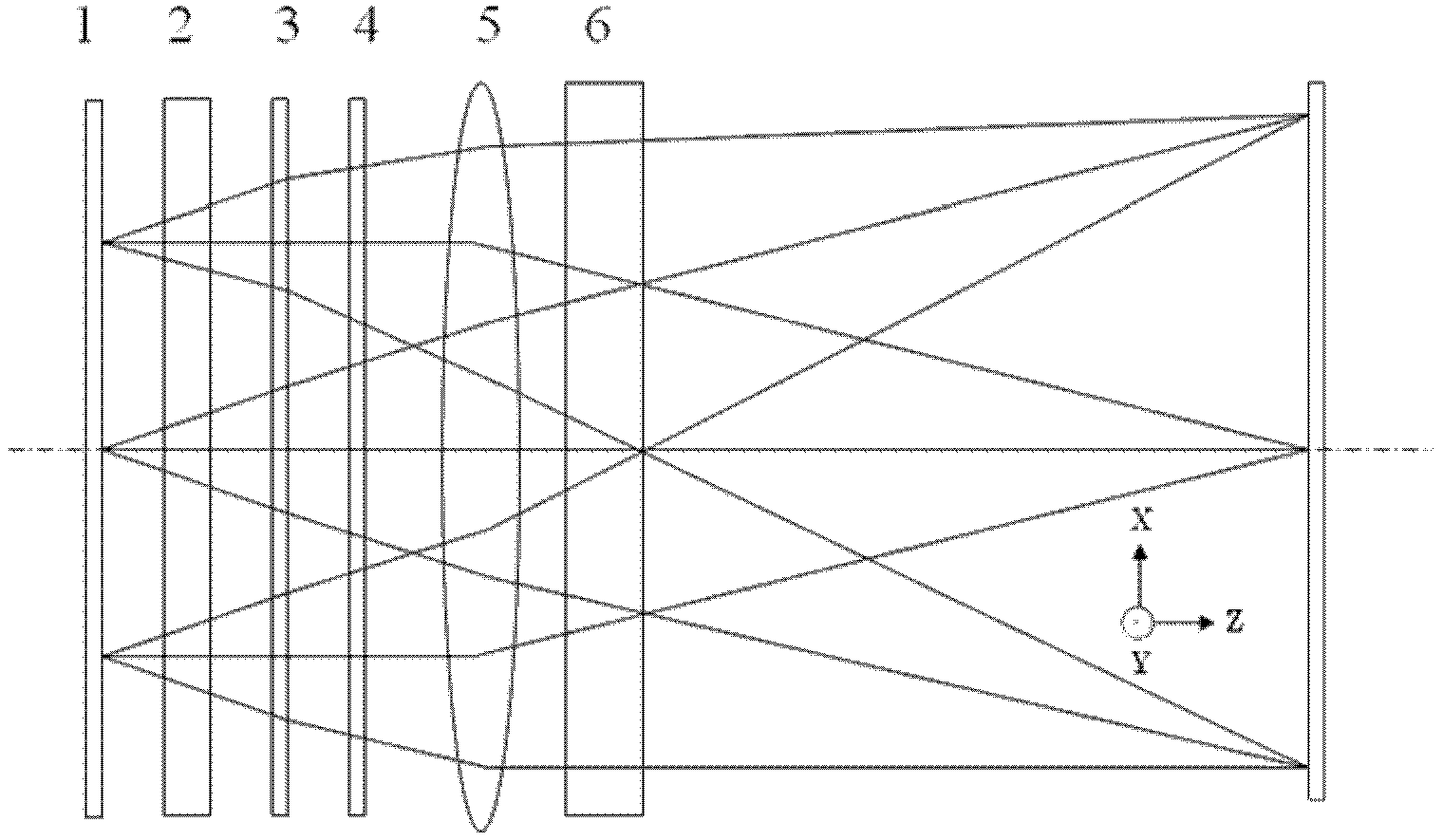
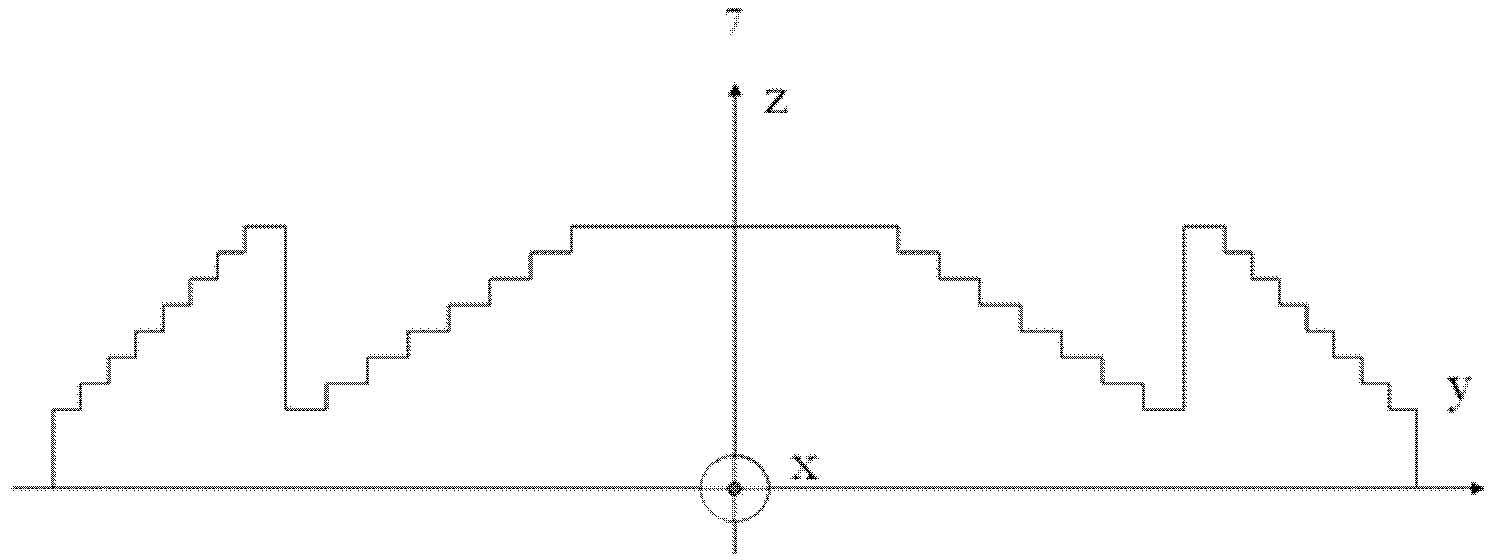
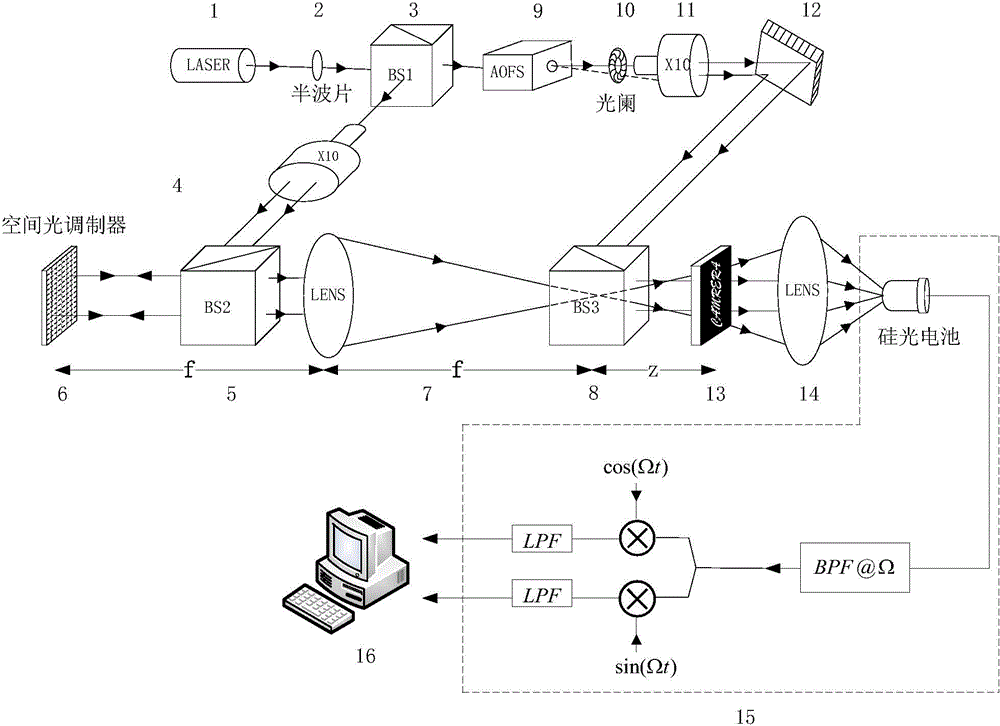
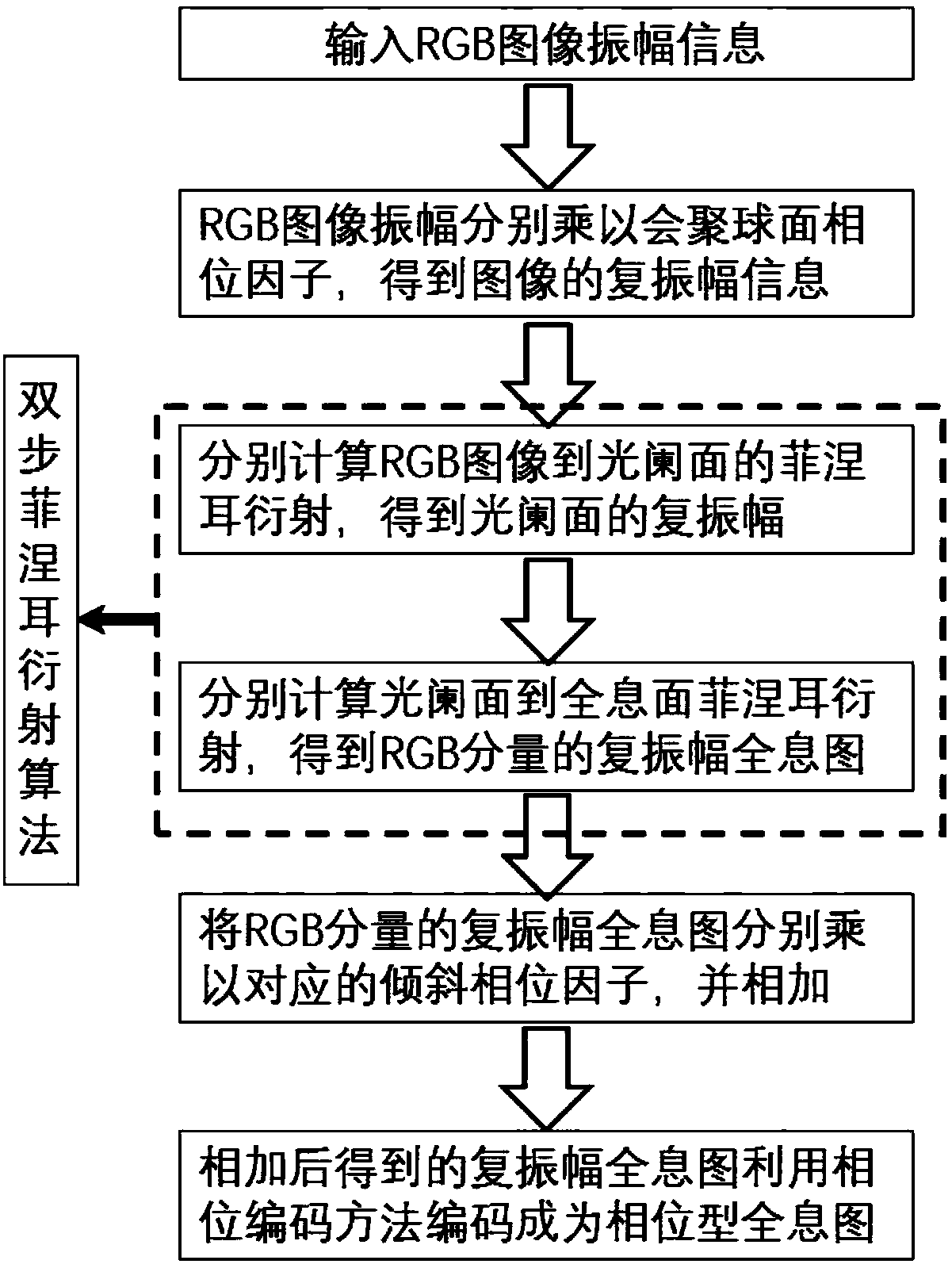
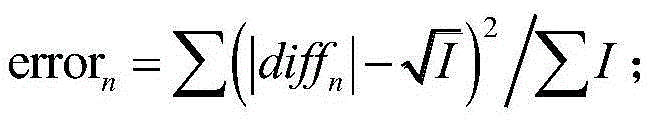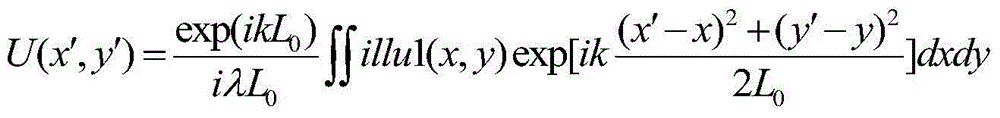Patents
Literature
93 results about "Fresnel diffraction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
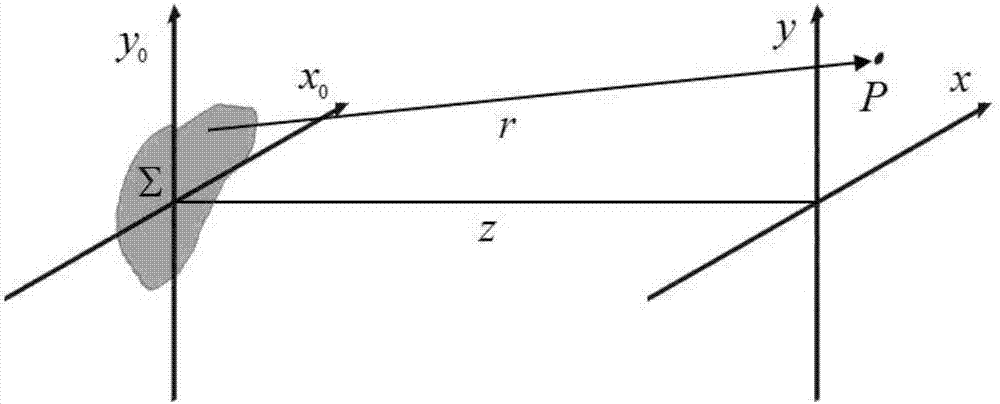
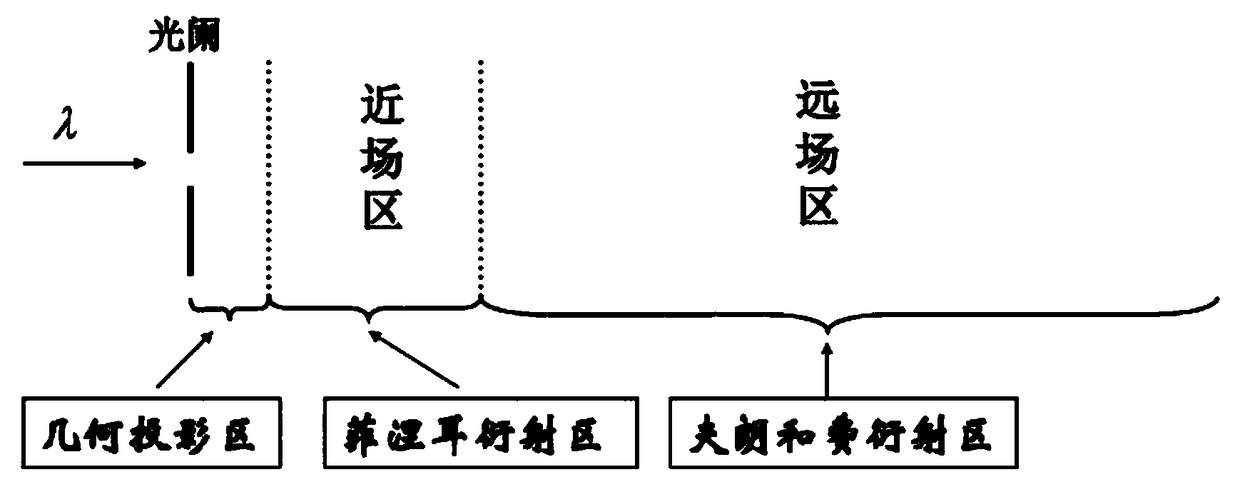
In optics, the Fresnel diffraction equation for near-field diffraction is an approximation of the Kirchhoff–Fresnel diffraction that can be applied to the propagation of waves in the near field. It is used to calculate the diffraction pattern created by waves passing through an aperture or around an object, when viewed from relatively close to the object. In contrast the diffraction pattern in the far field region is given by the Fraunhofer diffraction equation.
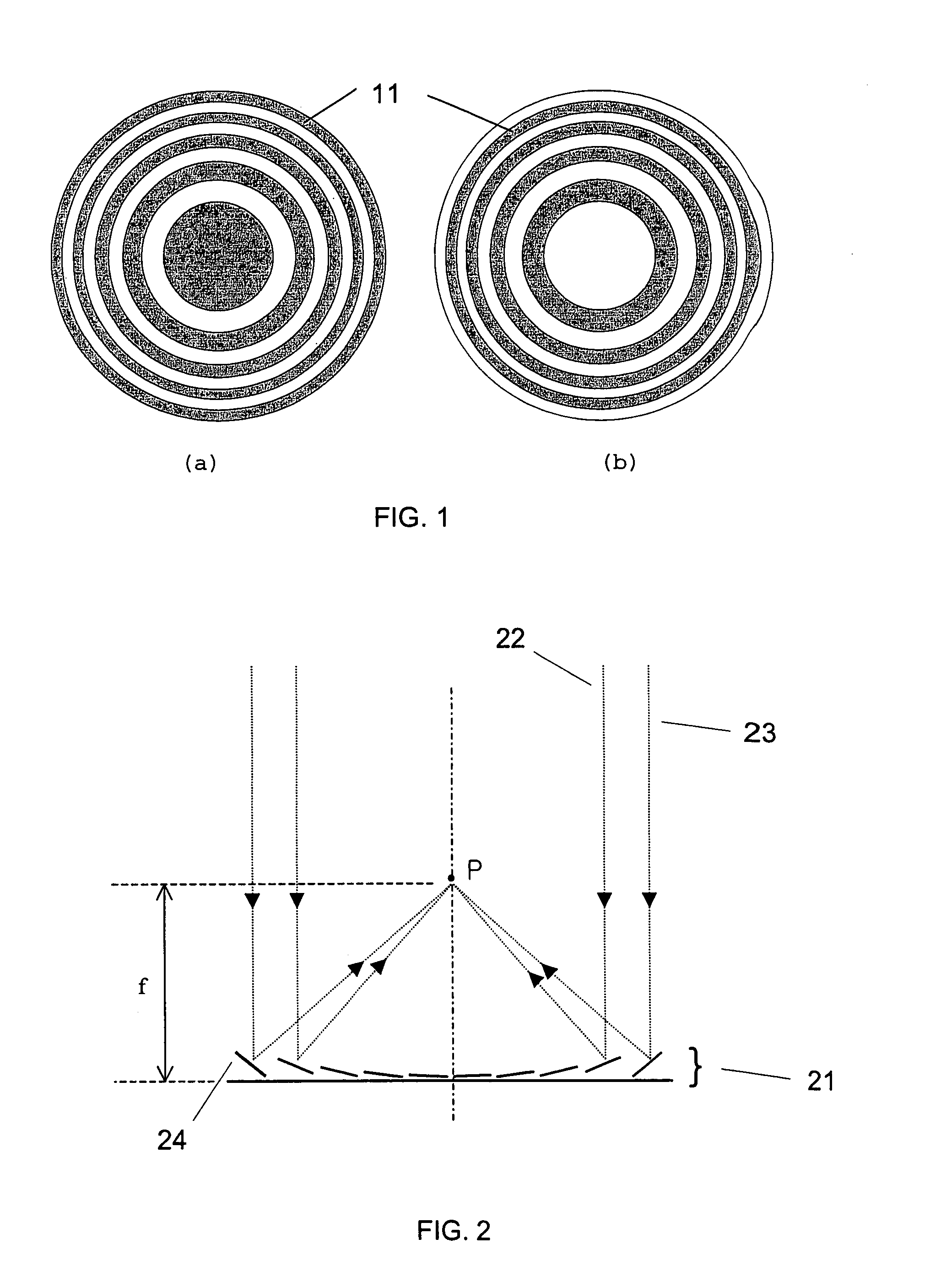
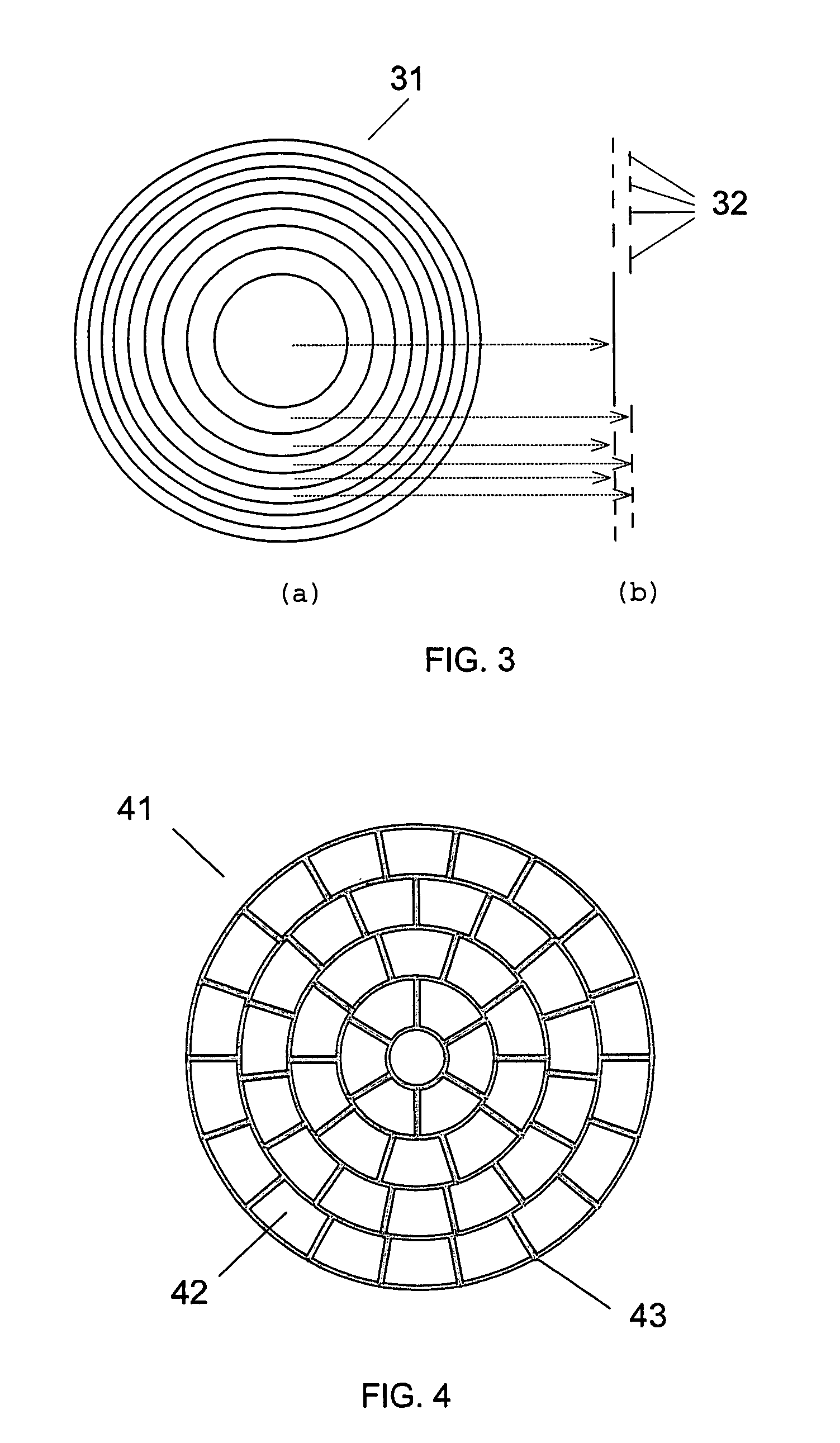
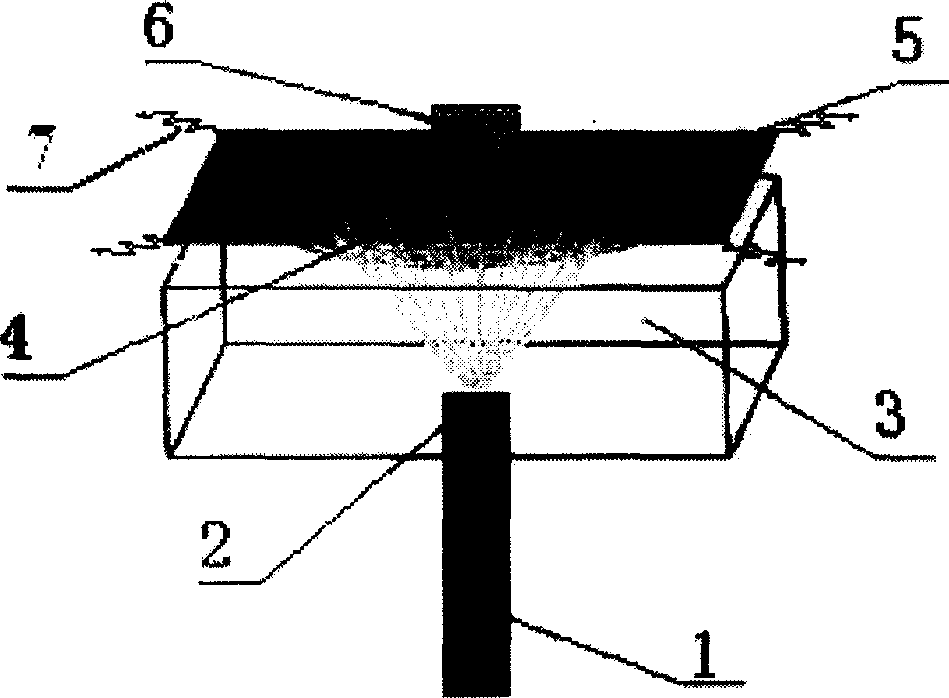
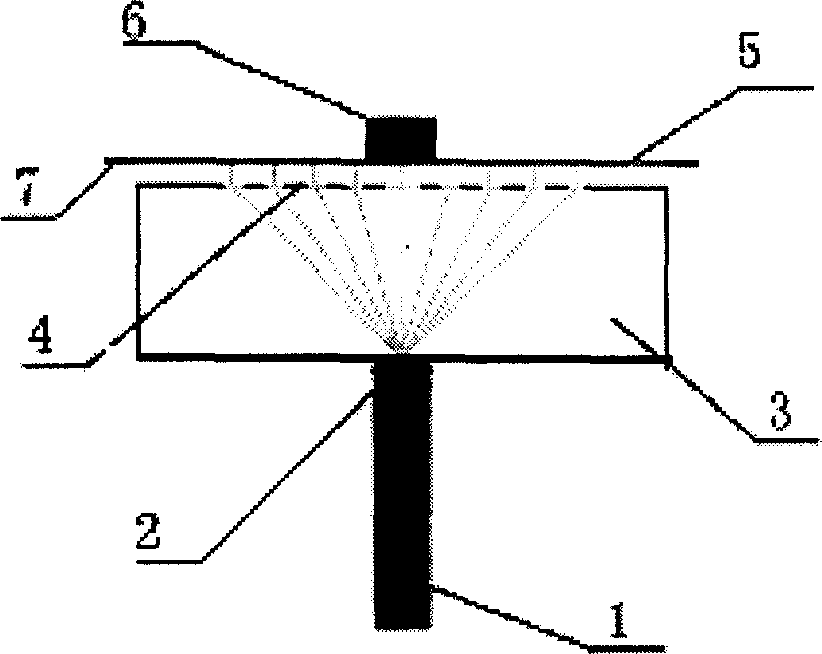
Variable focal length lens comprising micromirrors with one degree of freedom translation
ActiveUS6999226B2Improve reflectivitySimple mechanical structure and actuating componentNon-linear opticsLensCamera lensMicromirror array
A variable focal length lens comprising micromirrors with pure translation is invented. The lens consists of many micromirrors and actuating components. The array of micromirrors with pure translation makes all lights scattered from one point of an object have the same periodic phase and converge at one point of image plane by using Fresnel diffraction theory. The actuating components control the positions of micromirrors electrostatically and / or electromagnetically. The optical efficiency of the micromirror array lens is increased by locating a mechanical structure upholding micromirrors and the actuating components under micromirrors. The known semiconductor microelectronics technologies can remove the loss in effective reflective area due to electrode pads and wires. The lens can correct aberration by controlling each micromirror independently. Independent control of each micromirror is possible by known semiconductor microelectronics technologies. The micromirror array can also form arbitrary shape and / or size of a lens.
Owner:STEREO DISPLAY
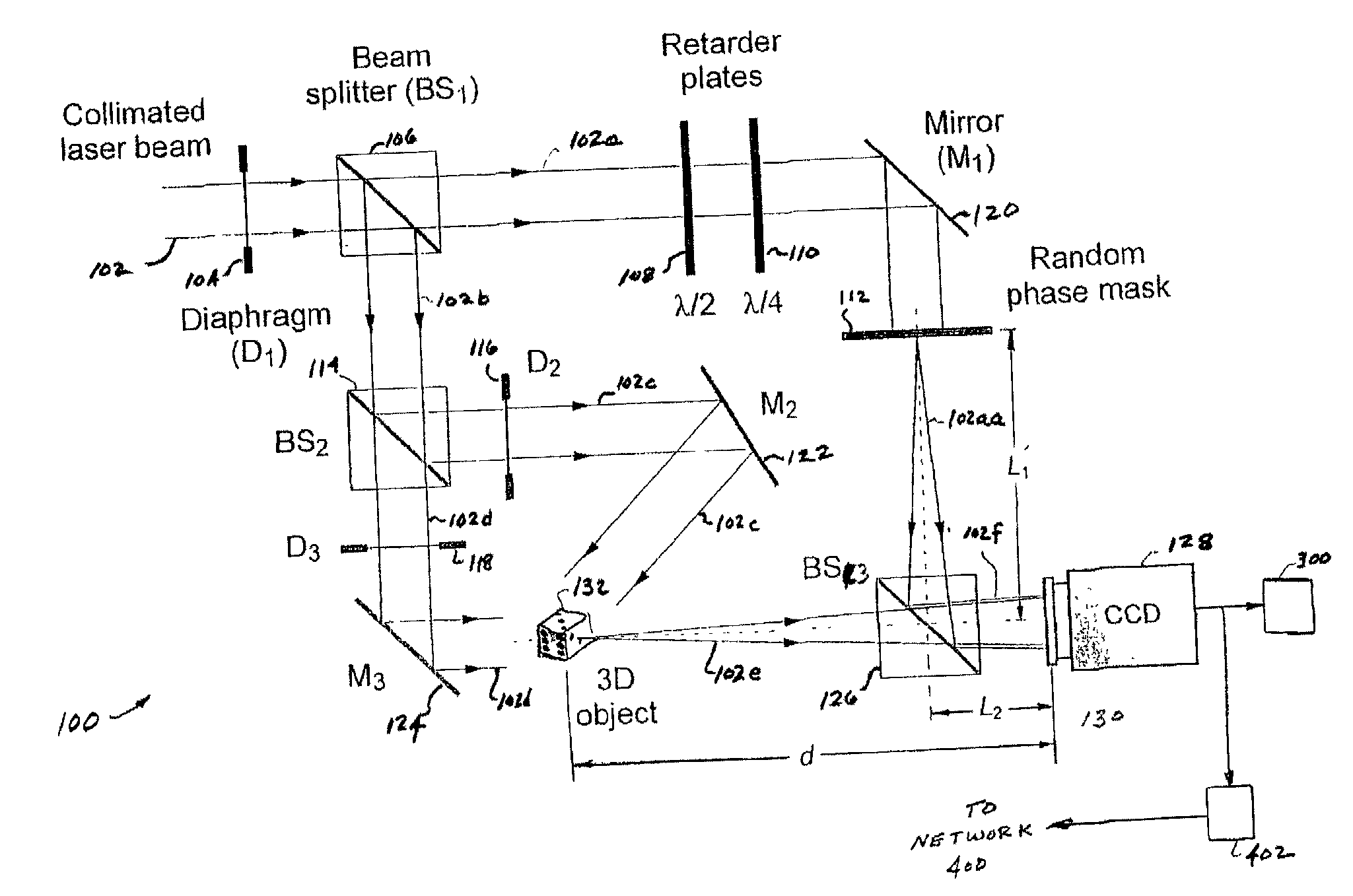
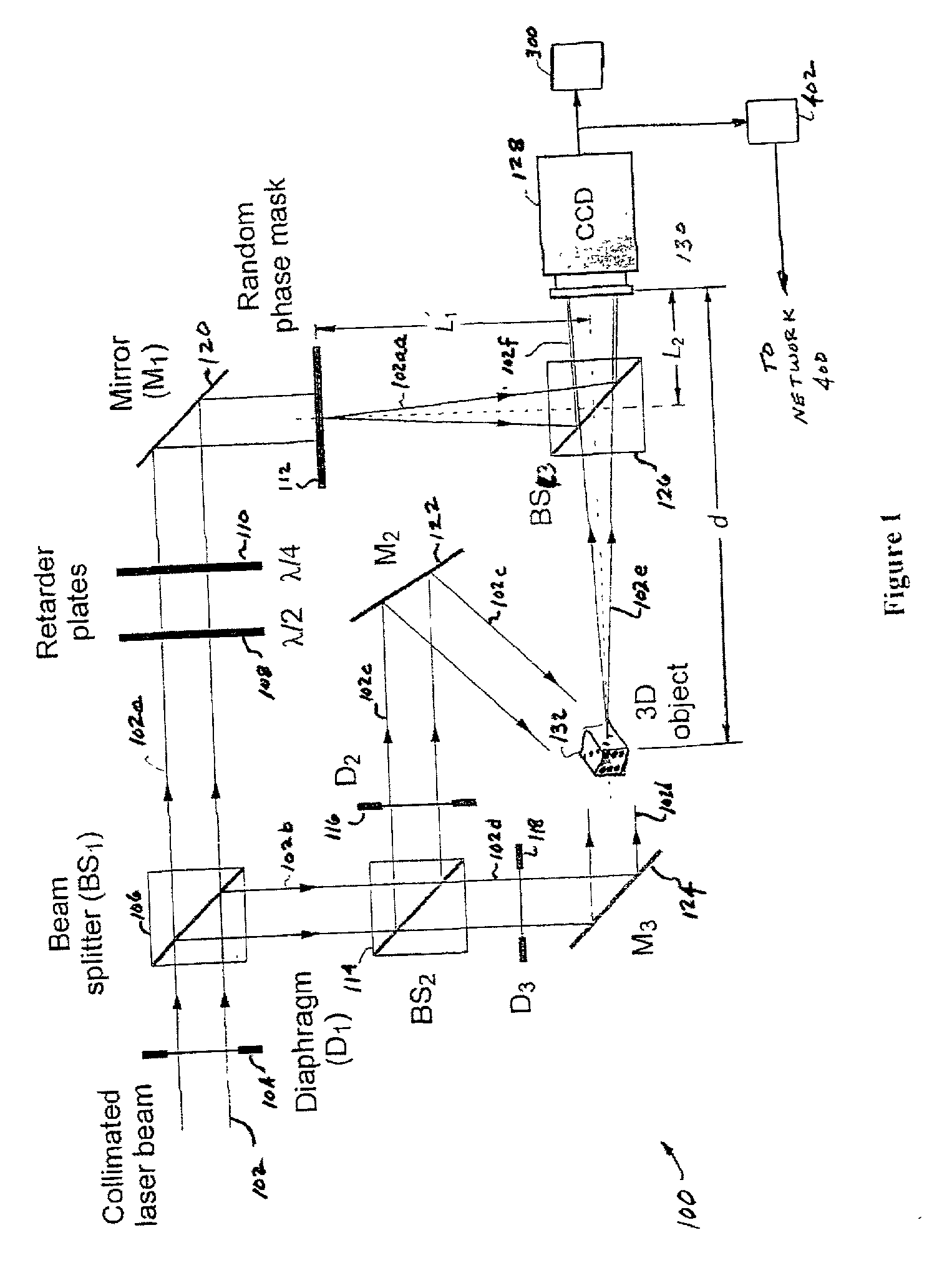
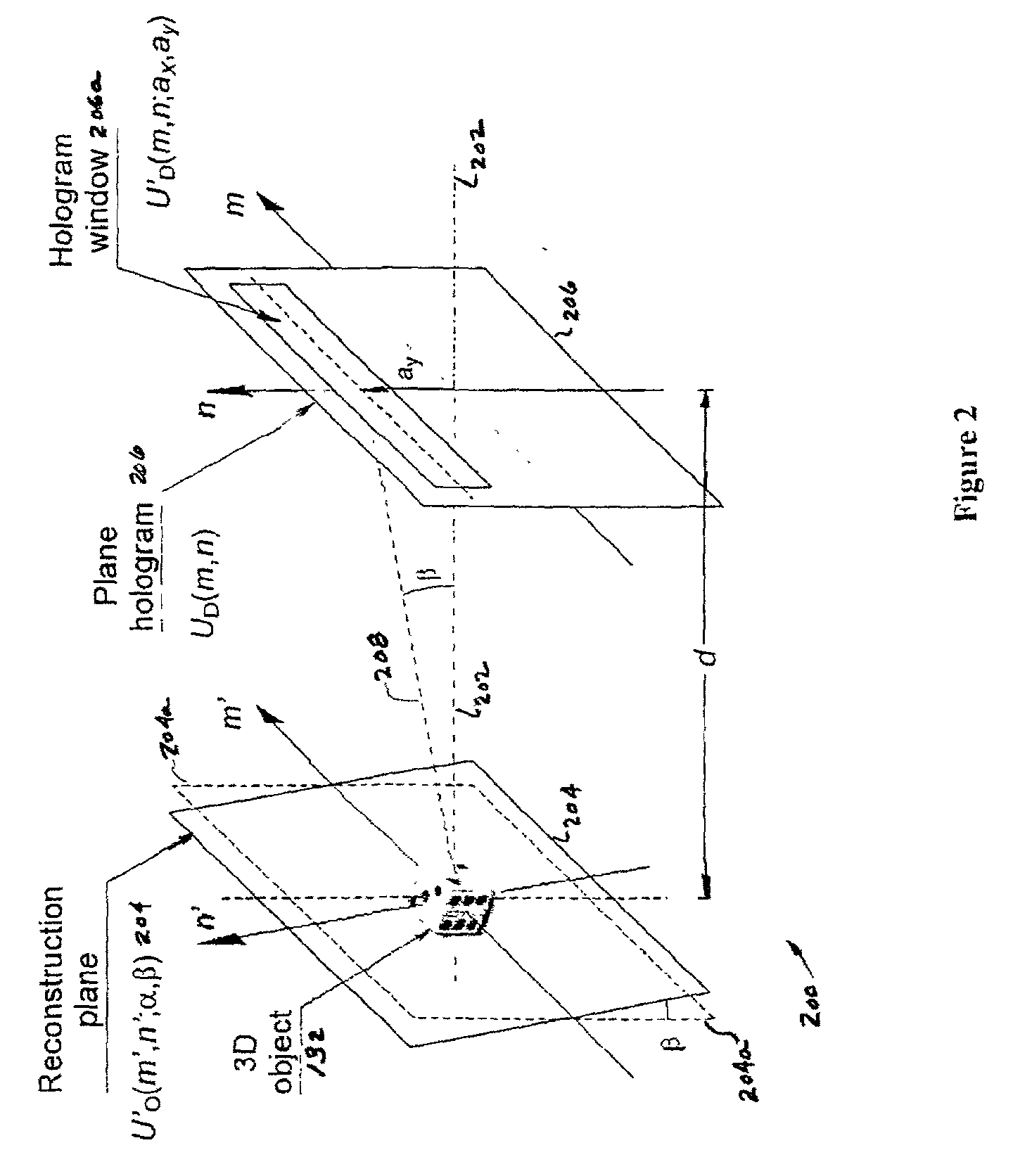
Information security using digital holography
InactiveUS20060078113A1User identity/authority verificationHolographic optical componentsComputer visionPhase mask
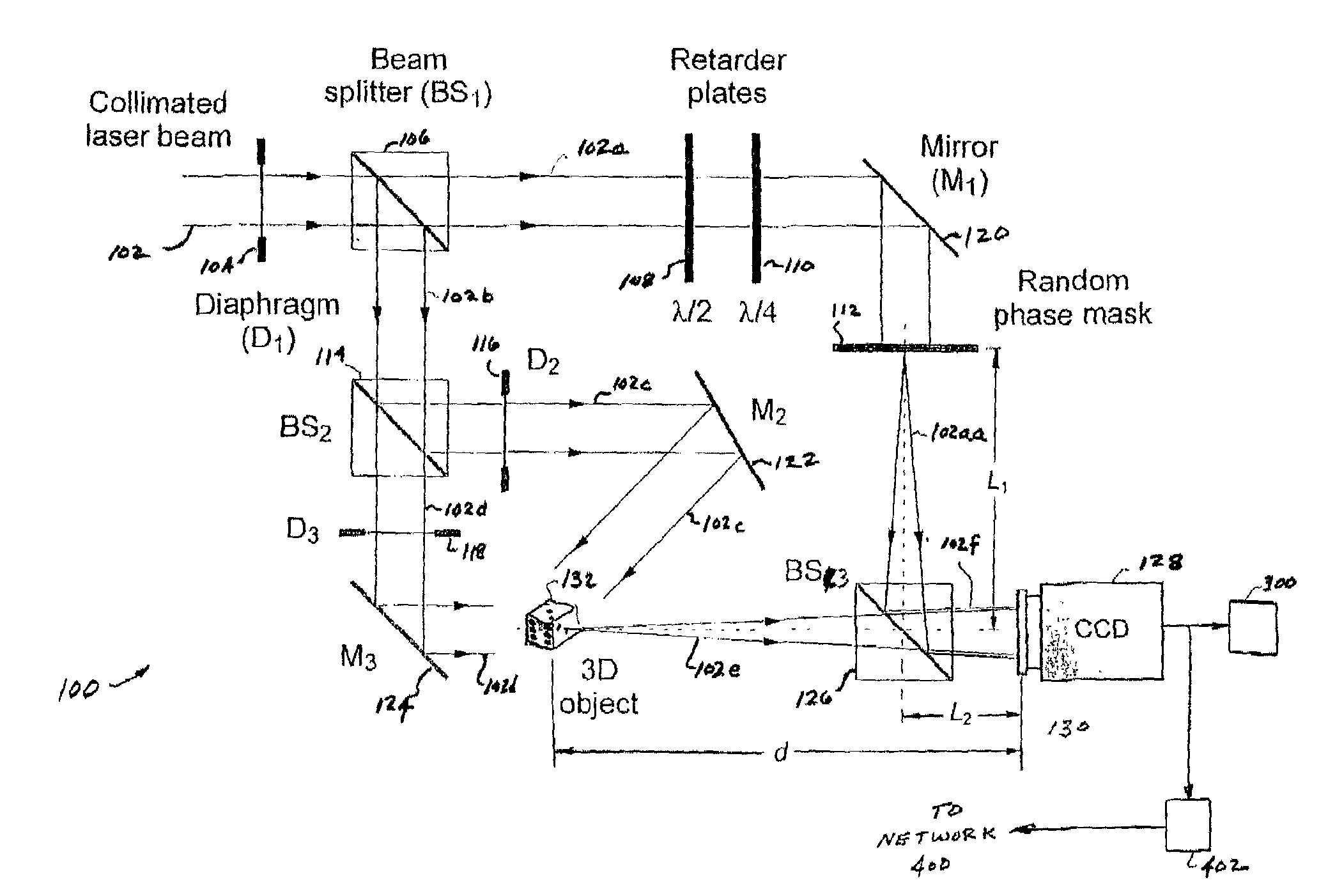
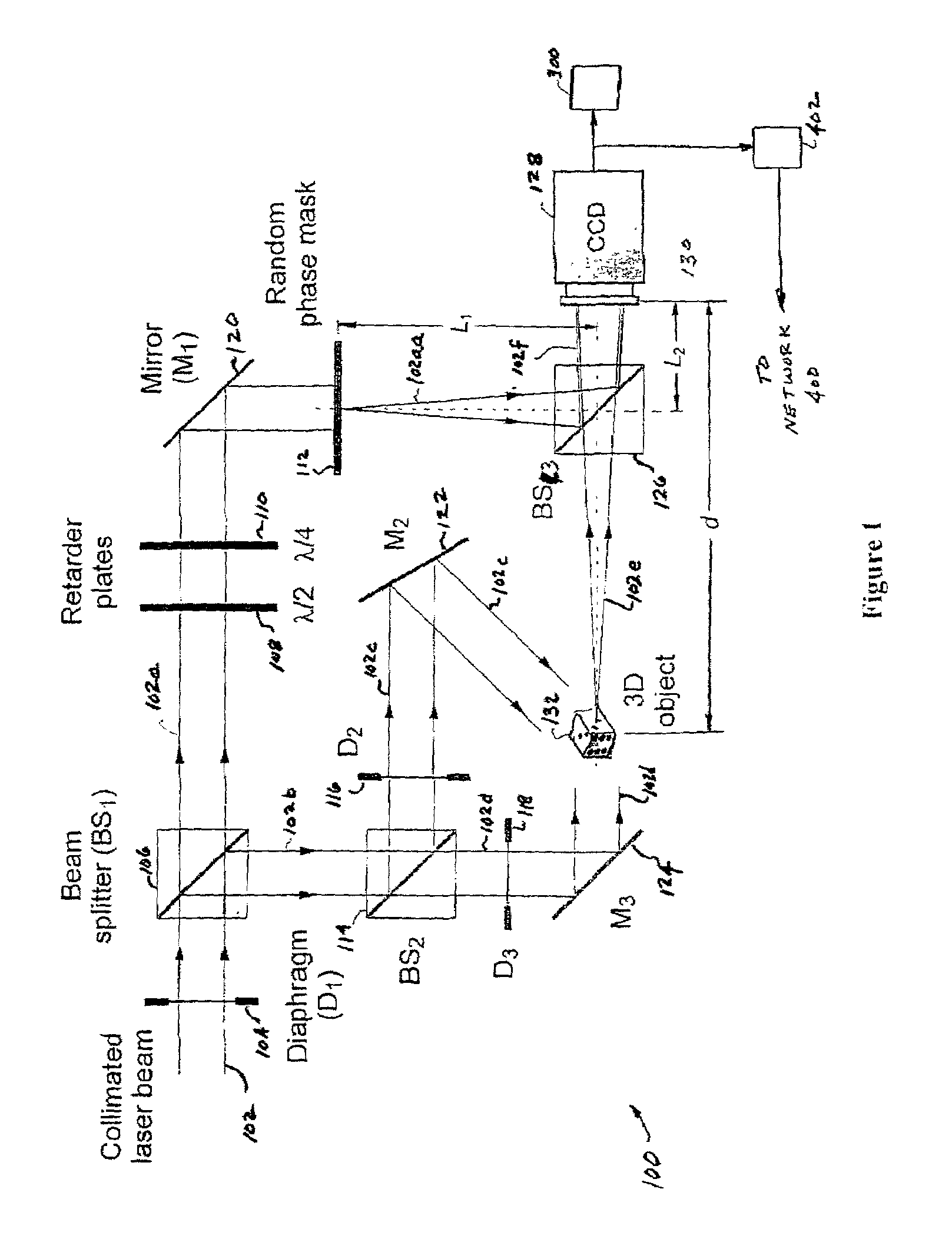
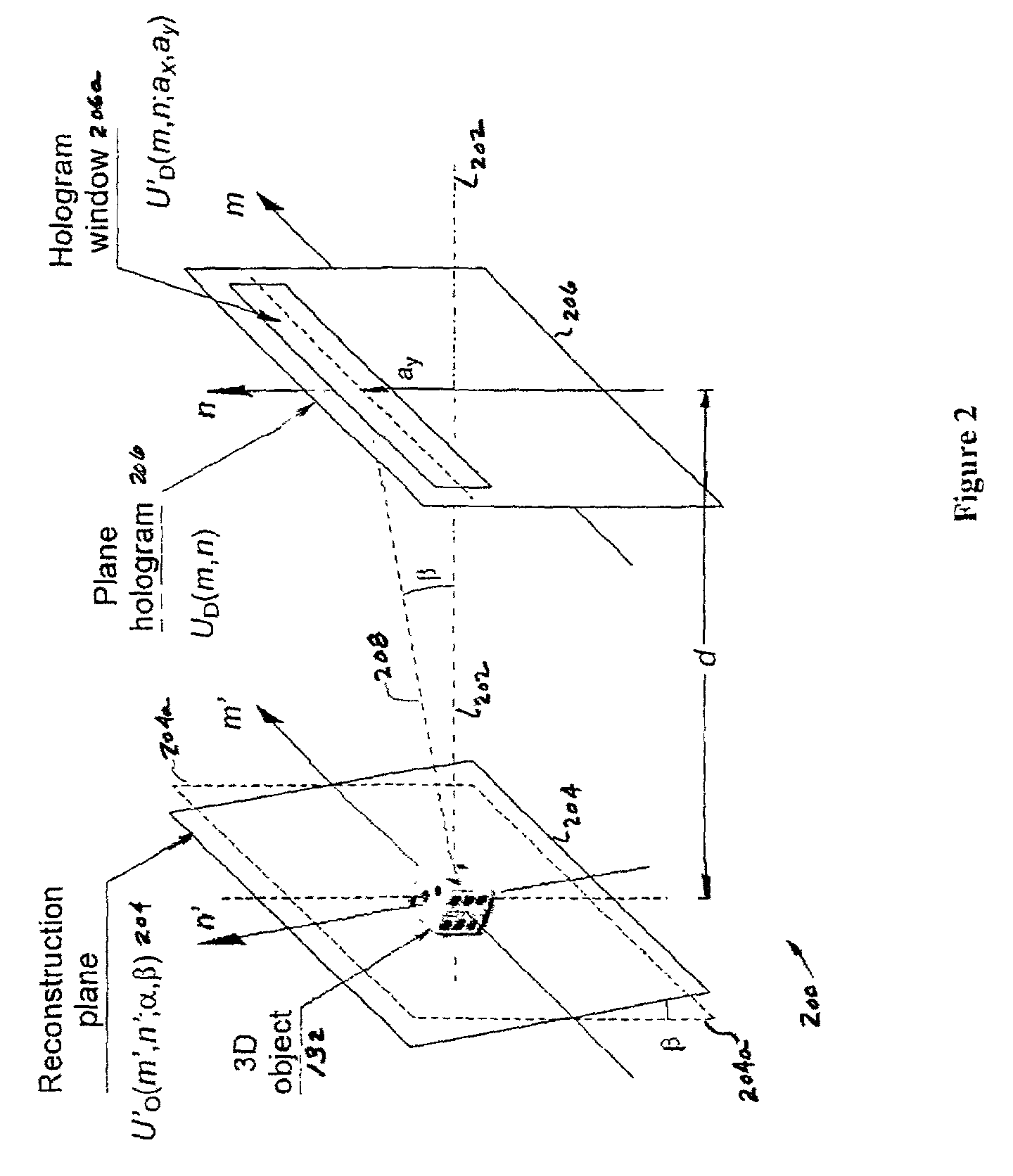
A method and system for encrypting multi-dimensional information utilizing digital holography is presented. A phase-shifting interferometer records the phase and amplitude information generated by a three-dimensional object at a plane located in the Fresnel diffraction region with an intensity-recording device. Encryption is performed by utilizing the Fresnel diffraction pattern of a random phase mask. Images of different perspectives of the three-dimensional object focused at different planes can be generated digital or optically with the proper key after decryption. After decryption, images of the object, focused at different planes, can be generated digitally or optically. The method allows for the reconstruction of the object with different perspectives from a single encrypted image. The method does not require sending the key exclusively through a digital communication channel. Instead, a copy of the random phase key itself can be sent to the authorized user. A method of forming an image of an object is disclosed. The method comprises forming an original hologram of the object; compressing the original hologram of the object to form a compressed hologram; decompressing the compressed hologram of the object to form a decompressed hologram; and reconstructing the object from the decompressed hologram to form a multi-dimensional image of the object.
Owner:CONNECTICUT UNIV OF THE
Method and device for producing a coupling grating for a waveguide
InactiveUS20040042724A1Reduce contrastAdequate averagingCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideDiffraction effectEffective solution
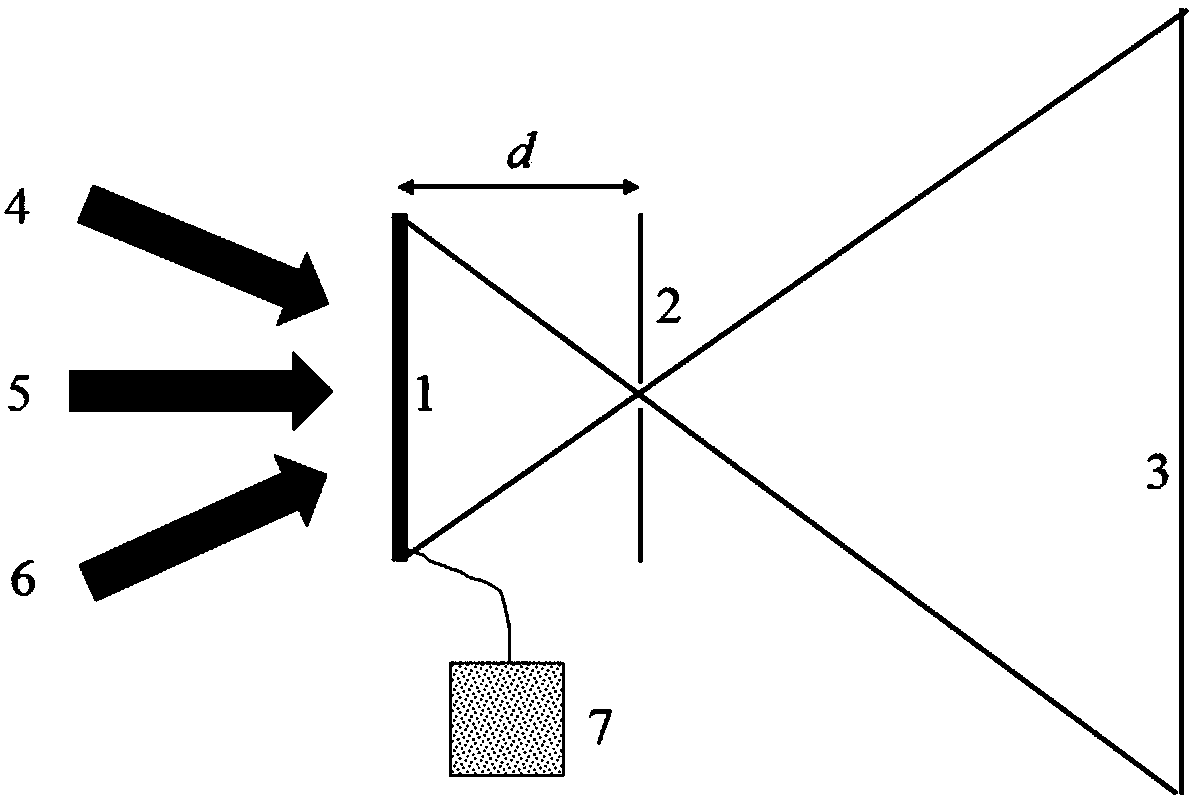
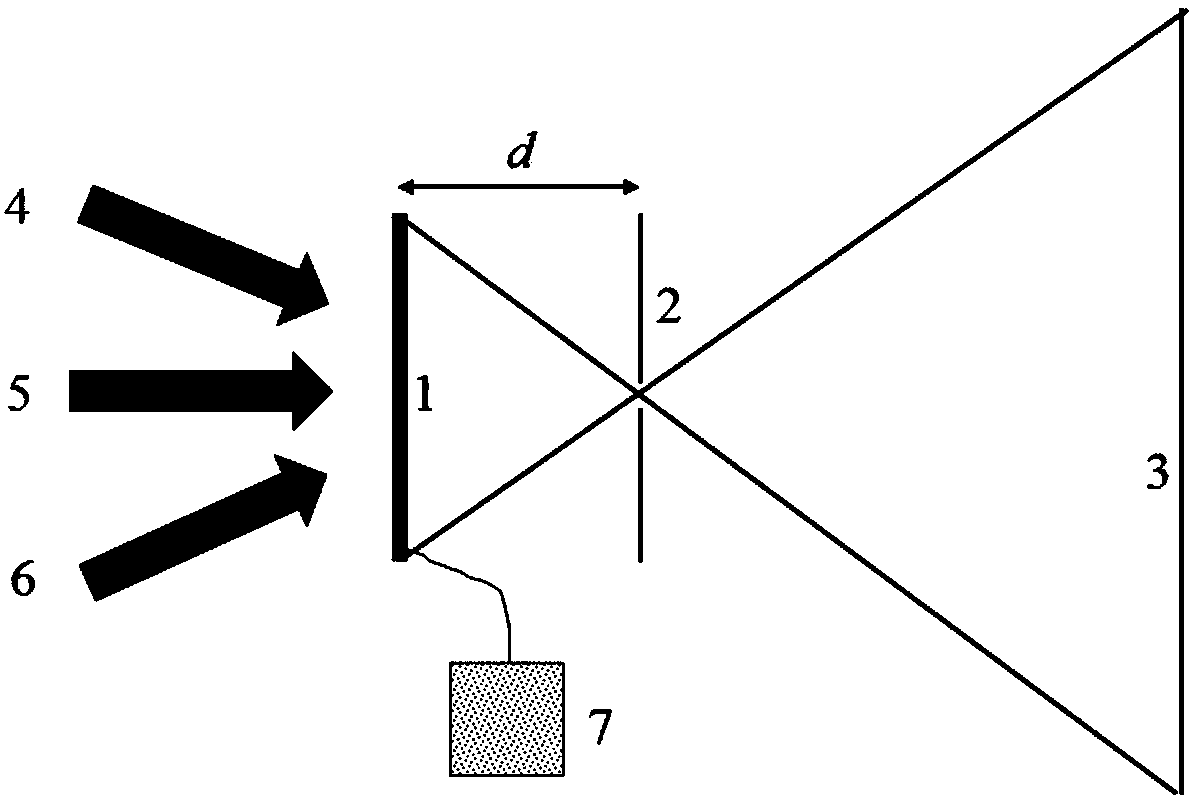
The invention relates to a method and a device for producing a coupling grating (5) for a waveguide. The method relies on the technique of interference lithography, whereby an interference pattern on a light-sensitive layer (2) is exposed by superimposing two coherent light beams (3, 4) on said light-sensitive layer (2). Said pattern is then transferred onto the surface of the substrate (1) that lies underneath by subsequent developing and an etching process. The method is characterized in that it uses a shadow mask (6) that is mounted at minimum clearance relative to the surface of the light-sensitive layer (2). By observing said minimum clearance, the Fresnel diffraction images of both light beams (3, 4) are separated on the edge(7). The thickness of the light-sensitive layer (2) is selected in such a way that the superimposition of the Fresnel diffraction pattern of one light beam with the other undisturbed light beam suffices to uncover areas of the substrate (1) during subsequent developing of the layer (2). The method makes it possible to avoid transfer of unwanted diffraction effects on the edge of the shadow mask to the substrate. The method provides a cost-effective solution for the production of large-surface coupling grating matrices.
Owner:GOMBERT ANDREAS +2
Linear Fresnel spectrometer chip with gradient line grating
InactiveUS9046418B1Spectrum investigationSpectrum generation using diffraction elementsGratingOptical axis
A spectrometer that includes a grating that disperses light via Fresnel diffraction according to wavelength onto a sensing area that coincides with an optical axis plane of the grating. The sensing area detects the dispersed light and measures the light intensity associated with each wavelength of the light. Because the spectrometer utilizes Fresnel diffraction, it can be miniaturized and packaged as an integrated circuit.
Owner:NASA
Color holographic display system based on diffraction distance control and method thereof
InactiveCN103412470ASwitch in real timeFlexible and convenient loading methodOptical elementsSpatial light modulatorWavelength
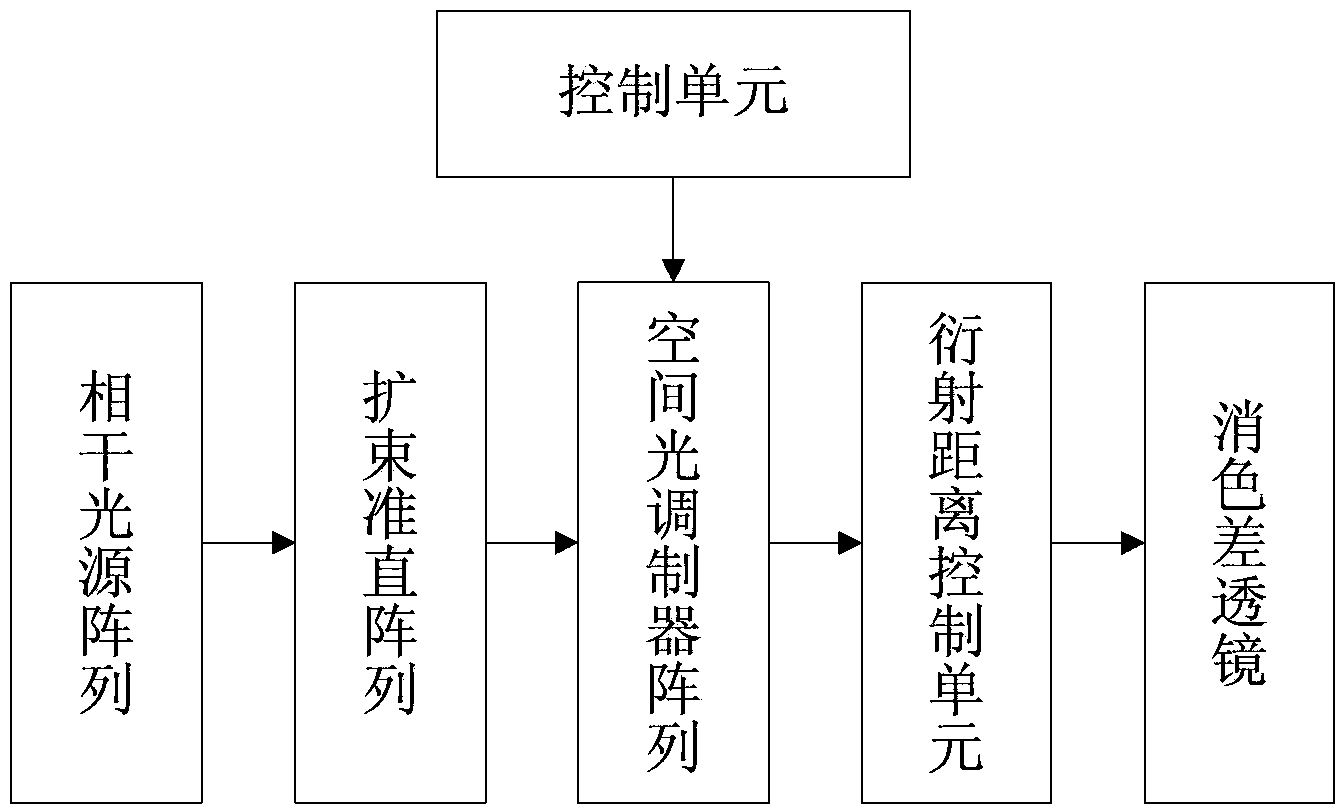
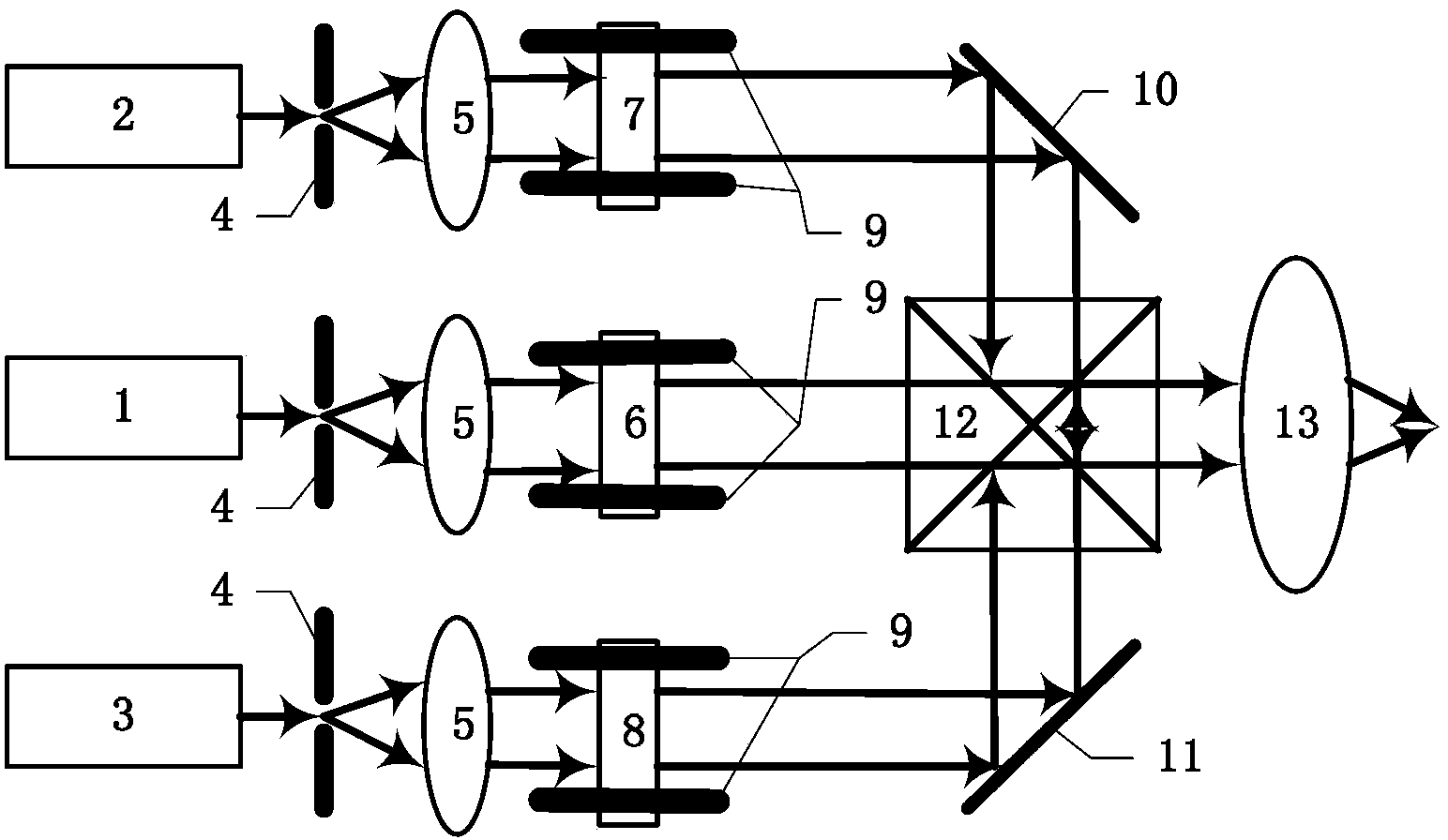
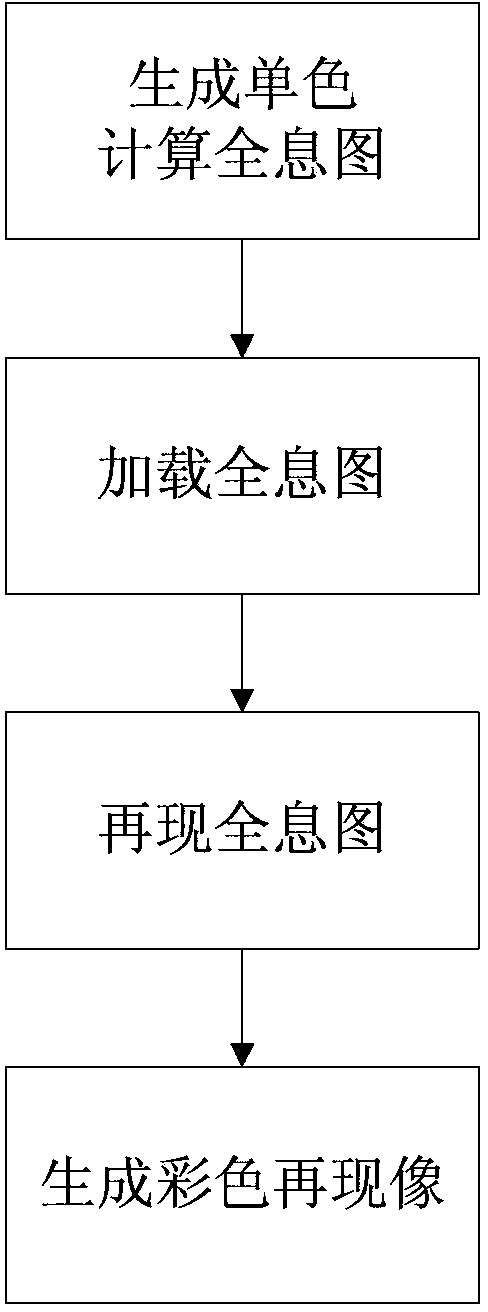
The invention discloses a color holographic display system based on diffraction distance control and a method of the color holographic display system based on the diffraction distance control. The problem that color crosstalk exists in existing color holographic display is mainly solved. The system comprises a coherent light source array, an expanded beam collimating array, a control unit, a space light modulator array, a diffraction distance control unit and an achromatic lens. The implementation steps of the method comprise the first step of generating monochrome computing holograms, the second step of loading the holograms, the third step of reproducing the holograms and the fourth step of generating a color reproduction image. An optimal Fresnel diffraction distance obtained under different wave lengths in a calculating mode is utilized to generate the three monochrome computing holograms, and Fresnel diffraction with an optimal diffraction distance is respectively carried out on the three monochrome computing holograms. The color holographic display system and the method have the advantages that the hologram loading mode is flexible, light paths are simple and convenient to adjust, and the effect of eliminating the color crosstalk is good.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Optical system for homogenizing semiconductor laser beam of area array
InactiveCN103246066AMade Simple and PreciseAchieve homogenizationOptical elementsOptical axisEffect light
The invention provides an optical system for homogenizing a semiconductor laser beam of an area array, which comprises a semiconductor laser of the area array, a collimating lens array, a first microlens array, a second microlens array, a slow-axis field lens and a fast-axis field lens, wherein the semiconductor laser of the area array is positioned on the front focal plane of the micro collimating lens array and takes an output laser beam of the semiconductor laser of the area array as a system optical axis; the first microlens array, the second microlens array, the slow-axis field lens and the fast-axis field lens are positioned on the optical axis in sequence and are vertical to the optical axis; and a multi-mode laser beam sent by the semiconductor laser parallelly enters after being collimated by the collimating lens array and then is evenly divided into a plurality of sub beams by the first microlens array to be focused on the rear focal plane, and afterwards, the sub beams are overlaid on the rear focal plane of a field lense by the the second microlens array, the slow-axis field lens and the fast-axis field lens, that is to say, the sub beams are overlaid on the lighting surface. The homogenizing of the semiconductor laser beam is realized by a cylinder-shaped Fresnel diffraction microlens array, so that the quality of the beam is improved.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Single-pixel holographic camera
InactiveCN105467806AQuality improvementEasy to handleInstrumentsFrequency spectrumHolographic imaging
The present invention relates to a single-pixel holographic camera, belonging to the field of holographic imaging. The working process of the system comprises the stages of recording and reconstruction. In the recording stage, the transformation matrix of a space amplitude modulating device is used to encode the Fourier spectral information of the Fresnel diffraction hologram of an object, the analysis and record of a time varying signal are completed by a single pixel intensity detection module, the corresponding measurement is carried out through changing the transformation matrix of the space amplitude modulating device for many times, and finally the compressed sensing imaging result of the Fourier spectrum of object Fresnel diffraction hologram is obtained. In the reconstruction stage, according to the selected encoding matrix, by using a minimization L1 norm algorithm, the recovery of spectral information is carried out, and the Fresnel diffraction hologram of the object is reconstructed through the Fourier transformation.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Interferometer
ActiveUS20070272861A1Increase rangeIndependent controlMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesOptical axisPrism
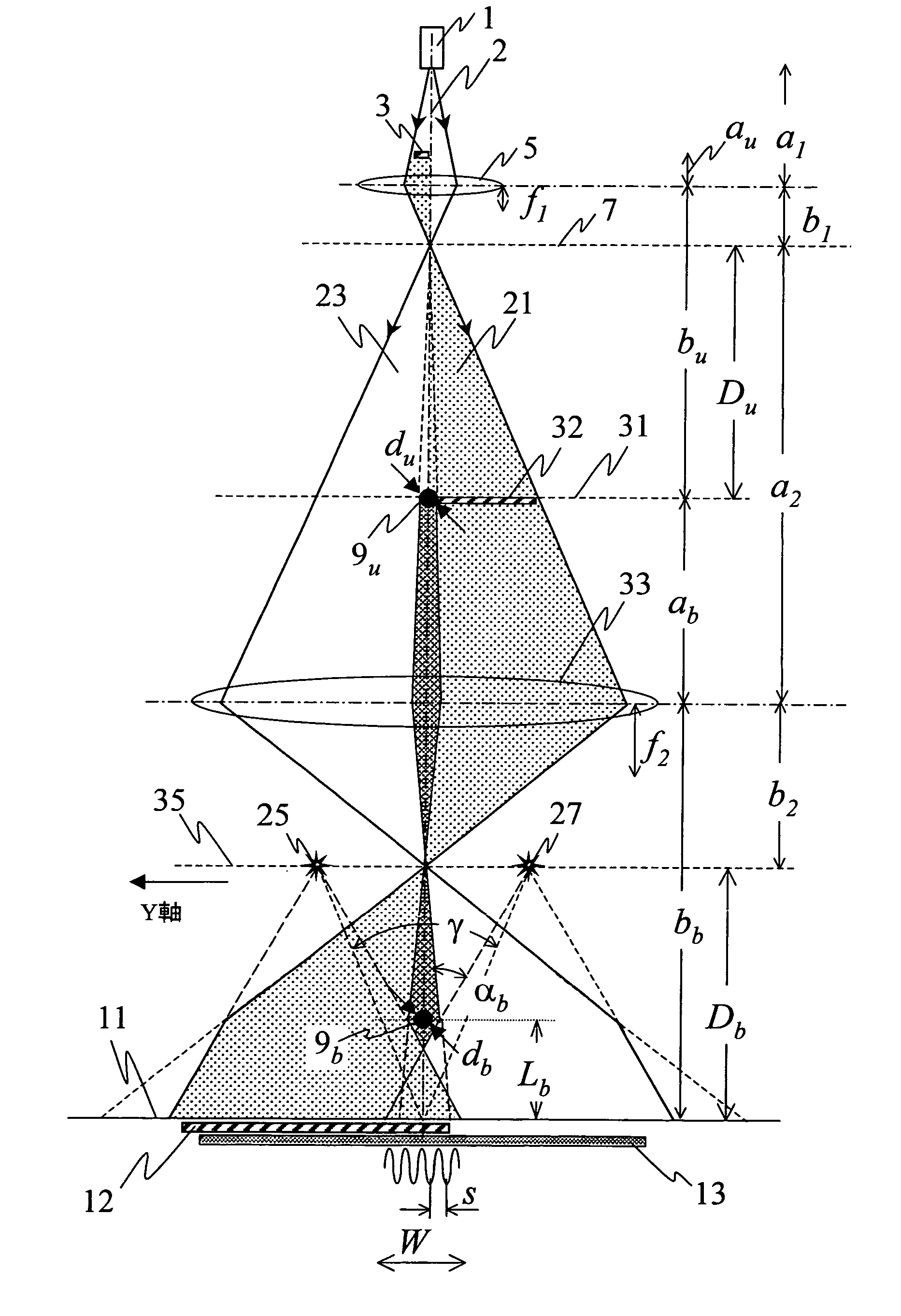
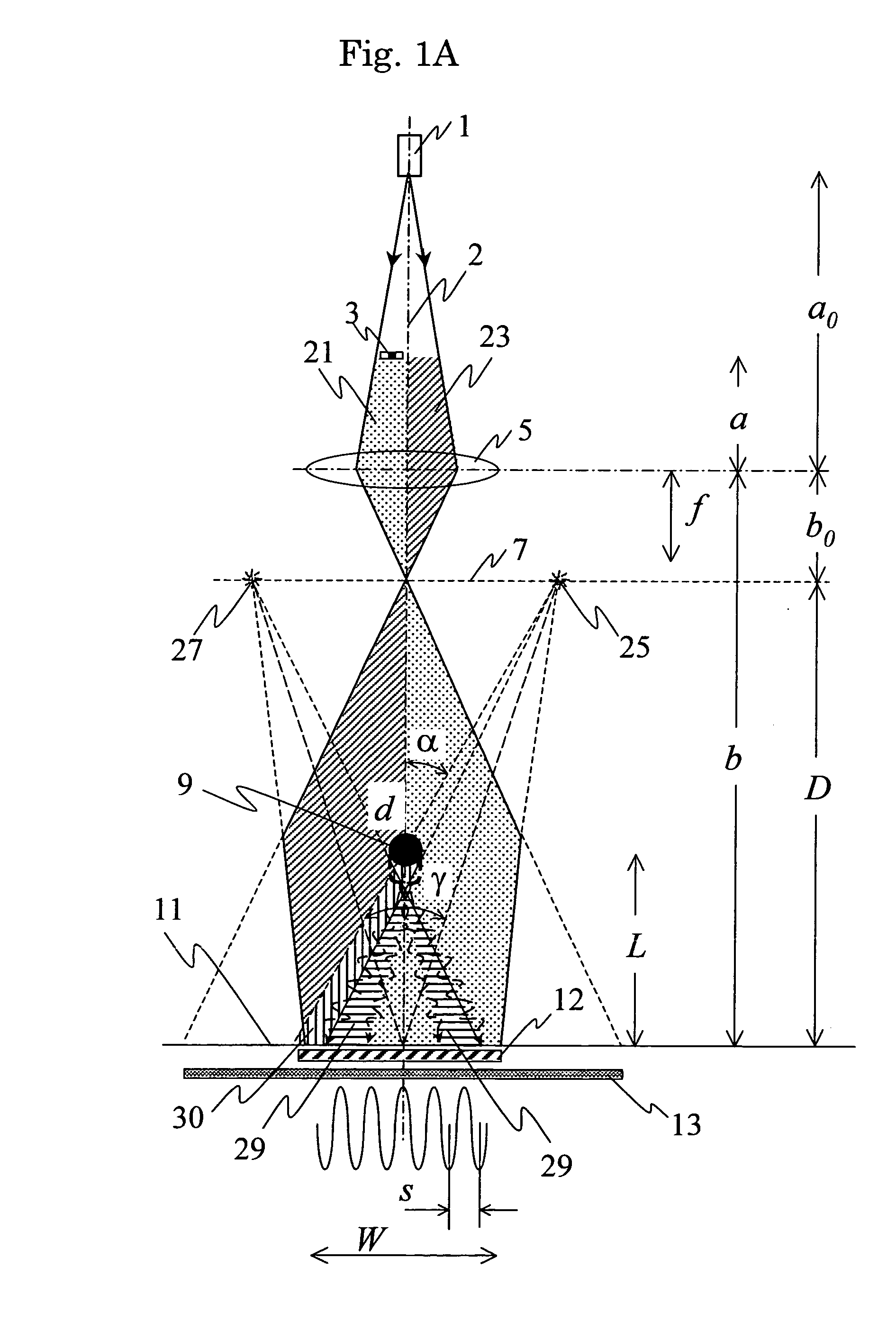
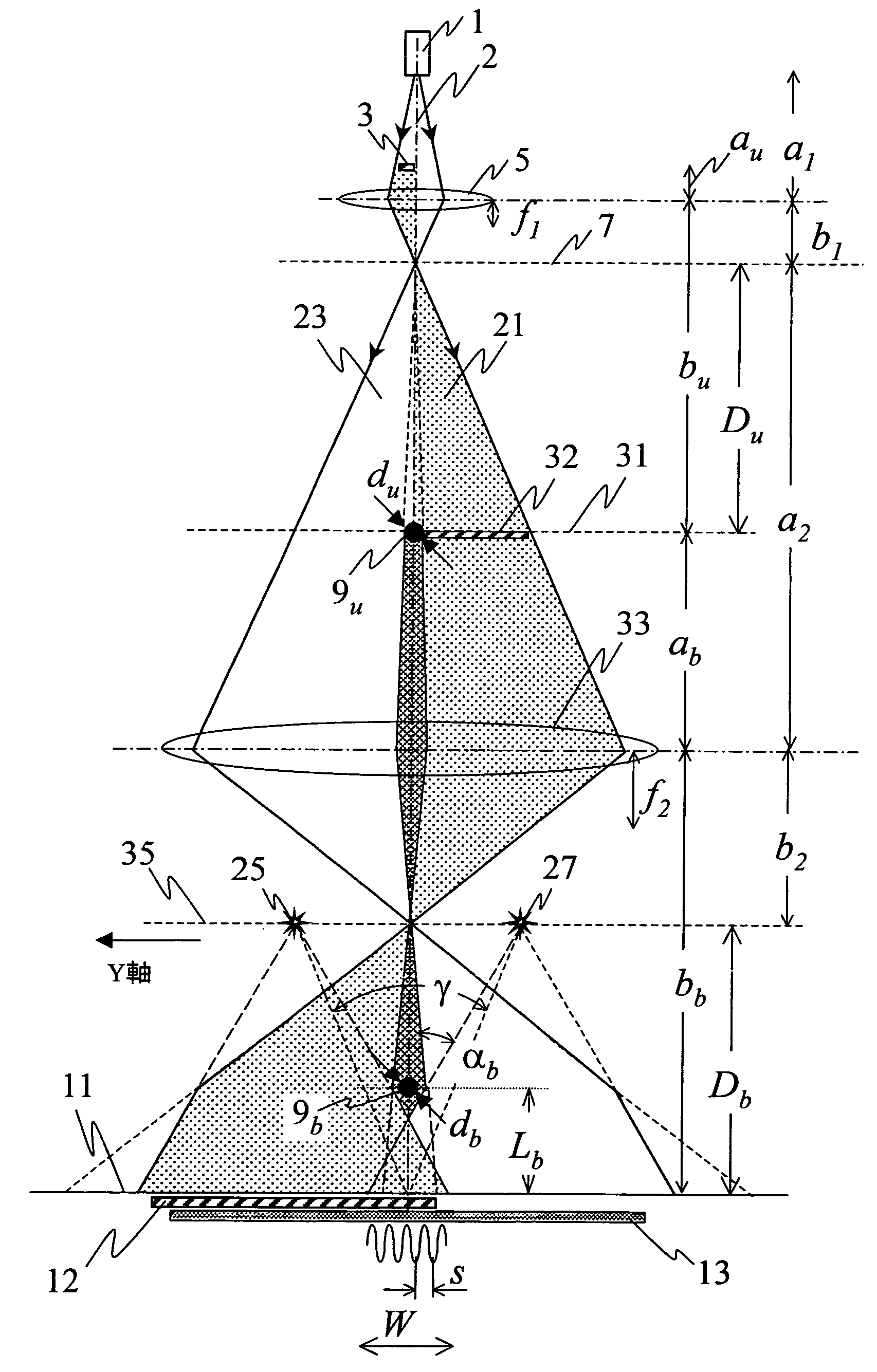
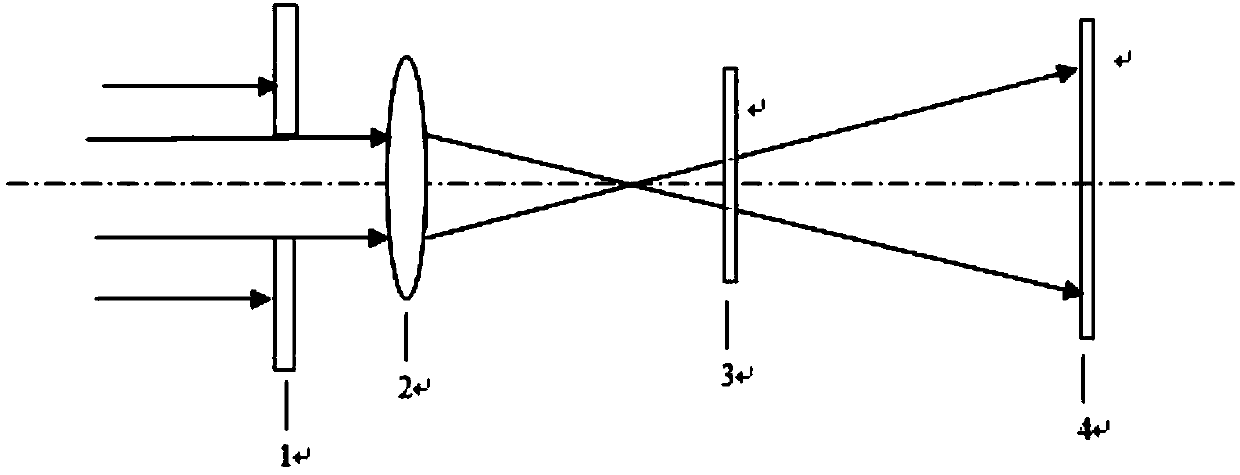
The present invention provides a technique enabling to control fringe spacing s and an interference width W independently of each other, which are important parameters for an interferometer using an electron biprism. In the present invention, two electron biprisms 9u, 9b are used in two stages along the optical axis, and fringe spacing s and an interference width W are controlled independently of each other by controlling a voltage applied to an electrode of each of the electron biprisms. Also Fresnel diffraction can be suppressed.
Owner:RIKEN
Information security using digital holography
InactiveUS7221760B2User identity/authority verificationHolographic optical componentsPhase maskInformation security
A method and system for encrypting multi-dimensional information utilizing digital holography is presented. A phase-shifting interferometer records the phase and amplitude information generated by a three-dimensional object at a plane located in the Fresnel diffraction region with an intensity-recording device. Encryption is performed by utilizing the Fresnel diffraction pattern of a random phase mask. Images of different perspectives of the three-dimensional object focused at different planes can be generated digital or optically with the proper key after decryption.After decryption, images of the object, focused at different planes, can be generated digitally or optically. The method allows for the reconstruction of the object with different perspectives from a single encrypted image. The method does not require sending the key exclusively through a digital communication channel. Instead, a copy of the random phase key itself can be sent to the authorized user.A method of forming an image of an object is disclosed. The method comprises forming an original hologram of the object; compressing the original hologram of the object to form a compressed hologram; decompressing the compressed hologram of the object to form a decompressed hologram; and reconstructing the object from the decompressed hologram to form a multi-dimensional image of the object.
Owner:CONNECTICUT UNIV OF THE
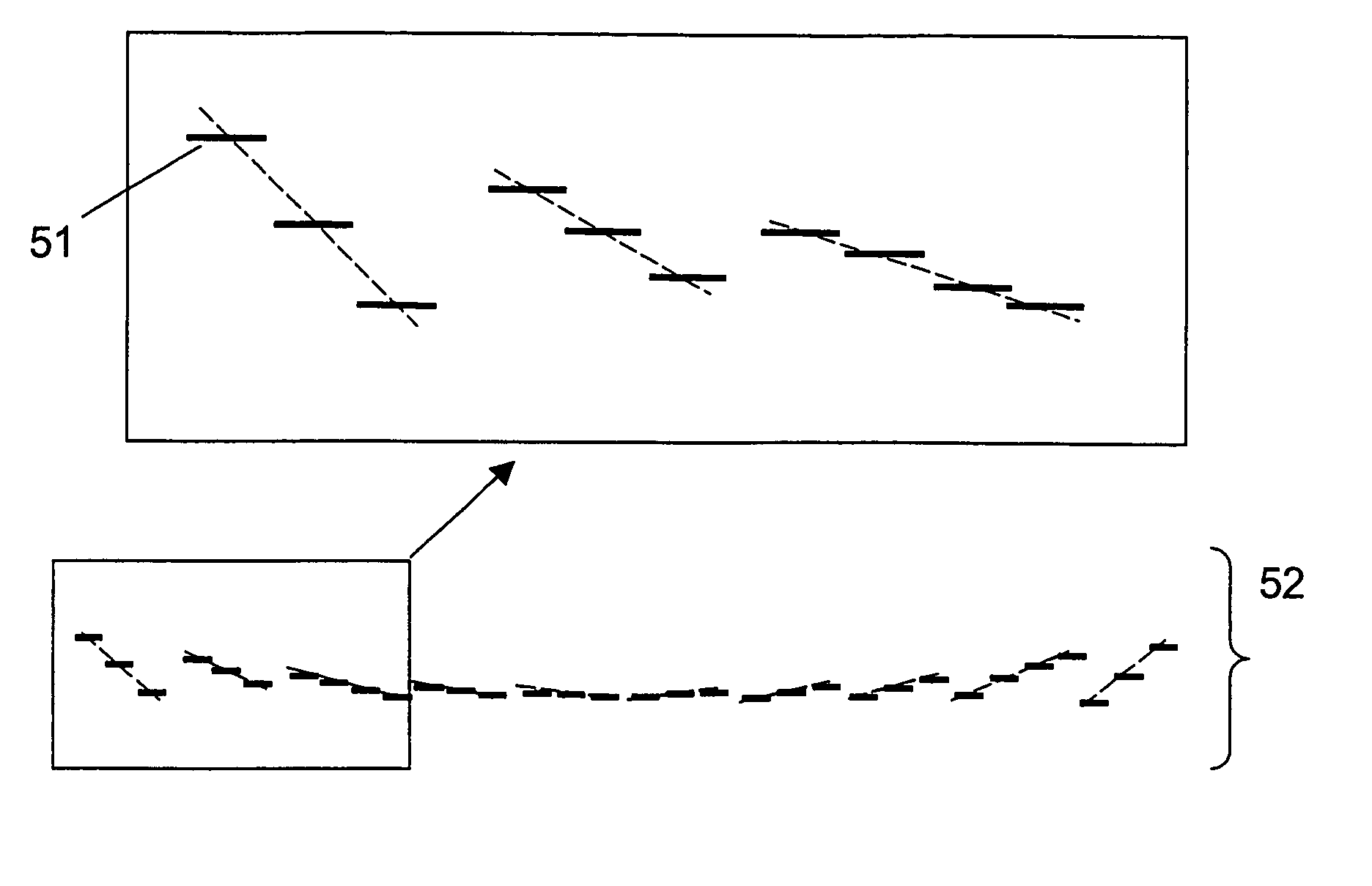
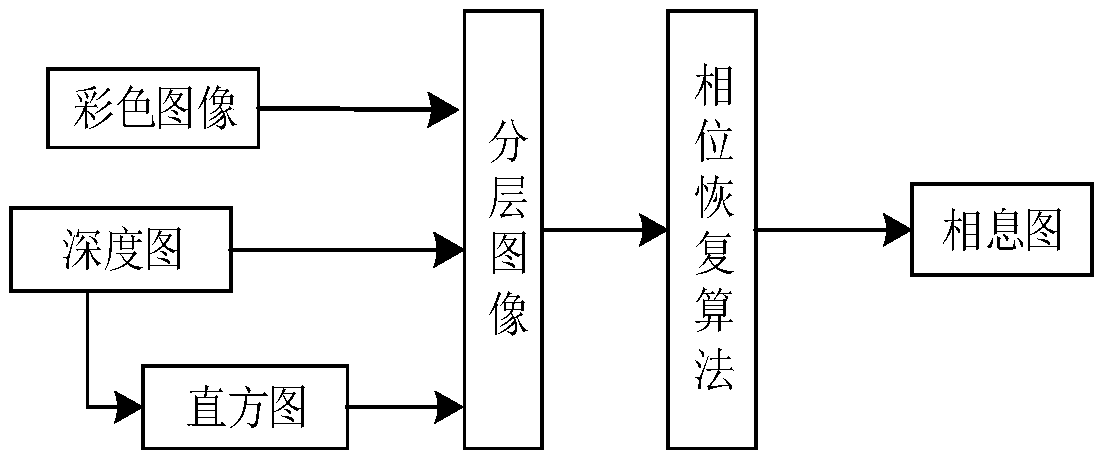
Multi-complex three-dimensional scene encryption and decryption method based on the kinoform and Fresnel domain multiplexing
ActiveCN108648267AImprove reconstruction qualityImprove securityImage enhancementImage analysisColor imageMultiplexing
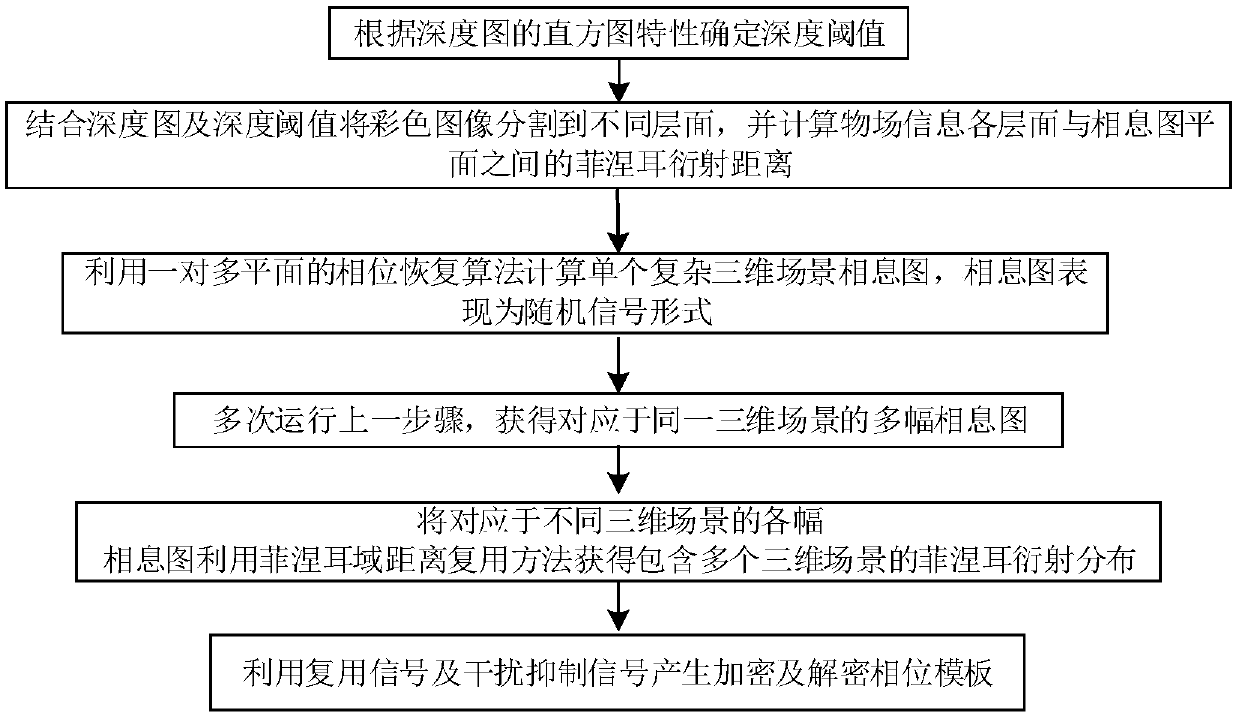
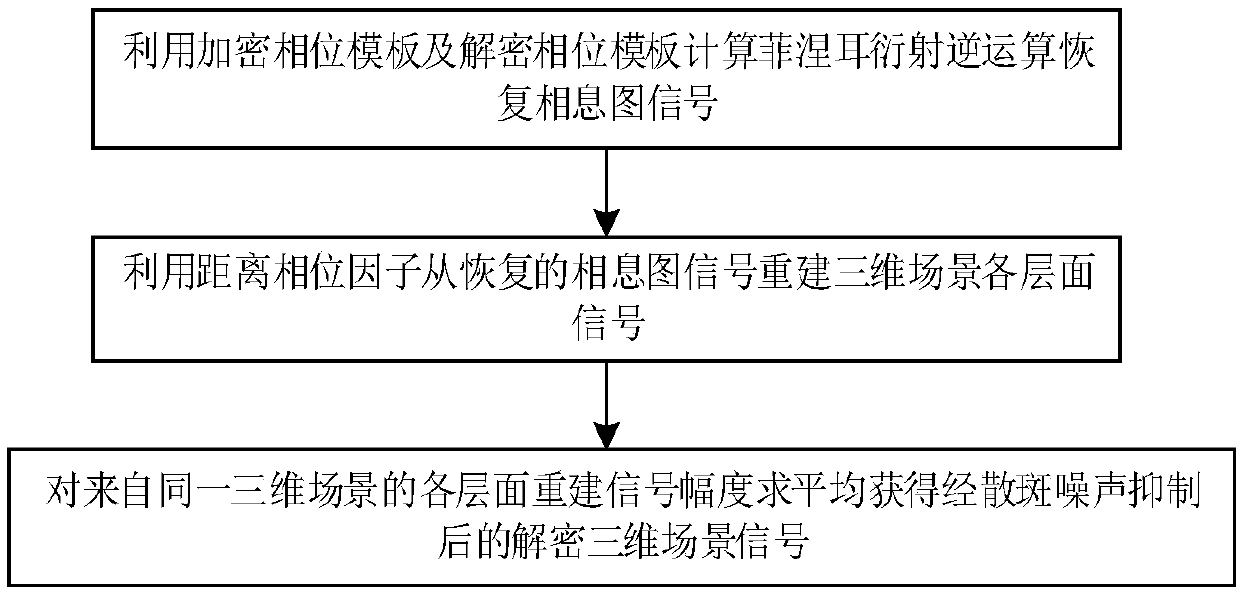
The present invention discloses a multi-complex three-dimensional scene encryption and decryption method based on the kinoform and Fresnel domain multiplexing. The method comprises: starting from a complex three-dimensional scene characterized by a color image and a depth map, using a computational holography coding method to generate a computational kinoform that can be used for true three-dimensional reconstruction, wherein the kinoform shows random signal characteristics; superimposing the kinoform recording a single complex three-dimensional scene by using the Fresnel domain distance multiplexing method to generate a Fresnel diffraction distribution containing multiple three-dimensional scenes; and finally, using a phase template decomposition method for the diffraction signal and theinterference suppression signal which contain multiple three-dimensional scenes to obtain an encrypted and decrypted phase template. In order to suppress the speckle noise in the reconstructed three-dimensional scene, the multiplexed signal contains multiple kinoforms from the same three-dimensional scene, and the intensities of the light wave signals reconstructed by different kinoforms from thesame three-dimensional scene are averaged in the decryption phase to improve the quality of reconstruction. According to the method provided by the present invention, a three-dimensional scene can still be reconstructed in the case that the encrypted phase template suffers from large area shearing or is superimposed with a certain intensity of Gaussian noise, and the method has good security and robustness.
Owner:FUJIAN NORMAL UNIV
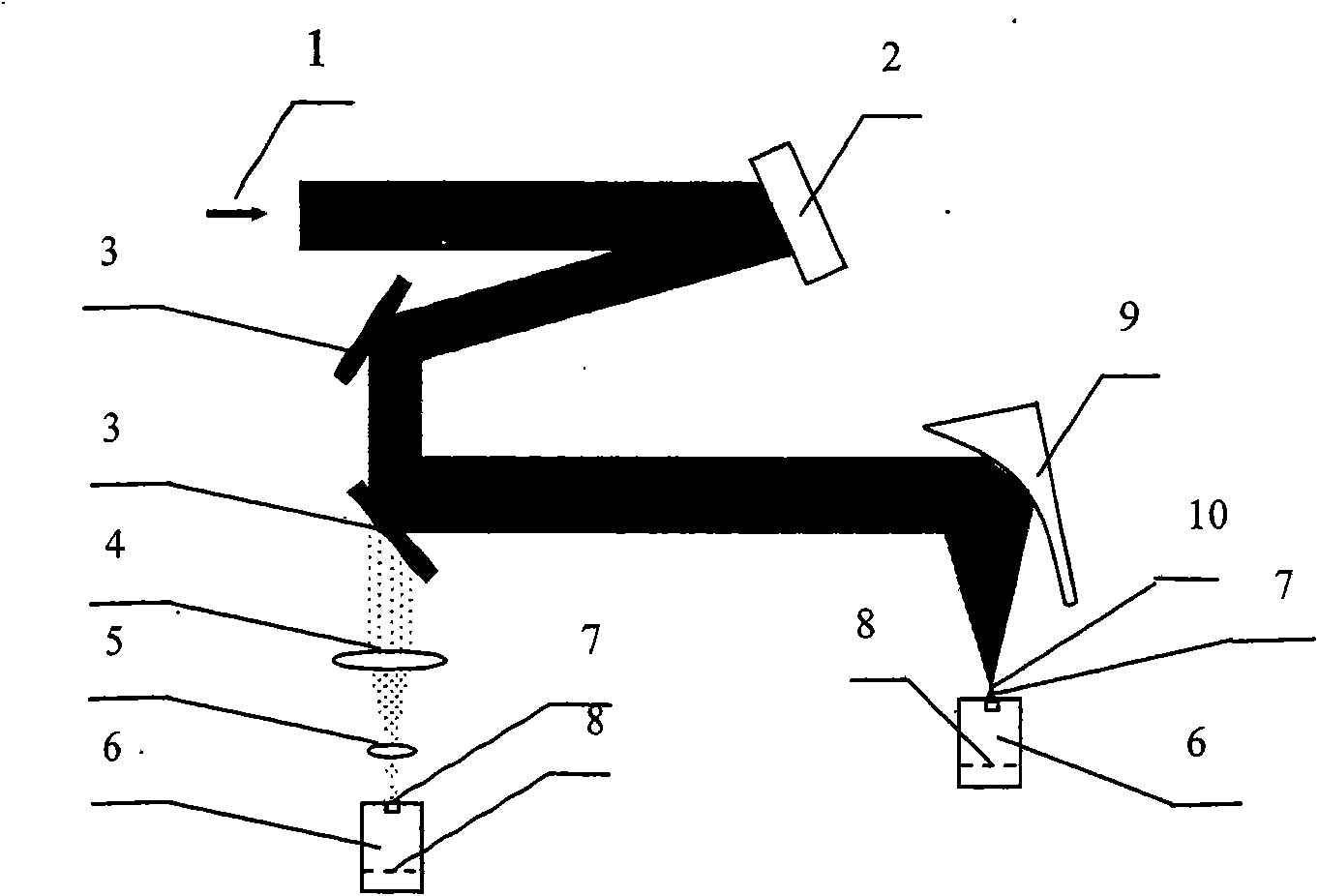
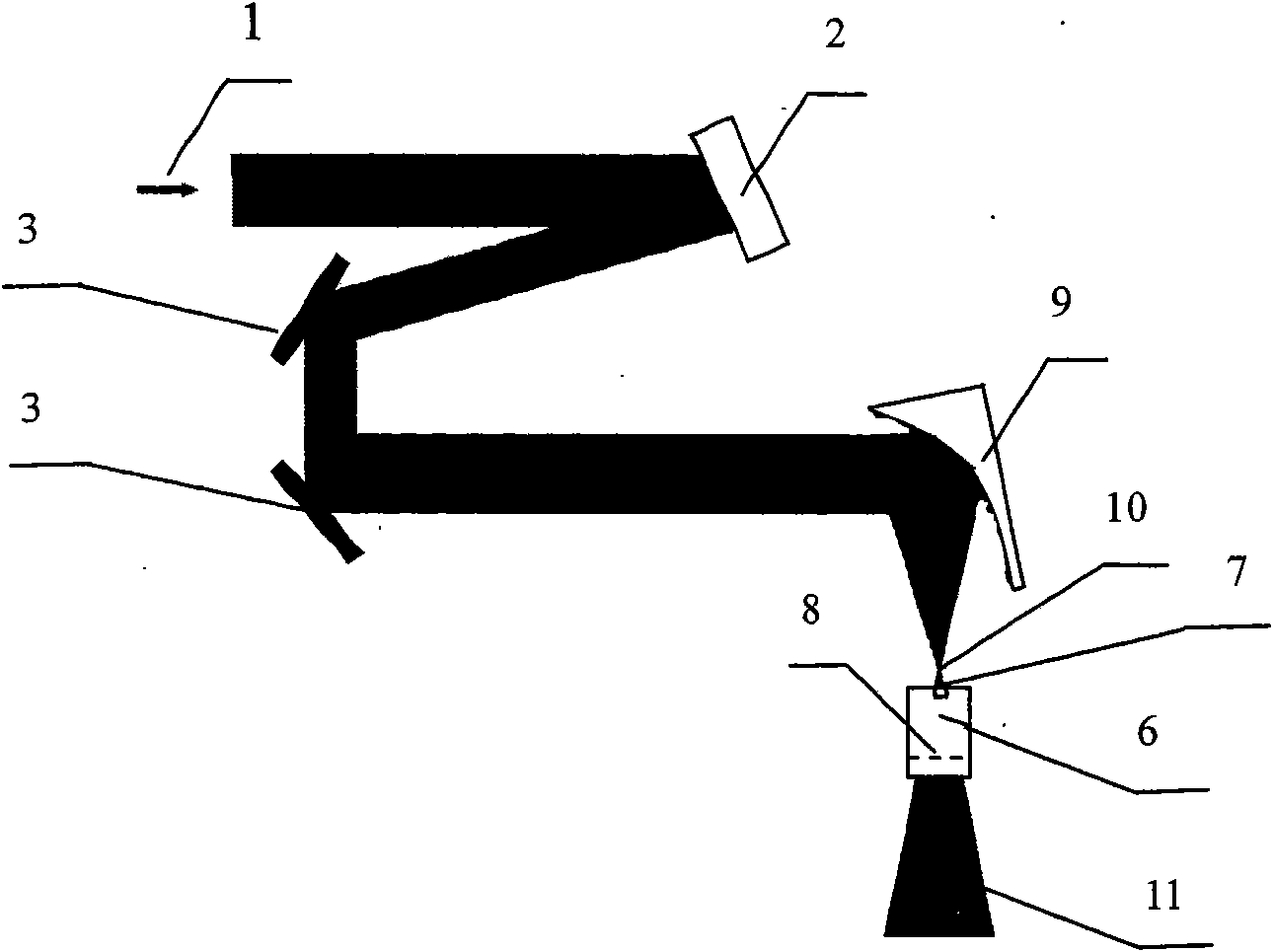
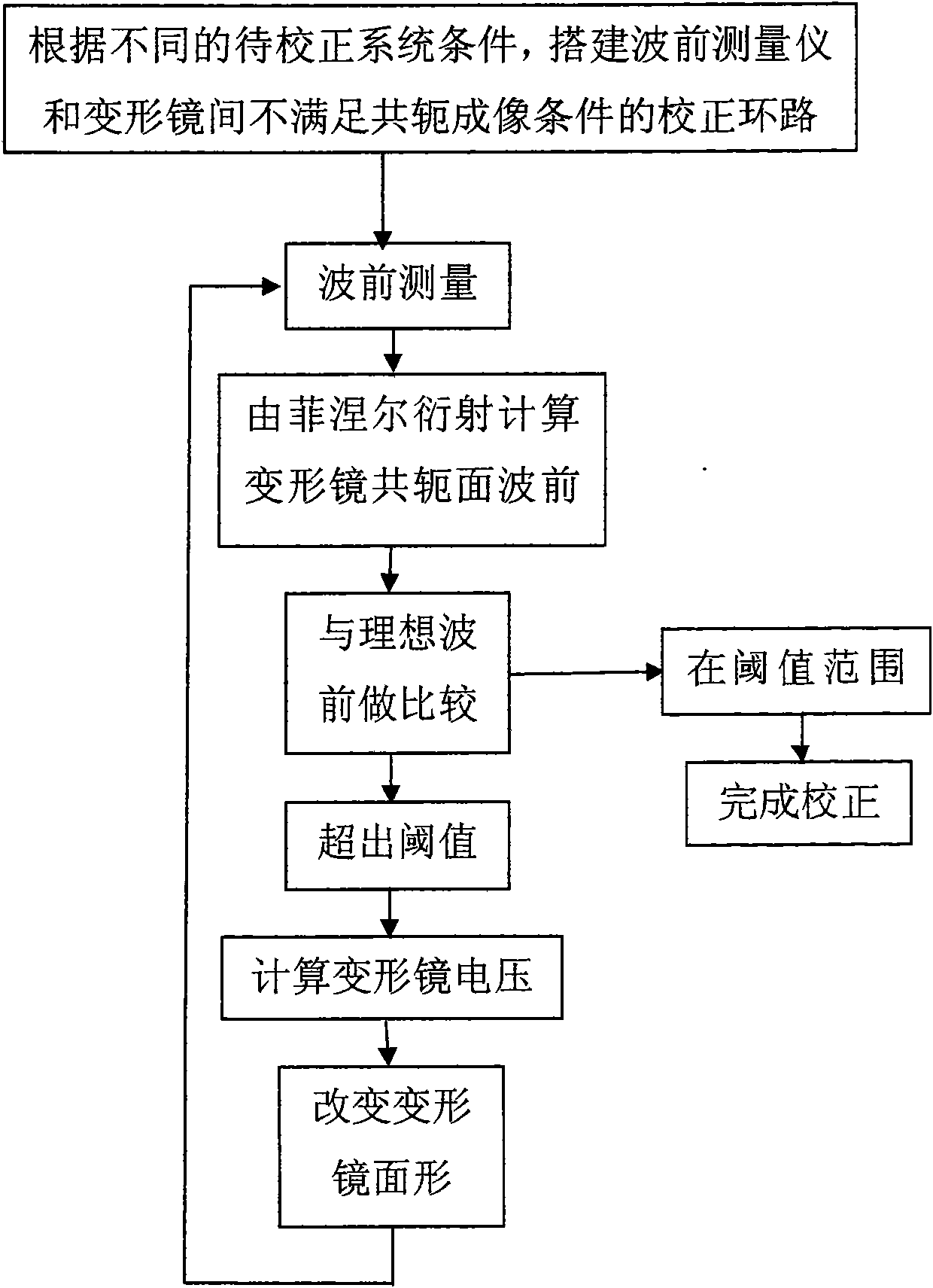
Method for calibrating wave front of self-adaptive optical loop
InactiveCN101571627AFlexible installationOvercoming the defects of caliber size restrictionOptical elementsOptical axisComputer programming
The invention relates to a method for calibrating the wave front of a self-adaptive optical loop. The method is to utilize the Fresnel diffraction theory and use computer programming to process wave front phase and amplitude distribution, which is measured in a certain position of an optical path, on a vertical optical axial plane, obtain phase and amplitude distribution of a conjugate plane of a distorting lens, take the computed value as a basis to change the surface shape of the distorting lens, and achieve the aim of wave front compensation. The method greatly increases the flexibility of the placing position of the distorting lens in the optical path, so that the complexity of the optical path can be effectively reduced and convenience is provided for wave front calibration comprising wave front pre-calibration. Therefore, the method has important practical value.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Diffractive non-contact laser gauge
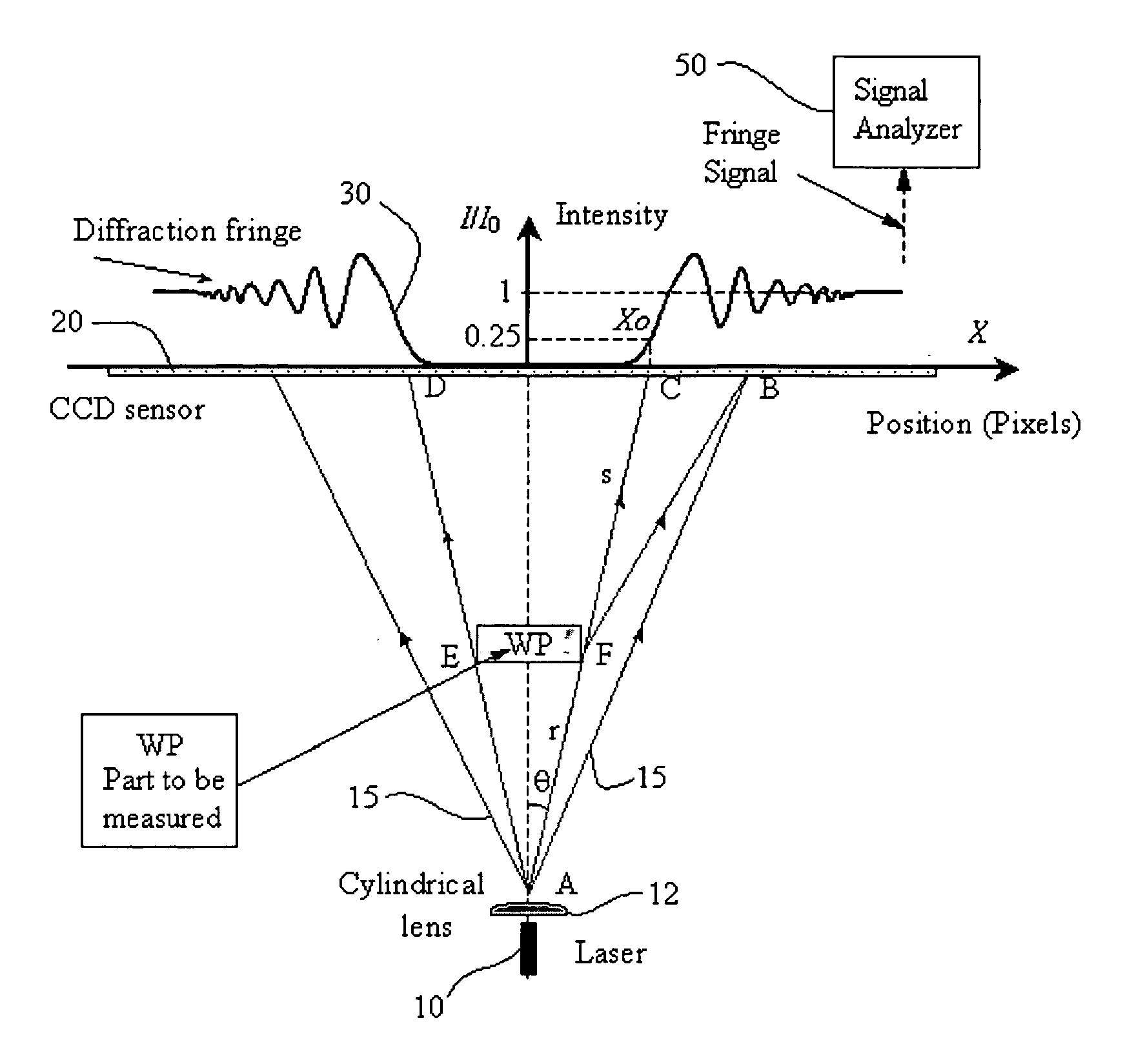
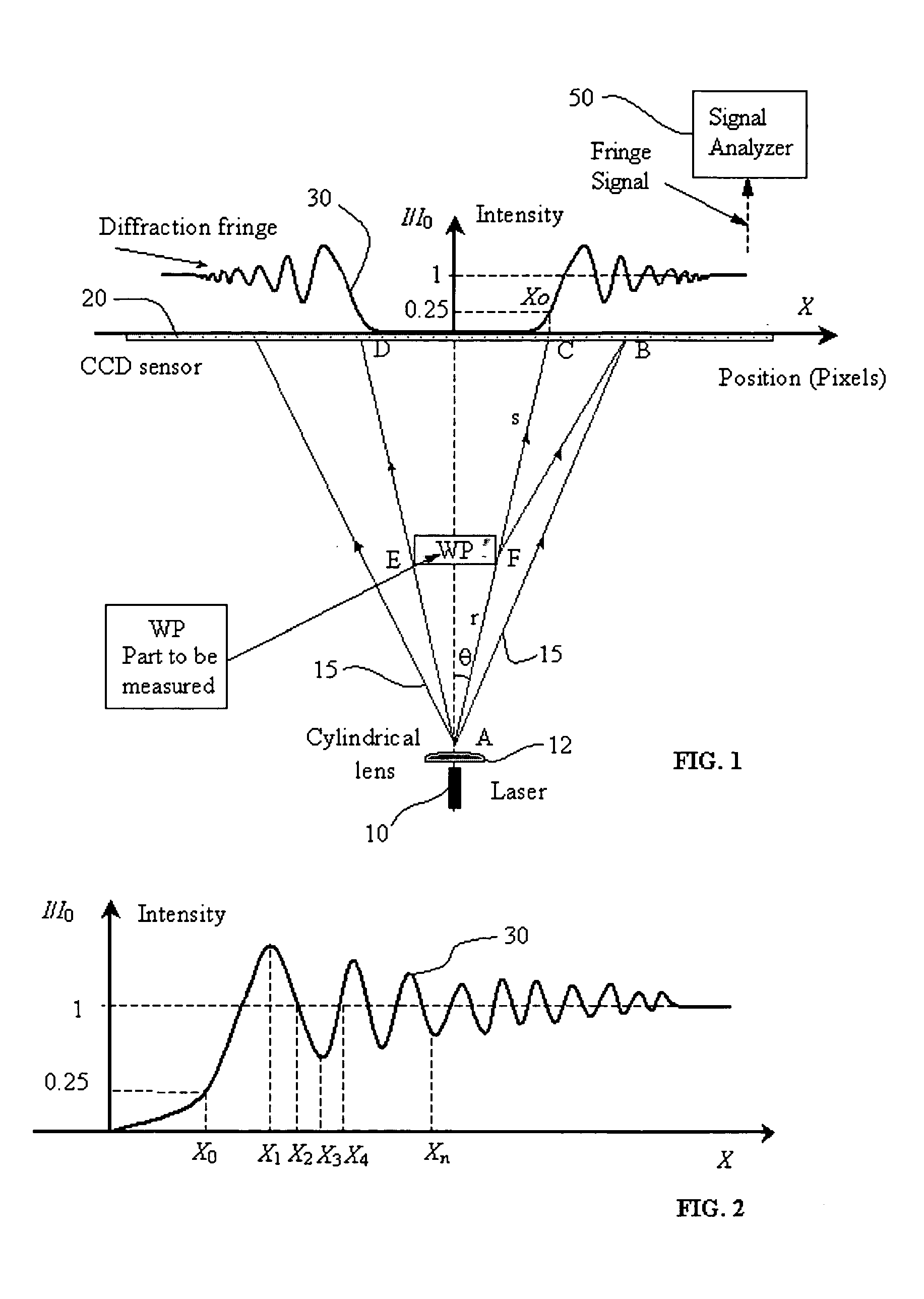
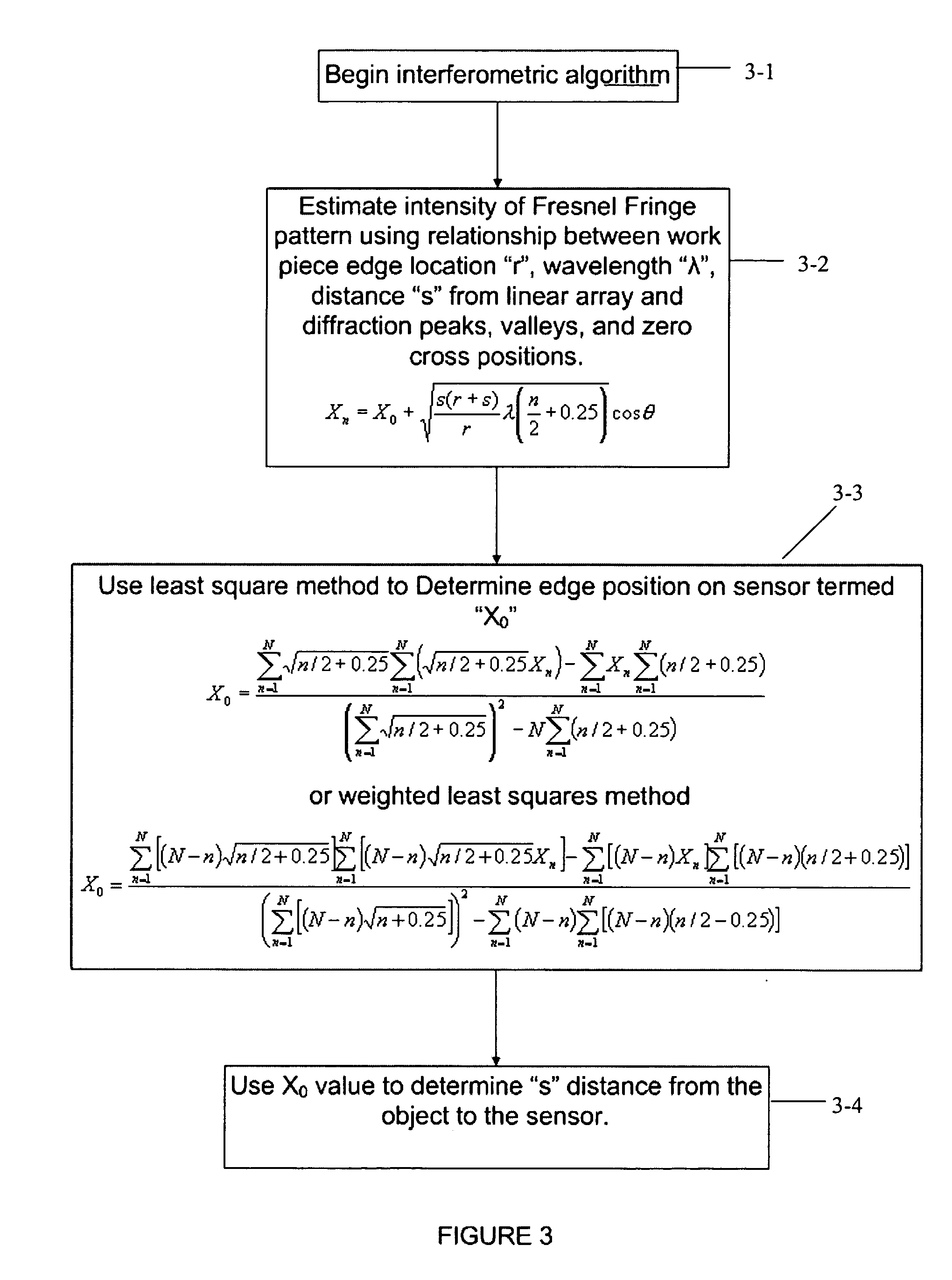
A non-contact gauge and method of use is provided for optical measurement of an object or objects. The apparatus and methods may comprise a laser providing a projected laser beam; a work-piece holder for holding the object to be measured; a light sensitive sensor located to sense the beam as the beam is diffracted by at least one edge of the object and as the beam forms a near field Fresnel diffraction fringe pattern upon elements of the sensor. The laser and the sensor are located to enable near-field Fresnel diffraction. A fringe pattern signal analyzer may be included for computing mathematical algorithms to determine the position (X0) of at least one edge of the object based upon the diffraction pattern sensed by the sensor wherein the fringe pattern signal analyzer is structured to refine sensed fringe pattern edge position data to be more accurate based upon a theoretical diffraction compensation factor.
Owner:PRATT & WHITNEY MEASUREMENT SYST
Non-lens color holographic projection method
ActiveCN107065492ADisplay frame rate speed increaseOvercoming qualityHolographic light sources/light beam propertiesColor imageSpatial light modulator
The invention discloses a non-lens color holographic projection method. The non-lens color holographic projection method comprises the steps of sequentially arranging a spatial light modulator, a diaphragm and a projection screen, and arranging a red-green-blue three-color laser at the other side of the spatial light modulator, wherein the spatial light modulator is connected with a computer; determining the distance to the diaphragm from the spatial light modulator according to the distance to the spatial light modulator from the projection screen; decomposing a color image to three primary color component images, respectively calculating Fresnel diffraction to a holographic surface from the component images to obtain three complex amplitude holograms; combining the three complex amplitude holograms into a phase type hologram by wavelength multiplex coding; and loading the obtained phase type hologram into the spatial light modulator, irradiating the spatial light modulator by the three-color laser at different angles, reconstructing an image on the projection screen after a light wave passes through the diaphragm, and combining a final color image after the images are laminated. By the non-lens color holographic projection method, the projection display frame rate of the color image is improved, and high-resolution and large-size dynamic non-lens color holographic projection is achieved.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Optical spectrum imaging device based on fresnel diffraction microlens array
InactiveCN101458209AReal-time monitoring capabilityExcellent anti-vibration performancePhase-affecting property measurementsColor/spectral properties measurementsAdditive ingredientDetector array
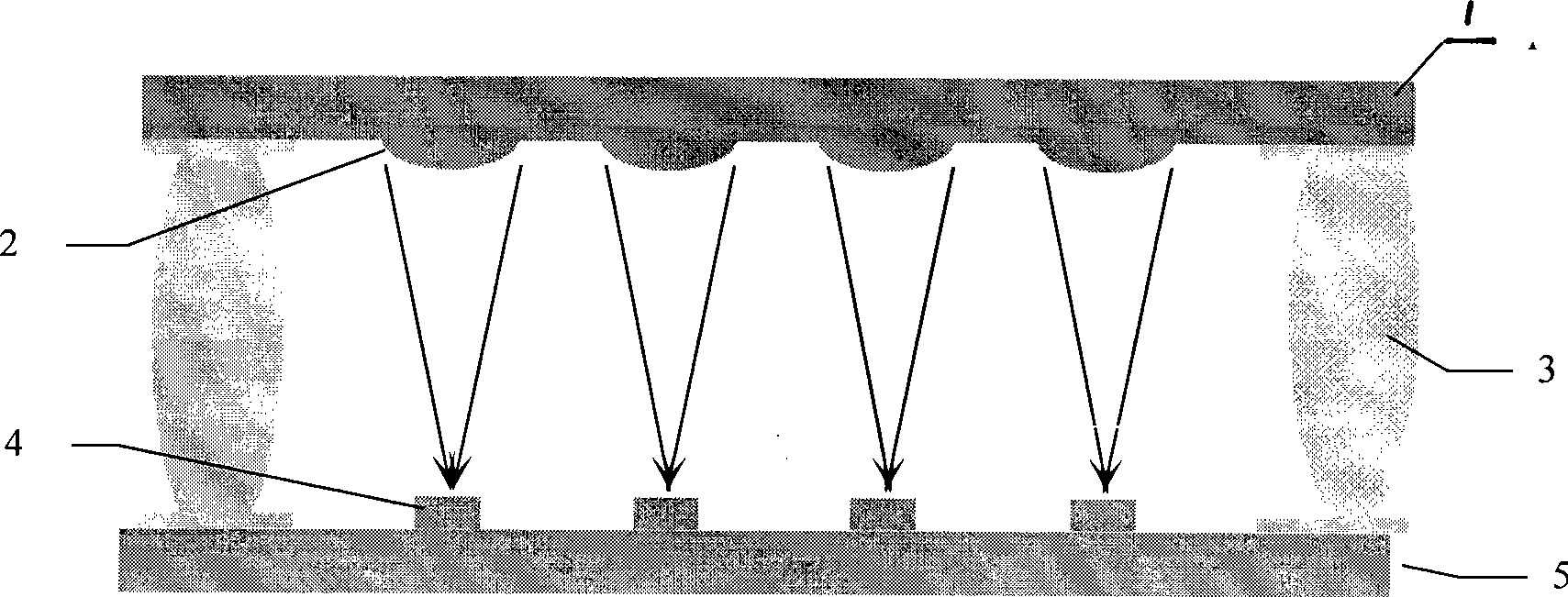
The invention discloses a spectral imaging device based on a Fresnel diffraction microlens array. The device comprises a hermetical optical channel composed of a microlens substrate, a detector substrate and a support side block, wherein, the microlens substrate and the detector substrate are respectively arranged from the top down and in parallel; the lower surface of the microlens substrate is provided with the processed microlens array composed of N Fresnel diffraction microlens, and the upper surface of the detector substrate is provided with a detector array composed of N detectors, the detector array corresponds to the microlens array; focal points of the N Fresnel diffraction microlens on the microlens array are respectively superposed with photosurfaces of the N detectors on the detector array on a one-to-one basis; each microlens is provided with the same converging focal length f0 and level number L, but different convergence center wavelengths lambda0 correspond to absorption wavelengths of N detection ingredients respectively, and at that time, a radius rm of each endless belt of an FZP needs to satisfy formula (1), wherein, m equals 1, 2, ..., M; the focal length f0 and the resolution delta lambda satisfy formula (2), and the microlenses take a converging action on the light with the wavelengths in a range of the lambda0 plus / minus delta lambda. The device adopts a multichannel array manner, simultaneously obtains a plurality of absorption spectra of a plurality of gas or substance ingredients, and has the advantages of small size, light weight, easy batch production, low cost and the like.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Interferometer
ActiveUS7538323B2Increase rangeIndependent controlMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesOptical axisPrism
The present invention provides a technique enabling to control fringe spacing s and an interference width W independently of each other, which are important parameters for an interferometer using an electron biprism.In the present invention, two electron biprisms 9u, 9b are used in two stages along the optical axis, and fringe spacing s and an interference width W are controlled independently of each other by controlling a voltage applied to an electrode of each of the electron biprisms. Also Fresnel diffraction can be suppressed.
Owner:RIKEN
Method for eliminating axial distance error between object and CCD through self-focusing iterative algorithm
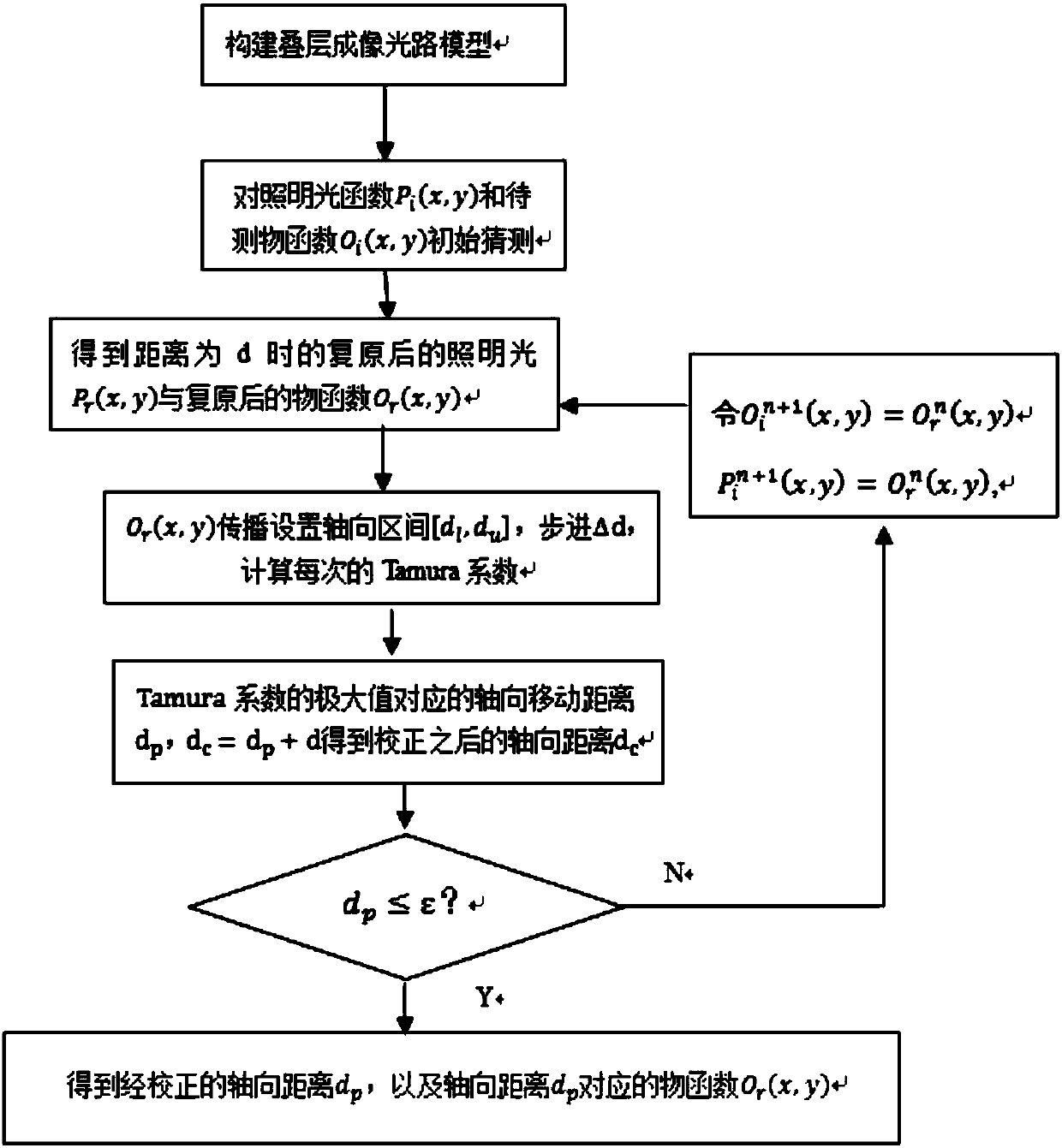
ActiveCN107655405AHigh-resolutionRealize automatic correctionUsing optical meansOptical testingAxial distance
The invention discloses a method for eliminating axial distance error between an object and a CCD through a self-focusing iterative algorithm. The method comprises the following steps: establishing anaxial distance error model through a Fresnel diffraction theory, and calculating axial distance through measurement of resolution of amplitude of a restored object, that is, in the laminated imagingprocess, transmitting reconstructed images to axial-distance-different planes through Fresnel diffraction integral and calculating a Tamura coefficient at each plane, the Tamura coefficients being resolution evaluation indexes, and when the Tamura coefficient reaches a maximum value, the generated restored image being clearest; and serving the axial distance corresponding to the place as a new axial distance for the next iteration, and repeating the process until the axial distance converges, and thus accurate axial distance is obtained. The method is good in correction effect for the axial distance errors in the laminated imaging process, is fast in operation speed and is high in image restoration resolution; and the method can be applied to the field of biological microscopy and opticaltest and the like.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Variable focal length lens comprising micromirrors with one degree of freedom translation
ActiveUS20050275928A1Simple mechanical structureSimple actuating componentNon-linear opticsLensDegrees of freedomMicromirror array
Owner:STEREO DISPLAY
Optical acceleration sensor based on Fresnel diffraction micr-lens
InactiveCN1743850AHigh sensitivityGood anti-electromagnetic interferenceAcceleration measurement using interia forcesNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsControl systemFixed frame
This invention discloses optical acceleration sensor based on Fresnel diffraction lens, which contains optical fiber, glass substrate, Fresnel diffraction micro lens, micro reflection film, micro quality block, micro balance spring and casing, wherein the micro reflection film parallel set with Fresnel diffraction micro lens with miniature gap, whose opposite side coated with metal reflection film, another side worked out an acceleration sensitive micro quality block, micro reflection film connected with fixed frame by four plane micro spring, optical fiber fixed the focus point of Fresnel diffraction micro lens for transmitting light, the external acceleration makes micro quality block driving micro reflection film to generate displacement, to change the light strength of focus of Fresnel diffraction micro lens, the acceleration can be tested by testing the change of light strength in optical fiber. Said invention can be used in aircraft control system and other fields demanding high precision sensing and high anti electromagnetic interference.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Fast generating method for computation hologram of 3D model
InactiveCN101458822ASmall amount of calculationCalculation speedHolographic object characteristics3D-image renderingOptical fieldComputer science
The invention discloses a computer generated hologram fast generation method for 3D models, comprising: translating and rotating a triangular patch in world coordinate system to standard position, and synchronously doing same transformation on the computer generated hologram, to hold the relative position between the triangular patches in the computer generated hologram and the object face, after the coordinate transformation of the triangular path; deriving Fresnel diffraction integral equation to obtain the relationship between the optical field at one point and the optical field at the top point of the triangular patch in the computer generated hologram; adding the coordinate and optical field of the top point of the special triangular patch into the equation to obtain the optical field at each sampling point on the computer generated hologram. The computer generated hologram fast generation method can significantly reduce calculation amount, avoid sampling error on object face and generate computer generated holograms of various resolutions.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Method for carrying out image-text hiding according to encrypted and converted phase position
InactiveCN101770589AEasy alignmentRandomnessRecord carriers used with machinesComputer hardwareOptical diffraction
The invention discloses a method for carrying out image-text hiding according to an encrypted and converted phase position. The method includes the following steps: a Fresnel diffraction converting method is adopted to carry out encryption and conversion on an image-text to be hidden, so as to obtain a black-and-white stripe pattern namely a phase information pattern which is composed by the encrypted and converted phase position; on the basis of the phase information pattern, the image-text to be hidden is respectively hidden in an encoding card and a decoding card; when the encoding card and the decoding card are overlapped and aligned with each other, the hidden image-text can reappear. As the pattern of image-text information hidden in the cards is stripe-shaped, the overlapping and aligning operations of the encoding card and the decoding card can be easily realized when in reappearing; moreover, as different image-texts have different stripe shapes, the counterfeiting difficulty is enhanced and the anti-counterfeiting strength is enhanced as well. As the image-text information hidden on the decoding card or the encoding card presents the form of grating stripes of the phase information pattern, the effect of optical diffraction is achieved and the image-text hidden on the decoding card and the encoding card can reappear by laser. Anti-counterfeiting logos manufactured by the method for the two cards cannot be easily counterfeited, and the anti-counterfeiting strength is greatly enhanced.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
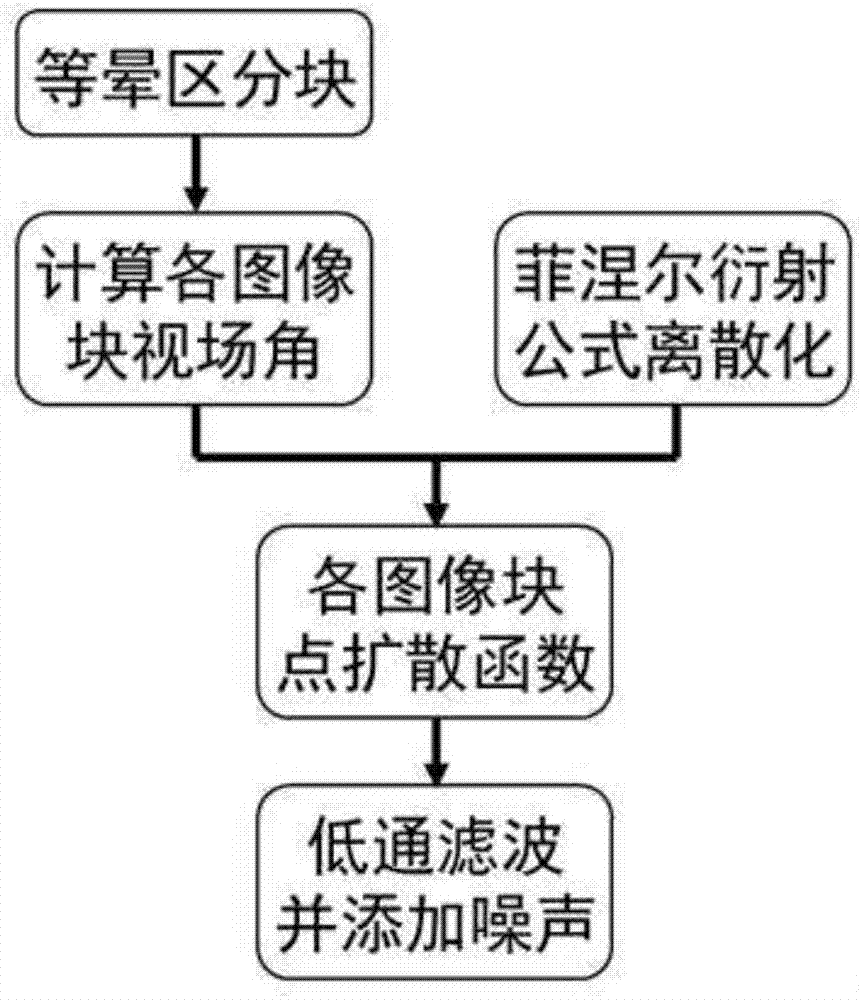
Imaging quality simulation method of Fresnel diffraction optical system
ActiveCN107016210ALow MTFReduce contrastDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsDiffusion functionImaging quality
The invention belongs to the technical field of optical imaging simulation, and relates to an imaging quality simulation method of a Fresnel diffraction optical system. The method includes the following steps that 1, based on the isoplanatic region block thought, an original image is divided into multiple image blocks with the similar same point diffusion function; 2, the meridian plane position of the center of each image block and the corresponding field angle are calculated; 3, a discretized Fresnel diffraction formula is constructed, and the point spread function of each image block is calculated; 4, MTF in different regions of the image are used for conducting lowpass filtering on all the image blocks, and random noise is added. The imaging quality simulation method is suitable for imaging quality simulation of an optical system with a diffraction lens as the main lens, capable of generating images with diffraction optical imaging characteristics including low MTF, low contrast, low SNR and large-size PSF spatial variability in a simulation mode, and provides support for optimal design of the Fresnel diffraction imaging system and image processing algorithm research and verification.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Mask shaping using temporal and spatial coherence in ultra high resolution lithography
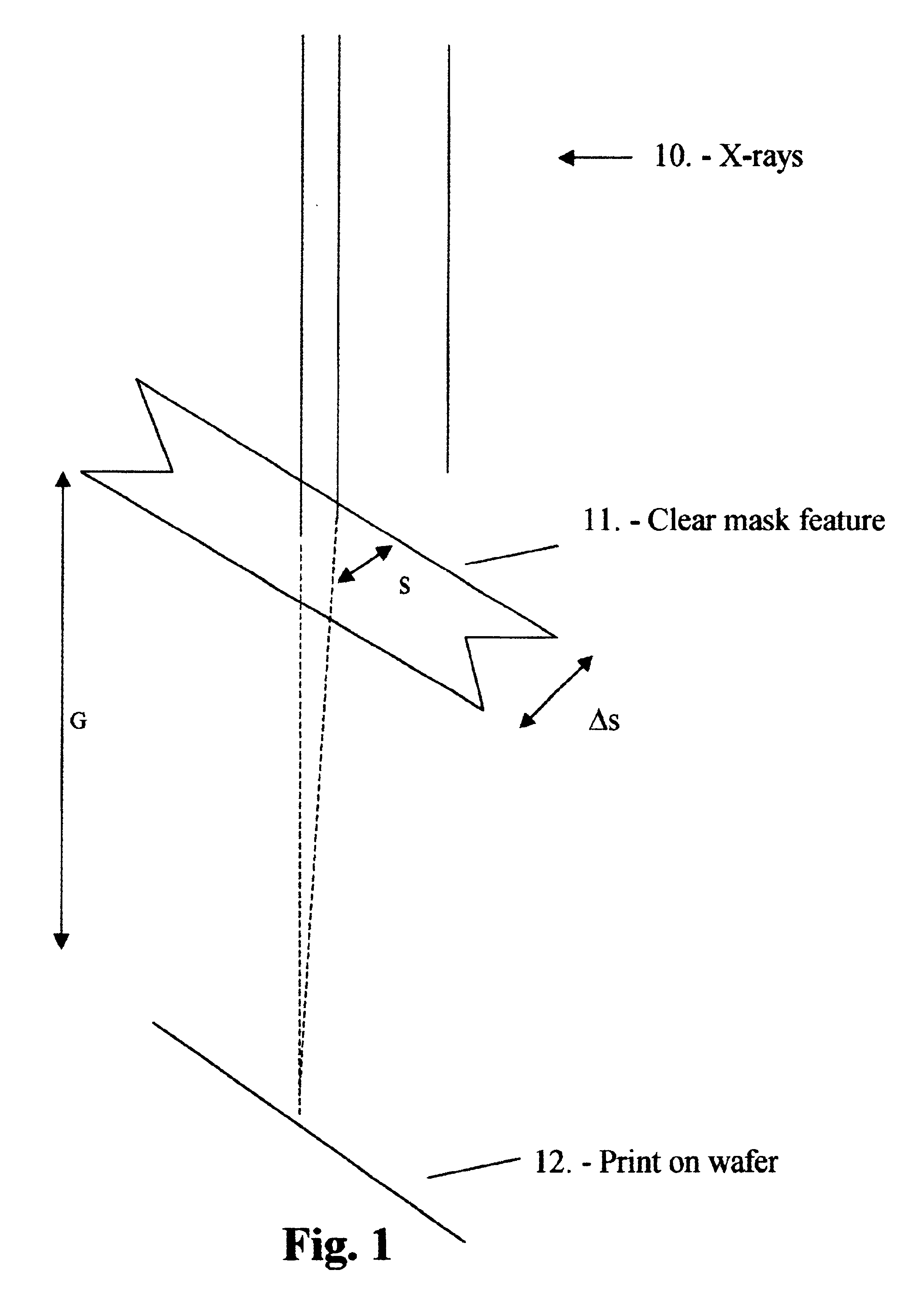
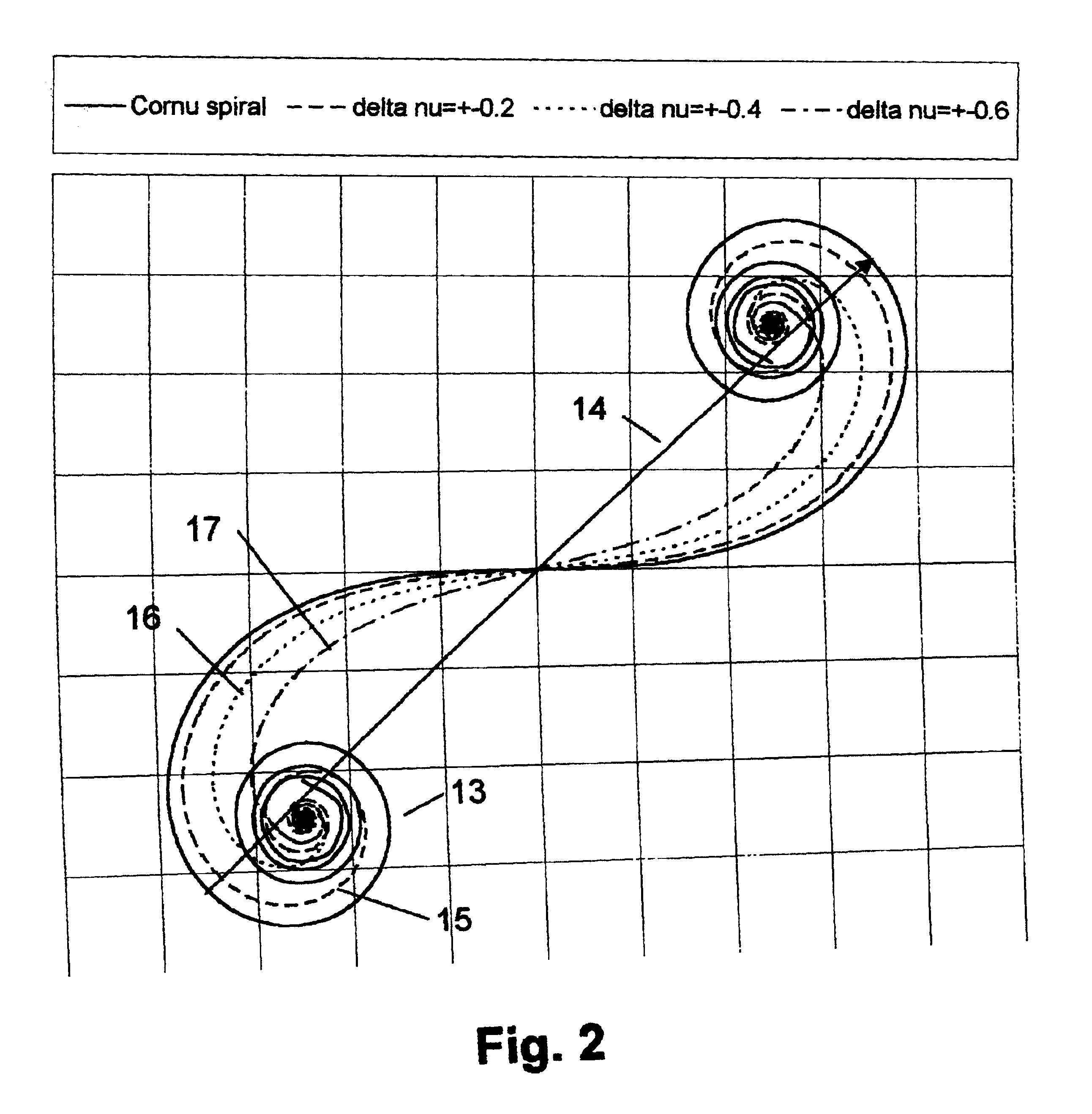
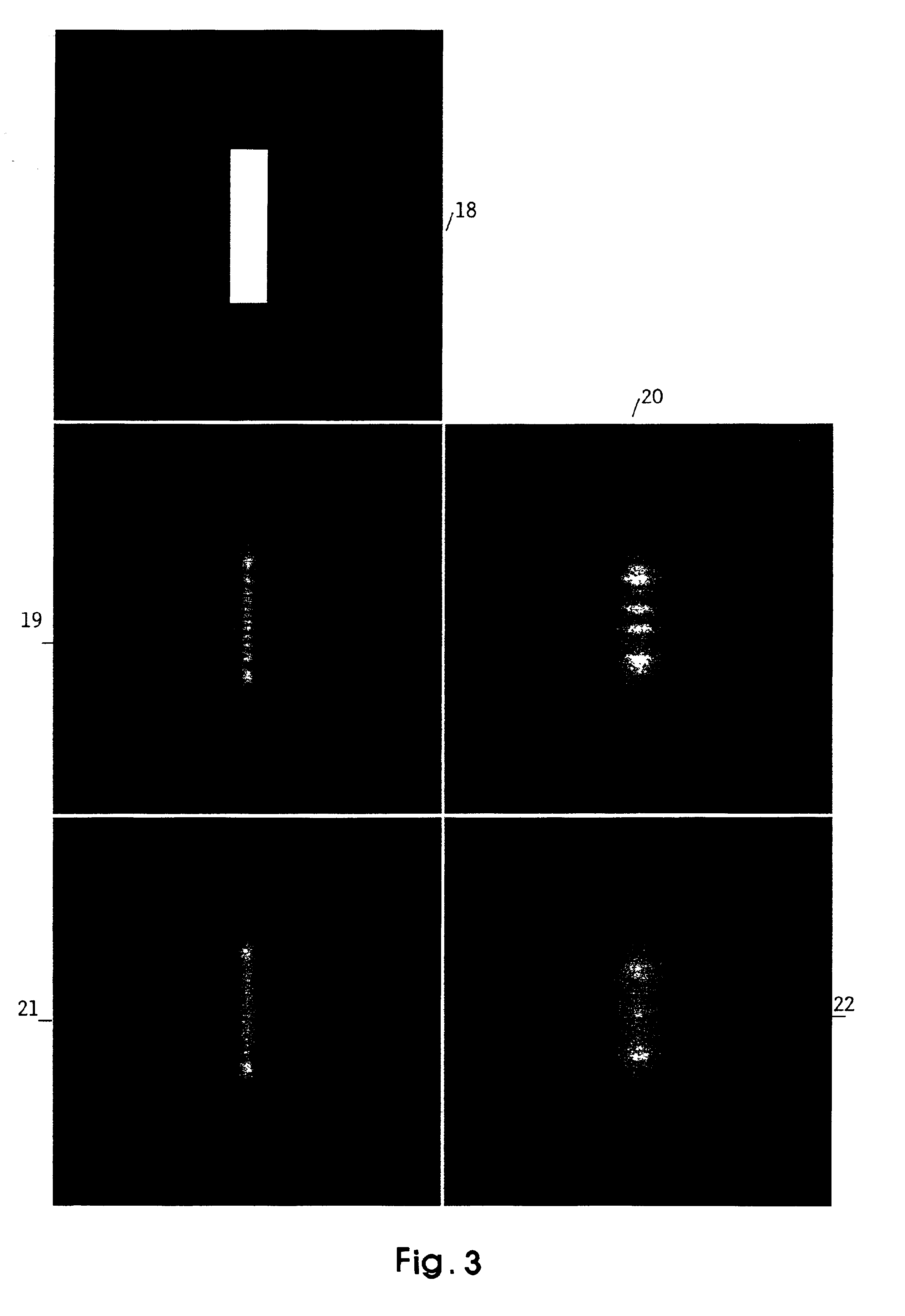
InactiveUS6953643B2Reduce the amplitudeAdjustable intensityElectric discharge tubesRadiation applicationsBright spotBand width
Mask Shaping using temporal and spatial Coherence for Ultra High Resolution Lithographic imaging and printing refers to methods and apparatus that can be adopted to print near-ideal images of basic shapes when the shapes are asymmetrical. Ultra High Resolution Lithography refers to proximity printing of clear mask fetures when they are demagnified by bias. In this lithography, optical components, including lenses and mirrors, are not used between the mask and wafer. When a clear mask feature is asymmetric and the mask-wafer gap is set so that the Critical Condition is maintained for the shortest print dimension, then undesirable features typically appear in other longer dimensions consistent with Fresnel diffraction. The undesirable featurs impede illumination uniformity for controlled printing in exposed areas. Such features, including Bright Spots and Ripple, are counteracted by the Mask Shaping that is designed to optimize printing with temporal and spatial coherence near the Critical Condition. Even with broad band illumination, ultra high resolution is not lost. On the contrary, with Mask Shaping near the Critical Condition, the undesirable features occurring parallel to the longer dimensions, are normally reduced or eliminated. Near-ideal shapes can be printed. With Mask Shaping for temporal and spatial coherence, production parameters, including resolution, exposure time, and illumination band width can be enhanced, traded, and optimized.
Owner:BOURDILLON ANTONY J
Laser scanning side lobe suppression device of phased array
InactiveCN102866394AImprove machining accuracyEasy to implementWave based measurement systemsImaging conditionLaser array
The invention discloses a laser scanning side lobe suppression device of a phased array. The suppression device comprises a master oscillation laser and a phase compensation plate, a beam expanding collimator and an optical phased array scanner are arranged between the master oscillation laser and the phase compensation plate in sequence, and the optical phased array scanner is also connected with a controller; the distance between the output end of the optical phased array scanner and the phase compensation plate can meet the self-imaging conditions of fractional Talbot effect; and the phase of the phase compensation plate corresponds to the phase of the Fresnel diffraction propagated from an optical field of a laser array to an optical field in the fractional Talbot distance. The laser scanning side lobesuppression device of the phased array disclosed by the invention is used for outputting non-mechanical scanning beams with high beam quality in a phased array laser radar transmission system, has the advantages of simple structure, stable and reliable performance, rapid high-resolution non-mechanical laser scanning and the like, is specially suitable for the fields such as laser scanning radars and laser communications, and has significant meaning for development of compact, light and high-quality laser scanning system.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Large-aperture optical element secondary exposure phase measuring device and measuring method
ActiveCN104634542AImplement phase measurementMeet the requirements of phase measurementTesting optical propertiesBeam expanderLight spot
The invention discloses a large-aperture optical element secondary exposure phase measuring device and measuring method. The method comprises the following steps: focusing coherent light emitted by a laser after the coherent light passes through a beam expander, forming scattered light spots by a random phase plate after the focused coherent light passes through a focal point, and recording first scattered light spots by a light spot detector; tightly attaching a large-aperture optical element to the front side of a focusing lens, recording second scattered light spots by the light spot detector, performing iterative computation by a computer through the recorded scattered light spots to obtain illuminating light field distribution on the random phase plate, calculating light field distribution on the surface of the focusing lens by using a Fresnel diffraction integral formula, solving light field distribution on the surface of the focusing lens by recovering diffracted light spots recorded by secondary exposure respectively, and solving phase difference, namely the phase difference of a large-aperture optical element to be measured. The large-aperture optical element secondary exposure phase measuring device is not limited to the size of the light spot detector, is low in environmental influence, is simple in structure, is high in measuring resolution, and meets the requirement on the phase measurement of the large-aperture optical element.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Apparatus of increasing coherent beam combination laser beam quality
The invention discloses an apparatus of increasing coherent beam combination laser beam quality. The apparatus comprises one set of diffractive telescopic system arrays, one focusing lens and one CCD. The diffractive telescopic system arrays are formed by one set of eye lens arrays and one set of objective lens arrays. Each eye lens and each objective lens form a diffractive telescopic system unit. A unit structure adopts a Galileo telescopic system. A composition lens adopts a multistage phase type Fresnel diffraction structure. The diffractive telescopic system arrays expand incident dispersed array light beams into tangent light beams. Then a focusing lens carries out focusing, far-field coherent beam combination is realized at a focal plane position and the CCD is used to detect energy distribution of beam combination laser. The apparatus possesses the advantages that processing is easy; installation and adjustment are convenient and so on. Simultaneously, the diffractive telescopic system arrays possess high expansibility. Different arrangements and coherent laser beam combination of multi-path high fill factors can be realized.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Manufacturing method of submicron photonic crystal phase array light beam splitter
InactiveCN103885190AImplement parallel transferAchieving processing powerNon-linear opticsOptical elementsDot matrixIndium
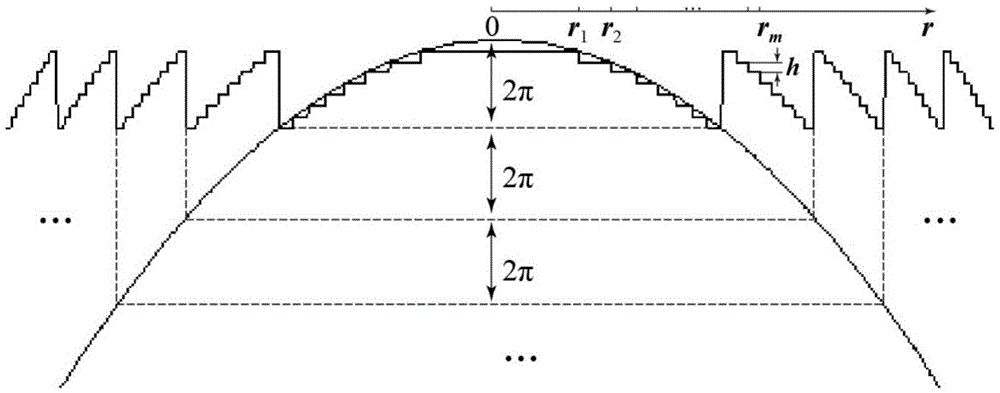
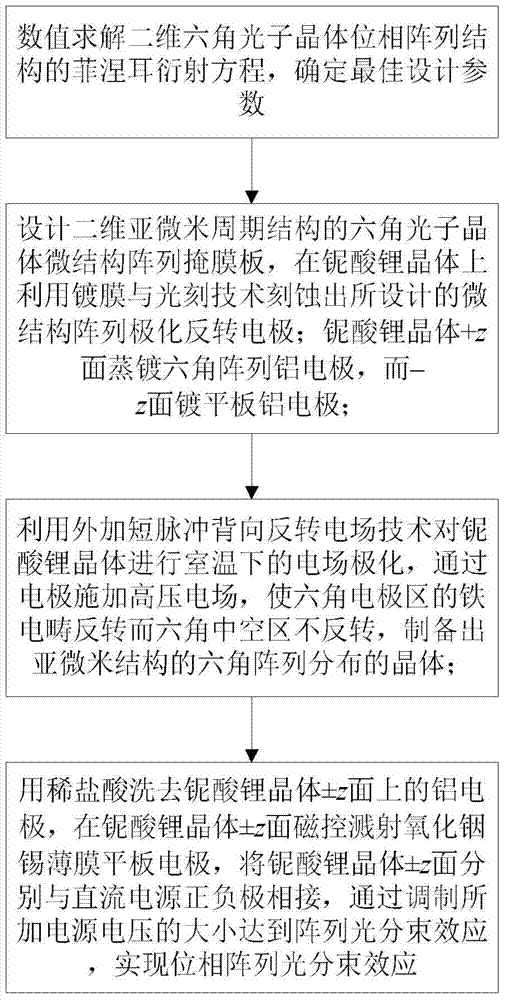
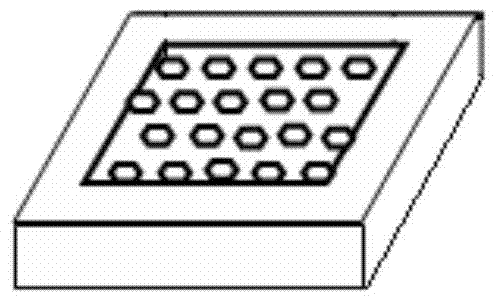
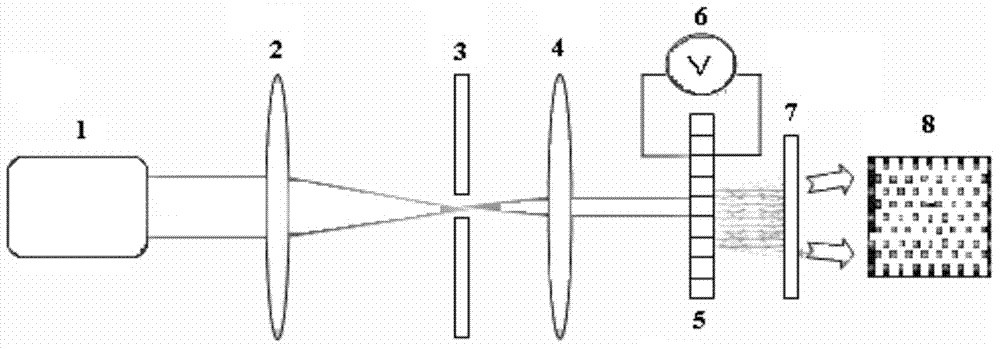
The invention belongs to the technical field of novel electronic devices and light information and relates to a manufacturing method of a submicron photonic crystal phase array light beam splitter. The method comprises the steps that (1) a Fresnel diffraction equation of a two-dimension hexagonal photonic crystal phase array structure is solved, and the optimum designing parameters are determined; (2) a hexagonal photonic crystal microstructural array mask plate of a two-dimension submicron periodic structure is designed, and a microstructural array polarization inversion electrode is etched on a lithium niobate crystal; (3) the lithium niobate crystal is subjected to electric field polarization, and a hexagonal array distribution crystal of a submicron structure is prepared; and (4) aluminum electrodes on the + / -z faces of the lithium niobate crystal are washed off, indium tin oxid thin film flat plate electrodes are subjected to magnetron sputtering on the + / -z faces, the + / -z faces of the lithium niobate crystal are connected to a positive electrode and a negative electrode of a direct-current power supply, the magnitude of voltages is adjusted, and the phase array light beam splitting effect is achieved. The designed light beam splitter has the advantages of being good in beam splitting evenness, large in light spot dot matrix number, high in diffraction efficiency and the like, and information parallel transmission and processing can be achieved.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
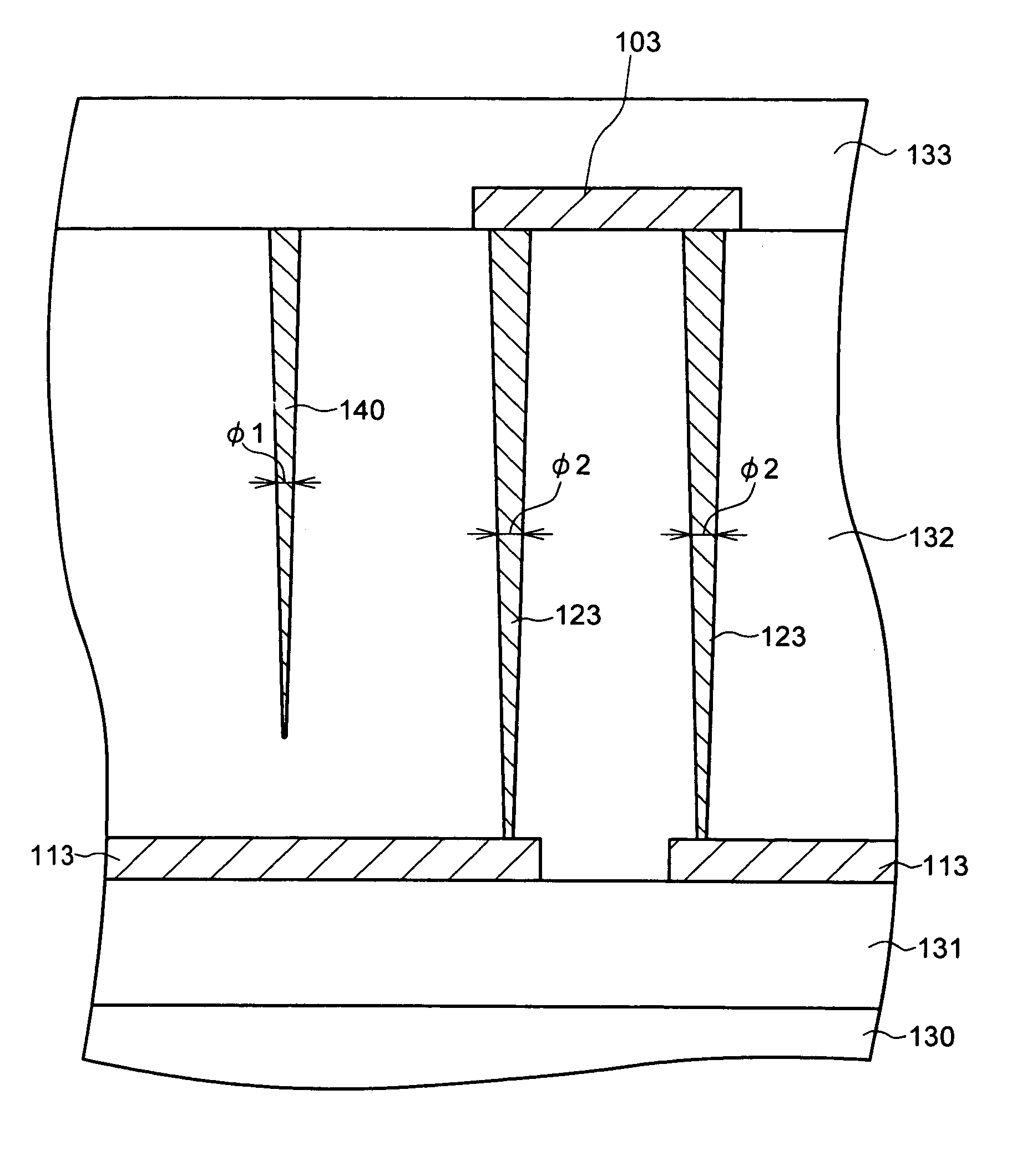
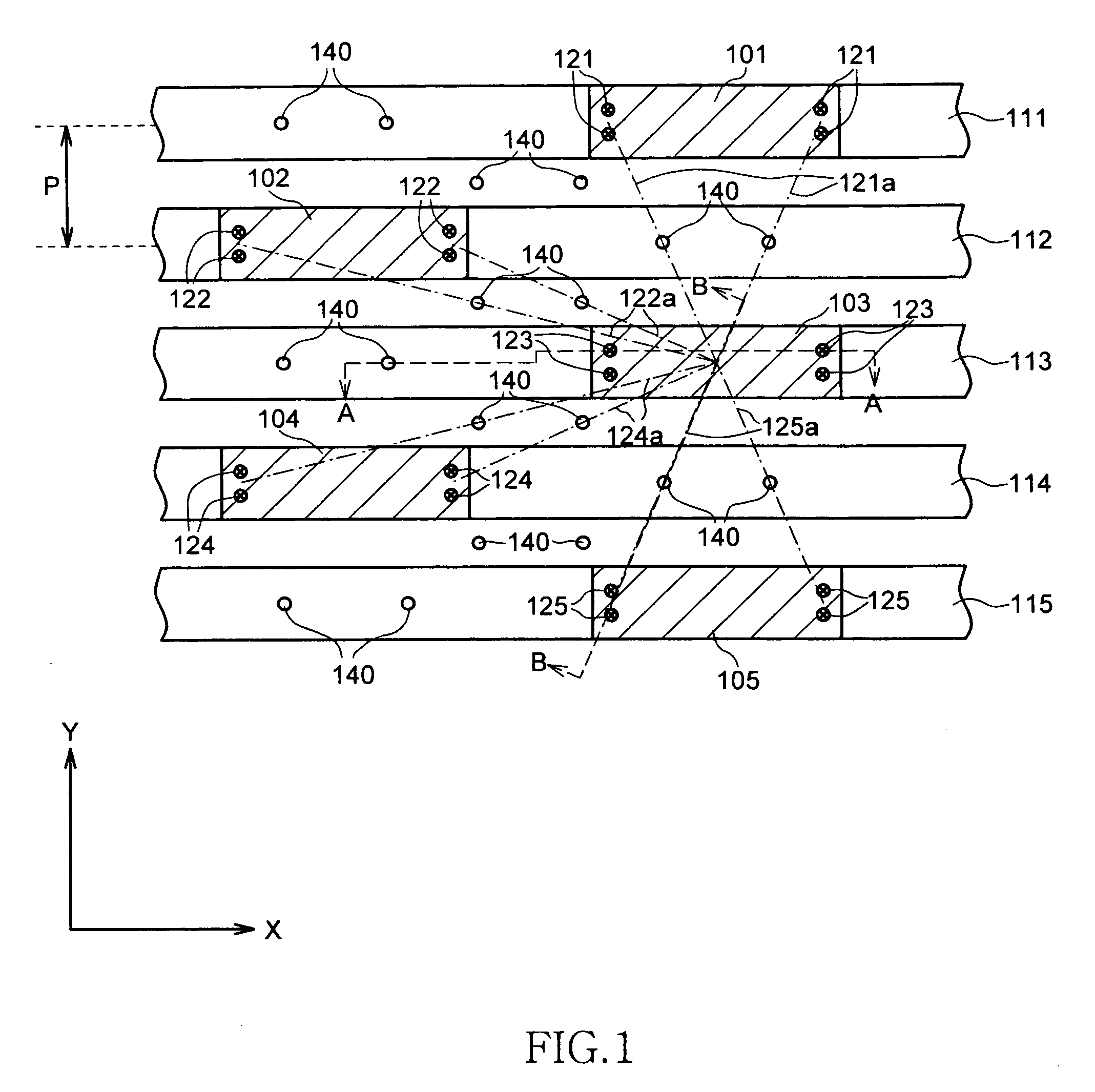
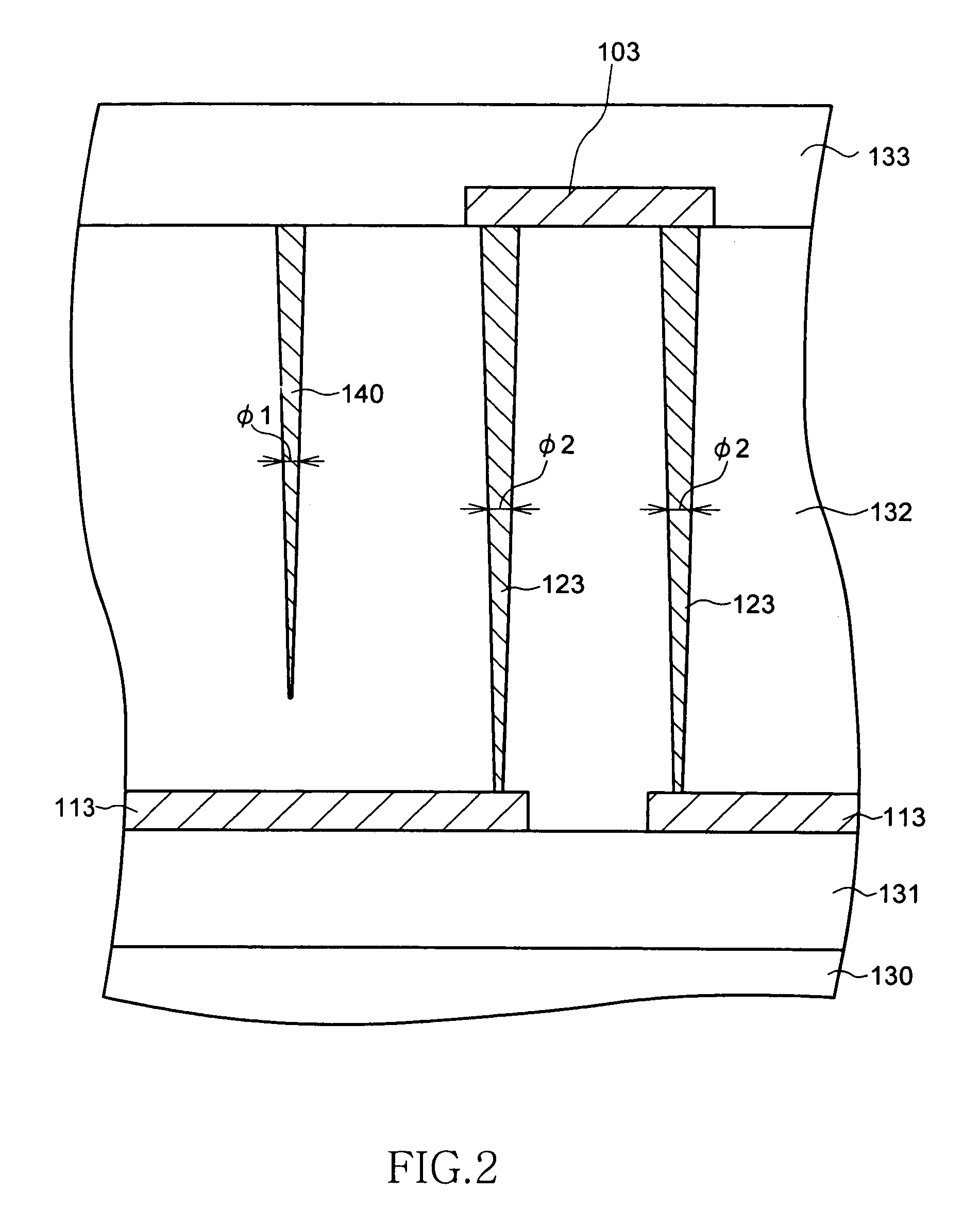
Semiconductor device and method of disconnecting fuse element
ActiveUS20080179708A1Reduce the impactReduce harmSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesUltrasound attenuationLight beam
A semiconductor device includes plural fuse elements which can be disconnected by irradiating a laser beam, and attenuation members which are located between the plural fuse elements as viewed two-dimensionally and can attenuate the laser beam. Each attenuation member includes plural columnar bodies. With this arrangement, the attenuation members including plural columnar units absorb the laser beam leaked out from a fuse element to be disconnected to a semiconductor substrate side. The laser beam is also scattered by Fresnel diffraction. Therefore, the columnar body can efficiently attenuate the laser beam, without generating a crack in the insulation film by absorbing excessive energy.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
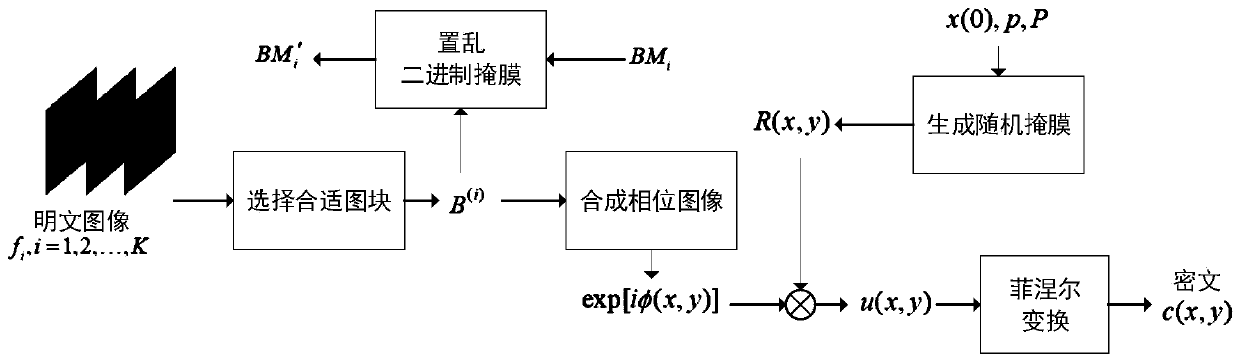
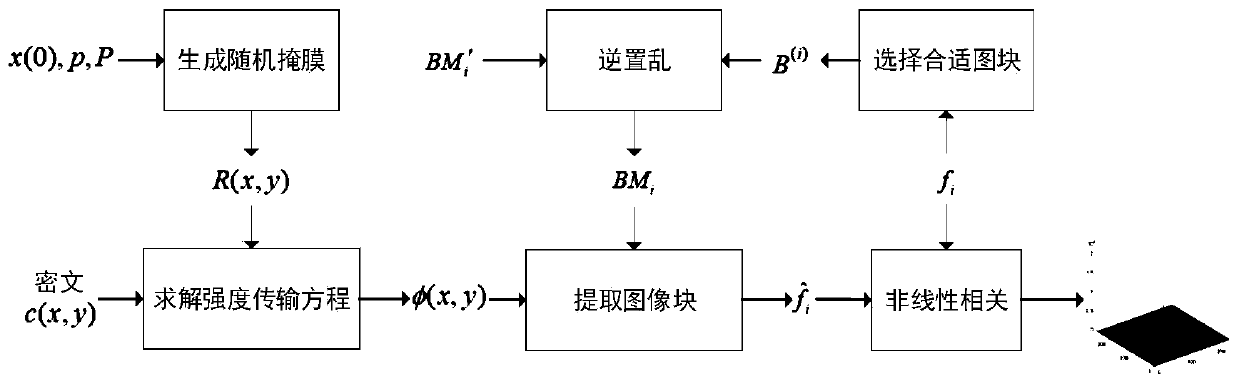
Multi-image encryption and authentication method based on intensity transmission equation and photon counting
InactiveCN110472424AImprove securityImprove robustnessDigital data protectionPlaintextLinear correlation
The invention provides a multi-image encryption and authentication method based on an intensity transmission equation and photon counting. The method comprises the steps of initially, evaluating spatial frequency coefficients; synthesizing a phase-coded plaintext using an important block selected from a plurality of plaintext images, the spatial frequency coefficient being combined with a random intensity mask generated using Logistic mapping to constitute a complex amplitude, and then encrypting the complex amplitude into a real-value ciphertext having a noise-like distribution by using Fresnel diffraction; in an authentication process, reconstructing phase information by solving an intensity transfer equation, and identifying the presence of a plaintext image by calculating, by means ofa corresponding binary mask, a non-linear correlation between it and its partial data containing only valid blocks extracted from the phase information. According to the multi-image encryption and authentication method based on the intensity transmission equation and photon counting. The safety of an optical authentication system is further enhanced.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF TECH
High-efficiency infrared micro Fresnel lens array manufacturing method based on MEMS technology
The invention belongs to the field of a sensor, and particularly to a high-efficiency infrared micro Fresnel lens manufacturing method based on MEMS technology. The high-efficiency infrared micro Fresnel lens manufacturing method based on the MEMS technology comprises the following steps of forming a diffraction image by means of a Fresnel diffraction principle, manufacturing a diffraction screen,manufacturing a receiving screen, performing exposure for forming a photoresist pattern, etching a Si circular plate, and performing cleaning. According to the method of the invention, through controlling a diffraction imaging distance, a traditional lithography machine is used for directly performing diffraction exposure on a wafer surface which requires forming of the Fresnel lens array, thereby forming a Fresnel waveband plate pattern; then micro machining is performed on the developed wafer through an MEMS process facility, and finally a Fresnel lens with a preset focal length is formed on the wafer surface. The high-efficiency infrared micro Fresnel lens manufacturing method has advantages of realizing simple, high-efficiency and easy-controlling integral process, greatly reducing process cost and production time consumed in various polishing steps of a traditional silicon lens, and improving imaging efficiency.
Owner:BESTAR HLDG +1
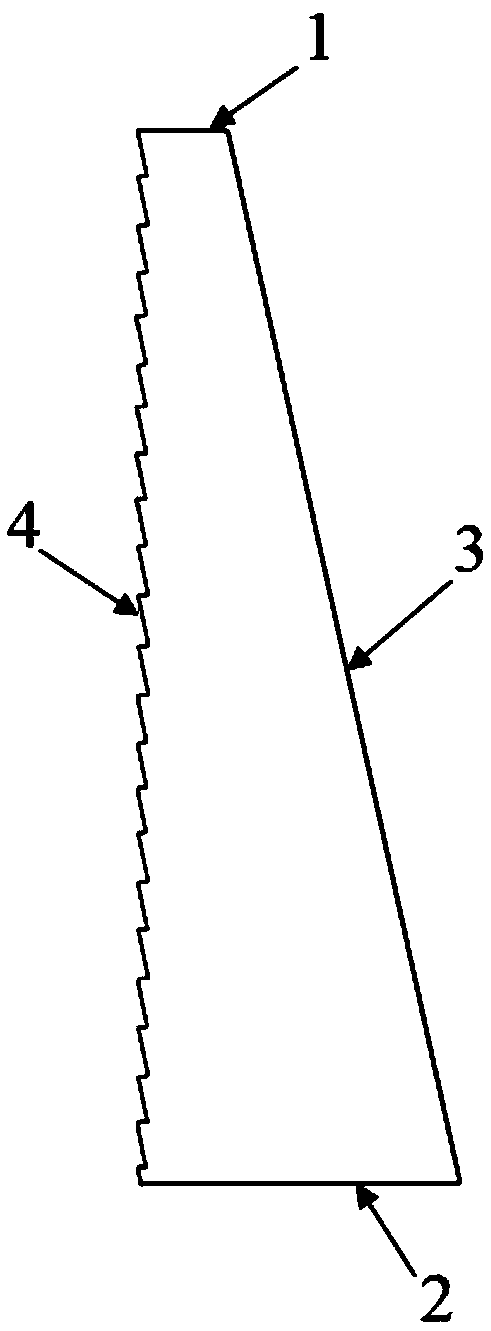
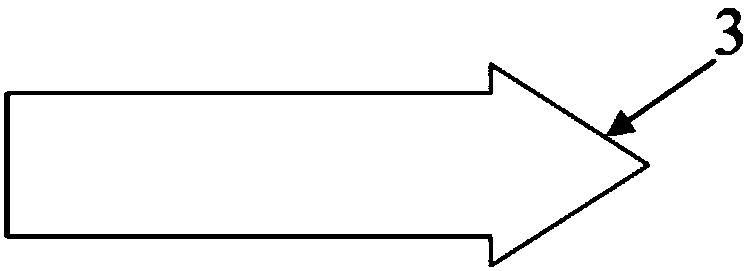
Trapezoidal wing
ActiveCN108100225AReduce specular reflectionReduce electromagnetic scattering energyWing shapesHysteresisLeading edge
The invention especially relates to a trapezoidal wing, belonging to the field of aircraft structure designing. According to the invention, a wedge shape is designed for the leading edge (3) of the trapezoidal wing, so specular reflection at the leading edge (3) of the trapezoidal wing is reduced, and a strong scattering source is changed into a weak scattering source; a sawtooth shape is designedfor the trailing edge (4) of the trapezoidal wing, so the azimuth angle, generating edge diffraction, of the trailing edge (4) of the trapezoidal wing is identical to the azimuth angle, generating specular reflection, of the leading edge (3) of the trapezoidal wing, the main energy of the radar echo of an aircraft is controlled to within few narrow orientations, which enables the number of RCS wave peaks to be reduced; and furthermore, a wave-absorbing structure is arranged between every two sawteeth at the trailing edge (4) of the wing, so various weak points and hysteresis loss of the electromagnetic energy of incident waves in wave-absorbing materials are converted into heat which is dissipated. The trapezoidal wing of the invention is improved in stealth performance in the two aspectsof appearance stealth and material stealth.
Owner:XIAN AIRCRAFT DESIGN INST OF AVIATION IND OF CHINA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com