Patents
Literature
4099results about How to "Improve resolution" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
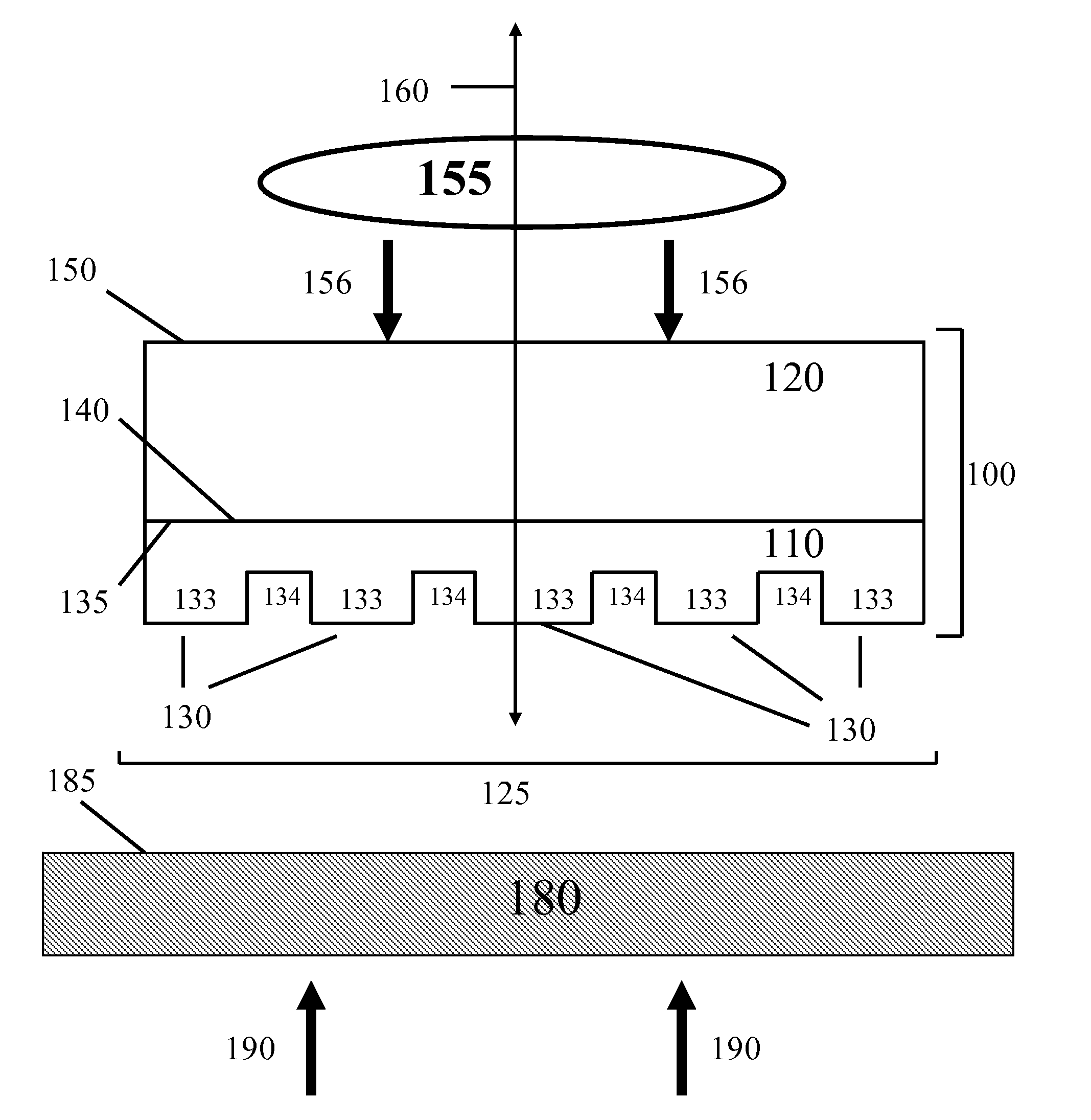
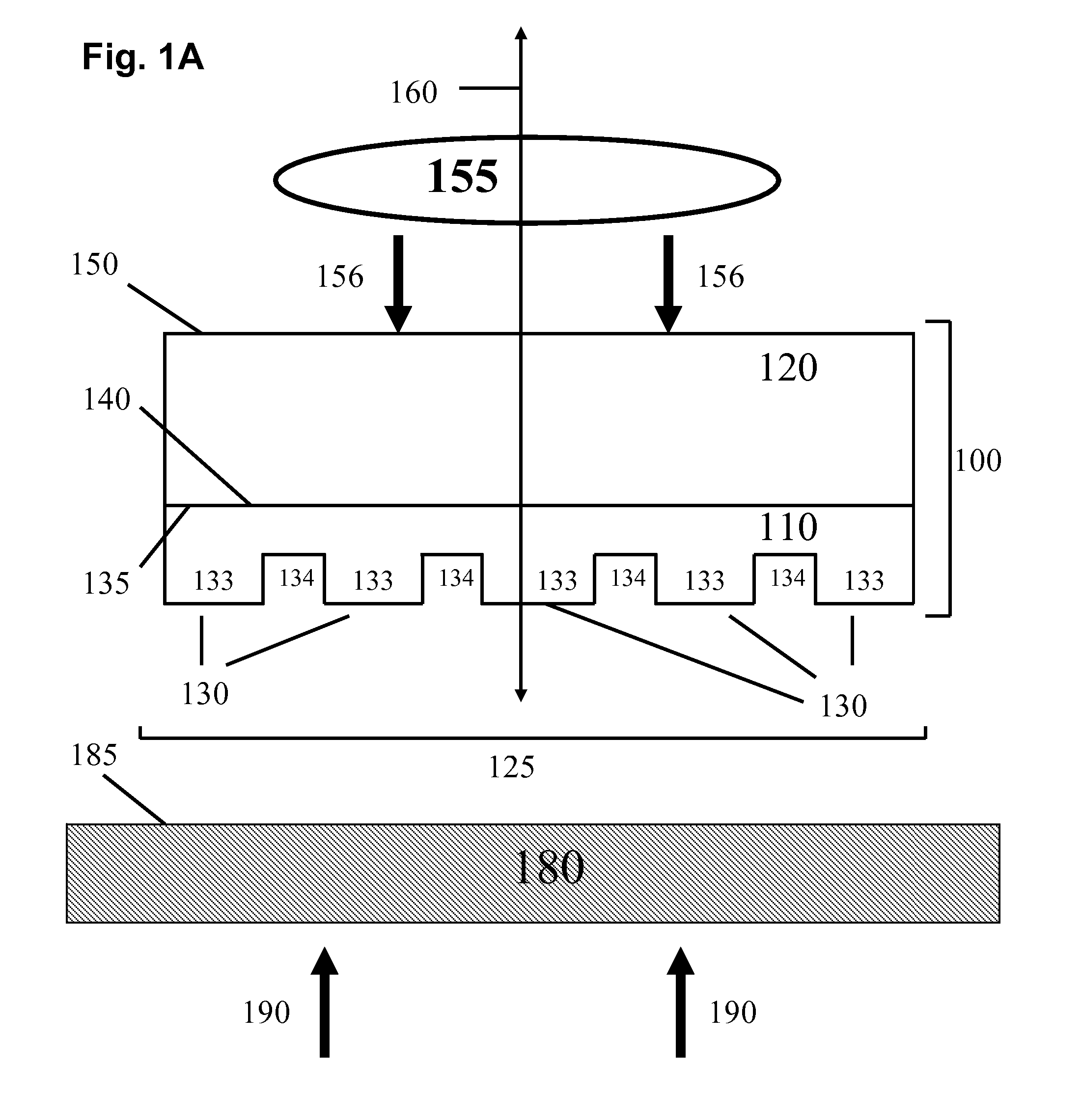
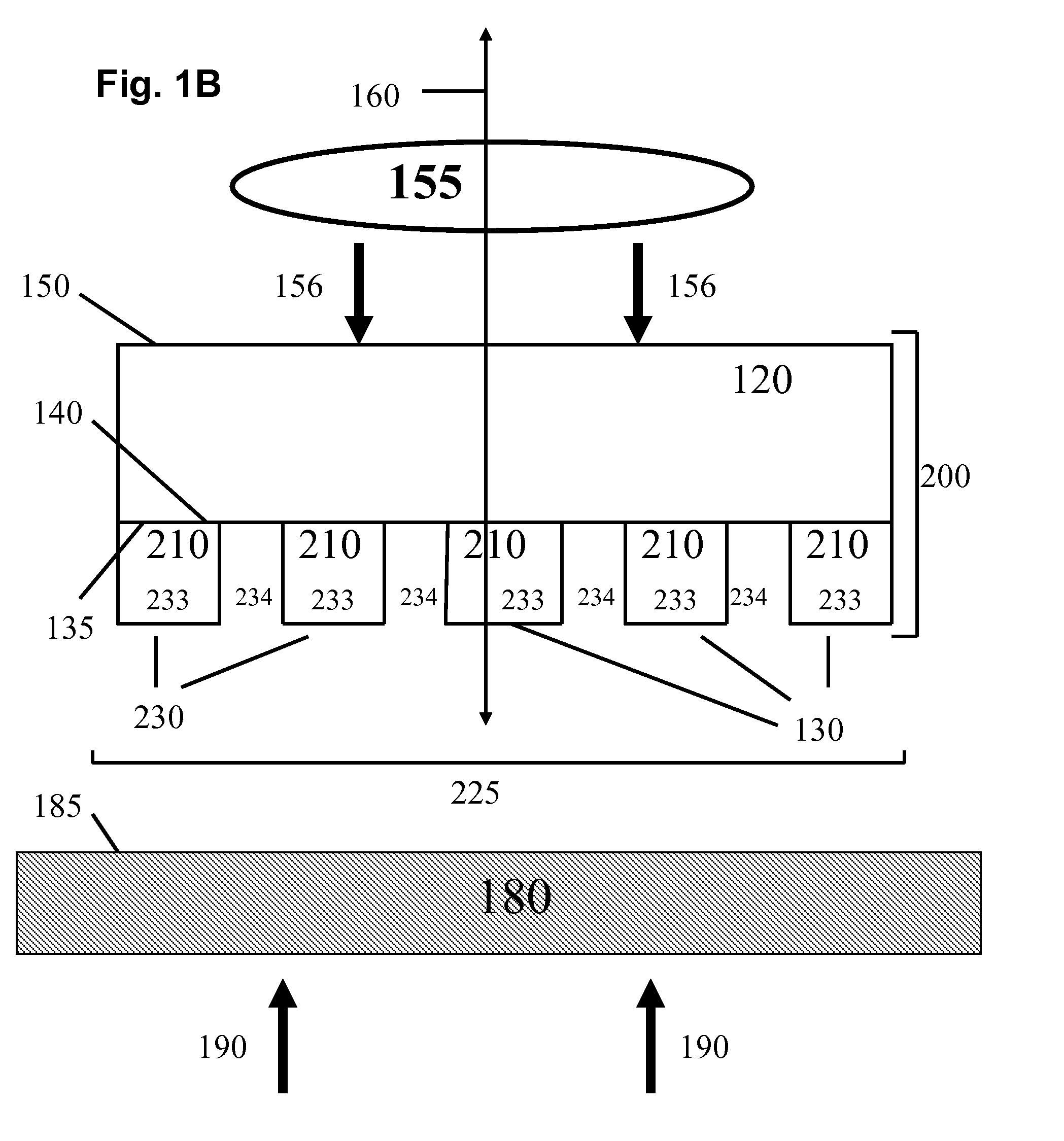
Composite patterning devices for soft lithography
ActiveUS7195733B2Improve fidelityIncrease resistanceMaterial nanotechnologyNanoinformaticsNano sizeYoung's modulus
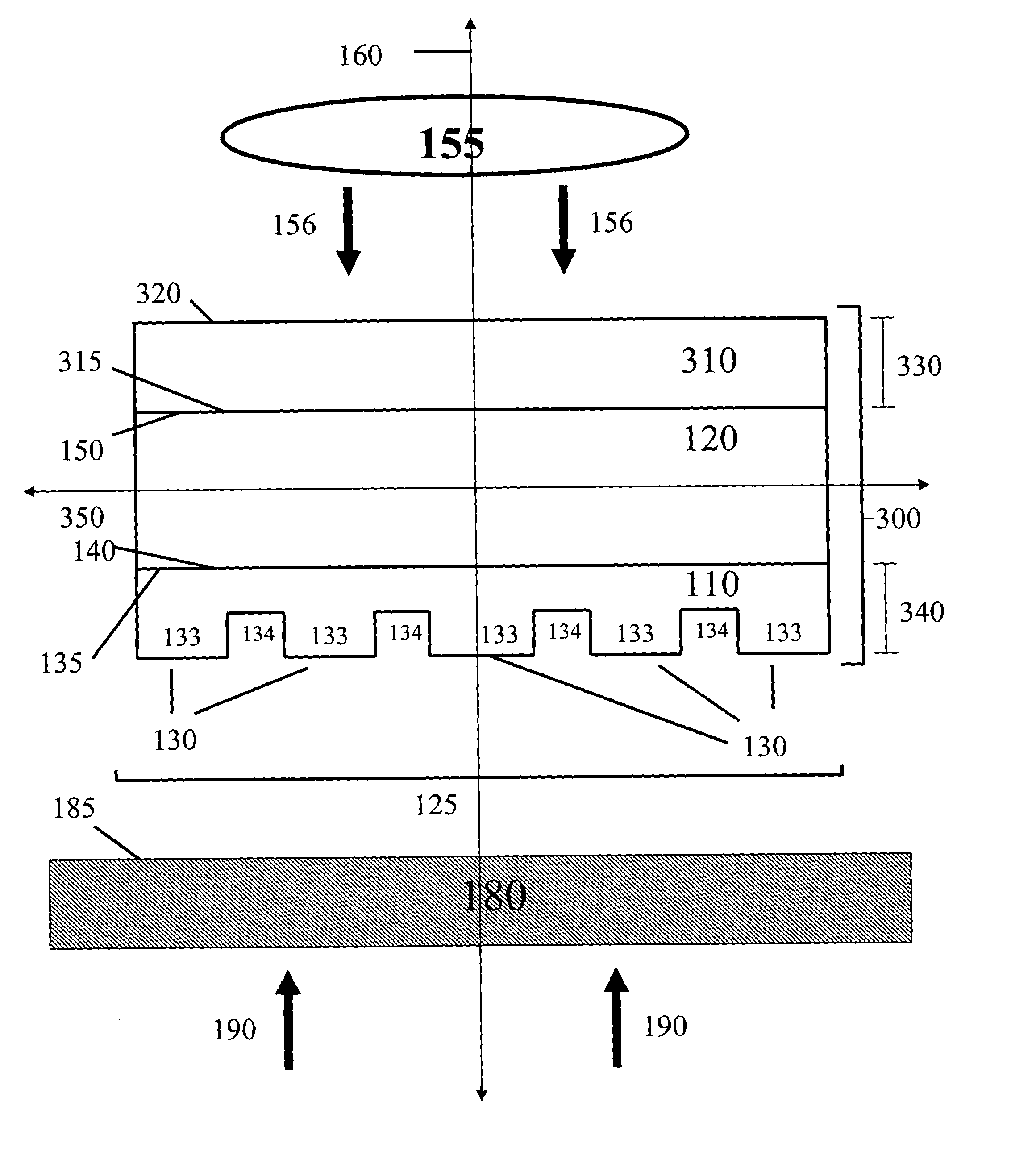
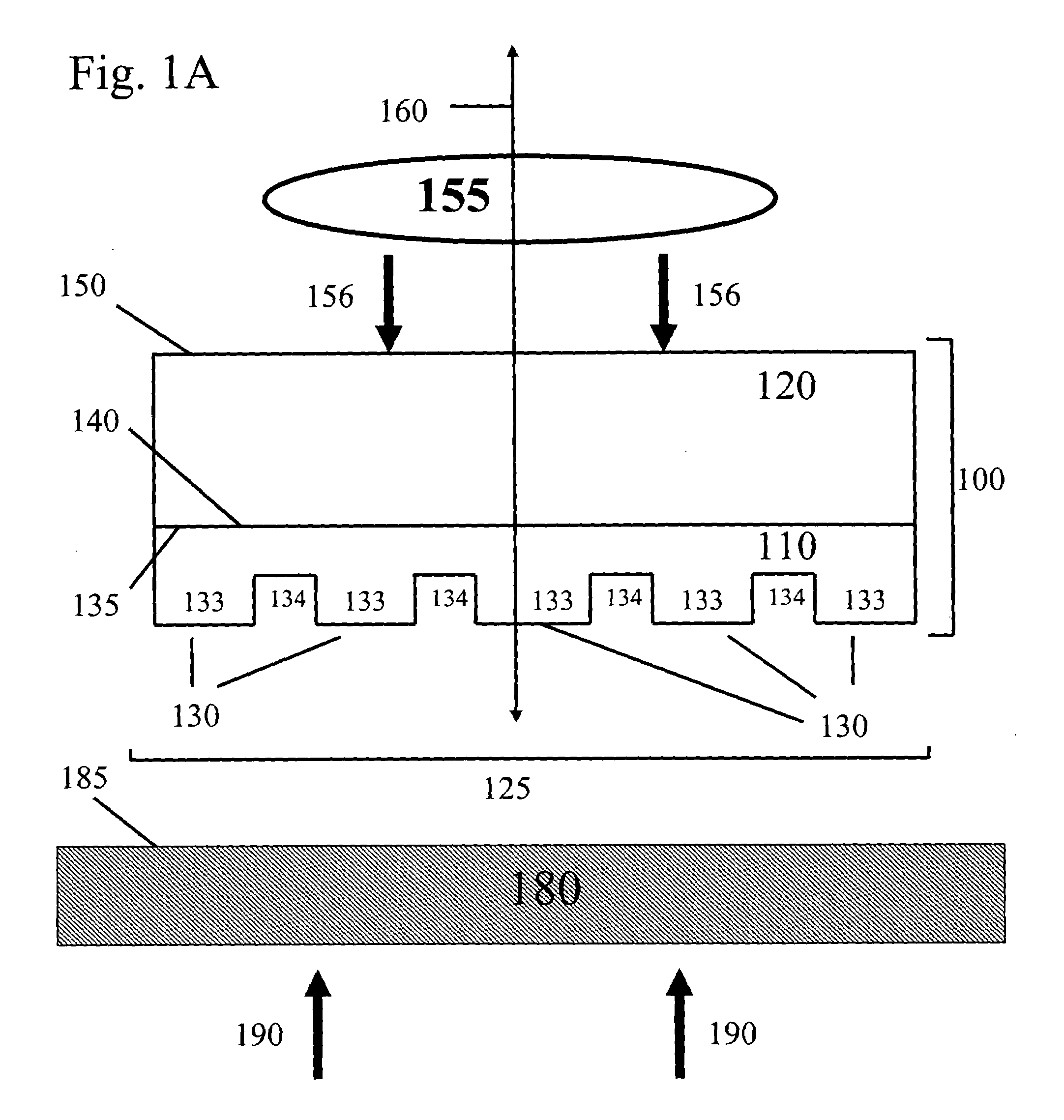
The present invention provides methods, devices and device components for fabricating patterns on substrate surfaces, particularly patterns comprising structures having microsized and / or nanosized features of selected lengths in one, two or three dimensions. The present invention provides composite patterning devices comprising a plurality of polymer layers each having selected mechanical properties, such as Young's Modulus and flexural rigidity, selected physical dimensions, such as thickness, surface area and relief pattern dimensions, and selected thermal properties, such as coefficients of thermal expansion, to provide high resolution patterning on a variety of substrate surfaces and surface morphologies.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
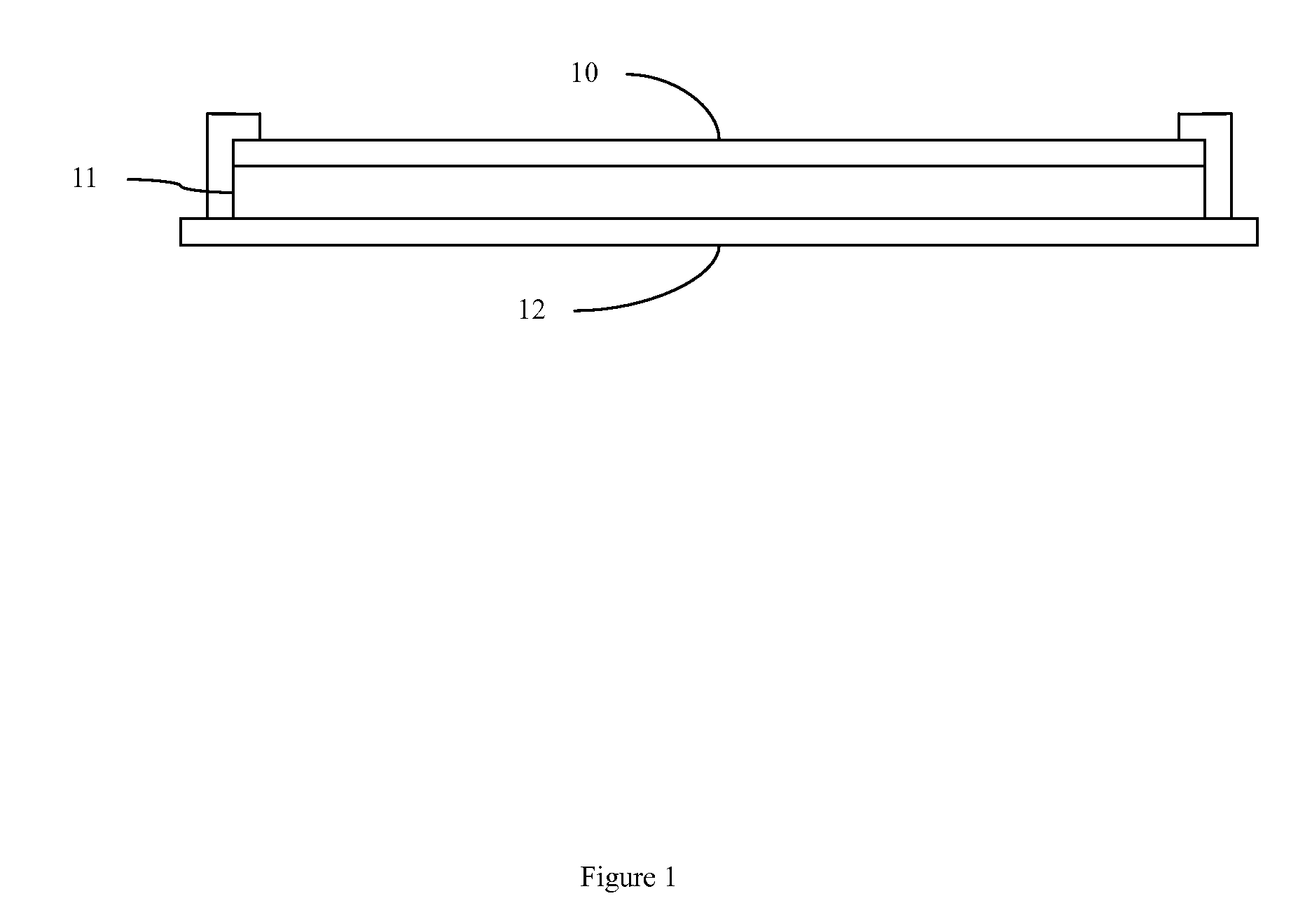
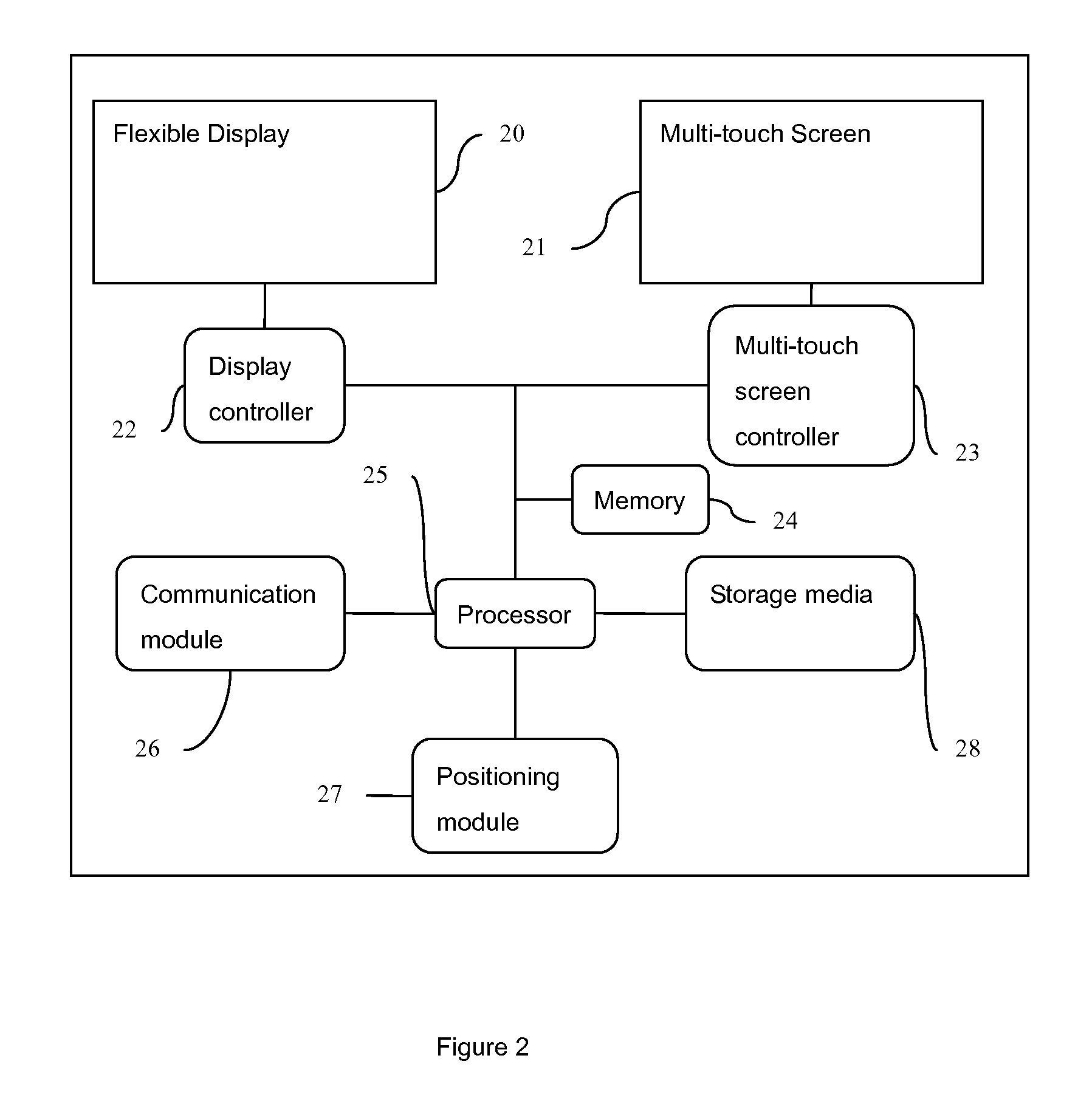
Flexible Multi-touch Screen
InactiveUS20080180399A1Easy to makeLow costInput/output processes for data processingDisplay deviceTouchpad
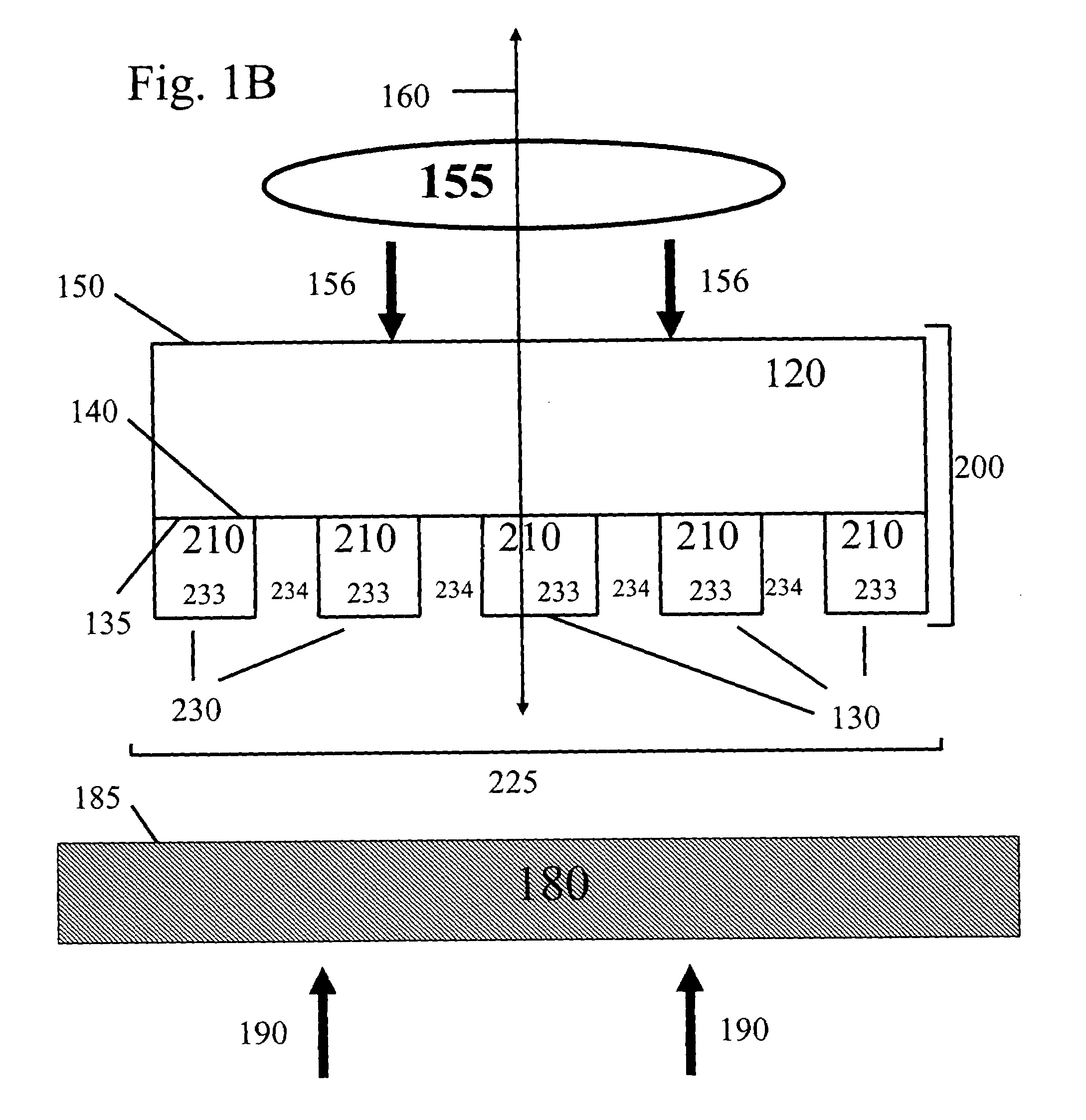
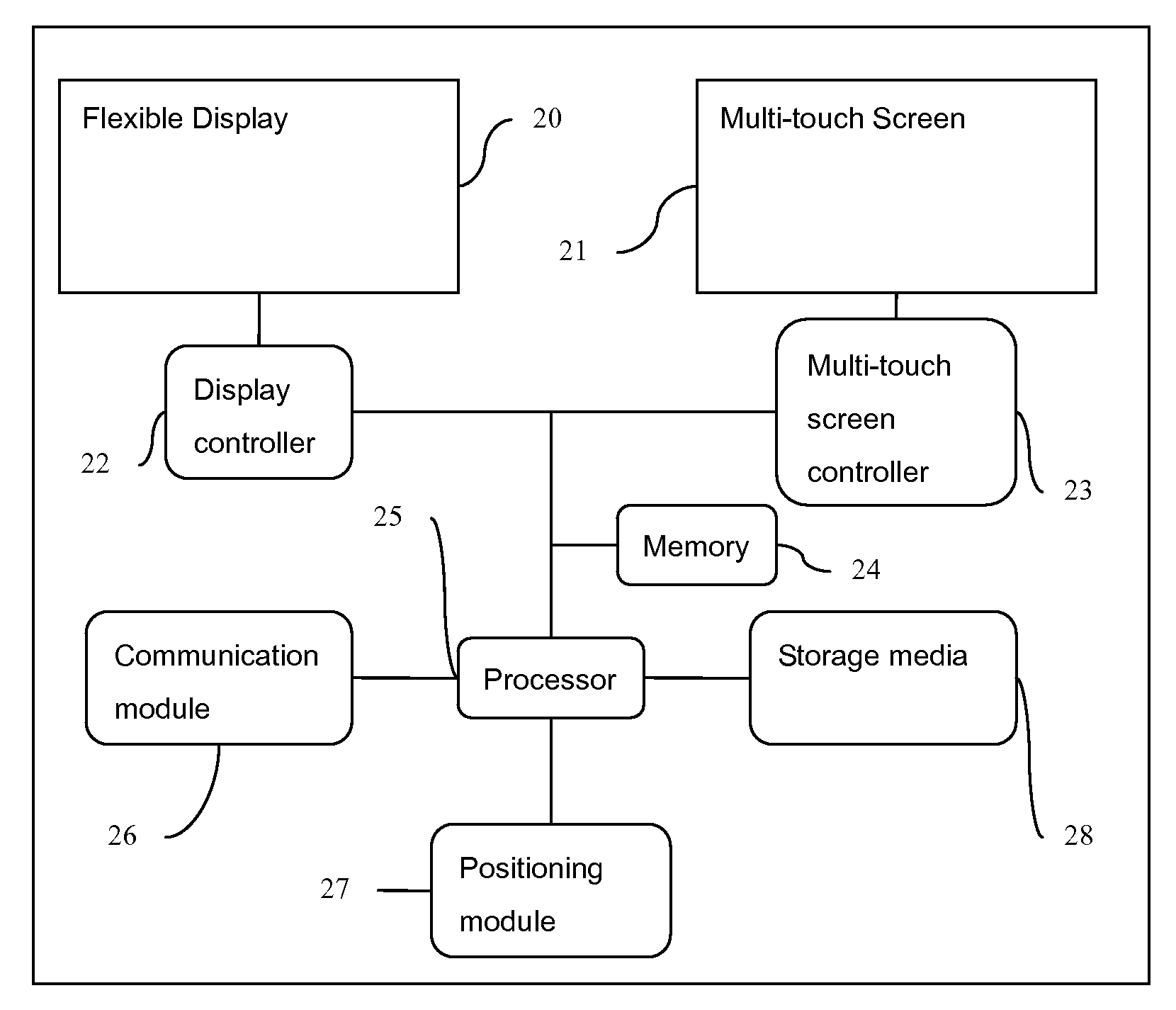
A method, apparatus, and system of flexible multi-touch touch are provided. The invention comprising: a flexible layer; and one or more sensors configured to detect a plurality of simultaneous touching positions at distinct locations of the layer and to generate distinct signals representative of the locations for each of the touches. And a method for flexible touch panel comprising: driving one or more sensors; and detecting a plurality of simultaneous touching positions at distinct locations of a touch panel, wherein the touch panel comprising a flexible property. The invention is also directed towards a flexible multi-touch screen device, comprising: a display as user interface; and a multi-touch panel with flexible property to combine with the display configured to detect a plurality of simultaneous touching positions at distinct locations of the multi-touch panel.
Owner:CHENG TUNG WAN
Composite patterning devices for soft lithography
ActiveUS20050238967A1High resolutionImprove placement accuracyMaterial nanotechnologyNanoinformaticsEngineeringThermal expansion
The present invention provides methods, devices and device components for fabricating patterns on substrate surfaces, particularly patterns comprising structures having microsized and / or nanosized features of selected lengths in one, two or three dimensions. The present invention provides composite patterning devices comprising a plurality of polymer layers each having selected mechanical properties, such as Young's Modulus and flexural rigidity, selected physical dimensions, such as thickness, surface area and relief pattern dimensions, and selected thermal properties, such as coefficients of thermal expansion, to provide high resolution patterning on a variety of substrate surfaces and surface morphologies.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
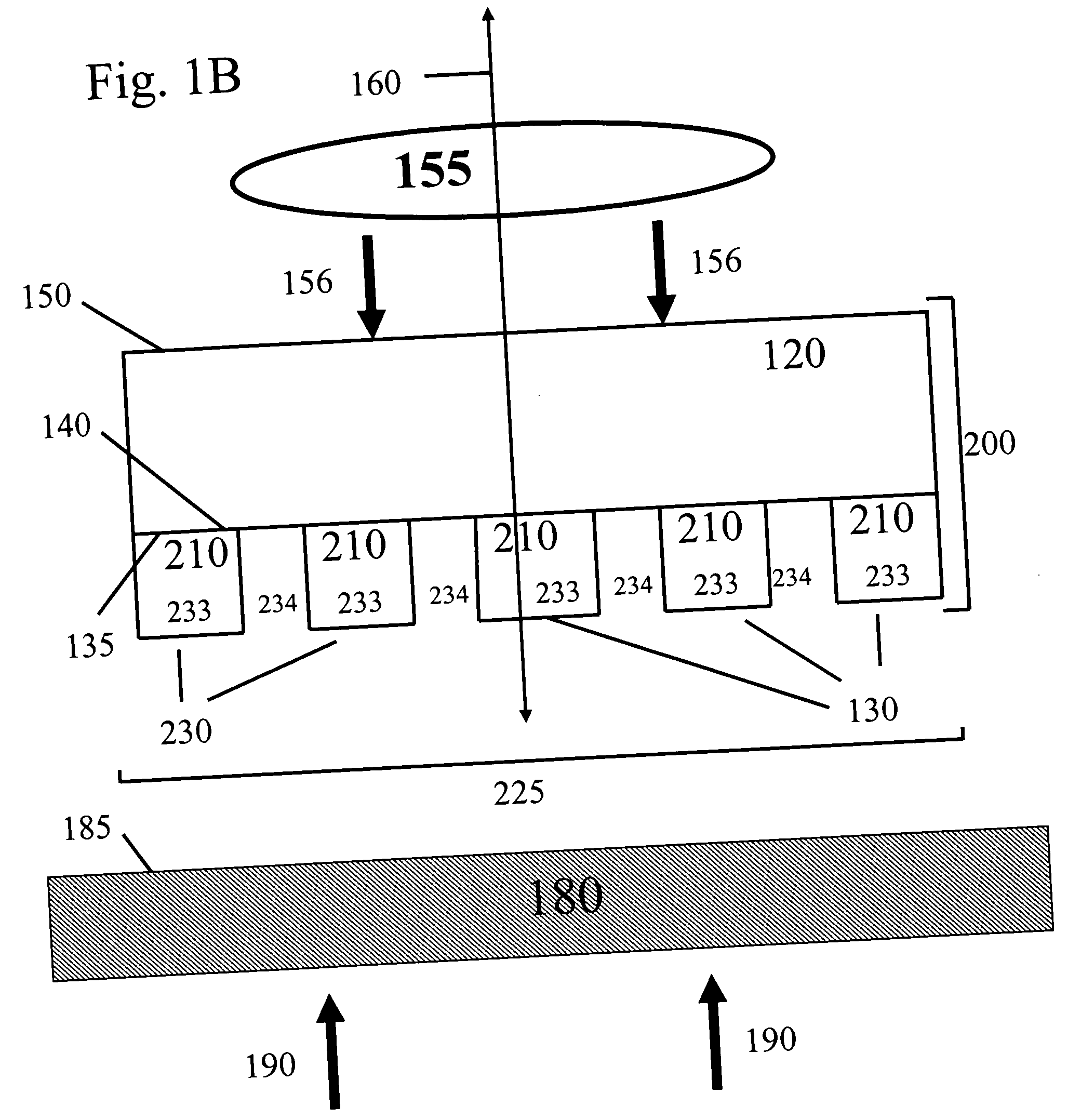
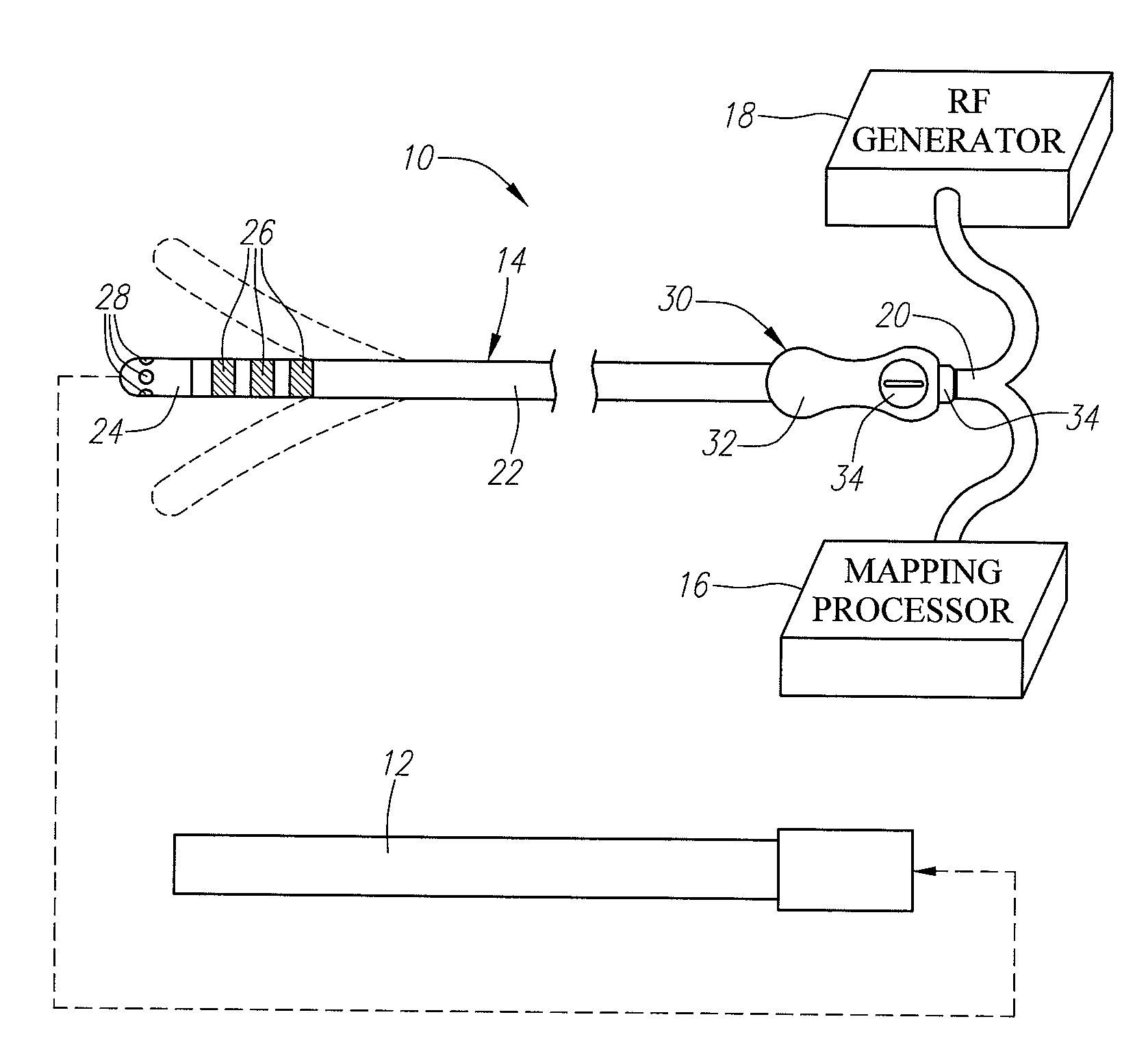
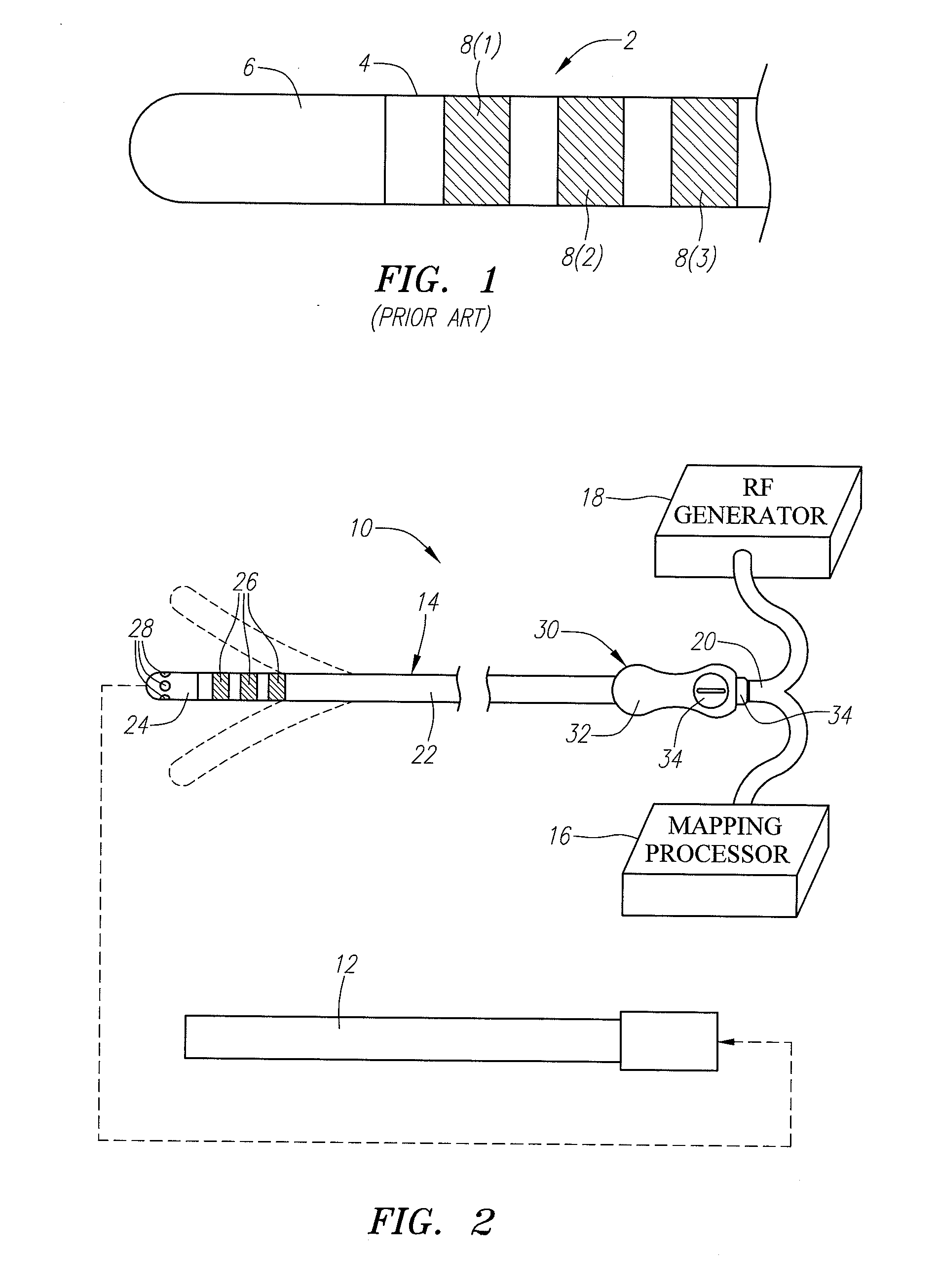
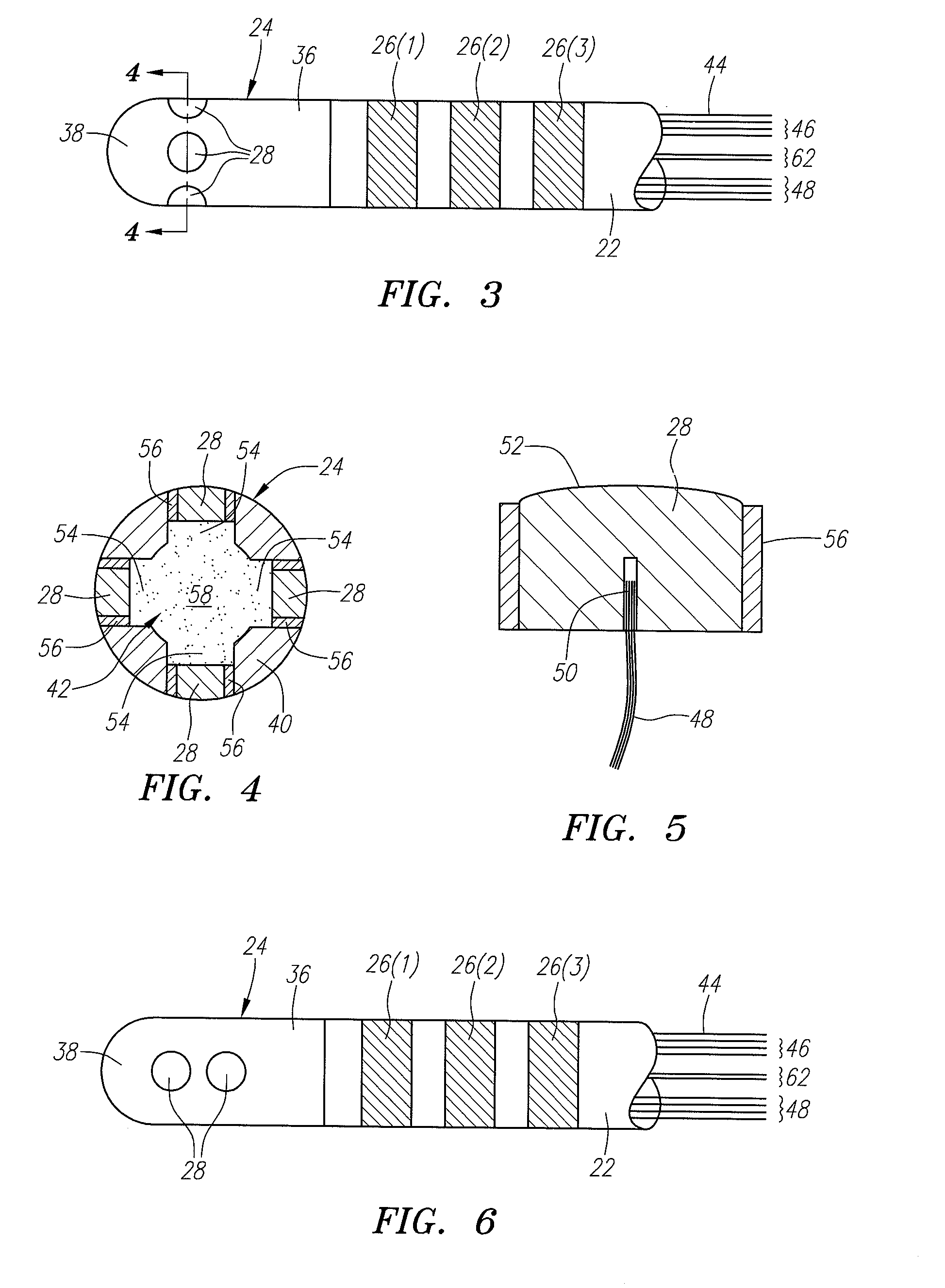
High resolution electrophysiology catheter
InactiveUS20080243214A1Improve resolution and fidelityAccurately tissue contactElectrocardiographyTransvascular endocardial electrodesMicroelectrodeBiomedical engineering
An electrophysiology medical probes, which may be incorporated into a system and used to perform an electrophysiology procedure, is provided. The medical probe comprises an elongated member (e.g., a flexible elongated member), and a metallic electrode mounted to the distal end of the elongated member. In one embodiment, the metallic electrode is cylindrically shaped and comprises a rigid body. The medical probe further comprises a plurality of microelectrodes (e.g., at least four microelectrodes) embedded within, and electrically insulated from, the metallic electrode, and at least one wire connected to the metallic electrode and the microelectrodes.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Sleep apnea risk evaluation
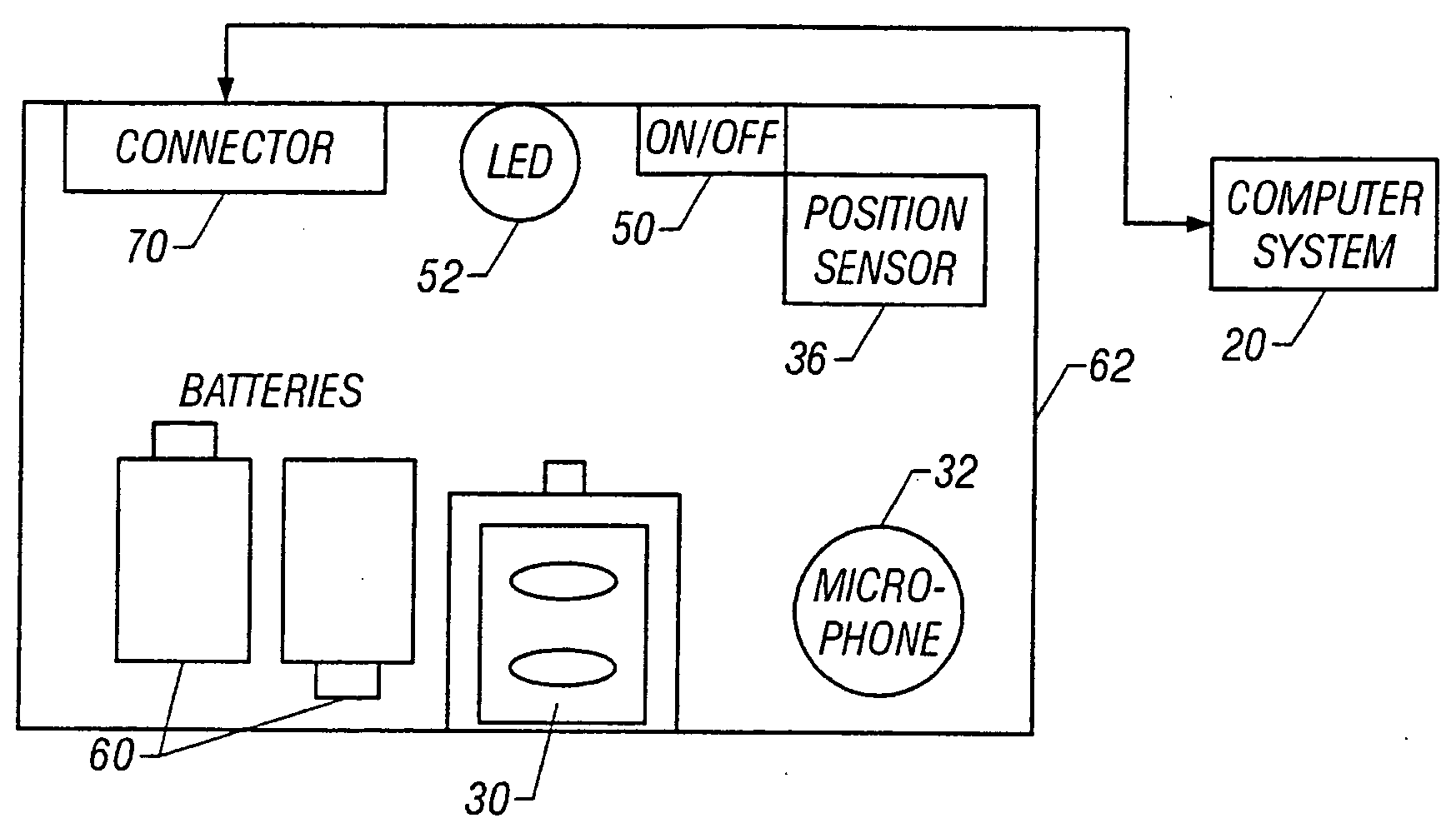
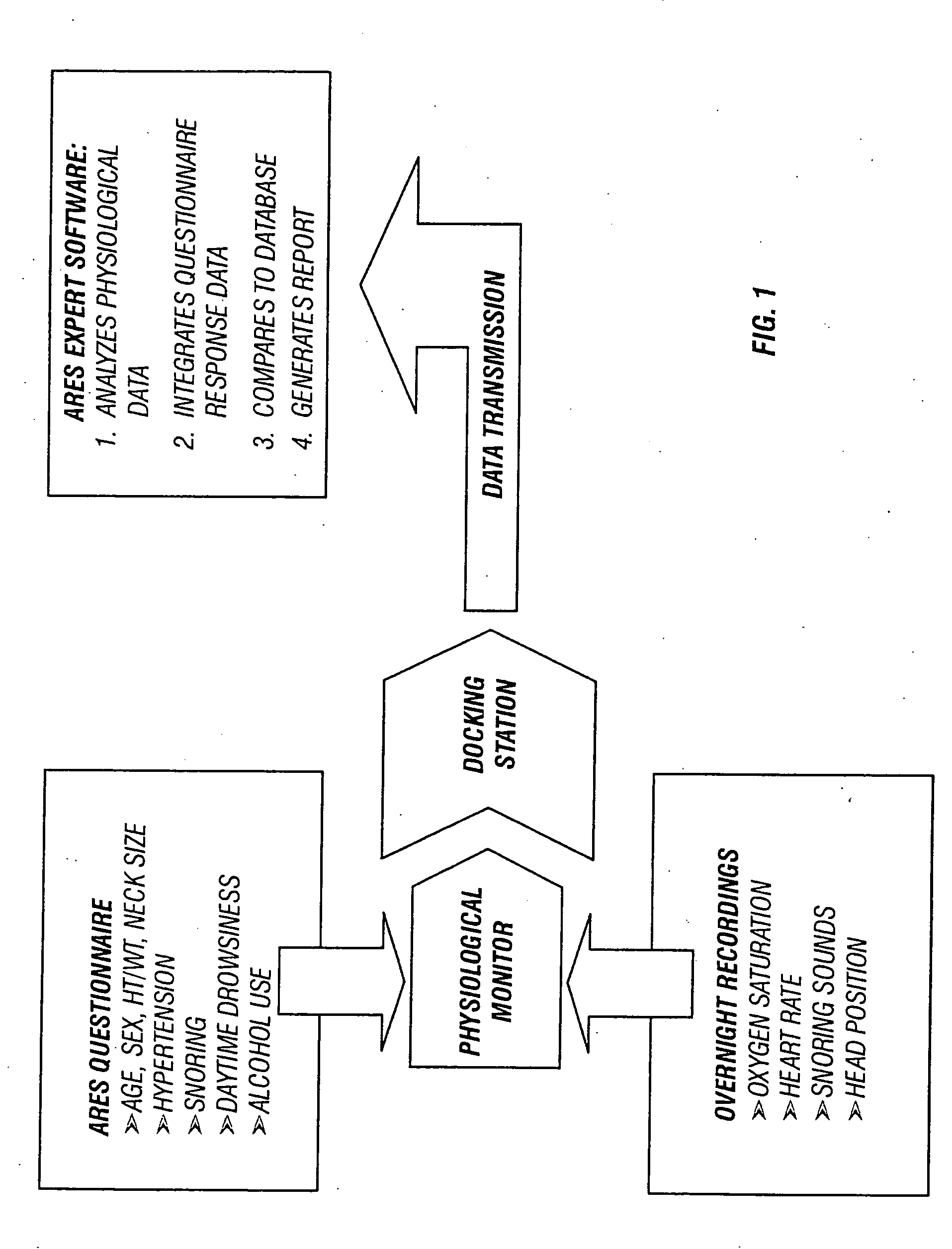
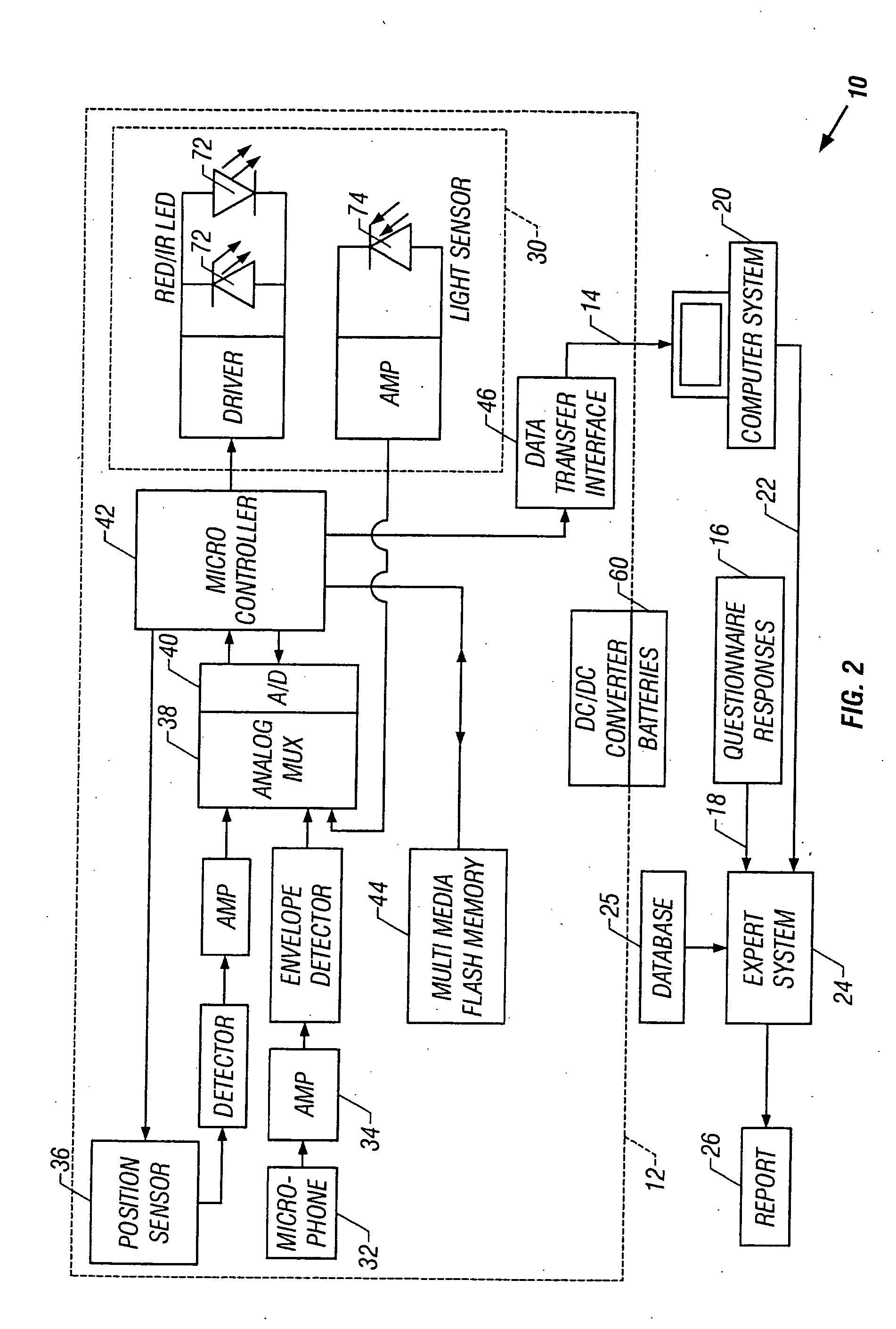
InactiveUS20050027207A1Improve accuracyImprove resolutionRespiratorsHealth-index calculationMedicinePulse oximeters
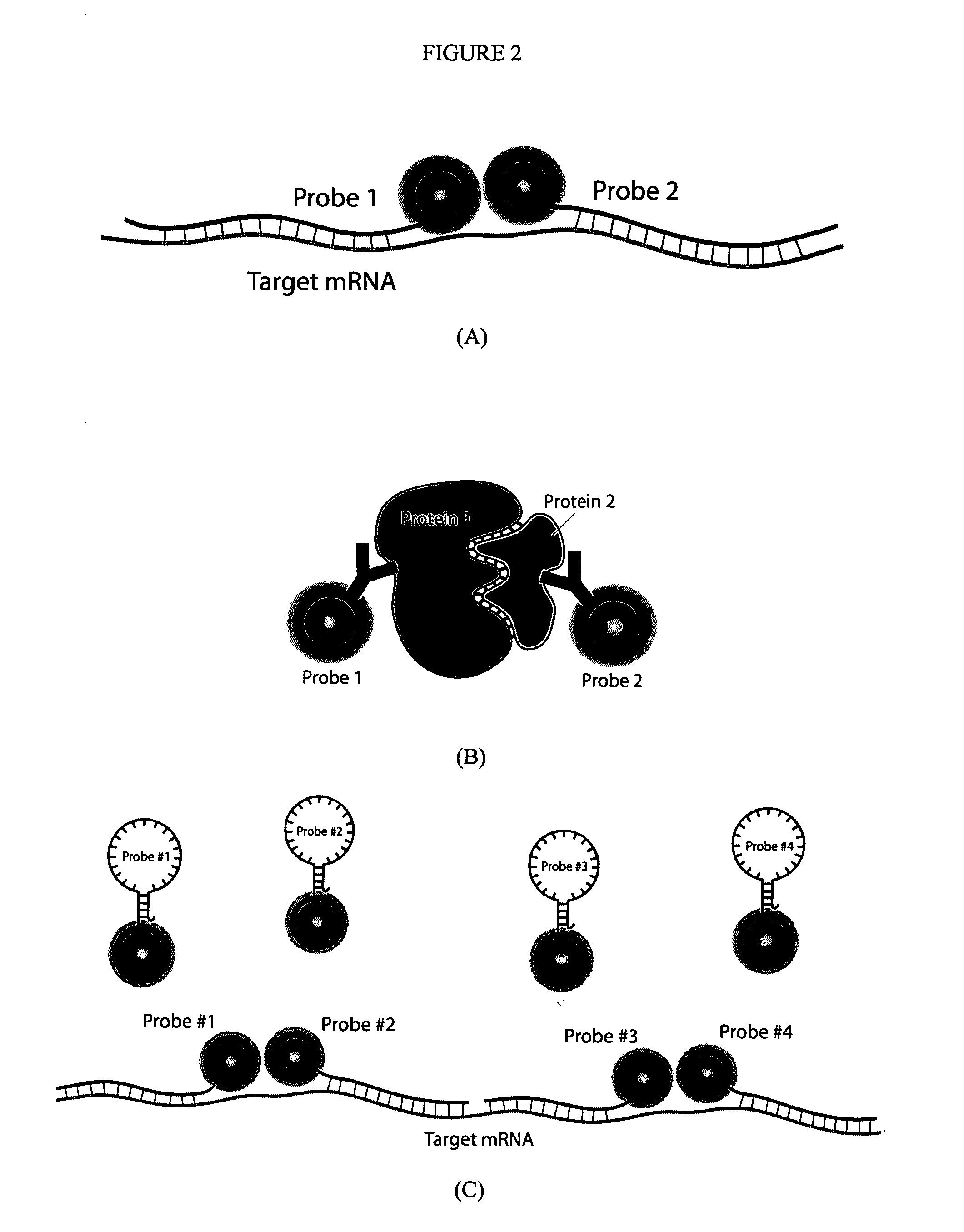
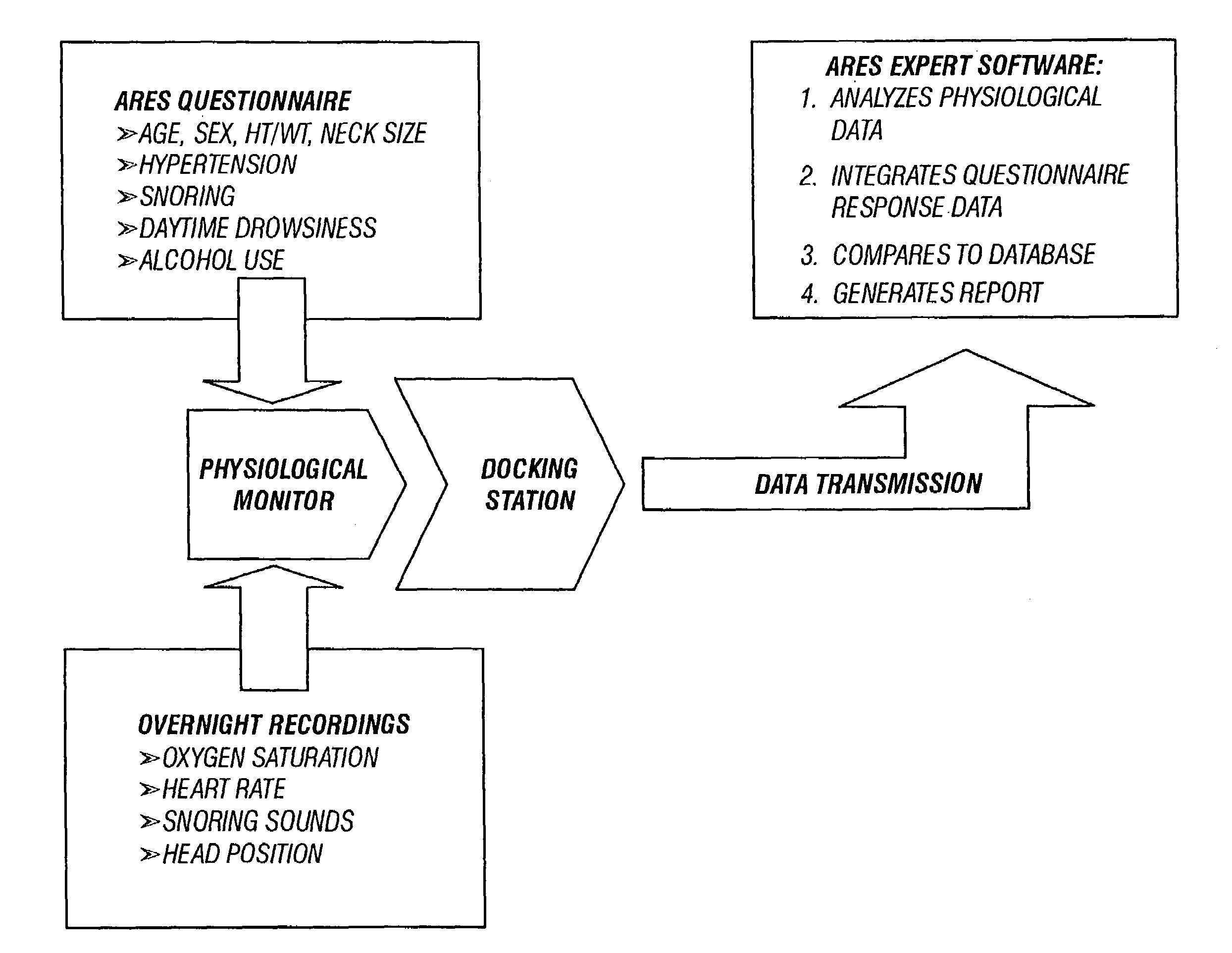
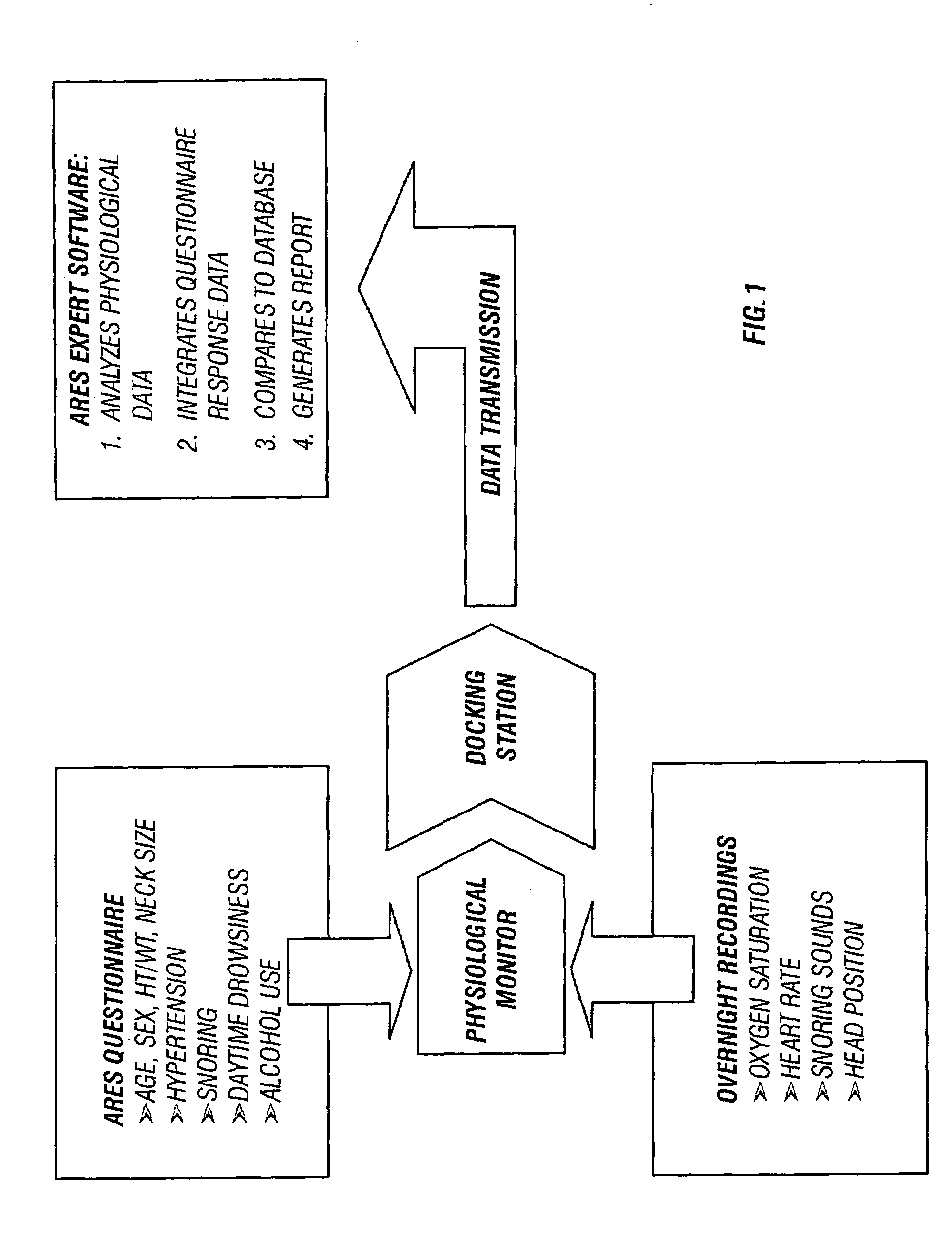
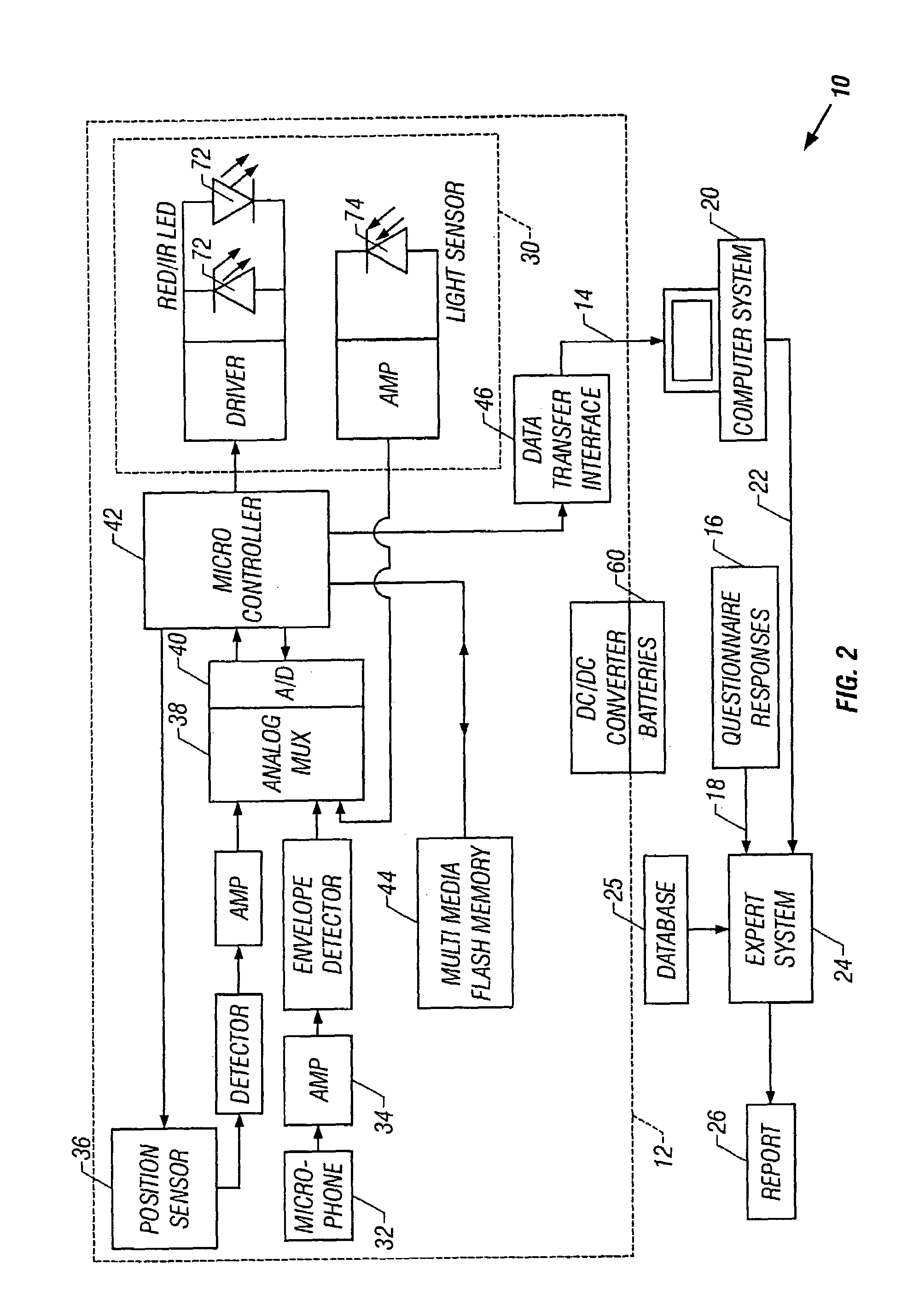
In a technique for collecting and analyzing physiological signals to detect sleep apnea, a small light-weight physiological monitoring system, affixed to a patient's forehead, detects and records the pulse, oximetry, snoring sounds, and head position of a patient to detect a respiratory event, such as sleep apnea. The physiological monitoring system may contain several sensors including a pulse oximeter to detect oximetry and pulse rate, a microphone to detect snoring sounds, and a position sensor to detect head position. The physiological monitoring system also can contain a memory to store or record the signals monitored by the mentioned sensors and a power source. The physiological monitoring system may be held in place by a single elastic strap, thereby enabling a patient to use the system without the assistance of trained technicians.
Owner:WATERMARK MEDICAL
Video manipulation of red, green, blue, distance (RGB-Z) data including segmentation, up-sampling, and background substitution techniques
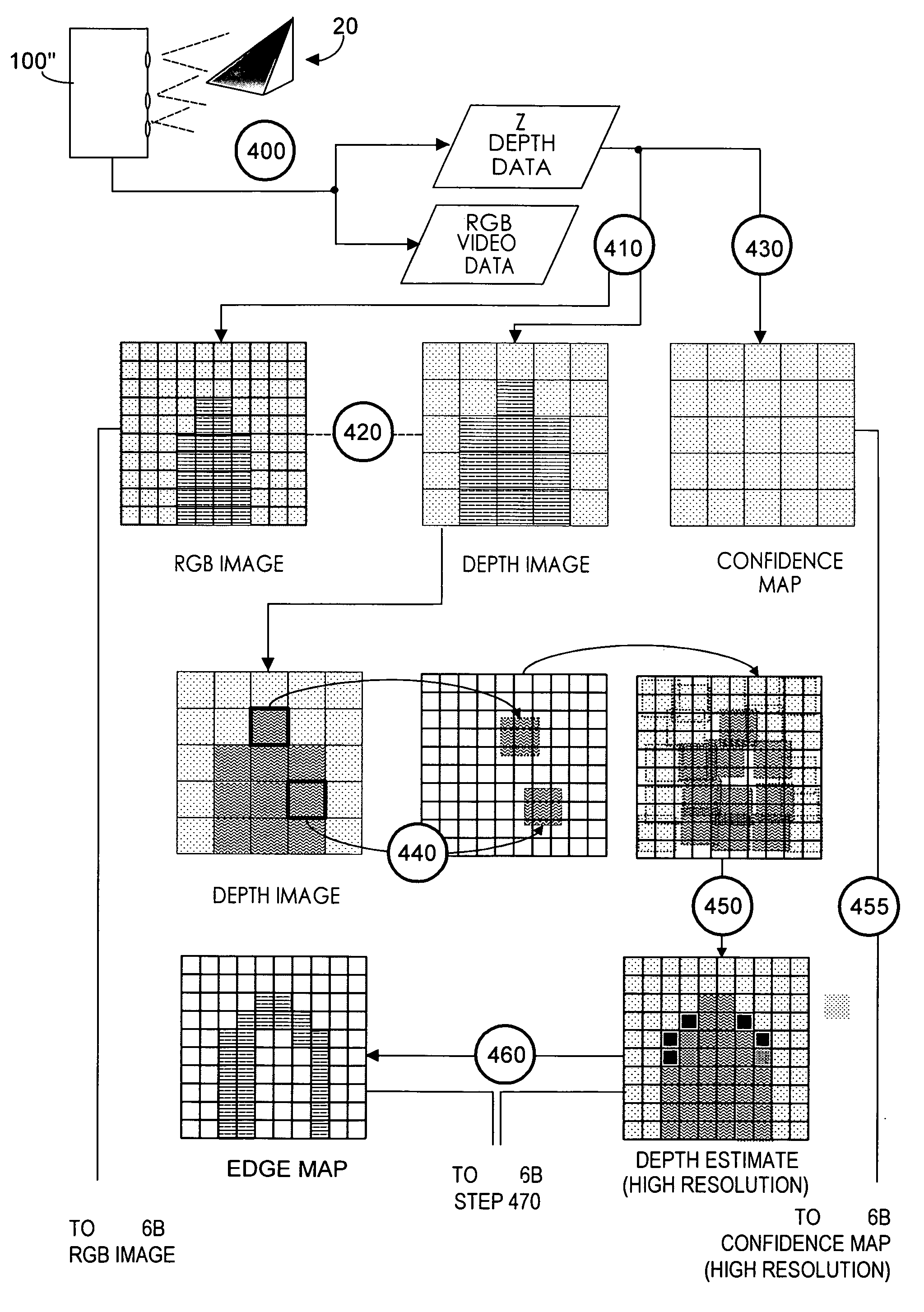
ActiveUS20110285910A1Improve resolutionEasy to processTelevision system detailsOptical rangefindersImage resolutionSignal characteristic
RGB-Z imaging systems acquire RGB data typically with a high X-Y resolution RGB pixel array, and acquire Z-depth data with an array of physically larger Z pixels having additive signal properties. In each acquired frame, RGB pixels are mapped to a corresponding Z pixel. Z image resolution is enhanced by identifying Z discontinuities and identifying corresponding RGB pixels where the Z discontinuities occur. Thus segmented data enables RGB background substitution, which preferably blends foreground pixel color and substitute background color. The segmented data also enables up-sampling in which a higher XY resolution Z image with accurate Z values is obtained. Up-sampling uses an equation set enabling assignment of accurate Z values to RGB pixels. Fixed acquisition frame rates are enabled by carefully culling bad Z data. Segmenting and up-sampling enhanced video effects and enable low cost, low Z resolution arrays to function comparably to higher quality, higher resolution Z arrays.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
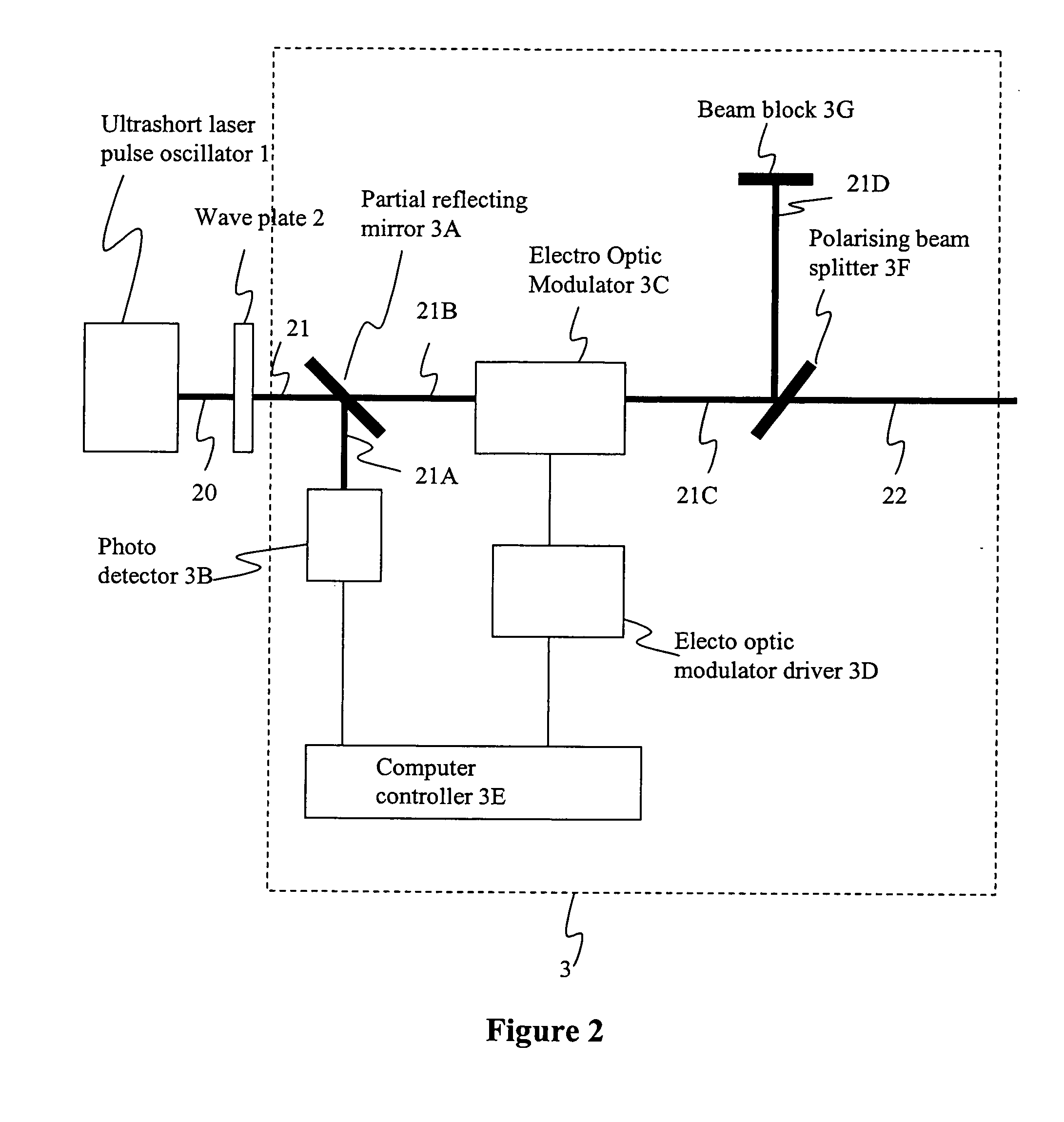
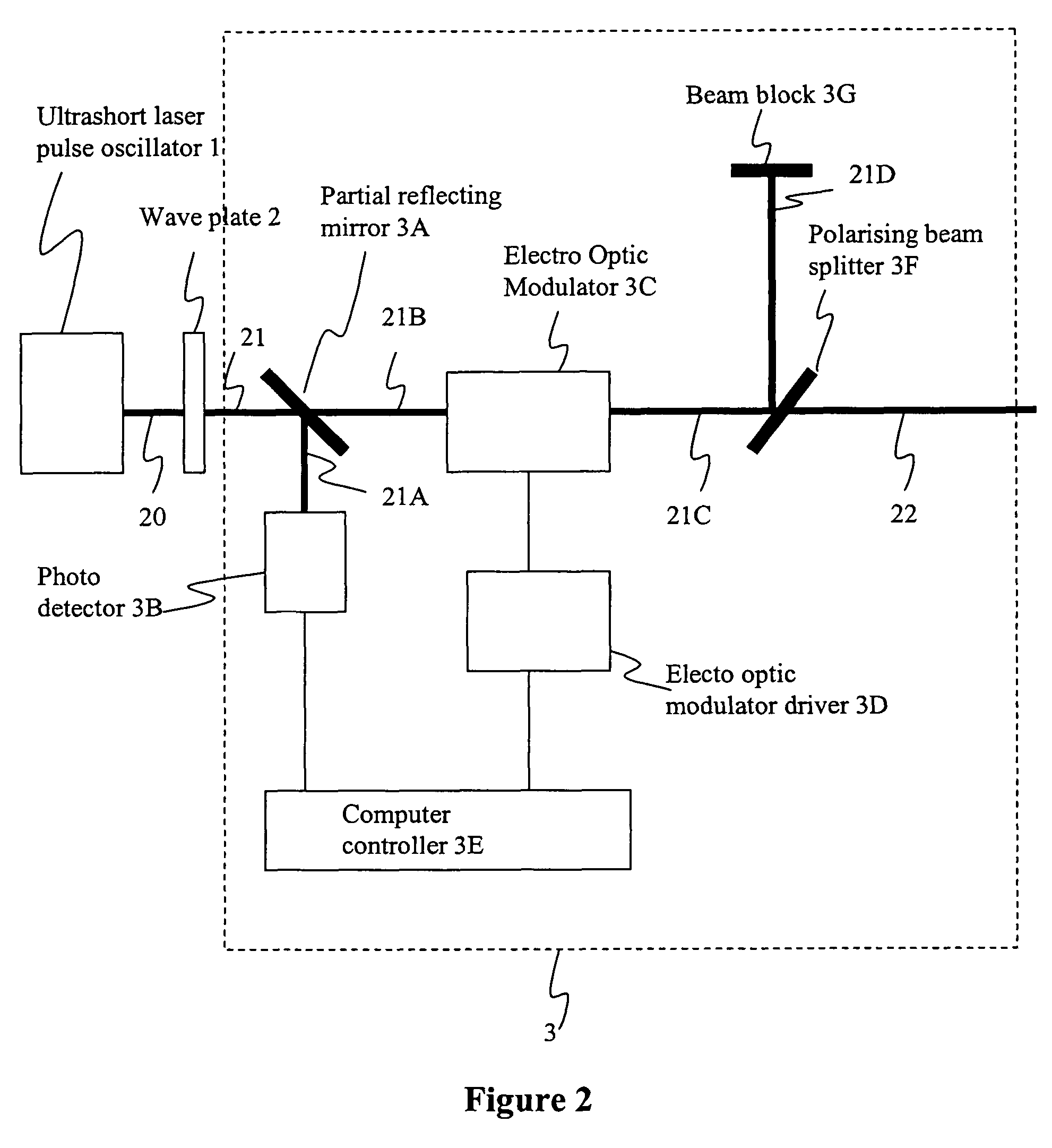
Method and apparatus for dicing of thin and ultra thin semiconductor wafer using ultrafast pulse laser
InactiveUS20050274702A1Improve inner wall qualityImprove surface qualityWelding/soldering/cutting articlesMetal working apparatusPicosecond laserFacula
The present invention relates to the apparatus, system and method for dicing of semiconductor wafers using an ultrafast laser pulse of femtosecond and picosecond pulse widths directly from the ultrafast laser oscillator without an amplifier. Thin and ultrathin simiconductor wafers below 250 micrometer thickness, are diced using diode pumped, solid state mode locked ultrafast laser pulses from oscillator without amplification. The invention disclosed has means to avoid / reduce the cumulative heating effect and to avoid machine quality degrading in multi shot ablation. Also the disclosed invention provides means to change the polarization state of the laser beam to reduce the focused spot size, and improve the machining efficiency and quality. The disclosed invention provides a cost effective and stable system for high volume manufacturing applications. An ultrafast laser oscillator can be a called as femtosecond laser oscillator or a picosecond laser oscillator depending on the pulse width of the laser beam generated.
Owner:LASERFACTURING
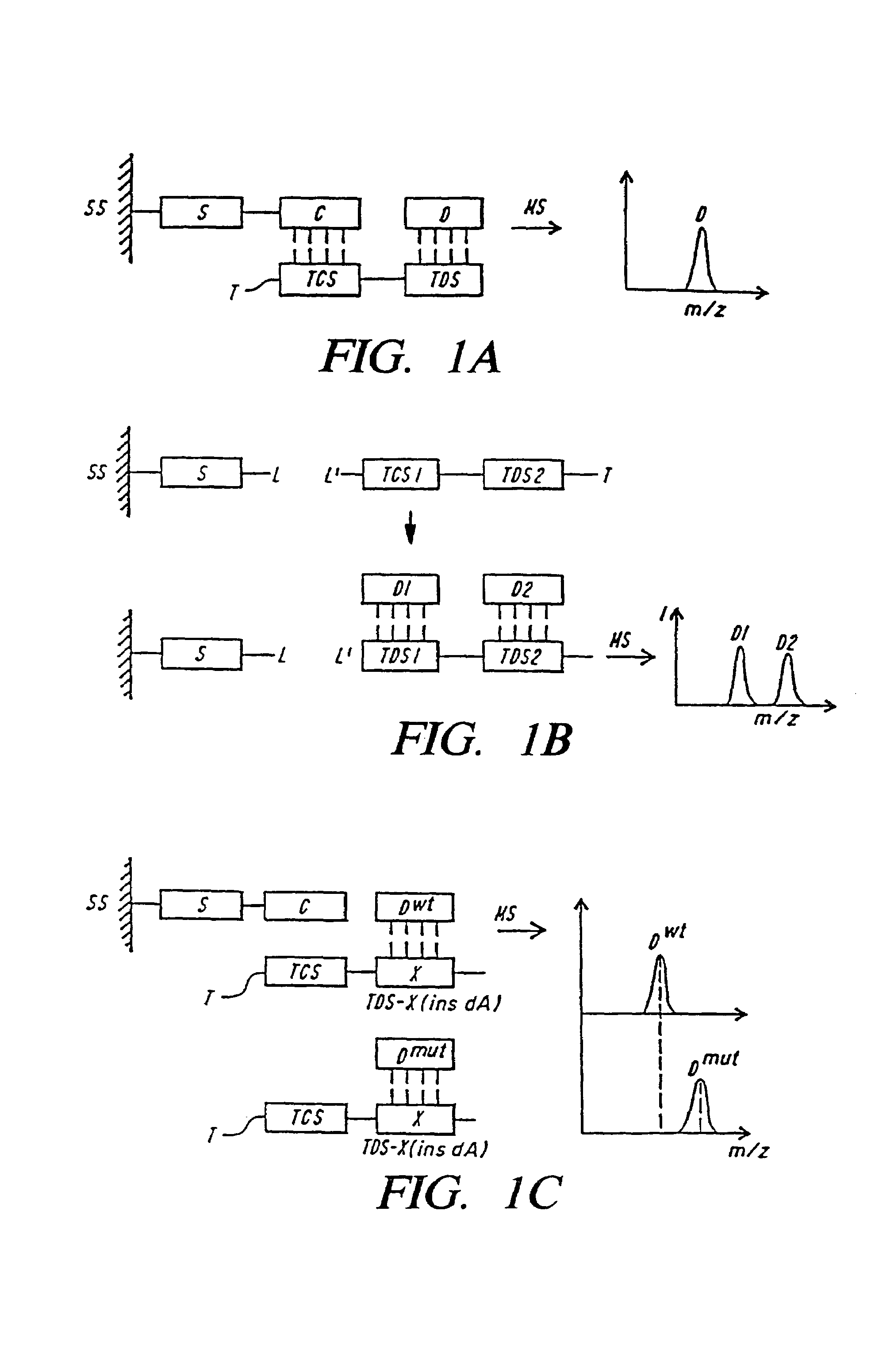
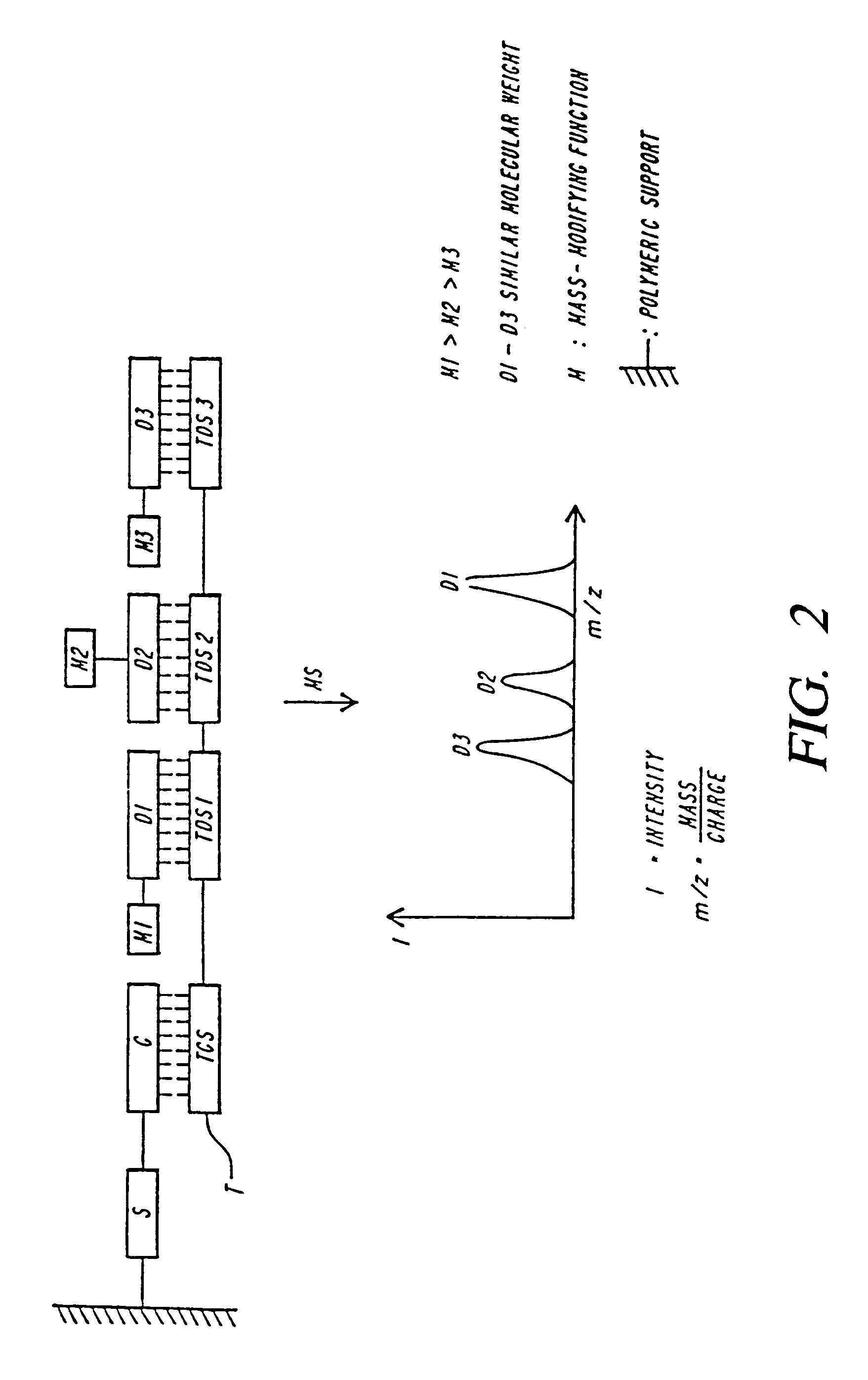
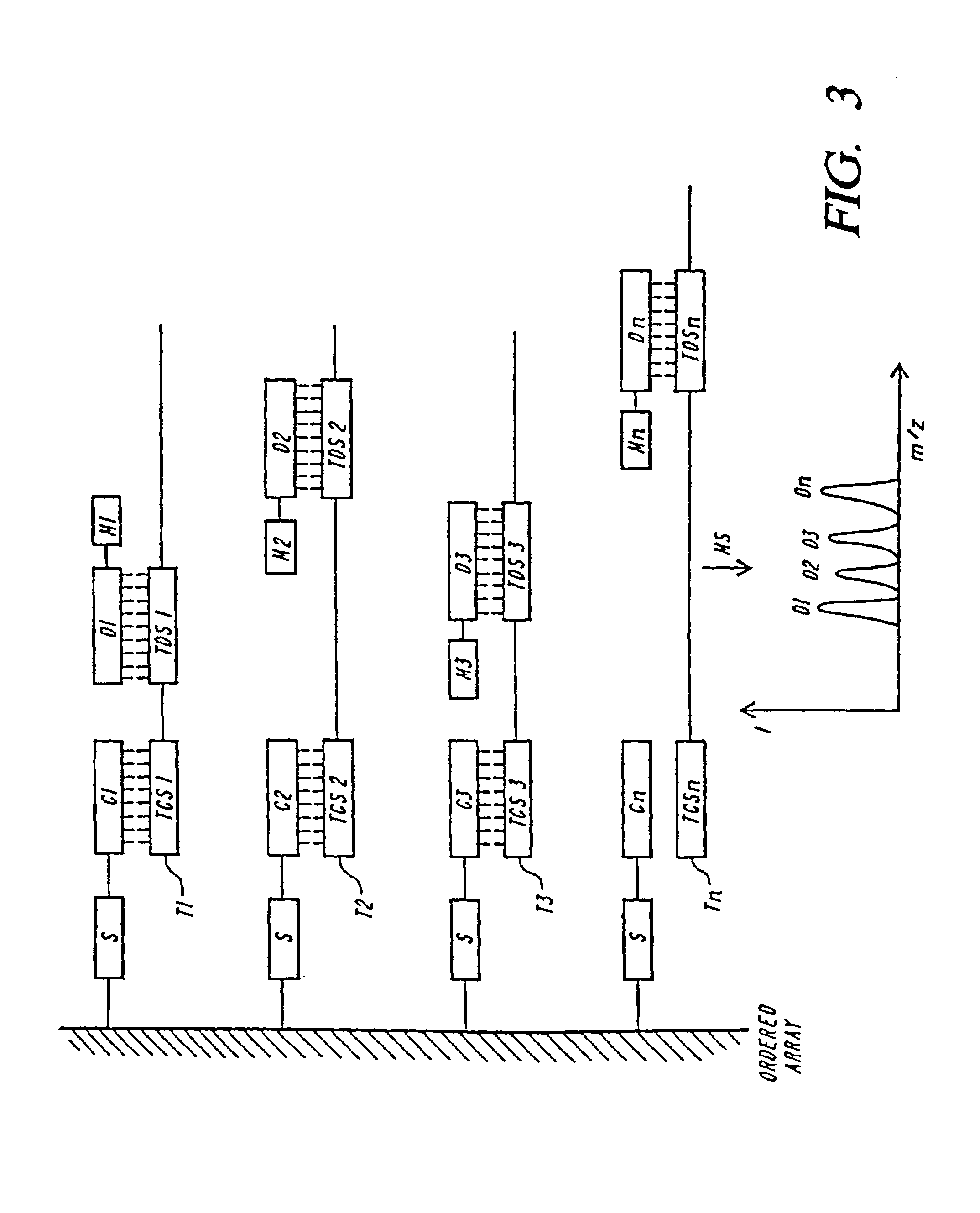
DNA diagnostics based on mass spectrometry
InactiveUS7198893B1Increase mass resolution massIncrease mass mass accuracyPeptide librariesSequential/parallel process reactionsMass spectrometry imagingOrganism
Fast and highly accurate mass spectrometry-based processes for detecting a particular nucleic acid sequence in a biological sample are provided. Depending on the sequence to be detected, the processes can be used, for example, to diagnose a genetic disease or chromosomal abnormality; a predisposition to a disease or condition, infection by a pathogenic organism, or for determining identity or heredity.
Owner:AGENA BIOSCI
Devices and methods for pattern generation by ink lithography
InactiveUS20080055581A1Improve fidelityIncrease resistanceNanostructure manufactureNanoinformaticsElastomerLithographic artist
The present invention provides methods, devices and device components for fabricating patterns on substrate surfaces, particularly patterns comprising structures having microsized and / or nanosized features of selected lengths in one, two or three dimensions and including relief and recess features with variable height, depth or height and depth. Composite patterning devices comprising a plurality of polymer layers each having selected mechanical and thermal properties and physical dimensions provide high resolution patterning on a variety of substrate surfaces and surface morphologies. Gray-scale ink lithography photomasks for gray-scale pattern generation or molds for generating embossed relief features on a substrate surface are provided. The particular shape of the fabricated patterned can be manipulated by varying the three-dimensional recess pattern on an elastomeric patterning device which is brought into conformal contact with a substrate to localize patterning agent to the recess portion of the pattern.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
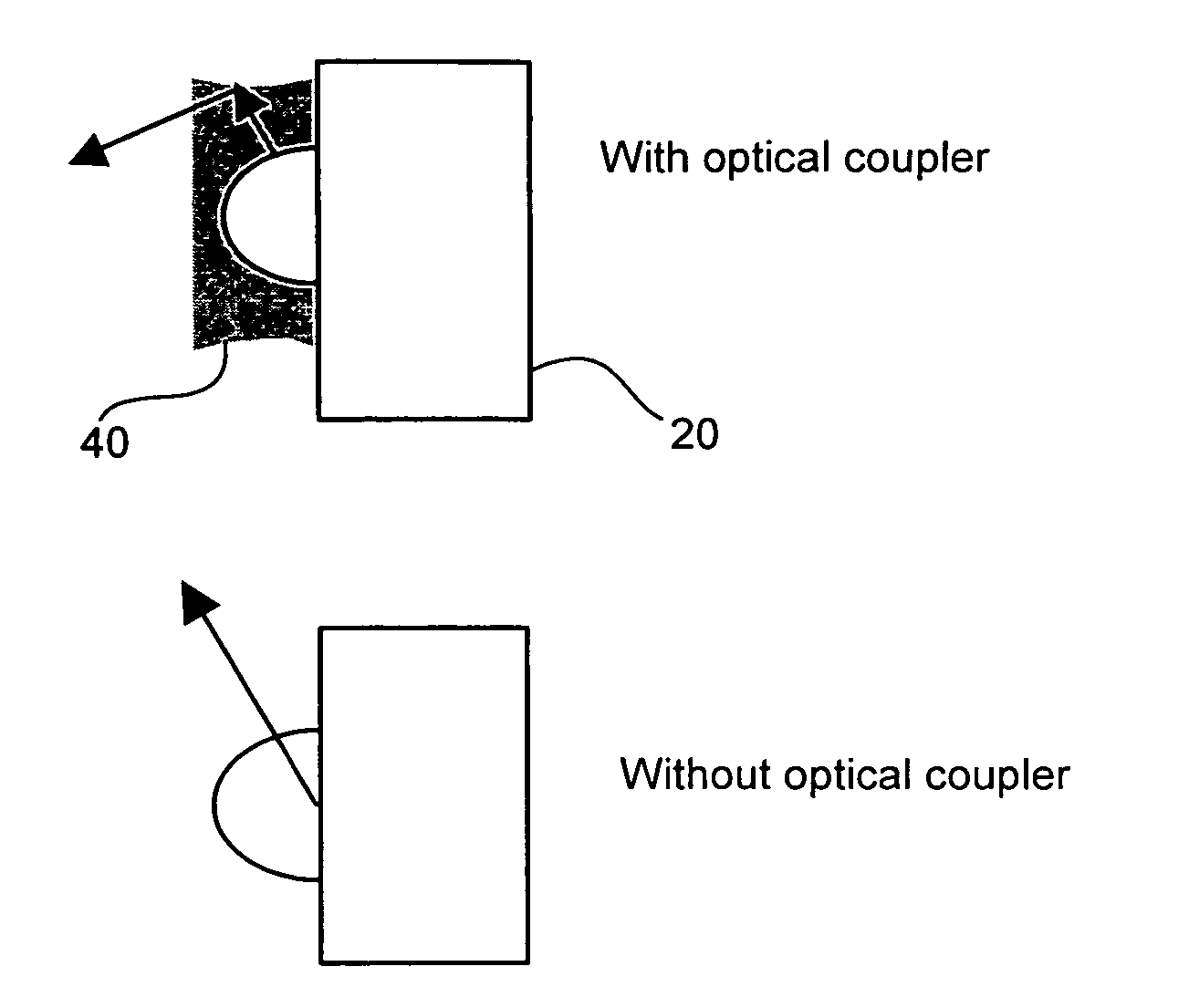
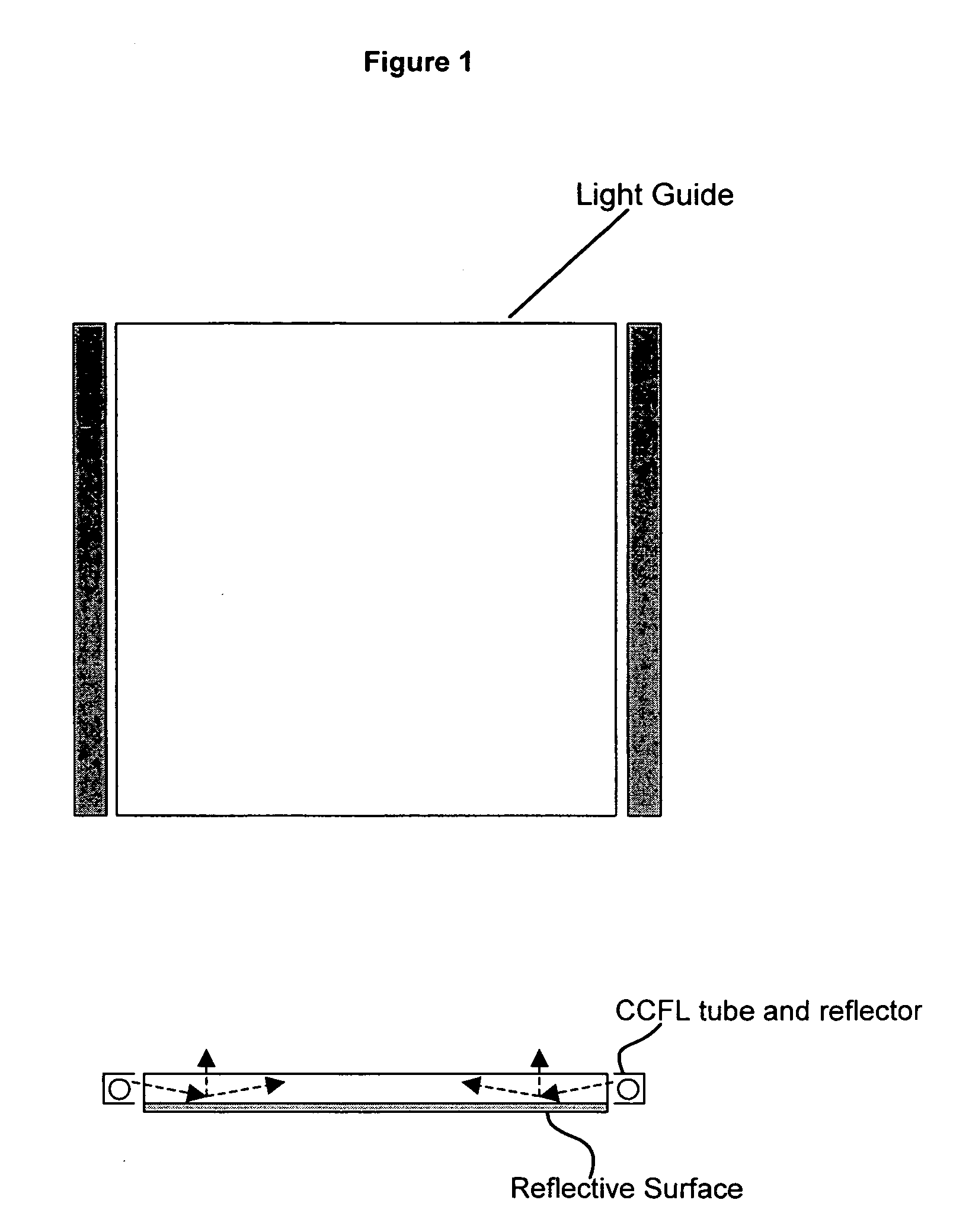
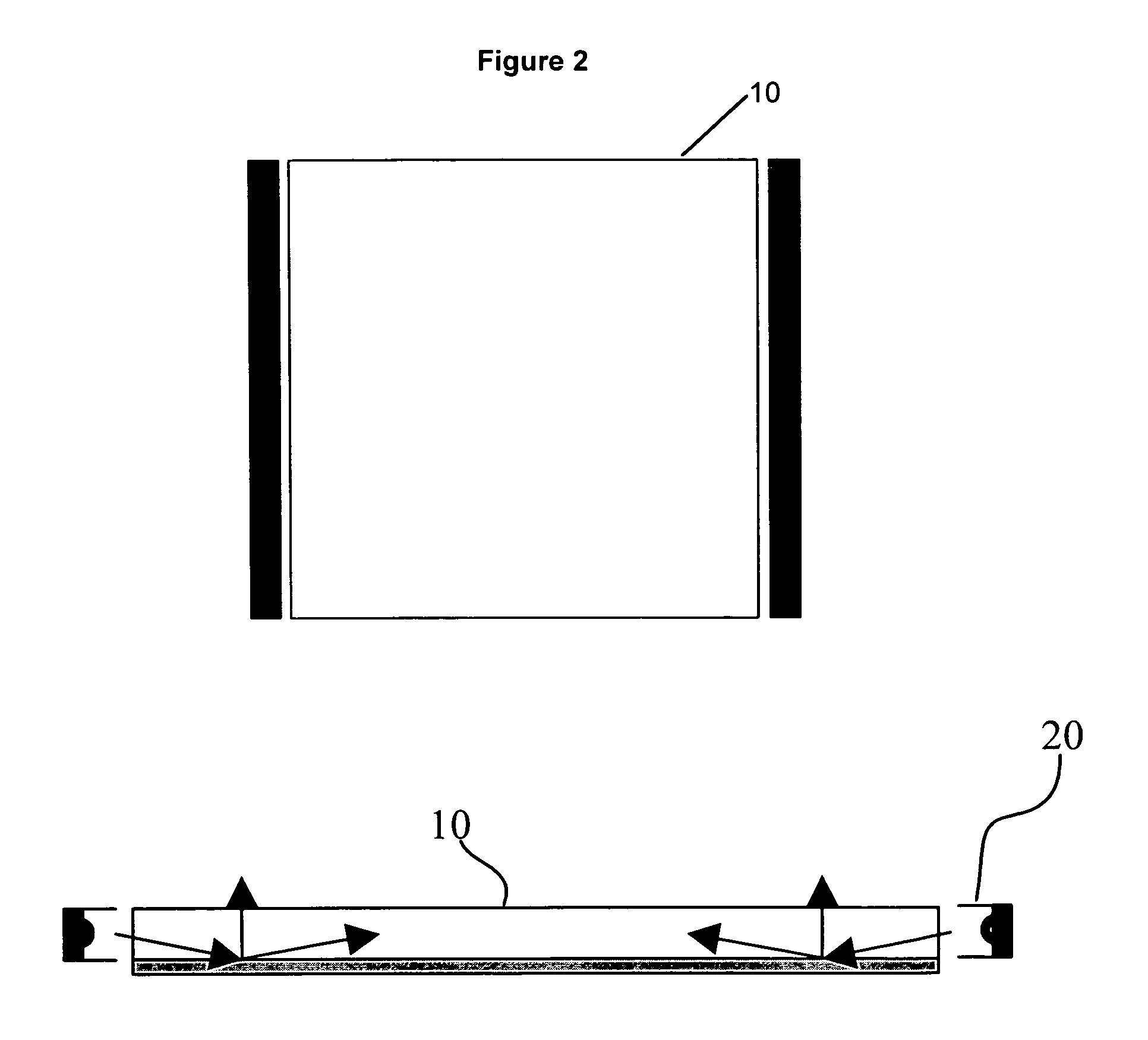
Display backlight with improved light coupling and mixing
ActiveUS20070081360A1Enhanced couplingWell mixedIlluminated signsOptical light guidesLight guideDisplay device
A display backlight assembly providing improved optical coupling between a solid state light source and a display optical light guide. The assembly includes an optical coupler to couple the solid state light source and display optical light guide together. In addition, the optical coupler may include a light mixing element for improved mixing of the multi-colored or mono-chromatic light produced by the solid state light source.
Owner:LIGHTING SCI GROUP
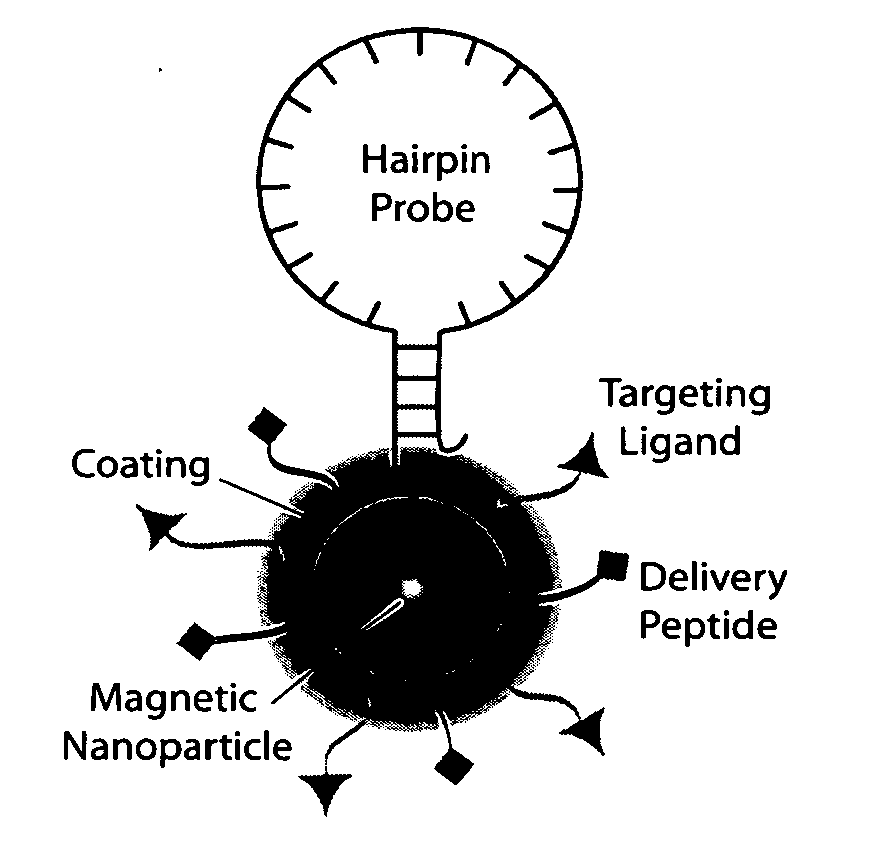
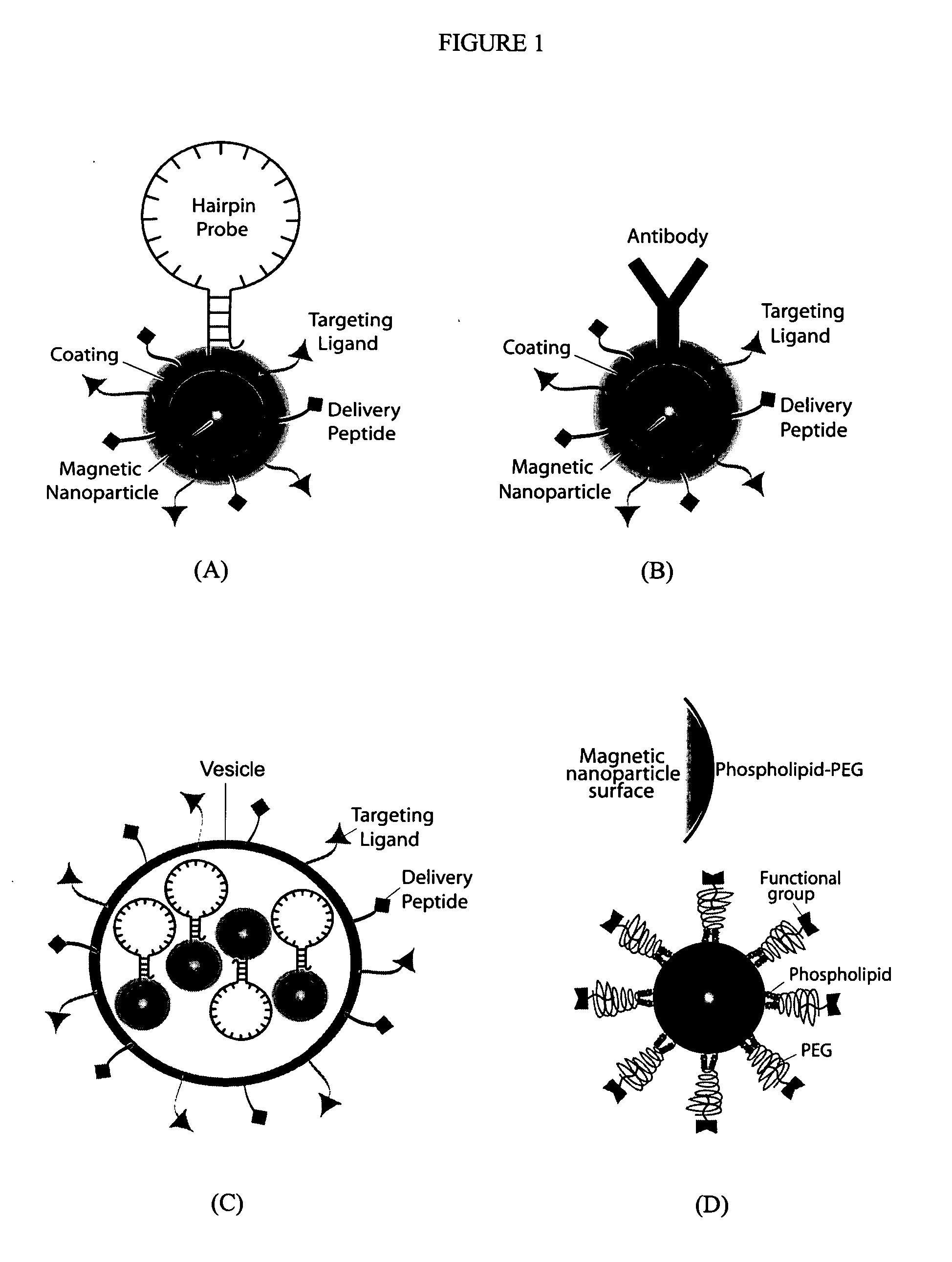
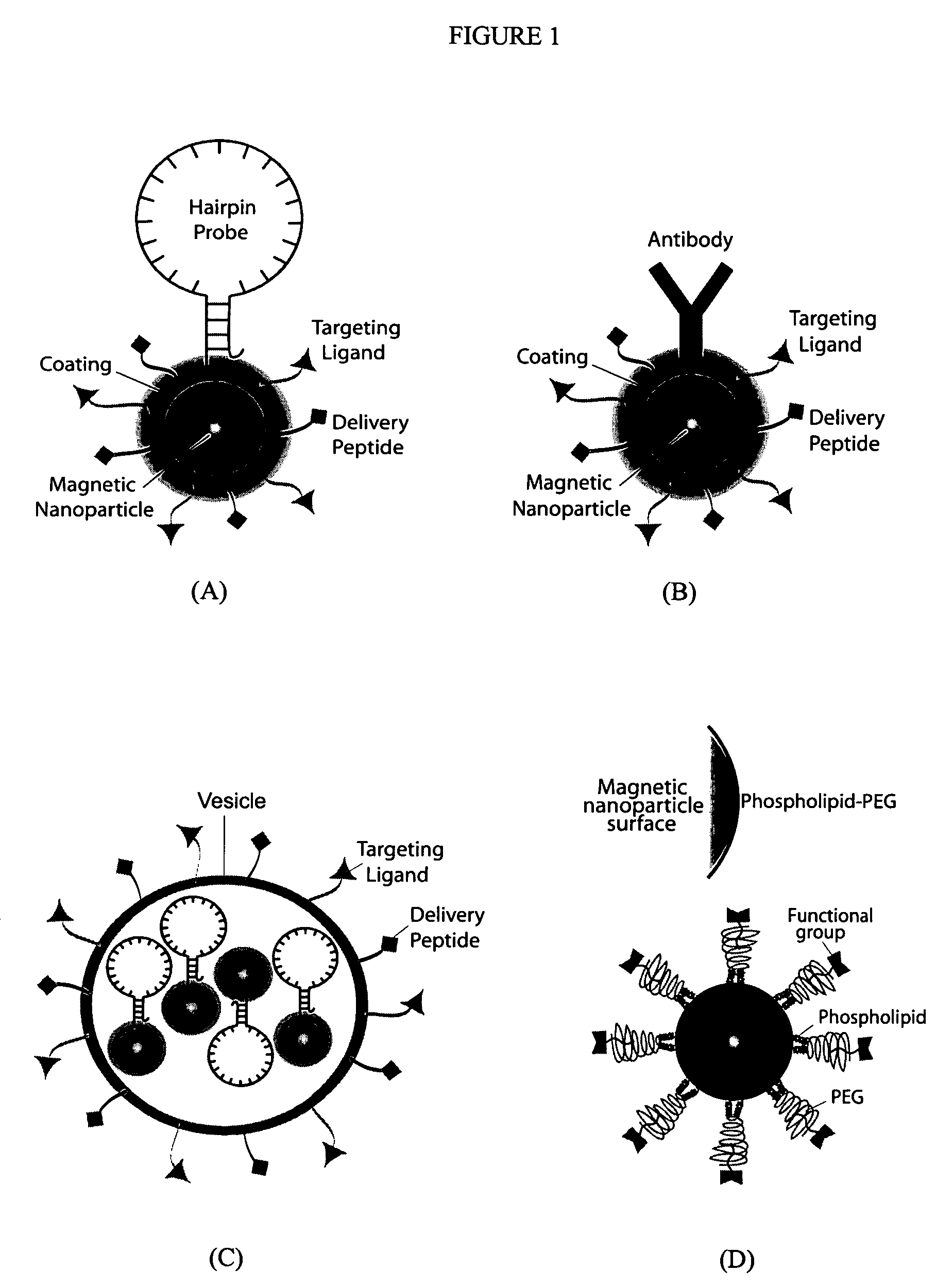
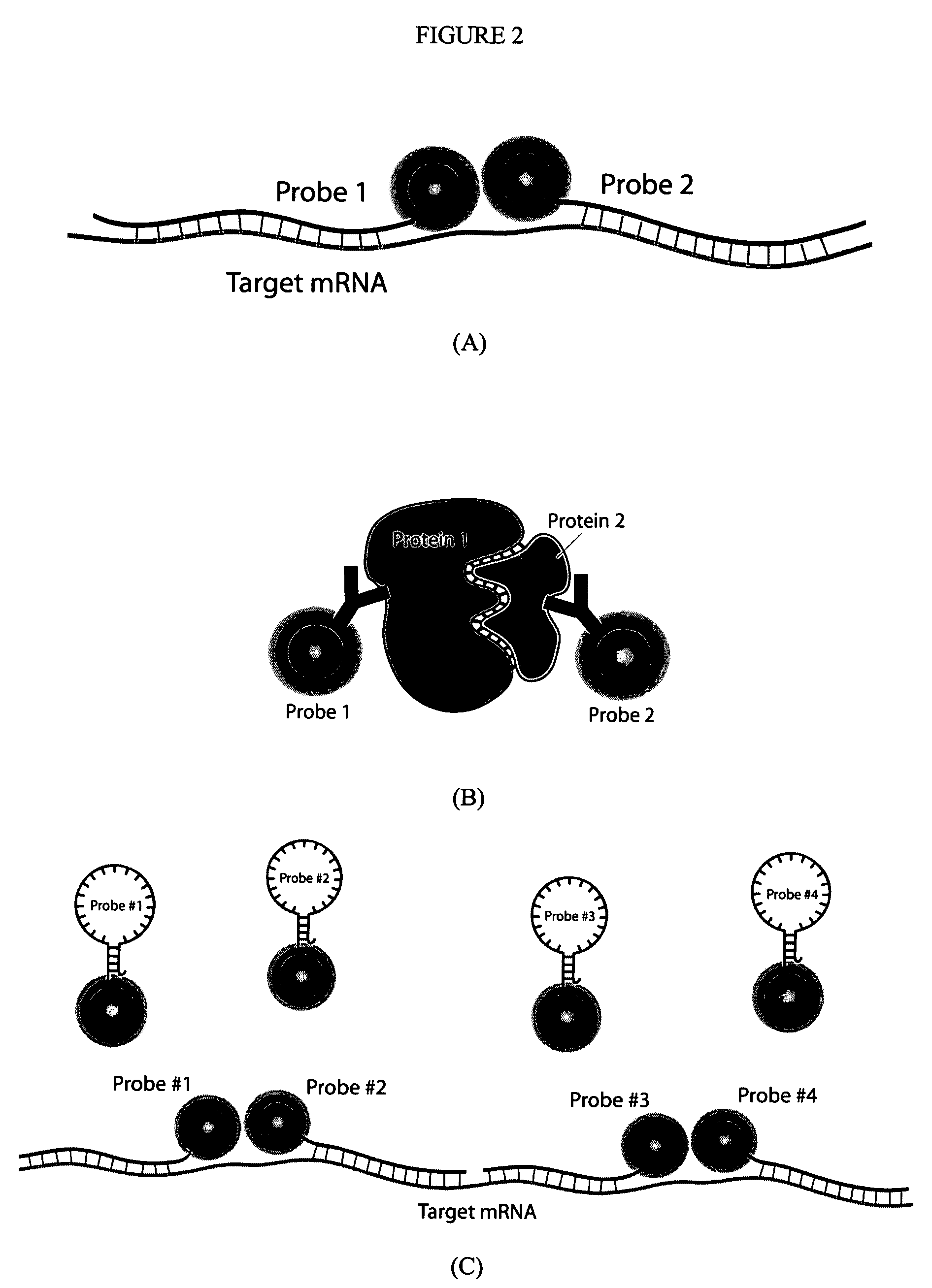
Multifunctional magnetic nanoparticle probes for intracellular molecular imaging and monitoring
InactiveUS20050130167A1Strong specificityHigh sensitivityMaterial nanotechnologyPowder deliveryFluorescenceBiocompatible coating
The present invention provides multifunctional magnetic nanoparticle probe compositions for molecular imaging and monitoring, comprising a nucleic acid or polypeptide probe, a delivery ligand, and a magnetic nanoparticle having a biocompatible coating thereon. The probe compositions may further comprise a fluorescent or luminescent resonance energy transfer moiety. Also provided are compositions comprising two or more such multifunctional magnetic nanoparticle probes for molecular imaging or monitoring. In particular, the nucleic acid or polypeptide probes bind to a target and generate an interaction observable with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or optical imaging. The invention thereby provides detectable signals for rapid, specific, and sensitive detection of nucleic acids, polypeptides, and interactions thereof in vivo.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP +1
Sleep apnea risk evaluation
InactiveUS7297119B2Improve accuracyImprove resolutionHealth-index calculationSurgeryPulse oximetersLate apnea
In a technique for collecting and analyzing physiological signals to detect sleep apnea, a small light-weight physiological monitoring system, affixed to a patient's forehead, detects and records the pulse, oximetry, snoring sounds, and head position of a patient to detect a respiratory event, such as sleep apnea. The physiological monitoring system may contain several sensors including a pulse oximeter to detect oximetry and pulse rate, a microphone to detect snoring sounds, and a position sensor to detect head position. The physiological monitoring system also can contain a memory to store or record the signals monitored by the mentioned sensors and a power source. The physiological monitoring system may be held in place by a single elastic strap, thereby enabling a patient to use the system without the assistance of trained technicians.
Owner:WATERMARK MEDICAL
Capacitive touch panel with force sensing
ActiveUS20140062934A1Improve spatial resolutionHigh sensitivityTransmission systemsInput/output processes for data processingCapacitanceTouch Senses
A capacitive type touch sensing device includes a first electrode array including a plurality of drive electrodes and a plurality of sense electrodes, and a second electrode array spaced apart from the first electrode array and including a plurality of discrete, electrically floating conductive regions. At least part of the second electrode array positionally overlaps with at least part of the first electrode array to define a separation distance therebetween, the separation distance varying with a force applied to a surface of the touch sensing device. Further, each conductive region is positioned relative to a respective drive electrode and sense electrode of the first electrode array so that a capacitance between certain pairs of drive and sense electrodes is more sensitive to a variation in the separation distance than a capacitance between other pairs of drive and sense electrodes.
Owner:SHARP KK
Pressure sensor, electronic skin and touch screen equipment
ActiveCN103411710AMiniaturizationEasy to carryPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesForce measurement using piezo-electric devicesNanogeneratorEngineering
The invention provides a pressure sensor, and further provides electronic skin, touch screen equipment and safety alarm equipment correspondingly, wherein the electronic skin, the touch screen equipment and the safety alarm equipment are based on the pressure sensor. The pressure sensor comprises a substrate. The substrate is provided with a plurality of sensing units arranged in an array mode; a static nano generator with two friction layers is adopted in the sensing units, when external force is applied to the sensor, the distance between two friction layers of each sensing unit feeling the external force is changed, and electrical signals output outwards by two corresponding electrode layers are also changed; electrode layers of all sensing units are led out of the sensor through wires, so that functions like pressure (stress) positioning and pressure field mapping can be achieved. The electronic skin, the touch screen equipment and the safety alarm equipment do not need to be powered by power supplies and can conduct pressure induction in a self-driven mode.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF NANOENERGY & NANOSYST
Image display unit
InactiveUS7880184B2Reduce production time and costDegrade position accuracySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingComputer graphics (images)Image display
An image display unit and a method of producing the image display unit, wherein the image display unit includes an array of a plurality of light emitting devices for displaying an image, and wherein the method of producing the image display unit employs, for example, a space expanding transfer, whereby a first transfer step includes transferring the devices arrayed on a first substrate to a temporary holding member such that the devices are spaced from each other with a pitch larger than a pitch of the devices arrayed on the first substrate, a second holding step includes holding the devices on the temporary holding member, and a third transfer step includes transferring the devices held on the temporary holding member onto a second board such that the devices are spaced from each other with a pitch larger than the pitch of the devices held on the temporary holding member.
Owner:SONY CORP
Digital imaging system, plenoptic optical device and image data processing method
ActiveUS20120050562A1Avoid disadvantagesSimple methodTelevision system detailsSignal generator with multiple pick-up deviceDigital imagingMicro lens array
A digital imaging system being configured for synthesizing an image of a plenoptic optical device, comprises a photosensor array comprising a plurality of photosensors arranged in a predetermined image plane, and a microlens array comprising a plurality of microlenses arranged for directing light from an object to the photosensor array, wherein the photosensor array and the microlens array are arranged with a predetermined distance, the microlenses have different focal lengths varying over the microlens array, and the image plane of the photosensor array is arranged such that the distance between the photosensor array and the microlens array does not equal the microlenses' focal lengths. Furthermore, a plenoptic optical device including the digital imaging system and a method for processing image data collected with the digital imaging system are described.
Owner:RAYTRIX
Method and device for photothermal examination of microinhomogeneities
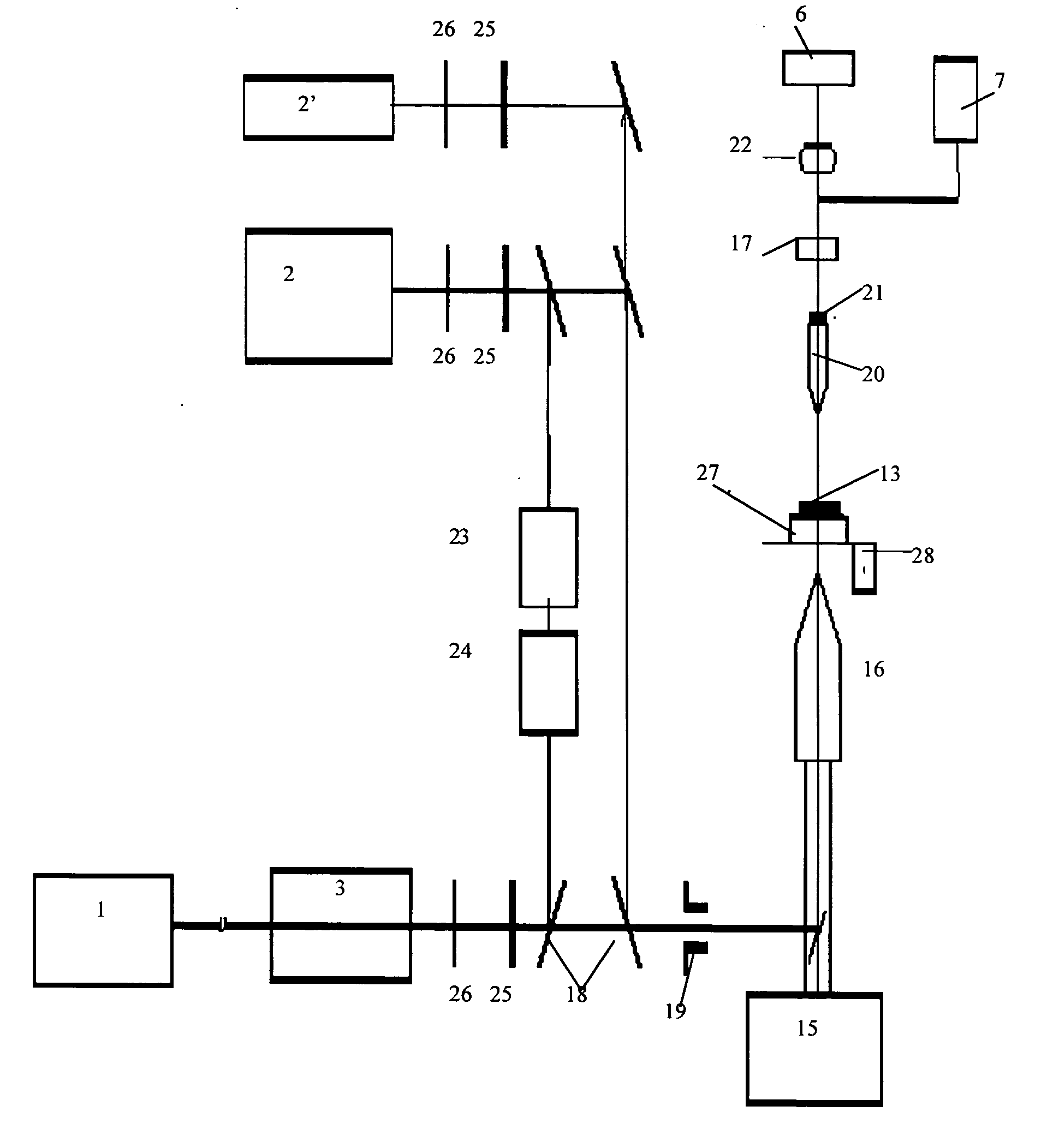
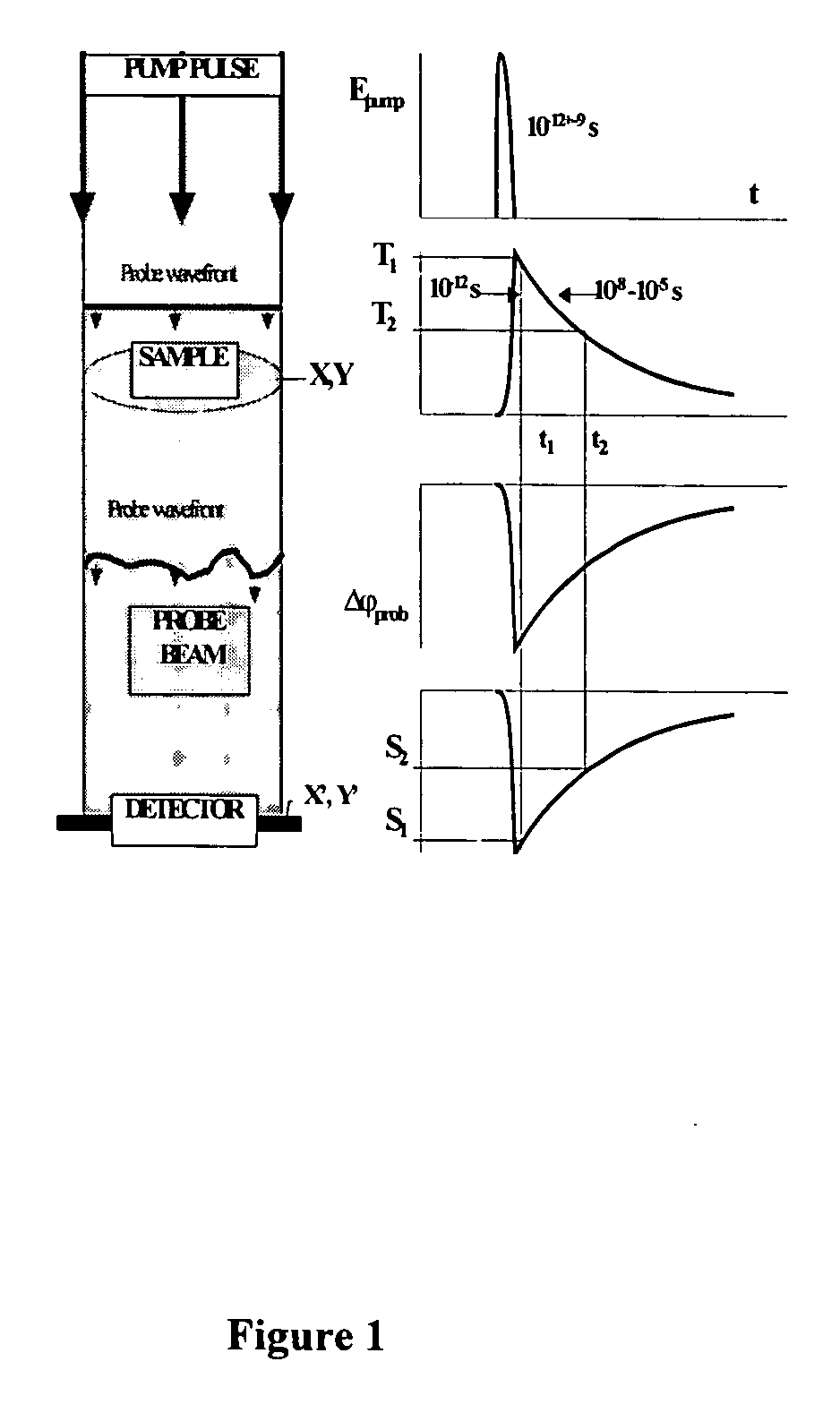
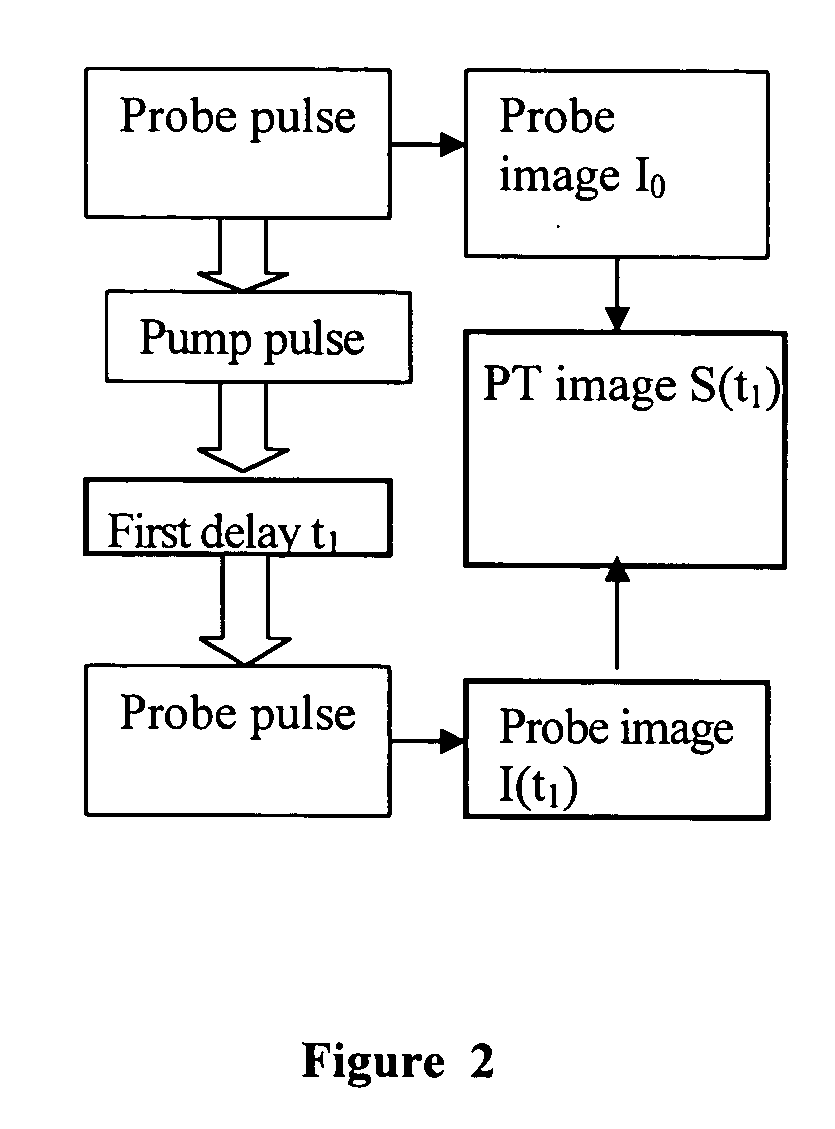
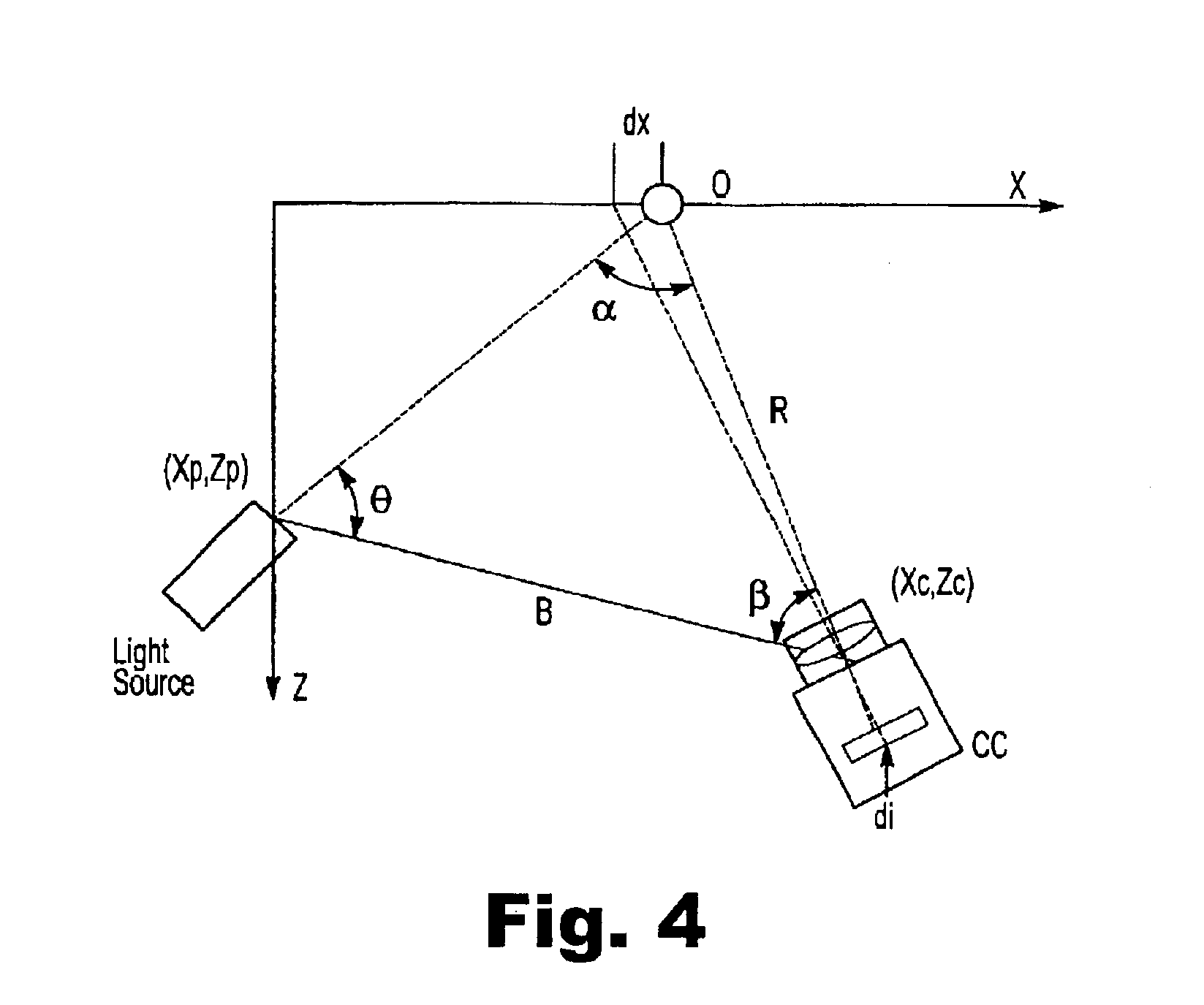
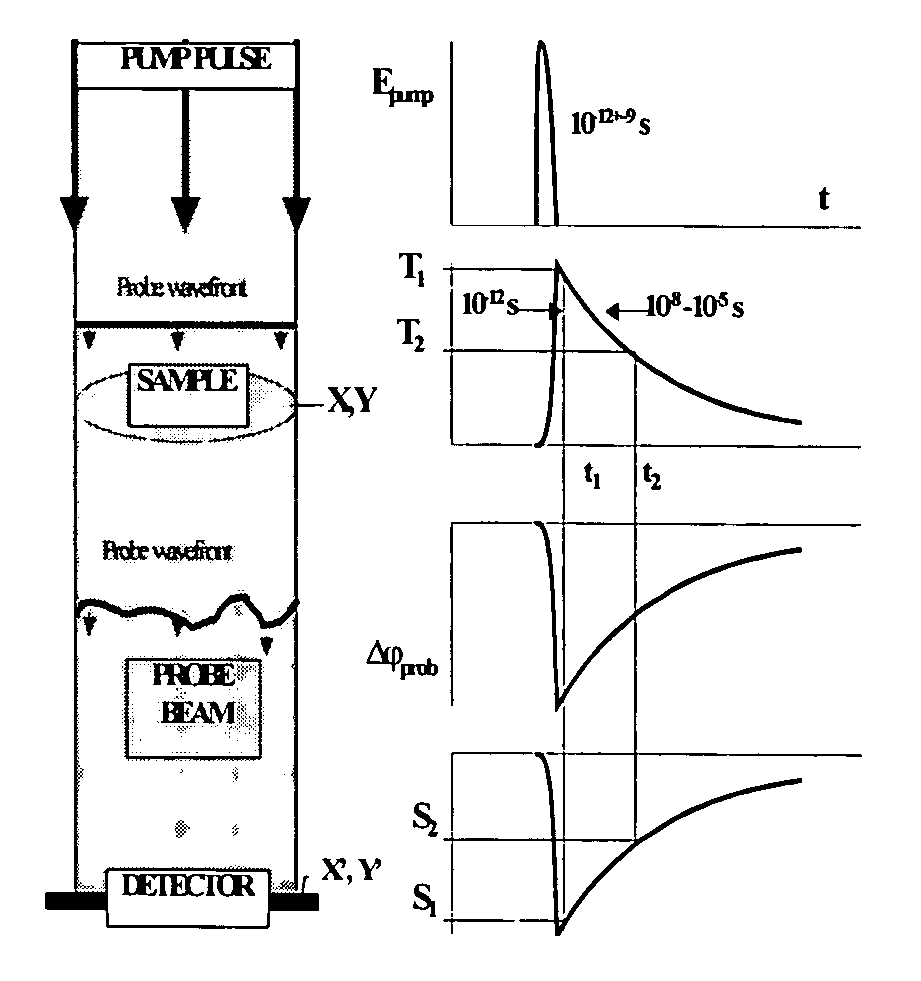
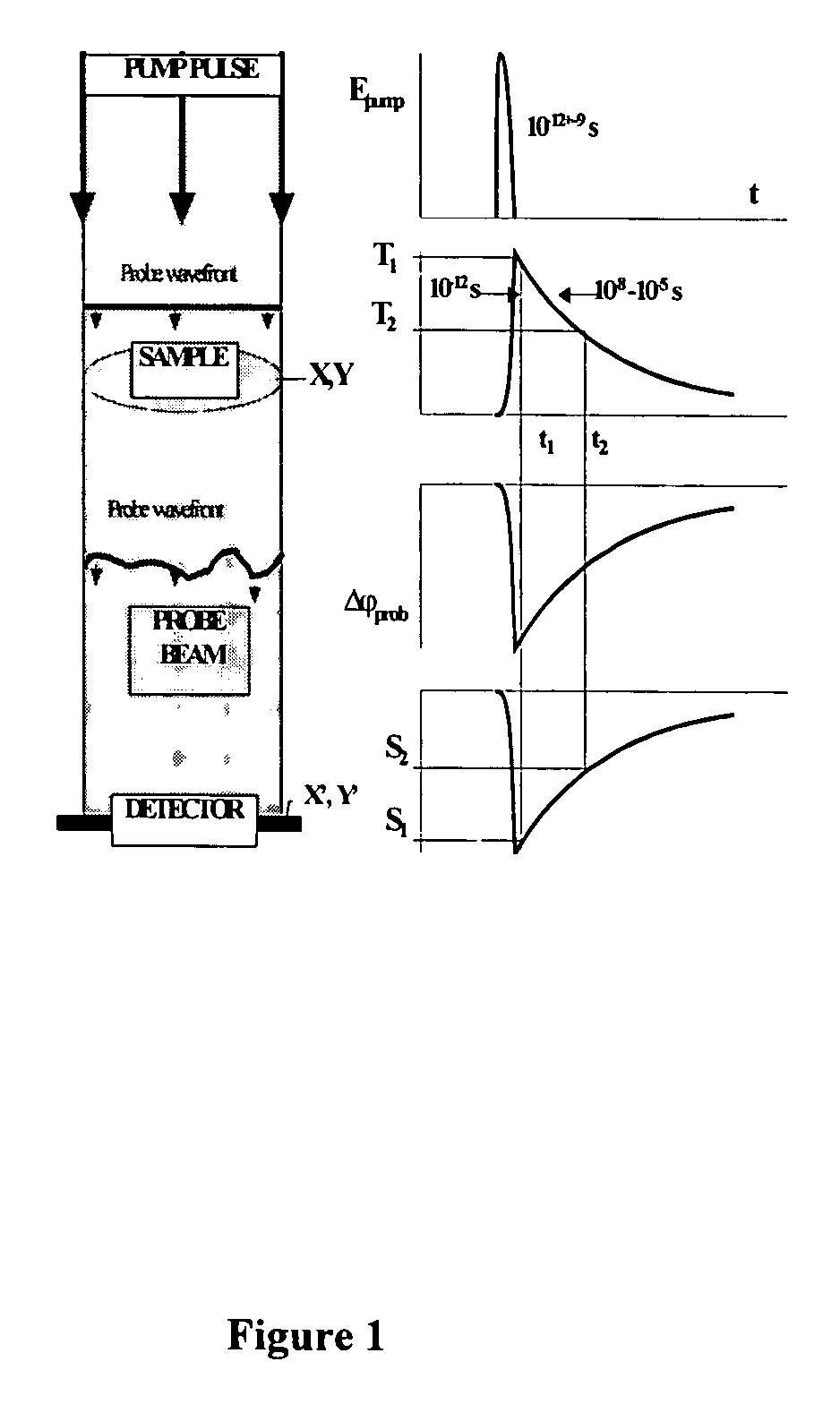
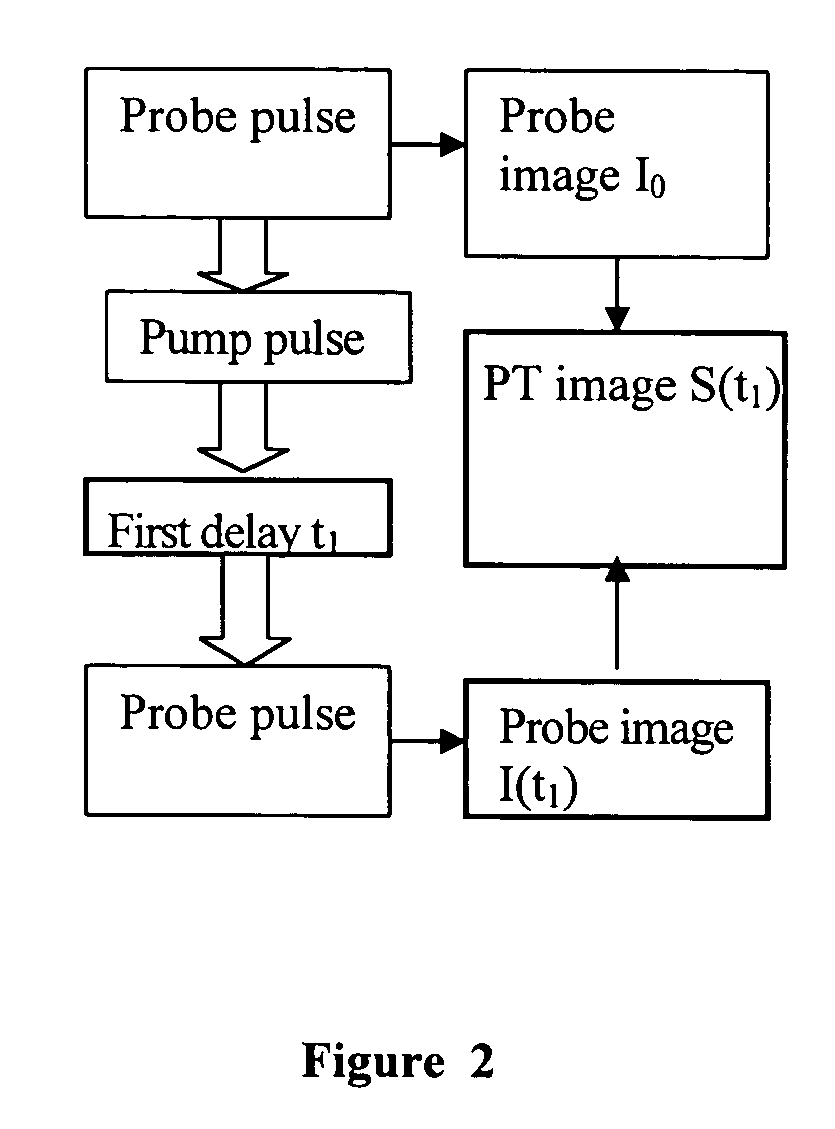
InactiveUS20040085540A1Increase sensitivity and resolutionImprove resolutionMaterial analysis by optical meansPhysicsRefractive index
The invention relates to optical microscopy, in particular to methods for photothermal examination of absorbent microinhomogeneities using laser radiation sources and can be widely used in laser engineering, industry and biomedicine for examining relatively transparent objects containing submicron impurities, including the detection of local inclusions and defects in ultrapure optical and semiconductor materials and the non-destructive diagnosis of biological samples on a cellular and subcellular level. The aim of the invention is to increase the sensitivity, spatial resolution and informativity of examination of local absorbent microinhomogeinities in transparent objects and to measure said microinhomogeinities even when they are less than the used emission wavelength. The inventive method consists in radiating a sample with a pumping laser beam. The duration of the radiation is equal to or less than a representative time for cooling the examined microinhomogeinity. The relatively large surface of the sample is radiated, the shape thereof being greater than the wavelength of the used pumping laser. Thermal variations of the refractive index occurring in the sample as a result of absorption produced with the aid of the pumping beam are recorded by measuring parameters of a test laser beam. The diameter of the test beam is chosen in such a way that it is equal to or greater than the diameter of the pumping beam. A diffraction-limited phase distribution along the cross-section of the testing laser beam is transformed into an amplitude image, the microinhomogeinity properties being determined by measuring said amplitude image.
Owner:LAPOTKO TATIANA MS
Touch sensing display panel, touch sensing color filter and fabricating method thereof
ActiveUS20090322702A1Touch sensing resolutionSimplify the manufacturing processCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingTouch SensesColor filter array
A touch sensing color filter including a substrate, a black matrix, a color filter layer and a second sensing electrode layer is provided. The black matrix is disposed on the substrate to define a plurality of sub-pixel areas. The black matrix includes a first sensing electrode layer, and the first sensing electrode layer has a plurality of openings corresponding to the sub-pixel areas. The color filter layer includes a plurality of color filter units disposed in the sub-pixel areas respectively. The second sensing electrode layer is disposed on the substrate, and the second sensing electrode layer includes a plurality of sub patterns corresponding to the sub-pixel areas. A method for fabricating the touch sensing color filter and a display panel using the same are further provided.
Owner:AU OPTRONICS CORP
Communications device with extendable screen
ActiveUS20120280924A1Thinner and lighter displayHigh resolution displayDevices with multiple display unitsStatic indicating devicesGraphical displayImage resolution
Described herein are apparatuses and mechanisms for providing an extendable screen in a portable communications device. A portable communications device may be provided with a multi-part screen, a portion of which may be extended to provide an expanded viewing display surface or may be retracted to provide a reduced viewing mode and increased portability. In a reduced viewing mode, a graphical display may be provided on a first, visible portion of a multi-part display screen, where one or more other screen portions are retracted and / or obscured from view in order to provide a portable mode for the communications device. In an extended viewing mode, the one or more other screen portions may be extended and / or brought into the same plane as a first portion of the multi-part display in order to provide increased display size and resolution.
Owner:DISH TECH L L C
Multifunctional magnetic nanoparticle probes for intracellular molecular imaging and monitoring
InactiveUS7459145B2Efficient internalizationHigh sensitivityBiocideMaterial nanotechnologyFluorescenceBiocompatible coating
The present invention provides multifunctional magnetic nanoparticle probe compositions for molecular imaging and monitoring, comprising a nucleic acid or polypeptide probe, a delivery ligand, and a magnetic nanoparticle having a biocompatible coating thereon. The probe compositions may further comprise a fluorescent or luminescent resonance energy transfer moiety. Also provided are compositions comprising two or more such multifunctional magnetic nanoparticle probes for molecular imaging or monitoring. In particular, the nucleic acid or polypeptide probes bind to a target and generate an interaction observable with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or optical imaging. The invention thereby provides detectable signals for rapid, specific, and sensitive detection of nucleic acids, polypeptides, and interactions thereof in vivo.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP +1
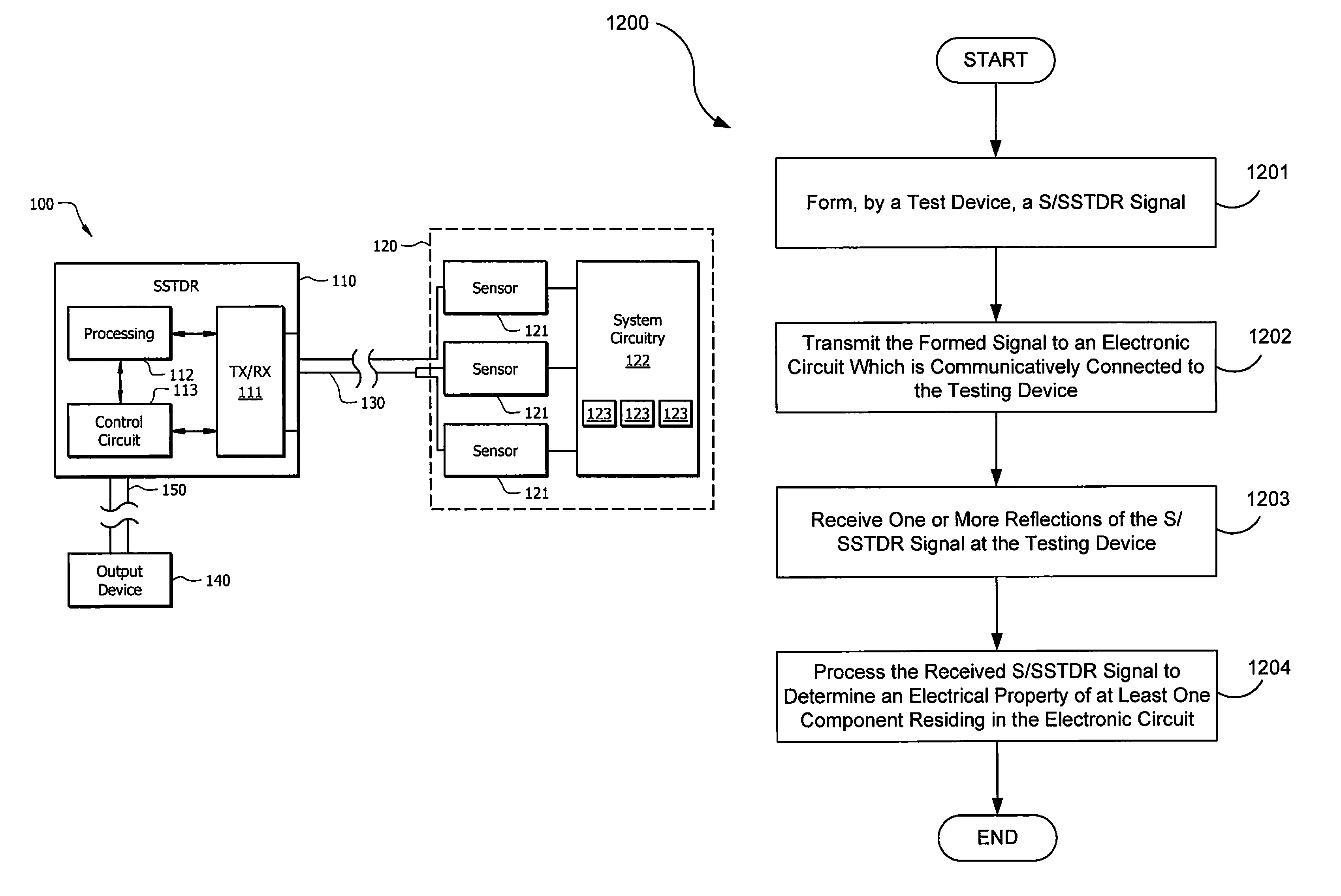
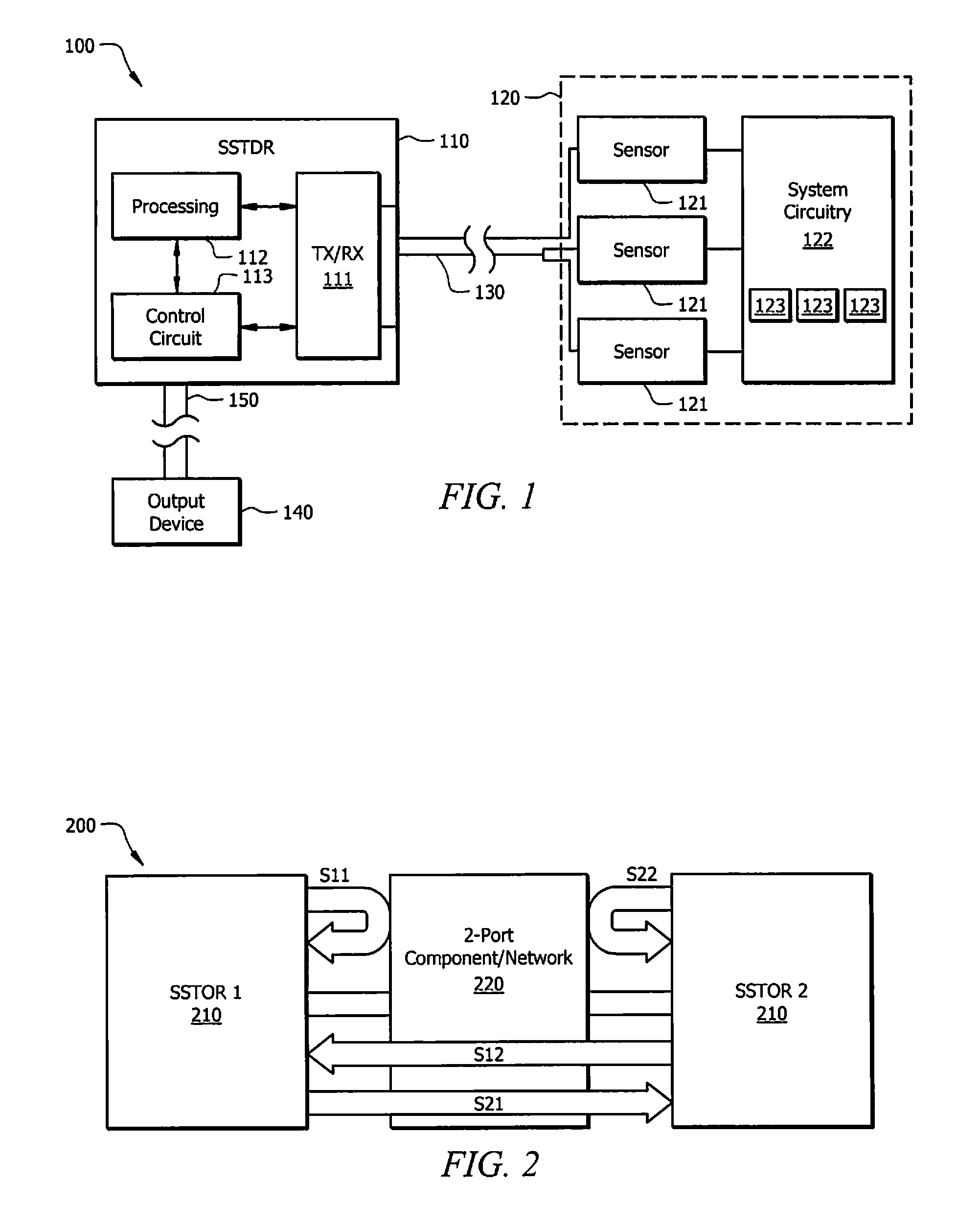
Systems and methods for implementing S/SSTDR measurements
ActiveUS9244117B2Shorten the timeAccurate measurementResistance/reactance/impedenceElectronic circuit testingCircuit under testSpread spectrum
Systems and methods which utilize spread spectrum sensing on live circuits to obtain information regarding a circuit under test are provided. In some embodiments S / SSTDR testing may be utilized to obtain R, L, C and Z measurements from circuit components. In yet further embodiments, these measurements may be utilized to monitor the output of sensors on a circuit.
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND
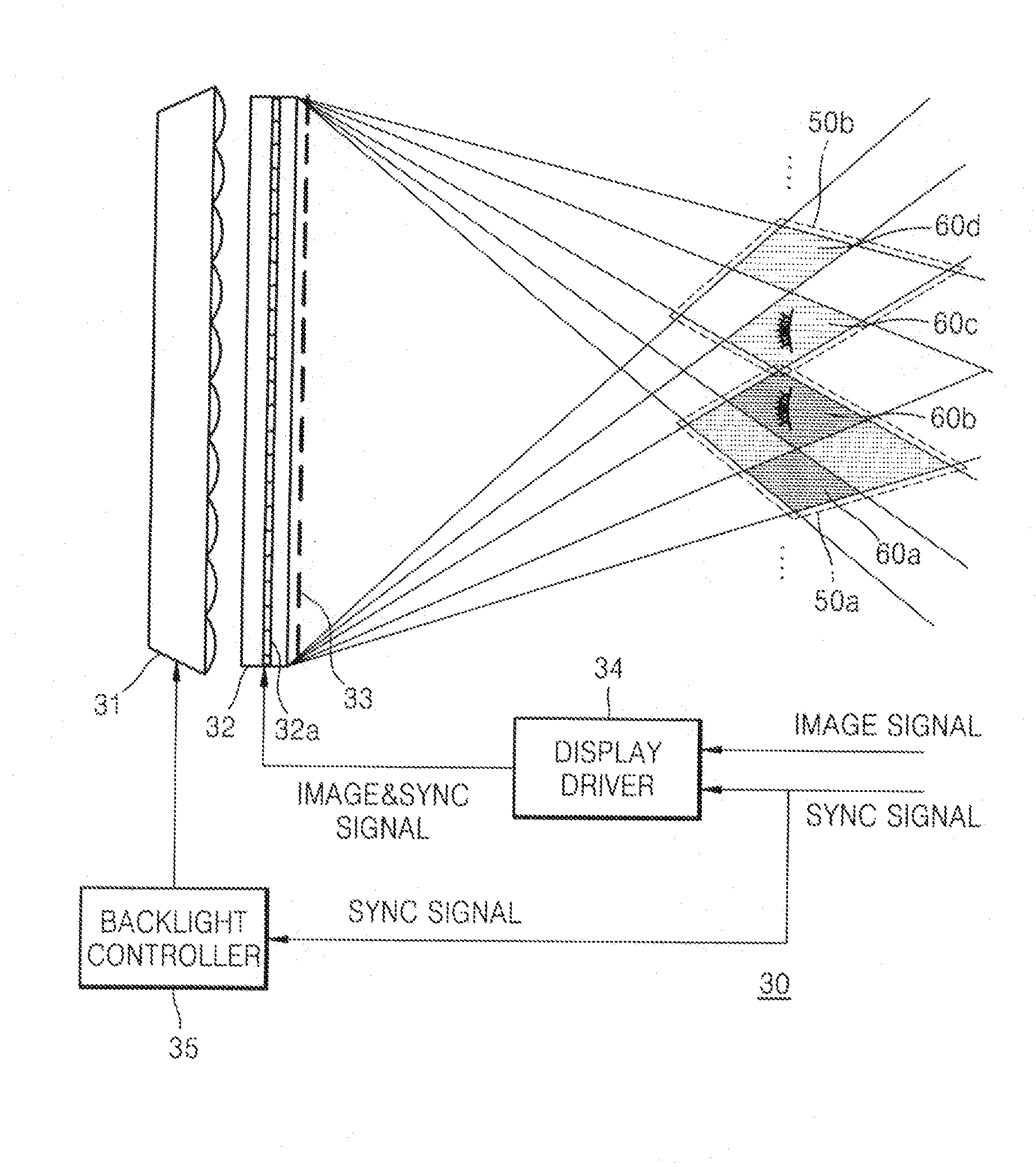
Multi-view autostereoscopic display with improved resolution
ActiveUS20080068329A1Improve resolutionHigh resolutionCathode-ray tube indicatorsSteroscopic systemsImage resolutionResolution improvement
A multi-view autostereoscopic display apparatus with improved resolution, includes: a display panel alternately displaying a plurality of images of different view points; an image separating device for separating the plurality of images such that the separated images can be alternately observed in different viewing zones; and a directional backlight unit switched between a plurality of different angular distributions of illumination to selectively provide light to the display panel, wherein the directional backlight unit is switched between the plurality of different angular distributions of illumination in synchronization with an image display period of the display panel.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and apparatus for dicing of thin and ultra thin semiconductor wafer using ultrafast pulse laser
InactiveUS7804043B2Minimize heating effectImprove machine qualityWelding/soldering/cutting articlesMetal working apparatusPicosecond laserBeam polarization
The present invention relates to the apparatus, system and method for dicing of semiconductor wafers using an ultrafast laser pulse of femtosecond and picosecond pulse widths directly from the ultrafast laser oscillator without an amplifier. Thin and ultrathin semiconductor wafers below 250 micrometer thickness, are diced using diode pumped, solid state mode locked ultrafast laser pulses from oscillator without amplification. The invention disclosed has means to avoid / reduce the cumulative heating effect and to avoid machine quality degrading in multi shot ablation. Also the disclosed invention provides means to change the polarization state of the laser beam to reduce the focused spot size, and improve the machining efficiency and quality. The disclosed invention provides a cost effective and stable system for high volume manufacturing applications. An ultrafast laser oscillator can be a called as femtosecond laser oscillator or a picosecond laser oscillator depending on the pulse width of the laser beam generated.
Owner:LASERFACTURING
OLED display and touch screen
ActiveUS7230608B2Easy to manufactureLow costCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingImage resolutionDisplay device
An OLED display and touch screen system, including: a) a substrate; b) an OLED display area including an array of individually addressable OLEDs formed on the substrate; and c) a touch screen including at least one OLED light emitter formed on the substrate and a plurality of light sensors formed on the substrate across the display area from the light emitter, each of the light sensors having an elongated surface area with a first relatively short dimension and a second relatively long dimension and being positioned adjacent to an edge of the display area, with the relatively long dimension positioned substantially perpendicular to the adjacent edge of the display area, and optics located around the display area above the light emitter and the light sensors for directing light emitted from the light emitter across the display area to the surface area of the light sensors. The system is advantageous in that it enables a thin, light, easily manufacturable display having an integrated optical touch screen having reduced weight, size, and cost, a greater reliability and improved sensitivity and resolution.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
Laser Optoacoustic Ultrasonic Imaging System (LOUIS) and Methods of Use
ActiveUS20130190595A1Increase contrastImprove resolutionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMedical imagingHelical computed tomographyContrast resolution
Provided herein are the systems, methods, components for a three-dimensional tomography system. The system is a dual-modality imaging system incorporates a laser ultrasonic system and a laser optoacoustic system. The dual-modality imaging system has means for generate tomographic images of a volume of interest in a subject body based on speed of sound, ultrasound attenuation and / or ultrasound backscattering and for generating optoacoustic tomographic images of distribution of the optical absorption coefficient in the subject body based on absorbed optical energy density or various quantitative parameters derivable therefrom. Also provided is a method for increasing contrast, resolution and accuracy of quantitative information obtained within a subject utilizing the dual-modality imaging system. The method comprises producing an image of an outline boundary of a volume of interest and generating spatially or temporally coregistered images based on speed of sound and / or ultrasonic attenuation and on absorbed optical energy within the outlined volume.
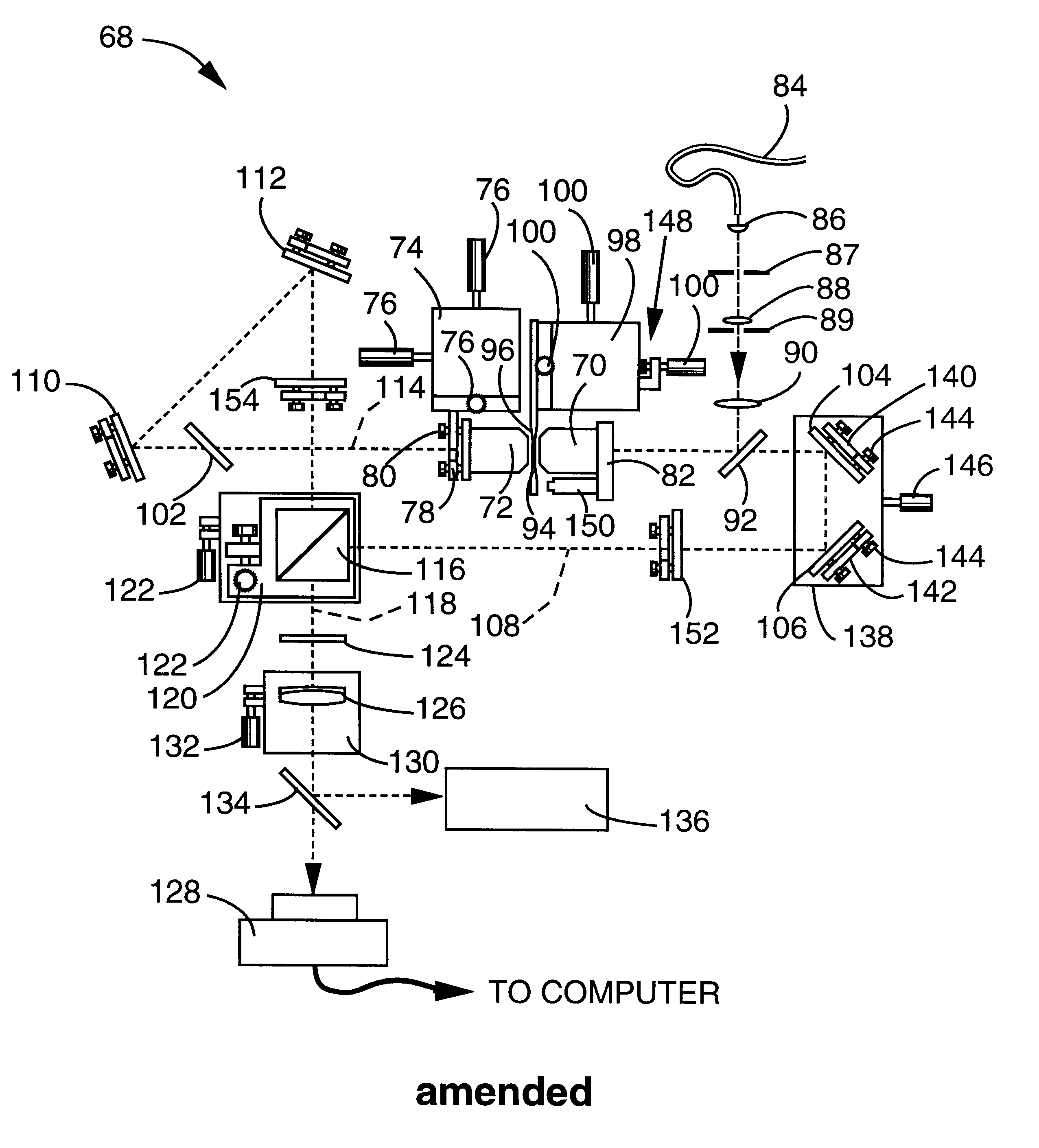
Owner:TOMOWAVE LAB INC
Method and apparatus for three-dimensional microscopy with enhanced resolution
InactiveUSRE38307E1Add depthImprove resolutionMicroscopesColor/spectral properties measurementsOphthalmologyImage resolution
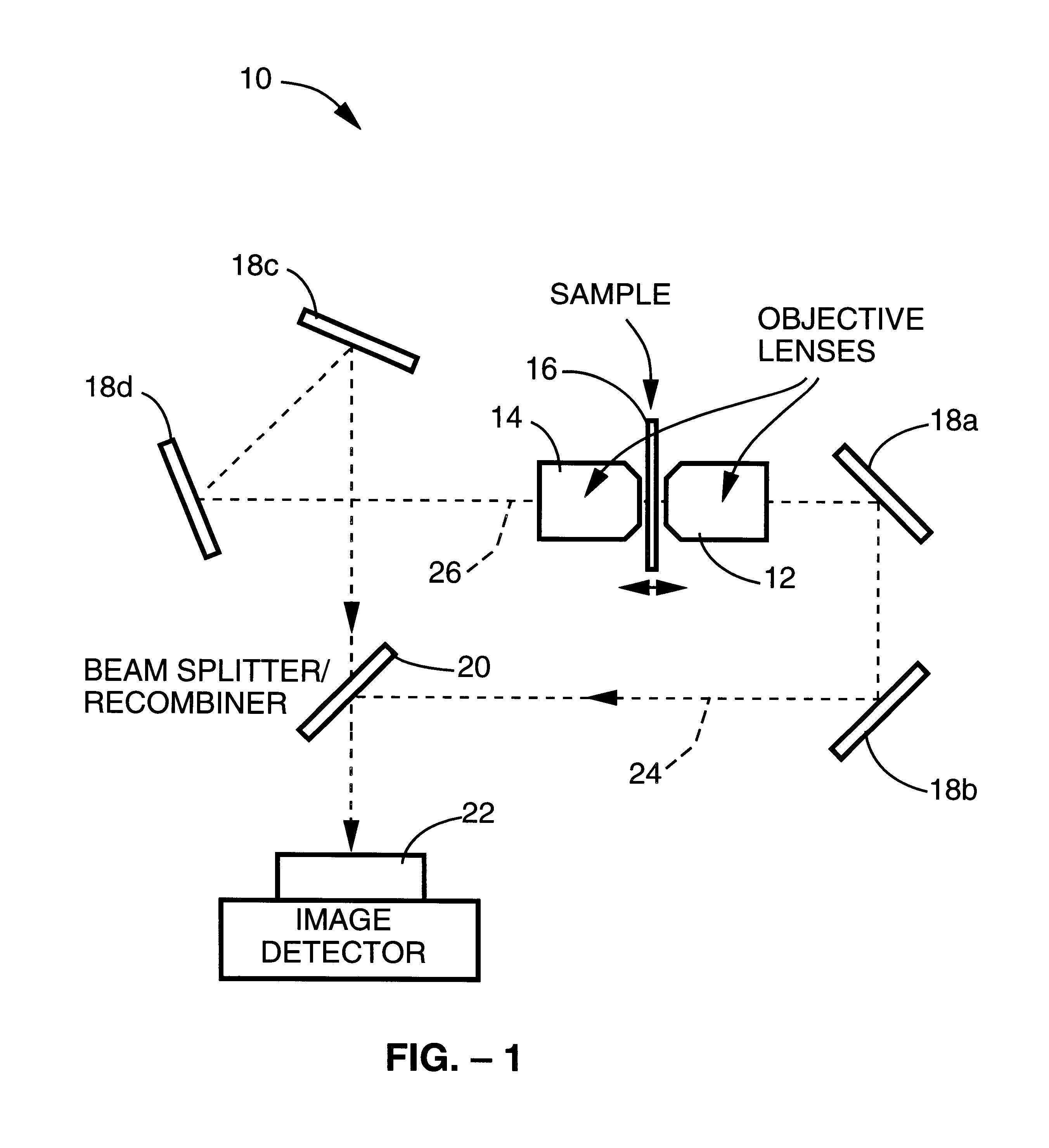
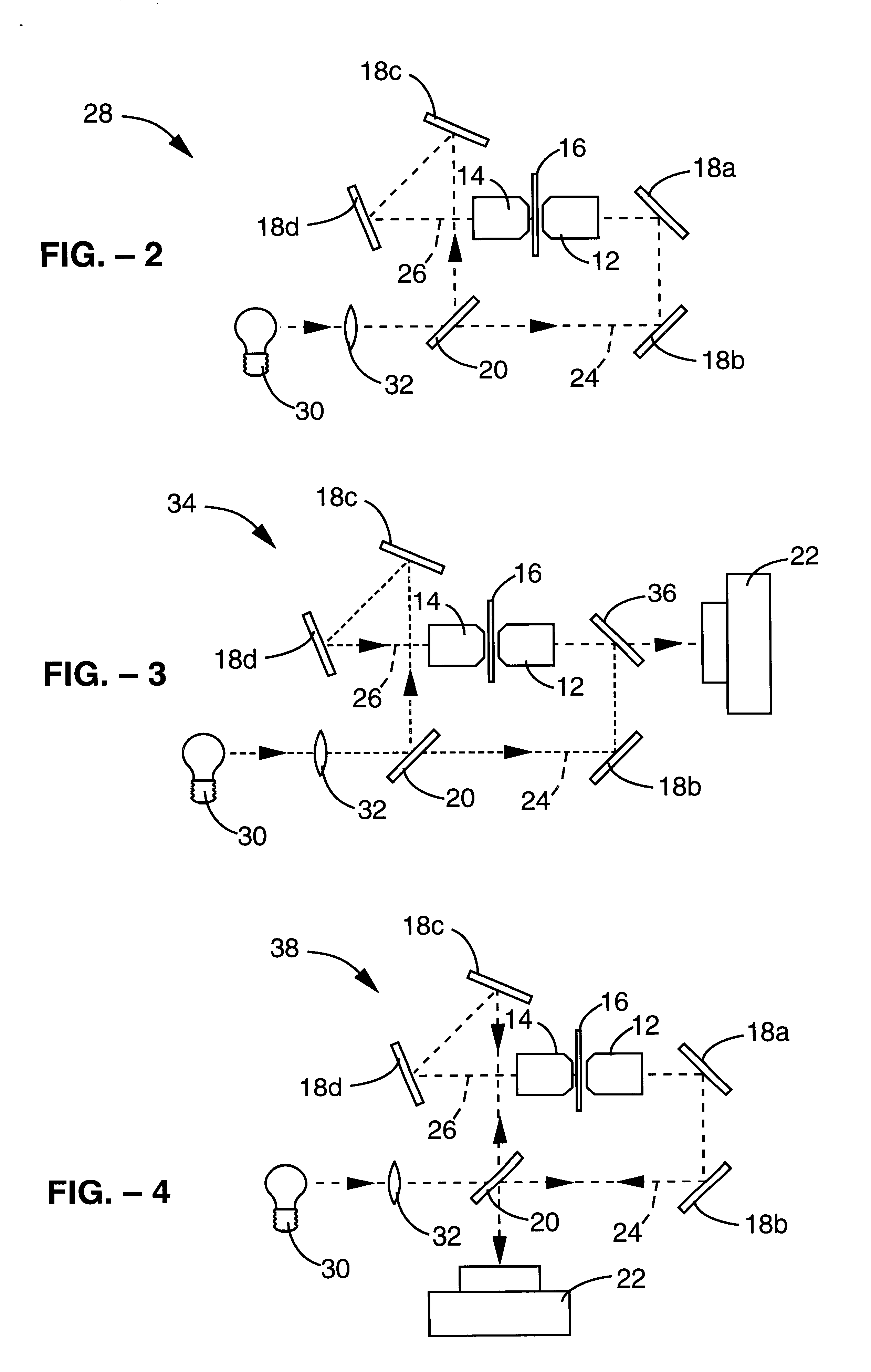
A method and apparatus for three dimensional optical microscopy is disclosed which employs dual opposing objective lenses about a sample and extended incoherent illumination to provide enhanced depth or Z.Iadd.-.Iaddend.direction resolution. In a first embodiment, observed light from both objective lenses are brought into coincidence on an image detector and caused to interfere thereon by optical path length adjustment. In a second embodiment, illuminating light from an extended incoherent light source is detected to the sample through both objective lenses and caused to interfere with a section of the sample by adjusting optical path lengths. Observed light from one objective lens is then recorded. In a third embodiment, which combines the first two embodiments, illuminating light from an extended incoherent light source is directed to the sample through both objective lenses and caused to interfere within a section of the sample by adjusting optical path lengths. The observed light from both lenses is caused to interfere on the image detector by the same optical path length adjustment. .Iadd.In a fourth embodiment of the invention, further spatial structure is introduced into the illumination light. Computational processing is used to enhance lateral or XY resolution as well as depth or Z resolution..Iaddend.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method and apparatus for generating structural pattern illumination
InactiveUS6937348B2High measurement accuracyImprove resolution accuracyImage analysisHearing aid design aspectsLighting spectrumSpatial change
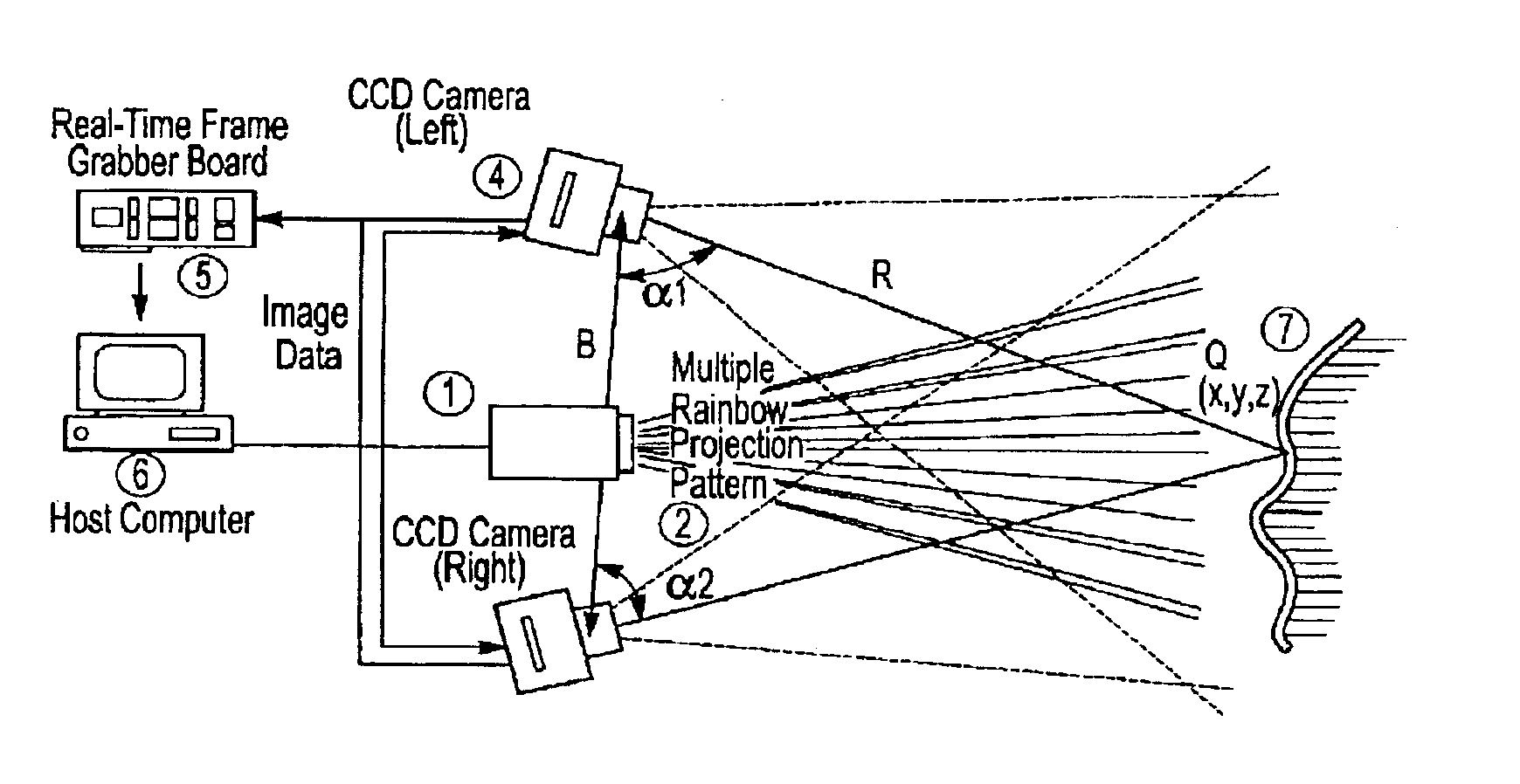
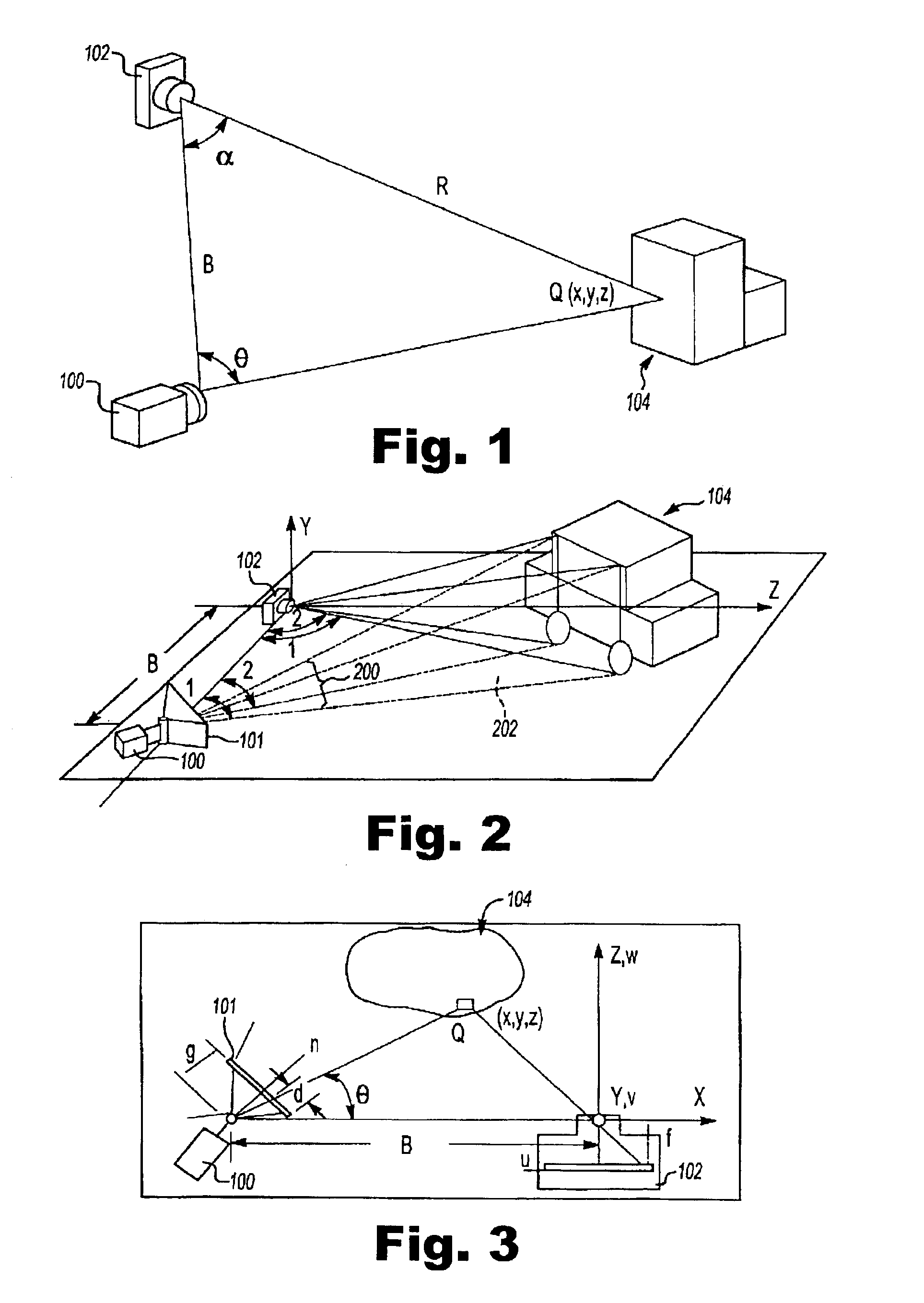
A three-dimensional imaging method and system illuminates an object to be imaged with a light pattern that is formed from two or more light sub-patterns. The sub-patterns can each encompass the visible light spectrum or can be spatially varying intensity sub-patterns that each correspond to a red, green, or blue component. The light pattern is generated by a slotted planar member or an optical filter.
Owner:TECHNEST HLDG
Method and device for photothermal examination of microinhomogeneities
InactiveUS7230708B2Improve resolutionHigh sensitivityMaterial analysis by optical meansRefractive indexLaser beams
The invention relates to optical microscopy, and more particularly to the methods for photothermal examination of absorbing microheterogeneities using laser radiation. The invention can be widely used in laser technique, industry, and biomedicine to examine transparent objects with absorbing submicron fragments, including detection of local impurities and defects in super-pure optical and semiconducting materials and non-destructive diagnostics of biological samples on cellular and subcellular levels.The object of the present invention is to increase sensitivity, spatial resolution and informative worth when examining local absorbing heterogeneities in transparent objects, as well as to detect the size of said heterogeneities even if said size is smaller than the radiation wavelength used.Said object is achieved by the pump beam irradiation of a sample, the duration of said irradiation not being longer than the characteristic time of cooling of the microheterogeneity observed. A relatively vast surface of the sample is irradiated at once, the size of said surface not being larger than the wavelength of the pump laser used. The refraction index thermal variations, induced by the pump beam in the sample and being the result of absorption, are registered by the parameter change of the probe laser beam. A chosen probe beam diameter should not be smaller than the pump beam diameter. The diffraction-limited phase distribution over the probe laser beam cross-section is transformed to an amplitude image using a phase contrast method. The properties of microheterogeneities are estimated by measuring said amplitude image.
Owner:LAPOTKO TATIANA MS
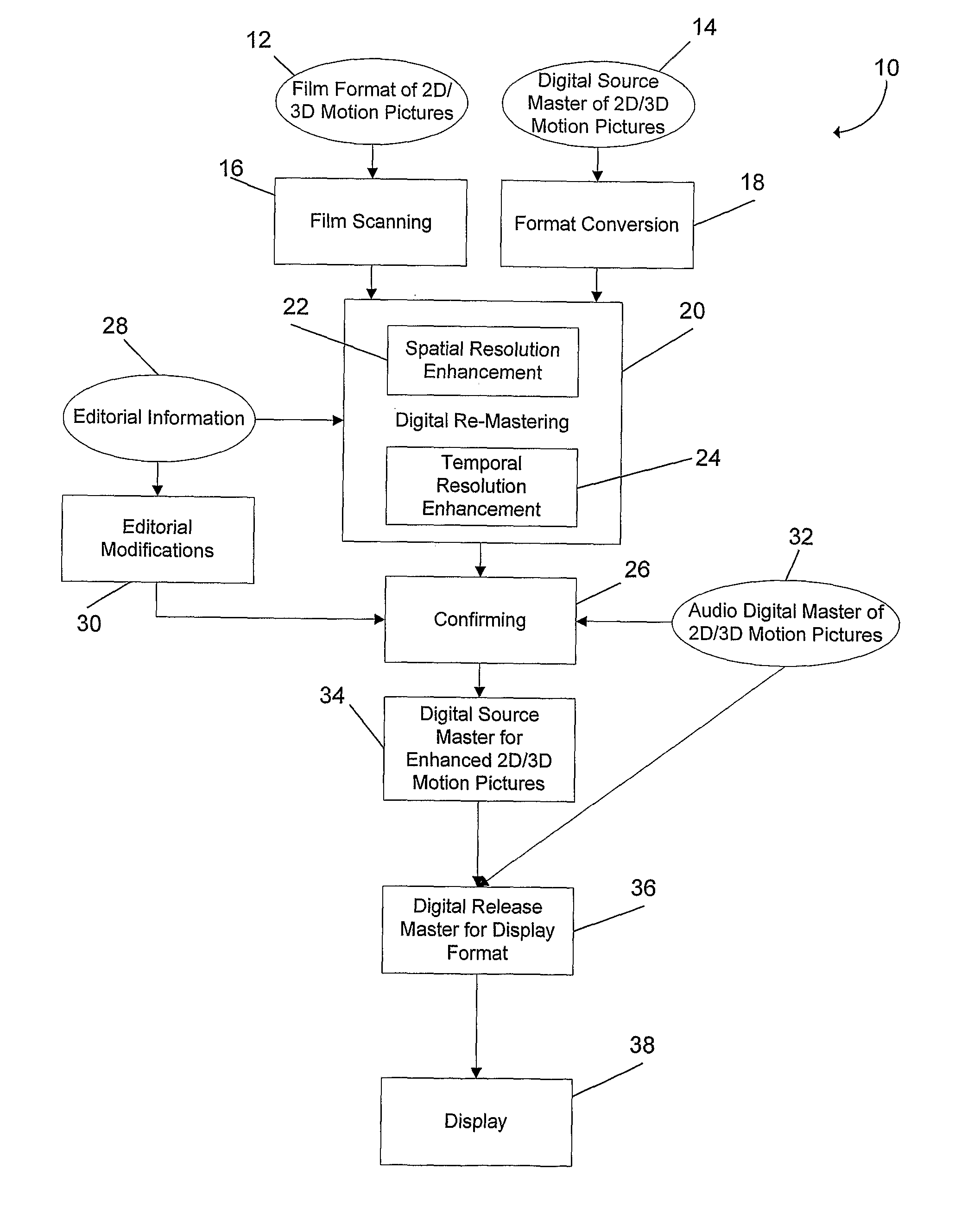
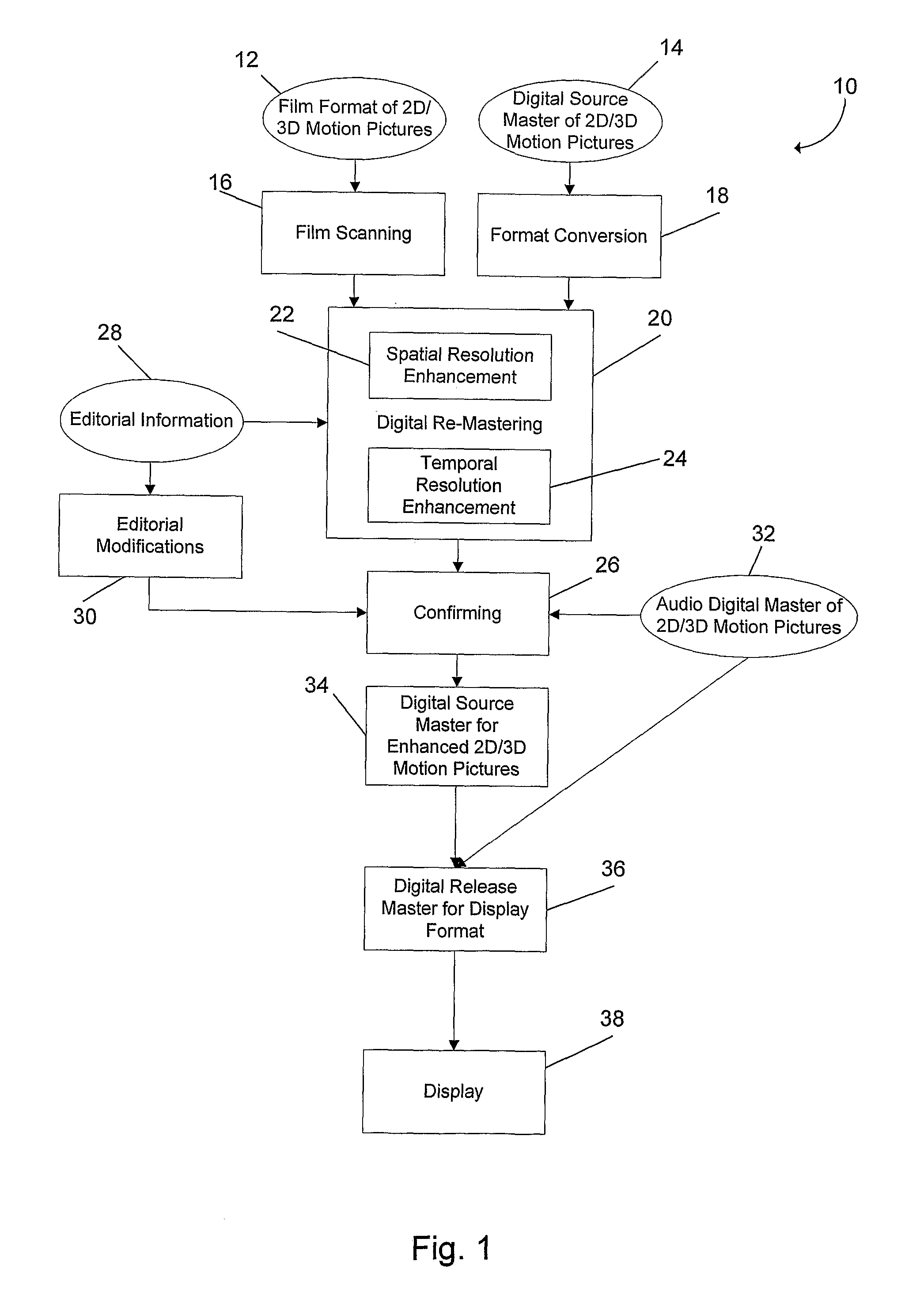
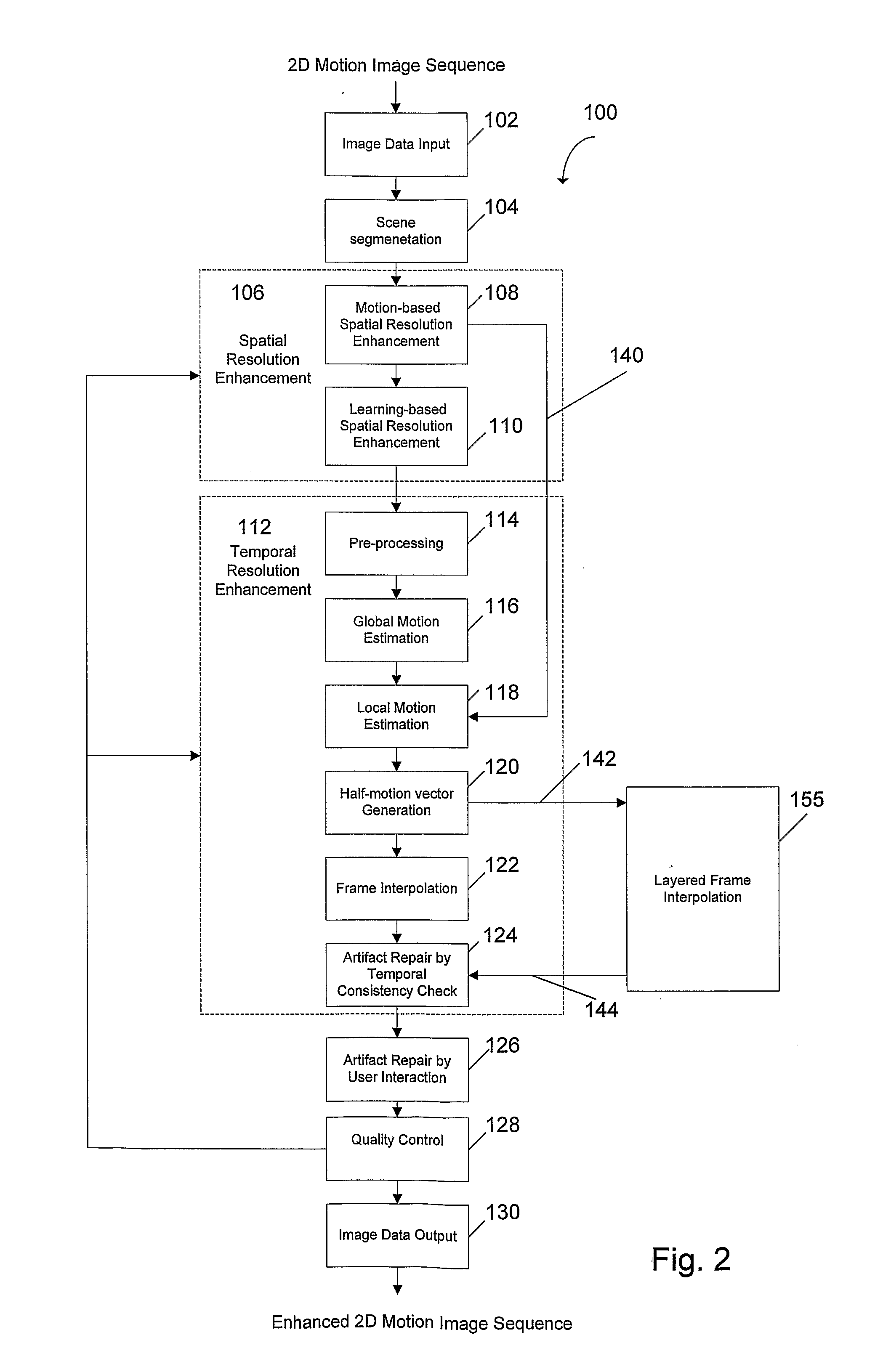
Methods and systems for digitally re-mastering of 2d and 3D motion pictures for exhibition with enhanced visual quality
ActiveUS20100231593A1Enhanced perceived resolutionEnhanced visual image qualityTelevision system detailsImage analysisLearning basedHigh frame rate
The present invention relates to methods and systems for the exhibition of a motion picture with enhanced perceived resolution and visual quality. The enhancement of perceived resolution is achieved both spatially and temporally. Spatial resolution enhancement creates image details using both temporal-based methods and learning-based methods. Temporal resolution enhancement creates synthesized new image frames that enable a motion picture to be displayed at a higher frame rate. The digitally enhanced motion picture is to be exhibited using a projection system or a display device that supports a higher frame rate and / or a higher display resolution than what is required for the original motion picture.
Owner:IMAX CORP
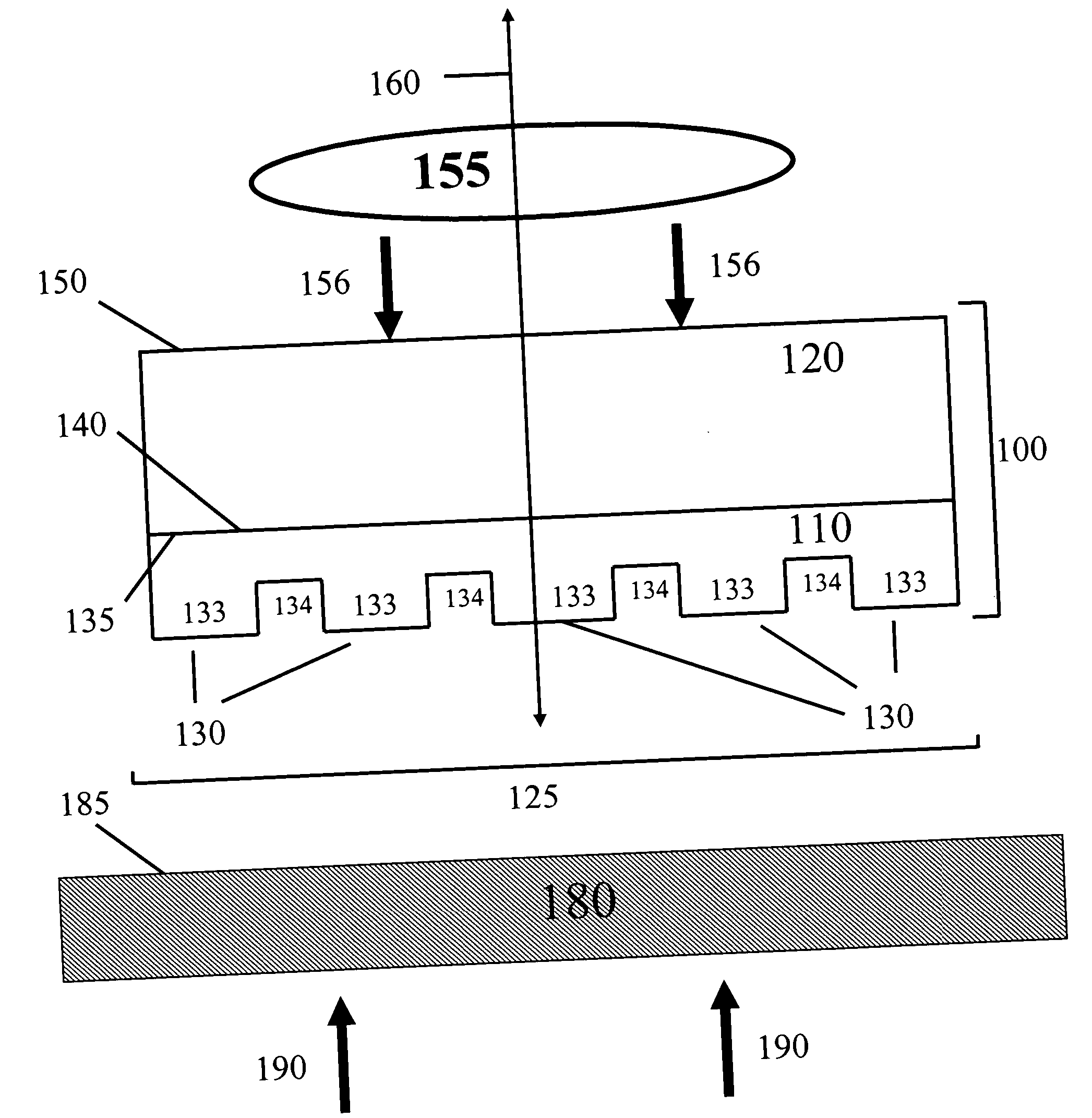
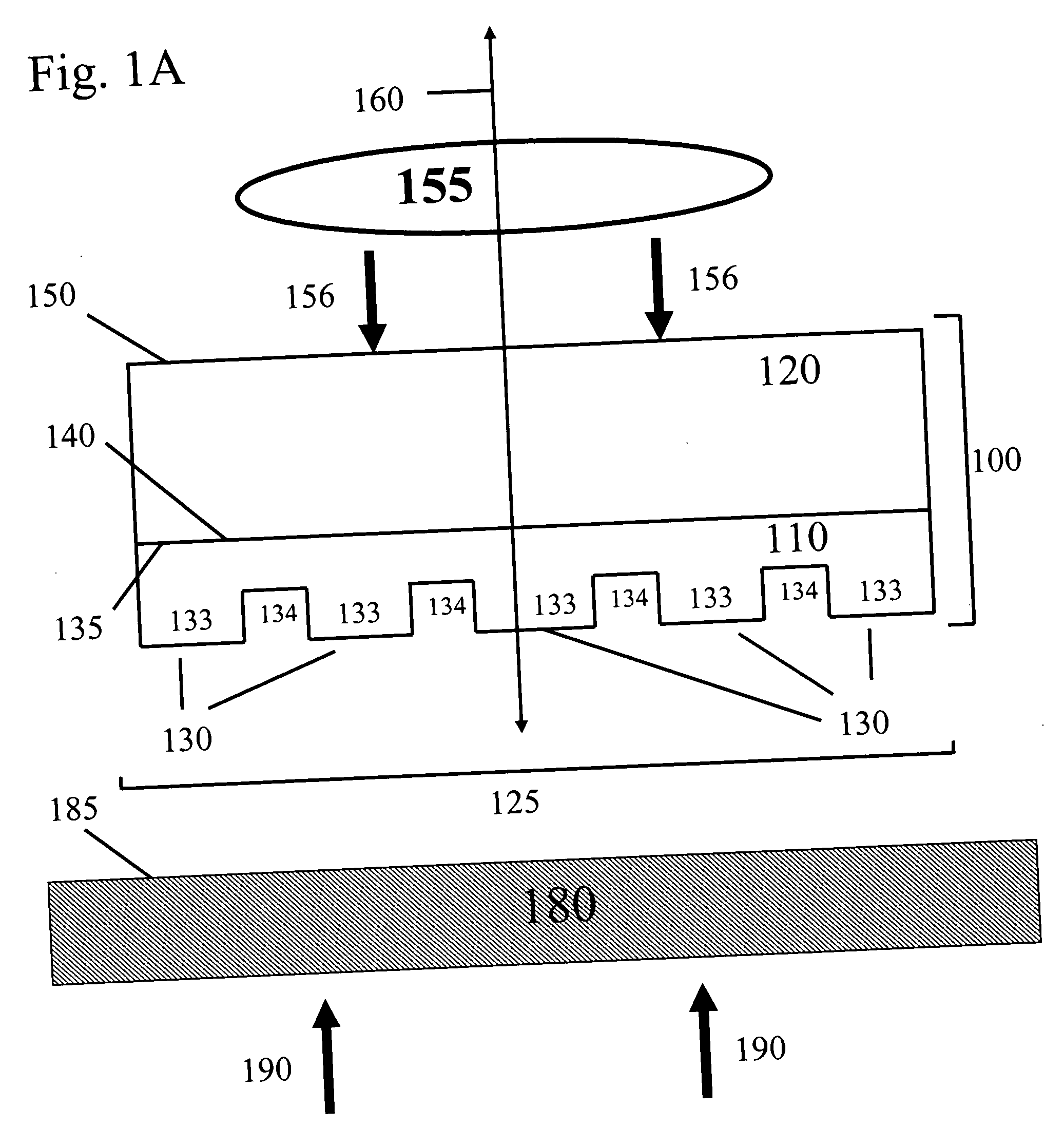
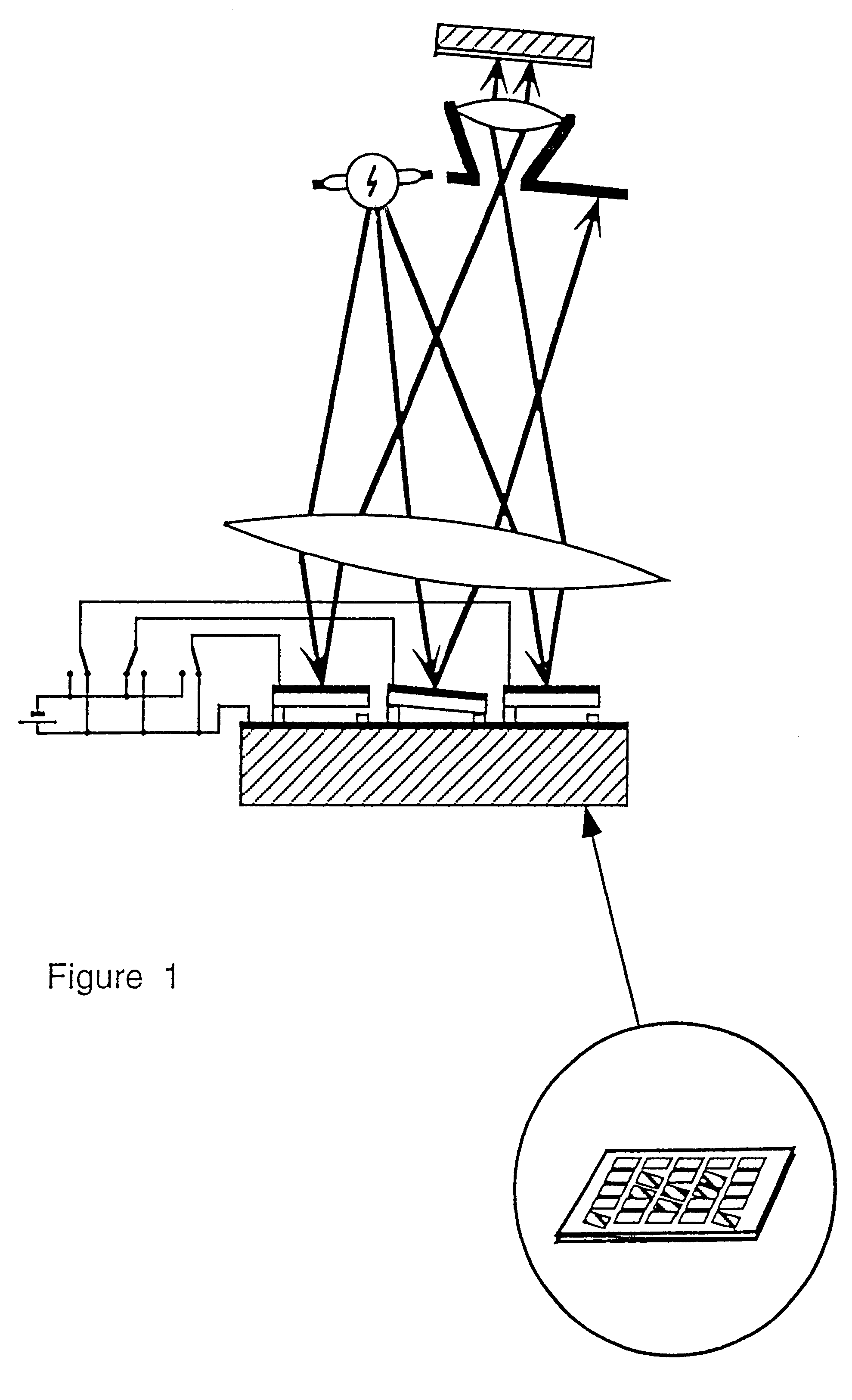
Method for pattern generation with improved image quality
InactiveUS6428940B1Improve fidelityImprove resolutionTelevision system detailsStatic indicating devicesPhysicsImage resolution
The present invention relates to a method for creating a microlithographic pattern on a workpiece, for increased resolution and image fidelity. The method comprises the steps of: providing a source for emitting electromagnetic radiation, illuminating by said radiation a spatial light modulator (SLM) having several pixels, projecting an image of the modulator on the workpiece, further coordinating the movement of the workpiece, the feeding of the signals to the modulator and the intensity of the radiation, so that said pattern is stitched together from the partial images created by the sequence of partial patterns, where an area of the pattern is exposed at least twice with a change in at least one, and preferably at least two, of the following parameters between the exposures: data driven to the SLM, focus, angular distribution of the illumination at the SLM, pupil filtering, polarisation.
Owner:MICRONIC LASER SYST AB
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com