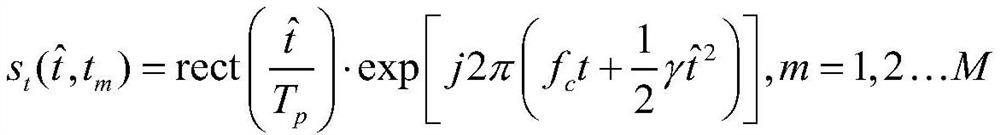Patents
Literature
41 results about "Single breath" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
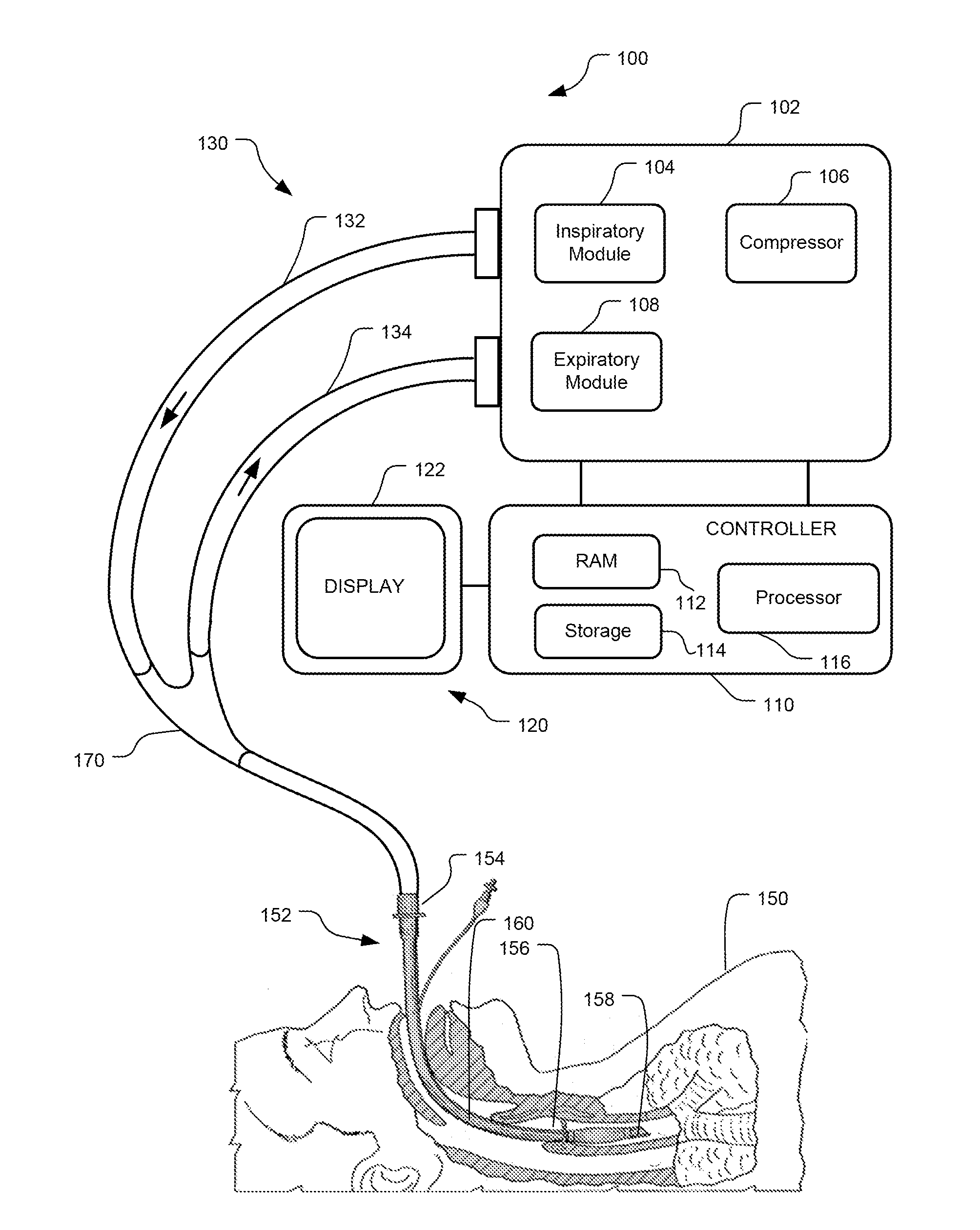
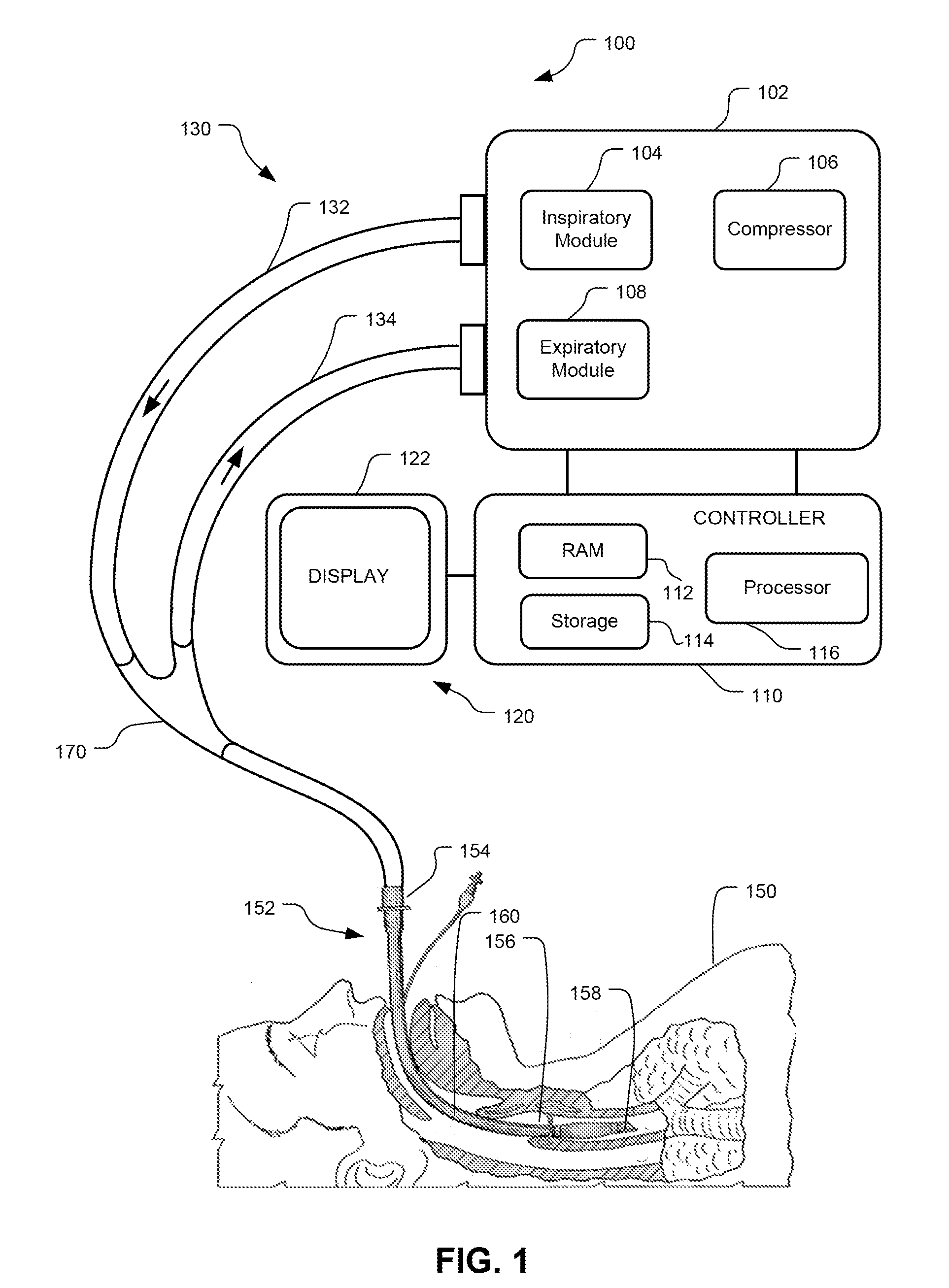
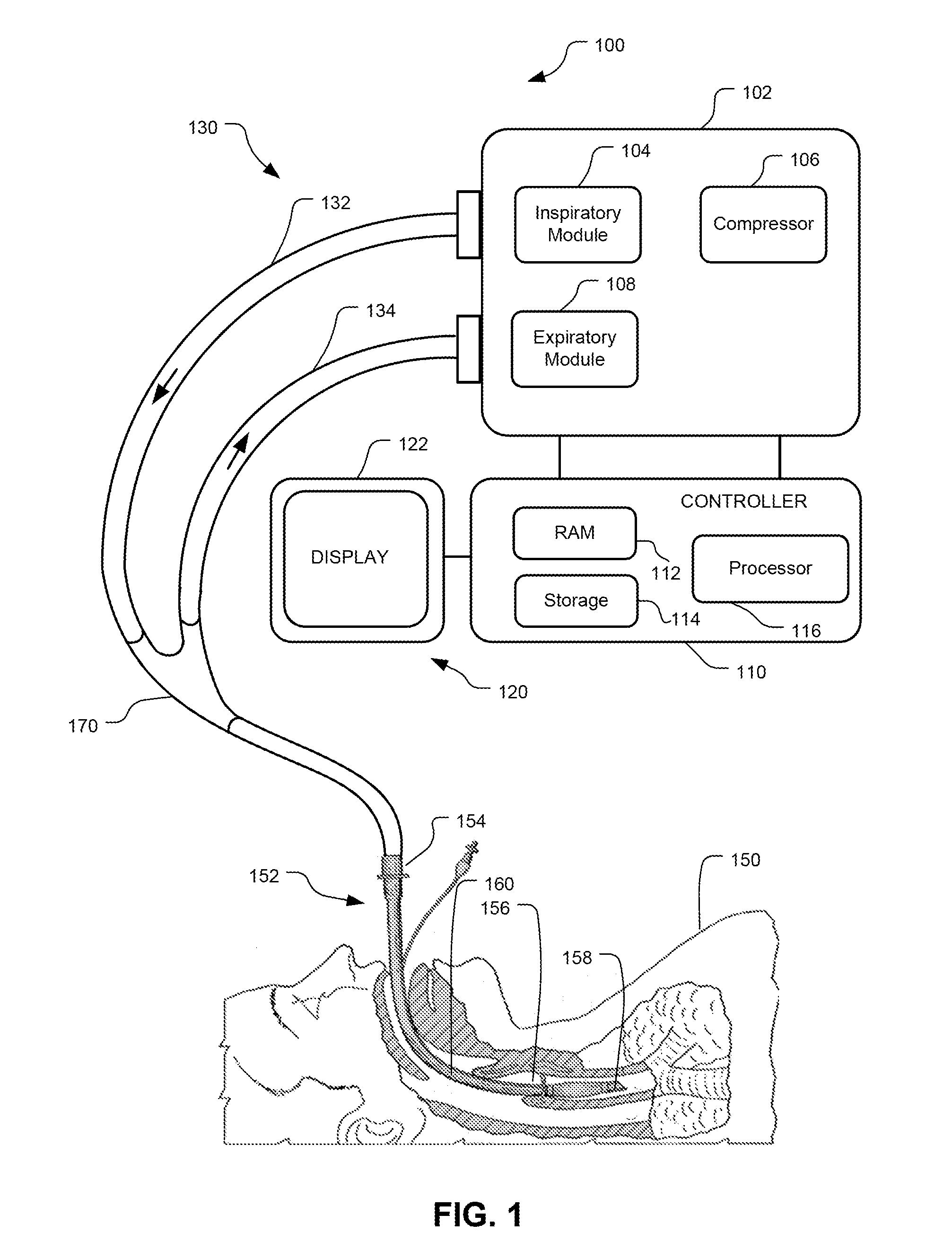
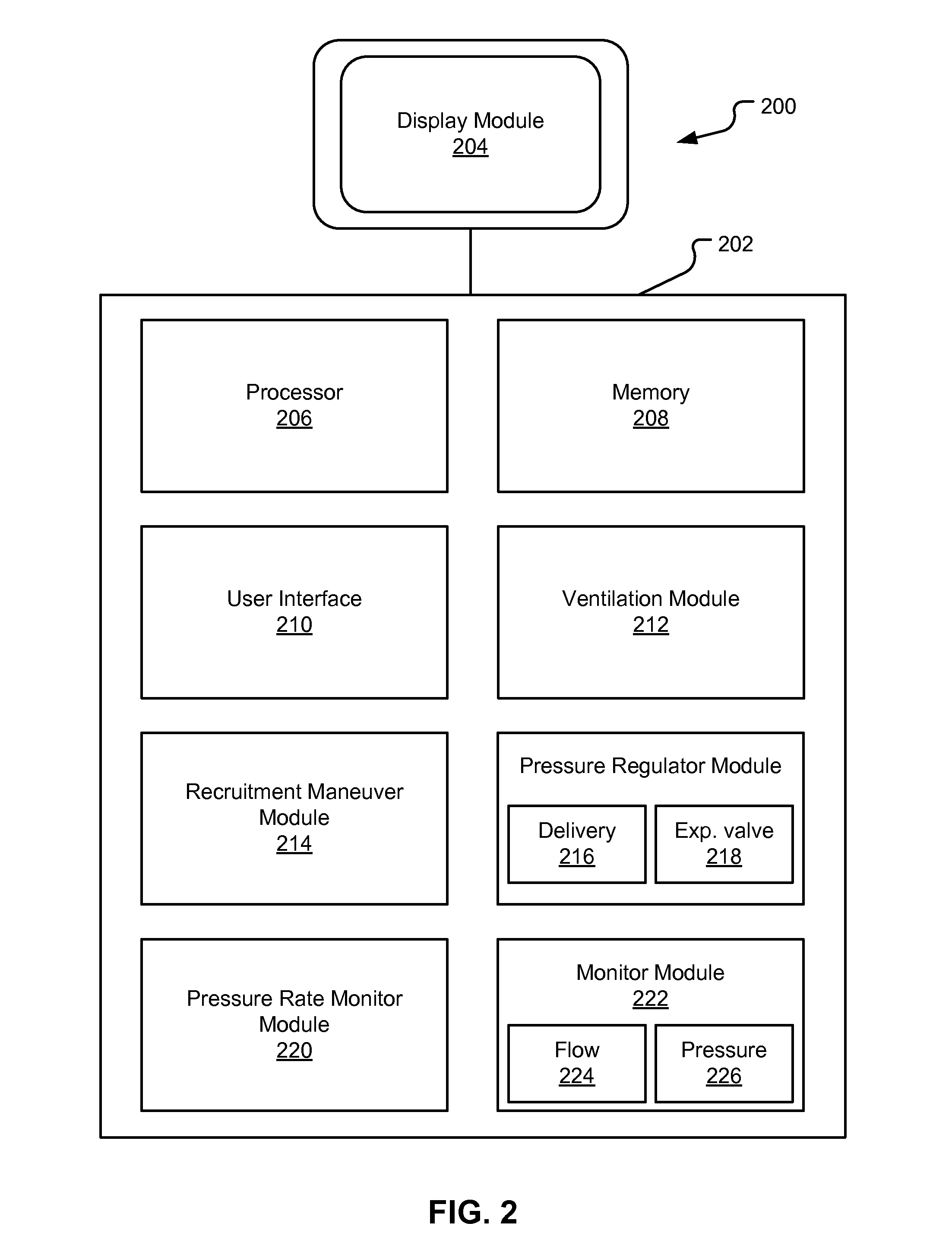
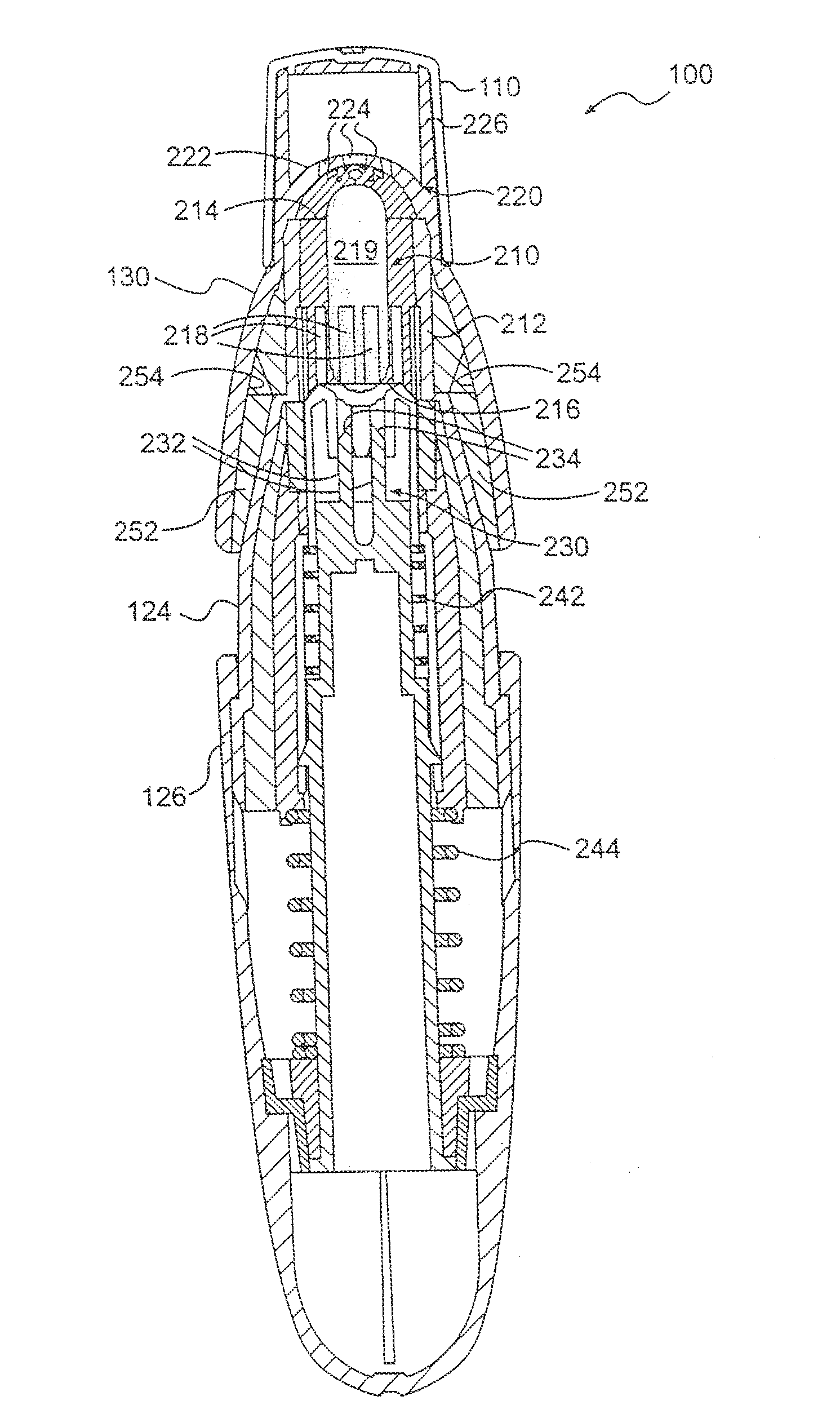
Method And System For Generating A Pressure Volume Loop Of A Low Flow Recruitment Maneuver
InactiveUS20110023881A1RespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesTraffic capacityGraphical user interface
This disclosure describes systems and methods for delivering one or more low flow recruitment maneuvers to a patient while on a ventilator. Embodiments described herein provide methods for delivering low flow recruitment maneuvers wherein either or both of the inspiratory and expiratory phases of the recruitment maneuver are maintained by the ventilator at a low flow. Embodiments described herein provide for single-breath recruitment maneuvers and multi-breath recruitment maneuvers at low flow. Embodiments described herein provide for graphical display of a pressure-volume loop (PV loop) for both single-breath and multi-breath recruitment maneuvers. Embodiments described herein also disclose an automated ventilator functionality whereby recruitment maneuvers settings and / or post-recruitment maneuver settings for resuming prescribed ventilation may be set via a graphical user interface. Other embodiments described herein enable a clinician to configure the ventilator to synchronize the end the recruitment maneuver with patient-triggered inspiration for post-recruitment maneuver ventilation.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
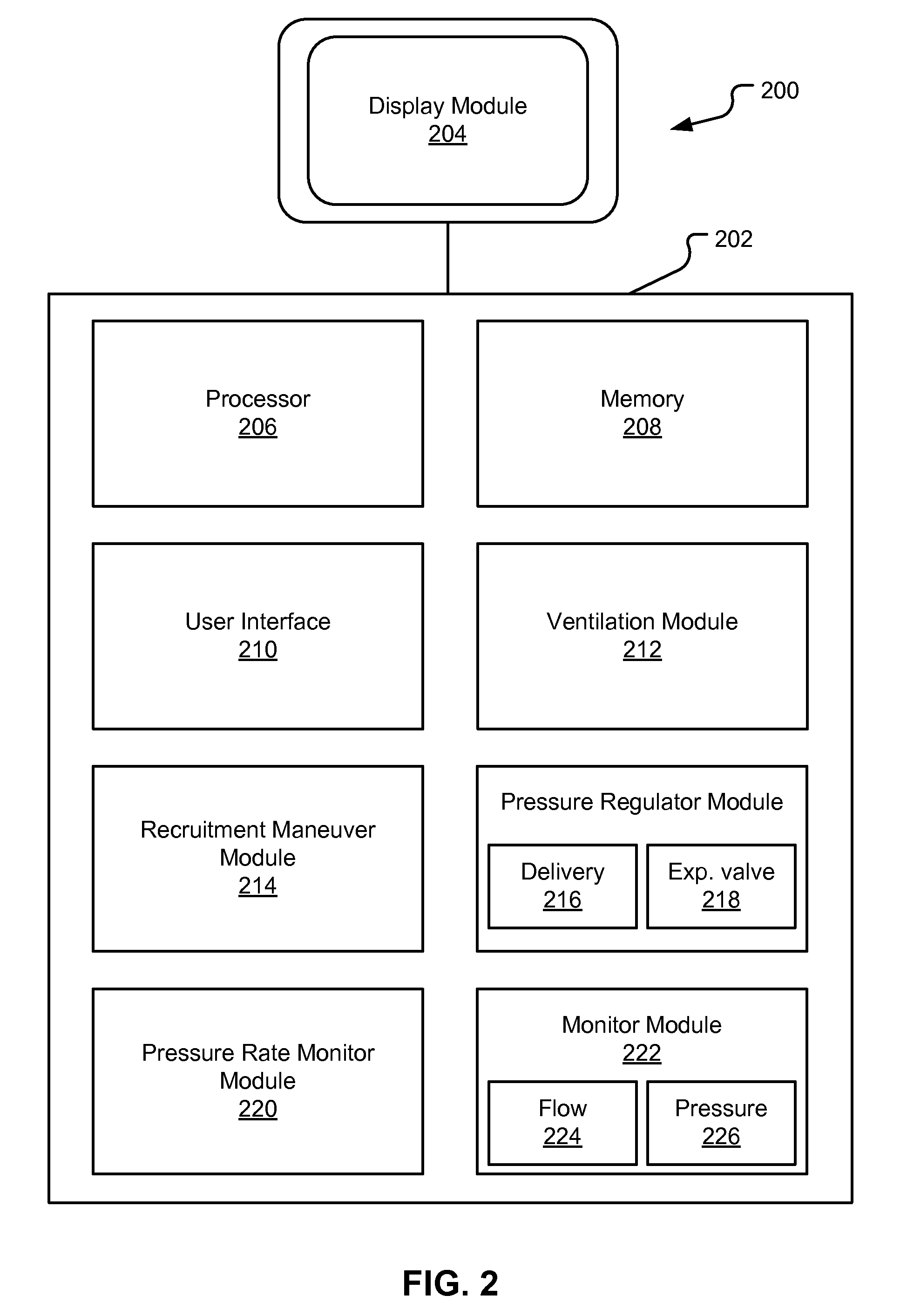
Method And System For Providing A Graphical User Interface For Delivering A Low Flow Recruitment Maneuver
This disclosure describes systems and methods for delivering one or more low flow recruitment maneuvers to a patient while on a ventilator. Embodiments described herein provide methods for delivering low flow recruitment maneuvers wherein either or both of the inspiratory and expiratory phases of the recruitment maneuver are maintained by the ventilator at a low flow. Embodiments described herein provide for single-breath recruitment maneuvers and multi-breath recruitment maneuvers at low flow. Embodiments described herein provide for graphical display of a pressure-volume loop (PV loop) for both single-breath and multi-breath recruitment maneuvers. Embodiments described herein also disclose an automated ventilator functionality whereby recruitment maneuvers settings and / or post-recruitment maneuver settings for resuming prescribed ventilation may be set via a graphical user interface. Other embodiments described herein enable a clinician to configure the ventilator to synchronize the end the recruitment maneuver with patient-triggered inspiration for post-recruitment maneuver ventilation.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
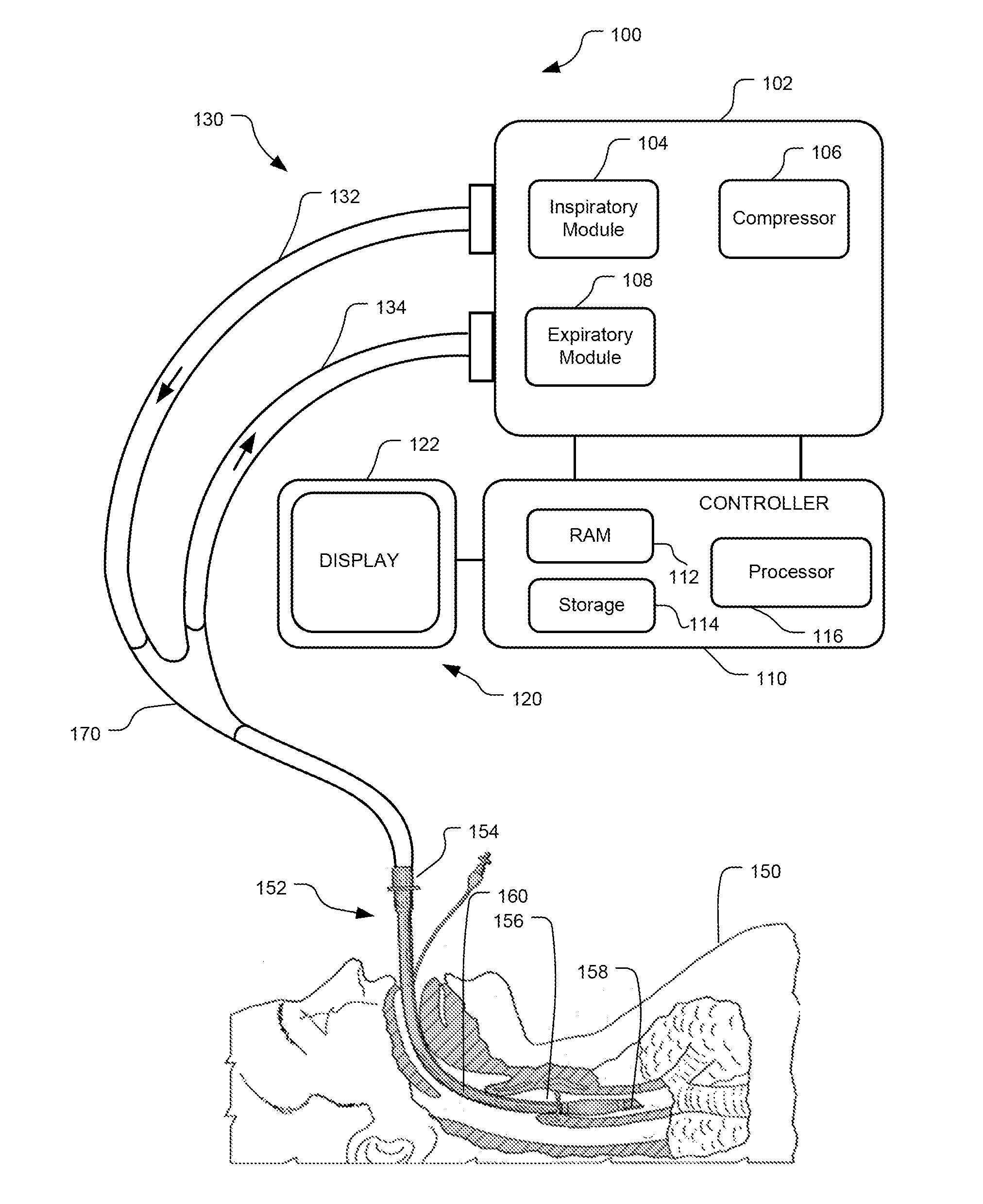
Method And System For Delivering A Multi-Breath, Low Flow Recruitment Maneuver
InactiveUS20110023880A1RespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesGraphical user interfaceEmergency medicine
This disclosure describes systems and methods for delivering one or more low flow recruitment maneuvers to a patient while on a ventilator. Embodiments described herein provide methods for delivering low flow recruitment maneuvers wherein either or both of the inspiratory and expiratory phases of the recruitment maneuver are maintained by the ventilator at a low flow. Embodiments described herein provide for single-breath recruitment maneuvers and multi-breath recruitment maneuvers at low flow. Embodiments described herein provide for graphical display of a pressure-volume loop (PV loop) for both single-breath and multi-breath recruitment maneuvers. Embodiments described herein also disclose an automated ventilator functionality whereby recruitment maneuvers settings and / or post-recruitment maneuver settings for resuming prescribed ventilation may be set via a graphical user interface. Other embodiments described herein enable a clinician to configure the ventilator to synchronize the end the recruitment maneuver with patient-triggered inspiration for post-recruitment maneuver ventilation.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
High efficient delivery of a large therapeutic mass aerosol
InactiveUS6858199B1Simple and cost-effectiveImprove efficiencyPowder deliveryLiquid surface applicatorsVolumetric Mass DensityIntensive care medicine
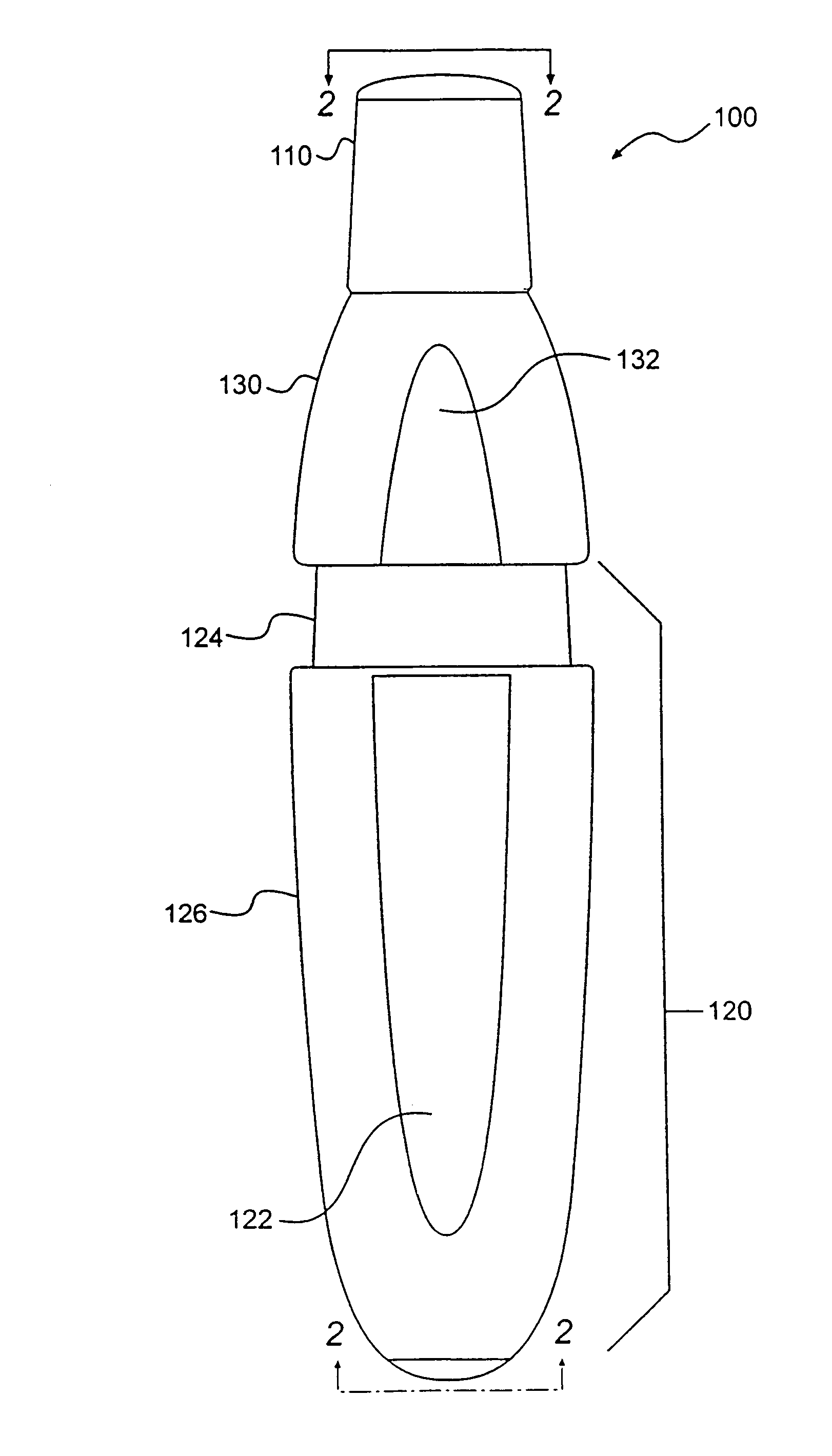
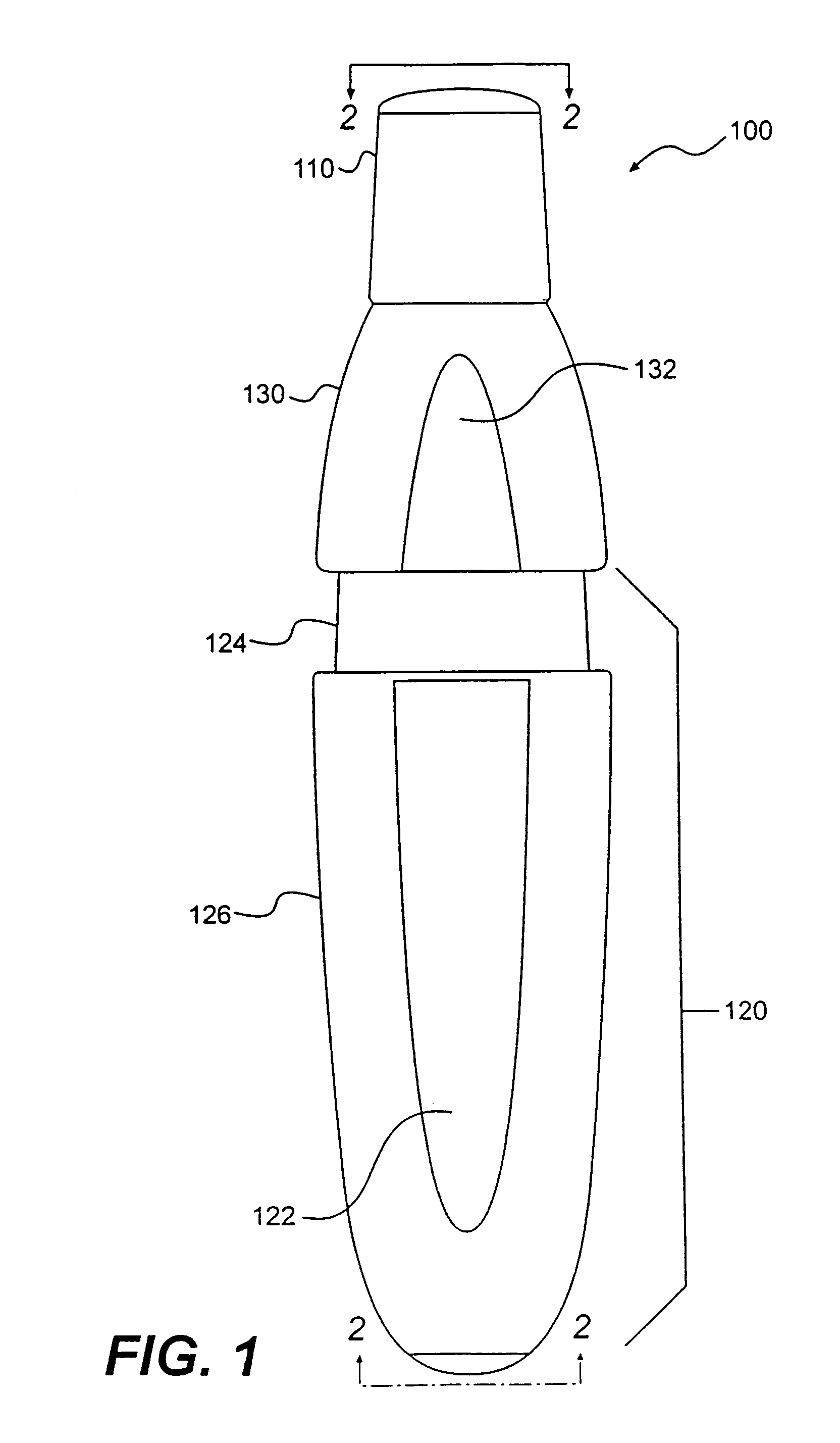
A method for delivering a therapeutic dose of a bioactive agent to the pulmonary system, in a single, breath-activated step, comprises administering from a receptacle enclosing a mass of particles, to a subject's respiratory tract, particles which have a tap density of less than 0.4 g / cm3 and deliver at least about 50% of the mass of particles. Another method of delivering a therapeutic dose of a bioactive agent to the pulmonary system, in a single breath, includes administering from a receptacle enclosing a mass of particles, to a subject's respiratory tract, particles which have a tap density of at least 0.4 g / cm3 and deliver at least about 10 milligrams of the bioactive agent. The receptacle can have a volume of at least 0.37 cm3.
Owner:CIVITAS THERAPEUTICS
Low dose pharmaceutical powders for inhalations
ActiveUS7954491B2Facilitate depositionGood dispersionRespiratorsPowder deliveryInhalationSingle breath
The invention relates to a method of delivering an agent to the pulmonary system of a compromised patient, in a single breath-activated step, comprising administering a particle mass comprising an agent from an inhaler containing less than 5 milligrams of the mass, wherein at least about 50% of the mass in the receptacle is delivered to the pulmonary system of a patient. The invention also relates to receptacles containing the particle mass and the inhaler for use therein.
Owner:CIVITAS THERAPEUTICS
Highly efficient delivery of a large therapeutic mass aerosol
InactiveUS6921528B2Improve efficiencyEliminate needPowder deliveryLiquid surface applicatorsVolumetric Mass DensityIntensive care medicine
A method for delivering a therapeutic dose of a bioactive agent to the pulmonary system, in a single, breath-activated step, comprises administering from a receptacle enclosing a mass of particles, to a subject's respiratory tract, particles which have a tap density of less than 0.4 g / cm3 and deliver at least about 50% of the mass of particles. Another method of delivering a therapeutic dose of a bioactive agent to the pulmonary system, in a single breath, includes administering from a receptacle enclosing a mass of particles, to a subject's respiratory tract, particles which have a tap density of at least 0.4 g / cm3 and deliver at least about 10 milligrams of the bioactive agent. The receptacle can have a volume of at least 0.37 cm3.
Owner:CIVITAS THERAPEUTICS
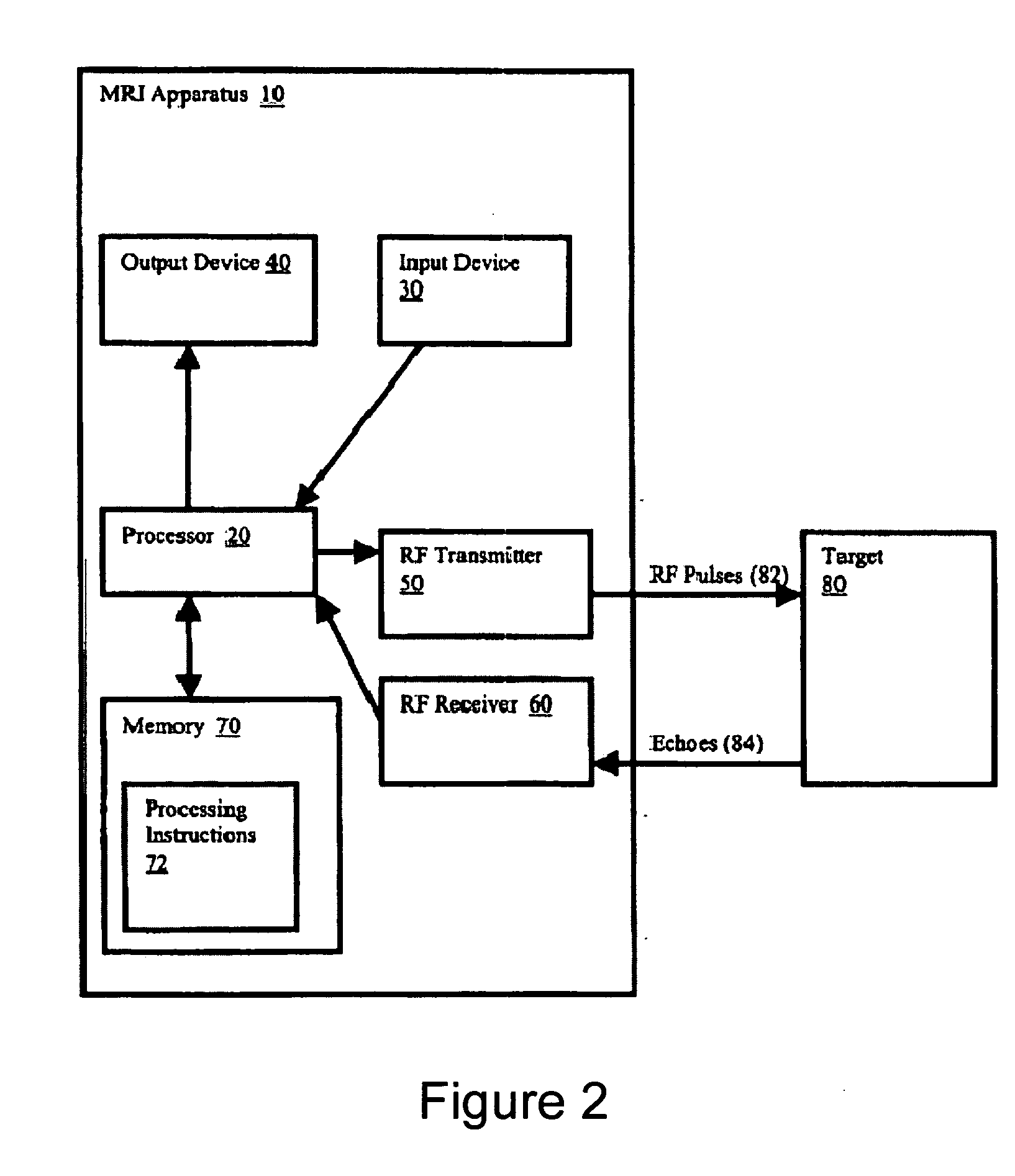
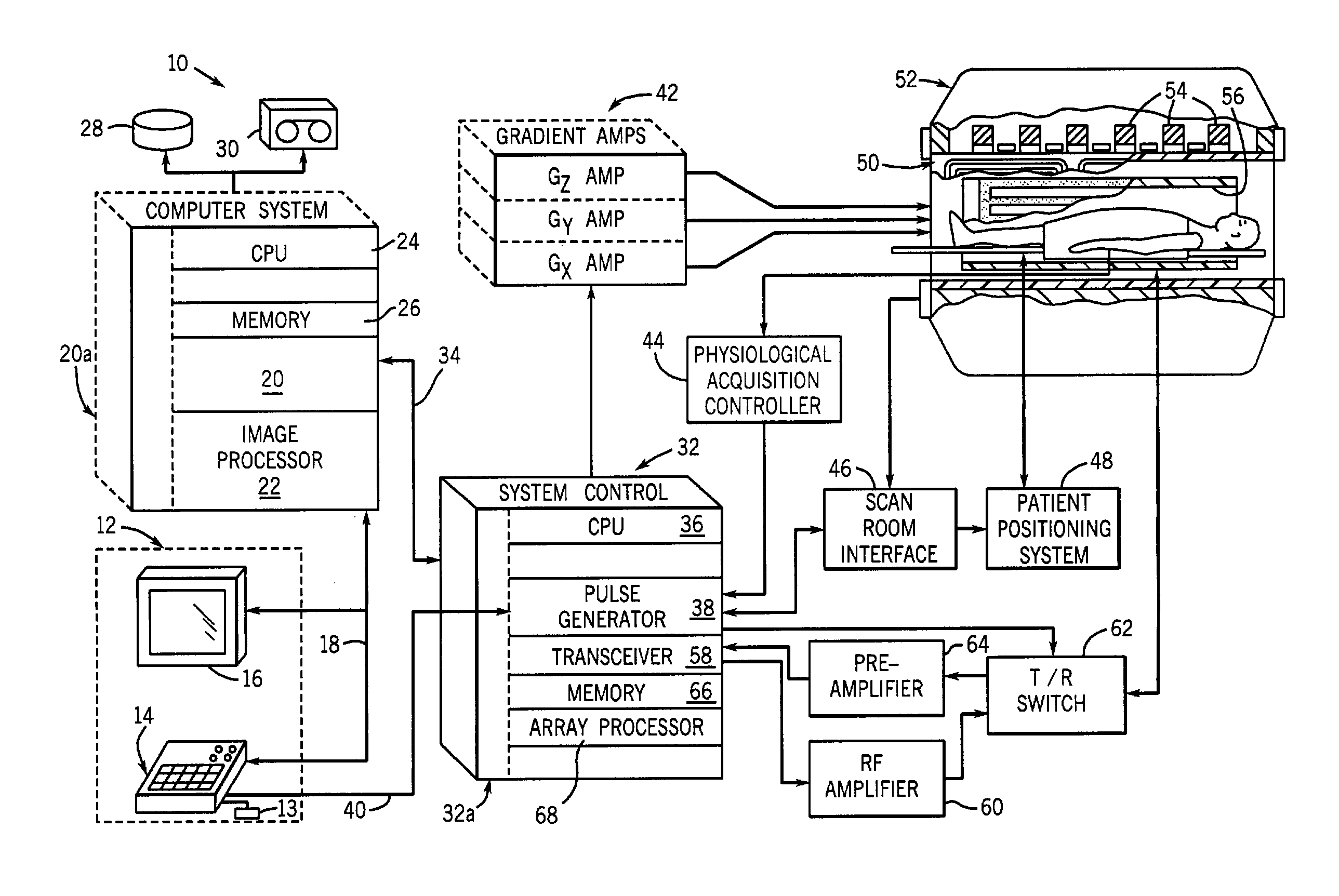
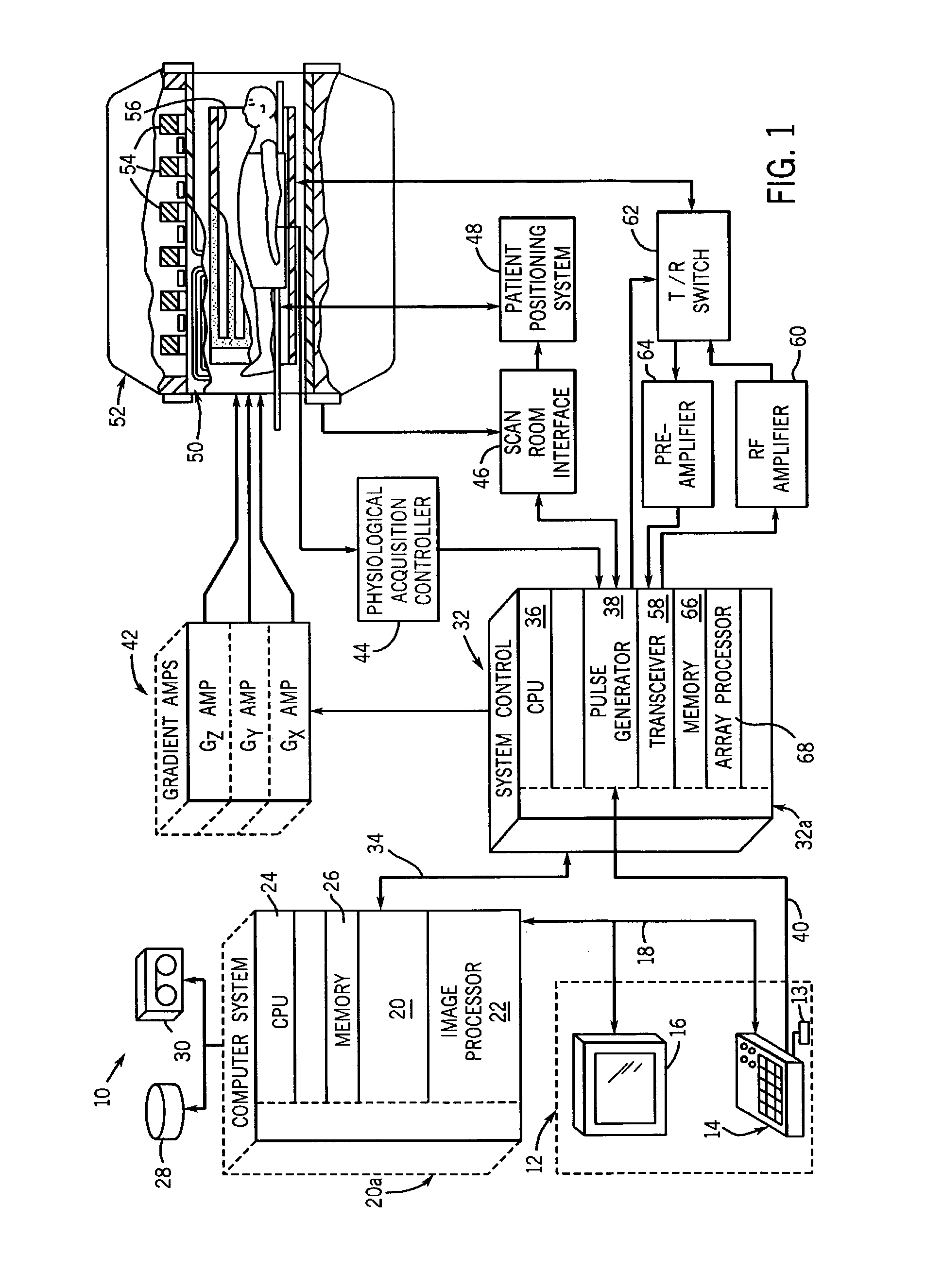
Multi-echo magnetic resonance imaging method and system
ActiveUS20060161060A1Faster and accurate perfusion mapImprove time resolutionMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringCardiac phaseRadio frequency
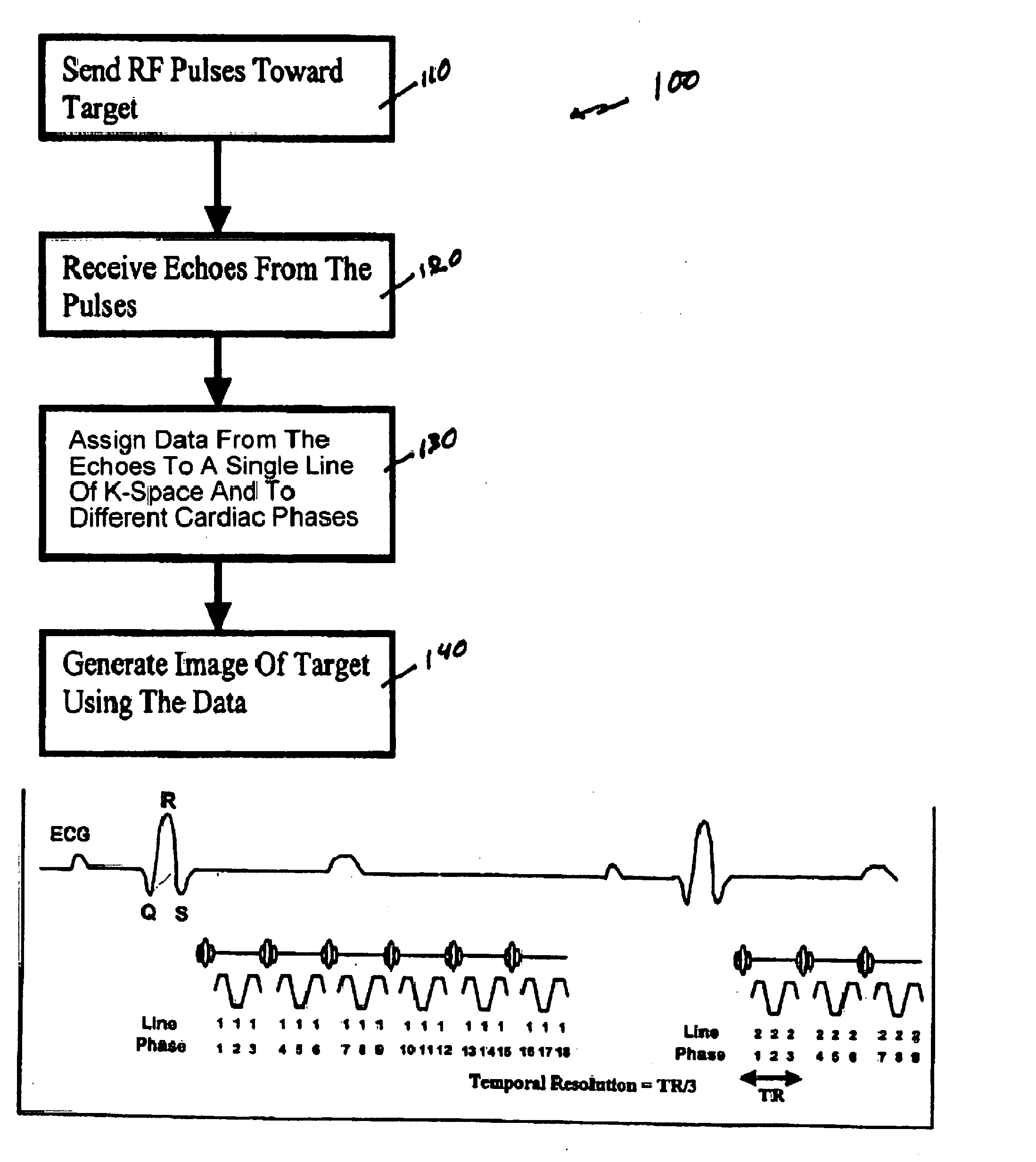
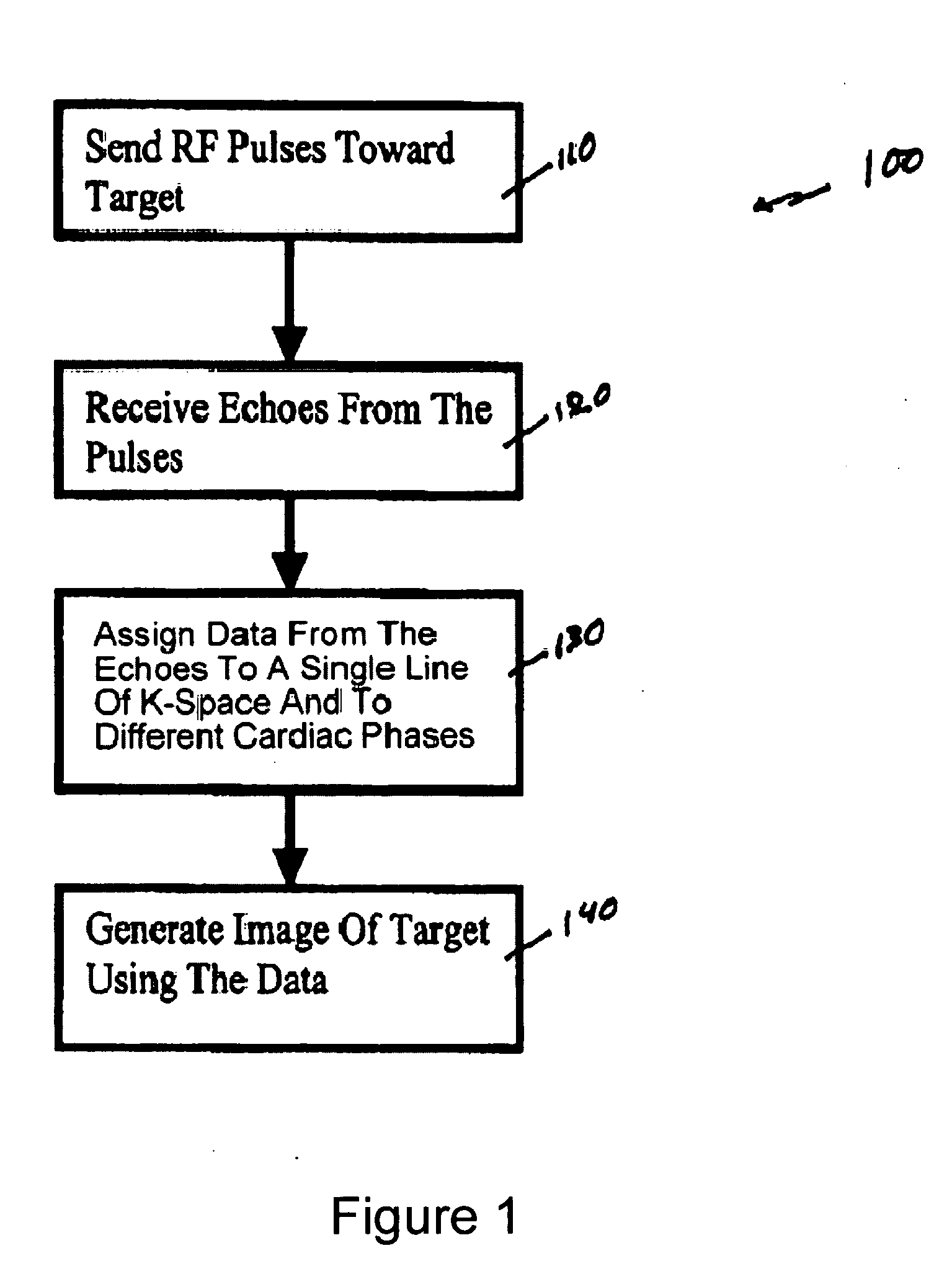
Method, systems and arrangements are provided for creating a high-resolution magnetic resonance image (“MRI”) or obtaining other information of a target, such as a cardiac region of a patient. Radio-frequency (“RF”) pulses can be transmitted toward the target by, e.g., an RF transmitter of an MRI apparatus. In response, multiple echoes corresponding to the plurality of pulses may be received from the target. Data from each of the echoes can be assigned to a single line of k-space, and stored in memory of the apparatus. An image of the target, acceleration data and / or velocity data associated with a target can be generated as a function of the data. In one exemplary embodiment, the data from different echoes may be assigned to the same k-space line, and to different cardiac phases. In one further embodiment, parallel processing may be used to improve the resolution of the image acquired during a single breath-hold duration. In yet another embodiment, utilizing a segmented implementation, multiples lines of k-space are acquired for a given cardiac phase (or time stamp) per trigger signal. The present invention may be utilized for the heart or for any other anatomical organ or region of interest for the evaluation and study of flow dynamics with very high temporal resolution.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
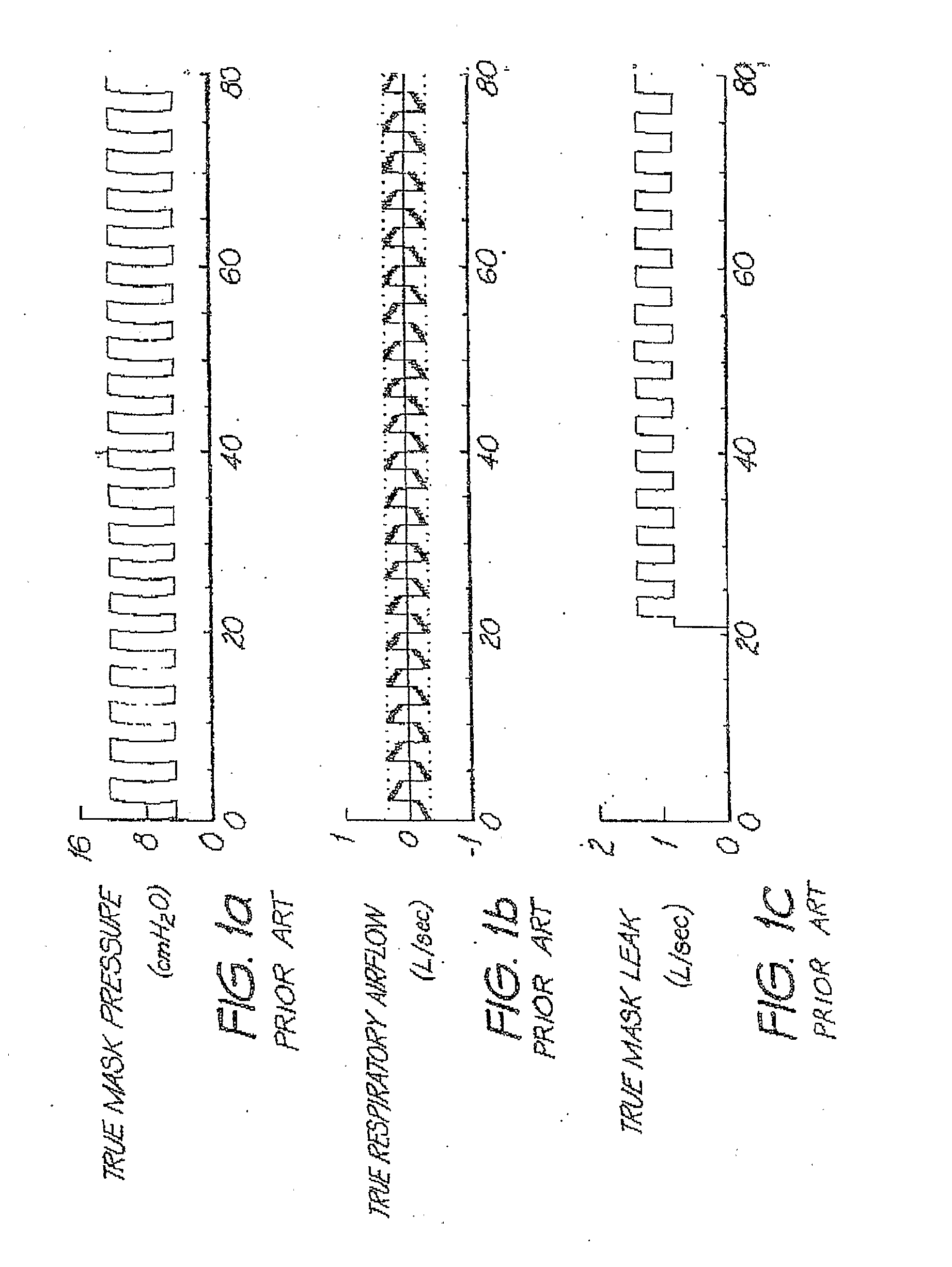
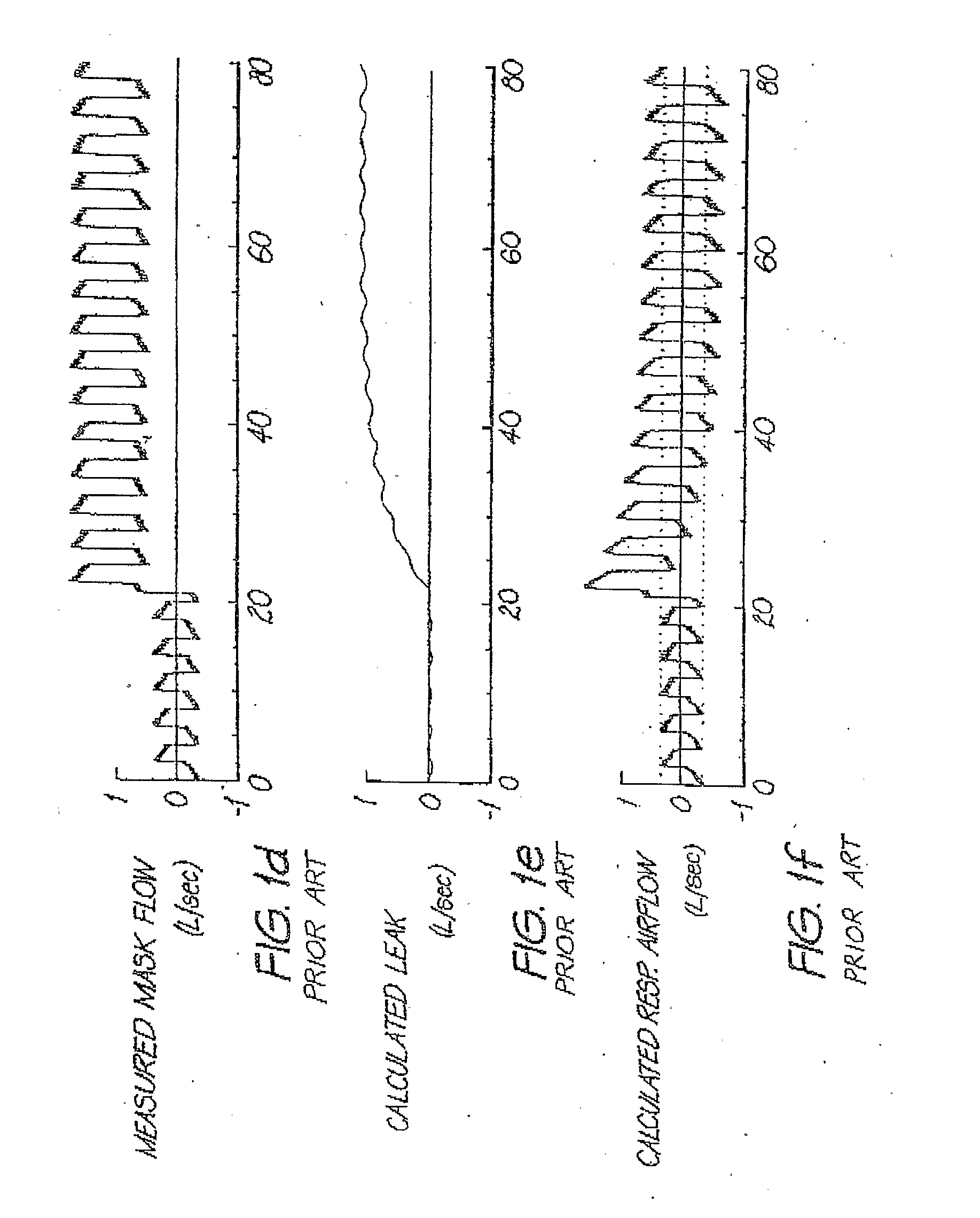
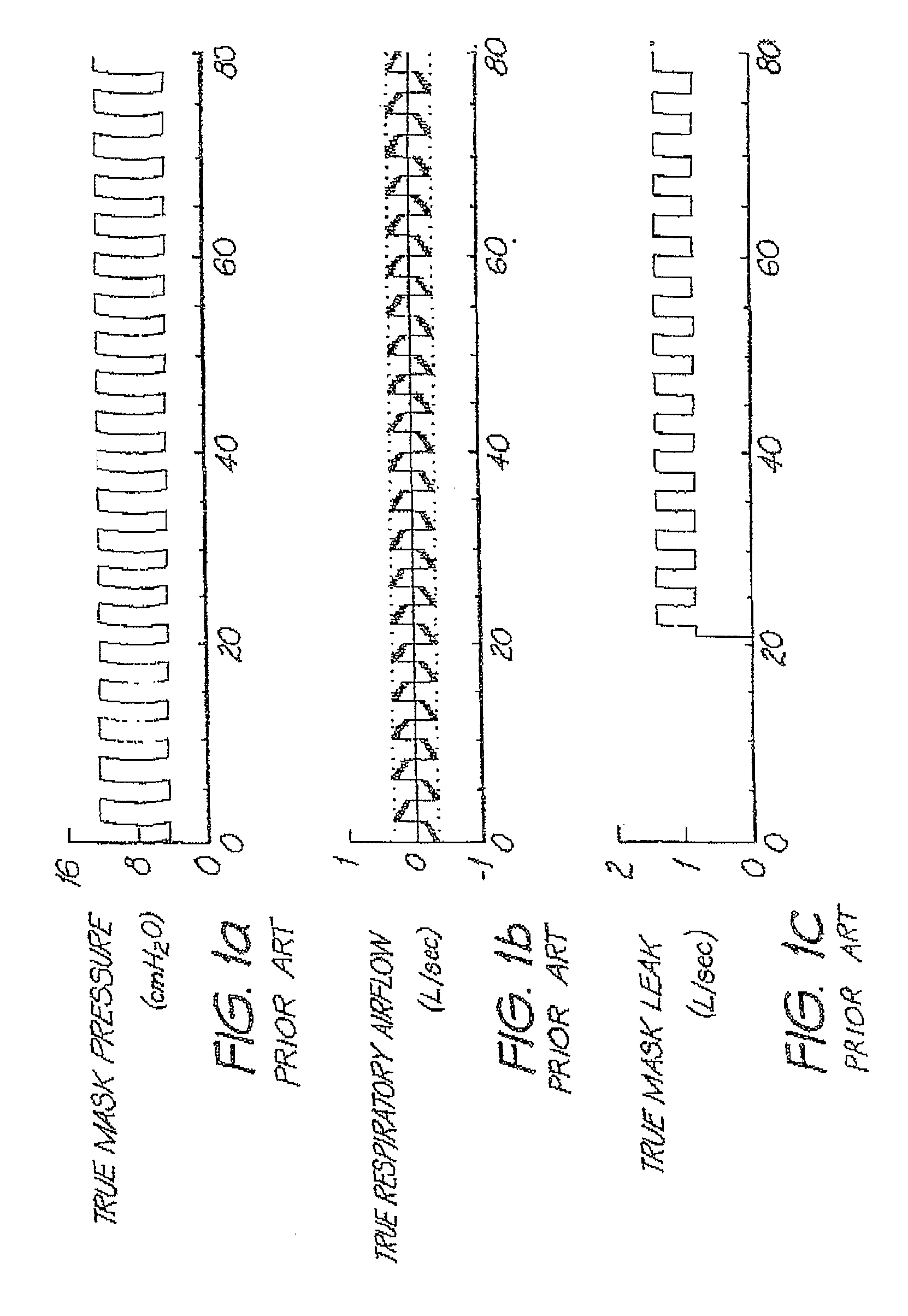
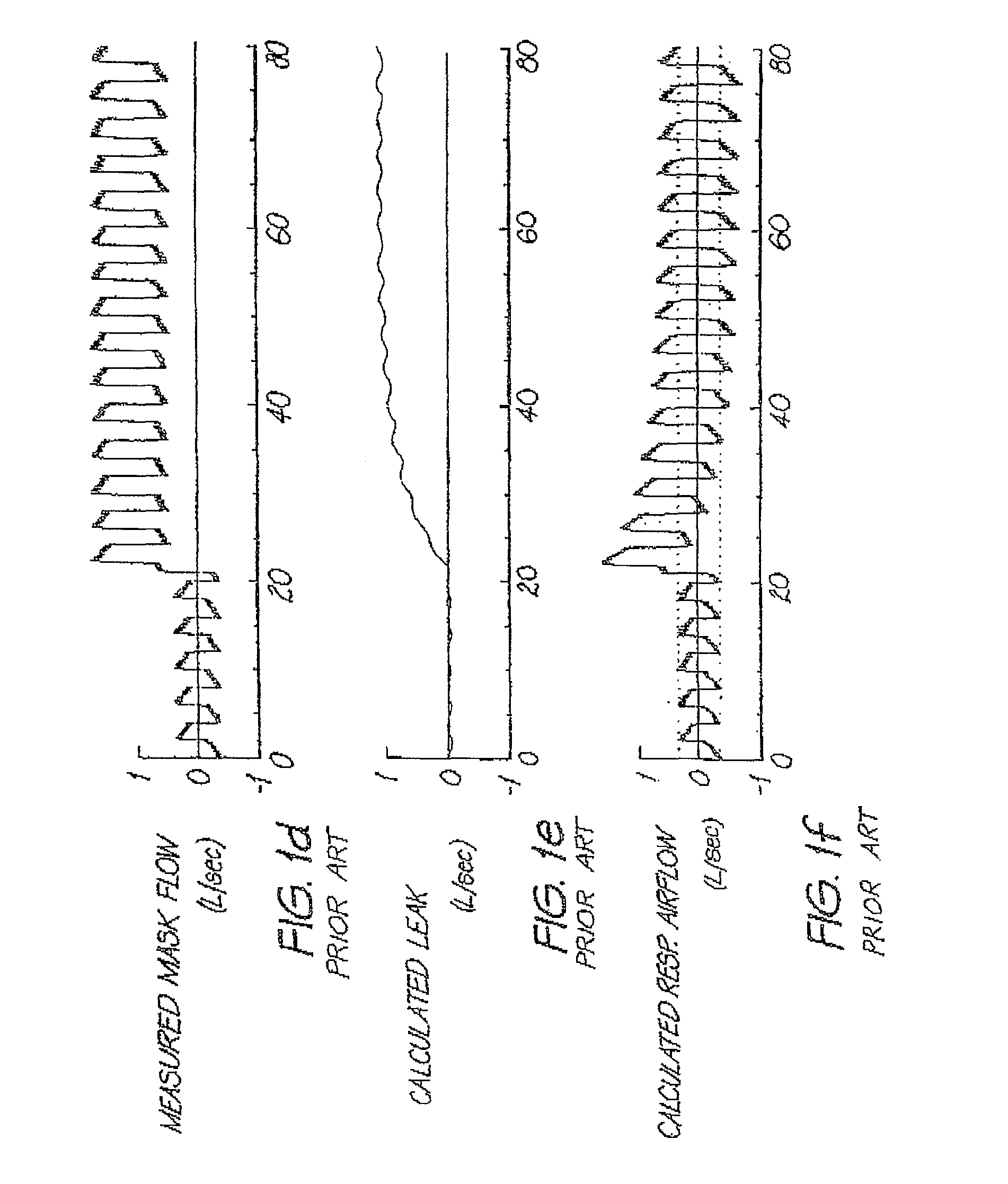
Determination of leak during cpap treatment
ActiveUS20100101574A1Quick fixDetection of fluid at leakage pointFlow propertiesRespiratory flowEngineering
In a CPAP or positive pressure ventilation system, leak is determined at each instant by a lookback for a time as long as single breath to establish the start of an averaging window over which low-pass filtered values used in the determination of a parameter of a leak model are averaged. A jamming index indicates whether the leak is rapidly changing. To the extent that jamming is high, the leak estimate used progressively changes from that using sliding breath-window averaging to a more robust and faster responding low-pass filter method, and adjustment of ventilatory support based on measures employing estimated respiratory flow is slowed down or stopped.
Owner:RESMED LTD
Low dose pharmaceutical powders for inhalation
ActiveUS20050022812A1Good dispersionFacilitate depositionRespiratorsPowder deliveryInhalationSingle breath
The invention relates to a method of delivering an agent to the pulmonary system of a compromised patient, in a single breath-activated step, comprising administering a particle mass comprising an agent from an inhaler containing less than 5 milligrams of the mass, wherein at least about 50% of the mass in the receptacle is delivered to the pulmonary system of a patient. The invention also relates to receptacles containing the particle mass and the inhaler for use therein.
Owner:CIVITAS THERAPEUTICS
Non-invasive method and apparatus for optimizing the respiration of atelectatic lungs
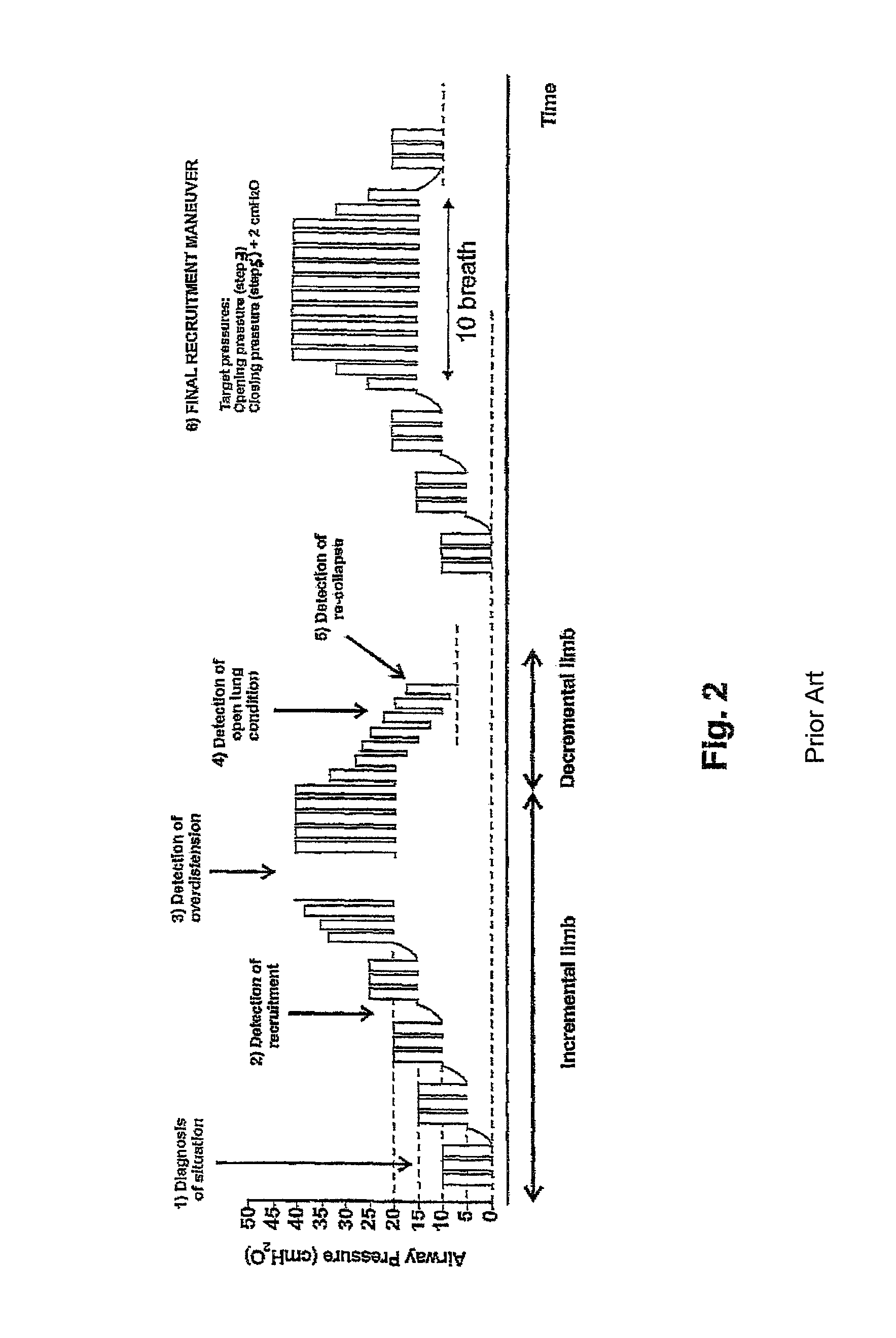
ActiveUS9173595B2Improve accuracyReduce pressureRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesLung alveolusNon invasive
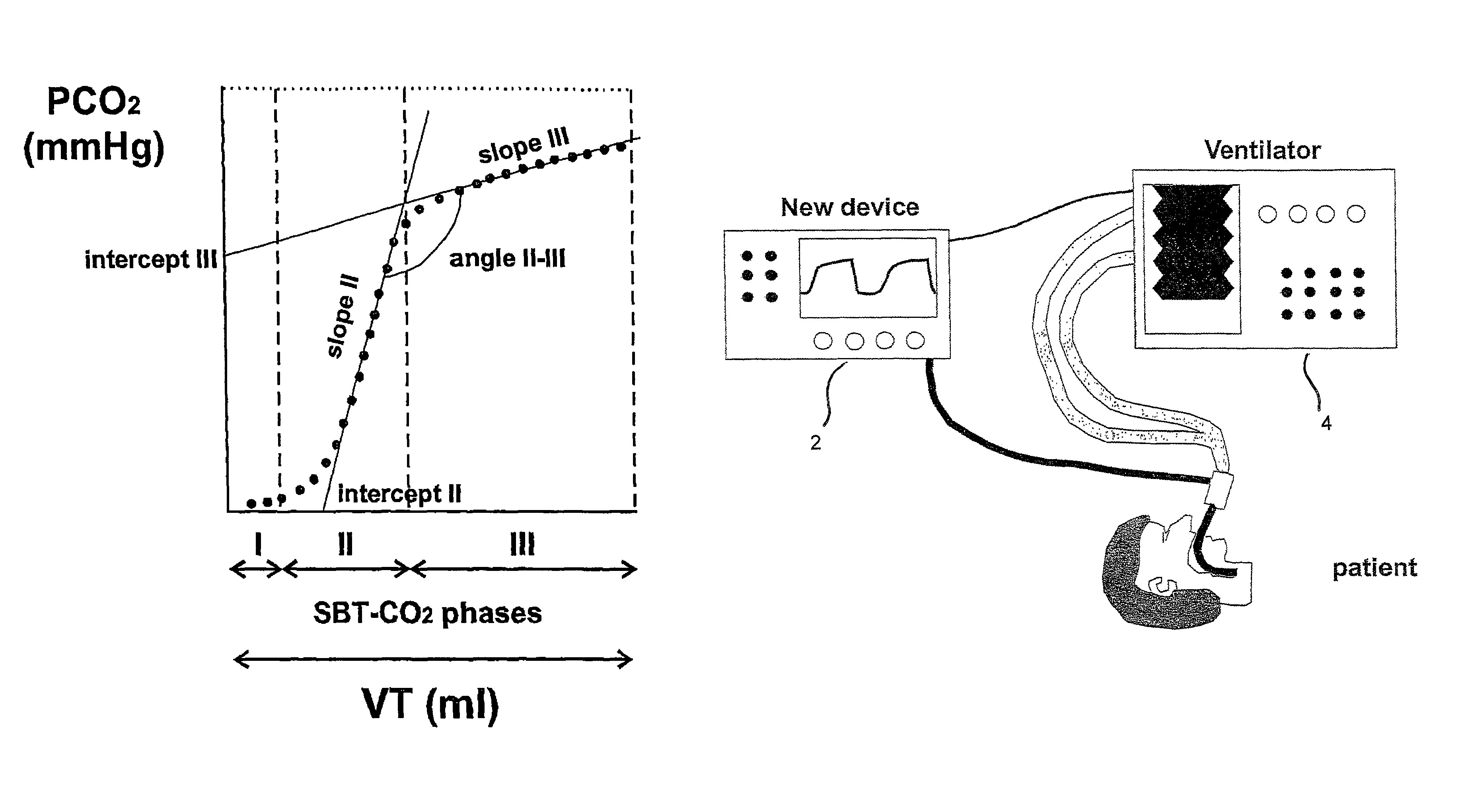
Method for providing ventilatory settings with regard to the airway pressure levels of an artificial ventilator, the artificial ventilator is connected to a lung, including the steps of obtaining data samples of a gas concentration of the expired gas over a single breath; selecting a plurality of data samples from the obtained data samples; calculating a tracing value being sensitive to changes of alveolar dead space on the basis of the selected data samples; repeating steps a), b) and c) for obtaining a plurality of tracing values; and changing at least one airway pressure level of the artificial ventilator, wherein from an observation of a resulting course of the plurality of calculated tracing values an airway pressure level at which alveolar opening or lung overdistension or lung open condition or alveolar closing occurs is detected. Apparatus for providing ventilatory settings with regard to the airway pressure levels of an artificial ventilator is also disclosed.
Owner:SALVIA MEDICAL
Method and apparatus for breath-held mr data acquisition using interleaved acquisition
InactiveUS20100222666A1Minimizes k-space transition artifactT weightingDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsVentricular volumeCardiac cycle
A method and apparatus are presented for acquiring MR cardiac images in a time equivalent to a single breath-hold. MR data acquisition is segmented across multiple cardiac cycles. MR data acquisition is interleaved from each phase of a first cardiac cycle with MR data from each phase of a subsequent cardiac cycle. Preferably, low spatial frequency data are interleaved between multiple cardiac cycles, and the subsequent cardiac cycle acquisition includes sequential acquisition of high spatial frequency data towards the end of the acquisition window. An MR image can then be reconstructed with data acquired from each of the acquisitions that reduce ghosting and artifacts. Volume images of the heart can be produced within a single breath-hold. Images can be acquired throughout the cardiac cycle to measure ventricular volumes and ejection fractions. Single phase volume acquisitions can also be performed to assess myocardial infarction.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Determination of leak during CPAP treatment
In a CPAP or positive pressure ventilation system, leak is determined at each instant by a lookback for a time as long as single breath to establish the start of an averaging window over which low-pass filtered values used in the determination of a parameter of a leak model are averaged. A jamming index indicates whether the leak is rapidly changing. To the extent that jamming is high, the leak estimate used progressively changes from that using sliding breath-window averaging to a more robust and faster responding low-pass filter method, and adjustment of ventilatory support based on measures employing estimated respiratory flow is slowed down or stopped.
Owner:RESMED LTD
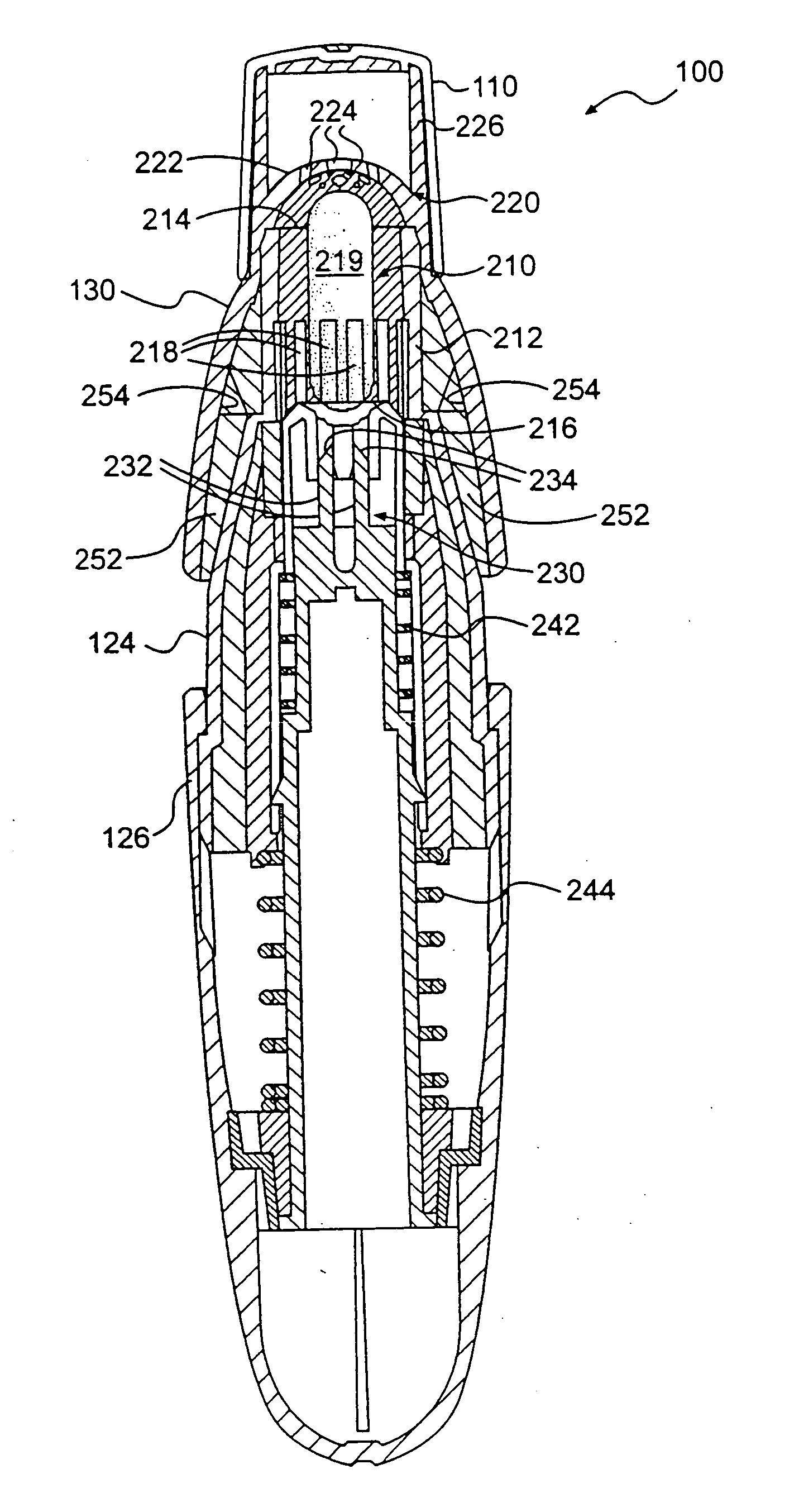
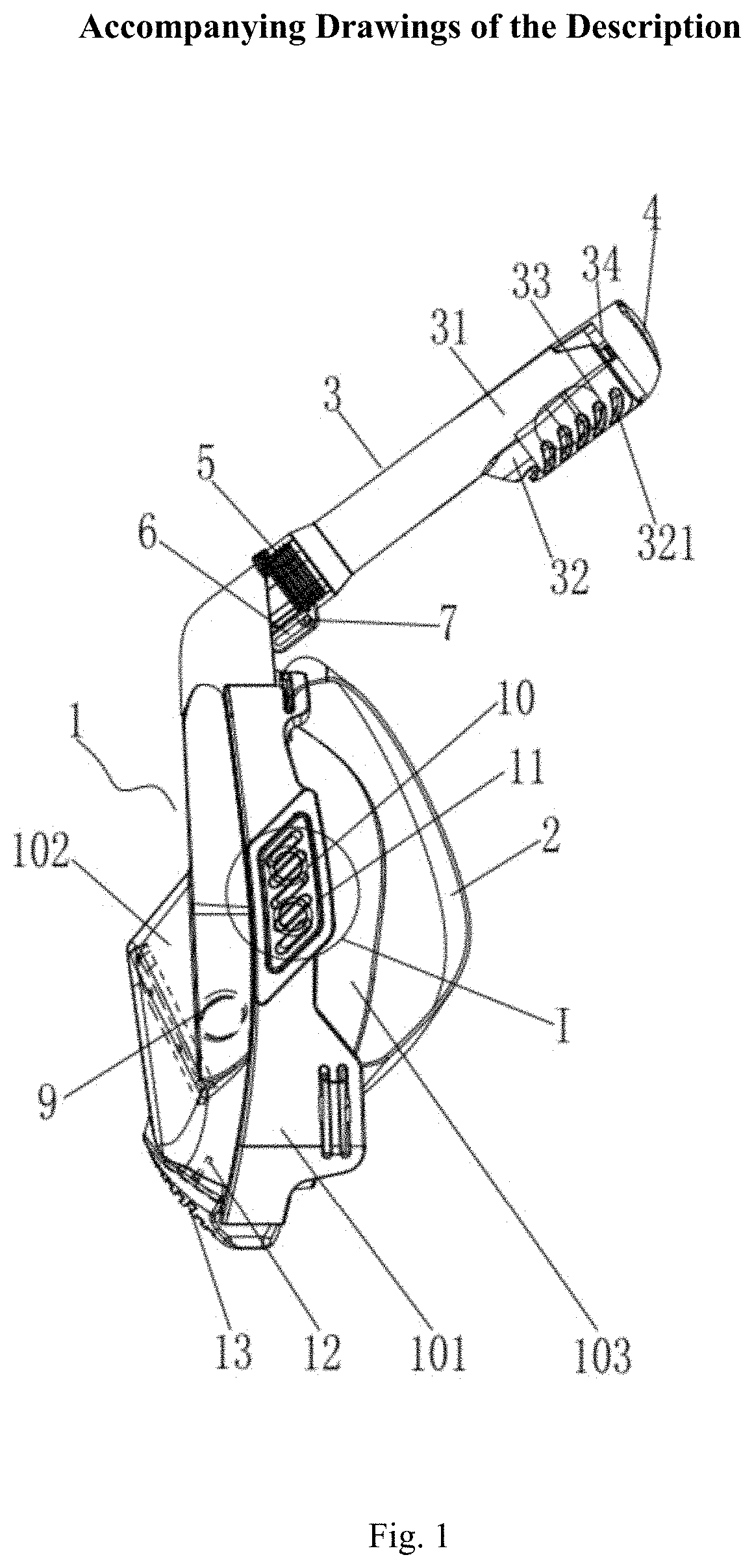
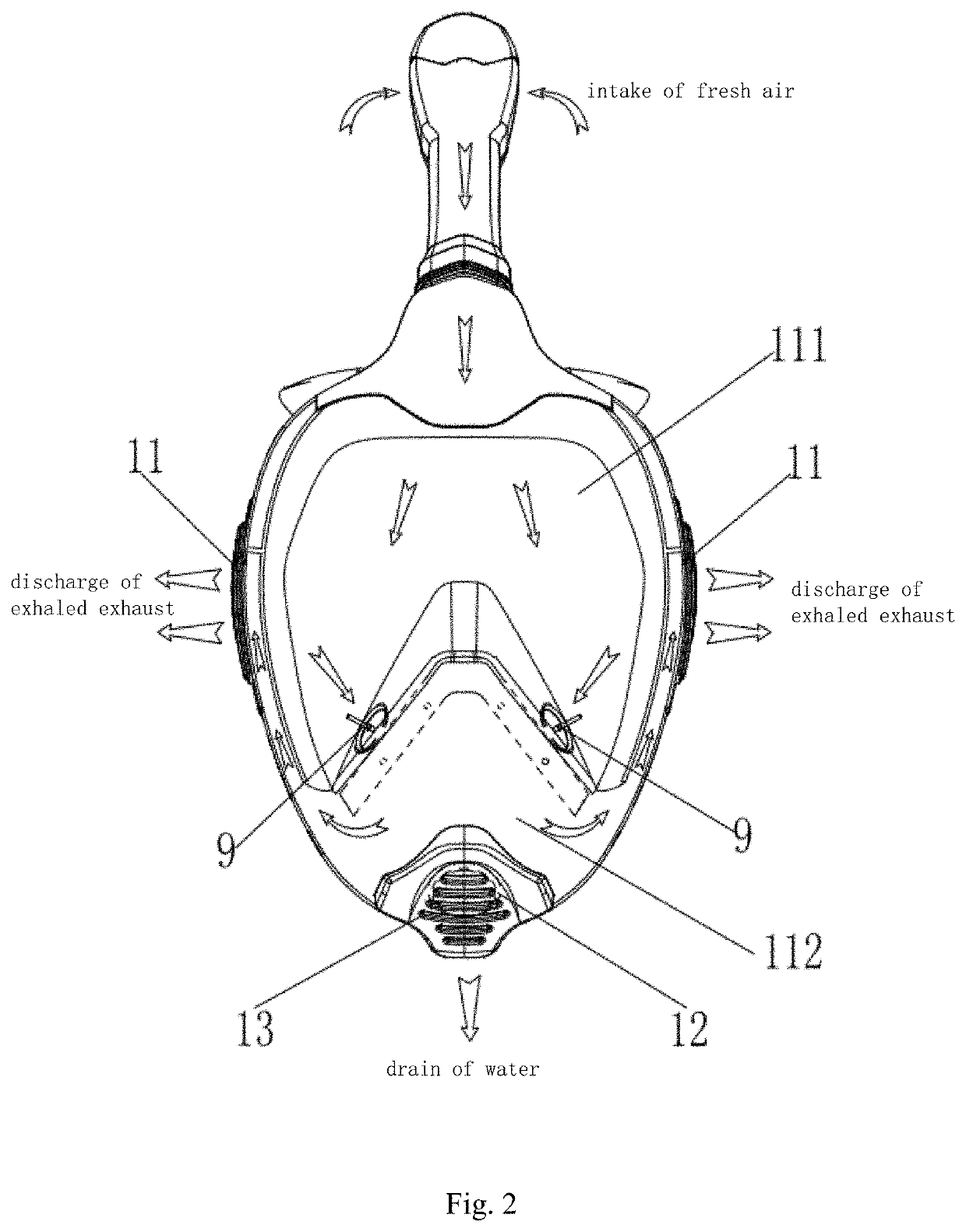
Full Face Dive Mask
InactiveUS20200031441A1Simple structureSmall sizeUnderwater equipmentPhysical medicine and rehabilitationEngineering
The present utility model discloses a full face dive mask, comprising a facial mask, a head strap connected with the facial mask and a respiratory pipe connected with the facial mask, wherein the side surface of the upper end of the facial mask is provided with a guide rail, the side surface of the lower end of the respiratory pipe is provided with a fixing shaft slidably connected with the guide rail, and the respiratory pipe is pulled outwards along the guide rail and revolved to fold in the facial mask. The utility model is simple in structure, small in size for the respiratory pipe can be folded to place, easy to store and capable of guaranteeing smooth breathing of a user.
Owner:GUANGZHOU VANGUARD WATERSPORT PRODS
Method and system for DLCO quality control testing
Owner:KOKO IT LLC
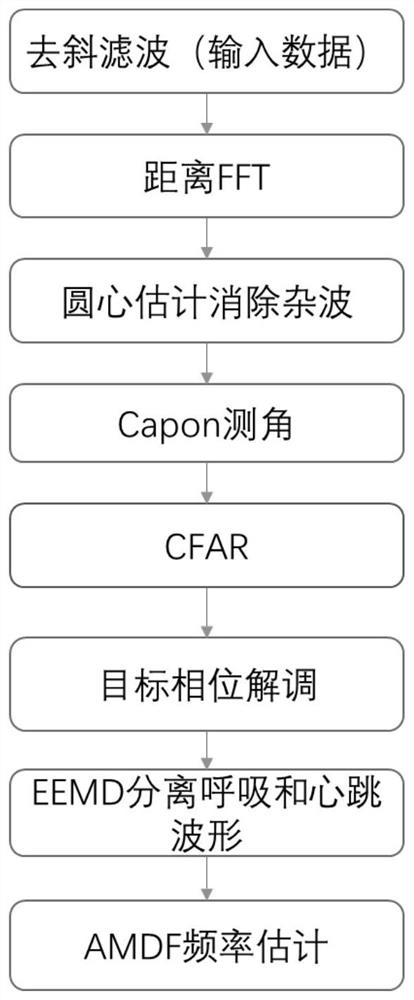
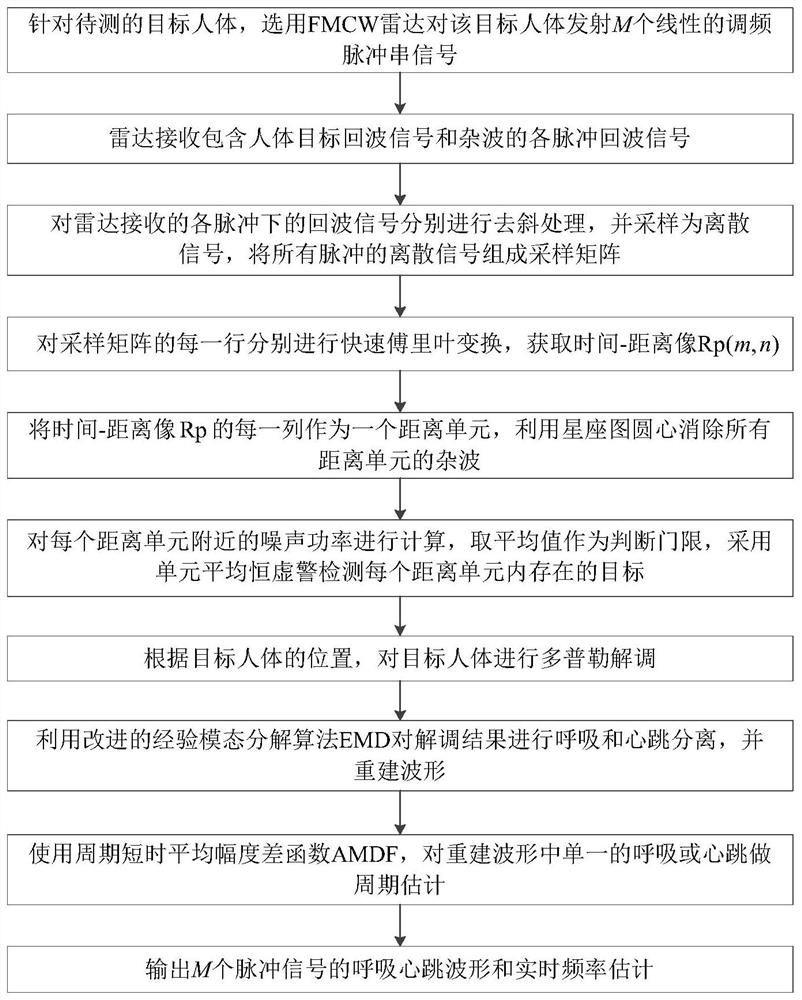
Personnel respiration and heartbeat detection method based on millimeter wave radar
ActiveCN113440120AEliminate clutterReduce the impactRespiratory organ evaluationSensorsHuman bodyRadar signal processing
The invention discloses a personnel respiration and heartbeat detection method based on a millimeter wave radar, and belongs to the field of radar signal processing, and the method specifically comprises the steps: firstly, the radar transmits a linear frequency modulation pulse string signal to a to-be-detected target human body, and receives pulse echo signals containing clutters; a sampling matrix is formed through dechirp processing and discretization; then, fast Fourier transform is performed on each row of the matrix to obtain a time-distance image Rp (m, n); each column of Rp is used as a distance unit, and clutters of all distance units are eliminated by using the center of a constellation diagram; then, the noise power average value of each distance unit is taken as a threshold, a target existing in each distance unit is detected by adopting a unit average constant false alarm, and Doppler demodulation is performed according to the position of the target; finally, a separation waveform of respiration and heartbeat are reconstructed according to a demodulation result; cycle estimation on single breath or heartbeat is performed in the reconstructed waveform; and breathing and heartbeat waveforms and real-time frequency estimation of the pulse signals are output. The algorithm is simple, and the calculation amount is reduced.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
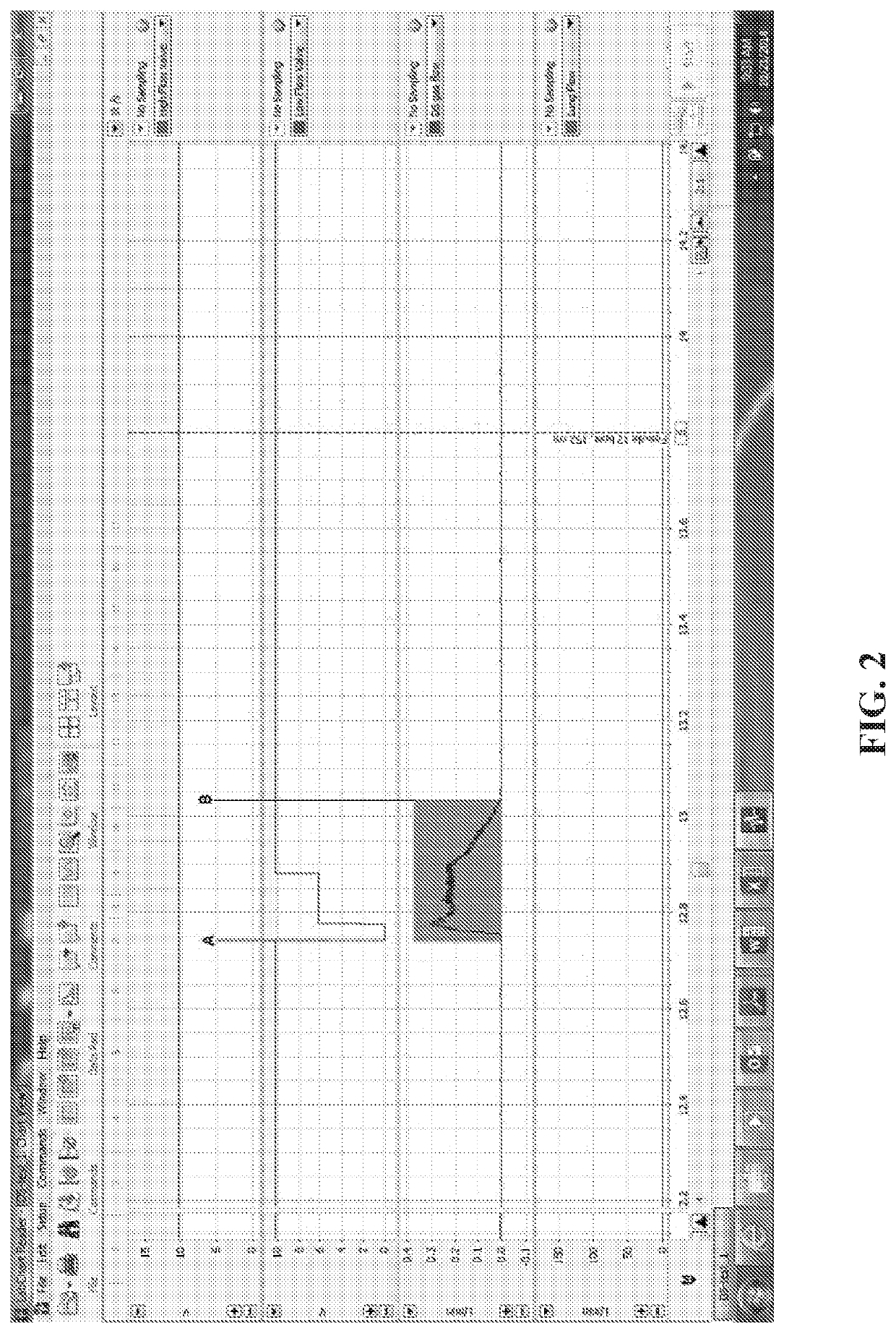
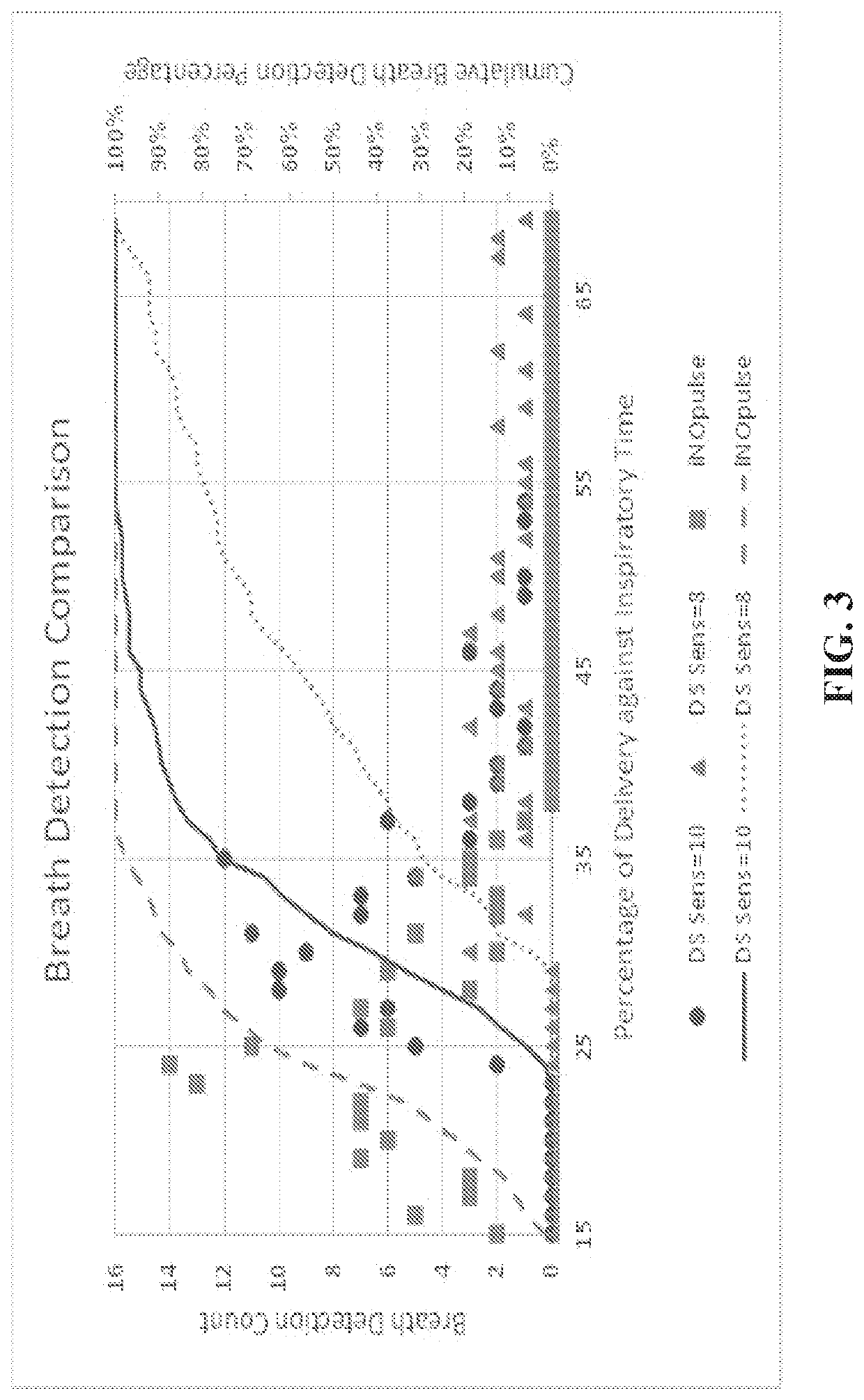
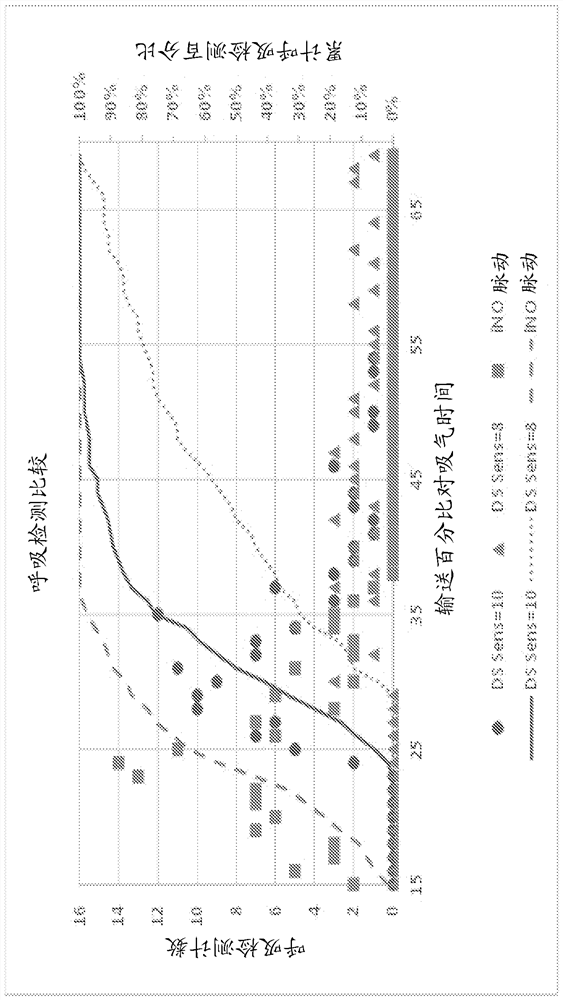
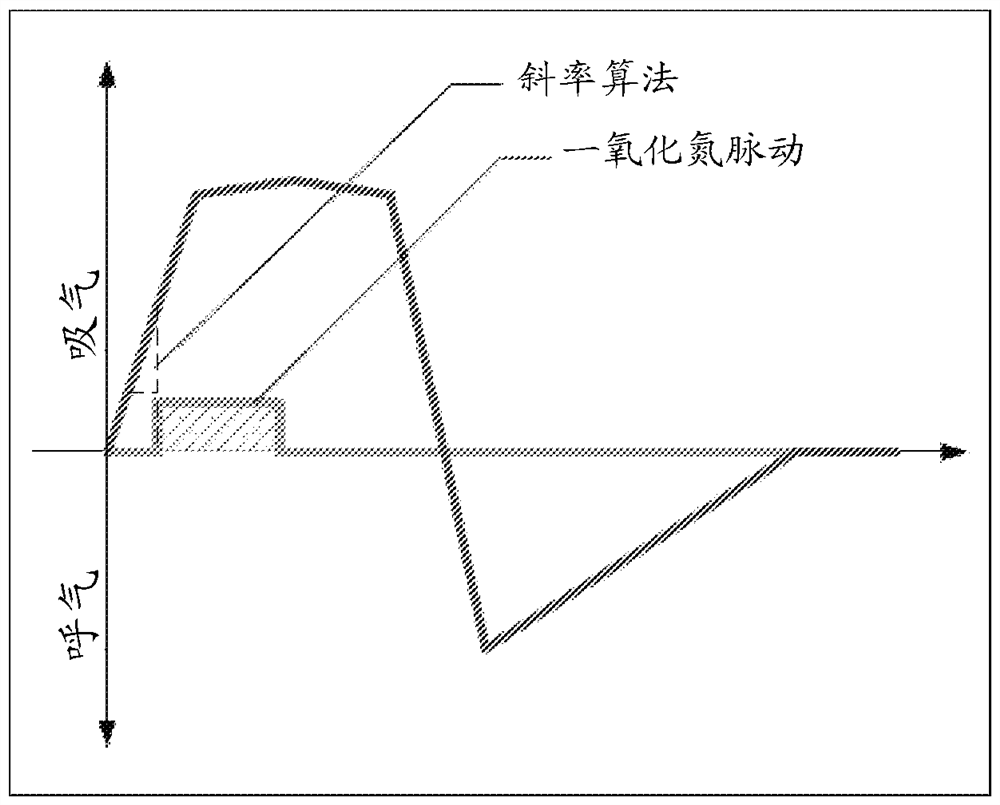
Method and apparatus for pulsatile delivery of nitric oxide
Described are methods for providing a pulsed dose of nitric oxide during at least the first two-thirds of total inspiratory time in each single breath for a therapeutically relevant period of time.
Owner:BELLEROPHON THERAPEUTICS
Low Dose Pharmaceutical Powders for Inhalation
ActiveUS20120111325A1Facilitate depositionGood dispersionRespiratorsPowder deliveryInhalationSingle breath
The invention relates to a method of delivering an agent to the pulmonary system of a compromised patient, in a single breath-activated step, comprising administering a particle mass comprising an agent from an inhaler containing less than 5 milligrams of the mass, wherein at least about 50% of the mass in the receptacle is delivered to the pulmonary system of a patient. The invention also relates to receptacles containing the particle mass and the inhaler for use therein.
Owner:CIVITAS THERAPEUTIC INC
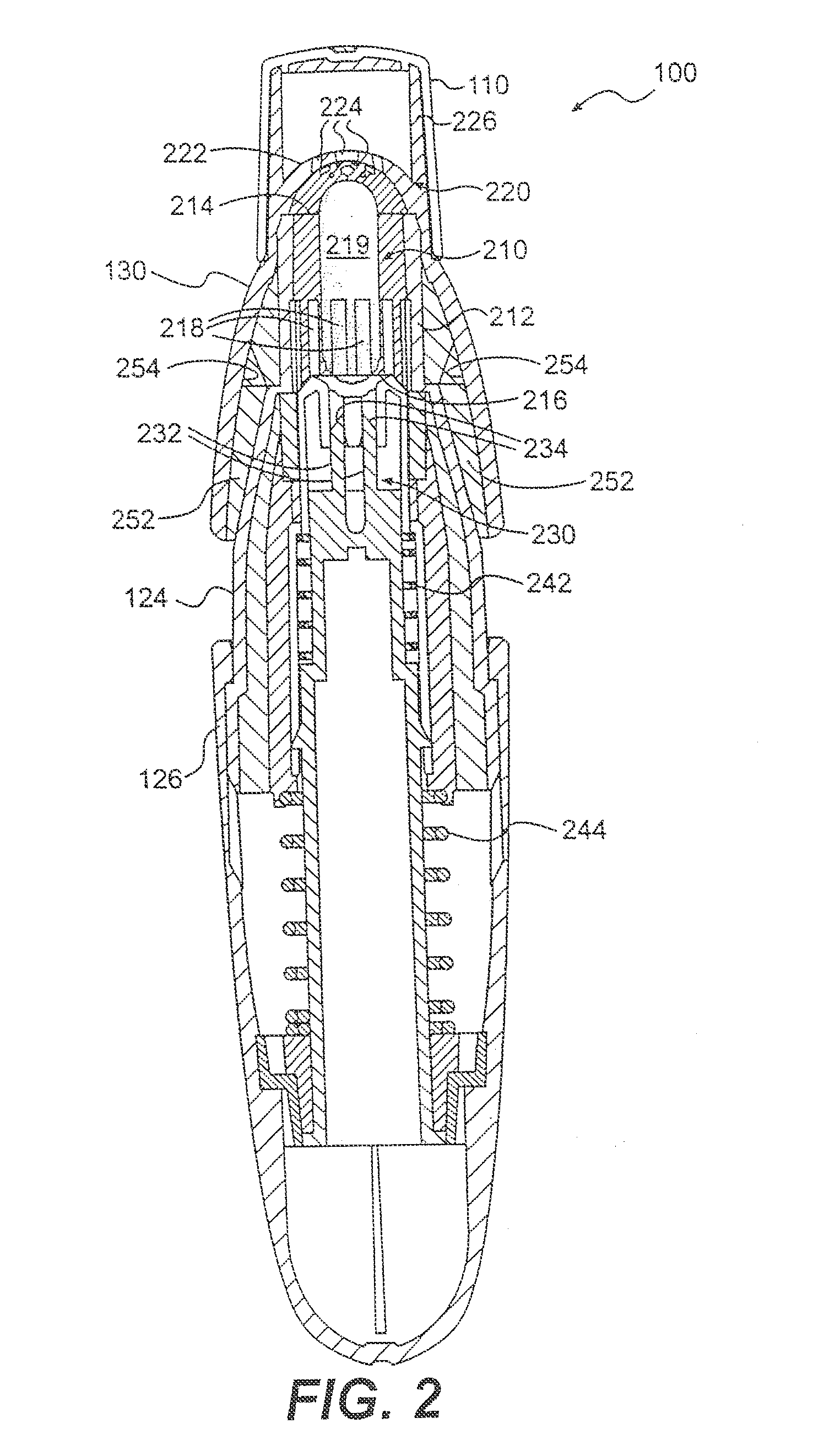
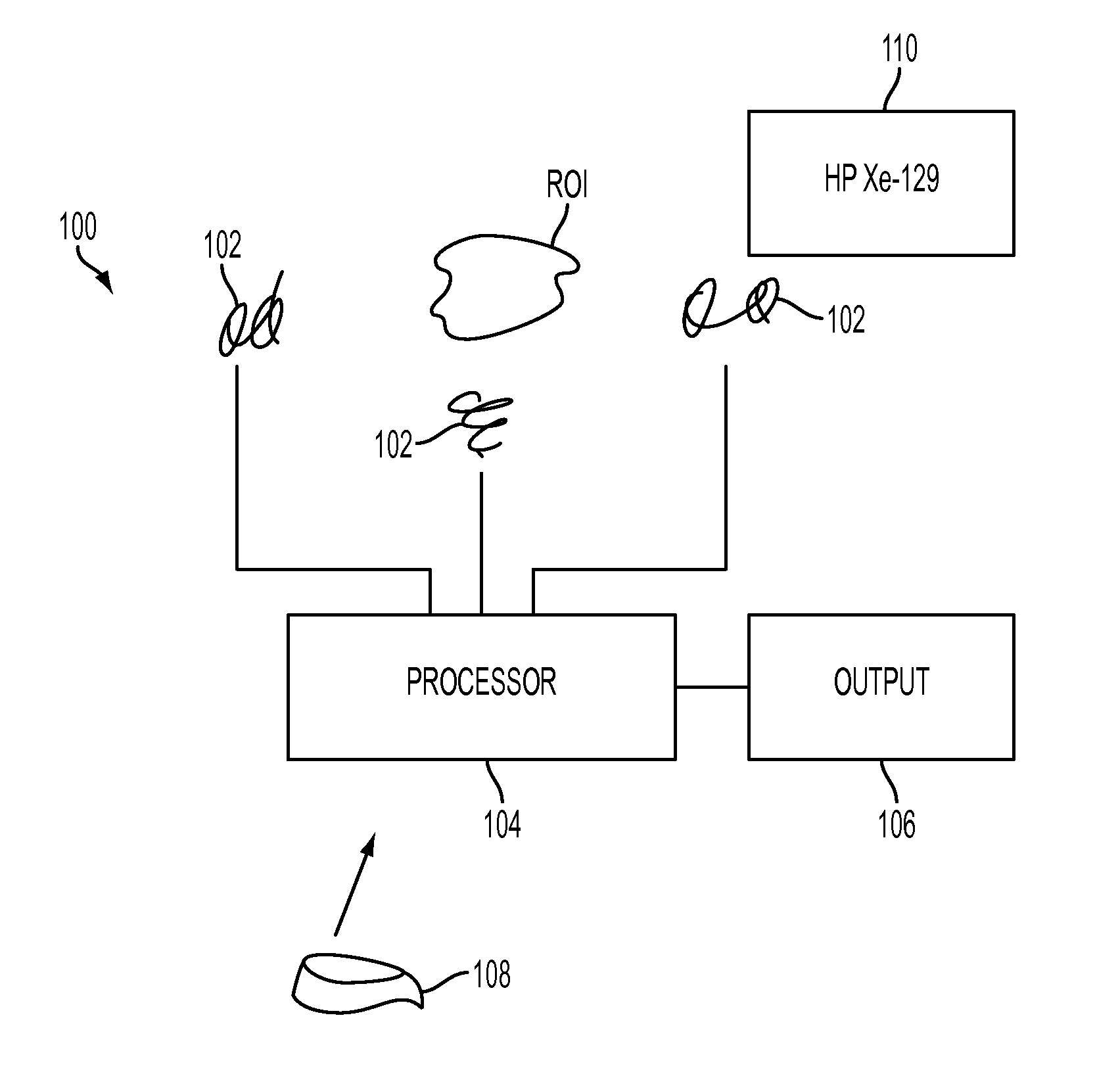
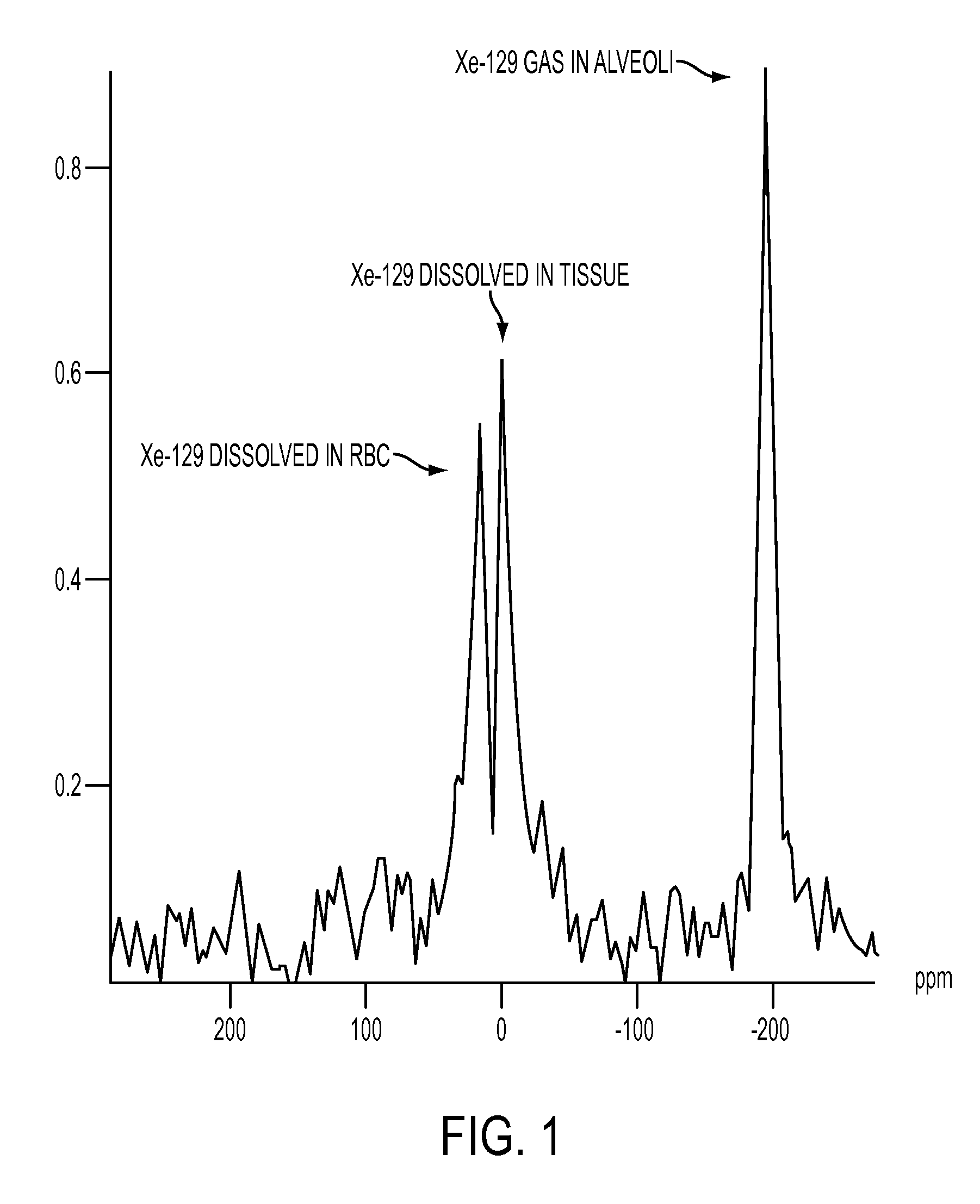
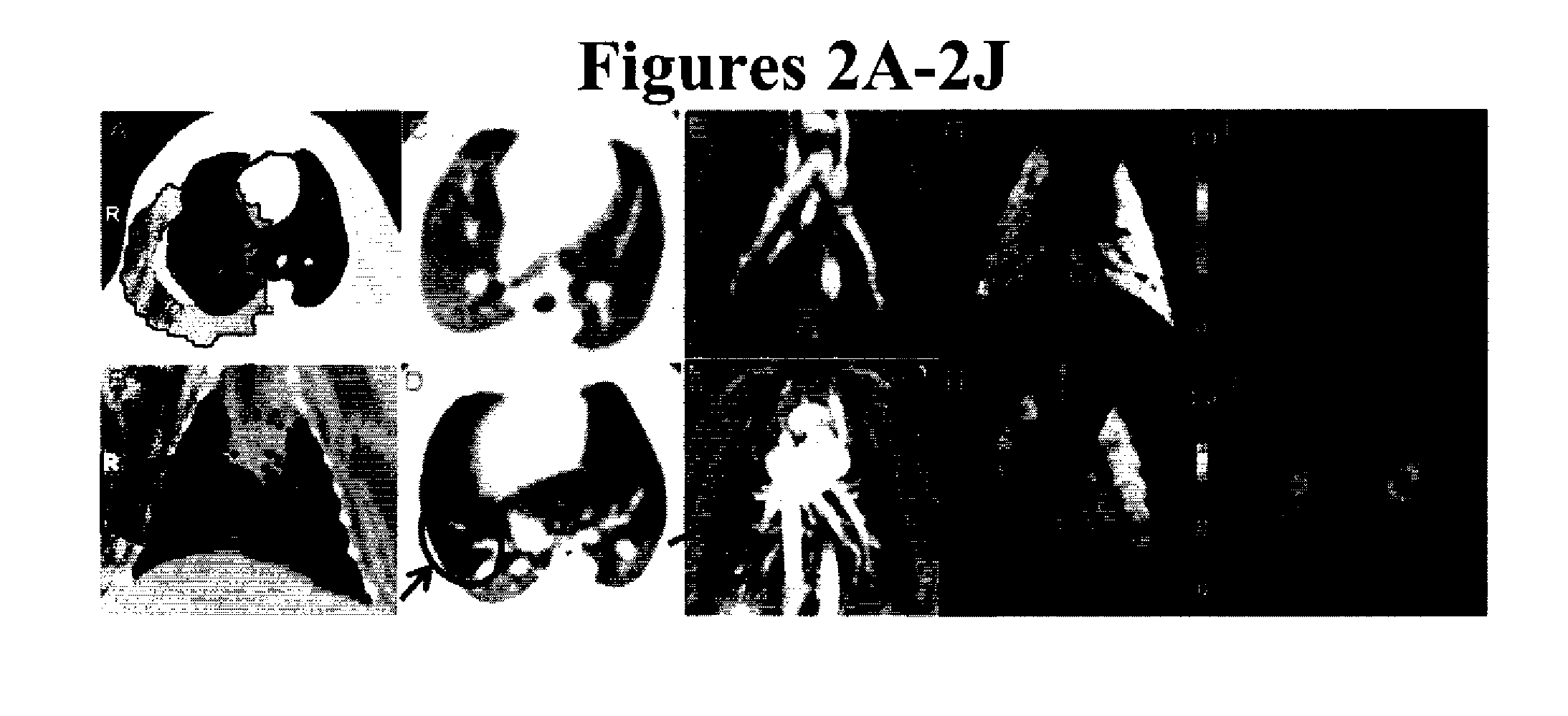
Single breath-hold system and method for detection and assessment of multi-organ physiologic, morphologic and structural changes
InactiveUS20100280358A1High sensitivityMinimal and no side-effectsImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionMedicineInhalation
In a single breath-hold the physiologic, morphologic and structural changes in multiple organs are detected and assessed. The main steps process include: polarizing the Xe-129 gas; inhalation or introduction of a certain pre-calculated amount of the gas and start of the breath-hold; acquisition of multiple spatially oriented spectrums, localized in the same plane (2D), in multiple different planes (3D) or in 3D plus at multiple time intervals (4D); stop the breath-hold; post-processing of the acquired data; evaluation of the multiple spectrums by comparison of the values in a region of interest with those in surrounding tissues or known as normal.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
Method and apparatus for breath-held MR data acquisition using interleaved acquisition
ActiveUS7797031B1Minimal temporal and spatial discrepancies or inaccuraciesImage producedDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsVentricular volumeCardiac cycle
A method and apparatus are presented for quickly acquiring MR cardiac images in a time equivalent to a single breath-hold. MR data acquisition is segmented across multiple cardiac cycles. MR data acquisition is interleaved from each phase of a first cardiac cycle with MR data from each phase of a subsequent cardiac cycle. Preferably, low spatial frequency data are interleaved between multiple cardiac cycles, and the subsequent cardiac cycle acquisition includes sequential acquisition of high spatial frequency data at the tail end of the acquisition window. An MR image can then be reconstructed with data acquired from each of the acquisitions that reduce ghosting and artifacts. MR images are reconstructed using this interleaved variable temporal k-space sampling technique to produce volume images of the heart within a single breath-hold. Images can be acquired throughout the cardiac cycle to measure ventricular volumes and ejection fractions. Single phase volume acquisitions can also be performed to assess myocardial infarction.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Multiple soft projectile blow gun
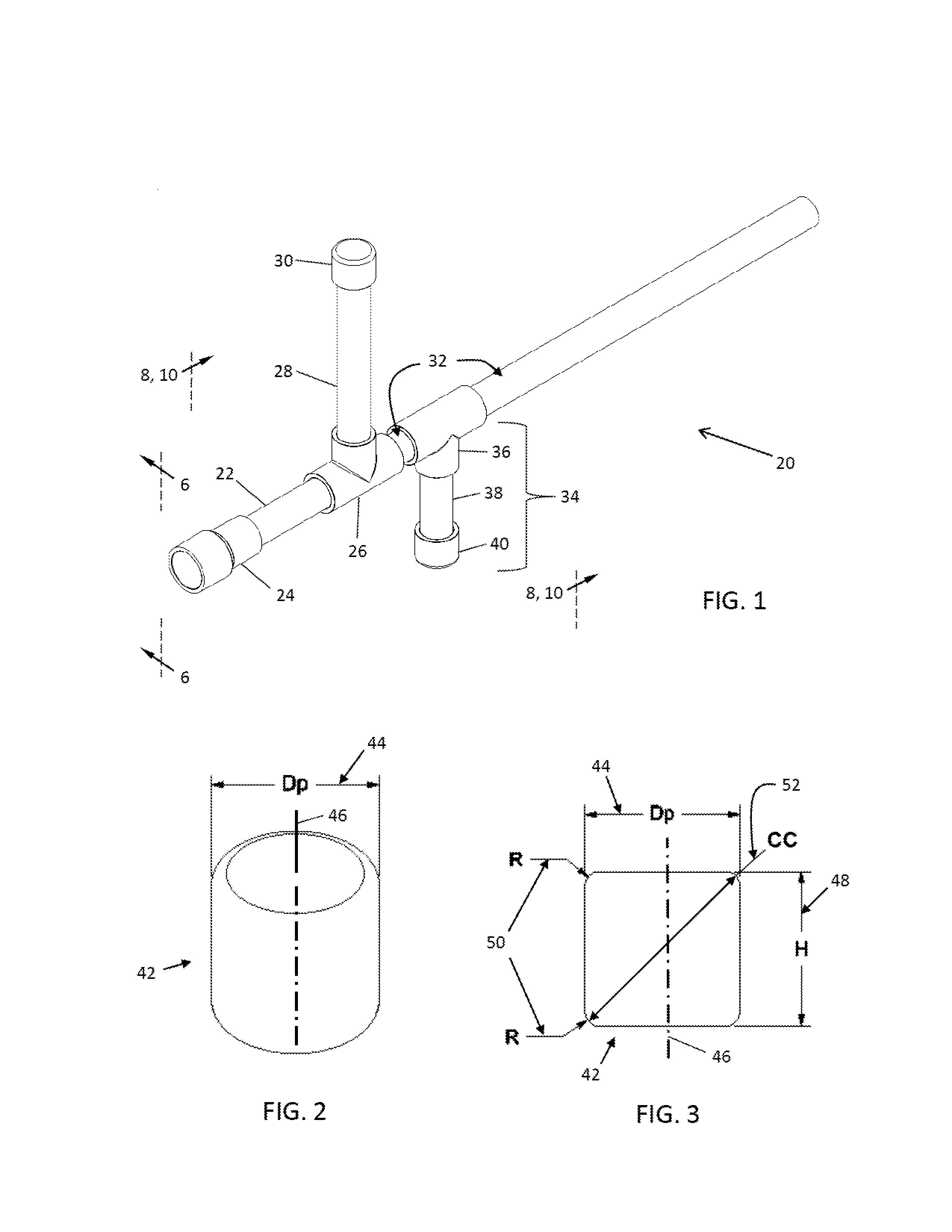
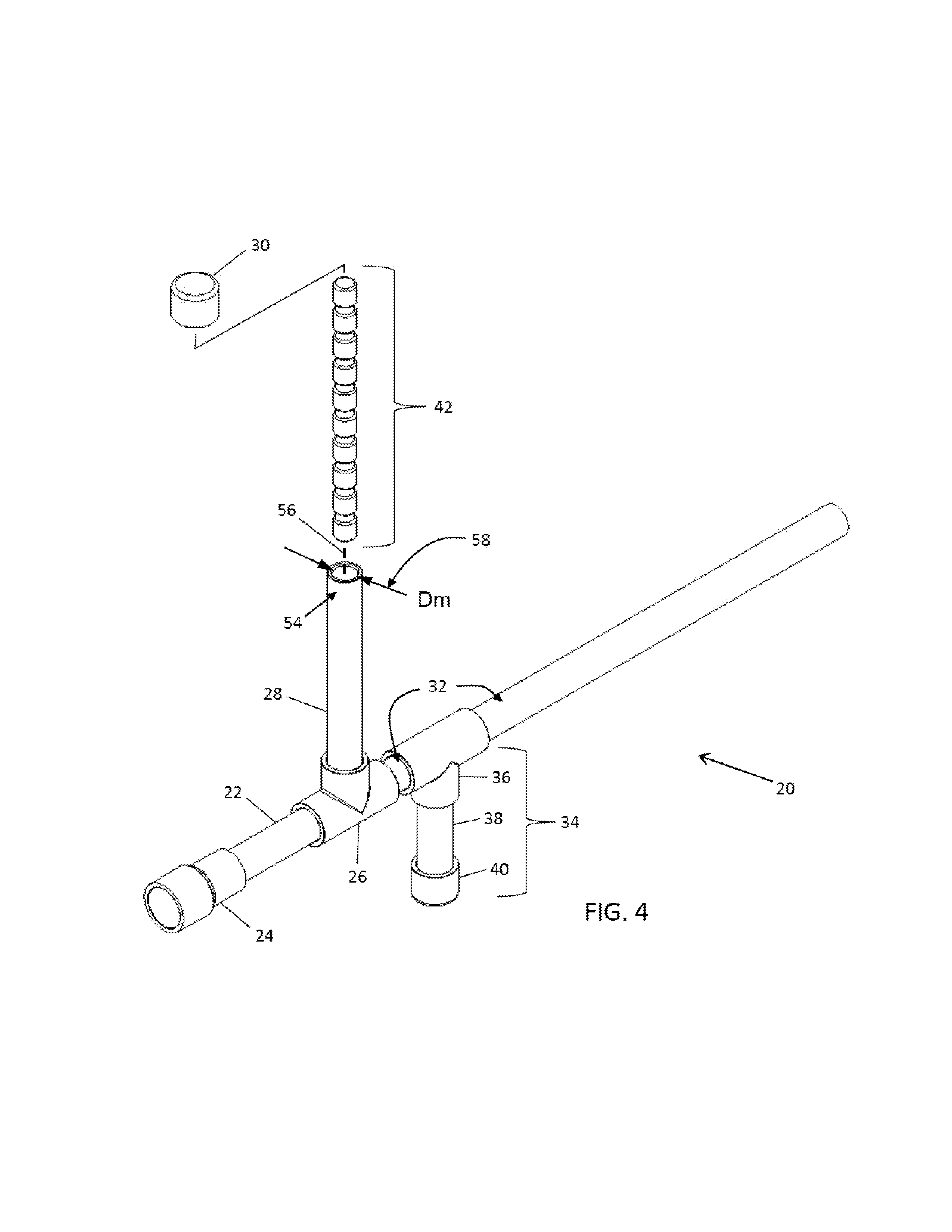
InactiveUS20130180513A1Rapid continuous firingEliminating a choking hazard for the userBlow gunsBatonsSingle breathGun barrel
A blow gun assembly allows the rapid continuous firing of multiple soft, cylindrical projectiles using a single breath. The assembly includes at least one soft cylindrical projectile with a height generally equal to or slightly greater than its diameter, and a centrally-located breech in fluid communication with a mouthpiece, a vertical magazine, and a barrel. Projectiles loaded into the magazine enter a breech chamber by gravity. Upon receiving a charge of air through the mouthpiece, the projectiles travel successively through the breech chamber and out through the barrel in rapid fashion. Sizing of the magazine, breech chamber, and barrel, relative to the projectile, causes the projectiles to flow through the blow gun in continuous succession without jamming, with projectiles being rotated within the breech chamber to properly align with the barrel.
Owner:FOELLER MARK R
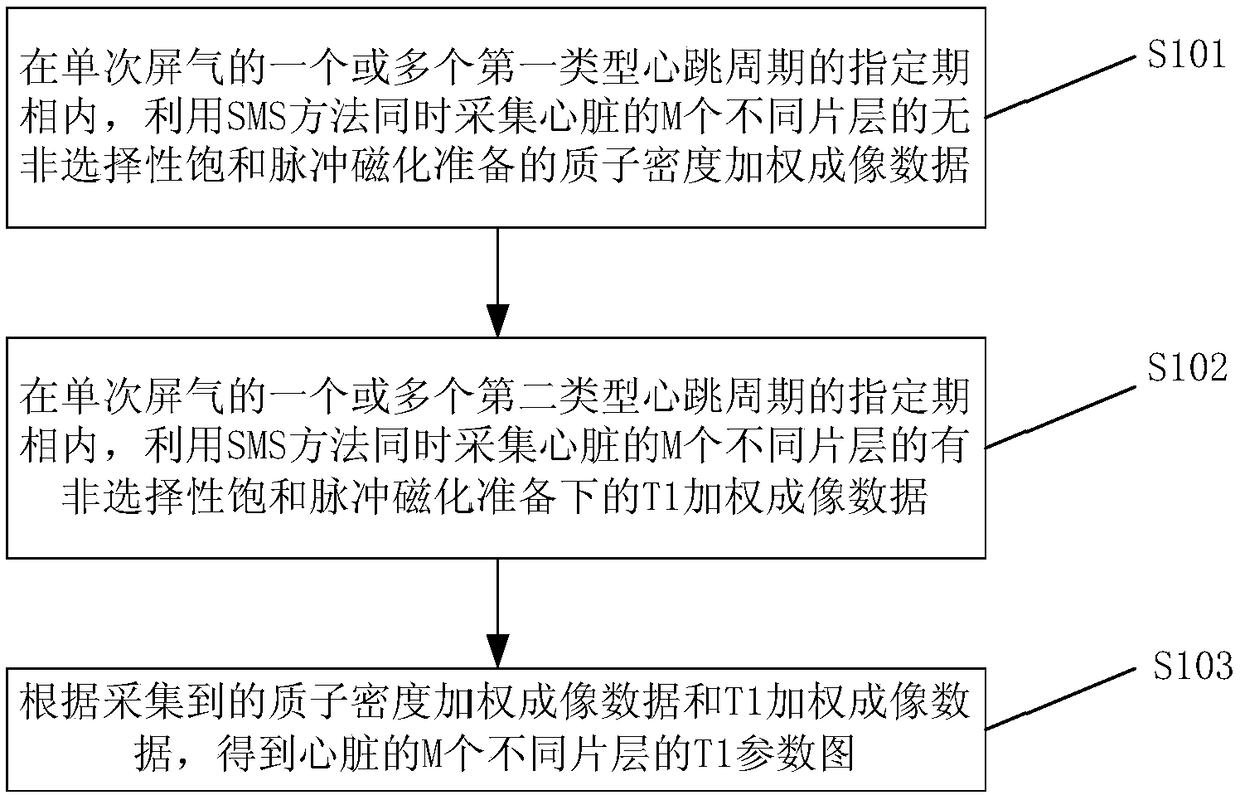
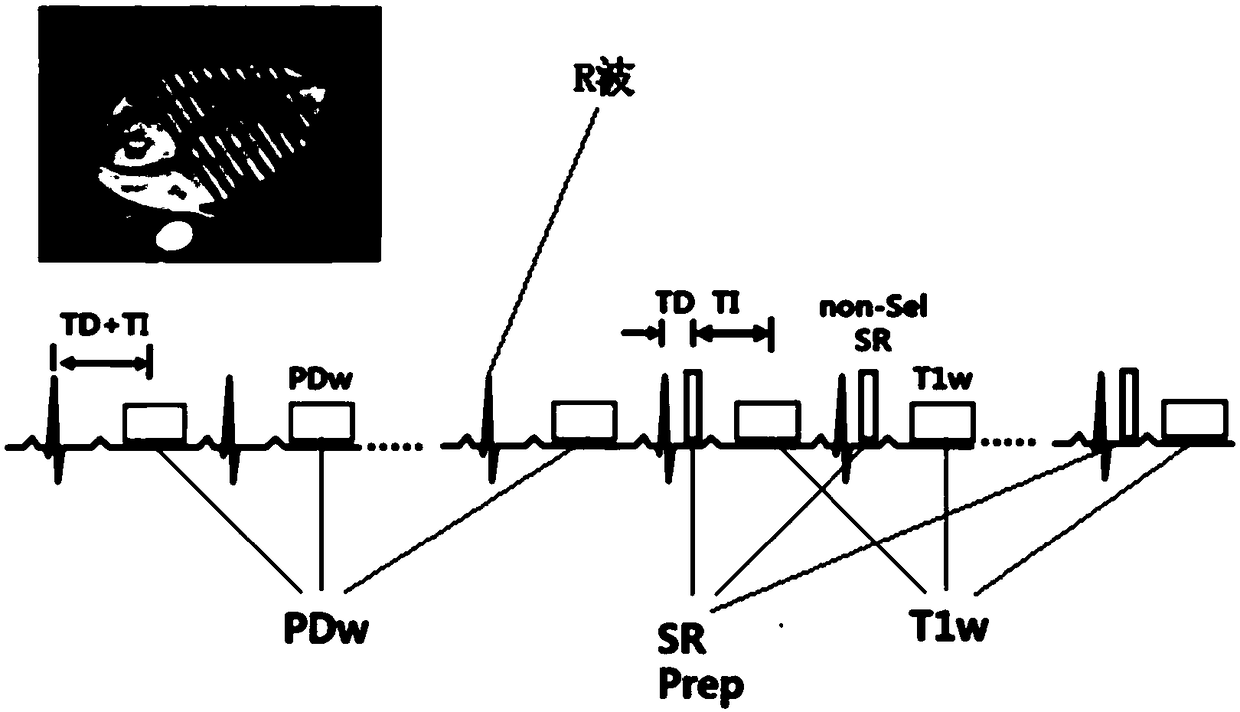
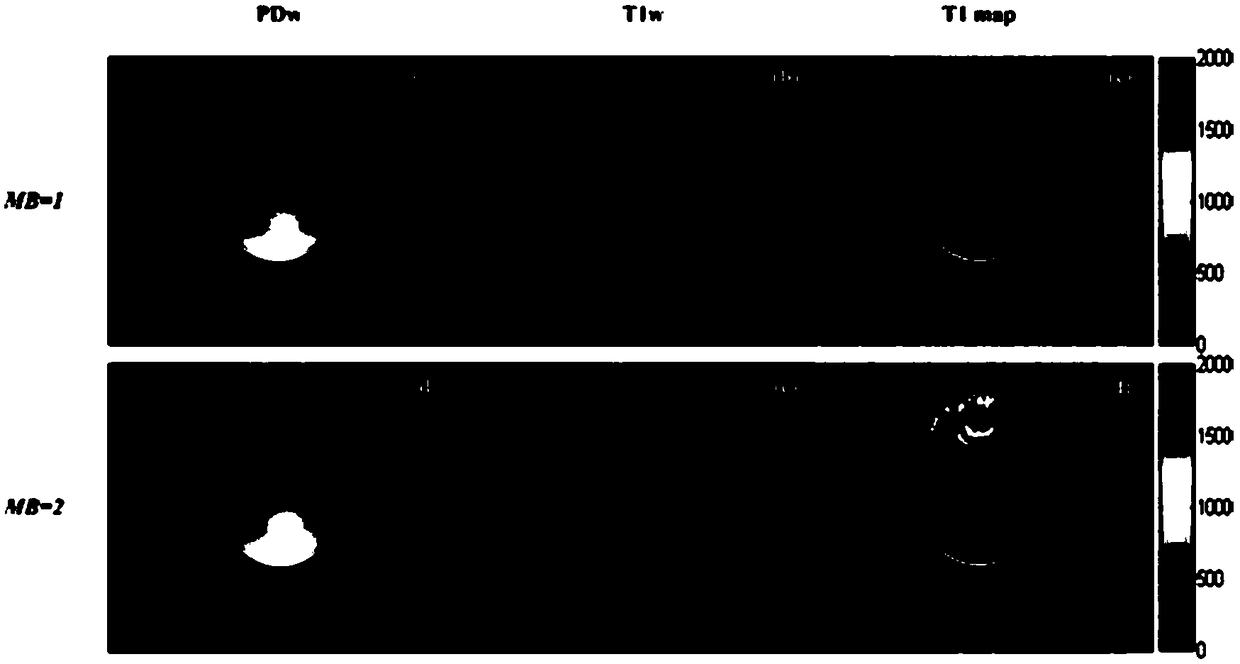
T1 parameter diagram imaging method and magnetic resonance imaging system
ActiveCN108742626AReduce scan timeImprove scanning efficiencyDiagnostic signal processingSensorsProtonMagnetization
The embodiment of the invention provides a T1 parameter image imaging method and a magnetic resonance imaging system. The method comprises the following steps: during the specified period of one or more first-type heart beat cycles with a single breath hold, proton density weighted imaging data of heart different M layers prepared by non-selective saturated pulse magnetization are collected simultaneously by using SMS method, during the specified period of one or more second-type heart beat cycles with a single breath hold, T1-weighted imaging data of heart different M layers prepared by non-selective saturated pulse magnetization are collected simultaneously by using SMS method, according to the proton density weighted imaging data and T1-weighted imaging data, the T1 parameters of the heart are obtained, by using SMS technology, two or more images in the same period can be acquired simultaneously in one heartbeat cycle, which enlarges the space coverage of T1 parameter map in singlebreath hold, and achieves the whole heart T1 parameter map, thus solving the problem of small space coverage of T1 parameter map in single breath hold.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
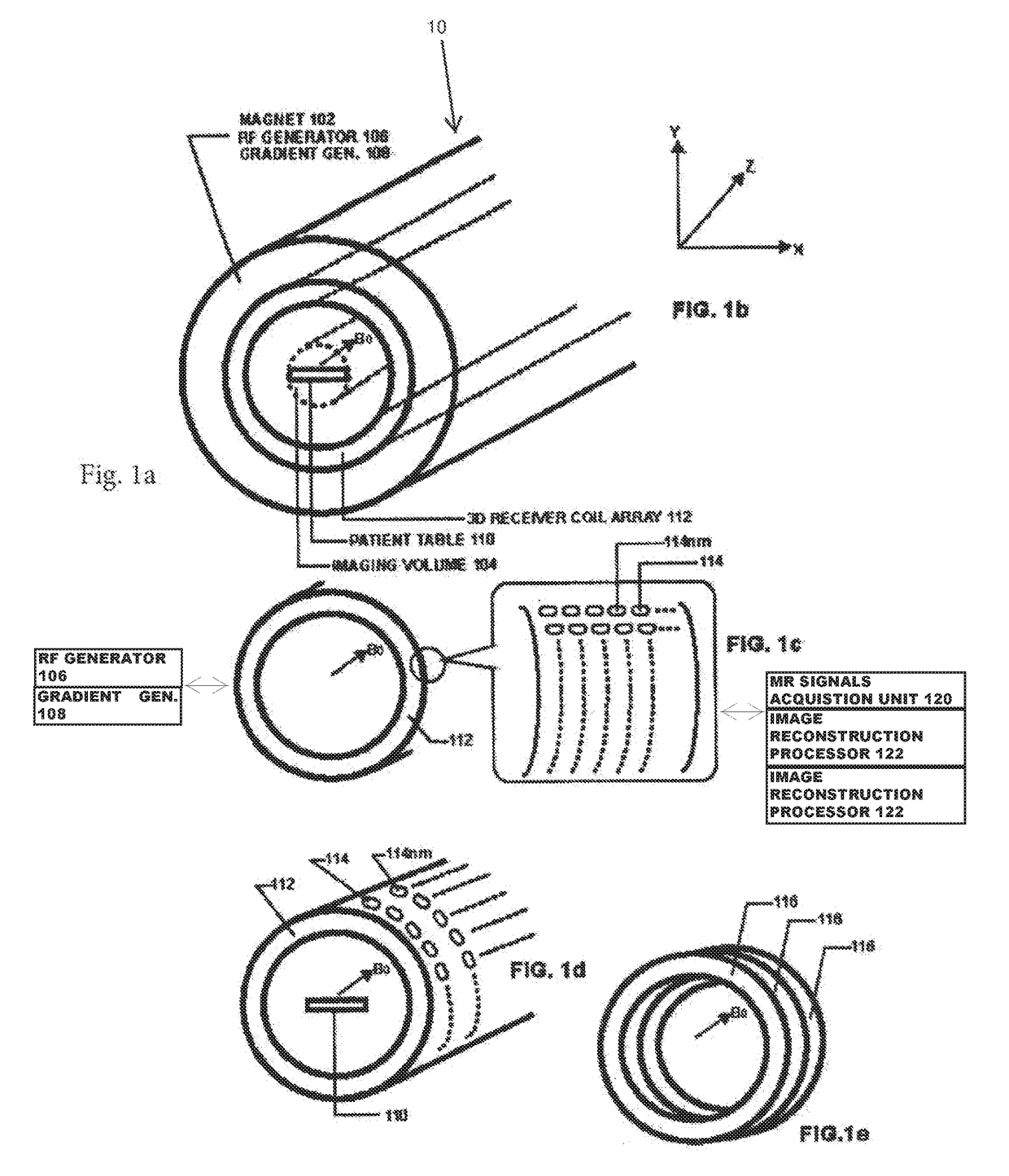
Ultrafast MRI system and method
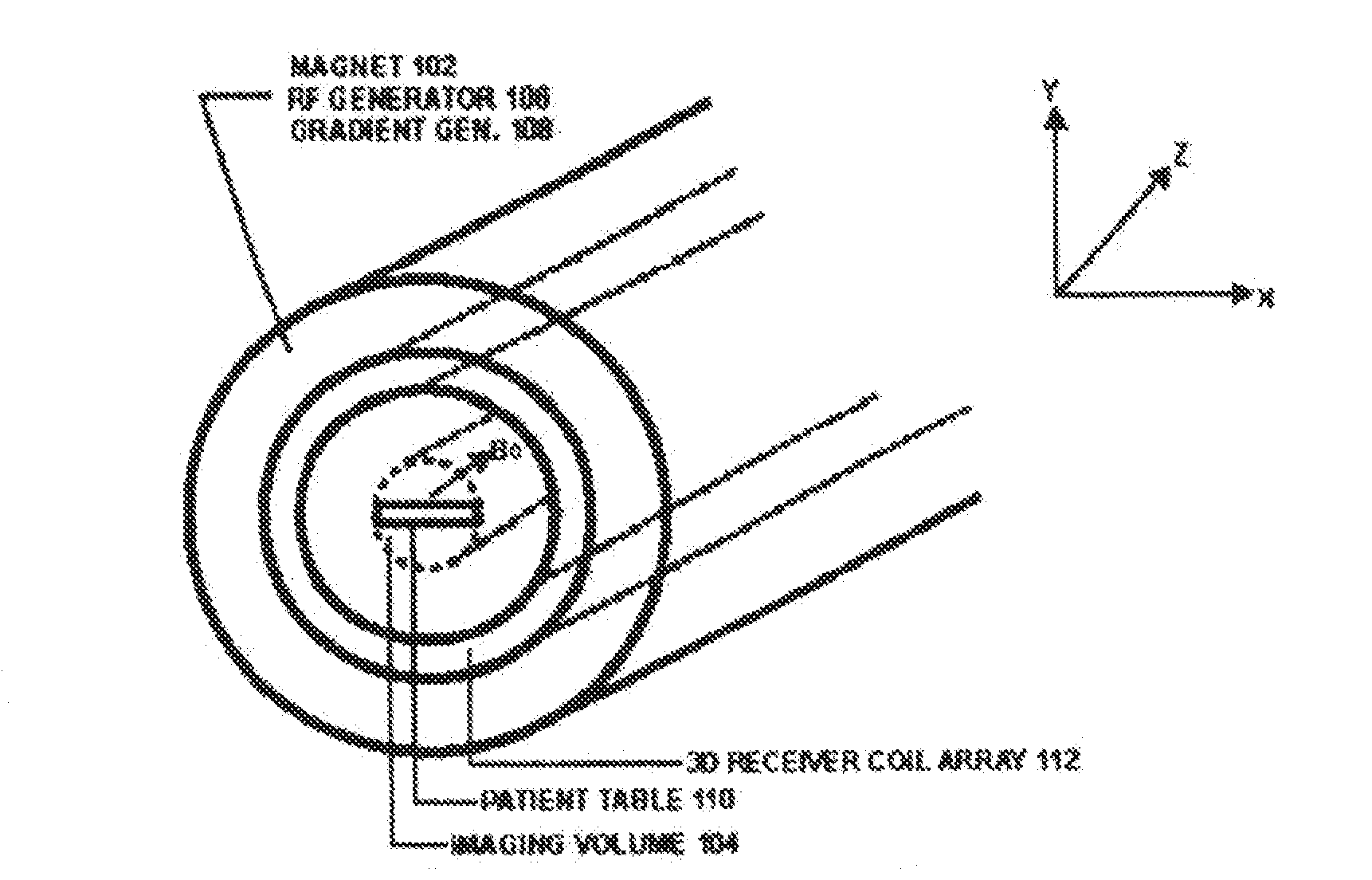
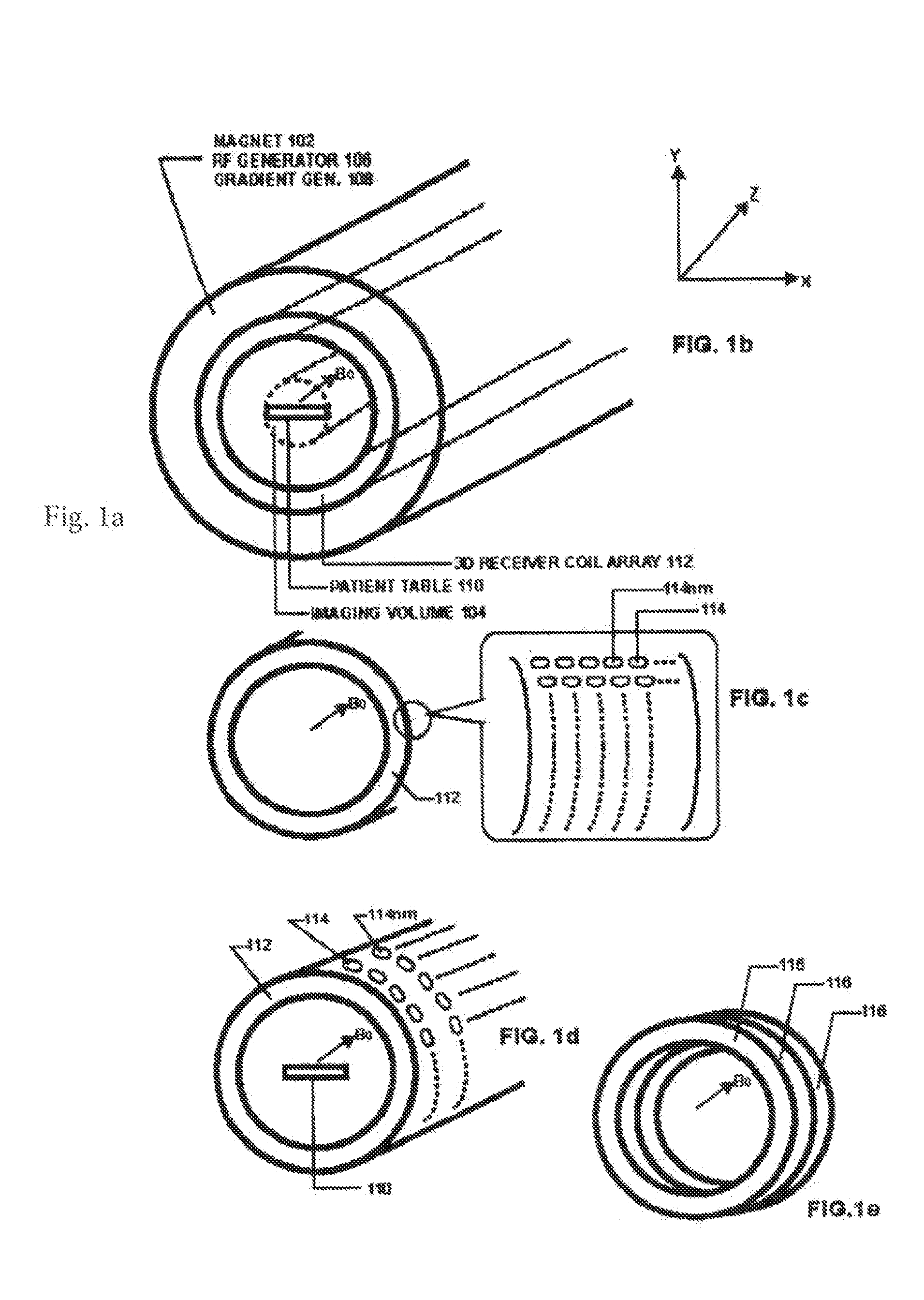
ActiveUS20190056471A1Reduce intensityImprove signal-to-noise ratioMeasurements using NMR imaging systems3d imageReceiver coil
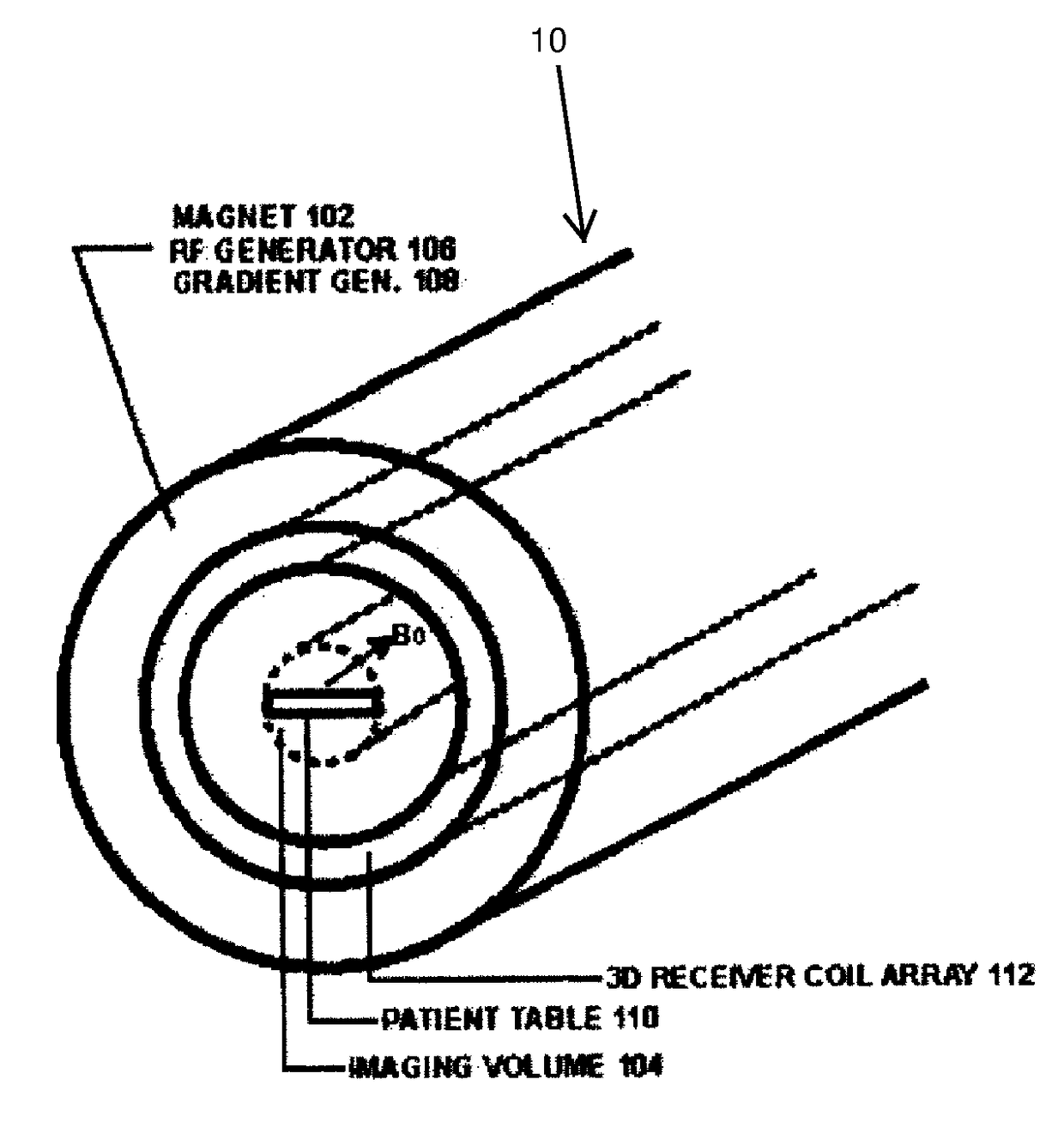
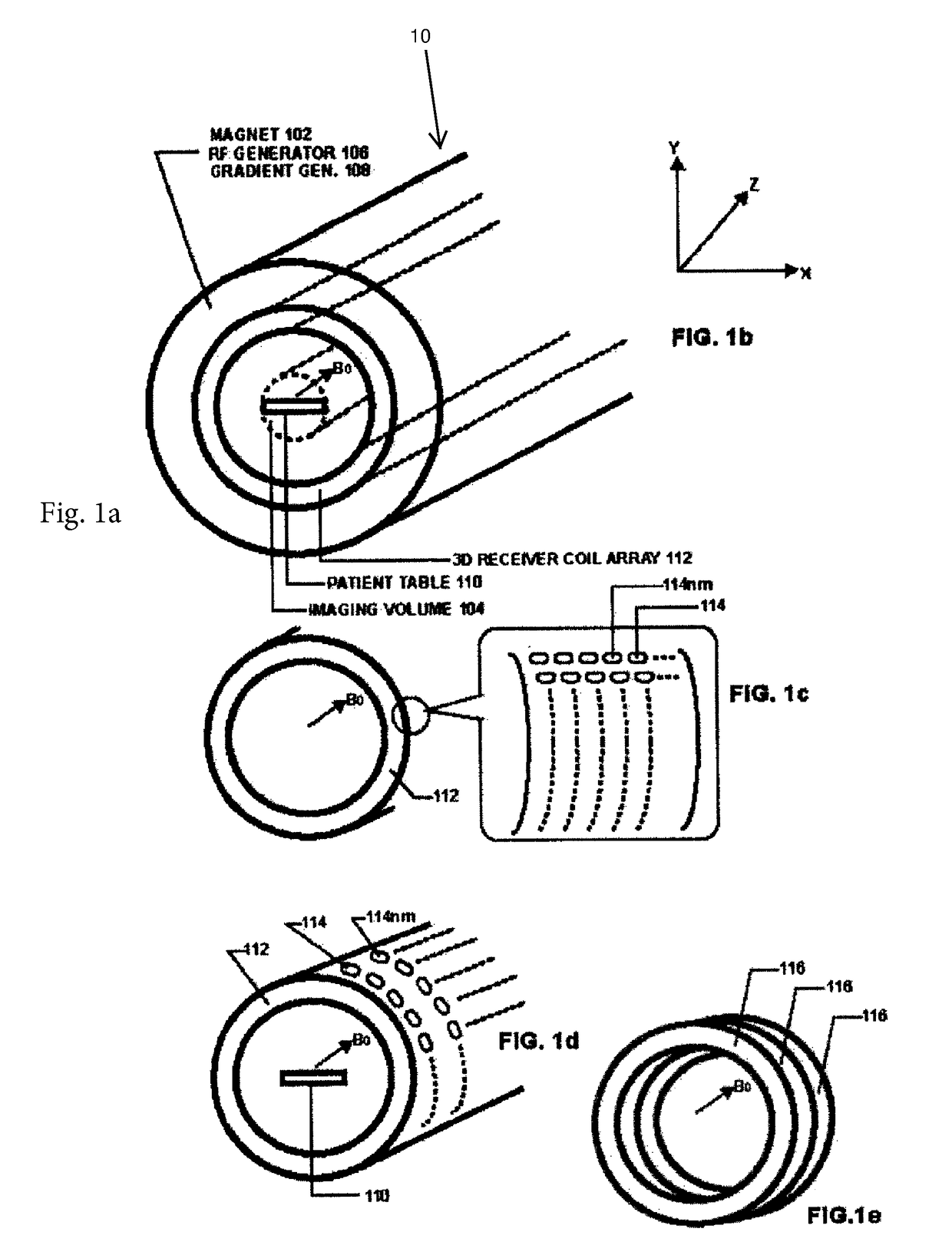
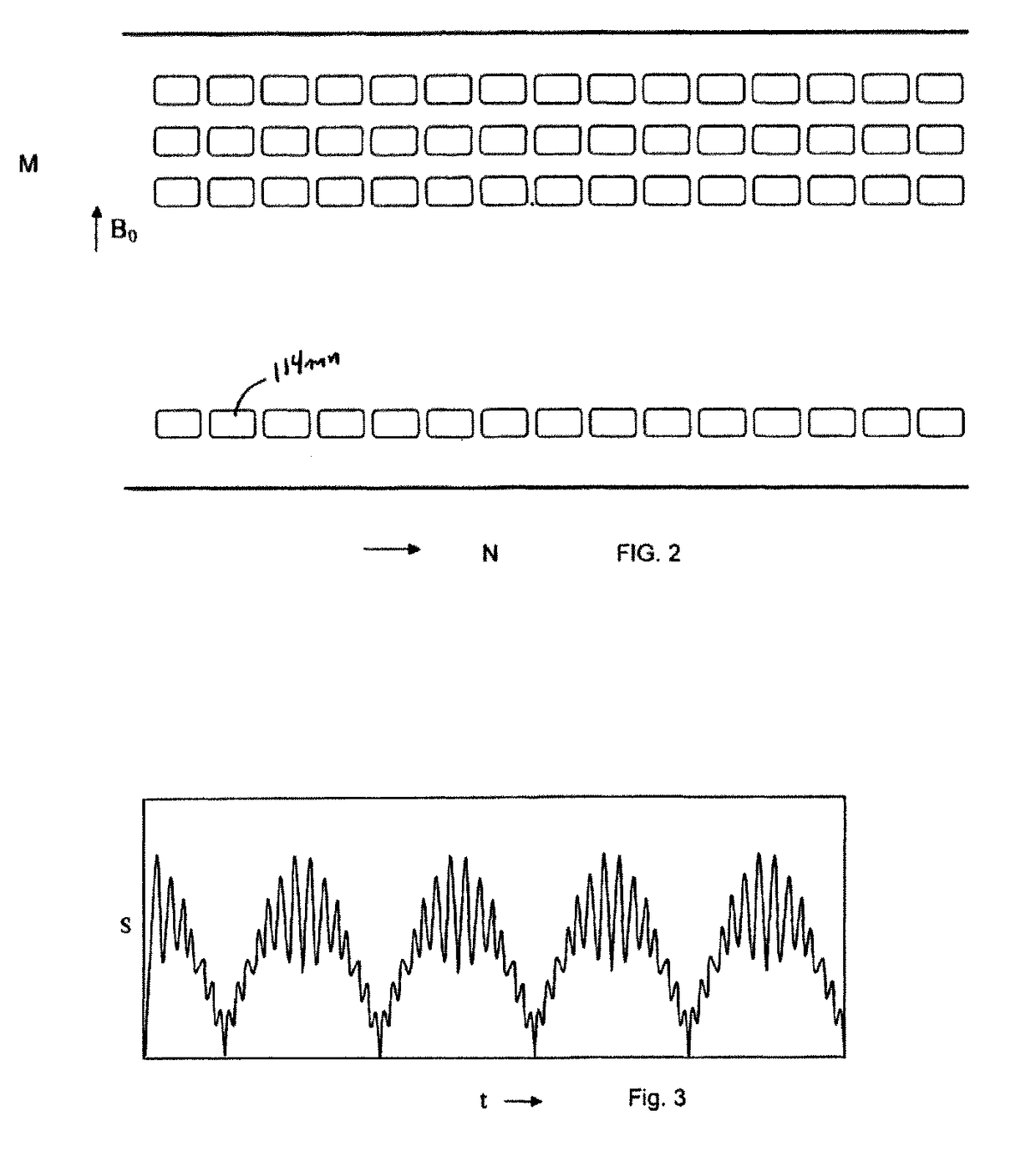
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI), which is given the acronym ULTRA (Unlimited Trains of Radio Acquisitions), can eliminate magnetic gradient reversals and allow simultaneous MR signal acquisition from the entire object volume in each of a multitude of very small receiver coils arranged in a 3D array around the imaging volume. This permits a rate of MR signal acquisition that is greatly increased (e.g. 256 times) compared with existing techniques, with a full 3D image constructed in as little as 1 millisecond. Furthermore, noise—both audible and electrical—is substantially reduced. The advantages over conventional MRI include:1. Clinical imaging can be completed in seconds or less, with good signal-to-noise ratio;2. Signal-to-noise ratio further increased by eliminating RF noise due to gradient switching;3. Real-time functional MRI on millisecond timescales;4. With single breath holds, high quality imaging of thorax and abdomen.5. Greatly reduced audible noise and vibration.
Owner:HUTCHINSON MICHAEL
Ultrafast MRI System and Method
ActiveUS20160282429A1Diagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systems3d imageReceiver coil
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI), which is given the acronym ULTRA (Unlimited Trains of Radio Acquisitions), can eliminate magnetic gradient reversals and allow simultaneous MR signal acquisition from the entire object volume in each of a multitude of very small receiver coils arranged in a 3D array around the imaging volume. This permits a rate of MR signal acquisition that is greatly increased (e.g. 256 times) compared with existing techniques, with a full 3D image constructed in as little as 1 millisecond. Furthermore, noise—both audible and electrical—is substantially reduced. The advantages over conventional MRI include:1. Clinical imaging can be completed in seconds, with good signal-to-noise ratio;2. Signal-to-noise ratio is further increased by eliminating RF noise due to gradient switching;3. Real-time functional MRI is possible, on millisecond timescales;4. With single breath holds, high quality imaging of thorax and abdomen is possible.5. ULTRA greatly reduces audible noise and vibration.
Owner:HUTCHINSON MICHAEL
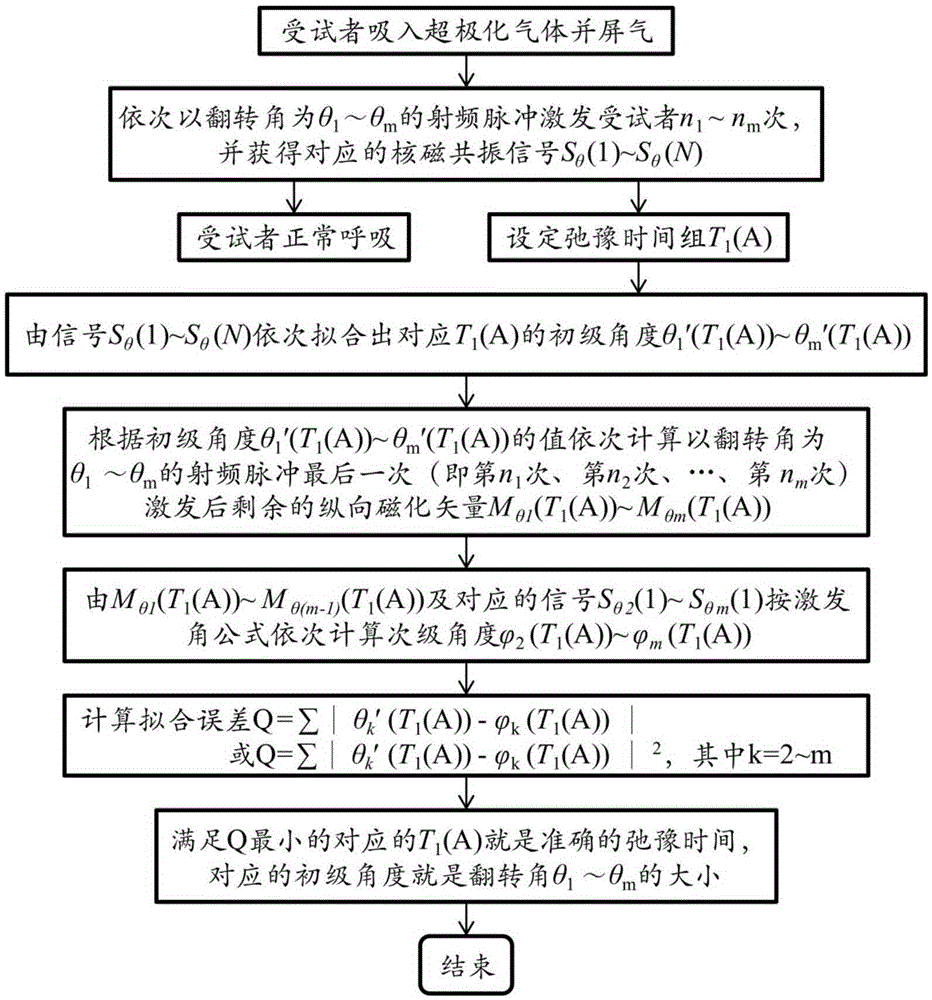
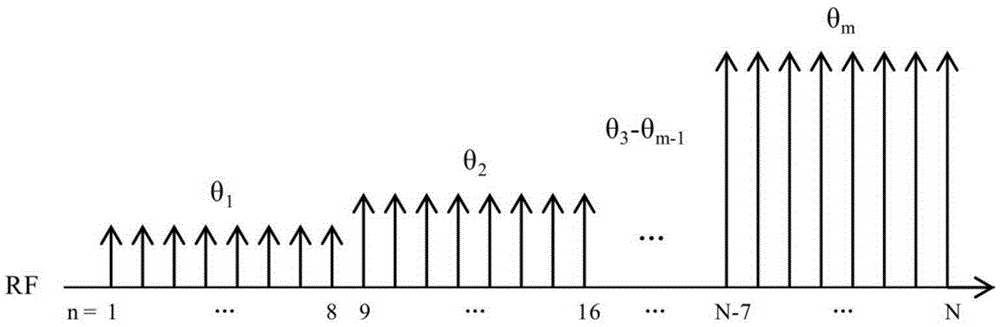
Hyperpolarized angle calibration method based on multi-angle excitation in single breath hold
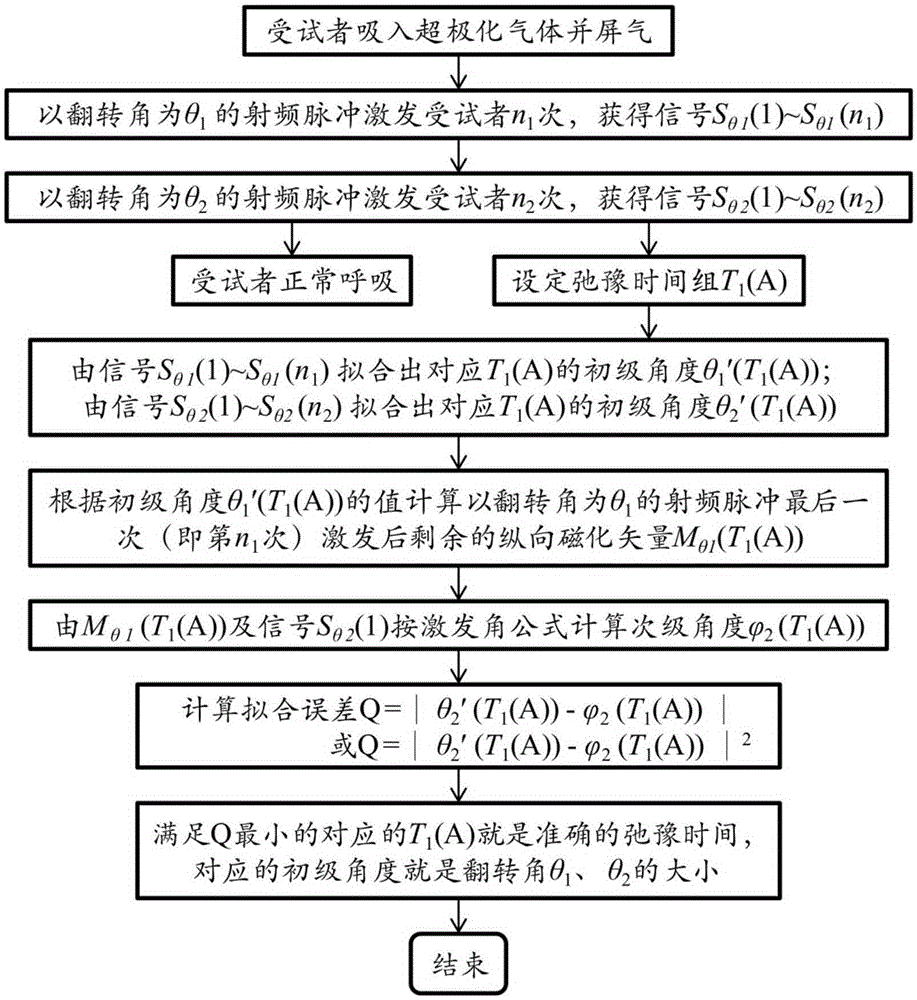
ActiveCN105301543AImprove accuracyShorten the timeMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectrical measurementsSingle breathFitting-out
The invention discloses a hyperpolarized angle calibration method based on multi-angle excitation in a single breath hold. The method comprises the steps of: using a multi-angle excitation mode in the single breath hold of a subject to obtain signals excited by different angles; then setting a group of longitudinal relaxation time T1 values, and fitting out a primary angle [theta]' by the signals of the different angles; utilizing the [theta]' to successively calculate a residual longitudinal magnetized vector M after the final time of excitation of each angle, and then utilizing M and signals of the first time of excitation of each angle to calculates a secondary angle [phi], wherein in one group of set T1 values, the T1 value, enabling the primary angle [theta]' to be closest to the secondary angle [phi], is the most accurate longitudinal relaxation time; and then utilizing the T1 value to calculate all the angles, and finishing angle calibration. The method has the advantages that the operation is simple, the calibration of the plurality of angles and the measurement of T1 are simultaneously completed in the single breath hold, the time is saved, and the cost is also saved.
Owner:WUHAN INST OF PHYSICS & MATHEMATICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
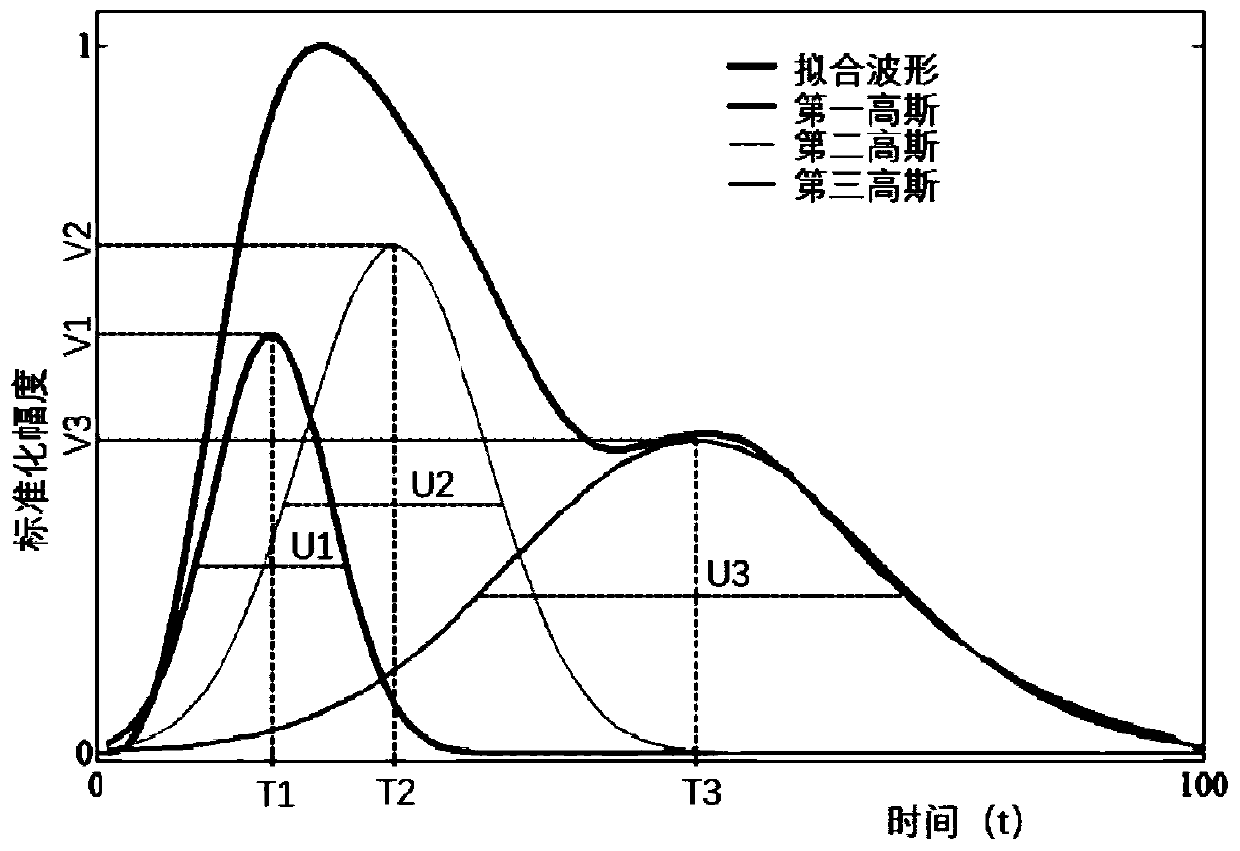
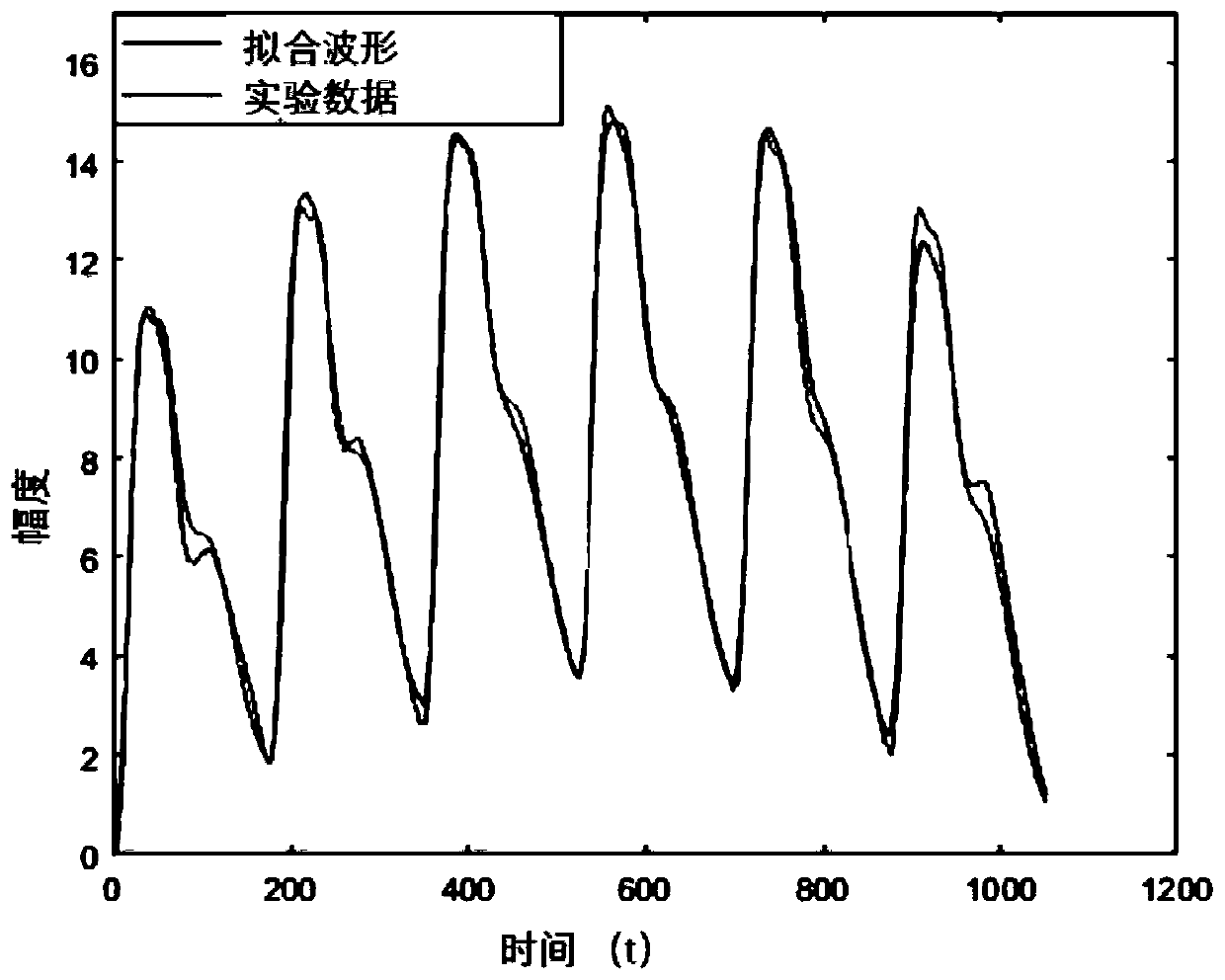
Simulation synthesis method and device for photoelectric volume wave signals
In a signal simulation synthesis method, three Gaussian signals are mutually superposed to fit an actual single-cardiac-cycle photoelectric volume wave waveform, and then the simulated single-cardiac-cycle photoelectric volume wave is extended to multiple cardiac cycles; two semi-sinusoidal signals are superposed to fit an actual single-respiratory-cycle respiratory wave, and obtained two semi-sinusoidal signals are used for simulating a single-respiratory-cycle respiratory wave; a mathematical model of amplitude, frequency and intensity change of respiration-induced photoelectric volume wavesis established, the proportion coefficient and phase difference of amplitude, frequency and intensity change of the respiration-induced photoelectric volume wave are solved by fitting the actual photoelectric volume wave waveform, and blood oxygen saturation and pulse rate variation signal are organically synthesized into a simulated photoelectric volume wave signal in a mode close to physiology,so that photoelectric volume wave simulated signals containing standard pulse rate, respiration, blood oxygen saturation and pulse rate variability is synthesized, and a simulation synthesis method and device for photoelectric volume wave signals are achieved.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
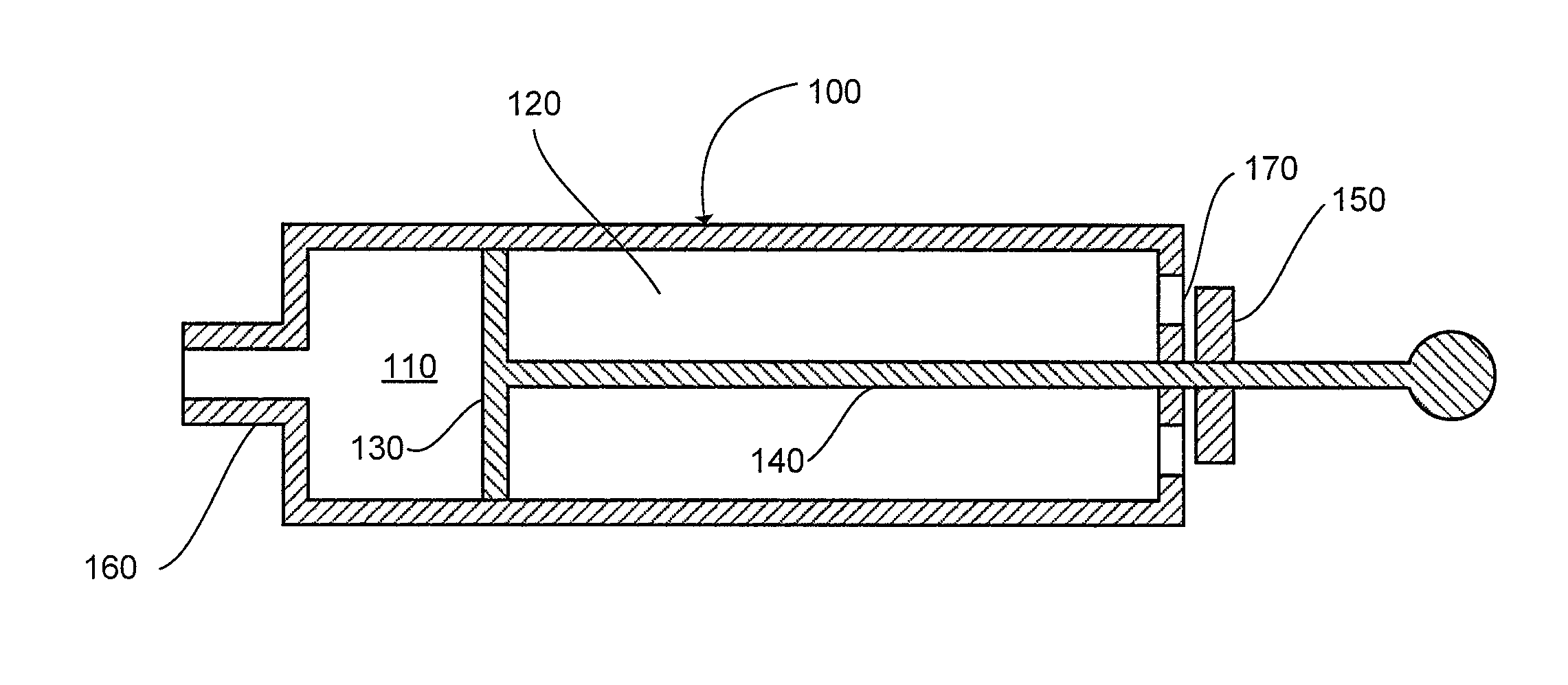
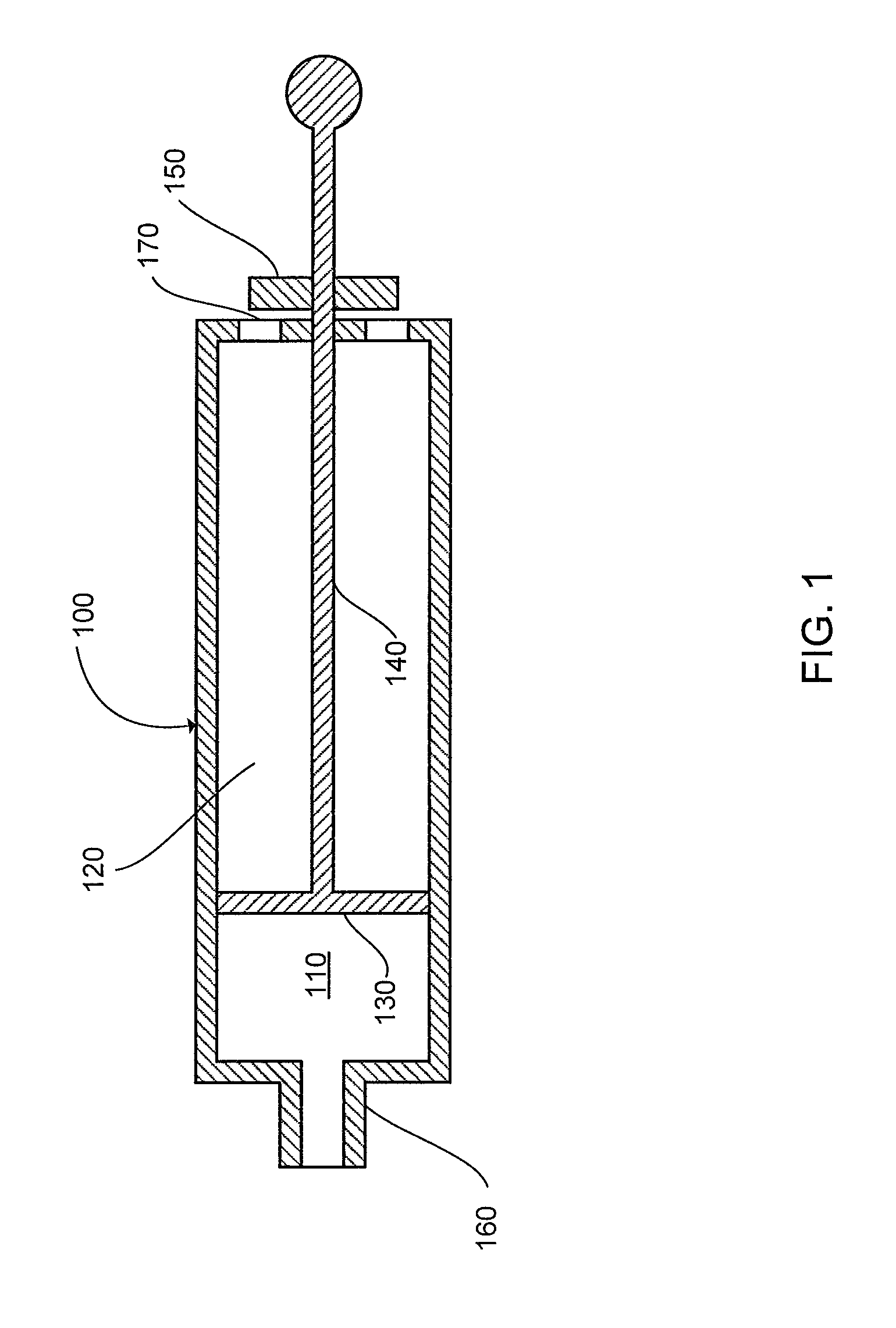
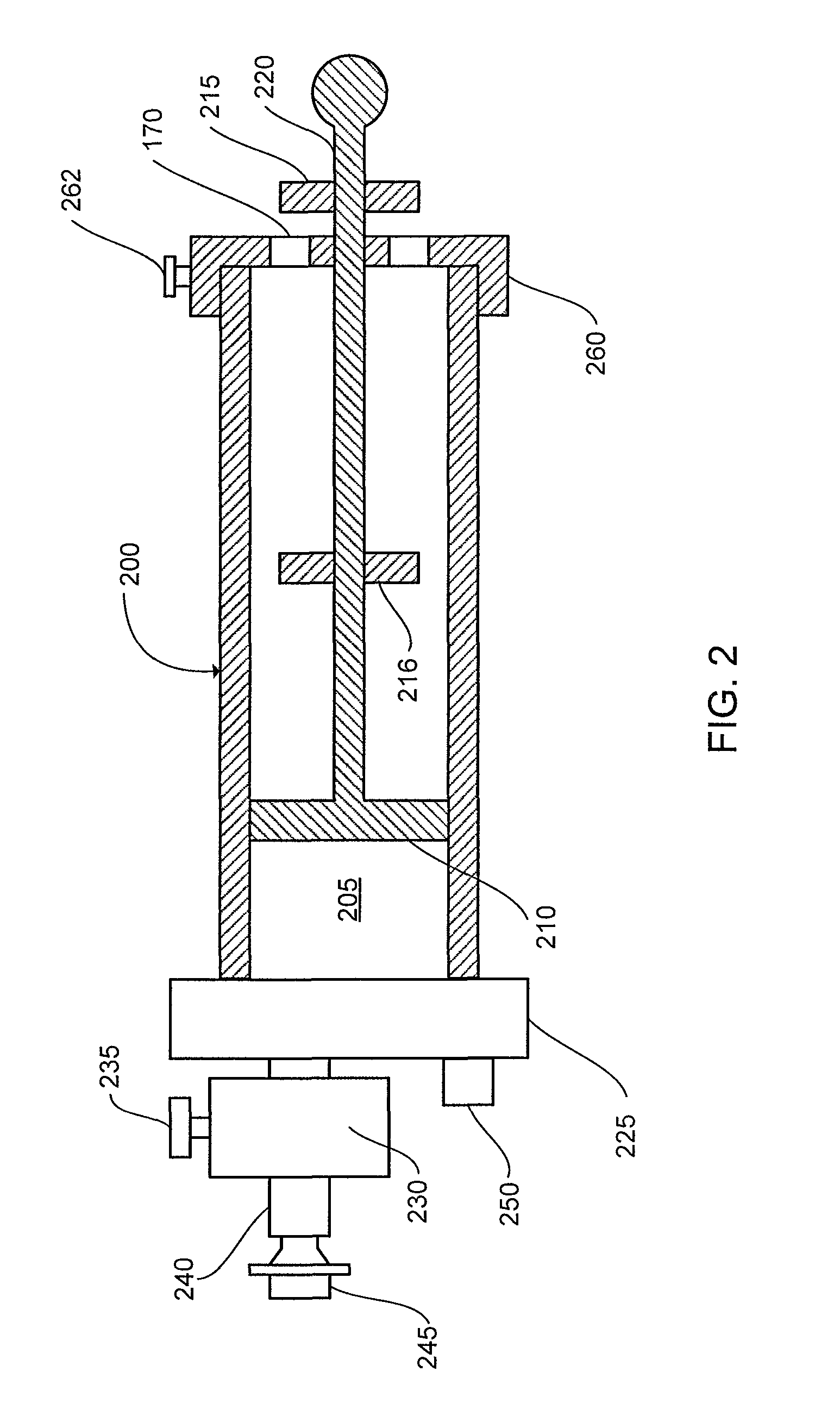
Method and system for DLCO quality control testing
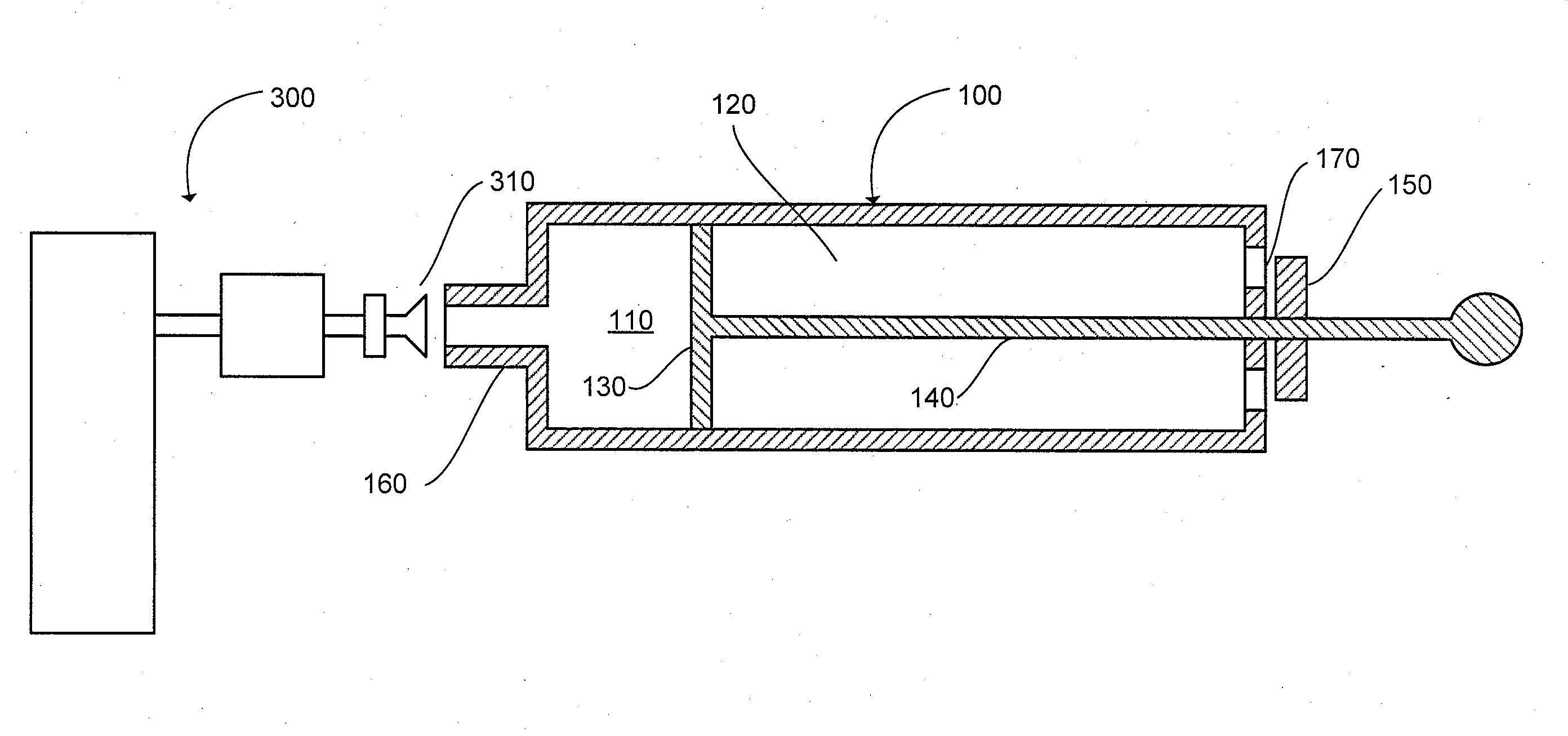
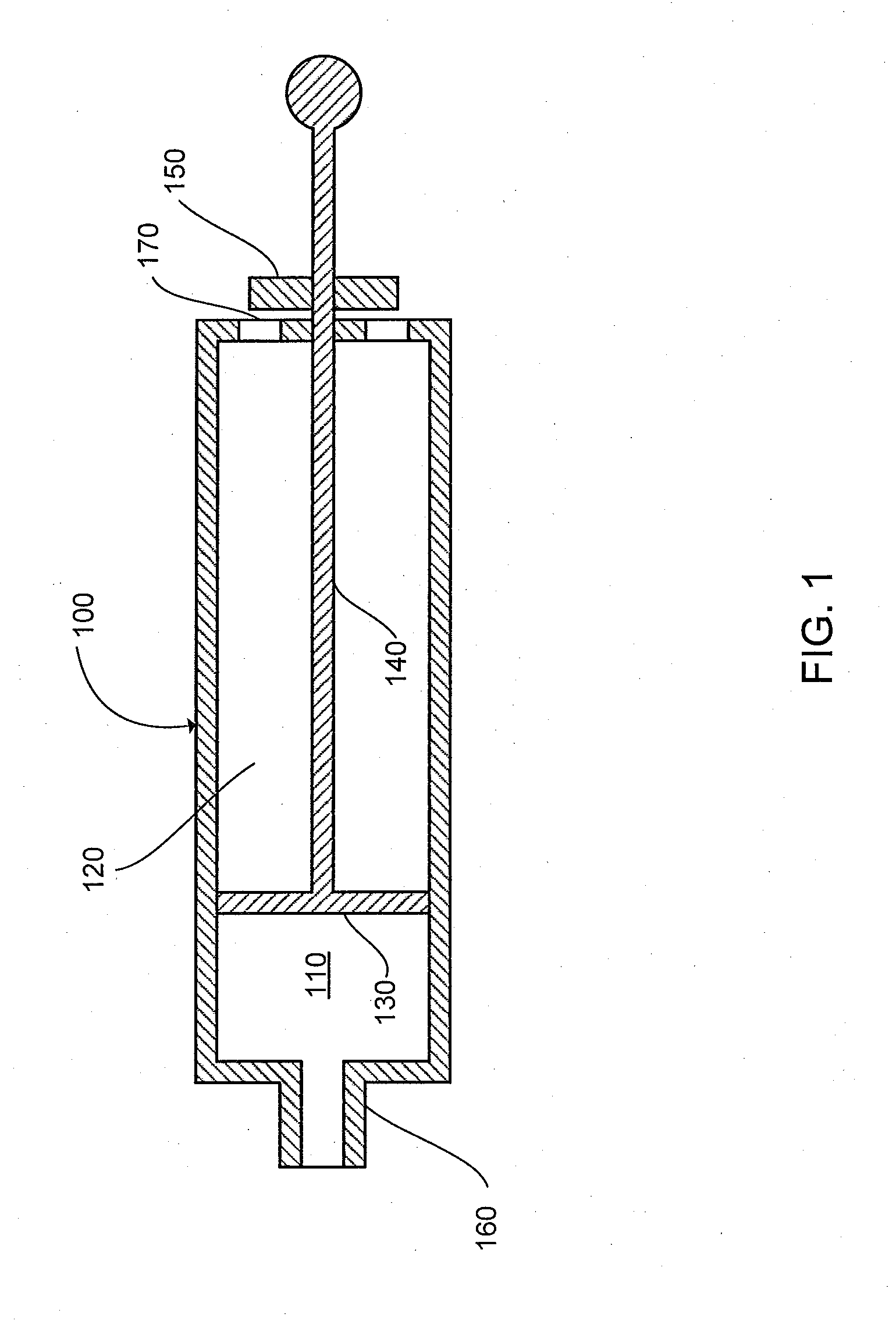
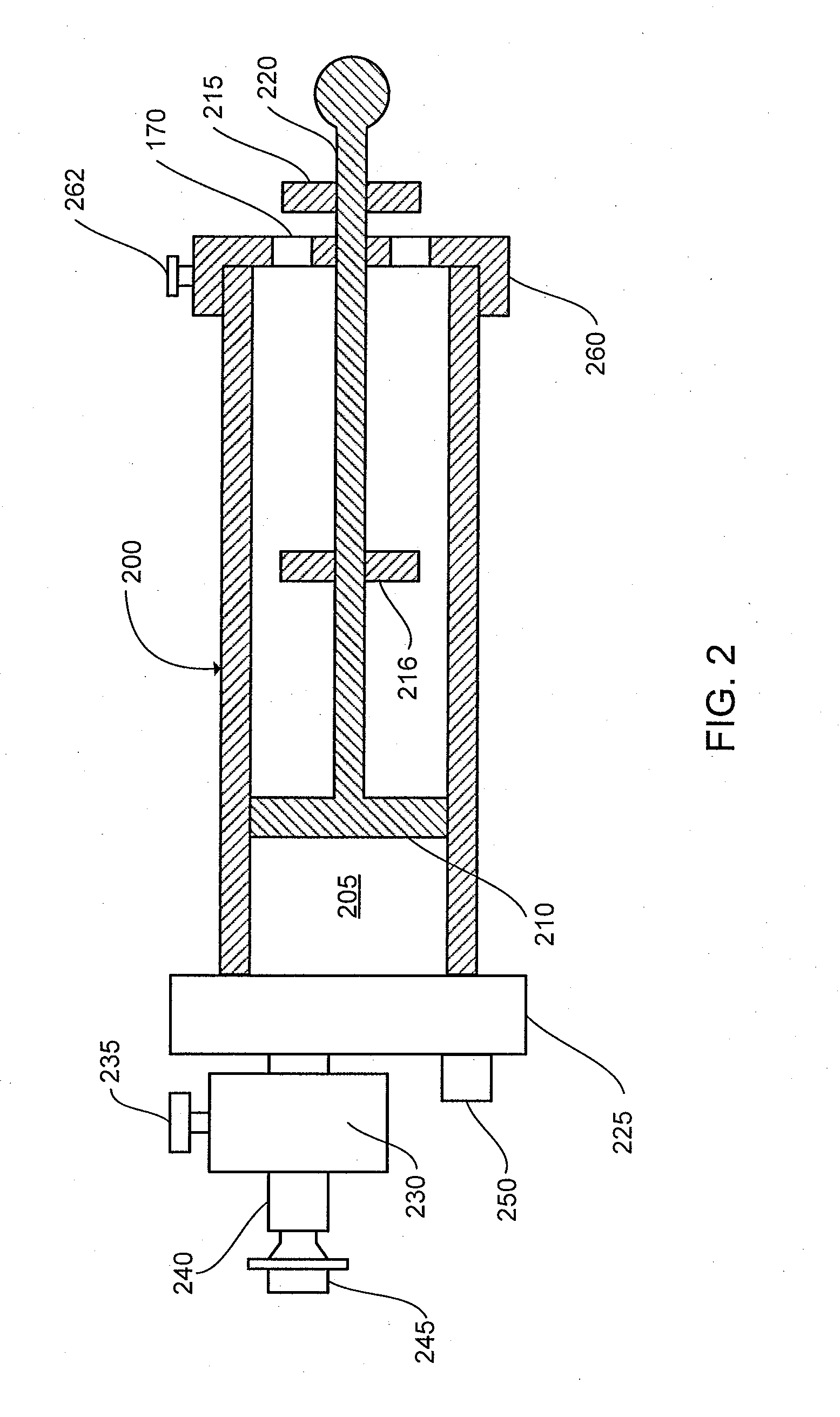
The present invention can provide a system and method for DLCO quality control testing and can include an apparatus for testing a pulmonary diagnostic device capable of performing single breath carbon monoxide uptake measurement, comprising: a single gas-tight chamber, with a gas port configured to receive gas from or to expel gas to the exterior of the chamber and a partition configured to change the volume of the single gas-tight chamber; the single gas-tight chamber capable of expanding and contracting; a member disposed within the single gas-tight chamber and configured to limit the movement of the partition, the member being adjustable to set a predetermined maximum volume of the single gas-tight chamber and a predetermined volume of DLCO test gas that the single gas-tight chamber can receive; and an interface configured for the transfer of gas between the pulmonary diagnostic device and the simulation device via the gas port.
Owner:KOKO IT LLC
Multiple soft projectile blow gun
InactiveUS8893697B2Rapid continuous firingEliminating a choking hazard for the userBlow gunsBatonsEngineeringSingle breath
Owner:FOELLER MARK R
Ultrafast MRI system and method
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI), which is given the acronym ULTRA (Unlimited Trains of Radio Acquisitions), can eliminate magnetic gradient reversals and allow simultaneous MR signal acquisition from the entire object volume in each of a multitude of very small receiver coils arranged in a 3D array around the imaging volume. This permits a rate of MR signal acquisition that is greatly increased (e.g. 256 times) compared with existing techniques, with a full 3D image constructed in as little as 1 millisecond. Furthermore, noise—both audible and electrical—is substantially reduced. The advantages over conventional MRI include:1. Clinical imaging can be completed in seconds, with good signal-to-noise ratio;2. Signal-to-noise ratio is further increased by eliminating RF noise due to gradient switching;3. Real-time functional MRI is possible, on millisecond timescales;4. With single breath holds, high quality imaging of thorax and abdomen is possible.5. ULTRA greatly reduces audible noise and vibration.
Owner:HUTCHINSON MICHAEL
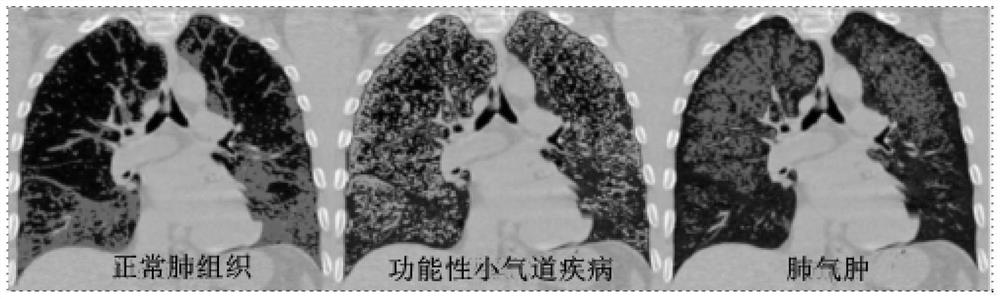
Lung function small airway disease prediction system and method, medium and electronic equipment
PendingCN113823413AReduce radiation doseProtect your healthImage enhancementImage analysisRadiation DosagesAirway disease
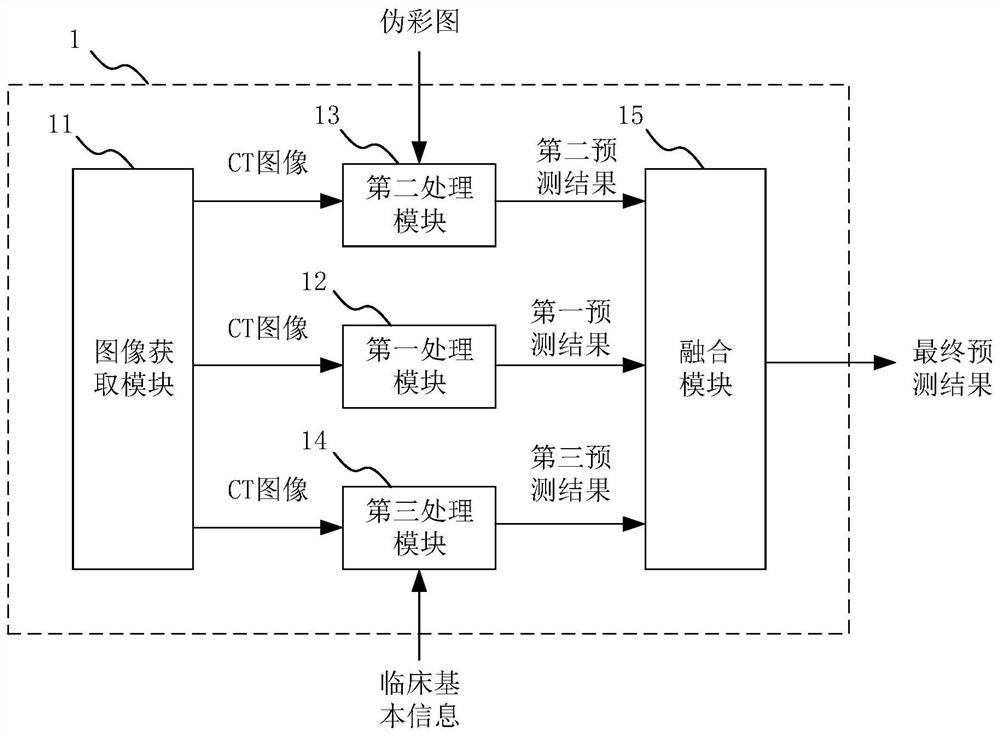
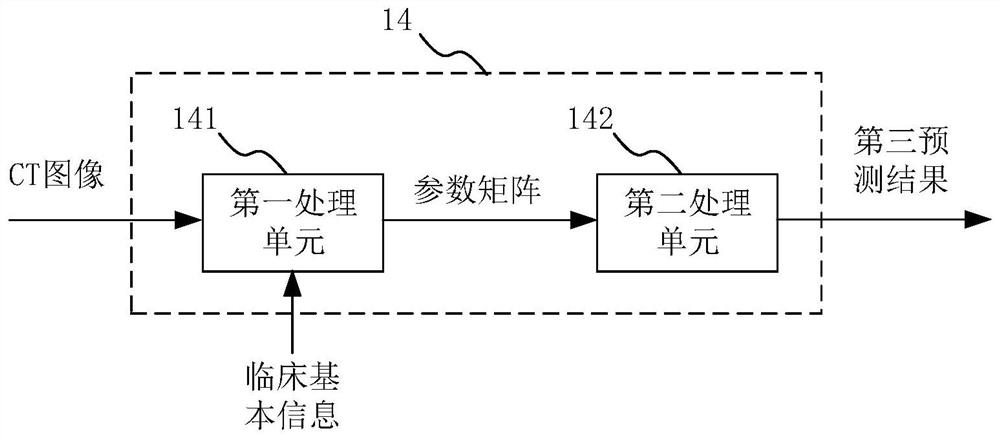
The invention provides a lung function small airway disease prediction system and method, a medium and electronic equipment. The system comprises: an image acquisition module used for acquiring a single respiratory phase chest CT image of a target object; a first processing module used for acquiring a first prediction result of the lung function small airway evaluation parameters by using a first deep learning model; a second processing module used for acquiring a second prediction result of the lung function small airway evaluation parameters by using a second deep learning model; a third processing module used for acquiring a third prediction result of the lung function small airway evaluation parameters by utilizing the machine learning model; and a fusion module used for fusing the first prediction result, the second prediction result and the third prediction result to obtain a final prediction result of the lung function small airway evaluation parameters. The system does not need to obtain a double-gas-phase CT image of the target object, and the radiation dose borne by the target object is reduced.
Owner:SHANGHAI CHANGZHENG HOSPITAL +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com