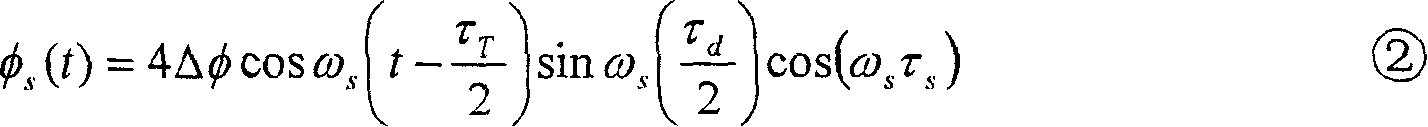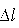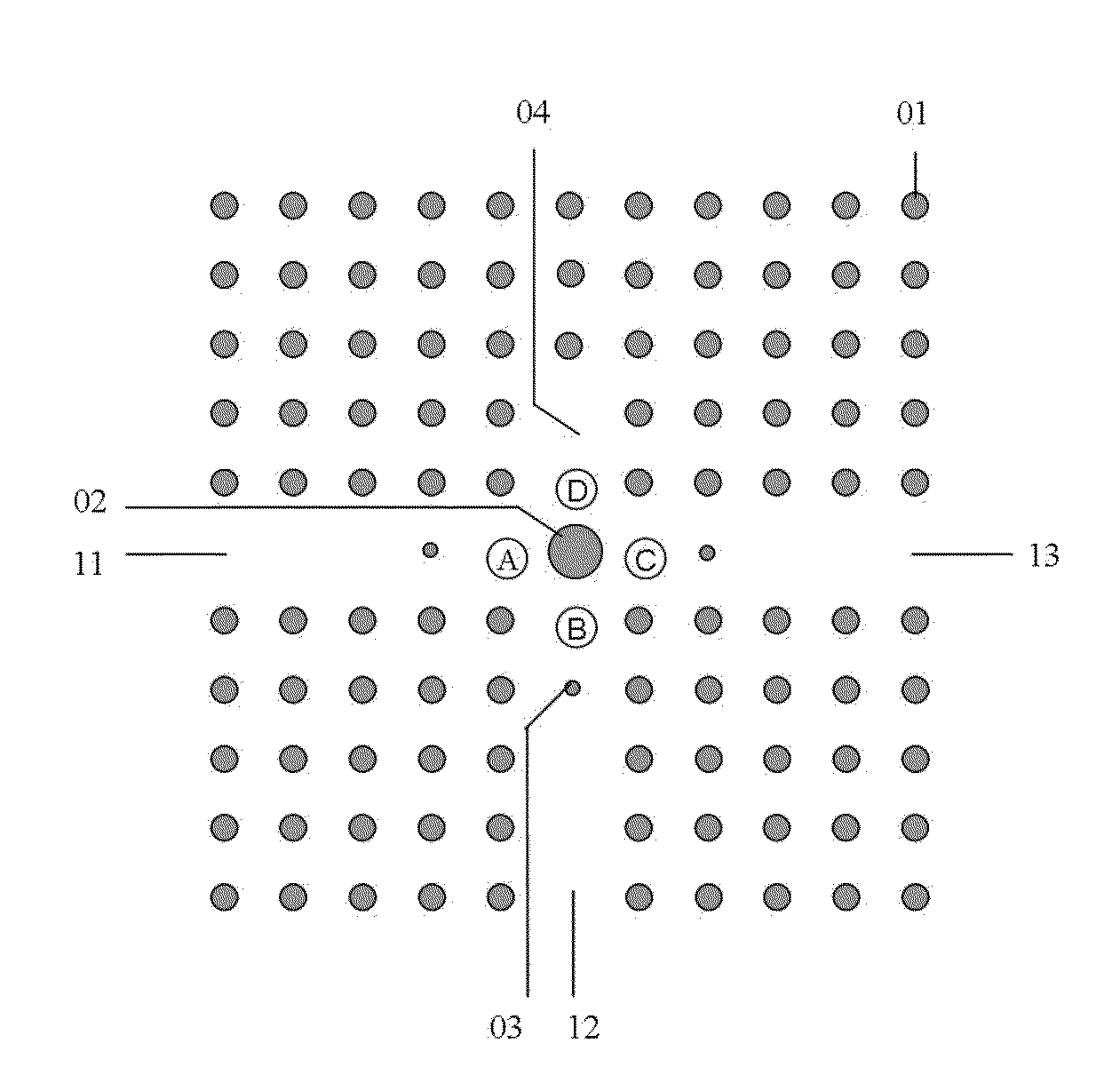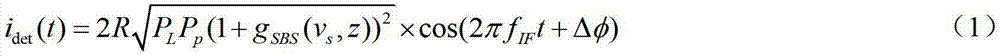Patents
Literature
1261 results about "Optical circulator" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
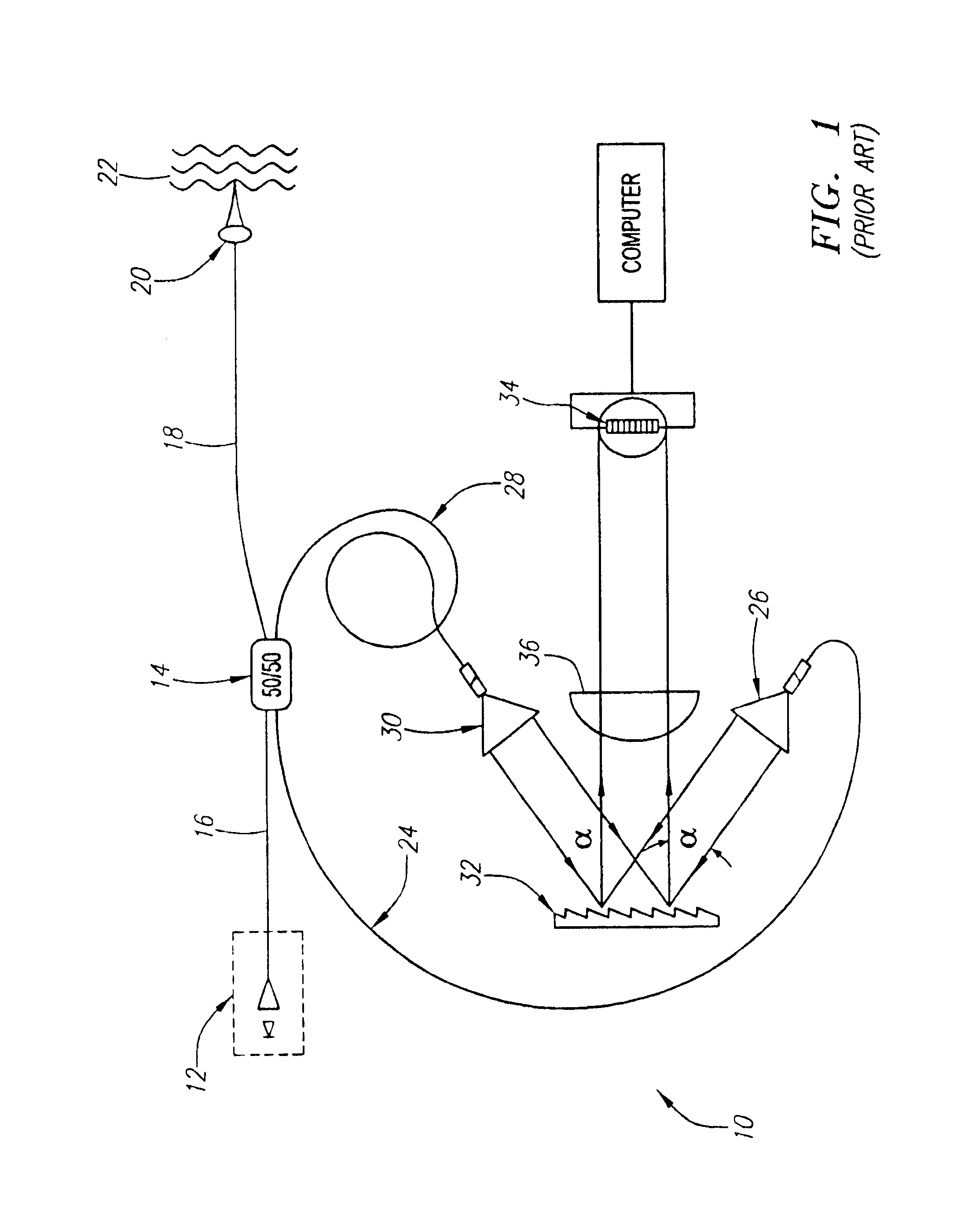
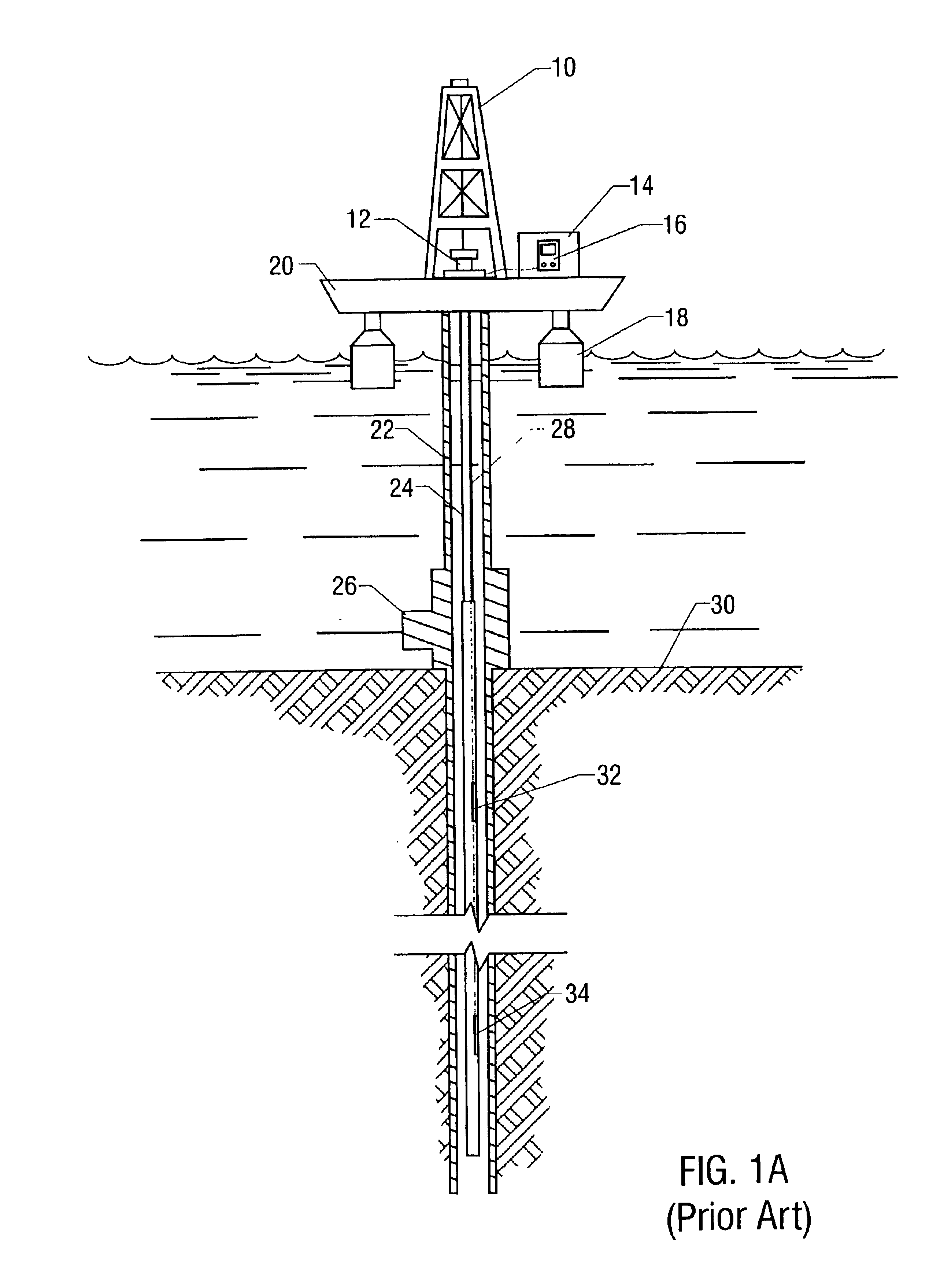
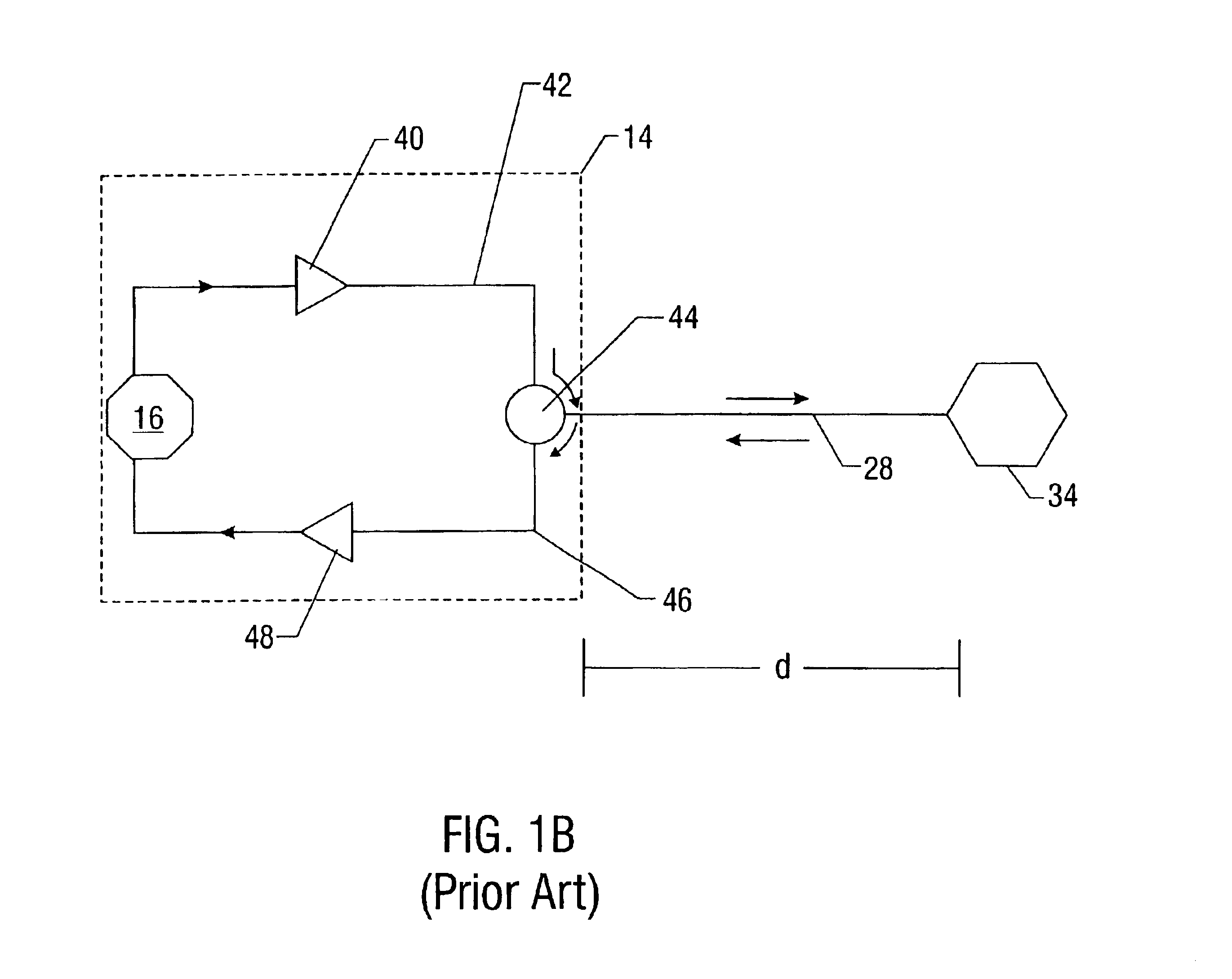
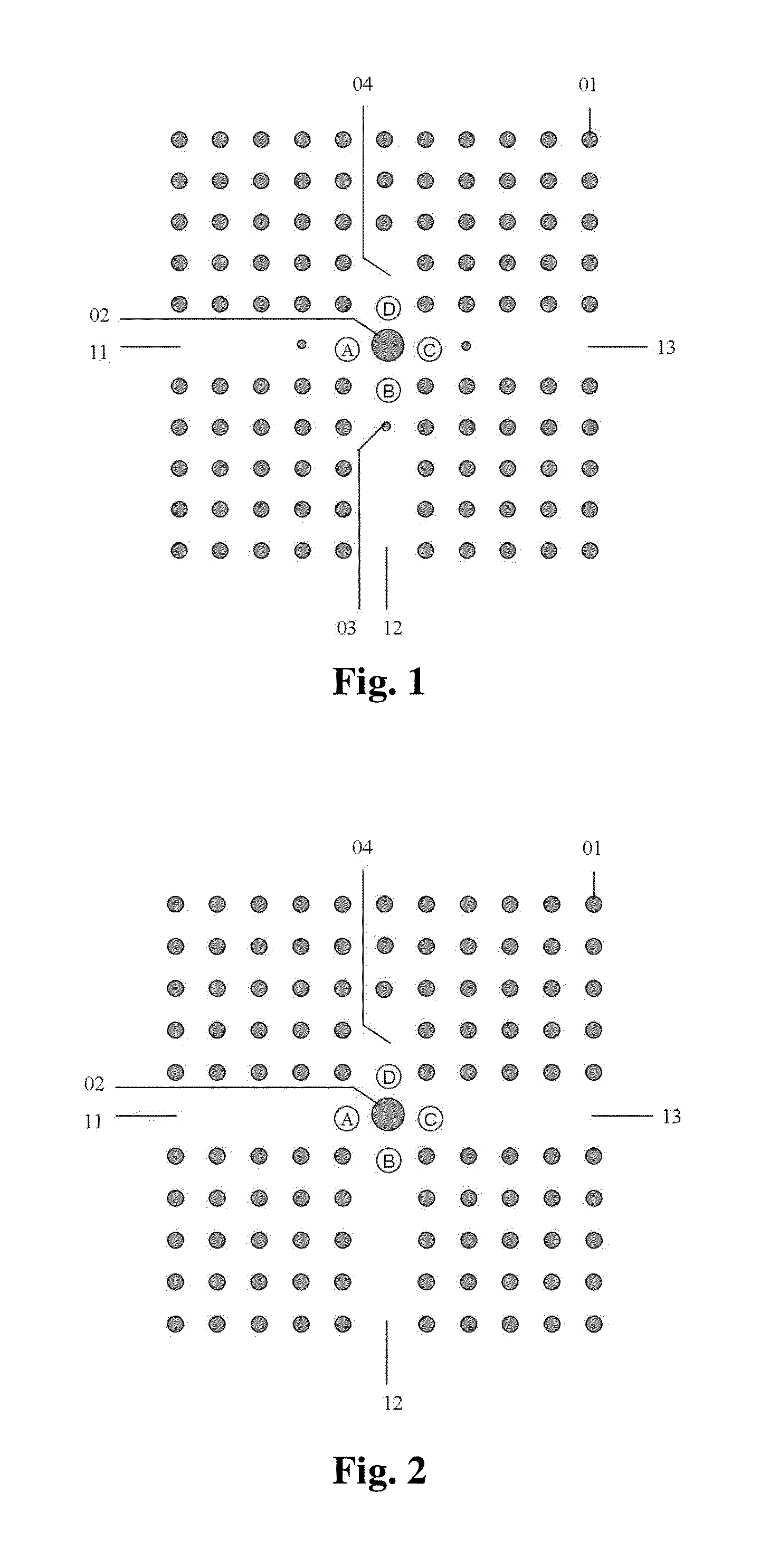
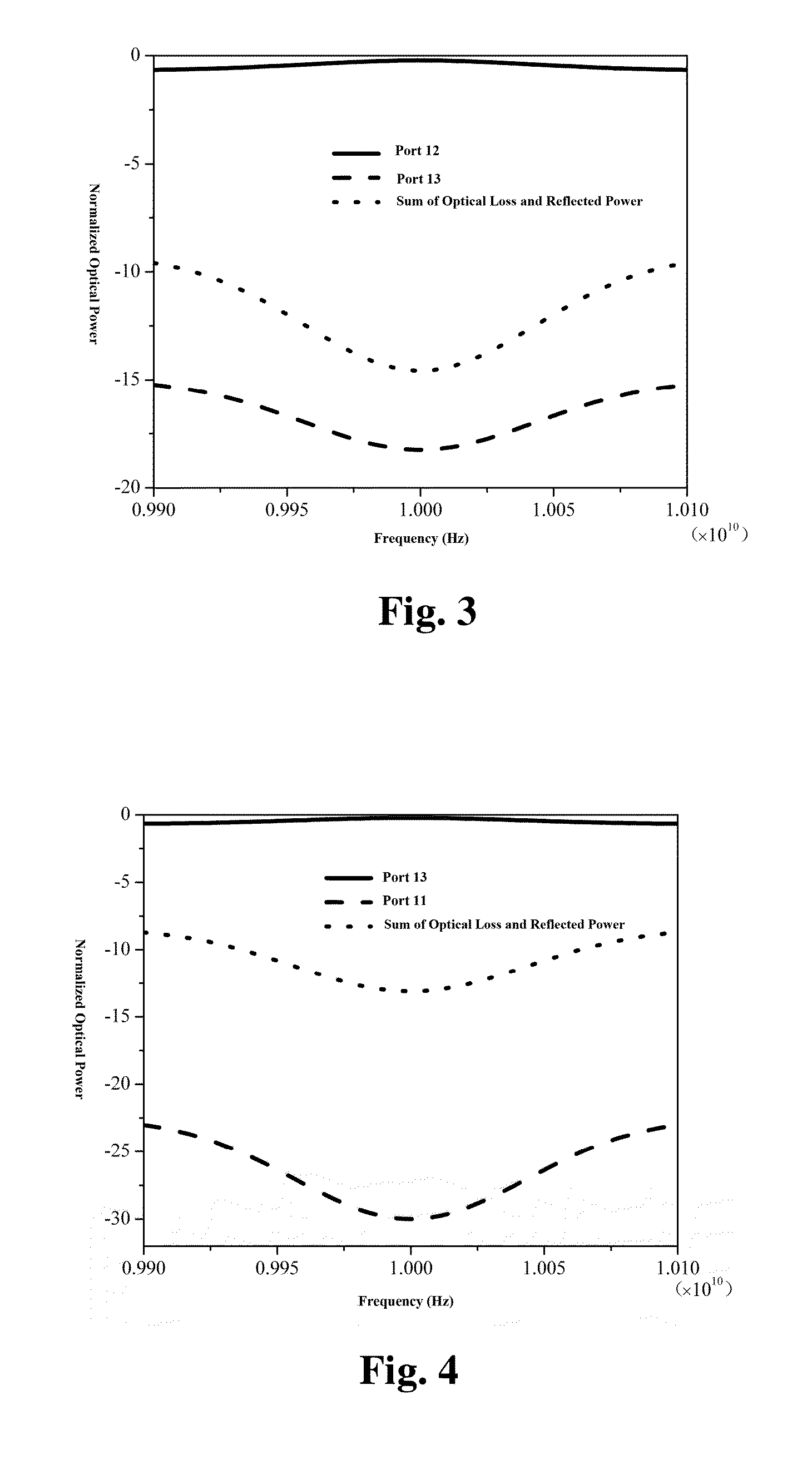
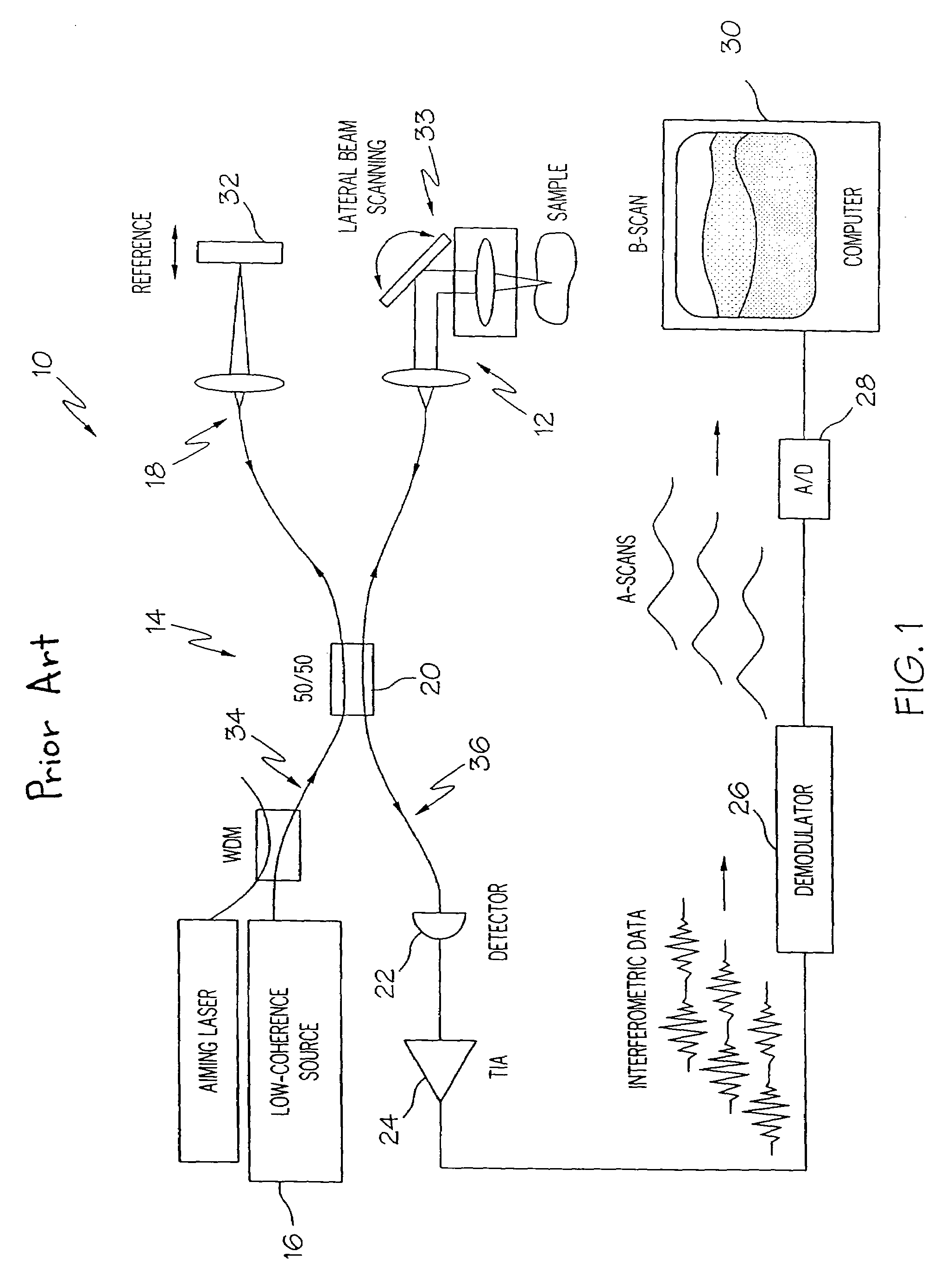
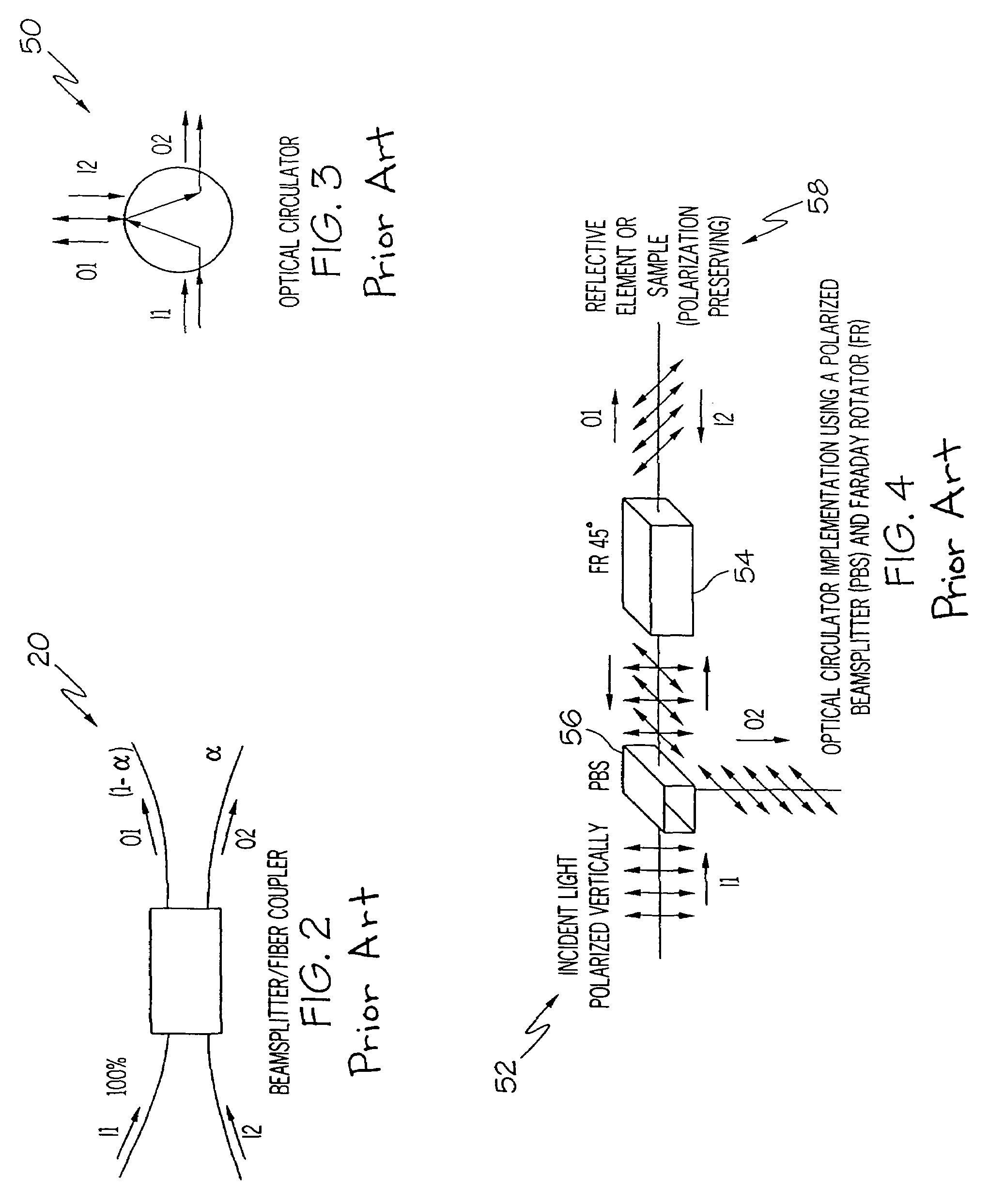
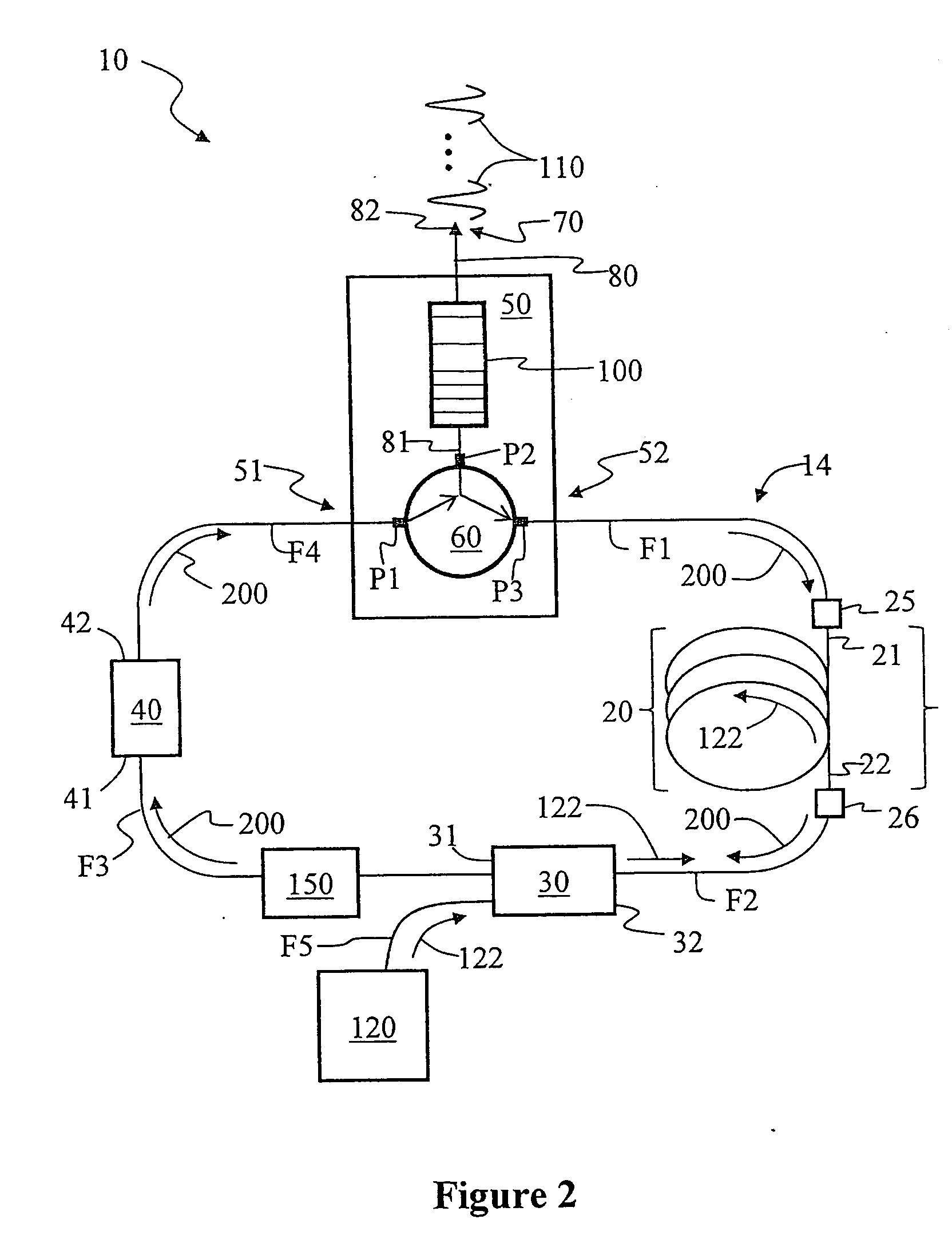
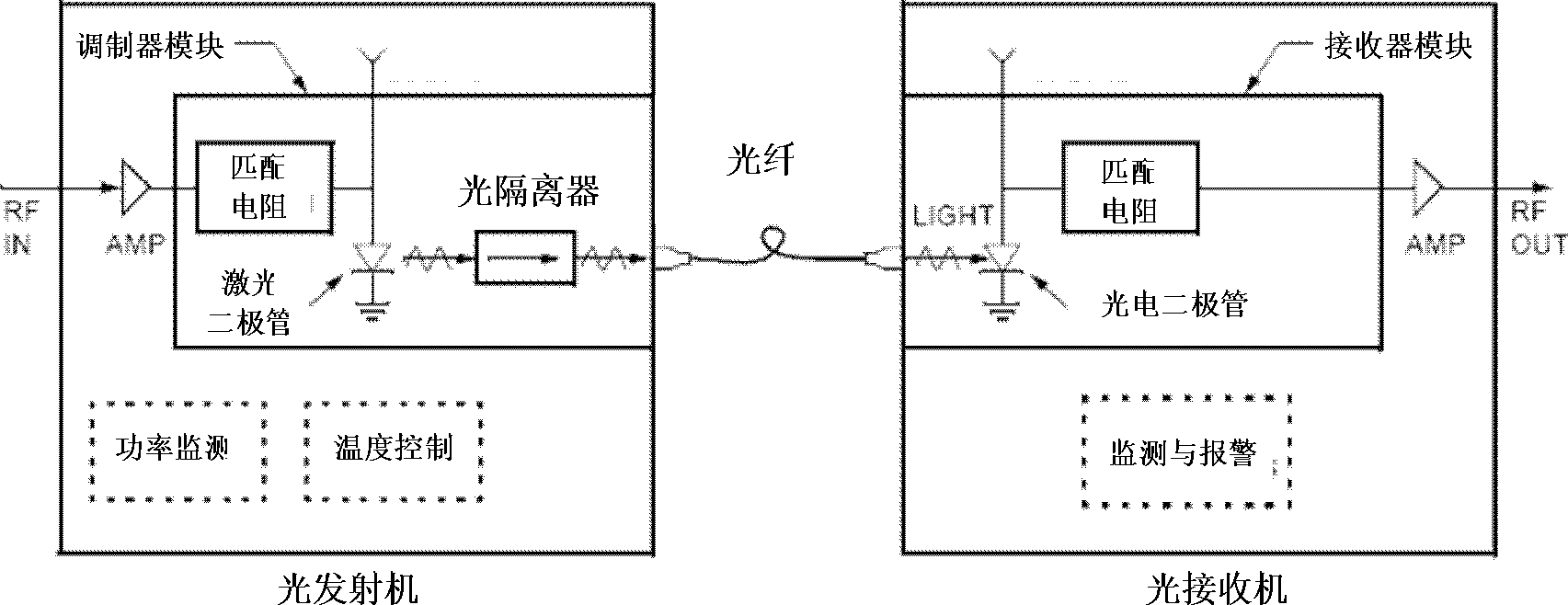
An optical circulator is a three- or four-port optical device designed such that light entering any port exits from the next. This means that if light enters port 1 it is emitted from port 2, but if some of the emitted light is reflected back to the circulator, it does not come out of port 1 but instead exits from port 3. This is analogous to the operation of an electronic circulator. Fiber-optic circulators are used to separate optical signals that travel in opposite directions in an optical fiber, for example to achieve bi-directional transmission over a single fiber. Because of their high isolation of the input and reflected optical powers and their low insertion loss, optical circulators are widely used in advanced communication systems and fiber-optic sensor applications.
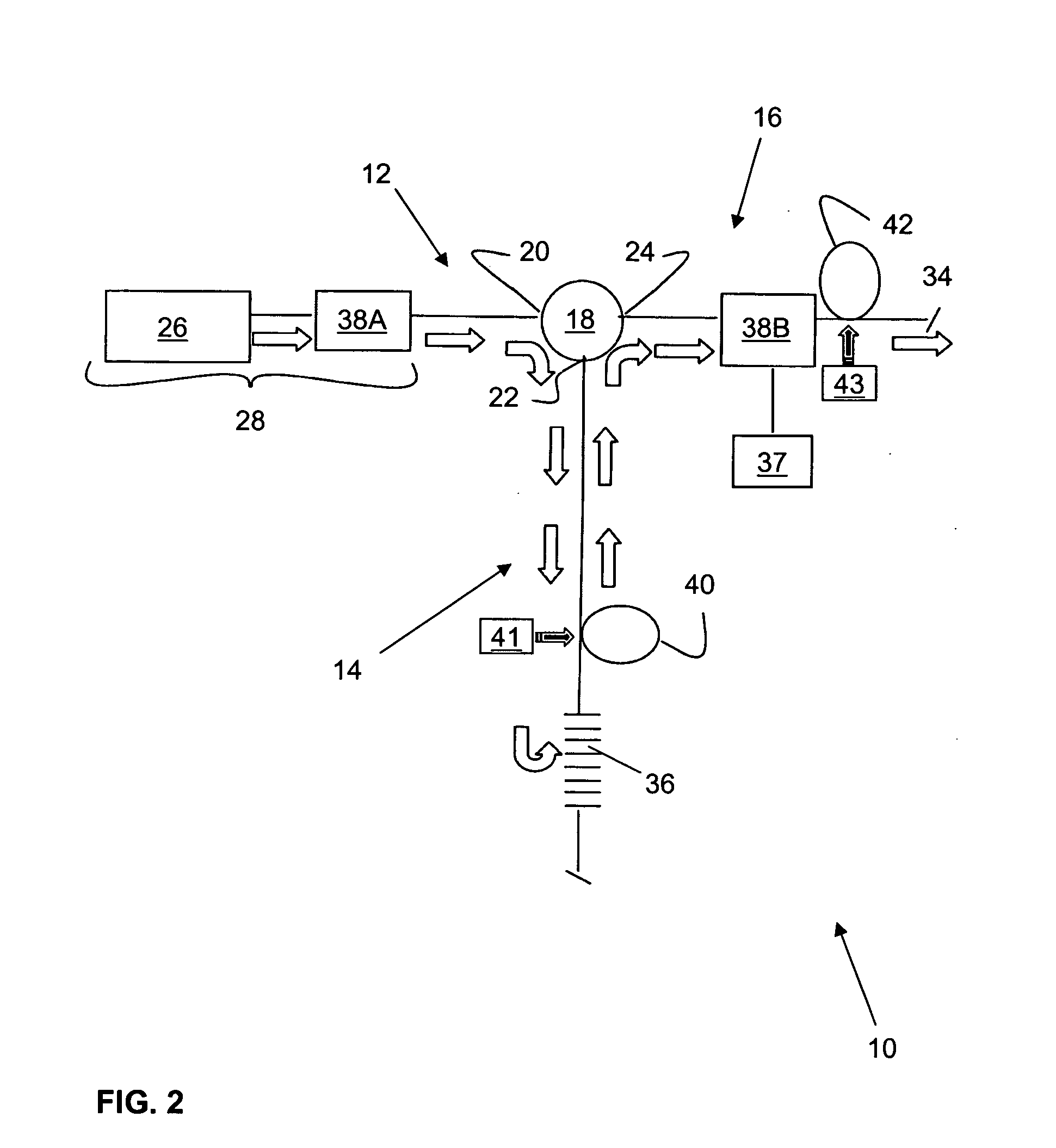
Diffraction grating based interferometric systems and methods
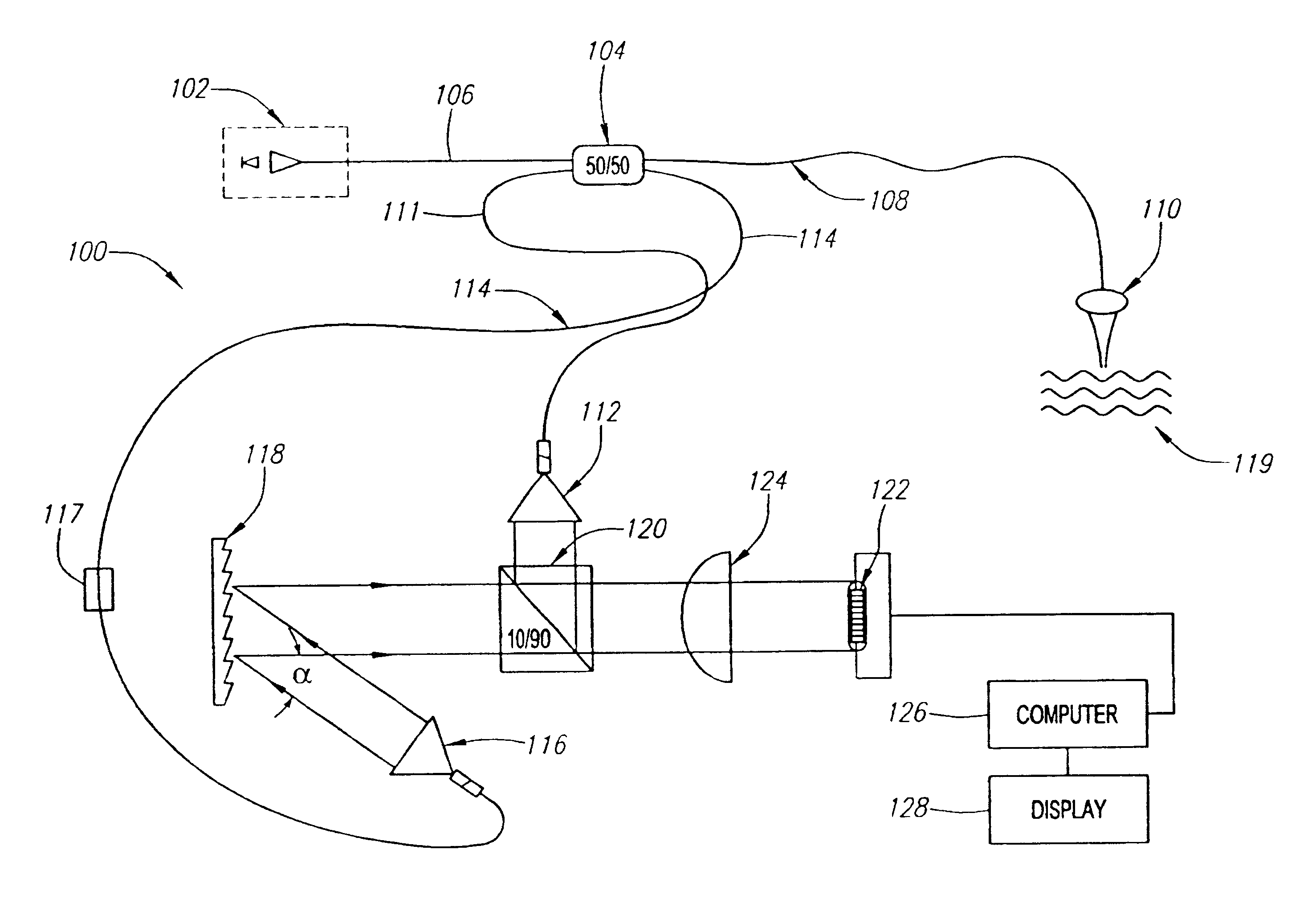
Diffraction grating based fiber optic interferometric systems for use in optical coherence tomography, wherein sample and reference light beams are formed by a first beam splitter and the sample light beam received from a sample and a reference light beam are combined on a second beam splitter. In one embodiment, the first beam splitter is an approximately 50 / 50 beam splitter, and the second beam splitter is a non 50 / 50 beam splitter. More than half of the energy of the sample light beam is directed into the combined beam and less than half of the energy of the reference light beam are directed into the combined beam by the second beam splitter. In another embodiment, the first beam splitter is a non 50 / 50 beam splitter and the second beam splitter is an approximately 50 / 50 beam splitter. An optical circulator is provided to enable the sample light beam to bypass the first beam splitter after interaction with a sample. Two combined beams are formed by the second beam splitter for detection by two respective detectors. More than half of the energy of the light source provided to the first beam splitter is directed into the sample light beam and less than half of the energy is directed into the reference light beam. The energy distribution between the sample and reference light beams can be controlled by selection of the characteristics of the beam splitters.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
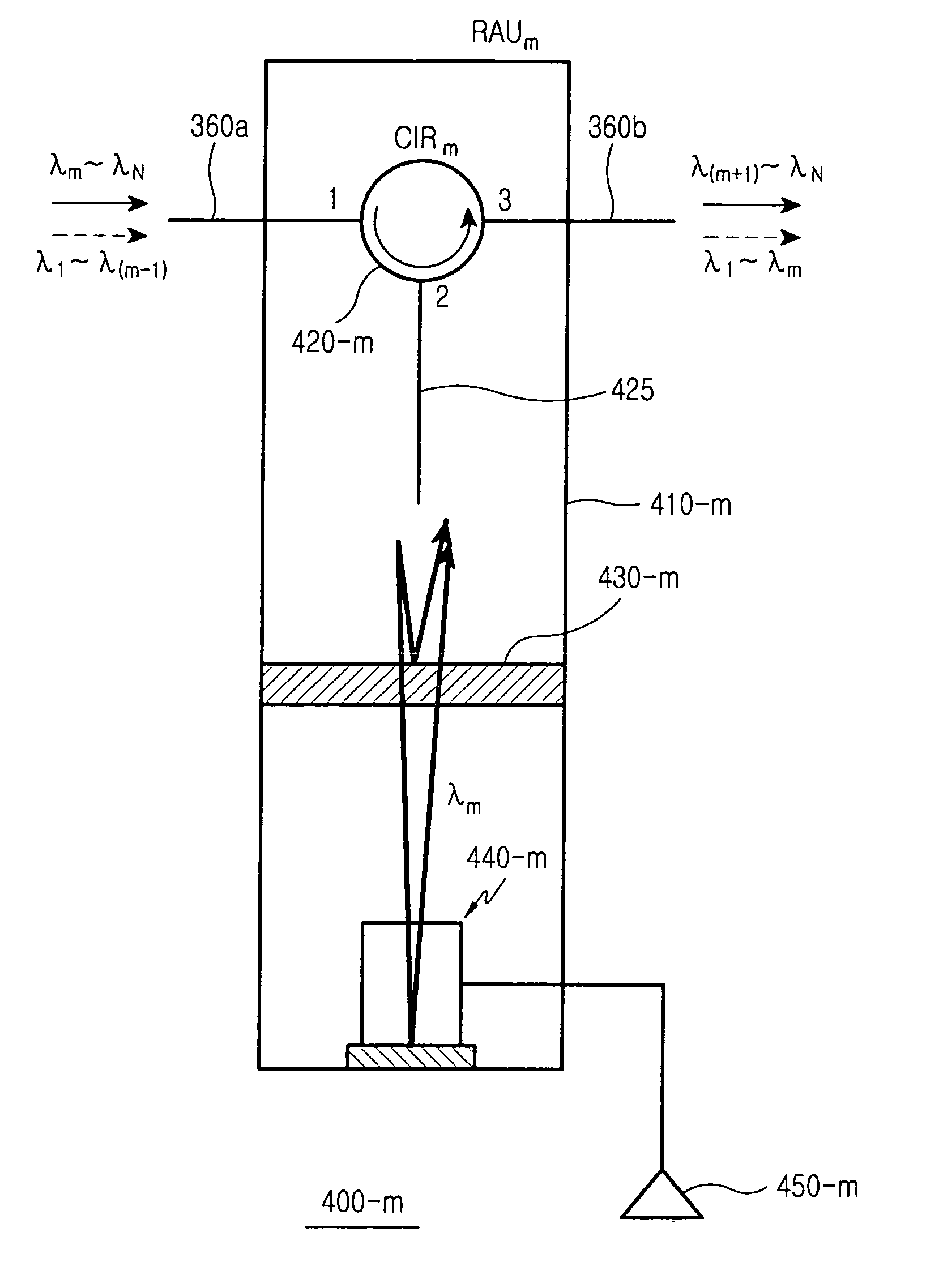
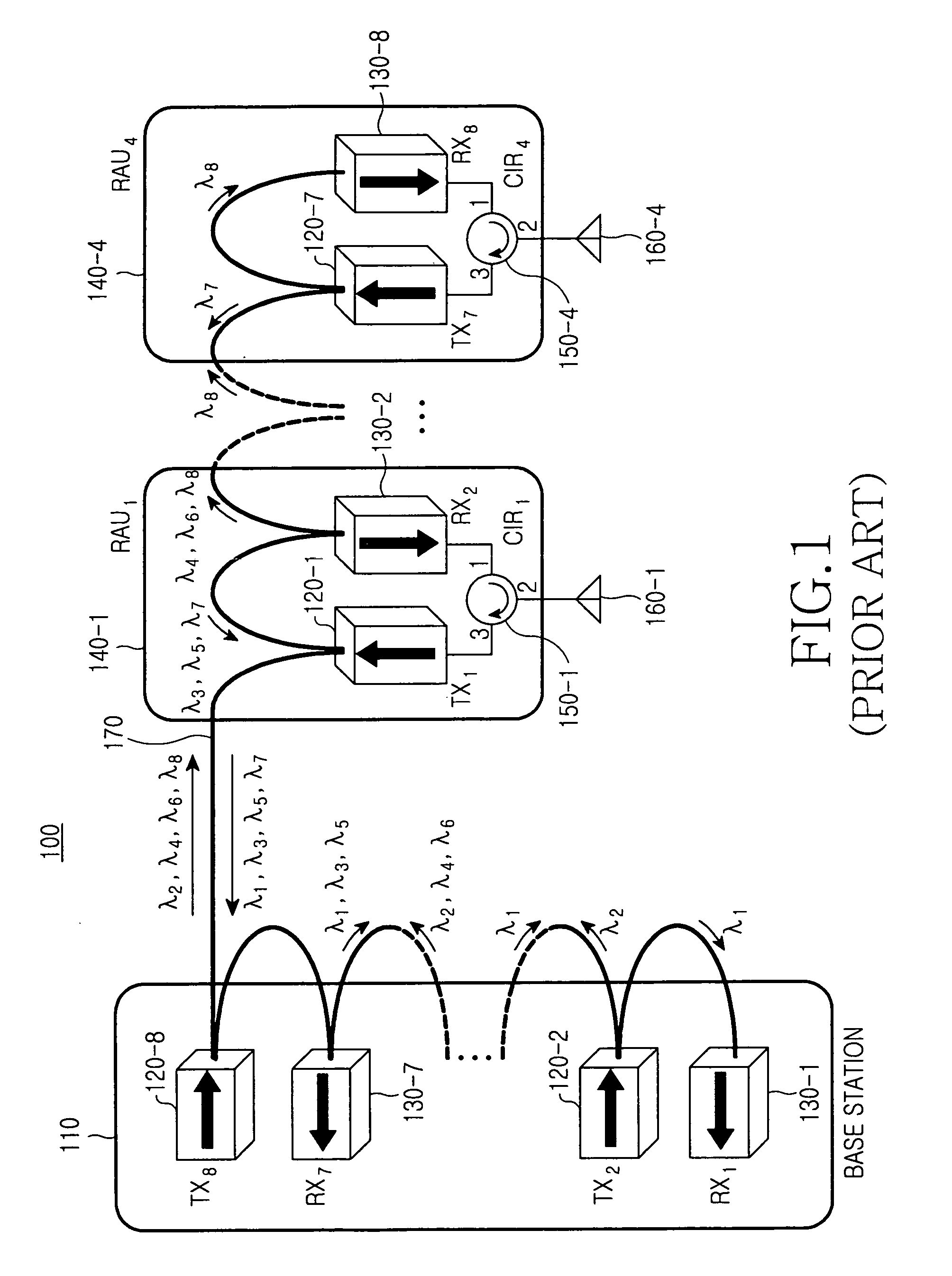
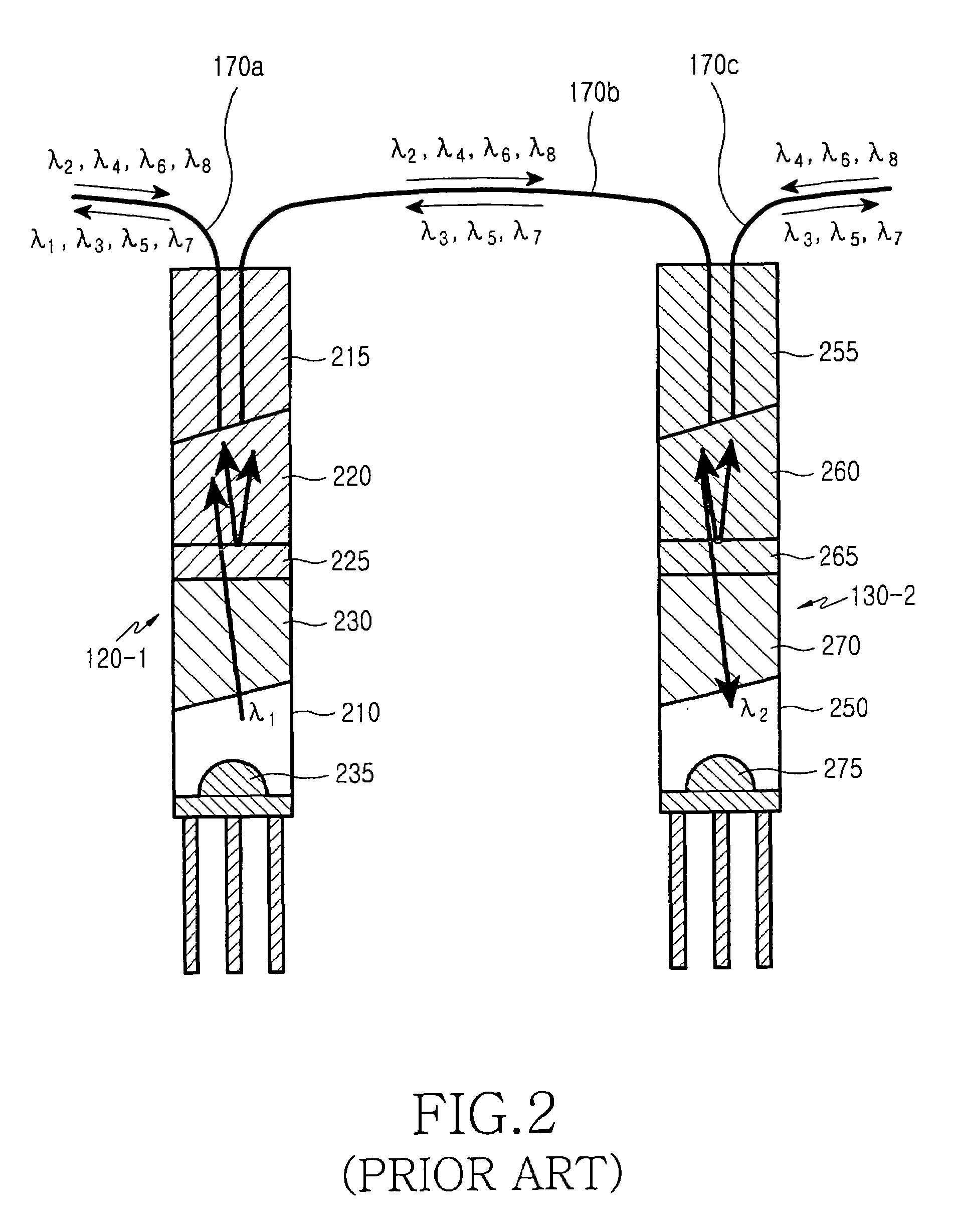
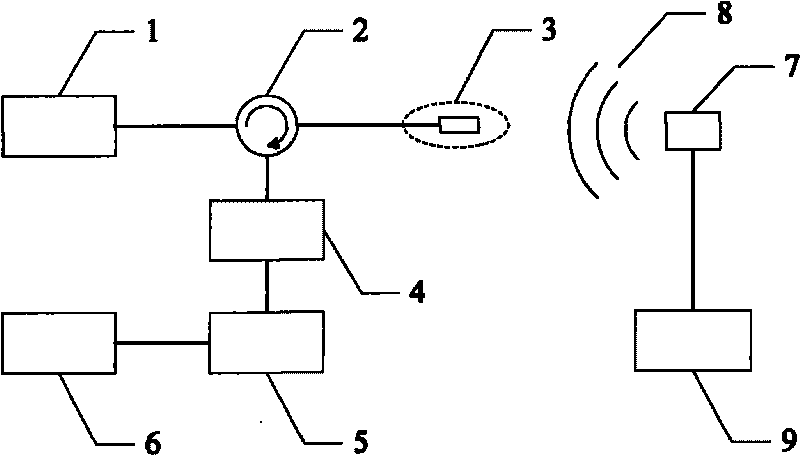
Remote antenna unit and wavelength division multiplexing radio-over-fiber network
InactiveUS7269311B2Simple structureLow costCoupling light guidesRadio-over-fibreElectricityRadio over fiber
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
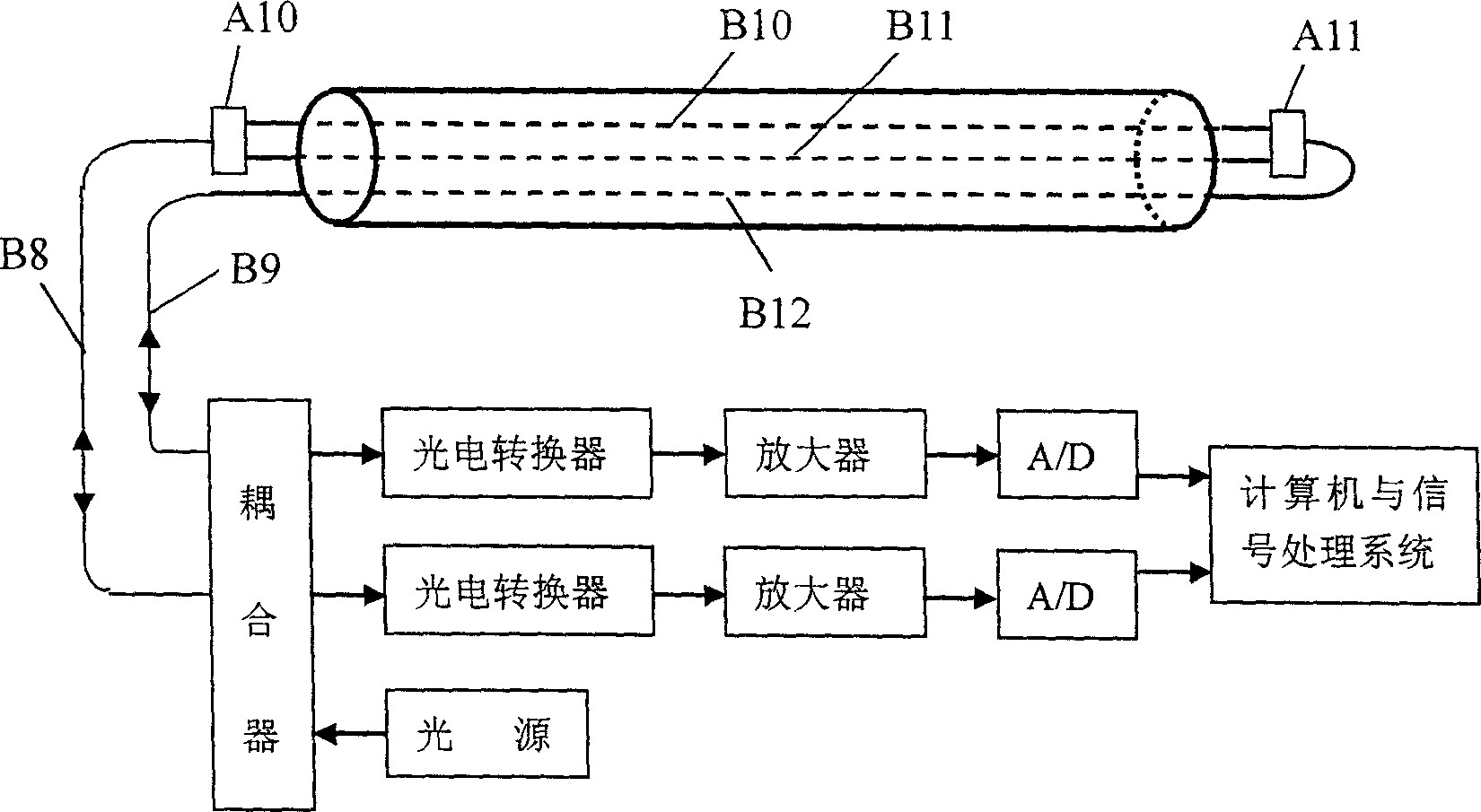
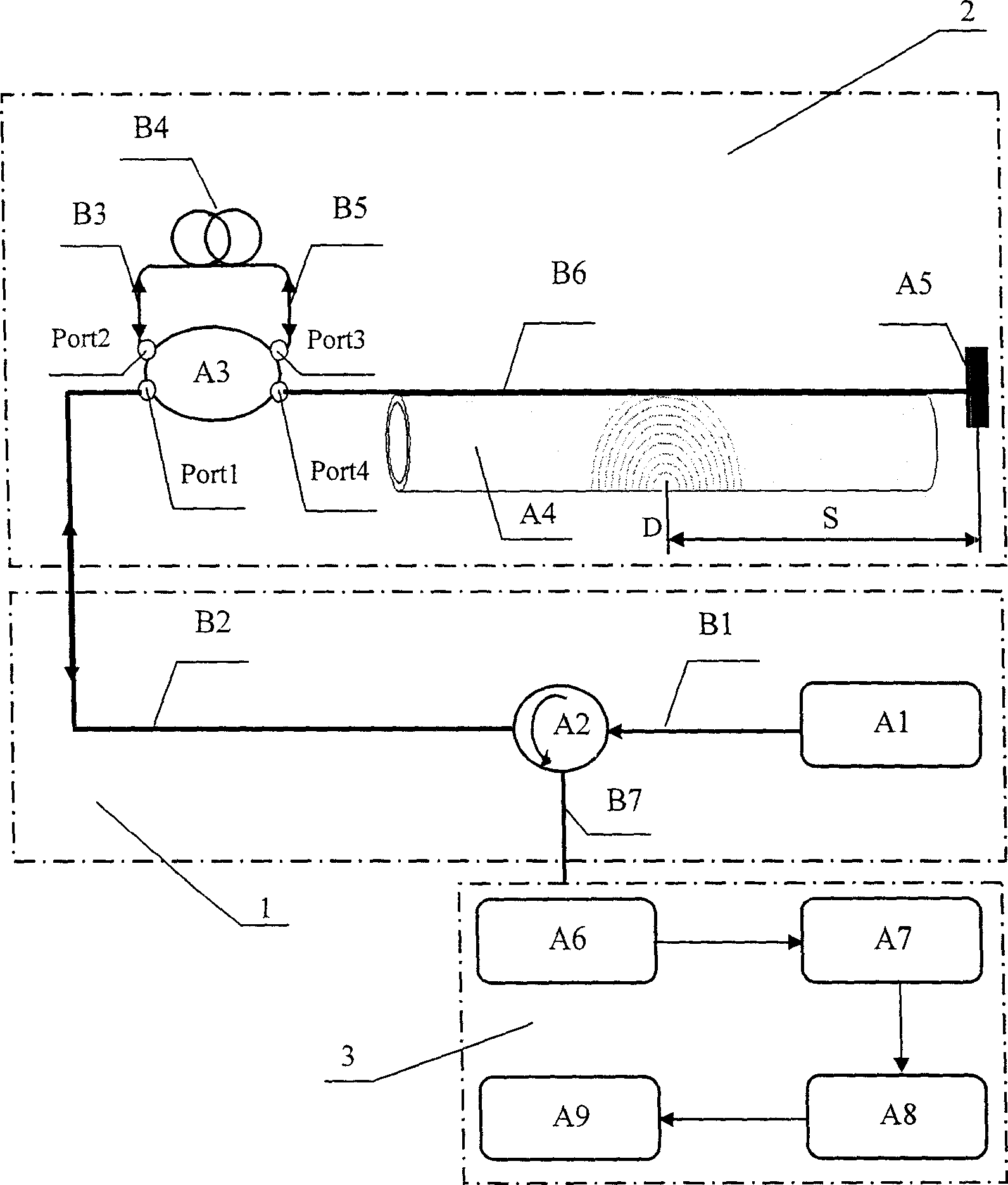
Apparatus and method for monitoring pipeline leakage based on distributed optical fiber acoustic sensing technology
InactiveCN1837674AReduce lossIncreased sensitivityPipeline systemsContinuous lightOptical circulator
The invention relates to a channel leakage detector and method based on distributed optical fiber acoustic sensing technique, which comprises an optical system (1), a distributed optical fiber sensing system (2), and a detecting system (3). Wherein, the optical system comprises a board band continuous light resource A1, and an optical circulator A2; the distributed optical sensing system comprises the first coupler A3, the delay coil B4, and a reflective mirror A5l; the detecting system comprises an optical-electric converter A6, a demodulate system A7, a A / D converter A8, and a computer A9; the board band continuous light resource via the optical circulator is connected to the Port1 interface of the first coupler A3, whose Port2 and Port3 are connected with delay coil; the Port4 of first coupler via sensing optical fiber is connected to the reflective mirror; and the optical circulator is connected to the optical-electric converter of detecting system, while said system can detect any leakage signal at any time.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
COTDR (coherent detection based optical time-domain reflectometry) fused long-distance coherent detection brilouin optical time-domain analyzer
InactiveCN102759371AImprove signal-to-noise ratioImprove dynamic rangeThermometers using physical/chemical changesUsing optical meansSpectrum analyzerLine width
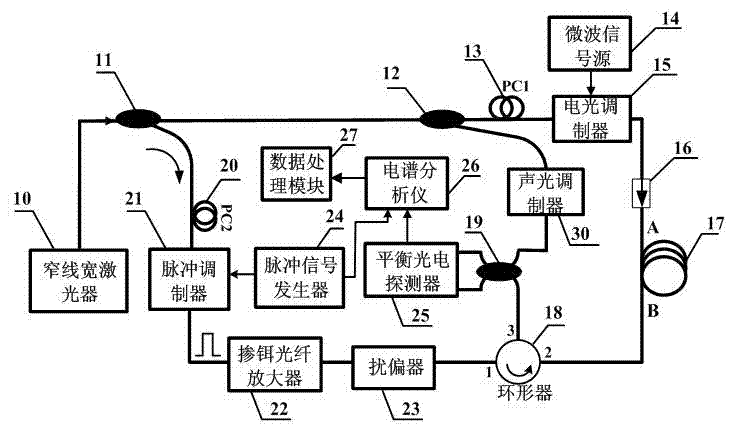
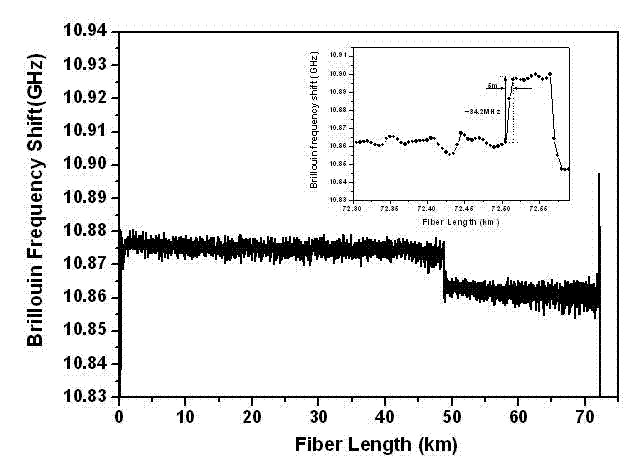
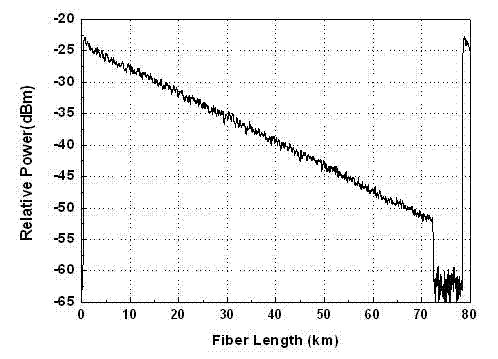
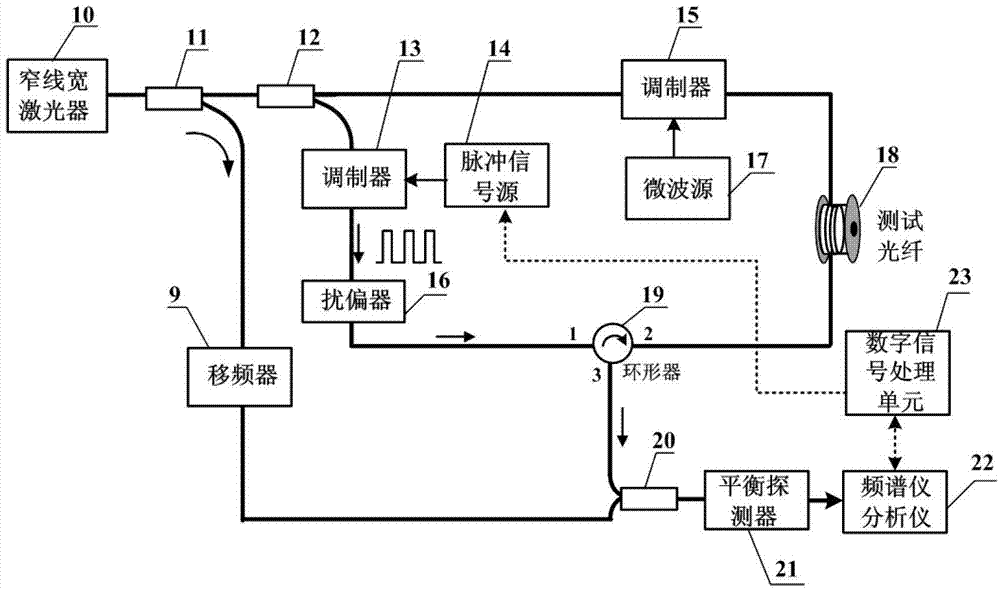
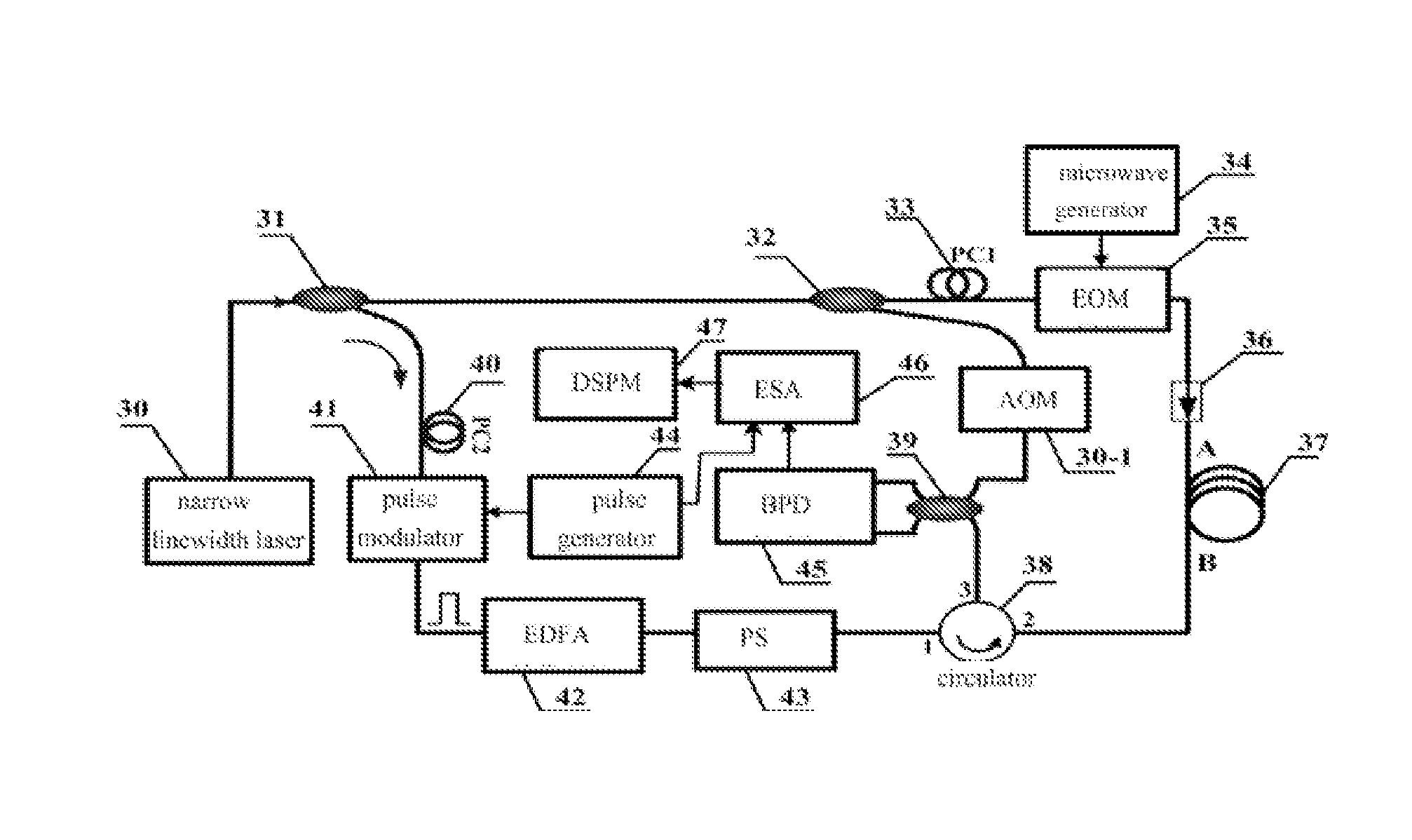
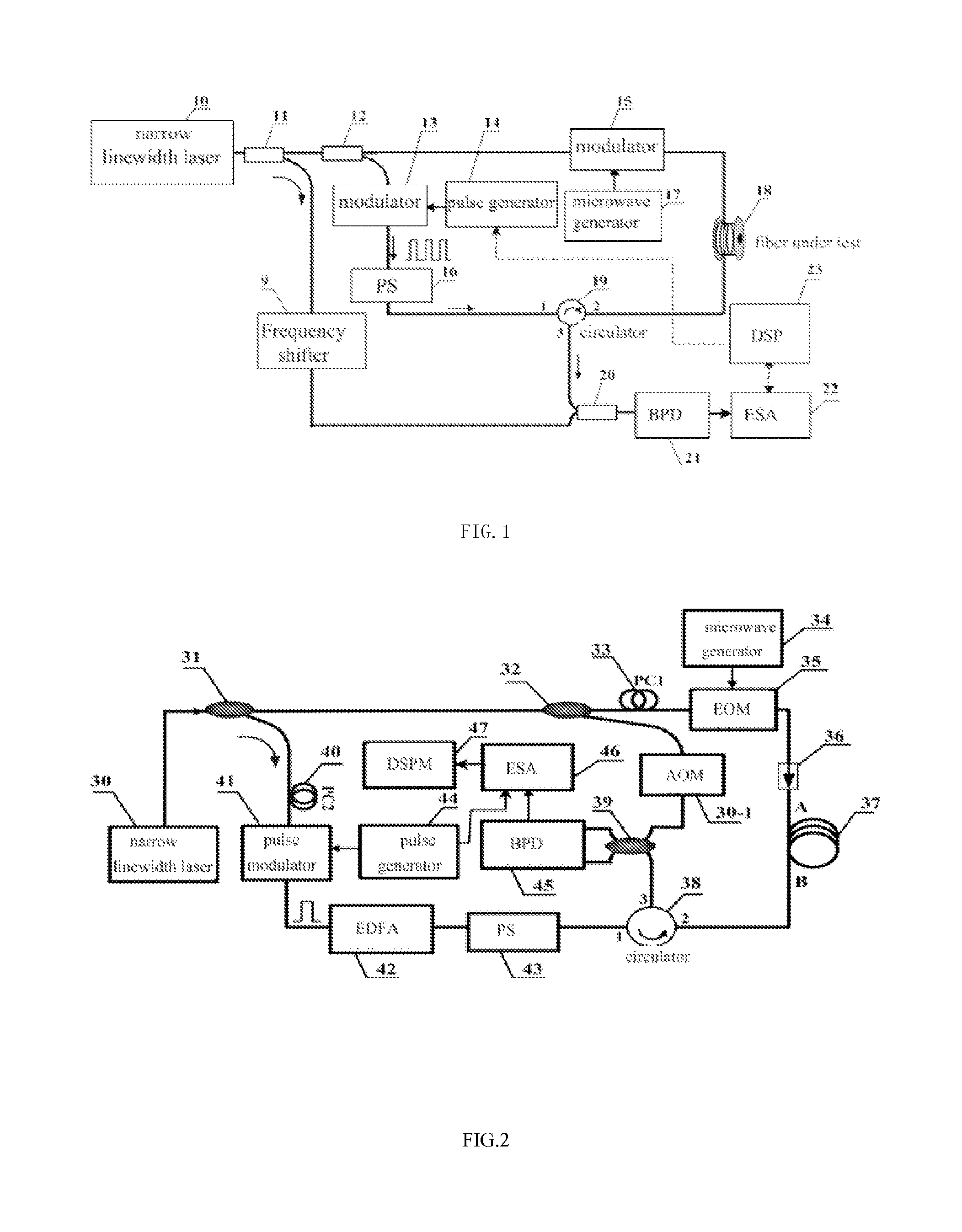
The invention discloses a COTDR (coherent detection based optical time-domain reflectometry) fused long-distance coherent detection brilouin optical time-domain analyzer which comprises a narrow-linewidth laser, two couplings, a microwave signal source, an electro-optic modulator, an isolator, a long-distance sensing optical fiber, an optical circulator, a 3 db coupling, a pulse modulator, an Er-doped fiber amplifier, a scrambler, a pulse signal generator, a balancing photoelectric detector, an electrical frequency spectrum analyzer, a data processing module and an acousto-optic modulator. According to the invention, the signal-to-noise ratio of BOTDA (brilouin optical time domain analysis) is improved by using a coherent detection method, a non-local effect of a BOTDA system is reduced in a double-sideband detection mode, and the sensing distance is more than 70 km under the condition of no light amplification such as raman; and according to the invention, the COTDR is fused to a coherent detection based BOTDA system, and the system can run in a breakpoint testing mode, so that the defect that the traditional BOTDA can not run when a sensing fiber has breakpoints and can not carry out positioning on breakpoints is effectively overcome, thereby enhancing the adaptability and practicability of the sensing system.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
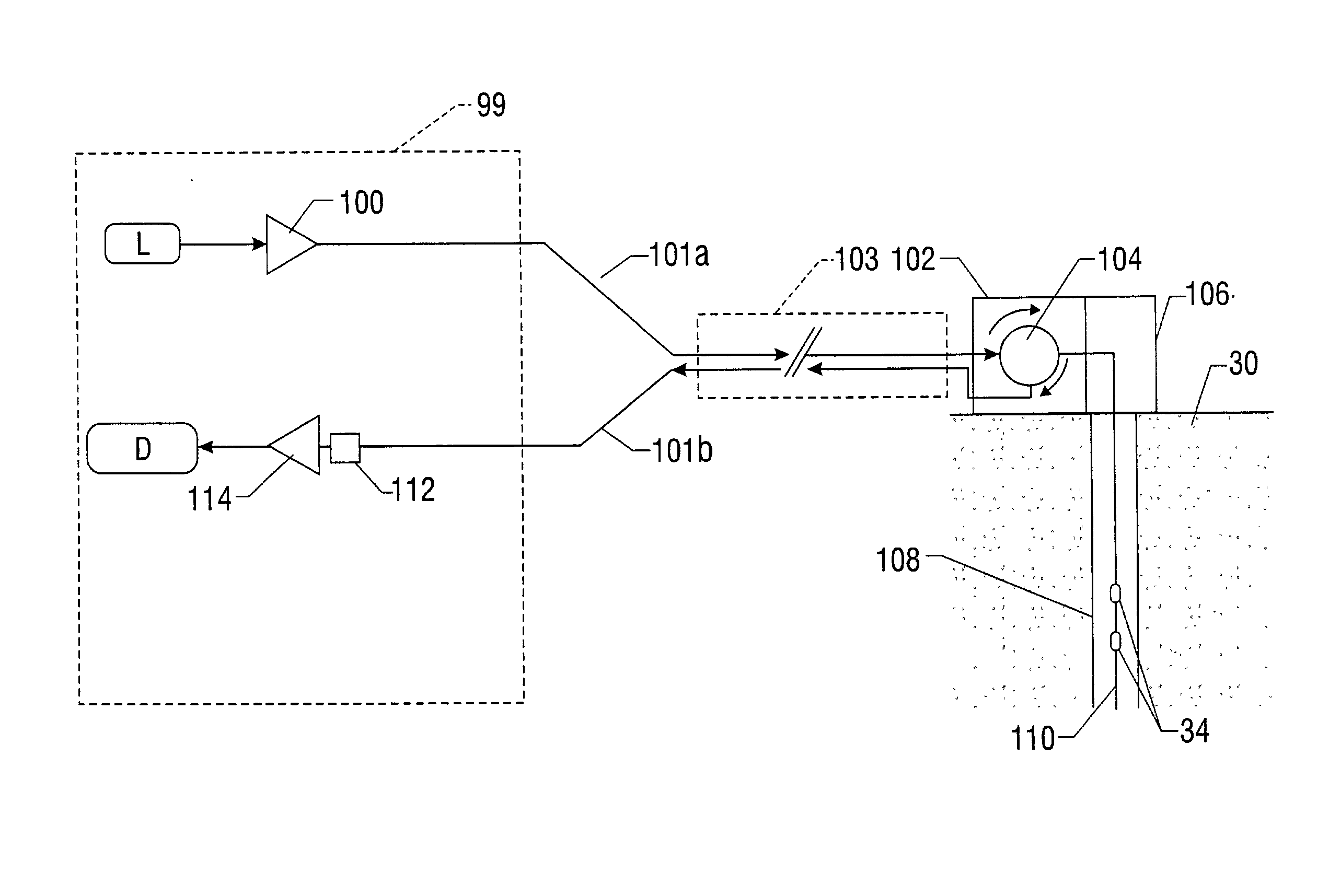
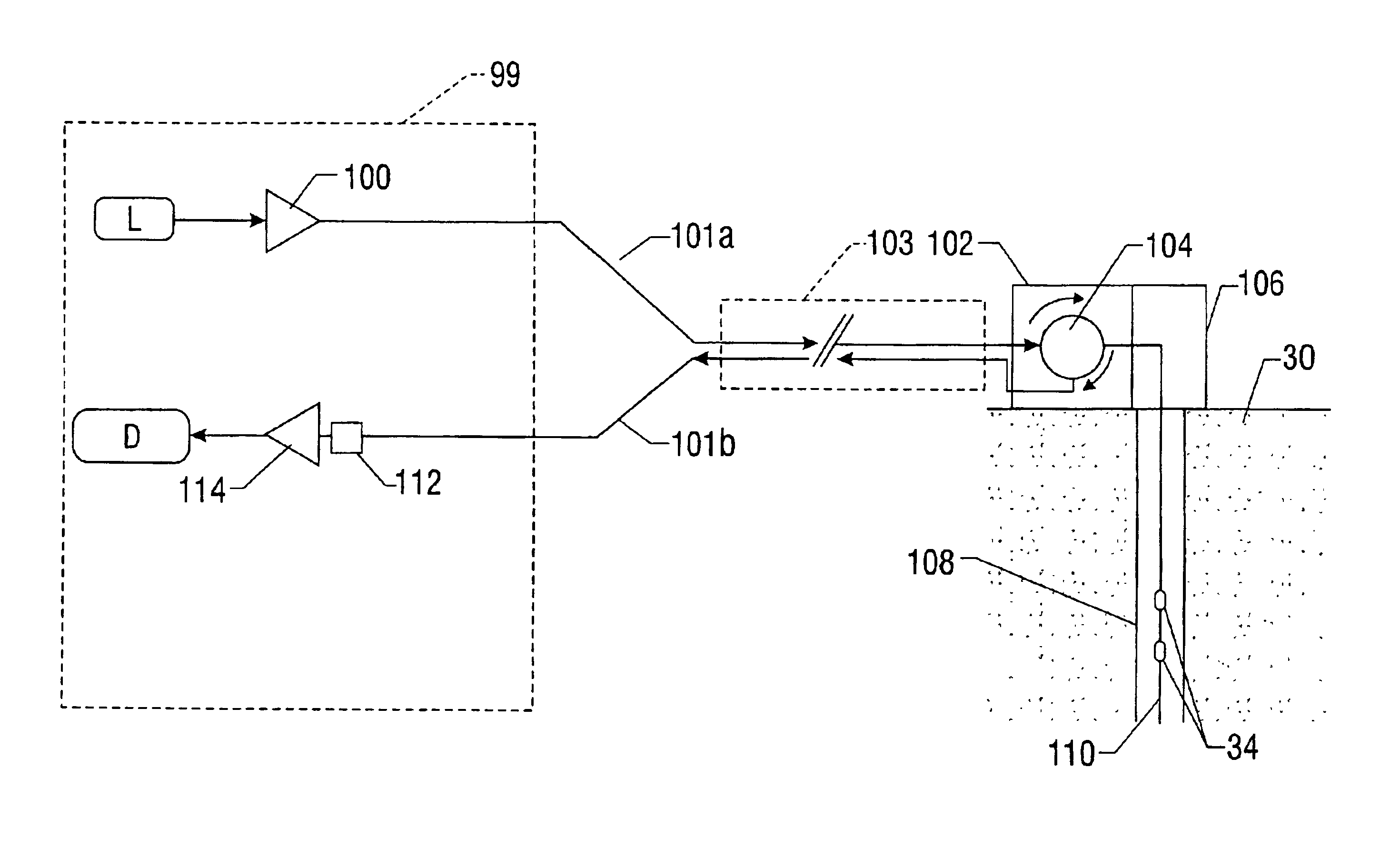
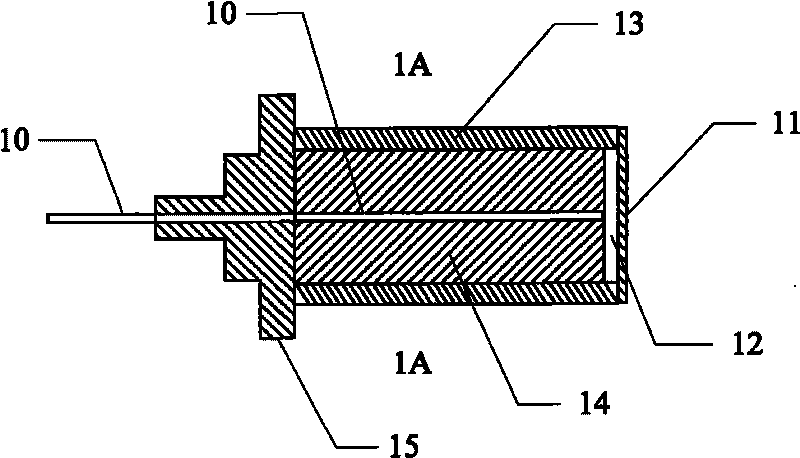
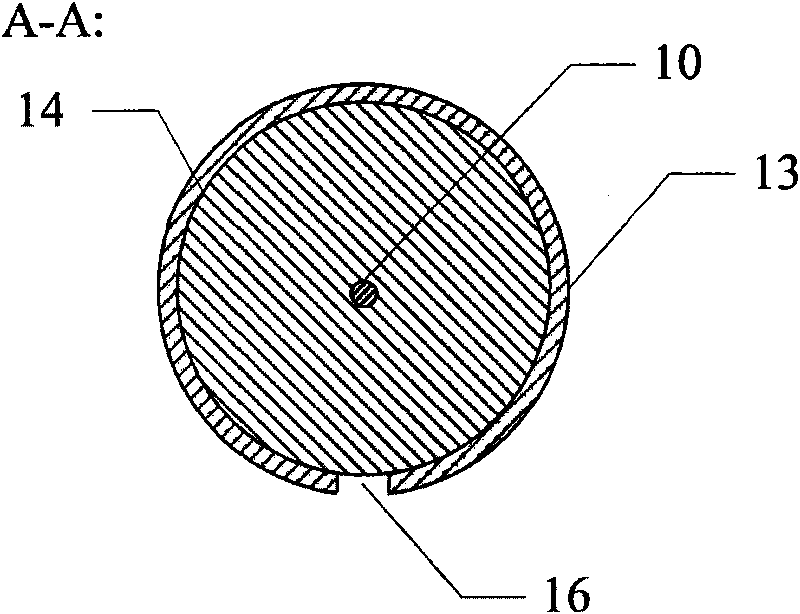
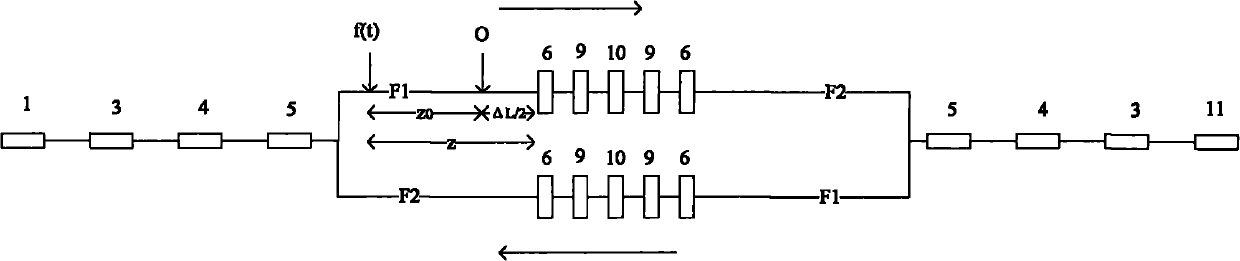
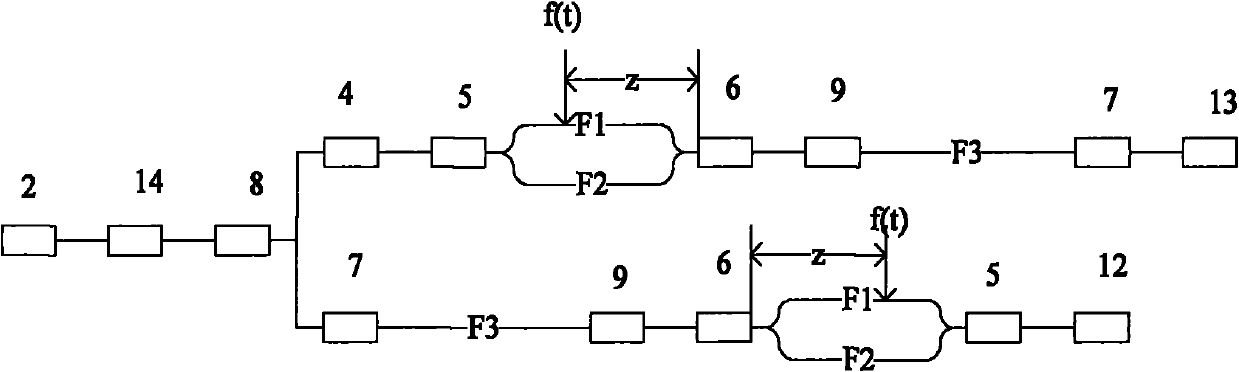
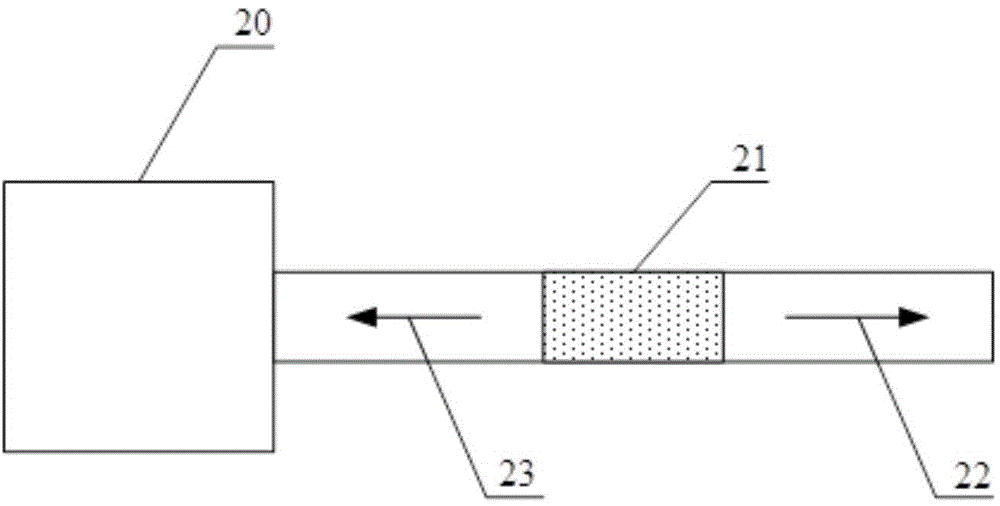
Remotely deployed optical fiber circulator
ActiveUS20040113104A1ConstructionsMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorFiberOptical circulator
Fiber-optic-based systems and methods for monitoring physical parameters using a remotely deployed circulator are disclosed. In a preferred embodiment the circulator is remotely deployed with respect to an optical source / detector and coupled thereto by two dedicated fiber optical cables: a forward line for passing light from the source through the circulator to fiber-optic-based sensors, and a return line for passing light reflected from the sensors through the circulator back to the detector. By using separate forward and return lines in conjunction with the circulator, backscattering phenomenon experienced on the forward line will not interfere with the reflected light signals coming from the sensors. The circulator, and hence the sensors, may therefore be remotely deployed from the source / detector present at a monitoring station, greatly expanding distances which optical sensing systems can span.
Owner:OPTOPLAN
Remotely deployed optical fiber circulator
InactiveUS6933491B2Increase distanceEasy to deployMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorConstructionsFiberOptical circulator
Fiber-optic-based systems and methods for monitoring physical parameters using a remotely deployed circulator are disclosed. In a preferred embodiment the circulator is remotely deployed with respect to an optical source / detector and coupled thereto by two dedicated fiber optical cables: a forward line for passing light from the source through the circulator to fiber-optic-based sensors, and a return line for passing light reflected from the sensors through the circulator back to the detector. By using separate forward and return lines in conjunction with the circulator, backscattering phenomenon experienced on the forward line will not interfere with the reflected light signals coming from the sensors. The circulator, and hence the sensors, may therefore be remotely deployed from the source / detector present at a monitoring station, greatly expanding distances which optical sensing systems can span.
Owner:OPTOPLAN
Distributed optical fiber sensing device based on chaotic laser coherence method, and measurement method of distributed optical fiber sensing device
ActiveCN103123285AAchieve strainEasy to detectThermometers using physical/chemical changesUsing optical meansData acquisitionDisplay device
The invention discloses a distributed optical fiber sensing device based on a chaotic laser coherence method, and a measurement method of the distributed optical fiber sensing device. Chaotic laser light which is emitted from a chaotic laser is divided into detection light and reference light; the detection light is amplified by a light amplifier and then emitted into a sending optical fiber through an optical circulator, and a backward Brillouin scattering light signal is generated in the optical fiber; the Brillouin scattering light signal is amplified by the light amplifier, de-noised by a tunable light filter and then emitted into an optical fiber coupler; the optical length of the reference light is regulated by a variable light delay line, and interferes with the backward Brillouin scattering light signal which is generated by the detection light at different positions in the sensing optical fiber in the optical fiber coupler; an interference beat frequency signal is detected by a photoelectrical detector; and Brillouin gain spectra at different lengths are obtained through a data acquisition device and a signal processing device and then output to a display device, so strain or temperature sensing detection is realized.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
Photonic Crystal Magneto-Optical Circulator and Manufacturing Method Thereof
InactiveUS20130223805A1Valid matchWell formedOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingOptical articlesElectricityDielectric
The invention relates to a photonic crystal magneto-optical circulator, which comprises first dielectric material columns in an air background, wherein the first dielectric material columns are arranged in the form of two-dimensional square lattice. The photonic crystal magneto-optical circulator also comprises a “T-shaped” or a “cross-shaped” photonic crystal waveguide, a second dielectric material column, four same magneto-optical material columns and at least three same third dielectric material columns, wherein the “T-shaped” or a “cross-shaped” photonic crystal waveguide comprises a horizontal photonic crystal waveguide and a vertical photonic crystal waveguide which are intercrossed; the second dielectric material column is arranged at a cross-connected position of the horizontal photonic crystal waveguide and the vertical photonic crystal waveguide and has the function of light guiding; the four same magneto-optical material columns are uniformly arranged on the periphery of the second dielectric material column; and at least three same third dielectric material columns.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
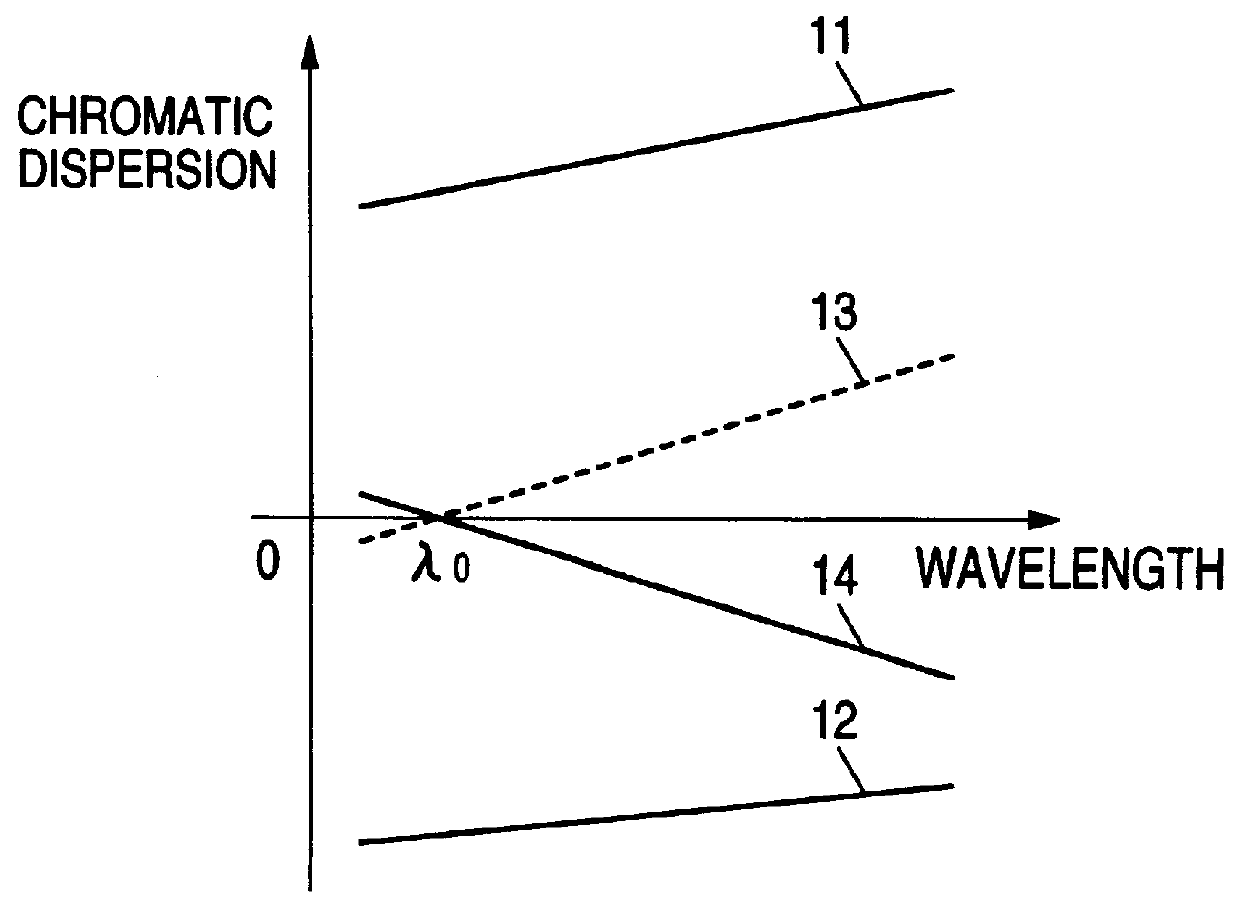
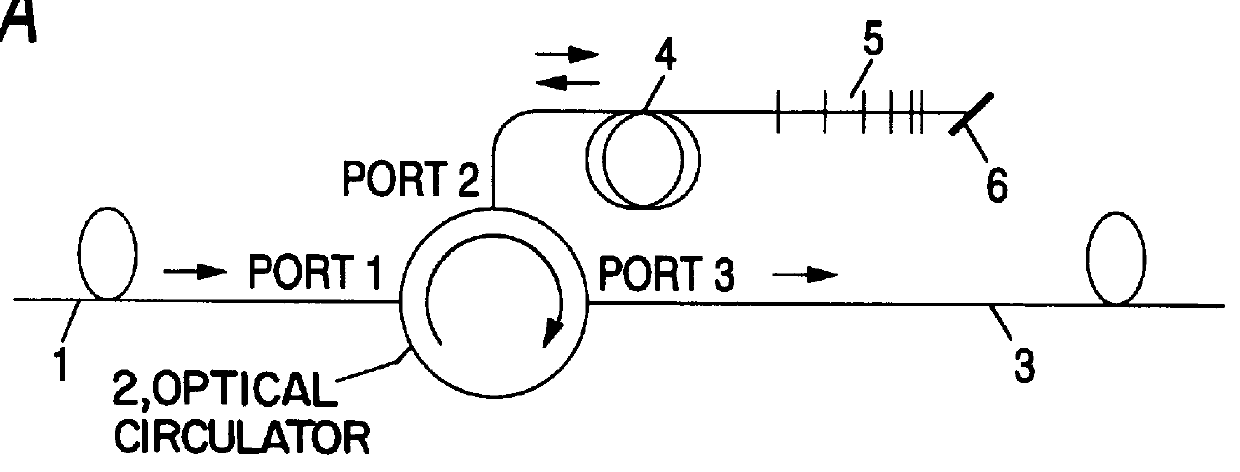
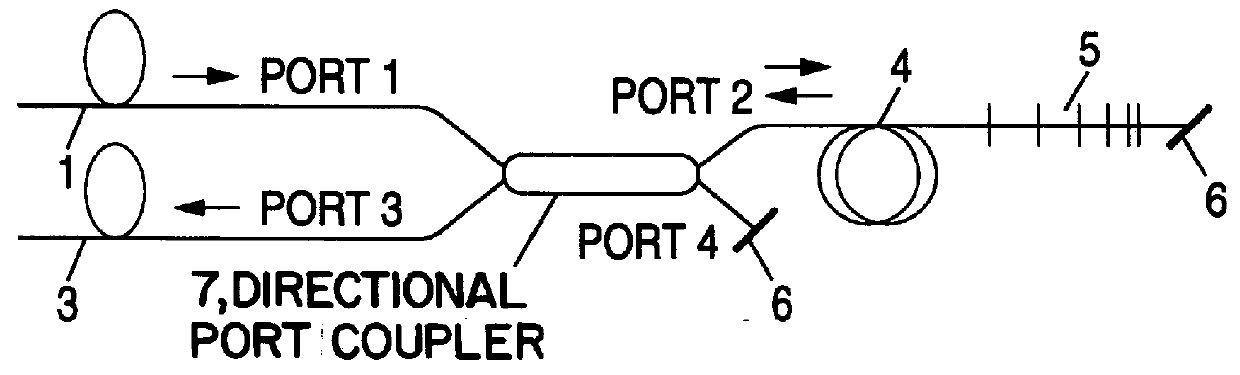
Chromatic dispersion compensator and chromatic dispersion compensating optical communication system
InactiveUS6055081AShorten the lengthReduced insertion lossWavelength-division multiplex systemsDistortion/dispersion eliminationCommunications systemGrating
In a chromatic dispersion compensator, an optical signal directing unit such as an optical circulator or a directional coupler having a first, second, third and fourth ports. The optical signal directing unit directs an optical signal inputted from one of the ports to another port of the ports. A reflection-type compensator including a dispersion compensating fiber, a reflecting portion and changing unit for changing a polarization direction of a reciprocating signal light, in which the dispersion compensating fiber is connected to the reflecting portion via the changing unit. An input transmission path which is connected to the first port; and an output transmission path which is connected to the fourth port so that the signal light is outputted from the fourth port. The reflection-type compensating unit is connected to one of the second and third ports, and the chirped grating is connected to the other port.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Parallel distribution optical fibre raster temp. sensing method and its system
InactiveCN101000267ADeployment restrictionsImprove consistencyThermometers using physical/chemical changesConverting sensor output opticallySensor arrayFiber coupler
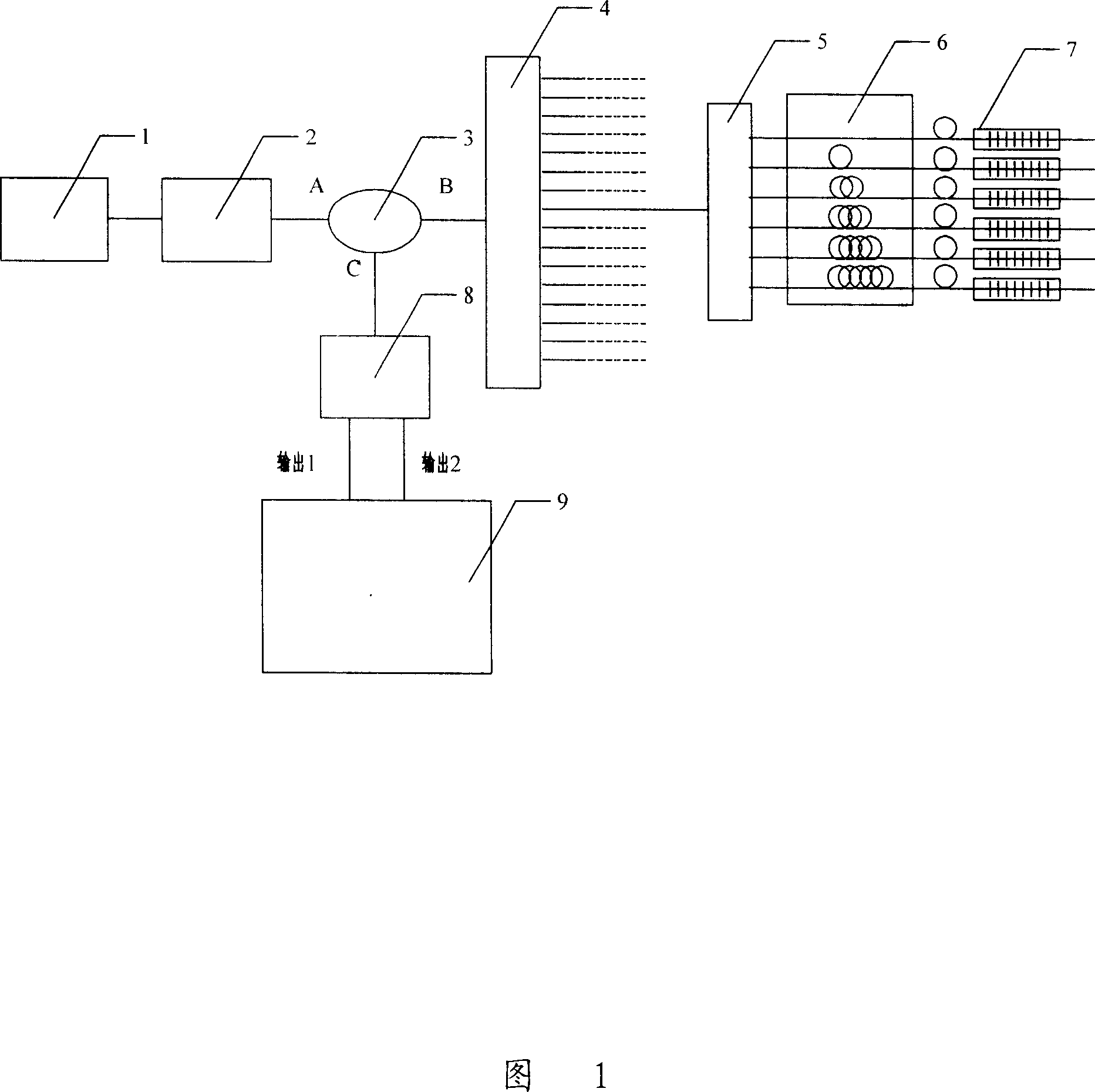
The invention relates to full parallel distributing type optical fiber grating temperature sensing method and its system. The method includes the following steps: processing high speed modulation for the wide band light source to form pulse sequence with certain width and duty ratio; adopting parallel connection for the sensor each of which is corresponding with different time delay optical fiber; making the pulse light source signal enter into the sensor array by splitter; making each reflected light signal of the sensor enter into photo-electricity detecting unit by one and the same fiber coupler or optical circulator; receiving a series of pulsing signals in one light source modulating cycle each of which is corresponding with one sensor; gaining light signal center wavelength information by a special filter; detecting each of them to gain corresponding sensor temperature information.
Owner:福建迅捷光电科技有限公司
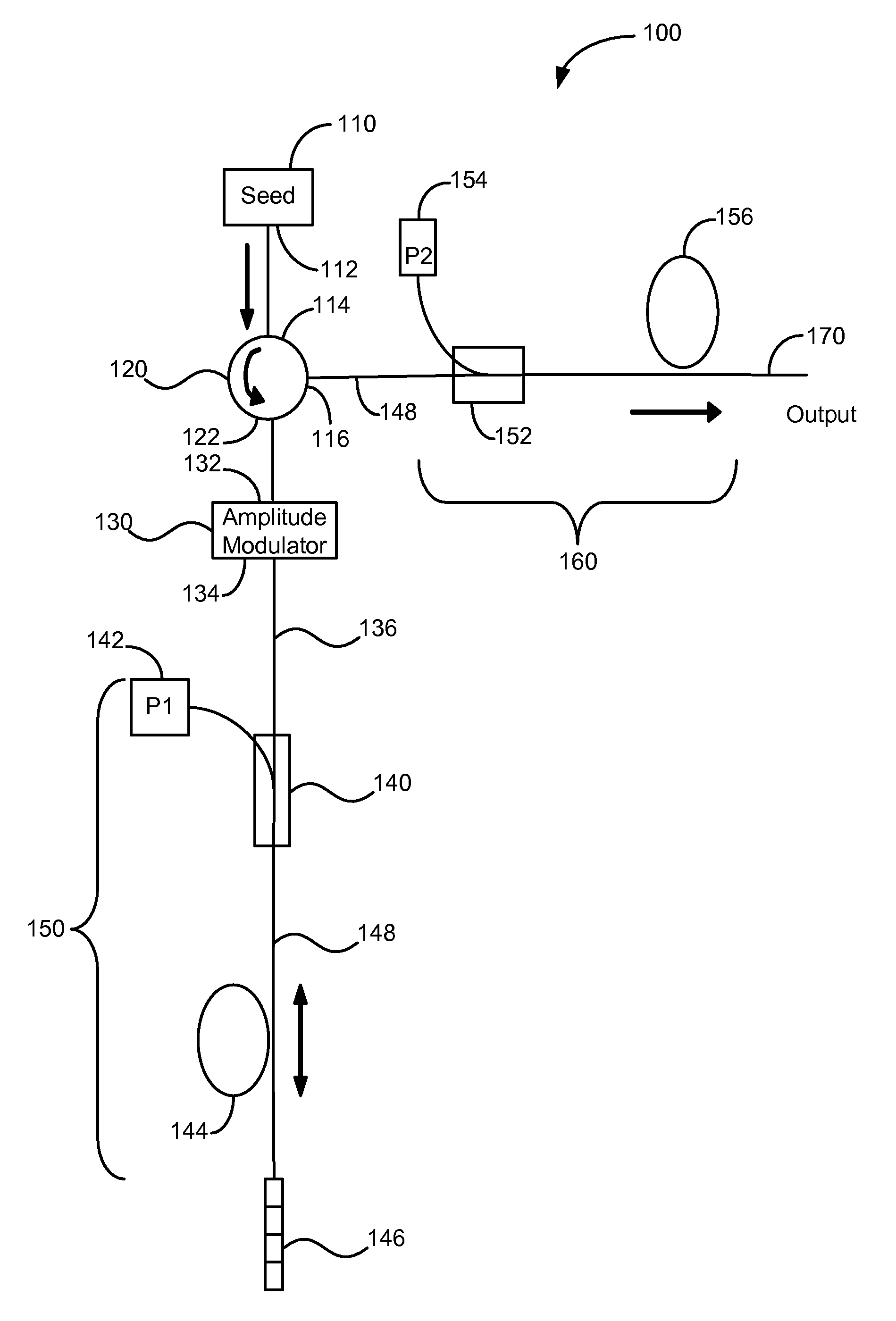
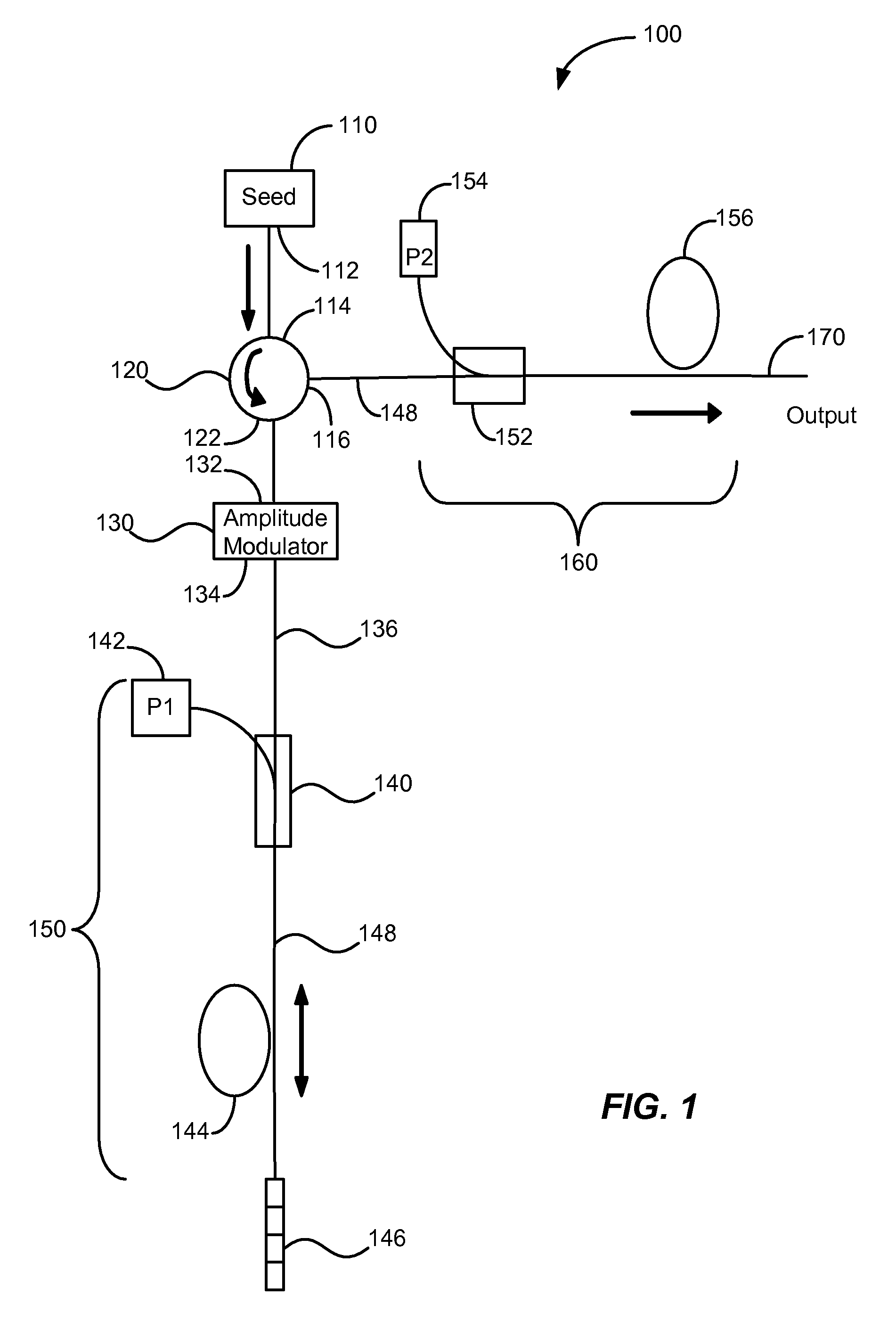
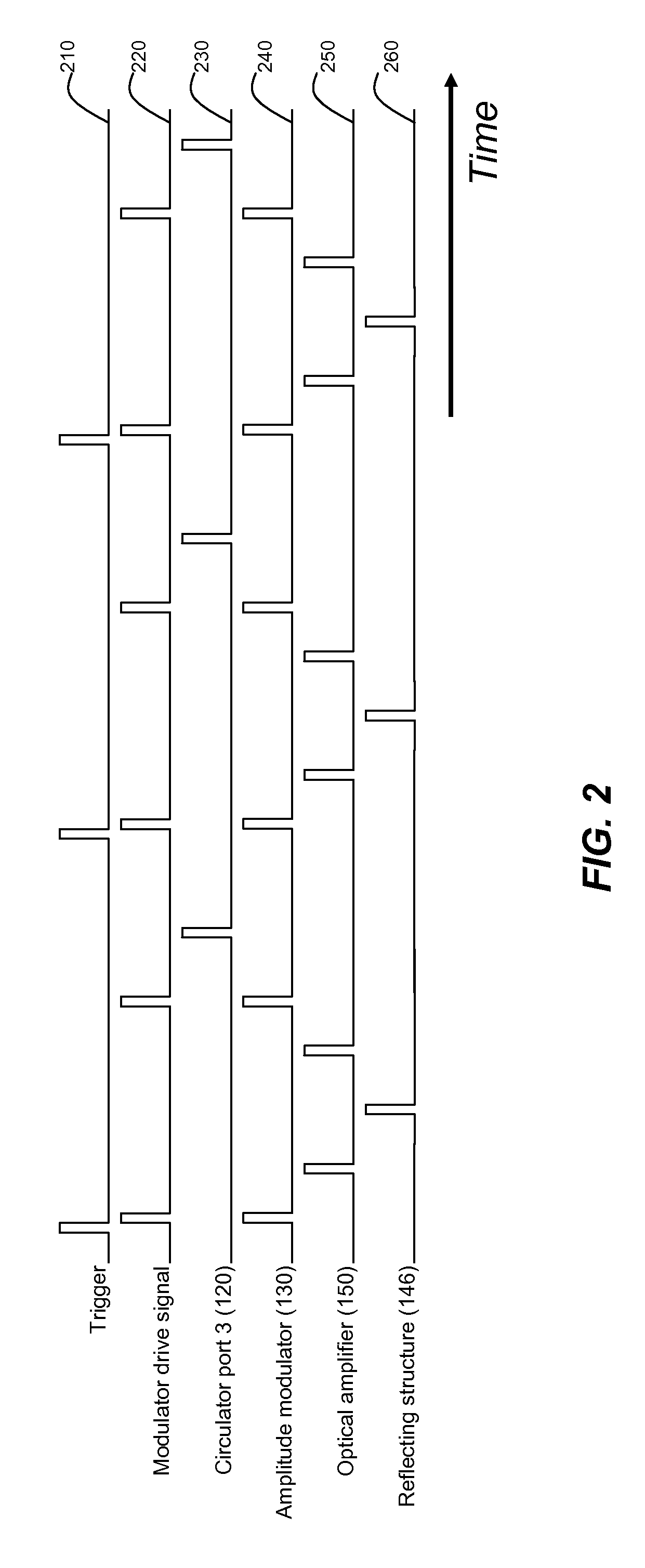
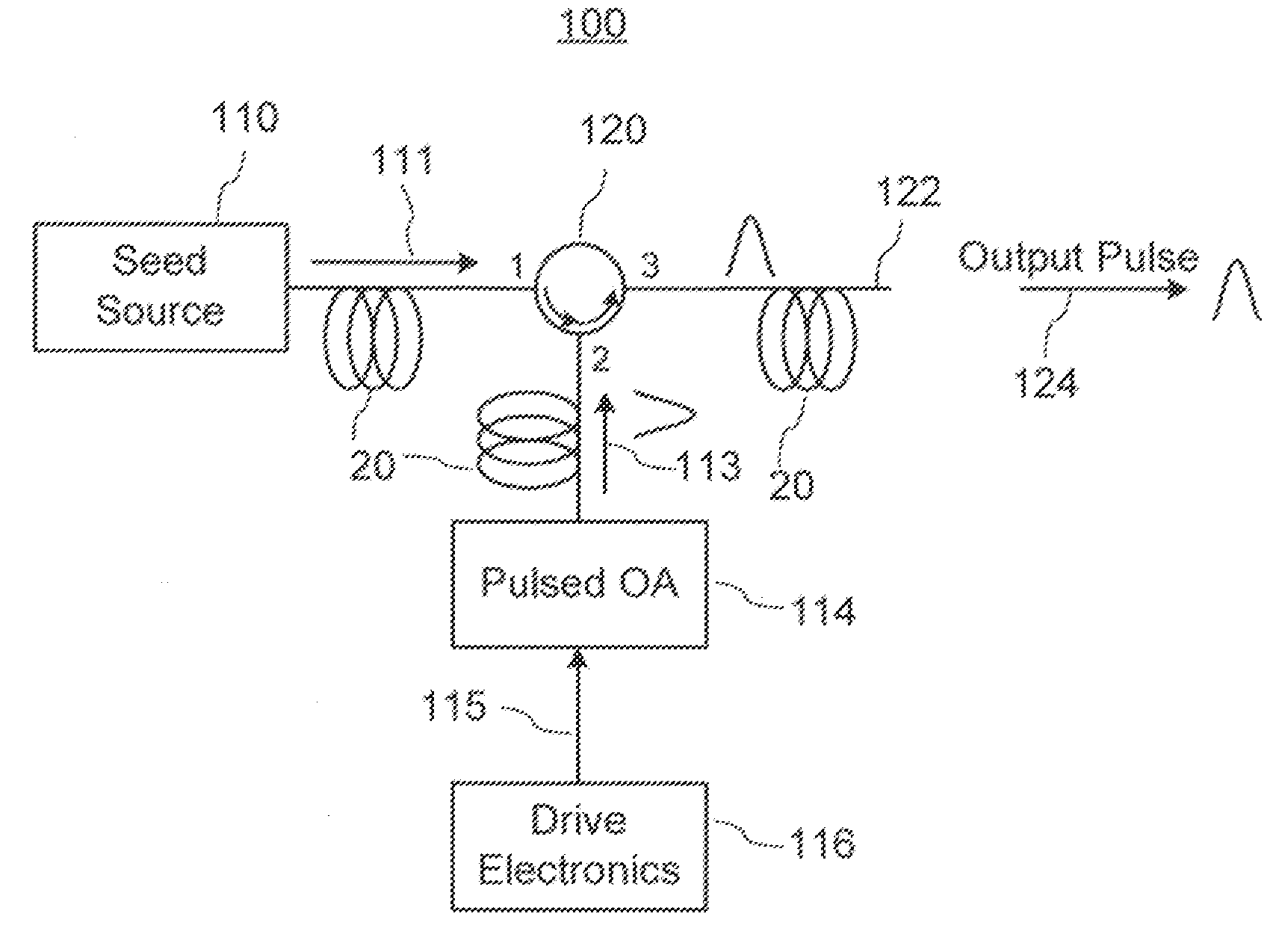
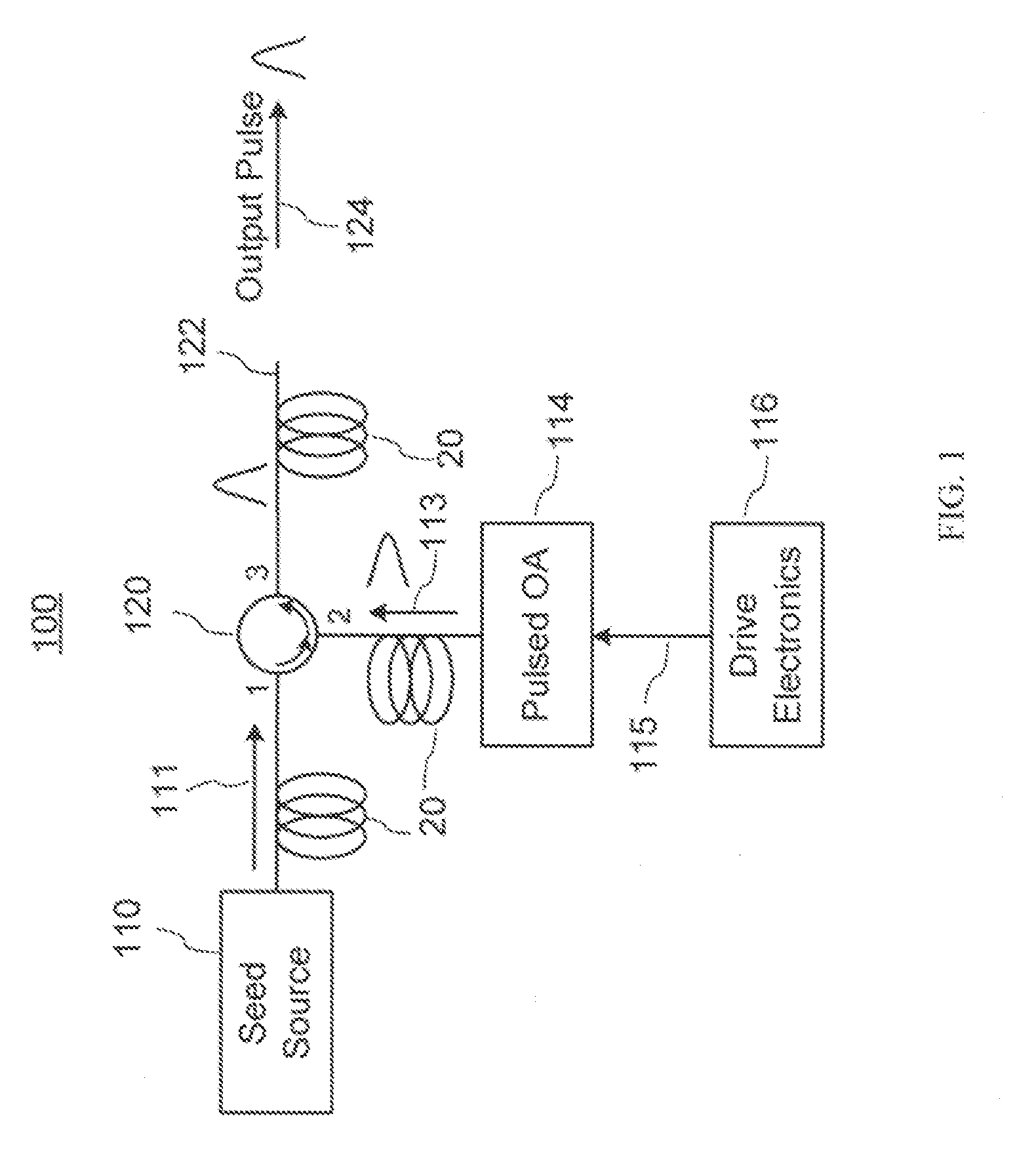
Enhanced seeded pulsed fiber laser source
A pulsed laser light source for producing amplified light pulses is provided. It includes a three-port optical circulator connected to a first, second, and third waveguide branch, a seed module for generating a pulsed light and propagating the light along the first waveguide branch to the first port of the optical circulator and out the second port to the second waveguide branch, a reflector in the second waveguide branch for reflecting the light back through the second port of the optical circulator for circulation out the third port to the third waveguide branch, and a light output provided in the third waveguide branch for outputting the amplified light pulses. An amplifier is disposed in the second waveguide branch between the optical circulator and the reflector for amplifying the light and an optical modulator operable for modulating the pulsed light is disposed in the third waveguide branch.
Owner:INSTITUT NATIONAL D'OPTIQUE
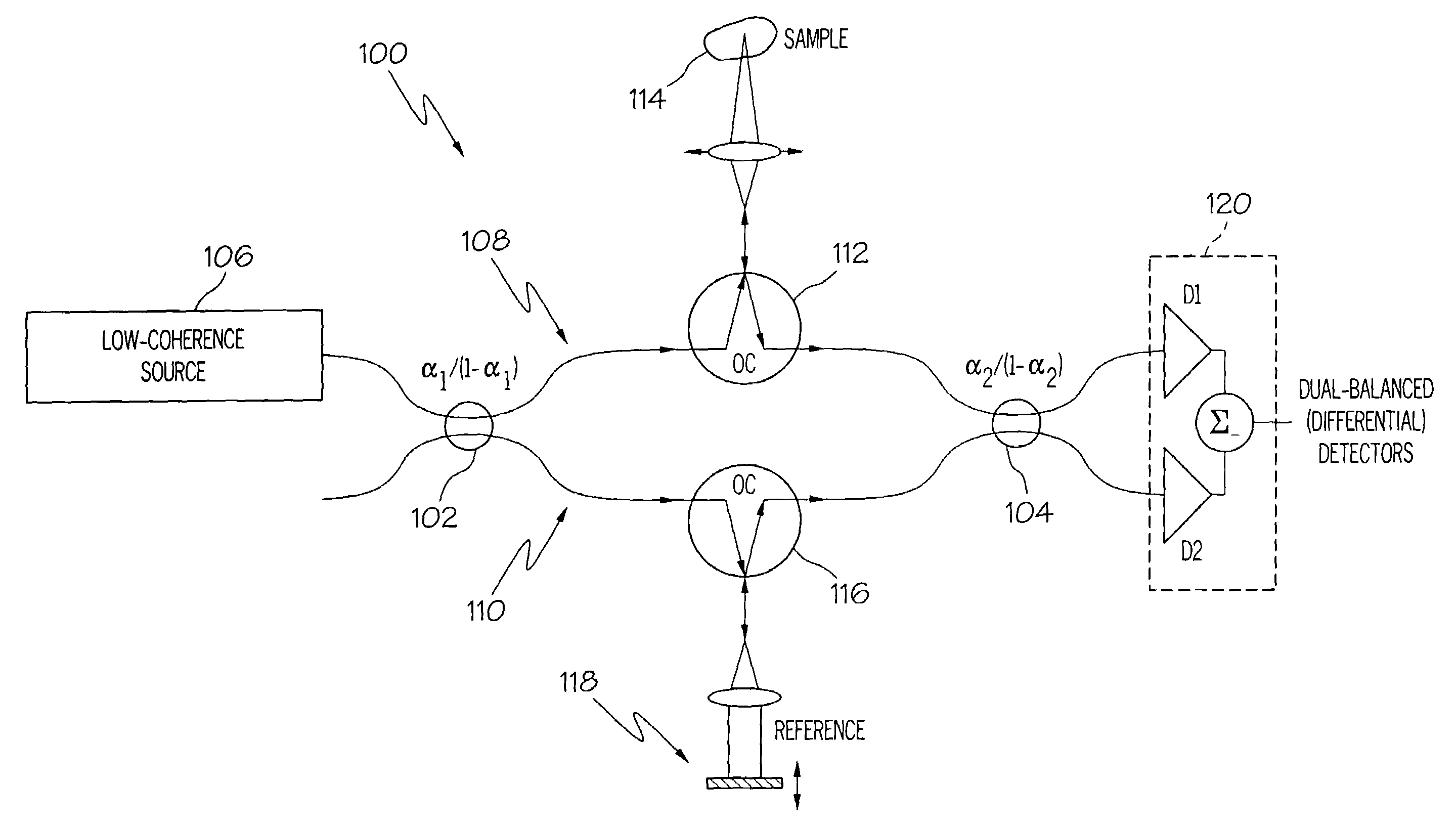
Interferometers for optical coherence tomography and reflectometry
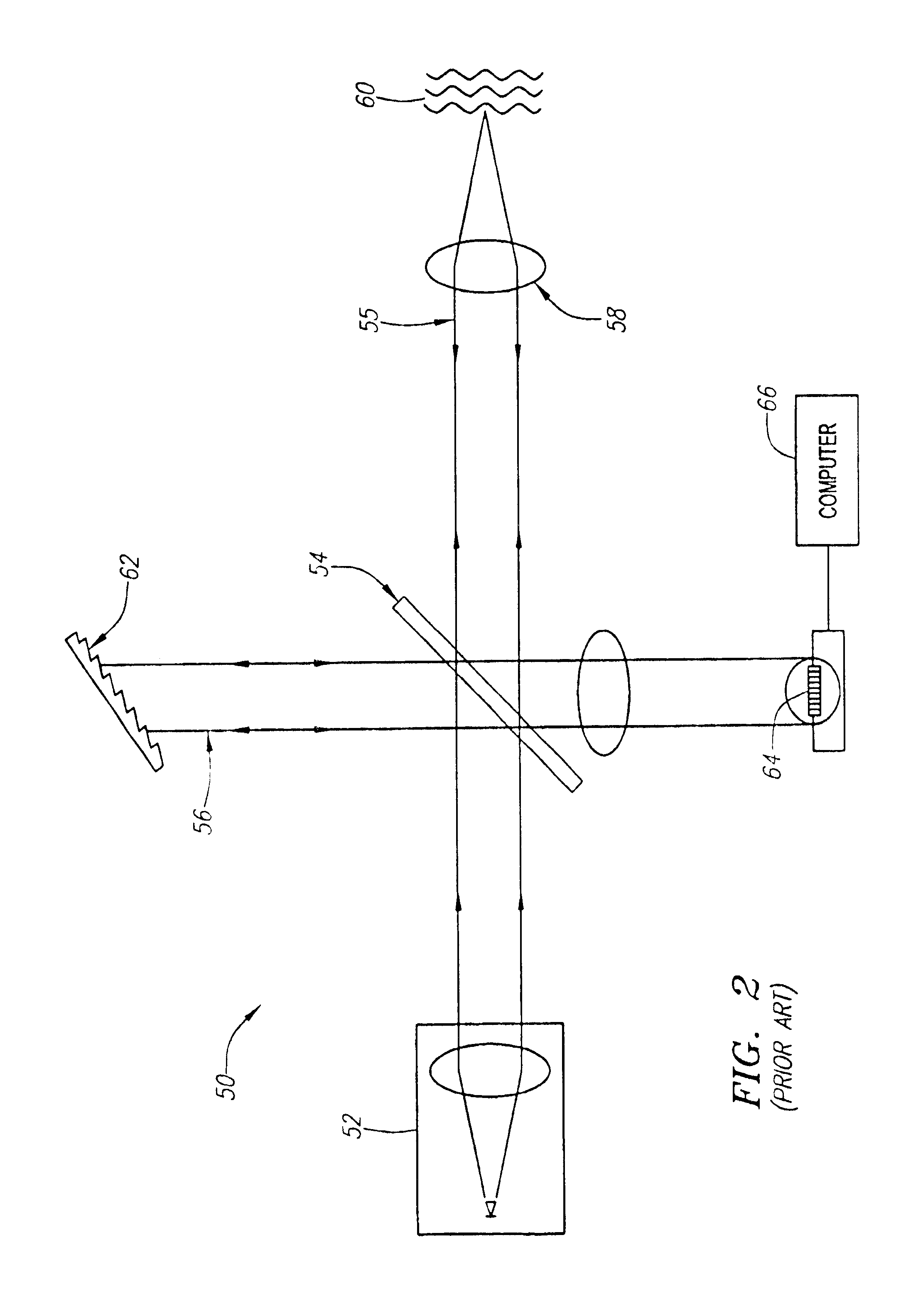
An interferometer system includes an optical radiation source, an optical circulator connected between the optical radiation source and a sample location for transmitting optical radiation from the optical radiation source to the sample location, an output of the optical circulator connected to direct optical radiation to an optical detector. Various embodiments of such a system are possible. A method of performing OCDR or OCT imaging of a sample which involves the steps of: (a) producing low coherence optical radiation; (b) directing at least some of the low coherence optical radiation through an optical circulator to the sample; (c) reflecting at least some of the low coherence optical radiation off of the sample; and (d) detecting at least some of the reflected low coherence optical radiation and producing an electrical signal corresponding thereto.
Owner:SC JOHNSON & SON INC +2
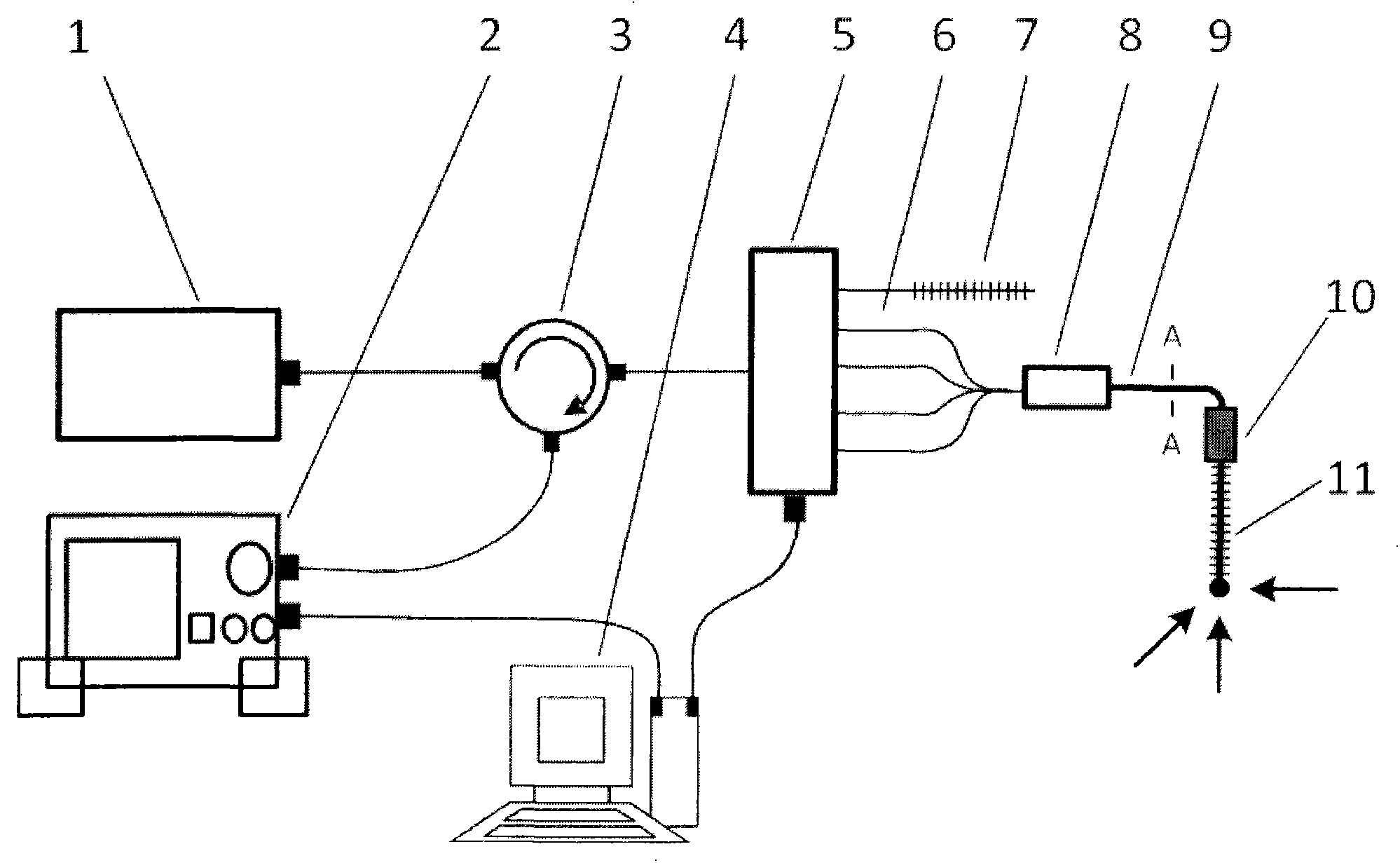
Optical fiber extrinsic Fabry-Perot interference ultrasonic sensing and detection device
InactiveCN101762318AImprove stabilityEasy to packTesting dielectric strengthSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementVibrating membraneUltrasound - action
The invention discloses an optical fiber extrinsic Fabry-Perot interference ultrasonic sensing and detection device, comprising a 1550nm light source, a 1550nm optical circulator, an optical fiber Fabry-Perot ultrasonic sensor, a photoelectric transition module, a signal amplification module, an oscillograph, a piezoelectric transducer and a signal generator. The basic structure of the optical fiber Fabry-Perot ultrasonic sensor is composed of a single mode optical fiber, a quartz vibrating membrane, an outer ceramic bushing, an inner ceramic bushing and a metal base. The light emitted by the 1550nm light source reaches the optical fiber Fabry-Perot ultrasonic sensor through the optical circulator, when ultrasonic wave acts on the ultrasonic sensor, as the light reflected by the optical fiber Fabry-Perot ultrasonic sensor is modulated by the ultrasonic signal, the reflected light reaches the photoelectric conversion module by the circulator and then is converted into an electric signal, and the ultrasonic signal can be observed by the oscillograph after amplification. The invention has simple structure, easy manufacture, low cost and high sensitivity, strong practicability, easy encapsulation and is convenient for mass production, and can be applied to related fields of industrial detection, power system safety and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Method and system for a pulsed laser source emitting shaped optical waveforms
InactiveUS7428253B2Wide applicabilityReduction in gain saturation impactLaser using scattering effectsOptical resonator shape and constructionAudio power amplifierSeeds source
A tunable pulsed laser source includes a seed source adapted to generate a seed signal and an optical circulator having a first port coupled to the seed source, a second port, and a third port. The tunable pulsed laser source also includes a modulator driver adapted to produce a shaped electrical waveform and an amplitude modulator coupled to the modulator driver and adapted to receive the shaped electrical waveform. The amplitude modulator is characterized by a first side coupled to the second port of the optical circulator and a second side. The tunable pulsed laser source further includes a first optical amplifier characterized by an input end and a reflective end. The input end is coupled to the second side of the amplitude modulator. Moreover, the tunable pulsed laser source includes a second optical amplifier coupled to the third port of the optical circulator.
Owner:ELECTRO SCI IND INC
Chaotic optical time domain reflectometer method and apparatus
ActiveUS20100290035A1Avoid disadvantagesHigh resolutionAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDigital computer detailsFiberFiber coupler
In a method and a corresponding apparatus for performing chaotic optical time domain reflectometer, the chaotic laser signal, generated by the chaotic laser transmitter, is split into probe signal I and reference signal II by a fiber coupler. Through an optical circulator, the probe signal I is launched into the test fiber and the echo light is converted into electrical signal by a photodetector and digitalized by an A / D converter. The reference signal II is converted into electrical signal by a photodetector and digitalized by another A / D converter. Two digital signals received from two A / D converters are correlated in a signal processing device to locate the exact position of faults in fibers. The result output is then displayed on a display device. This invention was developed to overcome the tradeoff between resolution and dynamic range of the pulse-based OTDR. This method can improve the dynamic range and spatial resolution significantly; enhance the anti-jamming capability and noise tolerance. Also it has merits of simple structure and lower cost.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
BOTDA (Brillouin Optical Time-Domain Analysis) system based on pulse coding and coherent detection
InactiveCN103245370AImprove signal-to-noise ratioImprove adaptabilityConverting sensor output opticallyContinuous lightDigital signal processing
A BOTDA system based on pulse coding and coherent detection comprises a narrow linewidth laser device (10), a first polarization-maintaining coupler (11), a second polarization-maintaining coupler (12), a microwave signal source (17), testing optical fibers (18), an optical circulator (19), a 3dB coupler (20), a balance photoelectric detector (21), a scrambler (16), a spectrum analyzer (22) and a digital signal processing unit (23), wherein continuous light emitted by the arrow linewidth laser device (10) is divided into two channels of continuous light, namely, a first channel of the continuous light and a second channel of the continuous light, through the first polarization-maintaining coupler (11); and the system further comprises a frequency shifter (9), a first electrooptical modulator (13), a pulse signal source (14) and a second electrooptical modulator (15). The system adopts a pulse coding technology and a coherent detection method, so that the signal to noise ratio of the BOTDA and the measurement accuracy can be improved, the sensing distance is increased, and the system has the function of breakpoint detection.
Owner:NANJING UNIV +1
Distributed optical fiber vibration sensor
InactiveCN102168808AImprove accuracyStable interference outputPipeline systemsPhotodetectorMach–Zehnder interferometer
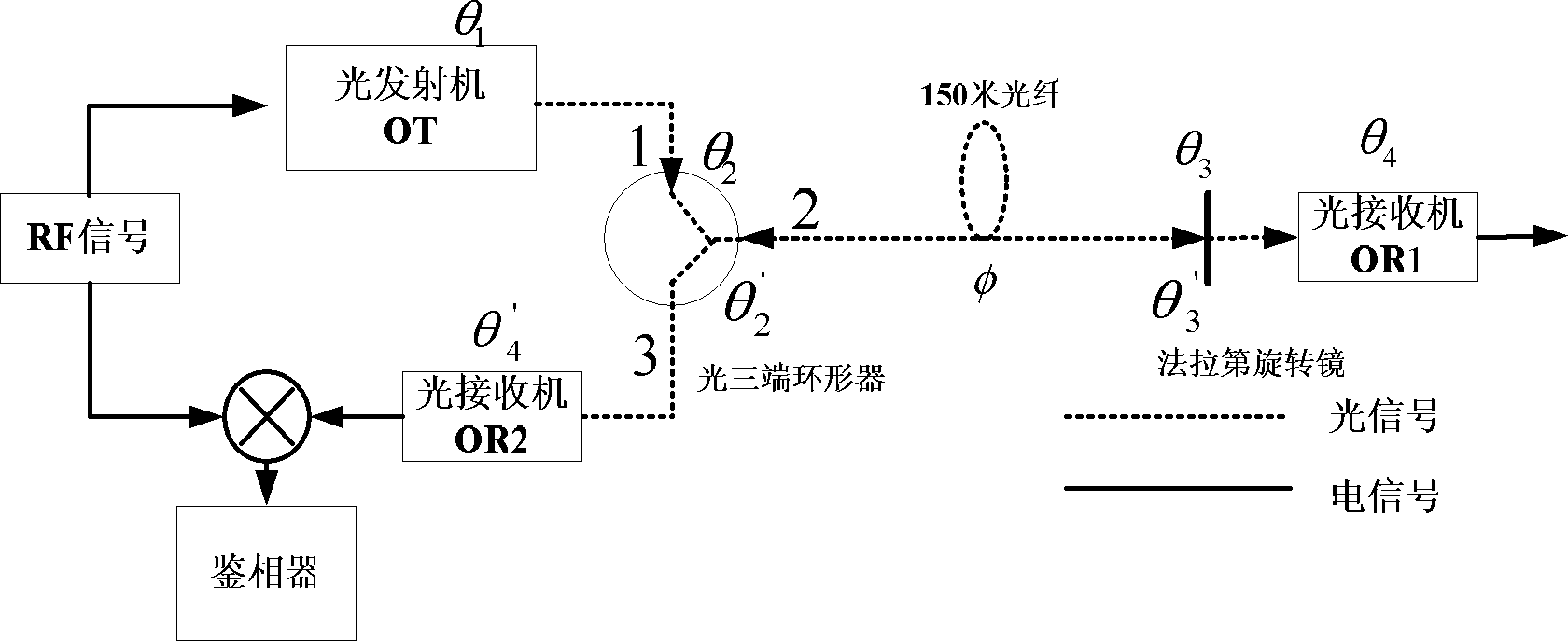
The invention discloses a distributed optical fiber vibration sensor. The distributed optical fiber vibration sensor is characterized in that: on the basis of the optimized combination of the interference principles of a Sagnac interferometer and a Mach-Zehnder interferometer, the distributed optical fiber vibration sensor comprises a signal processing device, a first sensing optical fiber, a second sensing optical fiber, a third sensing optical fiber, a wideband light source, a narrowband light source, an optical circulator, a first optical wavelength division multiplexer, a second optical wavelength division multiplexer, a first coupler, a second coupler, a third coupler, a fourth coupler, a Faraday rotating mirror, a first photodetector, a second photodetector, a third photodetector and an optoisolator. The distributed optical fiber vibration sensor has a simple structure and can be used for monitoring outside disturbance and positioning multi-point interferences in real time; the demodulation work is relative simple and polarization maintaining optical fibers can be prevented from being used; and by adopting the Faraday rotating mirror, the phenomenon of polarization state fading due to double refraction can be also compensated.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Three-dimensional microscale measuring device and method based on four-core fiber grating
The invention provides a three-dimensional microscale measuring device and method based on a four-core fiber grating, and belongs to the technical field of precision instrument manufacturing and measurement. The device comprises a broadband light source, an optical spectrum analyzer, an optical circulator, a control computer, a multi-way optical switch and an external reference grating. The multi-way optical switch is communicated with a four-core fiber fan-out device through four single mode fibers. One end of a four-core fiber is connected to the four-core fiber fan-out device. A four-core fiber grating probe is fixedly installed at the other end of the four-core fiber through a probe clamp holder. The four-core fiber and the four-core fiber grating probe are connected to form a closed circuit. According to the method, the multi-way optical switch is controlled by the control computer to switch optical paths, the optical spectrum analyzer is used for measuring reflectance spectra of the fiber gratings, and three-dimensional microscale measuring without temperature coupling is realized by utilizing a differential data processing algorithm. The three-dimensional microscale measuring device and method based on the four-core fiber grating have the advantages that accuracy is high, contact force is small, the device and method are not affected by the masking effect, and the service life of the probe is long.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Wavelength selective switch
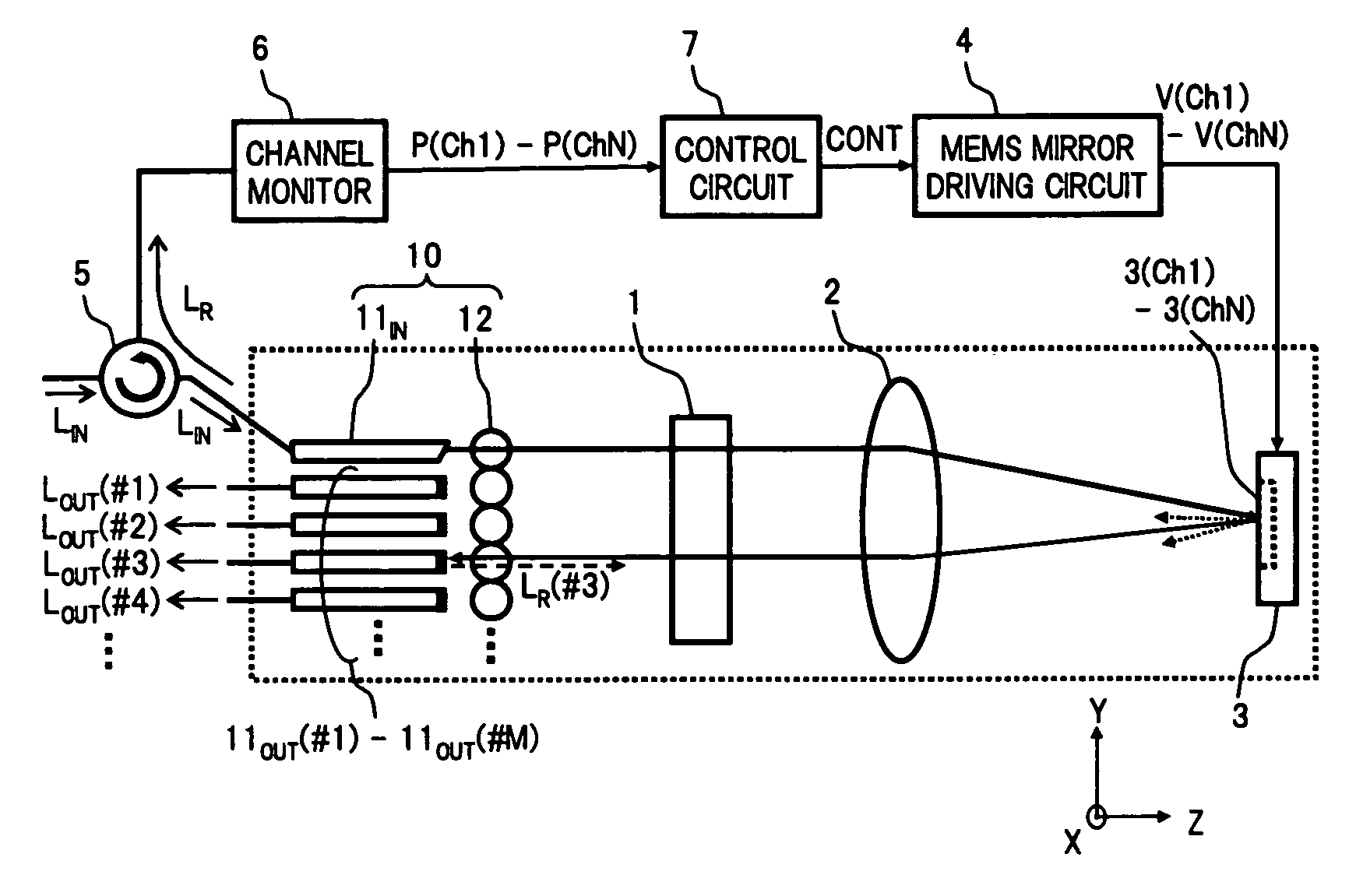
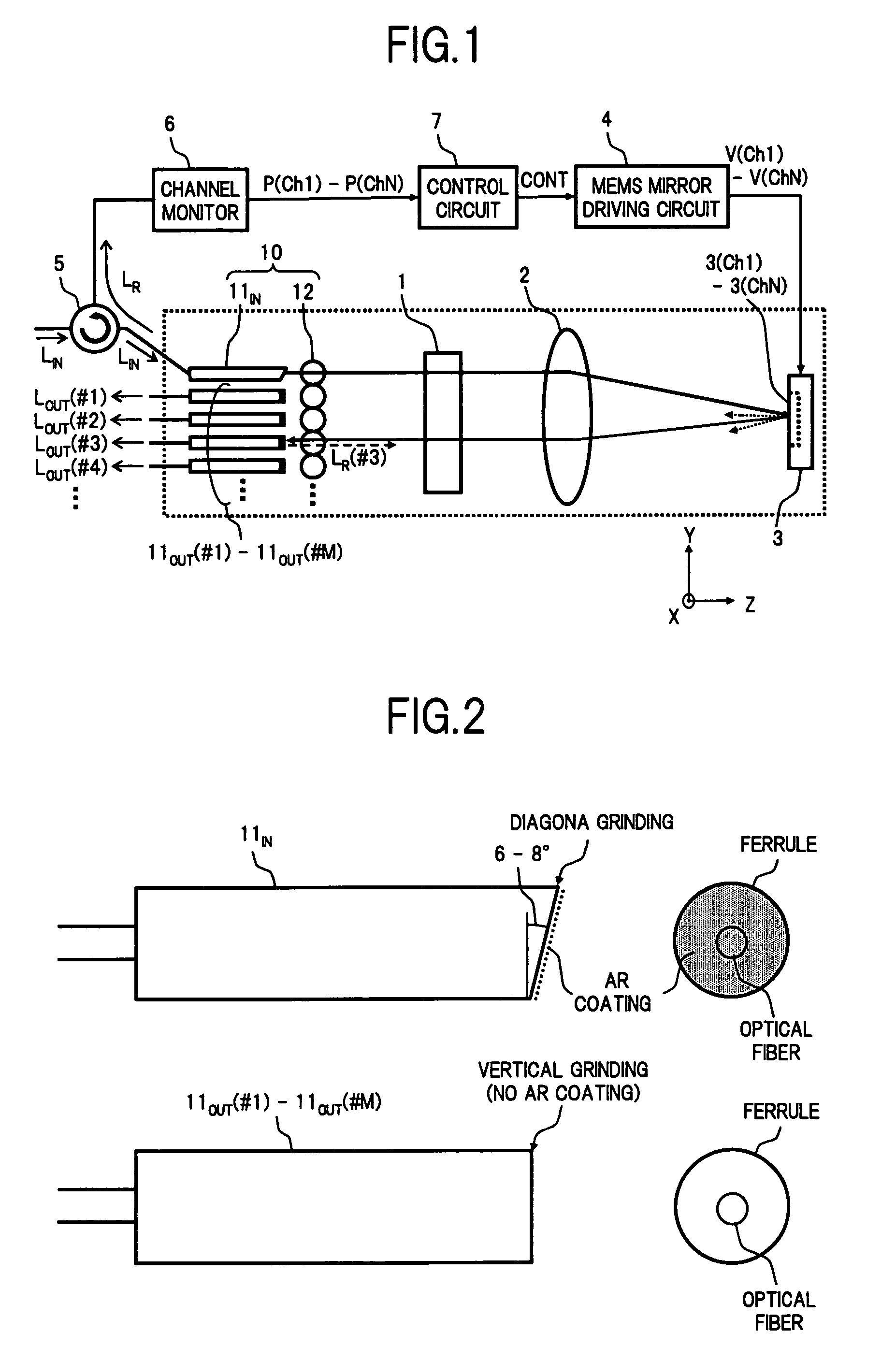
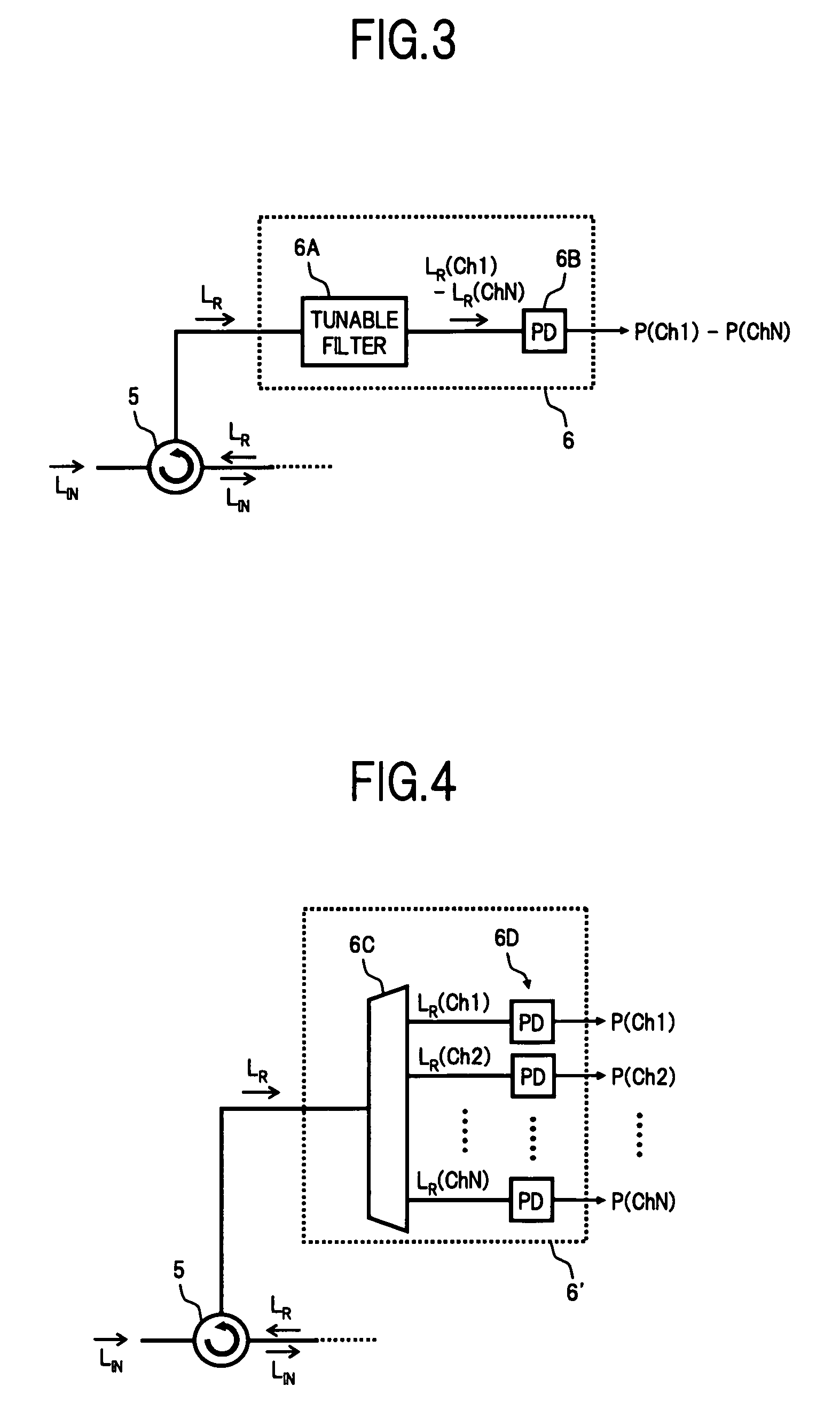
InactiveUS20060198583A1Improve accuracyEasy constructionMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsFiberOptical circulator
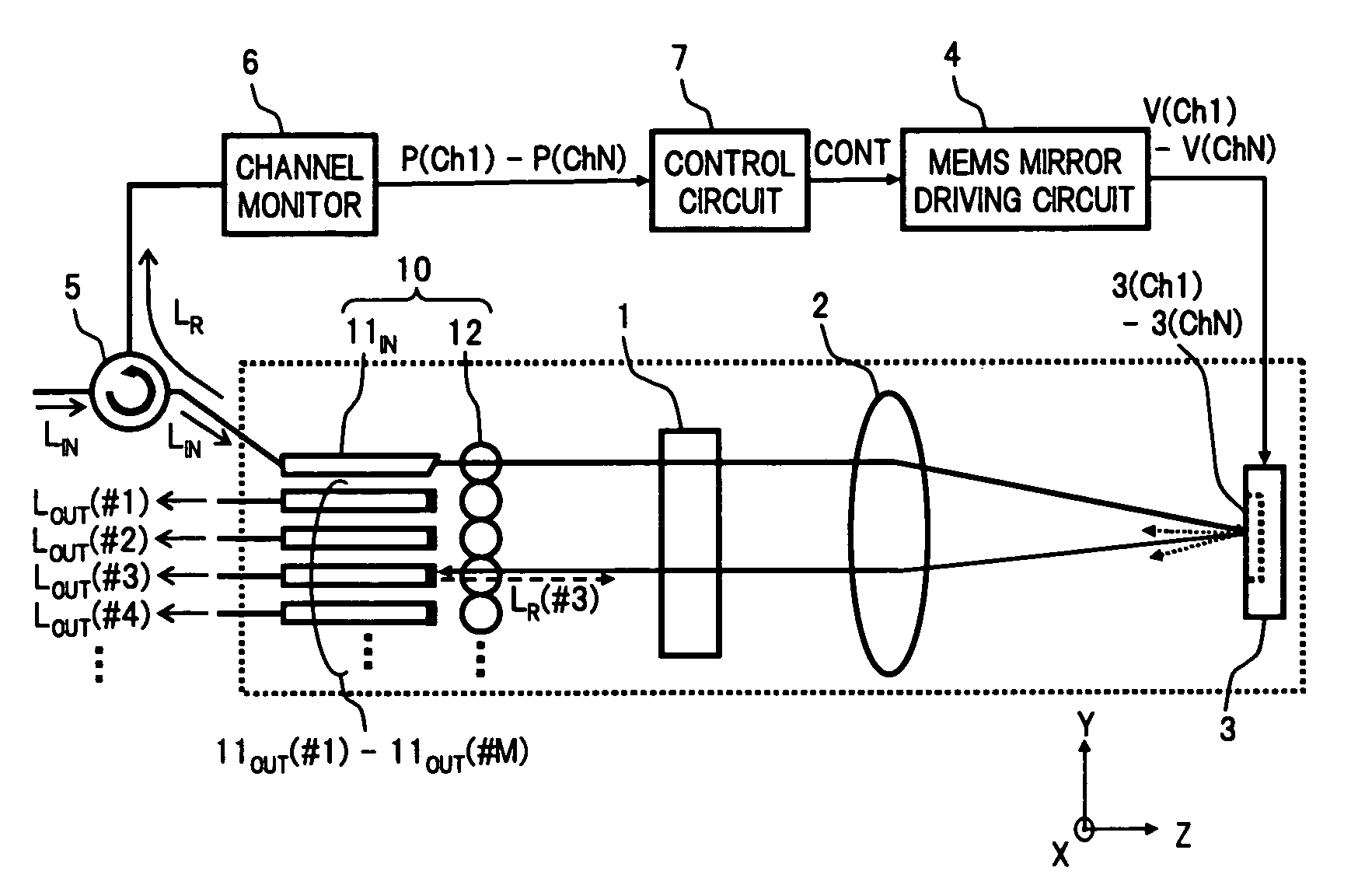
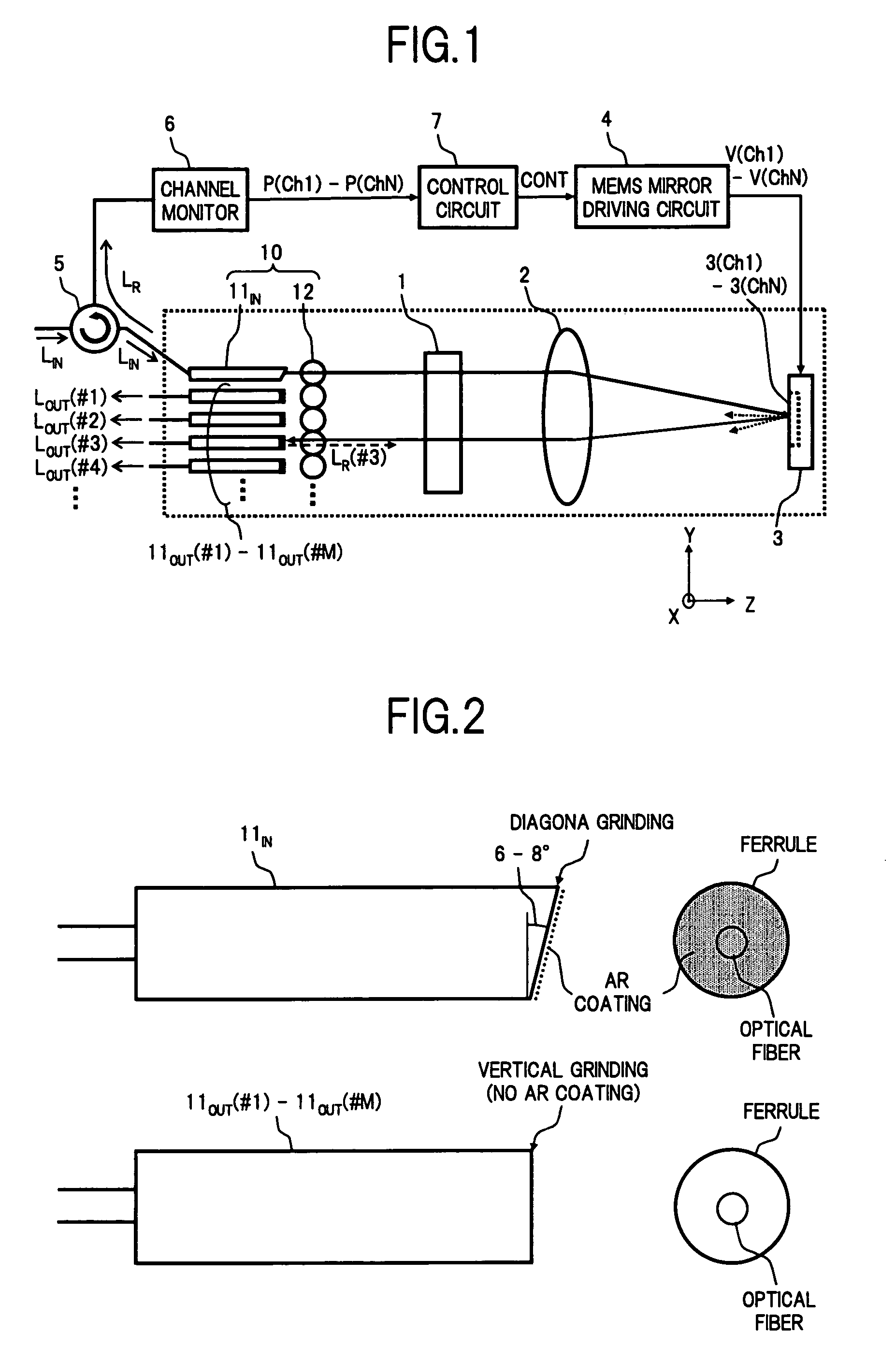
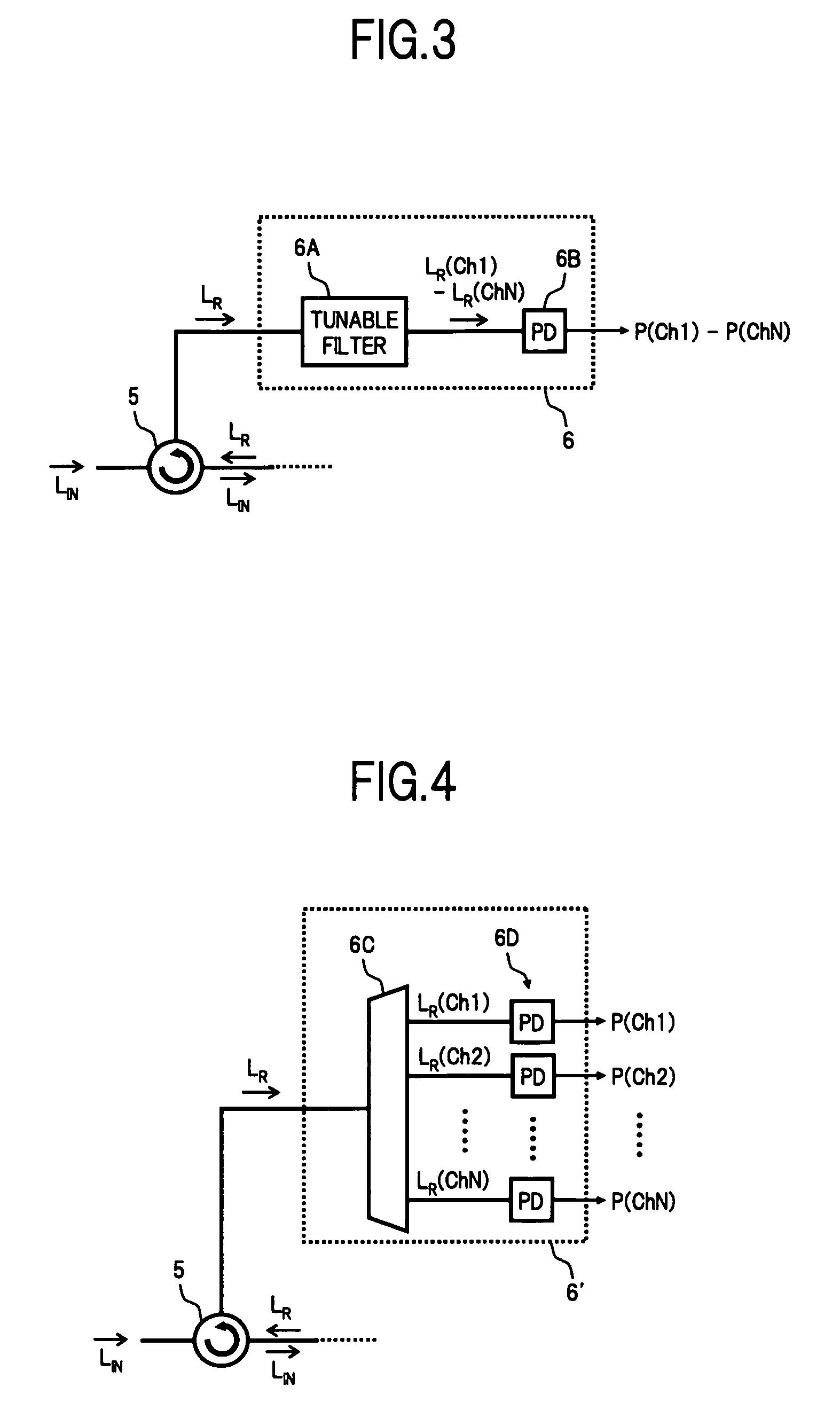
A wavelength selective switch of the invention, separates WDM light coming out from an input fiber of a fiber collimator array according to its wavelength, in a diffraction grating, and reflects each wavelength channel proceeding in different directions by MEMS mirrors corresponding to a mirror array. In the MEMS mirrors, the angles of their reflecting surfaces are set corresponding to the location of the output port which is set in the output address of the wavelength channel to be injected. For each of the wavelength channels that reach the target output port, one part of each is reflected by the end face of an output fiber, and the reflected light is returned to the input port, and sent to a channel monitor via an optical circulator, so that the optical power corresponding to each wavelength channel is monitored. As a result it is possible to provide a small size, and low-cost, wavelength selective switch, that can monitor the power of each wavelength channel guided to a plurality of output ports, with good accuracy.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Distributed optical fiber sensing system based on phase generated carrier technology
ActiveCN103759750ARealize dynamic measurementEliminate phase destructive fading problemsSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementUsing wave/particle radiation meansFiberGrating
A distributed optical fiber sensing system based on the phase generated carrier technology comprises a narrow-linewidth laser device, a modulator, an optoisolator, an erbium-doped optical fiber amplifier, an optical circulator, a fiber grating, a sensing fiber, a Michelson interferometer, a carrier circuit, a photoelectric detector, a data acquisition card, a signal processor and a pulse generator. The input end of the modulator is connected with the output end of the narrow-linewidth laser device. The input end of the optoisolator is connected with the output end of the modulator. The input end of the erbium-doped optical fiber amplifier is connected with the output end of the optoisolator. A port a of the optical circulator is connected with the output end of the erbium-doped optical fiber amplifier. The fiber grating is connected with a port b of the optical circulator. The output end of the carrier circuit is connected with an electrical interface of the Michelson interferometer. The input end of the photoelectric detector is connected with the output end of the Michelson interferometer. One input end of the data acquisition card is connected with the output end of the photoelectric detector, and the other input end of the data acquisition card is connected with the output end of the carrier circuit. The input end of the signal processor is connected with the output end of the data acquisition card. The input end of the pulse generator is connected with the trigger input end of the data acquisition card, and the output end of the pulse generator is connected with an electrical interface of the modulator.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Low-repetition-rate ring-cavity passively mode-locked fiber laser
InactiveUS20090003391A1Laser using scattering effectsOptical resonator shape and constructionMode locked fiber laserFiber disk laser
A ring-cavity, passively mode locked fiber laser capable of producing short-pulse-width optical pulses at a relatively low repetition rate. The fiber laser uses a one-way ring-cavity geometry with a chirped fiber Bragg grating (CFBG) at its reflecting member. The CFBG is part of a dispersion compensator that includes an optical circulator that defines a one-way optical path through the ring cavity. A doped optical fiber section is arranged in the optical path and serves as the gain medium. A pump light source provides the pump light to excite the dopants and cause the gain medium to lase. A saturable absorber is operable to effectuate passive mode-locking of the multiple modes supported by the ring cavity. The ring cavity geometry allows to achieve mode locking with single pulse operation in a longer cavity length than conventional linear cavities. Furthermore, the longer cavity length reduces the constraints on the chirp rate of the CFBG. This, in turn, allows the CFBG to have a relatively high reflectivity, which provides the necessary dispersion compensation and cavity loss for generating short optical pulses at a low repetition rate.
Owner:CORNING INC
Wavelength selective switch
InactiveUS7440648B2Small sizeImprove accuracyMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsFiberWavelength selective switching
A wavelength selective switch of the invention separates WDM light coming out from an input fiber of a fiber collimator array according to its wavelength, in a diffraction grating, and reflects each wavelength channel proceeding in different directions by MEMS mirrors corresponding to a mirror array. In the MEMS mirrors, the angles of their reflecting surfaces are set corresponding to the location of the output port which is set in the output address of the wavelength channel to be injected. For each of the wavelength channels that reach the target output port, one part of each is reflected by the end face of an output fiber, and the reflected light is returned to the input port, and sent to a channel monitor via an optical circulator, so that the optical power corresponding to each wavelength channel is monitored. As a result it is possible to provide a small size, and low-cost, wavelength selective switch, that can monitor the power of each wavelength channel guided to a plurality of output ports, with good accuracy.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
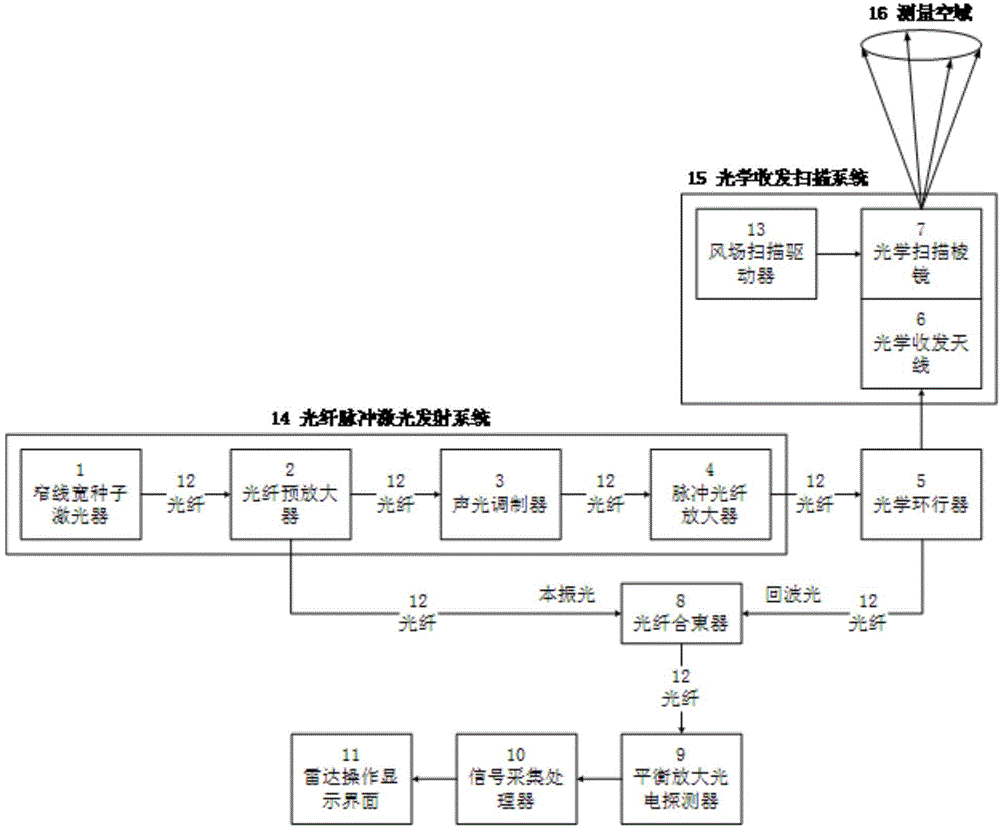
Pulse laser coherent wind measuring radar
InactiveCN103823221AImprove signal-to-noise ratioSimple structureElectromagnetic wave reradiationICT adaptationFiberOptoelectronics
The invention brings forward a pulse laser coherent wind measuring radar, for the purpose of providing a pulse laser coherent wind measuring radar which has the advantages of high measuring precision, simple structure and convenient installation and debugging. The pulse laser coherent wind measuring radar is realized through the following technical scheme: a fiber pulse laser emission system is taken as an emission source for generating two beams of laser, one beam of high repetition frequency pulse sequence laser for wind field detection is directly coupled through an optical circulator and enters an optical transmit-receive scanning system to perform collimated emission towards a target spatial domain, the optical circulator utilizes a polarization splitting characteristic to carry out isolation splitting on emission light and air aerosol scattering echo wave light, the air aerosol scattering echo wave light is selected to enter a fiber combiner, the other beam of laser, generated by the fiber pulse laser emission system, is taken as local oscillator light for inputting into a balance amplification photoelectric detector together with the echo wave light in a frequency mixing mode for optical amplification of a frequency mixing signal, through acquisition processing of a signal acquisition processor, the radial speed of each range gate in a current laser emission direction is calculated, and the radial speeds are transmitted to a radar operation display interface.
Owner:SOUTH WEST INST OF TECHN PHYSICS
Pulsed optical source
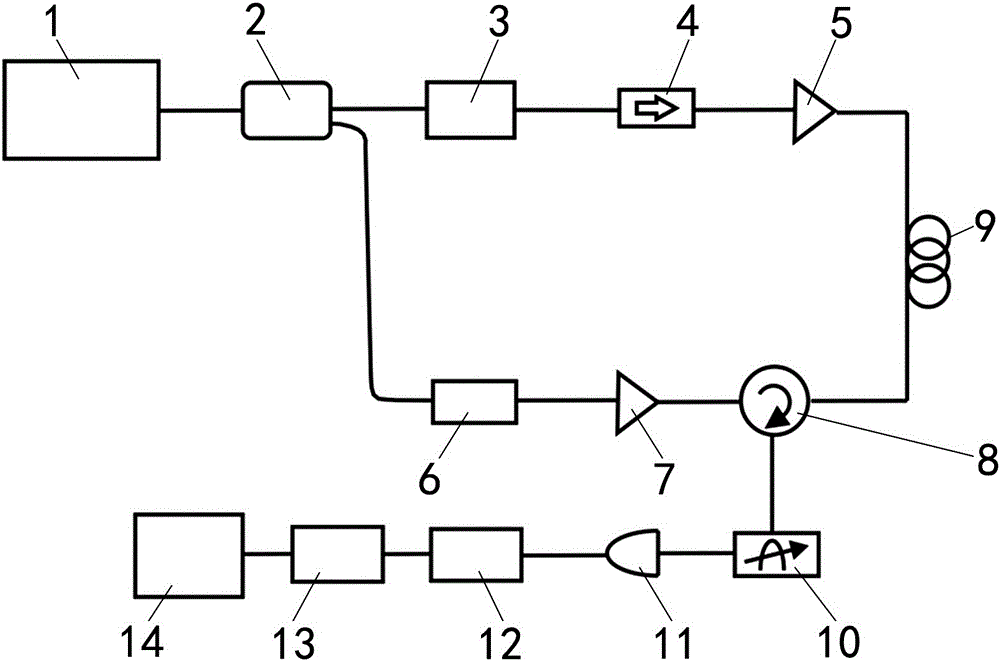
ActiveUS20110032605A1Prevent back reflectionLaser detailsSemiconductor amplifier structureOptical radiationSeeds source
The invention relates to pulsed optical sources formed of a source of seed optical radiation, a pulsed optical amplifier for pulsing the seed optical radiation, and an output optical port for outputting a pulsed optical signal produced by the pulsed optical amplifier. An optically isolating element such as an optical circulator is provided in the optical path between the optical seed source and the pulsed optical amplifier.
Owner:LUMENTUM OPERATIONS LLC
Microwave signal optical fiber stationary phase transmission system based on microwave phase shifter
ActiveCN104065416AAchieving phase-stable transmissionHigh bandwidthRadio-over-fibreMicrowave phase shifterLow-pass filter
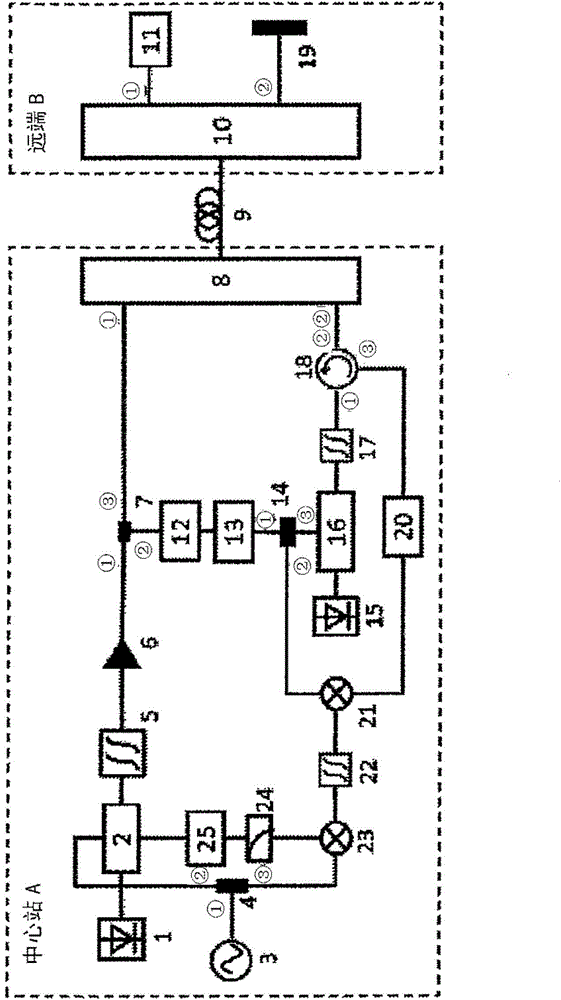
The invention discloses a microwave signal optical fiber stationary phase transmission system based on a microwave phase shifter. The system comprises a central station, a far end and a single-mode optical fiber. The central station is connected with the far end through the single-mode optical fiber. The central station is composed of a semiconductor laser device, a dual-drive Mach-Zehnder modulator, a microwave signal source, a first power divider, a first optical filter, an erbium-doped optical fiber amplifier, an optical coupler, a first array waveguide grating, a first photoelectric detector, a frequency eliminator, a second power divider, an optical source, a strength modulator, a second optical filter, an optical circulator, a second photoelectric detector, a first electric mixer, a band-pass filter, a second electric mixer, a low-pass filter and a linear voltage amplification circuit. The far end is composed of a second array waveguide grating, a third photoelectric detector and a Faraday polariscope. According to the invention, the advantage of low building and maintenance cost can be realized; and the phase jitter of microwave signals can be extracted and fed back on a real-time basis.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Chaos Brillouin optical coherence domain analysis distributed optical fiber sensing device and method
ActiveCN105136178AOvercoming resolutionOvercome the sensing distanceThermometers using physical/chemical changesUsing optical meansPhotodetectorDisplay device
The invention relates to a distributed optical fiber sensing system, and in particular relates to a chaos Brillouin optical coherence domain analysis distributed optical fiber sensing device and method. According to the invention, the problems of unavailable spatial resolution and sensing distance combination, severely limited sensing distance and low spatial resolution of the existing distributed optical fiber sensing system are solved. The chaos Brillouin optical coherence domain analysis distributed optical fiber sensing device comprises a wide spectrum chaos semiconductor laser, a 1*2 optical fiber coupler, an optical scrambler, an optical isolator, a first optical amplifier, a variable optical delay line, a second optical amplifier, an optical circulator, a sensing optical fiber, a tunable optical filter, a broadband gain photodetector, a data acquisition device, a signal processing device and a display device. The device and the method, which are provided by the invention, are applicable to the field of distributed optical fiber sensing.
Owner:太原网讯同诚科技有限公司
Distributed sensing system based on weak Bragg reflection structure
InactiveCN102102998AImprove reflectivityHigh measurement accuracyConverting sensor output opticallyControl signalDistributed Bragg reflector
The invention discloses a distributed sensing system based on a weak Bragg reflection structure. The distributed sensing system comprises a SG-DBR (Screen Grid-Distributed Bragg Reflector) tunable laser (1), an electrooptic modulator (4), an opto-isolator (5), an optical circulator (6), and weak Bragg reflection cycle structural optical fibers (7), which are connected in turn; wherein the SG-DBR tunable laser (1) is controlled by a wavelength tuning control circuit (2), the electrooptic modulator (4) is controlled by an impulse function generator (3), a photo-detector (8) is connected with the optical circulator (6), control signals outputted by the wavelength tuning control circuit (2) and the electrooptic modulator (4) and electric signals outputted by the photo-detector (8) enter a data acquisition card (9) jointly, and are processed and then transmitted to a data processing device (10). The distributed sensing system realizes the long-distance distributed sensing alarm for parameters such as temperature, stress and vibration, and has the characteristics of higher detection sensitivity and positioning precision, easiness for realization, lower cost and reliability for operation.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
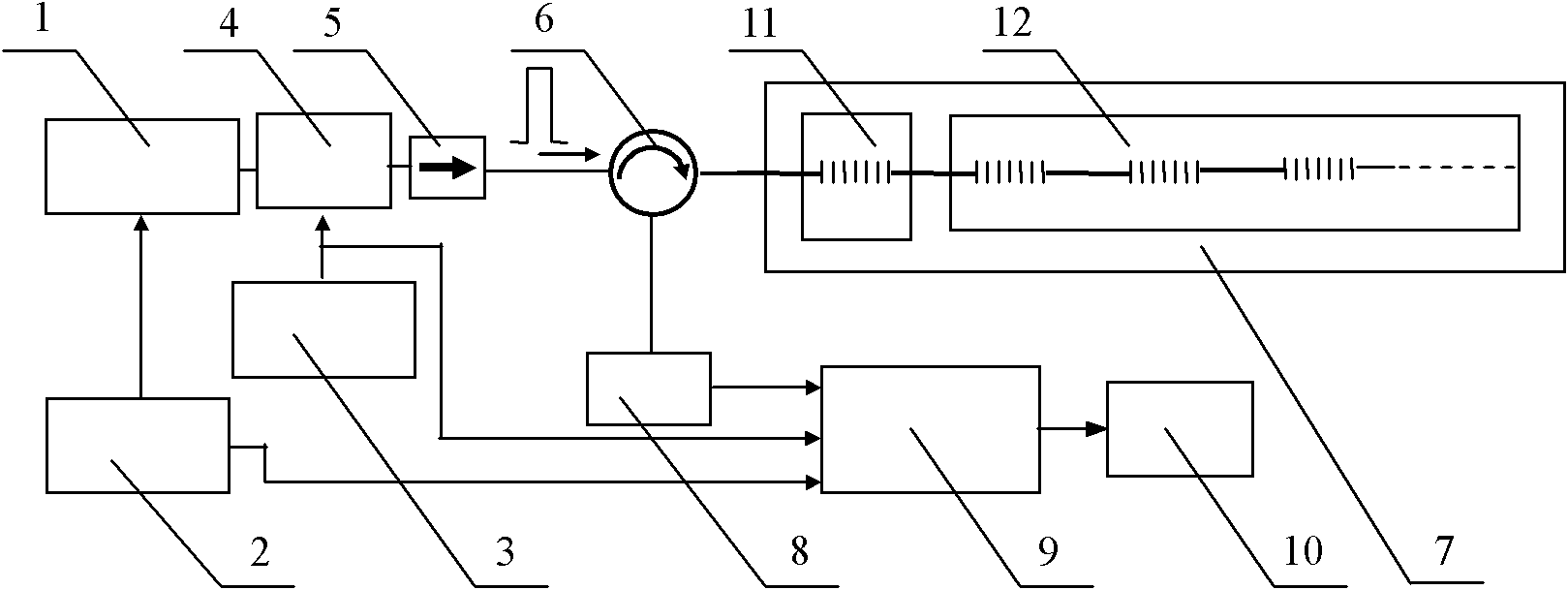
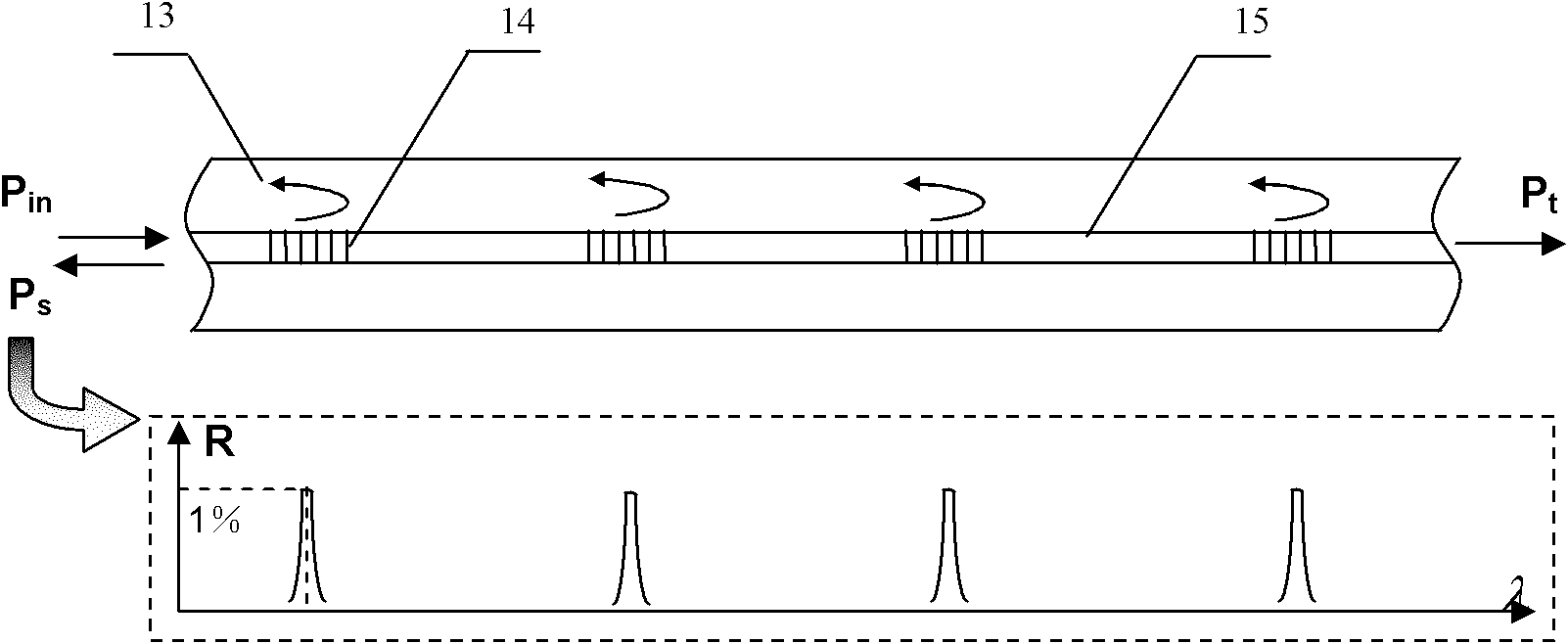
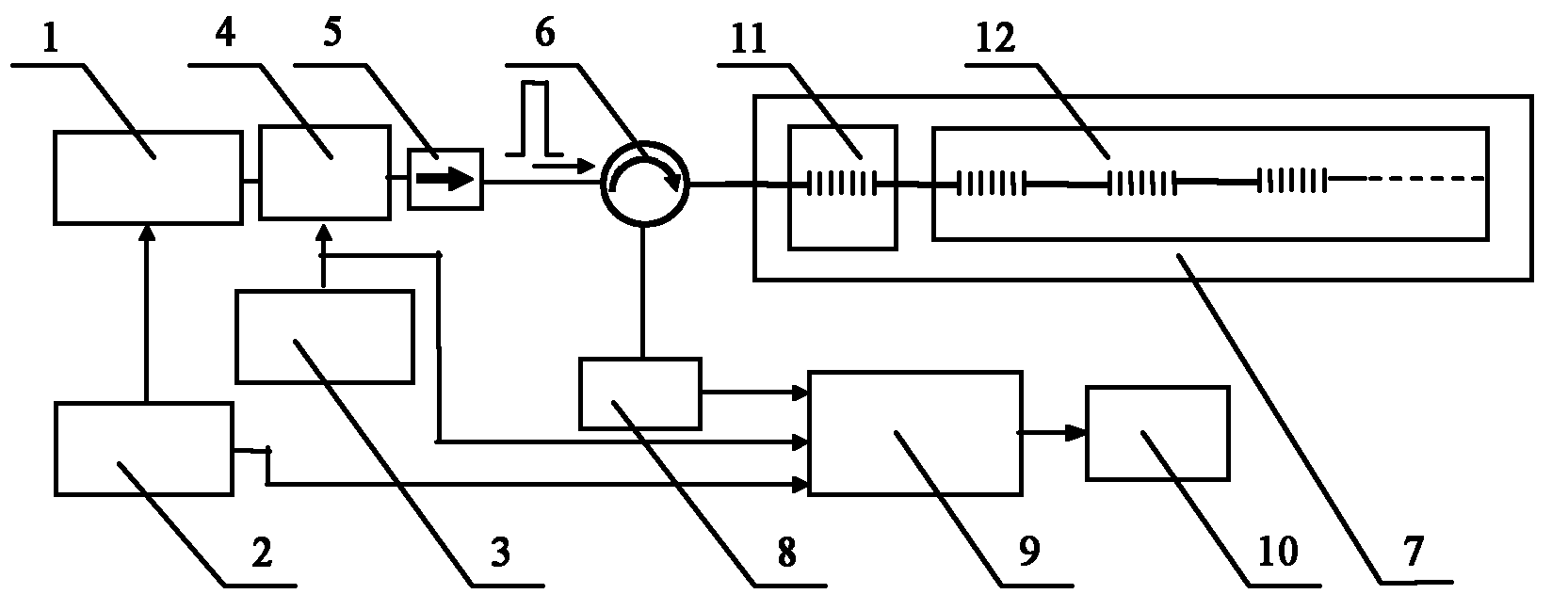
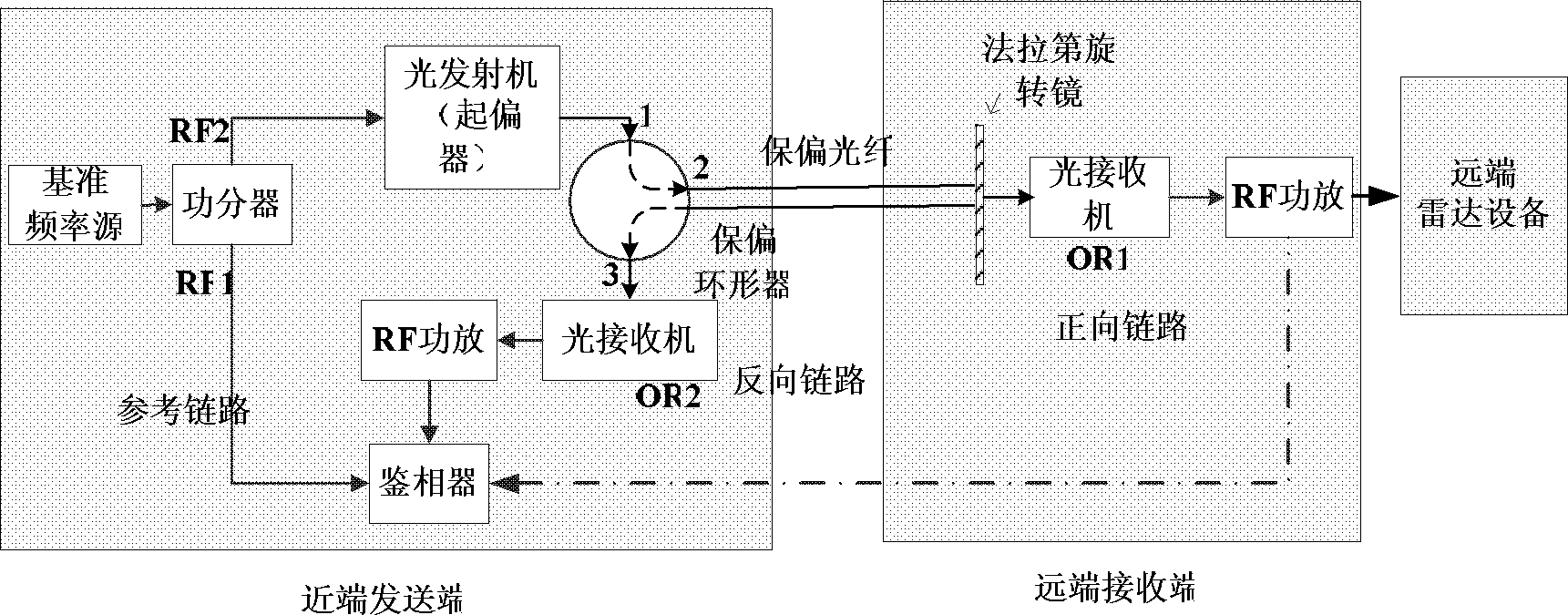
Microwave optical fiber link device for long-distance transmission of radar reference frequency signals
ActiveCN102857300AReduce interference noiseReduce volumeWave based measurement systemsFibre transmissionRadar systemsSynthetic aperture radar
The invention discloses a microwave optical fiber link device for long-distance transmission of radar reference frequency signals and relates to the technology of radar detection. The microwave optical fiber link device consists of an optical emitter, an optical receiver, a Faraday rotating mirror, an optical circulator, a polarization maintaining optical fiber, a radio-frequency power amplifier and the like. By subjecting microwaves to electric-optical and optical-electric conversion and utilizing the advantages of low insertion loss and high-temperature phase stability of the optical fiber, the microwaves are transmitted in low phase fluctuation and loss in the long distance. The microwave optical fiber link device can be used for transmission of rate-aided signals of spatial long-base line interference synthetic aperture radar (SAR) and transmission of reference frequency signals of radar systems such as phased array radars and multi-base radar monitoring net. Besides, phase changes caused by environmental factors such as temperature and irradiation can be accurately compensated during long-distance transmission of X-wave band microwave signals, and meanwhile, the microwave optical fiber link device has ultrawide radio-frequency (RF) working band and can be developed for transmission of radar reference frequency signals ranging from 50MHz to18GHz.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
BOTDA System that Combined Optical Pulse Coding Techniques and Coherent Detection
InactiveUS20140218717A1Improve SNRImprove dynamic rangeForce measurement by measuring optical property variationThermometers using physical/chemical changesDigital signal processingFiber
A BOTDA system that combined optical pulse coding techniques and coherent detection includes a narrow linewidth laser, two polarization-maintaining couplers, microwave generator, two electro-optic modulators (EOMs), fiber under test, an optical circulator, a 3 dB coupler, a polarization scrambler, a pulse generator, a balance photodetector, an electrical spectrum analyzer, digital signal processing unit and a frequency shifter. The optical pulse coding techniques and coherent detection are simultaneously used in the invented system, which can be enhance the signal-to-noise ration (SNR), the measuring accuracy and the sensing distance of BOTDA. Moreover, the proposed system has the capacity of break interrogation.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
High-precision wide-range low-coherent interference shift demodulation device and demodulation method thereof
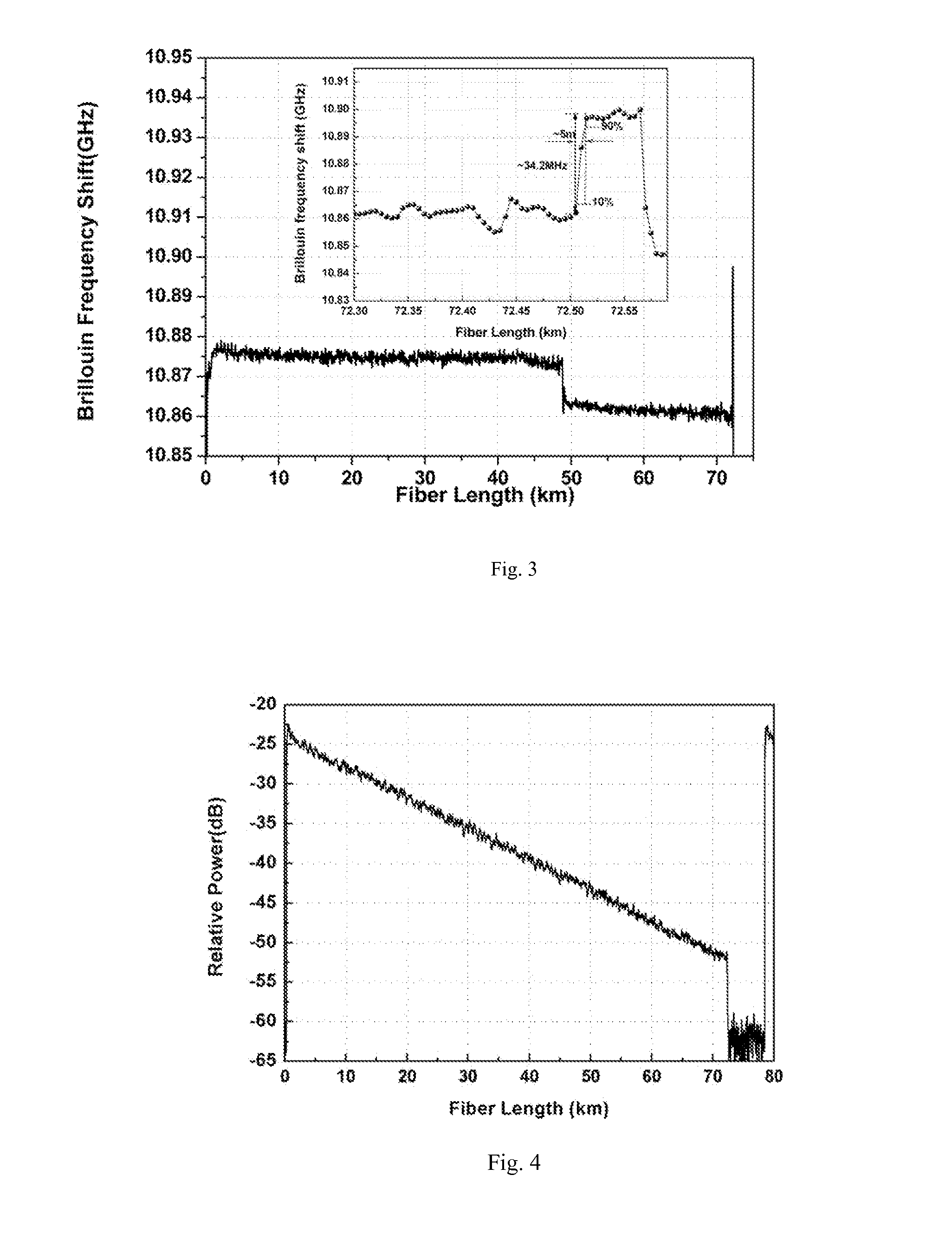
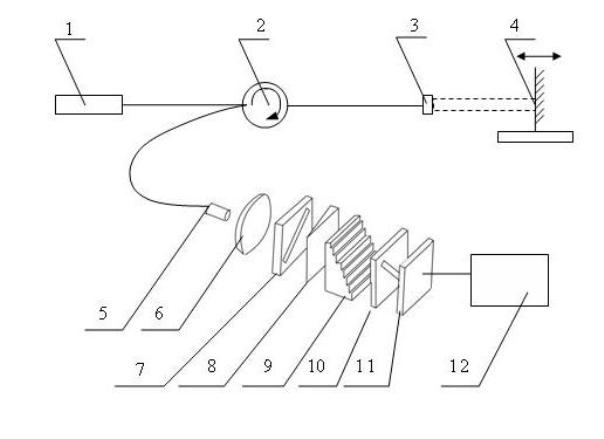
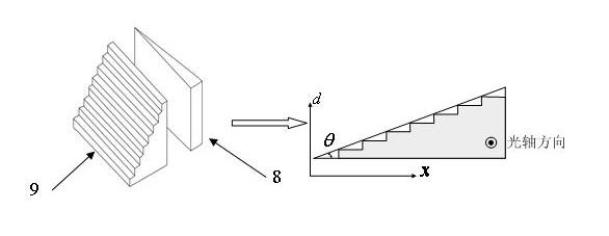
InactiveCN102052902ADifferent displacement measurement performanceImprove reliabilityPolarising elementsUsing optical meansOptical circulatorPolarizer
The invention relates to a high-precision wide-range low-coherent interference shift demodulation device, which comprises a light source, an optical circulator, a self-focusing collimation lens, a fixed reflecting mirror, an optical fiber splicer, a beam extender lens, a polarizer, a birefringent optical wedge, a stair-shaped birefringent phase shifter, an analyzer, a planar array camera and a processing unit. A demodulation method comprises the following steps: dividing the light emitted from the light source into two parts after the light passes through the optical circulator and reaches the self-focusing collimation lens at the sensing side, wherein one part is directly reflected and the other part is reflected after entering the reflecting mirror fixed on an object to be detected, and the two parts of reflection light have an optical path difference (OPD); guiding the two parts of reflection light to pass through the optical circulator again so as to reach the optical fiber splicer and then reach the birefringent optical wedge and the stair-shaped birefringent phase shifter through the beam extender lens and polarizer; realizing the wide-range optical path difference (OPD) scanning under the combined action of the birefringent optical wedge and the stair-shaped birefringent phase shifter; generating an interference fringe behind the analyzer; receiving the interference fringe by using the planar array camera; and detecting the shift information through digital processing by a computer or an embedded system.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com