Phospholipase D mutant, recombinant genetically engineered bacteria and preparation method and application thereof
A technology of genetically engineered bacteria and mutants, which is applied in the field of genetic engineering of enzymes, can solve problems affecting the healthy development of the downstream enzymatic phospholipid modification industry, and achieve the effect of increasing the optimum reaction temperature and improving the vitality of mutants
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] Example 1: Construction of Phospholipase PLD-VH Mutant Expression Vector and Expression Strain
[0023] (1) With reference to the complete amino acid sequence of Vibrio harveyi phospholipase PLD-VH (GenBank accession number: WP_005435673.1), the signal peptide sequence was analyzed by the signal peptide online analysis software Signal P. The amino acid is deleted from the complete sequence to obtain the phospholipase PLD-VH mature peptide coding sequence (SEQ ID NO.1);
[0024] (2) According to the amino acid sequence obtained in (1), the coding sequence of the phospholipase PLD-VH gene was designed according to the codon preference of Escherichia coli, and its base sequence is shown in the accompanying SEQ ID NO. 4 (wild type). Nde I was introduced upstream of the sequence, and Xho I restriction site was introduced downstream, and the obtained phospholipase PLD-VH gene sequence was synthesized by Sangon Bioengineering (Shanghai) Co., Ltd.;
[0025] (3) The phospholipa...
Embodiment 2
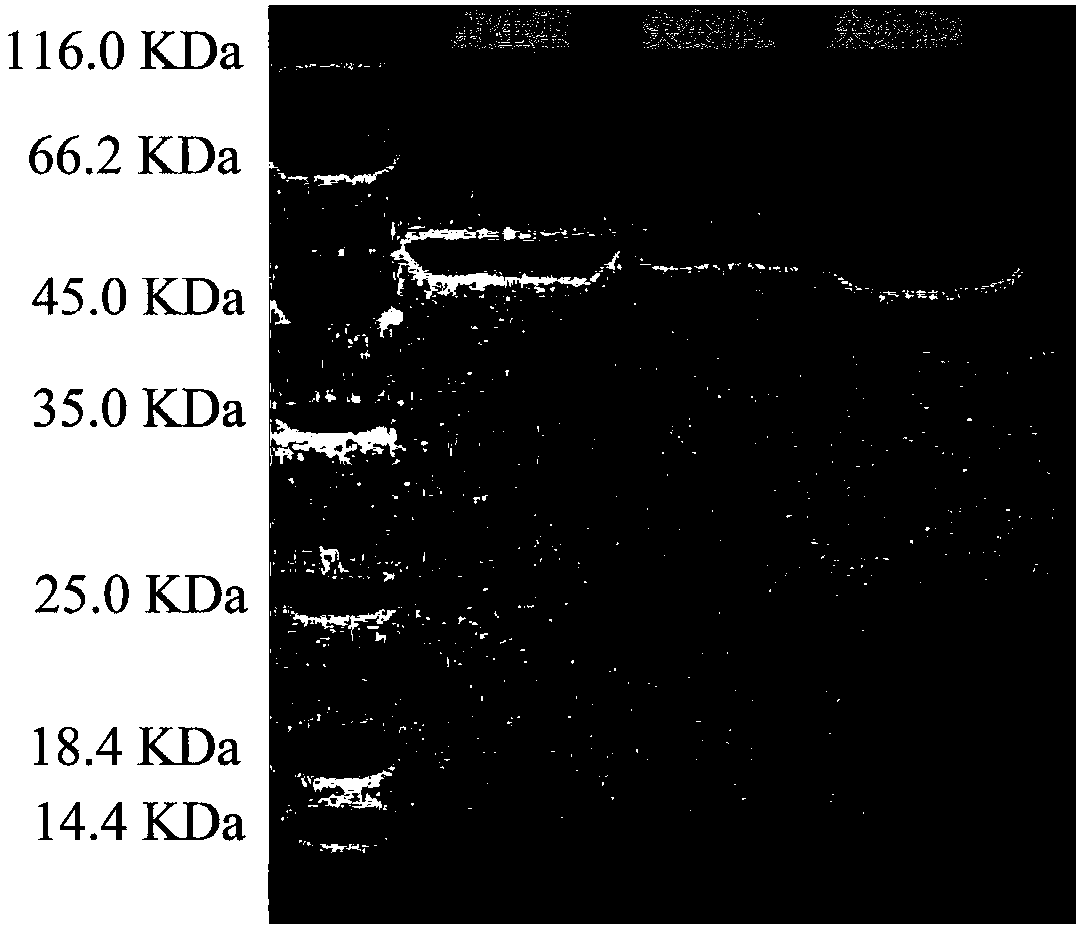
[0043] Example 2: Wild-type PLD-VH and its mutant recombinant expression strain fermentation and recombinant protein purification
[0044] (1) Inoculate recombinant Escherichia coli PLD-VH wild-type and mutant expression strains in seed medium containing ampicillin 100 μg / mL (NaCl 10 g / L, peptone 10 g / L, yeast extract 5 g / L, pH 7.2 ~7.4), at 37°C, 200r / min shake flask culture to the logarithmic growth phase, as the seed solution;
[0045] (2) Inoculate the seed liquid described in (1) into the self-inducing liquid fermentation medium (enzyme hydrolyzed casein 10g / L, yeast extract 5g / L, glucose 0.5g / L, lactose 2g by 5% inoculum size) / L, glycerin 5g / L, disodium hydrogen phosphate 3.6g / L, potassium dihydrogen phosphate 3.4g / L, ammonium chloride 2.7g / L, sodium sulfate 0.7g / L, magnesium sulfate 1g / L, pH 7.2~ 7.4), shake the flask at 37°C and 200r / min until OD 600 = 0.6 ~ 0.8, and then induce culture at 20°C and 200r / min for 24h; (3) Centrifuge the fermentation broth obtained in ...
Embodiment 3
[0047] Embodiment 3: Phospholipase enzymatic property analysis
[0048] (1) Assay method of phospholipase activity
[0049] The activity of the wild-type phospholipase PLD-VH and mutant phospholipase was measured by a standard spectrophotometric method, and phosphatidyl-p-nitrophenol (P-pNP) was used as a reaction substrate. Take 480 μL of purified phospholipase enzyme solution, add 20 μL P-pNP solution, react at a certain temperature for an appropriate time, add 10% SDS to terminate the reaction, and measure the absorbance at 405 nm. Heat-inactivated enzyme protein solution was used as the reaction control group. Phospholipase activity is defined as: under specific temperature and pH conditions, the amount of enzyme required to release 1 μmol of p-nitrophenol per minute is a phospholipase activity unit. Represented by U. Calculate the specific enzyme activity (U / g).
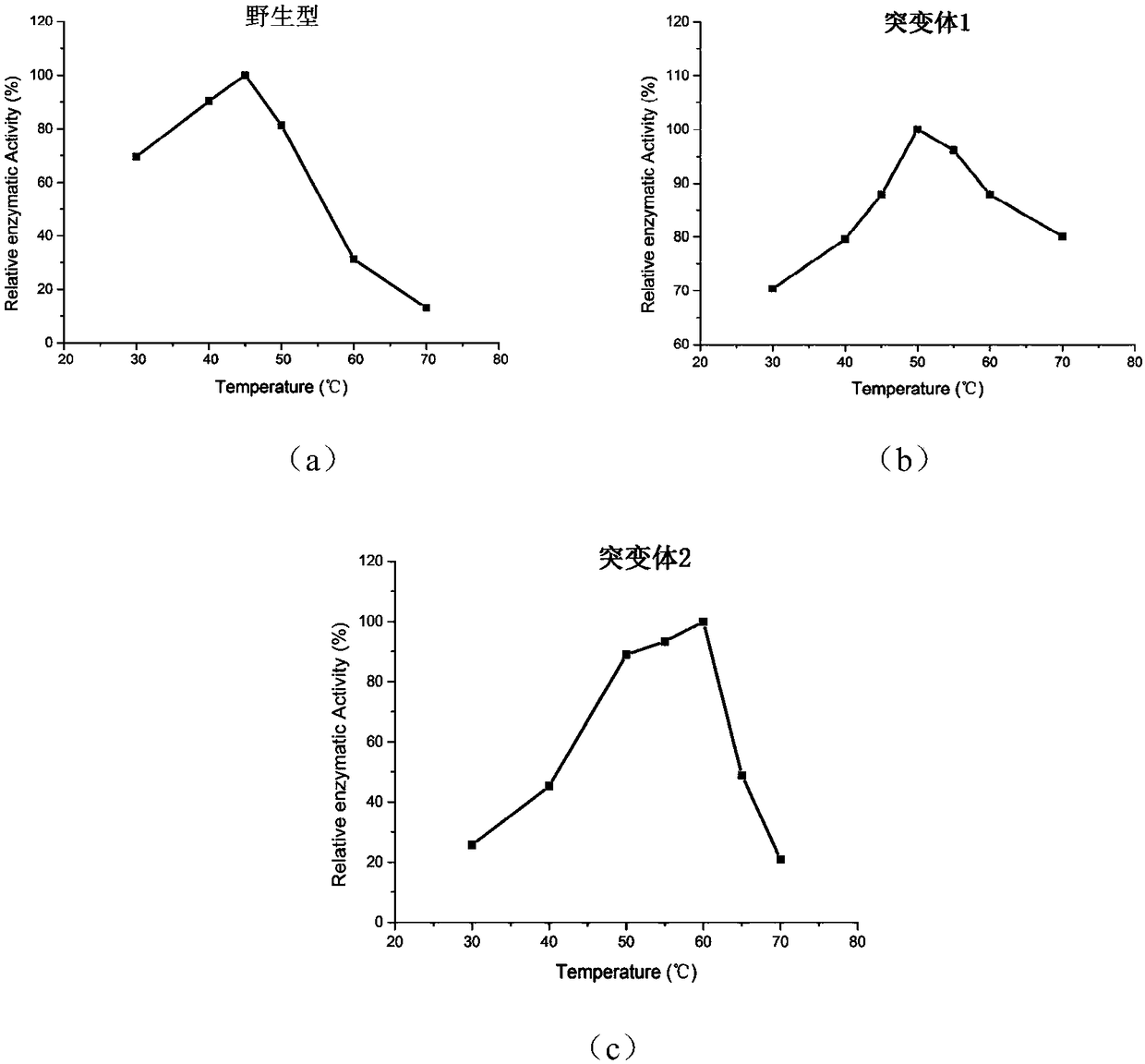
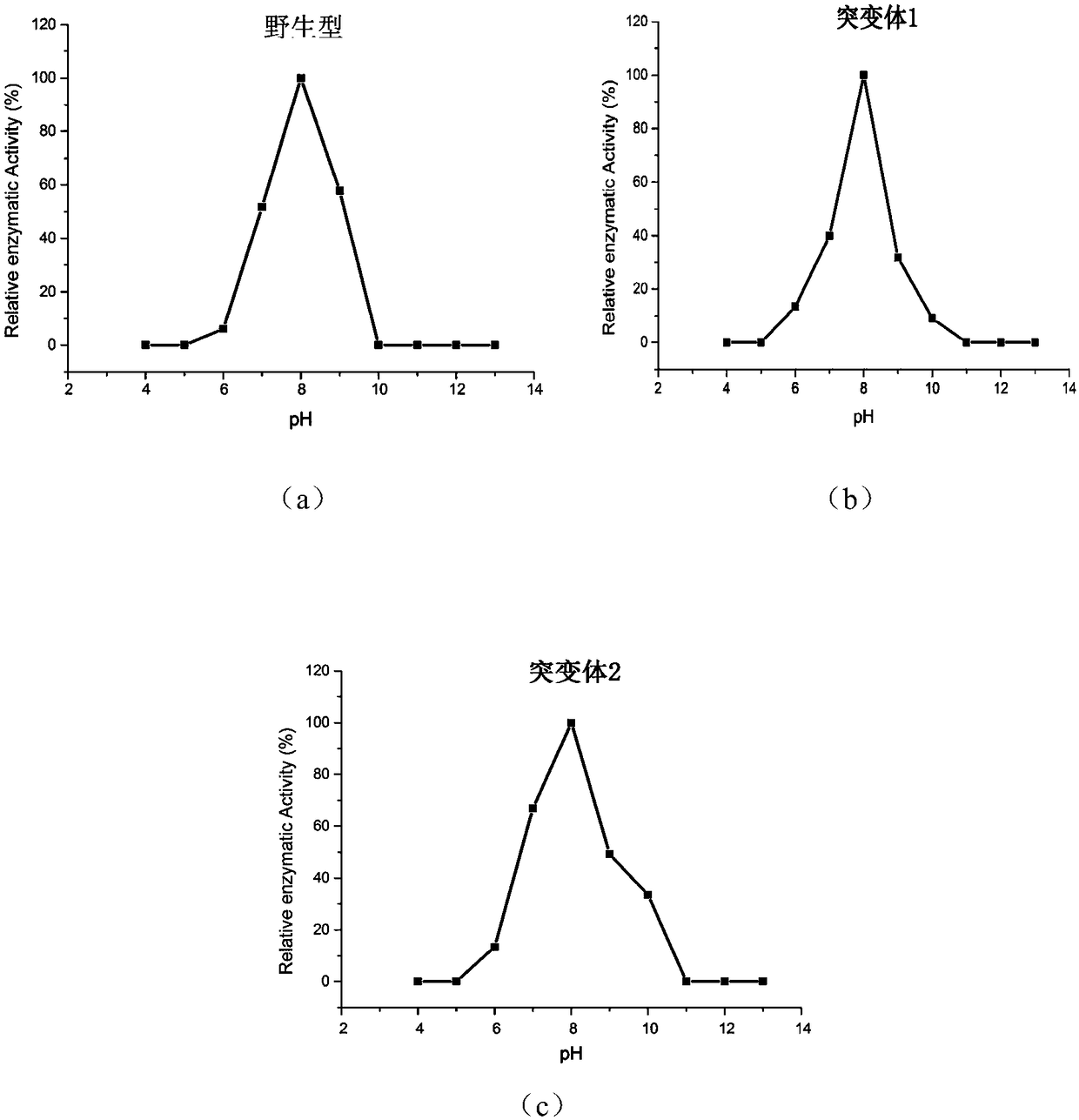
[0050] (2) Determination of the optimal reaction temperature of the enzyme
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com