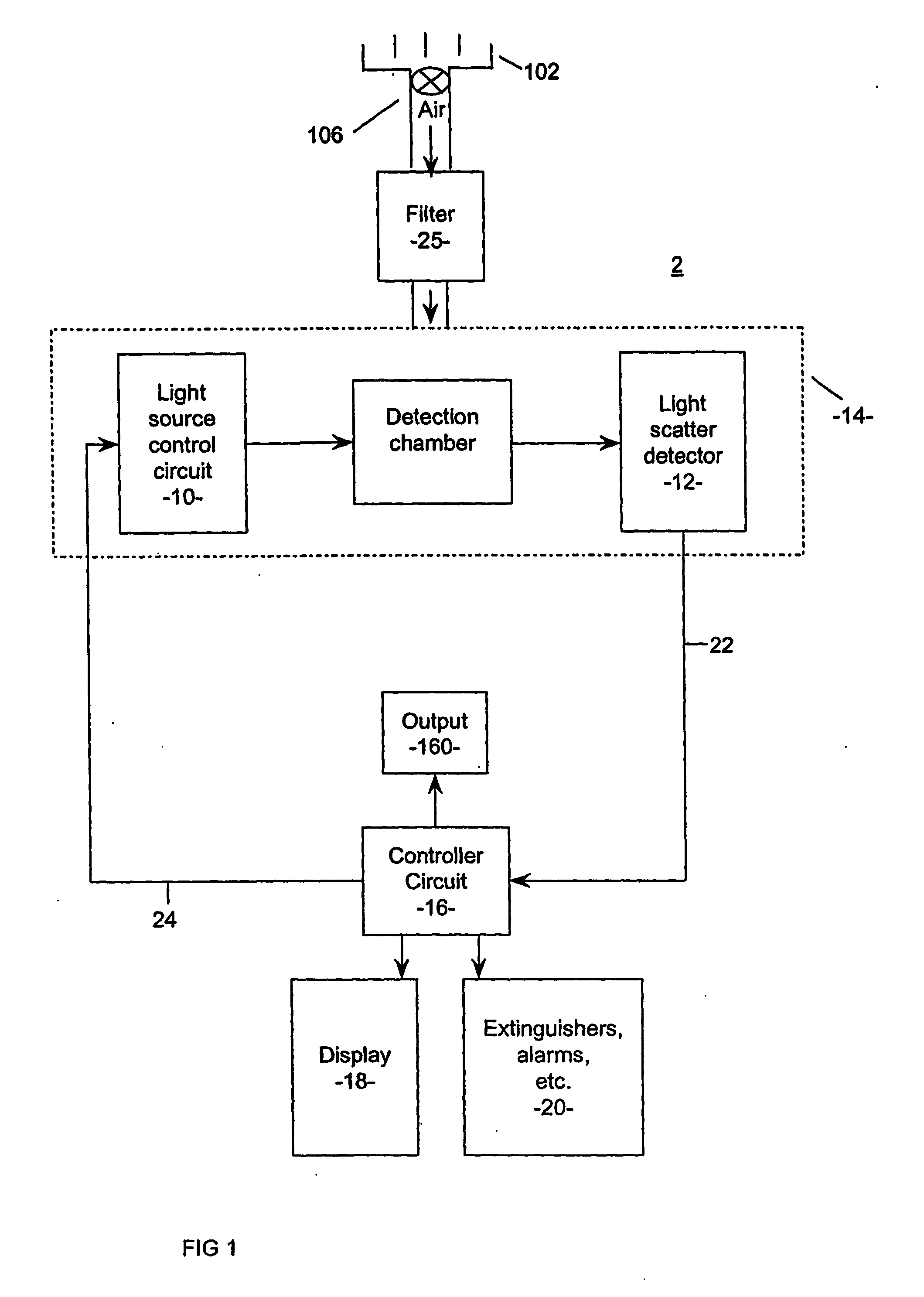
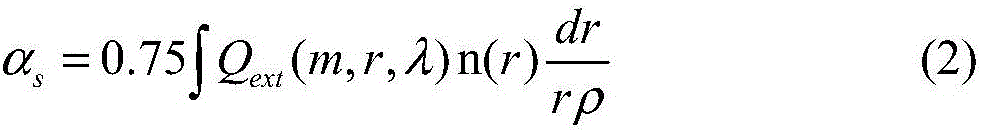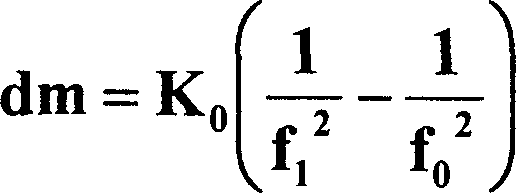Patents
Literature
172 results about "Particle mass" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
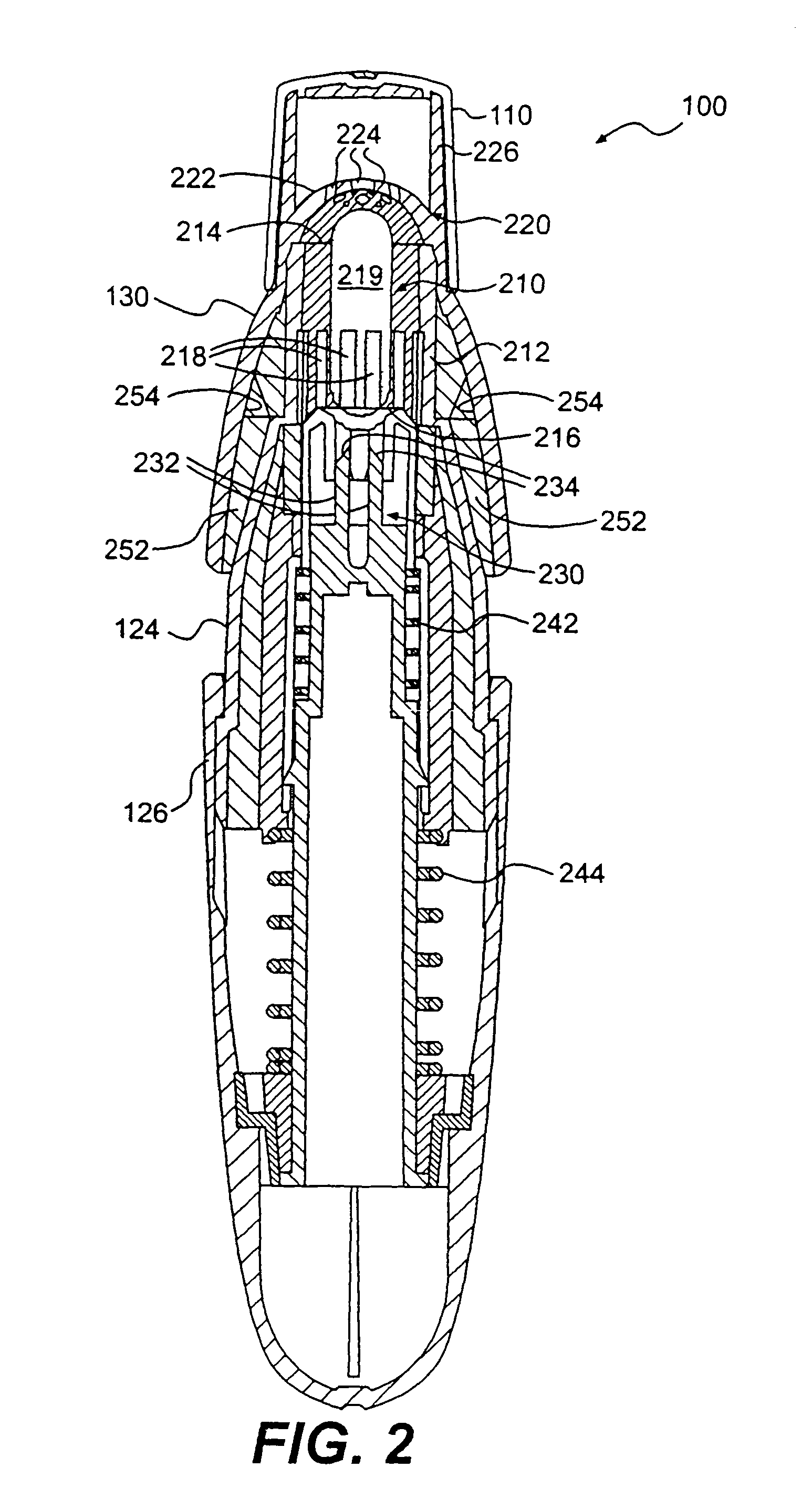
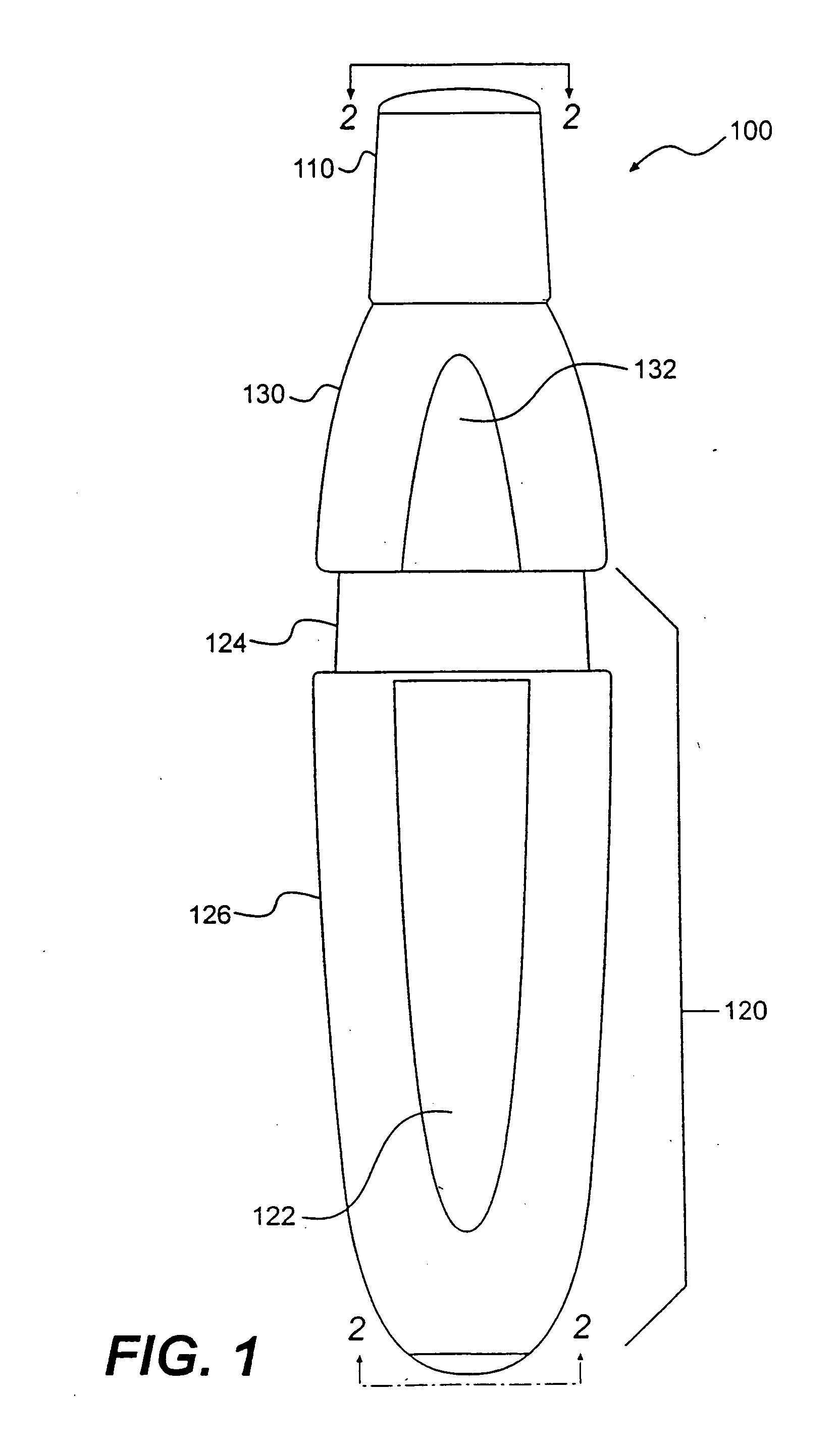
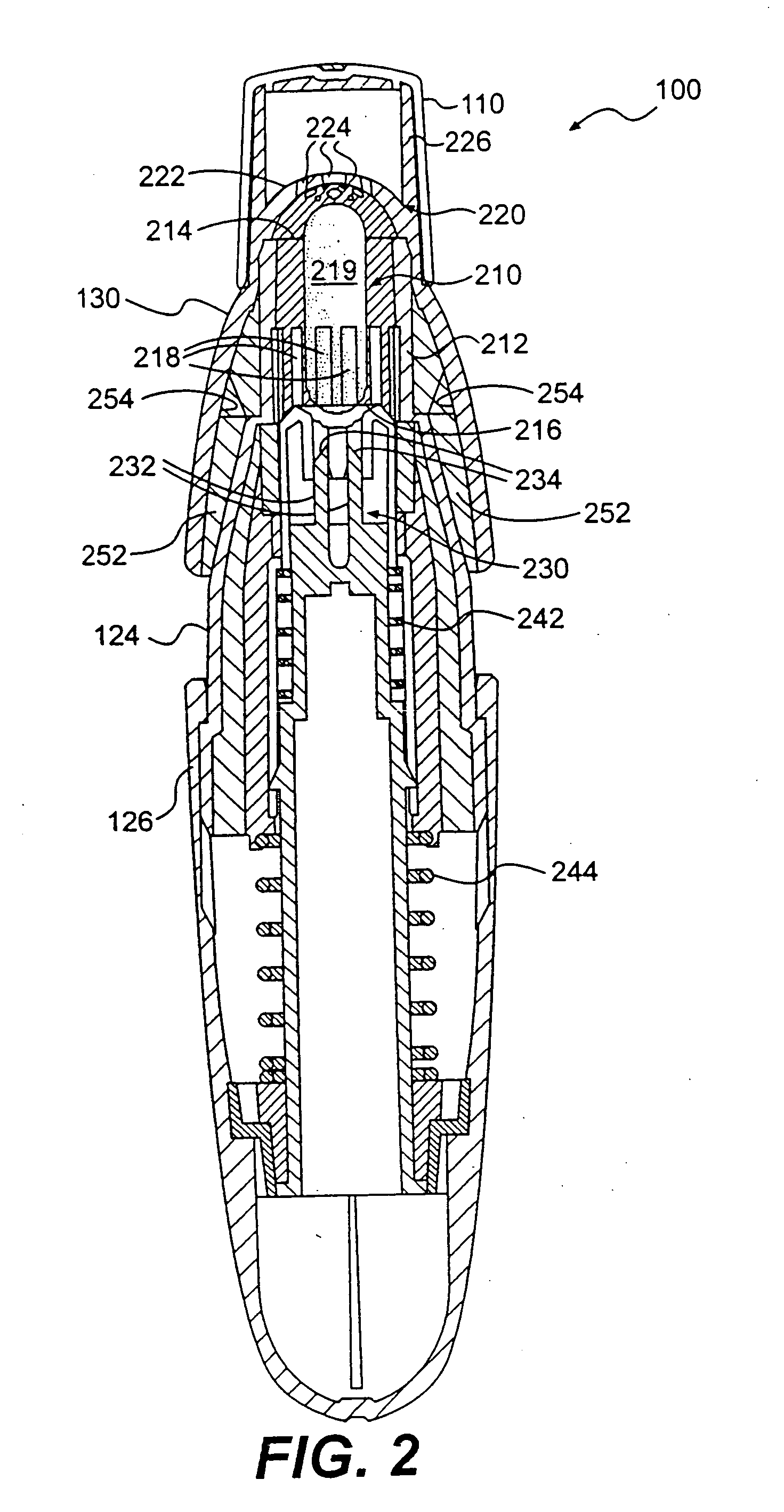
Low dose pharmaceutical powders for inhalations
ActiveUS7954491B2Facilitate depositionGood dispersionRespiratorsPowder deliveryInhalationSingle breath
The invention relates to a method of delivering an agent to the pulmonary system of a compromised patient, in a single breath-activated step, comprising administering a particle mass comprising an agent from an inhaler containing less than 5 milligrams of the mass, wherein at least about 50% of the mass in the receptacle is delivered to the pulmonary system of a patient. The invention also relates to receptacles containing the particle mass and the inhaler for use therein.
Owner:CIVITAS THERAPEUTICS
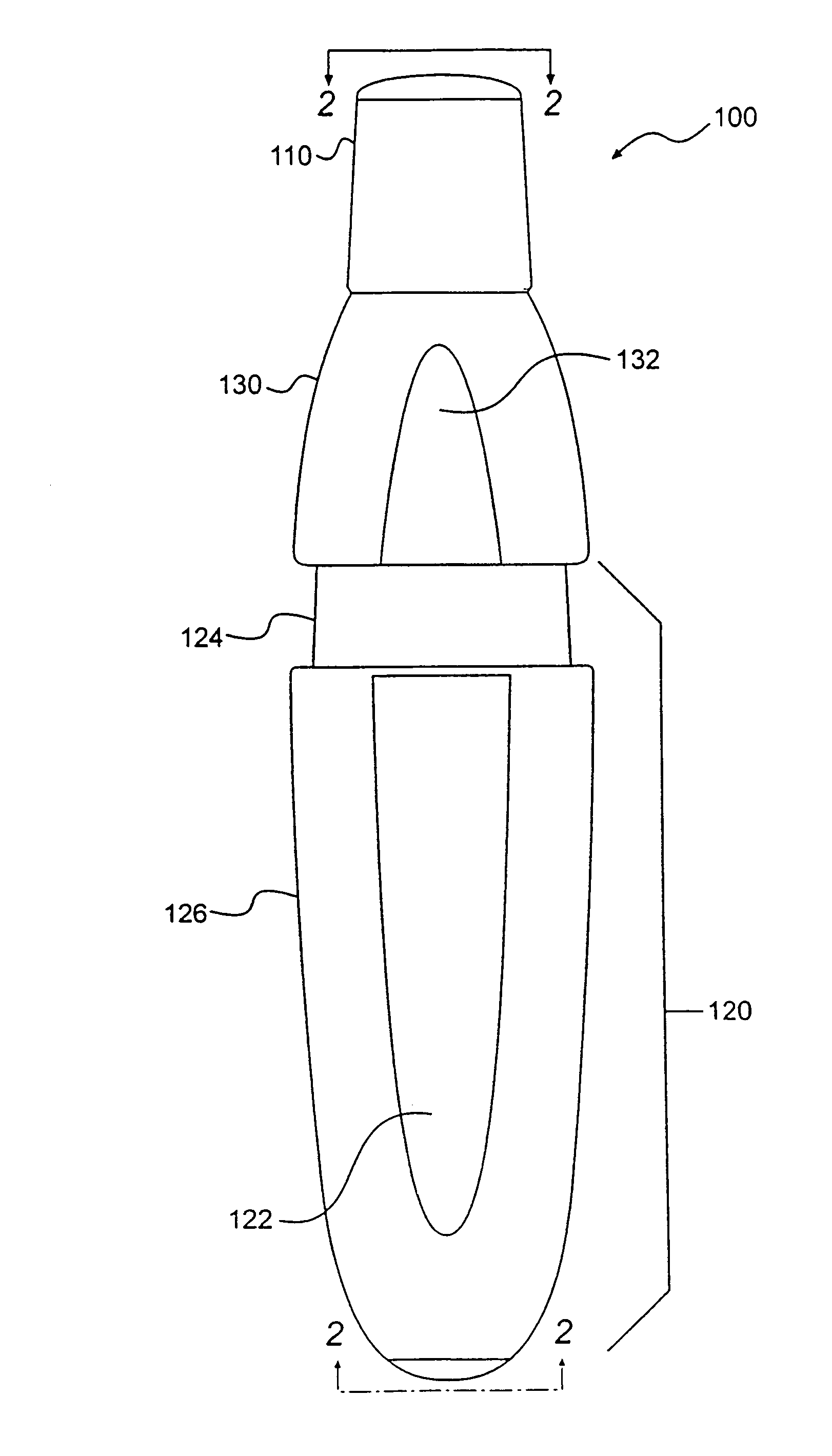
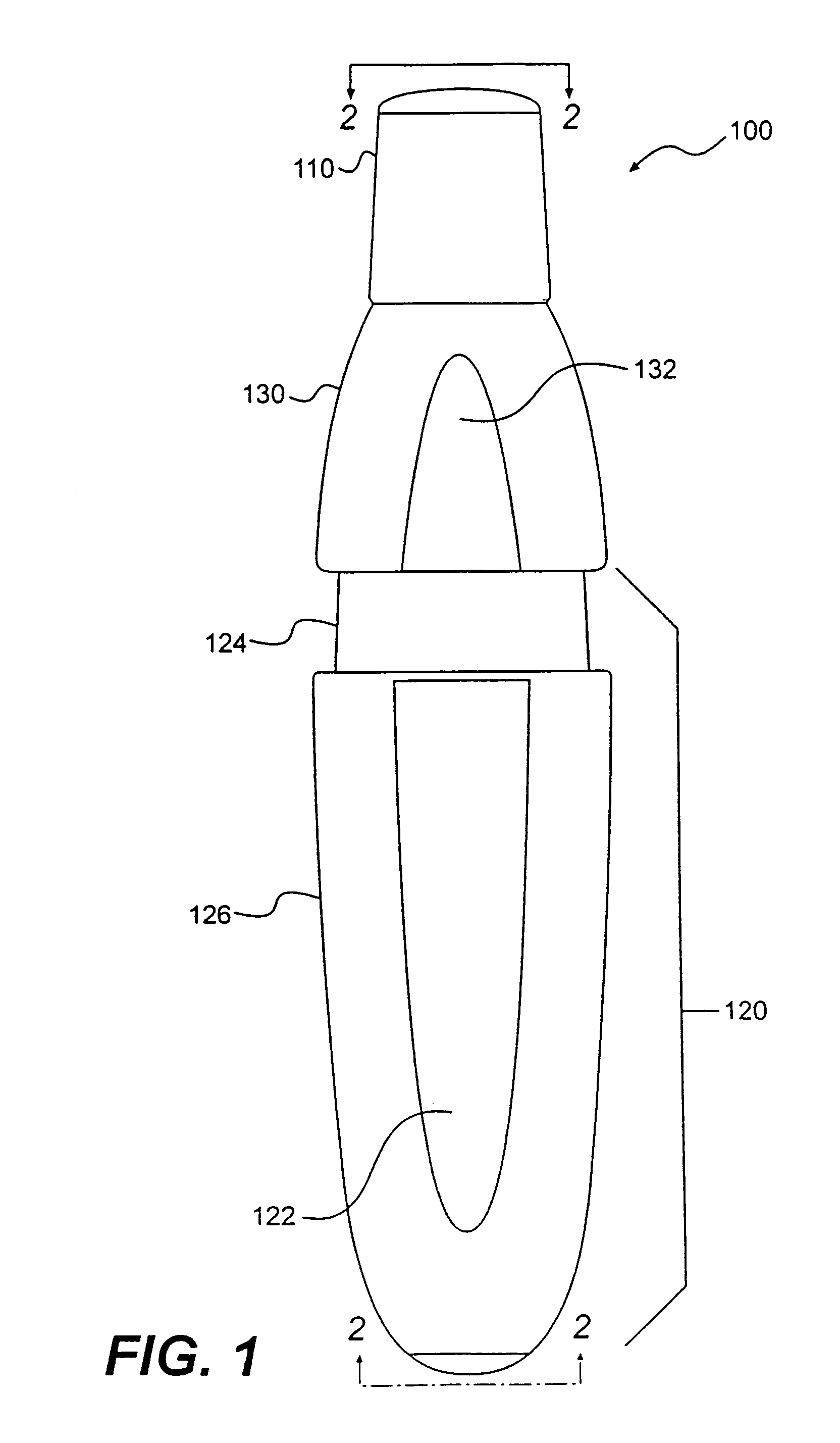
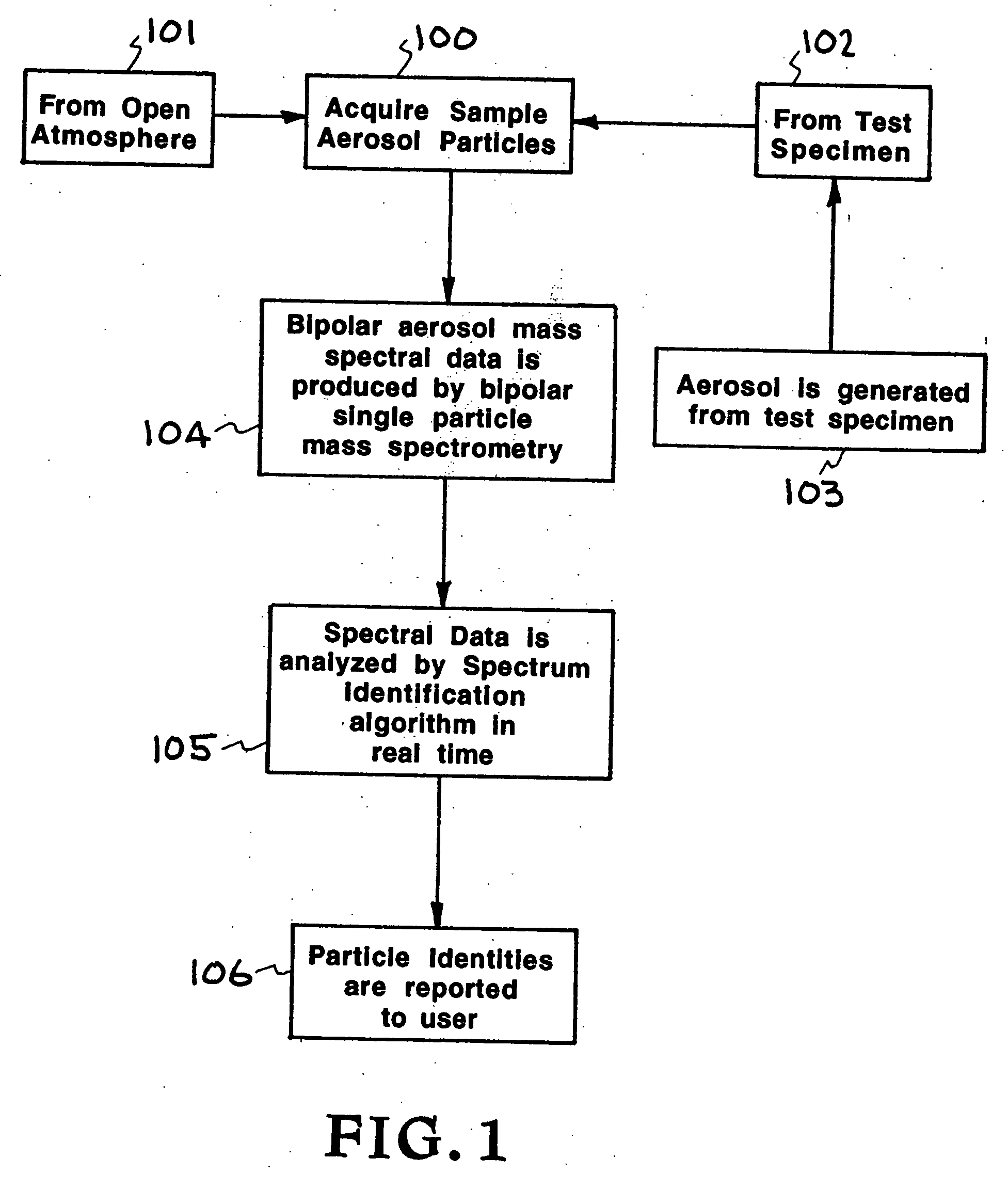
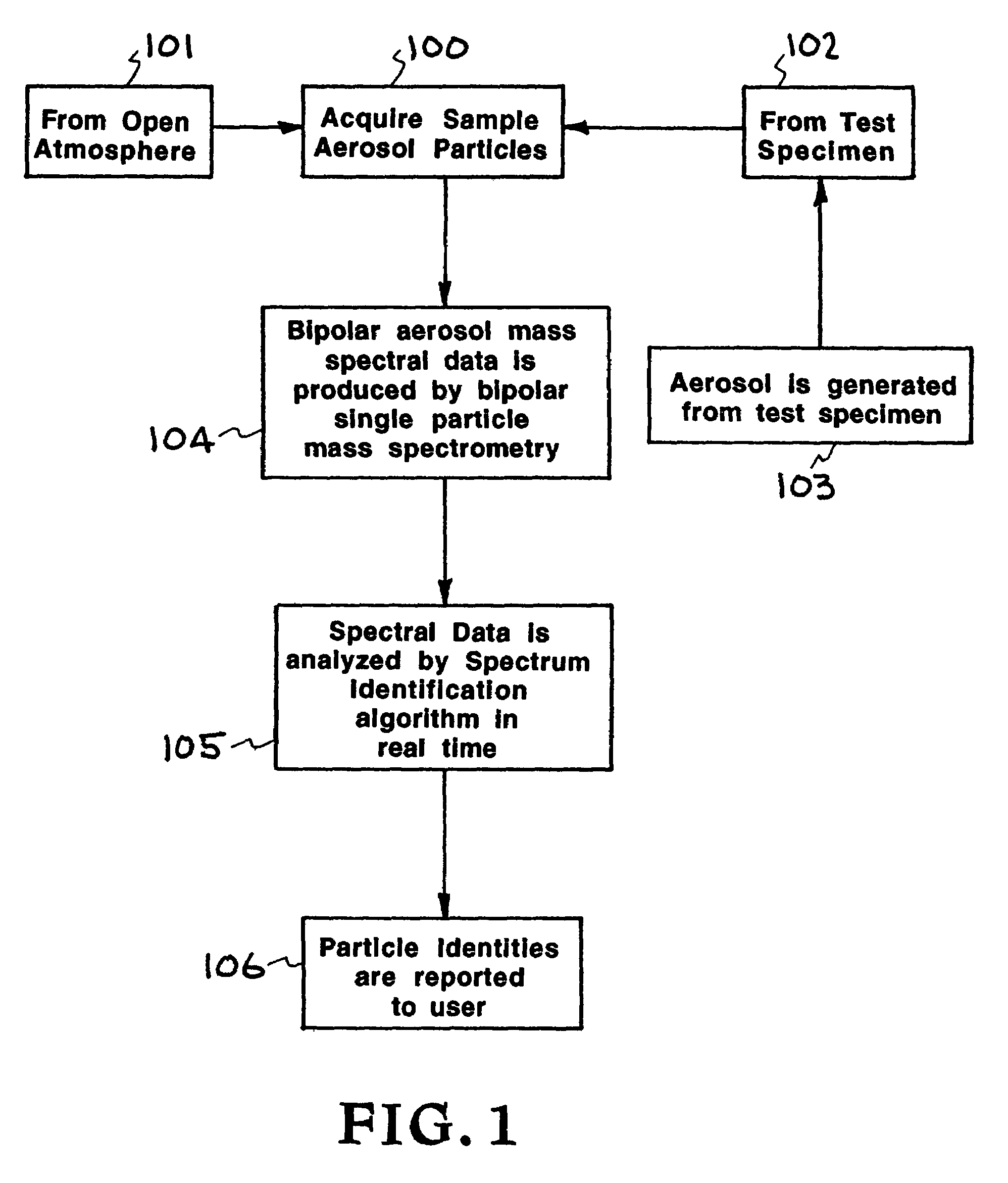
Real-time detection method and system for identifying individual aerosol particles
InactiveUS20050073683A1Reduce activationTime-of-flight spectrometersMaterial analysis by optical meansScreening techniquesFluorescence
An improved method and system of identifying individual aerosol particles in real time. Sample aerosol particles are collimated, tracked, and screened to determine which ones qualify for mass spectrometric analysis based on predetermined qualification or selection criteria. Screening techniques include one or more of determining particle size, shape, symmetry, and fluorescence. Only qualifying particles passing all screening criteria are subject to desorption / ionization and single particle mass spectrometry to produce corresponding test spectra, which is used to determine the identities of each of the qualifying aerosol particles by comparing the test spectra against predetermined spectra for known particle types. In this manner, activation cycling of a particle ablation laser of a single particle mass spectrometer is reduced.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
Low dose pharmaceutical powders for inhalation
ActiveUS20050022812A1Good dispersionFacilitate depositionRespiratorsPowder deliveryInhalationSingle breath
The invention relates to a method of delivering an agent to the pulmonary system of a compromised patient, in a single breath-activated step, comprising administering a particle mass comprising an agent from an inhaler containing less than 5 milligrams of the mass, wherein at least about 50% of the mass in the receptacle is delivered to the pulmonary system of a patient. The invention also relates to receptacles containing the particle mass and the inhaler for use therein.
Owner:CIVITAS THERAPEUTICS
Novel tuned particle mass damper
InactiveCN103541460AEnhance energy dissipation and vibration reduction effectEasy to useBridge structural detailsShock proofingMechanical energyShock resistance
The invention relates to a novel tuned particle mass damper and belongs to the technical field of shock resistance and absorption of structural engineering. The novel tuned particle mass damper comprises a damper fixing plate, mass block sliding cavities, mass blocks, connecting springs, viscous damper units, connecting bars, a damper cavity, damper chamber separating plates, multi-stage damping particle groups. Four sliding cavities are arranged on the damper fixing plate; four mass blocks are arranged inside the four sliding cavities, perform low-damping movement inside the internal tracks of the sliding cavities and are connected with the damper fixing plate through the viscous damper units and the springs and connected with the damper cavity through the connecting bars. The chamber separating plates are arranged inside the damper cavity, a single layer of the multi-stage damping particle groups are uniformly arranged on every chamber separating plate. Under the action of wind and / or earthquakes, the damper cavity moves opposite to a basic structure on the plane and generates control force opposite to that of the basic structure, internal damping particles collide fiercely to rapidly dissipate system mechanical energy and further improve system damping effects.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Pressurized Metered Dose Inhalers
InactiveUS20120180785A1Great massQuantity maximizationDispersion deliveryMedical devicesMedicineDesiccant
The invention provides a pMDI metering valve comprising at least one component which comprises a desiccant-entrained material, a pMDI closed container system containing a desiccant-entrained material, and a method of stabilising the fine particle mass (FPM) of an inhalation drug formulation emitted by a pMDI closed container system comprising providing a desiccant-entrained material inside the pMDI closed container system so as to be in contact with the formulation therein.
Owner:GLAXO GROUP LTD
Methods and Devices for Facile Fabrication of Nanoparticles and Their Applications
InactiveUS20080095705A1Efficient mixingThin layerMaterial nanotechnologyFrom normal temperature solutionsNanoparticleMaterials science
The invention provides devices and methods to fabricate nanoparticles by reverse micelle method. The method allows to fabricate a myriad of high quality nanoparticles in a repeatable way. These nanoparticles include multilayered spherical and rod like particles that may have inorganic, organic, polymeric, biological layers. The invention further provides methods to optimize the quality of the nanoparticles.
Owner:VIRTANEN JORMA ANTERO +2
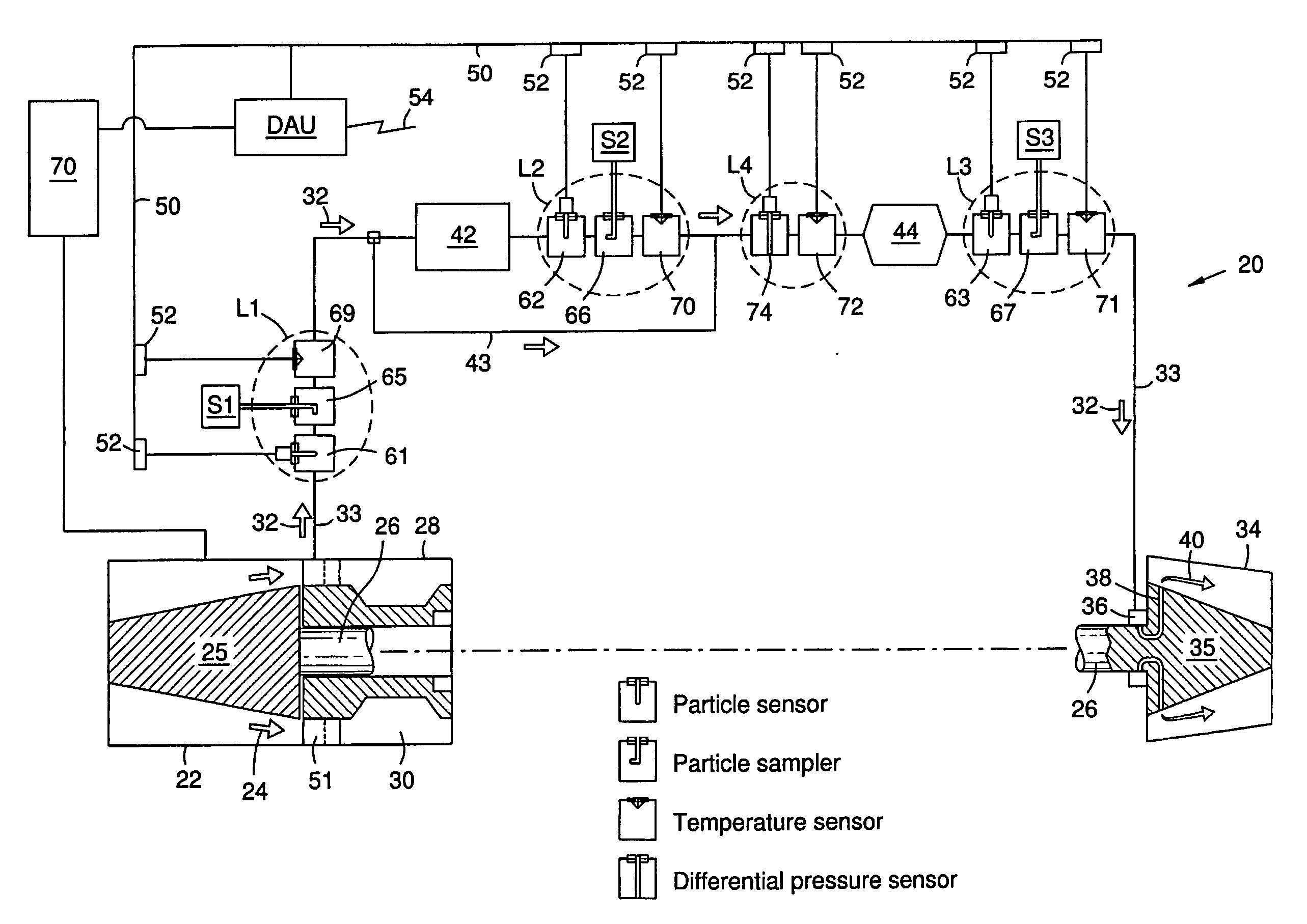
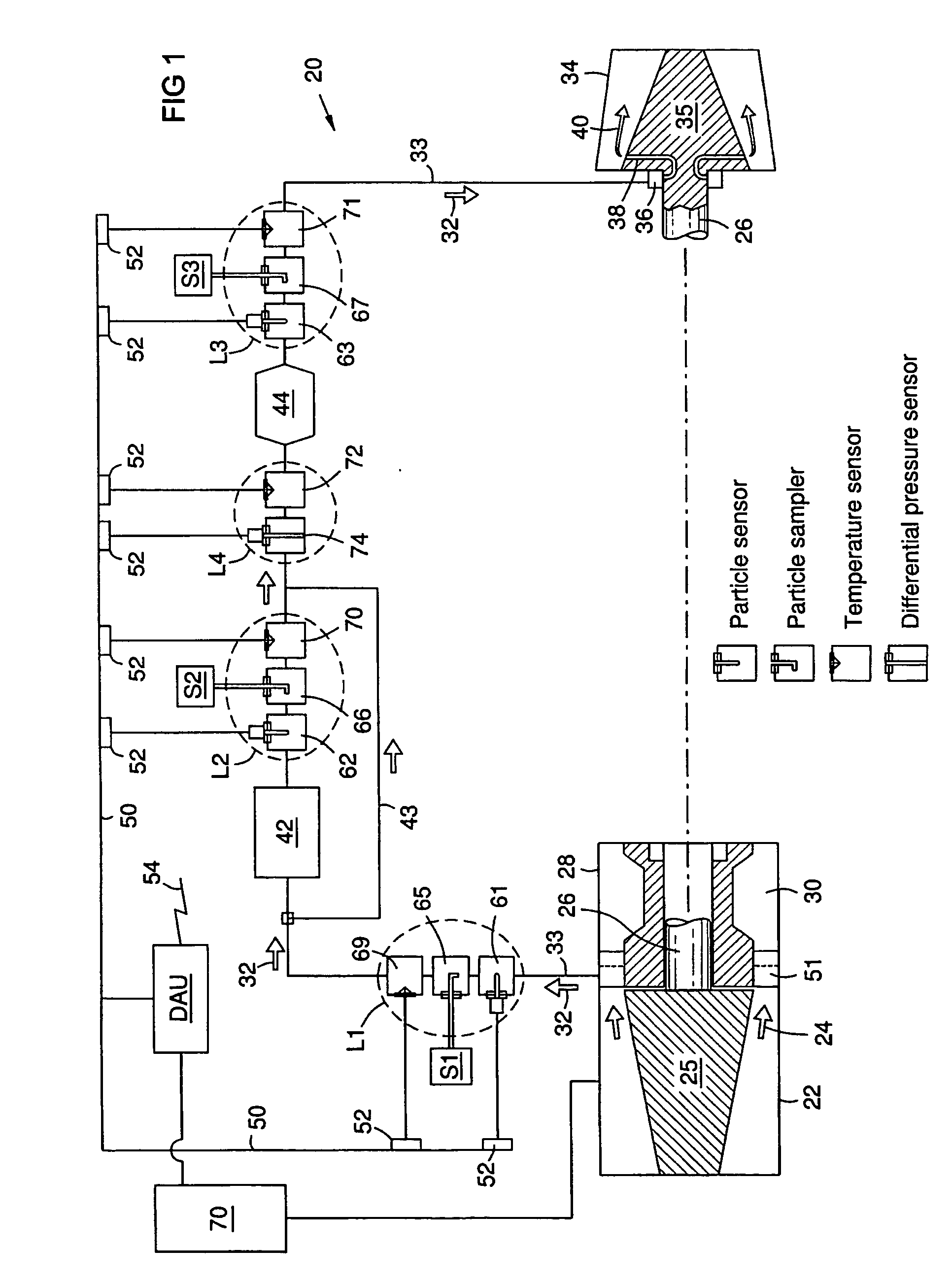
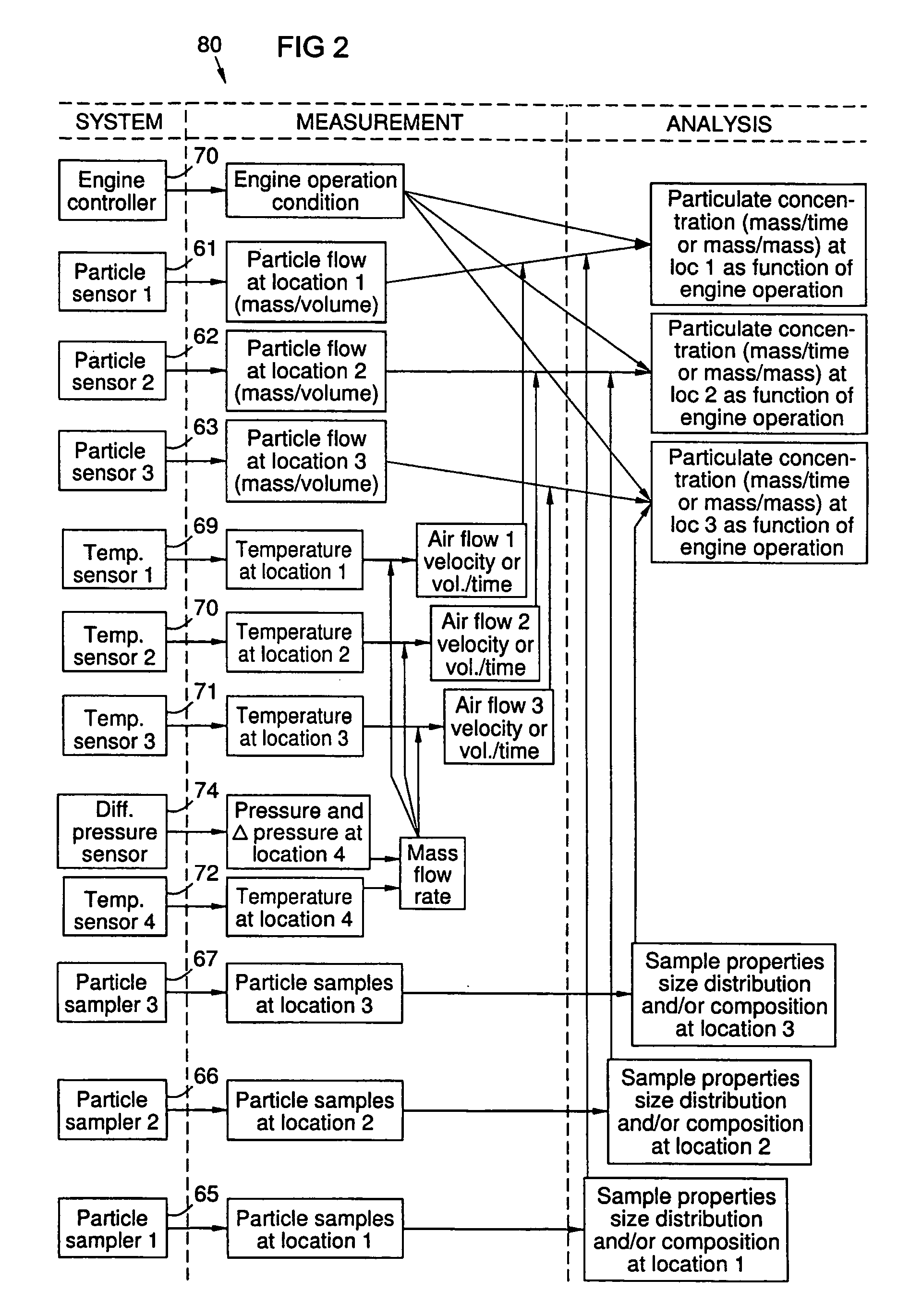
Method and apparatus for monitoring particles in a gas turbine working fluid
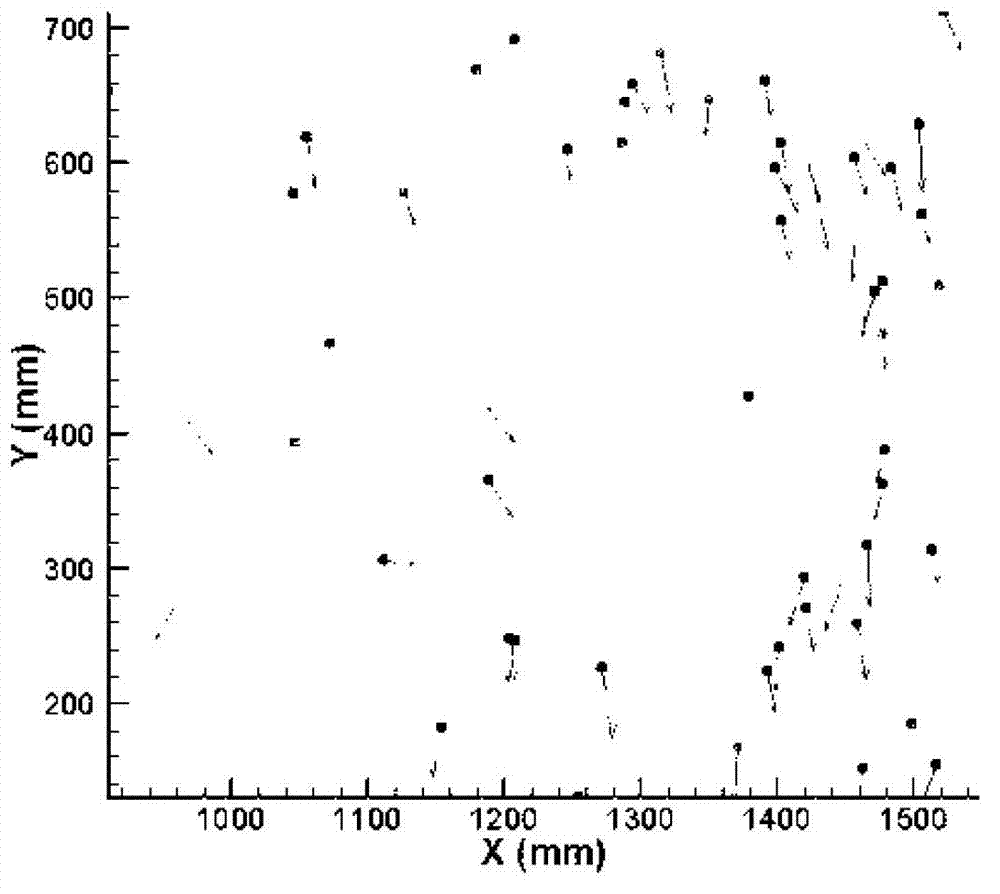
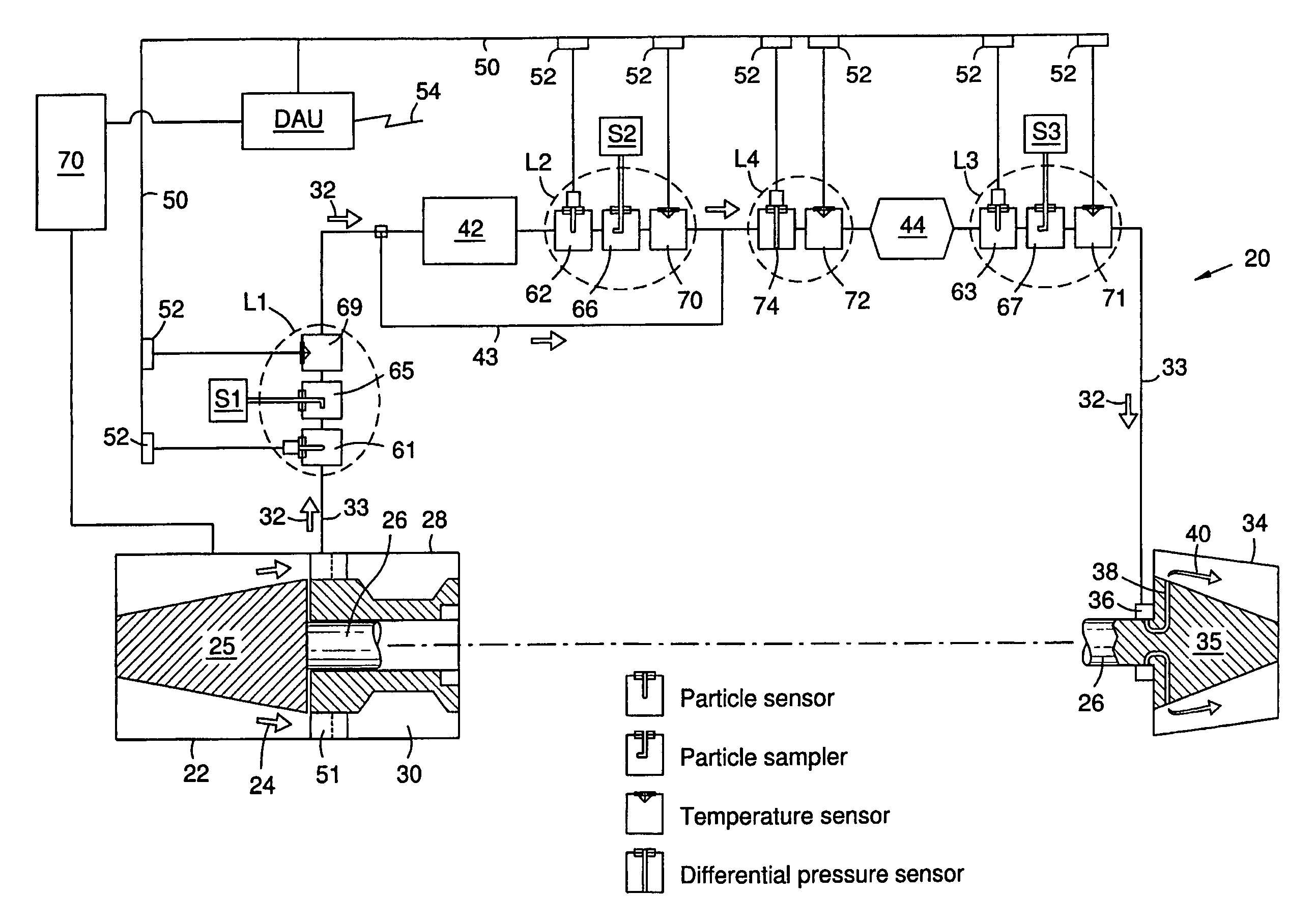
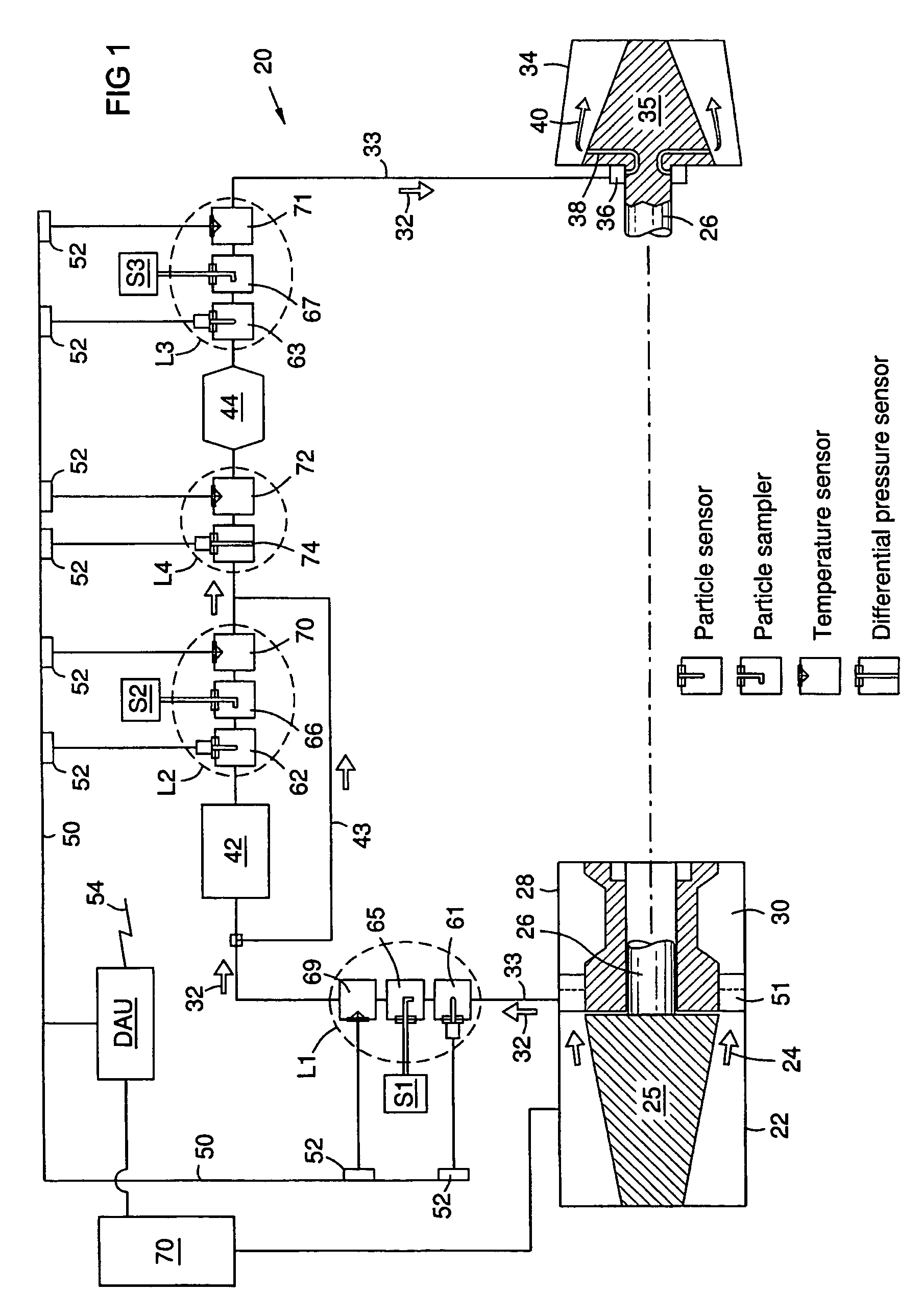
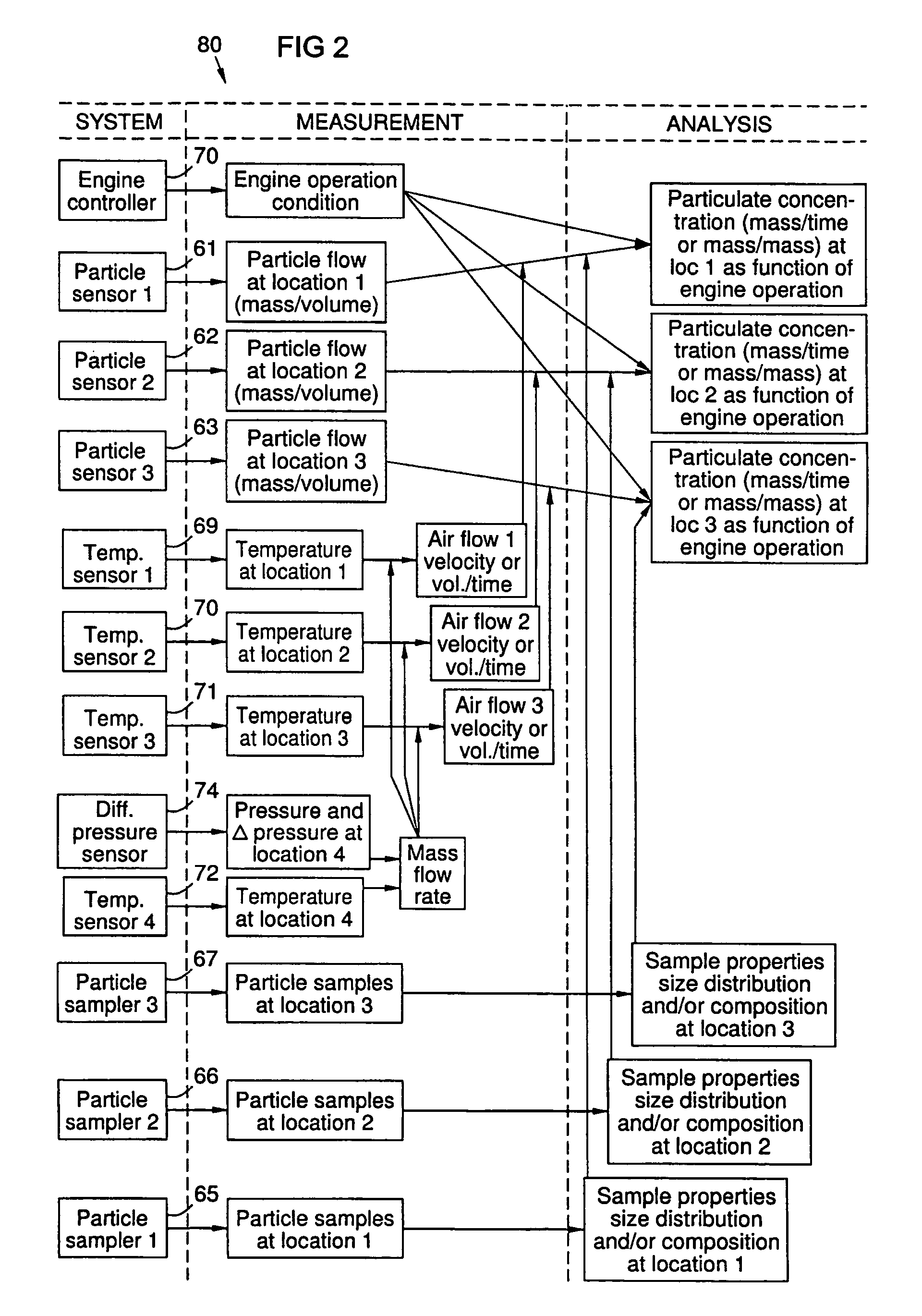
A method and system for monitoring a gas turbine engine (20) to predict maintenance requirements. Particles suspended in a gas flow (24, 32) of the engine (20) are monitored and quantified to predict a particle accumulation rate. Monitoring may be done using particle flow sensors (61-63) in a diverted portion (33) of the working gas flow (24), such as in the cooling gas flow (32). Particle sampling (S1-S3) may be done to determine particle size and composition distributions. Particle mass flow rates may then be continuously monitored per engine operating condition, and compared to predetermined values such as a normal upper limit per engine operating condition. An integrated particle mass flow may be used in conjunction with an instantaneous mass flow rate to predict a maintenance requirement. Multiple locations (L1-L3) may be monitored to recognize a maintenance requirement by flow section or component.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
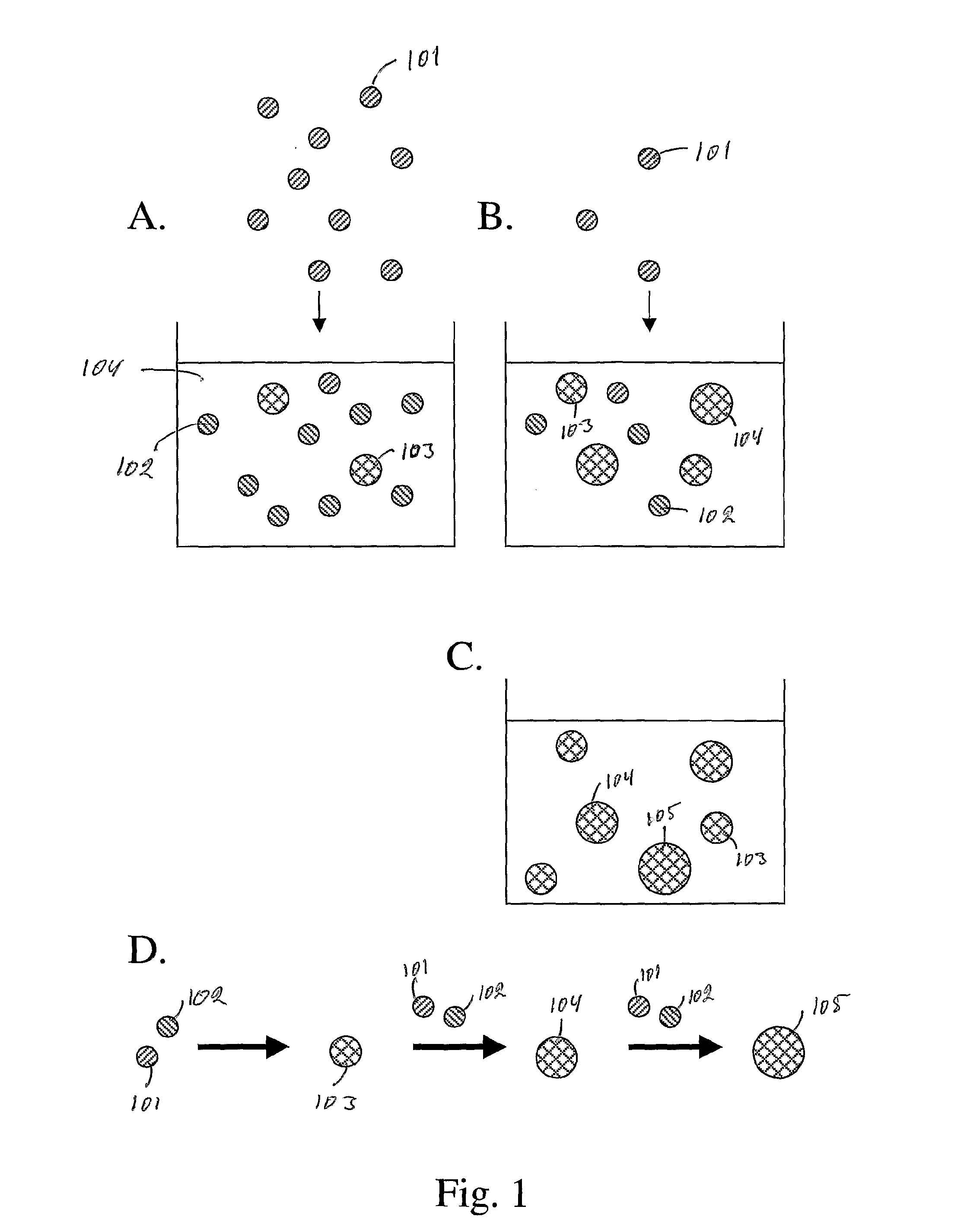
Fluid colloid crystal and process for producing three-dimensionsl aligned particle mass therefrom
InactiveUS20060182968A1Enhancement of surface charge intensityHigh charge densityOptical filtersPretreated surfacesDispersed mediaColloidal particle
Fluid colloidal crystals comprising a solid-liquid dispersion electrostatically charged at not more than 2000 μS / cm in terms of an electrical conductivity, wherein the solid-liquid dispersion comprises, as a dispersoid, electrostatically chargeable spherical colloidal particles of an organic or inorganic polymer having a mean volume diameter (d) of not more than 30 μm, and as a dispersion medium, an aqueous solution or a dissolving water-containing non-aqueous solution, the dispersion concentration of the spherical colloidal particles is not more than 70%, around the dispersoid an electric double layer of a given thickness (Δe) is formed, and the spherical colloidal particles form a three-dimensionally ordered lattice that shows fluidity and is a particle array structure in which the colloidal particles are aligned longitudinally and laterally in a lattice form while an interparticle distance (L) defined as a distance between centers of the particles arranged opposite to each other along the center line satisfies the relationship (d)<(L)≦(d)+2(Δe). A process for producing a three-dimensionally ordered lattice, comprising drying the fluid colloidal crystals to form a three-dimensionally ordered lattice which is a homogeneous particle array structure constituted of the organic or inorganic monodisperse spherical fine particles of the dispersoid.
Owner:SOKEN CHEM & ENG CO LTD
Real-time detection method and system for identifying individual aerosol particles
InactiveUS7260483B2Reduce activationTime-of-flight spectrometersMaterial analysis by optical meansScreening techniquesDesorption
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
Blown sand and quick sand charge-to-mass ratio real-time measurement system
ActiveCN102323493AReal-time measurementReal-time acquisitionElectrical measurementsMass ratioElectrometer
The invention discloses a blown sand and quick sand charge-to-mass ratio real-time measurement system which comprises a sand particle bearing device, a sand particle weighing device and a sand particle electrified capacity measuring device, wherein the sand particle bearing device is a Faraday cup, the sand particle weighing device is an electronic balance, and the sand particle electrified capacity measuring device is an electrometer; and the Faraday cup is arranged on the electronic balance and connected with the electrometer through a lead. By the matching of the devices, the invention can realize real-time acquisition of sand particle mass and electrified capacity in the Faraday, and can also realize high-frequency measurement of a blown sand and quick sand charge-to-mass ratio.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY
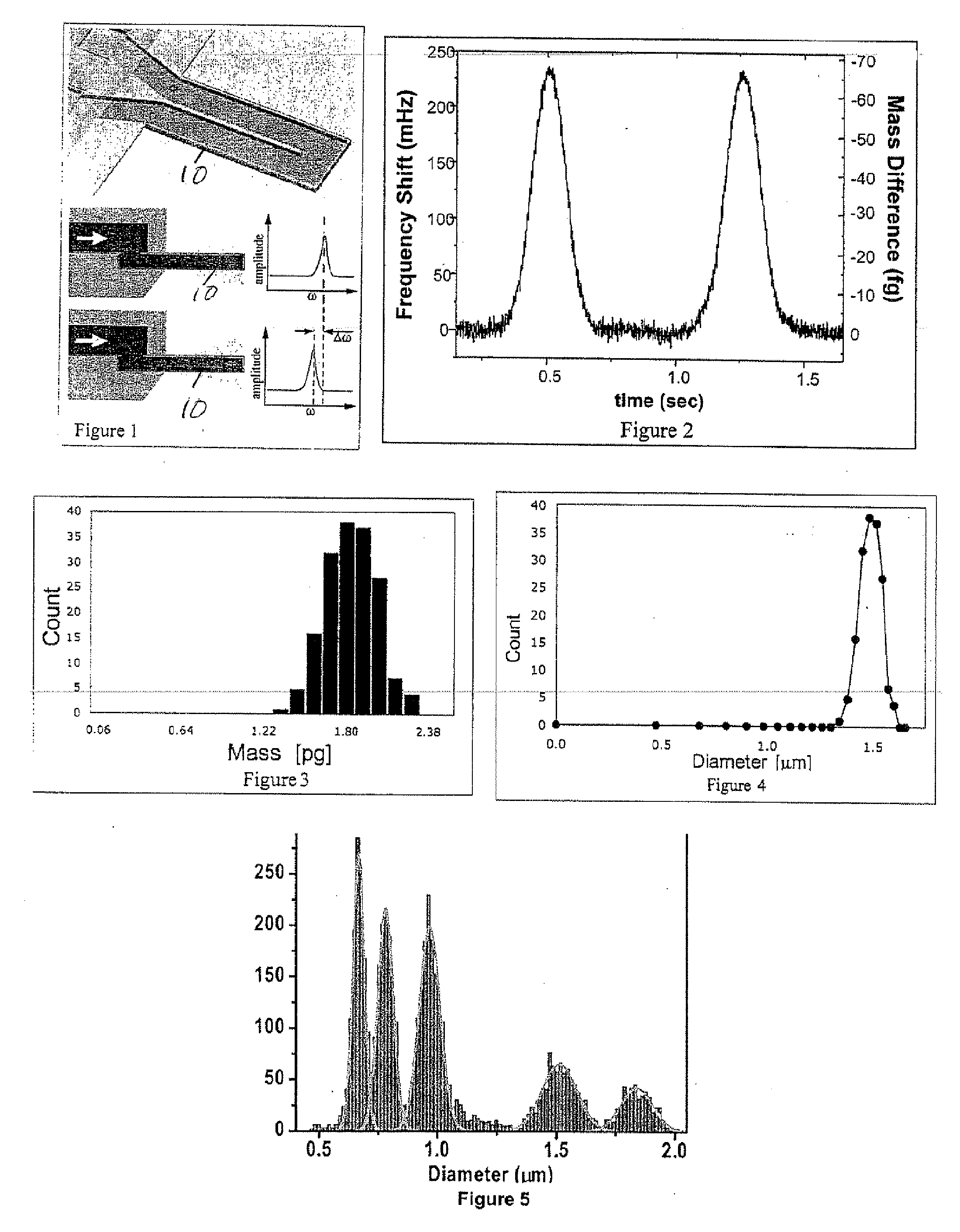
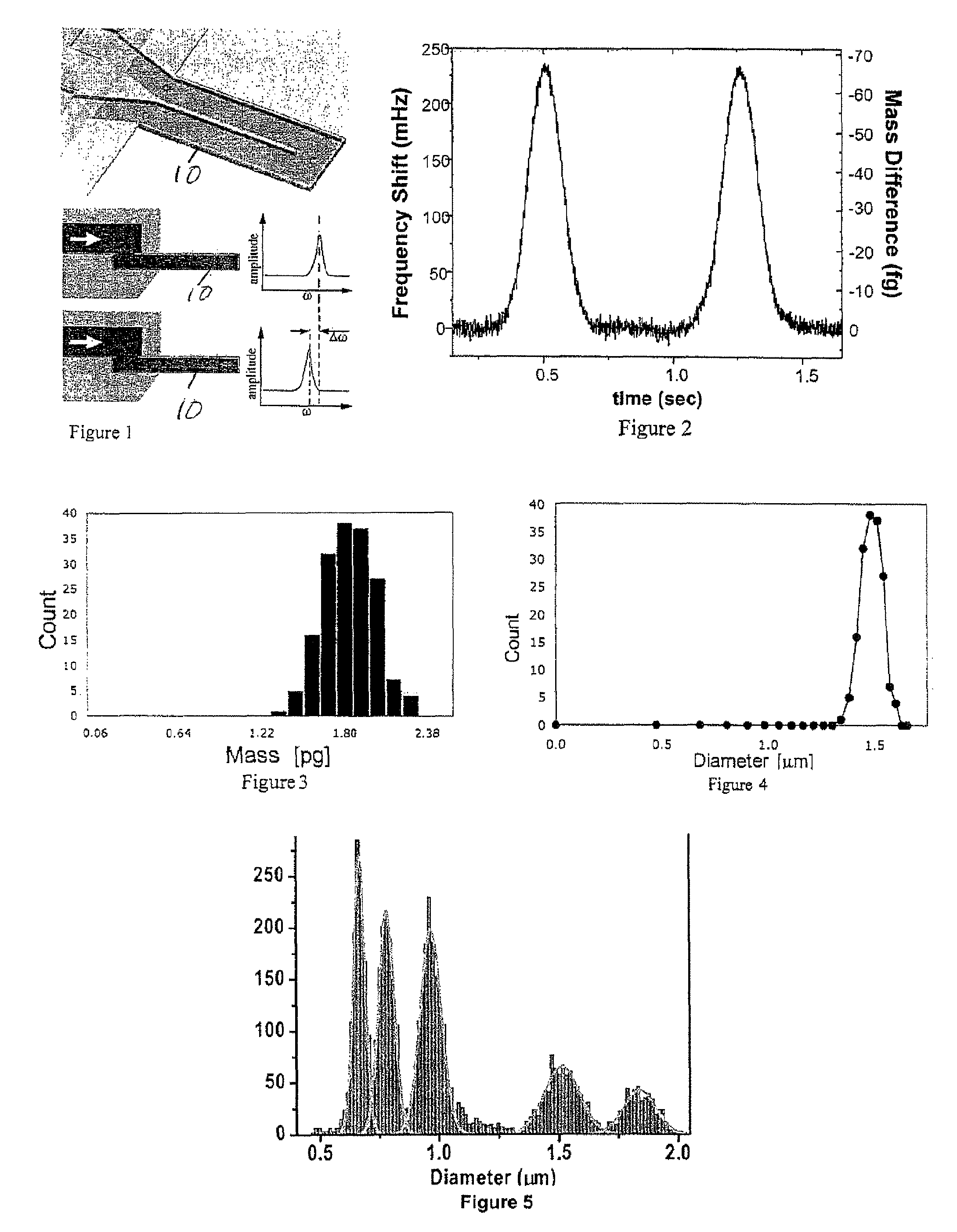
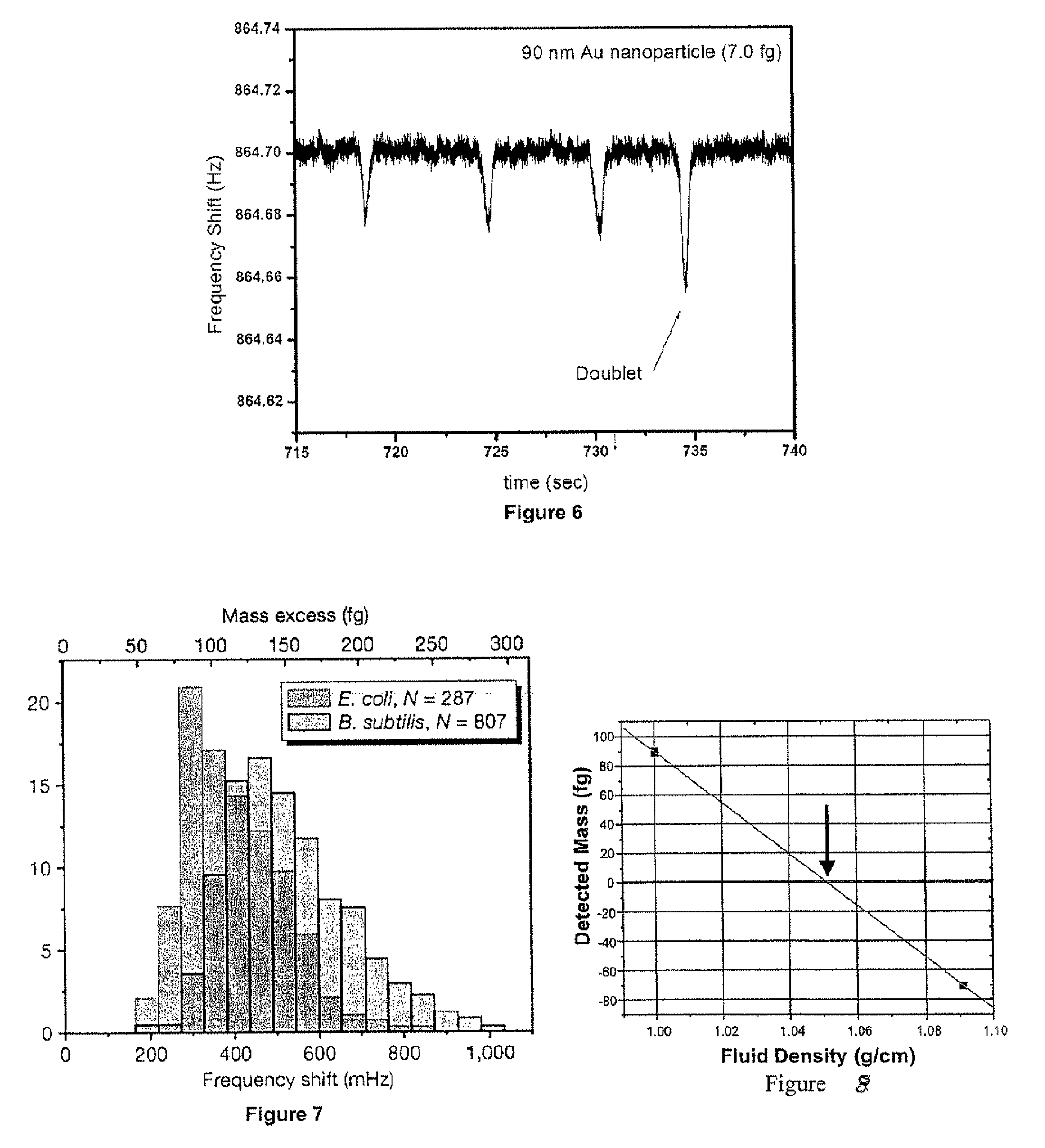
Method And Apparatus For Measuring Particle Characteristics through Mass Detection
ActiveUS20090044608A1Material analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesIndividual particle analysisParticle propertiesParticle density
Method for measuring a target particle property. A suspended microchannel resonator is calibrated to determine the relationship between a detected mass and a resonance frequency shift of the resonator. The target particle is suspended in a fluid and introduced into the resonator, and the resonator frequency shift due to the particle is measured. Target particle mass is calculated from the resonator frequency shift, the target particle density, and the fluid density. A target particle property such as size or volume is determined from the calculated target particle mass.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH +1
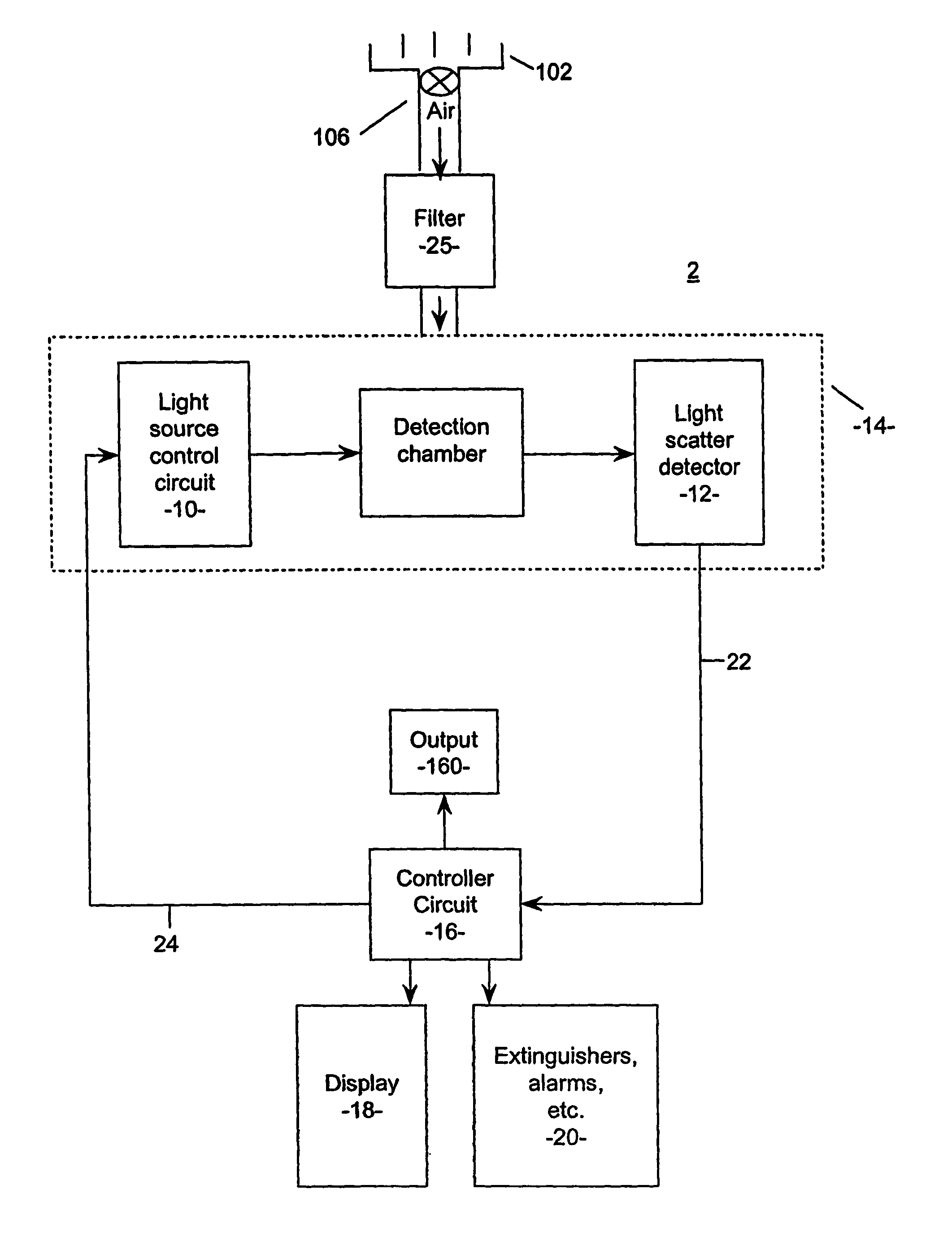
Method and system for a filter
ActiveUS20070176783A1Material analysis by optical meansPhotoelectric discharge tubesSmoke detectorsTransmittance
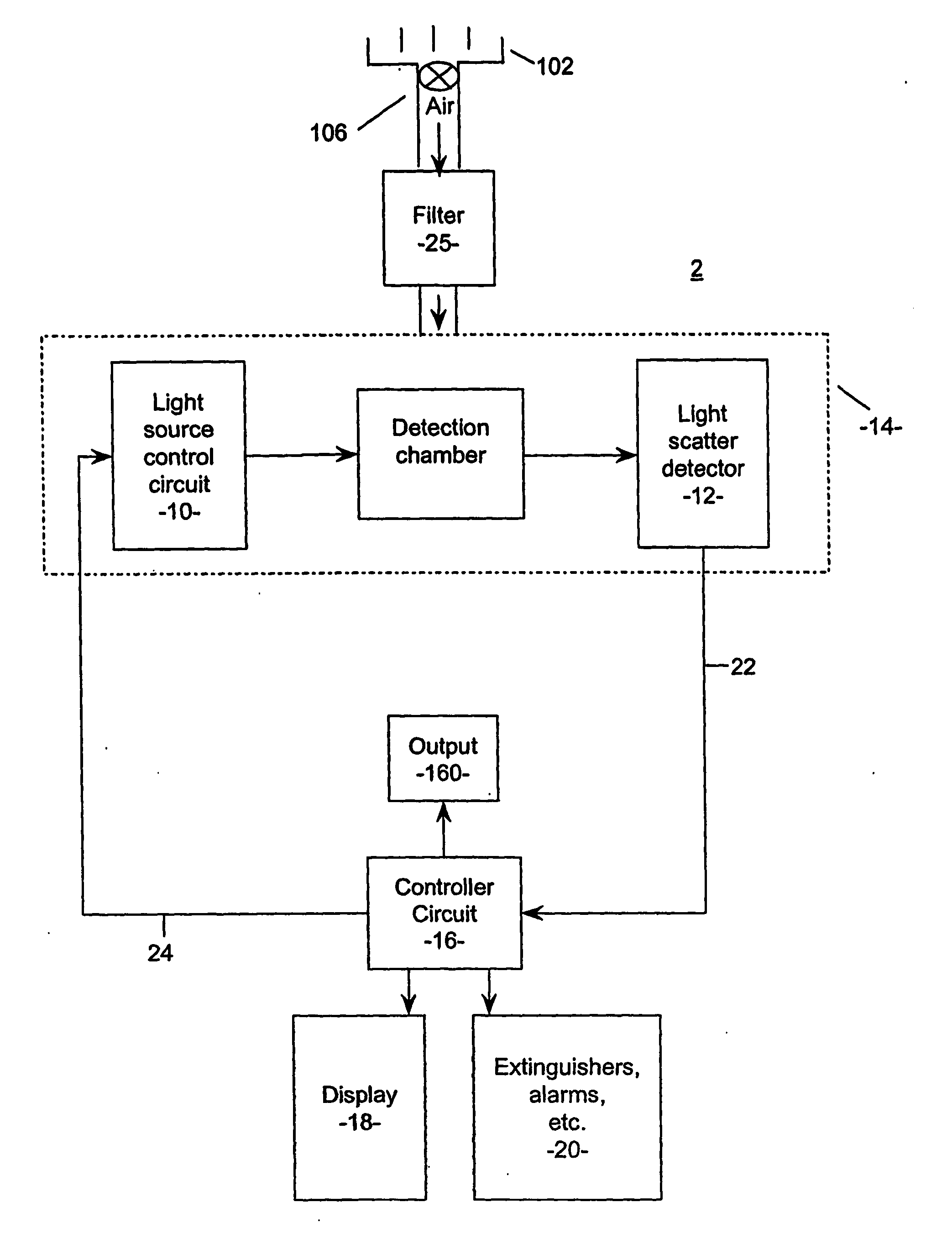
The present invention relates to a system for determining particle transmittance Tx of a filter for use with a particle detection system to provide a filter warning for aspirated particle detection systems by detecting a level of first particles having a size indicative of smoke particles and which pass through the detection system; determining an integrated smoke hours value by integrating the detected level of first particles over time; estimating the smoke particle transmittance Tx of the filter by applying a predetermined weighting operation to the integrated smoke hours value. An empirical measure of a filter's particle transmittance Tx, due to at least first particles having a size indicative of smoke particles may be achieved by way of integrating a level of such first particles passing through a particle detection system over time to determine the proportion of smoke particles arrested by a filter, “integrated smoke hours”. The “integrated smoke hours” value is, generally, a measure of cumulative filter blockage over time by smoke like particles and is a measure of a given amount of ambient smoke detected and recorded by a smoke detector system and integrated over the time of exposure of the smoke detector system to the ambient smoke. Using this method it is not necessary to infer the actual “filter load” per-se or, the actual particle mass trapped in the filter.
Owner:GARRETT THERMAL SYST LTD
Method and apparatus for measuring particle characteristics through mass detection
ActiveUS8087284B2Material analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesIndividual particle analysisParticle propertiesParticle density
Method for measuring a target particle property. A suspended microchannel resonator is calibrated to determine the relationship between a detected mass and a resonance frequency shift of the resonator. The target particle is suspended in a fluid and introduced into the resonator, and the resonator frequency shift due to the particle is measured. Target particle mass is calculated from the resonator frequency shift, the target particle density, and the fluid density. A target particle property such as size or volume is determined from the calculated target particle mass.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH +1
Particles capable of lowering temperature of smoke of cigarettes and preparation method and application of particles
ActiveCN109700070AEasy to addDense surfaceTobacco smoke filtersTobacco devicesInorganic particleInorganic particles
The invention belongs to the technical field of cigarette auxiliary materials and relates to particles capable of lowering the temperature of the mainstream smoke of cigarettes and a preparation method and application of the particles. The particles are inactive particles, active particles with outer film layers or inactive particles with outer film layers. The thickness of the outer film layers of the inactive particles is 0-0.2 mm, and the outer film layers account for 0-50% of the total particle mass; the thickness of the outer film layers of the active particles is 001-0.2 mm, and the outer film layers account for 0.001-50% of the total particle mass. The inactive particles are particles which adsorb 3.0 mg / cm<3> or less of nicotine in smoke aerosol; the inactive particles include inorganic particles or organic particles. The preparation method is simple, industrialization is convenient, and the particles are easily added into cigarette filter rods. The surfaces of the particles are dense and have no leakage, and by adding the particles into the cigarette filter rods, the temperature of the smoke of the cigarettes can be greatly lowered.
Owner:NANTONG CELLULOSE FIBERS CO LTD +2
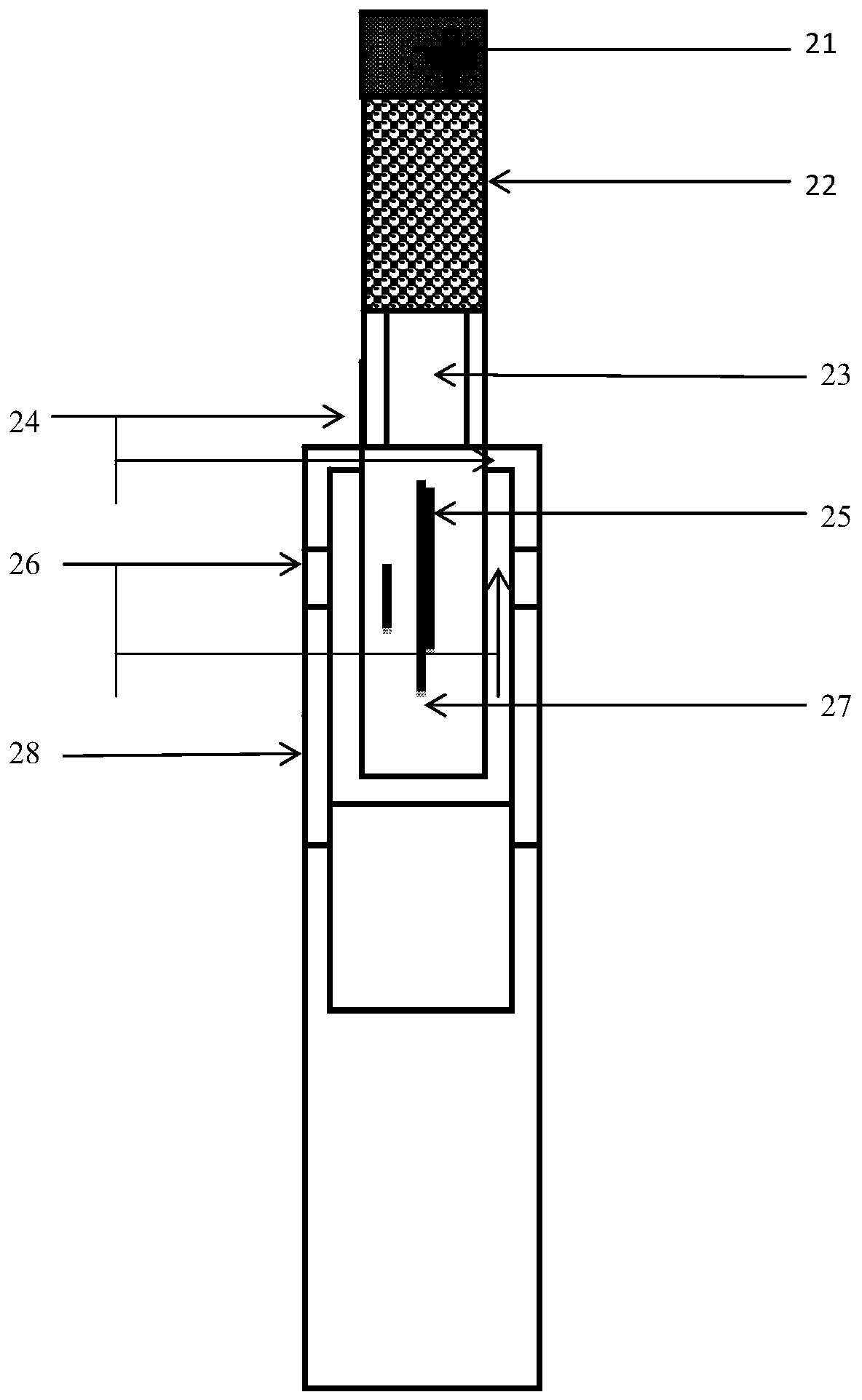
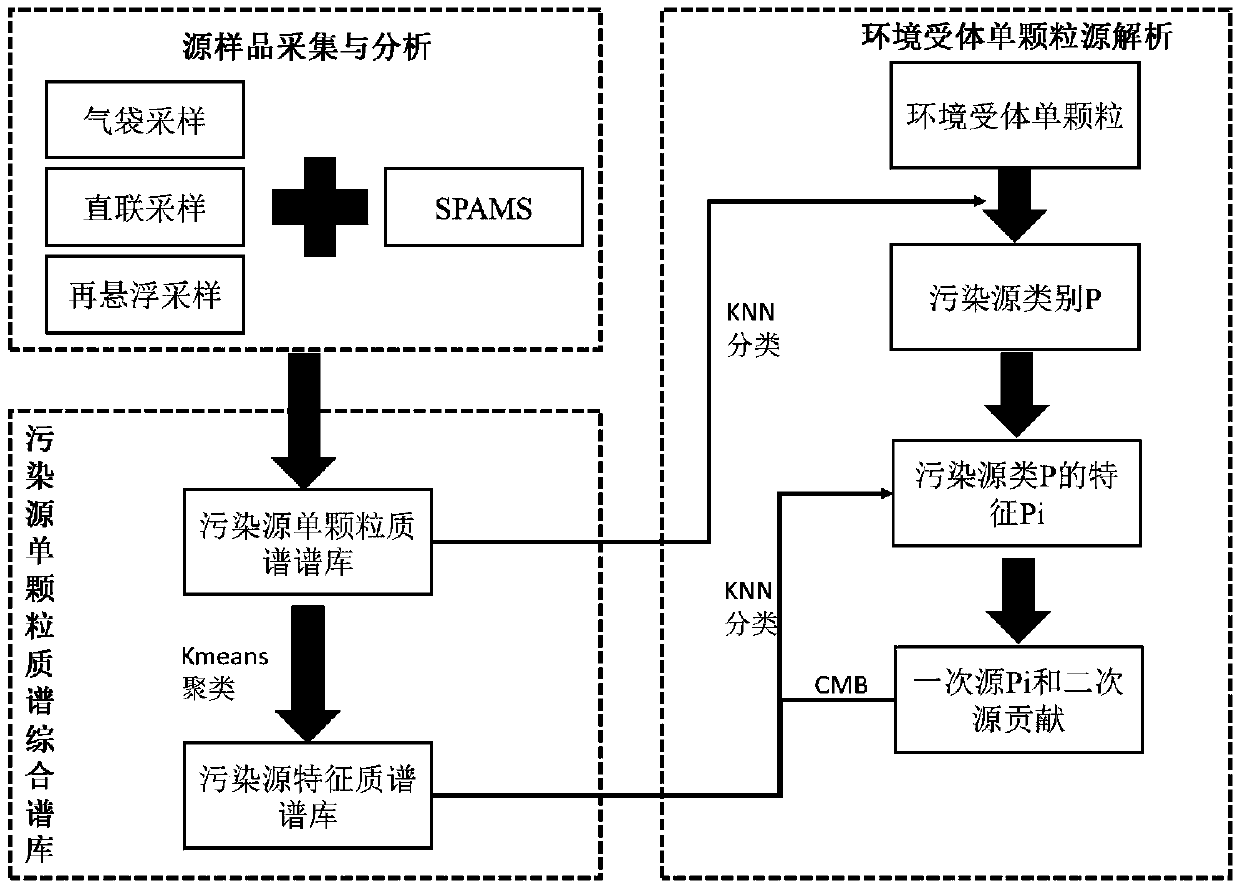
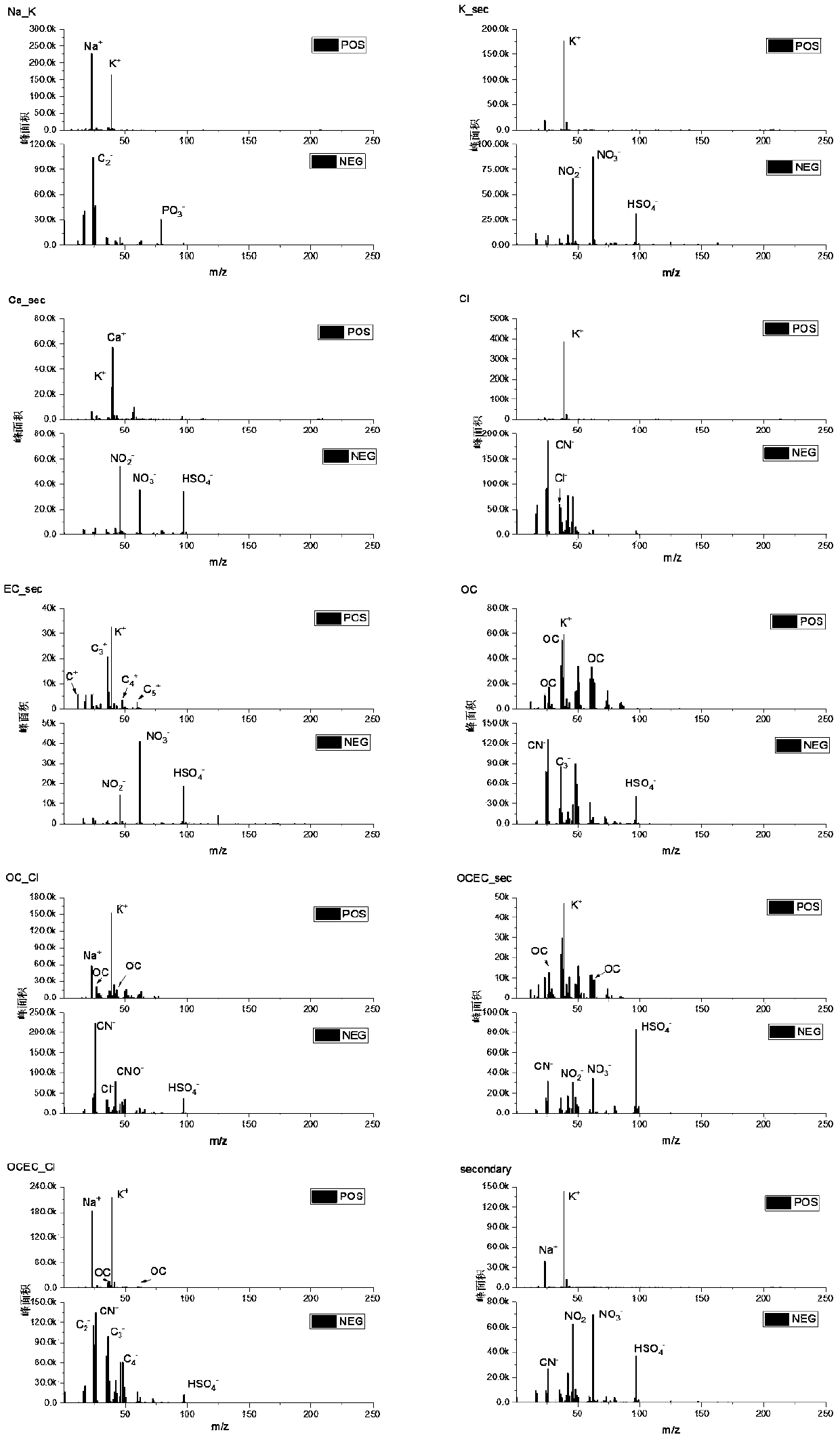
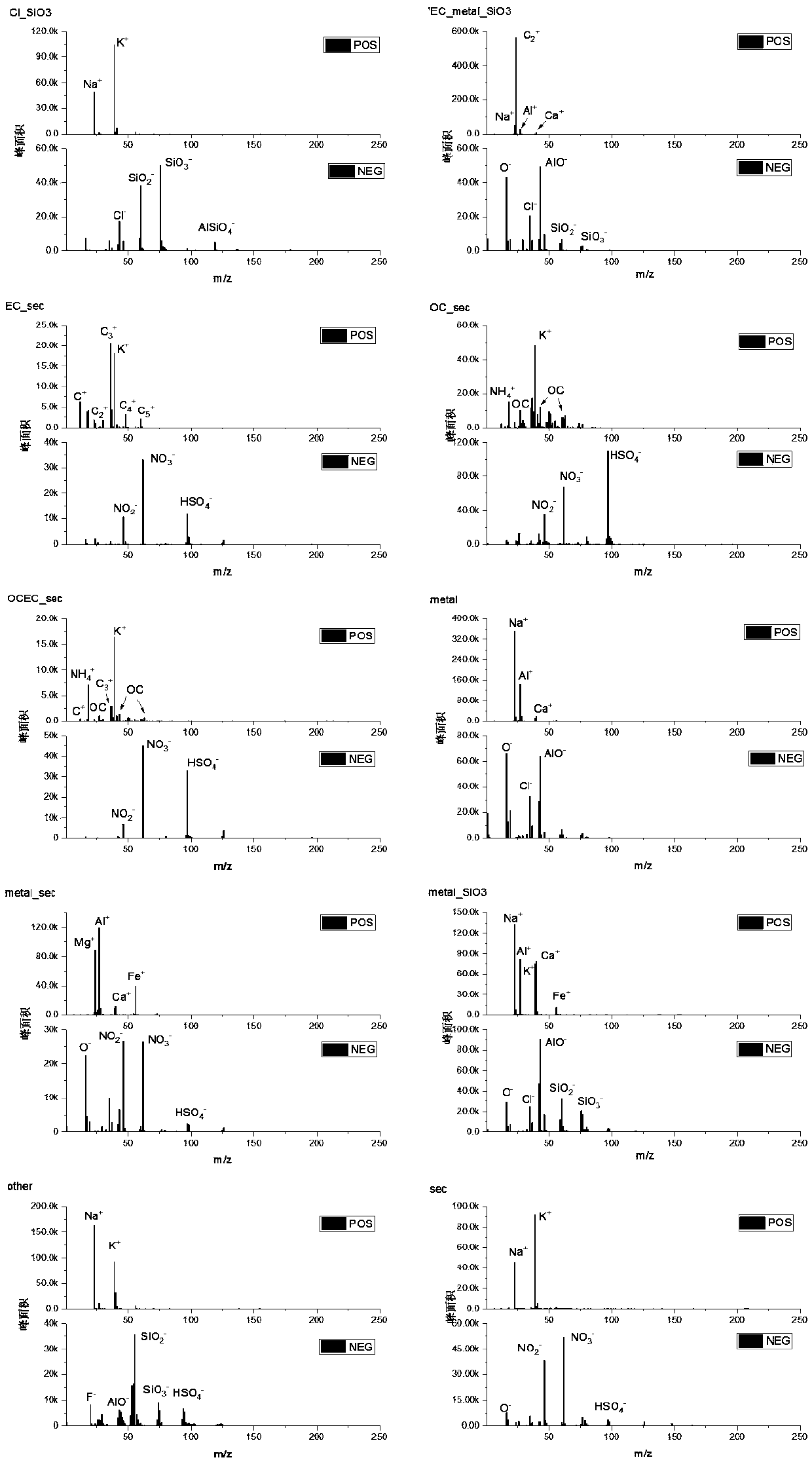
Method for performing particle source analysis by using single-particle aerosol mass spectrometer
InactiveCN108680473AImprove time resolutionHigh particle size resolutionCharacter and pattern recognitionParticle size analysisSecondary emissionNear neighbor
The invention provides a method for performing particle source analysis by using a single-particle aerosol mass spectrometer and relates to the field of atmospheric particle source analysis. Accordingto the method, a KNN (K Nearest Neighbor) classifier and a CMB (Cosmic Microwave Background) source analysis model are combined, single-particle mass spectrometry information of the pollution sourceas well as environmental receptor single-particle mass spectrometry characteristic and particle size information are fully utilized, the contribution of the primary emission source and secondary emission source of the particles on single environmental receptor particle can be rapidly solved, and refined source analysis results with high time resolution and high particle size resolution can be obtained. The method has excellent popularization and application prospects.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Method for monitoring atmospheric particles online by differential vibrating microbalance method and monitoring instrument
InactiveCN101017125ATrue reflective concentrationImprove accuracyWeighing by absorbing componentParticulatesAir pump
This invention discloses one difference vibration balance gas particles online test method and its detector, which comprises PM10 cut head, static dust remove device, flow controller, vibration balance mass sensor and gas pump part with structure as the following pattern with main principle to adopt two vibration balance mass sensor to test gas sample particles mass and particle mass within certain time to get the total mass concentration.
Owner:ANHUI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
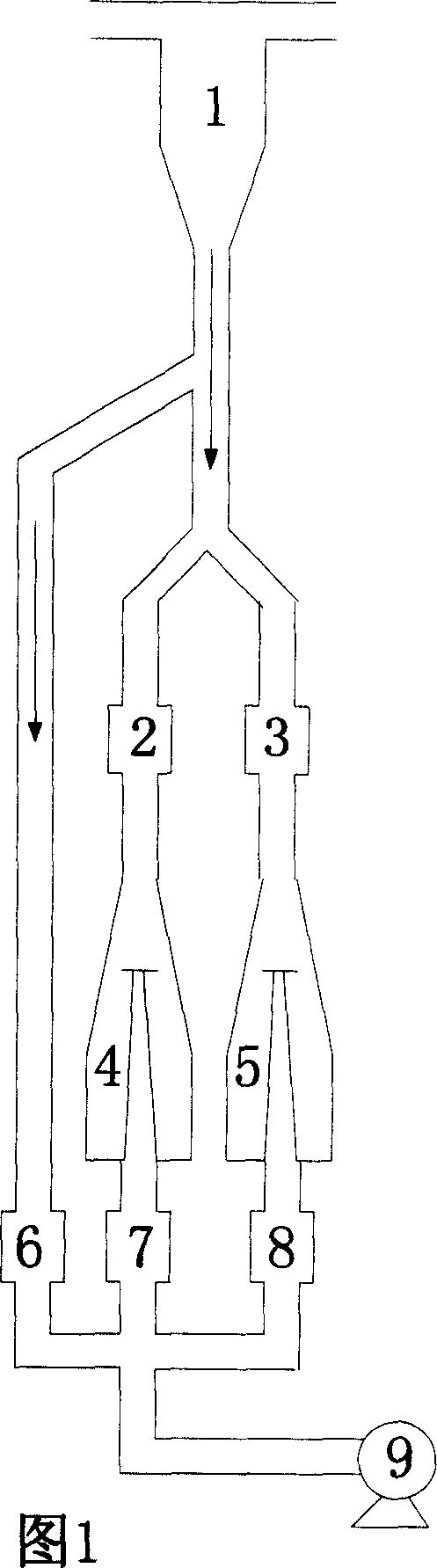
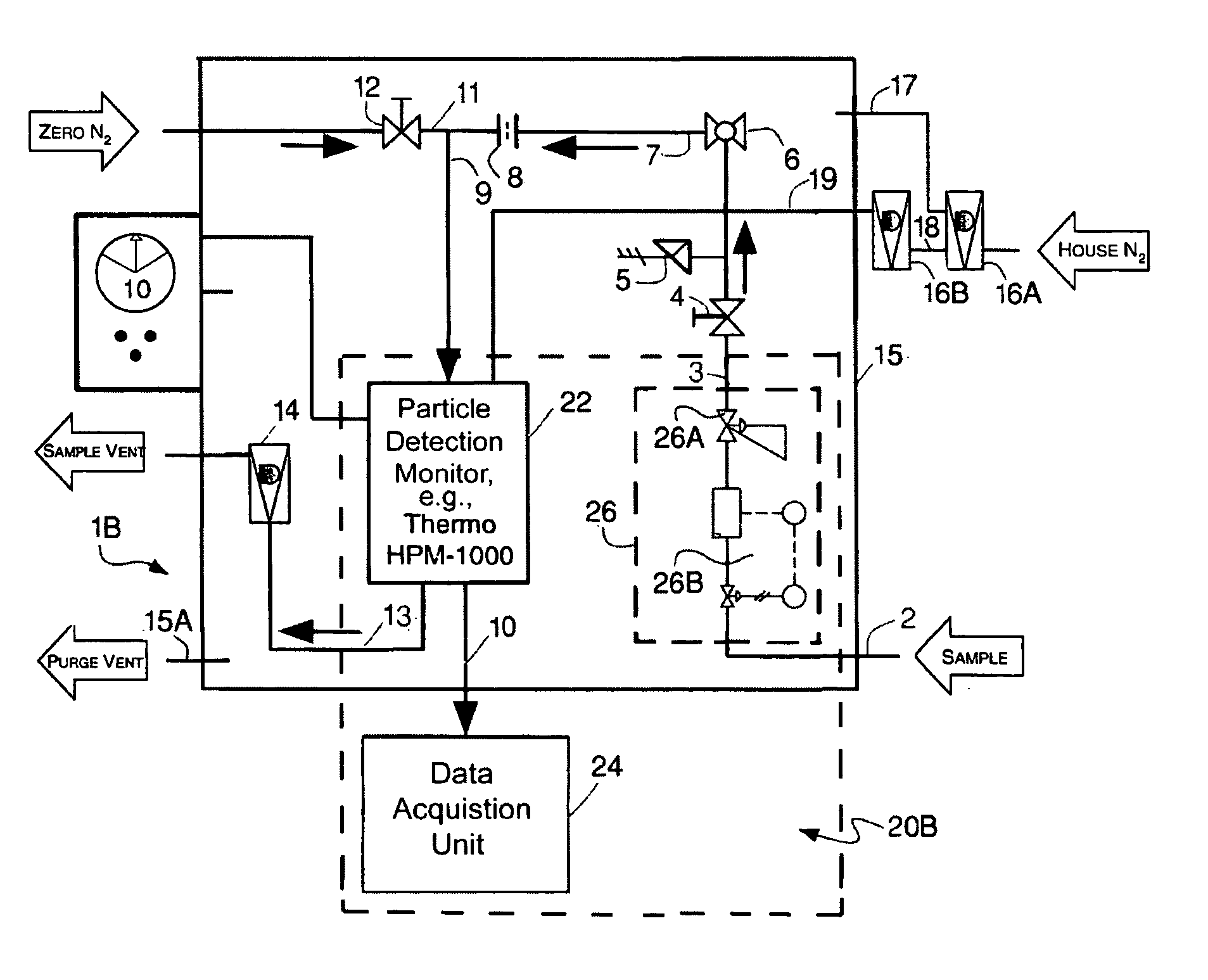
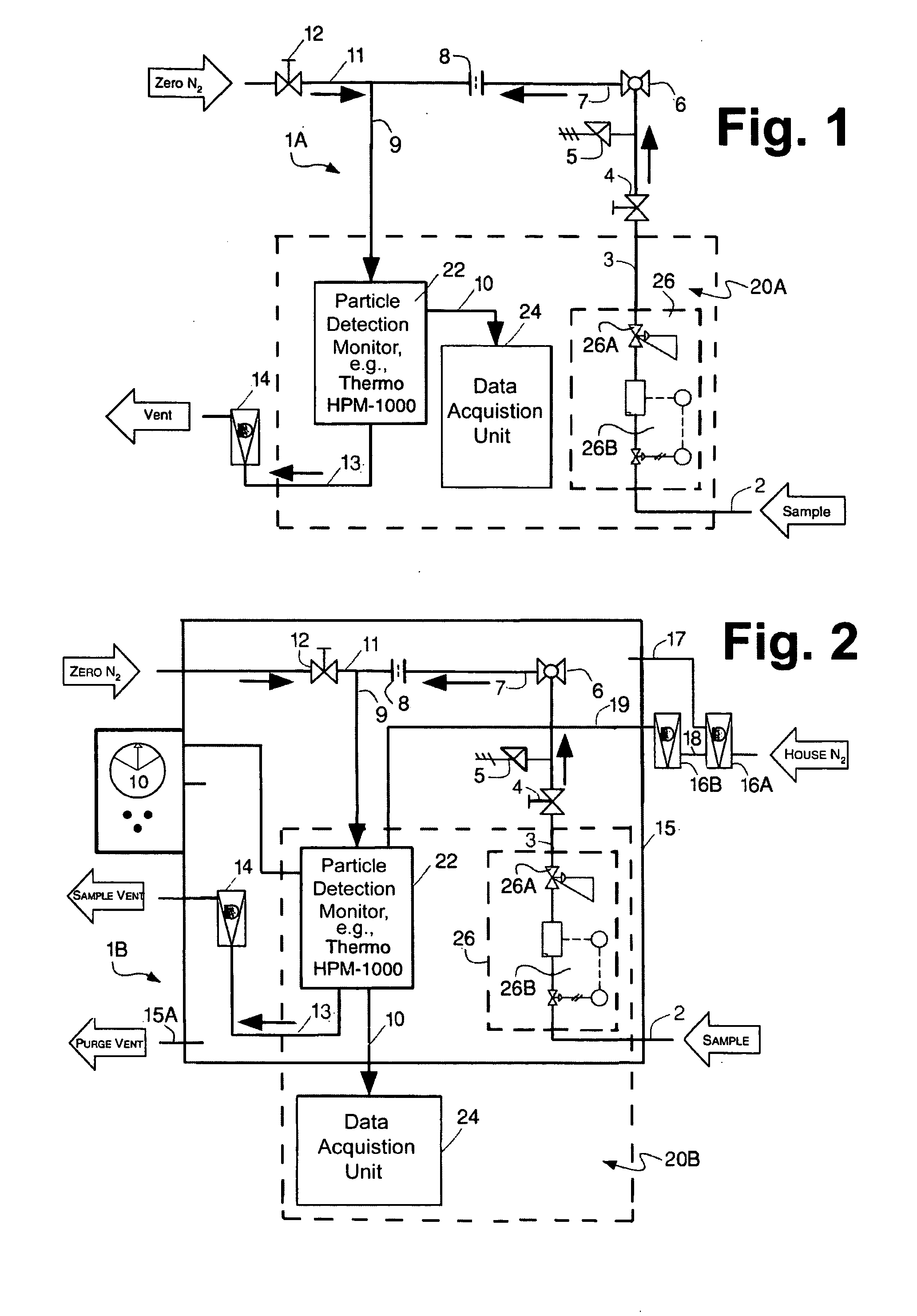
Liquid particle mass measurement in gas streams
InactiveUS20070086008A1Material analysis by optical meansParticle suspension analysisHydrogenStream flow
A system for detecting fine liquid, e.g., oil, particles in a gas system having a conduit through which a gas, e.g., hydrogen, air, etc., will flow. The detection system includes a monitor including a high sensitivity photometric sensor, a data acquisition unit and flow and pressure control components to control the pressure and rate of flow of the gas to the monitor. The detection system is arranged to detect the presence of fine liquid particles the gas passing through the conduit and to provide an alert signal representative of the mass count of such particles in response thereto.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
Method for identifying parameters of resonant fatigue crack propagation test vibration system based on soft sensing technology
ActiveCN104777054AStrong experimental operabilityLow cost per experimentStrength propertiesMechanical modelsThree degrees of freedom
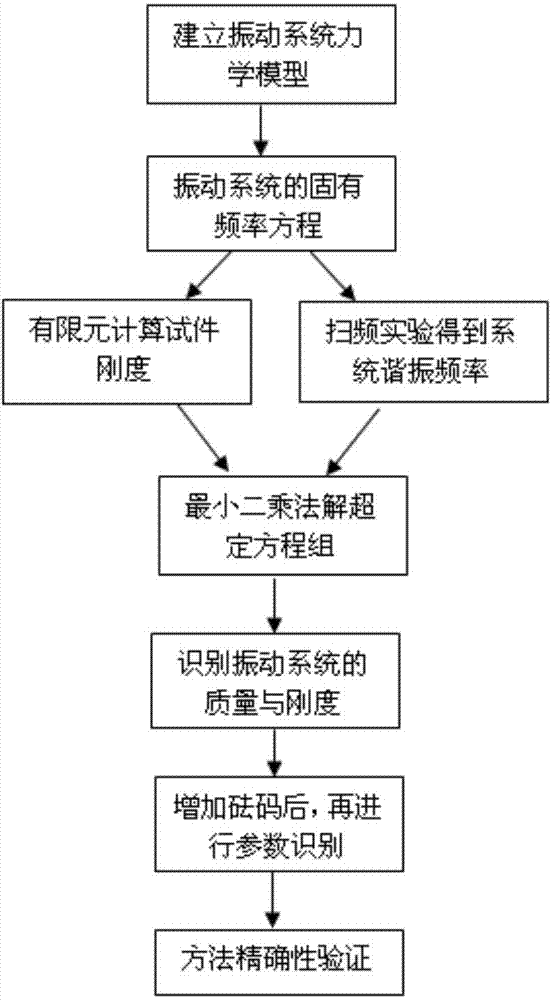
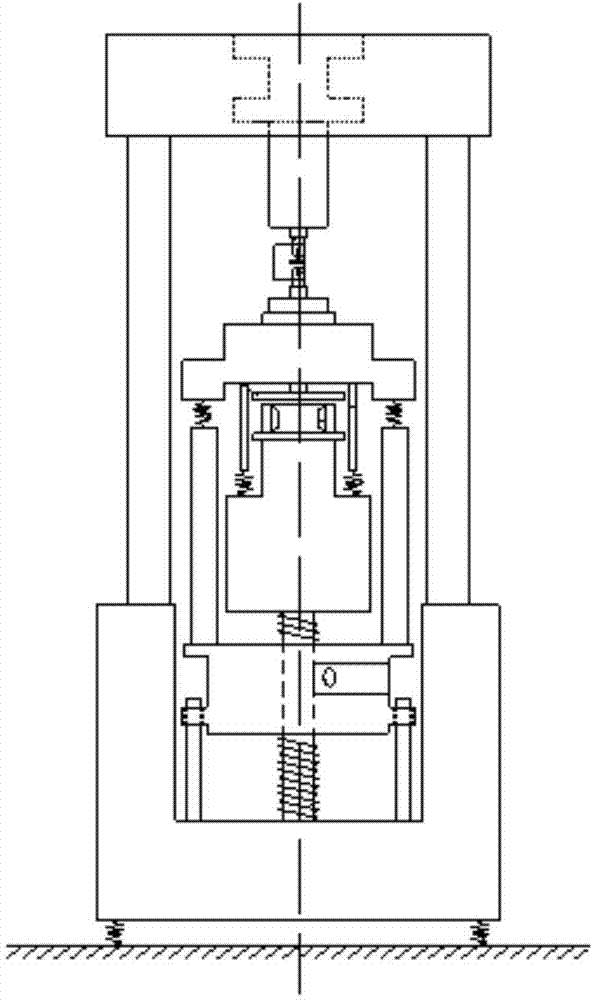
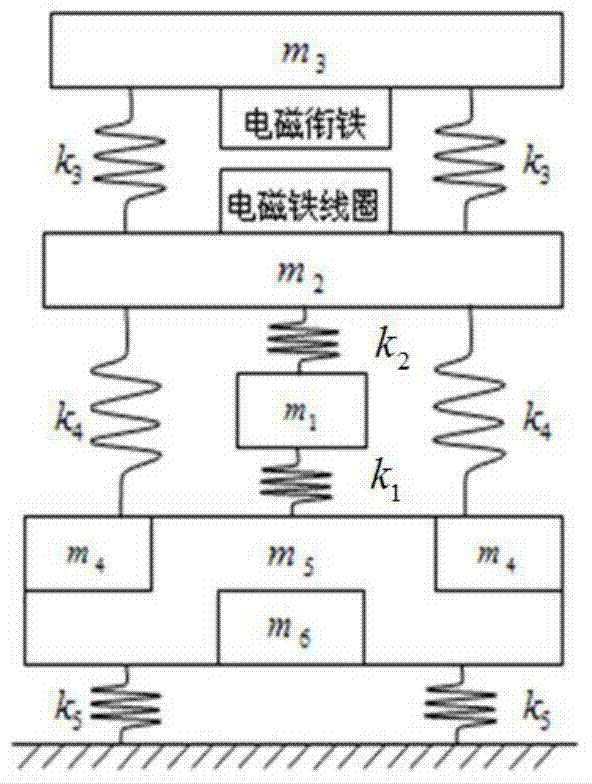
A method for identifying parameters of a resonant fatigue crack propagation test vibration system based on a soft sensing technology comprises the following steps: 1, establishing a system three-degree-of-freedom vibration mechanical model to obtain a kinetic equation, and deriving to obtain a system frequency equation about a relationship among the system inherent frequency, the spring rigidity and the particle mass; 2, calculating according to a finite element technology to obtain the rigidity of a test piece under different crack lengths, and testing the system resonant frequency when a crack is propagated to different lengths; 3, substituting the system resonant frequency value and the corresponding test piece rigidity under different crack lengths into the system frequency equation in order to obtain overdetermined equations about the mass to be identified and unknown rigidity; 4, solving the overdetermined equations through a least squares technique to obtain nonlinear equations about the mass and rigidity; and 5, solving the nonlinear equations by using a Newton-Raphson formula, and identifying the vibration system parameters comprising the mass and the rigidity. The method has the advantages of good maneuverability, low cost and good accuracy.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Light-scattering-method-based PM2.5 monitor calibration method and device
InactiveCN105572005ALow costSimple structureParticle suspension analysisLight scatteringParticle mass
The present invention provides a light-scattering-method-based PM2.5 monitor calibration method and device, and relates to the measuring technology. A light scattering signal generated by an aerosol particle group is converted into an electrical signal; total aerosol particle mass can be obtained according to direct proportion relation of cumulative voltage and cumulative mass of the aerosol particle group; a sample volume of a to-be-tested PM2.5 monitor is used as a standard volume, and standard mass concentration can be obtained according to the ratio of the total aerosol particle mass and the standard volume; an error value of a concentration display value of the to-be-tested PM2.5 monitor and the standard mass concentration is read by comparison, and a test result is judged. The light-scattering-method-based PM2.5 monitor calibration method solves the technical problems of complex calibration process, low calibration efficiency, difficulty in trace to the source of quality benchmark technology of PM2.5 monitors in the prior art. The beneficial effects are as follows: fast measuring speed, high sensitivity and accurate detection. Operation is simple and time saving, detection efficiency is improved, the light-scattering-method-based PM2.5 monitor calibration method is capable of tracing to the source of quality benchmark, can achieve online calibration, and saves testing costs, and the calibration device is reasonable in structure, low in cost, and easy to maintain.
Owner:ZHEJIANG MEASUREMENT SCI RES INST
Method for measuring concentration of particulate matter, and device adopting method
ActiveCN103245601AEasy to calculateGuaranteed calculation accuracyParticle suspension analysisAir volumePower unit
The invention belongs to the technical field of concentration measurement of atmospheric particulates, and particularly relates to a method for measuring the concentration of a particulate matter by a PIV (Particle Image Velocimetry) method, and a device adopting the method. The method comprises the following steps of: acquiring the size, shape and volume of each particle and calculating the mass of all types of particles; calculating the total sampled air volume according to the known flow and measurement time; and calculating the concentration of a particulate matter (PM) to be measured. Not only the method is convenient and quick in measuring and calculating, but also the calculating precision can be effectively ensured. The device comprises a particulate matter sampling mechanism, a filter strip conveying mechanism, a beta-ray radiation mechanism and a beta-ray receiving and measuring mechanism; the device further comprises a damping control component and a power unit, wherein the damping control component is close to the radiation outlet end of a beta-ray radiation source; and a PIV unit is also included. The device has the advantages of safety and reliability in use, simple and practical structure, correspondingly and remarkably improved occupied area and maintenance efficiency, and high measuring accuracy.
Owner:合肥福瞳光电科技有限公司
Method and apparatus for monitoring particles in a gas turbine working fluid
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
Particle three-dimensional position nanoscale resolving power measuring method under liquid state environment
InactiveCN104567682AExcellent horizontal resolutionExcellent lateral resolutionUsing optical meansMicro imagingDigital holographic microscopy
The invention relates to the field of digital holography microscopy measuring and the field of particle position measuring and provides a technology based on coaxial digital holography microscopy and an image processing method, and multi-particle three-dimensional position nanoscale resolving power measuring under a complex liquid state environment is achieved. According to the technical scheme, a particle three-dimensional position nanoscale resolving power measuring method under the liquid state environment comprises the steps that a coaxial digital holography microscopy imaging system is used for carrying out real-time tracking on particles and recording of particle holography images; the particle holography images are preprocessed; the processed holography images are subjected to holography reconstruction; the obtained reconstruction information is subjected to deconvolution operation; a centroid method is used for obtaining the horizontal positions of the particles; through the obtained particle mass center positions, a longitudinal intensity distribution curve is obtained; and polynomial fitting is used for carrying out fitting on the curve, and the peak values are the positions of the particles in the longitudinal direction. The method is mainly used in microscopy measuring.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
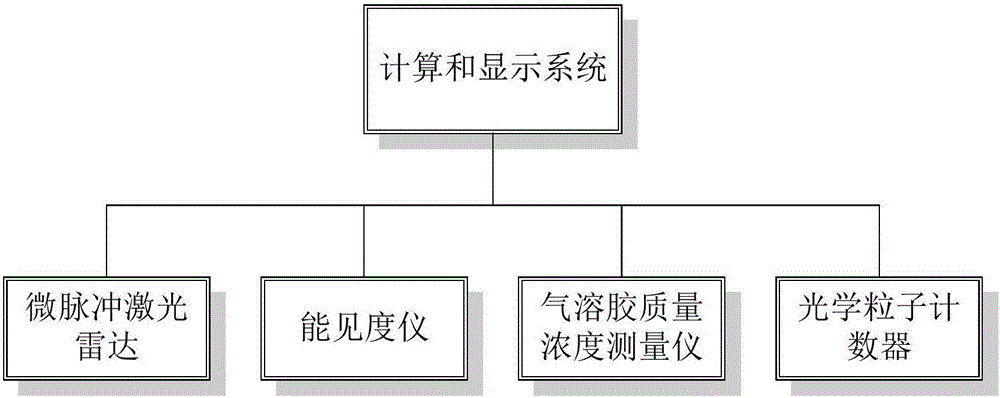
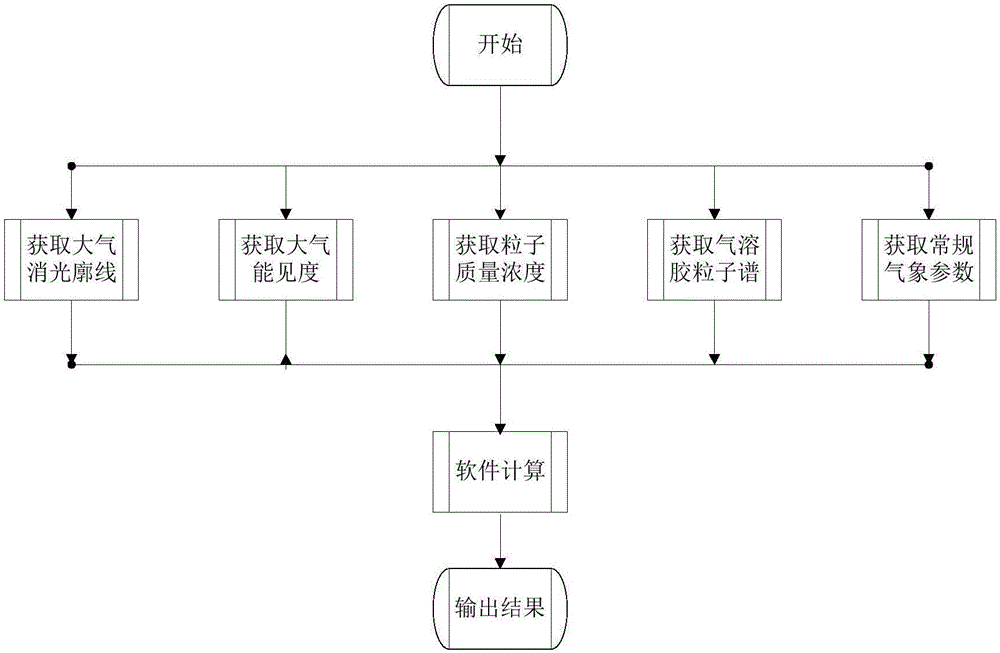
Computing method applied to atmospheric aerosol mass concentration horizontal route distribution
InactiveCN106383207AHigh precision advantageFully reflect the distribution characteristicsAir quality improvementMaterial analysisParticulatesMeasuring instrument
The invention discloses a computing method applied to atmospheric aerosol mass concentration horizontal route distribution and can effectively solve the obtaining problem of an aerosol mass concentration real-time distribution situation caused by quick city near-ground aerosol distribution time-space change, non-uniform city pollution source distribution and the like. Only the aerosol mass concentration of a limited position in a zone can be obtained through common fixed-point monitoring, and an aerosol pollution time-space distribution characteristic in a certain route cannot be expressed. In order to solve a distribution situation of aerosol and pollutants in a near-ground horizontal route, the invention provides the computing method for obtaining aerosol mass concentration distribution in routes within 0 to 6 kilometers in real time by comprehensively utilizing a micropulse laser radar and combining a particle counter, a visibility meter and a particle mass concentration measuring instrument. Parameters of aerosol extinction coefficient, particle distribution, mass concentration and the like are associated through theoretical and mathematic models. According to the computing method disclosed by the invention, an effective technical support is provided for research on pollution sources of city aerosol and monitoring on dynamic variation.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
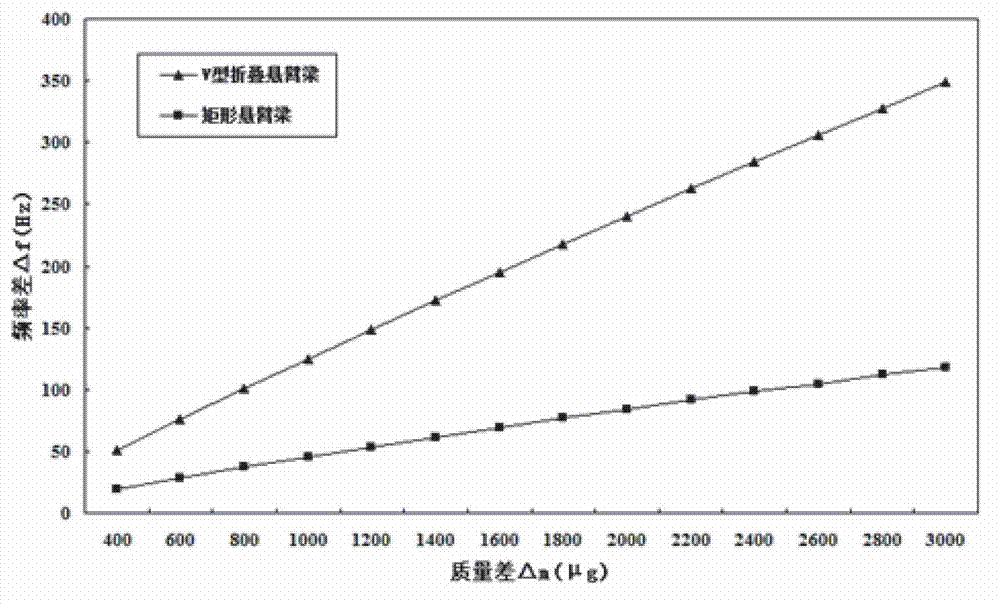
Micro-particle weighing sensor of V-shaped folding cantilever beam structure
InactiveCN102954829APrecise positioningHigh sensitivityWeighing apparatus using elastically-deformable membersWeighing by absorbing componentElectricityCantilevered beam
The invention discloses a micro-particle weighing sensor of a V-shaped folding cantilever beam structure, belonging to the field of a precise particle mass detection sensor. A micro mass sensor comprises a fixed block, a V-shaped folding cantilever beam structure and a piezoelectric thin film, and is characterized in that the upper surface of the V-shaped folding cantilever beam connected to the fixed block is connected with the piezoelectric thin film, wherein the top or tops of a single or a plurality of V-shaped folding grooves which are arranged along the axis is or are used as a main detection point or main detection points; and the mass of a detected object is accurately calculated through data output of the piezoelectric thin film. The rigidity and the effective mass distribution state of the sensor are effectively changed through introduction of the V-shaped folding cantilever beam, so that the detection sensitivity of the sensor is greatly improved. Specific examples show that the sensitivity can be improved by 227 percent compared with the conventional sensor of the rectangular section cantilever beam structure. The micro mass sensor has the characteristics of simple structure, accuracy in positioning of the detected object, high sensitivity and the like, so that the sensor can be widely applied to detection of atoms, fine particles, environmental dust and microbial cells such as bacteria or viruses.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Aerosol mass sensor and sensing method
InactiveUS20170097255A1Low costSensor compactWeighing by removing componentWeighing apparatus using elastically-deformable membersResonant sensorFrequency detection
A mass sensor for measuring particle mass within an aerosol uses resonance frequency detection to determine a mass of particles. A heating element is used for heating the resonant sensor element and it is controlled during a sensing cycle, with the change in mass of the deposited particles monitored during heating. This enables a low cost device to be able to detect particle concentration as well as provide information about the chemical and / or physical nature of the particles.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Low dose corticosteroid powders for inhalation
InactiveUS20060134009A1Treat conditionPowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsSteroid responsiveThroat
The invention relates to a method of treating a corticosteroid-responsive condition of the air passage ways and lungs by delivering a corticosteroid to the pulmonary system of a patient, comprising administering a particle mass comprising a corticosteroid from an inhaler characterized in that the corticosteroid is not substantially deposited in the mouth and throat and is not substantially systemically absorbed. The invention also relates to receptacles containing the particle mass and the inhaler for use therein.
Owner:ADVANCED INHALATION RES
Variable voltage agglomeration device for controlling quantity of micro-nano particles
ActiveCN109469533ADecrease in number concentrationLower mass emissionsExhaust apparatusSilencing apparatusMicro nanoEngineering
The invention discloses a variable voltage agglomeration device for controlling quantity of micro-nano particles. The variable voltage agglomeration device for controlling the quantity of the micro-nano particles comprises a particle charging cylinder, a particle agglomeration cylinder, a faraday cylinder and a particle trap, wherein the front end of the particle charging cylinder is connected with exhaust, the rear end of the particle charging cylinder is connected with the particle agglomeration cylinder, and the rear end of the particle agglomeration cylinder is connected with the faraday cylinder and then is connected with the particle trap. According to the variable voltage agglomeration device for controlling the quantity of the micro-nano particles, a charging and agglomeration technology is adopted, and through a method combining double-pole high-voltage charging and agglomeration, the agglomeration of exhaust particles is realized, so that the particle size is increased, meanwhile, the quantity and the concentration of the particles are reduced, the trapping efficiency of the particle trap is further improved, and particle mass emissions are reduced; particle surface charge measurement and high-voltage electric field control are connected together, so that the most suitable range control for the charging voltage is achieved and the energy consumption of the high-voltage power supply is reduced; and through double temperature sensors and double mass flow meters, the effect of the charging voltage and exhaust temperature on the charging and agglomeration of the particles and the study on the efficiency of the particle trap can be discussed.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Graded particulate compositions
A method of forming a particle mass comprising at least two particle populations arranged in a desired graded relationship, comprising: forming in a container a first layer of dry particles constituting a first particle population having a desired particle size distribution, superimposing on the first layer a second layer of dry particles constituting a second particle population having a desired particle size distribution, the second layer being in direct contact with the first layer at a contact interface, and causing the particle mass in the container to vibrate to cause a desired degree of migration of particles from one or both layers across the contact interface under the influence of force experienced by particles in the mass. The particle populations may have different physical and / or chemical properties, so that the particle mass is functionally graded for subsequent fusion into a functionally graded material such as a ceramic or ceramic / metal composite.
Owner:GC HLDG
Method and system for determining particle transmittance of a filter in particle detection system
ActiveUS7777633B2Material analysis by optical meansPhotoelectric discharge tubesSmoke detectorsTransmittance
Owner:GARRETT THERMAL SYST LTD
Mass sensor based on elastic mass system and method for measuring mass thereof
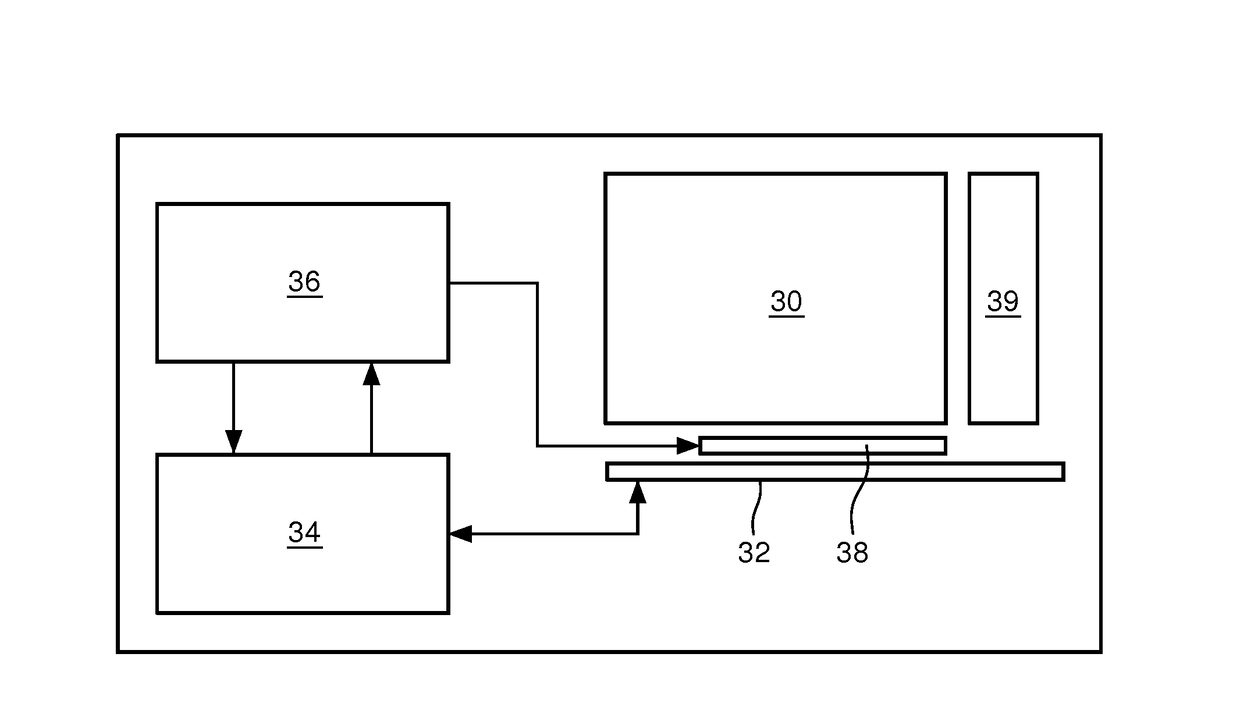
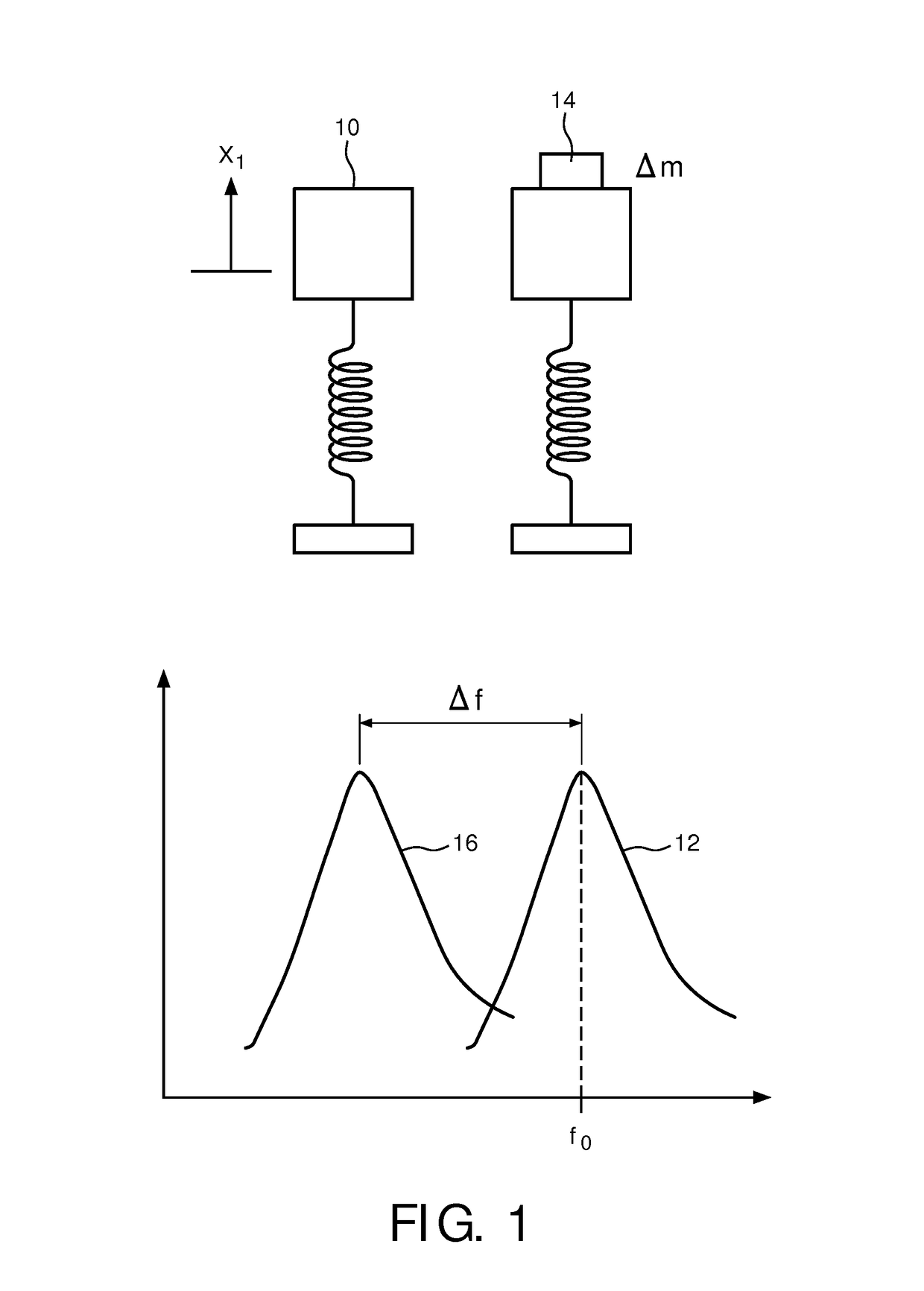
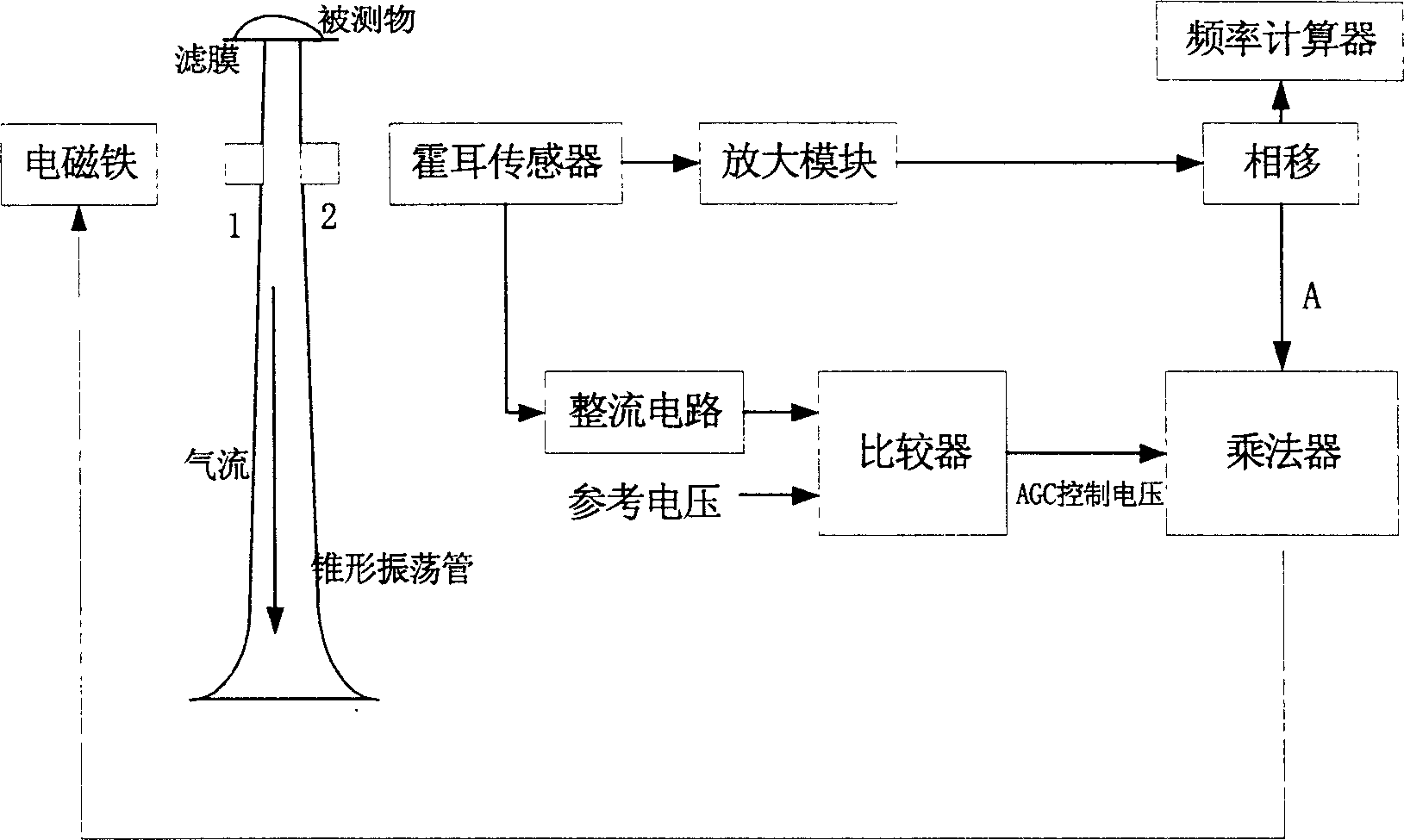
The invention discloses a quality sensor and measuring method based on the spring quality system. The conical bottom end of the hollow conical pipe is fixed on the frame; a filter is fixed on the conical snap end; the two magnetic steels are fixed on the two neck sides of the conical pipe. The measuring method is that it separately fixes an electric magnetic and a linear Hall part on the two sides of the magnetic steel; it measures the start oscillation frequency f0 of the hollow conical pipe and sampling air finishing frequency f1, which can compute the quality changing value dm of the oscillation body which is the particle quality on the filter.
Owner:ANHUI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com