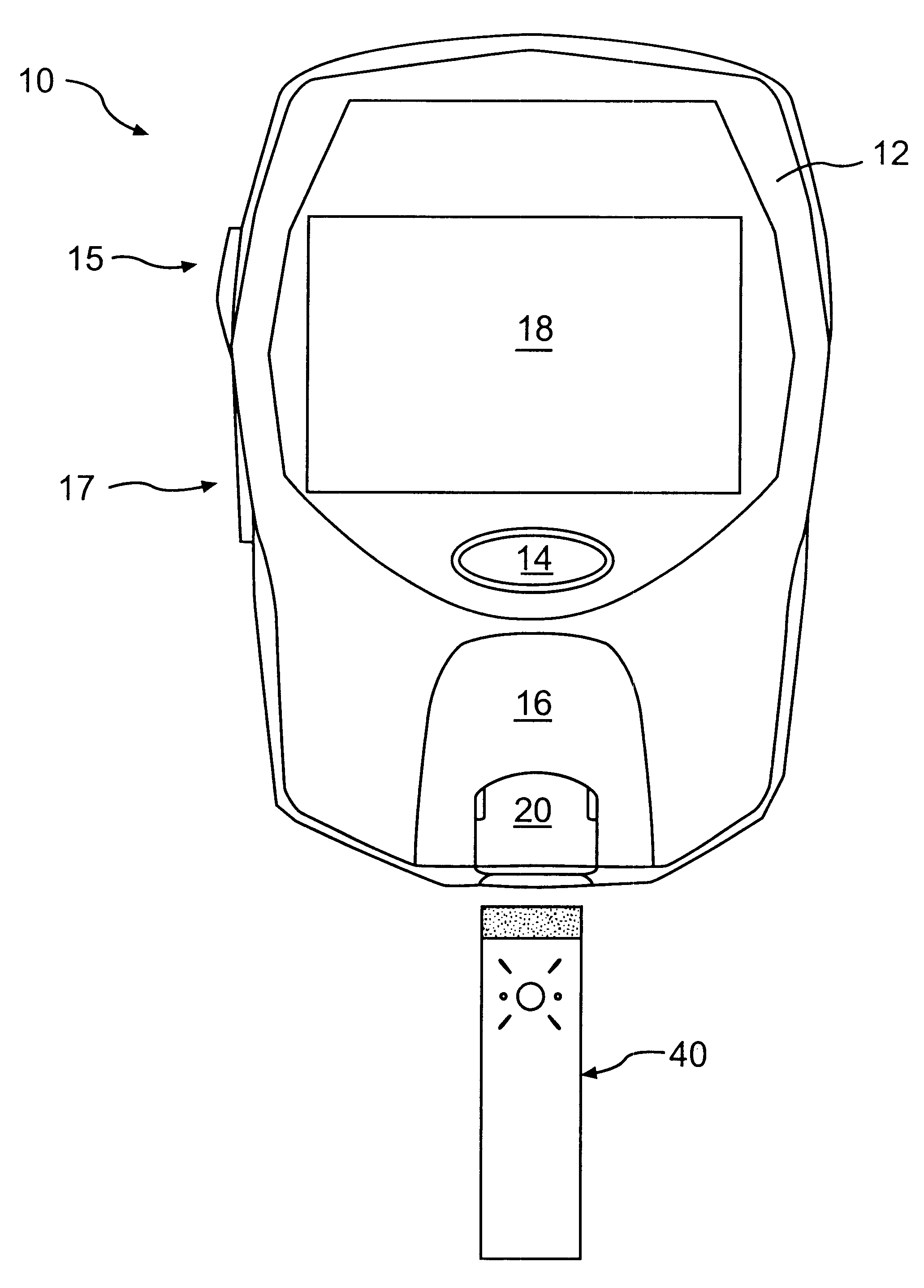
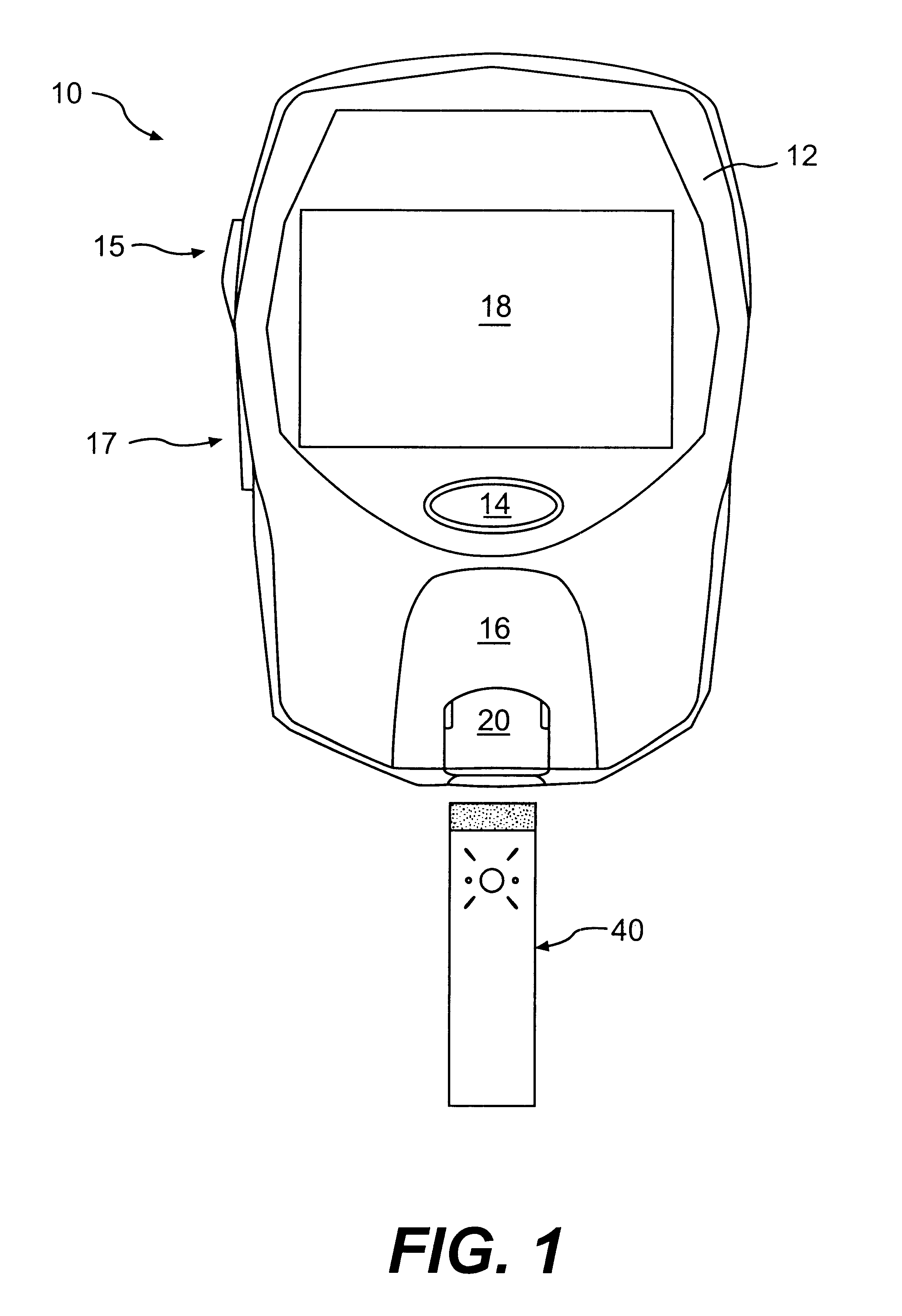
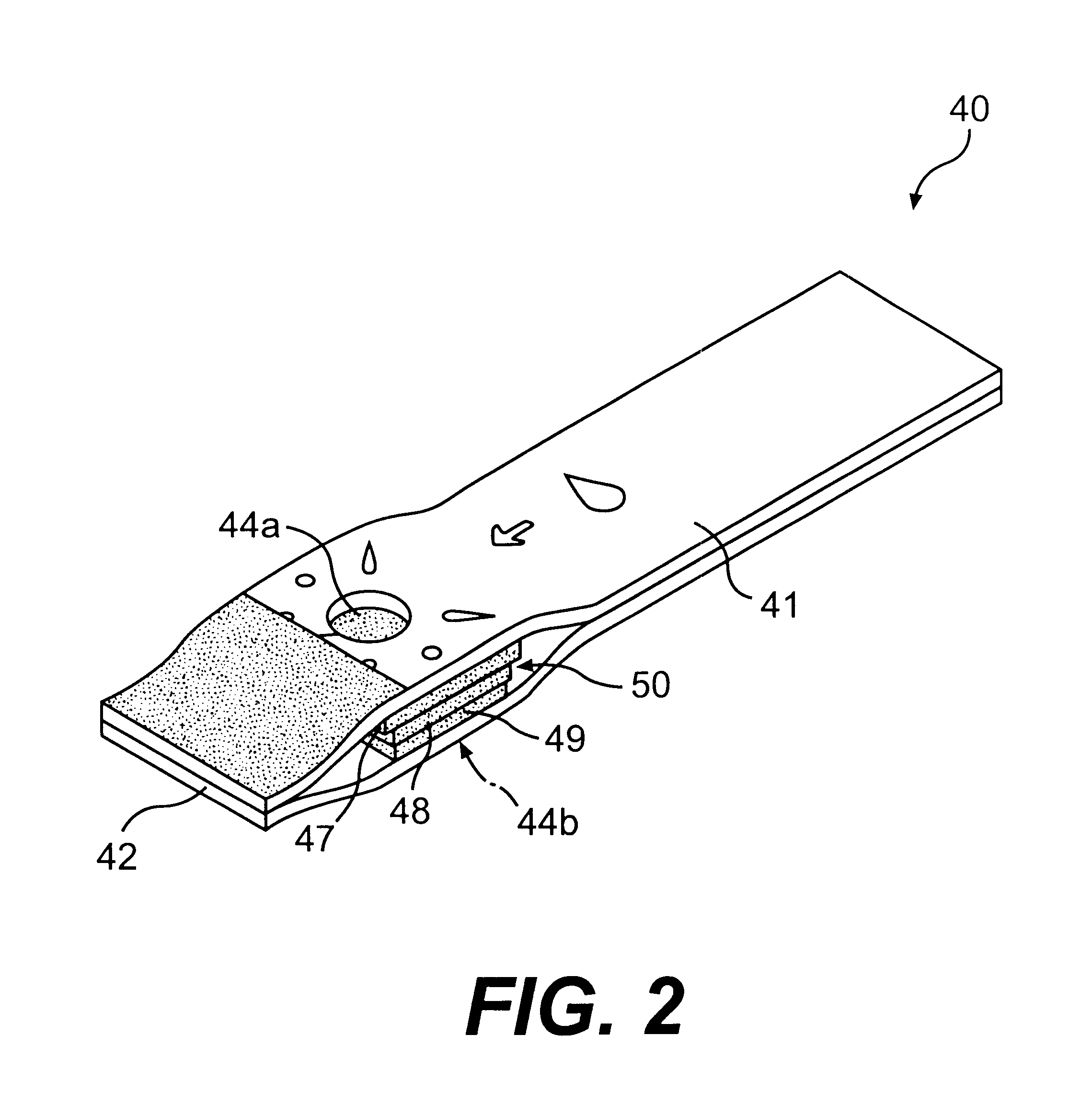
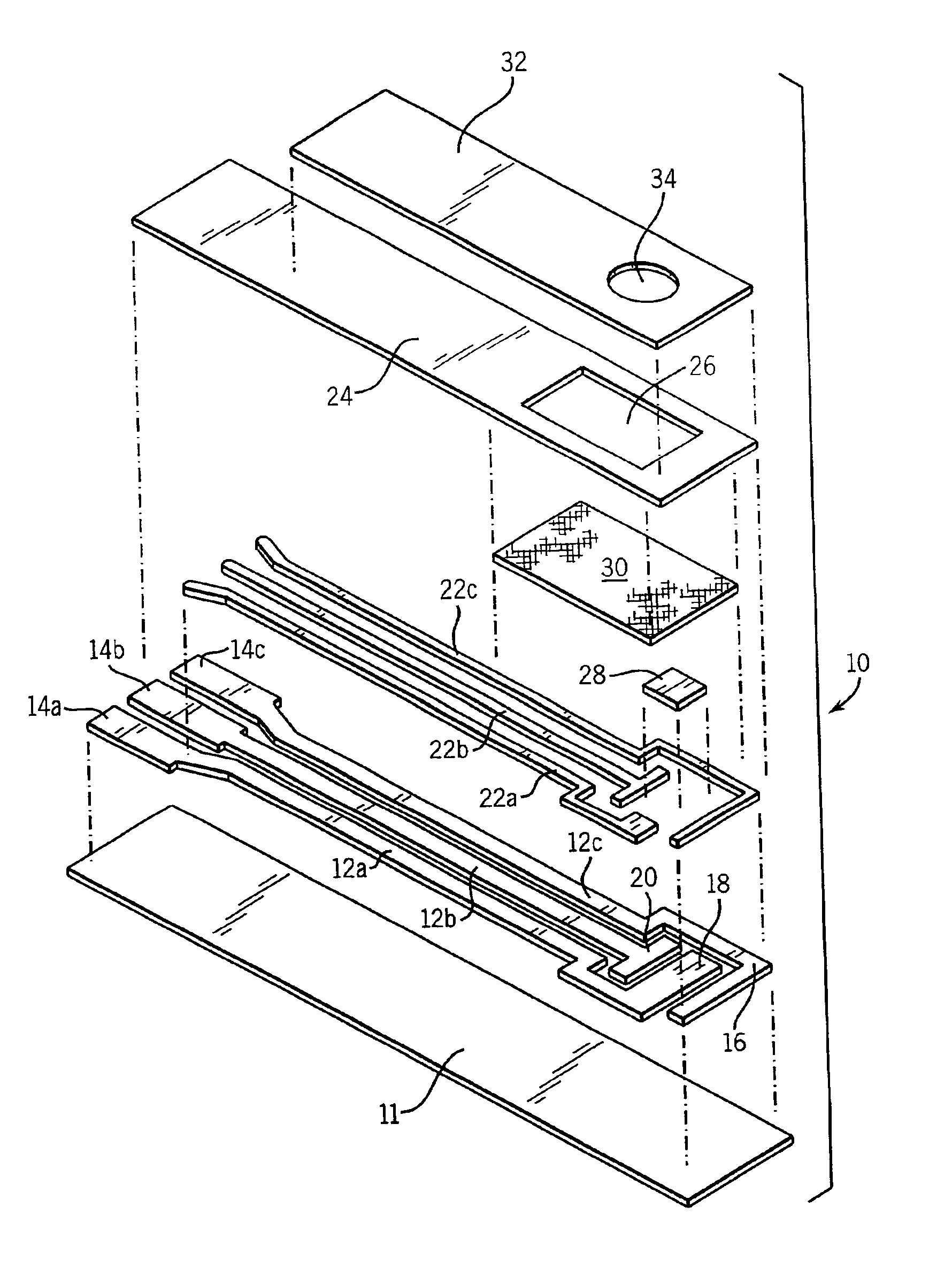
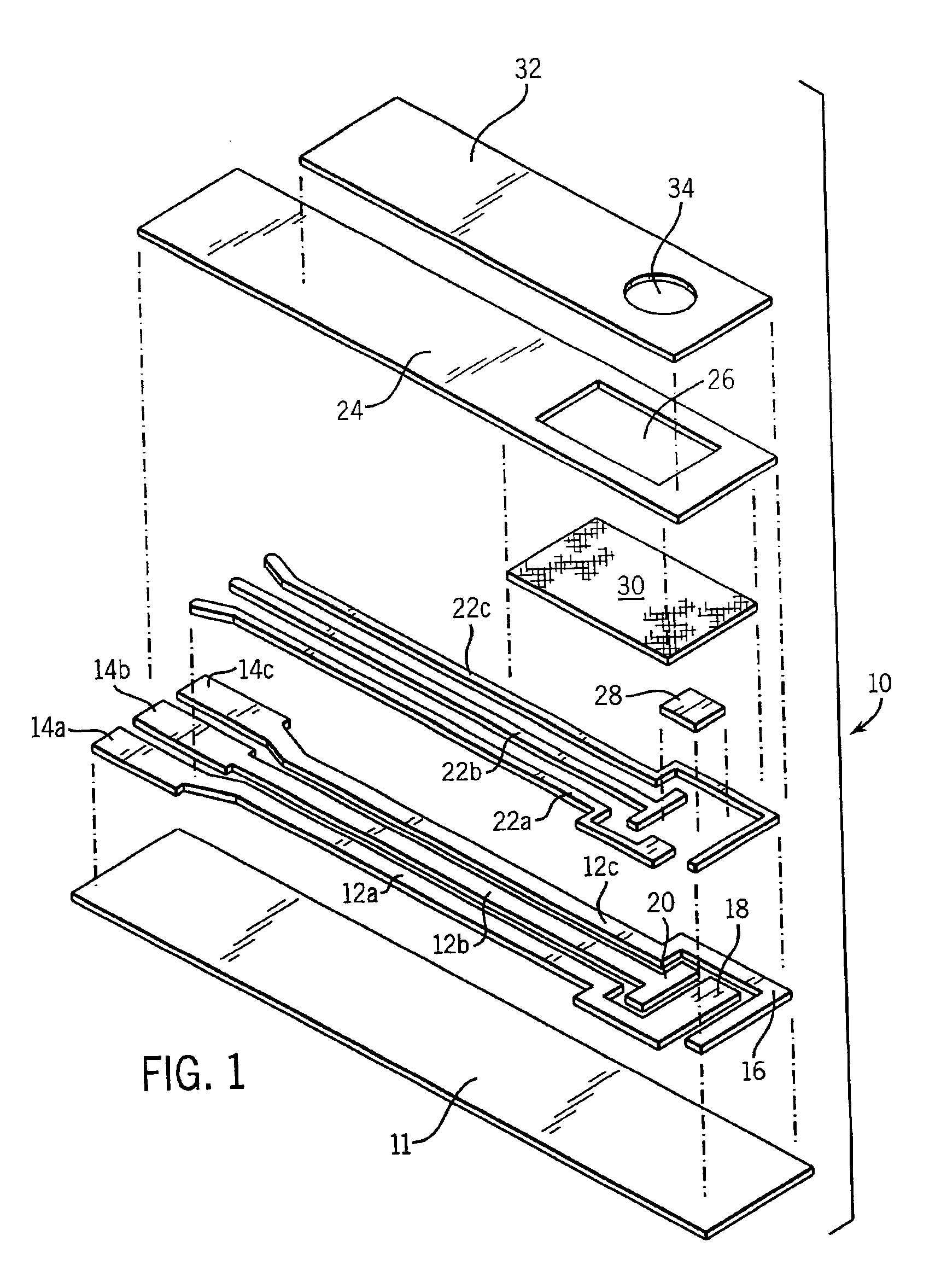
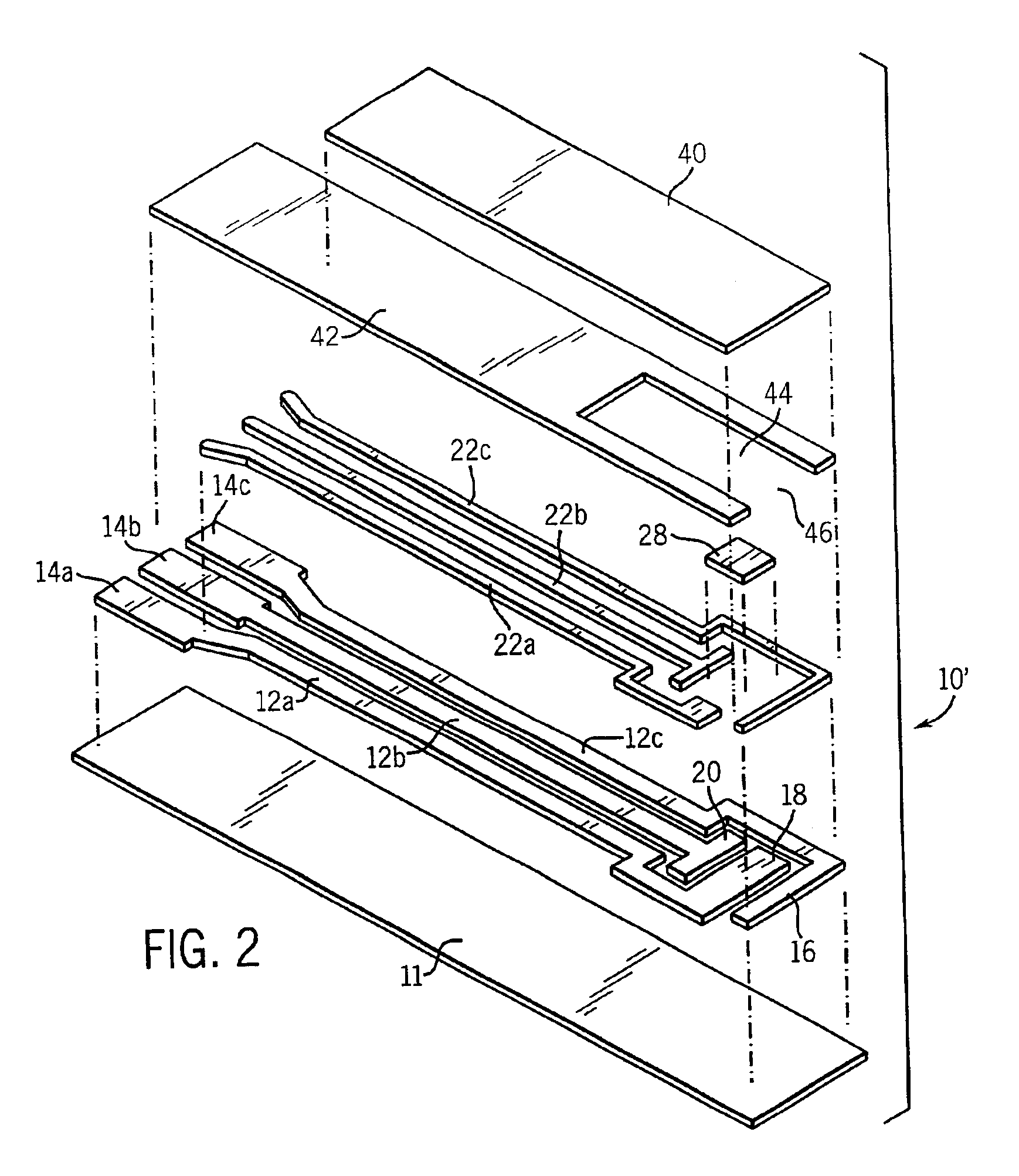
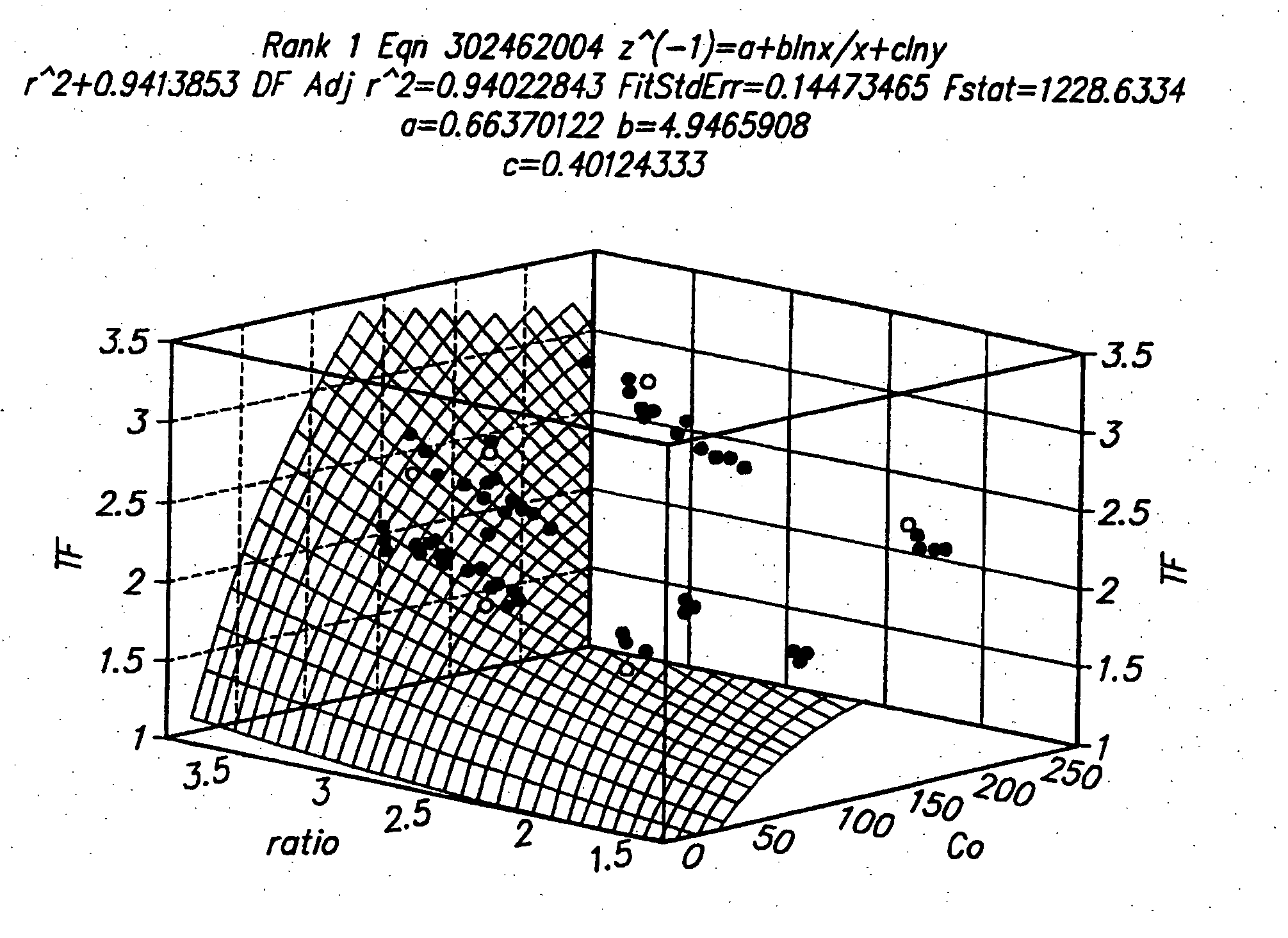
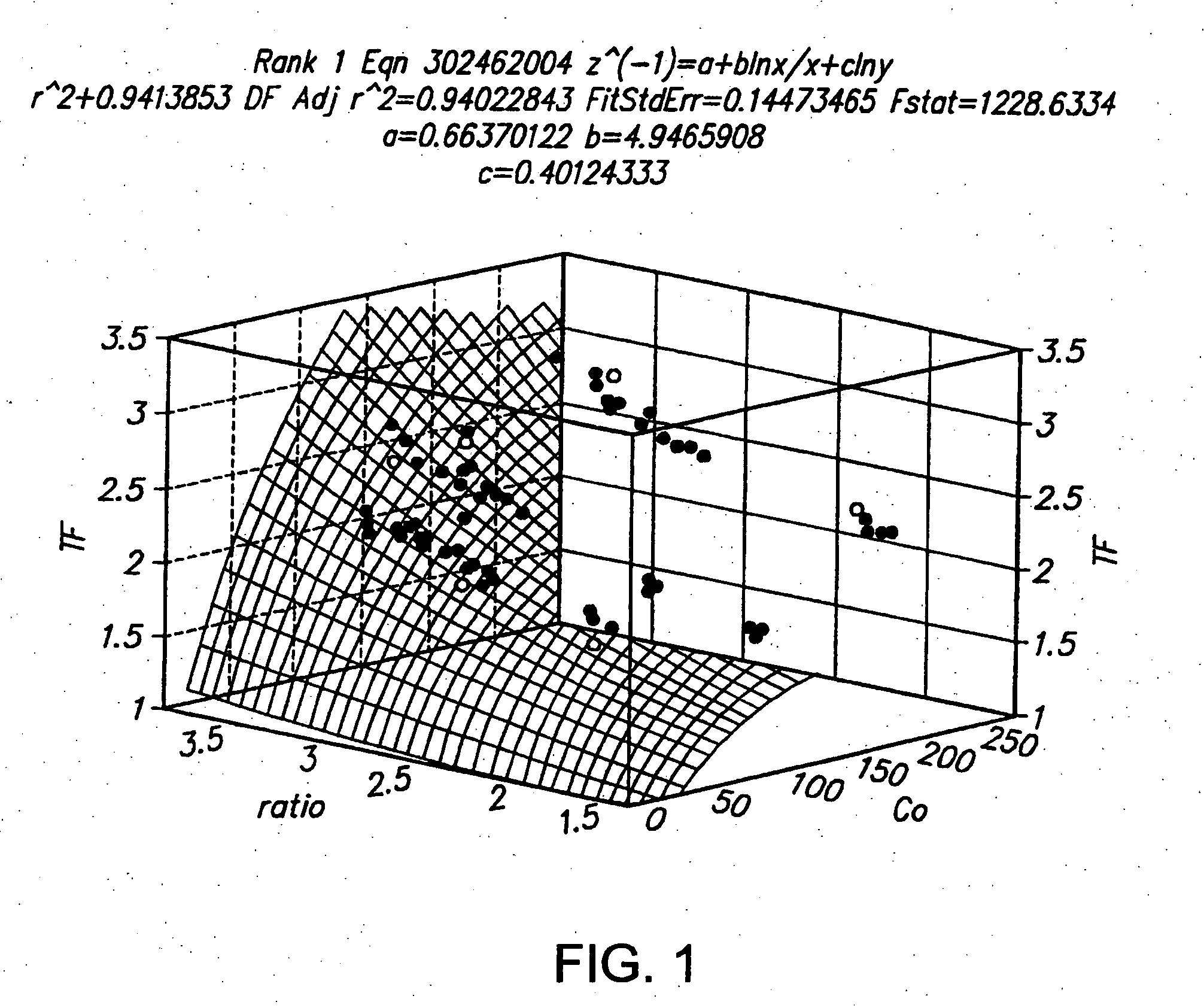
Patents
Literature
474 results about "Whole blood units" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Whole blood (WB) is human blood from a standard blood donation. It is used in the treatment of massive bleeding, in exchange transfusion, and when people donate blood to themselves. One unit brings up hemoglobin levels by about 10 g/L.
Method for determining concentration of an analyte in a test strip
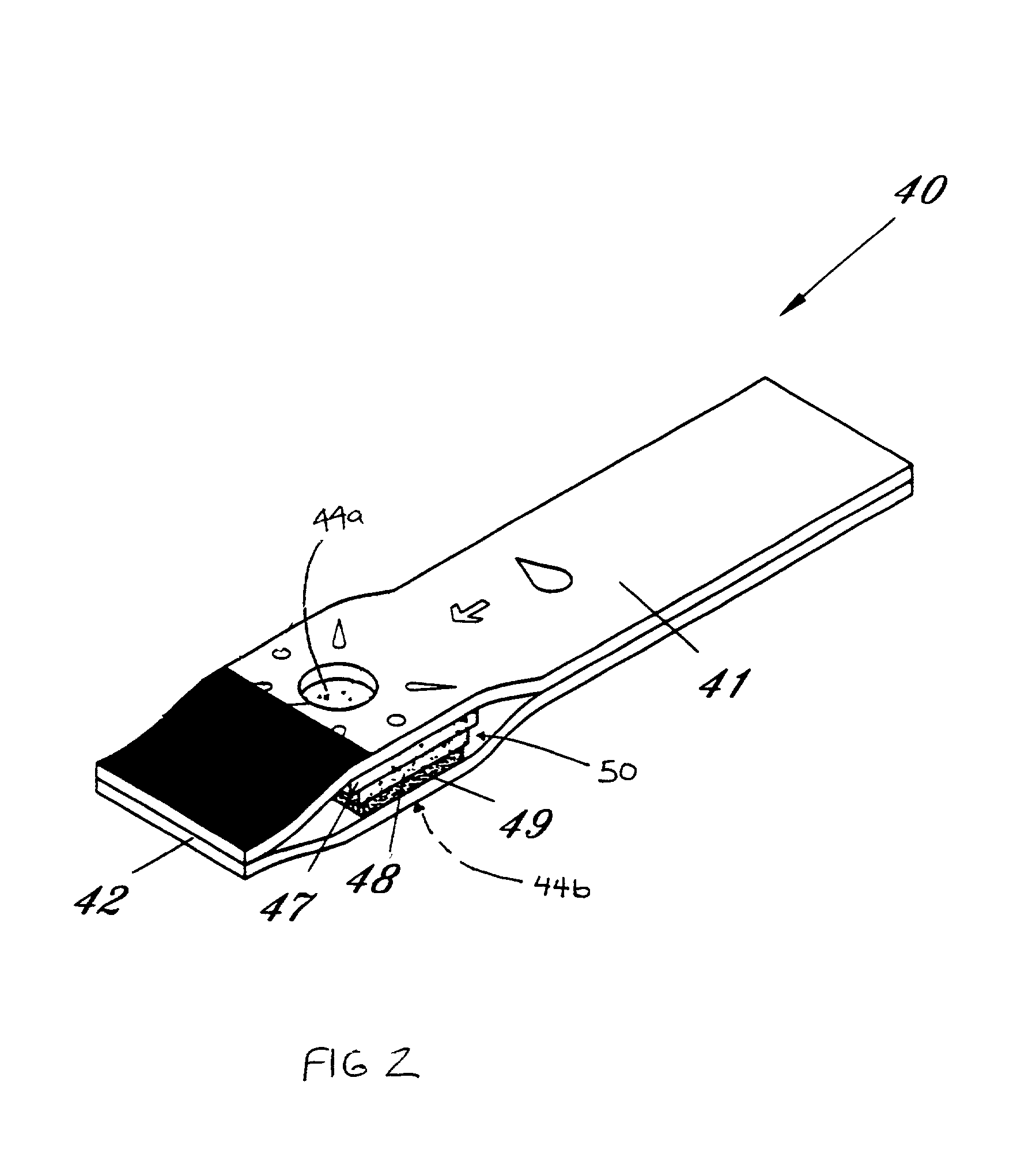
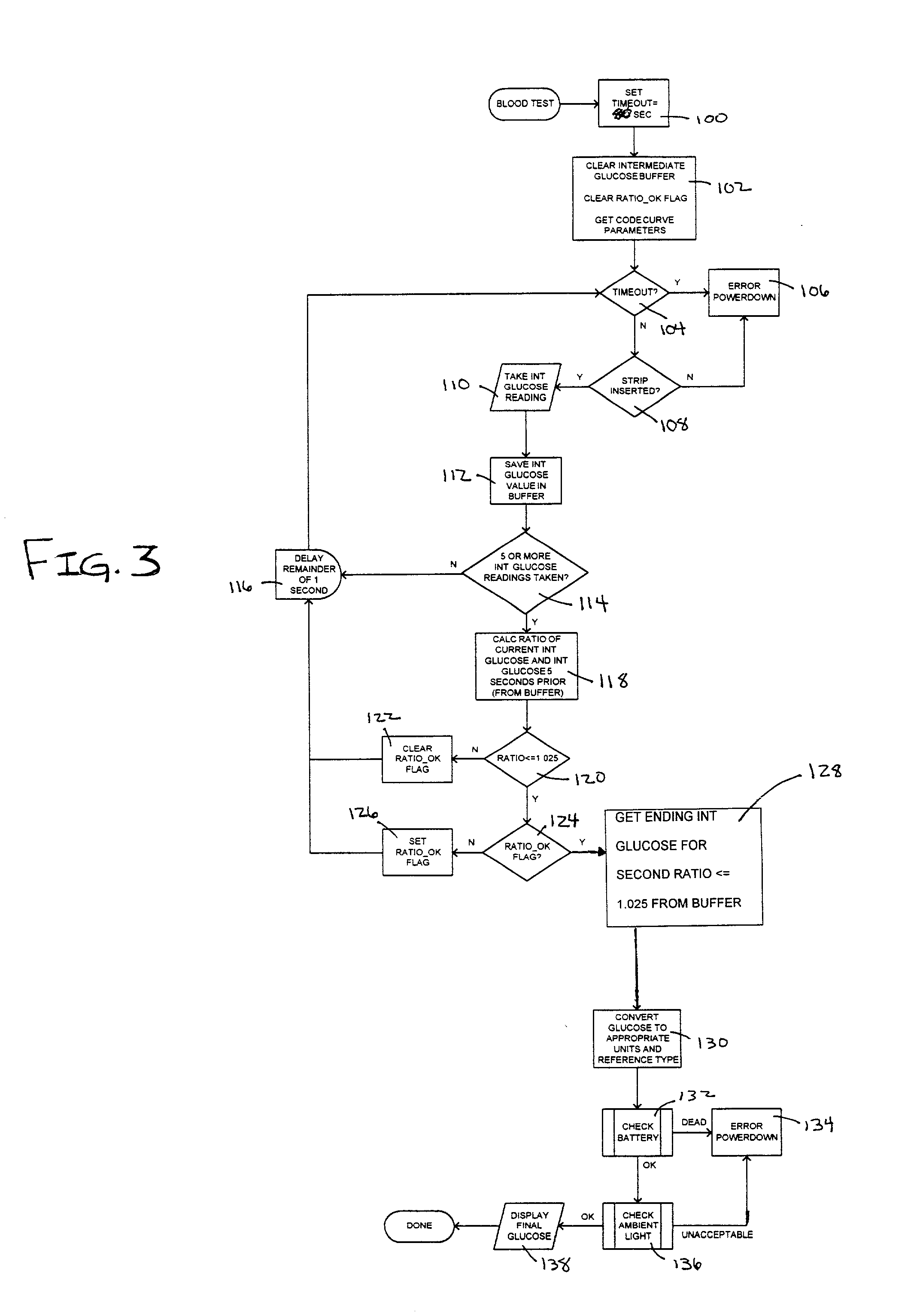
InactiveUS6541266B2Analysis using chemical indicatorsMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorTarget analysisAnalyte
The present invention provides a method of measuring an analyte, such as glucose in a fluid sample, such as whole blood, by a reflectance reading device. The method includes making periodic intermediate calculations of analyte level and dynamically ascertaining when an analytical reaction has reached an end point. Once stable, the process stops making periodic calculations and reports the final, actual glucose concentration. According to an exemplary embodiment, the method is performed by a reflectance photometer using an analytical test strip containing reagents that react with an analyte of interest in the test fluid. The end point is determined by calculating an intermediate analyte level of the testing element at predetermined intervals and calculating a ratio value corresponding to the (n)th measurement to an (n-5)th measurement. When two consecutive ratio values are less than or equal to a predetermined value, the end point is deemed reached and the final analyte level ascertained.
Owner:TRIVIDIA HEALTH
Electrochemical biosensor strip for analysis of liquid samples
InactiveUS6863800B2Easy to transportImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsElectrochemical biosensorConcentrations glucose
A biosensor in the form of a strip. In one embodiment, the biosensor strip comprises an electrode support, a first electrode, i.e., a working electrode, a second electrode, i.e., a counter electrode, and a third electrode, i.e., a reference electrode. Each of the electrodes is disposed on and supported by the electrode support. Each of the electrodes is spaced apart from the other two electrodes. The biosensor strip can include a covering layer, which defines an enclosed space over the electrodes. This enclosed space includes a zone where an analyte in the sample reacts with reagent(s) deposited at the working electrode. This zone is referred to as the reaction zone. The covering layer has an aperture for receiving a sample for introduction into the reaction zone. The biosensor strip can also include at least one layer of mesh interposed in the enclosed space between the covering layer and the electrodes in the reaction zone. This layer of mesh facilitates transporting of the sample to the electrodes in the reaction zone. In another embodiment, a biosensor strip can be constructed to provide a configuration that will allow the sample to be introduced to the reaction zone by action of capillary force. In this embodiment, the layer of mesh can be omitted. The invention also provides a method for determining the concentration of glucose in a sample of whole blood by using the biosensor of this invention.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
Electrochemical methods and devices for use in the determination of hematocrit corrected analyte concentrations
InactiveUS20050176153A1Electrolysis componentsVolume/mass flow measurementElectrical batteryBlood cell
Methods and devices for determining the concentration of an analyte in a physiological sample are provided. In the subject methods, the physiological sample is introduced into an electrochemical cell having a working and reference electrode. A first electric potential is applied to the cell and the resultant cell current over a period of time is measured to determine a first time-current transient. A second electric potential of opposite polarity is then applied and a second a time-current transient is determined. The preliminary concentration of the analyte is then calculated from the first and / or second time-current transient. This preliminary analyte concentration less a background value is then multiplied by a hematocrit correction factor to obtain the analyte concentration in the sample, where the hematocrit correction factor is a function of the preliminary analyte concentration and the variable γ of the electrochemical cell. The subject methods and devices are suited for use in the determination of a wide variety of analytes in a wide variety of samples, and are particularly suited for the determination of analytes in whole blood or derivatives thereof, where an analyte of particular interest is glucose.
Owner:LIFESCAN INC
Biosensor
InactiveUS6706232B2Avoid destructionNot easy to dissolveImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsWhole blood unitsEngineering
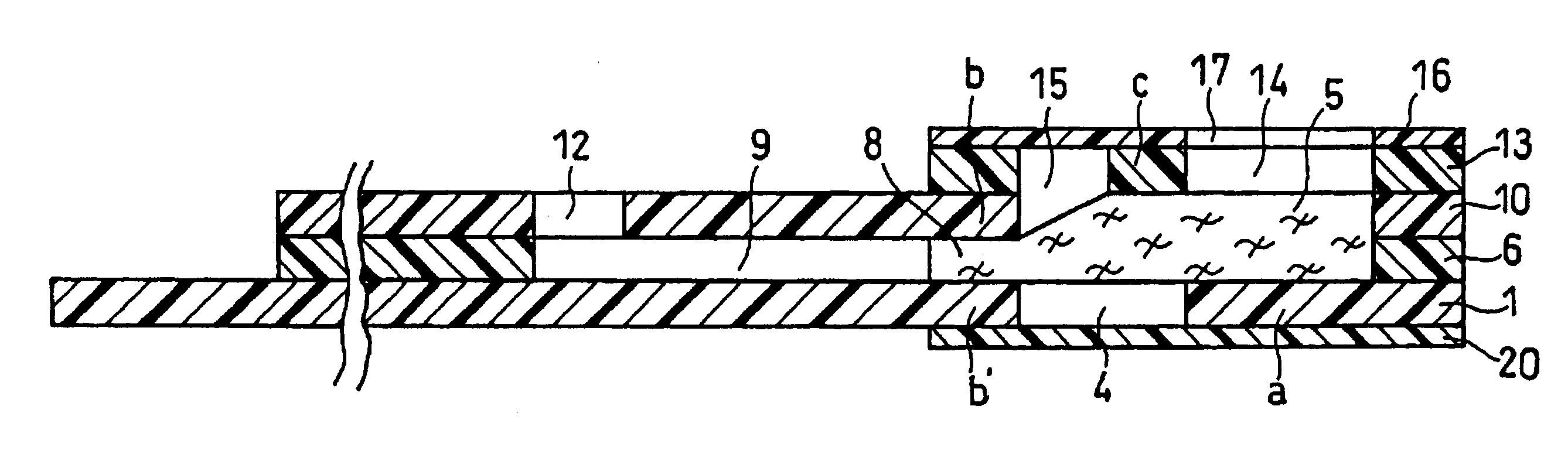
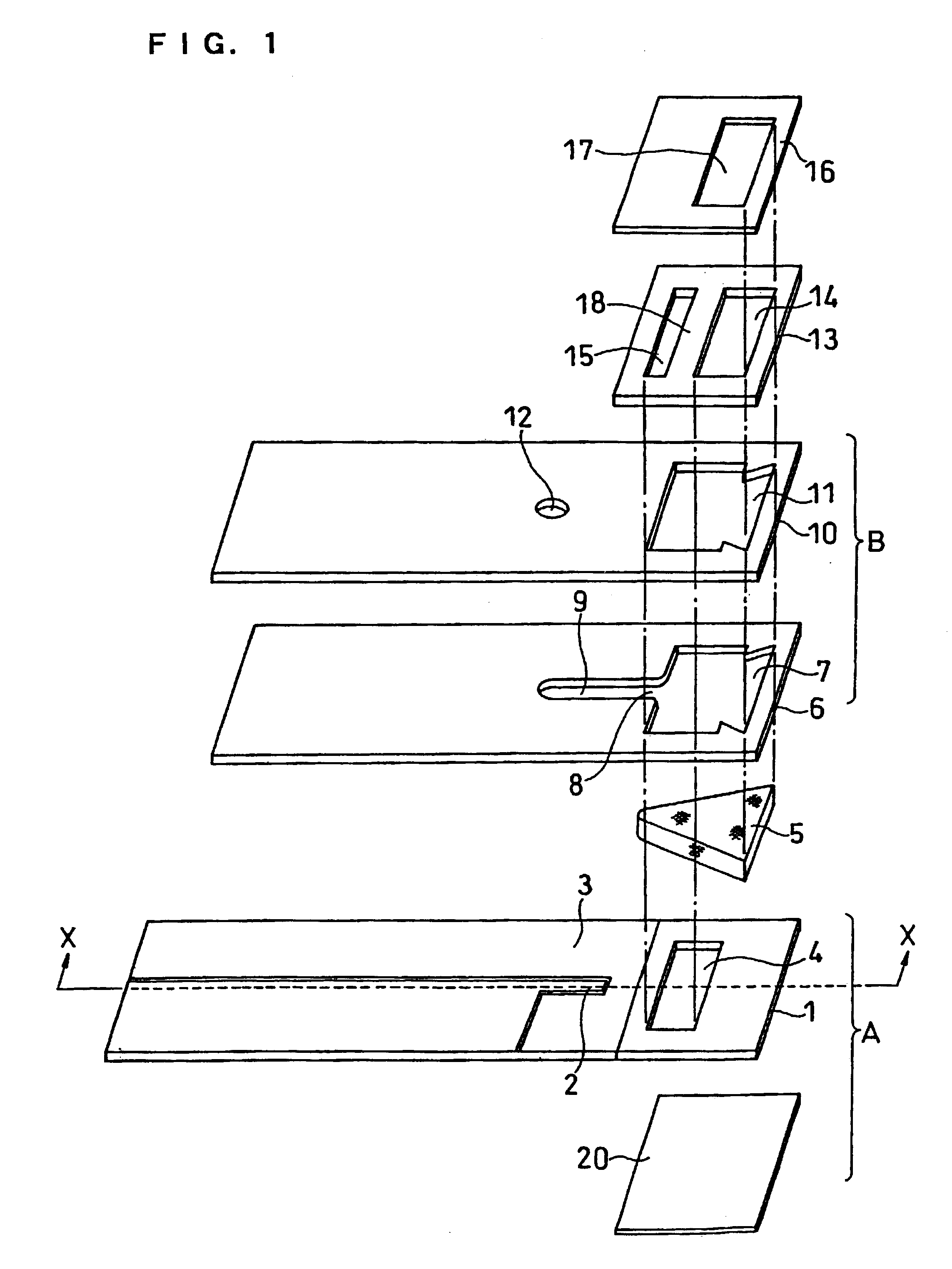
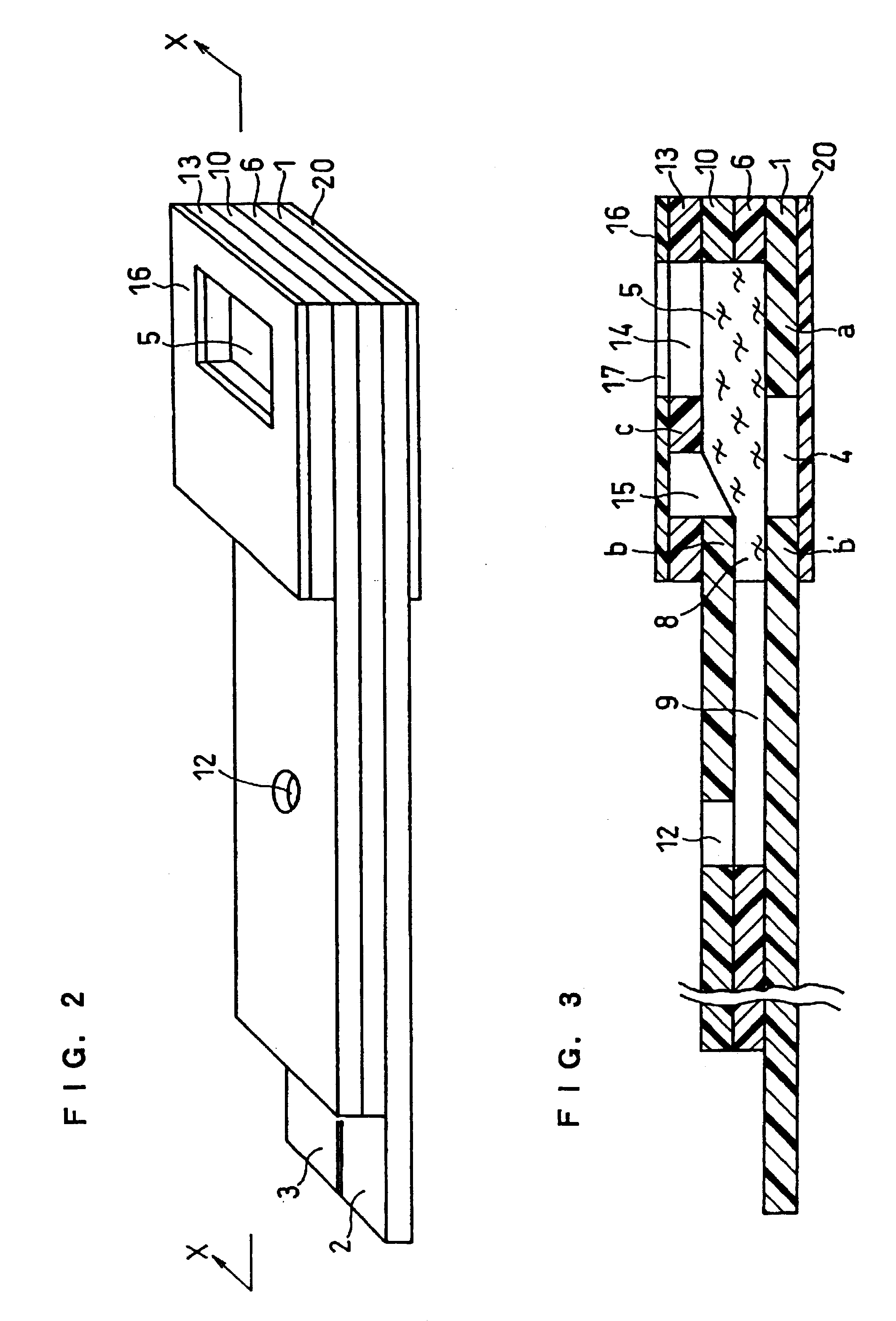
There is provided a cholesterol sensor with high-accuracy and excellent response, whose object to be measured is whole blood, where plasma with hemocytes therein filtered can rapidly reach an electrode system. In a biosensor where plasma with hemocytes therein filtered with a filter is sucked into a sample solution supply pathway due to capillarity, there are formed: a first pressing part for holding a primary side portion of the filter from the bottom; a second pressing part for holding a secondary side portion of the filter from the top and the bottom; a third pressing part for holding the central portion of the filter from the top; and a void for surrounding the filter between the second pressing part and third pressing part.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Method for determining concentration of an analyte in a test strip
InactiveUS20020146835A1Analysis using chemical indicatorsMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorChemical physicsWhole blood units
The present invention provides a method of measuring an analyte, such a glucose in a fluid sample, such as whole blood, by a reflectance reading device. The method includes making periodic intermediate calculations of analyte level and dynamically ascertaining when an analytical reaction has reached an end point. Once stable, the process stops making periodic calculations and reports the final, actual glucose concentration. According to an exemplary embodiment, the method is performed by a reflectance photometer using an analytical test strip containing reagents that react with an analyte of interest in the test fluid. The end point is determined by calculating an intermediate analyte level of the testing element at predetermined intervals and calculating a ratio value corresponding to the (n)th measurement to an (n-5)th measurement. When two consecutive ratio values are less than or equal to a predetermined value, the end point is deemed reached and the final analyte level ascertained.
Owner:TRIVIDIA HEALTH
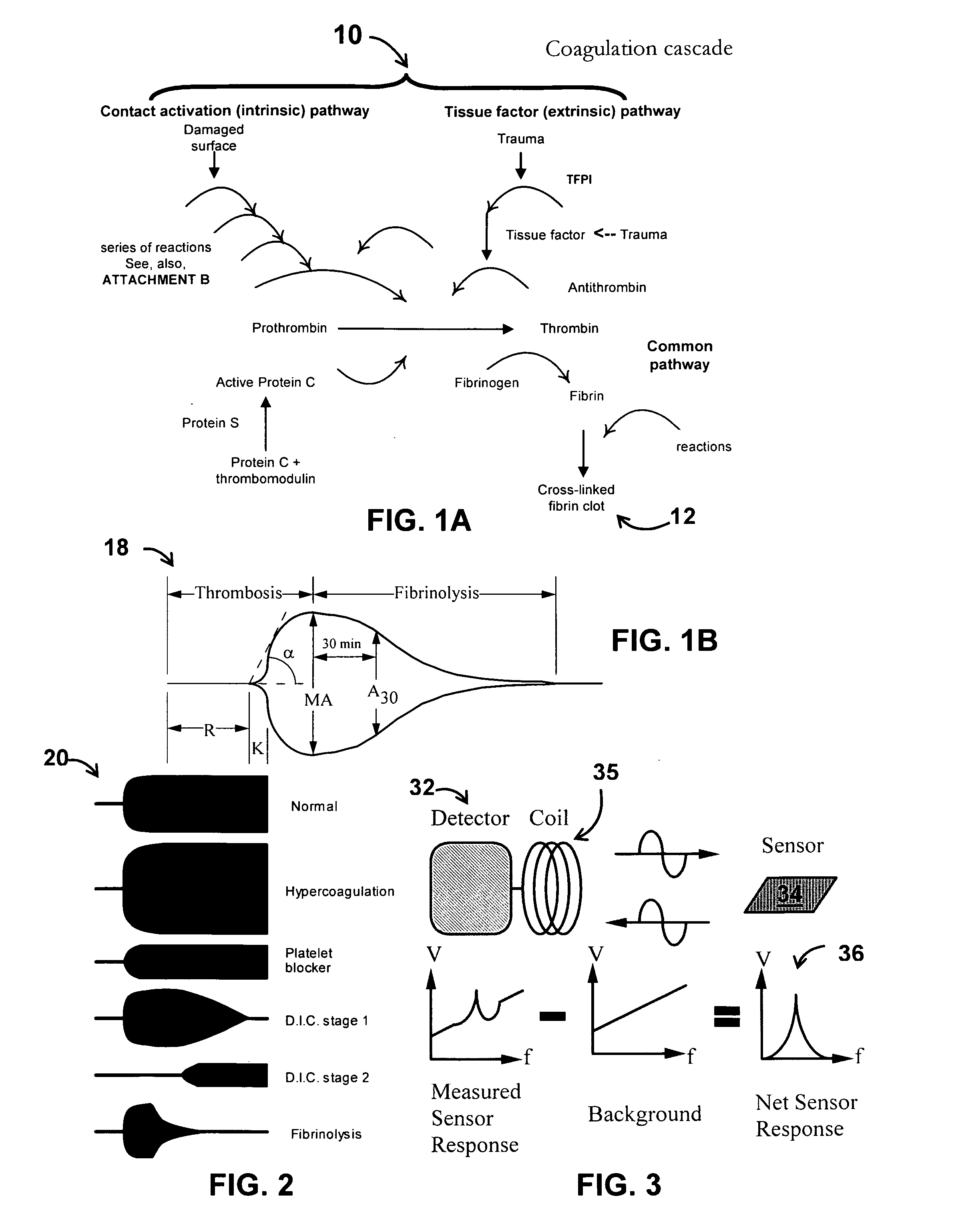
System/unit and method employing a plurality of magnetoelastic sensor elements for automatically quantifying parameters of whole blood and platelet-rich plasma
InactiveUS20080261261A1Quantifying platelet-fibrin clot strengthBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsClot formationBlood plasma
A system / analyzer-unit and method / platform—using information obtained from at least one, adapted for a plurality of, magnetoelastic sensor elements in contact with one or more samples comprising blood from a patient—for automatically quantifying one or more parameters of the patient's blood. Information obtained from emissions measured from each of the sensor elements is uniquely processed to determine a quantification about the patient's blood, such as, quantifying platelet aggregation to determine platelet contribution toward clot formation; quantifying fibrin network contribution toward clot formation; quantifying platelet-fibrin clot interactions; quantifying kinetics of thrombin clot generation; quantifying platelet-fibrin clot strength; and so on. Structural aspects of the analyzer-unit include: a cartridge having at least one bay within which a sensor element is positioned; each bay in fluid communication with both (a) an entry port for injecting a first blood sample composed of blood taken from the patient (human or other mammal), and (b) a gas vent through which air displaced by injecting the first blood sample into the bay.
Owner:KMG2 SENSORS CORP
Disposable cartridge for characterizing particles suspended in a liquid
InactiveUS7771658B2Facilitate drainingBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSingle useEngineering
A disposable cartridge for characterizing particles suspended in a liquid, especially a self-contained disposable cartridge for single-use analysis, such as for single-use analysis of a small quantity of whole blood. The self-contained disposable cartridge facilitates a straightforward testing procedure, which can be performed by most people without any particular education. Furthermore, the apparatus used to perform the test on the cartridge is simple, maintenance free, and portable.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
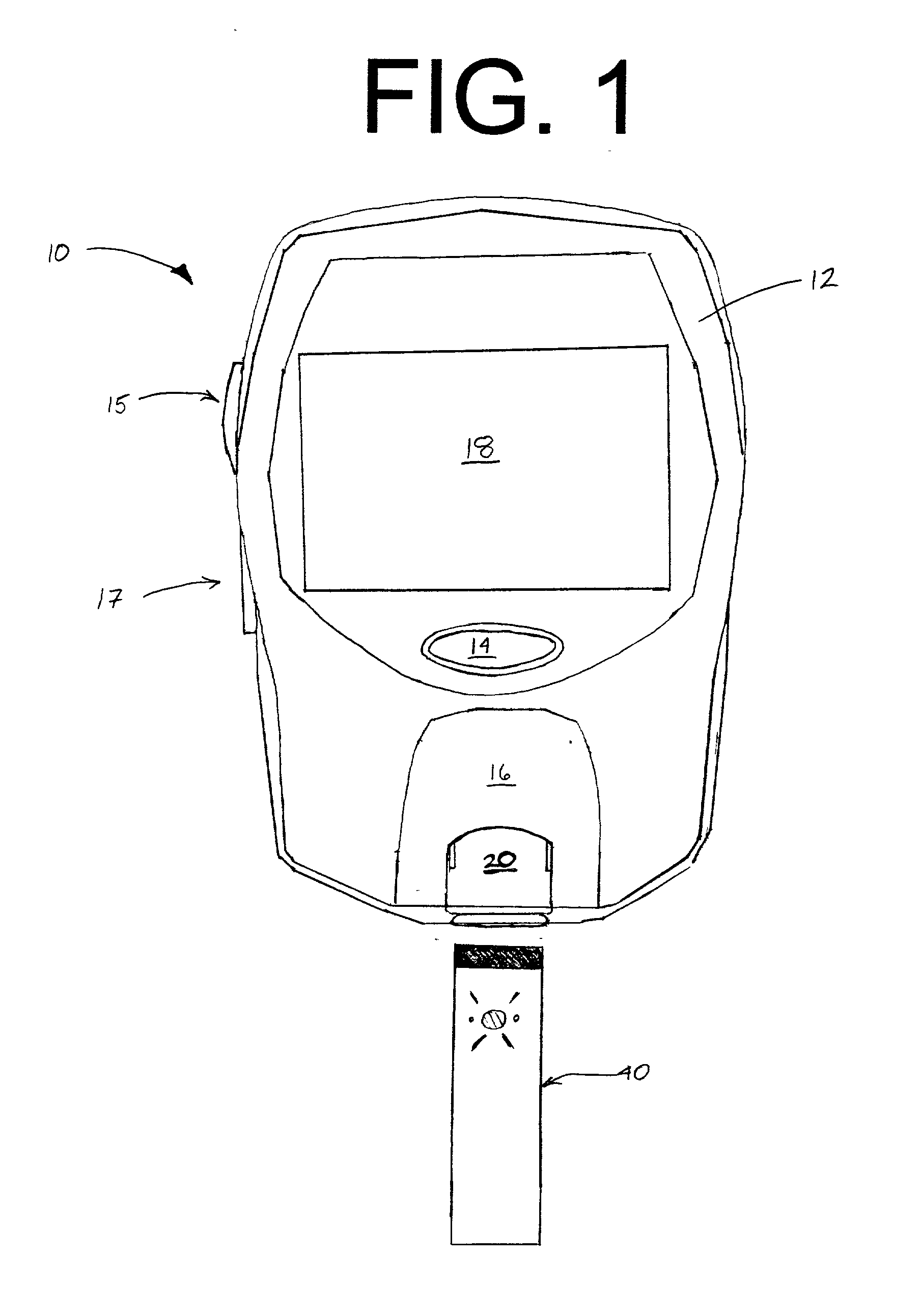
Reagent-less whole-blood glucose meter
A reagentless whole-blood analyte detection system that is capable of being deployed near a patient has a source capable of emitting a beam of radiation that includes a spectral band. The whole-blood system also has a detector in an optical path of the beam. The whole-blood system also has a housing that is configured to house the source and the detector. The whole-blood system also has a sample element that is situated in the optical path of the beam. The sample element has a sample cell and a sample cell wall that does not eliminate transmittance of the beam of radiation in the spectral band.
Owner:OPTISCAN BIOMEDICAL
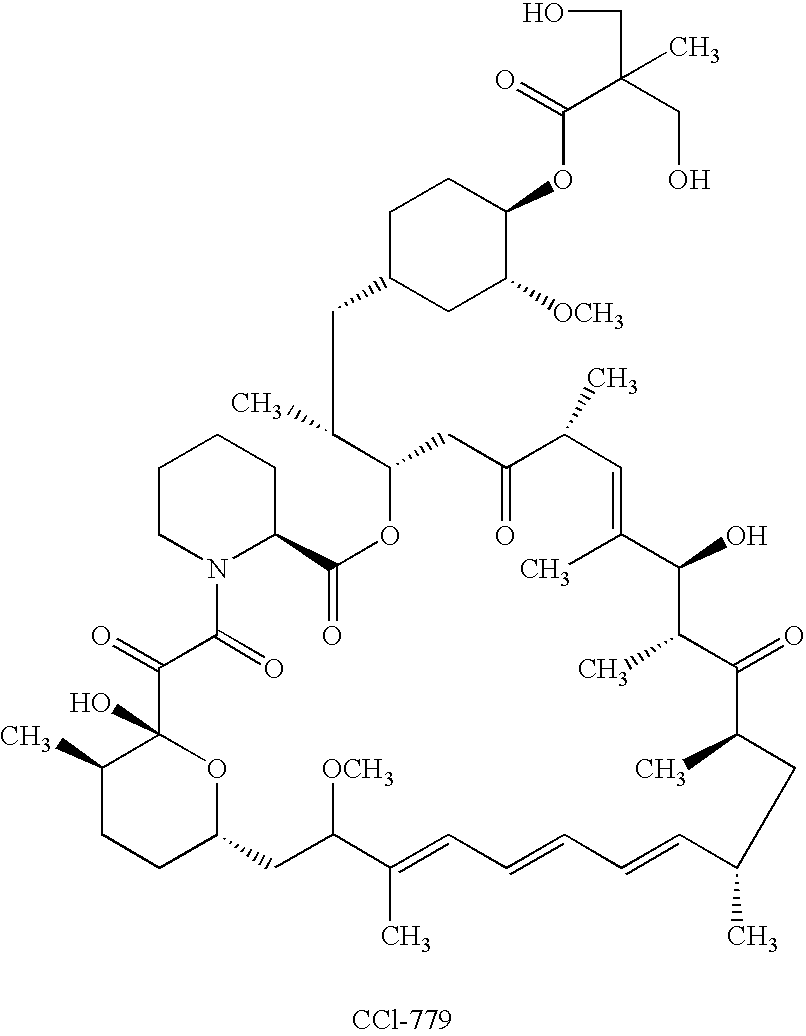
Orally bioavailable CCI-779 formulations
A CCI-779 oral dosage form is provided in which, after oral administration to a subject, the CCI-779 has a whole blood peak concentration (Cmax) of 5.4±1.8 ng / mL and an area under the curve (AUC) of about 66±about 22 ng-hr / ml and the sirolimus has a Cmax of 18.7±9.6 ng / mL and an AUC of about 600±about 228 ng-hr / ml, for a 25 mg unit dose of CCI-779. Another CCI-779 oral dosage form is provided which, after oral administration thereof to a subject, the CCI-779 has a Cmax of 5.7±1.7 ng / mL and an AUC of about 60±about 20 ng-hr / ml and the sirolimus has a Cmax of 17.1±8.1 ng / mL and an AUC of about 548±about 187 ng-hr / ml in whole blood, for a 25 mg unit dose of CCI-779. Products containing these oral dosage forms, and methods of use thereof, are also described.
Owner:WYETH LLC
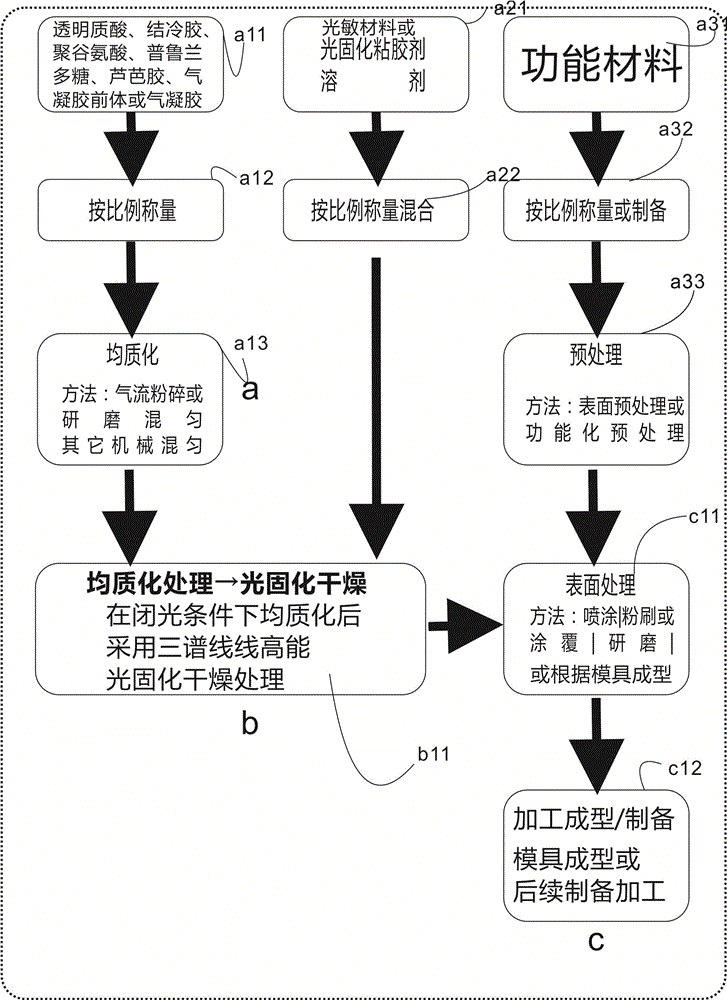
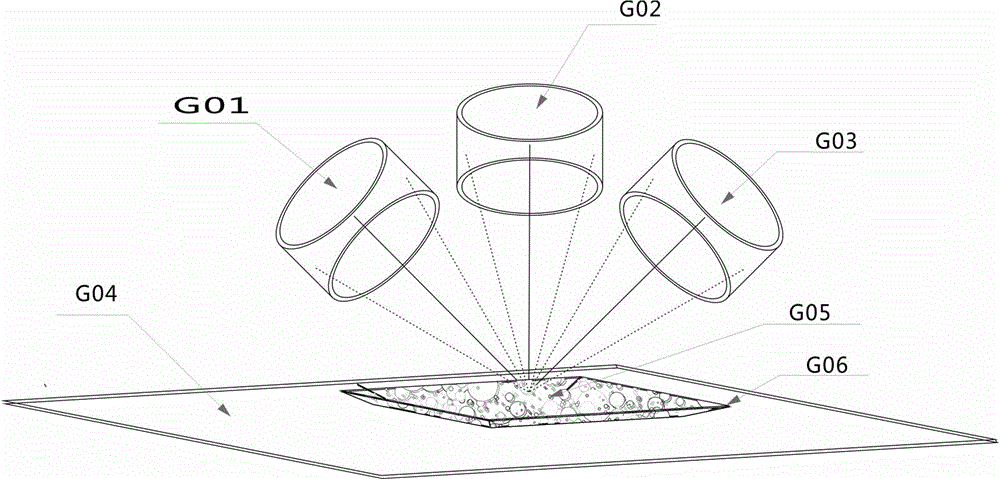
Novelmultifunctional ready-to-useaerogel composite for whole blood component protection and preparation method of novelmultifunctional ready-to-useaerogel composite
InactiveCN106832439ALow thermal conductivityImprove thermal conductivityChemical industryPullulanAntioxidant
The invention provides a multifunctional aerogel material for blood component protection and a preparation method of the multifunctional aerogel material. Gellan gum, hyaluronic acid, Pullulan, Lubrajel CG andpoly(gamma-glutamic acid), derivatives or a mixture thereof are taken as a skeleton to act with a novellight-sensitive material, aerogel or a precursor for preparation of the ready-to-useaerogel material, and then multifunctional ready-to-useaerogel composite is prepared from the ready-to-useaerogel material as well as raw materials includingglucose, a novel solvent, a novel fixing agent, a buffering agent, a stabilizer, a novel preservative, a surfactant, a high-molecular compound, essential oil, an antioxidant and the likewith a three-spectral-line high-energy photocuring method by utilizing a high polymer material such as hyaluronic acid and the like as the skeleton. The material has the characteristics of being convenient to use, green, environment-friendly and the like, the whole blood component treated with the material keeps good cellular morphology, is stored for a long time, reducesbatch-to-batch difference and is an ideal additive for a whole blood controlling product and other products, and the material can also be applied to collection, storage and transfer of tissue cells as well as fields of cosmetics, food, drugs and the like.
Owner:广州市芯检康生物科技有限公司
Continuous whole blood glucose monitor
InactiveUS20110009720A1Improve fitOther blood circulation devicesHaemofiltrationPeristaltic pumpPhotoconductive detector
A portable continuous whole blood glucose monitor comprising, a mid-infrared quantum cascade laser and driver in optical communication with a transmission cell and a photo-conductive detector and pre-amplifier. The monitor further comprises a peristaltic pump connected to a single lumen catheter peripherally inserted into a patient's vein. The single lumen catheter, in combination with the peristaltic pump, is operable to automatically withdraw a fixed and metered amount of whole blood from a patient, then a tube delivers a fixed and metered amount of the saline / surfactant supply to the whole blood. Methods of enhancing measurement sensitivity are also provided.
Owner:CASCADE METRIX LLC
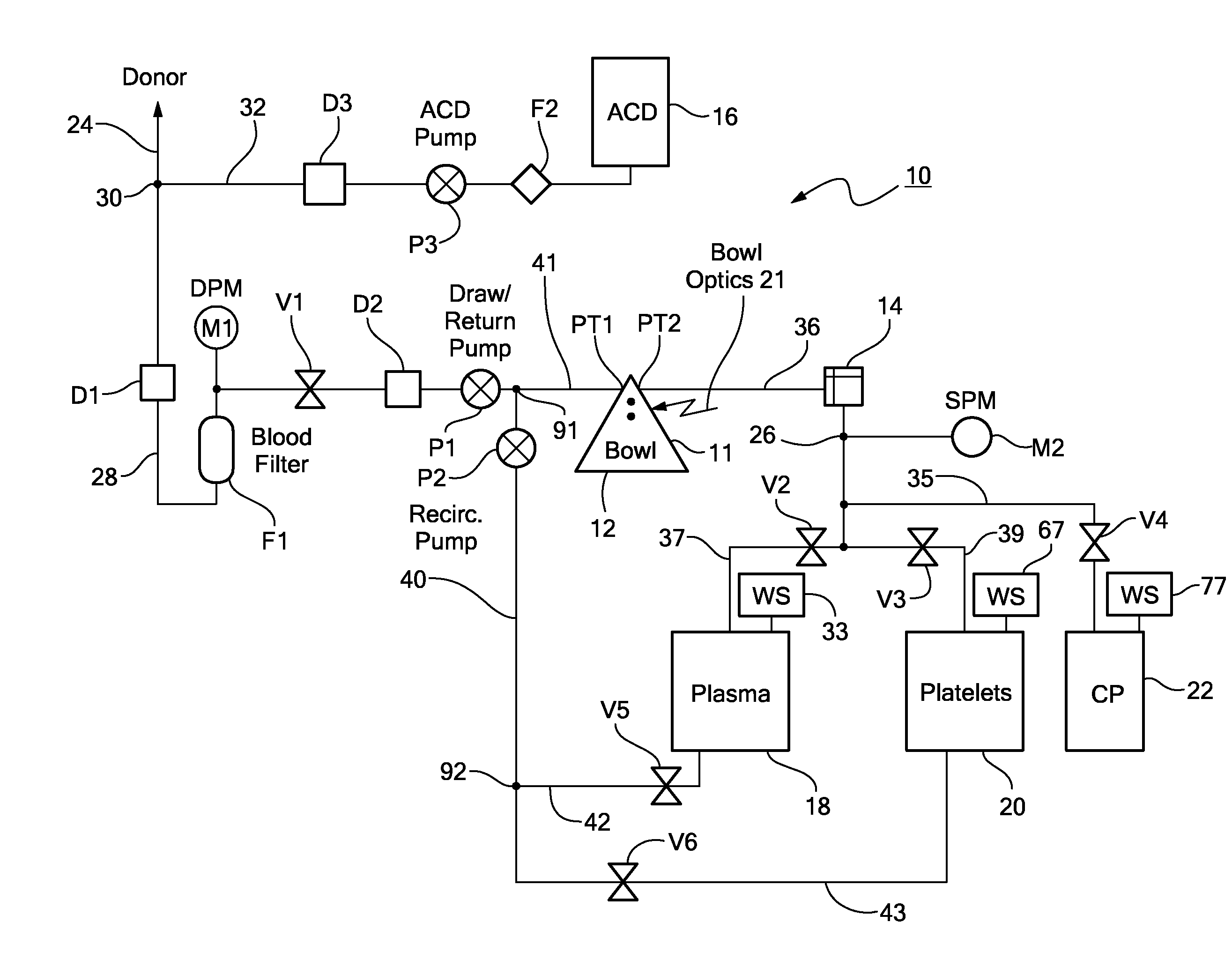
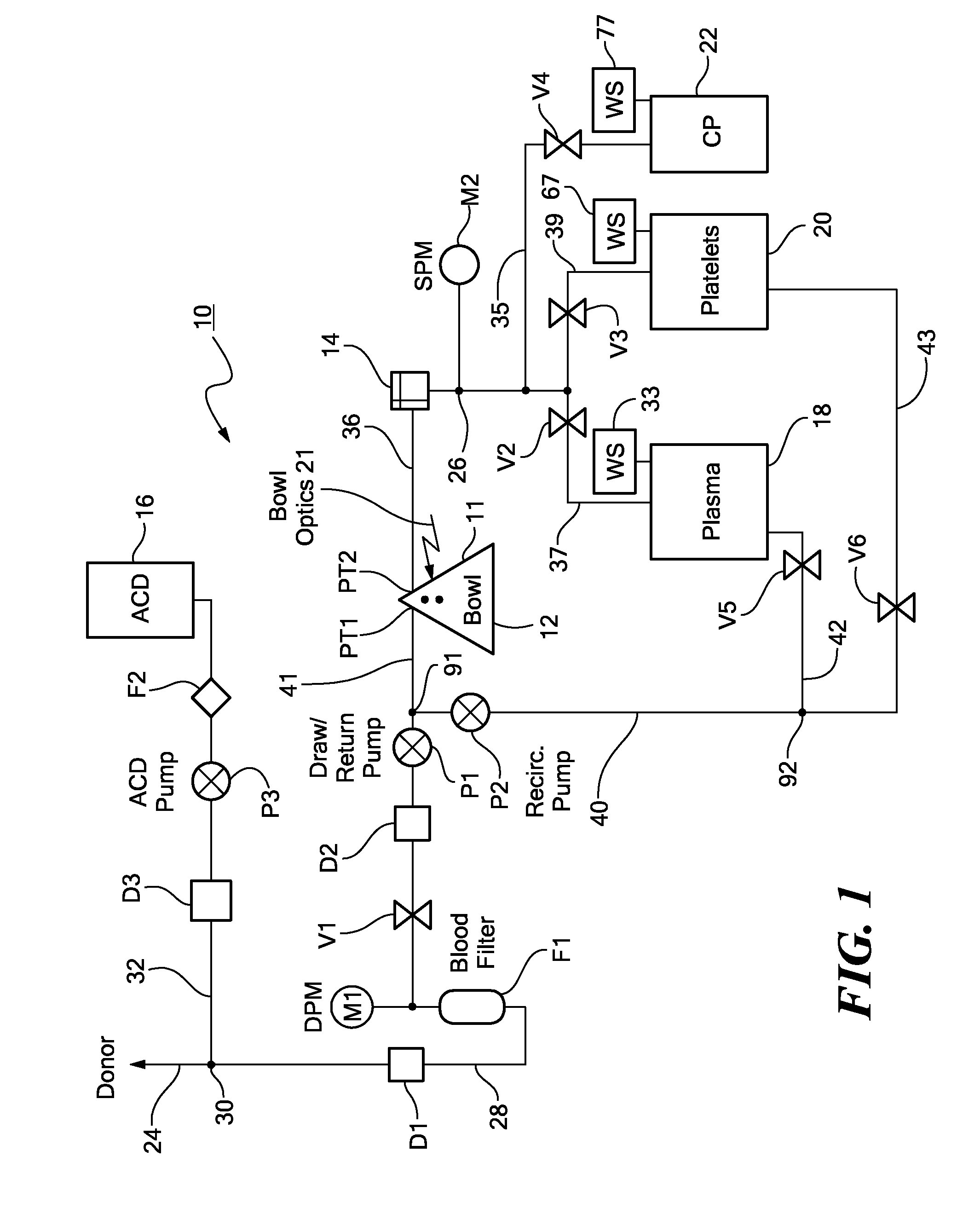
System and Method for Plasma Reduced Platelet Collection
A method and apparatus for collecting plasma reduced platelets potentially suspended in a synthetic solution from a donor. Whole blood is drawn from the donor and introduced into a separation chamber. Platelets are extracted from the separation chamber into a container, using, for example, surge (with anticoagulated plasma or a synthetic solution) or push methodologies. The remaining blood components in the separation chamber are returned back to the donor. The steps of drawing whole blood and introducing the whole blood into the separation chamber, extracting platelets from the separation chamber into the container, and returning the remaining components in the chamber back to the donor are repeated. The sequestered platelets in the container are reintroduced into the separation chamber, whereupon a plasma reduced platelet product is extracted.
Owner:HAEMONETICS
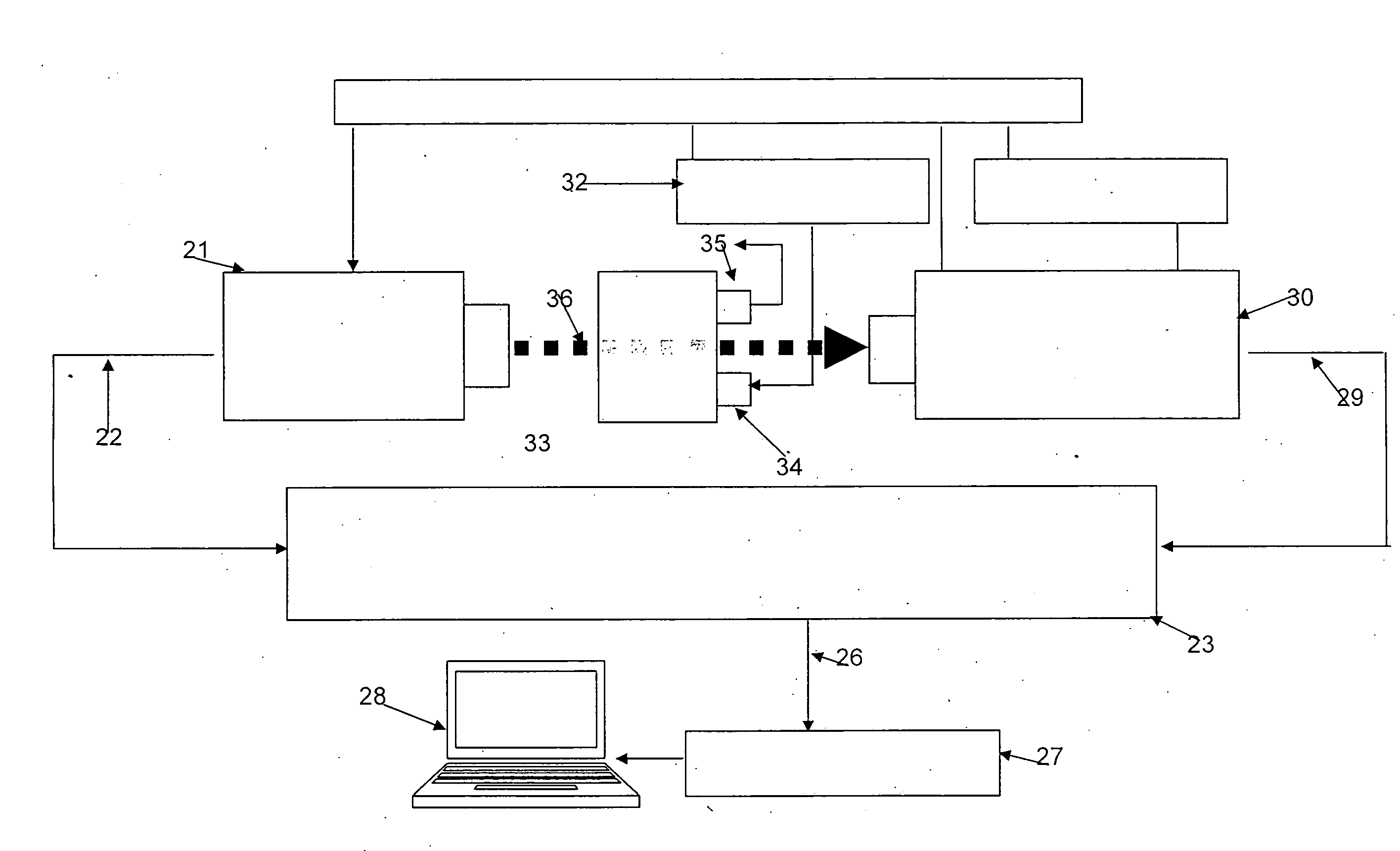
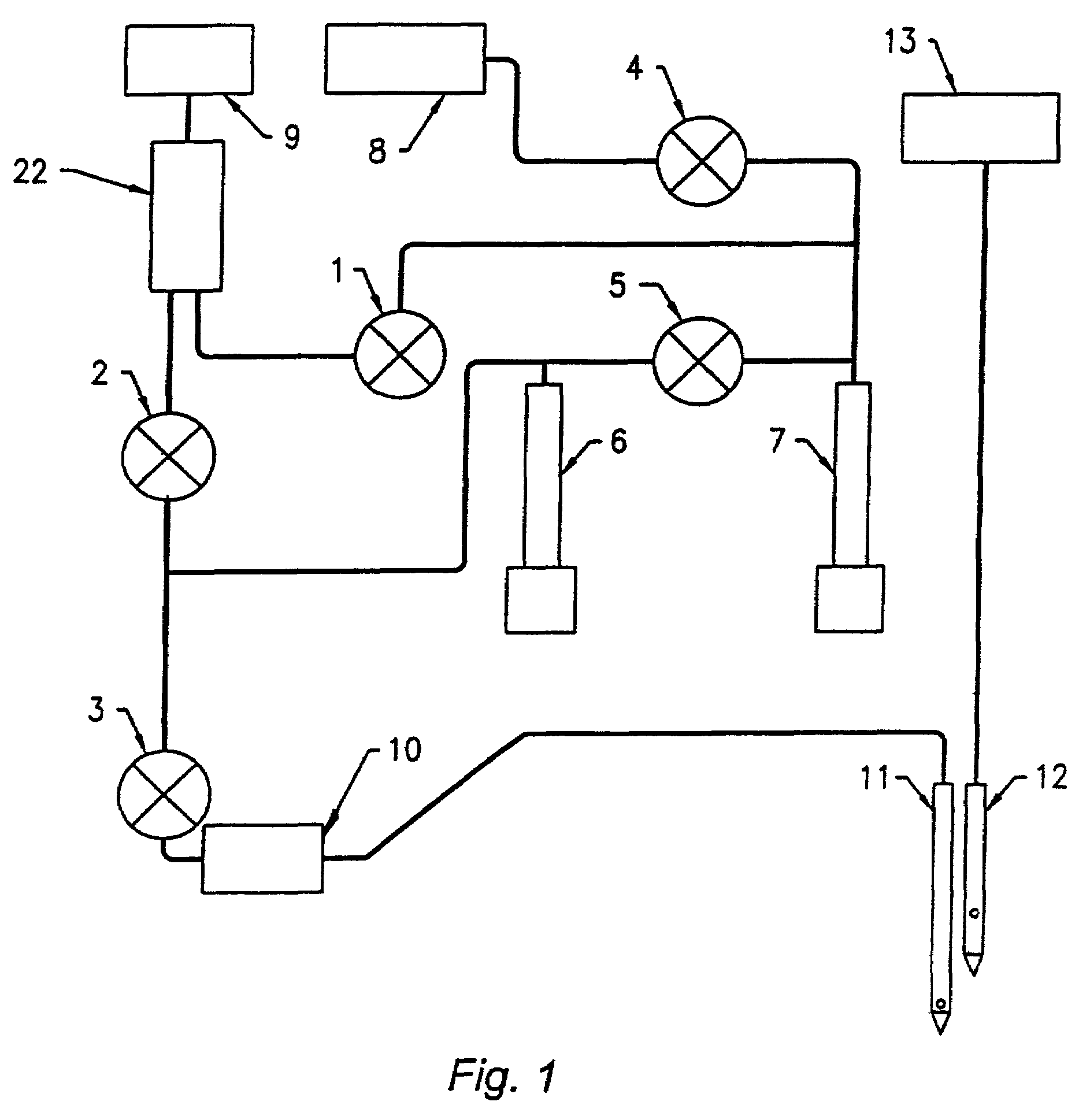
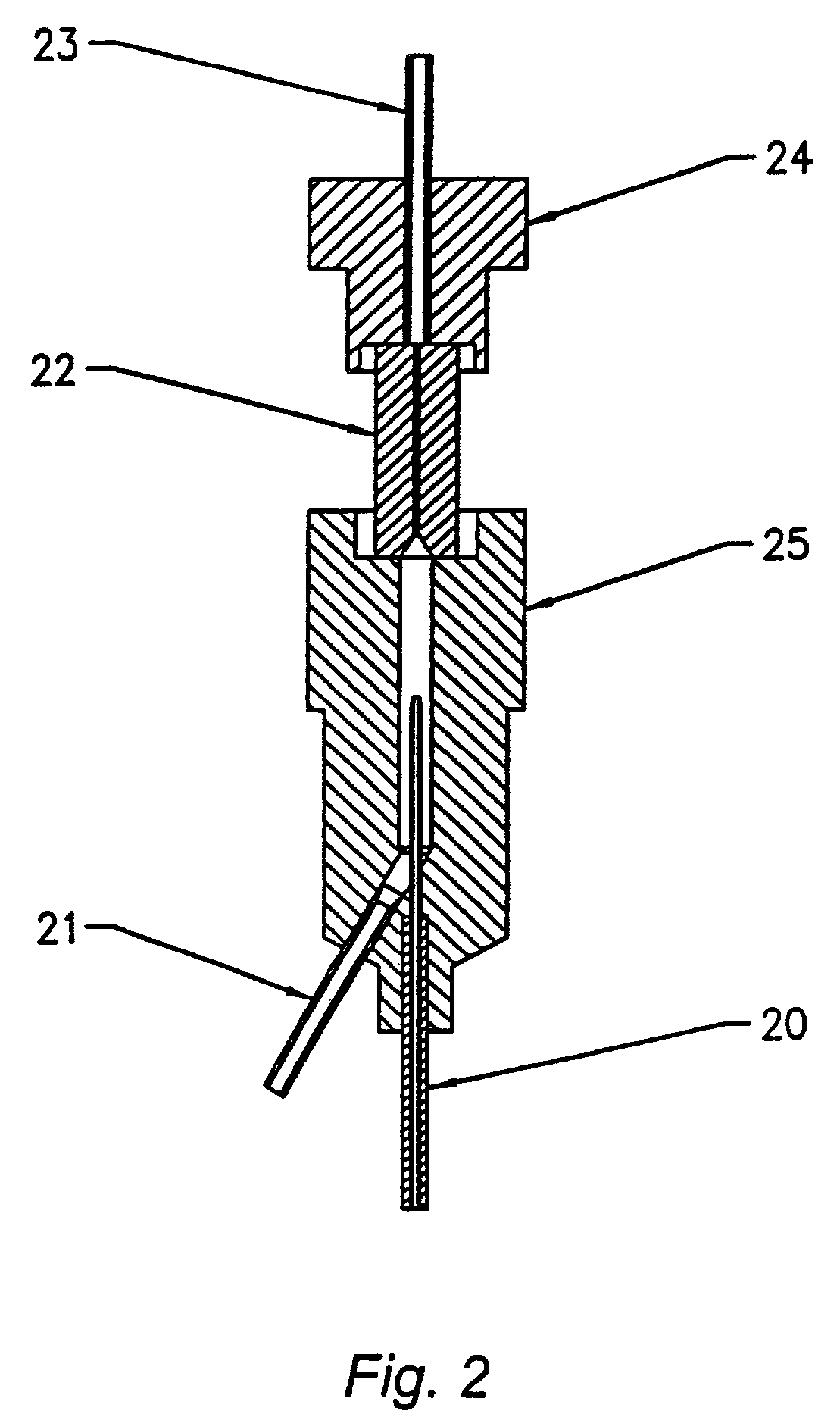
Automated method for preparing whole blood sample analysis and automated device therefor
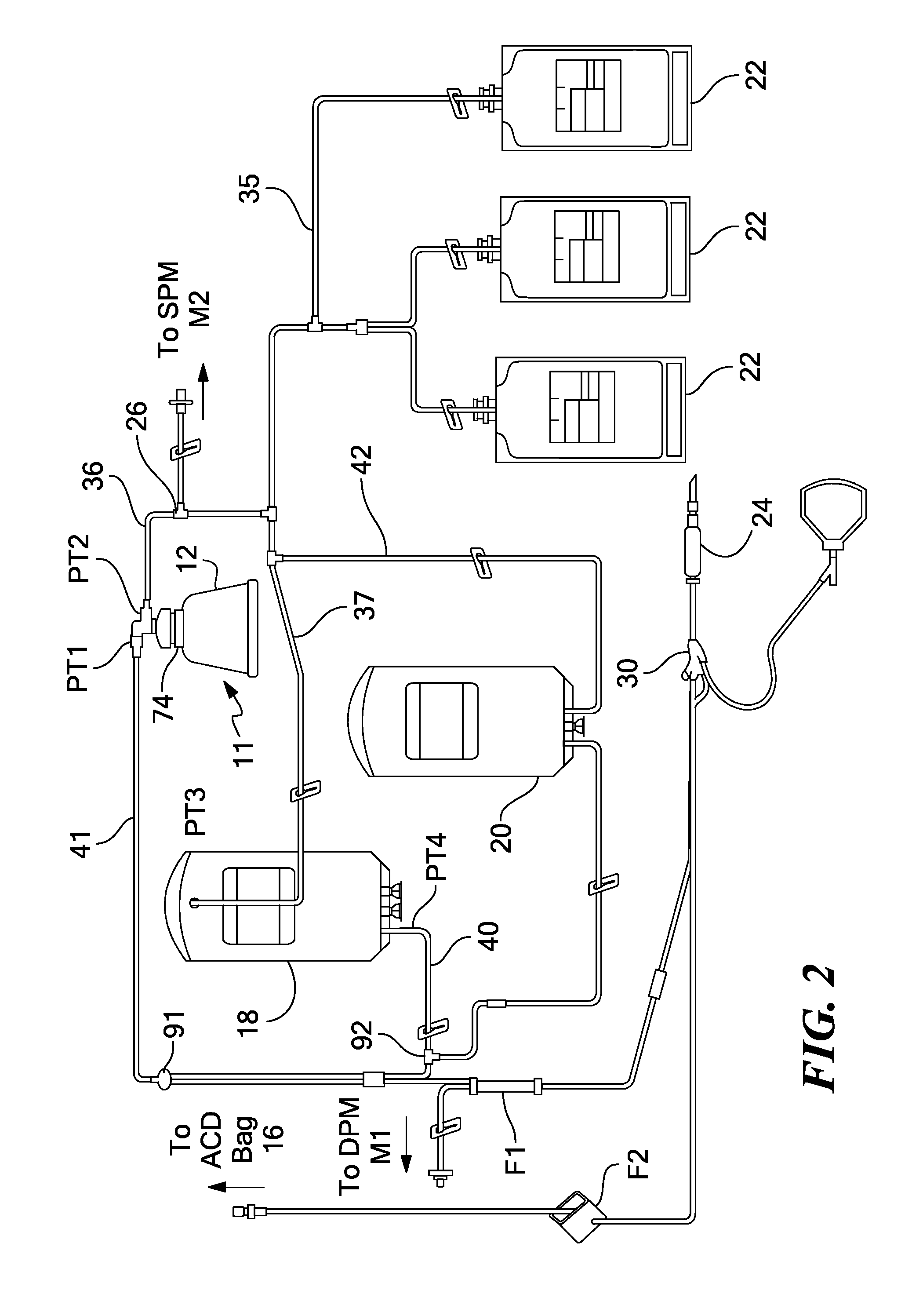
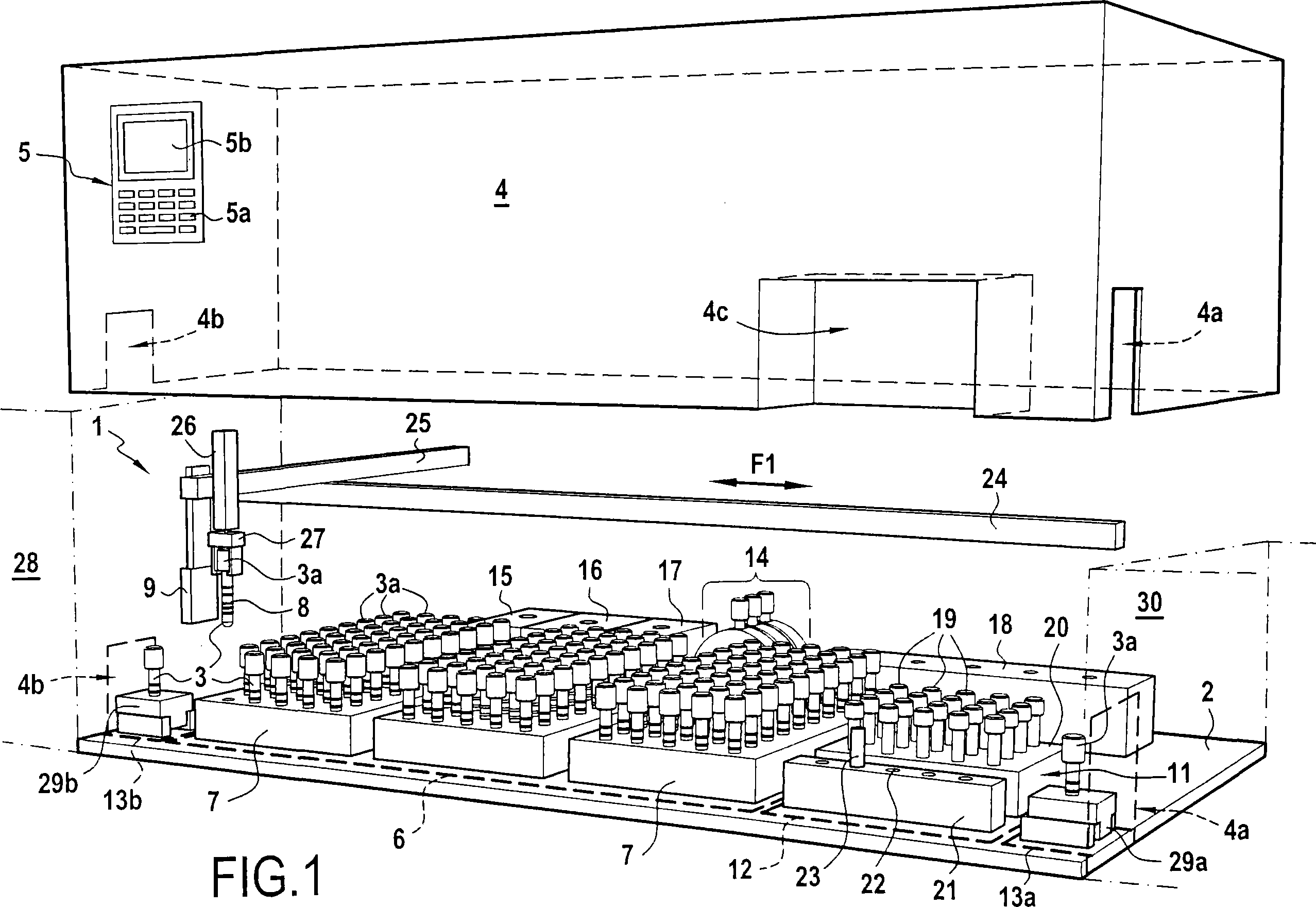
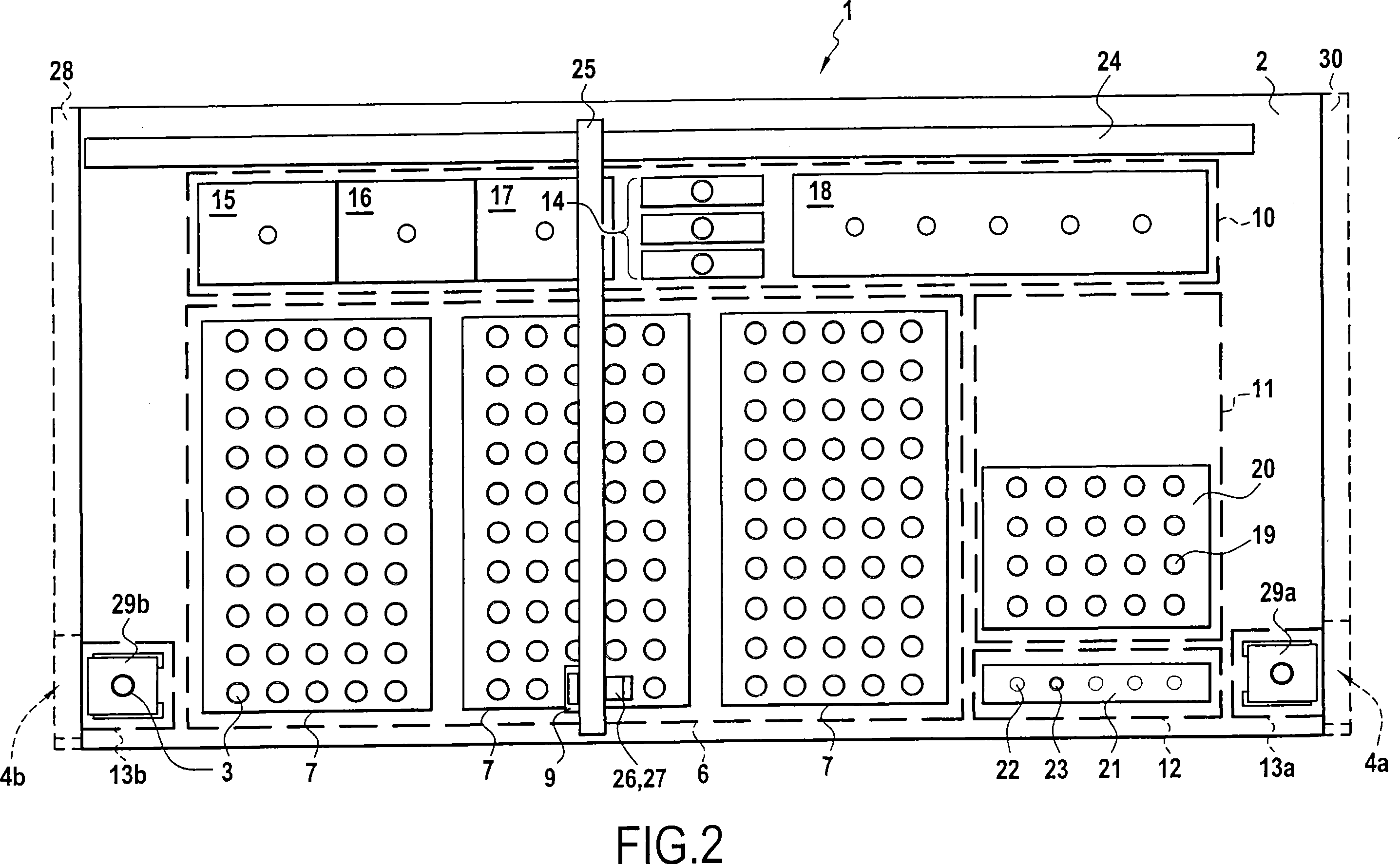
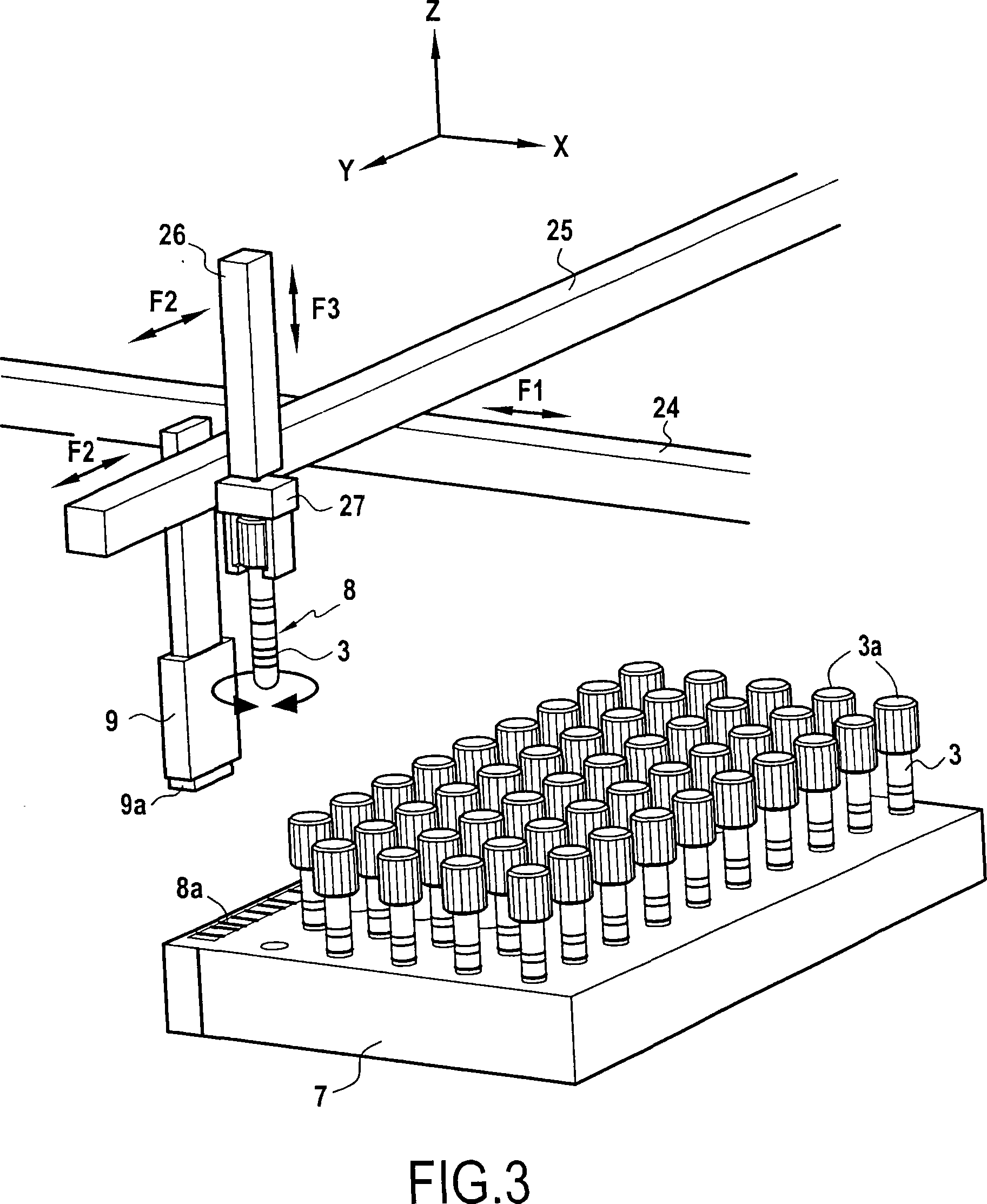
The invention concerns a method for preparing total blood sample analyses and a device (1) for implementing said method, said samples being preserved in tubes (3) comprising at least one means for identifying (8) the sample, said device comprising: at least one compartment forming the storage zone (6, 11, 12) for said tubes (3, 19, 23) before and after analysis, and at least one means for reading (9) said identifying means (8) of said tubes; and at least one zone for preparing (10) said blood samples prior to analysis including means (14, 15, 16, 17, 18) for verifying and / or processing said tubes (3, 19, 23) containing said samples, in particular at least one means for stirring (14) said tubes, and at least one zone for accessing (13a, 13b) at least one automatic analyzer (28, 30) on total blood, said access zone enabling one said tube (3, 19, 23) to be placed in said analyzer, and robotized gripping and displacing means (24, 25, 26, 27) controlled by a control automaton (5) and adapted to grip and set down said tubes (3, 19, 23) individually in said storage zone (6, 11, 12) and transport same in at least three directions XYZ between said storage zone, said preparation zone (10) and said access zone (13a, 13b) to said analyzer, said analyzer (28, 30) being preferably connected to and / or controlled by said control automaton (5).
Owner:HORIBA ABX SAS
Method for separating and purifying nucleic acid
InactiveUS20060051799A1Effective recoveryHigh yieldSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementPurification methodsWhole blood units
Nucleic acid contained in a sample is highly efficiently recovered at a high recovery ratio by a method for separating and purifying nucleic acid using whole blood as the sample, which is a method for separating and purifying nucleic acid, comprising: preparing a sample solution containing nucleic acid; putting the sample solution containing nucleic acid in contact with a solid phase to allow nucleic acid to be adsorbed to the solid phase; putting a washing solution in contact with the solid phase to wash the solid phase at the state of nucleic acid adsorbed thereon; and putting a elution solution in contact with the solid phase to allow nucleic acid to be desorbed from the solid phase, wherein the step of preparing a sample solution containing nucleic acid comprises at least one selected from the group consisting of vortexing, mixing with inversion, and pipetting.
Owner:KURASHIKI BOSEKI KK
Methods of administering anti-inflammatory cyclooxygenase-2 selective inhibitors
InactiveUS20070003646A1Good choiceBroader spectrum of therapeutic benefitBiocideAntipyreticSide effectCyclooxygenase
Owner:LIPOPROTEIN TECH
Consumable tube for use with a flow cytometry-based hematology system
InactiveUS7064823B2Minimizes reagent wasteReduces systemWithdrawing sample devicesPreparing sample for investigationMedicine.hematologyFlow cell
The present invention is a flow cytometry-based hematology system useful in the analysis of biological samples, particularly whole blood or blood-derived samples. The system is capable of determining at least a complete blood count (CBC), a five-part white blood cell differential, and a reticulocyte count from a whole blood sample. The system preferably uses a laser diode that emits a thin beam to illuminate cells in a flow cell and a lensless optical detection system to measure one or more of axial light loss, low-angle forward scattered light, high-angle forward scattered light, right angle scattered light, and time-of-flight measurements produced by the cells. The lensless optical detection system contains no optical components, other than photoreactive elements, and does not include any moving parts. Finally, the system uses a unique system of consumable reagent tubes that act as reaction chambers, mixing chambers, and waste chambers for the blood sample analyses. The consumable tubes incorporate reference particles, which act as internal standards to ensure that the dilutions made during processing of the samples have been carried out correctly, and to ensure that the instrument is working properly. The present invention also relates to methods for using the system.
Owner:IDEXX LABORATORIES
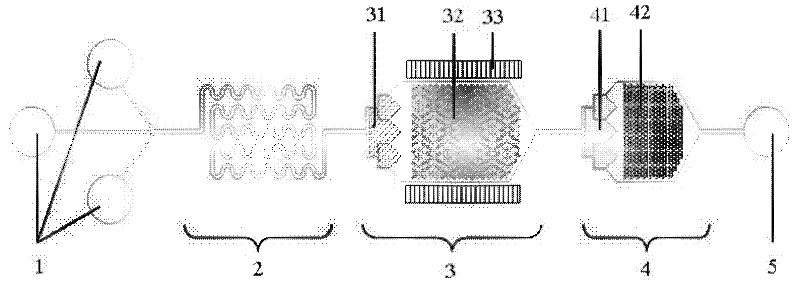
Integrated microfluidic chip for capture of cancer cells in whole blood
The invention relates to an integrated microfluidic chip for capture of cancer cells in whole blood. The integrated microfluidic chip for capture of cancer cells in whole blood comprises three inlets, an erythrocyte lysis unit, a leucocyte capture unit, a cancer cell capture unit and an outlet, wherein the three inlets, the erythrocyte lysis unit, the leucocyte capture unit, the cancer cell capture unit and the outlet are connected orderly. The leucocyte capture unit comprises a first diverter, a soft magnetic microcolumn array and permanent magnets. The first diverter is connected with the soft magnetic microcolumn array. The permanent magnets are arranged at two sides of the soft magnetic microcolumn array. The cancer cell capture unit comprises a second diverter and a capture microstructure array, wherein the second diverter and the capture microstructure array are connected orderly. Compared with the prior art, the integrated microfluidic chip for capture of cancer cells in whole blood has the advantages of high integration degree, simple operation, high cell capture efficiency, simple manufacture processes and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Particle/cell separation device and compositions
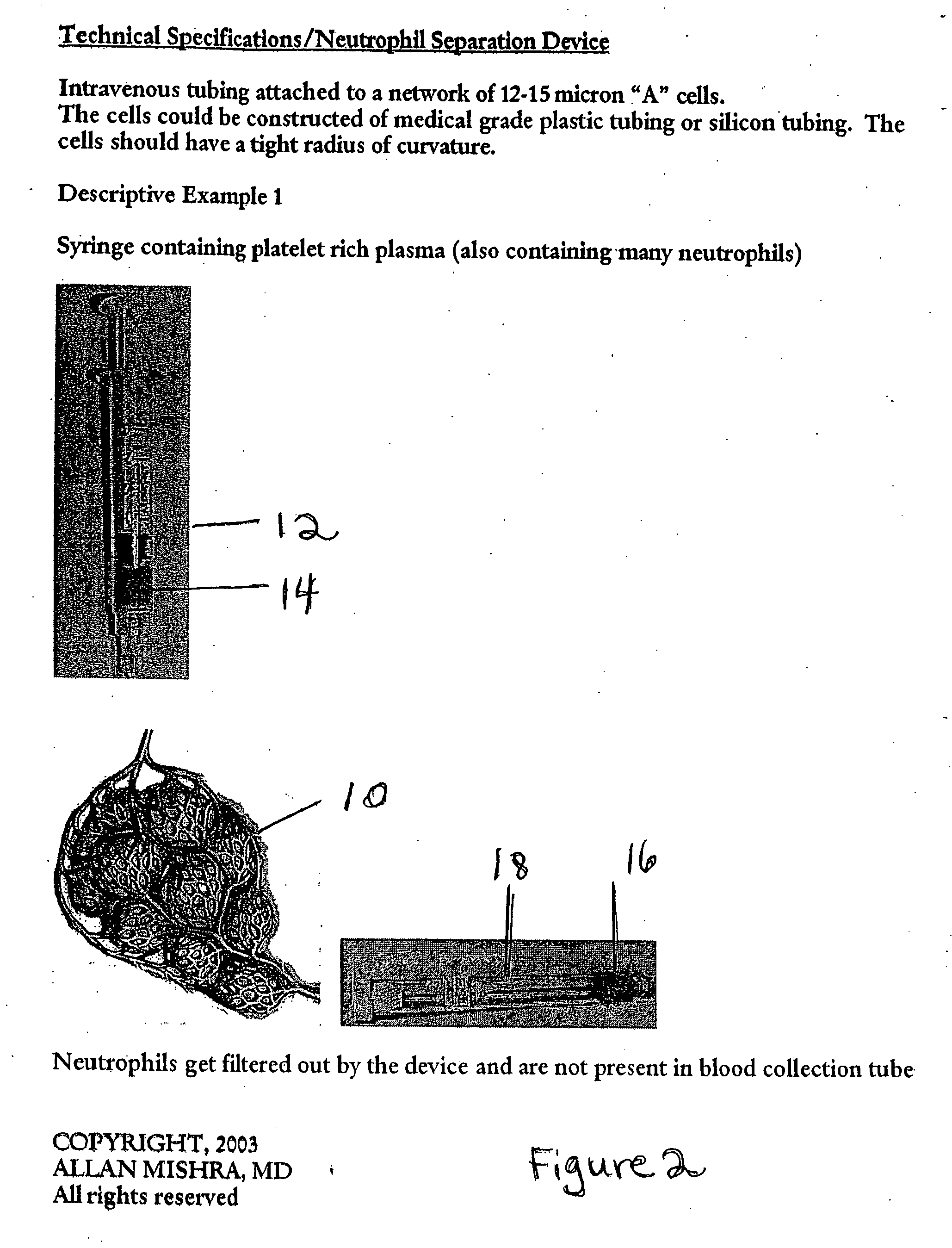
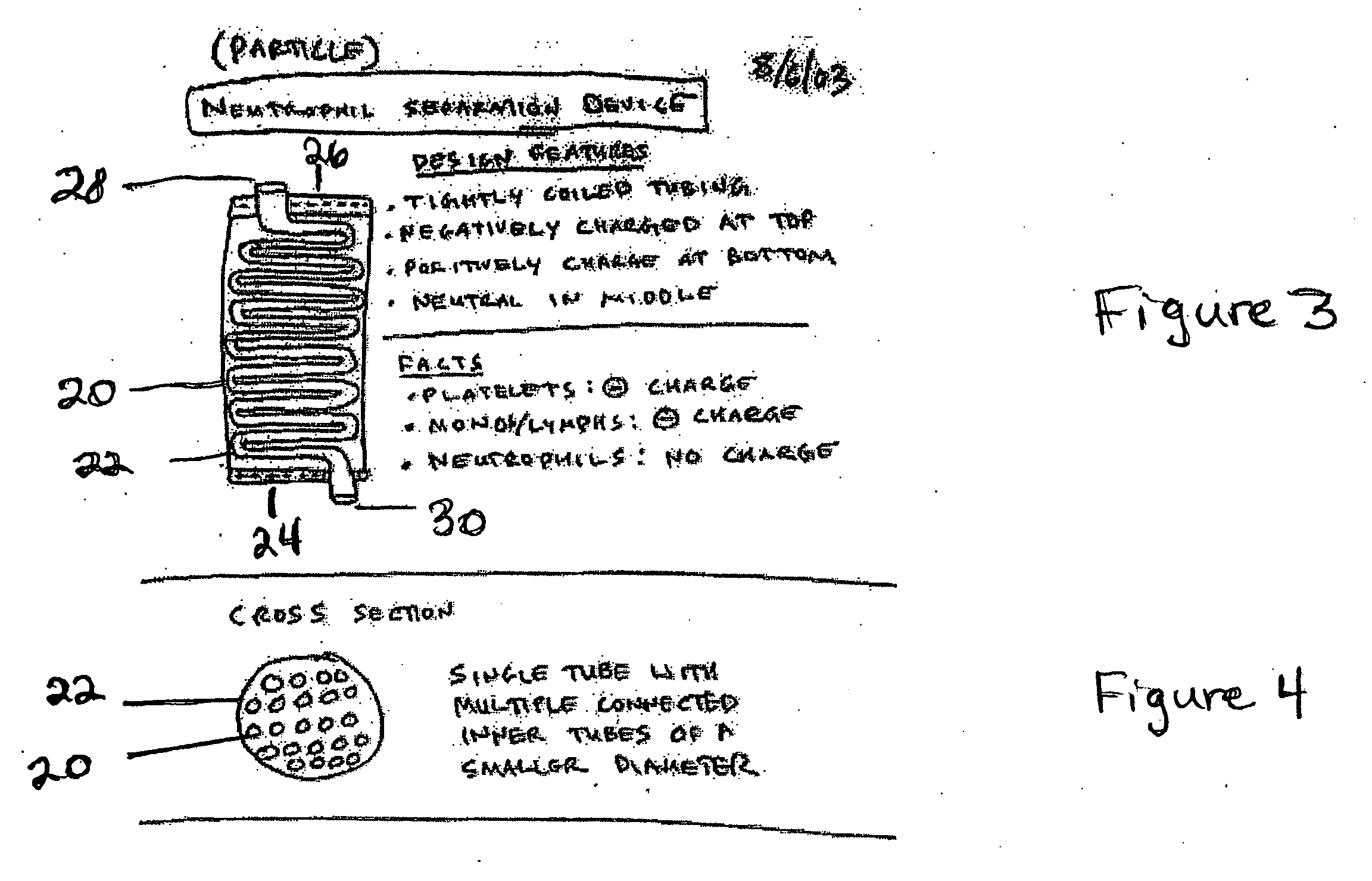
ActiveUS20060127382A1Extended storage timeCause effectsBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiocideGranular cellNeutrophil granulocyte
Owner:BLUE ENGINE BIOLOGICS LLC
Polychromic laser scanning system and method of use
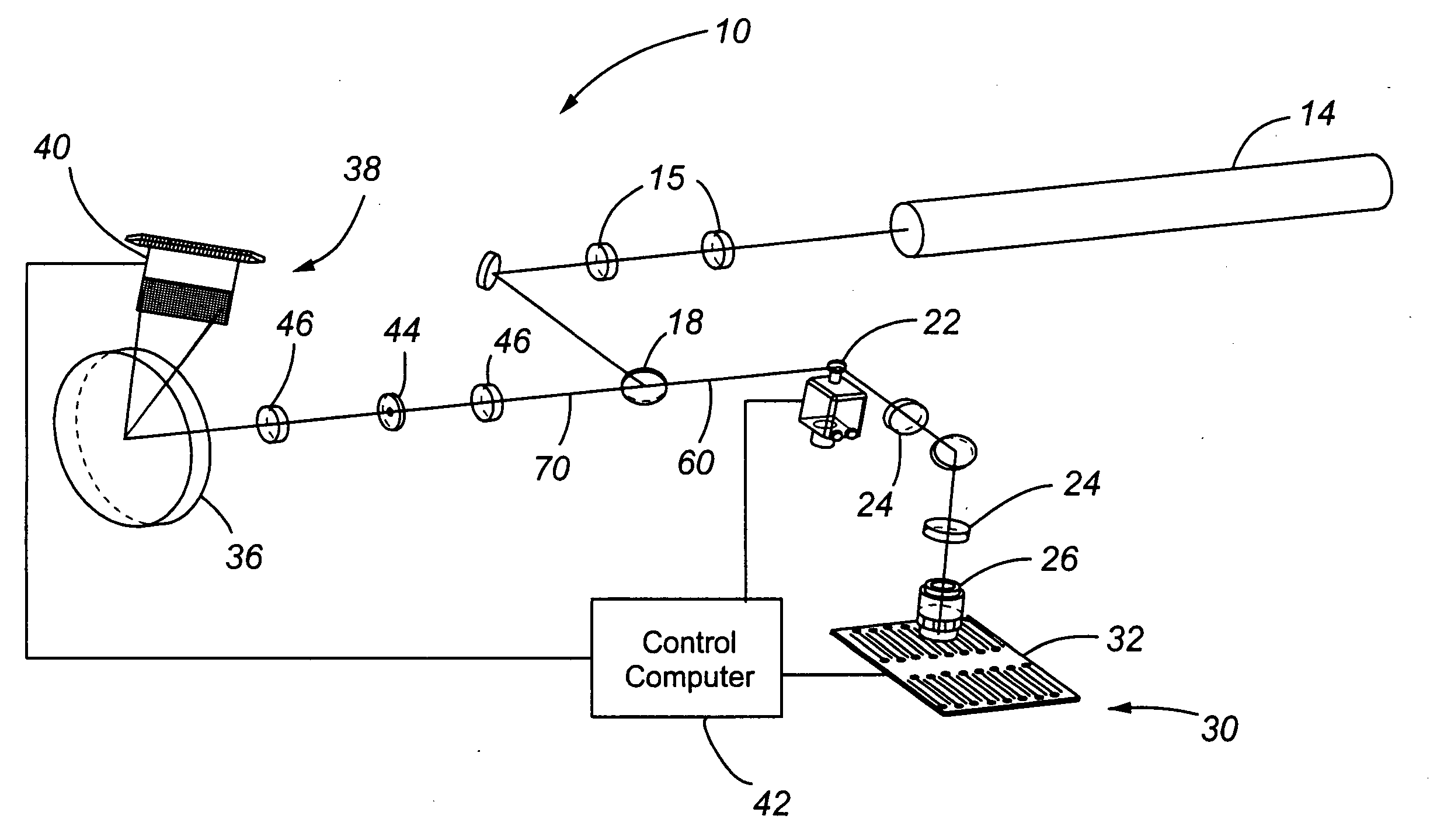
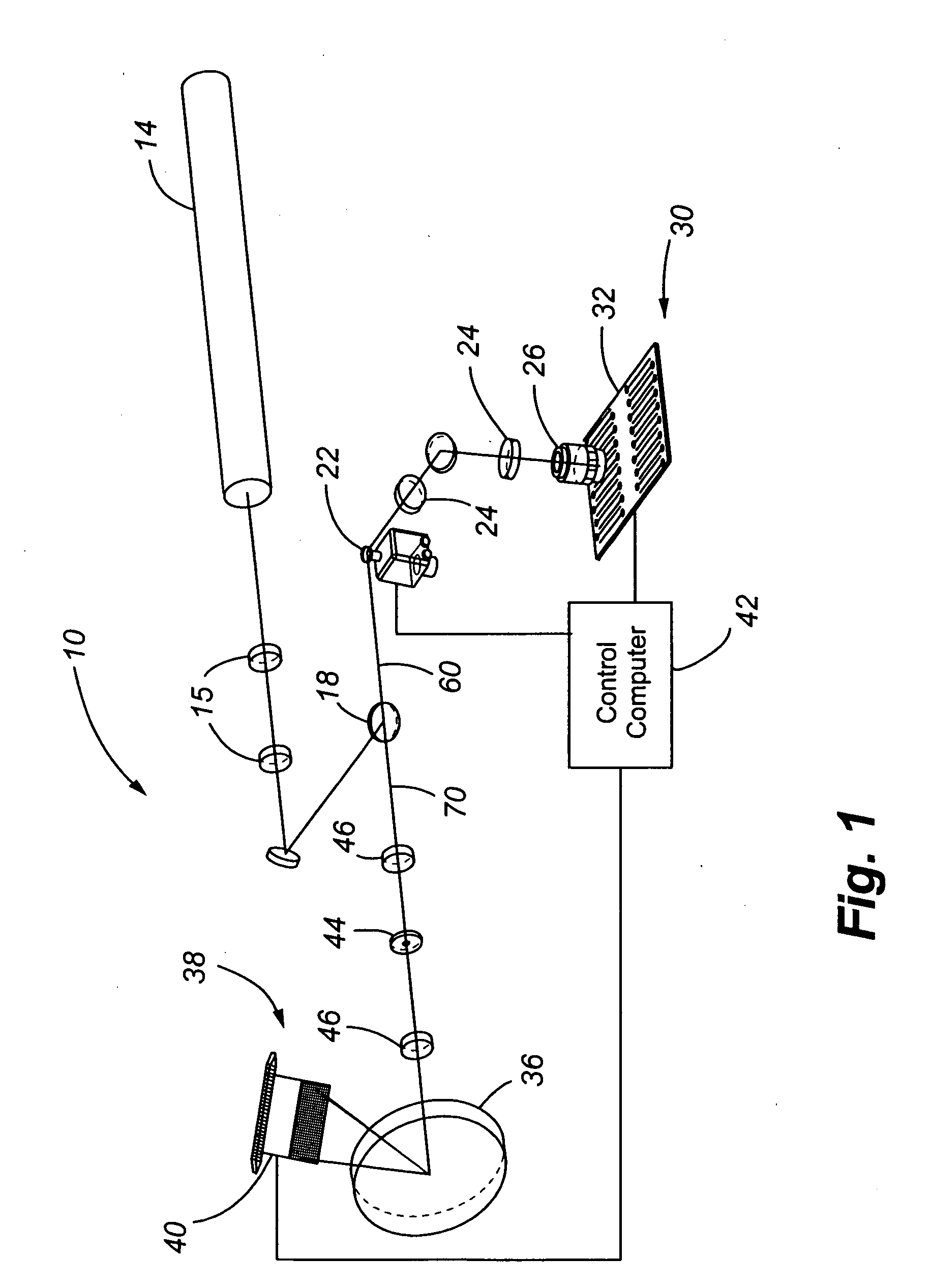
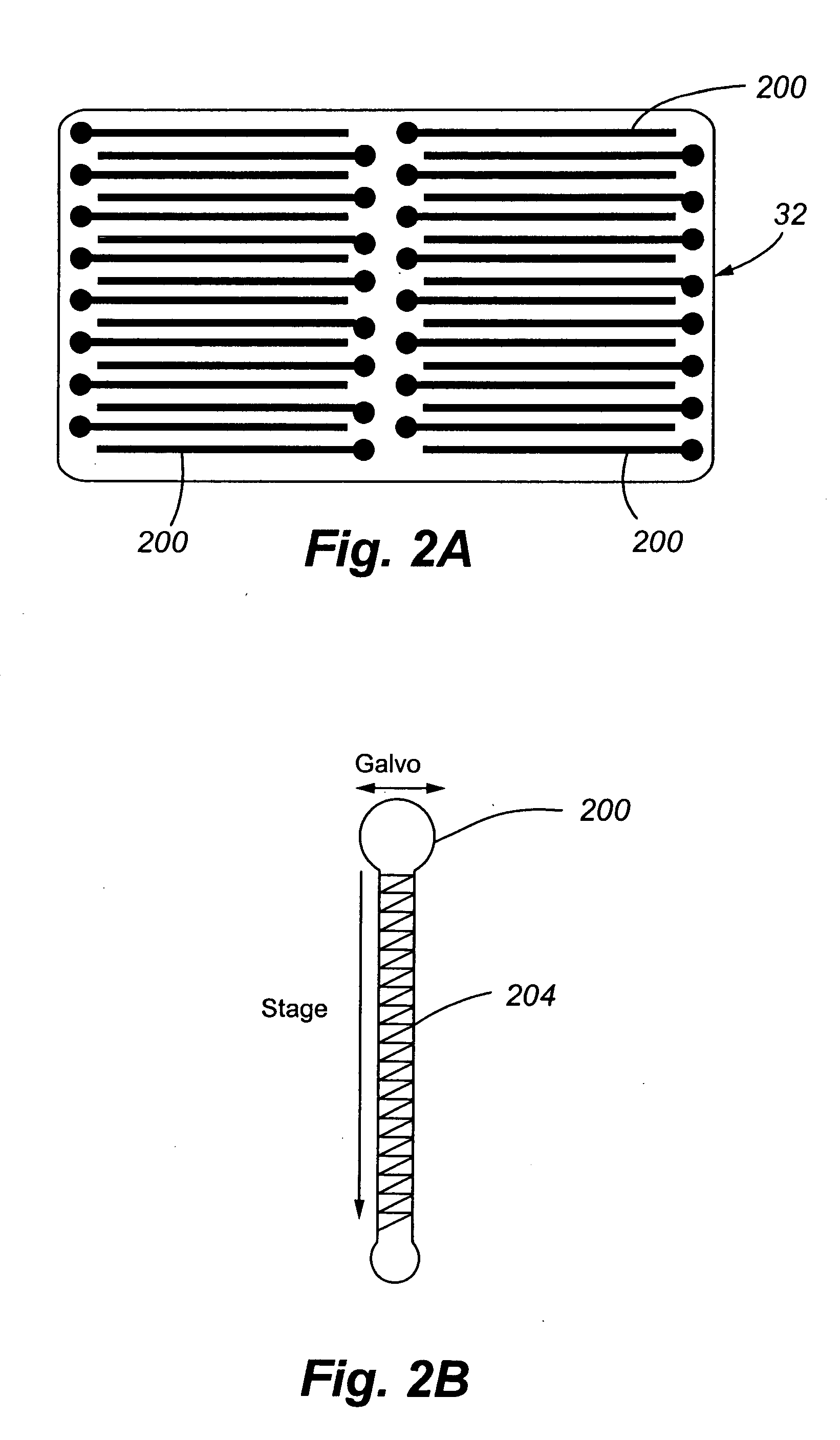
InactiveUS20050280817A1Avoid distractionRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationFluorescenceProtein tag
A system for laser scanning provides spectral flexibility needed for the spectroscopic monitoring of highly multiplexed samples, such as cellular and particle assays in whole blood or other suspensions. In accordance with embodiments of the present invention, the system comprises a scanner to direct an excitation laser through a sample, an objective to collect light emitted by the sample in response to the excitation laser, a spectrograph to disperse the emitted light over a plurality of wavelengths as a spectrum, and a charge coupled device for detecting the spectrum. The system can be used with samples having a variety of reporter tags, including one or more SERS tags, fluorescent organic and protein tags, and quantum dot tags. A laser scanning apparatus and method of using the same is also provided.
Owner:PPD BIOMARKER DISCOVERY SCI
Plasma on demand tube
ActiveUS20050139547A1Avoid easy cloggingEasy to useCapsClosure lidsEvacuated blood collection tubeMedicine
A device for separating plasma from whole blood is provided having an evacuated primary collection chamber capable of fluid communication through a porous filter to an evacuated secondary collection chamber. An agglutinating agent is provided within the primary collection chamber so as to aggregate blood cells within a whole blood sample. The porous filter has a pore size which is small enough to capture the aggregated blood cells therein, yet large enough to permit plasma to transfer therethrough under pressures associated with conventional evacuated blood collection tubes. The primary and secondary collection chambers may be provided in separate containers or tubes, with transfer occurring therebetween through a transfer device including the porous filter therein.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Closed method and system for the sampling and testing of fluid
InactiveUS20050199077A1Prevent backflowEasy to getWithdrawing sample devicesPharmaceutical containersBlood componentWhole blood units
A closed fluidic sampling system. The system includes a first port for receiving a sample of fluid and a sampling chamber in fluid communication with the first port. A a one-way valve allows fluid to flow from the first port towards the sampling chamber while preventing backflow of fluid towards the first port. A second port in fluid communication with the sampling chamber enables fluid to be withdrawn from the sampling chamber. The fluid may be a blood component, such as platelets, plasma, whole blood, or red blood cells.
Owner:HAEMONETICS
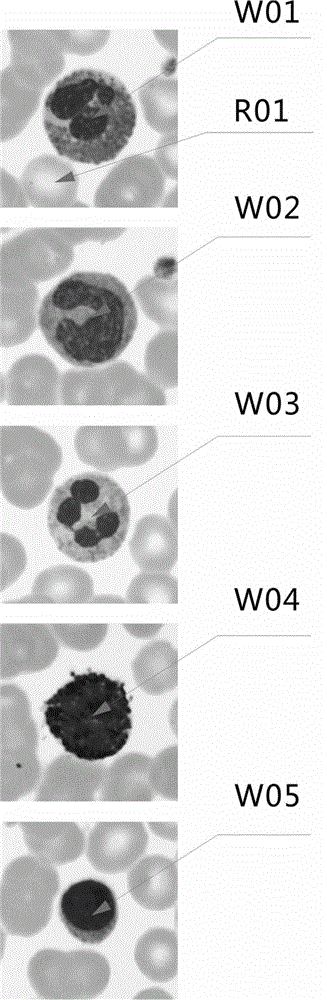
Automated microscopic cell analysis
InactiveUS20170328924A1Eliminate Bubble ProblemsSolve insufficient capacityReagent containersPreparing sample for investigationWhite blood cellRed blood cell
Disclosed in one aspect is a method for performing a complete blood count (CBC) on a sample of whole blood by metering a predetermined amount of the whole blood and mixing it with a predetermined amount of diluent and stain and transferring a portion thereof to an imaging chamber of fixed dimensions and utilizing an automated microscope with digital camera and cell counting and recognition software to count every white blood cell and red blood corpuscle and platelet in the sample diluent / stain mixture to determine the number of red cells, white cells, and platelets per unit volume, and analyzing the white cells with cell recognition software to classify them.
Owner:MEDICA CORP
System for rapid analysis of glycated proteinaceous species in biological samples
InactiveUS20080085507A1Component separationMicrobiological testing/measurementAnalyteChemical composition
A device is described which provides an automated or manual means to perform chromatographic affinity-based A1c analyses of whole blood or hemolysates in less than 1 minute. Further, such applications are useful for the quantitation of glycated plasma proteins used in analysis of gestational diabetes. The device includes several modules integrated to accomplish processing and analysis of the blood sample. One such module includes a disposable liquid chromatographic column which may be rapidly packed and is easily assembled from readily available materials. Such columns and assemblies may be used in fluid chromatography applications requiring separations of complex materials for purposes of purification and / or quantitation of particular analytes. The columns may be used as stand-alone units or may be integrated into commercially available chromatography systems. The columns have a chemical composition and particle size that allow for low operational pressures.
Owner:AFFINEX
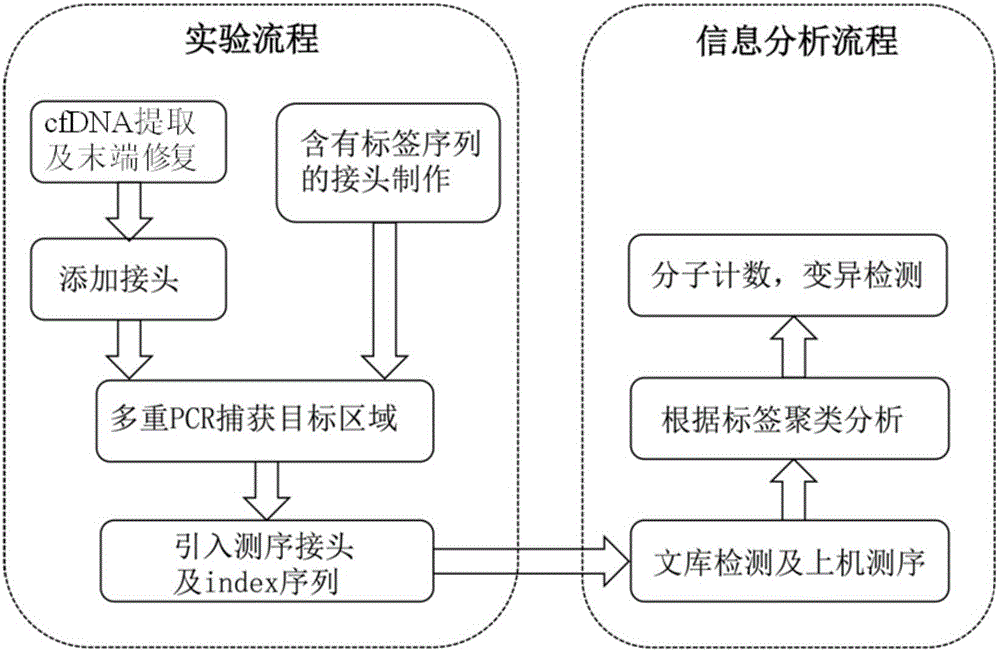
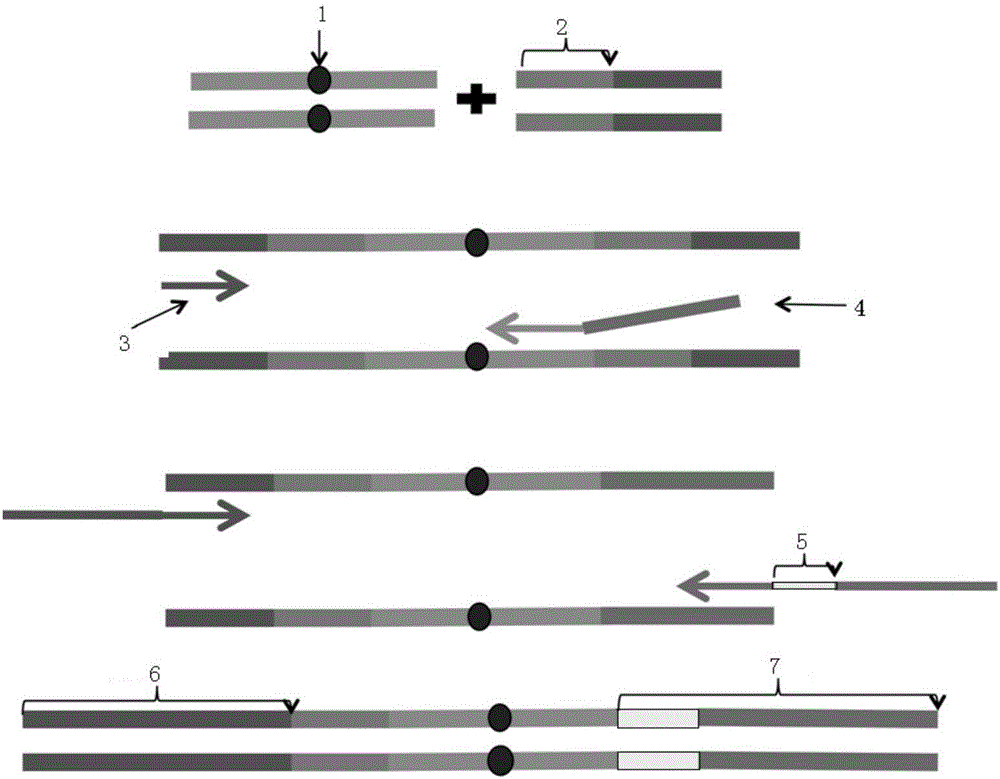
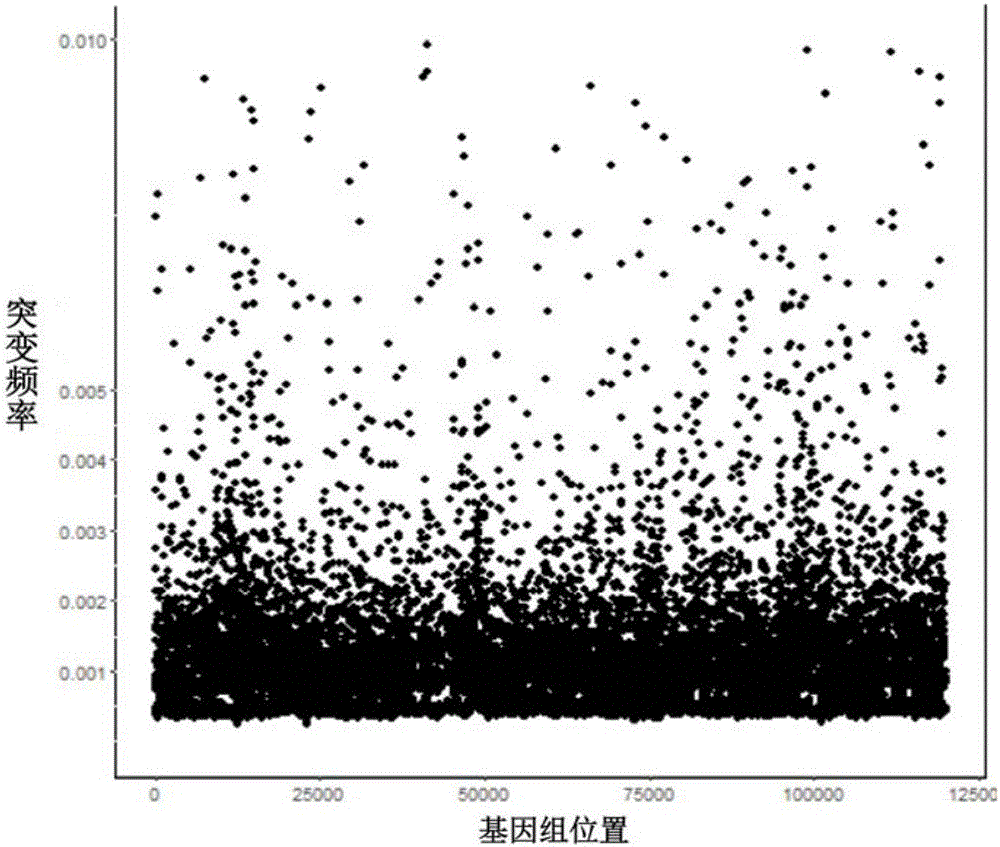
Construction method of ctDNA ultra-low-frequency mutation detection library, kit and analysis method of library detection data
InactiveCN106834275AIncrease diversityEasy to solveMicrobiological testing/measurementBioinformaticsMagnetic beadSmall fragment
The invention discloses a construction method of a ctDNA ultra-low-frequency mutation detection library, a kit and an analysis method of library detection data. The construction method comprises steps as follows: S1, cfDNA is extracted from whole blood; S2, the terminal of cfDNA is restored and an A basic group is added to the 3'terminal; S3, the terminal of the cfDNA obtained in S2 is connected with connectors containing random label sequences; S4, primers for multiplex PCR (polymerase chain reaction) are designed according to the sequences of the connectors and an object region for object region capturing; S5, a PCR product in S4 is subjected to magnetic bead purification, and small-fragment DNA not subjected to non-specific amplification and primer dimer are removed; S6, a product in S5 is subjected to PCR amplification, an index sequence is introduced, and the ctDNA ultra-low-frequency mutation library is obtained. According to the method, PCR mistakes and sequencing mistakes are eliminated, and the detection specificity is improved.
Owner:天津诺禾医学检验所有限公司
Microfluidic device and method for fluid clotting time determination
ActiveUS20110039285A1Low production costEasy to useBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsClotting timeWhole blood sample
A microfluidic passive device and a method for determining clotting time are described, of a fluid medium such as blood, of low production cost which can therefore be disposable. When optimised to determine blood clotting time, it requires a minimal whole blood sample (<5 μL) and it is particularly suited to INR or PT determination, which can be used autonomously by patient without venipuncture. Monitoring, and processing means to interpret the results are comprised in an external coagulometer device. A production method for the manufacture of the microfluidic device is also provided.
Owner:ILINE MICROSYSTEMS SL
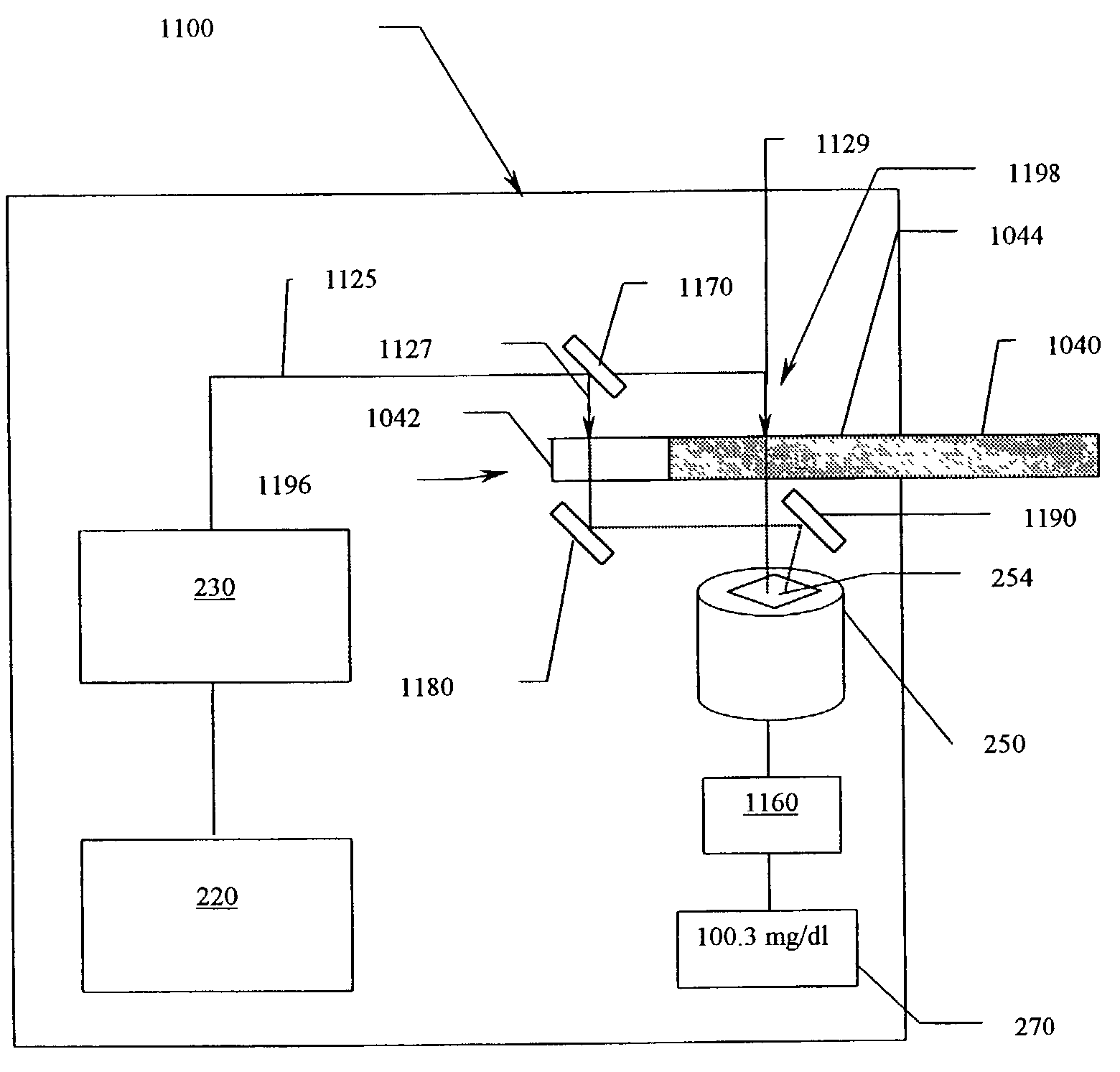
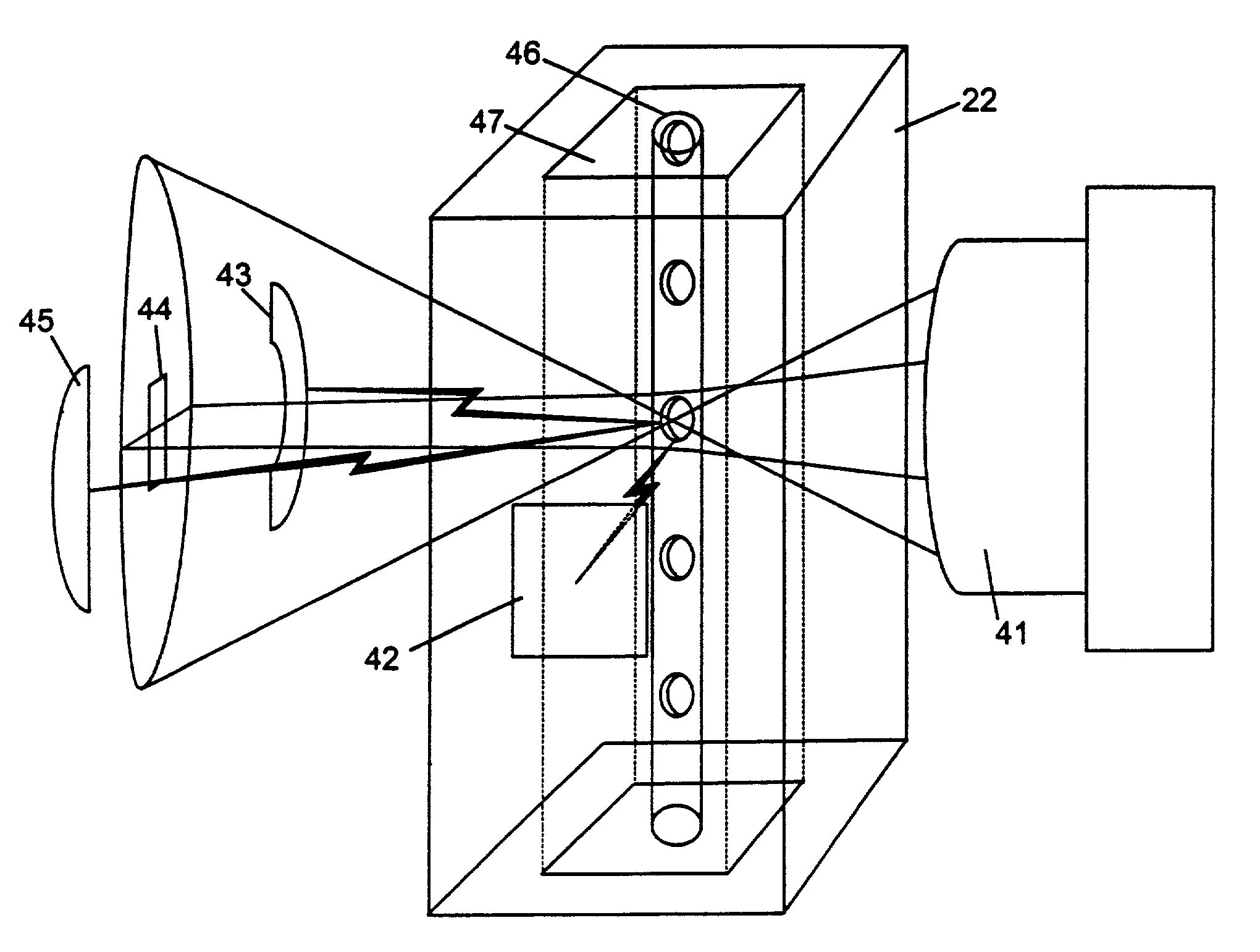
Method and apparatus for direct spectrophotometric measurements in unaltered whole blood
InactiveUS7075628B2Eliminate needAvoid problemsColor/spectral properties measurementsBiological testingWhole blood unitsMedicine
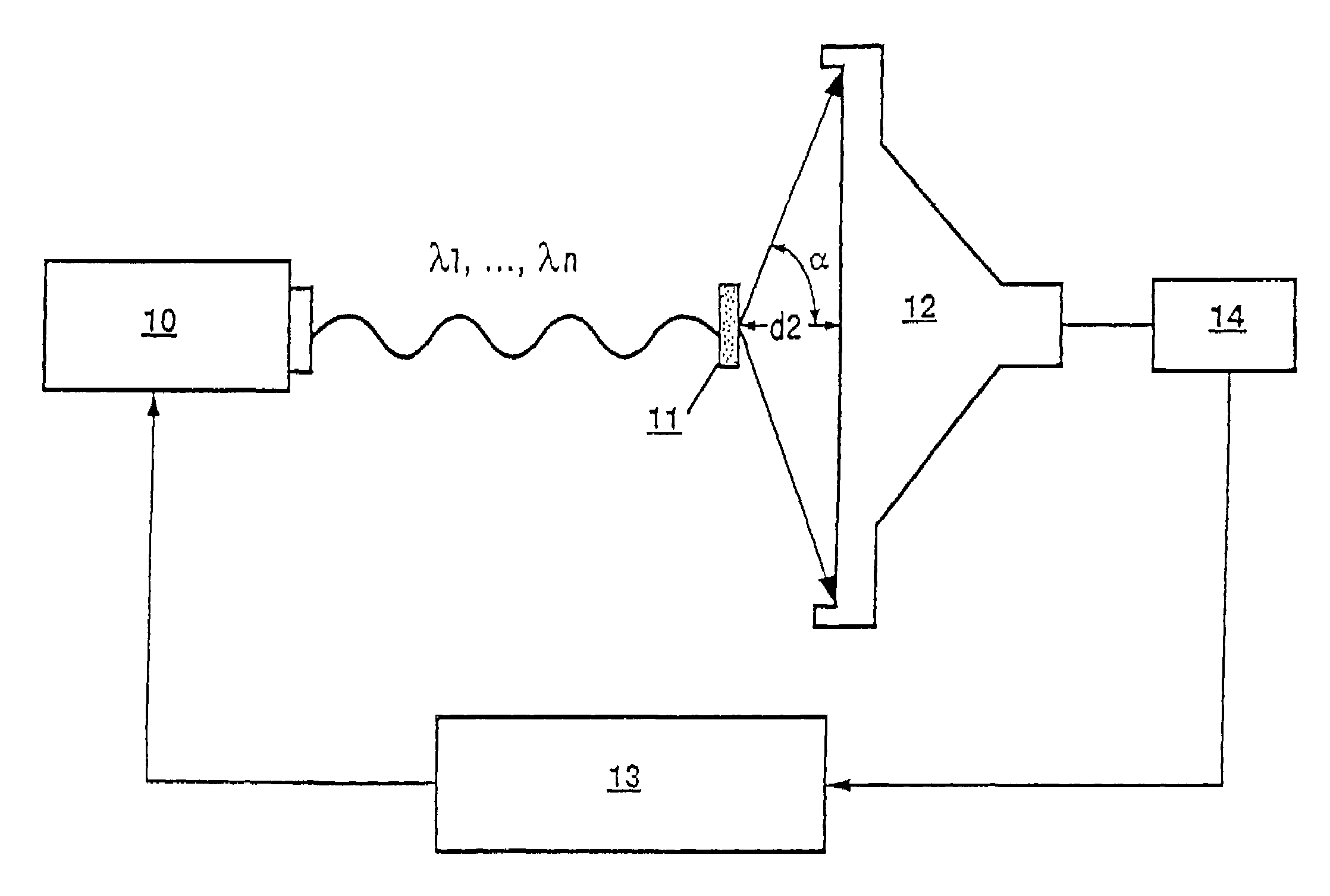
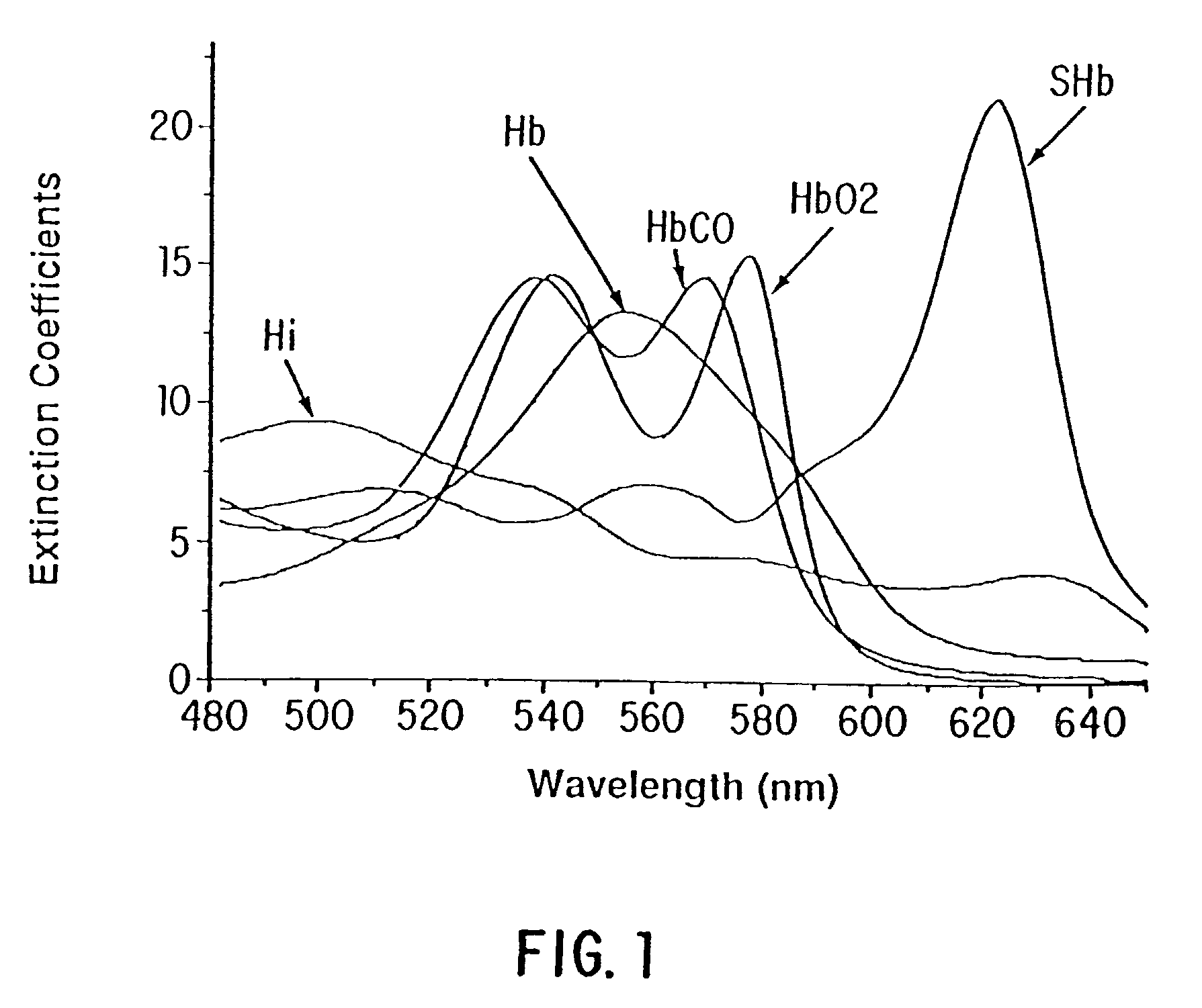
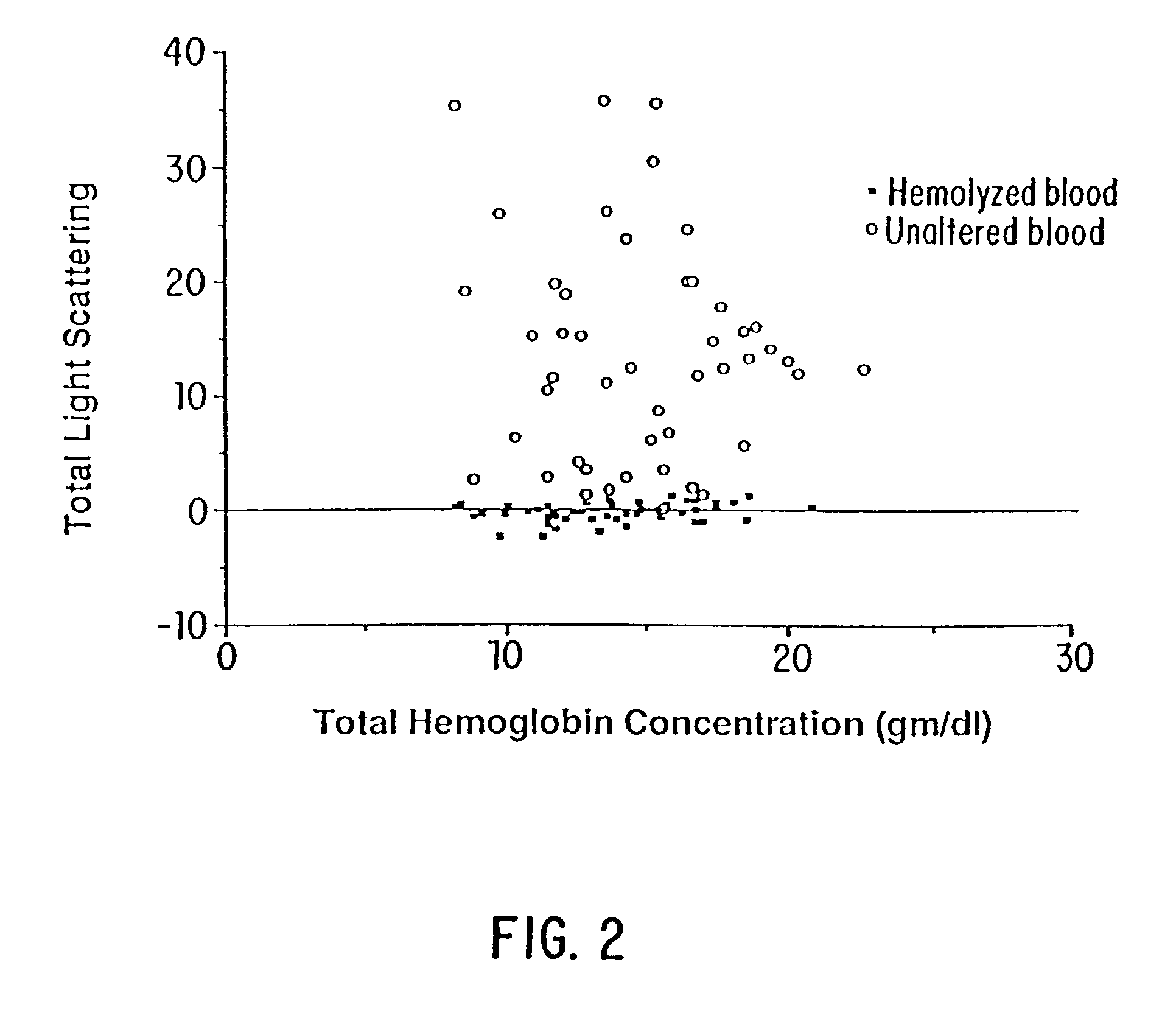
A method and apparatus that allows accurate spectrophotometric determination of the concentrations of various hemoglobin species in whole undiluted blood. The invention employs 1) an optical apparatus designed to maximize the true optical absorbance of whole blood and to minimize the effects of light scattering on the spectrophotometric measurements of the concentrations of various constituent components, and 2) methods to correct the hemoglobin concentration measurements for light scattering and for the effects of the finite bandwidth of the substantially monochromatic light. In the optical apparatus optical parameters, such as sample thickness, detector size and shape, sample-to-detector distance, wavelengths, monochromicity, and maximum angle of light capture by detector, are selected so as to minimize the contribution of light scattering to maximize the contribution of true optical absorbance. After making measurements of a blood sample's optical density at each of the wavelengths, corrections are made for the effects of light scattering.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
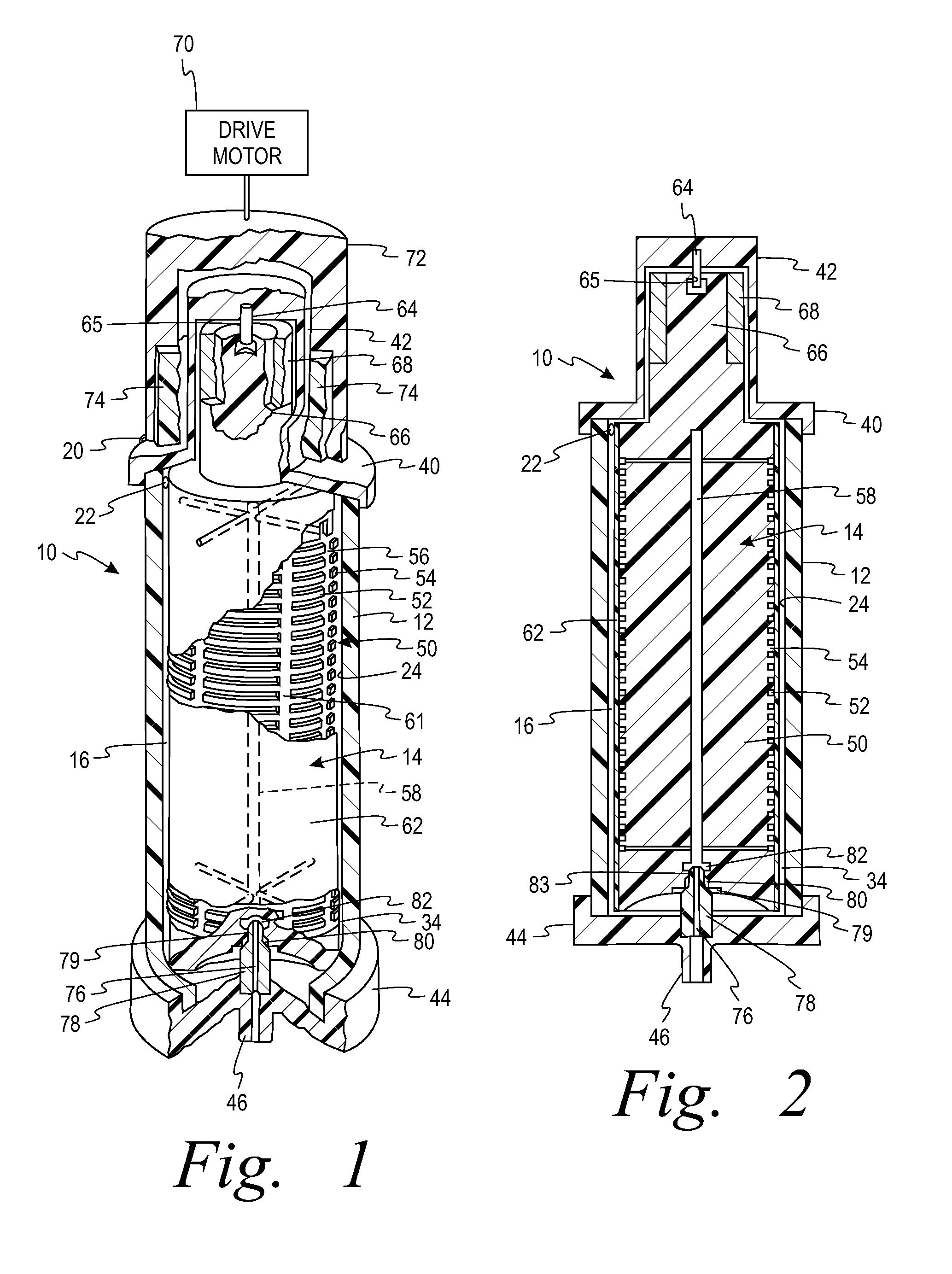
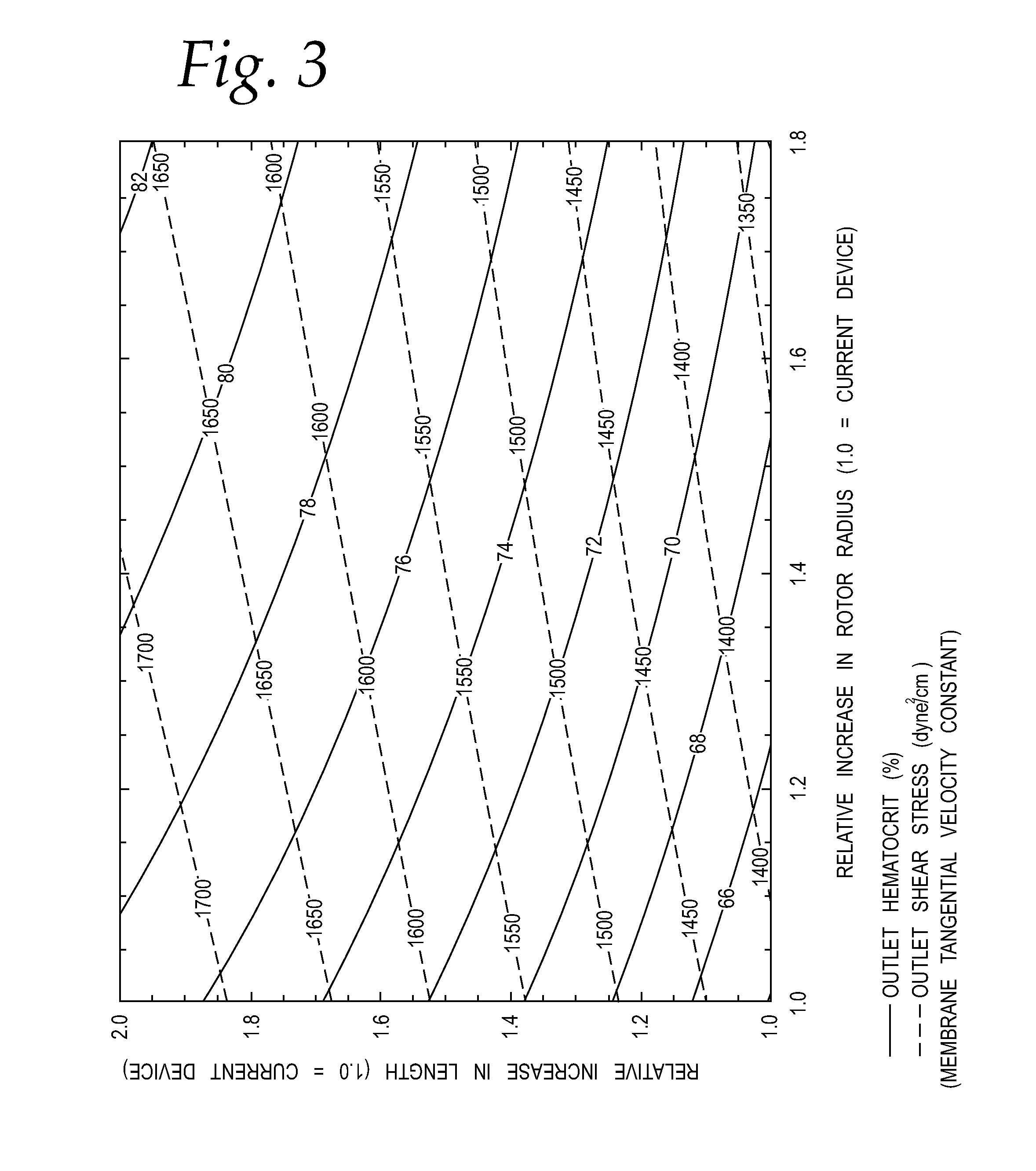
Membrane separation devices, systems and methods employing same, and data management systems and methods
A membrane separation device is disclosed along with systems and methods employing the device in blood processing procedures. In one embodiment, a spinning membrane separator is provided in which at least two zones or regions are created in the gap between the membrane and the shell, such that mixing of the fluid between the two regions is inhibited by a radial rib associated with the membrane that decreases the gap between the membrane and the shell to define two fluid regions, the ridge isolating the fluid in the two regions to minimize mixing between the two. Automated systems and methods are disclosed for separating a unit of previously collected whole blood into components, such as concentrated red cells and plasma, for collecting red cells and plasma directly from a donor in a single pass, and for cell washing. Data management systems and methods and priming methods are also disclosed.
Owner:FENWAL
Method for preparing polyvinylidene fluoride affinity membrane using amino acid as ligand
InactiveCN101596422AImprove adsorption efficiencyStable physical and chemical propertiesSemi-permeable membranesHaemofiltrationPolyvinylidene difluorideBlood plasma
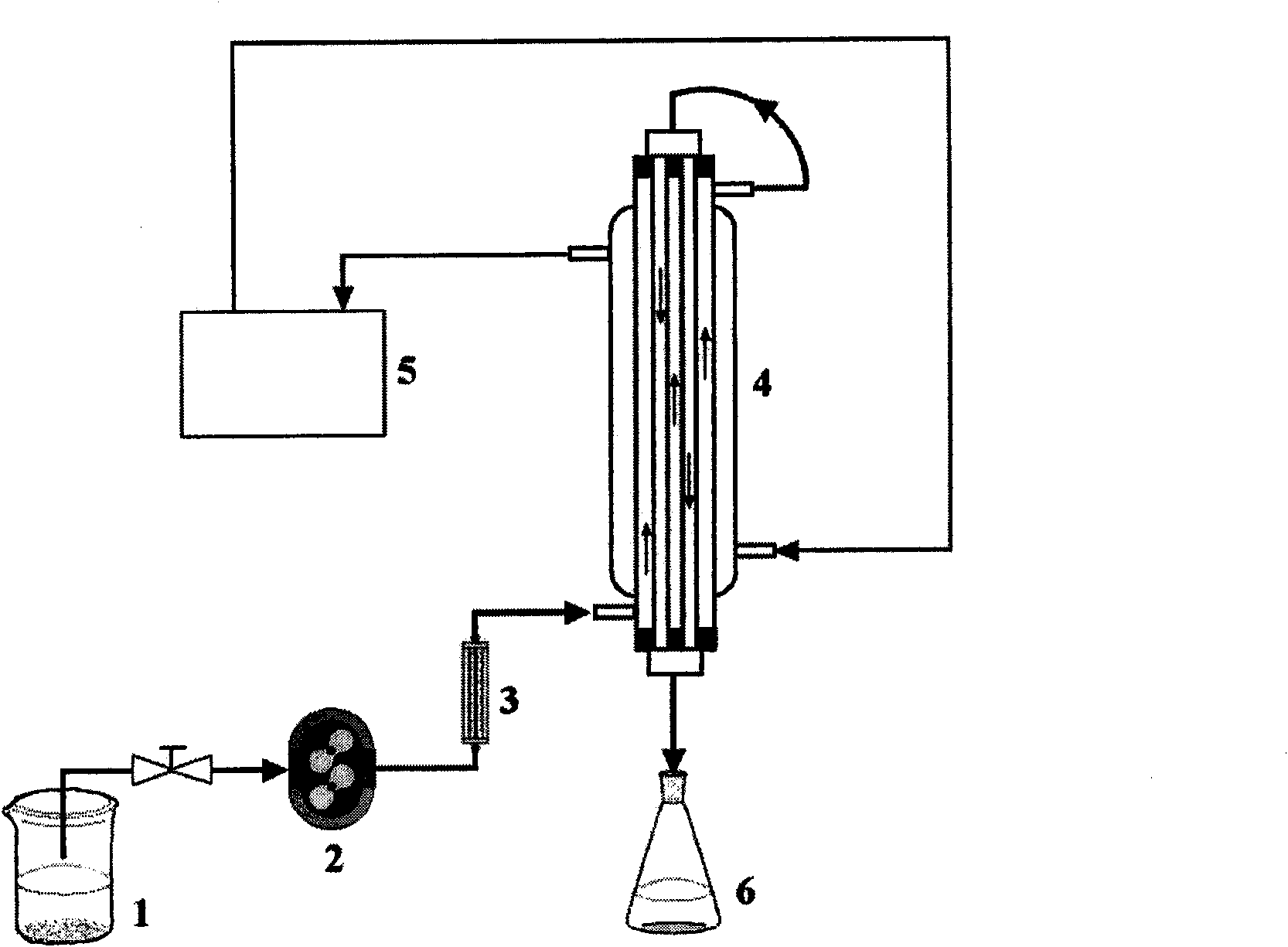
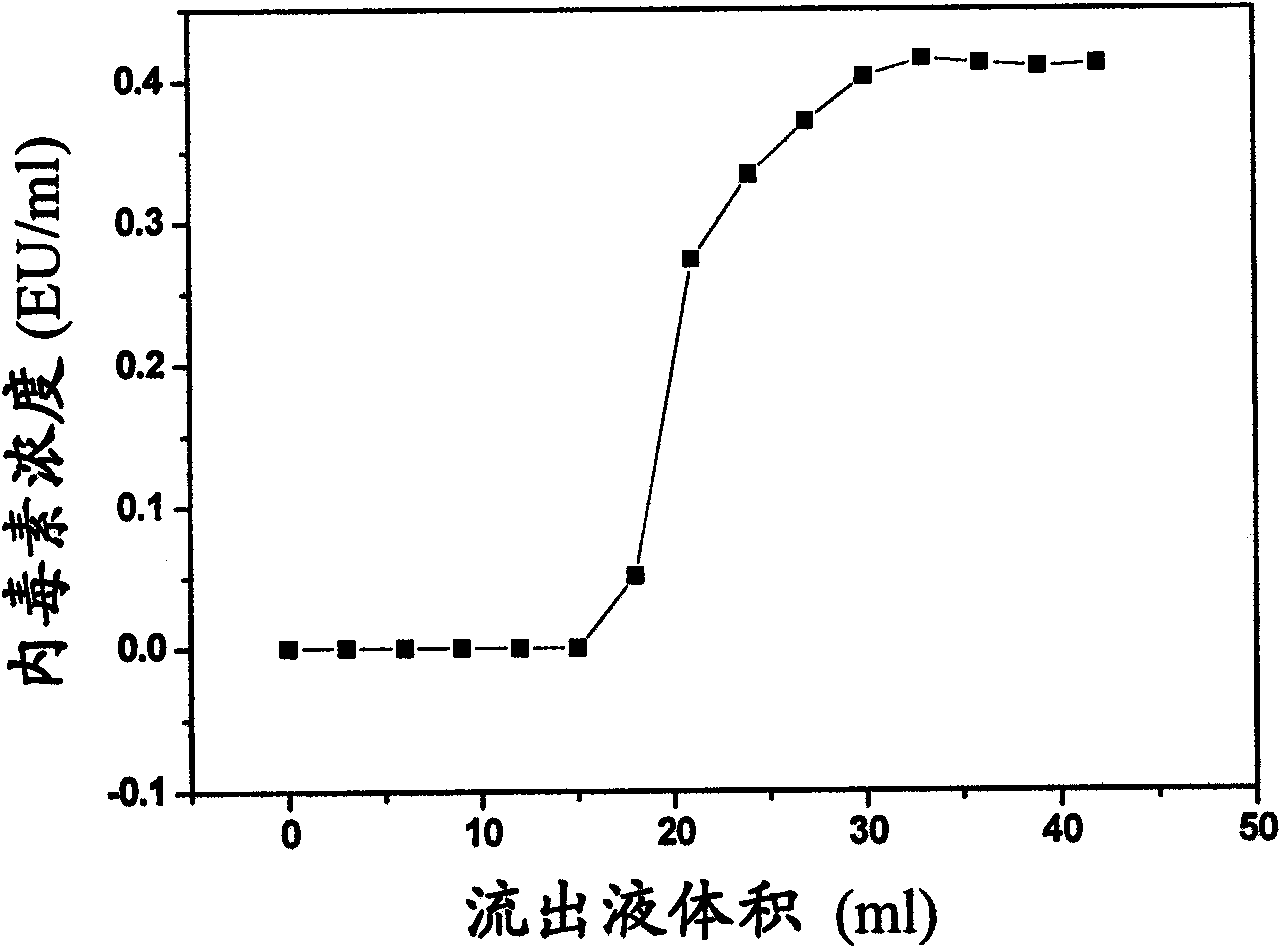
The invention discloses a method for preparing a polyvinylidene fluoride affinity membrane using amino acid as a ligand. The affinity membrane is prepared by hydrophilically modifying a polyvinylidene fluoride hollow fiber membrane and grafting the amino acid ligand. The grafting amount of the amino acid is 150 to 250mg / g for each membrane. The invention also discloses application of the affinity membrane in removing endotoxin in blood plasma, which removes the endotoxin in the blood plasma by a dynamic absorption means. The polyvinylidene fluoride affinity membrane prepared by the method has stable performance, good bio-compatibility and high endotoxin removing efficiency, and can be used for whole blood perfusion as well as blood plasma perfusion.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Lateral Flow Immunoassay With Encapsulated Detection Modality
InactiveUS20090155811A1High sensitivityThe result is moreAnalysis by material excitationBiological testingWhole blood unitsLateral flow immunoassay
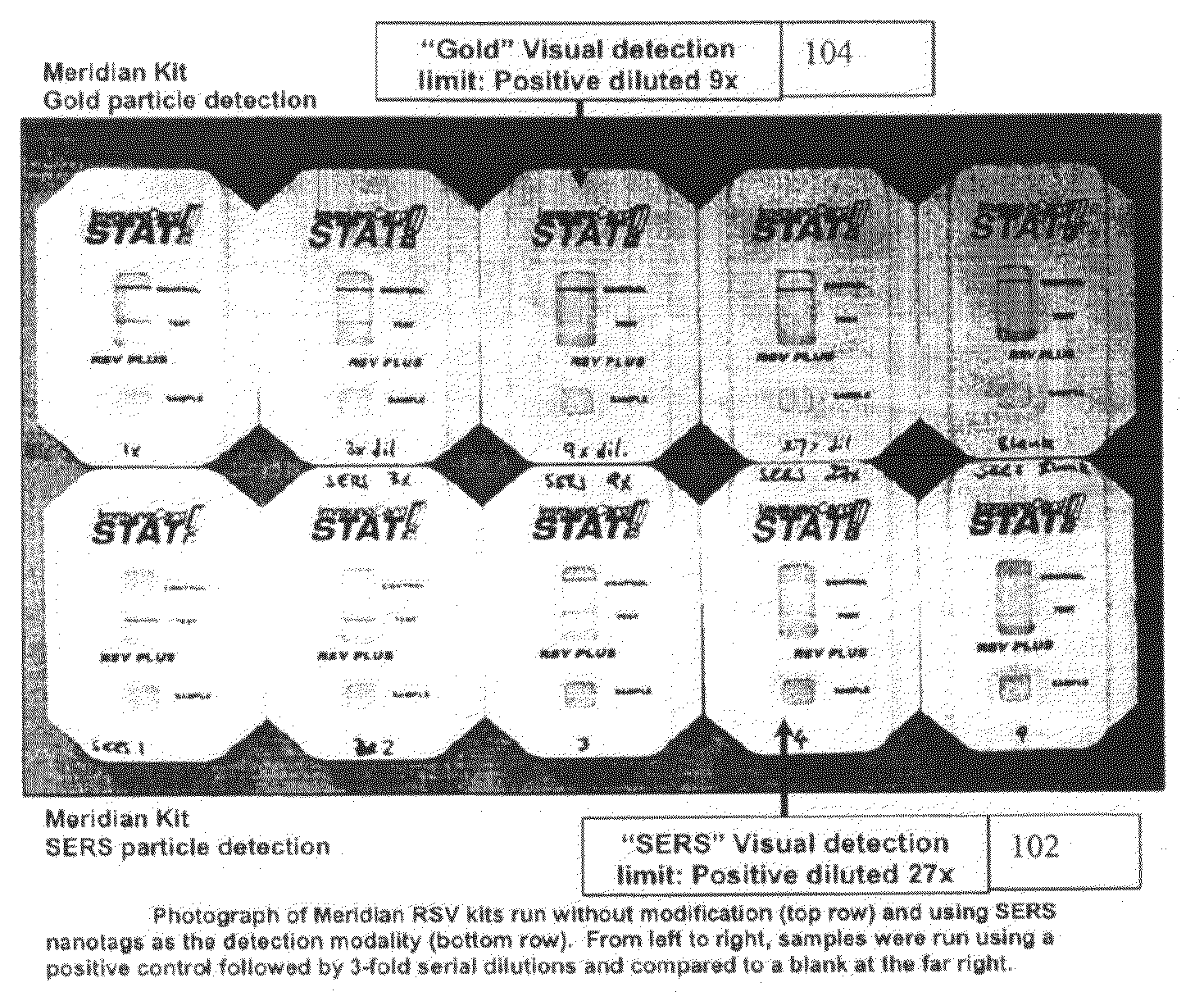
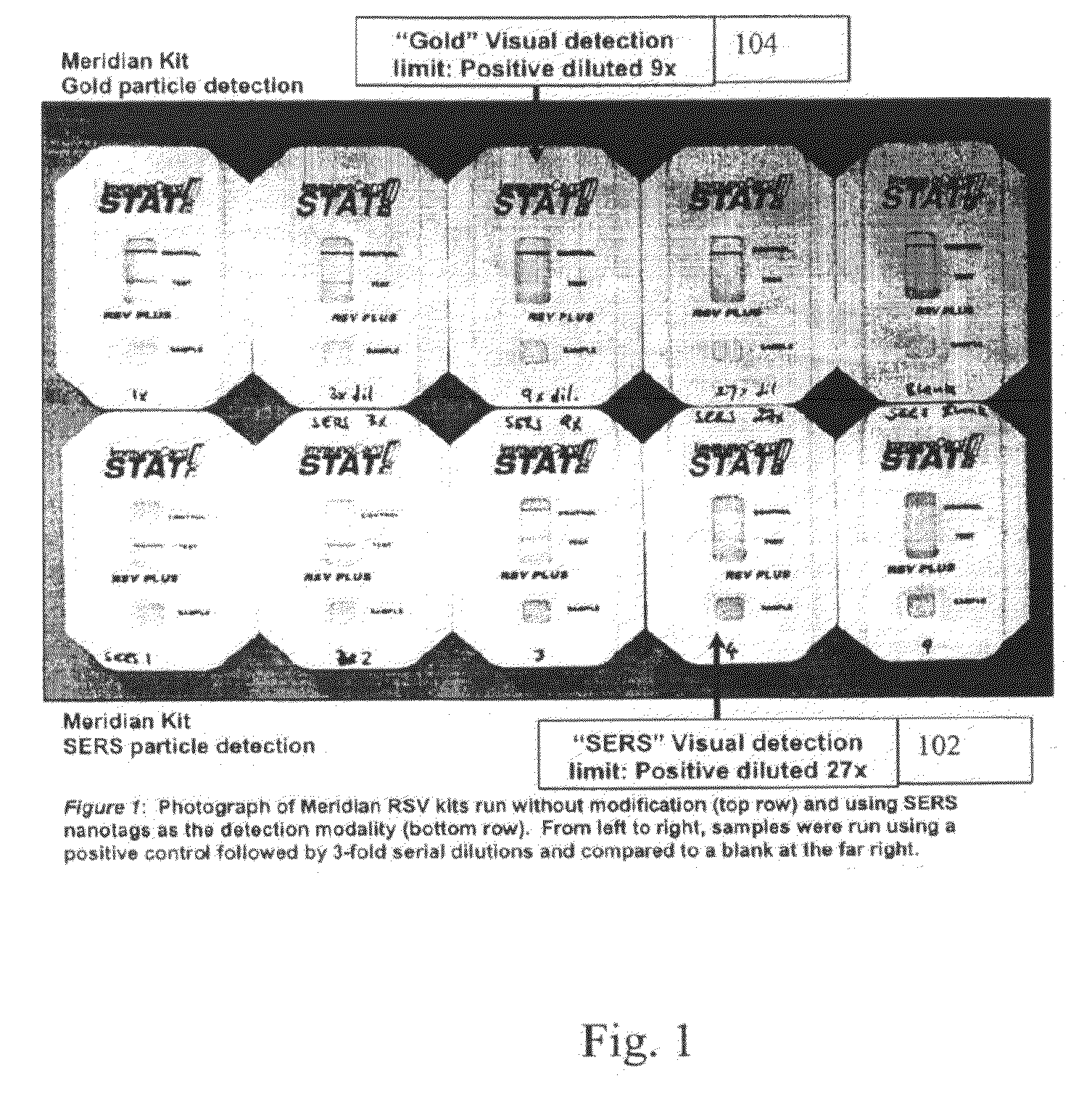
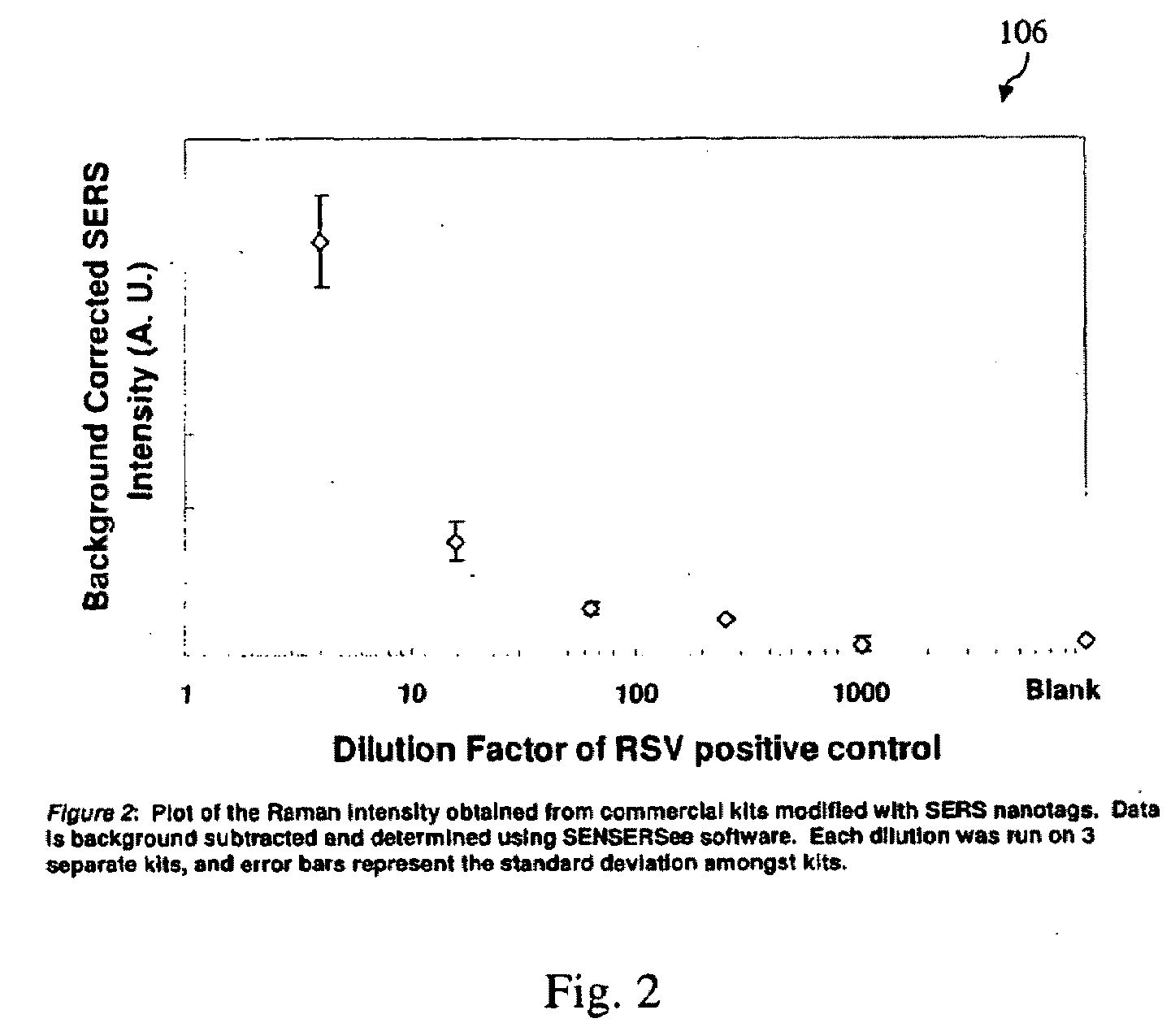
A lateral flow immunoassay featuring encapsulated metal particles. The encapsulated particles may use SERS nanotags as the detection modality. The use of encapsulated particles as a detection modality, in particular encapsulated SERS tags increases the sensitivity of an LFI prepared for visual reading and introduces the ability to obtain substantially more sensitive qualitative results or quantitative results through the analysis of a SERS spectrum read from an LFI prepared in accordance with the present invention. The use of SERS as detection modality also enhances the ability of an LFI device to be used for a multiplexed test. Other aspects of the present invention include LFI devices specifically configured to test whole blood, a reader for the detection and interpretation of a multiplexed assay and the hardware and software components used to implement the reader.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Whole blood CRP detection apparatus, method thereof, and blood cell analyzer
InactiveCN104713816AFast testImprove reliabilityIndividual particle analysisWhole blood unitsFasting tests
The invention discloses a whole blood CRP detection apparatus, a method thereof, and a blood cell analyzer. The apparatus comprise a syringe unit, a weak solution distribution unit, a DIFF channel measuring unit, a reagent unit, a counting chamber unit, a sampling needle, a negative pressure chamber and a waste liquid discharge unit; the reagent unit comprises a weak solution, a WBC reagent, a DIFF reagent and a second CRP reagent; and the counting chamber unit comprises a CRP pool, a DIFF pool, a WBC pool and an RBC pool, and is used for completing a reaction of a CRP channel sample with the CRP reagent, a reaction of a DIFF channel sample with the DIFFC reagent, a reaction of a WBC channel sample with the WBC reagent and a reaction of an RBC channel sample with a reagent. The apparatus and the method can be used to simultaneously detect CRP and five-classifications blood routine examination, and have the characteristics of parallel detection of all detection channels, and fast test speed.
Owner:SHENZHEN DYMIND BIOTECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com