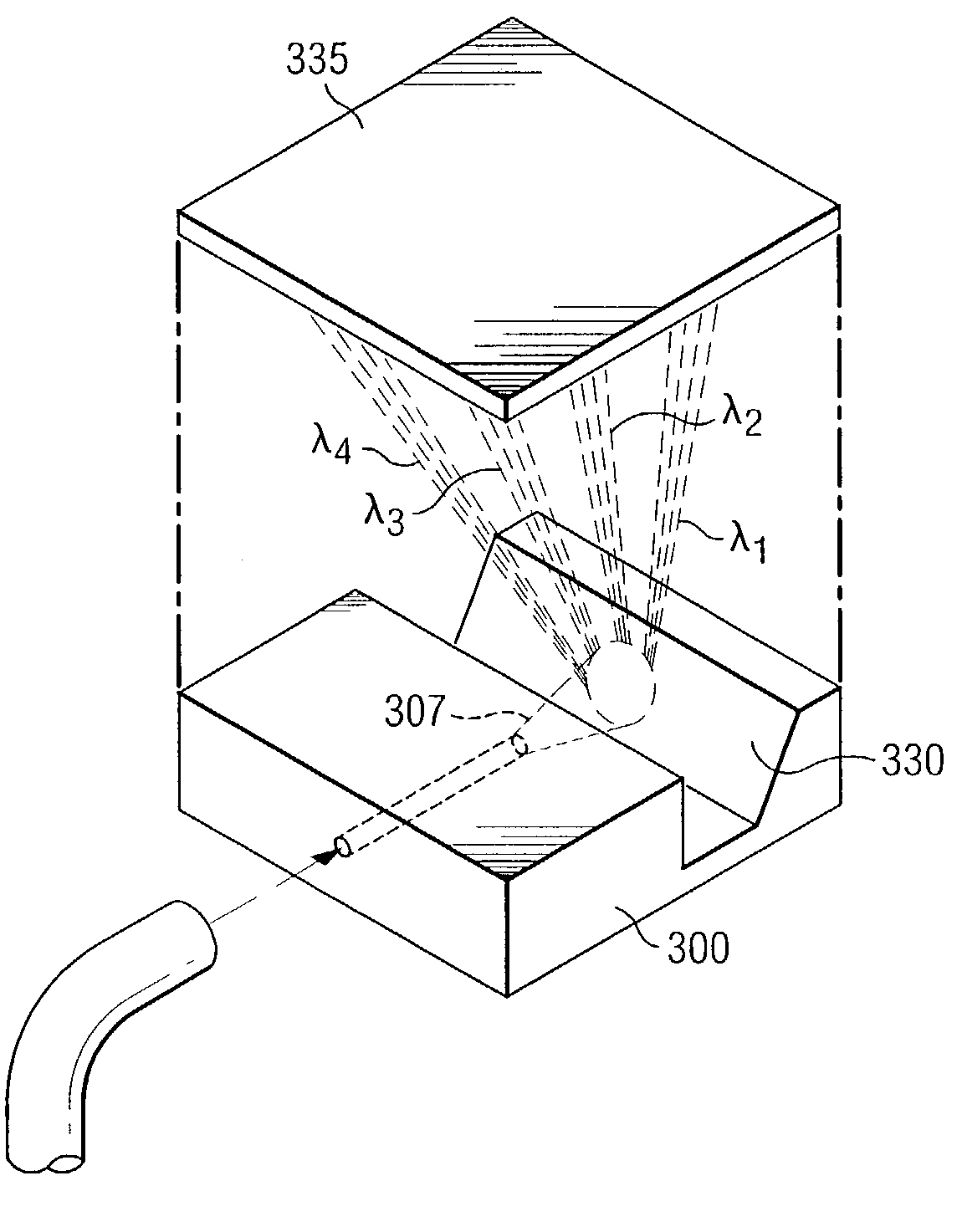
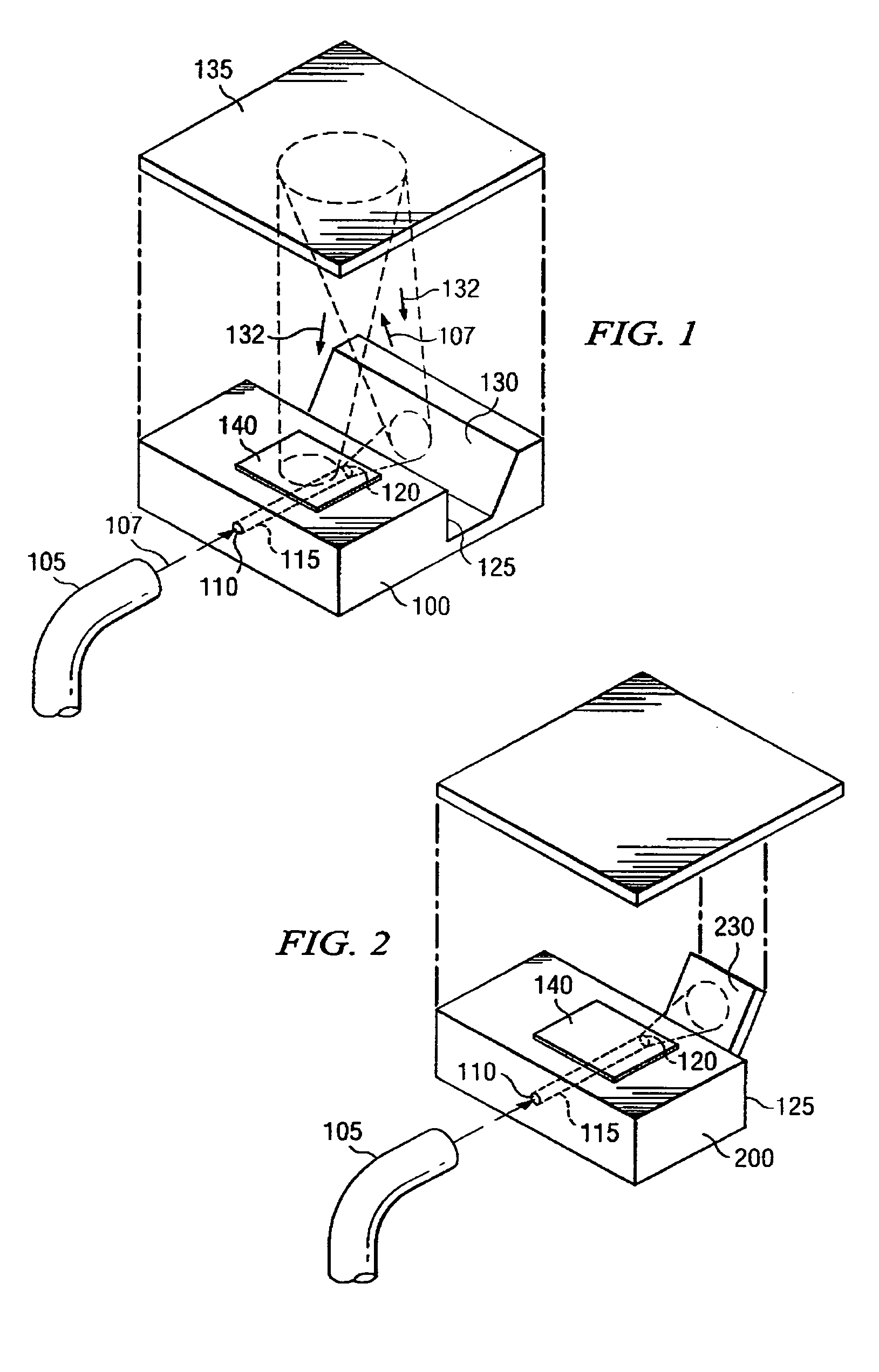
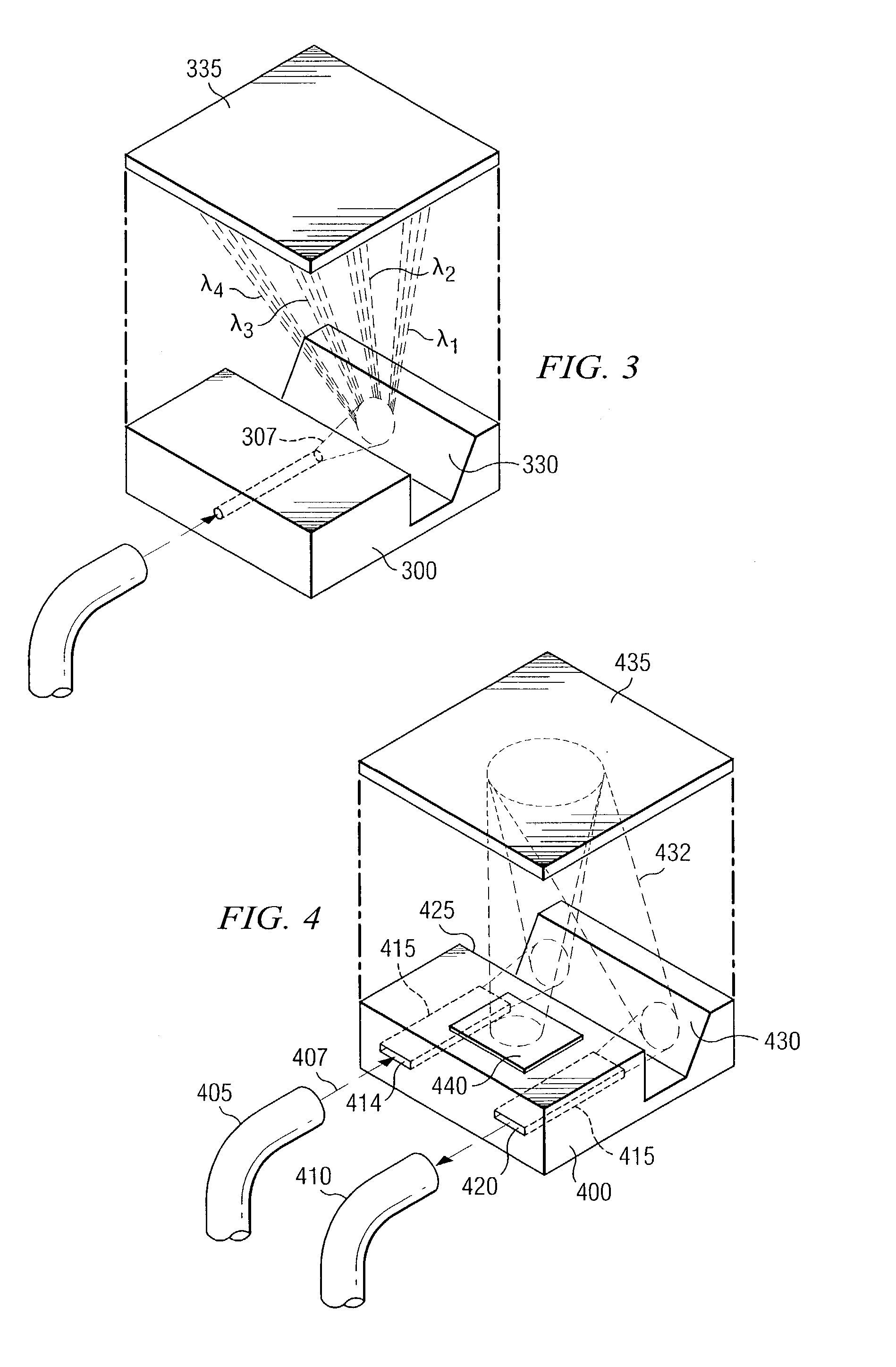
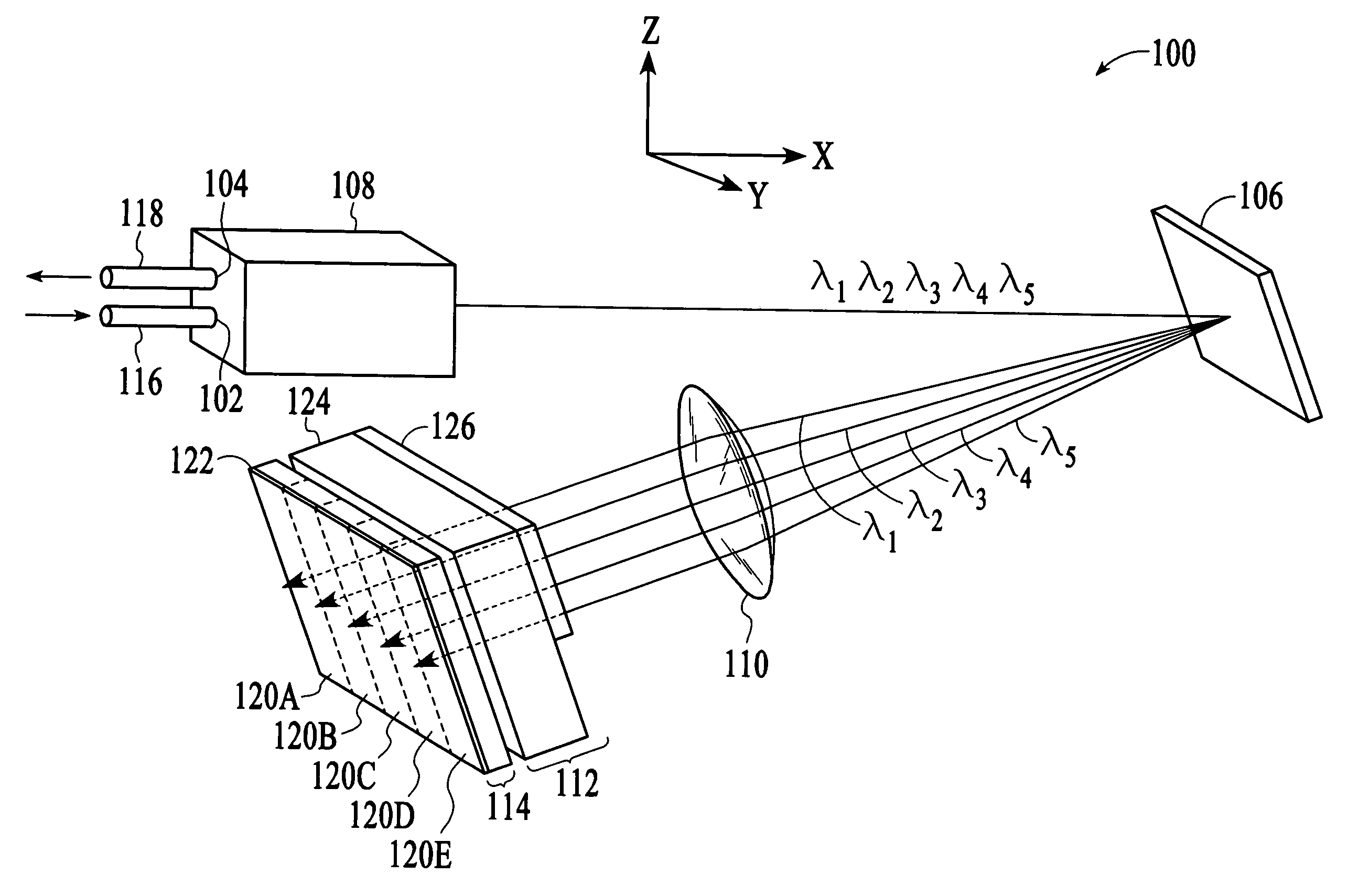
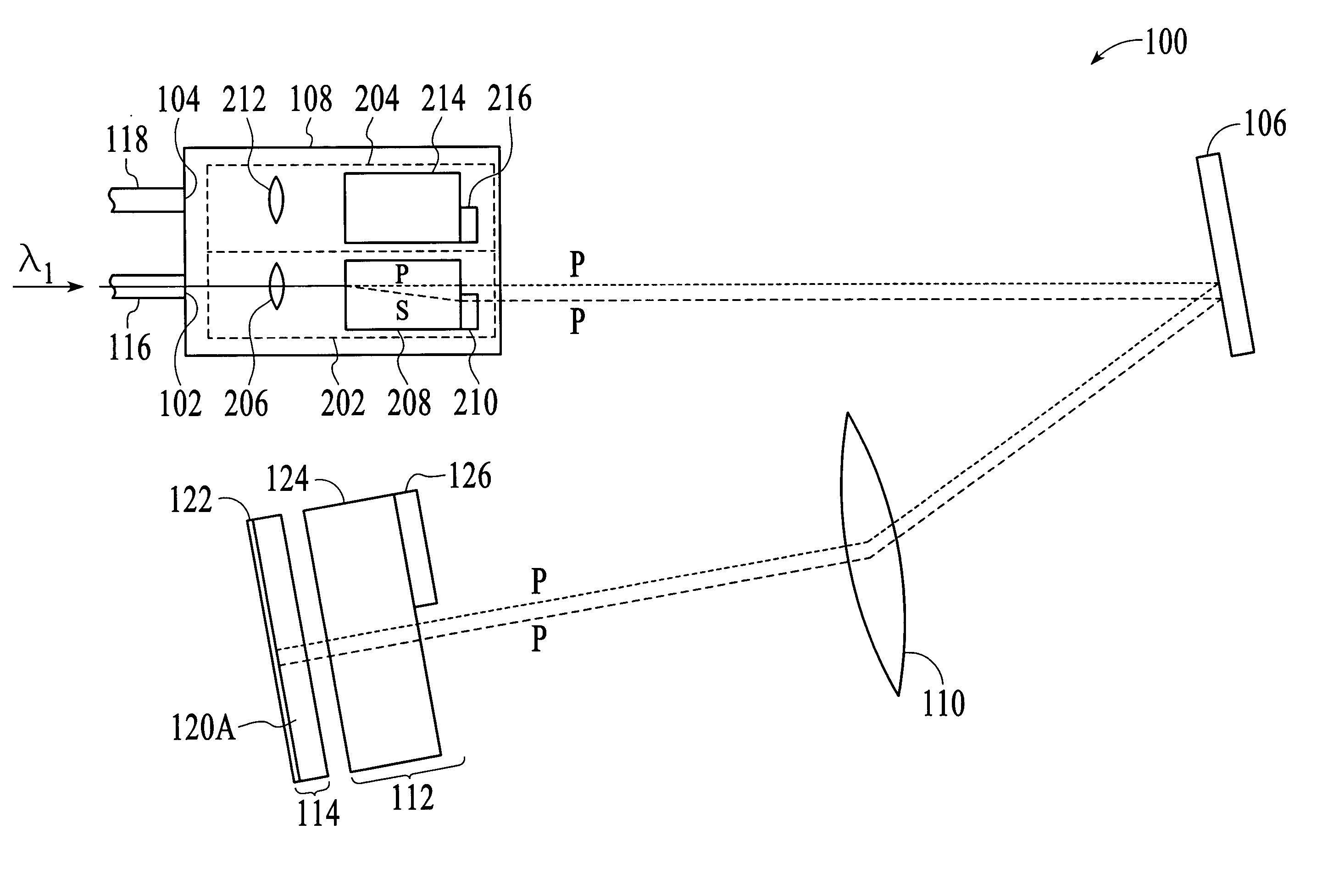
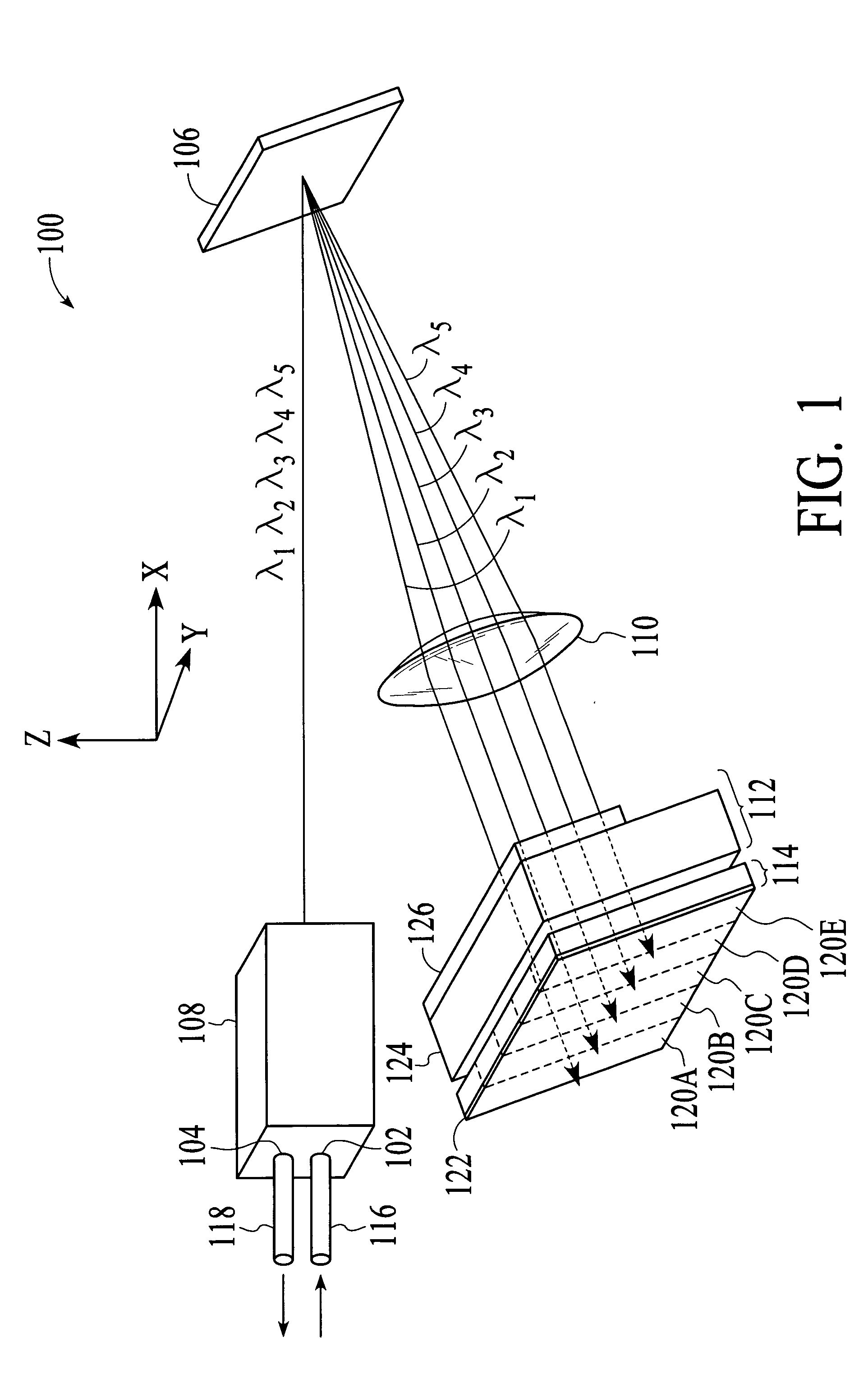
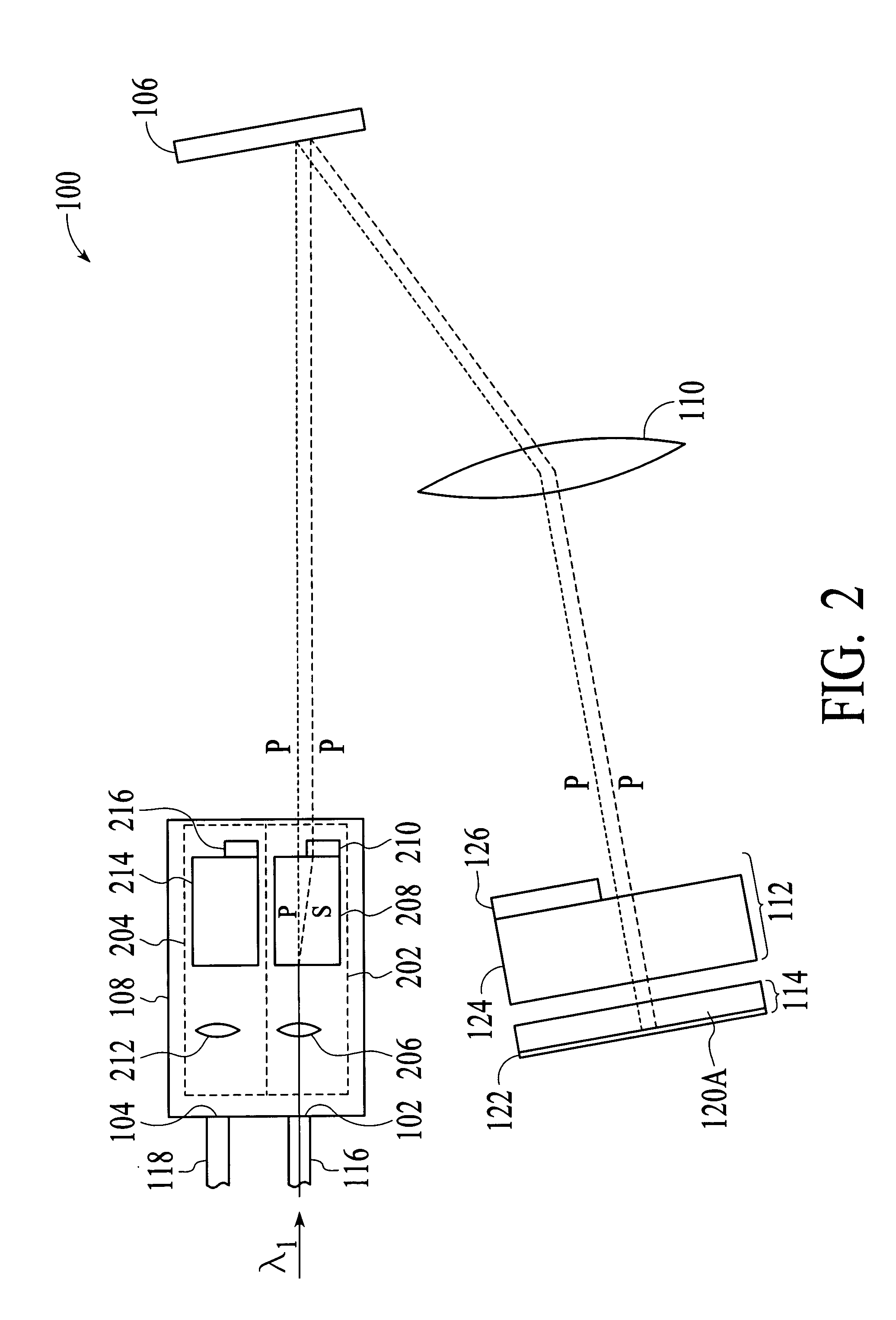
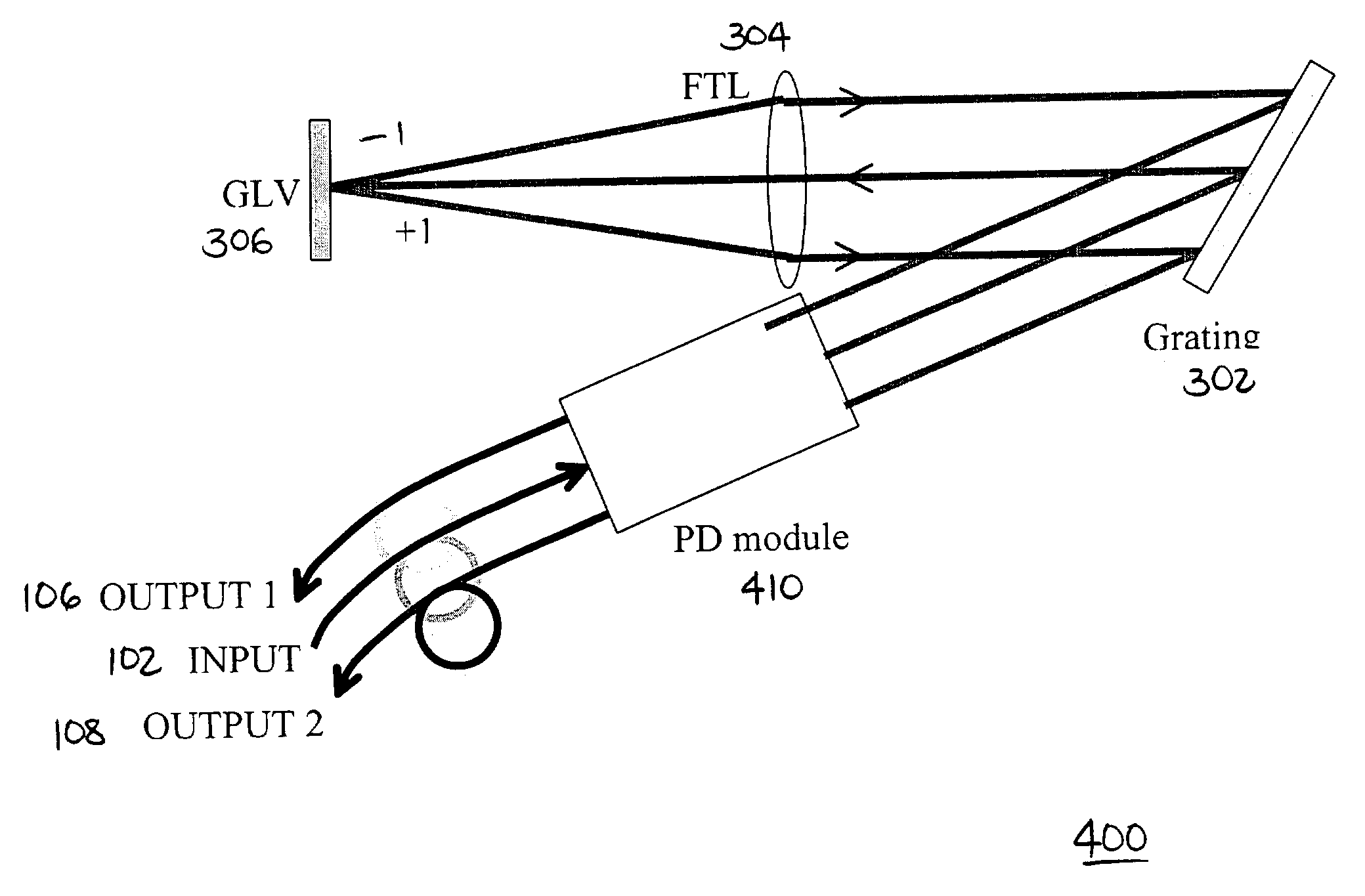
Patents
Literature
41 results about "Wavelength selective switching" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
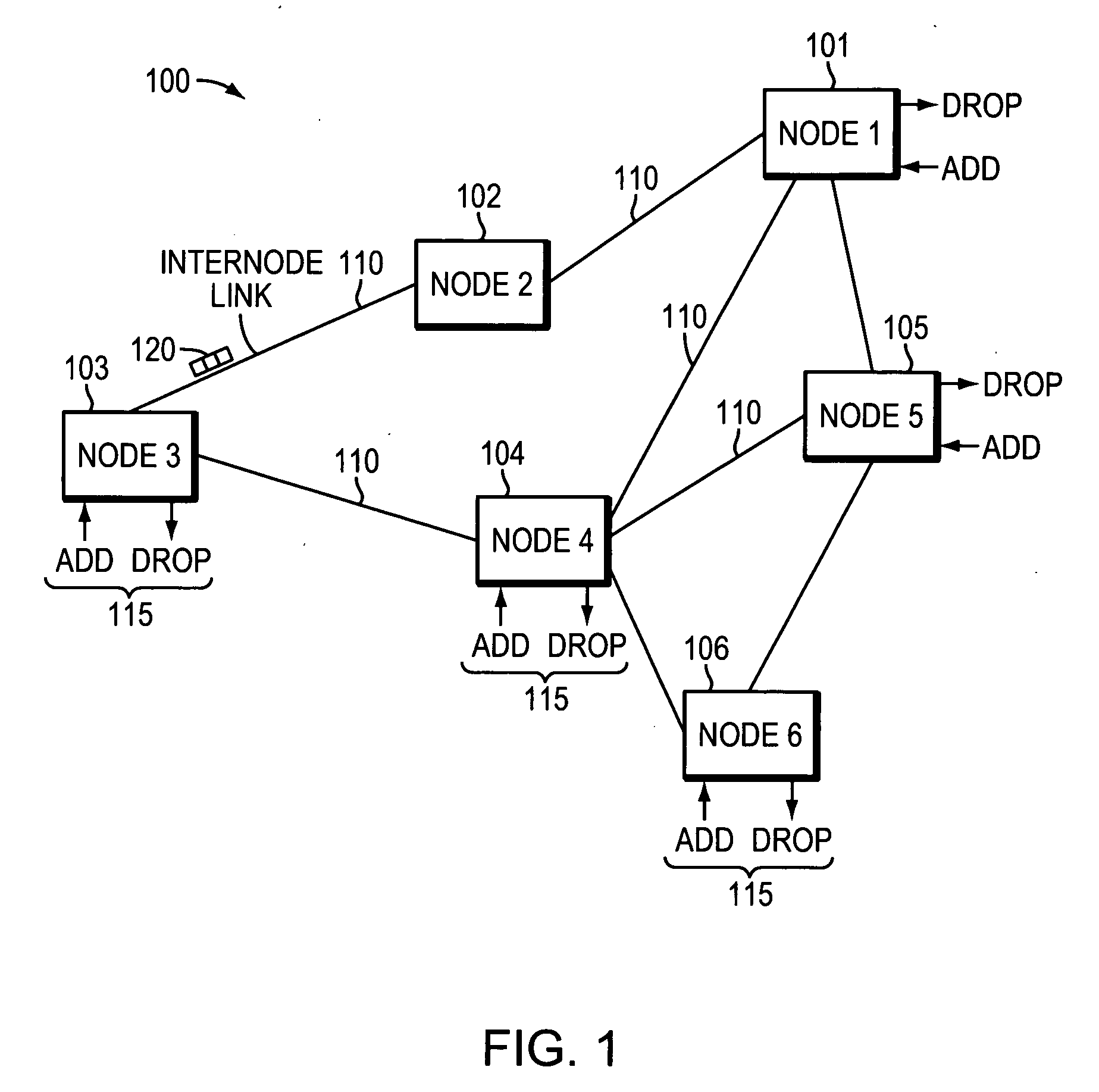
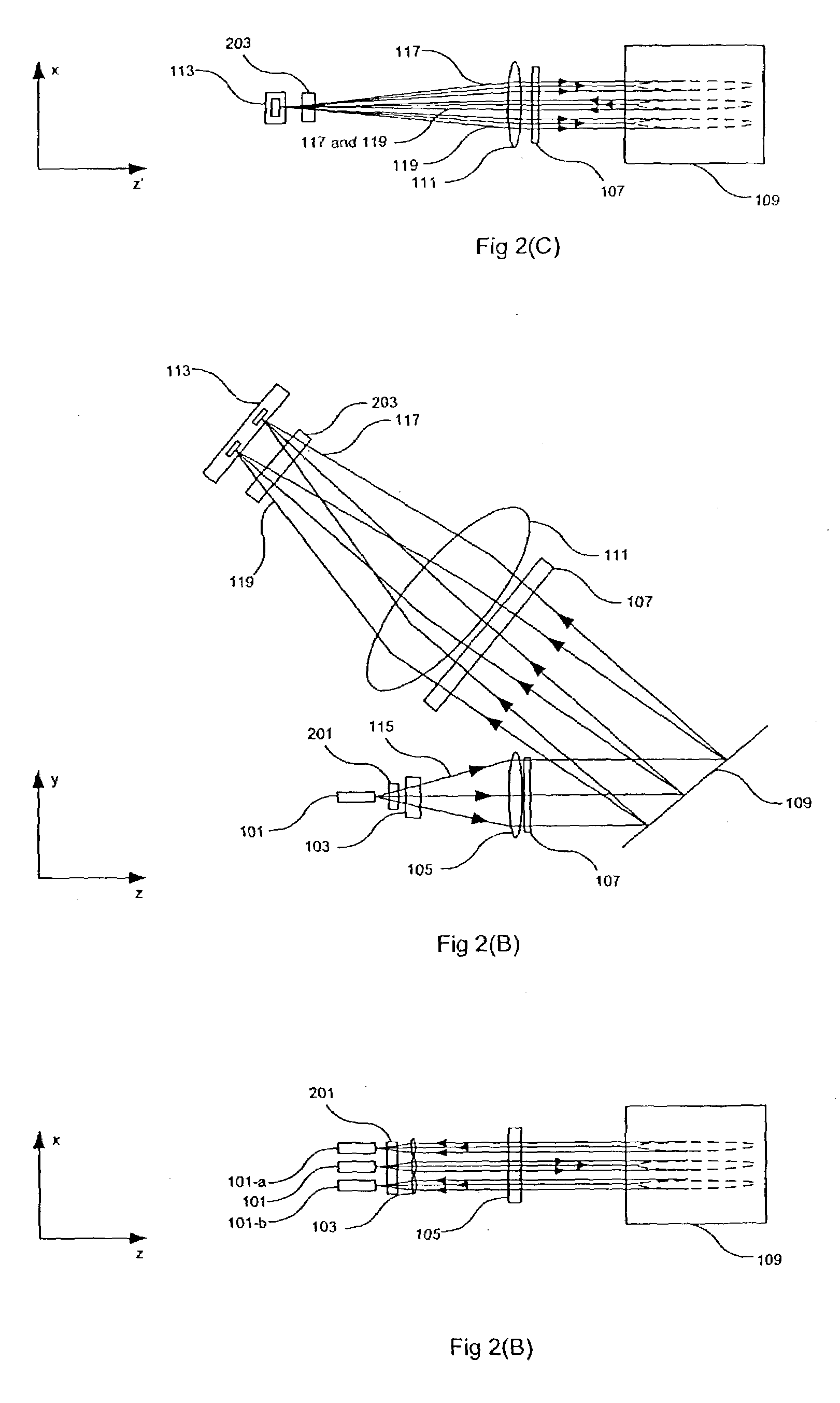
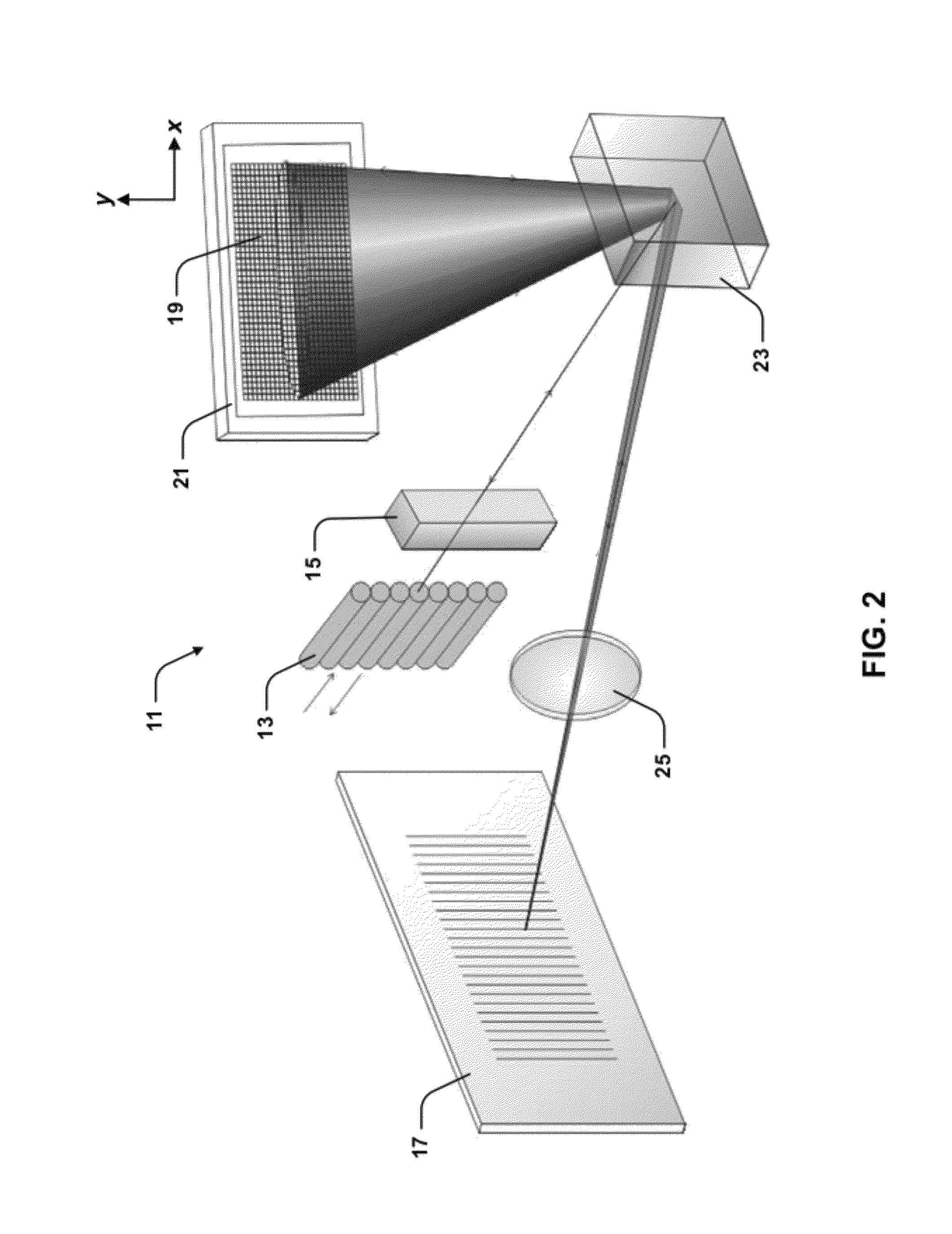
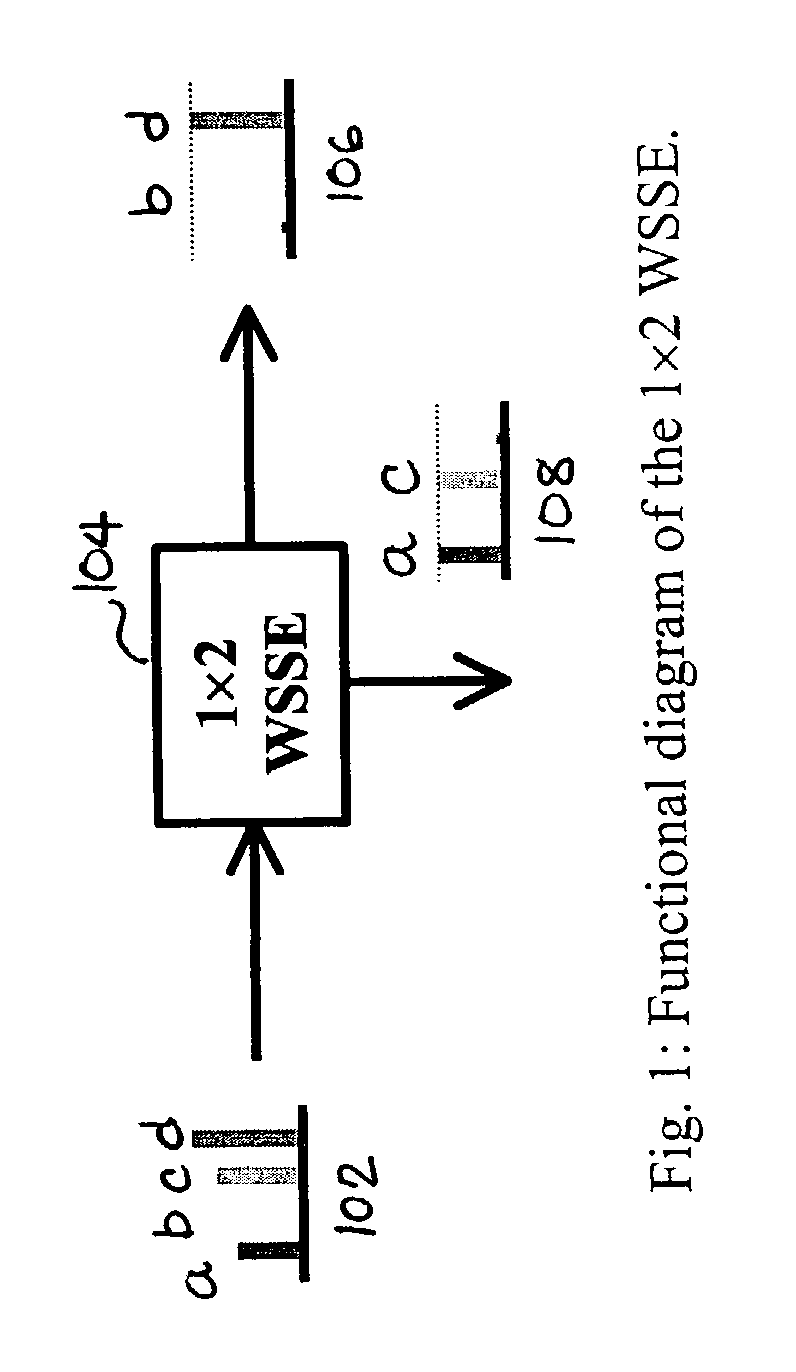
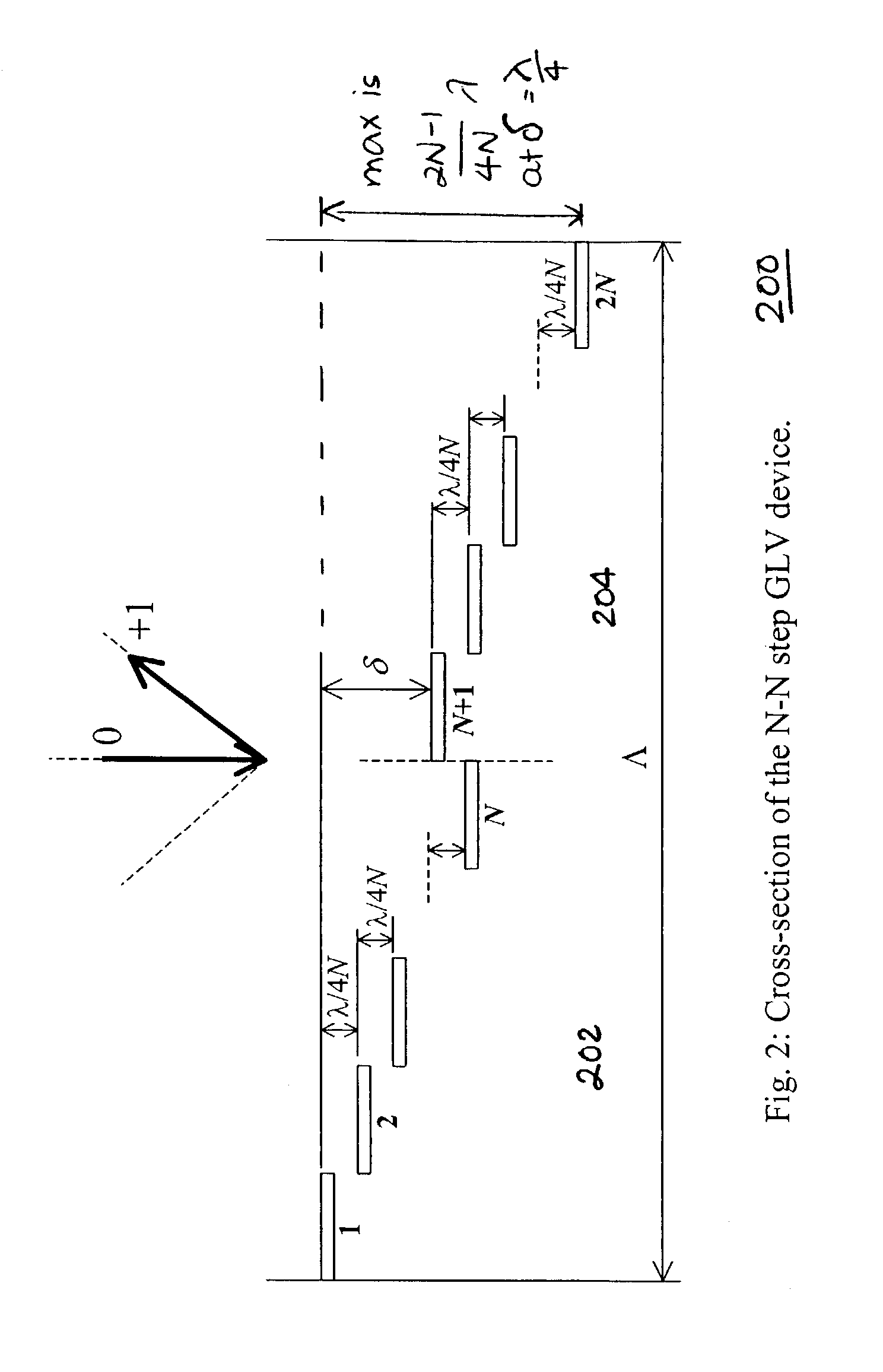
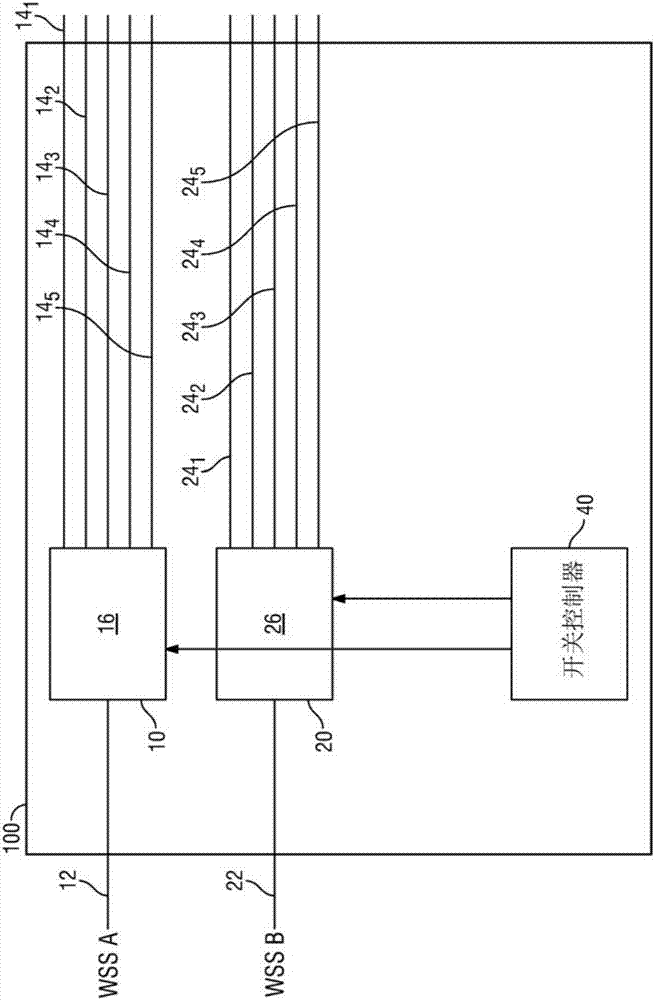
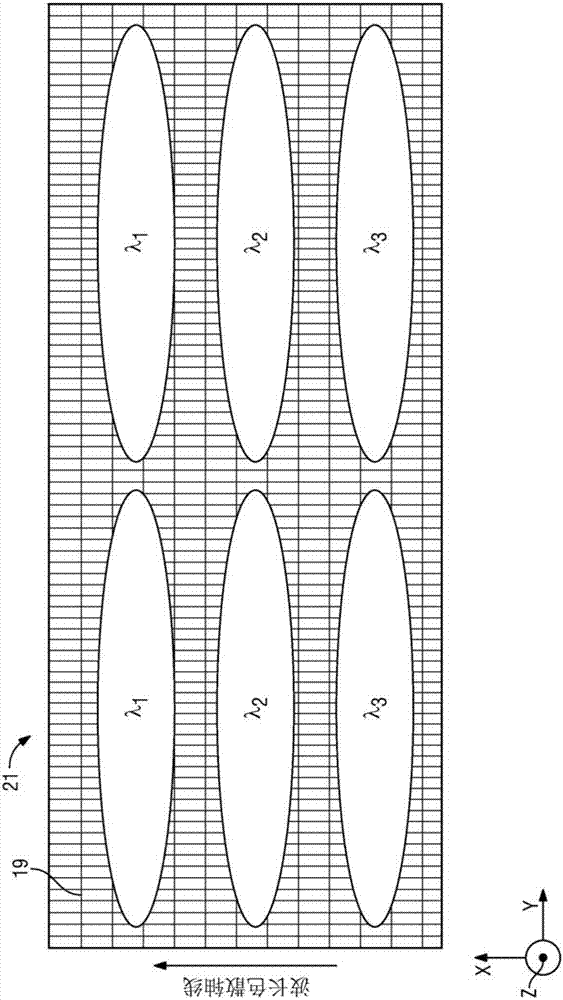
Wavelength selective switching components are used in WDM optical communications networks to route (switch) signals between optical fibres on a per-wavelength basis.
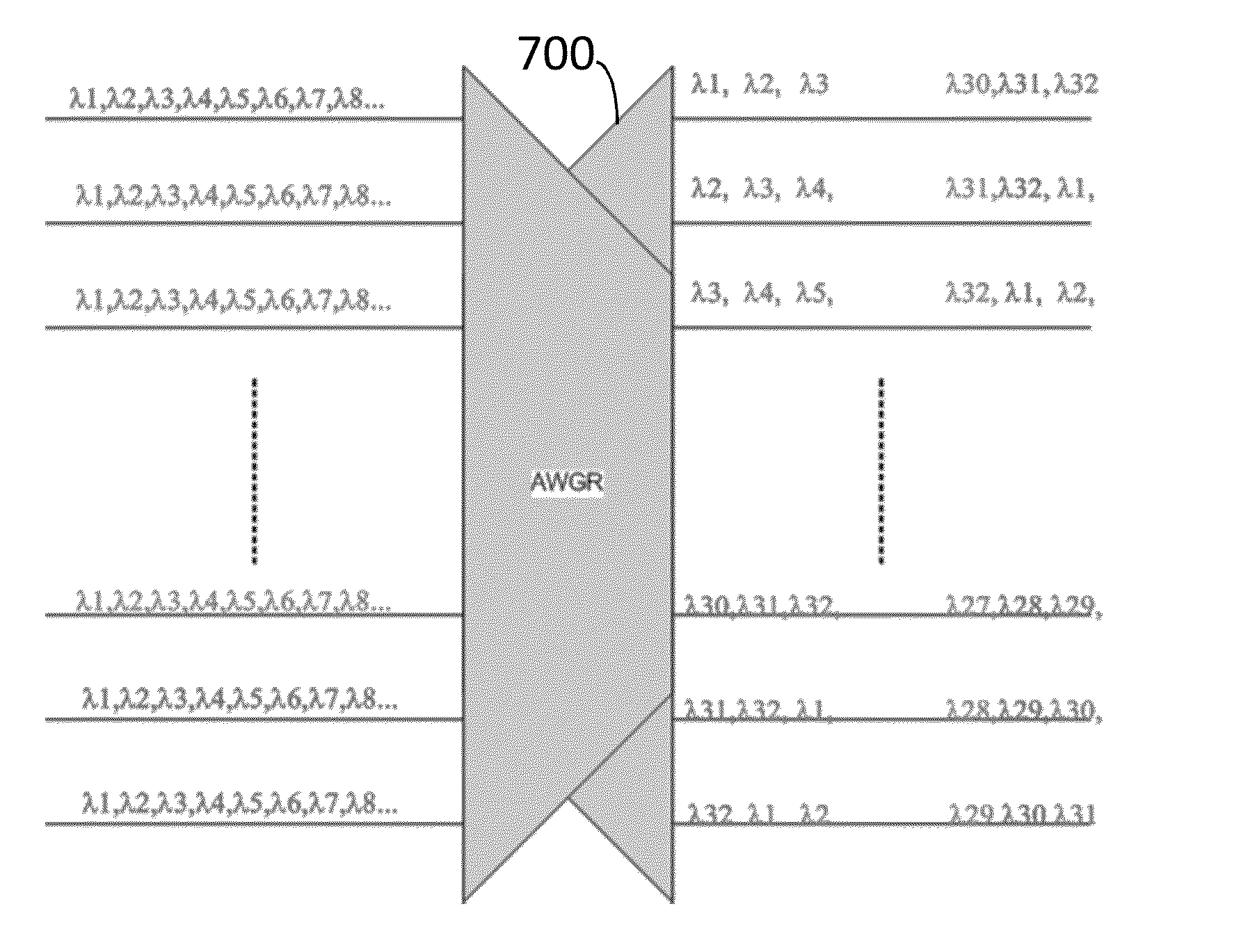
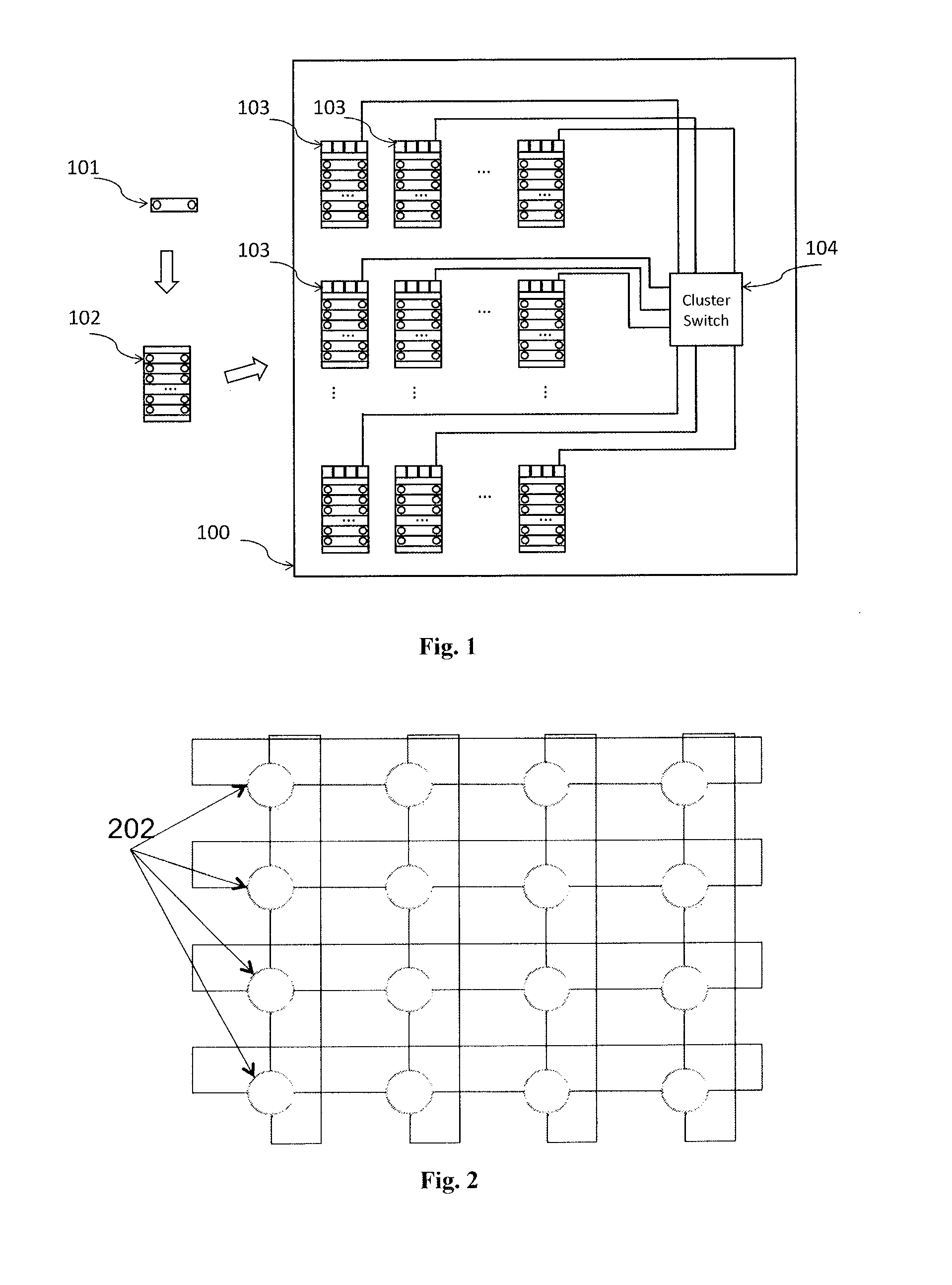
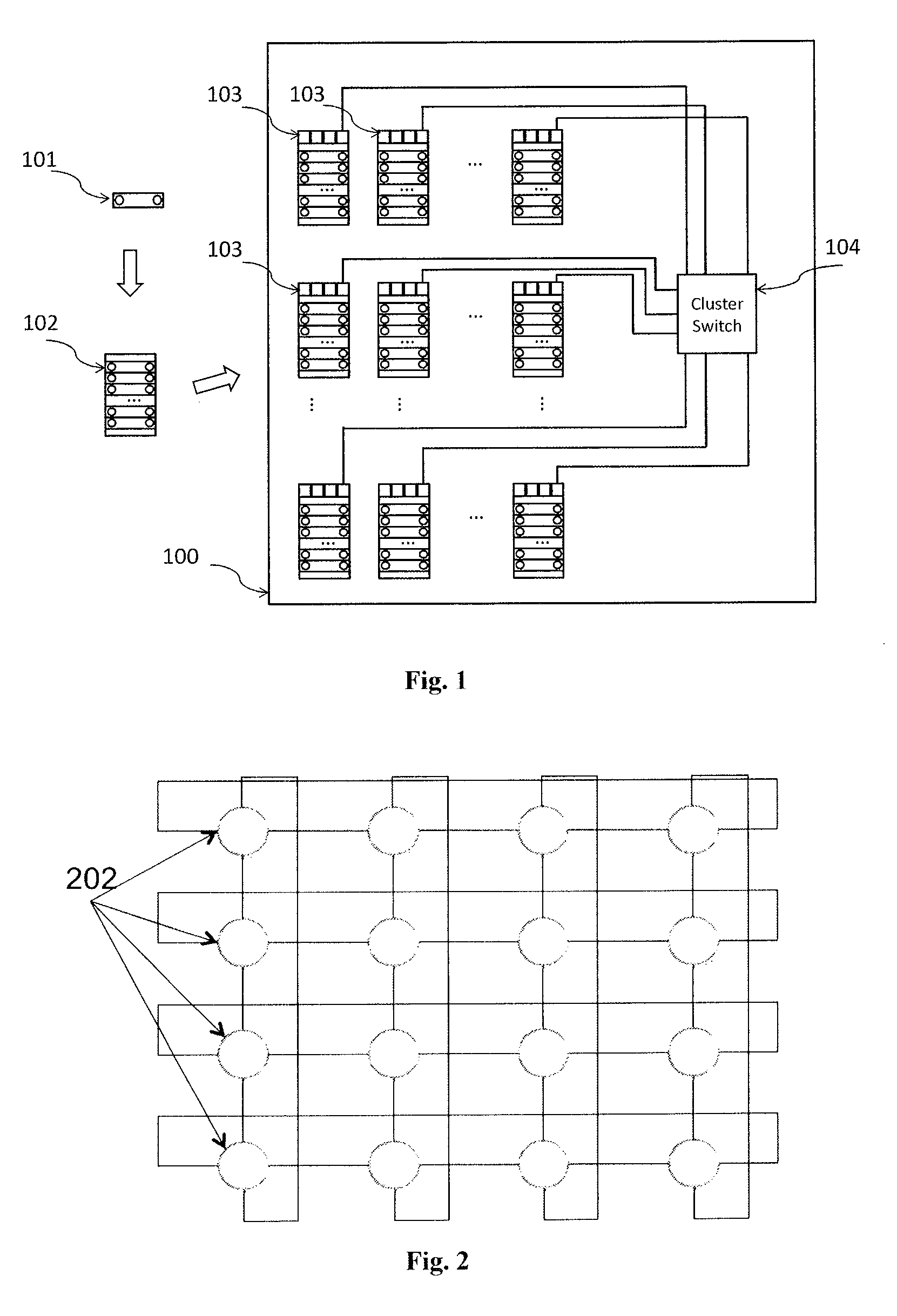
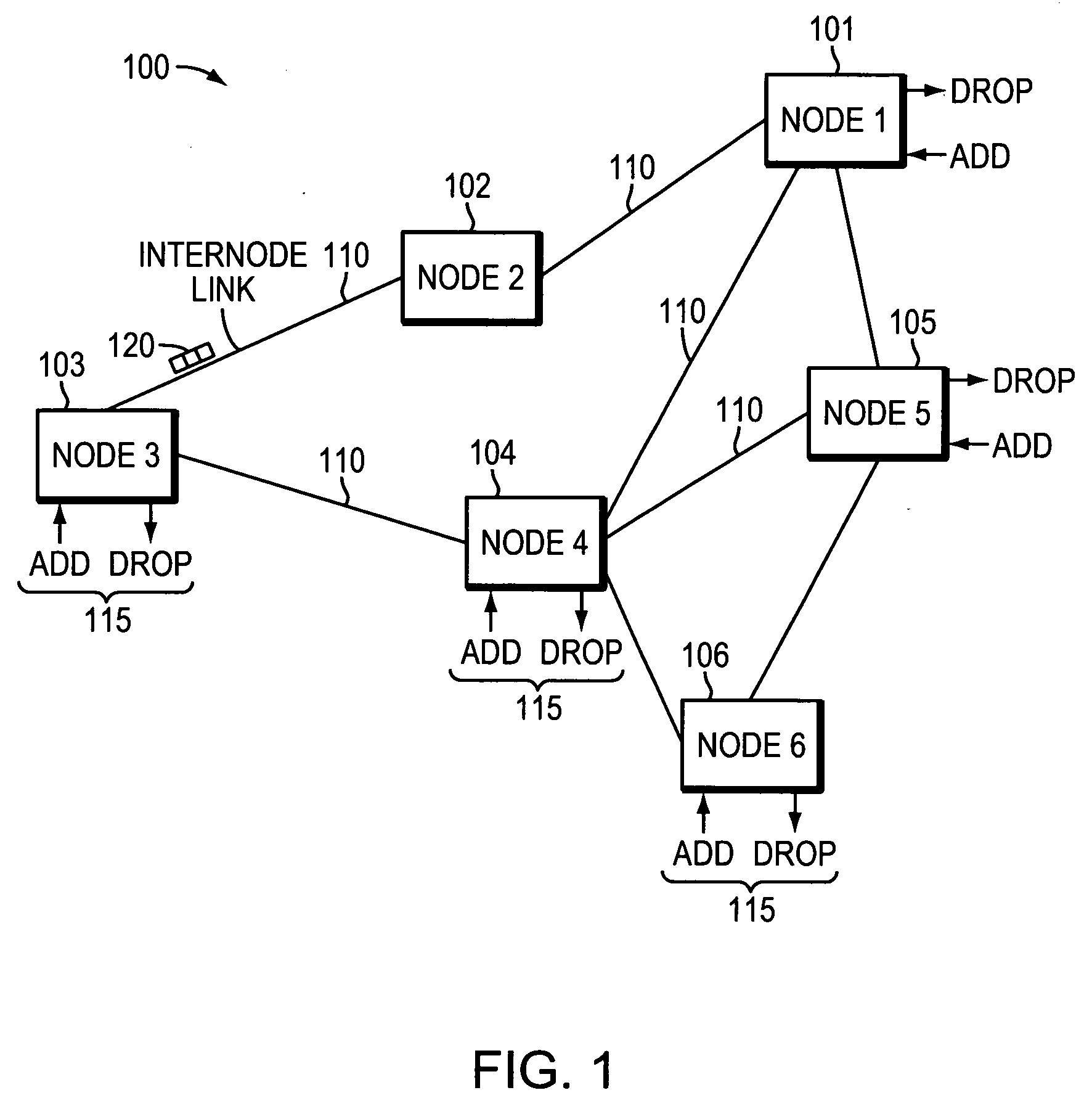
Distributed Optical Switching Architecture for Data Center Networking
InactiveUS20150098700A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsOptical multiplexWavelength selective switchingData center
A system has a first rack with a first set of servers and a first top of rack switch and a second rack with a second set of servers and a second top of rack switch. A first optical switch is connected to the first top of rack switch. A second optical switch is connected to the second top of rack switch and the first optical switch. The first optical switch and the second optical switch each employ wavelength selective switching.
Owner:COADNA PHOTONICS
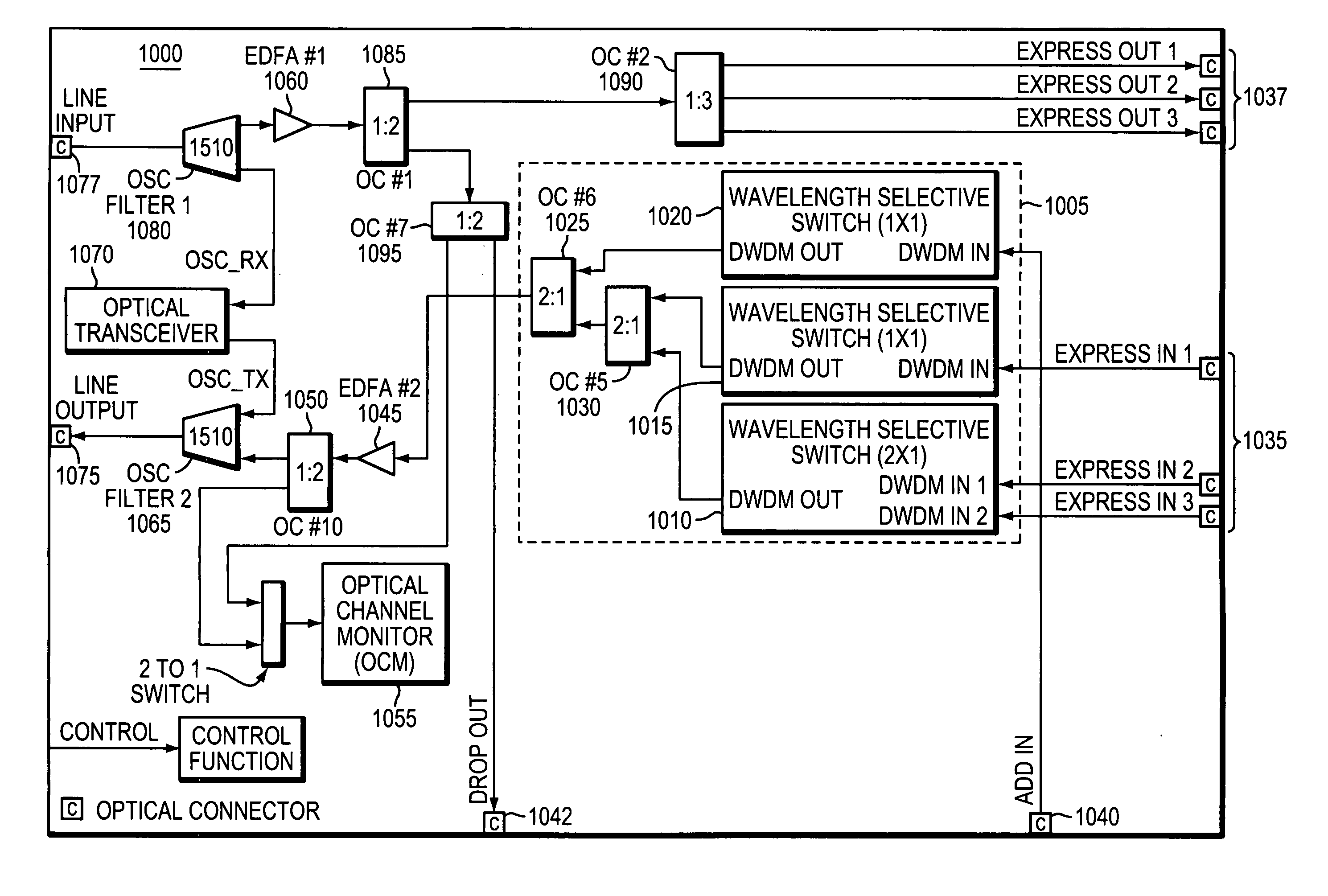
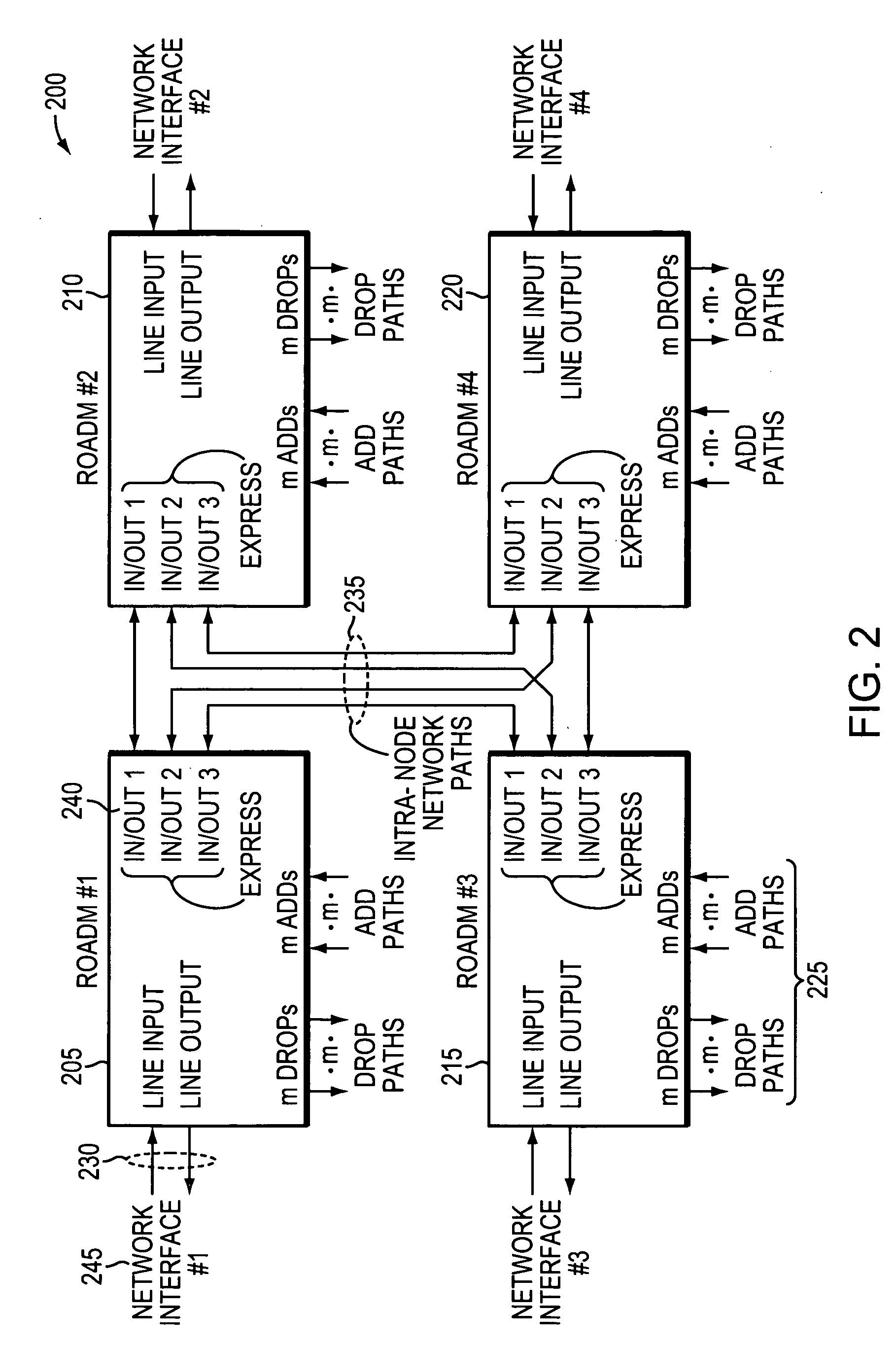
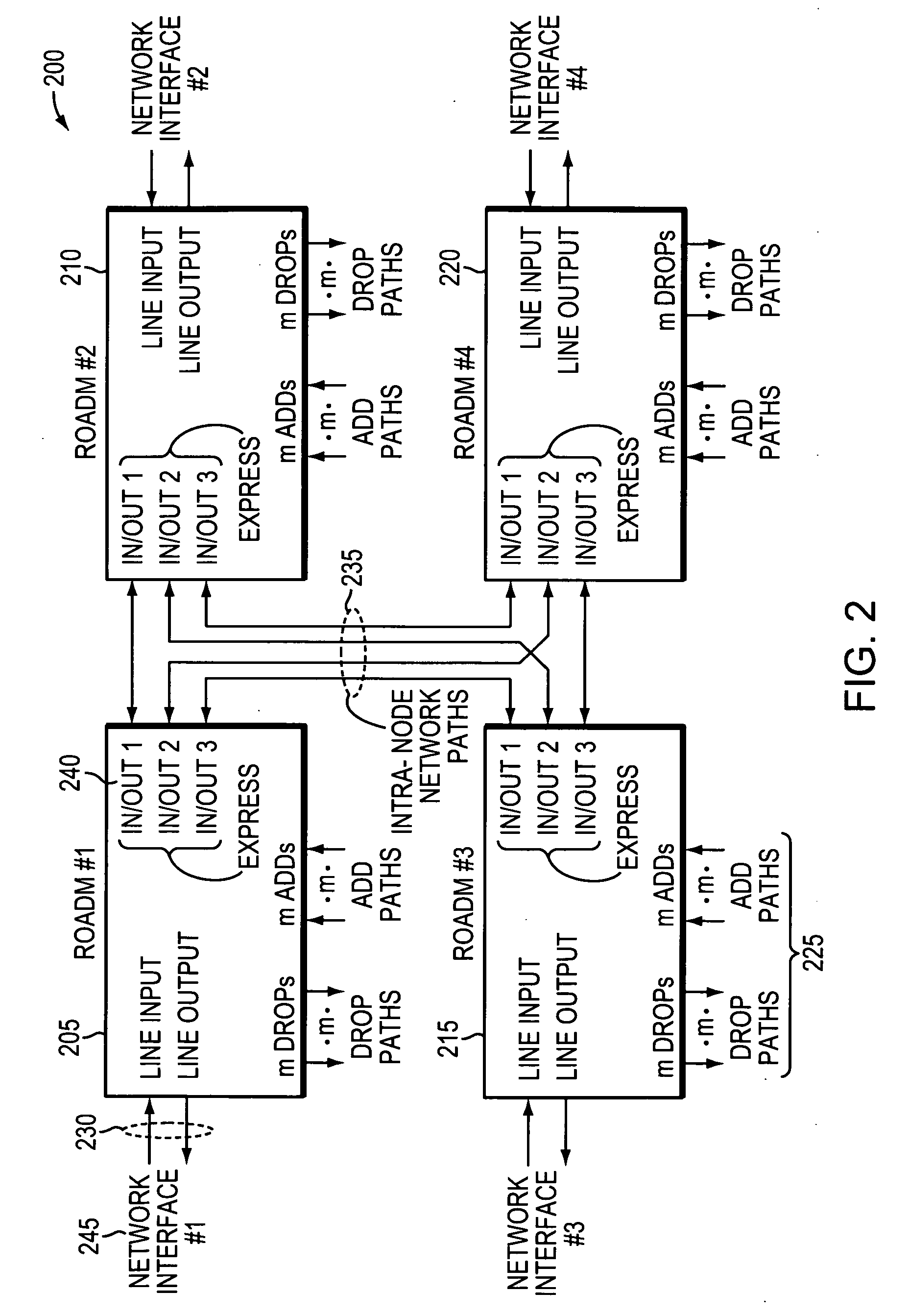
Methods and apparatus for reconfigurable add drop multiplexers
ActiveUS20090226168A1Less insertion lossMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsWavelength selective switchingOptical coupler
Optical networks are increasingly employing optical network nodes having multiple interfaces to allow a node to direct optical signals received at any interface to any other interface connected to the node. Constructing a larger wavelength selective switching (WSS) module used in such a node can be complex and expensive. A method an apparatus for constructing a large WSS using parallelism is provided. In example embodiments, a larger WSS may include multiple parallel non-cascaded smaller WSSs and an optical coupler configured to optically couple the multiple parallel, non-cascaded smaller WSSs. This technique may be used to construct both N×1 and 1×N WSSs. Because the technique employs multiple parallel, non-cascaded WSSs, all inputs of a larger N×1 WSS and all outputs of a larger 1×N WSS are available receive or transmit external signals rather than being rather than being unavailable due to, for example, cascading smaller WSS devices together.
Owner:TELLABS OPERATIONS
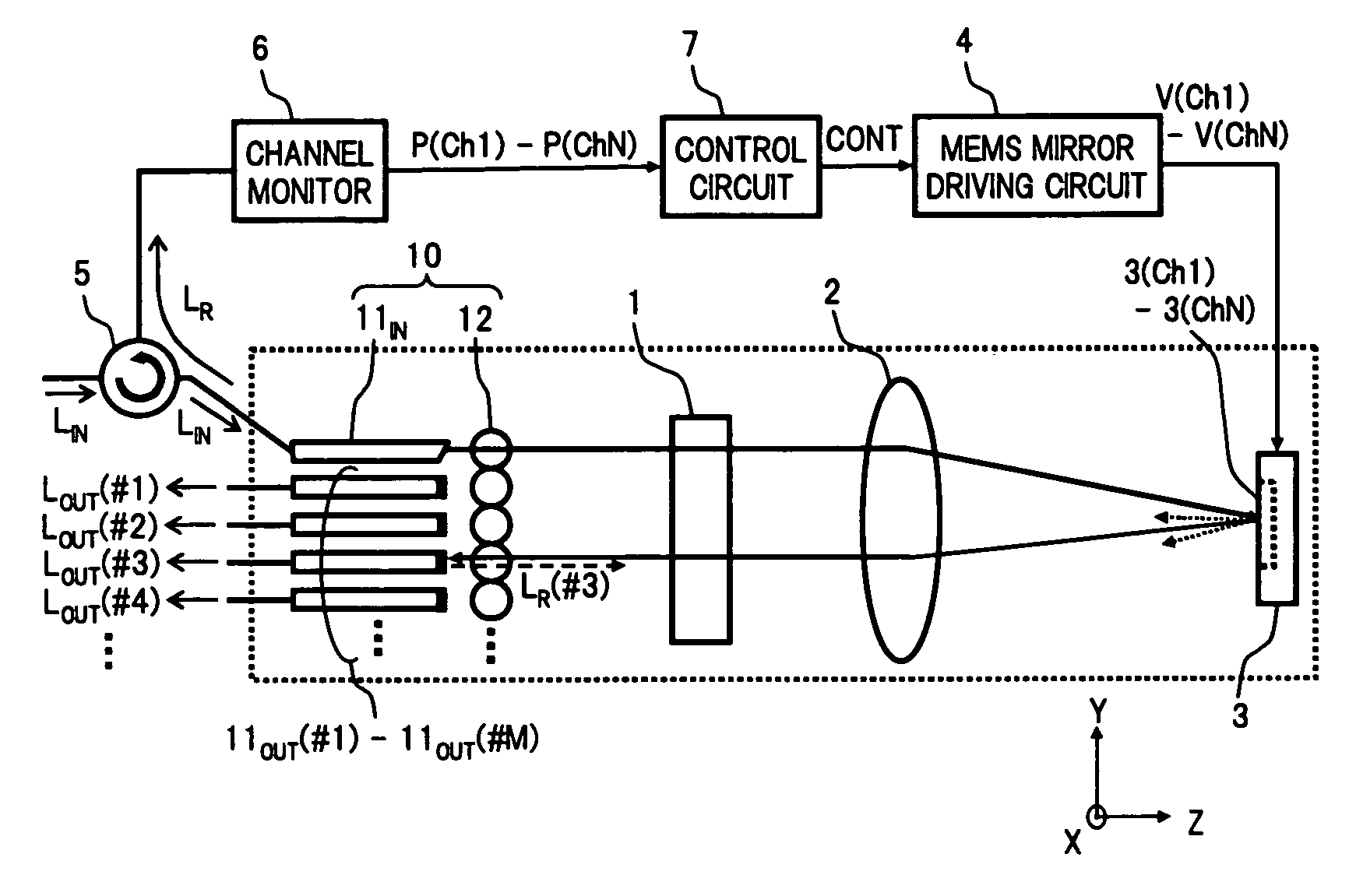
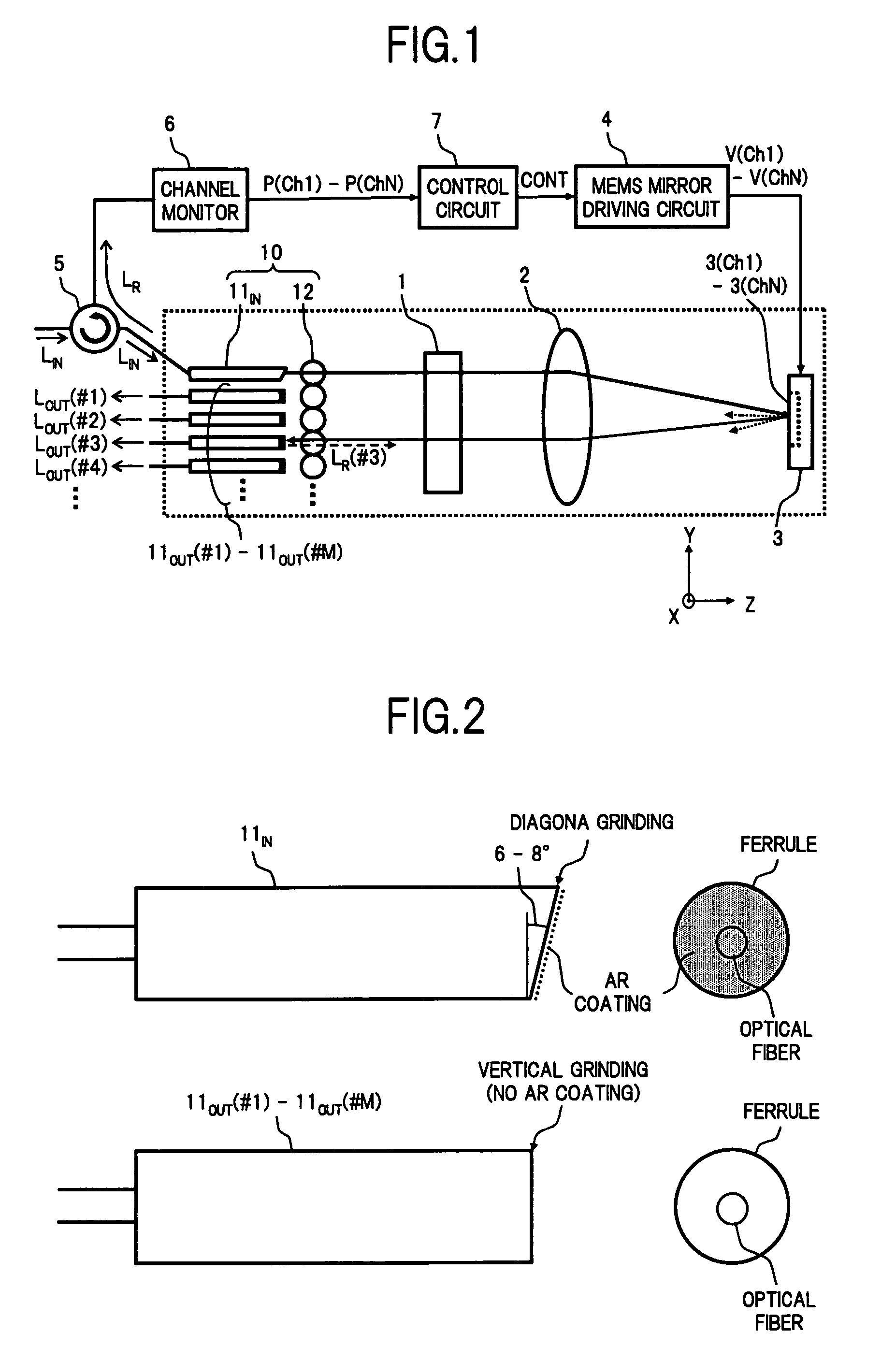
Wavelength selective switch
InactiveUS7440648B2Small sizeImprove accuracyMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsFiberWavelength selective switching
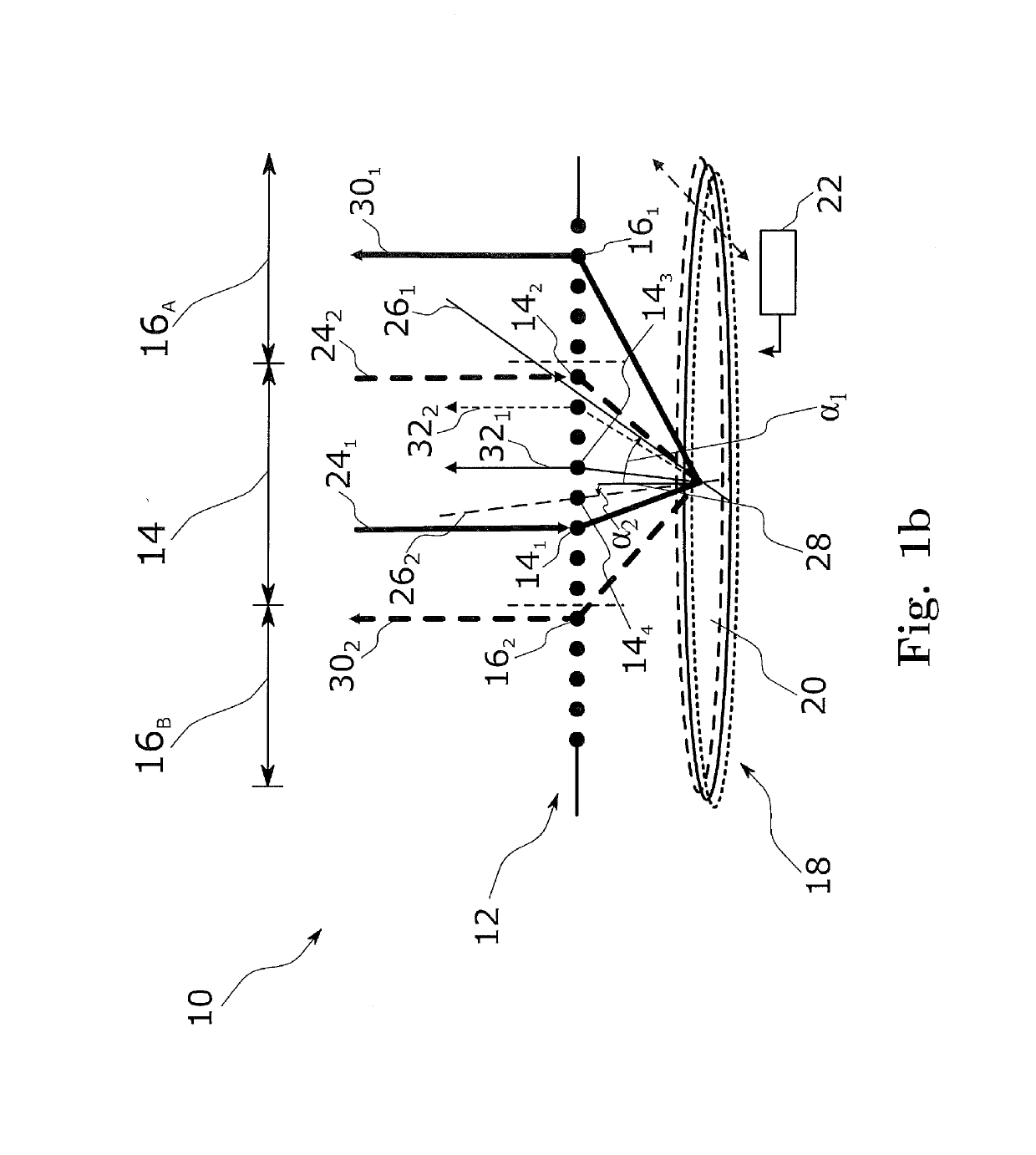
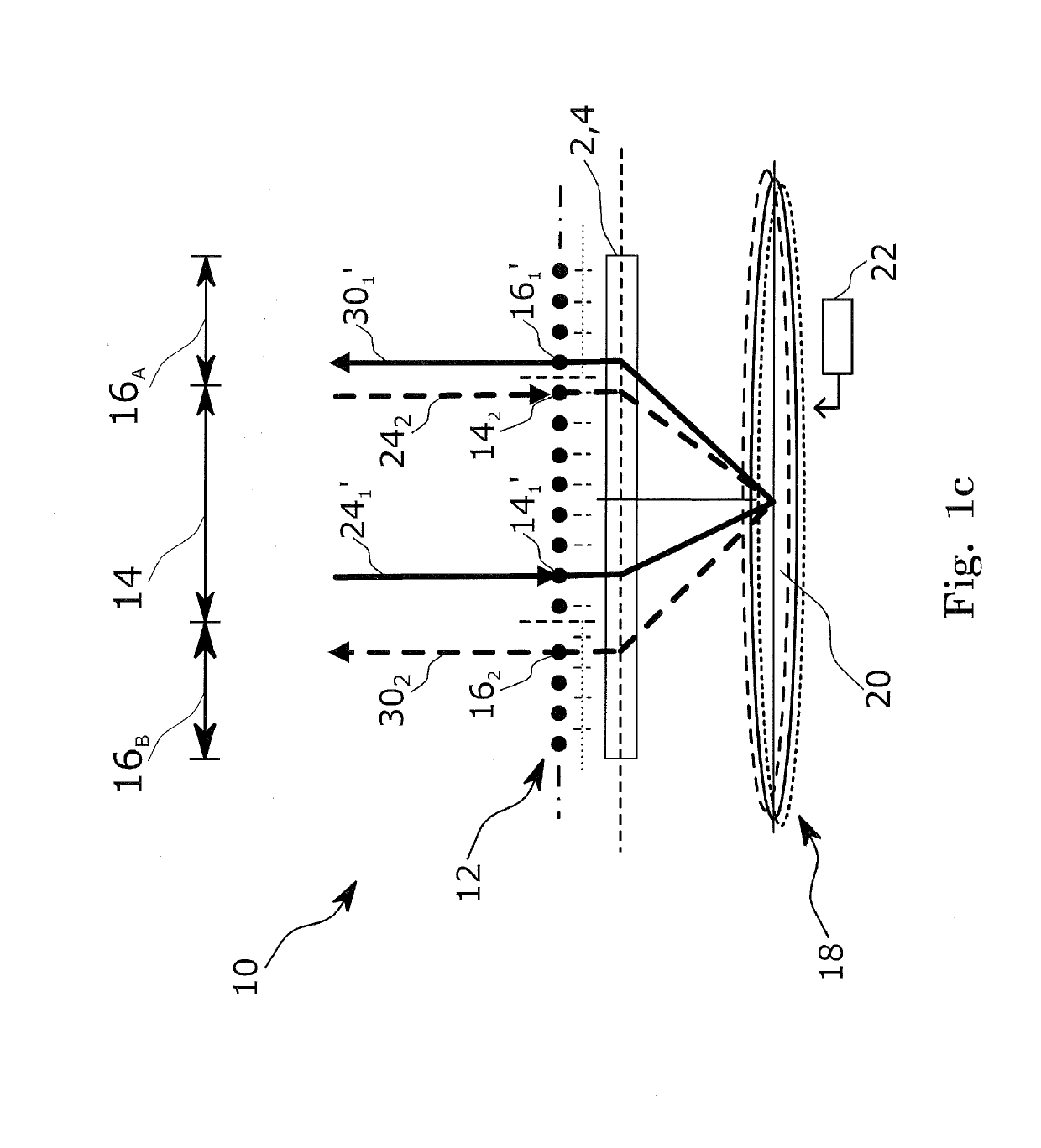
A wavelength selective switch of the invention separates WDM light coming out from an input fiber of a fiber collimator array according to its wavelength, in a diffraction grating, and reflects each wavelength channel proceeding in different directions by MEMS mirrors corresponding to a mirror array. In the MEMS mirrors, the angles of their reflecting surfaces are set corresponding to the location of the output port which is set in the output address of the wavelength channel to be injected. For each of the wavelength channels that reach the target output port, one part of each is reflected by the end face of an output fiber, and the reflected light is returned to the input port, and sent to a channel monitor via an optical circulator, so that the optical power corresponding to each wavelength channel is monitored. As a result it is possible to provide a small size, and low-cost, wavelength selective switch, that can monitor the power of each wavelength channel guided to a plurality of output ports, with good accuracy.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
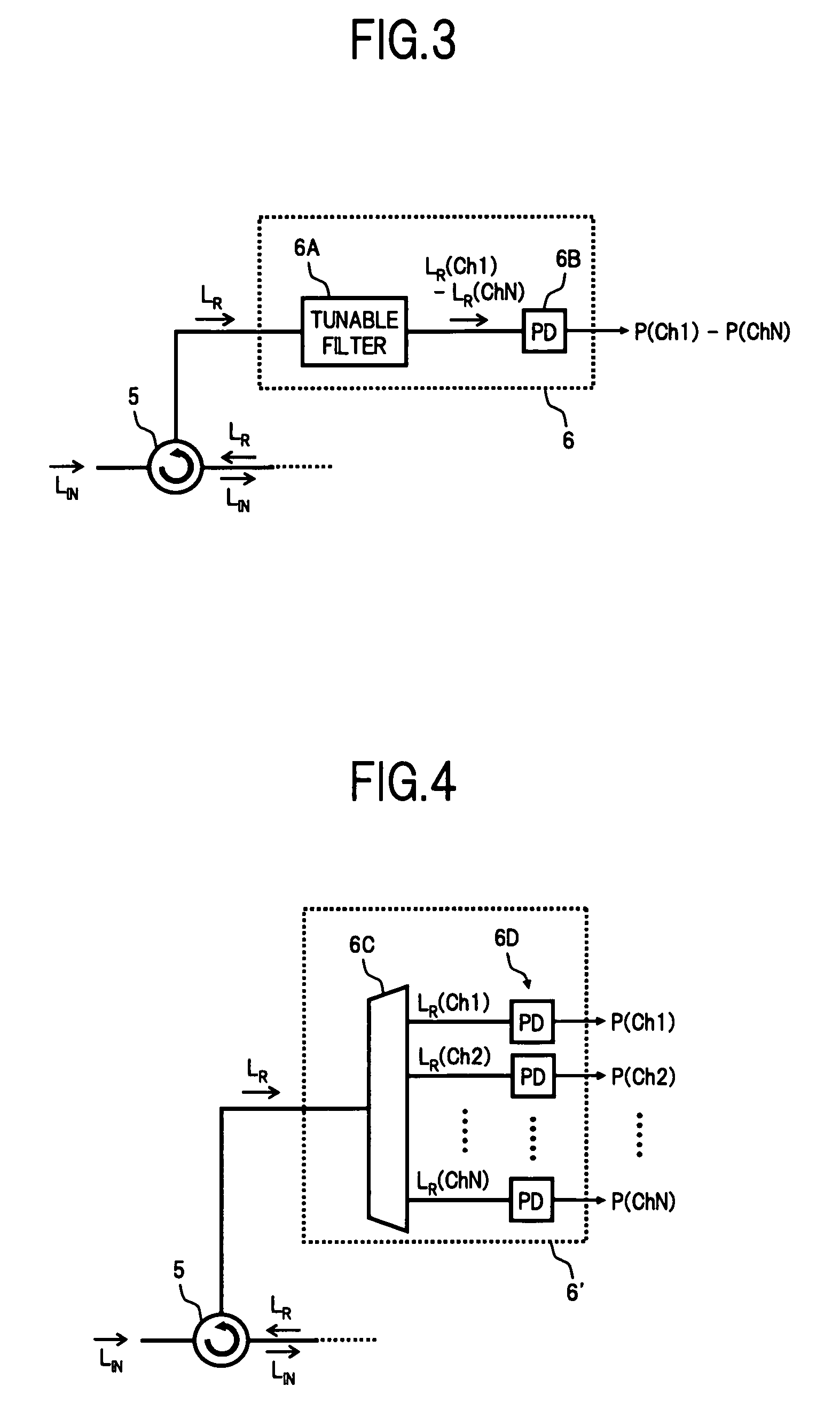
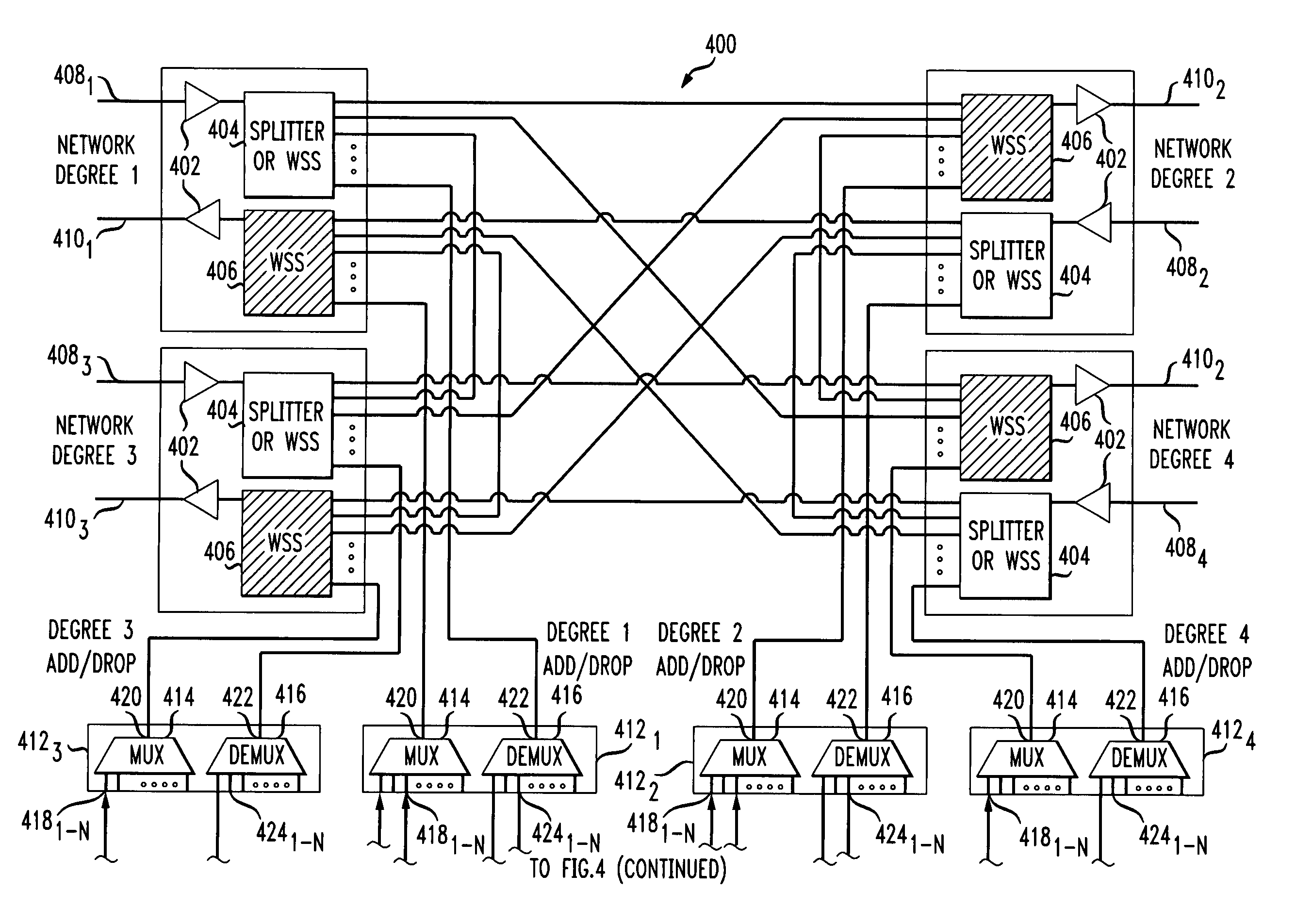
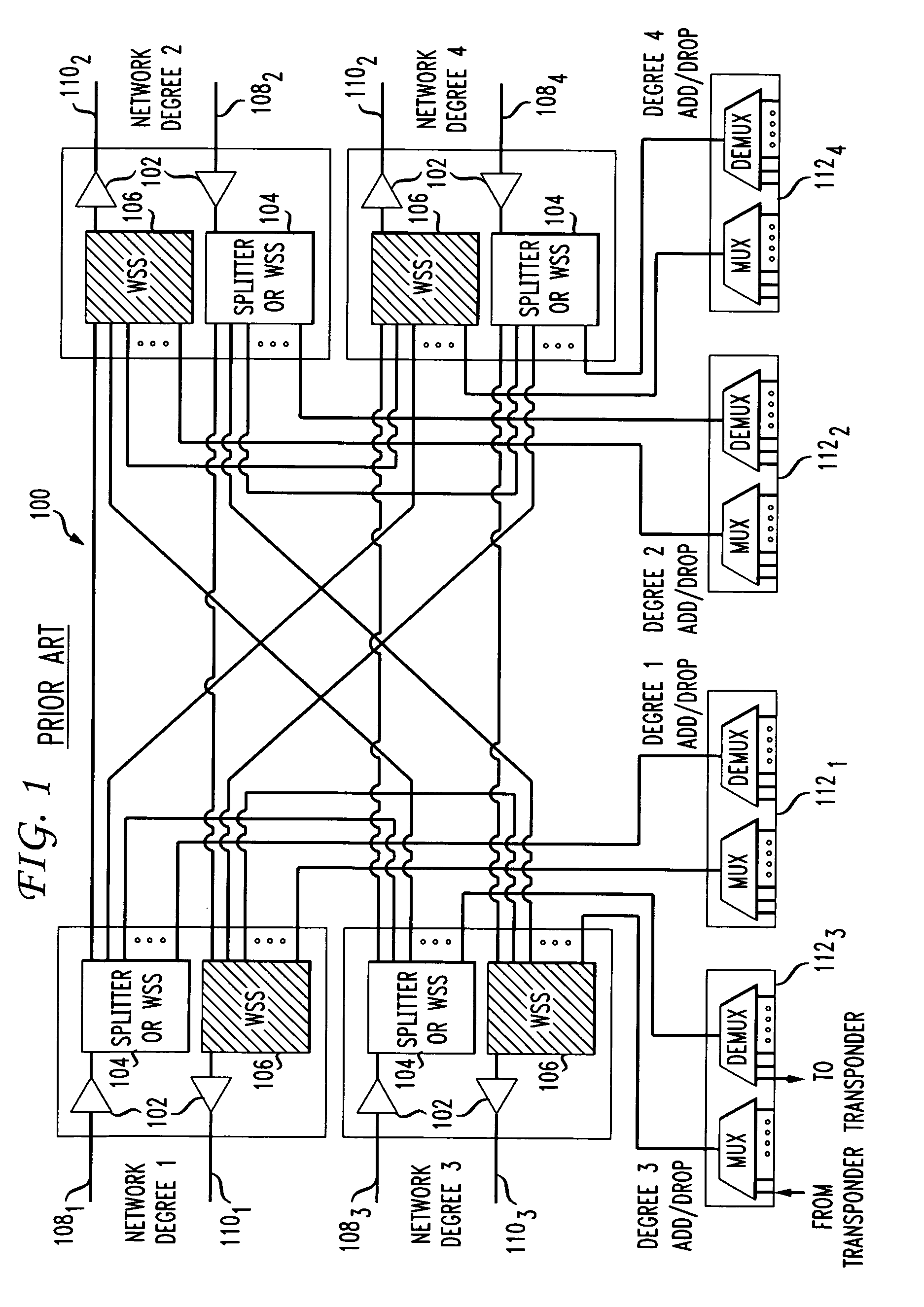
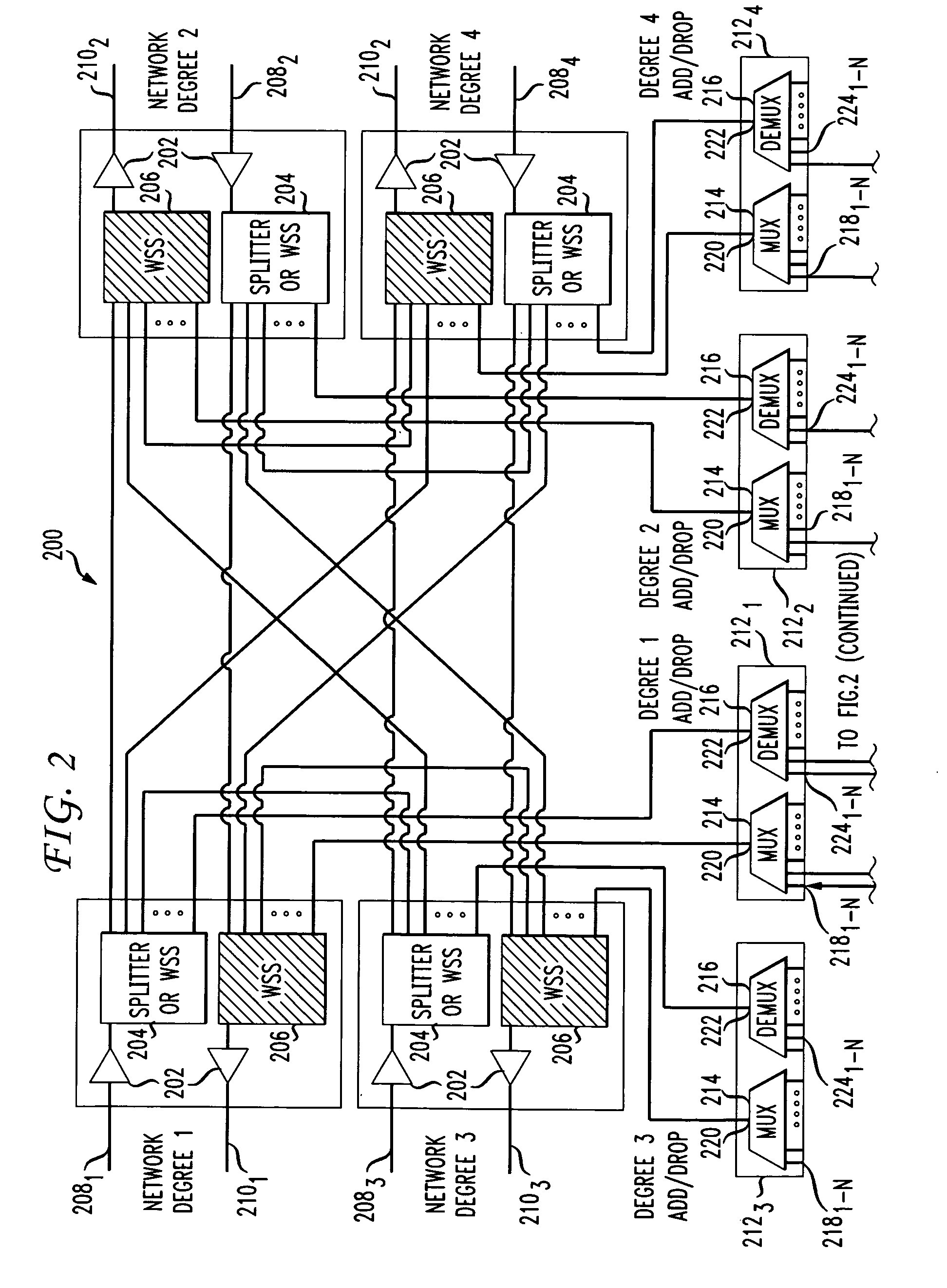
Dynamic wavelength service over a ROADM optical network
A system and method for dynamically adding / dropping wavelengths in a reconfigurable optical add-drop multiplexer (ROADM) transport network to form a wave division multiplexing virtual private network is disclosed. The system includes at least one optical transponder, a plurality of optical fan-out devices, each arranged to receive an input signal from a network degree and coupled to at least one of a plurality of optical fan-in devices, each optical fan-in device arranged to output a signal to a network degree, the optical fan-out devices comprising at least one wavelength selective switch and the optical fan-in devices comprising at least one wavelength selective switch, the optical fan-out devices and optical fan-in devices being connected so as to enable signals input from each of the plurality of network degrees to be switched to another network degree of the plurality of network degrees; a plurality of demultiplexers for locally dropping selected wavelengths; a plurality of multiplexers for locally adding selected wavelengths; and at least one customer-dedicated fiber switch interposed between the at least one optical transponder and the plurality of demultiplexers and multiplexers. The fiber switch is coupled to wavelengths and degrees that are allocated for a bandwidth-on-demand application. Other configurations include additional fan-in and fan-out devices interposed between a mux / demux assembly and the optical transponders to support wavelength redistribution applications.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
Method and apparatus for implementing a multi-dimensional optical circuit switching fabric
InactiveUS20140119728A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsCoupling light guidesHypercube architectureWavelength selective switching
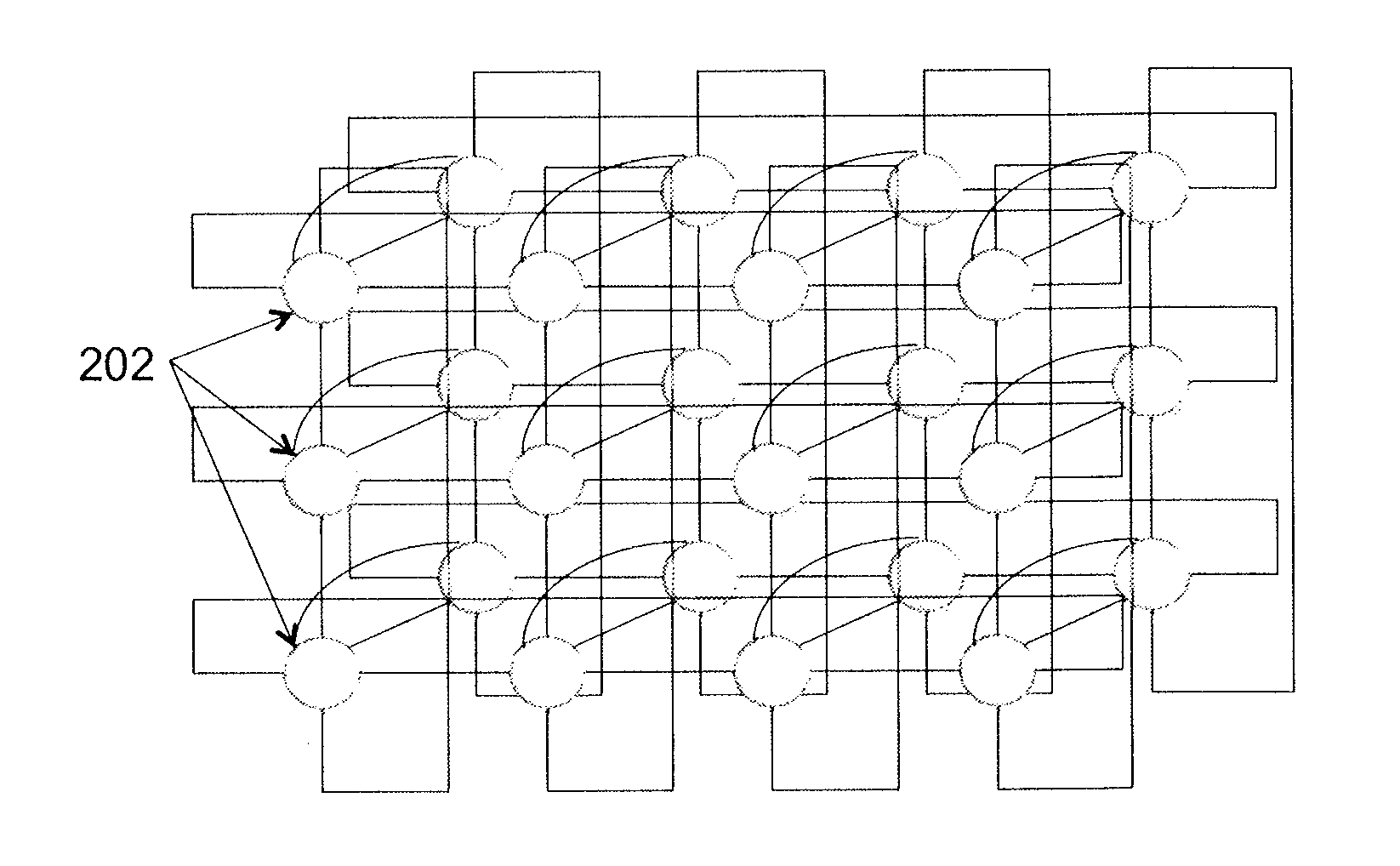
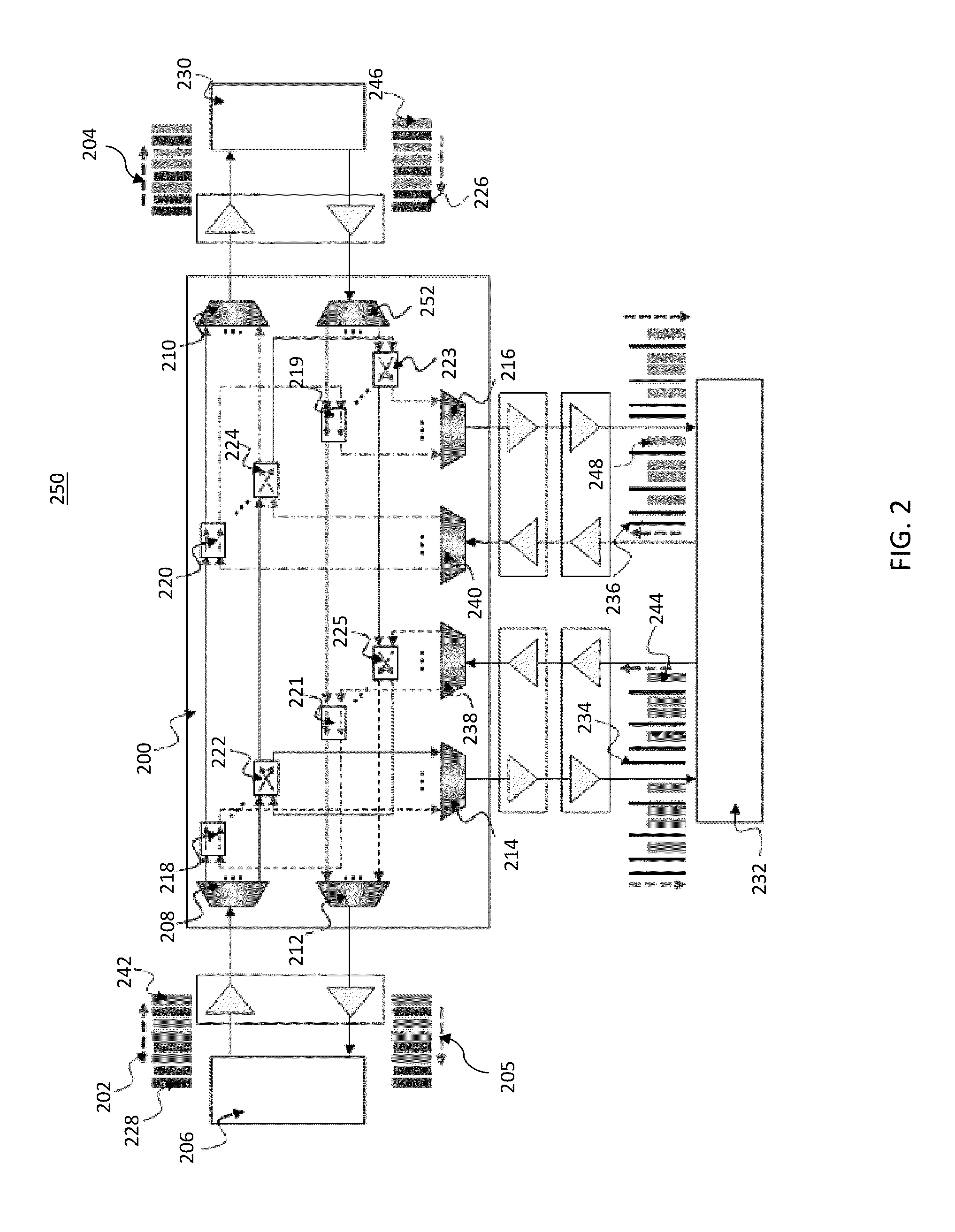
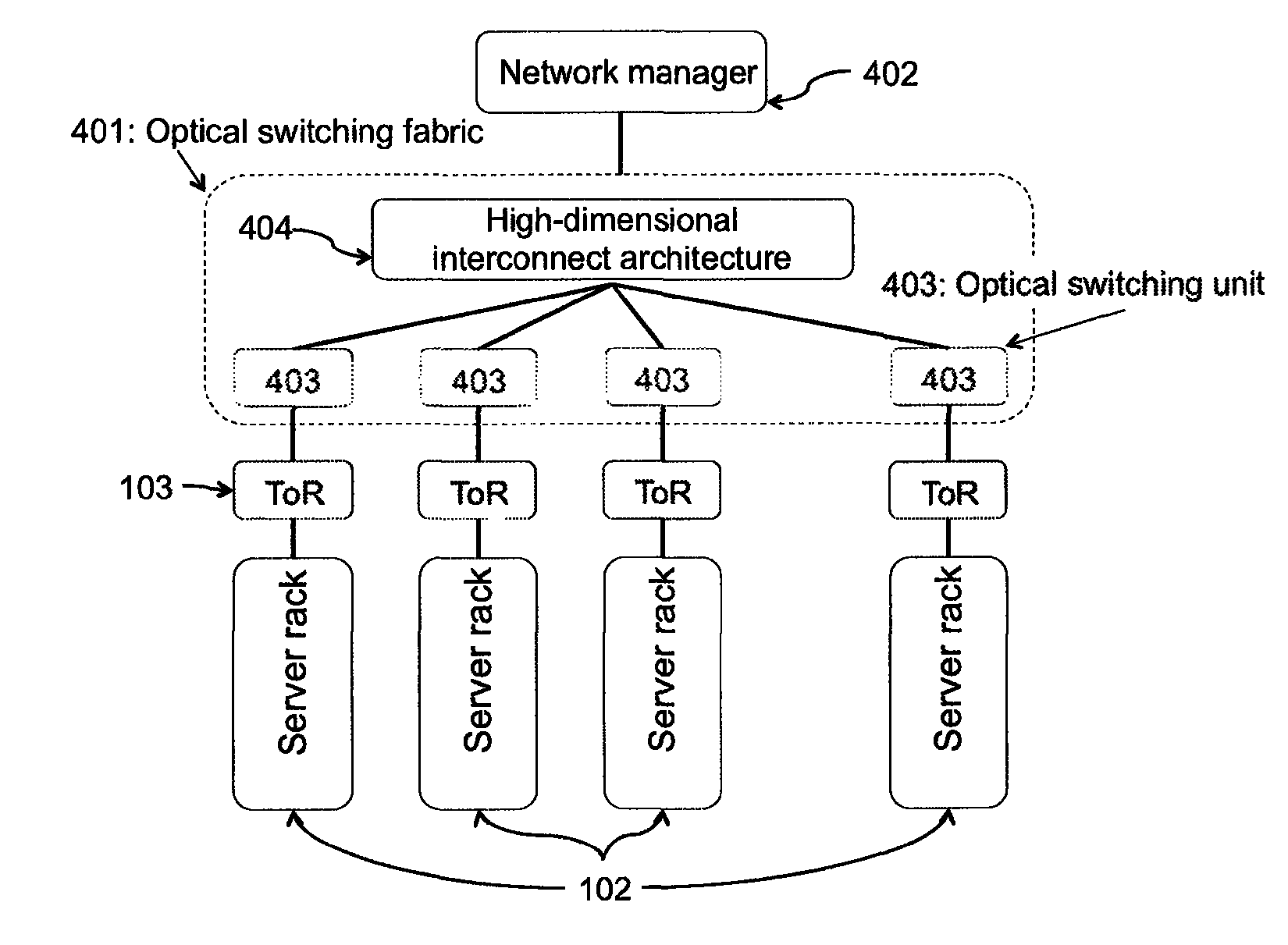
An optical switching system is described. The system includes a plurality of interconnected wavelength selective switching units. Each of the wavelength selective switching units is associated with one or more server racks. The interconnected wavelength selective switching units are arranged into a fixed structure high-dimensional interconnect architecture comprising a plurality of fixed and structured optical links. The optical links are arranged in a k-ary n-cube, ring, mesh, torus, direct binary n-cube, indirect binary n-cube, Omega network or hypercube architecture.
Owner:LIU GUOHUA
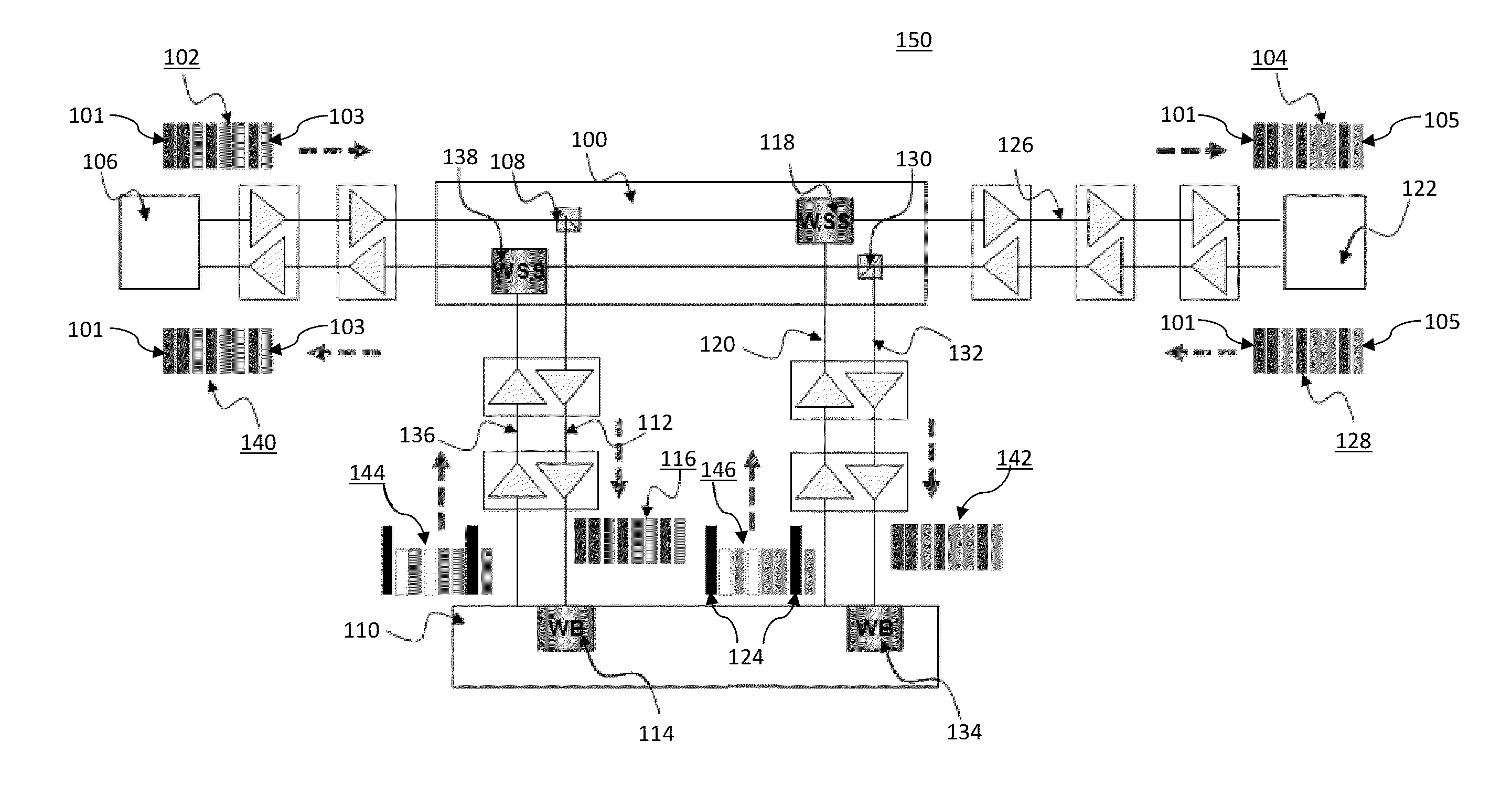
Reconfigurable branching unit for submarine optical communication networks
ActiveUS20130259475A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsData switching by path configurationFrequency spectrumWavelength selective switching
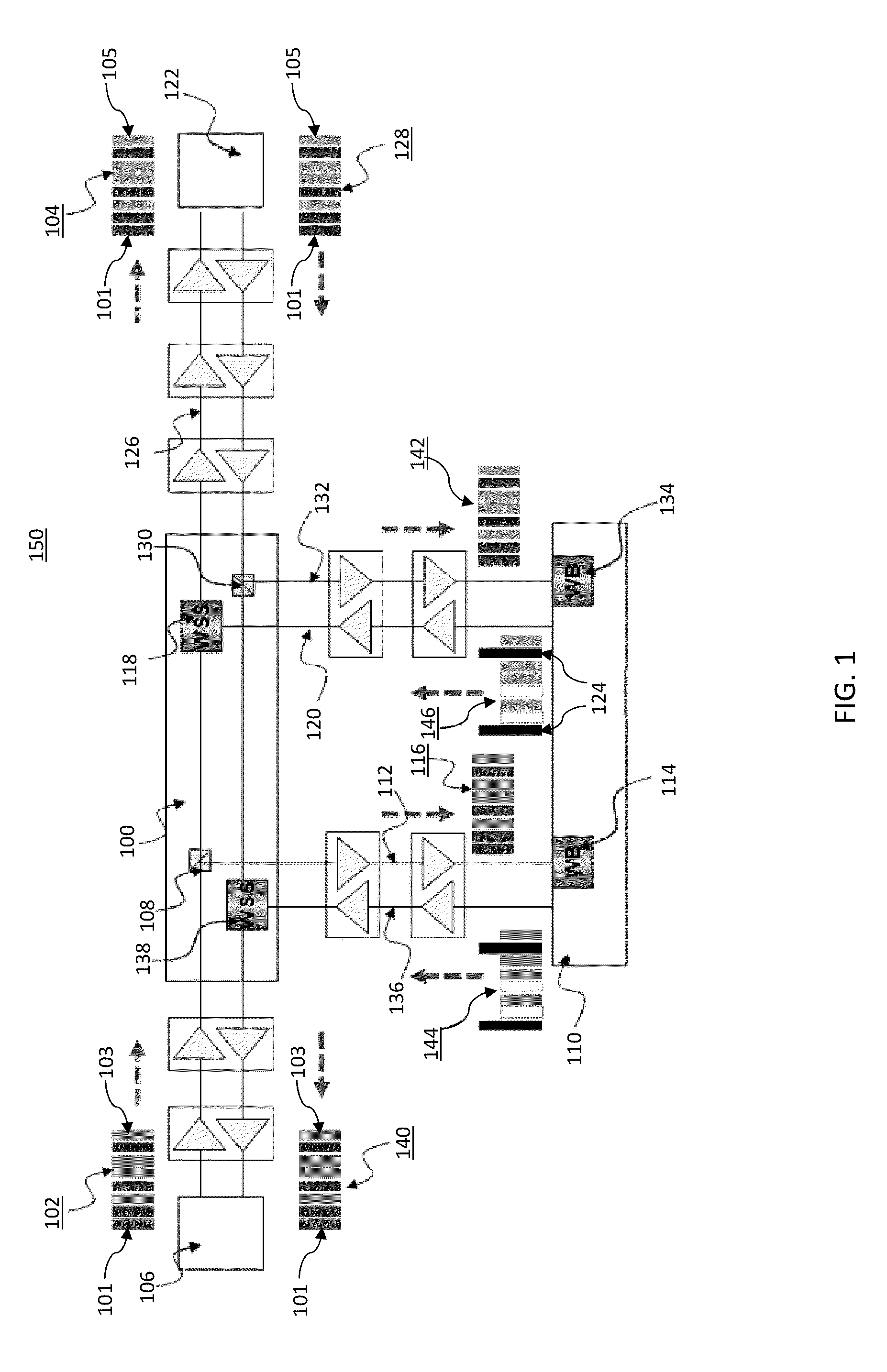
Methods and systems for optical communication in a submarine network are provided. An input signal is received from a terminal at a reconfigurable branching unit (BU), and the input signal is split into at least two parts, with one part being associated with one or more trunk terminals and another part being associated with one or more branch terminals. Each of one or more spectrum channels are selected and individually switched to one of a plurality of paths using at least one wavelength selective switch (WSS), with the at least one WSS being configured to transmit the one or more spectrum channels to their respective target output port and to combine signals switched to a specific port into a wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) signal. Individual spectrum channels are filtered out using at least one wavelength blocker (WB).
Owner:NEC CORP
Wavelength selective optical switch
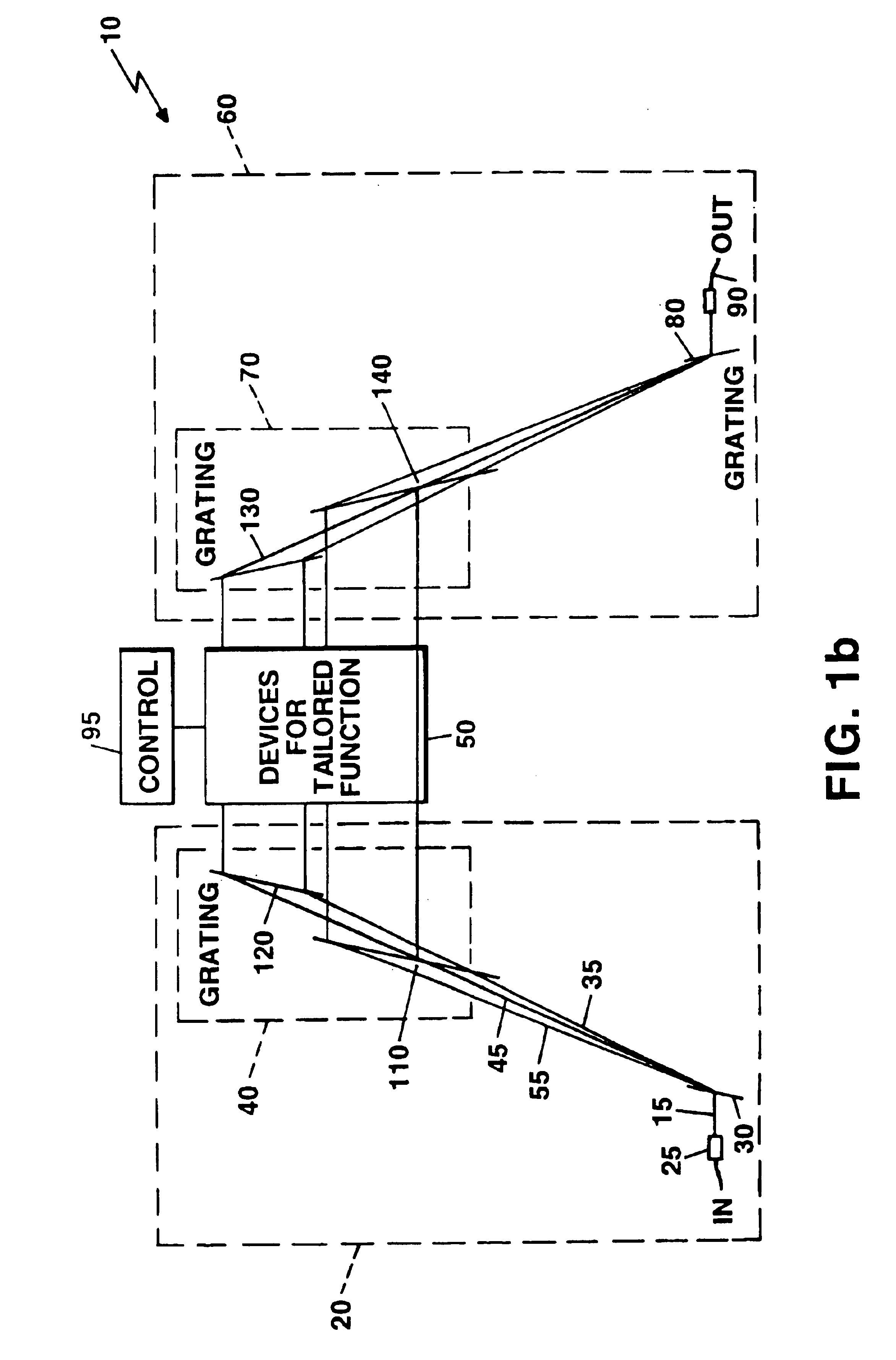
ActiveUS7058251B2Reduce polarizationReduce PDLDiffraction gratingsCoupling light guidesGratingCommunications system
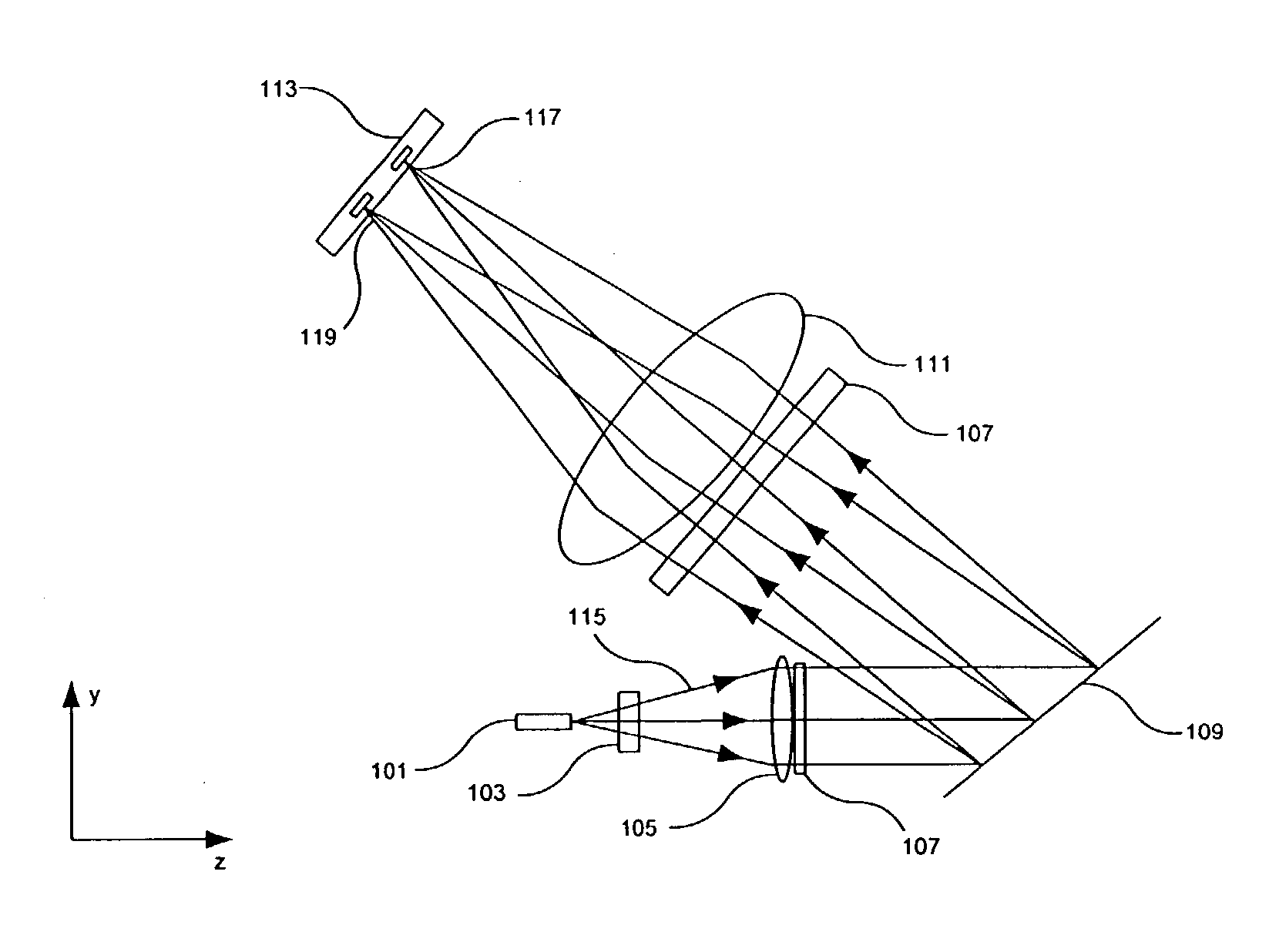
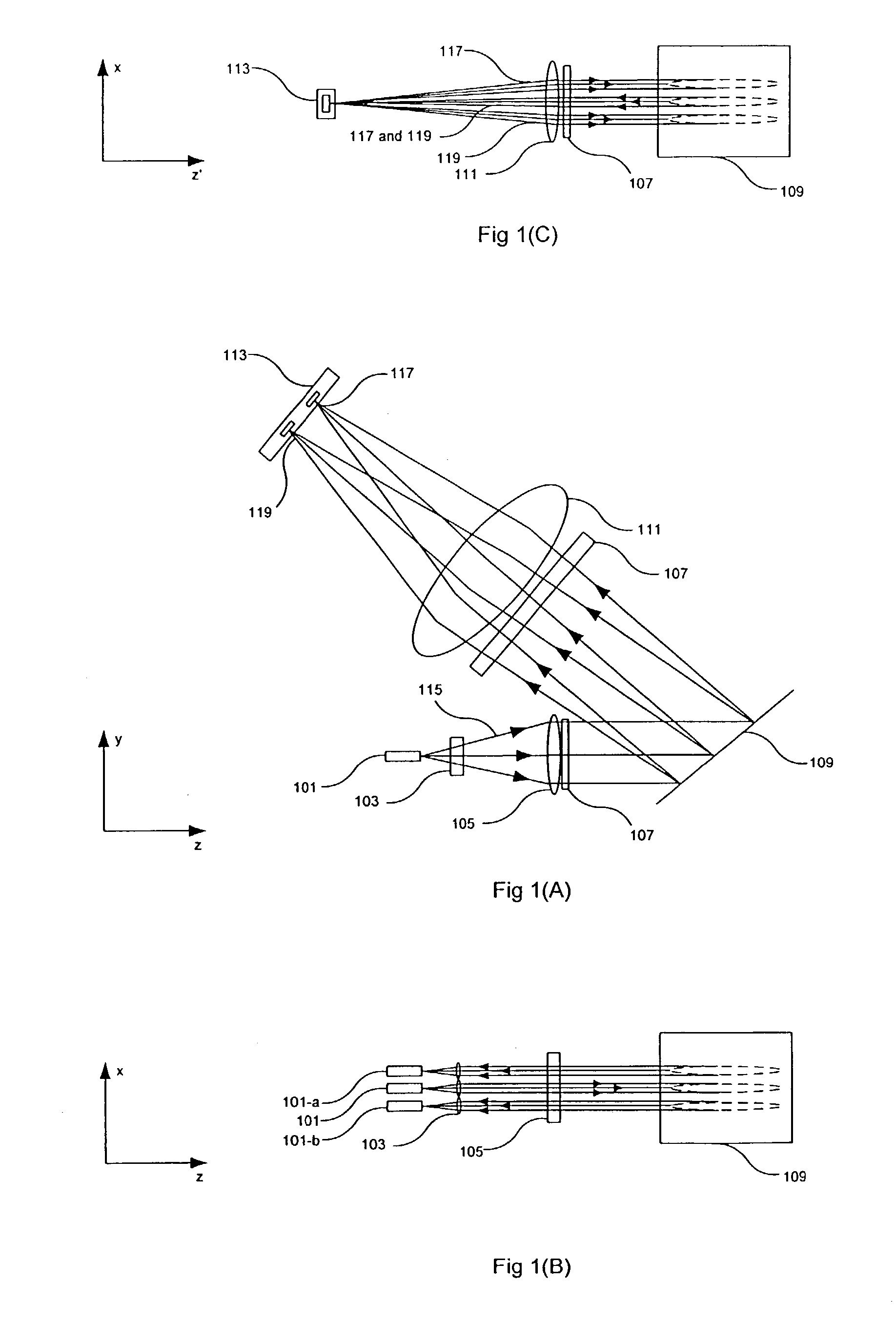
A wavelength selective optical switch particularly usable as a programmable N×M optical switch in a multi-wavelength communication system. The switch uses a grating that separates multi-channel optical signals into a plurality of optical channels, and combines a plurality of optical channels into multi-channel optical signals. Programmable mirrors switch each optical channel to any of a plurality of fibers coupled to the switch.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
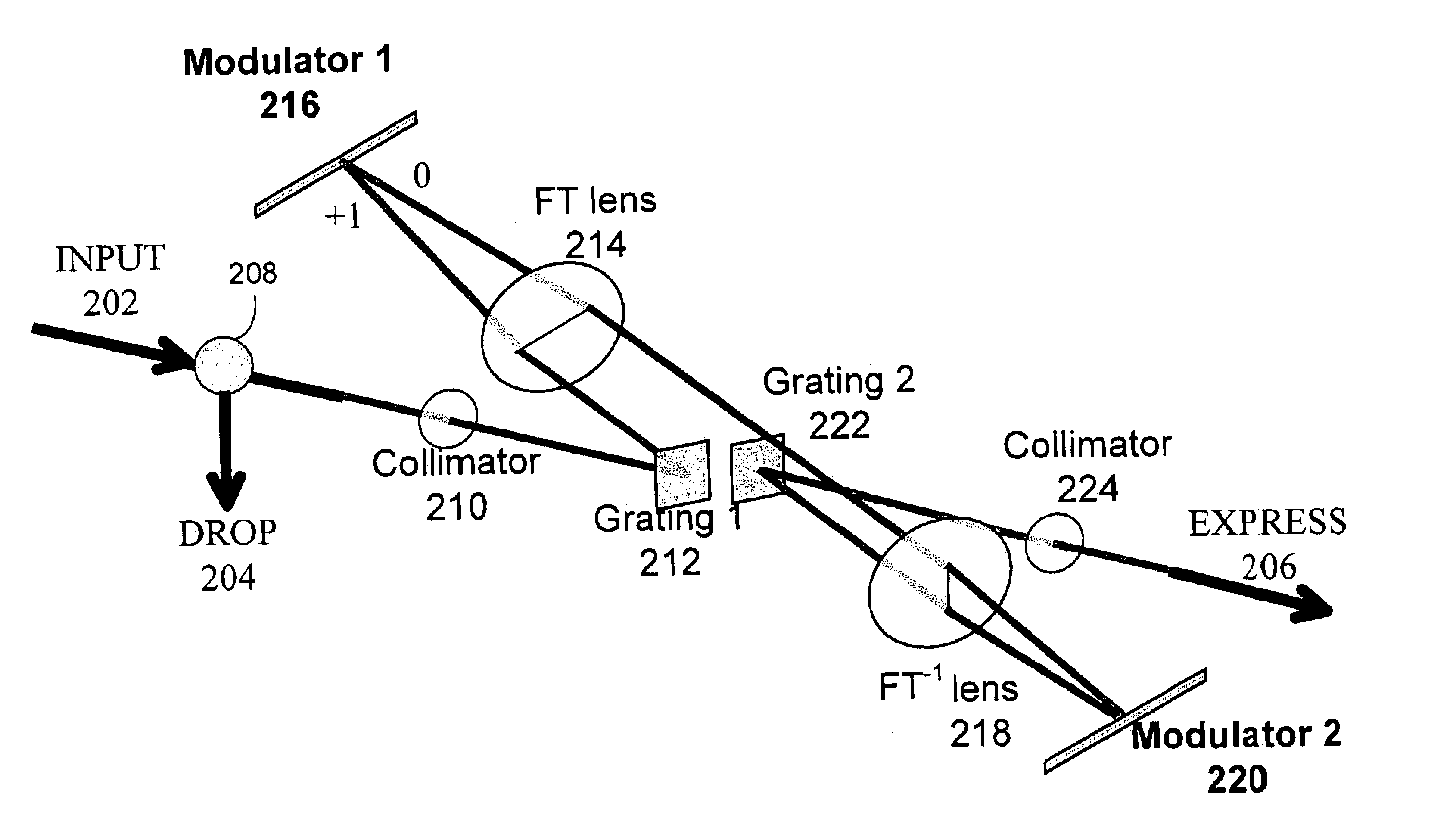
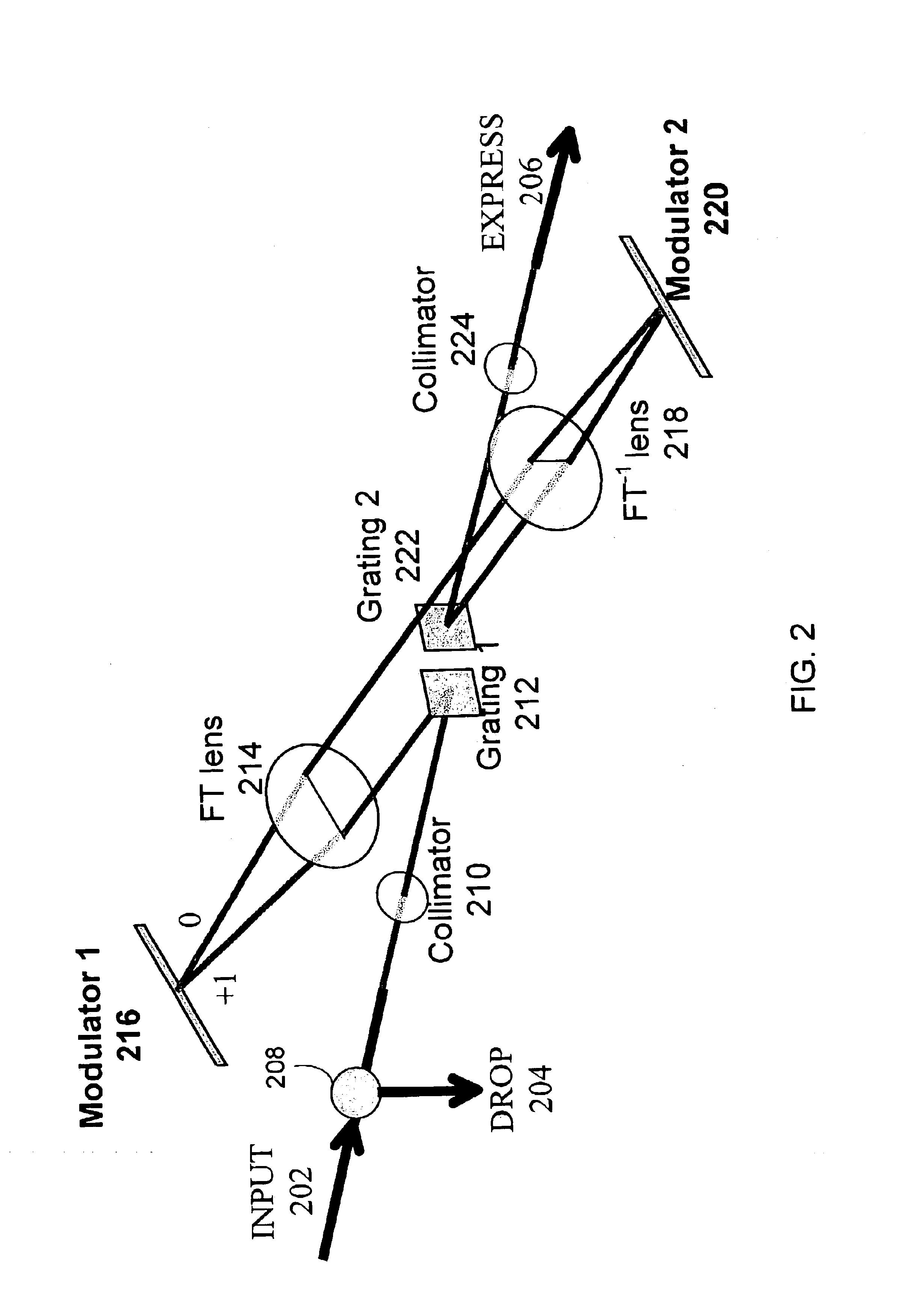
Dual modulator wavelength-selective switch and equalizer
InactiveUS6876475B1Wavelength-division multiplex systemsCoupling light guidesMultiplexingWavelength selective switching
One embodiment pertains to an apparatus for wavelength-selective switching and equalization of an incoming multiplexed signal having a plurality of wavelength components. The apparatus includes a first controllable light modulator, a second controllable light modulator, and a lens system. The first controllable light modulator controllably deflects a first set of the wavelength components and controllably reflects a second set of the wavelength components. The wavelength components in the second set are mapped onto separate sections of the second controllable light modulator by the lens system and are controllably reflected by the second controllable light modulator.
Owner:SILICON LIGHT MACHINES CORP
Apparatus and method for optical switching with liquid crystals and birefringent wedges
ActiveUS7492986B1Polarisation multiplex systemsWavelength-division multiplex systemsWavelength selective switchingOptical power
An optical switching apparatus includes at least one optical waveguide to deliver at least one input optical beam. A dispersion device spatially separates the at least one input optical beam into individual wavelength channels. An optical power device aligns the individual wavelength channels. An optical switch has at least one transflective polarizing element, at least one birefringent wedge and at least two polarization switches. The individual wavelength channels are directed to independently addressable regions of the polarization switches for wavelength selective switching. A second optical power device aligns the individual wavelength channels from the optical switch. A second dispersion device spatially combines individual wavelength channels from the second optical power device. At least one output optical waveguide receives at least one of the individual wavelength channels from the second dispersion device.
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC
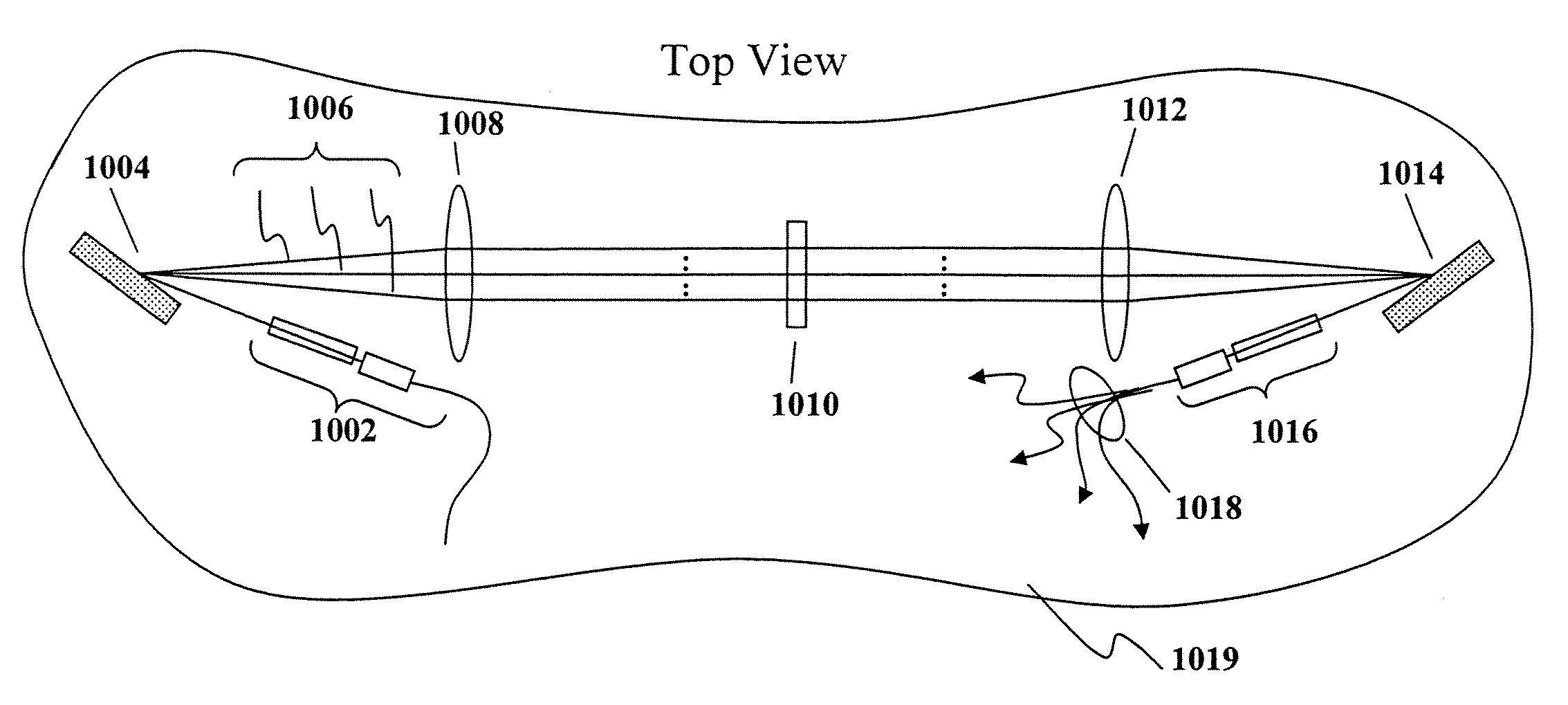
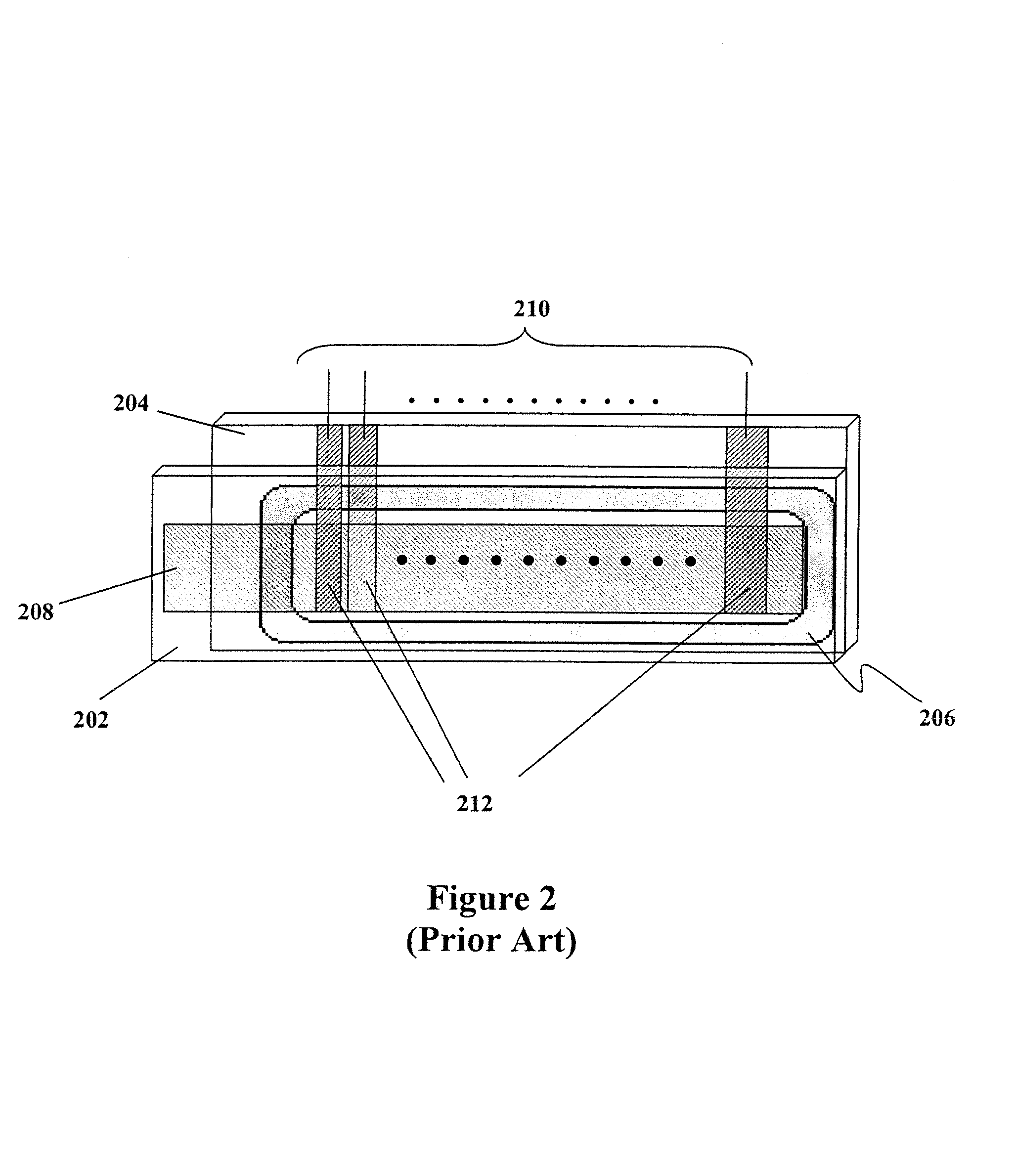
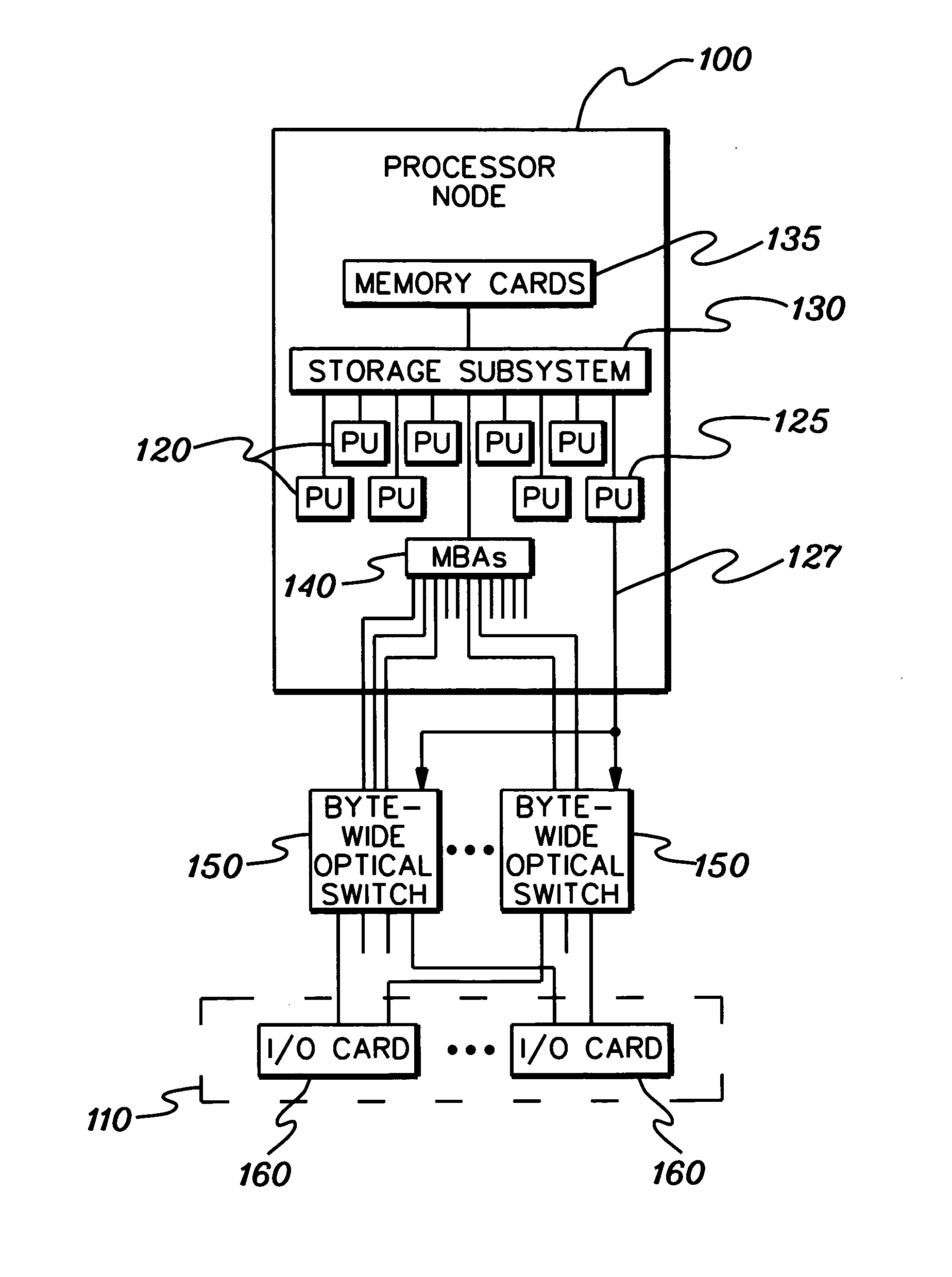
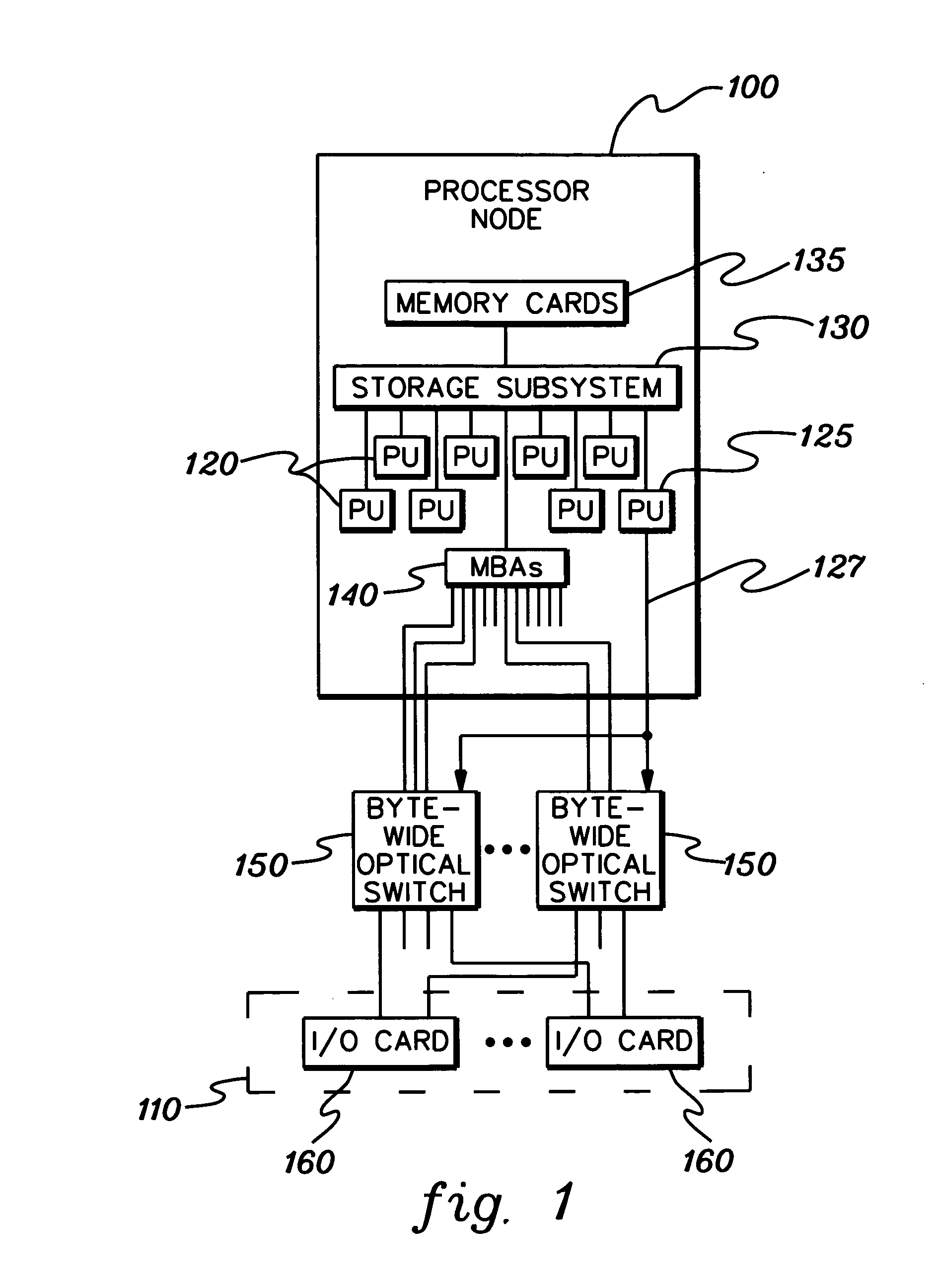
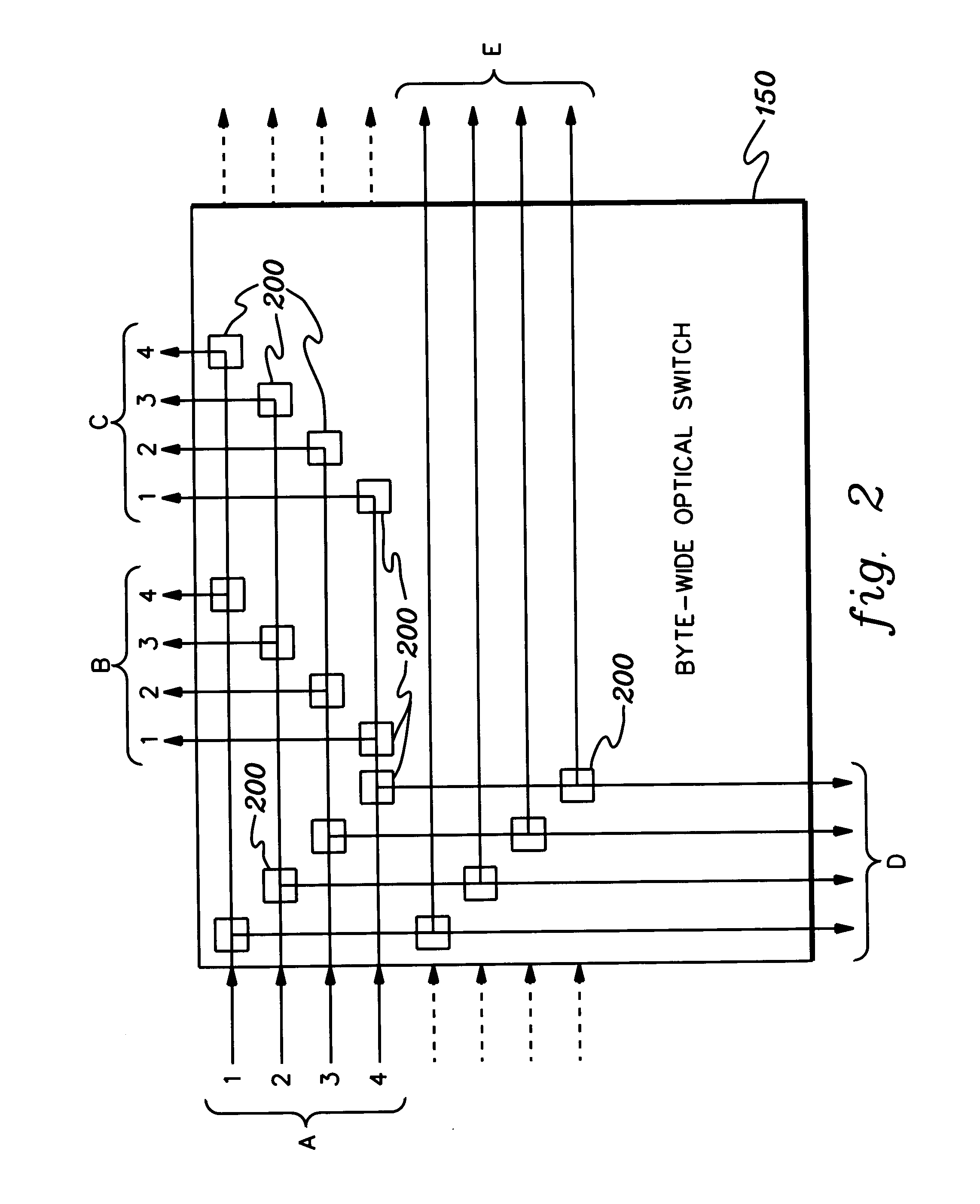
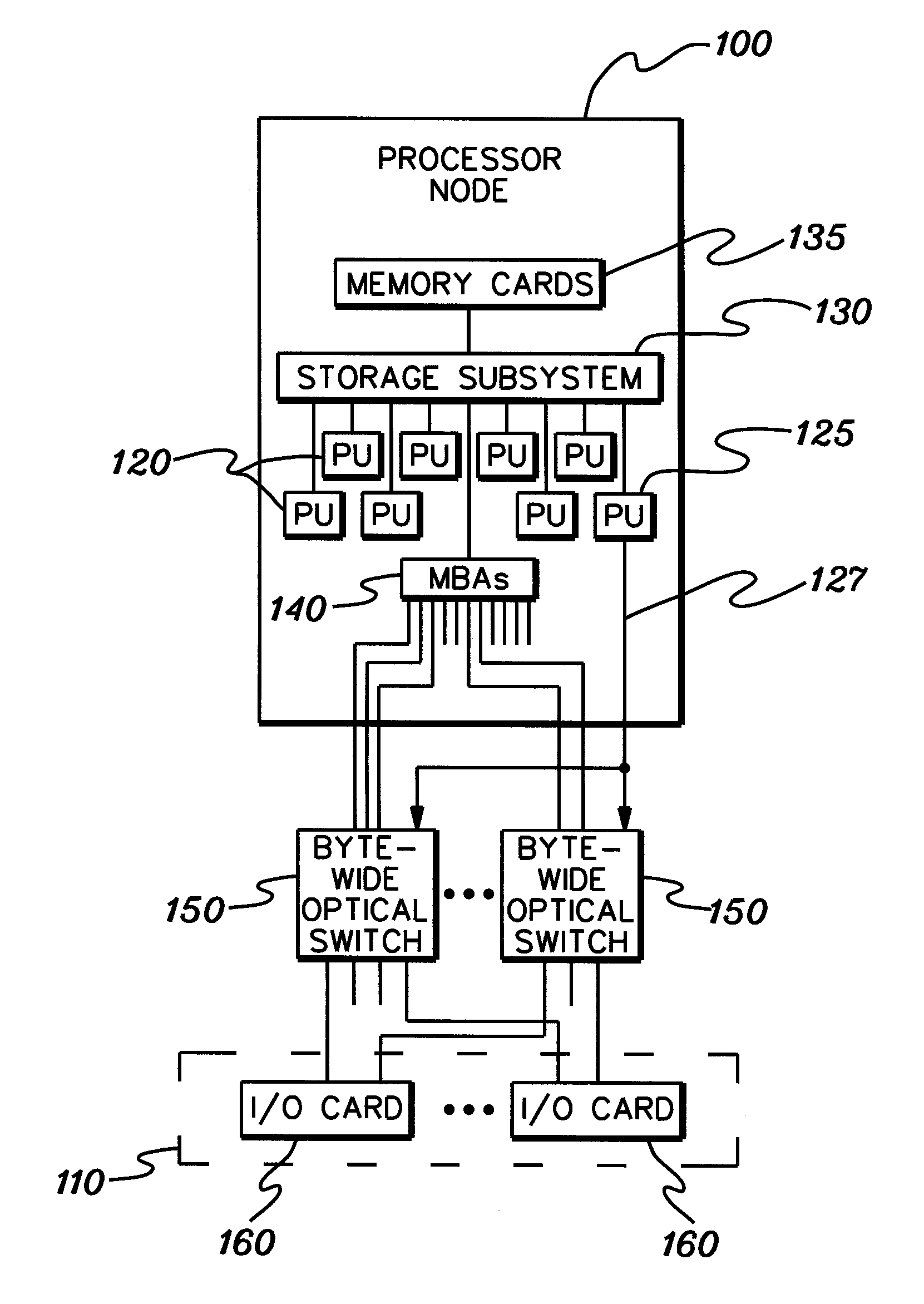
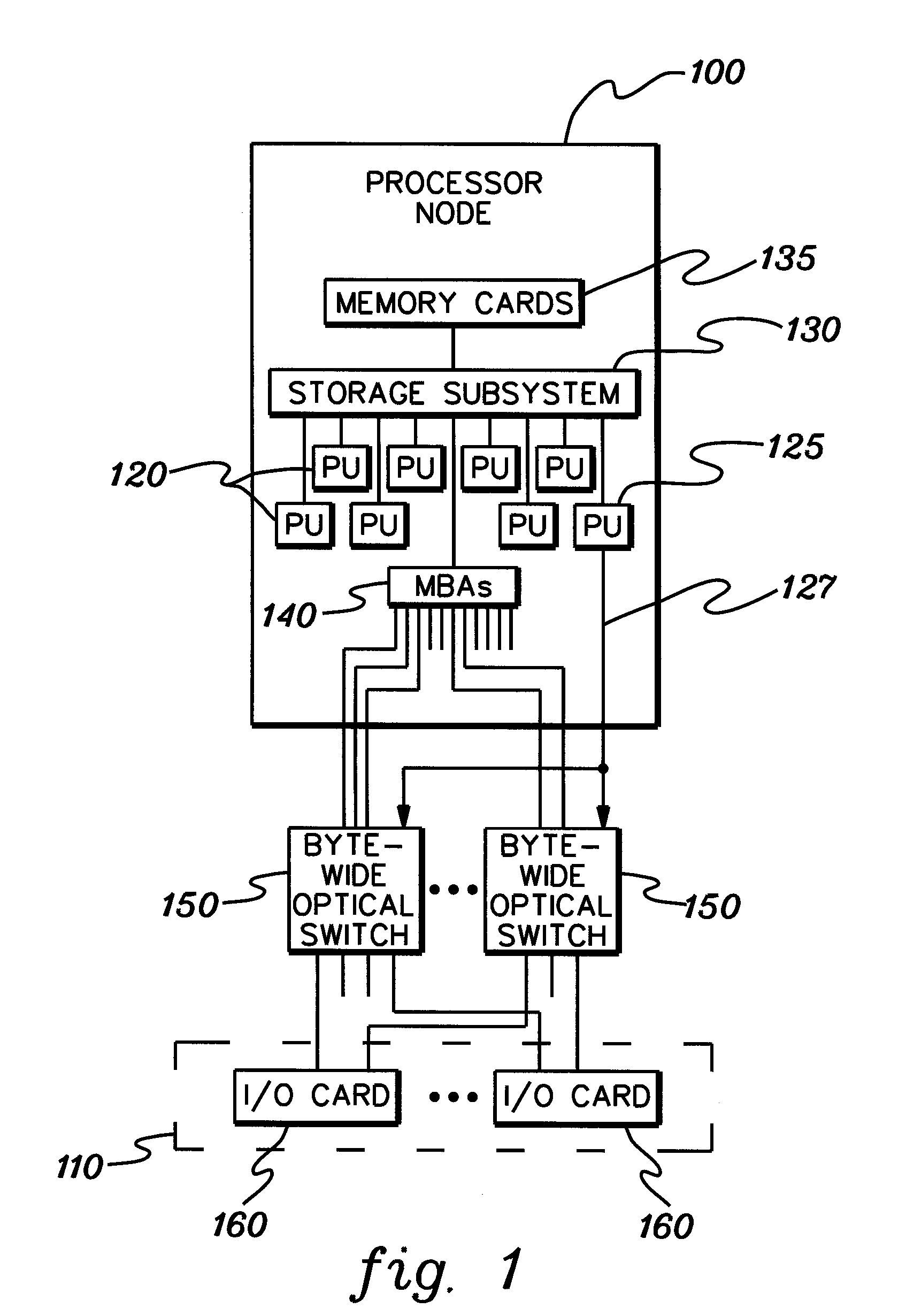
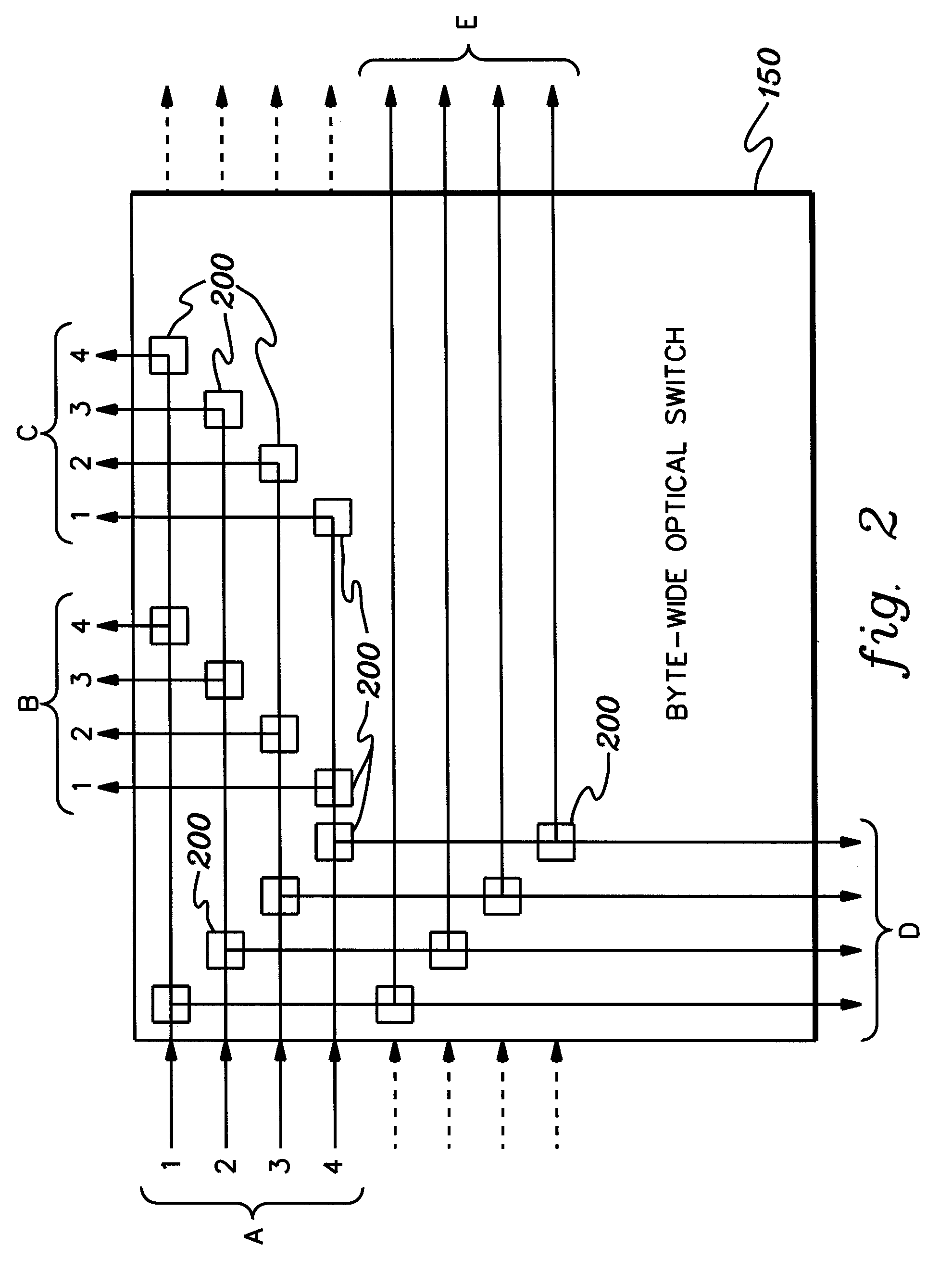
Byte-wide optical backplane switch and switching method
InactiveUS20050095000A1High bandwidthMultiplex system selection arrangementsLaser detailsWavelength selective switchingOptical backplane
A byte-wide optical switch and switching method are provided. The optical switch includes a first set of ports for receiving in parallel an optical byte of data, and multiple second sets of ports each capable of outputting in parallel the optical byte of data. An array of optical switching elements is disposed between the first set of ports and the multiple second sets of ports. The array of optical switching elements direct the optical byte of data in parallel from the first set of ports to at least one second set of ports of the multiple second sets of ports. The switching elements may comprise micro-electro mechanical system (MEMS) devices, each having a position controllable reflective surface. Thin film optical filters can be provided on the reflective surfaces for wavelength selective switching.
Owner:IBM CORP
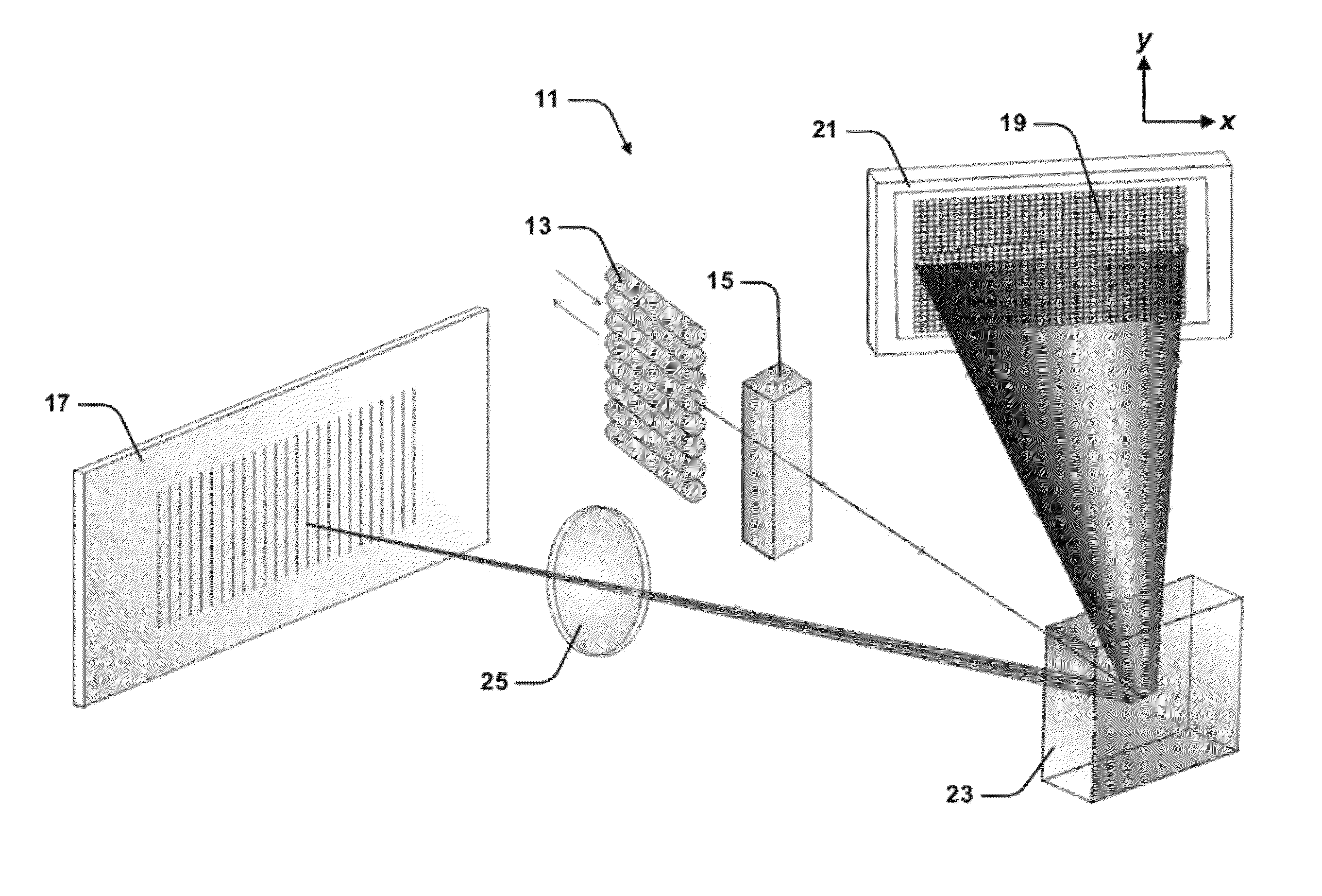
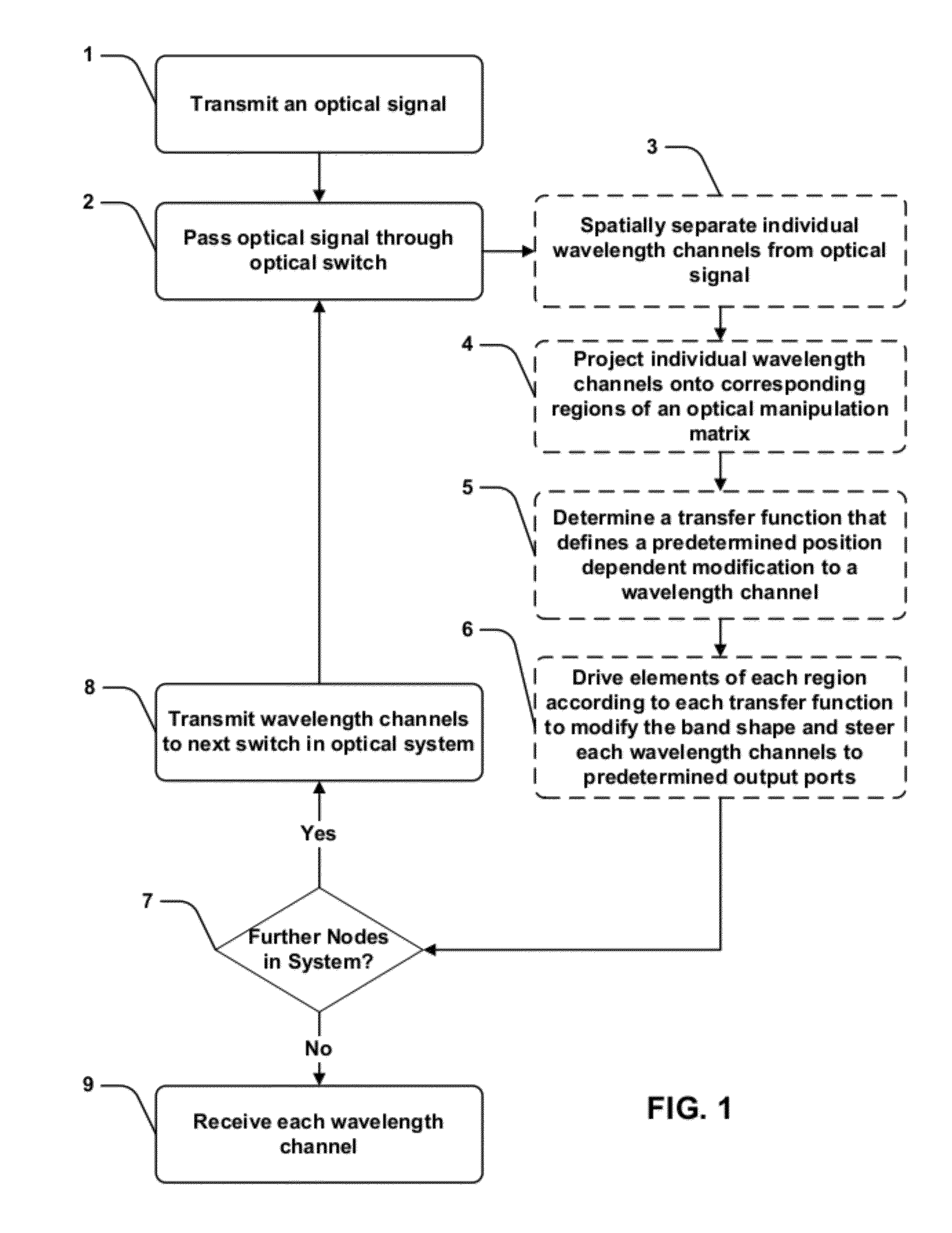
Optical wavelength selective switch calibration system
ActiveUS8867917B2Facilitate transmissionHigh bandwidthMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsBand shapeWavelength selective switching
Described herein are systems and methods of enhancing channel bandwidth in an optical system having a number of wavelength selective switching (WSS) devices. The method includes the steps of passing the optical signals through the WSS devices by: (i) spatially dispersing the wavelength channels of the optical signals; (ii) projecting the spatially dispersed channels onto corresponding predetermined regions of an optical manipulation matrix including a plurality of individually addressable manipulating elements; (iii) determining a modification function that specifies a state for each manipulating element within the predetermined region; and (iv) driving the elements of the corresponding regions at states specified by the function to selectively modify the channel band shape such that the received channel's bandwidth is substantially enhanced, and to spatially direct the wavelength channels to predetermined output ports of the WSS devices.
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC
Method and apparatus for implementing a multi-dimensional optical circuit switching fabric
InactiveUS9332323B2Multiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsHypercube architectureWavelength selective switching
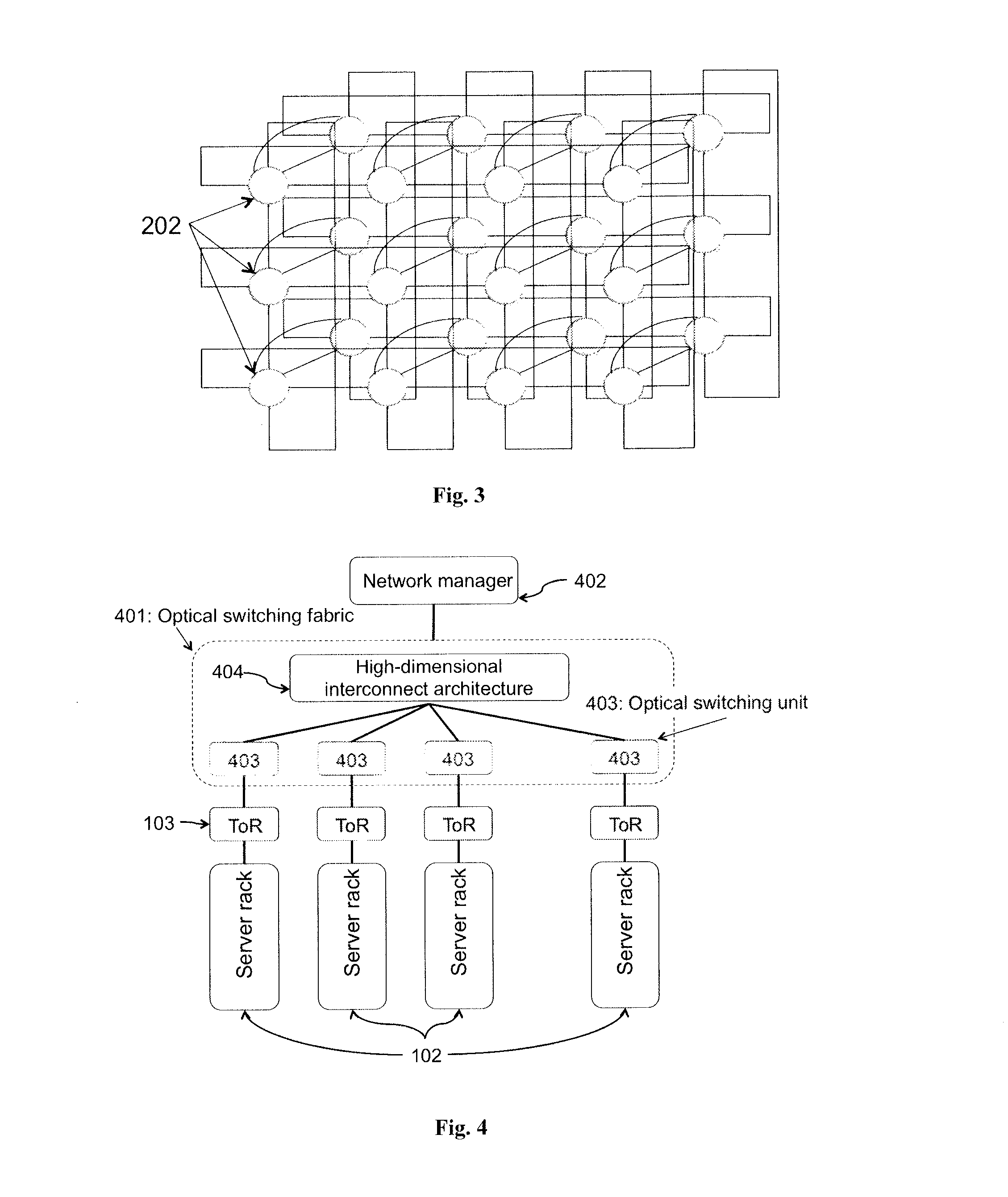
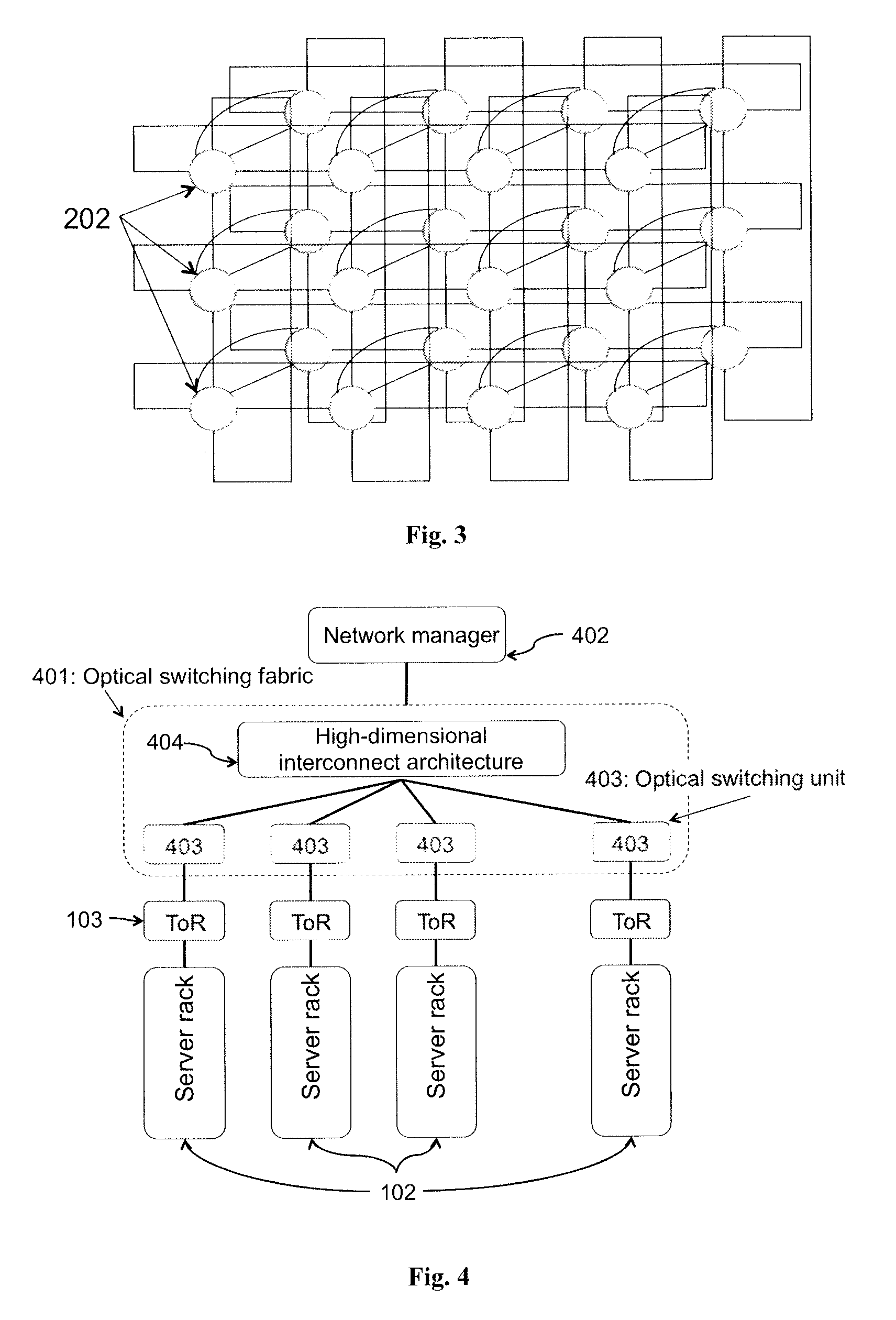
An optical switching system is described. The system includes a plurality of interconnected wavelength selective switching units. Each of the wavelength selective switching units is associated with one or more server racks. The interconnected wavelength selective switching units are arranged into a fixed structure high-dimensional interconnect architecture comprising a plurality of fixed and structured optical links. The optical links are arranged in a k-ary n-cube, ring, mesh, torus, direct binary n-cube, indirect binary n-cube, Omega network or hypercube architecture.
Owner:LIU GUOHUA
Compact DMD-based optical module
InactiveUS7203398B2Improved optical interfaceLess sensitive to movementCoupling light guidesOptical ModuleWavelength selective switching
An optical module having an integral optical waveguide with waveguide ports at each end. The optical waveguide receives an input light beam through a first waveguide port. The input light beam passes through the waveguide and is emitted from the second waveguide port, where it is reflected by the reflective surface. After being reflected by the reflective surface, the input light beam can be directed onto the surface of a DMD array, where the input light beam can be selectively reflected in a particular direction. The reflective surface may also comprise a diffractive grating, thereby enabling wavelength selective switching. In addition, the reflective surface may comprise a generally concave surface that converts a diverging input light beam into a generally collimated light beam, thereby facilitating more accurate selection and switching by the DMD array.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Wavelength selective switching device and method for selectively transmitting optical signals based on wavelength
InactiveUS20060077552A1Reduce device sizeSmall sizeMultiplex system selection arrangementsPrismsWavelength selective switchingLength wave
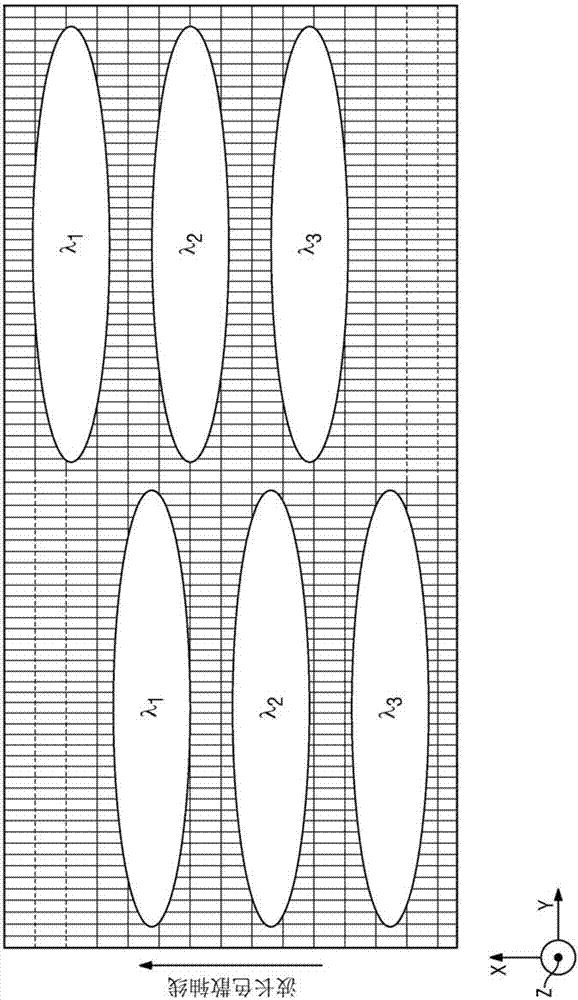
A wavelength selective switching device and method for selectively transmitting optical signals based on wavelength utilizes diffraction to spatially separate the optical signals of different wavelengths such that the optical signal of a selected wavelength can be selectively transmitted. The wavelength selective switching device selectively rotates the polarization components of the optical signals such that the polarization states of the polarization components are the same in both incoming and outgoing directions at the diffraction grating. Thus, a diffraction grating with a high grating line frequency (e.g. greater than 900 grating lines per mm for signals in the 1550 nm wavelength range) can be used for diffracting the polarization components of the optical signals in both the incoming and outgoing directions.
Owner:AVAGO TECHNOLOGIED FIBER IP SINGAPORE PTE LTD
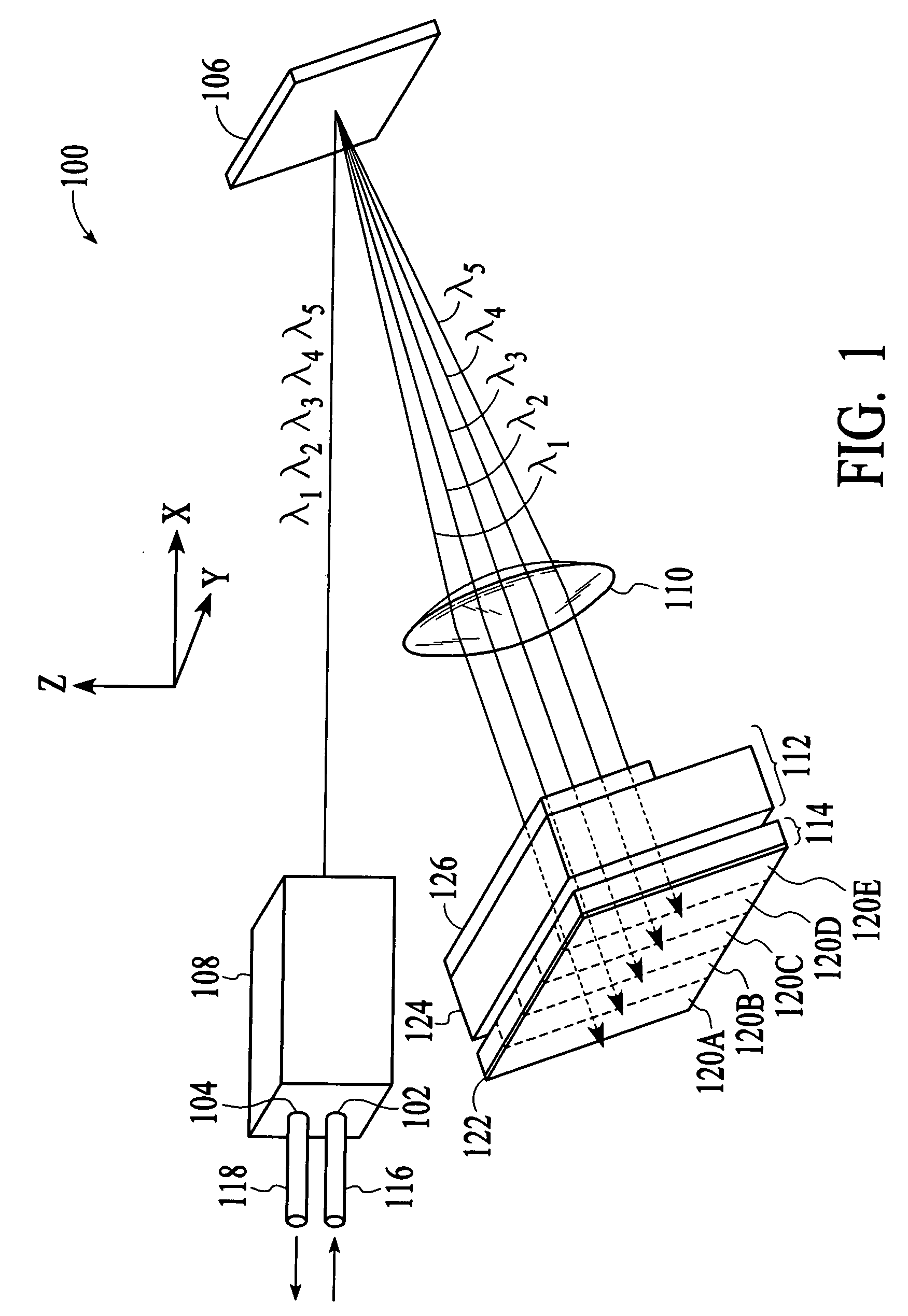
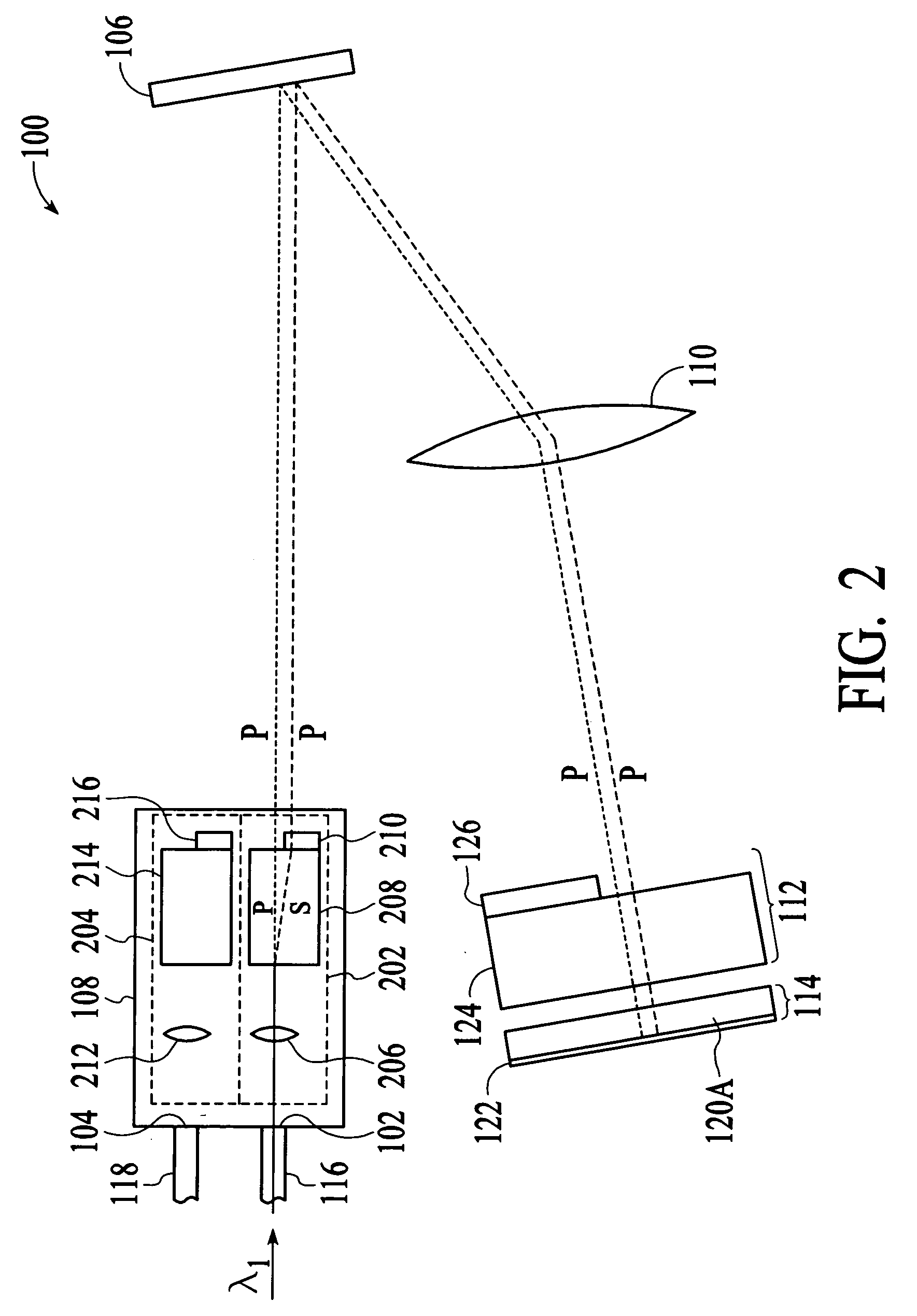
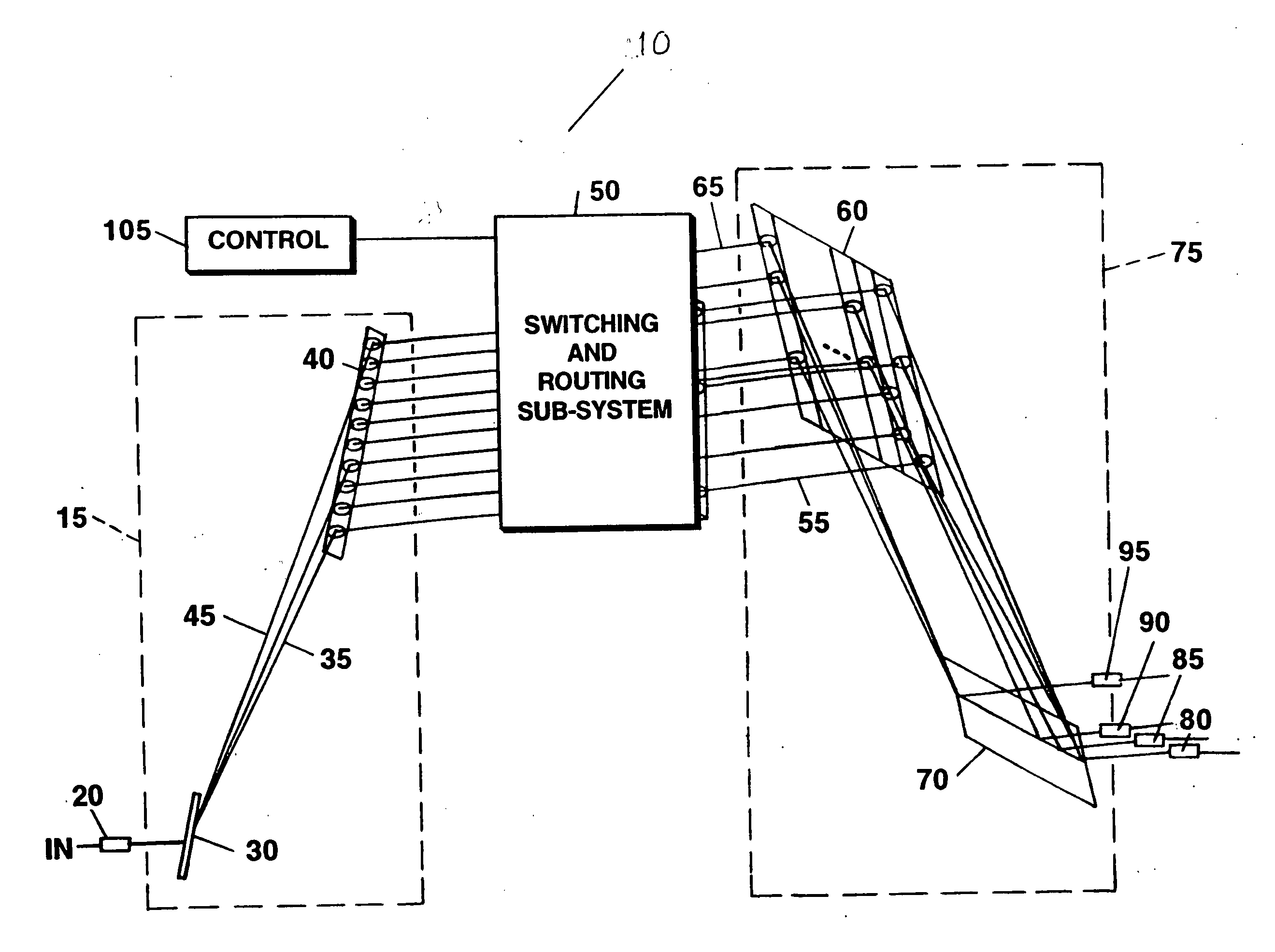
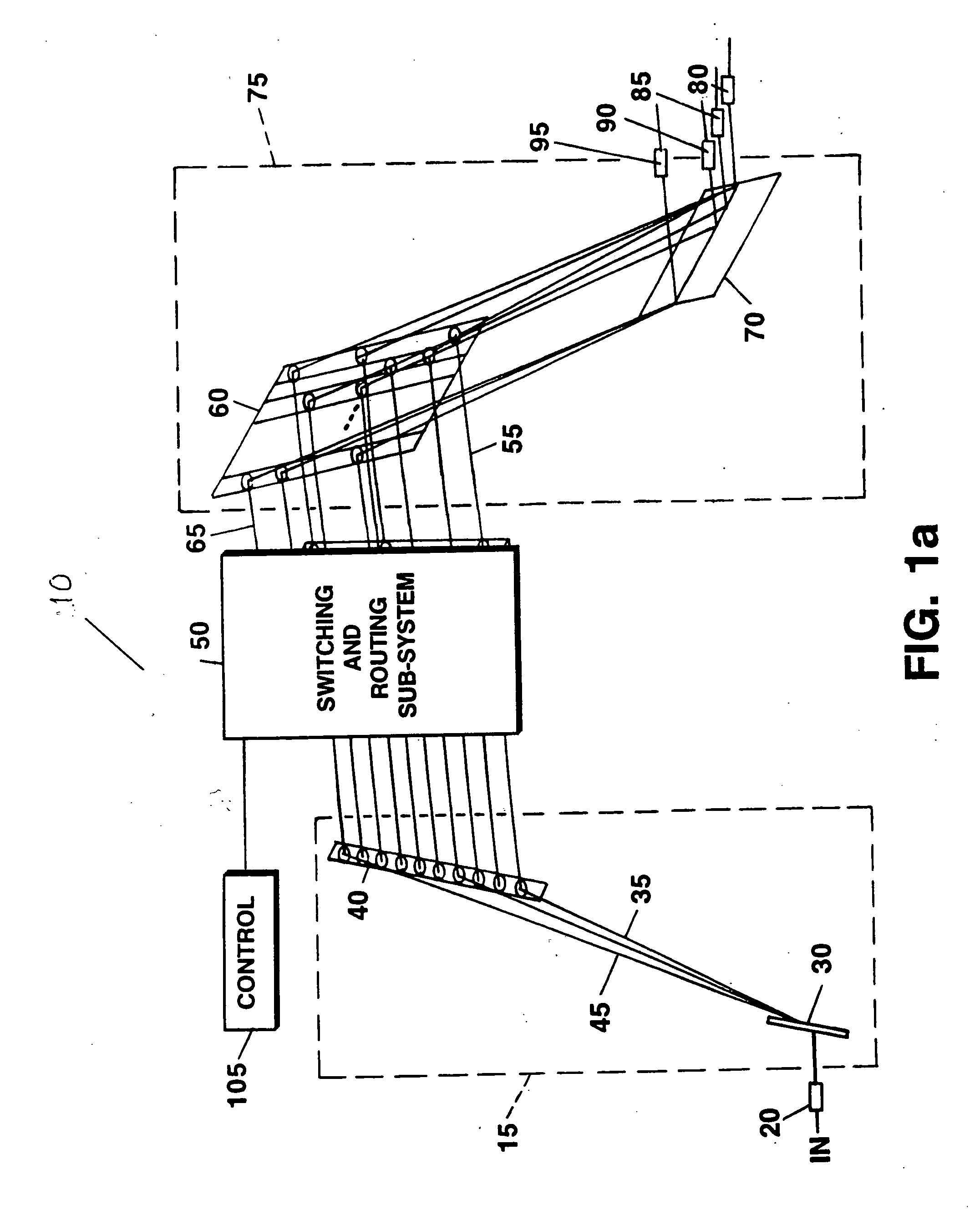
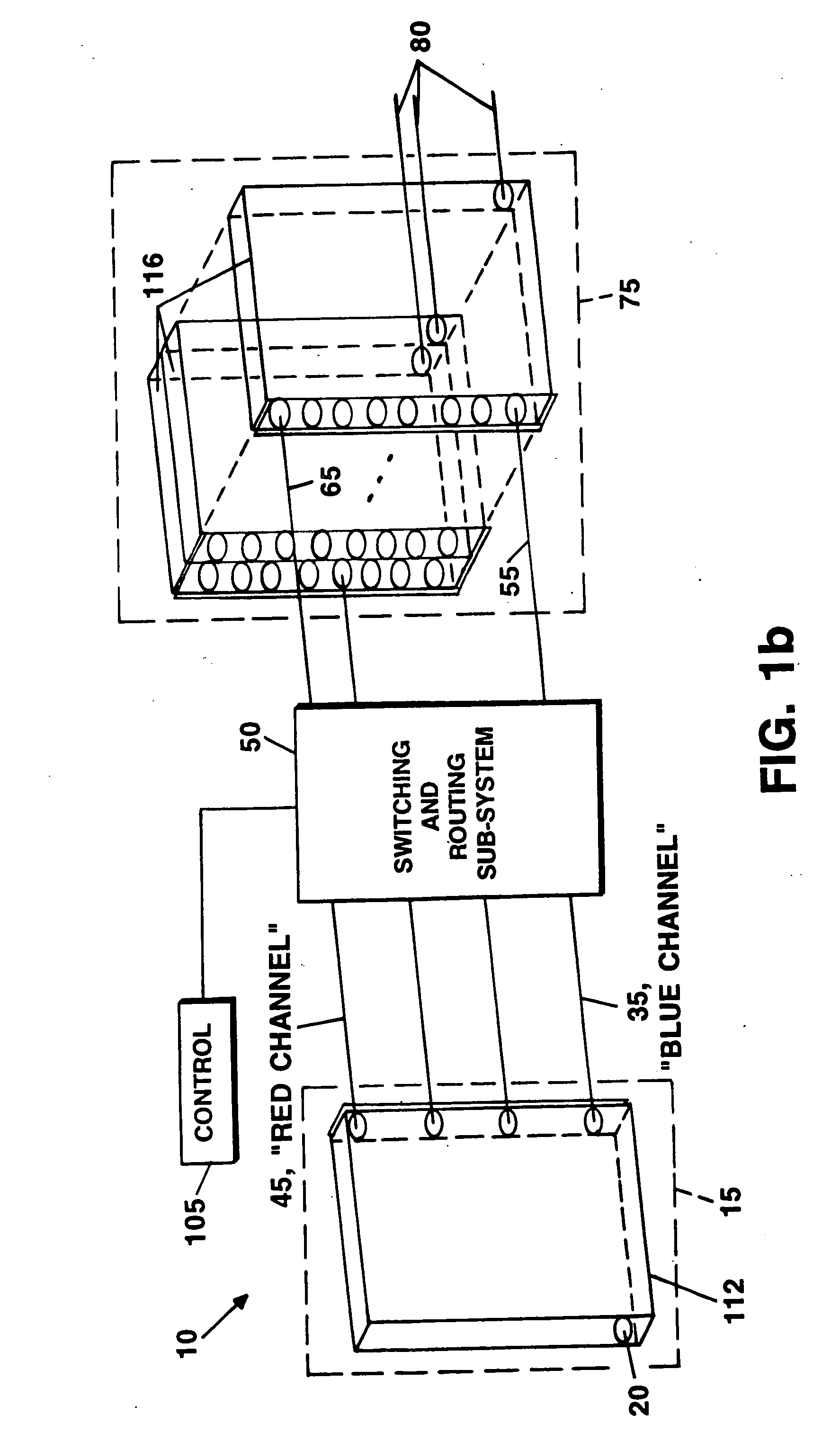
Wavelength selective switching and/or routing system
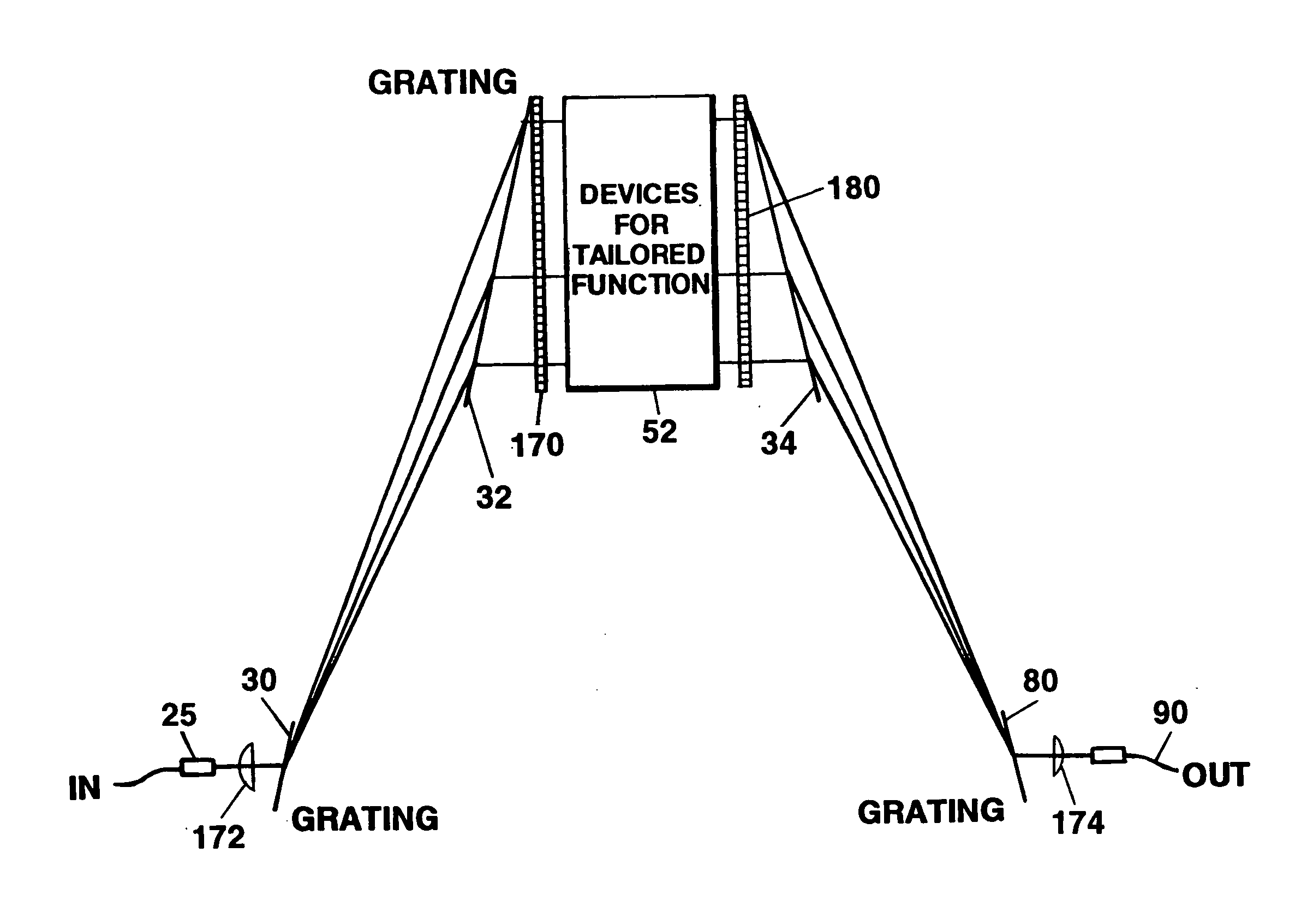
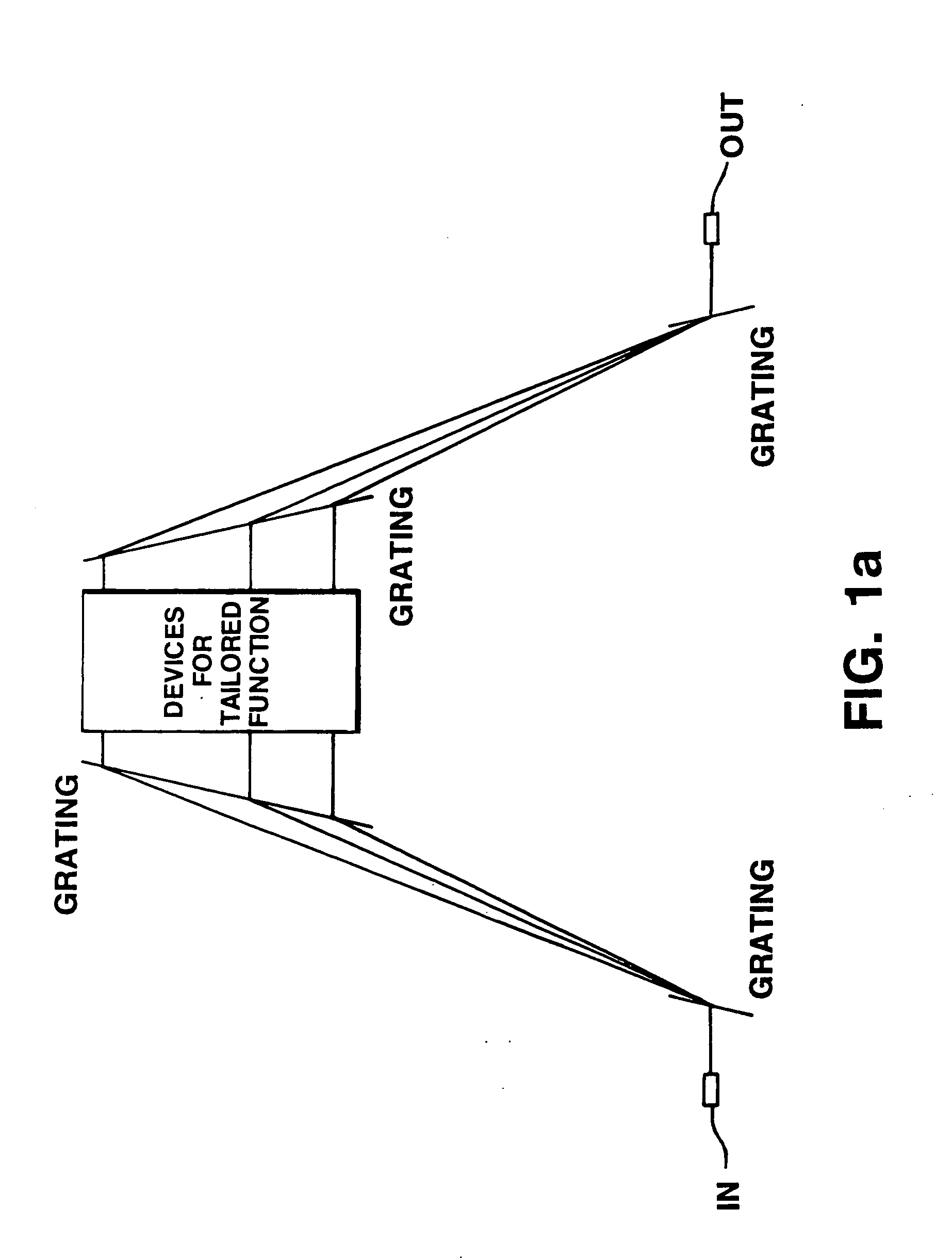
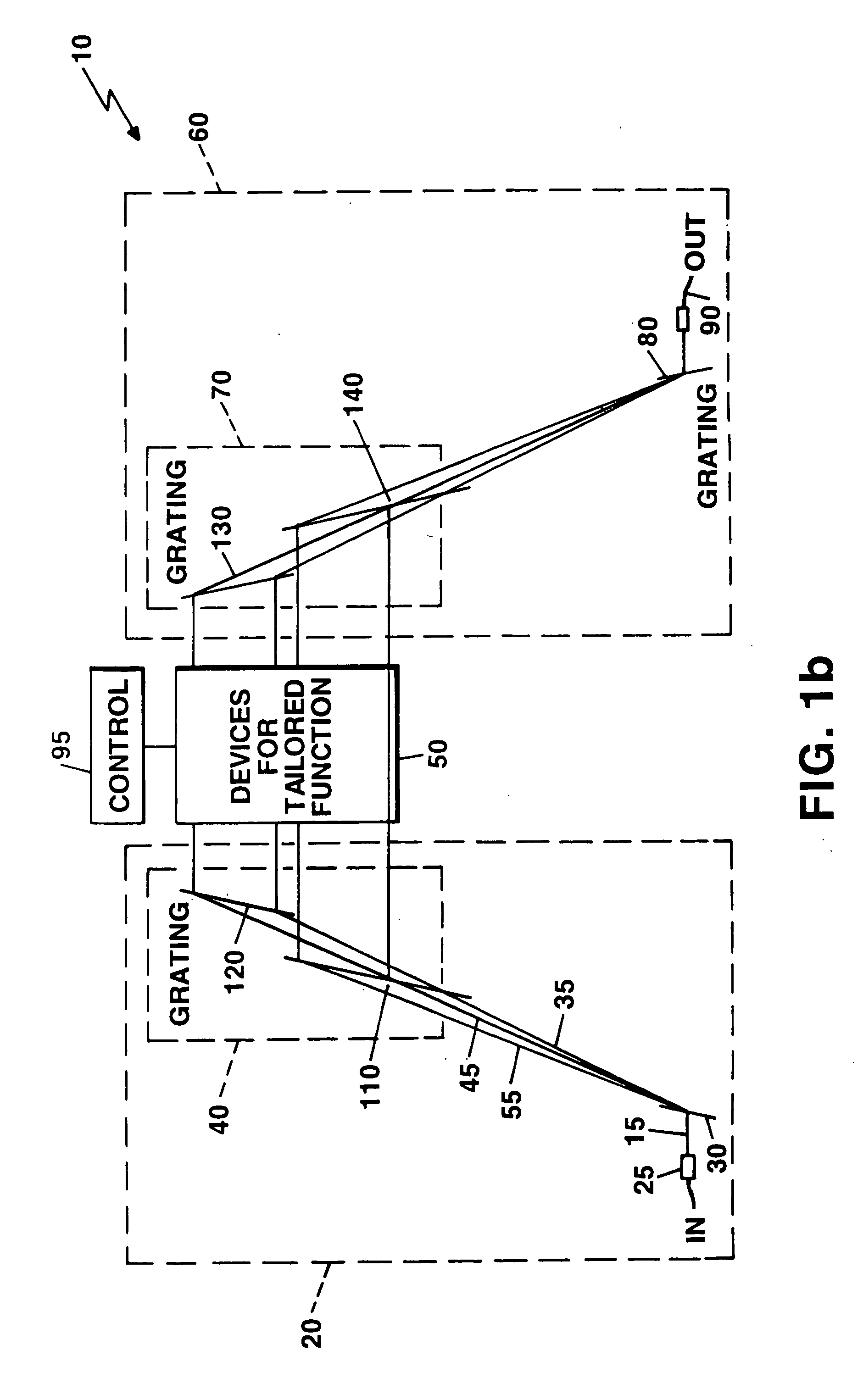
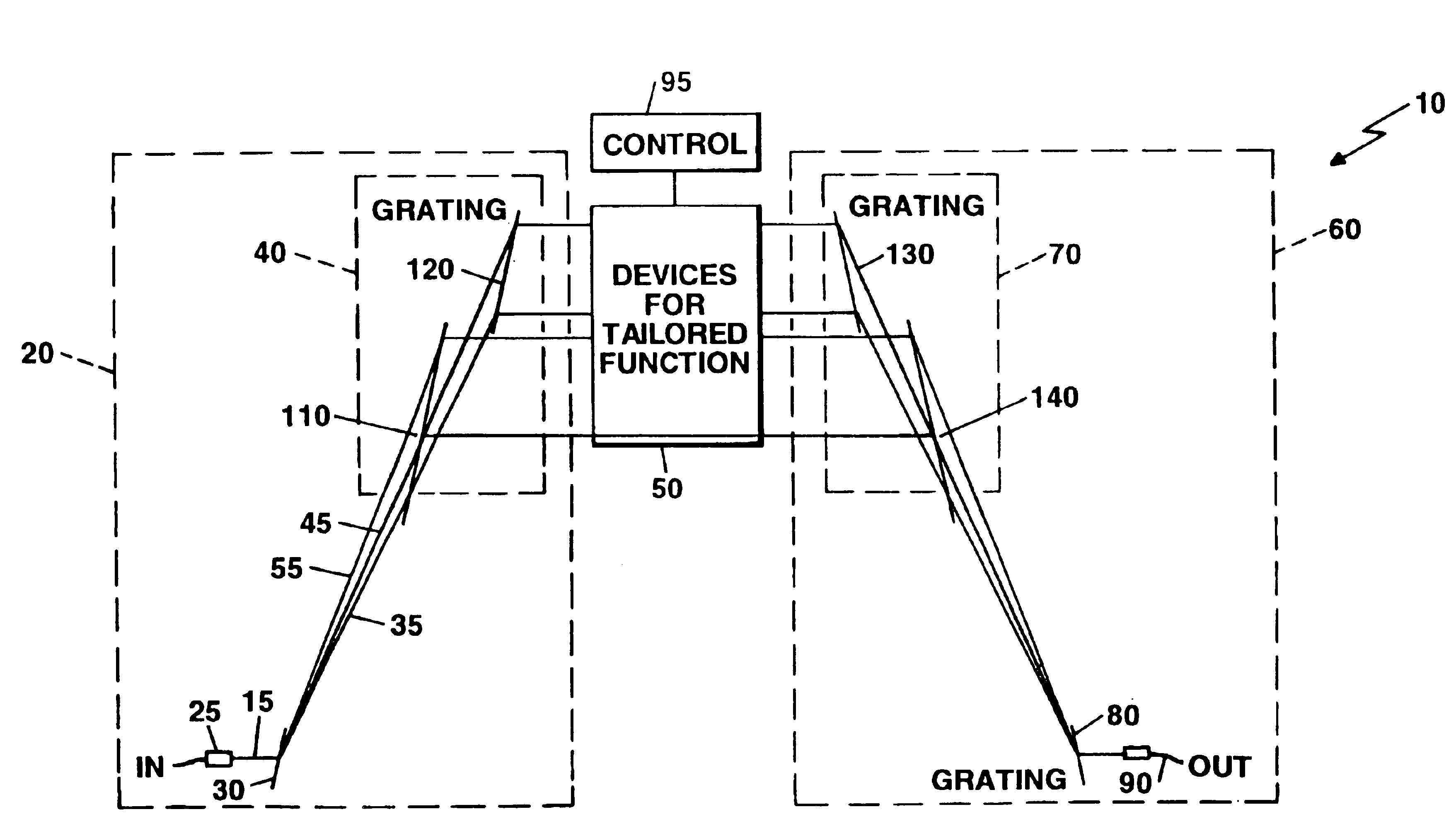
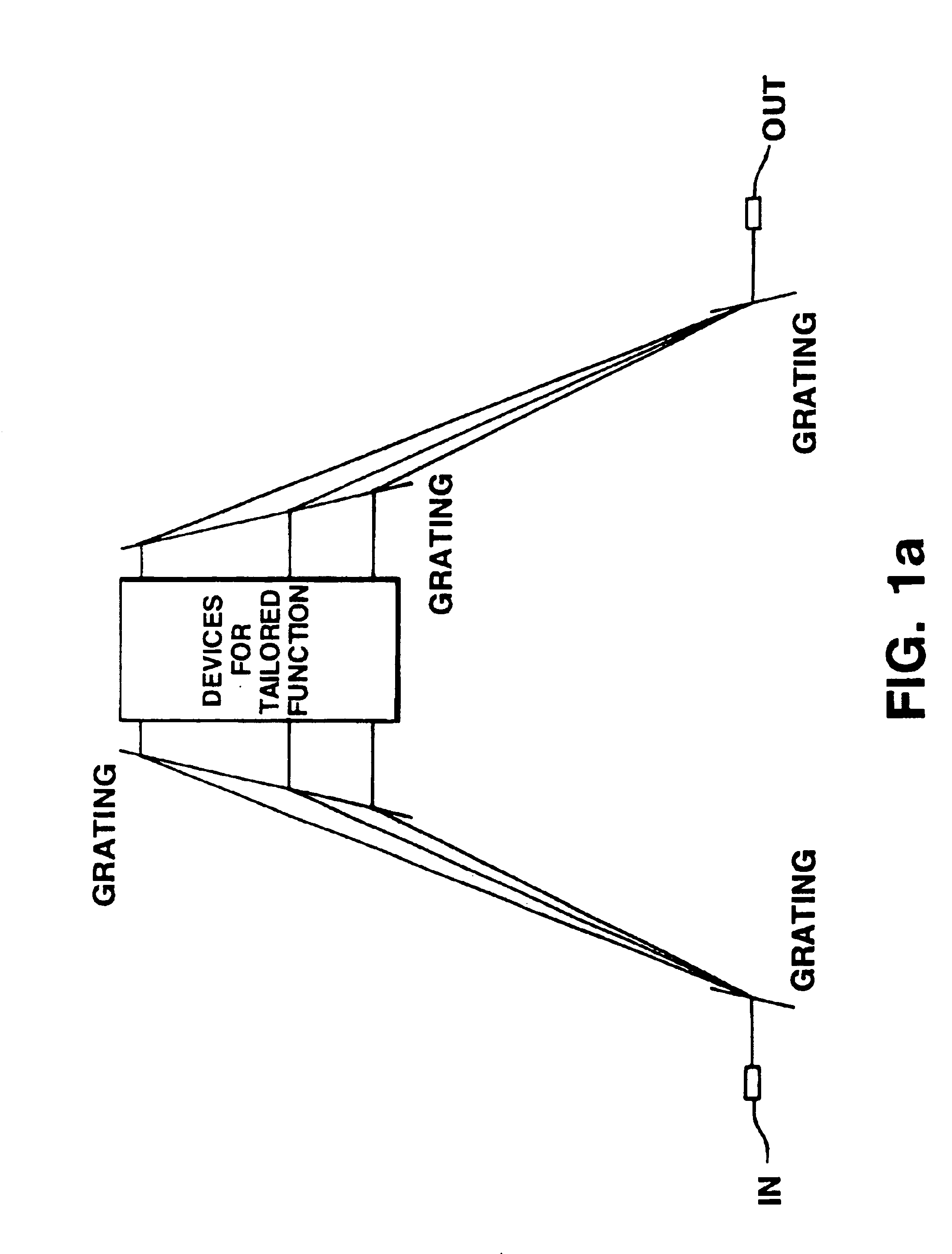
Switching and / or routing devices use separating diffraction gratings or AWG, a selectable switching and routing sub-sytem system, and recombining diffraction gratings or AWG to overcomes problems associated with insertion loss, size and compactness, switch isolation, switching speed, which may be present in current optical switching systems. The selectable switching and routing sub-system can include a switchable grating based sub-system or a switchable mirror based sub-sytem.
Owner:AVAGO TECHNOLOGIED FIBER IP SINGAPORE PTE LTD
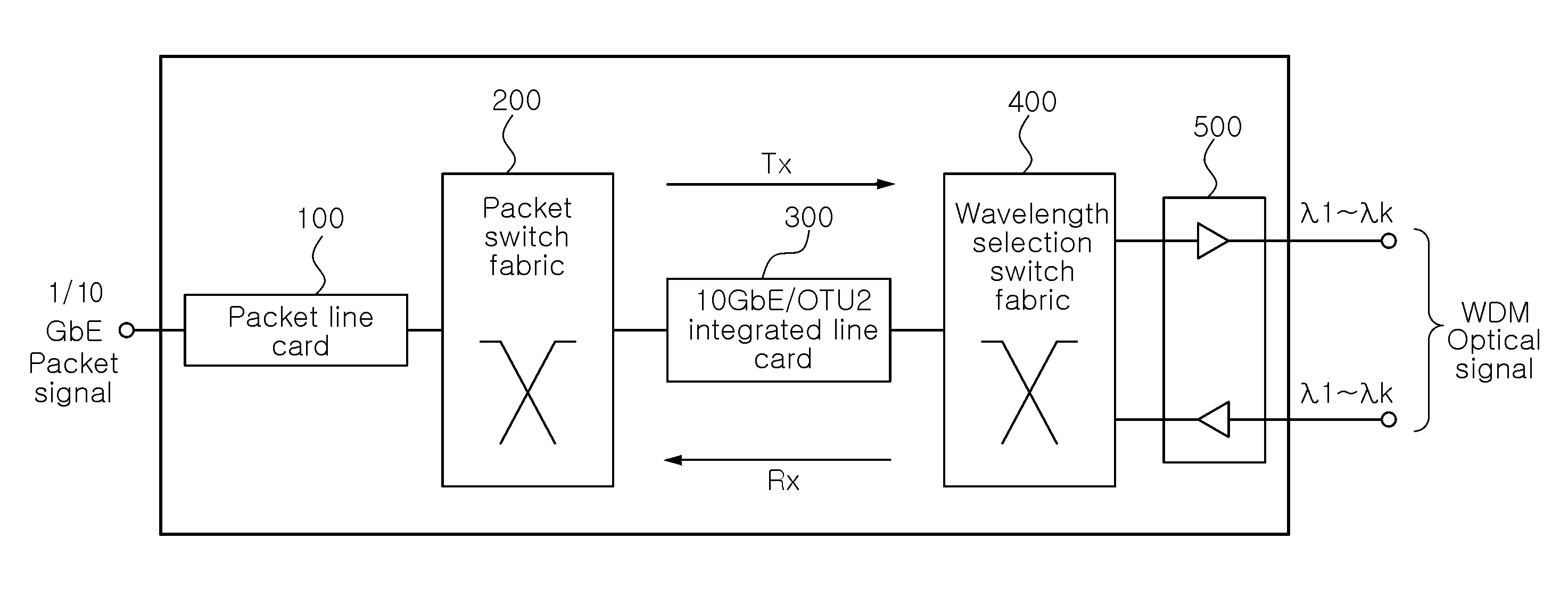
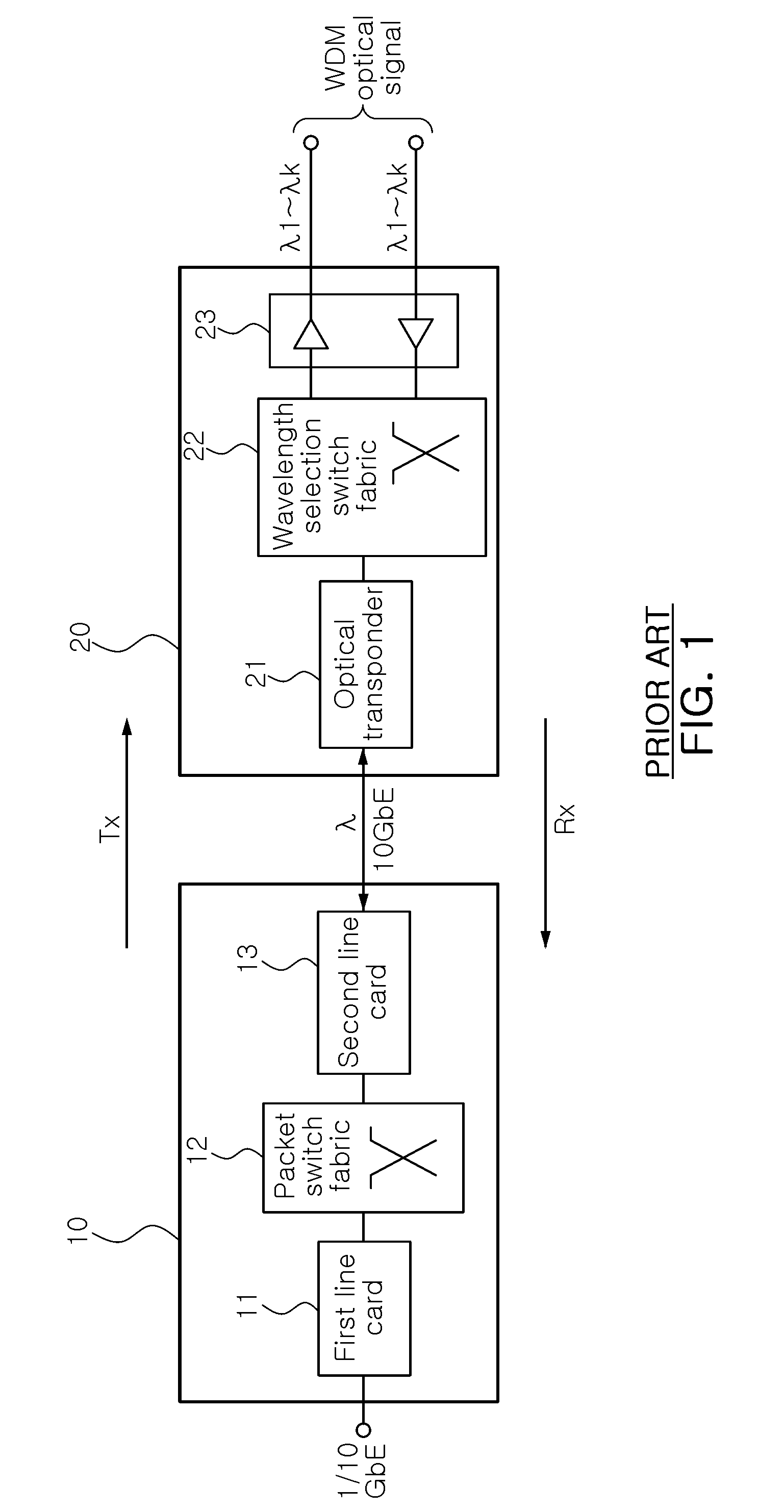
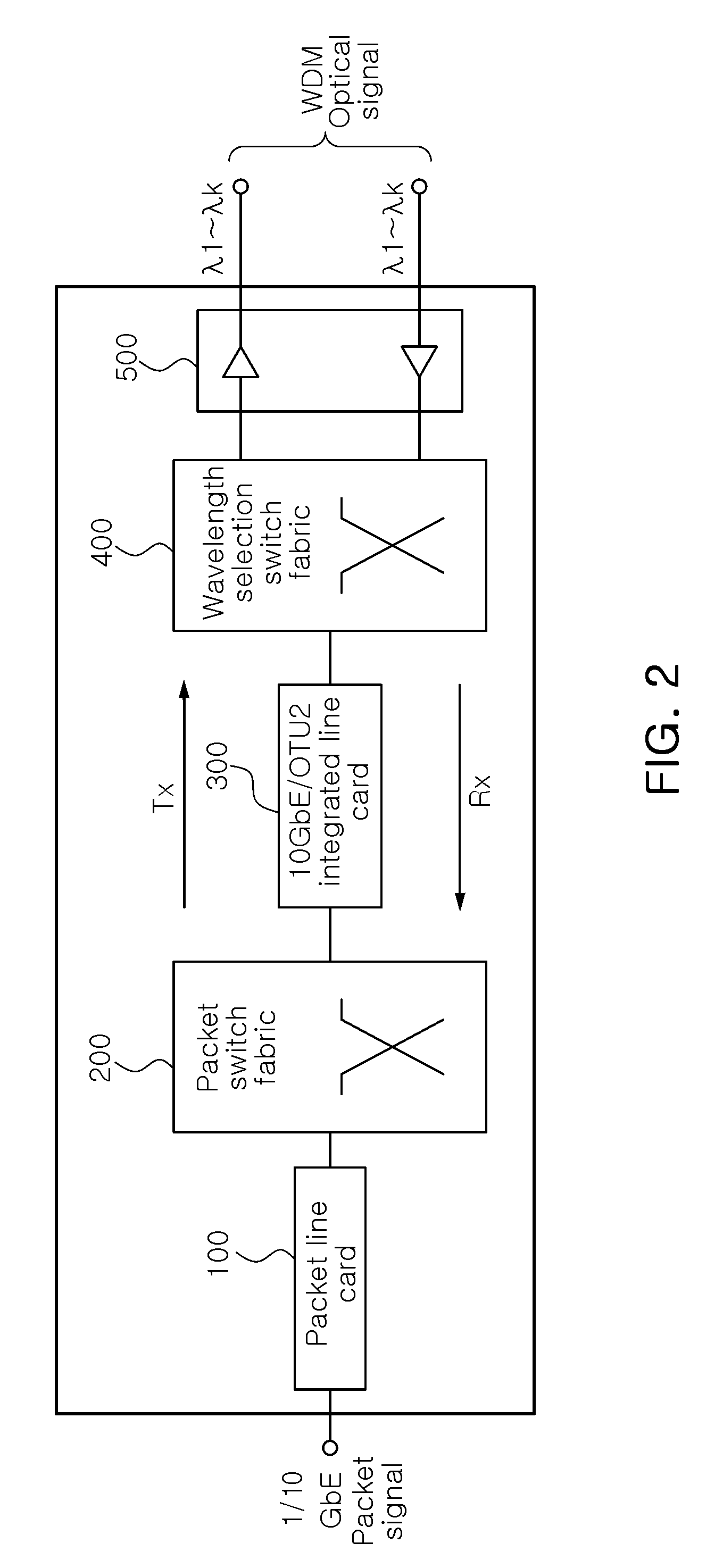
Packet-optical integrated switch without optical transponder
InactiveUS20100135659A1Promote conversionLow production costMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systems10 Gigabit EthernetWavelength selective switching
A packet-optical integrated switch without an optical transponder, includes: a packet line card configured to output an Ethernet packet signal to a pre-set output port; a packet switch fabric configured to transfer the packet signal from the packet line card to the output port previously set in a destination address included in the packet signal; a 10 gigabit Ethernet (10 GbE) / optical transport unit level 2 (OTU2) integrated line card configured to convert the packet signal from the packet switch fabric into an OTU2 optical signal having a pre-set wavelength; and a wavelength selection switch fabric configured to allocate the optical signal from the 10 GbE / OTU2 integrated line card to a pre-set wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) port by pre-set wavelength to exchange the optical signal to each port by wavelength, wherein the packet line card, the packet switch fabric, the 10 GbE / OTU2 integrated line card, and the wavelength selection switch fabric perform the reverse operations of the process, respectively.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
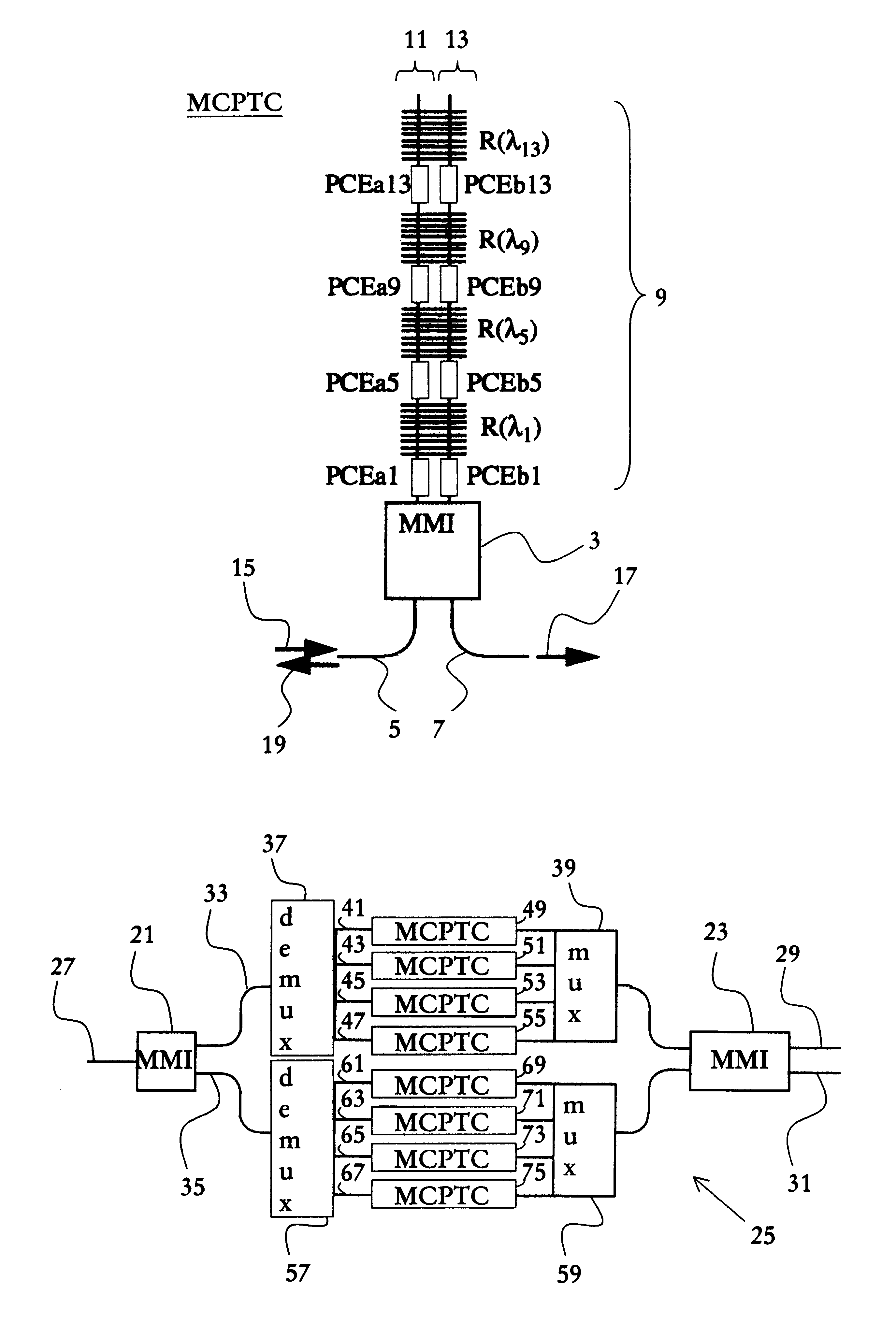
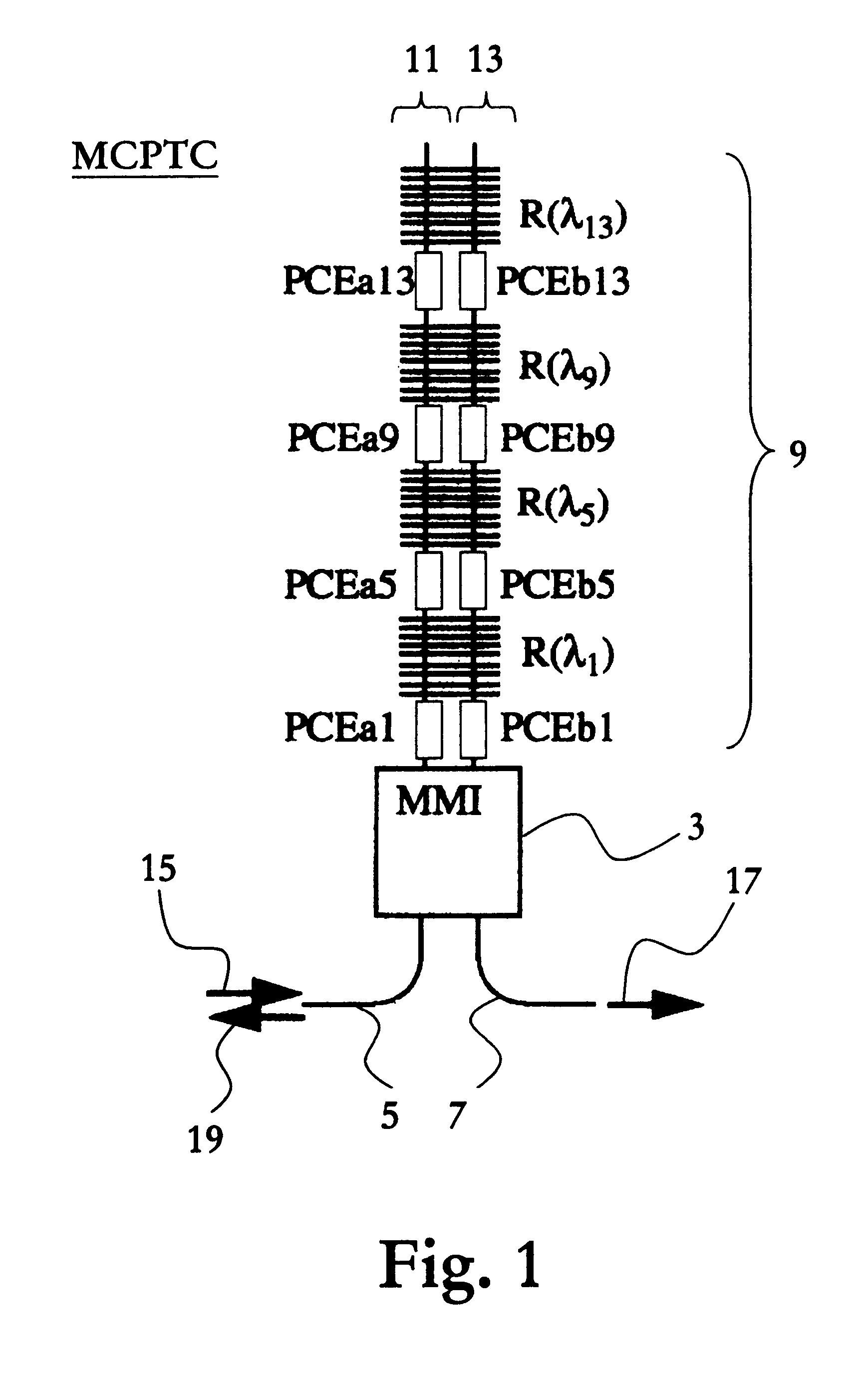
Wavelength selective switching element
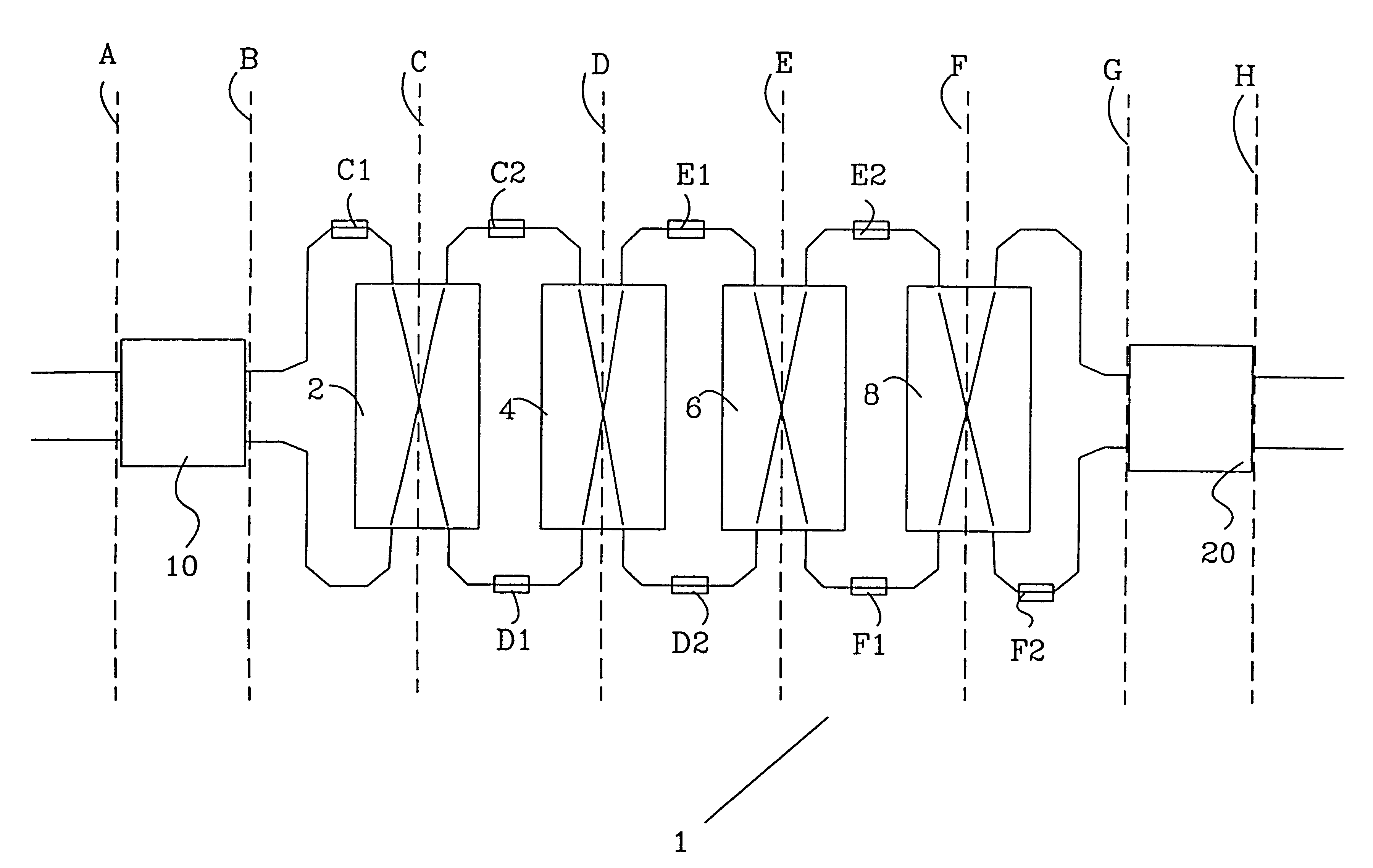
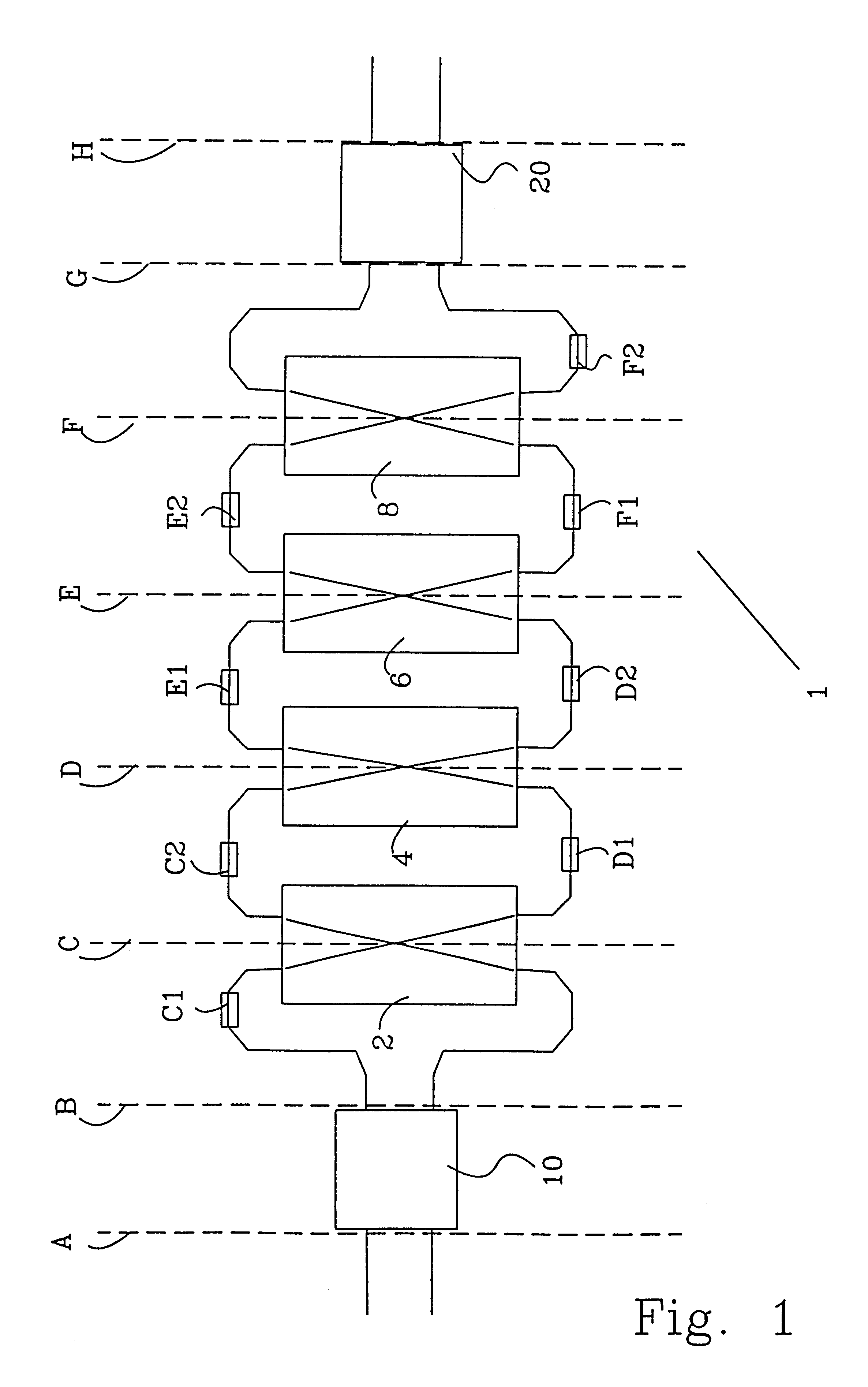
InactiveUS6292599B1Reduce manufacturing costReduce power consumptionMultiplex system selection arrangementsCoupling light guidesCross connectionPhase difference
The invention relates to a device and a method for switching optical wavelength channels. Said optical wavelength channels are introduced into at least one access waveguide provided on a first side of a first multi-mode waveguide (10). Subsequently, the wavelength channels are transmitted through said multi-mode waveguide (10) and projected on at least two connection waveguides provided on the opposite side. Subsequently, the optical wavelength channels are transmitted through the connection waveguides. For each wavelength selective cross-connection structure (2, 4, 6, 8) the phase is changed for a reflecting wavelength of two phase control elements (C1, C2, D1, D2, E1, E2, F1, F2) arranged in a first and a second connection waveguide on a first side of said wavelength selective cross-connection structure (2, 4, 6, 8), simultaneously as at a second side of said wavelength selective cross-connection structure (2, 4, 6, 8) said reflecting wavelength phase remains relatively unchanged. For each wavelength selective cross-connection structure (2, 4, 6, 8) the phase is changed for transmitting wavelengths once in a first and a second direction per wavelength selective cross-connection structure (2, 4, 6, 8). The phase difference between the optical signal in each access waveguide provided on the first side of the second multi-mode waveguide (20) determines where the optical signal is focused on the opposite side.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Methods and apparatus for constructing large wavelength selective switches using parallelism
ActiveUS20090232447A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsCoupling light guidesWavelength selective switchingComputer module
Optical networks are increasingly employing optical network nodes having multiple interfaces to allow a node to direct optical signals received at any interface to any other interface connected to the node. Constructing a larger wavelength selective switching (WSS) module used in such a node can be complex and expensive. A method an apparatus for constructing a large WSS using parallelism is provided. In example embodiments, a larger WSS may include multiple parallel non-cascaded smaller WSSs and an optical coupler configured to optically couple the multiple parallel, non-cascaded smaller WSSs. This technique may be used to construct both N×1 and 1×N WSSs. Because the technique employs multiple parallel, non-cascaded WSSs, all inputs of a larger N×1 WSS and all outputs of a larger 1×N WSS are available receive or transmit external signals rather than being rather than being unavailable due to, for example, cascading smaller WSS devices together.
Owner:TELLABS OPERATIONS
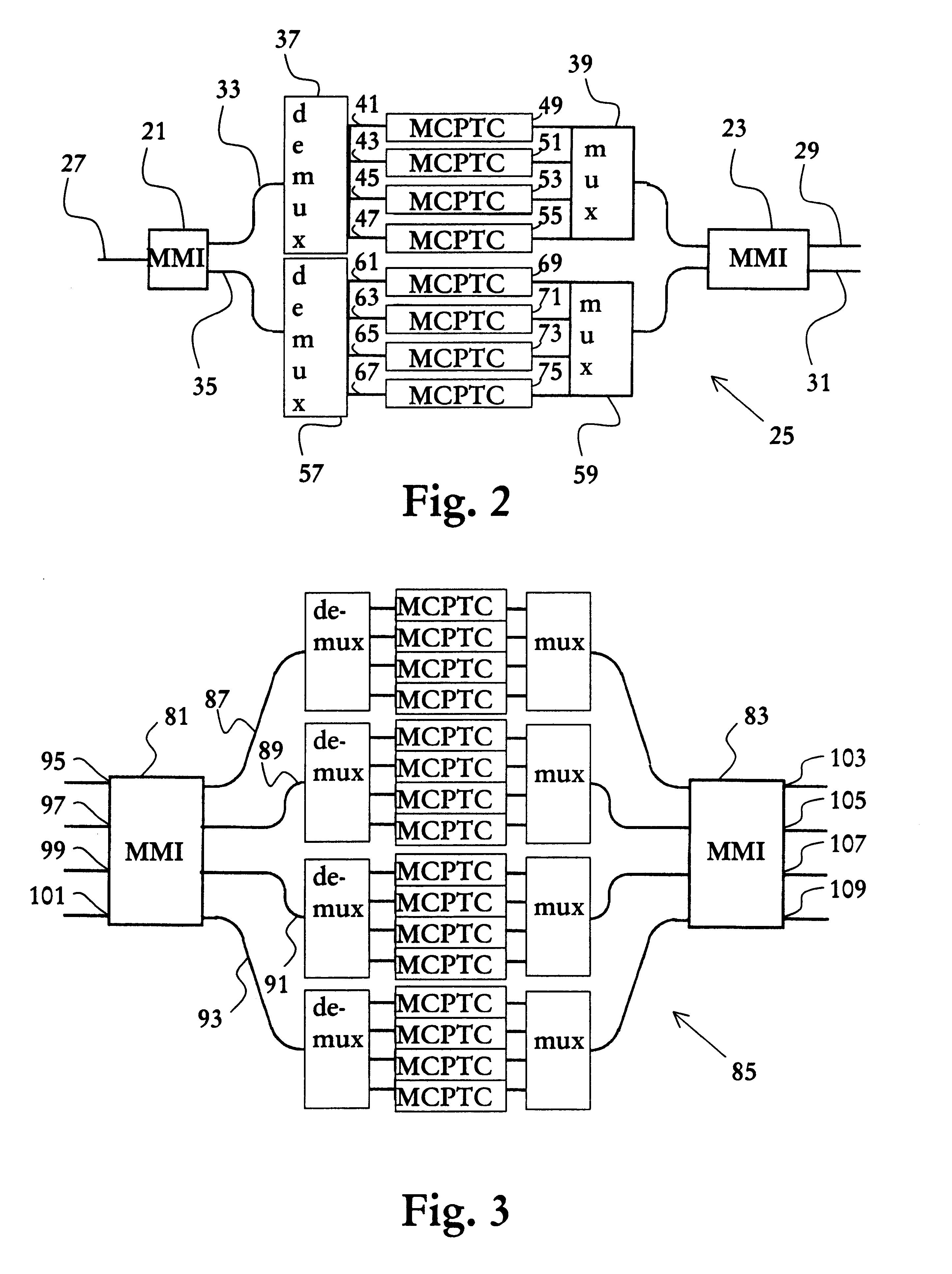
Apparatus and method for wavelength selective switching
InactiveUS6574391B2Increase switching capacityMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsMultiplexingWavelength selective switching
The present invention relates to an apparatus and a method for wavelength selective switching of a plurality of optical wavelength channels. The apparatus comprises two MMI waveguides interconnected by at least two Mach-Zehnder waveguide structures arranged in parallel, of which each is arranged to transmit a respective portion of the intensity of said plurality of optical wavelength channels. Each Mach-Zehnder waveguide structure comprises a demultiplexing unit, a multiplexing unit and at least two waveguides arranged in parallel, wherein the demultiplexing unit is arranged for demultiplexing of said plurality of optical wavelength channels into at least two channel groups, each waveguide arranged in parallel is arranged for transmission of a respective of said channel groups to the multiplexing unit, and is further provided with a respective multichannel wavelength selective phase control unit arranged for individual phase control of at least some channels in the respective of said channel groups, which is transmitted to the multiplexing unit, and the multiplexing unit is arranged for multiplexing of said channel groups.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
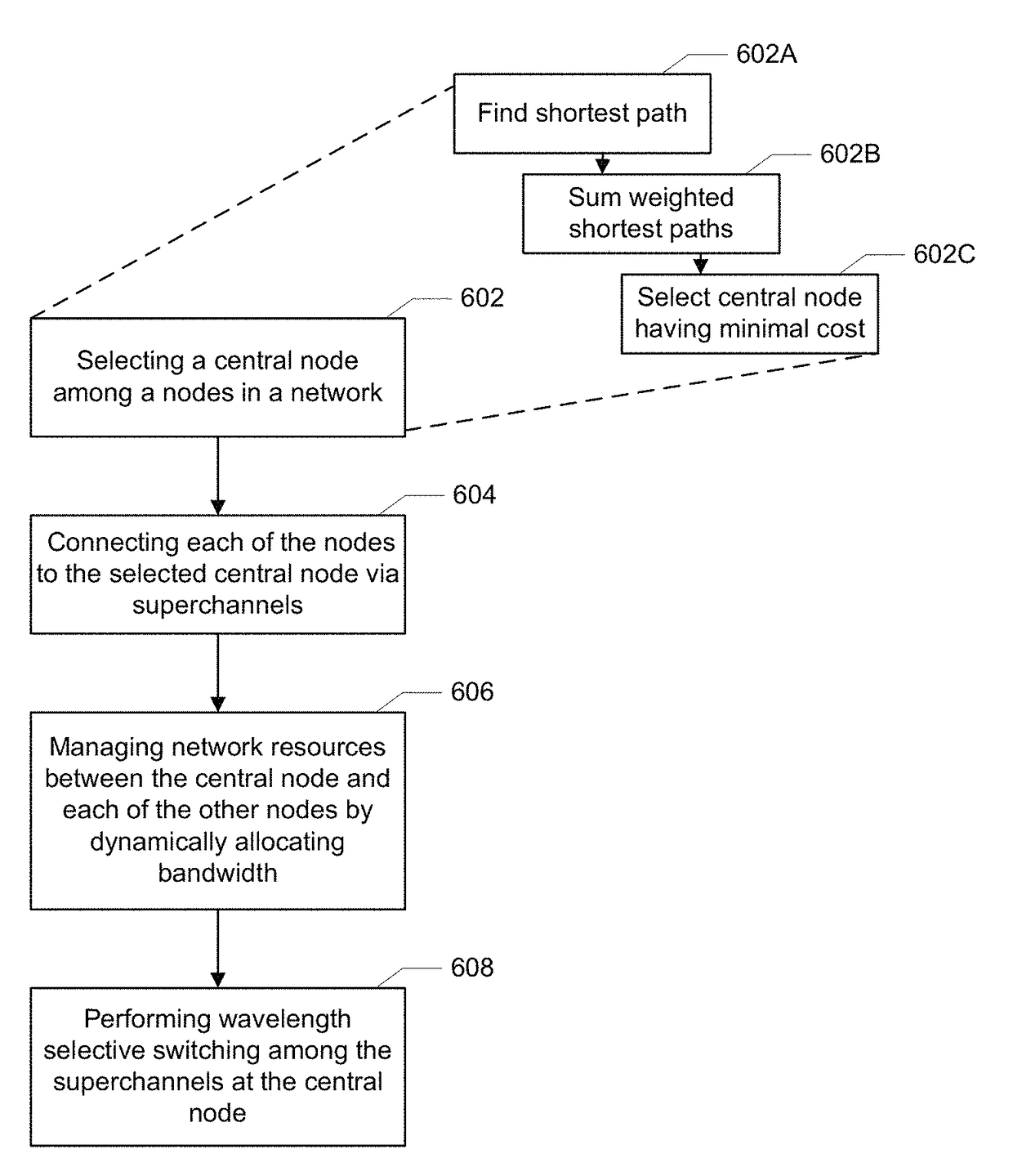
Method and apparatus for efficient network utilization using superchannels
ActiveUS20180076920A1Data rateWell formedMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsSuper-channelWavelength selective switching
The disclosure relates to technology for constructing an optical network. A central node is selected among a plurality of nodes in the optical network, and each of the nodes is connected to the central node via a set of superchannels, wherein each of the superchannels includes sub-carriers and has a same data rate. The network resources between the central node and each of the plurality of nodes are managed by dynamically allocating the sub-carrier bandwidths to support communication among the plurality of nodes via the superchannels, and wavelength selective switching is performed among the superchannels at the central node.
Owner:FUTUREWEI TECH INC
Wavelength selective switching device and method for selectively transmitting optical signals based on wavelength
InactiveUS20050073749A1Reduce device sizeSmall sizeMultiplex system selection arrangementsPrismsWavelength selective switchingLength wave
A wavelength selective switching device and method for selectively transmitting optical signals based on wavelength utilizes diffraction to spatially separate the optical signals of different wavelengths such that the optical signal of a selected wavelength can be selectively transmitted. The wavelength selective switching device selectively rotates the polarization components of the optical signals such that the polarization states of the polarization components are the same in both incoming and outgoing directions at the diffraction grating. Thus, a diffraction grating with a high grating line frequency (e.g. greater than 900 grating lines per mm for signals in the 1550 nm wavelength range) can be used for diffracting the polarization components of the optical signals in both the incoming and outgoing directions.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Wavelength-selective switch and equalizer
One embodiment disclosed relates to a method for wavelength-selective switching and equalization. The method includes dispersing an incoming multiplexed signal into wavelength components, focusing the wavelength components onto different portions of a controllable light diffractor array, and controllably diffracting each wavelength component such that each said component is individually attenuated and arrives at the individually selected output without substantial crosstalk between the outputs. Another embodiment relates to a wavelength-selective switching device with integrated equalizer functionality. Another embodiment relates to an optical apparatus for wavelength-selective switching and equalization. The apparatus includes a means for controllably diffracting each wavelength component of a multiplexed input such that each said component is controllably attenuated and directed to arrive at an individually selected output.
Owner:SILICON LIGHT MACHINES CORP
Wavelength selective switch with increased frequency separation to avoid crosstalk
ActiveCN107209328AMultiplex system selection arrangementsCoupling light guidesWavelength selective switchingLength wave
Owner:莫仕有限责任公司
Compact wavelength selective switching and/or routing system
InactiveUS20050111076A1Improve spatial uniformityOvercomes shortcomingProjectorsWavelength-division multiplex systemsWavelength selective switchingEngineering
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Wideband optical fiber amplifier
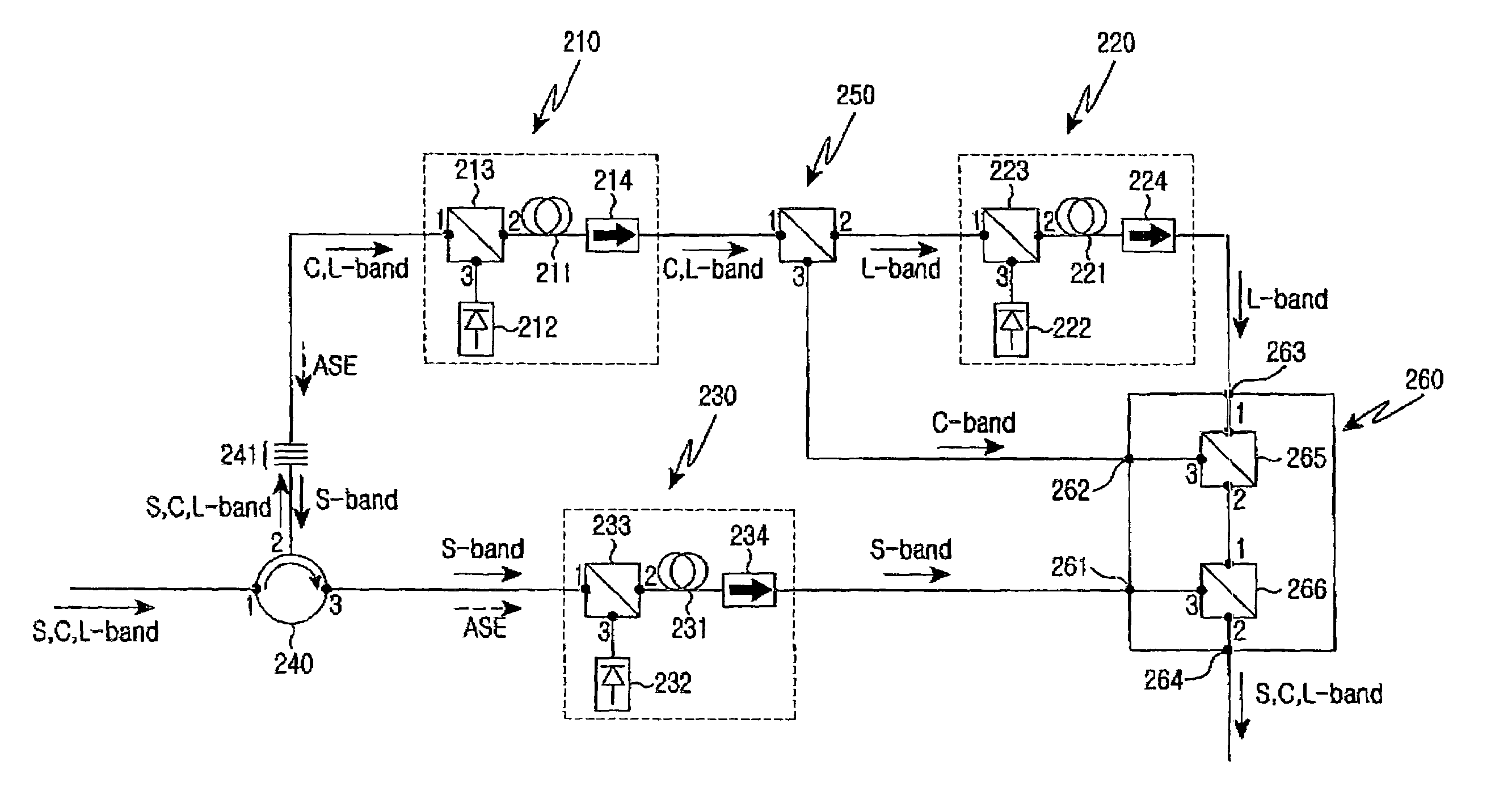
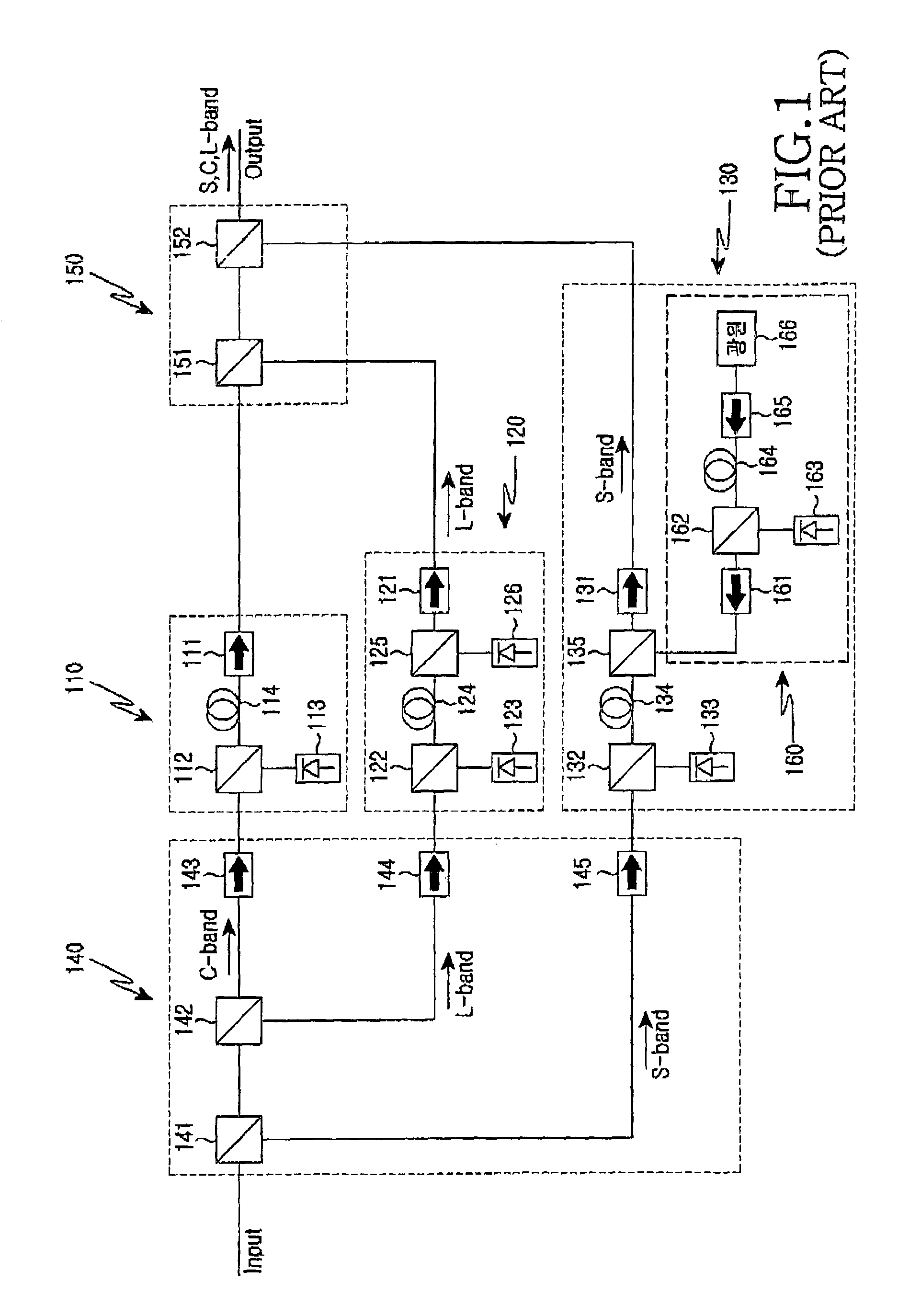
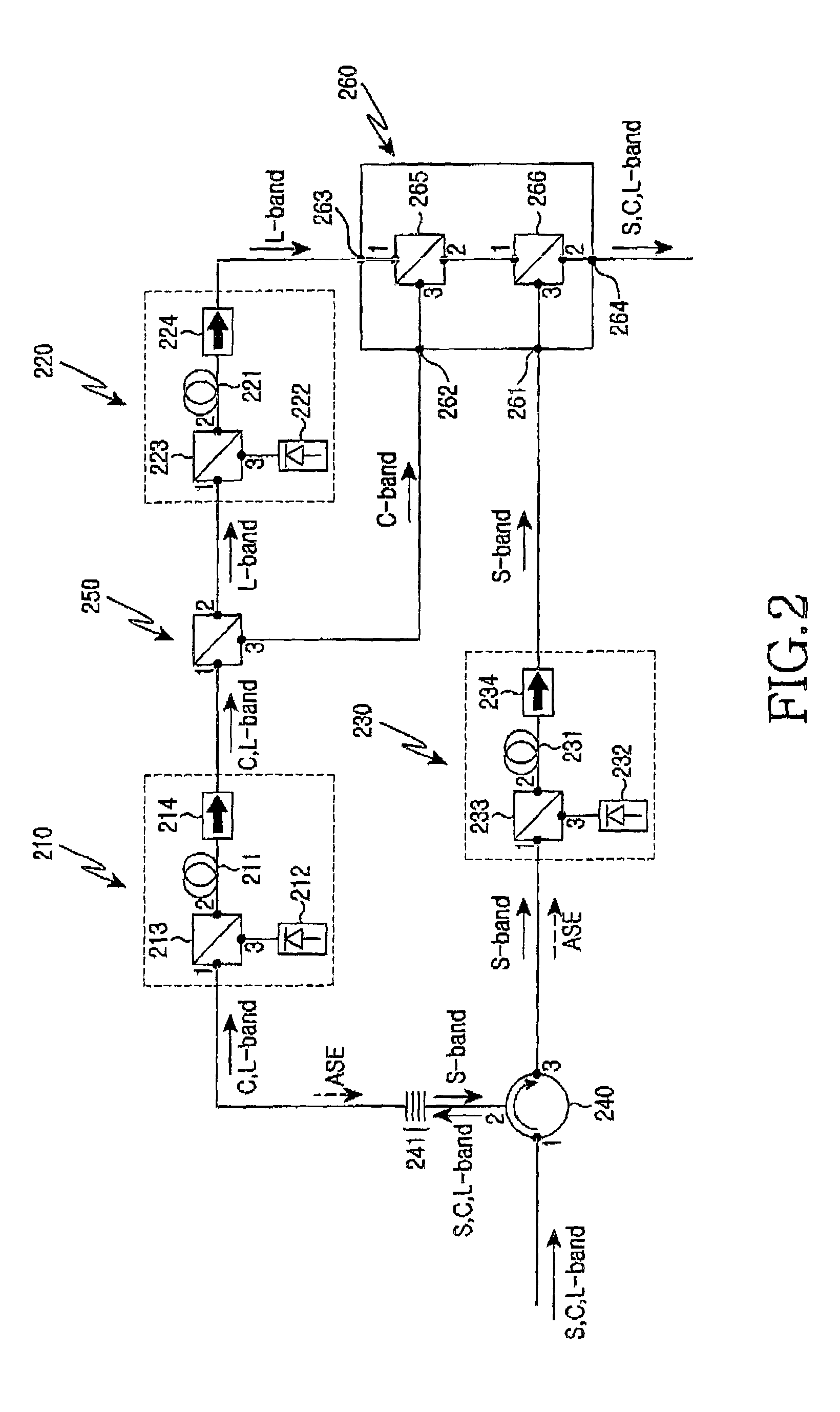
InactiveUS7034997B2High amplification efficiencyImprove noise figureLaser detailsElectromagnetic transmissionGratingAudio power amplifier
The wideband optical fiber optical includes a circulator. In addition the amplifier outputs the amplified spontaneous emission (ASE) and the S-band optical signals. At least one optical fiber grating is used for passing the C- and L-band optical signals. A wavelength selective splitter outputs the L-band optical signal. A first optical fiber amplifying unit connected with the optical fiber grating and the first port of the wavelength selective splitter, for amplifying the C- and L-band optical signals and for outputting the ASE to the optical fiber grating. A second optical fiber amplifying unit for amplifying the L-band optical signals inputted from the second port of the wavelength selective splitter and for outputting the amplified L-band optical signals to the third terminal of the outputting unit. A third optical fiber amplifying unit amplifies the S-band optical signals input from the third port of the circulator, and outputs the amplified S-band optical signals to the first terminal of the outputting unit.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Wavelength selective switch and reconfigurable optical add/drop multiplexer
ActiveUS20190327015A1Compact configurationEfficient parallel processingMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsMultiplexerWavelength selective switching
A wavelength selective switching device comprises a plurality of input paths for receiving optical signals, a plurality of output paths for emitting the optical signals, and a switching unit for selectively directing the optical signals from the input paths to the output paths. The switching unit comprises a reflective area adapted to be concurrently illuminated by a first optical signal from a first input path among the plurality of input paths, and by a second optical signal from a second input path among the plurality of input paths, the second input path being different from the first input path, and to concurrently direct the first optical signal to a first output path among the plurality of output paths and the second optical signal to a second output path among the plurality of output paths, the second output path being different from the first output path. Said first output path and said second output path are spatially separated by said first input path and said second input path, or vice-versa.
Owner:XIEON NETWORKS SARL
Compact wavelength selective switching and/or routing system
InactiveUS6947204B2Wavelength-division multiplex systemsProjectorsWavelength selective switchingEngineering
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Method and apparatus for efficient network utilization using superchannels
ActiveUS9941992B2Multiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsSuper-channelWavelength selective switching
The disclosure relates to technology for constructing an optical network. A central node is selected among a plurality of nodes in the optical network, and each of the nodes is connected to the central node via a set of superchannels, wherein each of the superchannels includes sub-carriers and has a same data rate. The network resources between the central node and each of the plurality of nodes are managed by dynamically allocating the sub-carrier bandwidths to support communication among the plurality of nodes via the superchannels, and wavelength selective switching is performed among the superchannels at the central node.
Owner:FUTUREWEI TECH INC
Byte-wide optical backplane switching method
InactiveUS20070286602A1High bandwidthMultiplex system selection arrangementsOptical multiplexWavelength selective switchingOptical backplane
A byte-wide optical switch and switching method are provided. The optical switch includes a first set of ports for receiving in parallel an optical byte of data, and multiple second sets of ports each capable of outputting in parallel the optical byte of data. An array of optical switching elements is disposed between the first set of ports and the multiple second sets of ports. The array of optical switching elements direct the optical byte of data in parallel from the first set of ports to at least one second set of ports of the multiple second sets of ports. The switching elements may comprise micro-electro mechanical system (MEMS) devices, each having a position controllable reflective surface. Thin film optical filters can be provided on the reflective surfaces for wavelength selective switching.
Owner:IBM CORP
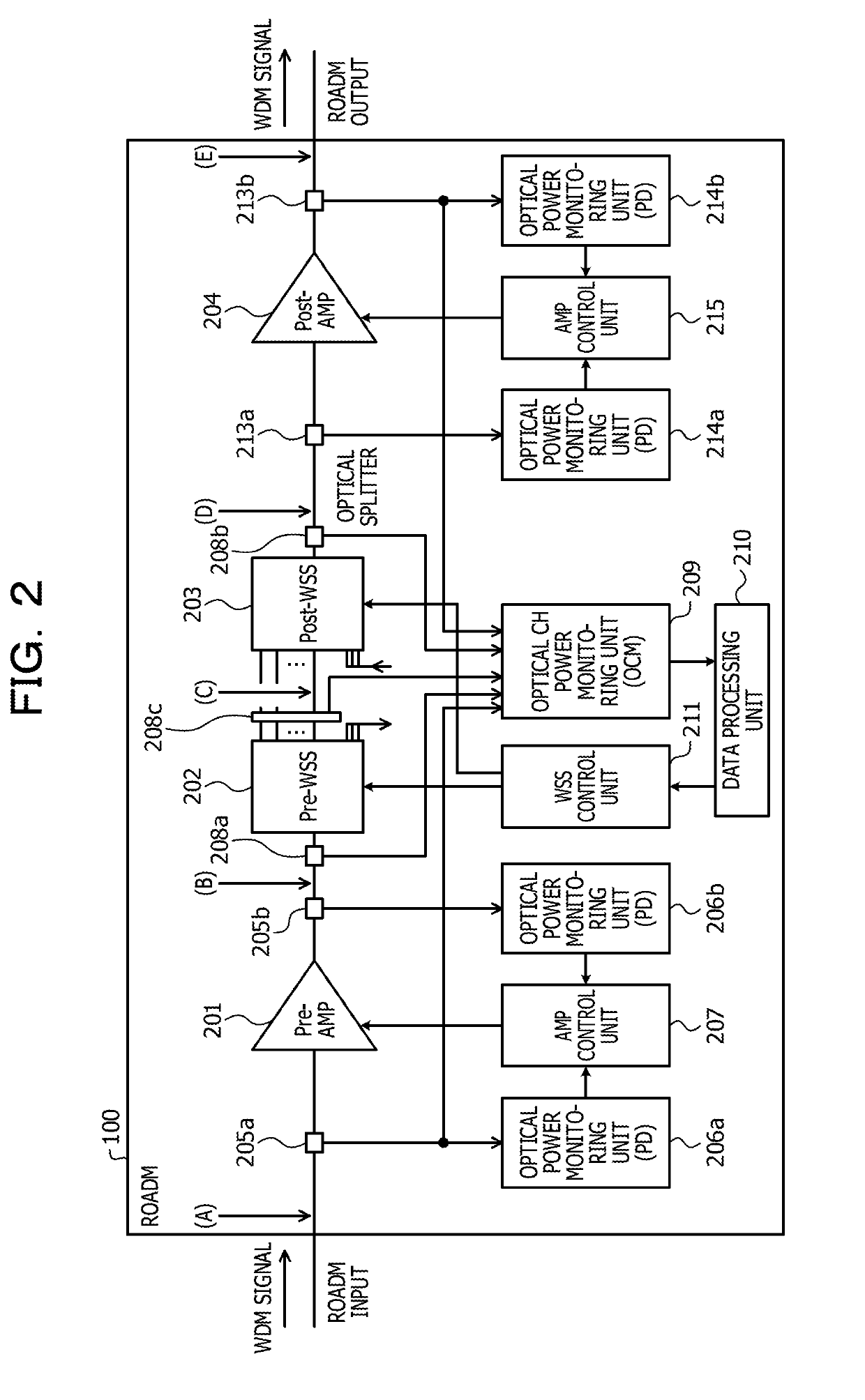
Optical transmission device and optical signal gain control method
ActiveUS20190115977A1Wavelength-division multiplex systemsElectromagnetic transmittersMultiplexingUltrasound attenuation
An optical transmission device includes an optical amplifier that optically amplifies a wavelength multiplexing signal which is input, a wavelength selective switch that splits, inserts, or transmits an optical signal of any wavelength of the wavelength multiplexing signal, an optical channel power monitor that detects power of each channel of the wavelength multiplexing signal which is input and the wavelength multiplexing signal which is output, and a controller that calculates an amount of change in the optical signal of each channel in which a gain of each channel between an input and an output to and from the device is steady, and adjusts an amount of attenuation of the wavelength selective switch, based on the power of each channel of the wavelength multiplexing signal that is detected by the optical channel power monitor.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com