Patents
Literature
485 results about "Particle counter" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A particle counter is an instrument that detects and counts physical particles.
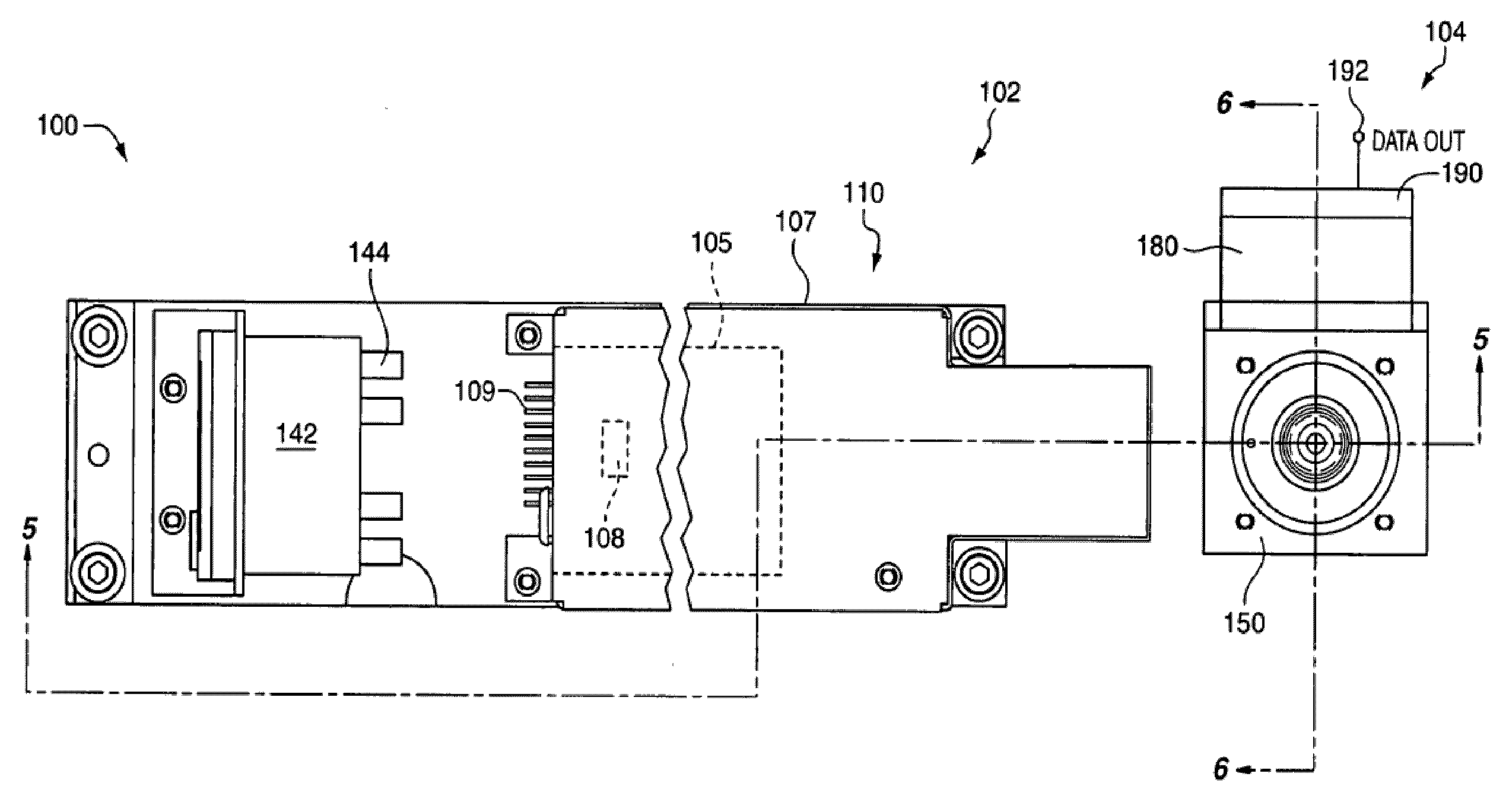
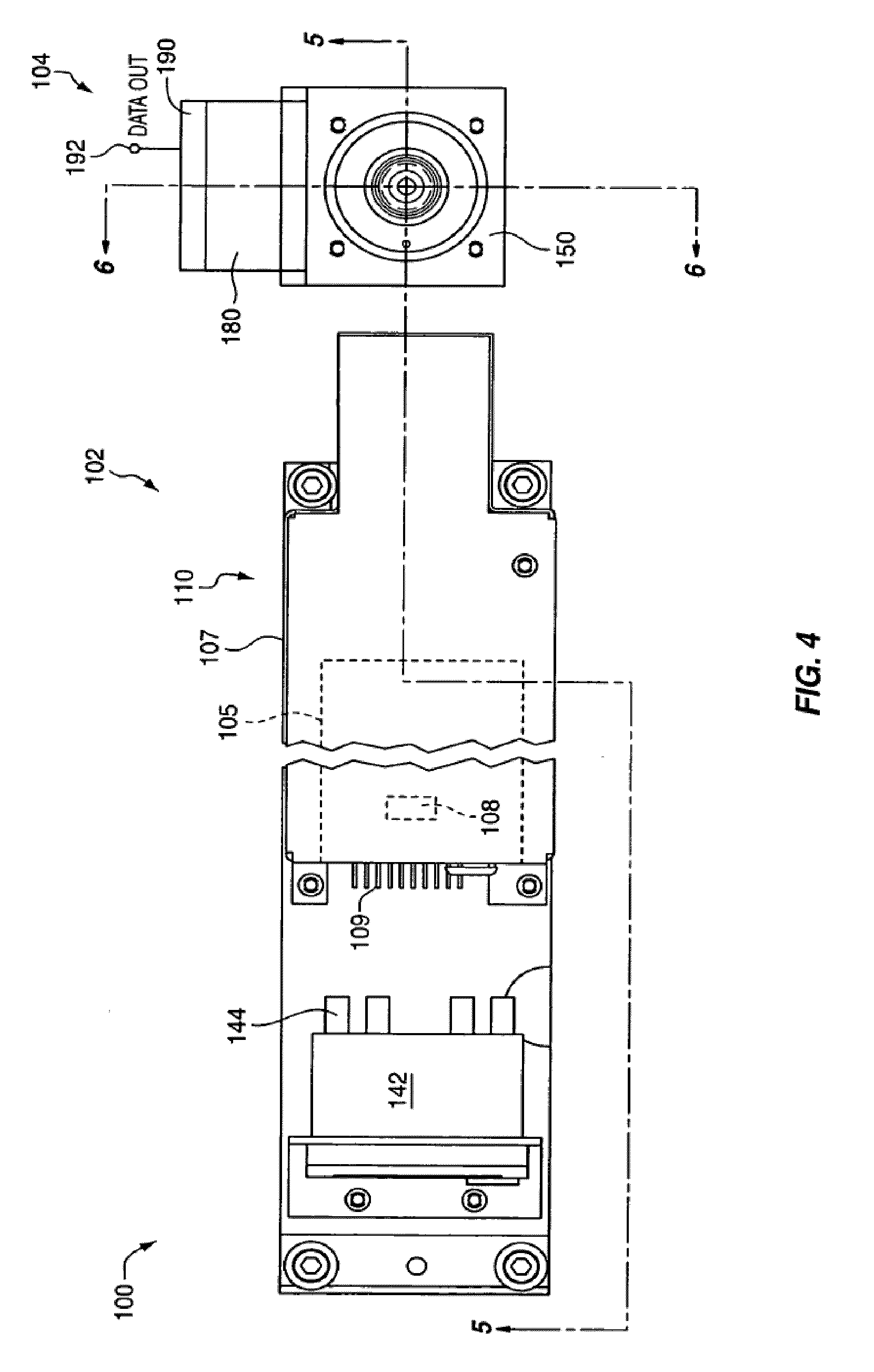
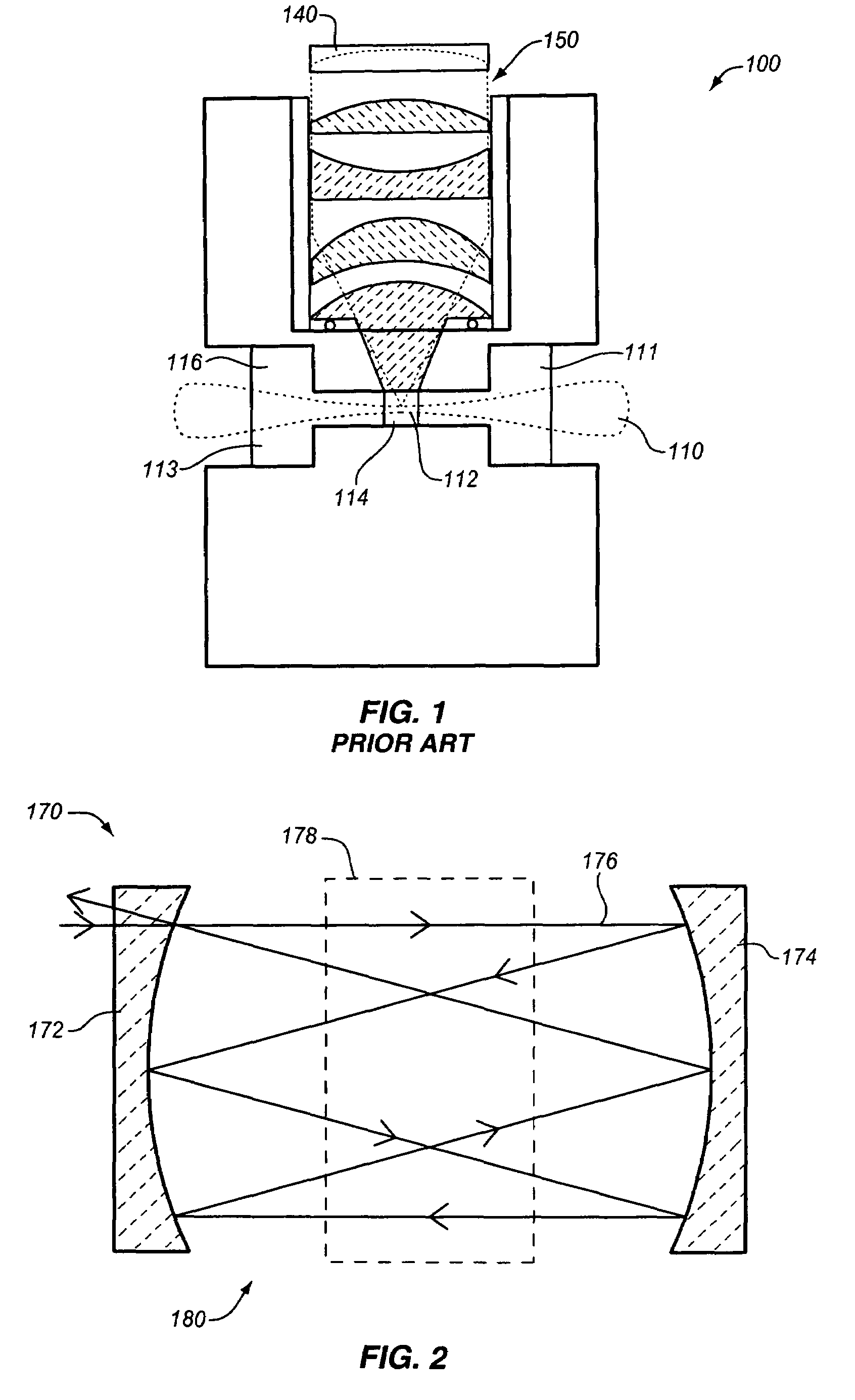
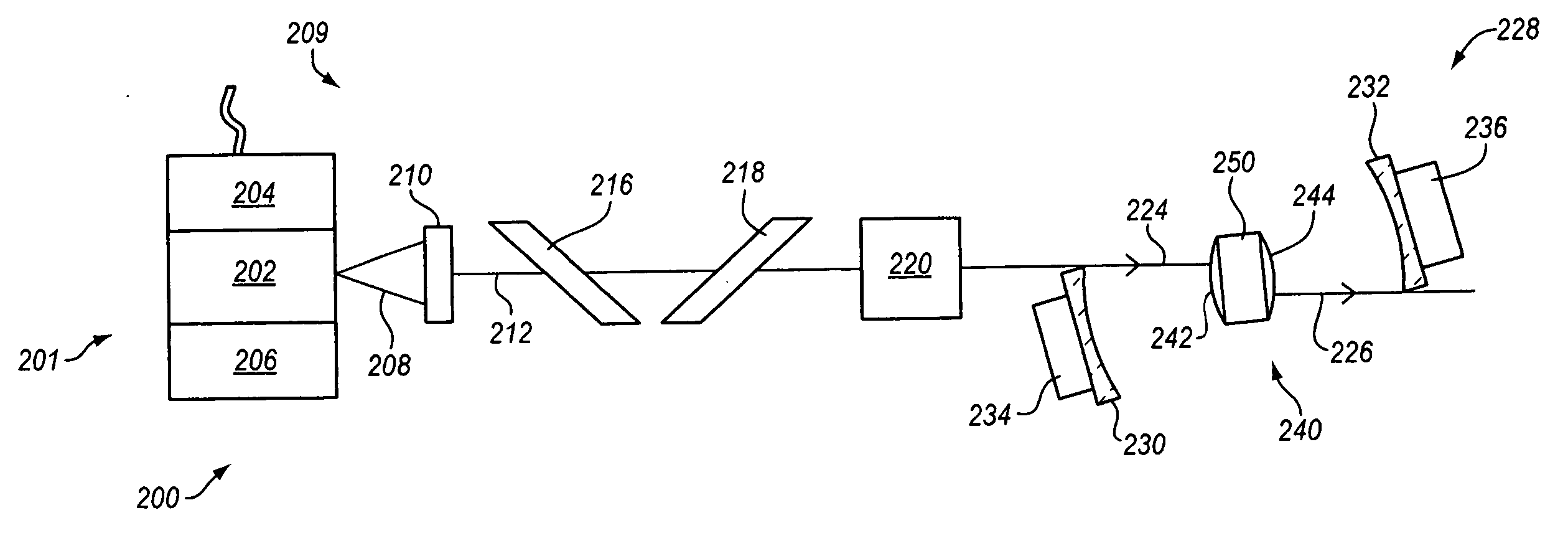
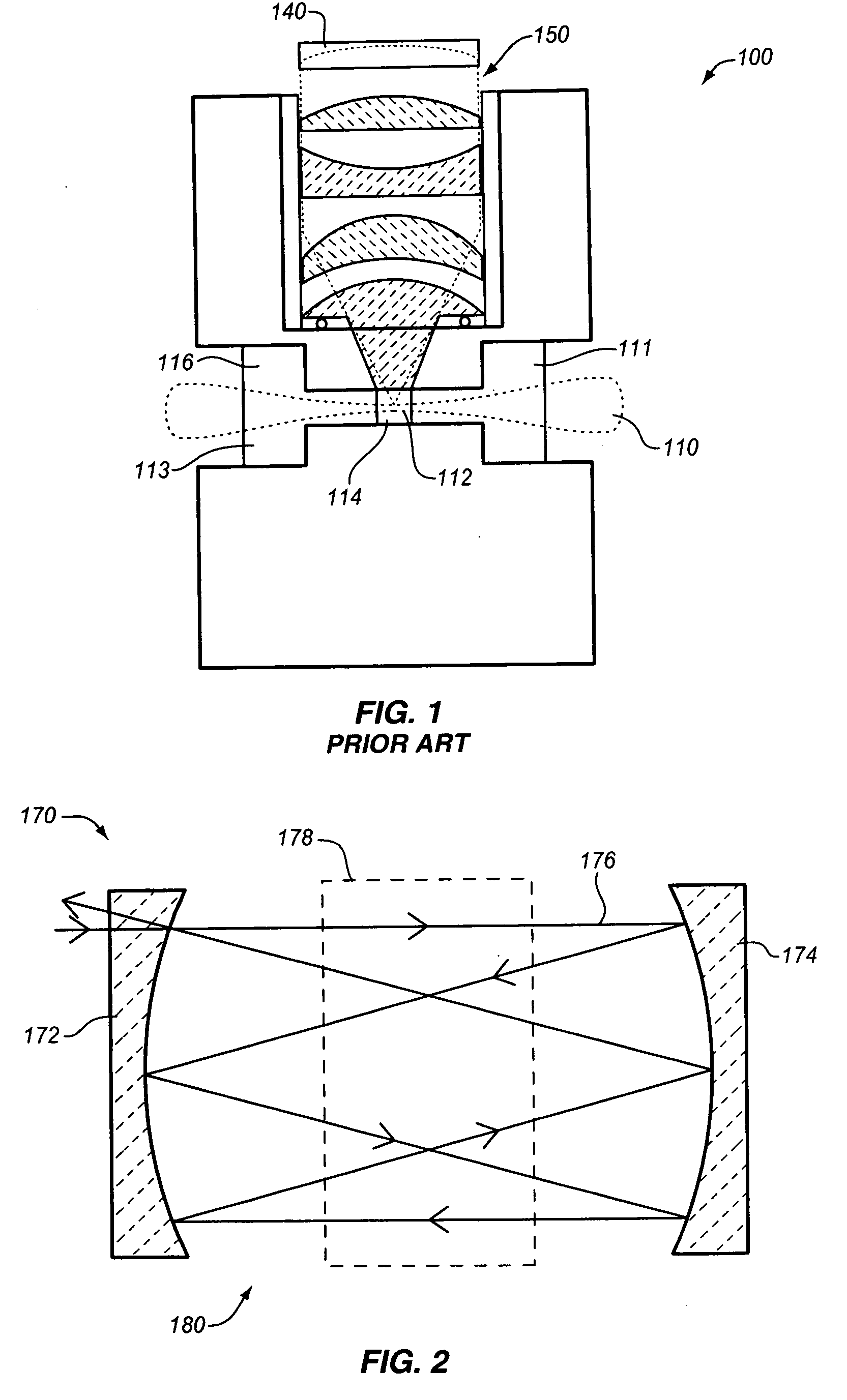
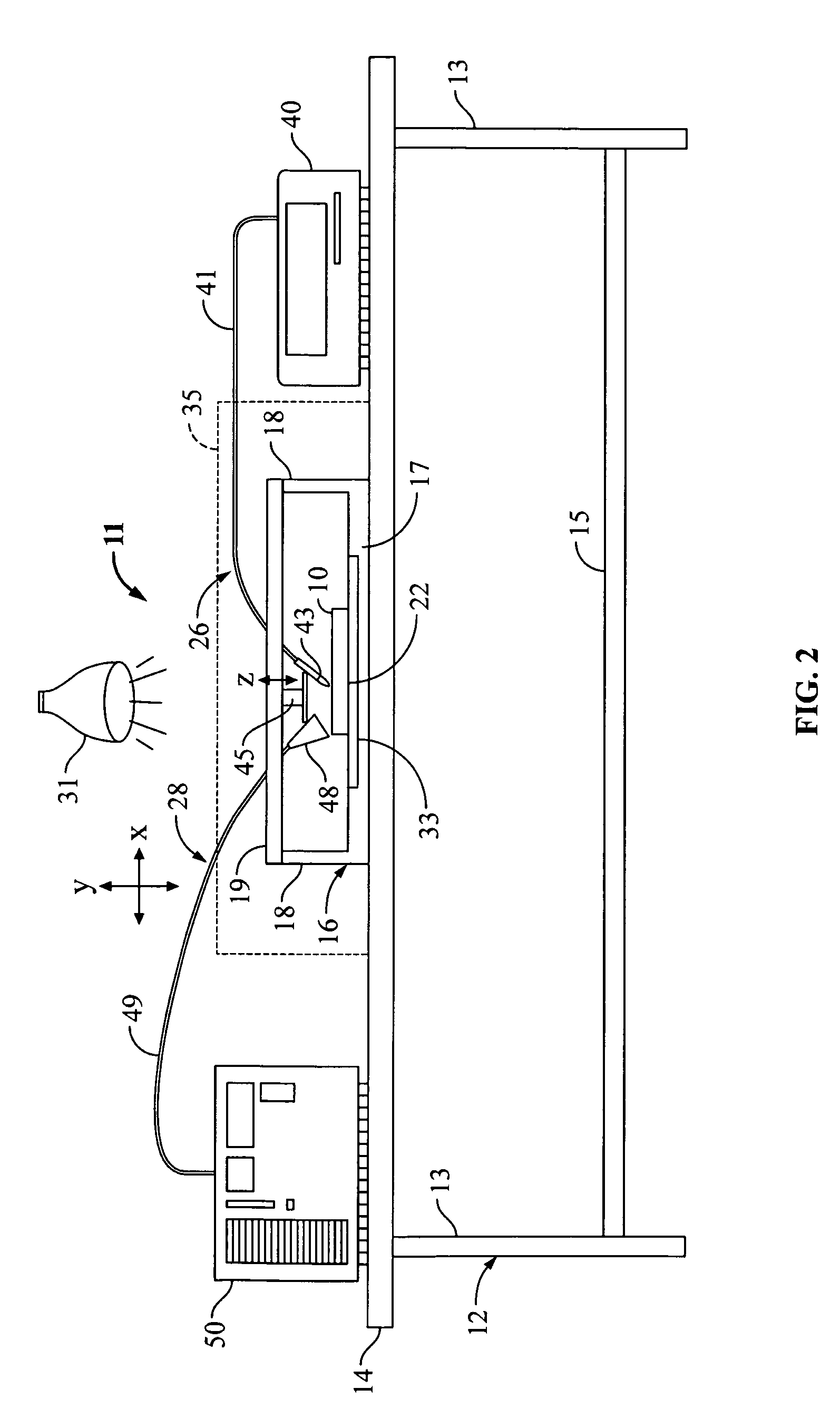
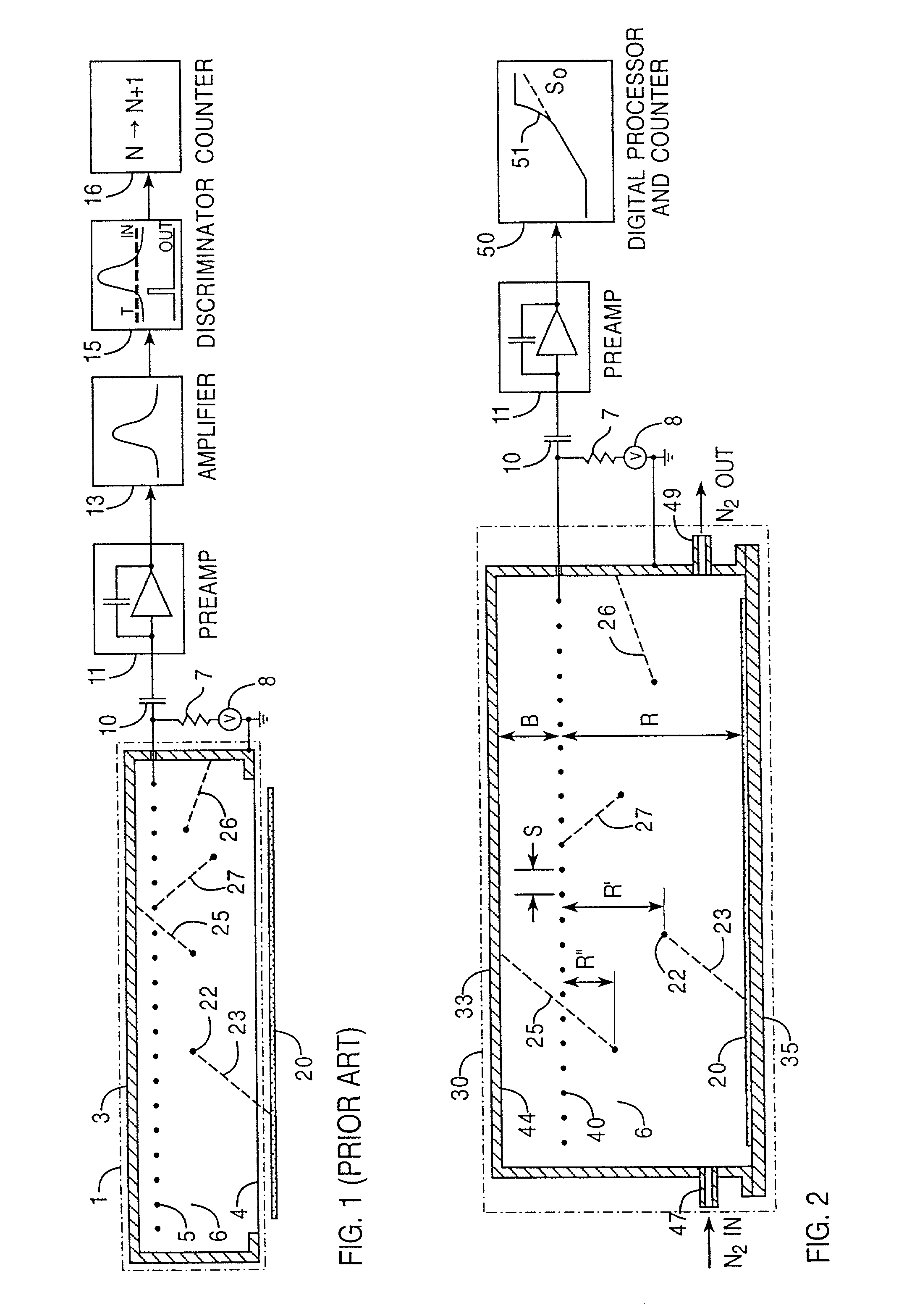
Low noise intracavity laser particle counter
ActiveUS6903818B2High power operationEffective noise reductionRadiation pyrometryScattering properties measurementsLow noiseEddy current
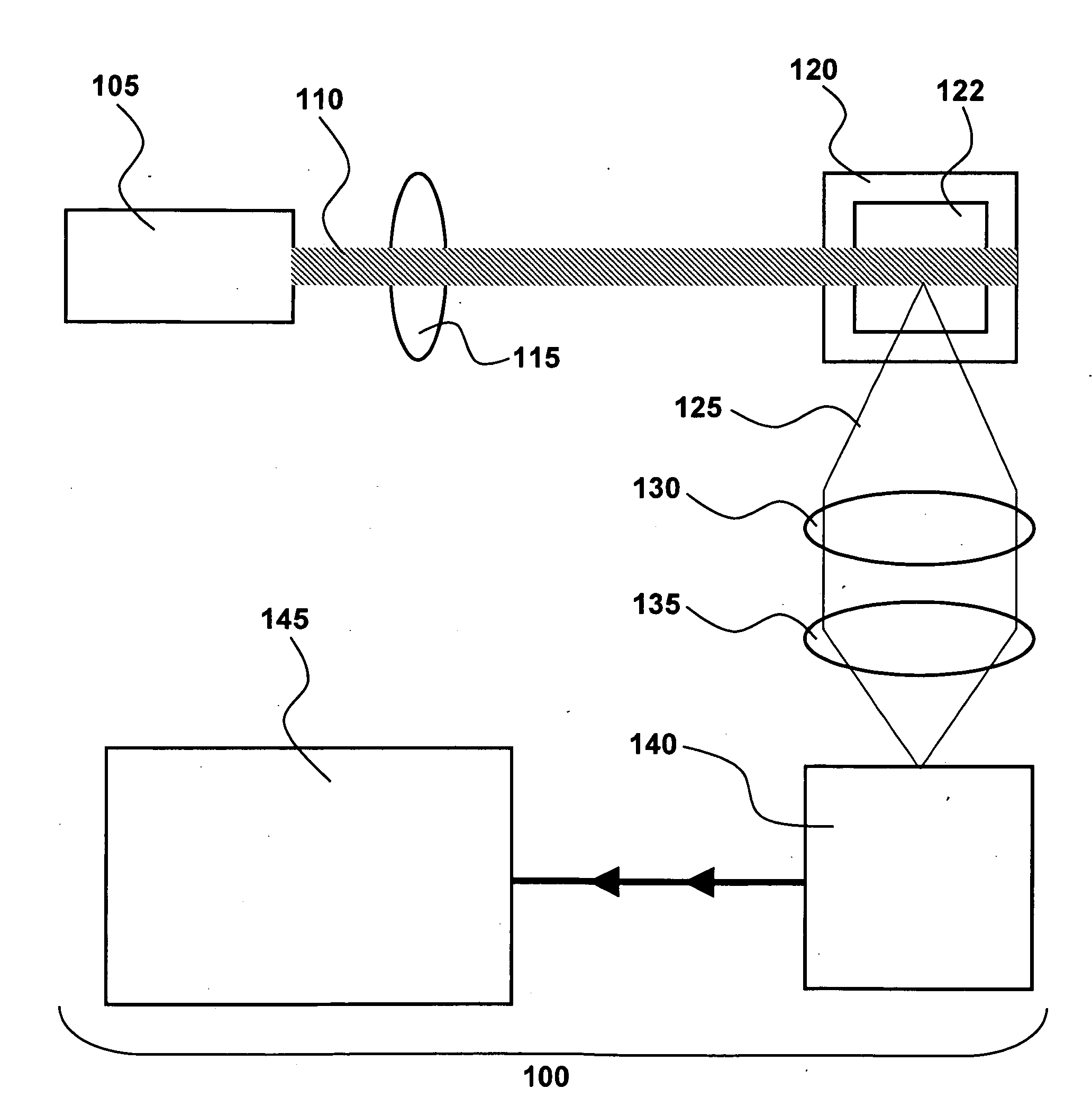
An optical particle counter has a gain-apertured laser cavity producing laser light, an inlet jet providing fluid flow into a particle detecting region within the laser cavity, the inlet jet having an inlet jet orifice; a detection optics assembly located to collect light scattered from particles with the detecting region for producing an output signal indicative of the particles; and an optical barrier complex located to reduce noise as compared to the gain-apertured system without the optical barrier complex for fluid flow rates greater than or equal to about 0.1 cubic feet per minute. The optical barrier complex inhibits laser light from illuminating turbulent eddy currents originating on the interior walls of the inlet jet. The optical barrier complex includes one or more physical apertures, one or more optical stops, or both which are located to prevent laser light from illuminating the eddy currents.
Owner:PARTICLE MEASURING SYST
System and method of conducting particle monitoring using low cost particle sensors
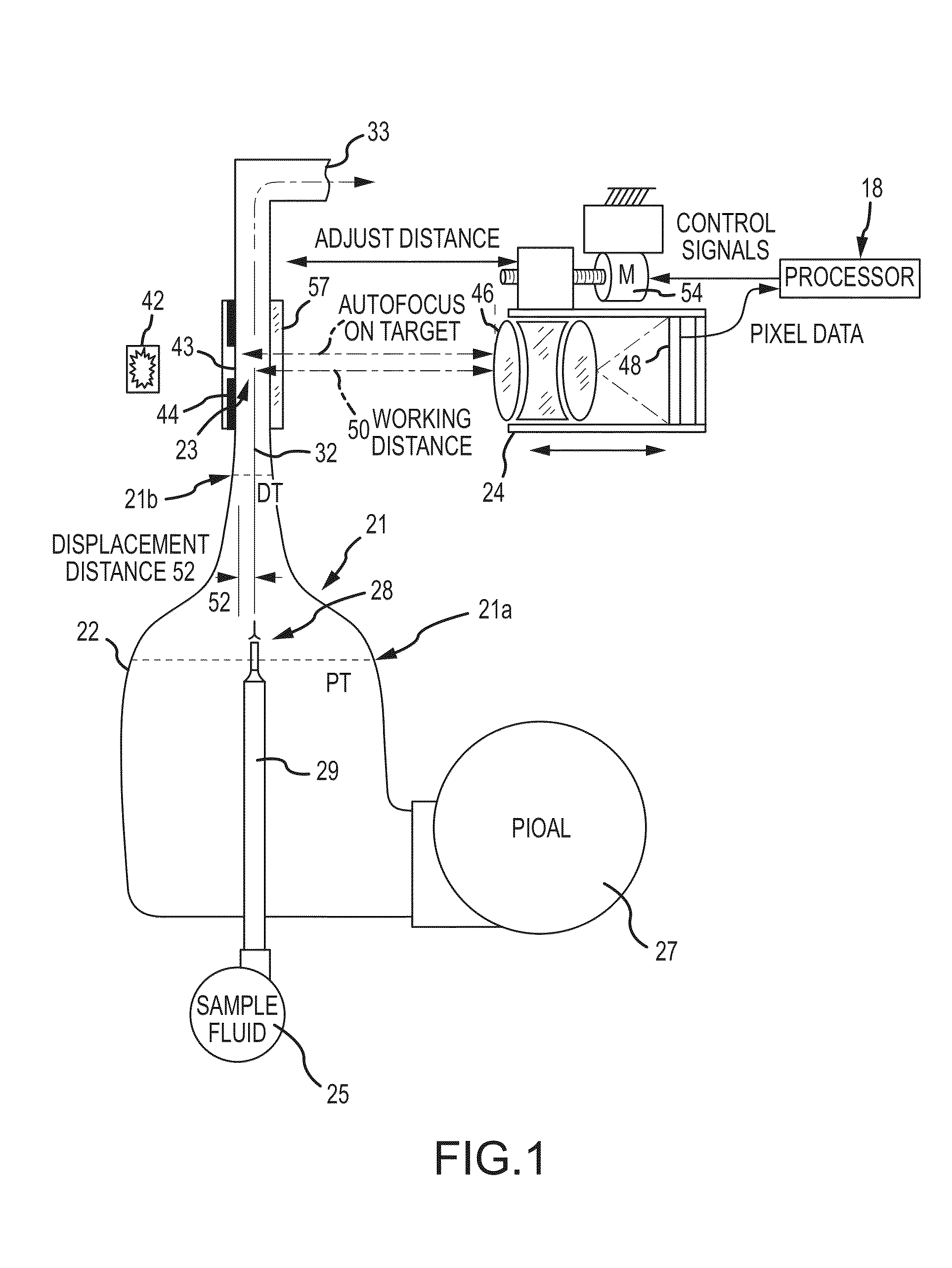
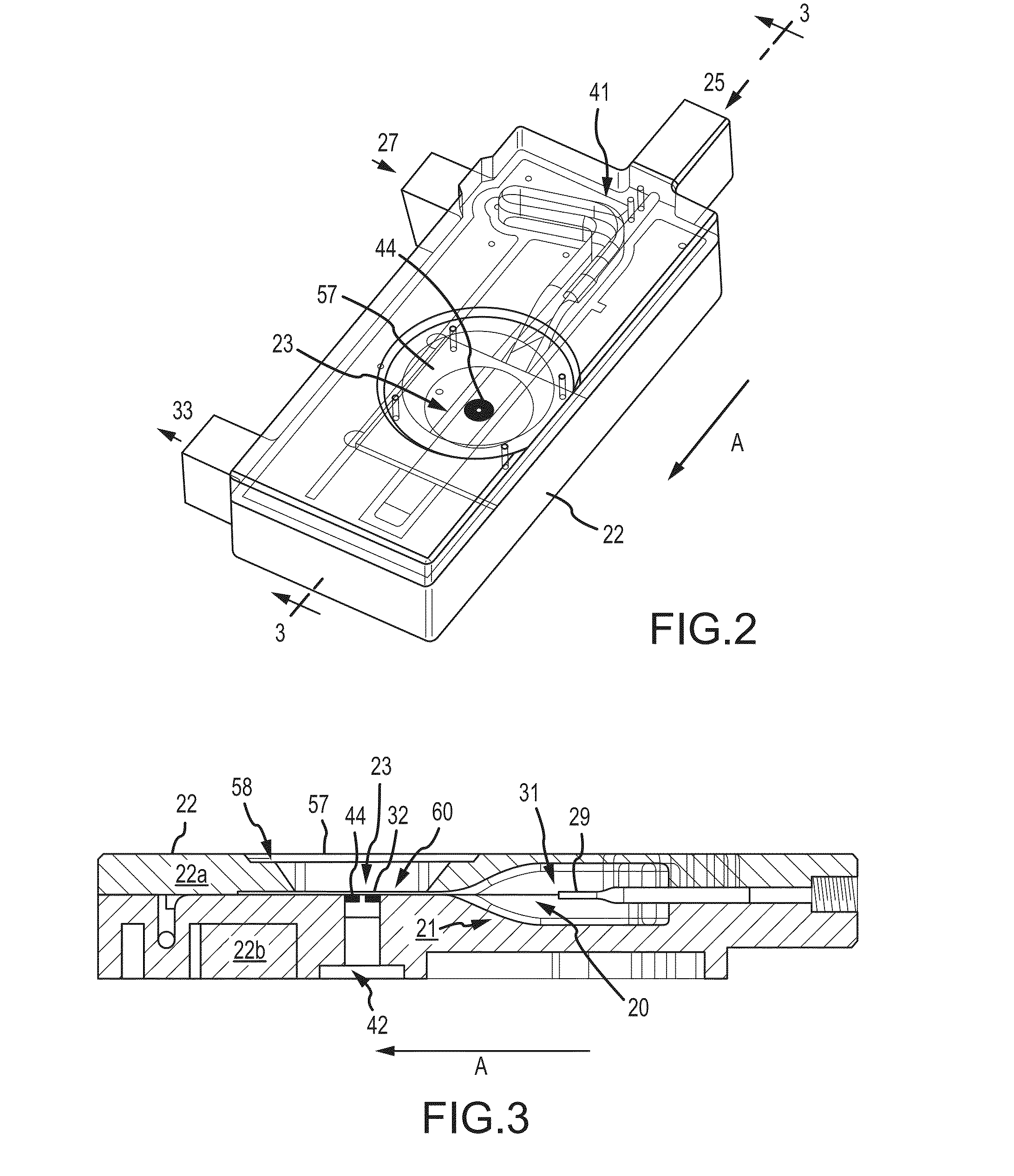
ActiveUS20160153884A1Low costCompact form factorWithdrawing sample devicesMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansUltrasound attenuationParticle counter
There is disclosed a field calibratable particle sensor solution in a low-cost, very compact form factor. This makes a low-cost sensor more accurate for low-concentration pollution measurements and decreases the cost of pollution measurement systems having a wide geographic coverage. In a related embodiment, the invention illustrates a method and system to remotely and automatically calibrate one or more of the low cost sensors disclosed herein as well as other commercially available sensors (such as optical particle counters, photometers etc.) against a reference instrument (such as a beta attenuation monitor) which may or may not be physically located in the same place as the individual sensors. The method may require minimum (or no) user interaction and the calibration period is adjustable periodically.
Owner:TSI INC
Ethernet-powered particle counting system
InactiveUS20060263925A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMaterial analysisDigital dataAir movement
A system includes a particle counter having a data output, an Ethernet cable adapted for connecting the data output of the particle counter to a monitoring station, and a power over Ethernet (POE) type power supply structured for providing power to the particle counter via the Ethernet cable. Apparatus includes a particle counter having an air movement device powered solely by a POE supply. Apparatus may include a particle counter having an air mover, power management subsystem, and Ethernet data output, the power management subsystem for monitoring power consumption of the air mover and maintaining the power consumption below a predetermined amount, and an electrical supply for powering the particle counter via an Ethernet medium. A method includes powering a particle counter over Ethernet medium via a POE power supply, detecting microscopic particles, and producing digital data based on the detecting, and transmitting the data over the Ethernet medium.
Owner:VENTUREDYNE LTD
Ion mobility analysis of lipoproteins
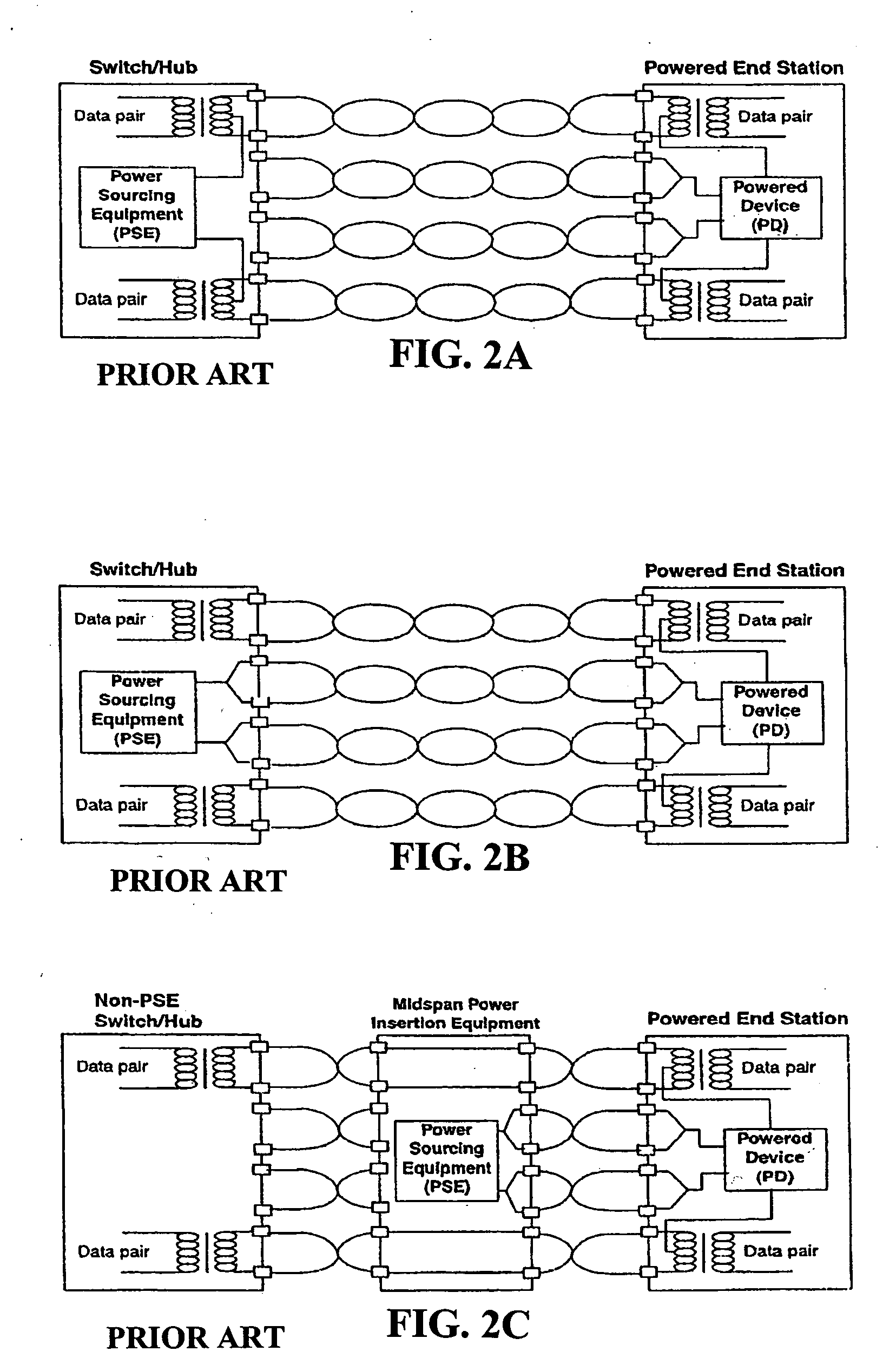
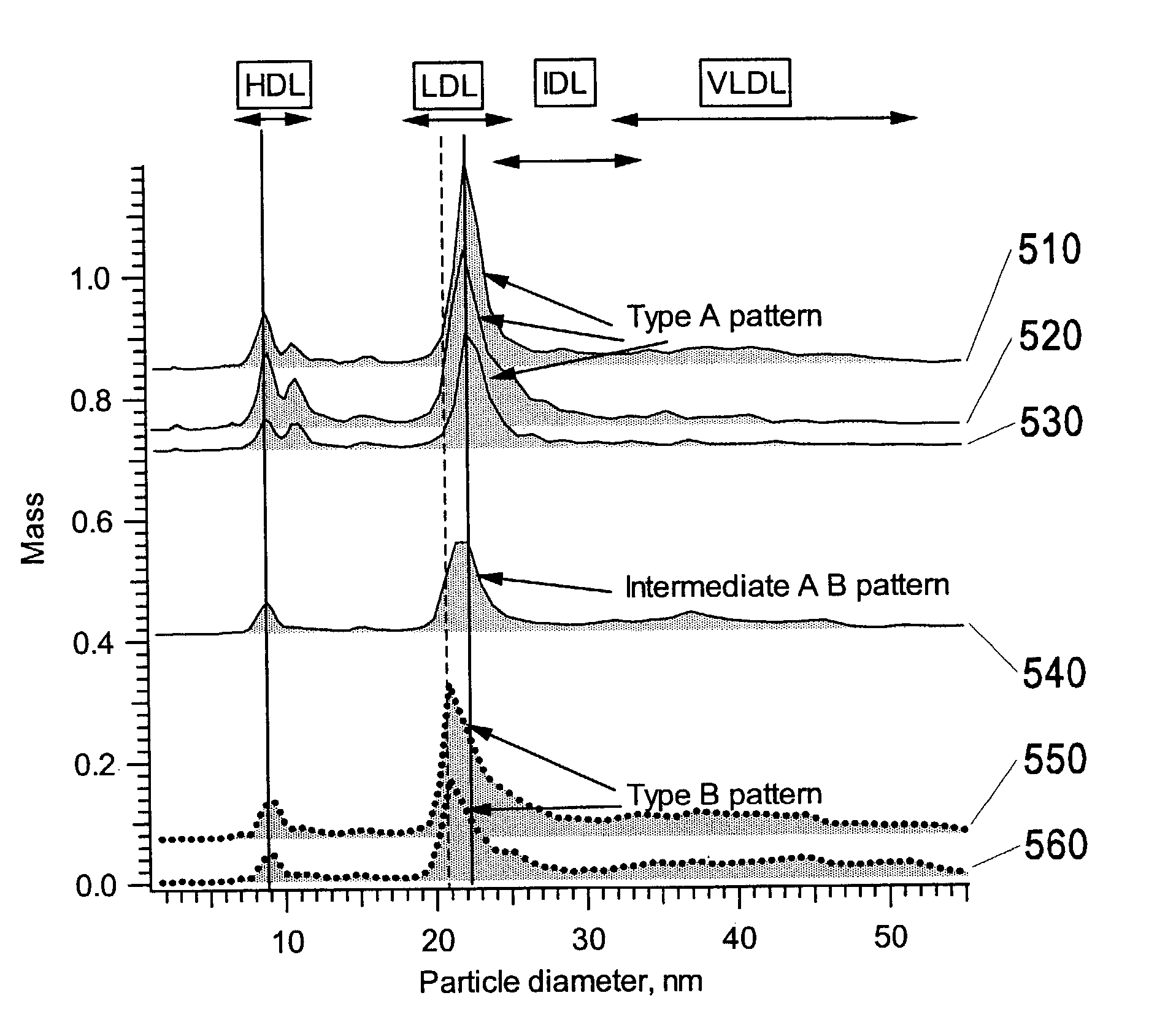
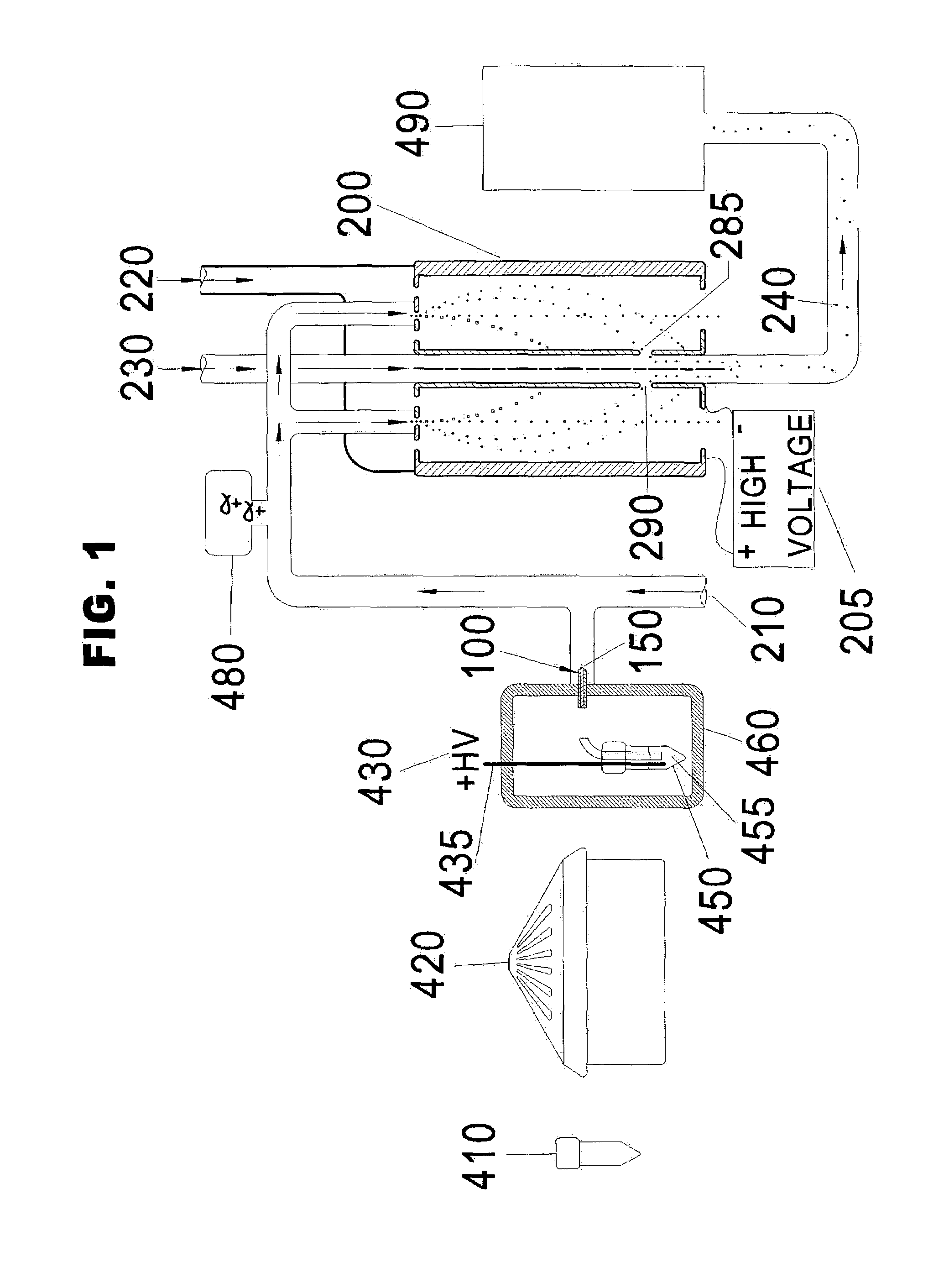
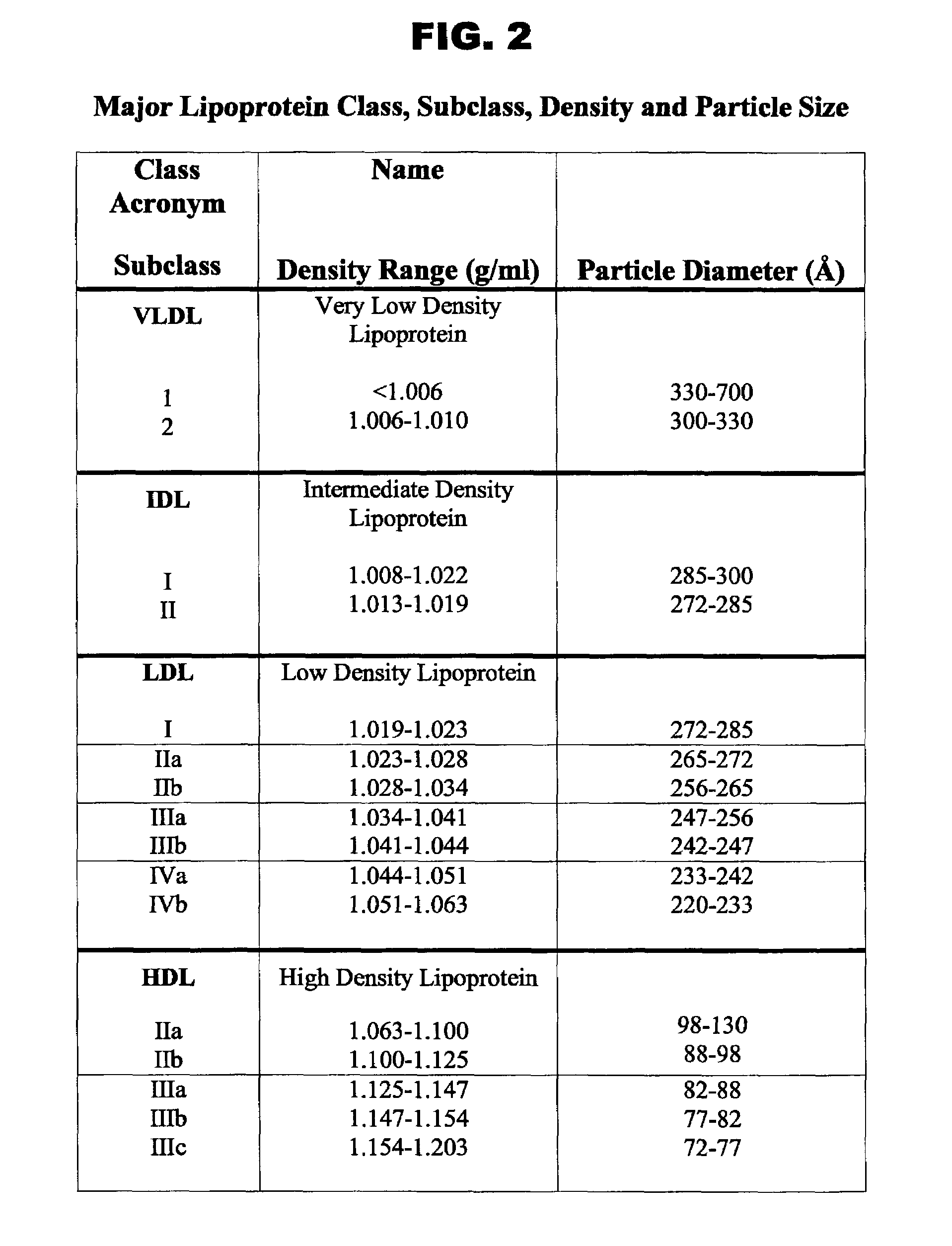
A medical diagnostic method and instrumentation system for analyzing noncovalently bonded agglomerated biological particles is described. The method and system comprises: a method of preparation for the biological particles; an electrospray generator; an alpha particle radiation source; a differential mobility analyzer; a particle counter; and data acquisition and analysis means. The medical device is useful for the assessment of human diseases, such as cardiac disease risk and hyperlipidemia, by rapid quantitative analysis of lipoprotein fraction densities. Initially, purification procedures are described to reduce an initial blood sample to an analytical input to the instrument. The measured sizes from the analytical sample are correlated with densities, resulting in a spectrum of lipoprotein densities. The lipoprotein density distribution can then be used to characterize cardiac and other lipid-related health risks.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method and device for decreasing contamination
ActiveUS20080038207A1Reduce Particle GenerationAltered propertyBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsViscoelasticityContamination
Methods and devices to determine rate of particle production and the size range for the particles produced for an individual are described herein. The device (10) contains a mouthpiece (12), a filter (14), a low resistance one-way valve (16), a particle counter (20) and a computer (30). Optionally, the device also contains a gas flow meter (22). The data obtained using the device can be used to determine if a formulation for reducing particle exhalation should be administered to an individual. This device is particularly useful prior to and / or following entry in a cleanroom to ensure that the cleanroom standards are maintained. The device can also be used to identify animals and humans who have an enhanced propensity to exhale aerosols (referred to herein as “over producers”, “super-producers”, or “superspreaders”). Formulations to reduce particle production are also described herein. The formulation is administered in an amount sufficient to alter biophysical properties in the mucosal linings of the body. When applied to mucosal lining fluids, the formulation alters the physical properties such as the gel characteristics at the air / liquid interface, surface elasticity, surface viscosity, surface tension and bulk viscoelasticity of the mucosal lining. The formulation is administered in an effective amount to minimize ambient contamination due to particle formation during breathing, coughing, sneezing, or talking, which is particularly important in cleanroom applications. In one embodiment, the formulation for administration is a non-surfactant solution. In one embodiment, the formulations are conductive formulations containing conductive agents, such as salts, ionic surfactants, or other substances that are in an ionized state or easily ionized in an aqueous or organic solvent environment. Preferably the formulation is administered in the form of an aerosol.
Owner:PULMATRIX OPERATING CO
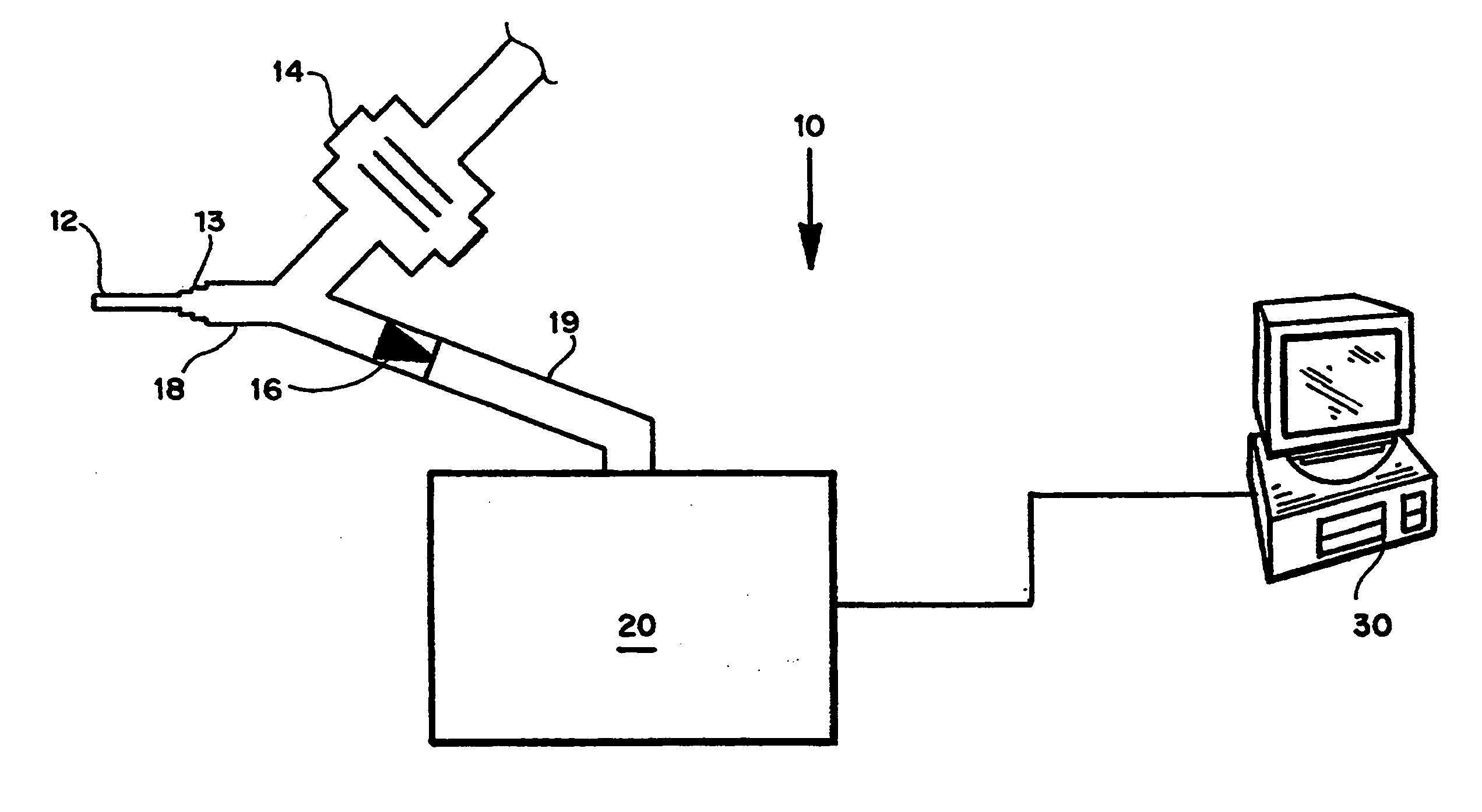
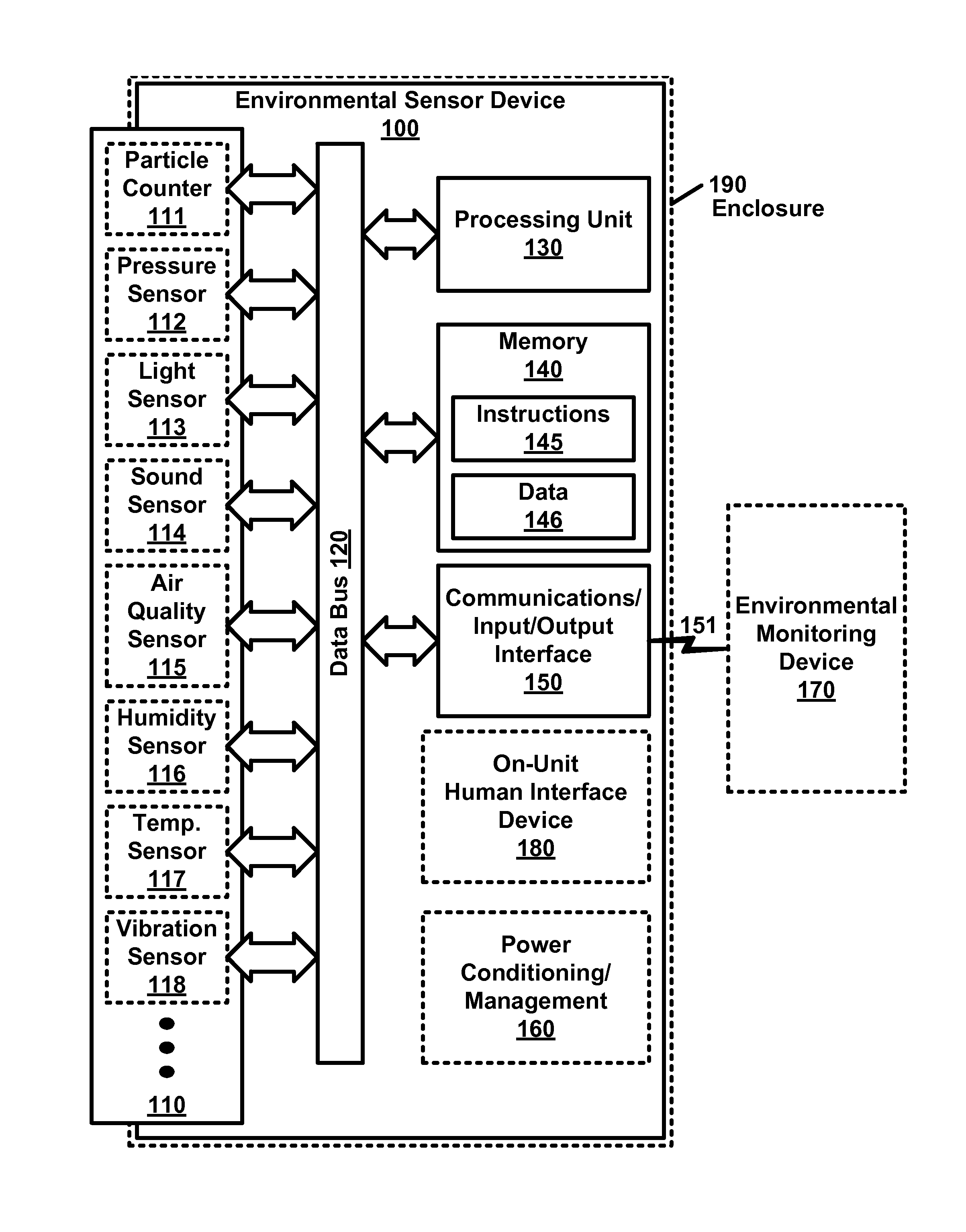
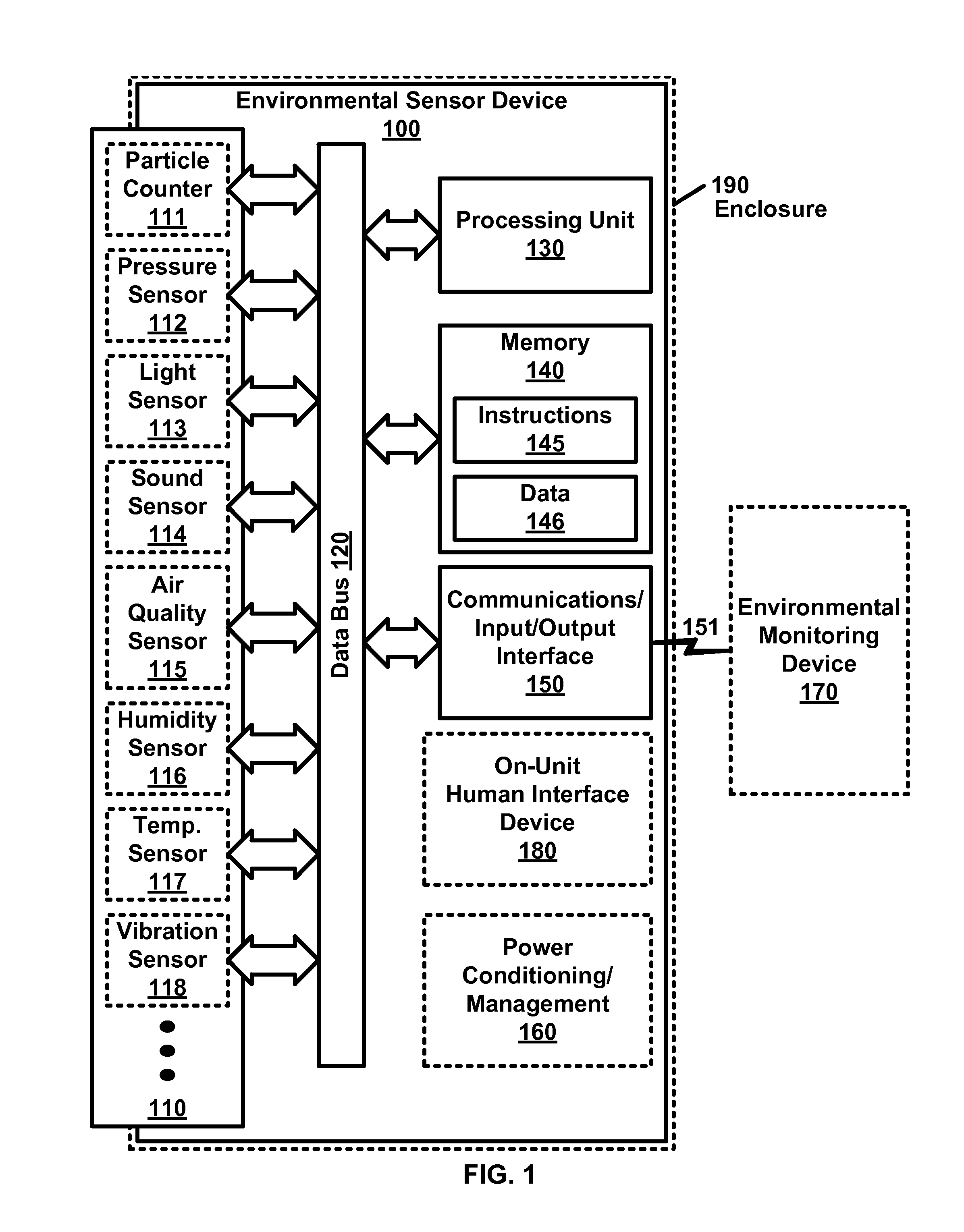
Environmental Monitor Device
ActiveUS20160063841A1AlarmsElectric digital data processingCommunication interfaceEnvironmental monitor
An environmental monitoring device comprises a data bus, a multitude of sensors, at least one processing unit, input / output device(s); communications interface(s), and memory. Communications interface(s) communicate with at least one environmental sensor device comprising with a multitude of sensors. The multitude of sensors may include particle counter(s), pressure sensor(s) and / or the like. The memory is configured to hold data and machine executable instructions. The machine executable instructions are configured to cause at least one processing unit to: collect sensor data from at least one environmental sensor device; and generate a report of sensor data that exceeds at least one threshold.
Owner:OBERON
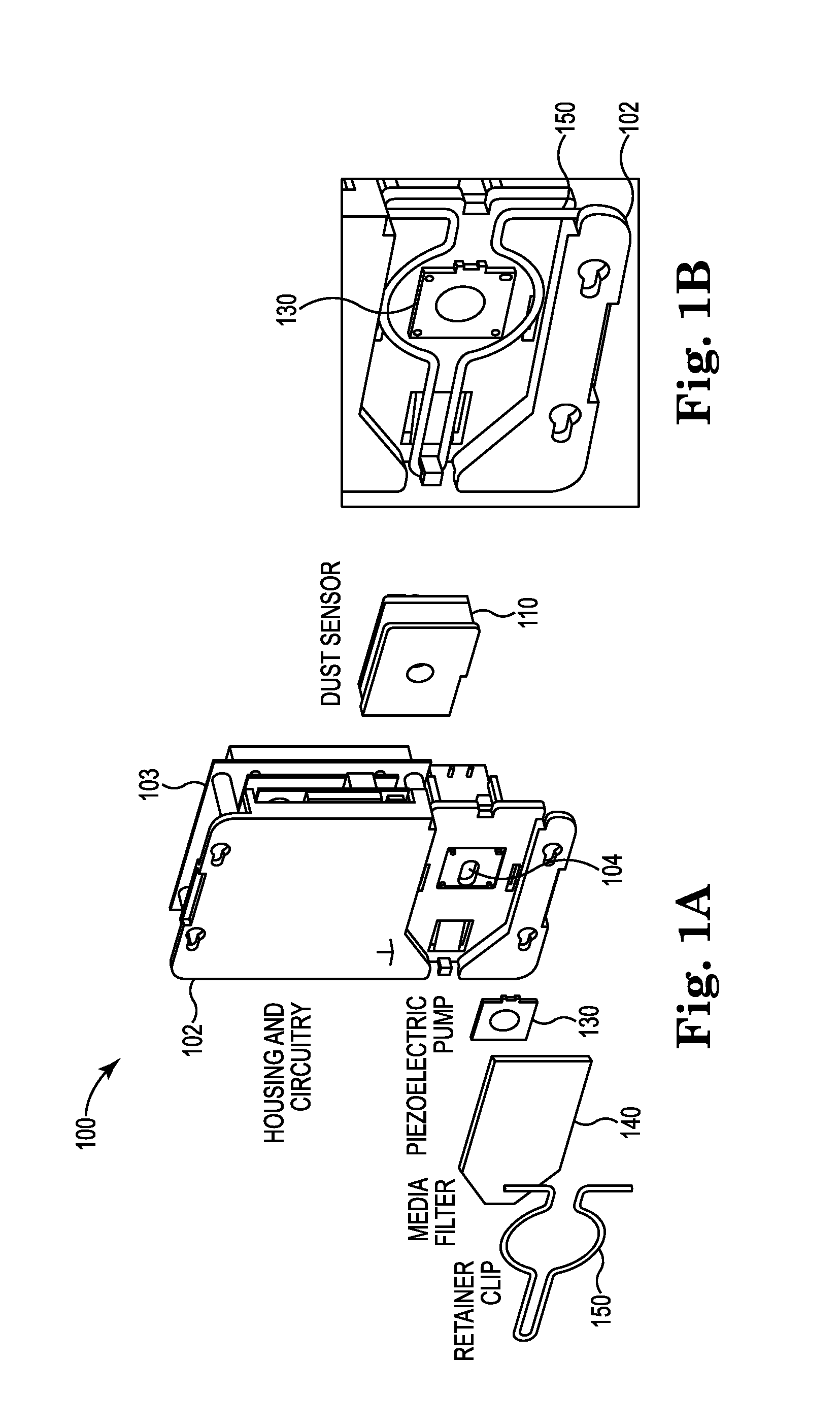
System for Inexpensive Characterization of Air Pollutants and Inexpensive Reduction of Indoor Dust
InactiveUS20150153317A1Rich picture of the local environmentReduce buildCombination devicesAuxillary pretreatmentMathematical modelAir filter
The invention describes software (including mathematical models implemented in software) and related electronic circuits that can be used to combine data from local, inexpensive dust sensors (particle counters) with Internet-available rich data on pollutants, weather, optional household devices, sensors, and appliances to create a rich picture of the local environment, shape that environment through non-trivial control of said household appliances and ventilation systems to reduce buildup of household dust on surfaces or reduce sensitive individuals' exposure to specific pollutants, and monitor individuals' exposure to pollutants. The software might live in a smartphone (such as the inventors' iPhone prototype), related hardware devices (such as a pollution sensor communicating via bluetooth with the smartphone) or in heating / cooling control system such as a common household thermostat. In particular, advanced control of windows or inexpensive air filters within a common forced air climate system to mitigate air pollution inexpensively are envisioned.
Owner:ACCULATION
Particle Counter with Laser Diode
InactiveUS20090268202A1Reduce noiseQuick checkScattering properties measurementsEnergy based chemical/physical/physico-chemical processesStray lightOptical detector
A liquid particle counter for optically detecting an unconstrained particle suspended in a flowing liquid includes a sample chamber having a liquid inlet and a liquid outlet; a laser diode module producing a symmetrically collimated laser beam; a beam shaping optical system directing the laser beam at the sample chamber; and an optical detector located to detect light scattered by the particle in the sample chamber, the detector producing an electric signal characteristic of a parameter of the particle. The laser beam has an energy of a watt or more and passed through an aperture in a black glass aperture element in the sample chamber. The black glass aperture element removes diffracted and stray light from the beam without damage to the sample chamber.
Owner:PARTICLE MEASURING SYST
Particle counter with improved image sensor array
ActiveUS7456960B2Scattering properties measurementsParticle size analysisDetector arrayMultiple pass
A particle counter for optically detecting an unconstrained particle of less than one micron in size suspended in a flowing liquid includes a sample chamber having a fluid inlet and a fluid outlet; a laser module producing a laser beam; a beam shaping optical system providing a multiple laser beam pattern in the sample chamber, and a CMOS optical detector located to detect light scattered by the particles in the sample chamber. The particle counter has a particle sensing area within the sample chamber in which the intensity of light is at least 10 Watts / mm2, the sensing area having an area of 0.5 square mm or more. The detector has thirty or more detector array elements. In the preferred embodiment, the laser optical system reflects and refocuses the laser beam to effect multiple passes of the same laser beam through the sensing area.
Owner:PARTICLE MEASURING SYST
Particle counter with improved image sensor array
ActiveUS20060274309A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioFast countScattering properties measurementsParticle size analysisDetector arrayMultiple pass
A particle counter for optically detecting an unconstrained particle of less than one micron in size suspended in a flowing liquid includes a sample chamber having a fluid inlet and a fluid outlet; a laser module producing a laser beam; a beam shaping optical system providing a multiple laser beam pattern in the sample chamber, and a CMOS optical detector located to detect light scattered by the particles in the sample chamber, the detector producing an electric signal characteristic of a parameter of the particle. The particle counter has a particle sensing area within the sample chamber in which the intensity of light is at least 10 Watts / mm2, the sensing area having an area of 0.5 square mm or more. The detector has thirty or more detector array elements. In the preferred embodiment, the laser optical system reflects and refocuses the laser beam to effect multiple passes of the same laser beam through the sensing area.
Owner:PARTICLE MEASURING SYST
Particle counter with self-concealing aperture assembly
ActiveUS7088447B1Reduce light noiseEliminating scattered light noiseMaterial analysis by optical meansCollection systemParticle counter
A particle measurement system using a single component light collecting system with an aperture having a portion within direct view of the light detector. An aperture assembly extending into a sample may be self-concealing by having an extended portion to block light from directly illuminating the light detector. Alternatively, a smooth, reflective inside surface of the aperture assembly provides for self-concealment by causing spontaneous emitted light to have low angles of reflection. In either case, spontaneously emitted light is substantially prevented from reflecting directly into the light detector, thereby reducing light noise to the level of molecular noise.
Owner:PARTICLE MEASURING SYST
Flow monitored particle sensor
ActiveUS8800383B2Reliable monitoringAccurate assessmentWithdrawing sample devicesVolume/mass flow by differential pressureDifferential pressureAtmospheric pressure
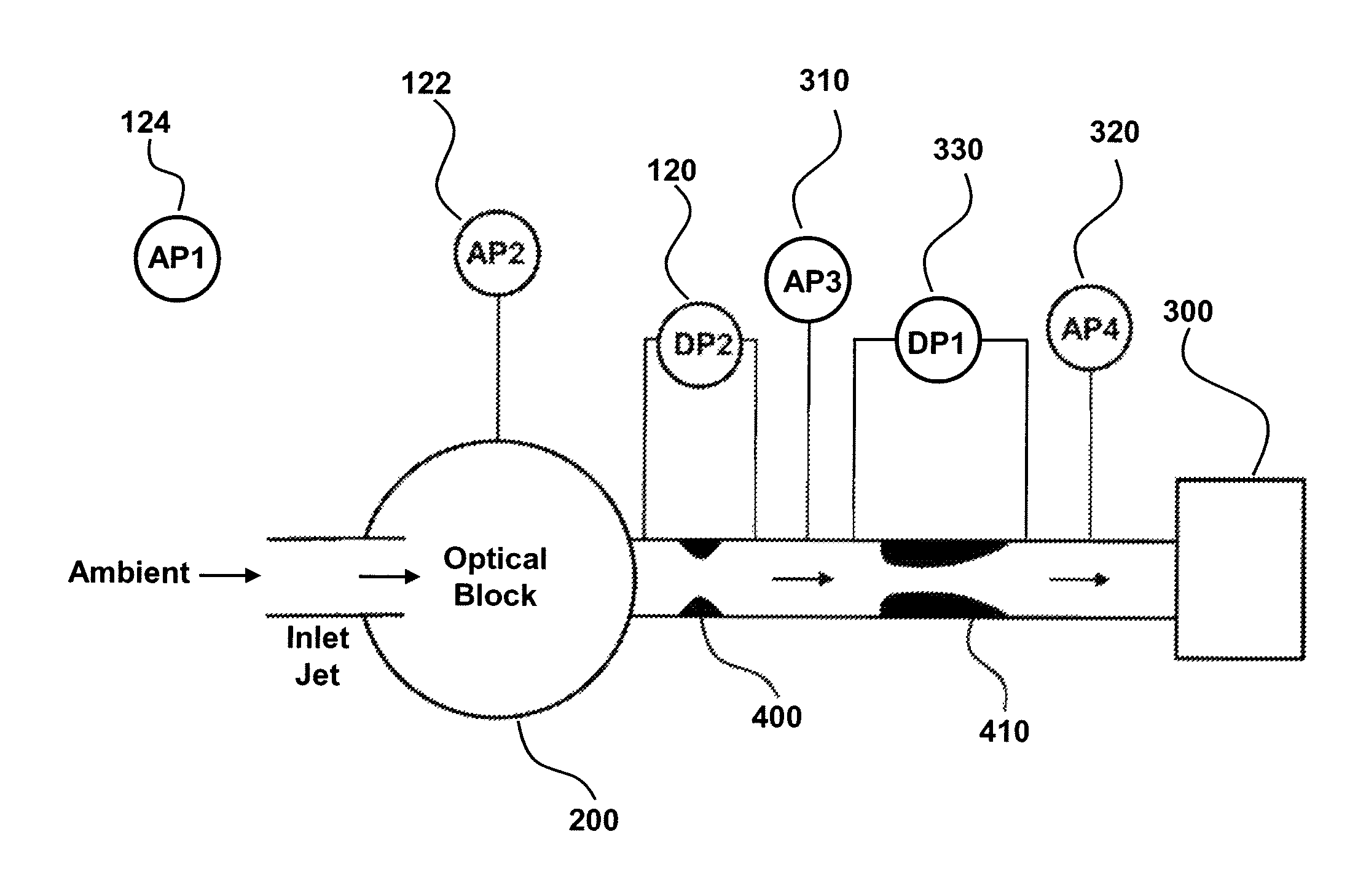
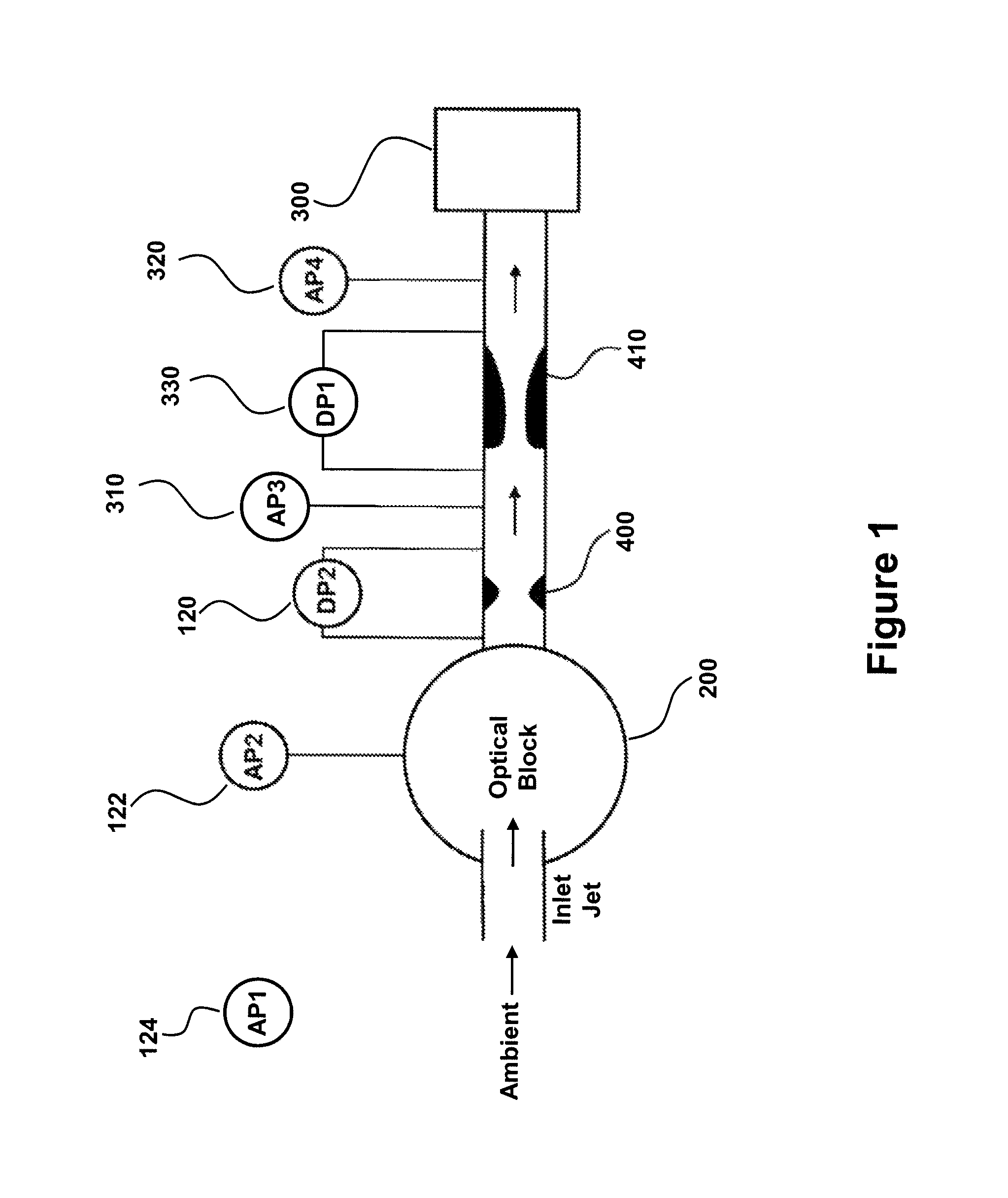
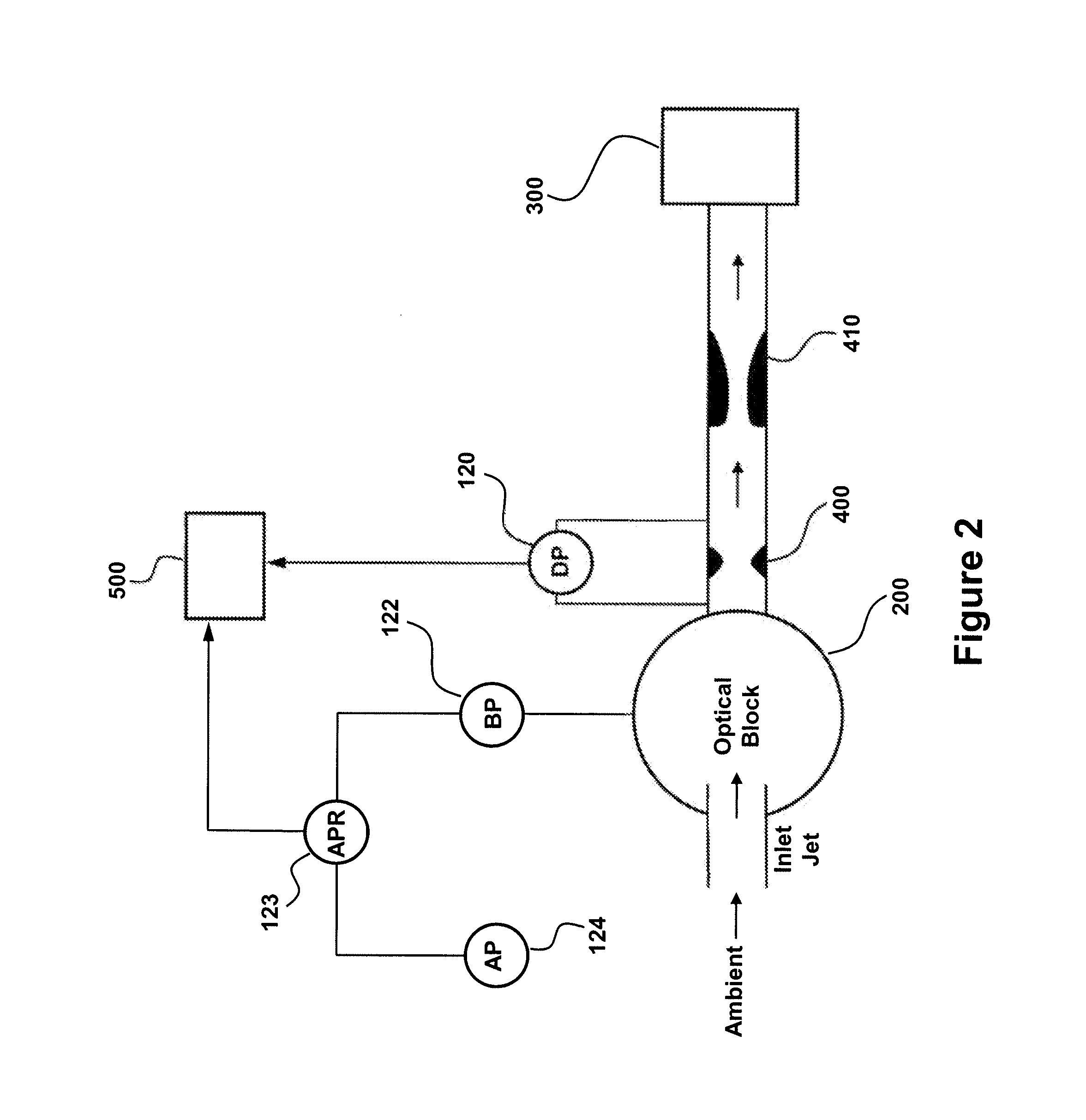
Provided are devices and methods for monitoring flow rate in aerosol particle counters. The particle sensor has a particle counter, a flow measurement orifice comprising a differential pressure sensor for measuring differential pressure (DP) across the flow measurement orifice during particle sensor operation and a critical flow orifice. A vacuum source pulls ambient gas through each of the particle counter, flow measurement orifice and critical flow orifice. An atmospheric pressure sensor measures atmospheric pressure (AP) and a bench pressure sensor measures pressure in the particle sensor (BP). The output from the sensors is used to identify a flow condition, such as by a monitor operably connected to each of the differential pressure sensor, atmospheric pressure sensor and bench pressure sensor. In this manner, deviation in flow rate from a target flow rate is readily monitored without the need for expensive sensors or other flow-controlling components.
Owner:PARTICLE MEASURING SYST
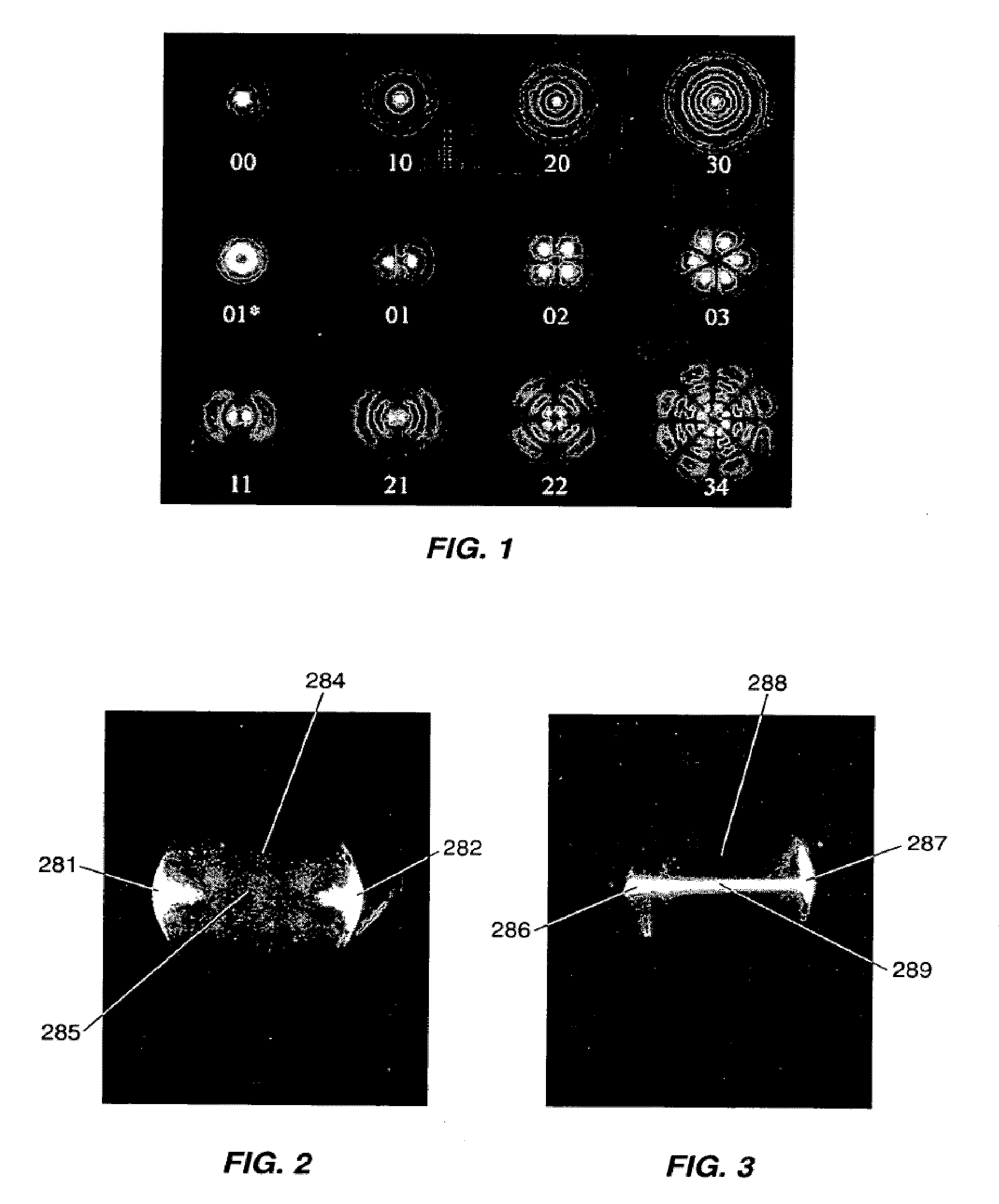
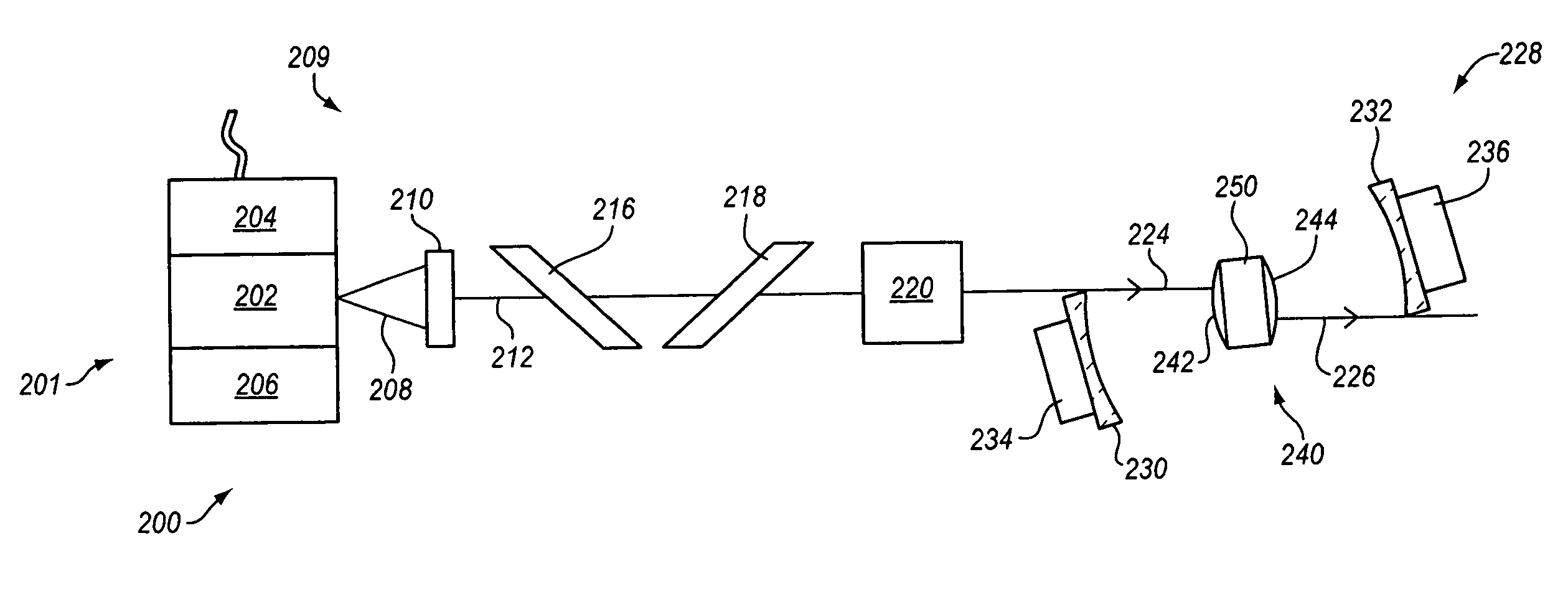
Two-dimensional optical imaging methods and systems for particle detection
ActiveUS20090244536A1Accurate detectionEfficiently generating and identifyingNanoparticle analysisInvestigating moving fluids/granular solidsGas phaseSelection system
The present invention provides methods and systems for particle detection and analysis using two-dimensional optical imaging to access enhanced detection sensitivity and expanded sensing functionality relative to conventional point and array detection-based optical particle counters. Methods and systems of the present invention provide a two-dimensional optical imaging-based particle sensing platform wherein system components and specifications are selected to generate reproducible and readily identifiable signals, including particle detection signatures, from optical scattering or emission from particles provided to the system. Systems and methods of the present invention are capable of accurately and sensitively detecting, identifying, and characterizing (e.g., determining the size of) particles in liquid phase or gas phase samples.
Owner:PARTICLE MEASURING SYST
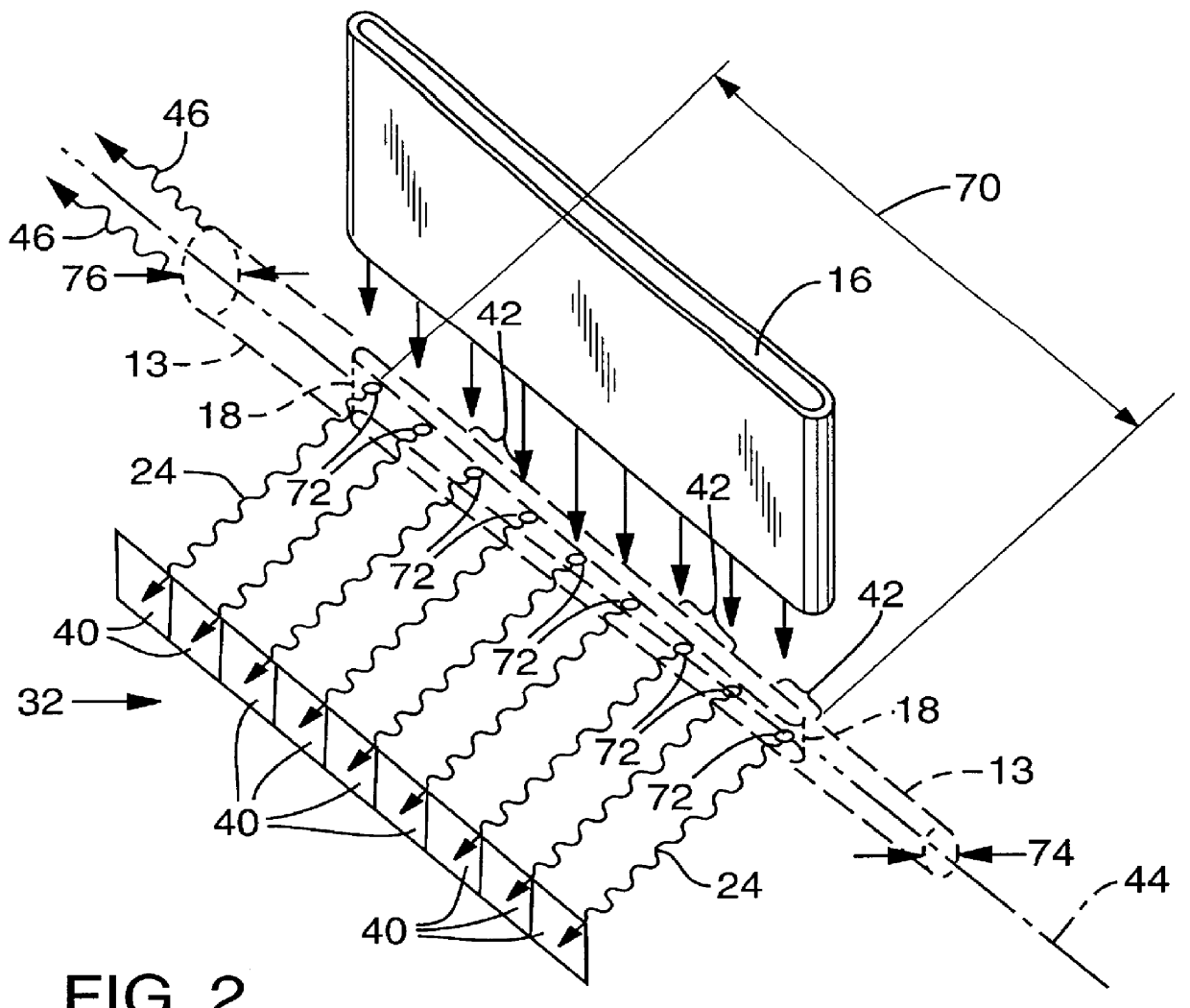
Flow apertured intracavity laser particle detector
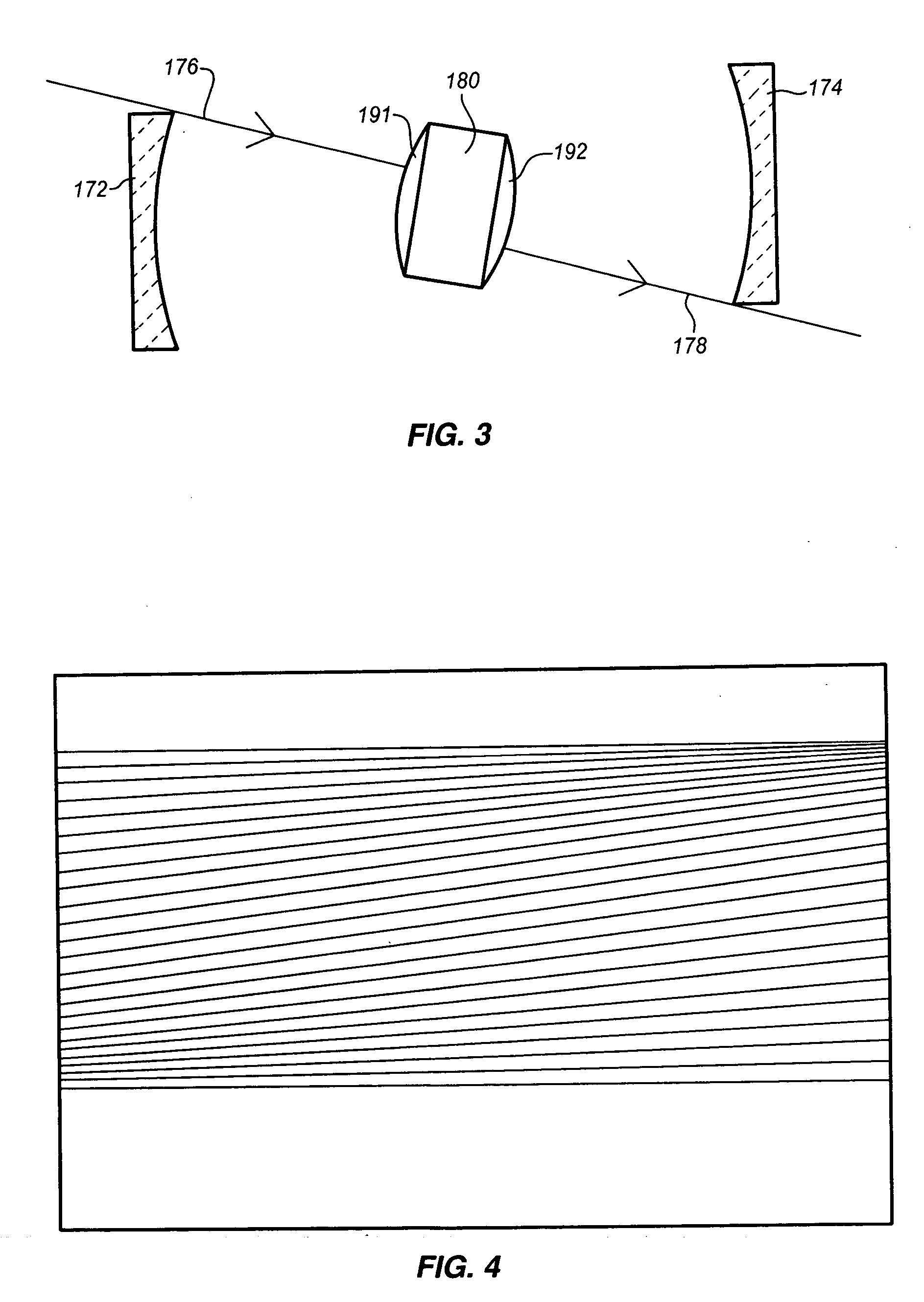
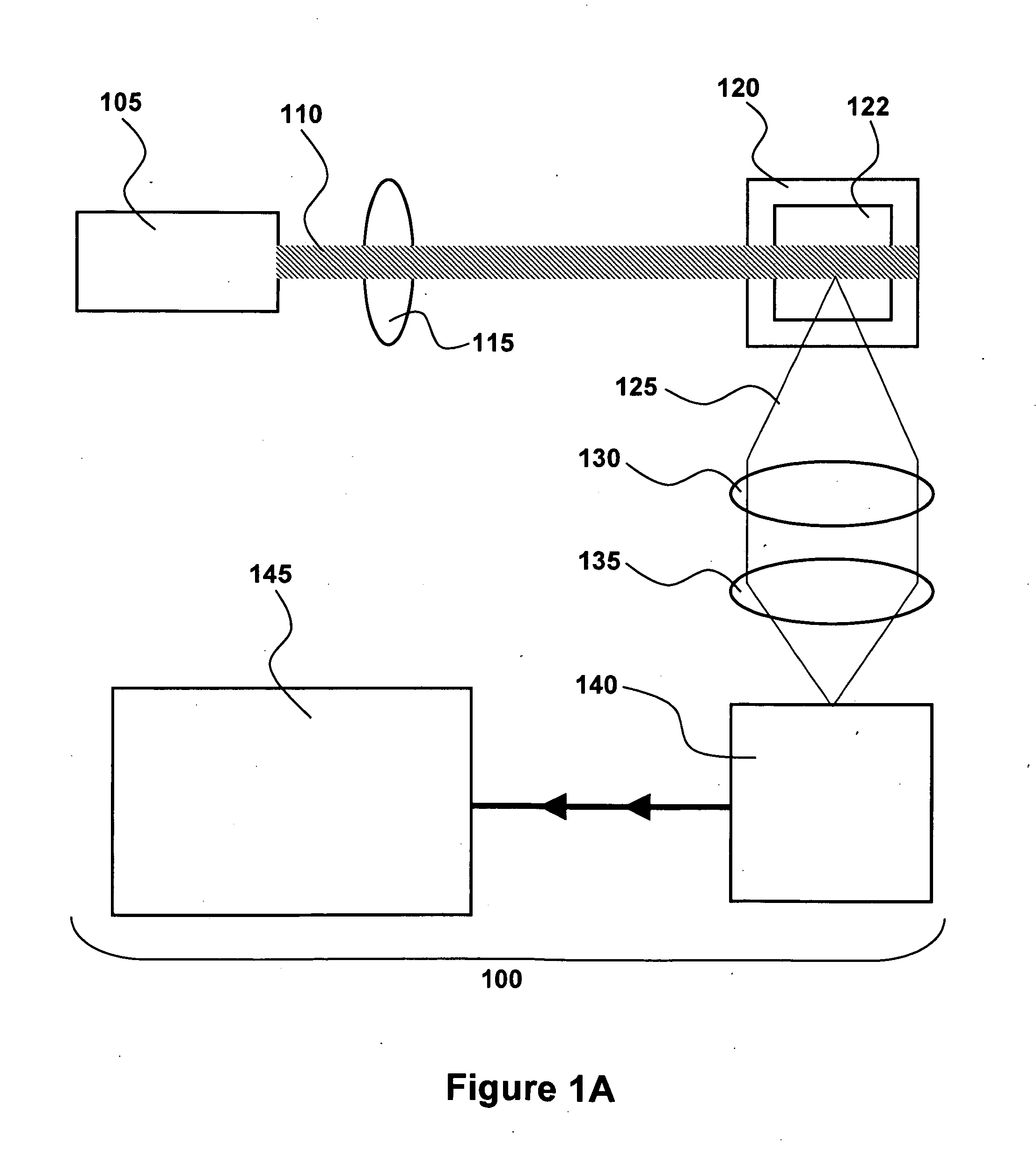
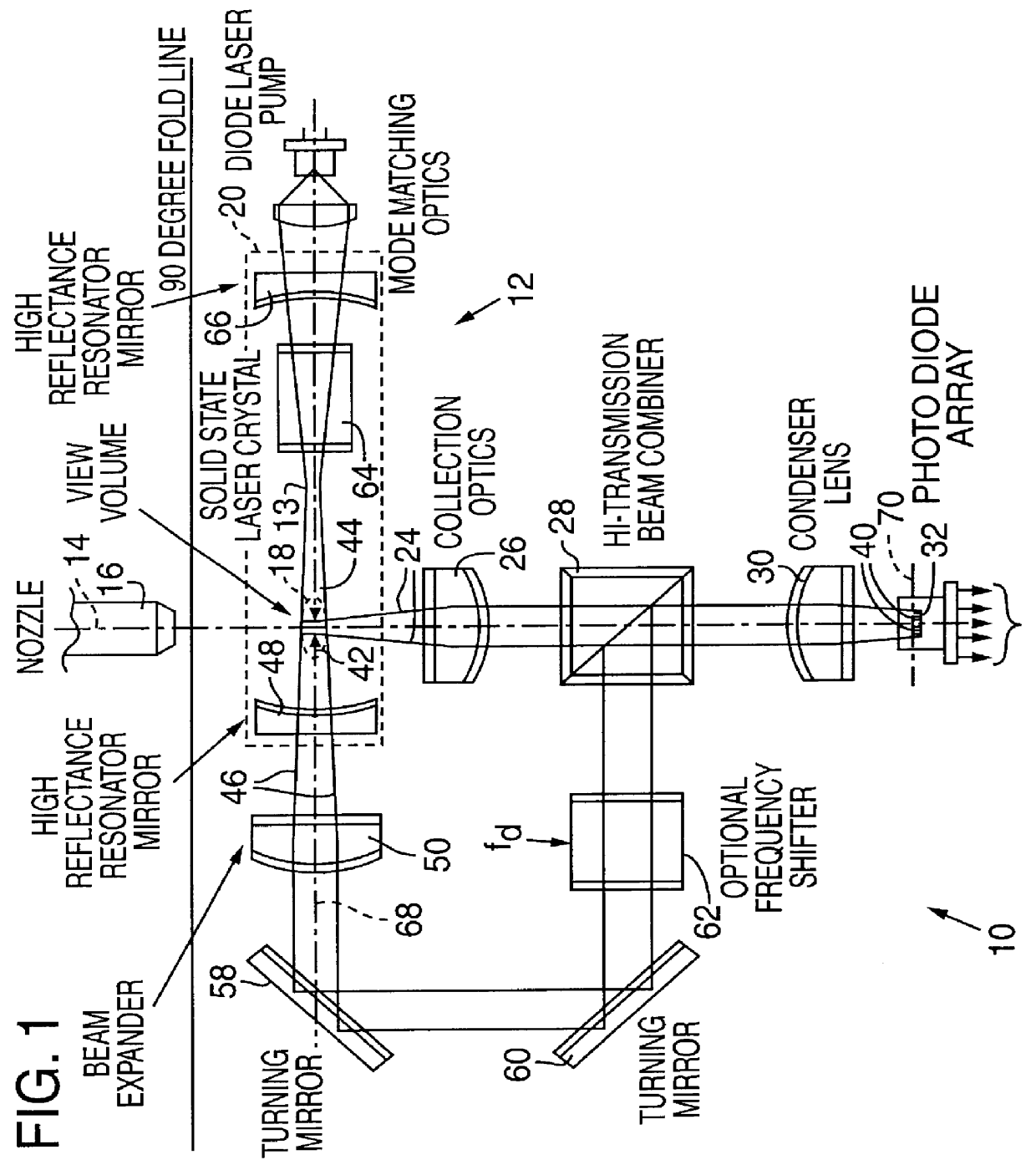
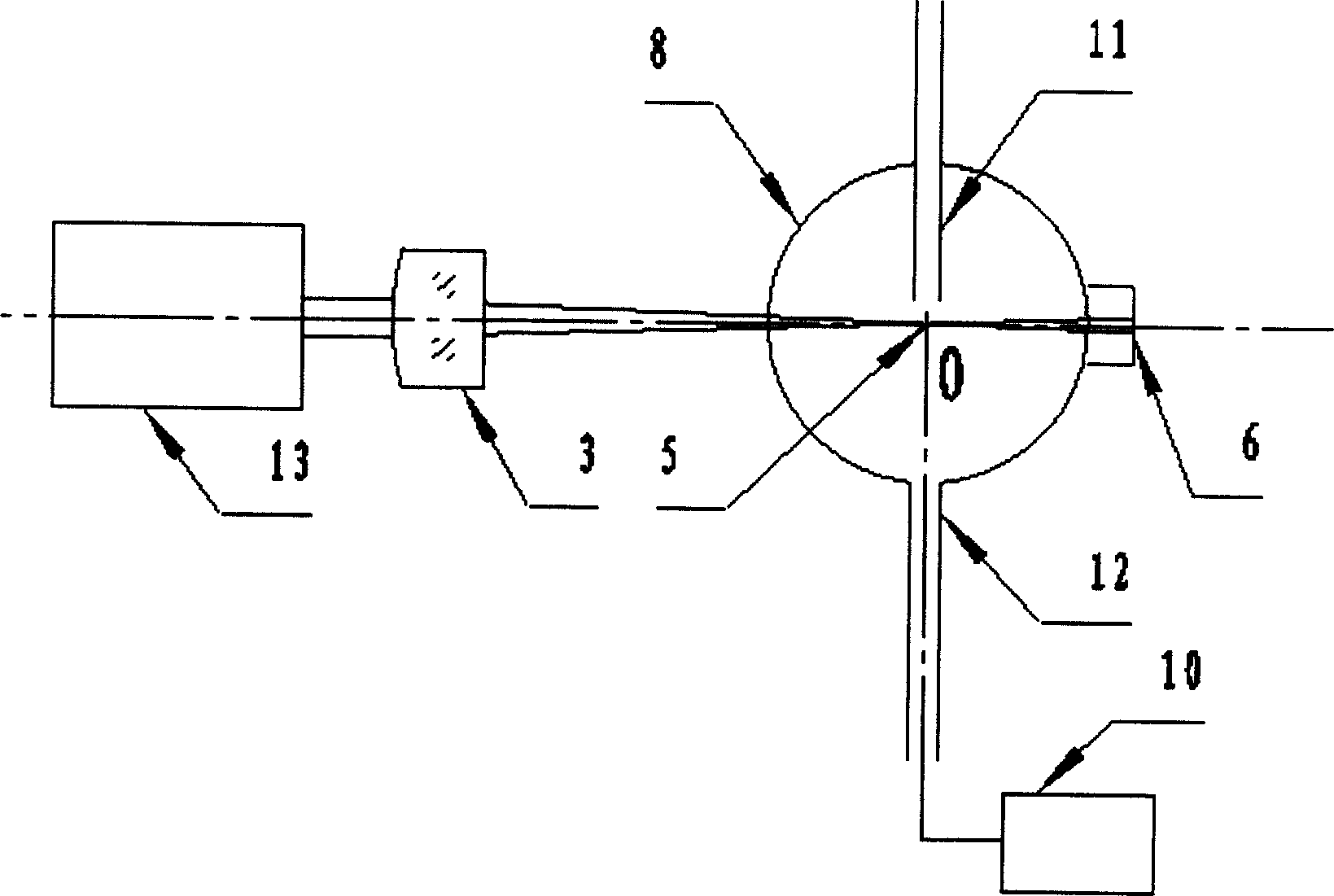
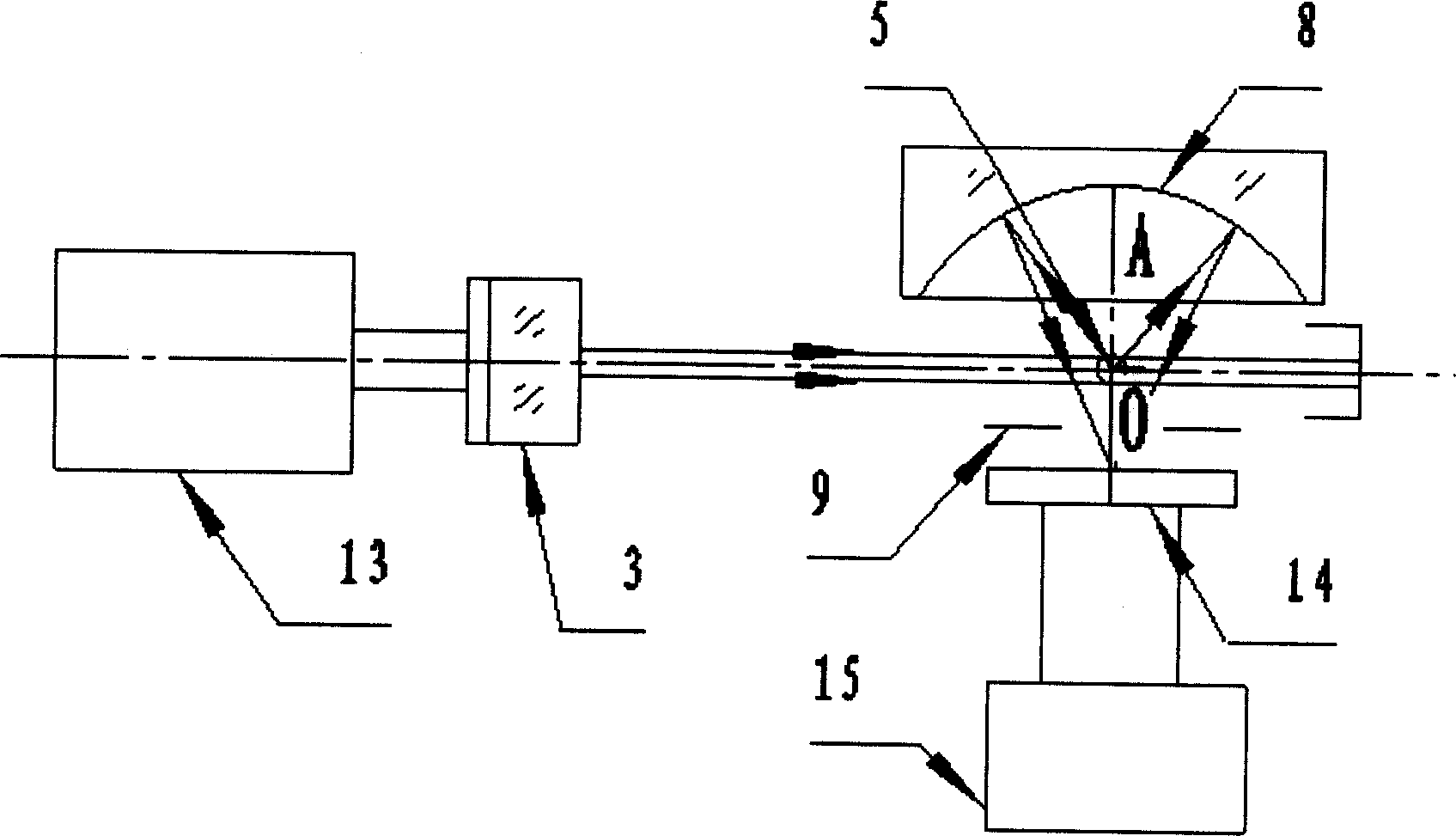
InactiveUS6111642AHigh submicron particle detection sensitivityAccurate particle size determinationInvestigating moving fluids/granular solidsScattering properties measurementsLaser lightLaser beams
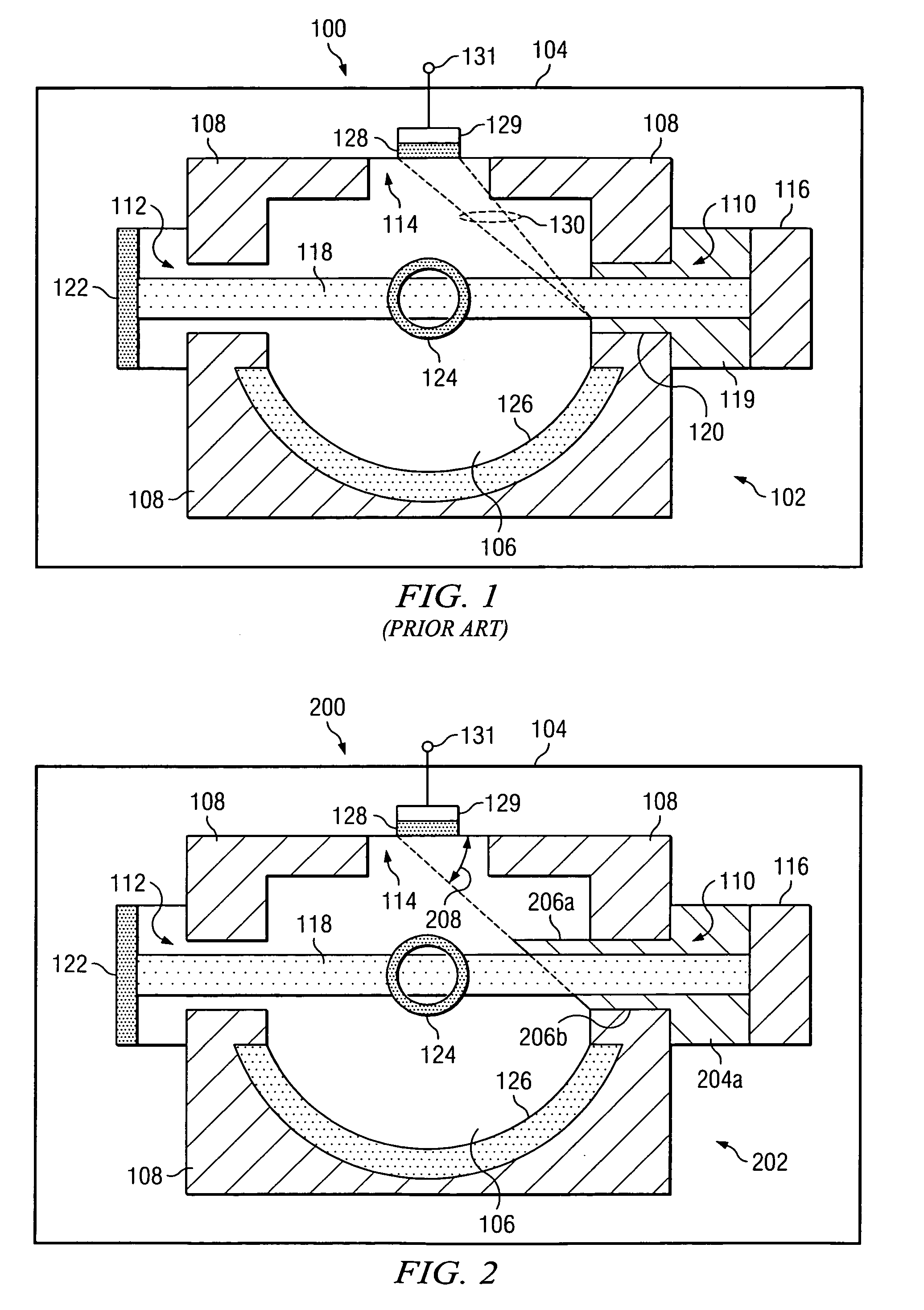
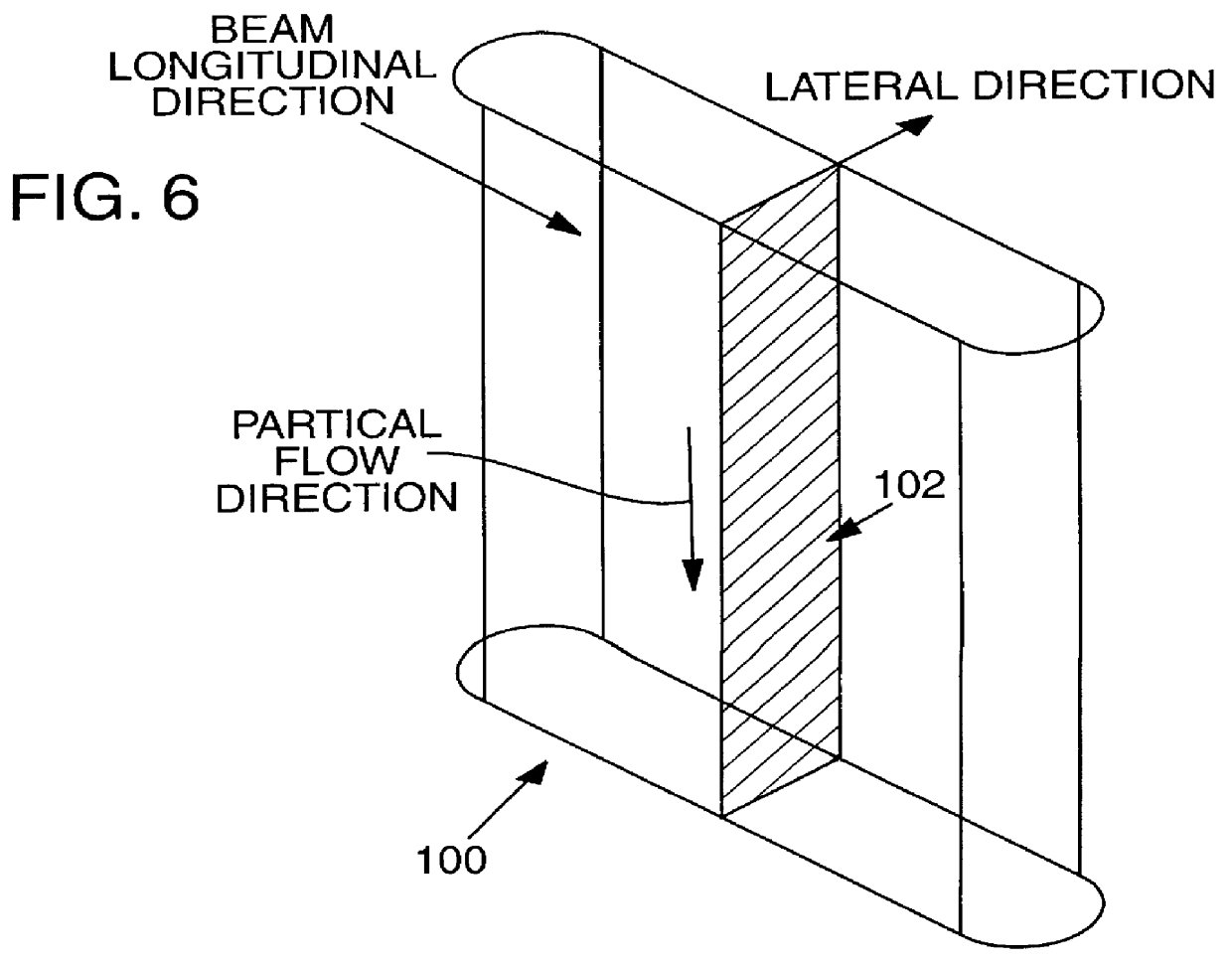
A particle counter (10) passes a sample stream of a carrier gas or fluid containing particles (72) through an elongated, flattened nozzle (16) and into a view volume (18) formed by an intersection of the sample stream and a laser beam (13). Particles entrained in the sample stream scatter light rays while passing through the view volume. The scattered light is collected by an optical system (26) and focused on to a detector (40). The magnitude of signal coming from the detector is indicative of the particle size. To correct for variances in particle velocity and light beam intensity across the view volume, flow aperturing is used. Flow aperture modeling (Eqs. 1-7) provides a format for designing the nozzle such that the lateral velocity profile matches the laser beam lateral intensity profile, thereby providing uniform detection sensitivity to laser light scattered from monodisperse particles distributed laterally across the view volume. Uniform detection sensitivity of monodisperse particles provides accurate particle sizing resolution.
Owner:HACH CO
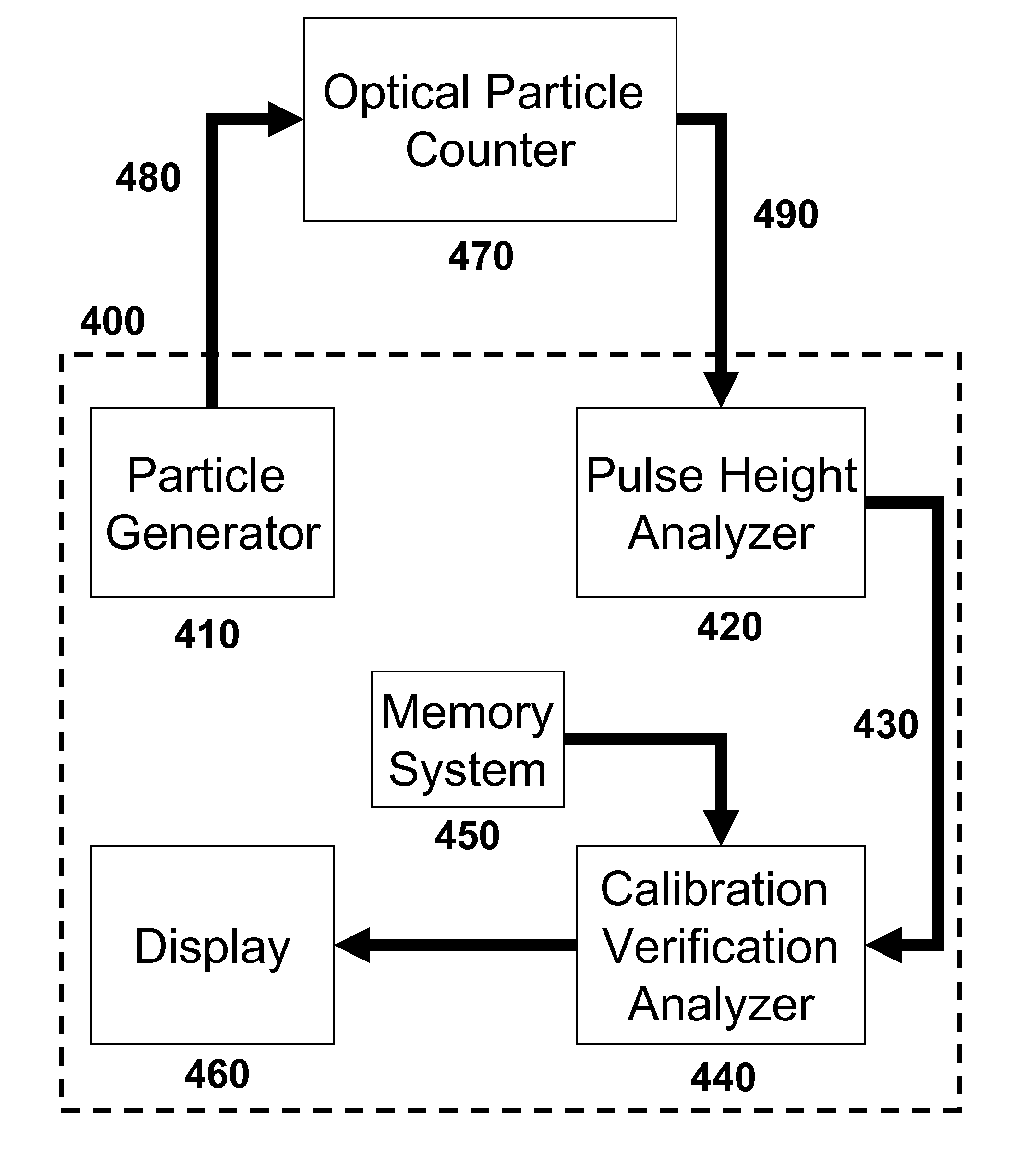
System and method for calibration verification of an optical particle counter
ActiveUS7973929B2Quick calibrationReduce power consumptionMaterial analysis by optical meansParticle size analysisVerification systemParticle counter
Described herein is a portable, low power consuming optical particle counter calibration verification system and reliable and sensitive methods for verifying the calibration status of a gas or liquid particle counter. The calibration verification systems described herein are useful for quickly determining the calibration status of an optical particle counter at its point of use, as well as for allowing the end user to determine if an optical particle counter is in need of a recalibration before the recommended calibration schedule suggests.
Owner:PARTICLE MEASURING SYST
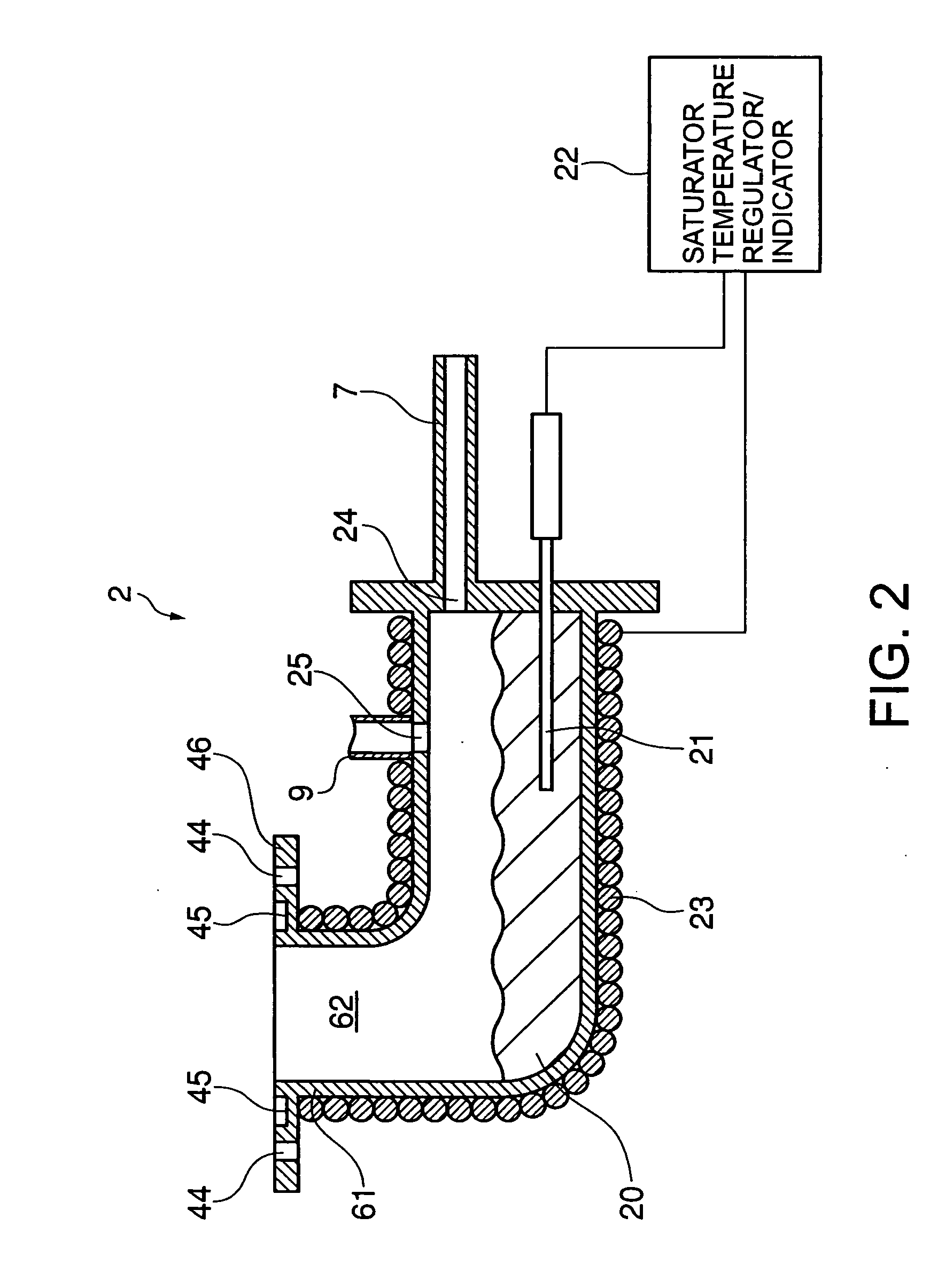
Particle counter
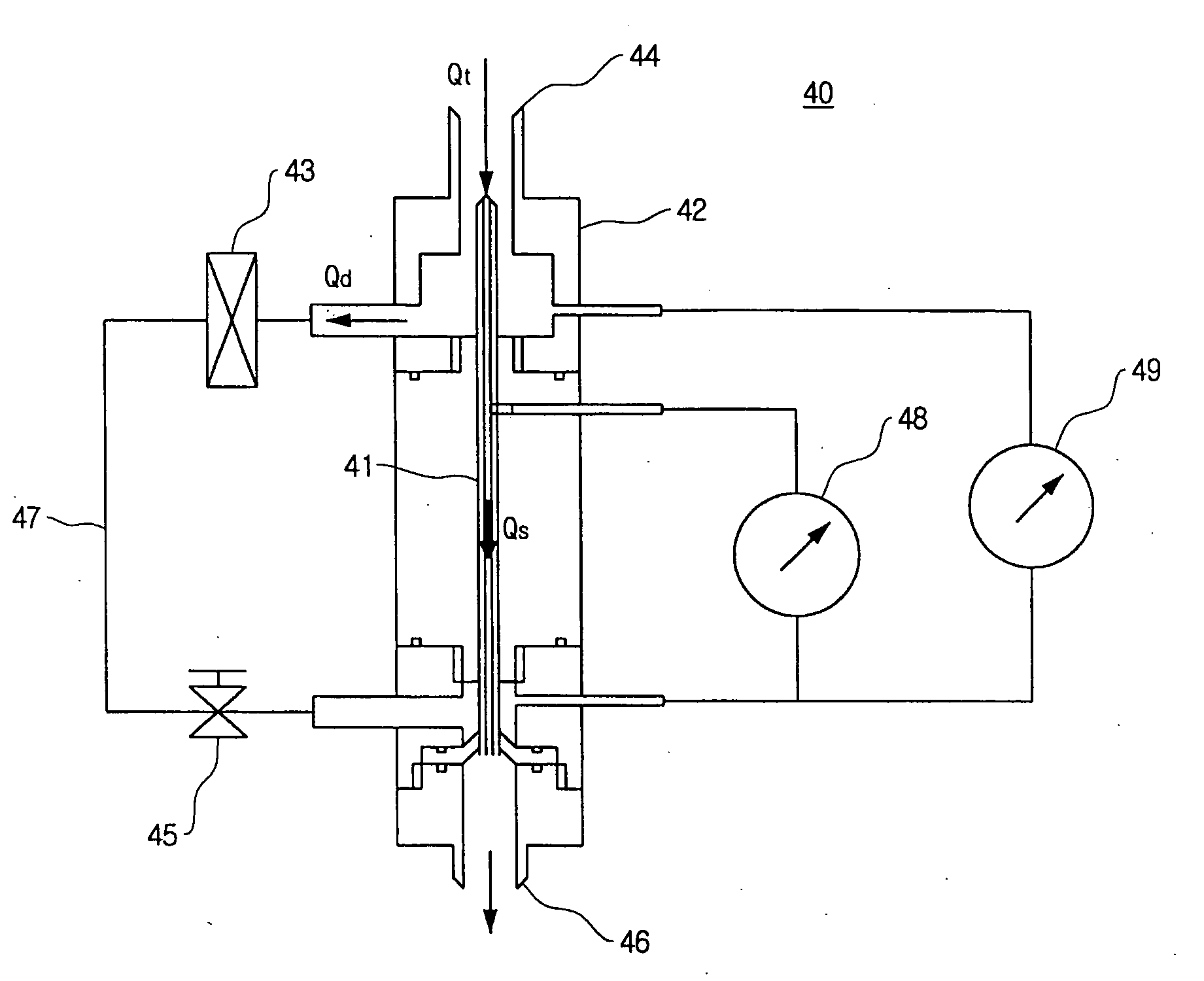
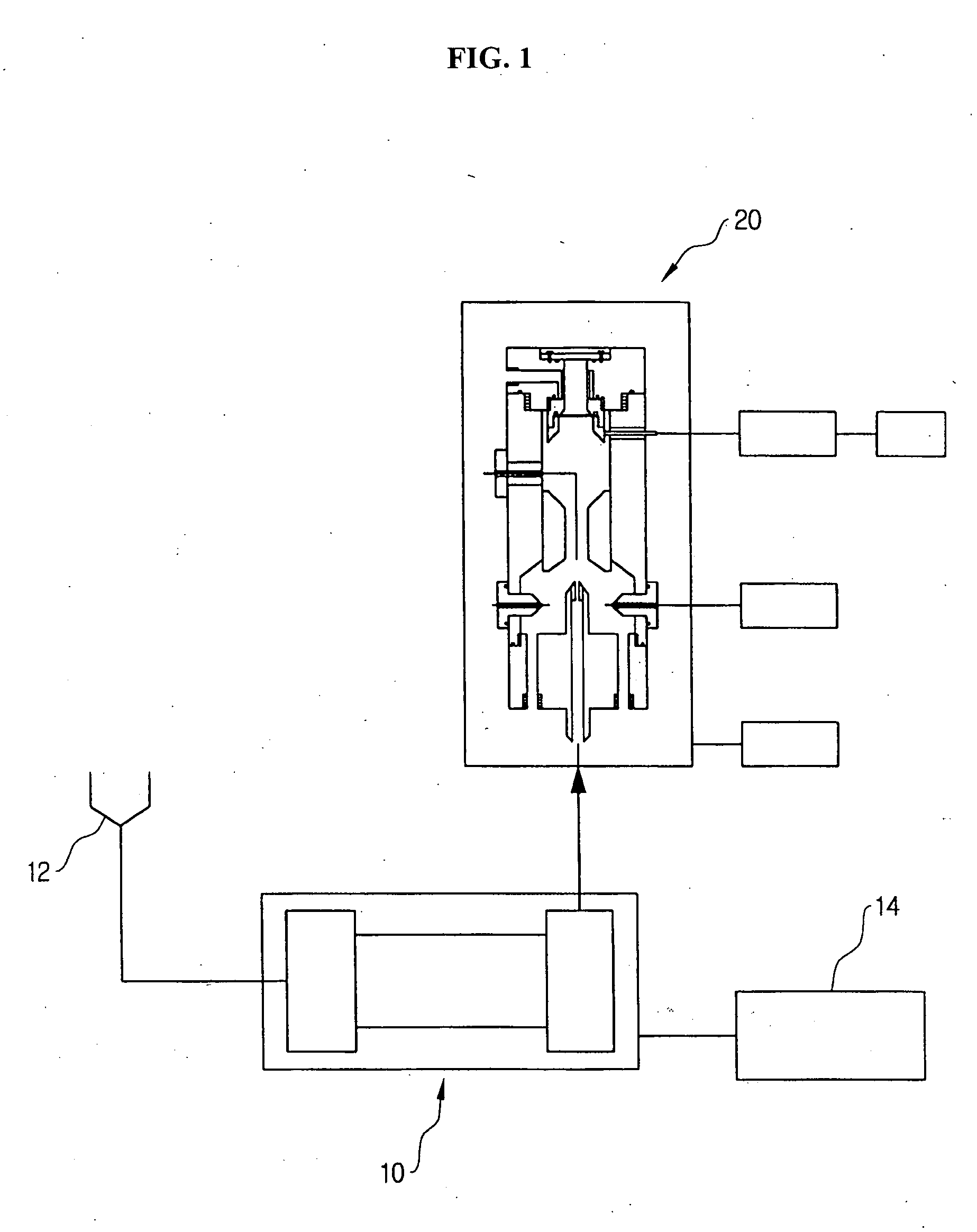
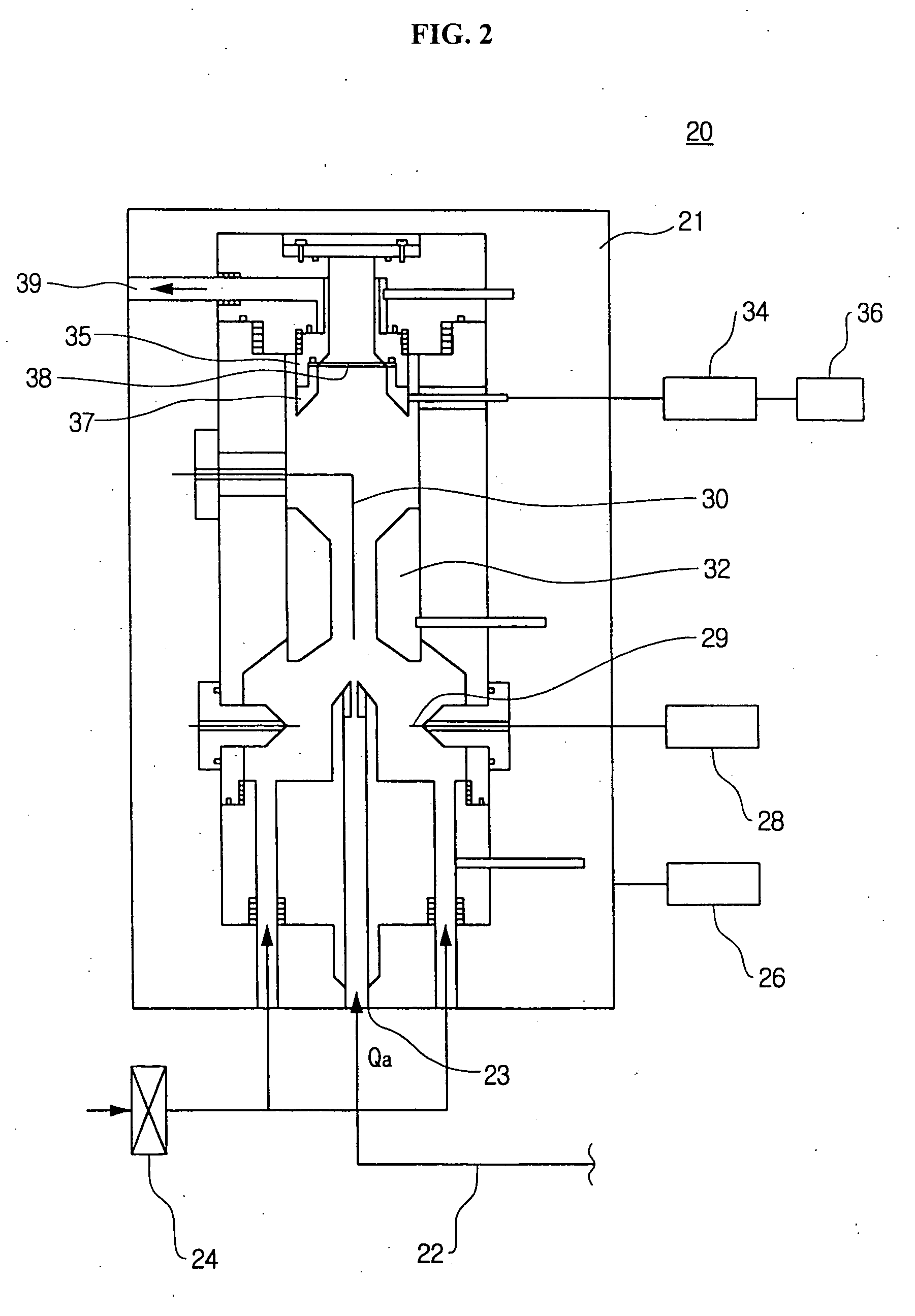
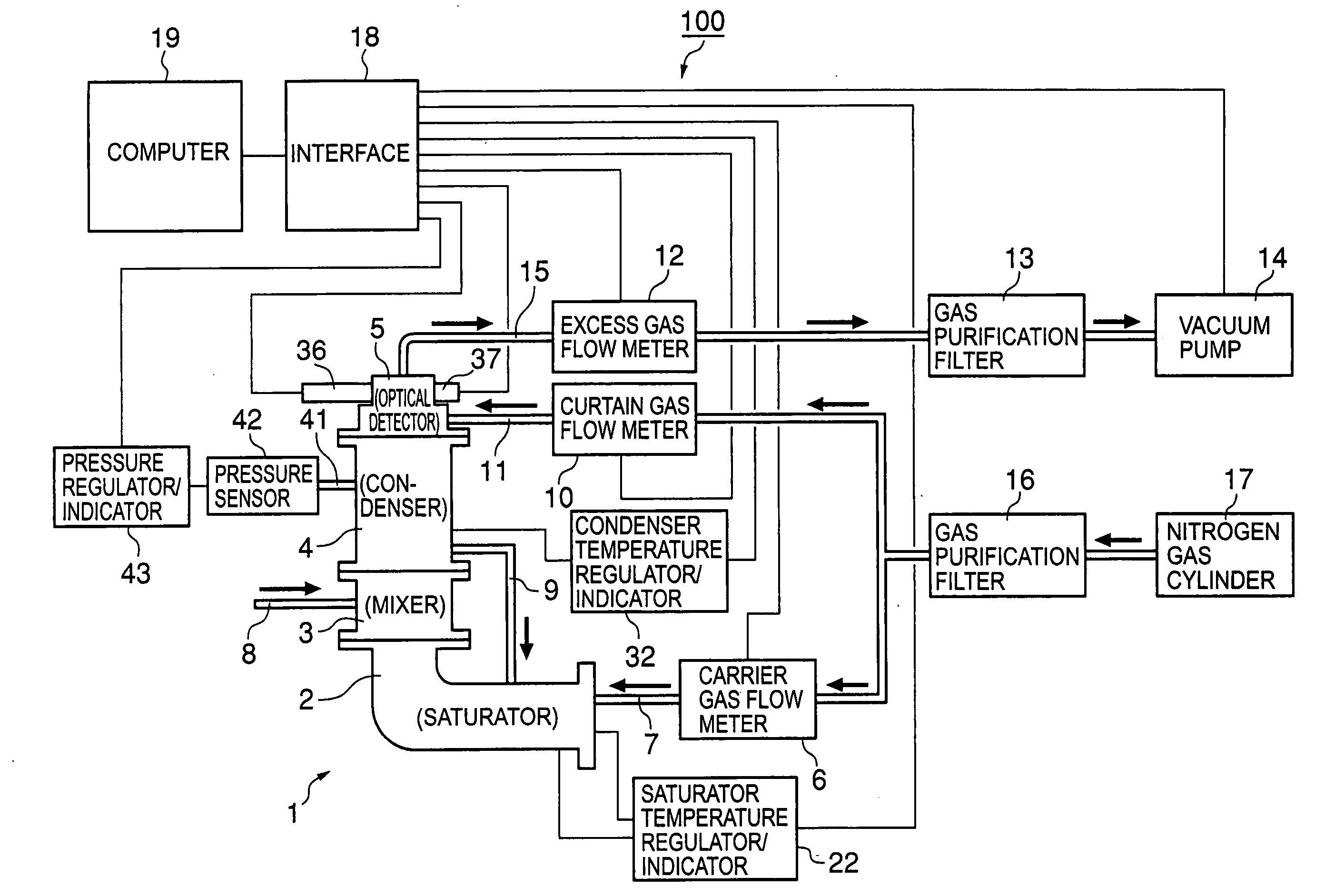
A particle counter has a saturator inhaling air in an atmosphere and vaporizing a working liquid therein; and an electrical detection unit electrically shielding an internal space thereof to maintain a temperature of the space to be constant, the air and vaporized working liquid flowing into the electrical detection unit through a side thereof from the saturator, condensing the vaporized working liquid on surfaces of ultrafine particles contained in the air, and charging the particles to measure a current of the charged particles, thereby measuring the number of the particles included in the air. According to the invention, it is possible to measure the number concentration of the ultrafine particles included in the air, and it is easy to move the counter depending on the measurement locations.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
Air filtering material tester
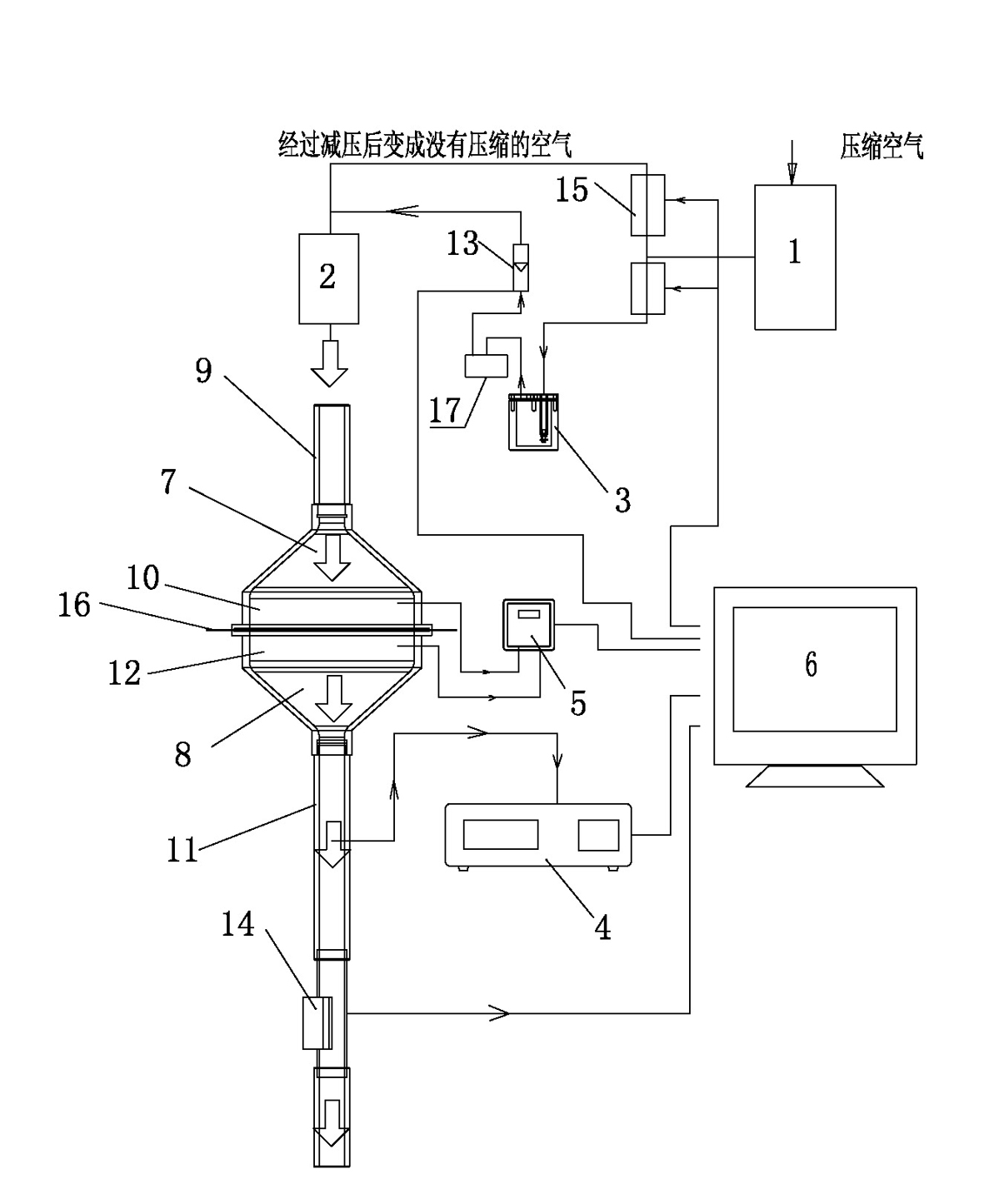
InactiveCN101995372AWide range of industriesGuarantee effective detection dataPermeability/surface area analysisAir filtrationAutomatic control
The invention relates to an air filtering material tester which comprises a high efficiency filter, a corona neutralizer, a filter clamp, an aerosol generator, a laser particle counter, a differential pressure meter and a computer, wherein an outlet of the high efficiency filter is respectively connected with an inlet of the corona neutralizer and an inlet of the aerosol generator through pipelines, and an outlet of the aerosol generator is connected with the inlet of the corona generator through a pipeline; the filter clamp is formed by hermetically assembling an upstream clamp and a downstream clamp, wherein the upstream clamp comprises an air inlet pipeline and an air inlet chamber, the downstream clamp comprises an air outlet pipeline and an air outlet chamber, and the outlet of the corona neutralizer is connected with the air inlet pipeline of the upstream clamp; the laser particle counter is connected with the air outlet pipeline of the downstream clamp, and the differential pressure meter is respectively connected with the air inlet chamber and the air outlet chamber; and the laser particle counter and the differential pressure meter are respectively connected with the computer. The air filtering material tester has the advantages of high detection efficiency and sensitivity and fully-automatic control of detection process.
Owner:BEIJING MUNICIPAL INST OF LABOUR PROTECTION +1
Particle measuring system and method
InactiveUS20080047373A1Exact numberSmall sizeSamplingMaterial analysis by optical meansParticle counterPhysics
A particle measuring system and method is capable of separating particles on a size-by-size basis and measuring the number and size of the particles one by one on a real time basis. The particle measuring system includes a sampling device for guiding a stream of an aerosol containing particles suspended in a gas, an analysis device for separating one by one the particles contained in the aerosol, a filter for filtering out the particles contained in the aerosol to produce a filtered gas, a saturating device for saturating the filtered gas with working liquid to thereby produce a saturated gas, a condensing device for condensing the saturated gas to produce liquid droplets each having a nucleus formed of one of the particles, and an optical particle counter for calculating the number and size of the particles contained in the liquid droplets.
Owner:AHN IN
System and method to monitor particles removed from a component
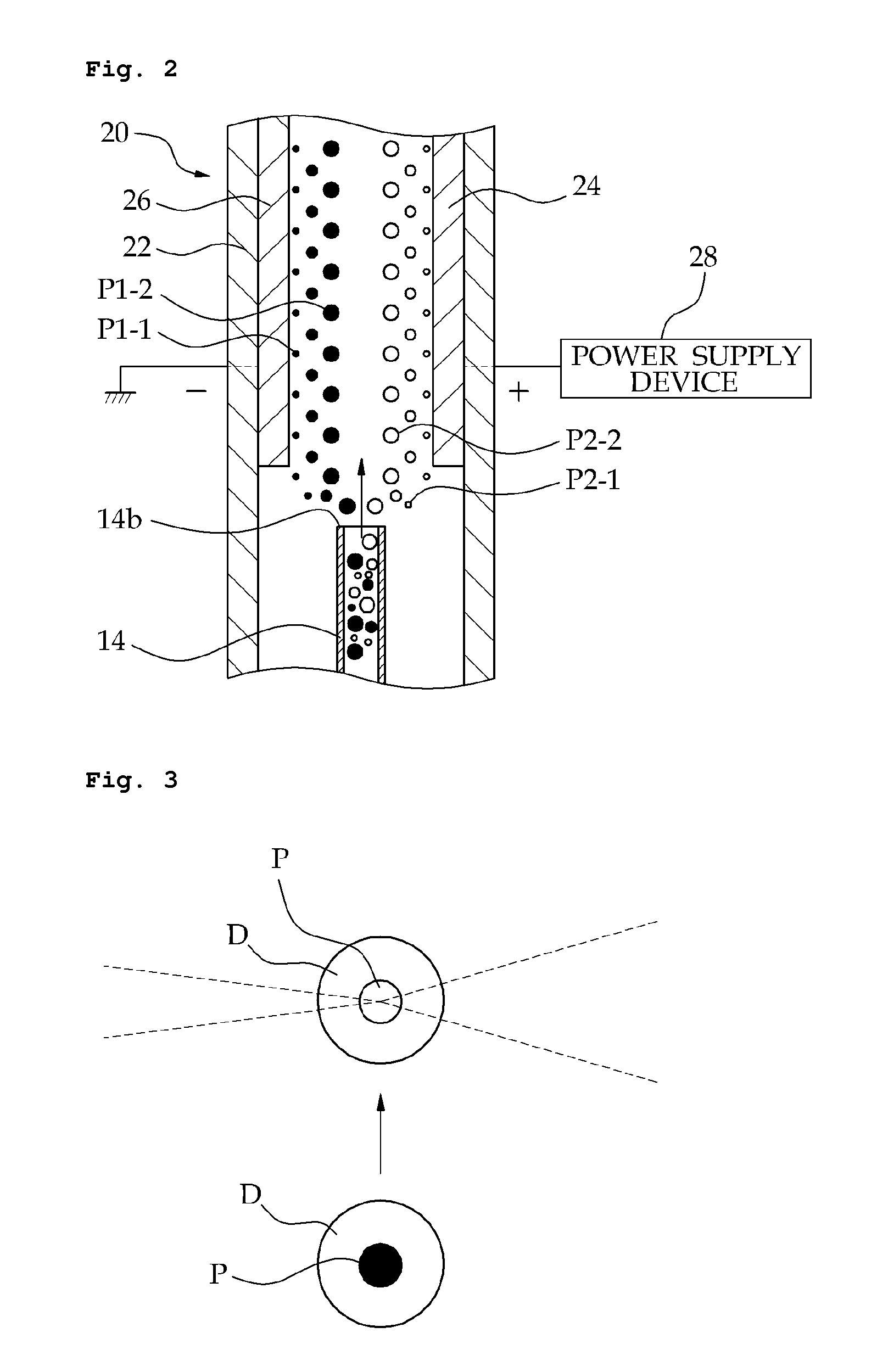
ActiveUS7673638B1Preparing sample for investigationAbrasive machine appurtenancesMonitoring systemEngineering
Disclosed is a system and method to monitor and count particles removed from a component. The particle monitoring system includes a jet spray device, a snow generator, a particle collection device, and a particle counter. The jet spray device includes an outlet that is disposed locally relative to the component. The snow generator is operable to generate cleaning snow comprising a stream of ice particles, wherein the cleaning snow is emitted from the outlet of the jet spray device onto the component to cause the ejection of particles from the component. The particle collection device includes a collector that is disposed locally around the component to collect particles ejected from the component. The particle counter is coupled to, and in fluid communication with, the particle collection device. The particle counter is operable to detect and count particles ejected from the component.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
System and method comprising same for measurement and/or analysis of particles in gas stream
InactiveUS20060172428A1Reduce impurityReduce pressureComponent separationWithdrawing sample devicesParticle counterImpurity
A system and method comprising same for measuring and analyzing particles within a gas feed stream. In one aspect, the system comprises a particle counter and a particle capture filter that are arranged in parallel. In another aspect, the system comprises a purifying device to remove trace molecular impurities from a gas feed stream to reduce the presence of impurities.
Owner:VERSUM MATERIALS US LLC
Micro optical sensor for laser dust particle counter
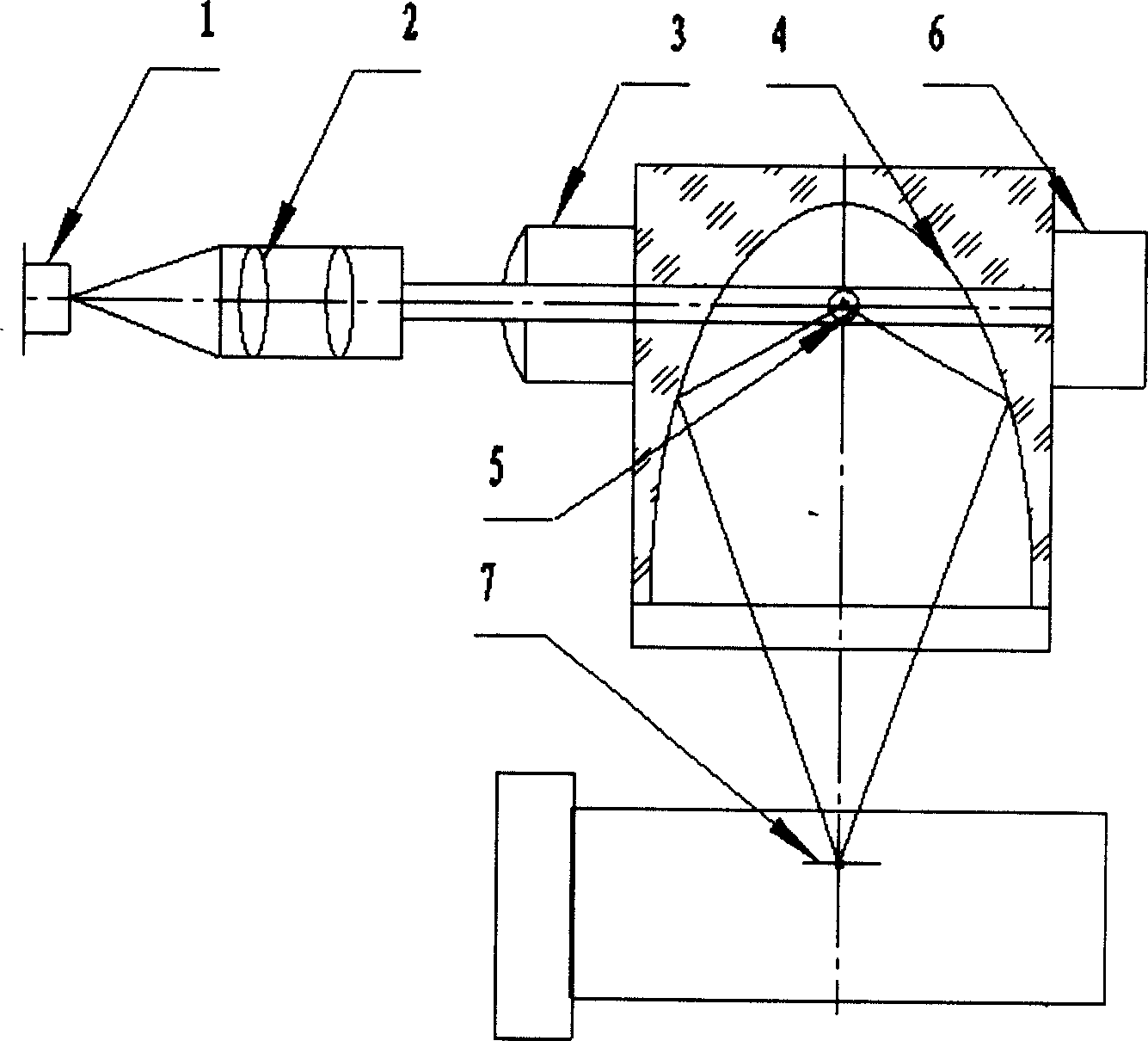
ActiveCN1570604AIncrease light intensityImprove light uniformityIndividual particle analysisCounting efficiencyLong axis
A micro optical sensor of laser dust particle counter, which is characterized by its components, which comprises the following: there is cylinder mirror, spherical mirror and light trap located orderly in the direction of light beam of laser source components. The spherical mirror is located in the right side of the cylinder mirror and light-sensitive area and that of light-electricity detector are located on both sides around the sphere center of spherical mirror, which satisfies the image relationship of geometry optics; vision diaphragm which is suited for the shape of light sensitive-area is located in front of light-electricity detector; the light-electricity detector employs photoelectric diode of high sensitivity or micro photoelectric multiplier tube sealed with metal; A band pass preposition enlarging circuit is fixed in the shell of scatter body of optics sensor with the same width of pulse frequency of scattering light.
Owner:上海镭慎光电科技有限公司 +1
Dynamic range extension systems and methods for particle analysis in blood samples
ActiveUS20140273076A1Easy to moveDecrease in flowpath sizeImage enhancementBioreactor/fermenter combinationsParticle physicsParticle counter
For analyzing a sample containing particles of at least two categories, such as a sample containing blood cells, a particle counter subject to a detection limit is coupled with an analyzer capable of discerning particle number ratios, such as a visual analyzer, and a processor. A first category of particles can be present beyond detection range limits while a second category of particles is present within respective detection range limits. The concentration of the second category of particles is determined by the particle counter. A ratio of counts of the first category to the second category is determined on the analyzer. The concentration of particles in the first category is calculated on the processor based on the ratio and the count or concentration of particles in the second category.
Owner:IRIS INT
Condensation particle counter
ActiveUS20080186489A1Efficient measurementMaterial analysis by optical meansIndividual particle analysisWorking fluidSurface layer
A condensation particle counter is capable of efficiently measuring the number and size of fine particles. The condensation particle counter includes a saturator, a plurality of condensers and a plurality of optical particle counters. The saturator is designed to generate a saturated gas by saturating a gas in which fine particles are suspended with working fluid. The condensers are connected to a downstream side of the saturator to condense the saturated gas so that liquid droplets can grow around the fine particles. The optical particle counters are connected to downstream sides of the condensers to optically detect the liquid droplets supplied from the condensers. Each of the condensers has a condenser tube for interconnecting the saturator and each of the optical particle counters. The condenser tube is provided with a hydrophilic inner surface layer.
Owner:AHN IN +1
Fine-particle counter
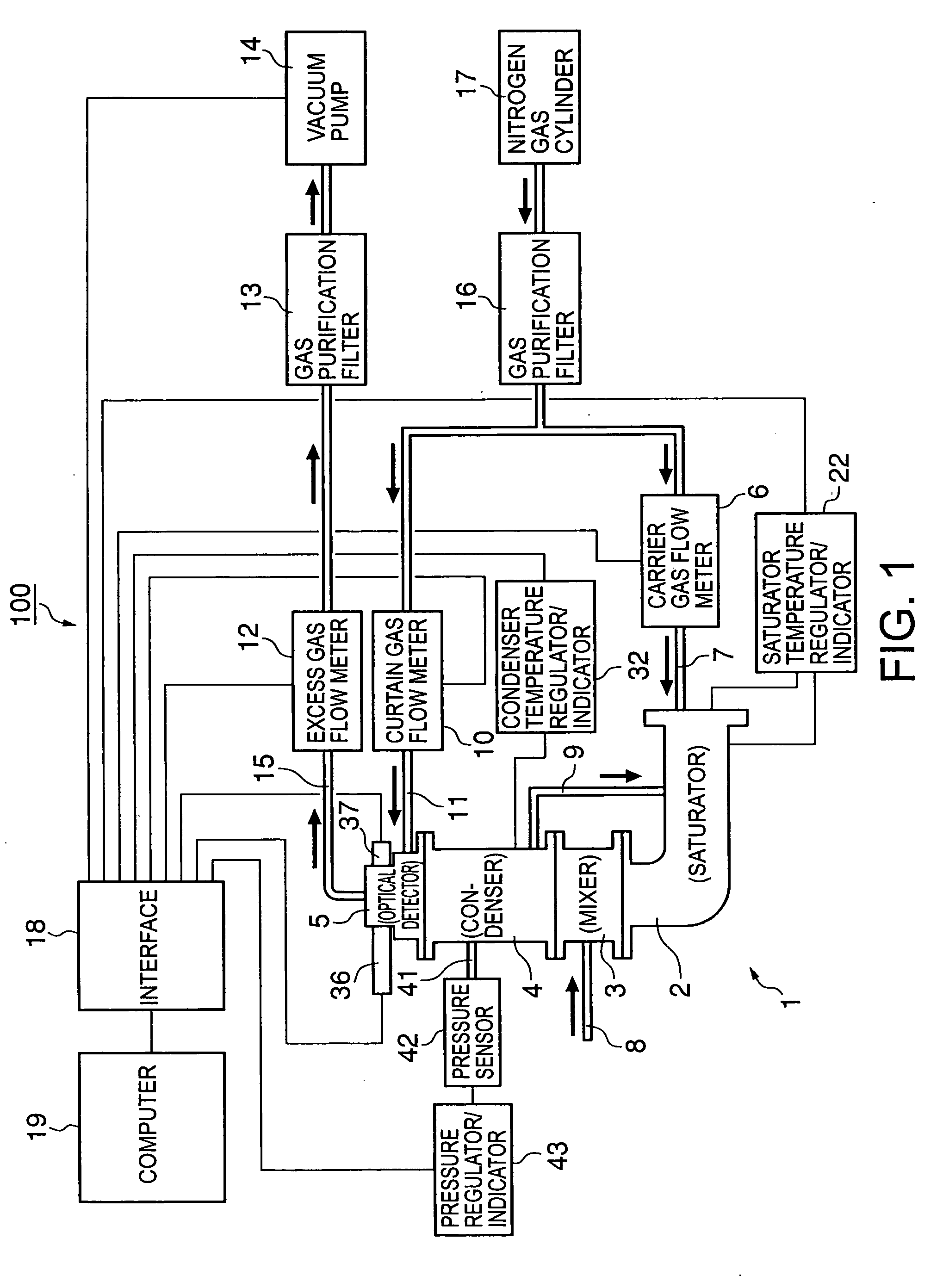
InactiveUS20090031786A1Accurate measurementReduce lossesSamplingParticle suspension analysisGas phaseNumber density
The present invention provides a fine-particle counter with which the number density of nanometer-sized fine particles born in a gas phase, which is extremely low, can be accurately measured under wide-ranging pressure conditions from pressurized conditions to low-pressure conditions.After contact-mixing, in a mixer 3, saturated vapor of a high-boiling-point solvent produced in a saturator 2, a component of a condensed nucleus detector 1, with nanometer-sized fine gas-born particles, condensed droplets of the saturated vapor whose nuclii are the fine particles are produced in a condenser 4 by heterogeneous nucleation. The number of the condensed droplets per unit of time is then counted with an optical detector 5 and is output as a pulse signal, and a computer 19 computes the number density of the nanometer-sized fine particles born in the aerosol from this pulse signal, the gas flow rates controlled by the flow meters 6, 12 and 10, and the other data that are transmitted to the computer 19 via an interface 18. The internal space of the mixer 3 has a narrowest passage having a circular cross section, situated in the center between the lower end of the mixer from which the carrier gas enters and the upper end of the mixer from which the carrier gas exits, a truncated-cone-shaped part whose cross section is circular and whose diameter gradually decreases so that the diameter on the lower end side is greater than the diameter on the narrowest passage side, and a reverse-truncated-cone-shaped part whose cross section is circular and whose diameter gradually increases so that the diameter on the narrowest passage side is smaller than the diameter on the upper end side. An aerosol inlet communicating with the aerosol inlet tube 8 is positioned at the narrowest passage.
Owner:RIKEN
Surface particle detector
A surface particle detector that includes a scanner slidable over a surface, a particle counter for counting particles passed therethrough, and a conduit connected between the scanner and the particle counter. The particle counter includes a pump for creating an airstream for drawing particles from the surface, through the scanner and conduit, to the particle counter, and back to the scanner. A sensor measures the airstream flow rate, and a controller controls the pump speed based upon the sensed airstream flow rate. The conduit attaches to the particle counter via a first connector, which contains electronic indicia identifying the type of scanner attached to the other end of the conduit. The controller controls the particle counter in response to the detected electronic indicia. The particle counter also includes a removable filter cartridge with a filter element that captures the counted particles for laboratory analysis.
Owner:PENTAGON TECH GROUP
Solid particle counting system with valve to allow reduction of pressure pulse at particle counter when vacuum pump is started
InactiveUS20080148812A1Avoiding work fluid backflowReduce pressure pulseInternal-combustion engine testingElectrical controlWorking fluidEngineering
A solid particle counting system for measuring solid particle number concentrations from engine or vehicle exhausts in real-time includes a diluter arrangement, a particle counter, and a flow splitter. The diluter arrangement mixes the dilution gas with flowing sample gases. The flow splitter receives the output flow from the diluter arrangement, provides a portion of this flow to the particle counter, and provides a by-pass flow that is received by a vacuum pump. A second flow route to the particle counter includes a valve arranged such that opening the valve during the starting of the vacuum pump reduces a pressure pulse at the particle counter caused by the starting of the vacuum pump, thereby avoiding work fluid backflow from the particle counter prior to the vacuum pump stabilizing.
Owner:HORIBA LTD
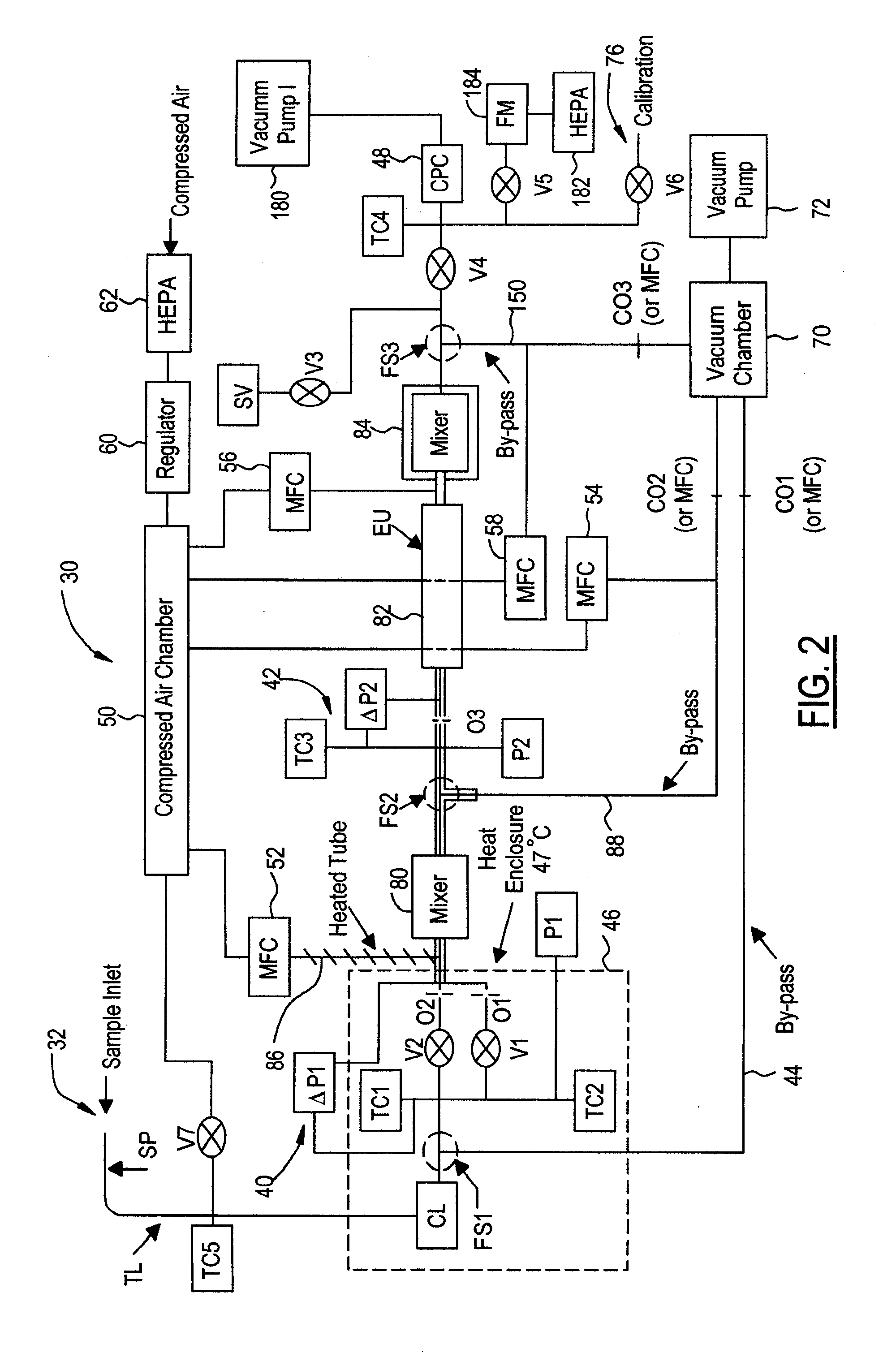
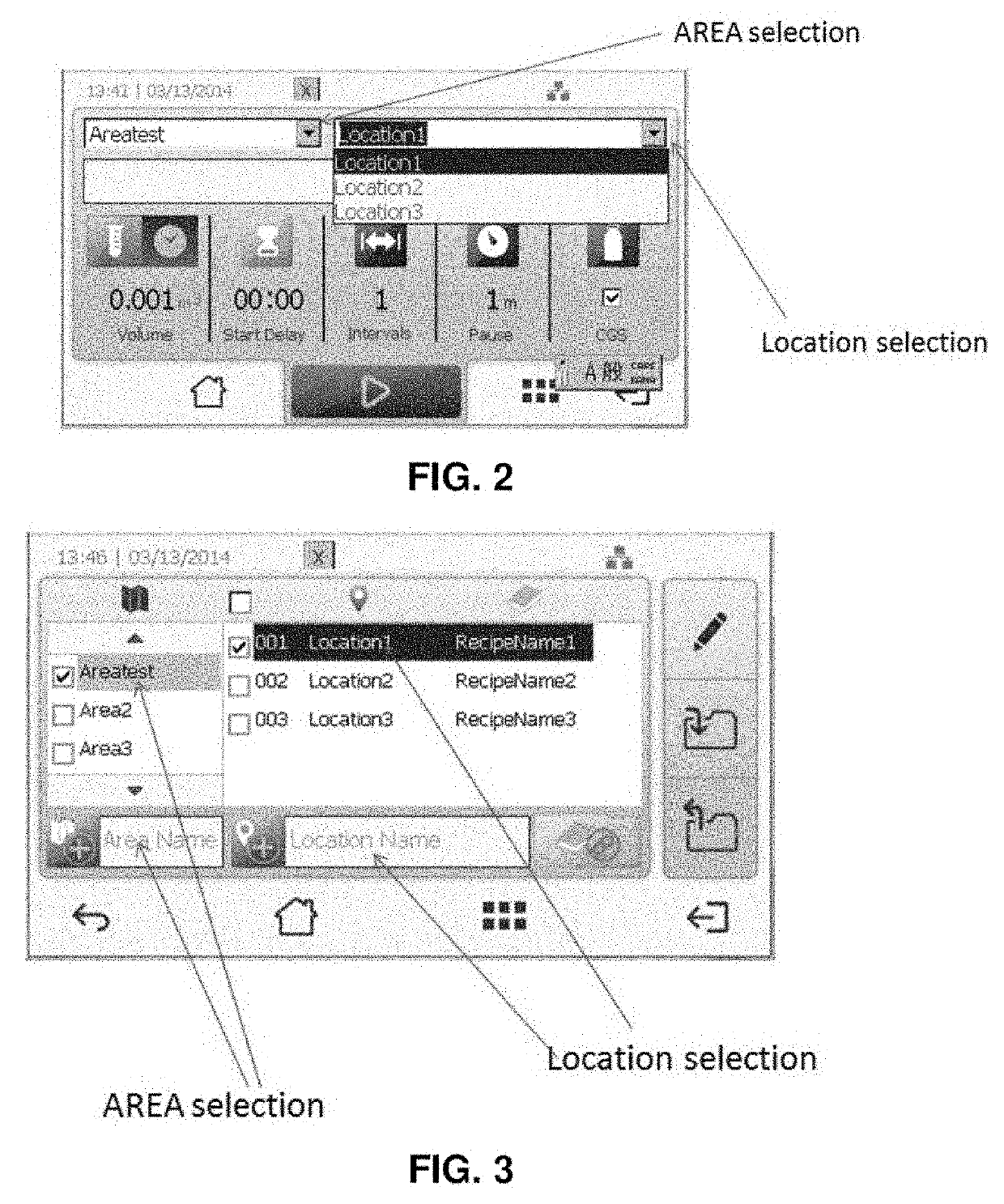
Firmware design for facility navigation, and area and location data management of particle sampling and analysis instruments
ActiveUS20190250785A1Navigational calculation instrumentsWithdrawing sample devicesUnique identifierMonitor equipment
Provided herein are methods and devices that allow for efficient management of many different sampling locations within a facility. A method for operating a biological sampler, a particle counter, and like air sampling, analysis, and / or monitoring equipment or instrumentation is described, such as by sampling an environment at a sampling position with the biological sampler and storing sample data and other useful information in memory in association with unique identifier(s) including sampling location(s) for the samples. Also provided are associated devices for carrying out the methods.
Owner:PARTICLE MEASURING SYST
Real-time microbial particle counter
InactiveCN103940709ARealize automated detectionSimple and fast operationParticle size analysisParticle suspension analysisEffect lightLaser-induced fluorescence
The invention discloses a real-time microbial particle counter comprising a light path, an air channel intersected with the light path, and a signal processing system connected with the light path, wherein the light path comprises a lighting light path for irradiating tested particles and a collecting light path arranged along the advancing direction of the lighting light path; the collecting light path also comprises a relay system for separating the light path and separately detecting separated light paths; the air channel is used for sampling the tested particles; the signal processing system is used for analyzing and processing a signal, and comprises a fluorescent preamplifier and a scattered light preamplifier. The concentration of microbial particles in air is monitored in real time by taking laser-induced fluorescence detection as the principle, the particle sizes and the biological attributes of the tested particles are judged by detecting the intensities of scattered light and fluorescence emitted by exciting light, and the particles in a sampling airflow are counted, so that the automatic detection on planktonic bacteria microorganisms is achieved, and the real-time microbial particle counter is simple and convenient to operate, strong in detection instantaneity, high in sensitivity and high in accuracy.
Owner:NANJING ZHONGKE SHENGUANG TECH
Ultra-low background gas-filled alpha counter
InactiveUS20030040877A1Reduce rateLow count rateSolid-state devicesAmplifiers controlled by lightParallel plateLarge sample
A method and counter for reducing the background counting rate in gas-filled alpha particle counters wherein the counter is constructed in such a manner as to exaggerate the differences in the features in preamplifier pulses generated by collecting the charges in ionization tracks produced by alpha particles emanating from different regions within the counter and then using pulse feature analysis to recognize these differences and so discriminate between different regions of emanation. Thus alpha particles emitted from the sample can then be counted while those emitted from the counter components can be rejected, resulting in very low background counting rates even from large samples. In one embodiment, a multi-wire ionization chamber, different electric fields are created in different regions of the counter and the resultant difference in electron velocities during charge collection allow alpha particles from the sample and counter backwall to be distinguished. In a second embodiment, a parallel-plate ionization chamber, the counter dimensions are adjusted so that charge collection times are much longer for ionization tracks caused by sample source alpha particles than for those caused by anode source alpha particles. In both embodiments a guard electrode can be placed about the anode's perimeter and secondary pulse feature analysis performed on signal pulses output from a preamplifier attached to this guard electrode to further identify and reject alpha particles emanating from the counter's sidewalls in order to further lower the counter's background.
Owner:WARBURTON WILLIAM K
Condensation particle counter
A condensation particle counter is capable of efficiently measuring the number and size of fine particles. The condensation particle counter includes a saturator, a condenser and an optical particle counters. The saturator is designed to generate a saturated gas by saturating a gas in which fine particles are suspended with working fluid. The condenser is connected to a downstream side of the saturator to condense the saturated gas so that liquid droplets can grow around the fine particles. The optical particle counter is connected to downstream sides of the condenser to optically detect the liquid droplets supplied from the condensers. The condenser has a condenser tube for interconnecting the saturator and the optical particle counter. The present condensation particle counter can use water as working fluid and also can optically measure fine particles in an easy and accurate manner by forming or installing an inner surface of a condenser tube with a hydrophilic tube.
Owner:HCTM +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com