Patents
Literature
1590 results about "Photometer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
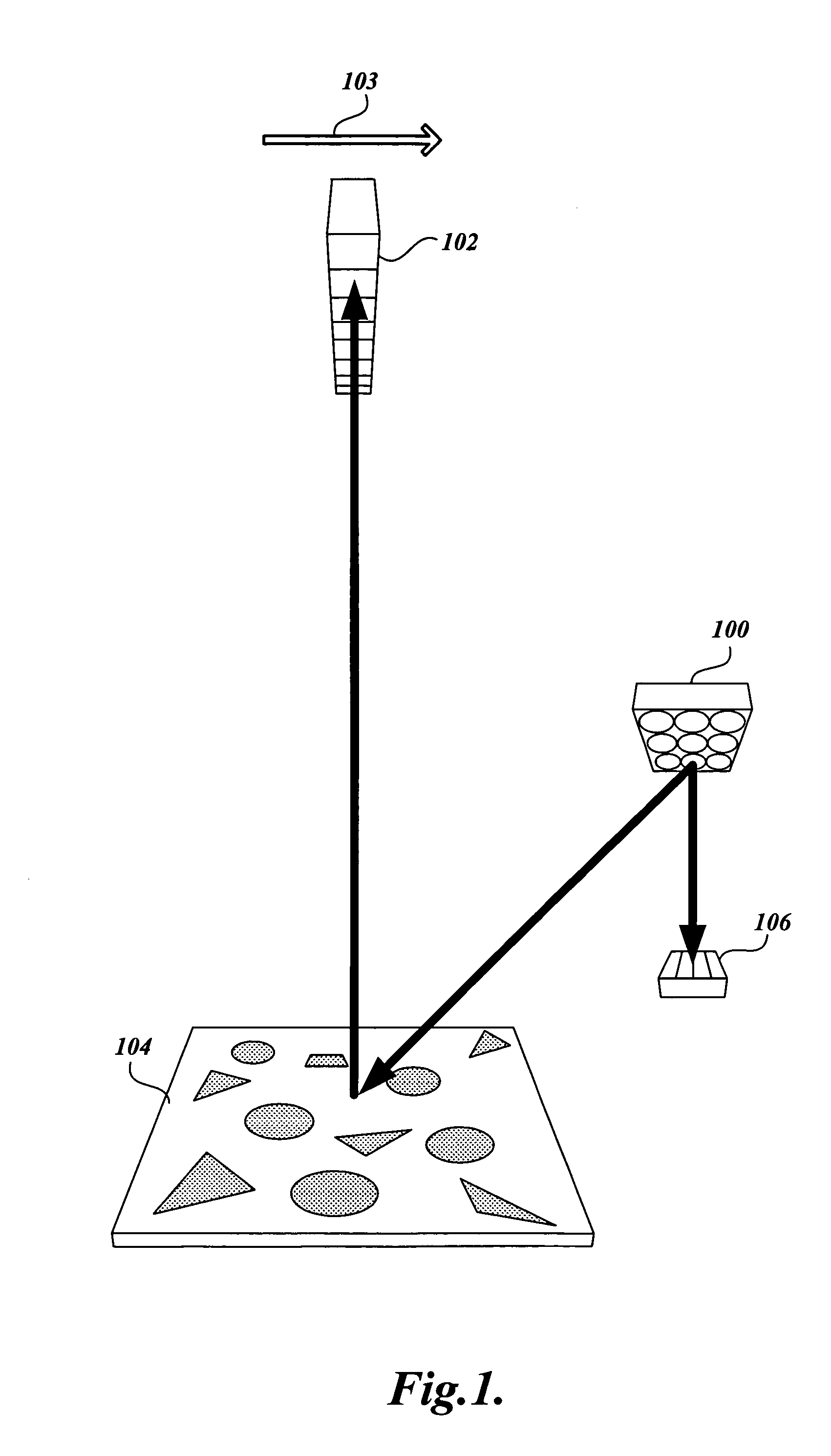
A photometer is an instrument that measures the strength of electromagnetic radiation in the range from ultraviolet to infrared and including the visible spectrum. Most photometers convert light into an electric current using a photoresistor, photodiode, or photomultiplier.
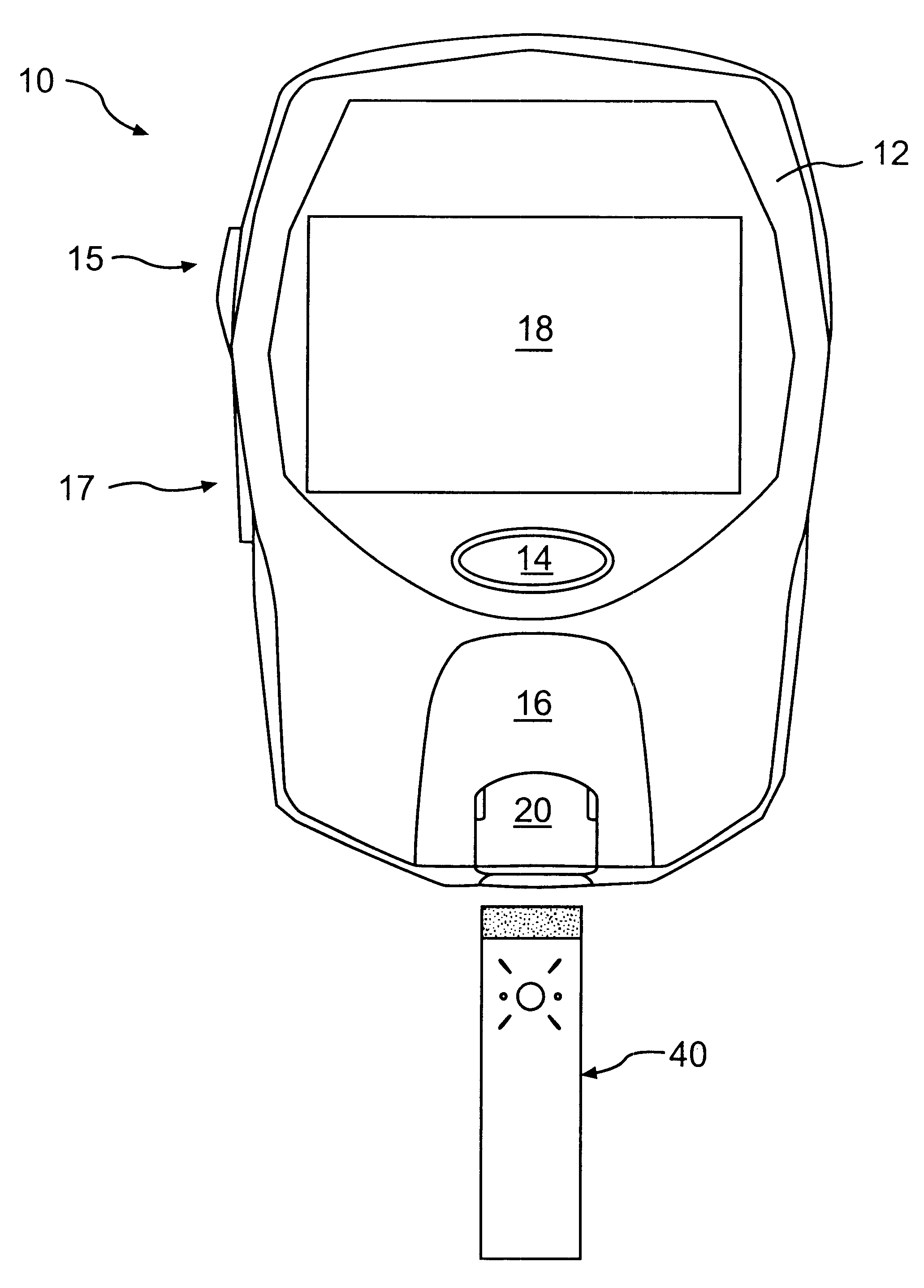
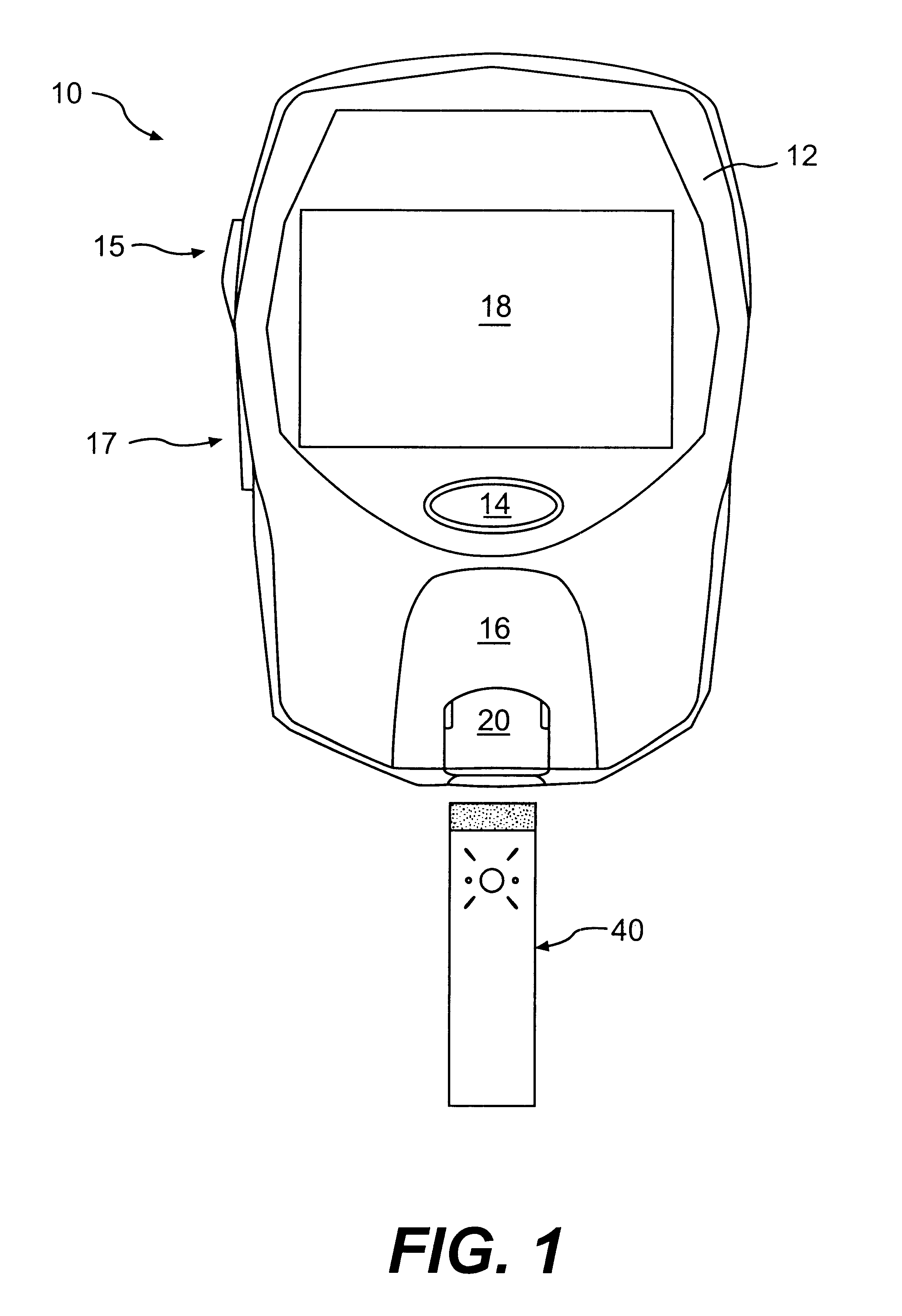
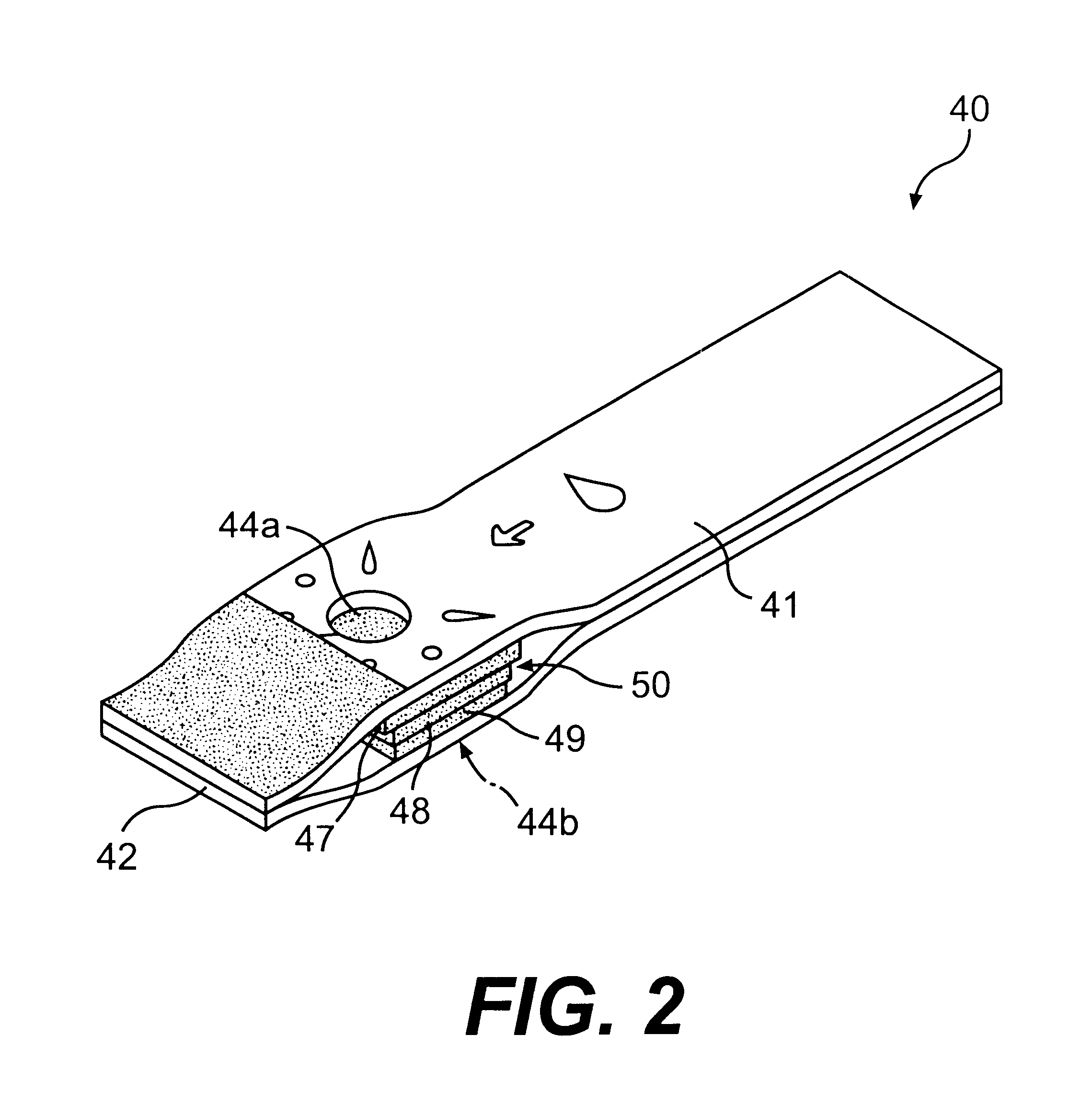
Method for determining concentration of an analyte in a test strip
InactiveUS6541266B2Analysis using chemical indicatorsMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorTarget analysisAnalyte
The present invention provides a method of measuring an analyte, such as glucose in a fluid sample, such as whole blood, by a reflectance reading device. The method includes making periodic intermediate calculations of analyte level and dynamically ascertaining when an analytical reaction has reached an end point. Once stable, the process stops making periodic calculations and reports the final, actual glucose concentration. According to an exemplary embodiment, the method is performed by a reflectance photometer using an analytical test strip containing reagents that react with an analyte of interest in the test fluid. The end point is determined by calculating an intermediate analyte level of the testing element at predetermined intervals and calculating a ratio value corresponding to the (n)th measurement to an (n-5)th measurement. When two consecutive ratio values are less than or equal to a predetermined value, the end point is deemed reached and the final analyte level ascertained.
Owner:TRIVIDIA HEALTH
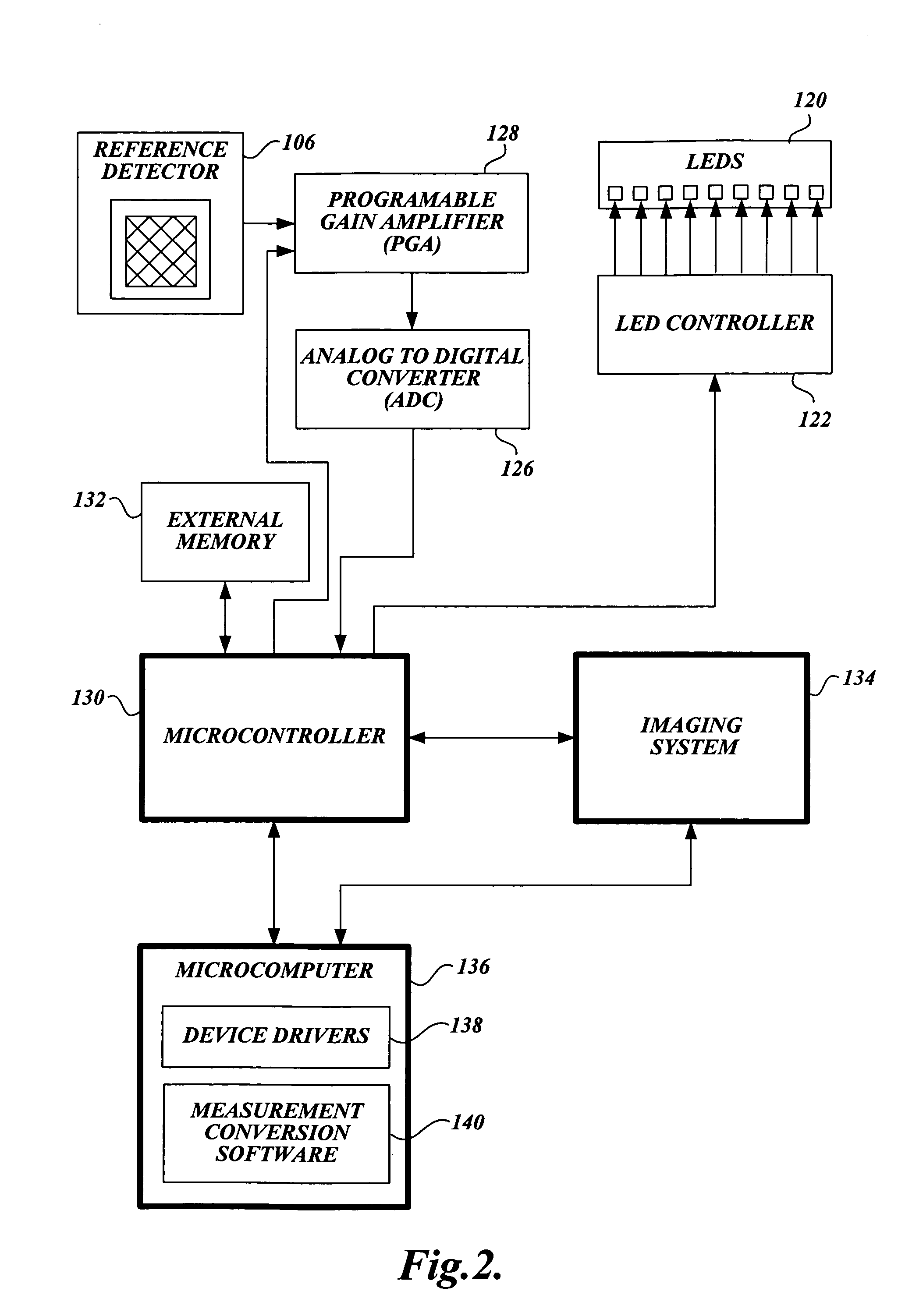
LED or laser enabled real-time PCR system and spectrophotometer
InactiveUS7122799B2Easy to useReduce entirely avoid costRadiation pyrometryHeating or cooling apparatusPhotodetectorUltraviolet
A system for conducting a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) assay upon a collection of samples is disclosed. The PCR assay is performed by absorption detection. The system includes a multi-well plate which is adapted to retain a collection of sample wells. This system includes a thermal cycler for the multi-well plate. The system additionally includes a collection of photodetectors, and a corresponding number of light sources. The light sources are positioned such that light emitted from each of the respective light sources passes through a corresponding well retained in the multi-well plate and to a corresponding photodetector. The system also includes a processor or other means for analyzing the output signals from the photodetectors. In certain versions of the system, ultra-violet light is used.
Owner:PALO ALTO RES CENT INC
Multi-array sensor with integrated sub-array for parallax detection and photometer functionality
Methods and systems of imaging to correct parallax. Color information is received from multi-array sensors. Luminance information is received from a sub-array sensor arranged with the multi-array sensors. Color information received from at least one of the multi-array sensors is correlated with the luminance information received from the sub-array sensor. Color information is shifted among the multi-array sensors, based on the correlation, to correct the parallax.
Owner:APTINA IMAGING CORP
Method for spectrophotometric blood oxygenation monitoring
ActiveUS20040024297A1Inhibition effectNon-invasive determinationSensorsColor/spectral properties measurementsBlood oxygenationNon invasive
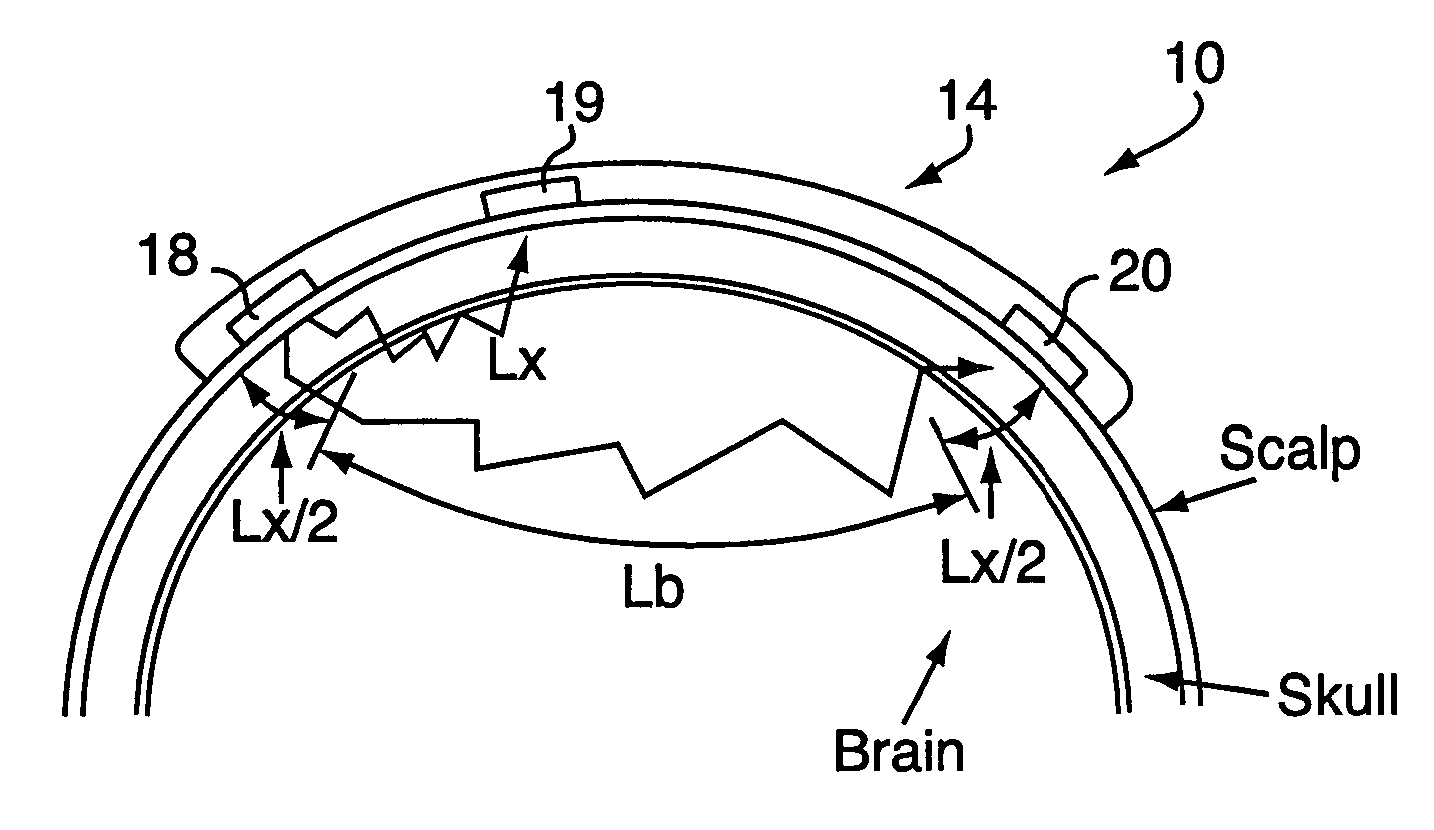
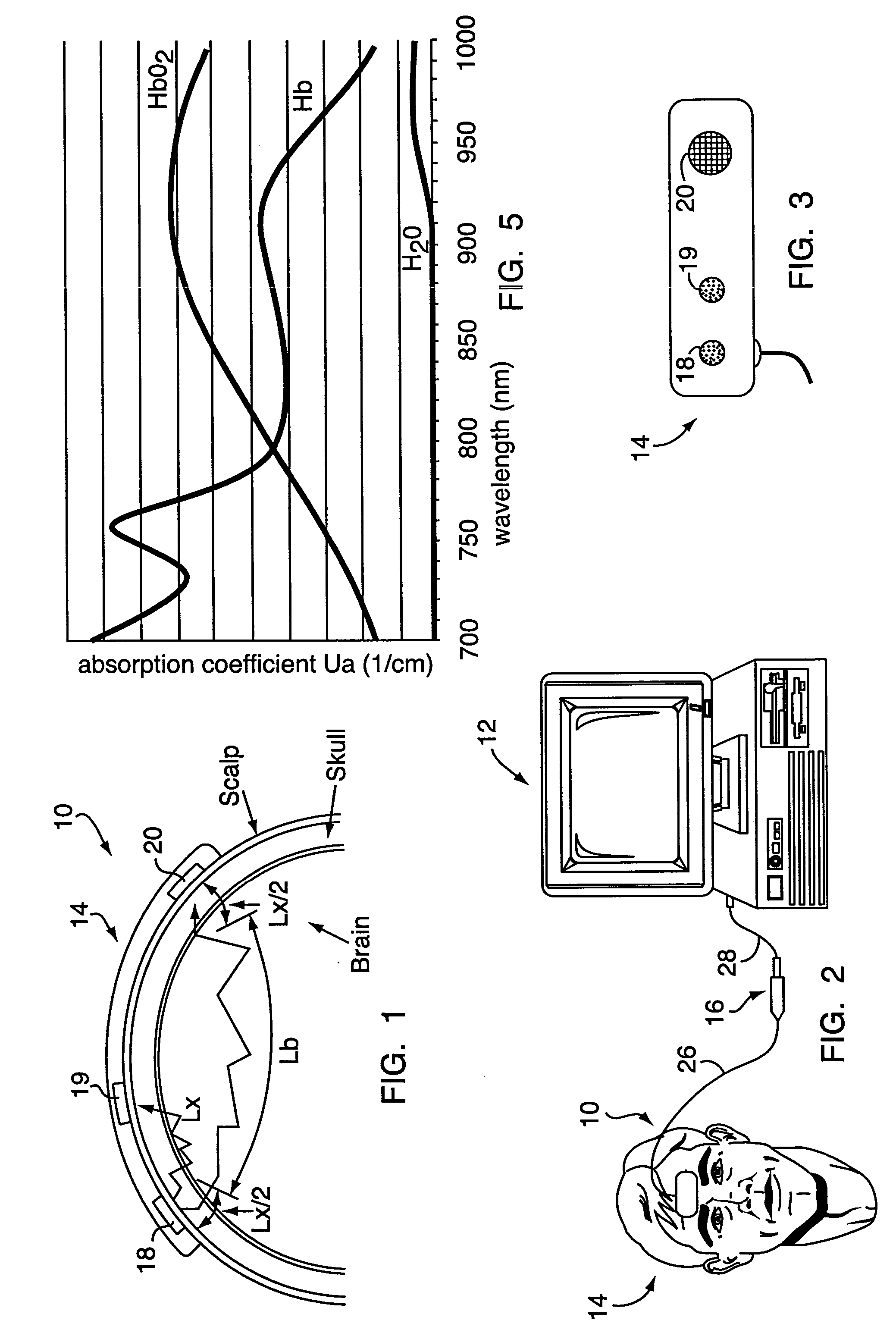
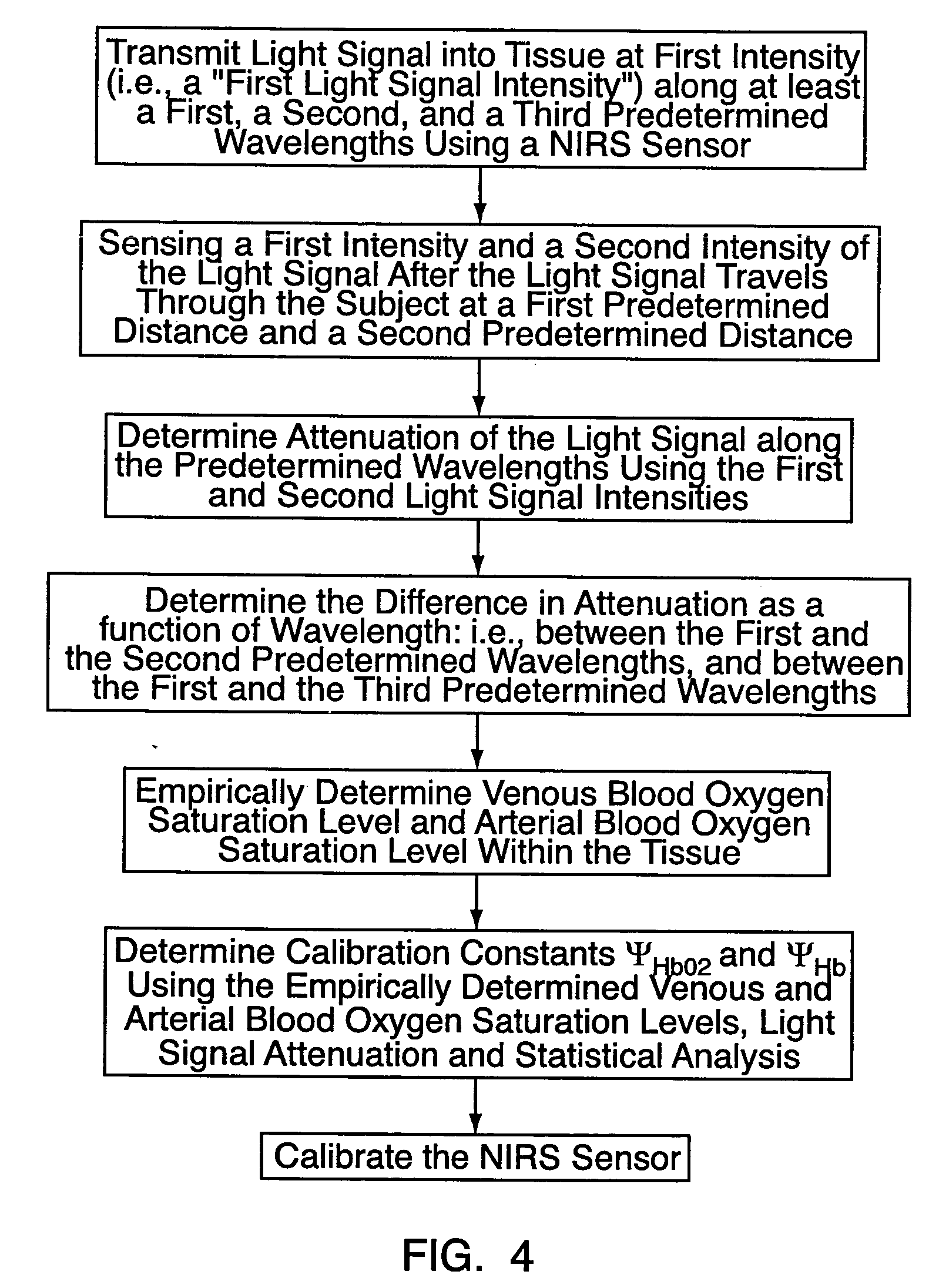
A method and apparatus for non-invasively determining the blood oxygen saturation level within a subject's tissue is provided that utilizes a near infrared spectrophotometric (NIRS) sensor capable of transmitting a light signal into the tissue of a subject and sensing the light signal once it has passed through the transmitting a light signal into the subject's tissue, wherein the transmitted light signal includes a first wavelength, a second wavelength, and a third wavelength; (2) sensing a first intensity and a second intensity of the light signal, along the first, second, and third wavelengths after the light signal travels through the subject at a first and second predetermined distance; (3) determining an attenuation of the light signal for each of the first, second, and third wavelengths using the sensed first intensity and sensed second intensity of the first, second, and third wavelengths; (4) determining a difference in attenuation of the light signal between the first wavelength and the second wavelength, and between the first wavelength and the third wavelength; and (5) determining the blood oxygen saturation level within the subject's tissue using the difference in attenuation between the first wavelength and the second wavelength, and the difference in attenuation between the first wavelength and the third wavelength.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
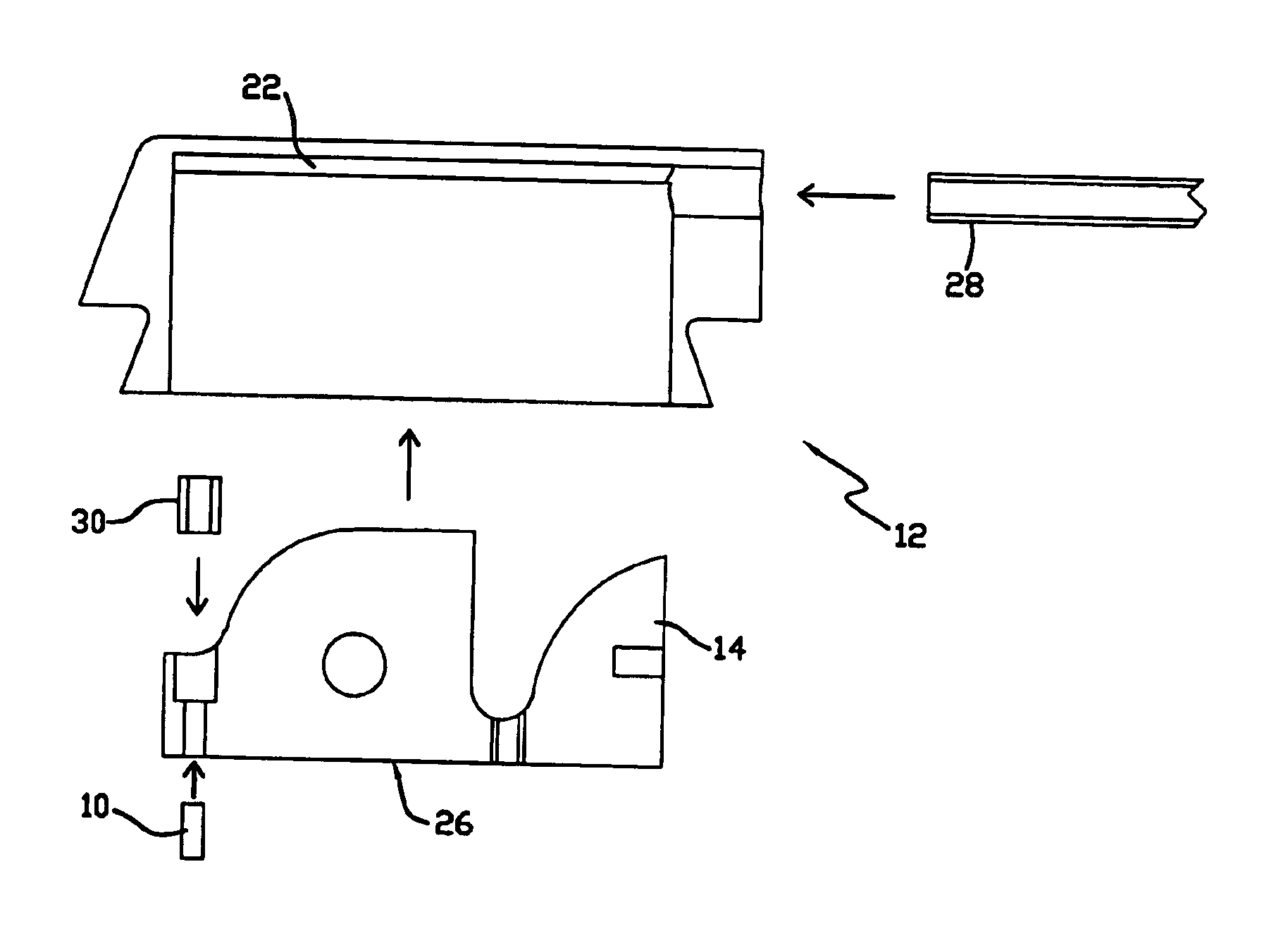
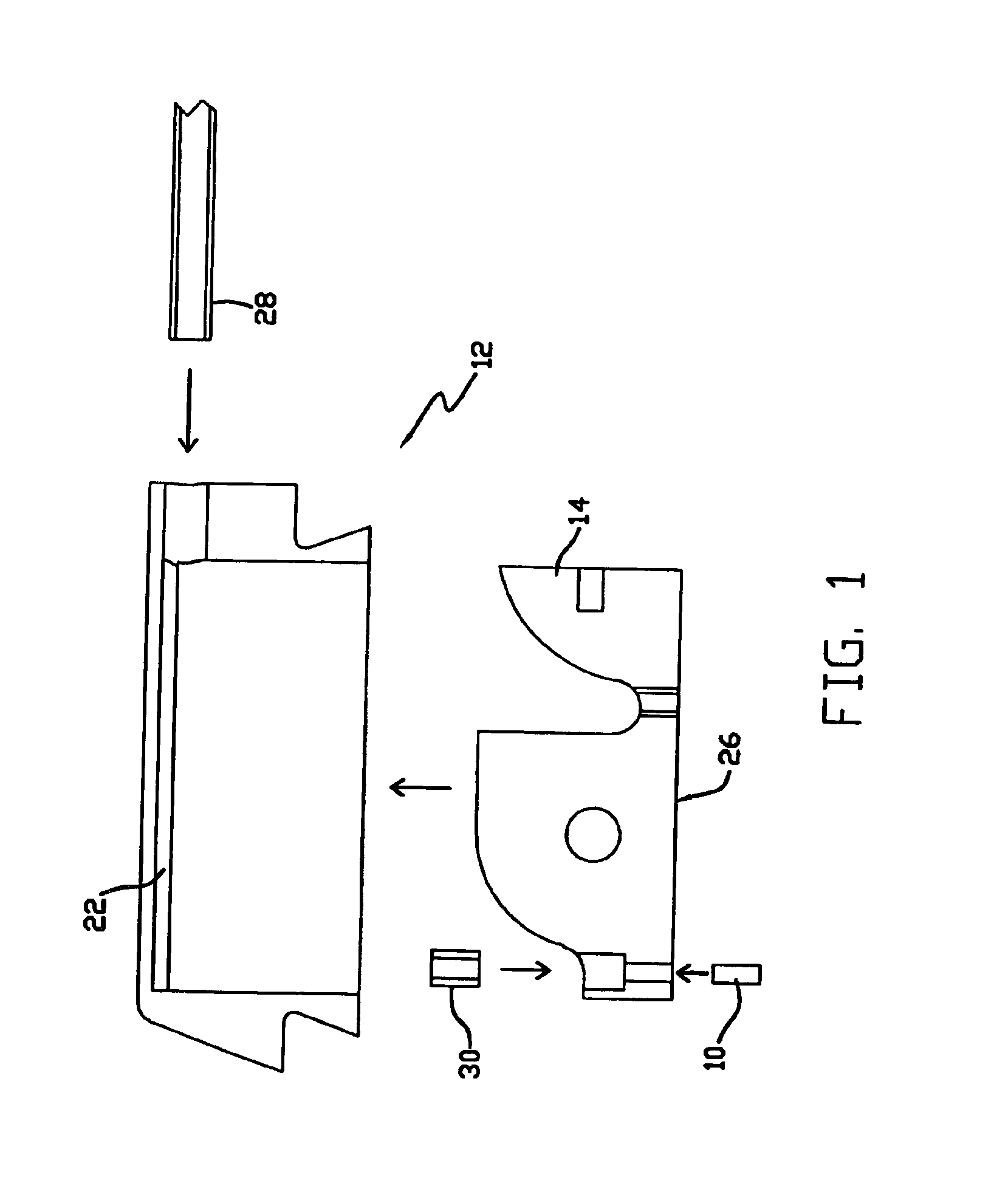
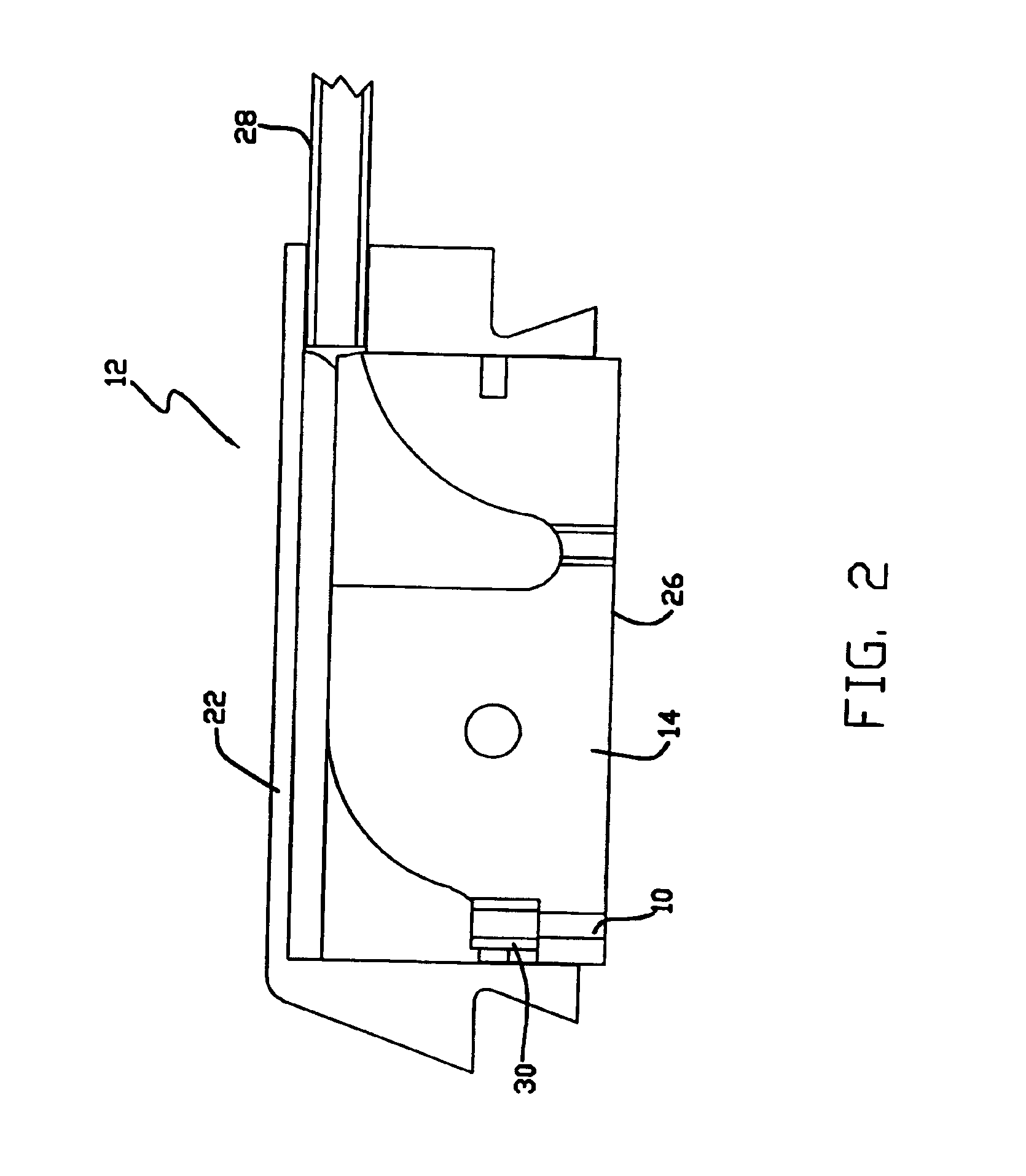
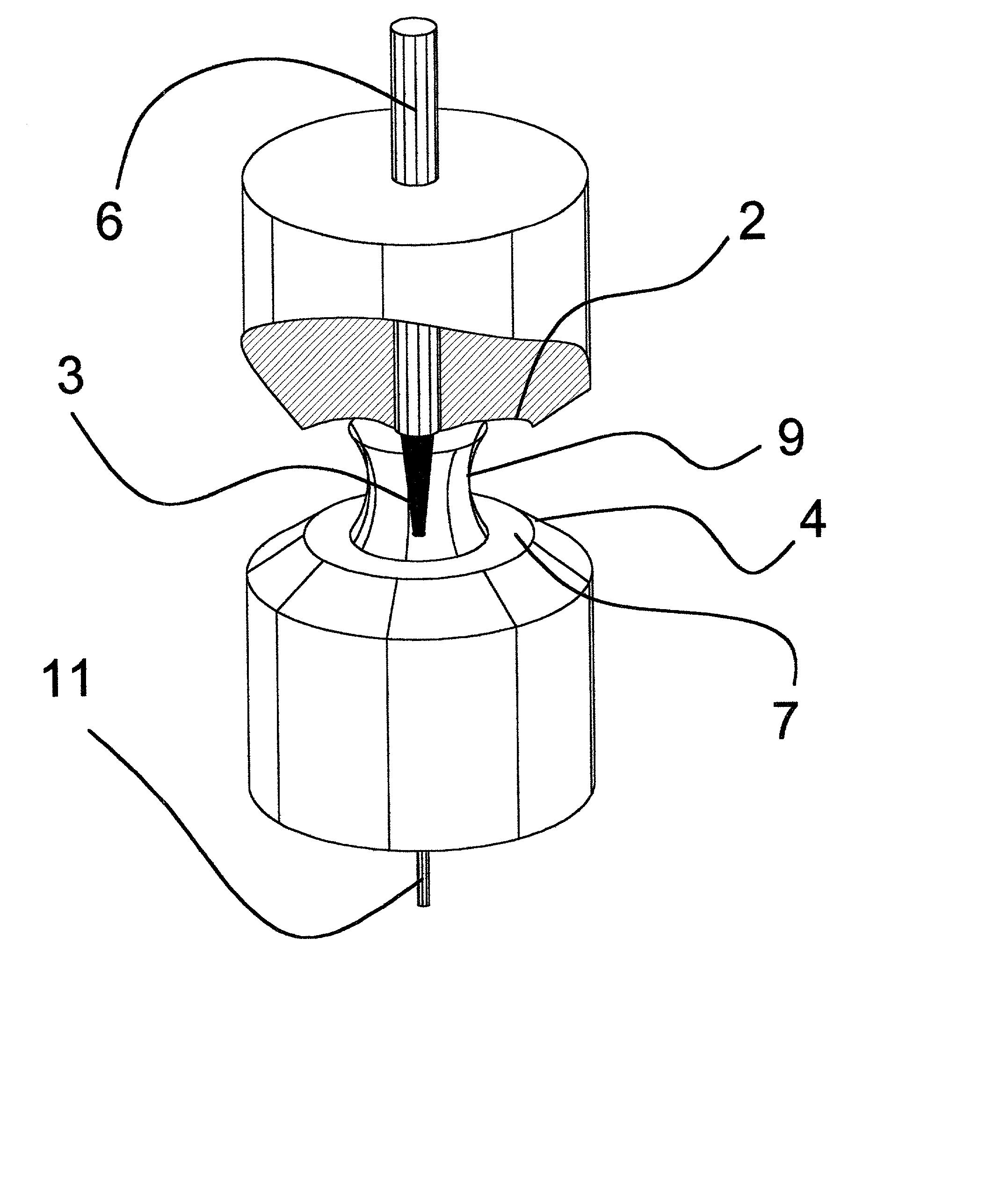
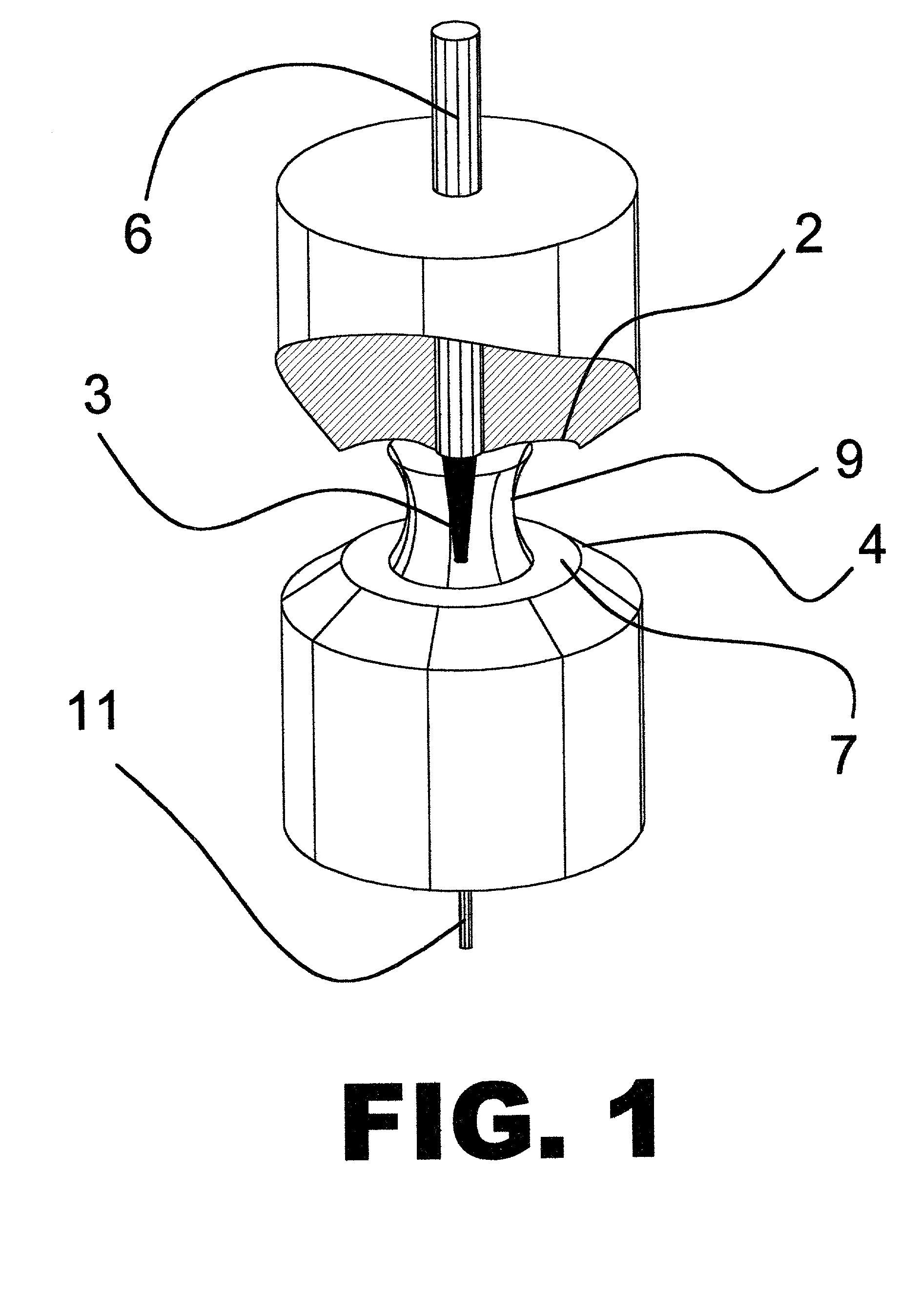
Liquid photometer using surface tension to contain sample
Method and apparatus of spectrophotometry or the like on extremely small liquid samples in which a drop is held between two opposing surfaces by surface tension and one surface is controllably moved toward and away from the other. To provide and transmit exciting energy through the drop for measurement, the optical fibers go through a surface and are finished flush with its surface. One of the surfaces can be swung clear of the other for easy cleaning between tests.
Owner:NANODROP TECH LLC
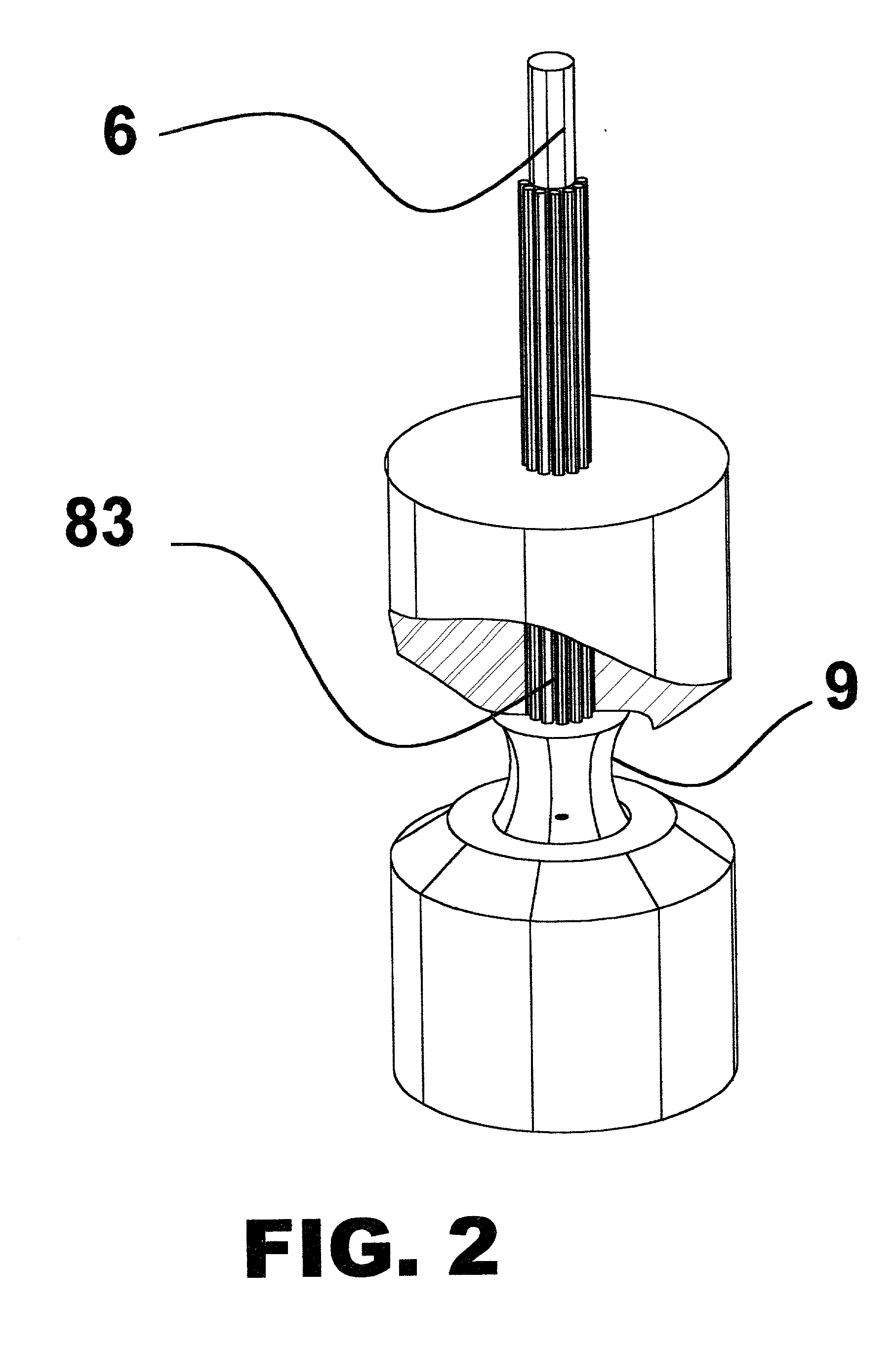
Liquid photometer using surface tension to contain sample
InactiveUS6809826B2Withdrawing sample devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansSmall sampleSpectroscopy
Method and apparatus of spectroscopy or the like on extremely small samples in which a drop is held between two opposing surfaces by surface tension and one surface is controllably toward and away from the other. To provide and transmit exciting energy through the drop for measurement, optical fibers go through a surface and finish flush with the surface. One of the surfaces can be swung clear of the other for easy cleaning between tests. Means for determining wetted surface are provided.
Owner:NANODROP TECH LLC
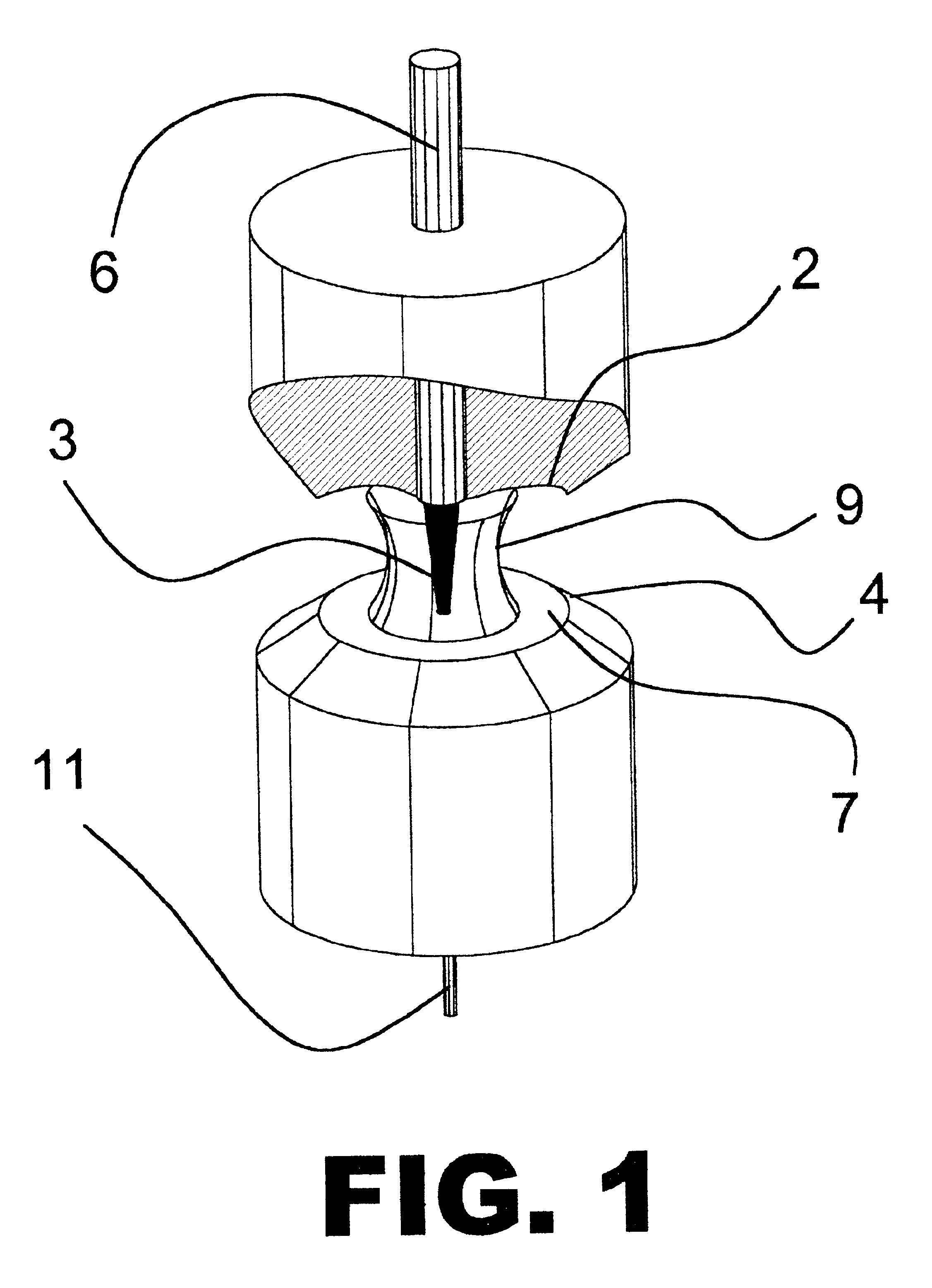
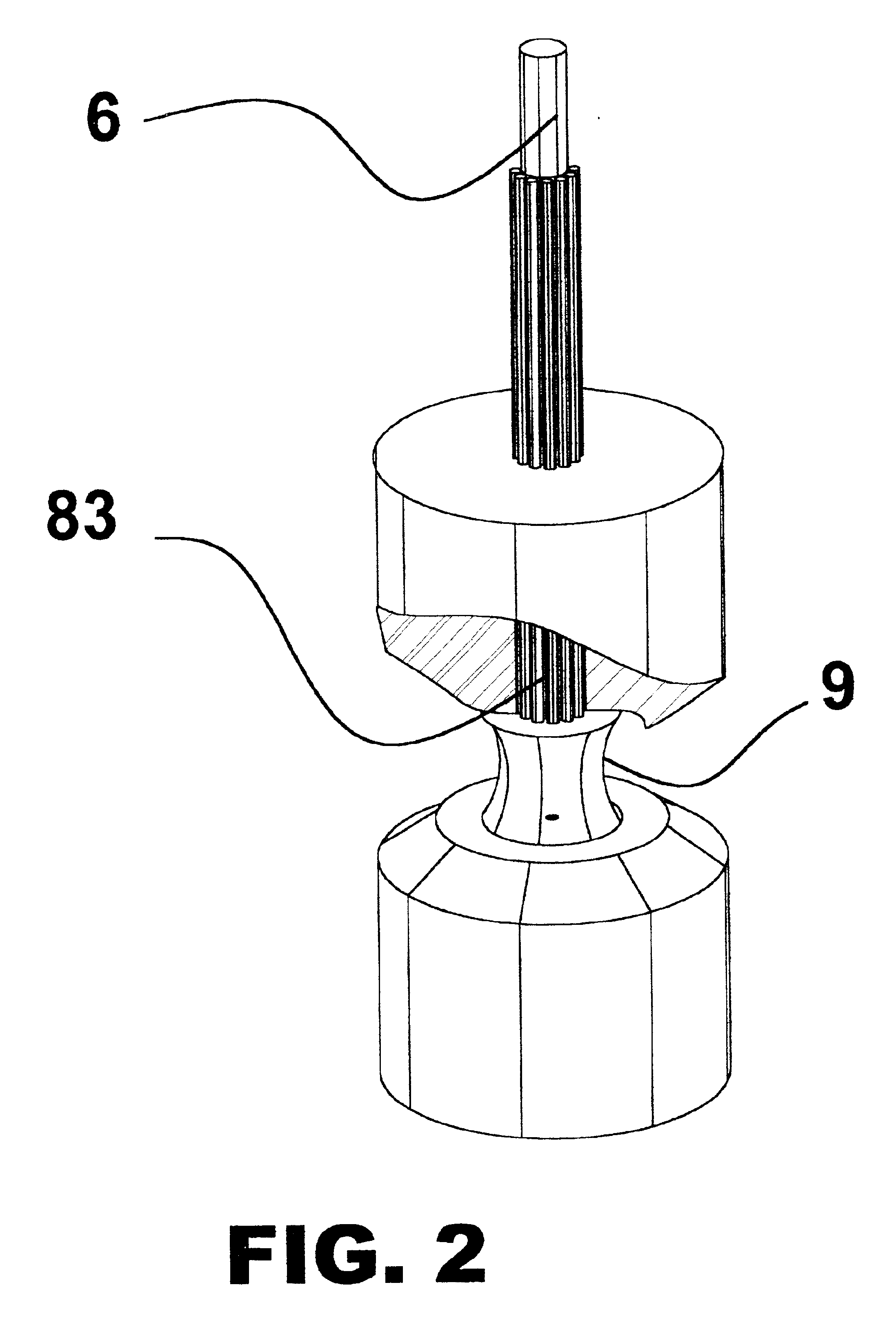
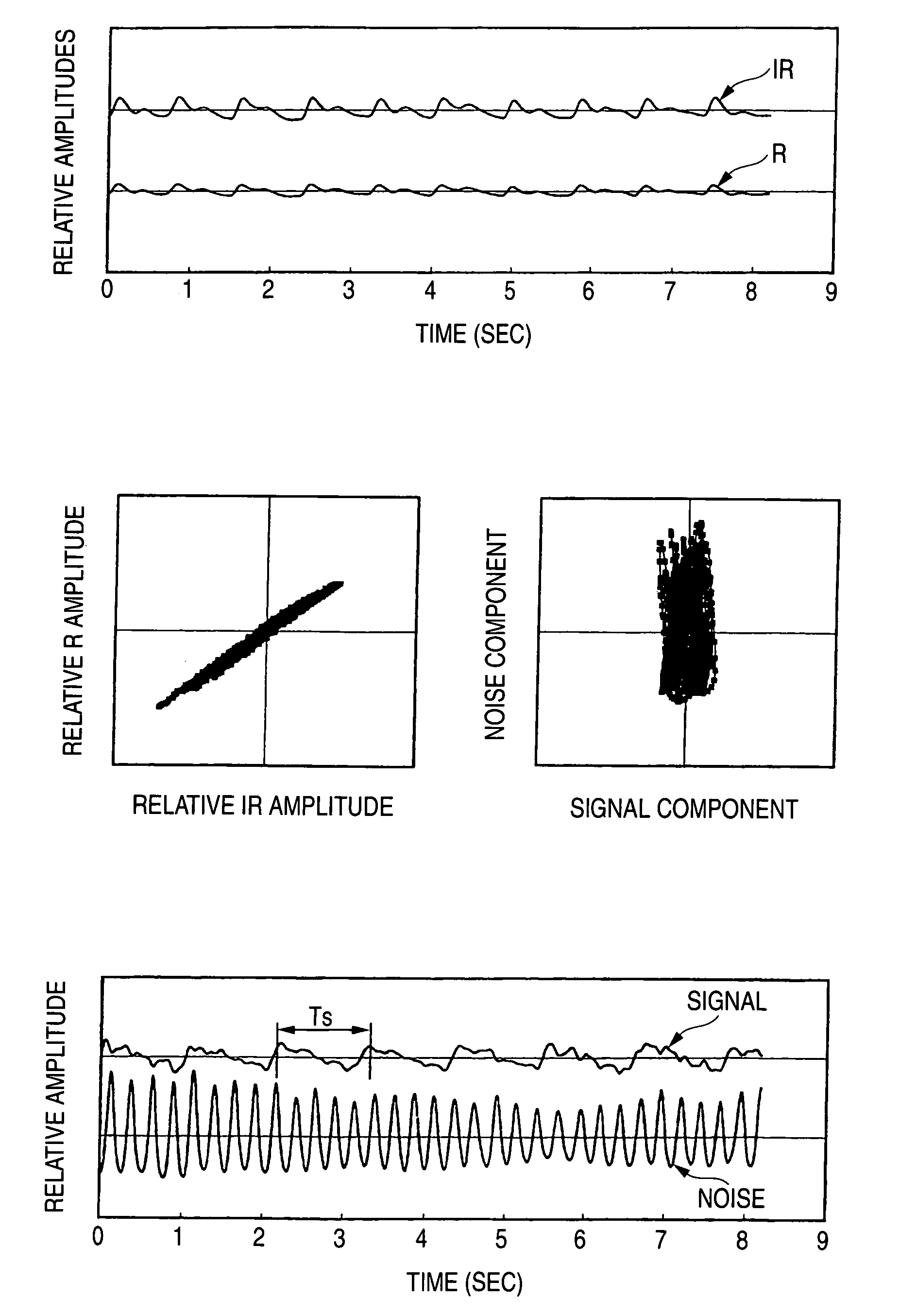
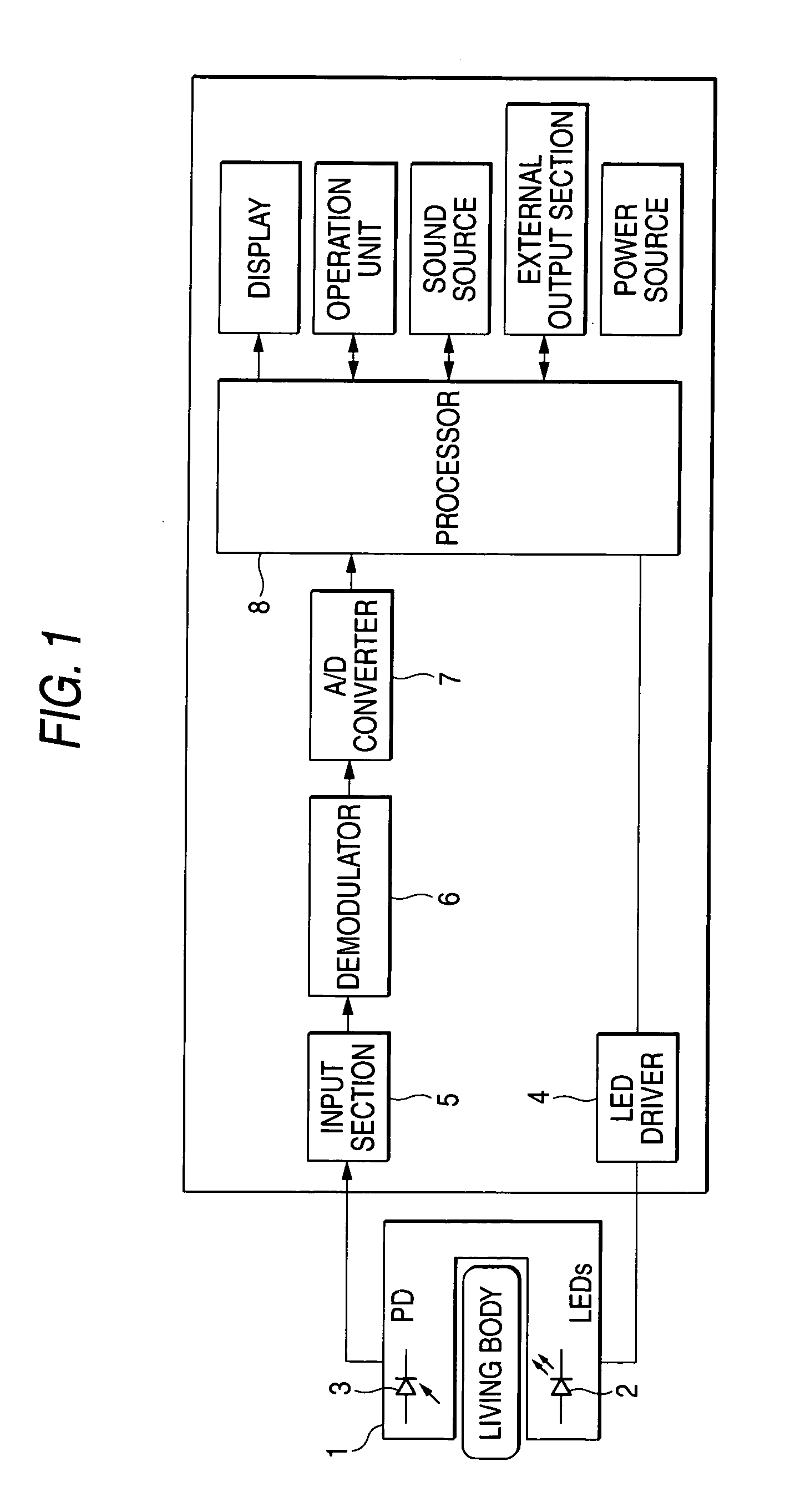
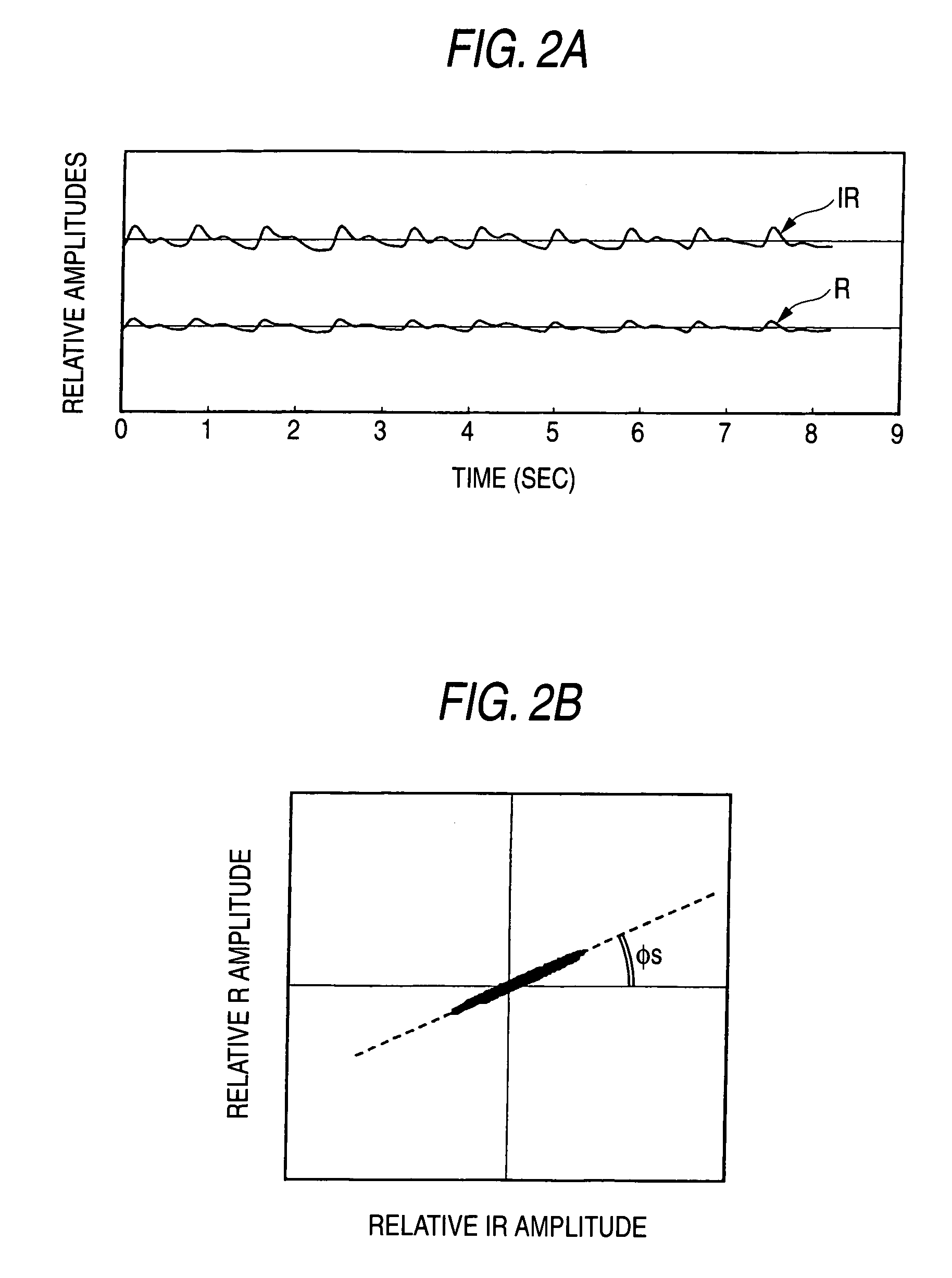
Method for reducing noise, and pulse photometer using the method
A living body is irradiated with a first light beam having a first wavelength and a second light beam having a second wavelength which is different from the first wavelength. The first light beam and the second light beam, which have been reflected or transmitted from the living body, are converted into a first electric signal corresponding to the first wavelength and a second electric signal corresponding to the second wavelength, as the observed pulse data. A light absorbance ratio obtained from the first electric signal and the second electric signal is computed, for each one of frequency ranges dividing an observed frequency band. It is determined that noise is not mixed into the observed pulse wave data in a case where a substantial match exists among light absorbance ratios computed for the respective frequency ranges.
Owner:NIHON KOHDEN CORP
Expert system for prediction of changes to local environment
ActiveUS20140067733A1Accurate predictionMechanical apparatusSpace heating and ventilation safety systemsCamera lensColor image
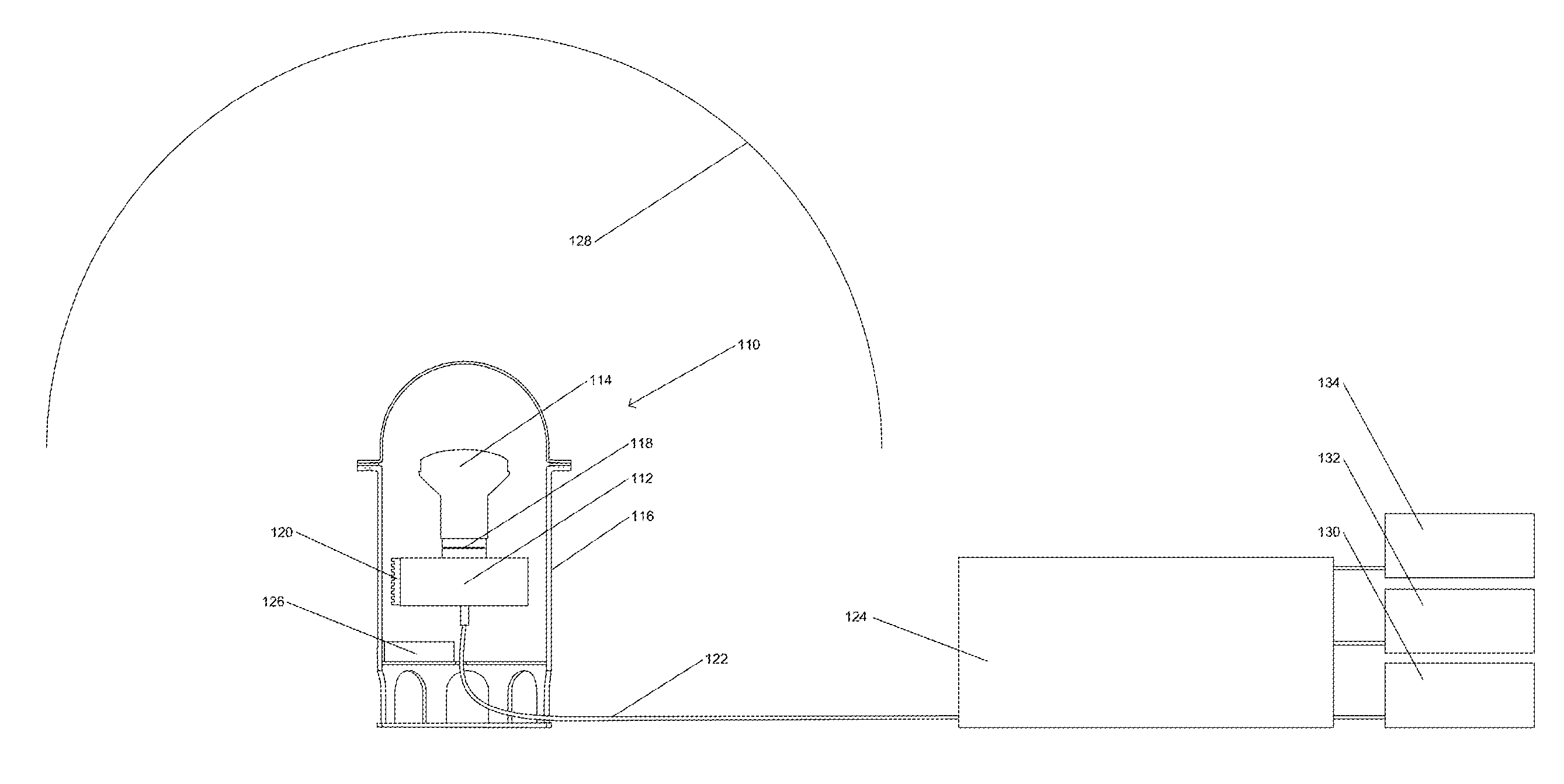
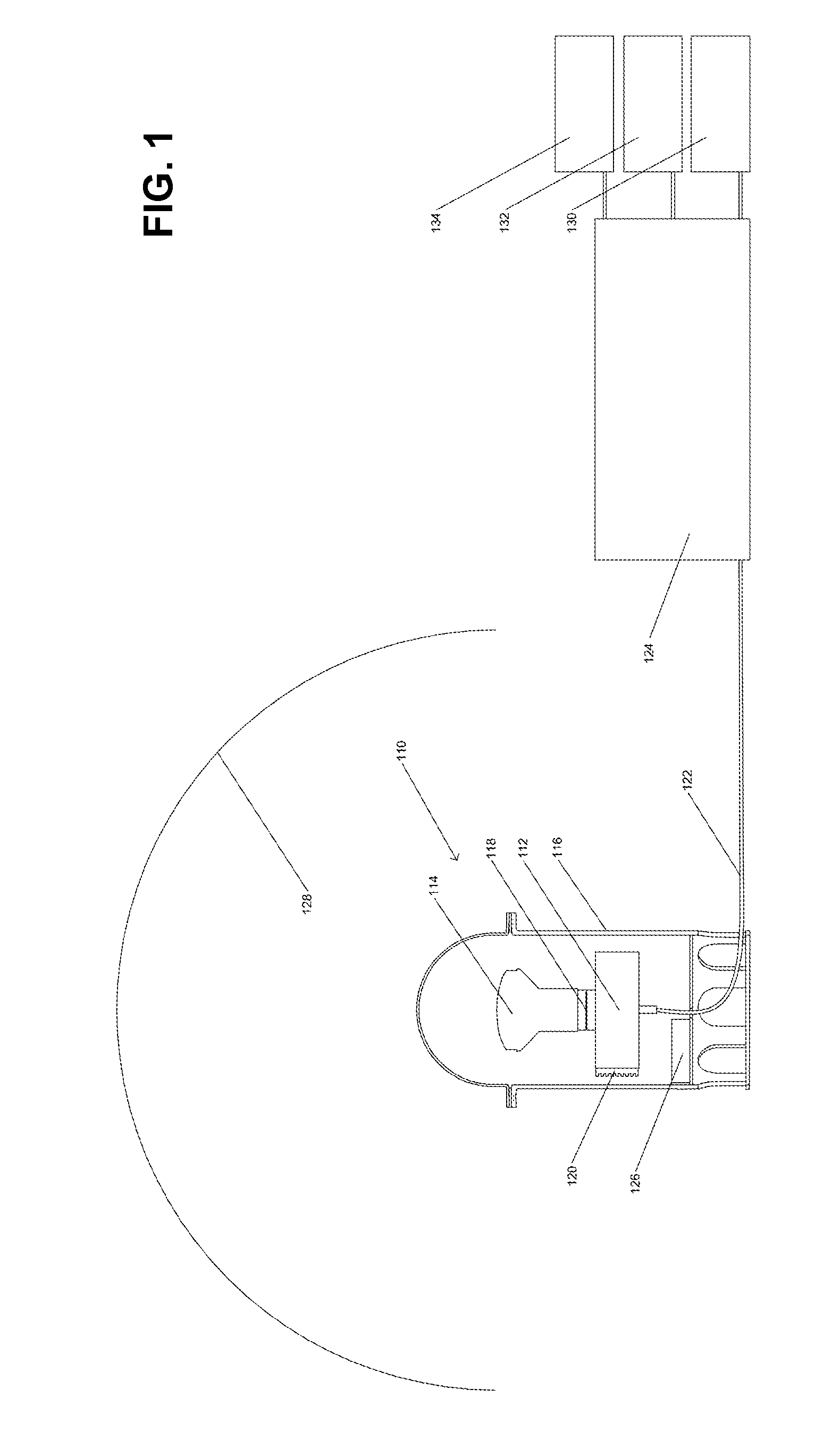
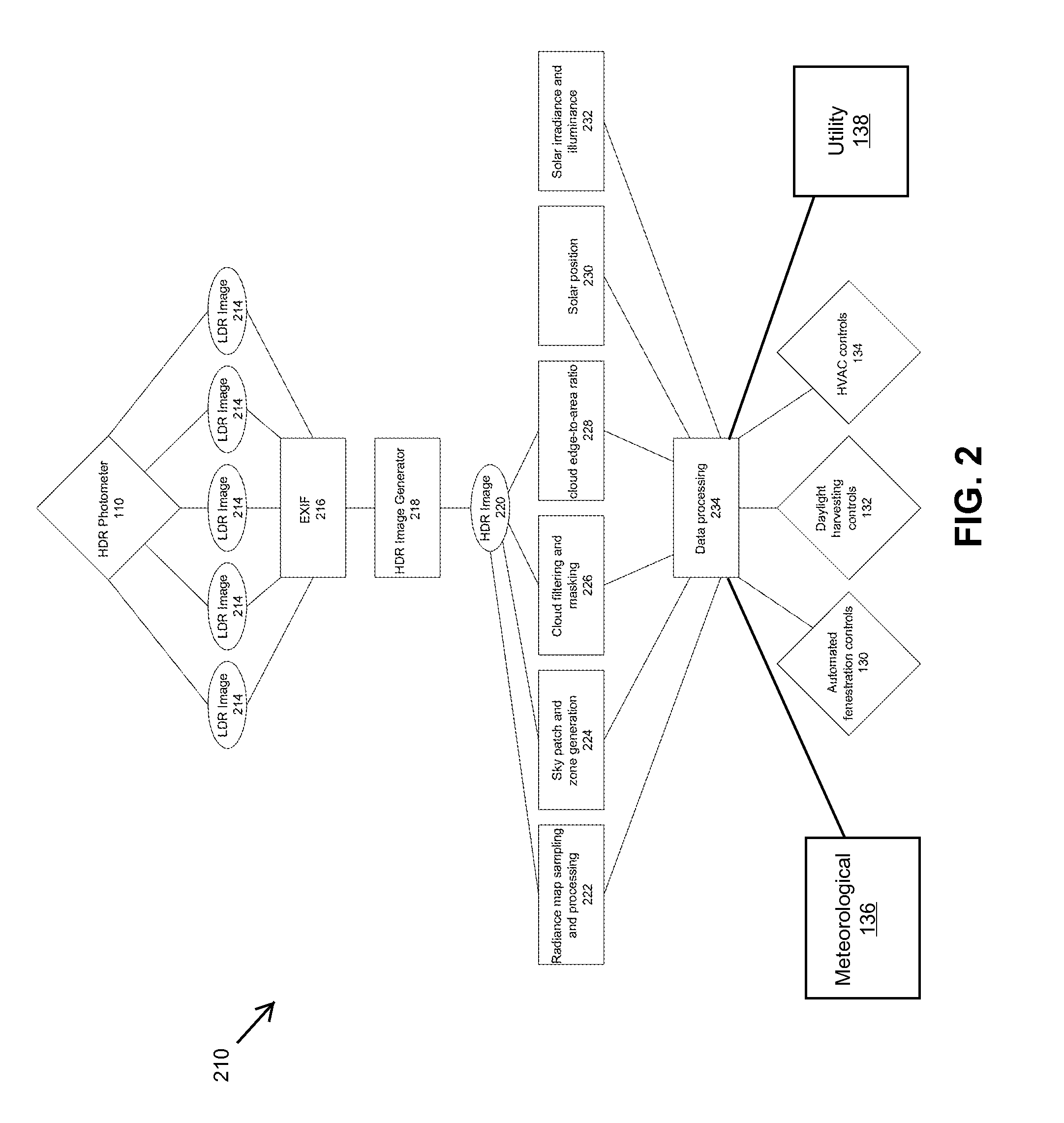
Disclosed is a photometer that employs high dynamic range (HDR) image processing and manipulation algorithms for capturing and measuring real-time sky conditions for processing into control input signals to a building's automated fenestration (AF) system, daylight harvesting (DH) system and HVAC system. The photometer comprises a color camera and a fitted fish-eye lens to capture 360-degree, hemispherical, low dynamic range (LDR) color images of the sky. Both camera and lens are housed in a sealed enclosure protecting them from environmental elements and conditions. In some embodiments the camera and processes are controlled and implemented by a back-end computer.
Owner:KINESTRAL TECH
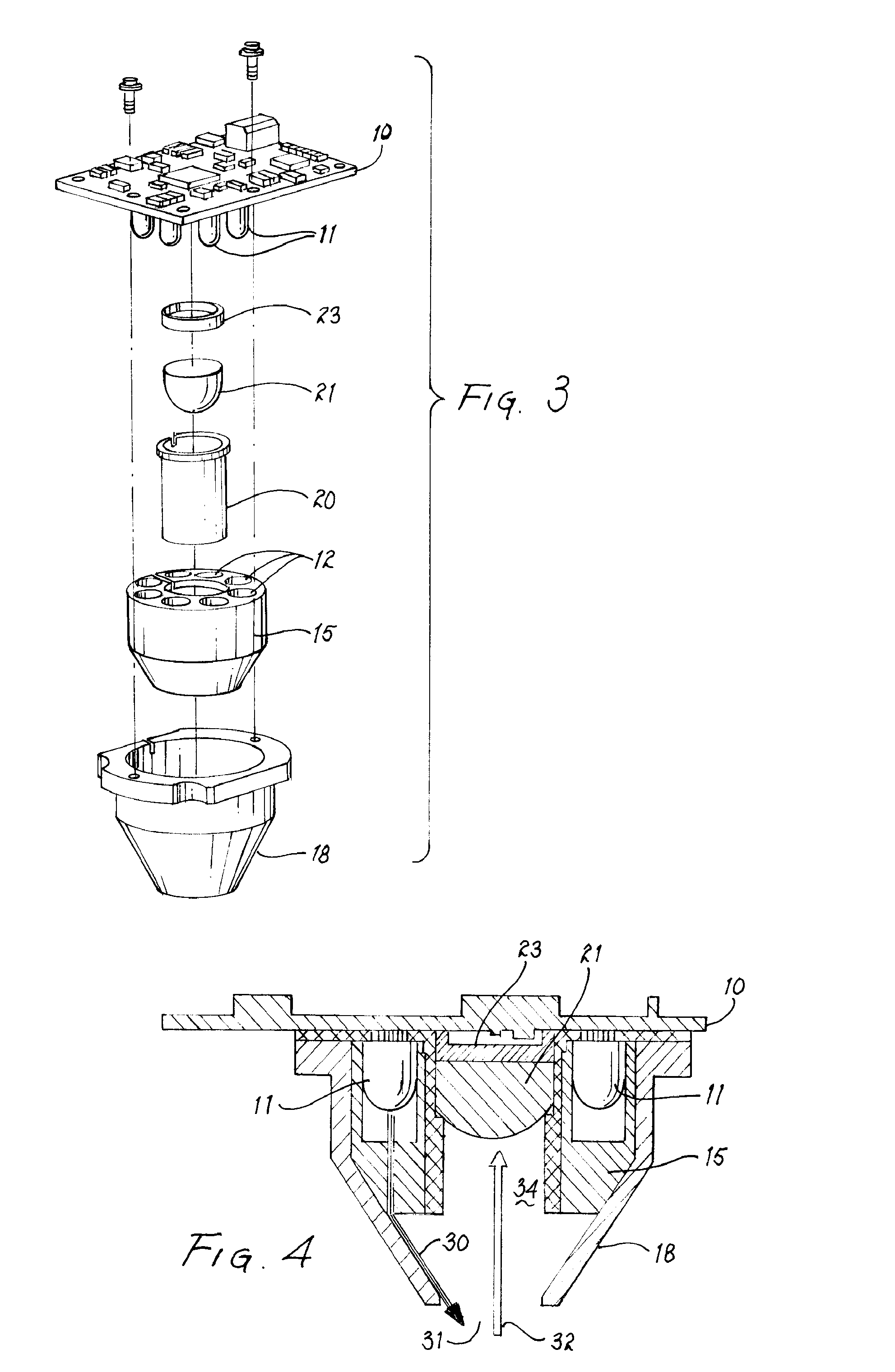
Apparatus for determining multi-bit data via light received by a light receiver and coupled to spectral sensors that measure light in spectral bands
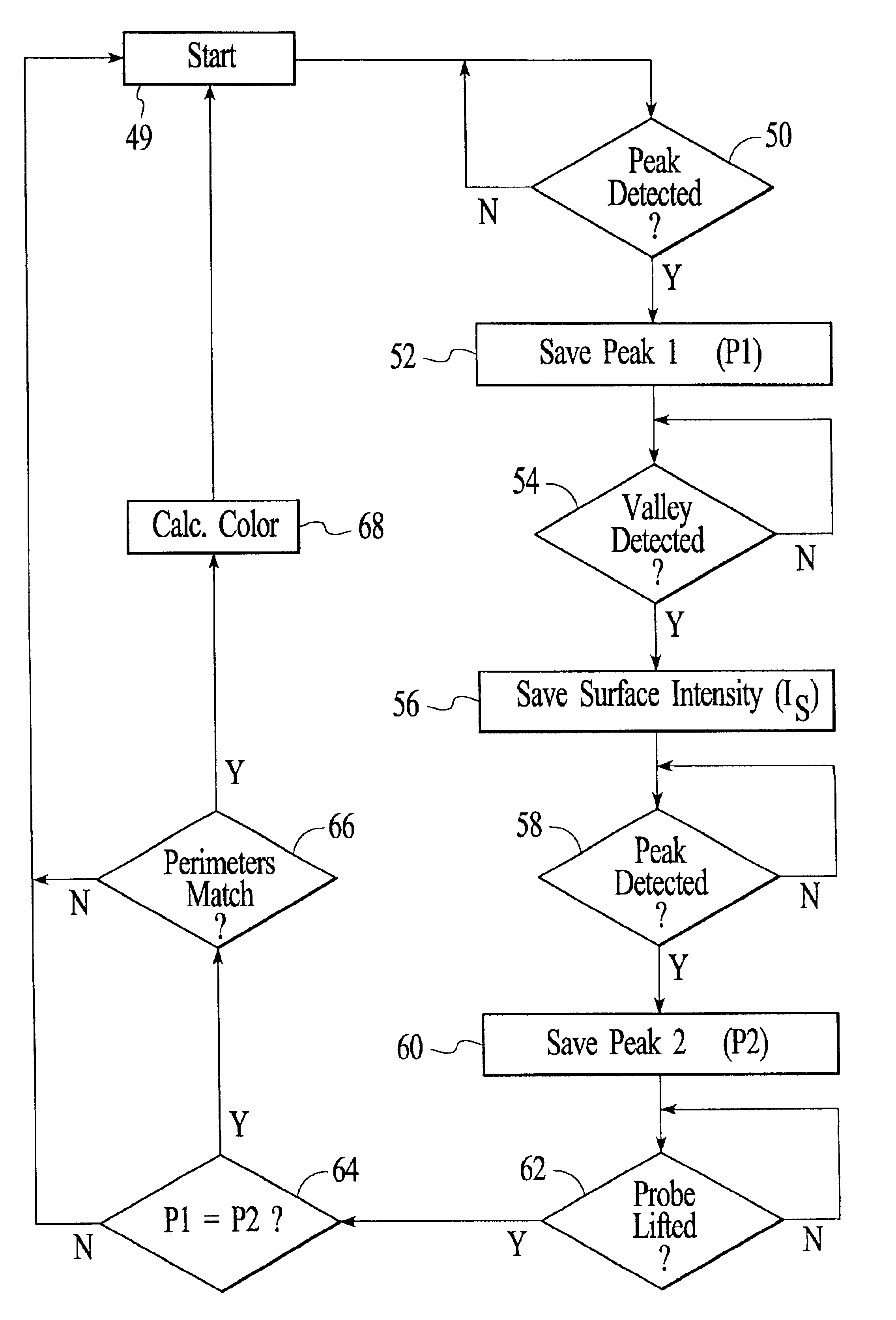
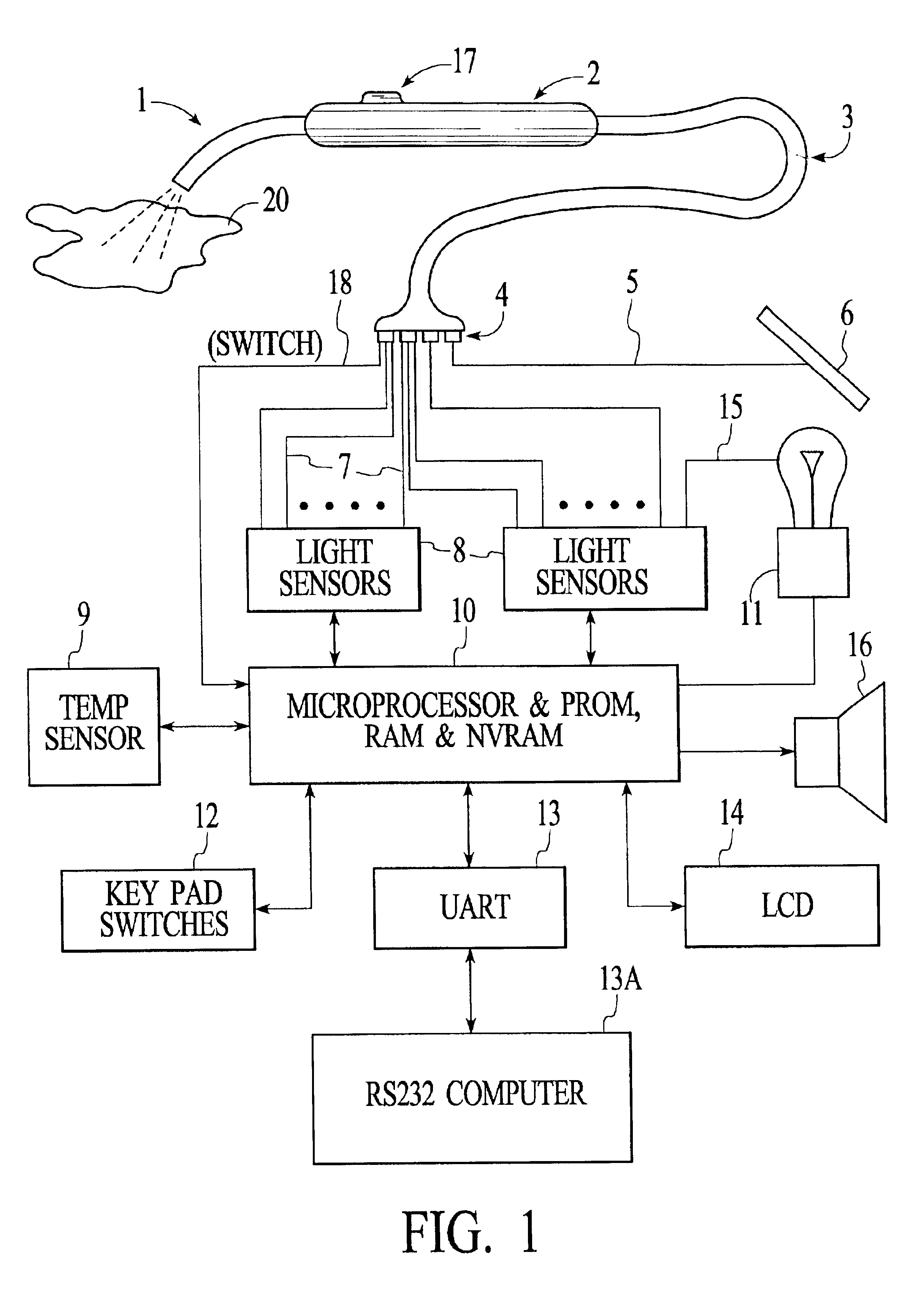
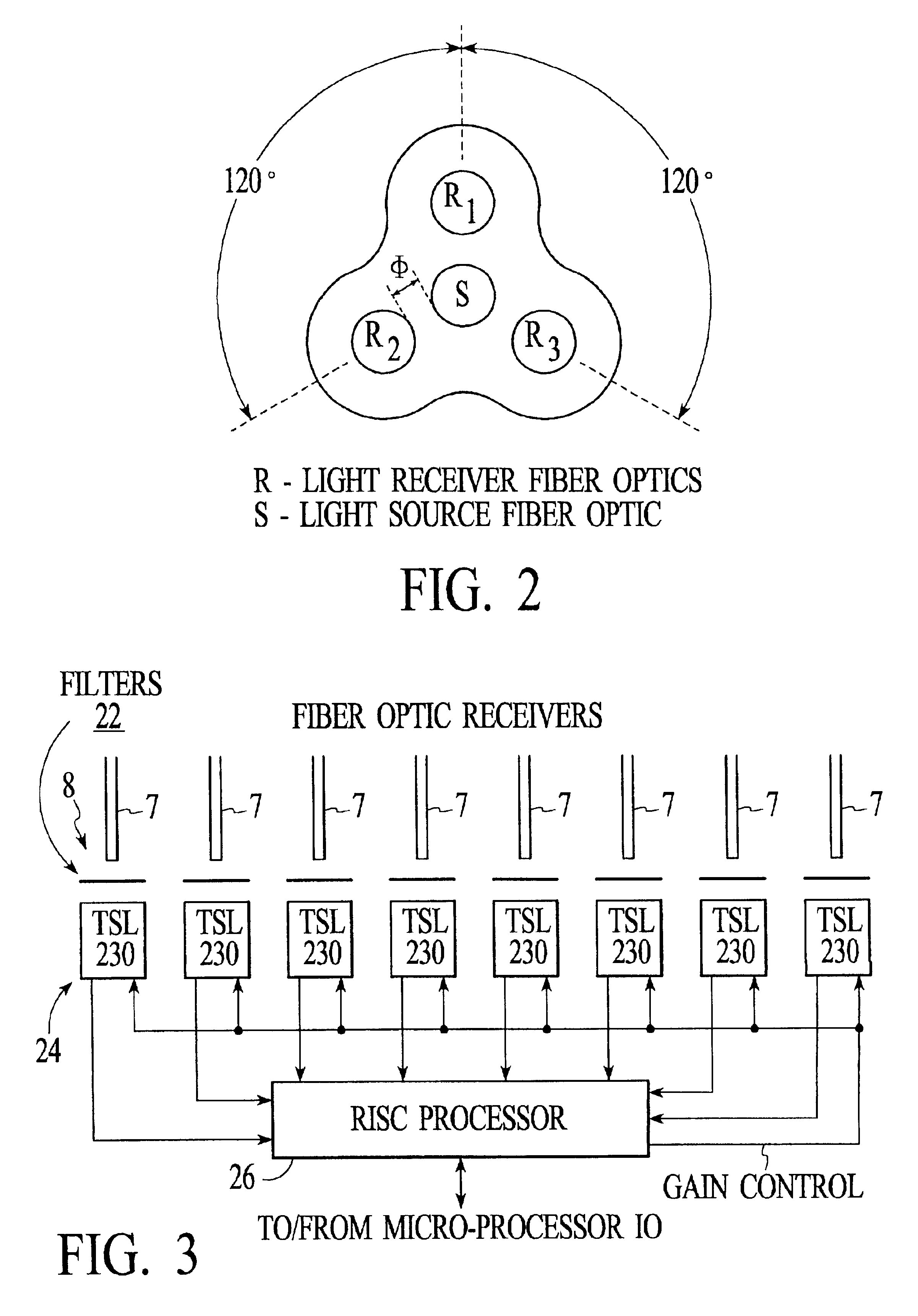
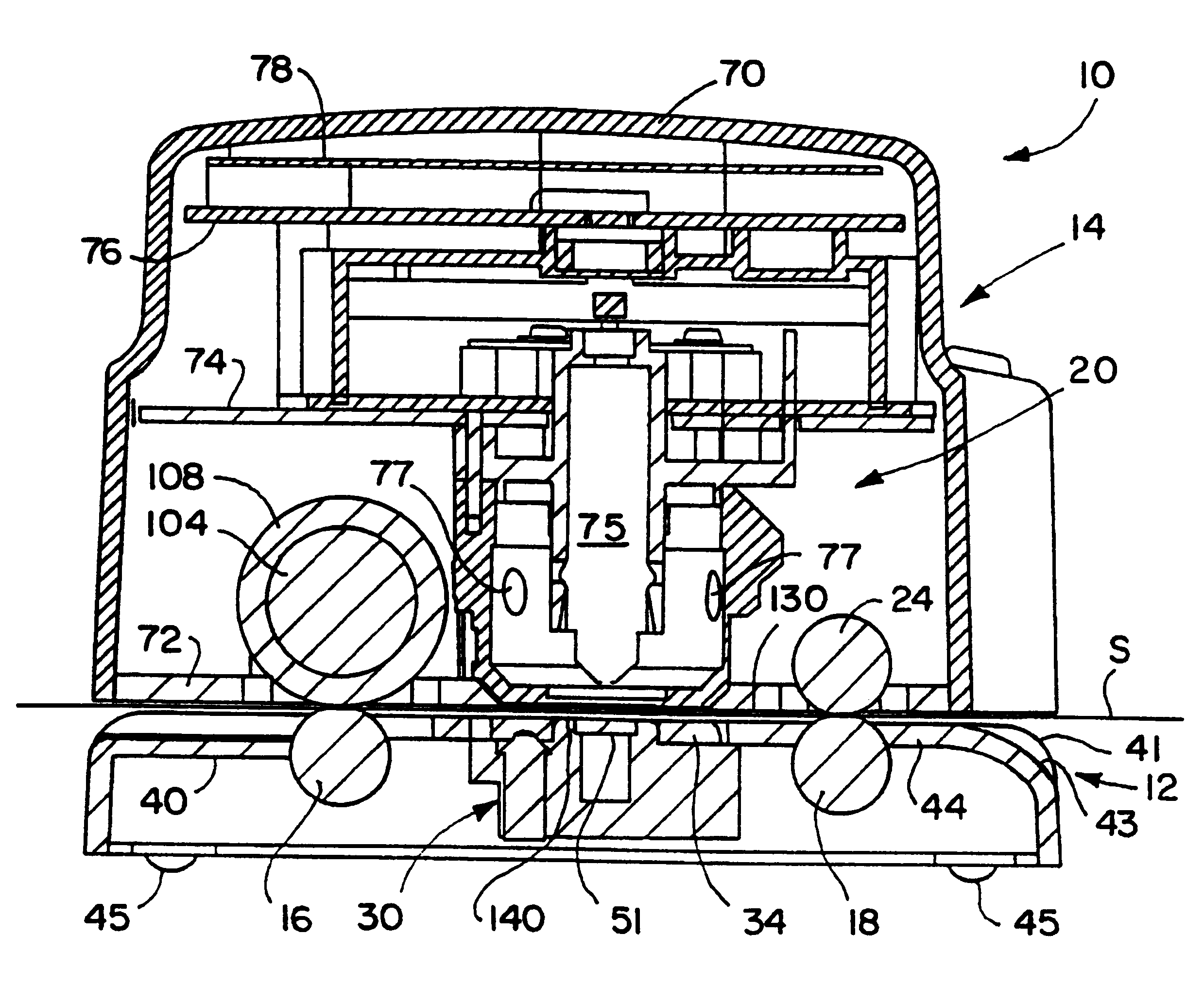
Optical characteristic measuring systems and methods such as for determining the color or other optical characteristics of teeth are disclosed. Perimeter receiver fiber optics preferably are spaced apart from a source fiber optic and receive light from the surface of the object / tooth being measured. Light from the perimeter fiber optics pass to a variety of filters. The system utilizes the perimeter receiver fiber optics to determine information regarding the height and angle of the probe with respect to the object / tooth being measured. Under processor control, the optical characteristics measurement may be made at a predetermined height and angle. Various color spectral photometer arrangements are disclosed. Translucency, fluorescence, gloss and / or surface texture data also may be obtained. Audio feedback may be provided to guide operator use of the system. The probe may have a removable or shielded tip for contamination prevention. A method of producing dental prostheses based on measured data also is disclosed. Measured data also may be stored and / or organized as part of a patient data base. Such methods and implements may be desirably utilized for purposes of detecting and preventing counterfeiting or the like. Low cost and small form factor spectrometers, and methods for manufacturing the same, also are disclosed. Spectrometers and spectrophotometers embedded in printing and scanning and other type devices, as well as computer companion devices, scope-type devices and the like, also are disclosed. Data encoding based on such devices also may be implemented.
Owner:RPX CORP
Portable scanning spectrophotometer
InactiveUS6198536B1Easy maintenanceConvenient registrationRadiation pyrometryMaterial analysis by optical meansEngineeringVarying thickness
Owner:X-RITE
Golf club apparatuses and methods
InactiveUS20120142443A1Simple algorithmWide variationLine/current collector detailsDigital data processing detailsSleep stateSimulation
Methods, apparatuses, machine readable non-transitory storage media, and systems which process measured light values in order to determine the status of a golf club relative to a golf club bag are described. In one embodiment, a system uses a floating threshold, which is between a running bright average and a running dark average, to determine whether to add a current light meter value to one or the other of these running averages. In another embodiment, a system resets or re-seeds the running averages so that re-seeded averages are used after exiting from a sleep state such as a dark sleep state. In another embodiment, a system uses light sensor information or other sensor information to determine when a club is in use. Other embodiments are also described.
Owner:RADER
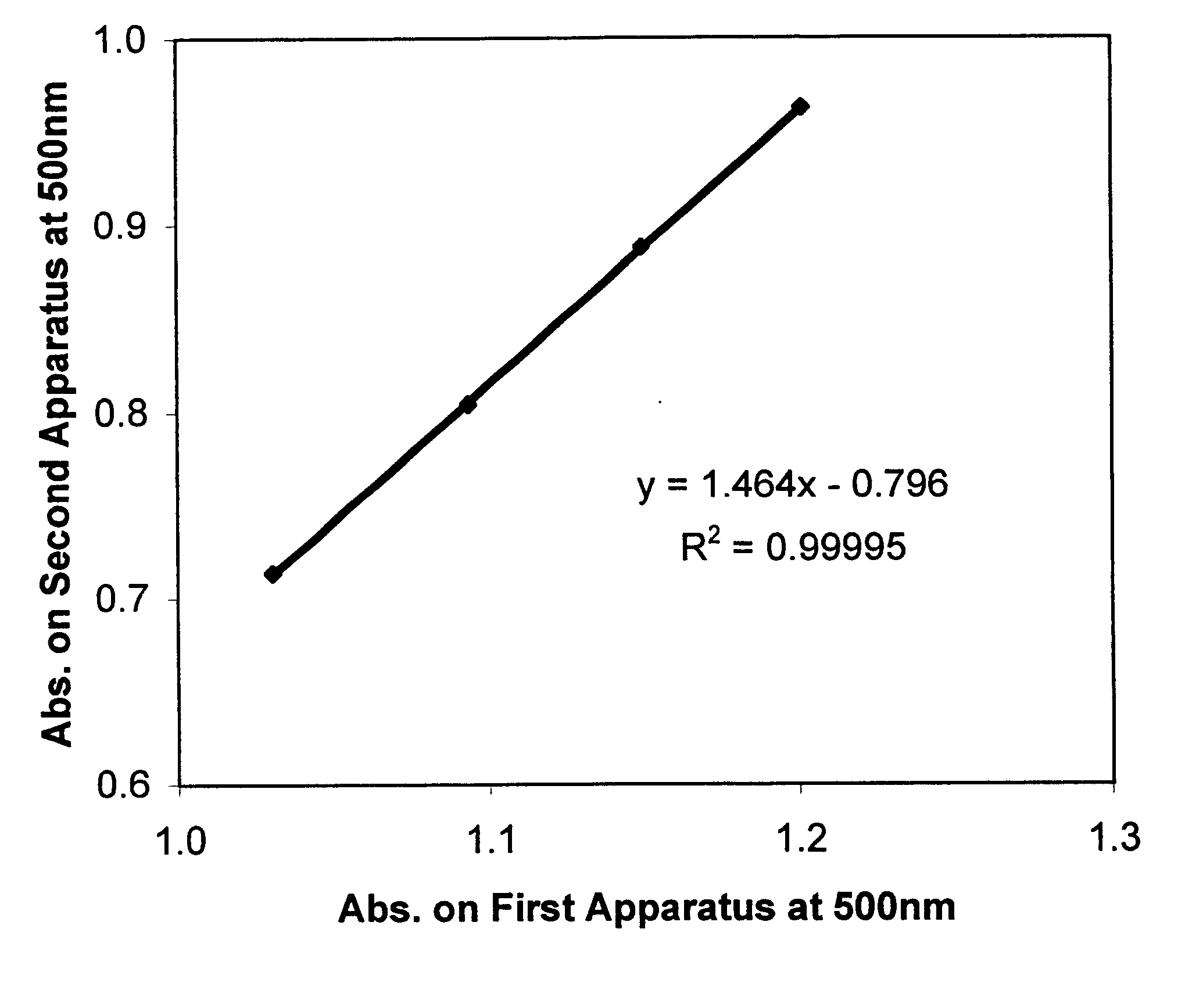
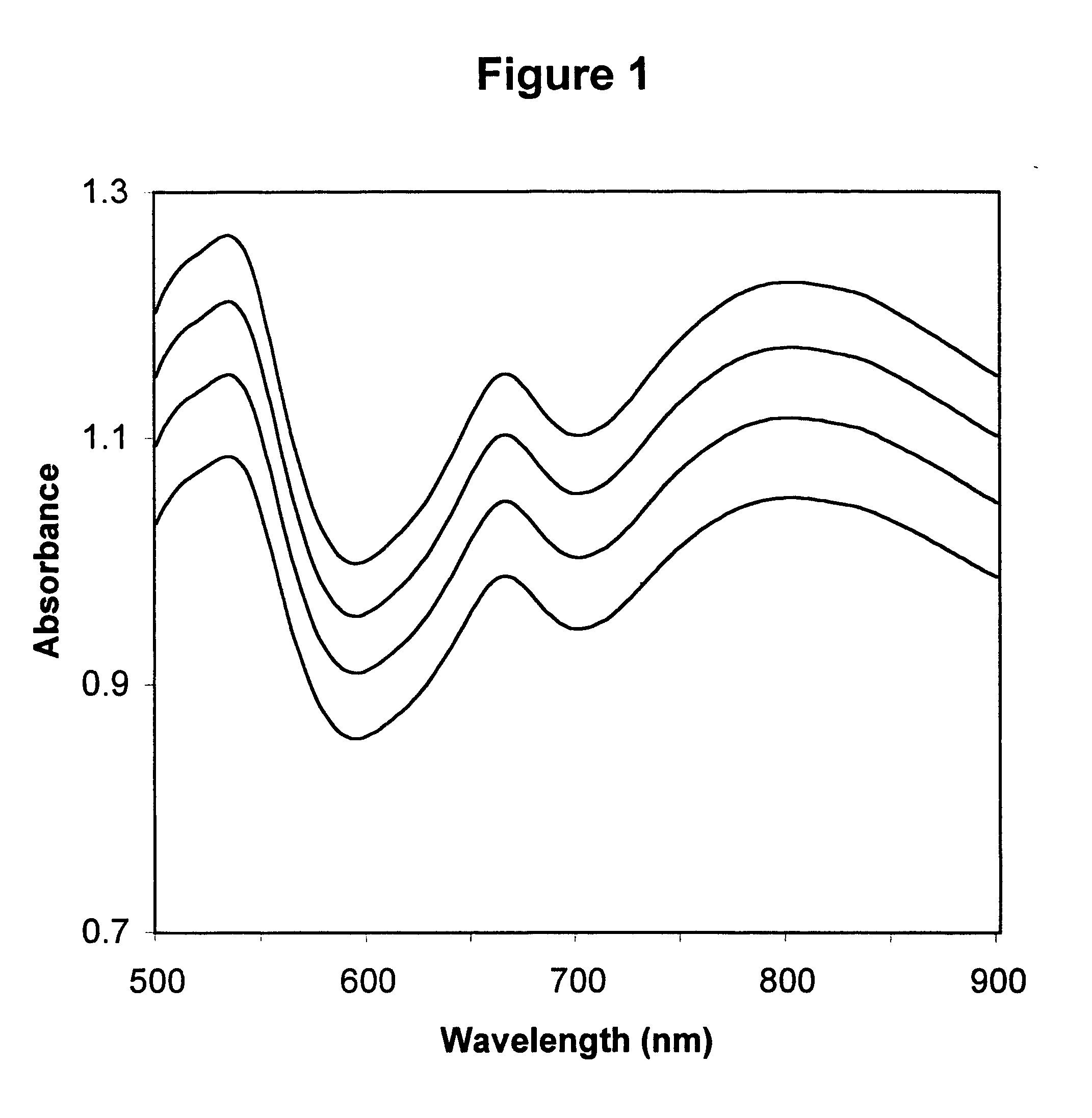
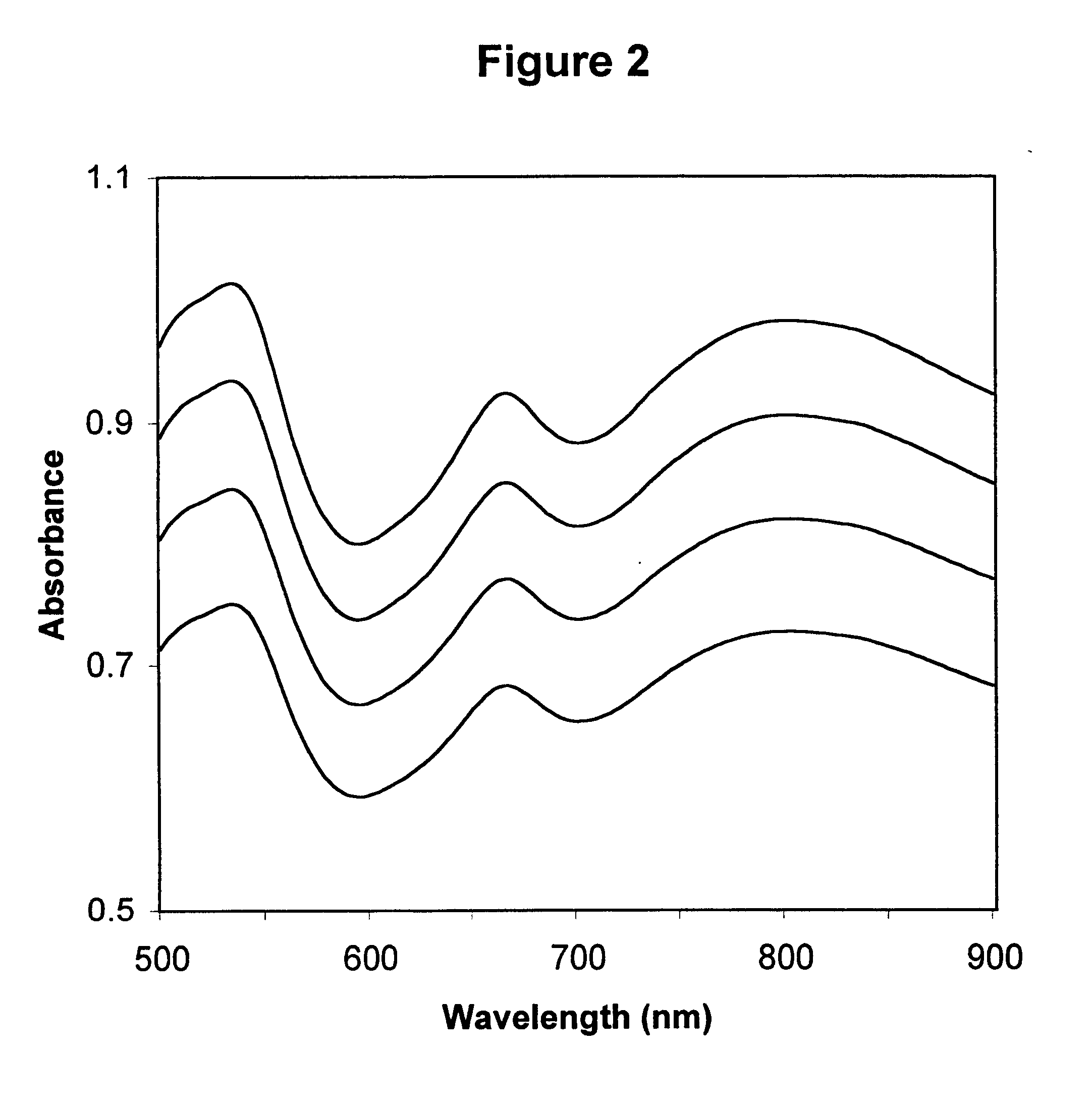
Method for calibrating spectrophotometric apparatus with synthetic fluids to measure plasma and serum analytes
InactiveUS6470279B1Testing/calibration apparatusScattering properties measurementsSample MeasureAnalyte
Described is a method for calibrating a spectrophotometric apparatus which is used to measure analytes in plasma and / or serum samples based on the calibration of a First Apparatus, and for recalibrating such apparatus, including recalibration of the First Apparatus all using synthetic calibrators. These apparatus use absorption of radiation to measure analytes in serum or plasma samples. The method described includes using synthetic calibrators which are submitted to the First Apparatus for measurement and compared with measurements of similar calibrators in a Second Apparatus and using the comparison to derive concentrations of analytes in samples measured on the Second Apparatus. As an alternative to making all apparatus identical, in terms of wavelength calibration, the absorbances of all apparatus should be mapped onto a standard set of wavelengths.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Fiber optic light mixer
InactiveUS6892006B2Improved light mixer structureHigh degreeRadiation pyrometryDiagnostic recording/measuringFiberEngineering
An optical structure for combining light from a plurality of individual optical fibers into a single optical transmission device. The structure can be incorporated into the optical probe of a spectrophotometric instrument and includes a plurality of optical send fibers having input and output ends and an optical light mixer having input and output ends. The output ends of the send fibers are secured in optical communication with the input end of the light mixer.
Owner:HUTCHINSON TECH
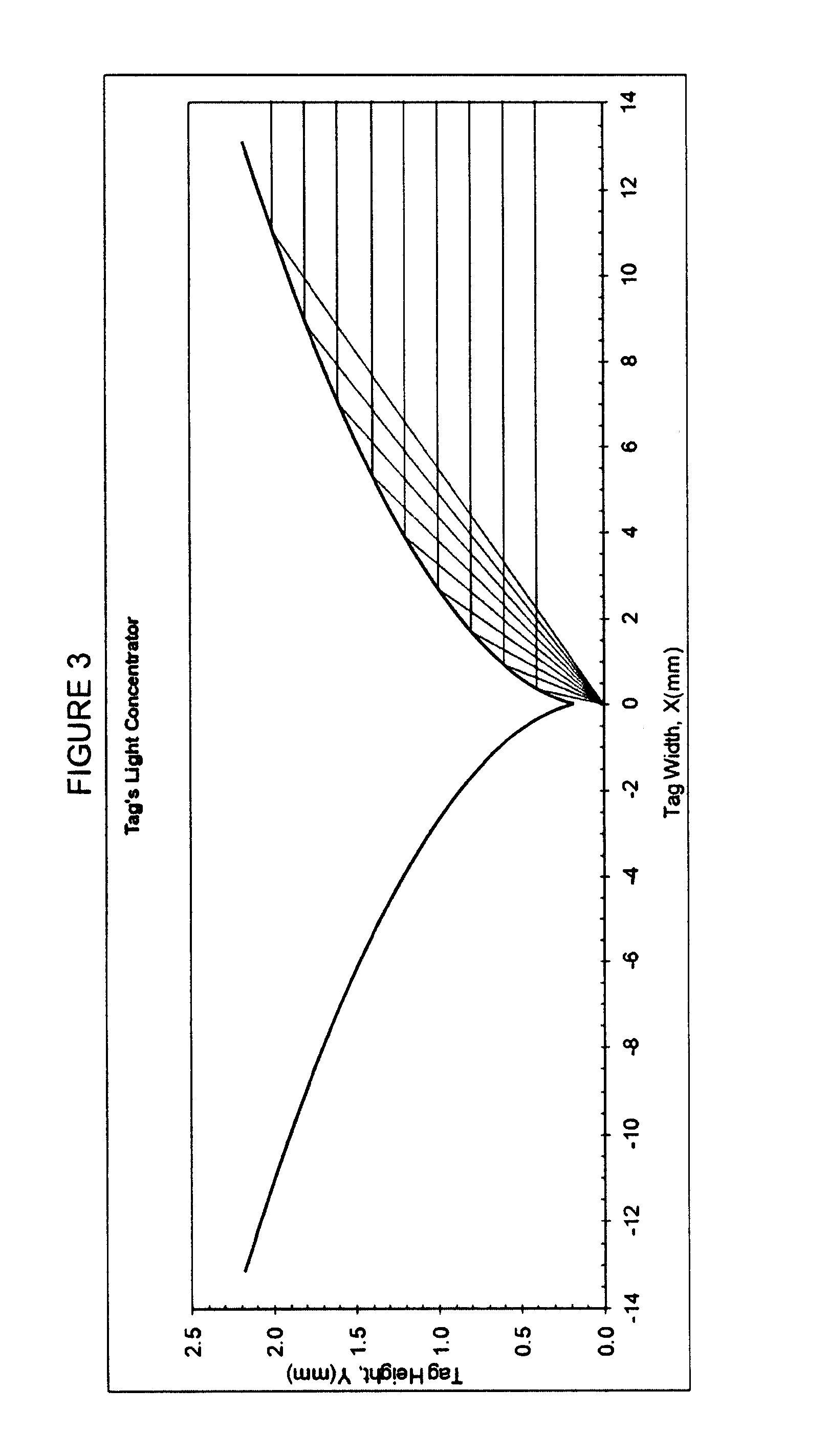
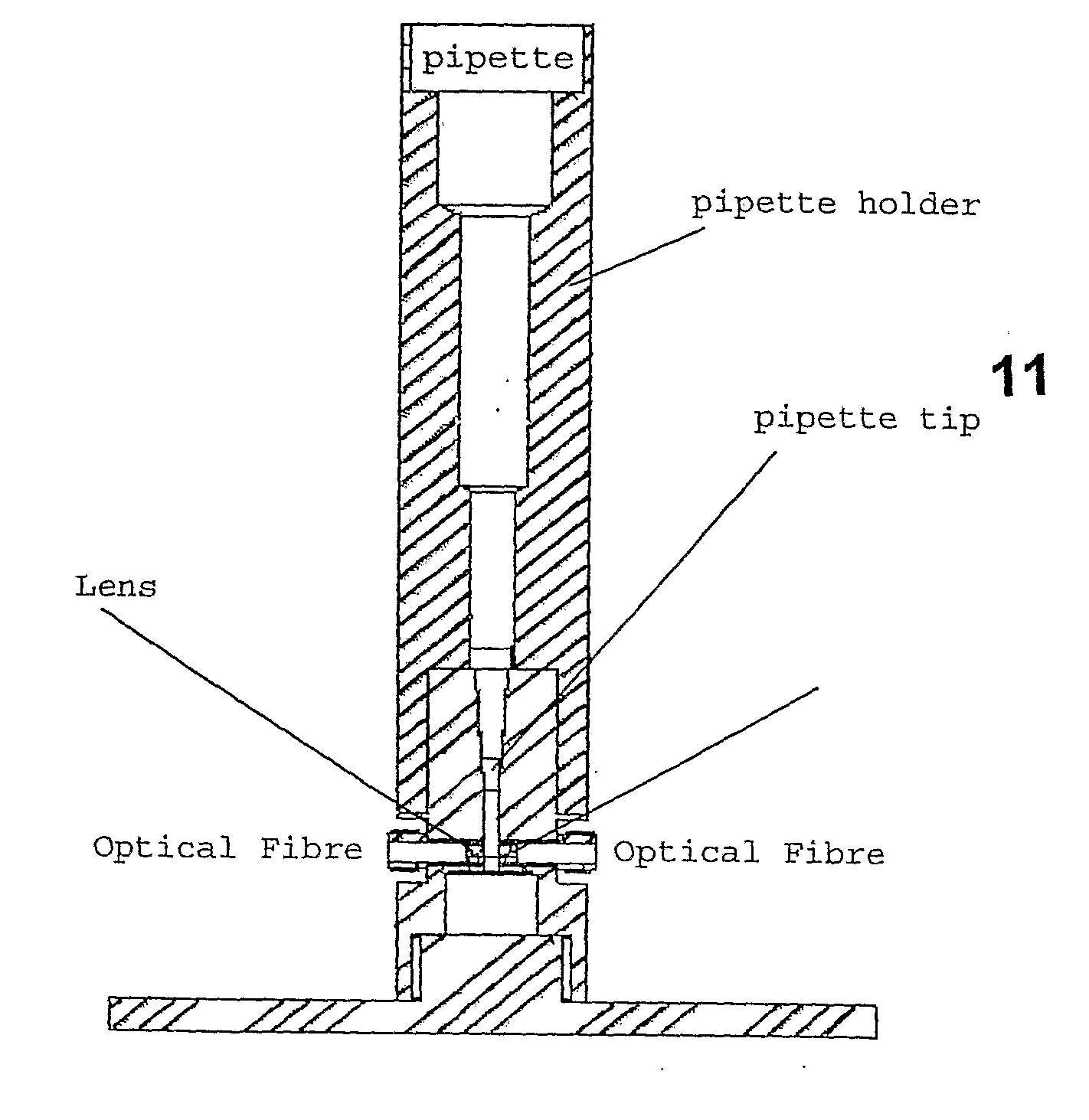
Liquid Photometry
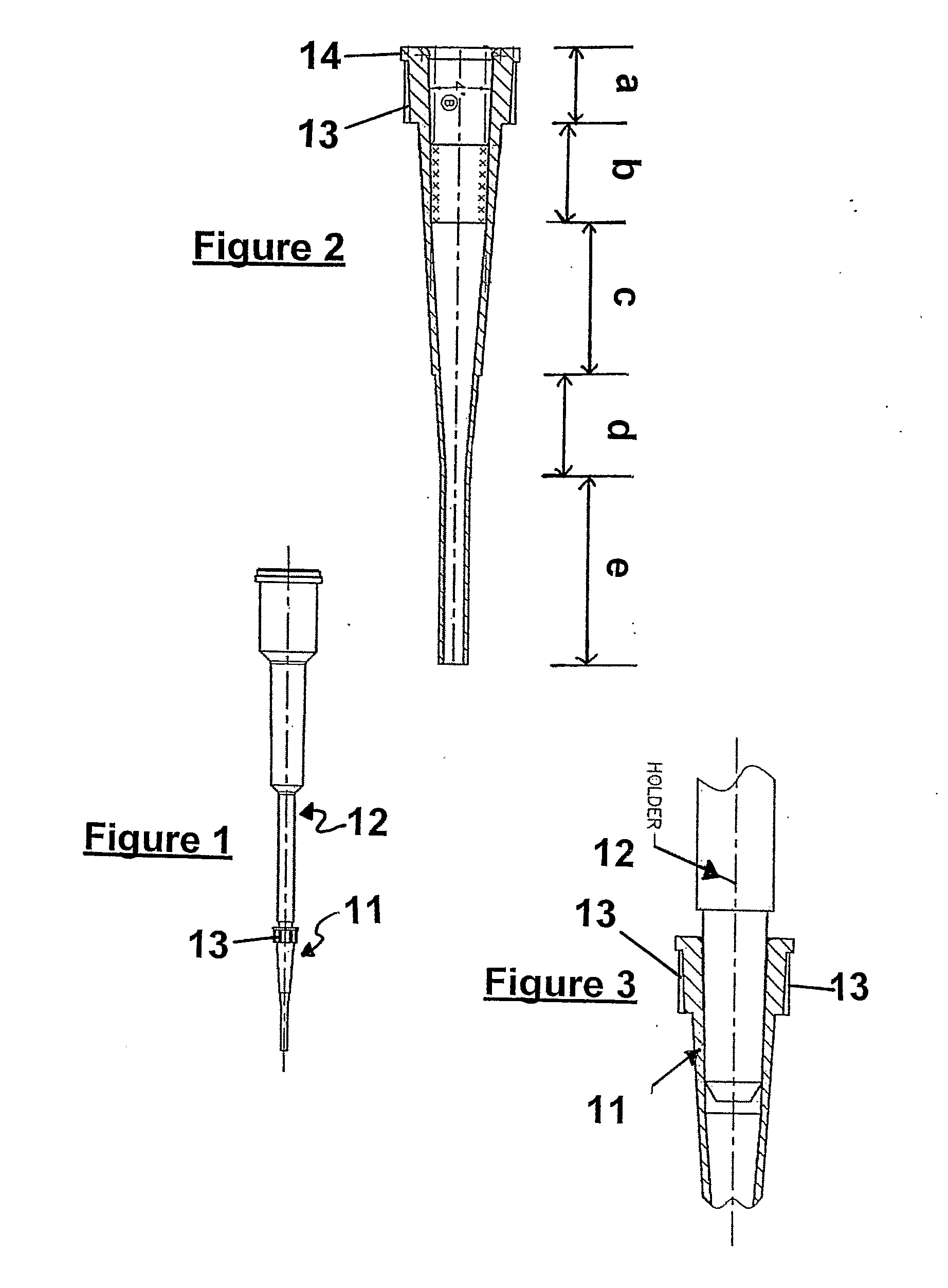
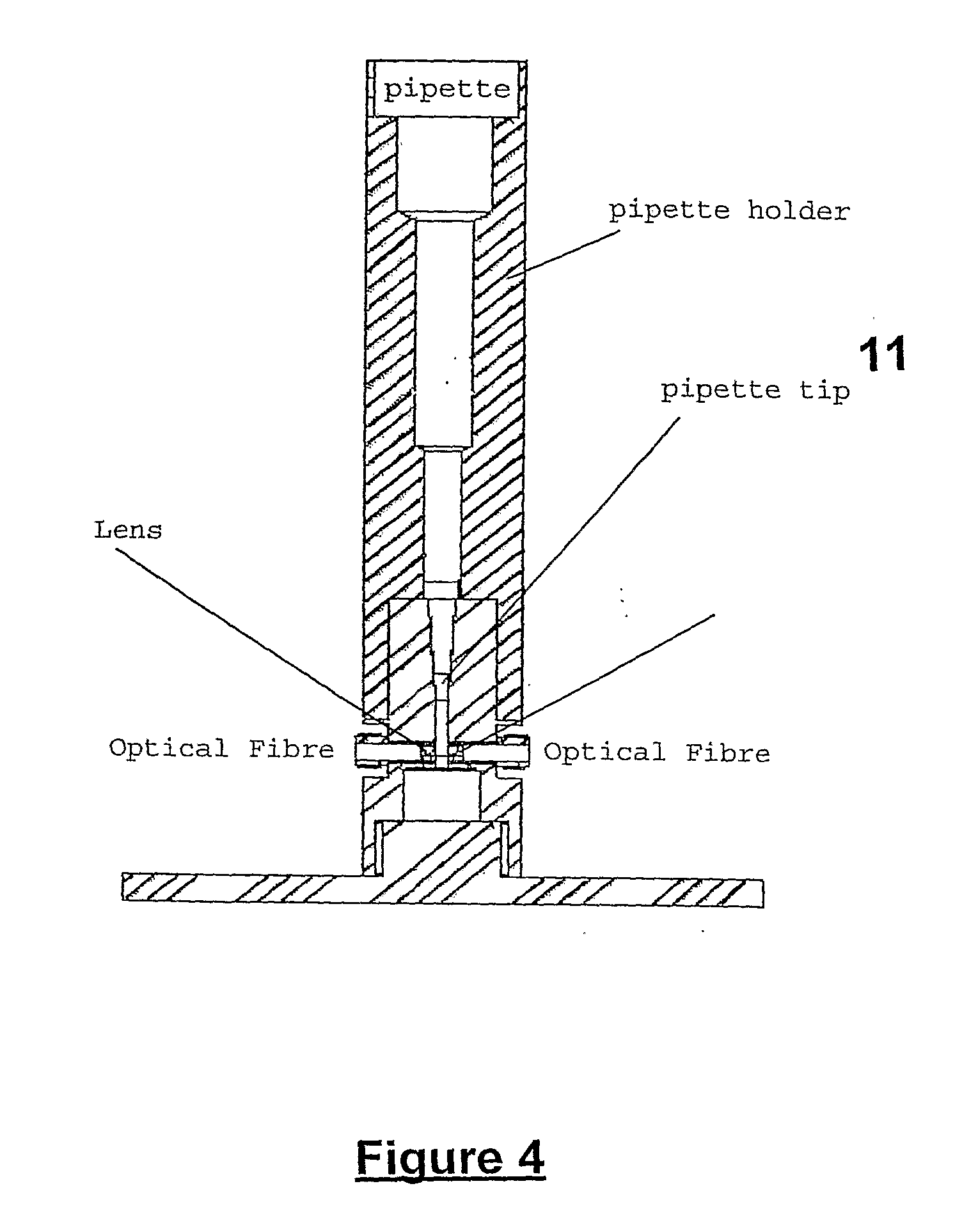
InactiveUS20080253933A1Analysis using chemical indicatorsAnalysis by subjecting material to chemical reactionPipetteLuminosity
A photometric or spectrophotometric apparatus and method wherein a sample is contained in a pipette held between two surfaces, one containing a photometric or spectrophotometric source and the other a photometric or spectrophotometric detector and an optical path is established through the walls of the pipette tip and through the sample between the two surfaces. Use of a disposable pipette tip which may be left attached to pipette tip during sample analysis or reattached to the pipette device following analyses, provides a means to recover the sample for subsequent applications and manipulations, and enables especially small volume samples to be analysed.
Owner:REDFERN JONATHAN
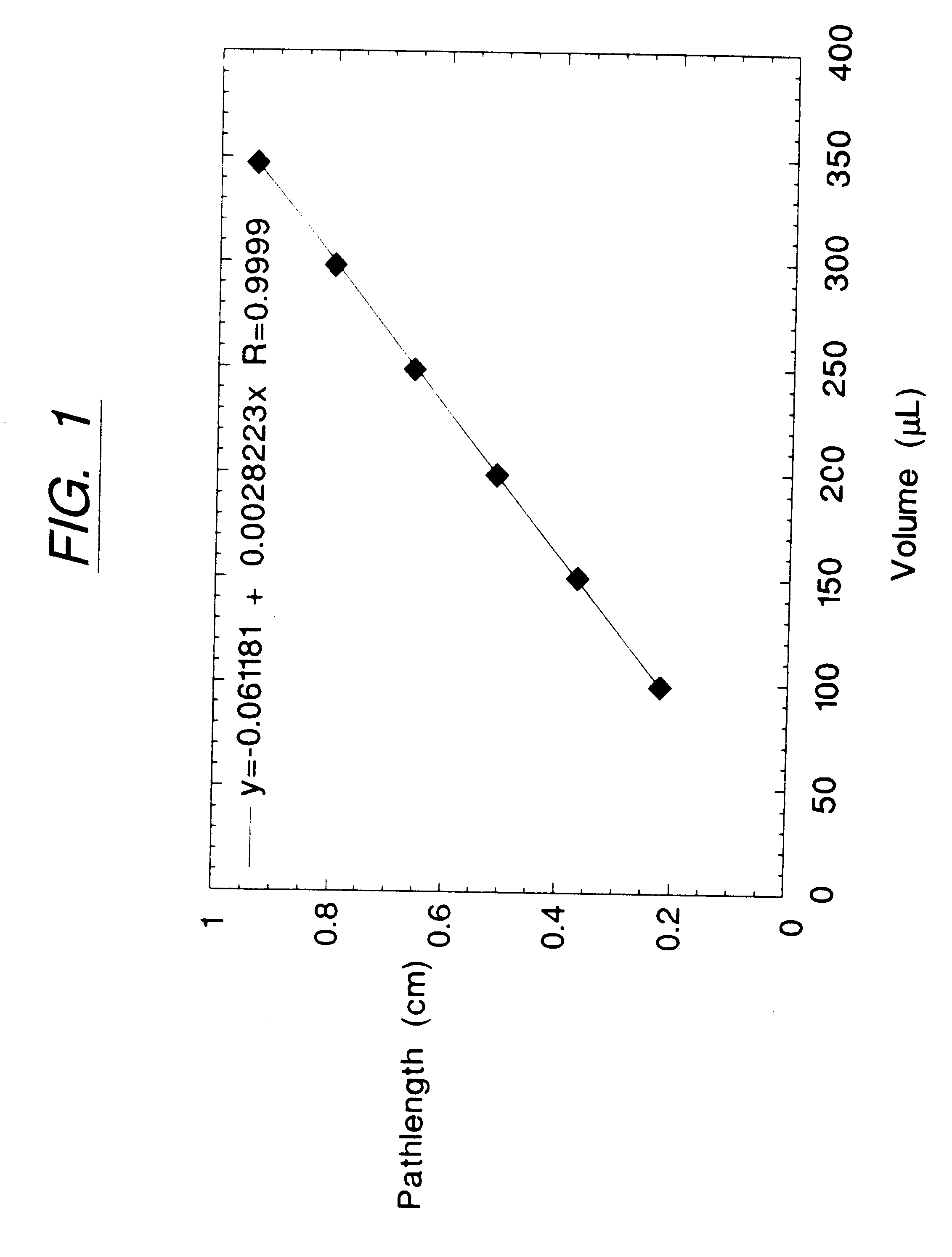
Determination of light absorption pathlength in a vertical-beam photometer
InactiveUS6188476B1Volume measurement apparatus/methodsColor/spectral properties measurementsAnalyteLight beam
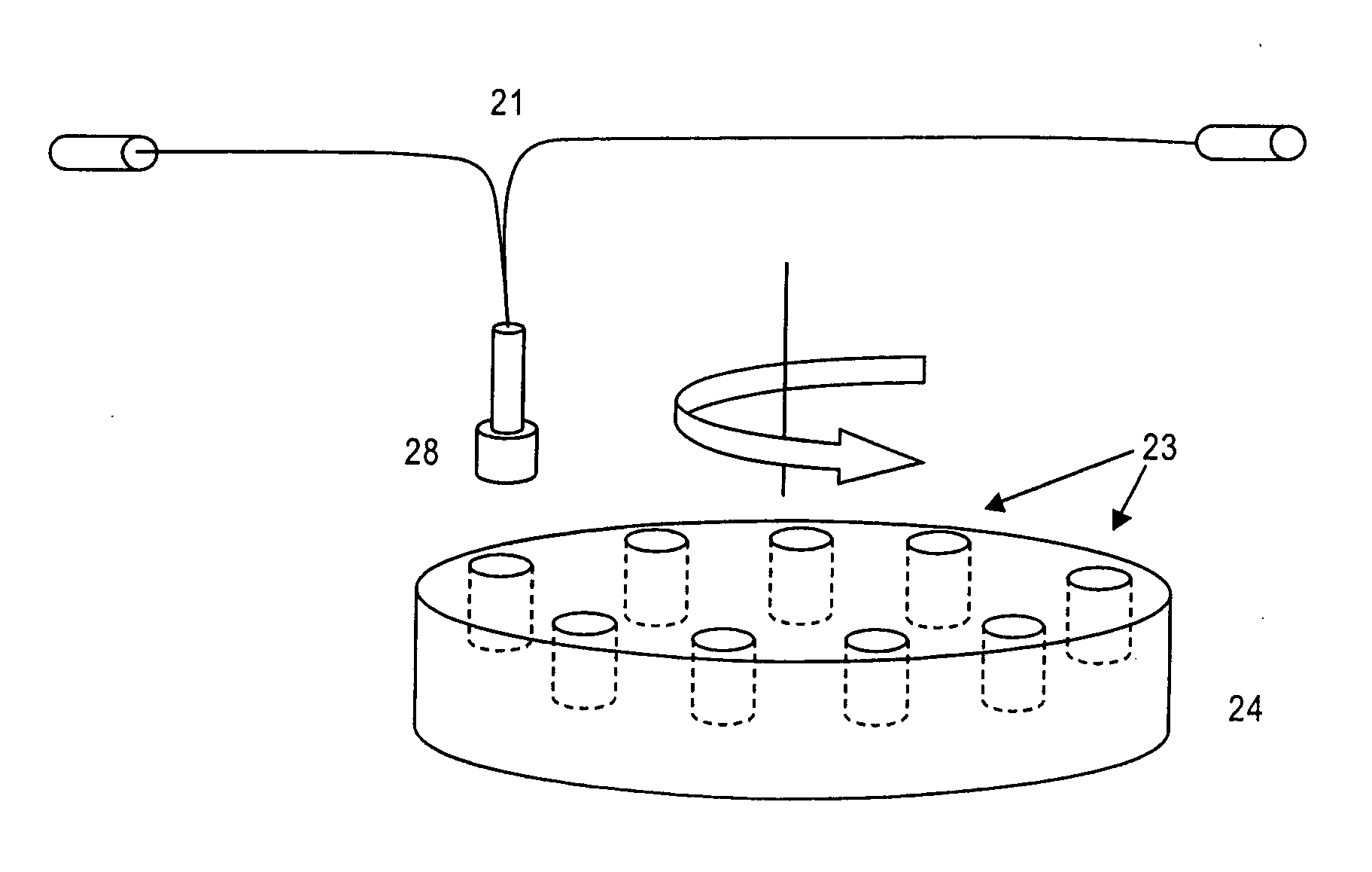
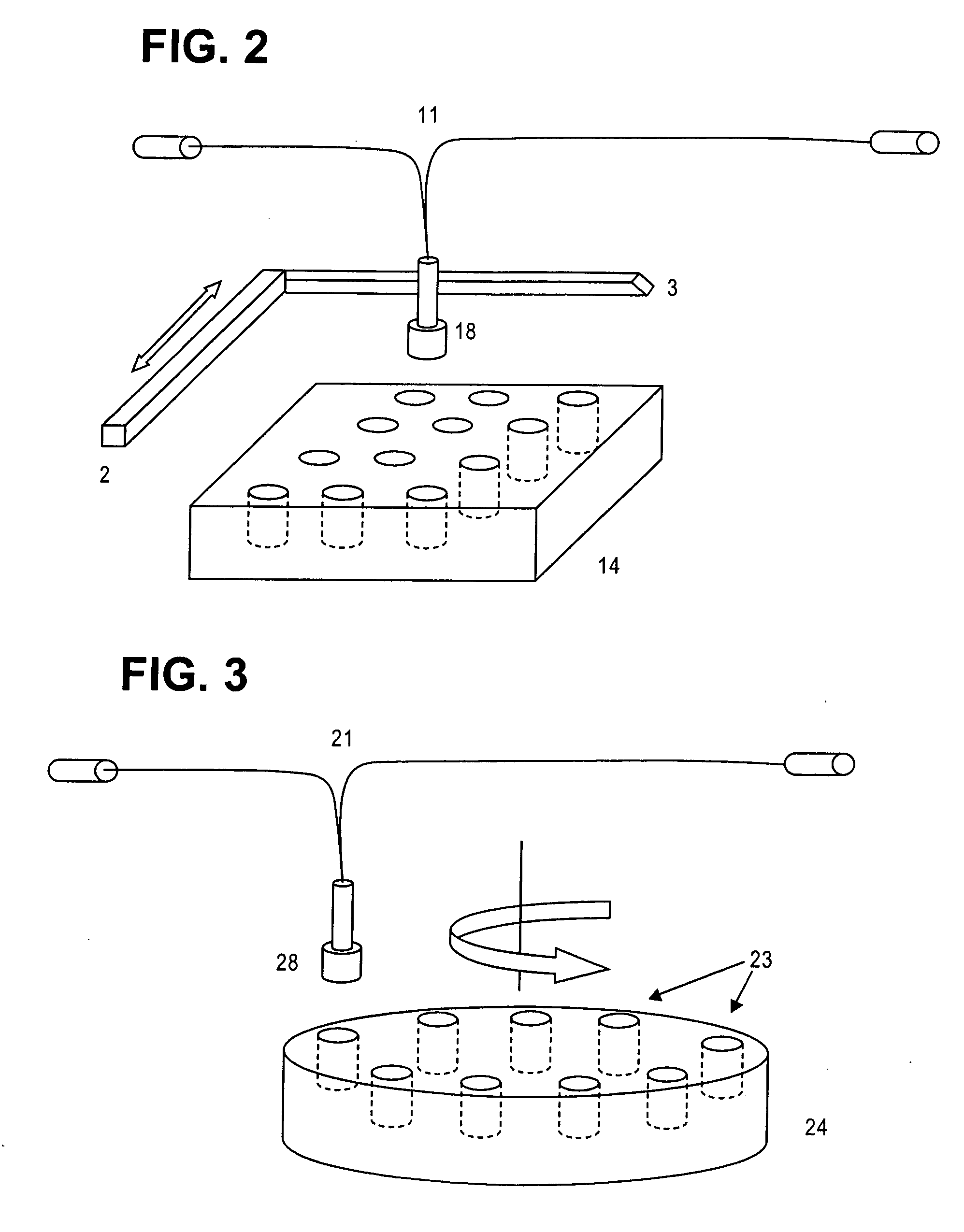
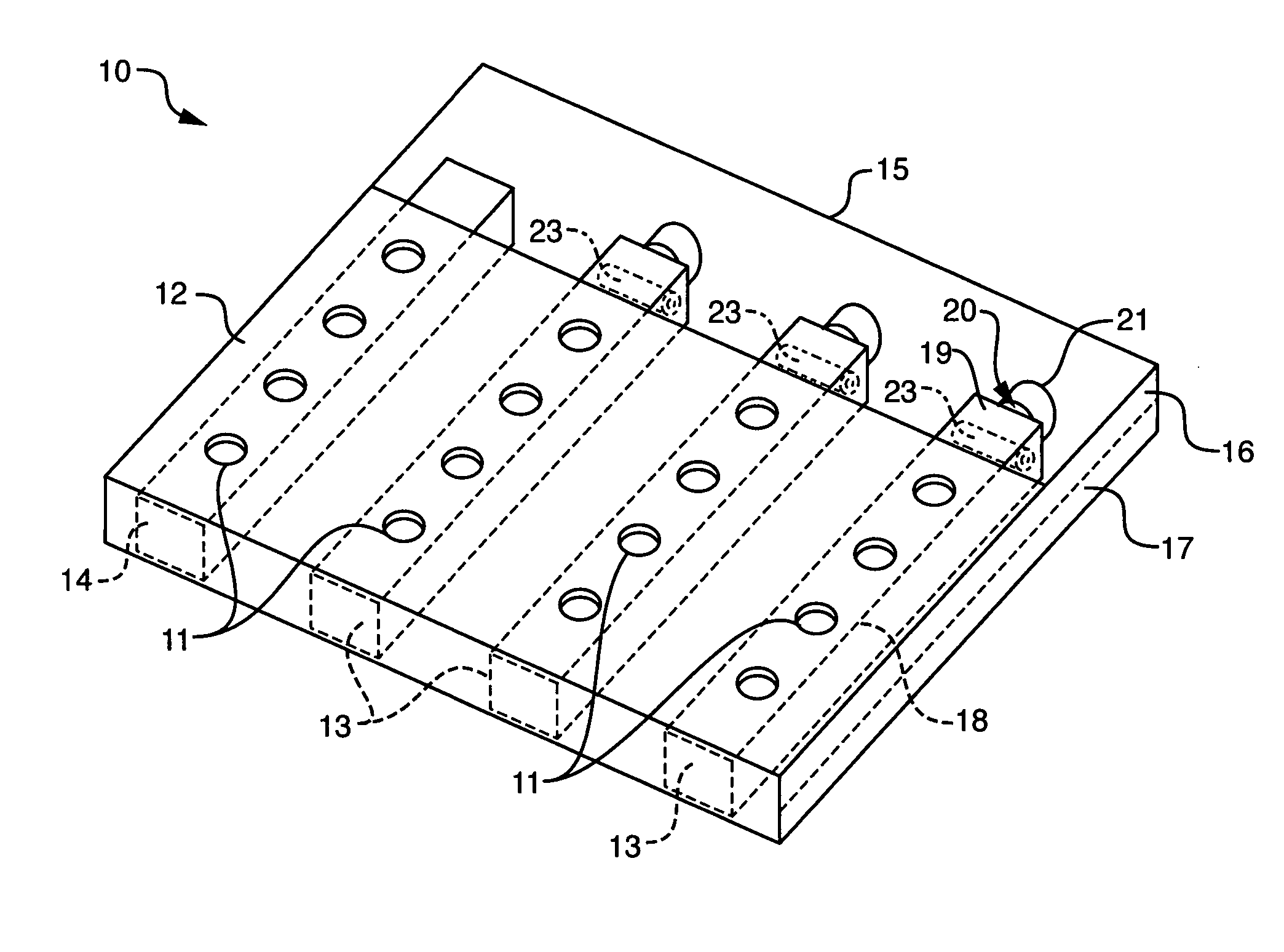
Disclosed are photometric methods and devices for determining optical pathlength of liquid samples containing analytes dissolved or suspended in a solvent. The methods and devices rely on determining a relationship between the light absorption properties of the solvent and the optical pathlength of liquid samples containing the solvent. This relationship is used to establish the optical pathlength for samples containing an unknown concentration of analyte but having similar solvent composition. Further disclosed are methods and devices for determining the concentration of analyte in such samples where both the optical pathlength and the concentration of analyte are unknown. The methods and devices rely on separately determining, at different wavelengths of light, light absorption by the solvent and light absorption by the analyte. Light absorption by the analyte, together with the optical pathlength so determined, is used to calculate the concentration of the analyte. Devices for carrying out the methods particularly advantageously include vertical-beam photometers containing samples disposed within the wells of multi-assay plates, wherein the photometer is able to monitor light absorption of each sample at multiple wavelengths, including in the visible or UV-visible region of the spectrum, as well as in the near-infrared region of the electromagnetic spectrum. Novel photometer devices are described which automatically determine the concentration of analytes in such multi-assay plates directly without employing a standard curve.
Owner:MOLECULAR DEVICES
Bi-directional boat running and emergency light apparatus and method
InactiveUS7794124B2Easy to viewLess likely to burn outNon-electric lightingPoint-like light sourceEffect lightDirectional antenna
A boat running light and emergency light apparatus and method comprising a plurality of radially projecting lights, at least one axially upward projecting light and at least one photometer, wherein the at least one photometer senses the amount of illumination from the plurality of radially projecting lights. Upon a reduction or cessation of illumination caused by failure of one or more of the plurality of radially projecting lights, the plurality of radially projecting lights are turned off and the axially upward projecting lights are illuminated to notify boaters of a faulty light while still providing redundant lighting. Additionally, the boat light is capable of flashing SOS in Morse code during an emergency situation. The lights are preferably high intensity directional light emitting diodes.
Owner:HULSEY MICHAEL
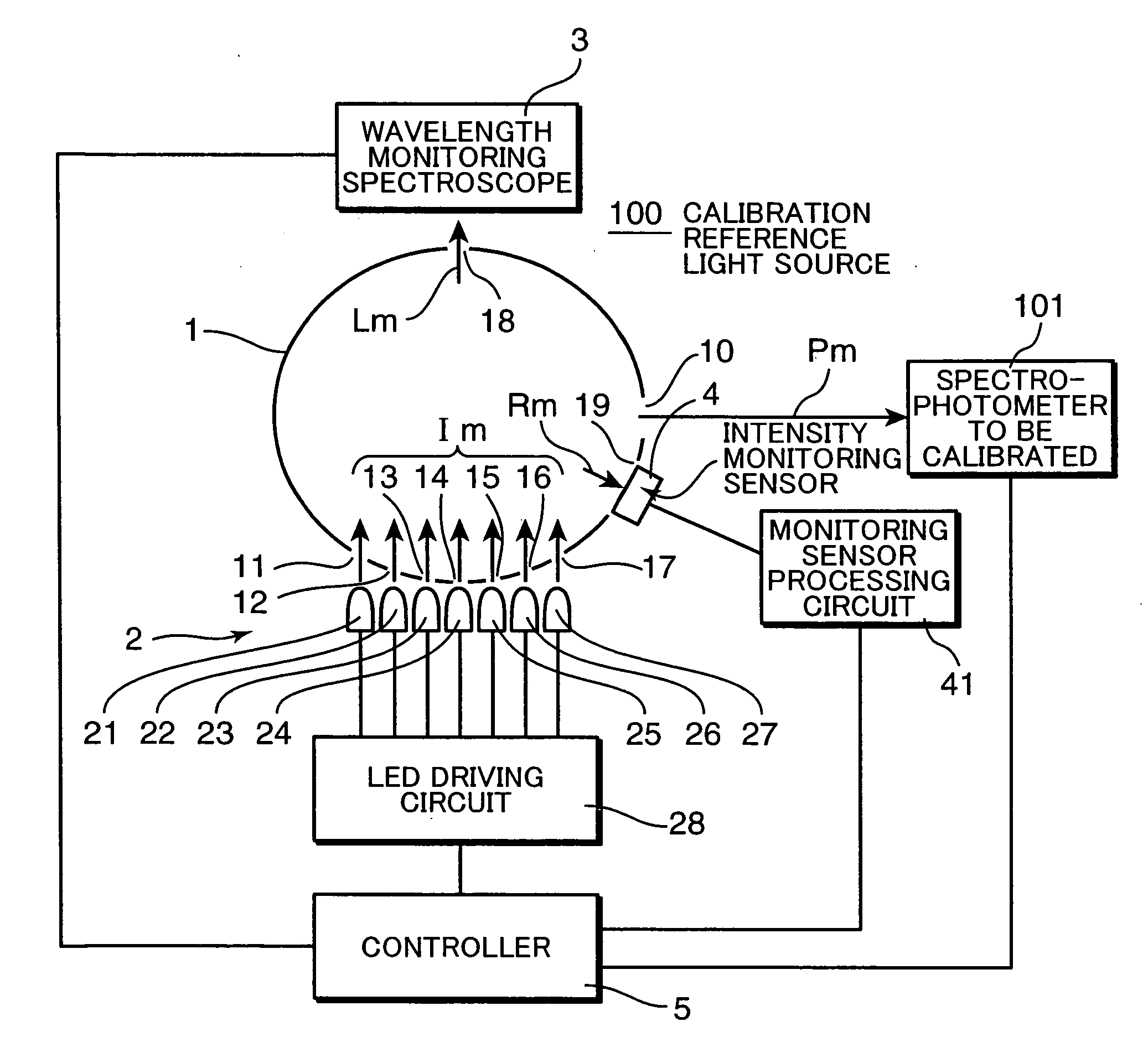
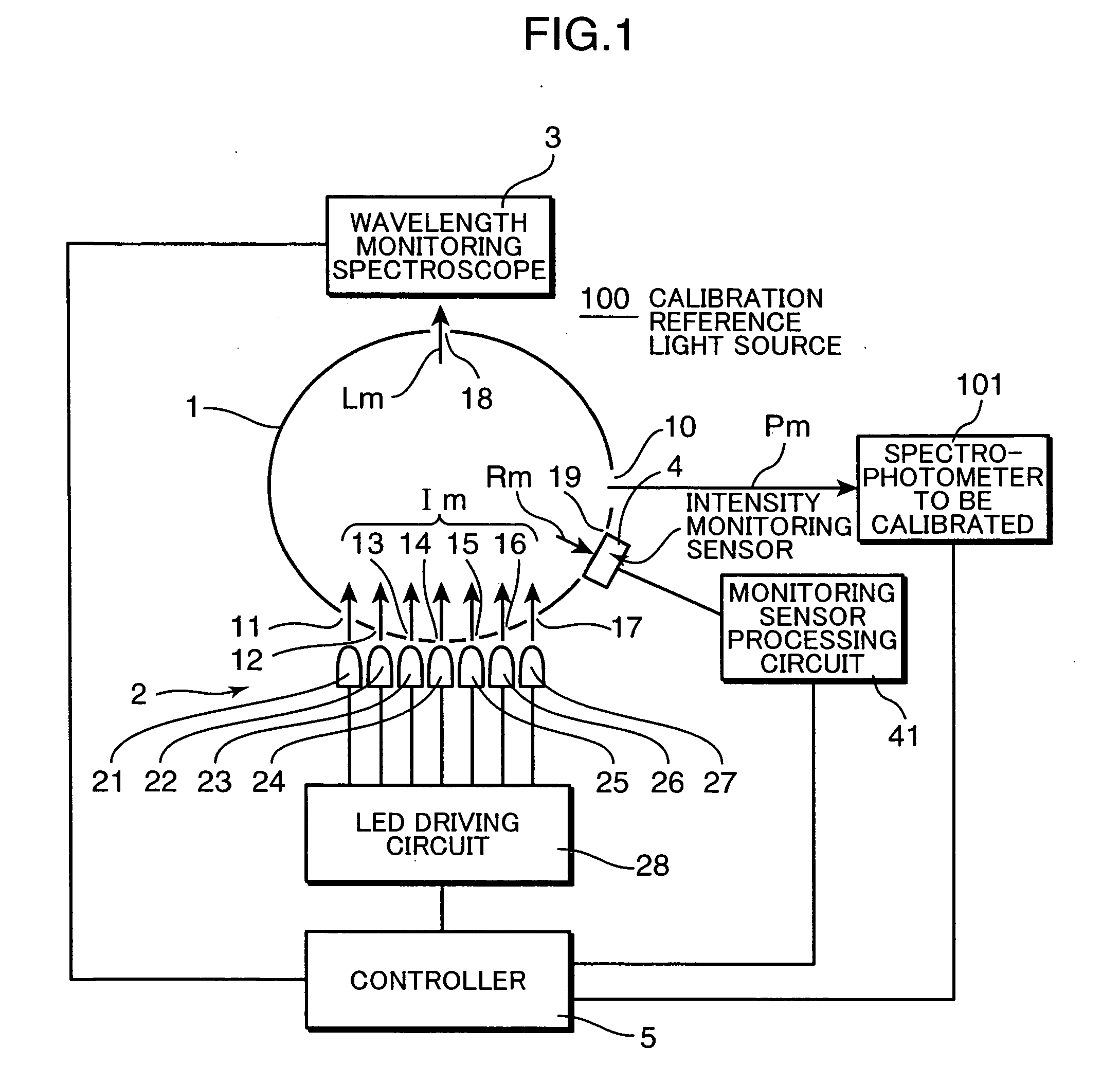
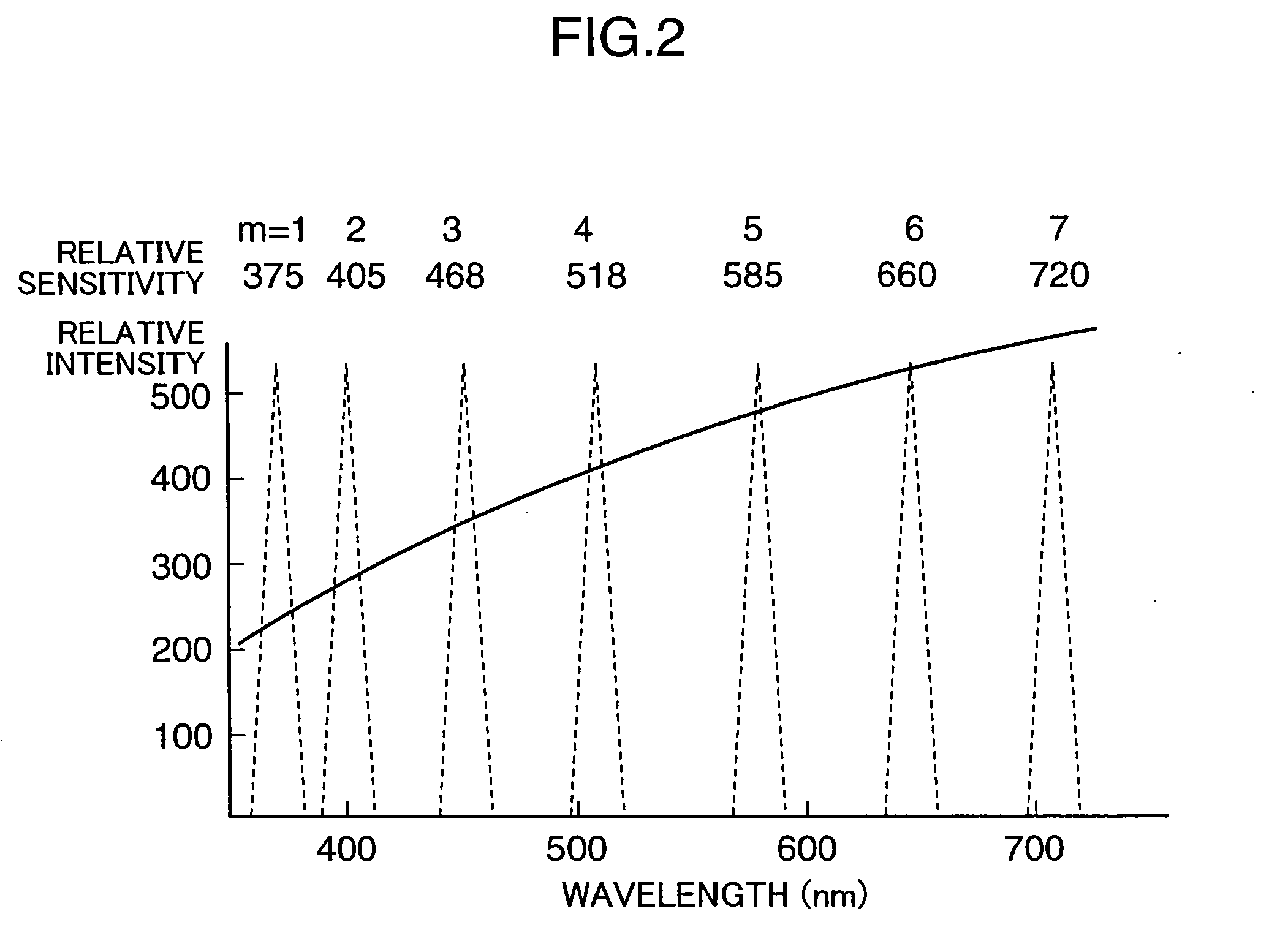
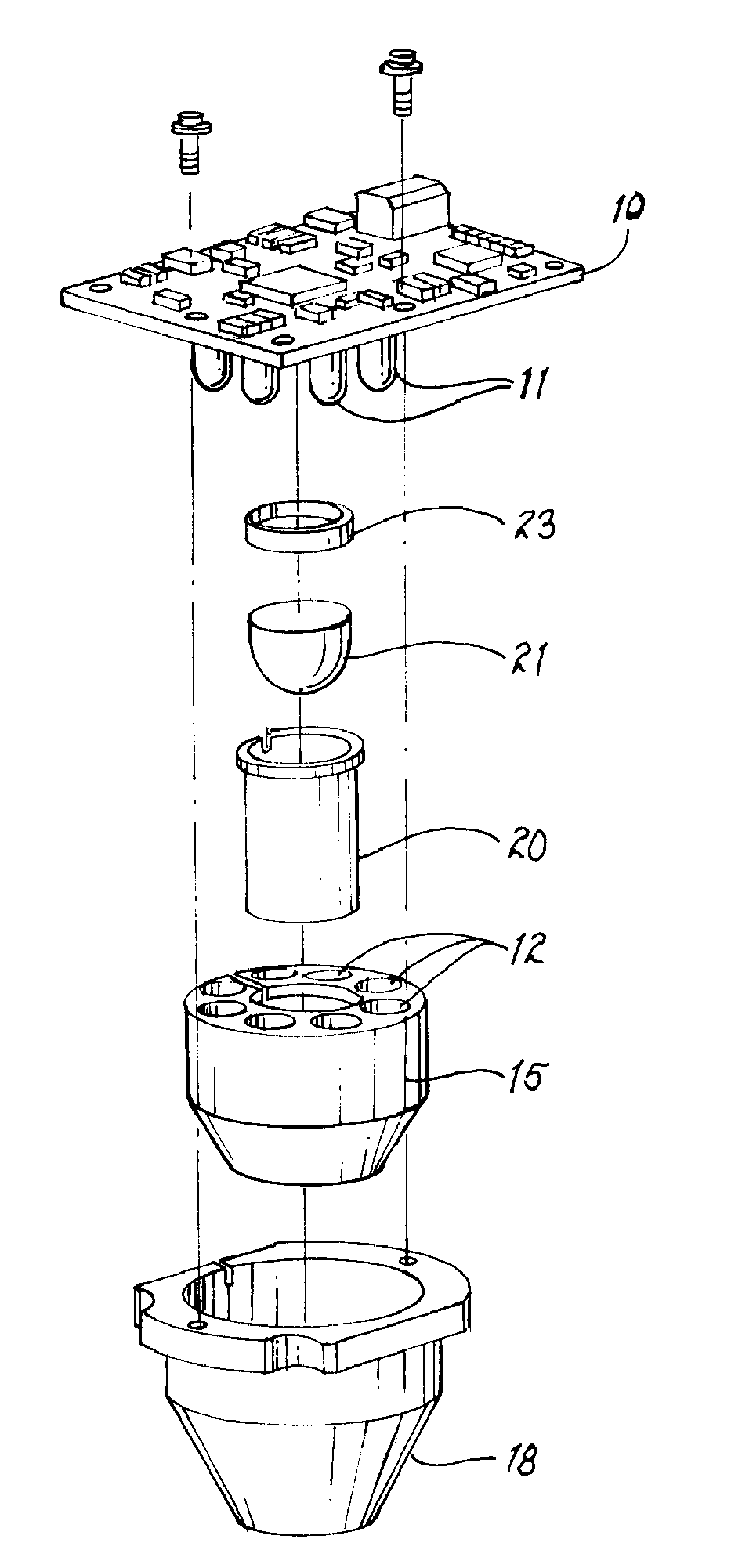
Calibration reference light source and calibration system using the same
InactiveUS20090051910A1Improve accuracyImprove reliabilityPhotometry using reference valueRadiation pyrometryBlack-body radiationRadiance
In a calibration reference light source and a sensitivity calibration system using the same, a plurality of single-wavelength light sources for emitting reference lights having mutually different single-wavelengths are used instead of a black body radiation source for radiating a white light, and not only the intensities of the single-wavelength reference lights, but also the wavelengths thereof are measured to obtain sensitivity correction coefficients of intensity-to-radiance conversion data. Thus, obtained reference radiance are highly reliable and sensitivity correction of spectrophotometers and spectral illuminometers can be performed with high accuracy and reliability at a user side, whereby the calibration reference light source and the calibration system using the same can be obtained at low cost.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA SENSING INC
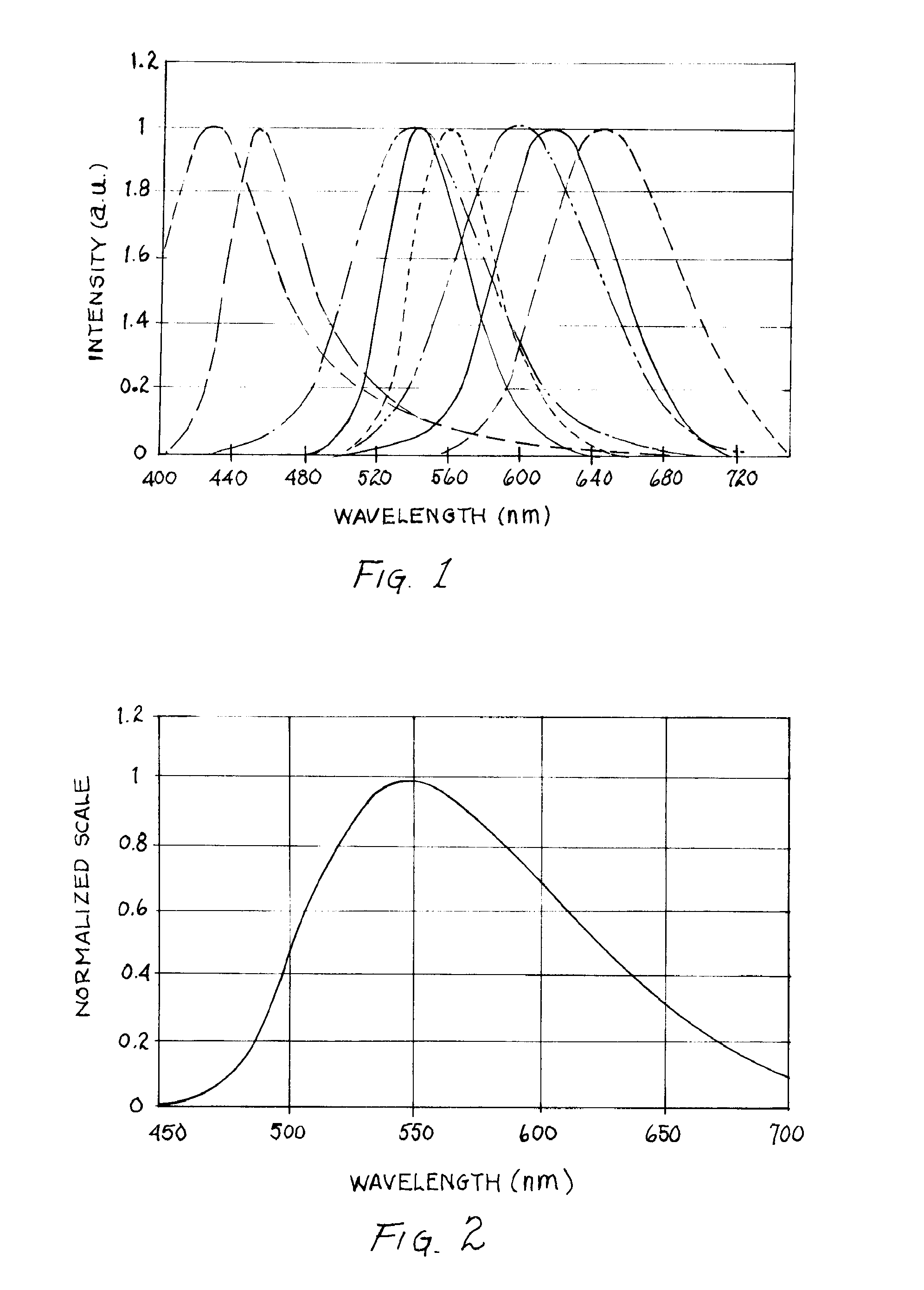
Spectrophotometer and method
InactiveUS20100148083A1Long-term stabilityReduce power consumptionRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryHigh energyFluorescence
A spectrophotometer includes a plurality of LEDs arranged in a circular array, each having a calibrated power input determined by the use of pulse width modulation and each having a unique wavelength band determined by the utilization of a unique fluorescent phosphor coating or lens. At least one of the LEDs comprising a phosphor-free high energy UV LED. Light reflected to the spectrophotometer is divided into predetermined wavelength ranges through the utilization of a linear variable filter and photo detectors wherein the analog signal from a photo detector is converted to a digital value through the use of auto-ranging gain technique.
Owner:MUTOH IND LTD
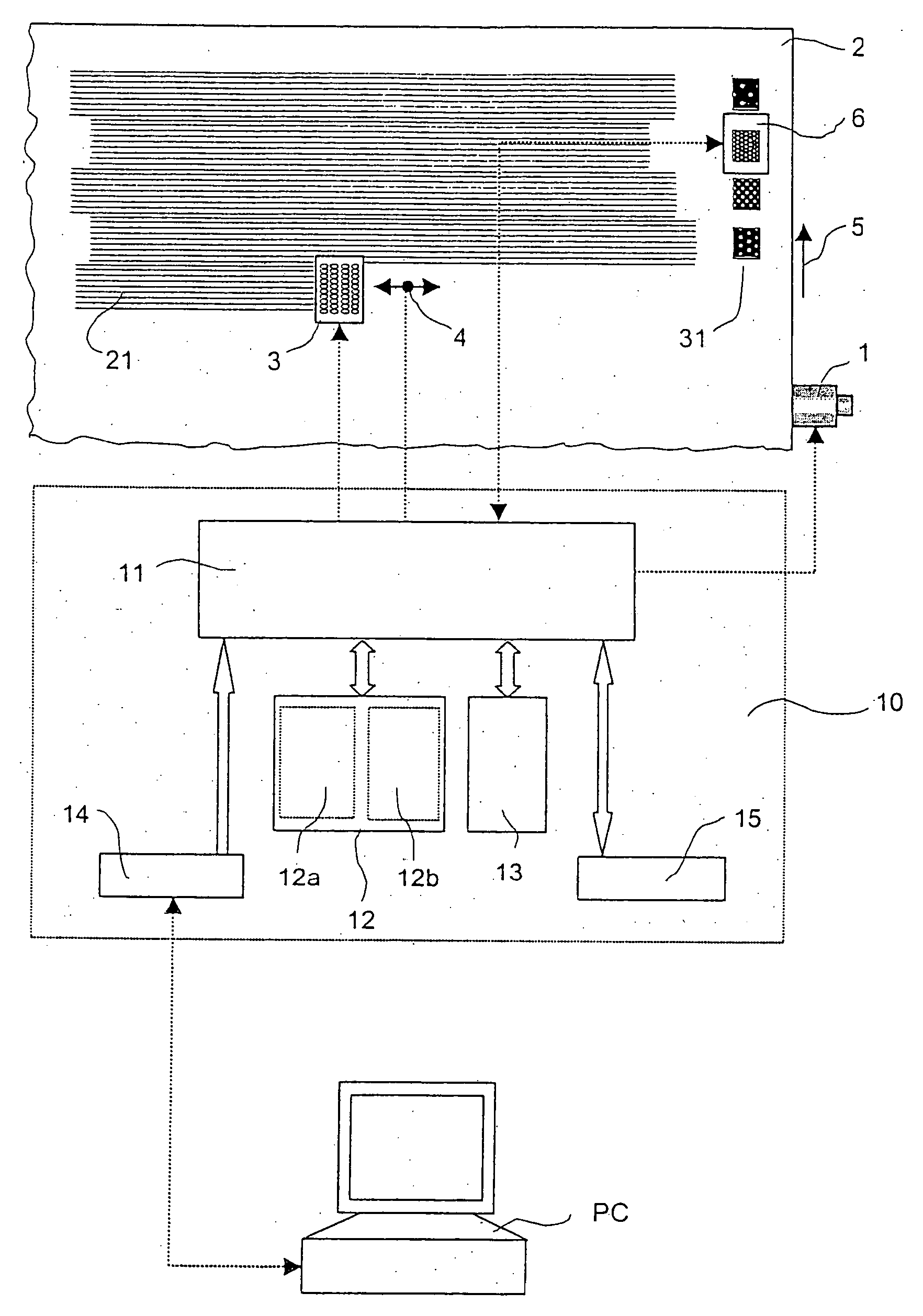
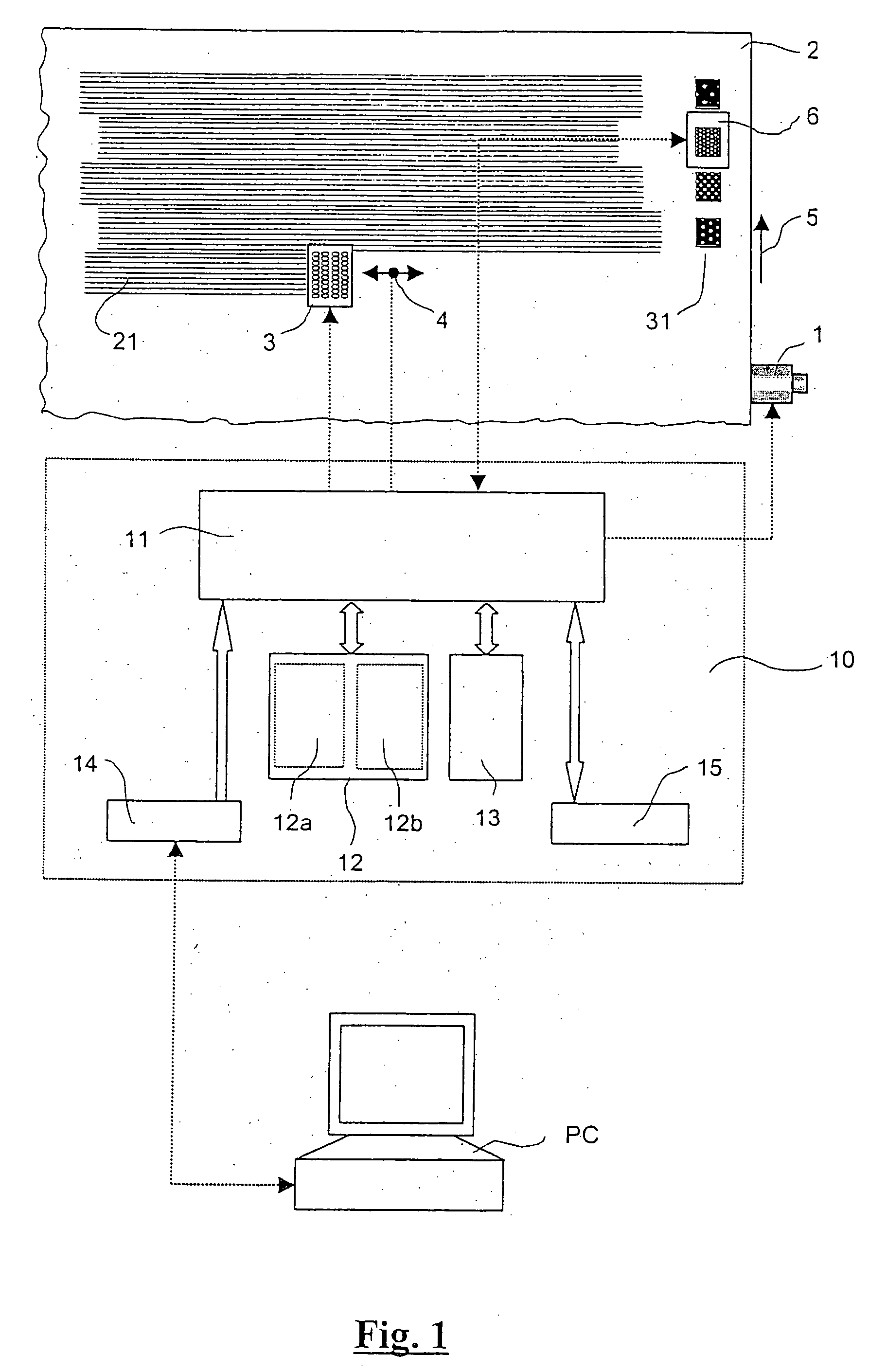
Digital printer
ActiveUS20050018219A1Cost optimizationIncreased susceptibilityDigitally marking record carriersVisual representation by matrix printersComputer printingEngineering
A digital printer is equipped with a built-in color measurement device (6) in the form of a colorimeter or spectral photometer, as well as with color management support. The built-in color measurement device (6) is used for control and optimization of the print output, especially for the simplification, optimization and automation of the work processes and for the verification of the output results.
Owner:X RITE SWITZERLAND
Three-dimensional optical coherence tomography confocal imaging apparatus
ActiveUS20110310395A1Easy to useInterferometersMaterial analysis by optical meansCamera lensMicroscopic image
A 3D OCT confocal imaging apparatus includes a light source module for providing an illumination beam with wider bandwidth from a crystal fiber; a reference source module; a pickup module; a beam splitter; an optical filter; and a sensor module. When the illumination beam illuminates a sample, a pickup objective lens and a piezoelectric actuator of the pickup module together provide an image beam scanning the sample in depth direction. The image beam and a reference beam from the reference source module together form an interference image beam, which is converted by a photosensor into a coherence image electric signal. Meanwhile, the interference image beam passes through a pinhole to form a confocal image, which is converted by an excited light photometer into a confocal image electric signal. With an image processing system, a 3D OCT confocal microscopic image of the sample can be produced from these image electric signals.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV
Method and system for luminance characterization
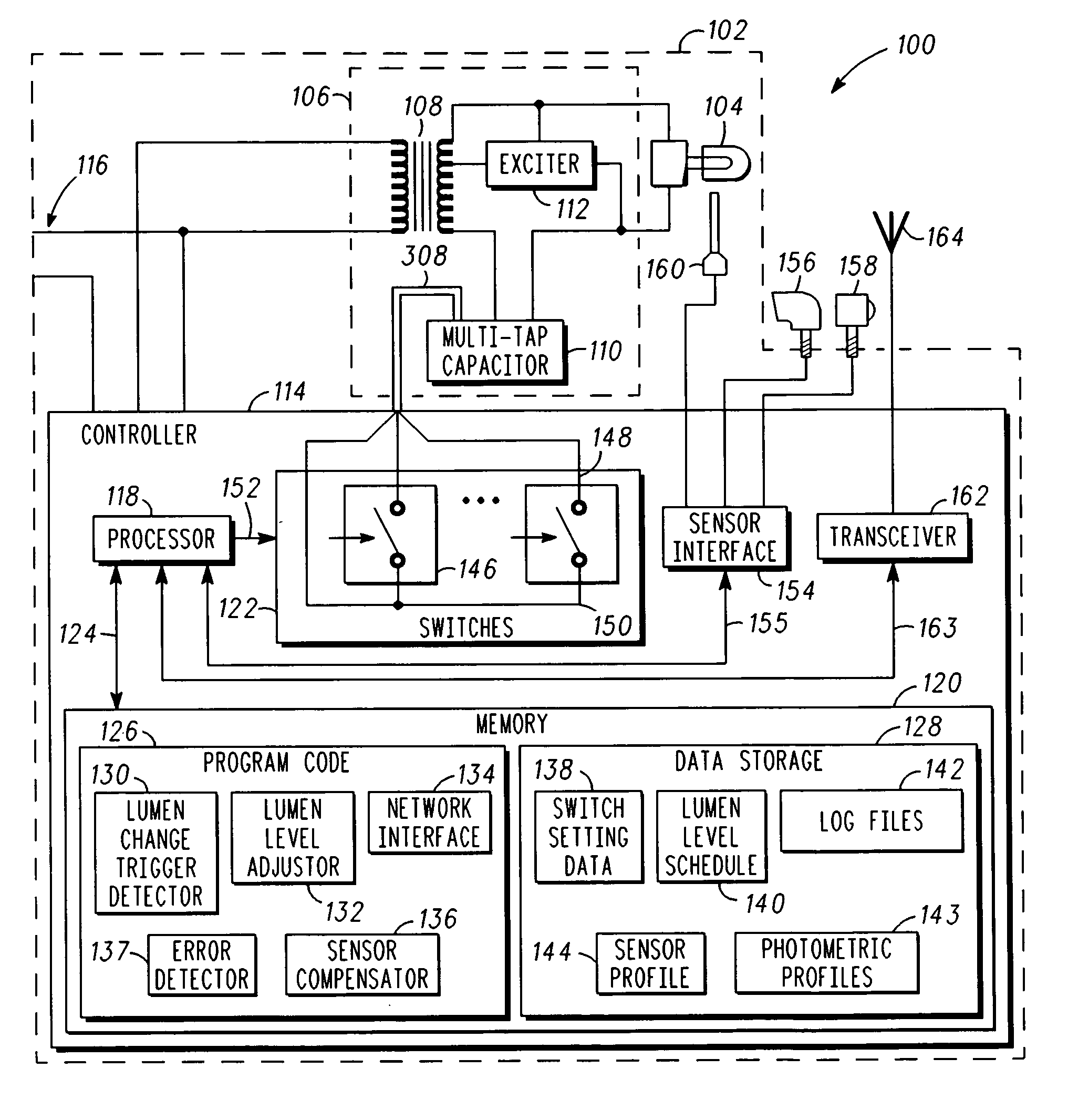
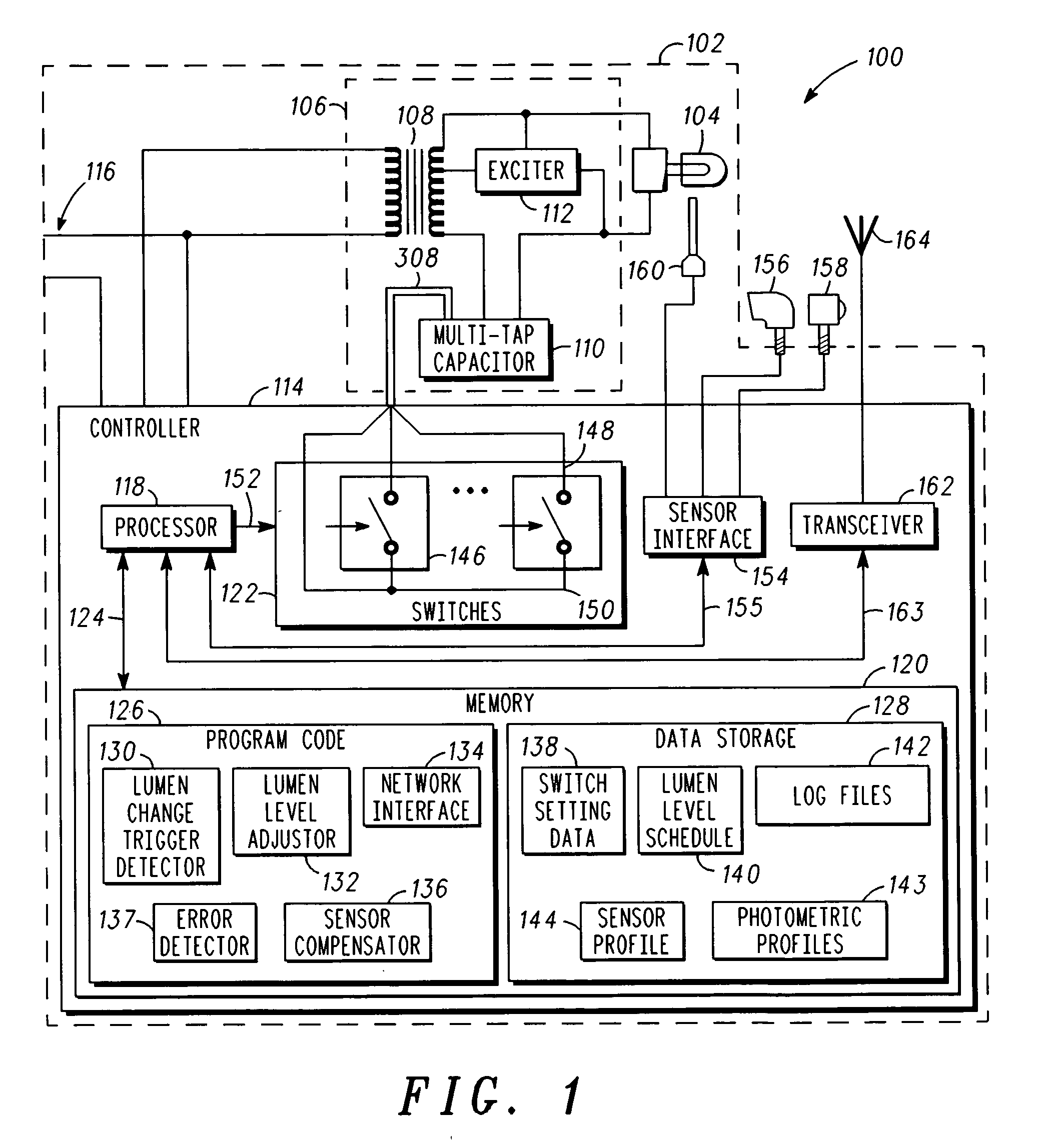
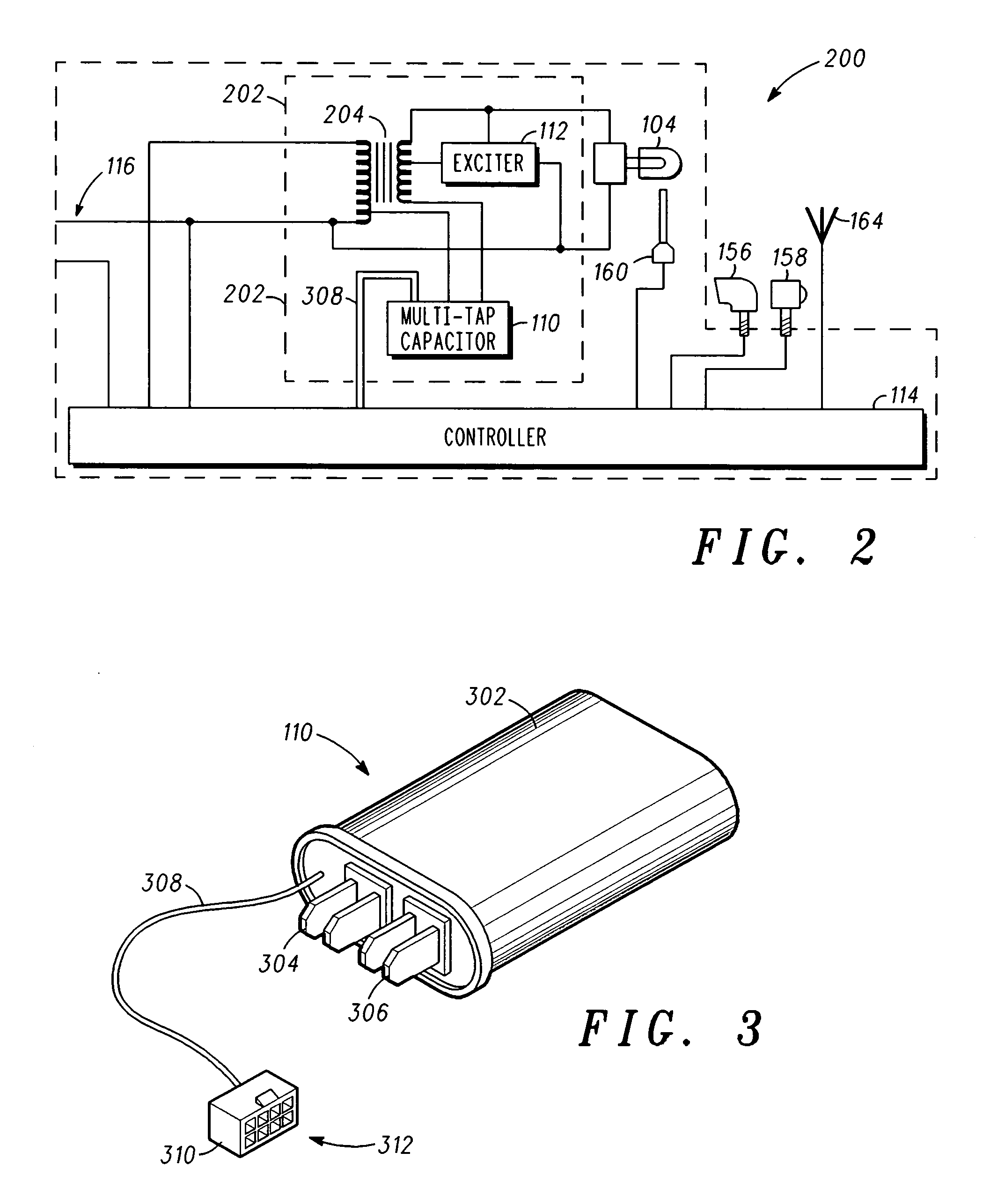
A system for luminance characterization of a luminaire includes a ballast coil and a multi-tap capacitor connected in series with the ballast coil. The multi-tap capacitor has a plurality of tap capacitors integrated into a capacitor housing. A plurality of switches are each coupled to one of the plurality of tap capacitors for selectively coupling the tap capacitors together to produce a multi-tap capacitance corresponding to a configuration of the plurality of switches. A lamp is connected in series with the multi-tap capacitor and the ballast coil. A photometer is located to measure light intensity of the lamp and to produce a lumen output measurement. A memory is used to store a database having a plurality of lumen output measurements, each corresponding to a multi-tap capacitance corresponding to all configurations of the plurality of switches.
Owner:STREETLIGHT INTELLIGENCE INC +1
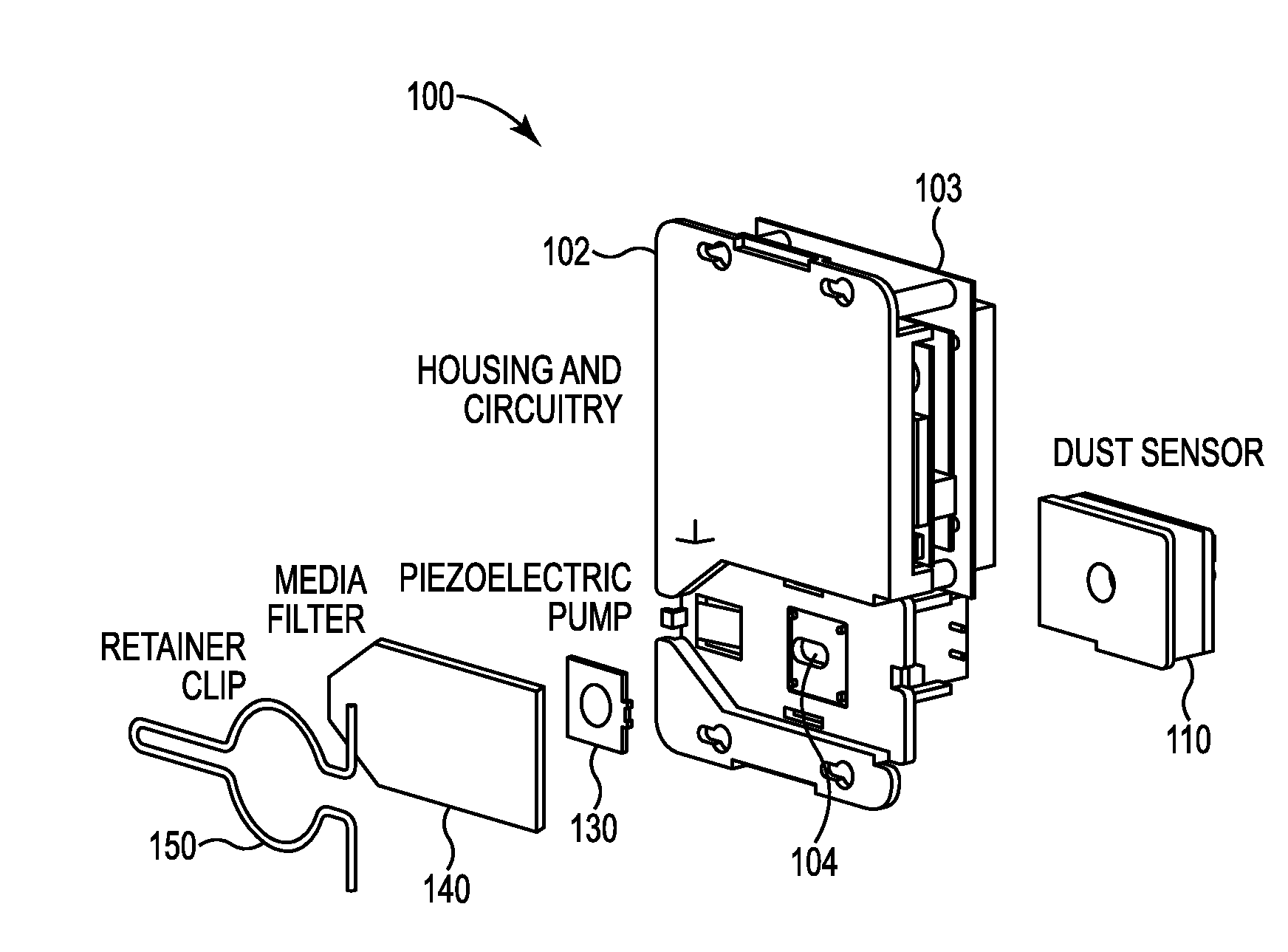
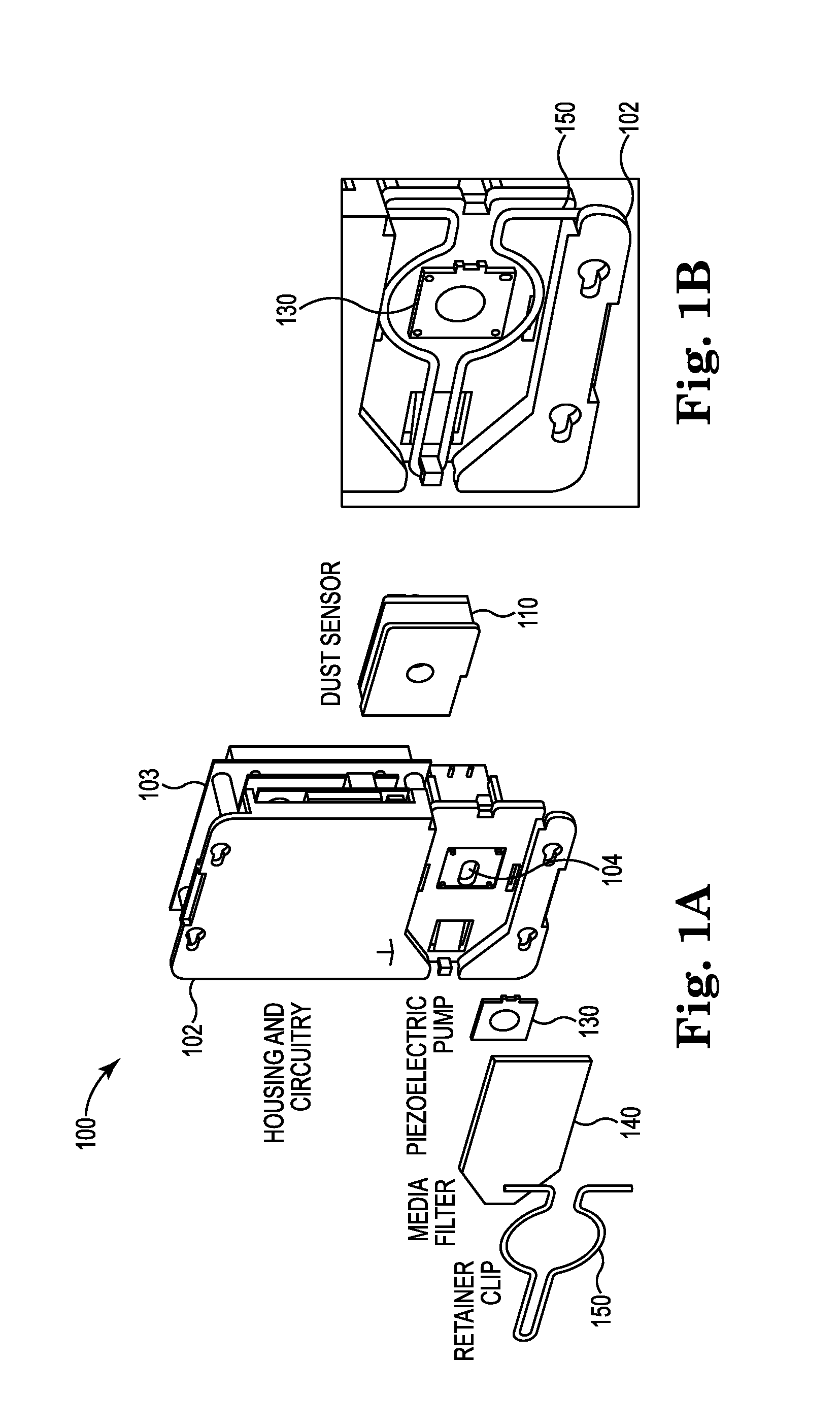
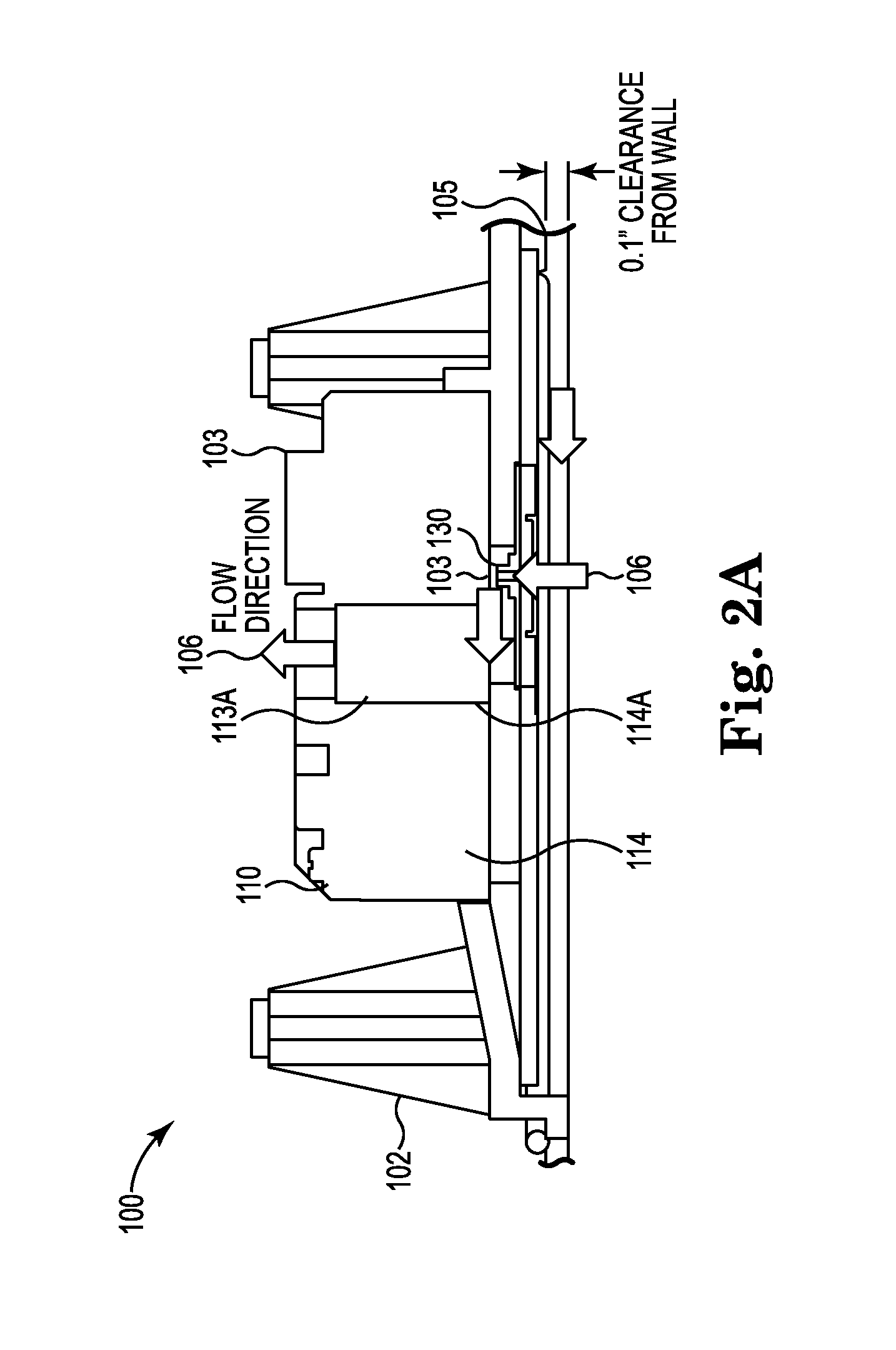
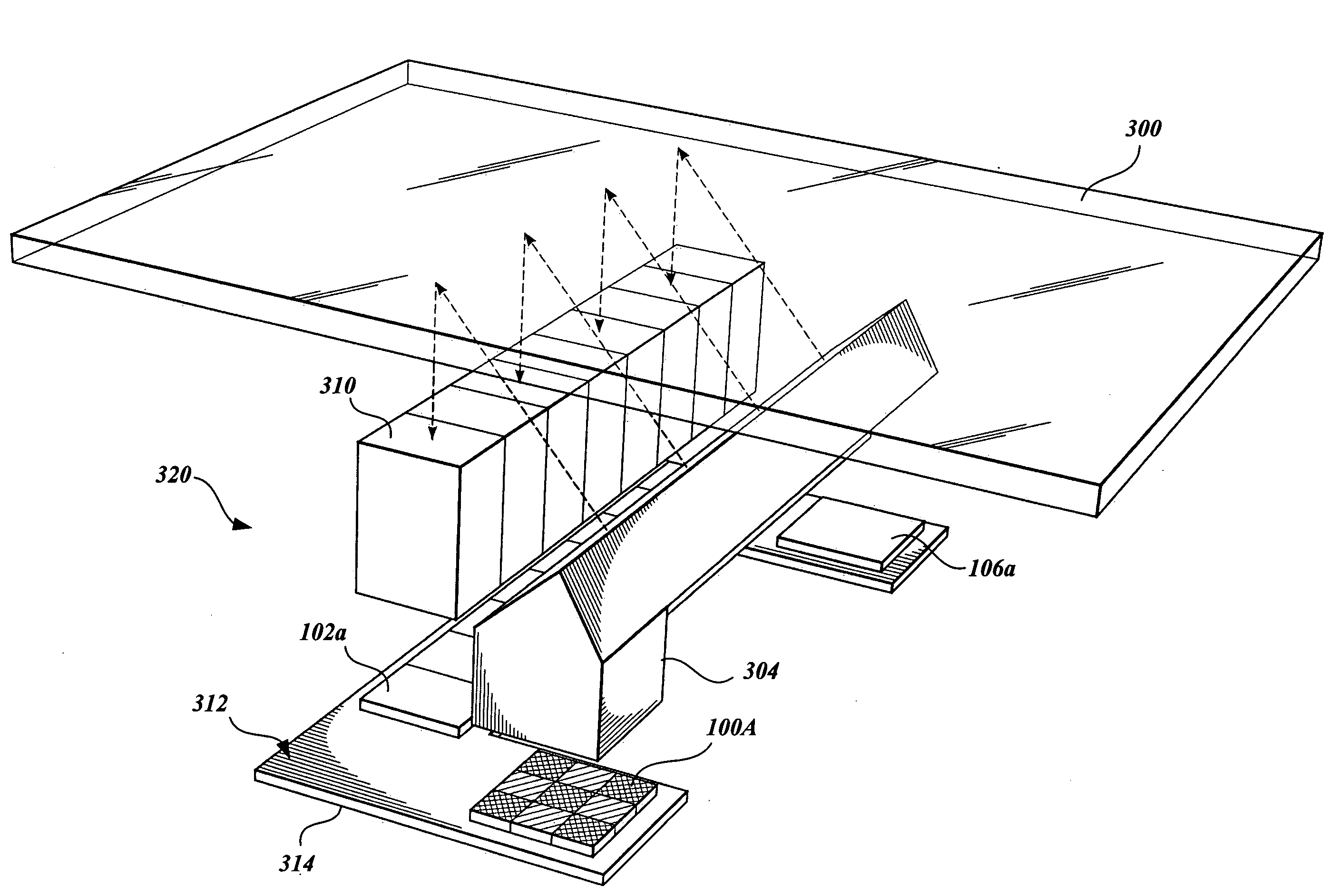
System and method of conducting particle monitoring using low cost particle sensors
ActiveUS20160153884A1Low costCompact form factorWithdrawing sample devicesMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansUltrasound attenuationParticle counter
There is disclosed a field calibratable particle sensor solution in a low-cost, very compact form factor. This makes a low-cost sensor more accurate for low-concentration pollution measurements and decreases the cost of pollution measurement systems having a wide geographic coverage. In a related embodiment, the invention illustrates a method and system to remotely and automatically calibrate one or more of the low cost sensors disclosed herein as well as other commercially available sensors (such as optical particle counters, photometers etc.) against a reference instrument (such as a beta attenuation monitor) which may or may not be physically located in the same place as the individual sensors. The method may require minimum (or no) user interaction and the calibration period is adjustable periodically.
Owner:TSI INC
Spectrophotometric scanner
A spectrophotometric scanner suitable for producing spectral reflectance images of surfaces of samples for a plurality of wavelength bands is disclosed. The spectrophotometric scanner comprises a scanner head for collecting spectral reflectance data, a positioning mechanism for positioning the scanner head in relation to a surface, and a computing device for controlling the mechanism and recording and analyzing the spectral reflectance data. The computing device directs the positioning mechanism to position the scanner head on a row of locations in a grid of locations of the surface; directs the scanner head to measure spectral reflectance data for each location in the row of locations; records and analyzes the spectral reflectance data; and produces spectral reflectance images from the spectral reflectance data. A light source in the scanner head comprises a plurality of sequentially controllable LEDs, each producing light in a different wavelength band.
Owner:VIE GRP
Liquid photometer using surface tension to contain sample
InactiveUS20020140931A1Withdrawing sample devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansSmall sampleSpectroscopy
Method and apparatus of spectroscopy or the like on extremely small samples in which a drop is held between two opposing surfaces by surface tension and one surface is controllably toward and away from the other. To provide and transmit exciting energy through the drop for measurement, optical fibers go through a surface and finish flush with the surface. One of the surfaces can be swung clear of the other for easy cleaning between tests. Means for determining wetted surface are provided.
Owner:NANODROP TECH LLC
Analytical multi-spectral optical detection system
InactiveUS20070098594A1Highly accurate fluorescent based measurementMinimize the numberMaterial analysis by optical meansChemical methods analysisPhysicsThrough transmission
Analytical multi-spectral optical detection systems and methods. A light source provides one or multiple lines (e.g., discrete wavelengths) of high spectral purity excitation light that is optically coupled to a sample via delivery fiber optic cables. Emission light is collected and provided to an emission detector, such as a diffraction gradient spectrophotometer emission detector, using collection fiber optic cables bundled with the delivery fiber optic cables in a probe interface positioned proximal a sample holder. The probe interface may be scanned over one or more samples, or one or more samples may be scanned proximal a fixed interface probe. Multiple excitation wavelengths allows for simultaneous excitation and detection of multiple fluorescent dyes in the visible spectrum. This increases sample throughput and reduces signal variations associated with signal acquisition at different times. The optical system provides several advantages over other systems including higher sensitivity, improved compatibility with fluorescent dyes, better signal discrimination, increased system reliability and reduced manufacturing and service costs.
Owner:ROCHE MOLECULAR SYST INC
Transparent polyimide film and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a transparent polyimide film. The transparent polyimide film is prepared from a copolymer of aromatic dianhydride and aromatic diamine, and can be modified by adding inorganic materials or inorganic nano-materials into the polymer. The thickness of the film is 25-100 microns, and the Tg temperature range is 180-350 DEG C; the film has low heat expansion coefficient with 3-30 ppm under the Tg temperature, has cutoff wavelength of 550 nm measured by an ultraviolet spectrophotometer and has average transmission rate of 85 percent or more in the range of 380-780 nm. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the transparent polyimide film. The film is high in mechanical property, high in heat stability and suitable for transparent electric conductive films, film transistor substrates, flexible printed circuit boards, solar battery flexible substrates, flexible substrates for flexible display of a new generation of OLED, and the like.
Owner:饶先花
Apparatus and method for calibration of spectrophotometers
ActiveUS20050168737A1Easy to controlEliminates meniscus errorPhotometry using reference valueRadiation pyrometryCuvetteEvaporation
An apparatus and related method for optical calibration of spectrophotometers is described. The apparatus is a calibration plate including one or more cuvettes filled with solutions of interest. The cuvettes are sealed to prevent evaporation. The cuvettes also possess a compressible component to allow for expansion of the solution and a bubble control apparatus to ensure that the compressible component does not intersect the beam path. A piece of neutral density glass is optionally included in the apparatus to track optical changes of the solutions over time.
Owner:ARTEL
Spectrophotometer
InactiveUS7092090B2Measurement stabilitySmall accuracyRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationDevice formPhotoelectric conversion
Disclosed herein is a spectrophotometer at least including: an optical waveguide; a light entrance slit provided at an end face on the inner side of the optical waveguide, for bringing an incident light into the optical waveguide; an optical element provided at an end face on the inner side of the optical waveguide or at an interior of the optical waveguide, for separating the incident light brought in the optical waveguide into a spectrum; and a photoelectric conversion device provided at an end face on the inner side of the optical waveguide, for detecting the incident light separated into the spectrum at the optical element; wherein the optical waveguide, the light entrance slit, and the optical element being integrally formed on an optical waveguide board, and a photoelectric conversion device substrate having the photoelectric conversion device formed thereon being mounted on the optical waveguide board.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Dual sample mode spectrophotometer
A dual-mode method and apparatus of selectively measuring samples in either a vessel or as a surface tension retained sample held between two opposing pedestals is introduced. In either configuration, such modes further contain optical paths from a source system through a small-volume or large-volume sample to a spectrometer based system. Such a system enables a user to measure samples with absorbances ranging from about 0.005 up to about 2.0 Absorbance Units for any given wavelength.
Owner:NANODROP TECH LLC
Liquid photometer using surface tension to contain sample
Method and apparatus of spectrophotometry or the like on extremely small liquid samples in which a drop is held between two opposing surfaces by surface tension and one surface is controllably moved toward and away from the other. To provide and transmit exciting energy through the drop for measurement, the optical fibers go through a surface and are finished flush with its surface. One of the surfaces can be swung clear of the other for easy cleaning between tests.
Owner:NANODROP TECH LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com