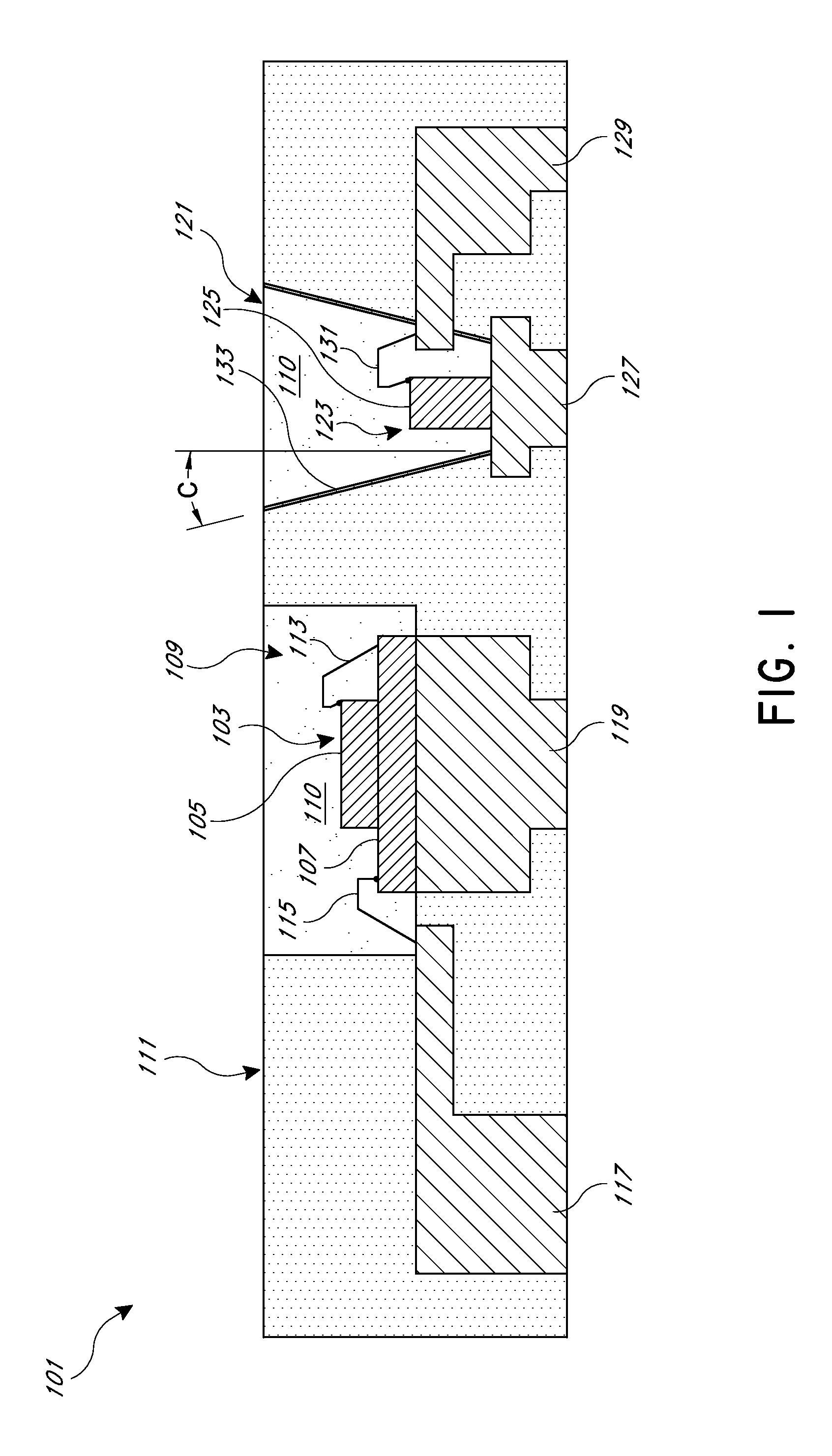
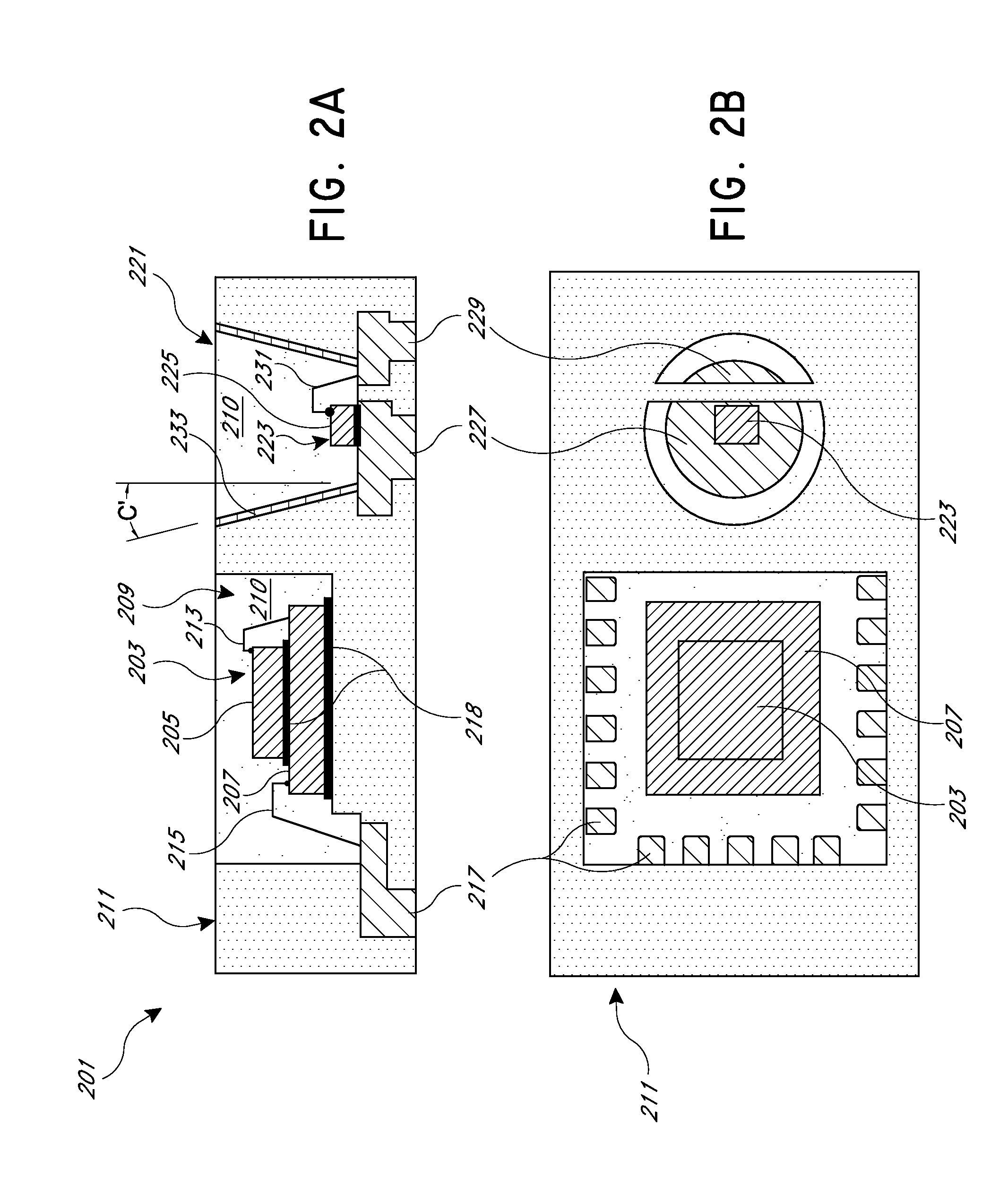
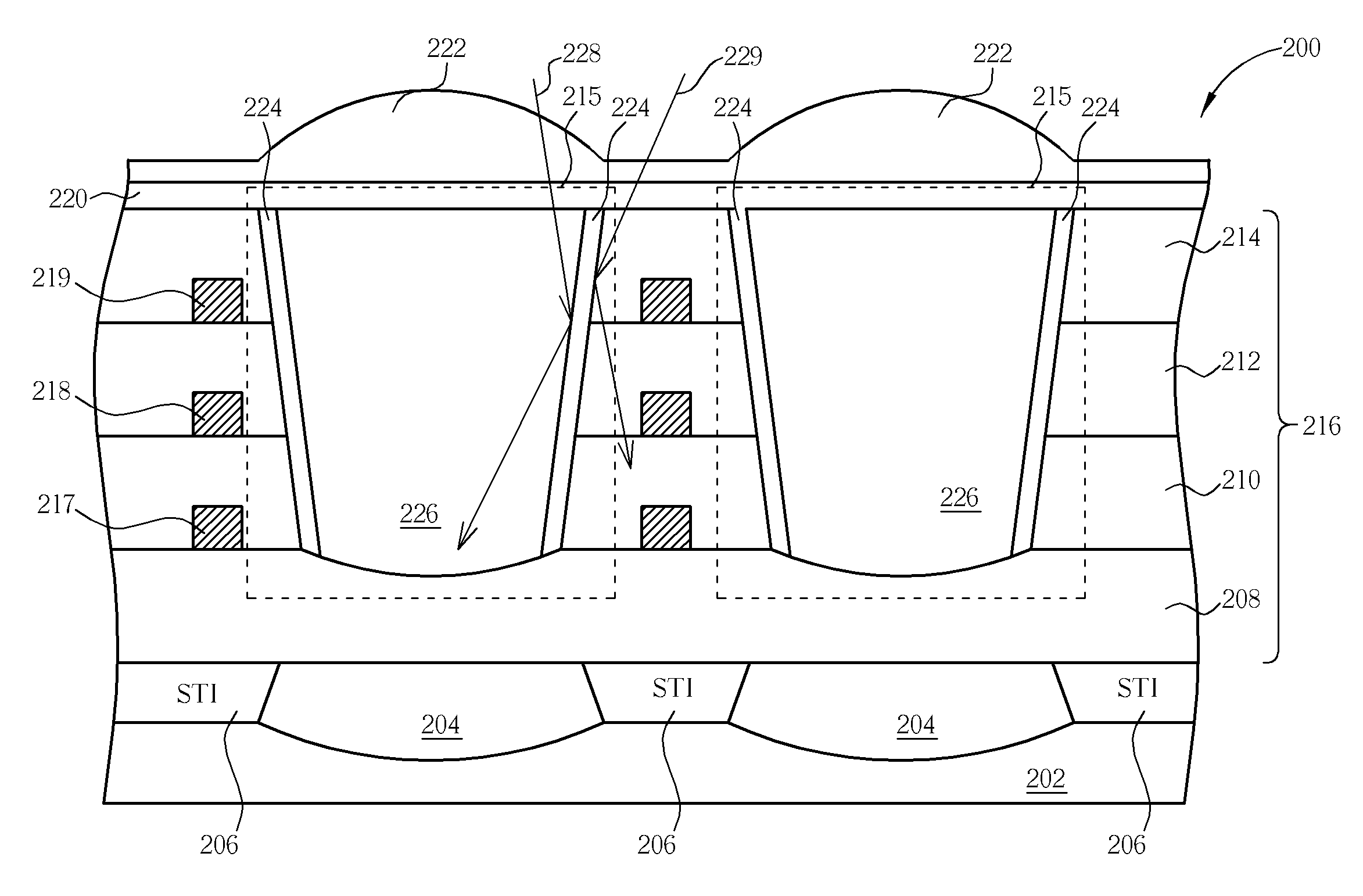
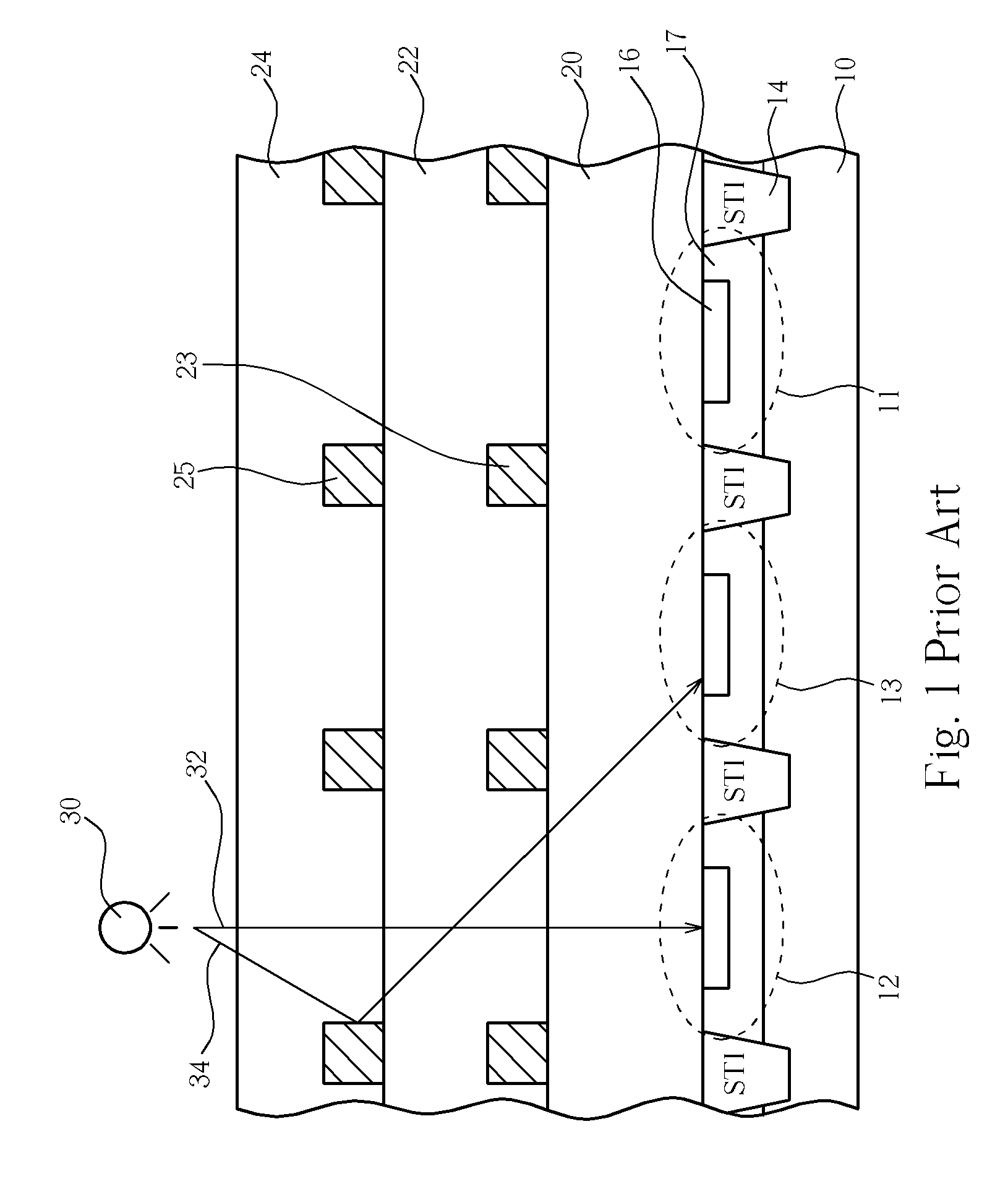
Patents
Literature
82 results about "Optical barrier" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
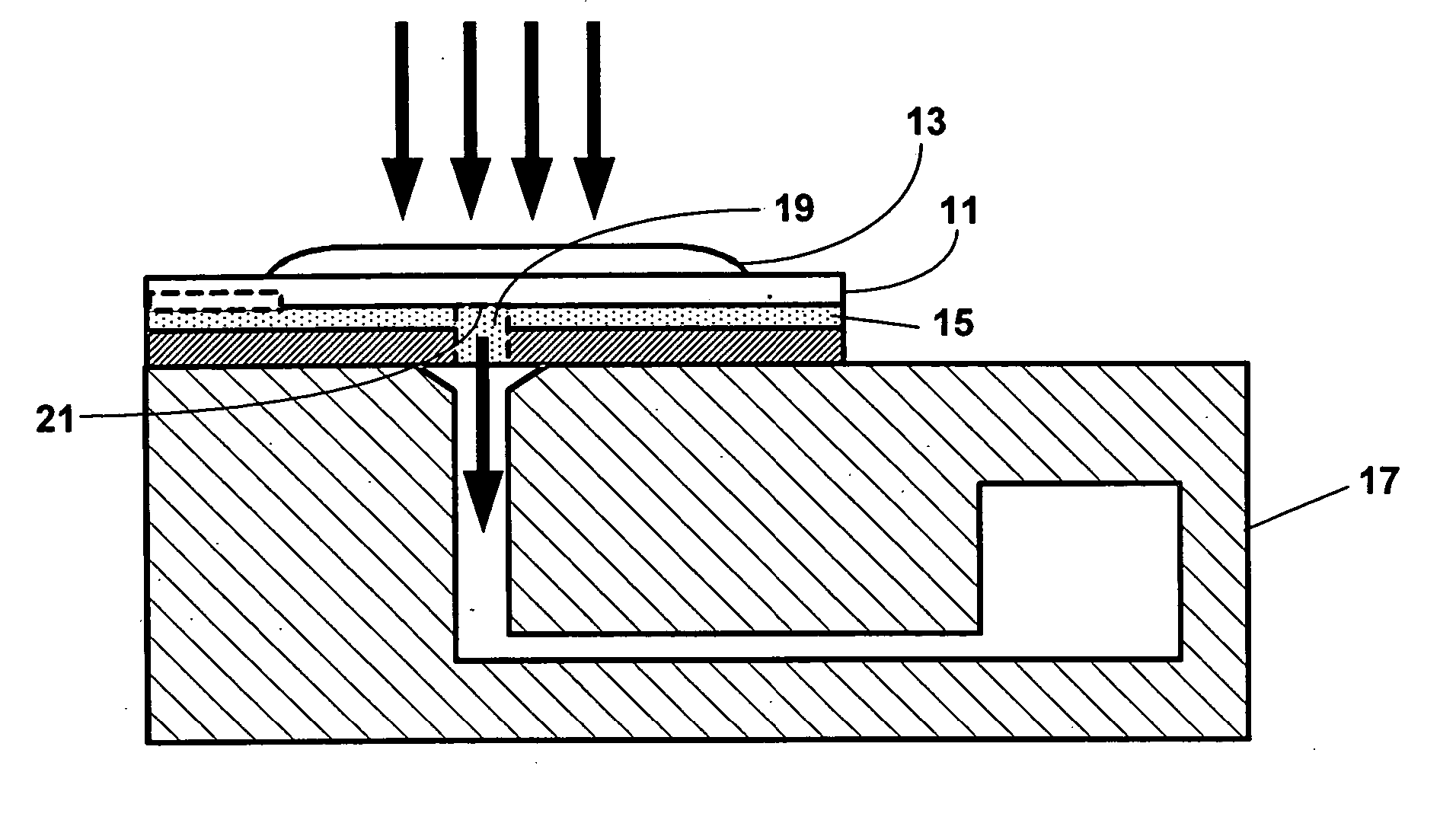
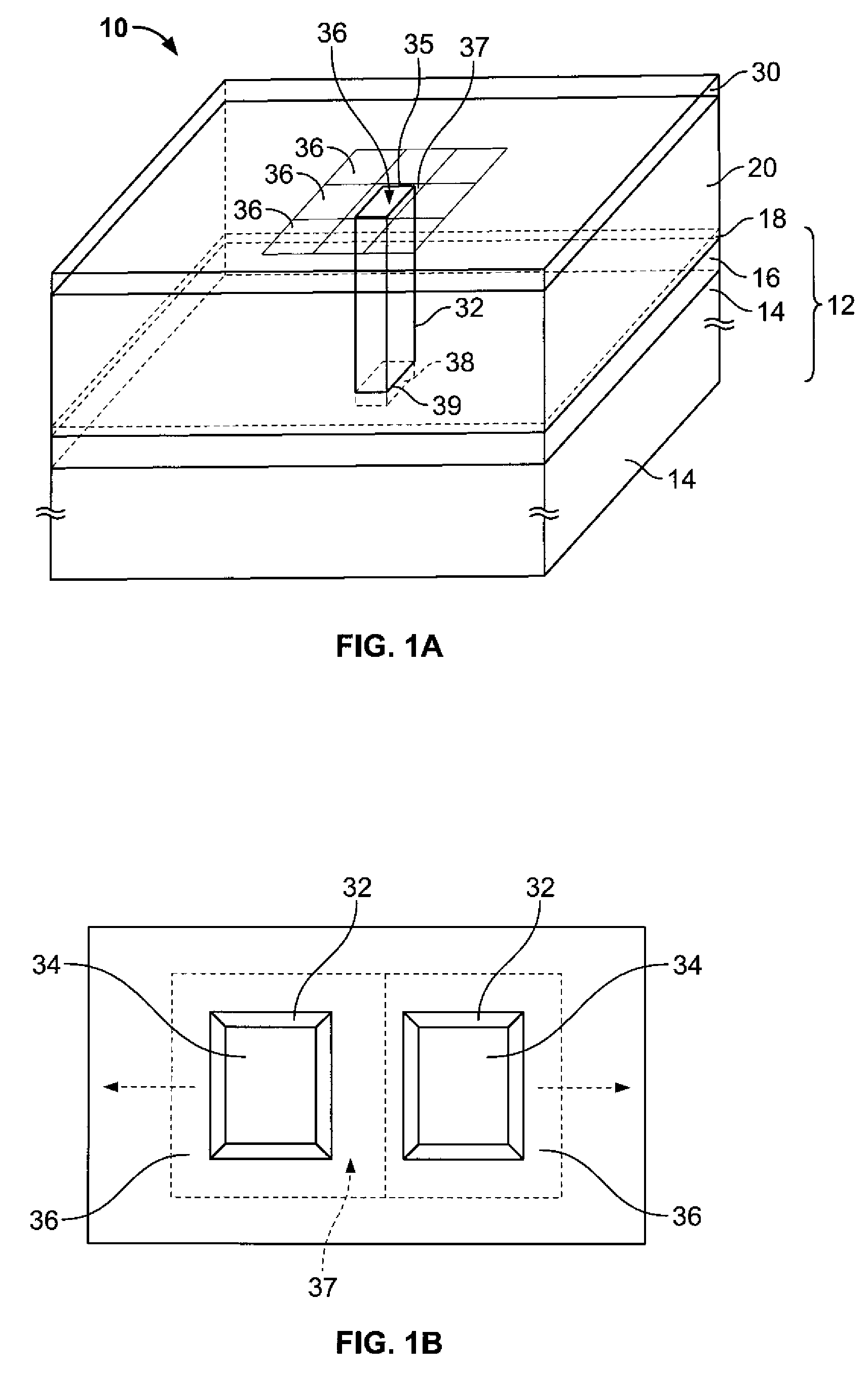
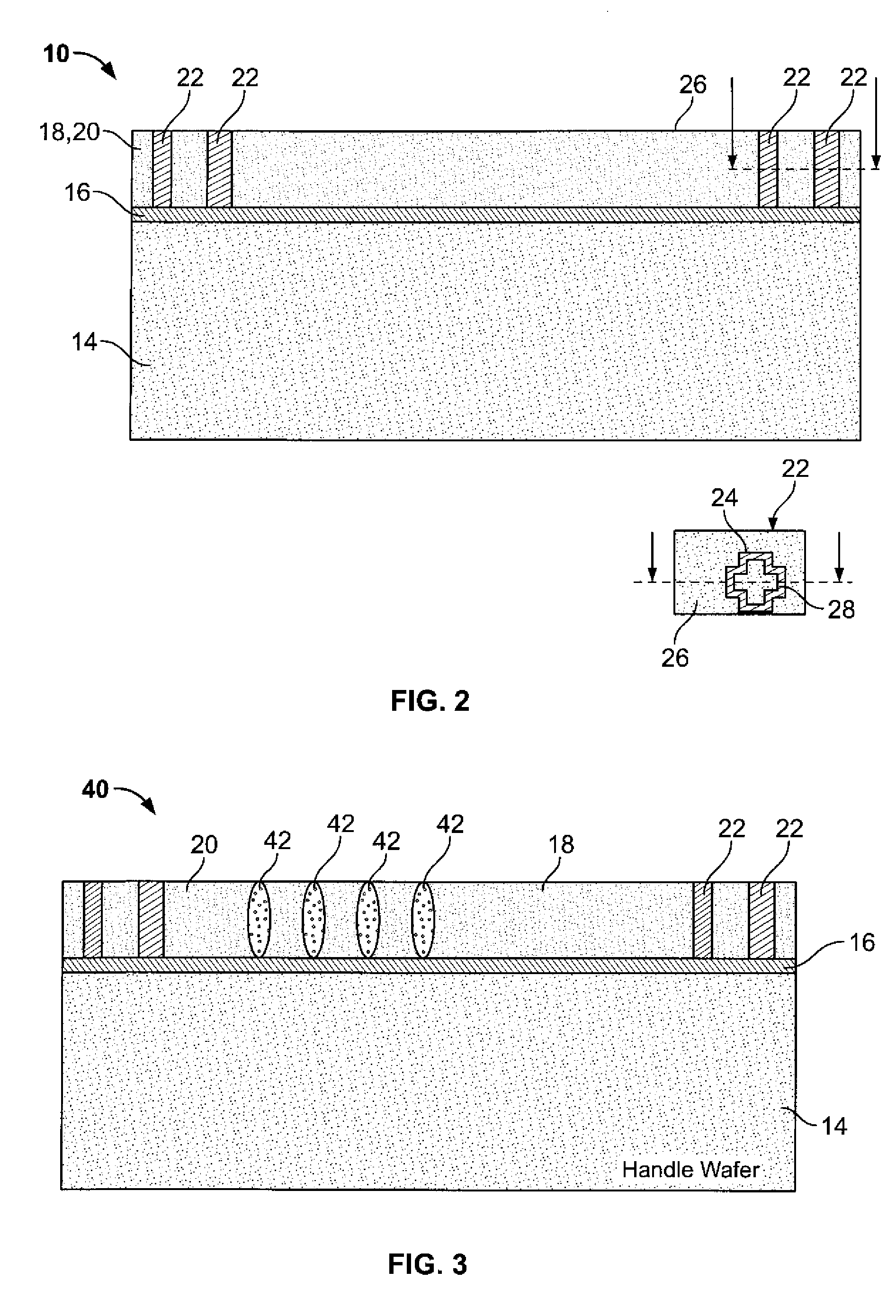
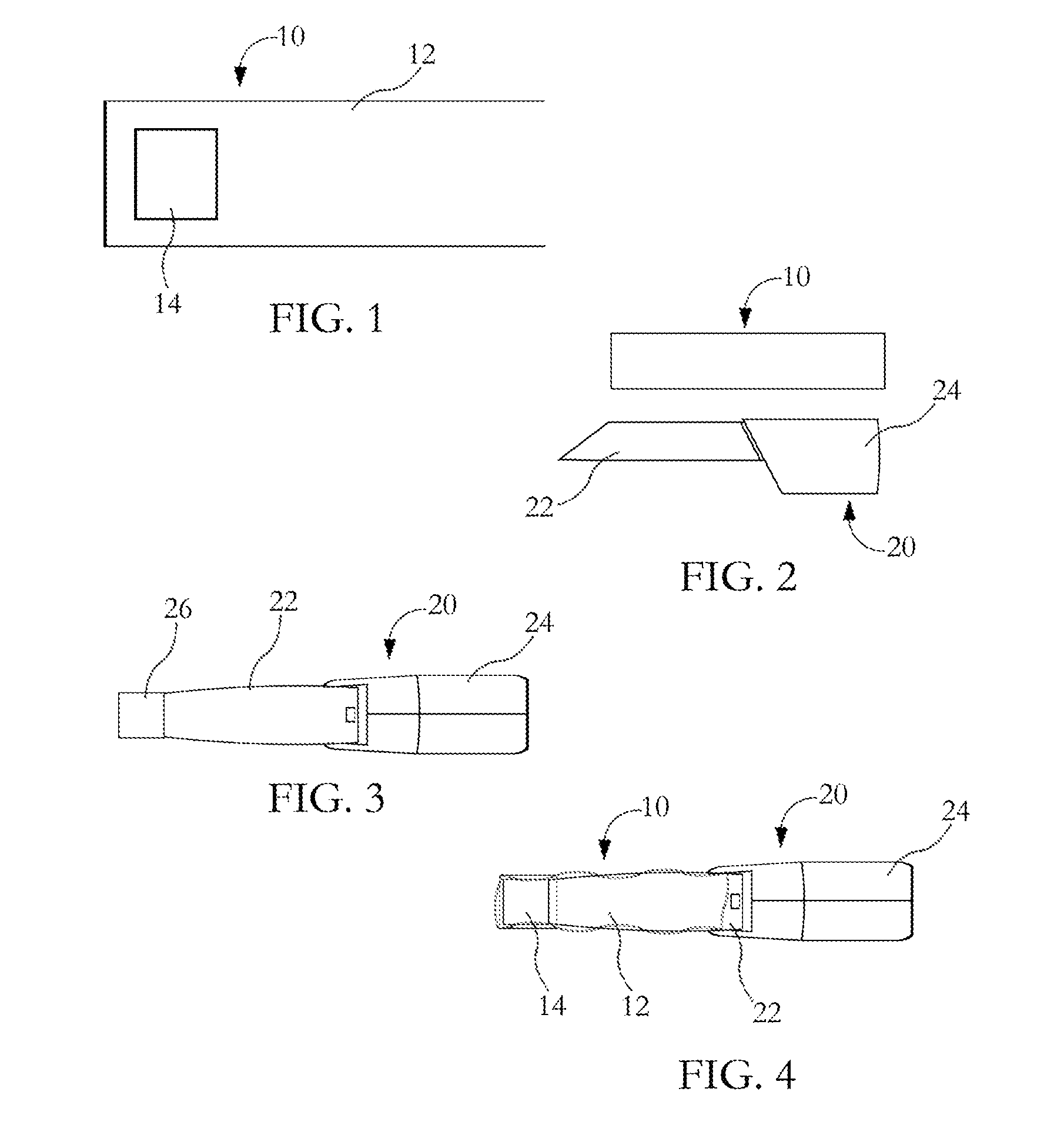
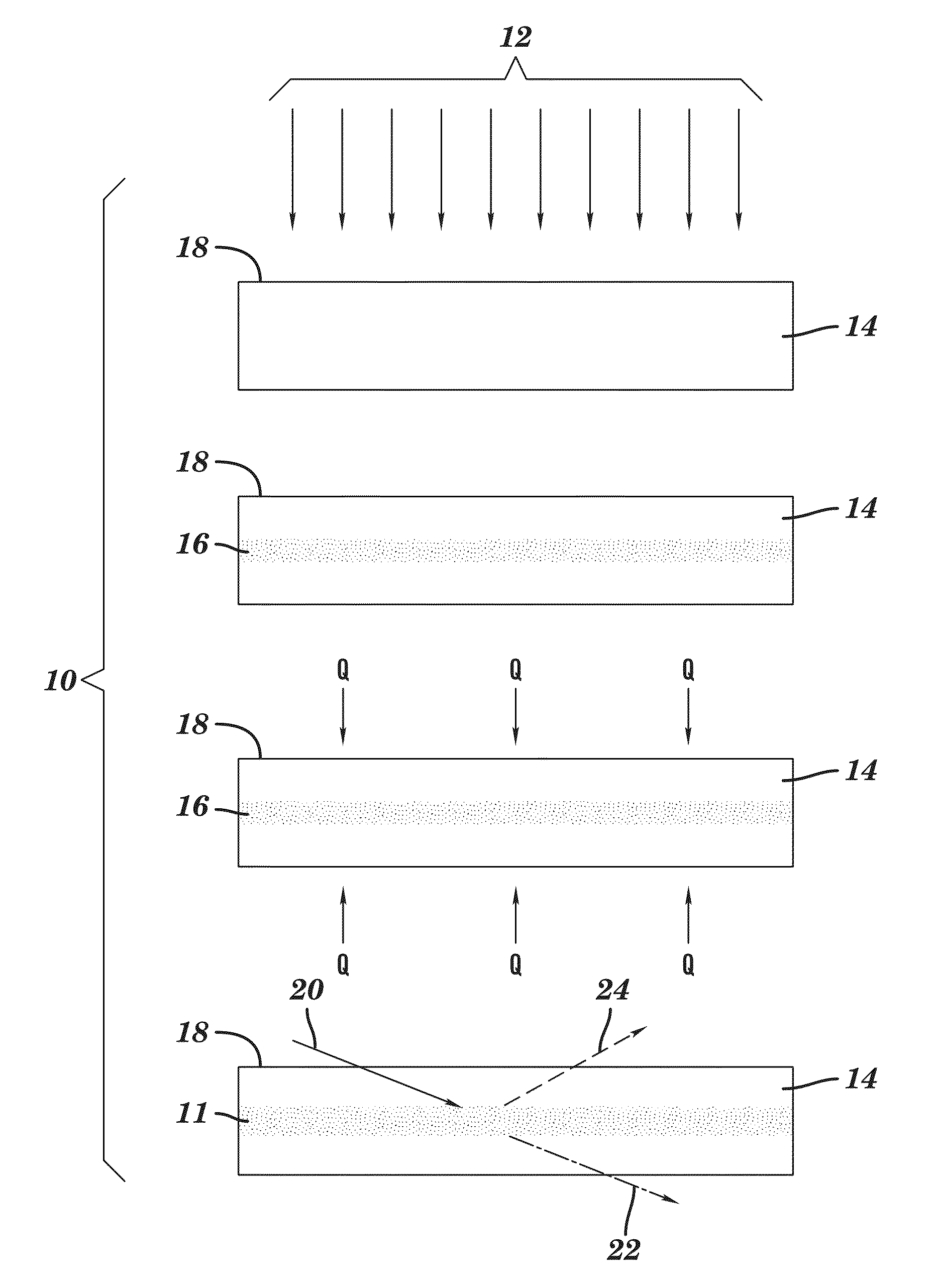
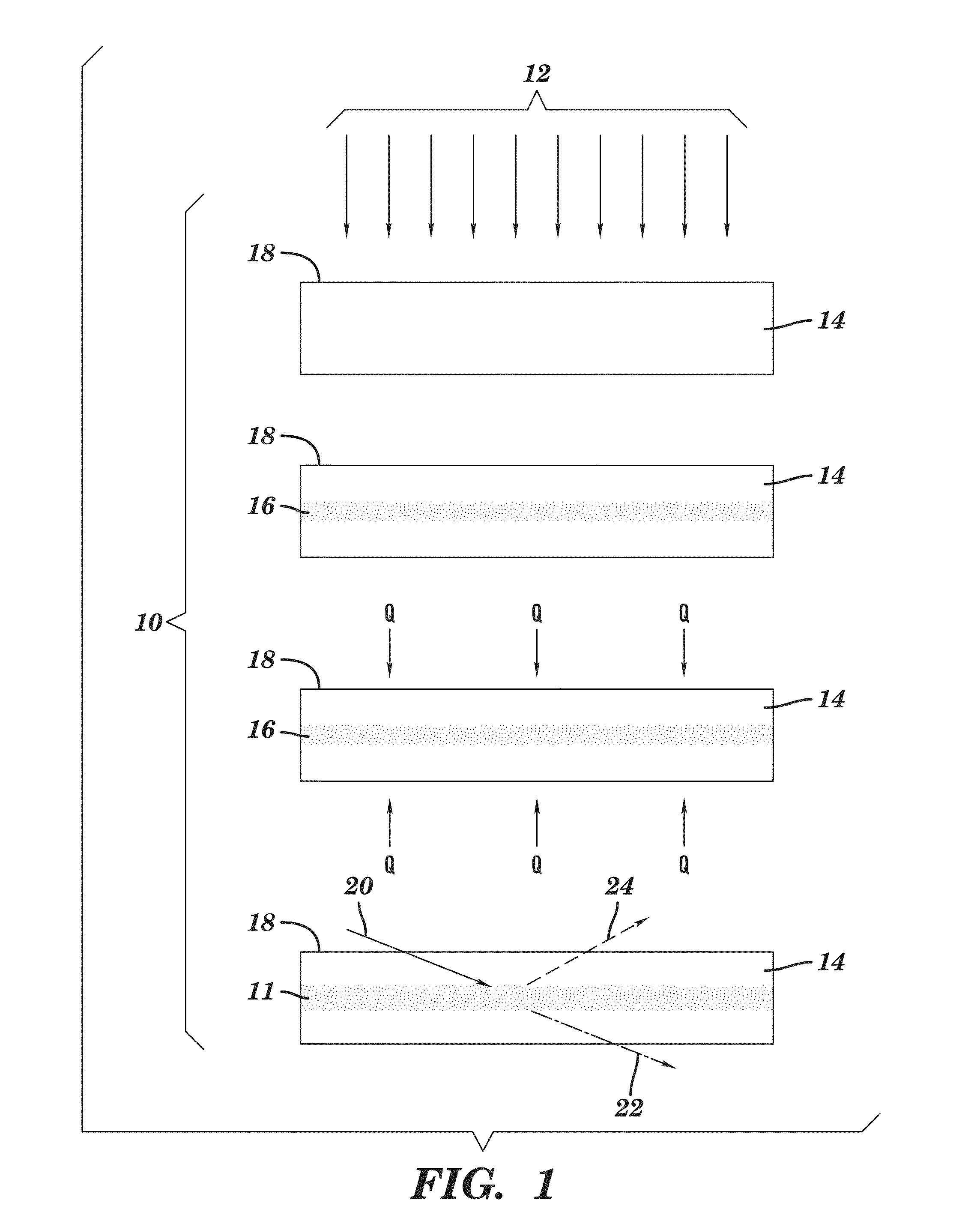
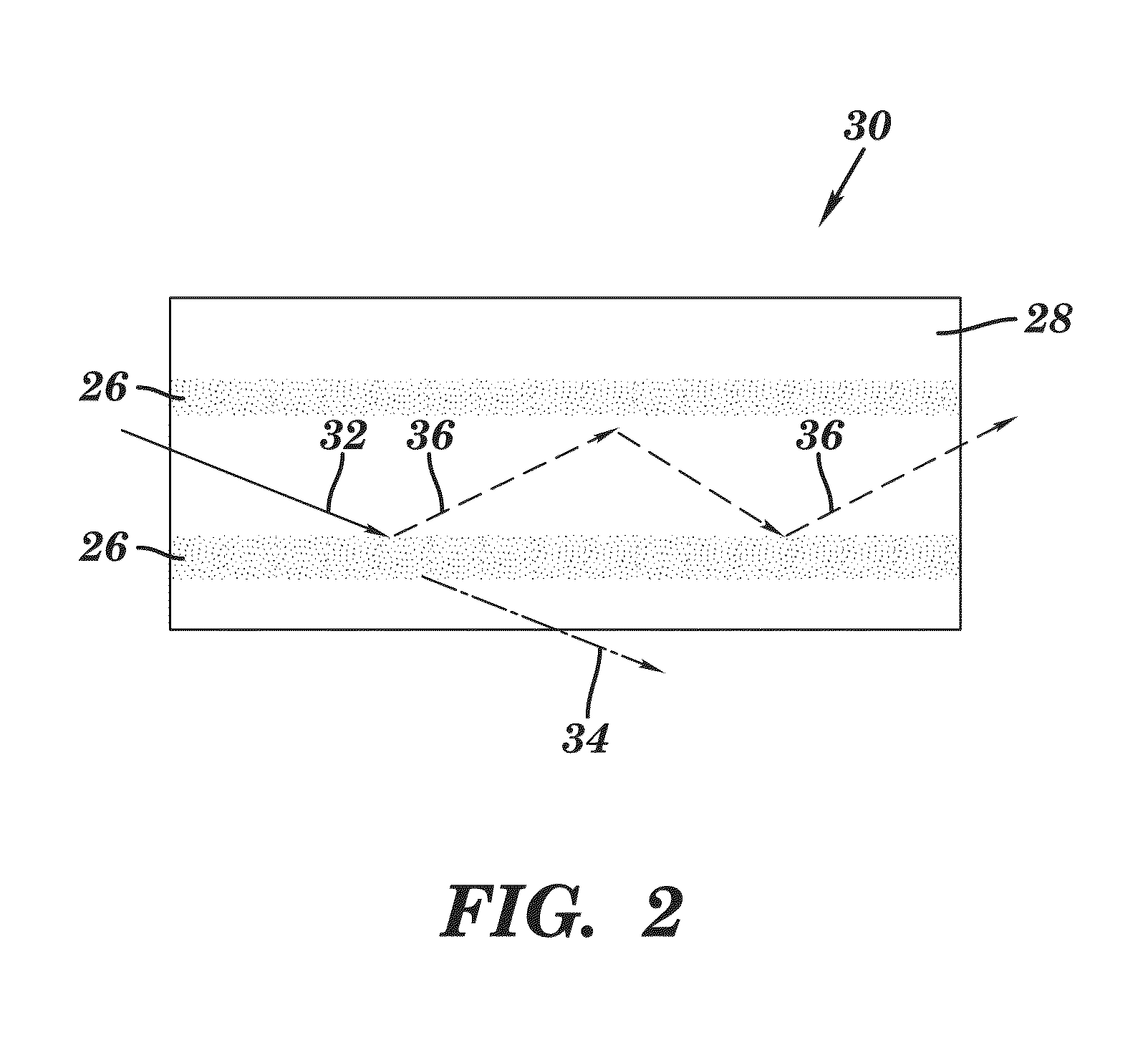
Fluidic medical devices and uses thereof
InactiveUS20060264779A1Reduce Optical InterferenceSatisfies needCompound screeningApoptosis detectionMedical deviceOptical barrier
Owner:GOLDEN DIAGNOSTICS TOP CORP +2
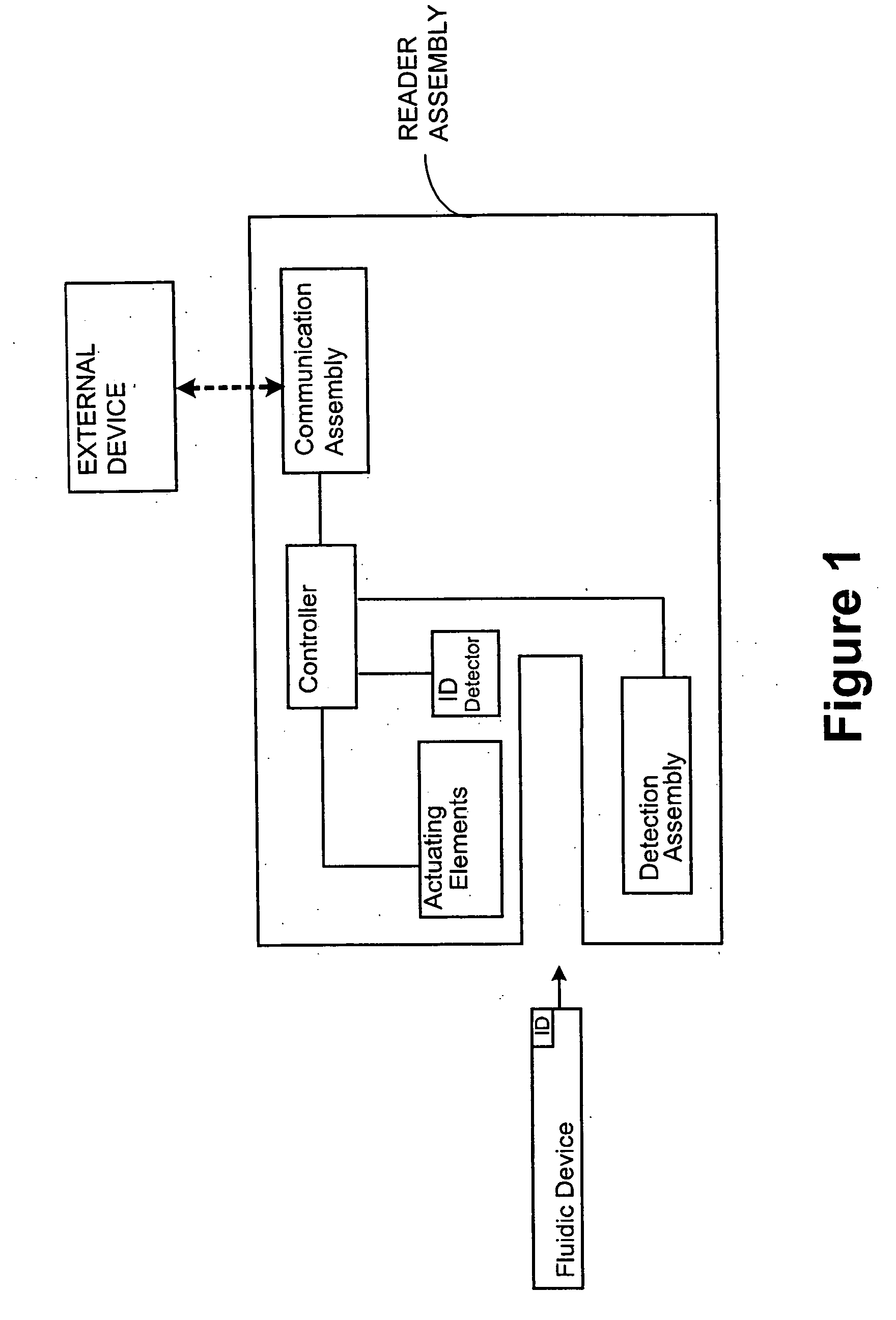
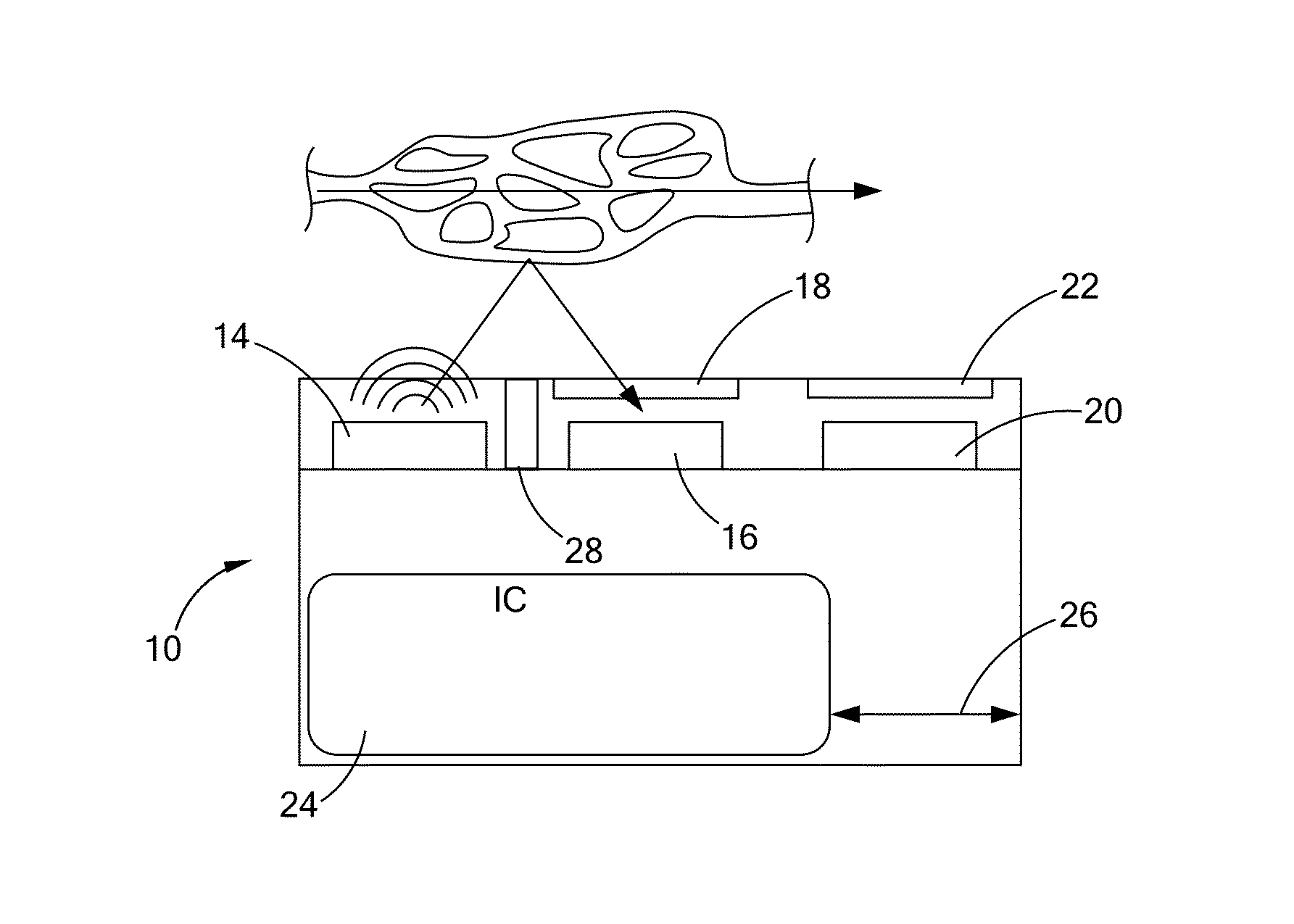
Sensor and method for continuous health monitoring
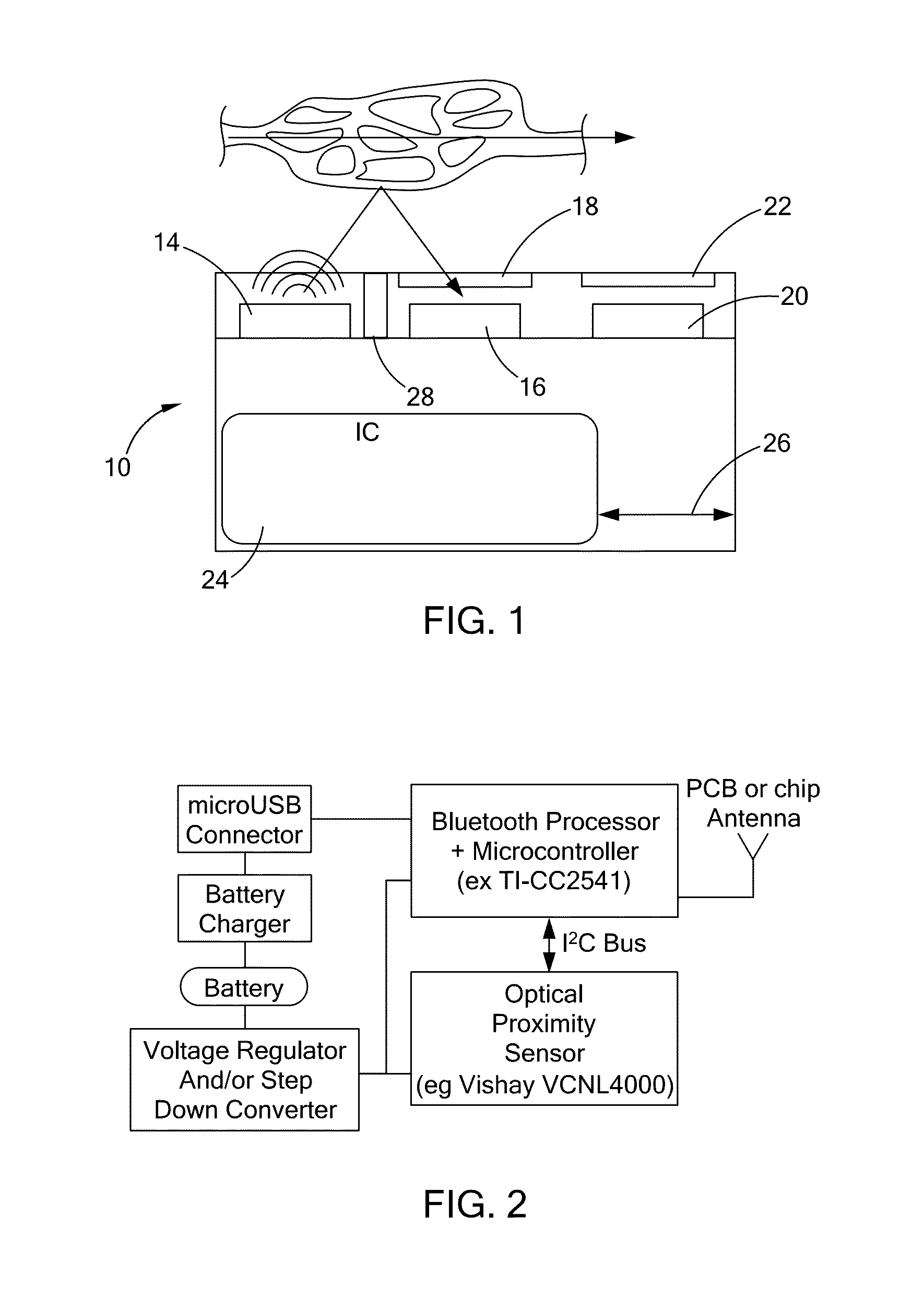
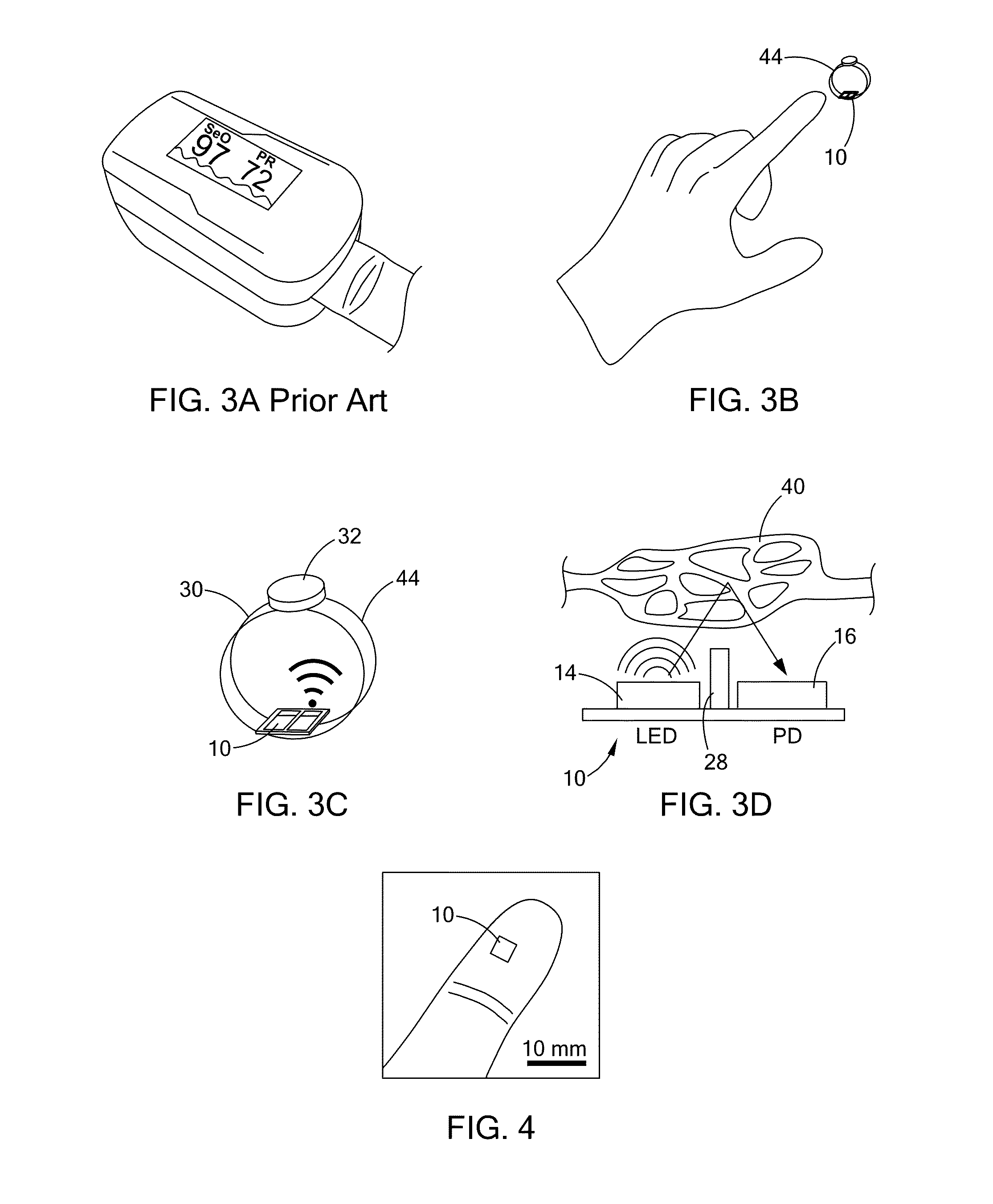
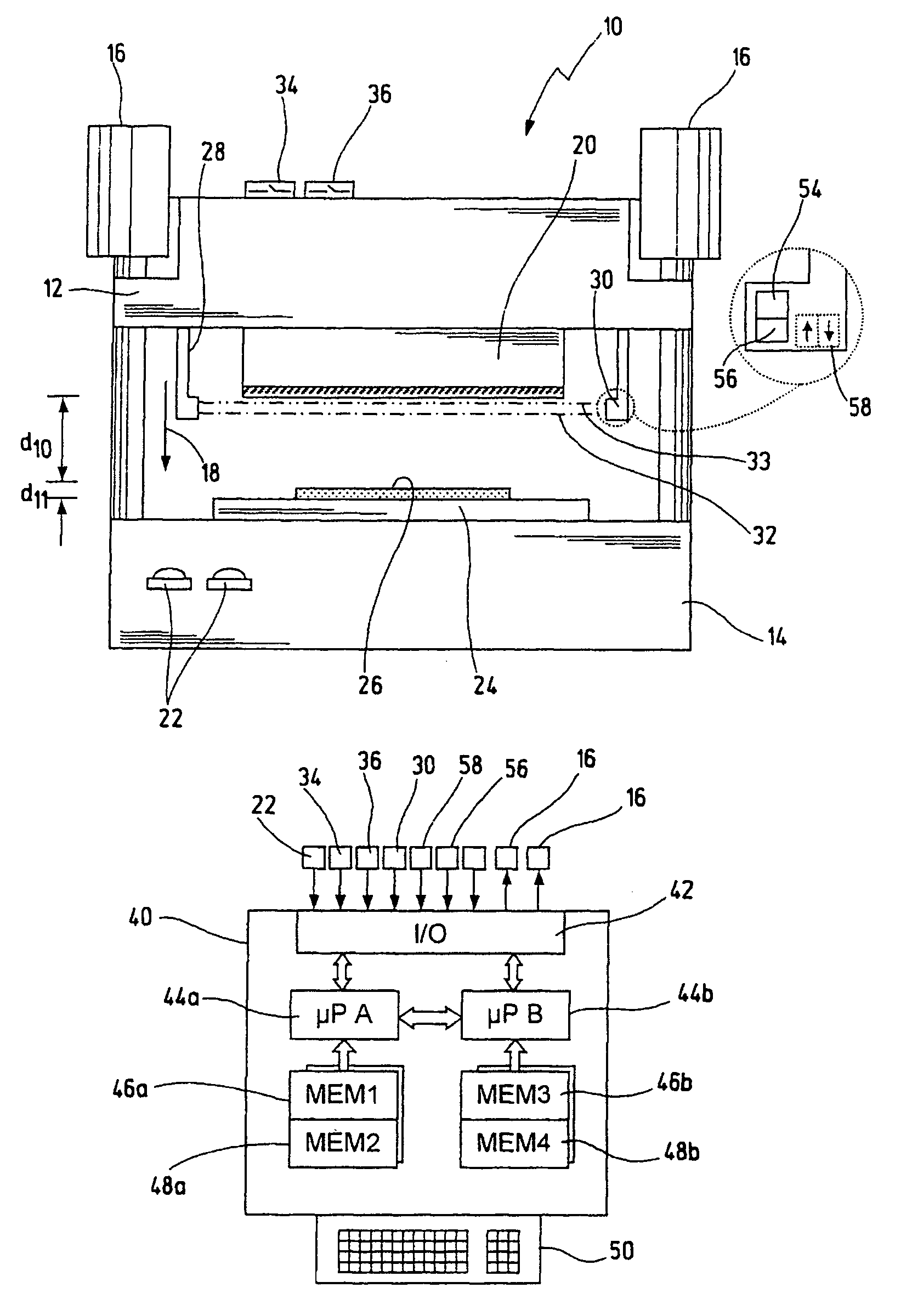
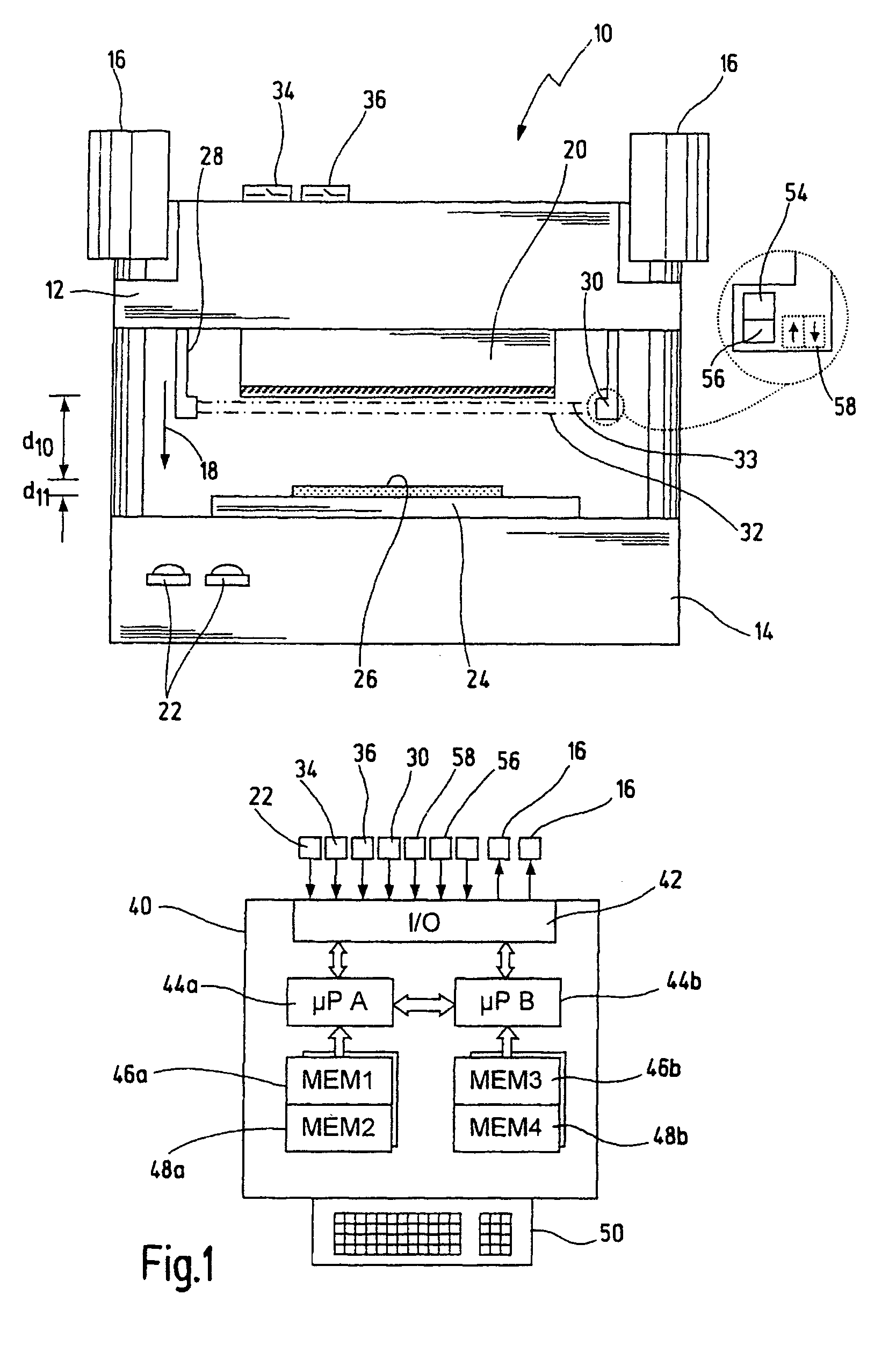
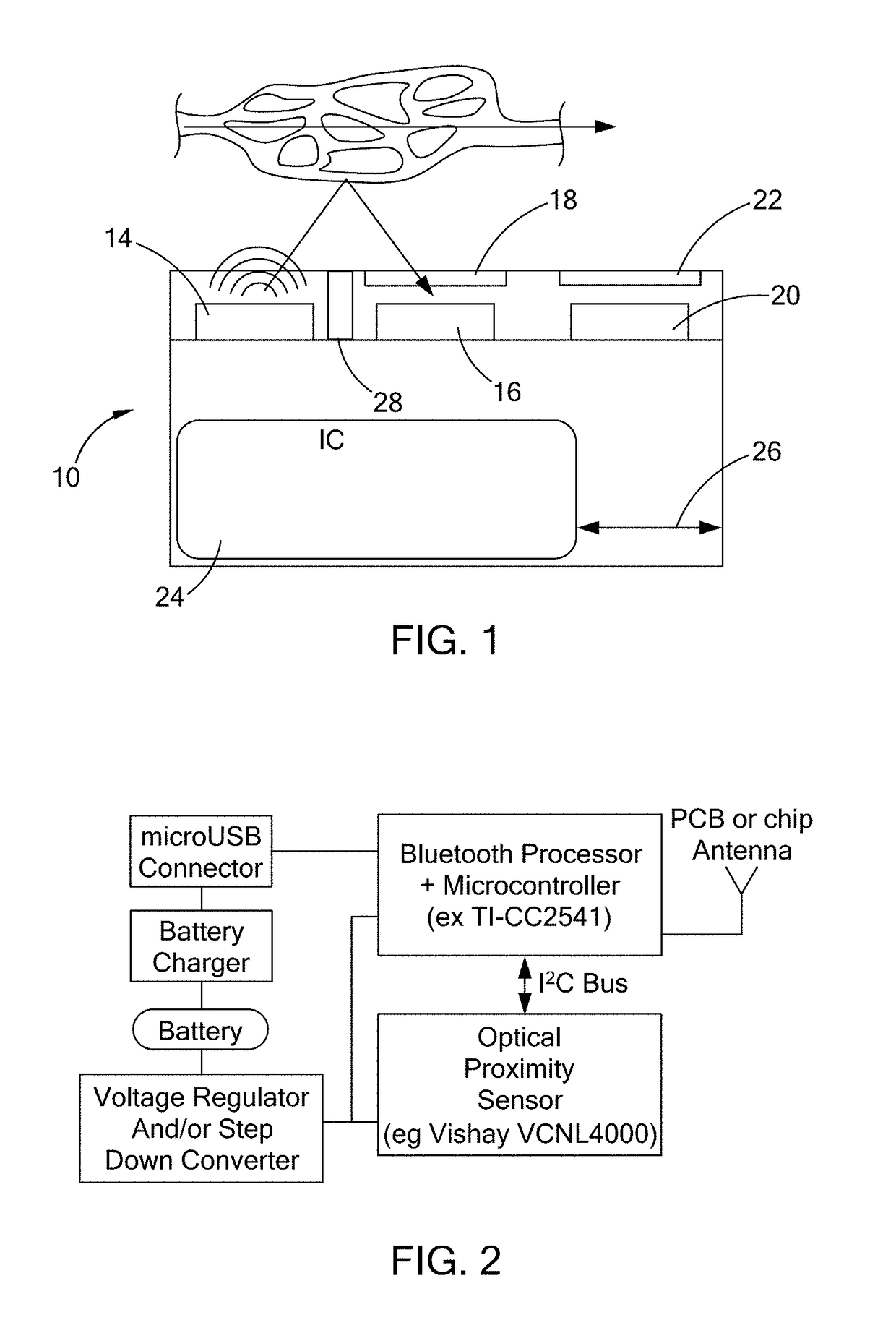
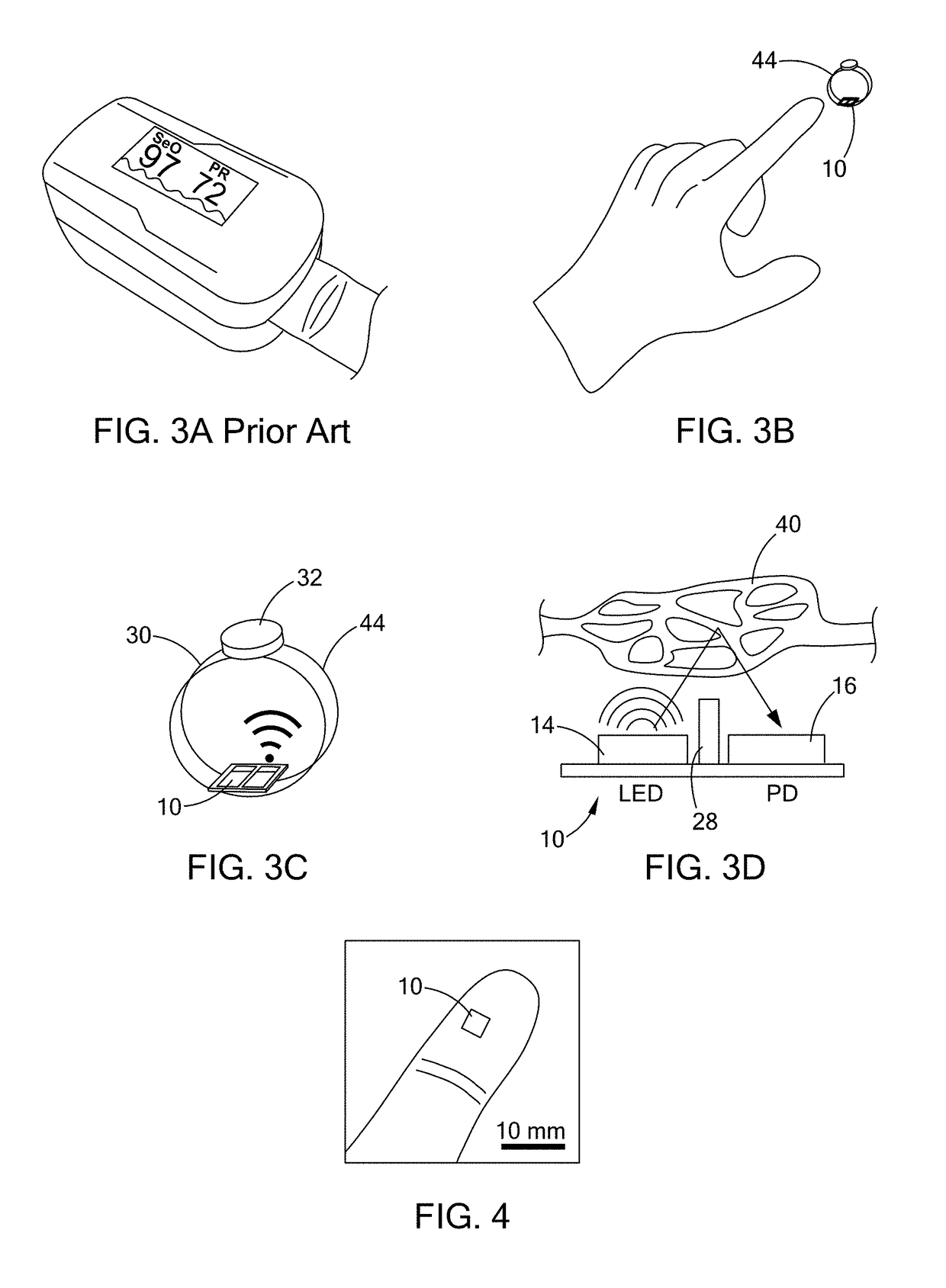
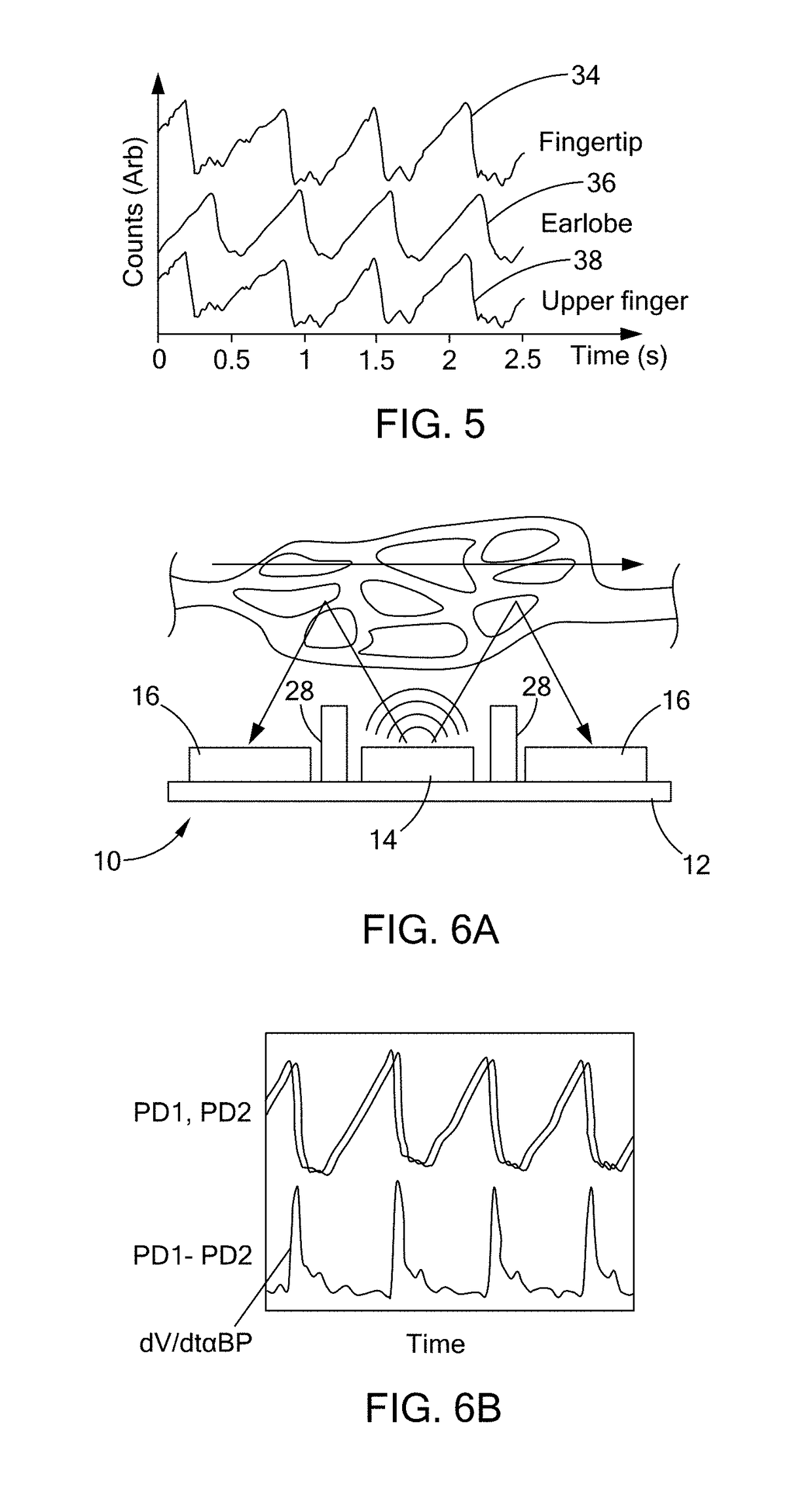
An optical proximity sensor assembly includes an optical proximity sensor with an IR LED emitting light having an infrared wavelength, an IR photo detector sensitive to the infrared wavelength, an optical barrier blocking direct light rays from the LED to the IR photo detector and permitting reflected light rays to reach the at least one photo detector; and an electronic integrated circuit with an amplifier for amplifying a signal detected by the photo detector, an analog to digital converter, LED drivers, noise reduction and ambient light cancellation circuitry, and a digital interface for communication with a microcontroller. The optical proximity sensor is accommodated on a wearable carrier. A single sensor may include a plurality of identical or different LEDs, a plurality of photodiodes, or both. Also, several sensors may be placed on a person's skin along a vascular path to obtain data relating to blood flow and artery stiffness.
Owner:WAYNE STATE UNIV
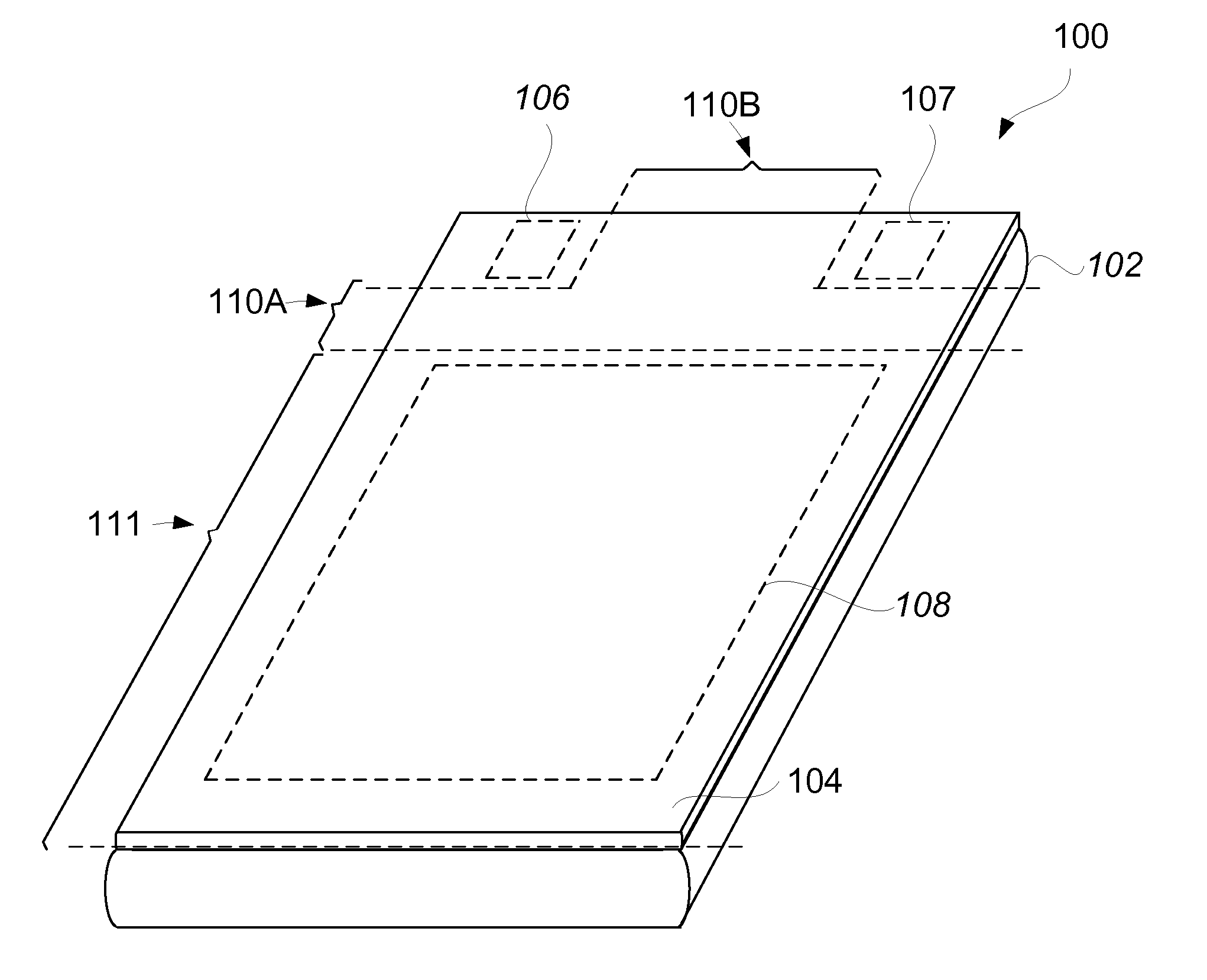
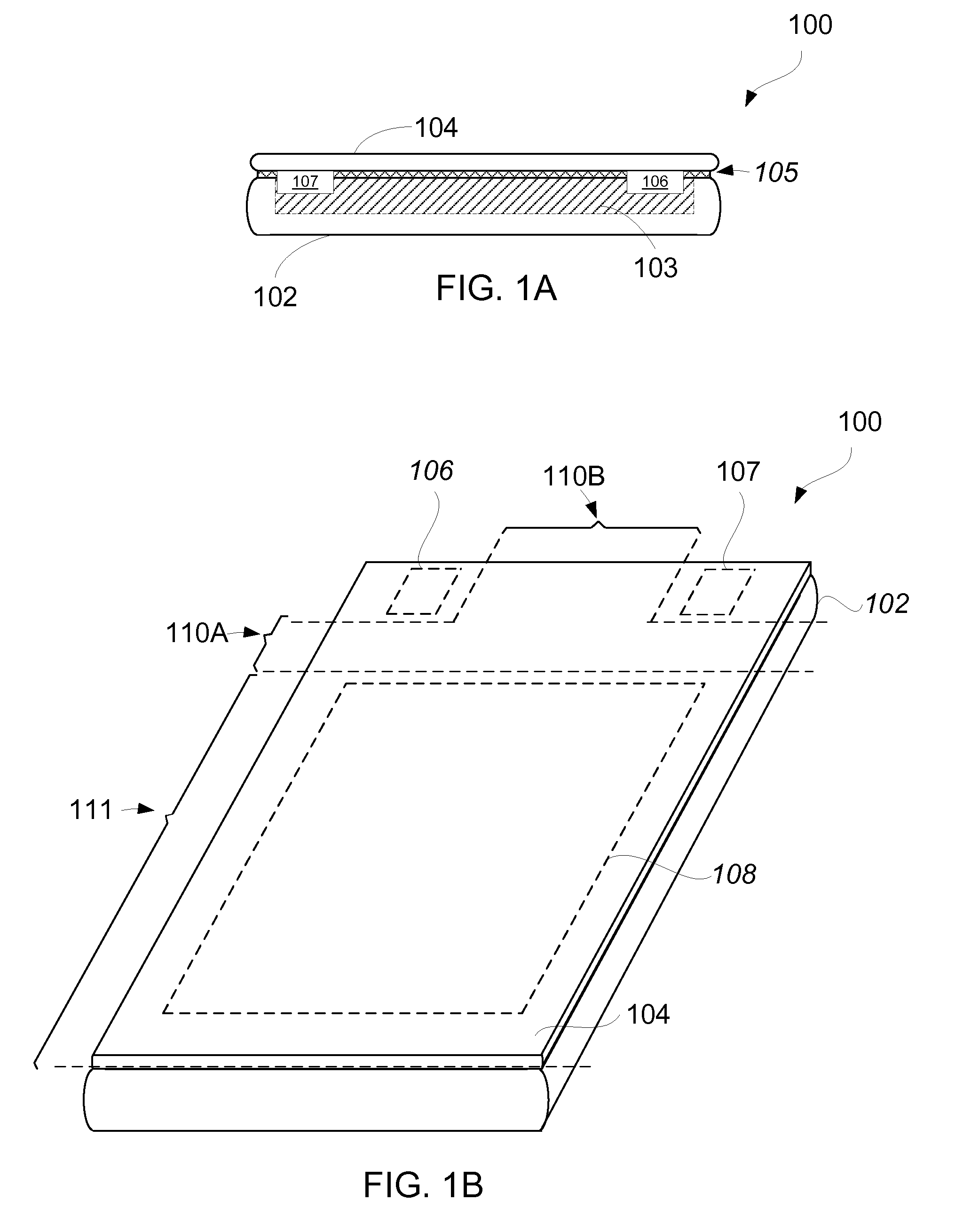
Electronic Device Having Selectively Strengthening Glass Cover Glass
ActiveUS20120027399A1Reduce glareReducing glare at the cameraWave amplification devicesDiffusing elementsGlass coverOptical barrier
Embodiments disclosed therein generally pertain to selectively strengthening glass. More particularly, techniques are described for selectively strengthening cover glass, which tends to be thin, for electronic devices, namely, portable electronic devices. In certain embodiments, selectively strengthening glass, such as cover glass, can be used to provide optical barriers (or channels) internal to the glass. The electronic devices can also provide for camera integration behind the cover glass.
Owner:APPLE INC
Low noise intracavity laser particle counter
ActiveUS6903818B2High power operationEffective noise reductionRadiation pyrometryScattering properties measurementsLow noiseEddy current
An optical particle counter has a gain-apertured laser cavity producing laser light, an inlet jet providing fluid flow into a particle detecting region within the laser cavity, the inlet jet having an inlet jet orifice; a detection optics assembly located to collect light scattered from particles with the detecting region for producing an output signal indicative of the particles; and an optical barrier complex located to reduce noise as compared to the gain-apertured system without the optical barrier complex for fluid flow rates greater than or equal to about 0.1 cubic feet per minute. The optical barrier complex inhibits laser light from illuminating turbulent eddy currents originating on the interior walls of the inlet jet. The optical barrier complex includes one or more physical apertures, one or more optical stops, or both which are located to prevent laser light from illuminating the eddy currents.
Owner:PARTICLE MEASURING SYST
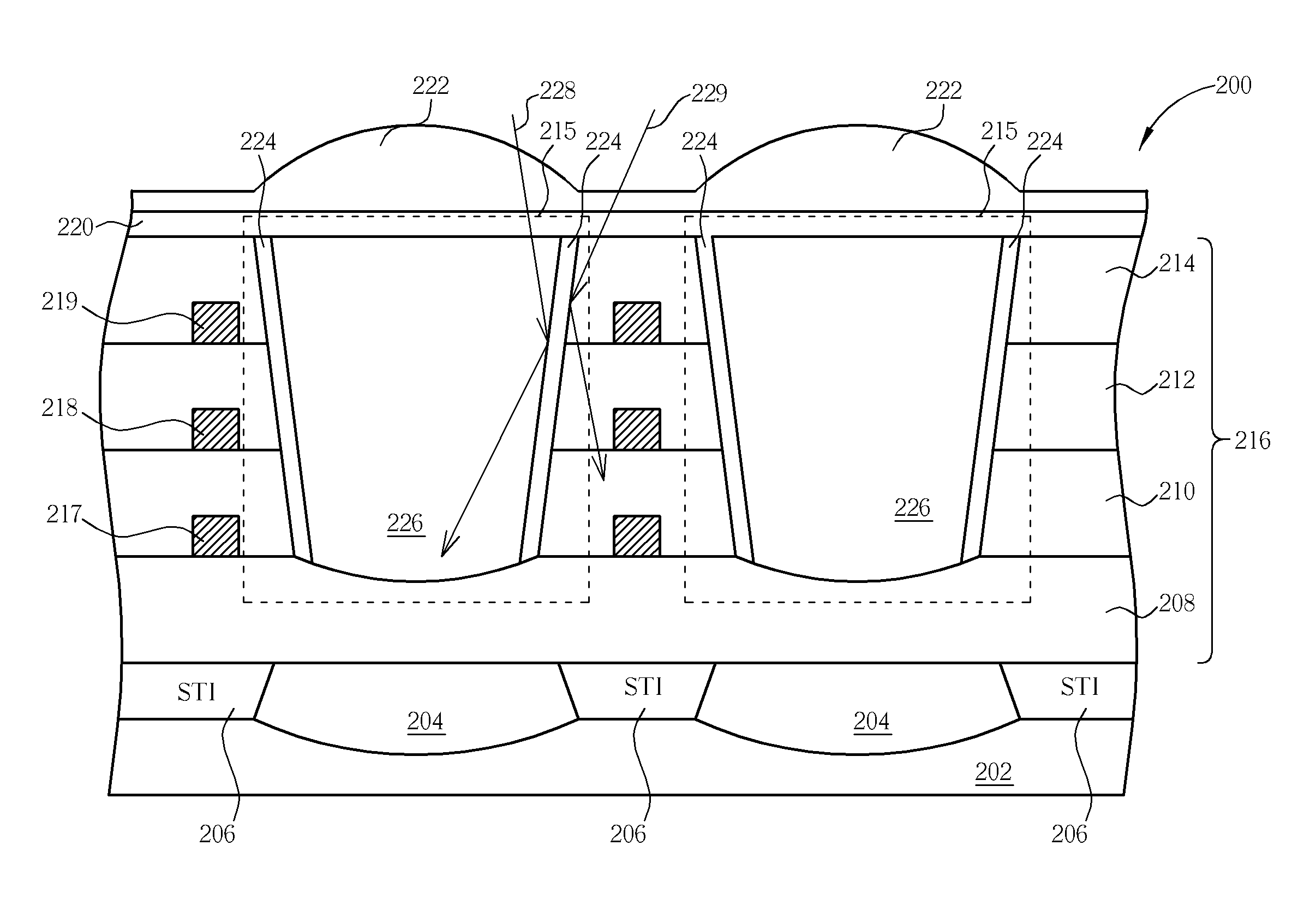
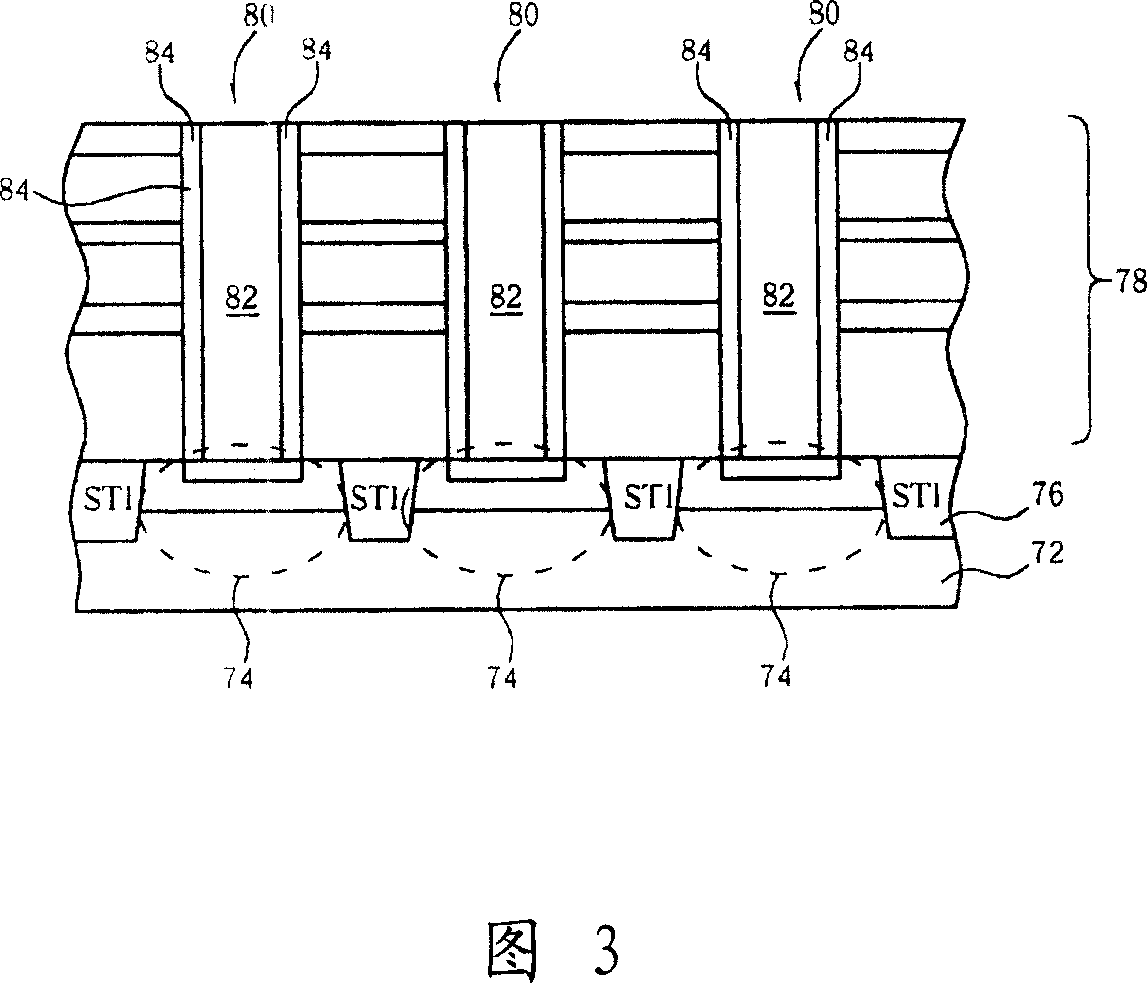
Image sensor with a waveguide tube and a related fabrication method
ActiveUS20080036020A1Avoid surface defectsIncrease image sensing efficiencySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingWaveguideOptical barrier
An image sensor includes a substrate, at least an optical device, at least a dielectric layer, and at least a wave-guide tube disposed upon the optical device. The wave-guide tube has an optical barrier disposed on a sidewall thereof and a filter layer filled in the wave-guide tube. The structure of the wave-guide tube has the advantages of shortening light path, focusing, and preventing undesirable crosstalk effect between different optical devices.
Owner:UNITED MICROELECTRONICS CORP
Method and device for reducing crosstalk in back illuminated imagers
ActiveUS20090206377A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDopantCharge carrier
A method and resulting device for reducing crosstalk in a back-illuminated imager is disclosed, comprising providing a substrate comprising an insulator layer and a seed layer substantially overlying the insulator layer, an interface being formed where the seed layer comes in contact with the insulator layer; forming an epitaxial layer substantially overlying the seed layer, the epitaxial layer defining plurality of pixel regions, each pixel region outlining a collection well for collecting charge carriers; and forming one of an electrical, optical, and electrical and optical barrier about the outlined collection well extending into the epitaxial layer to the interface between the seed layer and the insulator layer. The seed layer and the epitaxial layer of the device have a net dopant concentration profile which has an initial maximum value at the interface of the seed layer and the insulator layer and which decreases monotonically with increasing distance from an interface within an initial portion of the semiconductor substrate and the epitaxial layer.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
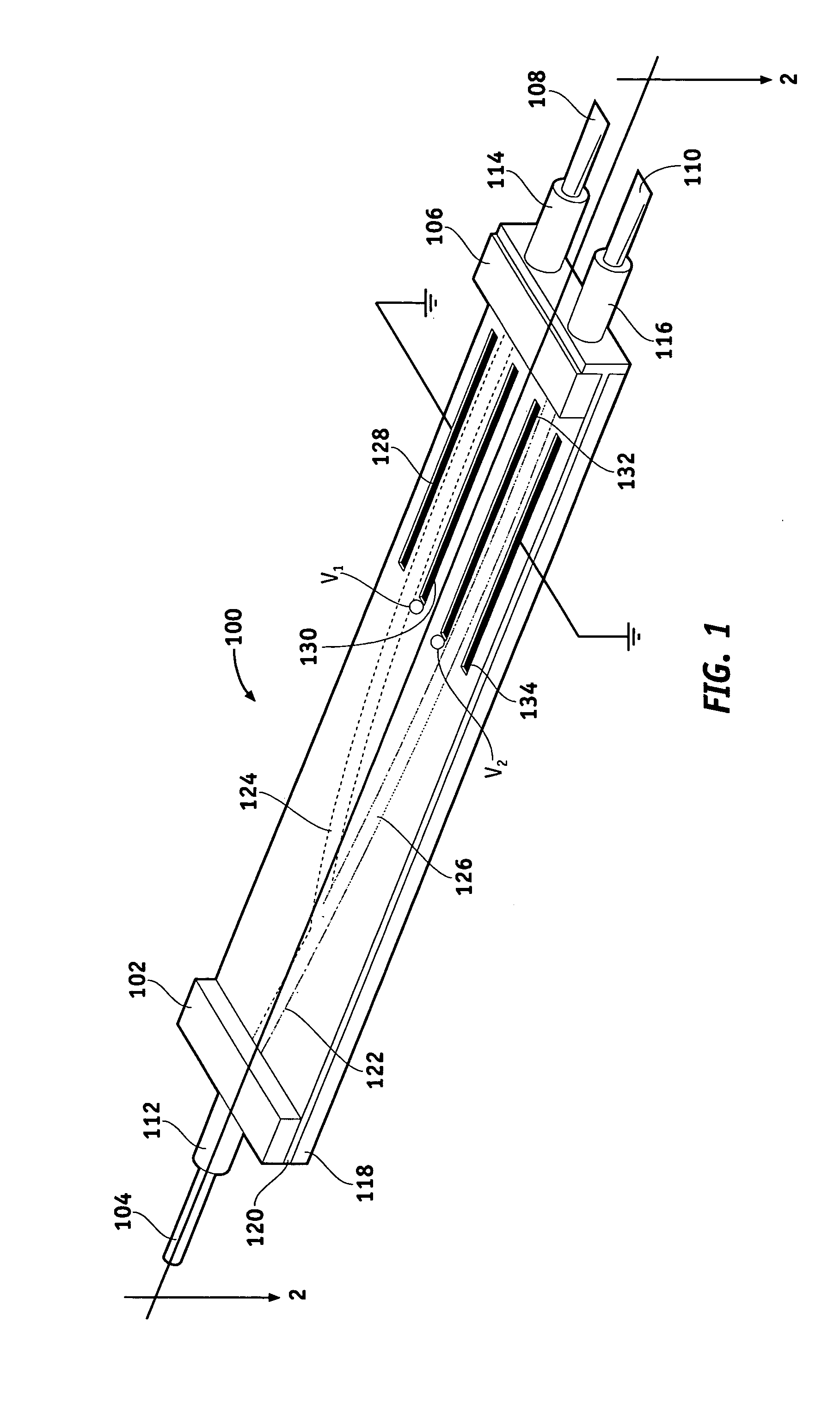
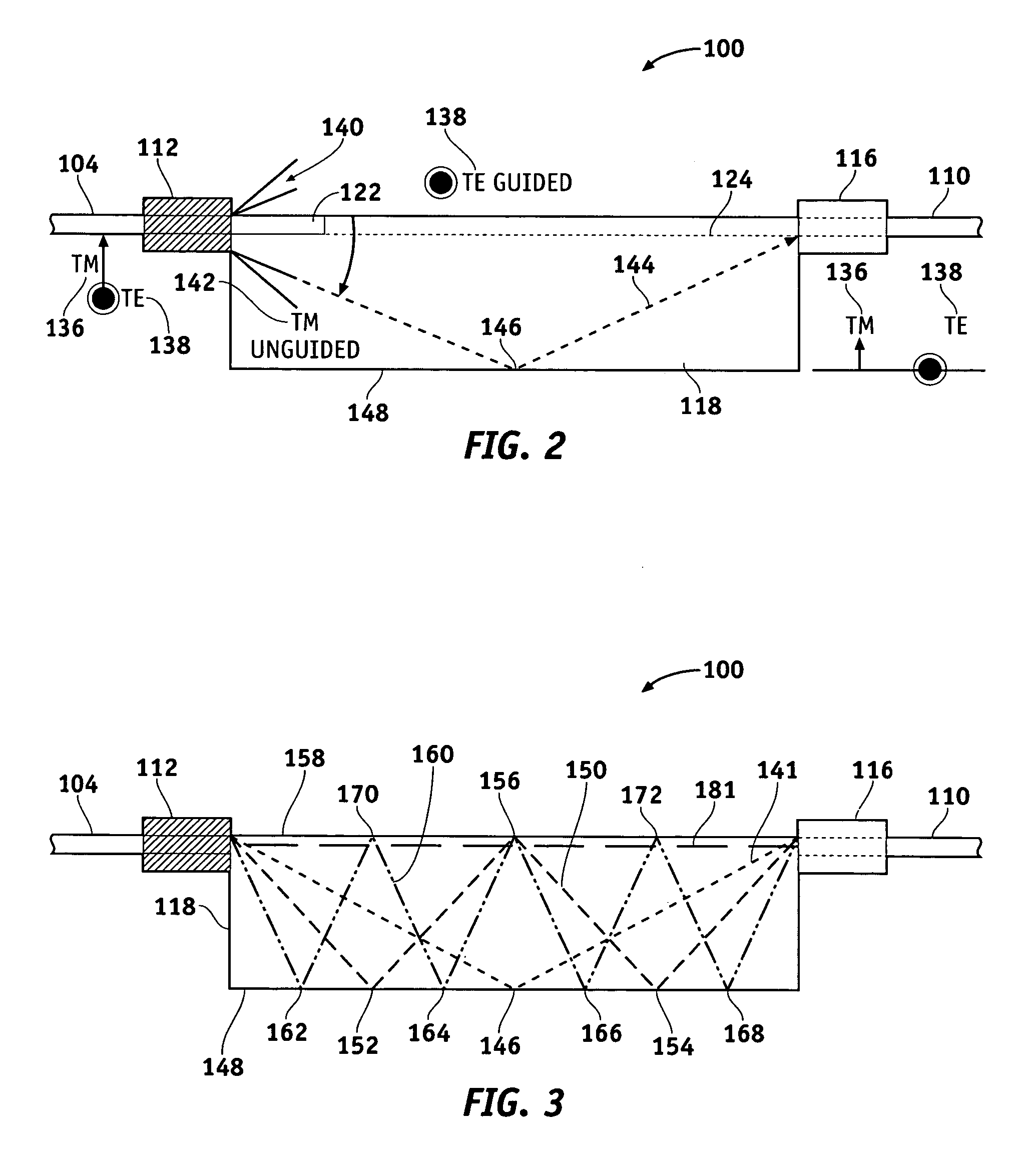
Waveguide device having improved spatial filter configurations
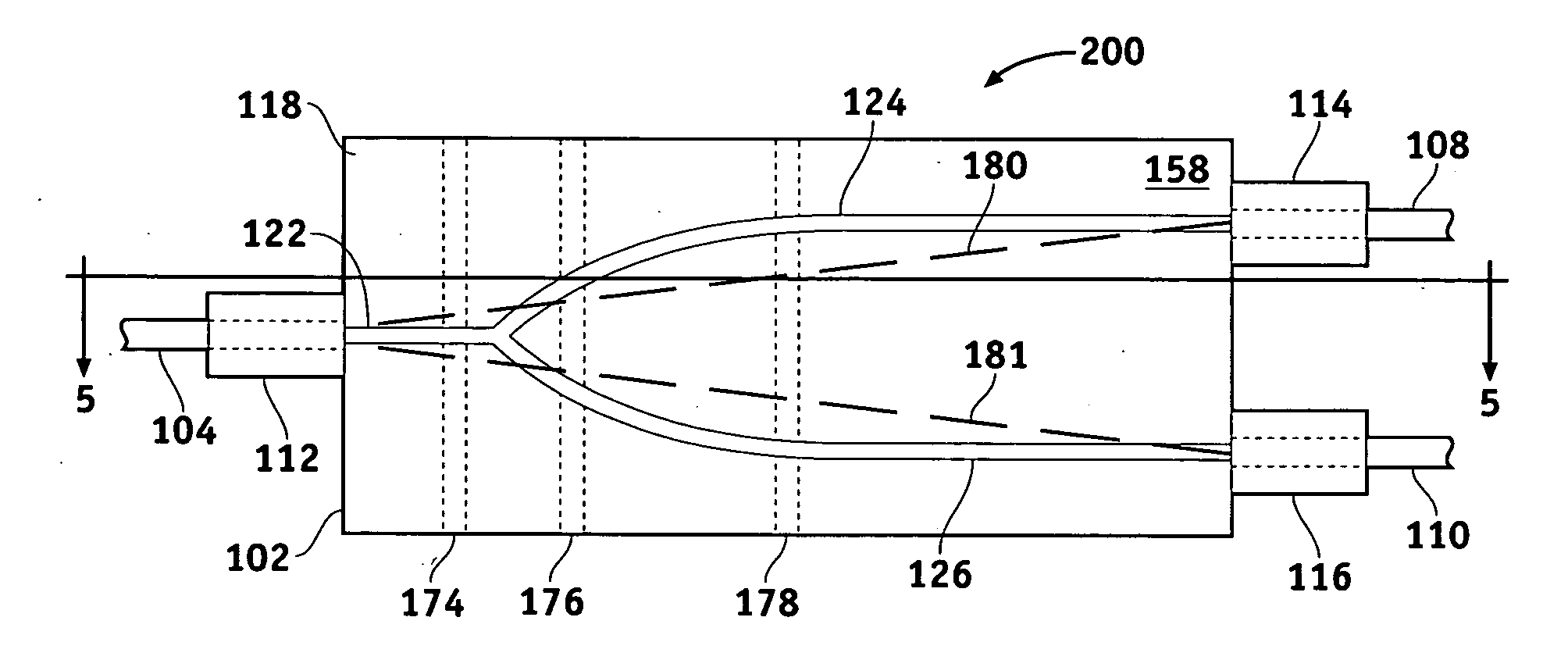
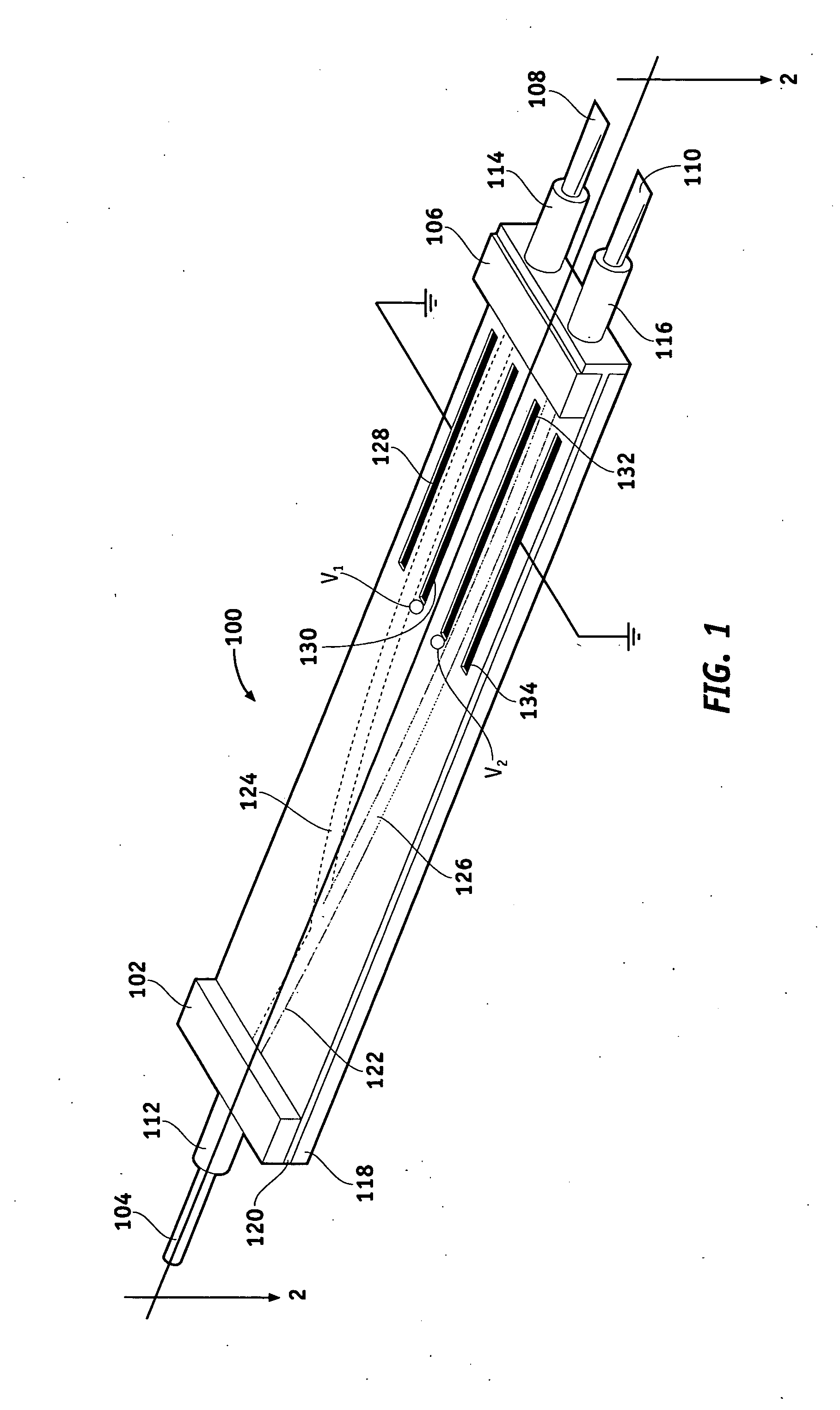
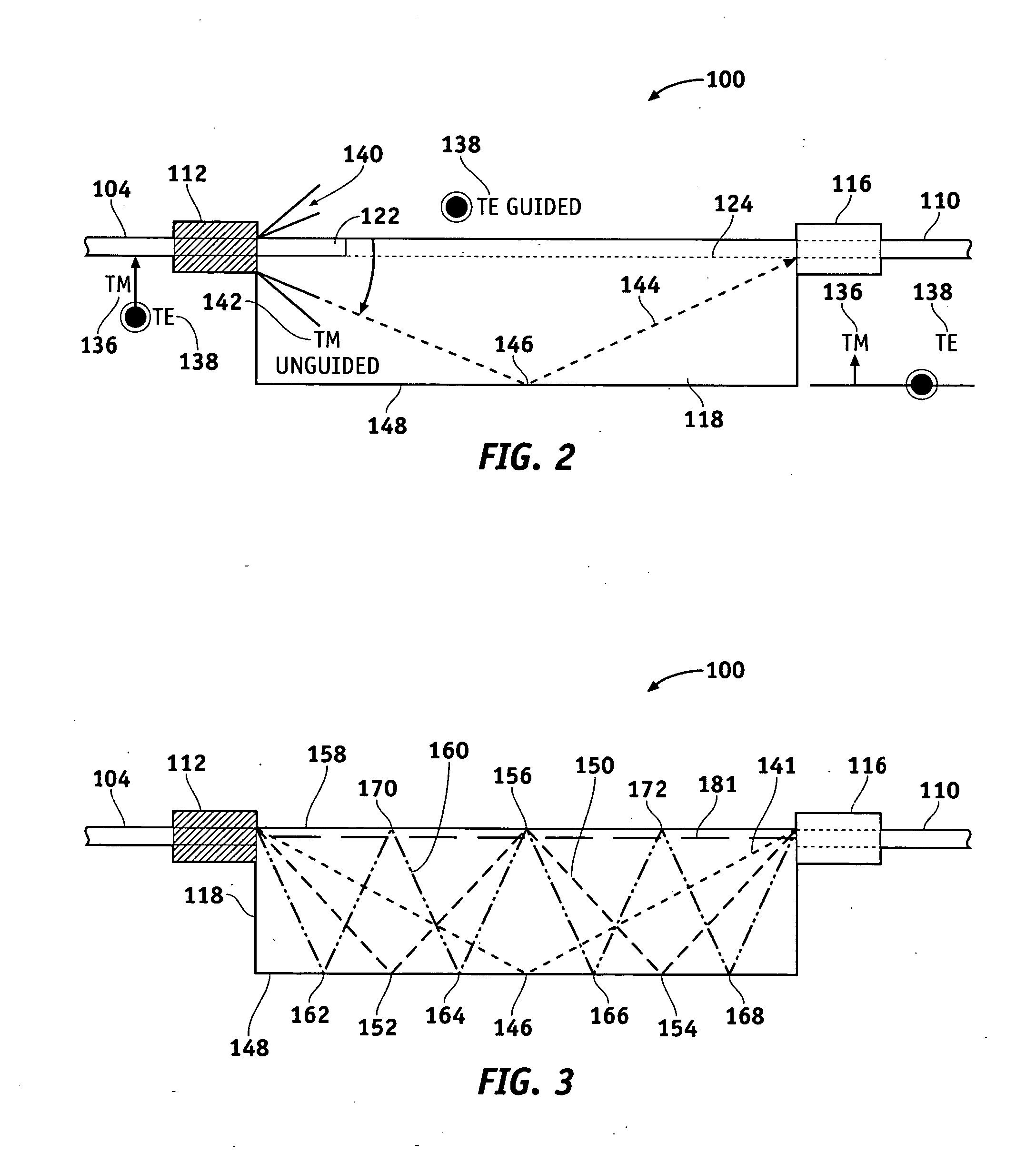
An optical waveguide device is provided for receiving light that has a guided mode and an unguided mode. The device comprises an optically transmissive substrate having first and second substantially opposite surfaces, an input end, and an output end. An optical waveguide region is disposed within the substrate and extends from the input to the output. A plurality of electrodes is disposed on the first surface at predetermined locations with respect to the waveguide region. The device includes a plurality of optical barriers each disposed proximate one of the first and second surfaces and positioned to block a different optical path of the unguided mode.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
System and method for in situ creation of a small aperture intraocular lens
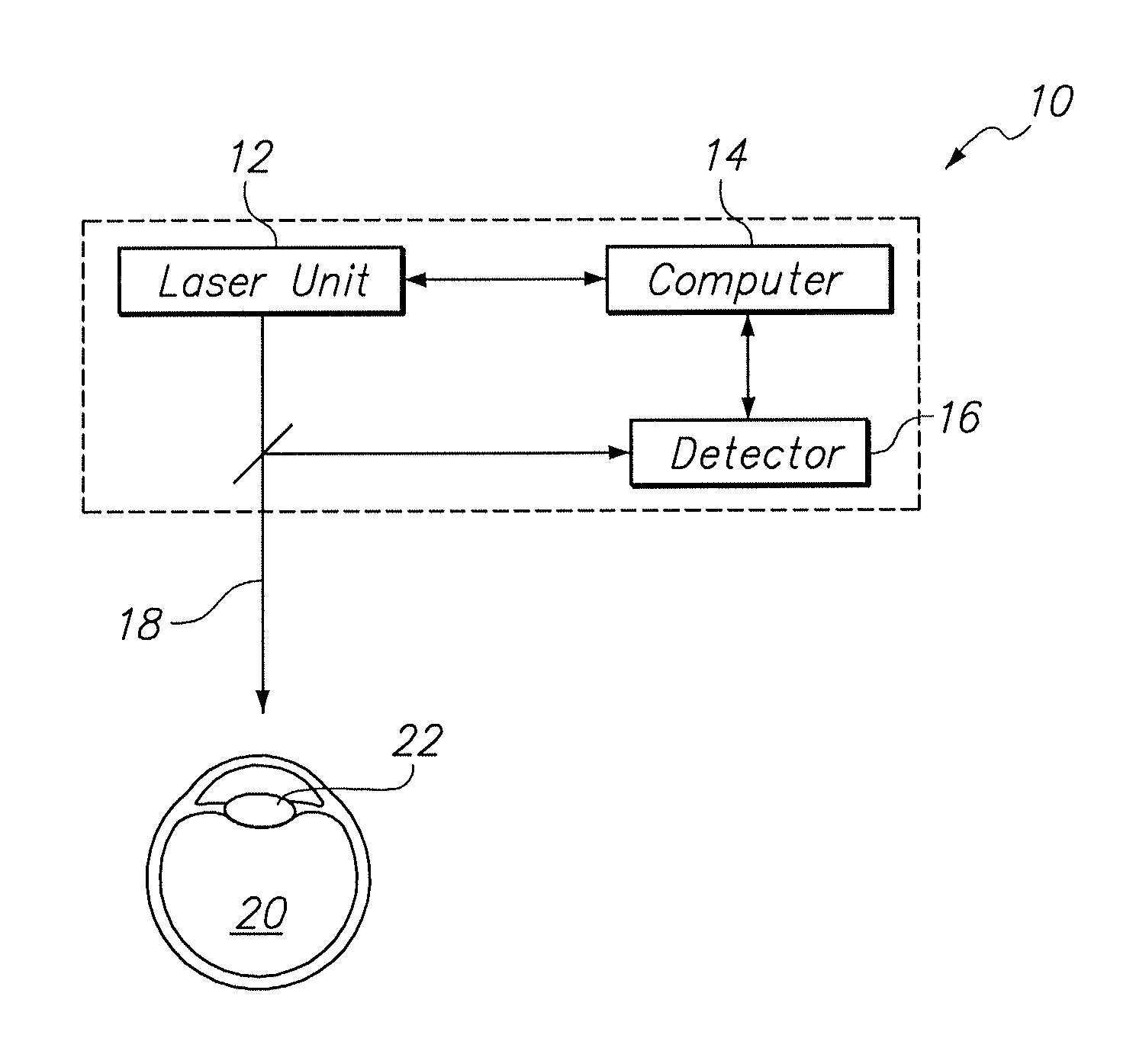
InactiveUS20130289543A1Increase depth of focusMinimize impactLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsLaser technologyOptical property
A system and method are provided for altering the optical characteristics of an Intraocular Lens (IOL), in situ, using laser techniques. Specifically, a computer-controlled laser unit either creates microbubbles, or converts inclusions, inside the IOL, to establish a predetermined optical barrier having a predetermined opacity. The resultant optical barrier is oriented in the IOL to control light passing through the IOL, and to thereby minimize or correct adverse optical effects that would otherwise be present.
Owner:BAUSCH & LOMB INC
Integrated gesture sensor module
ActiveUS20140340302A1High surfaceInput/output for user-computer interactionSolid-state devicesComputer moduleApplication-specific integrated circuit
An integrated gesture sensor module includes an optical sensor die, an application-specific integrated circuit (ASIC) die, and an optical emitter die disposed in a single package. The optical sensor die and ASIC die can be disposed in a first cavity of the package, and the optical emitter die can be disposed in a second cavity of the package. The second cavity can be conical or step-shaped so that the opening defining the cavity increases with distance from the upper surface of the optical emitter die. The upper surface of the optical emitter die may be higher than the upper surface of the optical sensor die. An optical barrier positioned between the first and second cavities can include a portion of a pre-molded, laminate, or ceramic package, molding compound, and / or metallized vias.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
Image sensor with a waveguide tube and a related fabrication method
ActiveUS7524690B2Avoid Crosstalk EffectsHigh sensitivitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingWaveguideDielectric layer
An image sensor includes a substrate, at least an optical device, at least a dielectric layer, and at least a wave-guide tube disposed upon the optical device. The wave-guide tube has an optical barrier disposed on a sidewall thereof and a filter layer filled in the wave-guide tube. The structure of the wave-guide tube has the advantages of shortening light path, focusing, and preventing undesirable crosstalk effect between different optical devices.
Owner:UNITED MICROELECTRONICS CORP
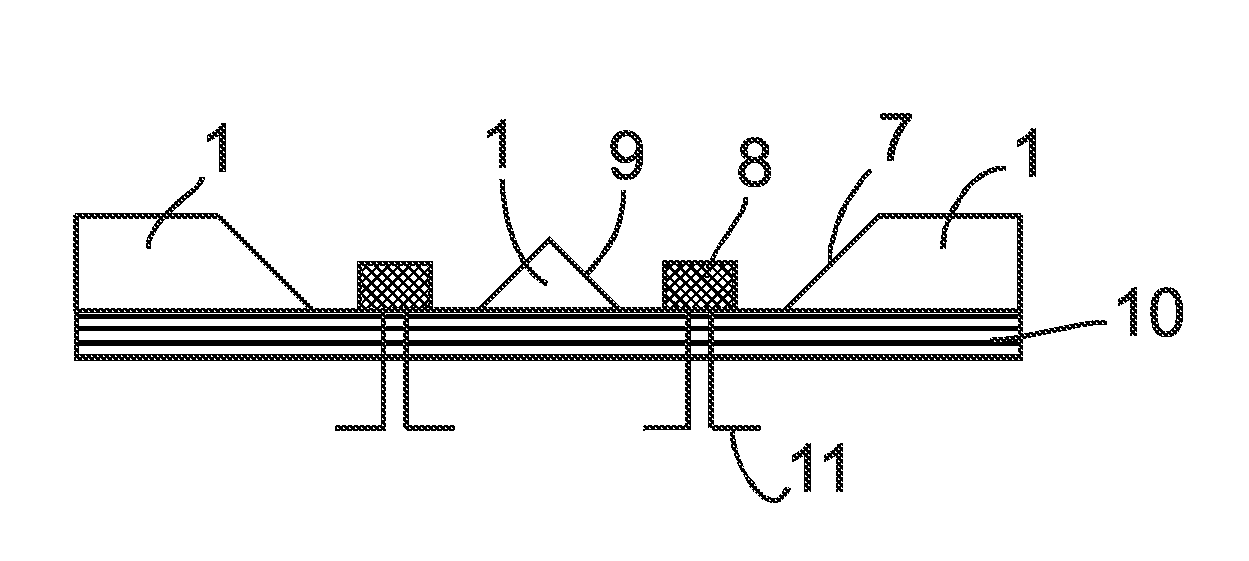
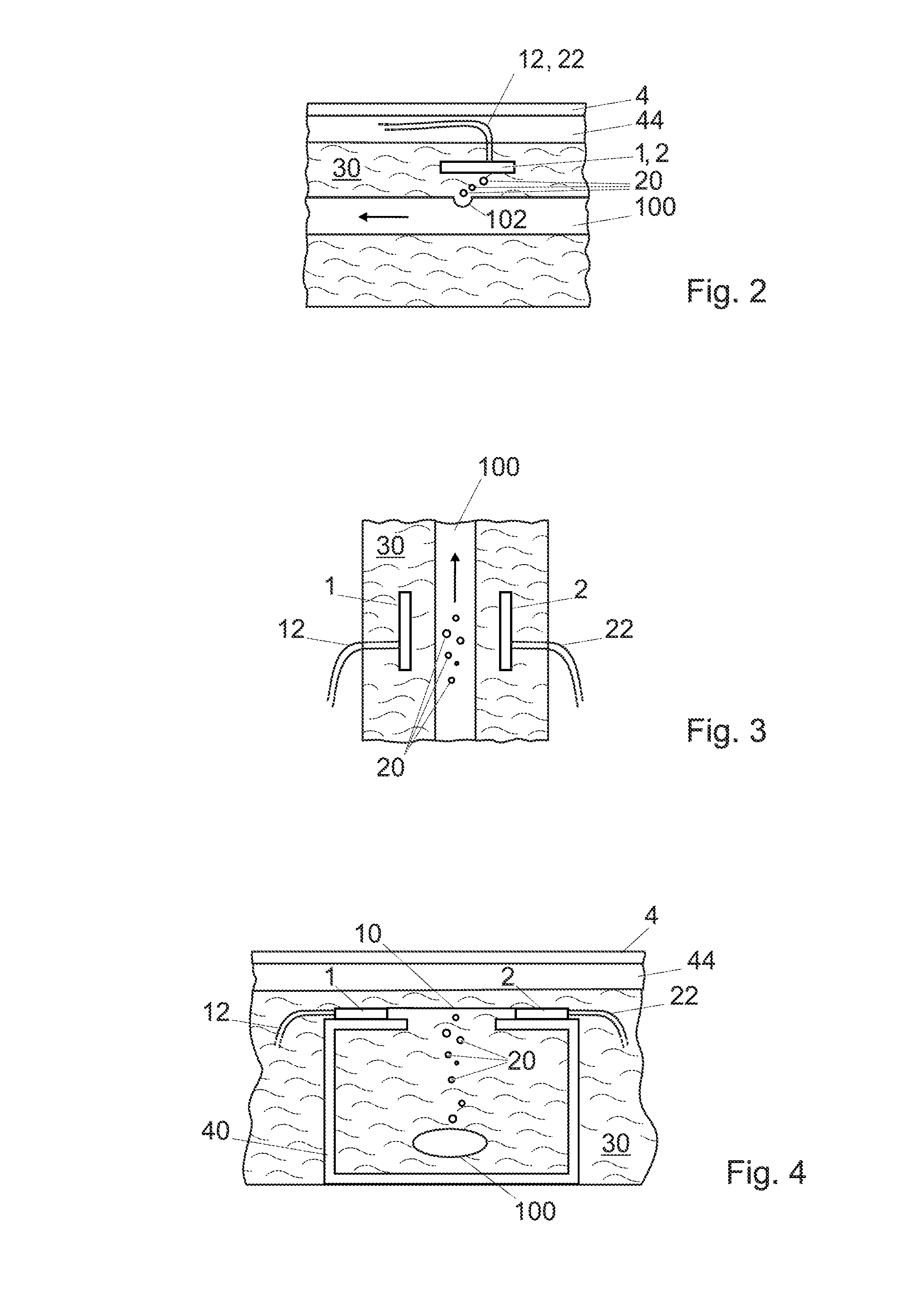
System for manufacturing an irrigation pipe and a device and method for detecting holes in the wall of an irrigation pipe
InactiveUS9022764B2Less expensiveImproving transmission and receptionTurning machine accessoriesWatering devicesEngineeringOptical transmitter
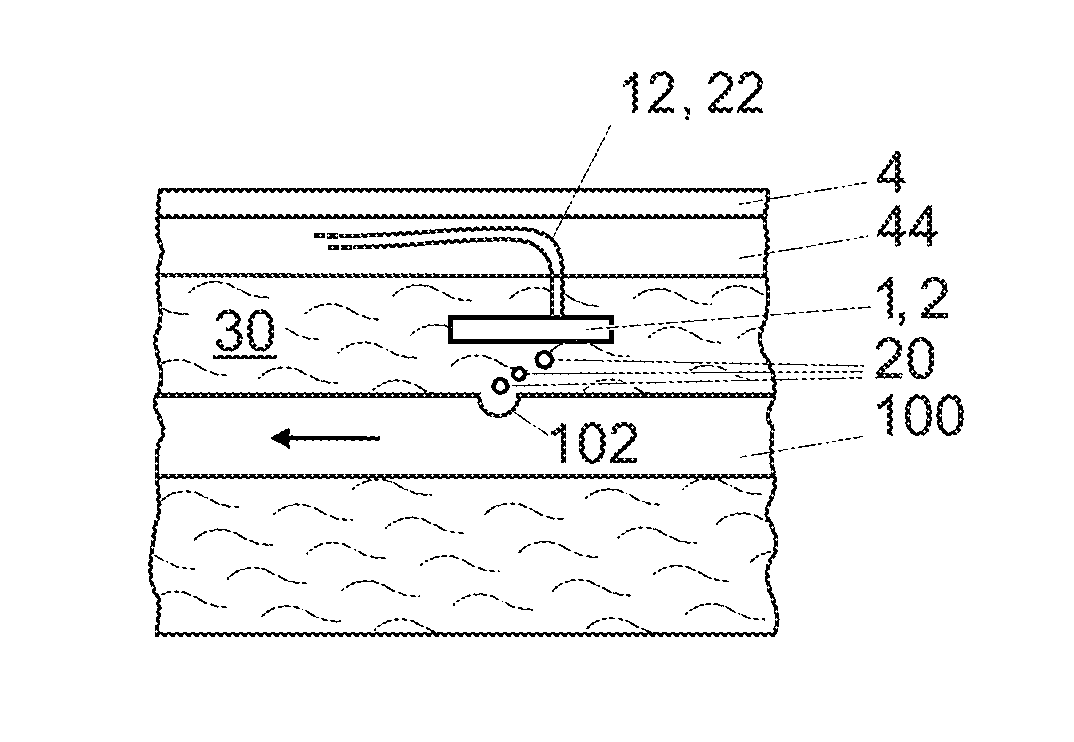
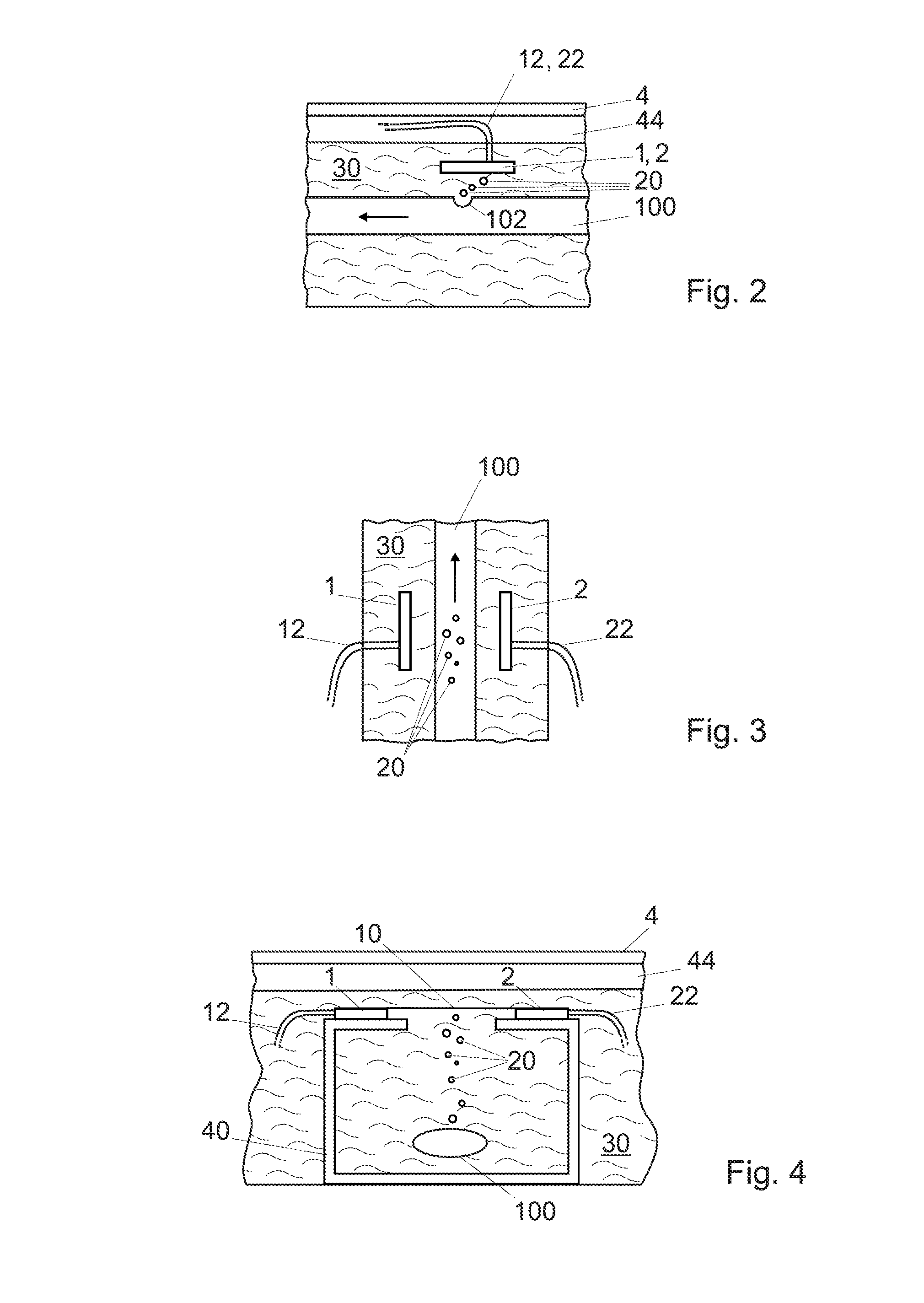
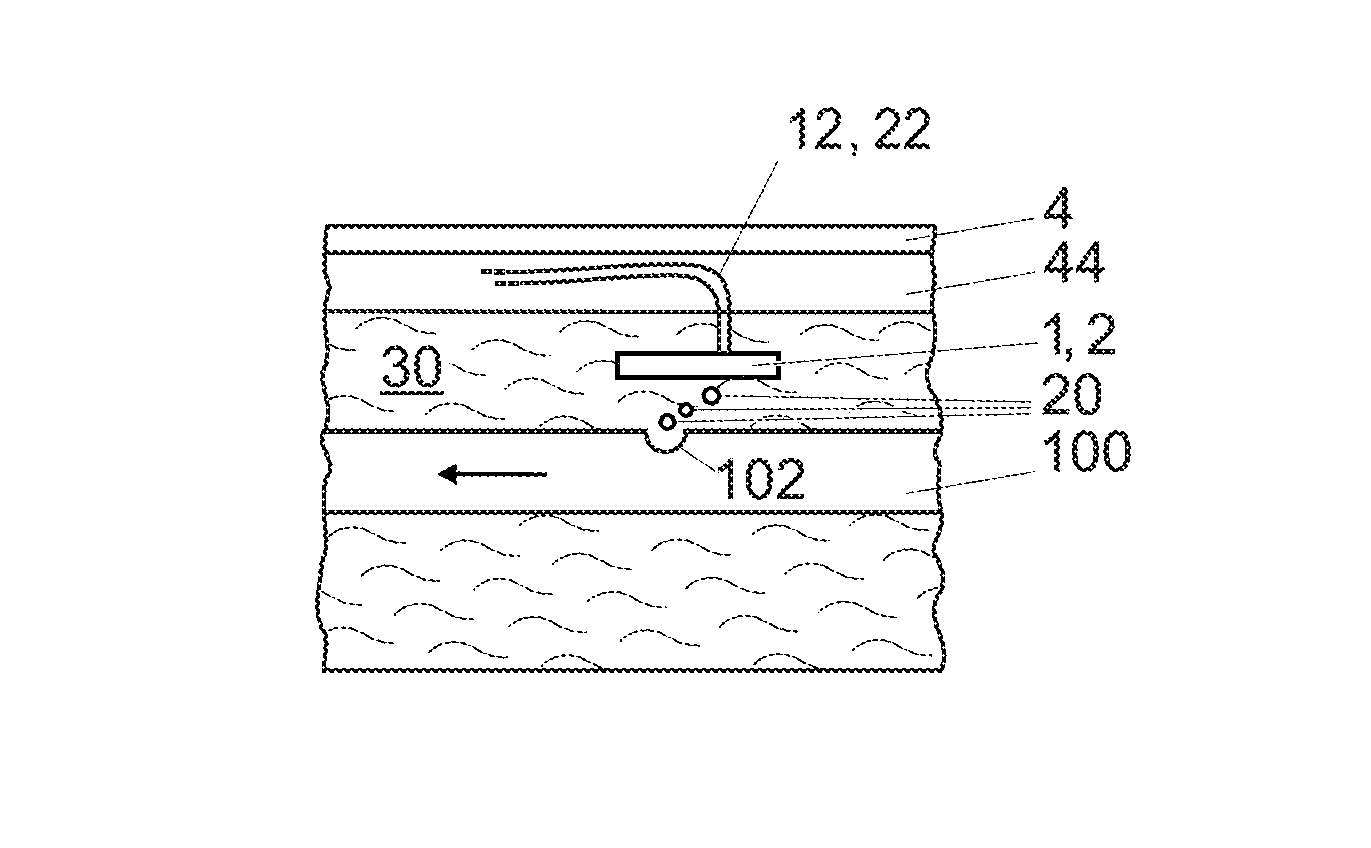
A system for manufacturing an irrigation pipe comprises an extrusion unit, a calibrator unit, a cooling unit for cooling the irrigation pipe in a cooling liquid, and a traction unit for drawing the irrigation pipe in the cooling unit. The cooling unit comprises a device for detecting holes in the wall of the irrigation pipe and arranged for being immersed in the cooling liquid. The device for detecting holes comprises at least one optical transmitter and at least one optical receiver which define an optical barrier. The device is arranged so that the holes in the irrigation pipe located below the device produce gas bubbles which modify the optical barrier.
Owner:MAILLEFER SA MAILLEFER SA
Electronic device having selectively strengthened cover glass
ActiveUS8923693B2Reducing glare at the cameraWave amplification devicesDiffusing elementsOptical barrierCover glass
Embodiments disclosed therein generally pertain to selectively strengthening glass. More particularly, techniques are described for selectively strengthening cover glass, which tends to be thin, for electronic devices, namely, portable electronic devices. In certain embodiments, selectively strengthening glass, such as cover glass, can be used to provide optical barriers (or channels) internal to the glass. The electronic devices can also provide for camera integration behind the cover glass.
Owner:APPLE INC
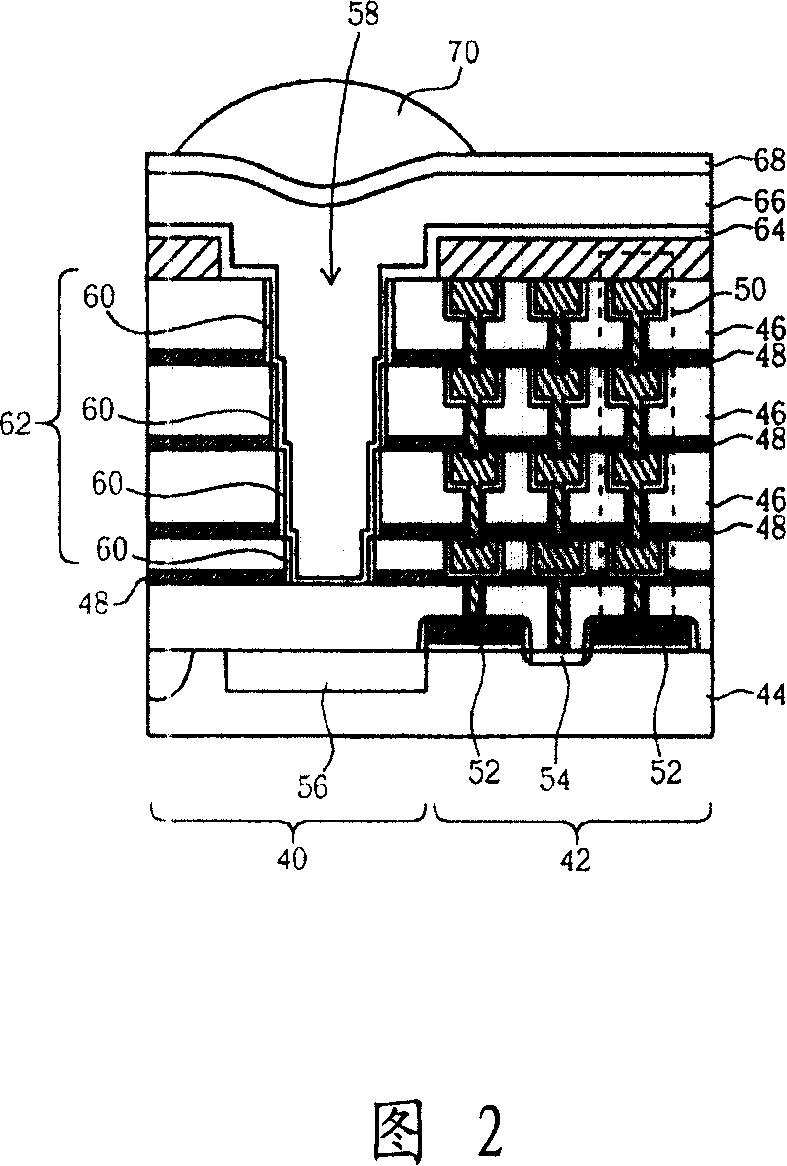
Image sensing device and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN101132014AIncrease photosensitivityHigh sensitivitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingRadiation controlled devicesWaveguideOptical barrier
An image-sensing device includes a substrate, at least one optic component, at least one dielectric layer and at least a waveguide set above the optic component. Sidewall of the waveguide is set with a optic-shielding layer, and the waveguide is embedded with a filling layer. Therefore, the device can effectively shorten optic path, focus light, and avoid bridging phenomenon between different optic paths to improve sensitivity of the image-sensing device.
Owner:UNITED MICROELECTRONICS CORP
Silicon Deflector on a Silicon Submount For Light Emitting Diodes
The present invention deals with a process for the manufacturing of reflecting optical barriers comprising silicon and useful in combination with light emitting devices, wherein the process comprises anisotropic wet etching of the silicon material in such a manner that the rate of etching along the crystallographic (111) plane of the silicon material is slower than the rate of etching along the (110) and (100) planes. The present invention further comprises a reflecting optical barrier useful in combination with light emitting devices and a system containing at least one light emitting device comprising a reflecting optical barrier.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
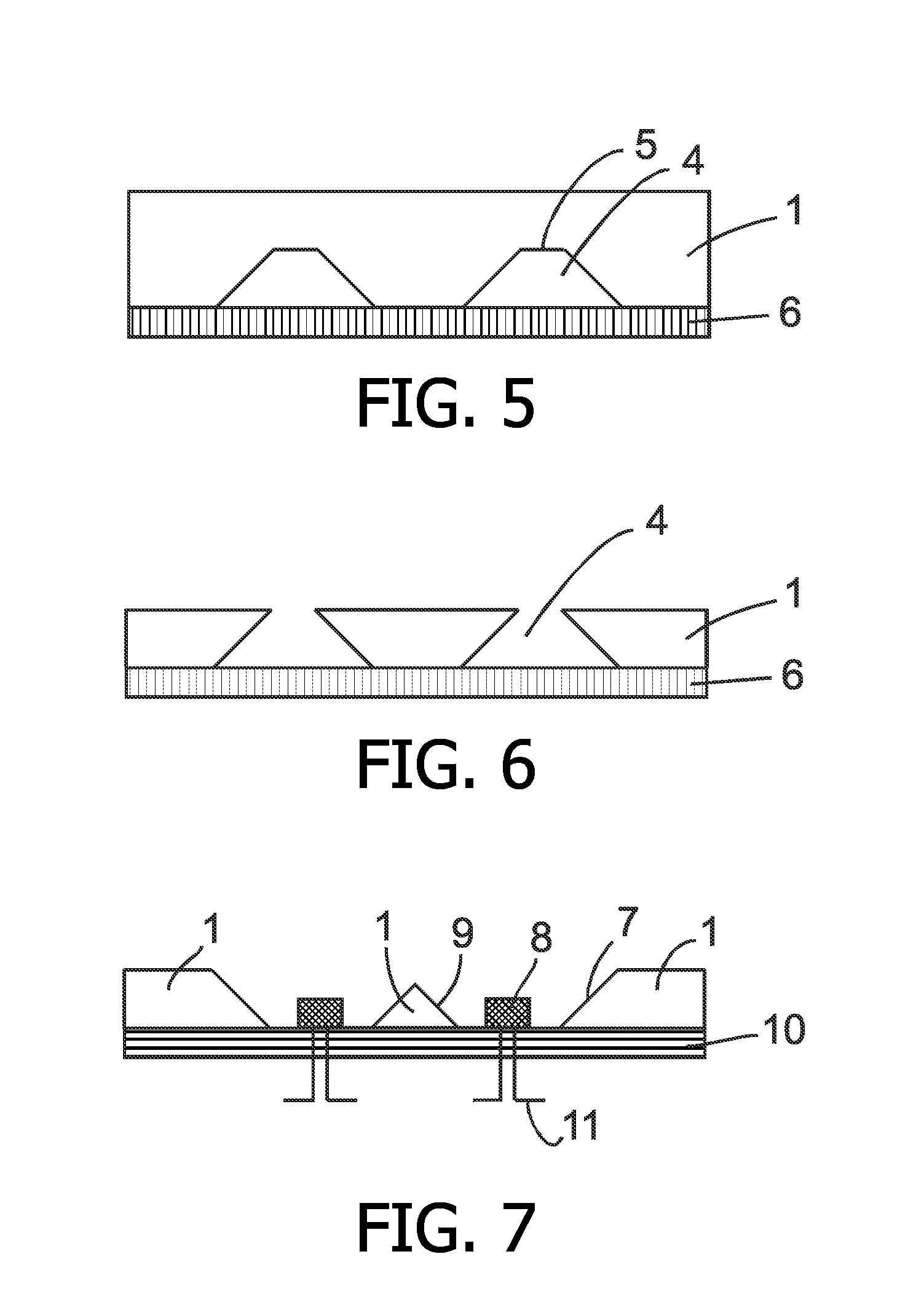
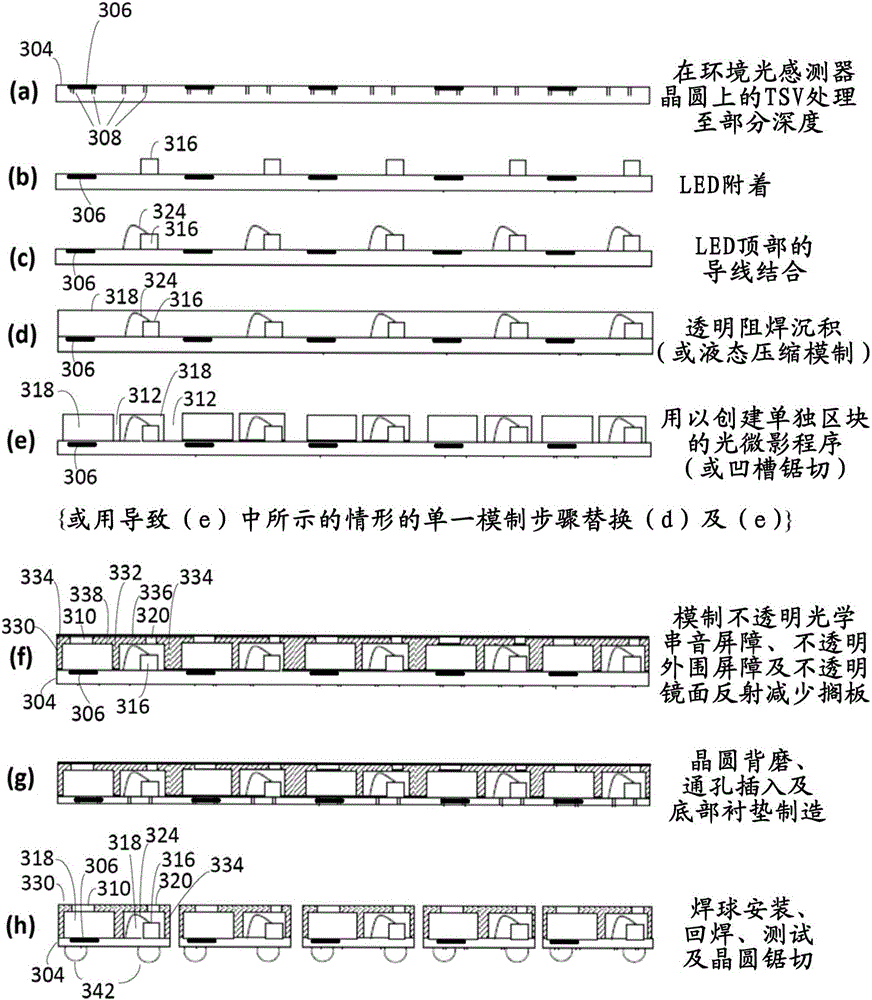
Package structure with optical barrier, optical package structure and manufacturing methods thereof
ActiveUS20160111561A1Simple packaging processSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOptical barrierPhysics
A package structure with an optical barrier is provided. An emitter for emitting an optical signal and a detector for receiving the optical signal are disposed on a substrate. The optical barrier is disposed between the emitter and the detector for shielding the excess optical signal. A package material is used to completely cover the optical barrier, the emitter and the detector so that the optical barrier is completely disposed within the package material.
Owner:SENSORTEK TECH
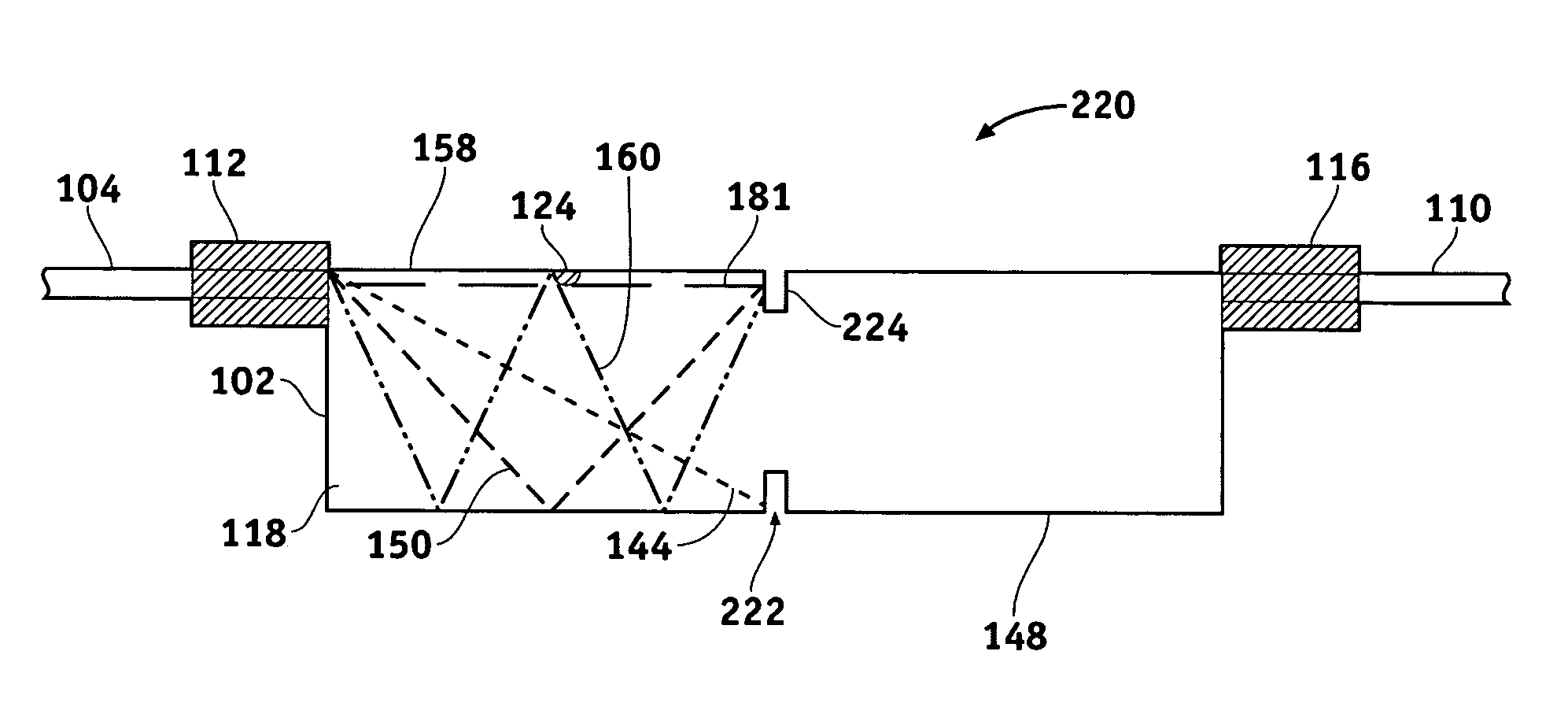
Graphic-arts laser imaging with reduced-length laser cavities and improved performance
InactiveUS20050257708A1High beam qualityReduced dopant levelOptical resonator shape and constructionActive medium materialGraphicsPhotonics
Cavity lasers exhibit a relatively high beam quality (e.g., M2<1.25) despite a relatively small cavity length (e.g., 50-53 mm) for a high (e.g., ≧10 watt) output power device. This enables the construction of physically smaller laser and optical assemblies without sacrificing performance. Reduction of optical photonic interference, which can impair imaging performance, is also facilitated. Laser and optical assemblies may utilize an aperture defined within an optical barrier element to reduce the divergence of the light beam emanating from a diode-pumping laser.
Owner:MARK ANDY
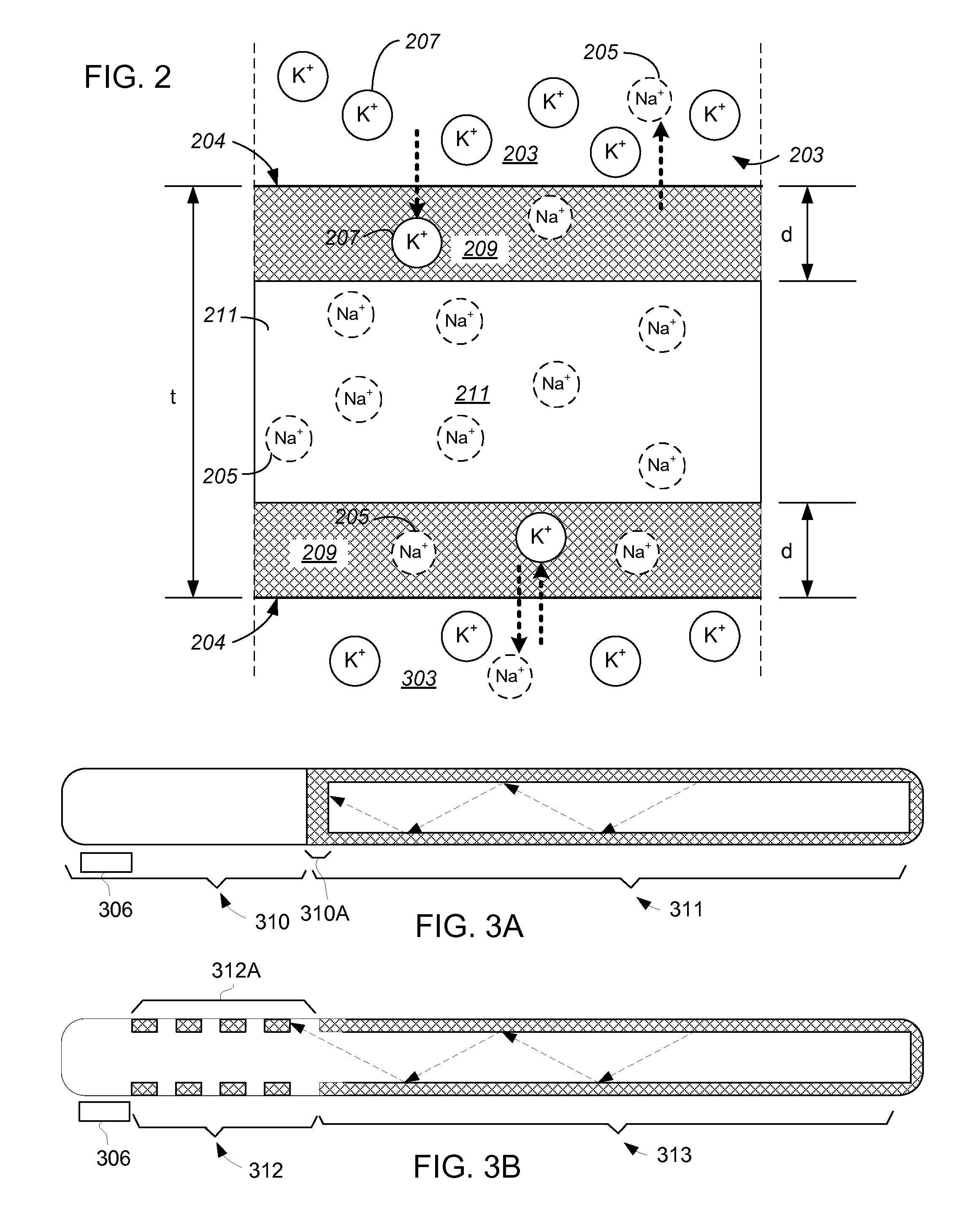
Optical barriers, waveguides, and methods for fabricating barriers and waveguides for use in harsh environments
ActiveUS20140070119A1Polycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsCrystal structureRefractive index
Electromagnetic radiation barriers and waveguides, including barriers and waveguides for light, are disclosed. The barriers and waveguides are fabricated by directing charged particles, for example, ions, into crystalline substrates, for example, single-crystal sapphire substrates, to modify the crystal structure and produce a region of varying refractive index. These substrates are then heated to temperatures greater than 200 degrees C. to stabilize the modified crystal structure and provide the barrier to electromagnetic radiation. Since the treatment stabilizes the crystal structure at elevated temperature, for example, above 500 degrees C. or above 1000 degrees C., the barriers and waveguides disclosed are uniquely adapted for use in detecting conditions in harsh environments, for example, at greater than 200 degrees C. Sensors, systems for using sensors, and methods for fabricating barriers and waveguides are also disclosed.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
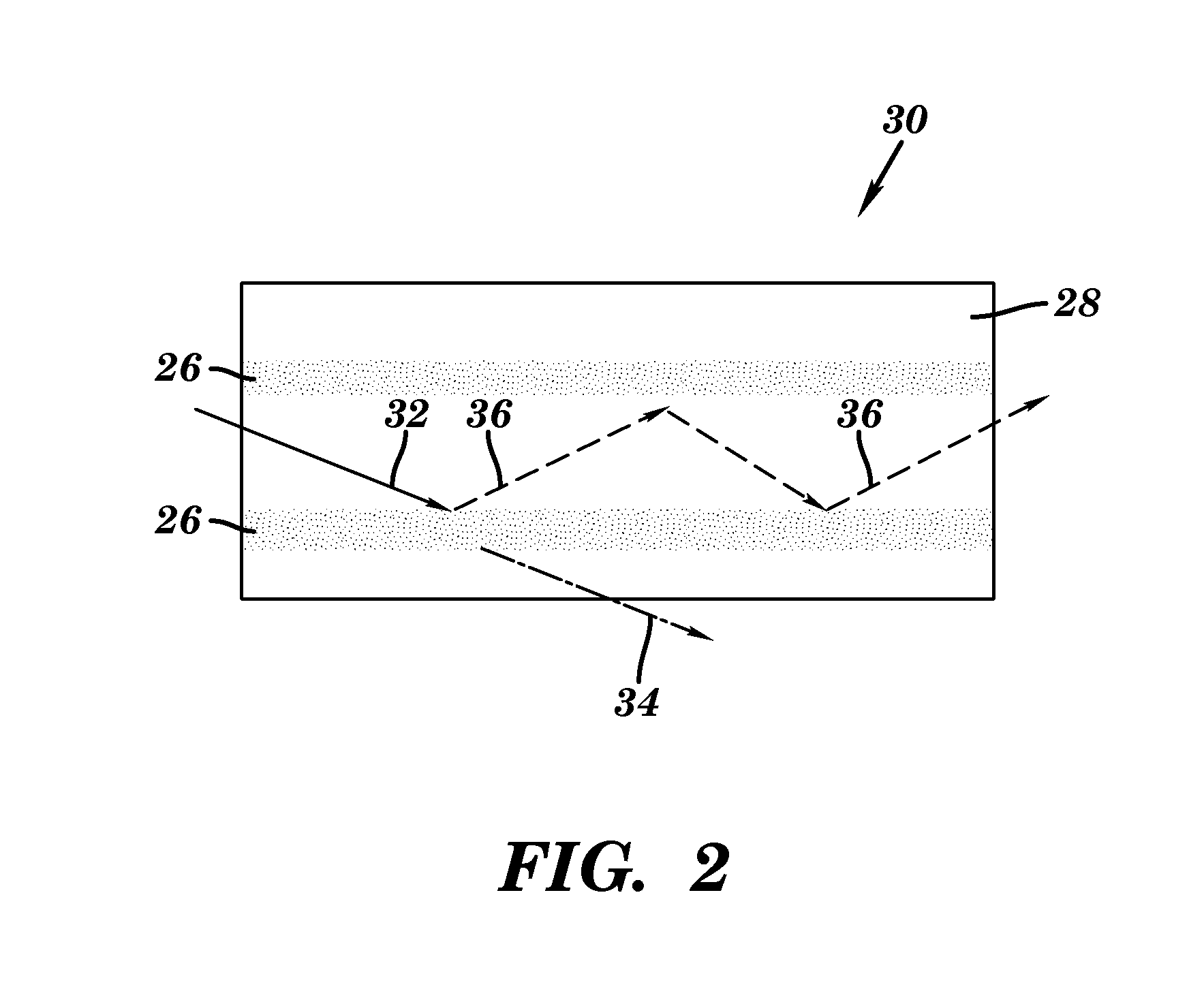
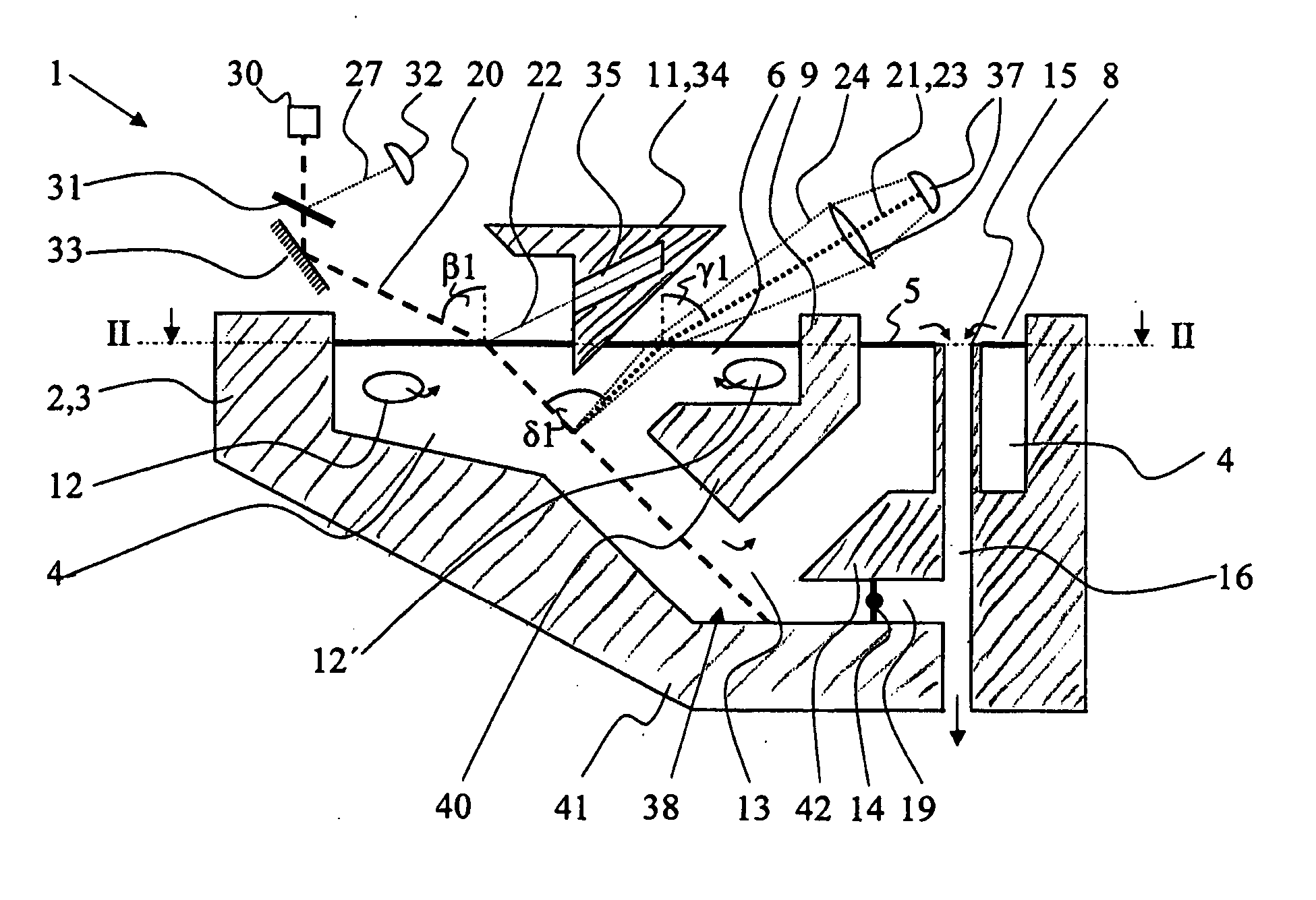
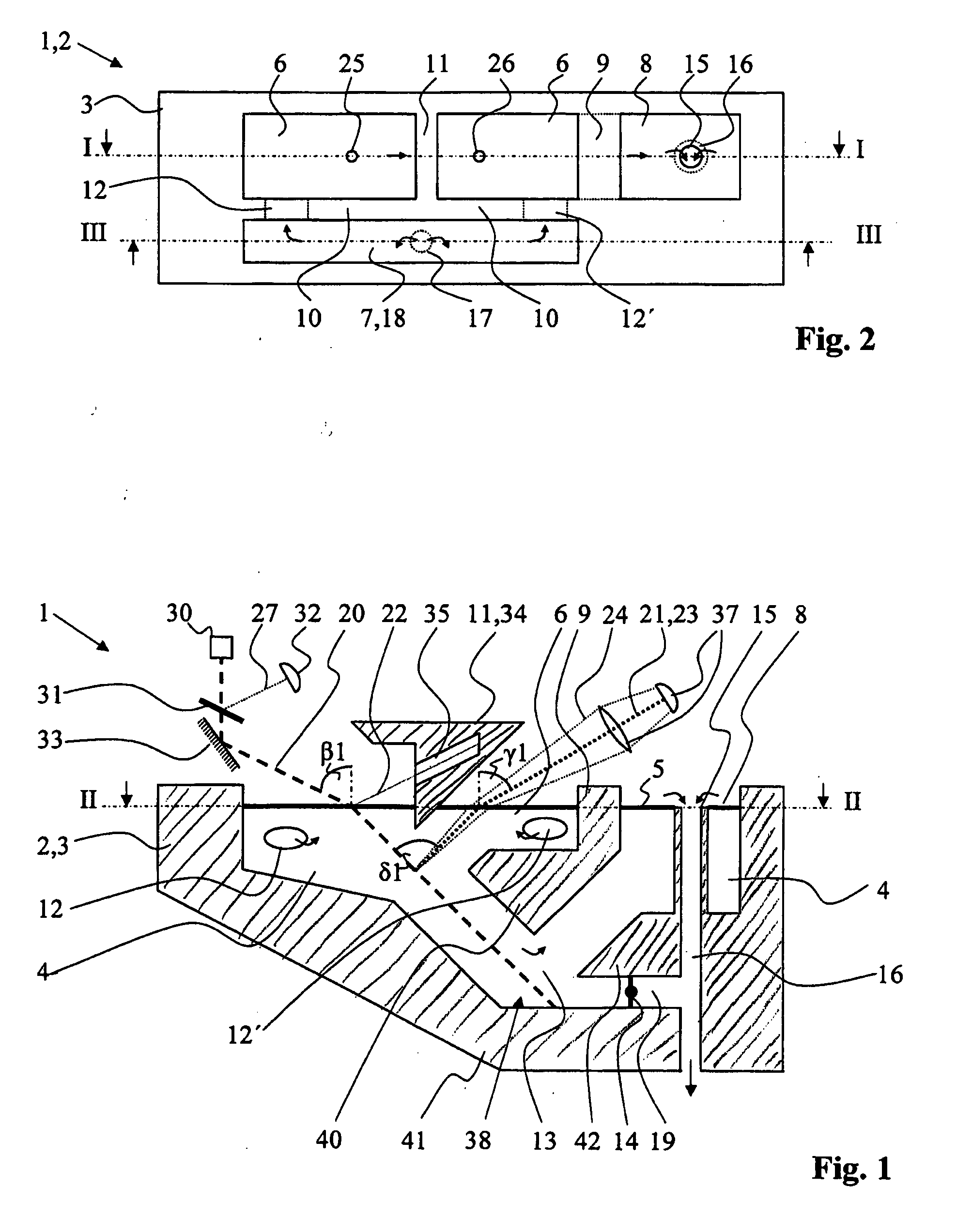
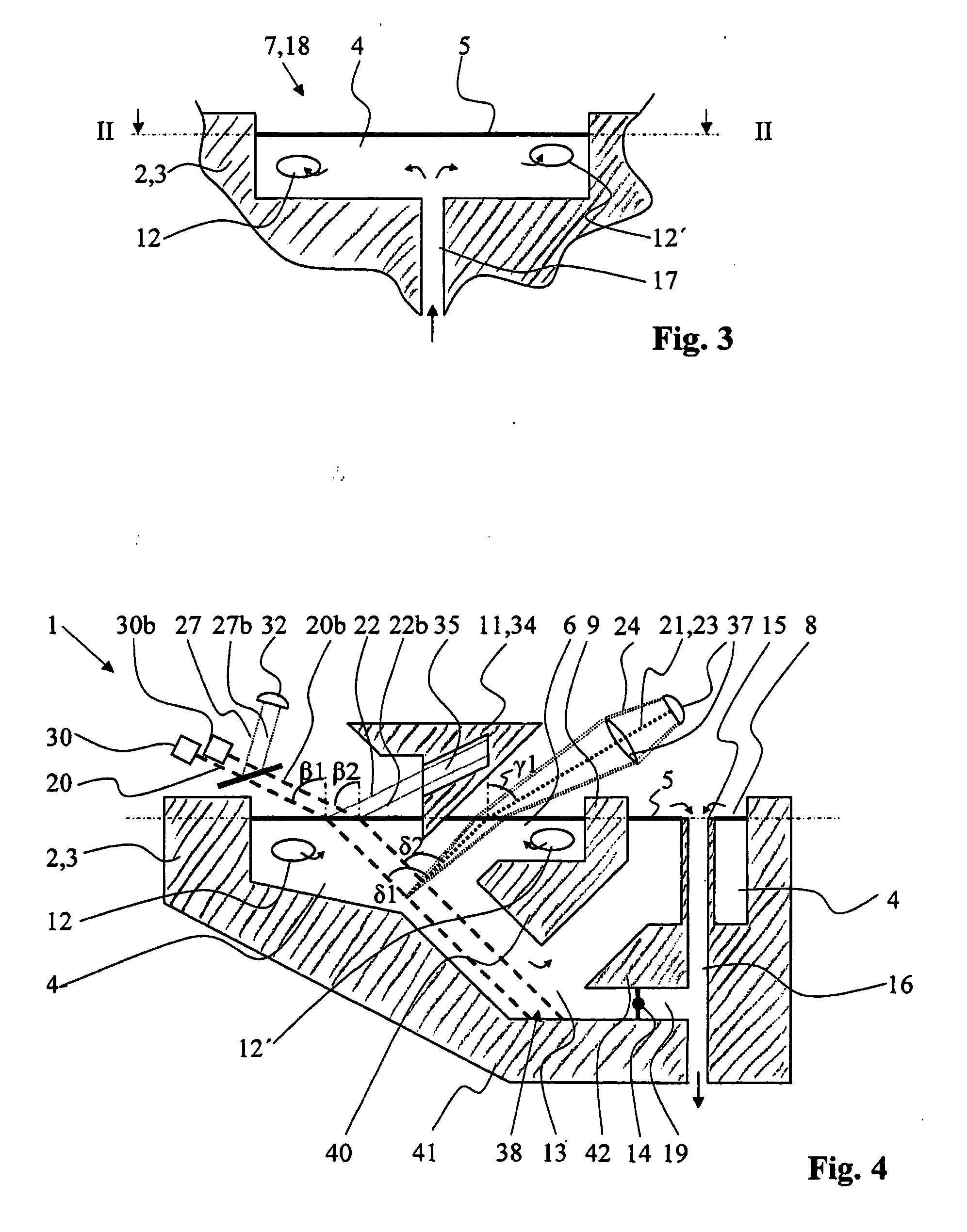
Photometric method and apparatus for measuring a liquid's turbidity, fluorescence, phosphorescence and/or absorption coefficient
ActiveUS20070077178A1Improve accuracyImprove measurement stabilityInvestigating moving fluids/granular solidsAnalysis by electrical excitationGratingTurbidity
The apparatus for deriving at least one property like turbidity or fluorescence of a sample liquid from measuring emitted light emitted from said sample liquid upon irradiation of said sample liquid with a probe light beam comprises a container for containing said sample liquid, said sample liquid forming a sample surface. It furthermore comprises a light source for generating said probe light beam directed, in an angle β1≠0° with respect to a sample surface normal, at said sample surface, and a detector adapted to detecting an intensity of said emitted light emitted through said sample surface out of said sample liquid generally along a first detection axis, said first detection axis forming an angle γ1≠0° with a sample surface normal. It also comprises an optical barrier arranged between said probe light beam and said first detection axis adapted to blocking a propagation of light originating from reflection or scattering of said probe light beam at said sample surface generally along said first detection axis. The apparatus may comprise an outlet section for removing sample liquid from said container, having at least one opening to said main section located beneath said sample surface and a first separating member for substantially separating a portion of said sample surface belonging to said outlet section from a portion of said sample surface belonging to a main section, where said light enters and exits the sample liquid.
Owner:SWAN ANALYTISCHE INSTR
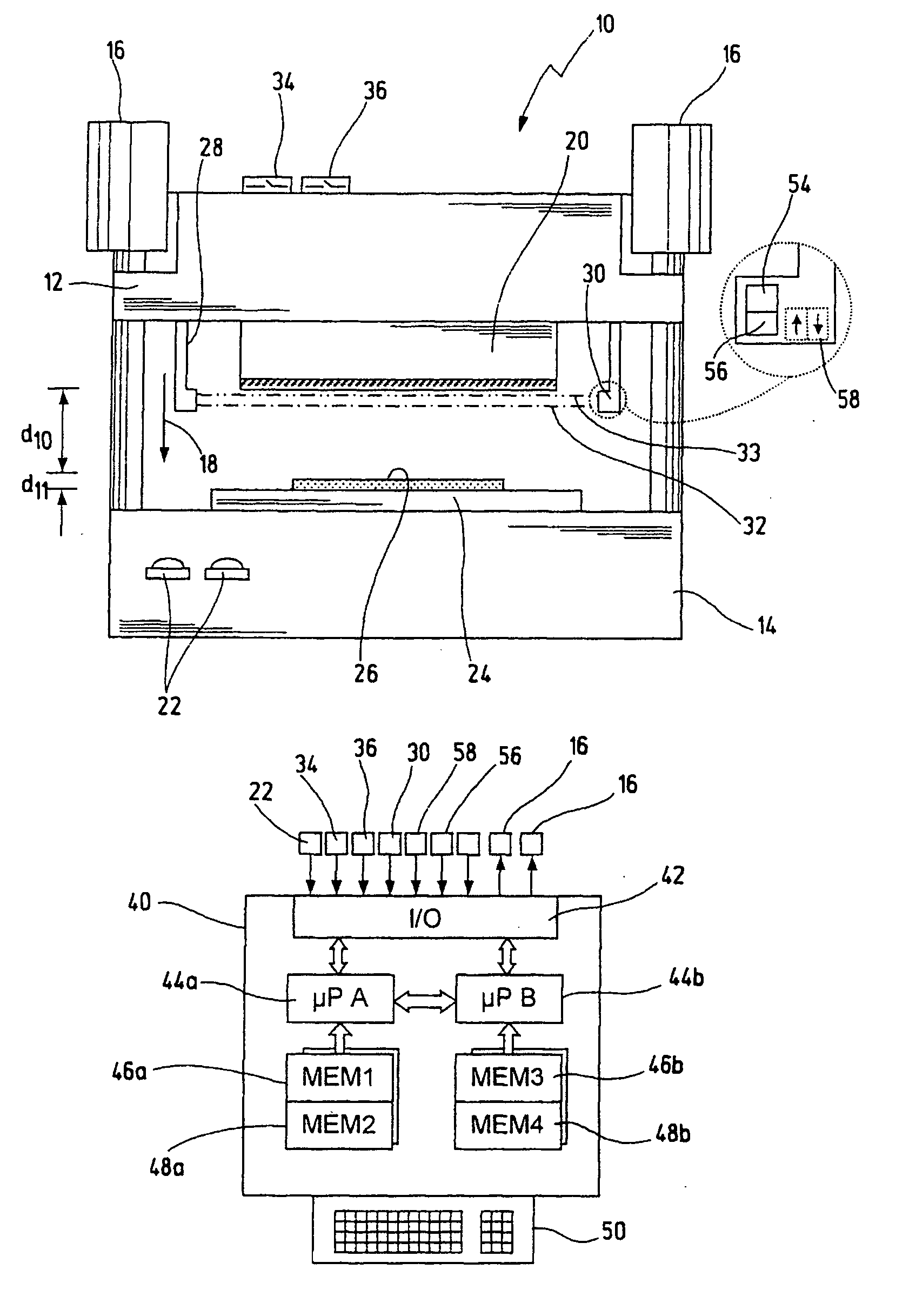
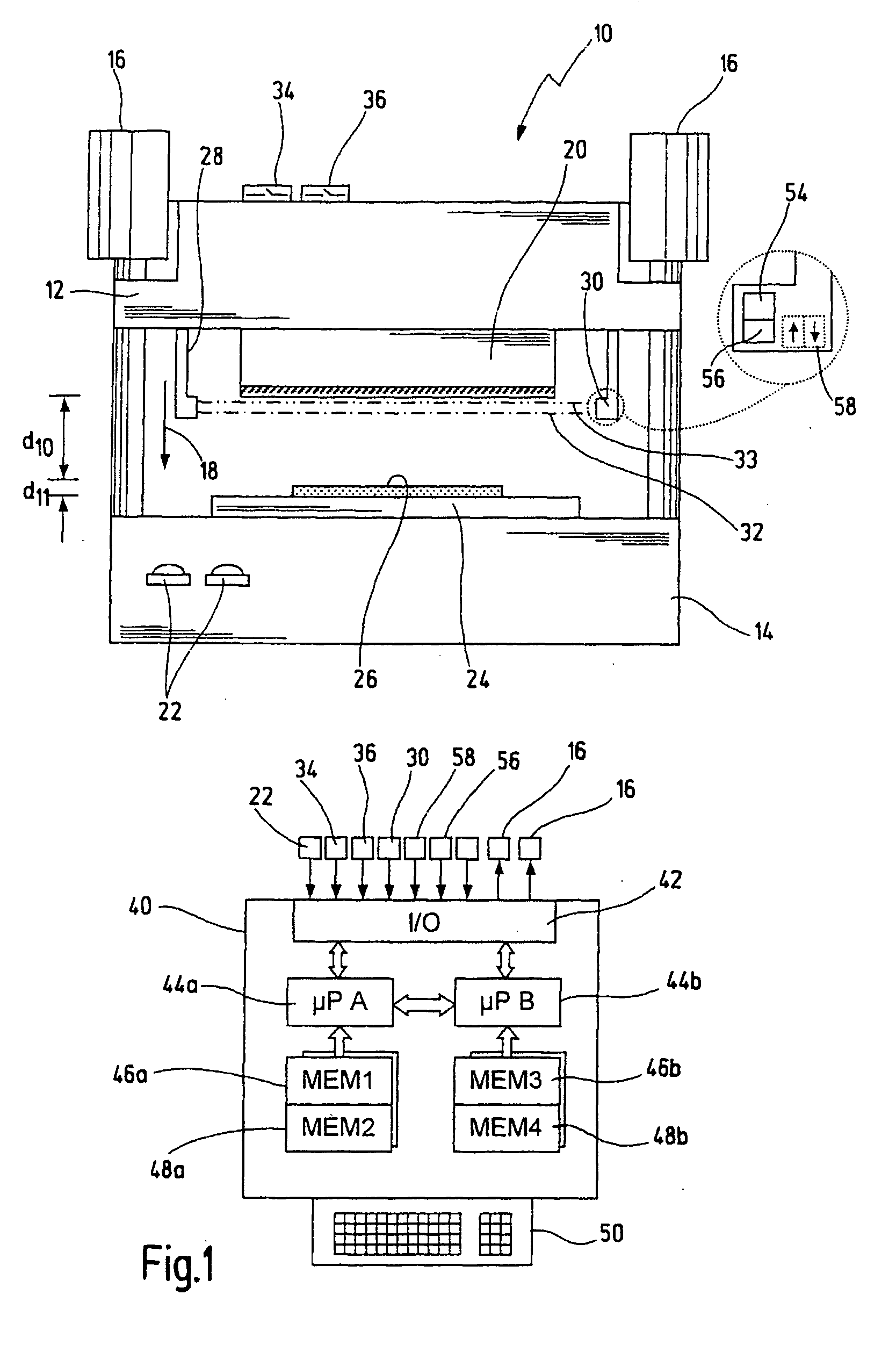
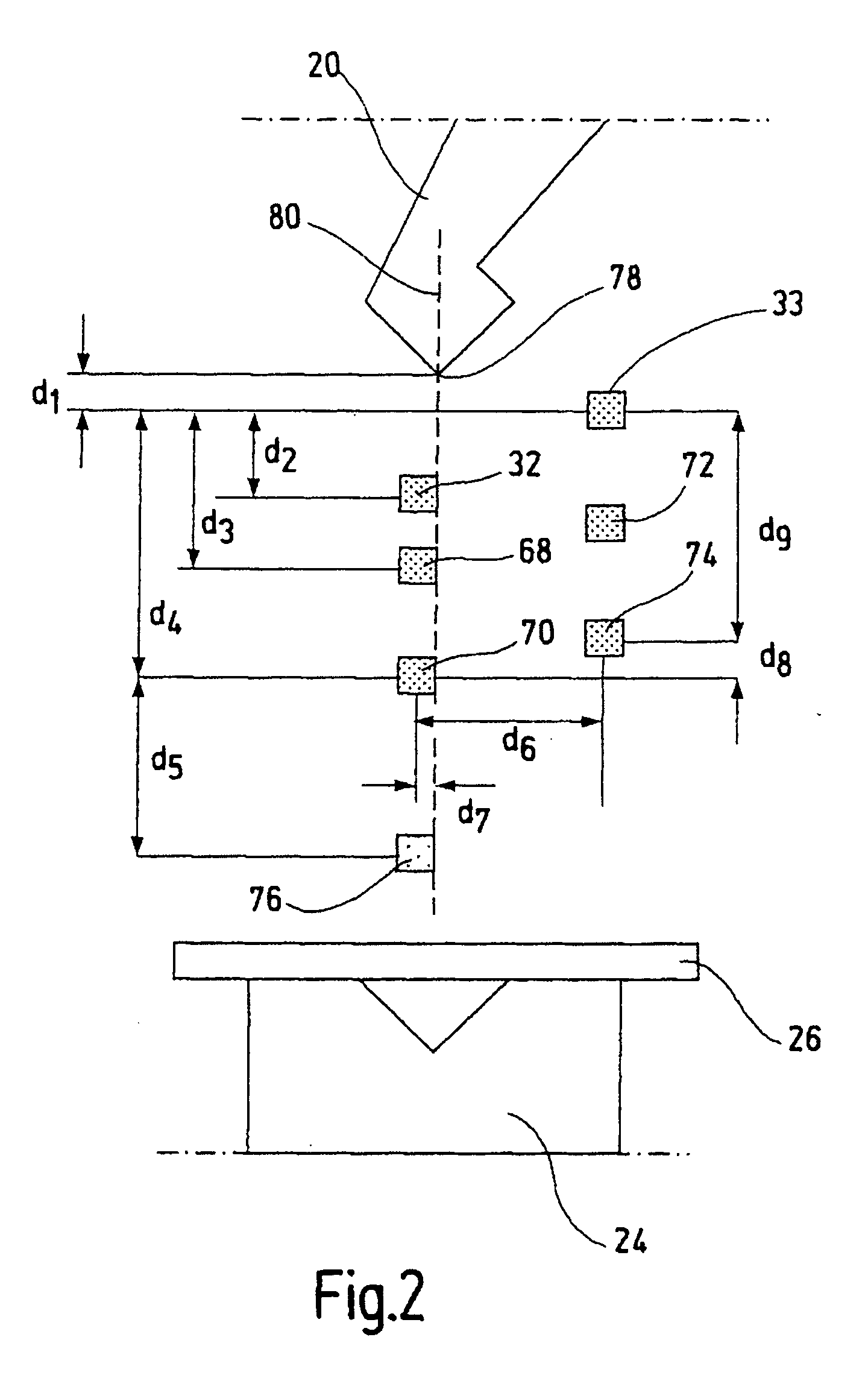
Safety device and method for determining an overtravel in a machine
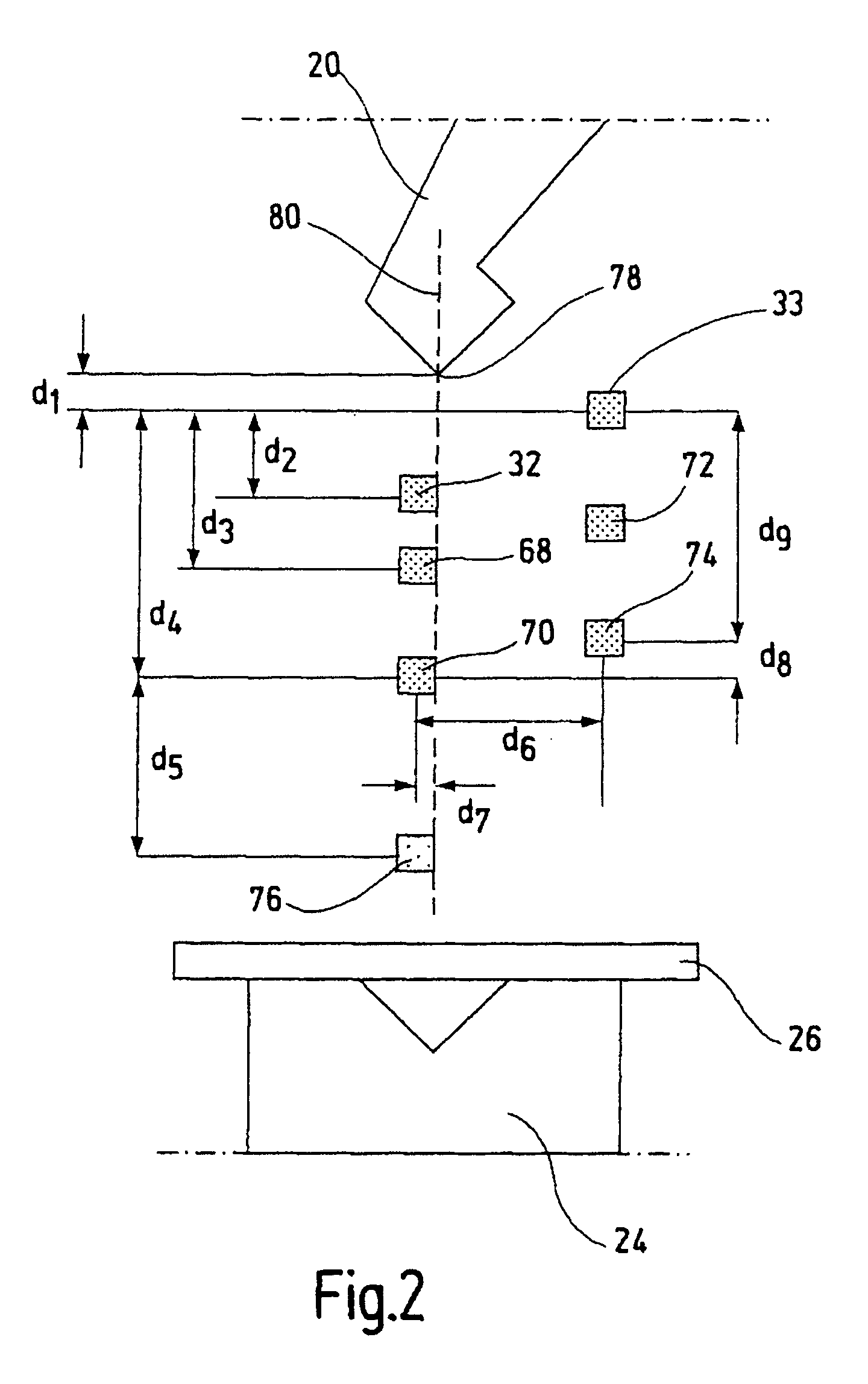
ActiveUS7286895B2Cost-effective and convenient and safe determinationShaping safety devicesEngineering safety devicesExtra-locationOptical barrier
A safety device for a machine has a first machine part for carrying out a working movement towards a second machine part. It also has at least a first and a second optical barrier moving along with the first machine part during the working movement. The first optical barrier runs ahead of the first machine part by a first distance, and the second optical barrier is arranged at a second distance from the first optical barrier. A control unit is designed to stop the working movement of the first machine part when the first optical barrier is interrupted. A test unit allows to test whether the second optical barrier has been interrupted once the first machine part has been stopped. A blocking unit serves for blocking the working movement as a function of the test result from the test unit. Using this safety device it is possible to determine an overtravel of the first machine part in a simple and reliable manner. Furthermore, an optical sensor barrier can be used to detect the position for a switchover between a rapid motion and a creep motion of the machine without requiring additional position sensors.
Owner:PILZ (COMPANY)
Sensor and method for continuous health monitoring
ActiveUS10219709B2Low costQuick upgradeEvaluation of blood vesselsCatheterMicrocontrollerProximity sensor
An optical proximity sensor assembly includes an optical proximity sensor with an IR LED emitting light having an infrared wavelength, an IR photo detector sensitive to the infrared wavelength, an optical barrier blocking direct light rays from the LED to the IR photo detector and permitting reflected light rays to reach the at least one photo detector; and an electronic integrated circuit with an amplifier for amplifying a signal detected by the photo detector, an analog to digital converter, LED drivers, noise reduction and ambient light cancellation circuitry, and a digital interface for communication with a microcontroller. The optical proximity sensor is accommodated on a wearable carrier. A single sensor may include a plurality of identical or different LEDs, a plurality of photodiodes, or both. Also, several sensors may be placed on a person's skin along a vascular path to obtain data relating to blood flow and artery stiffness.
Owner:WAYNE STATE UNIV
System for Manufacturing an Irrigation Pipe and a Device and Method for Detecting Holes in the Wall of an Irrigation Pipe
InactiveUS20140150509A1Less expensiveImproving transmission and receptionWatering devicesExtrusion control devicesThermodynamicsSoil science
A system for manufacturing an irrigation pipe (100) comprisingan extrusion unit (300)a calibrator unit (400)a cooling unit (600) for cooling the irrigation pipe (100) in a cooling liquid (30)a traction unit (500) for drawing the irrigation pipe (100) in the cooling unit (600)the cooling unit comprising a device for detecting holes (102) in the wall of the irrigation pipe (100) and arranged for being immersed in the cooling liquid (30), this device for detecting holes comprising at least one optical transmitter (1) and at least one optical receiver (2) which define an optical barrier (10),this device being arranged so that the holes (102) in the irrigation pipe (100) located below this device produce gas bubbles (20) which modify this optical barrier (10).
Owner:MAILLEFER SA MAILLEFER SA
Display panel and display device with same
ActiveCN109300942AImprove visibilityAlleviate visible problemsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesState of artVisibility
The invention relates to a display panel and a display device with the same, and aims at solving the problem that a photosensitive module which is visible under blaze influences the integral appearance of electronic equipment in the prior art. The display panel comprises a display layer, the photosensitive module positioned in the inner side of the display panel, and an optical barrier layer arranged between the display layer and the photosensitive module and used to reducing the intensity of light radiated from the display panel to the photosensitive module and / or the intensity of light reflected from the photosensitive module to the display layer. Thus, reflected light in different areas of the display panel are basically consistent, the visibility of the photosensitive module under thedisplay panel is reduced, the photosensitive module is less visible, and the integral appearance of the electronic equipment is improved.
Owner:VIVO MOBILE COMM CO LTD
Waveguide device having improved spatial filter configurations
An optical waveguide device is provided for receiving light that has a guided mode and an unguided mode. The device comprises an optically transmissive substrate having first and second substantially opposite surfaces, an input end, and an output end. An optical waveguide region is disposed within the substrate and extends from the input to the output. A plurality of electrodes is disposed on the first surface at predetermined locations with respect to the waveguide region. The device includes a plurality of optical barriers each disposed proximate one of the first and second surfaces and positioned to block a different optical path of the unguided mode.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Optical film, and optical barrier film, color conversion film and backlight unit each using the same
ActiveUS20170235025A1Improve barrier propertiesAvoid cloggingMechanical apparatusOptical filtersStatic friction coefficientStatic friction
An optical film comprises a first transparent film substrate, a matte layer arranged on the first transparent film substrate and having irregularities, the matte layer having a coefficient of static friction of not larger than 0.3 and a maximum height roughness Rz of not less than 0.05 μm to not larger than 8 μm.
Owner:TOPPAN PRINTING CO LTD
Wafer level optoelectronic device packages with crosstalk barriers and methods for making the same
ActiveCN106057964AReduce listHigh yield manufacturingSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSolder ballElectrical connector
A method for wafer level fabricating a plurality of optoelectronic devices, starting with a wafer that includes a plurality of light detector sensor regions, includes attaching each of a plurality of light source dies to one of a plurality of bond pads on a top surface of the wafer that includes the plurality of light detector sensor regions. The method also includes attaching, to the wafer, a preformed opaque structure made off-wafer from an opaque material, wherein the preformed opaque structure includes opaque vertical optical barriers. Additionally, solder balls or other electrical connectors are attached to the bottom of the wafer. The wafer is diced to separate the wafer into a plurality of optoelectronic devices, each of which includes at least one of the light detector sensor regions, at least one of the light source dies and at least two of the solder balls or other electrical connectors.
Owner:INTERSIL INC
Backlight Module Unit and Backlight Module
ActiveUS20090185371A1Reduce thicknessEliminating dark bandNon-electric lightingPoint-like light sourceOptical barrierLight source
A backlight module unit and a backlight module are provided. The backlight module unit includes a first light source, a second light source, and an optical barrier. A light source interval is defined between the first light source and the second light source, while a barrier interval is defined between the optical barrier and the second light source. Because the barrier interval is substantially shorter than a half of the light source interval, the backlight module unit mixes the light evenly, and prevents the dark bands from forming due to the disposition of the optical barrier. Thereby, the backlight module that comprises the plural aforesaid backlight units will have no dark bands, mix light evenly, and be thin overall.
Owner:AU OPTRONICS CORP
Safety device and method for determining an overtravel in a machine
ActiveUS20060138310A1Cost-effective and convenient and safe determinationShaping safety devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansMachine partsExtra-location
A safety device for a machine has a first machine part for carrying out a working movement towards a second machine part. It also has at least a first and a second optical barrier moving along with the first machine part during the working movement. The first optical barrier runs ahead of the first machine part by a first distance, and the second optical barrier is arranged at a second distance from the first optical barrier. A control unit is designed to stop the working movement of the first machine part when the first optical barrier is interrupted. A test unit allows to test whether the second optical barrier has been interrupted once the first machine part has been stopped. A blocking unit serves for blocking the working movement as a function of the test result from the test unit. Using this safety device it is possible to determine an overtravel of the first machine part in a simple and reliable manner. Furthermore, an optical sensor barrier can be used to detect the position for a switchover between a rapid motion and a creep motion of the machine without requiring additional position sensors.
Owner:PILZ (COMPANY)
Optical barrier device
The present invention relates to a protective barrier device for covering an intraoral camera comprising: a flexible plastic body, said body having an opening for inserting the intraoral camera; and a hard clear plastic window at the distal end of the plastic body. The flexible plastic body is of sufficient length to cover the entire length of an appendage of the intraoral camera. The window aligns with a camera lens of the intraoral camera when the plastic body is placed over the appendage and may be constructed of a fog-resistant plastic.
Owner:STUTES RICHARD DALE
Optical barriers, waveguides, and methods for fabricating barriers and waveguides for use in harsh environments
ActiveUS8852695B2Polycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsCrystal structureRefractive index
Electromagnetic radiation barriers and waveguides, including barriers and waveguides for light, are disclosed. The barriers and waveguides are fabricated by directing charged particles, for example, ions, into crystalline substrates, for example, single-crystal sapphire substrates, to modify the crystal structure and produce a region of varying refractive index. These substrates are then heated to temperatures greater than 200 degrees C. to stabilize the modified crystal structure and provide the barrier to electromagnetic radiation. Since the treatment stabilizes the crystal structure at elevated temperature, for example, above 500 degrees C. or above 1000 degrees C., the barriers and waveguides disclosed are uniquely adapted for use in detecting conditions in harsh environments, for example, at greater than 200 degrees C. Sensors, systems for using sensors, and methods for fabricating barriers and waveguides are also disclosed.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
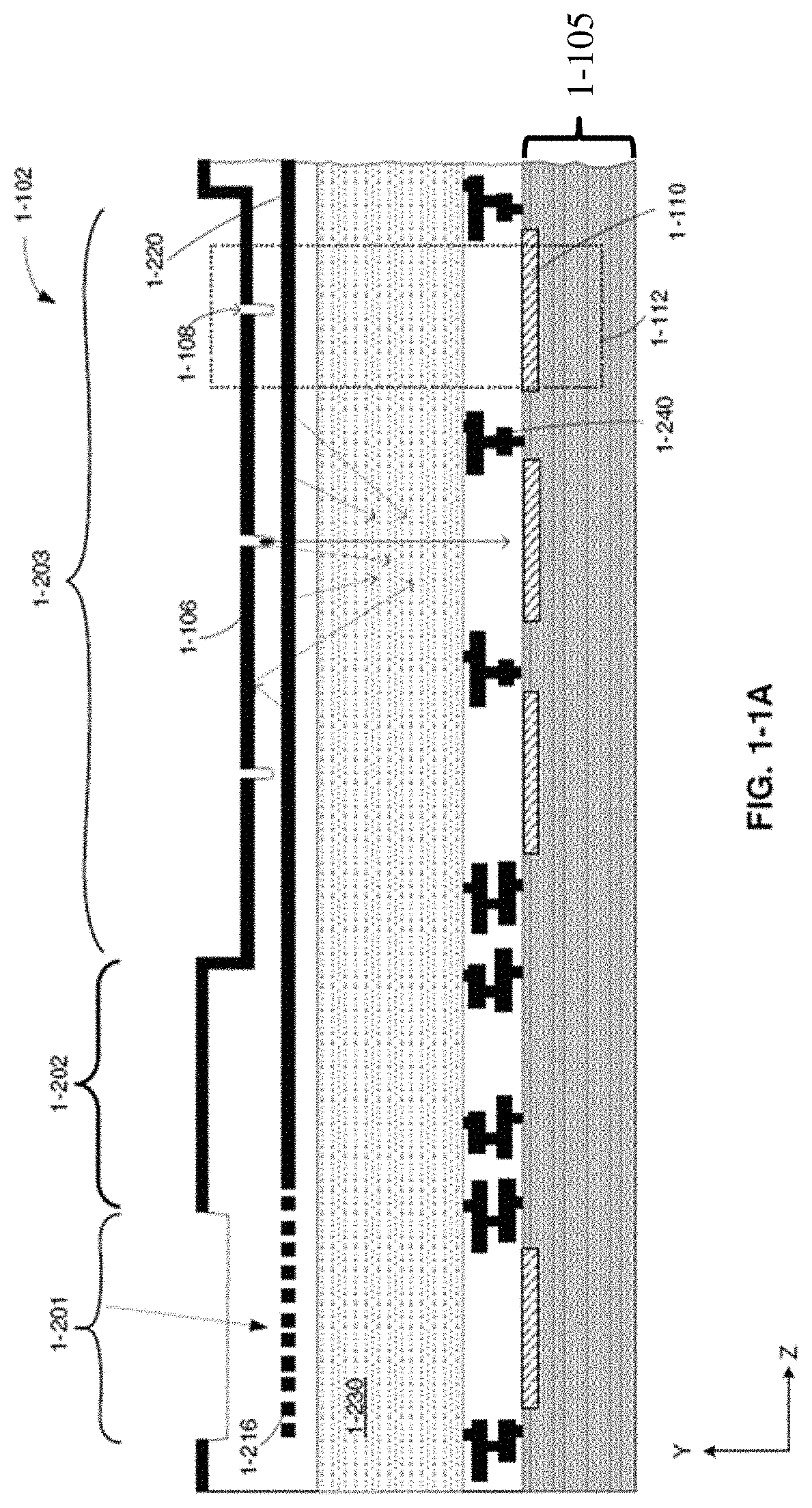
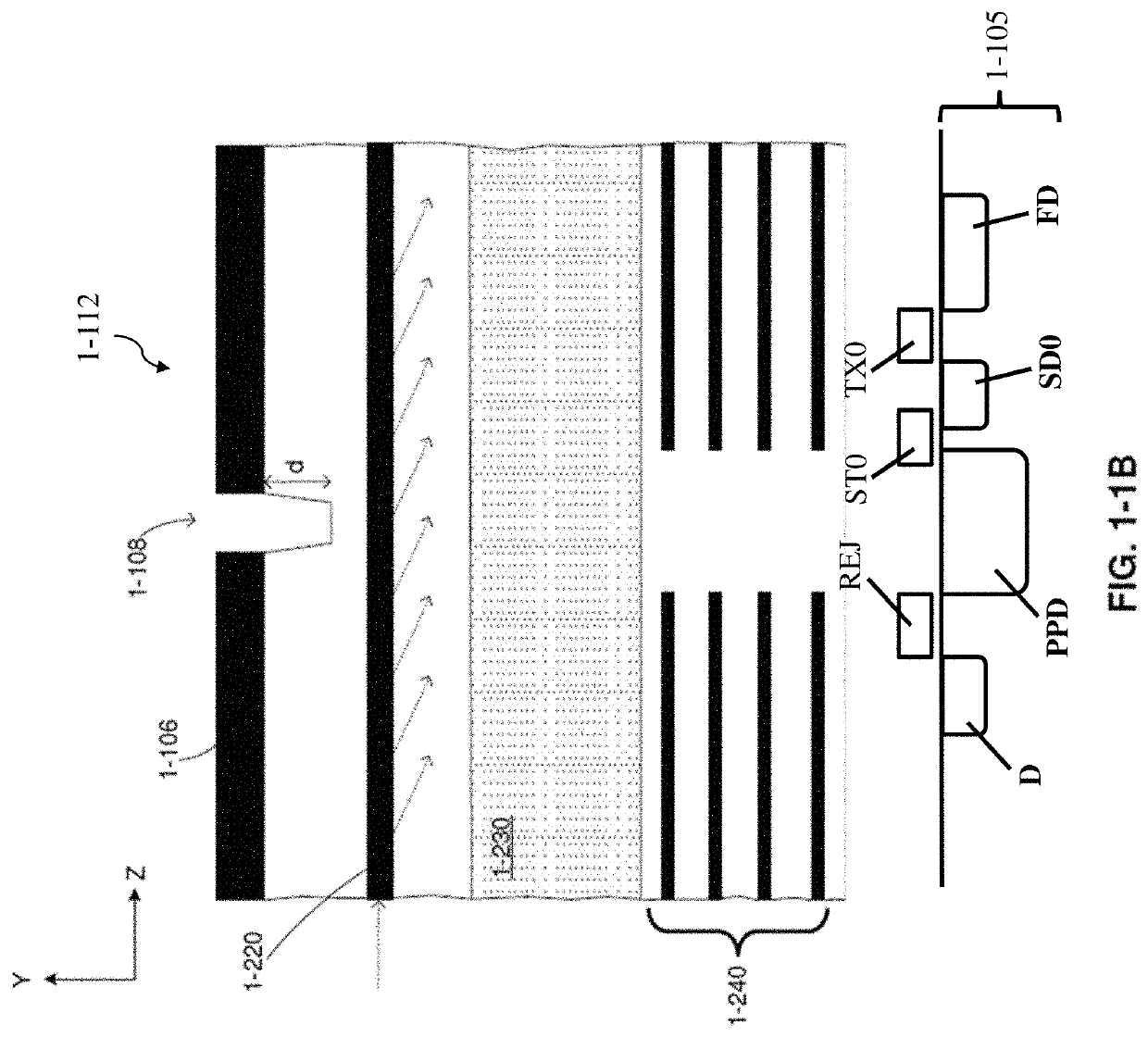
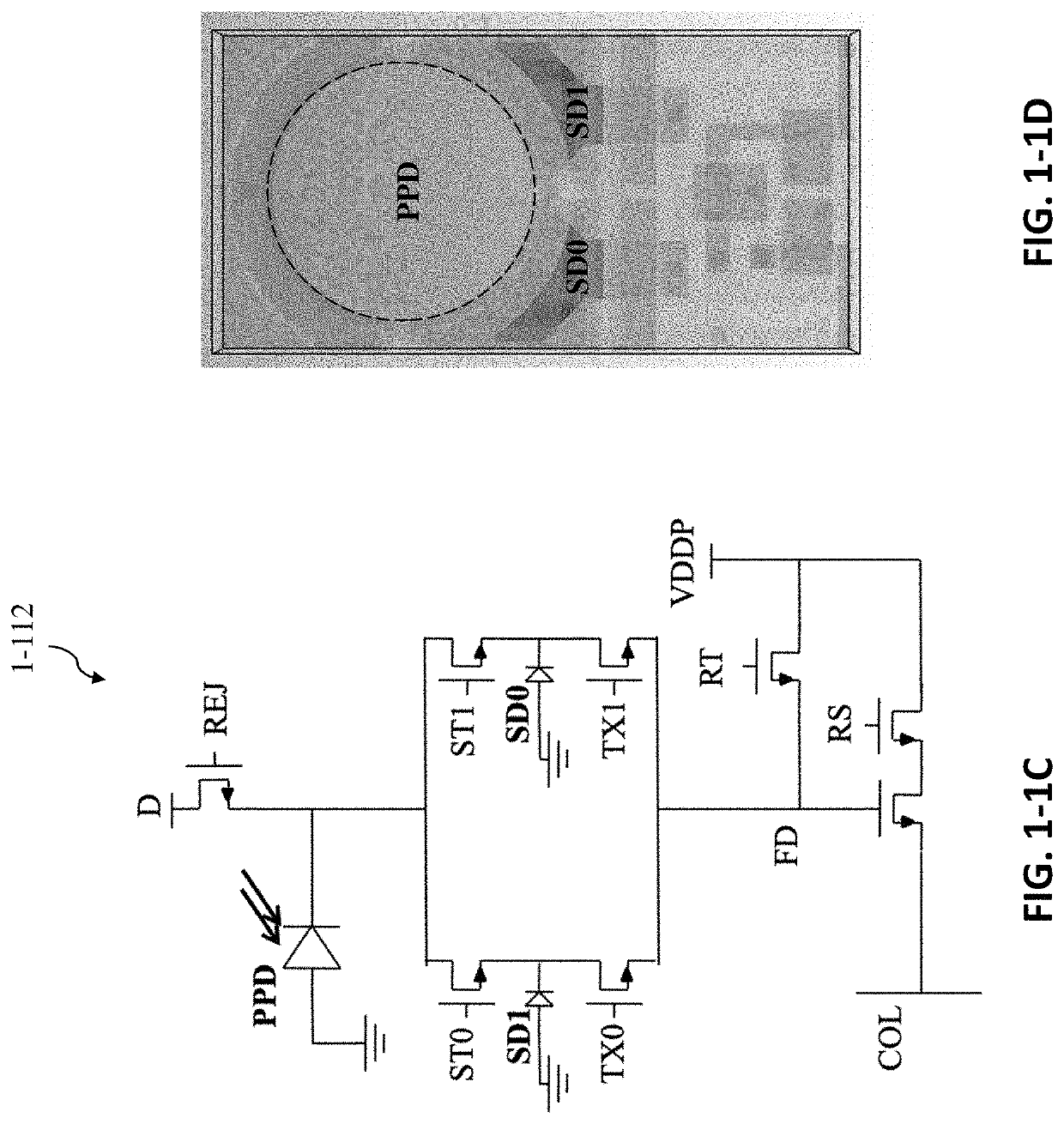
Optical and electrical secondary path rejection
PendingUS20200408690A1Solid-state devicesFluorescence/phosphorescencePhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
Described herein are techniques to reduce or remove the impact of secondary path photons and / or charge carriers on storage bins of an integrated device to improve noise performance, and thus, sample analysis. Some embodiments relate to optical rejection techniques such as including an optical barrier positioned to block at least some photons from reaching the storage bins. Some embodiments relate to electrical rejection techniques such as including an electrical barrier configured to block at least some charge carriers from reaching the storage bins along at least one secondary path. Some embodiments relate to an integrated device in which at least one storage bin is shaped and / or positioned relative to the photodetector to facilitate receipt of some charge carriers (e.g., fluorescent emission charge carriers) and / or photons and to impede receipt of other charge carriers (e.g., noise charge carriers) and / or photons.
Owner:QUANTUM SI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com