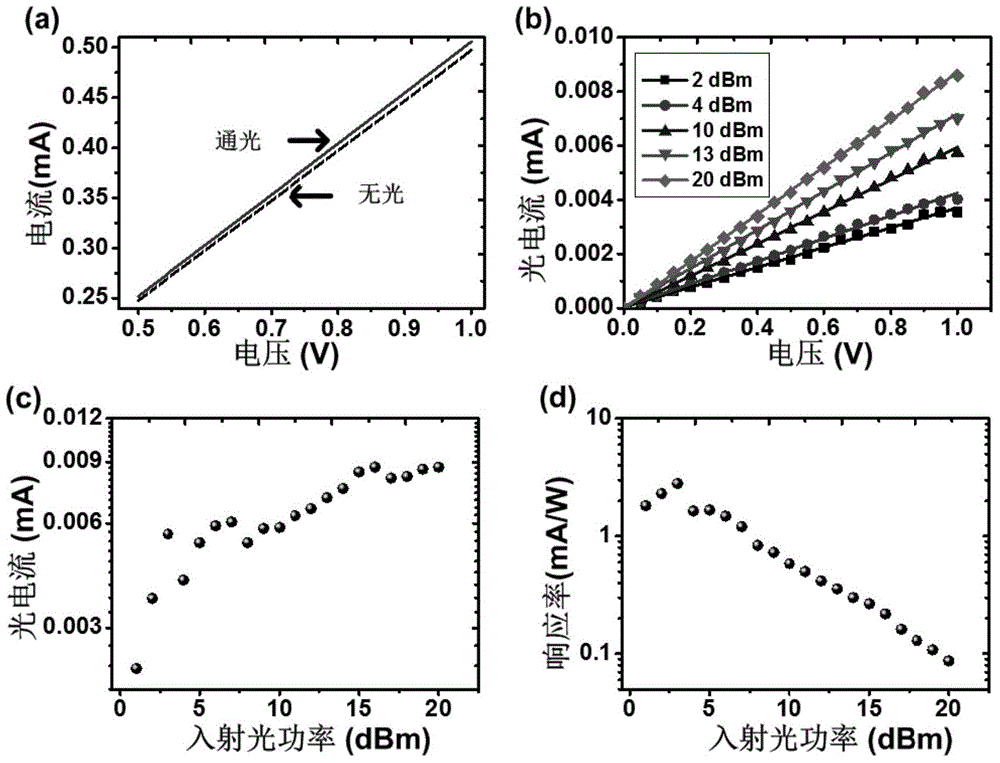
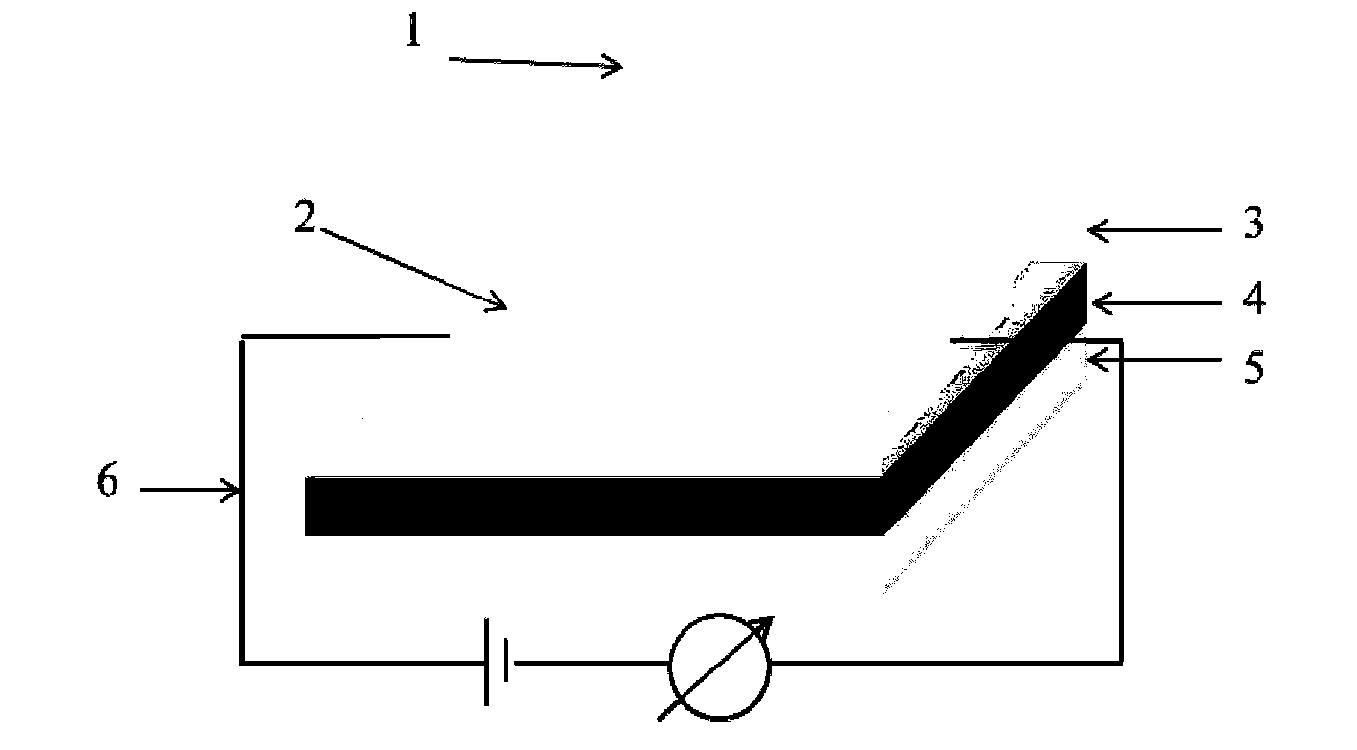
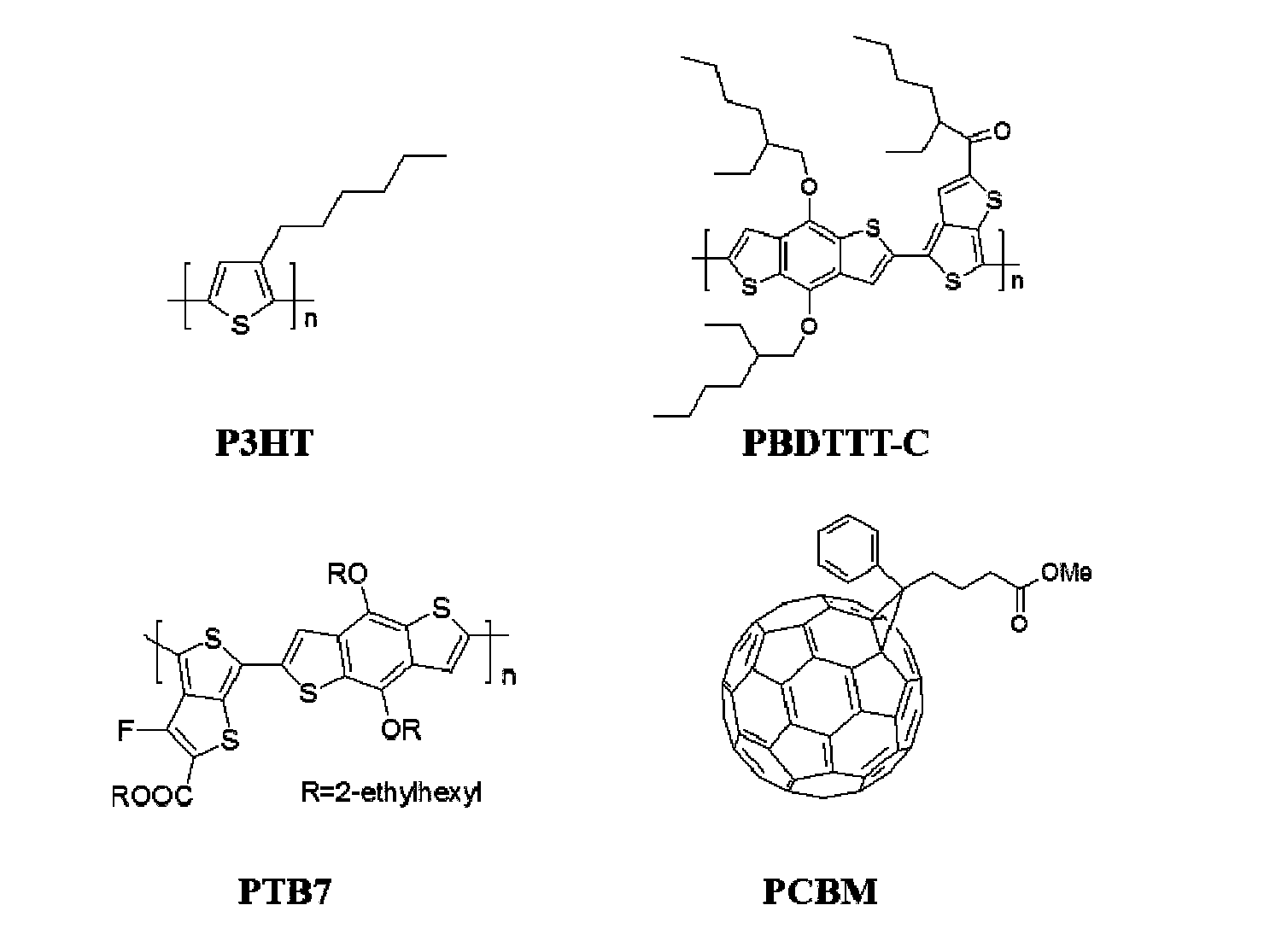
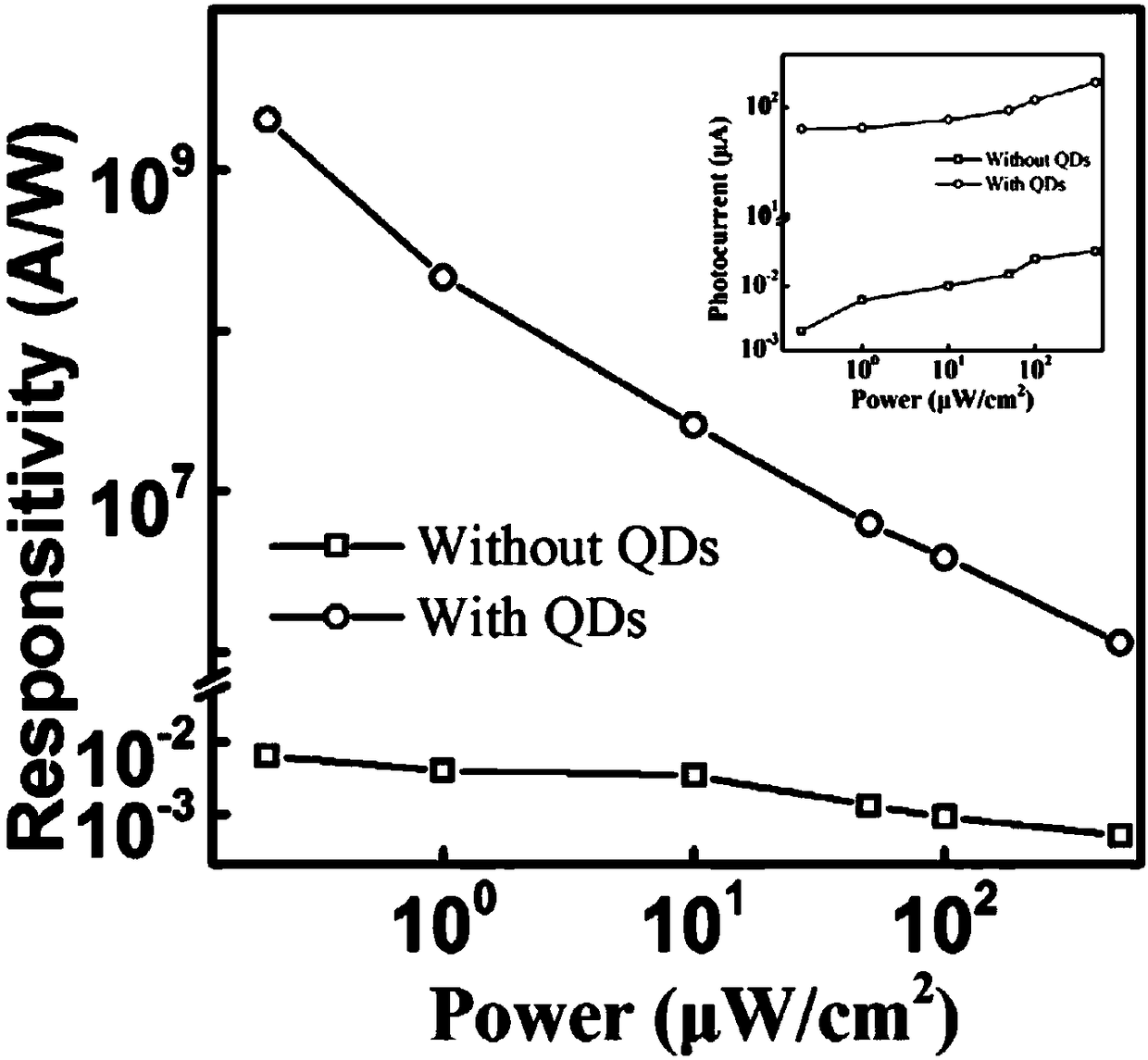
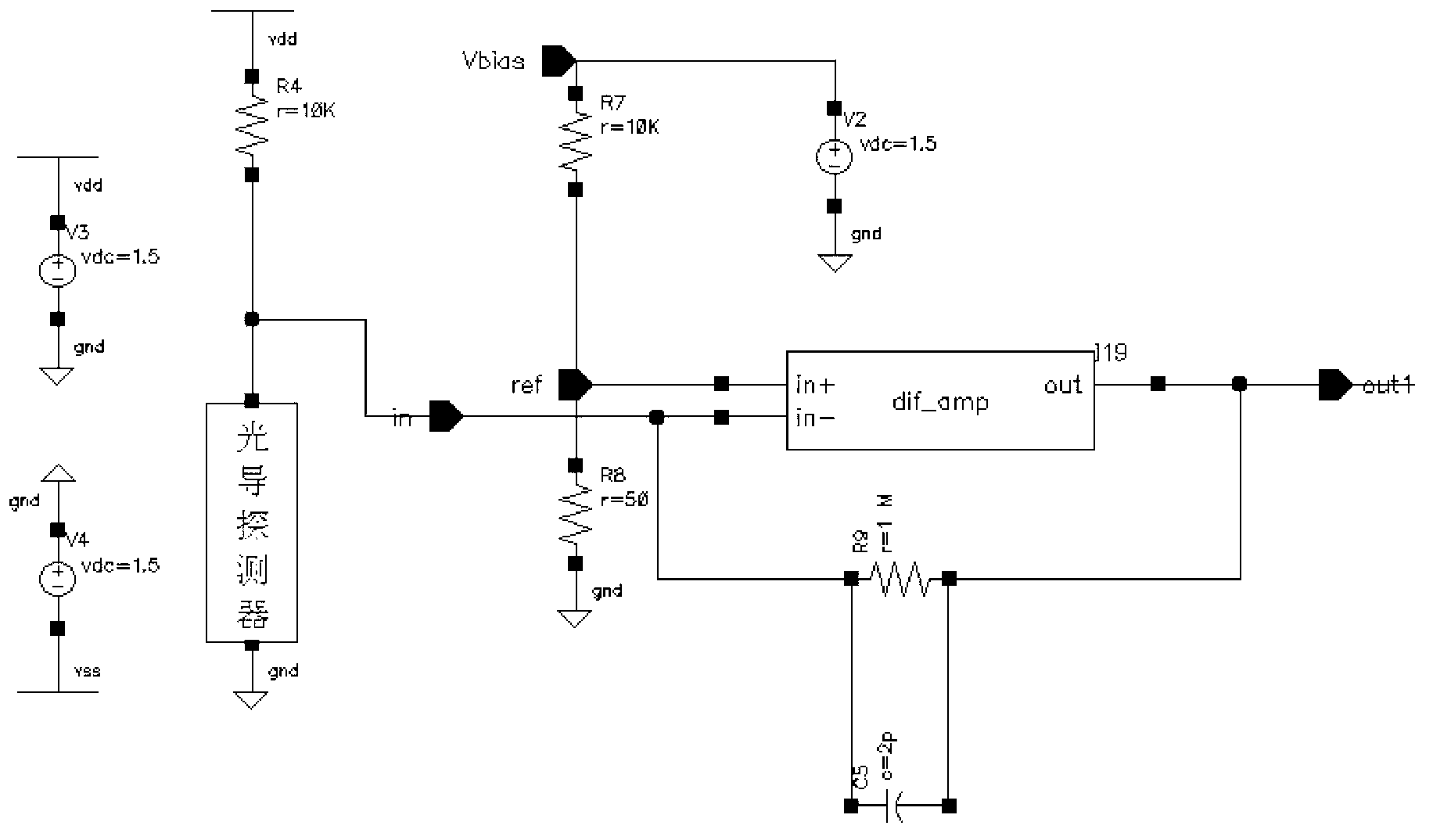
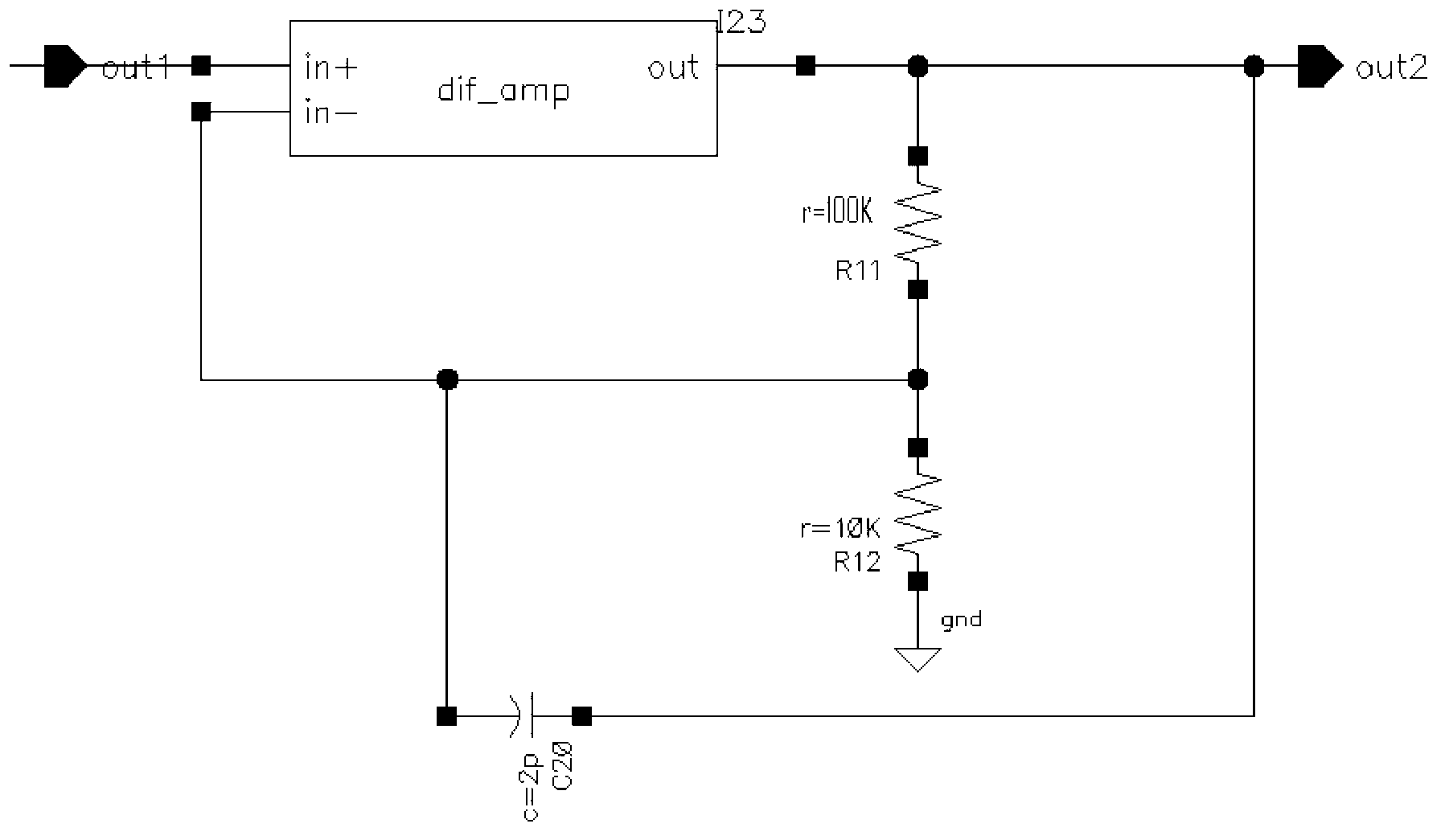
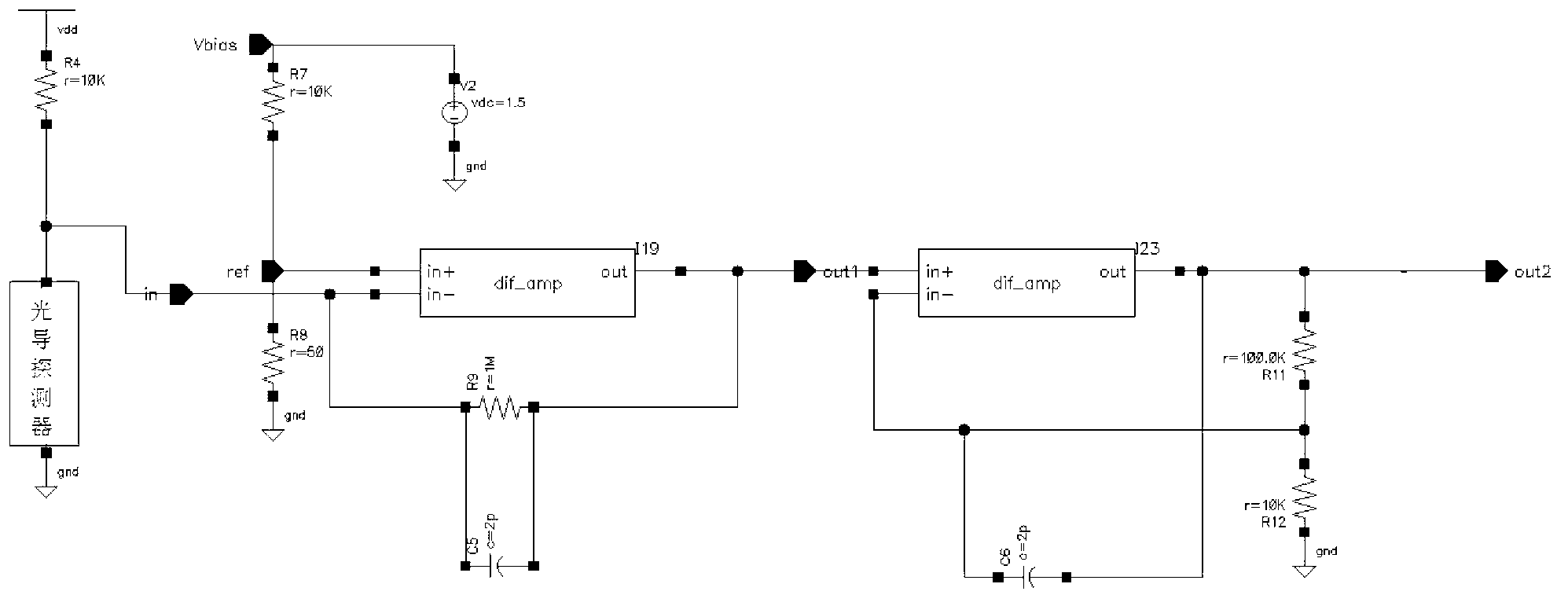
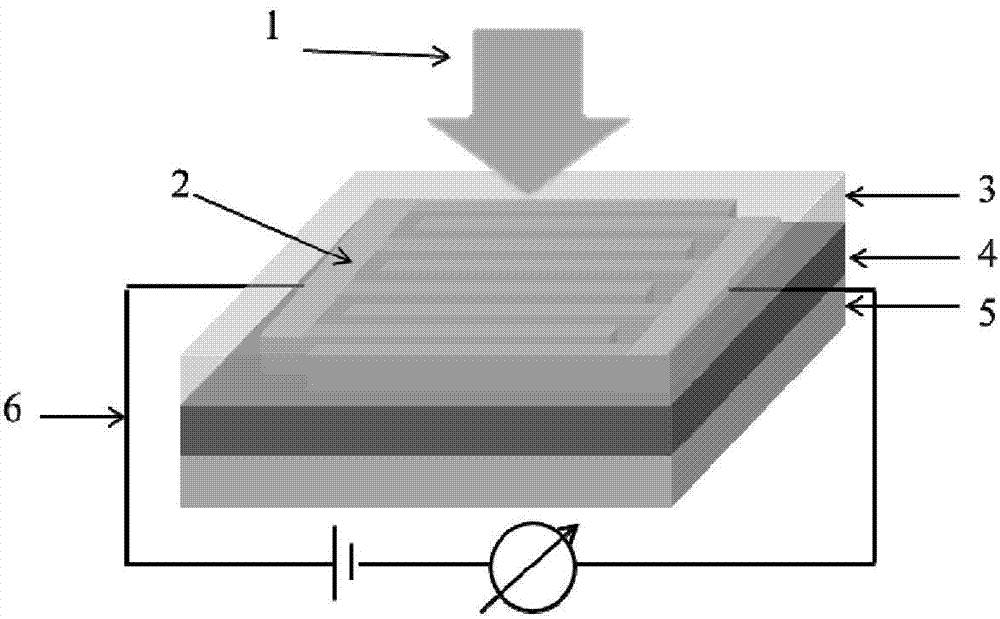
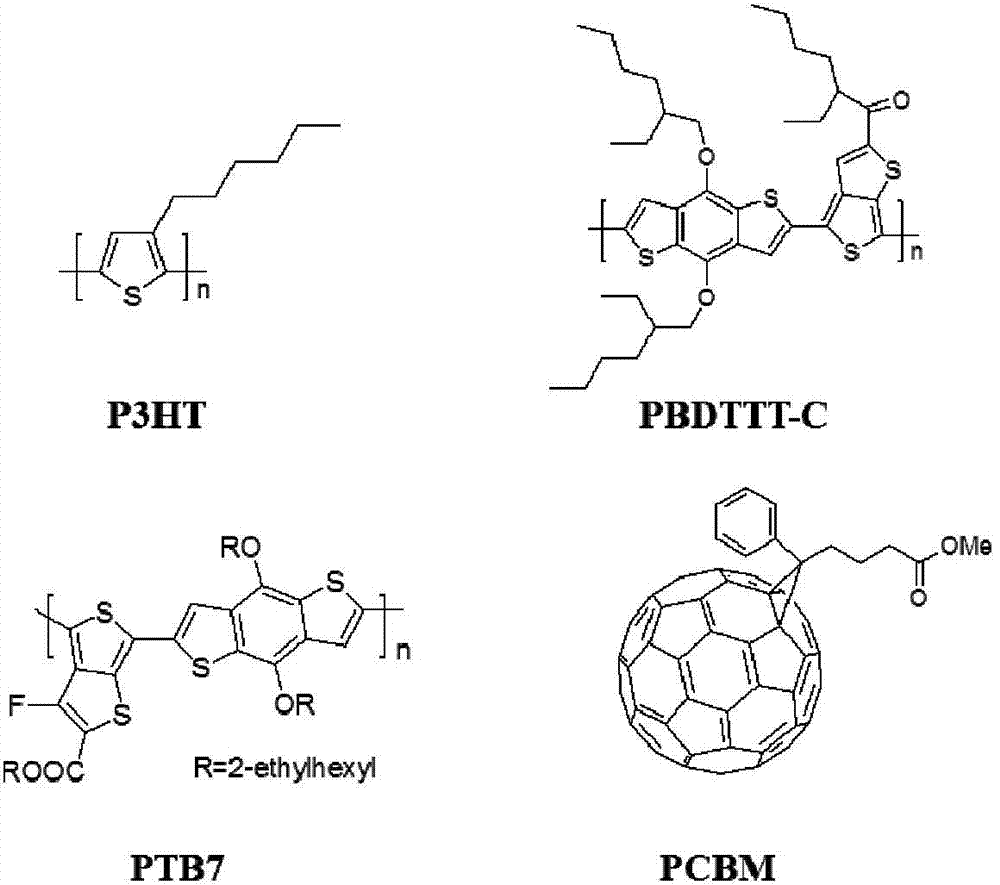
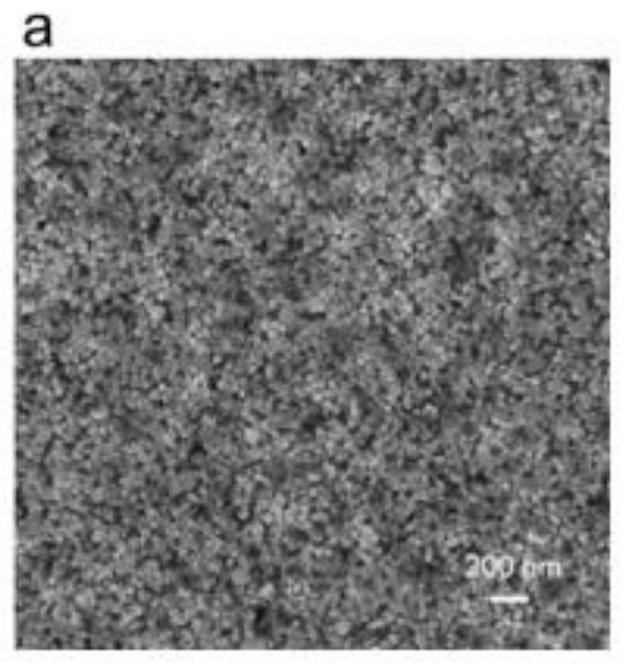
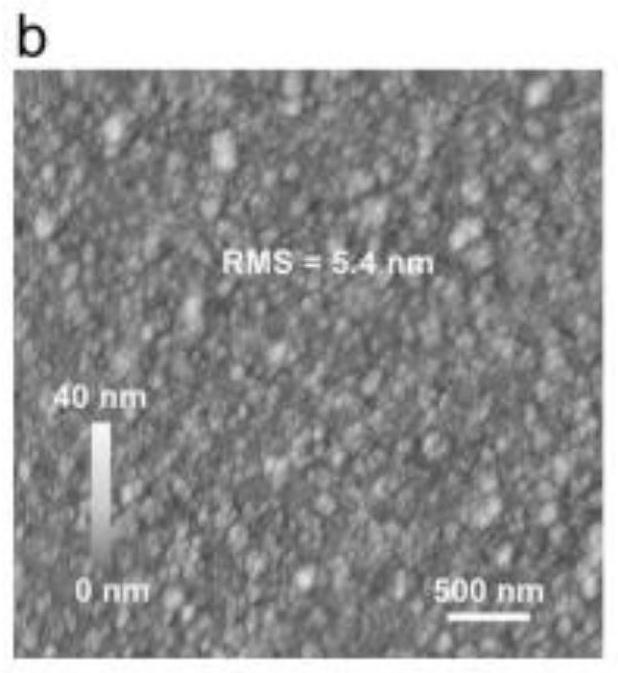
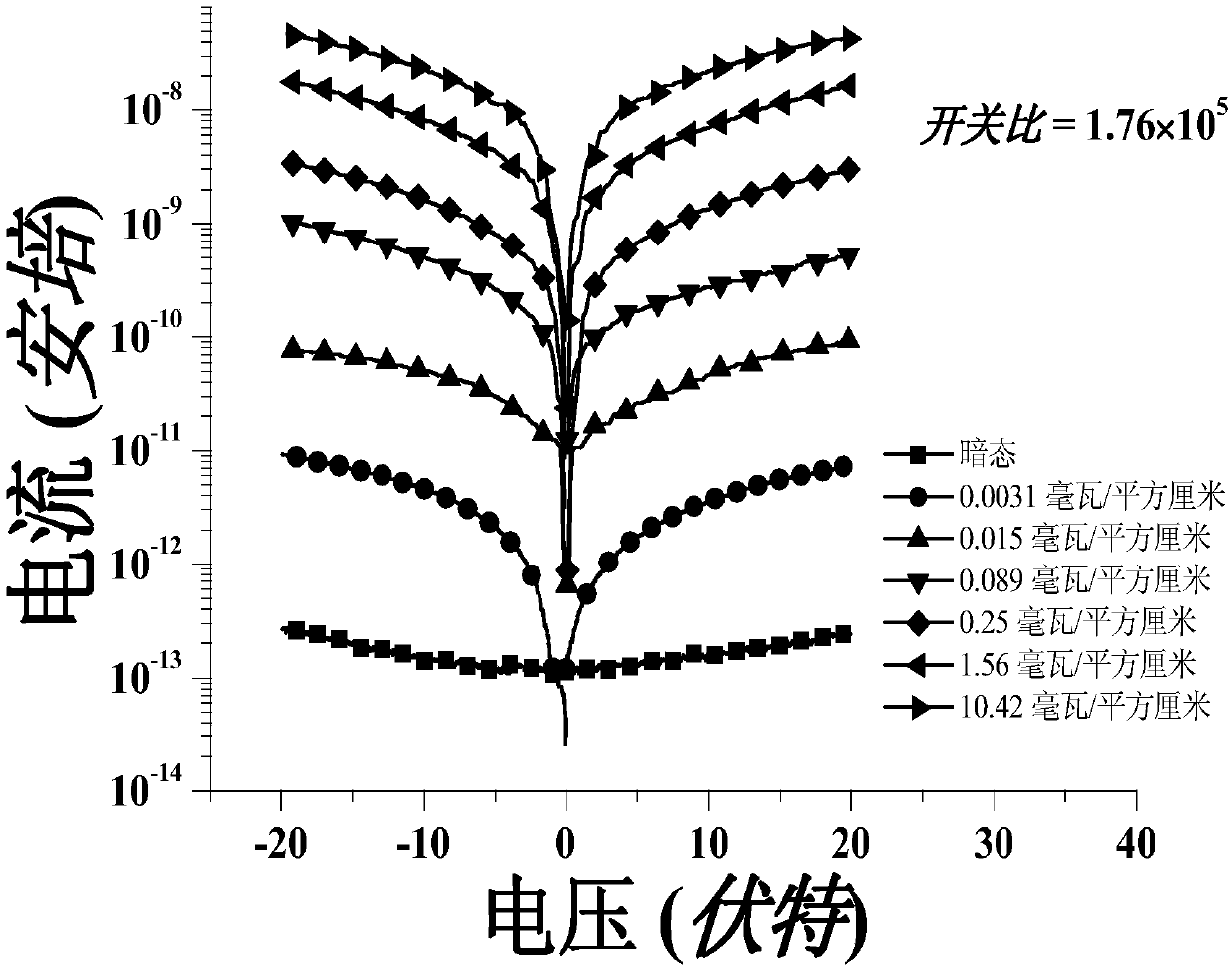
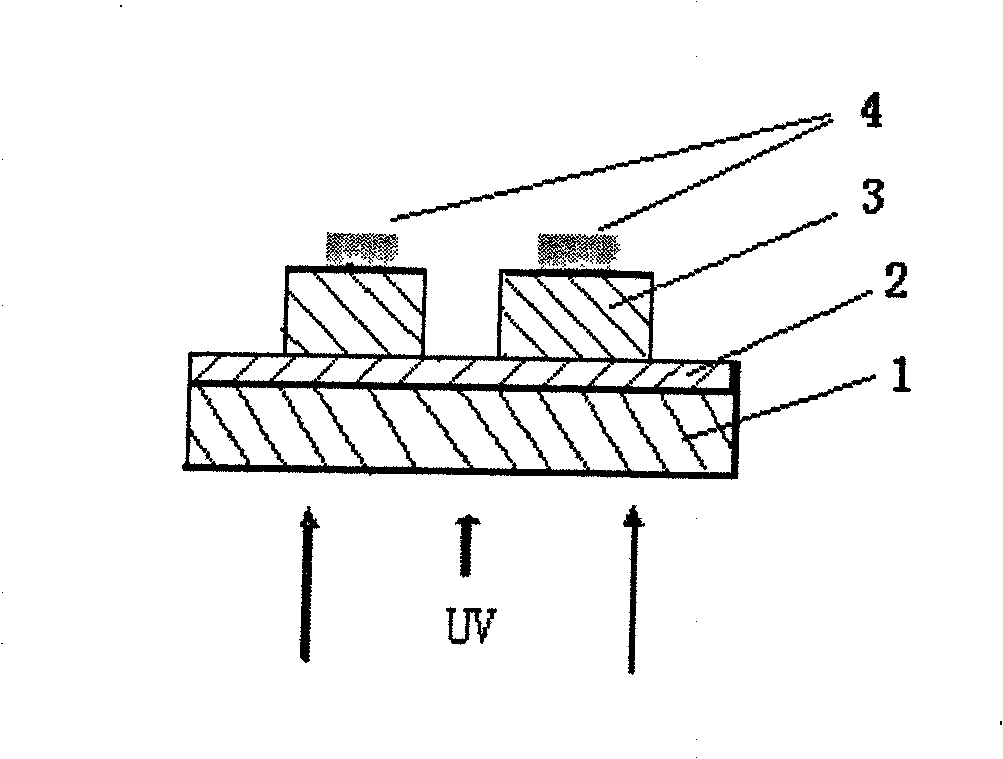
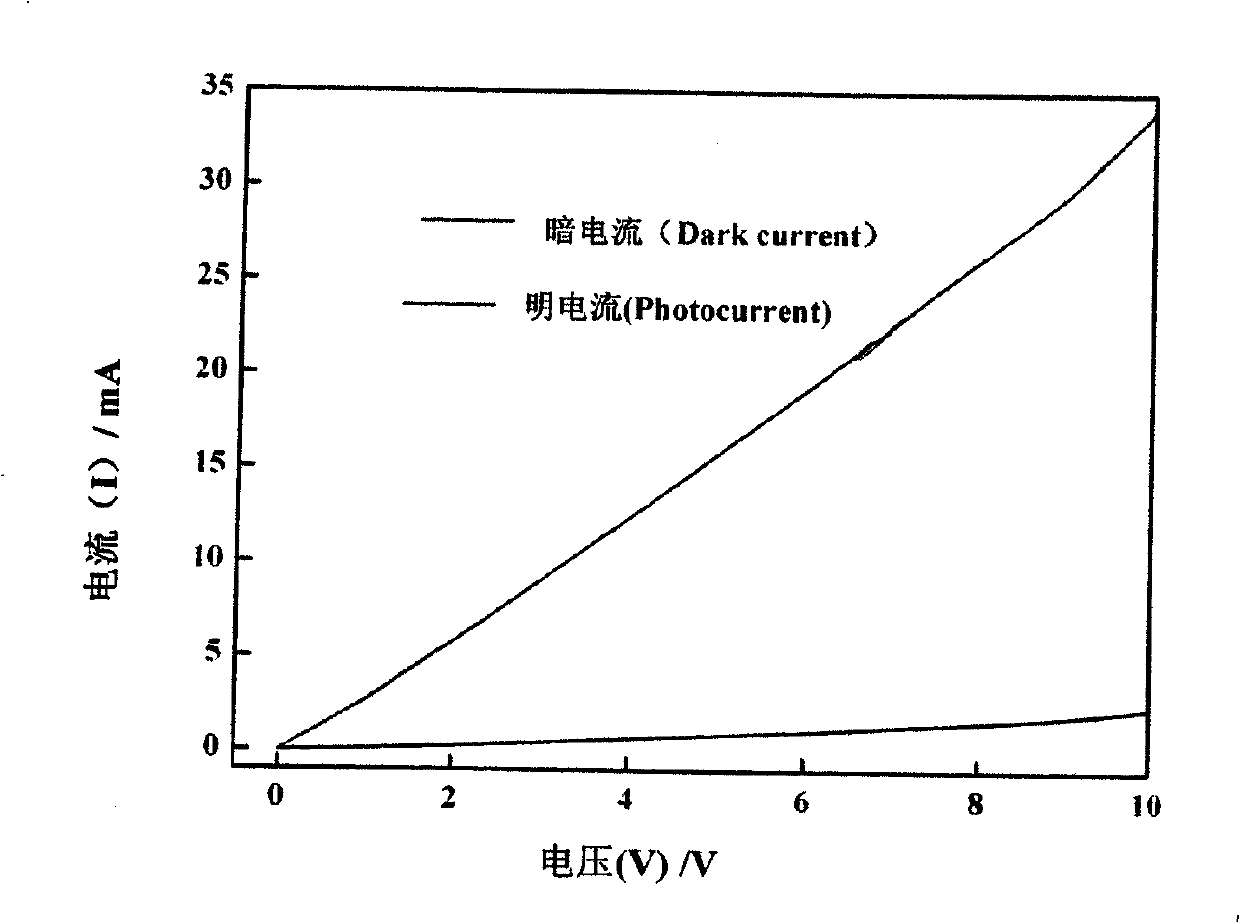
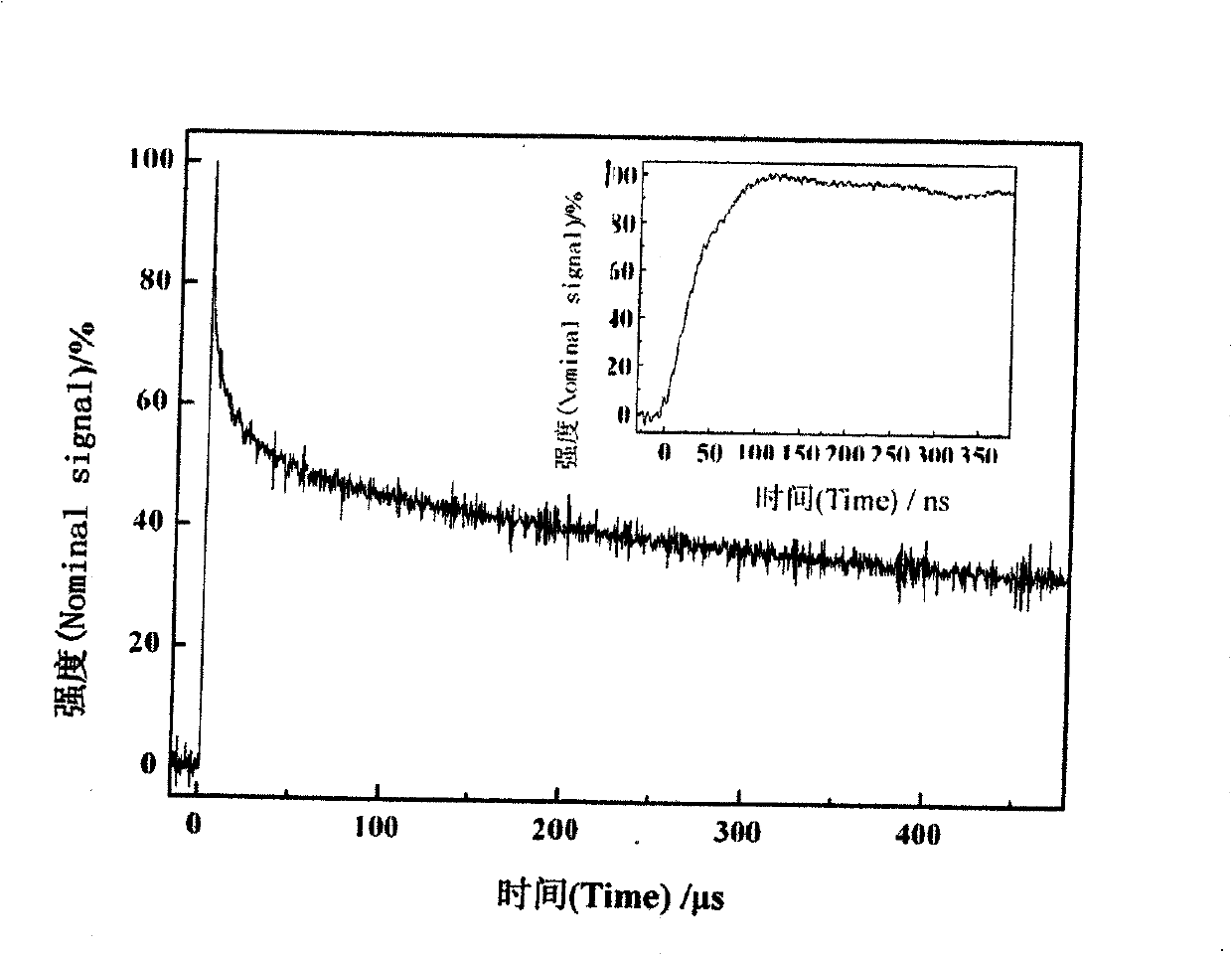
Patents
Literature
41 results about "Photoconductive detector" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
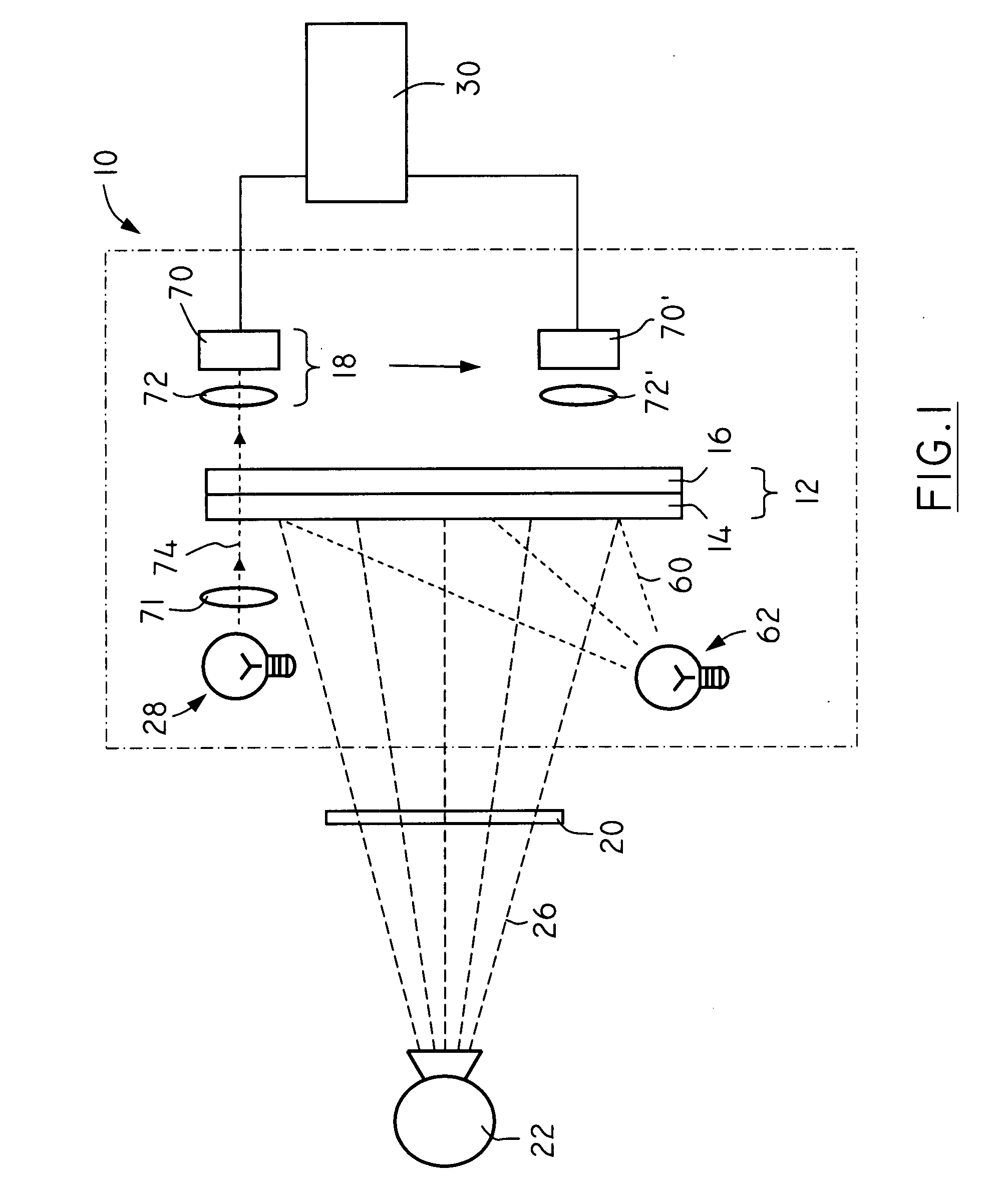
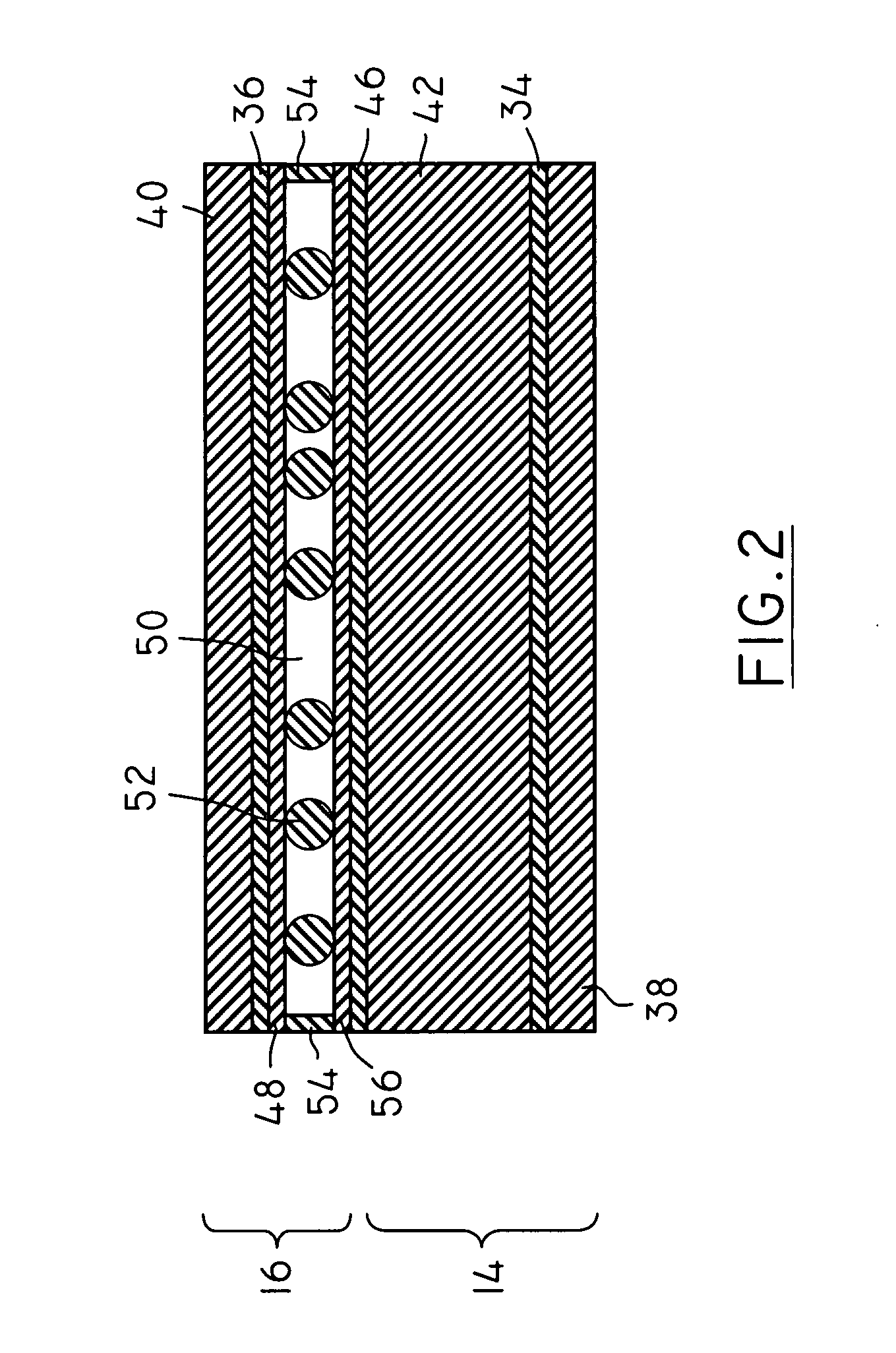
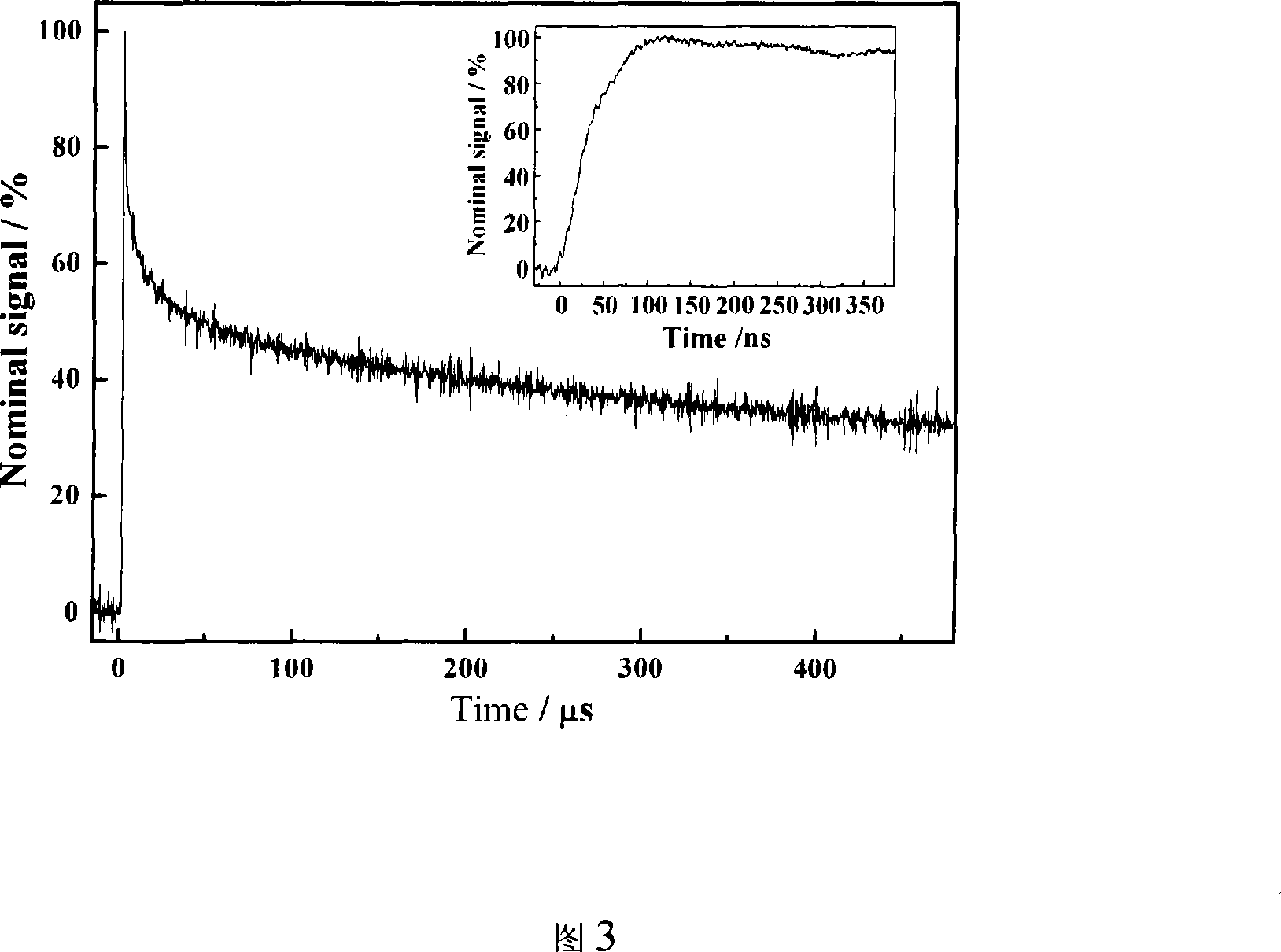
Differential interference phase contrast X-ray imaging system
InactiveUS8073099B2High radiant fluxPhoton energy is highImaging devicesX-ray tube electrodesHigh energyPhotoconductive detector
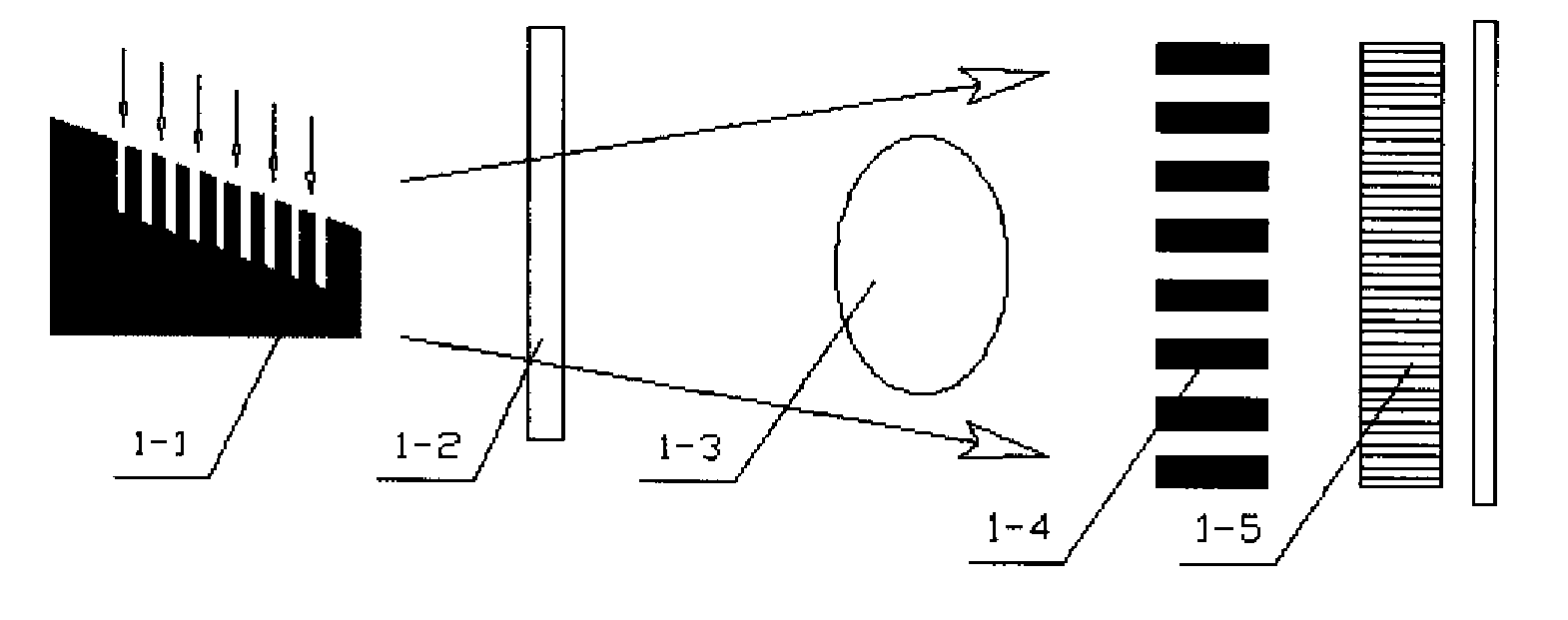
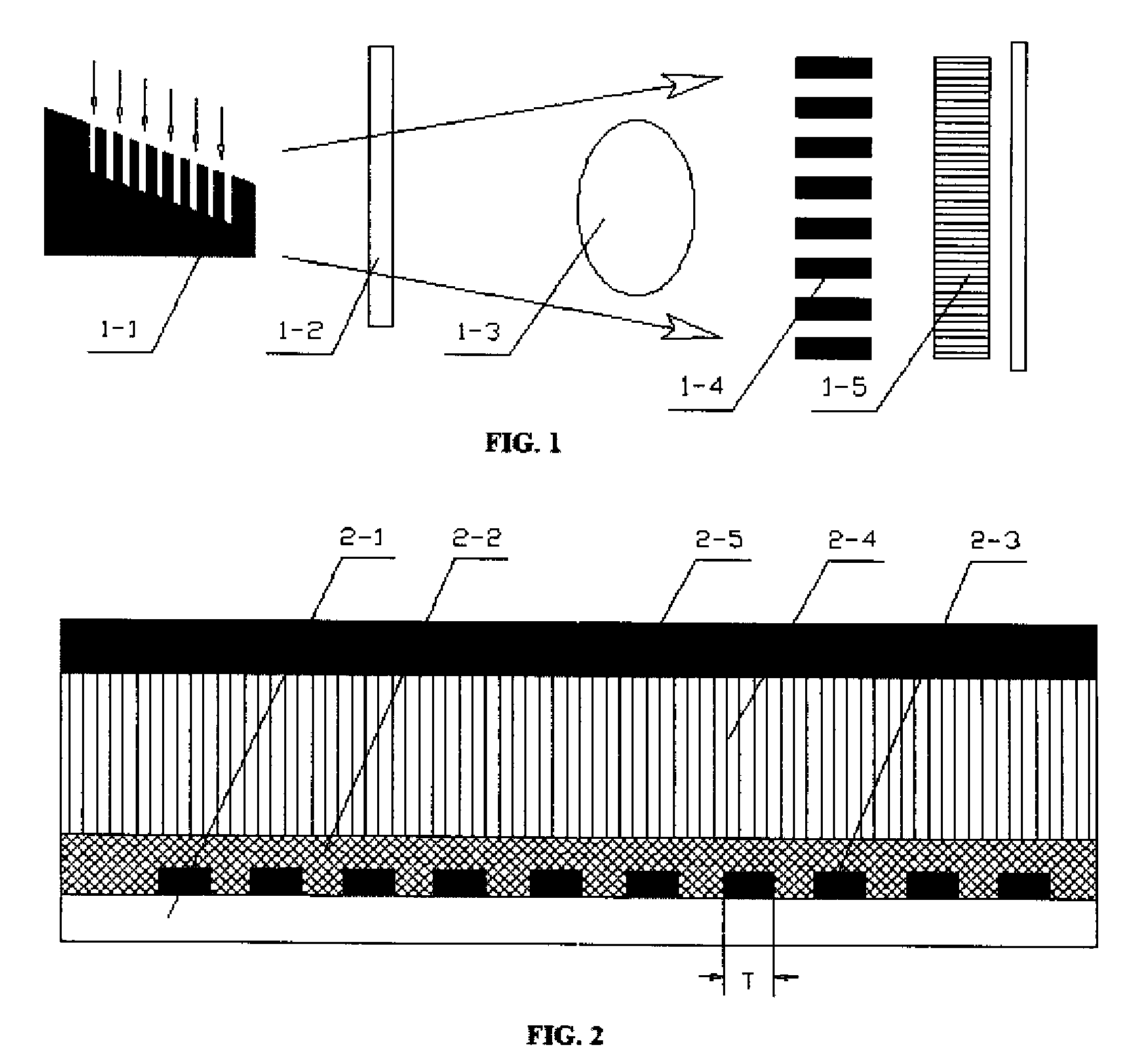
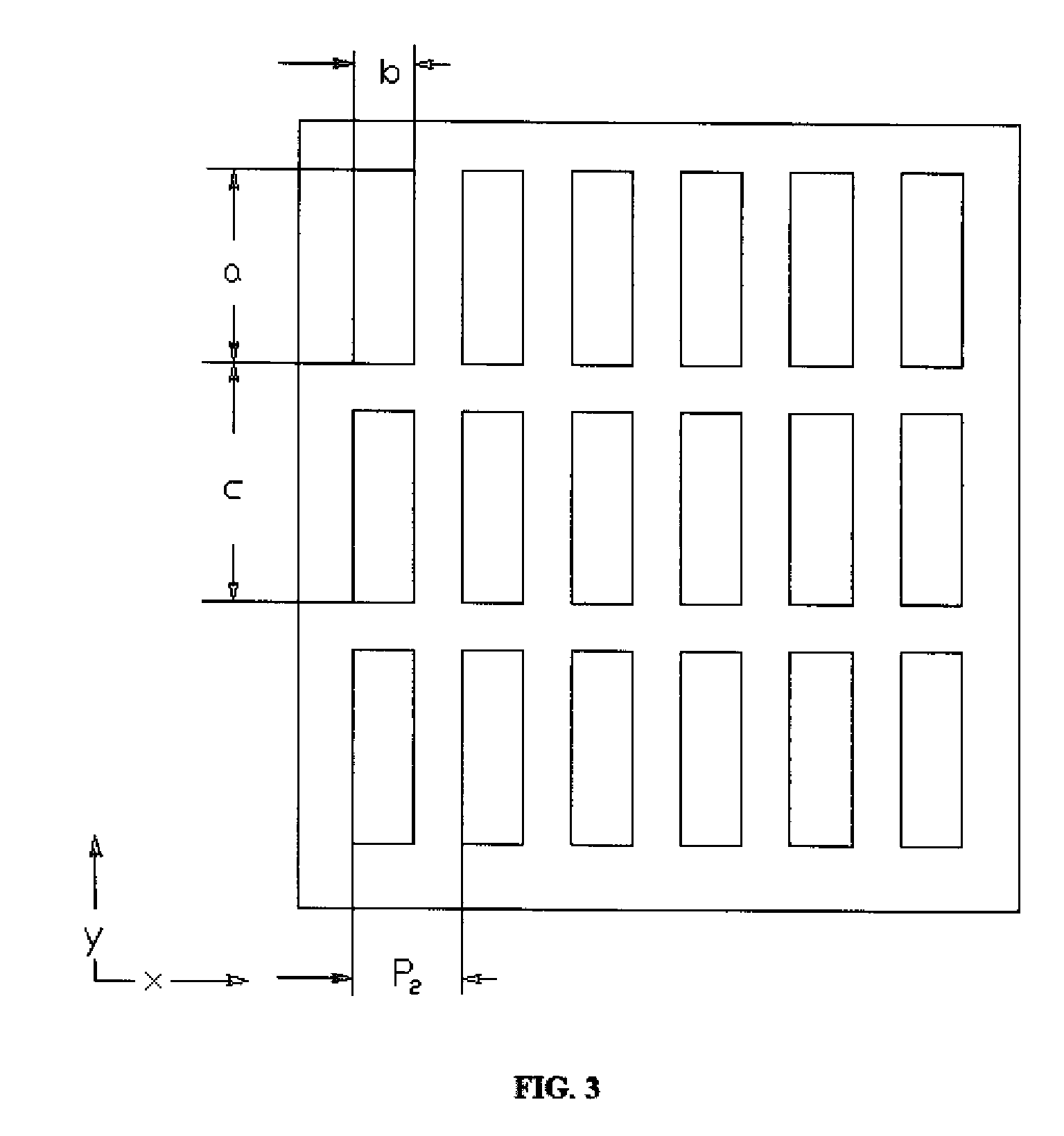
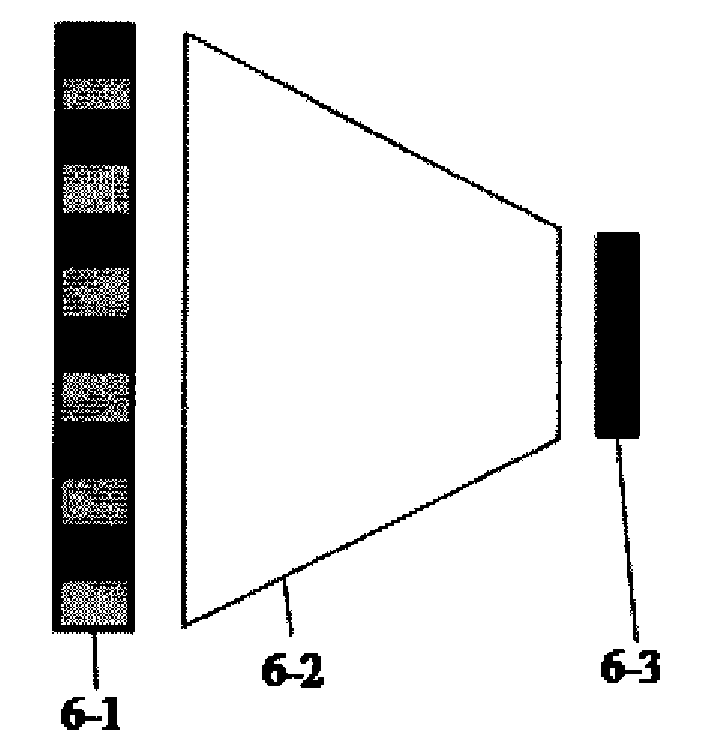
A differential phase-contrast X-ray imaging system is provided. Along the direction of X-ray propagation, the basic components are X-ray tube, filter, object platform, X-ray phase grating, and X-ray detector. The system provides: 1) X-ray beam from parallel-arranged source array with good coherence, high energy, and wider angles of divergence with 30-50 degree. 2) The novel X-ray detector adopted in present invention plays dual roles of conventional analyzer grating and conventional detector. The basic structure of the detector includes a set of parallel-arranged linear array X-ray scintillator screens, optical coupling system, an area array detector or parallel-arranged linear array X-ray photoconductive detector. In this case, relative parameters for scintillator screens or photoconductive detector correspond to phase grating and parallel-arranged line source array, which can provide the coherent X-rays with high energy.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Differential Interference Phase Contrast X-ray Imaging System
InactiveUS20100091947A1Photon energy is highWide emission angleImaging devicesX-ray tube electrodesPhotoconductive detectorHigh energy
A differential phase-contrast X-ray imaging system is provided. Along the direction of X-ray propagation, the basic components are X-ray tube, filter, object platform, X-ray phase grating, and X-ray detector. The system provides: 1) X-ray beam from parallel-arranged source array with good coherence, high energy, and wider angles of divergence with 30-50 degree. 2) The novel X-ray detector adopted in present invention plays dual roles of conventional analyzer grating and conventional detector. The basic structure of the detector includes a set of parallel-arranged linear array X-ray scintillator screens, optical coupling system, an area array detector or parallel-arranged linear array X-ray photoconductive detector. In this case, relative parameters for scintillator screens or photoconductive detector correspond to phase grating and parallel-arranged line source array, which can provide the coherent X-rays with high energy.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Continuous whole blood glucose monitor
InactiveUS20110009720A1Improve fitOther blood circulation devicesHaemofiltrationPeristaltic pumpPhotoconductive detector
A portable continuous whole blood glucose monitor comprising, a mid-infrared quantum cascade laser and driver in optical communication with a transmission cell and a photo-conductive detector and pre-amplifier. The monitor further comprises a peristaltic pump connected to a single lumen catheter peripherally inserted into a patient's vein. The single lumen catheter, in combination with the peristaltic pump, is operable to automatically withdraw a fixed and metered amount of whole blood from a patient, then a tube delivers a fixed and metered amount of the saline / surfactant supply to the whole blood. Methods of enhancing measurement sensitivity are also provided.
Owner:CASCADE METRIX LLC
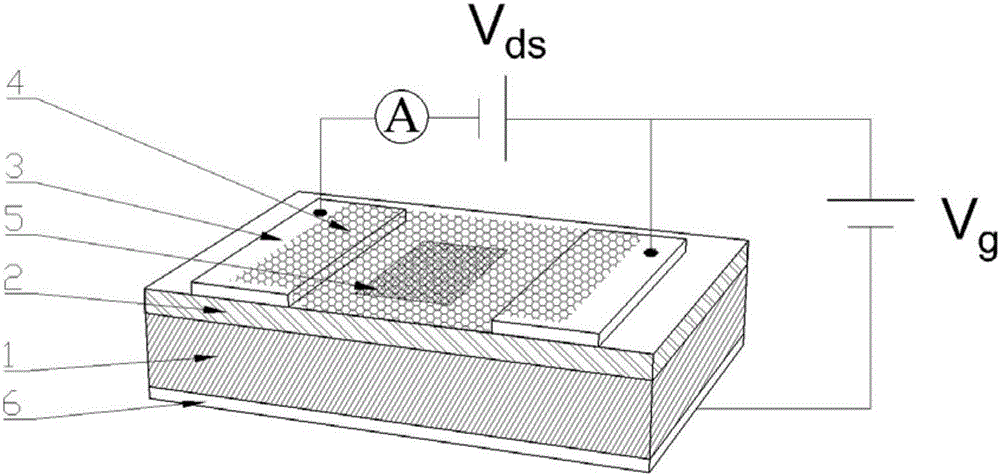
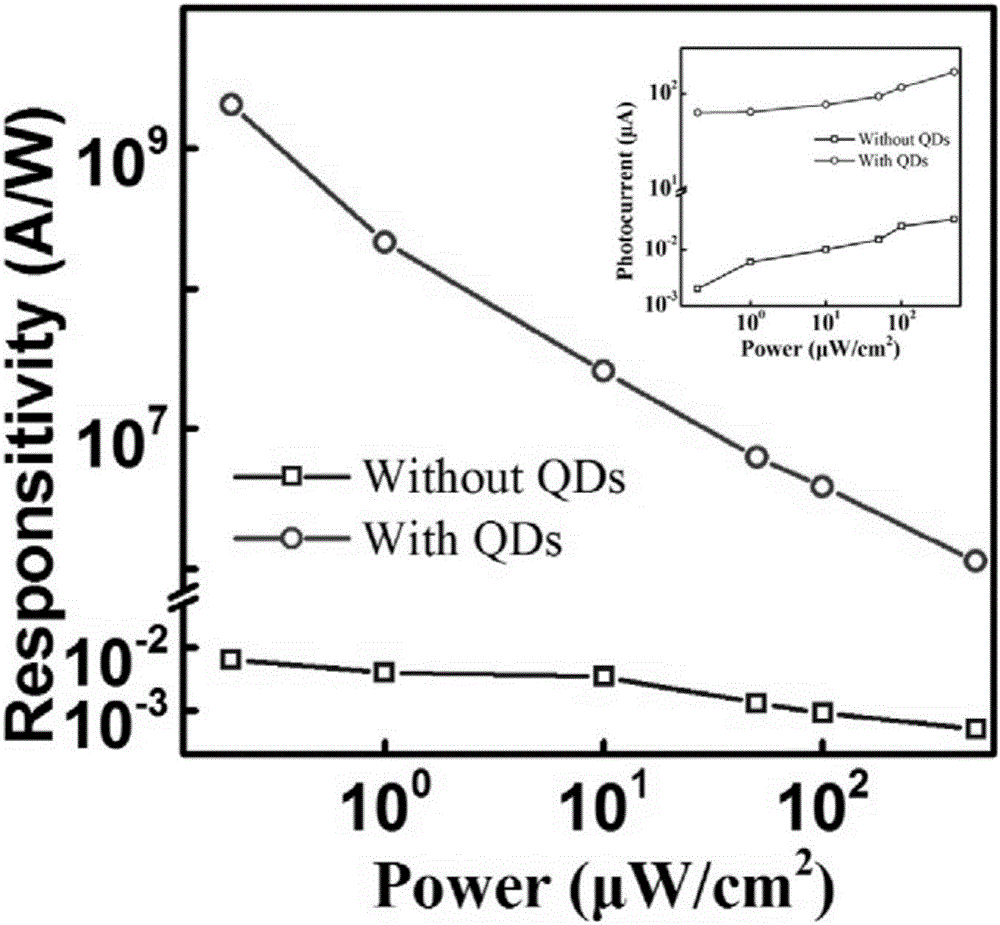
Photoconductive detector based on boron-doped silicon quantum dot/graphene/silicon dioxide and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106601857ALarge light signal currentHigh gainFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesPhotoconductive detectorP type silicon
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
X-ray light valve based digital radiographic imaging systems
InactiveUS20070201616A1Improve scalabilitySacrificing densityX-ray/infra-red processesMaterial analysis by optical meansPhotoconductive detectorX-ray
The present invention provides a digital x-ray radiographic imaging system. The system is based on a photoconductive detector and an electro-optic light modulator, where the photoconductive detector layer absorbs x-rays that have passed through an object to form an exposure of the object. The absorbed x-rays create a static optical image, which is stored in the electro-optic light modulator, allowing the capture of the optical image to continue over longer time. The optical image is digitized using a scanning system and an external light source. The image is then processed and stored by a computer. After the optical image is recorded, an erasing mechanism is used to reset the system before a new exposure is made.
Owner:SUNNYBROOK HEALTH SCI CENT
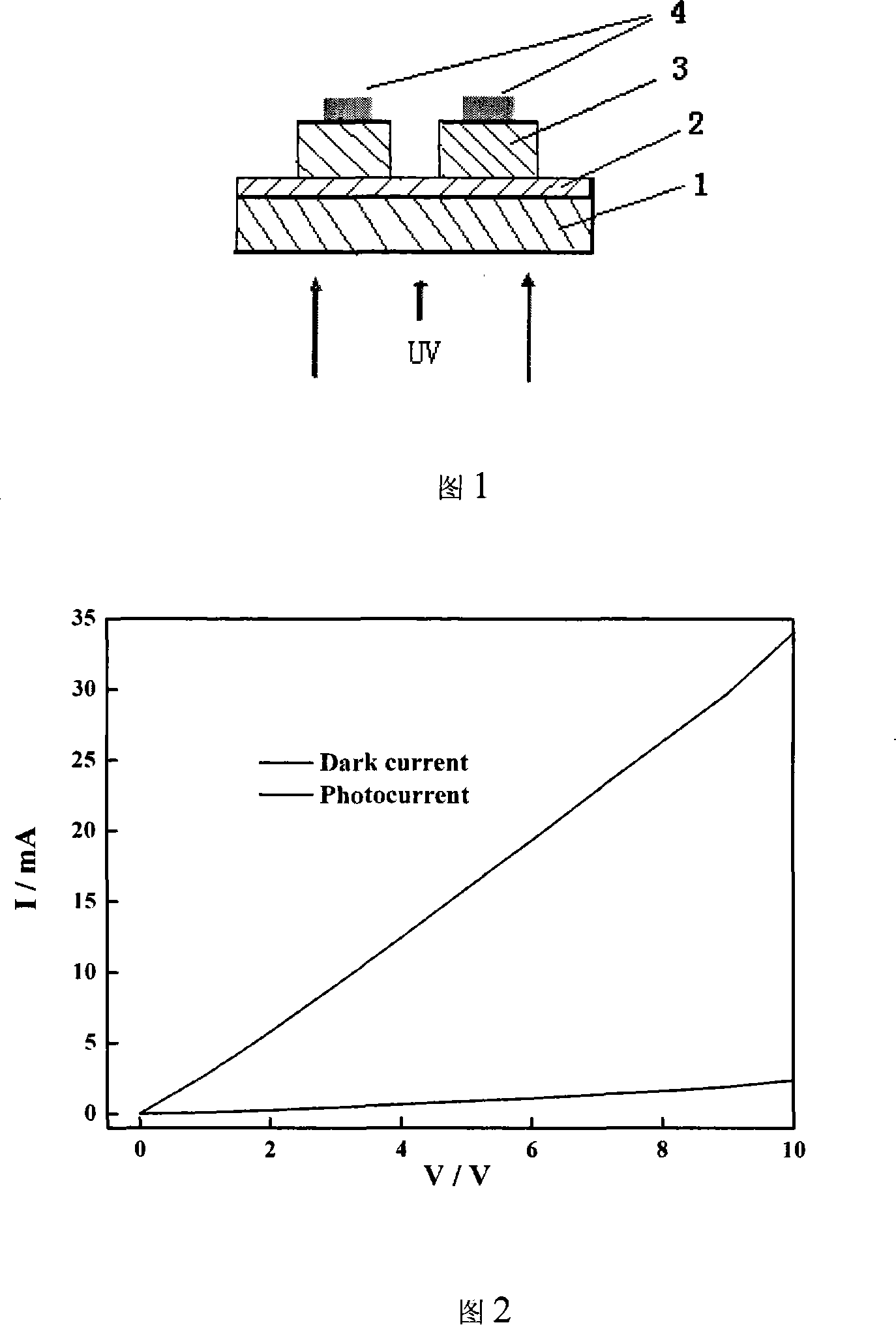
Responsivity-enhanced ZnO-based photoconductive detector and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103346171AImprove photoresponsivitySimple preparation processFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesSputteringResponsivity
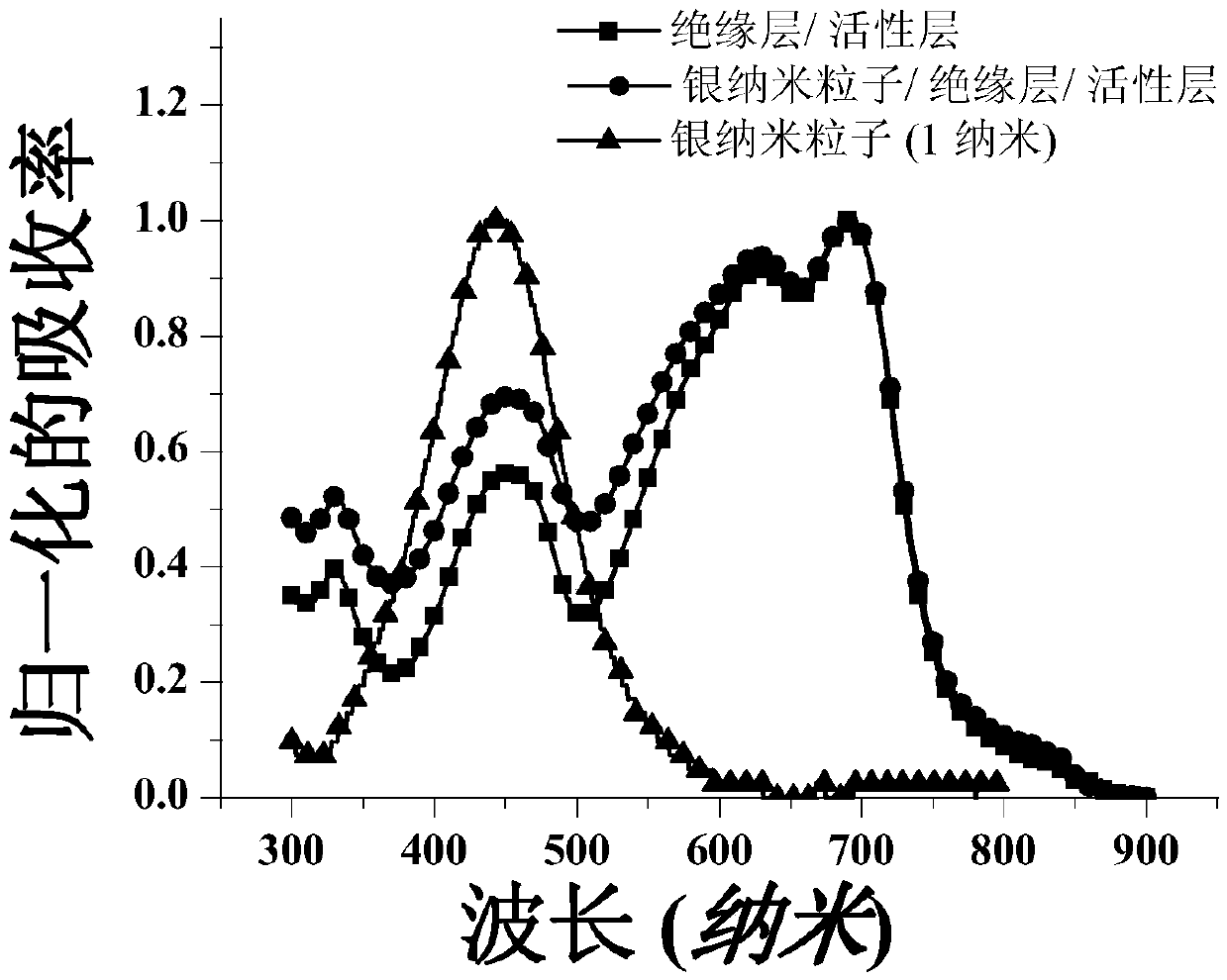
Disclosed are a responsivity-enhanced ZnO-based photoconductive detector and a preparation method thereof. The responsivity-enhanced ZnO-based photoconductive detector comprises a substrate and a ZnO film on the substrate. The ZnO film is coated with Ag nano-particles, fork-finger-shaped Al electrodes are deposited on the Ag nano-particles, and the Ag nano-particles are exposed among adjacent fork fingers of the fork-finger-shaped Al electrodes; or the fork-finger-shaped Al electrodes are deposited on the ZnO film, the Ag nano-particles are filled among the adjacent fork fingers of the fork-finger-shaped Al electrodes, and the Ag nano-particles are arranged on the ZnO film through spin-coating. The method includes the steps that the ZnO film is formed on the substrate through RF magnetron sputtering, then the Ag nano-particles are arranged on the ZnO film through spin-coating, or the fork-finger-shaped Al electrodes are deposited on the ZnO film; the responsivity-enhanced ZnO-based photoconductive detector can be obtained by depositing the fork-finger-shaped Al electrodes on the Ag nano-particles or arranging the Ag nano-particles on a sample surface with the fork-finger-shaped Al electrodes through spin-coating. According to the responsivity-enhanced ZnO-based photoconductive detector and the preparation method thereof, the surface plasma resonance effect of the Ag nano-particles is used for improving light absorbing ability of the detector, and therefore responsivity of the obtained photoconductive detector in an ultraviolet light area can be greatly improved.
Owner:徐州国隆电力配件铸造有限公司
X-ray light valve based digital radiographic imaging systems
InactiveUS7687792B2Improve scalabilitySacrificing densityX-ray/infra-red processesMaterial analysis by optical meansSoft x rayPhotoconductive detector
Owner:SUNNYBROOK HEALTH SCI CENT
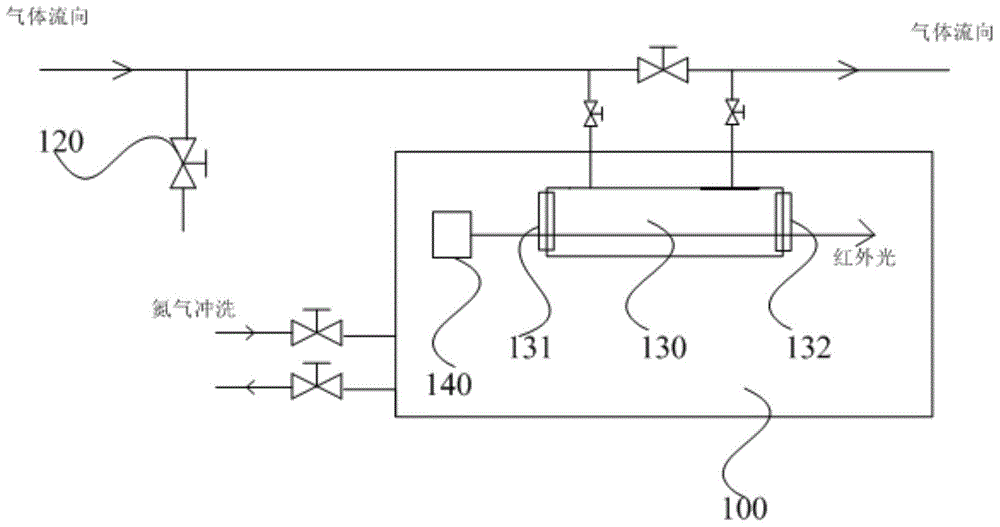
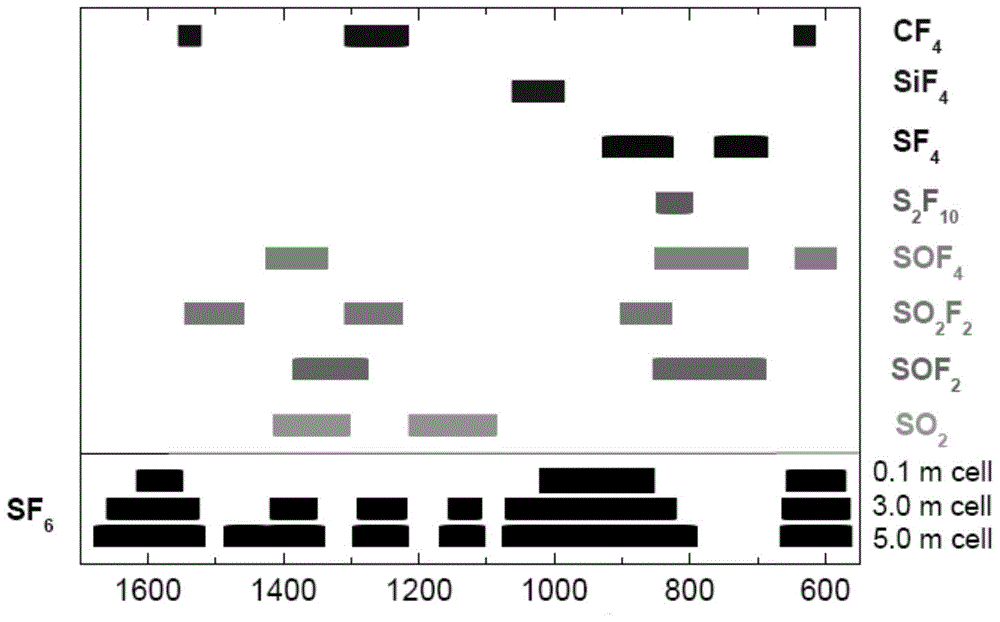
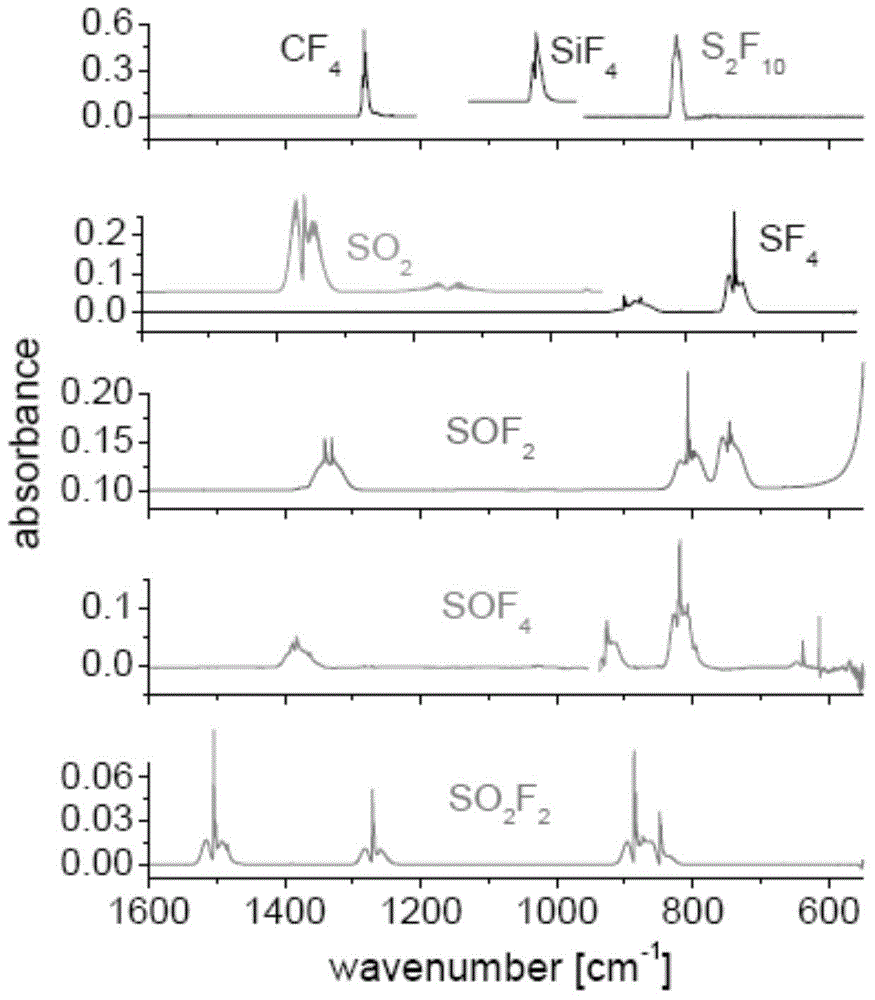
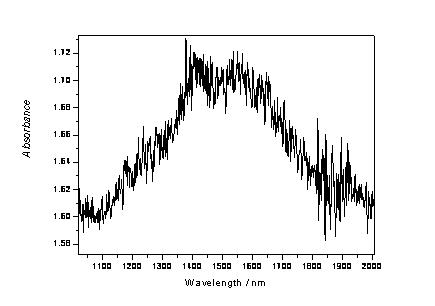
Fourier infrared spectrum analysis method for SF6 (sulfur hexafluoride) decomposition product
InactiveCN103604769AEffectively judge the internal operationGuaranteed safe operationMaterial analysis by optical meansDecompositionPhotoconductive detector
The invention discloses a Fourier infrared spectrum analysis method for a SF6 (sulfur hexafluoride) decomposition product. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: introducing sample gas into an absorption cavity of a Fourier infrared spectrum spectrophotometer for performing Fourier infrared spectrum analysis, wherein the analysis parameters are that a detector is a photoconductive detector, the pressure balance is 0.1+ / -0.01mbar, a refrigerant is 400+ / -1mL and the temperature is 196 DEG C below zero+ / -1 DEG C. According to the method, the problems that HF, SF4, S2F10 and SiF4 in the SF6 decomposition product cannot be accurately analyzed in the conventional technical means can be effectively solved, the decomposition products such as SO2, HF, SF4, SOF2, SOF4, SO2F2, S2F10, SiF4, CF4, CO and COS in the SF6 are accurately analyzed, the internal operating conditions of SF6 gas insulated equipment are effectively judged, the failure of electrical equipment is successfully judged, and the safety operation of the electrical equipment is guaranteed.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RES INST OF GUANGDONG POWER GRID
Molybdenum sulfide-graphene heterojunction photoconductive detector and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN110690315ALow costImprove responsivenessFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesHeterojunctionPhotoconductive detector
The invention relates to a molybdenum sulfide-graphene heterojunction photoconductive detector and a preparation method of the heterojunction thereof.The molybdenum sulfide-graphene heterojunction photoconductive detector comprises the heterojunction. The heterojunction comprises a MoS2 layer arranged on a SiO2 / Si substrate layer.A graphene layer is arranged on the MoS2 layer, and a plurality of metal electrodes are arranged on the graphene layer. The two-dimensional material heterojunction negative photoconductive detector with low cost and high responsiveness and the preparation method thereof are provided. With application of the two-dimensional material transfer technology, the impurity problem in the interface layer of the graphene / TMDC heterojunction is reduced and the photoelectriccharacteristics of the graphene / TMDC photoconductive detector are improved.
Owner:苏州枫桥光电科技有限公司
Tellurium-cadmium-mercury grid-controlled structure photoconductive detector for Hall test
InactiveCN103165724AShorten the development processOvercome the shortcomings of only performance testingFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesEpoxyPhotoconductive detector
The invention discloses a tellurium-cadmium-mercury grid-controlled structure photoconductive detector for Hall test. The tellurium-cadmium-mercury grid-controlled structure photoconductive detector structurally comprises a substrate, a tellurium-cadmium-mercury material, epoxy resin glue, a ZnS passivation layer, four Hall electrodes, a transparent grid electrode and a thickened electrode, the substrate is a sapphire wafer, the tellurium-cadmium-mercury material grows an anodic oxide layer after double-faced rough polishing and fine polishing, the epoxy resin glue is used for bonding the tellurium-cadmium-mercury material and the substrate, the ZnS passivation layer can function in passivating the surface of the material and increasing permeability, the four Hall electrodes positioned in the front and the rear grow on the tellurium-cadmium-mercury material and serve as signal extraction electrodes for the Hall test and device performance test, the transparent grid electrode grows on the ZnS passivation layer and is used for applying grid voltage to a device, and the thickened electrode grows on the transparent grid electrode. The detector with the structure can apply the grid voltage in the device performance test process and the Hall test process to obtain needed electrical parameter conditions such as the grid voltage, material carrier concentration and mobility when device performances are optimal, and the development process of the device is greatly shortened.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
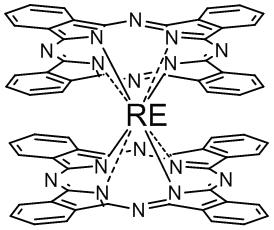
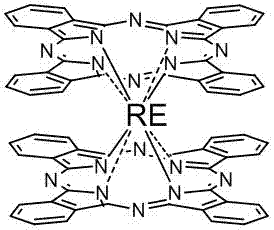
Phthalocyanine rare earth organic infrared semiconductor light guide detector
ActiveCN101969101AControllable electrical parametersHigh controllabilityFinal product manufactureSolid-state devicesSemiconductor materialsPhotoconductive detector
The invention relates to the technical field of photoelectron, in particular to a phthalocyanine rare earth organic infrared semiconductor light guide organic semi-conductor detector. The detector of the invention comprises a substrate, a metal or transparent conductive electrode, an organic infrared photosensitive material layer and the like. The detector is characterized in that the photosensitive material is phthalocyanine rare earth with a sandwich structure; the electrical parameters of the photosensitive material of the organic infrared semiconductor light guide detector are controllable, so that electric resistance of a device can be adjusted within a scope of three orders of magnitude by acceptor doping, the performance regulation of the device and the compatibility with the infrared system are enhanced; the photosensitive material is an organic infrared semiconductor material which can be used to fabricate a large-area and low-cost infrared photoconductive detector responsive to infrared light with the wavelength of 1.3-1.8 micron on a silicon substrate integrated circuit, a cheap substrate glass, a quartz plate and a flexible plastic substrate and has the advantages of simple technology, low cost, controllable performances and the like.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF PHYSICS
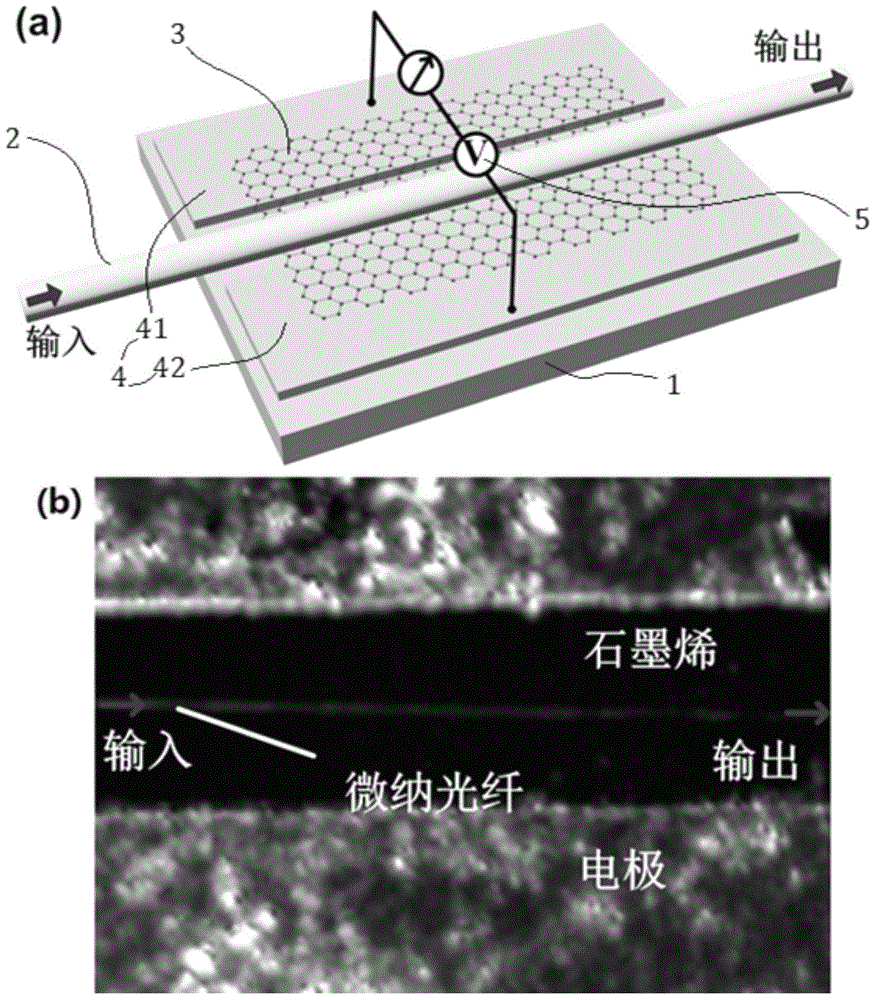
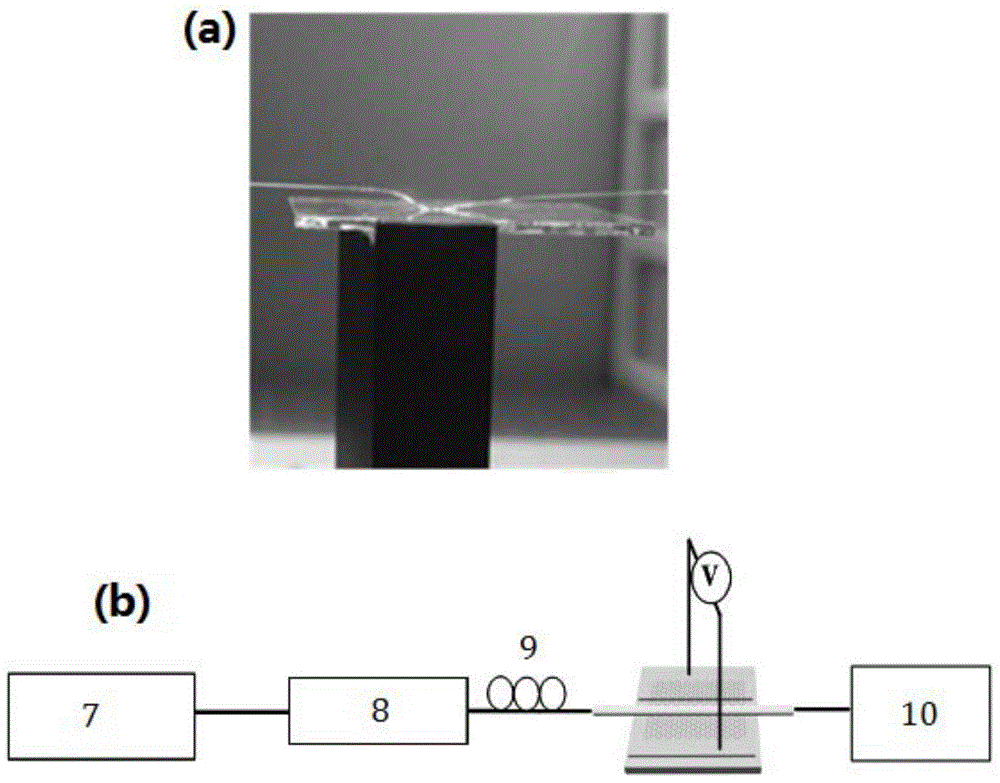
Micro-nanofiber structure based wide-spectrum graphene photoconductive detector
InactiveCN105140314ASimple structureDetection wavelength effectSemiconductor devicesPhotoconductive detectorNanofiber
A micro-nanofiber structure based wide-spectrum graphene photoconductive detector in the technical field of optical fiber communication is disclosed. The wide-spectrum graphene photoconductive detector comprises a substrate, micro-nanofiber, a graphene thin film, a metal electrode and bias voltage, wherein the metal electrode is manufactured on the substrate; the graphene thin film is manufactured on the metal electrode and divides the metal electrode into a first electrode and a second electrode; the micro-nanofiber and the graphene thin film are in contact; and the bias voltage is connected with the first electrode and the second electrode. The micro-nanofiber structure based wide-spectrum graphene photoconductive detector has the advantages of wide-spectrum detection, high detection efficiency, low insertion loss and simple structure.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Thin film photoconductive detector and manufacturing method and application thereof
ActiveCN103311439AOvercoming the shortcomings of very low R and G valuesImprove responsivenessSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingTransport layerPhotoconductive detector
The invention discloses a thin film photoconductive detector and a manufacturing method and application thereof. The thin film photoconductive detector comprises a substrate, a carrier transport layer, an electrode layer and a light absorption layer from bottom to top, wherein the electrode layer consists of an anode layer and a cathode layer positioned on the same layer. The detector integrates high migration ratio of an inorganic material and high light absorptivity of an organic material; when light irradiates onto an organic layer of a photoelectric device, the uppermost organic material layer absorbs light to generate carriers; and by virtue of energy level difference between an inorganic layer and the organic layer and the concentration difference of the carriers, the photo-generated carriers enter the inorganic material layer and can be fast collected by electrodes, thereby having large G and R values. Meanwhile, due to high migration rate of the inorganic material, the light current response time and the fall time of the device are greatly shortened, and therefore the sensitivity of the thin film photoconductive device is improved; and the thin film photoconductive detector has an important application value.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
HgCdTe infrared photoconductive detector with reference element structure
InactiveCN102004002ASolve temperature driftReduce the impact of accuracyPyrometry using electric radation detectorsInfraredIndium
The invention discloses an HgCdTe infrared photoconductive detector with a reference element structure, wherein the reference element comprises a substrate, an epoxy glue layer, a first-side HgCdTe oxidation layer, a bulk material HgCdTe layer, a second-side HgCdTe oxidation layer, a silica insulating layer, a negative photoresist insulating layer, a metal indium layer, and a metal gold layer; and the reference element is characterized in that an edge photosensitive surface is covered with a double-layer insulating layer, an infrared absorption layer and an infrared light reflection layer. The HgCdTe infrared photoconductive detector with a reference element structure has the advantages: the problem of temperature drift existing in the HgCdTe infrared photoconductive detector is solved, and because a differential circuit is adopted to replace a temperature-compensation circuit, the influence of ambient temperature variation on the accuracy of the HgCdTe detector can be reduced, and the circuit structure can greatly be simplified; the detector can be used for measuring the temperatures of low-speed moving objects and high-speed moving objects; and the detector is quick in response speed and has a self-compensating function.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for manufacturing photoelectric detector based on integrated chip with alloy semiconductor nano-structure
InactiveCN104143586AOvercome uneven responseUniform broadband responseFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesPhotoconductive detectorEvaporation
The invention relates to a method for manufacturing a photoelectric detector based on an integrated chip with an alloy semiconductor nano-structure and belongs to the field of photoelectric detection. According to the method for manufacturing the photoelectric detector which is high in broadband sensitivity, large in scale and low in cost based on the integrated chip which is integrally grown on a single substrate and provided with the one-dimensional CdSSe ternary alloy semiconductor nano-structure with the gradually-changing band gap, electrode structures in different shapes and with different widths are manufactured on the chip on which the CdSxSe1-X ( x ranging from zero to one) nano-structure which comprises different components and provided with the gradually-changing band gap is grown in a gradually-changing mode through heat evaporation or electron beam evaporation, and finally, the photoconductive detector which is high in broadband sensitivity and can cover the whole visible region and the near ultraviolet region is manufactured by taking the whole chip as a detecting unit and electrically connecting the whole chip with a nonlinear current amplifying circuit.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Homogeneous 'scintillator-semiconductor-scintillator' composite X-ray detector
ActiveCN107015263AImprove detection efficiencyTightly boundRadiation intensity measurementChemical compositionPhotoconductive detector
The invention provides a homogeneous 'scintillator-semiconductor-scintillator' composite X-ray detector including a front scintillator, a semiconductor photoconductive detector, and a rear scintillator that are in a sandwich structure and are combined through the interatomic attractive force without the need of a couplant. The front scintillator, and the rear scintillator are same in chemical composition and different in thickness, and are obtained by doping the matrix; and the semiconductor photoconductive detector comprises a semiconductor matrix, an electrode and a lead. The composite X-ray detector can be obtained by a universal thin film growth technique, in the growth process, only the doping concentration needs to be adjusted, the scintillator, the couplant, the photodiode or photomultiplier are simplified into one material, so that the composite X-ray detector has the advantages of simple production method, single production principle, short production cycle, and low production cost. Meanwhile, the couplant is not needed, the scintillators and the photoconductive detector are tightly combined through the interatomic attractive force, the light loss is small, and the detection efficiency is high.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Method of making ZnO ultraviolet photoconductive detector with vertical structure
InactiveCN101202315AEasy to makeLow costFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesPhotoconductive detectorOhmic contact
The invention discloses a method for producing a ZnO ultraviolet photoconductive detector with high-performance vertical structure; an ITO film and a ZnO film are adopted by the method to be deposited sequentially on a sapphire substrate or a quartz substrate, the ZnO film of the film undergoes the 400 DEG C thermal processing in the oxygen atmosphere, so as to improve the photoelectric response characteristic of the ZnO film, and then the ITO film is exposed after the corrosion of the ZnO film to form a ZnO table facet, and the metal A1 is deposited on the ZnO table facet and taken as the ohmic contact electrode so as to acquire the ZnO ultraviolet photoconductive detector with vertical structure. The invention has the advantages of simple manufacturing process, low cost, easy controlling, convenient optoelectronic integration, easy industrialization, and high practical value.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
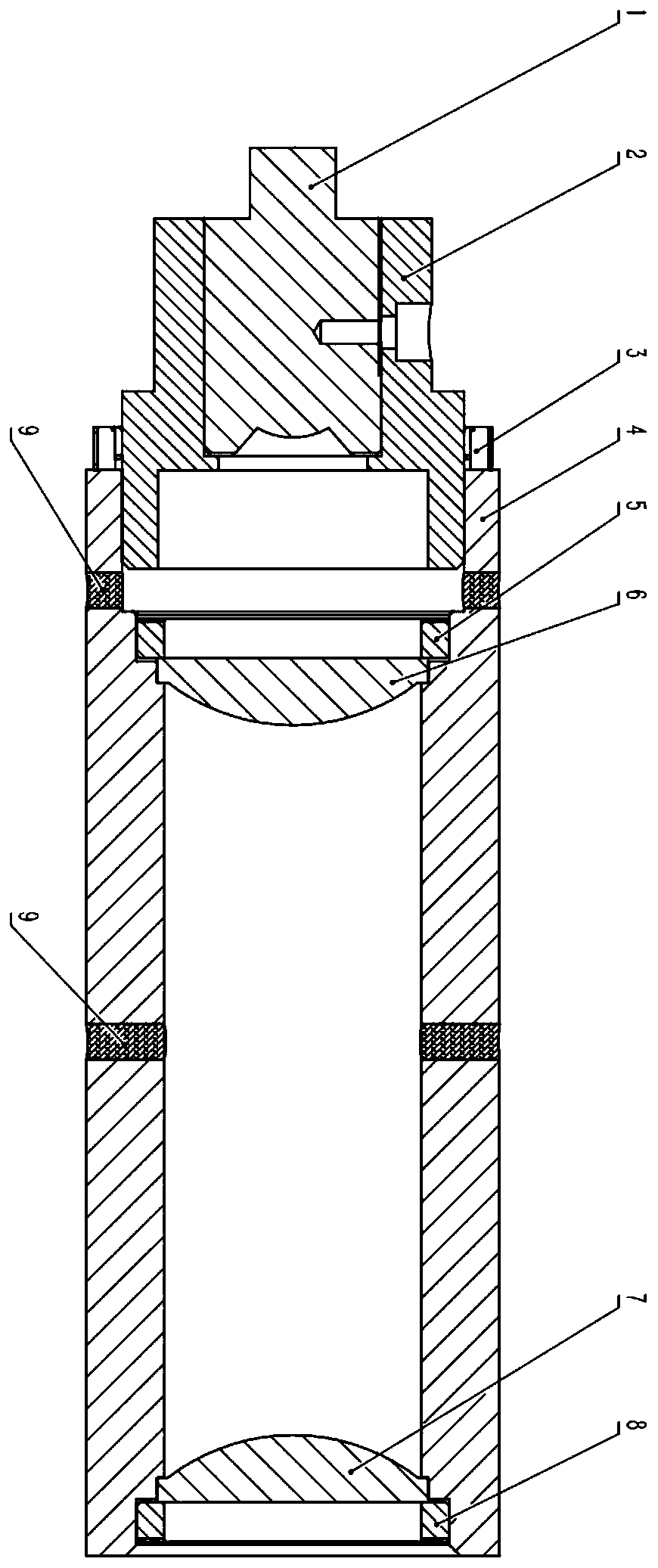
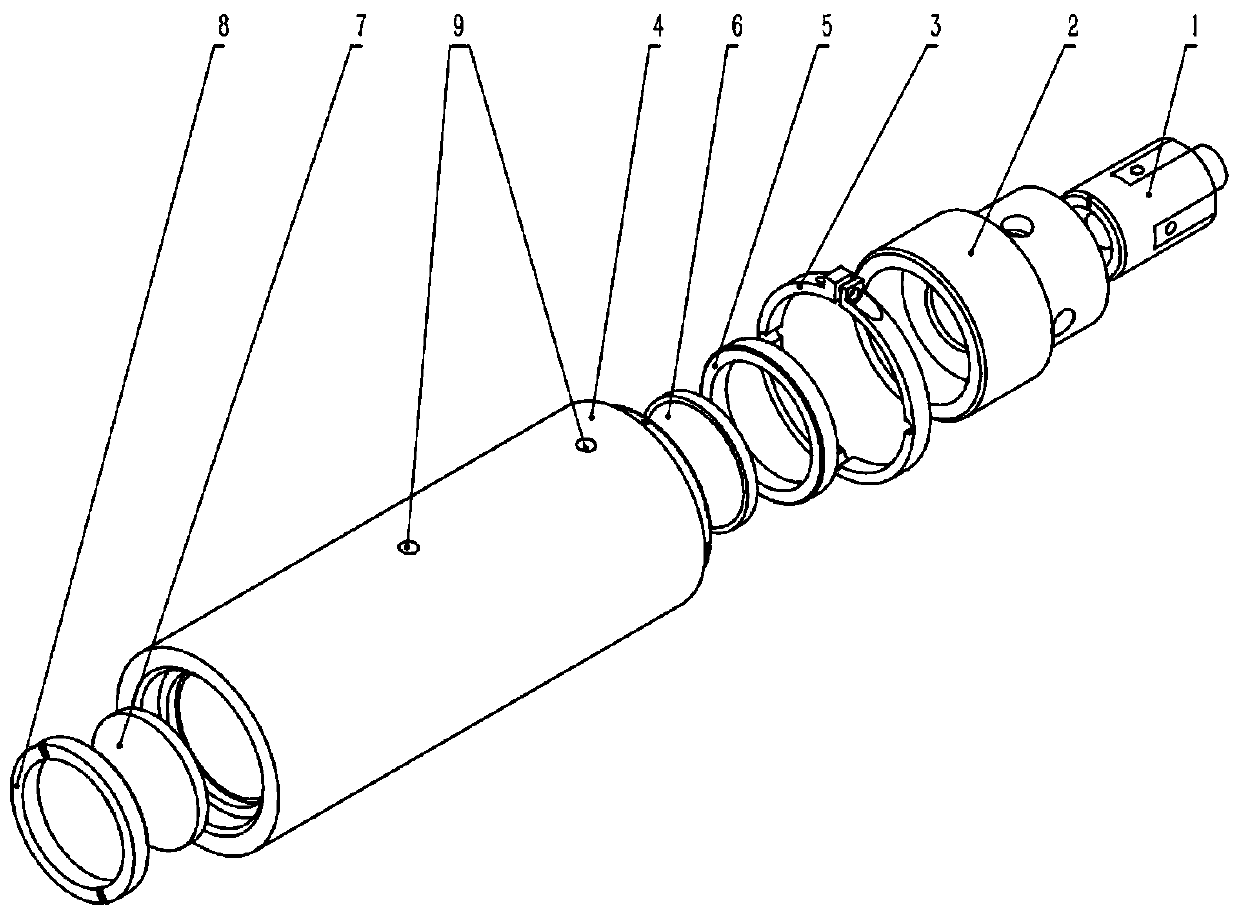
Integrated lens for terahertz detection
PendingCN110907390AAvoid interferenceGuaranteed accuracyMaterial analysis by optical meansPhotoconductive detectorEngineering
The invention discloses an integrated lens for terahertz signal detection. A terahertz photoconductive detector is connected with a detector sleeve through a screw, the silicon rubber is sealed in a counter bore, and a terahertz focusing lens and a terahertz collimating lens are respectively arranged at the two ends of the lens sleeve. A focusing lens pressing sheet and an collimating lens pressing sheet are used for threaded pressing, dispensing and curing, after the detector sleeve and the lens sleeve are screwed in and adjusted to the proper positions through threads, an elastic fastening ring is screwed in, nitrogen is filled into a sealing ring hole, the internal air is exhausted, and then the hole is sealed by a rubber sealing plug, so that the dryness of an internal terahertz transmission path is ensured, and the interference of water vapor absorption on terahertz signals is eliminated. The idea of integrated design is introduced into the design of a terahertz signal detection device, an integrated lens is invented, and the convenience of use and the accuracy of measurement are improved.
Owner:青岛青源峰达太赫兹科技有限公司
Photoconductive detector and preparation method based on boron-doped silicon quantum dot/graphene/silicon dioxide
ActiveCN106601857BLarge light signal currentHigh gainFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesPhotoconductive detectorP type silicon
The invention discloses a photoconductive detector based on boron-doped silicon quantum dot / graphene / silicon dioxide and a preparation method thereof. The photoconductive detector includes a p-type silicon substrate, a silicon dioxide isolation layer, a top electrode, a graphene film, a boron-doped silicon quantum dot film and a bottom electrode. The photoconductive detector is capable of carrying out wide-spectrum detection, so that a problem of low response to infrared detection by the traditional silicon-based PIN structure can be solved. Because the graphene is used to form an active layer and a transparent electrode, a dead layer is eliminated and incident light absorption is enhanced. With the silicon dioxide isolation layer, the silicon surface state can be reduced. The detector can work normally at a low bias voltage; the absorbed light of the boron-doped silicon quantum dot layer is converted into photon-generated carriers and the generated photon-generated carriers being hole electron pairs are separated under the effect of the built-in electric field, so that the high gain can be obtained. In addition, the preparation method is simple; the cost is low; the response degree is high; the response speed is fast; the internal gain is high; the switch ratio is low; and integration is easy to realize.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS) amplifying circuit matched with infrared low-impedance photoconductive detector
InactiveCN103166585AGuaranteed bandwidthReduce magnificationDifferential amplifiersDc-amplifiers with dc-coupled stagesPhotoconductive detectorAlternating current
The invention discloses a complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS) amplifying circuit matched with an infrared low-impedance photoconductive detector. The amplifying circuit adopts a bridge circuit mode at an input end, is suitable for amplifying 20-200 ohm low-input-impedance infrared photoconductive detector signals, and can work at liquid nitrogen temperature. A first-level double-end input single-ended output differential amplifier adopts a positive-negative power source for power supply, and enables input quiescent voltage to be free of limitation of the threshold voltage of a metal oxide semiconductor (MOS) transistor. Another branch circuit corresponding to a biasing resistor and the detector adopts 10 kilohms to be connected with 50 ohms in series, the noise rejection ratio led in from another biasing input end is enabled to reach 200 times, and reduction of circuit overall noise is benefited. Under the requirement of a certain bandwidth, in order to increase pre-level gain and lower equivalent input noise, a 1megohm feedback resistor is adopted between a negative input end of the amplifier and output. A direct connection mode is respectively adopted among a bridge input mode, the first-level amplifier and a second-level amplifier, and the amplifiers can amplify both alternate current signals and direct current signals.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Thin film photoconductive detector and manufacturing method and application thereof
ActiveCN103311439BOvercoming the shortcomings of very low R and G valuesImprove responsivenessSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhoto irradiationPhotoconductive detector
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
MgZnO film and band gap adjusting method and application thereof
PendingCN114203841APrevent phase separationSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor devicesPhase splittingPhotoconductive detector
The invention relates to the technical field of MgZnO film band gap adjustment, in particular to a MgZnO film and a band gap adjustment method and application thereof, and the method comprises the following steps: observing the MgZnO film according to an SEM diagram, an AFM diagram and an EDS diagram of the MgZnO film; an MgZnO thin film is obtained based on an ALD technology and a low-temperature growth technology, and a planar photoconductive detector is prepared; a semiconductor parameter analyzer is adopted to test the characteristics of the planar photoconductive detector; performing a photoresponse switch test on the device; and performing transmission spectrum test analysis on the returned sample to determine whether the device has spectral selectivity or not, so that phase splitting of the film can be avoided.
Owner:ZHONGKAI UNIV OF AGRI & ENG
Phthalocyanine rare earth organic infrared semiconductor light guide detector
ActiveCN101969101BControllable electrical parametersImprove controllabilityFinal product manufactureSolid-state devicesSemiconductor materialsPhotoconductive detector
The invention relates to the technical field of photoelectron, in particular to a phthalocyanine rare earth organic infrared semiconductor light guide organic semi-conductor detector. The detector of the invention comprises a substrate, a metal or transparent conductive electrode, an organic infrared photosensitive material layer and the like. The detector is characterized in that the photosensitive material is phthalocyanine rare earth with a sandwich structure; the electrical parameters of the photosensitive material of the organic infrared semiconductor light guide detector are controllable, so that electric resistance of a device can be adjusted within a scope of three orders of magnitude by acceptor doping, the performance regulation of the device and the compatibility with the infrared system are enhanced; the photosensitive material is an organic infrared semiconductor material which can be used to fabricate a large-area and low-cost infrared photoconductive detector responsiveto infrared light with the wavelength of 1.3-1.8 micron on a silicon substrate integrated circuit, a cheap substrate glass, a quartz plate and a flexible plastic substrate and has the advantages of simple technology, low cost, controllable performances and the like.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF PHYSICS
Ultraviolet-near infrared broadband photoconductive detector
InactiveCN114005897AImplement detectionWide spectral response rangeSemiconductor devicesHeterojunctionSpectral response
The invention discloses an ultraviolet-near infrared broadband photoconductive detector. The ultraviolet-near infrared broadband photoconductive detector comprises a GaAs material substrate layer, a Bi2Se3 material layer arranged on the upper surface of the GaAs material substrate layer, and an electrode layer arranged on the upper surface of the Bi2Se3 material layer. By adjusting the voltage applied to the electrode layer, the GaAs material substrate layer can detect a near-infrared broadband, and the Bi2Se3 material layer can detect an ultraviolet waveband. The GaAs material substrate layer and the Bi2Se3 material layer are specifically designed, the Bi2Se3 material layer is arranged on the upper surface of the GaAs material substrate layer, the GaAs material substrate layer and the Bi2Se3 material layer can form a longitudinally vertical heterojunction structure, and the spectral response range is effectively widened; and the electrode layer is arranged on the upper surface of the Bi2Se3 material layer, the GaAs material substrate layer can detect the near-infrared broadband, the Bi2Se3 material layer can detect the ultraviolet waveband by adjusting the voltage applied to the electrode layer, and ultraviolet-near-infrared broadband detection is achieved.
Owner:TIANJIN JINHANG INST OF TECH PHYSICS
A photoconductive organic semiconductor detector and its preparation method
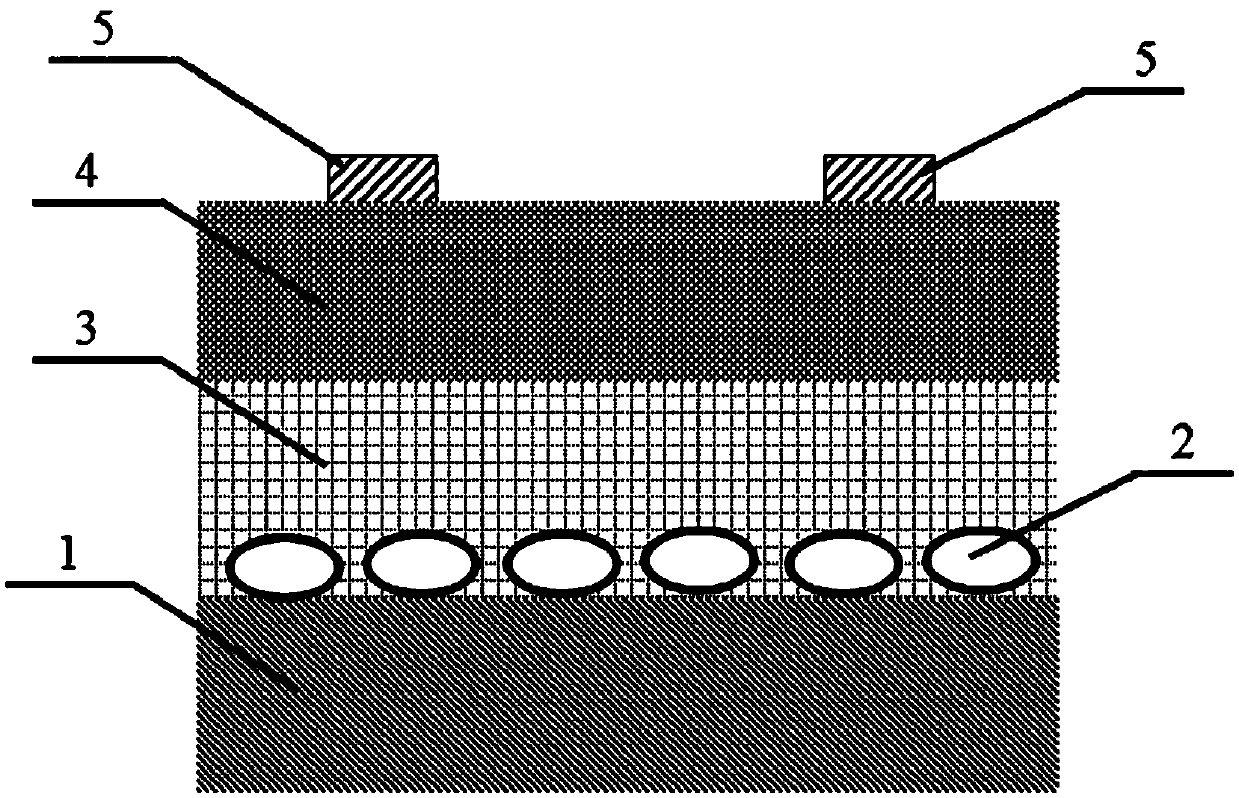
ActiveCN106449987BIncrease photocurrentHigh switching ratioSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMetallic electrodePhotoconductive detector
The invention discloses a photoconductive organic semiconductor detector, which is formed by stacking a quartz plate substrate, metal nanoparticles, an organic insulating layer, an organic photosensitive layer and a metal electrode from bottom to top; the metal nano particles and the organic photosensitive layer produce localized plasmon resonance. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the photoconductive organic semiconductor detector. The invention solves the problem of large dark current in existing organic semiconductor detectors and breaks through the limitation of photoconductive detectors on the high mobility of materials. The photoconductive organic semiconductor detector of the invention has the advantages of simple structure, high detection ratio, fast response speed, etc., and has important application value and economic value in military, civil and some specific fields.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Method of making ZnO ultraviolet photoconductive detector with vertical structure
InactiveCN100517771CEasy to makeLow costFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesPhotoconductive detectorOhmic contact
The invention discloses a method for producing a ZnO ultraviolet photoconductive detector with high-performance vertical structure; an ITO film and a ZnO film are adopted by the method to be deposited sequentially on a sapphire substrate or a quartz substrate, the ZnO film of the film undergoes the 400 DEG C thermal processing in the oxygen atmosphere, so as to improve the photoelectric response characteristic of the ZnO film, and then the ITO film is exposed after the corrosion of the ZnO film to form a ZnO table facet, and the metal A1 is deposited on the ZnO table facet and taken as the ohmic contact electrode so as to acquire the ZnO ultraviolet photoconductive detector with vertical structure. The invention has the advantages of simple manufacturing process, low cost, easy controlling, convenient optoelectronic integration, easy industrialization, and high practical value.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
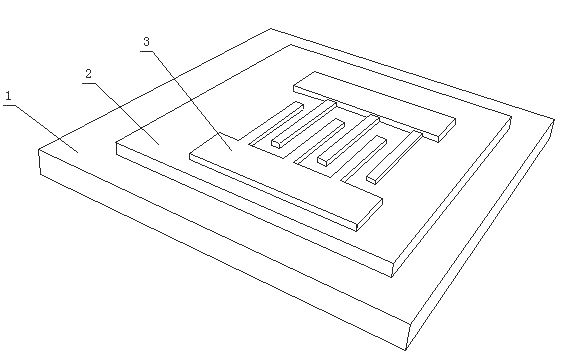
A Novel Photoconductive Detector
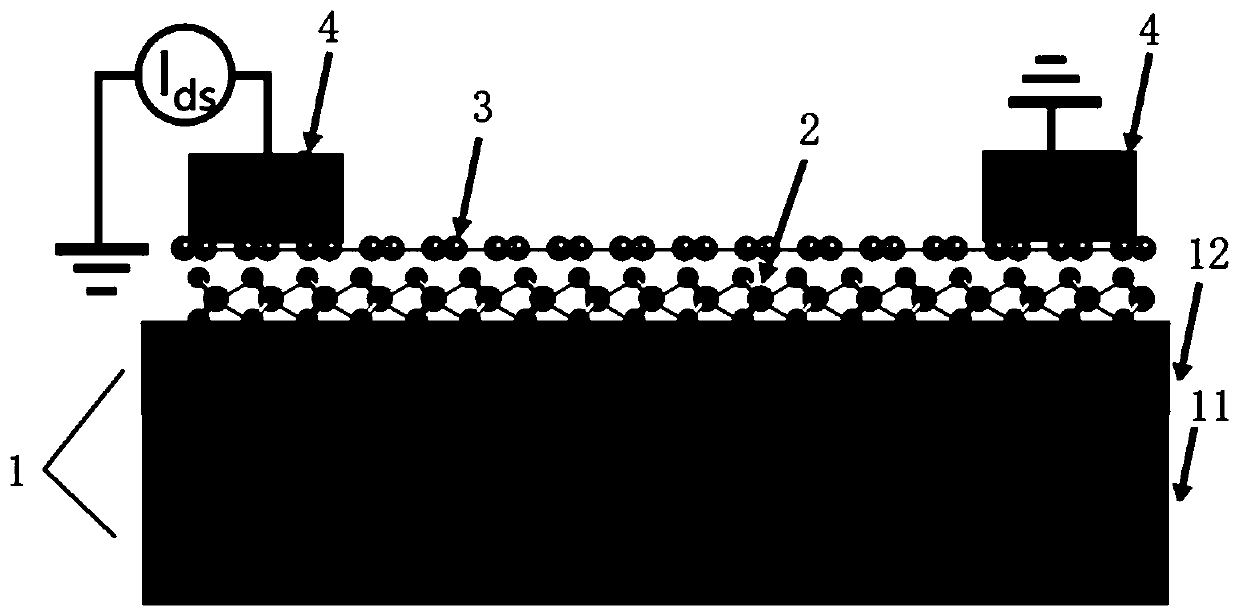
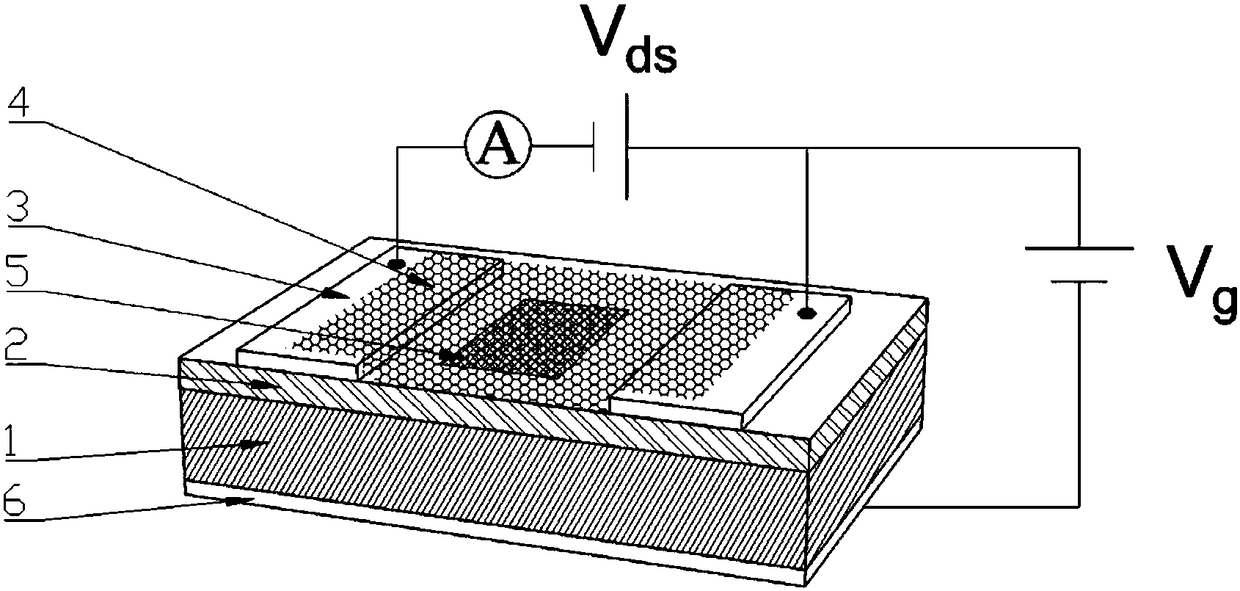
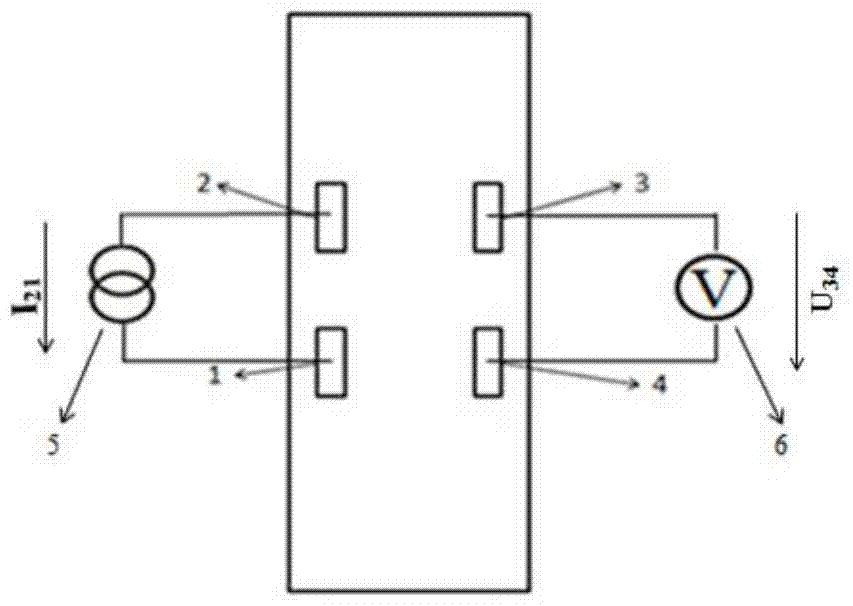
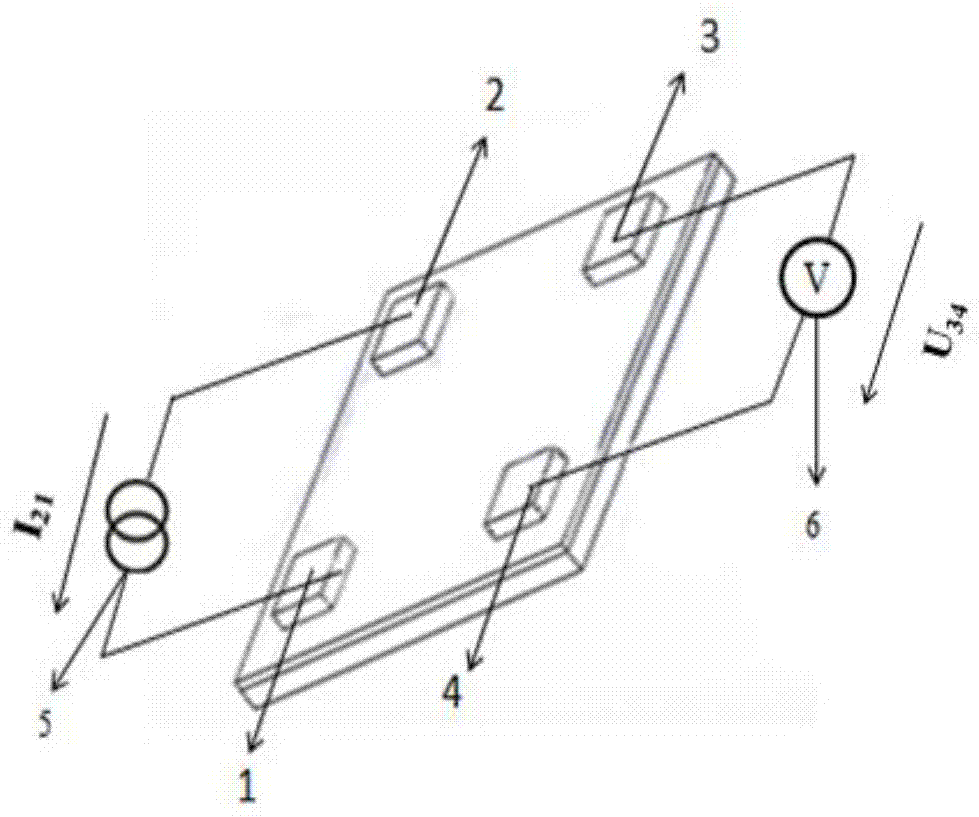
InactiveCN105355701BReduce carrier concentrationReduce concentrationSemiconductor devicesLithographic artistPhotoconductive detector
A novel photoconductive detector belongs to the field of electronic information materials and components. The photoconductive detector consists of an active layer and a patterned electrode layer from bottom to top, wherein the patterned electrode layer includes a first electrode, a second electrode, a third electrode, and a fourth electrode. The relative position of the second electrode, the third electrode and the fourth electrode pattern is an arbitrary quadrilateral structure. The first electrode, the second electrode, the third electrode and the fourth electrode are arranged clockwise or counterclockwise. When working, the A constant current power supply is connected between the first electrode and the second electrode, and a voltage value is tested by a voltage measuring device between the third electrode and the fourth electrode, and the optical signal is identified through the change of the voltage value. The photoconductive detector of the present invention has lower requirements on the size of the electrode structure, and its preparation does not require photolithography technology, and the preparation process is simpler, which helps to improve the yield of products and reduce production costs, and the aperture ratio of the device is greatly improved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
An Electromagnetic Induced Potential Well Semiconductor Photoconductive Detection Device Under the Bandgap Room Temperature
ActiveCN106784126BImprove performanceAchieving room temperature photoconductivitySemiconductor devicesPotential wellSemiconductor materials
The invention discloses an electromagnetic induction potential well semiconductor forbidden room temperature light conductivity detector, the detector is formed on the semiconductor substrate from a semiconductor epitaxy, a passivation protective layer and a metal layer of the positive and negative electrode in turn. The detector is based on the electromagnetic induction potential well and remote control of lower chamber temperature and photoconductive mechanism, suitable parameter (carrier concentration, migration rate and the like) semiconductor material is selected, the reasonable detector size is designed through theory analysis, high speed optical signal to electrical signal conversion and detection are realized through the photoelectric signal being amplified and read by the pre-amplifying circuit. The device has the advantages that work can be carried out in room temperature, the stronger photoconductivity is produced in far less than the semiconductor forbidden, the sensibility is high, responding speed is fast, the structure is simple and compact, the large scale integration can be carried out and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Organic-inorganic hybrid semi-conductive dicyclohexyl-imine bismuth bromide compound and crystal and preparation method and use thereof
ActiveCN106554326AEasy to processShorten the growth cycleOrganic chemistry methodsPhotometry using electric radiation detectorsSpace groupPhotoconductive detector
The invention relates to an organic-inorganic hybrid semi-conductive dicyclohexyl-imine bismuth bromide compound and crystal and a preparation method and use thereof. The chemical formula of the material is (C6H12NH2)2BiBr5, and belongs to a monoclinic system P21 / n space group. The absorption cut-off side length of the crystalline material approximates to 430nm; and the crystal exhibits good photoconductive property, can be used for manufacturing photoconductive detectors, and has potential application value in photoelectric detection, integrated photoelectric functional elements and the like. The synthesis and preparation method disclosed by the invention is high in practicability, simple in path and easy for operation; no complex production equipment is needed; manufacture cost is low; and the synthesis and preparation method is suitable for batch production.
Owner:FUJIAN INST OF RES ON THE STRUCTURE OF MATTER CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Thin-film organic photodetector with pin structure and its preparation method and application
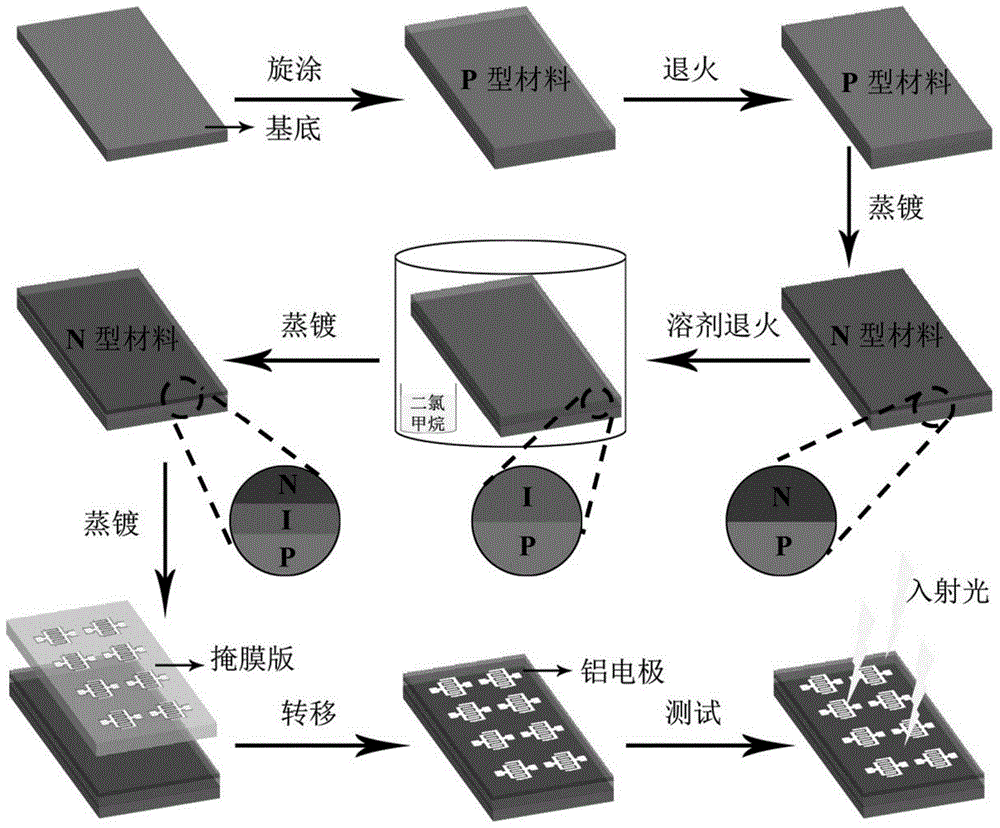
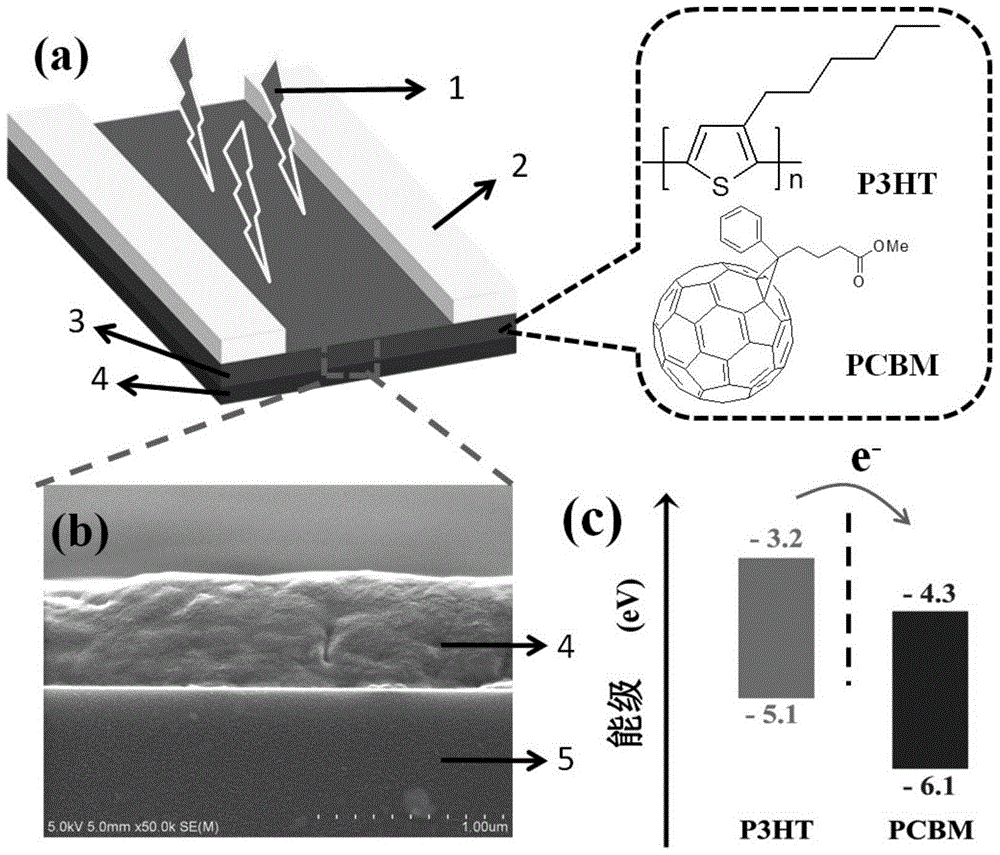
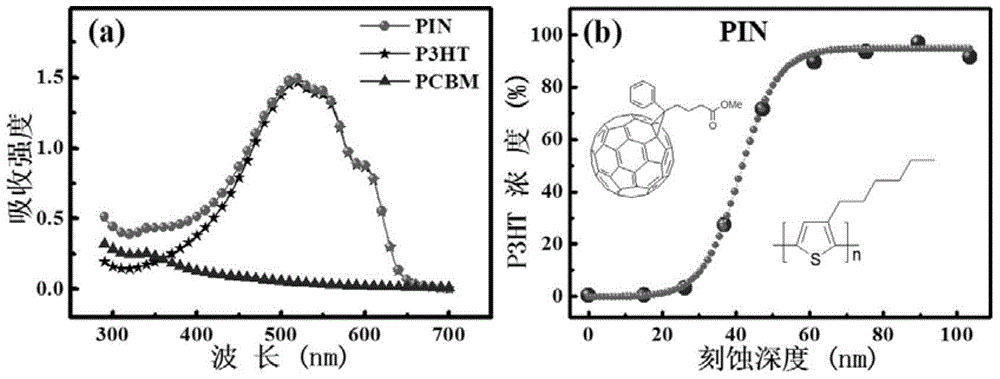
ActiveCN103794726BSimple structureEasy to prepareSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHigh concentrationHeterojunction
The invention discloses a thin-film organic photodetector based on a PIN structure, a preparation method and an application thereof. The thin-film organic photoconductive detector includes a substrate, a photosensitive layer with a PIN structure and a patterned electrode layer thereon. The detector combines the high mobility of the intrinsic organic layers (P and N layers) with the high concentration of photofree charges generated by the organic heterojunction layer (I layer, which is a mixture of P and N organic materials). The advantages. The high mobility results in short electron transit times, and the generation of high-concentration photofree charges imply high external quantum efficiency. Therefore, when light is irradiated on the device, the material absorbs light and generates carriers quickly, and a large number of them are collected by the electrodes to generate high photocurrent and photoelectric performance, thereby improving the sensitivity of the detector. Therefore, this thin-film organic photodetector has important application value.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com