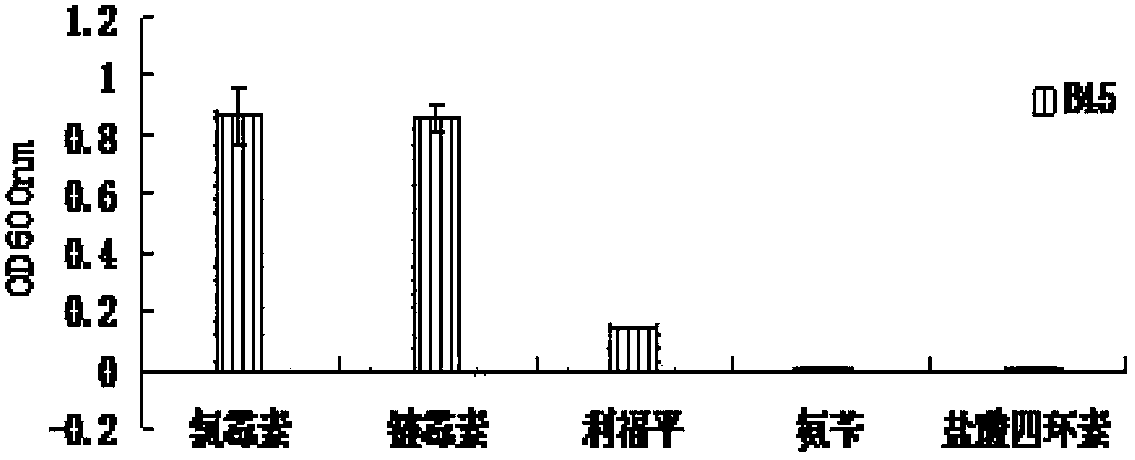
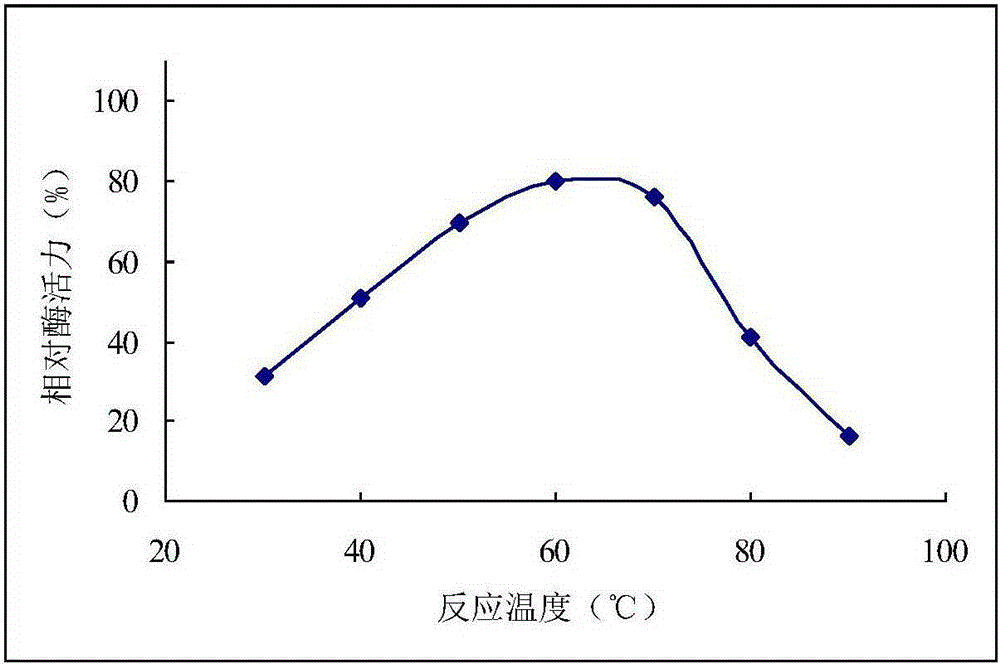
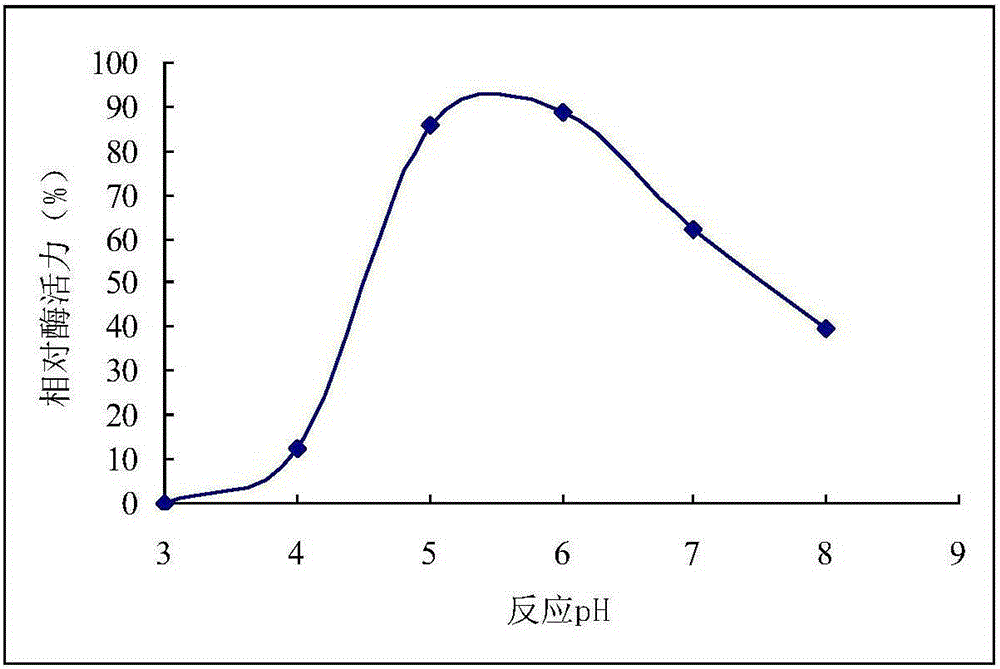
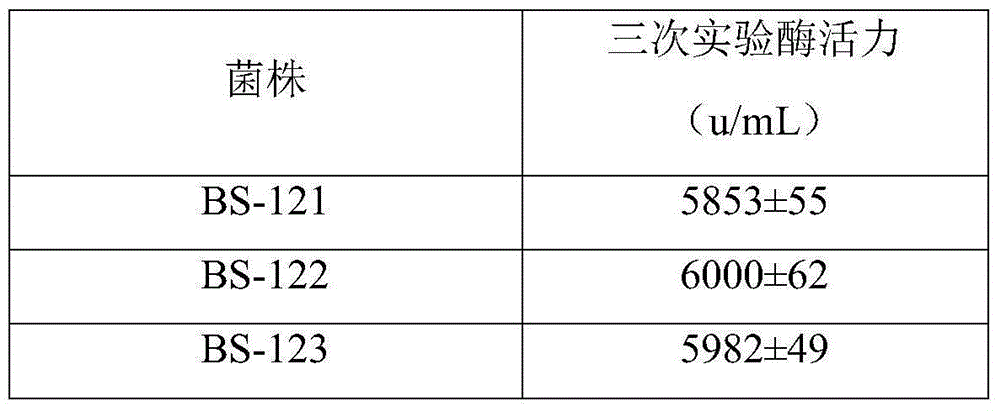
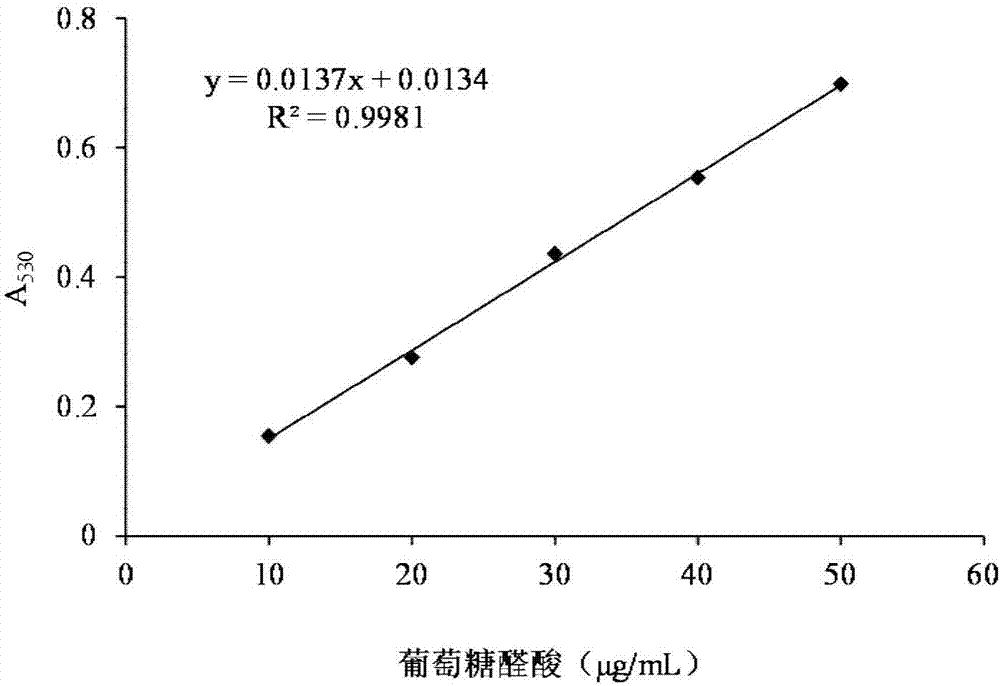
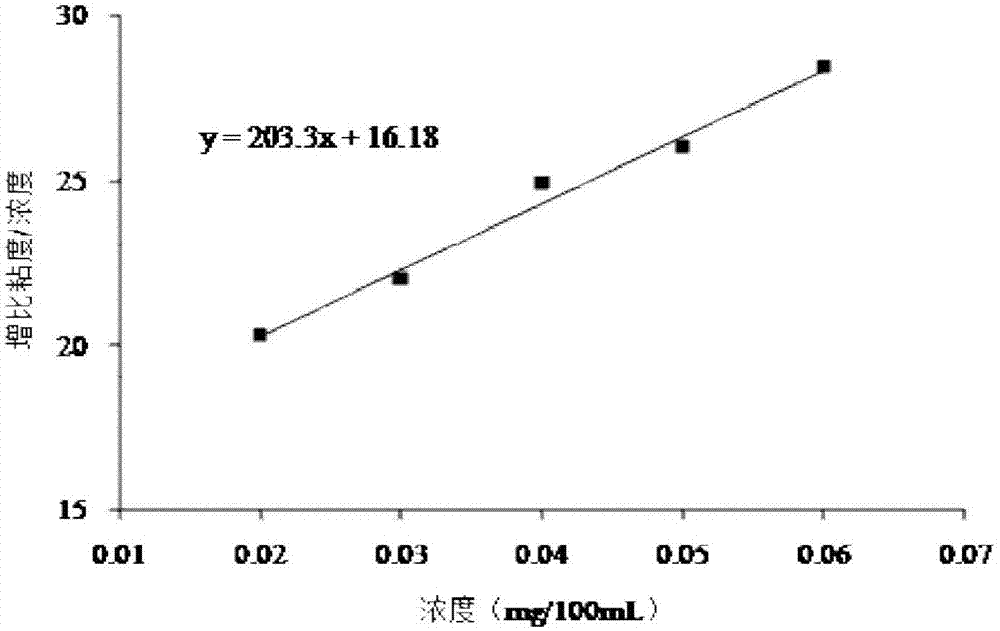
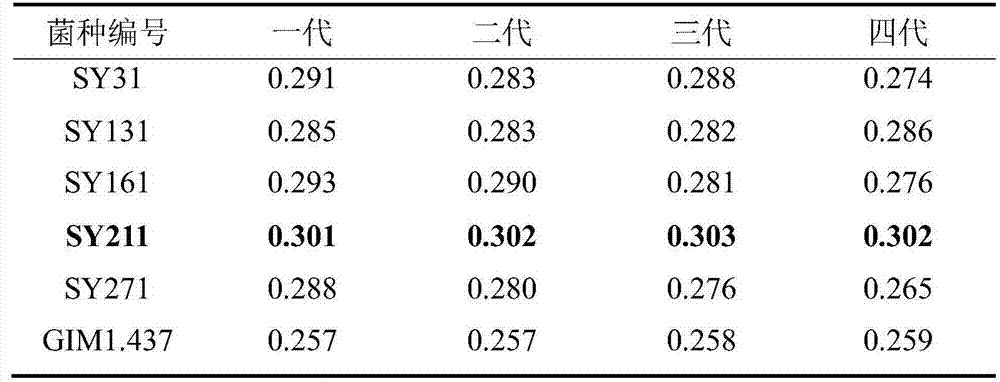
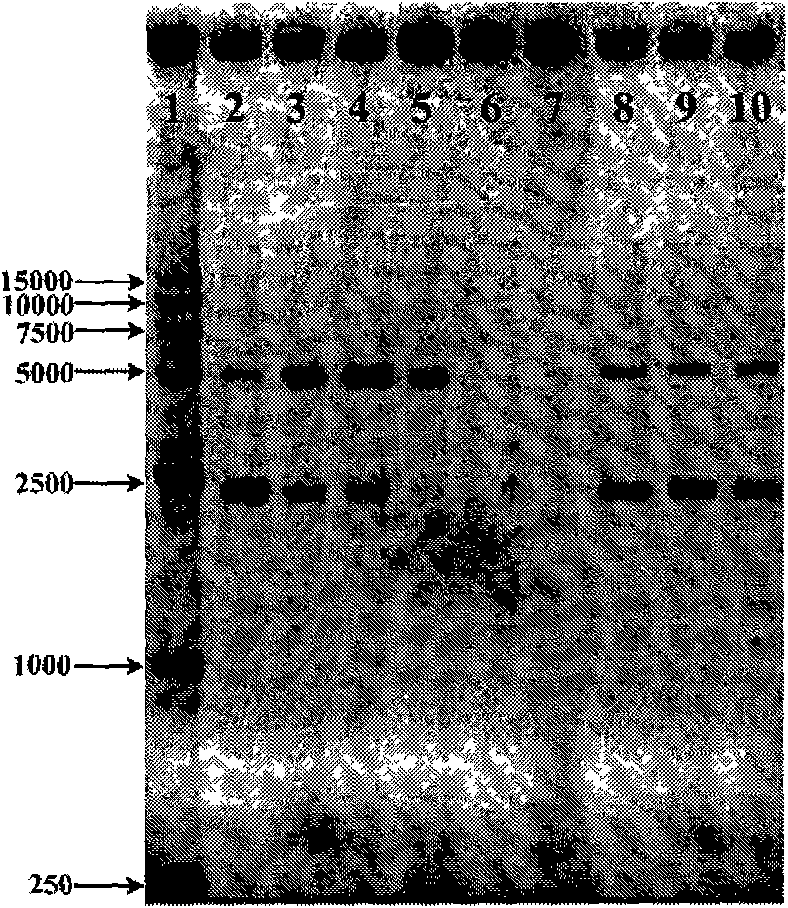
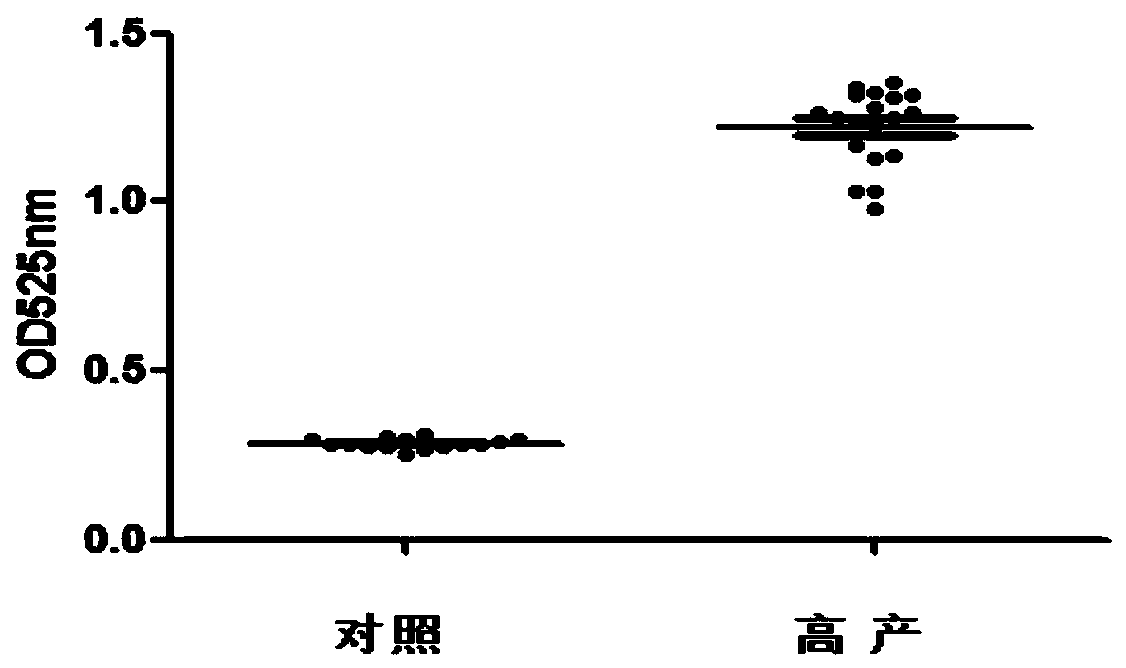
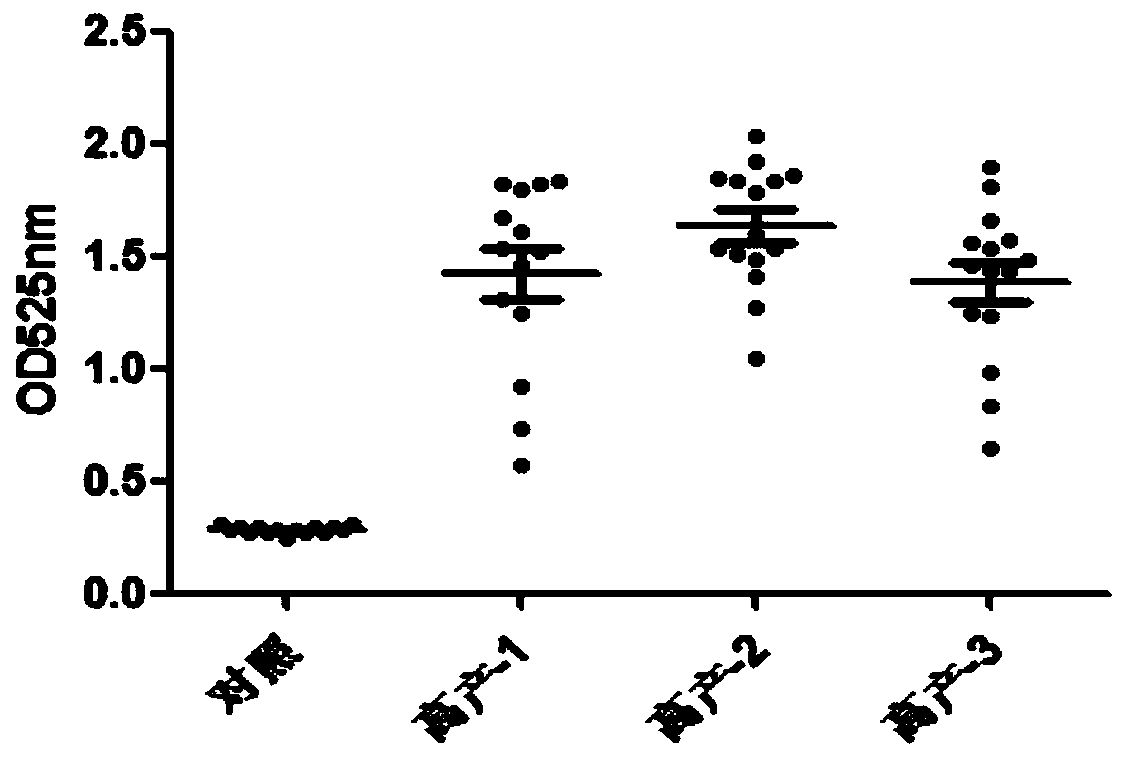
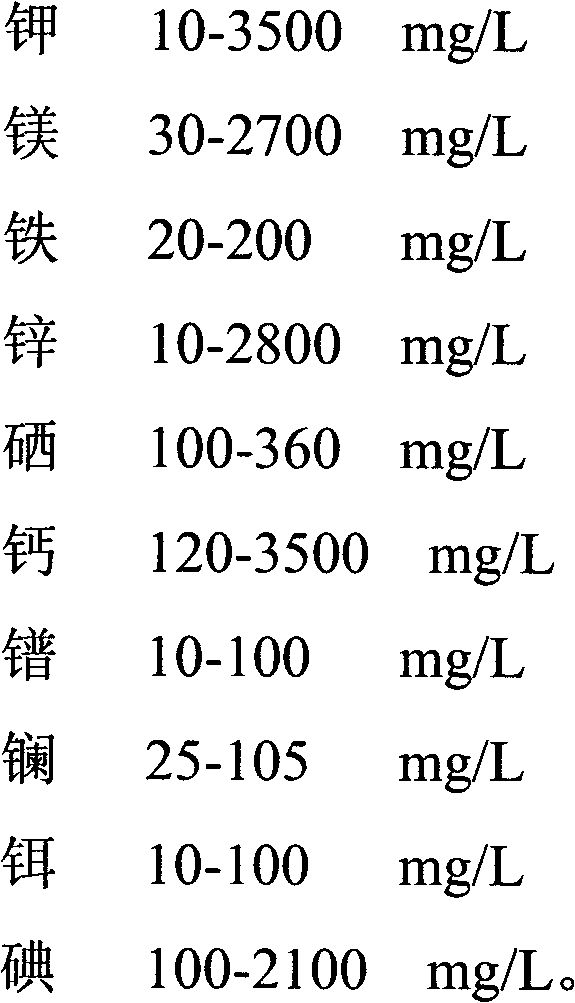
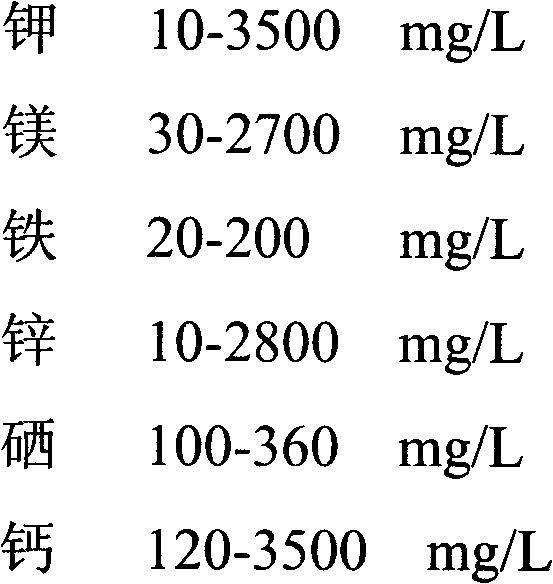
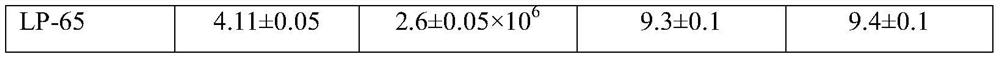Patents
Literature
340 results about "Mutation breeding" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Mutation breeding, sometimes referred to as "variation breeding", is the process of exposing seeds to chemicals or radiation in order to generate mutants with desirable traits to be bred with other cultivars. Plants created using mutagenesis are sometimes called mutagenic plants or mutagenic seeds. From 1930 to 2014 more than 3200 mutagenic plant varieties were released that have been derived either as direct mutants (70%) or from their progeny (30%). Crop plants account for 75% of released mutagenic species with the remaining 25% ornamentals or decorative plants. However, although the FAO/IAEA reported in 2014 that over 1,000 mutant varieties of major staple crops were being grown worldwide, it is unclear how many of these varieties are currently used in agriculture or horticulture around the world, as these seeds are not always identified or labeled as having a mutagenic provenance.
Microalga strain with high CO2 tolerance and high fixation rate and breeding method thereof
InactiveCN102703326AImprove toleranceEasy to fixUnicellular algaeMutant preparationHigh concentrationOrganism
The invention belongs to the technical field of microalga biology, and particularly relates to a microalga strain with high CO2 tolerance and high fixation rate and a breeding method thereof. The microalga is named Chlorella sp.Y-1, and is collected into Common Microorganism Center of China General Microbiological Culture Collection Committee; and collection number is CGMCC No.5429. The invention has the following characteristics: the initial strain is separated from natural environment; after high-CO2-concentration enrichment culture, gene cloning, induced mutation breeding and other operations, the carbon content of the target strain is increased to 56.981%, the optimal fixation concentration is up to 20% (v / v), the fixation rate is up to 5.762g / (L.d), and the maximum tolerance concentration is 100% (v / v); and the target strain has high adaptability to a series of physical and chemical culture conditions, has high culture transfer stability, and high better overall properties than the like research findings at present. The invention aims to solve the bottleneck problem in high concentration CO2 biological fixation technology, cultures an efficient organism capable of efficiently fixing high concentration CO2, implements effective fixation of CO2 in high concentration flue gas and other complex environments, and meanwhile, generates beneficial biological substances.
Owner:QINGDAO TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY
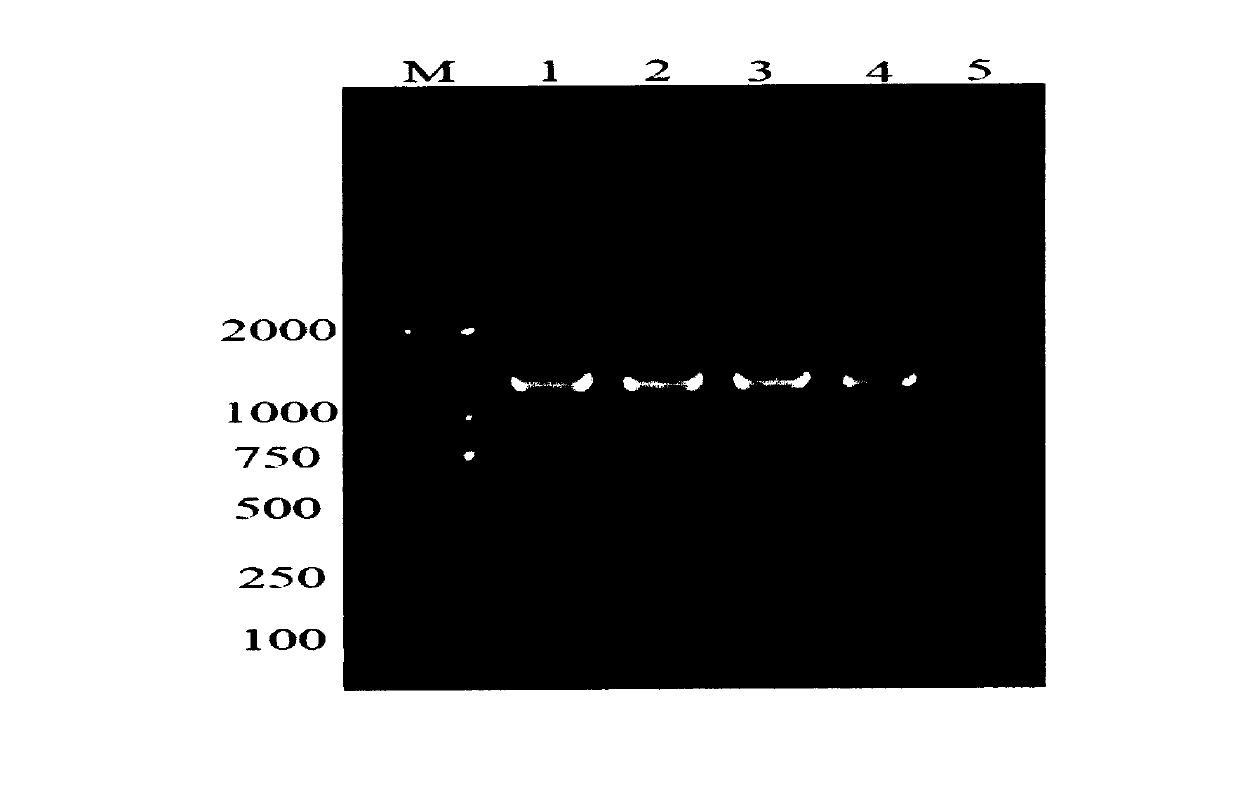
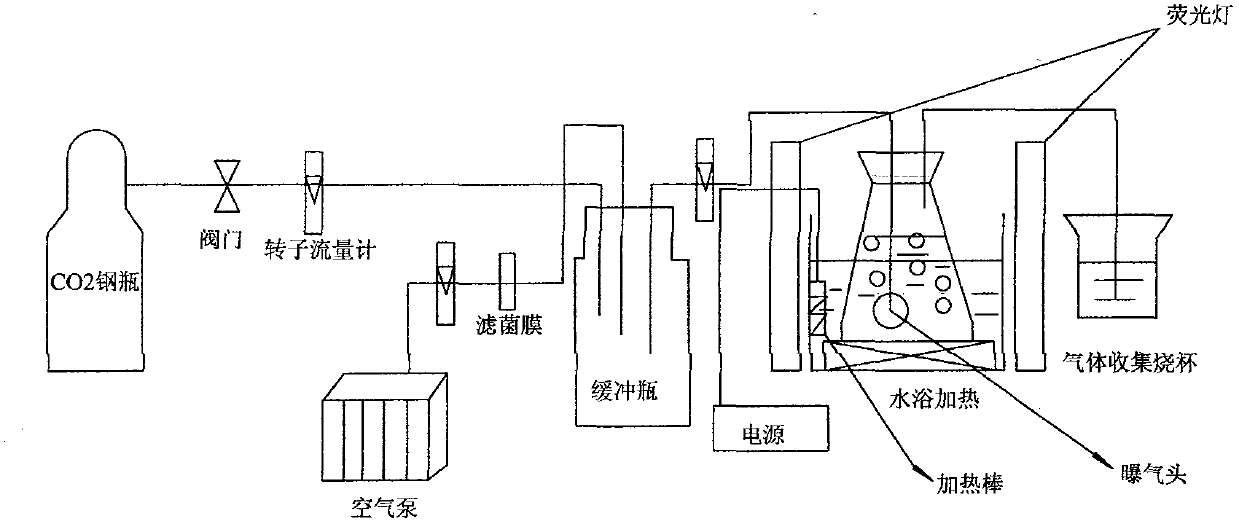
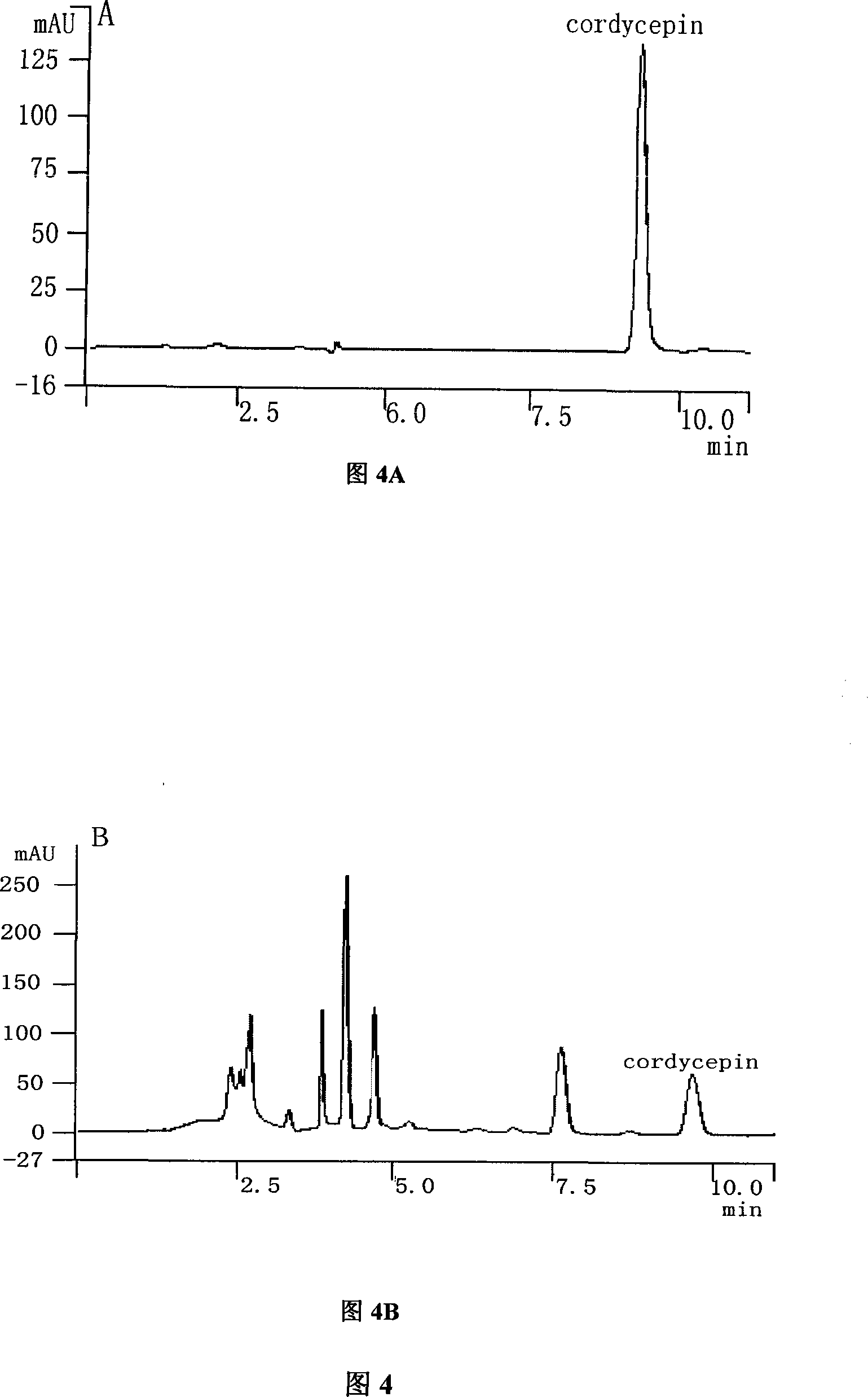
Method for producing cordycepin, breeding of high production cordyceps militaris link bacterial strain BYB-08 and application
The invention pertains to the field of agriculture microbial technology, in particular to a method for producing cordycepin, a breeding and an application of a high-yield Cordyceps militaris bacterial strain. The method obtains the high-yield Cordyceps militaris bacterial strain BYB-08 by mutation breeding, and the bacterial strain is collected in China Center for Type Culture Collection as a patent procedure before the application date (the collection number is CCTCC NO: M207091). The invention discloses a successful embodiment in a combined method of the optimized deep fermentation and the still placement surface layer fermentation culture of the Cordyceps militaris bacterial strain BYB-08 which is obtained by the method, compared with the cordycepin biological yield which is obtained by the methods which are reported in the existing patent documents and the non-patent documents, the cordycepin content in the obtained fermentation liquid of the invention is significantly improved.
Owner:武汉华裕新美菌业有限公司
Novel normal-pressure room-temperature plasma induced mutation breeding device
ActiveCN103981091ASmooth dischargeEnables continuous automated processingBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsInduced mutationControl system
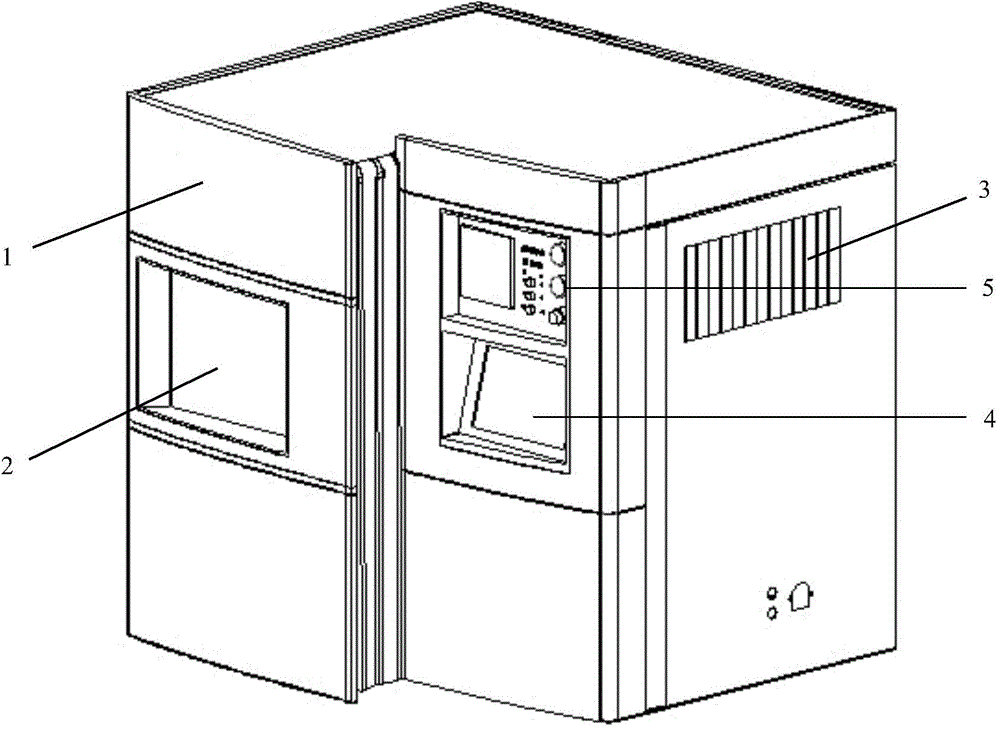
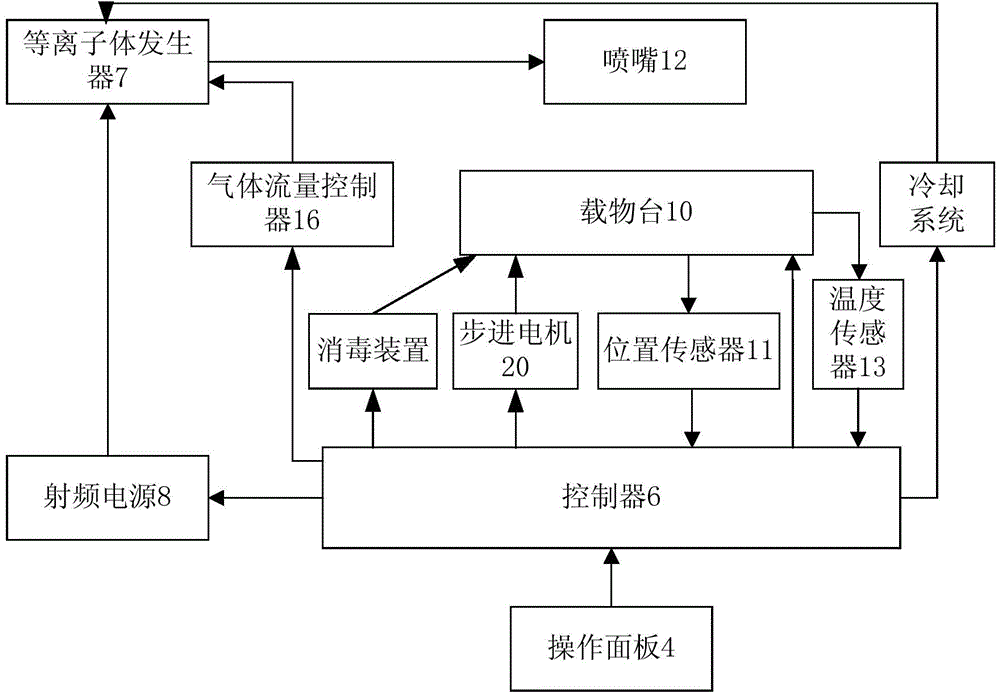
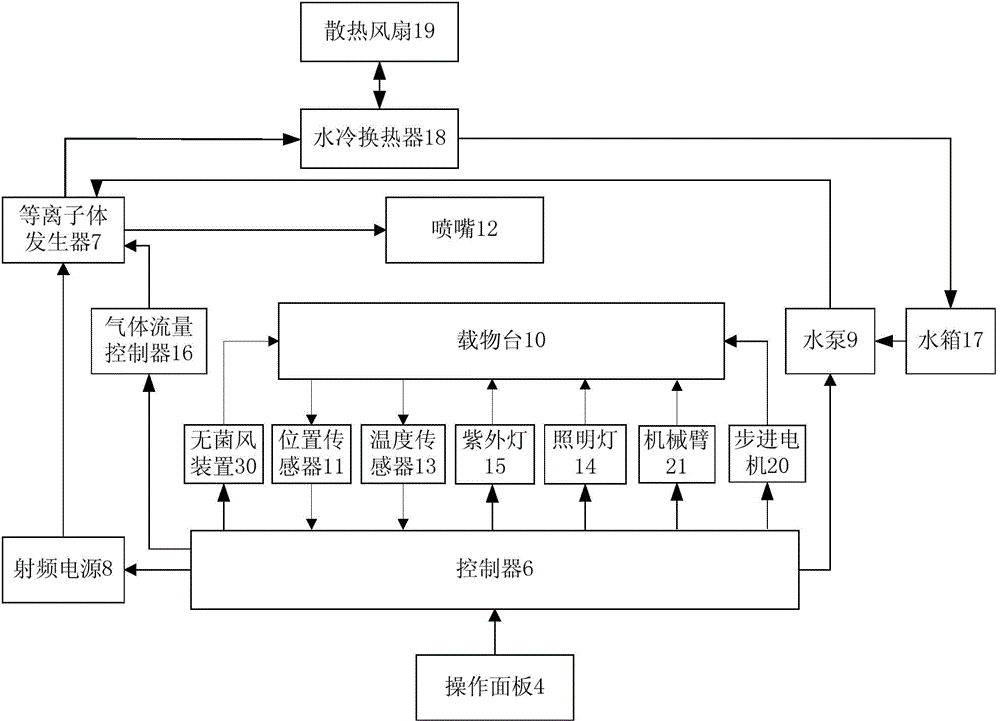
The invention relates to a novel normal-pressure room-temperature plasma induced mutation breeding device. The novel normal-pressure room-temperature plasma induced mutation breeding device comprises a sample processing system, a cooling system, a control system and a detection system; the sample processing system comprises a clean working chamber without bioactive contaminants; a step motor and an object stage are arranged in the clean working chamber; the object stage is arranged on the step motor; at least one sterilizing device mounting position is reserved in the inner cavity or on the wall of the clean working chamber; the detection system comprises a gas flow controller, a temperature sensor and a position sensor; and the control system comprises an operating panel and a controller, and the controller is used for controlling the step motor to realize rising and falling or horizontal rotation of the object stage so as to automatically process a plurality of samples. The novel normal-pressure room-temperature plasma induced mutation breeding device is capable of realizing the functions of continuous automatic processing, automatic sterilization, automatic monitoring and control on the samples, and also capable of completing the plasma induced mutation breeding in the normal pressure and room temperature environment at higher efficiency.
Owner:WUXI TMAXTREE BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Induced rapid propagation culture medium for somatic embryos of leaves in vitro of photinia x frasery
InactiveCN102124954AGrow vigorouslySolve the problem of germplasm degradationHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureBiotechnologyBud growth
The invention discloses an induced rapid propagation culture medium for somatic embryos of leaves in vitro of photinia x frasery, which comprises a bud starting culture medium, a test-tube seedling enrichment medium, a first somatic embryo and / or adventive bud formation culture medium, a second somatic embryo and / or adventive bud formation culture medium, a third somatic embryo and / or adventive bud formation culture medium, a first somatic embryo and / or adventive bud growth and differential medium, a second somatic embryo and / or adventive bud growth and differential medium, and a sound seedling rooting medium. By using the induced rapid propagation culture medium for the somatic embryos of the leaves in vitro of the photinia x frasery, a basal culture medium and content are improved, and the culture condition is adjusted to ensure that the photinia x frasery which is difficult to propagate propagates rapidly through the occurring pathway of the somatic embryos, the plant transplantation survival rate is over 95 percent, a seedling grows healthily, so that the problem of quality reduction of a good seed can be effectively solved, a large amount of high-quality purified and rejuvenated virus-free nursery stocks can be provided for production, and an ideal acceptor system can be provided for genetic transformation or mutation breeding seed selection of the photinia x frasery.
Owner:JIANGSU POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE OF AGRI & FORESTRY +1
Protoplast mutation breeding method for improving cordycepin content of cordyceps militaris
InactiveCN103215250AGood mutagenic effectEasy to operateFungi productsLichen productsBiotechnologyNitroso
The invention relates to a protoplast mutation breeding method for improving the cordycepin content of cordyceps militaris. The method comprises the following steps of activated culture of bacterial strains, solid culture of mycelia, liquid mycelia culture, mycelia enzymolysis, protoplast nitrosoguanidine (NTG) mutation, protoplast regeneration culture, regenerated bacteria subculture, fermentation culture, filtering, further washing of mycelia, measurement of cordycepin content in the mycelia, preservation of the bacteria strain with high cordycepin content, measurement of the genetic stability and the like. Due to the adoption of the method, the cordycepin content of the cordyceps militaris can be increased.
Owner:XUZHOU HONGYU AGRI TECH
Induction rapid-propagation culture method for Photinia fraseri in-vitro leaf somatic embryos
InactiveCN102124955ASolve the problem of germplasm degradationHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureBiotechnologySomatic embryogenesis
The invention provides an induction rapid-propagation culture method for Photinia fraseri in-vitro leaf somatic embryos, comprising the following steps: (1) building a regeneration system of a Photinia fraseri asepsis test tube seedling; (2) building a high-frequency rapid-propagation system induced by an in-vitro somatic embryo and an adventitious bud; and (3) rooting, acclimatizing and transplanting for the test tube seedling. The induction rapid-propagation culture method for Photinia fraseri in-vitro leaf somatic embryos is characterized in that coordinated sets of measures of selecting a proper explant, improving a basic culture medium and ingredients, regulating culture conditions and the like are adopted, and the Photinia fraseri of which the seed is difficult to breed is subjected to path rapid propagation by the somatic embryos; the plant transplantation survival rate is higher than 95%; the germchit grows strongly to solve the problem that an excellent germchit quality degenerates, and a great quantity of purified and rejuvenated detoxification nursery stock with good quality can be provided for production; and in addition, and ideal receptor system is provided for breeding new specimens for Photinia fraseri by genetic transformation or mutation breeding.
Owner:JIANGSU POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE OF AGRI & FORESTRY +1
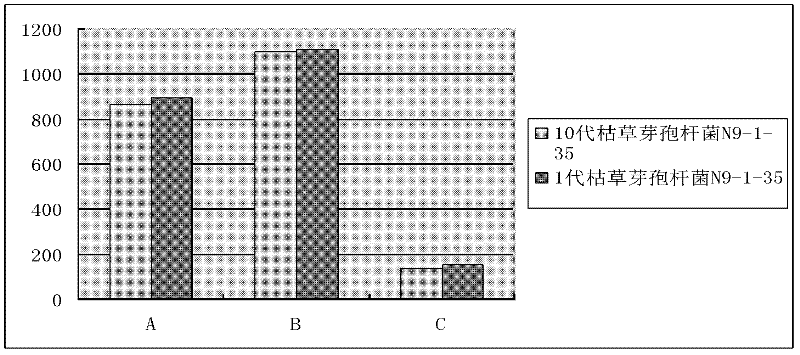
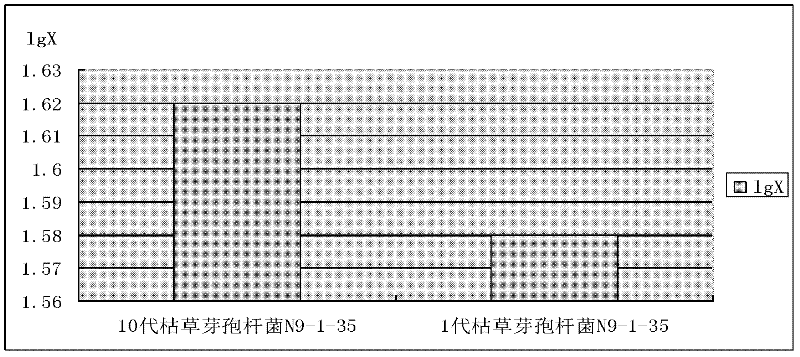
Bacillus subtilis bred by space mutation breeding technology and application of Bacillus subtilis
ActiveCN102329749APromote digestion and absorptionImprove conversion rateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesFeed conversion ratioDigestion
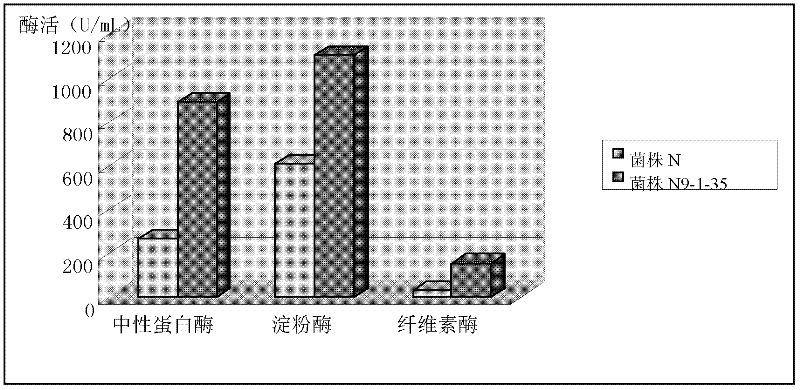
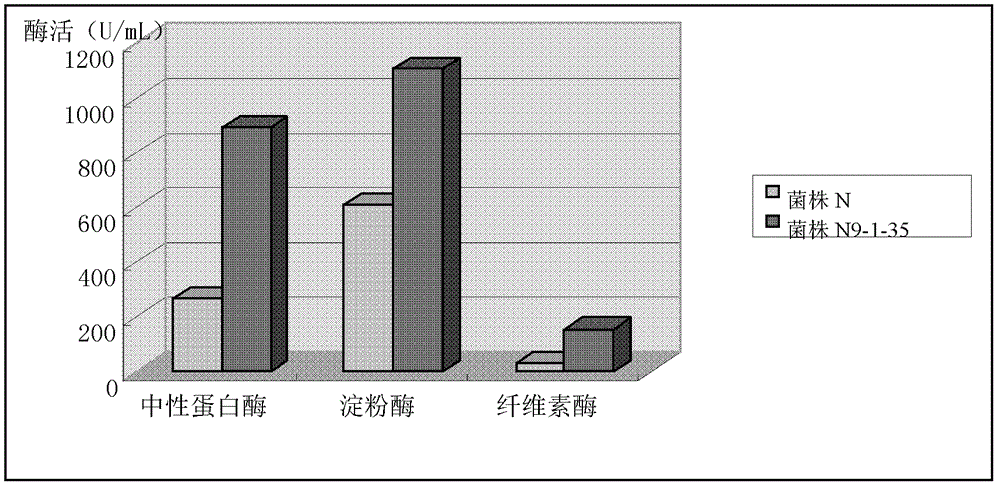
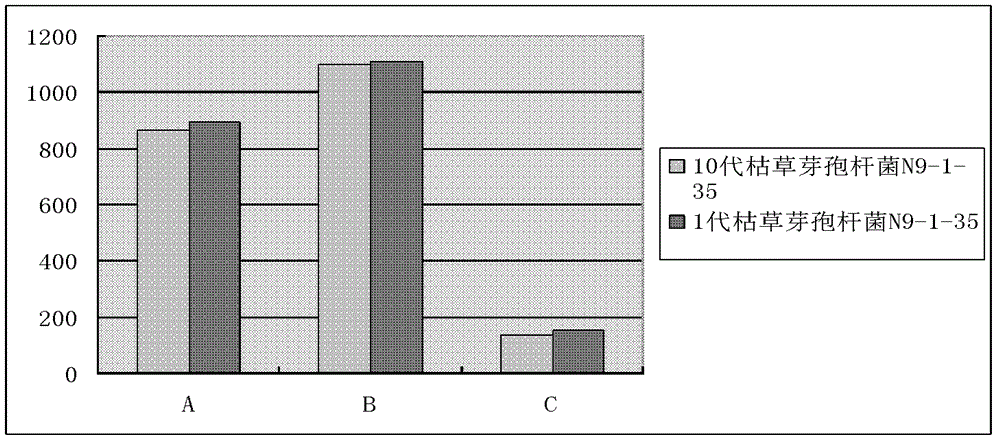
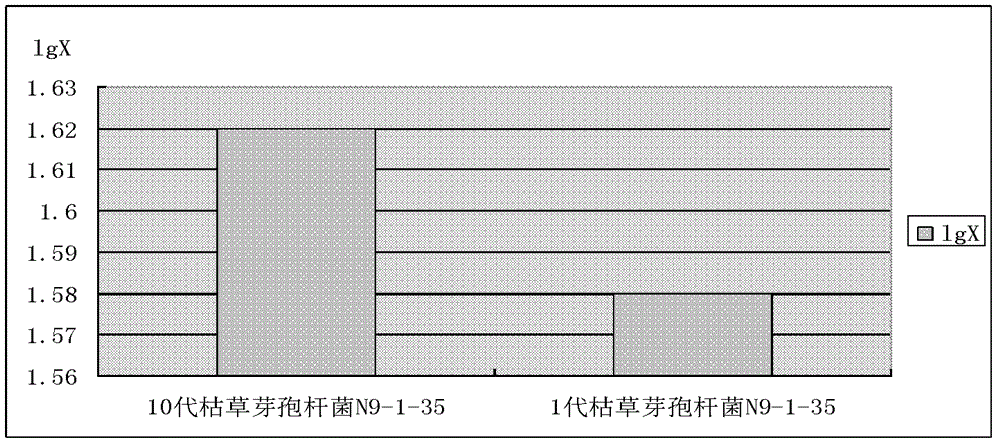
The invention discloses Bacillus subtilis bred by a space mutation breeding technology. The strain is named Bacillus subtilis N9-1-35 and was collected in China Center for Type Culture Collection on August 31, 2011, and the collection number is CCTCC M2011301. The test shows that the Bacillus subtilis is an excellent probiotic strain. After entering intestinal tracts of animals, the Bacillus subtilis achieves the effects of a probiotic and can also generate a plurality of kinds of digestive enzymes in the growth and reproduction process of the animals, so that the digestion and absorption of the animals on feeds are improved, the conversion rate of the feeds is improved, and the cost of the feeds is reduced; and the Bacillus subtilis can be used for producing enzyme-producing probiotics, and is a strain which has excellent research and development value. The invention also discloses an enzyme-producing probiotic. The enzyme-producing probiotic consists of Bacillus subtilis powder, Streptococcus lactis powder, Lactobacillus acidophilus powder and corn starch.
Owner:山东宝来利来生物工程股份有限公司
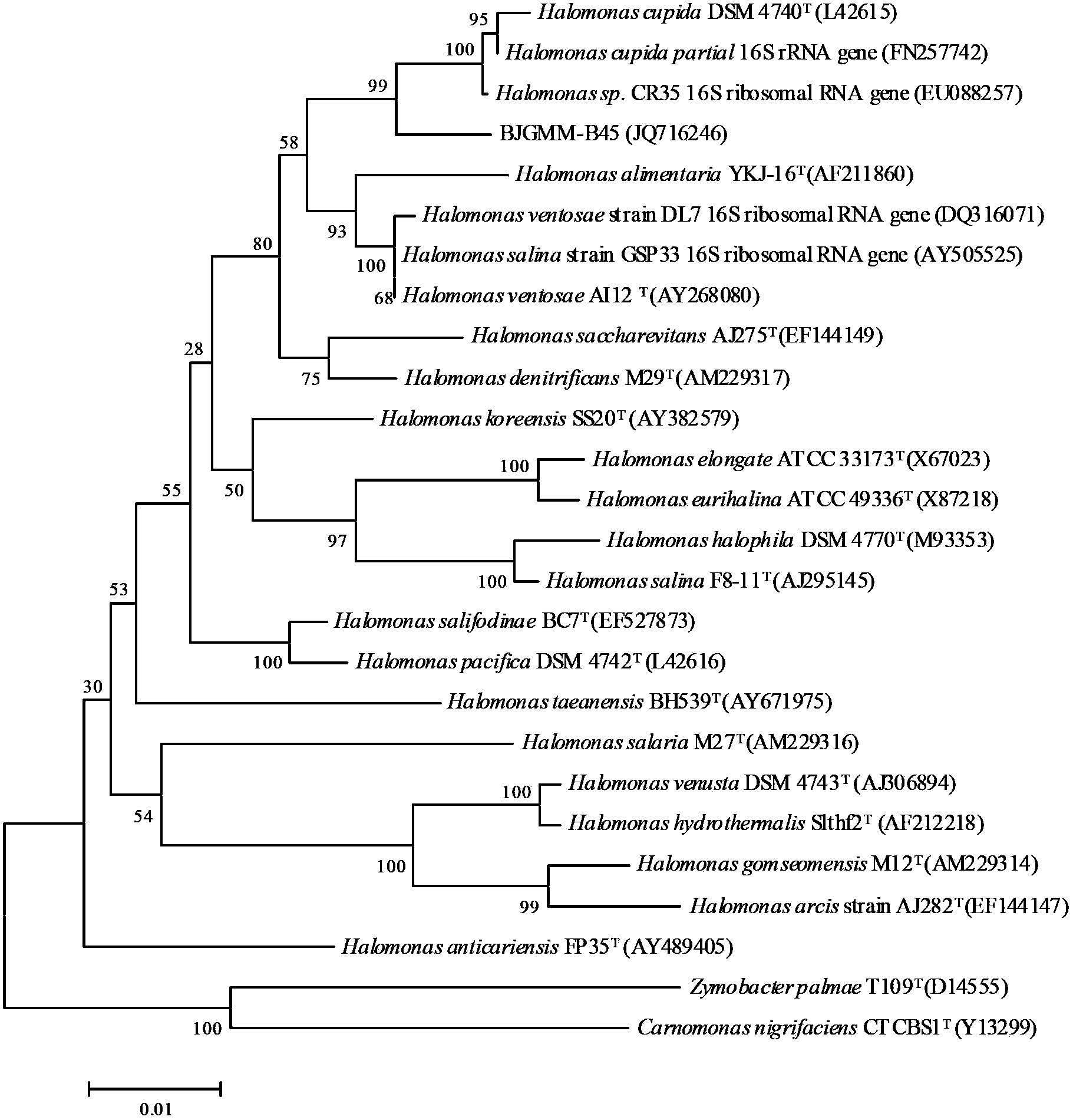
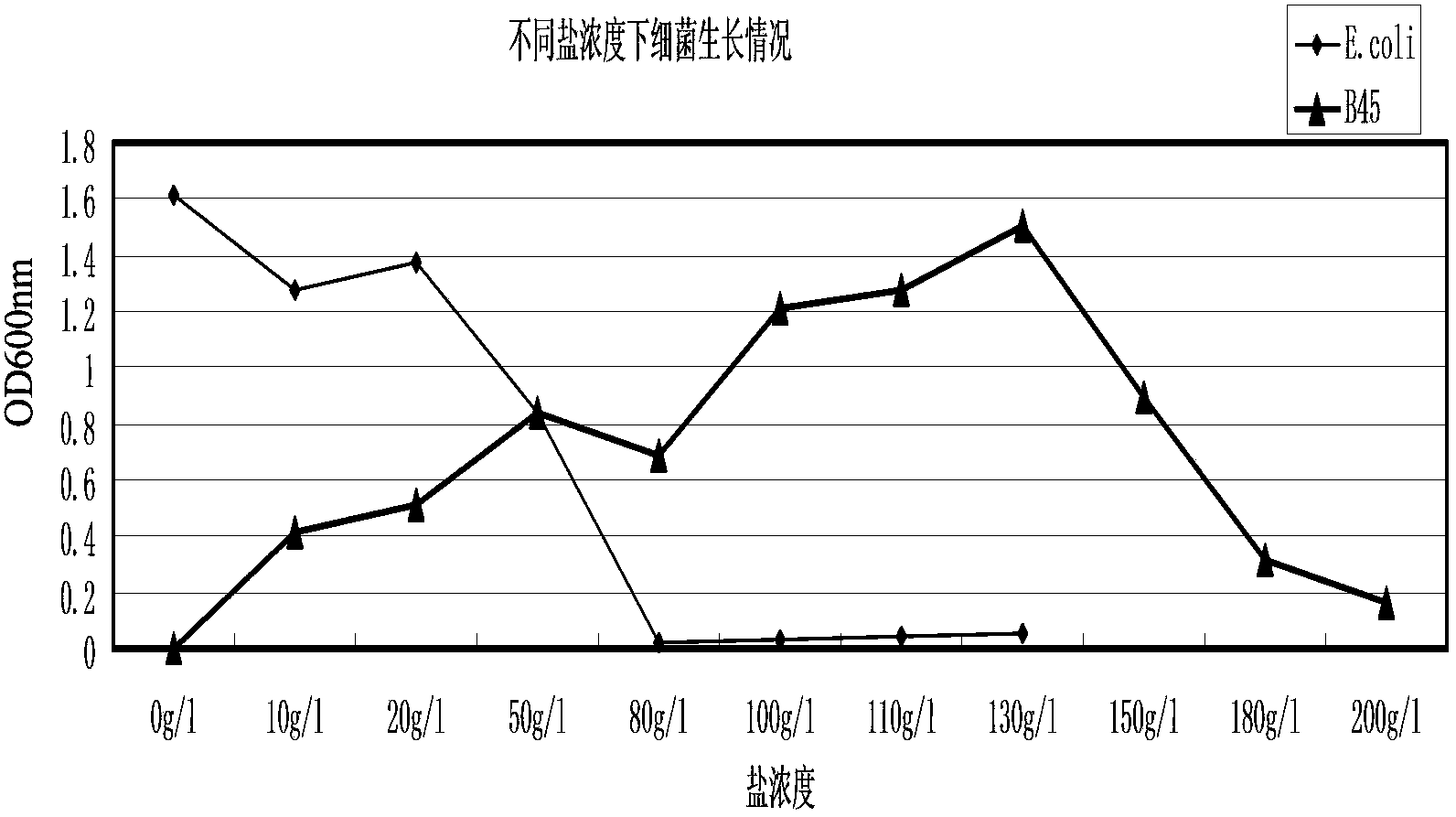
Halomonas huanghegensis BJGMM-B45 and application thereof
InactiveCN103805531AGood characterImproved stress resistance traitsAgriculture tools and machinesBacteriaBiotechnologyAlkali soil
The invention provides a bacteria halomonas huanghegensis BJGMM-B45, which has excellent salt tolerance. The preservation number of the halomonas huanghegensis BJGMM-B45 is CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) NO.7022. The bacteria not only can be directly used as functional bacteria for improvement of saline-alkali soil, but also can be used as a gene donor of a novel transgenic organism; the organism can obtain excellent stress resistance if an excellent salt tolerance gene is transferred into the organism; in addition, the bacteria also can be used as a novel gene engineering bacteria, and can obtain more excellent properties by accepting other foreign excellent genes; furthermore, more mutant strains with excellent properties can be obtained through improvement of properties by traditional mutation breeding manner.
Owner:THE INST OF BIOTECHNOLOGY OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Bacillus subtilis of high-yield mesophilic alpha-amylase and liquid fermentation method for bacillus subtilis
ActiveCN105176883AHigh Fermentation Enzyme ActivityGood antibacterial effectBacteriaMicroorganism based processesRoom temperatureMutation breeding
The invention provides bacillus subtilis mutant strain of high-yield mesophilic alpha-amylase and a liquid fermentation method for the bacillus subtilis mutant strain. The strain is obtained through atmospheric and room temperature plasma (ARTP) mutation breeding, and the collection number of the strain is CGMCC No.10786. By fermentation condition optimization, average fermentation enzyme activity can reach 7309mu / mL, and the maximum average fermentation enzyme activity is 7400 mu / mL; compared with an original strain before mutation, the strain has a better antibacterial effect; the optimum temperature of the mesophilic alpha-amylase produced by liquid fermentation of the strain is 60 to 70 DEG C, and after being stored for 12h at 60 to 70 DEG C, the enzyme still has more than 75 percent of enzyme activity; the optimum reaction pH of the enzyme is 5.2 to 6.2, and after being stored for 12h at pH 5.2 to 6.2, the enzyme still has more than 85 percent of enzyme activity.
Owner:SHANDONG LONGKETE ENZYME PREPARATION
Streptococcus equi subsp. Zooepidemicus subspecies SXY36 and application in fermentation production of hyaluronic acid
ActiveCN107338201ANo hemolyticImprove fermentation yieldBacteriaMicroorganism based processesHemolysisGamma ray
Owner:株洲市中建新材料有限公司
Method for breeding microorganisms by plasma-induced mutation
InactiveCN101624591ARich varietySimplified typesMutant preparationMicroorganism based processesPlasma jetActive particles
The invention discloses a method for breeding microorganisms by plasma-induced mutation, which radiates microorganisms to be induced to mutate with a plasma jet flow that uses neutral active particles as acting particles to obtain mutated microorganisms. The method in which the neutral active particles in the plasma jet flow play a main induction role has the advantages of: ensuring the high activity of forward mutant strains and the high capability and genetic stability of produced target products, reducing mutagenesis period and improving mutagenesis efficiency, inducing a great variety of microorganisms such as prokaryotic microorganisms, eukaryotic microorganisms and archaebacteria in form of microbial community, bacterial suspension or spore suspension, simplifying experimental operation by avoiding culturing the processed microorganisms in the dark, having the characteristics of simple, safe and pollution-free whole operation, low equipment and experiment cost and the like and having great potential role in the field of industrial microorganism induced mutation breeding.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Red yeast engineering bacterium for high-yield production of astaxanthin and construction method thereof
ActiveCN106318878AImprove metabolic fluxIncrease productionFungiMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismYeast
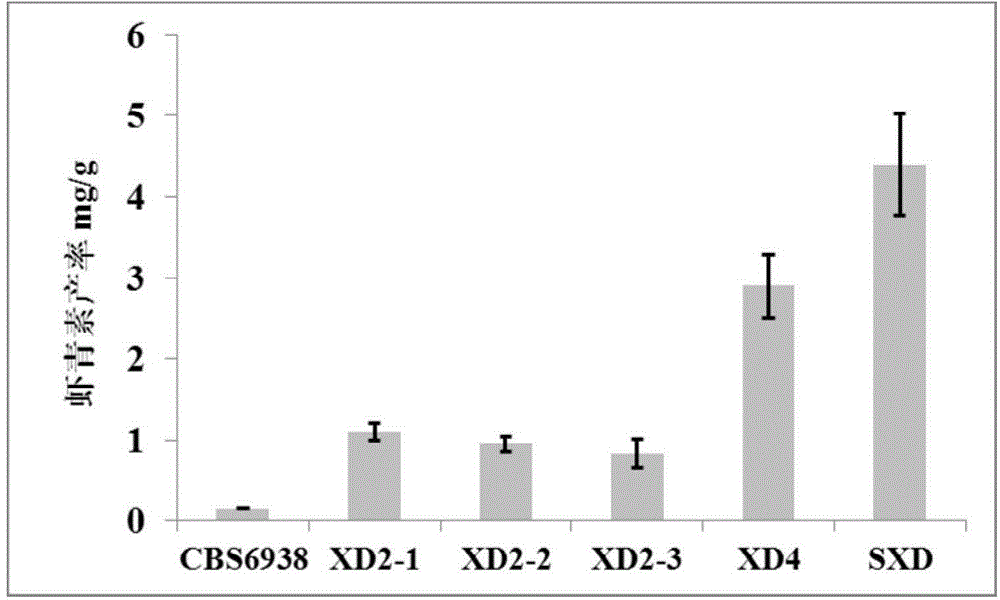
The invention relates to a red yeast engineering bacterium for high-yield production of astaxanthin and a construction method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of biology. The red yeast engineering bacterium is an xanthophyllomyces dendrorhous strain SXD, and is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center, the preservation number is CGMCC No.10519, and the preservation date is February 4th, 2015. The xanthophyllomyces dendrorhous engineering bacterial strain SXD is obtained by a metabolic engineering method, and metabolic flux of astaxanthin synthesizing route of xanthophyllomyces dendrorhous is substantially improved. The highest astaxanthin content of the xanthophyllomyces dendrorhous engineering bacterial strain SXD is 4.4mg / g dry cell weight, after optimal cultivation, the astaxanthin content of the bacterial strain reaches 7.1mg / g dry cell weight, the maximum biomass is 83.8g / L, and an industrial exploitation prospect is provided. The SXD bacterial strain is not treated by any mutagenesis, the astaxanthin yield can be increased continuously and significantly by means of a mutation breeding, and production cost of yeast astaxanthin is hopeful to reduce continuously.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Strain for generating phospholipase D with high and stable yield by utilizing physical and chemical mutation
InactiveCN101875929AImprove efficiencyEasy to operateMutant preparationMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismLithium chloride
The invention relates to a strain for generating phospholipase D with high and stable yield by utilizing physical and chemical mutation, belonging to the technical field of microbial mutation. The strain is characterized in that the phospholipase D is prepared by fermenting streptomyces chromofuscus of high yield phospholipase D, which is obtained by taking the streptomyces chromofuscus as an original strain and sequentially carrying out composite mutation of ultraviolet rays and lithium chloride and composite mutation of atmosphere cold plasmas and the lithium chloride on a monospore bacterial suspension thereof. The invention has the advantages that the streptomyces chromofuscus of the high yield phospholipase D is obtained through mutation screening, thereby providing a high yield strain with higher application value to industrial production of the phospholipase D, laying a good foundation for fermentation culture and application of the phospholipase D, and also providing a good and feasible method for microbial mutation breeding. The invention adopts a mutation and screening method, has the advantages of simple operation, high efficiency and the like, and has a practical value on screening the strain with an industrial application value.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Full-automatic physical mutation breeding machine
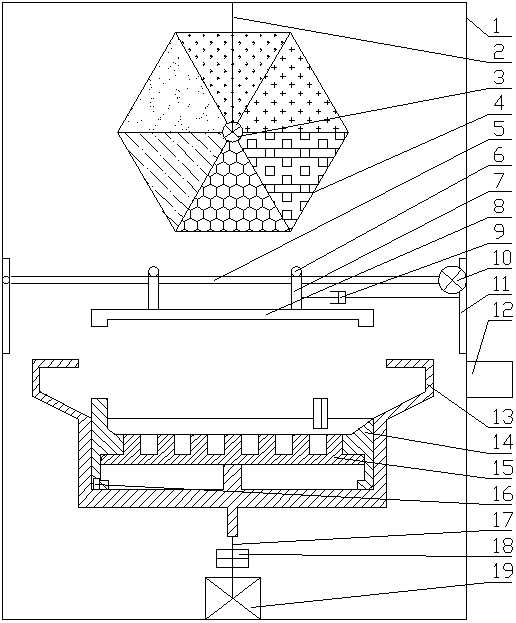
InactiveCN103461117ARealize free combinationFully automatic conversionPlant genotype modificationMicrowaveMutation breeding
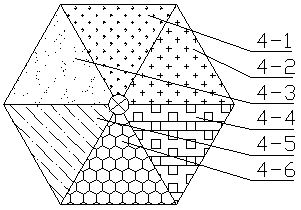
The invention provides a full-automatic physical mutation breeding machine. The breeding machine comprises a shell (1), a hanging bracket (2), a stepping motor (3), a radiation table (4), a beam (5), rollers (6), a movable hanging bracket (7), an electromagnetic chuck (8), a vibration exciter (9), a motor (10), guide rails (11), a program control table (12), a rotating bin (13), a vibrating bin (14), a seed supporting table (15), a fixed column (16), a speed changer output shaft (17), a speed changer (18) and a rotating motor (19), wherein the radiation table (4) consists of an alpha-ray emitter (4-1), a beta-ray emitter (4-2), a gamma-ray emitter (4-3), an X-ray emitter (4-4), an ultraviolet radiator (4-5) and a microwave particle radiator (4-6). The full-automatic physical mutation breeding machine can realize free combination of various programs as well as full-automatic switching of various breeding processes during physical mutation breeding in a static state and a dynamic state, thereby having a very high application value.
Owner:HEBEI UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
White rot fungi, breeding method and use thereof
InactiveCN101469312AStable enzyme productionShort cycleFungiMutant preparationFiberAutomatic control
The invention relates to Trametes Versicolor YS-L613 and a breeding method and application thereof. The Trametes Versicolor YS-L613 is prepared by the method through mutation breeding. The breeding method is to take Trametes Versicolor as a starting strain, adopt composite mutation breeding technology which combines UV, 60 CO, ultraviolet rays, nitrosoguanidine, ion implantation and microwave treatment, and breed the YS-L613 strain for high-yield production of laccase. The invention performs breeding operation through physiochemical treatment methods such as ion implantation, the ultraviolet rays and mutagen, finally obtains the YS-L613 strain for high-yield production of the laccase, and adopts experimental automatic control technology, strain fermentation control technology and strain extraction technology to develop laccase products. As proved by experiments of the laccase in pulp bleaching, fiber modification and pulp deinking, utilization of the laccase in the paper-making industry can improve the quality of paper, reduce environmental pollution and save the cost.
Owner:HENAN YANGSHAO BIOCHEM ENG
In-vitro sodium azide (NaN3) mutation breeding technology of dendranthema morifolium
InactiveCN103039369AEasy to operateHigh mutation frequencyPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsInduced mutationShoot apex
The invention relates to a chemical mutation breeding technology in the field of biotechnologies, and particularly relates to an in-vitro sodium azide (NaN3) mutation breeding technology of dendranthema morifolium. The in-vitro NaN3 mutation breeding technology comprises the following steps of: performing culture in vitro on an immature stem, a stem tip or a leaf of the dendranthema morifolium to form an aseptic seedling; processing the stem tip and a stem segment of the aseptic seedling, which are taken as explants, by sodium azide (NaN3) in a breeding process to carry out induced mutation; rooting and transplanting a test-tube plantlet; and finally breeding excellent mutant in a field at a flowering phase. The in-vitro sodium azide (NaN3) mutation breeding technology can effectively overcome the obstacle of breed improvement of a clonal plant and the constraints of low bud-variation frequency and small mutational range under natural conditions, can be used for obtaining the excellent mutant within a short period of time, ensures high induced mutation efficiency, and has an important value to the genetic improvement of asexual propagation of the dendranthema morifolium with medicinal and ornamental values.
Owner:ANHUI SCI & TECH UNIV
Bacillus subtilis capable of stably producing chymosin with high yield by mutation and application
InactiveCN101665779AShorten the production cycleReduce fermentation costsBacteriaHydrolasesSporeMutation breeding
The invention discloses a bacillus subtilis capable of stably producing chymosins with high yield by mutation and an application. The original strain used is a bacillus subtilis which is obtained by the screening of a laboratory and used for producing products such as cheeses and the like by fermentation, and is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC) in February 2008, with the preservation name of bacillus subtilis QL-2 (Bacillus subtilis QL2) and the preservation No. of M208023. The mutation breeding comprises the following steps of: taking the bacillus subtilis QL-2 which is preserved in CCTCC with the culture preservation No. of M208023 as the original strain, and then culturing the bacillus subtilis QL-2 on a rejuvenation culture medium and a fermentation culture medium in sequence so as to obtain the original strain suspension; using a vortex device to make the strain suspension into single spore suspension; and then conducting ultraviolet mutation and culture for a plurality of times to the single spore suspension; and finally obtaining the bacillus subtilis YB-3 (Bacillus subtilis YB-3 , CCTCC NO: M209075) capable of stably producing chymosins with high yield. The bacillus subtilis capable of stably producing chymosins with high yield can be used for preparing chymosin crude enzymes by liquid fermentation, which can be used for preparing cheeses and caseins, and shortens the clotting time of milk.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY
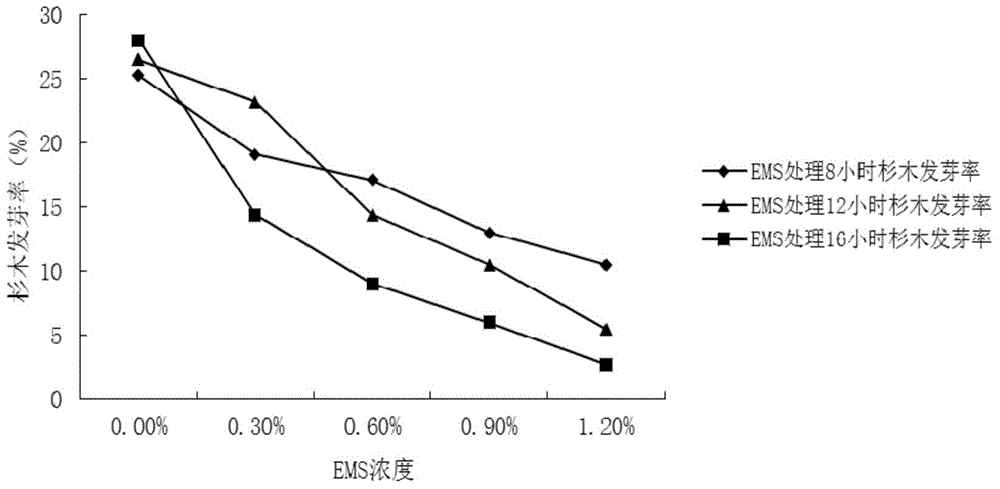
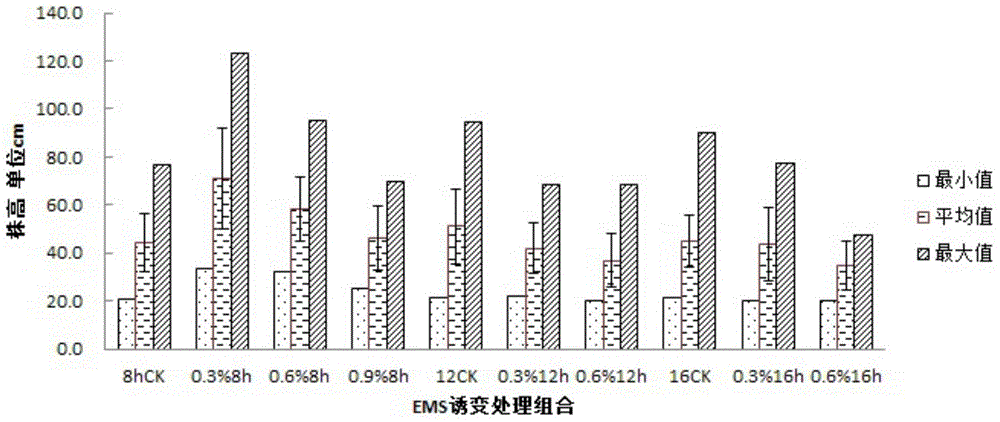
Mutation breeding method for cunninghamia lanceolata
InactiveCN104542265AIncrease mutation rateHigh mutant seedling emergence ratePlant genotype modificationEthylmethane SulfonateMutation breeding
The invention discloses a mutation breeding method for cunninghamia lanceolata. The method comprises the following steps: especially adopting ripen seeds of a cunninghamia lanceolata seed garden; carrying out low-temperature overwintering treatment, carrying out constant-temperature seed soaking stimulation on a gibberellin solution with specific concentration, immediately putting the gibberellin solution subjected to constant-temperature seed soaking stimulation into clear water, carrying out variable-temperature soaking for 3 days, and carrying out sprout promoting treatment; respectively carrying out colchicine mutation treatment, ethylmethane sulfonate (EMS) mutation treatment and sodium azide (NaN3) mutation treatment; and finally seeding and germinating the cunninghamia lanceolata seeds which are subjected to mutation treatment, so as to obtain a large group of cunninghamia lanceolata mutation seedlings. The cunninghamia lanceolata mutation seedlings obtained by the mutation method have the characteristics of obvious phenotypic characteristic variation, large population growth characteristic variation range and the like; a great number of mutated cunninghamia lanceolata materials can be formed within a short period of time by the method disclosed by the invention; and a foundation is laid for breeding of a new variety of cunninghamia lanceolata.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
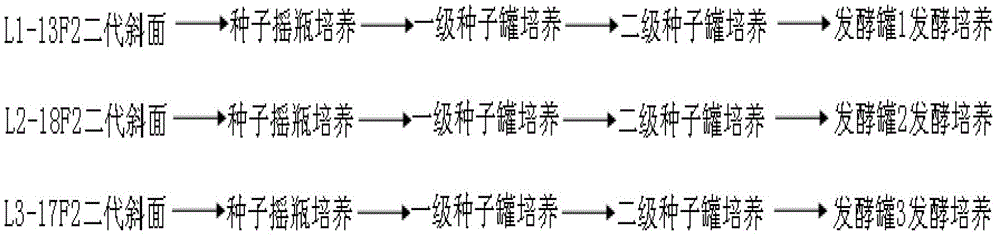
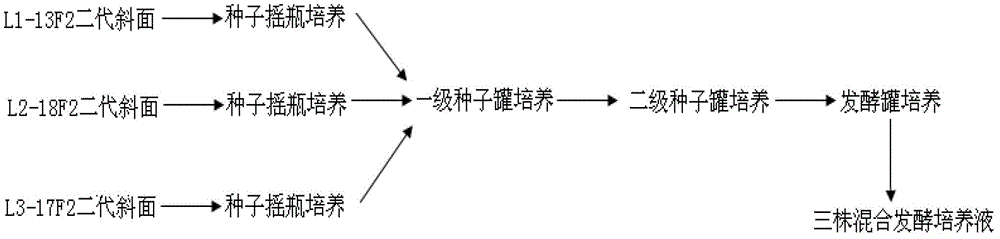
Mixed liquid fermentation process of three plants of bacillus licheniformis
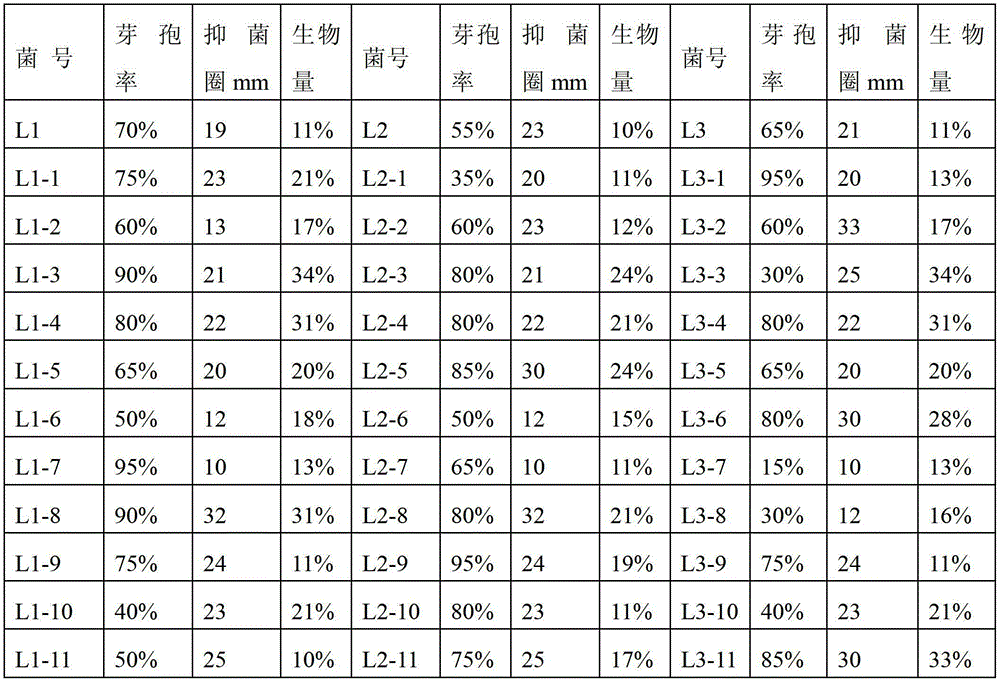
InactiveCN103146624AChange growth characteristicsThe fermentation process is simpleBacteriaMutant preparationBacillus licheniformisMutation breeding
The invention discloses a mixed liquid fermentation process of three plants of bacillus licheniformis. According to the mixed liquid fermentation process, the three plants of the bacillus licheniformis, namely L1, L2 and L3 with different physiological functions, which are originally cultured under different conditions, are subjected to solid culture and shaking flask seed preparation by performing artificial mutation breeding and optimizing process formula and culture conditions, then shaking flask seed liquid of the three plants of the bacillus licheniformis is merged into a flask, first-stage seed liquid preparation and second-stage seed liquid preparation are performed, and fermentation culture is finally performed in a same fermentation tank. By adopting the mixed fermentation process disclosed by the invention, the bacteriostatic ability is improved by 10-15%, the sporation rate is improved by 16-23% and the cost is saved by 200%.
Owner:SHANXI KINGSHINE FERTILIZER
Strain for producing colorful natto and production process
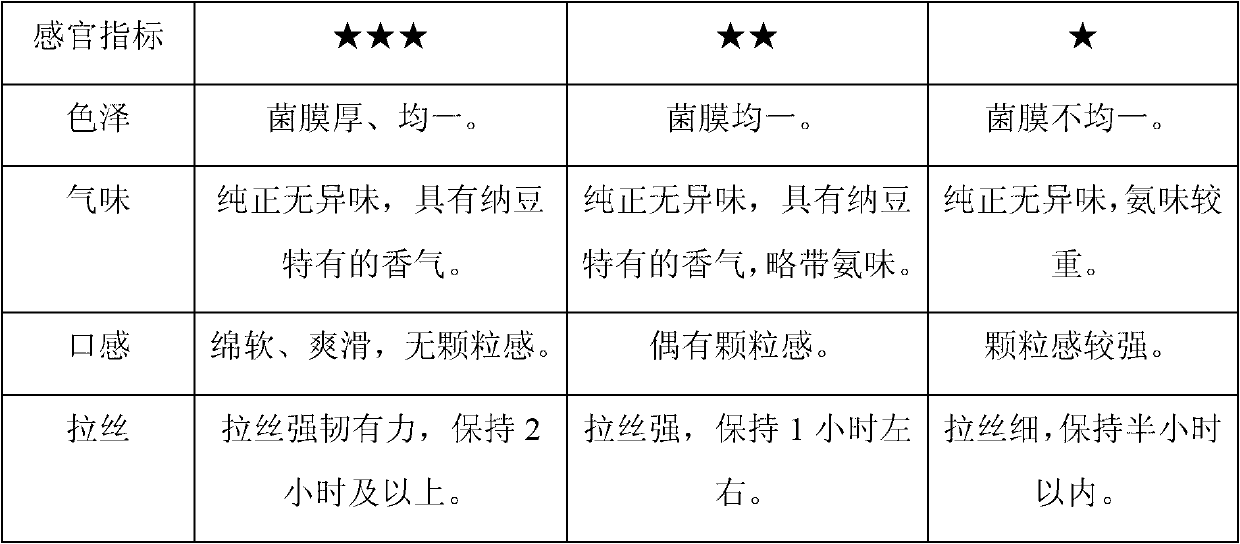
ActiveCN102703340AUniform coverageGood food valueBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyMutation breeding
The invention discloses a strain for producing colorful nattos and a production process, belongs to the field of fermentation, and in particular relates to the strain for producing the colorful nattos, the production process and sensory evaluation thereof. The invention provides bacillus subtitlis strain with a preservation number of CGMCC No.5860 for producing the colorful nattos. In the implementation scheme of fermenting production of the colorful nattos, the fermenting culture conditions are as follows: the fermenting temperature is within 38 and 40 DEG C, the humidity is within 70 and 90percent, and the fermentation time is within 20 and 30 hours. According to the strain for producing the colorful nattos and the production process, a new strain after mutation breeding is adopted anddifferent beans are adopted as raw materials for producing the nattos, and produced nattos have uniformly covered mycoderm and excellent dietary property.
Owner:CHINA NAT RES INST OF FOOD & FERMENTATION IND CO LTD
Penicillium strain producing cellulase and application in cellulose enzymatic hydrolysis thereof
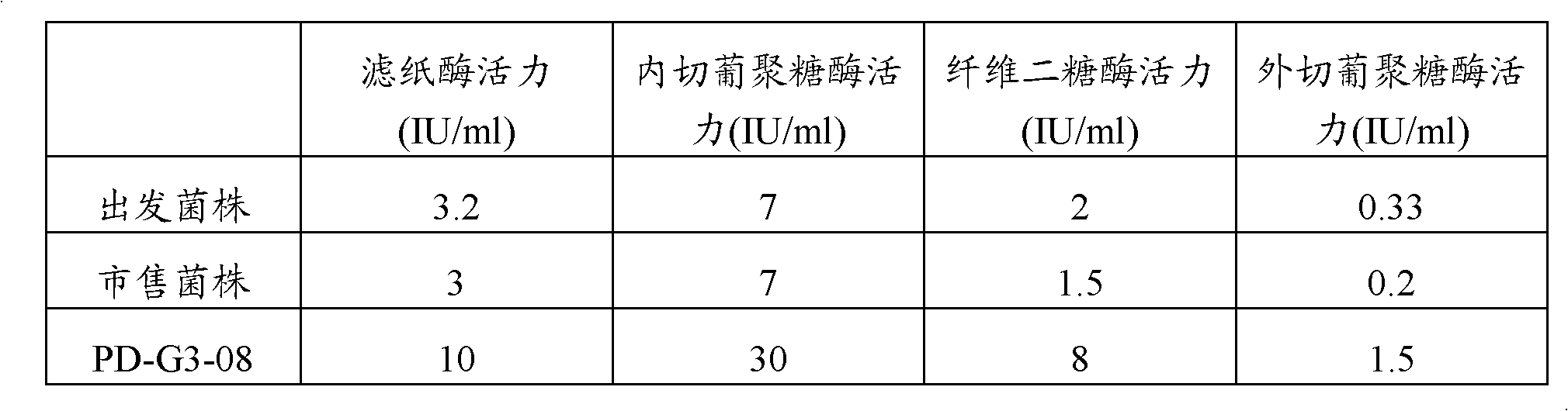
ActiveCN103045484AHigh activityInduce enzyme productionFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyPenicillium decumbens
The invention belongs to the field of microorganism, and particularly relates to a microorganism penicillium strain producing high-activity cellulase. The penicillium strain has a classification name of Penicillium decumbens PD-G3-08, and is preserved in Wuhan University China Center for Type Culture Collection with a preservation number of CCTCC M2011195. The invention also provides an application of the strain in cellulose enzymatic hydrolysis. Through mutation breeding, the penicillium strain producing high-activity cellulase is bred; cellulase crude enzyme liquid is obtained through fermentation of the strain, which has filter paper enzyme activity of up to 10 IU / ml, endoglucanase activity of up to 30 IU / ml, exoglucanase activity of up to 1.5 IU / ml and beta-glucosidase activity of up to 8 IU / ml, respectively being 3 times, 4 times, 4.5 times, and 4 times higher than the activities of an original strain; when the strain is applied to enzymatic hydrolysis of cellulose raw materials, the cellulose conversion rate in 3 days is up to more than 80%, and the cellulase has extremely high activity.
Owner:JINAN SHENGQUAN GROUP SHARE HLDG
High-yield glutamine transaminase strain and application thereof
ActiveCN110358708ASolve the problem of low enzyme production efficiencyIncrease enzyme activityBacteriaMutant preparationMicroorganismMutation breeding
The invention relates to the technical field of microorganism mutation breeding, in particular to a high-yield glutamine transaminase strain. The high-yield glutamine transaminase strain (YRZ170817NTG31) is preserved in the China Center For Type Culture Collection and has the preservation number of 15353 and the preservation date of February 12th, 2018. The high-yield glutamine transaminase straincan has the maximum enzyme activity after 24 hours of seed culturing and 48-56 hours of fermentation culturing and has the enzyme activity of 20-40 U / mL. The strain has the advantage of being high inenzyme activity.
Owner:TAIXING DONGSHENG FOOD TECH +1
Method for improving yield and trace element enrichment of liquid fermentation mycelium of lucid ganoderma
The invention relates to the field of liquid fermentation mycelium of lucid ganoderma and provides a method for improving yield and trace element enrichment of the liquid fermentation mycelium of the lucid ganoderma. The method is characterized by comprising the steps of inoculating a slope lucid ganoderma strain onto a liquid seed culture medium added with trace element-containing substances, performing mutation breeding by ultraviolet rays and cobalt-60 gamma rays, placing the lucid ganoderma mycelium into a fermentation tank for expansion breeding step by step, and performing separation filtering, vacuum microwave drying and crushing on the lucid ganoderma mycelium to obtain a product. The method adopts the fermentation process controlled by adopting pH value steady state feedback step by step according to the composition and distribution of the trace elements in the culture medium, thus more facilitating improving the conversion efficiency of multiple trace elements; the process is efficient and controllable, and the mycelium is high in additional value and suitable for process production; and the drying method for the mycelium adopts hot wind combined with a vacuum microwave drying technology and keeps the biological activity of effective constituents in the mycelium.
Owner:HUBEI JIAFU BIOLOGICAL TECH
Preparation of epothilones B lactam derivates
InactiveCN101323869AIncrease productionReduce outputBacteriaMicroorganism based processesCytochrome P450Mutation breeding
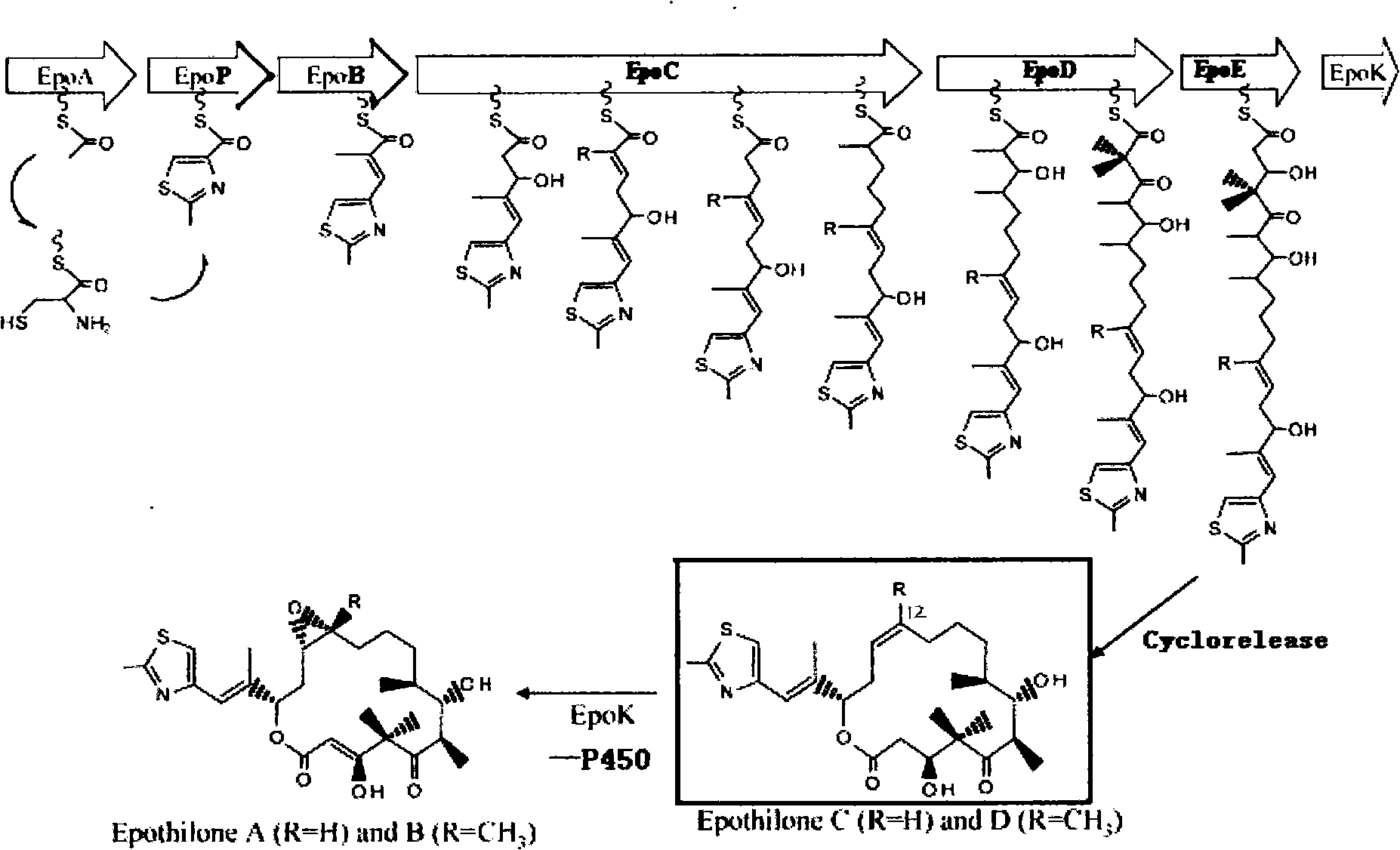
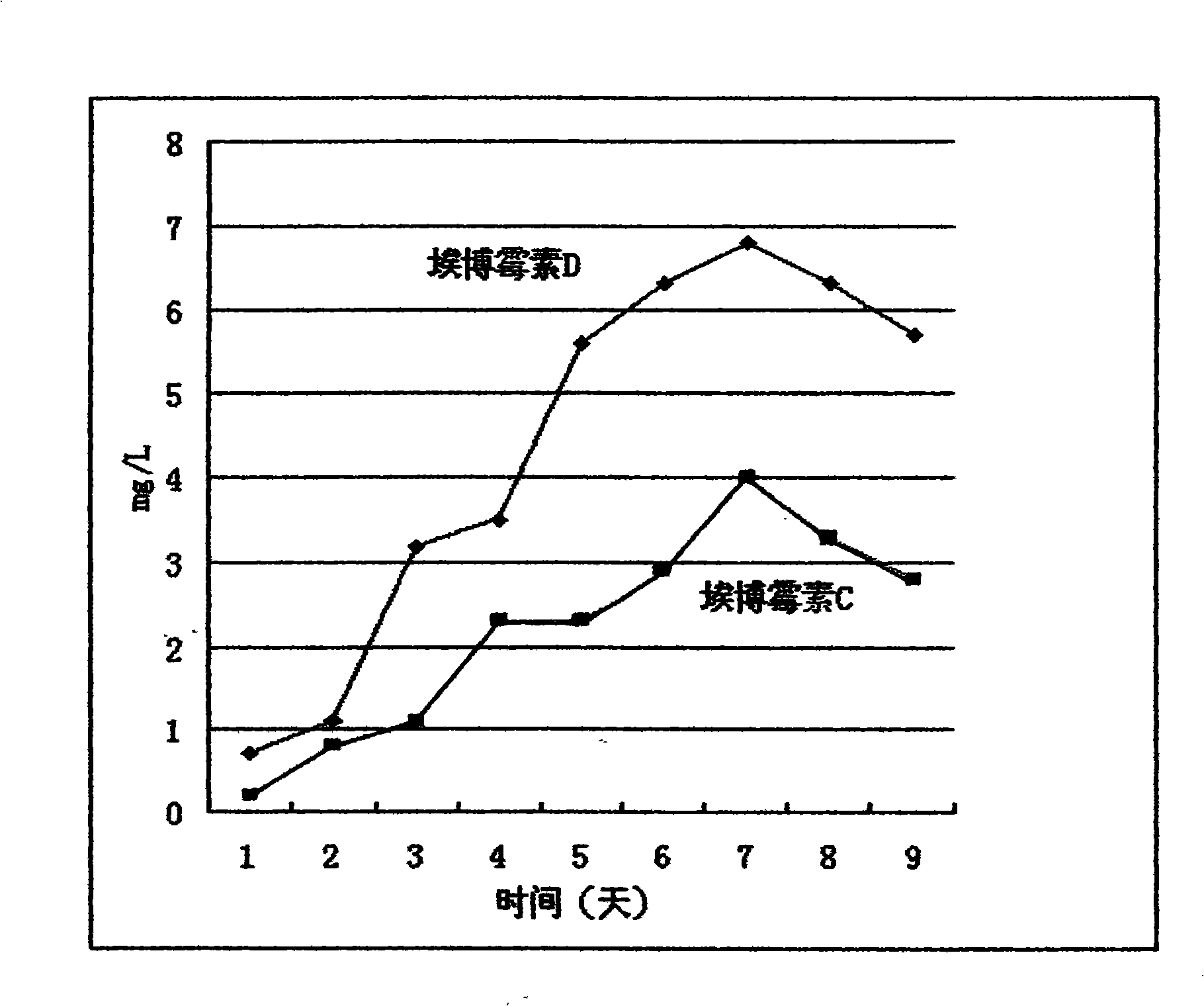
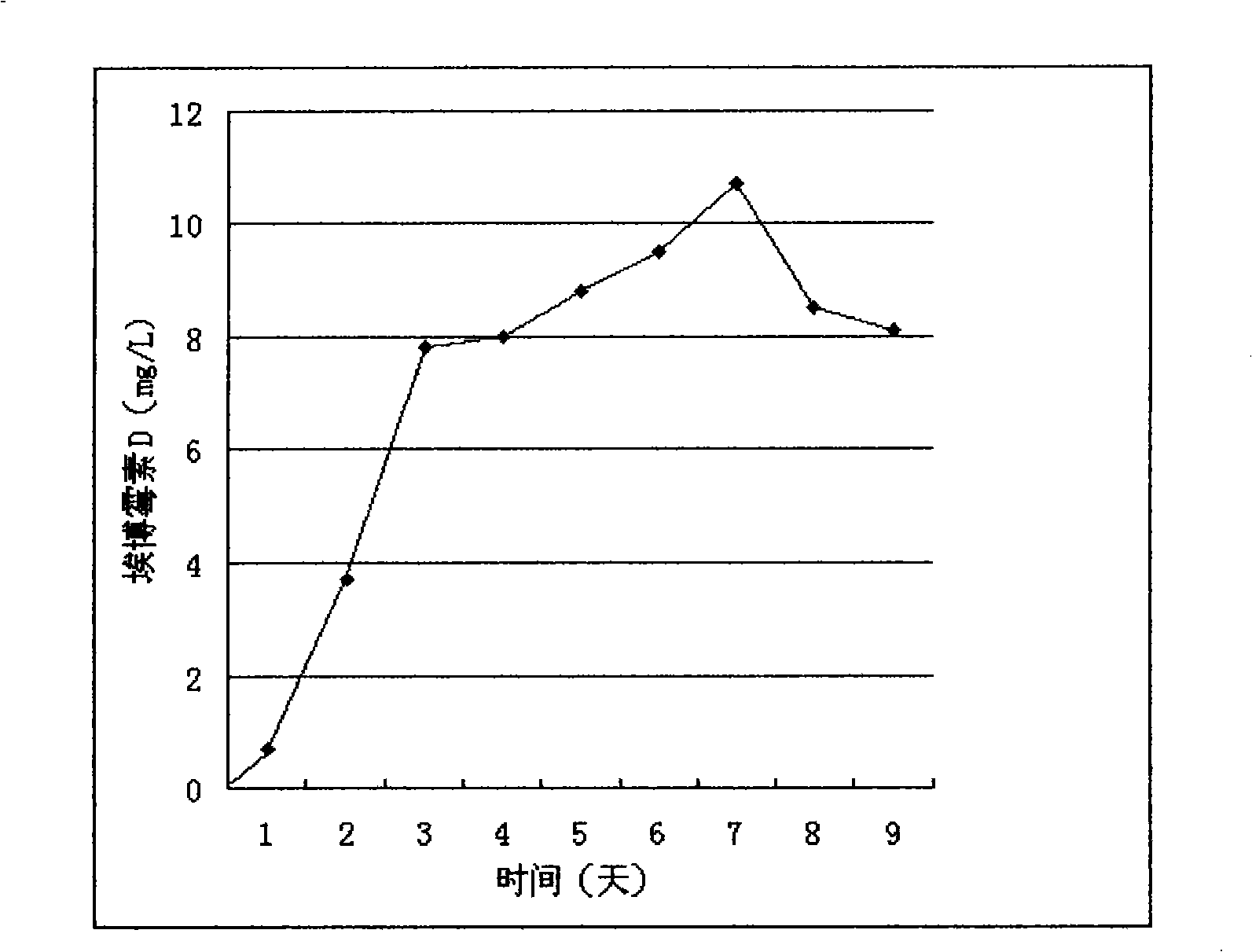
The invention relates to a method for the production of an epothilones B lactam derivative which is an anticancer drug. The method adopts a gene mutation method, utilizes an eopK inhibitor to promote the inactivation of cytochrome P450 oxidase which is the gene product of eopK, and directionally obtain epothilones C and epothilones D without the generation of epothilones A and epothilones B. The mutant strains are further treated with UV mutation breeding to obtain the high-yield strains of the epothilones D, and the strains are fermented to produce the epothilones D which is used as a starting material to synthesize the epothilones B lactam derivative by two-step reaction.
Owner:京山瑞生制药有限公司 +1
Bacillus subtilis bred by space mutation breeding technology and application of Bacillus subtilis
ActiveCN102329749BPromote digestion and absorptionImprove conversion rateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesFeed conversion ratioDigestion
The invention discloses Bacillus subtilis bred by a space mutation breeding technology. The strain is named Bacillus subtilis N9-1-35 and was collected in China Center for Type Culture Collection on August 31, 2011, and the collection number is CCTCC M2011301. The test shows that the Bacillus subtilis is an excellent probiotic strain. After entering intestinal tracts of animals, the Bacillus subtilis achieves the effects of a probiotic and can also generate a plurality of kinds of digestive enzymes in the growth and reproduction process of the animals, so that the digestion and absorption of the animals on feeds are improved, the conversion rate of the feeds is improved, and the cost of the feeds is reduced; and the Bacillus subtilis can be used for producing enzyme-producing probiotics, and is a strain which has excellent research and development value. The invention also discloses an enzyme-producing probiotic. The enzyme-producing probiotic consists of Bacillus subtilis powder, Streptococcus lactis powder, Lactobacillus acidophilus powder and corn starch.
Owner:山东宝来利来生物工程股份有限公司
Strain for producing cellulase and application of strain
InactiveCN103555595AIncrease hydrolysis rateIncrease enzyme activityFungiMutant preparationHigh activityTrichoderma reesei
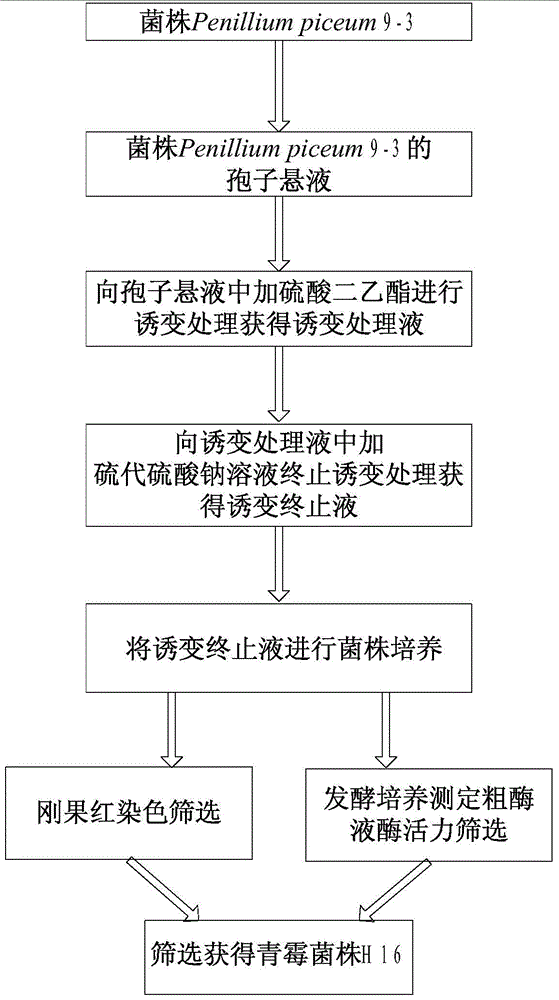
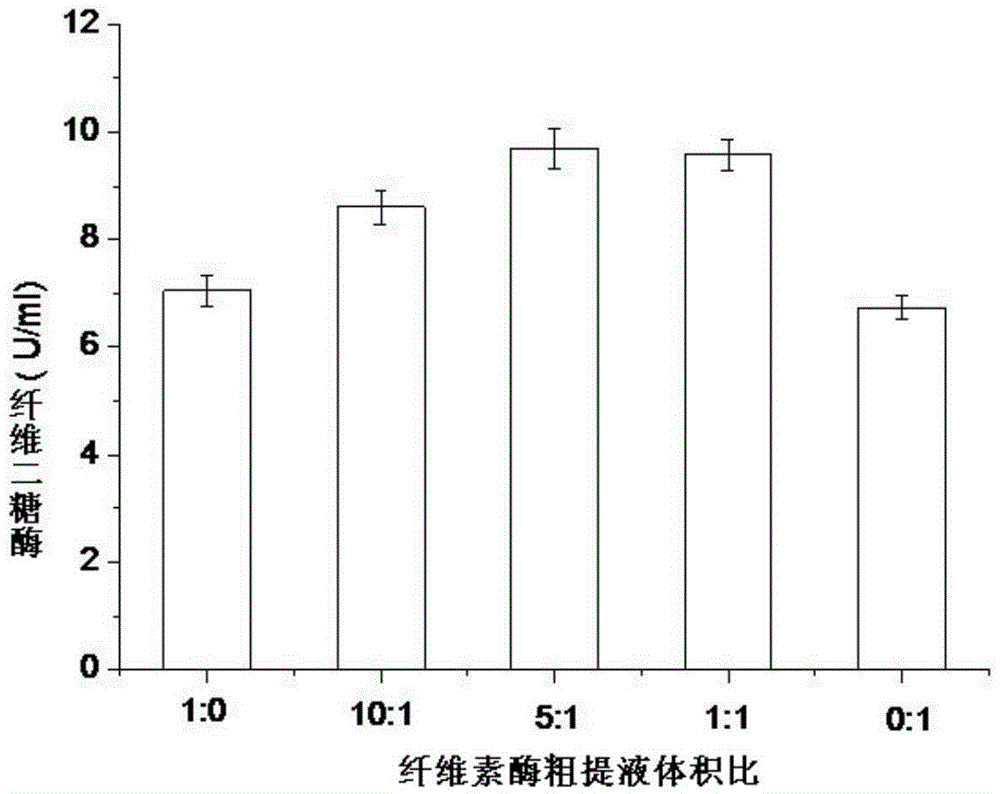
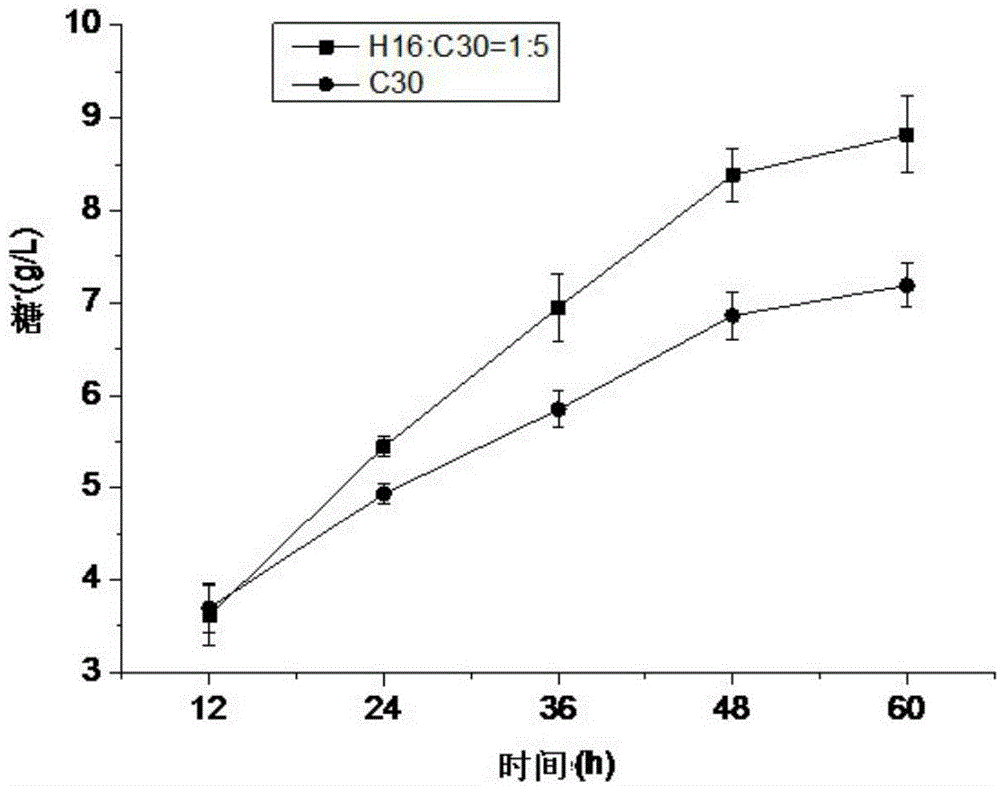
The invention discloses a strain for producing cellulase. The strain has a collection number of CGMCC No.8339 in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center, and the classification name of the strain is Penillium piceum H16. The Penillium piceum is obtained through induced mutation treatment by taking a strain Penillium piceum 9-3 screened from straws as an original strain. The Penillium piceum 9-3 serves as the original strain for mutation breeding, the Penillium piceum H16 for producing high-activity cellulase is obtained through breeding, the enzyme activity of filter paperof cellulase crude enzyme liquid obtained by fermenting the Penillium piceum H16 reaches 7IU / mL, and the enzyme activity of beta-glucosidase reaches 50IU / mL. Different cellulase systems of the Penillium piceum H16 and Trichoderma reesei RUT-C30 are researched according to different proportions, the enzyme activity and the hydrolysis rate of microcrystalline celluloses are greatly improved at an optimal proportion, and the enzyme cost is reduced.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Chemical mutation breeding method for bougainvillea
InactiveCN102499071ALarge baseReduce processing costsPlant genotype modificationHorticultureMutation frequencySodium azide
The invention discloses a chemical mutation breeding method for bougainvillea, and relates to the field of the vegetative propagation and chemical mutation breeding of xylophyta and vines. The method treats cottage pieces of bougainvillea with sodium azide (NaN3), adopts continuous cottage propagation to create a time and a space which are good for growth of leaf color mutants, and obtains new lines with stable heredity and ornamental value through generation selection, thereby achieving the purpose of chemical mutation breeding. By adopting the technical scheme in the invention, large quantities of female parent materials can be treated in one step; the base number of variants is relatively increases greatly; the mutation frequency is increased; the treatment cost is relatively low; and the breeding period can be shorten effectively. By utilizing the continuous cottage propagation manner, the growth of leaf color mutants is ensured to be competitive, which is helpful for overcoming the chimera formation, thereby obtaining stable and uniform variants. The chemical mutation breeding method can obtain high-frequency mutation and a wide spectrum of variation, and is helpful for the variety improvement of bougainvillea.
Owner:SHENZHEN XIANHU BOTANICAL GARDEN ADMINISTRATION
Fungus strain with high-efficiency expression of huperzine A and application thereof
ActiveCN105670940ALower medical costsSolve first-line drug needsFungiNervous disorderDiseaseBiotechnology
The invention discloses a fungus strain with high-efficiency expression of huperzine A. The strain is separated from endophytic fungi of wild huperzia serrata (huperziaceae, huperzia), belongs to the NSH-D strain of mucor racemosus and has genetic stability till the passage to 15th generation in a laboratory; and the amino acid sequence is shown by SEQ ID NO:1. The fungus strain with high-efficiency expression of huperzine A, disclosed by the invention, serves as a biological strain for treating the Alzheimer's disease, the good huperzine A generating high-efficiency expression gene is transferred into other type strains, and more good characters are obtained through gene modification; and moreover, further optimization of the strain can be realized through mutation breeding. The study on the fungus strain is of great significance to the biosynthesis and industrial production of huperzine A, protection of plant resources, meeting of clinical pharmaceutical needs and reduction of the medical expense for treating the Alzheimer's disease.
Owner:陕西仁达康健医药生物科技有限公司
High-concentration tea dreg-tolerant lactobacillus plantarum LP-08 strain and application thereof
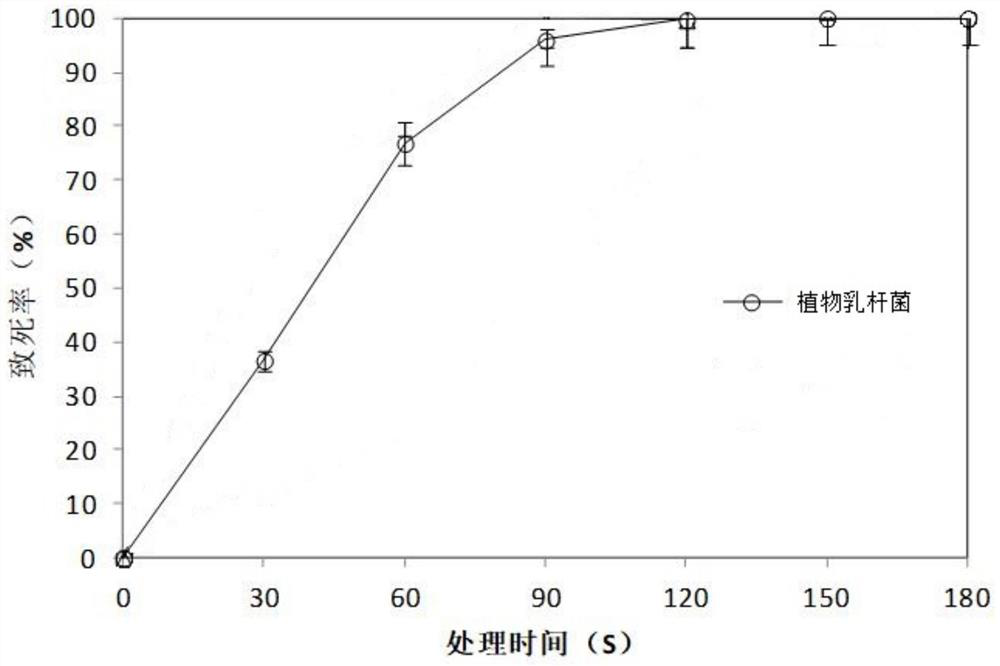
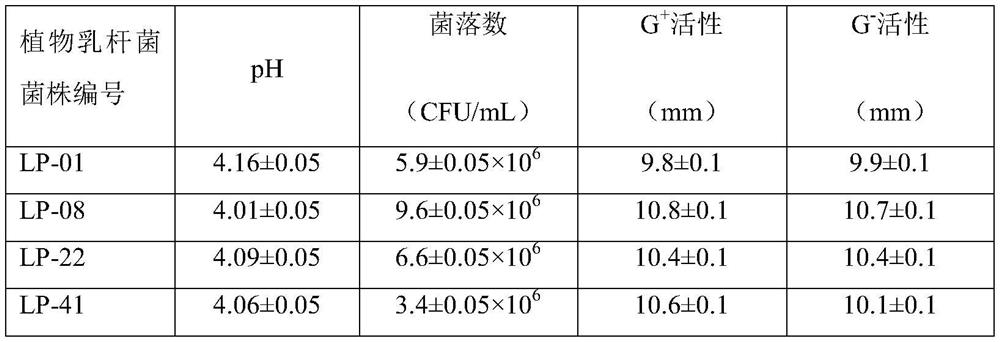
PendingCN111690579AChanging nutritional contentIncrease biomassBacteriaFood processingBiotechnologyBiology
The present invention relates to the technical field of microbial mutation breeding and particularly to a high-concentration tea dreg-tolerant lactobacillus plantarum LP-08 strain and an application thereof. The lactobacillus plantarum LP-08 is deposited in Guangdong Microbial Culture Collection Center (GDMCC) on June 16, 2020 and has a deposit number of GDMCC No:61061. The present invention aimsto develop ground-origin green tea dregs to prepare functional bacterial tea biological feeds, an ARTP mutagenesis and domestication screening method is used to select functional microorganisms, and the lactobacillus plantarum LP-08 that can tolerate high-concentration tea dregs and is good in biomass and metabolite activity is obtained. The strain can be used for tea dreg fermentation, can changenutrient ingredients in tea dregs, can be applied to development of the tea dreg feeds, and is of great significance for high-value utilization of tea dreg resources.
Owner:清远一生自然生物研究院有限公司 +1
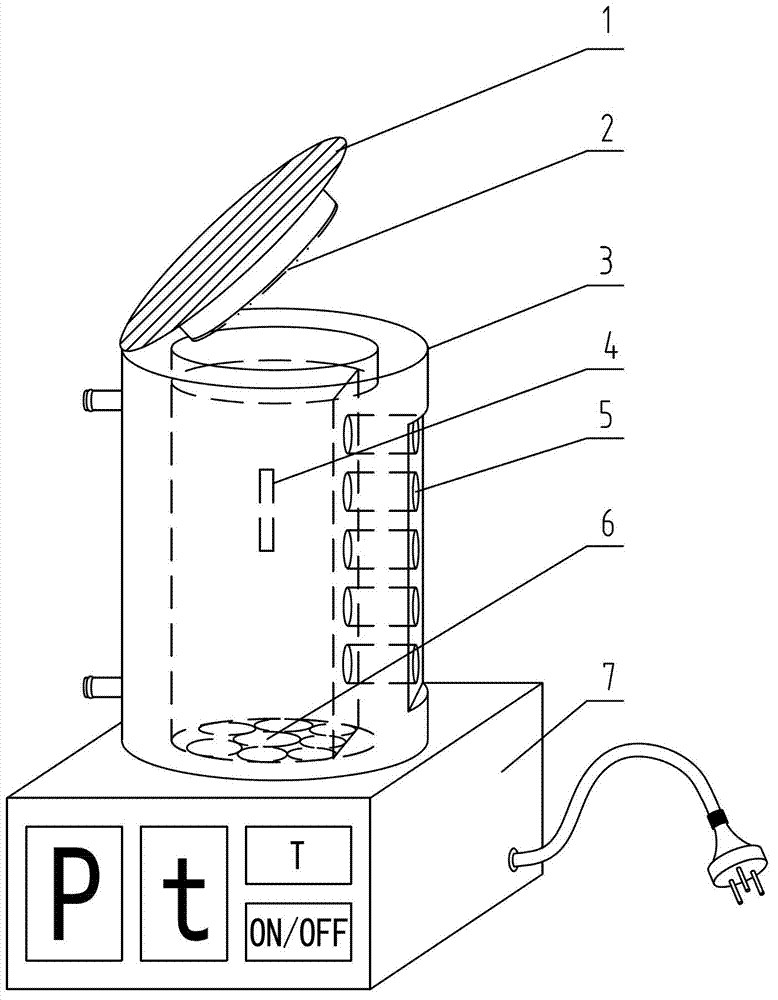
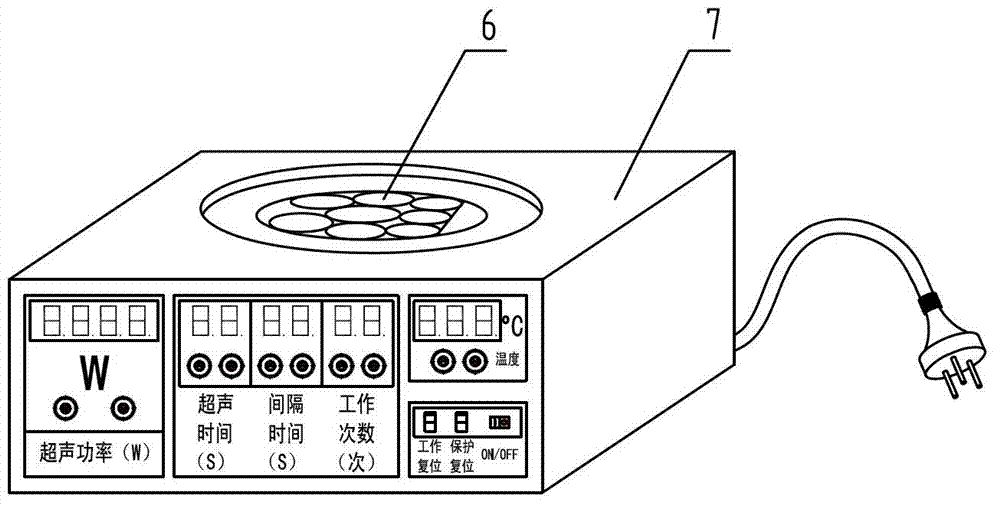
Ultrasound mutation breeding device
InactiveCN102754593AImprove germination rateRealize inquiryPlant genotype modificationGerminating apparatusTemperature controlPlanting seed
The invention relates to an ultrasound mutation breeding device. A reaction container is arranged on a base and is characterized in that a container cover which is connected in a sealing manner is arranged on the top of a reaction container body; one side wall of the reaction container body is provided with a water inlet and a water outlet arranged above the water inlet; a horizontal ultrasonic transducer set vertical to the central shaft of the reaction container body is arranged at the other side of the reaction container body; a longitudinal ultrasonic transducer set is arranged on the top of the base below the reaction container body; and a sound absorption layer is arranged along the reaction container body and the inner wall of the container cover. Parameters such as ultrasonic power and ultrasonic time of an ultrasonic wave generator are regulated, and temperature in the reaction container body is regulated in real time by applying a temperature control unit, thus exploration on parameters which influence germination of plant seeds is achieved, so that the rate of emergence of the plant seeds is improved, a germination period is shortened, and yield is increased. The ultrasound mutation breeding device disclosed by the invention is novel in structure and easy to operate.
Owner:SHAANXI NORMAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com