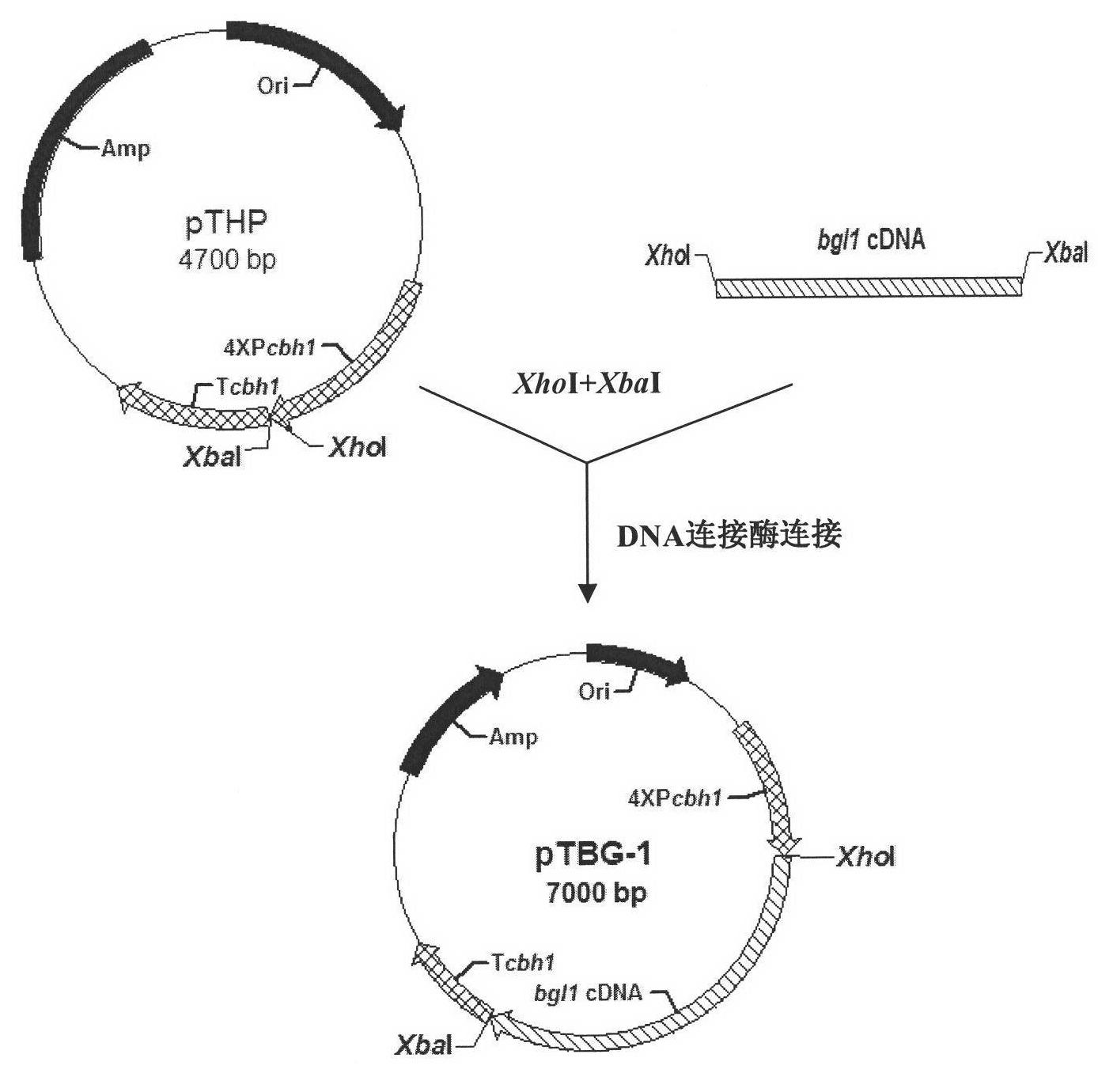
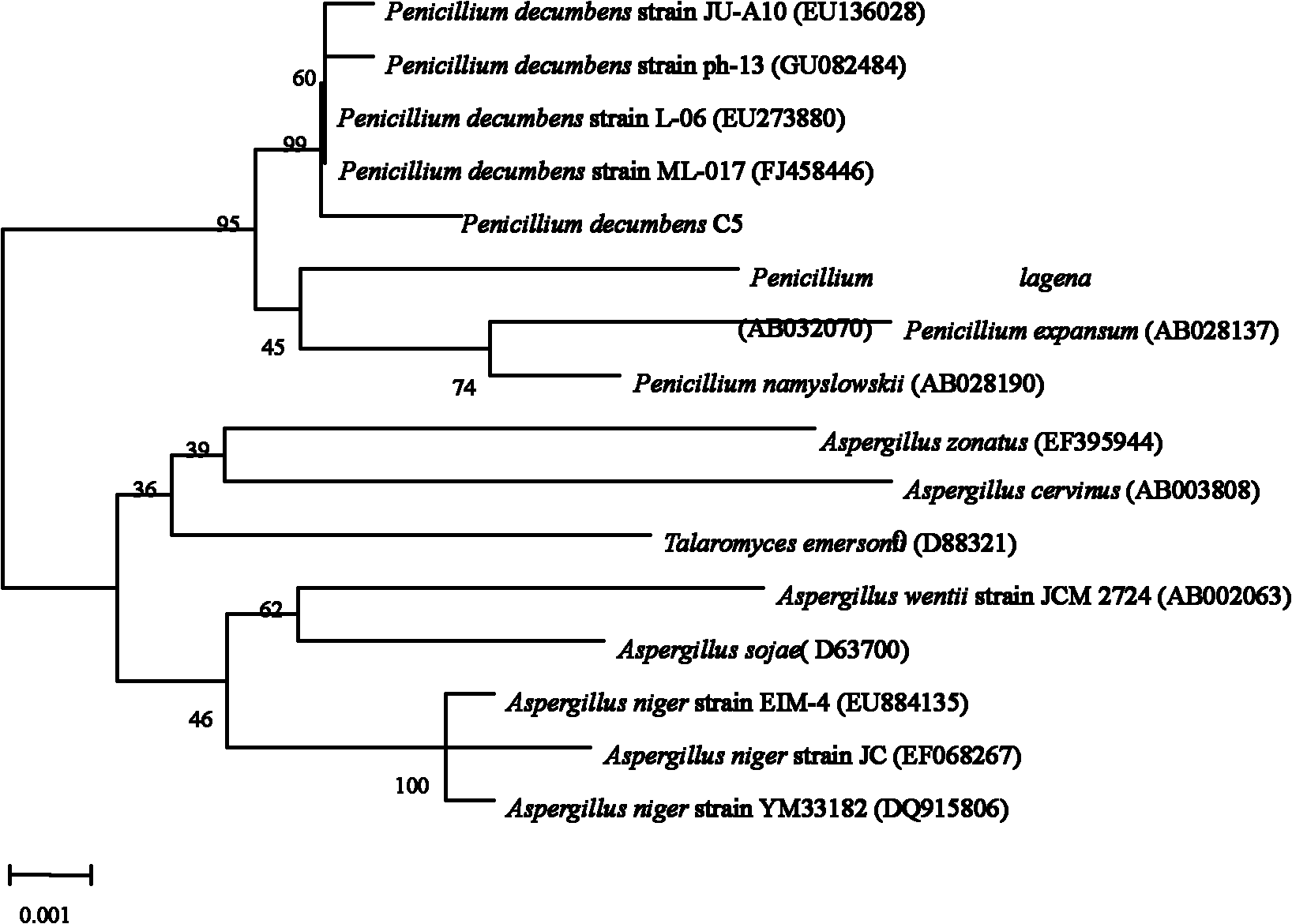
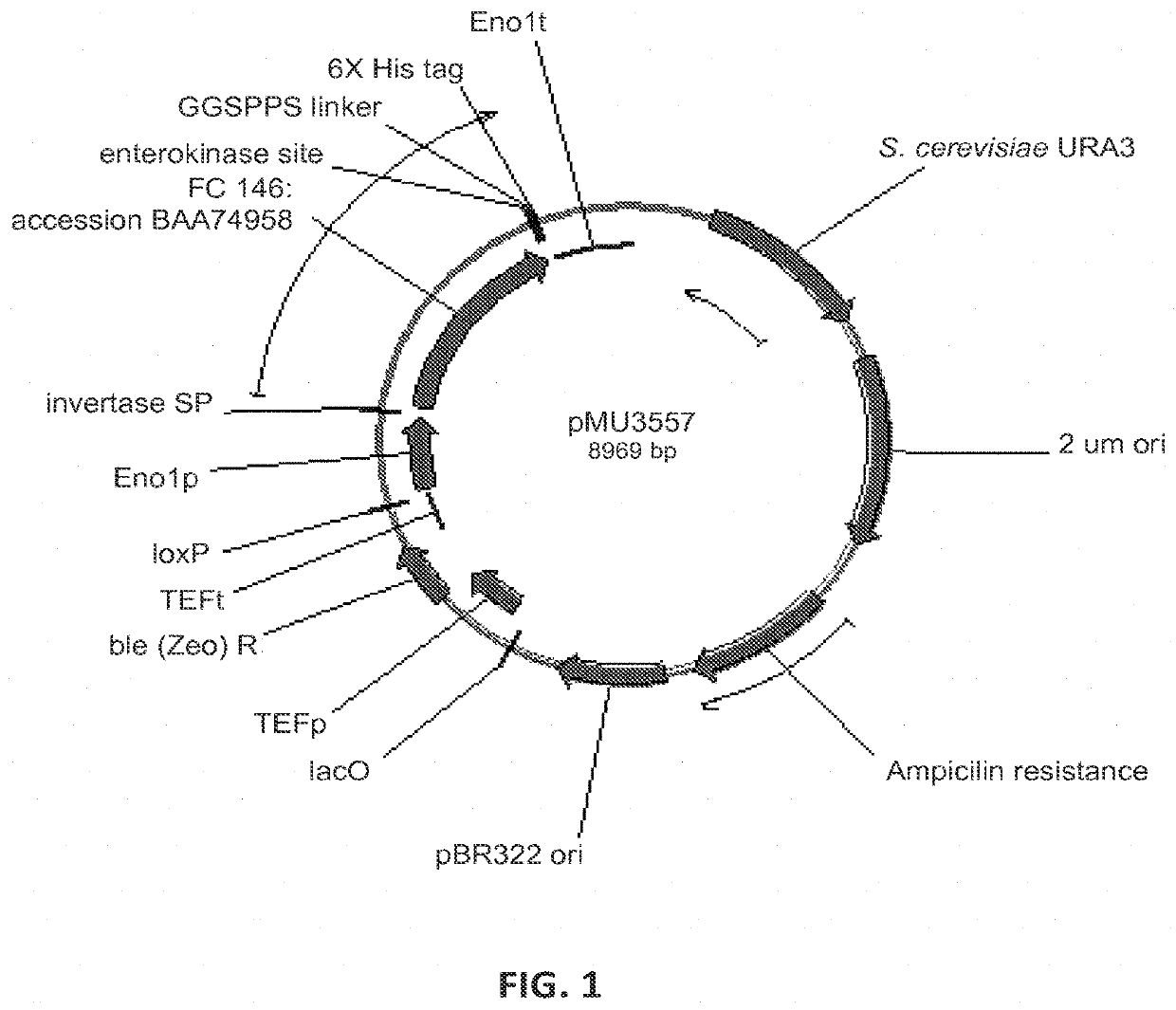
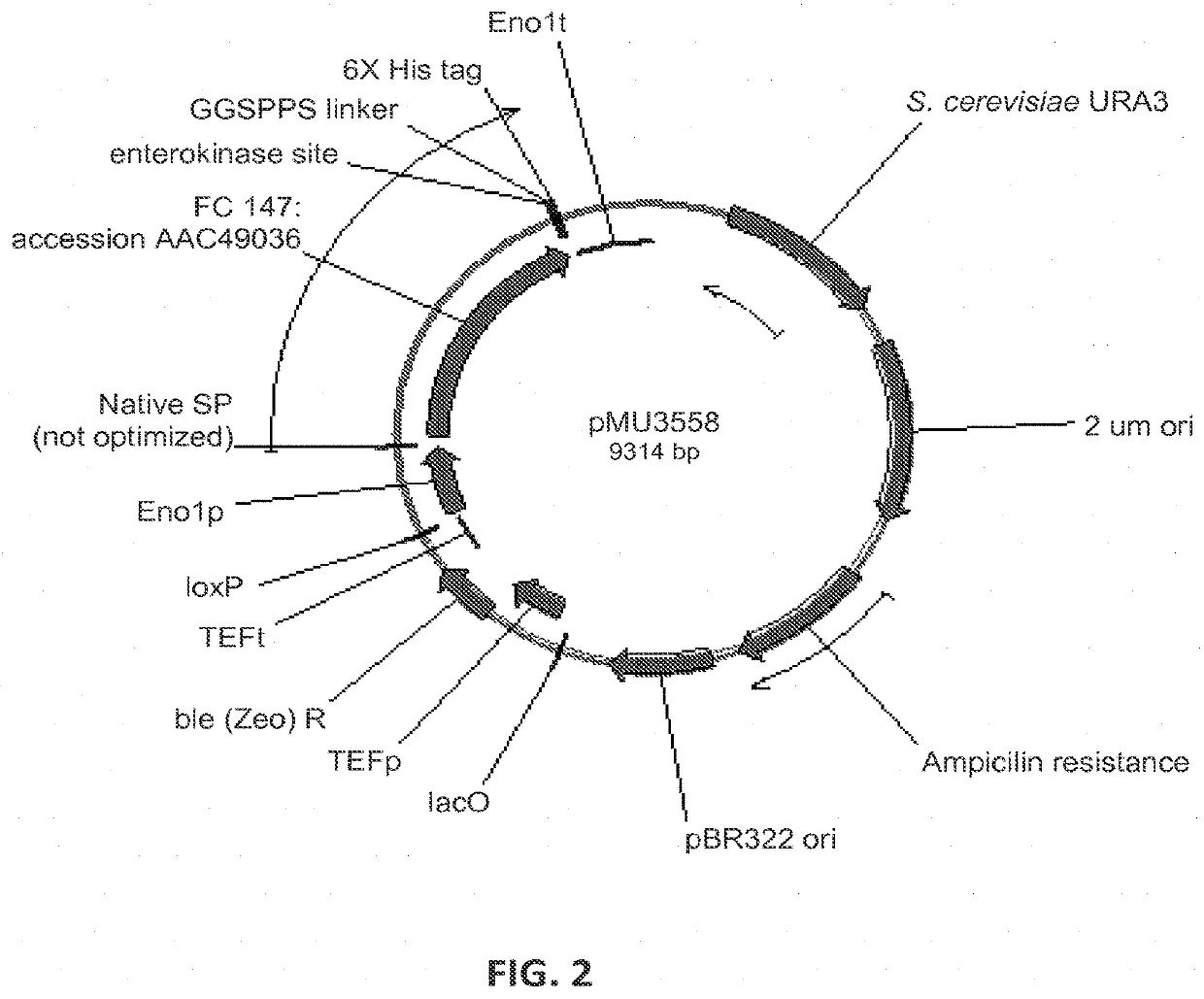
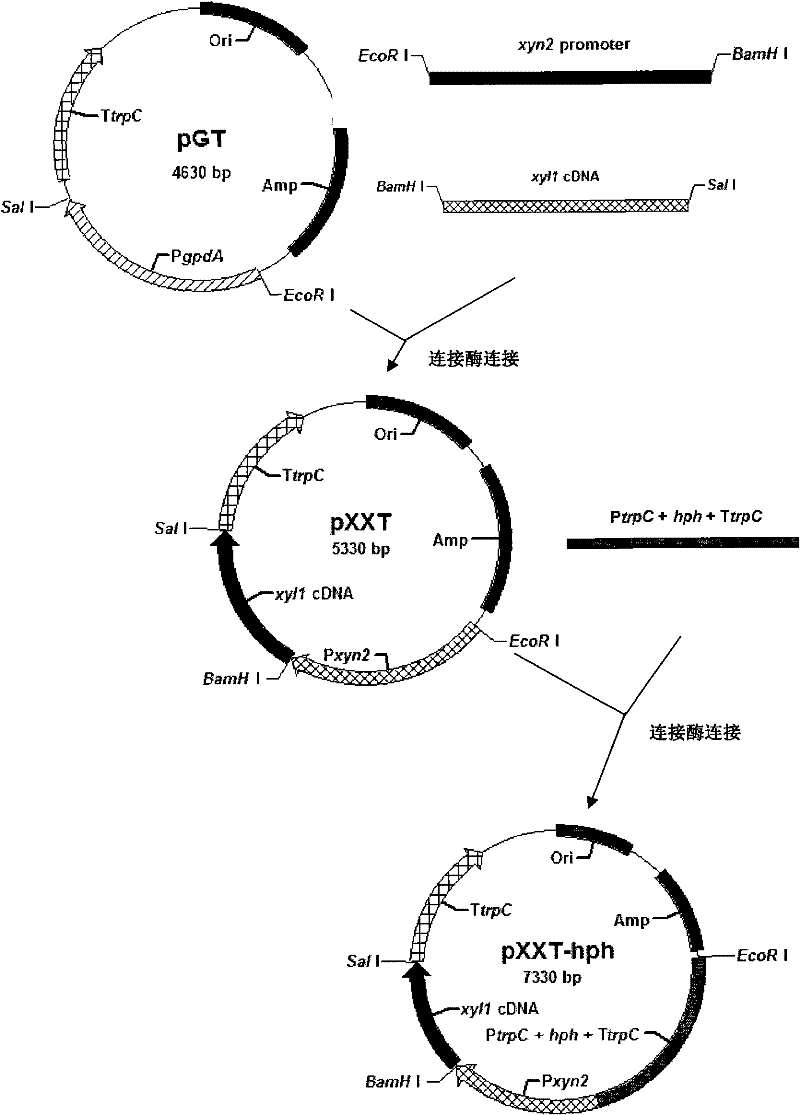
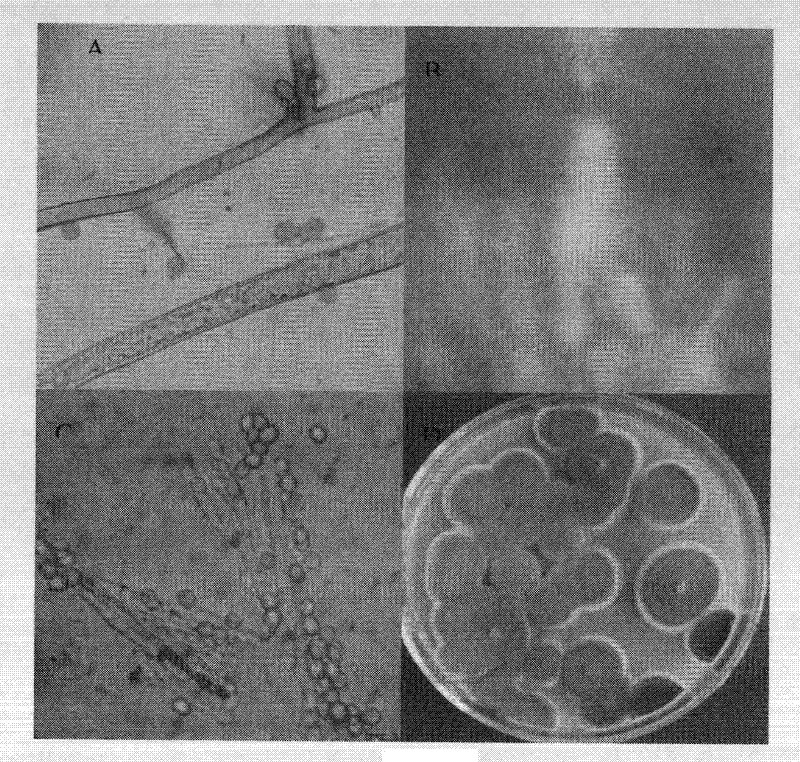Patents
Literature
36 results about "Penicillium decumbens" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Penicillium decumbens is an anamorph species of the genus of Penicillium which occurs widespread in nature, mainly in subtropical and tropical soil but it also occur in food.
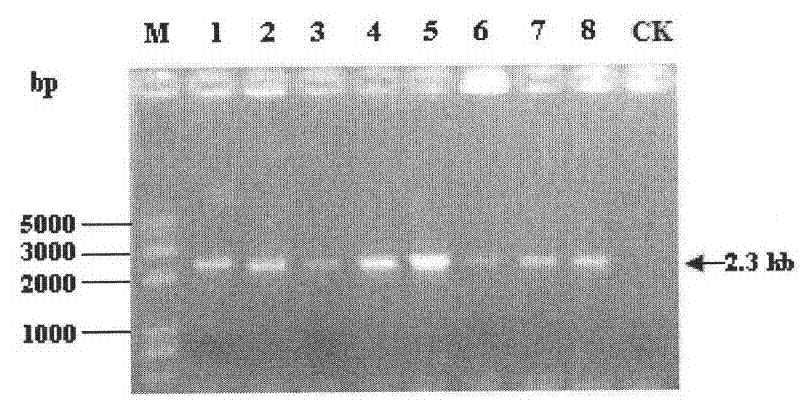
Penicillium decumbens engineered strain containing over-expressed beta-glucosidase and application thereof
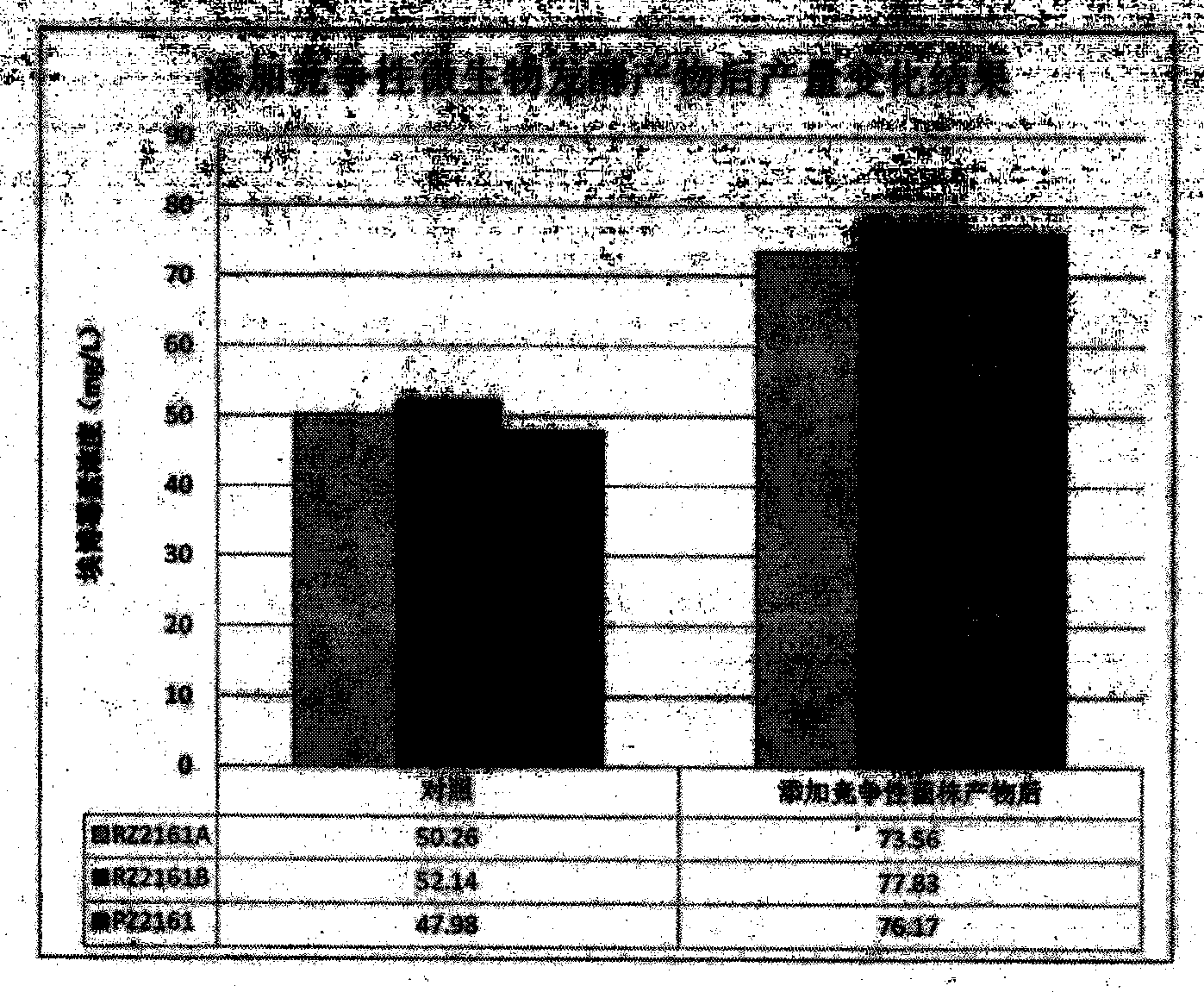
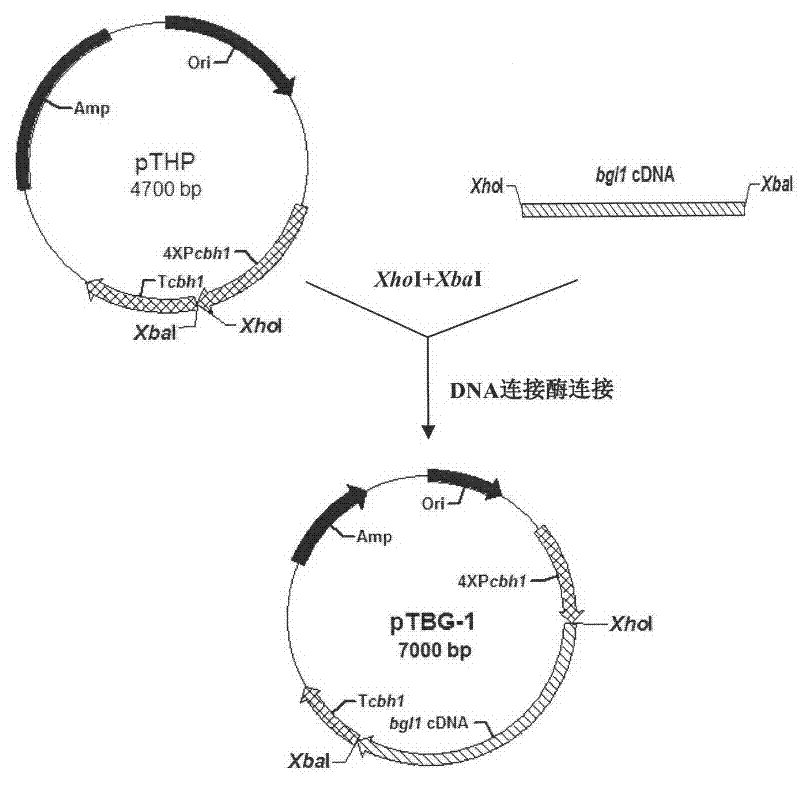
The invention discloses a penicillium deumbens engineered strain containing over-expressed beta-glucosidase, which contains over-expressed beta-glucosidase genes, is named penicillium deumbens Gi31-2 and is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection on May 7, 2010 with a preservation number of CCTCC M 2010111. The invention also discloses the application of the strain in production of the beta-glucosidase and degradation of cellulose. The highest activity of the beta-glucosidase of the engineered strain of the invention reaches 3.47 IU / ml and is 2.90 times as high as that of an original host strain, while highest filter paper activity is 3.32 IU / ml and is 1.23 times as high as that of the original host strain. Therefore, the strain is widely applied to the production of the beta-glucosidase.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Engonus fungus with high enzyme activity and high capacity of efficiently degrading straw cellulose in northeast China region
InactiveCN102061267AIncrease profitEfficient degradation abilityFungiMicroorganism based processesPenicillium bilaiaeCellulose
The invention relates to an engonus fungus with high enzyme activity and high capacity of efficiently degrading straw cellulose in the northeast China region, in particular to a fungus for degrading cellulose. The engonus fungus with high enzyme activity and high capacity of efficiently degrading the straw cellulose in the northeast China region is named as Penicillium decumbens C5, belongs to the Penicillium sp., and has the preservation number of CGMSS No.4203 and the preservation date of October 8th 2010. When the Penicillium decumbens C5 strain is cultured for 3d, FPase reaches 7085.66U / L, the EG / Cen peak is 3856.97U / L, the CBU / Cex peak is 2681.59U / L, and the beta-Gase peak is 1487.86U / L, thus the Penicillium decumbens C5 has a function of efficiently degrading straws.
Owner:NORTHEAST FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Method for preparing feed by mixing straw and butanol or alcoholic fermentation waste water
InactiveCN101940248ASolve the emission problemImprove palatabilityFood processingAnimal feeding stuffFiberPenicillium decumbens
The invention relates to a method for preparing a protein feed by mixing straw and straw dilute acid hydrolytic pentose butanol or alcoholic fermentation waste water for solid state fermentation, which comprises the following steps of: mixing the steam-exploded straw or the straw hydrolyzed by dilute acid and the straw dilute acid hydrolytic pentose butanol or alcoholic fermentation waste water in a certain volume to ensure that moisture content is between 70 and 80 percent, after sterilizing, inoculating penicillium decumbens and trametes pubescens to the mixture and performing aerobic solidstate fermentation for 4 to 6 days, inoculating candida tropicalis and lactobacillus plantarum and performing anaerobic fermentation for 2 to 3 days, and drying to obtain the protein feed. In the protein feed product prepared by the method, the protein content is between 22 and 27 percent, and the degradation rate of coarse fibers is between 63 and 68 percent. The method can solve the problem of discharging the butanol or alcoholic fermentation waste water; and the waste water and the straw are converted into the protein feed, so that the waste is turned into treasure.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Penicillium strain producing cellulase and application in cellulose enzymatic hydrolysis thereof
ActiveCN103045484AHigh activityInduce enzyme productionFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyPenicillium decumbens
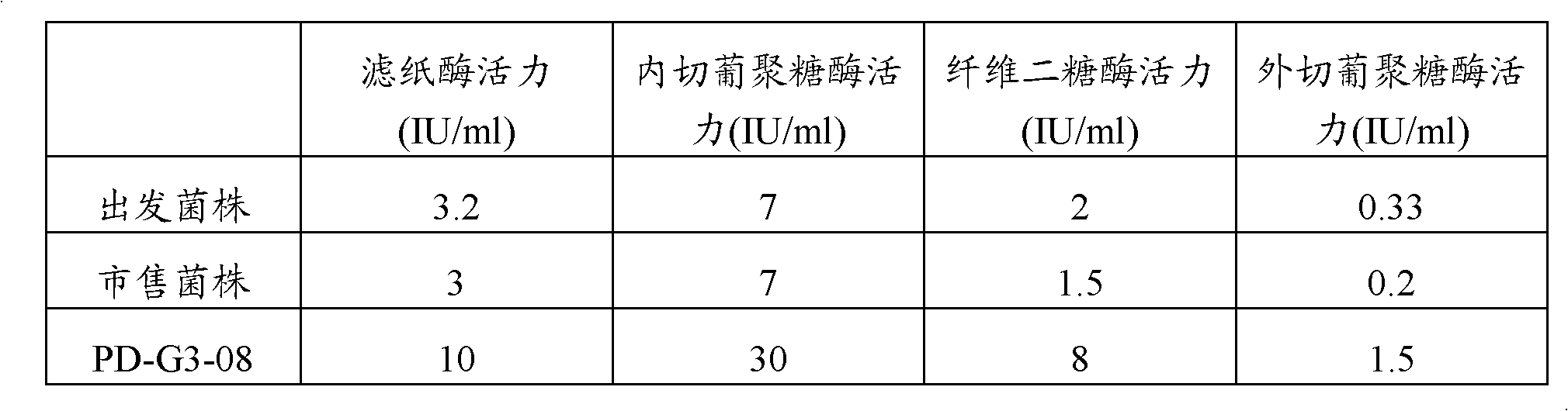
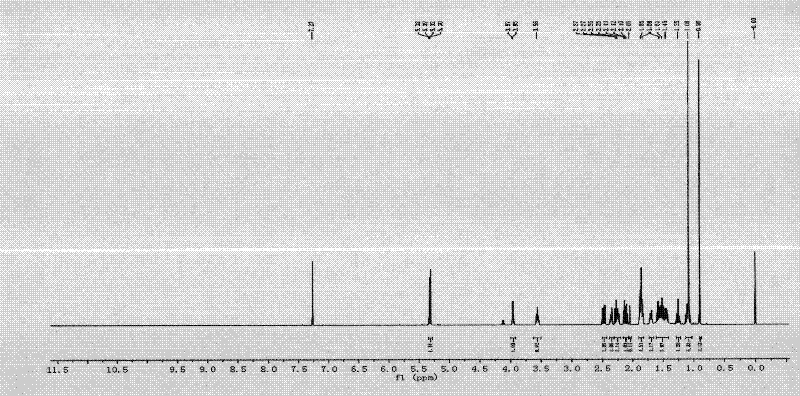
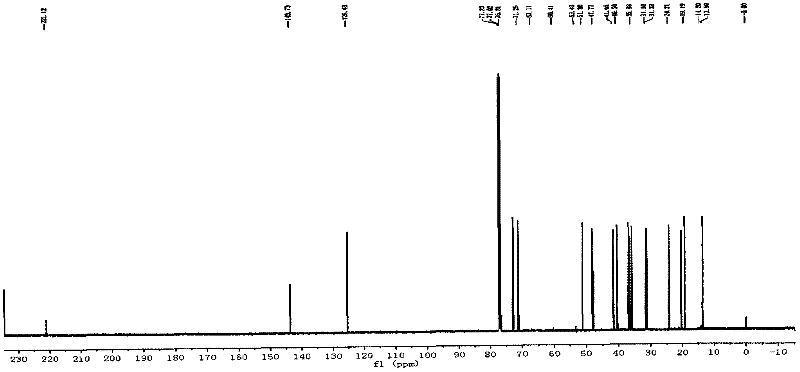
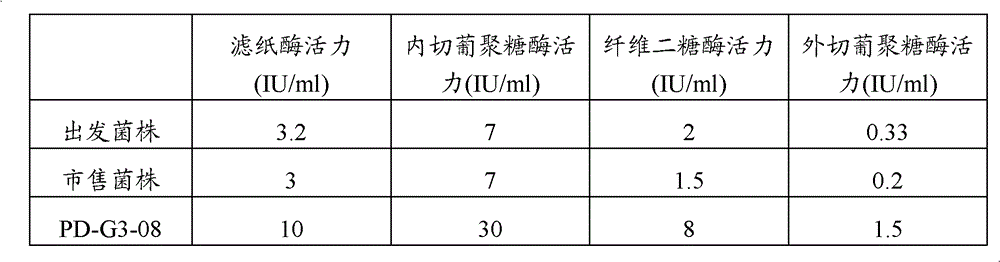
The invention belongs to the field of microorganism, and particularly relates to a microorganism penicillium strain producing high-activity cellulase. The penicillium strain has a classification name of Penicillium decumbens PD-G3-08, and is preserved in Wuhan University China Center for Type Culture Collection with a preservation number of CCTCC M2011195. The invention also provides an application of the strain in cellulose enzymatic hydrolysis. Through mutation breeding, the penicillium strain producing high-activity cellulase is bred; cellulase crude enzyme liquid is obtained through fermentation of the strain, which has filter paper enzyme activity of up to 10 IU / ml, endoglucanase activity of up to 30 IU / ml, exoglucanase activity of up to 1.5 IU / ml and beta-glucosidase activity of up to 8 IU / ml, respectively being 3 times, 4 times, 4.5 times, and 4 times higher than the activities of an original strain; when the strain is applied to enzymatic hydrolysis of cellulose raw materials, the cellulose conversion rate in 3 days is up to more than 80%, and the cellulase has extremely high activity.
Owner:JINAN SHENGQUAN GROUP SHARE HLDG
Method for ex-situ preparation of methane and combined production of humic acid, and composite microbial agent used in same
InactiveCN105274178AIncrease productionImprove extraction efficiencyOrganic chemistryMicroorganism based processesCelluloseEscherichia coli
The invention discloses a method for ex-situ preparation of methane and combined production of humic acid, and a composite microbial agent used in the same, belonging to the field of recycling of brown coal. The composite microbial agent is composed of fermentation broth of four bacteria, i.e., Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas putida, Penicillium decumbens and Clostridium acetobutylicum. The composite microbial agent has strong degradation capability on a variety of celluloses, hydrocarbons, asphaltene and a variety of carbonaceous macro-molecules. As coal is treated by the composite microbial agent, anaerobic digestion time can be shortened, output of methane gas is increased and extraction efficiency of humic acid is improved; moreover, the synergistic effect of the above-mentioned four microbial strains is superior to the effect of any one microbial strain or any two microbial strains.
Owner:创盛量子科技(温州)有限公司
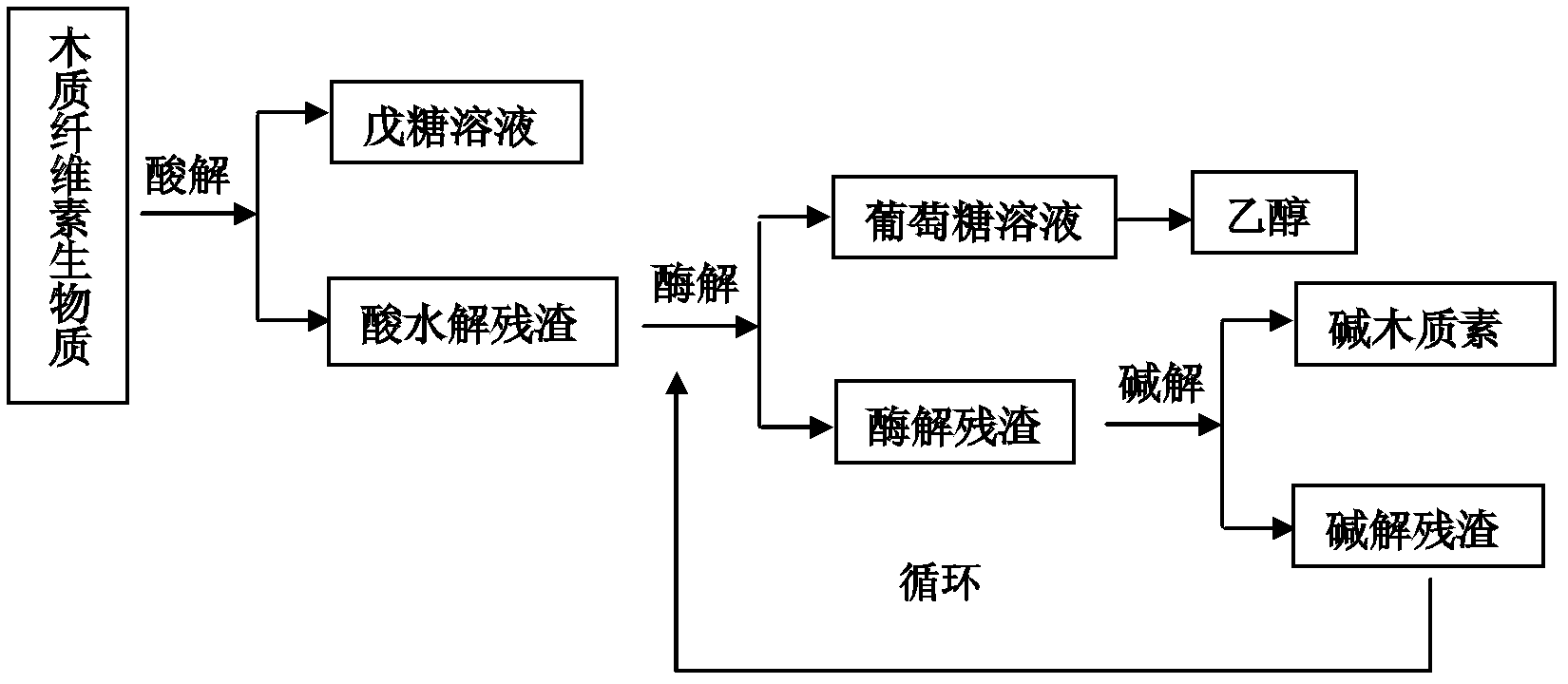
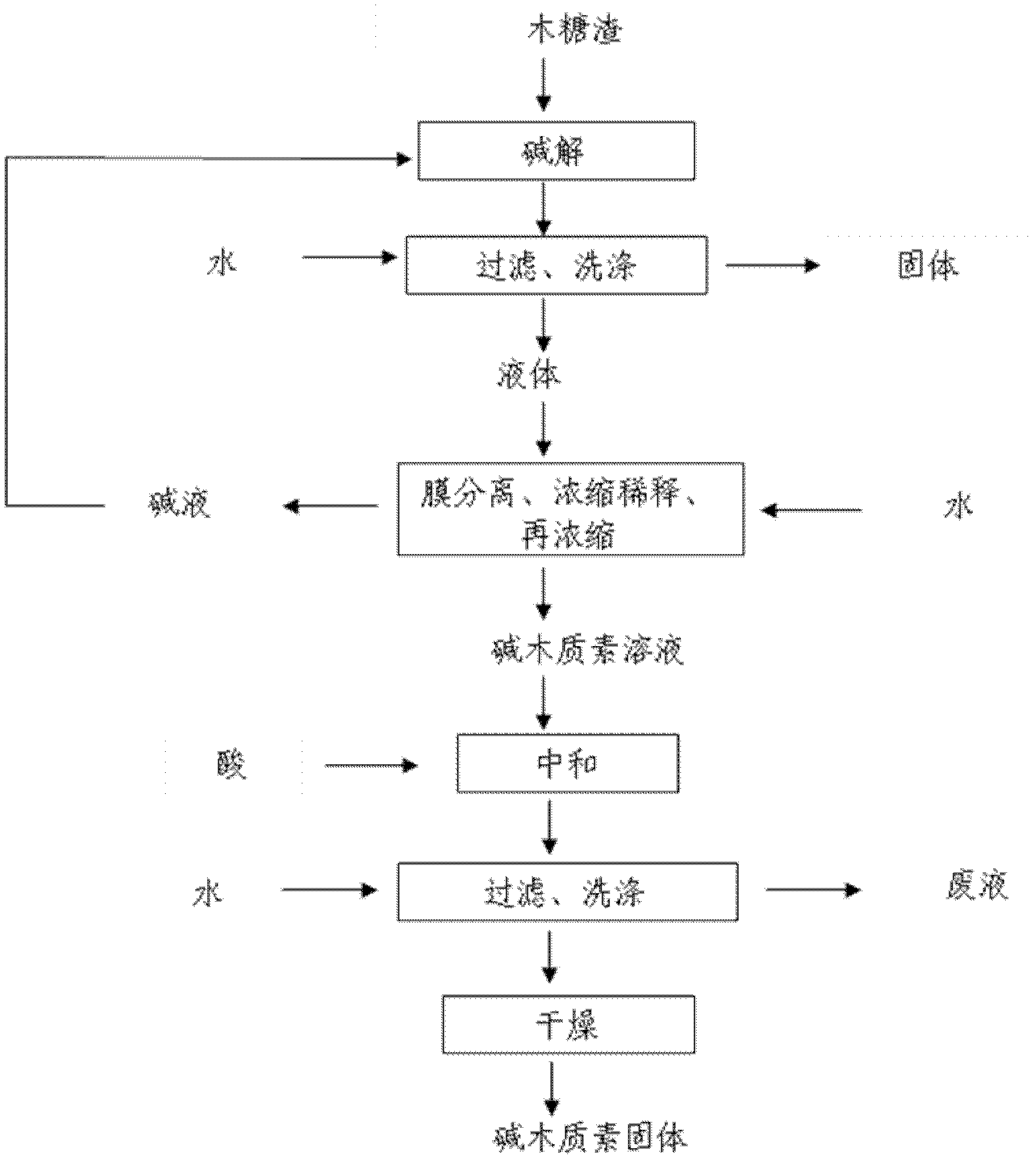
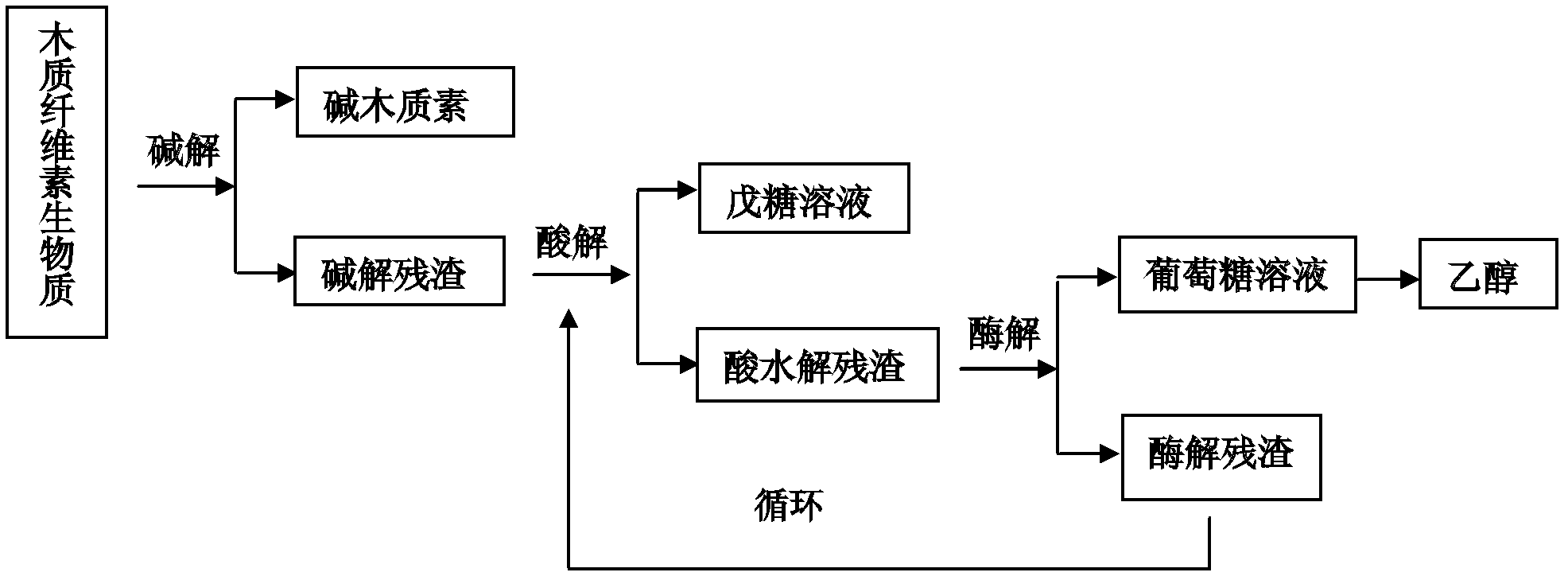
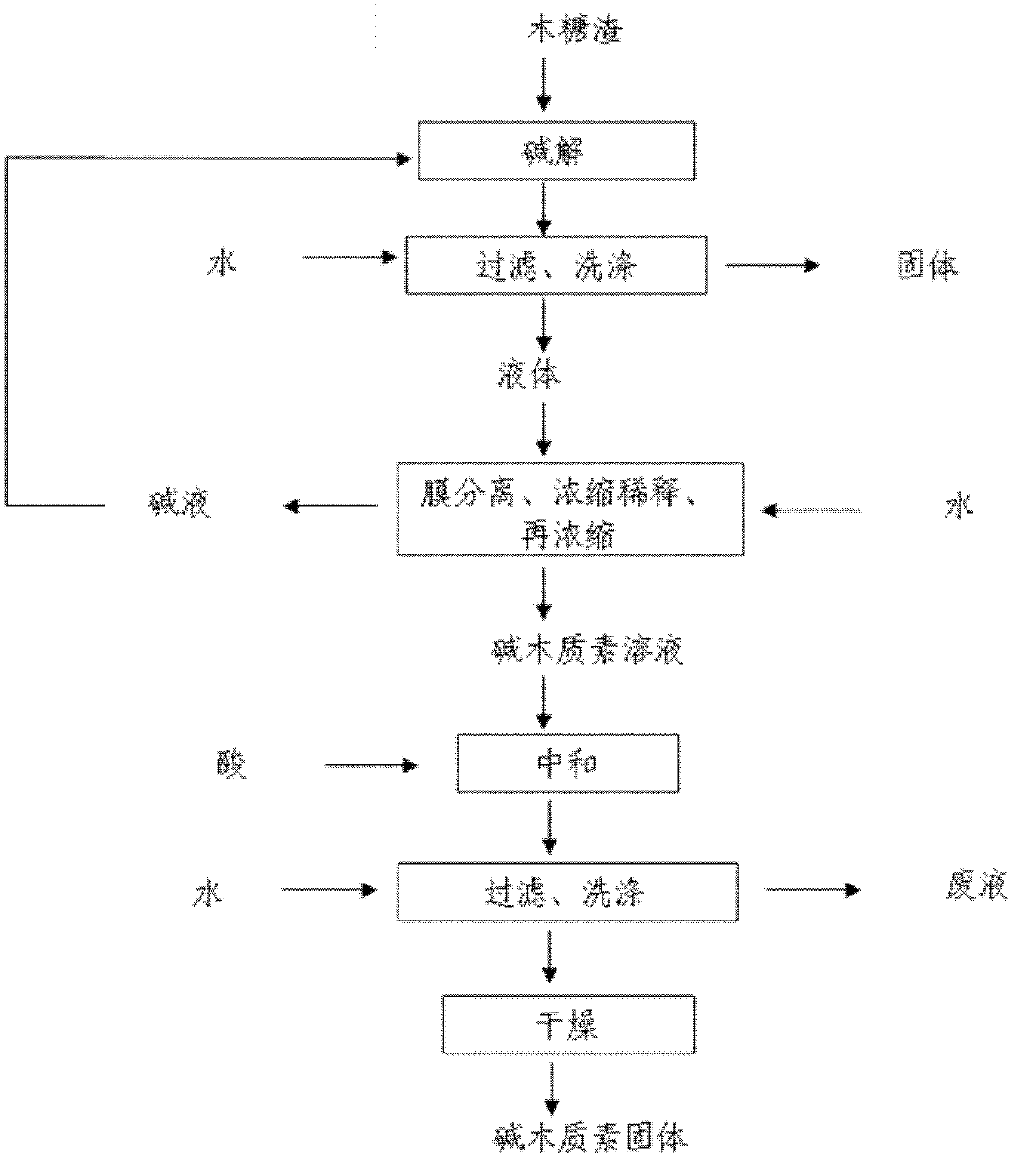
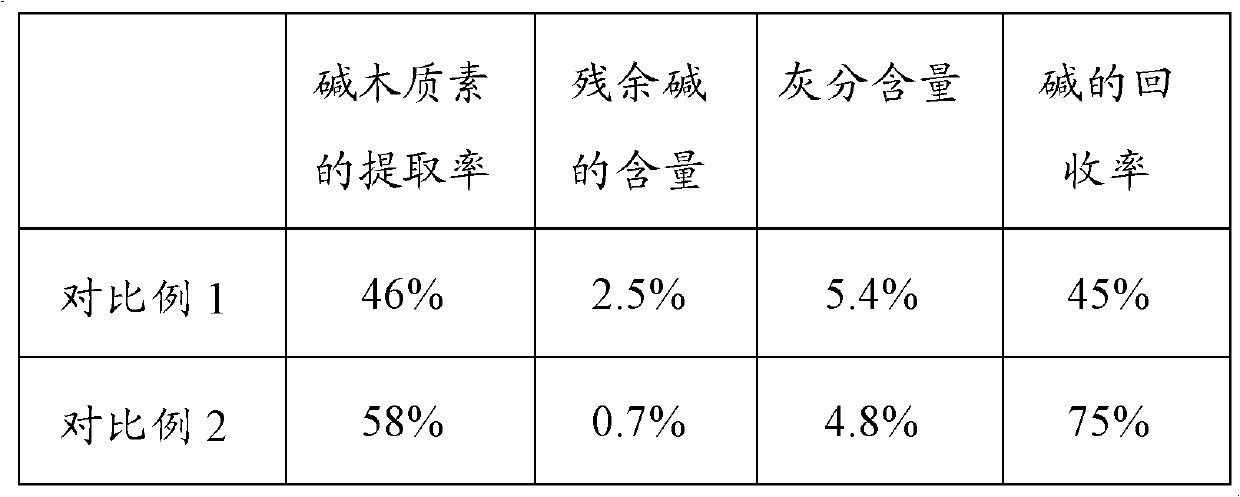
Comprehensive utilization method of lignocellulose biomass
ActiveCN103045680AHigh purityIncrease vitalityMicroorganism based processesFermentationEnzymatic hydrolysisResource utilization
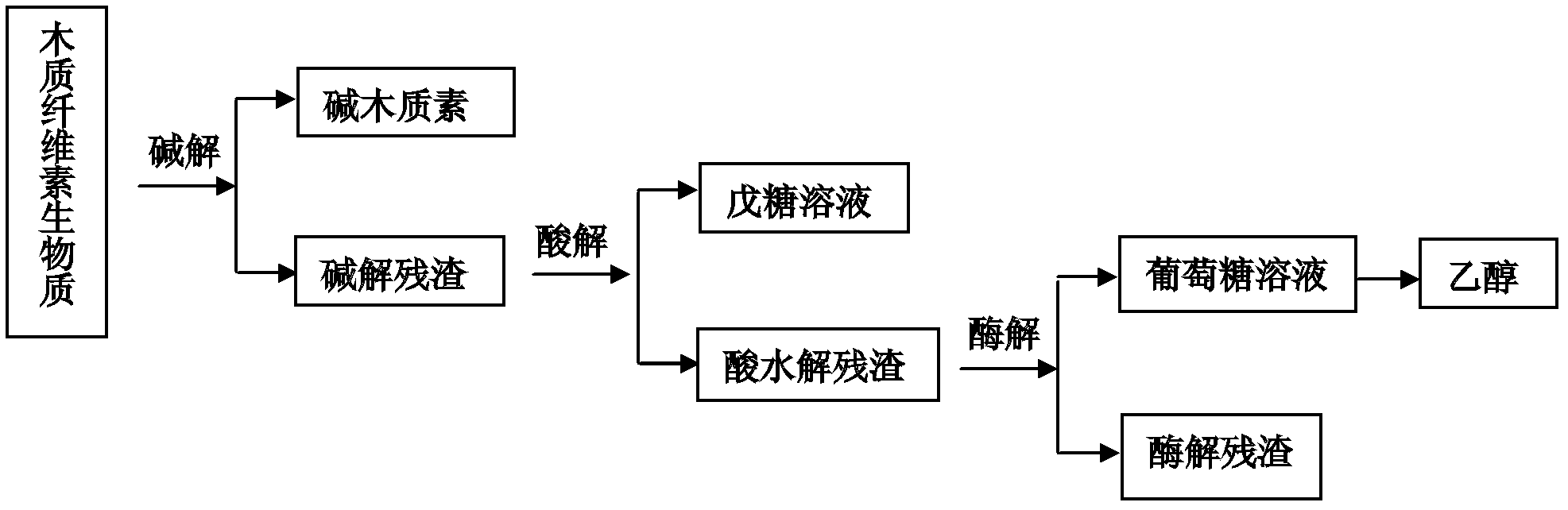
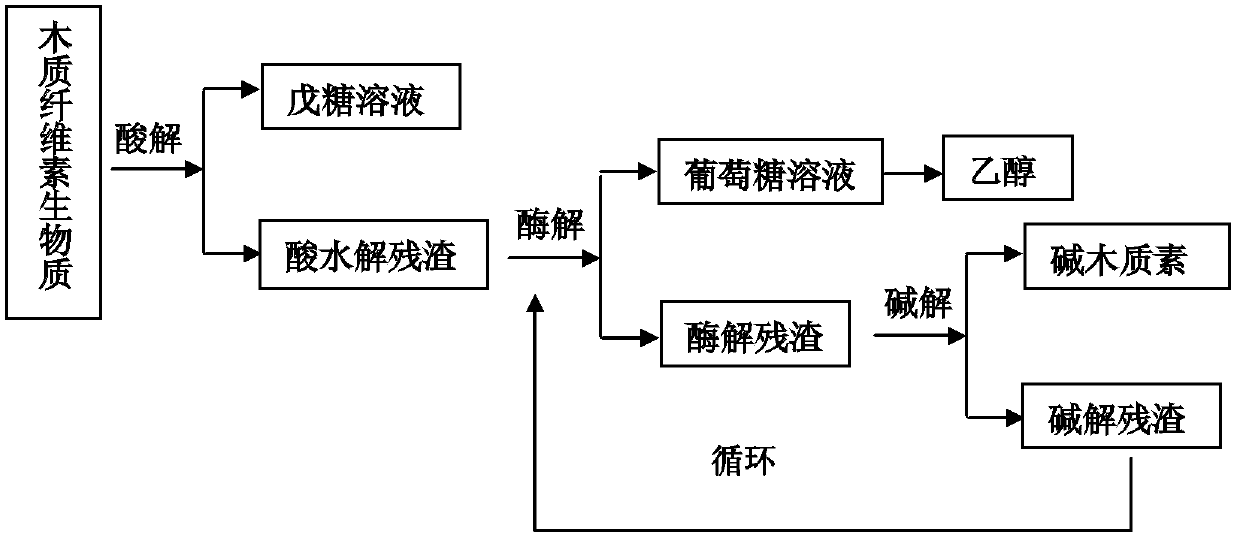
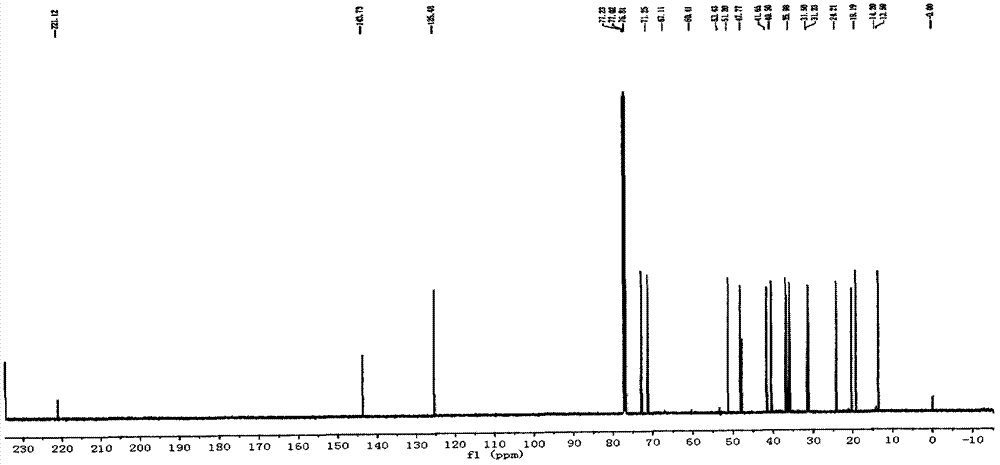
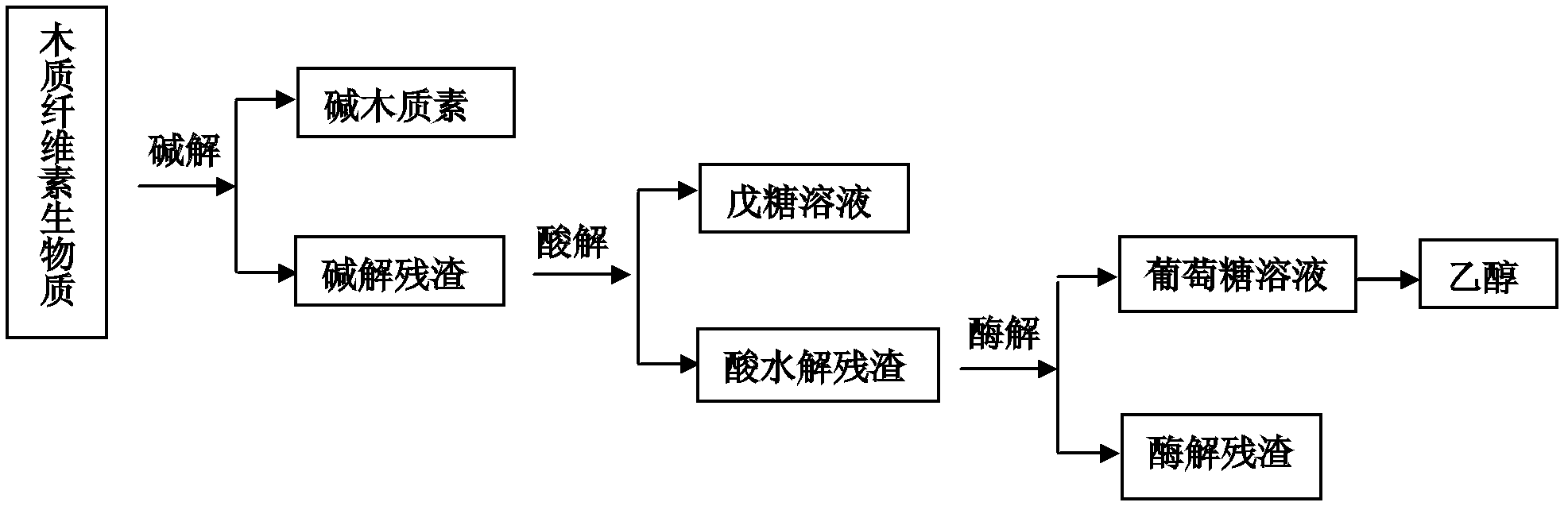
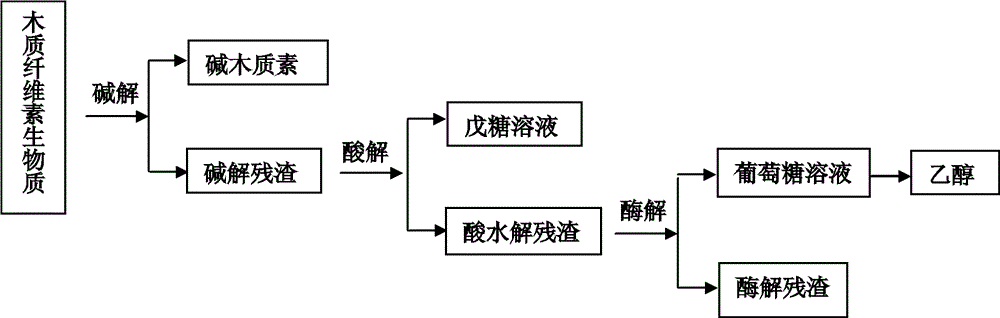
A comprehensive utilization method of lignocellulose biomass comprises the following steps of: (a) alkaline hydrolysis processing: (i) processing the lignocellulose biomass by an alkaline solution to dissolve the lignin in the alkaline solution; (ii) then performing filtration and washing to obtain alkaline hydrolysis residues and liquid; (iii) separating the obtained liquid by a membrane device, and concentrating to obtain an alkaline lignin solution; (b) acid hydrolysis: performing acid hydrolysis of the alkaline hydrolysis residues, separating to obtain a pentose solution and acid hydrolysis residues; (c) cellulose enzymatic hydrolysis: performing enzymatic hydrolysis of the acid hydrolysis residues by using cellulase produced by a penicillium (Penicillium decumbens PD-G3-08), and then performing fermentation to produce ethanol. The method realizes the maximum resource utilization of lignocellulose biomass.
Owner:JINAN SHENGQUAN GROUP SHARE HLDG
Method for preparing hesperetin from enzymatic hydrolysis neohesperidin or hesperidin
InactiveCN106148446AHigh purityHigh efficiency and high purityFermentationChromatographic separationOrganic solvent
The invention discloses a method for preparing hesperetin from enzymatic hydrolysis neohesperidin or hesperidin. Neohesperidin or hesperidin beta-D-glucoside bond can be hydrolyzed in one step through crude enzyme liquid to prepare corresponding aglycone hesperetin. The method includes the steps of preparing the crude enzyme liquid of Penicillium decumbens through fermentation, adjusting the content and reaction time of the crude enzyme liquid, directly converting neohesperidin or hesperidin into hesperetin, dissolving or extracting conversion liquid through organic solvent, and conducting chromatographic purification to obtain hesperetin. By means of the method, the defects that a traditional chemical method is strict in reaction condition, serious in pollution, low in conversion rate and the like when used for preparing hesperetin can be overcome, and the defects that when microbial fermentation is directly adopted, operation is complicated, products are not simplex, and products are difficult to purify can be overcome.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Penicillium decumbens, culture method thereof, and application thereof in transforming steroid medicines
ActiveCN102127511AEasy extractionHigh purityFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyPenicillium bilaiae
The invention relates to a strain of Penicillium decumbens UC086 capable of effectively transforming dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) into 1alpha-OH-DHEA, and a culture method thereof and application thereof in transforming steroid medicines, and belongs to the technical field of microorganisms. The strain was preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on August 9, 2010 with the collection number of GCMCC 4075. The strain has the characteristics that the strain is quickly grown and easy to culture, and can efficiently transform the DHEA into the 1alpha-OH-DHEA; moreover, the product is easy to extract, and the final product has high purity. Through detection, the biological conversion rate of the 1alpha-OH-DHEA is 20 to 50 percent, the product extraction yield is75 to 80 percent, and the purity of the 1alpha-OH-DHEA product is over 99.5 percent.
Owner:SHANDONG BAIZAOGANGMU BIOTECH CO LTD
Method for increasing enzyme activity of cellulase produced from fungal
InactiveCN102108347AIncrease enzyme activityRegulation of secretionMicroorganism based processesEnzymesPenicillium decumbensFilter paper
The invention relates to a new technical method for increasing the enzyme activity of cellulase. In the fermentation and production process of the cellulase produced from fungal, farnesol is added to increase the enzyme activity of cellulase. By adding farnesol, the filter paper enzyme activity of the Trichoderma reesei cellulase-producing is increased by about 30% and the filter paper enzyme activity of Penicillium decumbens cellulase-producing is increased by about 46%. The method in the invention is simple and practical, the effect of increasing the enzyme activity of cellulase is obvious; and the method can be widely used and can be used in various cellulase-producing industries adopting fungal fermentation.
Owner:RES CENT FOR ECO ENVIRONMENTAL SCI THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Penicillium strain producing cellulase and application in cellulose enzymatic hydrolysis thereof
ActiveCN103045484BHigh activityInduce enzyme productionFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyPenicillium decumbens
The invention belongs to the field of microorganism, and particularly relates to a microorganism penicillium strain producing high-activity cellulase. The penicillium strain has a classification name of Penicillium decumbens PD-G3-08, and is preserved in Wuhan University China Center for Type Culture Collection with a preservation number of CCTCC M2011195. The invention also provides an application of the strain in cellulose enzymatic hydrolysis. Through mutation breeding, the penicillium strain producing high-activity cellulase is bred; cellulase crude enzyme liquid is obtained through fermentation of the strain, which has filter paper enzyme activity of up to 10 IU / ml, endoglucanase activity of up to 30 IU / ml, exoglucanase activity of up to 1.5 IU / ml and beta-glucosidase activity of up to 8 IU / ml, respectively being 3 times, 4 times, 4.5 times, and 4 times higher than the activities of an original strain; when the strain is applied to enzymatic hydrolysis of cellulose raw materials, the cellulose conversion rate in 3 days is up to more than 80%, and the cellulase has extremely high activity.
Owner:JINAN SHENGQUAN GROUP SHARE HLDG
Animal feed additive and preparation process thereof
InactiveCN101664110ANutritional diversityPromote growthAnimal feeding stuffAccessory food factorsPenicillium decumbensAspergillus niger
An animal feed additive comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 25-29% of lactobacillus, 24-28% of saccharomyces cerevisiae, 33-37% of penicillium decumbens and 10-14% of aspergillus niger. A preparation process comprises the following steps: (1) placing the four strains into four fermentation tanks respectively; (2) placing vectors and nutrients with addition proportion of 3%into each fermentation tank in which the strains account for 97%; (3) controlling the temperature of the fermentation tanks between 25 DEG C and 35 DEG C and humidity between 60% and 70%, and carryingout fermentation under the acid environment with pH value less than 7; (4) taking out the solid obtained after fermentation in each fermentation tank, baking and then processing the solid into powder; and (5) mixing the four kinds of powder. The animal feed additive is prepared by mixing the microbial strains, has all-round nutrition and has no effect on the quality of animals. The preparation process is simple and the cost is lowered.
Owner:WUHAN DUOBAO BIOLOGICAL TECH
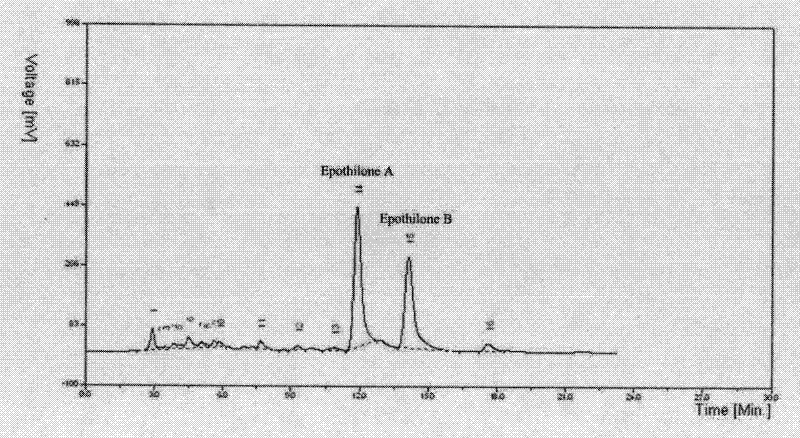
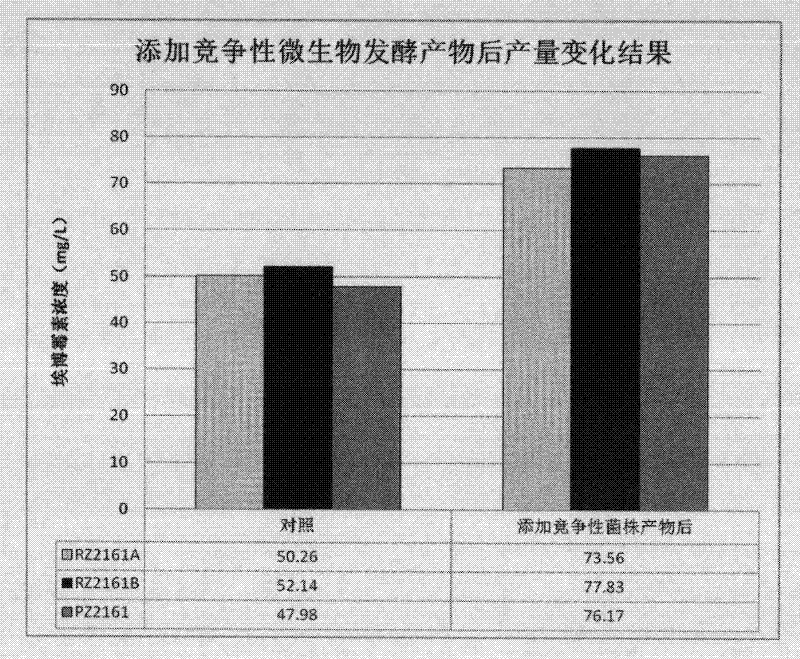
Method for increasing fermentation yield of epothilone by using competitive microorganism and application thereof
InactiveCN102399848AImprove fermentation yieldIncrease the amount of bacteriaMicroorganism based processesFermentationMicroorganismPenicillium bilaiae
The invention discloses a method for increasing the fermentation yield of epothilone by using the metabolin of competitive microorganism namely rhizopus arrhizus or penicillium decumbens of sorangium cellulosum to induce. The method provided by the invention comprises the following steps of: cultivating the competitive microorganism, and extracting the metabolin of the competitive microorganism; adding the metabolin into a sorangium cellulosum fermentation medium, activating epothilone to produce related regulator genes inside the strain by using the stimulation of the external additive, and further stimulating the synthesis of epothilone. Detection results show that the fermentation yield of epothilone can be increased by 46.3-58.7% as compared with original conditions after the method is used, and the method has important theoretical significance and economic value.
Owner:QILU UNIV OF TECH
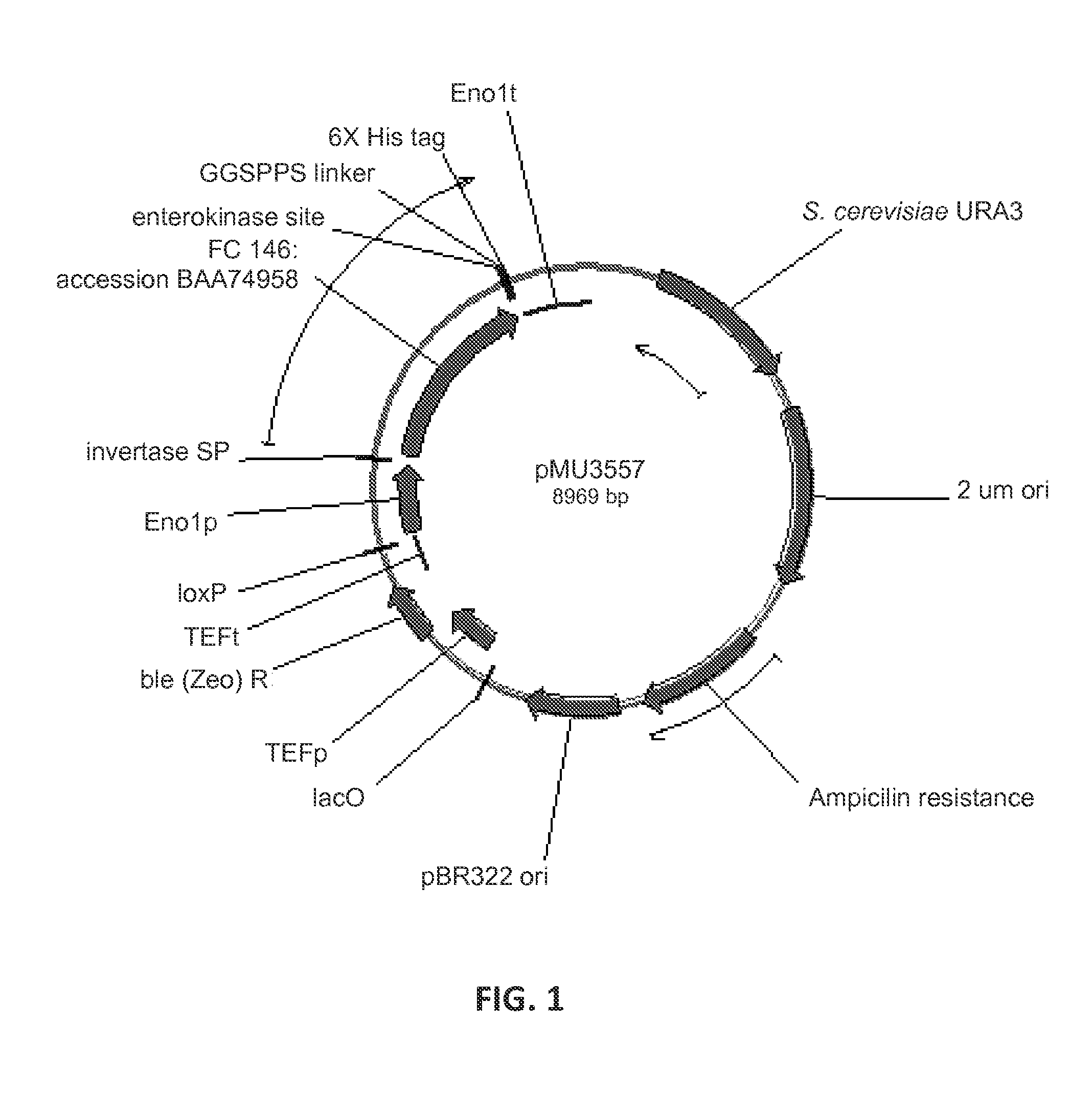
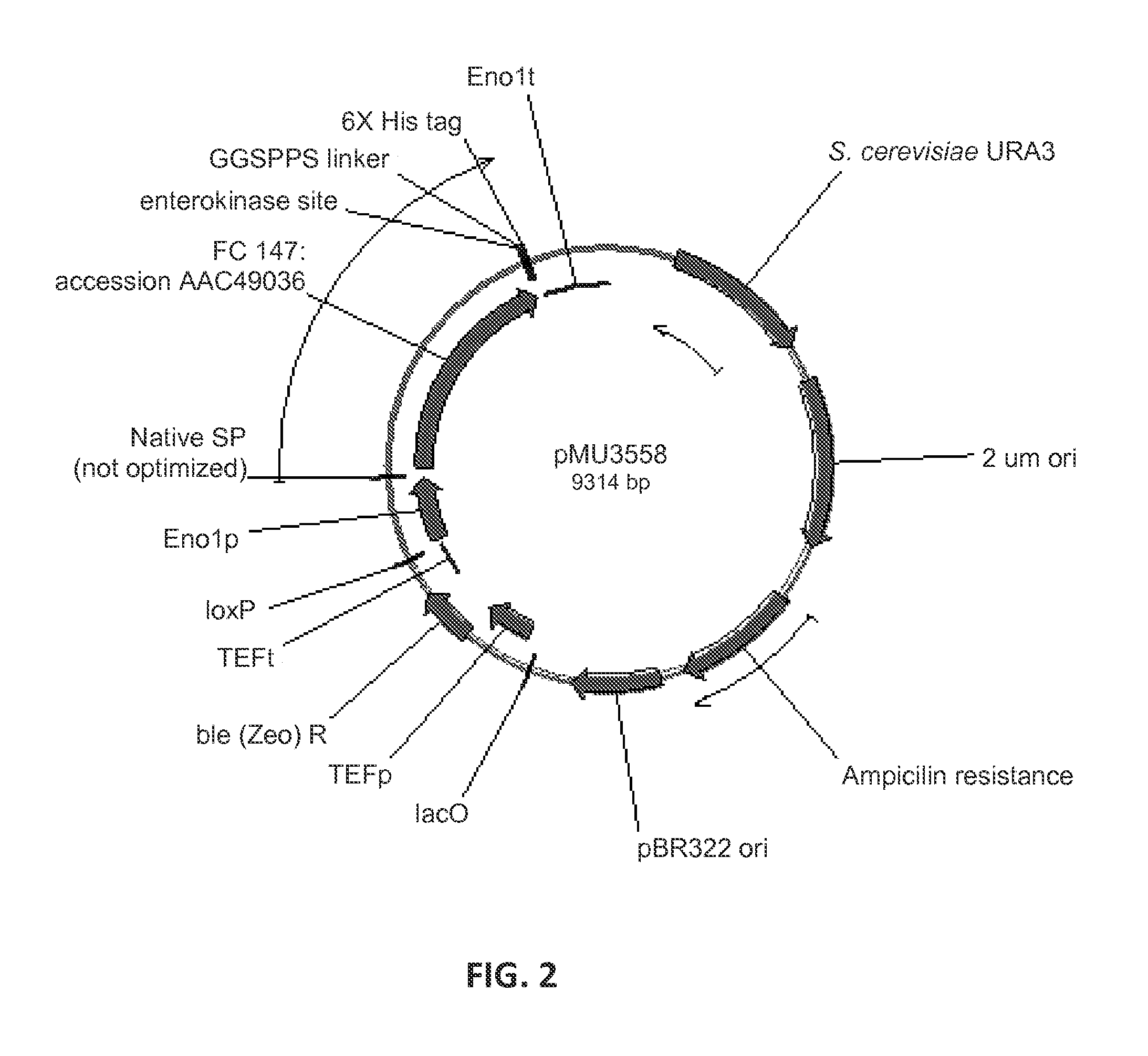
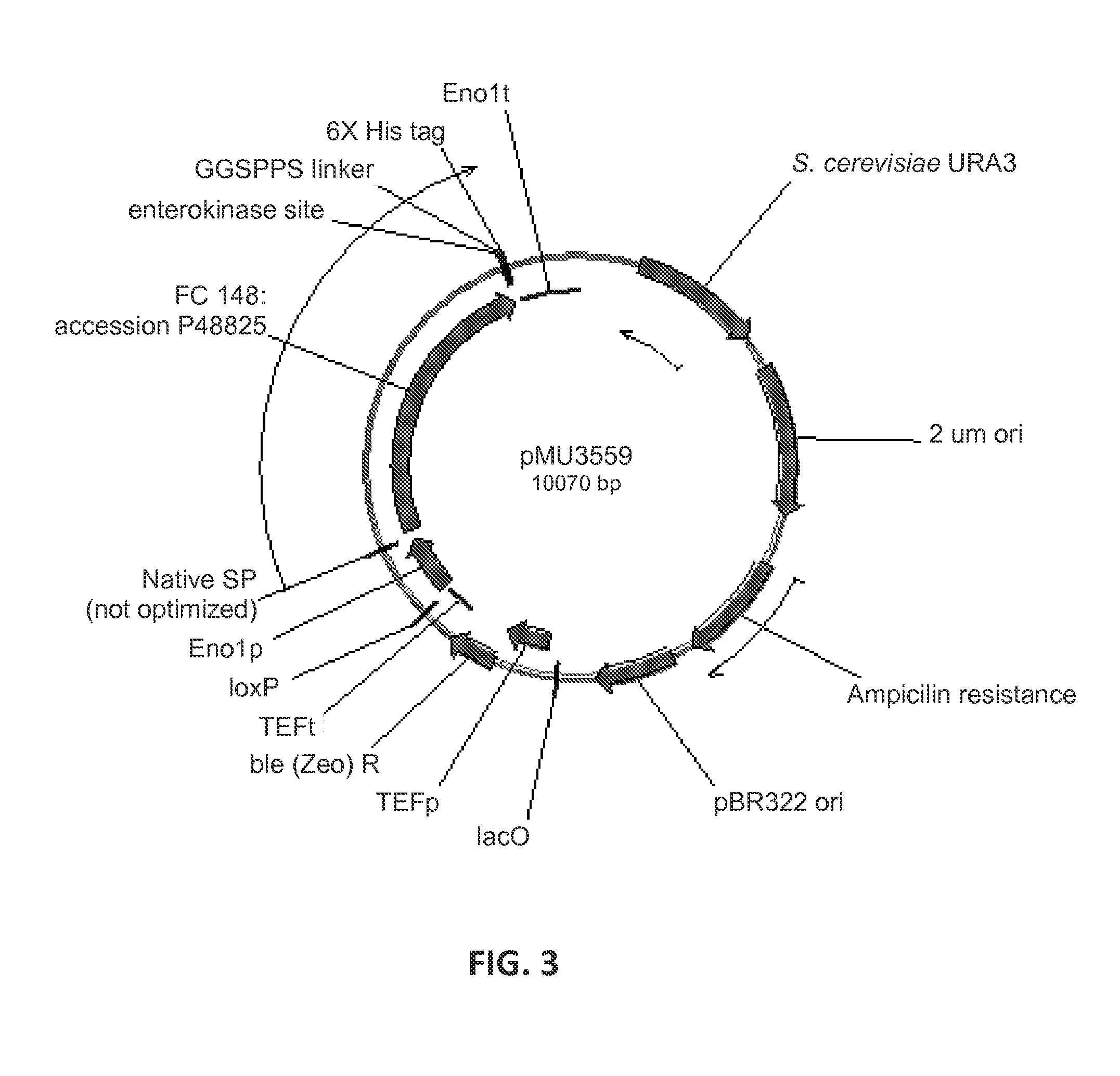
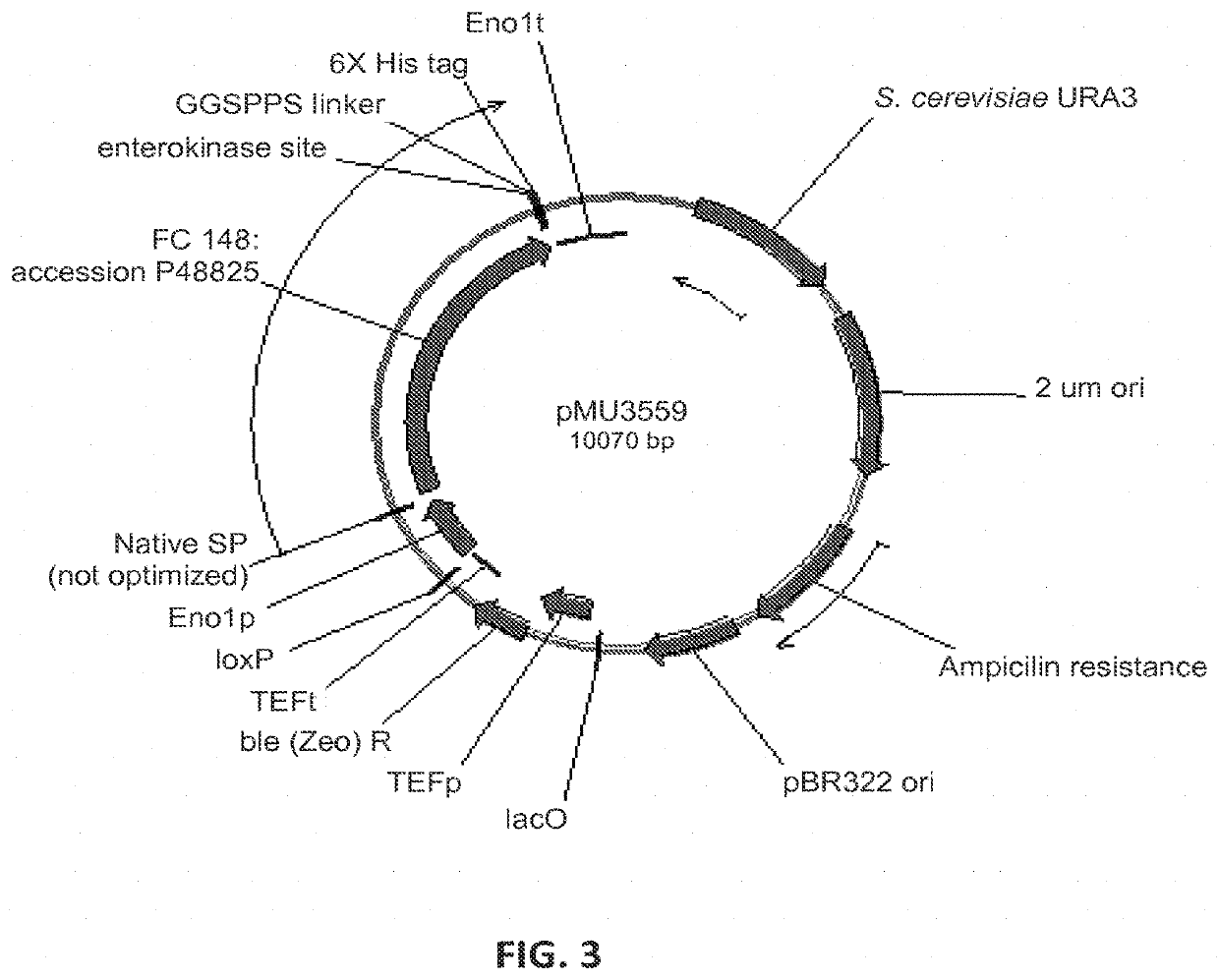
Expression of beta-glucosidases for hydrolysis of lignocellulose and associated oligomers
The present invention provides for heterologous expression of beta-glucosidase (BGL) polypeptides encoded by Humicola grisea, Candida wickerhamii, Aspergillus aculeatus, Aspergillus oryzae, Penicillium decumbens, Chaetomium globosum, Neocallimastix frontalis, Debaryomyces hansenii, Kluyveromyces marxianus, or Phytophthora infestans in host cells, such as the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. The expression in such host cells of the corresponding genes, and variants and combinations thereof, result in improved specific activity of the expressed BGL. Thus, such genes and expression systems are useful for efficient and cost-effective consolidated bioprocessing systems.
Owner:LALLEMAND HUNGARY LIQUIDITY MANAGEMENT LLC
Comprehensive utilization method of lignocellulose biomass
ActiveCN103045688AMaximize utilizationReduce pollutionMicroorganism based processesFermentationEnzymatic hydrolysisResource utilization
A comprehensive utilization method of lignocellulose biomass comprises the following steps: (a) performing acid hydrolysis of the lignocellulose biomass, separating to obtain a pentose solution and acid hydrolysis residues; b) performing enzymatic hydrolysis of the acid hydrolysis residues in step (a) by using cellulase, then performing fermentation to produce ethanol, wherein the cellulase is obtained by culturing a strain of penicillium which has a classification name of Penicillium decumbens PD-G3-08, and is preserved in Wuhan University China Center for Type Culture Collection with a preservation number of CCTCC M 2011195; (c) processing the fermentation residues produced in step (b) by using an alkaline solution so as to extract lignin from the fermentation residues; (d) after step (c) is complete, returning to step (b) to perform enzymatic hydrolysis and fermentation by using residues obtained after alkaline solution processing as enzymatic hydrolysis raw materials, and then performing steps (c) and (d). The method realizes the maximum resource utilization of lignocellulose biomass.
Owner:JINAN SHENGQUAN GROUP SHARE HLDG
Microbial metabolite microbial agent for promoting plant growth, and preparation method and application thereof
PendingCN114032183APromote growthIncrease productionBiocidePlant growth regulatorsMetabolitePlant roots
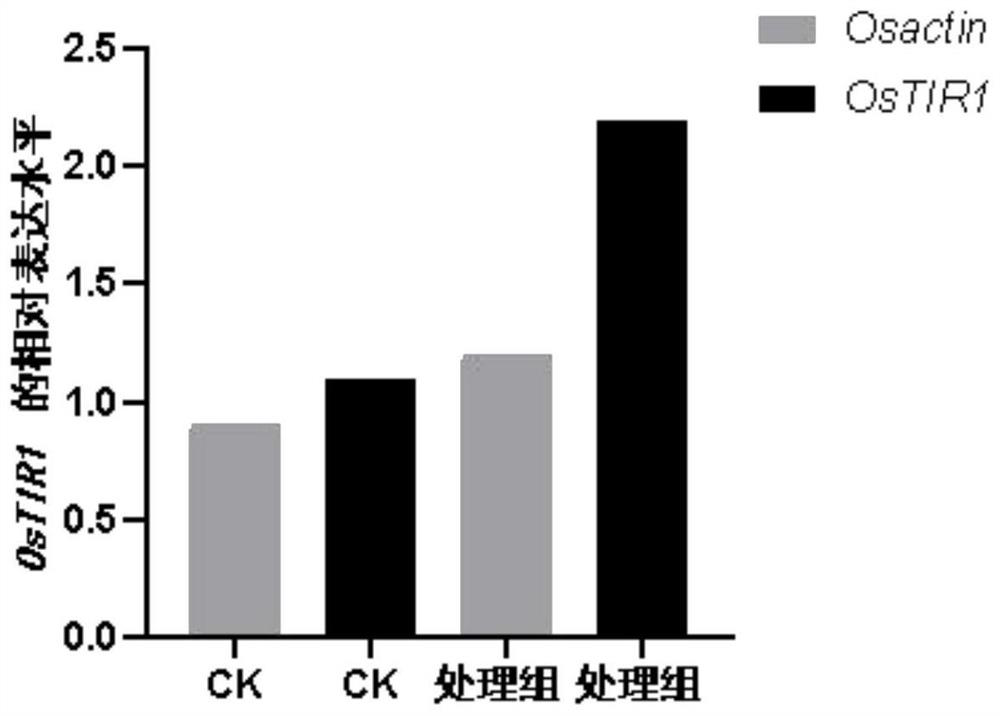
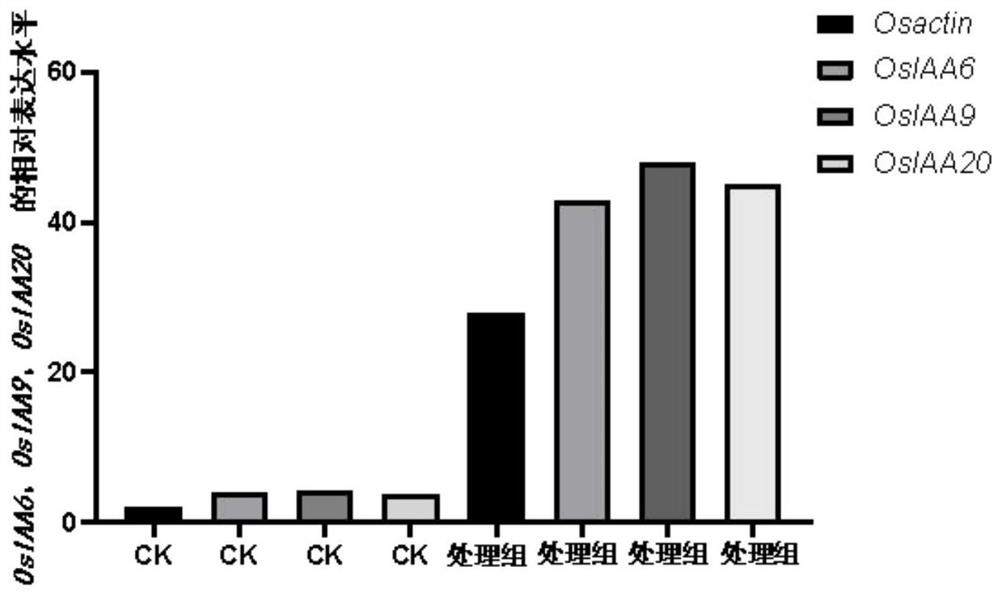
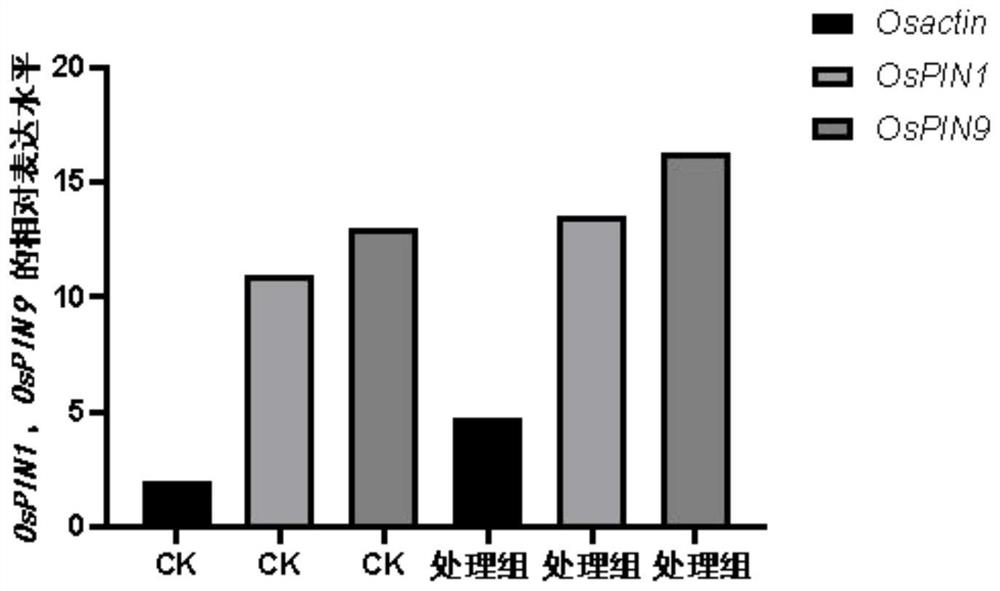
The invention belongs to the technical field of fertilizer preparation, and particularly relates to a microbial metabolite microbial agent for promoting plant growth, and a preparation method and application thereof. By compounding metabolite dry powders of penicillium citrinum, penicillium rubrum and penicillium decumbens, or the penicillium rubrum, penicillium tomummii and penicillium griseofulvum, the growth of plant root systems can be remarkably promoted, and particularly, the root length, the root diameter and the root weight of the root systems of the root vegetables can be increased, so that the effect of increasing the plant yield is achieved. Meanwhile, the microbial metabolite microbial agent disclosed by the invention can also enable the expression of auxin related genes such as auxin transport genes OsPIN1 and OsPIN9, auxin signal genes OsIAA6, OsIAA9 and OsIAA20 and an auxin receptor gene OsTIR1 to be up-regulated, so that the content of endogenous hormones in plants is increased, and the growth of the plants is promoted.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Comprehensive utilization method of lignocellulose biomass
ActiveCN103045679AHigh extraction rateIncrease vitalityMicroorganism based processesFermentationEnzymatic hydrolysisPenicillium decumbens
A comprehensive utilization method of lignocellulose biomass comprises the following steps: (a) processing the lignocellulose biomass by an alkaline solution to extract lignin; (b) performing acid hydrolysis of the alkaline hydrolysis residues obtained by the alkaline solution processing, separating to obtain a pentose solution and acid hydrolysis residues; (c) performing enzymatic hydrolysis of the alkaline hydrolysis residues by using cellulase produced by a penicillium (Penicillium decumbens PD-G3-08) to obtain a glucose solution and enzymatic hydrolysis residues; (d) returning the enzymatic hydrolysis residues to step (b) for acid hydrolysis processing, or combining the enzymatic hydrolysis residues with new alkaline hydrolysis residues and performing acid hydrolysis processing in step (b), then orderly performing steps (c) and (d), cycling the steps so as to further convert hemicellulose into pentose and to perform enzymatic hydrolysis of the cellulose into glucose. The method improves the conversion rate of cellulose enzymatic hydrolysis, and realizes comprehensive utilization of lignocellulose biomass resources.
Owner:JINAN SHENGQUAN GROUP SHARE HLDG
Expression of beta-glucosidases for hydrolysis of lignocellulose and associated oligomers
The present invention provides for heterologous expression of beta-glucosidase (BGL) polypeptides encoded by Humicola grisea, Candida wickerhamii, Aspergillus aculeatus, Aspergillus oryzae, Penicillium decumbens, Chaetomium globosum, Neocallimastix frontalis, Debaryomyces hansenii, Kluyveromyces marxianus, or Phytophthora infestans in host cells, such as the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. The expression in such host cells of the corresponding genes, and variants and combinations thereof, result in improved specific activity of the expressed BGL. Thus, such genes and expression systems are useful for efficient and cost-effective consolidated bioprocessing systems.
Owner:LALLEMAND HUNGARY LIQUIDITY MANAGEMENT LLC
Penicillium decumbens engineered strain containing over-expressed xylanase and application thereof
InactiveCN101845400AIncrease vitalityFungiMicroorganism based processesPenicillium bilaiaePenicillium decumbens
The invention discloses a penicillium decumbens engineered strain containing over-expressed xylanase, which contains over-expressed penicillium decumbens xylanase I genes, is named penicillium decumbens X8 and is preserved in China Centre for Type Culture Collection on May 7, 2010 with a preservation number of CCTCC M 2010110. The invention also discloses the application of the strain in production of xylanase. The highest activity of the xylanase of the engineered strain of the invention reaches 219.82 IU / ml and is 1.57 times as high as that of an original host strain, which indicates that the strain is widely applied to the production of the xylanase.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Compound microorganism live bacteria preparation for degrading papermaking wastewater COD, preparation method and applications thereof
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF PHARMA IND CO LTD +1
Expression of beta-glucosidases for hydrolysis of lignocellulose and associated oligomers
The present invention provides for heterologous expression of beta-glucosidase (BGL) polypeptides encoded by Humicola grisea, Candida wickerhamii, Aspergillus aculeatus, Aspergillus oryzae, Penicillium decumbens, Chaetomium globosum, Neocallimastix frontalis, Debaryomyces hansenii, Kluyveromyces marxianus, or Phytophthora infestans in host cells, such as the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. The expression in such host cells of the corresponding genes, and variants and combinations thereof, result in improved specific activity of the expressed BGL. Thus, such genes and expression systems are useful for efficient and cost-effective consolidated bioprocessing systems.
Owner:LALLEMAND HUNGARY LIQUIDITY MANAGEMENT LLC
Method for preparing feed by mixing straw and butanol or alcoholic fermentation waste water
InactiveCN101940248BSolve the emission problemImprove palatabilityFood processingAnimal feeding stuffPenicillium decumbensCandida tropicalis
The invention relates to a method for preparing a protein feed by mixing straw and straw dilute acid hydrolytic pentose butanol or alcoholic fermentation waste water for solid state fermentation, which comprises the following steps of: mixing the steam-exploded straw or the straw hydrolyzed by dilute acid and the straw dilute acid hydrolytic pentose butanol or alcoholic fermentation waste water in a certain volume to ensure that moisture content is between 70 and 80 percent, after sterilizing, inoculating penicillium decumbens and trametes pubescens to the mixture and performing aerobic solid state fermentation for 4 to 6 days, inoculating candida tropicalis and lactobacillus plantarum and performing anaerobic fermentation for 2 to 3 days, and drying to obtain the protein feed. In the protein feed product prepared by the method, the protein content is between 22 and 27 percent, and the degradation rate of coarse fibers is between 63 and 68 percent. The method can solve the problem of discharging the butanol or alcoholic fermentation waste water; and the waste water and the straw are converted into the protein feed, so that the waste is turned into treasure.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Method for increasing fermentation yield of epothilone by using competitive microorganism and application thereof
InactiveCN102399848BImprove fermentation yieldIncrease the amount of bacteriaMicroorganismsMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismPenicillium bilaiae
Owner:QILU UNIV OF TECH
Penicillium decumbens engineered strain containing over-expressed beta-glucosidase and application thereof
The invention discloses a penicillium deumbens engineered strain containing over-expressed beta-glucosidase, which contains over-expressed beta-glucosidase genes, is named penicillium deumbens Gi31-2 and is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection on May 7, 2010 with a preservation number of CCTCC M 2010111. The invention also discloses the application of the strain in production of the beta-glucosidase and degradation of cellulose. The highest activity of the beta-glucosidase of the engineered strain of the invention reaches 3.47 IU / ml and is 2.90 times as high as that of an original host strain, while highest filter paper activity is 3.32 IU / ml and is 1.23 times as high as that of the original host strain. Therefore, the strain is widely applied to the production of the beta-glucosidase.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Comprehensive utilization method of lignocellulose biomass
ActiveCN103045688BMaximize utilizationReduce pollutionMicroorganism based processesFermentationBiotechnologyEnzymatic hydrolysis
A comprehensive utilization method of lignocellulose biomass comprises the following steps: (a) performing acid hydrolysis of the lignocellulose biomass, separating to obtain a pentose solution and acid hydrolysis residues; b) performing enzymatic hydrolysis of the acid hydrolysis residues in step (a) by using cellulase, then performing fermentation to produce ethanol, wherein the cellulase is obtained by culturing a strain of penicillium which has a classification name of Penicillium decumbens PD-G3-08, and is preserved in Wuhan University China Center for Type Culture Collection with a preservation number of CCTCC M 2011195; (c) processing the fermentation residues produced in step (b) by using an alkaline solution so as to extract lignin from the fermentation residues; (d) after step (c) is complete, returning to step (b) to perform enzymatic hydrolysis and fermentation by using residues obtained after alkaline solution processing as enzymatic hydrolysis raw materials, and then performing steps (c) and (d). The method realizes the maximum resource utilization of lignocellulose biomass.
Owner:JINAN SHENGQUAN GROUP SHARE HLDG
Penicillium decumbens, culture method thereof, and application thereof in transforming steroid medicines
ActiveCN102127511BEasy extractionHigh purityFungiMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismPenicillium decumbens
The invention relates to a strain of Penicillium decumbens UC086 capable of effectively transforming dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) into 1alpha-OH-DHEA, and a culture method thereof and application thereof in transforming steroid medicines, and belongs to the technical field of microorganisms. The strain was preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on August 9, 2010 with the collection number of GCMCC NO.4075. The strain has the characteristics that the strain is quickly grown and easy to culture, and can efficiently transform the DHEA into the 1alpha-OH-DHEA; moreover, the product is easy to extract, and the final product has high purity. Through detection, the biological conversion rate of the 1alpha-OH-DHEA is 20 to 50 percent, the product extraction yield is 75 to 80 percent, and the purity of the 1alpha-OH-DHEA product is over 99.5 percent.
Owner:SHANDONG BAIZAOGANGMU BIOTECH CO LTD
Comprehensive utilization method of lignocellulose biomass
ActiveCN103045683AEliminate spatial barriersEasy accessFermentationSaccharides productionEnzymatic hydrolysisPenicillium decumbens
A comprehensive utilization method of lignocellulose biomass comprises the following steps: (a) performing alkaline hydrolysis of the lignocellulose biomass to extract lignin; (b) performing acid hydrolysis of the residues obtained in the alkaline hydrolysis processing , separating to obtain a pentose solution and acid hydrolysis residues; (c) performing enzymatic hydrolysis of the residues obtained by alkaline hydrolysis processing in step (b) by using cellulase to obtain a solution with a main component of glucose, wherein the cellulase is obtained by culturing a strain of penicillium which has a classification name of Penicillium decumbens PD-G3-08, and is preserved in Wuhan University China Center for Type Culture Collection with a preservation number of CCTCC M 2011195 and a preservation date of June 13, 2011. The method improves the extraction ratio of cellulose enzymatic hydrolysis, and realizes comprehensive utilization of lignocellulose biomass resources.
Owner:JINAN SHENGQUAN GROUP SHARE HLDG
Method for increasing enzyme activity of cellulase produced from fungal
InactiveCN102108347BIncrease enzyme activityRegulation of secretionMicroorganism based processesEnzymesPenicillium decumbensFilter paper
The invention relates to a new technical method for increasing the enzyme activity of cellulase. In the fermentation and production process of the cellulase produced from fungal, farnesol is added to increase the enzyme activity of cellulase. By adding farnesol, the filter paper enzyme activity of the Trichoderma reesei cellulase-producing is increased by about 30% and the filter paper enzyme activity of Penicillium decumbens cellulase-producing is increased by about 46%. The method in the invention is simple and practical, the effect of increasing the enzyme activity of cellulase is obvious;and the method can be widely used and can be used in various cellulase-producing industries adopting fungal fermentation.
Owner:RES CENT FOR ECO ENVIRONMENTAL SCI THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Engonus fungus with high enzyme activity and high capacity of efficiently degrading straw cellulose in northeast China region
InactiveCN102061267BEfficient degradationEfficient degradation abilityFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyPenicillium bilaiae
The invention relates to an engonus fungus with high enzyme activity and high capacity of efficiently degrading straw cellulose in the northeast China region, in particular to a fungus for degrading cellulose. The engonus fungus with high enzyme activity and high capacity of efficiently degrading the straw cellulose in the northeast China region is named as Penicillium decumbens C5, belongs to the Penicillium sp., and has the preservation number of CGMSS No.4203 and the preservation date of October 8th 2010. When the Penicillium decumbens C5 strain is cultured for 3d, FPase reaches 7085.66U / L, the EG / Cen peak is 3856.97U / L, the CBU / Cex peak is 2681.59U / L, and the beta-Gase peak is 1487.86U / L, thus the Penicillium decumbens C5 has a function of efficiently degrading straws.
Owner:NORTHEAST FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Comprehensive utilization method of lignocellulose biomass
ActiveCN103045683BEliminate spatial barriersEasy accessFermentationSaccharides productionEnzymatic hydrolysisPenicillium decumbens
A comprehensive utilization method of lignocellulose biomass comprises the following steps: (a) performing alkaline hydrolysis of the lignocellulose biomass to extract lignin; (b) performing acid hydrolysis of the residues obtained in the alkaline hydrolysis processing , separating to obtain a pentose solution and acid hydrolysis residues; (c) performing enzymatic hydrolysis of the residues obtained by alkaline hydrolysis processing in step (b) by using cellulase to obtain a solution with a main component of glucose, wherein the cellulase is obtained by culturing a strain of penicillium which has a classification name of Penicillium decumbens PD-G3-08, and is preserved in Wuhan University China Center for Type Culture Collection with a preservation number of CCTCC M 2011195 and a preservation date of June 13, 2011. The method improves the extraction ratio of cellulose enzymatic hydrolysis, and realizes comprehensive utilization of lignocellulose biomass resources.
Owner:JINAN SHENGQUAN GROUP SHARE HLDG
Penicillium decumbens engineered strain containing over-expressed xylanase and application thereof
InactiveCN101845400BIncrease vitalityFungiMicroorganism based processesPenicillium bilaiaePenicillium decumbens
The invention discloses a penicillium decumbens engineered strain containing over-expressed xylanase, which contains over-expressed penicillium decumbens xylanase I genes, is named penicillium decumbens X8 and is preserved in China Centre for Type Culture Collection on May 7, 2010 with a preservation number of CCTCC M 2010110. The invention also discloses the application of the strain in production of xylanase. The highest activity of the xylanase of the engineered strain of the invention reaches 219.82 IU / ml and is 1.57 times as high as that of an original host strain, which indicates that the strain is widely applied to the production of the xylanase.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com