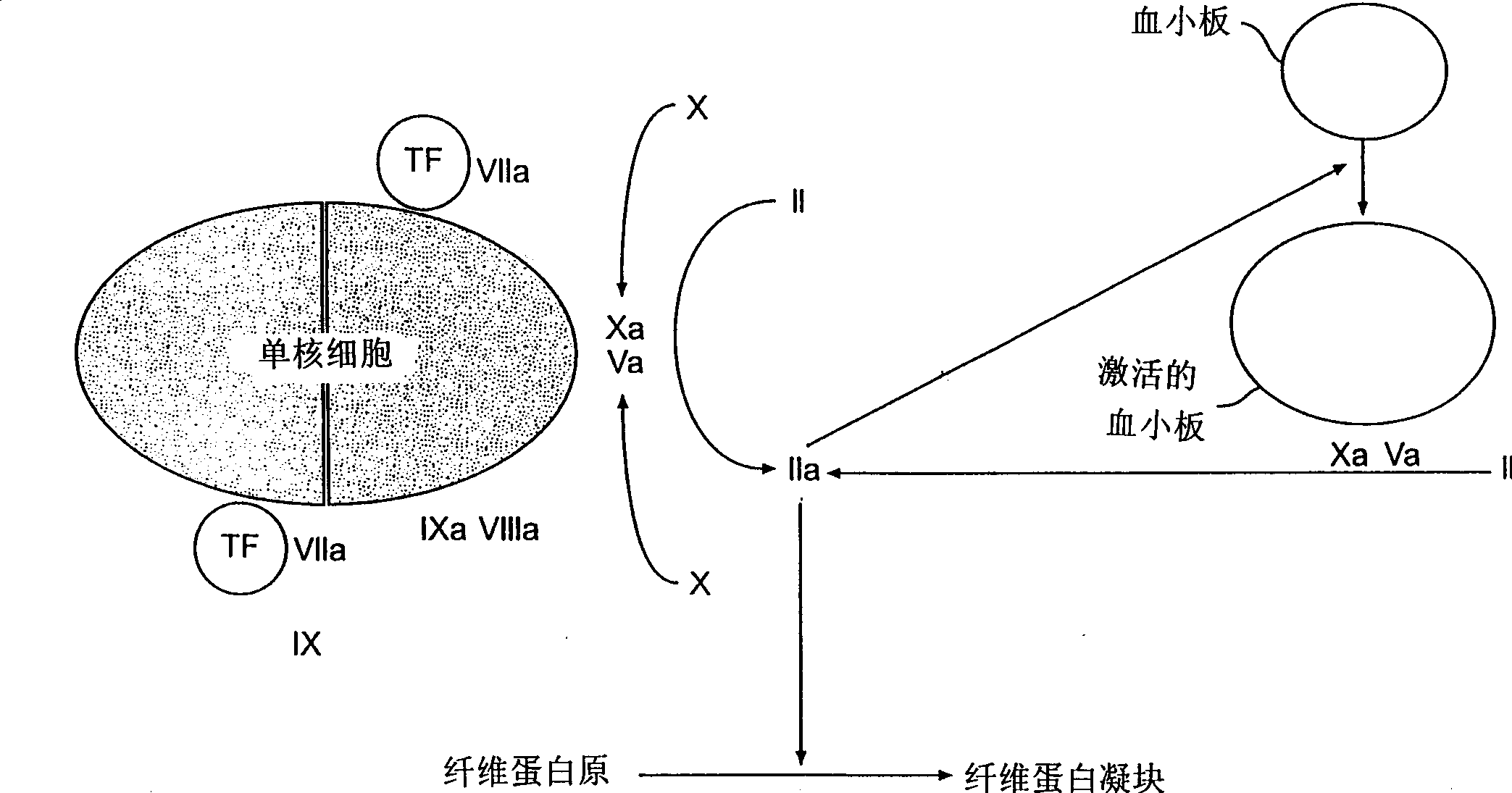
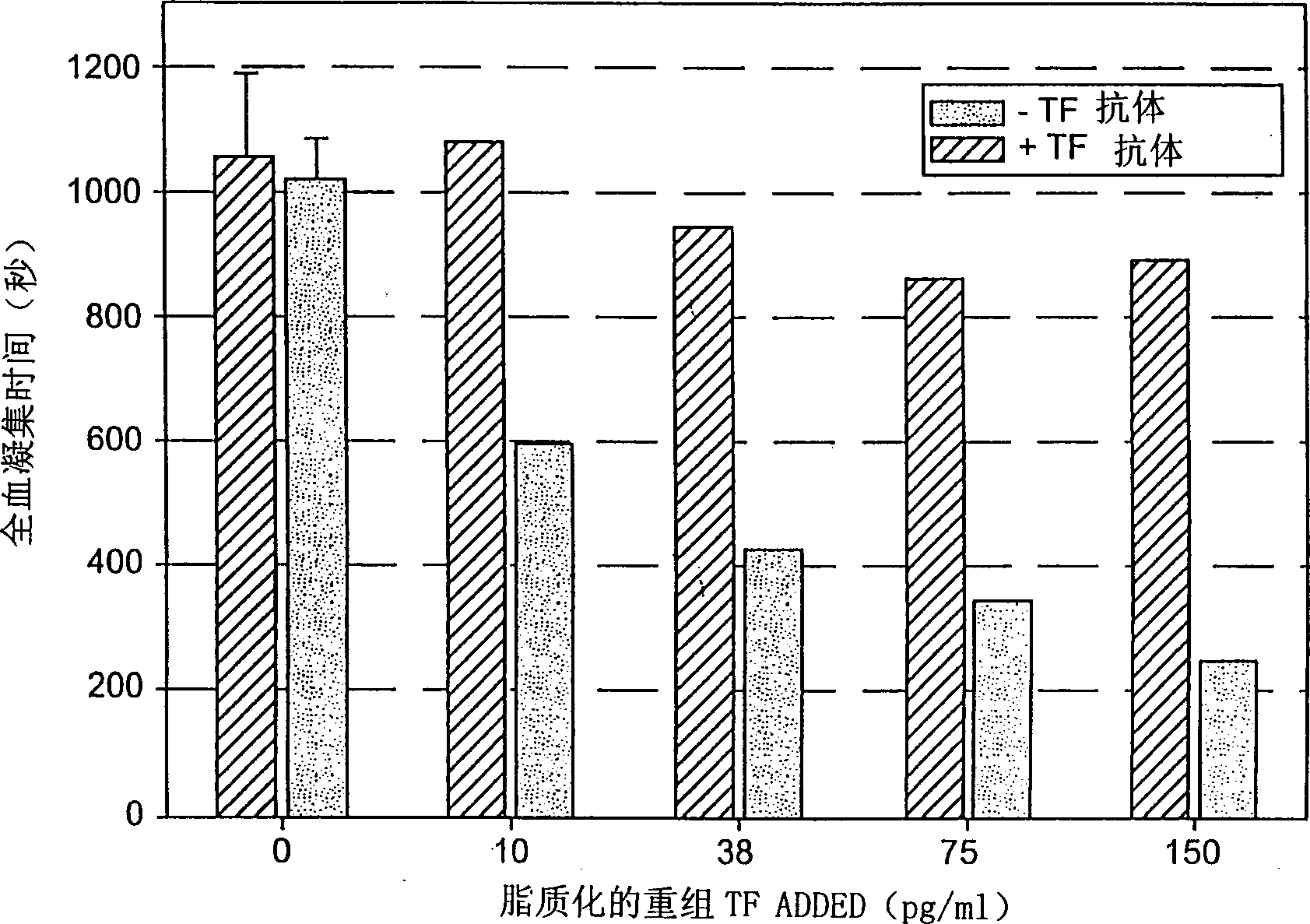
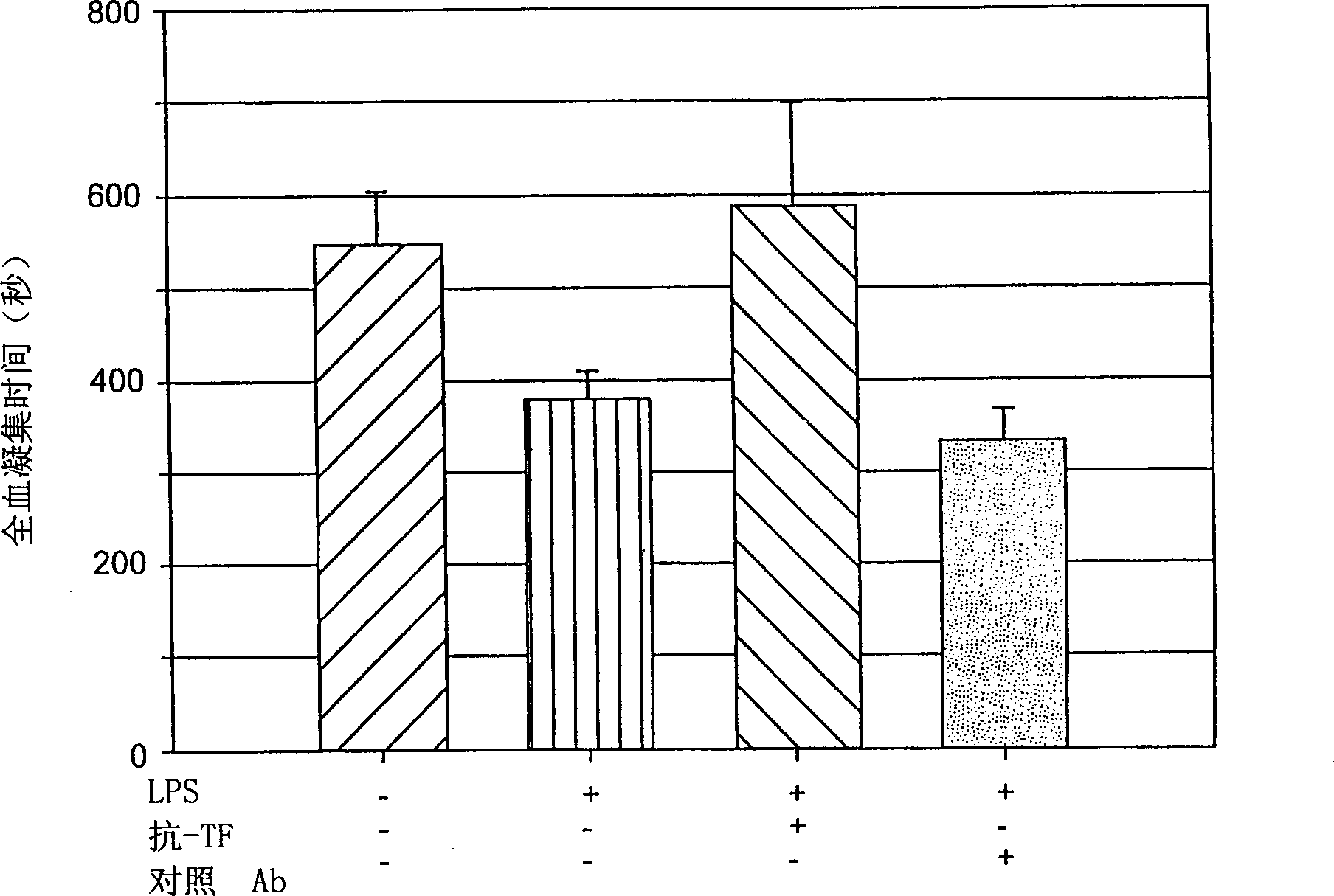
Patents
Literature
128 results about "Clotting time" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
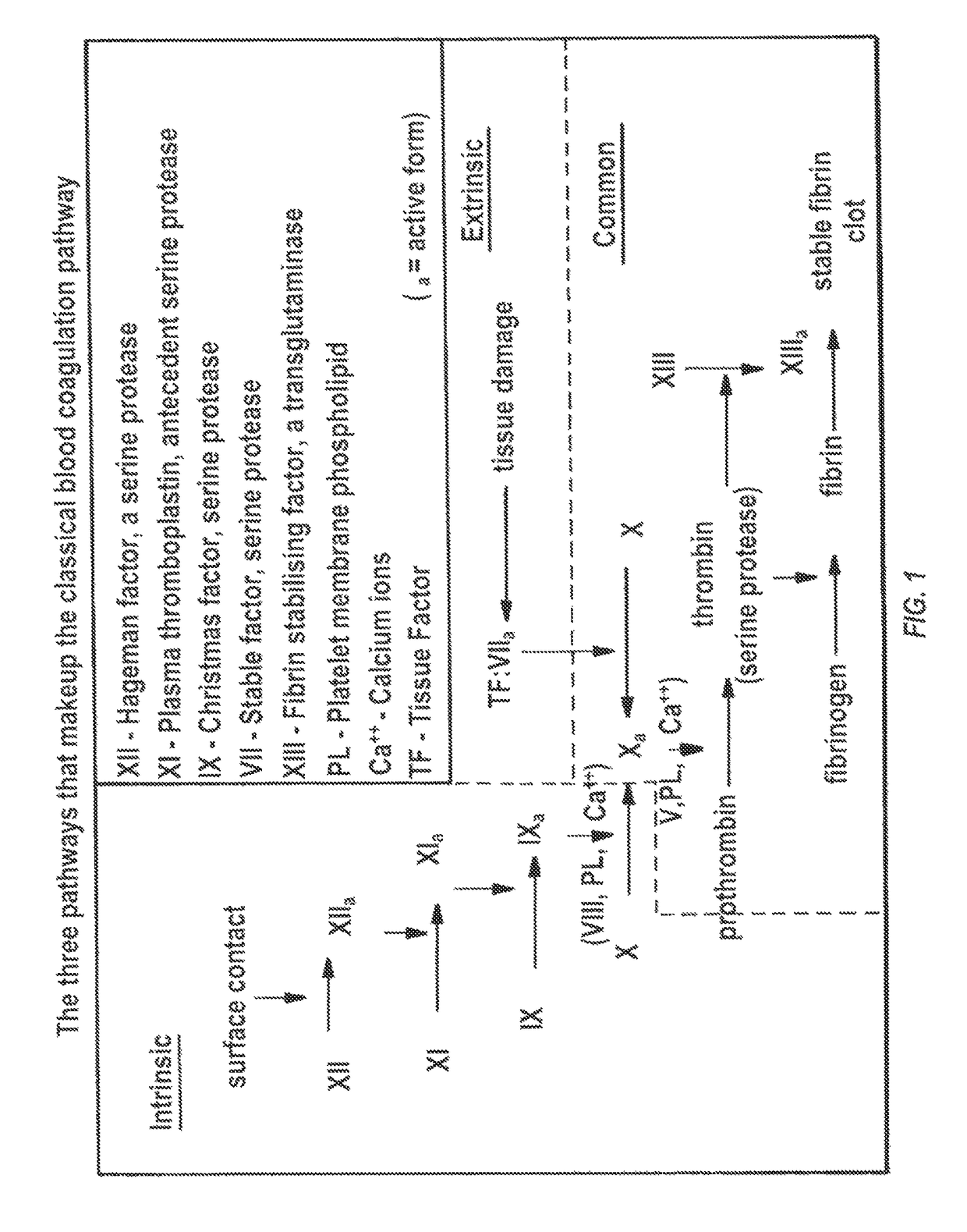
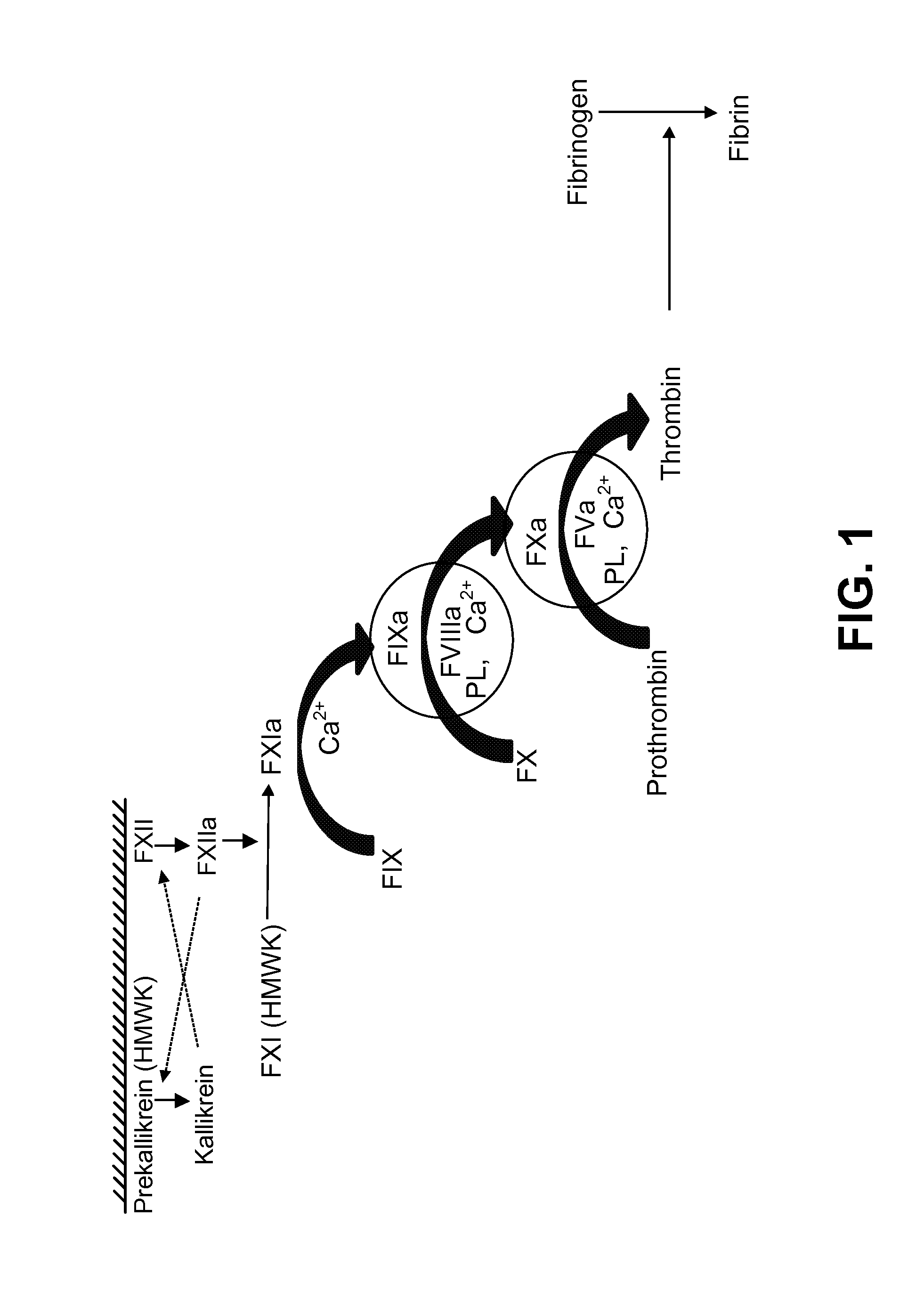
Clotting time is the time required for a sample of blood to coagulate in vitro under standard conditions. There are various methods for determining the clotting time, the most common being the capillary tube method. It is affected by calcium ion levels and many diseases. Normal value of clotting time is 8 to 15 minutes.
Device for measuring blood coagulation and method thereof
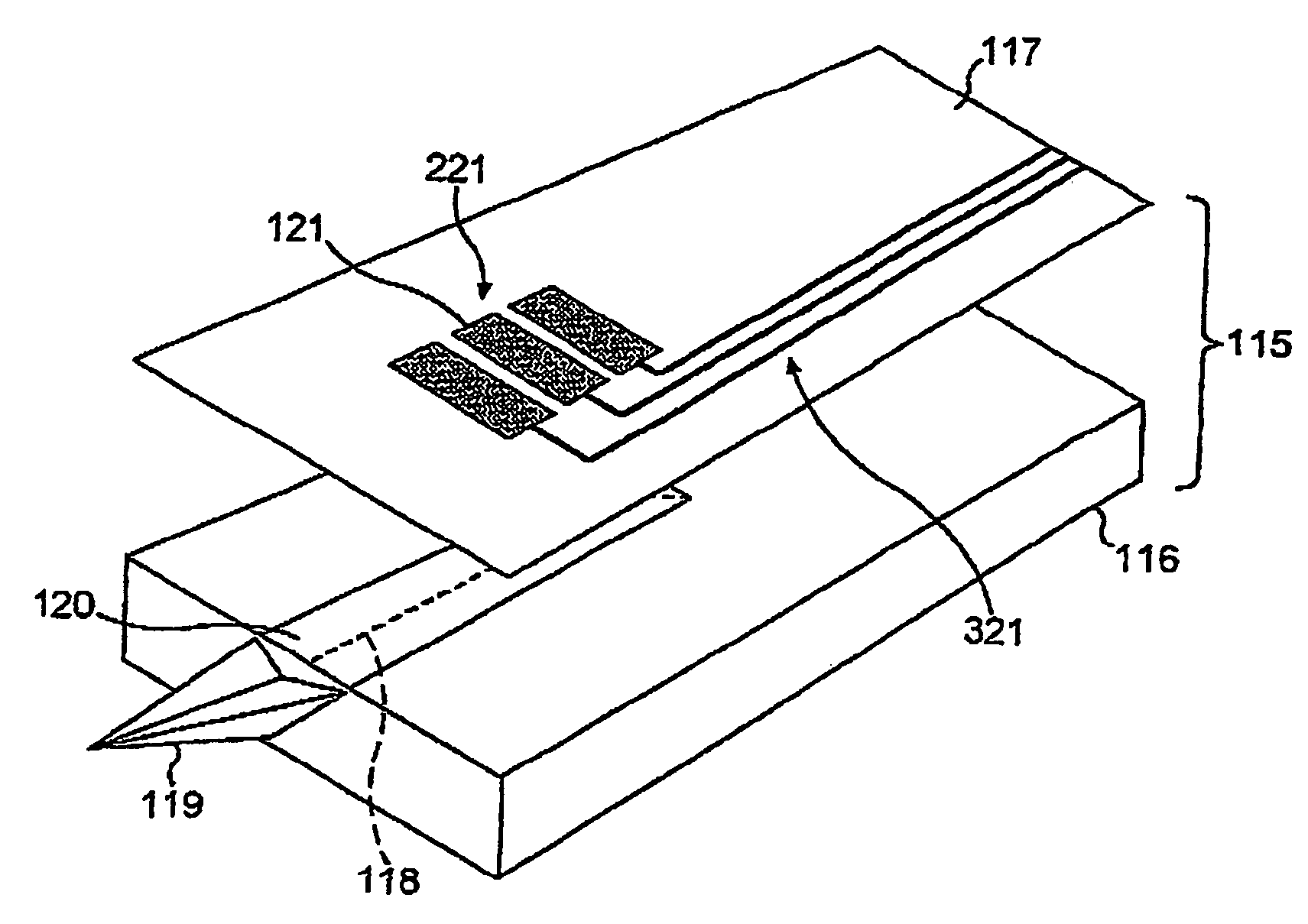
InactiveUS7005857B2Simple and inexpensiveResistance/reactance/impedenceSurgeryCapacitanceBlood coagulations
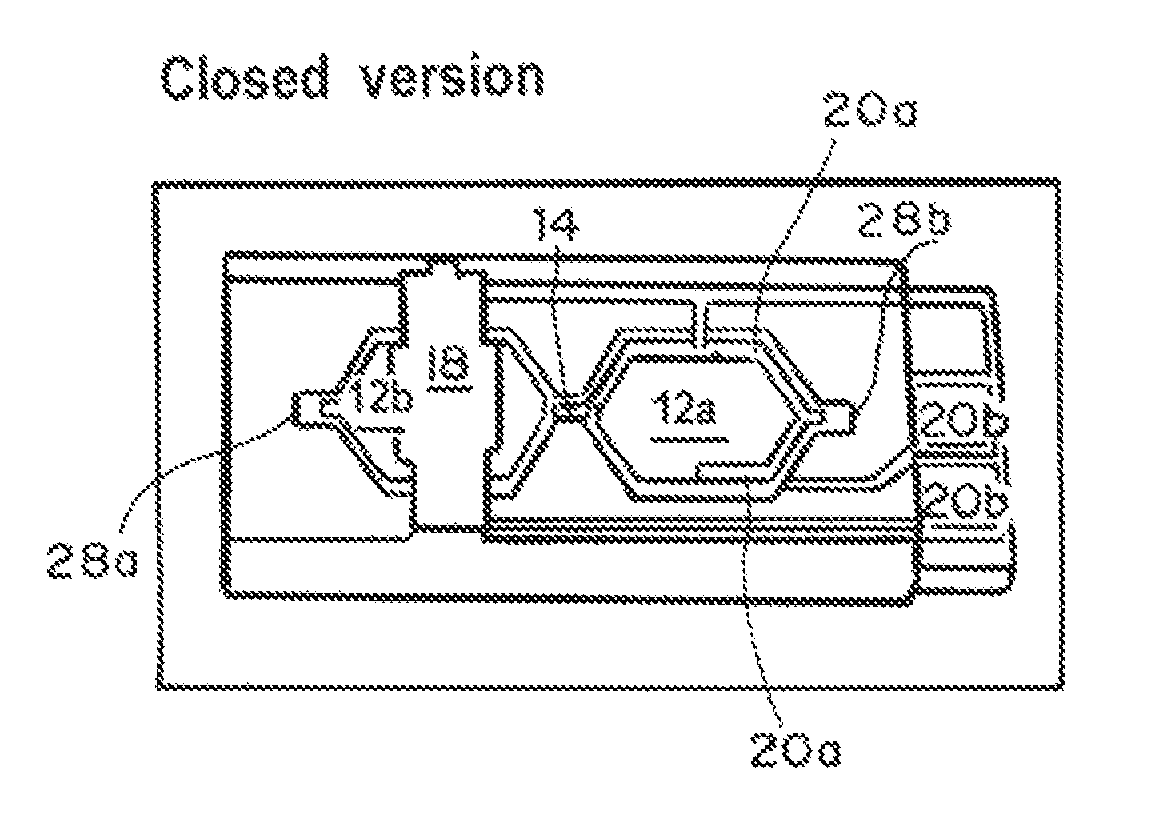
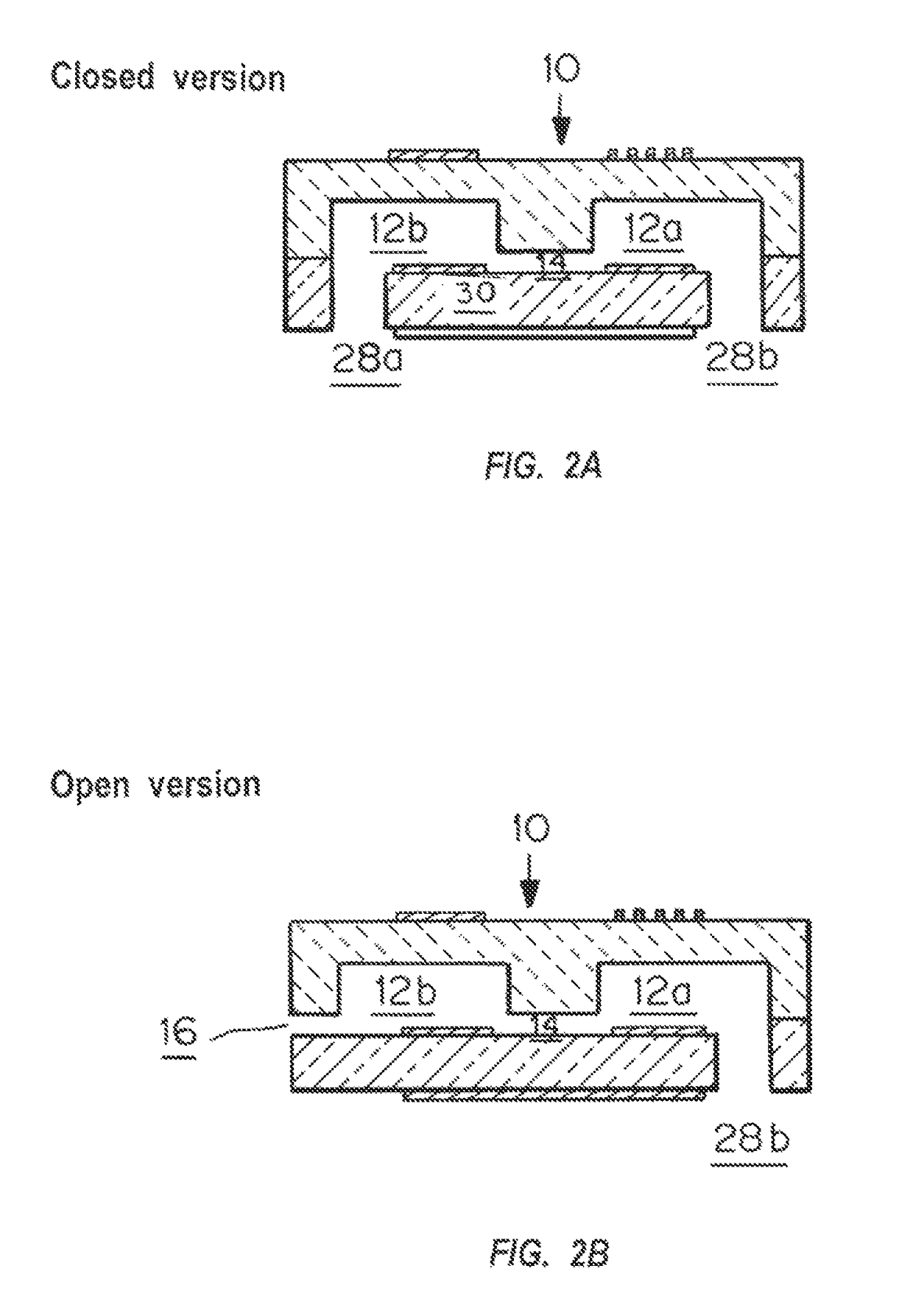
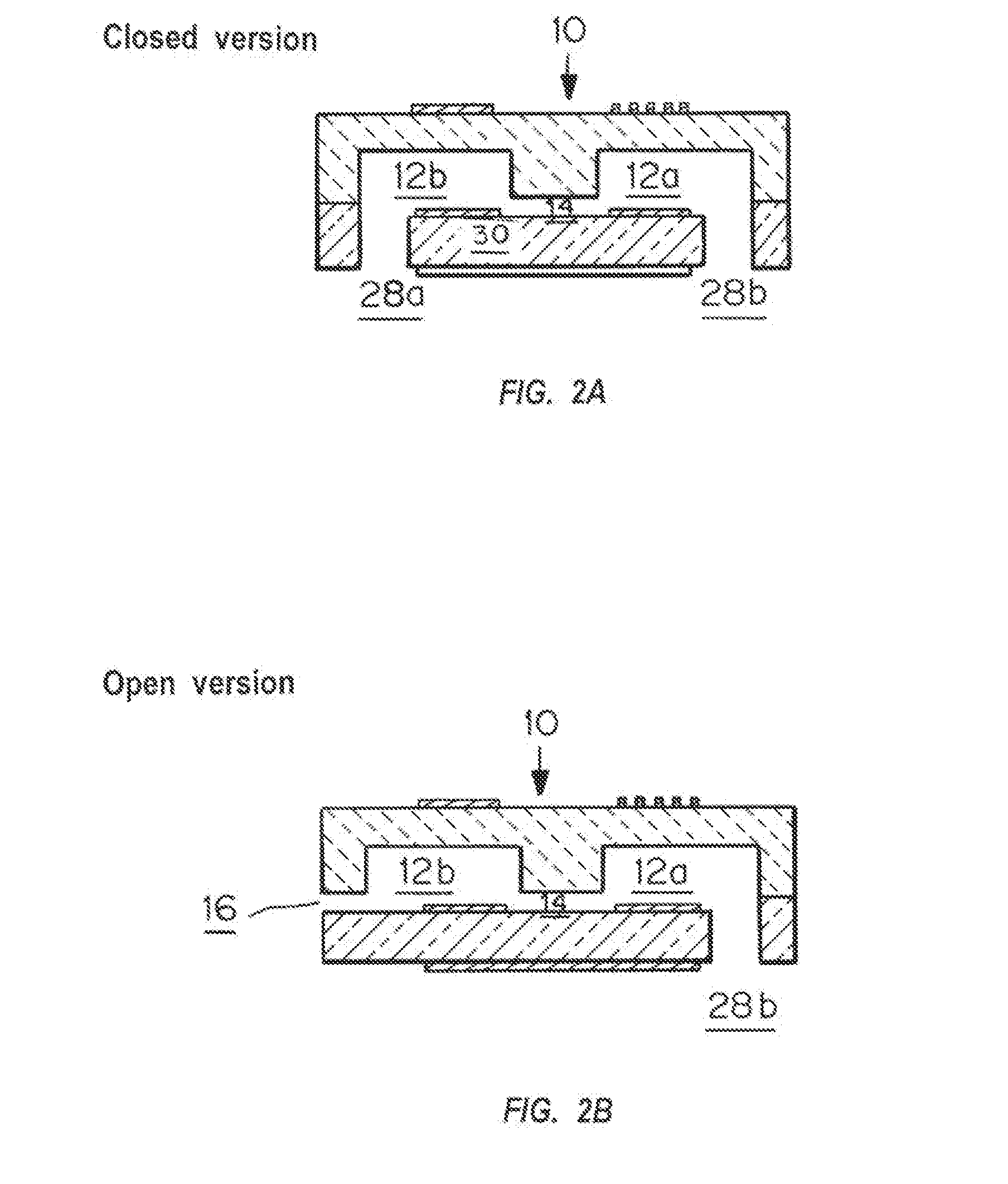
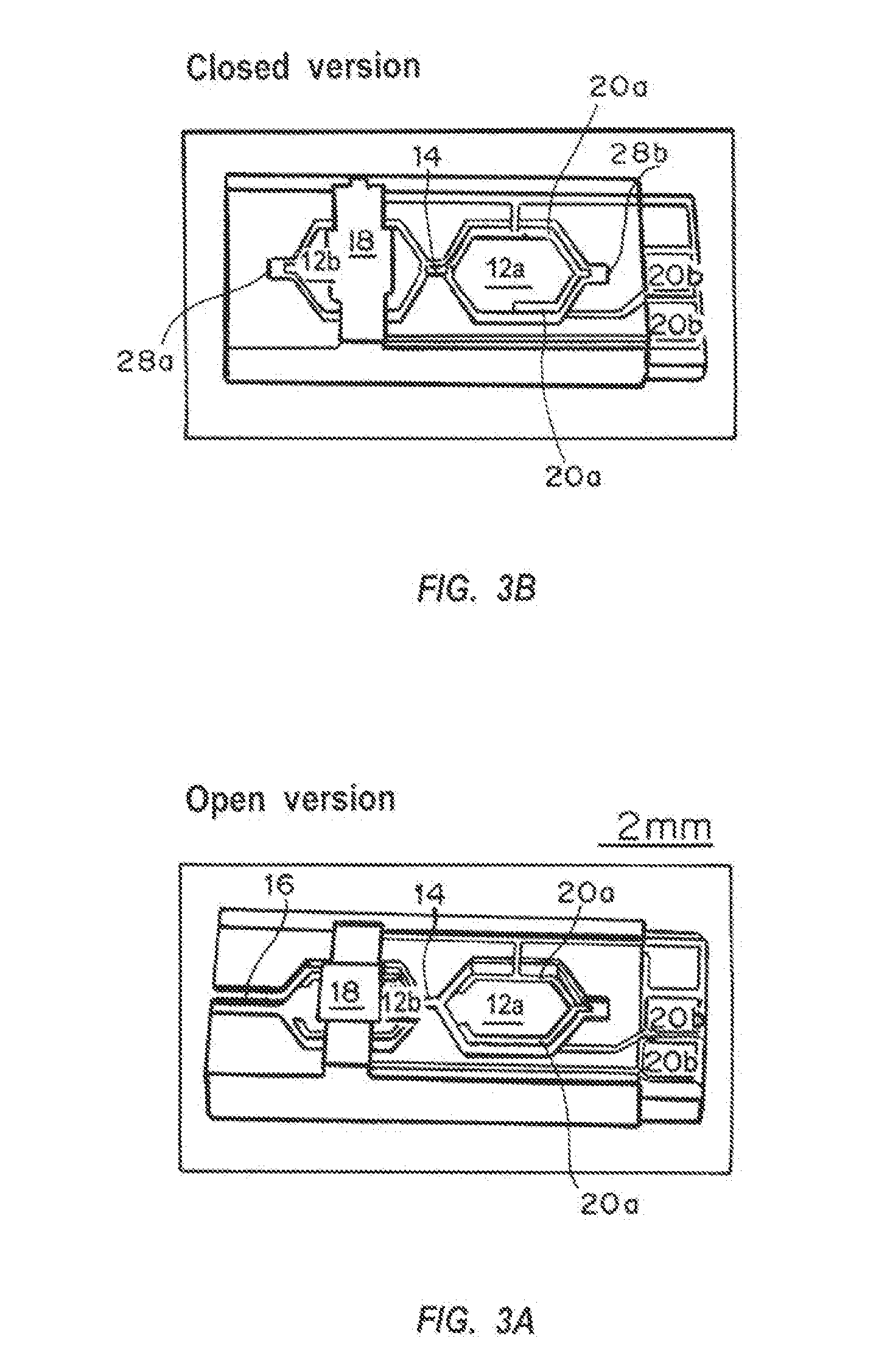
A device and method for measuring clotting times in a fluid, typically blood, within a microchannel, with the onset of clotting being determined by measurement of the rate of change, or the value, of capacitance or impedance between two electrodes situated on either side of the microchannel. The device includes an upper support member and a lower support member with a microchannel formed therein. The device also includes electrodes situated along the length of the microchannel.
Owner:LIFESCAN IP HLDG LLC
Method for preparing thrombin for use in a biological glue
InactiveUS6472162B1Derive fast acting, stable autologous thrombinSimple preparatory procedureBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsTissue sealantDonors plasma
A sterile method for preparing stable thrombin component from a single donor's plasma in which the thrombin component and the clotting and adhesive proteins component are harvested simultaneously from the same donor plasma in less than one hour. The combined components provide an improved biological hemostatic agent and tissue sealant by virtue of its freedom from the risk of contaminating viruses or bacteria from allogenic human or bovine blood sources. The thrombin provides polymerization of the clotting and adhesive proteins in less than five seconds, and is sufficiently stable to provide that fast clotting over a six hour period. Further, the clotting times can be predictably lengthened by diluting the thrombin with saline.
Owner:ASAHI KASEI MEDICAL CO LTD
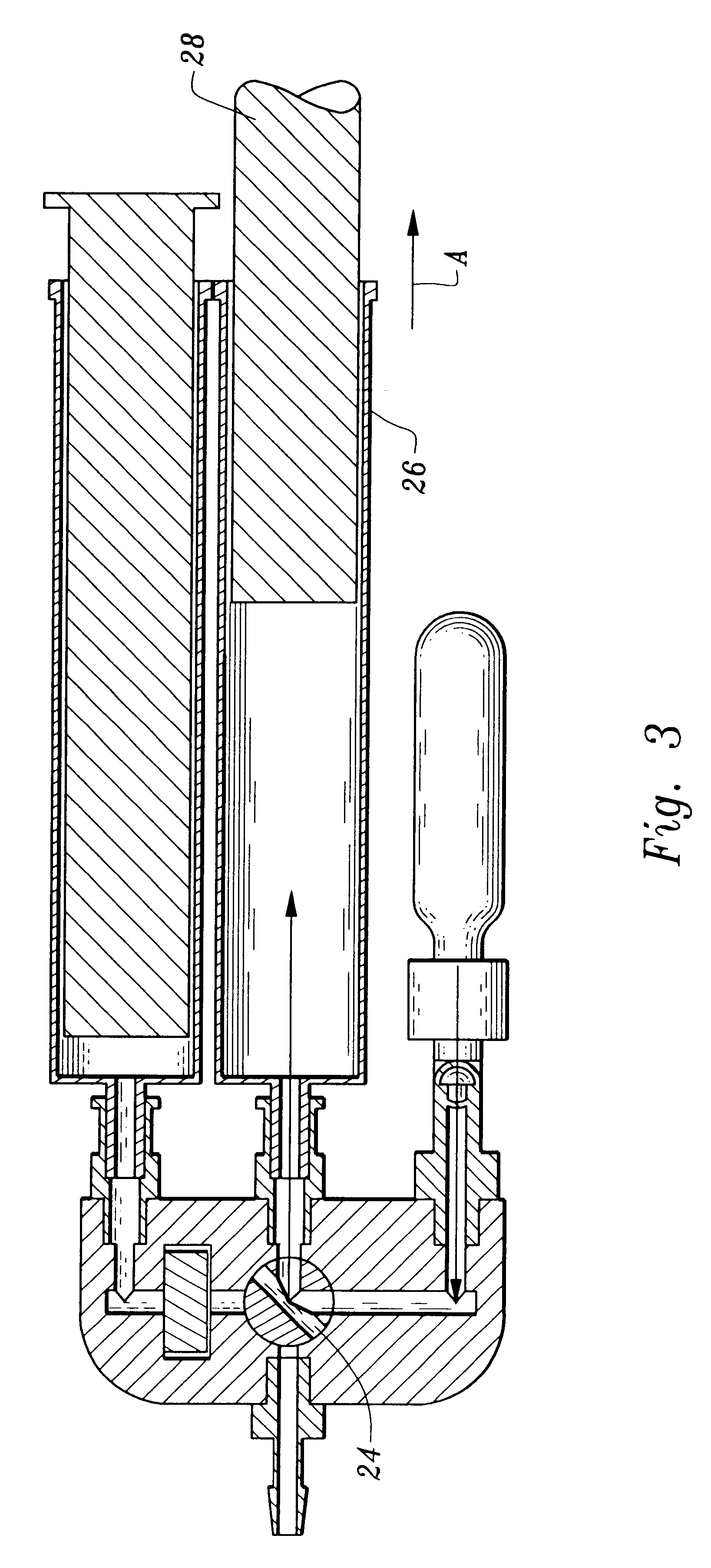
Apparatus and method of preparation of stable, long term thrombin from plasma and thrombin formed thereby
InactiveUS6274090B1Derive fast acting, stable autologous thrombinSimple preparatory procedureImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsTissue sealantDonors plasma
A sterile method for preparing stable thrombin component from a single donor's plasma in which the thrombin component is harvested simultaneously from the clotting and adhesive proteins component from the same donor plasma in less than one hour. The combined components provide an improved biological hemostatic agent and tissue sealant by virtue of its freedom from the risk of contaminating viruses or bacteria from allogenic human or bovine blood sources. The thrombin provides polymerization of the clotting and adhesive proteins in less than five seconds, and is sufficiently stable to provide that fast clotting over a six hour period. Further, the clotting times can be predictably lengthened by diluting the thrombin with saline.
Owner:ASAHI KASEI MEDICAL CO LTD
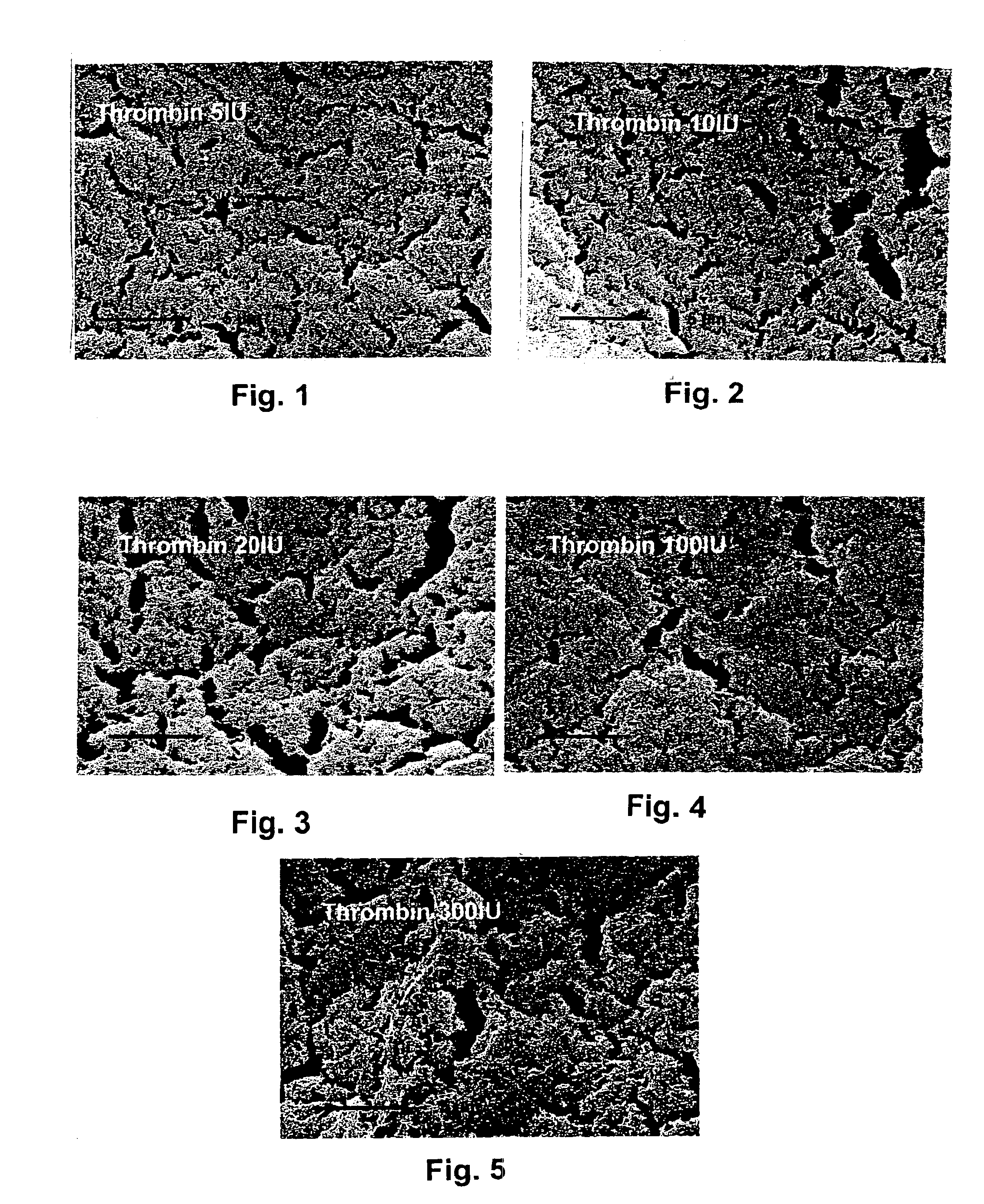
Fibrin material and method for producing and using the same
This invention describes a bioerodible fibrin material which is obtained by mixing fibrinogen and thrombin reconstituted or diluted with a particular high tonic strength medium, free of calcium. Such a fibrin-based biomaterial develops a tight structure with thin fibers and small pore size suitable for use as an anti-adhesion barrier. In this invention, thrombin is no longer the variable which governs the tightness and the porosity of the fibrin material obtained, but still controls the clotting time. The mechanical behavior, high-water capacity, and releasable retention properties for therapeutic agents of this fibrin structure causes the fibrin material to be ideally suited for use as a drug delivery device, capable of delivering proteins, hormones, enzymes, antibiotics, antineoplastic agents and even cells for local and systemic treatment of human and non-human patients.
Owner:BAXTER INT INC
Device for the determination of blood clotting by capacitance or resistance
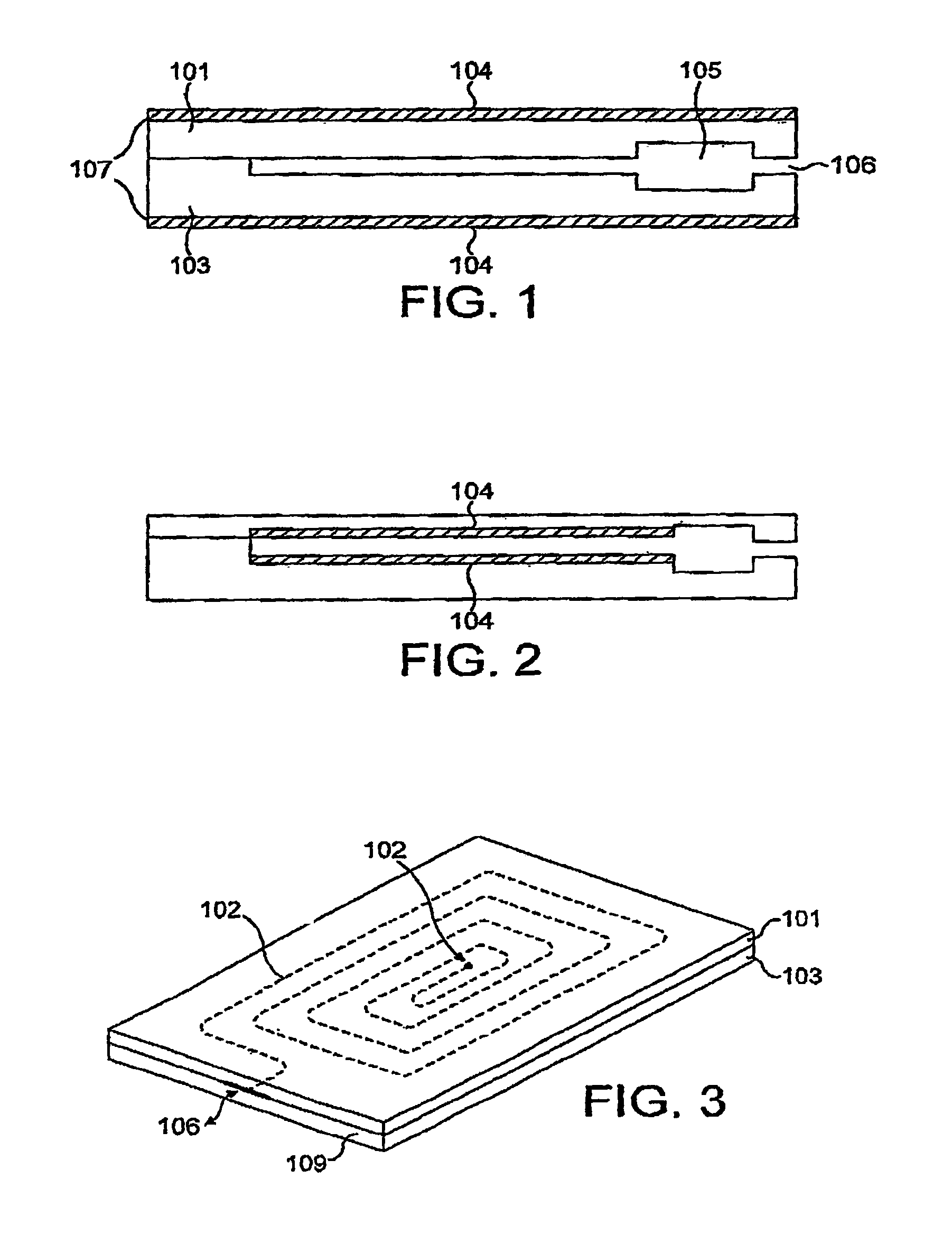
InactiveUS7021122B1Machines/enginesLubrication indication devicesElectrical resistance and conductanceViscosity
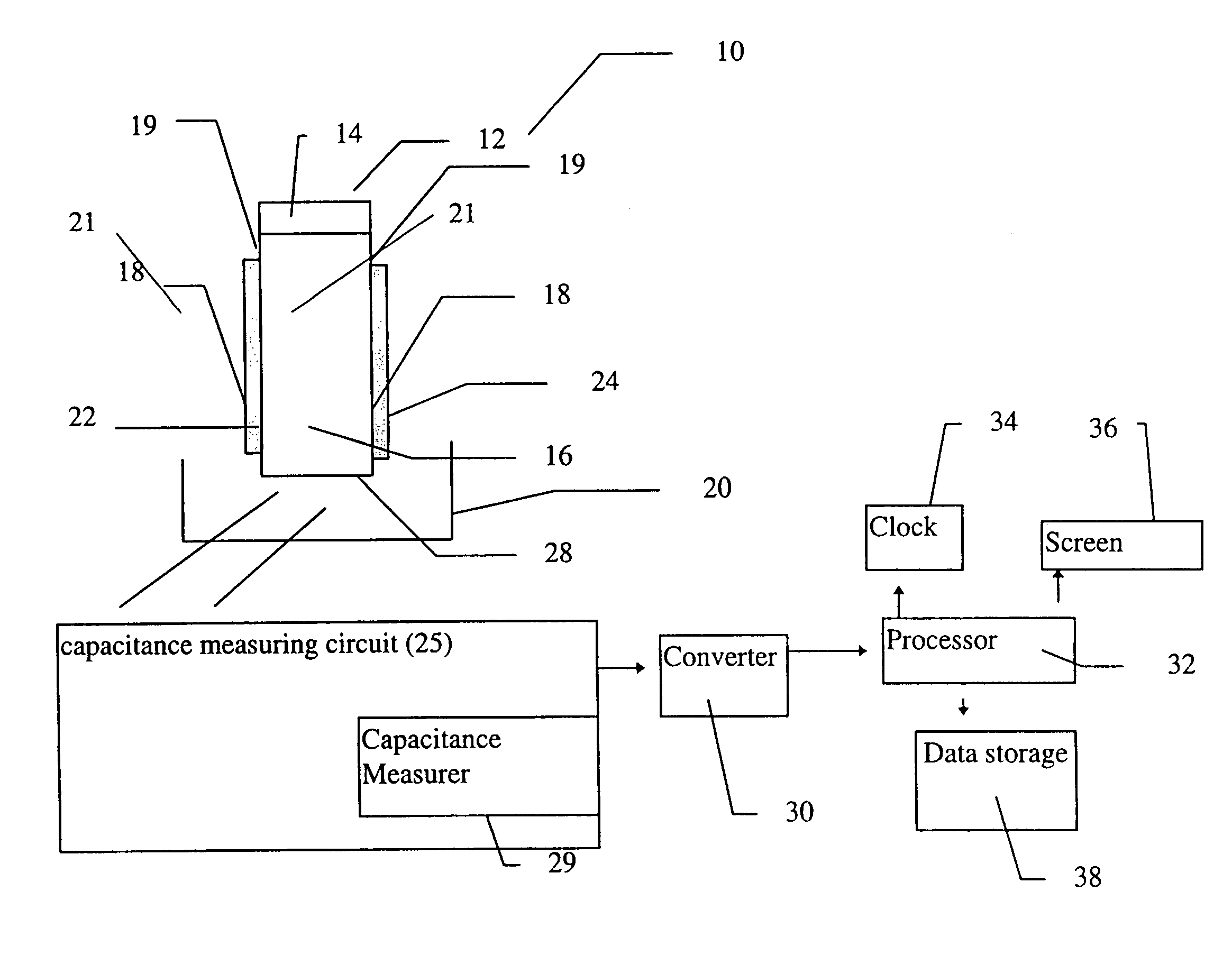
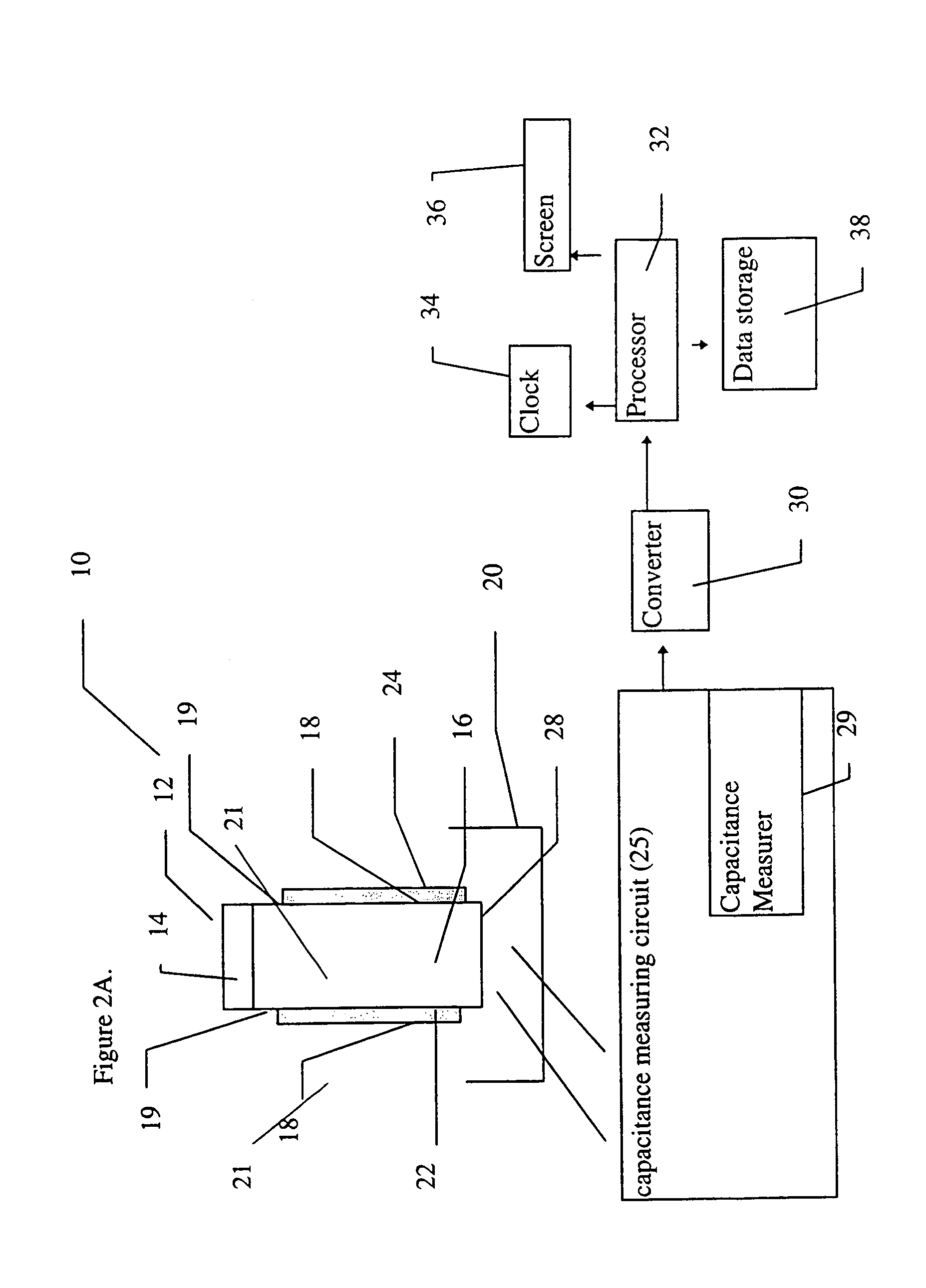
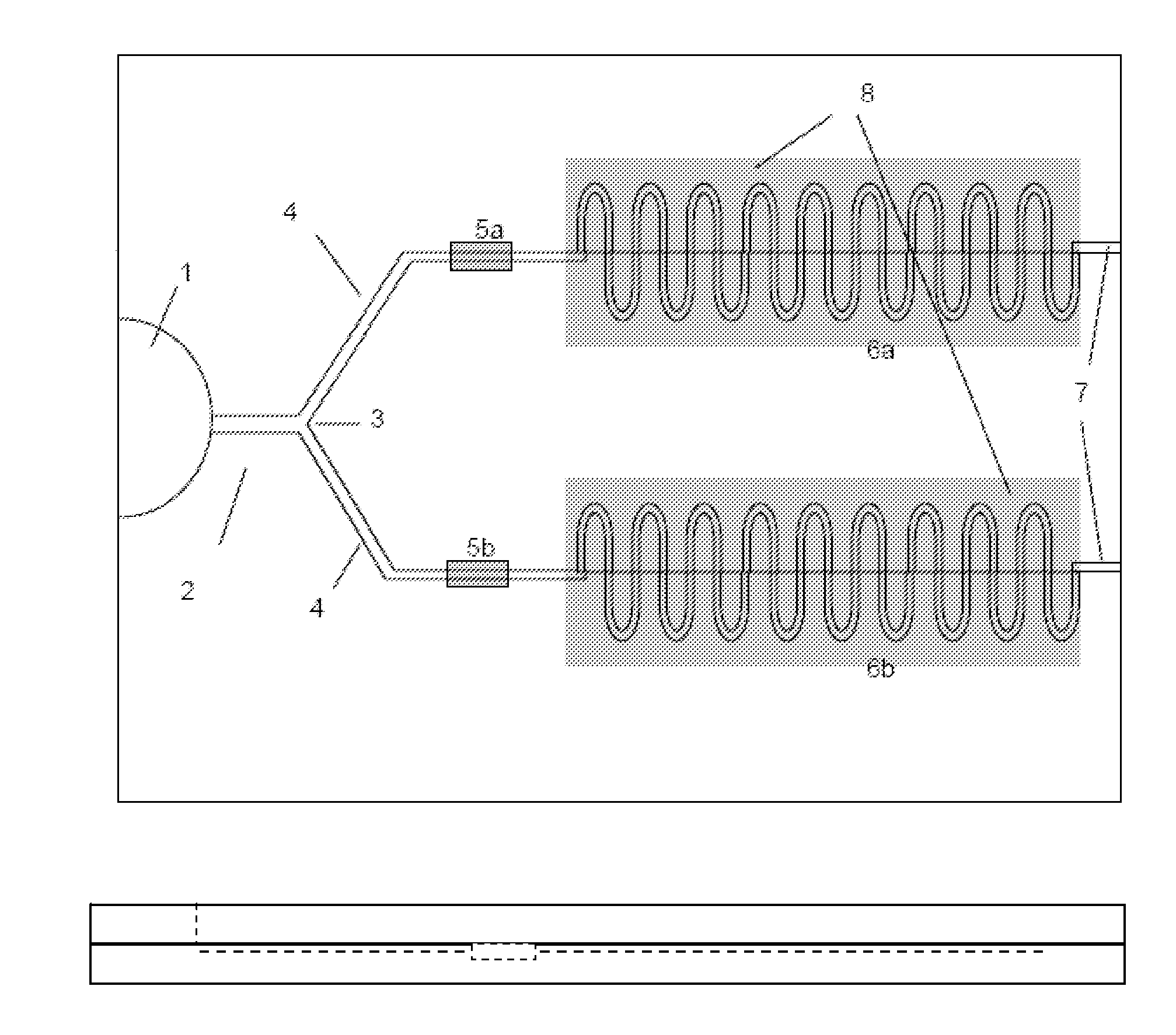
A sensor device (10) and a method for measuring a viscosity of a sample of a liquid. The sensor features a chamber (12) for receiving the sample of the liquid, two electrodes (18) disposed either on the surfaces of the chamber, but possibly isolated from contacting the sample, or electrodes located externally to the chamber, and a capacitance measuring circuit (25). The sensor is used by connecting to a measurer for determining a capacitance on the electrodes, such that the capacitance directly reflects a volume occupied by the sample of the liquid. Preferably, the liquid is blood and the capacitance is used to determine the clotting time of the blood. Also preferably, a cover for the chamber is provided with at least one aperture, which more preferably is a mesh. Alternatively, an electrical property such as the amplitude of current passed through the sample is used to determine clotting time. Also preferably, the time period required for the maximum capacitance to be reached could be measured. Alternatively, the capacitance could be measured after a fixed time period (34) had elapsed. Also alternatively, the time period required for the maximum current to be reached could be measured, or the amount of current could be measured after a fixed time period had elapsed. In preferred embodiments of the present invention, a kit for measuring the clotting time of blood is provided. In other preferred embodiments of the present invention, methods are provided for using the kit and device of the present invention.
Owner:ORGENICS BOISENSORS
Apparatus and method of preparation of stable, long term thrombin from plasma and thrombin formed thereby
InactiveUS7056722B1Precise repeatable fast slow polymerizationVarious disease riskBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsTissue sealantDonors plasma
A sterile method for preparing stable thrombin component from a single donor's plasma in which the thrombin component is harvested simultaneously from the clotting and adhesive proteins component from the same donor plasma in less than one hour. The combined components provide an improved biological hemostatic agent and tissue sealant by virtue of its freedom from the risk of contaminating viruses or bacteria from allogenic human or bovine blood sources. The thrombin provides polymerization of the clotting and adhesive proteins in less than five seconds, and is sufficiently stable to provide that fast clotting over a six hour period. Further, the clotting times can be predictably lengthened by diluting the thrombin with saline.
Owner:ASAHI KASEI MEDICAL CO LTD
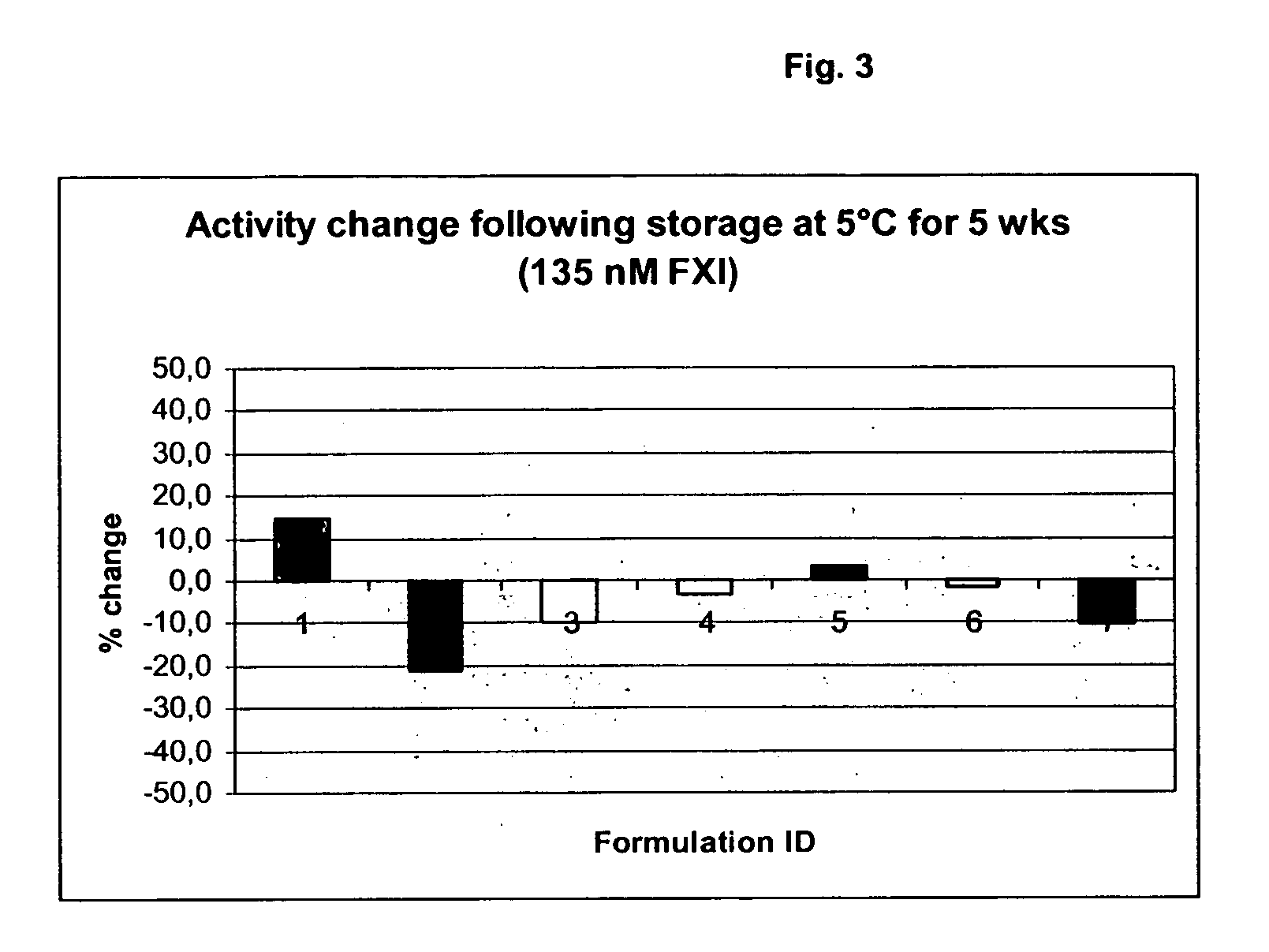
Therapeutic use of factor XI
InactiveUS20050181978A1Shorten clotting timeGood hemostasisPeptide/protein ingredientsBlood disorderMedicineFactor XI
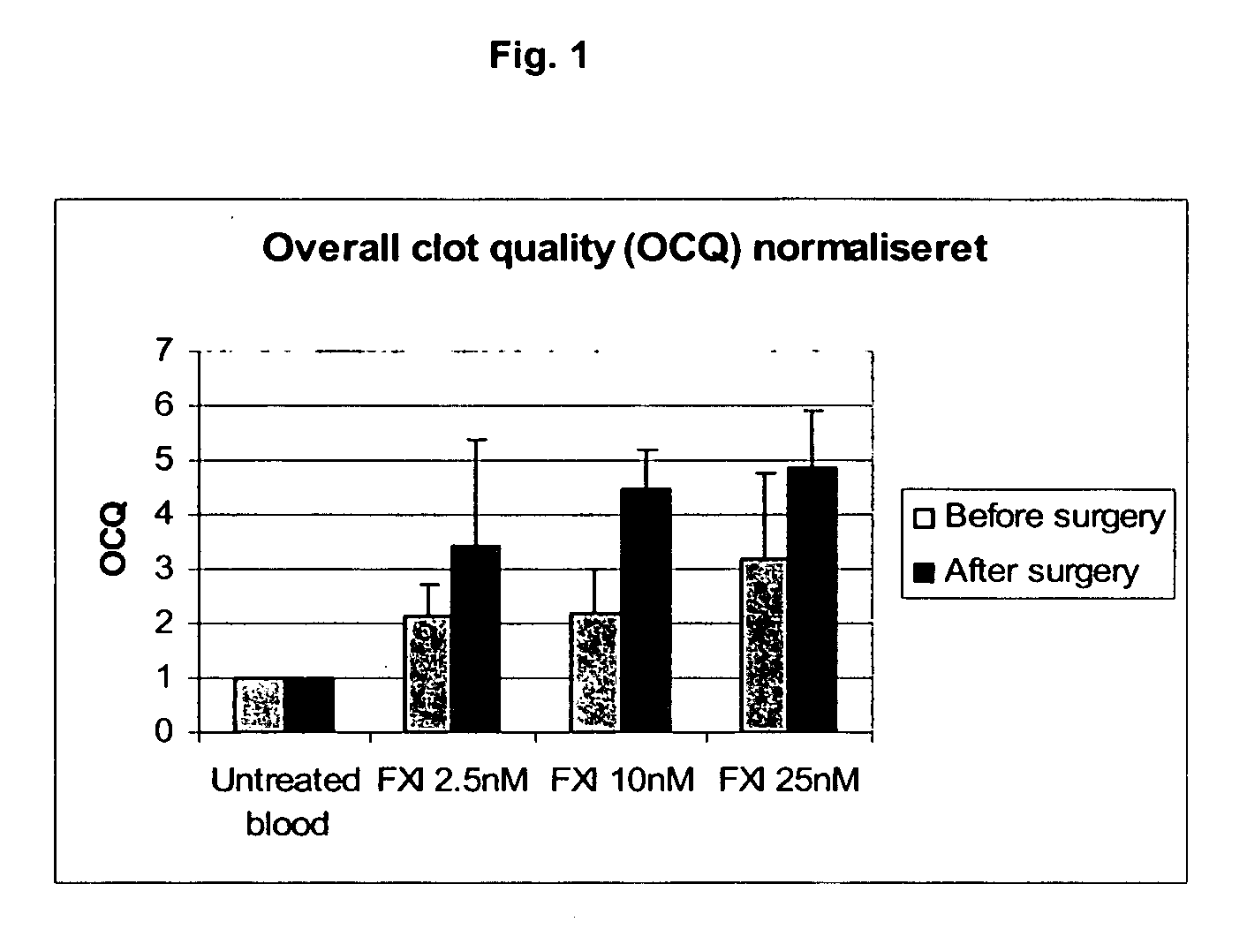
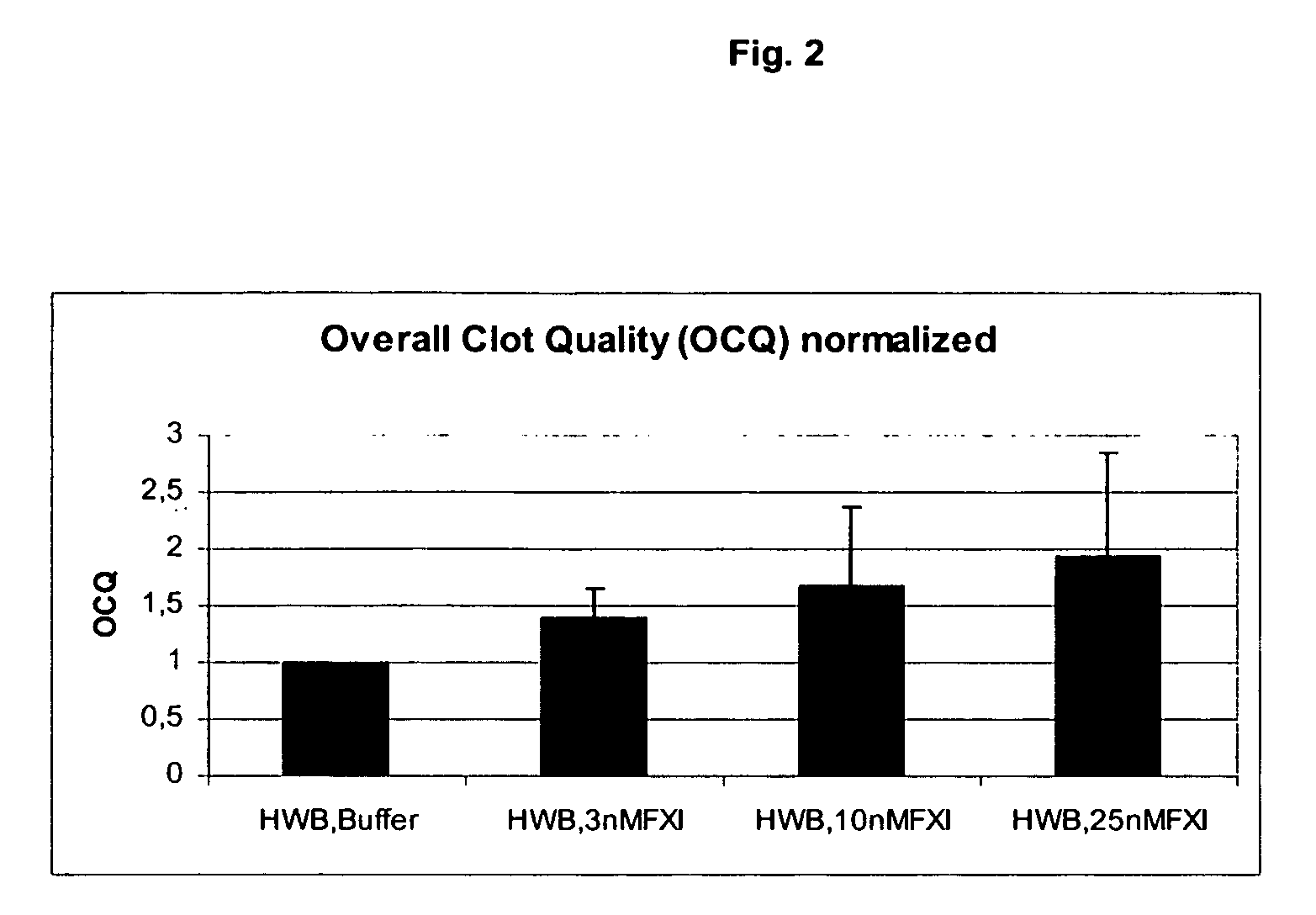
The present invention provides methods and compositions for treating bleeding episodes. The methods are carried out by administering to a patient in need thereof a preparation comprising a factor XI polypeptide, in an amount effective for such treatment. The methods of the invention result in one or more of: reduced clotting time; enhancement of hemostasis; increase in clot lysis time; increase in clot strength; and / or increase in overall clot quality (OCQ) in said patient.
Owner:ROJKJAER RASMUS +4
Photometric determination of coagulation time in undiluted whole blood
InactiveUS20060110283A1Easy to implementEasy to operateMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceAgglutinationBlood coagulations
A device, system and method for photometric detection of coagulation in whole blood. The present invention is easy to implement and operate. Furthermore, the present invention has the advantage of being considered to fulfill the desired standard of using photometry for measuring blood coagulation. Also, a photometric coagulation test device for whole blood specimens according to the present invention provides medical accuracy to the home user and, at the same time, is simple to construct. The present invention is also useful for detecting and determining blood agglutination, for example as the results of a serological reaction with an antibody.
Owner:INVERNESS MEDICAL SWITZERLAND GMBH
Microfluidic chip-based, universal coagulation assay
ActiveUS9910053B2Ensures comparabilityEnsure repeatabilityLaboratory glasswaresBiological testingPoint of careShear flow
Owner:PEROSPHERE TECH INC
Microfluidic device and method for fluid clotting time determination
ActiveUS20110039285A1Low production costEasy to useBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsClotting timeWhole blood sample
A microfluidic passive device and a method for determining clotting time are described, of a fluid medium such as blood, of low production cost which can therefore be disposable. When optimised to determine blood clotting time, it requires a minimal whole blood sample (<5 μL) and it is particularly suited to INR or PT determination, which can be used autonomously by patient without venipuncture. Monitoring, and processing means to interpret the results are comprised in an external coagulometer device. A production method for the manufacture of the microfluidic device is also provided.
Owner:ILINE MICROSYSTEMS SL
Hydraulic Composition With Prolonged Open Time
The presently disclosed and claimed inventive concept(s) relates generally to a hydraulic composition with a prolonged open time. More particularly, the composition comprises at least one cement retarder and at least one accelerator. The presently disclosed and claimed inventive concept(s) further relates to a dry mortar composition comprising the hydraulic composition having prolonged open time without deterioration of the other cement tile adhesive properties such as workability, setting time, strength development and sag resistance.
Owner:HERCULES LLC
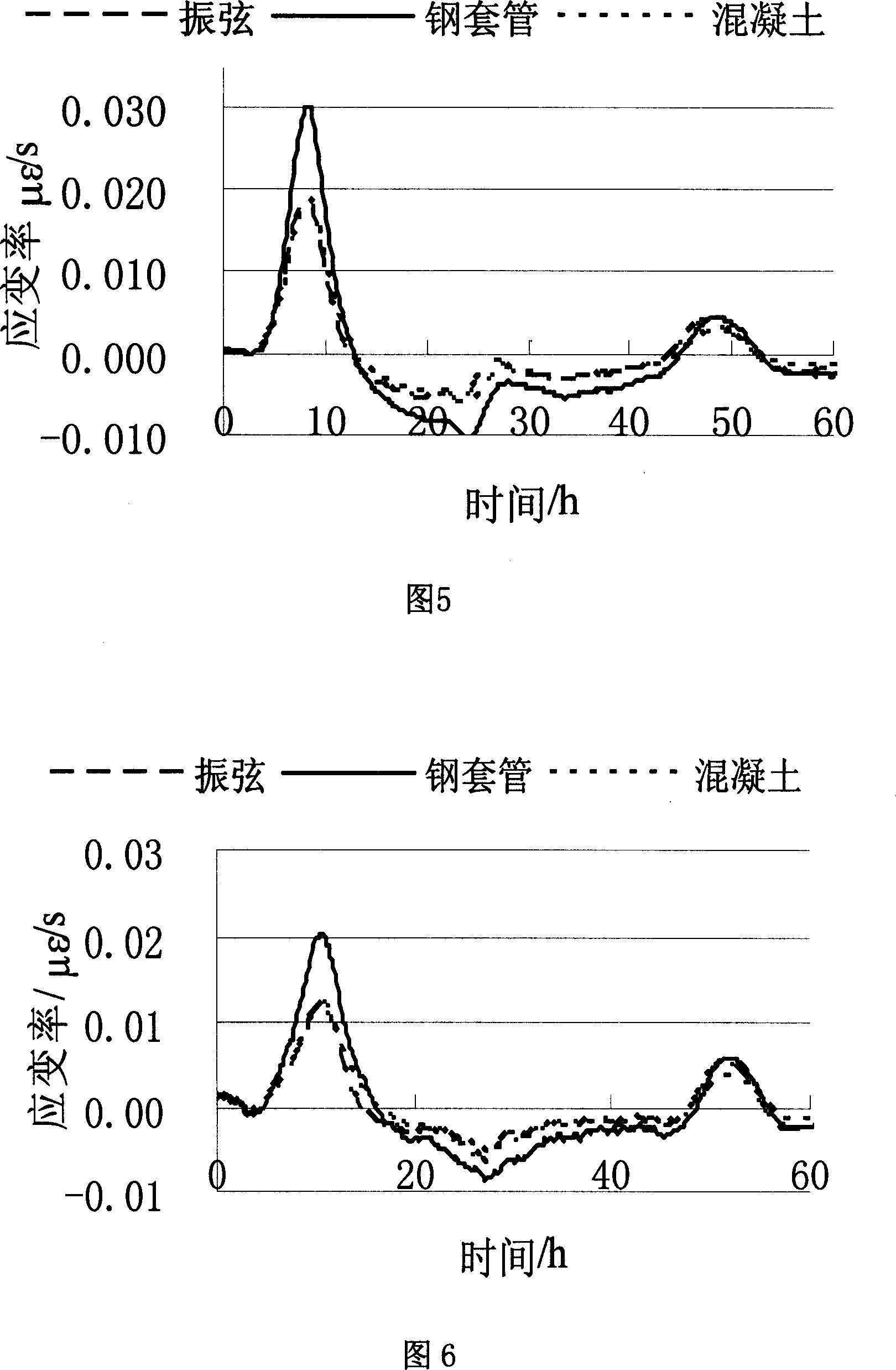
Method for measuring concrete setting time based on strain time on-line measuring
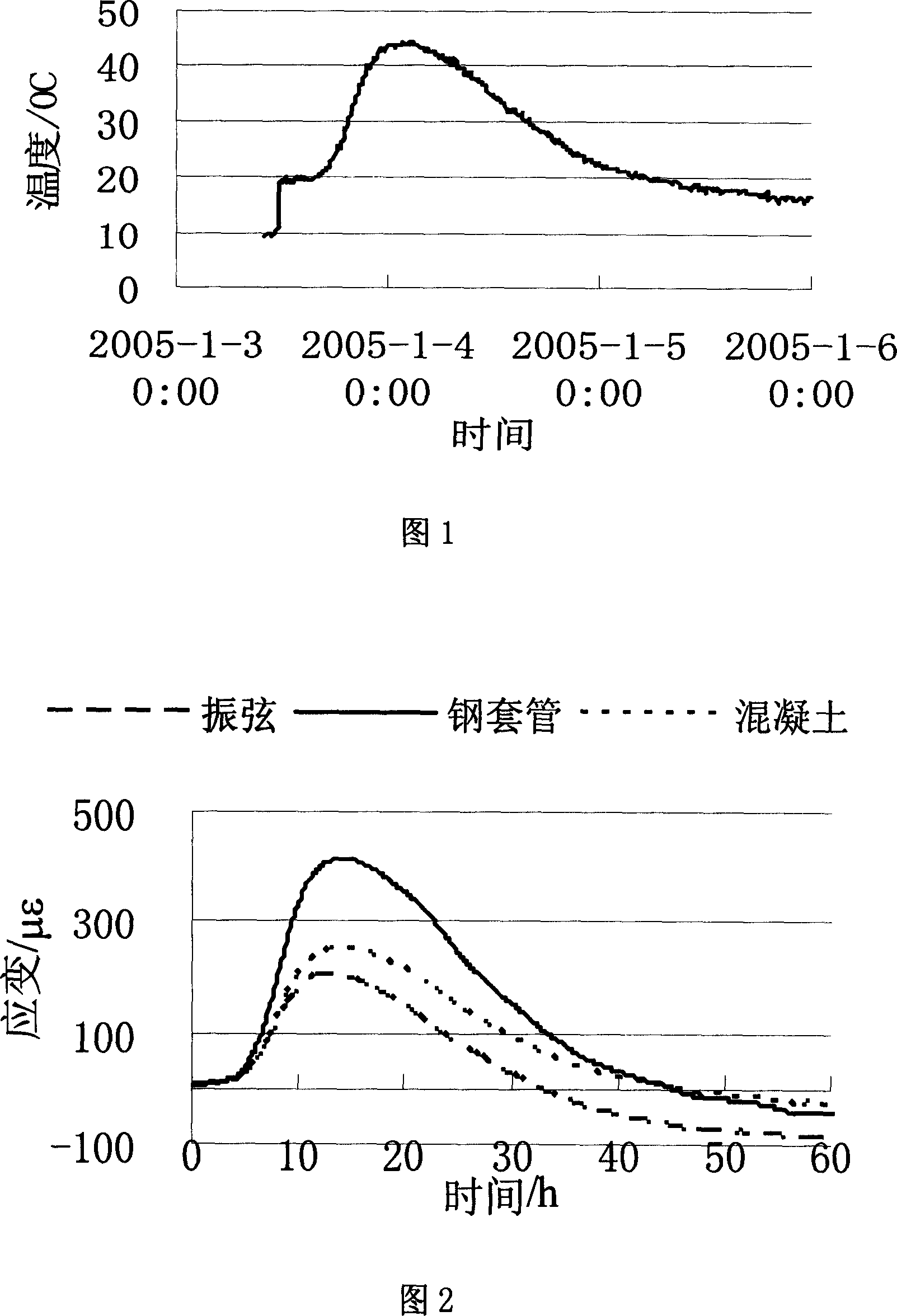
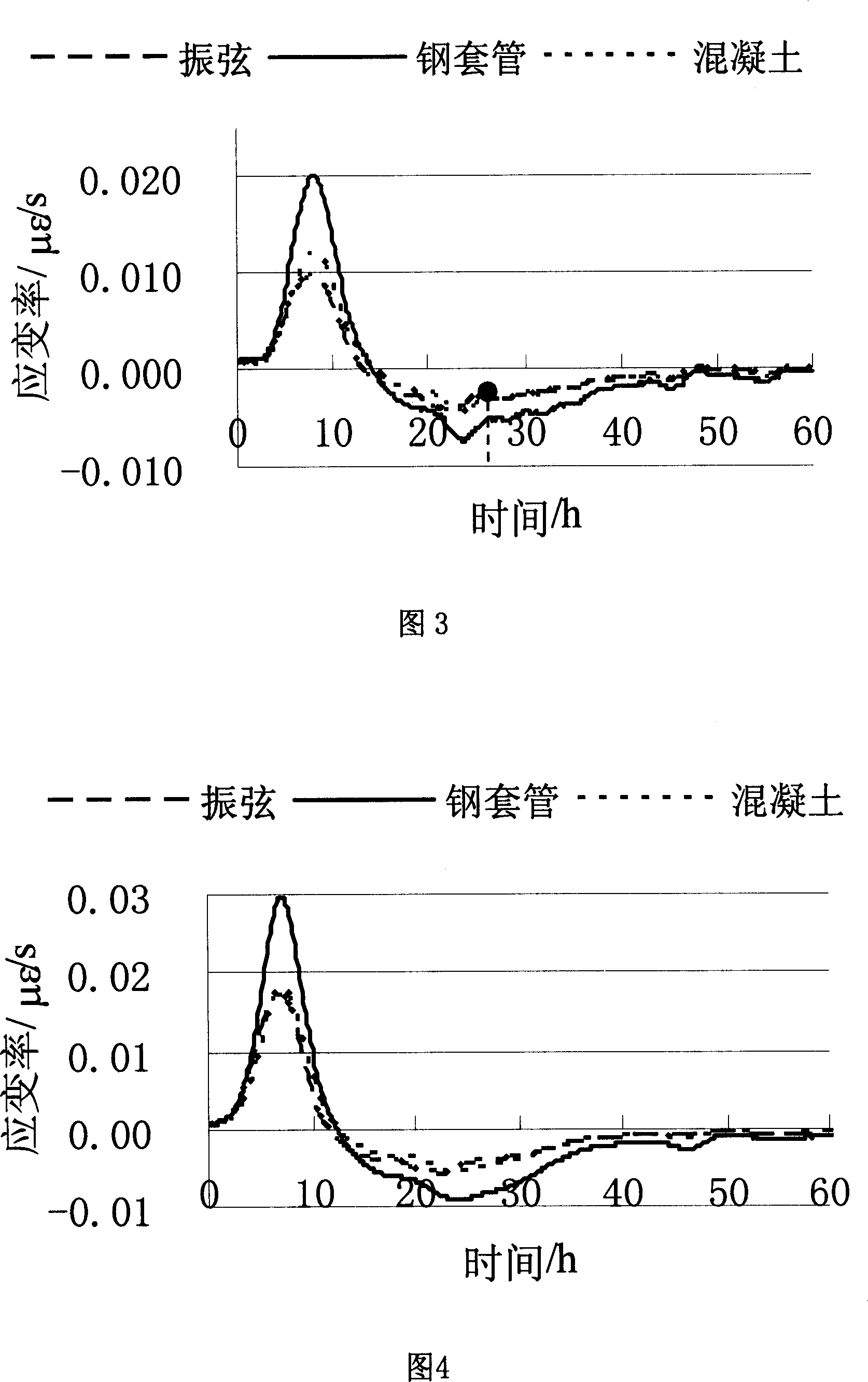
A method for measuring setting time of concrete based on on-line measurement of strain temperature includes fixing transducers in concrete template to be measured in advance, setting parameters of said transducers before concrete is poured and carrying out on-line measurement automatically on strain and temperature in solidifying course of concrete to obtain variation curve of general strain to time and variation curve of temperature to time, using the first coincided time point of two said curves as the solidified time of concrete.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
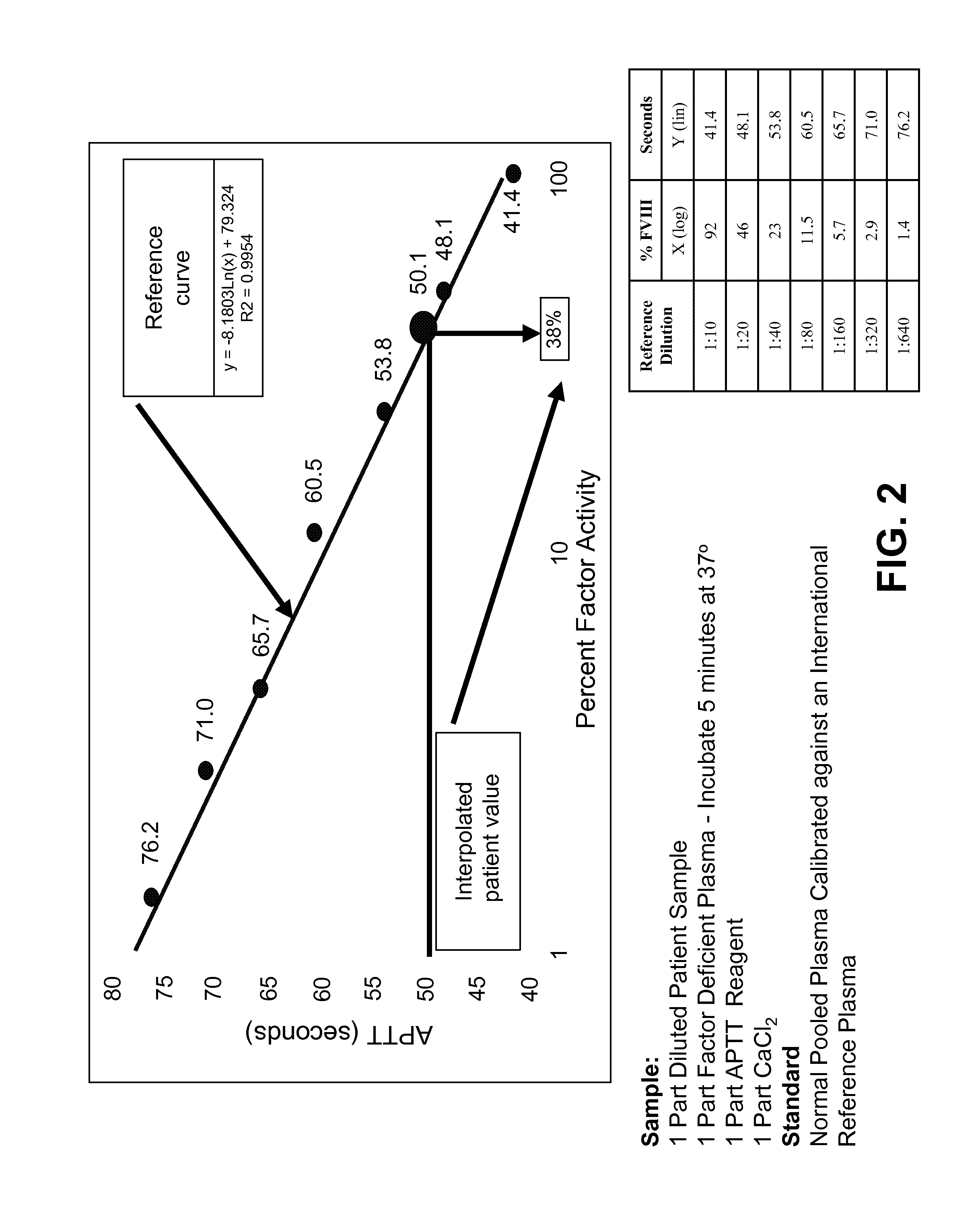
Method for measuring coagulant factor activity in whole blood
InactiveCN1368886ADetermining the risk of thrombosisPeptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementCellular componentAnticoagulant
The present invention relates to the rapid assessment of the overall clotting properties of a patient's blood sample by measuring and comparing clotting times with and without inhibitors of procoagulants or anticoagulants. When the sample is whole blood, the resulting clotting time represents the total coagulation activity of the plasma and cellular components in the blood, which may be indicative of existing or impending pathology resulting from abnormal coagulation. The present invention also provides a method for determining a patient's risk of developing a thrombotic process by functionally determining the current level of one or more procoagulant or anticoagulant substances in whole blood. In addition, the present invention also provides a method for measuring the effectiveness of anticoagulant therapy and a kit for implementing the method of the present invention.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST +1
Antibodies Against Tissue Factor Pathway Inhibitor
ActiveUS20110318356A1Shorten clotting timeImmunoglobulins against blood coagulation factorsFungiCoagulopathyTissue factor pathway inhibitor
The invention relates to antibodies that specifically bind to tissue factor pathway inhibitor (TFPI) and that reduce the clotting time of blood. Such antibodies have utility in the treatment of subjects with a coagulopathy.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Method and reagent kit for measuring activated partial thromboplastin time
InactiveCN104076156APrevent precipitationLowering assayMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisBlood plasmaEnzyme
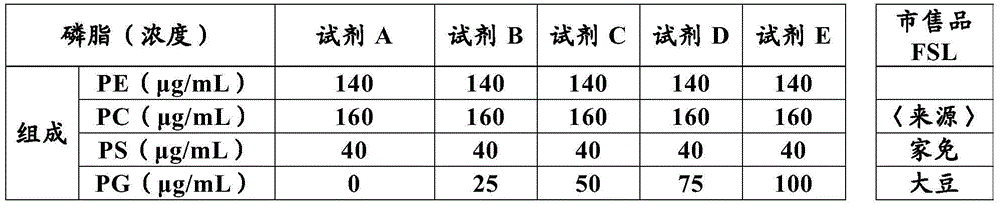
The present invention provides a method for measuring activated partial thromboplastin time. The method comprises: a first mixing step of mixing a blood plasma with a first reagent, wherein the first reagent comprises an activator and phosphatidylglycerol at a concentration equal to or greater than 25 µg / mL; a second mixing step of mixing a sample obtained in the first mixing step with a second reagent comprising a calcium salt; and a step of measuring coagulation time of the sample obtained in the second mixing step.
Owner:SYSMEX CORP
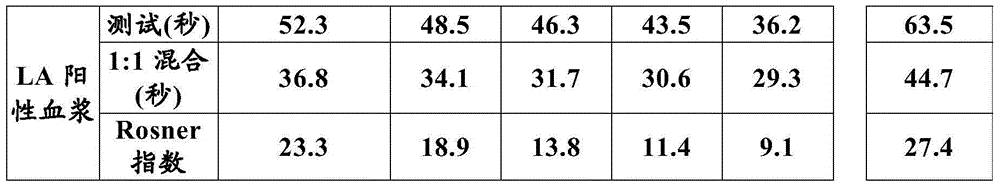
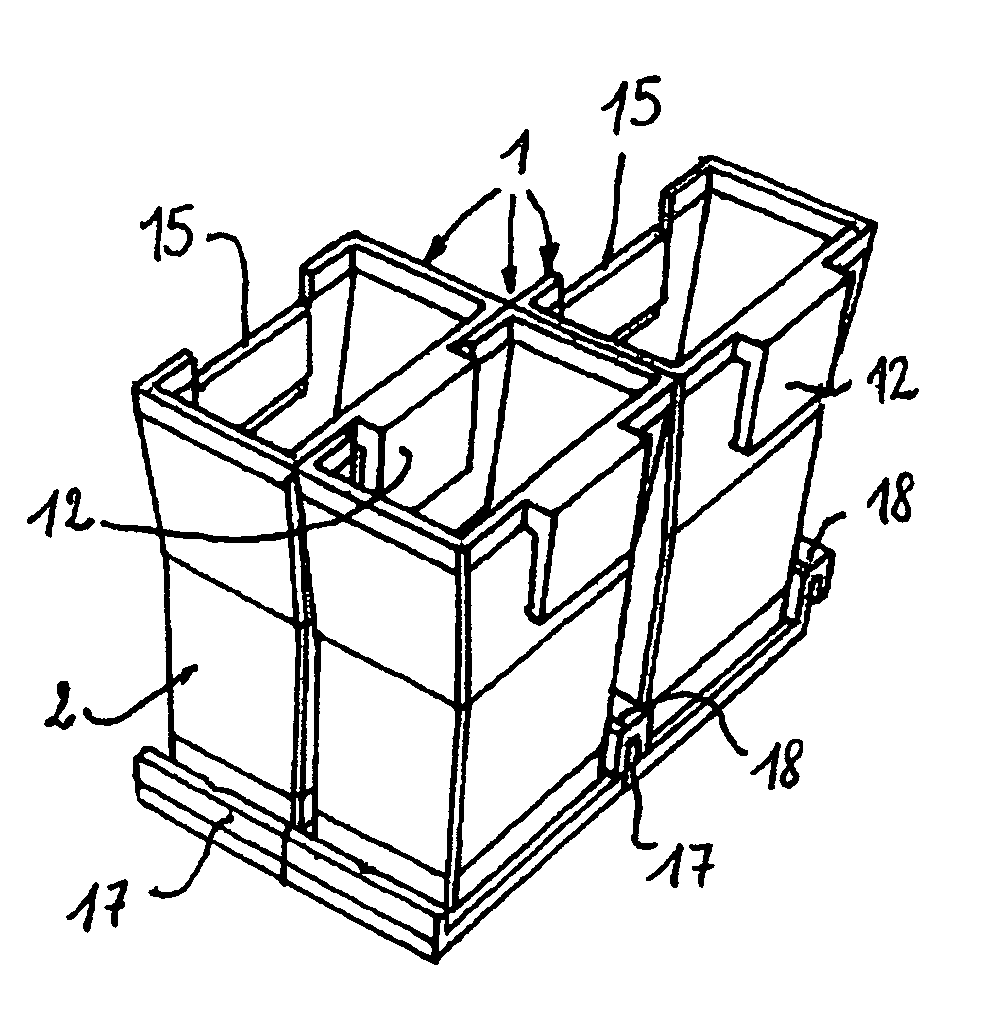
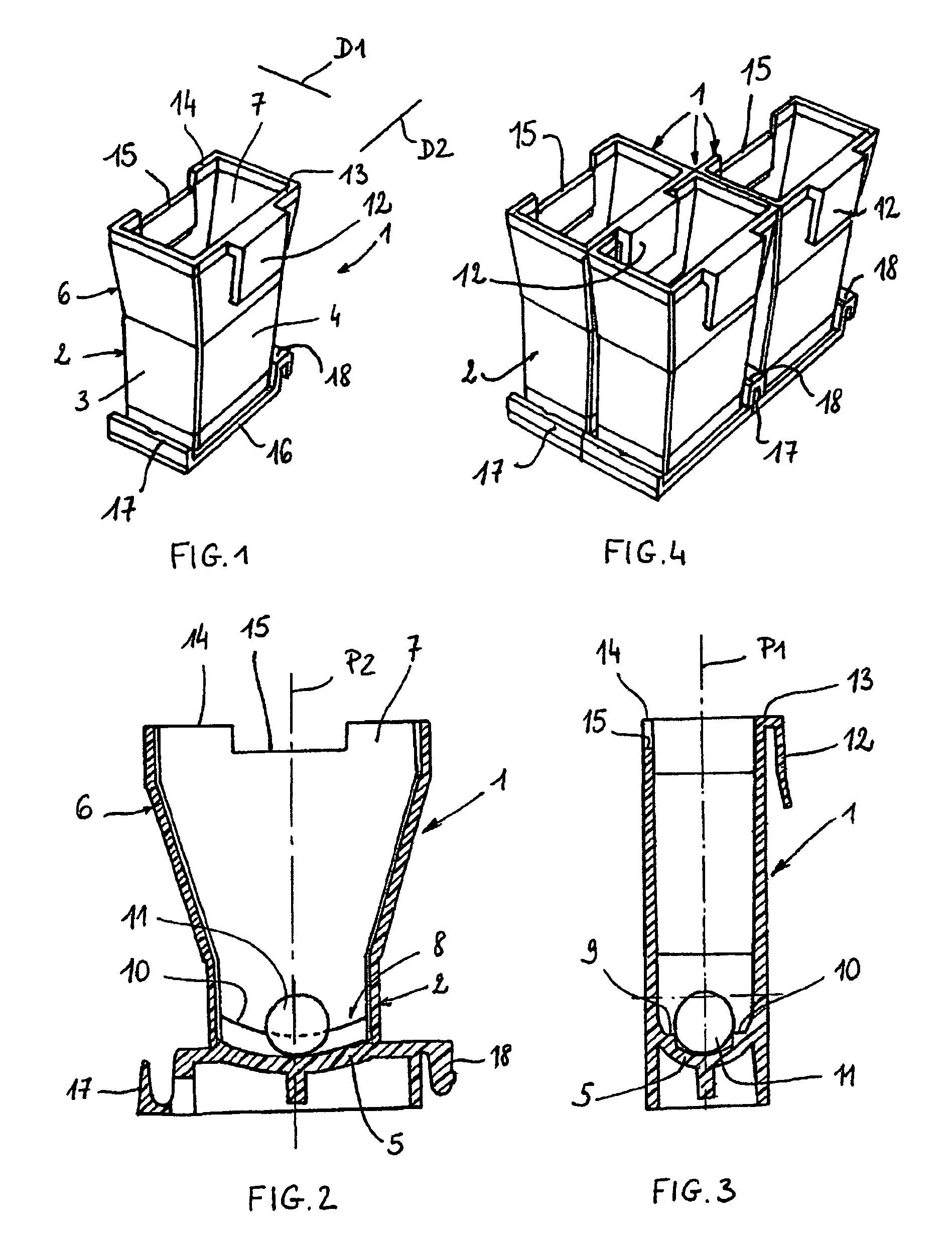
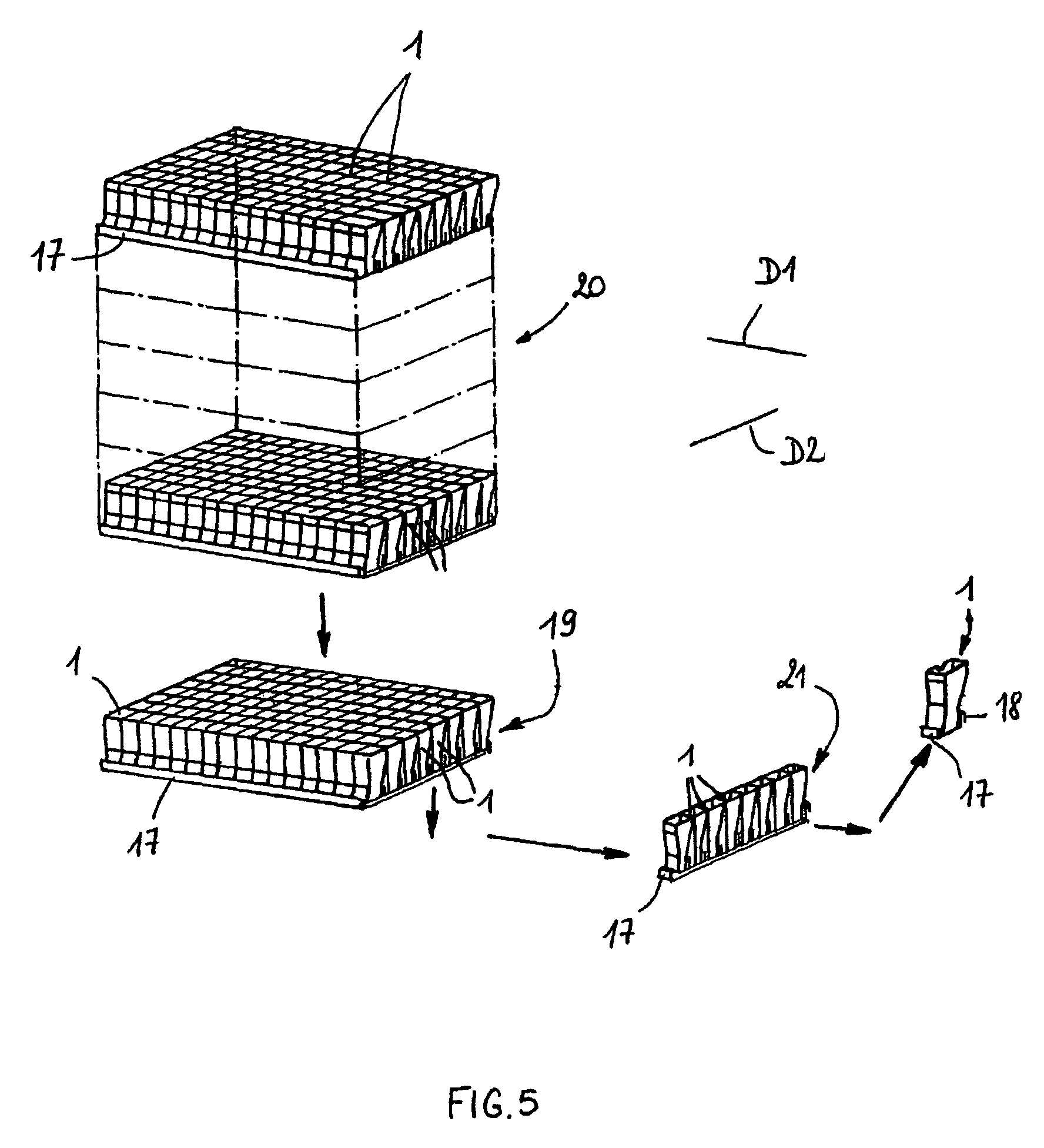
Unit cuvette for analyzing a biological fluid, automatic device for in vitro analysis
ActiveUS7959878B2Easy to storeEasy to usePharmaceutical containersMaterial analysis by optical meansCuvetteIn vitro analysis
The bottom of the cuvette comprises a curved raceway placed so as to guide the oscillating movement of a ball inserted into the cuvette. In addition, the cuvette comprises means of attachment, in two perpendicular directions, to adjacent unit cuvettes. The cuvettes can thus be stored as plates in a feed magazine of an analytical device. The analytical device comprises several stations placed around a rotary ring. Only where it is desired to determine the clotting time of the blood contained in the cuvette a ball is introduced into the latter, at a ball distribution post. The cuvette equipped in this way is then brought to a station where the test is carried out. The major advantage of the invention is the polyvalence of the cuvette and of the analytical device.
Owner:ALAIN ROUSSEAU +1
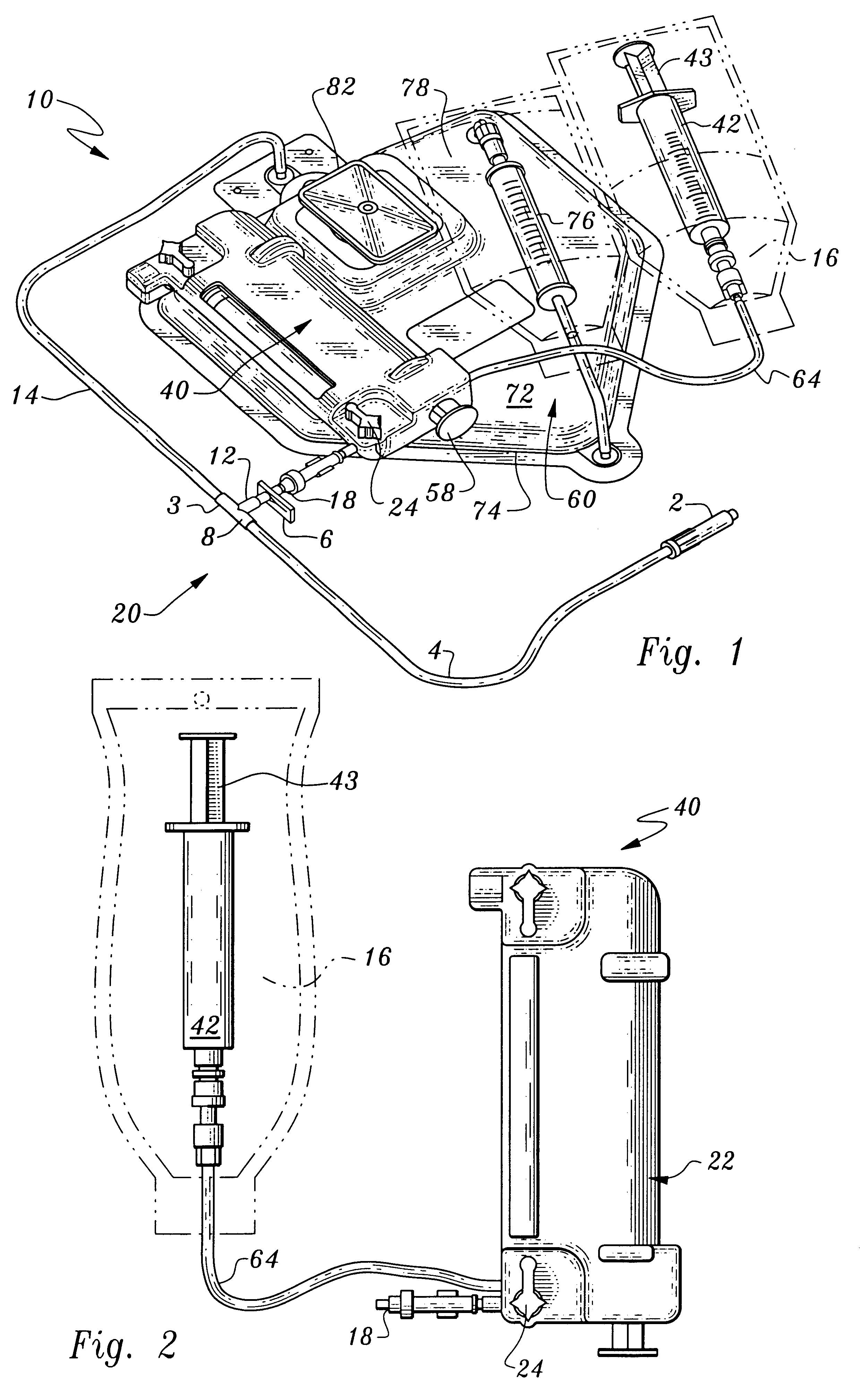
Hemostatic system and components for extracorporeal circuit
InactiveUS7153473B2Reduce or minimize inflammation, excessive bleedingEasy to adaptSolvent extractionOther blood circulation devicesCardiopulmonary bypassExtracorporeal circulation
A method and system for use in the course of extracorporeal blood flow, e.g., cardiopulmonary bypass, dialysis, and angioplasty procedures, in order to reduce or minimize inflammation, excessive bleeding, and other undesirable side effects. The system can include one or more automated blood parameter sensor modules and one or more blood parameter regulating modules. The system is particularly well suited to monitor and / or regulate blood parameters that include blood analytes (e.g., biomolecules, drugs or metabolites) as well as blood functions (e.g., clotting time, fibrinolytic activity, immune response). The system is particularly well suited for use in the management of clotting (e.g., heparing / protamine) and bleeding (e.g., aprotinin).
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Microfluidic chip-based, universal coagulation assay
ActiveUS20160069913A1Easy doseEnsures comparabilityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPoint of careShear flow
A microfluidic, chip-based assay device has been developed for measuring physical properties of an analyte (particularly, whole blood or whole blood derivatives). The technologies can be applied to measure clotting times of whole blood or blood derivatives, determine the effects of anticoagulant drugs on the kinetics of clotting / coagulation, as well as evaluate the effect of anticoagulant reversal agents. These technologies can additionally be used to optimize the dosage of anticoagulation drugs and / or their reversal agents. The assay is independent of the presence of anticoagulant; clotting is activated by exposure of the blood sample in the device to a glass (or other negatively charged material such as oxidized silicon) surface, which activates the intrinsic pathway and can be further hastened by the application of shear flow across the activating materials surface. The absence of chemical activating agents and highly controlled and reproducible micro-environment yields a point of care universal clotting assay.
Owner:PEROSPHERE TECH INC
Electrochemical Determination of Factor XA Inhibitors
ActiveUS20090236238A1Current maximum and retardedMaximum and retarded reactionImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsFactor XFactor ii
Methods and devices for determining factor Xa inhibitors, in particular heparins and fractionated or low-molecular-weight heparins, as well as direct factor Xa inhibitors in blood samples. The methods include contacting a blood sample with a detection reagent that contains at least one thrombin substrate having a peptide residue that can be cleaved by thrombin and is amidically bound via the carboxyl end to an electrogenic substance, and with a known amount of factor X reagent and an activator reagent which induces the conversion of factor X into factor Xa. Subsequently, in a second step, the amount or activity of the electrogenic substance that is cleaved from the thrombin substrate by the factor Xa-mediated thrombin activation and / or the time course thereof is determined as the measurement signal using electrochemical methods. In a third step, the amount of the factor Xa inhibitor in the sample of the blood to be analyzed or a measured quantity that correlates therewith, in particular a clotting time that correlates therewith, is determined on the basis of this measurement signal.
Owner:ROCHE DIAGNOSTICS OPERATIONS INC
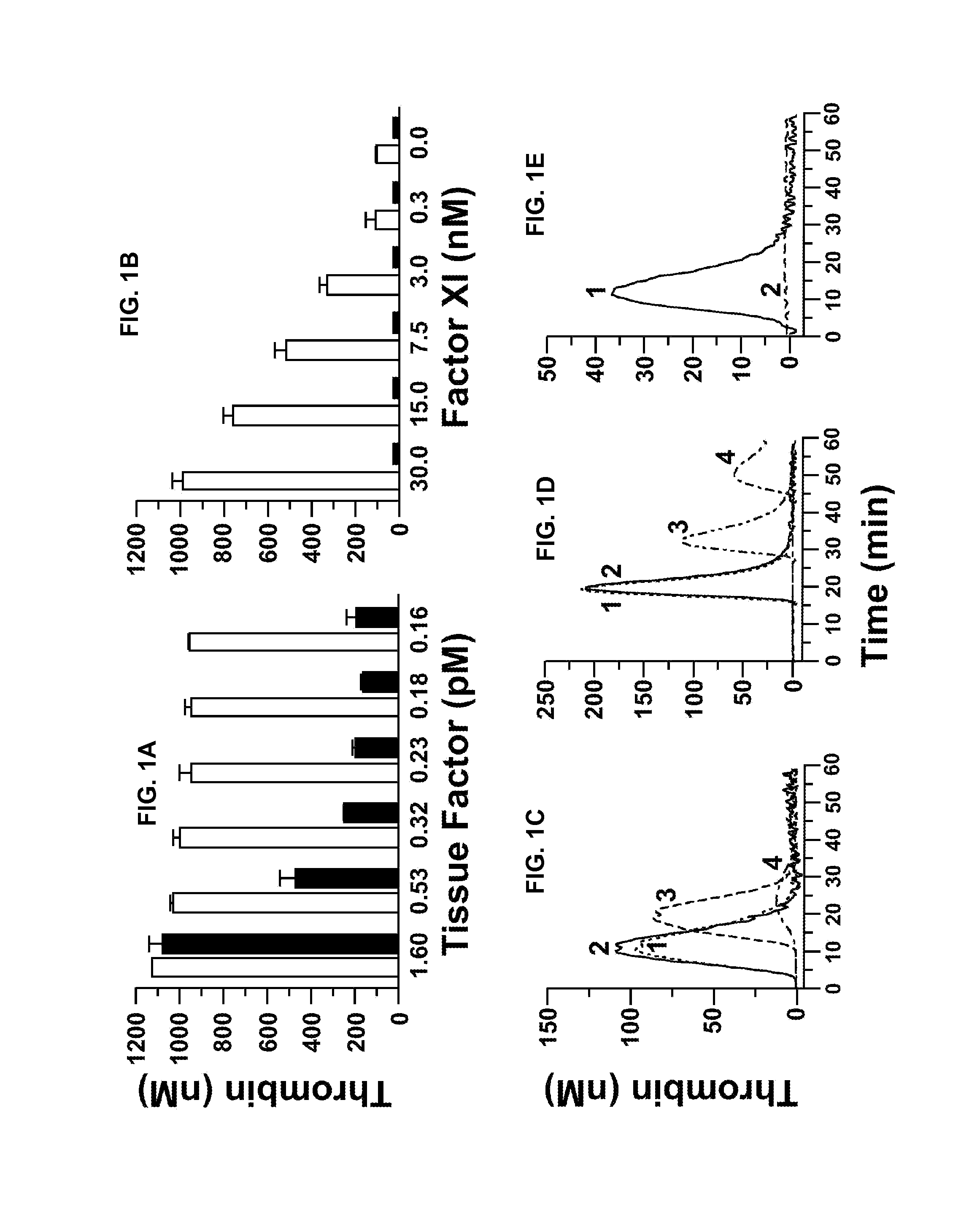
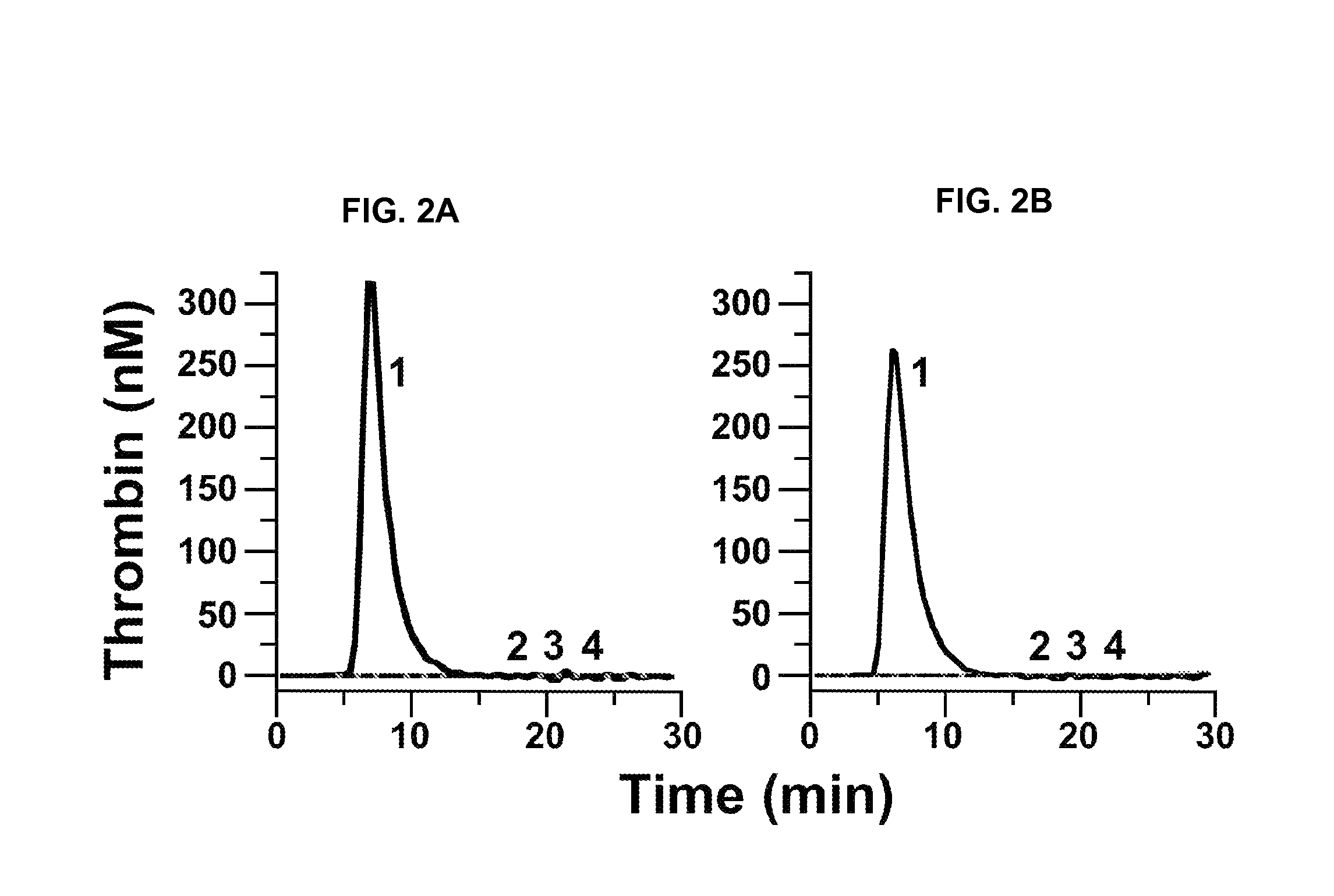
Blood Factor Monitoring Assay and Uses Thereof
The present disclosure provides methods and compositions for diagnosing and treating subject having a bleeding disorder. The disclosed methods comprise contacting a sample, e.g., a blood or plasma sample obtained from the patient, with an activation mixture comprising an activated coagulation factor and a phospholipid mixture, wherein the activation mixture is dried onto a solid substrate. Also provided is a global hemostasis test based on the integration of clotting time (Ct) and pharmacokinetics data. The methods and compositions presented can be applied to point-of-care diagnostic systems.
Owner:BIOVERATIV THERAPEUTICS INC
Antibodies against tissue factor pathway inhibitor
ActiveUS8361469B2Shorten clotting timeImmunoglobulins against blood coagulation factorsPeptide/protein ingredientsCoagulopathyTissue factor pathway inhibitor
The invention relates to antibodies that specifically bind to tissue factor pathway inhibitor (TFPI) and that reduce the clotting time of blood. Such antibodies have utility in the treatment of subjects with a coagulopathy.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Bacillus subtilis capable of stably producing chymosin with high yield by mutation and application
InactiveCN101665779AShorten the production cycleReduce fermentation costsBacteriaHydrolasesSporeMutation breeding
The invention discloses a bacillus subtilis capable of stably producing chymosins with high yield by mutation and an application. The original strain used is a bacillus subtilis which is obtained by the screening of a laboratory and used for producing products such as cheeses and the like by fermentation, and is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC) in February 2008, with the preservation name of bacillus subtilis QL-2 (Bacillus subtilis QL2) and the preservation No. of M208023. The mutation breeding comprises the following steps of: taking the bacillus subtilis QL-2 which is preserved in CCTCC with the culture preservation No. of M208023 as the original strain, and then culturing the bacillus subtilis QL-2 on a rejuvenation culture medium and a fermentation culture medium in sequence so as to obtain the original strain suspension; using a vortex device to make the strain suspension into single spore suspension; and then conducting ultraviolet mutation and culture for a plurality of times to the single spore suspension; and finally obtaining the bacillus subtilis YB-3 (Bacillus subtilis YB-3 , CCTCC NO: M209075) capable of stably producing chymosins with high yield. The bacillus subtilis capable of stably producing chymosins with high yield can be used for preparing chymosin crude enzymes by liquid fermentation, which can be used for preparing cheeses and caseins, and shortens the clotting time of milk.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY
Anti-fXI antibodies and methods of use
ActiveUS8940883B2Inhibition of activationImmunoglobulins against blood coagulation factorsAnimal cellsFactor XIBiological activation
Disclosed herein are monoclonal antibodies specific for factor XI (fXI) that prevent activation of fXI by factor XIIa (fXIIa). The monoclonal antibodies are universal fXI antibodies, capable of binding all mammalian species tested. The anti-fXI monoclonal antibodies prolong clotting time in mammalian plasmas. Moreover, administration of the fXI monoclonal antibodies disclosed herein results in inhibition of thrombosis without altering hemostasis in animal models of thrombosis. Thus, provided herein are monoclonal antibodies specific for fXI that block activation of fXI by fXIIa, compositions and immunoconjugates comprising such antibodies and their methods of use.
Owner:OREGON HEALTH & SCI UNIV +1
Methods for Treating Bleeding Disorders
A method of factor X1-dependent blood coagulation enhancement in a subject in need of enhanced blood coagulation comprising administering a therapeutically effective amount of a composition comprising a non-anticoagulant sulfated polysaccharide (NASP) to the subject. A method of factor X1-dependent blood coagulation enhancement in a subject in need of enhanced blood coagulation comprising: (i) selecting a subject that is not deficient for factor X1; and (ii) administering a therapeutically effective amount of a composition comprising a non-anticoagulant sulfated polysaccharide (NASP) to the subject, wherein the NASP enhances blood coagulation in a factor X1-dependent manner. A method of identifying a non-anticoagulant sulfated polysaccharide (NASP) which is capable of enhancing blood coagulation in dependence on FXI, the method comprising: a) combining a blood or plasma sample comprising activation competent FXI with a composition comprising a sulfated polysaccharide and measuring the clotting or thrombin generation parameters of the blood or plasma sample; b) combining a corresponding blood or plasma sample deficient in activation competent FXI with a composition comprising the sulfated polysaccharide and measuring the clotting or thrombin generation parameters of the blood or plasma sample; and c) comparing the clotting or thrombin generation parameters of the blood or plasma samples as determined in steps (a) and (b) with each other, wherein a decrease in the clotting time of the blood sample or an increase in peak thrombin or decrease in peak time of the plasma sample comprising activation competent FXI compared to the clotting time of the blood sample or peak thrombin or peak time of the plasma sample deficient in activation competent FXI is indicative of a NASP which is capable of enhancing blood coagulation in dependence on FXI.
Owner:BAXALTA GMBH
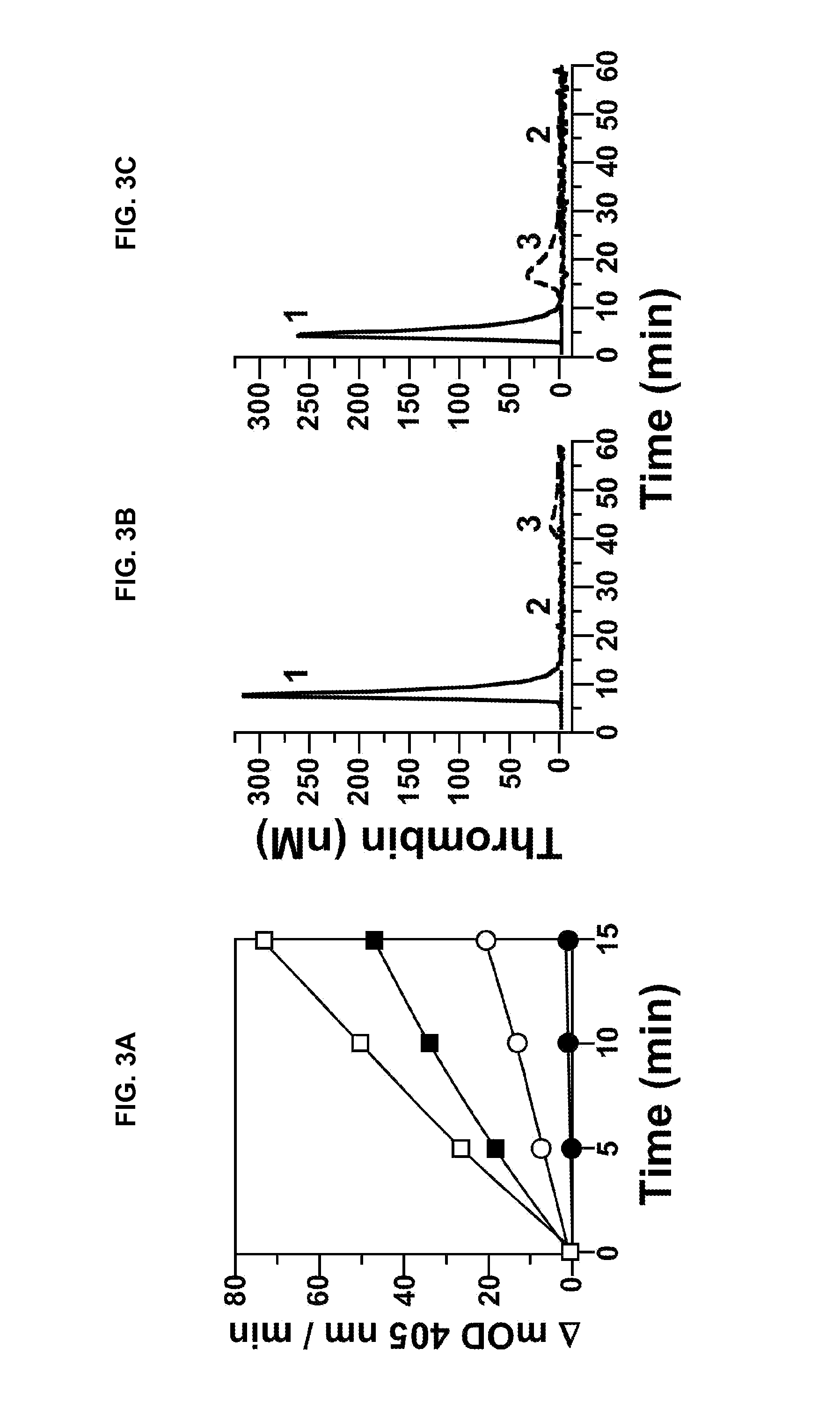
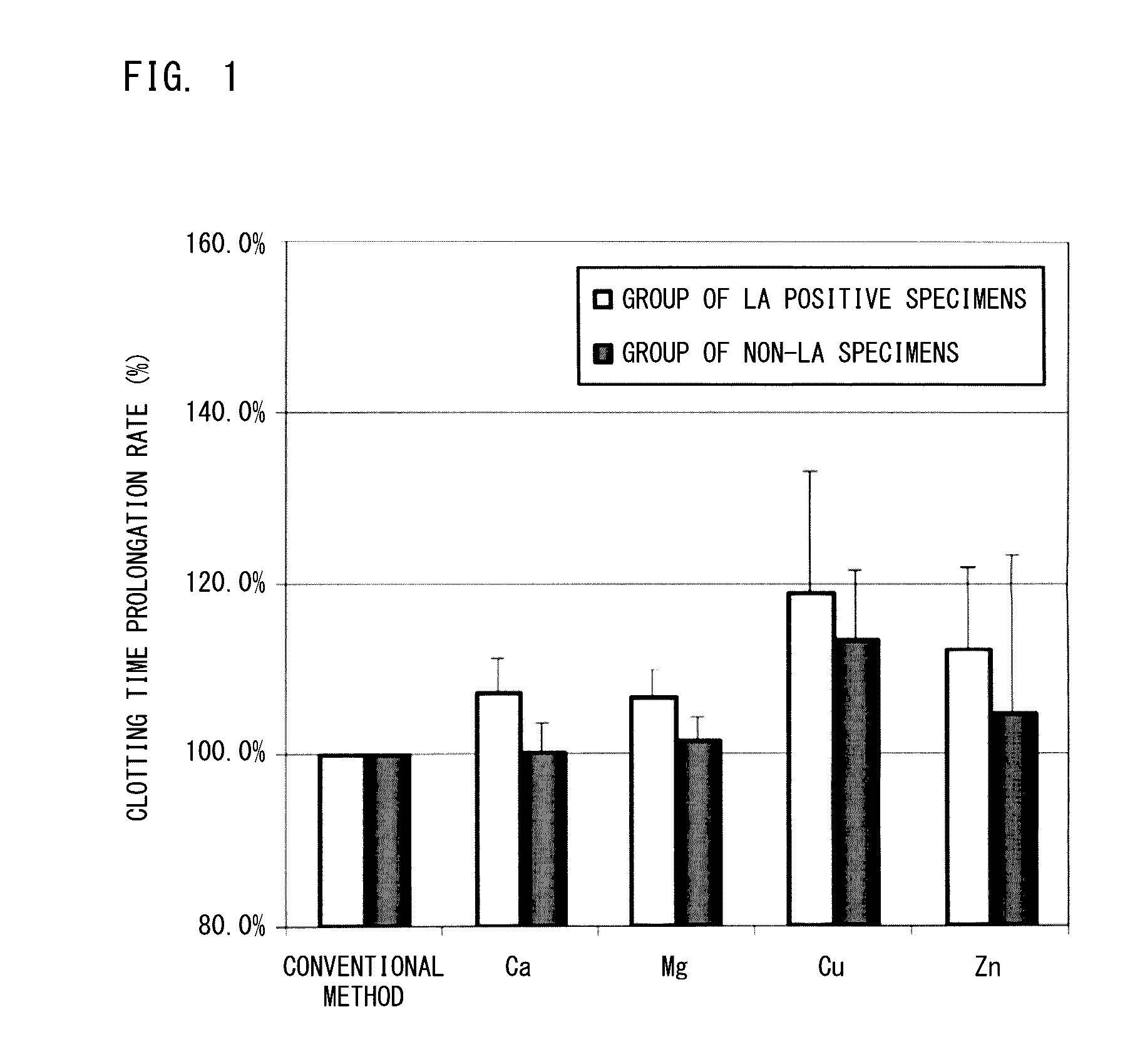
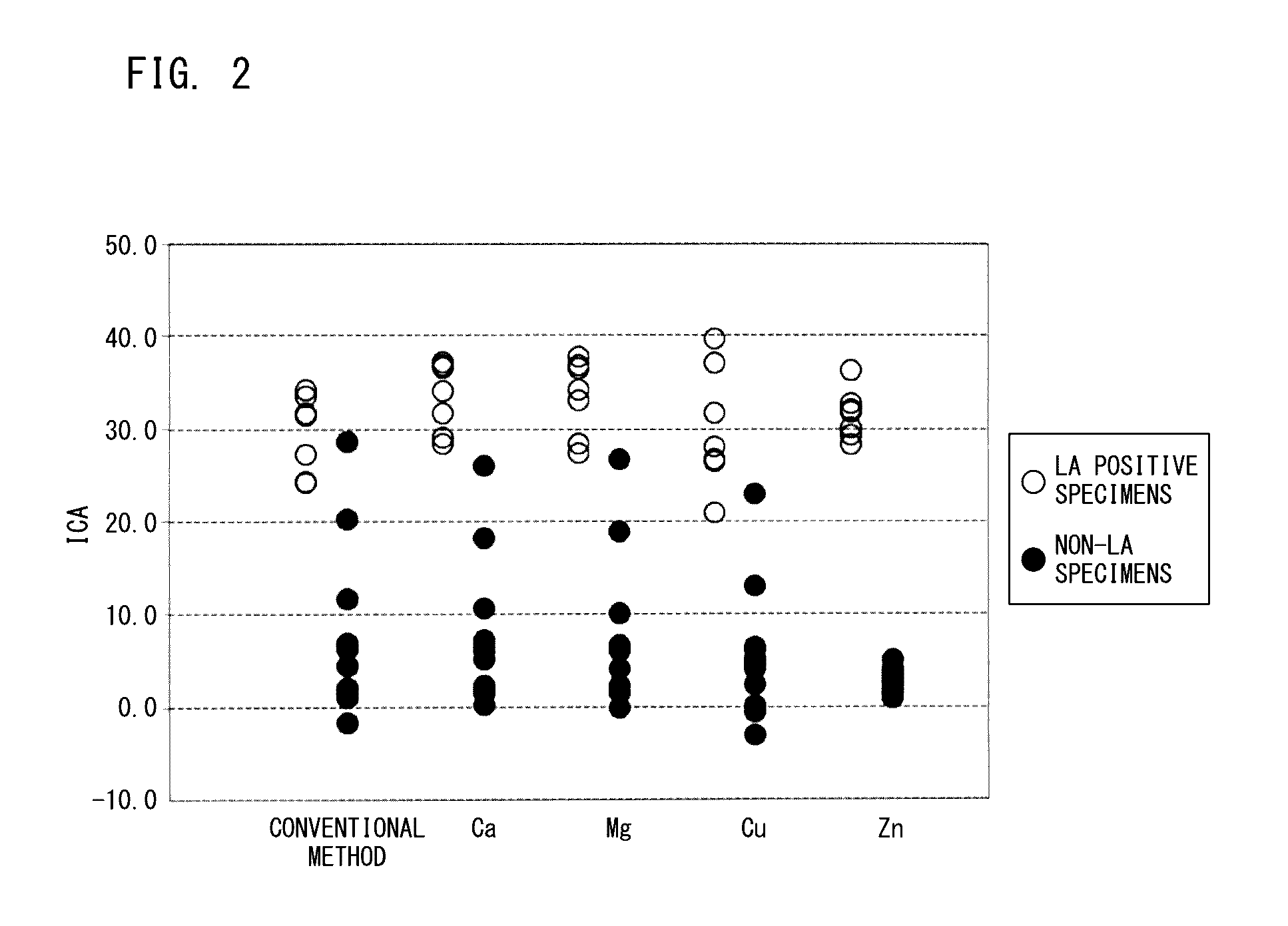
Method for measuring clotting time, method for determining presence or absence of lupus anticoagulant, and reagent kit for detecting lupus anticoagulant
Disclosed is a method for measuring clotting time including: preparing a measurement sample by mixing a blood specimen suspected to contain a lupus anticoagulant, an activator, and a divalent-metal-ion-producing compound for facilitating formation of a phospholipid-containing complex; and measuring a clotting time after adding, to the measurement sample, an aqueous solution of a calcium salt as a coagulation initiator.
Owner:SCHOOL JURIDICAL PERSON HIGASHI NIPPON GAKUEN +1
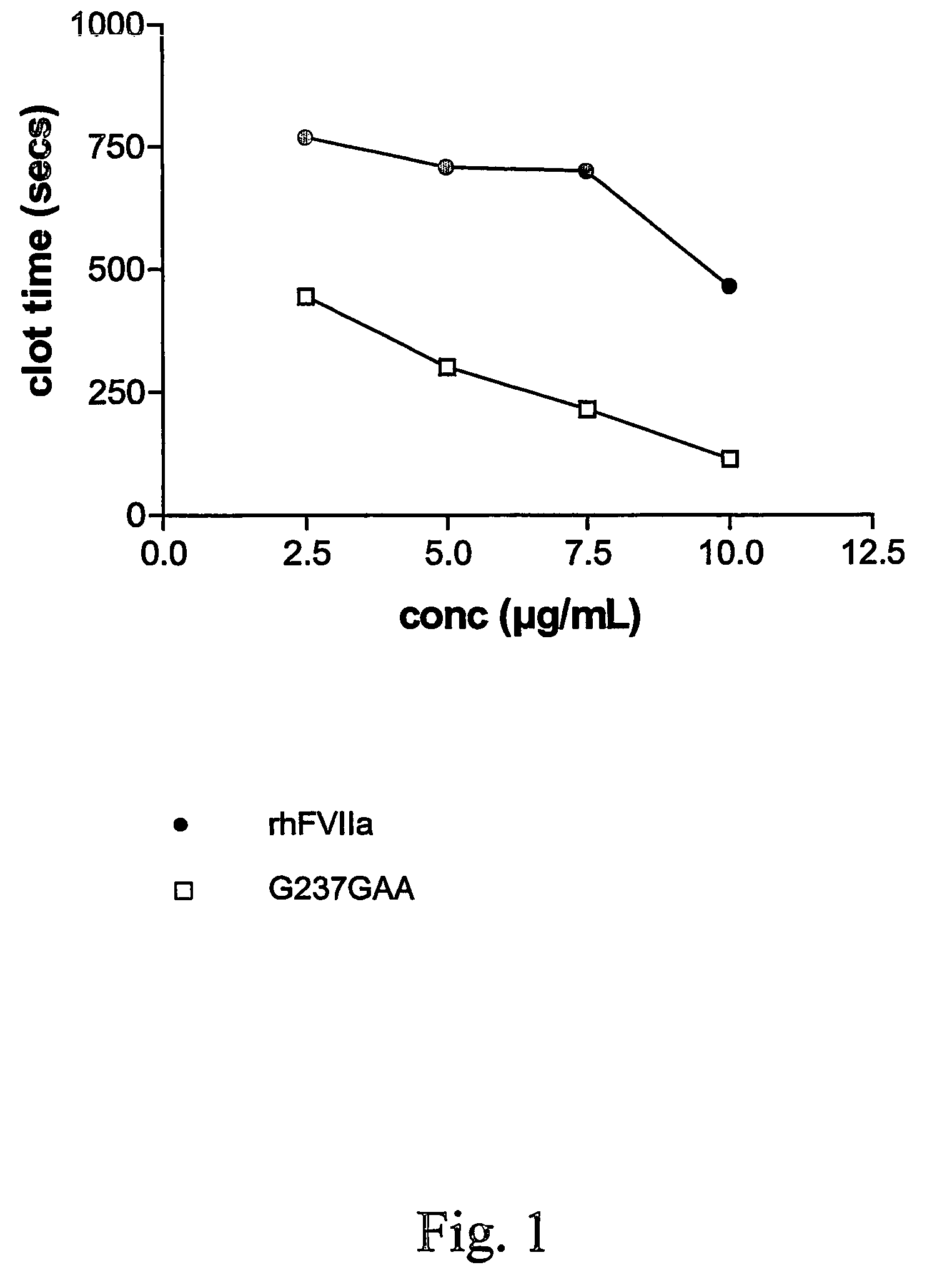
FVII or FVIIa variants
InactiveUS7771996B2Enhanced phospholipid membrane binding affinityProlong half-life in vivoPeptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulinsBiologyClotting time decreased
Variants of FVII or FVIIa comprising at least one amino acid modification in position 196, 237 or 341 relative to hFVII or hFVIIa. The variants exhibit an increased clotting activity, i.e. reduced clotting time, compared to rhFVIIa.
Owner:BAYER HEALTHCARE LLC
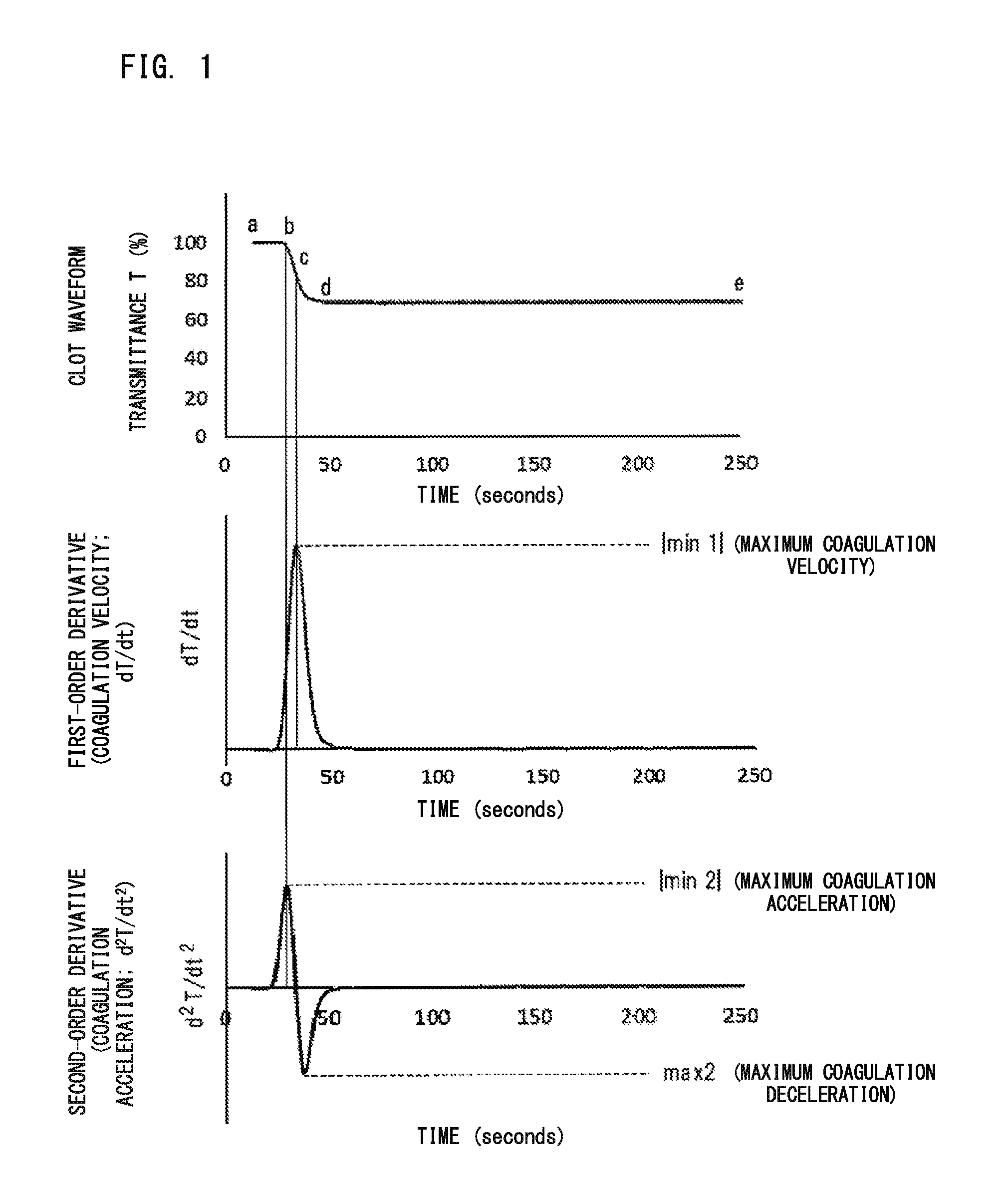
Blood sample determination method and blood sample analyzer
ActiveUS20160178651A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsLupus anticoagulantCoagulation Factor Inhibitors
Disclosed is a blood sample determination method including: emitting light to a measurement specimen prepared by mixing a clotting time measuring reagent and a blood sample suspected to be derived from a subject having lupus anticoagulant or a coagulation factor inhibitor, to obtain optical information about an amount of light from the measurement specimen; obtaining at least one parameter regarding derivative of clot waveform, based on the obtained optical information; and determining, based on a value of the obtained parameter, whether the blood sample is suspected to be a sample derived from a subject having lupus anticoagulant or is suspected to be a sample derived from a subject having a coagulation factor inhibitor.
Owner:NARA MEDICAL UNIVERSITY +1
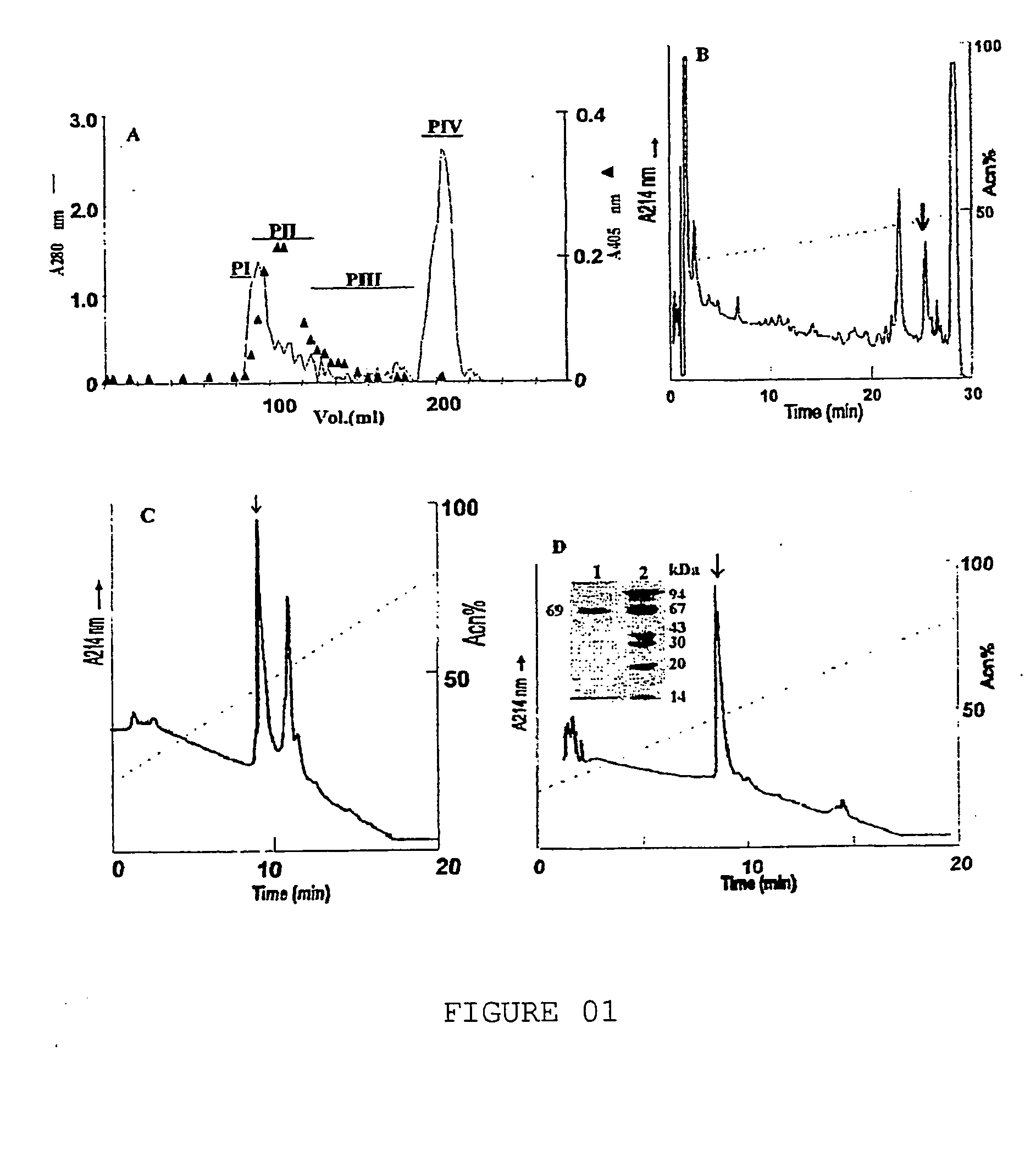
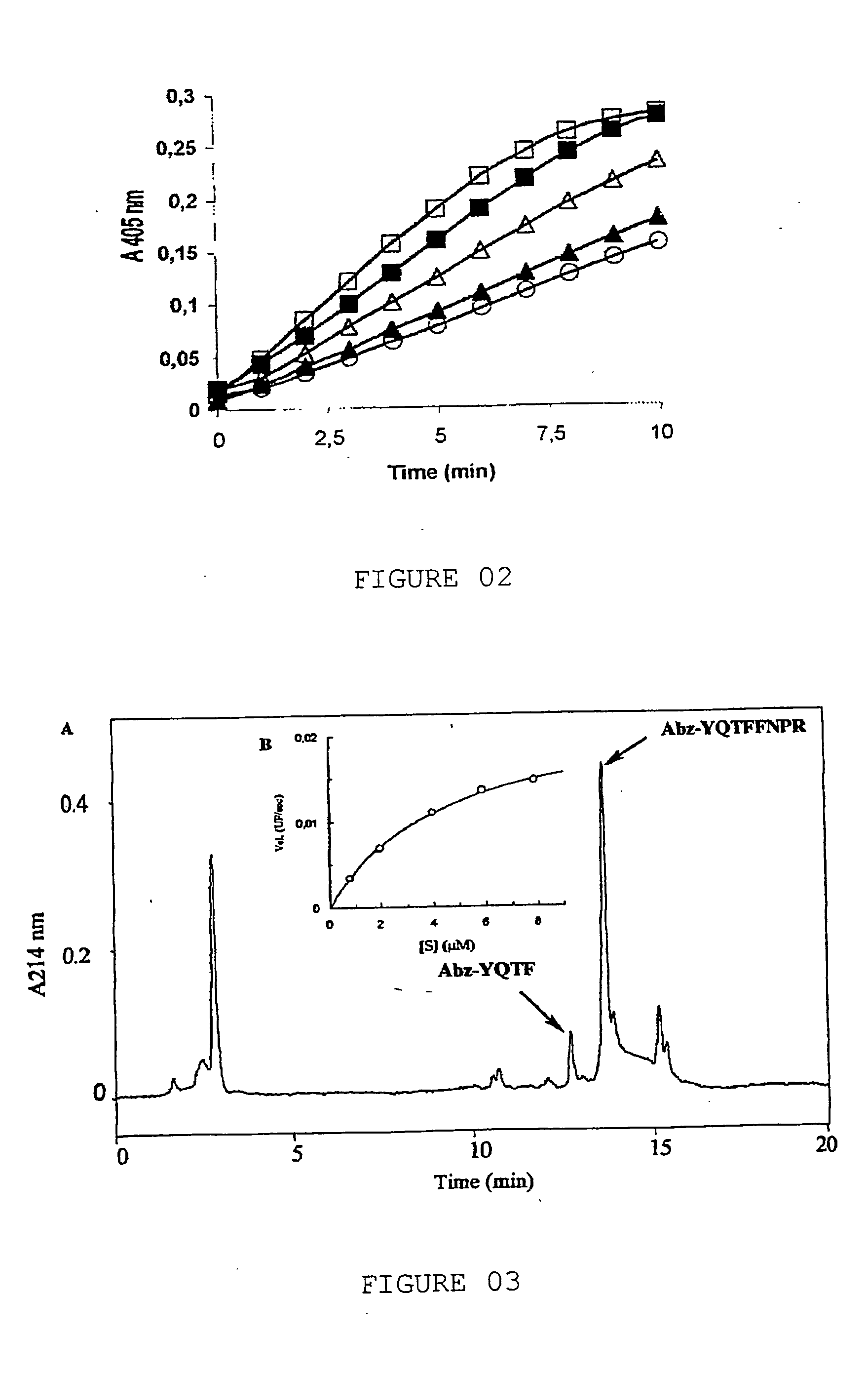
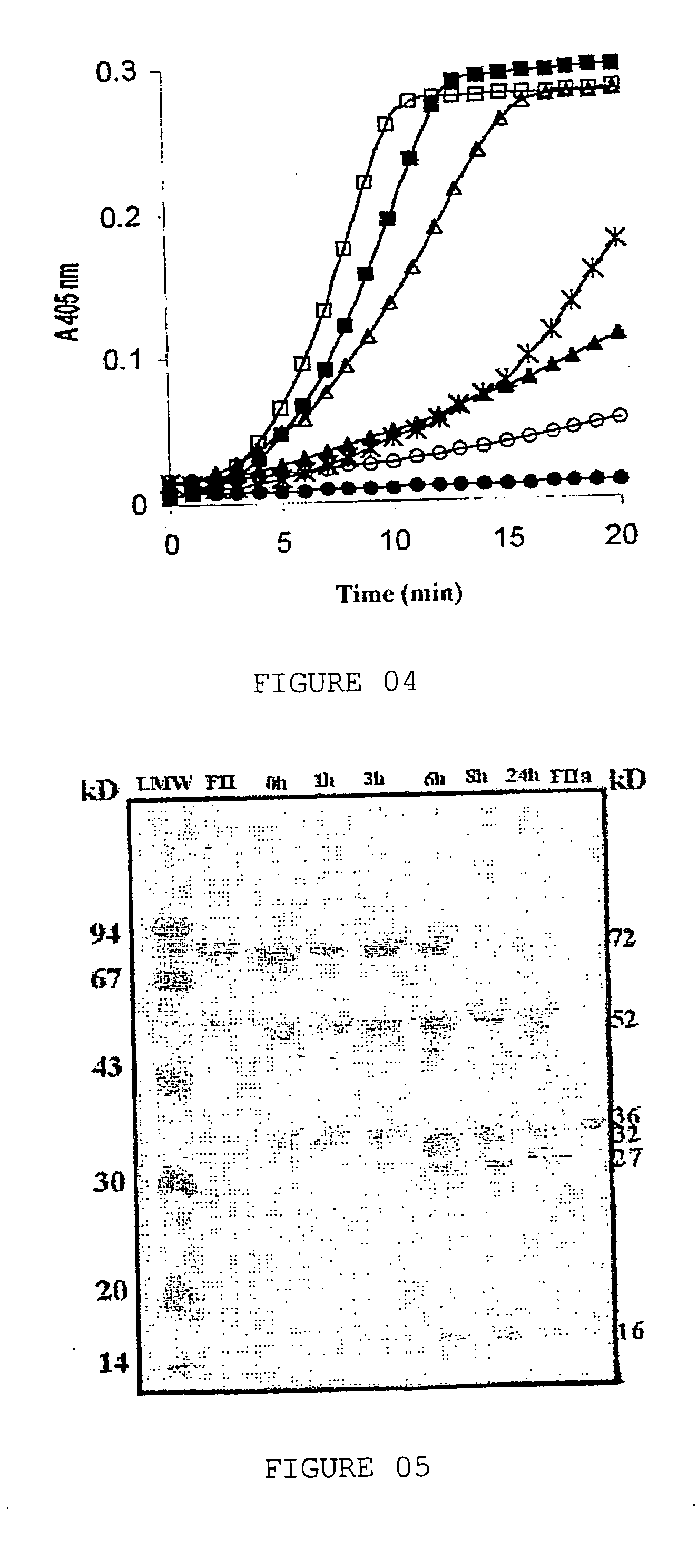
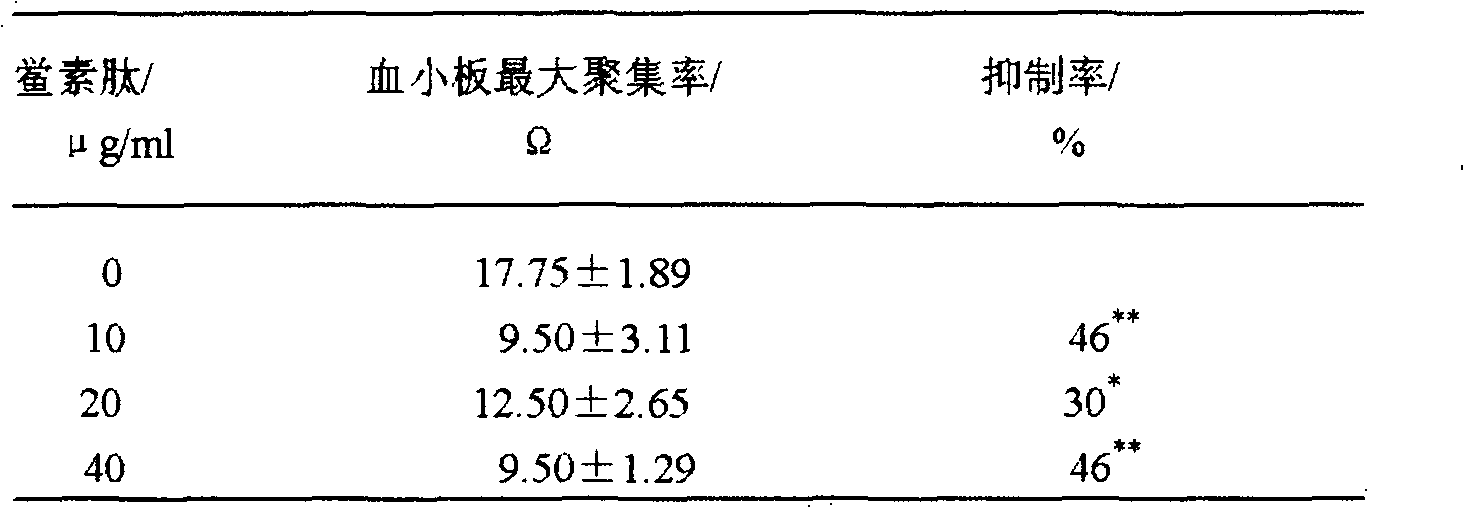
Purifying process of soluble proteins of the l.obliqua bristles through prothrombin activation: process for a partial determination of the amino acids sequence of the prothrombin activator; process for determining the prothrombin activation of fraction II, n-terminal and internal fragments sequences
InactiveUS20050130287A1Prolong coagulation timePeptide/protein ingredientsHydrolasesDysprothrombinemiaConsumption Coagulopathy
The herein invention refers to a purifying process of soluble proteins of the L. obliqua bristles through prothrombin activation; a partial deterrination of the amino acids sequence of the prothrombin activator; a process for determining the fraction II of the prothrombin activation as well as the N-terminal sequence and the sequence of internal fragments of the prothrombin activator fraction, the prothrombin activator and the utilization of the prothrombin activator through the homogenization of the L. obliqua bristles. The herein invention has shown that only one component of the Lonomia obliqua venom, the Lopap, causes the hemorrhagic syndrome directly by activating prothrombin and, therefore, a patient should be conducted to a therapy when in contact with the Lonomia obliqua venom. According to the herein invention, Lopap is a new prothrombin activator, showino to be a quite important factor responsible for consumption coagulopathy, found in patients exposed to the venom of the L. obliqua caterpillar. In low doses of purified protein, due to its capacity of activating prothrombin and generating thrombin, it is possible, in controlled conditions, to withdraw fibrinogen from circulation, transforming it in fibrin microthrombs. The decrease on the concentration of plasmatic fibrinogen promotes the increasing of blood coagulation time and therefore it will avoid acute vascular thrombosis. Since protein does not present proteolytic activity, it could maintain the coagulating capacity of the fibrinogen not consumed in the process. The fibrinogen plasmatic concentration would decrease, however there would not be predisposition for hemorrhagic state. Besides that, it could be used to produce diagnosis KITS for detecting dysprothrombinemias.
Owner:BIOLAB SANUS FARMACEUTICA LTD
Application of tachyplesin in preparing antihrombotic medicines and health-care products and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102188691APeptide/protein ingredientsPeptide preparation methodsAntithrombotic AgentMedicine
The invention belongs to an application of tachyplesin in preparing antihrombotic medicines and healthcare products and a preparation method thereof. Tachyplesin is applied in preparing antiplatelet aggregation and antihrombotic medicines and healthcare products as a component of antiplatelet aggregation and antihrombotic medicines and healthcare products, or as a precursor of antiplatelet aggregation and antihrombotic medicines. Prepared from production wastes of horseshoe crab hemocytes or horseshoe crab reagents, such tachyplesin is capable of obviously inhibiting platelet aggregation and preventing thrombosis; and the tachyplesin has excellent antiplatelet aggregation performance and prolongs bleeding time (BT) and clotting time (CT).
Owner:GUANGDONG MEDICAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com