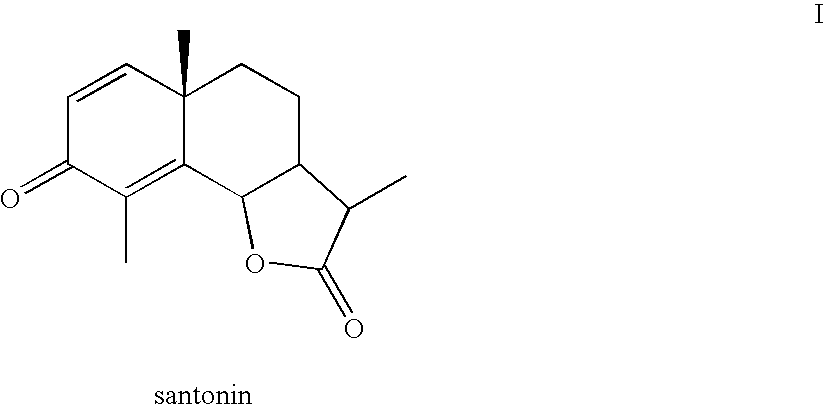
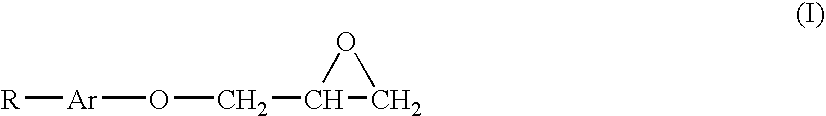
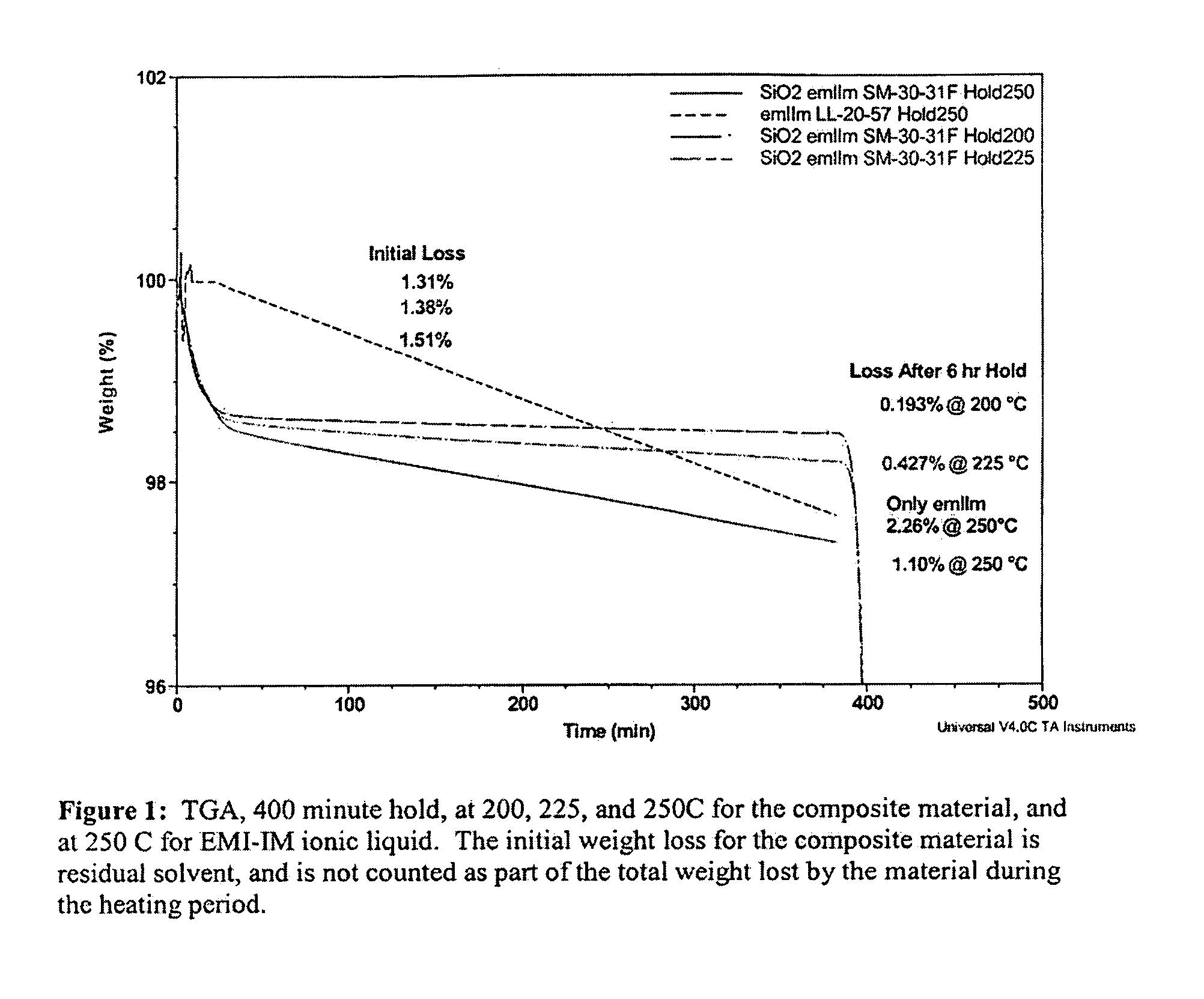
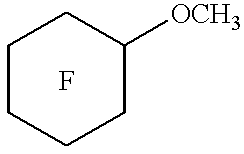
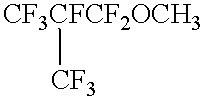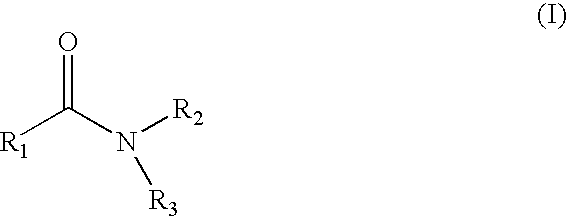Patents
Literature
487 results about "Solvent composition" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Solvent composition according to any of the claims 1 to 4, characterized in that the solvent composition is a technochemical solvent, an industrial solvents, an agricultural solvent, a fuel or a constituent thereof or in drilling fluids for oil recovery, hydraulic oils, cable oils, or heat transfer fluids.
Pharmaceutical composition
InactiveUS6946120B2Improve solubilityImprove abilitiesCosmetic preparationsOrganic active ingredientsAlcoholPolyol
A pharmaceutical composition for topical administration, including, as the pharmaceutically active component, at least 5% by weight, based on the total weight of the composition of a piperidinopyrimidine derivative or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof; an acid in an amount to completely solubilise the piperidinopyrimidine derivative or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof; a solvent composition including at least two of water, a lower alcohol and a co-solvent selected from one or more of the group consisting of aromatic and polyhydric alcohols; wherein when the co-solvent includes propylene glycol, it is present in an amount of less than approximately 10% by weight.
Owner:STIEFEL RESEARCH AUSTRALIA PTY LTD
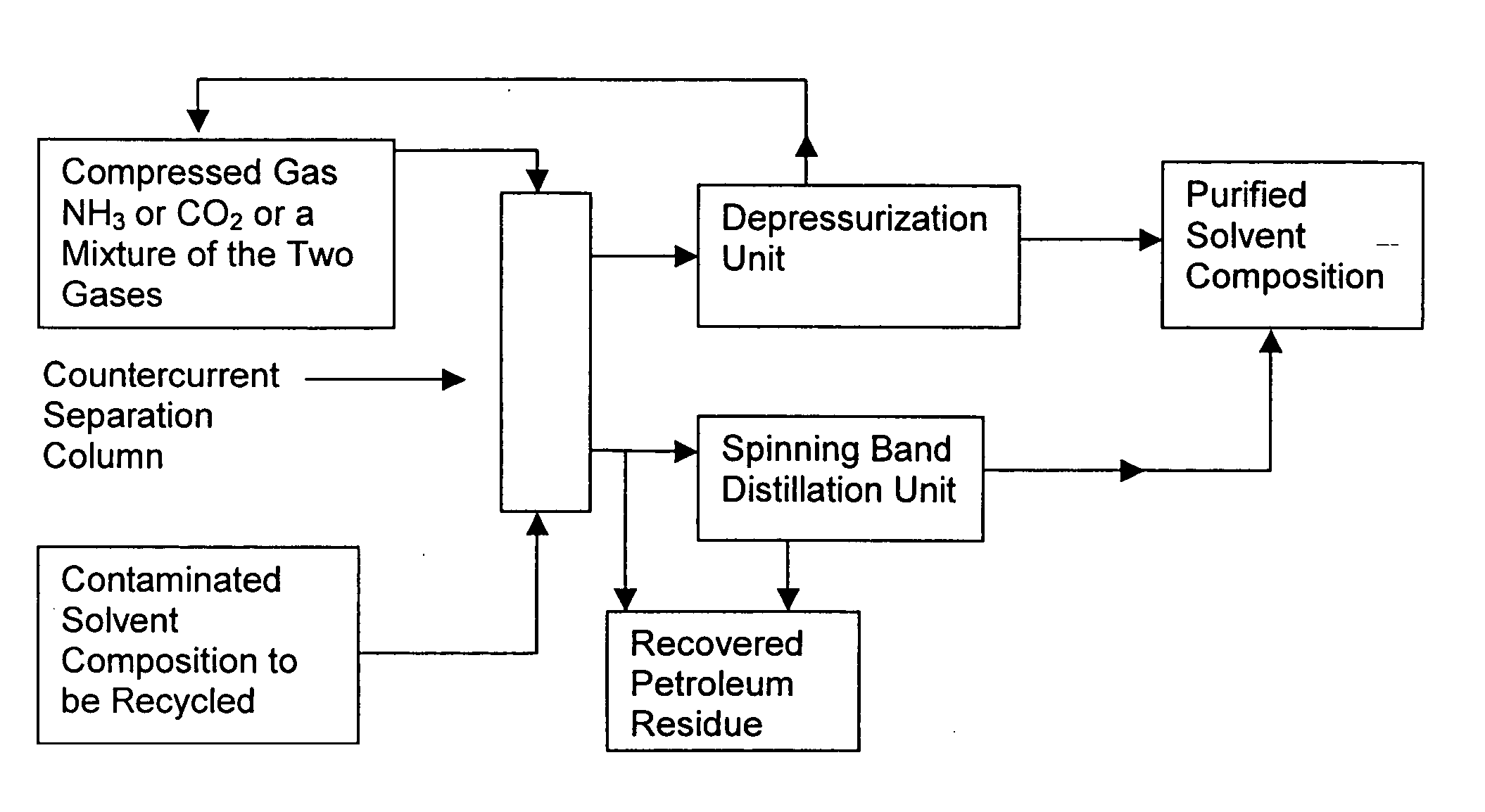
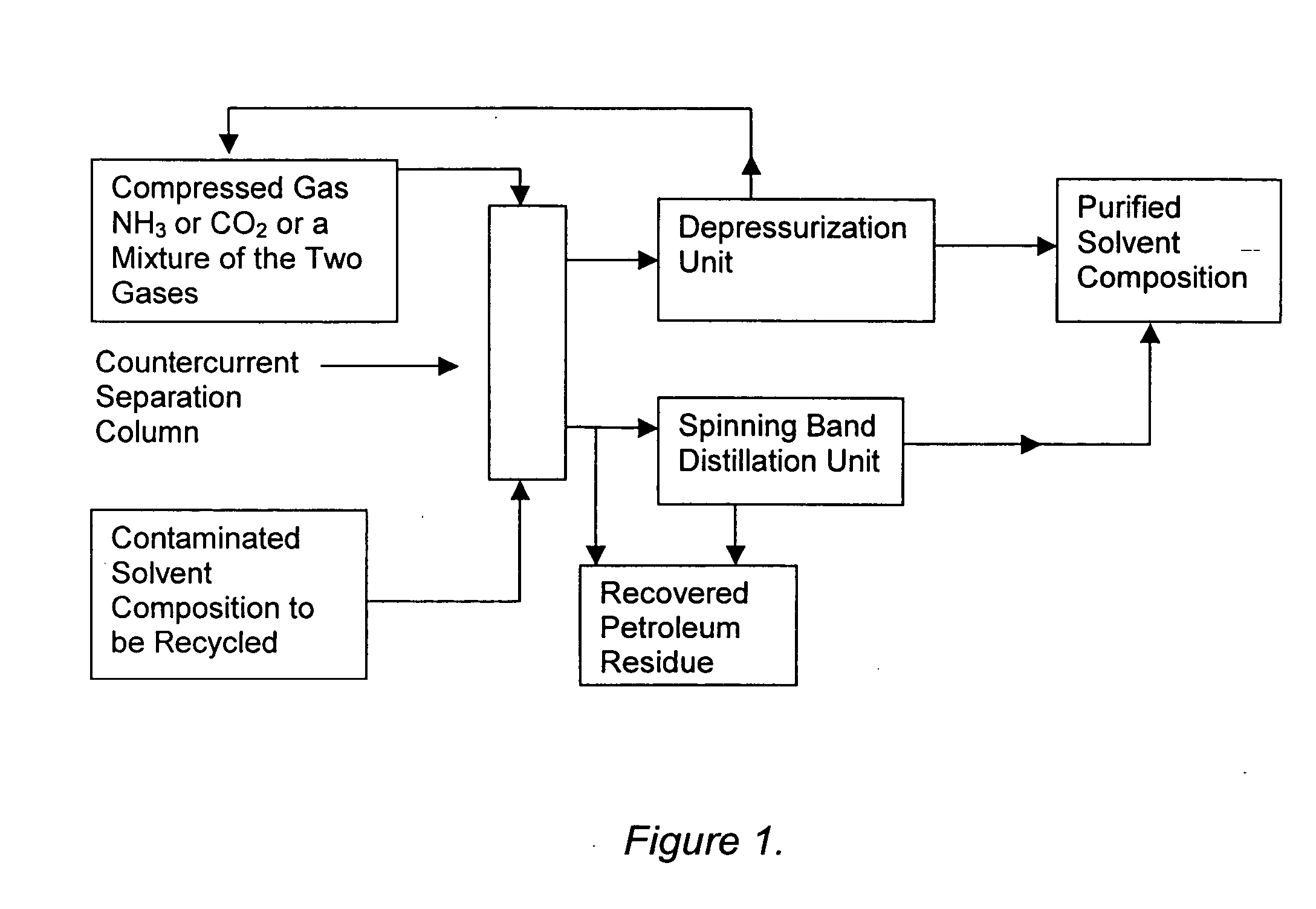
Solvent compositions for removing petroleum residue from a substrate and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS20050197267A1Cationic surface-active compoundsNon-ionic surface-active compoundsSpinning band distillationPetroleum
Water-soluble solvent compositions, including from about 10% to about 60% by weight of an aromatic ester; from about 30% to about 60% by weight of an aliphatic ester; from 0% to about 15% by weight of a co-solvent; from 0% to about 20% of one of a cyclic terpene and a terpenoid; from 0% to about 1% by weight of an odor-masking agent; and from 0% to about 20% by weight of a nonionic surfactant, for removing petroleum residue from a substrate, and methods of use thereof. The composition can further comprise water. The composition also can comprise an aqueous solution. The method for removing petroleum residue from a substrate can further comprise recycling the solvent composition by using a countercurrent separation column charged with compressed ammonia and / or carbon dioxide and a spinning band distillation column to separate the solvent composition from the petroleum residue.
Owner:CRUDE SPILL CLEANING CO INC
Stabilized Iodocarbon Compositions
InactiveUS20080157022A1Reduce environmental damageLow propertyHalogenated hydrocarbon separation/purificationHeat-exchange elementsStabilizing AgentsSolvent composition
Disclosed are compositions comprising at least one iodocarbon compound and preferably at least one stabilization agent comprising a diene-based compound. These compositions are generally useful as refrigerants for heating and cooling, as blowing agents, as aerosol propellants, as solvent composition, and as fire extinguishing and suppressing agents.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Compositions containing fluorine substituted olefins
The use to e of tetrafluoropropenes, particularly (HFO-1234) in a variety of applications, including refrigeration equipment, is disclosed. These materials are generally useful as refrigerants for heating and cooling, as blowing agents, as aerosol propellants, as solvent composition, and as fire extinguishing and suppressing agents.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Liquid Composite Compositions Using Non-Volatile Liquids and Nanoparticles and Uses Thereof
InactiveUS20080209876A1Reduce CTEImprove performanceElectrolytic capacitorsCell electrodesOrganic solventNanoparticle
A solvent composition comprising an organic solvent; dispersed nanoparticles; and a non-volatile electrolyte.
Owner:ESIONIC
Lithium ion battery with high voltage electrolytes and additives
ActiveUS20110136019A1Final product manufactureElectrode carriers/collectorsMethyl carbonateHigh pressure
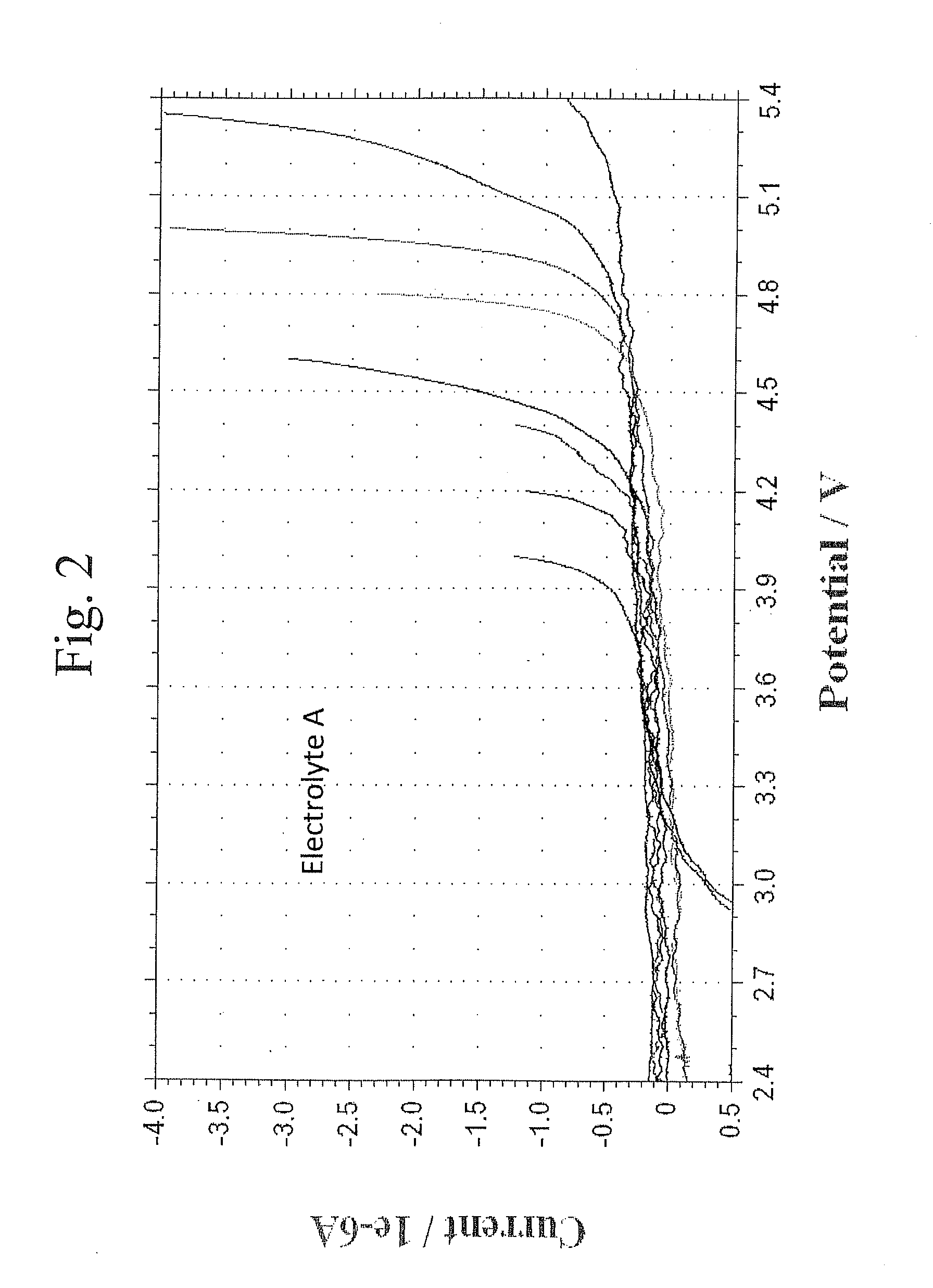
Desirable electrolyte compositions are described that are suitable for high voltage lithium ion batteries with a rated charge voltage at least about 4.45 volts. The electrolyte compositions can comprise ethylene carbonate and solvent composition selected from the group consisting of dimethyl carbonate, methyl ethyl carbonate, γ-butyrolactone, γ-valerolactone or a combination thereof. The electrolyte can further comprise a stabilization additive. The electrolytes can be effectively used with lithium rich positive electrode active materials.
Owner:IONBLOX INC
Solvent compositions containing chlorofluoroolefins or fluoroolefins
Compositions and methods based on the use of fluoroalkene containing from 3 to 4 carbon atoms and at least one carbon-carbon double bond, such as HFO-1214, HFO-HFO-1233, or HFO-1354, having properties highly beneficial in solvent cleaning applications.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Two solvent antimicrobial compositions and methods employing them
InactiveUS6927237B2Reduce populationGreat reductionBiocideHalogenated hydrocarbon active ingredientsPharmaceutical industrySolvent composition
Owner:ECOLAB USA INC
In situ micromachined mixer for microfluidic analytical systems
The present invention relates to an in situ micromachined mixer for microfluidic analytical systems. In a preferred embodiment, a 100 pL mixer for liquids transported by electroosmotic flow (EOF) is described. Mixing was achieved in multiple intersecting channels with a bimodal width distribution and varying lengths. Five .mu.m width channels ran parallel to the direction of flow whereas larger 27 .mu.m width channels ran back and forth through the network at a 45.degree. angle. All channels were approximately 10 .mu.m deep. It was observed that little mixing of confluent streams occurred in the 100 .mu.m wide mixer inlet channel where mixing would be achieved almost exclusively by diffusion. In contrast, mixing was complete after passage through the channel network in the .apprxeq.200 .mu.m length mixer. Solvent composition was altered by varying the voltage on solvent reservoirs. The high efficiency attained in this mixer was attributed to the presence of a 2 pL vortex in the center of the mixer. Video tracking of fluorescent particles with a fluorescence microscope allowed the position and volume of this vortex to be determined.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Fluorinated solvent compositions containing hydrogen fluoride
InactiveUS6310018B1Not easily recoveredEasy to separateDecorative surface effectsDetergent mixture composition preparationHydrogen fluorideEtching
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Compositions containing fluorine substituted olefins
The use of pentafluoropropene (HFO-1225) and tetrafluoropropene (HFO-1234) in refrigeration equipment is disclosed. These materials are generally useful as refrigerants for heating and cooling, as blowing agents, as aerosol propellants, as solvent composition, and as fire extinguishing and suppressing agents.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Solvent compositions comprising unsaturated fluorinated hydrocarbons
InactiveUS20070102021A1Drying solid materials with heatPretreated surfacesPolymer scienceSolvent composition
Disclosed is a method for removing residue from a surface comprising: contacting the surface with a composition comprising at least one unsaturated fluorinated hydrocarbon selected from the group consisting of compounds having the formula E- or Z-R1CH═CHR2, wherein R1 and R2 are, independently, C1 to C6 perfluoroalkyl groups, or C1 to C6 hydrofluoroalkyl groups, and recovering the surface from the composition.
Owner:THE CHEMOURS CO FC LLC
Solvent compositions comprising unsaturated fluorinated hydrocarbons
This invention relates to cleaning compositions comprising unsaturated fluorinated hydrocarbons. The invention further relates to use of said cleaning compositions in methods to clean, degrease, deflux, dewater, and deposit fluorolubricant. The invention further relates to novel unsaturated fluorinated hydrocarbons and their use as cleaning compositions and in the methods listed above.
Owner:THE CHEMOURS CO FC LLC
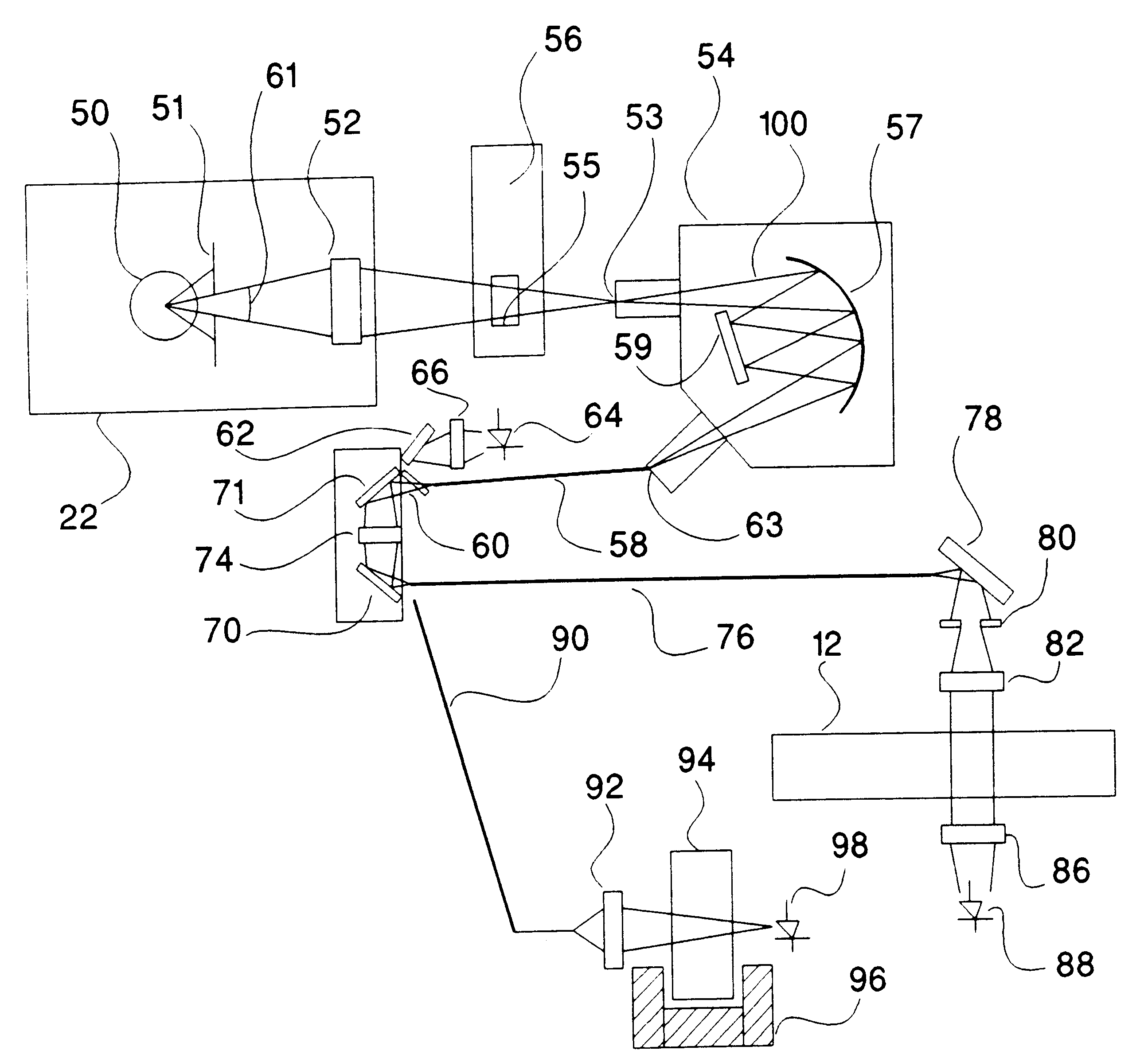
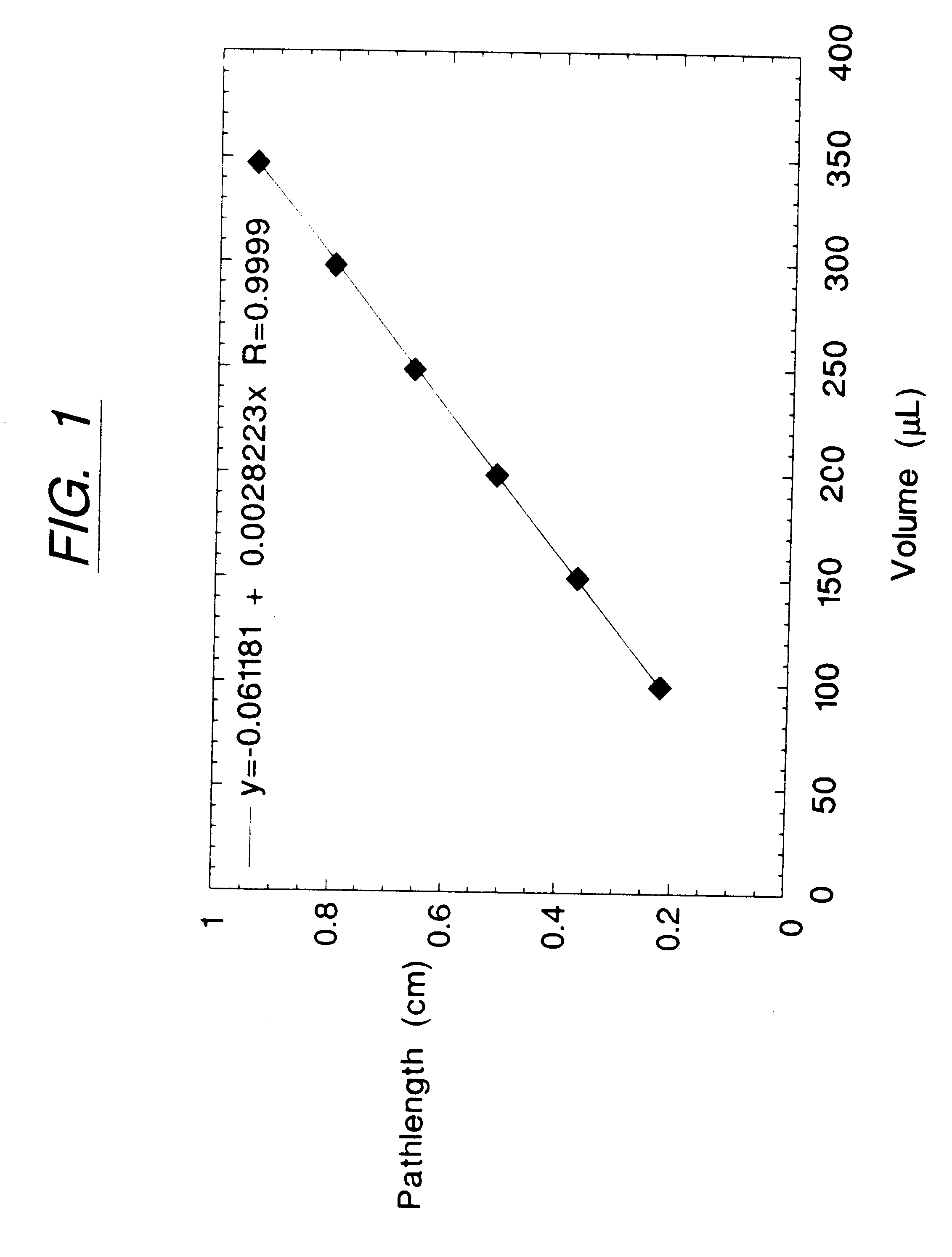
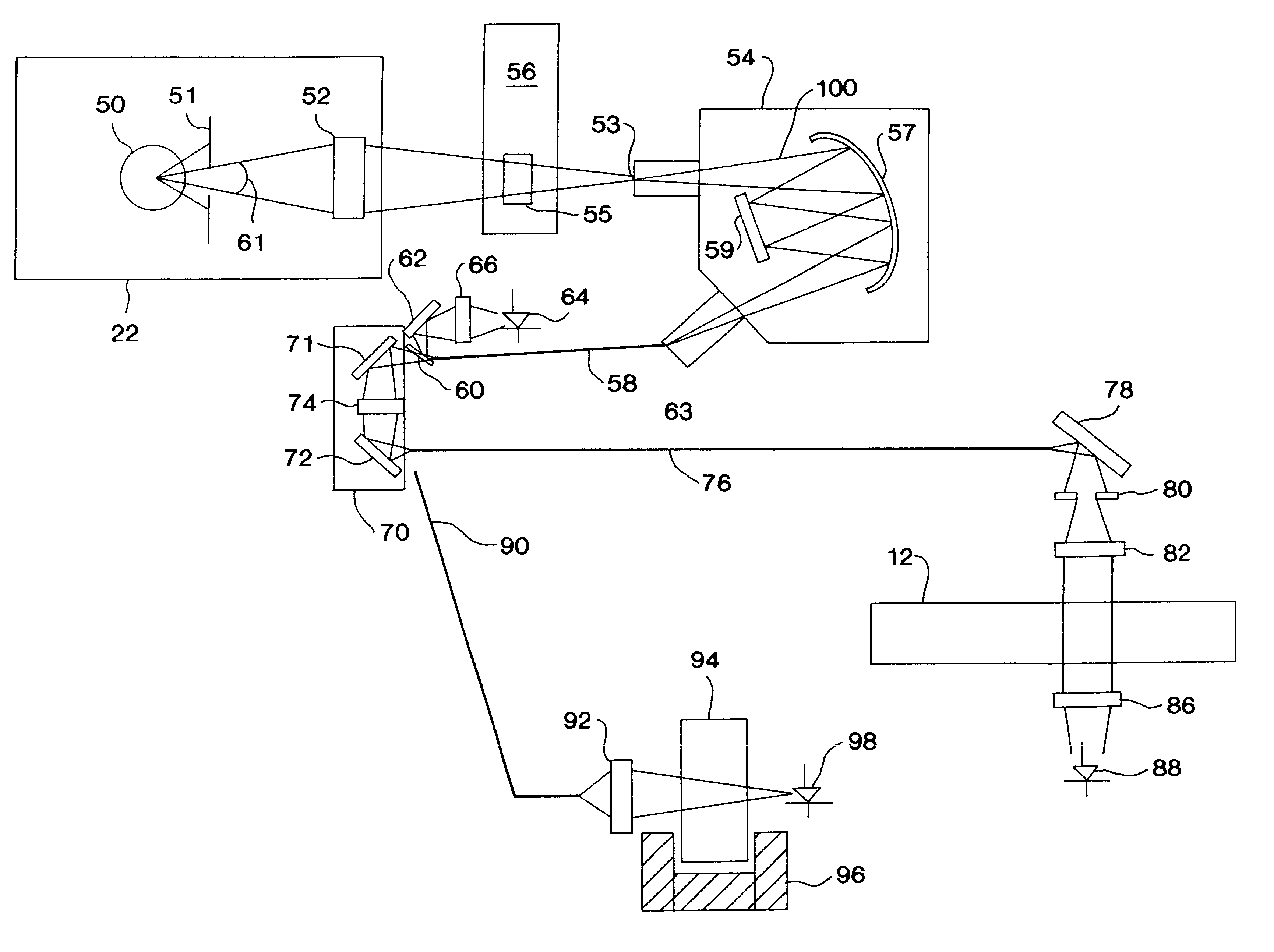
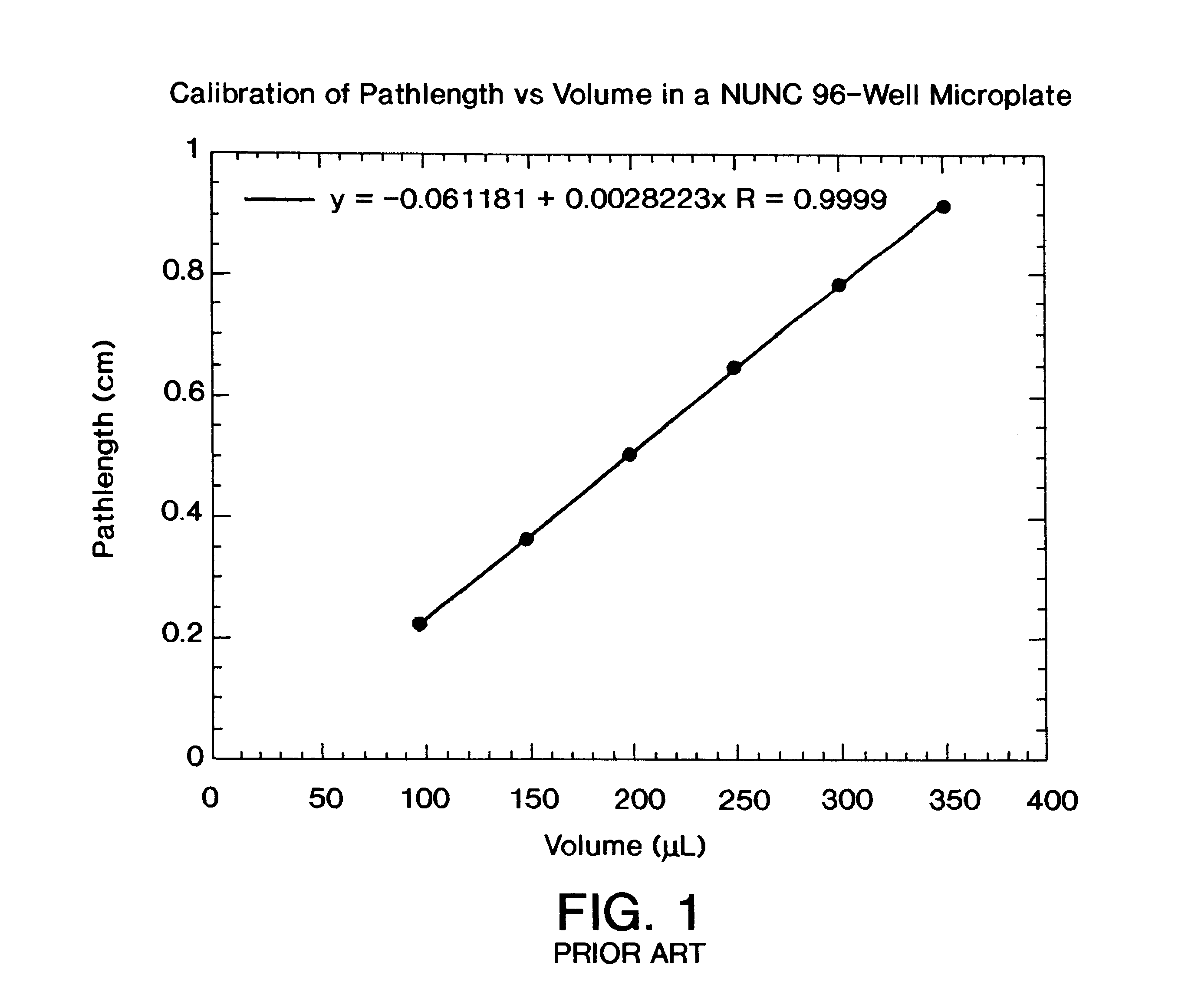
Determination of light absorption pathlength in a vertical-beam photometer
InactiveUS6188476B1Volume measurement apparatus/methodsColor/spectral properties measurementsAnalyteLight beam
Disclosed are photometric methods and devices for determining optical pathlength of liquid samples containing analytes dissolved or suspended in a solvent. The methods and devices rely on determining a relationship between the light absorption properties of the solvent and the optical pathlength of liquid samples containing the solvent. This relationship is used to establish the optical pathlength for samples containing an unknown concentration of analyte but having similar solvent composition. Further disclosed are methods and devices for determining the concentration of analyte in such samples where both the optical pathlength and the concentration of analyte are unknown. The methods and devices rely on separately determining, at different wavelengths of light, light absorption by the solvent and light absorption by the analyte. Light absorption by the analyte, together with the optical pathlength so determined, is used to calculate the concentration of the analyte. Devices for carrying out the methods particularly advantageously include vertical-beam photometers containing samples disposed within the wells of multi-assay plates, wherein the photometer is able to monitor light absorption of each sample at multiple wavelengths, including in the visible or UV-visible region of the spectrum, as well as in the near-infrared region of the electromagnetic spectrum. Novel photometer devices are described which automatically determine the concentration of analytes in such multi-assay plates directly without employing a standard curve.
Owner:MOLECULAR DEVICES
Solvent composite and preparation method and use thereof
The solvent composition consists of sodium hydroxide 5-12 wt% and urea 8-20 wt% except water. The preparation process of the solvent composition is also provided. Water solution of sodium hydroxideand water solution of urea are mixed to compound the solvent composition; or sodium hydroxide is first compounded into water solution and urea is then added to compound the solvent composition. The solvent composition may be used in directly dissolving natural cellulose and regenerated cellulose to obtain transparent cellulose solution with high dissolubility and high concentration.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Photoresist Composition for Deep UV and Process Thereof
InactiveUS20090042148A1Photomechanical apparatusOriginals for photomechanical treatmentResistPolymer science
The present invention refers to a photoresist composition comprising (i) a polymer A comprising at least one acid labile group; (ii) at least one photoacid generator; (iii) at least one base; (iv) a polymer B, where polymer B is non-miscible with polymer A and soluble in the coating solvent, and; (v) a coating solvent composition. The present invention also relates to the process of imaging the photoresist.
Owner:AZ ELECTRONICS MATERIALS USA CORP
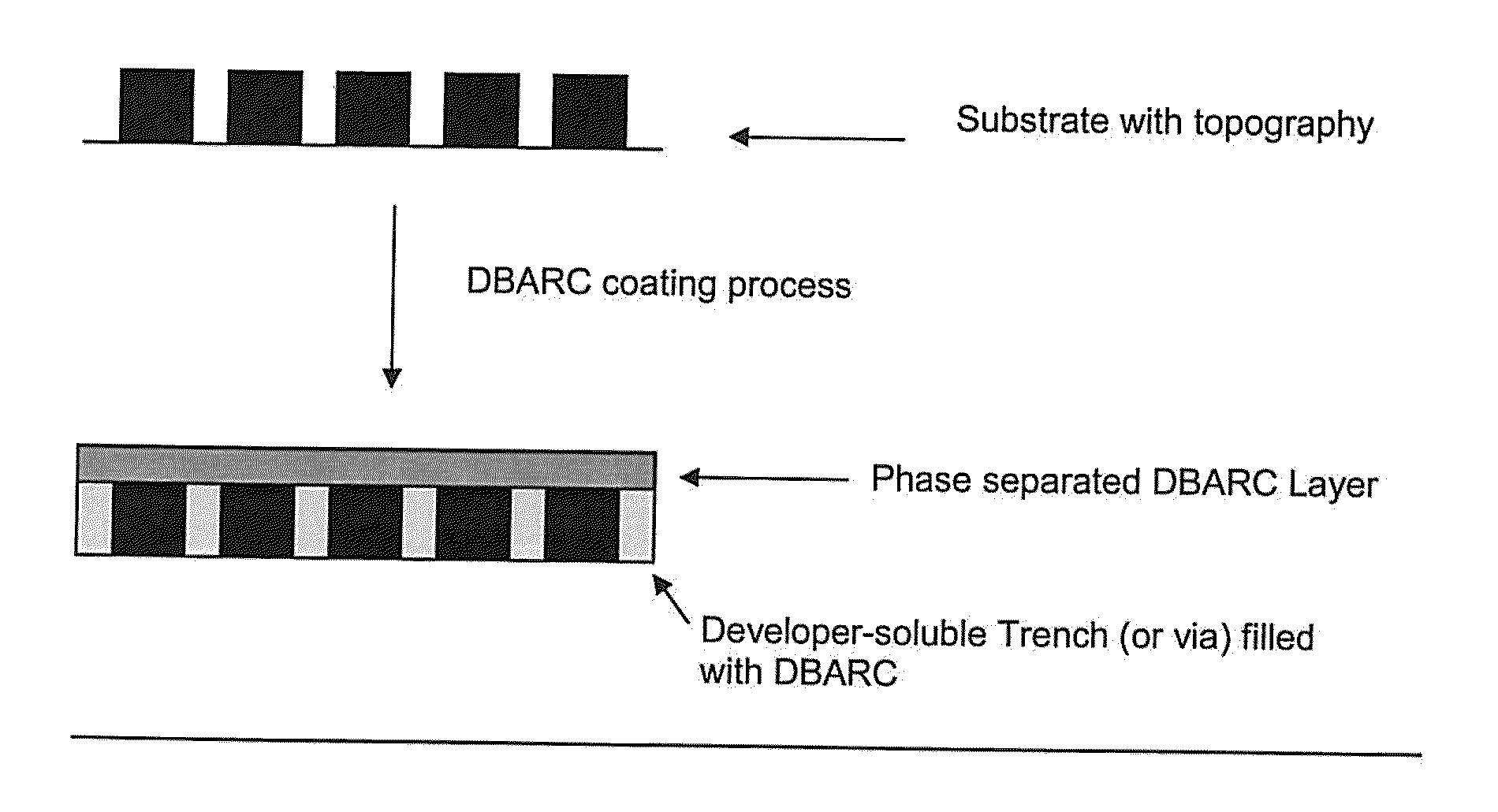
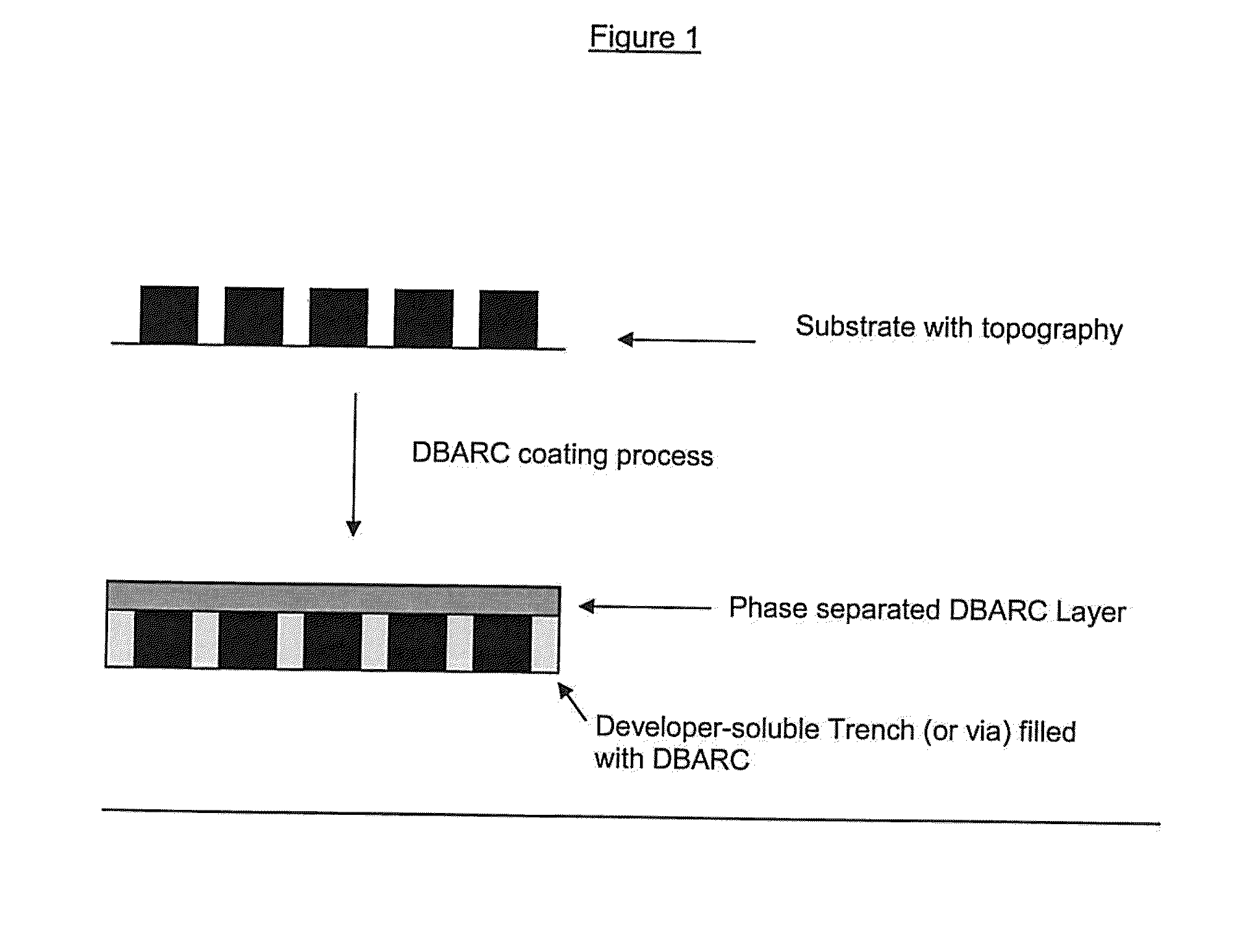
Positive-Working Photoimageable Bottom Antireflective Coating
ActiveUS20110076626A1Improve solubilityAid solubilityPhotosensitive materialsOriginals for photomechanical treatmentSolubilityPolymer science
The invention relates to a photoimageable antireflective coating composition capable of forming a pattern by development in an aqueous alkaline solution, comprising, (i) a polymer A soluble in a coating solvent and comprises a chromophore, a crosslinking moiety, and optionally a cleavable group which under acid or thermal conditions produces a functionality which aids in the solubility of the polymer in an aqueous alkaline solution and; (ii) at least one photoacid generator; (iii) a crosslinking agent; (iv) optionally, a thermal acid generator; (v) a polymer B which is soluble in an aqueous alkaline solution prior to development, where polymer B is non-miscible with polymer A and soluble in the coating solvent, and; (vi) a coating solvent composition, and (vii) optionally, a quencher. The invention also relates to a process for imaging the antireflective coating.
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
Photoresist composition for deep UV radiation
The present invention relates to a novel photoresist composition sensitive in the deep ultraviolet region, where the photoresist performance is not adversely impacted by basic contaminants in the processing environment of the photoresist. The novel photoresist comprises a polymer, a photoactive compound, a basic compound that is a sulfonium or iodonium compound that is essentially nonabsorbing at the exposure wavelength of the photoresist, and a solvent composition. The invention further relates to a process for imaging such a photoresist in the deep ultraviolet region.
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
Stabilized iodocarbon compositions
ActiveUS20120187330A1Heat-exchange elementsLubricant compositionStabilizing AgentsSolvent composition
Disclosed are compositions comprising at least one iodocarbon compound and preferably at least one stabilization agent. These compositions are generally useful as refrigerants for heating and cooling, as blowing agents, as aerosol propellants, as solvent composition, and as fire extinguishing and suppressing agents.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Compositions containing fluorine substituted olefins
Various uses of tetrafluoropropenes, particularly (HFO-1234) in a variety of applications, including refrigeration equipment, are disclosed. These materials are generally useful as refrigerants for heating and cooling, as blowing agents, as aerosol propellants, as solvent composition, and as fire extinguishing and suppressing agents.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Solvent compositions containing chlorofluoroolefins
InactiveUS20050096246A1Satisfies needOvercome deficienciesCompressorTransportation and packagingDouble bondSolvent composition
Compositions and methods based on the use of fluoroalkene containing from 3 to 4 carbon atoms and at least one carbon-carbon double bond, such as 1,2,-dichloro-3,3,3-trifluoropropene (HFO-1223xd) having properties highly beneficial in solvent cleaning applications.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Siloxane solvent compositions
ActiveUS7897558B1Organic detergent compounding agentsNon-surface-active detergent compositionsFlash pointSolvent composition
The present invention relates to non-volatile organic compositions having a VOC of about zero, a flash point above 140° F., and a vapor pressure of less than seven millimeters of mercury (7 mm Hg). The non-volatile organic compositions comprise an alkylated cyclicsiloxane having 5 to 8 repeating siloxane units, an alkylated cyclicsiloxane having 3 or 4 repeating siloxane units, and at least one glycol alkyl ether.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Cellulose solvent compositions and methods of making and employing same
InactiveUS6827773B2Duplicating/marking methodsMonocomponent cellulose artificial filamentEthylenediamineCellulose
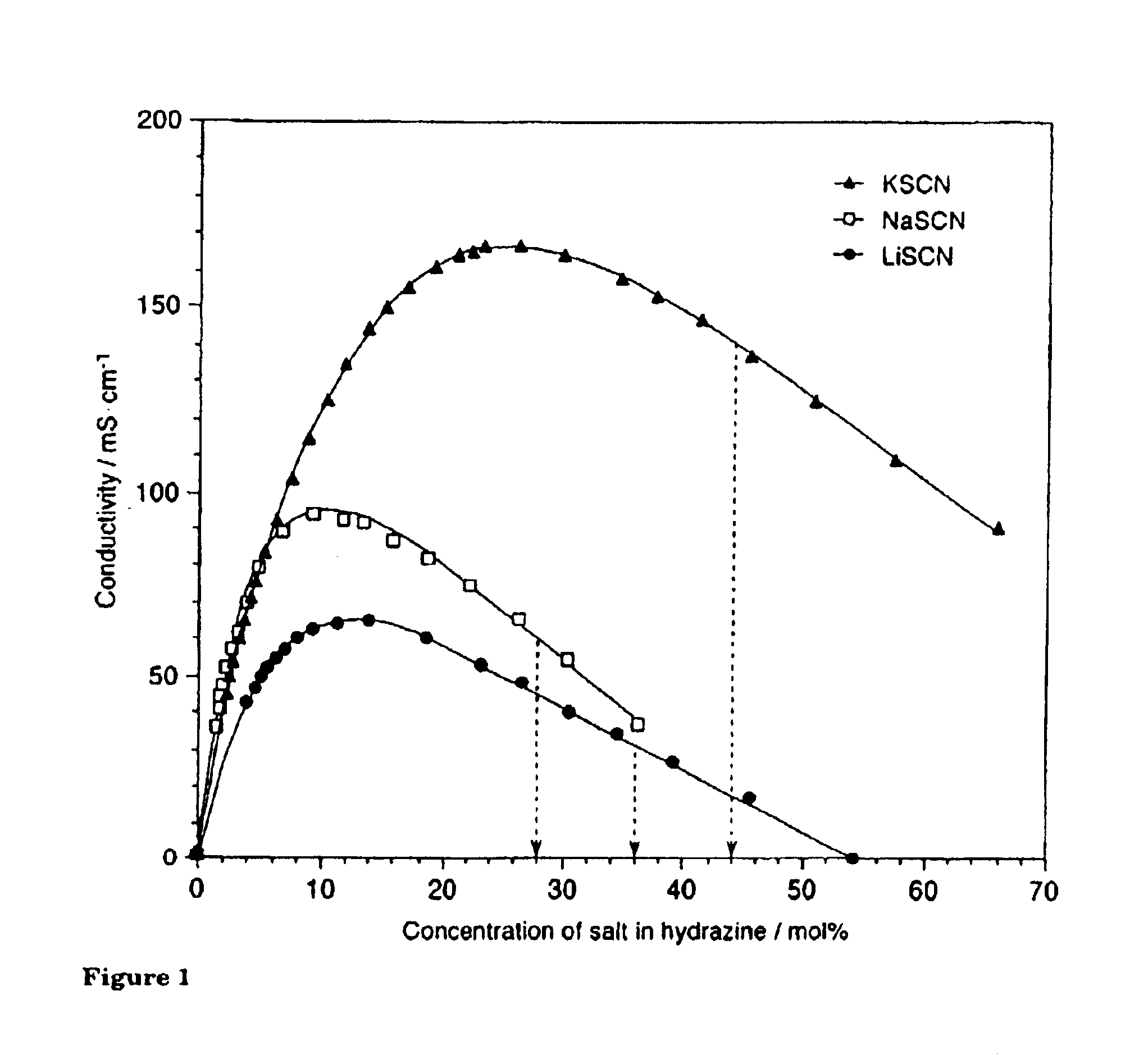
Cellulose solvents, cellulose compositions, and methods of making and using the same. For example, a cellulose composition including cellulose dissolved in the following solvent: an amine-based composition, provided however, the amine-based composition is not ammonia; and a salt selected from the group including a thiocyanate salt, a halide salt, and a nitrate salt. Representative amine-based compositions include hydrazine, hydrazine hydrate, and ethylenediamine.
Owner:NORTH CAROLINA STATE UNIV
Vertical-beam photometer for determination of light absorption pathlength
InactiveUS6496260B1Transmissivity measurementsColor/spectral properties measurementsAnalyteLight beam
Disclosed are photometric methods and devices for determining optical pathlength of liquid samples containing analytes dissolved or suspended in a solvent. The methods and devices rely on determining a relationship between the light absorption properties of the solvent and the optical pathlength of liquid samples containing the solvent. This relationship is used to establish the optical pathlength for samples containing an unknown concentration of analyte but having similar solvent composition. Further disclosed are methods and devices for determining the concentration of analyte in such samples where both the optical pathlength and the concentration of analyte are unknown. The methods and devices rely on separately determining, at different wavelengths of light, light absorption by the solvent and light absorption by the analyte. Light absorption by the analyte, together with the optical pathlength so determined, is used to calculate the concentration of the analyte. Devices for carrying out the methods particularly advantageously include vertical-beam photometers containing samples disposed within the wells of multi-assay plates, wherein the photometer is able to monitor light absorption of each sample at multiple wavelengths, including in the visible or UV-visible region of the spectrum, as well as in the near-infrared region of the electromagnetic spectrum. Novel photometer devices are described which automatically determine the concentration of analytes in such multi-assay plates directly without employing a standard curve.
Owner:MOLECULAR DEVICES
Two solvent antimicrobial compositions and methods employing them
InactiveUS20050096245A1Reduce populationGreat reductionBiocidePretreated surfacesPharmaceutical industryIngested food
The present invention relates to two solvent antimicrobial compositions and methods employing these two solvent compositions. The two solvent compositions typically contain a second solvent that is not or is only sparingly soluble in a diluting solvent. The two solvent composition can form a clear single-phase solution. The two solvent antimicrobial compositions can reduce the population of microbes on various surfaces such as facilities, containers, or equipment found in food, beverage, or pharmaceutical industries at temperatures between about −70° C. to about 100° C.
Owner:ECOLAB USA INC
Low odor, low volatility solvent for agricultural chemicals
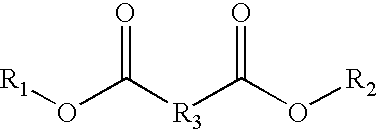
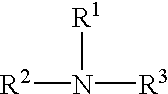
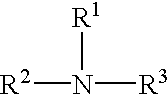
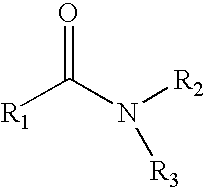
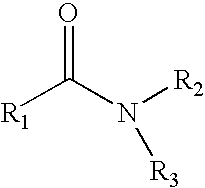
A composition includes an agricultural component in an amount of at least about 27% by weight and a solvent composition in an amount not greater than about 55% by weight. The solvent composition includes an amide having a structure of Formula I:wherein R1 comprises a C3 to C15 hydrocarbon group, and wherein R2 and R3 comprise a C1 or higher hydrocarbon group.
Owner:INDORAMA VENTURES OXIDES LLC
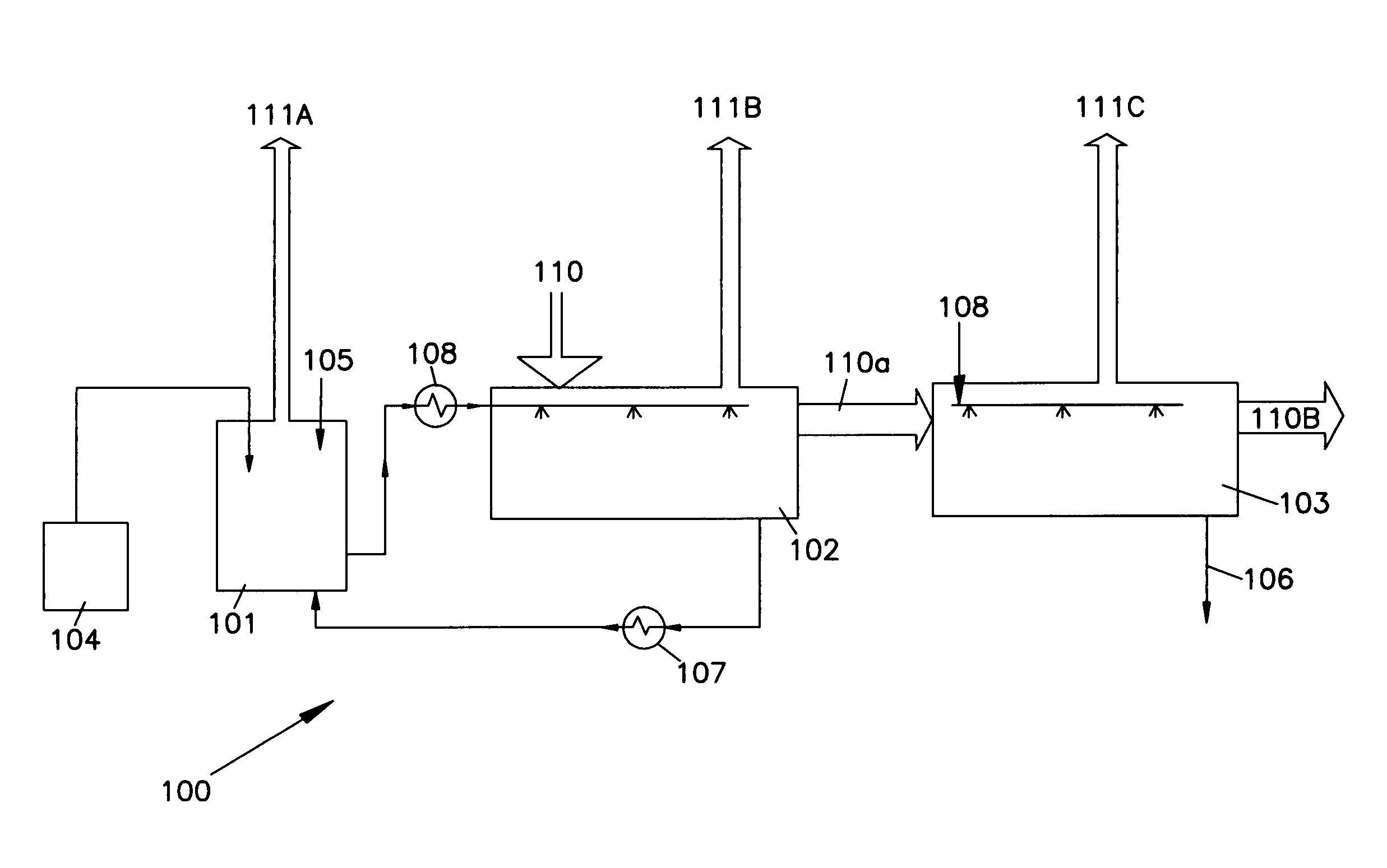
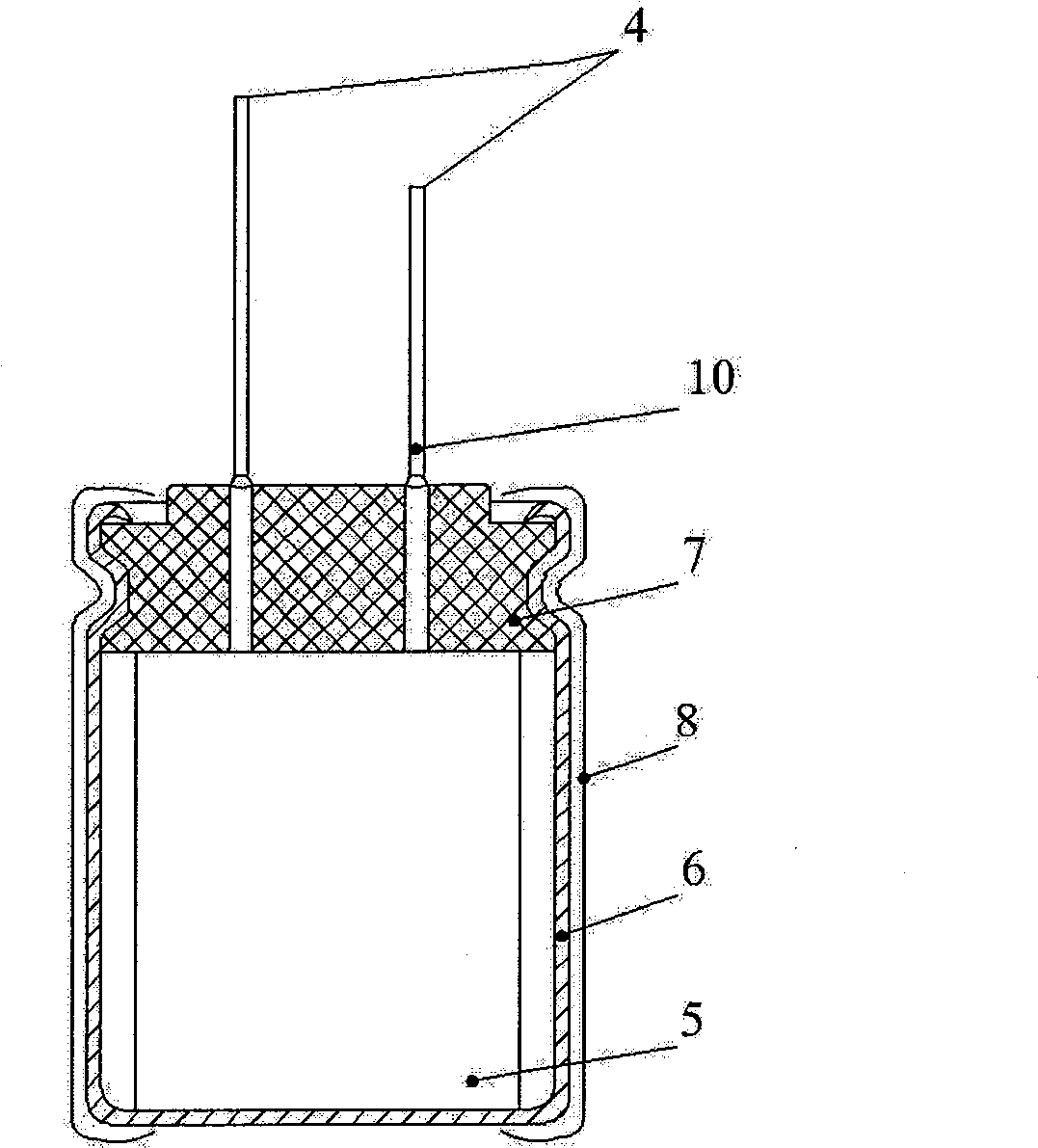
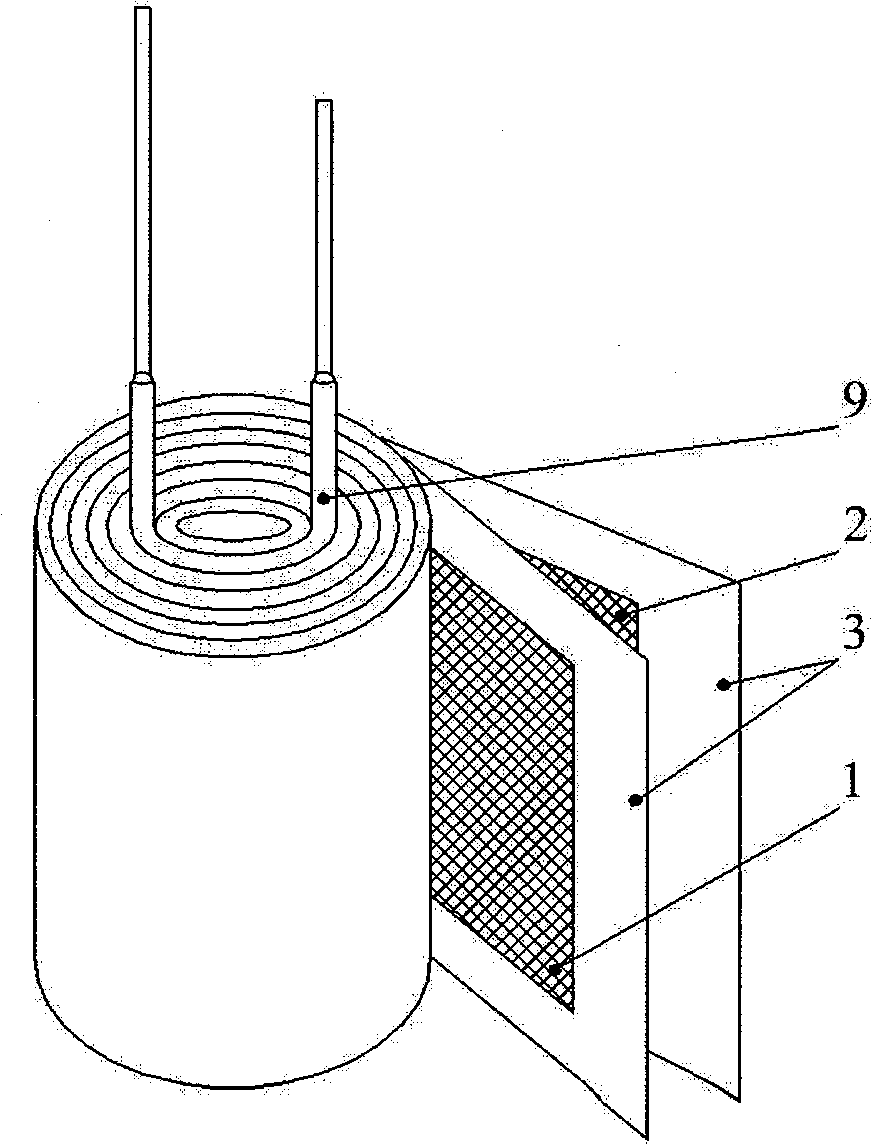
125 DEG C high temperature long life aluminum electrolysis capacitor, production method thereof and special electrolysis liquid
InactiveCN101483101ALower impedanceSolution to short lifeLiquid electrolytic capacitorsCapacitor terminalsElectrolytic agentEngineering
The present invention relates to the manufacture field of capacitor, specifically to a high temperature (125 DEG C) long life electrolytic capacitor, its manufacturing method and its special electrolyte. The capacitor is formed by manufacturing a capacitor core package by coiling together the cathode foil, cathode foil, electrolytic paper and leading-out wires; dipping the core packages in the electrolyte; and then putting in the aluminum shell; and sealing by the plug. The electrolyte has 85-88 parts of solvent composition, 5.5-11 parts of solute, 1-1.5 parts of additives and 3-5 parts of high temperature stabilizer. The capacitor has a low impedance, high-profile current resistance, long-life (5,000 hours in durability test at 125 DEG C).
Owner:FOSHAN SANSHUI RIMING ELECTRONCS
Solvent composition for dissolving chitin
The invention discloses a novel solvent for dissolving chitin by a freezing-unfreezing method or a direct dissolving method, and a use of the solvent composition. The solvent is a KOH aqueous solution, and further comprises any combination of LiOH, NaOH, urea or thiourea. The chitin and the solvent are mixed and then frozen to a point lower than a freezing point, and unfrozen at a point higher than the freezing point to obtain the chitin solution; or, the solvent is pre-cooled to the freezing point of 0 DEG C, and then the chitin is added to the cooled solvent for continuous stirring for more than 3 minutes, so that the chitin is quickly dissolved to form a transparent chitin solution. The chitin solution prepared in the invention can be processed into a chitin finished product of any form, for example, a film type, a plate type, a tubular type, a block type, a granulate type and a fiber type, and further can be processed into various chitin derivatives. The solvent composition is suitable for large-scale popularization and application.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Separation of polyolefins from nylons
InactiveUS7067613B2High proportionEconomical acceptableLayered productsPlastic recyclingPolyolefinPolyamide
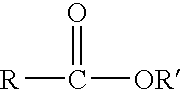
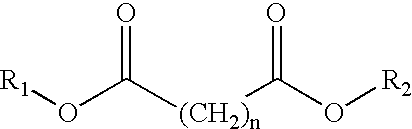
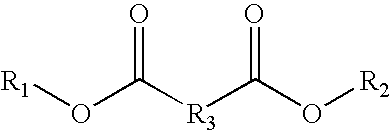
In the recycling of Nylon 6 and Nylon 6,6 polyamides from post-consumer or post-industrial waste, a process is disclosed to separate Nylon 6 and Nylon 6,6 polyamides from commingled polyolefin waste components, particularly polypropylene, by admixing the waste with an ester solvent composition and heating the admixture to a temperature above the melting temperature of the contained polyolefins to form an ester solvent composition further containing dissolved polyamide polymer and a separate immiscible liquid polyolefin phase. The ester solvent composition preferably contains ethylene carbonate, propylene carbonate, butylene carbonate, or mixtures thereof.
Owner:CHEM PROD CORP
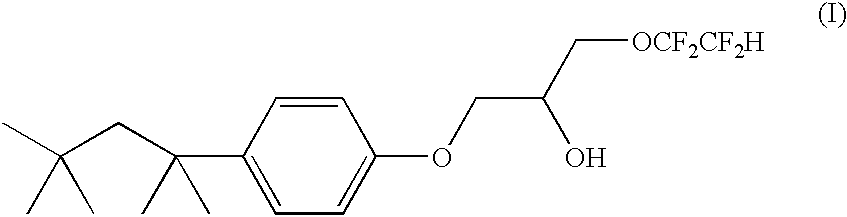
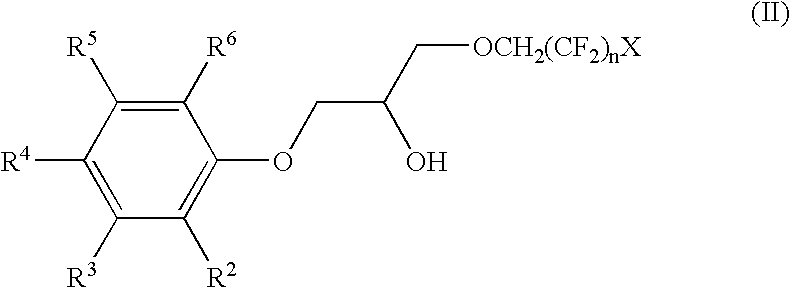
Fluoro-alcohol phase modifiers and process for cesium solvent extraction
InactiveUS6566561B1Restored to potencyMinimal partOrganic chemistryWater/sewage treatment by ion-exchangeAlcoholHydrogen
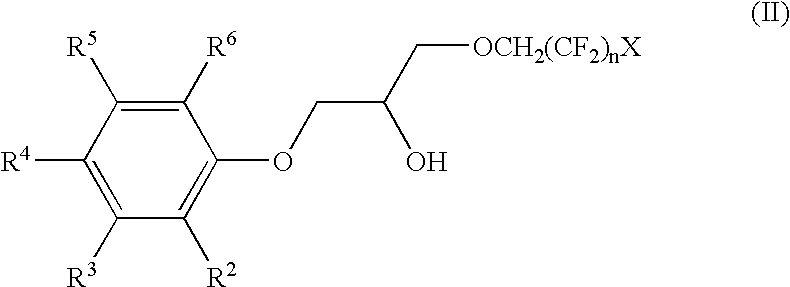
The invention relates to a class of phenoxy fluoro-alcohols, their preparation, and their use as phase modifiers and solvating agents in a solvent composition for the extraction of cesium from alkaline solutions. These phenoxy fluoro-alcohols comply with the formula:in which n=2 to 4; X represents a hydrogen or a fluorine atom, and R2-R6 are hydrogen or alkyl substituents. These phenoxy fluoro-alcohol phase modifiers are a necessary component to a robust solvent composition and process useful for the removal of radioactive cesium from alkaline nuclear waste streams. The fluoro-alcohols can also be used in solvents designed to extract other cesium from acidic or neutral solutions.
Owner:LISLE CORPORATION +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com