Patents
Literature
55 results about "Kinoform" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A kinoform is a type of converging lens that is able to efficiently focus x-ray radiation. They can be used to study nanomaterials. Diamond is often used in kinoform lenses as it has a high thermal conductivity. They are also used in holography.
Efficient wave propagation for terahertz imaging and sensing
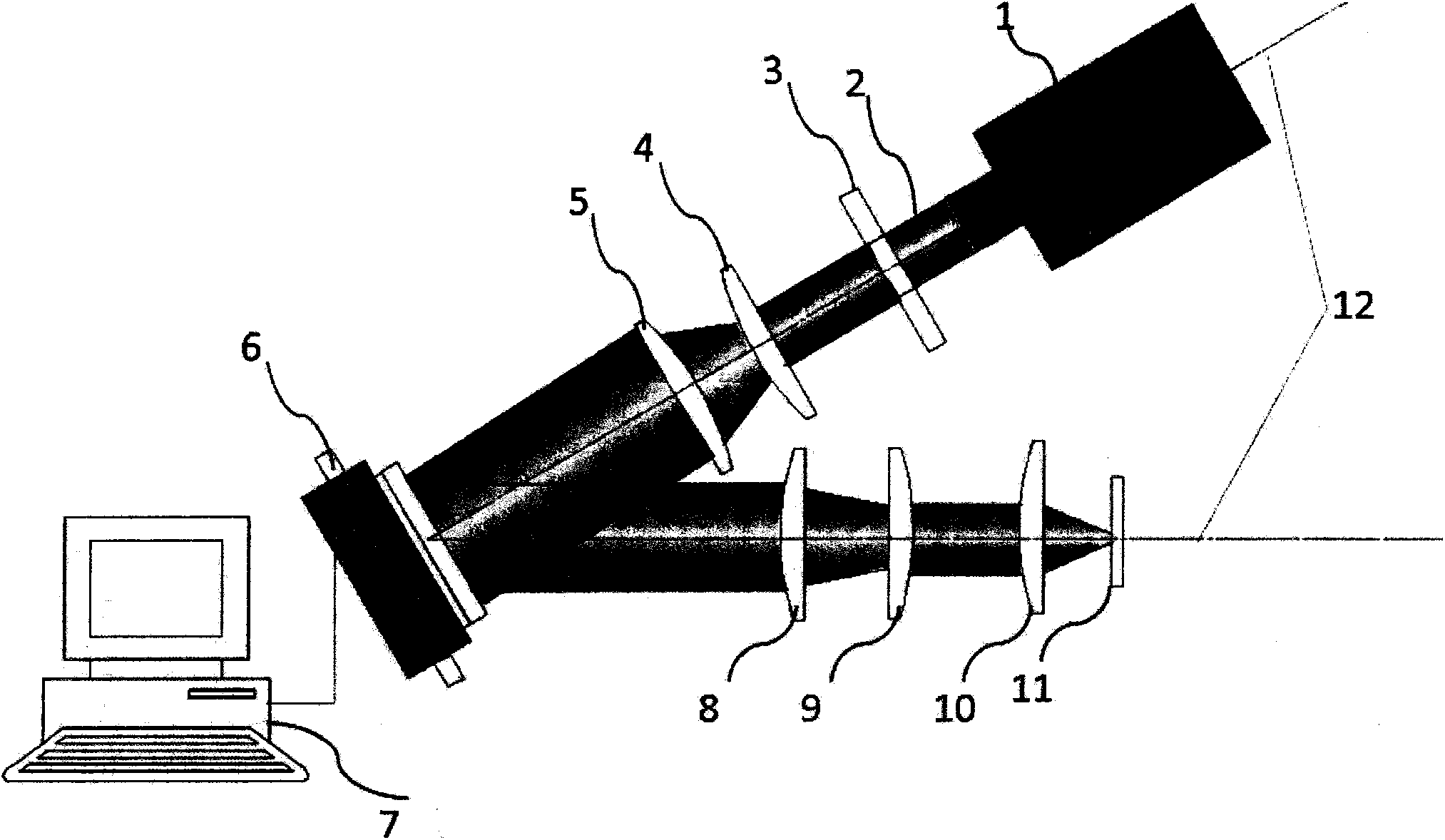
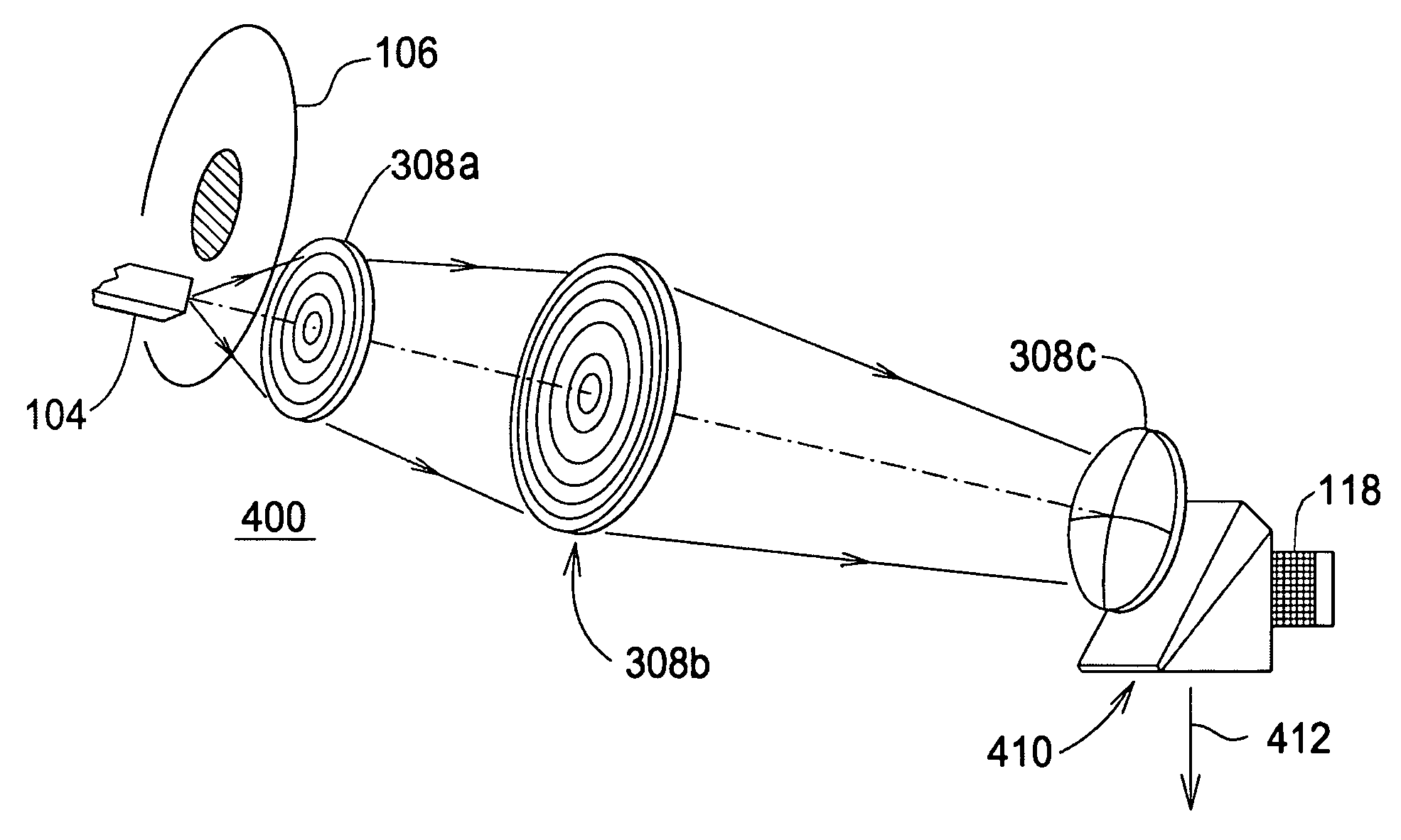
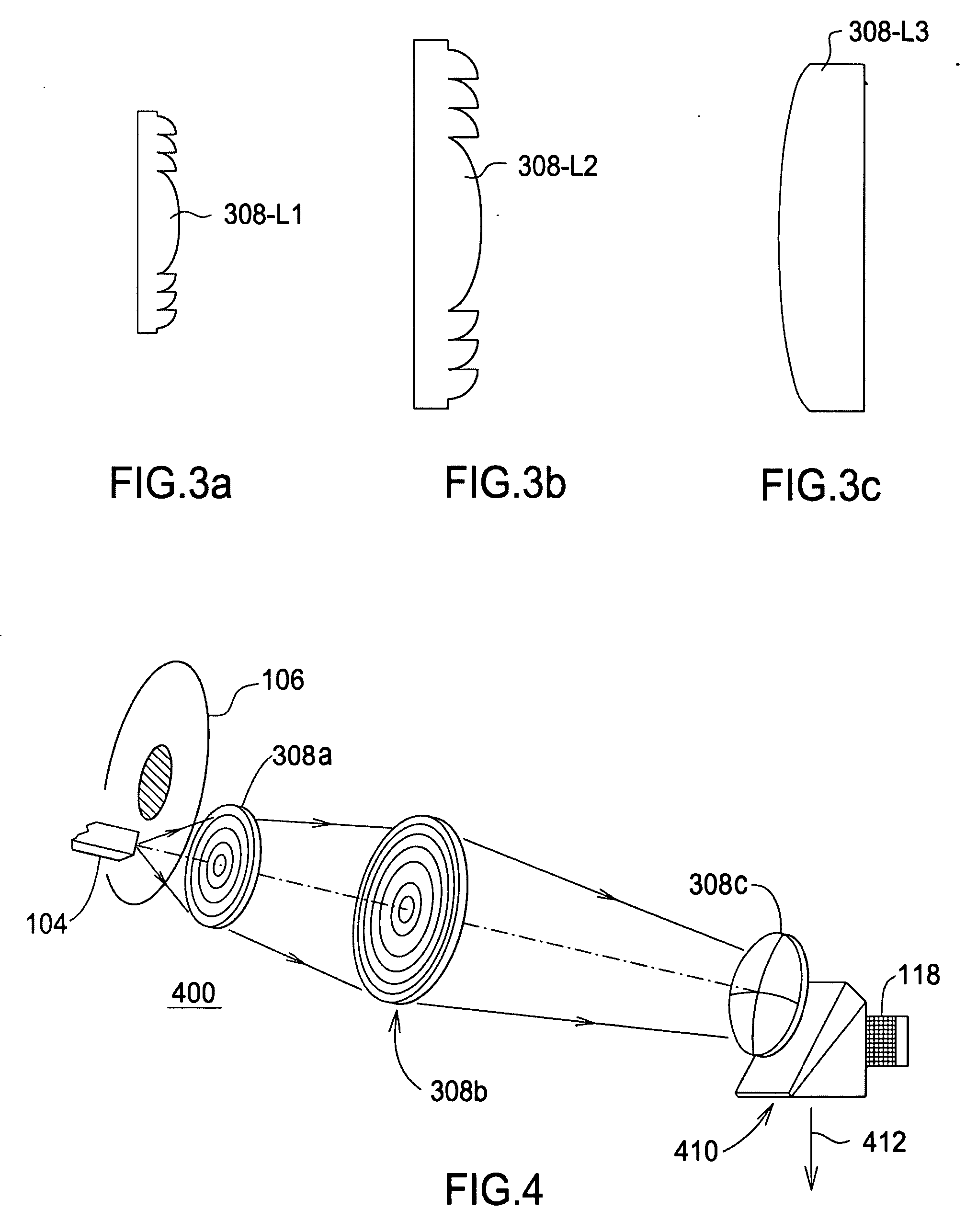
A method of wave propagation from 100–10000 GHz. The currently disclosed method and apparatus adapts micro-opto-electro-mechanical systems (MOEMS) technologies and processes to construct Kinoform optical components from microwave to terahertz range. The method uses induced coupled plasma (ICP) and gray scale processes for upper terahertz band; LIGA-based high aspect ratio (HAR) and gray scale processes are for the mid band; and computer numerical control (CNC) for lower band. In all cases, the thickness of any processed components is about the respective wavelength and system efficiency is about 95%. A Kinoform lens element is designed at 5000 GHz. However, the method is applicable for the entire terahertz band.
Owner:MOTAMEDI MANOUCHEHR E +1
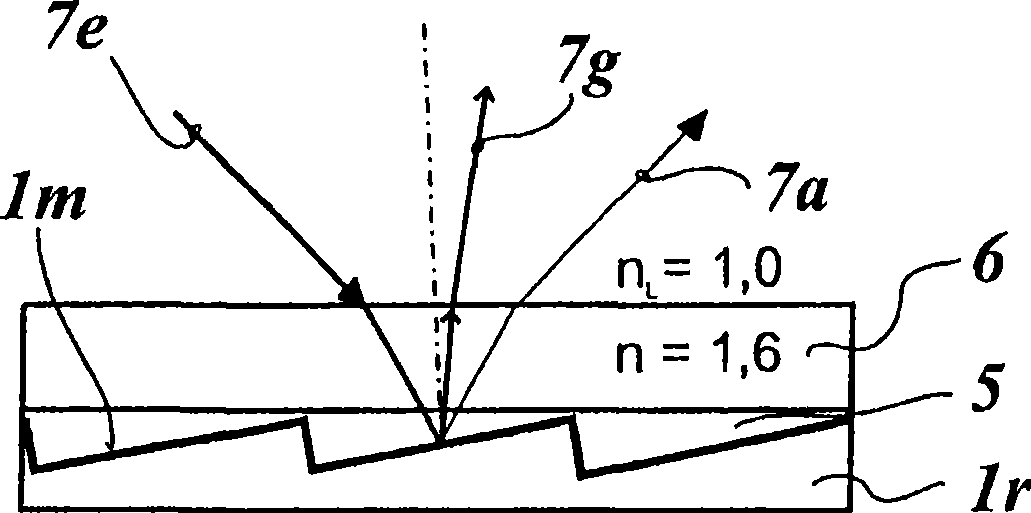
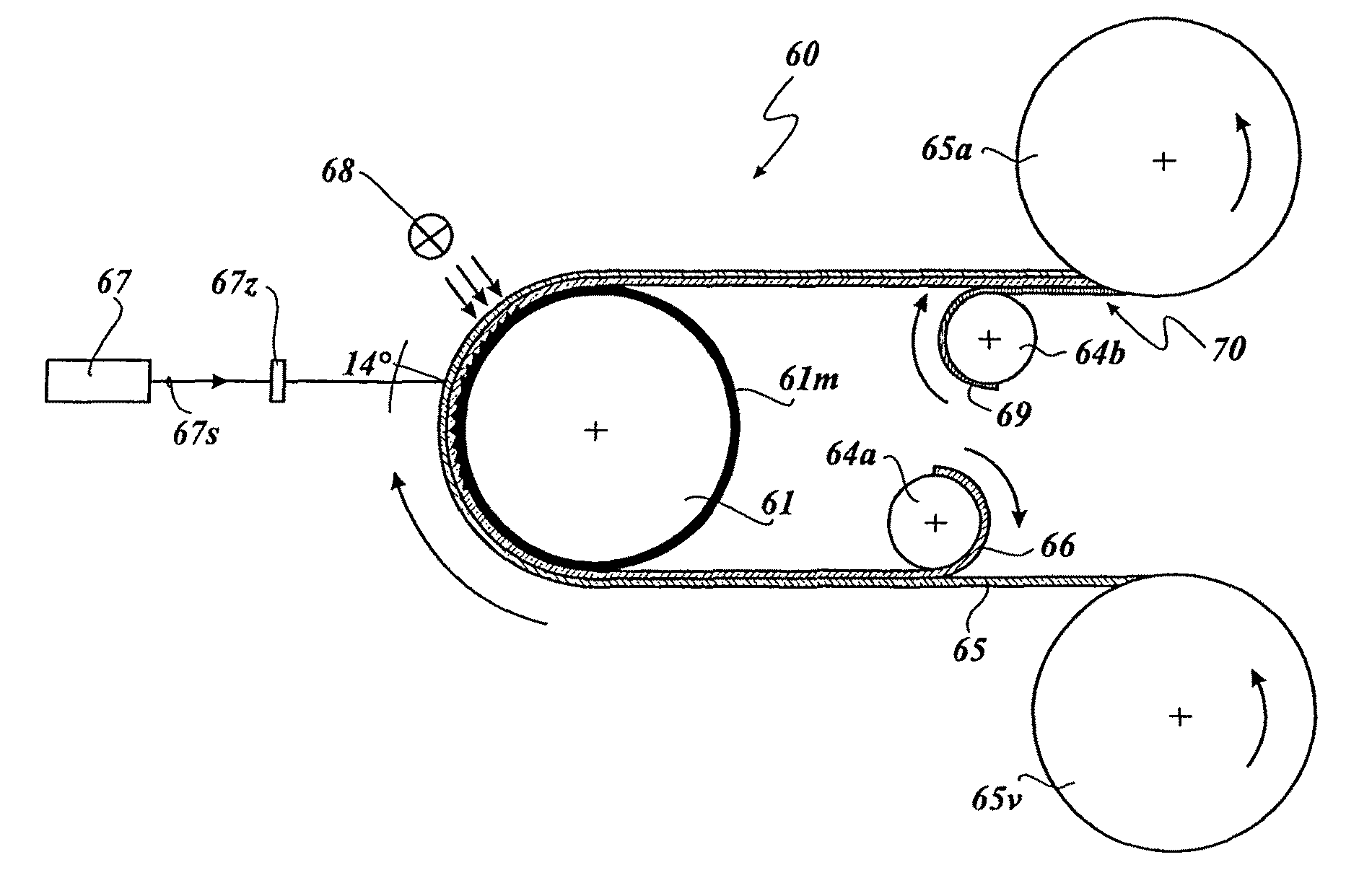
Optical systems employing stepped diffractive surfaces
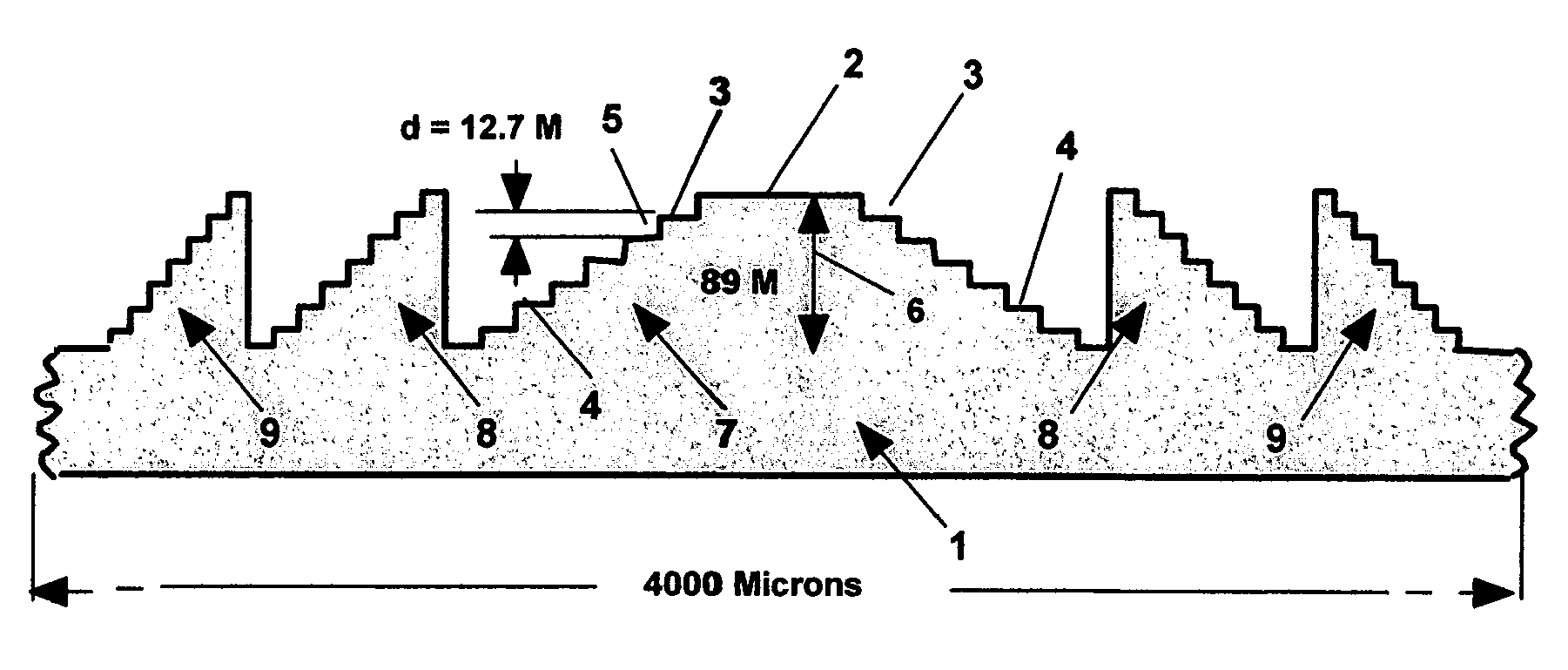
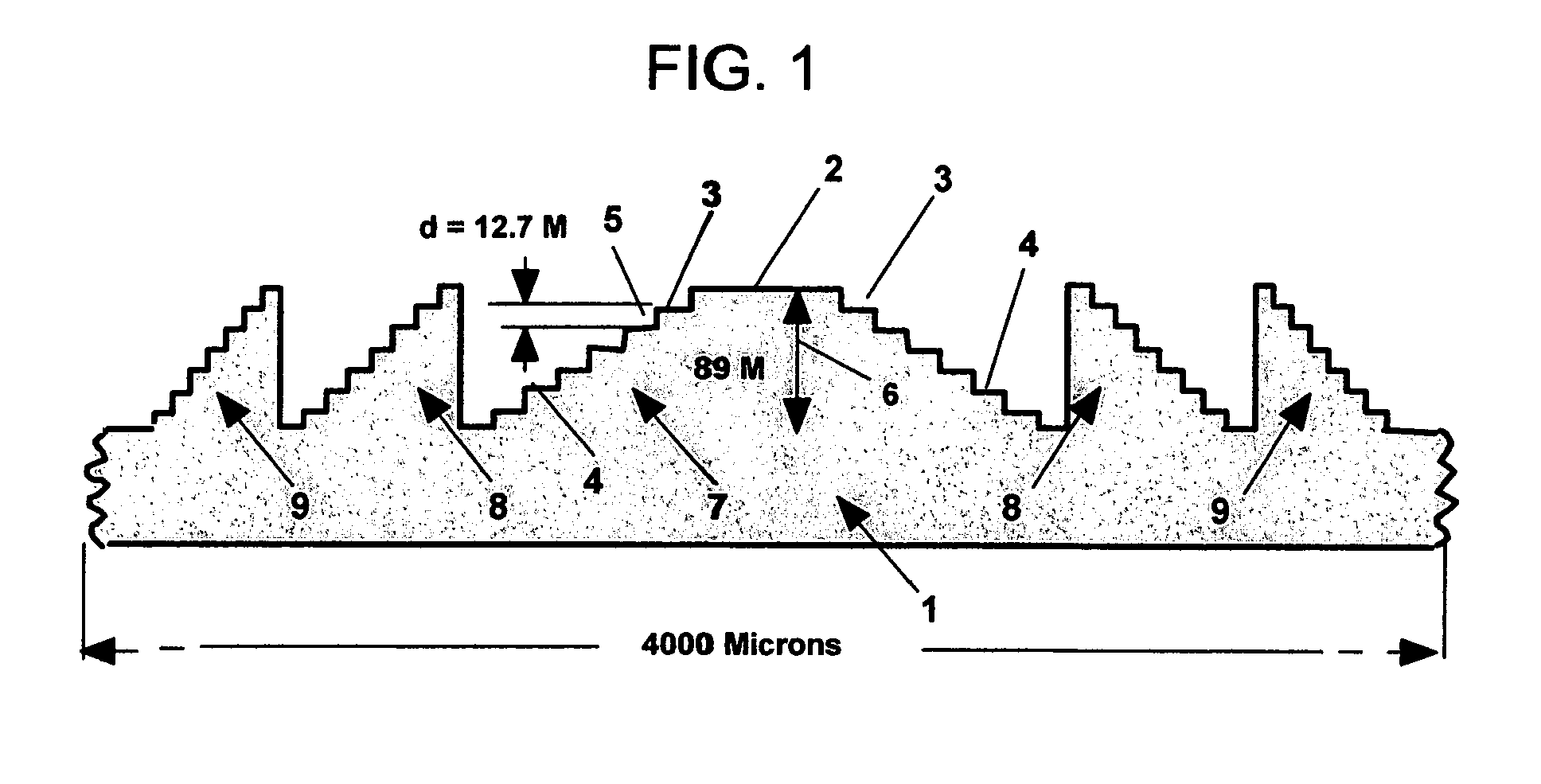
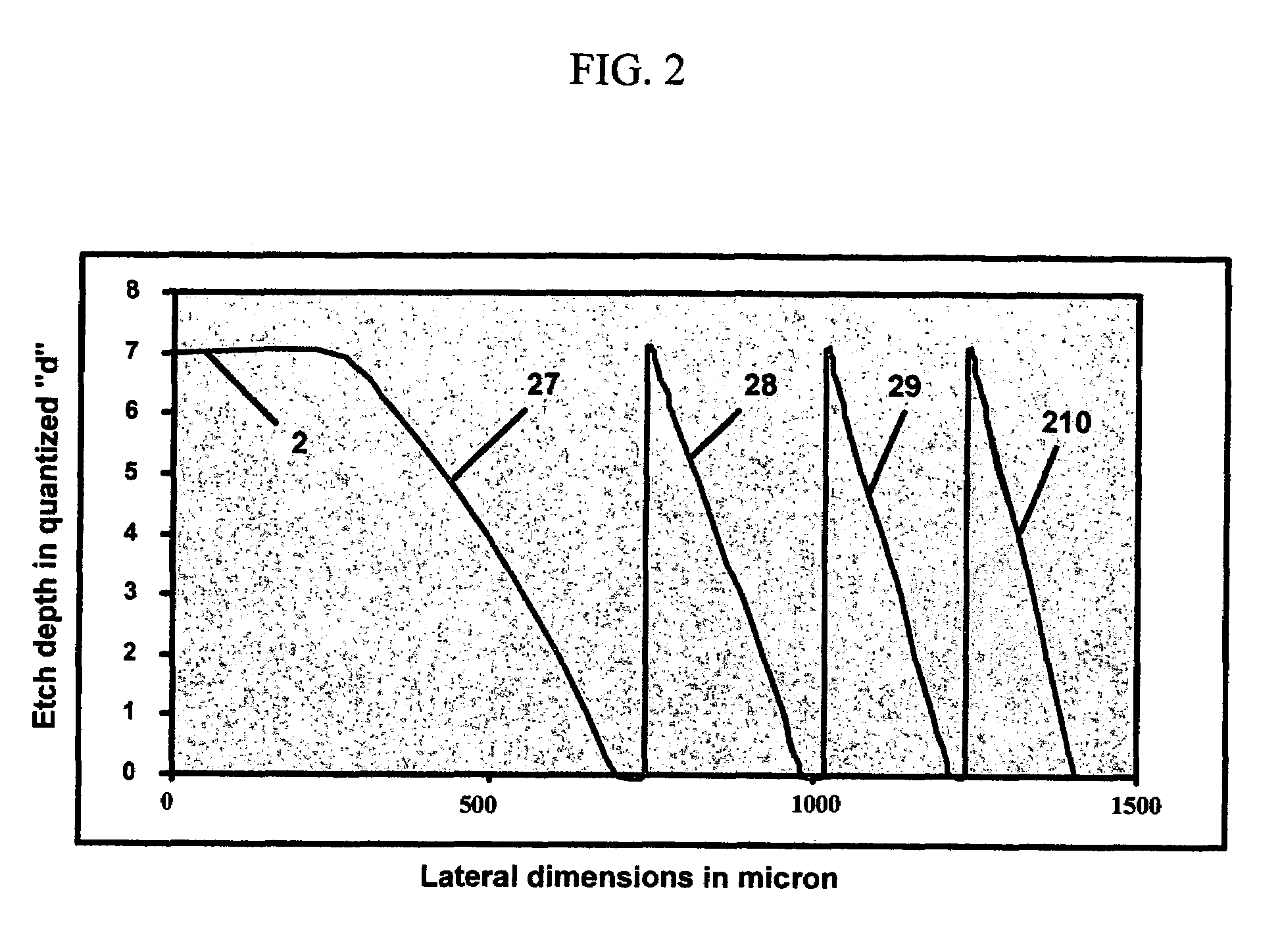
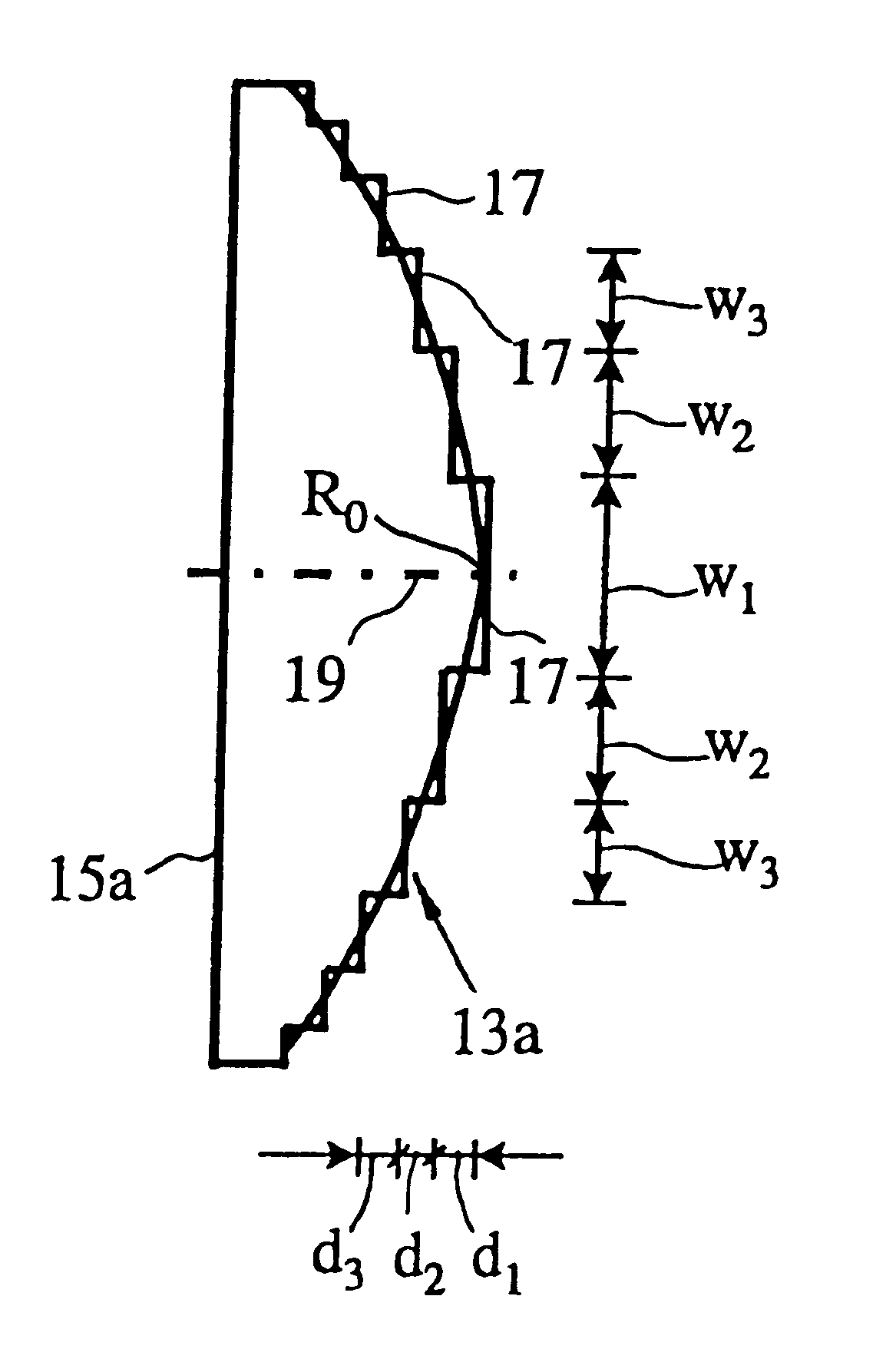
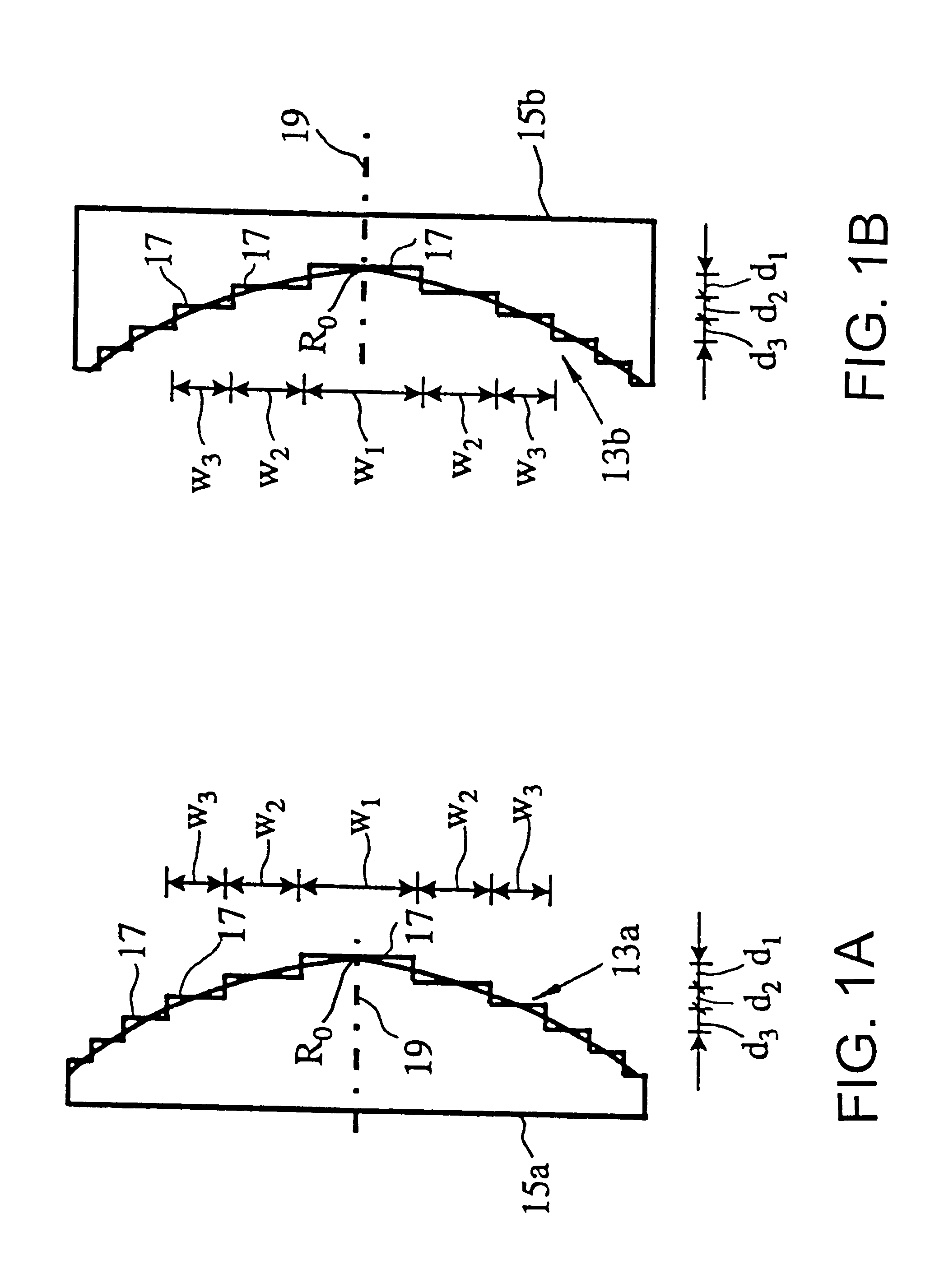
Stepped diffractive surfaces (13) are used to reduce variations in the optical properties of an optical system as a result of a change in the temperature of all or a portion of the system. Such surfaces have optothermal coefficients which differ from the optothermal coefficients of both kinoforms and refractive elements. Accordingly, stepped diffractive surfaces can be combined with such elements to achieve overall thermal control of optical systems employing such elements.
Owner:KSM ASSOCS
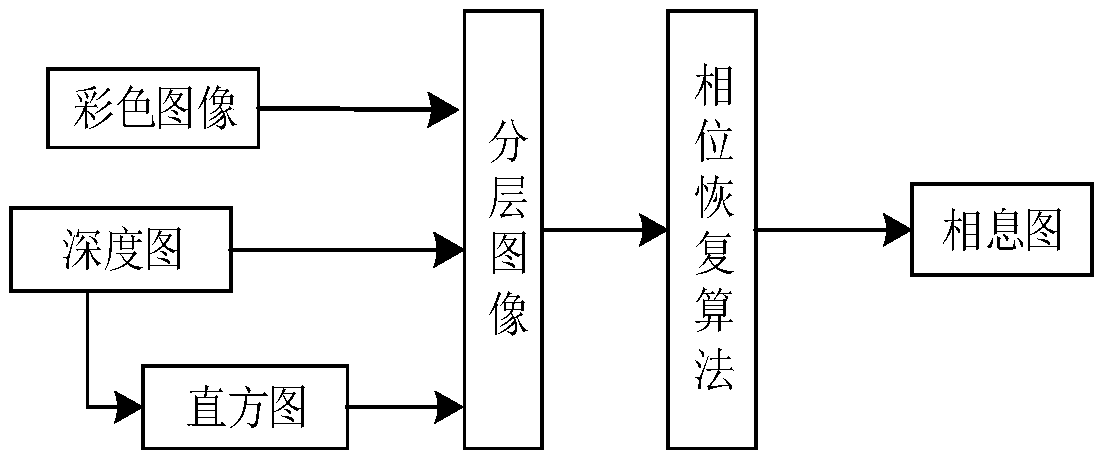
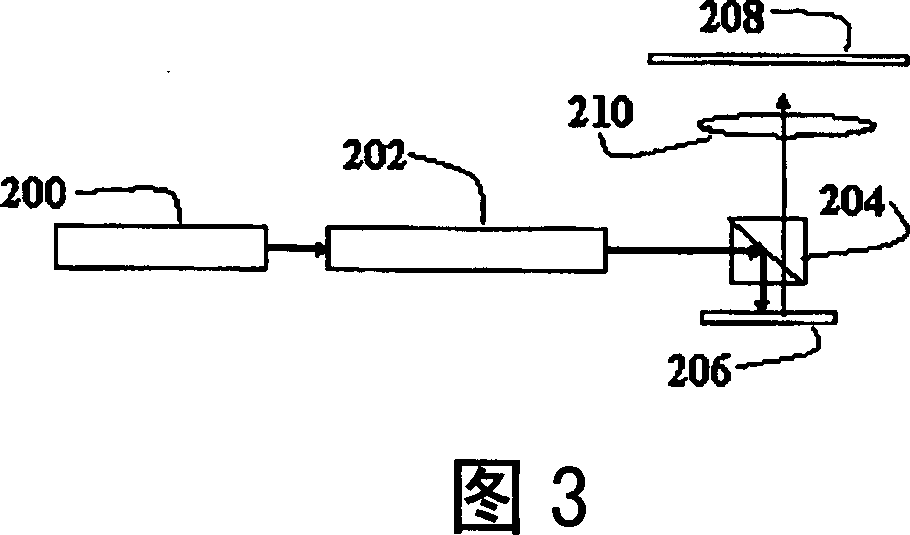
Method and device for true color 3D object holographic display
InactiveCN101566823AImprove light energy utilization efficiencyNo conjugate imageInstrumentsSpatial light modulatorLight beam
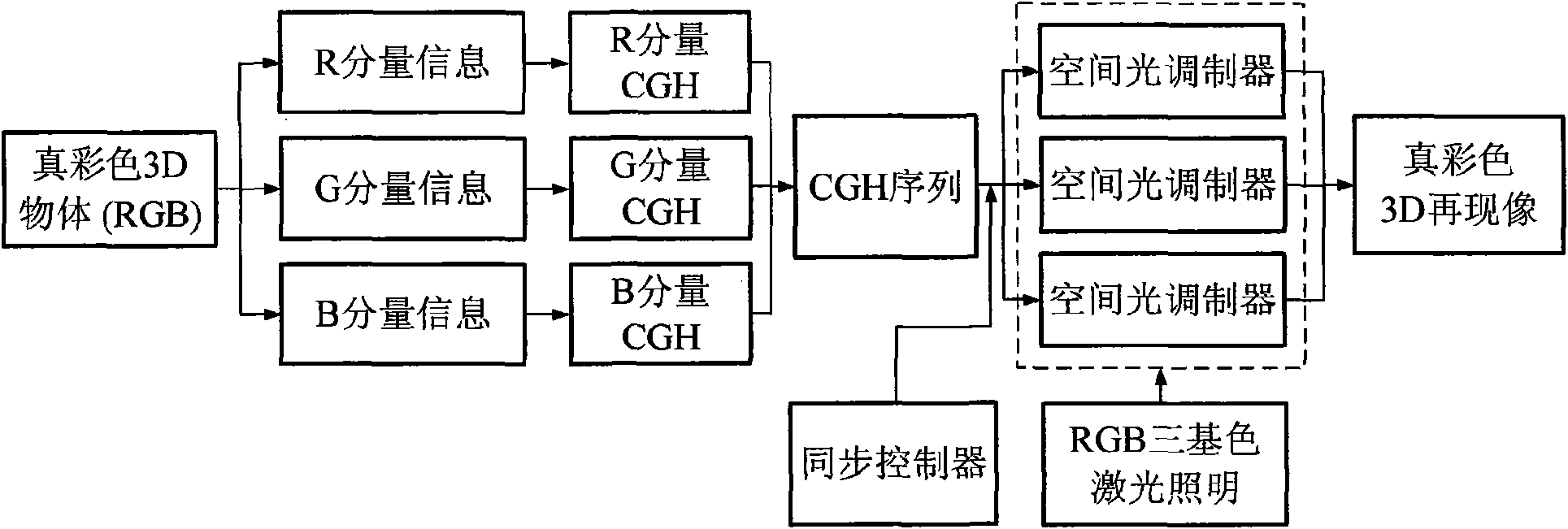
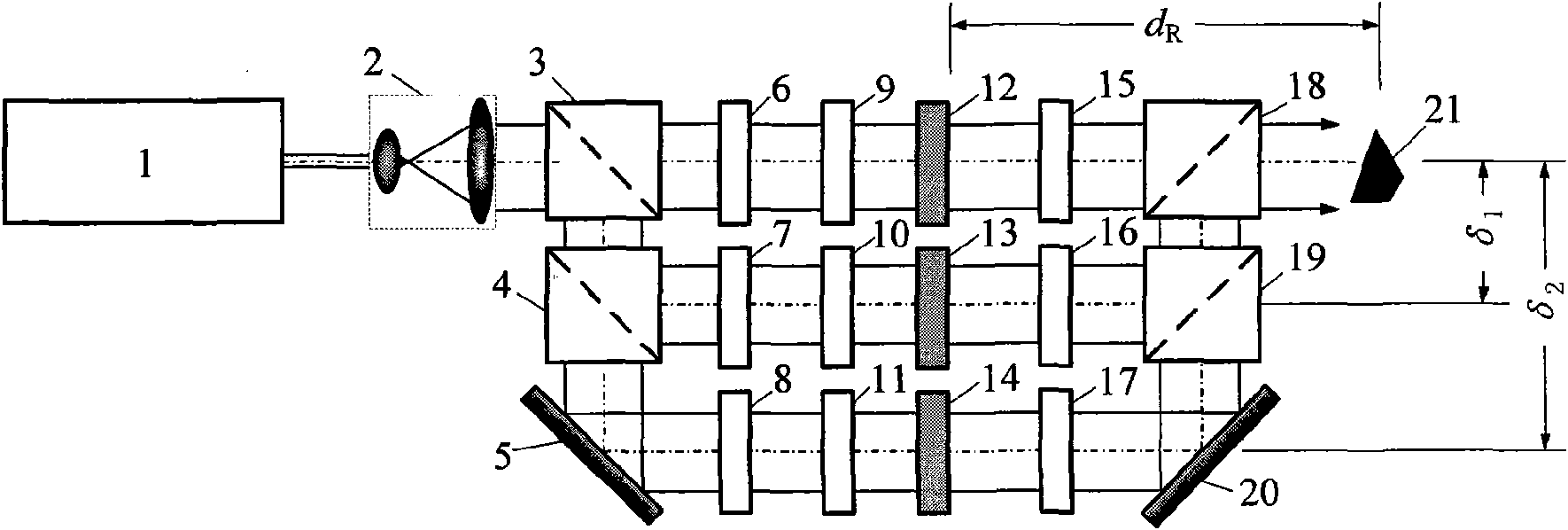
The invention relates to a method and a device for true color 3D object holographic display. Colorful image information of a true color 3D object is decomposed into RGB coloring information which comprises component amplitude information and depth information of each color, and a multi-component-level phase type kinoform of each color component of the 3D object is calculated according to the depth information and amplitude information of each color component; image series formed by each color component kinoform are output respectively to three spatial light modulators with phase modulation capacity under the control of an isochronous controller, simultaneously relevant light of relevant color is adopted to illumine the kinoform carried by three spatial light modulator, beams modulated by the kinoform show the component information of RGB of an original true color 3D object, and holographic true color reappearance effect is obtained after integration of the component information. The invention designs a plurality of devices and provides a position relation setting method of key devices in an opto-electrical reappearance device. The invention can be used for holographic display of a static or dynamic true color 3D object or scene.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Optical beam routing apparatus and methods
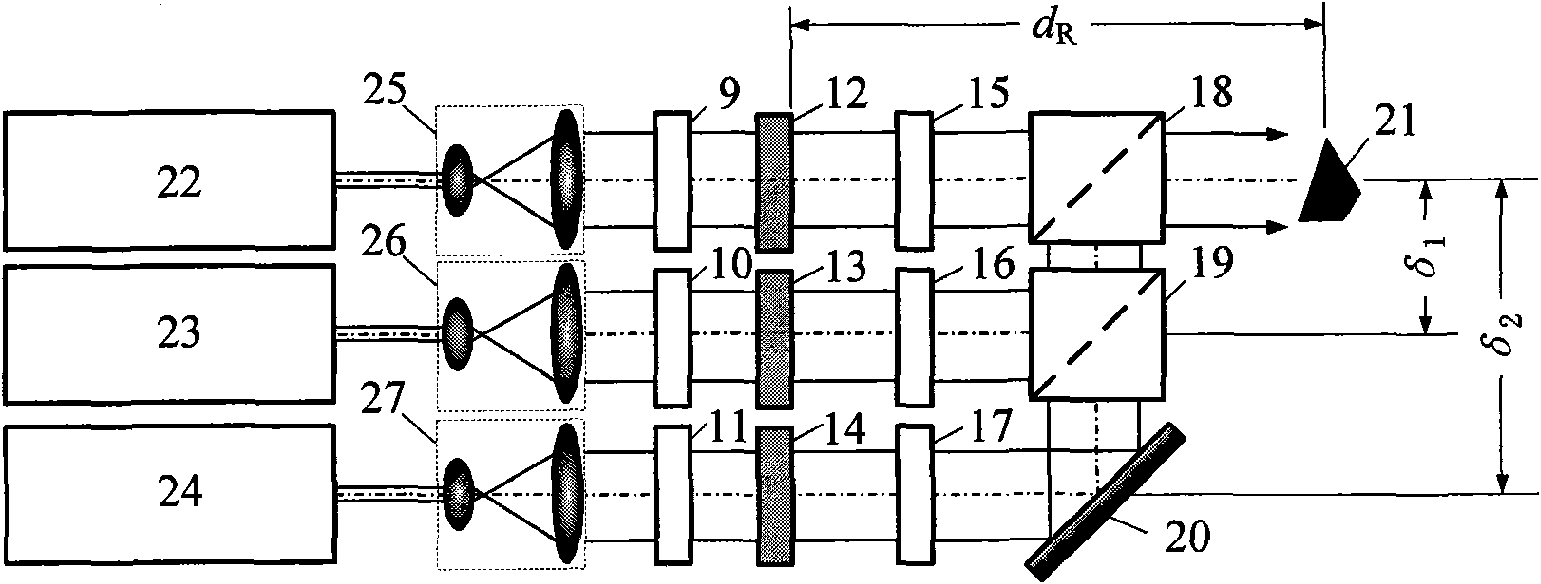
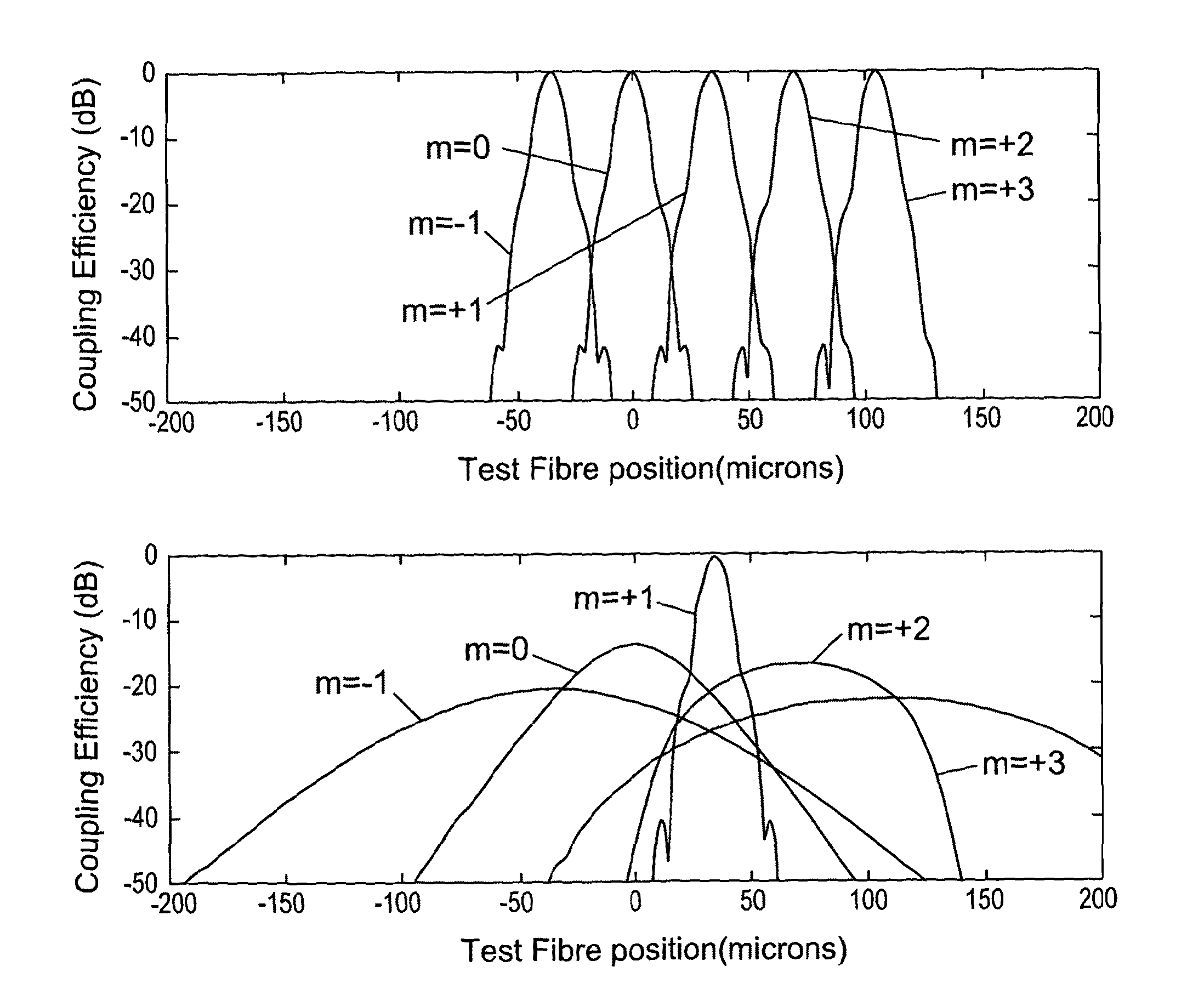
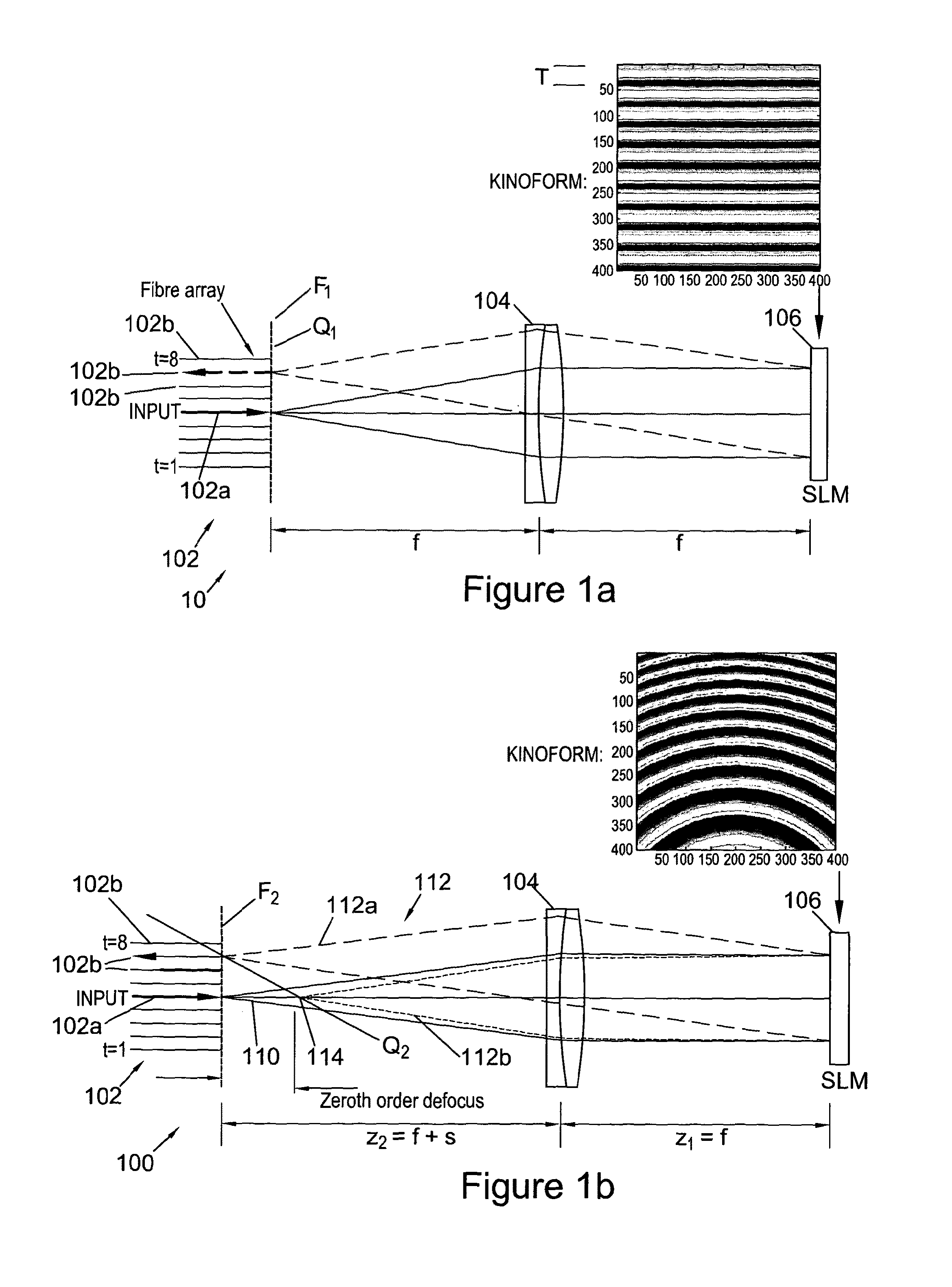
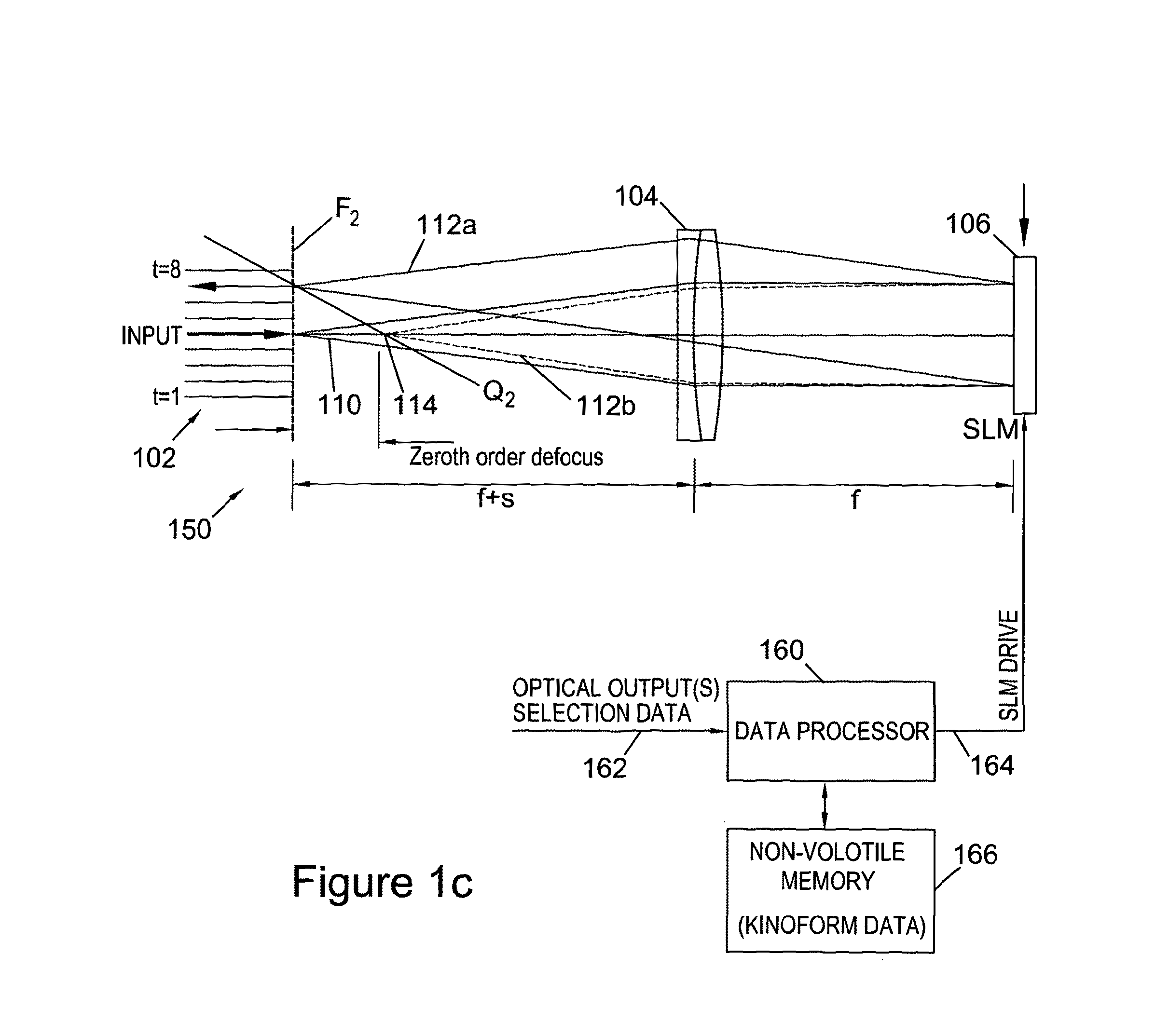
ActiveUS20140355985A1Reduce couplingIncreasing ‘ aberration ’Multiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsDiffraction orderSpatial light modulator
This invention relates to methods and apparatus for routing light beams in telecommunications devices using holographic techniques, in particular by displaying kinoforms on LCOS (Liquid Crystal on Silicon) devices. Thus we describe optical beam routing apparatus comprising: at least one optical input to receive an input beam; a plurality of optical outputs; a spatial light modulator (SLM) on an optical path between said optical input and said optical outputs; and a driver for said SLM to display a kinoform on said SLM to diffract said input beam into an output beam comprising a plurality of diffraction orders, wherein a routed one of said diffraction orders is directed to at least one selected said optical output; wherein said apparatus is configured to modify a wavefront of said output beam to reduce a coupling of said output beam into said selected optical output; and wherein said kinoform is adapted to compensate for said wavefront modification to compensate for said reduced coupling and thereby to reduce a coupling of other diffracted light from said input beam into others of said optical outputs than said at least one selected optical output.
Owner:CAMBRIDGE ENTERPRISE LTD
Light control devices and methods implemented with kinoform diffusers having controllable diffusion characteristics
Kinoform diffusers (82) exhibit controllable diffusion characteristics that include off-axis transmittance and reflectance properties, elimination of zero-order beam, and freedom from spectral dispersion under achromatic illumination. Light control devices (76, 80, 82) implemented with kinoform diffusers having controllable diffusion characteristics provide anisotropic luminous intensity distributions and glare control at high viewing angles while maintaining high luminaire efficiency or daylight utilization.
Owner:LUMEC HLDG ULC
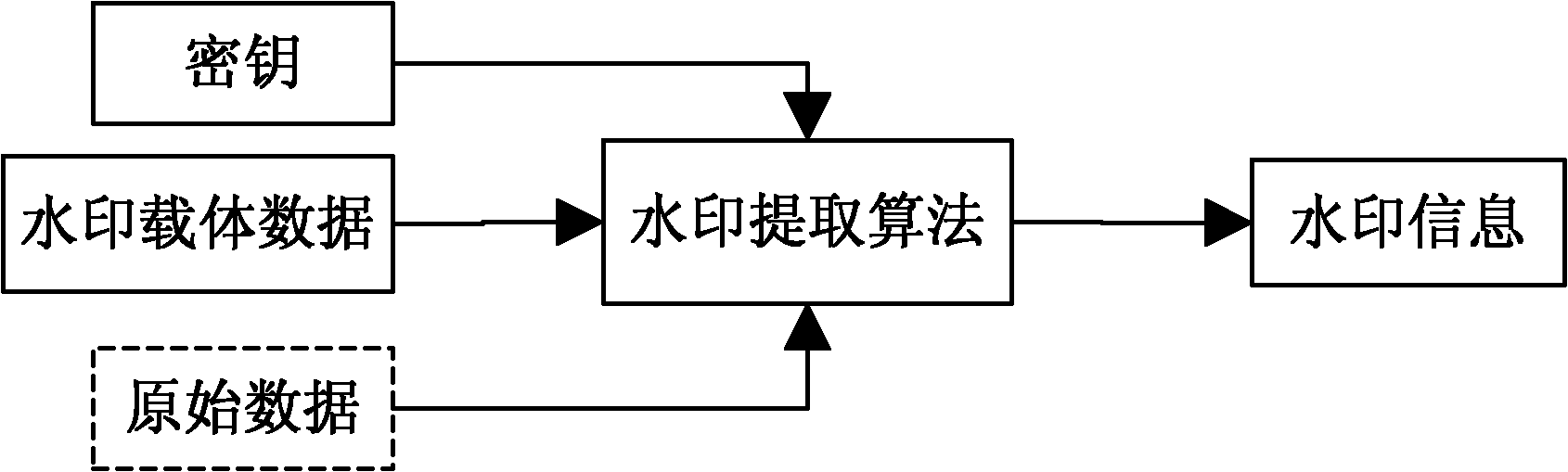
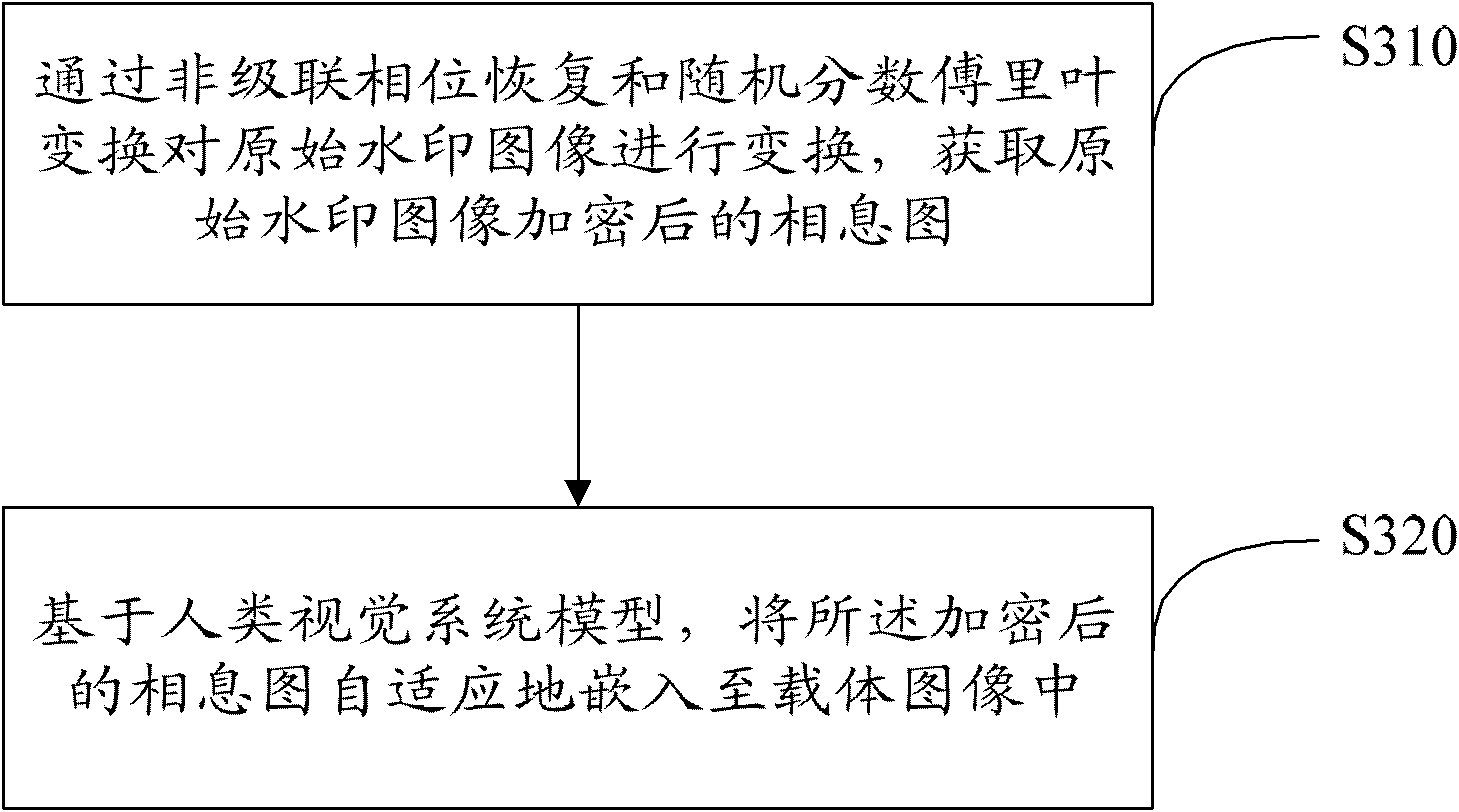
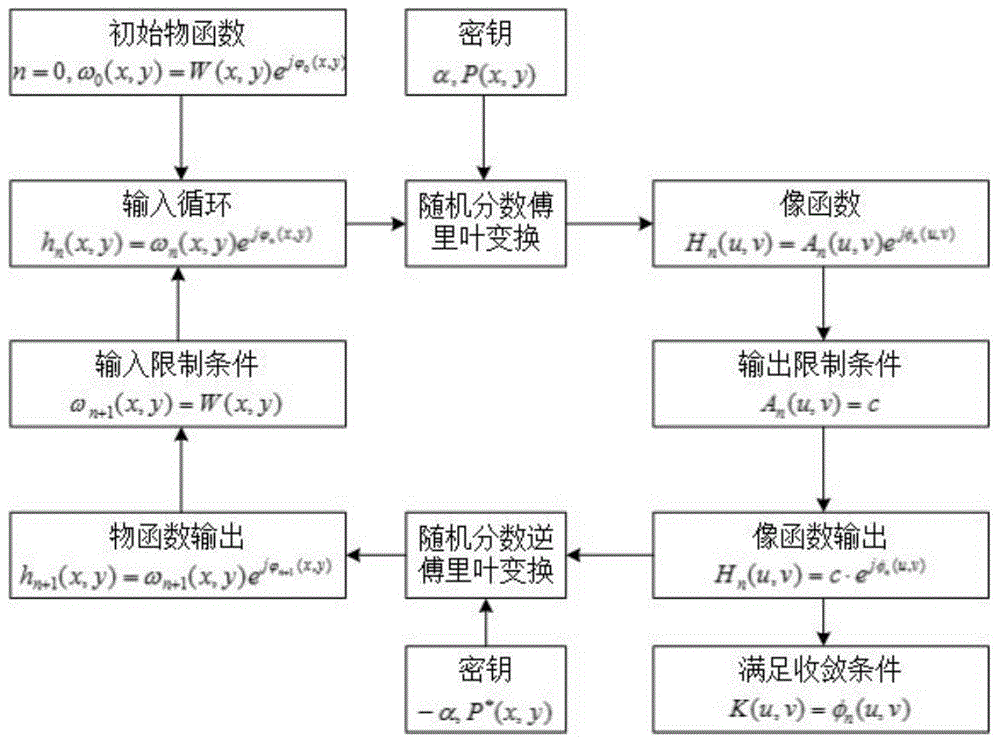
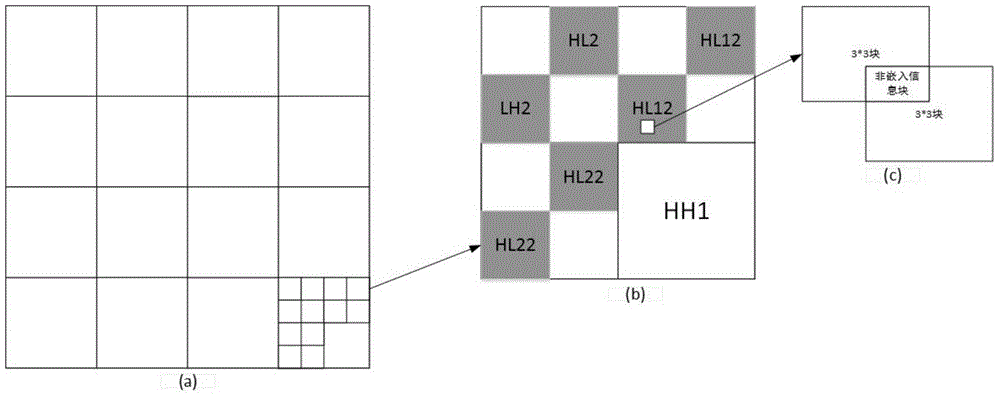
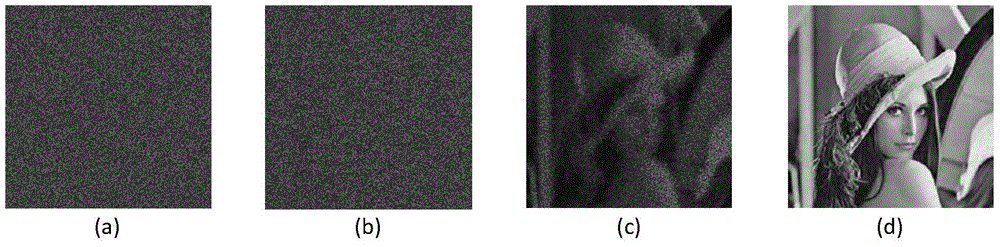
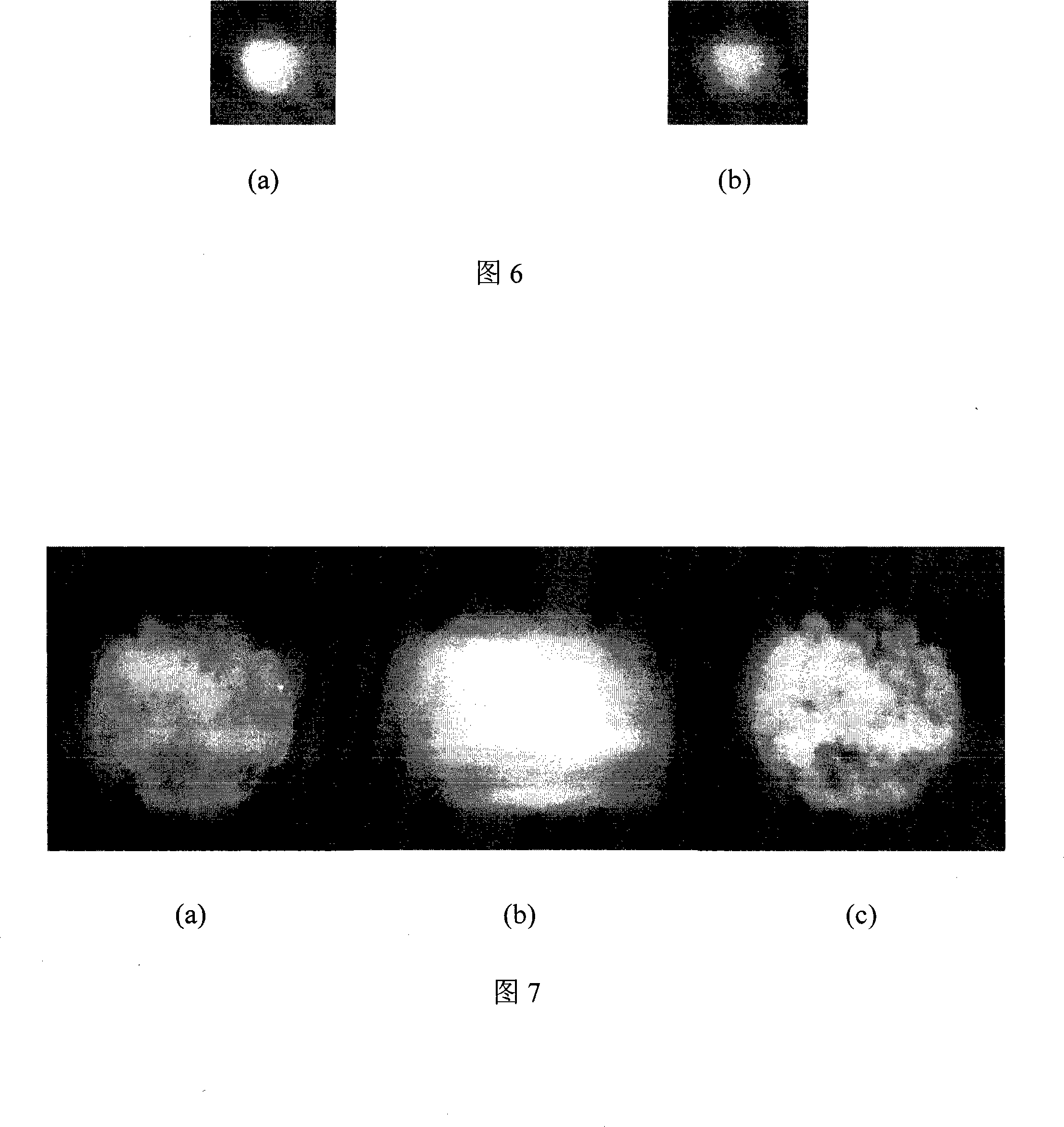
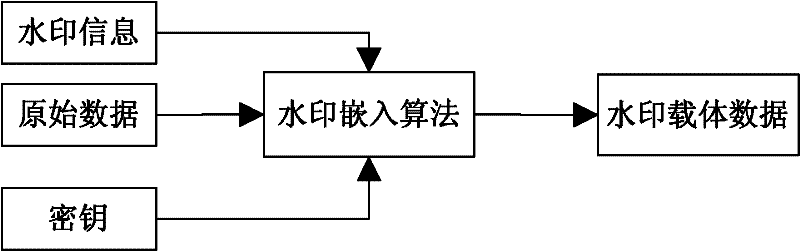
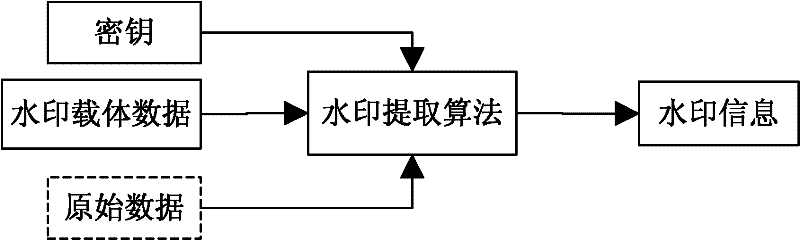
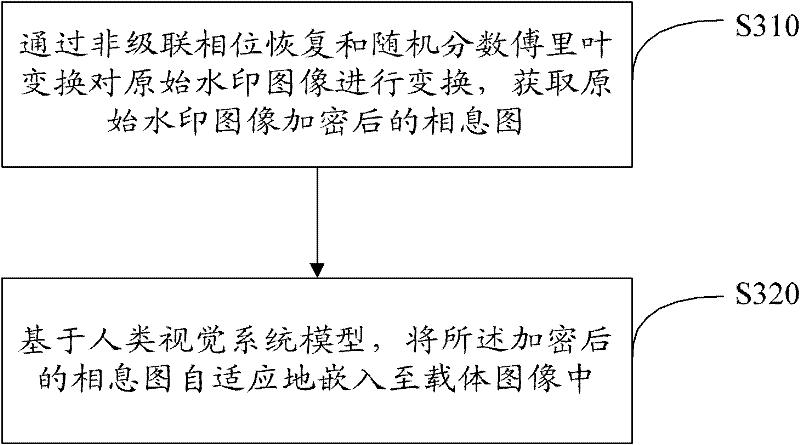
Encrypted kinoform based digital image watermarking embedding and extracting methods and systems
ActiveCN102142131AReduce data volumeGood clipping resistanceImage data processing detailsHuman visual system modelKinoform
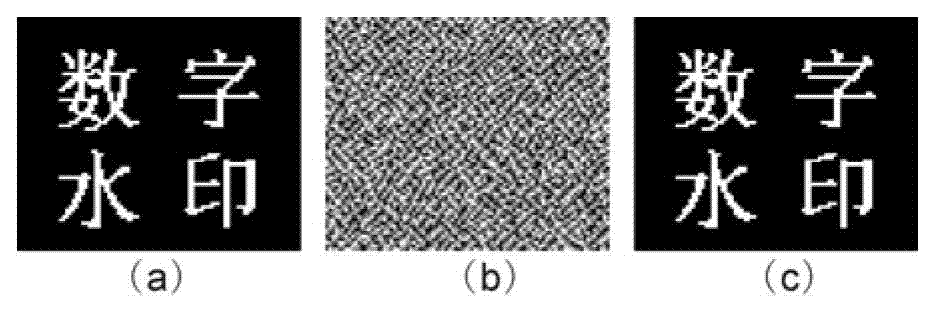
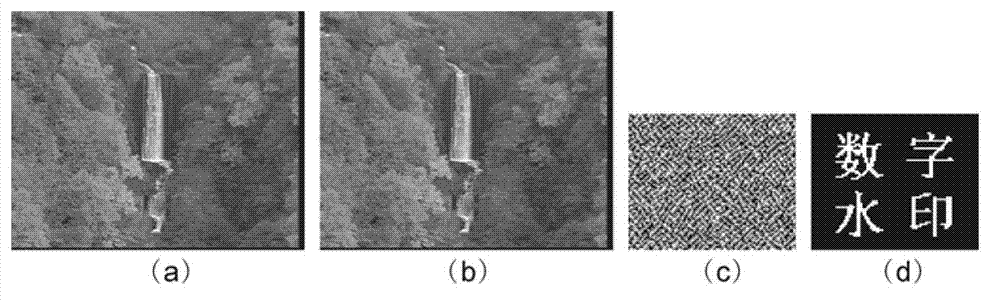
The invention discloses encrypted kinoform based digital image watermarking embedding and extracting methods and systems. The digital image watermarking embedding method comprises the following steps of: transforming an original watermarking image through non-cascaded phase recovery and random fractional fourier transform (RFrFT) to acquire an encrypted kinoform of the original watermarking image; and adaptively embedding the encrypted kinoform into a carrier image based on a human visual system (MVS) model. In the invention, the safety of the watermarking of the kinoform is enhanced by using a non-cascaded iterative encryption method; meanwhile, blink watermarking is realized by adopting an adaptive embedding algorithm; and experiments verify that extremely high robustness against various attacks is achieved, and the safety performance is extremely high.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Multi-layer body with volume hologram
Described is a method for producing a multi-layer body having a volume hologram with at least two different image information items, wherein a photosensitive layer (46) of the multi-layer body is brought into contact with the front side of a master (44) directly or by interposing a transparent optical medium (44s, 45), into which front side nested areas with different asymmetrical surface structures or kinoform structures are formed which embody the at least two different image information items. The photosensitive layer (46) and the master are exposed using a coherent light beam (47), by means of which a volume hologram is formed in the photosensitive layer (46). A master for producing the multi-layer body and a security element with said multi-layer body are further described.
Owner:OVD KINEGRAM AG
Image display method, storage medium thereof and image display system
ActiveCN108287414ASolving Laser Speckle ProblemsLow costHolographic object characteristicsOptical elementsLaser imagingKinoform
The invention provides an image display method, a storage medium thereof, and an image display system. The method includes a step 1 of: generating a plurality of sub-images according to an input image, wherein the plurality of sub-images record a part of the content of the input image respectively; and a step 2 of displaying the plurality of sub-images at different times respectively, or a step 2'of displaying corresponding holograms or kinoforms generated from the plurality of sub-images through mathematical transformation at different times respectively. The method solves laser speckles caused by mutual interference between pixels by software, and can be used independently without additional hardware, and can reduce the cost. Of course, the method can be combined with other speckle-eliminating techniques to enhance a speckle-eliminating effect. The method is suitable for all laser imaging systems, including holographic display technology using coherence imaging.
Owner:SHANGHAI INTELIGHT ELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
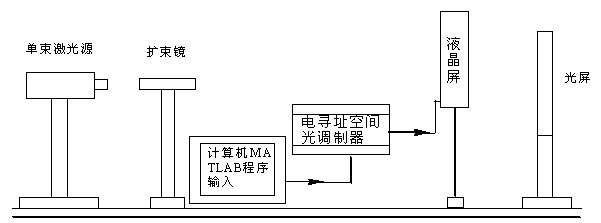
Method for realizing varifocal lens based on liquid crystal space optical modulator
The invention discloses a method for realizing varifocal lens based on a liquid crystal space optical modulator. The method comprises the following steps: according to the phase modulating principle of the liquid crystal space optical modulator, controlling the liquid crystal space optical modulator to modulate an incident light wave to generate a kinoform, diffracting the incident light wave into a converging spherical wave, and changing radius and zone number of a Fresnel zone plate in the kinoform to realize the variable focus of a program-control varifocus imaging system established by the liquid crystal space optical modulator. The method provided by the invention can be used for improving the automatic varifocus precision and the varifocus response speed of the varifocus imaging system, so that the focal distance of the lens is variable and easy to control.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Multi-complex three-dimensional scene encryption and decryption method based on the kinoform and Fresnel domain multiplexing
ActiveCN108648267AImprove reconstruction qualityImprove securityImage enhancementImage analysisColor imageMultiplexing
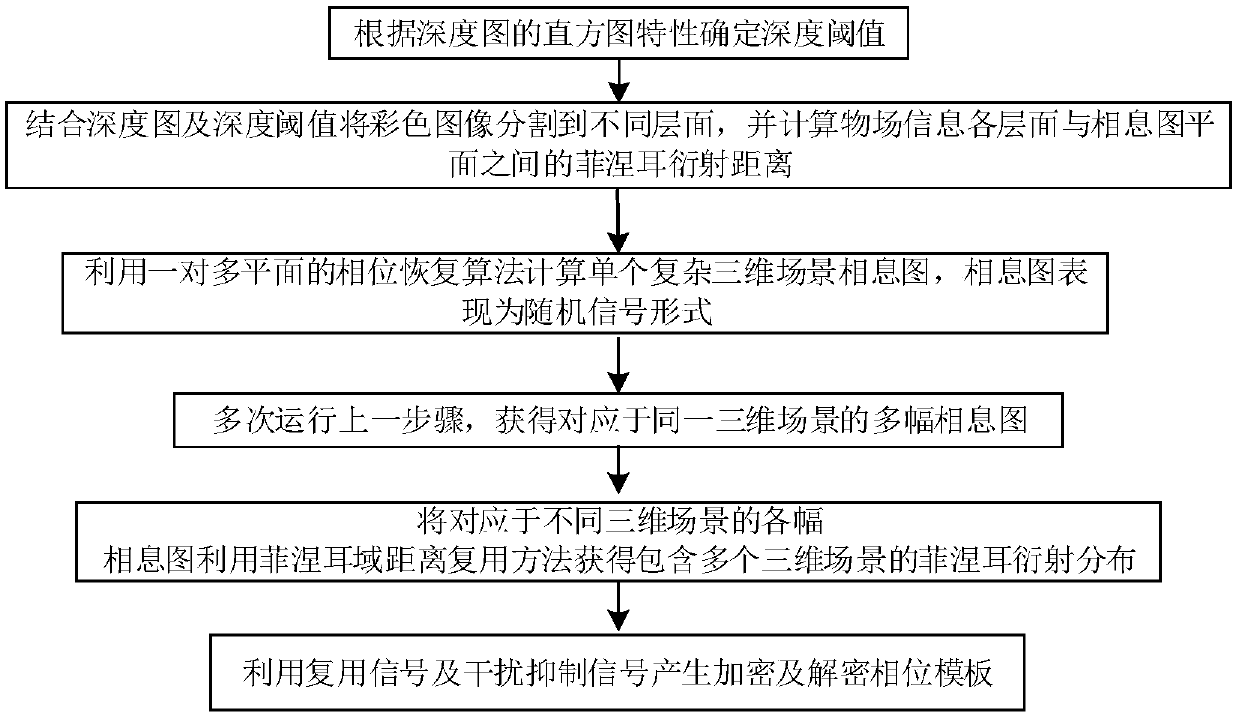
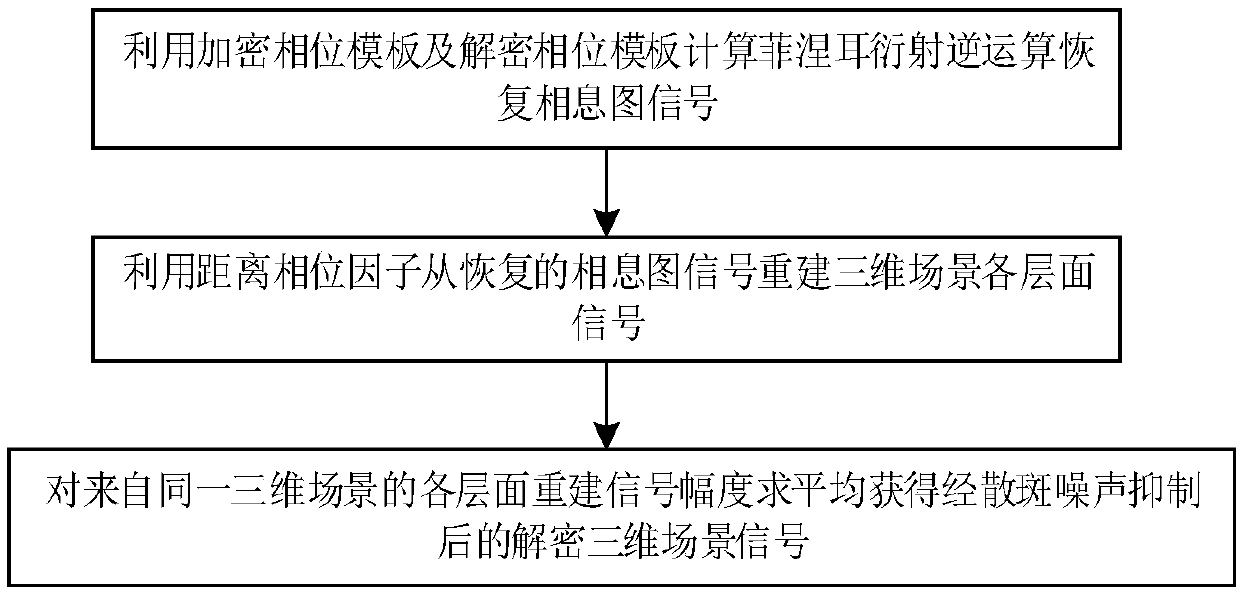
The present invention discloses a multi-complex three-dimensional scene encryption and decryption method based on the kinoform and Fresnel domain multiplexing. The method comprises: starting from a complex three-dimensional scene characterized by a color image and a depth map, using a computational holography coding method to generate a computational kinoform that can be used for true three-dimensional reconstruction, wherein the kinoform shows random signal characteristics; superimposing the kinoform recording a single complex three-dimensional scene by using the Fresnel domain distance multiplexing method to generate a Fresnel diffraction distribution containing multiple three-dimensional scenes; and finally, using a phase template decomposition method for the diffraction signal and theinterference suppression signal which contain multiple three-dimensional scenes to obtain an encrypted and decrypted phase template. In order to suppress the speckle noise in the reconstructed three-dimensional scene, the multiplexed signal contains multiple kinoforms from the same three-dimensional scene, and the intensities of the light wave signals reconstructed by different kinoforms from thesame three-dimensional scene are averaged in the decryption phase to improve the quality of reconstruction. According to the method provided by the present invention, a three-dimensional scene can still be reconstructed in the case that the encrypted phase template suffers from large area shearing or is superimposed with a certain intensity of Gaussian noise, and the method has good security and robustness.
Owner:FUJIAN NORMAL UNIV
Multi-layer body with volume hologram
Described is a process for the production of a multi-layer body having a volume hologram with at least two different items of image information, wherein a photosensitive layer (46) of the multi-layer body is directly or with the interposition of a transparent optical medium (44s, 45) brought into contact with the front side of a master (44), in which interlaced regions with different asymmetrical surface structures or kinoform structures are shaped, which embody the at least two different items of image information. The photosensitive layer (46) and the master are exposed with a coherent light beam (47) whereby a volume hologram is formed in the photosensitive layer (46). Also described are a master for the production of the multi-layer body and a security element having said multi-layer body.
Owner:OVD KINEGRAM AG
Apparatus and methods for light beam routing in telecommunication
ActiveUS20150286187A1Fast convergenceIncreased field sizeMultiplex system selection arrangementsHolographic light sources/light beam propertiesSpatial light modulatorLight beam
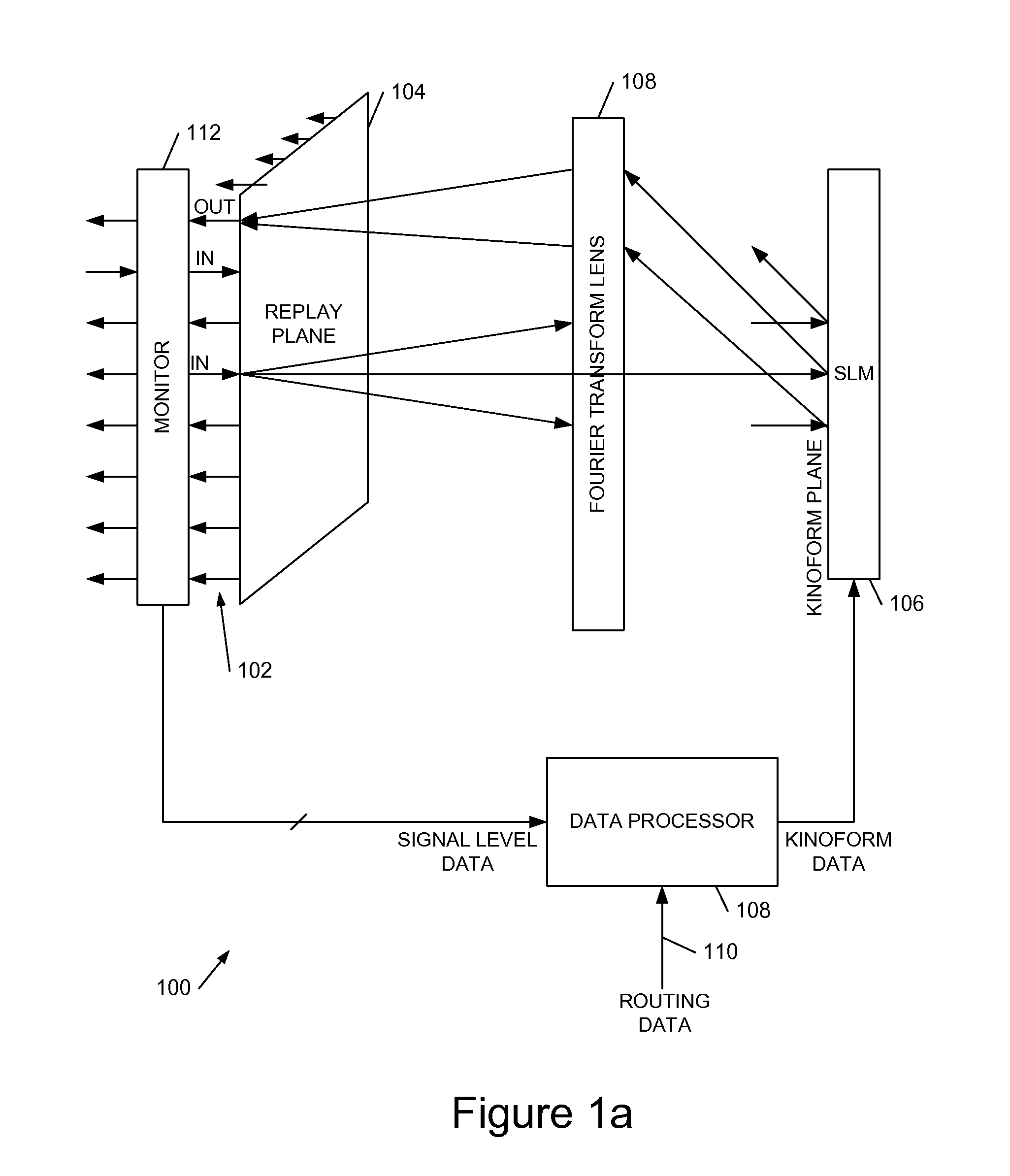
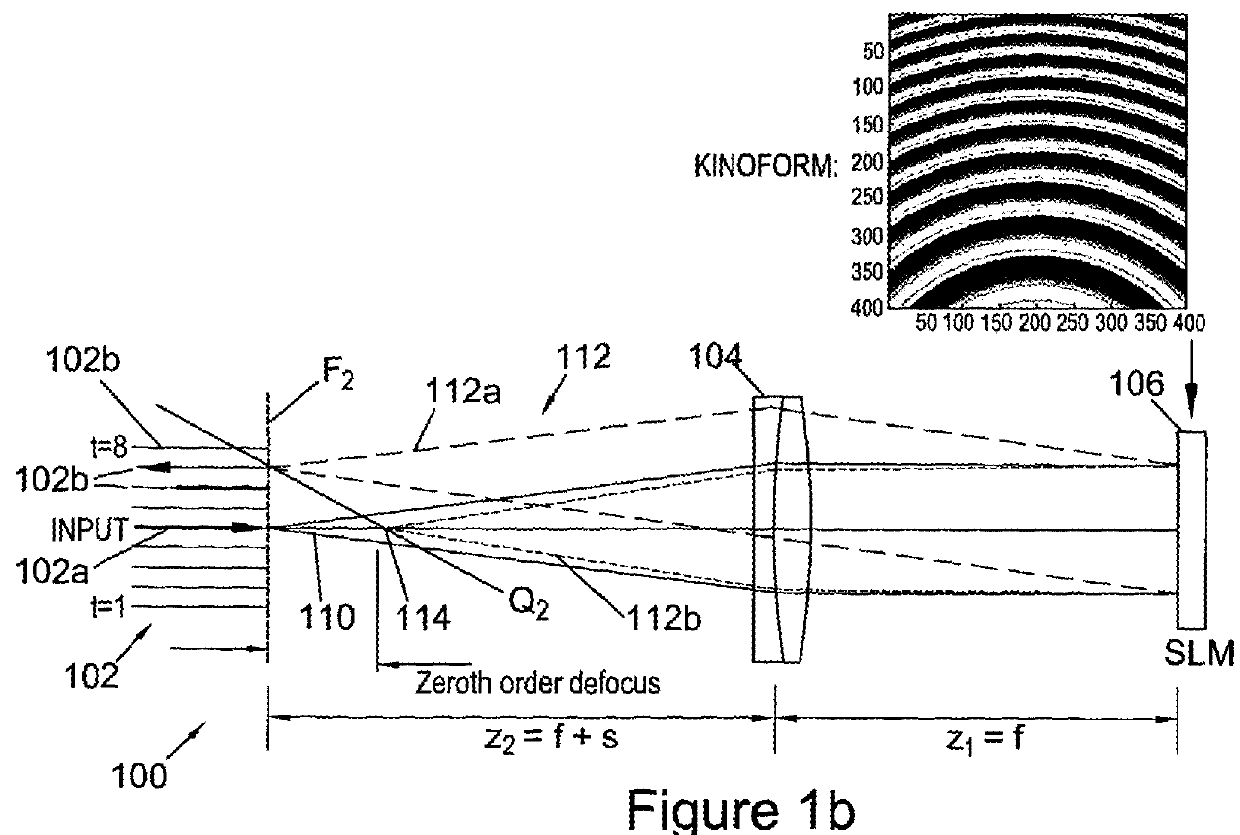
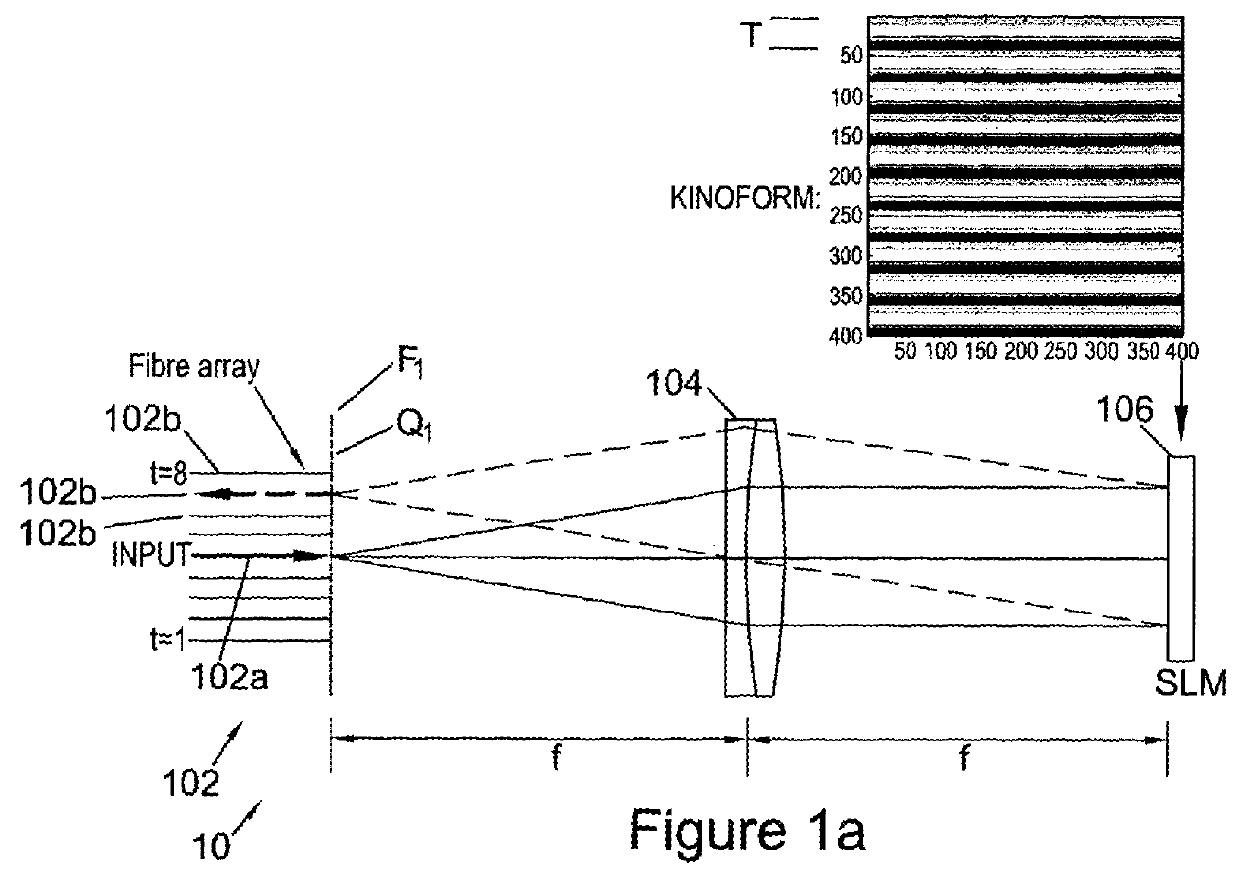
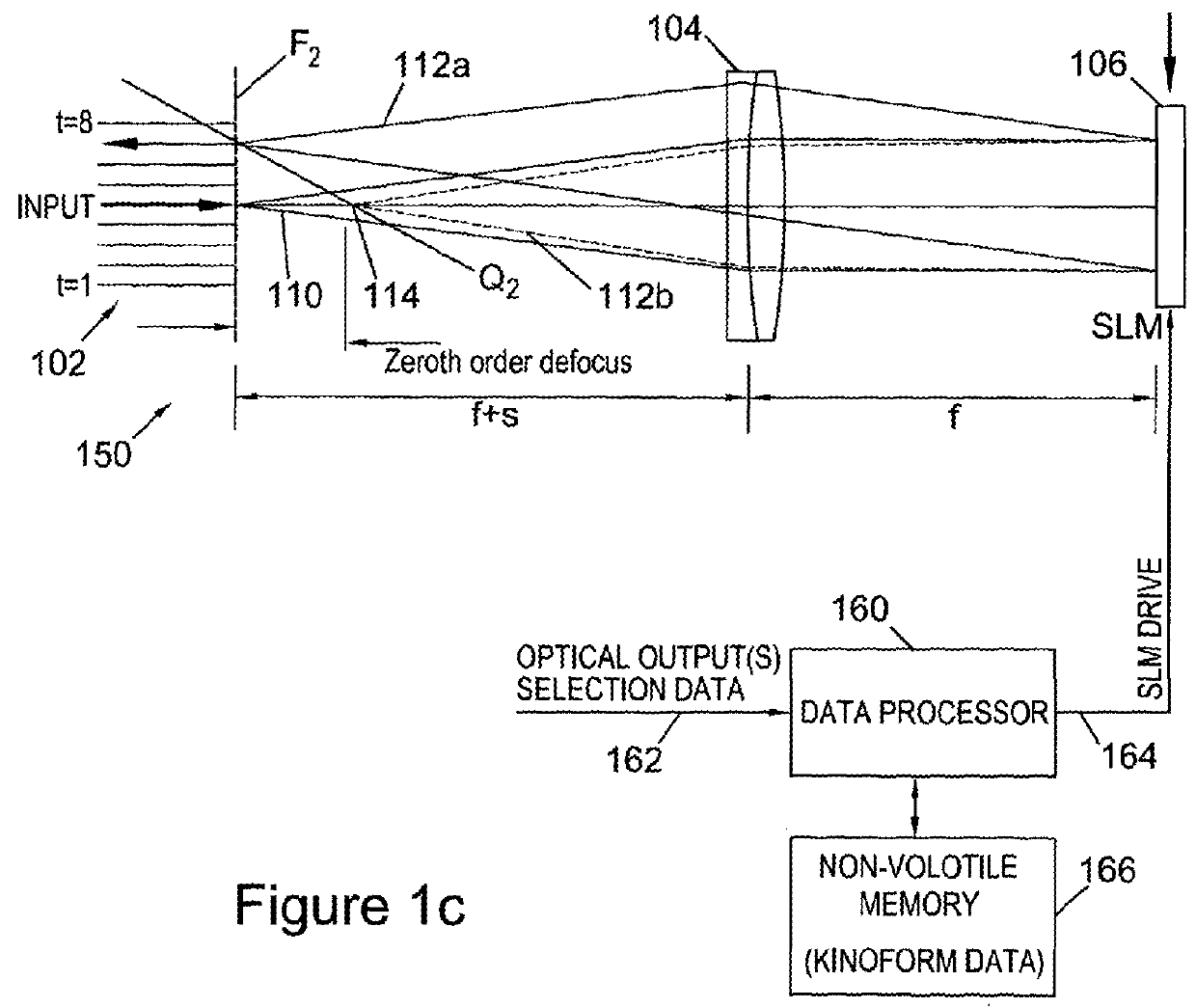
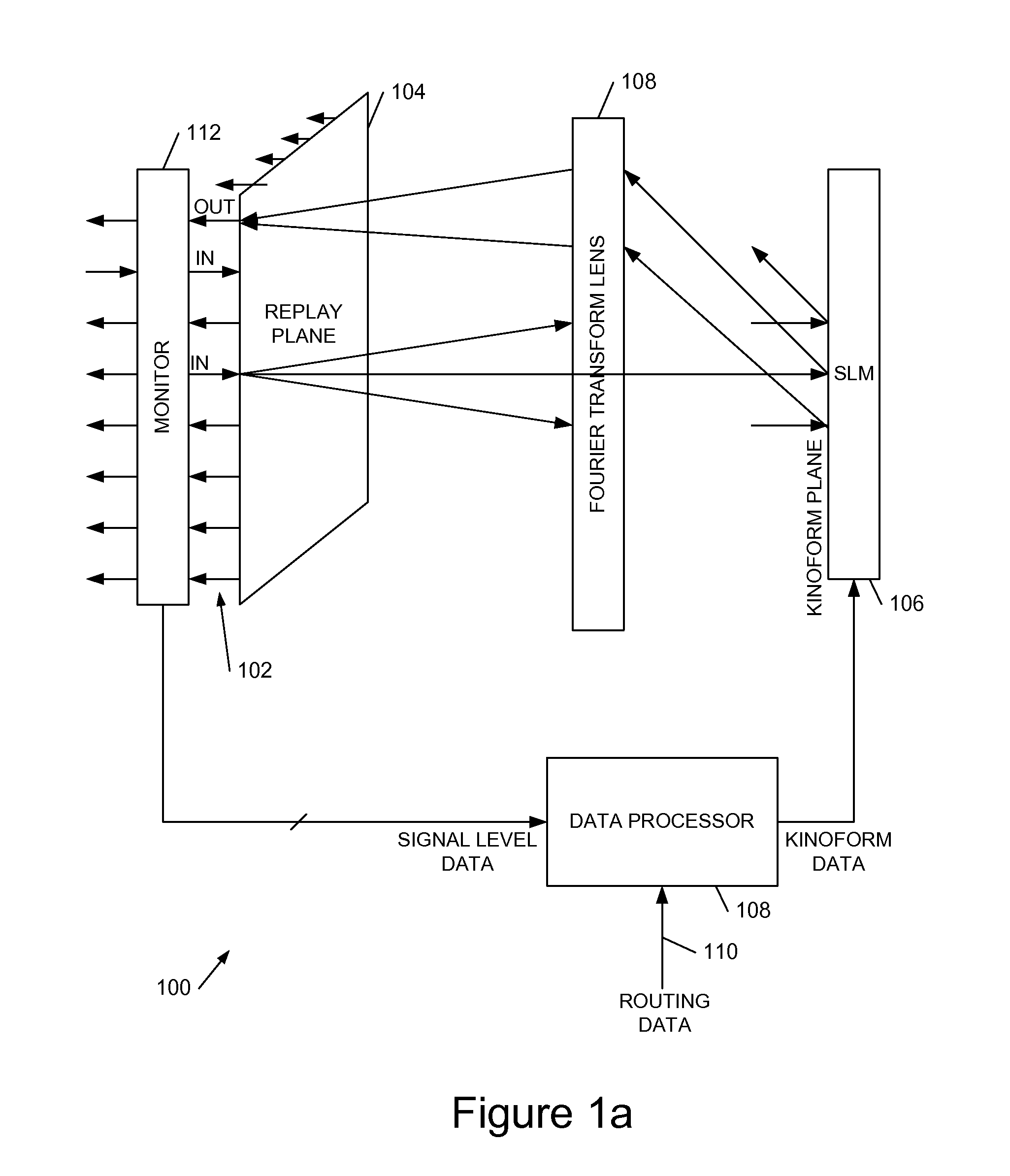
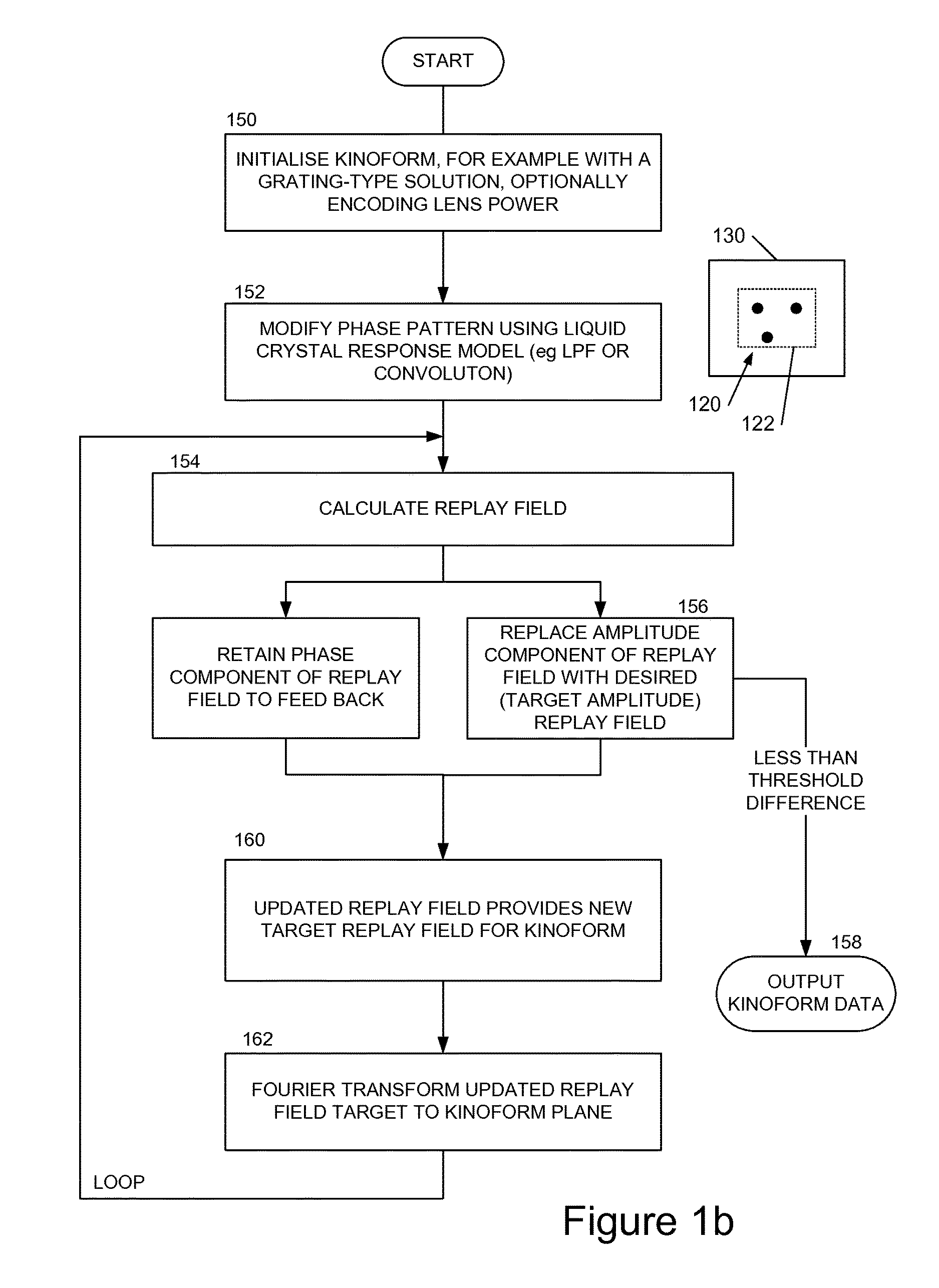
We describe a LCOS (liquid crystal on silicon) telecommunications light beam routing device, the device comprising: an optical input; a plurality of optical outputs; a LCOS spatial light modulator (SLM) in an optical path between said input and said output, for displaying a kinoform; a data processor, coupled to said SLM, configured to provide kinoform data for displaying said kinoform on said SLM; wherein said kinoform data defines a kinoform which routes a beam from said optical input to a selected said optical output; wherein said data processor is configured to input routing data defining said selected optical output and to calculate said kinoform data for routing said beam responsive to said routing data; and wherein said data processor is configured to calculate said kinoform data by: determining an initial phase pattern for said kinoform; calculating a replay field of said phase pattern; modifying an amplitude component of said replay field to represent a target replay field for said beam routing, retaining a phase component of said replay field to provide an updated replay field; performing a space-frequency transform on said updated replay field to determine an updated phase pattern for said kinoform; and repeating said calculating and updating of said replay field and said performing of said space-frequency transform until said kinoform for display is determined; and outputting said data for display on said LCOS SLM.
Owner:CAMBRIDGE ENTERPRISE LTD
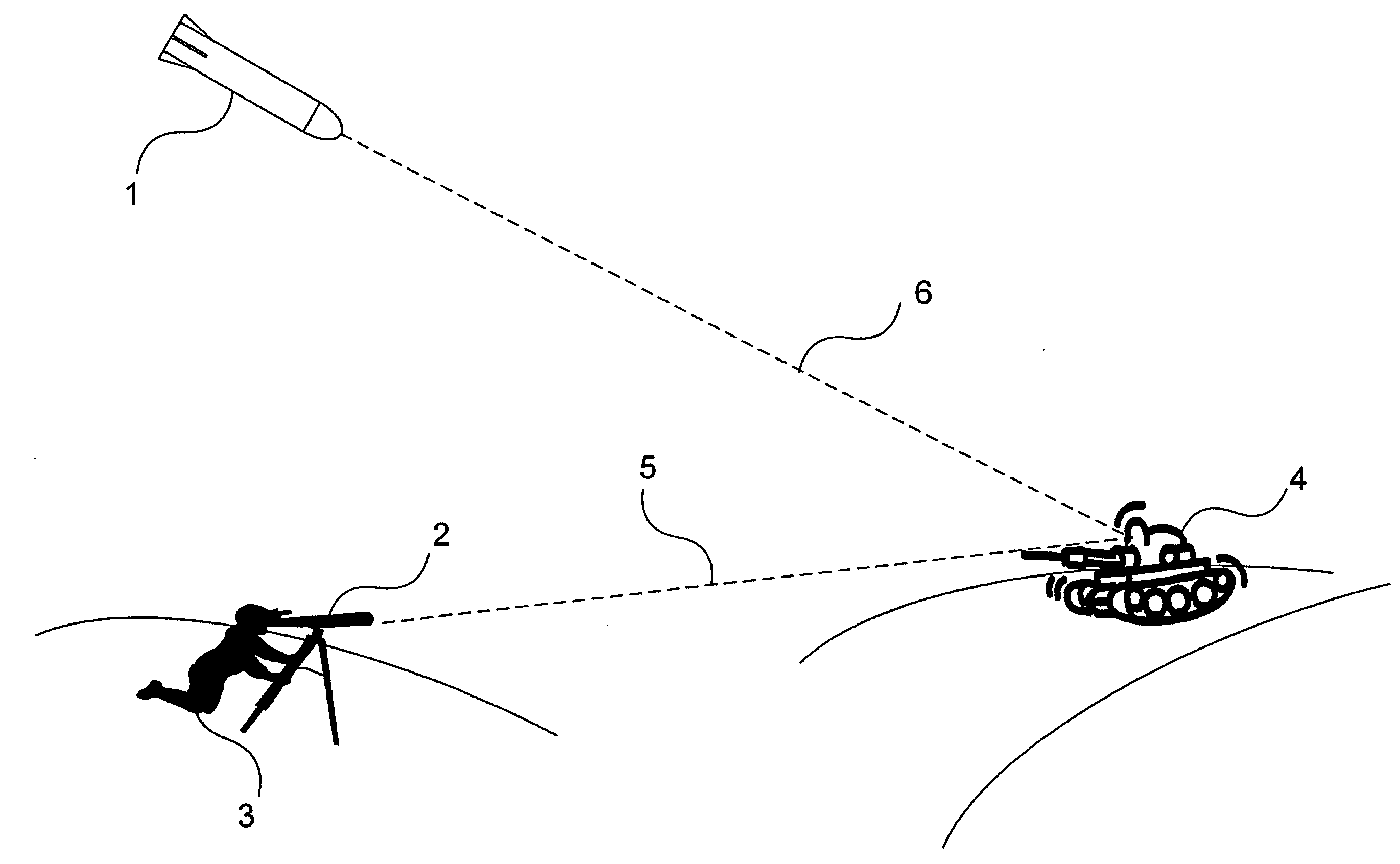
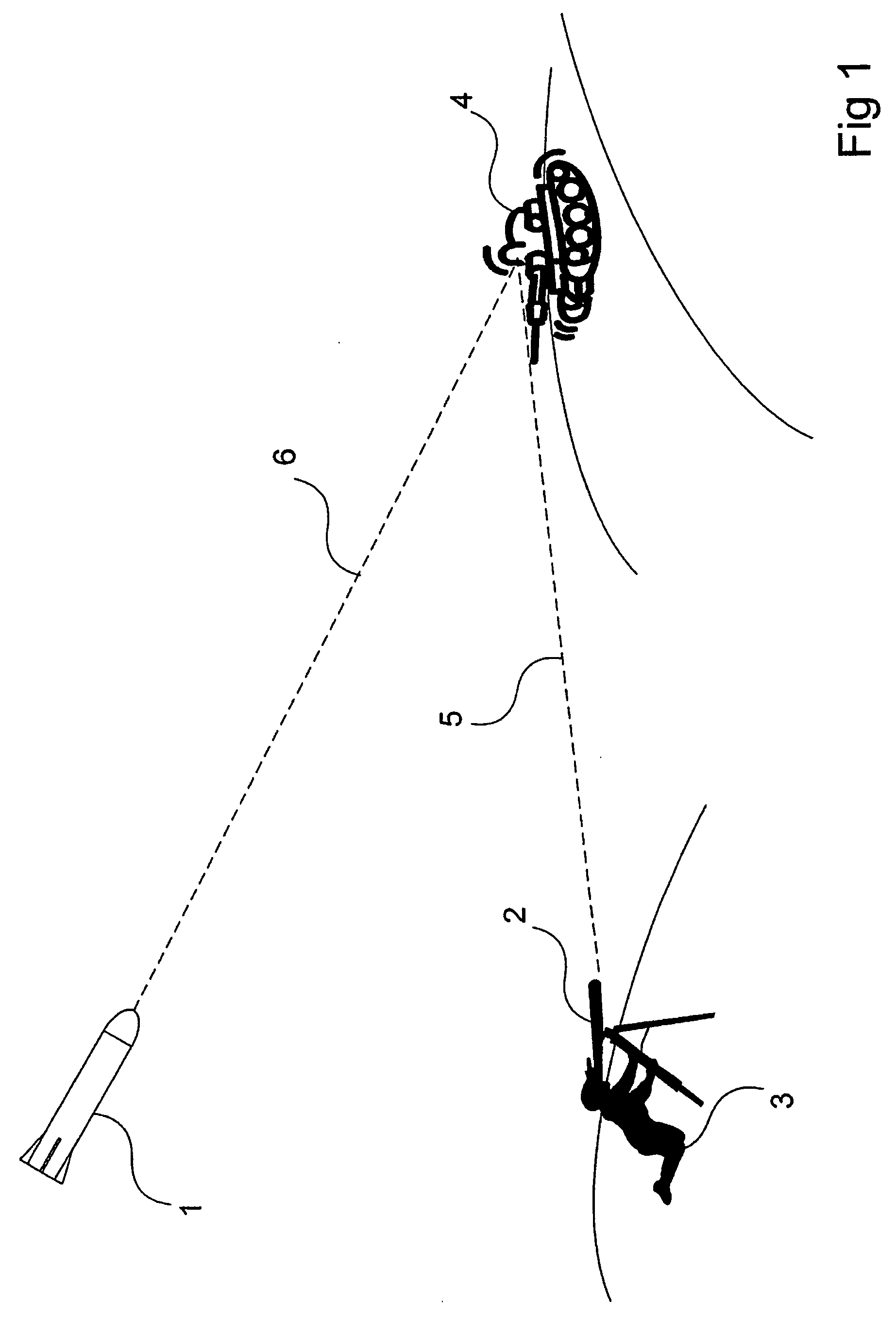
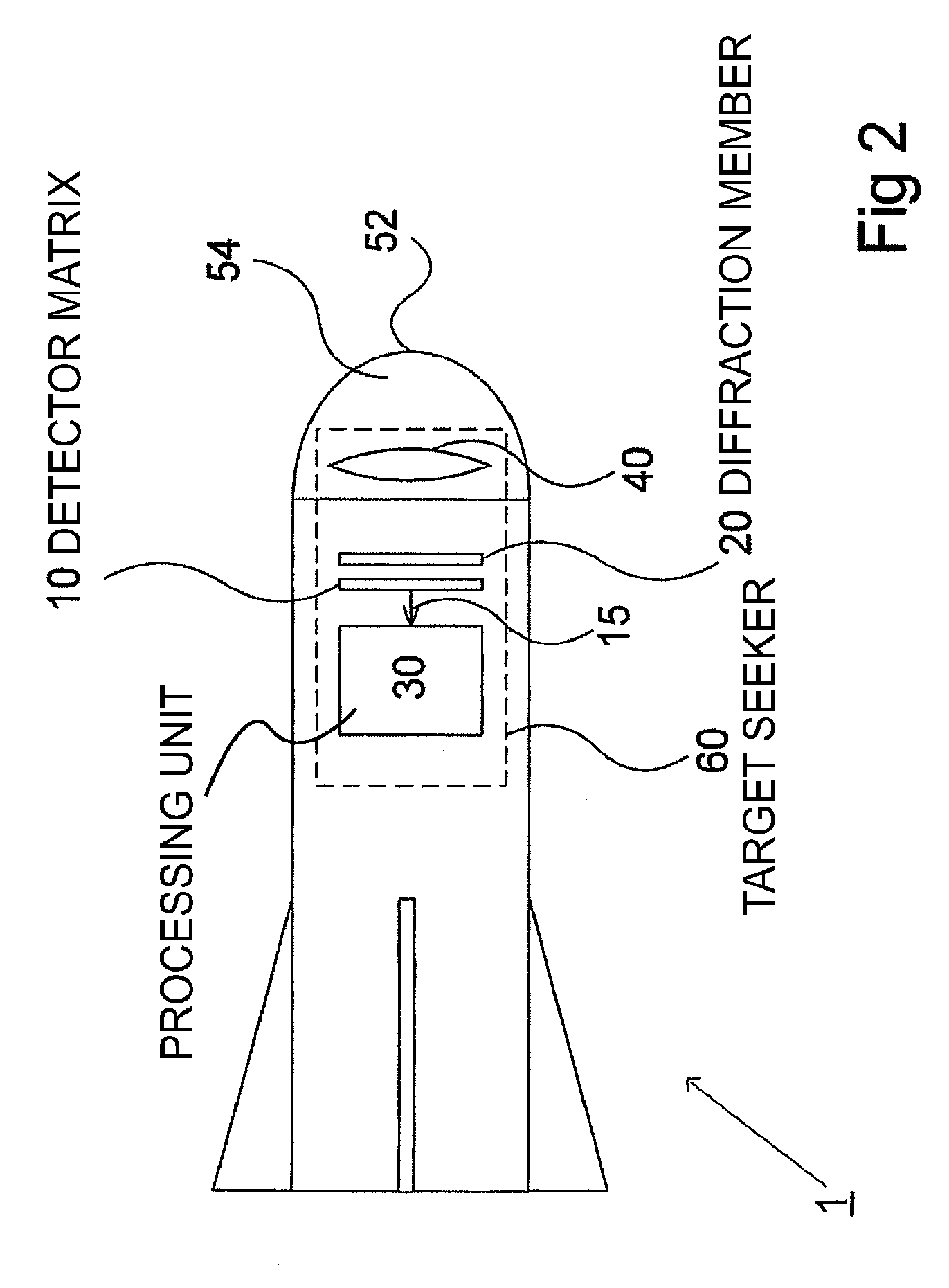
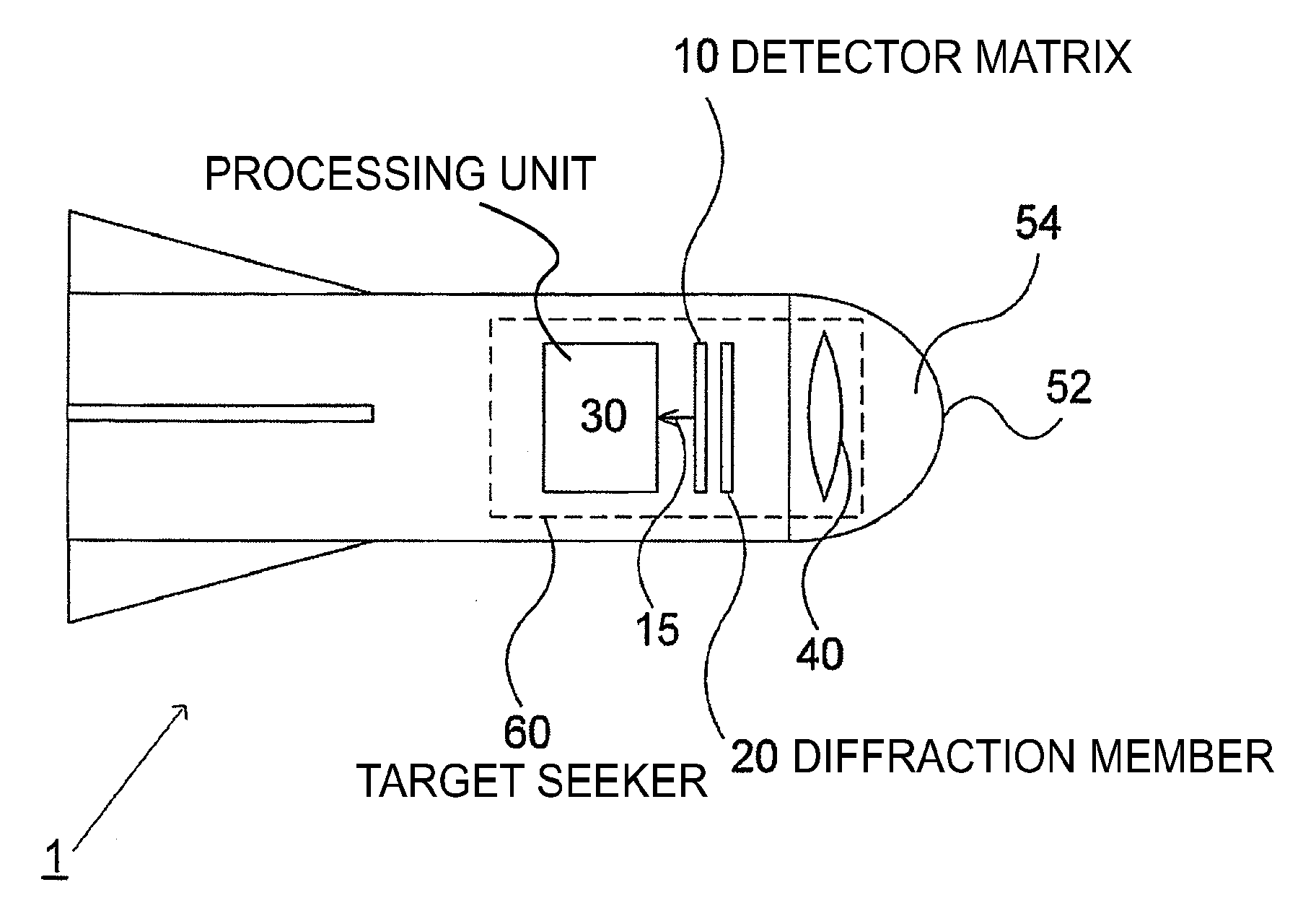
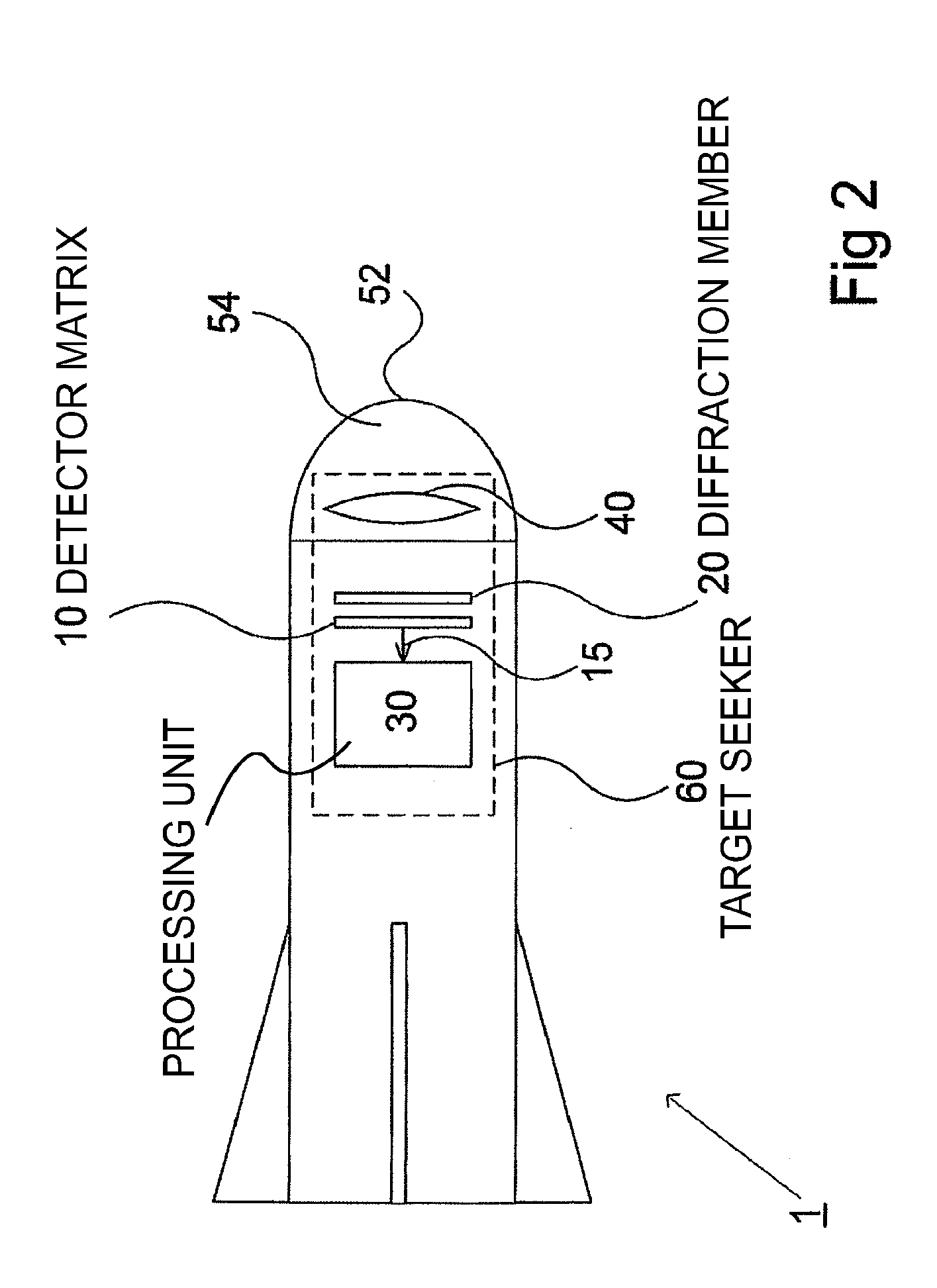
Laser target seeker device
ActiveUS20100001119A1Improve accuracyDirection controllersInstruments for comonautical navigationLaser targetKinoform
A laser target seeker device arranged to receive a laser beam reflected from an object. Detector elements are arranged to detect the reflected laser beam. A processor is arranged to determine the received radiation on the respective detector element in order to determine the origin of the laser beam. A diffractor is arranged relative to the detector elements and configured to diffract the reflected laser beam into portions prior to being detected by the detector elements. The detector elements are arranged to detect the respective portion. A flyable body is for hitting a target by means of a laser beam. A system for hitting a target by means of a laser beam. A method for detecting a laser beam reflected from an object. Use of a kinoform member in a laser target seeker for diffracting a laser beam.
Owner:SAAB AB
Apparatus and method for displaying a video image
InactiveCN101034279AHolographic light sources/light beam propertiesHolographic optical componentsComputer graphics (images)Light beam
Owner:CAMBRIDGE ENTERPRISE LTD
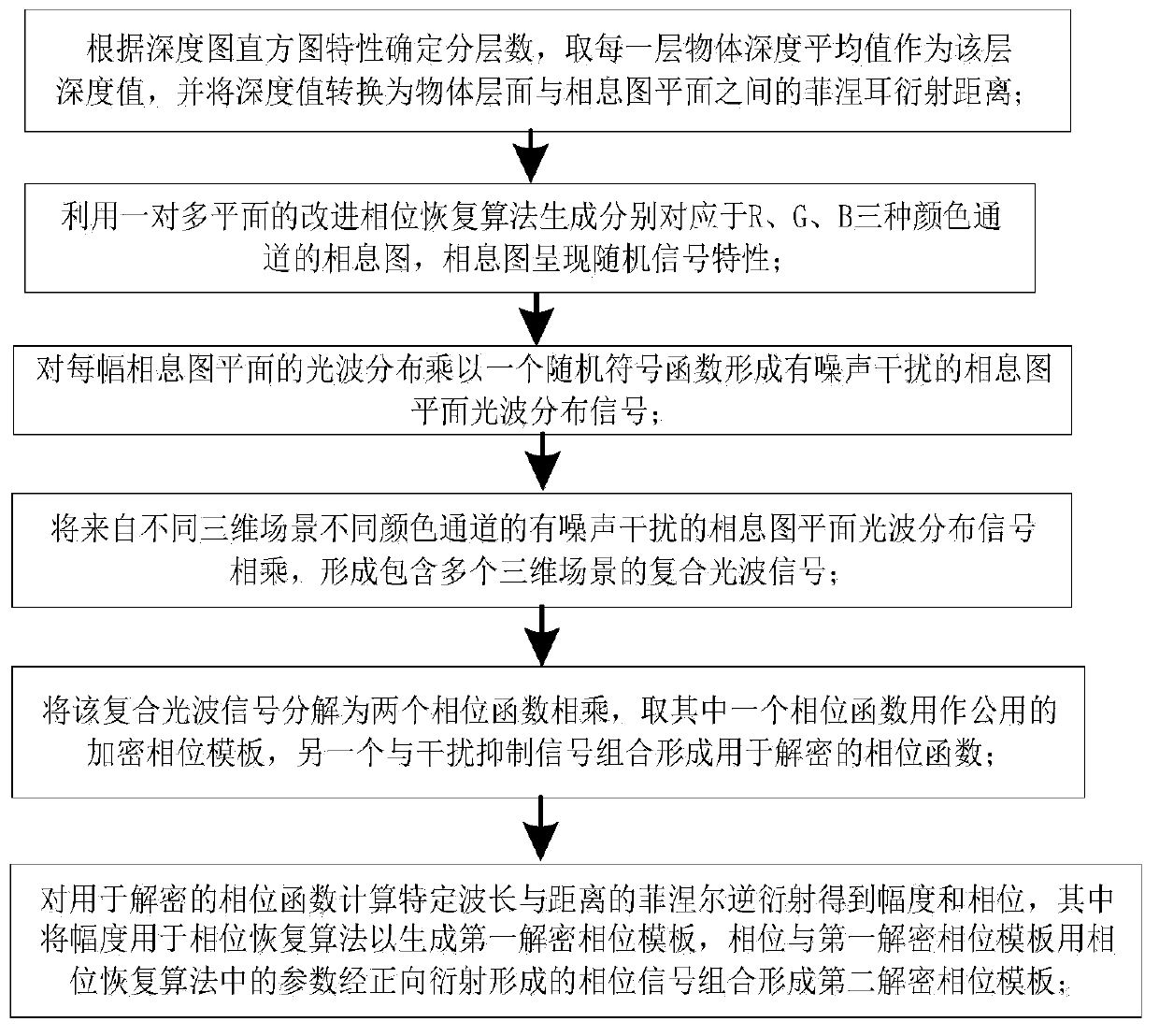
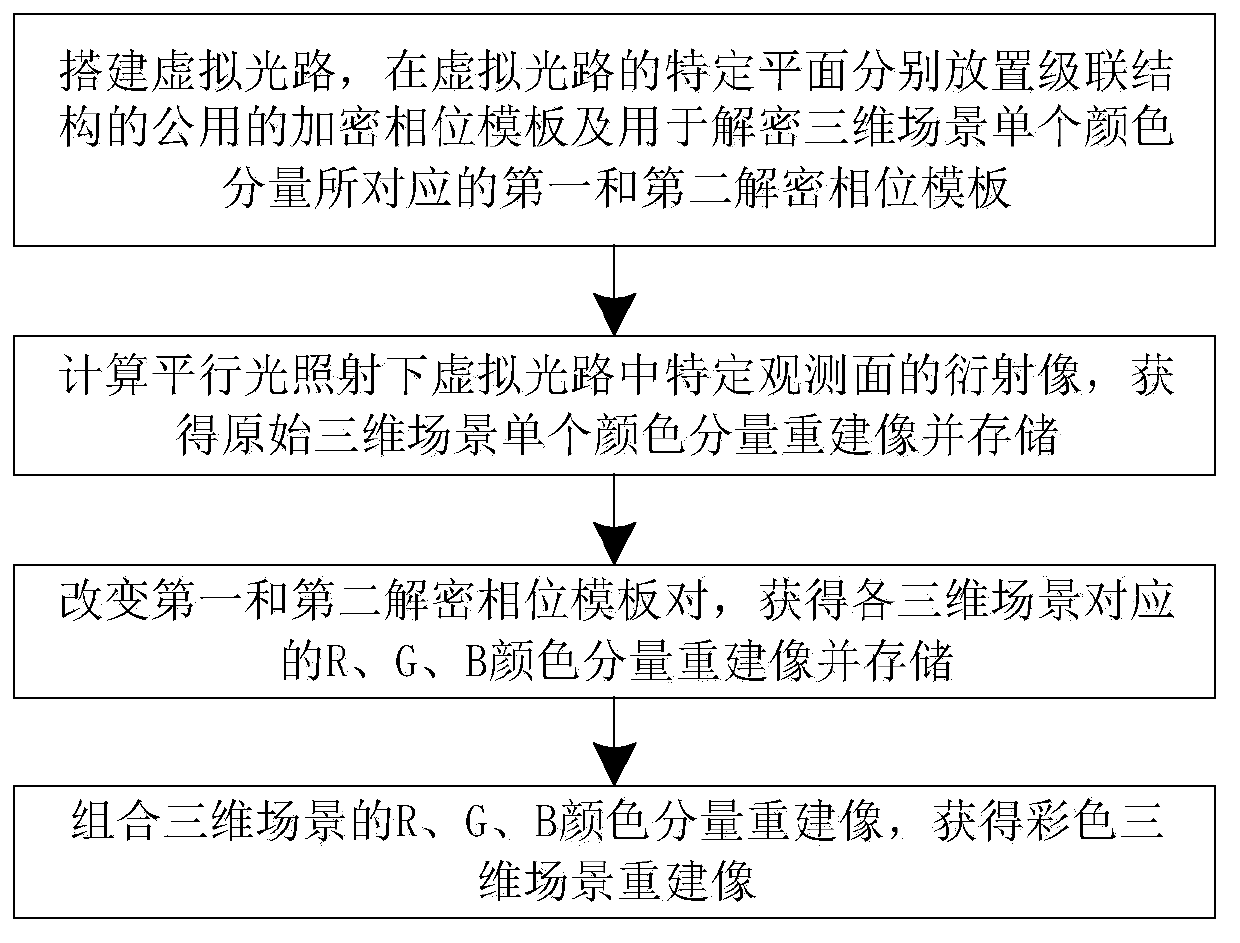
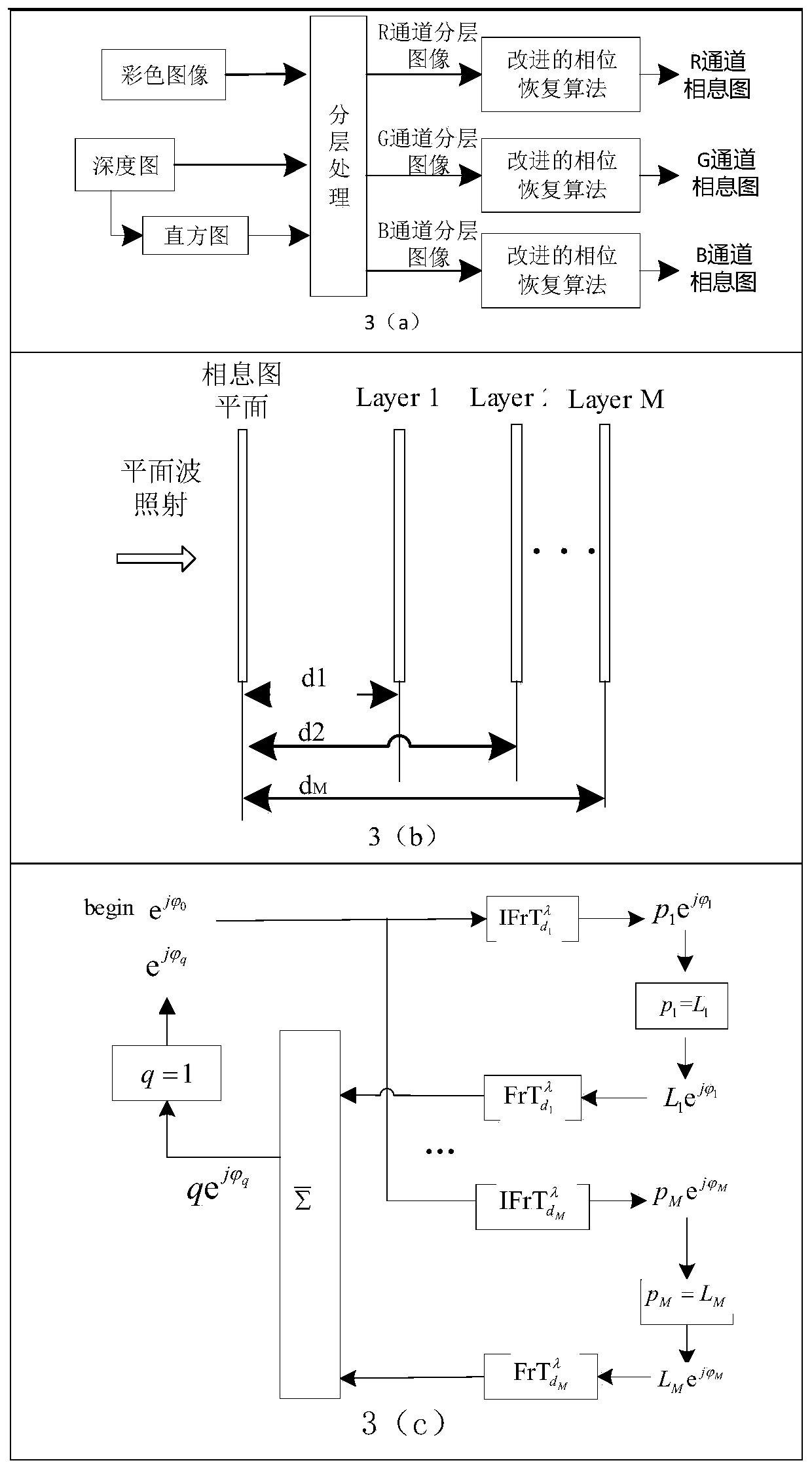
Multi-complex three-dimensional scene encryption and decryption method
The invention discloses a multi-complex three-dimensional scene encryption and decryption method, which comprises the following steps of: generating a kinoform for each color layered image of a three-dimensional scene by using a phase recovery algorithm, and multiplying the kinoform by a random symbol function to form a light wave signal with noise interference; multiplying the kinogram plane light wave signals with noise interference of different color channels in different three-dimensional scenes to form a composite light wave signal; decomposing the composite light wave signal into two phase functions to be multiplied, using one phase function as a common encryption phase template, and combining the other phase function with an interference suppression signal to form a phase function for decryption; calculating Fresnel inverse diffraction of a specific wavelength and a specific distance for the phase function for decryption to obtain an amplitude and a phase, applying a phase recovery algorithm to the amplitude to generate a first decrypted phase template, and combining the phase with a phase formed by forward Fresnel diffraction of the first decrypted phase template to form asecond decrypted phase template. All color components of a three-dimensional scene are decrypted by placing an encryption phase template of a cascade structure and first and second decryption phase templates on a specific plane of a virtual light path and are combined to recover the color three-dimensional scene. The method has good safety and robustness.
Owner:FUJIAN NORMAL UNIV
Two-dimensional code laser marking method and device based on liquid crystal spatial light modulator
Disclosed is a two-dimensional code laser marking method and device based on a liquid crystal spatial light modulator. The device mainly comprises a laser device, a polarizer, beam expanding collimation systems, the liquid crystal spatial light modulator, a computer, focusing collimation systems and an imaging lens. Lasers emitted by the laser device pass through the polarizer to become polarized light, the polarized light passes through the beam expanding collimation systems to become parallel light, the parallel light is incident to the liquid crystal spatial light modulator, the liquid crystal spatial light modulator performs image information modulation on the parallel light, a two-dimensional code image output by two-dimensional code generating software generates a kinoform through the computer so as to precisely control a phase image displayed on the liquid crystal spatial light modulator, diffraction light splitting is performed on the parallel light through the image displayed on the liquid crystal spatial light modulator, and therefore the parallel light becomes diffraction light, the light beam of the diffraction light is narrowed and collimated through the focusing collimation systems, and finally the lasers are focused on a workpiece surface required to be marked through a flat-field lens.
Owner:SHANGHAI FEINIEER LASER TECH CO LTD
Digital video watermark method using kinoform
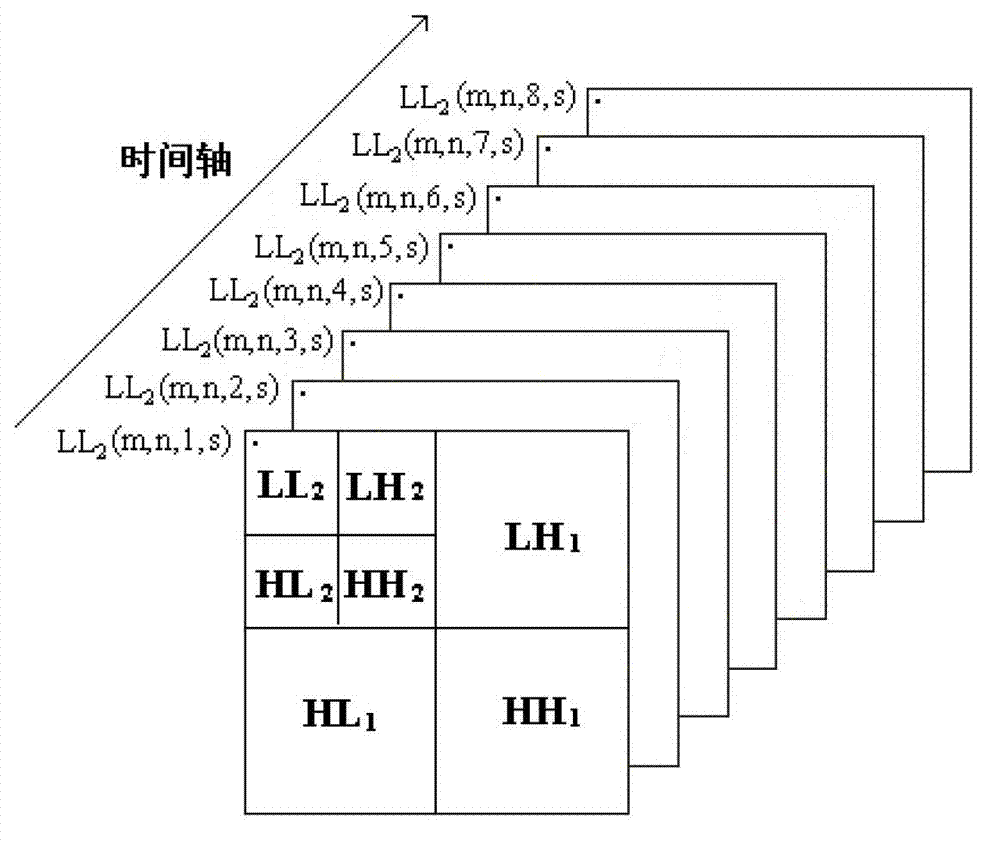
InactiveCN103179406AMany degrees of freedomImprove securityTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationDigital videoWatermark method
The invention discloses a digital video watermark method using a kinoform and relates to a multimedia signal processing method. The digital video watermark method using the kinoform provided by the invention is high in imperceptibility and can effectively resist various attacks. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) manufacturing the kinoform based on Gyrator conversion by using a computer, wherein the manufactured kinoform serves as a watermark information sequence which is embedded into a carrier video; (2) embedding the kinoform into the carrier video; (3) judging whether a video contains watermark information or not by using a watermark detection algorithm; and (4) reproducing the kinoform on the computer, and particularly, reproducing the contents of an extracted watermark on the computer.
Owner:HANSHAN NORMAL UNIV
Optical beam routing apparatus and methods
ActiveUS9363582B2Reduce couplingIncreasing ‘ aberration ’Multiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsSpatial light modulatorDiffraction order
This invention relates to methods and apparatus for routing light beams in telecommunications devices using holographic techniques, in particular by displaying kinoforms on LCOS (Liquid Crystal on Silicon) devices. Thus we describe optical beam routing apparatus comprising: at least one optical input to receive an input beam; a plurality of optical outputs; a spatial light modulator (SLM) on an optical path between said optical input and said optical outputs; and a driver for said SLM to display a kinoform on said SLM to diffract said input beam into an output beam comprising a plurality of diffraction orders, wherein a routed one of said diffraction orders is directed to at least one selected said optical output; wherein said apparatus is configured to modify a wavefront of said output beam to reduce a coupling of said output beam into said selected optical output; and wherein said kinoform is adapted to compensate for said wavefront modification to compensate for said reduced coupling and thereby to reduce a coupling of other diffracted light from said input beam into others of said optical outputs than said at least one selected optical output.
Owner:CAMBRIDGE ENTERPRISE LTD
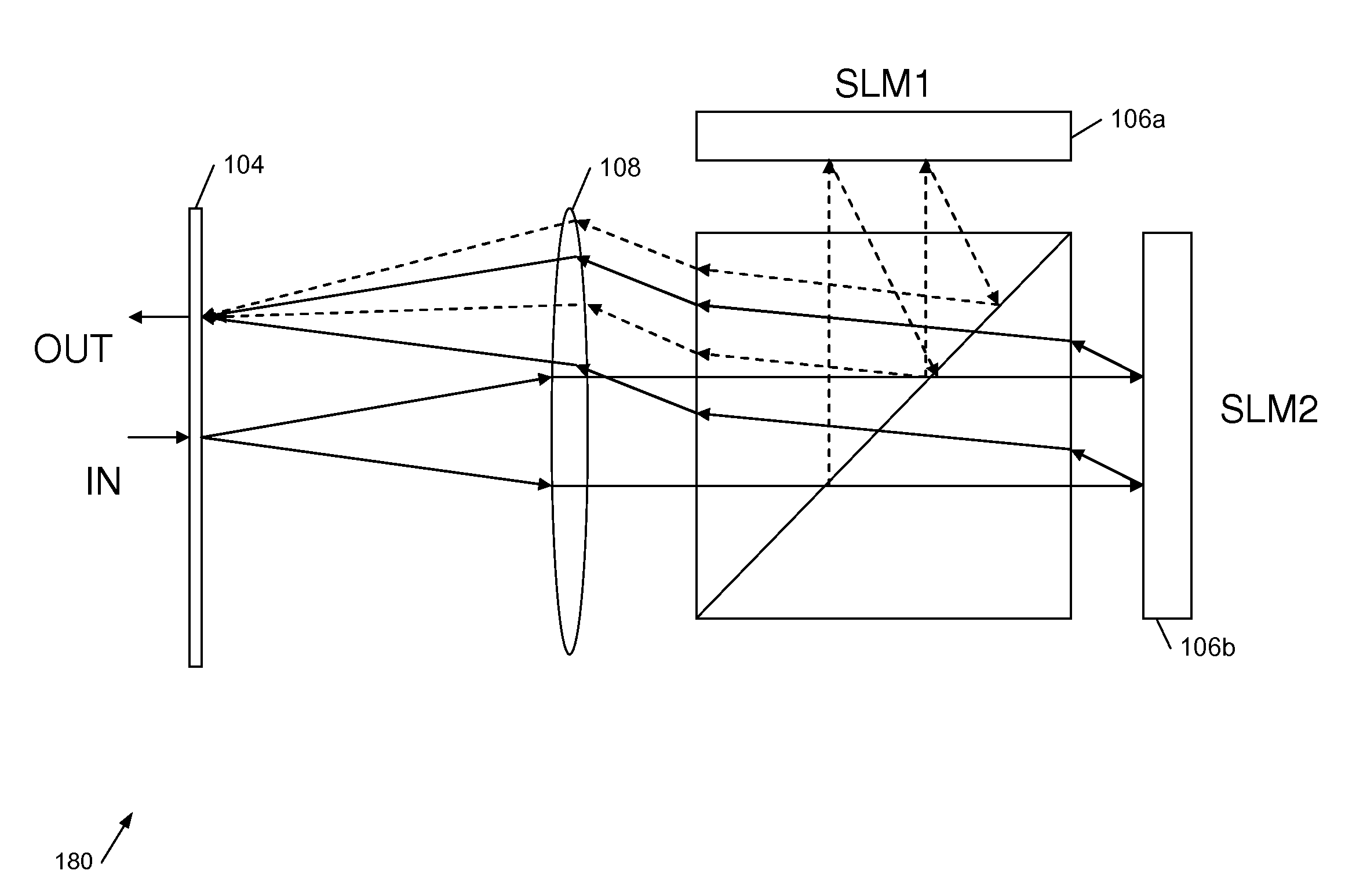
Apparatus and methods for light beam routing in telecommunication
ActiveUS9547276B2Reduce crosstalkImprove signal-to-noise ratioMultiplex system selection arrangementsHolographic light sources/light beam propertiesSpatial light modulatorDisplay device
Owner:CAMBRIDGE ENTERPRISE LTD
Laser target seeker device
ActiveUS7659494B2Improve accuracyDirection controllersDirection/deviation determining electromagnetic systemsLaser targetKinoform
A laser target seeker device arranged to receive a laser beam reflected from an object. Detector elements are arranged to detect the reflected laser beam. A processor is arranged to determine the received radiation on the respective detector element in order to determine the origin of the laser beam. A diffractor is arranged relative to the detector elements and configured to diffract the reflected laser beam into portions prior to being detected by the detector elements. The detector elements are arranged to detect the respective portion. A flyable body is for hitting a target by means of a laser beam. A system for hitting a target by means of a laser beam. A method for detecting a laser beam reflected from an object. Use of a kinoform member in a laser target seeker for diffracting a laser beam.
Owner:SAAB AB
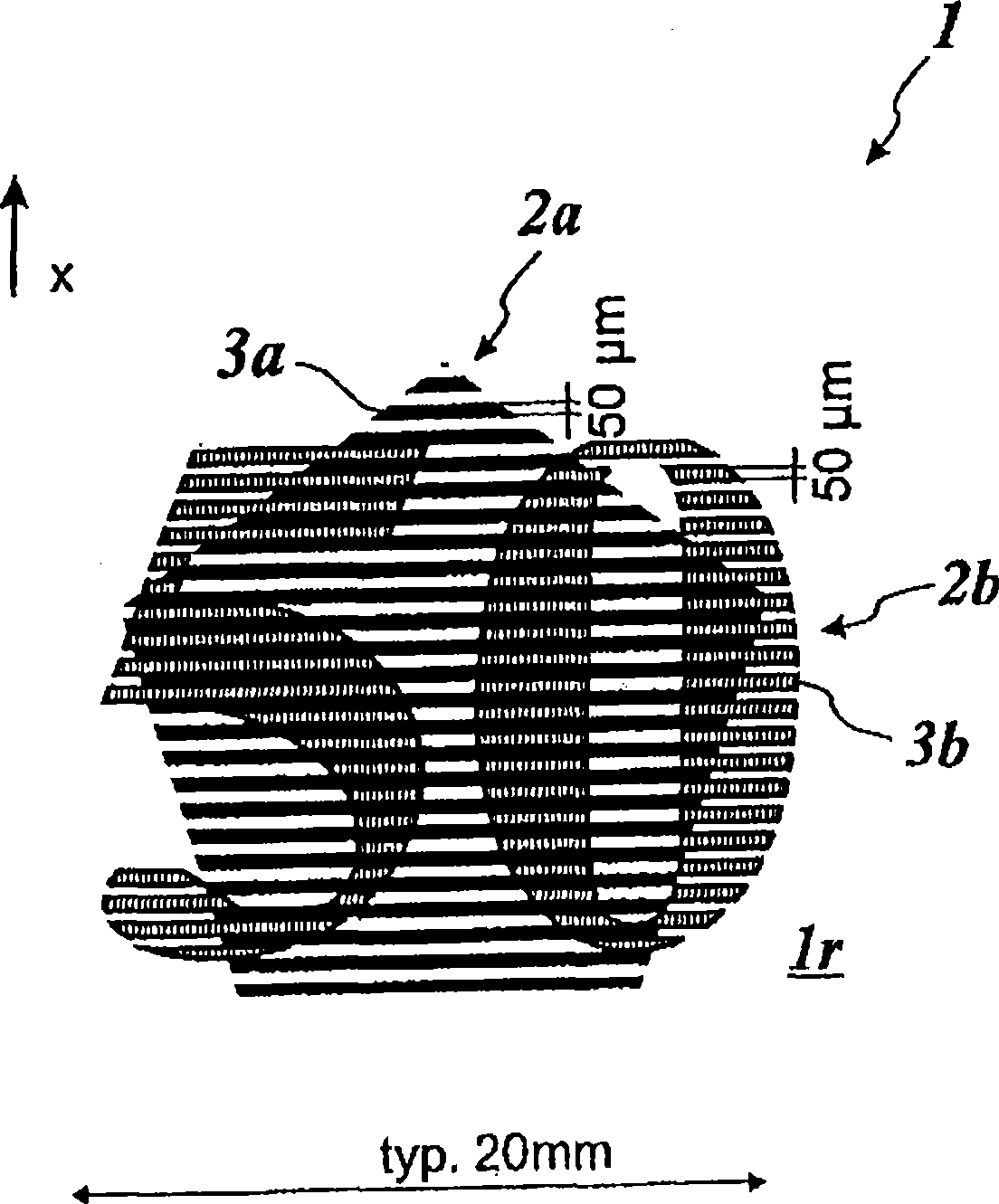
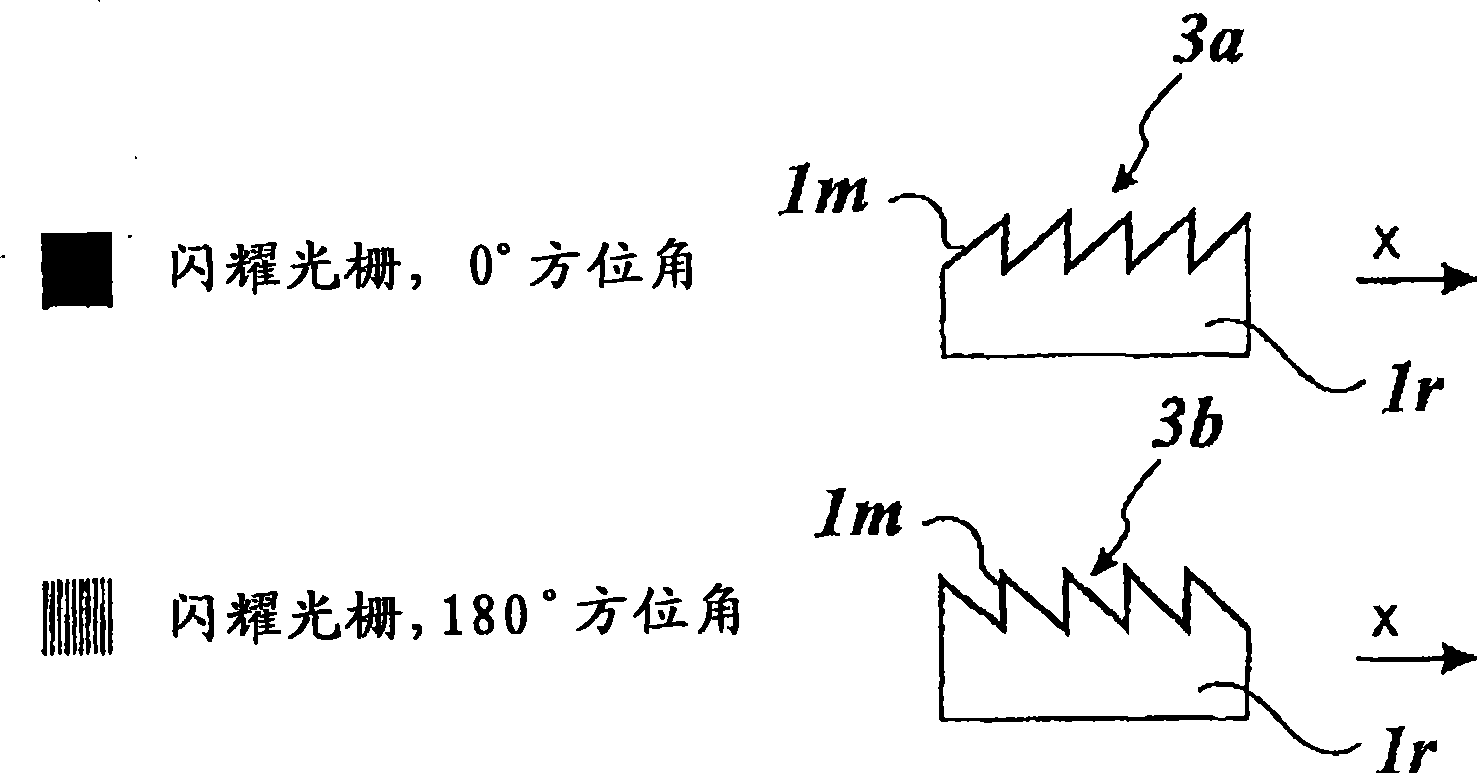
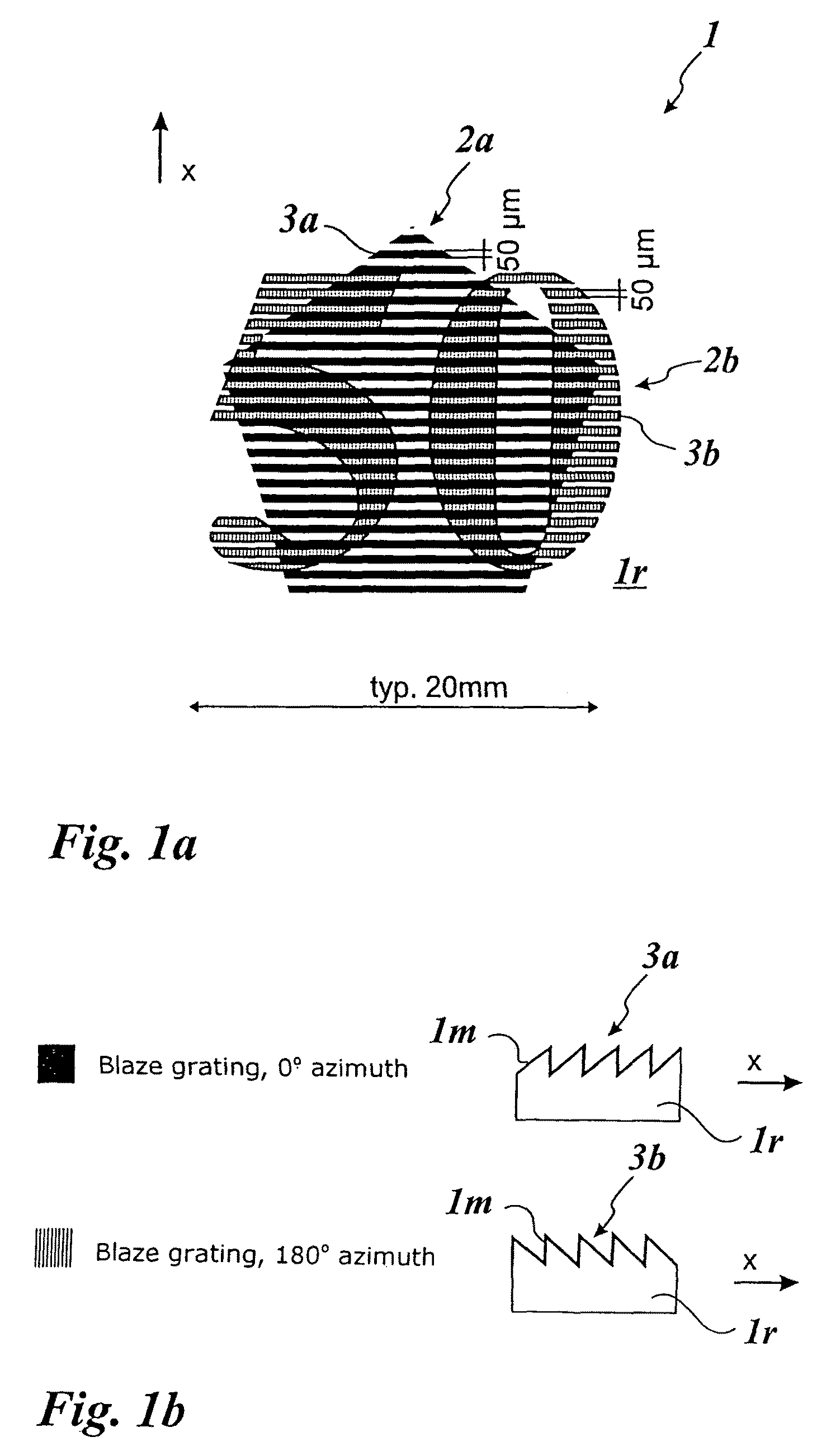
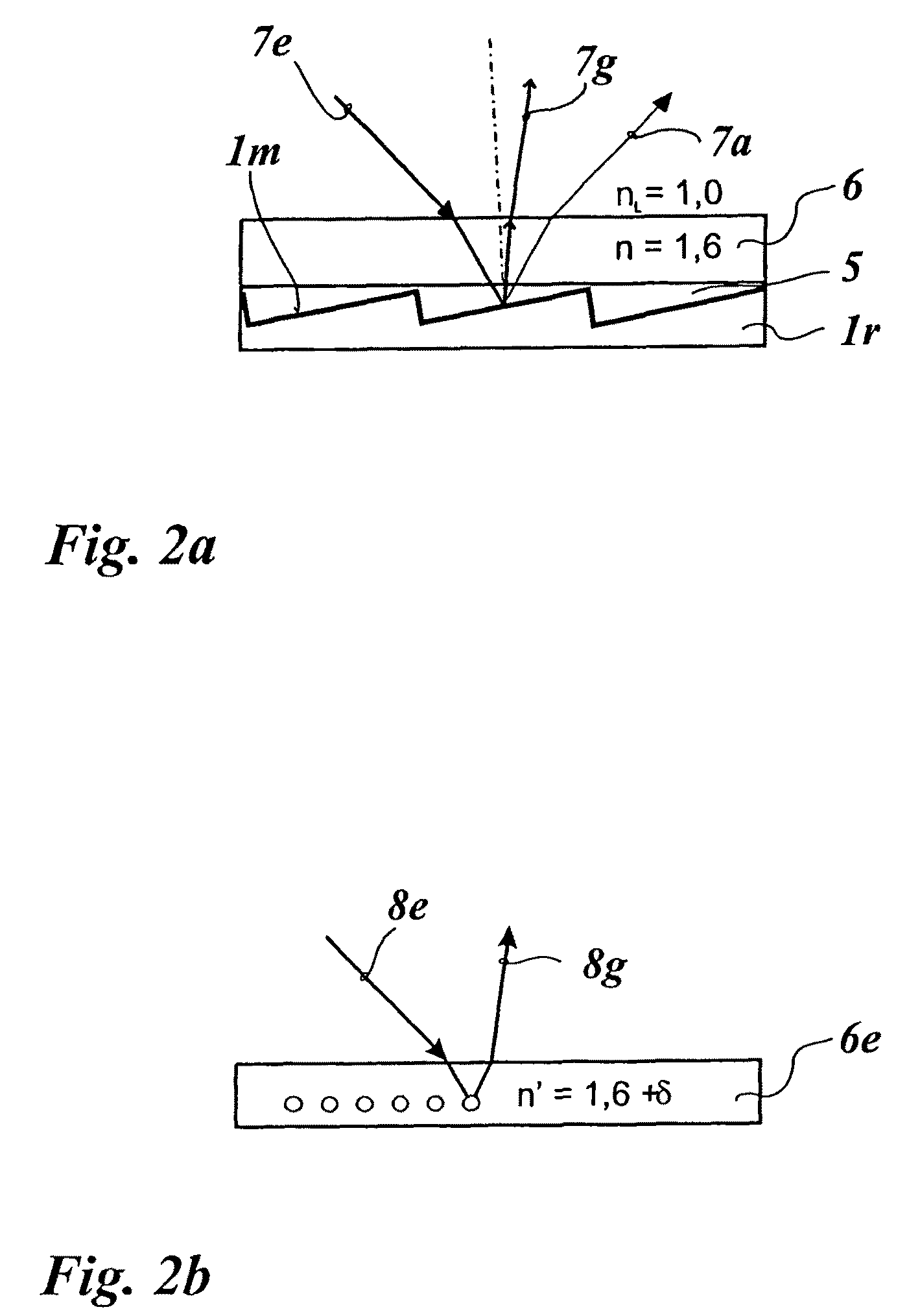
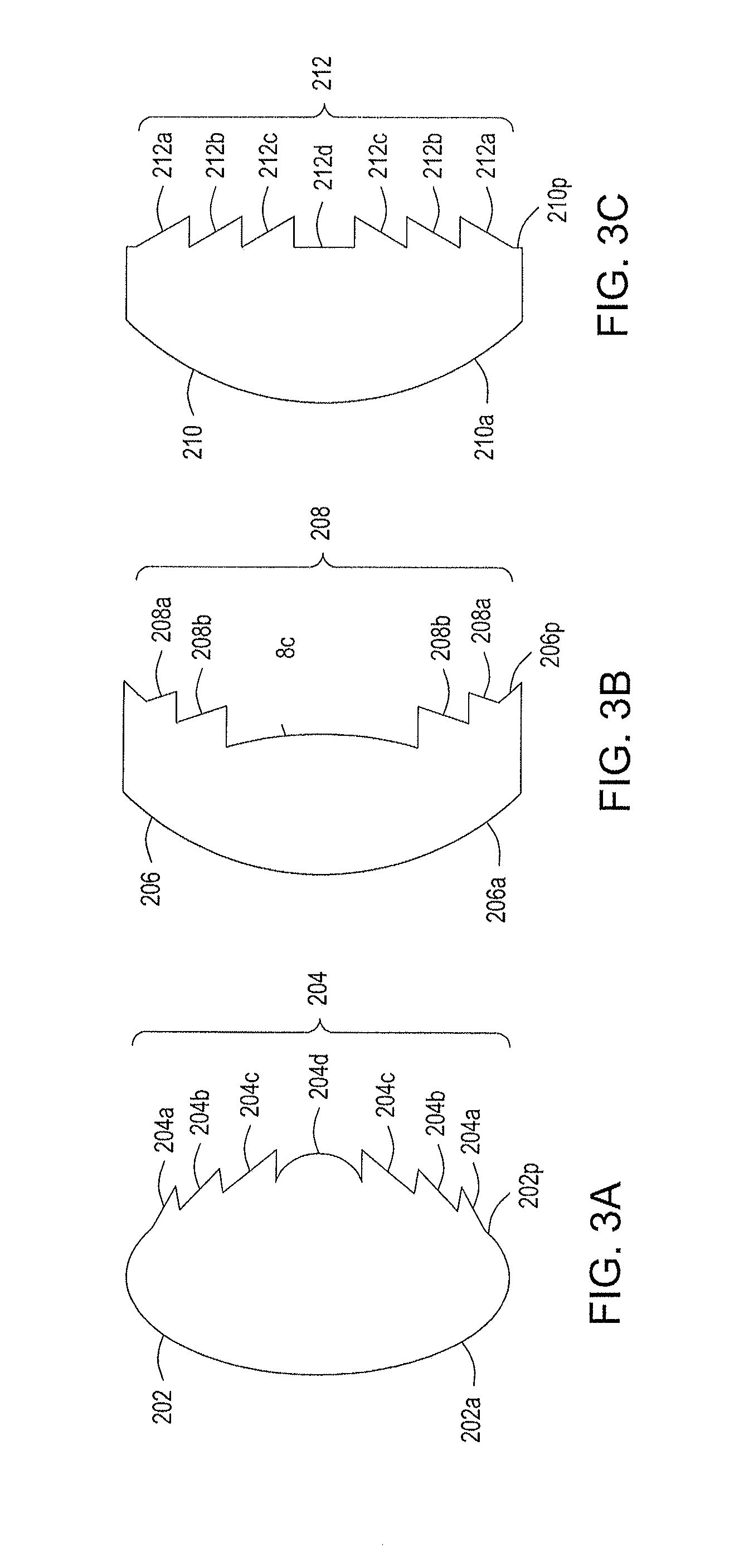
Diffractive optical element and method of manufacture of the same
A diffractive optical element having plural diffraction grating surfaces accumulated, wherein a pair of diffraction grating surfaces are positioned so that a protrusion and / or a recess formed on an outside of one diffraction grating surface engages with a recess and / or a protrusion formed on an outside of the other diffraction grating surface, and wherein the pair of diffraction grating surfaces are defined on materials having different refractive indices and different dispersions and being formed into a kinoform, or a shape and a height of blazed or binary, close to it, such that a largest optical path difference to be applied to light rays passing through the diffraction grating surfaces with respect to plural wavelengths becomes equal to a multiple, by an integral number, of the wavelength.
Owner:CANON KK
Projection illumination systems lenses with diffractive optical elements
InactiveUS20070247715A1Easy to manufactureLight weightDiffraction gratingsLensFresnel lensSpatial light modulator
An optical assembly for a projection illumination system has a refractive lenses and a diffractive lens for imaging a sheet of light from a light source onto a Spatial Light Modulator (SLM). One embodiment utilizes a fresnel lens having kinoforms formed on a surface. Such a lens may be molded using a light-weight plastic in a single step.
Owner:OC OERLIKON BALZERS AG
Device and method for moving self-focusing point of round Airy beam in large-range and high-precision manner
ActiveCN111273451AAchieve high precision controlAvoid inaccuraciesStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsSpatial light modulatorFrequency spectrum
The invention discloses a device and method for moving a self-focusing point of a round Airy beam in a large-range and high-precision manner. The method comprises the following steps of polarizing a Gaussian beam outputted by a laser by a polarizer, expanding the Gaussian beam by a 4f system formed by combining a first lens and a second lens, and enabling the Gaussian beam to irradiate to a spatial light modulator, loading the frequency spectrum information of the round Airy beam on the spatial light modulator, and operating and controlling a two-dimensional plane of the self-focusing point ofthe round Airy beam through frequency spectrum translation; after the modulation of the spatial light modulator, the reflection of a plane mirror and the Fourier transform of a third lens, obtainingthe round Airy beam on a focal plane, and observing a self-focusing point after two-dimensional displacement at a self-focusing position of the round Airy beam by using a charge coupler. By changingdifferent kinograms loaded by the spatial light modulator, the track of the generated round Airy beam can be finely, simply and conveniently adjusted, the purpose of changing the position of the self-focusing point is achieved, and the two-dimensional movement of the self-focusing point is large in regulation range and high in precision.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Design method of diffractive optical element with high diffraction efficiency and low speckle noise
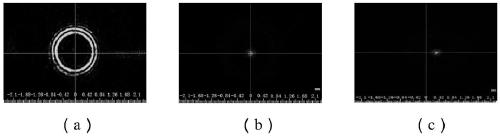
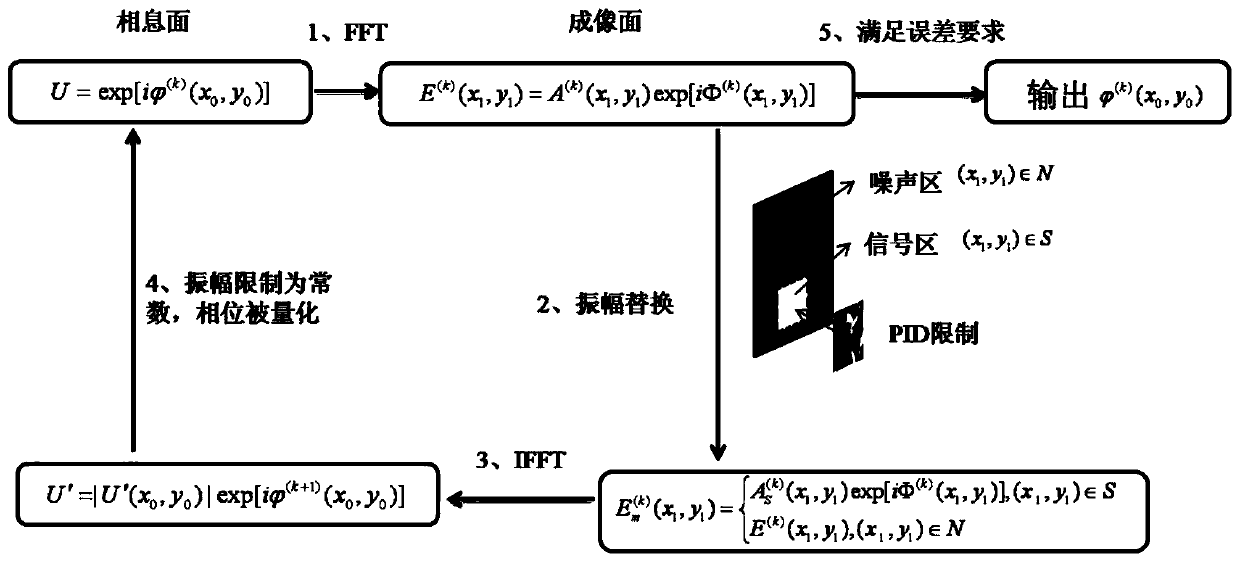
The invention discloses a design method of a diffractive optical element with high diffraction efficiency and low speckle noise. The design method comprises the following steps: 1) taking a complex amplitude light field of which the amplitude is a constant amplitude and the phase is a random phase as an initial complex amplitude light field on a kinoform surface; 2) spreading the complex amplitudelight field on the kinoform to an imaging surface through diffraction, and obtaining a complex amplitude light field on the imaging surface; 3) replacing the amplitude part of the complex amplitude light field obtained in the step 2) with specially designed PID limitation; 4) reversely diffracting and propagating the replaced complex amplitude light field in the step 3) back to the kinoform surface to obtain a complex amplitude light field; 5) taking out the phase part of the complex amplitude light field in the step 4), and quantifying the phase part to obtain the phase of a diffractive optical element; (6) taking the phase obtained in the step (5) as the phase of the kinoform surface, and taking the constant amplitude as the amplitude of the kinoform surface to obtain a complex amplitude light field of the kinoform surface, and (7) repeating the step (2) and the step (6), and completing iteration when the diffractive optical element meets the design requirements.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Deformable accommodative intraocular lens
InactiveUS20150134059A1Enhanced power variationImprove variationIntraocular lensIntraocular lensRefractive surgery
A deformable accommodating intraocular lens (IOL) is disclosed, where the IOL comprises a diffractive kinoform-like grating pattern on one or both of the anterior or posterior surfaces of the deformable IOL. The capsular bag of the eye exerts a distorting force on the IOL, changing its power and allowing for accommodation. The focal length variation obtained by the change in curvature of the refractive surface of the IOL is enhanced by the kinoform-like diffractive grating pattern in combination with the traditional refractive surface. The focal length variation obtained by stretching and shrinking of the diffractive pattern adds considerable power variation independent of the refractive index of the material used to make the IOL.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
Color watermark preparation method based on kinoform
ActiveCN104408682AImprove robustnessImprove securityImage data processing detailsPattern recognitionKinoform
The invention discloses a color watermark preparation method based on kinoform. In the method, kinoform is applied in color watermark technology; compared with conventional color watermark technology, no reference light is led in during reproduction of kinoform, so that a single reproduction image can be acquired during reproduction; a random phase secret key is added, so that safety of watermark information is improved; due to own characteristics of kinoform, both robustness and safety can reach high level.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Optical Pickup Device
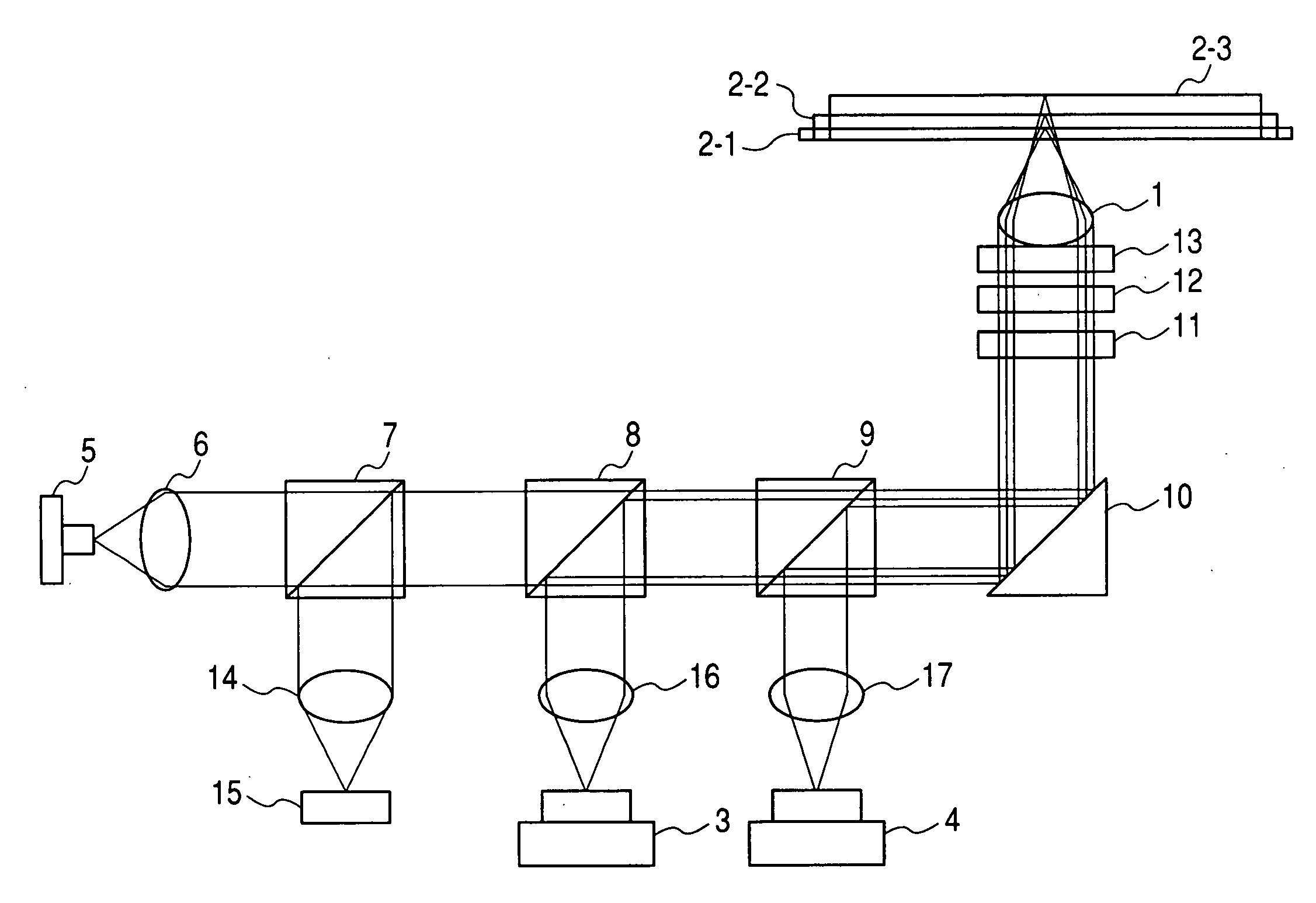
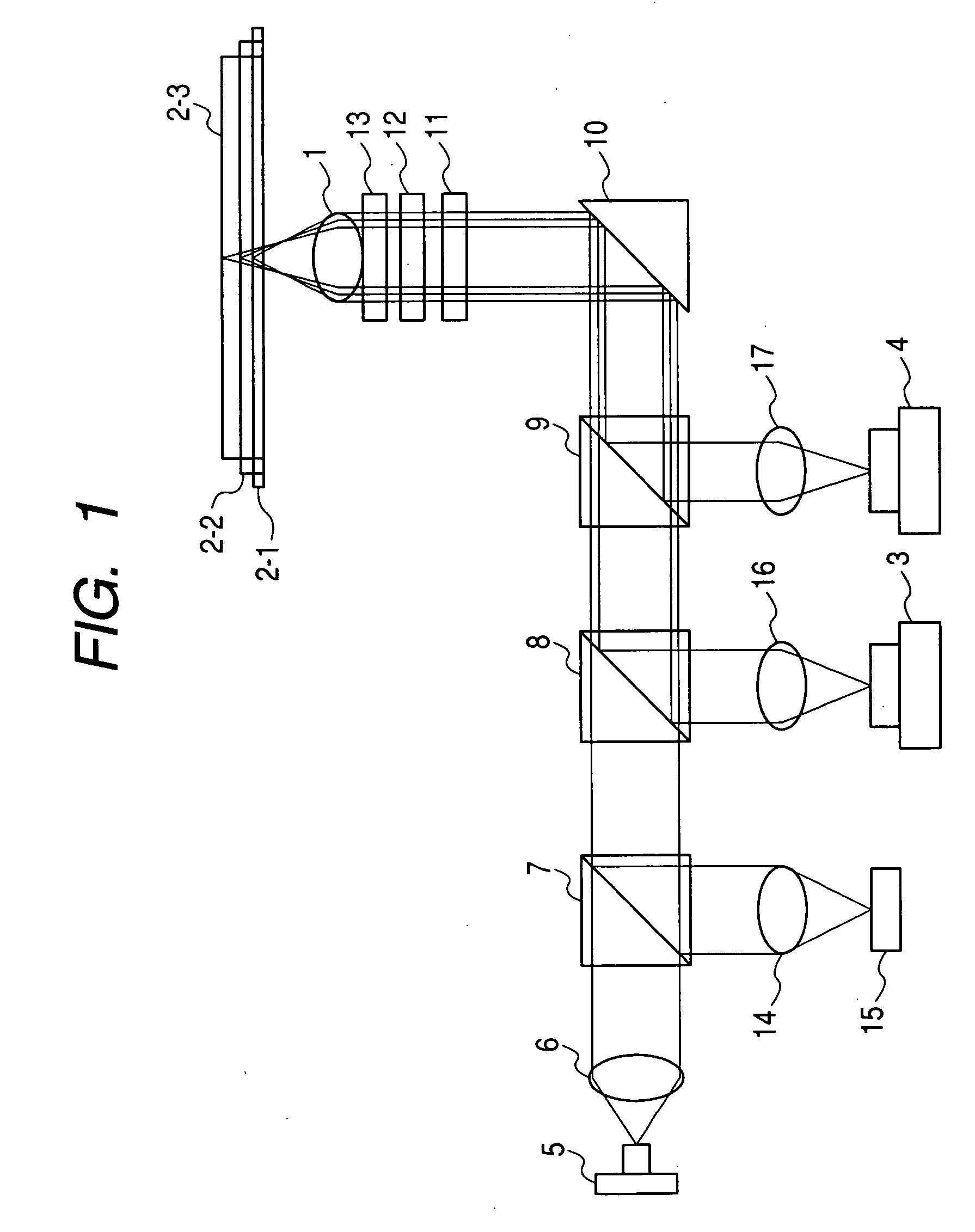
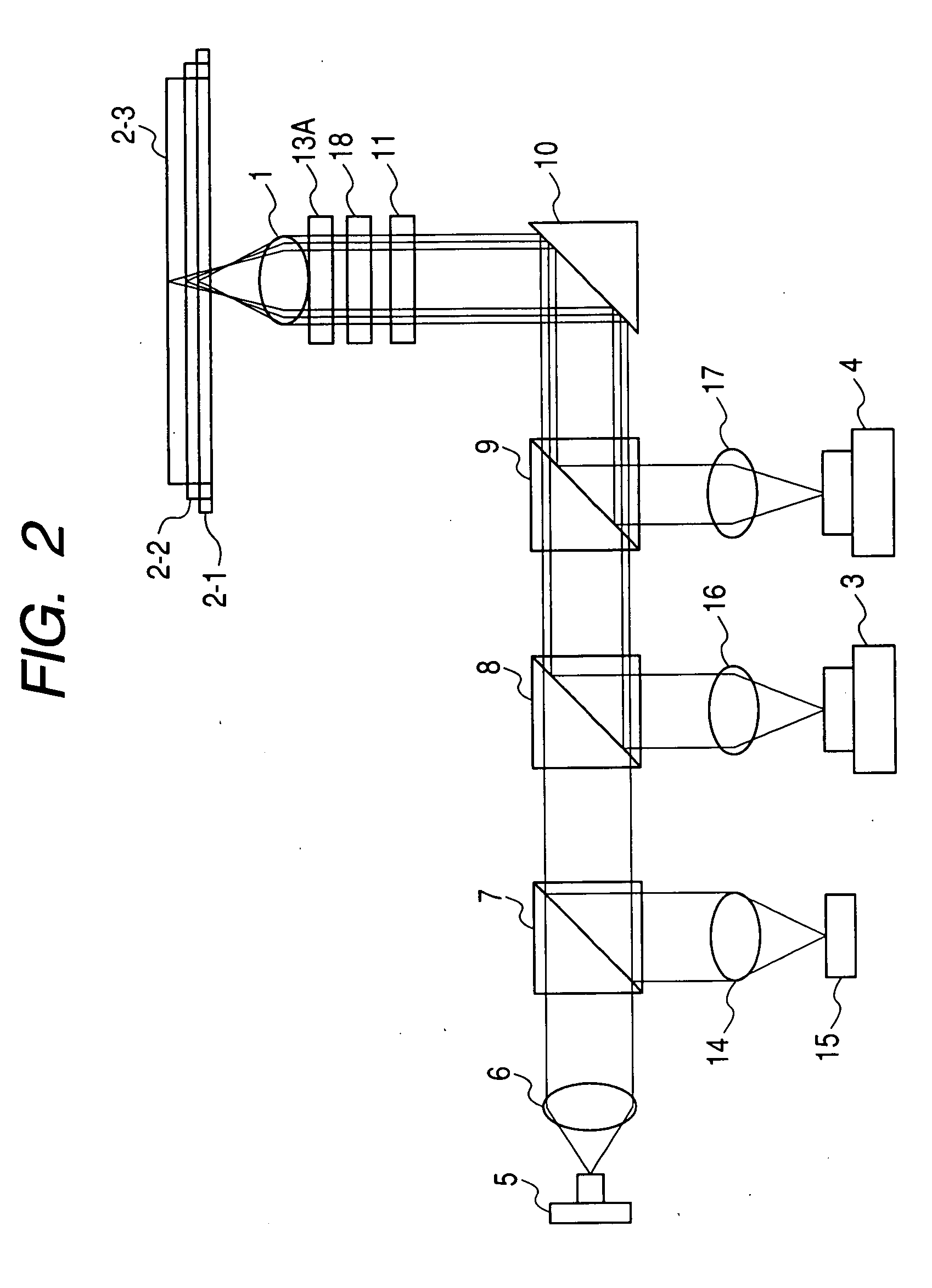
ActiveUS20090059768A1Improve light intensity distributionControl diffraction efficiencyRecord information storageOptical beam guiding meansOptical pickupPhase correction
An optical pickup device enables prevention of an increase of spherical aberration during tracking without needing any finite optical system. The diameters of parallel light beams (A, B, C) for the next-generation DVDs, DVDs, and CDs are limited to diameters of a, b, c (a>b>c) in accordance with the NA for each type by a light beam limiting element, the diameter of light beam B is limited to the diameter ranges of b to c and d (=0.85×c) to e (d>e>0), the diameter of the light beam C is limited to the diameter ranges of c to d and less than e. They are passed through a phase correcting element (13B) and focused on the corresponding optical recording medium signal planes by means of a common objective lens. The objective lens is so optimized that the wave front aberration to the light beam A is minimum on the signal plane of the next generation DVD. The phase correcting element (13B) has a phase correcting zones (Z1 to Z4) of diffraction optical structure exhibiting a pseudo-kinoform shape of a step constitution. The spherical aberration to the light beam B is corrected in the zones (Z1, Z3). The spherical aberration to the light beam C is corrected in the zones (Z2, Z4). The light beam A is passed through all the zones of the light beam diameter a without changing the parallel light beam state by optimizing the step heights of the zones (Z1 to Z4).
Owner:RAKUTEN GRP INC
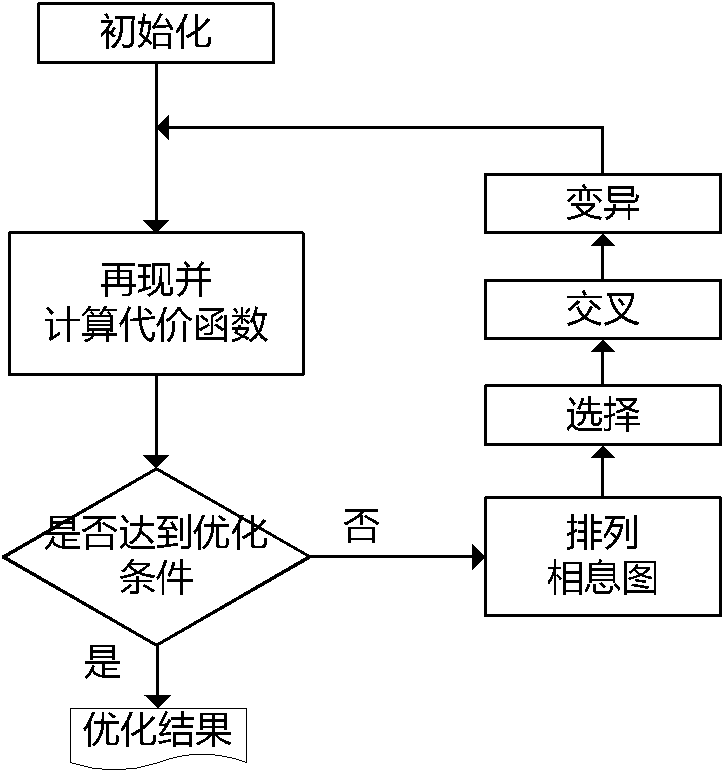
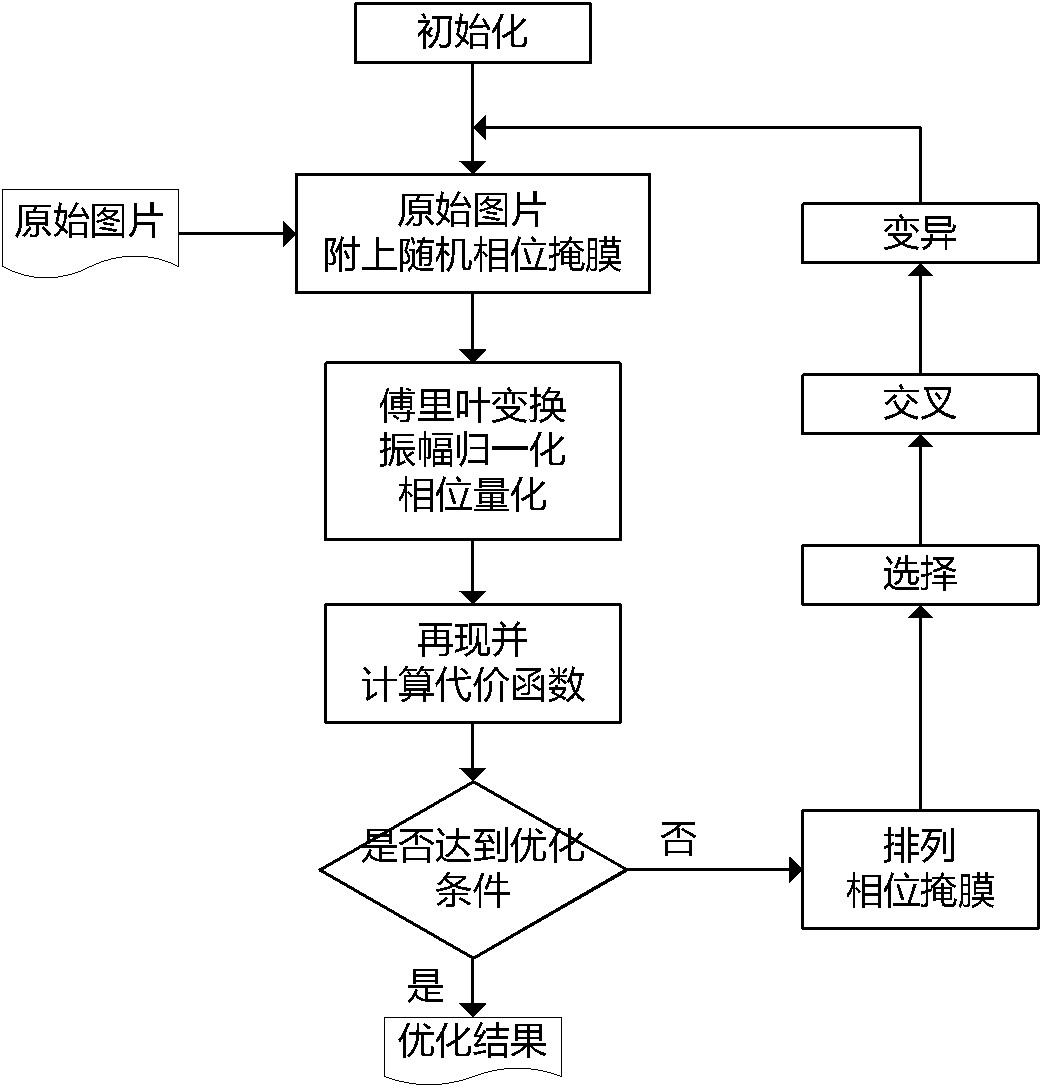
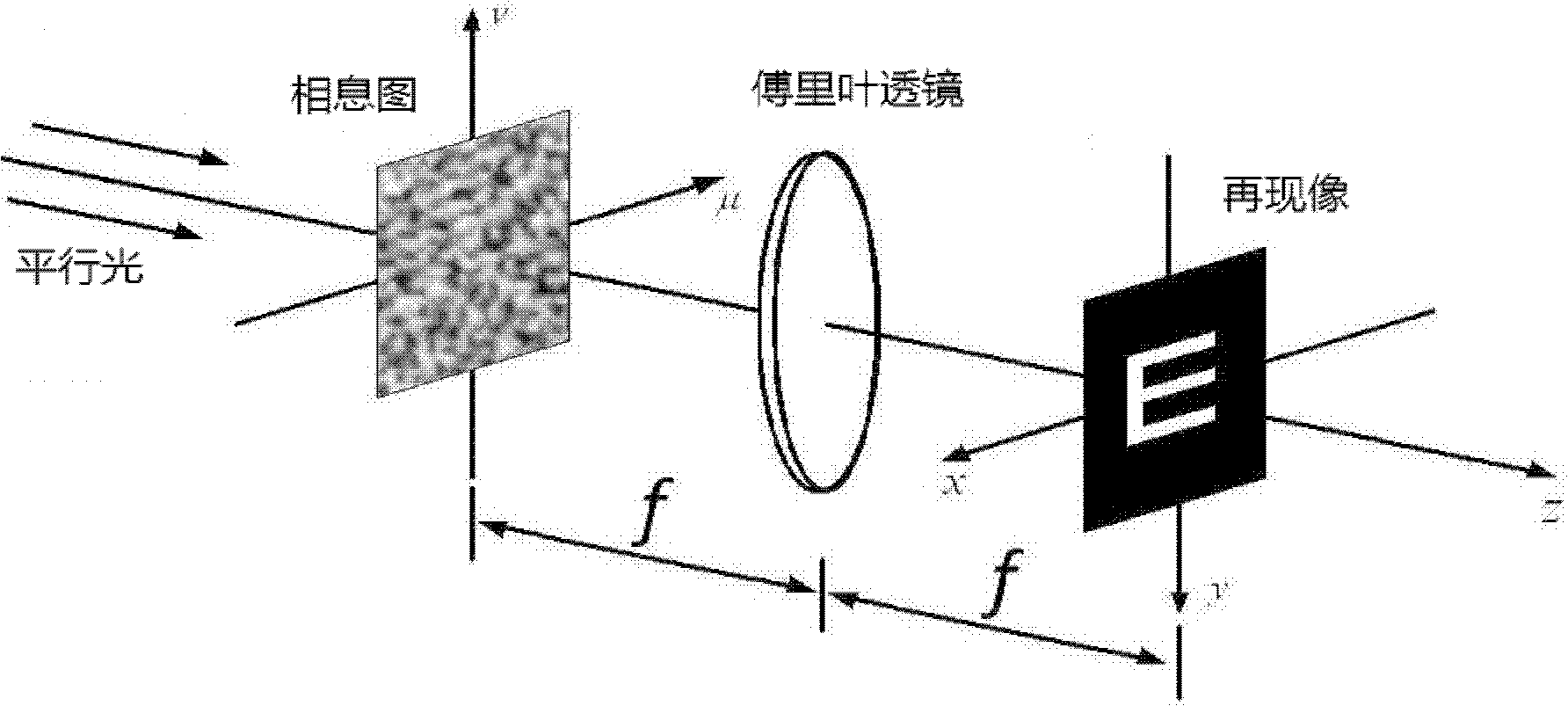
Method for synthesizing and optimizing kinoform
ActiveCN102074002AReduce mistakesOvercome the shortcoming of slow initial convergenceImage enhancementGenetic modelsGenetic algorithmKinoform
The invention provides a method for synthesizing and optimizing a kinoform, wherein the method is based on a genetic algorithm. The technical scheme provided by the invention comprises the following steps: adding a group of random phase masks to original images; optimizing the masks; and when reaching optimizing conditions,taking the phase mask with minimum cost function as the best mask, and the corresponding kinoform of the best mask as the obtained kinoform. The Kinoforms are indirectly optimized by optimizing the masks. Ihe method, the error of reproduced images is reduced by directly optimizing the random phase masks so as to optimize the Kinoform. In the selection link of the genetic algorithm, an elite retaining method is used to retain excellent solutions of groups and to accelerate the convergence rate, and is easy for realizing. Compared with the traditional optimization method, the method provided by the invention has the advantages of small initial cost function, fast optimizing speed, good optimizing effect and the like.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Method for eliminating color difference of twisting type liquid crystal wave-front corrector
The invention belongs to the field of adaptive optical technique and relates to a method for eliminating the chromatic aberration of a twisted liquid crystal-based wave-front corrector. During the process of wave surface correction with the twisted liquid crystal-based wave-front corrector, the light polarization of the liquid crystal layer may change and a part of the light emerges without correction, and the correction effect is poor. In order to filter the non-corrected stray light, a liquid crystal blazed grating is applied to the twisted liquid crystal-based wave-front corrector based on Kinoform, to allow the polarized light corrected by the liquid crystal layer to diffract in the blazing direction and to filter off the non-corrected stray light. But after applying the blazed grating to the twisted liquid crystal-based wave-front corrector, light beams of different wavelengths may be dispersed in the liquid crystal layer due to the difference in refractive index, producing images with chromatic aberration. The invention also utilizes a liquid crystal blazed grating that has the same parameter and is conjugated in position with the previous blazed grating and arranged behind the twisted liquid crystal-based wave-front corrector, so that the color dispersion of the twisted liquid crystal-based wave-front corrector is eliminated to ensure good quality of images.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Encrypted kinoform based digital image watermarking embedding and extracting methods and systems
ActiveCN102142131BReduce data volumeGood clipping resistanceImage data processing detailsPattern recognitionHuman visual system model
The invention discloses encrypted kinoform based digital image watermarking embedding and extracting methods and systems. The digital image watermarking embedding method comprises the following steps of: transforming an original watermarking image through non-cascaded phase recovery and random fractional fourier transform (RFrFT) to acquire an encrypted kinoform of the original watermarking image; and adaptively embedding the encrypted kinoform into a carrier image based on a human visual system (MVS) model. In the invention, the safety of the watermarking of the kinoform is enhanced by usinga non-cascaded iterative encryption method; meanwhile, blink watermarking is realized by adopting an adaptive embedding algorithm; and experiments verify that extremely high robustness against various attacks is achieved, and the safety performance is extremely high.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com