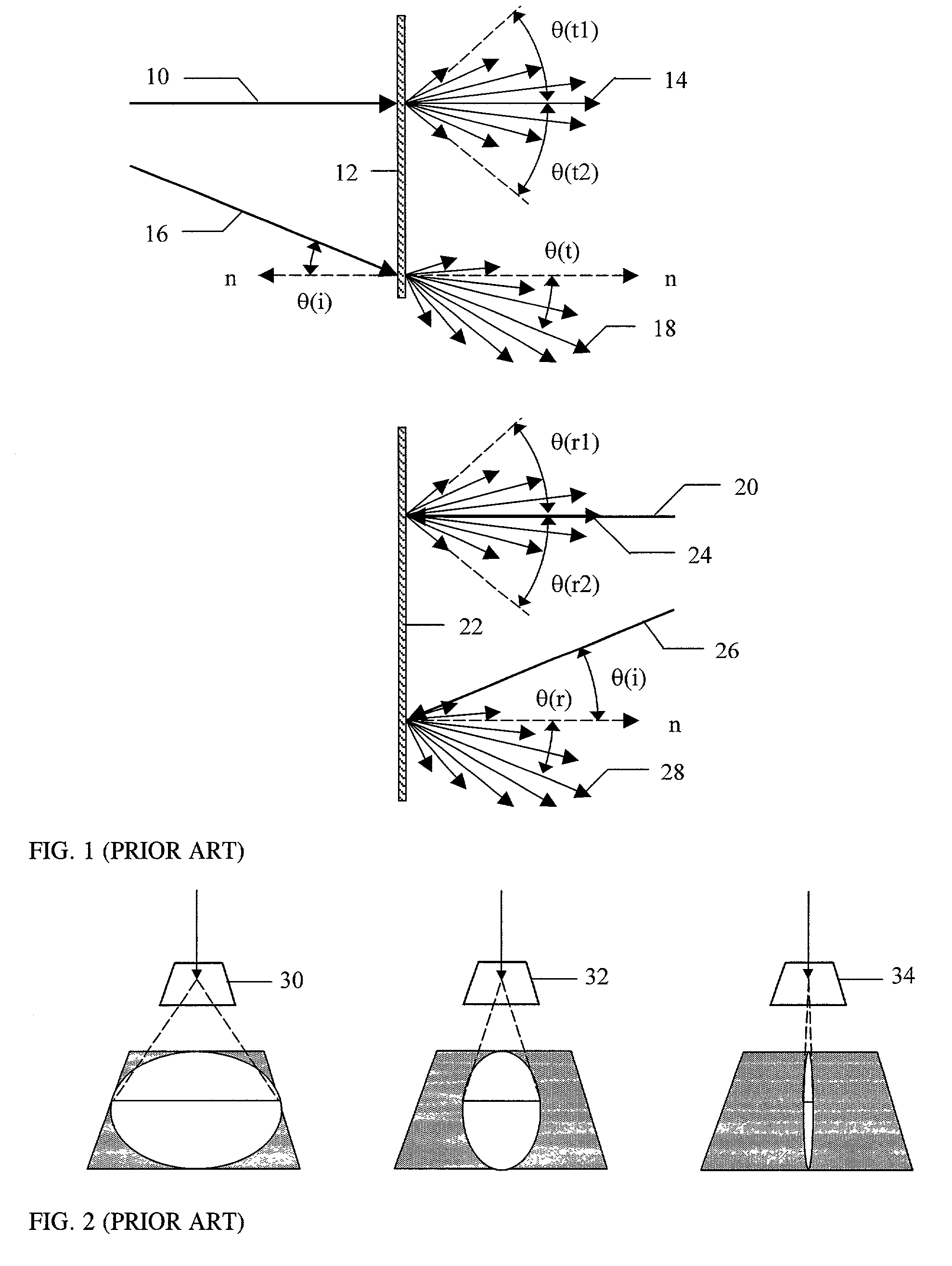
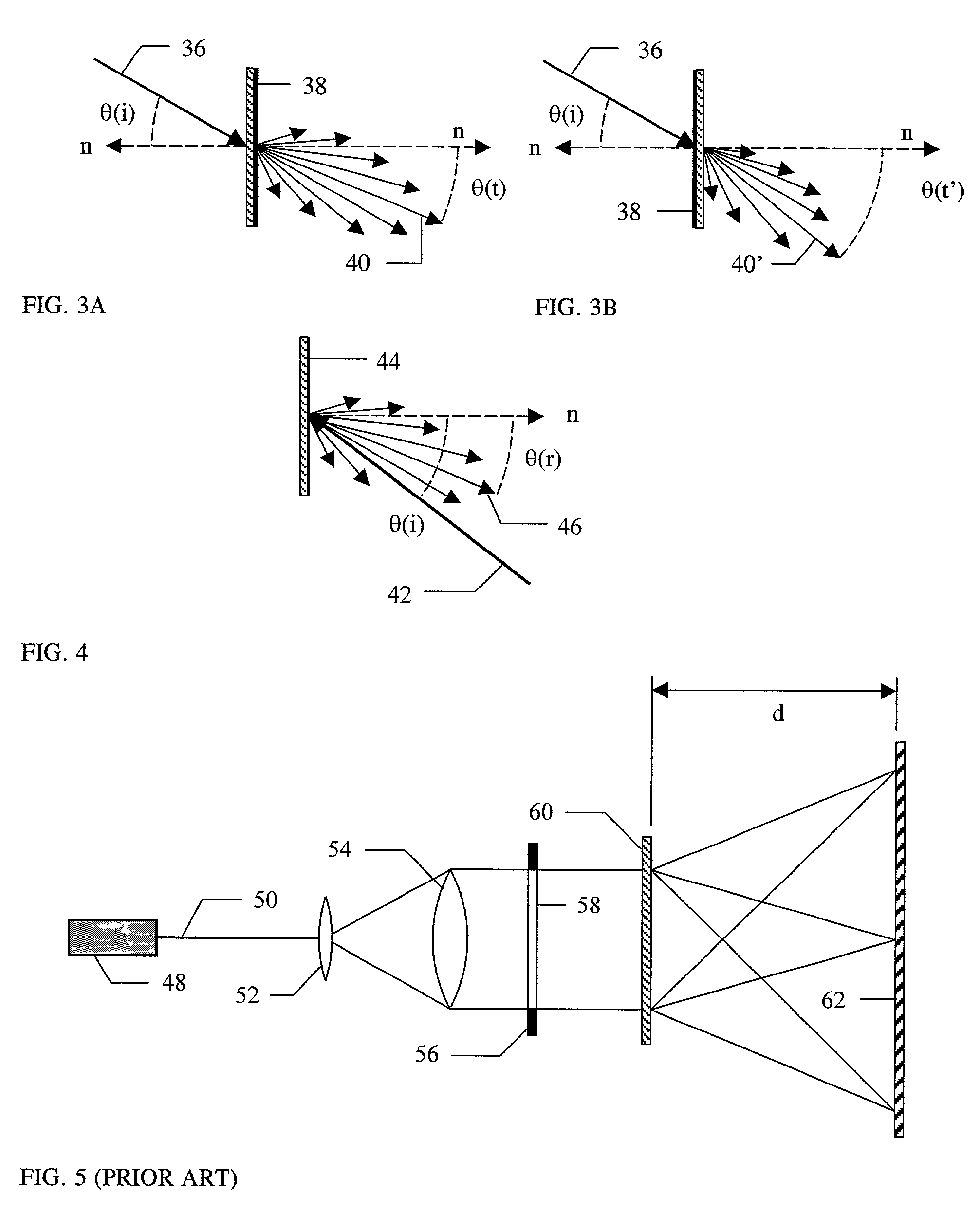
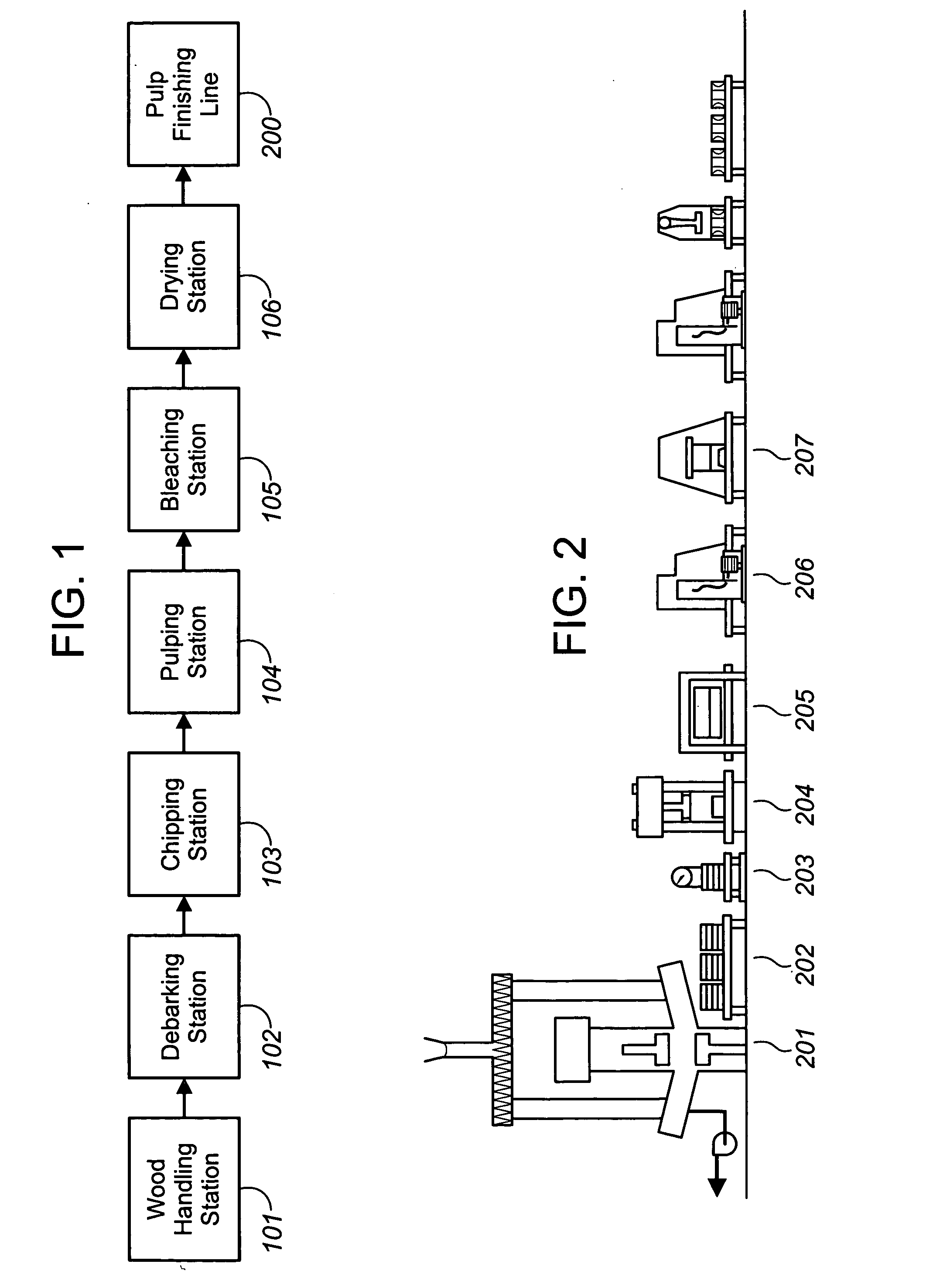
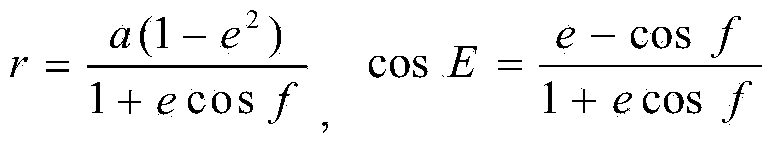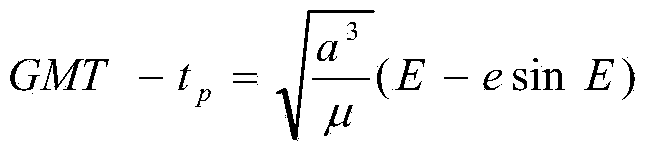Patents
Literature
100 results about "Reflectance properties" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
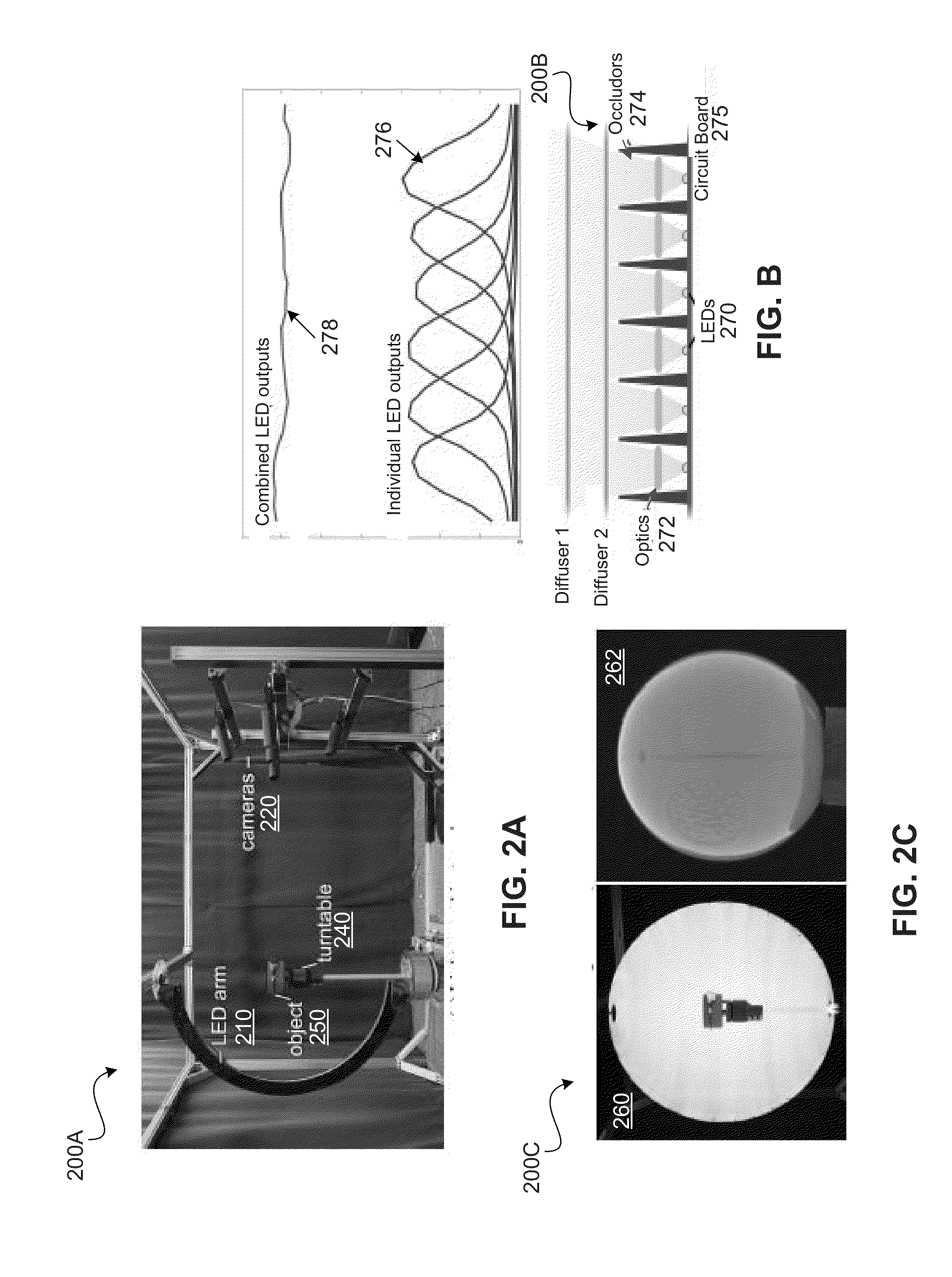
Facial image processing methods and systems
InactiveUS6850872B1Exclude influenceComponent can be removedImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionImaging processingAnimation
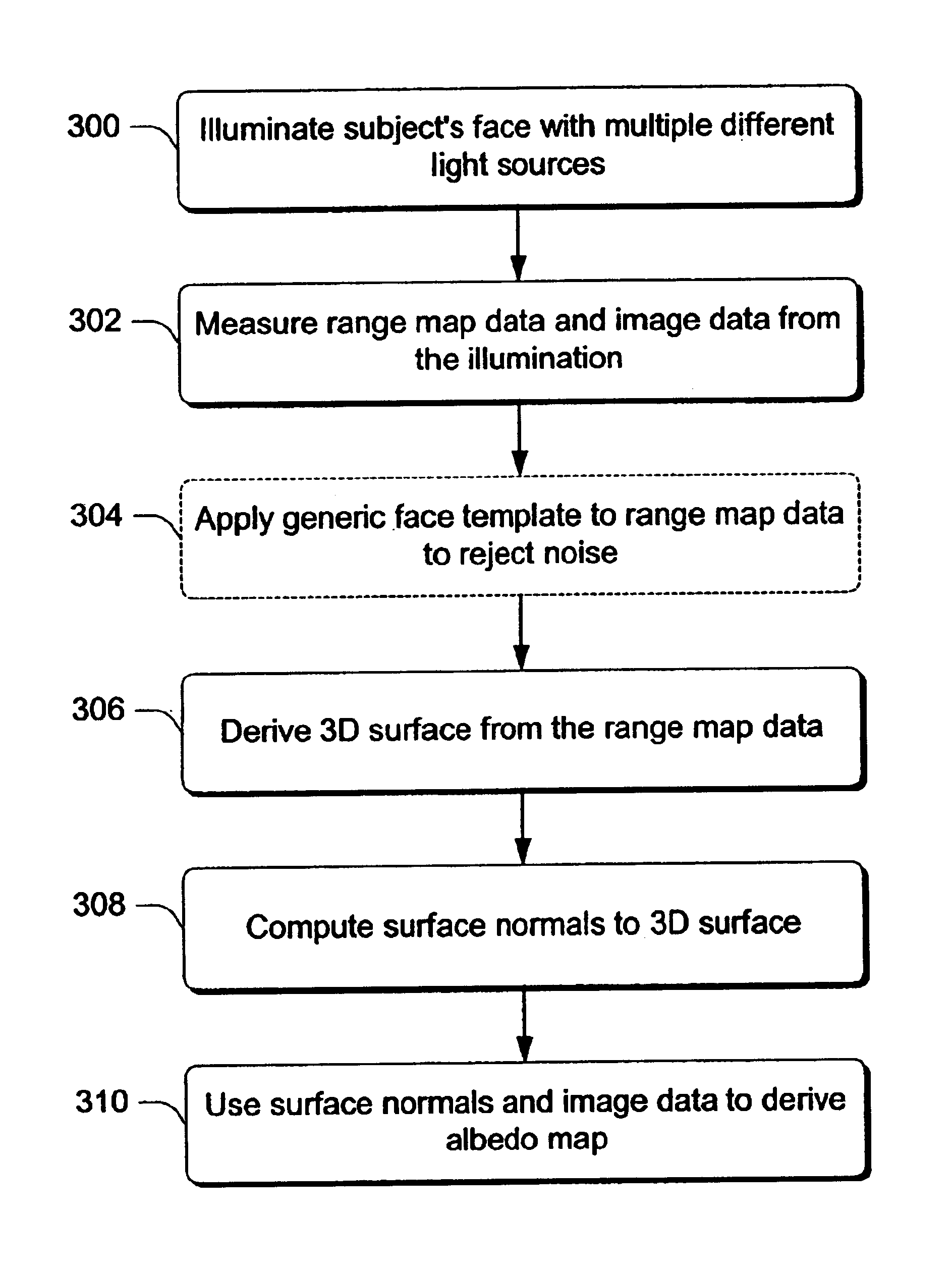
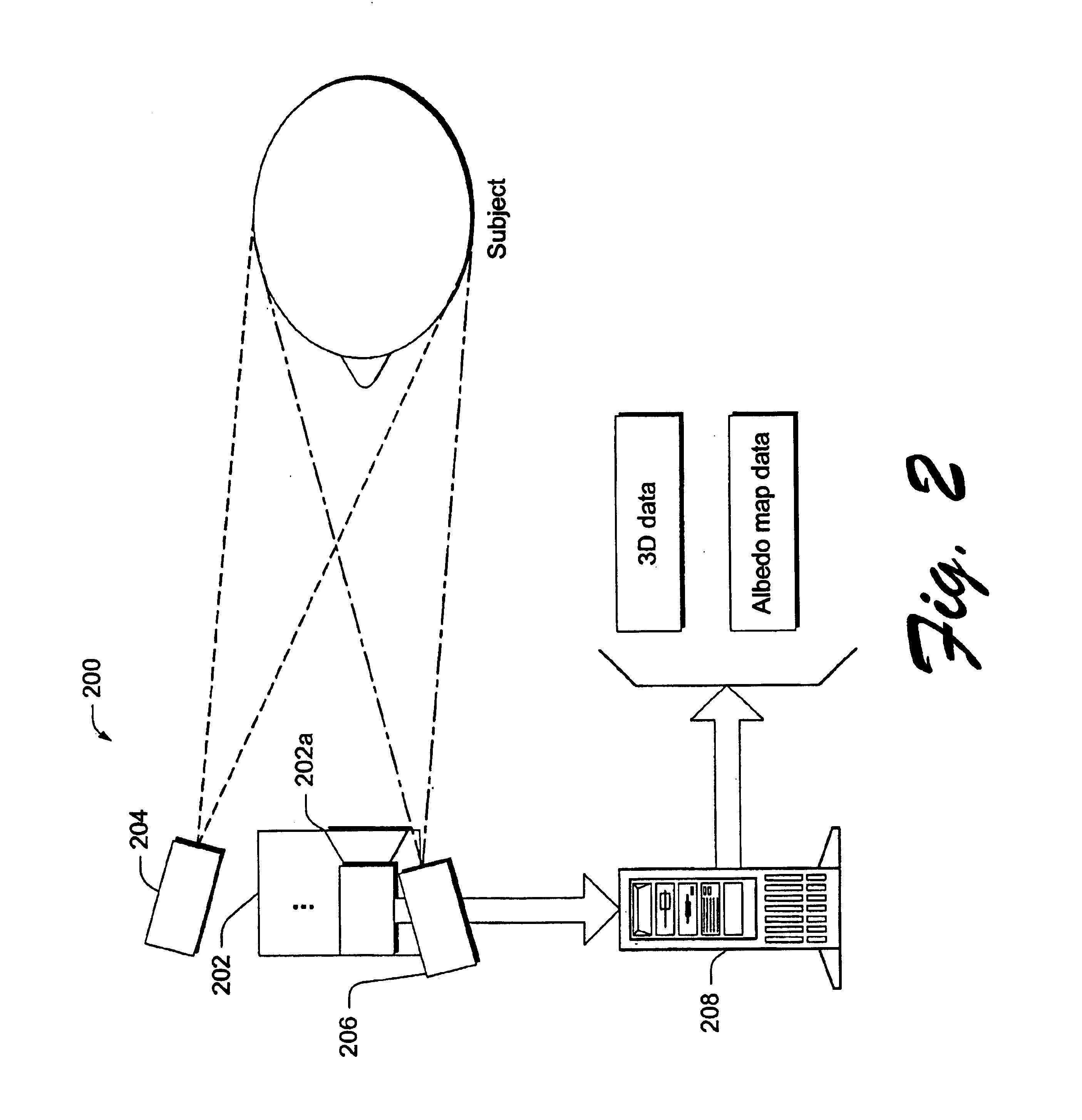
In the described embodiment, methods and systems for processing facial image data for use in animation are described. In one embodiment, a system is provided that illuminates a face with illumination that is sufficient to enable the simultaneous capture of both structure data, e.g. a range or depth map, and reflectance properties, e.g. the diffuse reflectance of a subject's face. This captured information can then be used for various facial animation operations, among which are included expression recognition and expression transformation.
Owner:ZHIGU HLDG
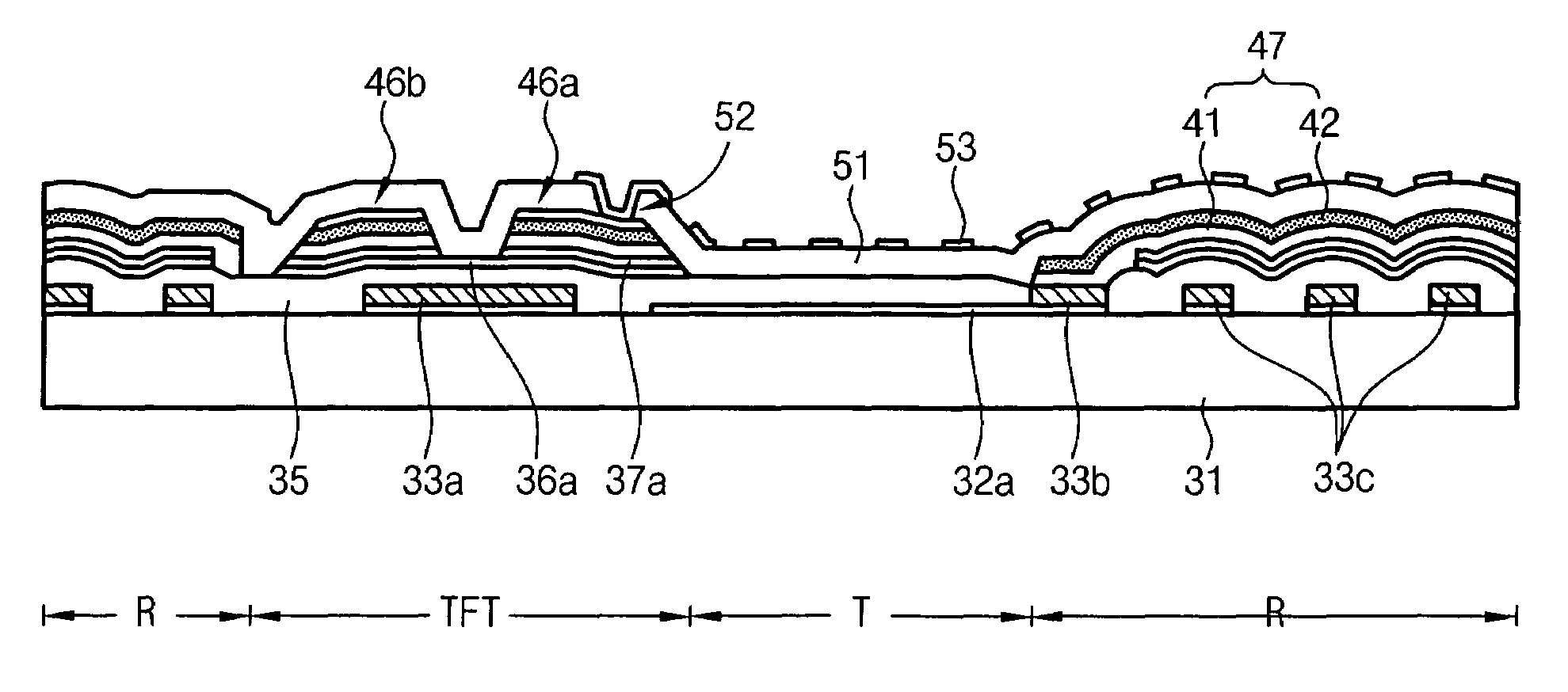
Method for manufacturing array substrate of translucent LCD
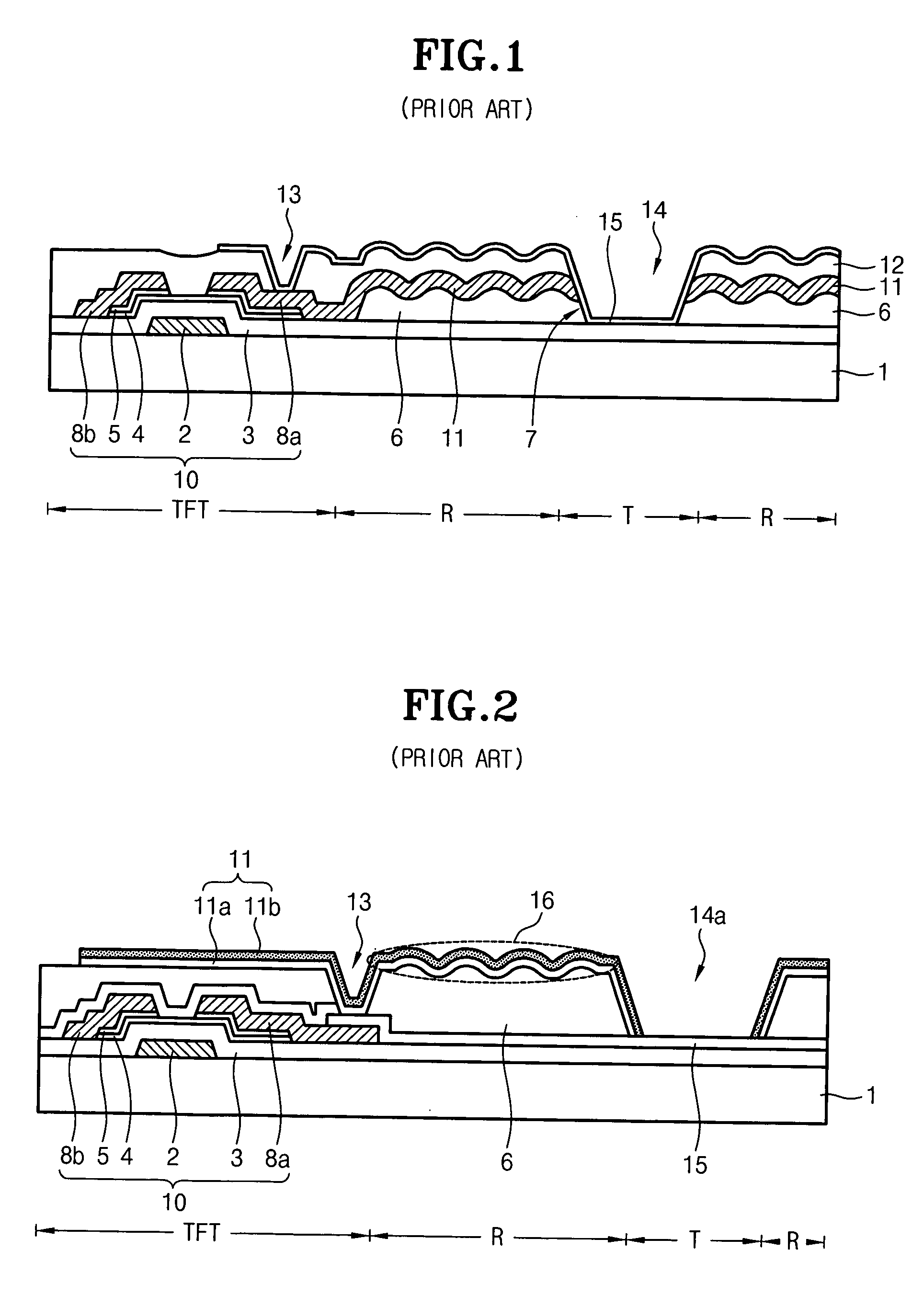
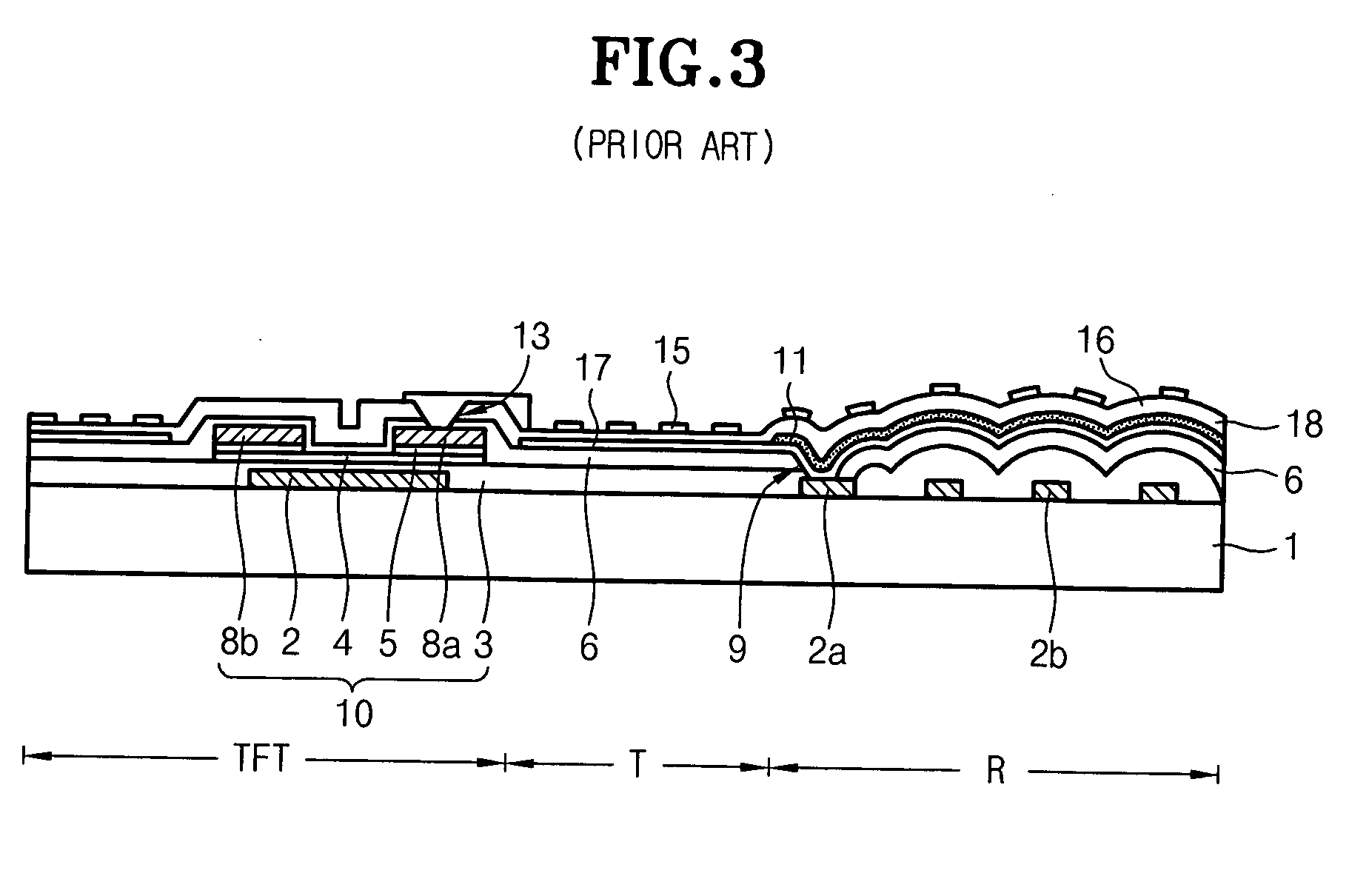
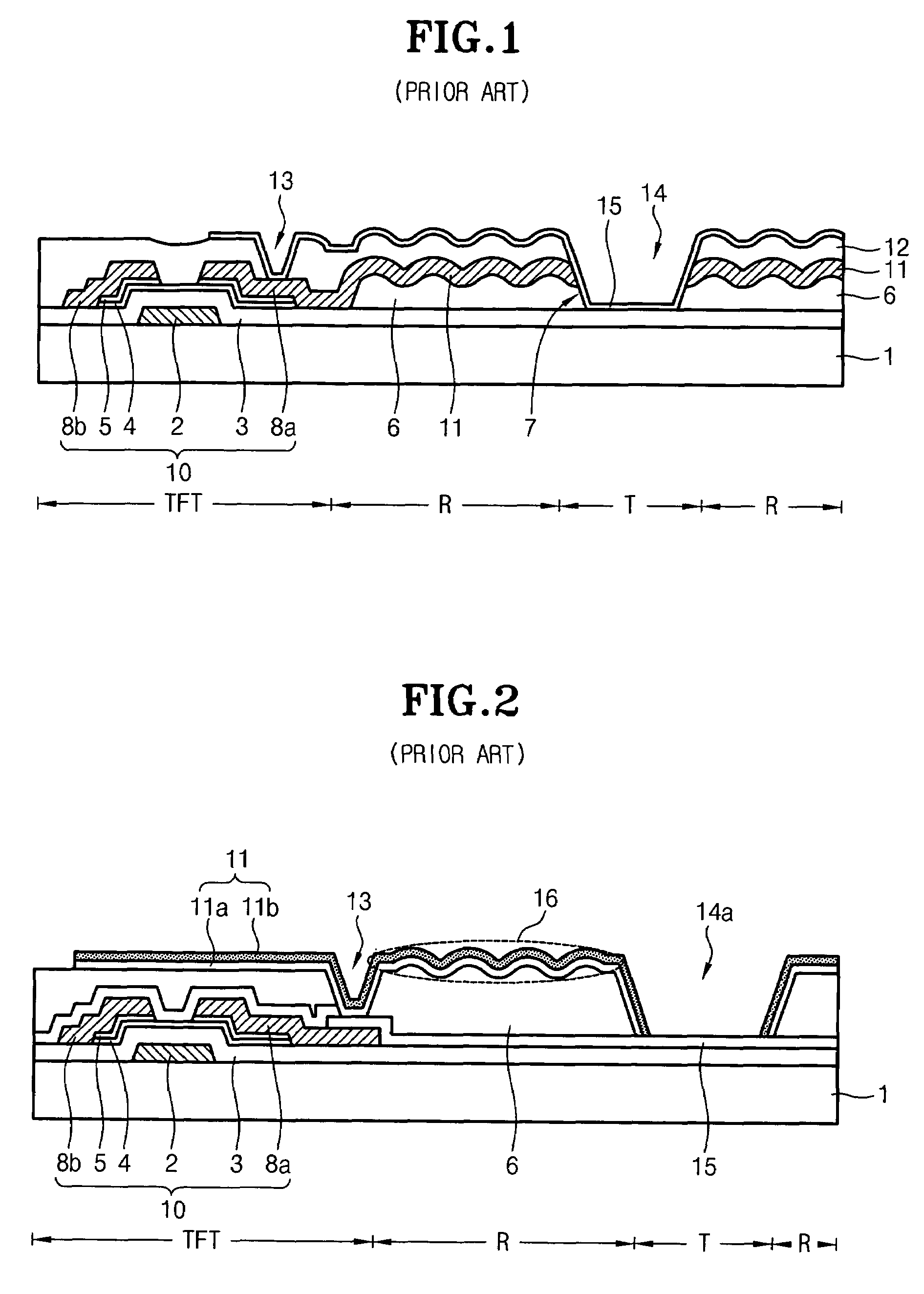
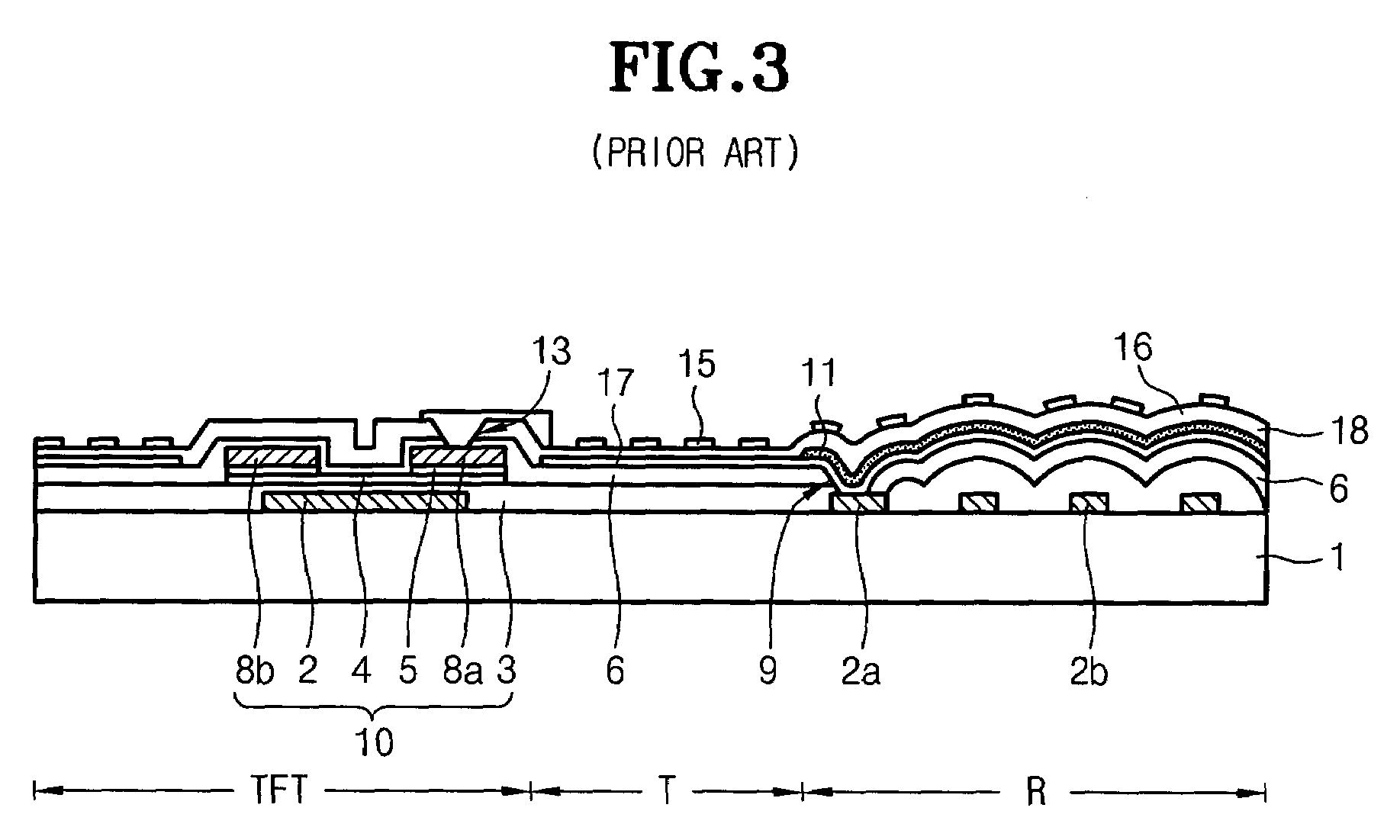
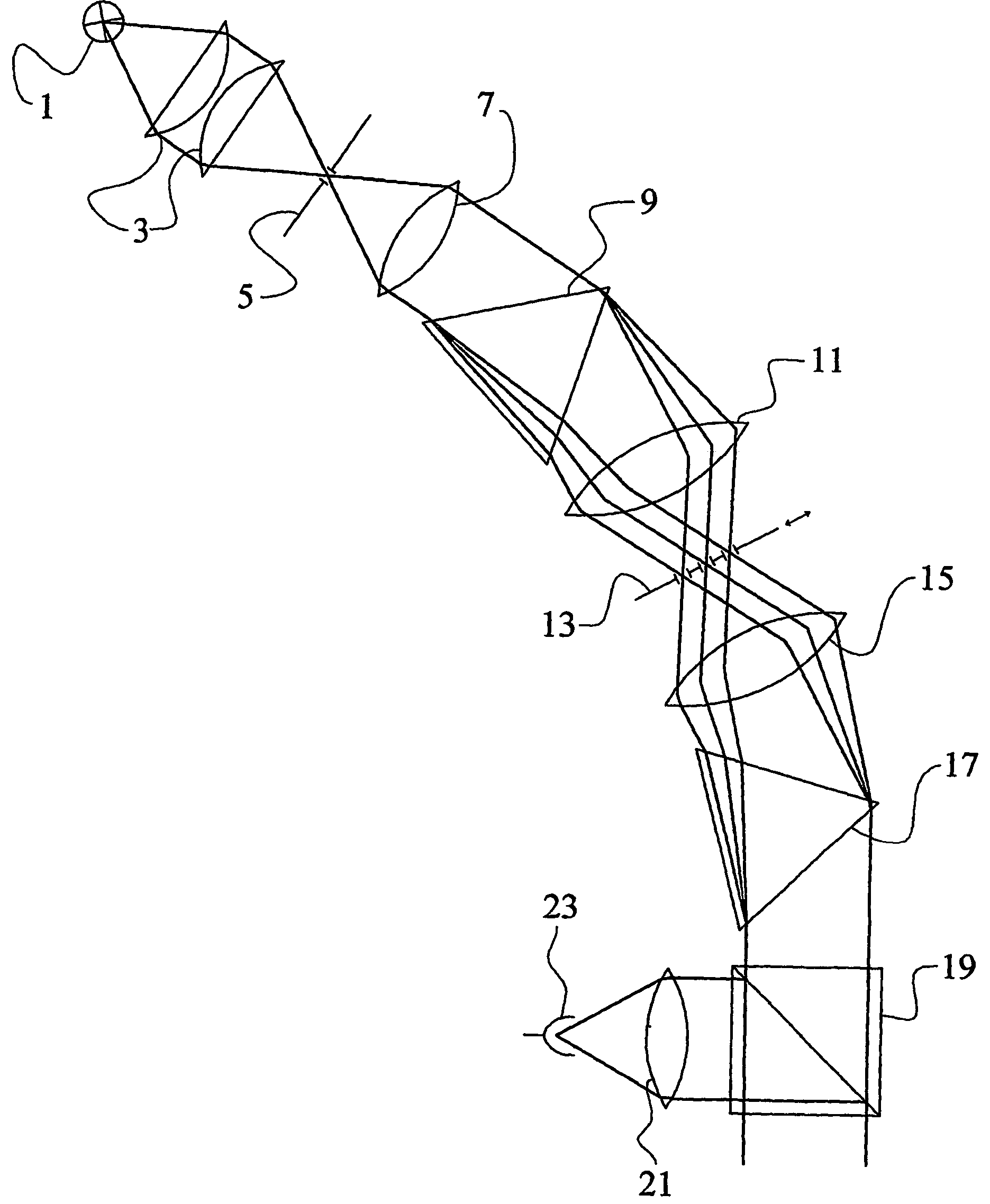
ActiveUS20070109455A1Increase contact resistanceGuaranteed uptimeSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNon-linear opticsElectrical resistance and conductanceReflectance properties
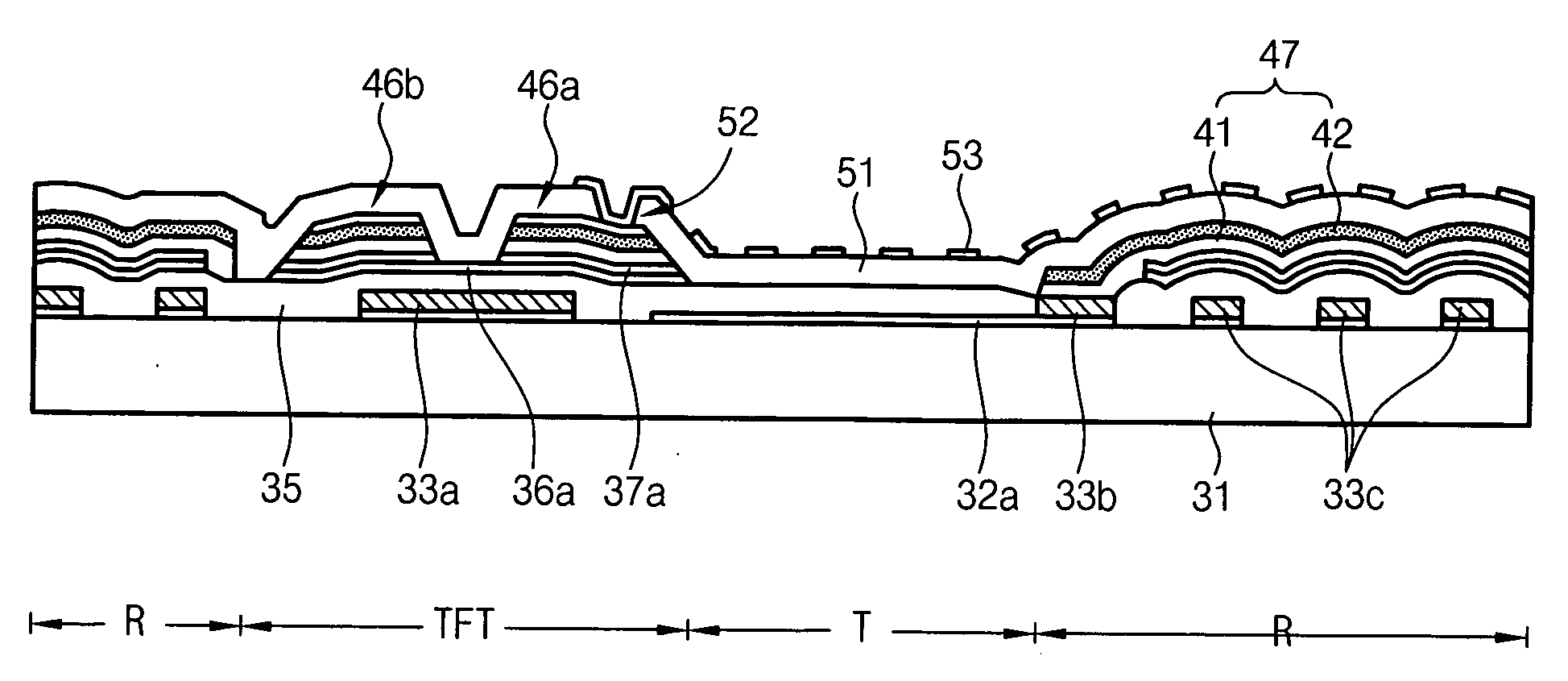
Disclosed is a method for manufacturing an array substrate of a translucent LCD capable of simultaneously forming source and drain metal layers as reflective electrodes while improving both the contact resistance in a transmissive region and the reflectivity properties in a reflective region. The source and drain metal layers have a triple-layered structure of Mo—Al—Mo and, the top Mo is selectively removed from the reflective region. As a result, the screen quality of products improves. In addition, about 5-6 masks are enough to manufacture an array substrate using half-tone exposure technology, in contrast to the prior art which uses 8-11 masks. As the number of masks and processes is reduced in this manner, the manufacturing cost decreases accordingly and the process is simplified.
Owner:HYDIS TECH
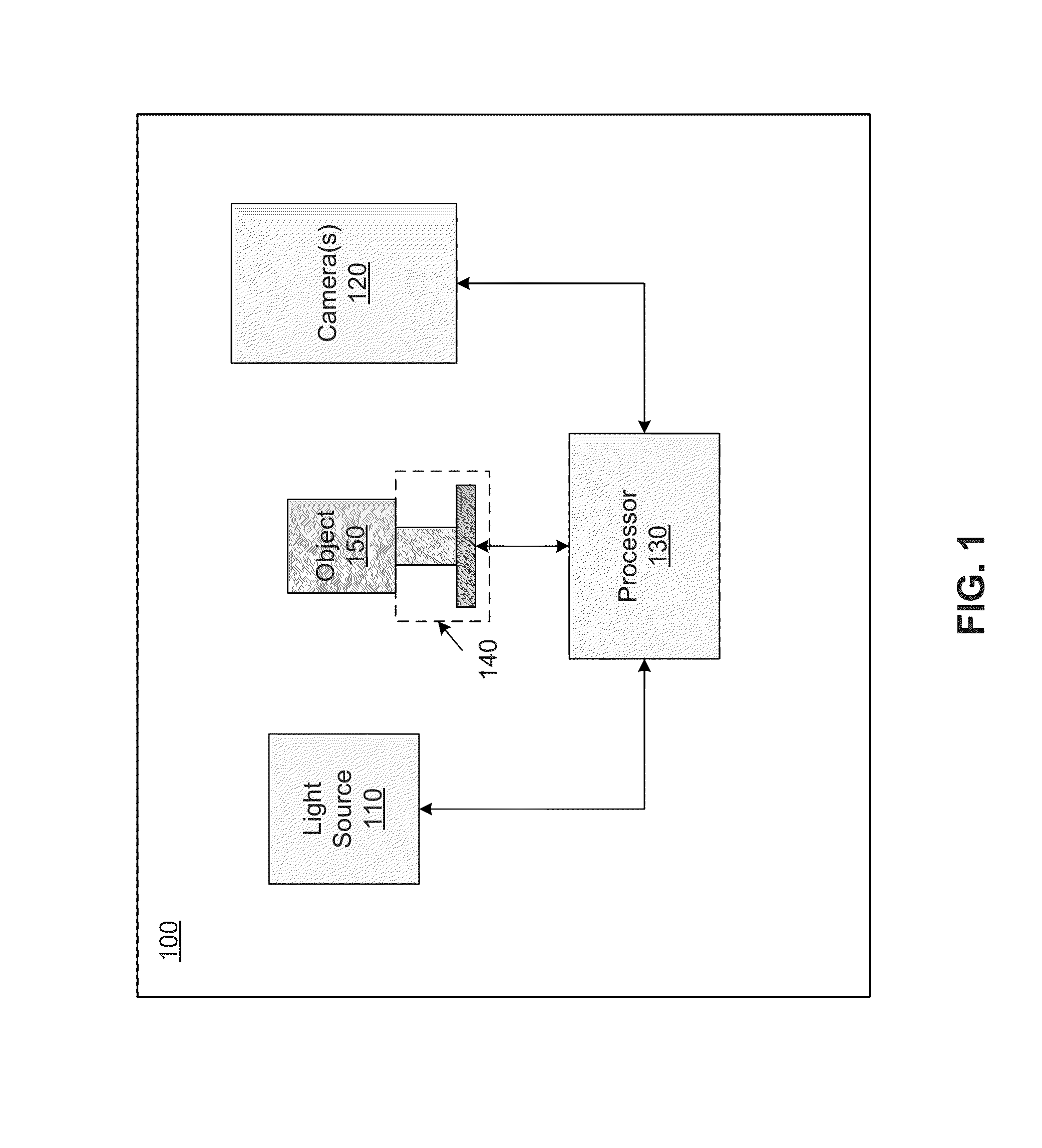
Method and system for imaging an object or pattern
A system and method for simultaneously obtaining a plurality of images of an object or pattern from a plurality of different viewpoints is provided. In an exemplary embodiment, proper image contrast is obtained by replacing the light sources of earlier systems with equivalent light sensitive devices and replacing the cameras of earlier systems with equivalent light sources. With such a system, bright-field images and dark-field images may be simultaneously obtained. In one aspect of the invention, a light source is positioned to illuminate at least a portion of an object. A plurality of light guides having input ends are positioned to simultaneously receive light reflected from the object and transmit the received light to a plurality of photodetectors. The light guides are arranged such that their respective input ends are spaced substantially equally along at least a portion of a surface of an imaginary hemisphere surrounding the object. The signals generated by the photodetectors (as a result of light detection) are processed and a plurality of images of the object are formed. Another aspect of the invention provides a method for generating composite images from simultaneously obtained images. Equivalent regions of each image (corresponding to geographically identical subpictures) are compared. The subpicture having the highest entropy is selected and stored. This process continues until all subpictures have been considered. A new composite picture is generated by pasting together the selected subpictures. In another aspect of the invention, the vector of relative light values gathered for each pixel or region of an object illuminated or scanned (i.e., one value for each photodetector) is used to determine reflectance properties of points or regions illuminated on the object or pattern. The reflectance properties may be stored in a matrix and the matrix used to read, for example, a Bar Code of a data matrix symbol.
Owner:RUDOLPH TECHNOLOGIES INC
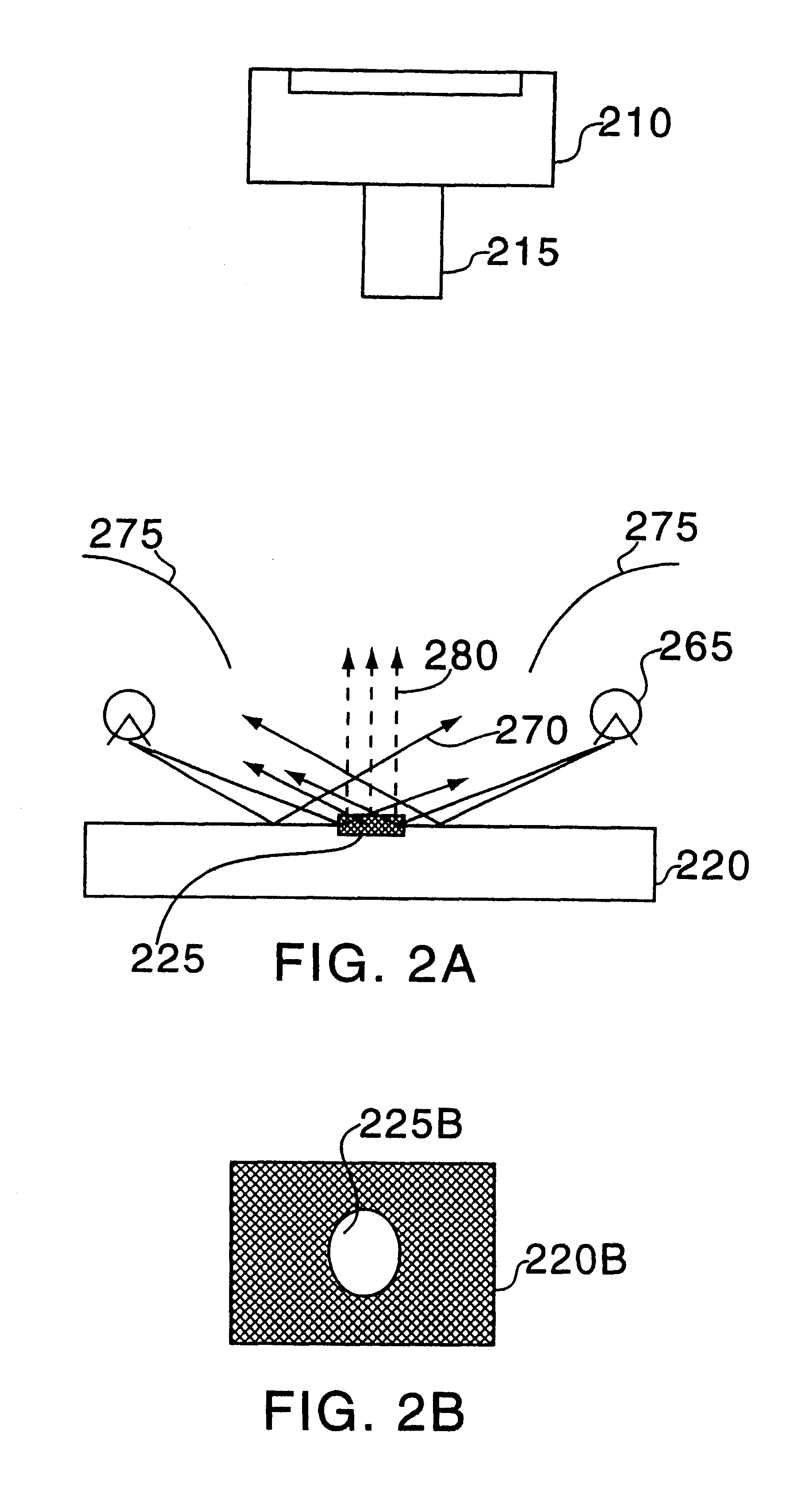
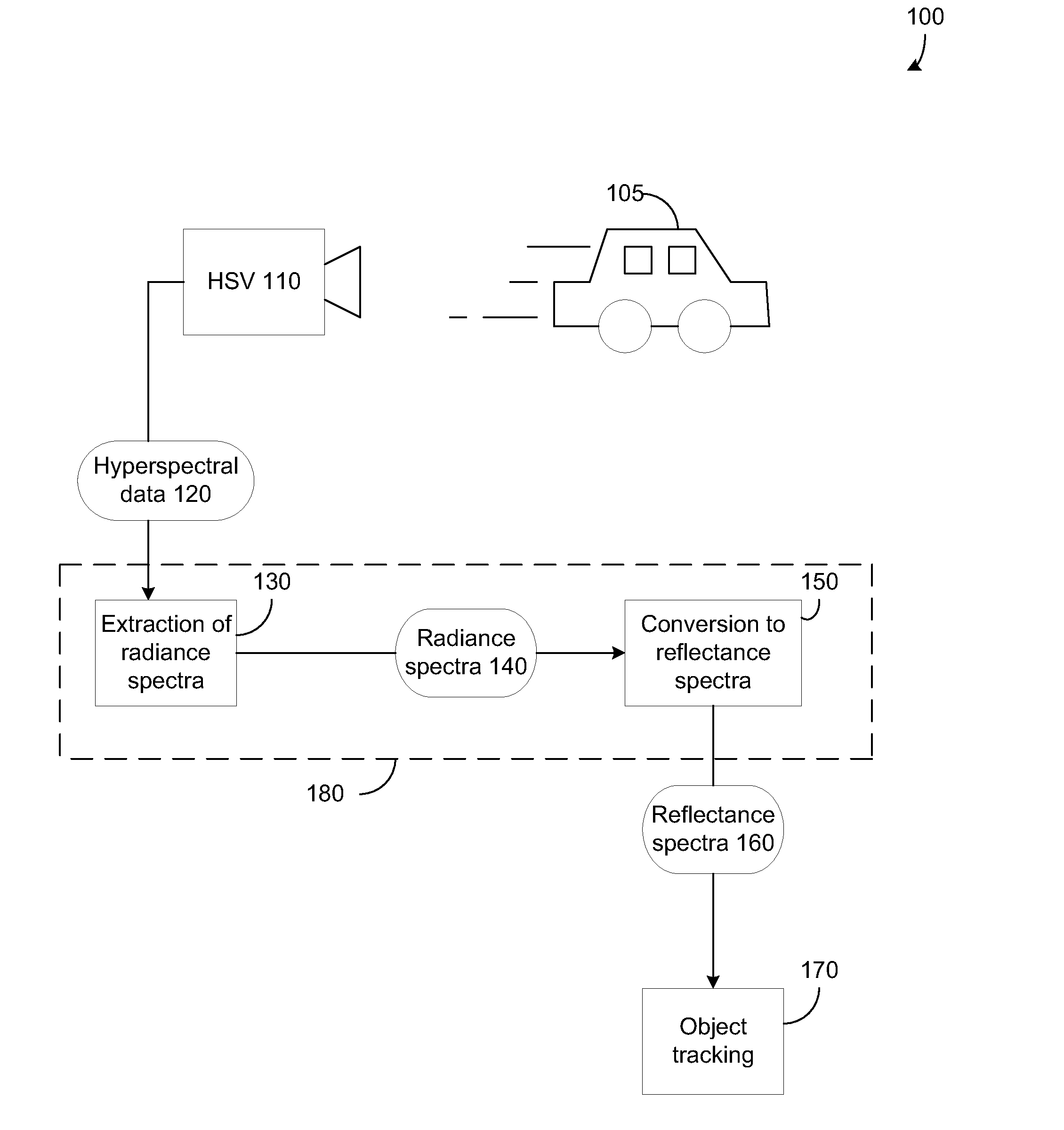
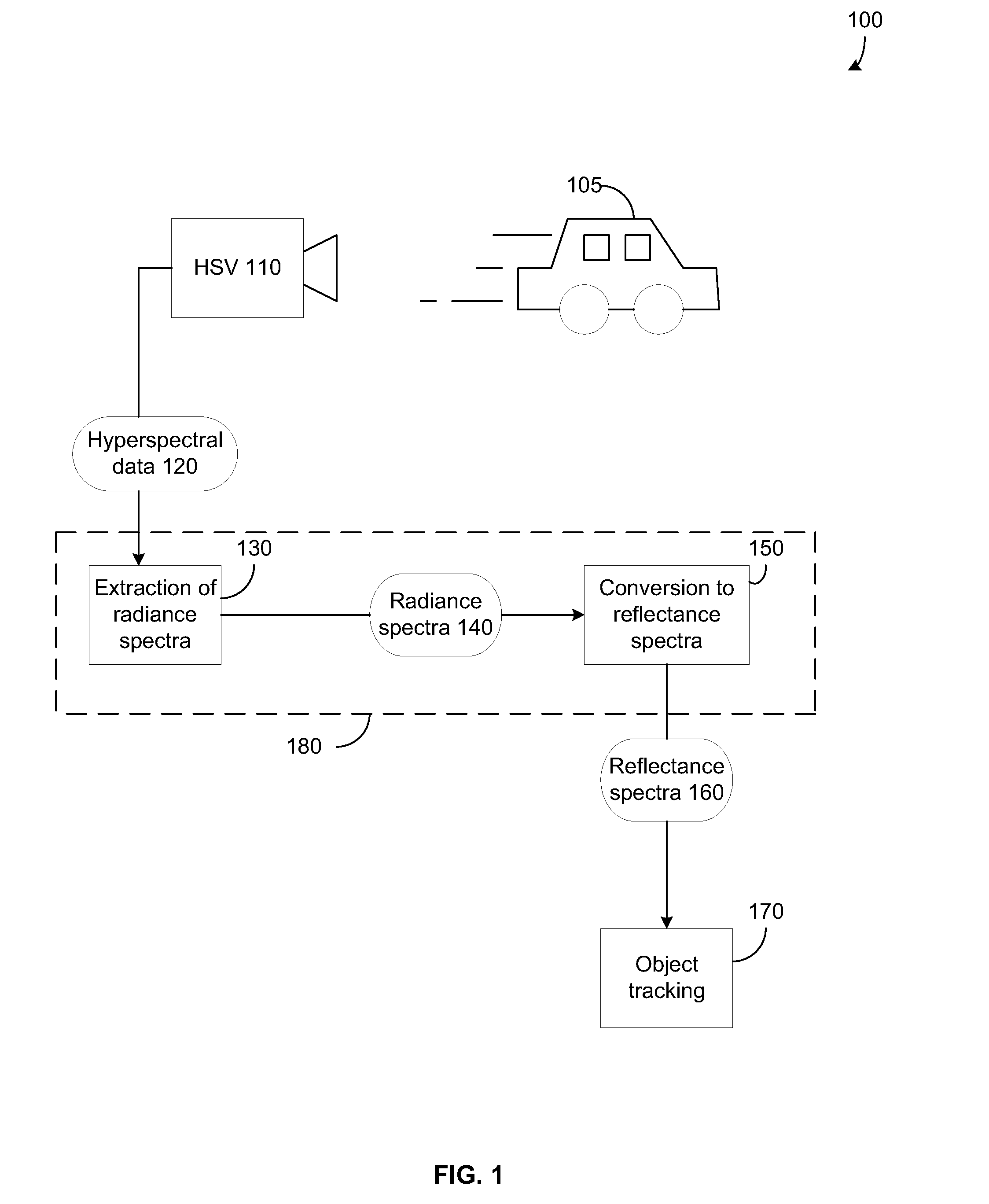
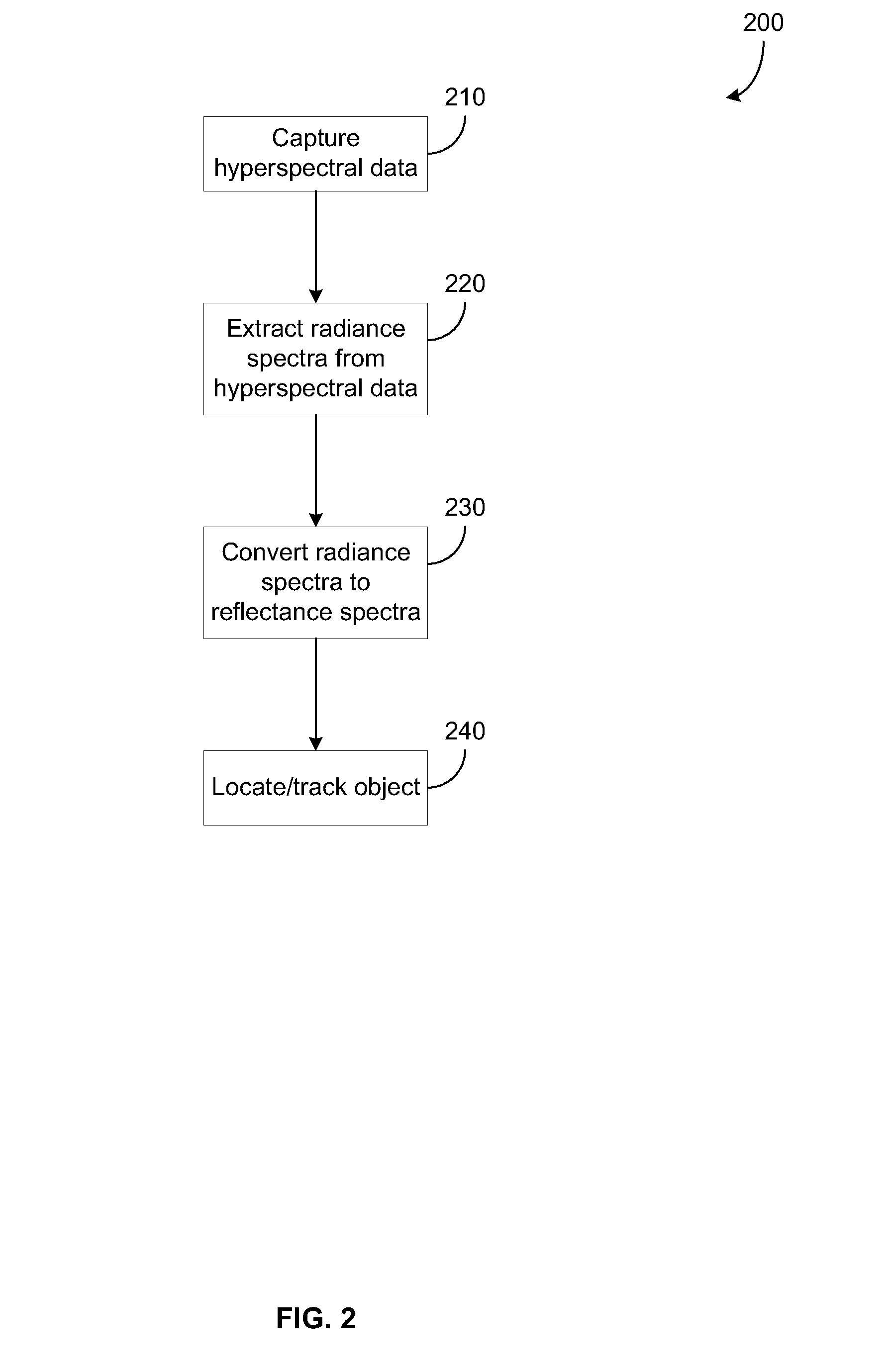
Systems and Methods for Remote Tagging and Tracking of Objects Using Hyperspectral Video Sensors
ActiveUS20100322480A1Reduce false alarmHigh spatialImage enhancementImage analysisReflectance spectroscopyRadiance
Detection and tracking of an object by exploiting its unique reflectance signature. This is done by examining every image pixel and computing how closely that pixel's spectrum matches a known object spectral signature. The measured radiance spectra of the object can be used to estimate its intrinsic reflectance properties that are invariant to a wide range of illumination effects. This is achieved by incorporating radiative transfer theory to compute the mapping between the observed radiance spectra to the object's reflectance spectra. The consistency of the reflectance spectra allows for object tracking through spatial and temporal gaps in coverage. Tracking an object then uses a prediction process followed by a correction process.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Microwave Sensor
InactiveUS20080165002A1Increase in sizeIncrease costDetection using electromagnetic wavesRadio wave reradiation/reflectionReflectance propertiesMicrowave sensor
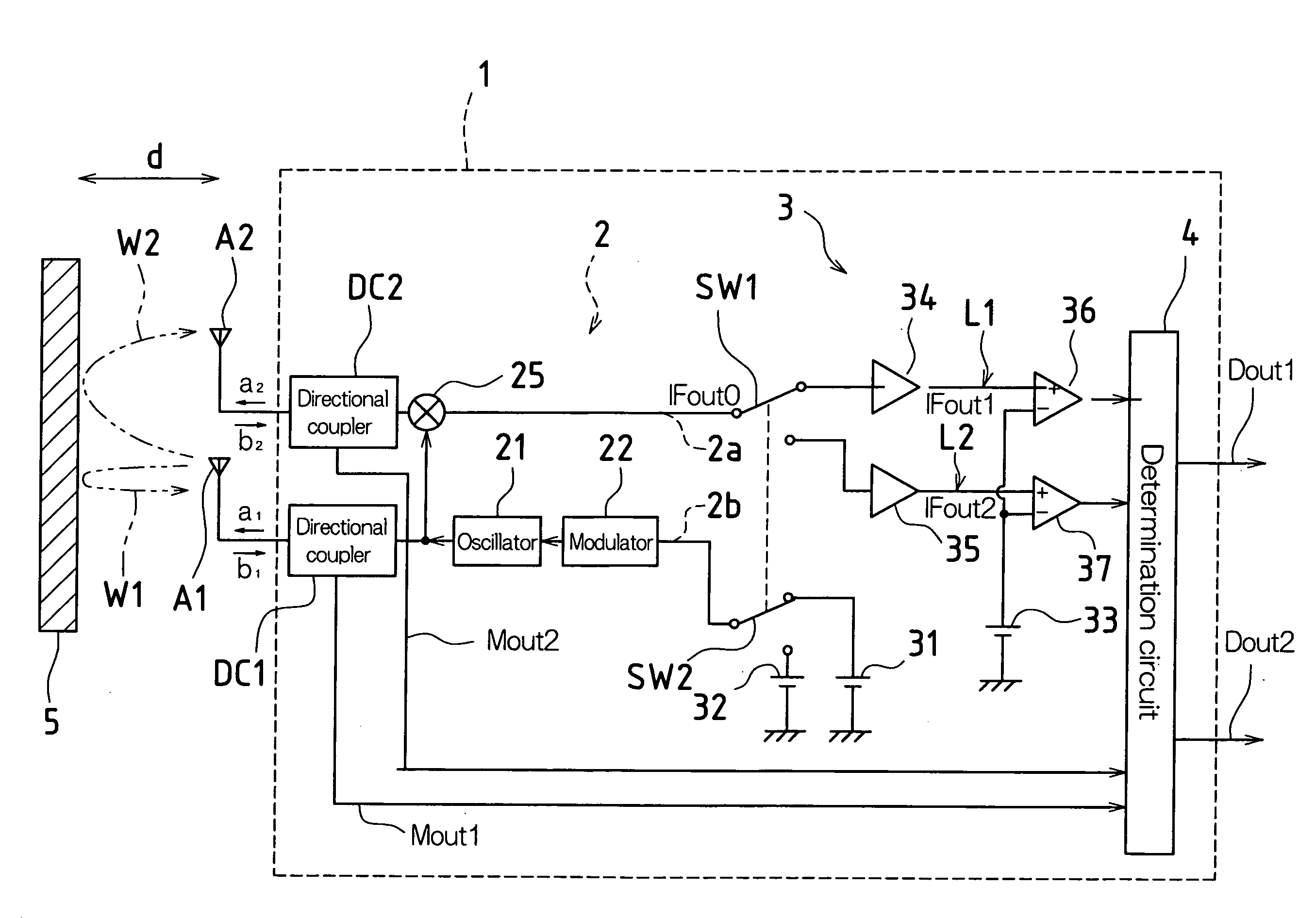
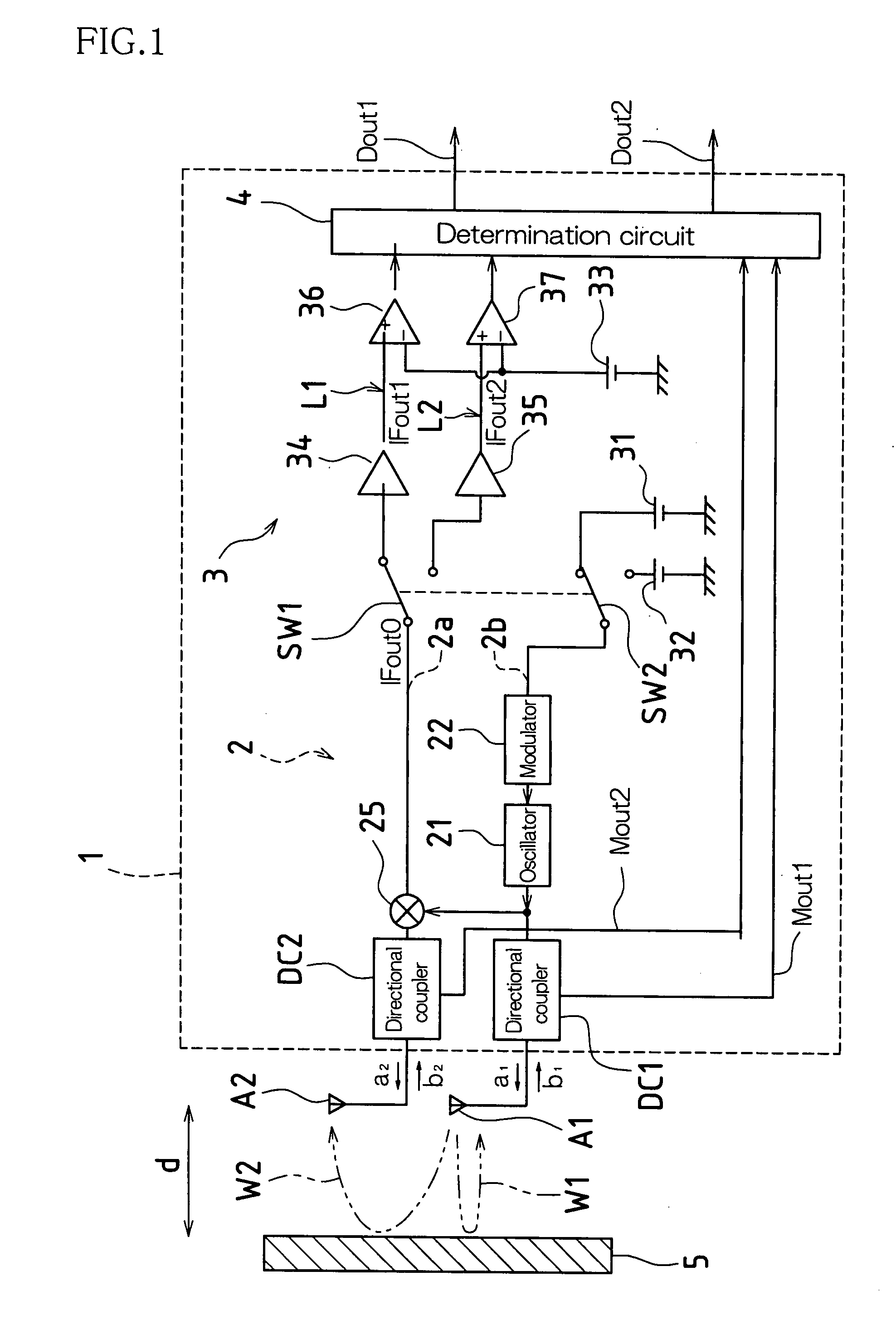
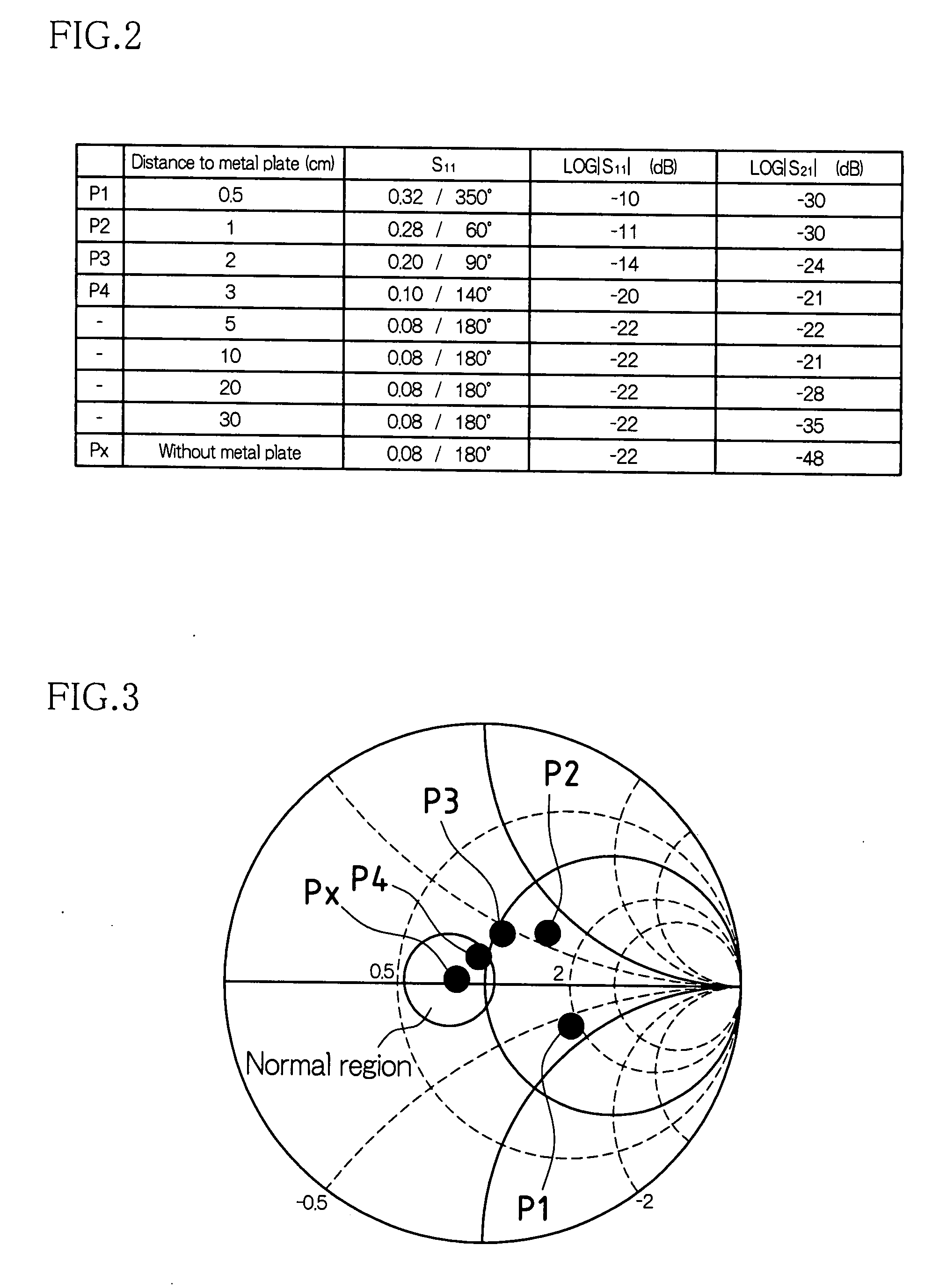
According to one embodiment, a microwave sensor includes: a first directional coupler (DC1) connected on a path of a transmission antenna unit (A1); a second directional coupler (DC2) connected on a path of a reception antenna unit (A2), and a determination unit (4) that obtains, based on monitor outputs from these, a scattering parameter S11 corresponding to a reflectance property at the transmission antenna unit (A1) and a scattering parameter S21 corresponding to a transmission property from the transmission antenna unit (A1) to the reception antenna unit (A2), and outputs an alarm signal (Dout2) when at least one of the scattering parameter S11 and the scattering parameter S21 continuously exhibits a value outside its respective pre-set range over a predetermined period of time.
Owner:OPTEX CO LTD
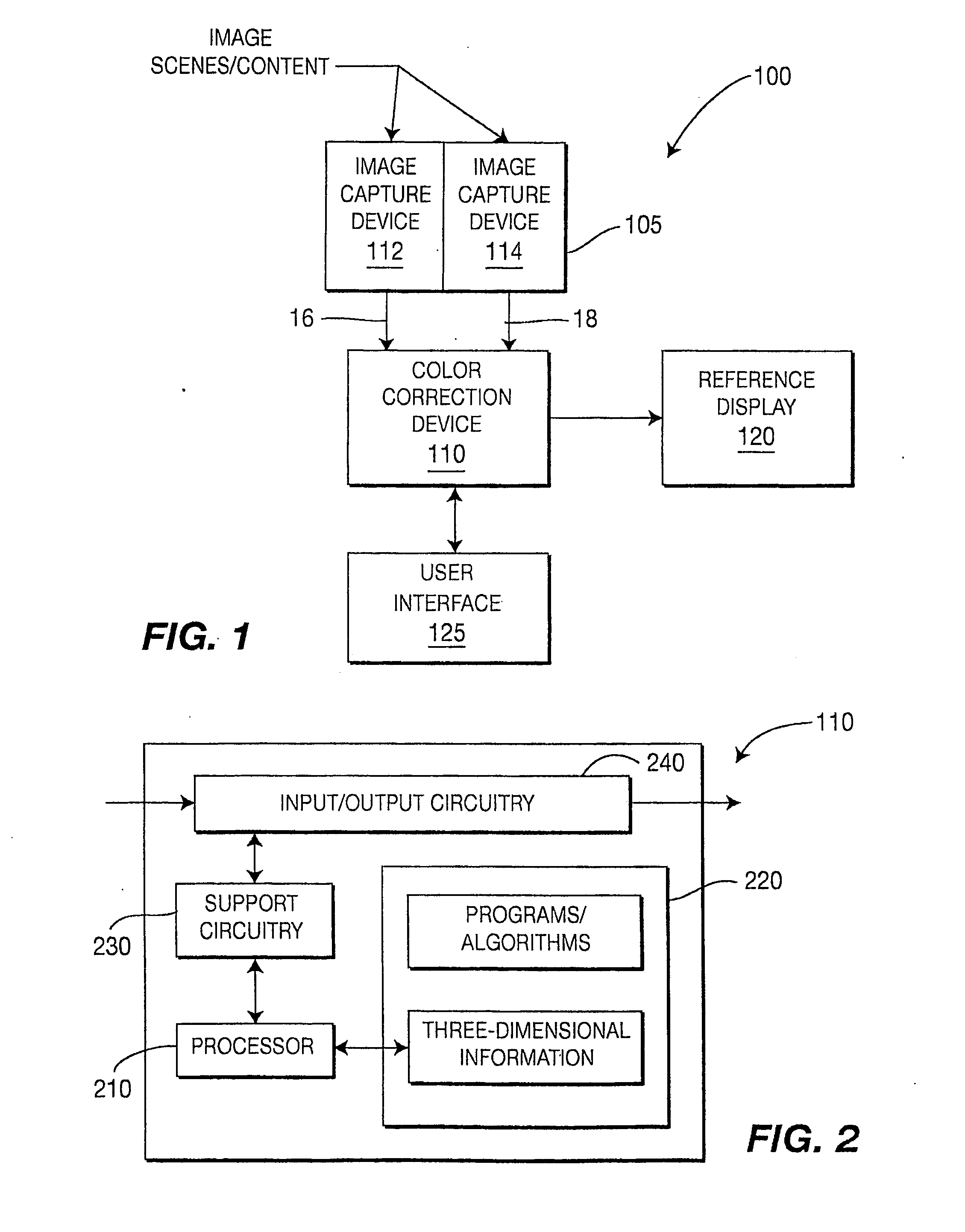
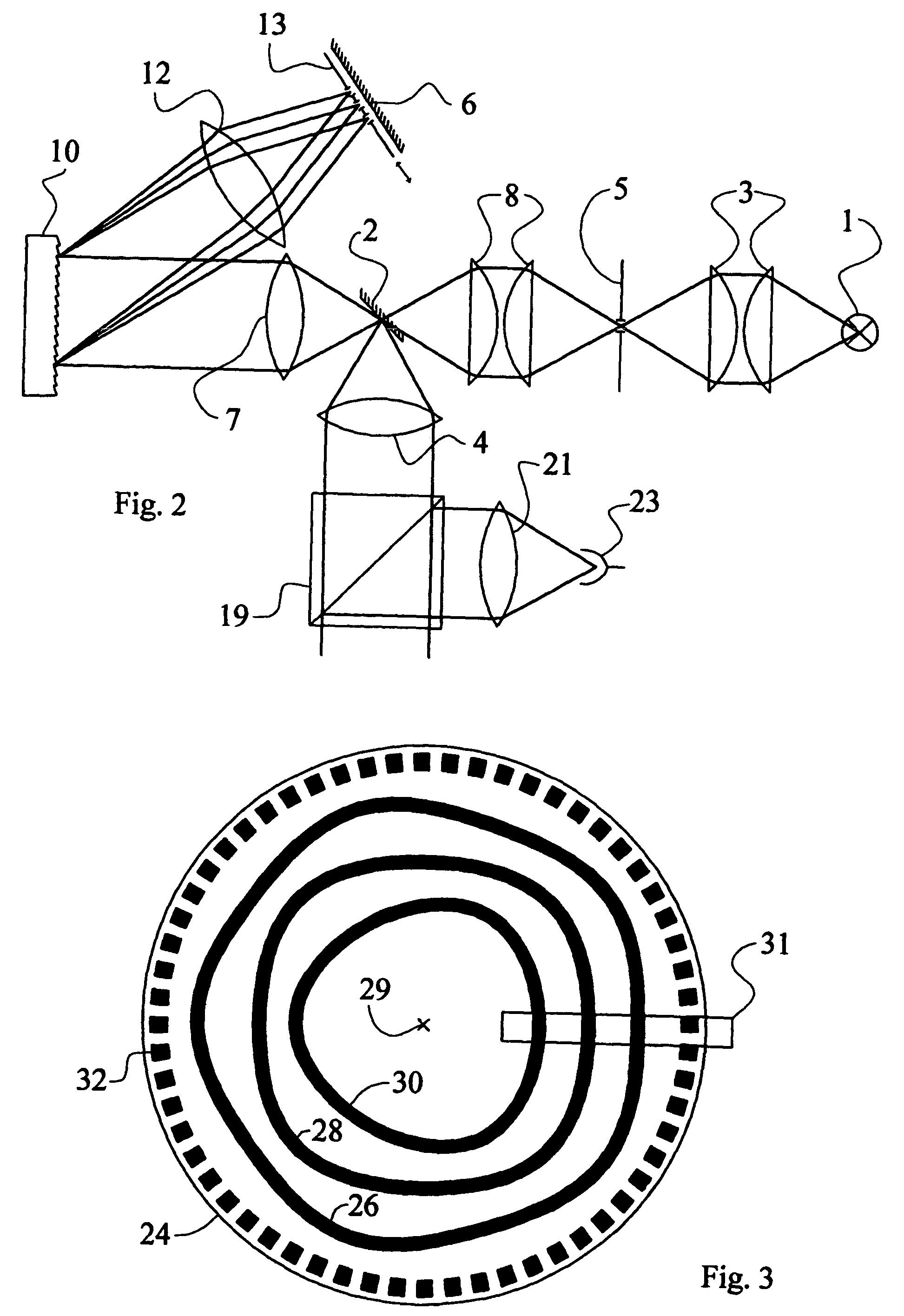
Methods and systems for color correction of 3D images
A system and method for color correction of 3D images including at least two separate image streams captured for a same scene include determining three-dimensional properties of at least a portion of a selected image stream, the three-dimensional properties including light and surface reflectance properties, surface color, reflectance properties, scene geometry and the like. A look of the portion of the selected image stream is then modified by altering the value of at least one of the determined three-dimensional properties and, in one embodiment, applying image formation theory. The modifications are then rendered in an output 3D picture either automatically and / or according to user inputs. In various embodiments, corrections made to the selected one of the at least two image streams can be automatically applied to the other of the image streams.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL CE PATENT HLDG
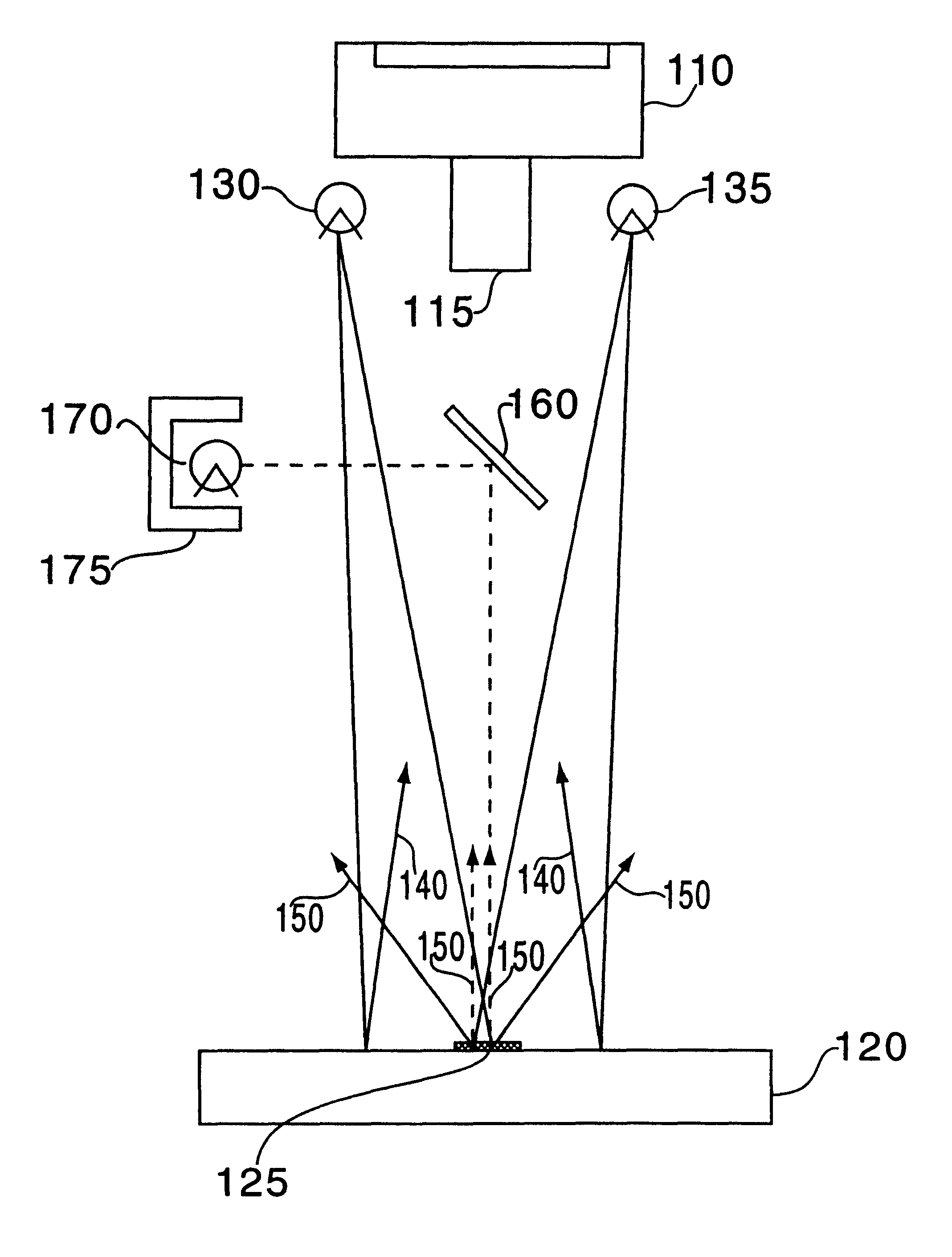
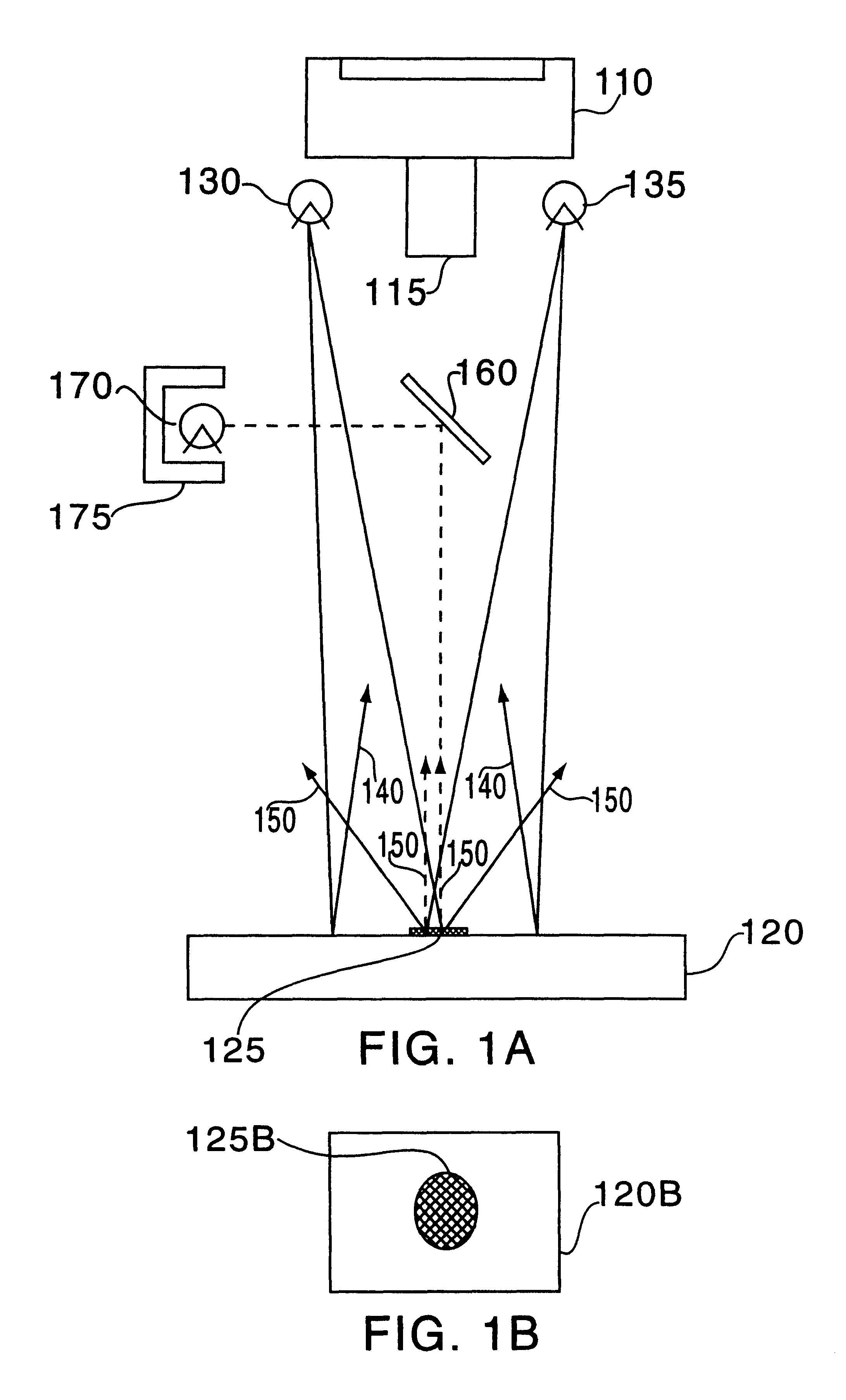
Specular object scanner for measuring reflectance properties of objects
An apparatus to measure surface orientation maps of an object may include a light source that is configured to illuminate the object with a controllable field of illumination. One or more cameras may be configured to capture at least one image of the object. A processor may be configured to process the image(s) to extract the reflectance properties of the object including an albedo, a reflection vector, a roughness, and / or anisotropy parameters of a specular reflectance lobe associated with the object. The controllable field of illumination may include limited-order Spherical Harmonics (SH) and Fourier Series (FS) illumination patterns with substantially similar polarization. The SH and FS illumination patterns are used with different light sources.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Apparatus and method for angular colorimetry
ActiveUS20070258093A1Cost-effectiveData variationScattering properties measurementsAngle of incidenceReflectance properties
An apparatus for measuring the reflectance properties of an object having a front reflecting surface and at least one back reflecting surface. The apparatus includes a sample stage for placement of the object, a light source, a detector configured to detect reflected light from the object, and a positioning device configured to provide a plurality of angular positions for the light source and the detector relative to the object on the sample stage such that incident light on the object is specularly reflected towards the detector and the reflected light received at the detector includes a front surface reflection from the object and at least one back surface reflection from the object. The method includes illuminating the object at varying angles of incidence, collecting reflected light from the front and back reflecting surfaces of the object at respective specularly reflected angles, wavelength resolving the reflected light into a color spectrum, and analyzing an intensity of the color spectrum as a function of wavelength.
Owner:CARDINAL CG
Device, method and system for determining the road surface condition
InactiveUS20060050270A1Radiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationWavelength modulation spectroscopyReflectance properties
The invention relates to a device, a method and a system for determining a road surface condition, where the surface condition is one of dry, wet or icy. The device comprises a reflectance spectrometer which senses the reflectance properties of the road at one or several wavelengths and uses these reflectance properties to determine the surface condition. The reflectance spectrometer is a wavelength modulation spectrometer, preferably for the near infrared region. The system determines the surface condition and indicates it to a user of the system.
Owner:ELMAN ULF
Light control devices and methods implemented with kinoform diffusers having controllable diffusion characteristics
Kinoform diffusers (82) exhibit controllable diffusion characteristics that include off-axis transmittance and reflectance properties, elimination of zero-order beam, and freedom from spectral dispersion under achromatic illumination. Light control devices (76, 80, 82) implemented with kinoform diffusers having controllable diffusion characteristics provide anisotropic luminous intensity distributions and glare control at high viewing angles while maintaining high luminaire efficiency or daylight utilization.
Owner:LUMEC HLDG ULC
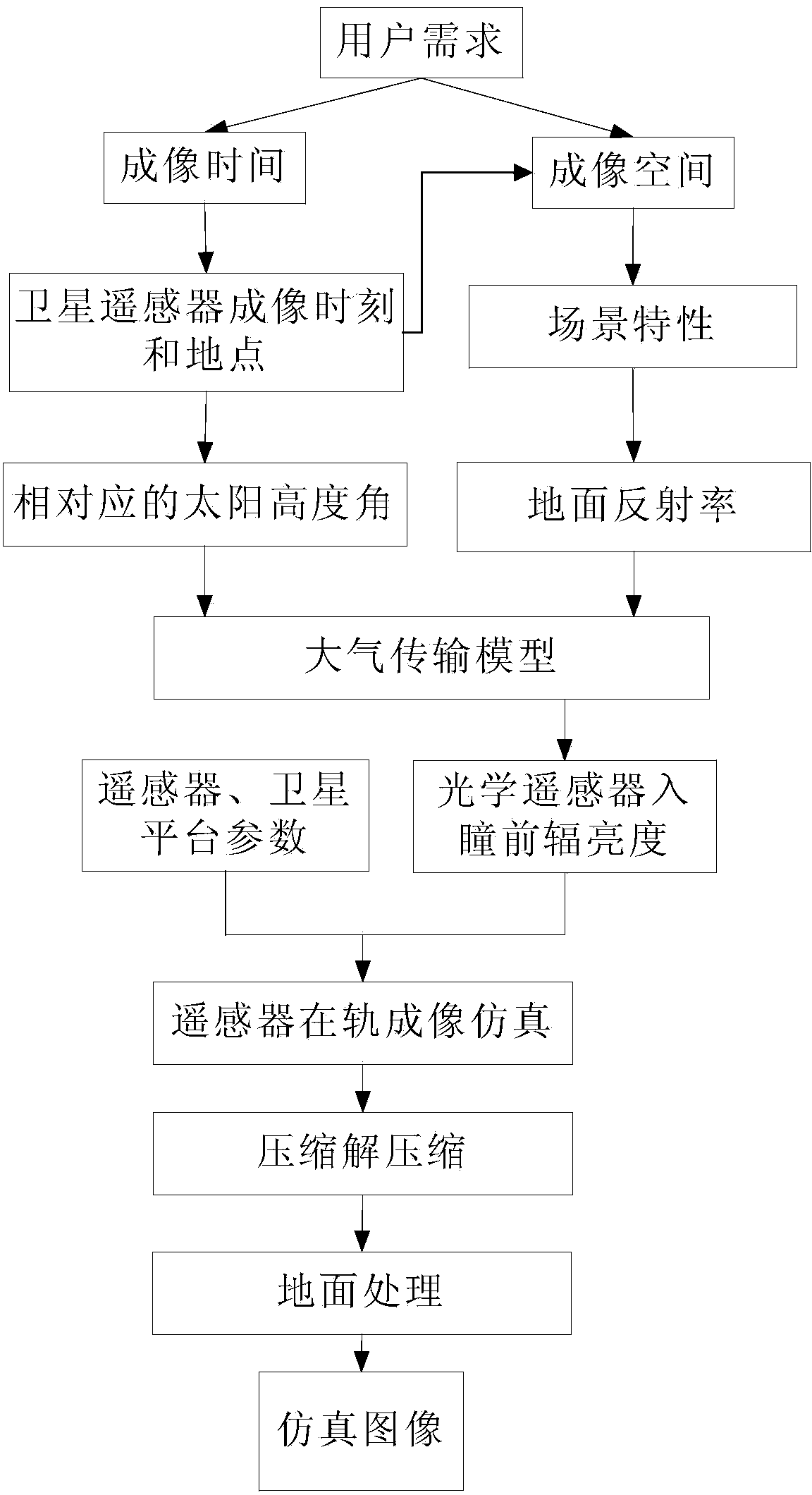
Spaceflight optical remote sensing imaging simulation method based on space-time unified feature
ActiveCN103675794AGuaranteed correctnessImprove image qualityWave based measurement systemsImaging qualityReflectance properties
A spaceflight optical remote sensing imaging simulation method based on a space-time unified feature comprises the steps that (1), the relation of the position of a satellite at any GMT and the time and the longitude and latitude of the satellite at a GMT sub-satellite point are obtained in a calculating mode according to satellite orbit parameters; (2), the entrance pupil radiance L (lamda) of a remote sensor is obtained in a calculating mode according to the longitude and latitude of the satellite at the GMT sub-satellite point, an imaging time ground target reflectivity feature pho and a solar elevation angle theta; (3), the signal Starget of the remote sensor is obtained by combining the remote senor parameters and L (lamda), linear amplification, smoothing and quantization processing are carried out on the Starget in sequence, and an initial simulation image is obtained after a remote sensor optical system, a remote sensor detector, a remote sensor circuit and a simulation MTF of a satellite platform are overlaid; (4), after compression, uncompression, radiation correction and MTF compensation are carried out on the initial simulation image, a simulation image needed by a user is obtained. The method can carry out effective optical remote sensing full-chain imaging simulation, and optical remote sensing in-orbit imaging quality is greatly improved.
Owner:BEIJING RES INST OF SPATIAL MECHANICAL & ELECTRICAL TECH
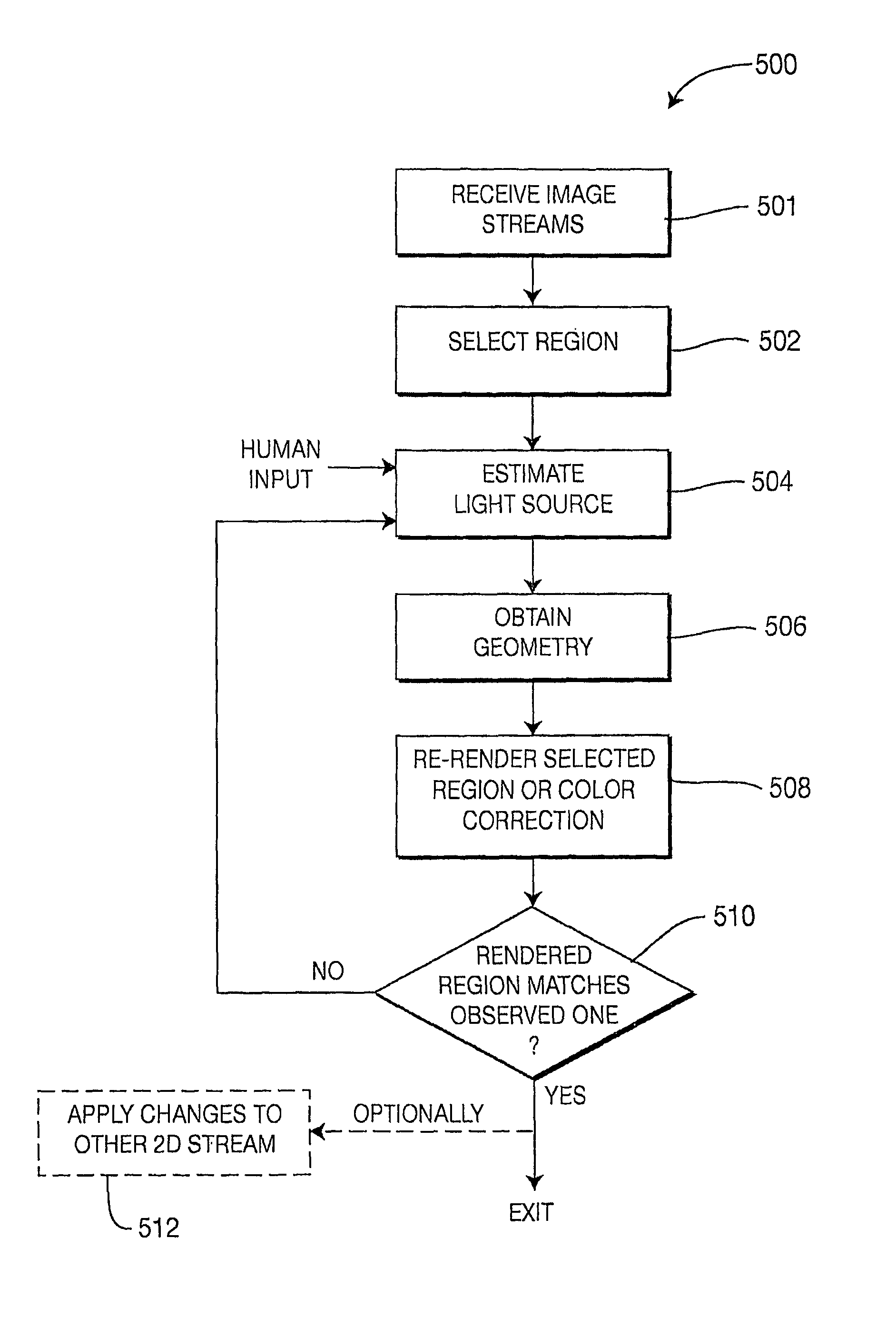
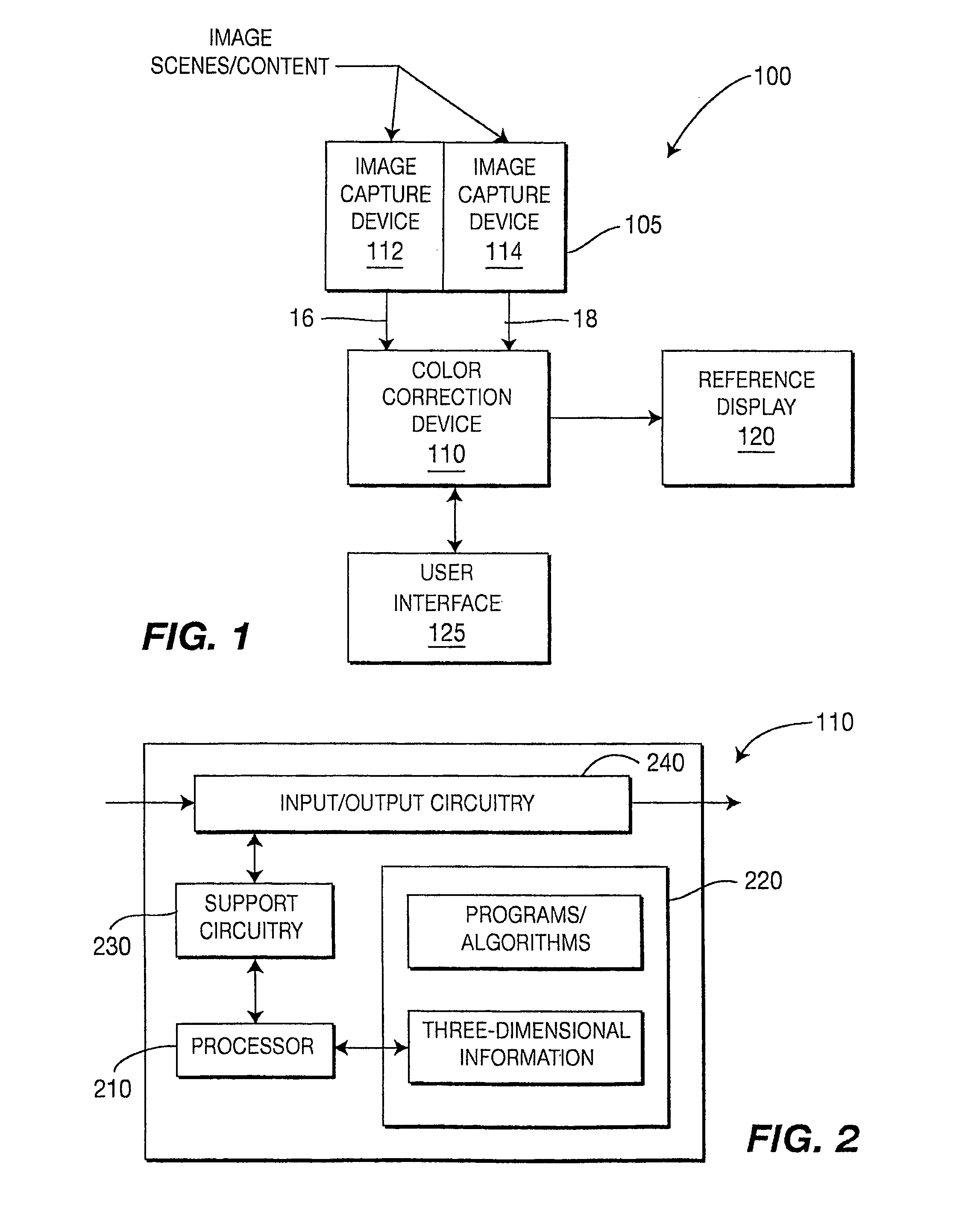
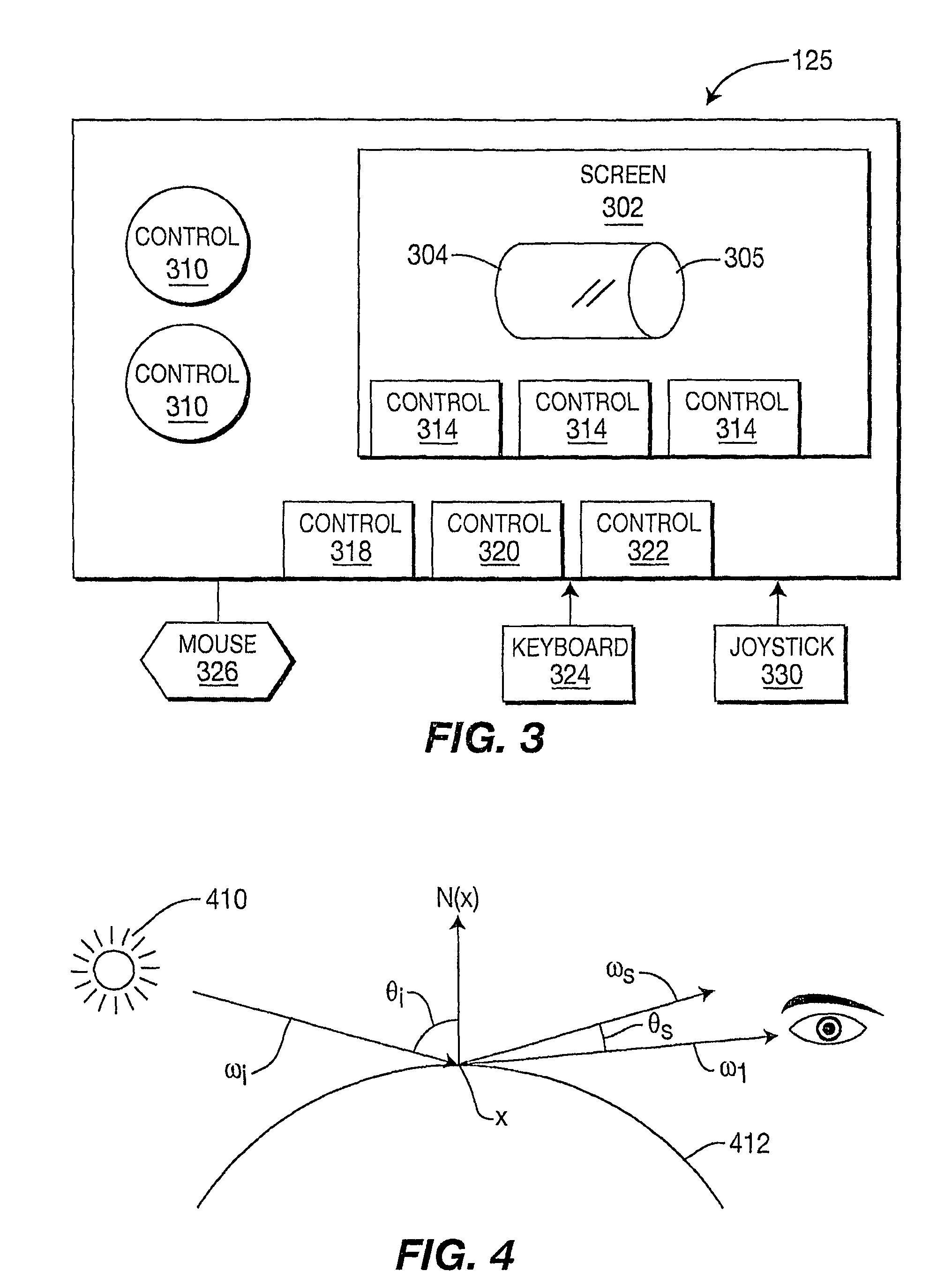
Method and System for Color Correction Using Thre-Dimensional Information
ActiveUS20090303247A1Cathode-ray tube indicators3D-image renderingUser inputComputer graphics (images)
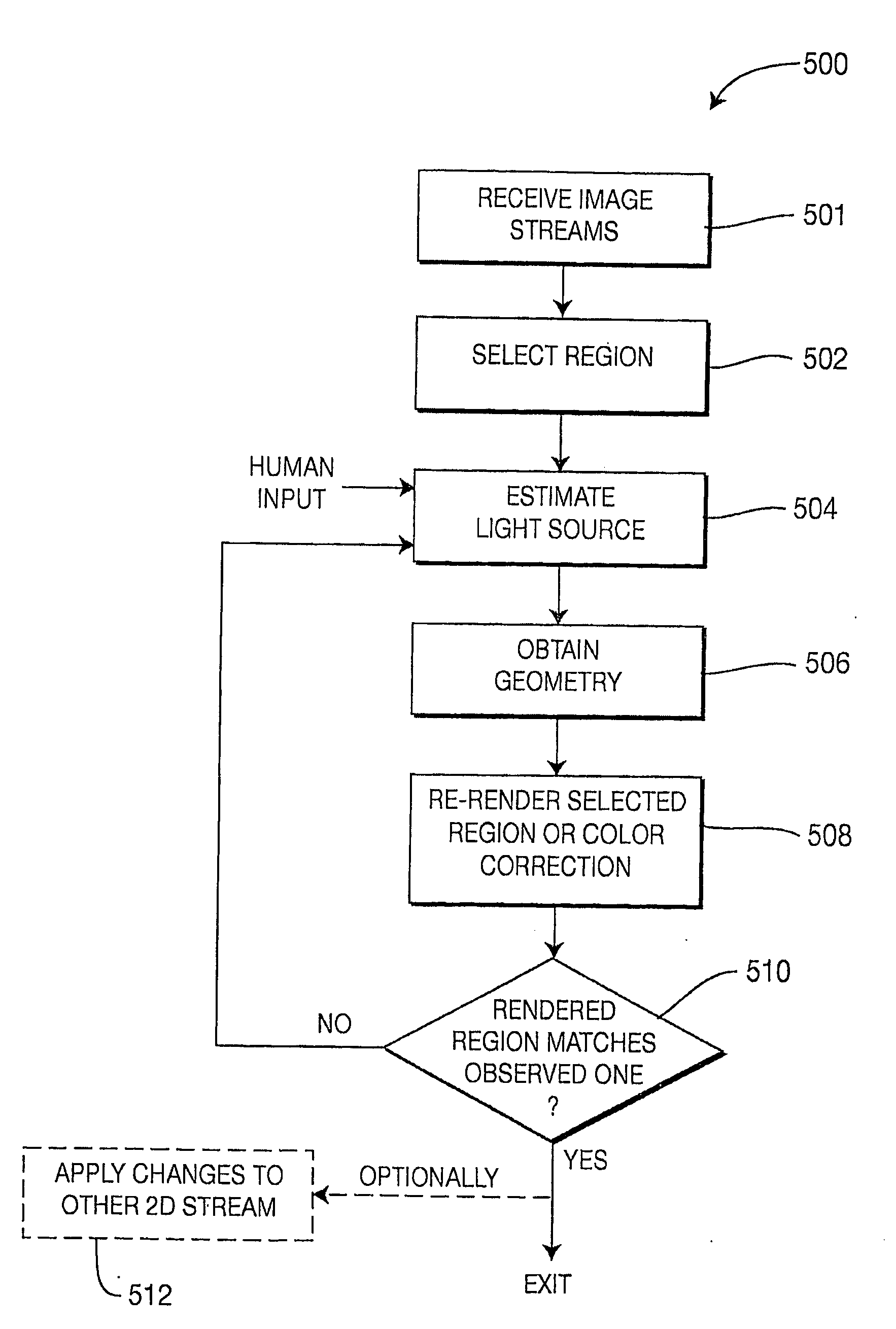
A system and method for the color correction of an image using three-dimensional, geometrical information of the capture environment of the image includes determining geometrical properties of at least a portion of the image and modifying a look of at least the portion of the image by altering a value of at least one of the determined geometrical properties and using image formation theory. In one embodiment of the present invention, the geometrical properties of the image include at least one of light properties, surface color, reflectance properties, and scene geometry of the at least one portion of the image. In accordance with the present invention, the geometrical properties of the image are alternatively determined by using sensing devices, by inferring the geometrical properties from the image itself, or by user input.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL MADISON PATENT HLDG
Antireflective film and optical element
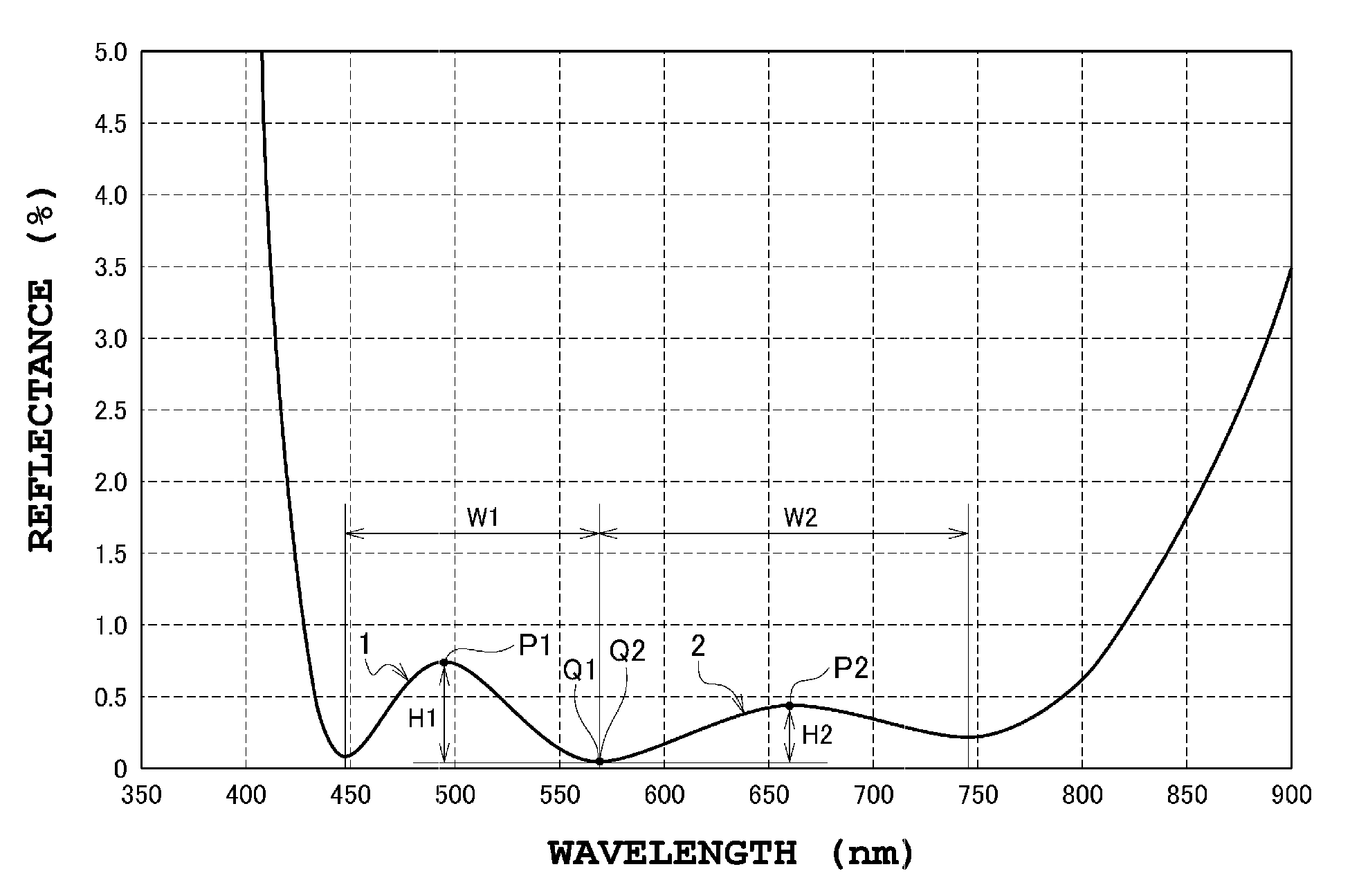
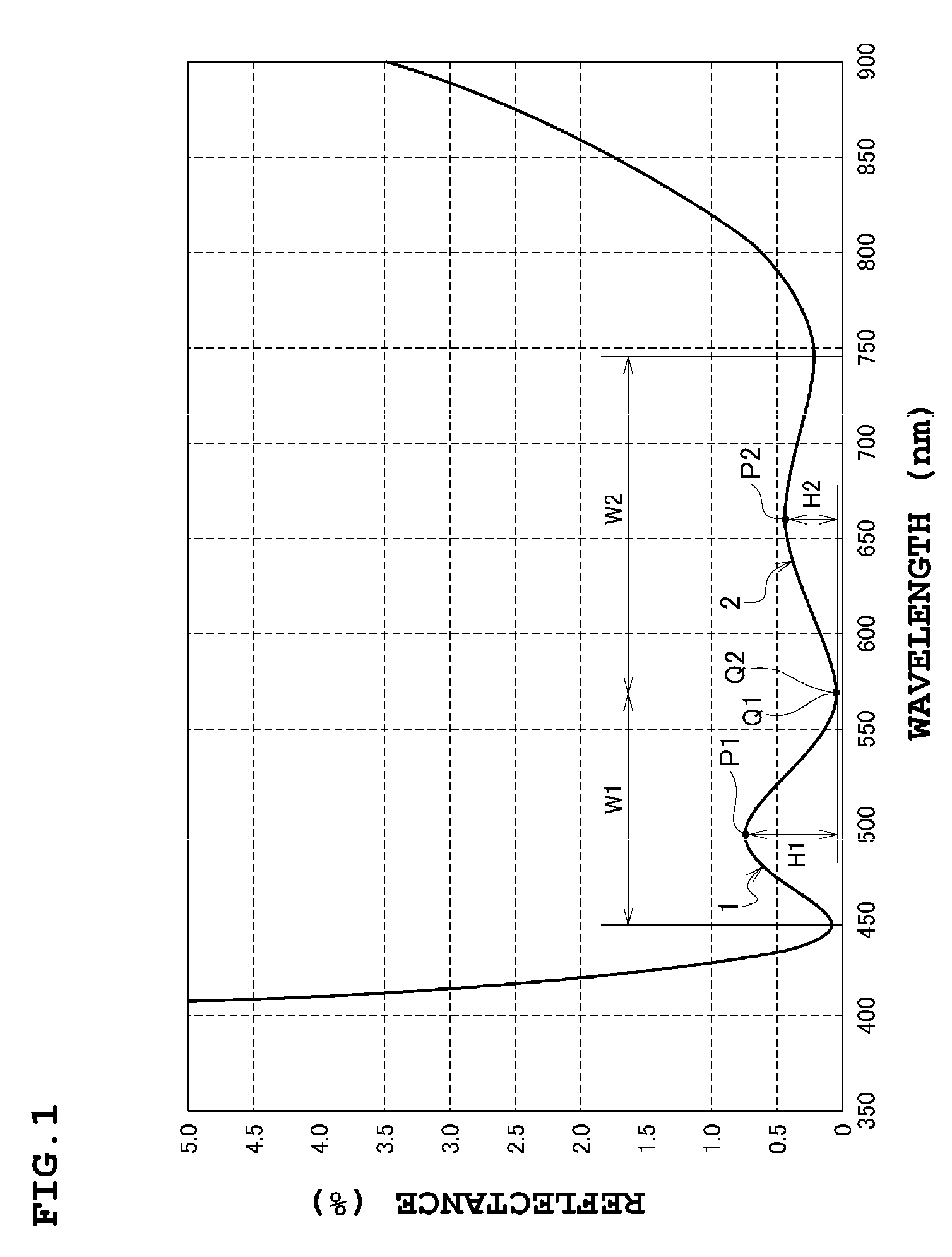
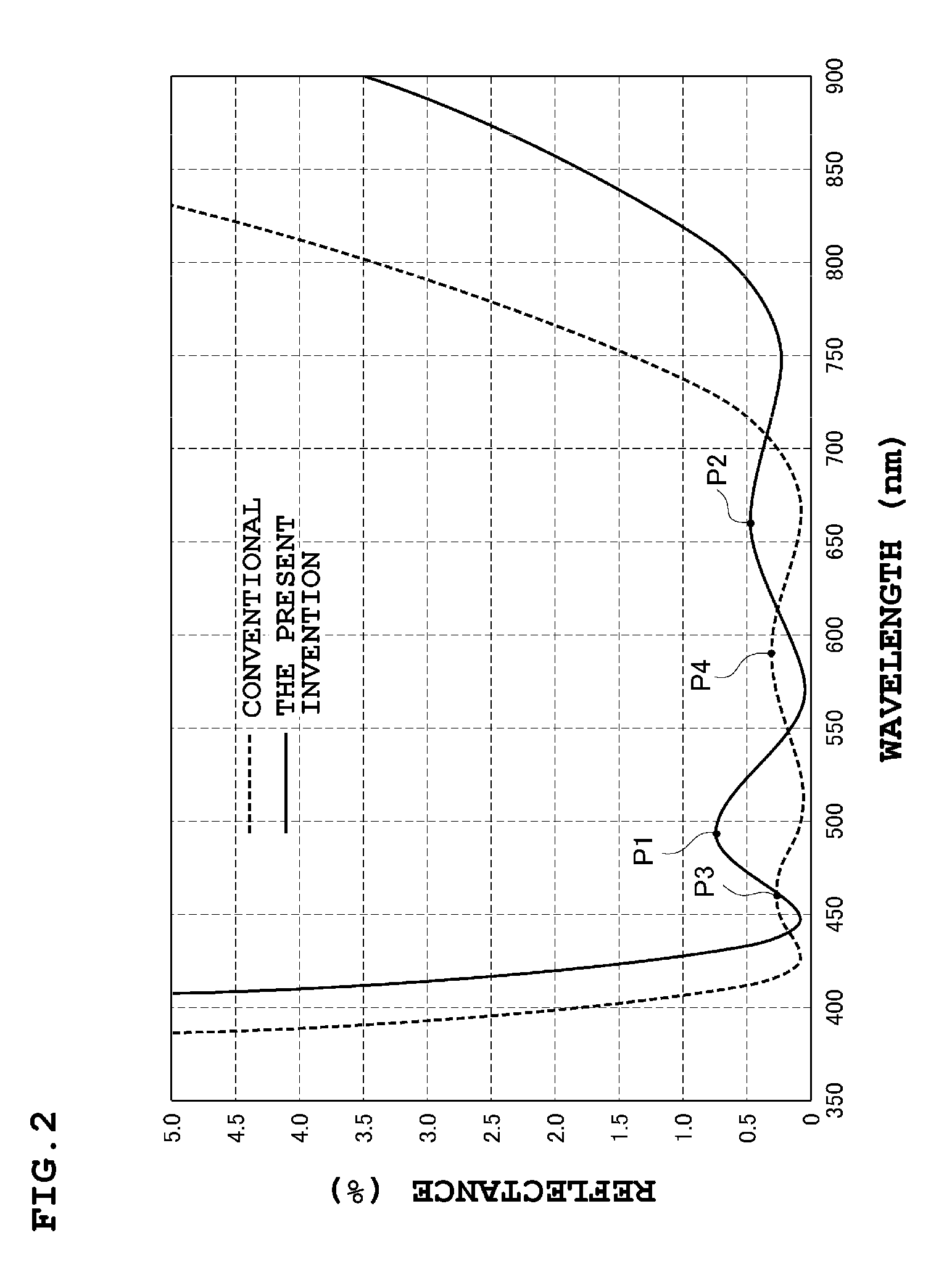
InactiveUS8840257B2Avoid reflectionsSecond wavelength region isCoatingsLensLight beamReflectance properties
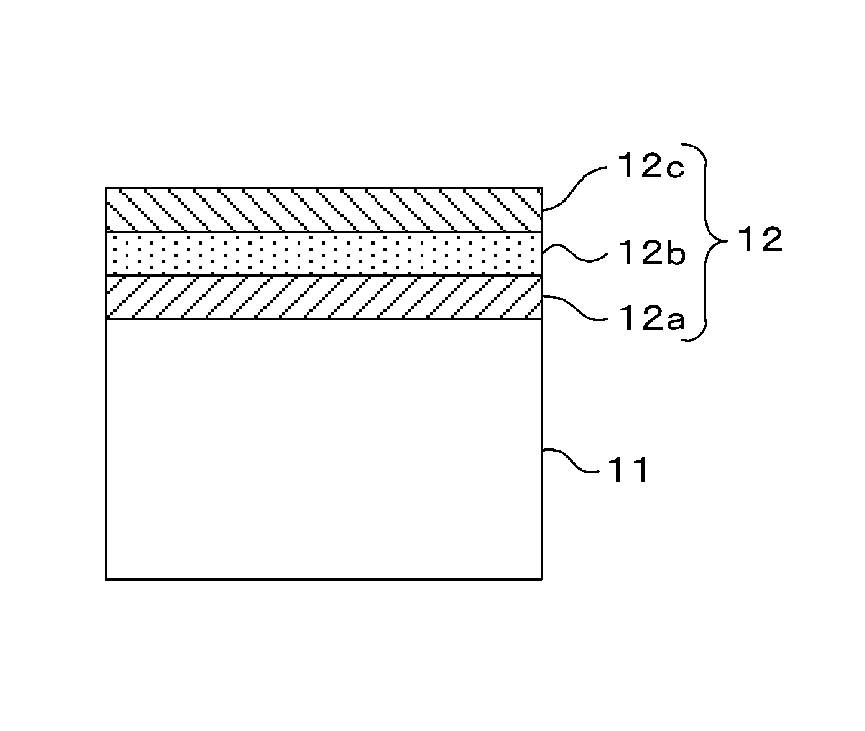
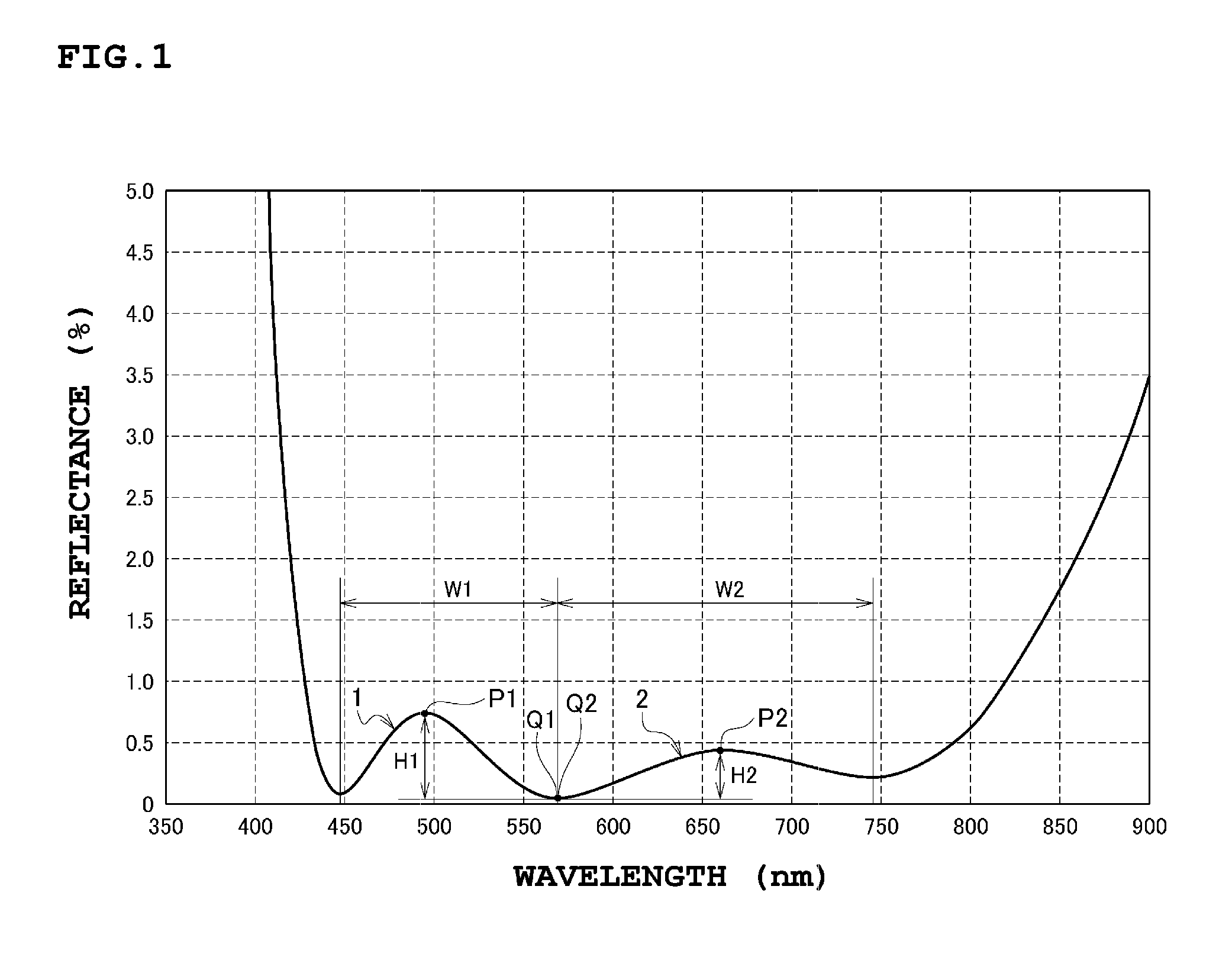
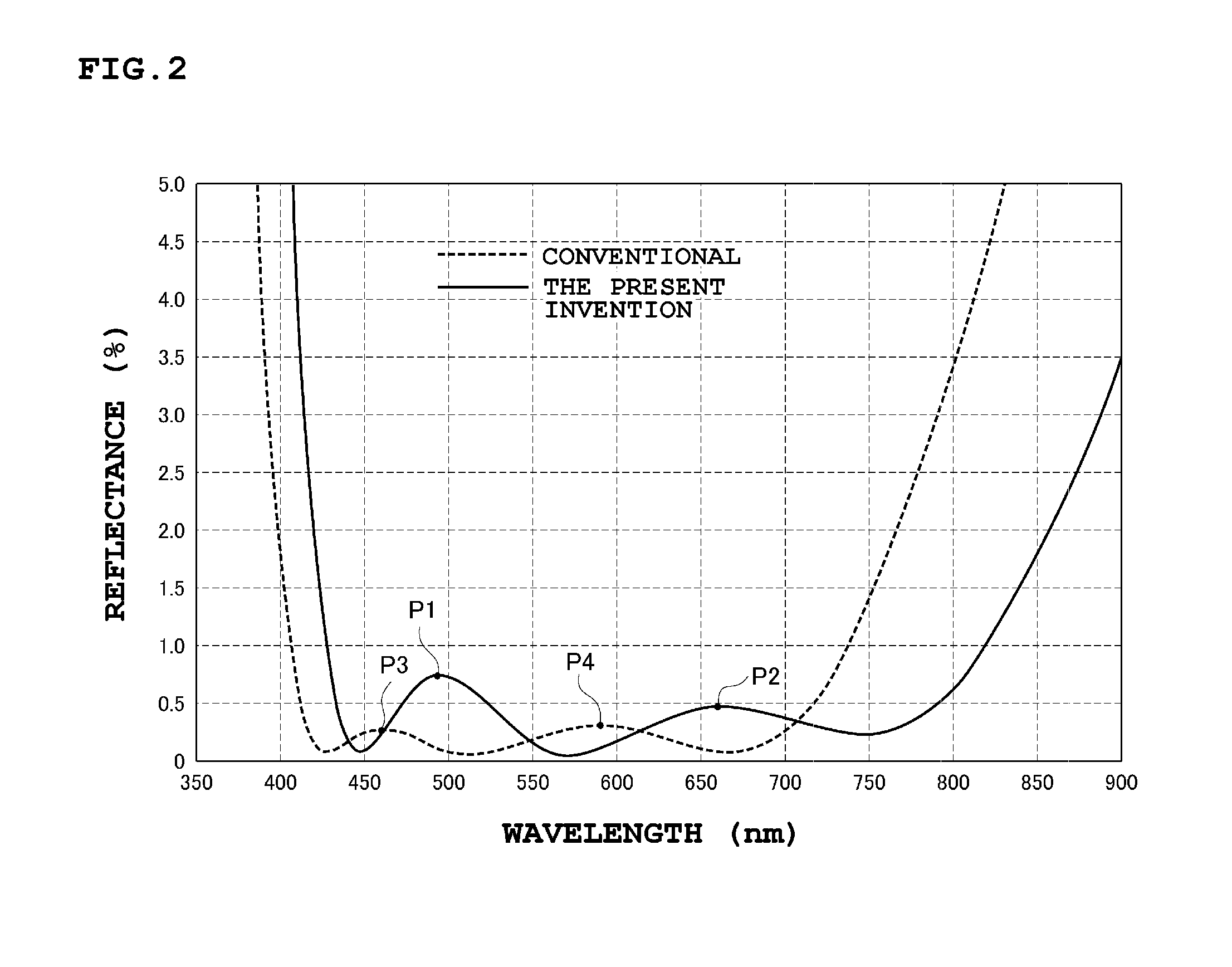
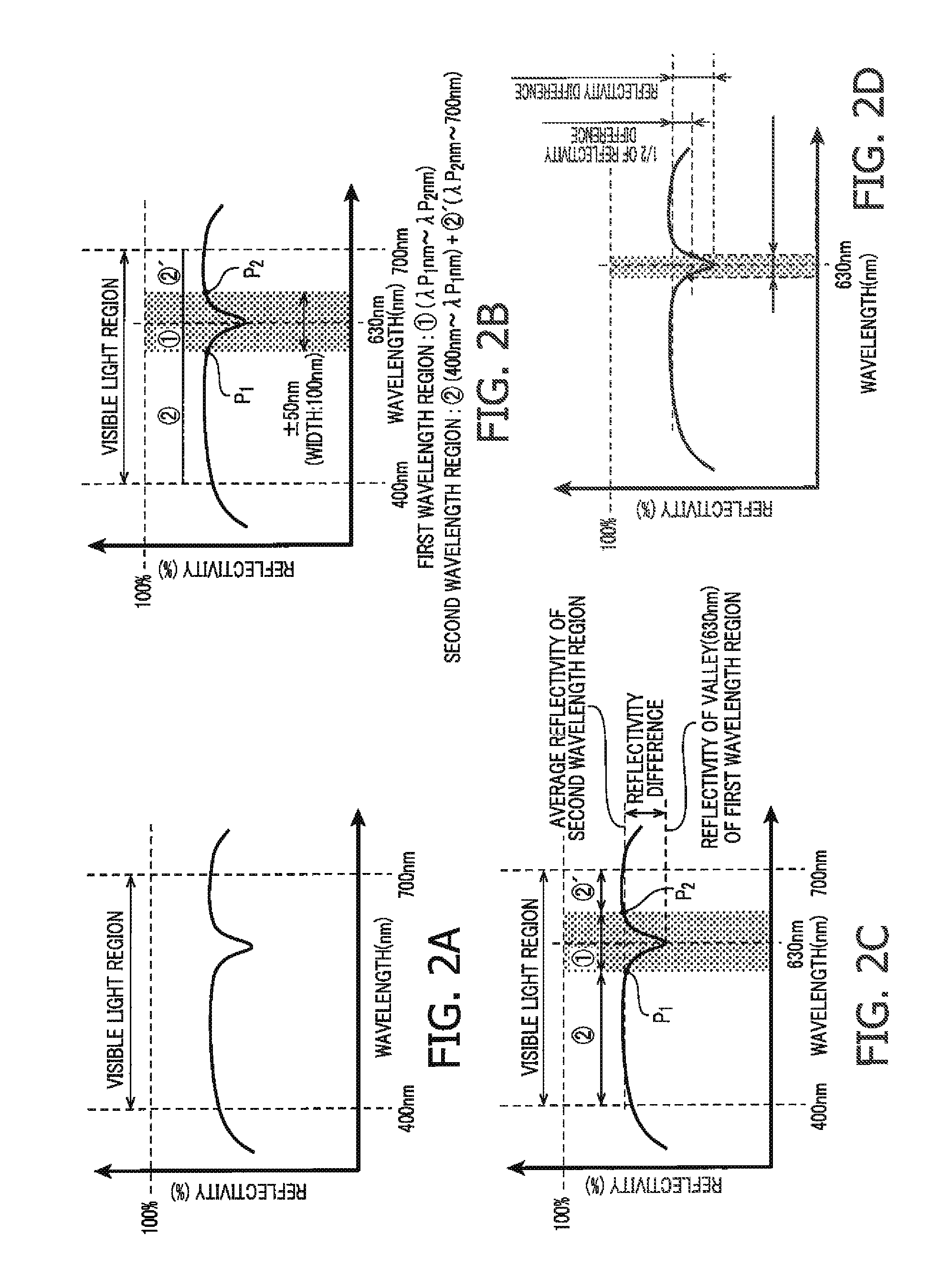
An antireflection film, including an optical element, formed on an optical surface of an optical member and preventing reflection of a light beam incident on the optical surface. It has a maximum reflectance P1 in a first wavelength region and a maximum reflectance P2 in a second wavelength region at a wavelength side longer than the first wavelength region, and satisfies a relation of P1>P2, as a spectral reflectance property when a light beam is incident on the optical surface at a 0 degree incident angle. It also shifts a wavelength range where the reflectance is a specific value or less, to a wavelength longer than the second wavelength region, the reflectance in the second wavelength region decreases, and the reflectance in the first wavelength region increases so that a luminance difference is small between a ghost in the first wavelength region and the second wavelength region.
Owner:HOYA CORP
Method for manufacturing array substrate of translucent LCD
ActiveUS7480015B2Resistance in propertiesResistance in regionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNon-linear opticsElectrical resistance and conductanceReflectance properties
Owner:HYDIS TECH CO LTD
Device, method and system for determining the road surface condition
InactiveUS7224453B2Radiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationWavelength modulation spectroscopyReflectance spectroscopy
The invention relates to a device, a method and a system for determining a road surface condition, where the surface condition is one of dry, wet or icy. The device comprises a reflectance spectrometer which senses the reflectance properties of the road at one or several wavelengths and uses these reflectance properties to determine the surface condition. The reflectance spectrometer is a wavelength modulation spectrometer, preferably for the near infrared region. The system determines the surface condition and indicates it to a user of the system.
Owner:ELMAN ULF
Methods and systems for color correction of 3D images
Owner:INTERDIGITAL CE PATENT HLDG
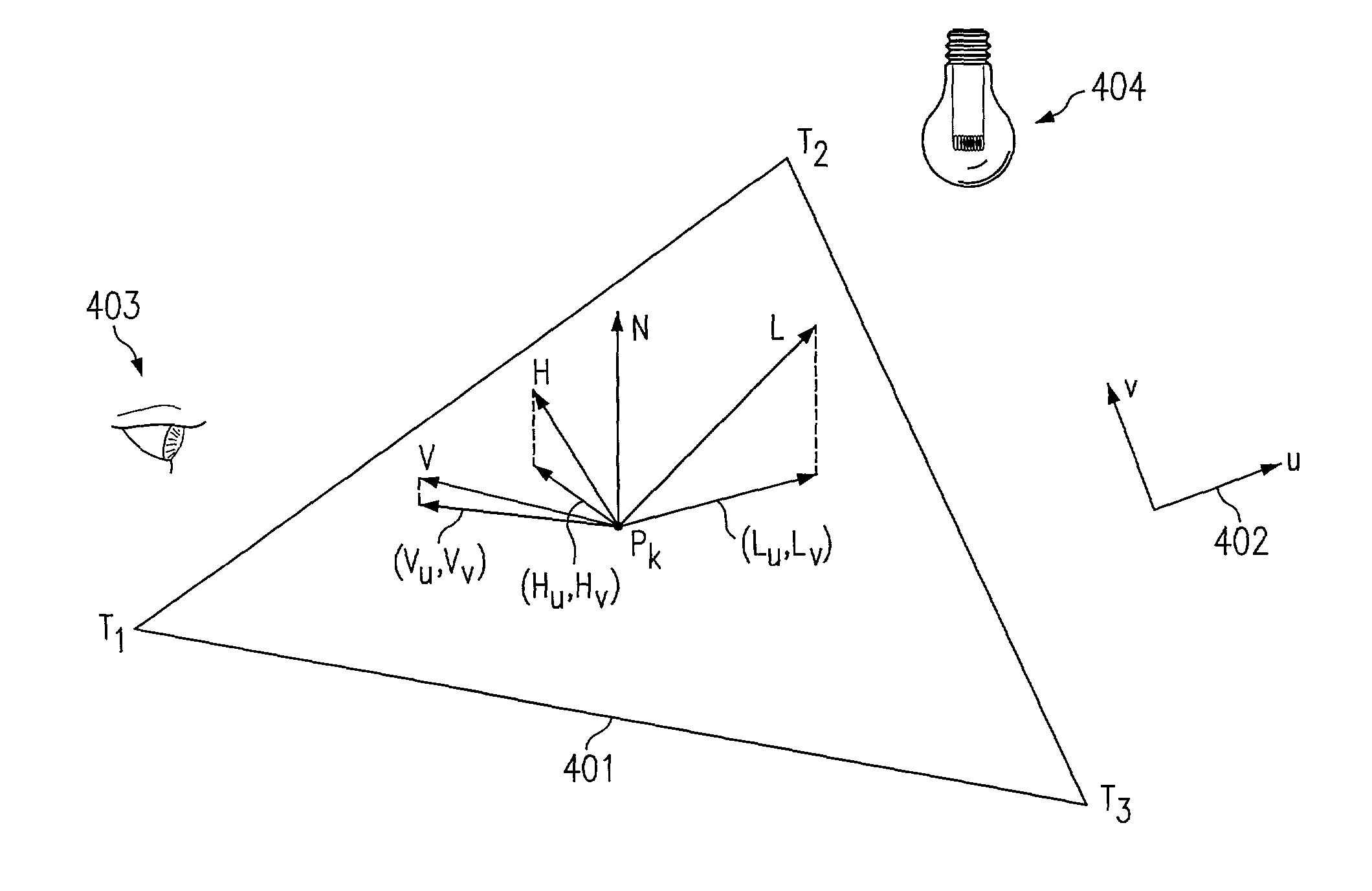
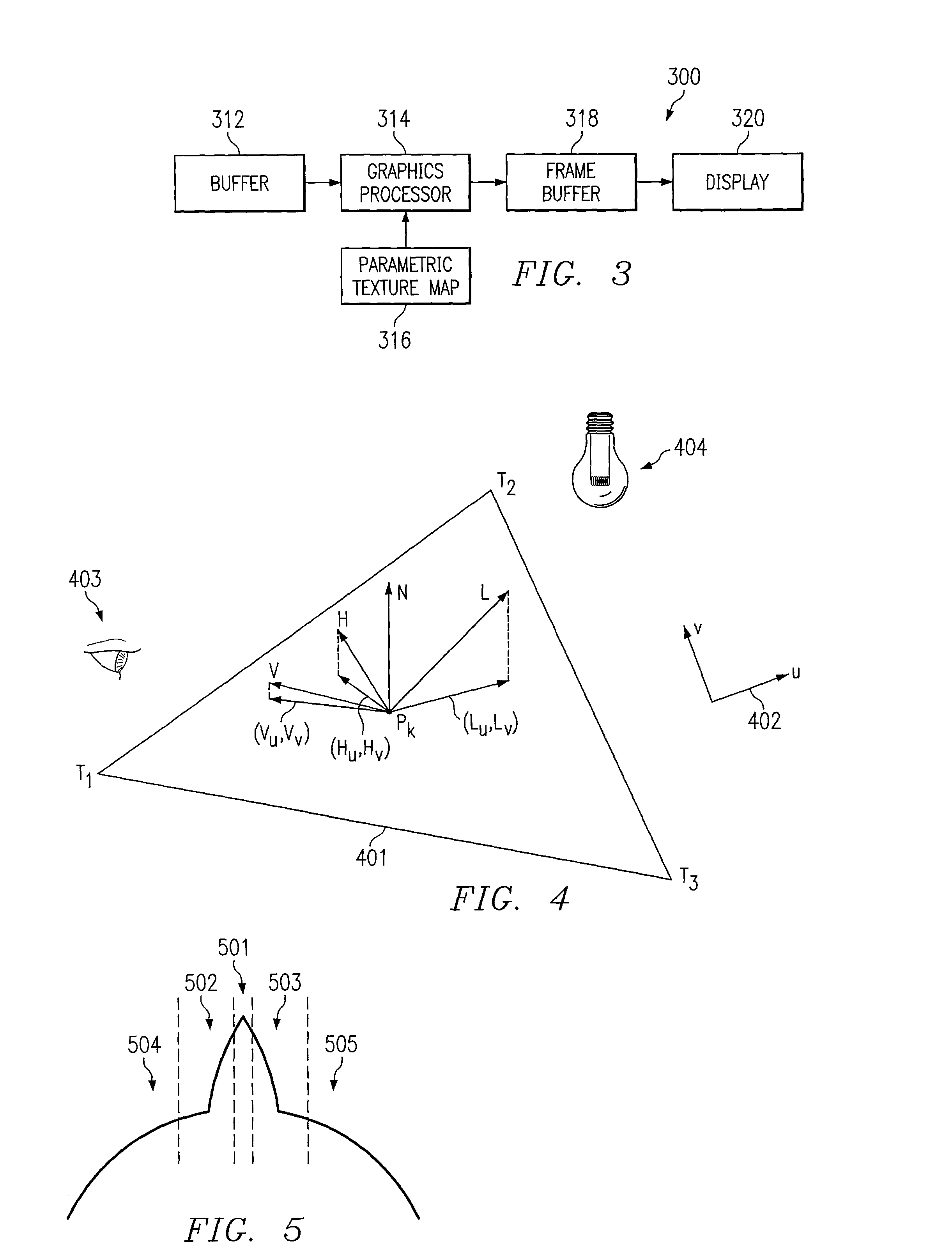
System and method for rendering digital images having surface reflectance properties
InactiveUS7106325B2Cathode-ray tube indicators3D-image renderingComputer graphics (images)Reflectance properties
According to one embodiment of the present invention, a method for rendering a digital image having surface reflectance properties is disclosed. The method comprises creating a parametric texture map that comprises parameters for an equation that defines a surface structure in a manner in which the appearance of the surface structure includes surface reflectance properties. The method further comprises rendering a digital image using the parametric texture map.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
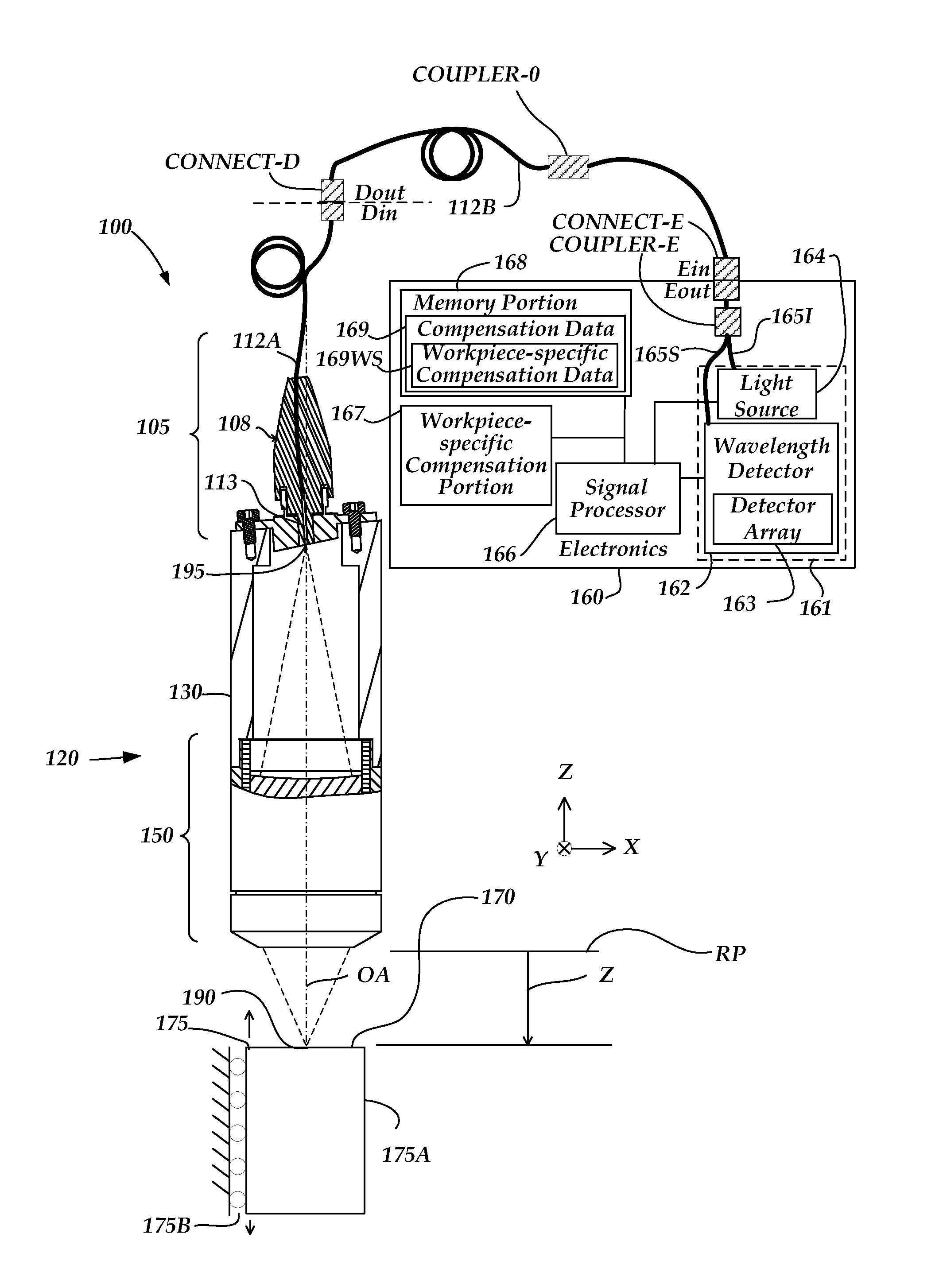
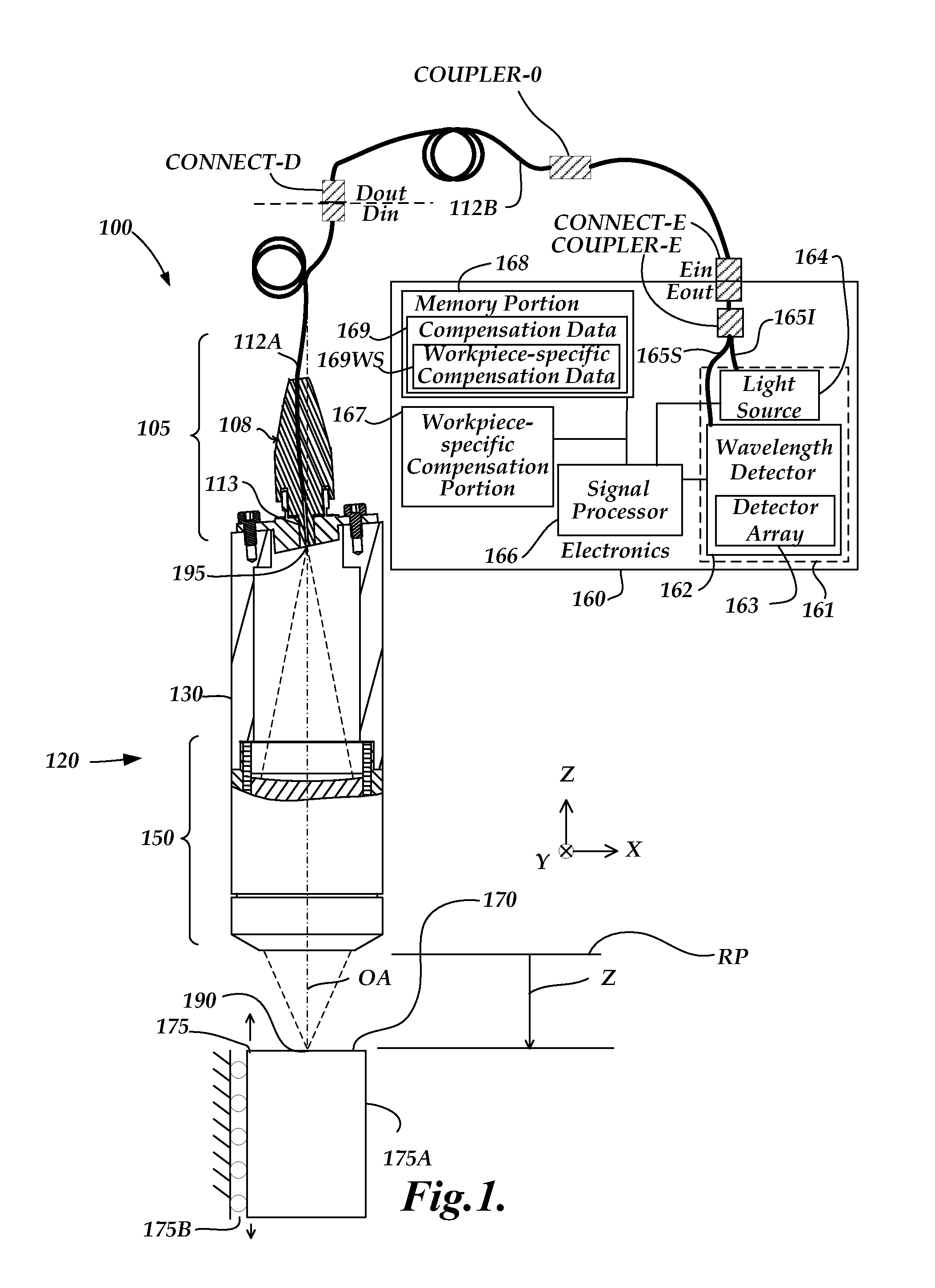
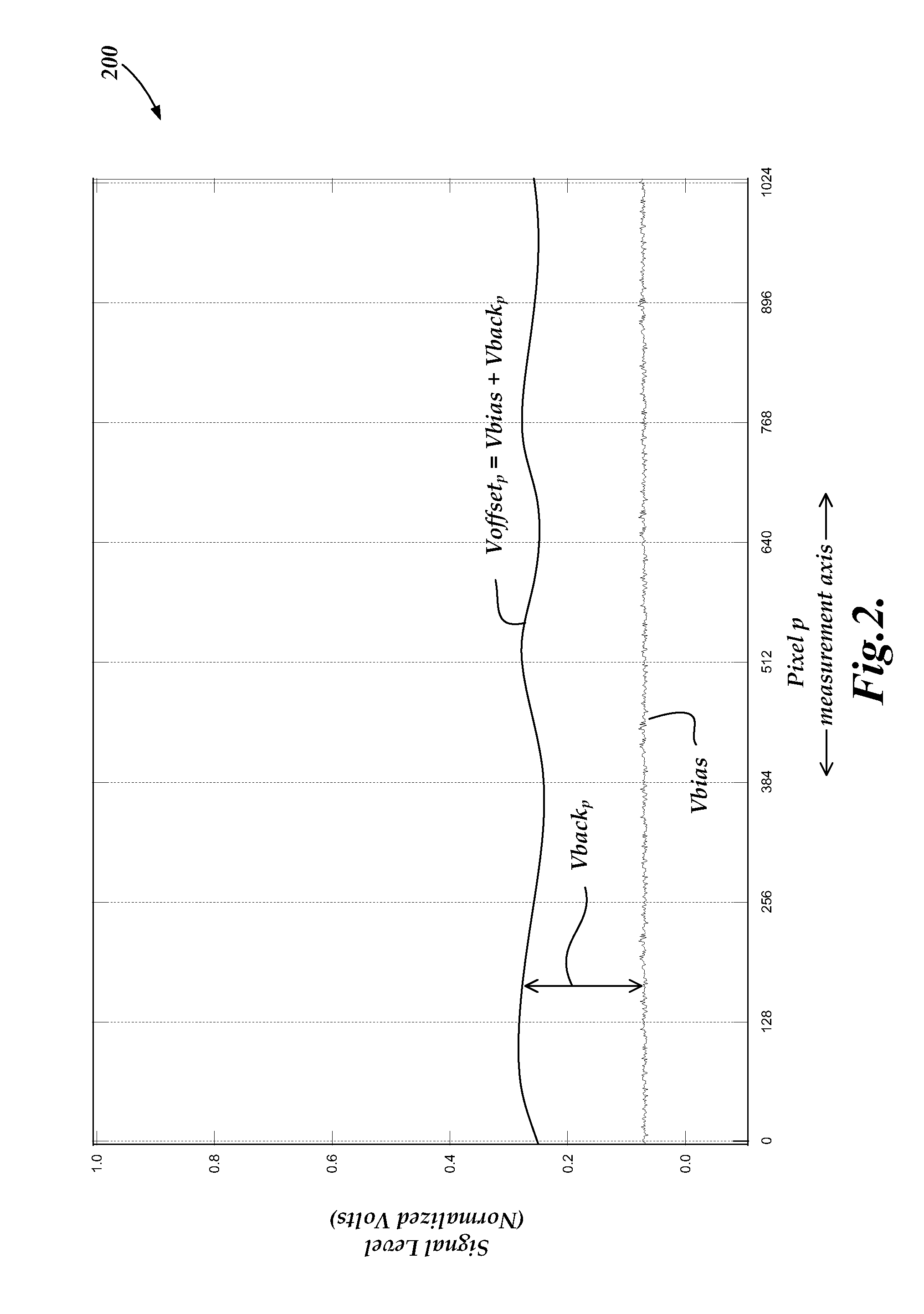
Chromatic point sensor compensation including workpiece material effects
ActiveUS20130163006A1Reduces distance measurement errorPotential for errorUsing optical meansReflectivity measurementReflectance properties
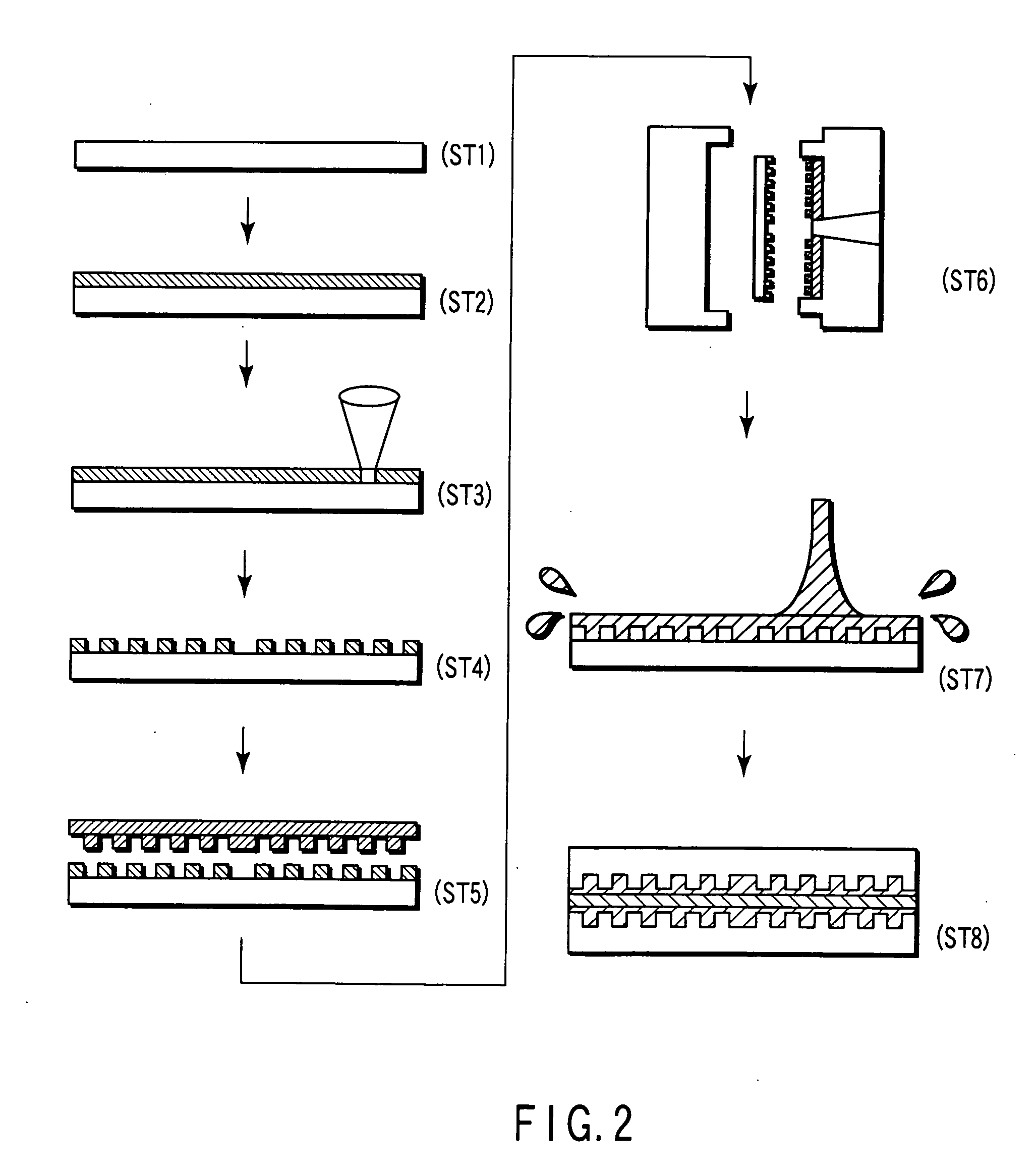
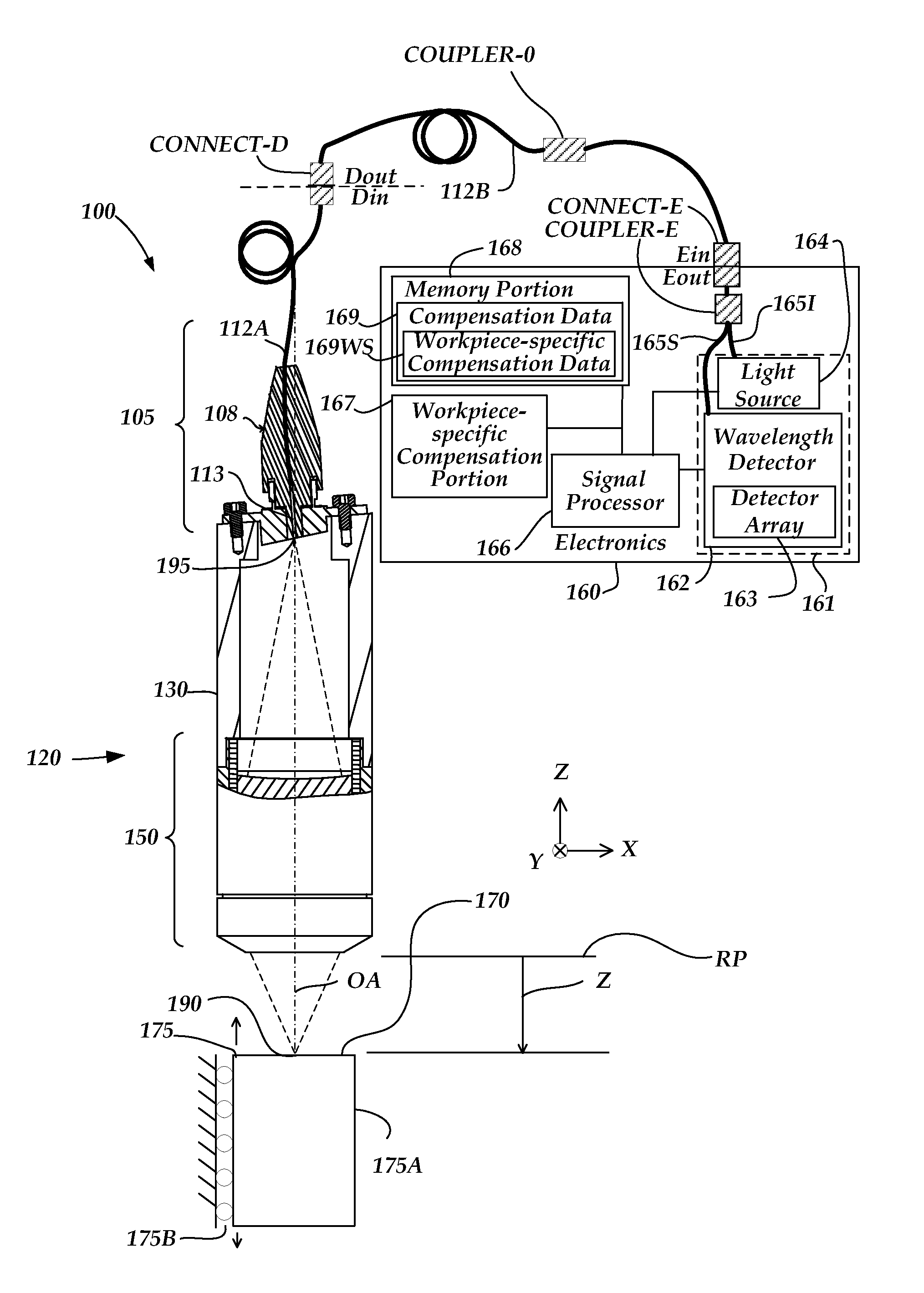
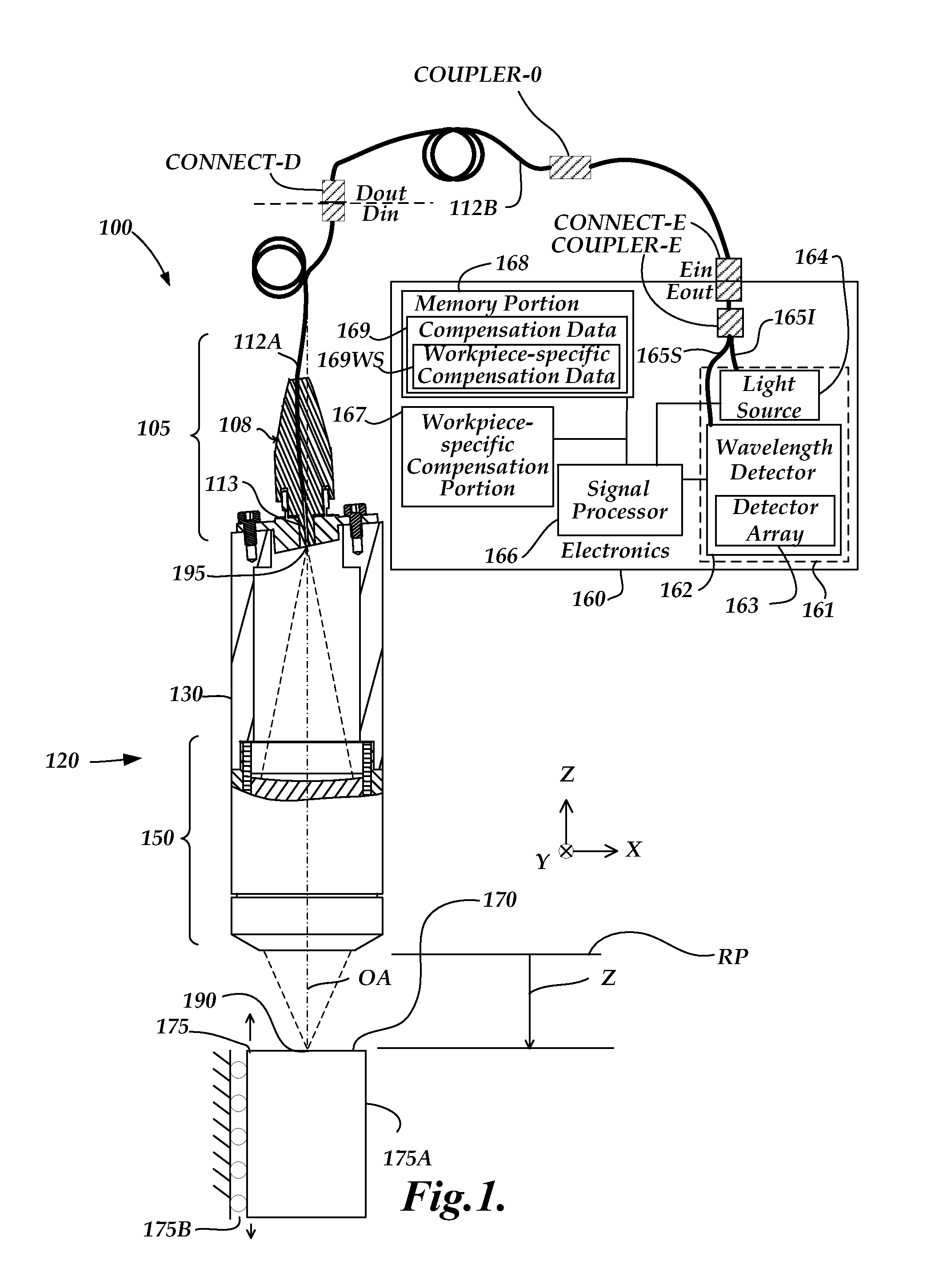
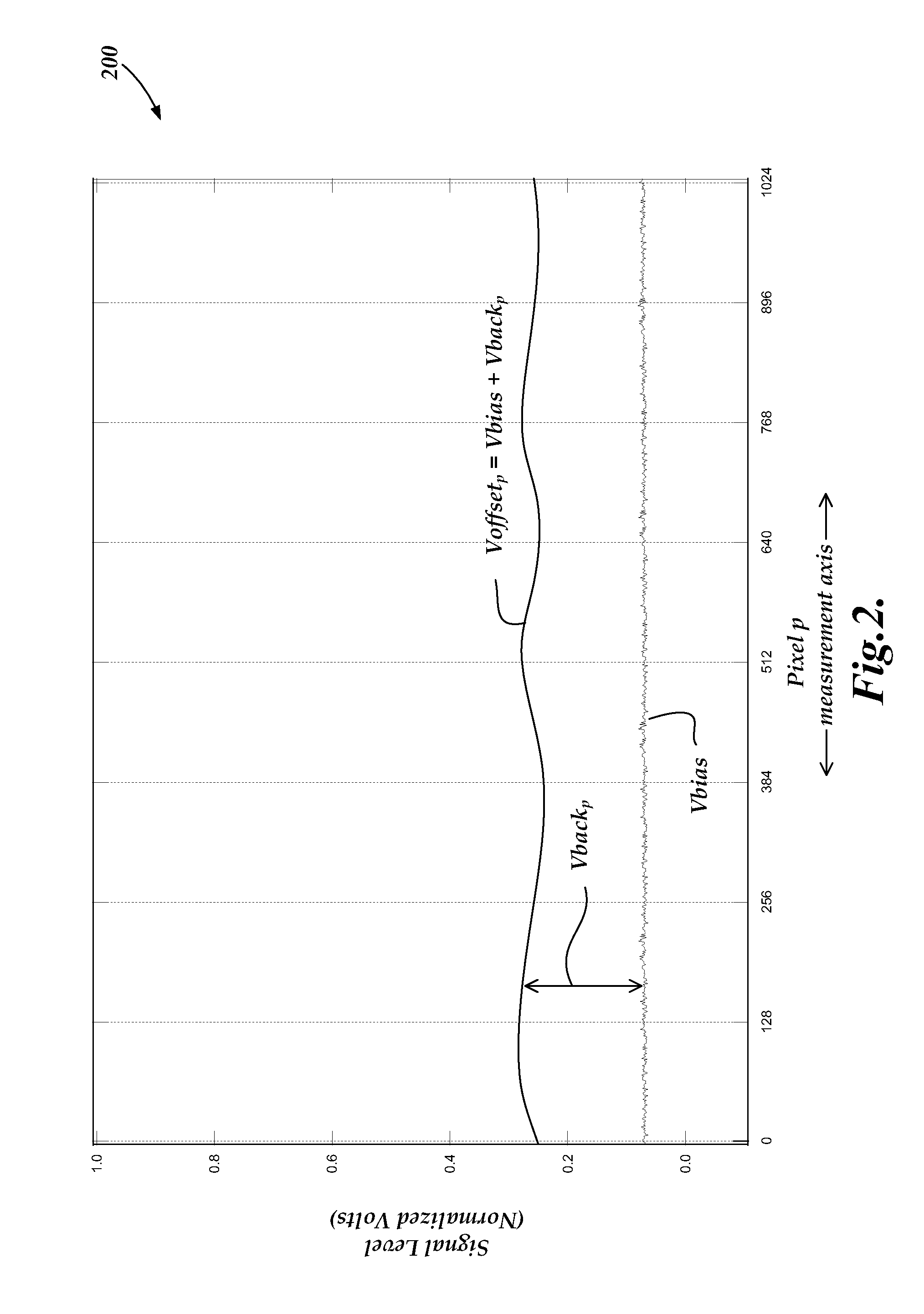
A method of error compensation in a chromatic point sensor (CPS) reduces errors associated with varying workpiece spectral reflectivity. The errors are associated with a distance-independent profile component of the CPS measurement signals. Workpiece spectral reflectivity may be characterized using known spectral reflectivity for a workpiece material, or by measuring the workpiece spectral reflectivity using the CPS system. CPS spectral reflectivity measurement may comprise scanning the CPS optical pen to a plurality of distances relative to a workpiece surface and determining a distance-independent composite spectral profile from a plurality of resulting wavelength peaks. By comparing the distance-independent composite spectral profile obtained from a workpiece with that corresponding to the CPS distance calibration procedure, the contribution of the reflectivity characteristics of the workpiece will be indicated in the differences between the profiles, and potential CPS position errors due to varying workpiece reflectivity characteristics may be calculated and / or compensated.
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
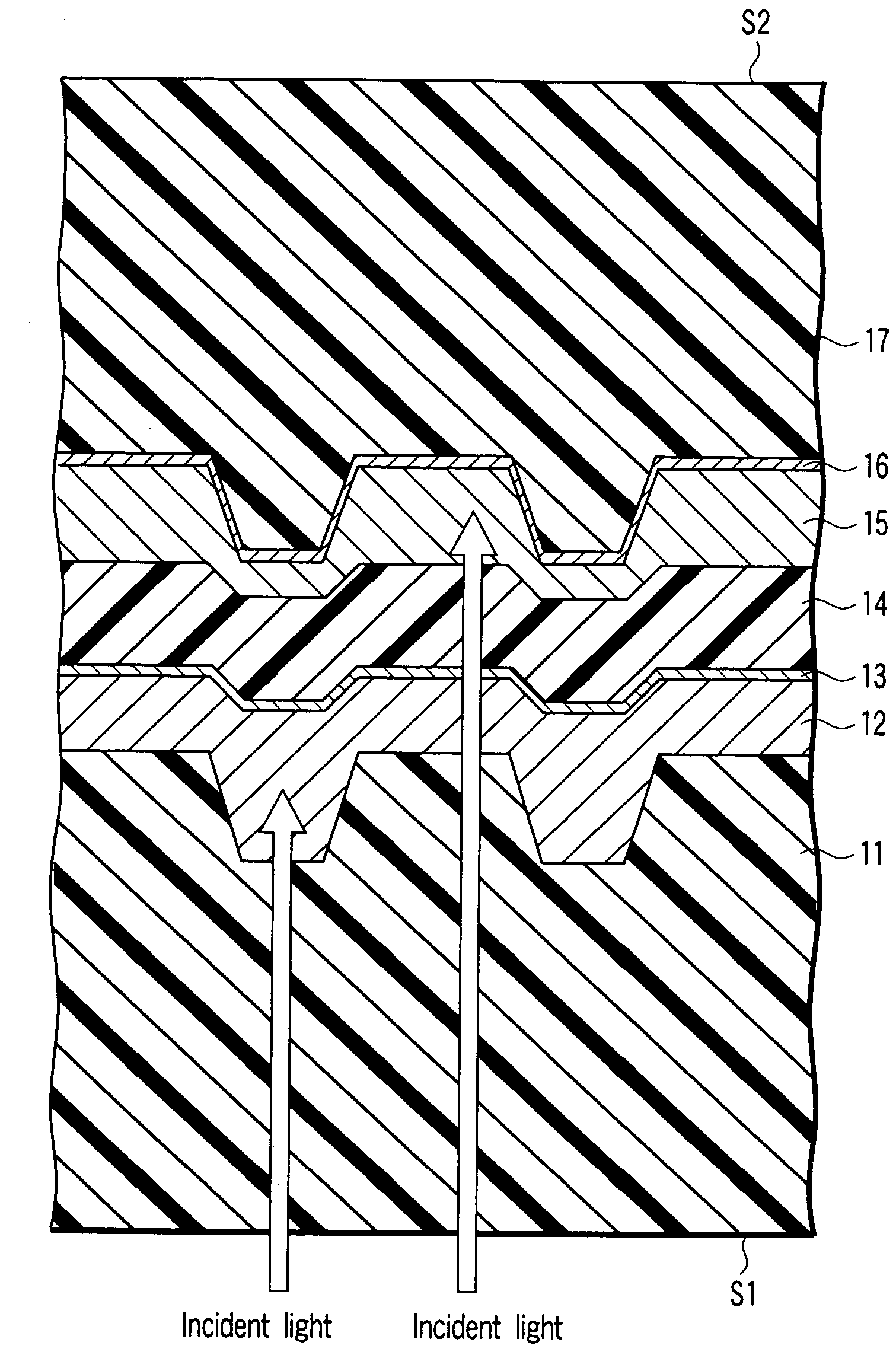
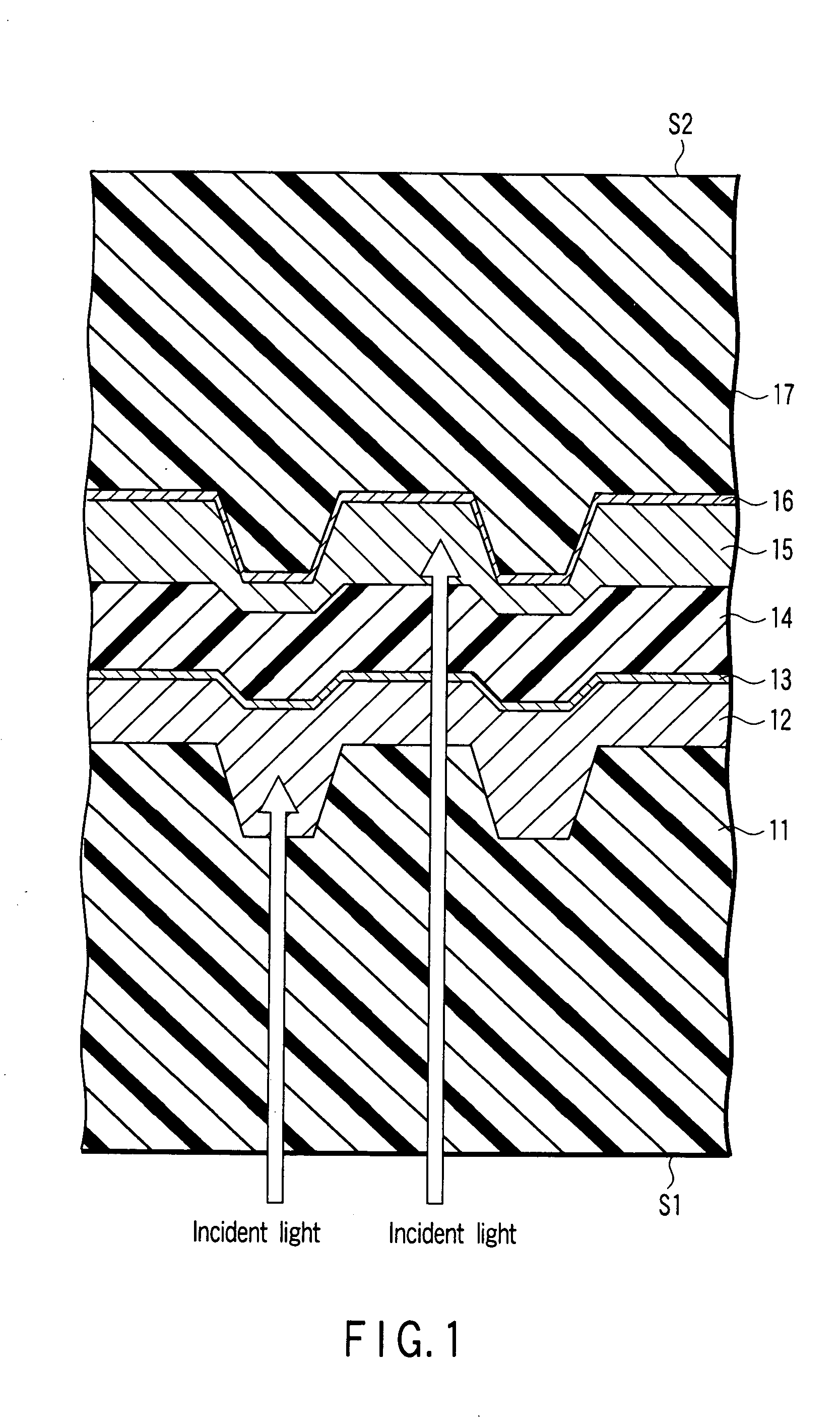
Optical disk and information playback apparatus
InactiveUS20060023615A1Mechanical record carriersRecord information storageRecord statusReflectance properties
An optical disk according to an example of the present invention includes the first and second recording layers on which pieces of information can be recorded by undergoing a change in properties when irradiated with a laser beam. The first recording layer has the first reflectance characteristic in which the reflectance in an information recorded state is lower than that in an information unrecorded state. The second recording layer has the second reflectance characteristic in which the reflectance in the information recorded state is higher than that in the information unrecorded state.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Chromatic point sensor compensation including workpiece material effects
ActiveUS8587789B2Reduce measurementPotential for errorUsing optical meansReflectivity measurementReflectance properties
A method of error compensation in a chromatic point sensor (CPS) reduces errors associated with varying workpiece spectral reflectivity. The errors are associated with a distance-independent profile component of the CPS measurement signals. Workpiece spectral reflectivity may be characterized using known spectral reflectivity for a workpiece material, or by measuring the workpiece spectral reflectivity using the CPS system. CPS spectral reflectivity measurement may comprise scanning the CPS optical pen to a plurality of distances relative to a workpiece surface and determining a distance-independent composite spectral profile from a plurality of resulting wavelength peaks. By comparing the distance-independent composite spectral profile obtained from a workpiece with that corresponding to the CPS distance calibration procedure, the contribution of the reflectivity characteristics of the workpiece will be indicated in the differences between the profiles, and potential CPS position errors due to varying workpiece reflectivity characteristics may be calculated and / or compensated.
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
Temperature compensated lasers
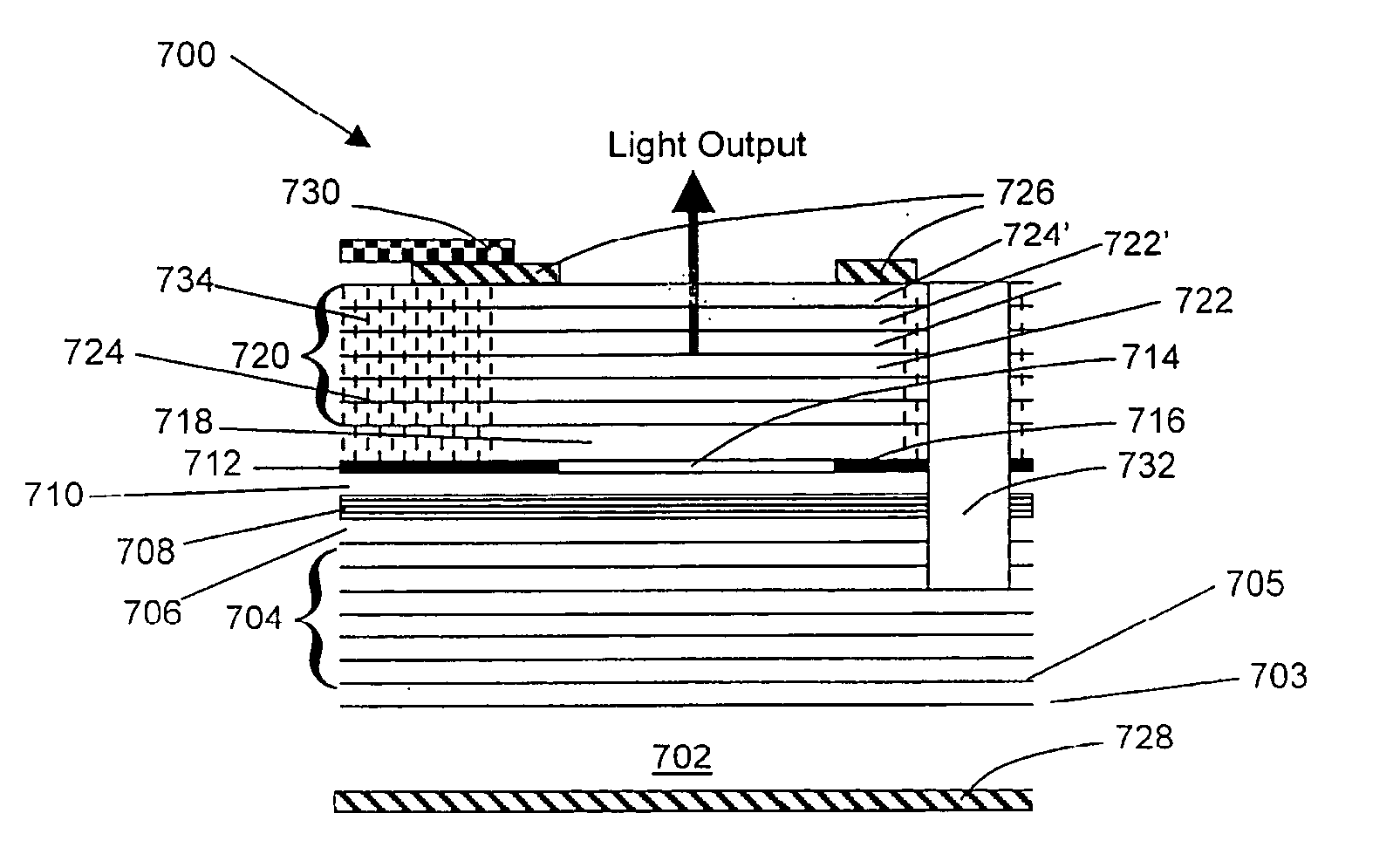
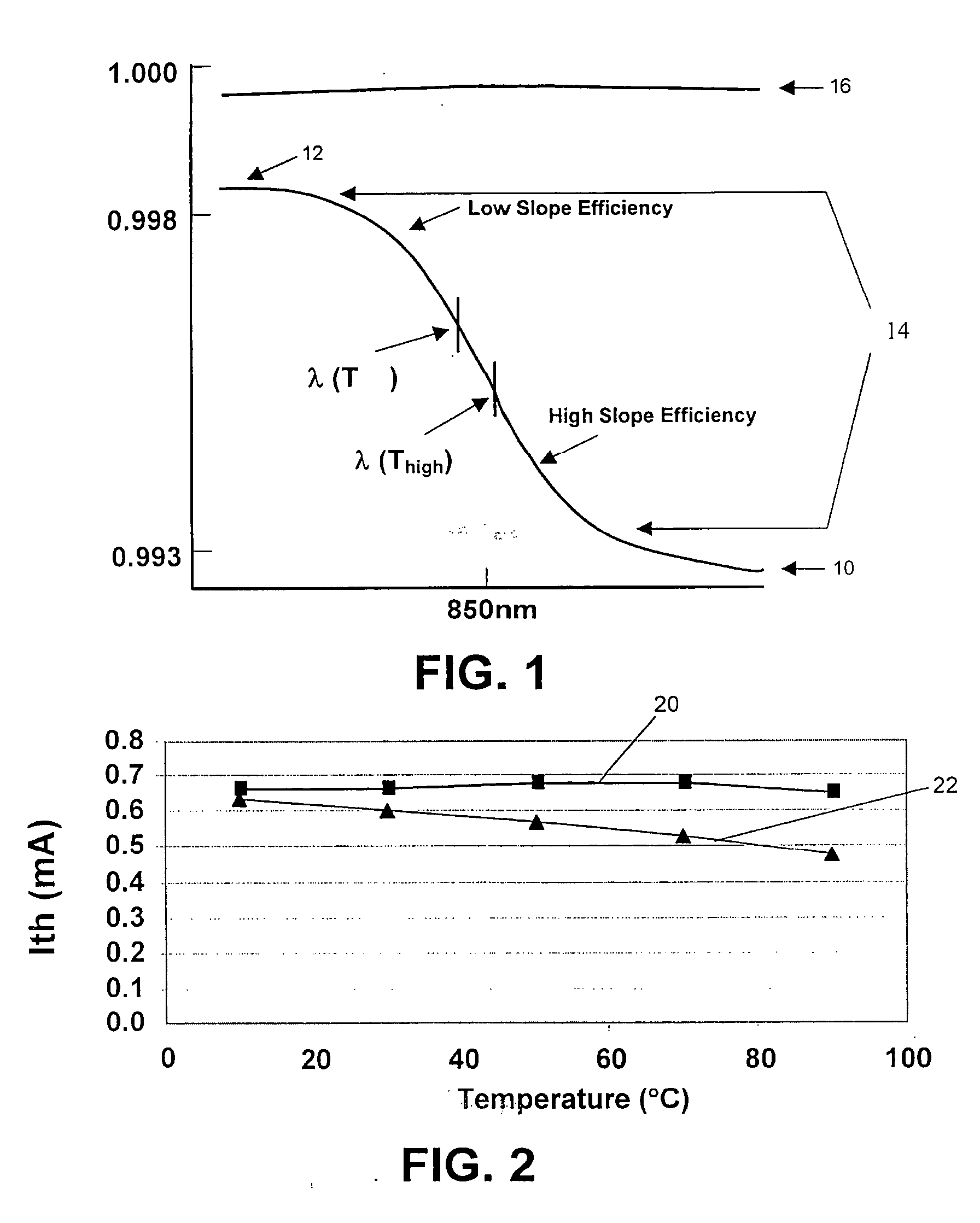
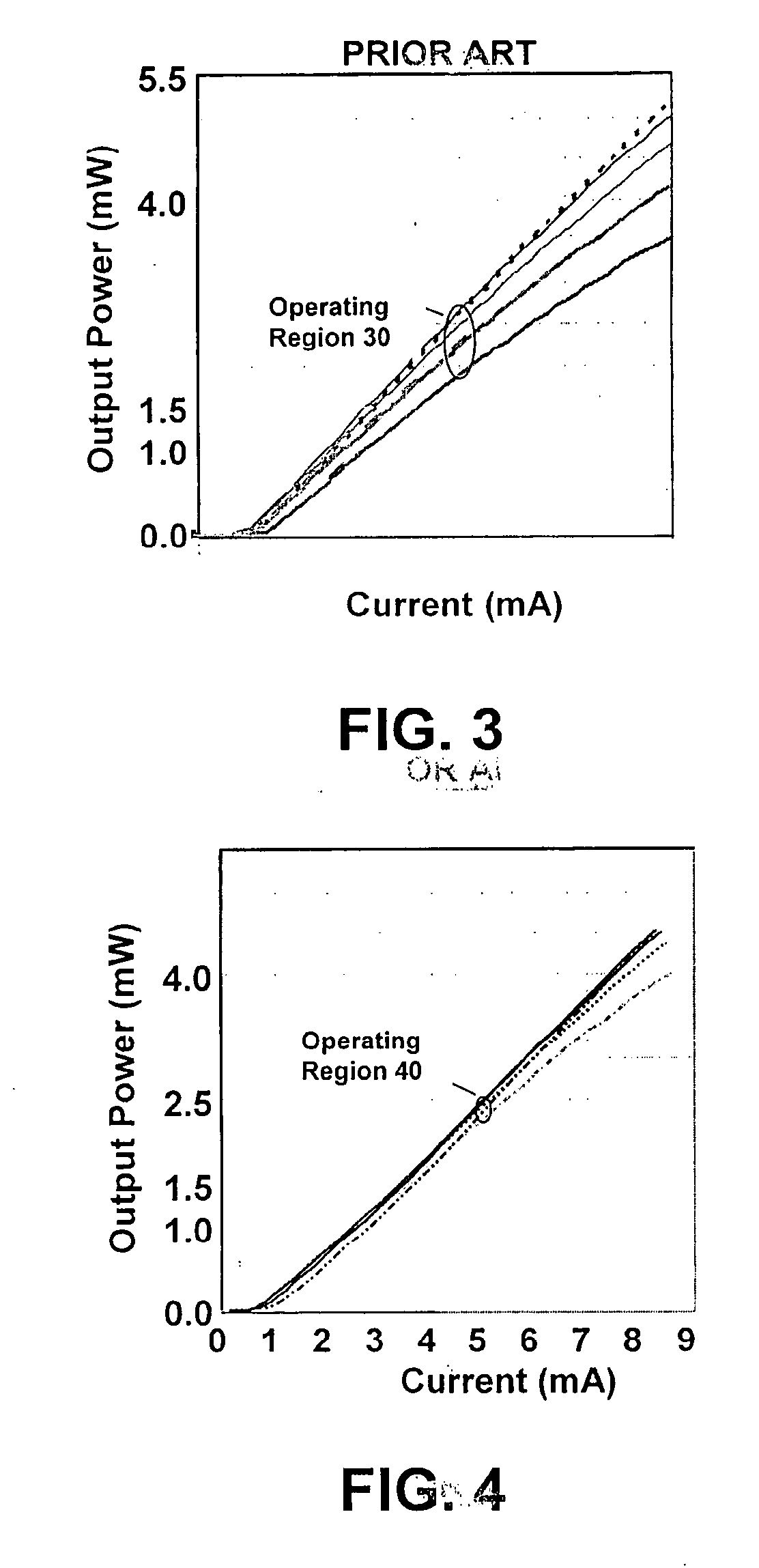
InactiveUS20060062266A1Semiconductor lasersLaser cooling arrangementsReflectance propertiesSemiconductor
A novel approach for providing temperature compensation for semiconductor lasers is disclosed. This approach utilizes reflectivity characteristics in the at least one of the mirrors of the semiconductor laser to provide temperature compensation to the device.
Owner:LUMENTUM OPERATIONS LLC
Apparatus and method for obtaining a reflectance property indication of a sample
InactiveUS20080079943A1Quantity minimizationEasy to watchScattering properties measurementsPaper-making machinesTemperature controlReflectivity measurement
A method for obtaining a reflectance property indication of a sample which includes making a reflectance measurement of the sample and correcting the reflectance measurement in order to obtain the reflectance property indication. The reflectance measurement represents an observed reflectance of the sample, the reflectance property indication represents a standardized reflectance of the sample, and correcting the reflectance measurement accounts for a difference between the standardized reflectance and the observed reflectance. An apparatus for making a reflectance measurement of a sample which includes a housing defining a viewing port, a temperature control mechanism for controlling the temperature within the interior of the housing, and an optical reflectometer contained within the interior of the housing. The reflectometer has a measurement direction and is movable within the housing so that the measurement direction can be selectively aligned with the viewing port.
Owner:INNOTECH ALBERTA INC
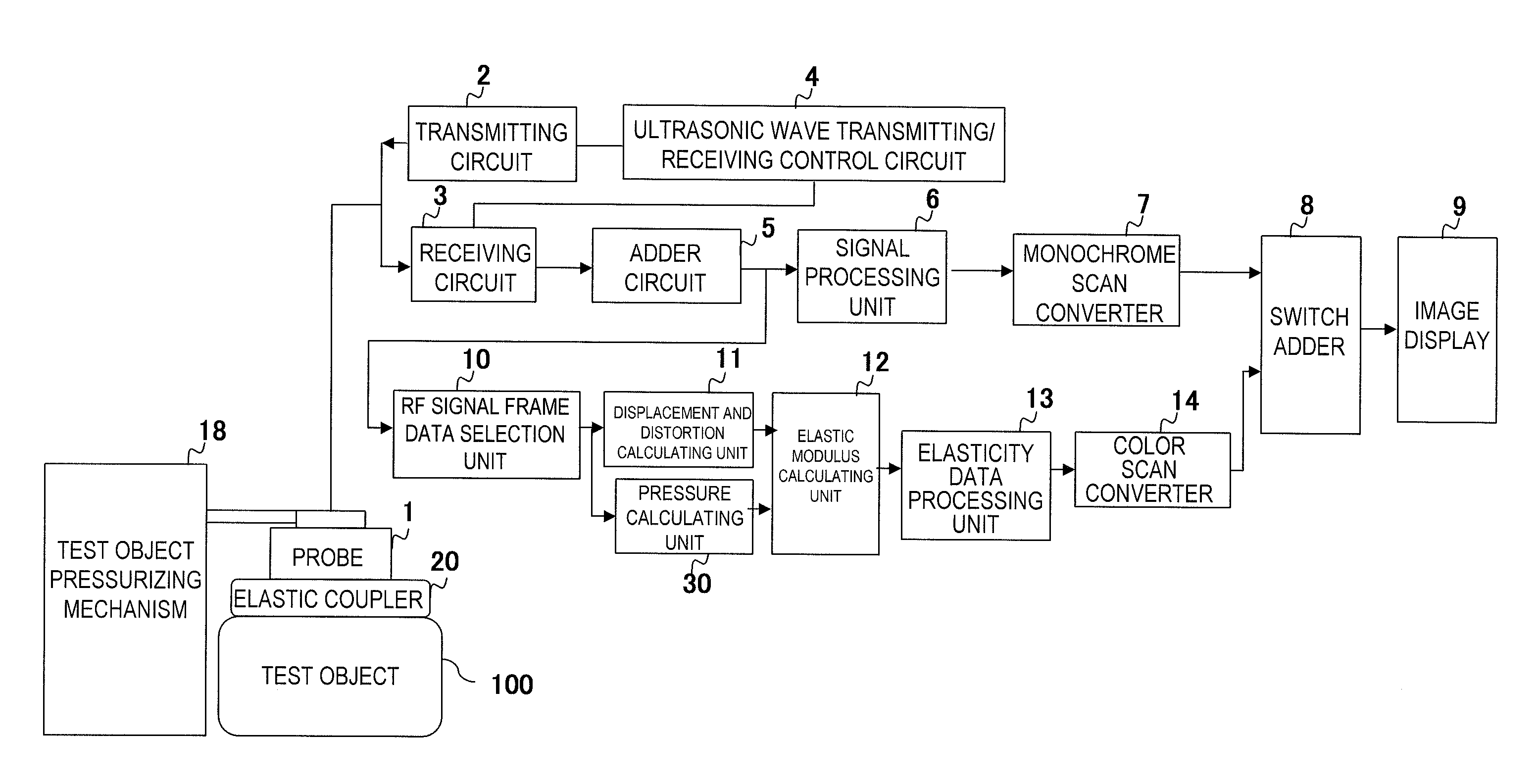
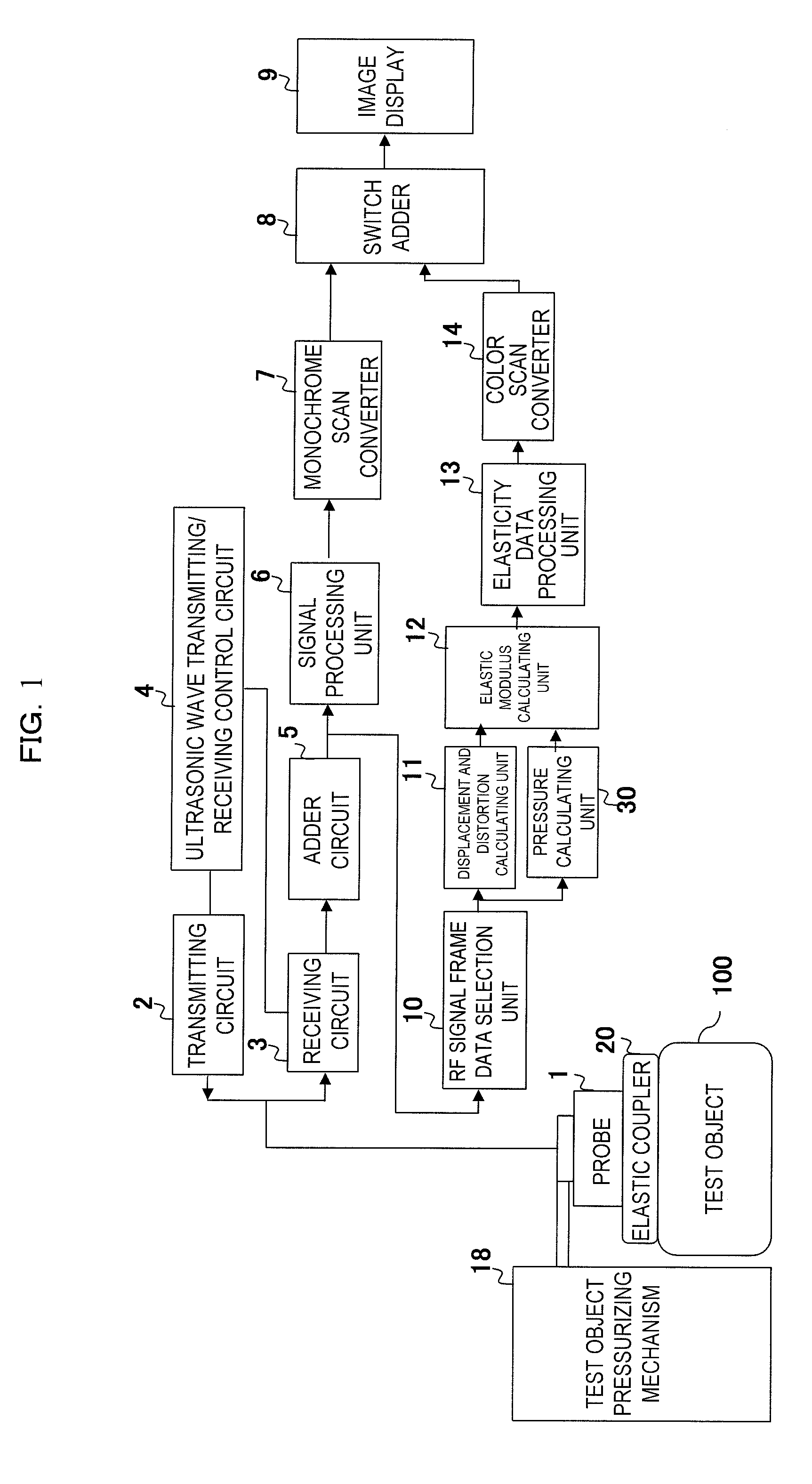
Ultrasonic diagnostic apparatus
InactiveUS20110040186A1Accurate detectionEasy to operateBlood flow measurement devicesOrgan movement/changes detectionObject basedSonification
The present invention is made to accurately detect an absolute pressure even when a contact property between an elastic coupler and a body surface of an object is poor. An elastic coupler 20 is formed by an elastic material with flexibility to have two layers at least with different ultrasonic wave reflectance properties and attached to an ultrasonic wave transmitter / receiver surface, and a pressure calculating unit 30 detects the position of a boundary surface 22 between those two layers based on RF signal frame data output from an RF signal frame data selection unit 10, obtains positional change of the boundary surface based on the detected position of the boundary surface and the initial position of the boundary surface, which was obtained in advance, and obtains the absolute pressure applied to the object based on the positional change and a pre-set elasticity property of the elastic coupler. At this time, for example, an ID code is given to the elastic coupler by making the initial position or the like of the boundary surface of the elastic coupler be different in accordance with the type of the elastic coupler, the pressure calculating unit 30 identifies the ID code, identifies the type of the elastic coupler with reference to a coupler database, and reads the elasticity property corresponding to the ID code.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Optical element, optical system including the optical element, and optical apparatus including the optical system
InactiveUS20100296168A1Low refractive indexCoatingsOptical elementsRefractive indexReflectance properties
An optical element includes a substrate, and an antireflection film provided on a surface of the substrate. The antireflection film is a graded layer having a refractive index that is progressively decreased from the substrate side towards an outer surface of the antireflection film. The graded layer has a reflectivity characteristic occupying ⅔ of a usable wavelength range around the center of the usable wavelength range. Reflectivity of the graded layer at a maximum value of the reflectivity characteristic is a peak value equal to or less than 0.4% The graded layer does not have a maximal value not corresponding to the peak value. At least one of reflectivities at both ends of the usable wavelength range is equal to or less than half the reflectivity at the peak value.
Owner:CANON KK
Processing of superhydrophobic, infrared transmissive, Anti-reflective nanostructured surfaces
Methods for producing nanostructured, hydrophobic, superhydrophobic, or hydrophilic, transmissive, anti-reflective surfaces are described. The method for providing a hydrophilic surface includes steps of providing a substrate that is transmissive at at least one wavelength in the infrared to ultraviolet range of the electromagnetic spectrum and comprises at least one surface including nanostructures of a size smaller than the at least one wavelength; and functionalizing the at least one surface with hydroxyl groups thereon. A hydrophobic or superhydrophobic surface can be provided by contacting the at least one surface with a hydrophobic fluoropolymer for a time sufficient to apply at least a monolayer of fluorine-containing material to the at least one surface. These methods provide devices having excellent transmittance and anti-reflectance properties and which are resistant to seawater.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
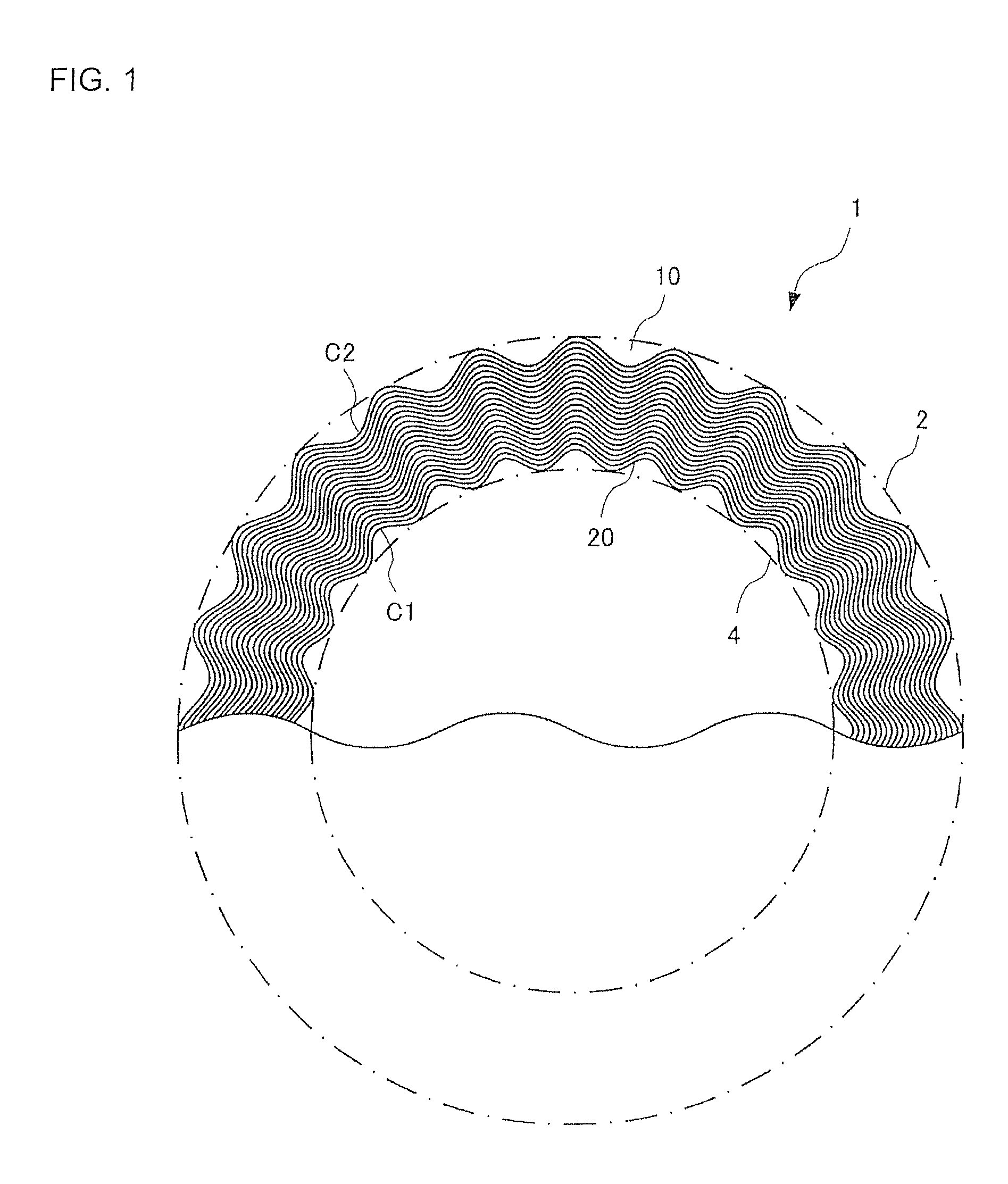
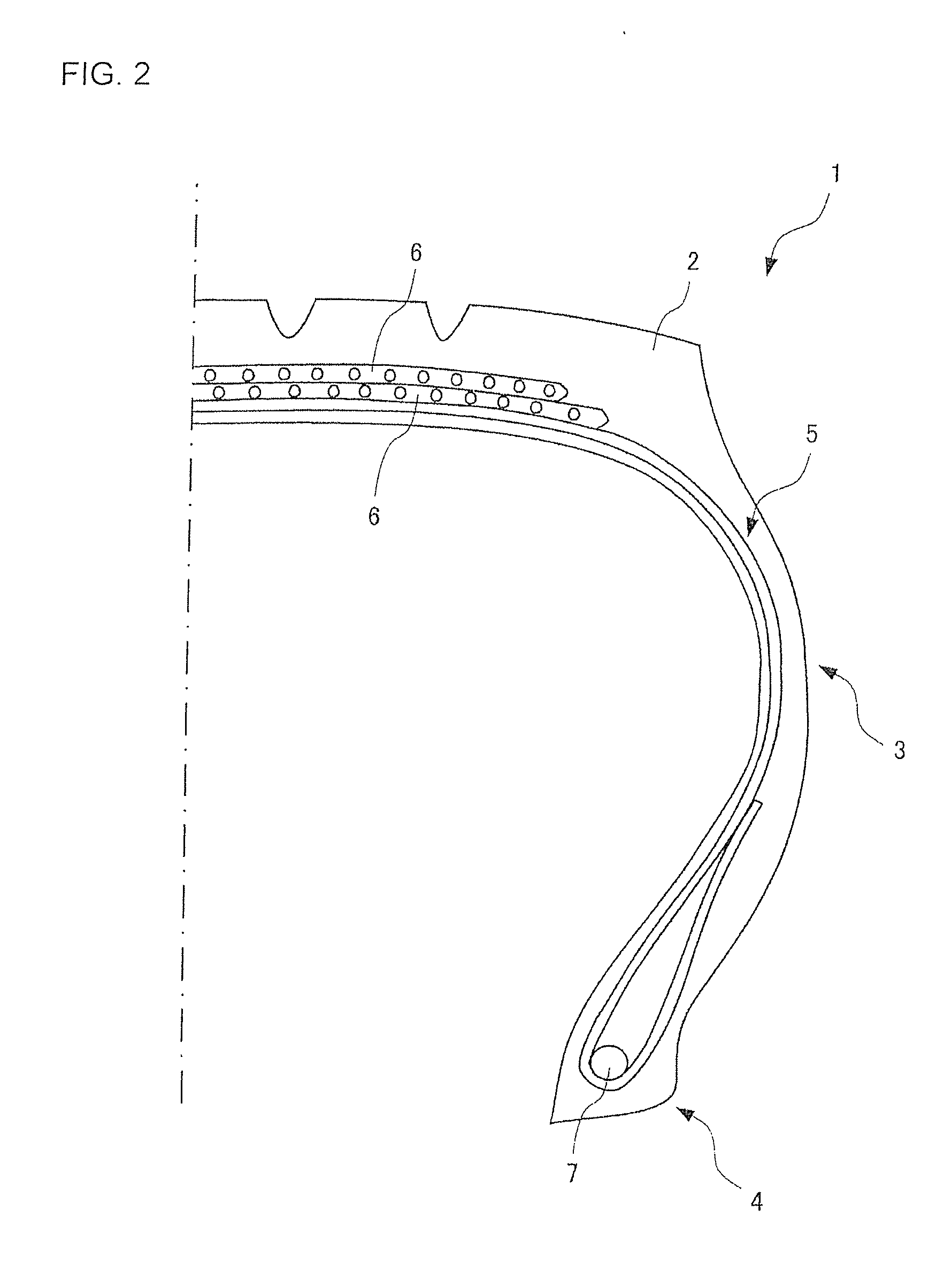
Pneumatic tire
A pneumatic tire having inconspicuous sidewall surface irregularities. The pneumatic tire includes a plurality of sidewall parts and a tread portion extending between the sidewall parts. At least one sidewall part has a pattern extending in the tire circumferential direction that can be visually differentiated from the surrounding regions of the sidewall surface by an irregularity or reflectance properties of light of the sidewall surface. The pattern includes a plurality of linear protrusions or grooves that extend in a wave shape in a tire circumferential direction while deflecting in a tire radial direction with a period of λ1. The line protrusions or grooves have intervals in a tire radial direction, and are non-intersecting. Outer and inner circumferences of the pattern of the tire radial direction are formed by the plurality of linear protrusions or grooves to extend in a wave shape in a tire circumferential direction.
Owner:YOKOHAMA RUBBER CO LTD
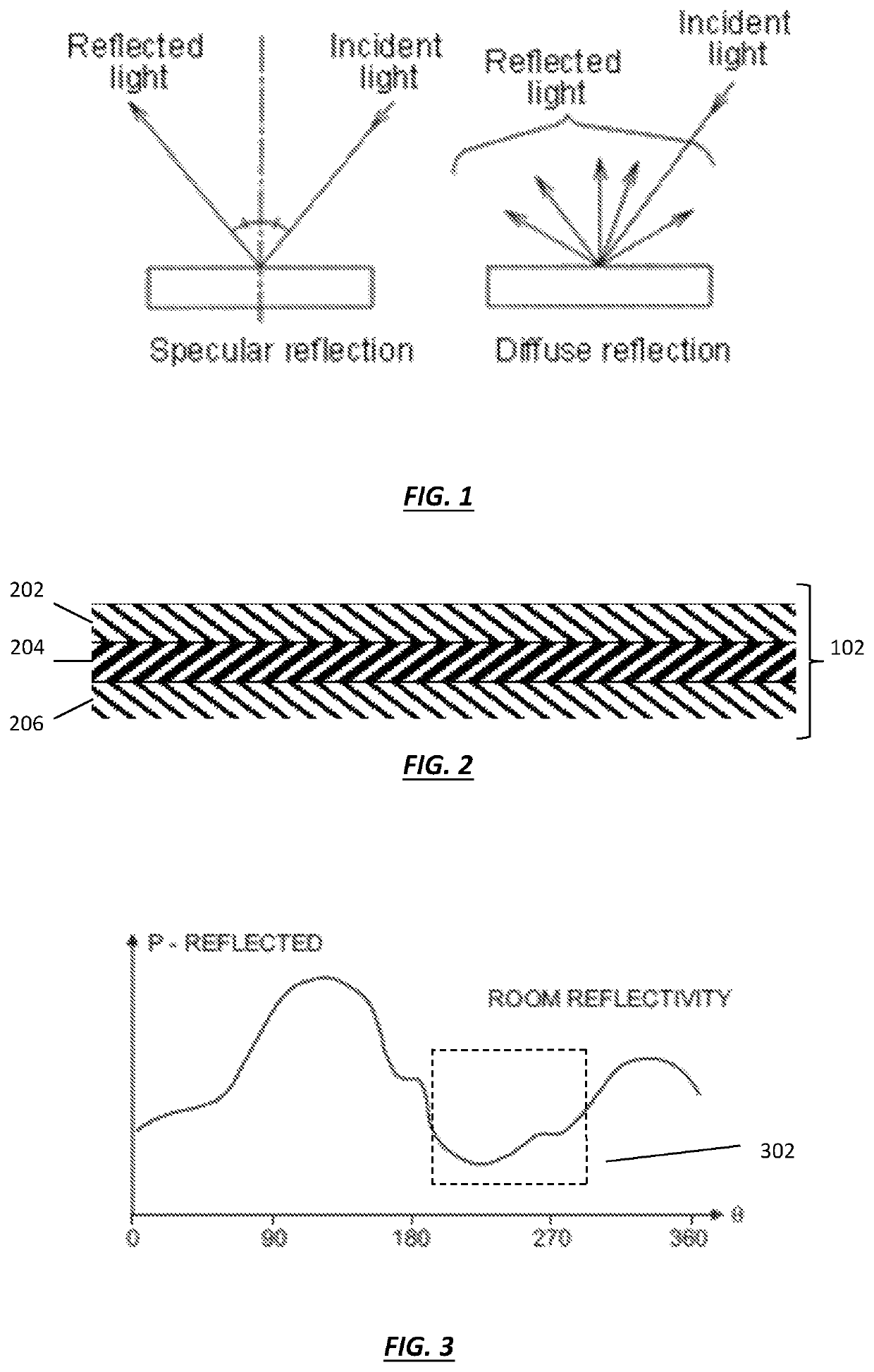
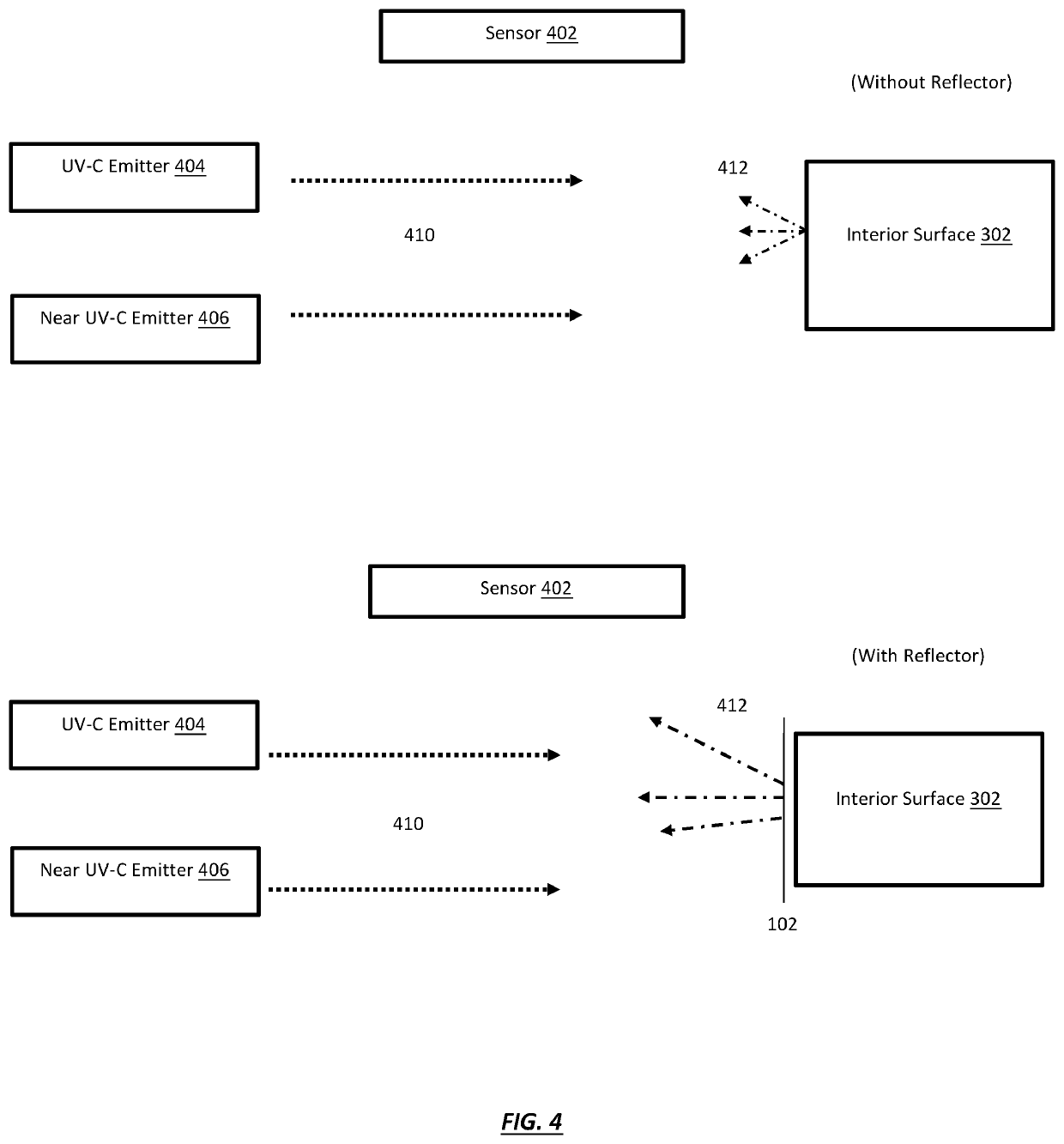
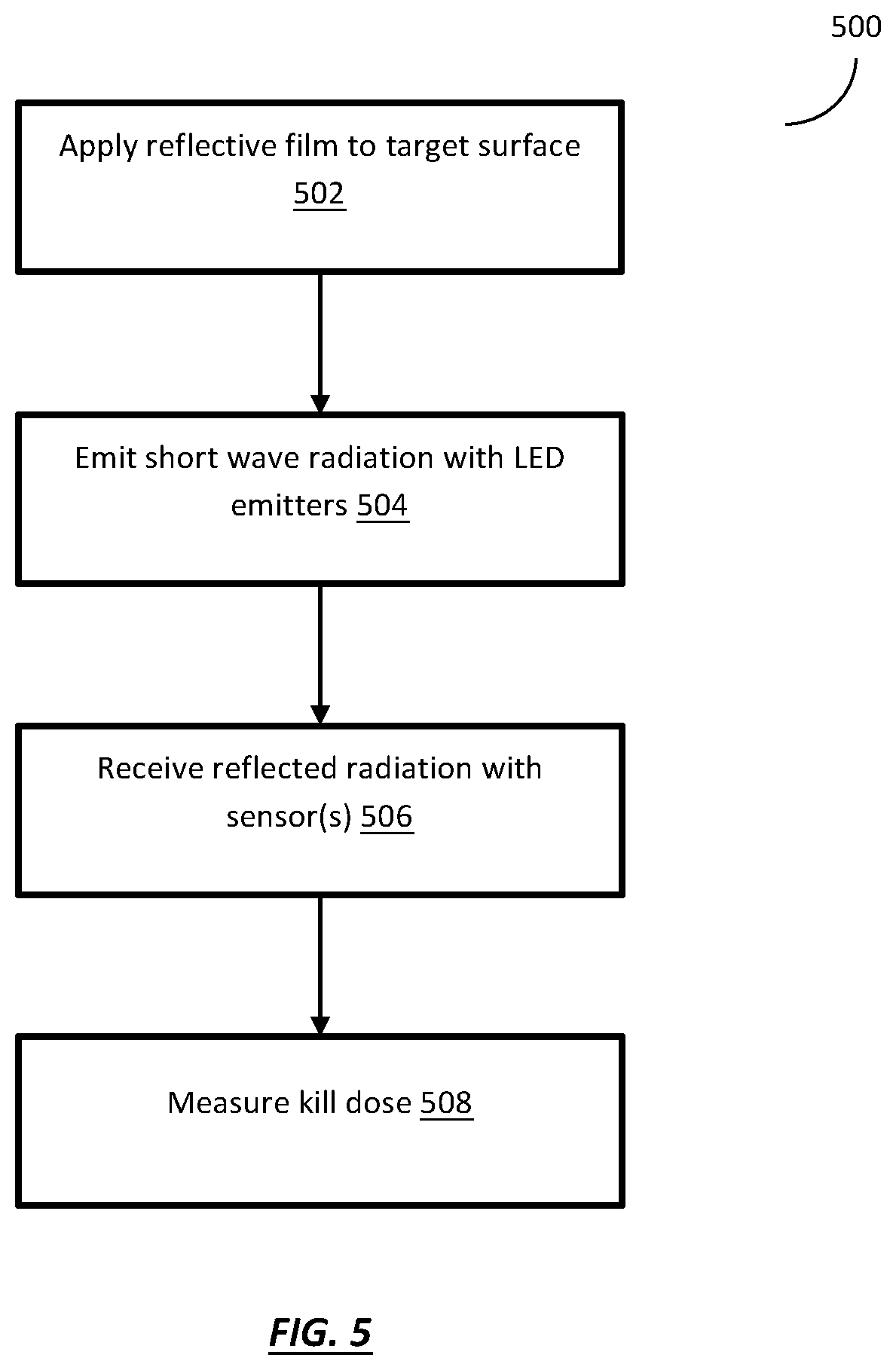
Apparatus and method for reducing dosage time in UV-C germicidal irradiation
An apparatus and method for reducing dosage time in ultraviolet germicidal irradiation systems. UV-C reflective adhesive film may be configured as sheets, or in a roll that may be cut to a desired size or shape. A user may apply UV-C reflective adhesive film to a desired surface of an interior room by exposing an adhesive surface to the desired interior surface. A reflective layer of the UV-C reflective adhesive film is configured to improve the reflectance percentage or reflectance pattern of a desired interior surface with respect to incident UV-C or near UV-C light. The improved reflectance properties of the desired surface functions to reflect a greater amount of light back to one or more closed-loop sensors in operation with a UV-C or near UV-C germicidal irradiation system. The improved reflectance thereby reduces the amount of time required for one or more closed-loop sensors in operation with a UV-C or near UV-C germicidal irradiation system to measure an effective kill-dose for surface disinfection.
Owner:UD INNOVATIONS LLC
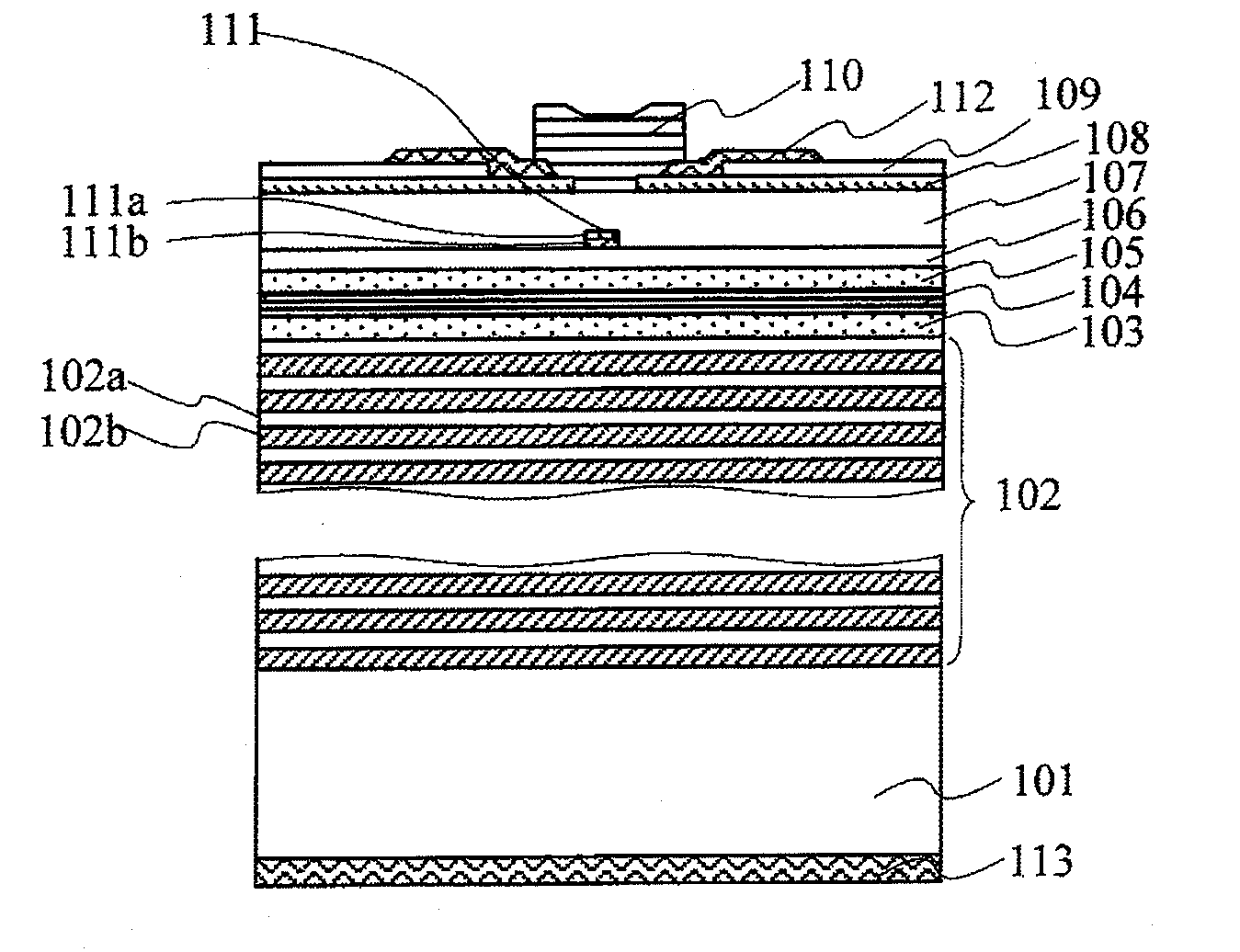
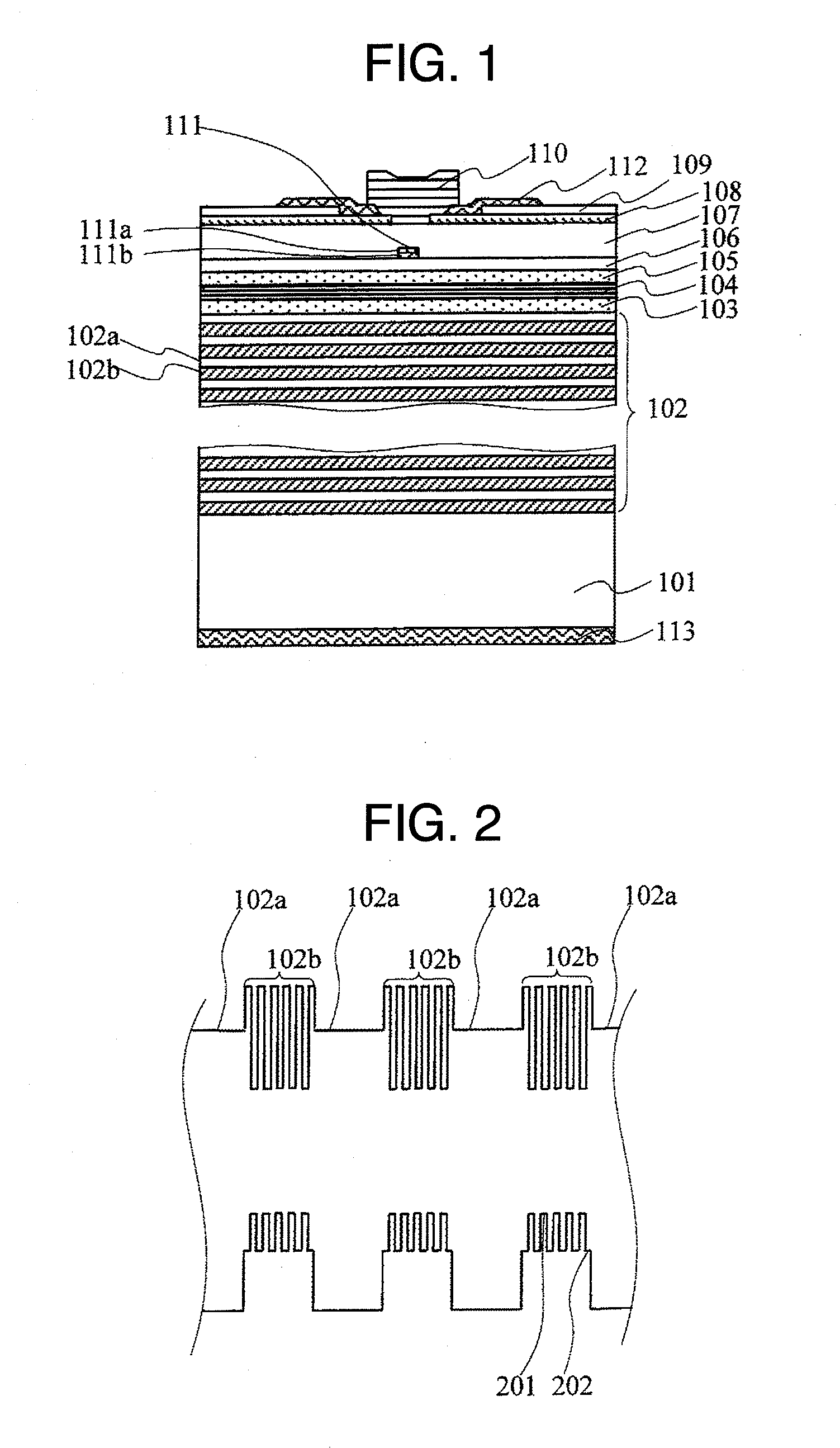
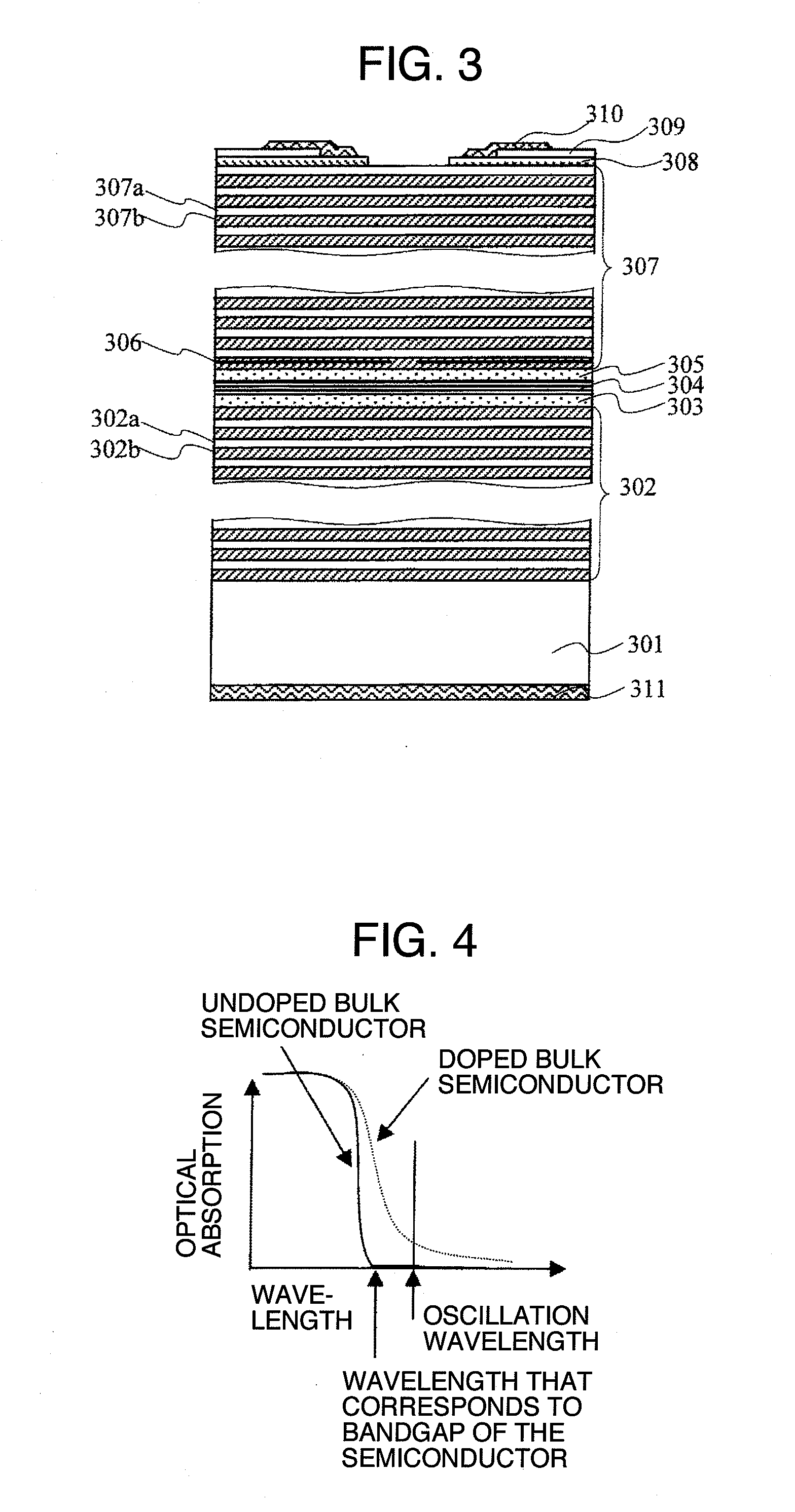
Vertical cavity surface emitting semiconductor laser device
ActiveUS20080144683A1Laser detailsNanoopticsVertical-cavity surface-emitting laserReflectance properties
The relationship between the reflectivity characteristic of a DBR layer(s), in which an InP layer and an InGaAlAs layer are laminated alternatively, and the optical absorption characteristic of the InGaAlAs layer, is a trade-off in a vertical cavity surface emitting laser on an InP substrate. The present invention applies a semiconductor DBR layer(s), in which an InP layer and an InGaAlAs-MQW (multi-quantum-wells) layer are laminated alternatively, in order to dissolve the above trade-off. The InGaAlAs-MQW layer is composed of InGaAlAs-wells and barriers. The InP layer is doped uniformly and the InGaAlAs-MQW layer has a structure in which at least a part thereof is doped.
Owner:LUMENTUM JAPAN INC
Antireflective film and optical element
An antireflection film including an optical element, formed on an optical surface of an optical member, and is configured to prevent a reflection of a light beam incident on the optical surface, wherein a maximum reflectance P1 in a first wavelength region and a maximum reflectance P2 in a second wavelength region at a wavelength side longer than the first wavelength region, satisfies a relation of P1>P2, as a spectral reflectance property when a light beam is incident on the optical surface at an incident angle of 0 degree; and by shifting a wavelength range where the reflectance is a specific value or less, to a wavelength side longer than the second wavelength region, the reflectance in the second wavelength region is decreased, and the reflectance in the first wavelength region is increased so that a luminance difference is small between a ghost in the first wavelength region and a ghost in the second wavelength region.
Owner:HOYA CORP
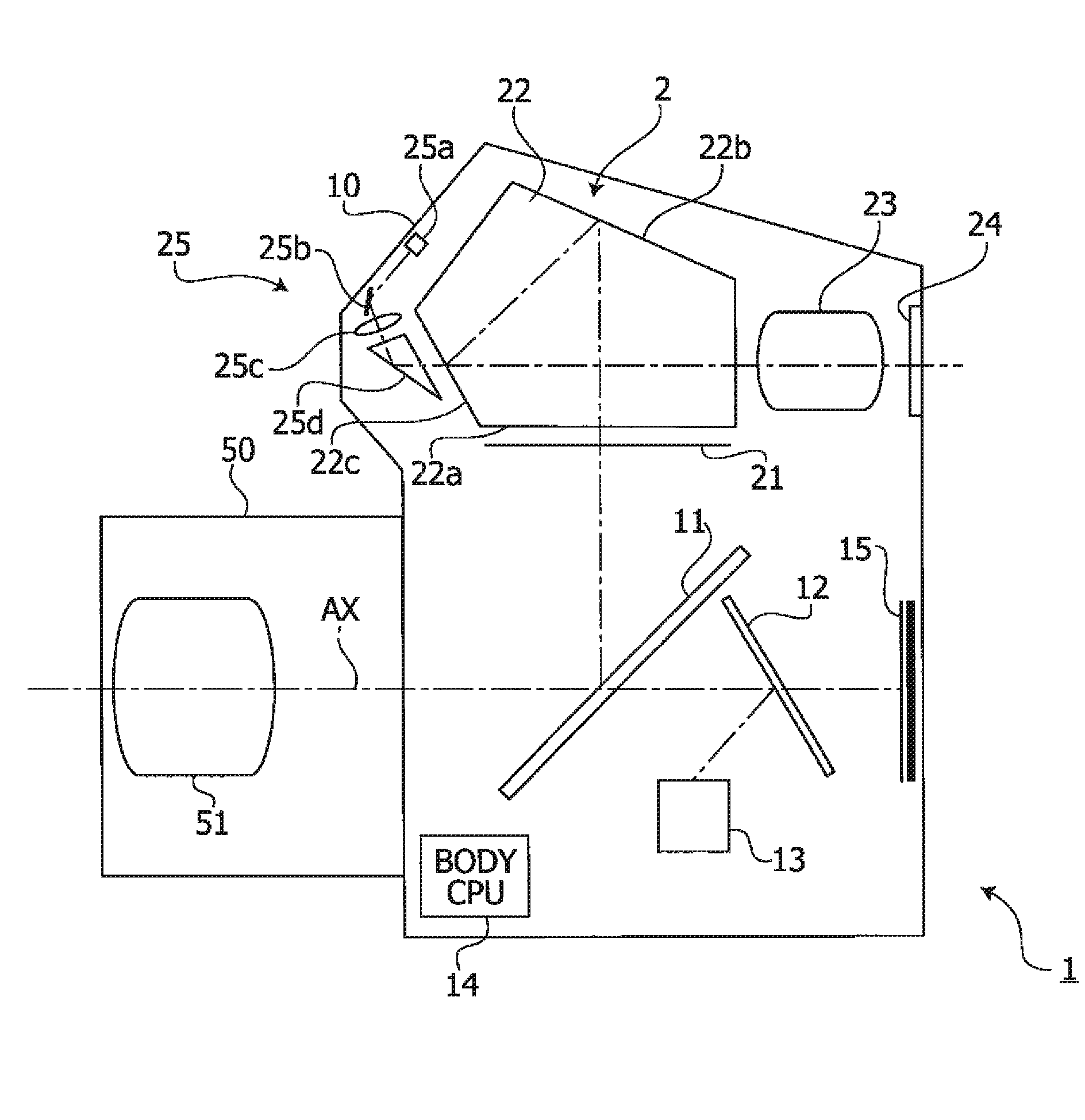
Optical Device and Single Lens Reflex Camera
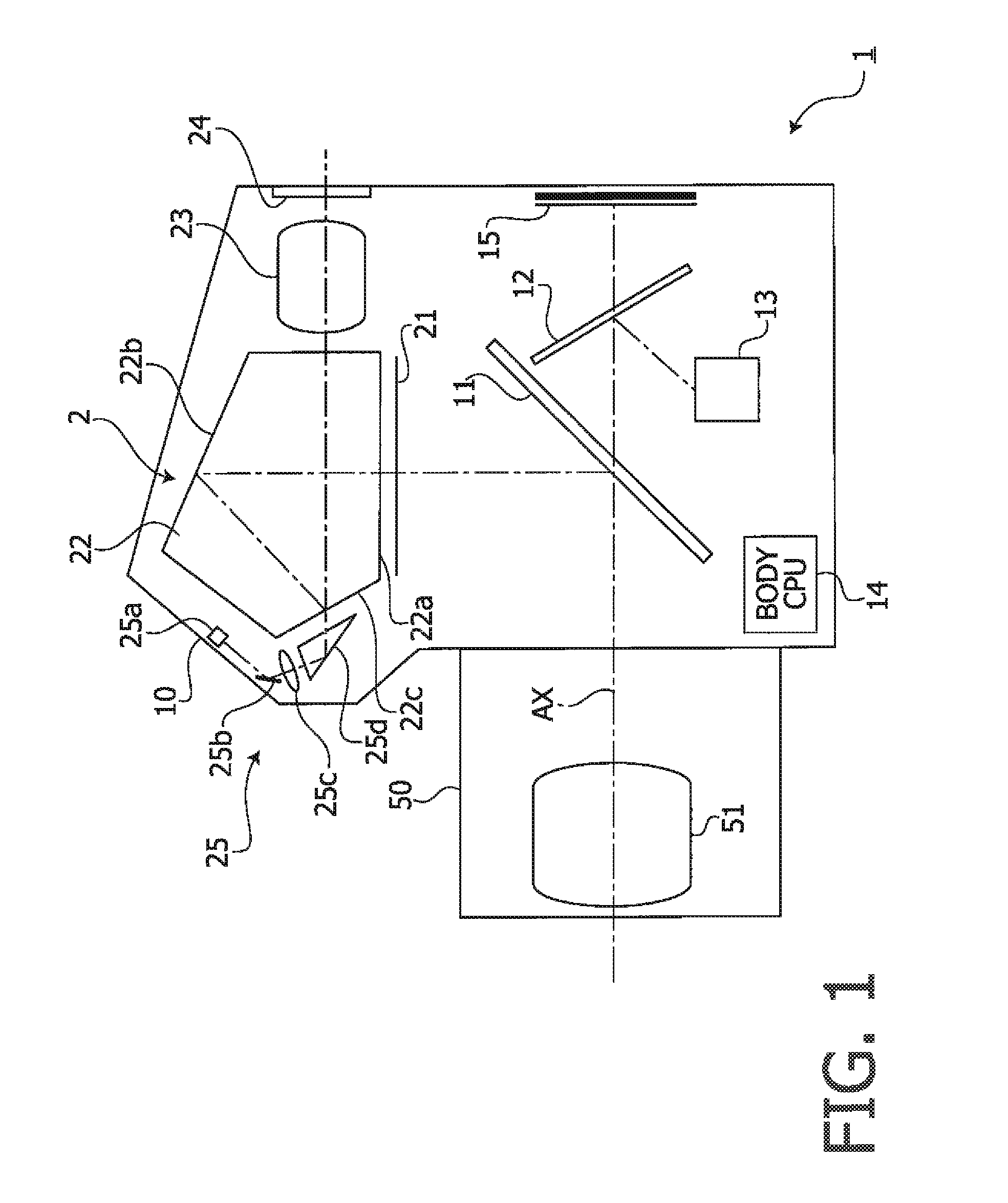
ActiveUS20140168499A1Increase brightnessIncrease image brightnessTelevision system detailsPrismsCamera lensReflectance properties
Owner:RICOH IMAGING COMPANY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com