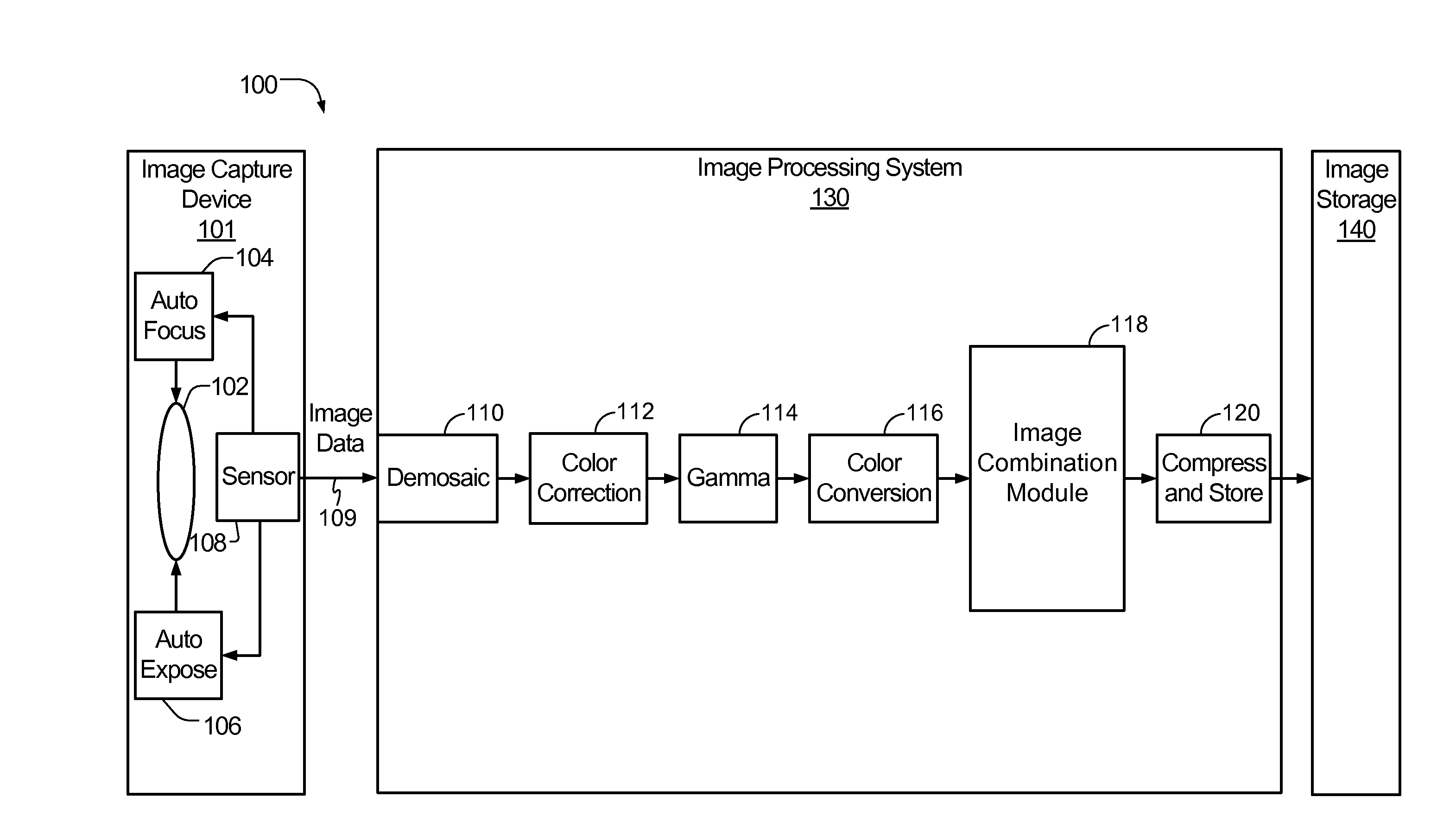
Patents
Literature
267results about How to "Reduce ghosting" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Ghost-compensation for improved stereoscopic projection
InactiveUS20060268104A1Reduce ghostingStatic indicating devicesElectrical measurementsComputer visionLeft eye
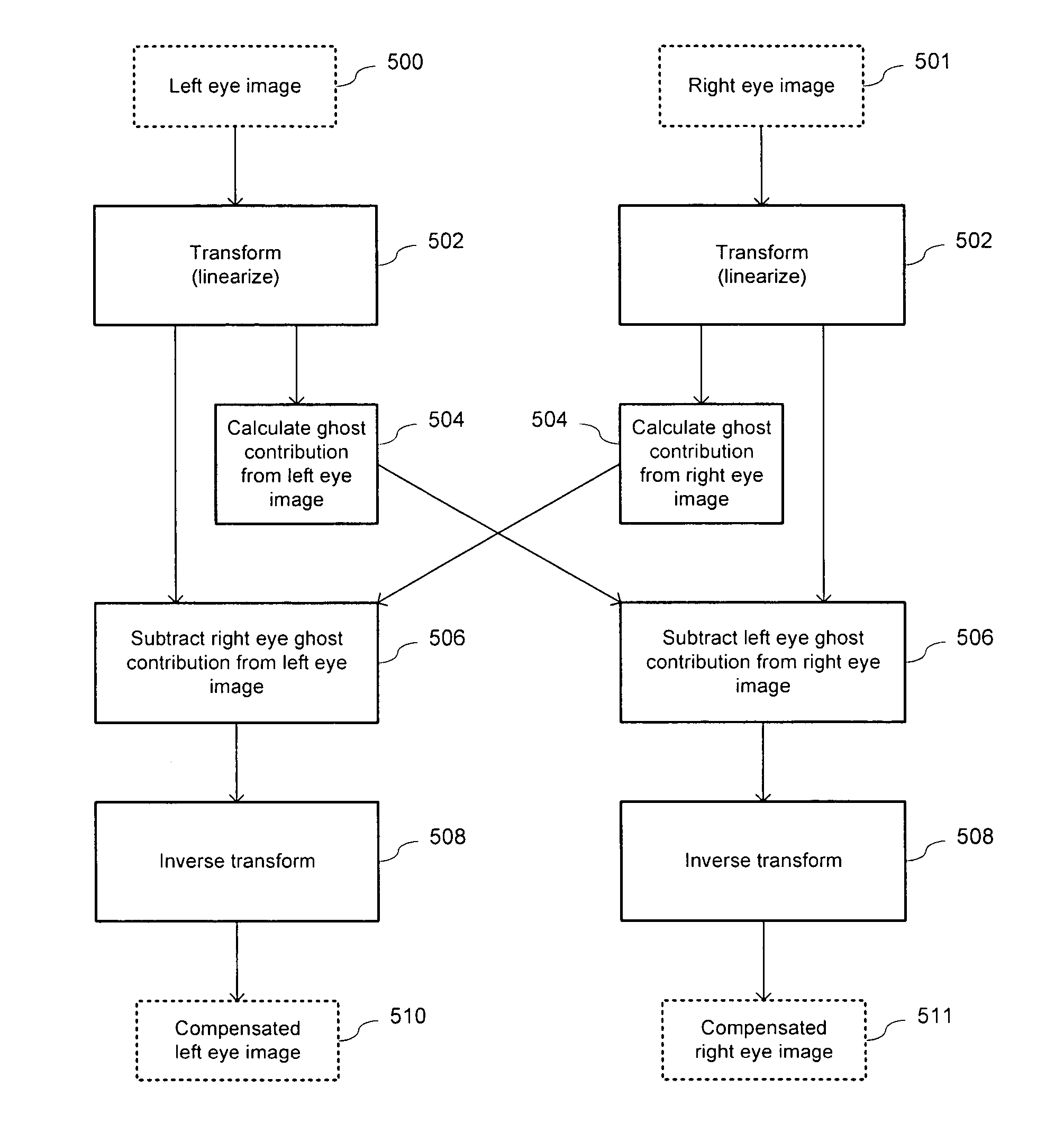
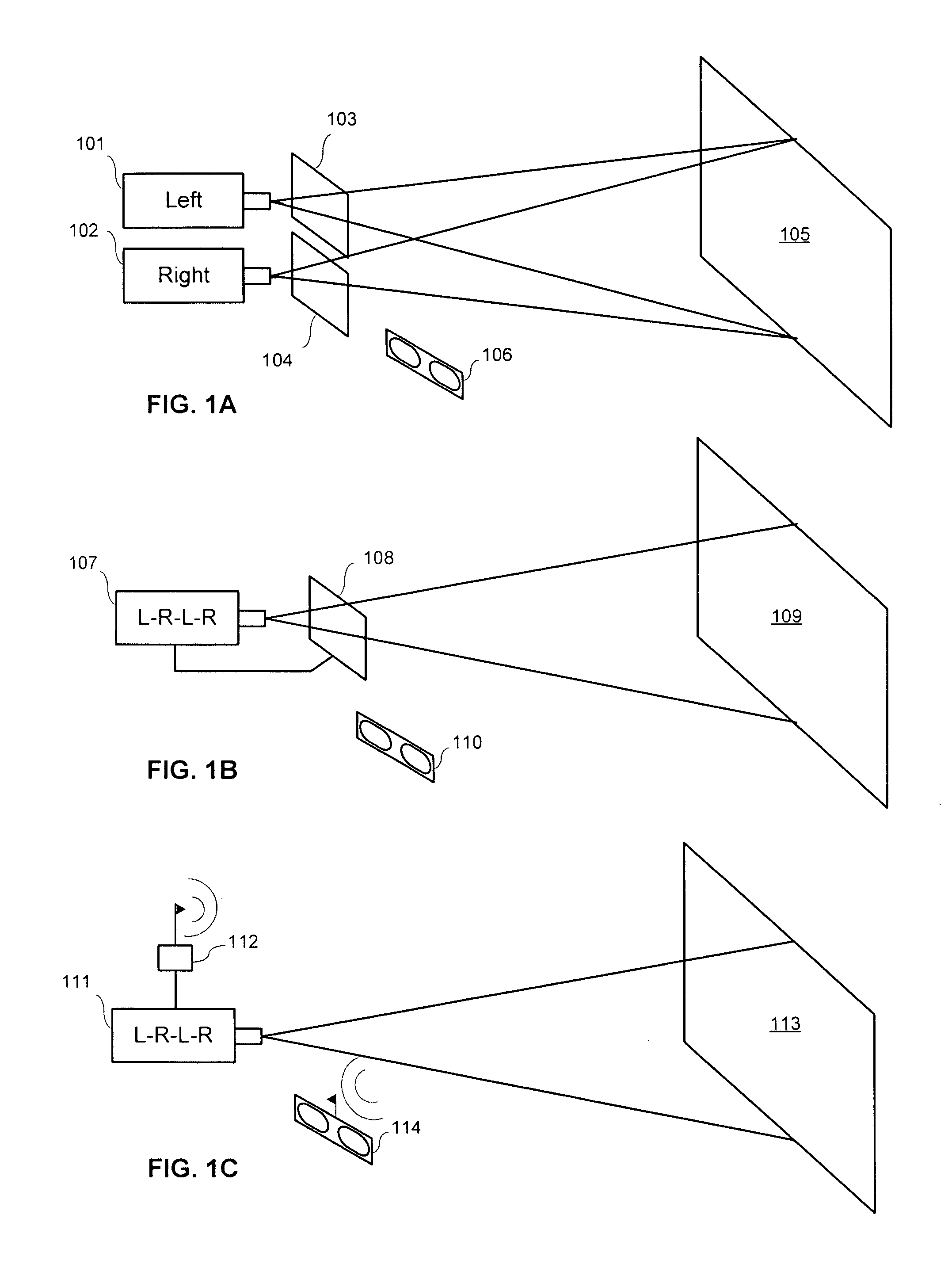
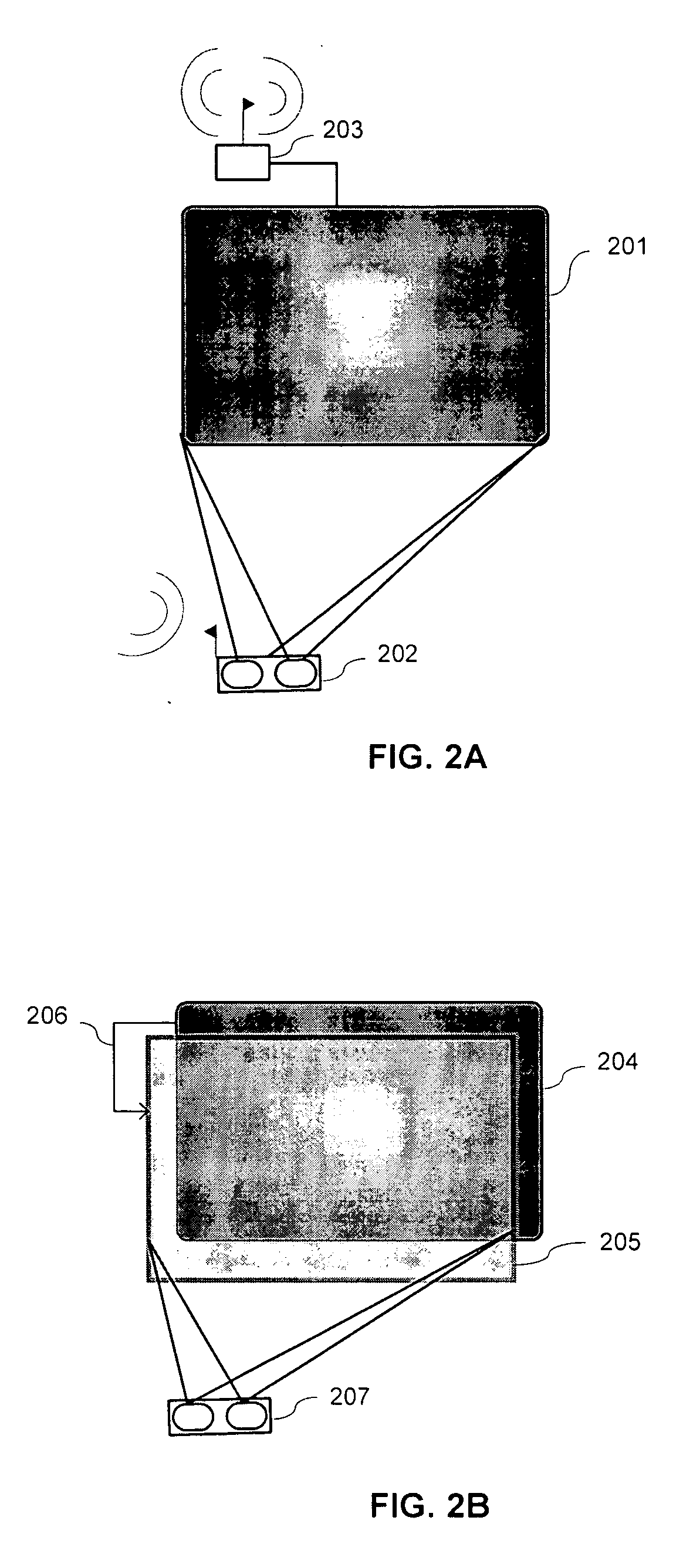
A method and system for reducing ghost images in plano-stereoscopic image transmissions is provided. The method comprises establishing a plurality of expected ghosting profiles associated with a plurality of predetermined regions on a screen, and compensating for leakage in each predetermined region of a projected left and right eye images by removing an amount of ghost images leaking from the projected left eye image into the projected right eye image and vice versa. The system comprises a processor configured to receive the quantity of ghost artifacts and compute ghost compensation quantities for left eye images and right eye images. The processor is further configured to remove an amount of actual image ghost artifacts leaking from a projected left eye image into a projected right eye image and vice versa. The processor is also configured to compute ghost compensation quantities for each of a plurality of zones, each zone corresponding to a region on a screen having an expected ghosting profile associated therewith.
Owner:REAID INC
Multilayer optical adhesives and articles
ActiveUS6842288B1Improve transmittanceReduce distortion problemsMaterial nanotechnologyLayered productsInter layerAdhesive
Described are multilayer optical composites including a first layer having an index of refraction n1, an ith layer having an index of refraction ni greater than n1, and one or two or more intermediate layers between the first layer and the ith layer, wherein the indices of refraction of the intermediate layers are between n1 and ni, and the index of refraction of each intermediate layer increases in the order of position of each layer from the first layer.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
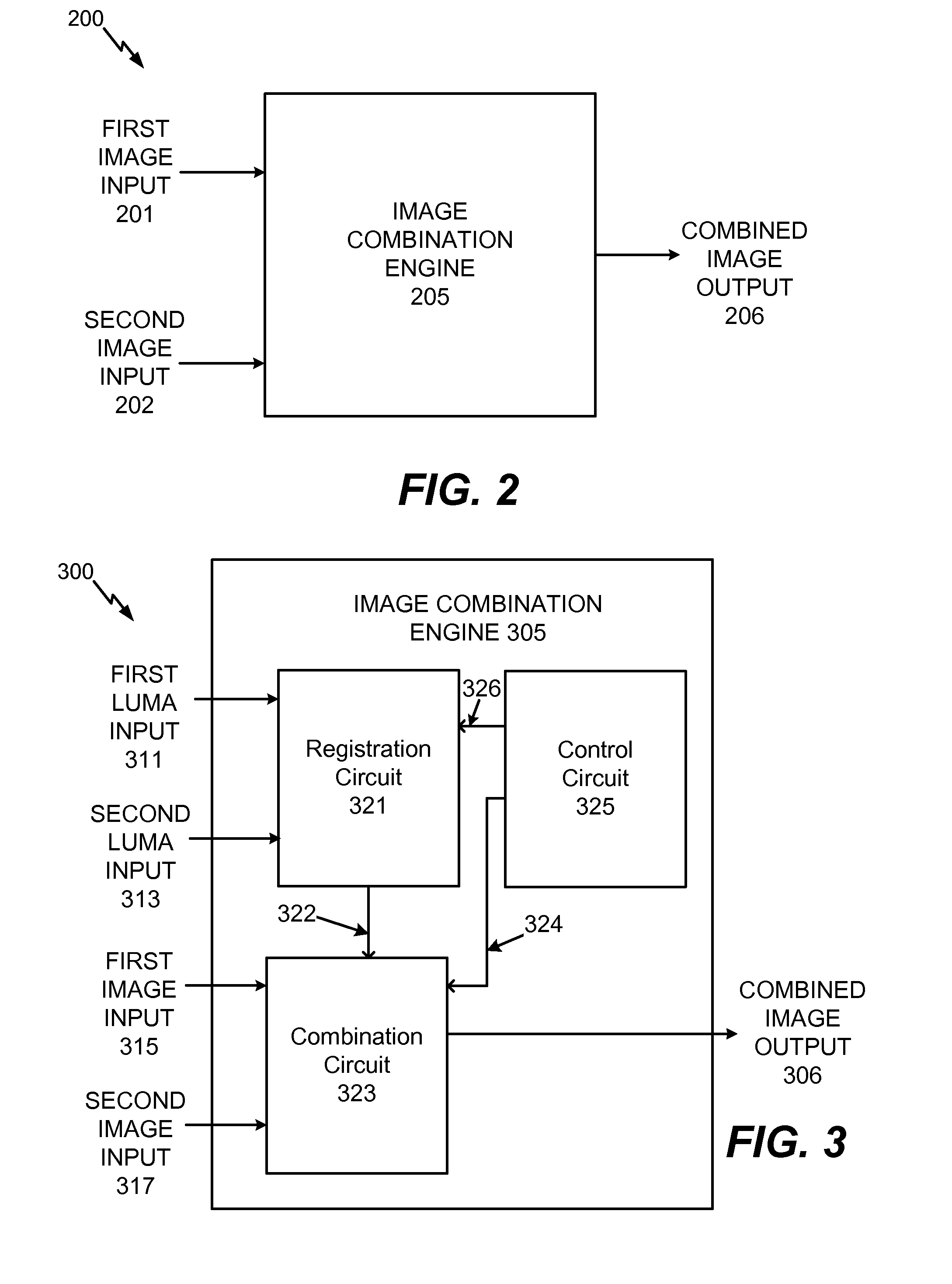
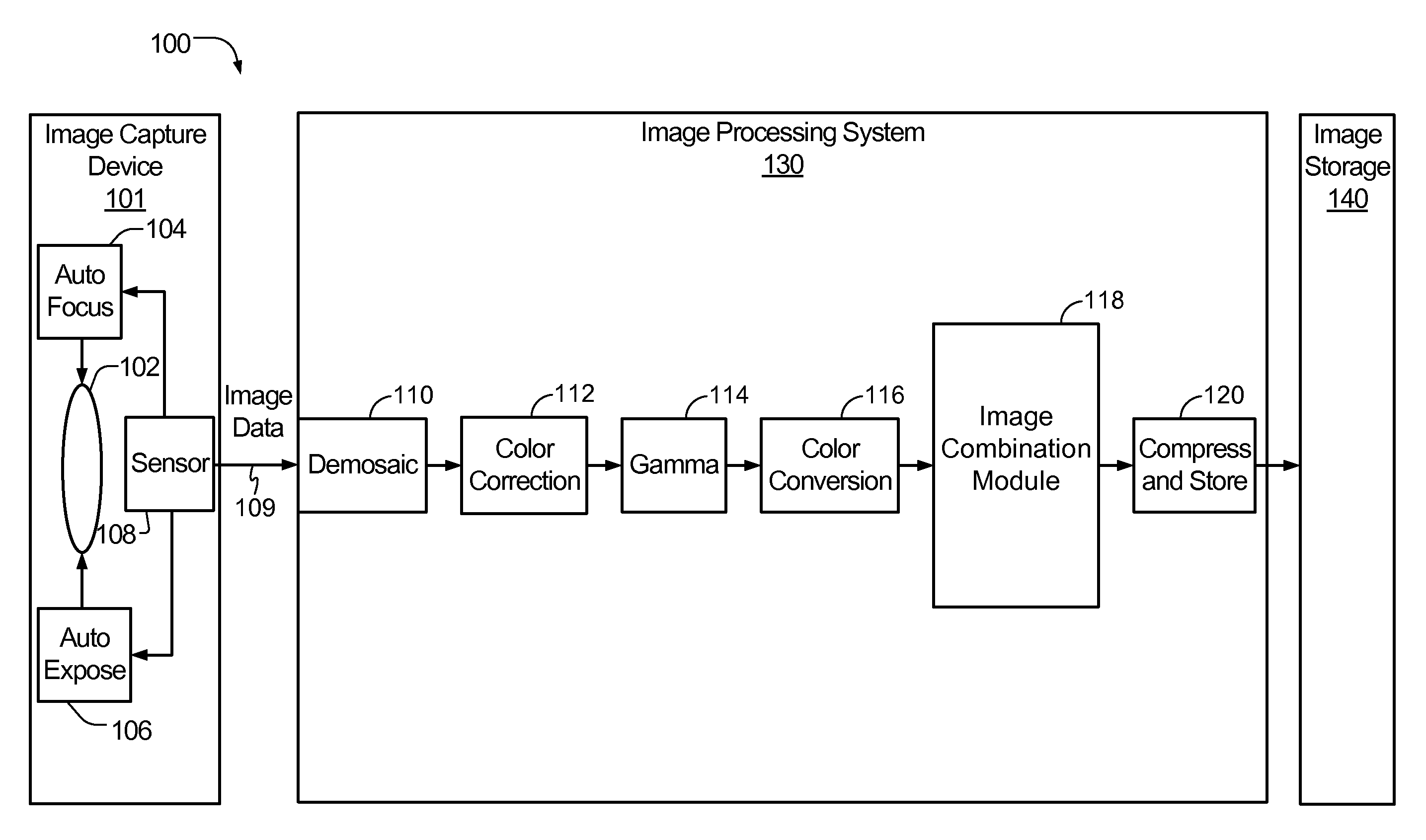
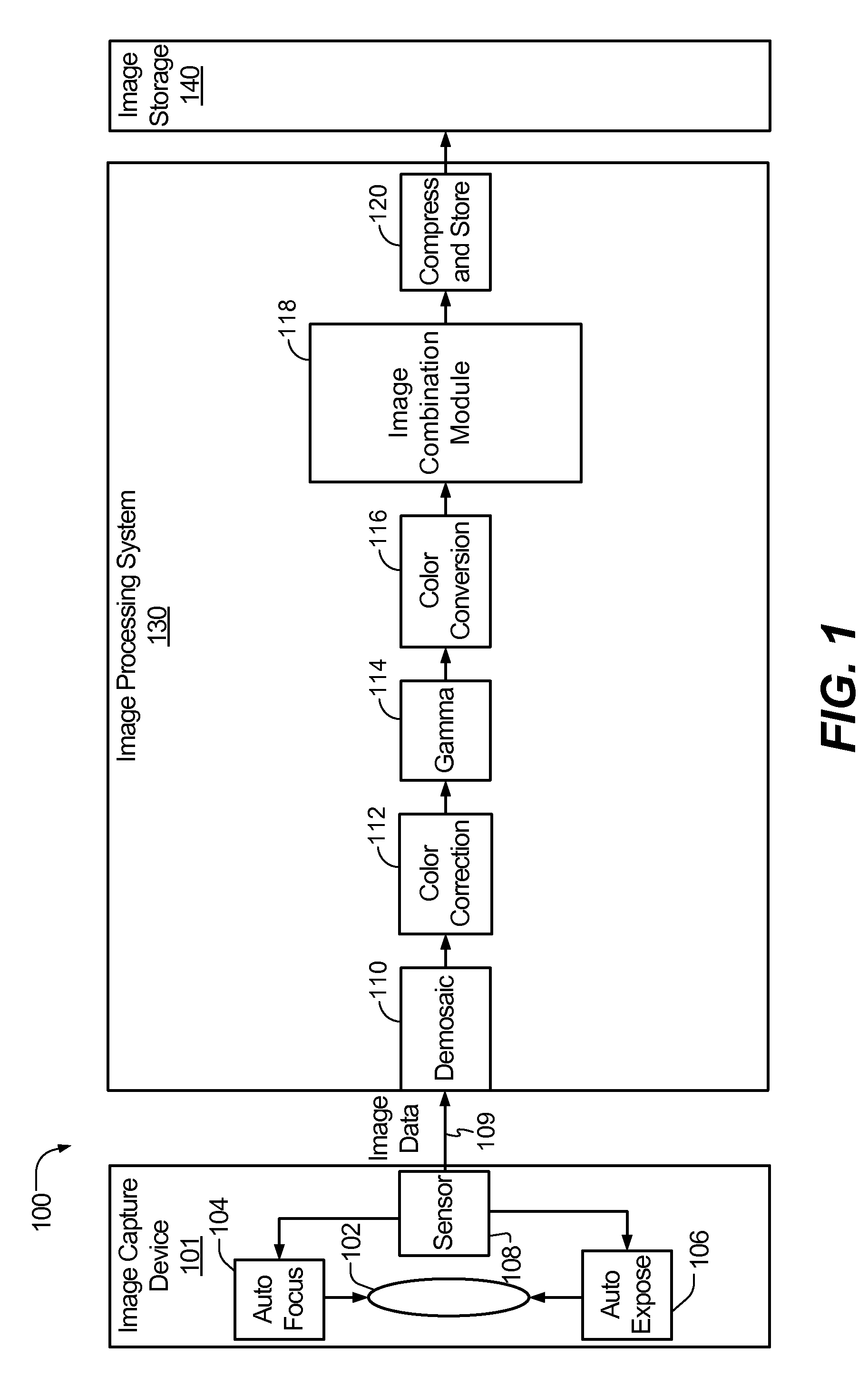
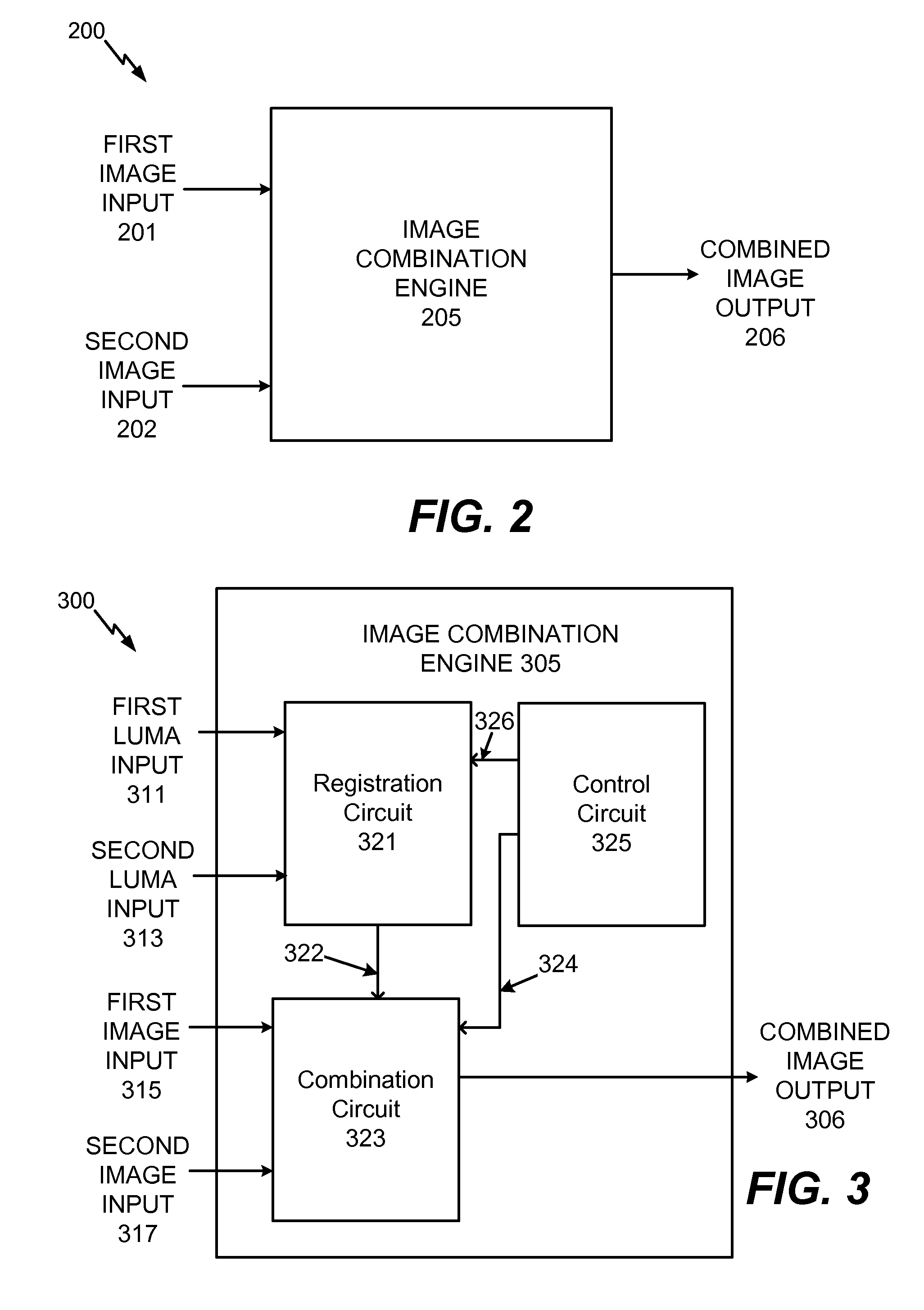
System and method to selectively combine images
InactiveUS20100157079A1Issue of imageReduce ghostingImage enhancementTelevision system detailsMotion vectorControl circuit
Systems and methods to selectively combine images are disclosed. In a particular embodiment, an apparatus includes a registration circuit configured to generate a set of motion vector data based on first image data corresponding to a first image and second image data corresponding to a second image. The apparatus includes a combination circuit to selectively combine the first image data and adjusted second image data that corresponds to the second image data adjusted according to the motion vector data. The apparatus further includes a control circuit to control the combination circuit to generate third image data.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
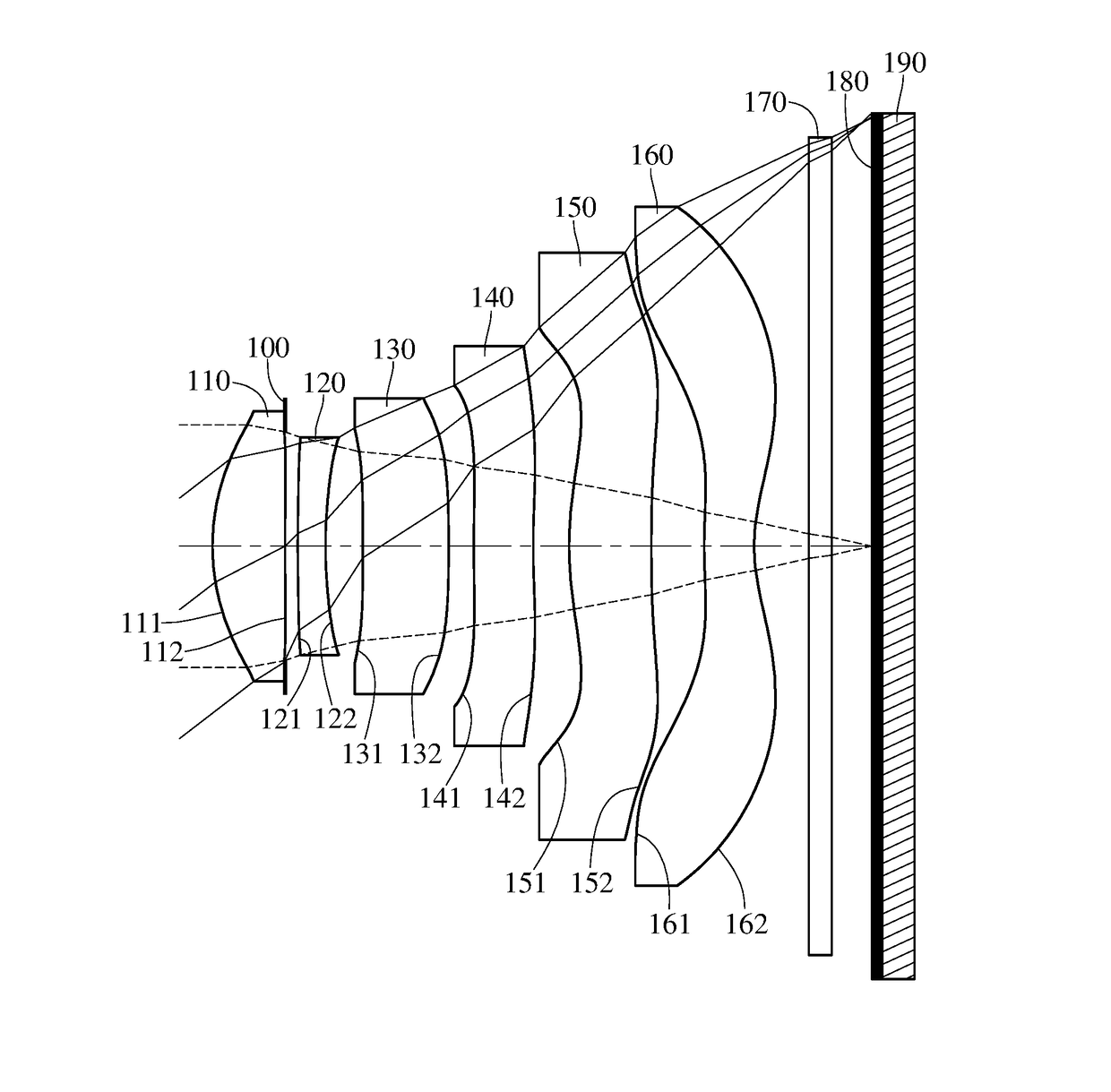
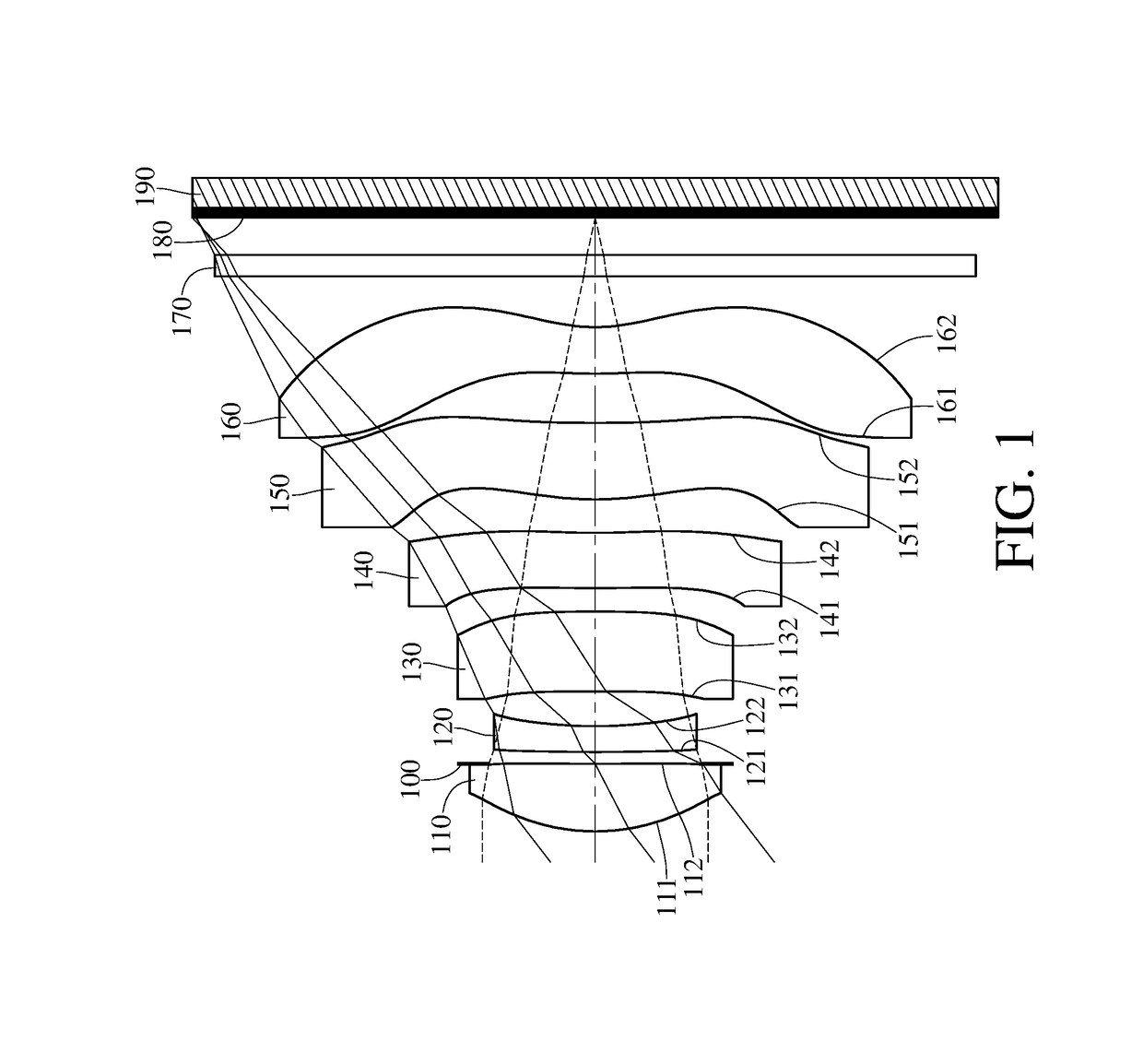
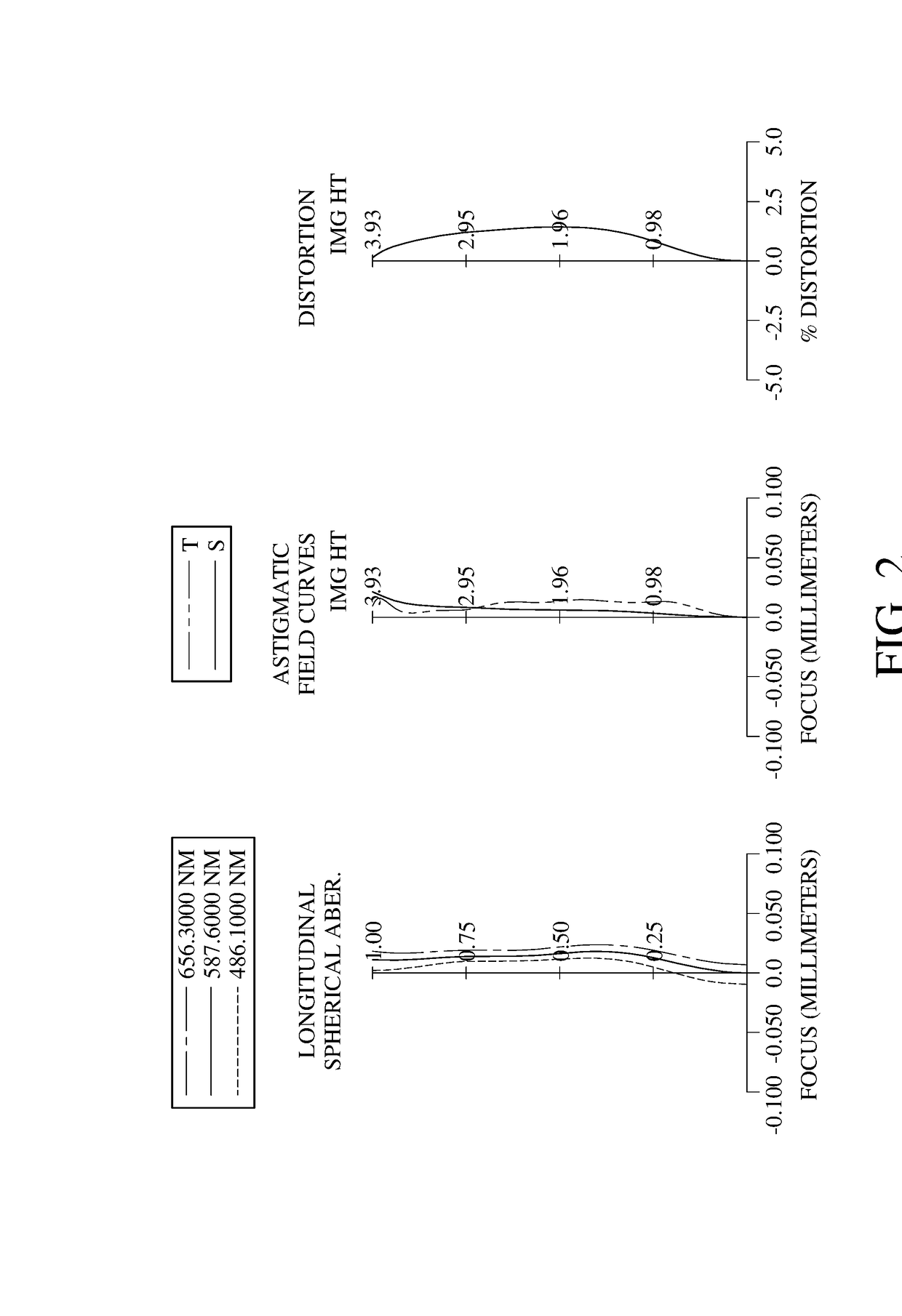
Optical imaging lens assembly, image capturing unit and electronic device
An optical imaging lens assembly includes, in order from an object side to an image side, a first lens element, a second lens element, a third lens element, a fourth lens element, a fifth lens element and a sixth lens element. The first lens element with positive refractive power has an object-side surface being convex. The second lens element has negative refractive power. At least one of two surfaces of the fourth lens element has at least one inflection point, and the two surfaces thereof are aspheric. The fifth lens element has an object-side surface being convex and an image-side surface having at least one inflection point, and the two surfaces thereof are aspheric. The sixth lens element has an image-side surface being concave, wherein the image-side surface of the sixth lens element has at least one convex shape in off-axial region, and the two surfaces thereof are aspheric.
Owner:LARGAN PRECISION
System and method to selectively combine video frame image data
ActiveUS20100271498A1Issue of imageReduce hand jitterImage enhancementTelevision system detailsImaging dataImage sensor
Systems and methods to selectively combine video frame image data are disclosed. First image data corresponding to a first video frame and second image data corresponding to a second video frame are received from an image sensor. The second image data is adjusted by at least partially compensating for offsets between portions of the first image data with respect to corresponding portions of the second image data to produce adjusted second image data. Combined image data corresponding to a combined video frame is generated by performing a hierarchical combining operation on the first image data and the adjusted second image data.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Panoramic image fusion method based on depth convolution neural network and depth information
InactiveCN106934765AReduce ghostingImplement automatic selectionImage enhancementImage analysisData setSemantic representation
The invention discloses a panoramic image fusion method based on a depth convolution neural network and depth information. The method comprises the steps of (S1) constructing a deep learning training data set, selecting overlap regions xe1 and xe2 of two fish eye images to be fused used for training and an ideal fusion area ye of a panoramic image formed after fusing the two fish eye images, and constructing a training set {xe1, xe2, ye} of the images to be fused and a panoramic image block pair, (S2) constructing a convolution neural network model, and (S3) obtaining a fusion area of a test data set based on a test data set and a trained depth convolution neural network model. According to the method, an image can be expressed more comprehensively and deeply, the image semantic representation in a plurality of abstract levels is realized, and the accuracy of image fusion is improved.
Owner:CHANGSHA PANODUX TECH CO LTD
Depth adaptive video-splicing method, device and system thereof
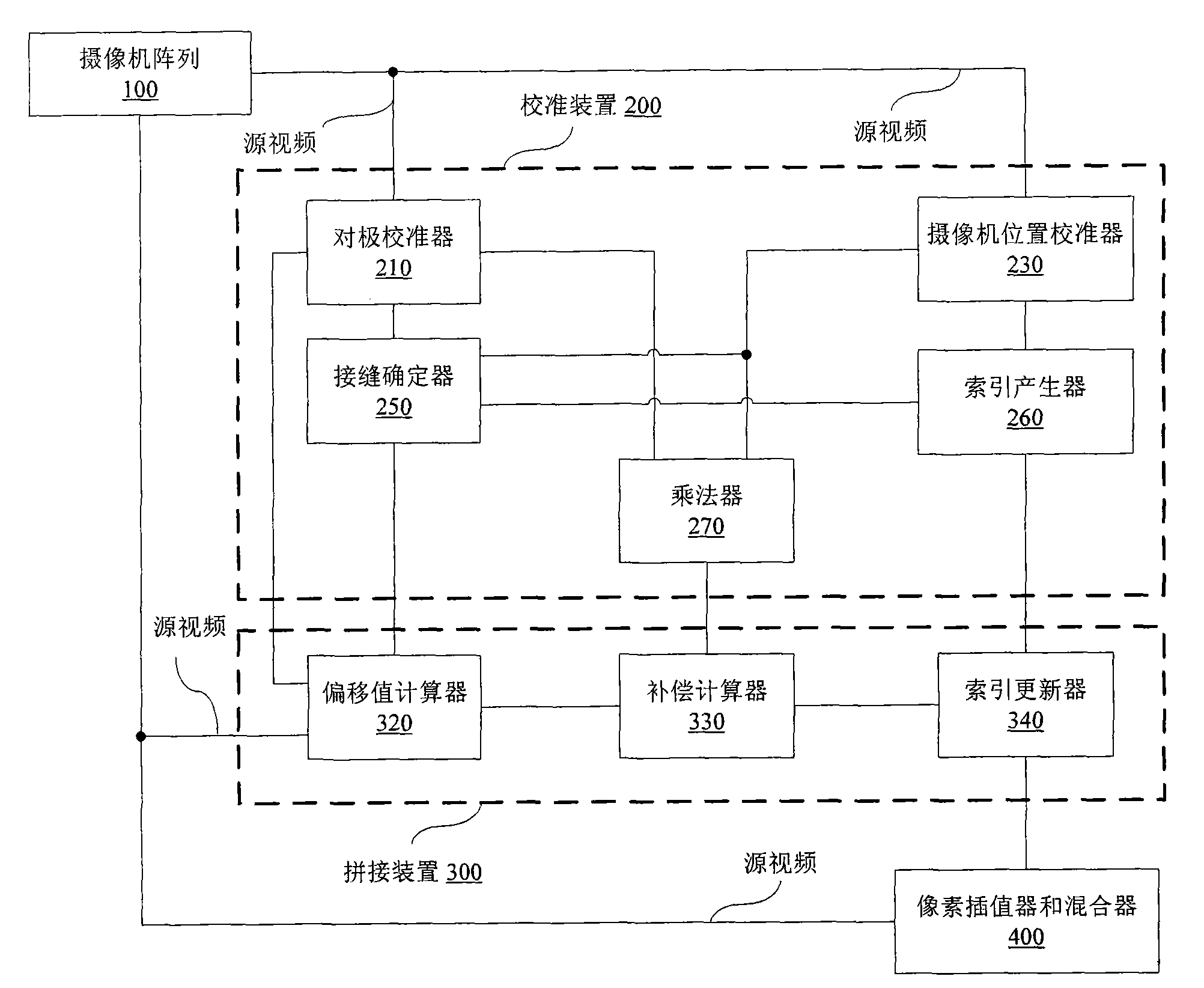
InactiveCN101593350AWork fastReduce ghostingTelevision system detailsImage analysisSelf adaptiveCamera array
The invention relates to a depth adaptive video-splicing method, a device and a system thereof. The depth adaptive video-splicing system comprises a camera array, a calibration device, a video-splicing device, a pixel interpolation device and a mixer, wherein a plurality of source videos are generated by the camera array; the calibration device executes antipodal calibration and camera position calibration, confirms a splicing area in each special adjacent image pair in a plurality of source videos and generates a pixel index table; the video-splicing device calculates an average pixel deviation value corresponding to the depth, forms a compensation item of the pixel index table based on the average pixel deviation value and compensates the pixel index table by the compensation item; and the pixel interpolation device and the mixer use the upgraded pixel index table and generate a panoramic video according to a plurality of source videos.
Owner:NEC (CHINA) CO LTD
Electro-optical apparatus and projection-type display apparatus
InactiveUS6859247B2Simple structureReduce volatilityProjectorsNon-linear opticsParasitic capacitorDisplay device
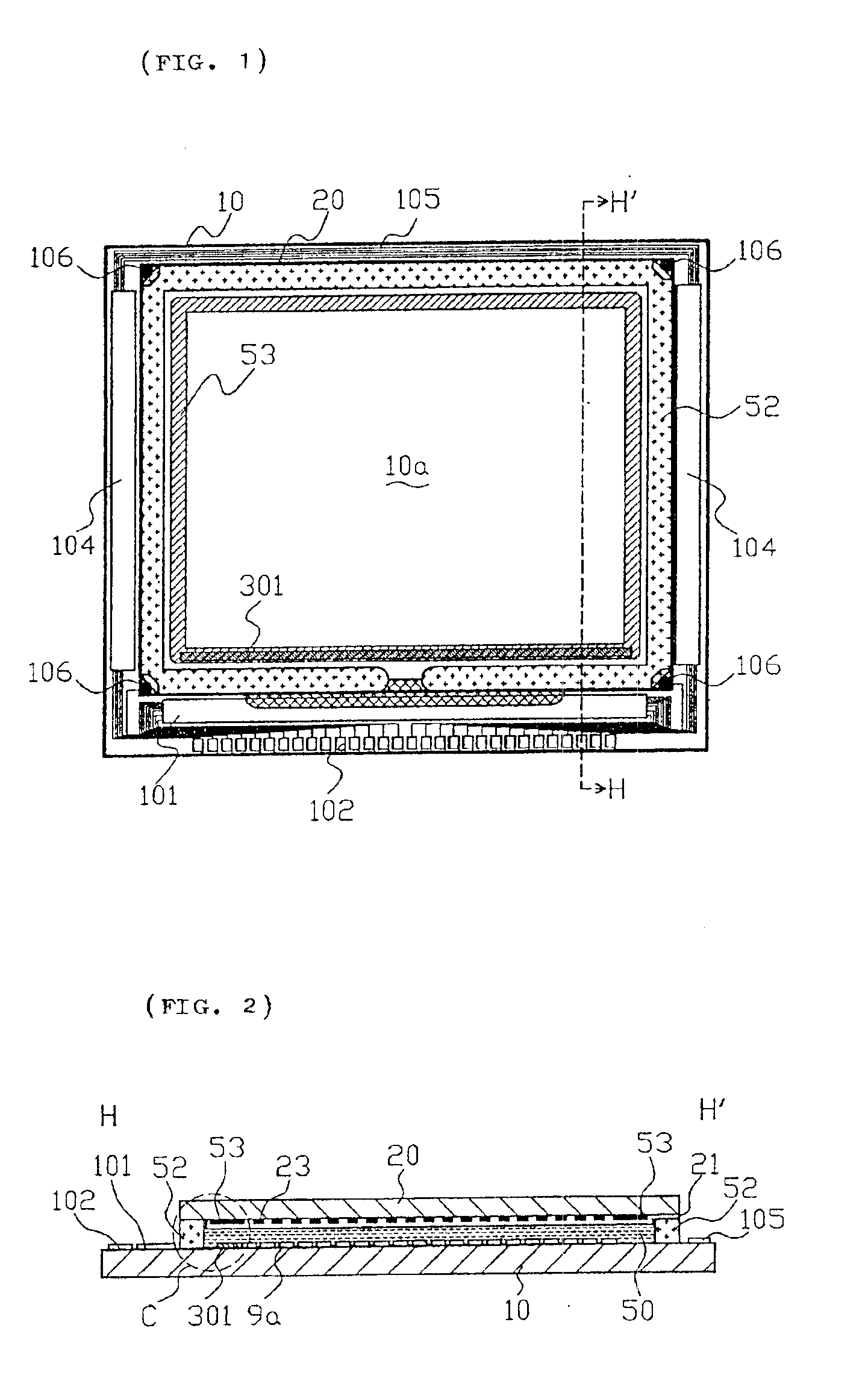
In an electro-optical apparatus, such as a liquid-crystal apparatus, a TFT array substrate is provided with pixel electrodes and TFTs connected thereto. In addition, a peripheral area (including a frame area and a sealing area) is provided with peripheral circuits that drive the pixel electrodes, such as data-line driving circuits and a sampling circuit, and wires that send image signals. On an opposite substrate, an opposite electrode is formed so as to avoid areas opposite the wires. Therefore, with a relatively simple structure, parasitic capacitors generated between the wires on one substrate and the opposite electrode on the other substrate are reduced, and high-quality image display having a reduced ghost is achieved.
Owner:138 EAST LCD ADVANCEMENTS LTD
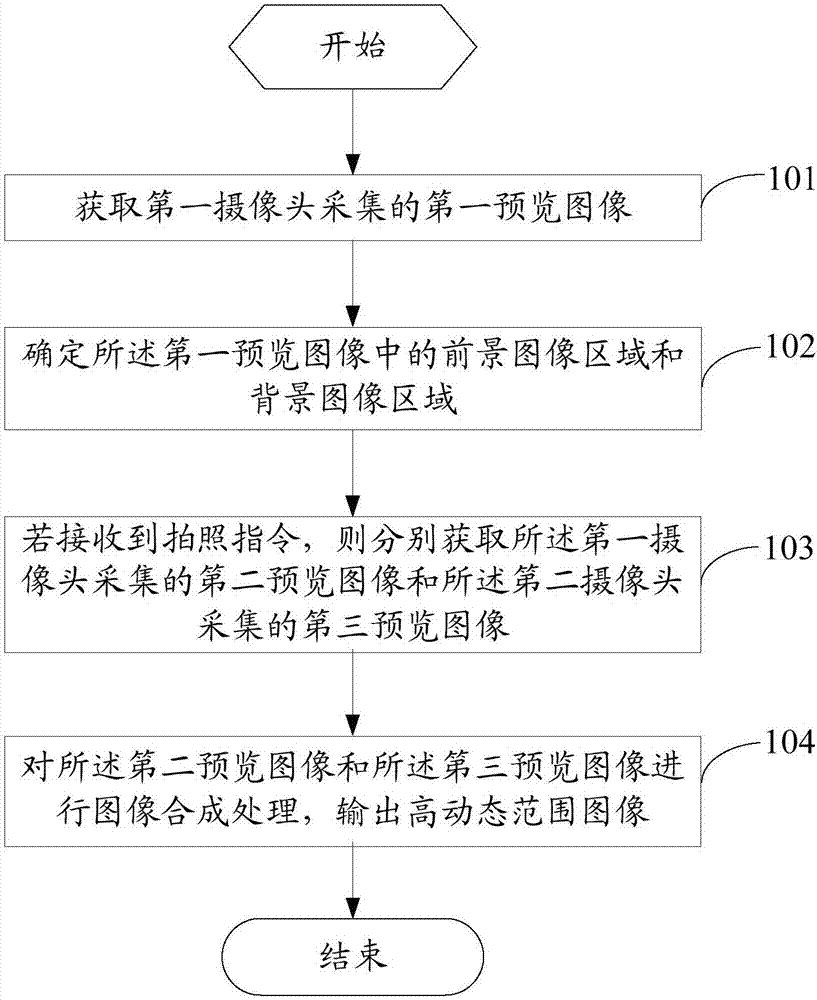
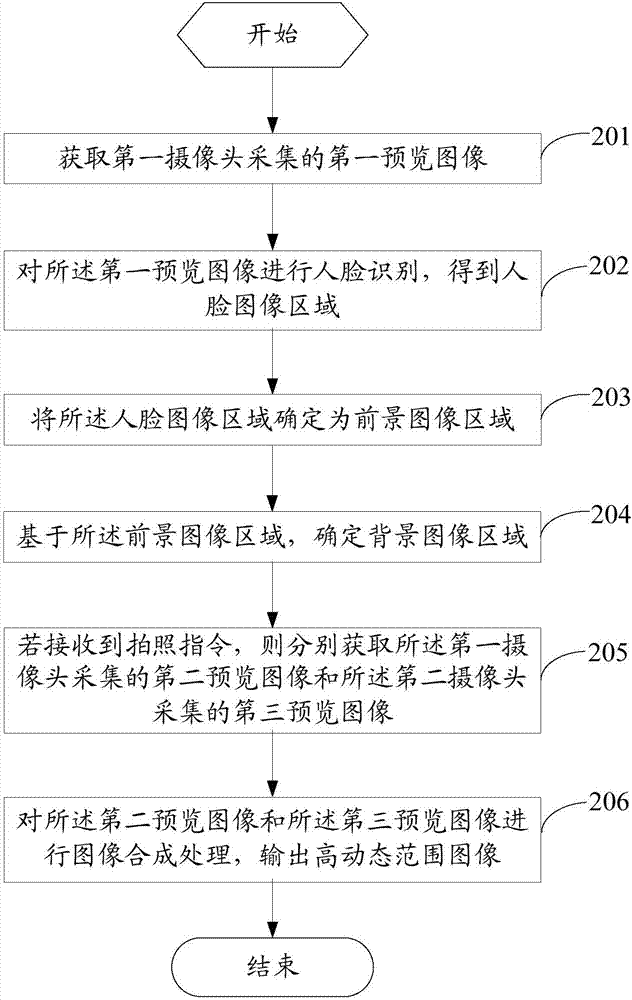
High dynamic range image shooting method and mobile terminal
ActiveCN107197169AImprove photo qualityAvoid time differenceTelevision system detailsColor television detailsImage synthesisTime difference
The invention provides a high dynamic range image shooting method and a mobile terminal. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining a first preview image collected by a first camera; determining a foreground image area and a background image area in the first preview image; if a shooting instruction is received, separately obtaining a second preview image collected by the first camera and a third preview image collected by a second camera; performing image synthesis processing on the second preview image and the third preview image to output a high dynamic range image, wherein the second preview image is an exposed image of the foreground image area, and the third preview image is an exposed image of the background image area. According to the high dynamic range image shooting method provided by the embodiment of the invention, the mobile terminal can be used for avoiding the time difference of photos used for synthesizing the HDR image, thereby reducing the occurrence of double images or ghosts and improving the quality of the photos shot by the mobile terminal.
Owner:VIVO MOBILE COMM CO LTD
Inorganic, dielectric, grid polarizer and non-zero order diffraction grating
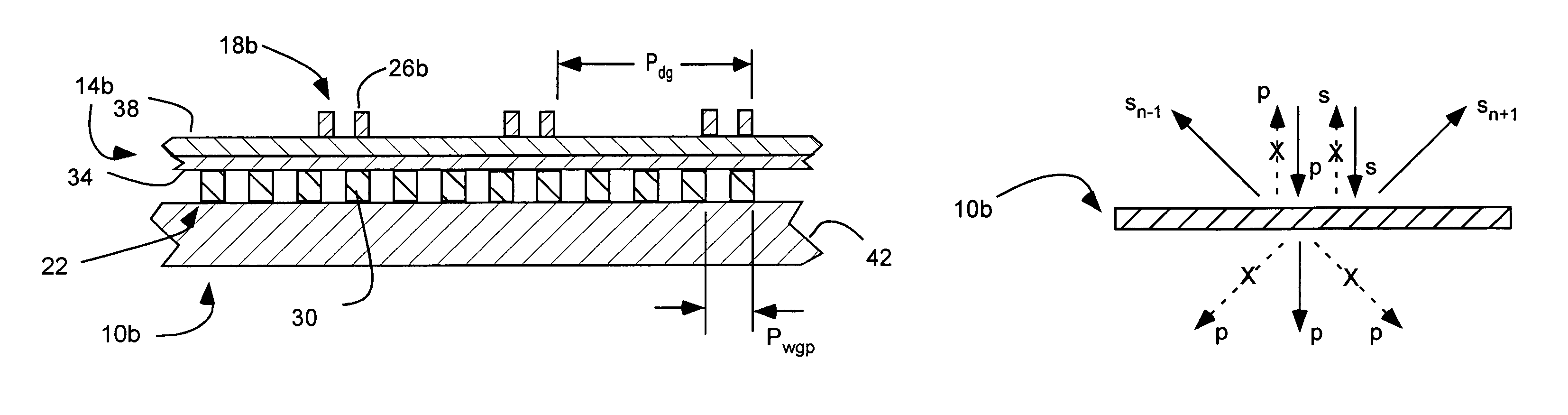
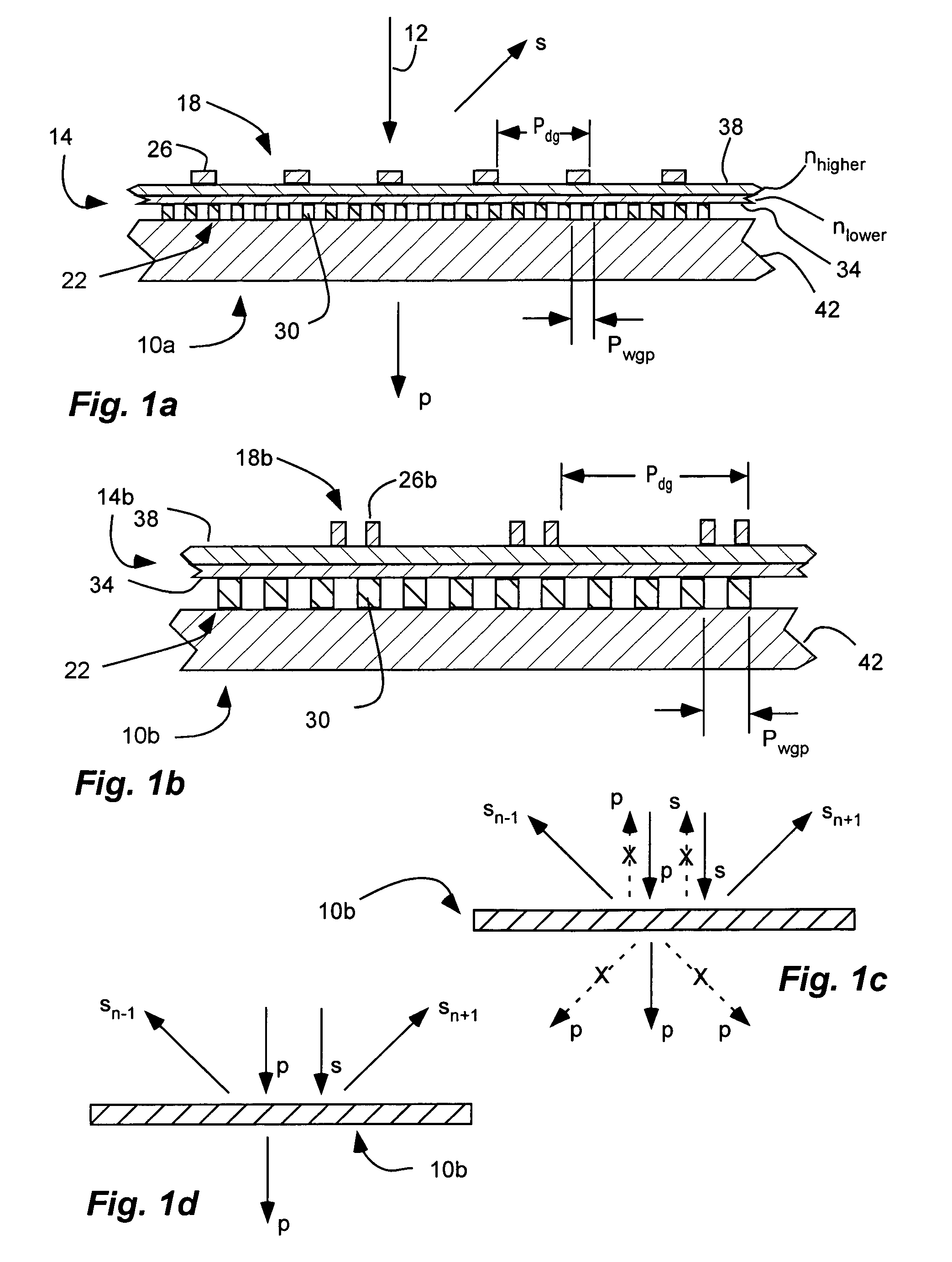
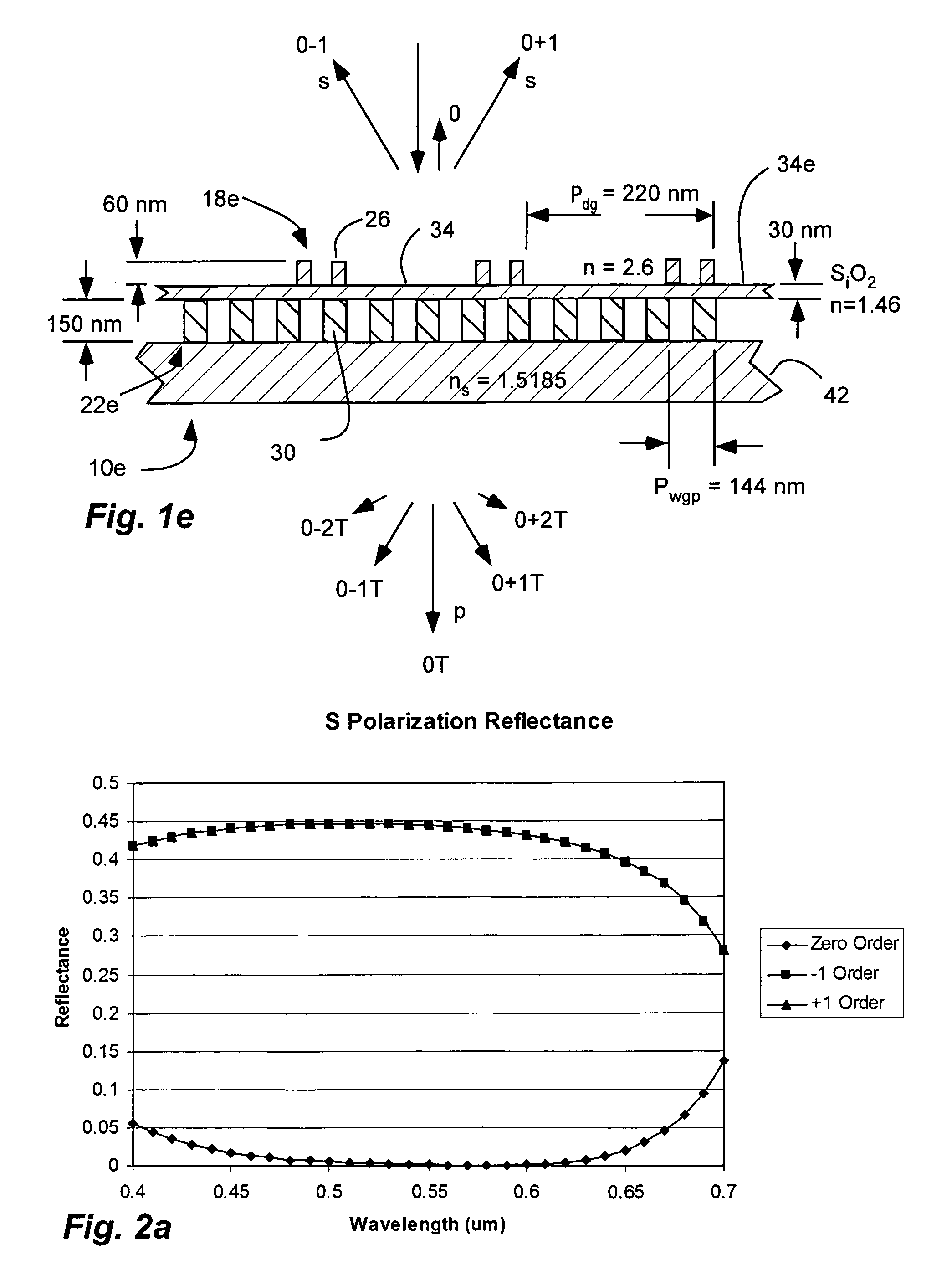
InactiveUS7630133B2Reduce back reflectionSave spacePolarising elementsDiffraction gratingsDielectricPolarizer
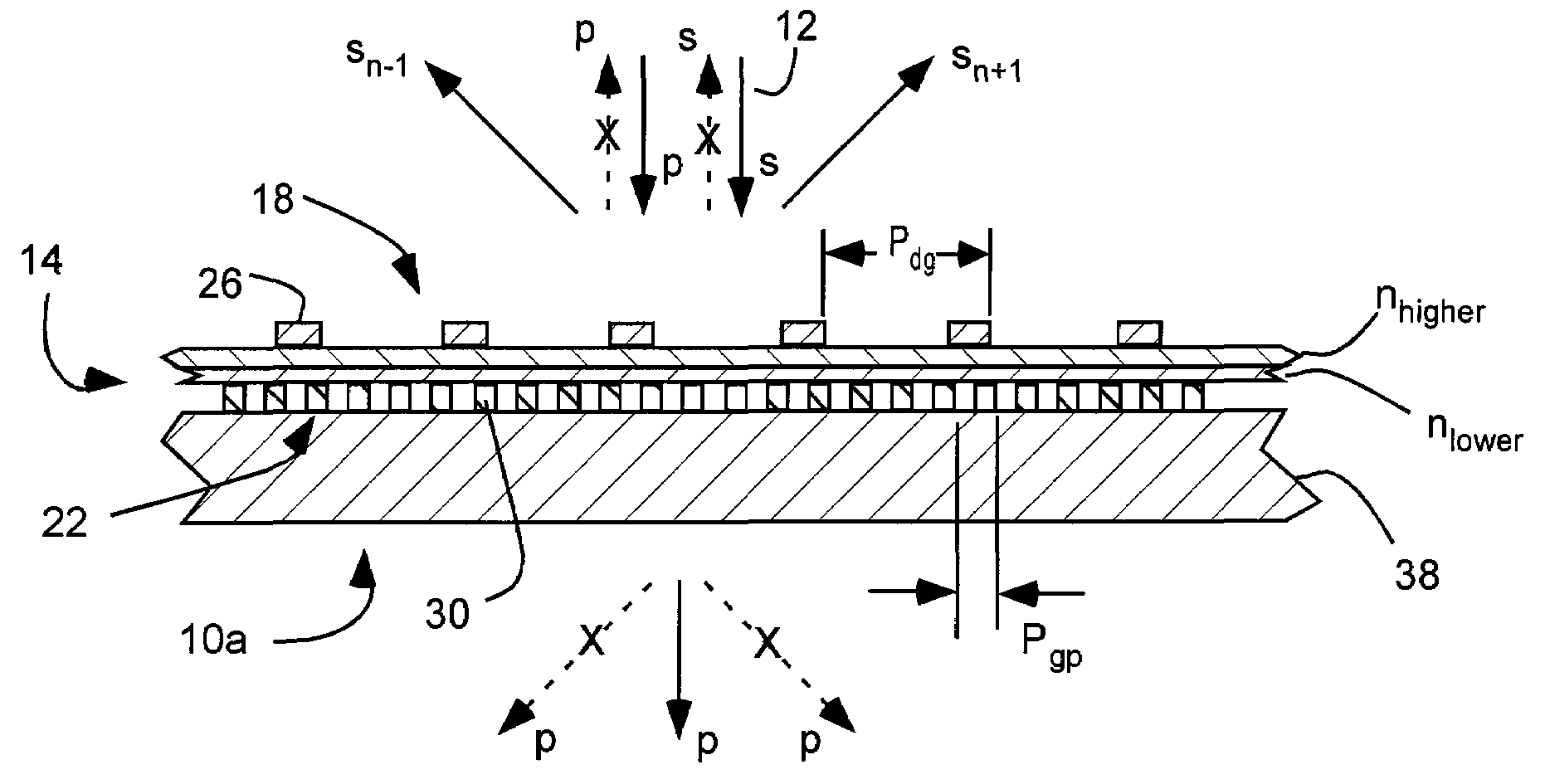
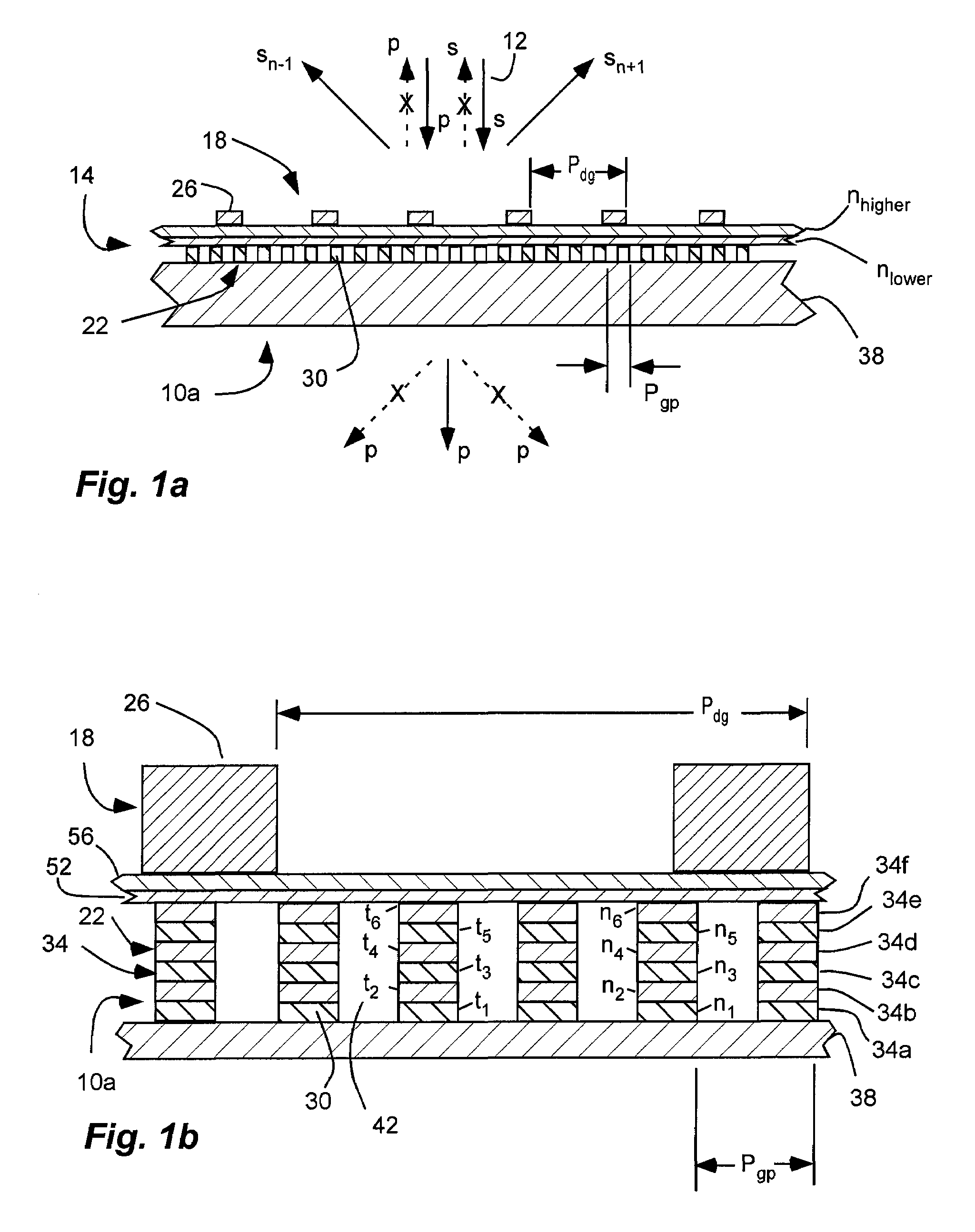
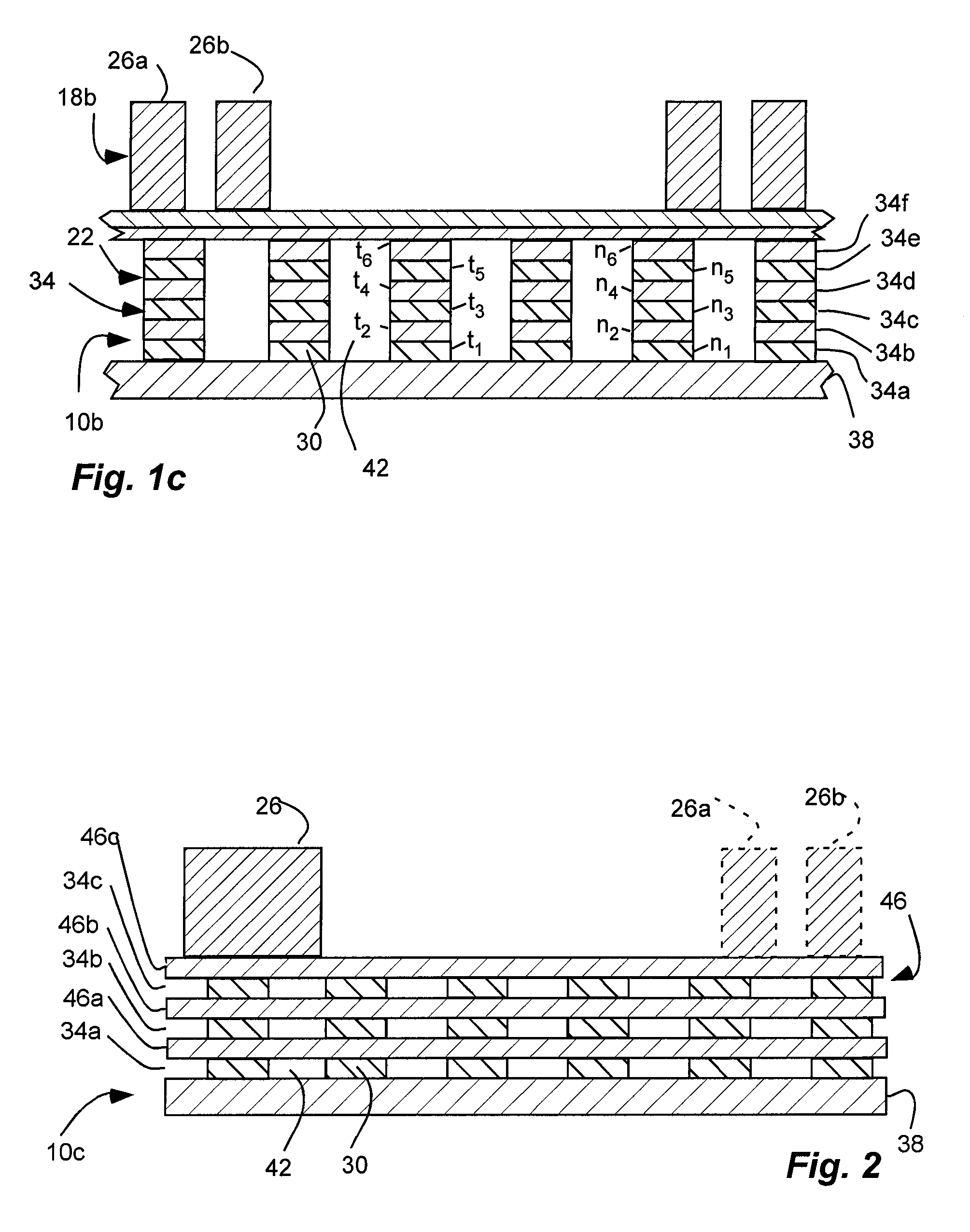
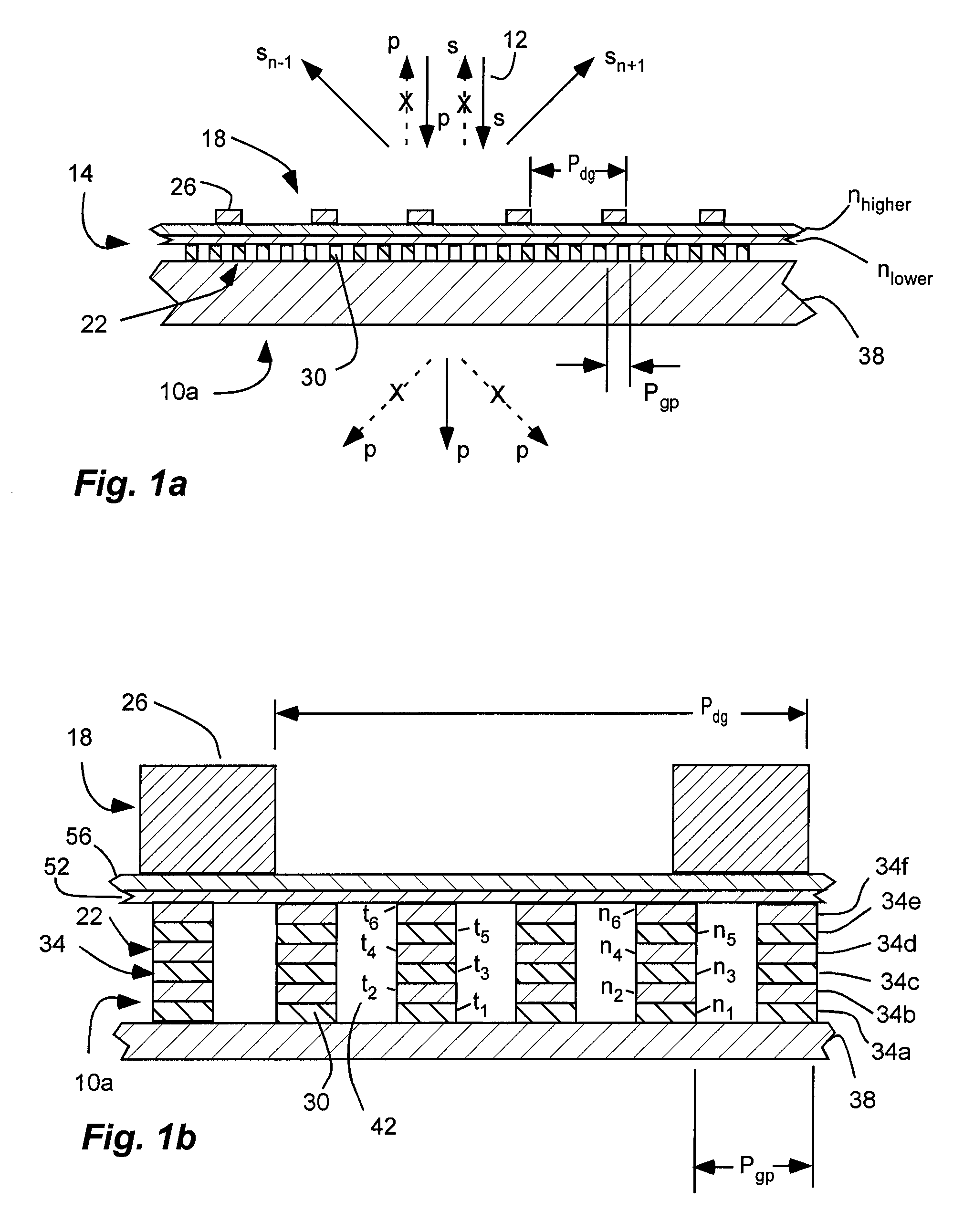
An inorganic, dielectric grid polarizer includes an optical stack with a diffraction grating and an inorganic, dielectric grid polarizer. The inorganic, dielectric grid polarizer includes a stack of film layers with an array of parallel ribs in accordance with PGP<lambda / 2 where PGP is the period of the ribs and lambda is the wavelength of the light. The diffraction grating includes an array of elongated parallel dielectric ribs in accordance with PDG>lambda / 2 where PDG is the period of the ribs.
Owner:MOXTEK INC
Interference filters for viewing anaglyphs
InactiveUS20110063726A1Improve transmission efficiencyLow costOptical elementsComputer sciencePolymer
This invention provides apparatus for viewing anaglyphic stereoscopic images with color filters comprising polymer interference films. The interference films may be mounted in lightweight paper frames or rigid frames. The interference films may have a curved profile in order to reduce reflections into a user's eyes. The interference films may be laminated to a substrate. The viewing apparatus may comprise adsorption films in order to block primary colors and attenuate primary colors reflected into a user's eyes.
Owner:RAMSTAD MONTE JEROME
Light Reflecting Film, And Light Controlling Film, Optical Film, Functional Glass And Head-Up Display Including The Light Reflecting Film
ActiveUS20170235030A1Improve visibilityImprove reflectivityMirrorsInstrument arrangements/adaptationsHead-up displayLength wave
A light controlling film comprises a light reflecting film and a light controlling layer that are laminated. The light reflecting film comprises at least two laminated light reflecting layers including at least one of light reflecting layers PRL-1 to PRL-3 that a central reflection wavelength of 400 nm-500 nm, 500 nm-600 nm, and 600 nm-700 nm, respectively, and a reflectance to ordinary light at the central reflection wavelength of 5%-25%. The at least two light reflecting layers have central reflection wavelengths that are different from each other. All of the at least two laminated light reflecting layers have a property of reflecting polarized light having the same orientation. The light controlling layer comprises two quarter wave plates, and the light reflecting film is laminated so as to be interposed between the two quarter wave plates.
Owner:NIPPON KAYAKU CO LTD
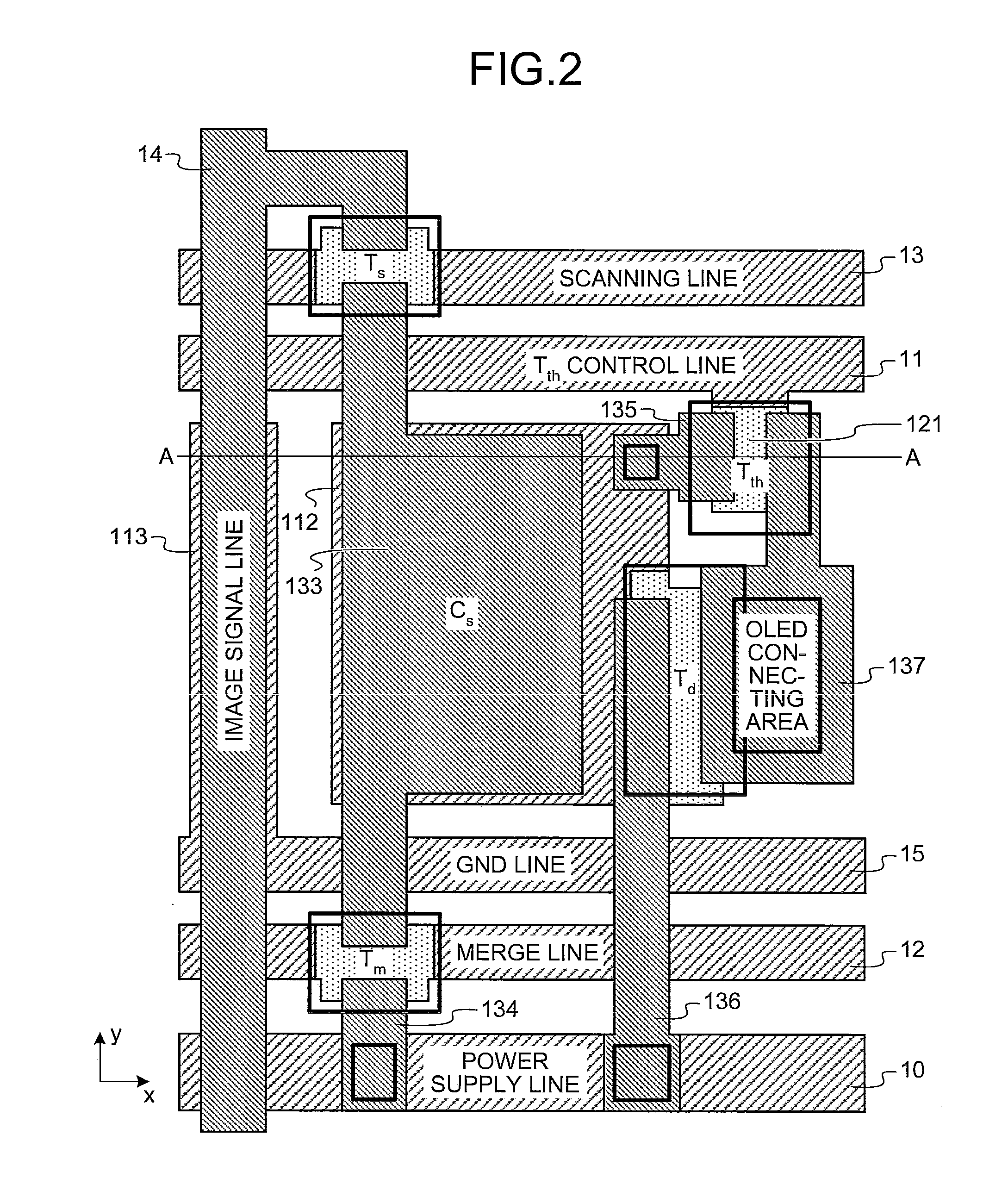
Image display device
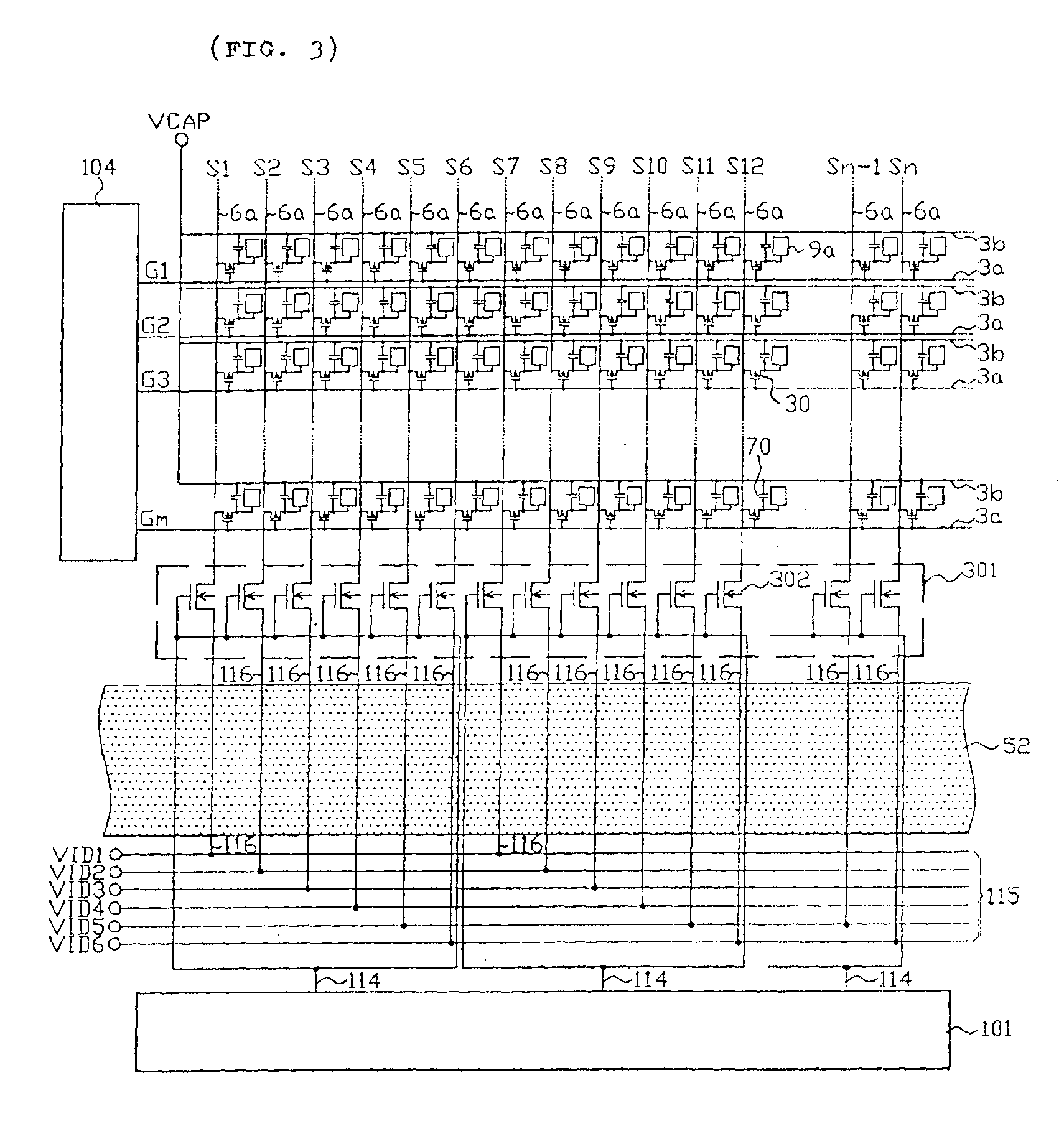
InactiveUS20100182303A1Reduce crosstalkReduce ghostingSolid-state devicesCathode-ray tube indicatorsCapacitanceDisplay device
According to one embodiment, an image display device includes: a plurality of pixels including a light-emitting element, a driver element that controls light emission of the light-emitting element, and a capacitive element electrically connected to the driver element; and an image signal line that is commonly connected to the pixels for sequentially supplying, to the pixels, an image signal corresponding to luminous brightness of the light-emitting element. The pixel includes a shield electrode that shields an electric field from the image signal line to the capacitive element.
Owner:KYOCERA CORP
Display Device
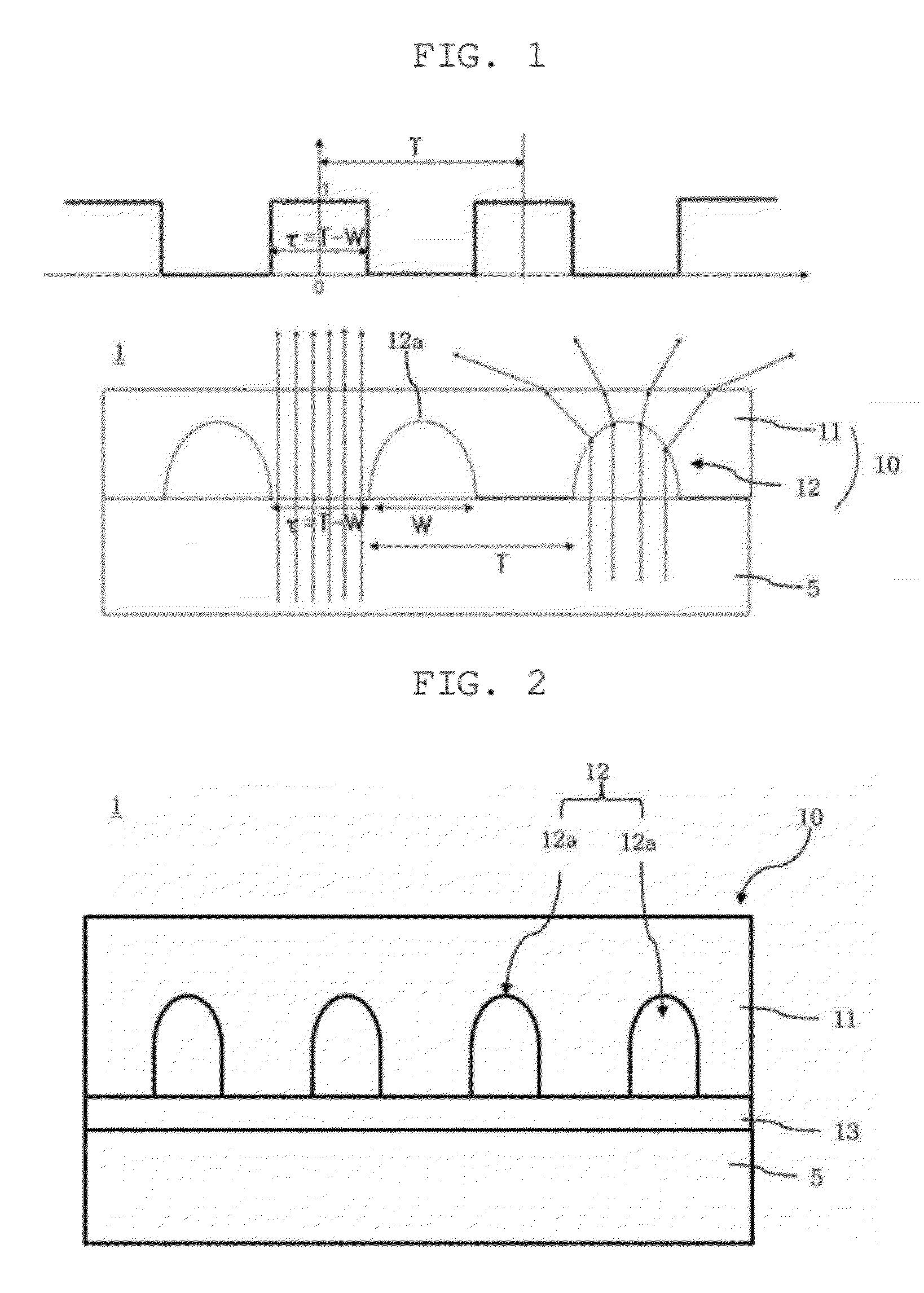
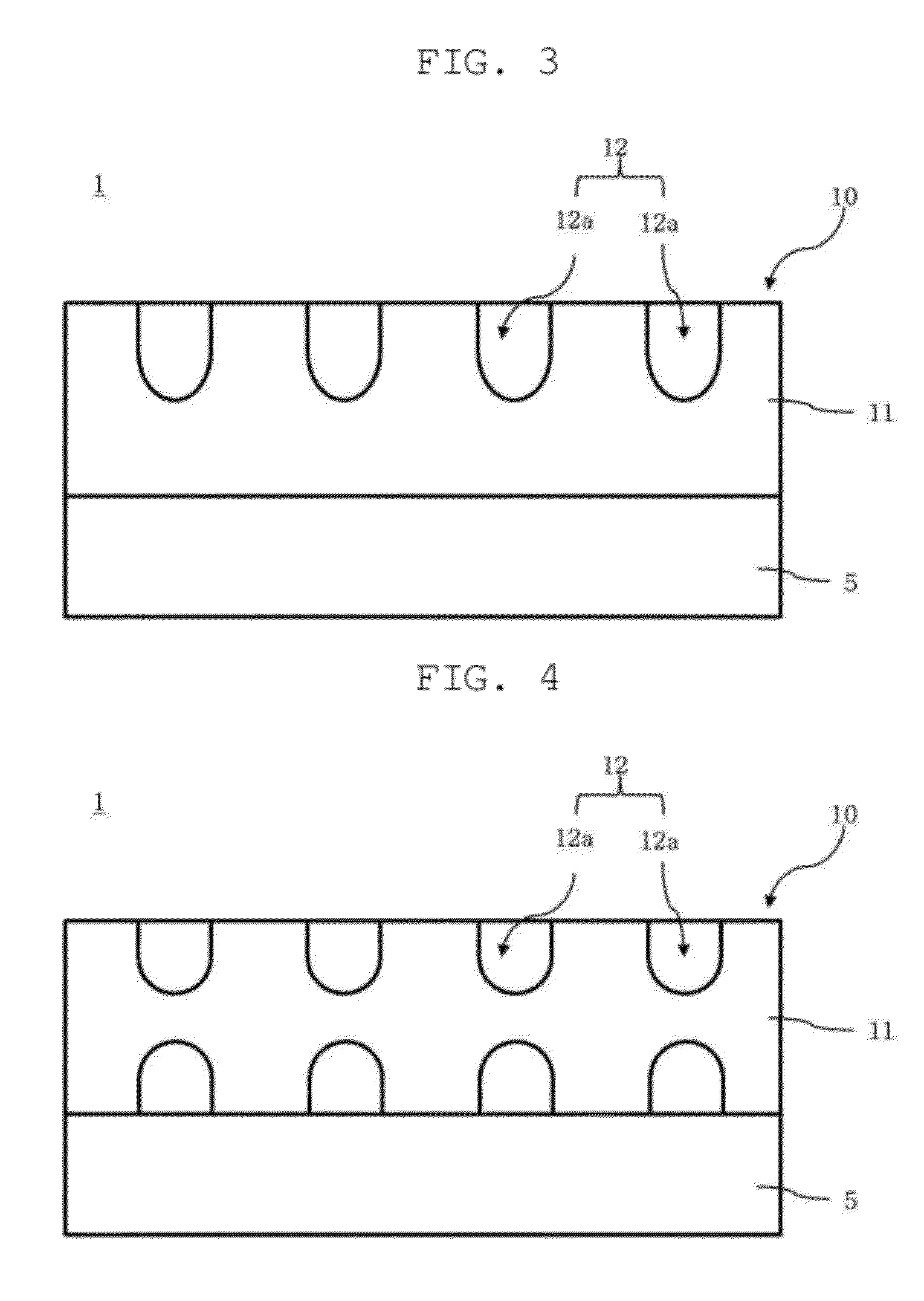
InactiveUS20120307191A1Improve image qualityMinimizing color shiftSolid-state devicesNon-linear opticsColor shiftDisplay device
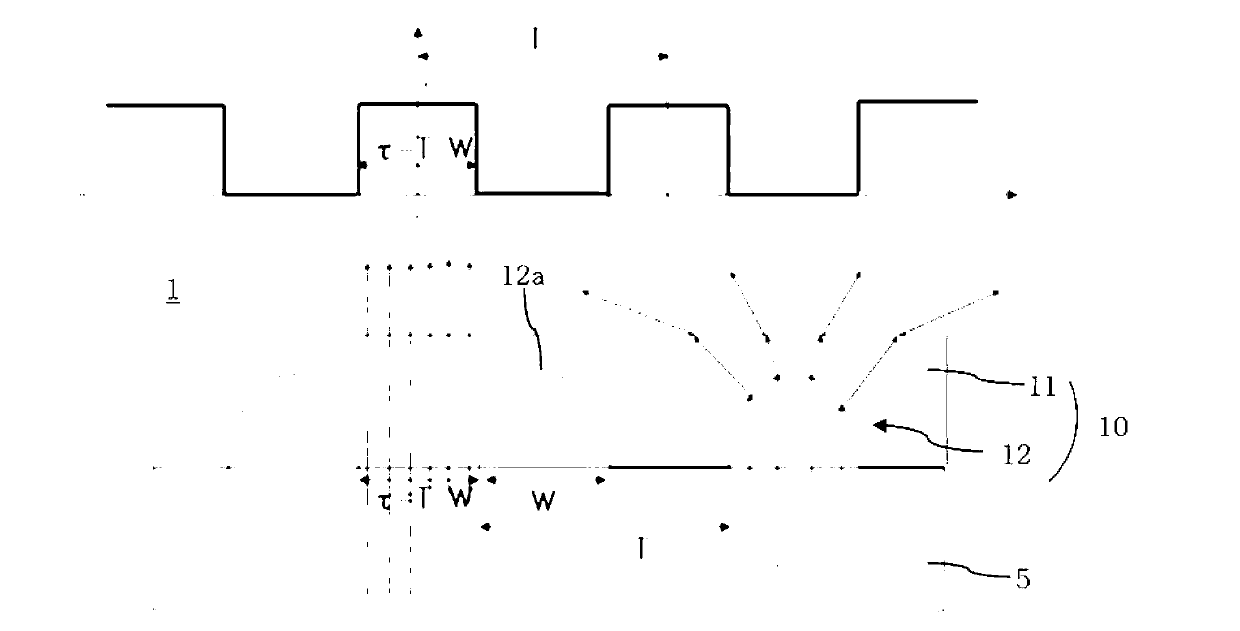
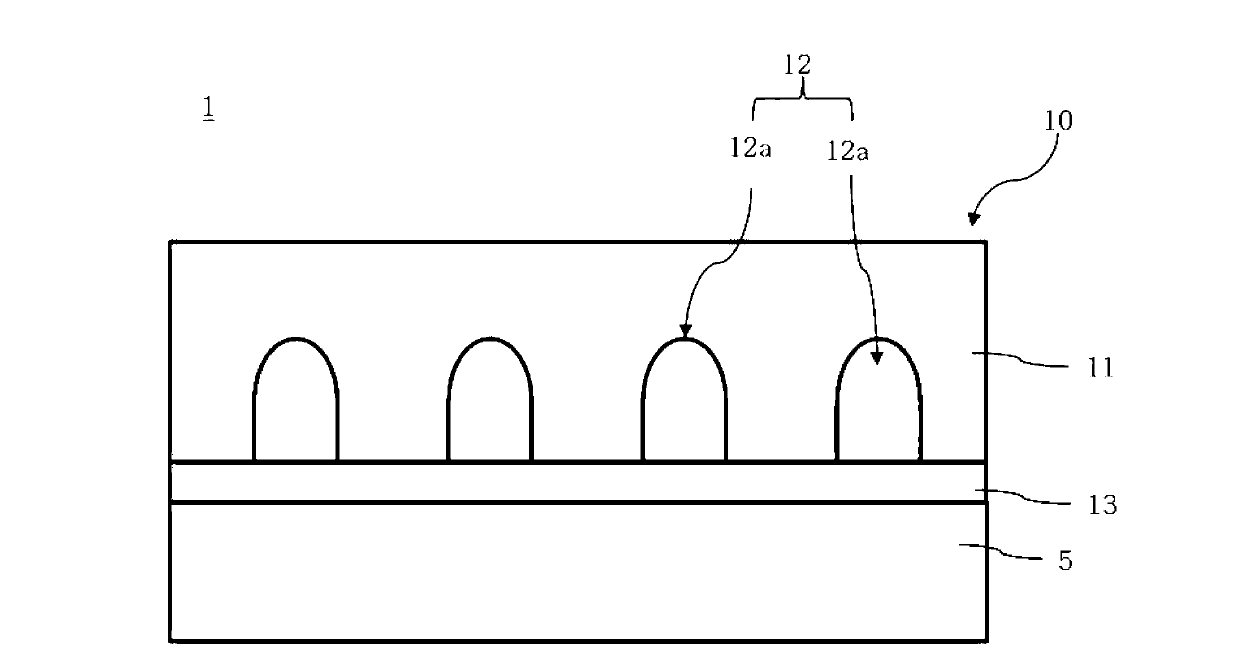
A display device that can reduce color shift and prevent the quality of an image from degrading due to moiré. The display device includes a display panel and an optical film, which includes a background layer disposed in front of the display panel, and a lens section formed on the background layer. Patterns of the lens section is spaced apart from each other to diffuse incident light. The spacing τ and pitch T of the patterns are determined by the following m value in the following formulae.Imax-IminImax+Imin≈2sin(π·k·p / P)(π·k·p / P)sin(π·m·p / P)(π·m·p / P)≤0.01k=τ / Tp / Pm=P / Tp / P is an aperture ratio of sub-pixels of the display panel, τ / T is an aperture ratio of the lens section, I is an intensity of light exiting the optical film after being diffused through the sub-pixels, P and p are a pitch and a width of the sub-pixels, T is a pitch of the patterns, and τ=T−W.
Owner:SAMSUNG CORNING PRECISION MATERIALS CO LTD
Polarization device to polarize and further control light
InactiveUS7800823B2Save spaceReduce back reflectionPolarising elementsDiffraction gratingsWire gridLength wave
A polarization device includes an optical stack with a diffraction grating and a wire grid polarizer with one disposed over the other. The wire grid polarizer includes an array of elongated, parallel conductive wires in accordance with PWGP<λ / 2 where PWGP is the period of the wires and λ is the wavelength of the light. The diffraction grating includes an array of elongated parallel dielectric ribs in accordance with PDG>λ / 2 where PDG is the period of the ribs.
Owner:MOXTEK INC
Imaging apparatus and imaging system, method thereof and program for the same
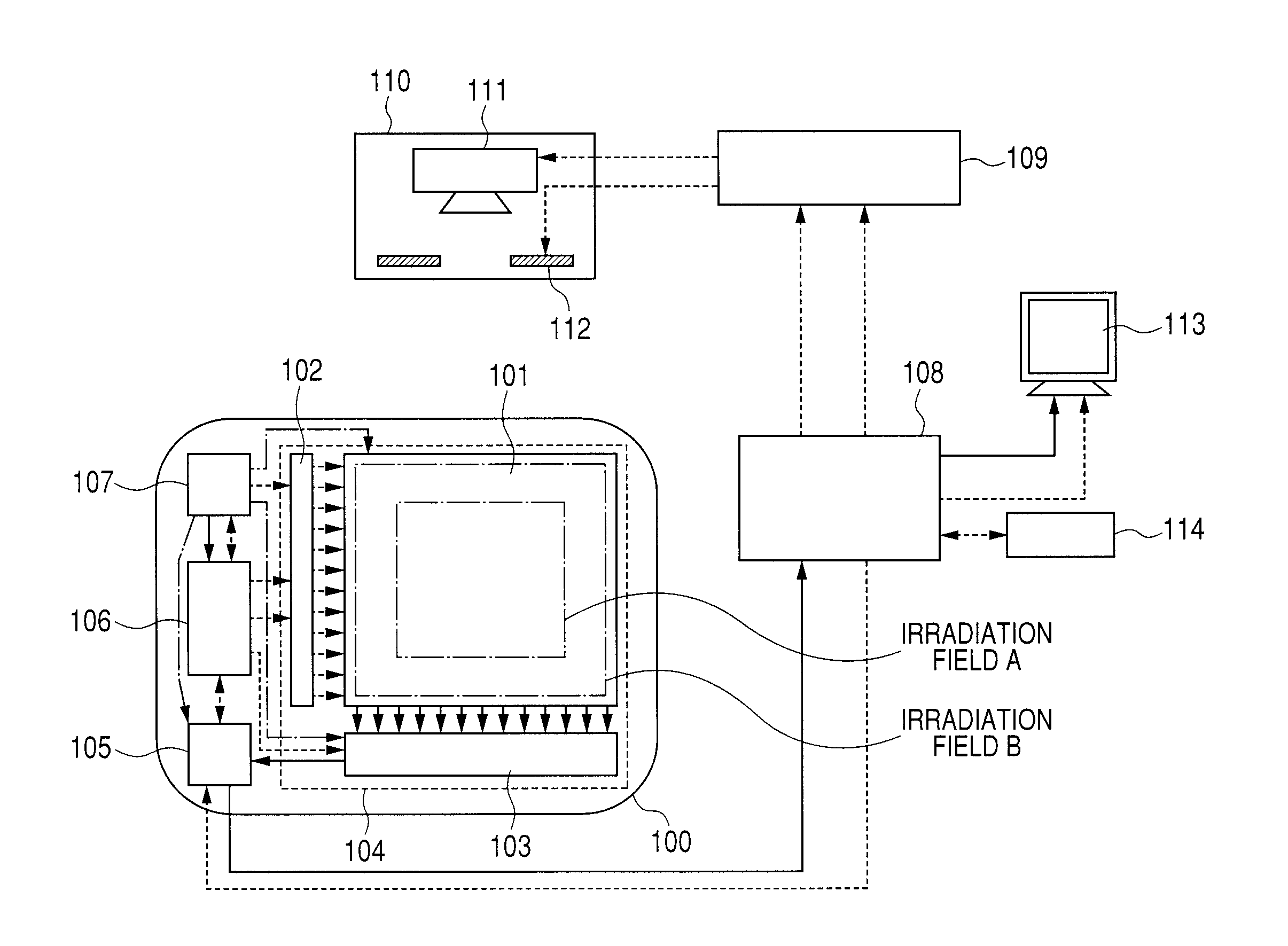
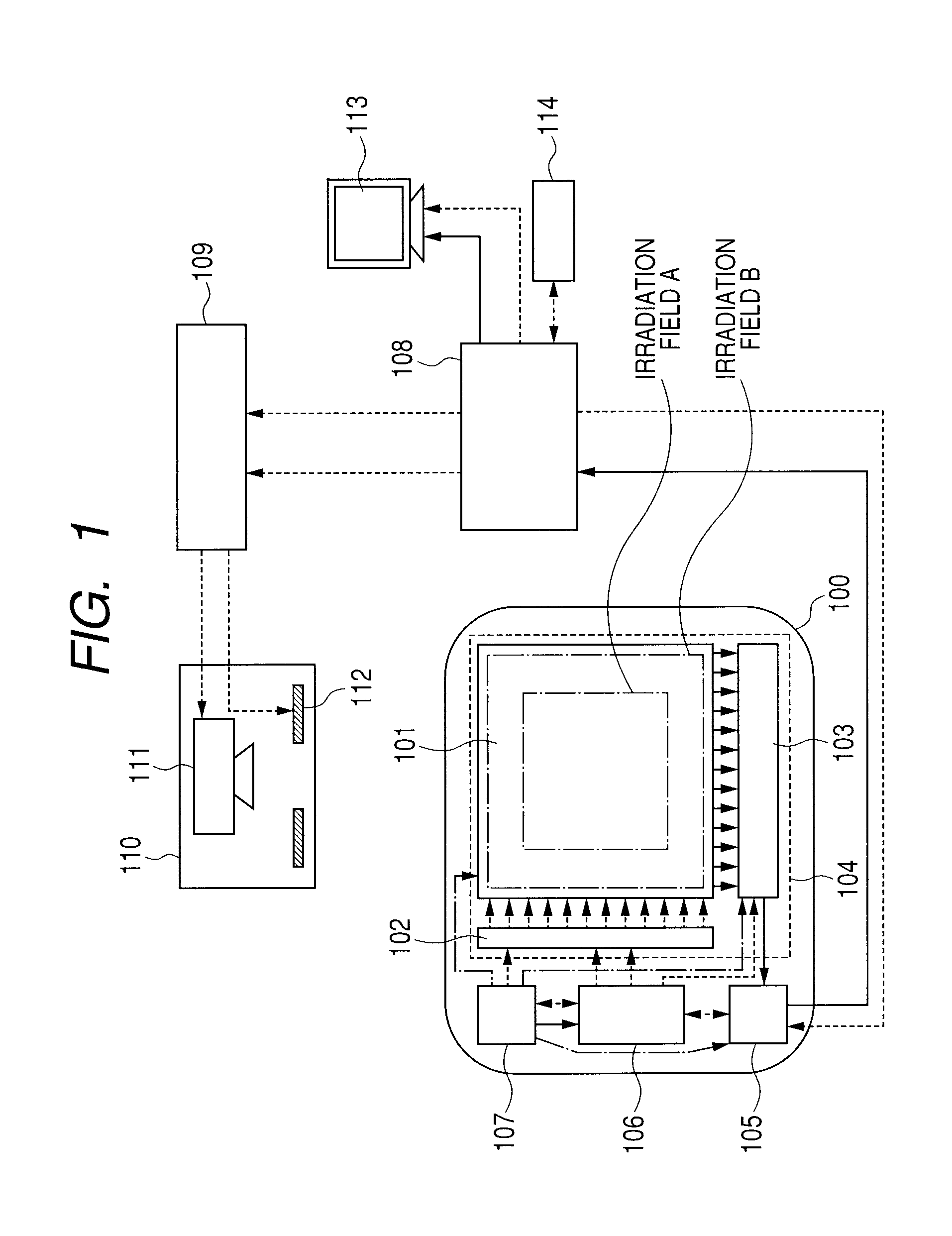
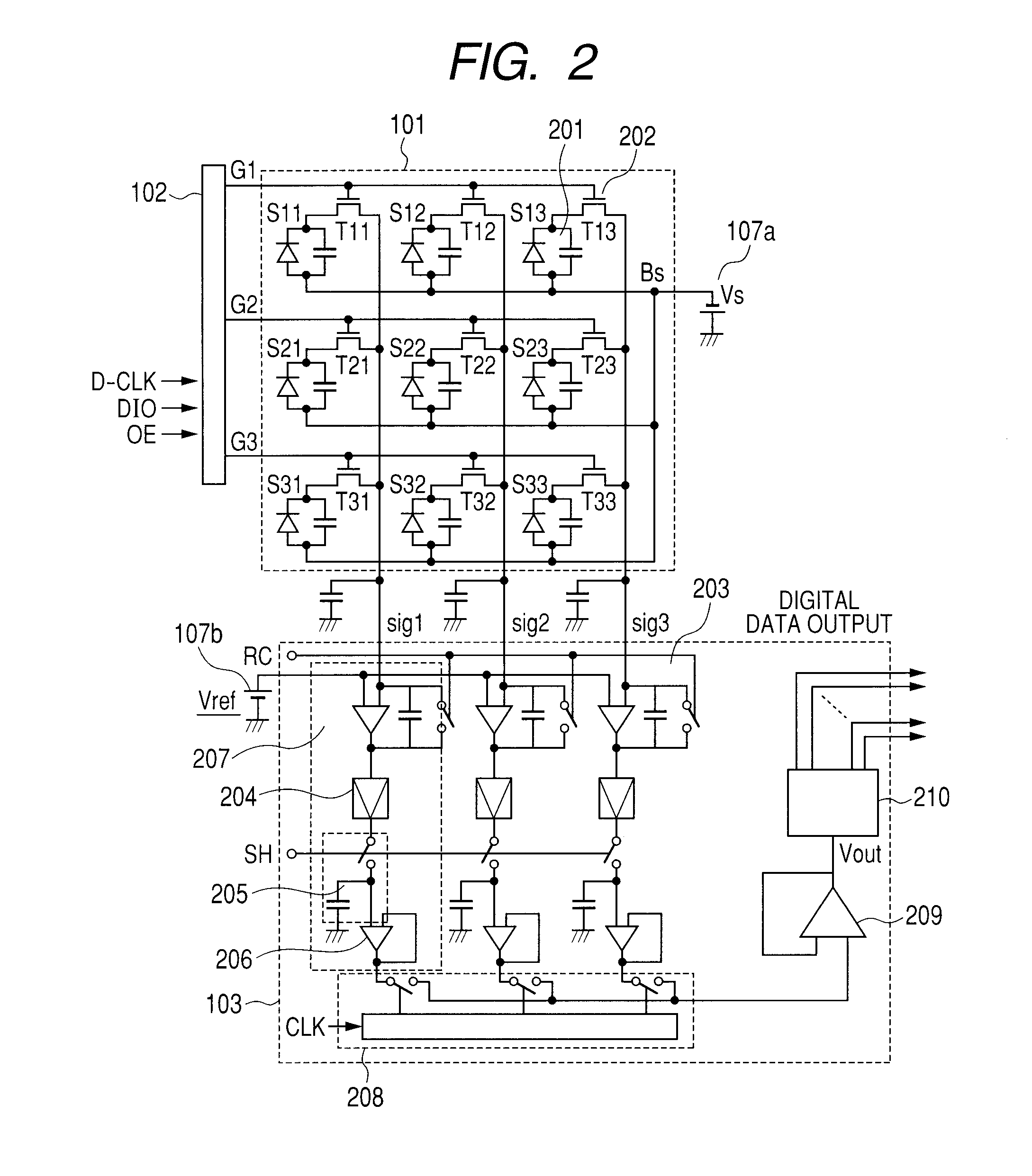
ActiveUS8829438B2Reduce ghostingPreventing considerable image quality degradationTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesRadiologyNuclear medicine
An imaging operation includes a first imaging operation for outputting image data according to irradiation to the detector with radiation or light in an irradiation field A corresponding to a part of the plurality of pixels, and a second imaging operation for outputting image data according to irradiation to the detector 104 with radiation or light in an irradiation field B wider than the irradiation field A, wherein, responsive to a changing from irradiation in the irradiation field A to irradiation in the irradiation field B, an operation of the detector is controlled so that the detector performs an initializing operation for initializing conversion elements during a period between the first and second imaging operations.
Owner:CANON KK
Optical element, imaging optical system, and camera module
ActiveUS8455810B2Easy to useReduce flareSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansOptical axisLight flux
Owner:TIANJIN OFILM OPTO ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and apparatus for breath-held mr data acquisition using interleaved acquisition
InactiveUS20100222666A1Minimizes k-space transition artifactT weightingDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsVentricular volumeCardiac cycle
A method and apparatus are presented for acquiring MR cardiac images in a time equivalent to a single breath-hold. MR data acquisition is segmented across multiple cardiac cycles. MR data acquisition is interleaved from each phase of a first cardiac cycle with MR data from each phase of a subsequent cardiac cycle. Preferably, low spatial frequency data are interleaved between multiple cardiac cycles, and the subsequent cardiac cycle acquisition includes sequential acquisition of high spatial frequency data towards the end of the acquisition window. An MR image can then be reconstructed with data acquired from each of the acquisitions that reduce ghosting and artifacts. Volume images of the heart can be produced within a single breath-hold. Images can be acquired throughout the cardiac cycle to measure ventricular volumes and ejection fractions. Single phase volume acquisitions can also be performed to assess myocardial infarction.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
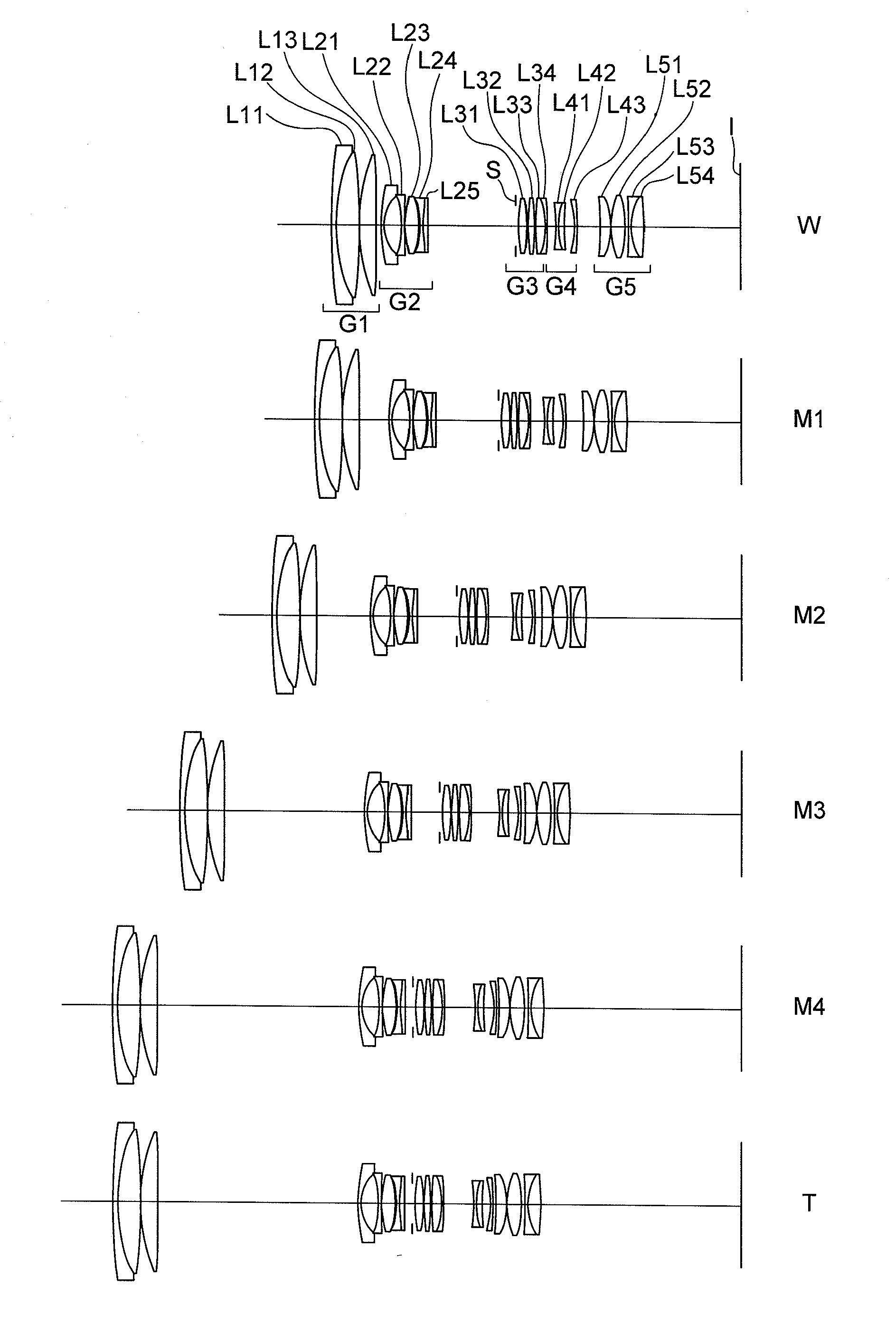
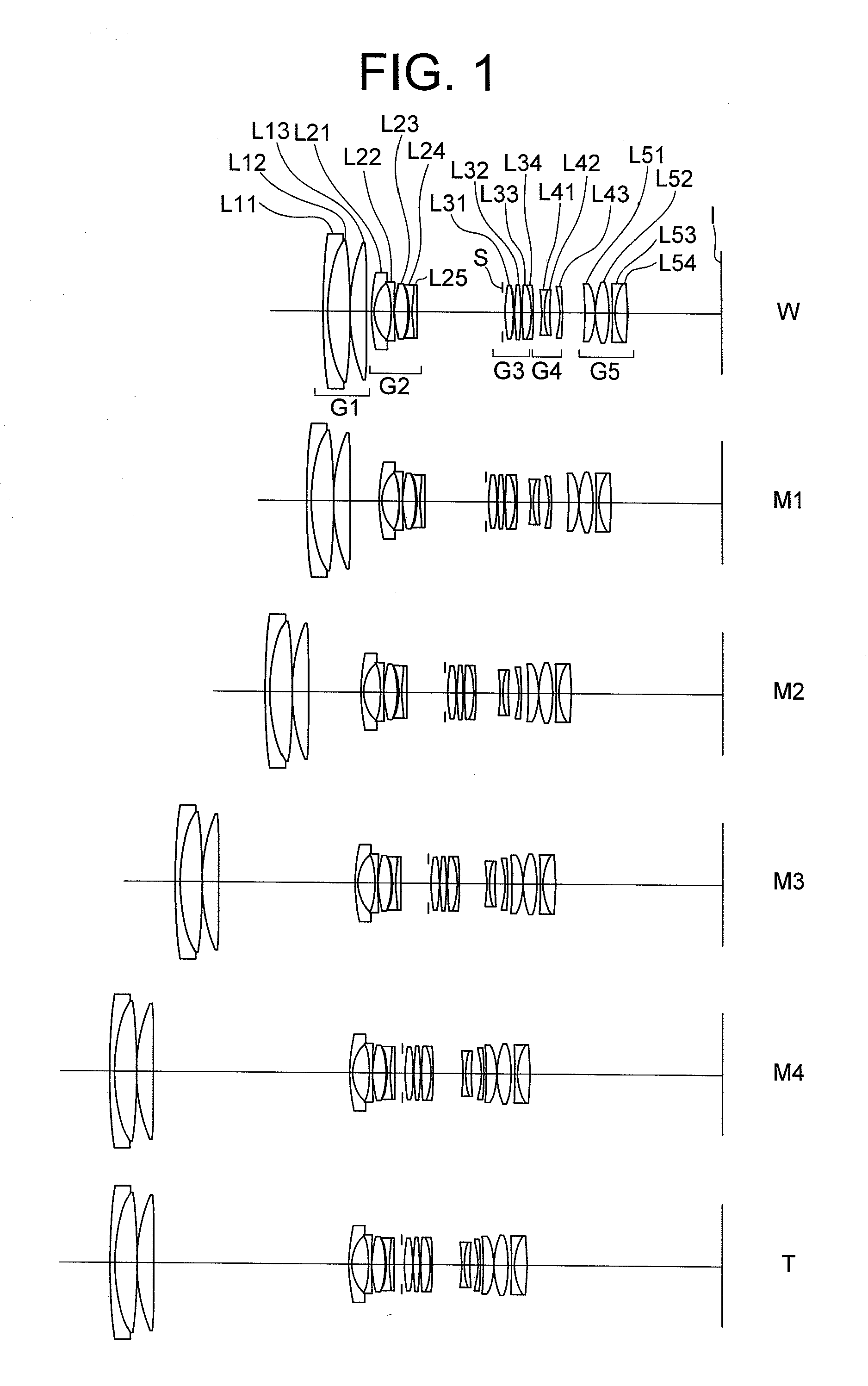
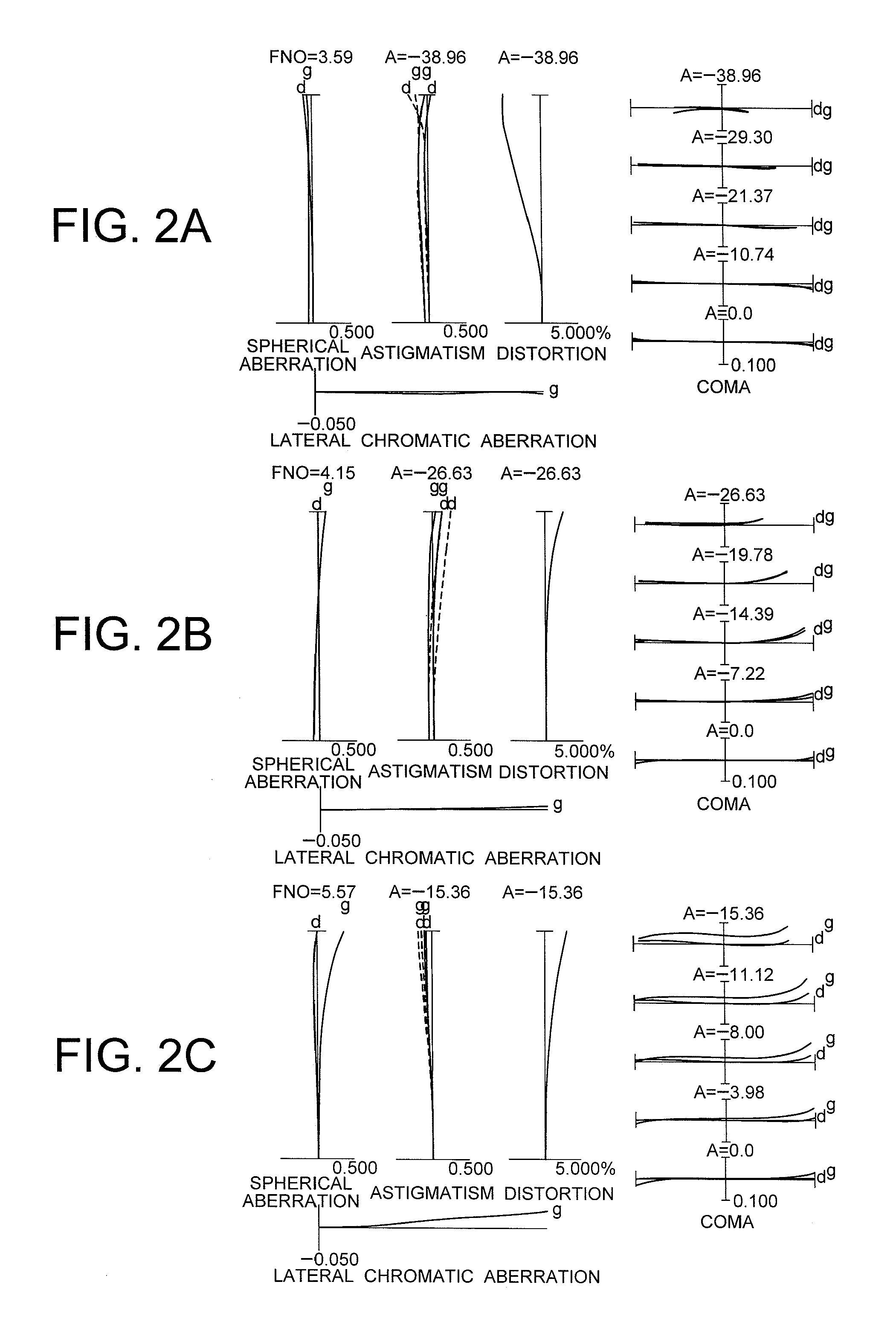
Zoom lens system, optical apparatus and method for manufacturing zoom lens system
ActiveUS20110273776A1Good optical performanceSuppress mutationCoatingsSpecial surfacesNegative powerOptoelectronics
Including, in order from an object side: a first lens group G1 having positive power; a second lens group G2 having negative power; a third lens group G3 having positive power; a fourth lens group G4 having negative power; and a fifth group G5 having positive power, an aperture stop being disposed to an image side of the second lens group, upon zooming from a wide-angle end state to a telephoto end state, a distance between the first lens group G1 and the second lens group G2 increasing, a distance between the second lens group G2 and the third lens group G3 decreasing, a distance between the third lens group G3 and the fourth lens group G4 varying, and a distance between the fourth lens group G4 and the fifth lens group G5 varying, and given conditionals being satisfied, thereby providing a zoom lens system having high optical performance with suppressing variation in aberrations, an optical apparatus equipped therewith, and a method for manufacturing the zoom lens system.
Owner:NIKON CORP
Aperture board
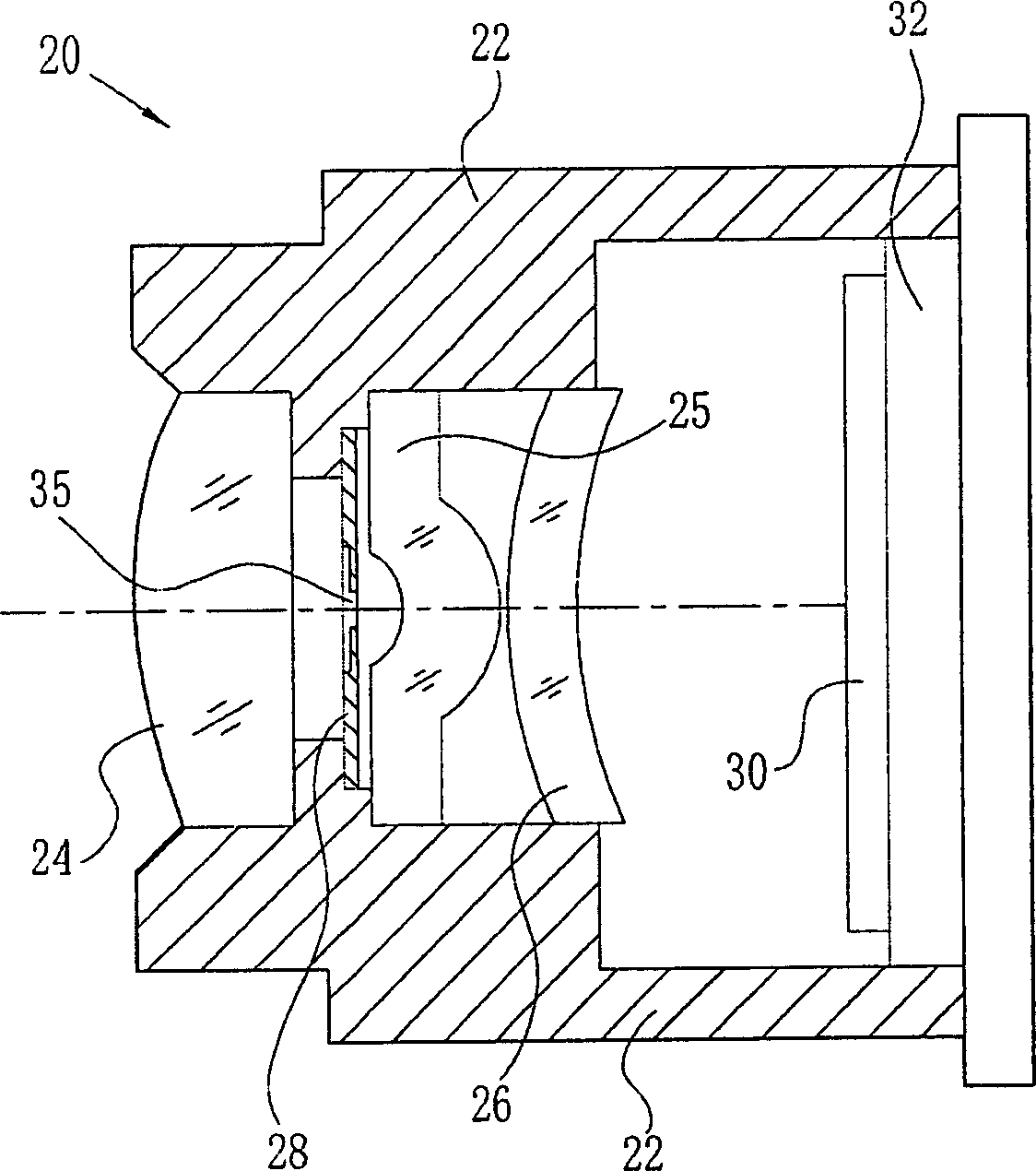
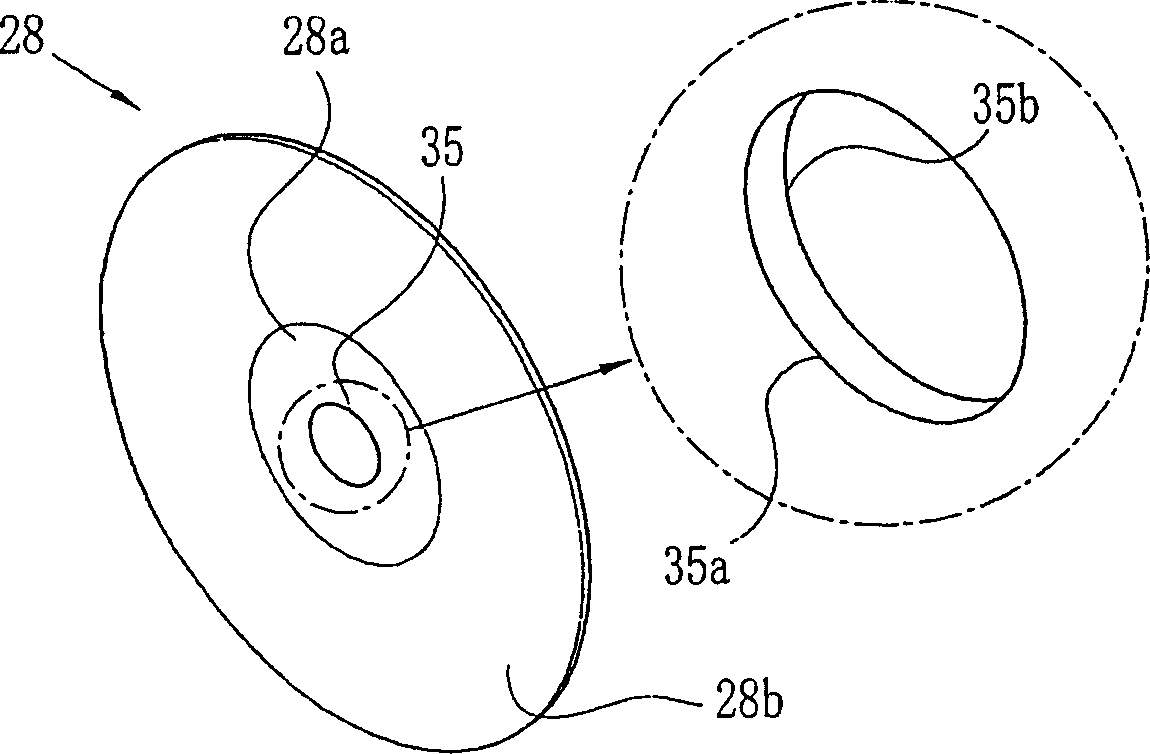
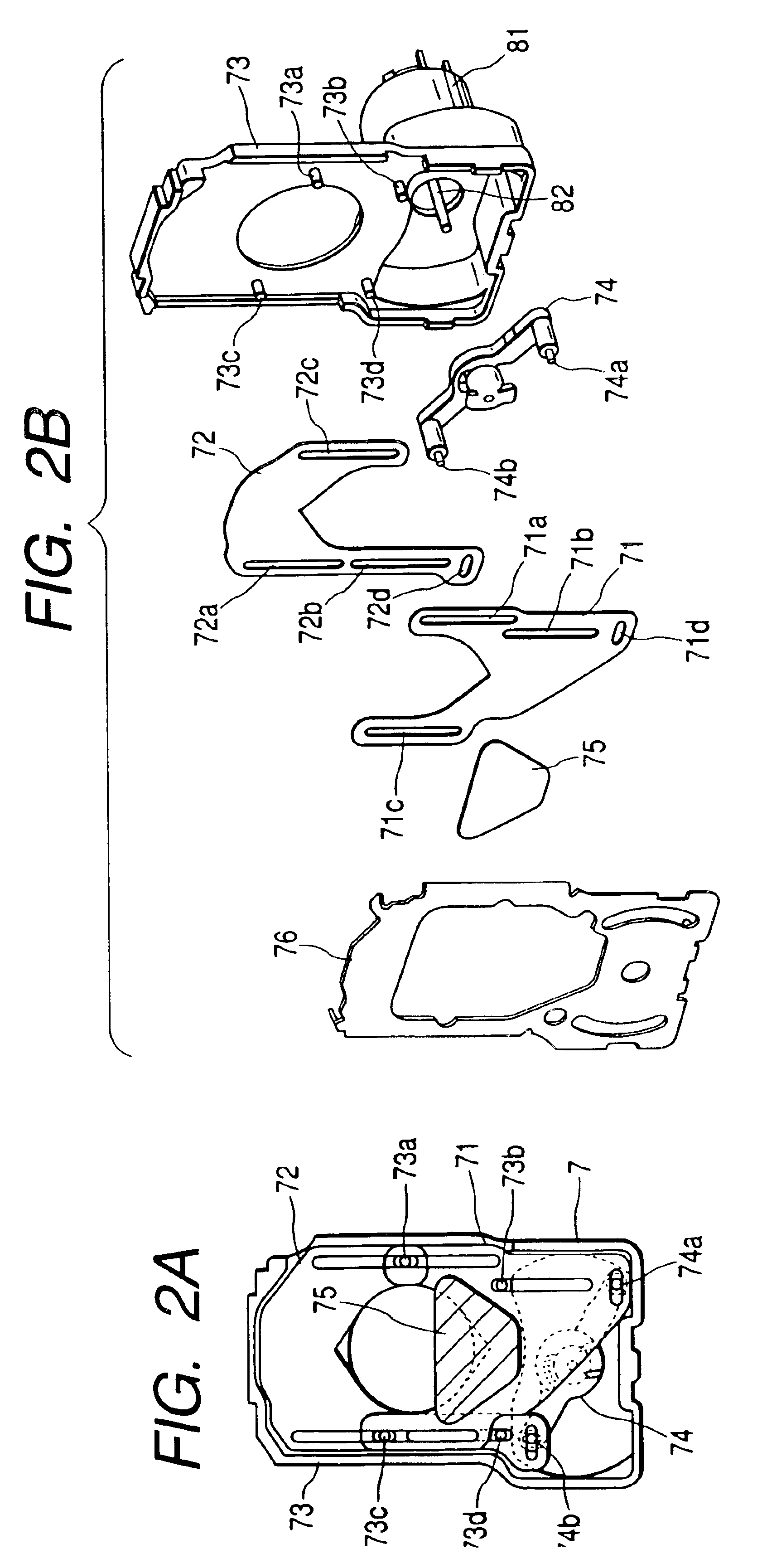
To provide a diaphragm plate which has sufficient strength and doesn't transmit light and suppresses the occurrence of flare and ghost. A diaphragm plate 28 is made of, for example, phosphor bronze or stainless steel. The diaphragm plate 28 comprises a first tabular portion 28a having a diaphragm aperture 35 formed therein and a second tabular portion 28b formed surrounding the periphery of the first tabular portion 28a. The first tabular portion 28a is made thinner than the second tabular portion 28b. An entrance peripheral portion 35d and an exit peripheral portion 25e are formed in an inner peripheral surface 35c of the diaphragm aperture 35. The entrance peripheral portion 35d and the exit peripheral portion 25e are formed circularly. Therefore, the diameter of the diaphragm aperture 35 is made gradually larger according as going toward an entrance 35a and an exit 35b. The inner peripheral surface 35c is coated with a paint preventing reflection of light.
Owner:FUJI PHOTO OPTICAL CO LTD
Transparent display panel and transparent display device
ActiveCN109448575AReduced diffractionReduce ghostingSolid-state devicesNon-linear opticsLight diffractionTransparent display
The invention provides a transparent display panel and a transparent display device. The transparent display panel comprises a plurality of display areas arrayed along a first direction and a second direction. Each display area comprises a non-transparent area, a first transparent area and a second transparent area, wherein the non-transparent area and the first transparent area are sequentially arrayed along the first direction, and the non-transparent area and the second transparent area are sequentially arrayed along the second direction. In the multiple display areas arrayed along the first direction, lengths of the display areas in the first direction are in aperiodic variation, and / or in the multiple display areas arrayed along the second direction, the first transparent areas of anytwo adjacent display areas are staggered along the first direction. Therefore, light diffraction can be eliminated or weakened, image ghosting can be eliminated or abated, image display definition can be improved, and user experience is optimized.
Owner:SHANGHAI TIANMA MICRO ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Facial expression synthetic method based on rapid expression information extraction and Poisson image fusion
InactiveCN106056650ASmall sample sizeOvercome the disadvantage of requiring a large number of training samples to get the average expression shape under each expressionImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionSynthesis methods
The present invention discloses a facial expression synthetic method based on rapid expression information extraction and Poisson image fusion. The method mainly solves the problem in the prior art that the expression detail information can not be extracted rapidly and effectively and can not be synthesized to a target face, and comprises the realization steps of 1) obtaining a corresponding expression template according top the face characteristic point data; 2) according to an expression shape template of a target object, deforming a neutral expression image of the target object and a non-neutral expression image of a source object to the non-neutral expression shapes of the target object; 3) extracting the deformed expression detail information of a figure expression image block in a frequency domain; 4) using a Poisson image fusion method to filter the extracted expression details of the source object; 5) using the Poisson image fusion method to synthesize the filtered expression detail information to the deformation expression of the target object to thereby obtain a final synthesis result. The facial expression synthetic method of the present invention is small in needed sample capacity and natural and vivid in synthesis result, and can be used for the figure animation rendering, the video conference and the man-machine interaction.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Optical apparatus
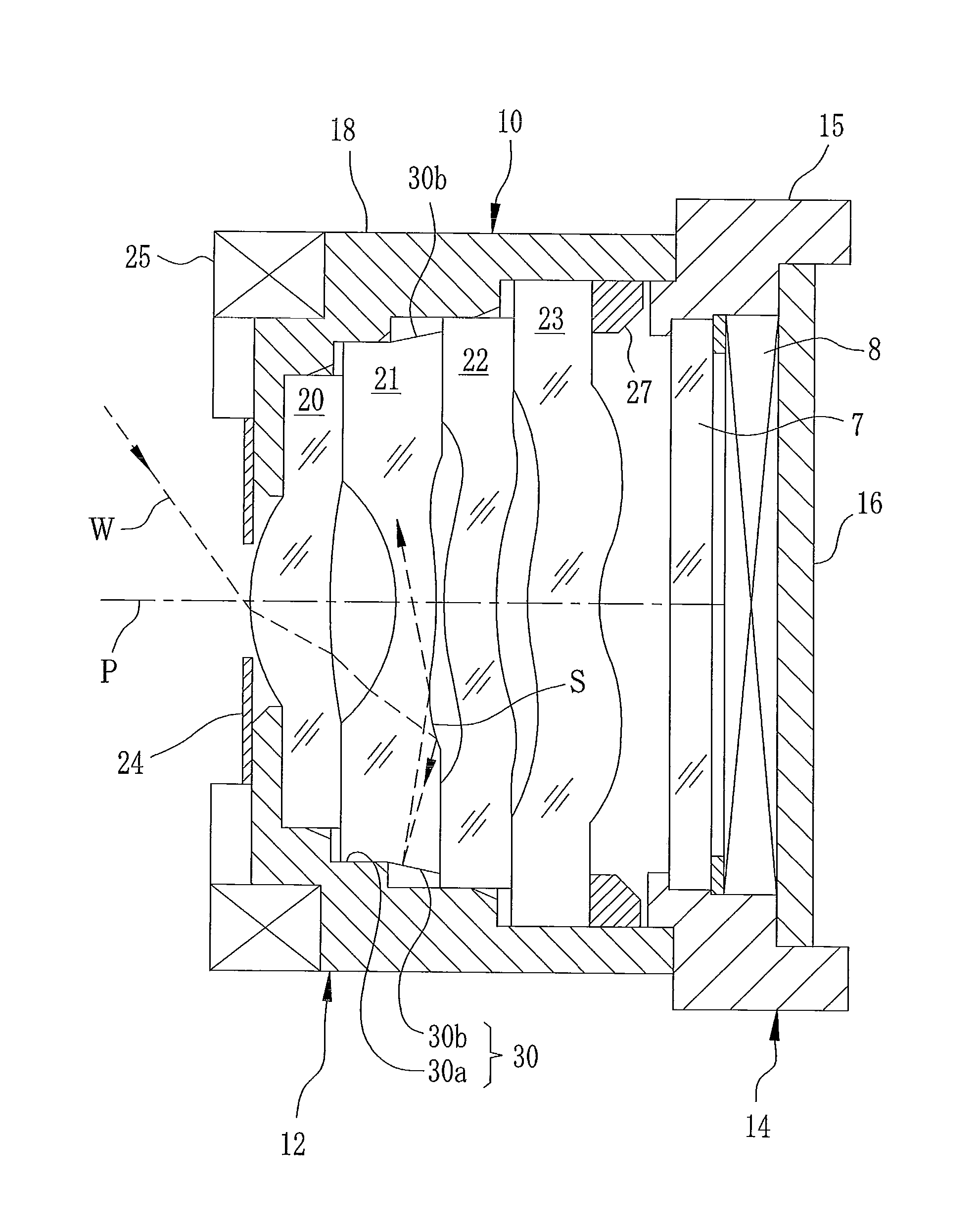
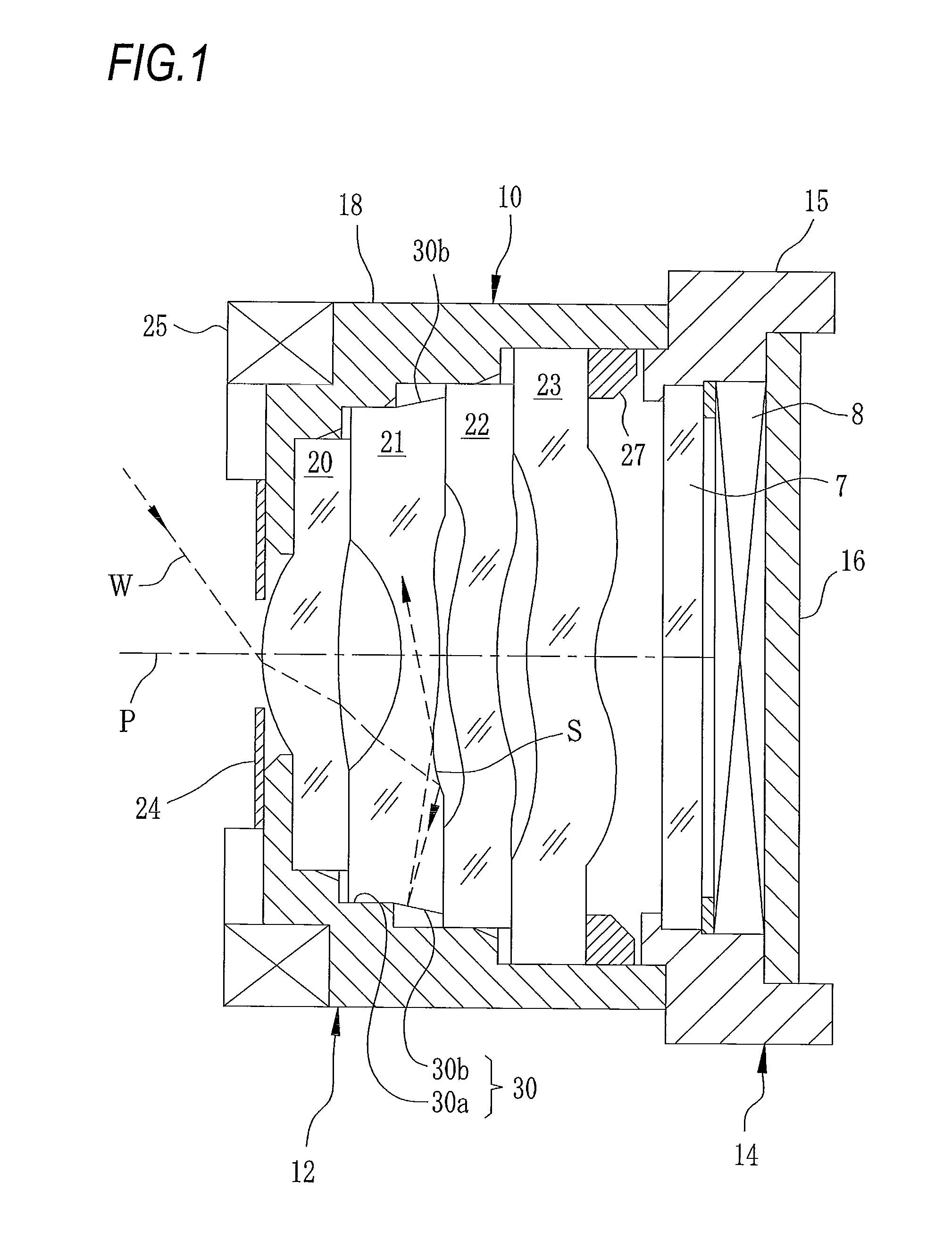
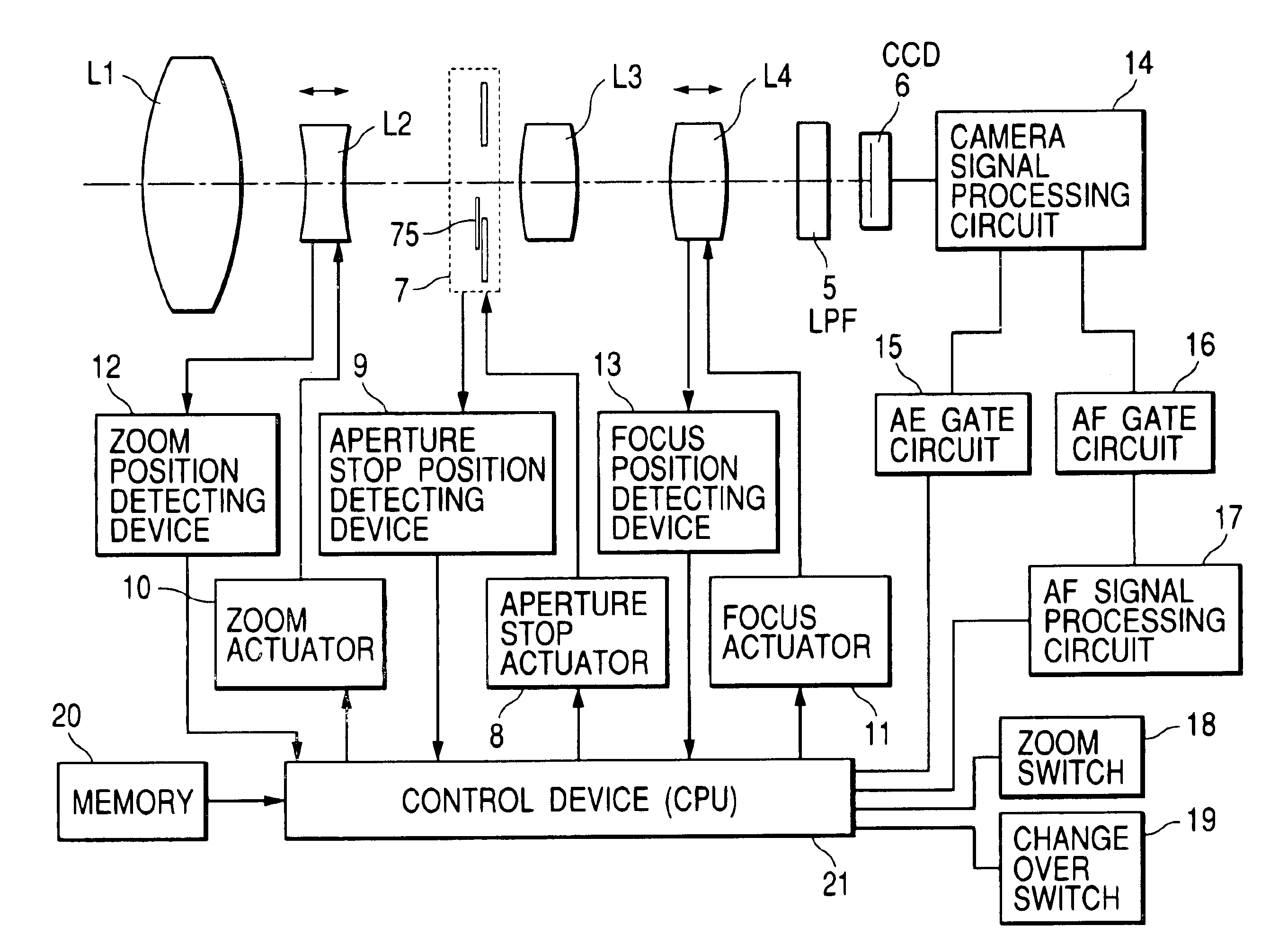
InactiveUS6924941B2Reduce thicknessReduce ghostingTelevision system detailsColor television detailsCamera lensOptical axis
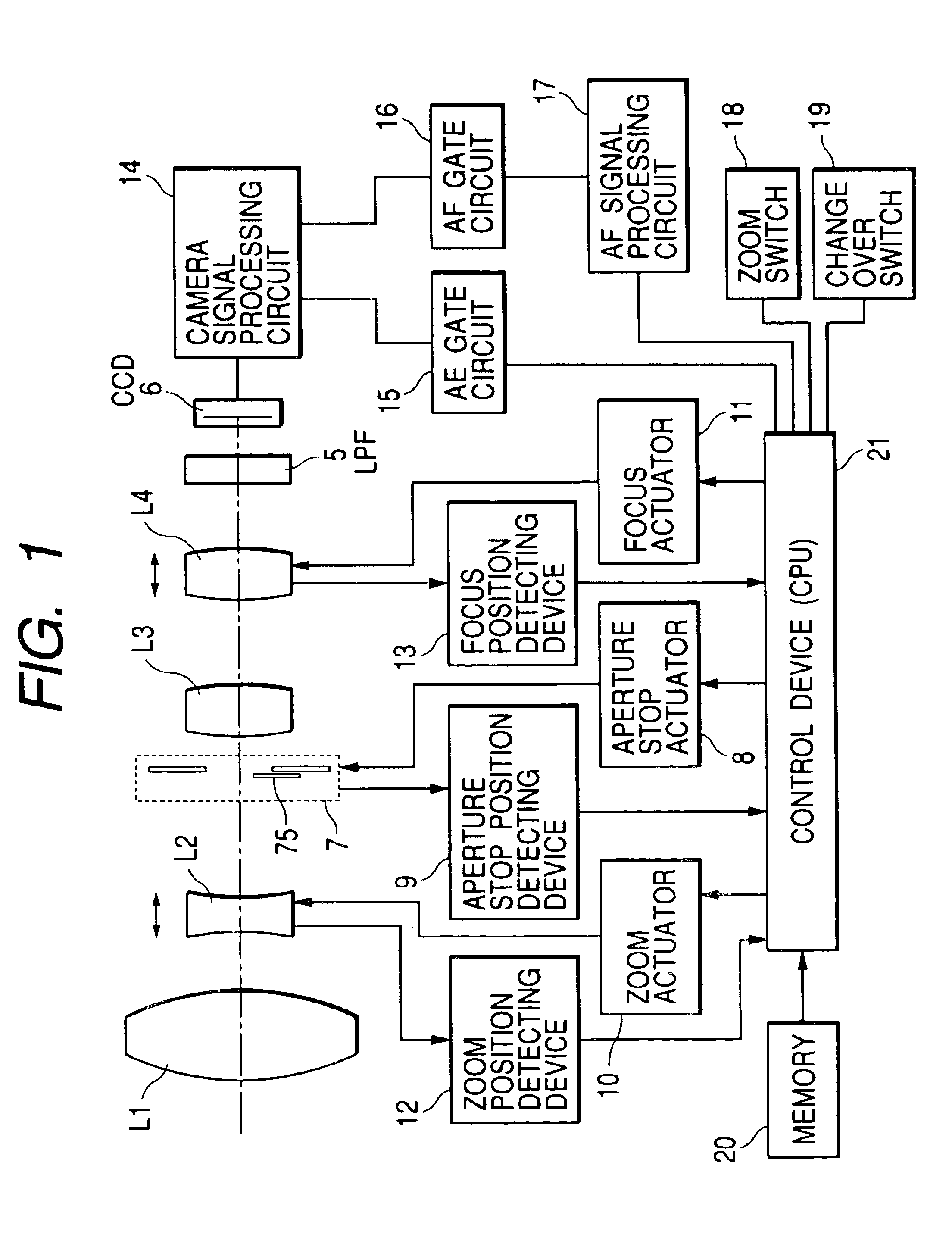
An optical apparatus is disclosed which comprises an optical system provided with a zoom lens for performing zooming by moving along the optical axis and a focus lens for performing correction and focusing at the time of zooming, an imaging device for imaging an optical image supplied from the optical system, a zoom actuator for driving the zoom lens, a focus actuator for driving the focus lens, a zoom position detecting device for detecting the position of the zoom lens, a focus position detecting device for detecting the position of the focus lens, an aperture stop member whose opening diameter changes so as to adjust the luminous energy passing through the optical system a filter member to be freely inserted into or extracted from the optical path of the optical system, an aperture stop state detecting device for detecting the opening state of the aperture stop member, a filter state detecting device for detecting the insertion state of the filter member, a memory storing the movement information on the relation between the position of the zoom lens for keeping a focused state and the position of the focus lens, and a control device for correcting the movement information in accordance with an output of the aperture stop state detecting device and an output of the filer state detecting device and controlling driving of the focus lens.
Owner:CANON KK
Display device
InactiveCN102809846APreventing Image Quality DeteriorationImprove image qualitySolid-state devicesNon-linear opticsColor shiftDisplay device
A display device that can reduce color shift and prevent the quality of an image from degrading due to Moire. The display device includes a display panel and an optical film, which includes a background layer disposed in front of the display panel, and a lens section formed on the background layer. The lens section has a plurality of patterns spaced apart from each other to diffuse incident light. The spacing [tau] and pitch T of the patterns are determined by the following m value in the following formulae, and m = P / T, p / P is an aperture ratio of sub-pixels of the display panel, [tau] / T is an aperture ratio of the lens section, I is an intensity of light exiting the optical film after being diffused through the sub-pixels, P and p are a pitch and a width of the sub-pixels, T is a pitch of the patterns, and [tau]=T-W.
Owner:SAMSUNG CORNING PRECISION MATERIALS CO LTD
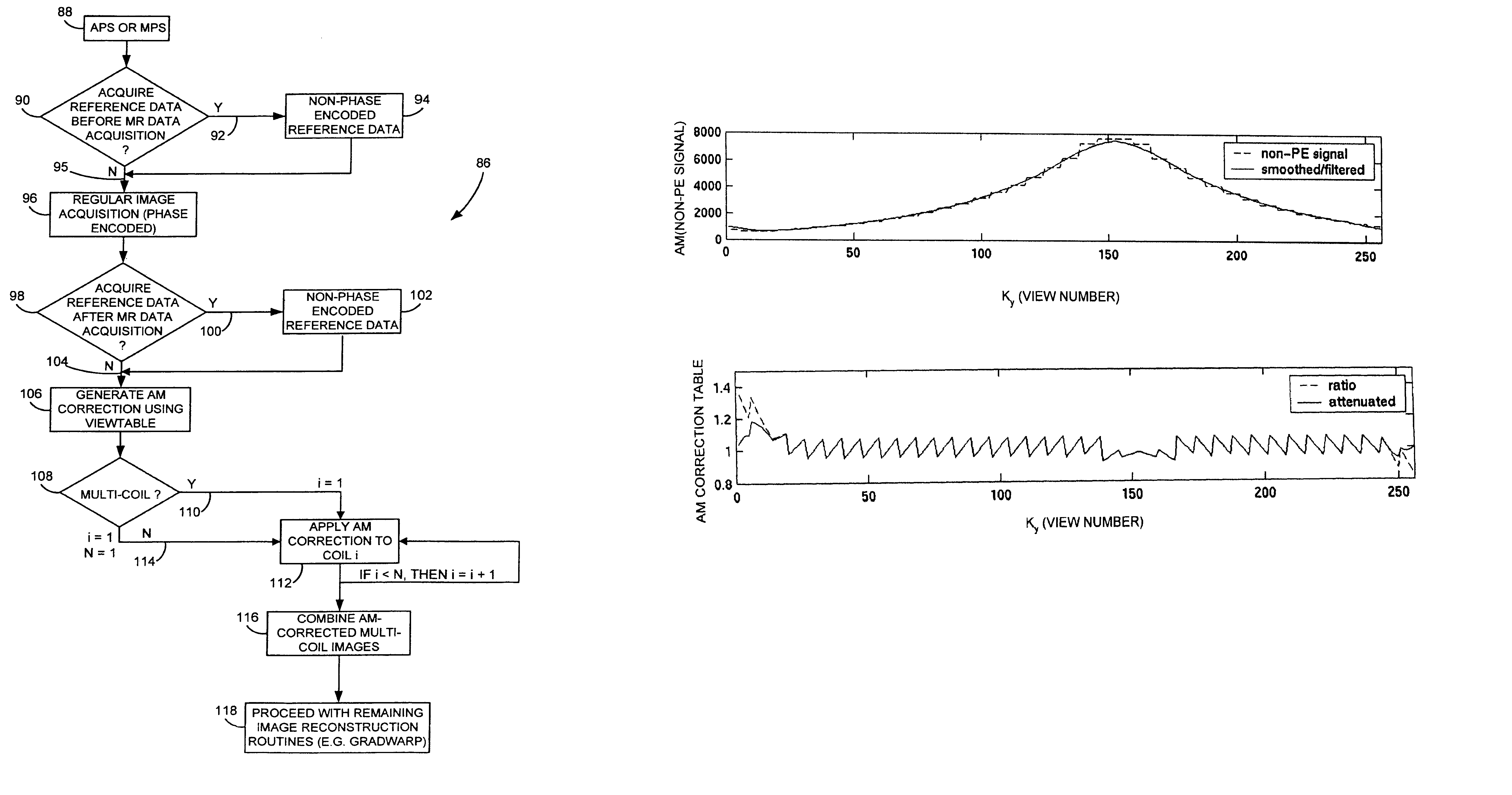
Method and apparatus to correct amplitude modulation in multi-echo magnetic resonance imaging
ActiveUS7075299B1Reduce ghostingImprove image qualityElectrocardiographyMagnetic measurementsStimulated echoImaging quality
An imaging technique is disclosed for multi-echo, magnetic resonance imaging that addresses amplitude modulations, such as those caused by T2 decay and stimulated echo refocusing, in acquired MR data. Acquired MR data is corrected by non-phase encoded data such that amplitude modulations in the echo signal are addressed. Reducing the effects of amplitude modulations in the echo signal reduces ghosting and thereby improves image quality.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Solid-state imaging device, method of manufacturing solid-state imaging device, and electronic apparatus
ActiveCN102446937AReduce ghostingHigh quality imagingTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesOrganic filmImaging quality
The invention discloses a solid-state imaging device, a method of manufacturing the solid-state imaging device, and an electronic apparatus. The solid-state imaging device includes a plurality of pixels formed on a semiconductor substrate and include a photoelectric conversion unit; a color filter on the pixels; an on-chip microlens made of an organic film on the color filter, corresponding to each of the pixels; a first inorganic film formed on a surface of the on-chip microlens and having a higher refraction index than the on-chip microlens; and a second inorganic film formed on a surface of the first inorganic film and having a lower refraction index than the on-chip microlens and the first inorganic film, in which at least the second inorganic film includes a non-lens area at an interface of an adjacent second inorganic film. The solid-state imaging device, the method of manufacturing the solid-state imaging device, and the electronic apparatus can improve image quality and sensitivity characteristic.
Owner:SONY SEMICON SOLUTIONS CORP
Inorganic, Dielectric, Grid Polarizer and Non-Zero Order Diffraction Grating
InactiveUS20070165307A1Save spaceEasy to manufacturePolarising elementsDiffraction gratingsDielectricPolarizer
An inorganic, dielectric grid polarizer includes an optical stack with a diffraction grating and an inorganic, dielectric grid polarizer. The inorganic, dielectric grid polarizer includes a stack of film layers with an array of parallel ribs in accordance with PGP<λ / 2 where PGP is the period of the ribs and λ is the wavelength of the light. The diffraction grating includes an array of elongated parallel dielectric ribs in accordance with PDG>λ / 2 where PDG is the period of the ribs.
Owner:MOXTEK INC
Variable transmittance element, optical system, and optical apparatus utilizing electrochromic material
ActiveUS20130094073A1Improve color balanceReduce ghostingNon-linear opticsTransmittanceRefractive index
A variable transmittance element includes two substrates, two transparent electrode layers held between the two substrates, an electrochromic layer held between the two transparent electrode layers and having transmittance that is reversibly changed by electric control, and a first dielectric layer provided between one of the two substrates and one of the two transparent electrode layers closest to the one of the two substrates and configured to reduce reflections. The first dielectric layer is a multilayer film made by alternately laminating two or more layers each having a high refractive index and two or more layers each having a low refractive index, a refractive index difference for a wavelength of 550 nm between the layer having the high refractive index and the layer having the low refractive index being 0.2 or more.
Owner:CANON KK
Image capture lens module and wafer level packaged image capture devices
ActiveUS20120218648A1Reduce ghostingIncrease the areaSolid-state devicesLensOptoelectronicsImage capture
Image capture lens modules and wafer level packaged image capture devices are presented. The image capture lens module includes a compound lens with a first lens element and a second lens element molded on both sides of a substrate, and a field stop disposed at an interface between the first lens element and the substrate or at an interface between the second lens element and the substrate, wherein the field stop is a coating layer with a polygonal transparent area.
Owner:VISERA TECH CO LTD +1
Spectral imaging apparatus and methodology
InactiveUS20060250616A1Enhanced efficiencyDecrease ghostRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometrySpectral imagingScattered light
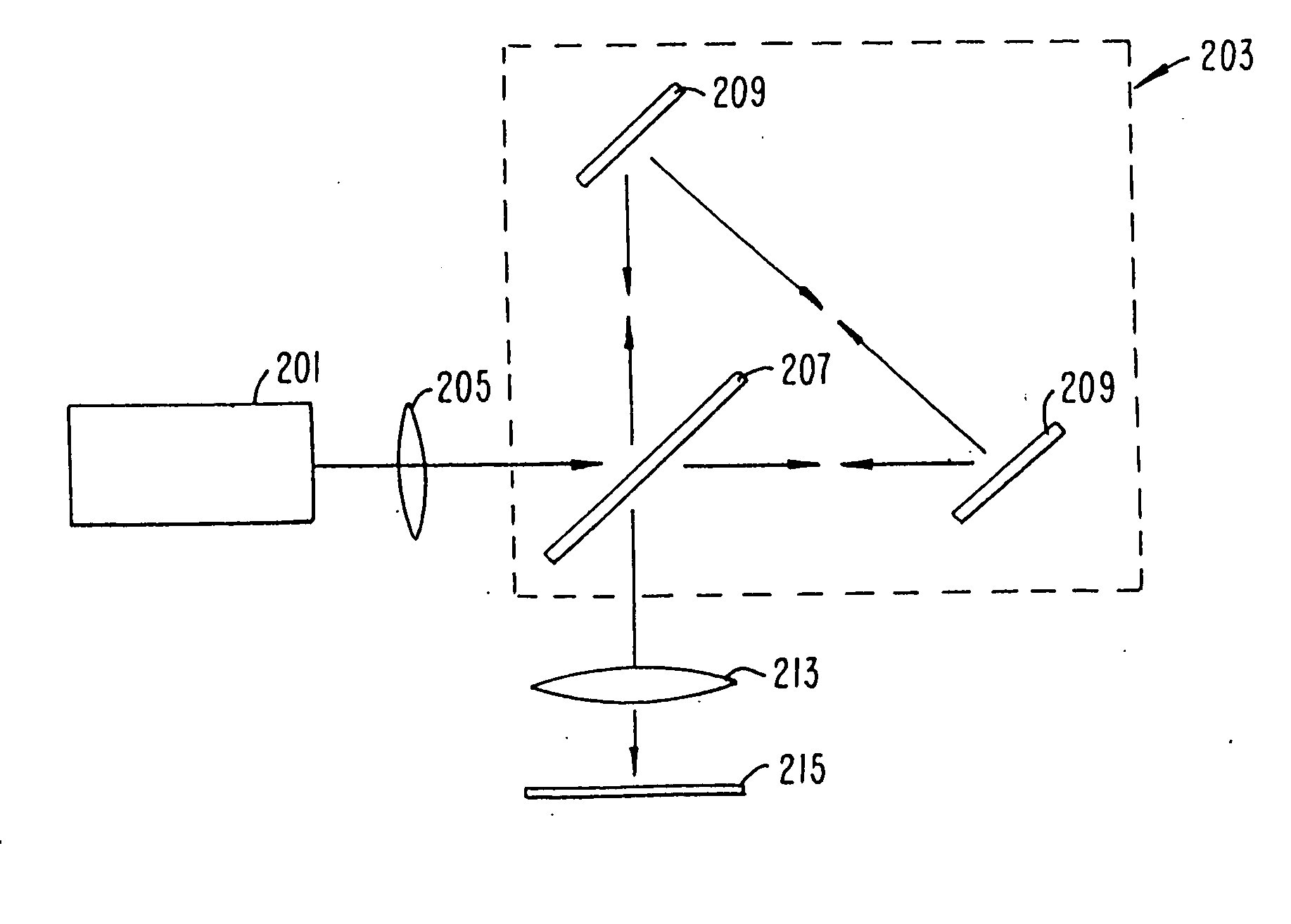
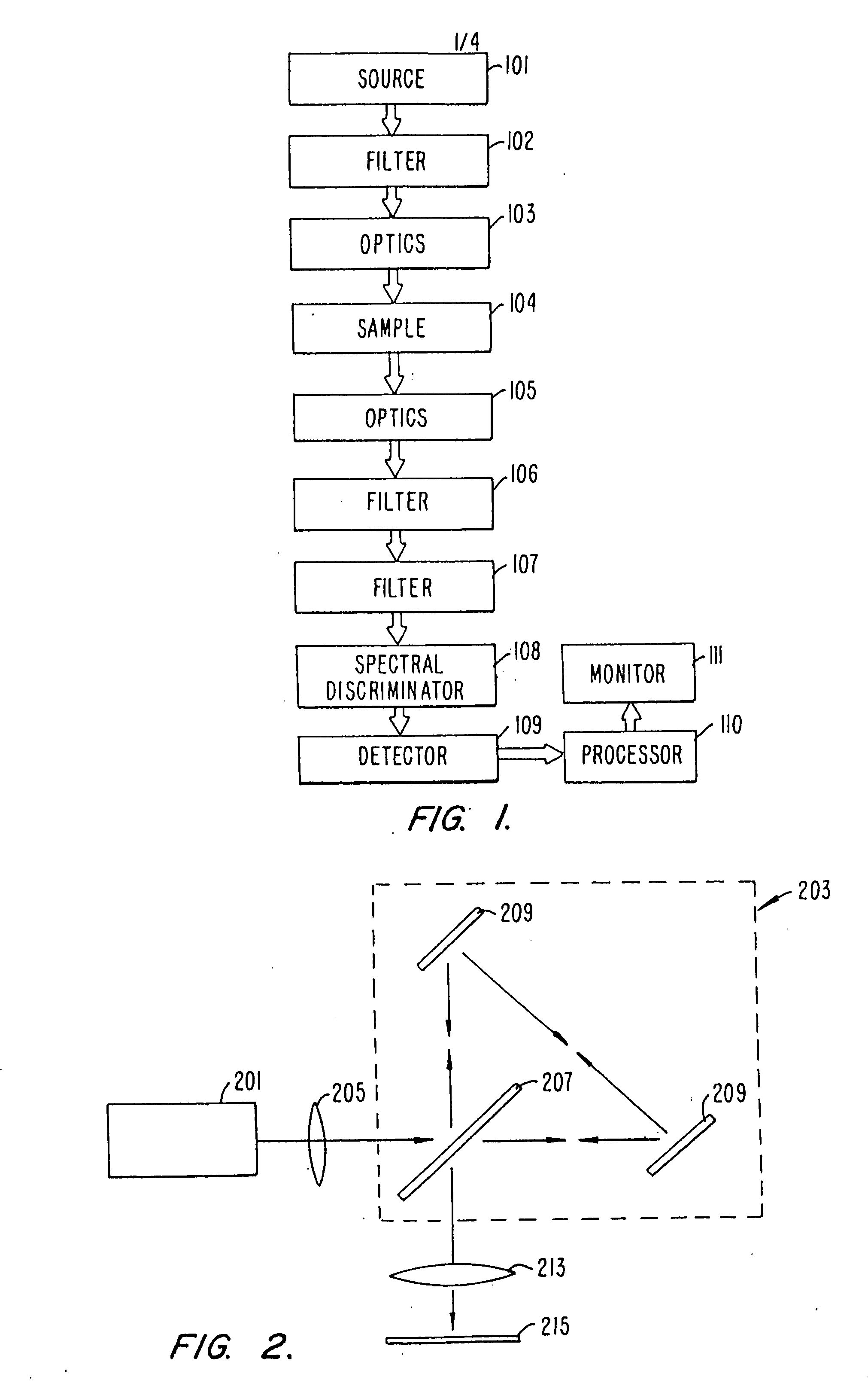
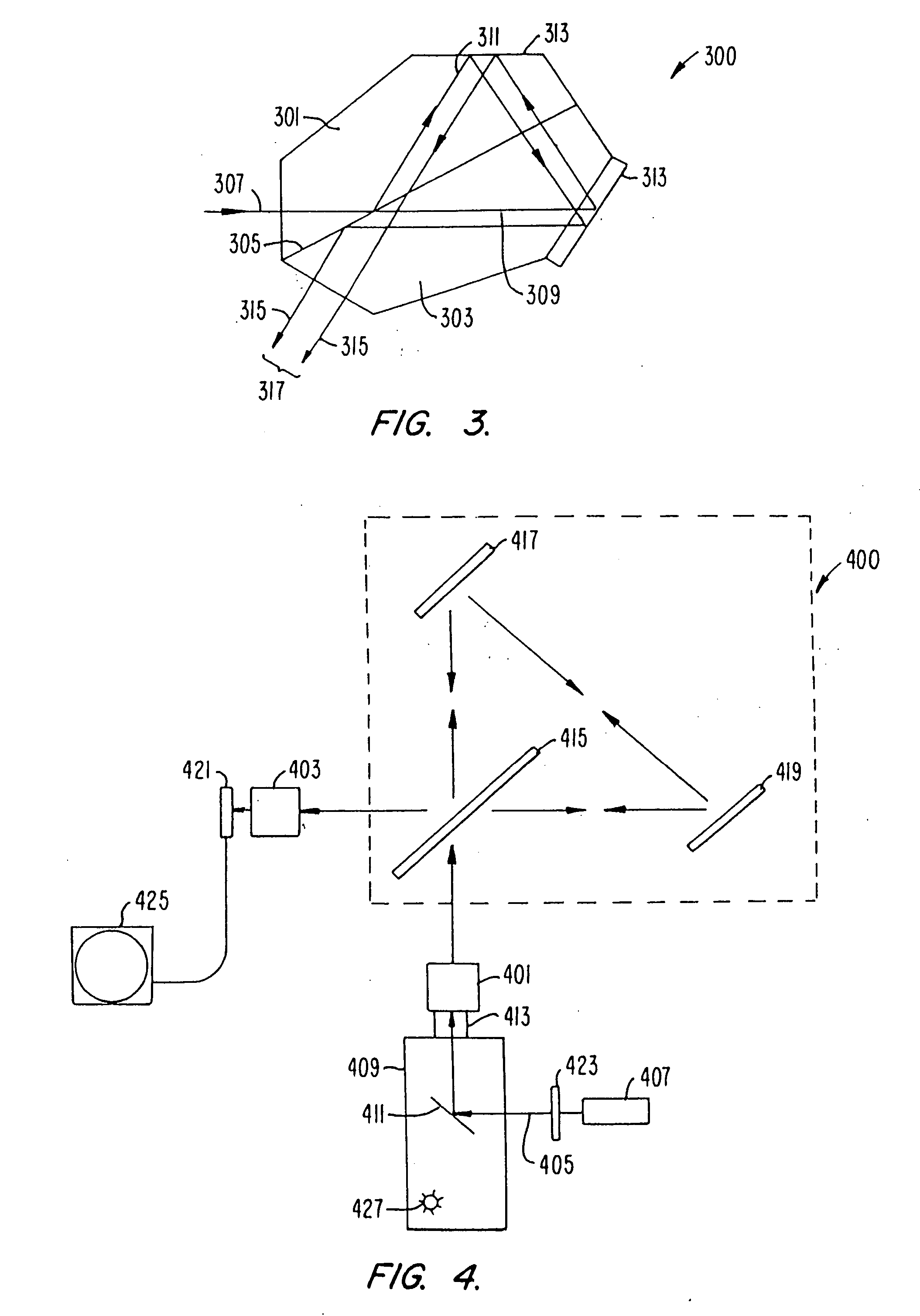
A method and apparatus for an improved spectral imaging system is provided. The system is capable of measuring the fluorescence, luminescence, or absorption at selected locations on a sample plate. The emissions detection subassembly can tune to any wavelength within a continuum of wavelengths utilizing an interferometric spectral discriminator. The interferometric spectral discriminator creates an interferogram from which the wavelength spectra for each pixel of the array can be calculated, typically using Fourier transform analysis. In one aspect, the chromatic accuracy of the system is calibrated using a calibration slit placed in the input aperture of the input relay lens but outside of the sample image. The slit is illuminated using a source of known wavelength. The fringe count versus the wavelength of the slit illumination source is monitored and used to calibrate the spectral discriminator. In another aspect, a transparent optic is included in the interferometric spectral discriminator that can be inserted into the beam path whenever a monochrome image of the sample is required. The optic produces a large offset in the legs of the interferometer resulting in the fringe density becoming too large to resolve by the individual pixels of the detector array. In another aspect, the interferometric spectral discriminator includes a polarizing beam splitter. The polarizing beam splitter preferentially reflects one polarization while preferentially transmitting a second polarization, thus achieving improved efficiency while minimizing ghosting. In another aspect, a metaphase finder is used to locate areas of interest. The sample plate containing the material of interest is illuminated with light of a wavelength determined to preferentially scatter from objects the size of the metaphase spreads. The intensity of the scattered light versus the location on the sample plate is monitored and used to locate the areas of interest. Preferably the sample plate is also illuminated by light of a second wavelength which is not preferentially scattered by the objects of interest, thus representing the background scatter. By subtracting the background scatter from the primary scattered light, improved object discrimination is achieved.
Owner:BIO RAD LAB INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com