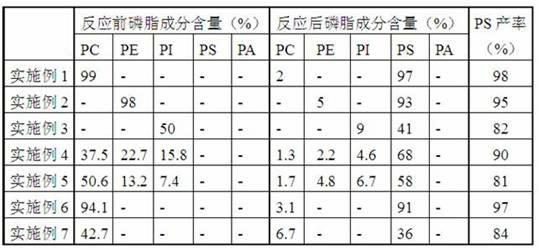
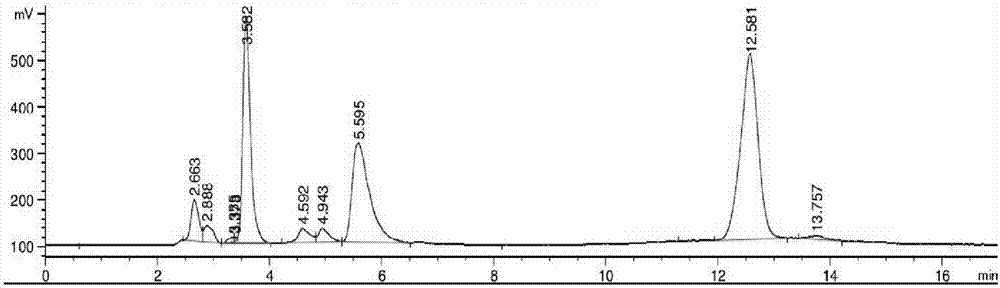
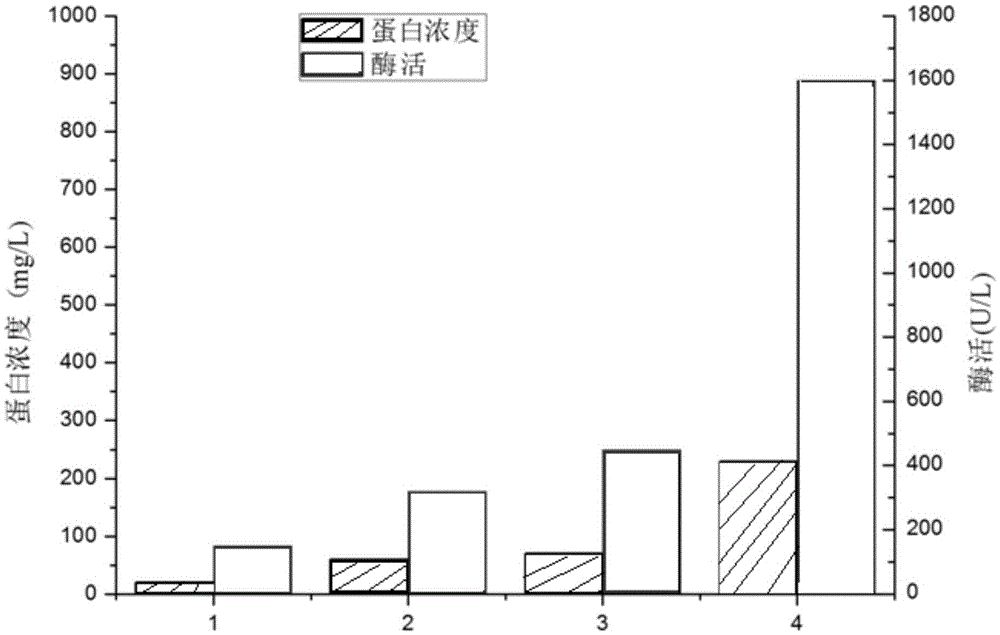
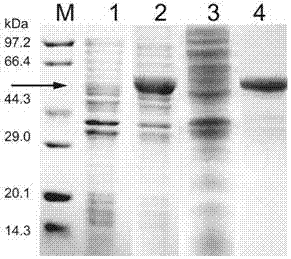
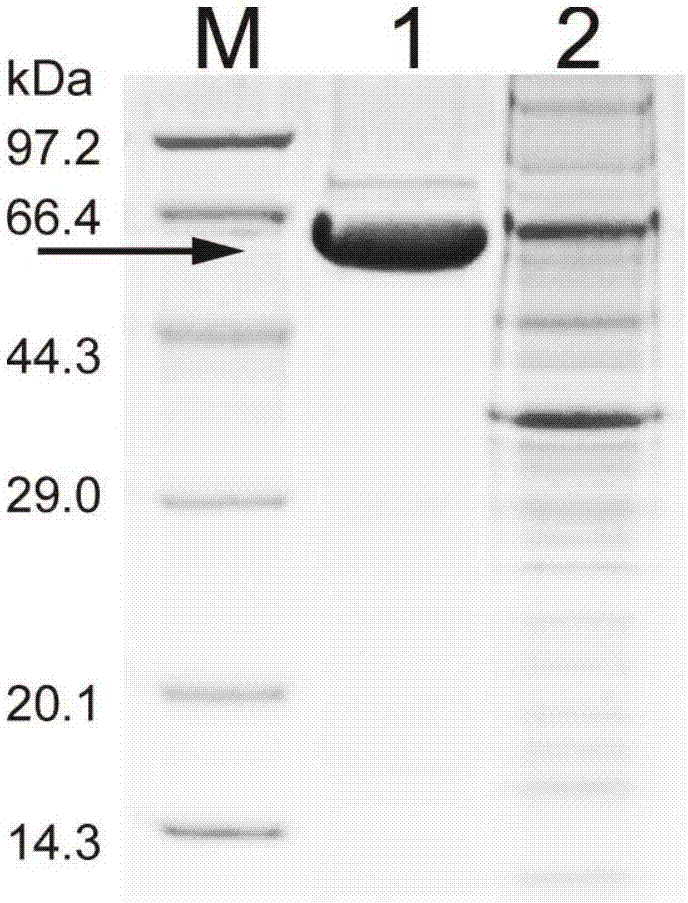
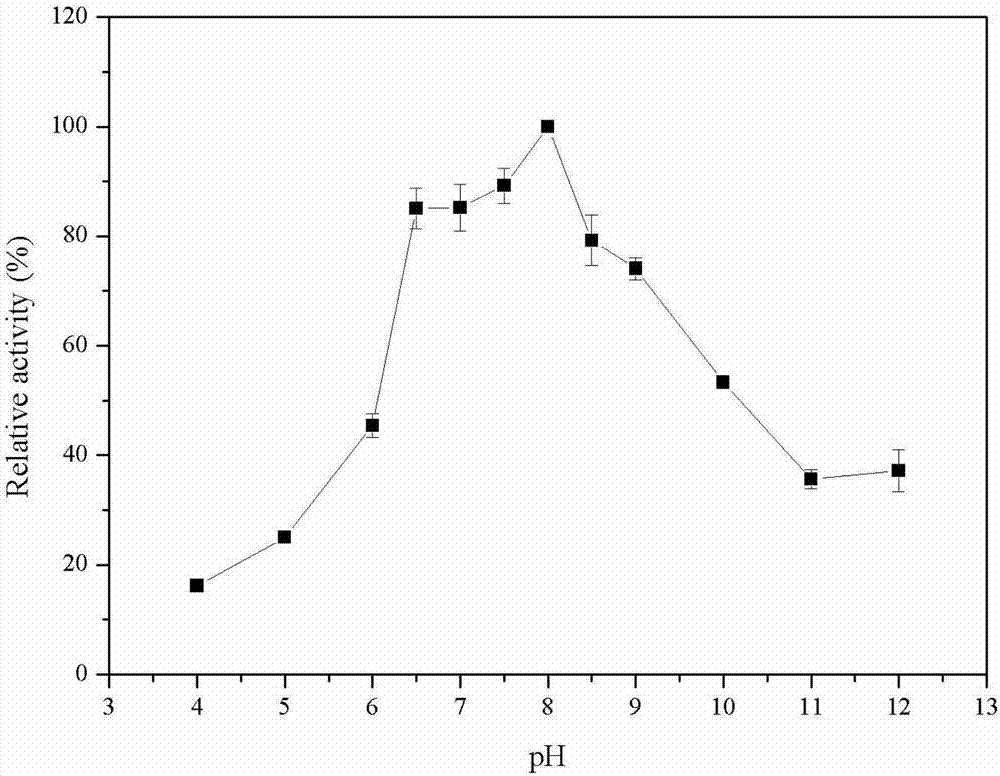
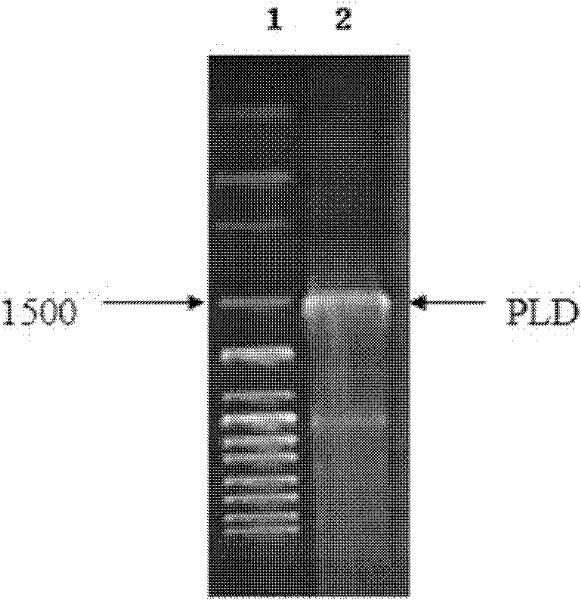
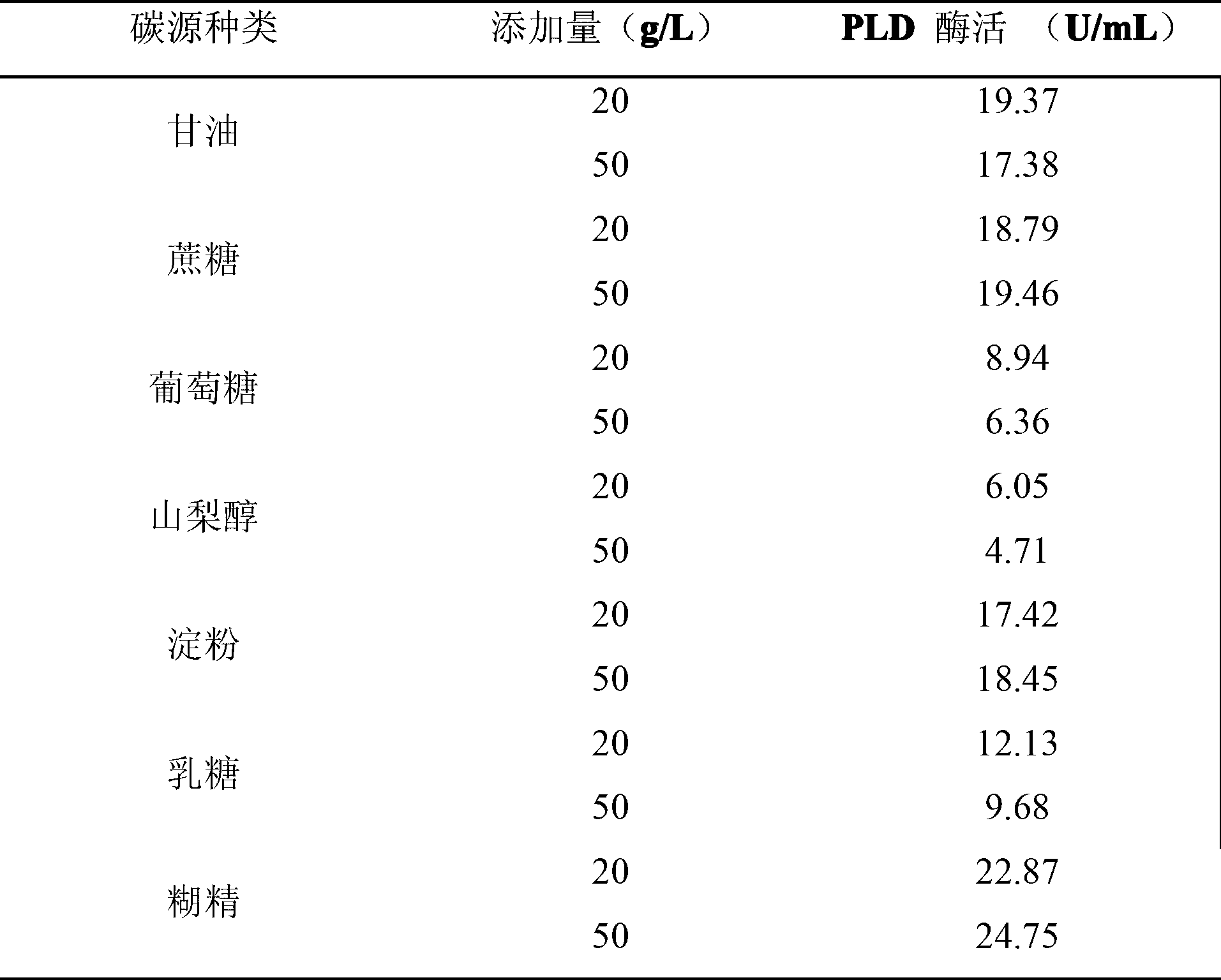
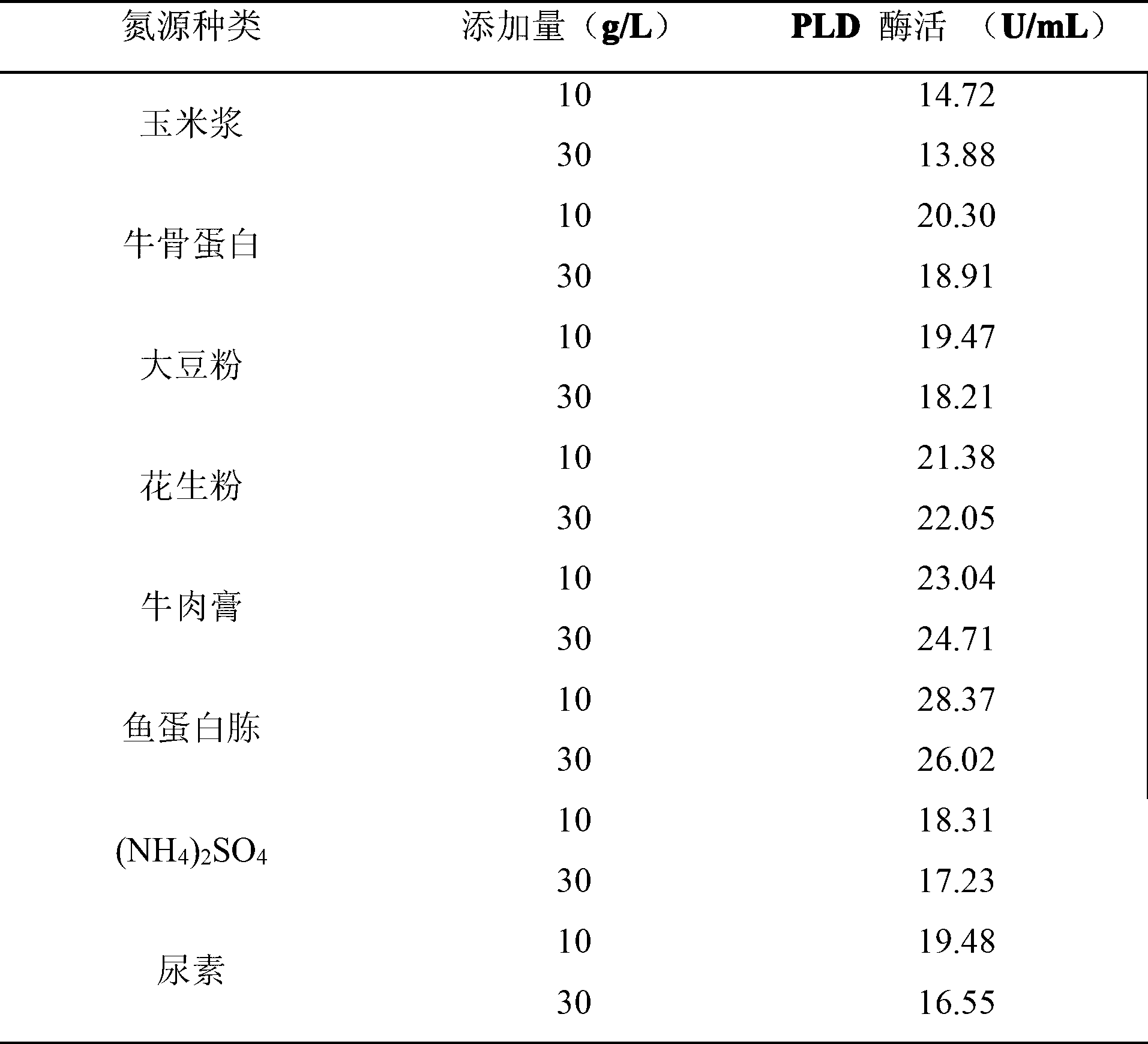
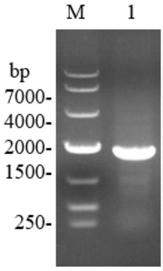
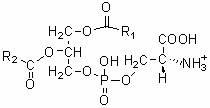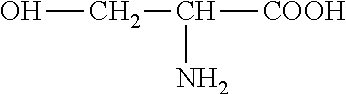Patents
Literature
180 results about "Phospholipase D" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
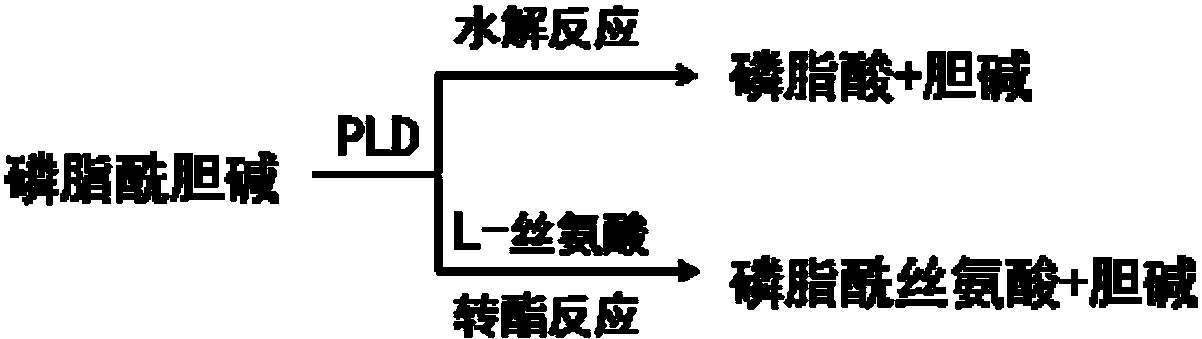
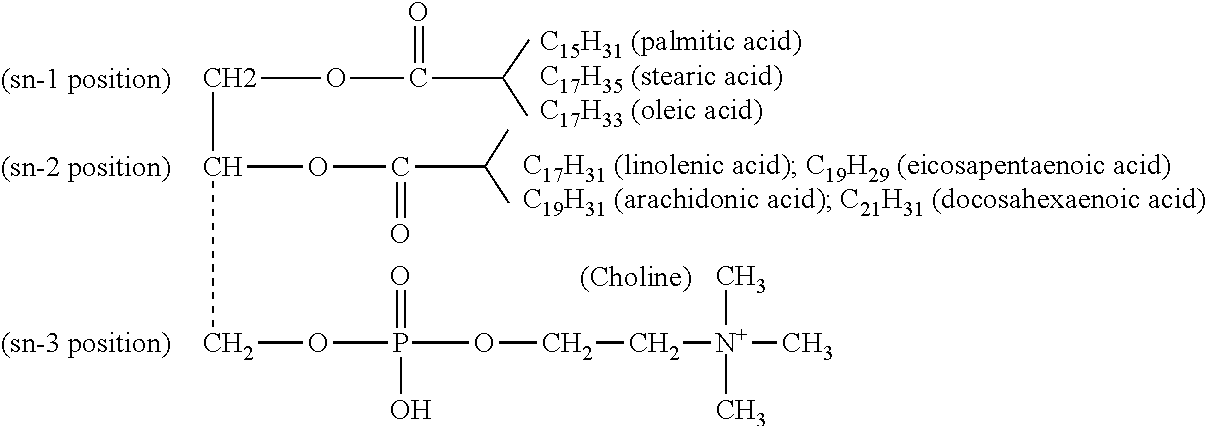
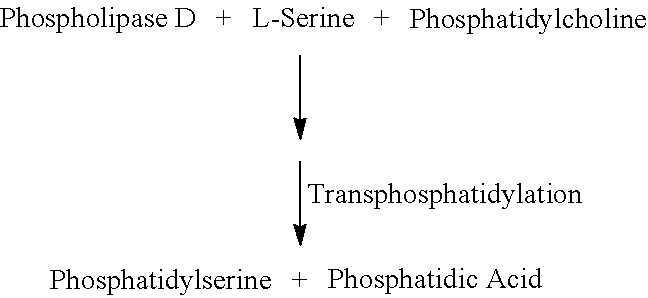
Phospholipase D (EC 3.1.4.4, lipophosphodiesterase II, lecithinase D, choline phosphatase) (PLD) is an enzyme of the phospholipase superfamily. Phospholipases occur widely, and can be found in a wide range of organisms, including bacteria, yeast, plants, animals, and viruses. Phospholipase D’s principal substrate is phosphatidylcholine, which it hydrolyzes to produce the signal molecule phosphatidic acid (PA), and soluble choline. Plants contain numerous genes that encode various PLD isoenzymes, with molecular weights ranging from 90-125 kDa. Mammalian cells encode two isoforms of phospholipase D: PLD1 and PLD2. Phospholipase D is an important player in many physiological processes, including membrane trafficking, cytoskeletal reorganization, receptor-mediated endocytosis, exocytosis, and cell migration. Through these processes, it has been further implicated in the pathophysiology of multiple diseases: in particular the progression of Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s, as well as various cancers.
Method for preparing phosphatidylserine abundant in polyunsaturated fatty acid
InactiveCN101818179ANo emissionsImprove product qualityMicroorganism based processesFermentationUnsaturated fatty acid esterPhospholipid
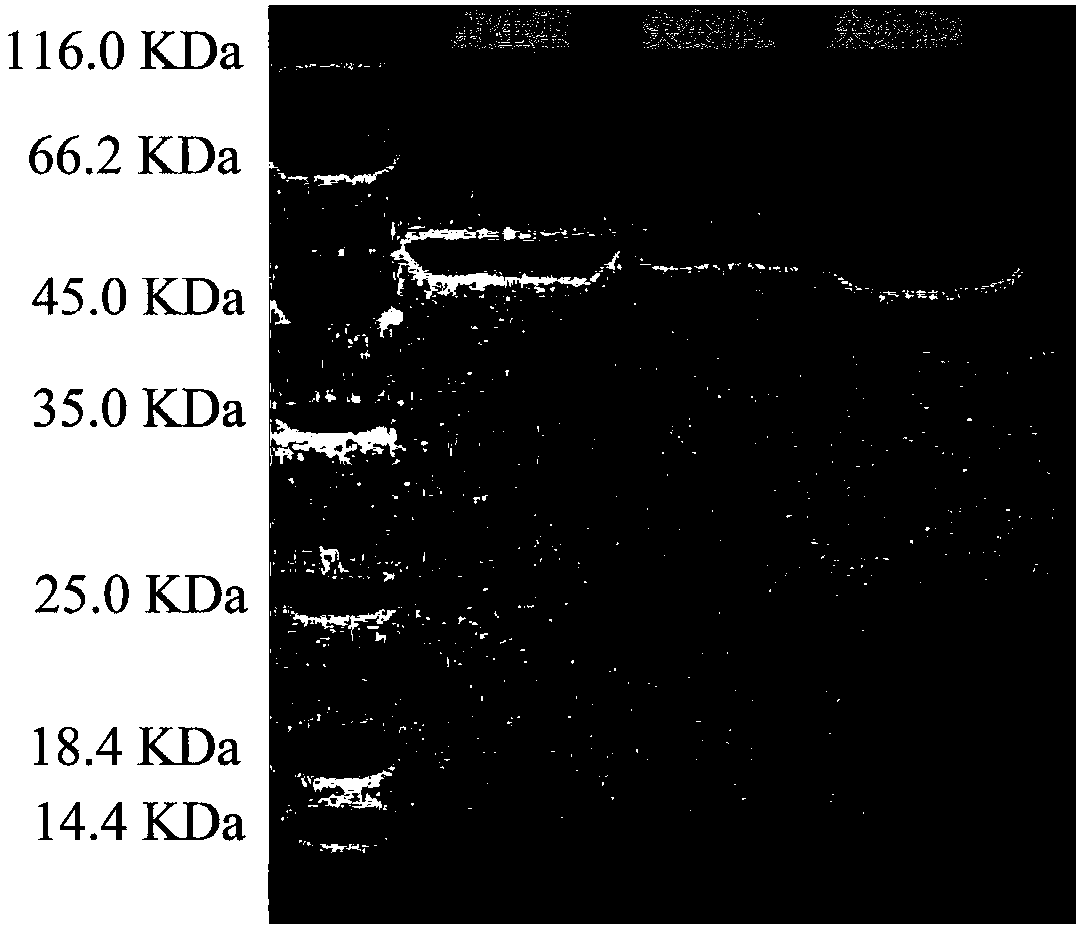
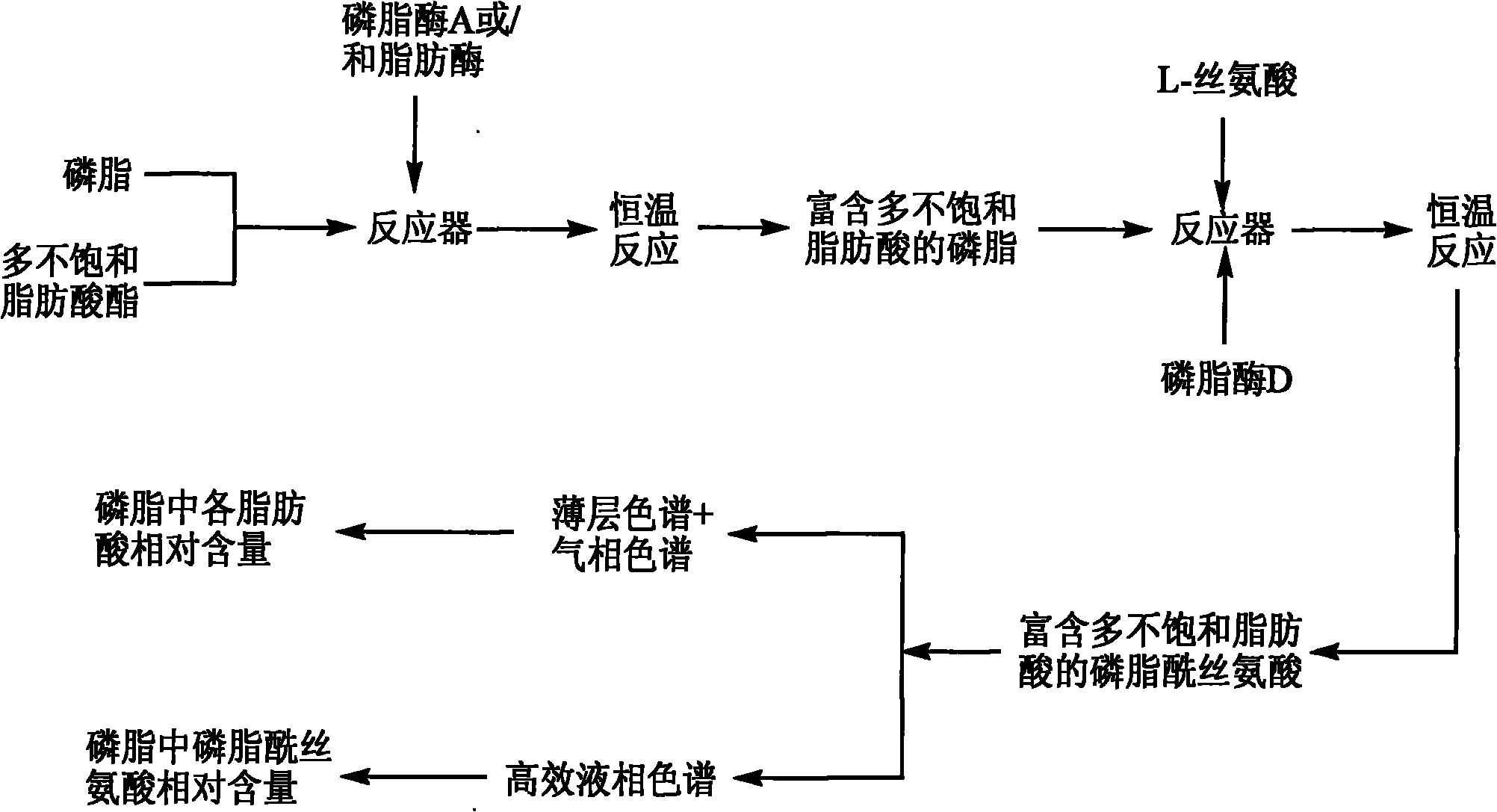
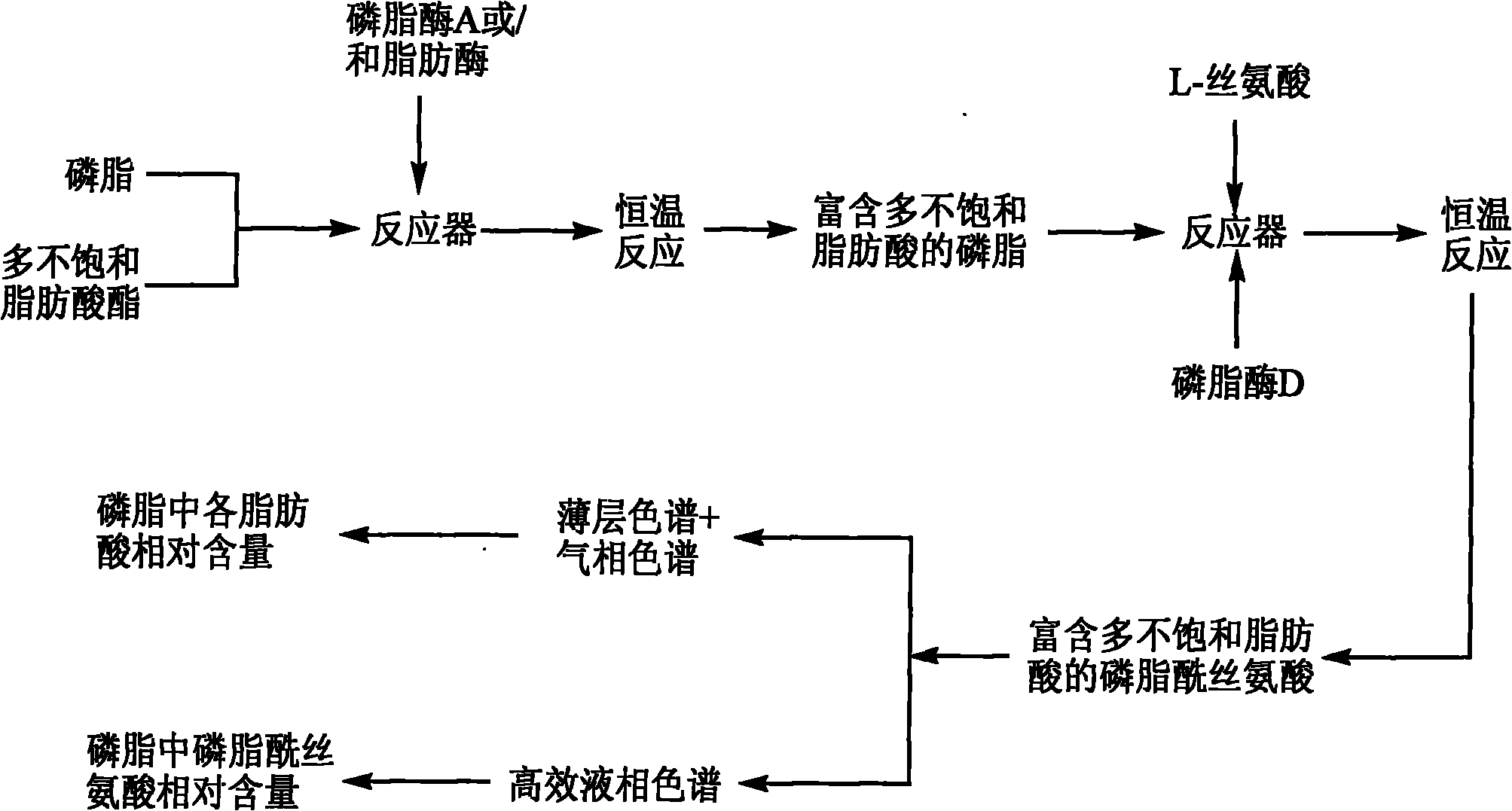
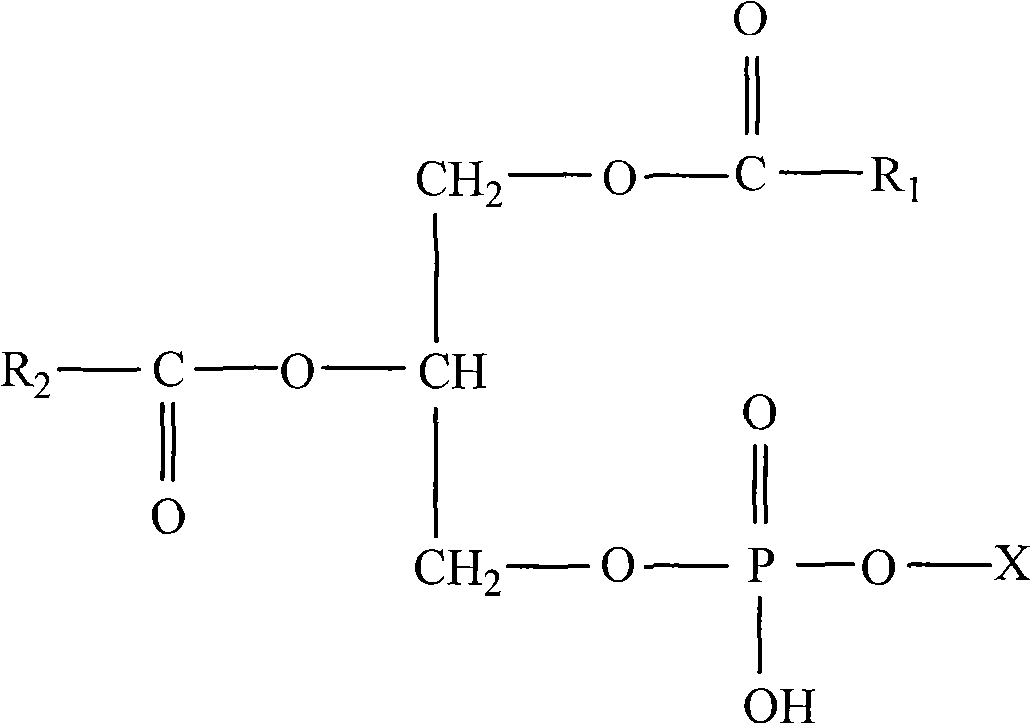
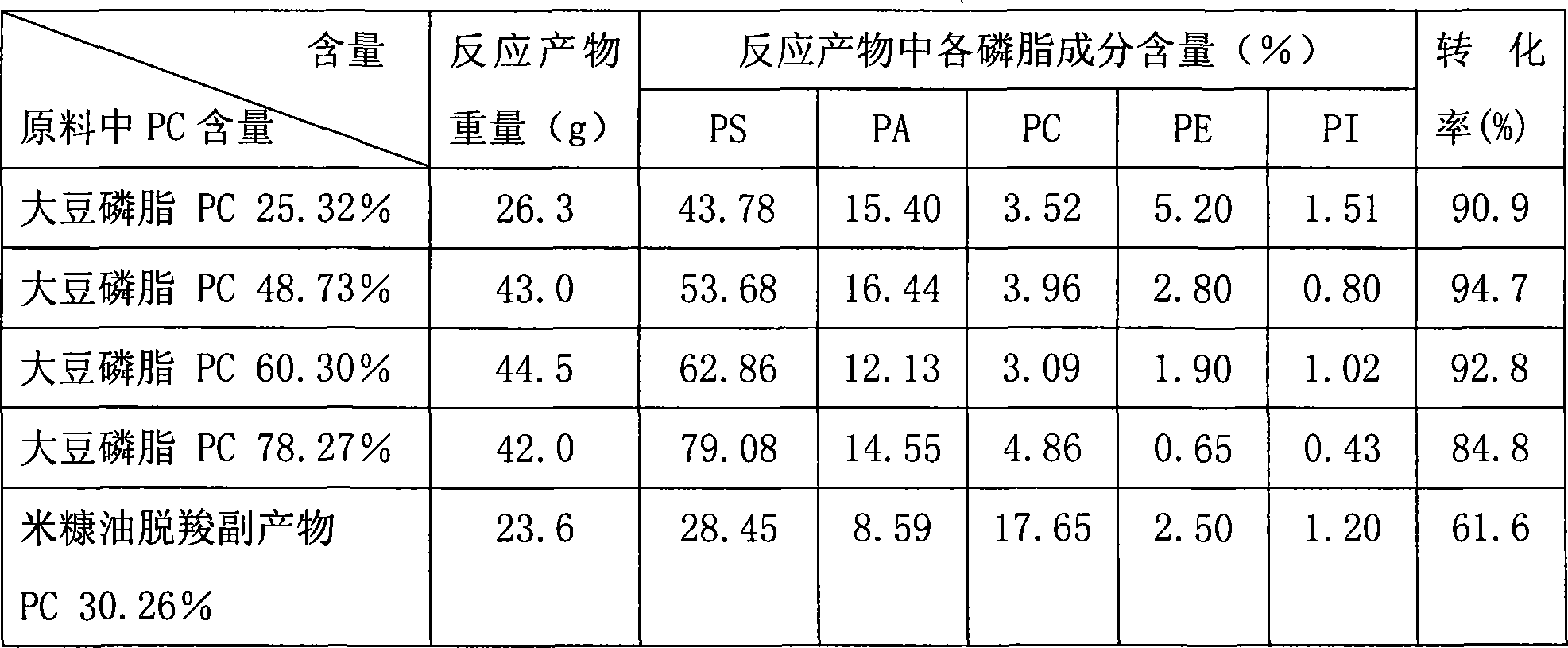
The invention relates to a method for preparing phosphatidylserine abundant in polyunsaturated fatty acid and belongs to the technical field of bioengineering. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: firstly, catalyzing ester exchange reaction between phosphatide and polyunsaturated fatty acid ester by utilizing one or a mixture of phosphatidase A and lipase to generate phosphatide abundant in polyunsaturated fatty acid; and then catalyzing phosphor-transfer esterification reaction between the phosphatide abundant in the polyunsaturated fatty acid and L-serine by utilizing phosphatidase D to generate the phosphatidylserine abundant in the polyunsaturated fatty acid. The method has the advantages of no discharge of waste water, good product quality, no solvent residue, safe process operation, few reaction byproducts, no waste generation, cost reduction, simple production process and easy realization of scale production because of utilizing two enzymes to perform sub-step catalysis and perform reaction in the same reactor, and completing the reaction process in a non-solvent system. Therefore, the invention provides a good and feasible method for preparing the phosphatidylserine abundant in the polyunsaturated fatty acid.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Method for preparing powdered phosphatidyl serine
The invention relates to a method of preparing compounds, in particular to a method of preparing powder phosphatidylserine. The invention has to overcome the problems that the prior art inputs a lot of equipment and costs a lot, and the transformation ratio of the reaction is hard to be guaranteed. The invention has the technical proposal that a method of preparing powder phosphatidylserine takes natural lecithin as the reaction substrate; and after being separated by water, the reaction substrate can be added with an inorganic system prepared by L-serine, calcium salt and buffer solution to produce rough product under the effect of phospholipase D. Concentrate can be obtained by conducting the solvent extraction to the rough product, and then can be purified by solvent to obtain phosphatidylserine. The invention is characterized in that to separate the reaction substrate needs water three to ten times (w / v) of reaction substrate; and the separating temperature is ranged from 20 DEG C to 60 DEG C. In the system, the weight of the L-serine is two to ten times of the reaction substrate, and the weight of water used in the inorganic system is three to ten times(w / v) of reaction substrate. Ph value of the inorganic system can be adjusted between 4.5 and 6.0 by the buffer solution.
Owner:杨凌萃健生物工程技术有限公司 +1
Extraction process of phosphatidylcholine with antarctic krill as source and preparation method of phosphatidylserine
InactiveCN103509047AReduce dosageEmission reductionPhosphatide foodstuff compositionsFermentationAlcoholFreeze-drying
The invention provides an extraction process of phosphatidylcholine with antarctic krill as a source. The extraction process comprises the following steps: collecting heads of the antarctic krill, adding water for decoction, stirring, sending the krill head decoction liquid to a cold pressing machine for solid-liquid separation, to obtain an oily liquid rich in phospholipid and krill heads and other solids; adding absolute ethyl alcohol into the krill heads and other solids, carrying out high shearing extraction, carrying out centrifugal separation, and concentrating to obtain an oily liquid; merging the oily liquids, drying under a reduced pressure, then filtering through a plate frame filter to remove insoluble substances, followed by carrying out membrane separation and concentration, carrying out column chromatography separation and purification, carrying out freeze drying, and thus obtaining the phosphatidylcholine product. The invention also provides a preparation method for phosphatidylserine with the antarctic krill as the source. The preparation method comprises the steps of hydrolyzing the extracted phosphatidylcholine by phospholipase D, and extracting to obtain phosphatidylserine rich in DHA and EPA. The extraction process and the preparation method are environmentally friendly, and are low in cost; and the obtained products have high content and good activity, and can be industrially produced.
Owner:ACERCHEM INT
Compositions for the preservation of fruits and vegetables
InactiveUS20050031744A1Improve quality lifeExtended shelf lifeMilk preservationDead plant preservationGrowth plantAntioxidant
The invention discloses compositions for the preservation of fruits, vegetables, partially processed products, other produce and followers. The compositions comprise at least one phospholipase D inhibitor, at least one compound comprising an isoprene subunit, at least one component of the flavonoid biosynthetic pathway in a suitable medium. The composition of the present invention may additionally comprise one or more plant growth regulators of the cytokinin type, one or more antioxidants, a membrane stabilizing agent, a surfactant, or any combination thereof. The composition may be applied to produce as a spray, drench, dip, or a vapour and at either the pre-harvest stage or post-harvest stage.
Owner:GUELPH UNIV OF
Tolerogenic vaccine and method
InactiveUS20060093580A1Increased proliferationBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsRegulatory T cellAutoimmune condition
Methods and compositions are provided for treating autoimmune diseases such as diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, and other conditions involving undesired immune responses such as allergies, including food allergies, and graft-versus-host disease. In one embodiment disclosed, regulatory / suppressor T cells are selected or expanded in culture using a phospholipase D (PLD) inhibitor to prevent growth of effector T cells and a growth factor to stimulate the regulatory cells. Antigen-specific regulatory / regulatory T cells can be produced by this method. The regulatory T cells can then be administered to a patient in need of suppressive immunotherapy. In another embodiment, PLD inhibitor, growth factor, and an antigen for which antigen-specific suppressive immunotherapy is desired are administered to a patient via injection, oral or topical administration, or other means known to the art.
Owner:MEDICAL COLLEGE OF GEORGIA RES INST
Method for preparing phosphatidylserine with docosahexaenoic acid at sn-2 bit
ActiveCN104004797AGood application effectIncreased specific enzyme activityFungiBacteriaDocosahexaenoic acidPhospholipase A2
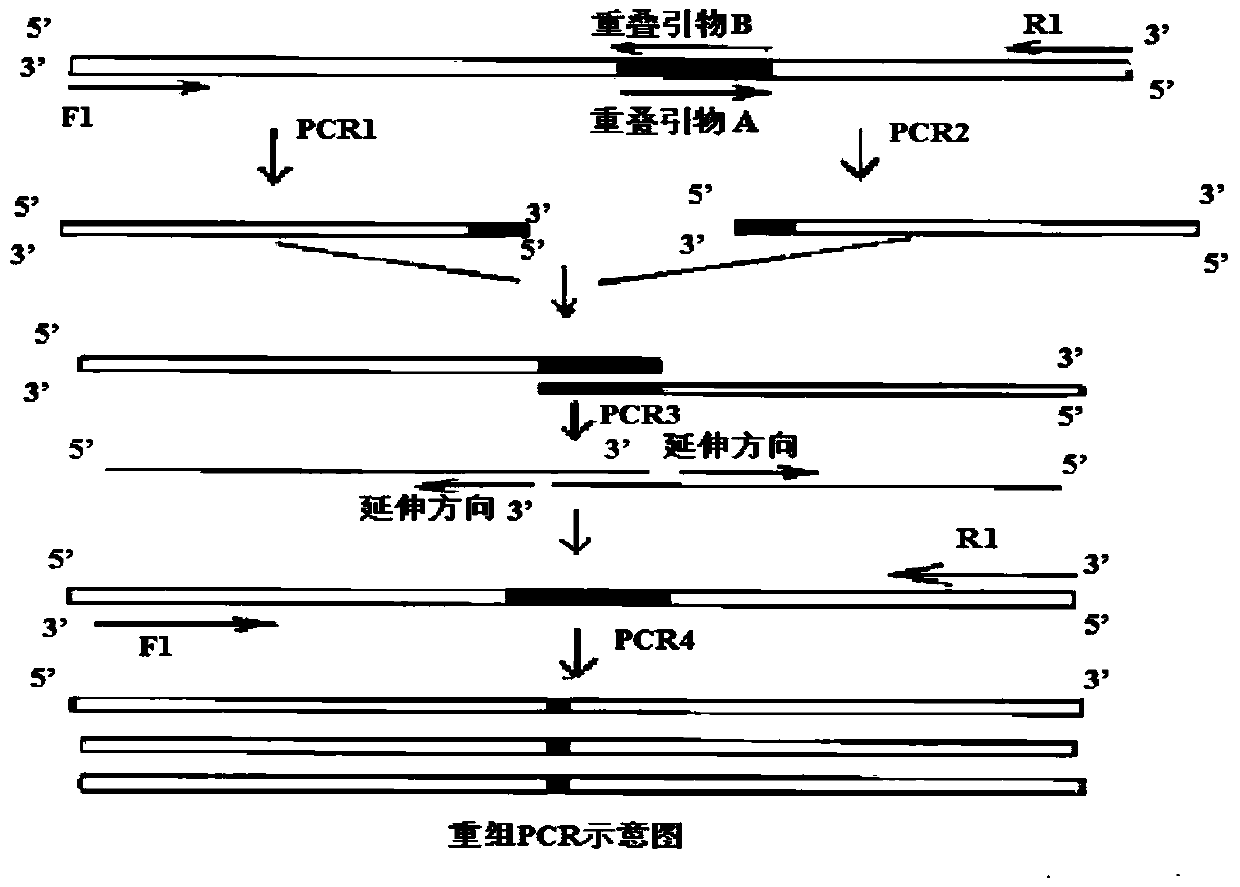
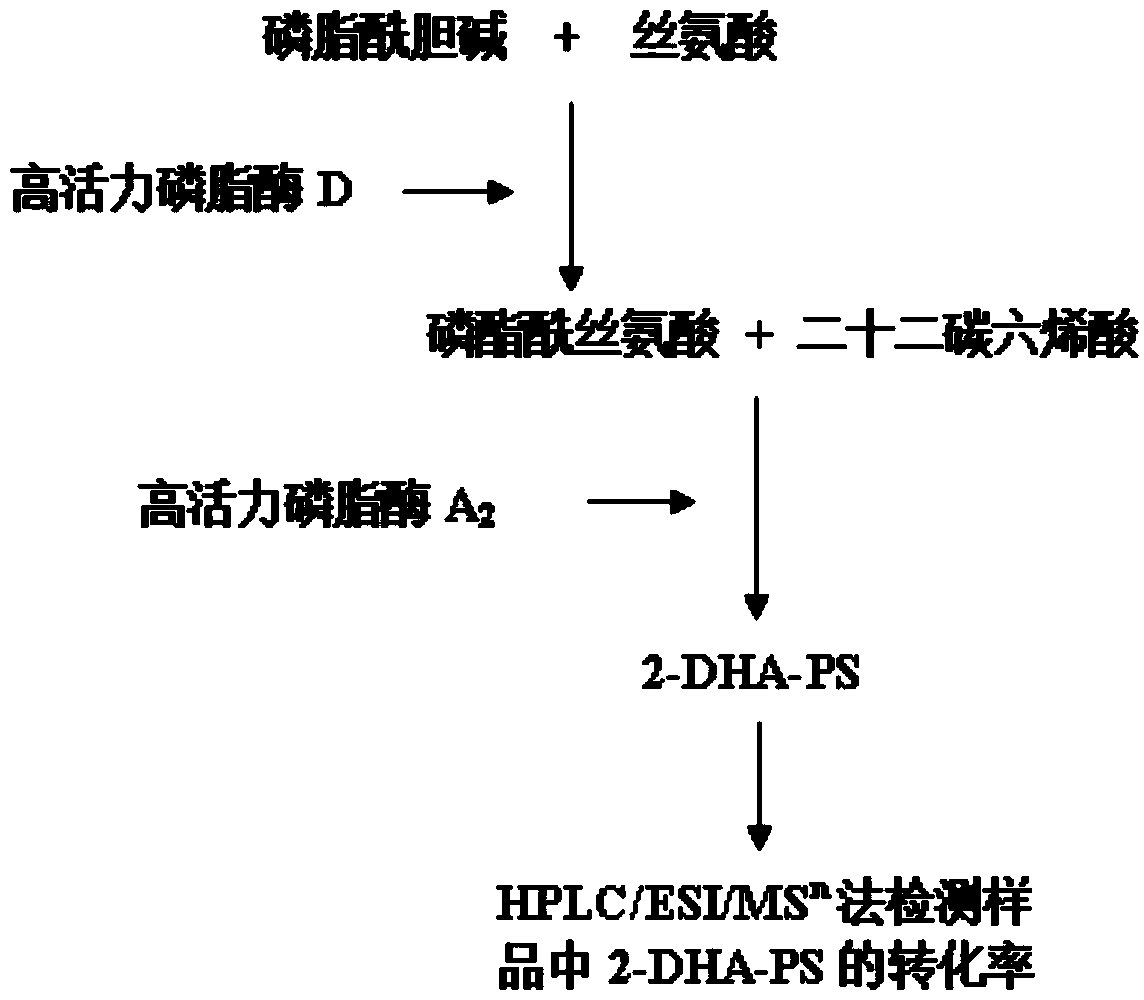
The invention relates to a method for preparing phosphatidylserine (2-DHA-PS) with docosahexaenoic acid at the sn-2 bit through high-activity phospholipase A2 and high-activity phospholipase D. Directed evolution is achieved through the overlapping PCR technology so that the high-activity phospholipase A2 and the high-activity phospholipase D can be obtained; the 2-DHA-PS is prepared through catalysis by means of the high-activity phospholipase A2 and the high-activity phospholipase D, phosphatidylserine is generated through phosphatidylcholine and serine under the catalysis of the high-activity phospholipase D first, and then the 2-DHA-PS is generated through the phosphatidylserine and the docosahexaenoic acid under the catalysis of the high-activity phospholipase A2. The relative content of the 2-DHA-PS in the product synthesized through the method is high, and the defects of an existing synthesizing method are effectively overcome.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Technique for preparing phosphatidyl serine rich in highly-unsaturated fatty acid
The invention relates to a technique for preparing diacylglyceryl-phosphorylserine rich in unsaturated acid, which is characterized in that a reactor is preheated to 30 to 60 DEG C, squid lecithin and L-serine at the mass ratio of 1:1-15 is added, phosphatidase D2-15U / g is also added as reaction substrate, gas R134a is pumped to lead the pressure of the reactor to reach 4-6MPa, the pressure is reduced after agitating reaction for 2 to 8 hours, R134a is recycled after the reaction mixture comes into a separation pot which is communicated with the reactor under the temperature of 30 to 60 DEG C, reaction mixture is collected from the a sample receiving port of the separation pot, at last, the reaction mixture is washed by using acetone and centrifuged for 5 to 10 min to separate the solid phase for further purification. The diacylglyceryl-phosphorylserine prepared by the invention rich in high unsaturated fatty acid as the medium in catalytic reaction of phosphatidase D has the advantages of simple technique, low equipment input, short reaction time, high content of unsaturated fatty acid and high yield and the neglecting of organic solvent. Furthermore, R134a can be completely recycled after reaction, which is beneficial to the separation of products and repeated use of enzyme.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Preparation method of phosphatidylserine
The invention relates to a preparation method of phosphatidylserine. The preparation method comprises the steps of carrying out enzymic catalytic reaction on natural lecithin and L-serine in the presence of phospholipase D enzyme liquid, and carrying out a simple purification process after the reaction, so as to obtain phosphatidylserine with the yield exceeding 60%. The preparation method has the beneficial effects that the operation is simple and convenient, the yield is high, the cost is low, the product quality is stable, and the process is environmentally friendly.
Owner:SINPHAR TIAN LI PHARMA
Compositions for the preservation of fruits and vegetables
InactiveUS7198811B2Prolong lifeQuality improvementDead plant preservationFatty substance preservation using additivesGrowth plantChemical compound
The invention discloses compositions for the preservation of fruits, vegetables, partially processed products, other produce and followers. The compositions comprise at least one phospholipase D inhibitor, at least one compound comprising an isoprene subunit, at least one component of the flavonoid biosynthetic pathway in a suitable medium. The composition of the present invention may additionally comprise one or more plant growth regulators of the cytokinin type, one or more antioxidants, a membrane stabilizing agent, a surfactant, or any combination thereof. The composition may be applied to produce as a spray, drench, dip, or a vapour and at either the pre-harvest stage or post-harvest stage.
Owner:GUELPH UNIV OF
Infant formula supplemented with phospholipids
InactiveCN1523964AIncrease ratingsImprove protectionOrganic active ingredientsMilk preparationYolkAdditive ingredient
The present invention relates to pharmaceutical or nutritional or food compostion for feeding infants, which is more similar to human milk in a powder or fluid form, having an effect of addresseing the shortcomings of the presently known infant formulas by the inclusion of a phospholipid supplement which contains phosphatidylserine or salts thereof as one of the effective ingredients and comprising at least 1% (w / w) phosphatidyserine out of the total phospholipid content of the composition, wherein the phosphatidylserine has a structural fatty acid chain derived from at least one raw material lecithin selected from the group consisting of soy bean lecithin, rapeseed lecithin, or egg yolk lecithin, and which is produced by reaction with phospholipase-D.
Owner:LIPOGEN
Phospholipase D mutant, recombinant genetically engineered bacteria and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN108118041AHigh value for industrial useIncrease vitalityBacteriaHydrolasesBiotechnologyWild type
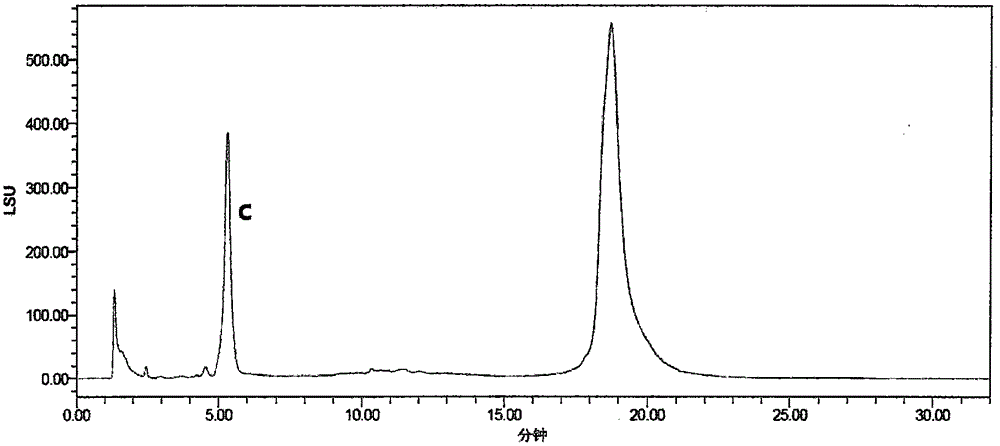
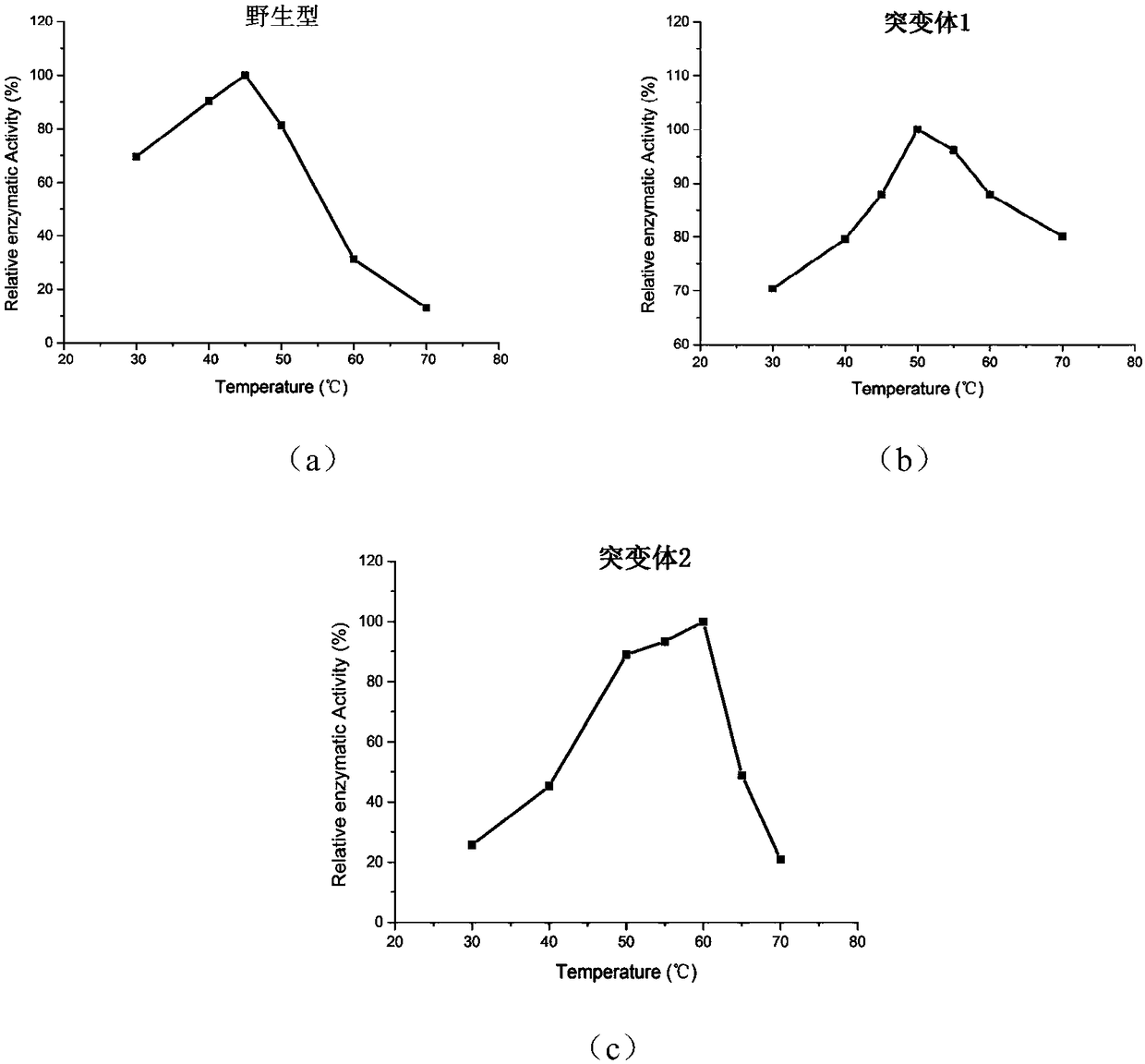
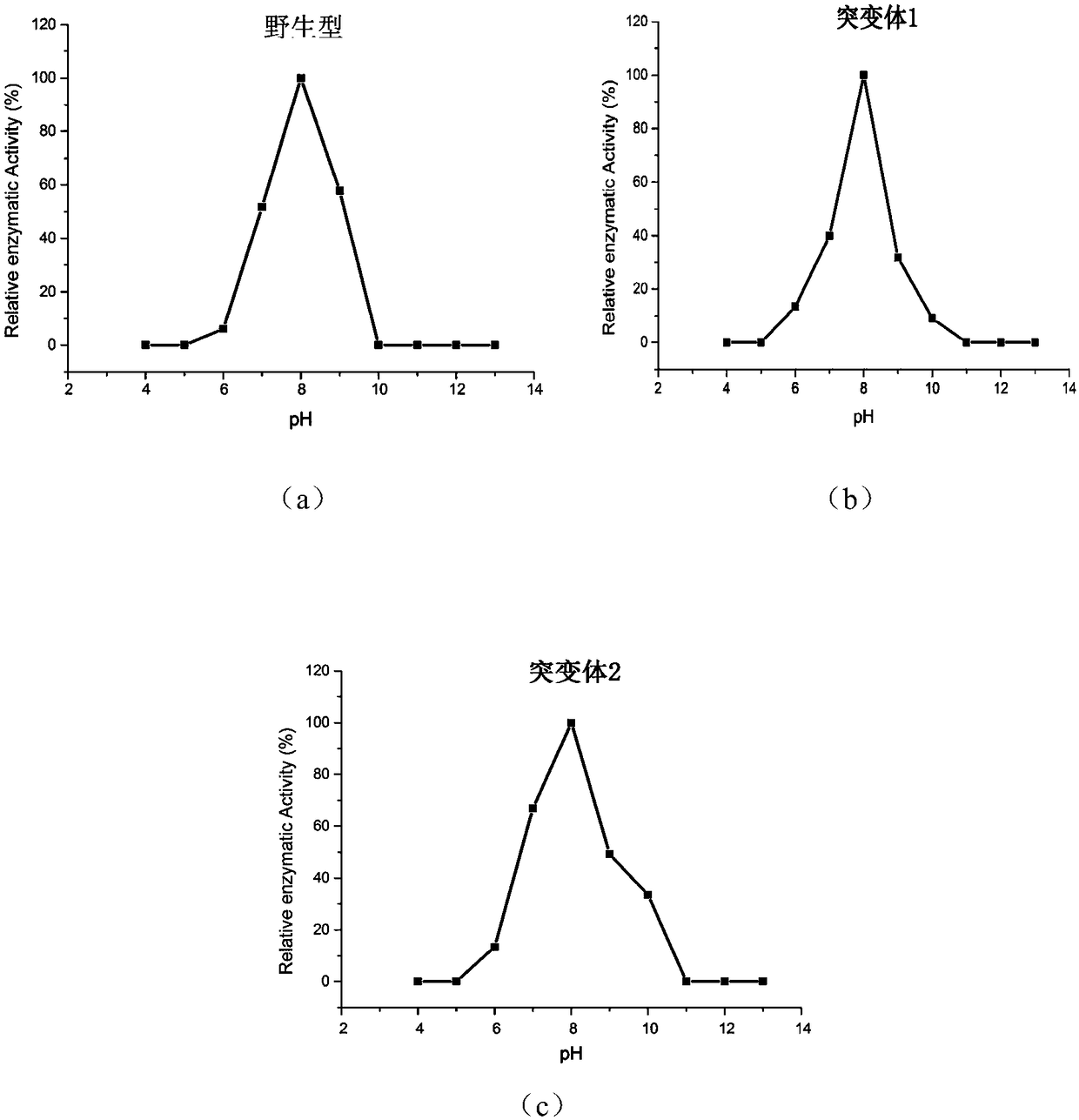
The invention discloses a phospholipase D mutant, recombinant genetically engineered bacteria and a preparation method and application thereof. The phospholipase D mutant is obtained by deleting 12 to47 amino acids at a C tail end on the basis of a parent sequence with the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 1. Two phospholipase D mutants are obtained and an experiment determines that the enzyme activity of the mutant 1 is improved by 3.7 times when being compared with that of a wild type mutant; meanwhile, the optimal reaction temperature is improved to 50 DEG C from original 45 DEG C; the enzyme activity of the mutant 2 is improved by 6 times when being compared with that of the wild type mutant; meanwhile, the optimal reaction temperature is improved to 60 DEG C from original 45 DEG C. According to the mutant disclosed by the invention, the optimal reaction temperature and the enzyme activity of the mutant are remarkably improved under the condition that the optimal pH (Potential ofHydrogen) is not changed; when the catalytic performance is improved, the industrial utilization value of the enzyme is further improved.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Method for preparing phosphatidylserine under catalysis of immobilized phospholipase D
InactiveCN103966277AHigh immobilization rateIncrease temperatureChemical industryOn/in organic carrierSodium acetrizoateSodium acetate
The invention discloses a method for preparing phosphatidylserine under catalysis of immobilized phospholipase D. The method comprises the following steps: (1) with chitin as a vector and glutaraldehyde as a cross-linking reagent, immobilizing free phospholipase D to obtain immobilized enzyme of phospholipase D; (2) with the immobilized enzyme of the phospholipase D prepared in the step (1) as a catalyst, n-butyl acetate as an organic phase solvent, and 50mM of sodium acetate buffer solution of which the pH is 5.5 as a water phase solvent, reacting L-serine to react with soyabean lecithin at 20-60 DEG C according to the molar ratio of (10-100):1, thus obtaining phosphatidylserine; and at the end of reaction, filtering and recovering the phospholipase D for repeated use. By adopting the method disclosed by the invention, the ester transfer rate in the dual-phase catalytic system can be up to 78%, the immobilized enzyme can be repeatedly used, and the method is simple, easy to operate, and low in preparation cost.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Method for preparing phosphatidylserine
InactiveCN102676600AHydrolysis does not occurImprove conversion efficiencyFermentationPhospholipaseEnzyme catalysis
The invention discloses a method for preparing phosphatidylserine. According to the method, phospholipid and L-serine are subjected to phospholipid translating acylation reaction under the action of phospholipase D to generate the phosphatidylserine, wherein the phospholipid translating acylation reaction is carried out in a homogeneous medium system and the yield of the phosphatidylserine reaches 80-98 percent. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that due to the adoption of a green reaction medium, a reaction system is a homogeneous medium system. No phosphatidic acid as a byproduct is generated, high catalytic efficiency of enzyme and favorable quality of products are obtained and the process is safe and environment-friendly.
Owner:ACAD OF STATE GRAIN ADMINISTRATION
Infant formula supplemented with phospholipids
InactiveUS20050129738A1Augment nerve cell devlopmentImprove nerve cell developmentOrganic active ingredientsBiocidePhospholipaseAdditive ingredient
An infant formula supplemented with phospholipids. A composition for feeding infants is claimed. The composition includes an infant formula base and a phospholipid supplement. The supplement includes a product of an enzymatic reaction between a crude phospholipid source and phospholipase-D and includes phosphatidylserine or salts thereof as an effective ingredient. Phosphatidylserine from the phospholipid supplement represents between 0.1% and 19.99% (w / w) of a total phospholipid content of the composition. Preferably the phosphatidylserine has a structural fatty acid chain derived from the raw material lecithin. The composition is more similar to human milk with regard to phospholipid composition. Methods of production and articles of manufacture are also disclosed.
Owner:LIPOGEN
Phospholipase B from pseudomonas fluorescens and production method thereof
InactiveCN102002486AHigh activityImprove stabilityHydrolasesMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliEnzyme Gene
The invention relates to a phospholipase B from pseudomonas fluorescens and a production method thereof, which belong to the field of enzyme gene engineering and enzyme engineering. The phospholipase B is produced from the pseudomonas fluorescens, has the total gene length of 1272bp and codes of 423 amino acids, and the zymoprotein theoretical molecular weight is 45.8kDa, wherein 1 to 69bp code phospholipase B signal peptide, and 70 to 1272bp code phospholipase B mature peptide are comprised. An expression vector and a recombinant host of the phospholipase B can be obtained by the traditional molecular biological method, i.e. colibacillus recombinant plasmid and recombinant colibacillus containing genes of the phospholipase B are obtained. The phospholipase B has good activity and stability at low temperature, does not have the lipase activity, can be hydrolyzed for catalyzing two fatty acyl group radicals in complete phospholipids, has wide application in the industrial process of grease refining, phospholipids emulsifying agent modification and the like, and also has simple preparation method, high product quality and low production cost.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
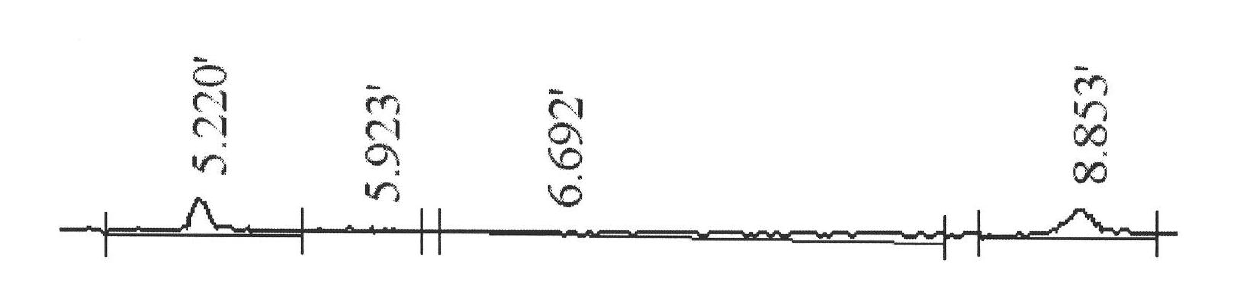
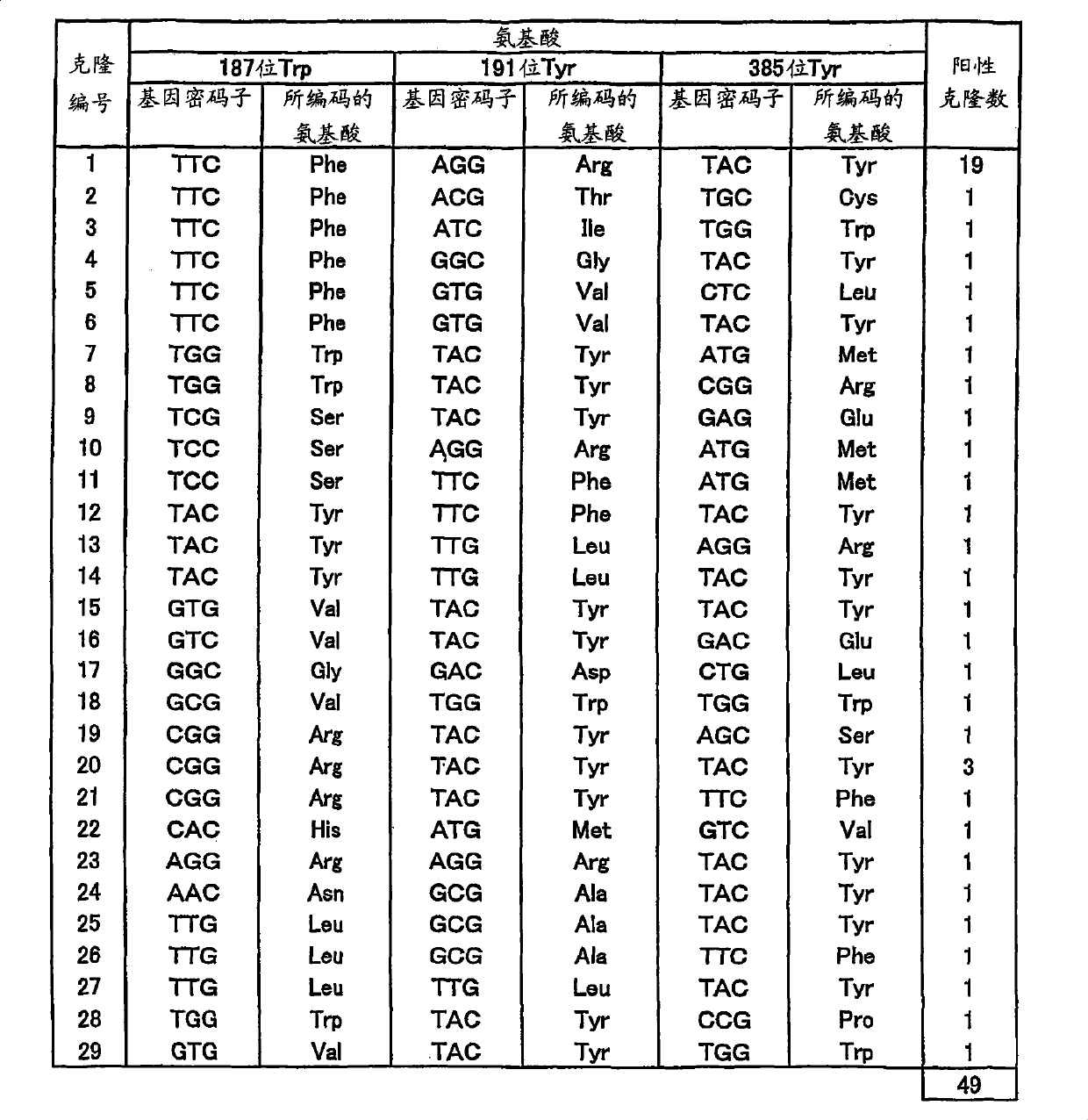
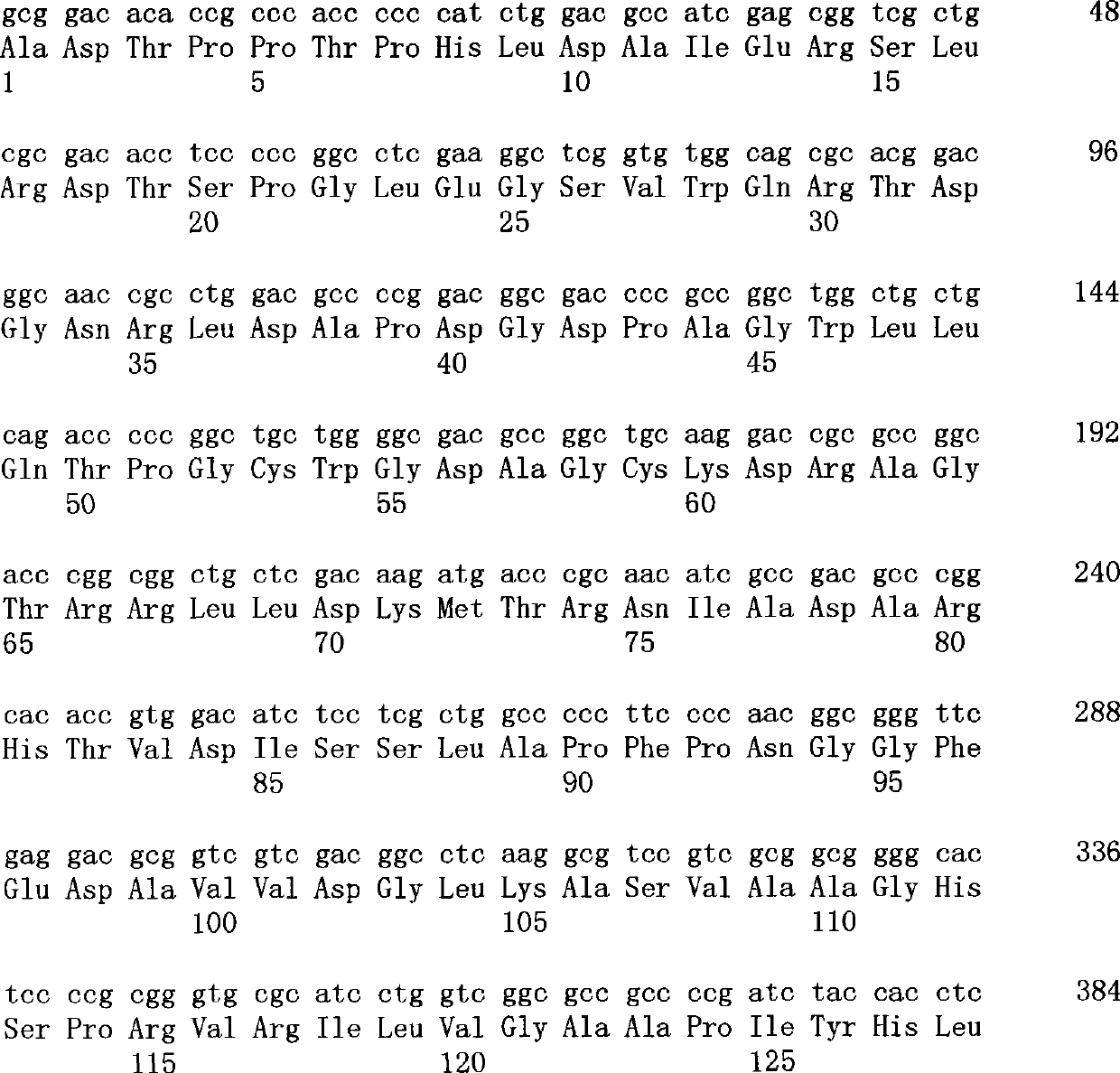
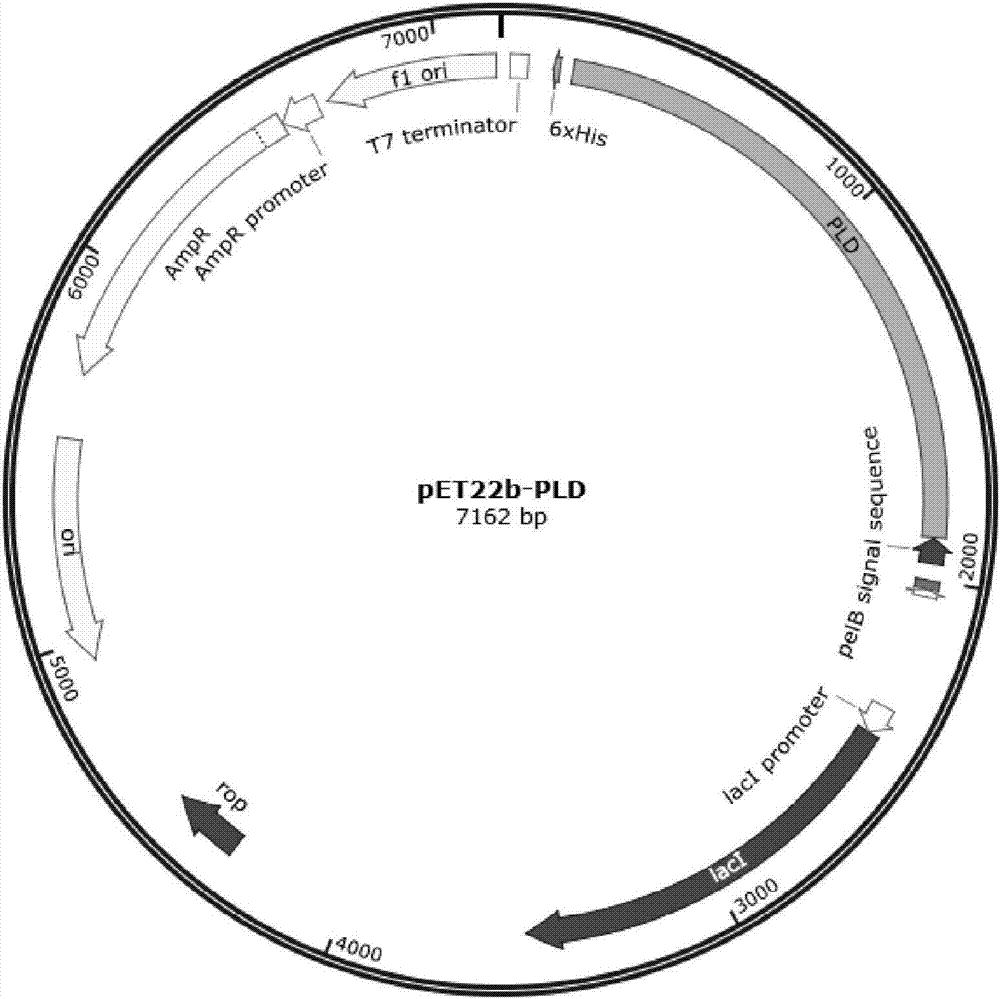
Novel phospholipase D
A modified phospholipase D having an ability to synthesize phosphatidylinositol which contains: (A) an amino acid sequence derived from the amino acid sequence represented by SEQ ID NO:2 by substitution of at least one of the amino acid residues at the 187-, 191- and 385-positions by other amino acid residue(s); or (B) an amino acid sequence of a polypeptide derived from the amino acid sequence as described in the above (A) by substitution, deletion, insertion and / or addition of at least one amino acid residue at a position different from the 187-, 191- and 385-positions and having an ability to synthesize phosphatidylinositol. By using this modified phospholipase D, phosphatidylinositol can be efficiently produced from a phospholipid. It is also intended to provide a method of screening a phospholipase D having an ability to synthesize an acylglycerophospholipid having glycol group.
Owner:NAGOYA UNIVERSITY
Genetically engineered bacteria for producing phospholipase D and construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN106957850AEasy source of enzymesConvenient sourceBacteriaHydrolasesEscherichia coliStreptomyces
The invention discloses a gene sequence for coding phospholipase D, which belongs to the fields of biotechnology and preparation of phospholipids products. The gene sequence of the phospholipase D is sourced from Streptomyces sp.(strain PMF), and the gene sequence capable of being expressed in escherichia coli is obtained by virtue of the optimization of a codon. The invention also constructs a genetically engineered bacterium for producing phospholipase D, the phospholipase D produced by utilizing the recombinant Escherichia coli is used as a catalyst to produce phosphatidylserine, the enzyme is convenient in source, the yield is high, the fermentation process is simple, the cost is low, and the industrialization prospect is good.
Owner:NANJING TECH UNIV
Process For Producing Cheese
InactiveUS20080299252A1Increase productionDecrease oiling-offMilk preparationCheese manufactureBiotechnologyPhospholipases C
The present invention relates to a method for producing cheese comprising treating the cheese milk, or a fraction of the cheese milk, with phospholipase C and / or phospholipase D.
Owner:NOVOZYMES AS +2
Signal peptide capable of effectively improving protein secretion expression efficiency and application of signal peptide
ActiveCN105601720ASmooth transmembrane transportImprove secretion efficiencyBacteriaHydrolasesSequence signalProtein target
The invention discloses a signal peptide for mediating protein secretion expression and belongs to the field of protein engineering and gene engineering. By modifying known signal peptides PelB and OmpA, the N terminal of the signal peptide contains the first three amino acid residues MKK of the signal peptide OmpA, the C terminal of the signal peptide contains the last three amino acid residues AQA of the signal peptide OmpA, and a middle hydrophobic structure is the hydrophobic sequence LLPTAAAGLLLLAAQP of the signal peptide PelB. After the signal peptide capable of effectively improving protein secretion efficiency is used, the secretion expression capability of a strain on target protein is obviously improved; the extracellular enzyme activity of phospholipase D of target protein can be improved by 2 times, the extracellular enzyme production capability of the modified strain is significantly improved, and industrialized application is better facilitated.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Preparation method of phosphatidylserine
The invention discloses a preparation method of phosphatidylserine. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) mixing soya bean lecithin and water, thus preparing a mixture M1; (2) adding L-serine and phospholipase D into the mixture M1, and mixing L-serine, phospholipase D and the M1, thus preparing a phosphatidylserine crude product; (3) adding a solvent into the prepared phosphatidylserine crude product for extraction, thus preparing a phosphatidylserine semi-finished product; and (4) enabling the prepared phosphatidylserine semi-finished product to sequentially pass through a silicagel column and an ion exchange resin, thus preparing phosphatidylserine, wherein the solvent is composed of chloroform, ethanol, diethyl ether and water. According to the design, soya bean lecithin is mixed with water firstly, then L-serine and phospholipase D are added for carrying out reaction, then the solvent containing chloroform, ethanol, diethyl ether and water is adopted for carrying out extraction, and the obtained phosphatidylserine semi-finished product is filtered by the silicagel column and the ion exchange resin, the operation is simple and convenient, the prepared phosphatidylserine is high in purity, and the application range of phosphatidylserine is greatly expanded.
Owner:WUHU FOMAN BIOPHARMA CO LTD
Recombinant escherichia coli for producing phospholipase D and application thereof
The invention discloses a recombinant escherichia coli for producing phospholipase D and an application thereof, which belongs to the technical field of bioengineering. A phospholipase D gene is obtained through clone in Streptomyces ambofaciens by means of molecular biology measures, constructed expression plasmid is guided into E. coli BL21(DE3), and phosphatase-containing engineering bacteria formed by highly copying and recombining an expression carrier are obtained through kanamycin resistant plate screening. The recombinant phospholipase D is used for converting phosphatidylcholine and serine to generate phosphatidylserine, and efficient production of vitamin C-2-phosphate is achieved. By carrying out reaction for 2 h at the temperature of 40 DEG C with the pH value of 4.5, the yield of phosphatidylserine can reach 15.8 g / L, the conversion rate is 63.9%, and the space time yield is 7.9 g / L / h.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
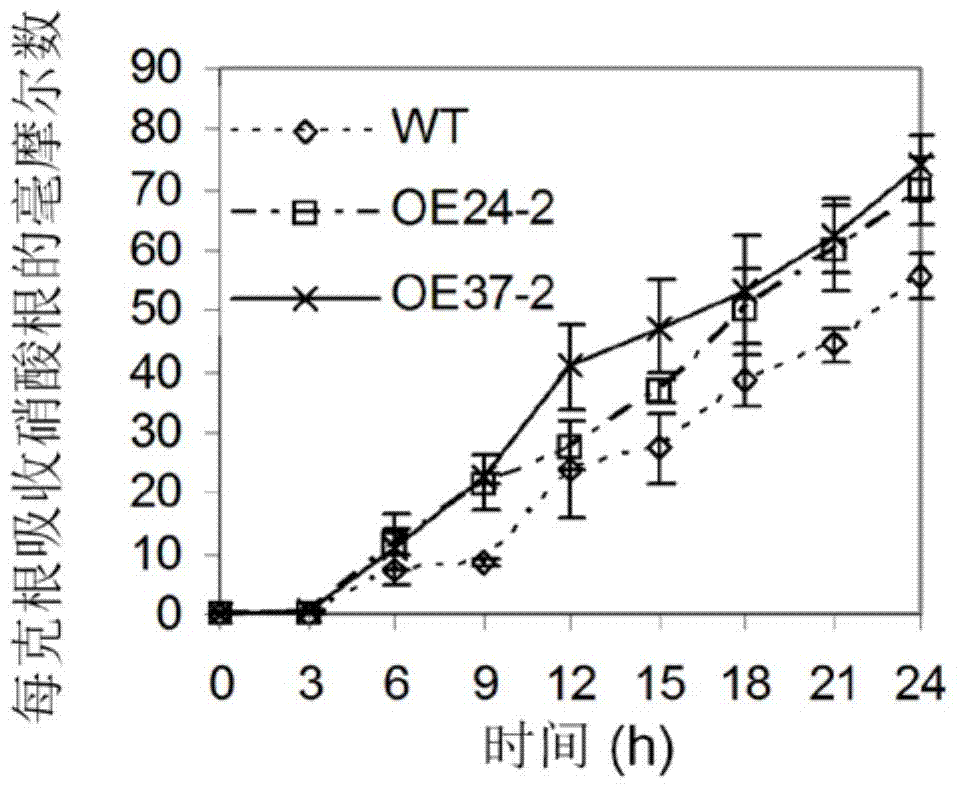
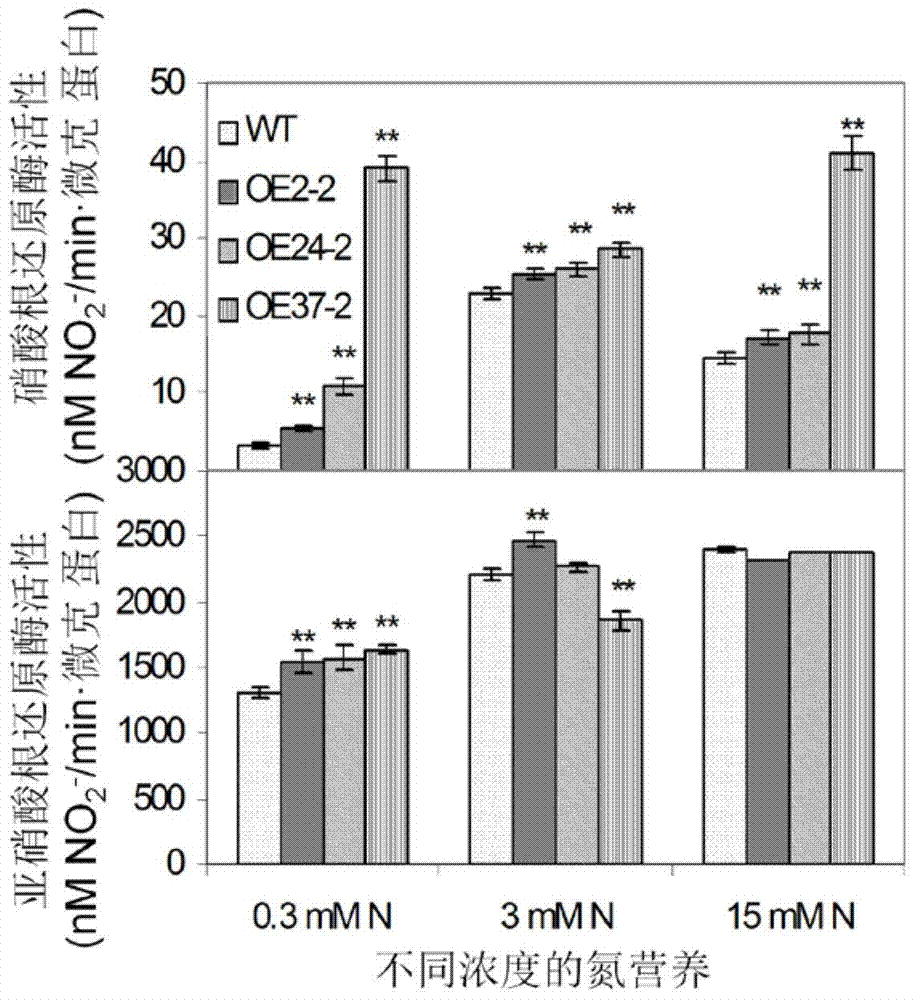
Application of PLD (phospholipase D) epsilon gene in increasing nitrogen nutrition effective utilization and seed yield of crops
InactiveCN103773798AEasy to transportEfficient reuseFermentationGenetic engineeringNutritionNucleotide
The invention belongs to the technical field of plant molecular breeding and biology, and discloses application of a PLD (phospholipase D) epsilon gene in increasing nitrogen nutrition effective utilization and seed yield of crops. The nucleotide sequence of the PLD epsilon gene is shown as SEQ ID NO:1, or has a similarity more than or equal to 60 percent as the nucleotide sequence shown as SEQ ID NO:1. The invention also discloses a method for increasing nitrogen nutrition effective utilization and seed yield of rape. Tests prove that growth and occurrence of lateral roots of rape can be promoted due to overexpression of AtPLD epsilon either in nitrogen starvation or nitrogen sufficiency condition, increase of rape leaf tissue cell growth and biological yield can be reinforced, absorption transportation and assimilation metabolism processes of rape plants can be promoted, which are particularly indicated in that the expression quantities of genes NTR1.1 and NTR2.1 related to overexpressed plant N transportation are remarkably higher than that of a wild type, and the nitrogen absorption rate is remarkably higher than that of the wild type.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
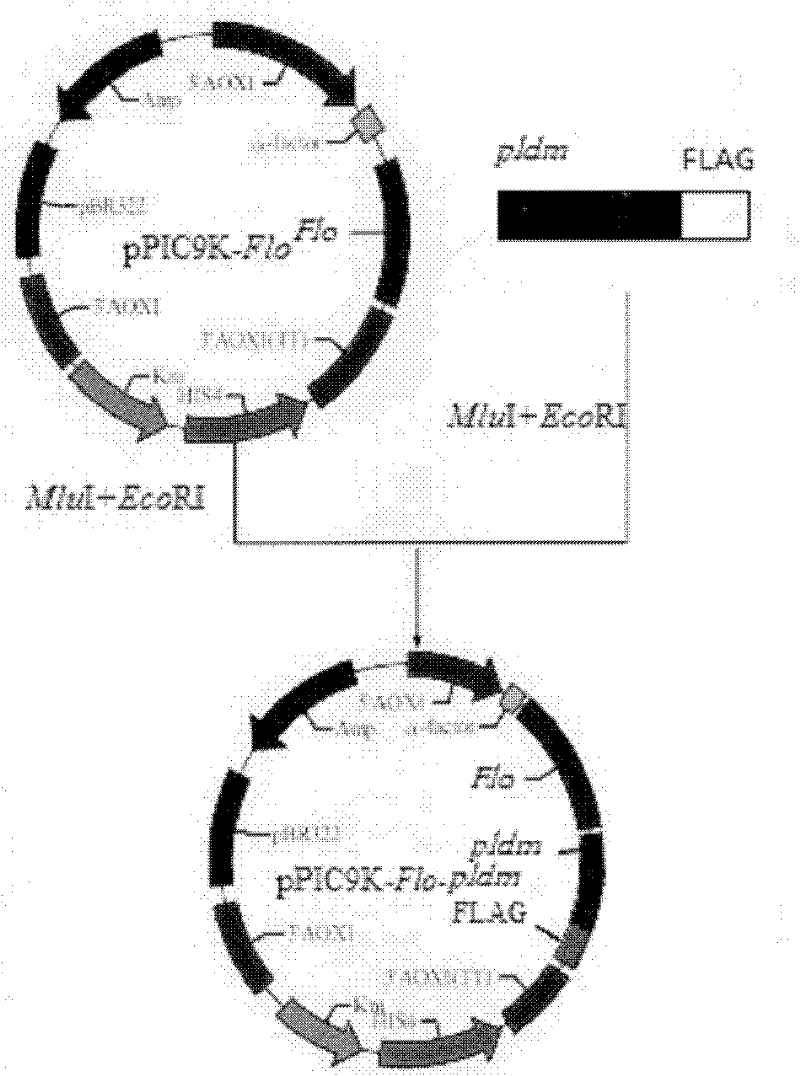
Preparation of highly active phospholipase d and yeast whole cell catalyst displaying phospholipase d on the cell surface
The invention relates to preparation of high-activity phospholipids enzyme D and cell surface display phospholipids enzyme D yeast whole cell catalysts, which belongs to a method for carrying out site directed mutagenesis wild phospholipids enzyme D by recombinant deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) for improving the activity, connecting the mutated gene with yeast show carriers pPIC9K-Flo and efficiently displaying the mutated gene on the surface of pichia pastoris cells, and relates to a preparation method of the high-activity phospholipids enzyme D and cell surface display phospholipids enzyme D yeast whole cell catalysts. The method has the advantages that the activity of the wild phospholipids enzyme D is improved and is shown on the surfaces of the pastoris cells, the stability is improved,and the advantages of immobilized enzymes are realized. The method has the technical scheme that wild phospholipids enzyme D genes are separated from microbes, particularly streptomyces aureofuscus, the mutation is carried out on the amino acid residue of Glu69 and Ser285, through the efficient expression on the surfaces of the pichia pastoris cells, the enzyme activity of the high-activity phospholipids enzyme is improved by 11 percent than the wild type phospholipids enzyme D, and the enzyme activity of the recombination strains GS115 / pPIC9K-Flo-pldm prepared through high-density fermentation is 120U / (g. stem cells).
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Production method of recombinant phospholipase D
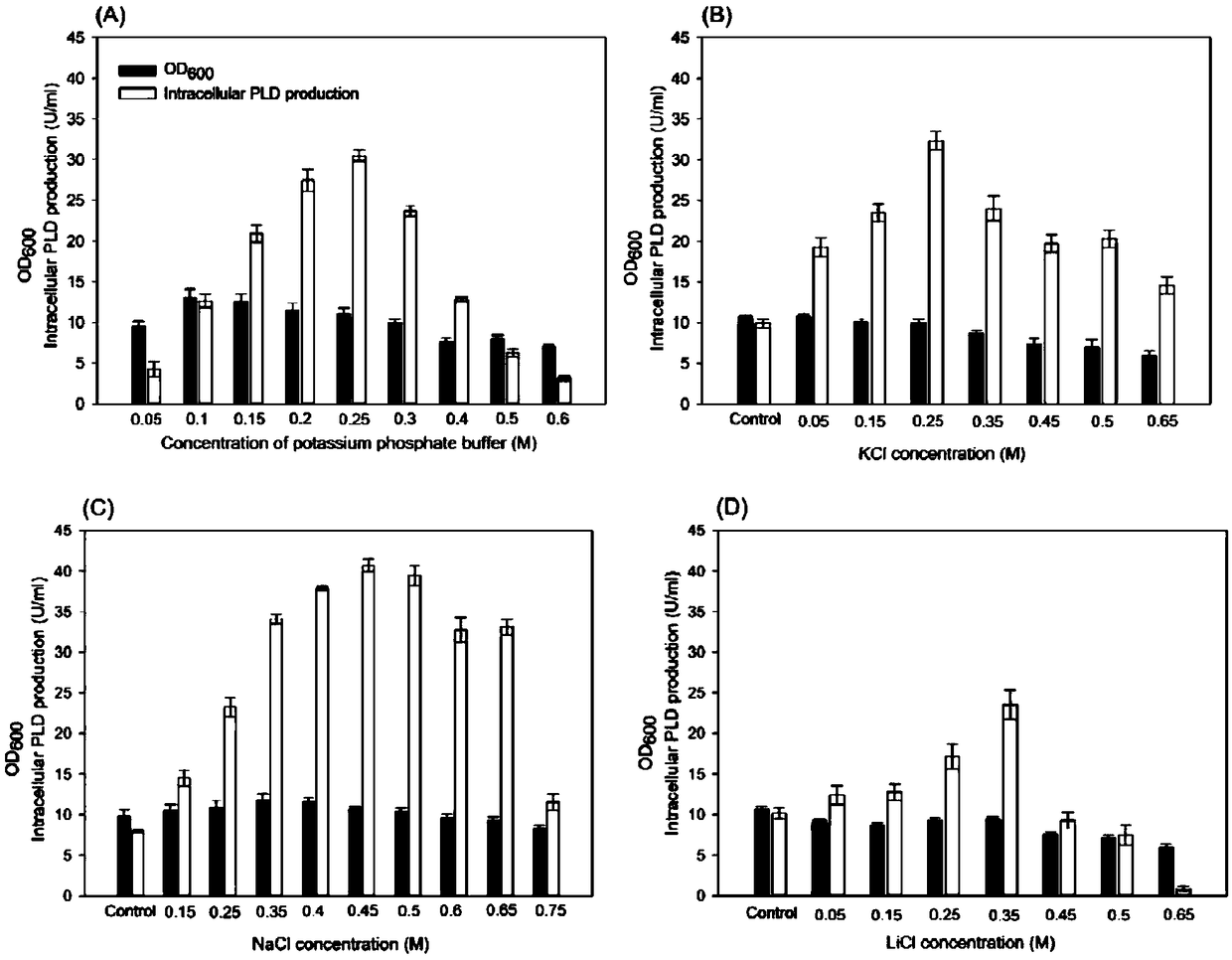
InactiveCN103013947AIncrease culture densitySlow down the speed of expressionHydrolasesMicroorganism based processesInclusion bodiesProgrammable logic device
The invention relates to a method for producing recombinant phospholipase D by genetic engineering bacteria fermentation, and particularly relates to a production method of recombinant phospholipase D. The production method is characterized by comprising the following steps of (1) building recombinant gene engineering bacteria; (2) preparing a shake flask seed culture medium and a fermentation medium; (3) activating the built recombinant genetic engineering bacteria for 16-20h on a plane plate, and inoculating into a shake flasks with the shake flask seed culture medium to obtain seed liquid; (4) inoculating into the fermentation medium for fermenting; adding an inducer until the final volume concentration in fermentation liquor is 1-5%, and continuing to ferment for 32-48h; and (5) obtaining the phospholipase D from culture of the fermentation liquor. Compared with the prior art, the production method disclosed by the invention has the following beneficial effects that carbon source dextrin is utilized as a carbon source at a slow speed; on one hand, the culture density of the cell is increased; and high-density fermentation is achieved; on the other hand, the expression speed of a PLD (programmable logic device) is reduced, and generation of an inclusion body is also reduced.
Owner:宁夏乙征生物工程有限公司
Recombination strain for expressing phospholipase D and application
ActiveCN108949721AGood transphosphatidyl transfer abilityShort fermentation cycleFungiBacteriaPhospholipaseNucleotide
The invention relates to phospholipase D having an amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID NO.1. The invention further relates to a gene sequence coding the phospholipase D. The nucleotide sequence of thegene is shown as SEQ ID NO.2. The invention provides a method for improving the expression level of the phospholipase D by virtue of a system modification expression component. The method comprises the following steps: screening and replacing signal peptides, ribosome binding sites and promoters, and transforming the constructed recombinant plasmid into host bacteria, wherein the recombination strain is capable of successfully expressing the phospholipase D. The phospholipase D disclosed by the invention has excellent phosphatidyl transformation ability, and the product phosphatidylserine canbe synthesized by taking lecithin and L-serine as the substrate. The recombinant bacteria have excellent enzyme activity stability, the fermentation cycle is short, and a foundation is laid for large-scale industrial production.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
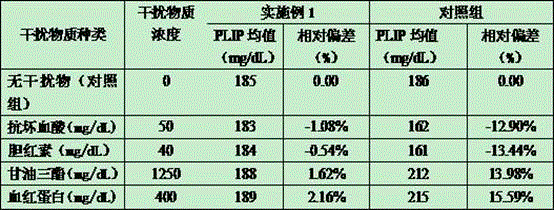
A stable serum phospholipid detecting reagent high in interference-resisting capability and a detecting method
ActiveCN105543336AAvoid interferenceImprove anti-interference abilityMicrobiological testing/measurementGlycerolTurbidity
The invention relates to the technical field of serum phospholipid detection and particularly relates to a serum phospholipid detecting reagent. A reagent R1 comprises a buffer solution, phospholipase D, DAOS, ascorbic acid oxidase, bilirubin oxidase, polyethylene glycol 6000, cane sugar, xanthan gum, mannitol, trehalose, BSA, glycerol propoxylate-block-ethoxylate (Pluranic L64) and an aseptic. A reagent R2 comprises the buffer solution, 4-aminoantipyrine, peroxidase, choline oxidase, the polyethylene glycol 6000, the cane sugar, the xanthan gum, the mannitol, the trehalose, the BSA, the glycerol propoxylate-block-ethoxylate (Pluranic L64) and the aseptic. The HEPES buffer solutions and a novel Trinder reaction chromogen DAOS are adopted. A plurality of stabilizers are added to obviously improve stability of the detecting reagent. The bilirubin oxidase and the ascorbic acid oxidase are added, thus effectively avoiding interference caused by bilirubin and ascorbic acid and greatly improving interference-resisting capability of the detecting reagent. In addition, addition of the glycerol propoxylate-block-ethoxylate (Pluranic L64) which is an optional nonionic surfactant prevents reaction system turbidity, enhances substrate stability and improves the interference-resisting capability of the detecting reagent.
Owner:BIOBASE BIODUSTRY (SHANDONG) CO LTD
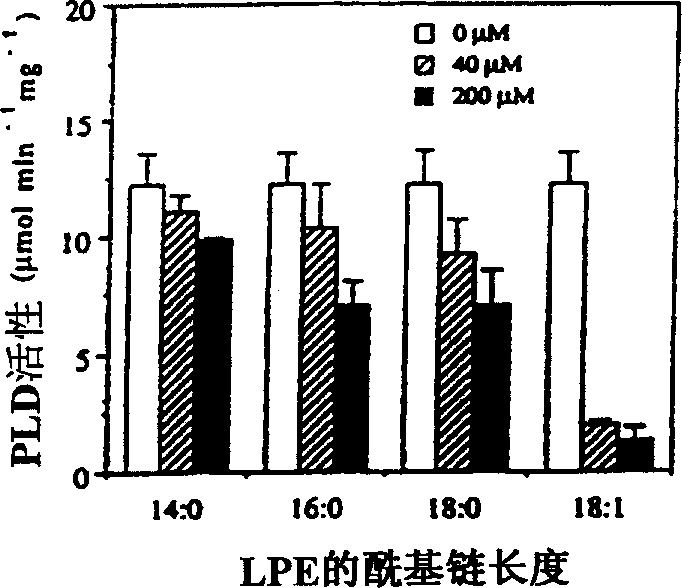
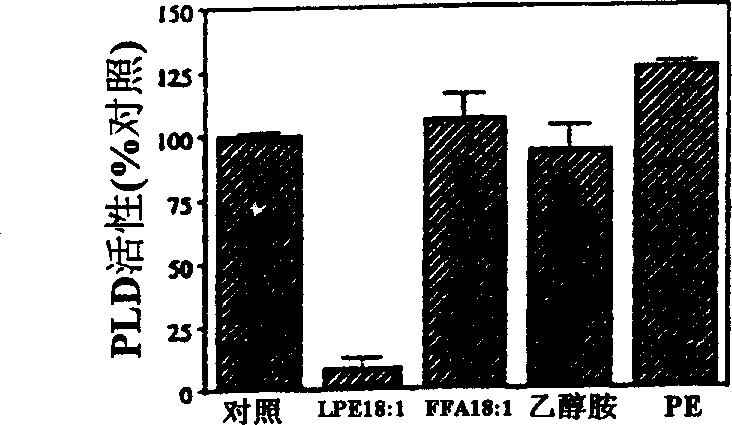
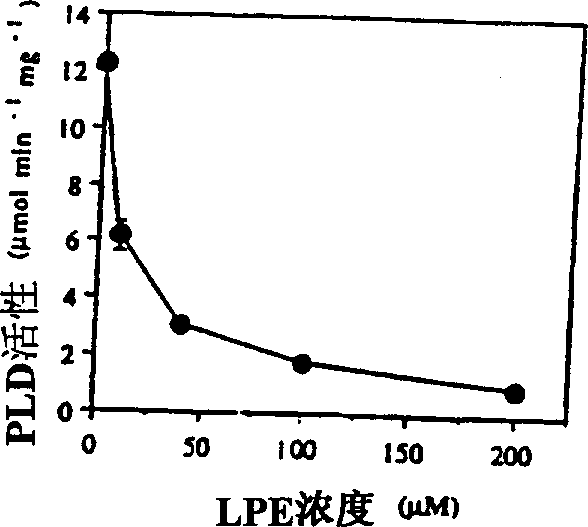
Use of lysophosphatidylethanolamine (18:1) and lysophosphatidylinositol to retard senescence and to enhance fruit ripening
The present invention relates to a method of enhancing fruit ripening and stability and of delaying senescence in fruit and other plant tissues. This method consists of applying an effective amount of a lysophospholipid, such as lysophosphatidylethanolamine (18:1) (hereinafter referred to as LPE (18:1)) or lysophosphatidylinositol (hereinafter referred to as LPI) to the fruit and other plant tissues. Lysophospholipids such as LPE (18:1) and LPI were found to be superior to other lysophospholipids in delaying senescence and in inhibiting phospholipase D, a key enzyme in mediating membrane deterioration during of plant senescence. LPE (18:1) and LPI are naturally occurring and environmentally safe. Their use could replace many environmentally toxic compounds that are currently being used to retard senescence of flowers, fruits and leaves and to enhance fruit ripening.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Method for preparation of polyunsaturated fatty acid-containing phosphatidylserine
A method for the preparation of the polyunsaturated fatty acids-containing phosphatidylserine, the method comprising: combining L-serine with a fish liver phosphatidylcholine having a polyunsaturated fatty acid to form a mixture; reacting the mixture with phospholipase D to effect transphosphatidylation of L-serine and the phosphatidylcholine having polyunsaturated fatty acids to produce the polyunsaturated fatty acids-containing phosphatidylserine.
Owner:CHEN SU +1
Method for producing phospholipase D through recombinant escherichia coli
ActiveCN109136207AInhibition of lysisOptimal physiological stateBacteriaHydrolasesEscherichia coliHigh density
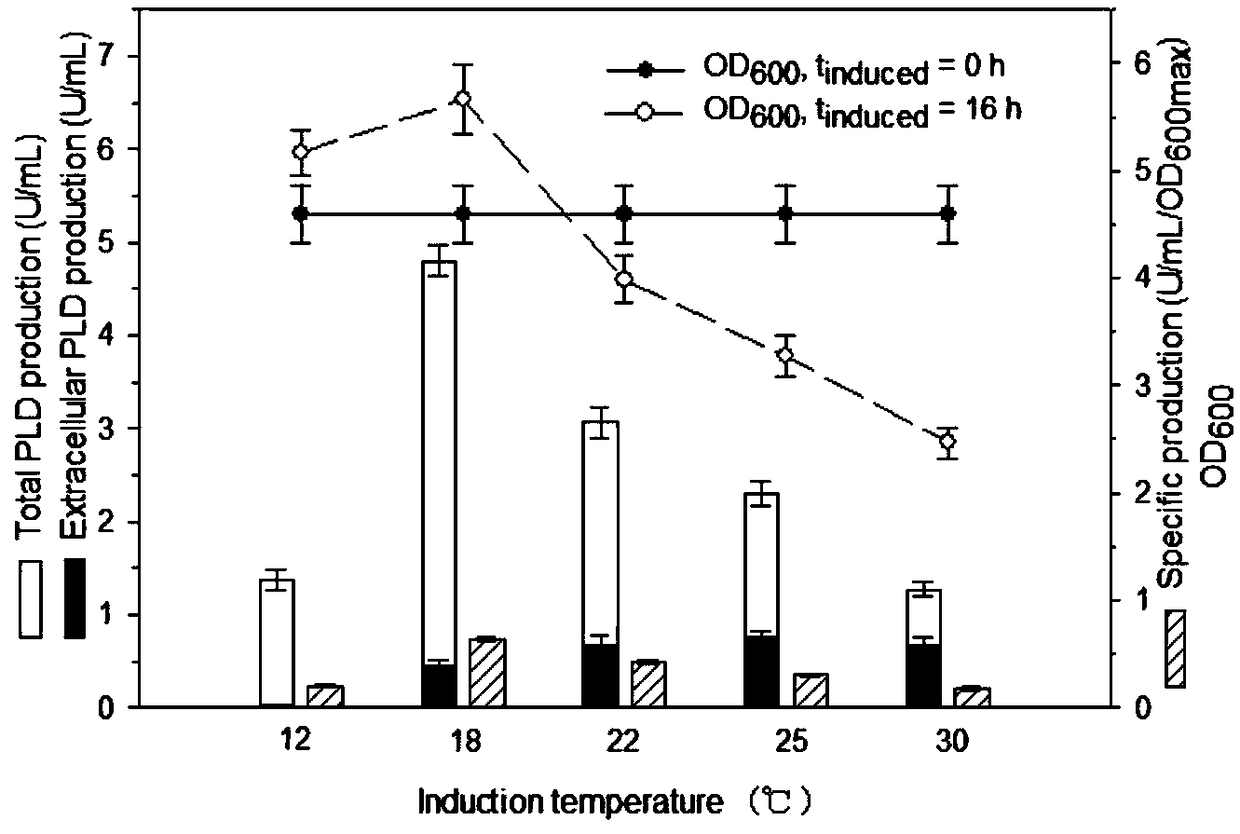
The invention discloses a method for producing phospholipase D through recombinant escherichia coli. According to the method, a phospholipase D gene is in preciseness-type starting sub control, a pararea of pSC101 is inserted in an expression plasmid, an escherichia coli mutant strain recA is used for keeping the genetic stability of the plasmid, cells containing the plasmid at the growth periodare cultured to high density, and saturation induction is conducted at the induction period; meanwhile, the temperature is decreased, alkali metal salt stress is applied, the cytotoxicity of PLD to ahost is reduced, cell lysis is inhibited, the synthesis time of PLD is prolonged, and accordingly PLD expression is improved.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Application of phospholipase gene PLDzeta1 in improving salt resistance of plant
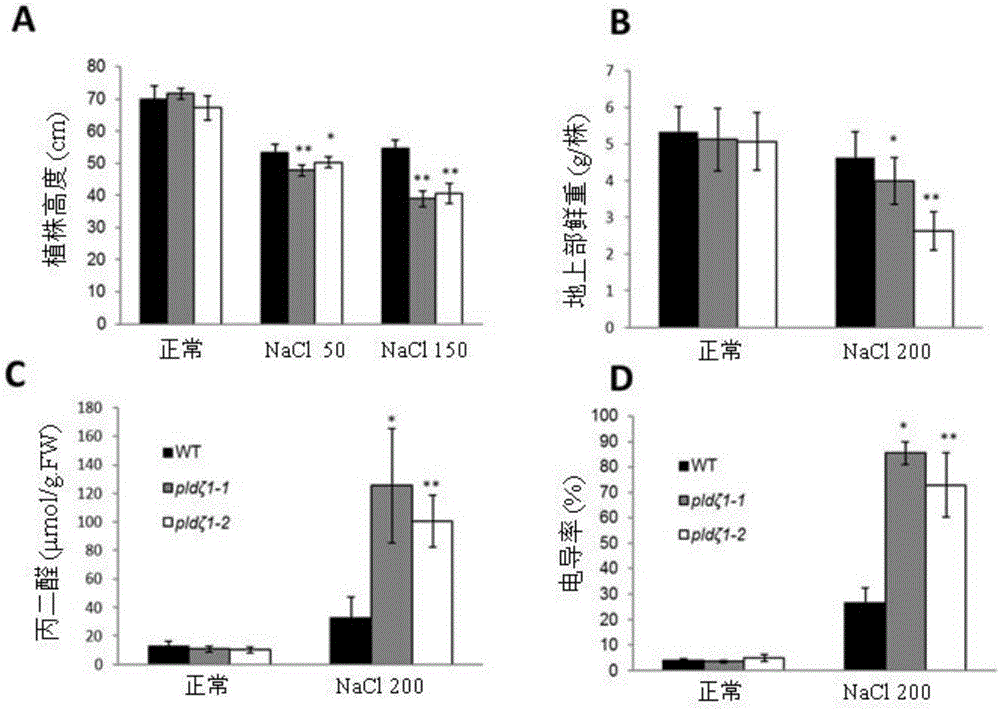
ActiveCN106191001ALow salt toleranceReduced survival rateHydrolasesFermentationSalt resistanceBiotechnology
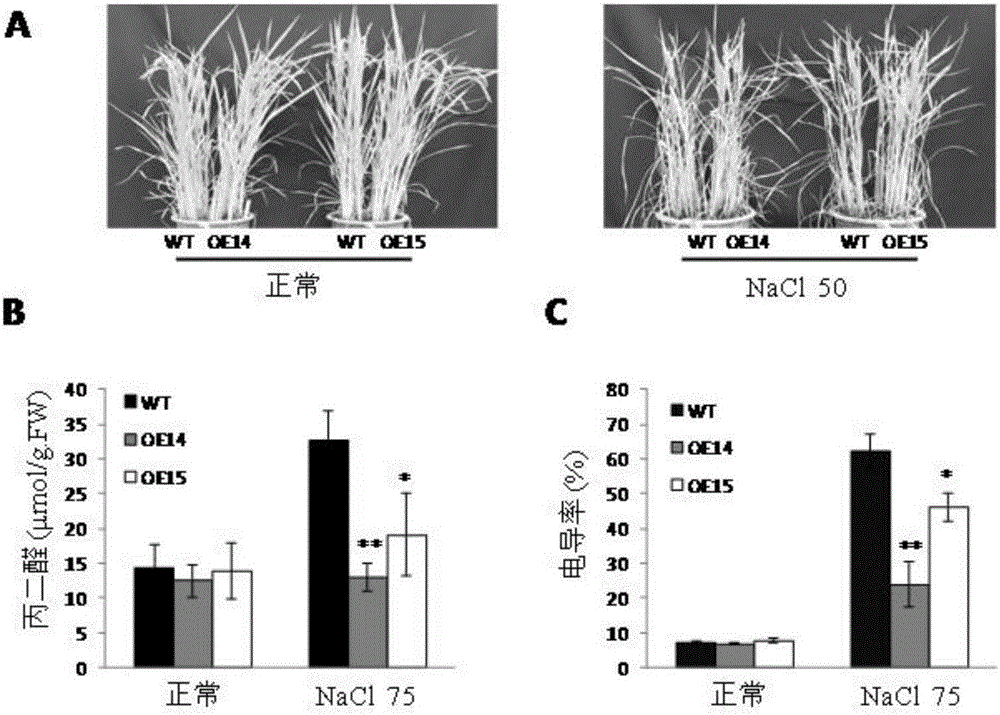
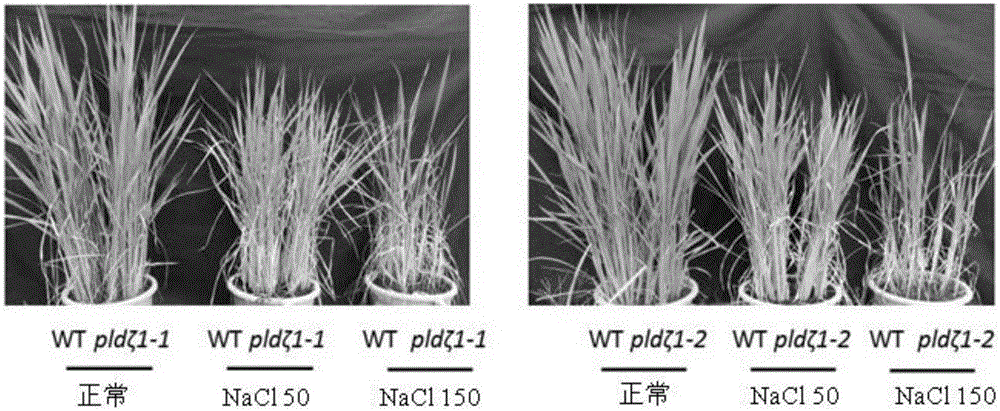
The invention discloses application of a phospholipase gene PLDzeta1 in improving salt resistance of a plant. The gene PLDzeta1 is transferred to a plant through a molecular genetic transformation method, and the transformation plant with the overexpression gene PLDzeta1 is obtained. The overexpression gene PLDzeta1 remarkably improves the salt resistance of the plant. The membrane permeability and the malondialdehyde content of a leaf of the plant with overexpression gene PLDzeta1 are remarkably lower than those of a control wide group under the threat of salt, and the survival rate and the plant height are remarkably higher than those of the control wide group. The loss expression of the gene PLDzeta1 leads to remarkable reduction of the salt resistance of the plant and remarkable reduction of biological yield compared with the wild group, and the result further improves that the gene PLDzeta1 has a remarkable positive regulation effect on salt resistance. The application of the phospholipase gene PLDzeta1 in improving salt resistance of the plant provides a novel way for the seed breeding of salt-resistance molecules of the plant, and creates a novel seed material.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com