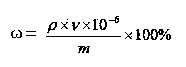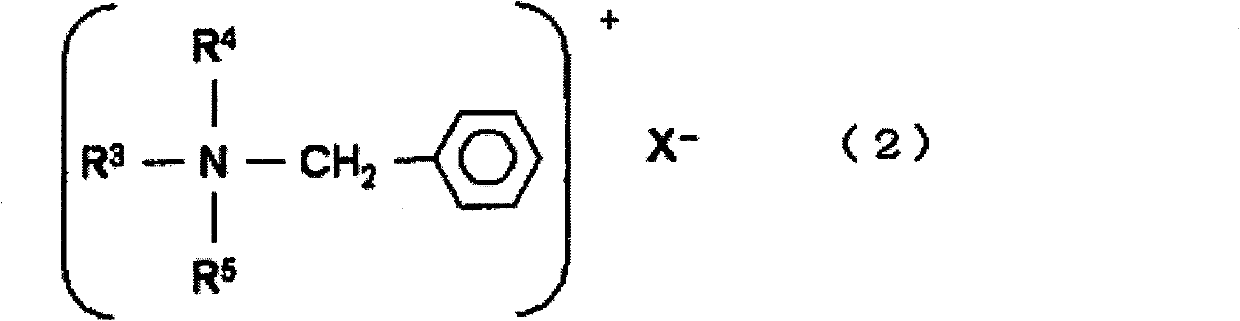Patents
Literature
55results about How to "High value for industrial use" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Hard-particle powder for sintered body and sintered body
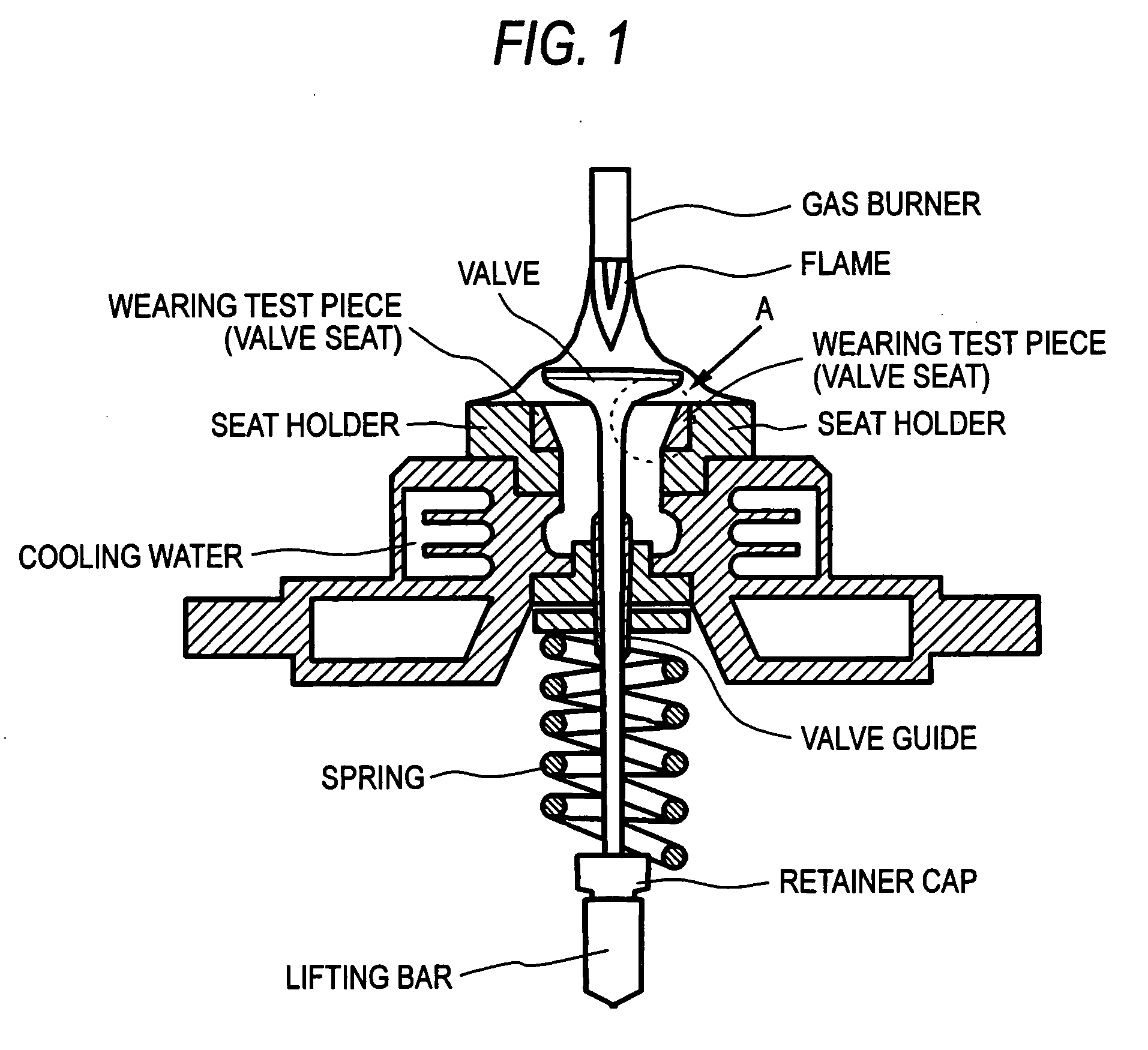
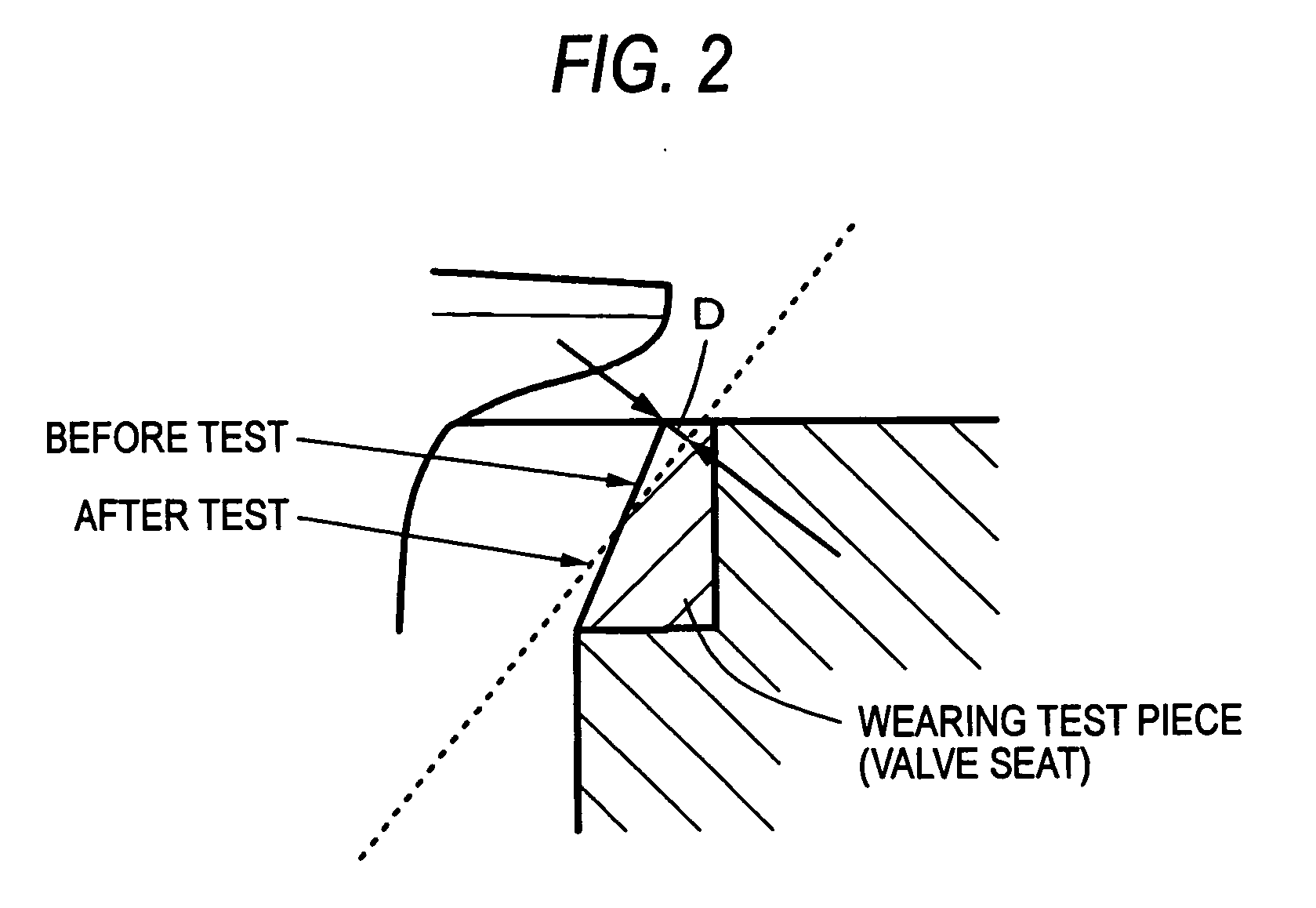
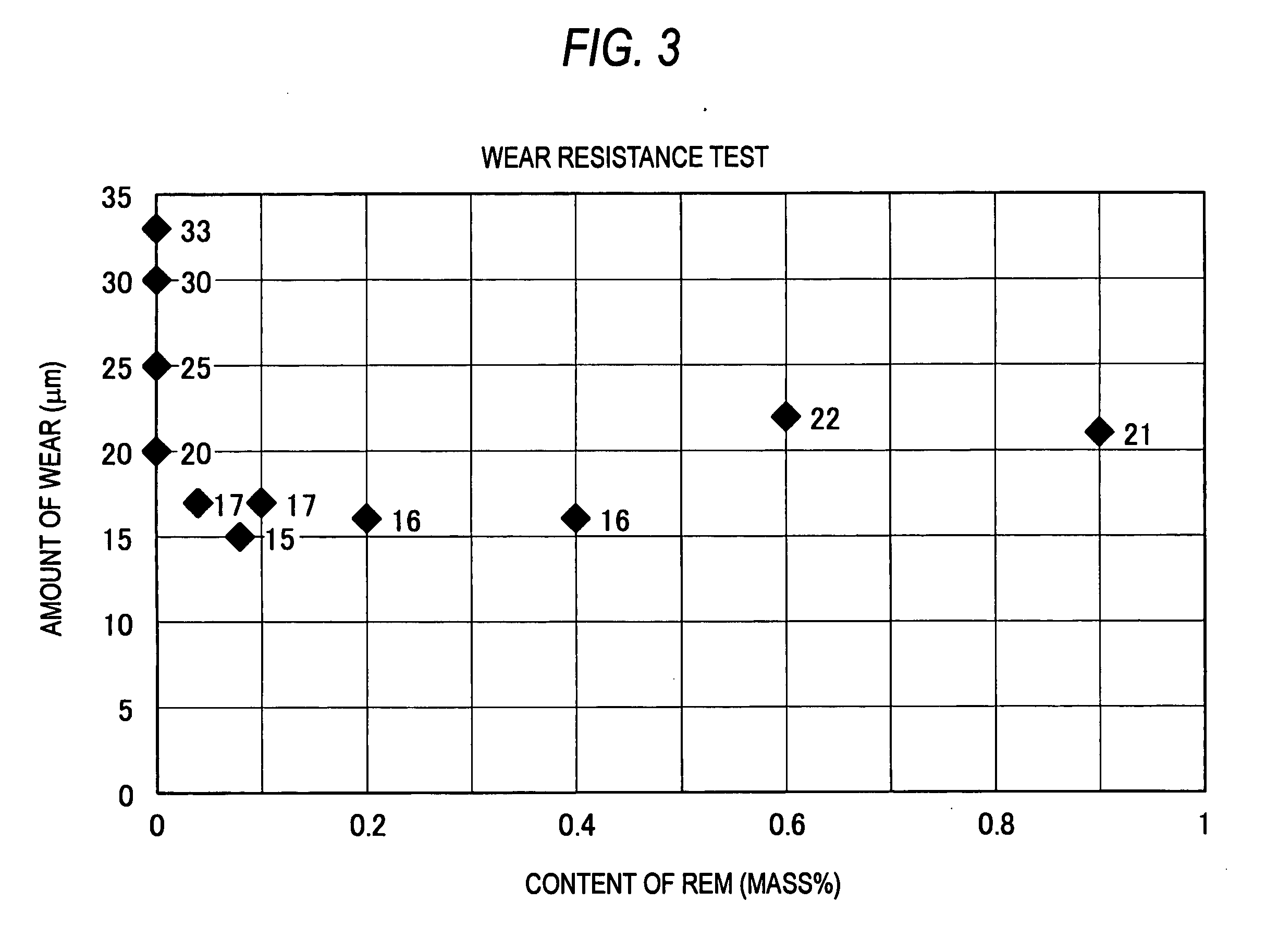
ActiveUS20090165595A1Improve wear resistanceHigh value for industrial useMachines/enginesLift valvePowder mixtureIron powder
The invention provides a hard-particle powder for sintered body, which contains, by mass %, 2% to 3.5% of Si, 6% to 10% of Cr, 20% to 35% of Mo, 0.01% to 0.5% of REM, and the remainder being Co and unavoidable impurities. The invention further provides a sintered body obtained through a mixing step of mixing the above-mentioned hard-particle powder for sintered body with a pure iron powder and a graphite powder to obtain a powder mixture, a forming step of compacting the powder mixture to obtain a compact, and a sintering step of sintering the compact. The hard-particle powder according to the invention has the effect of giving a sintered body having improved wear resistance without substantially impairing powder characteristics and sintering characteristics. Additionally, the sintered body according to the invention has the effect of having excellent wear resistance.
Owner:DAIDO STEEL CO LTD
Coating composition and optical article
InactiveCN102421861AHigh refractive indexImprove scratch resistanceSynthetic resin layered productsOptical partsRefractive indexMicroparticle
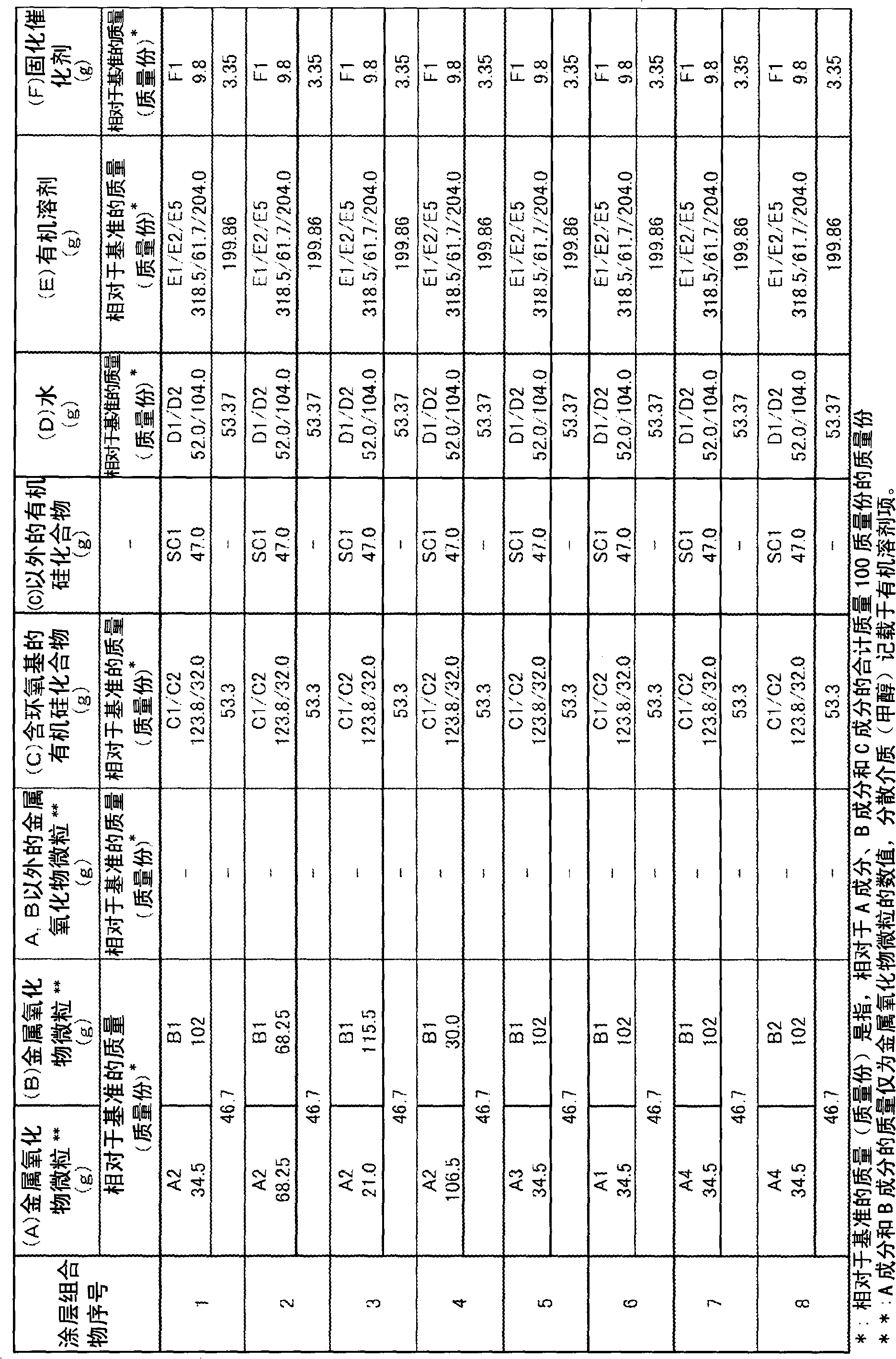
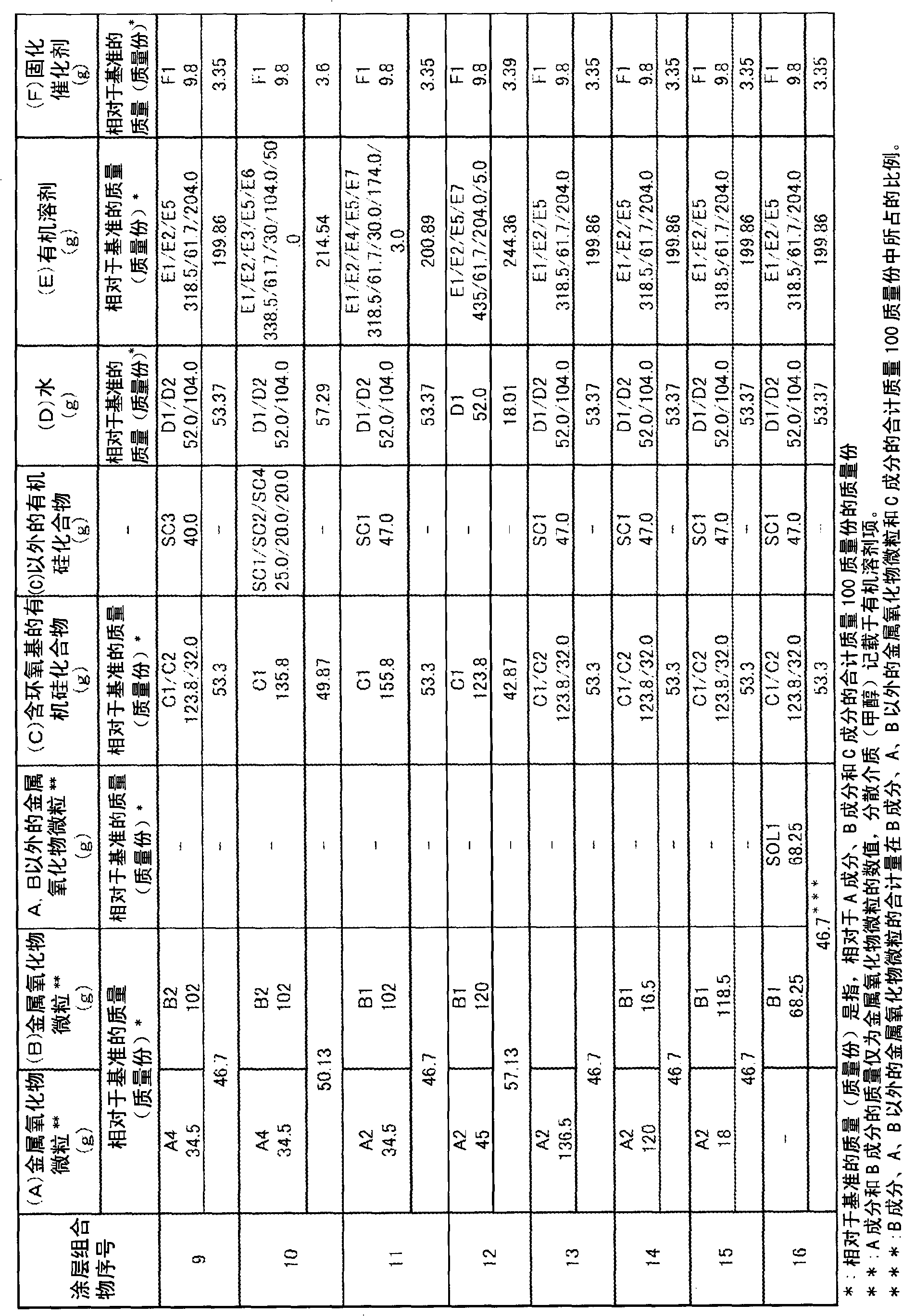
Disclosed is a coating composition appropriately usable for forming a hard coat film that is obtained by applying the composition onto a light-permeable member, such as a plastic lens having a high refractive index or a photochromic plastic lens having a color-developing function and a high refractive index, and hardening. This coating composition exhibits an extremely improved weather resistance (prevention of discoloration) while sustaining a high refractive index, a good scratch resistance and an excellent adhesiveness to an optical base. Specifically disclosed is a coating composition, comprising: titanium oxide-containing metal oxide microparticles (A) together with titanium oxide-containing metal oxide microparticles (B), provided that the titanium oxide-containing metal oxide microparticles (A) and the titanium oxide-containing metal oxide microparticles (B) have been selected through a specific light irradiation test and show different properties; an epoxy group-containing organosilicon compound (C) such as ?-glycidoxypropyltrimethoxysilane; water (D); an organic solvent (E) such as methyl alcohol; and a hardening catalyst (F) such as aluminum acetylacetonate or magnesium perchlorate, each in a specific amount.
Owner:TOKUYAMA CORP
Process for production of ketomalonic acid compounds or hydrates thereof
ActiveUS20120004443A1Readily availableSafe and easily availableOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationMalonic acidChlorous acid
Disclosed is a process for the production of ketomalonic acid compounds or hydrates thereof by reacting a malonic acid compound with one or more chlorous acid compounds selected from among chlorous acid and chlorites and thus oxidizing the methylene group of the malonic acid compound. The process does not necessitate highly toxic reagents, lowly safe reagents, special reactants, special reaction equipment, expensive reagents, expensive catalysts, or transition metals such as noble metals, and permits the selection of mild reaction conditions and simple operation, thus enabling efficient and easy production of ketomalonic acid compounds such as ketomalonic diesters under simple and easy conditions suitable for industrialization.
Owner:IHARA CHEM IND CO LTD
Special fertilizer of sweet wormwood
InactiveCN1817822AMeet special needsIncrease productionAlkali orthophosphate fertiliserAmmonium orthophosphate fertilisersPhosphamidonPotassium sulfate
A special fertilizer for sweet wormwood consists of urea 10-20%, phosphamidon 12-25wt%, potassium sulfate 20-30wt%, special organic substance 15-32wt%, special additive 0.5-2.0wt% and zeolite powder 7-18wt%. The special additive comprises of Mg, Mo, B, Zn and Mn. The process is carried out by aging the special organic substance at 40-60DEG C by dilute solution, adding into lump lime, mixing, balancing above 24hrs, regulating pH value to 6-8 and drying. It has more yields.
Owner:丁德蓉
Photoresist developing solution
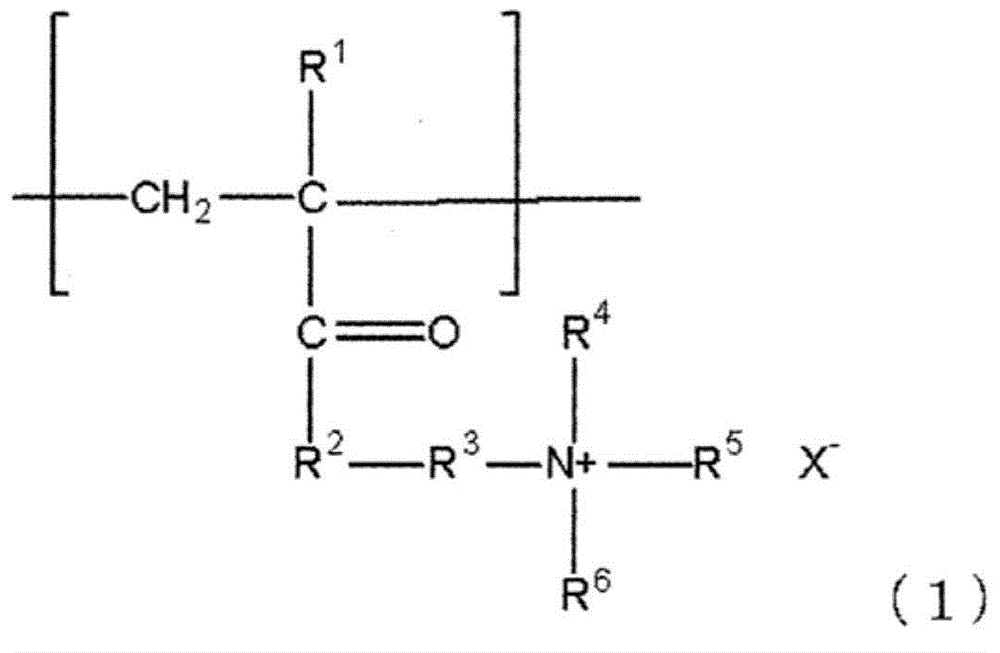
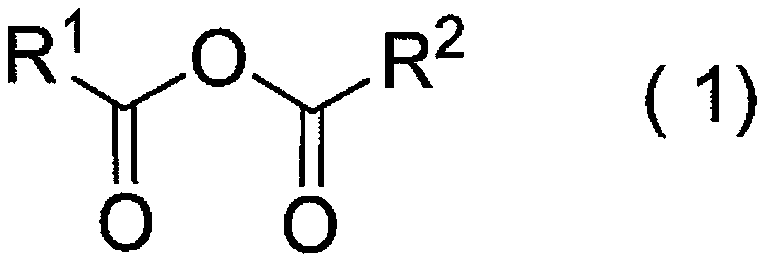
InactiveCN101657761AHigh dimensional accuracyPattern in good shapeSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotosensitive material processingResistAmmonium compounds
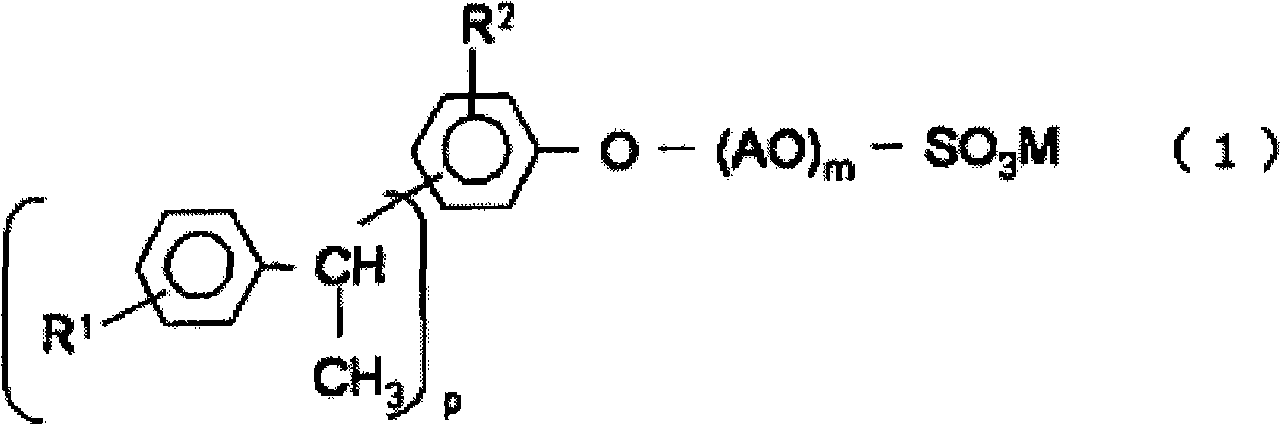
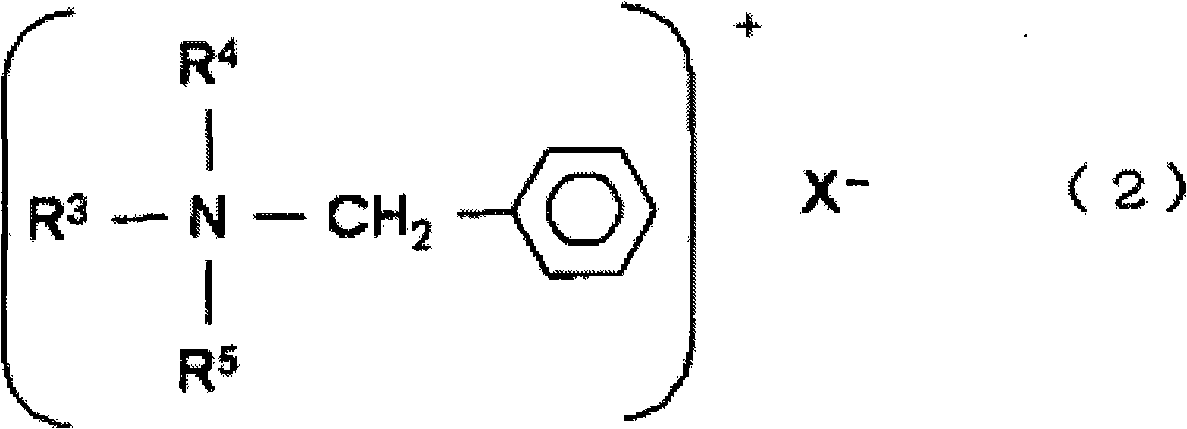
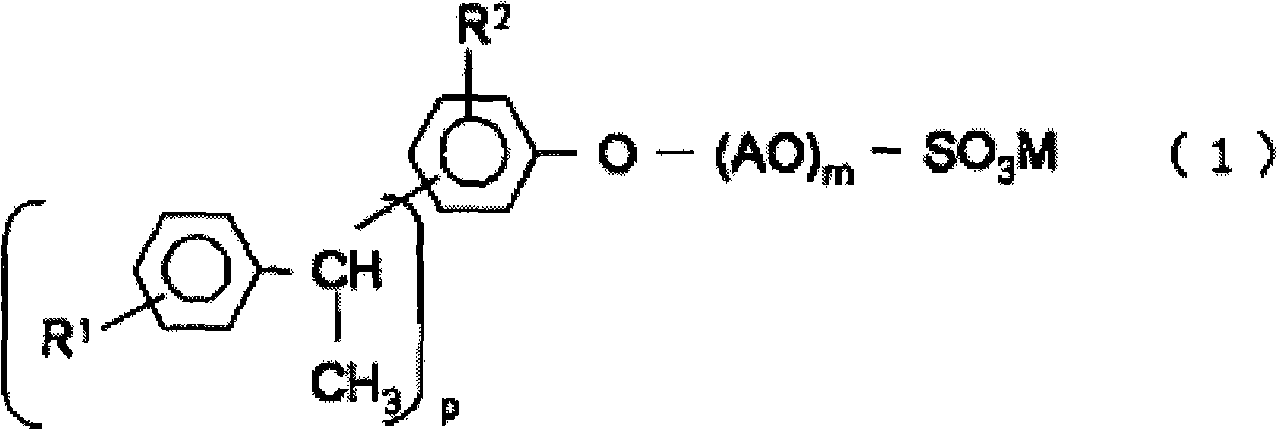
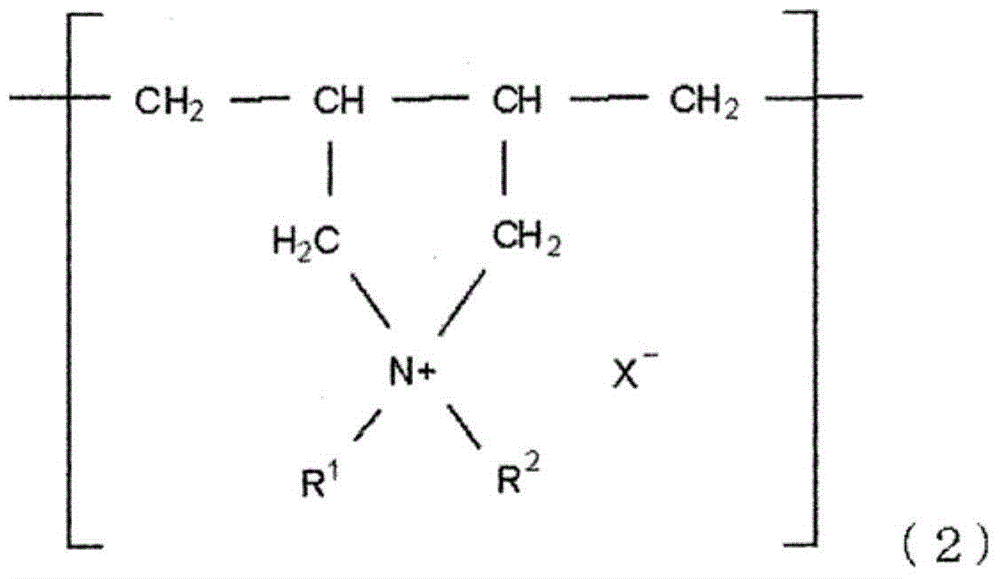
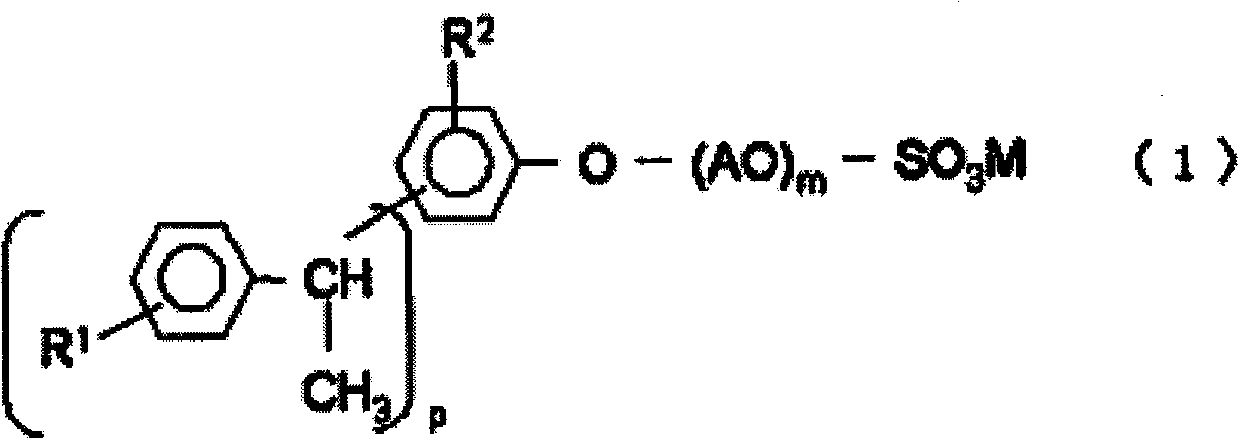
The invention provides a developing solution which can be used suitably for the development of a thick resist comprising a chemically amplified resist. Disclosed is a photoresist developing solution comprising an aqueous quaternary ammonium compound solution containing an anionic surfactant and a cationic surfactant, wherein the anionic surfactant is represented by the formula (1) and is containedin an amount of 0.1 to 5% by mass and the cationic surfactant is contained in an amount of 0.01 to 2% by mass relative to 100% by mass of the total mass of the photoresist developing solution. (1) wherein R<1> represents a hydrogen atom or a methyl group; R<2> represents a hydrogen atom or an alkyl group having 1 to 4 carbon atoms; A represents an alkylene group having 1 to 4 carbon atoms, provided that AO's may be the same as each other or may be a combination of different two or more groups in the molecule; p is an integer of 1 to 3; m is an integer of 5 to 30; and M represents a hydrogen atom or an ammonium ion.
Owner:TOKUYAMA CORP
Double-axle oriented polyester film and making method thereof
InactiveCN1248514AImprove stabilityHigh transparencyRecord information storageMagnetic recordingPolyesterImide
A biaxially oriented polyester film, comprising a polyester (A) at least mainly composed of ethylene terephthalate and a polyether imide (B), having a single glass transition temperature, and having a refractive index of 1.60 to 1.80 at least in either the machine direction or the transverse direction, has excellent thermal dimensional stability, clarity and is easy to produce. It can be prepared by melt-extruding a polyester (A) at least mainly composed of ethylene terephthalate and polyether imide (B), to mold a resin sheet with a single glass transition temperature, and stretching the resin sheet at a ratio of 3.0 to 10 times in the machine direction and at a ratio of 3.0 to 10 times in the transverse direction.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
Method for mfg. printed circuitboard
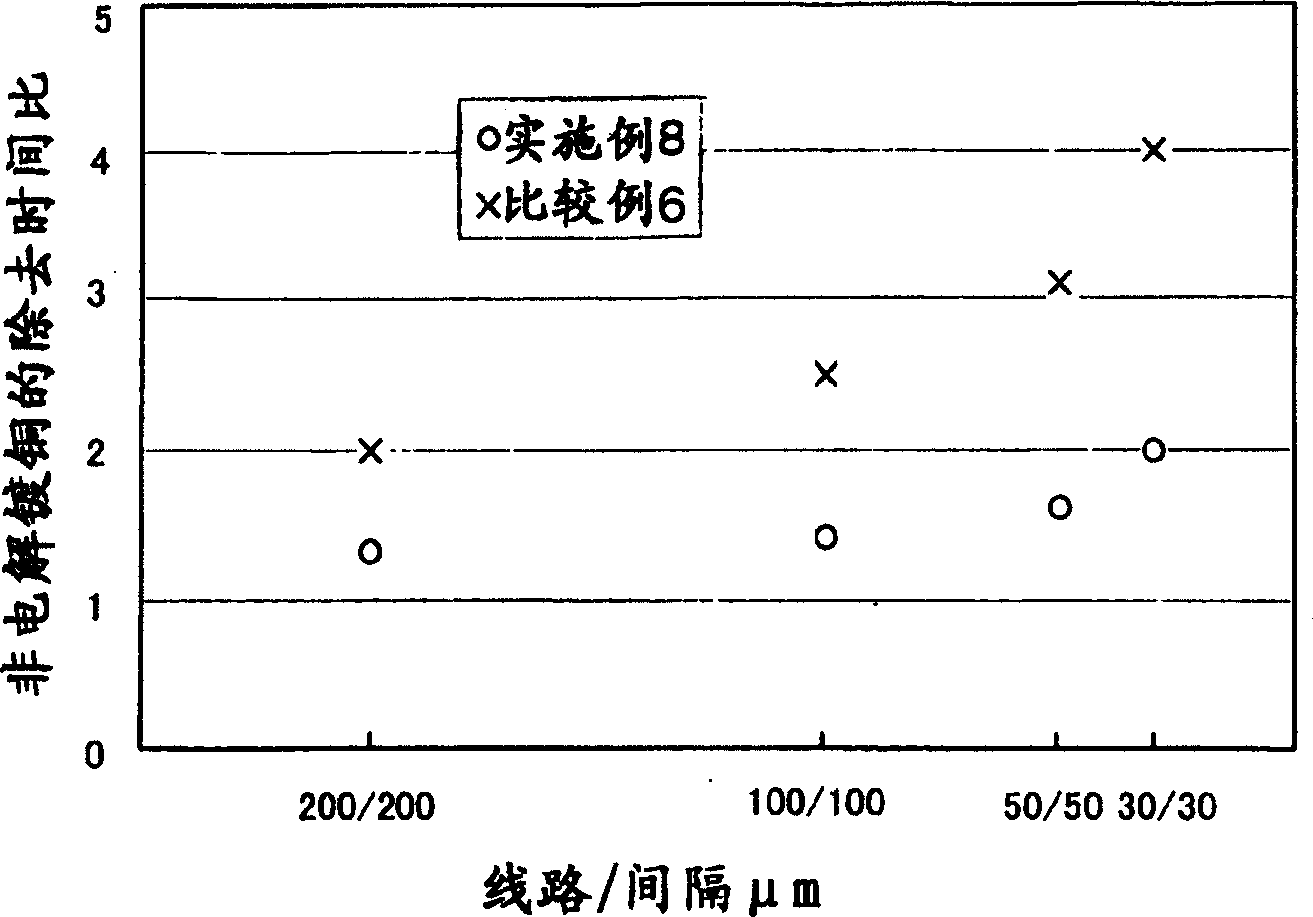
InactiveCN1592548AUniform wiring widthHigh value for industrial useConductive material chemical/electrolytical removalSurface treatment compositionsCopper platingElectrolysis
To provide a method for reducing a wiring width in the formation of a copper wiring by the semi-additive method of a printed circuit board, etc., suppressing an undercut and further forming a uniform wiring width in a plane. The method for manufacturing the printed circuit board having the fine wiring of a line / space of 50 [mu]m / 50 [mu]m or less using the semi-additive method includes a step of processing with an etchant liquid in which an etching speed of non-electrolytic copper plating of a seed layer is twice as fast as the etching speed of the electrolytic copper plating, and non-electrolytic copper plating removing time in space of the fine wiring having the line / space of 50 [mu]m / 50 [mu]m or less is larger than 50 [mu]m or less is three times as fast as the non-electrolytic copper plating removing time in the space larger than 50 [mu]m, and manufacturing of the printed circuit board.
Owner:MITSUBISHI GAS CHEM CO INC
Method for producing harmful-organism control agent, and intermediate thereof
InactiveCN105980354ANovel manufacturing intermediatesNovel preparation methodHydropoly/poly sulfide preparationSulfide preparationHalogenIndustrial scale
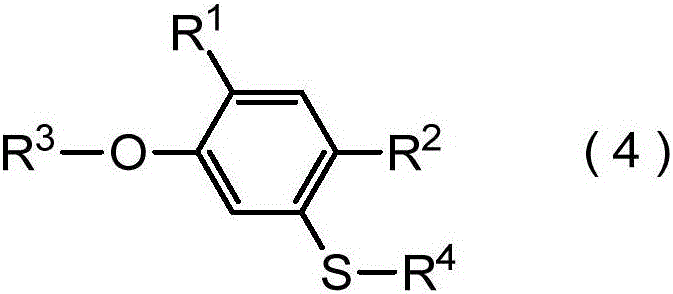
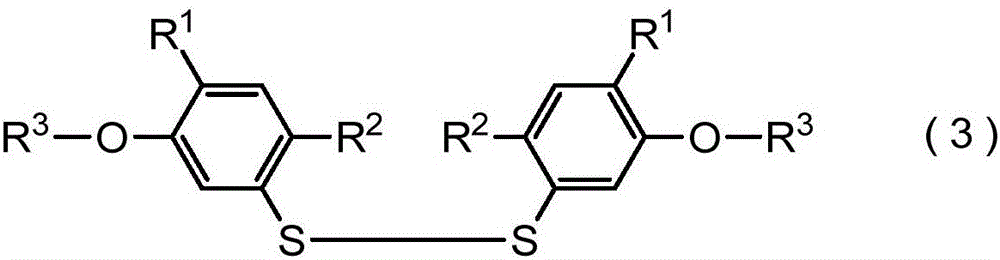
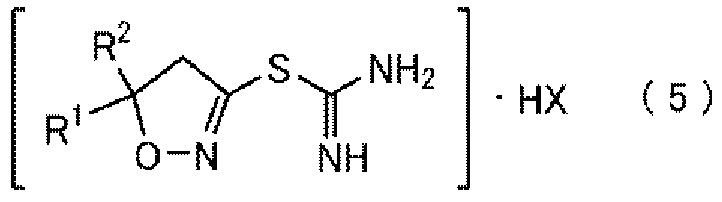
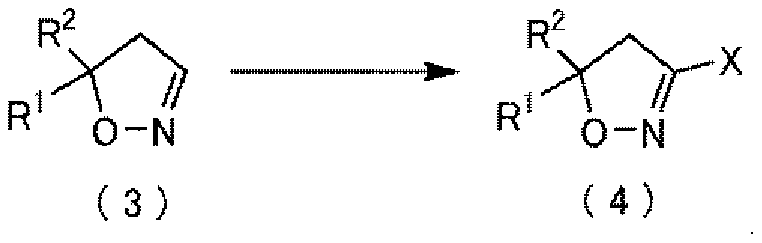
The purpose of the present invention is to provide: a production intermediate suitable for the industrial-scale production of a compound represented by general formula (4) and having a harmful-organism control activity; and a method for producing the same. A compound represented by general formula (4) (In the formula, R1-R4 are as stated below) is produced by causing a reaction between the following, while in the presence of a a compound represented by general formula (b) R4-Y (In the formula, R4 represents a C1-C4 haloalkyl group, and Y is a halogen atom or the like.); and a compound represented by general formula (3) (In the formula, R1 and R2 each independently represent a halogen atom or a C1-C4 alkyl group.), which is obtained by oxidizing a mercaptophenol derivative, and next, while in the presence of a base, causing a reaction with a compound represented by general formula (a) R3-X (In the formula, R3 represents a C1-C4 haloalkyl thio C2-C10 alkyl group, and X is a halogen atom or the like.).
Owner:KUMIAI CHEM IND CO LTD
Preparation method of loaded nano-metal catalyst based on UIO-66
InactiveCN110152657AHigh value for industrial useEasy to prepareMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsN dimethylformamideSynthesis methods
The invention discloses a preparation method of a loaded metal catalyst based on metal-organic framework UIO-66. The catalyst is prepared by: adding a carrier precursor metal salt into water, adding an organic ligand into N, N-dimethylformamide, after full dissolution of the two substances, mixing the two solutions evenly, adding an active component precursor, and performing one-pot synthesis to obtain a catalyst precursor, and carrying out high temperature roasting and reduction to obtain the metal catalyst. The high stability metal catalyst M@BO2@C prepared by one-pot synthesis method, the method prepares the loaded metal catalyst based on UIO-66 structure, the preparation method is simple, provides a new synthesis method for preparation of nano-scale catalyst, and has high industrial utilization value. The catalyst prepared according to the invention is subjected to high temperature calcination and reduction, has good thermal stability and potential application space, moreover, thecatalyst still maintains the shape of UIO-66 after high temperature calcination.
Owner:昆山普瑞凯纳米技术有限公司
Acrylic resin filmy material, and product with the same
ActiveCN101024700ANo albinoMeet light resistanceSynthetic resin layered productsCLARITYHeat resistance
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
Process for preparing chromium oxide from laterite-nickel ores
ActiveCN101723460AHigh value for industrial useIncrease diversityChromium oxides/hydratesSlurryToxic material
The invention provides a process for preparing chromium oxide from laterite-nickel ores. The process comprises the steps of carrying out liquid-solid separation and aluminum removal on roast materials obtained by leading the laterite-nickel ores and alkali metal hydroxide to be in molten salt reaction for obtaining alkaline leaching solution which is rich in chromate and the alkali metal hydroxide, taking the alkaline leaching solution as a raw material, taking hydrogen as a reducing agent, leading the alkaline leaching solution and the hydrogen to be in direct hydrothermal reduction reaction under certain temperature and pressure conditions for generating chromium hydroxide slurry, and carrying out the liquid-solid separation on the slurry for obtaining a chromium hydroxide filter cake and filtrate containing a small quantity of hexavalent chromium. A final product of chromium oxide is obtained by drying, high-temperature calcining and washing the chromium hydroxide filter cake; and the filtrate can be returned to the material mixing procedure for realizing the circulating material mixing. The process can effectively recycle and utilize valuable metal chromium in the laterite-nickel ores, thereby not only realizing the pluralism of a laterite-nickel ore product, but also reducing the emissions of toxic wastes, realizing the internal circulation of materials and media, being in line with the requirements on clean production; furthermore, the reduction process has simple flow process and strong industrial operationality.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
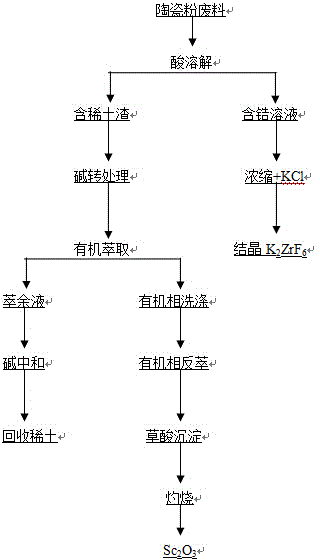
Method for separating and recovering scandium in stable zirconia ceramic wastes containing scandium and rare earth
ActiveCN104651619AEmission reductionEasy to operateProcess efficiency improvementOXALIC ACID DIHYDRATEAcid dissolution
The invention discloses a method for separating and recovering scandium in stable zirconia ceramic wastes containing scandium and rare earth. The method comprises the following steps: crushing ceramic wastes firstly, sieving by virtue of a 200-mesh sieve, then dissolving the crushed powder by acid; after heating and concentrating a filtrate, adding potassium chloride, carrying out crystallization to obtain potassium fluozirconate, and separating zirconium from a solution; and washing filter residues, carrying out conversion treatment by using 5-20 percent sodium hydroxide, washing the residues again after treatment, dissolving with acid, extracting scandium by using an extractant so as to realize the separation of scandium and the rare earth, neutralizing an extraction raffinate with alkali, recovering the rare earth from precipitates, and searing to obtain rare earth oxide; and carrying out washing and back extraction on an organic phase for extracting the scandium, precipitating the scandium by oxalic acid, and searing to obtain scandium oxide. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the purity of Sc2O3 is larger than 99 percent, the recovery rate is larger than 90 percent, the recovery rate of the rare earth is larger than 90 percent, and the recovery rate of Zr is larger than 95 percent.
Owner:HUNAN ORIENTAL SCANDIUM
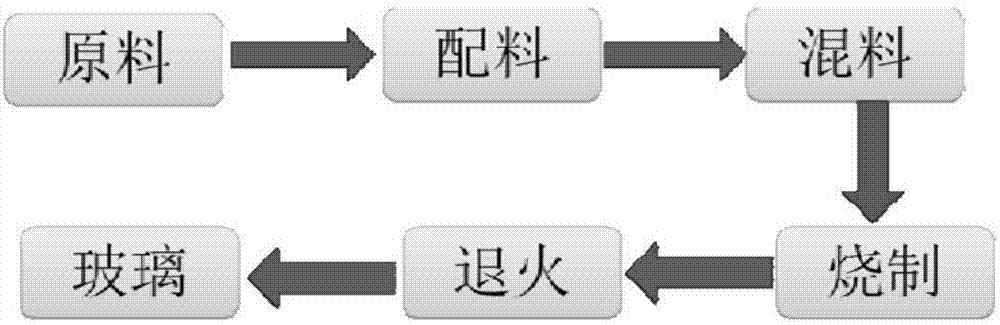
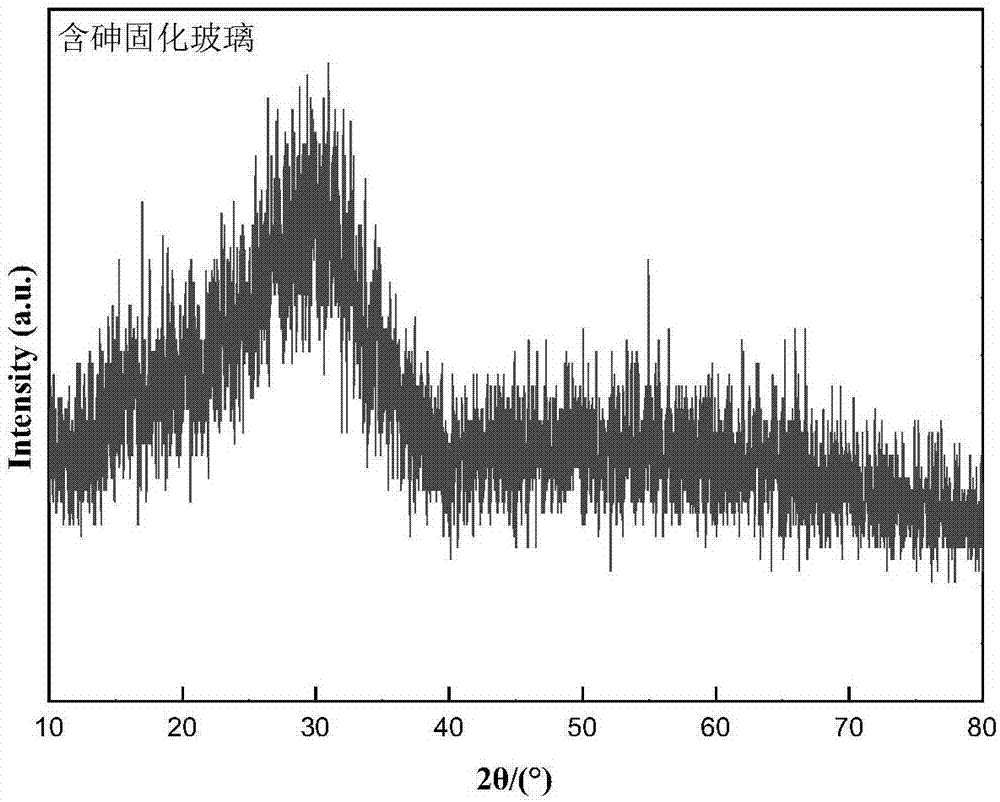
Method for preparing arsenic-containing cured glass by arsenic-containing waste slag
InactiveCN107311455AUniform colorHigh hardnessGlass shaping apparatusArsenic pollutionMixed materials
The invention discloses a method for preparing arsenic-containing cured glass by arsenic-containing waste slag. Arsenic-containing waste slag, copper melting waste slag, a silicon-based material and boracic acid are subjected to mixed ball milling according to a certain mass ratio; sieving is performed; the mixed material is put into a fire-resistant mold; solid-phase reaction is performed under a certain temperature condition; then, the materials are taken out to be cooled in the high-temperature state; the cured glass with uniform color and luster, high hardness and smooth surface is obtained; the obtained cured glass meets the requirements of the general inorganic glass materials for industry. The method has the advantages that the waste and abandoned copper slag and dangerous waste of arsenic-containing waste slag in industry are used to be converted into curing glass with the industrial utilization value through directional regulation and control; the quantity reduction and secondary resource utilization of the copper slag can be realized; the problems of copper slag tail end open path and environment pollution are solved; the harmless disposition goal of the arsenic-containing waste slag is achieved; waste materials are changed into valuable materials; a green and sustainable path is opened up for the copper slag and arsenic pollution treatment in copper melting industry.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Method for improving the aqueous solubility of poorly-soluble substances
ActiveCN102573912AImprove securityProductivity advantagePowder deliveryBiocideSolubilityCalcium biphosphate
Provided is a method for improving the solubility of poorly-soluble substances used in pharmaceuticals, veterinary pharmaceuticals, quasi-drugs, cosmetics, food products, agricultural chemicals, and the like, without using large amounts of additives. The provided method is characterized in that fine particles of a calcium compound such as calcium phosphate or calcium carbonate are used to cover the surfaces of particles of a poorly-soluble substance used in pharmaceuticals, veterinary pharmaceuticals, quasi-drugs, cosmetics, food products, agricultural chemicals, or the like.
Owner:SANGI CO LTD
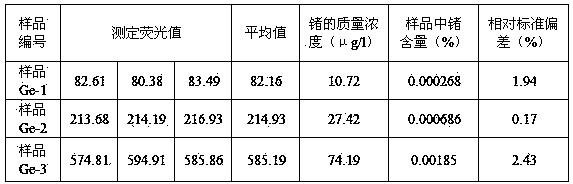
Method for determining germanium content of cobalt-nickel slag by atomic fluorescence spectrometry
InactiveCN103776811AReduce volatile lossEliminate distractionsPreparing sample for investigationFluorescence/phosphorescenceThioureaSlag
The invention belongs to the technical field of metallurgical industry analysis and discloses a method for determining germanium content of a cobalt-nickel slag by atomic fluorescence spectrometry. The method comprises the following steps: preparing a germanium standard solution, a zinc standard solution and a thiourea-ascorbic acid mixed solution, and drawing a germanium standard solution curve; weighing a cobalt-nickel slag sample to prepare a sample solution; determining the fluorescence intensity of germanium in the sample by using an atomic fluorescence spectrometer; and comparing with the germanium standard solution curve and analyzing the content of the germanium in the sample solution. According to the method, after the approximate equal amount of zinc is added into the germanium standard solution, the germanium standard curve is drawn to eliminate the inferences to a detection result by the base body zinc. The method disclosed by the invention has the characteristics of low detection limit, wide linear range, low maintenance cost, rapidness in measurement, simplicity in operation, good accuracy, high precision, capability of simultaneously and rapidly determining elements to be detected and the like; furthermore, the method has the characteristics of few needed reagents, low cost and high automation degree, is suitable for analyzing a large batch of samples and has a very good industrial utilization value.
Owner:BAIYIN NONFERROUS GROUP
Applied film
ActiveCN105008130APrevent precipitationHigh value for industrial useSynthetic resin layered productsElectrical equipmentPolyesterPolymer science
The present invention provides a coating film having exceptional characteristics, the coating film allowing the precipitating of oligomers from the surface of a film to be suppressed to a high extent; e.g., under exposure to high temperatures; and, when the film is stored, used, processed, etc., preventing any incidence of adverse events owing to the oligomers (ester cyclic trimers). A coating film having a coating layer formed from a coating liquid containing a multivalent aldehyde compound, the coating layer being formed on at least one surface of a single-layer polyester film containing 0.7% by weight or less of ester cyclic trimers or a multi-layer polyester film having a polyester surface layer containing 0.7% by weight or less of ester cyclic trimers.
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
NOx-reduced burning method and apparatus
InactiveCN1508473AAchieve reductionHigh value for industrial useBurnersFluegas recirculationCombustorExhaust fumes
Combustion method and apparatus for NOx reduction are capable of easily achieving NOx reduction to an exhaust NOx value of 30 ppm or under. The combustion method is to perform in combination a first NOx reduction step for suppressing generated NOx value to 60 ppm or under (at 0% O2 in exhaust gas, dry basis) by a low NOx burner, a second NOx reduction step for recirculating exhaust gas of the low NOx burner to a burning reaction zone formed by the low NOx burner, and a third NOx reduction step for adding water or steam to the burning reaction zone.
Owner:MIURA COMPANY LIMITED
Method for preparing regenerated cellulose fiber from fine corn fiber in corn starch milk production process
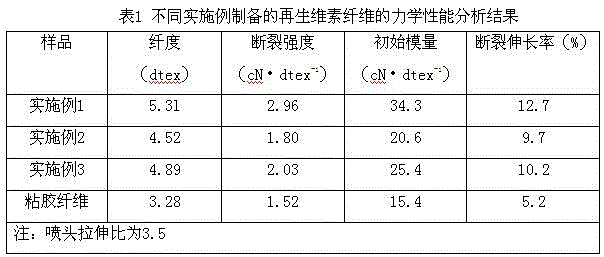
InactiveCN103556247AGood textile mechanical propertiesGood mechanical propertiesSpinning head liquid feederMonocomponent cellulose artificial filamentCellulose fiberMechanical property
The invention belongs to the technical field of deep corn machining, and in particular relates to a method for preparing a regenerated cellulose fiber from fine corn fibers in the corn starch milk production process. The method for preparing the regenerated cellulose fiber from the fine corn fiber in the corn starch milk production process comprises the following steps of S1. preparing fine corn fiber pulp; S2. preparing a cellulose spinning solution; and S3. preparing recycled cellulose fibers. The recycled cellulose fibers prepared by using the method provided by the invention is good in spinning mechanical property which is superior to that of ordinary viscose; and moreover due to adoption of the method, the complex preparation steps in the ordinary preparation method are avoided, the recycled cellulose fiber which can be woven can be prepared at one time, and the industrial utilization values of the fine corn fibers are improved.
Owner:SHANDONG XIWANG SUGAR
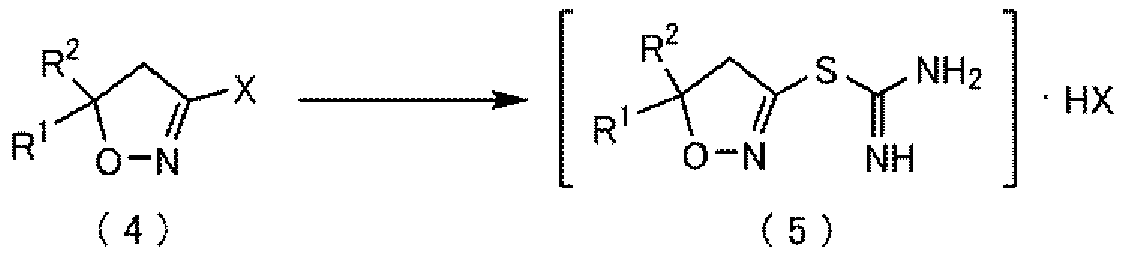
Method for producing thiocarboxamidine salt compound
ActiveCN111542514AManufacturing method solutionHigh value for industrial useOrganic chemistry methodsBiochemical engineeringMedicinal chemistry
Owner:KUMIAI CHEM IND CO LTD
Bronze alloy, and sliding member using said bronze alloy
ActiveCN111630194AImprove friction and wear characteristicsExcellent mechanical propertiesMolten spray coatingShaftsFernicoSulfide compound
The invention of the present application addresses the problem of providing: a bronze alloy which has a lead-free composition and is imparted with high seize resistance and adhesive wear resistance enough to withstand fluctuating high-speed / high-surface-pressure sliding; and a sliding member. The bronze alloy according to the invention of the present application is characterized by being a metal structure which contains 8 to 15% by mass of Sn, 0.5 to 5.0% by mass of Bi, 0.5 to 5.0% by mass of Ni, 0.08 to 1.2% by mass of S and 0.5 to 6.0% by mass of Fe, with the remainder made up by Cu and unavoidable impurities, and has such an eutectoid structure that a fine flake-like copper-tin-based intermetallic compound is precipitated in alpha-copper, wherein an iron-nickel-based intermetallic compound and a copper-iron-based mixed sulfide are dispersed in the metal structure.
Owner:AKASHI GOHDOH
Protected l-carnosine derivative, l-carnosine, and method for producing crystalline l-carnosine zinc complex
InactiveCN111051289AEasy to manufactureHigh value for industrial useOrganic active ingredientsBulk chemical productionCarboxyl radicalPerylene derivatives
The purpose of the present invention is to provide: a method for easily producing a protected L-carnosine derivative; and the like. A method for producing a protected L-carnosine derivative accordingto the present invention is characterized by comprising a step wherein a protected L-carnosine derivative represented by formula (3) is produced by reacting an acid anhydride represented by formula (1) and an L-histidine derivative represented by formula (2) with each other. In the formulae, R1 represents a specific protected amino group; R2 represents a specific protected amino group or a branched group; each of R7 and R8 represents a hydrogen atom or a protecting group of an amino group; and R9 represents a hydrogen atom or a protecting group of a carboxyl group.
Owner:TOKUYAMA CORP
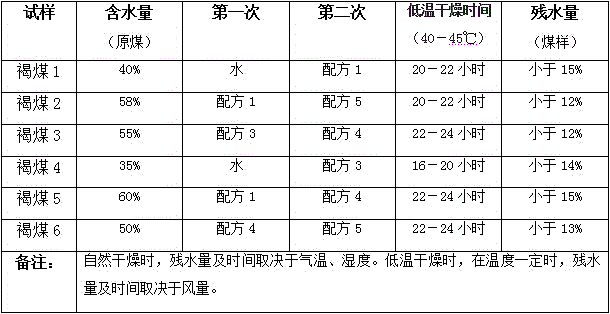
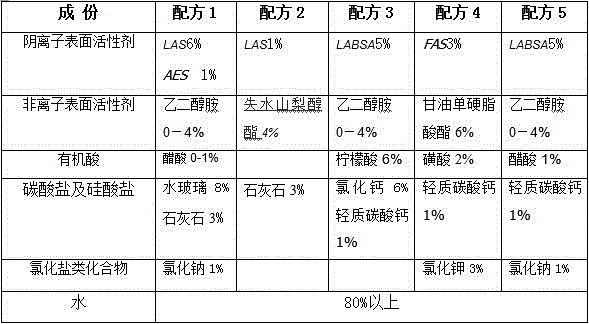
A kind of lignite additive and lignite dehydration treatment method
The invention provides a lignite dehydration additive and a lignite dehydration treatment method. The lignite dehydration additive is one of water and anionic surfactant, nonionic surfactant, organic acid, water glass, carbonate and chloride salt compounds Or several kinds are mixed and prepared in proportion, and the proportion of water is more than 80%. The lignite dehydration treatment method includes: stacking in the open air, spraying lignite dehydration additives; crushing; adding lignite additives, and forming honeycomb blocks by cold pressing; finally drying in the air or at low temperature. The invention solves the situation that the internal moisture of lignite (especially soft lignite) cannot be dried in the natural state or only with low-temperature hot air (less than 45°C); it can make the total moisture greater than 55% and the low calorific value less than 1600Kcal / kg lignite can be fully utilized in many industrial fields. The method of the invention significantly increases the hydrophobicity and permeability of the "internal water" and "bound water" of the lignite, and greatly improves the industrial utilization value of the lignite.
Owner:CHONGQING SIJI JINBIAO TECH CO LTD
Organic montmorillonite and its composite with polyurethane
InactiveCN100383182CImprove mechanical propertiesReduce manufacturing costPigment treatment with non-polymer organic compoundsMontmorilloniteAmmonium
The invention relates to an organic montmorillonite and compound with polyurethane, which is characteristic in that: acidifying and treating the Na-base montmorillonite, and reacting with long-chain alkyl ammonium salt to obtain the product. This product can not generate trimerization catalysis with isocyanate when composing with polyether polyol- isocyanate, can push off the layer gap of montmorillonite to nano state, and has high industrial application value.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF GEOCHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for producing nitrobenzene compound
ActiveCN109071411AEfficient preparation methodLess quantityOrganic compound preparationOrganic chemistry methodsHydrogen atomHalogen
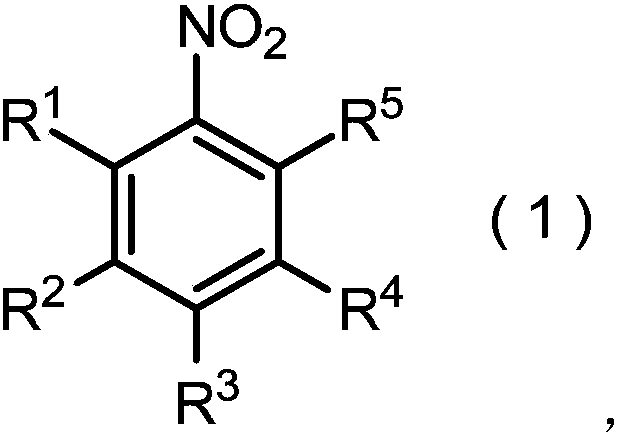
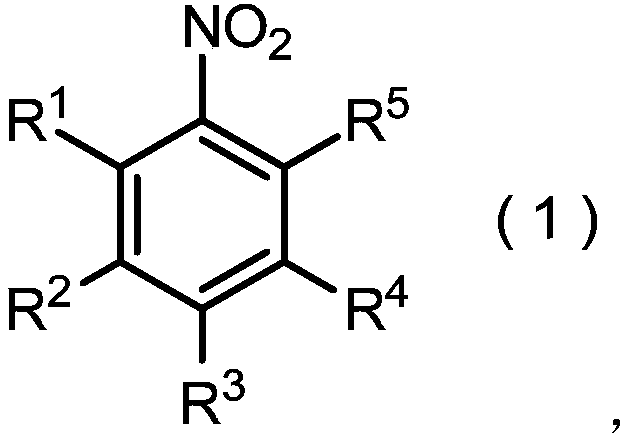
The purpose of the present invention to provide a method for producing a nitrobenzene compound represented by general formula (1), which is economically preferable, and suitable for industrialization.The present invention pertains to a method for producing a nitrobenzene compound represented by general formula (1) (in the formula, R1 represents a halogen atom; R2, R3, and R4 represent a hydrogenatom or the like; R5 represents a halogen atom or an alkoxycarbonyl group), comprising: (i) a step for reacting an aniline compound represented by general formula (2) (in the formula, R1, R2, R3, R4,and R5 are as defined above) with a metal salt of nitrous acid in the presence of nitric acid; and (ii) a step for reacting the product of step (i) with a metal salt of nitrous acid in the presence ofa copper compound.
Owner:KUMIAI CHEM IND CO LTD
Composite modified montmorillonite adsorbent as well as preparation method and application thereof
PendingCN111871387ARealize inorganic-organic composite modificationAvoid adsorptionOther chemical processesWater contaminantsSorbentMontmorillonite
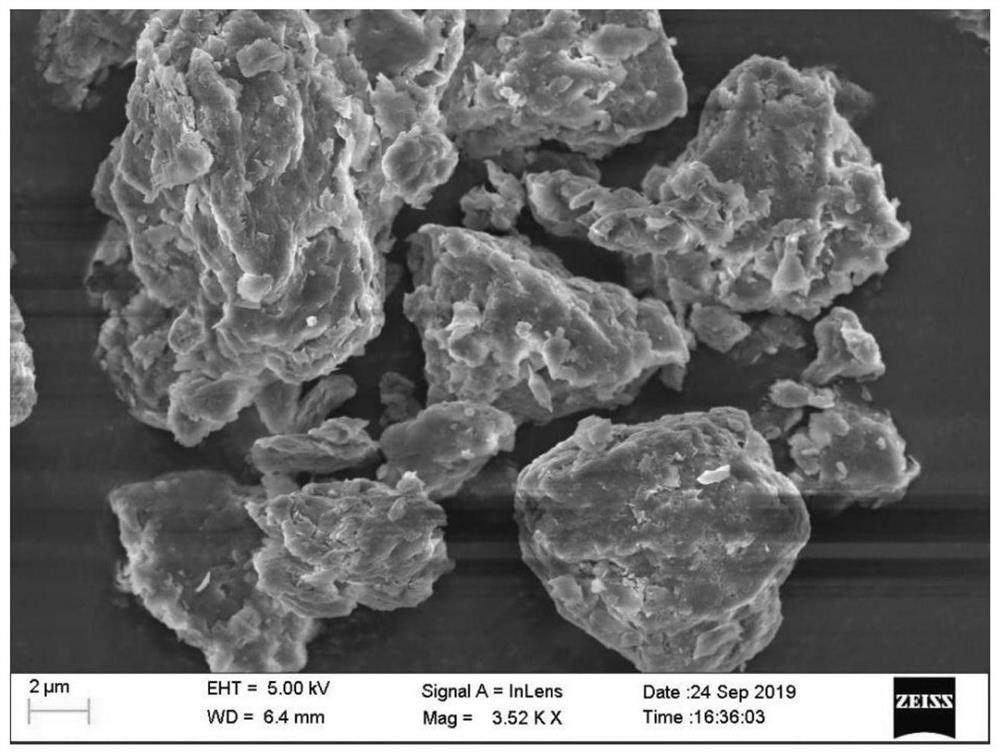
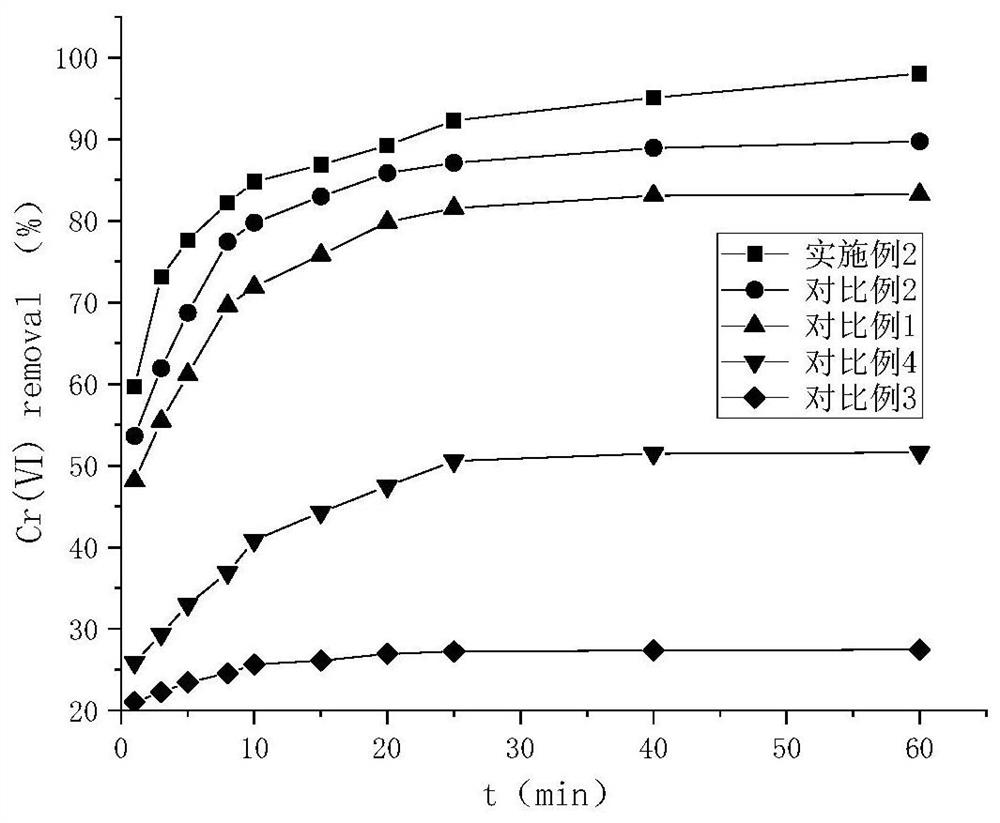
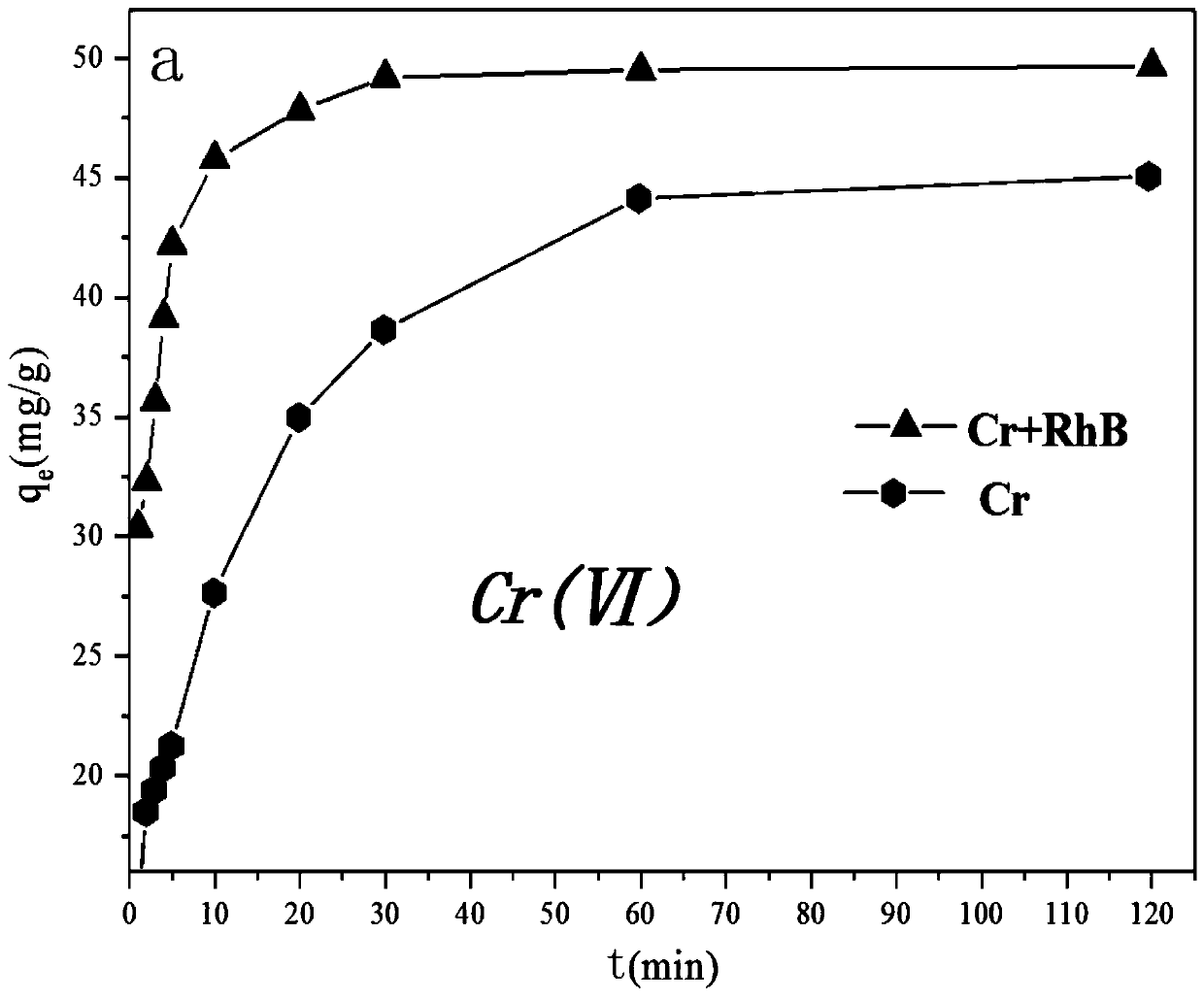
The invention discloses a composite modified montmorillonite adsorbent as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: preparing a cetyltrimethyl ammonium bromide column agent from cetyl trimethyl ammonium bromide and water; preparing a dextrin column agent from dextrin, a sulfuric acid solution and water; mixing montmorillonite and water into montmorillonite suspension liquid, and adding the two column agents into the montmorillonite suspension liquid to prepare the composite modified montmorillonite adsorbent. The invention alsoprovides application of the composite modified montmorillonite adsorbent in Cr (VI)-containing wastewater treatment. In the application process of the composite modified montmorillonite adsorbent, the Cr (VI) in wastewater can be effectively removed; compared with a single modified montmorillonite adsorbent, the composite modified montmorillonite adsorbent is better in adsorption effect and higher in adsorption capacity.
Owner:陕西聚泰新材料科技有限公司
Photoresist developing solution
InactiveCN101657761BHigh dimensional accuracyPattern in good shapeSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotosensitive material processingResistAmmonium compounds
The invention provides a developing solution which can be used suitably for the development of a thick resist comprising a chemically amplified resist. Disclosed is a photoresist developing solution comprising an aqueous quaternary ammonium compound solution containing an anionic surfactant and a cationic surfactant, wherein the anionic surfactant is represented by the formula (1) and is contained in an amount of 0.1 to 5% by mass and the cationic surfactant is contained in an amount of 0.01 to 2% by mass relative to 100% by mass of the total mass of the photoresist developing solution. (1) wherein R<1> represents a hydrogen atom or a methyl group; R<2> represents a hydrogen atom or an alkyl group having 1 to 4 carbon atoms; A represents an alkylene group having 1 to 4 carbon atoms, provided that AO's may be the same as each other or may be a combination of different two or more groups in the molecule; p is an integer of 1 to 3; m is an integer of 5 to 30; and M represents a hydrogen atom or an ammonium ion.
Owner:TOKUYAMA CORP
Collapsible heat rediation plate
InactiveCN1294385CHigh value for industrial useLighting and heating apparatusBuilding componentsEngineeringMechanical engineering
According to the present invention, there is provides a foldable heat radiation board, in which: a plurality of elongated and narrow plate-like members with fluid tube embedding grooves provided therein are combined with each other in a quadrangular plan configuration; fluid tubes are embedded in the embedding grooves; a heat radiation sheet is attached to the entire surface on the front surface side; a back surface material is attached to the entire or partial surface on the back surface side; a plurality of contact portions in which the end portions of adjacent plate-like members contact with each other are set as folding portions; and a fluid tube outlet opening portion in the end portion of one of the plate-like members and a fluid tube inlet opening portion in the end portion of the other of the plate-like members are provided so as not to oppose each other but to be shifted from each other, this portion being set as a fluid tube passage portion. With this construction, the number of construction elements (components) is reduced, the manufacturing process is easy to perform, folding is possible, buckling in the fluid tubes and the plate-like members and damages due to friction with the grooves provided in the plate-like members, do not occur at the time of packaging, storage, transportation, and installation, installation at the installation site is easy to perform, and the surface after the installation is finished flat.
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM FUNCTIONAL PROD
A kind of phospholipase d mutant, recombinant genetic engineering bacteria and its preparation method and application
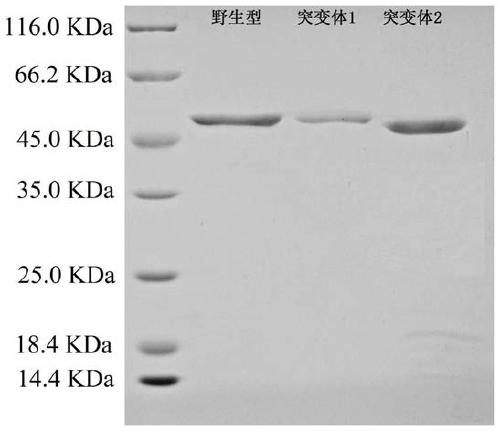
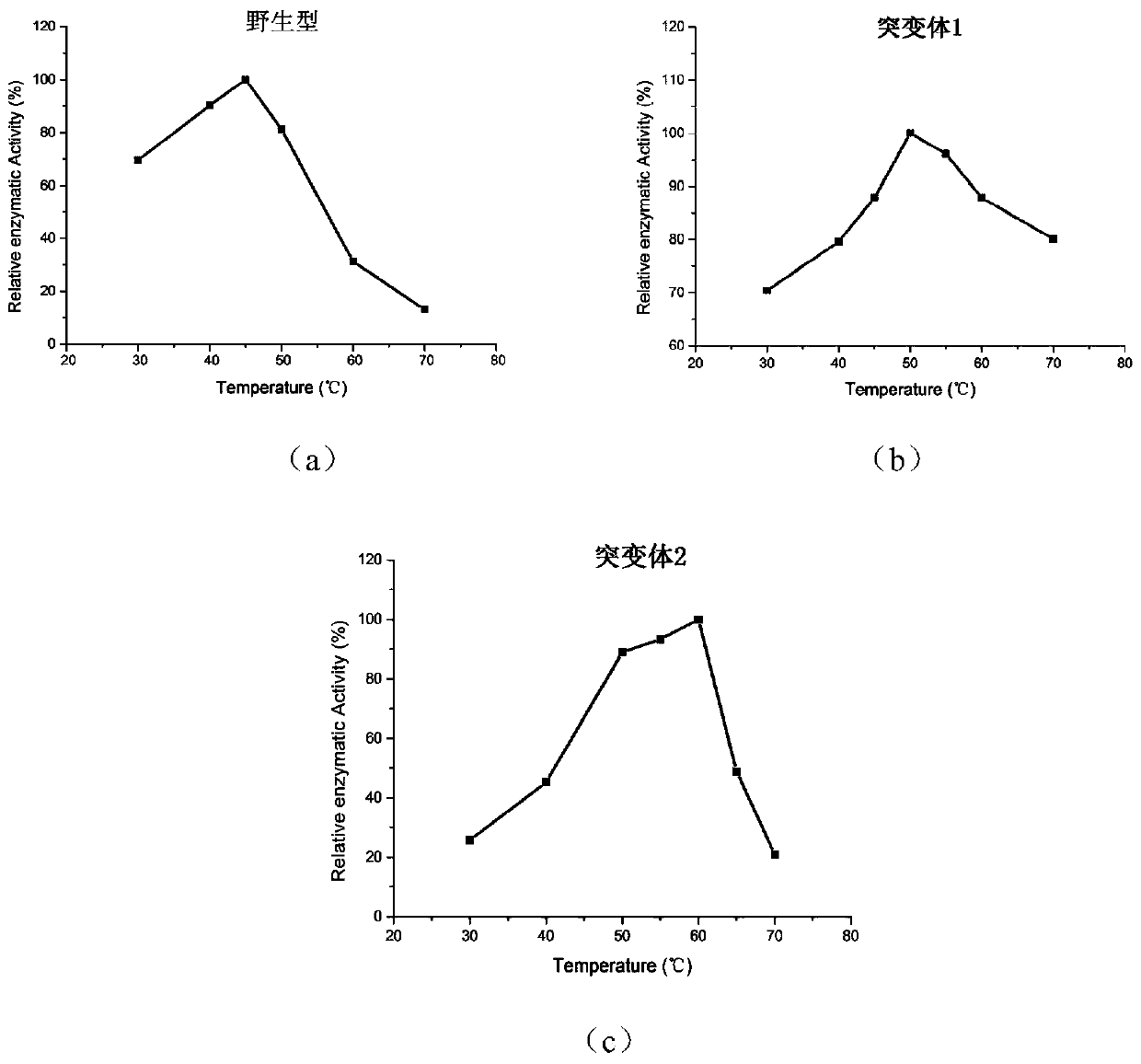
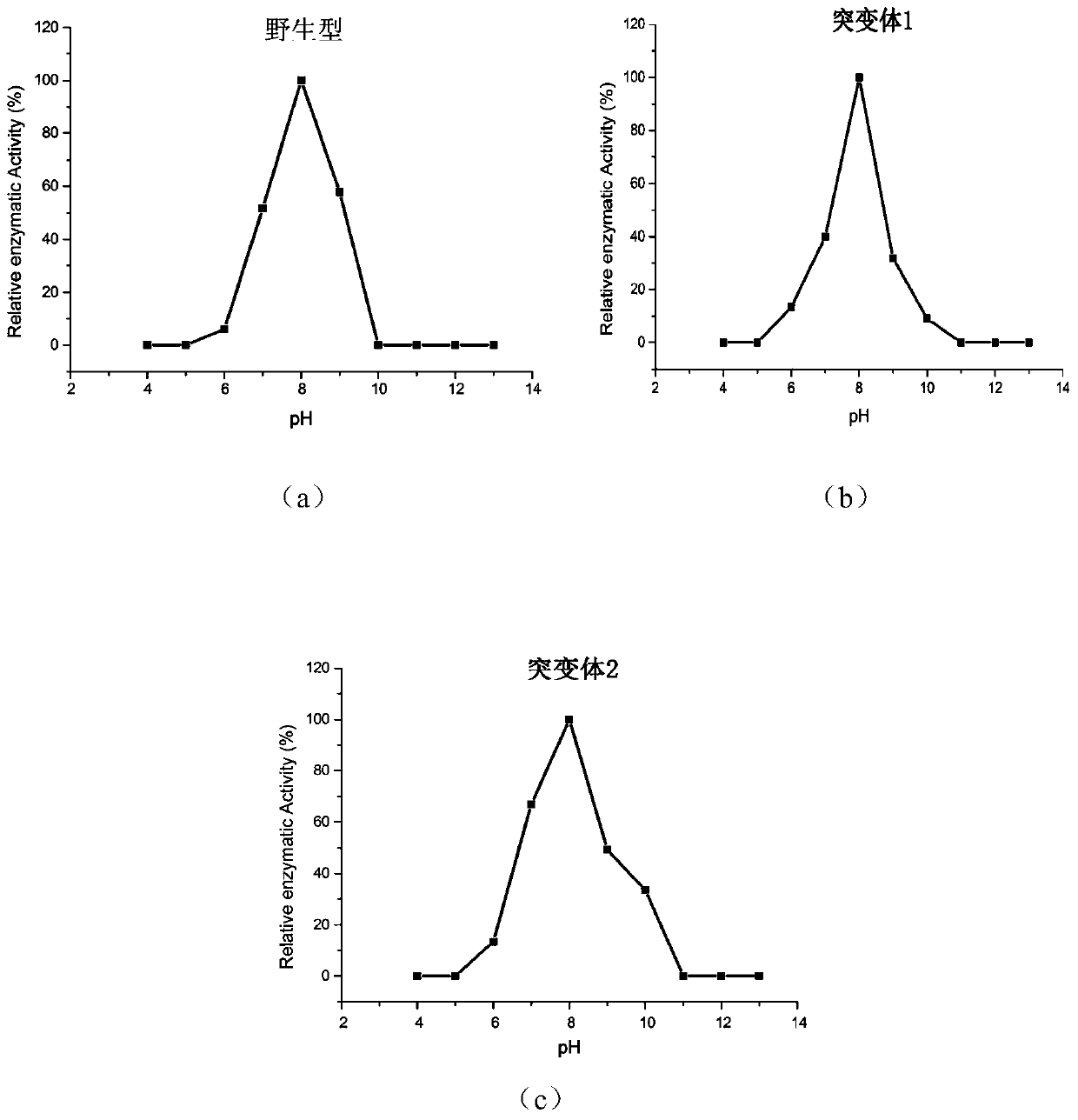
ActiveCN108118041BHigh value for industrial useIncrease vitalityBacteriaHydrolasesPhospholipaseReaction temperature
The invention discloses a phospholipase D mutant, recombinant genetically engineered bacteria and a preparation method and application thereof. The phospholipase D mutant is obtained by deleting 12 to47 amino acids at a C tail end on the basis of a parent sequence with the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 1. Two phospholipase D mutants are obtained and an experiment determines that the enzyme activity of the mutant 1 is improved by 3.7 times when being compared with that of a wild type mutant; meanwhile, the optimal reaction temperature is improved to 50 DEG C from original 45 DEG C; the enzyme activity of the mutant 2 is improved by 6 times when being compared with that of the wild type mutant; meanwhile, the optimal reaction temperature is improved to 60 DEG C from original 45 DEG C. According to the mutant disclosed by the invention, the optimal reaction temperature and the enzyme activity of the mutant are remarkably improved under the condition that the optimal pH (Potential ofHydrogen) is not changed; when the catalytic performance is improved, the industrial utilization value of the enzyme is further improved.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Aluminum removal method for shale vanadium extraction pickle liquor
InactiveCN111304440ASimple and fast operationShort reaction timeProcess efficiency improvementPhysical chemistryPotassium bisulfate
The invention relates to an aluminum removal method for shale vanadium extraction pickle liquor. According to the technical scheme, the aluminum removal method comprises the steps that potassium saltis added into the shale vanadium extraction pickle liquor and mixed, and pretreatment liquid is obtained, wherein the mole ratio of Al to K in the pretreatment liquid is 1:(0.8 to 3.0); the pretreatment liquid is placed in an airtight container and stirred under the conditions of 140-280 DEG C and 100-400 r / min for 3.5-6 h, and mixed slurry is obtained; and the mixed slurry is subjected to solid-liquid separation, and aluminum removal purification liquid and alunite slag are obtained. As for the shale vanadium extraction pickle liquor, the aluminum concentration is 4-25 g / L, and the pH is -0.50-2.0. The potassium salt is one or more of potassium sulfate, potassium chloride and potassium bisulfate. The aluminum removal method has the characteristics of easy and convenient operation, environmental friendliness and short technological process, and V and Al can be effectively separated.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
A kind of composite modified montmorillonite chitosan cross-linked adsorbent and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN108970587BAvoid the problem of low adsorption capacityImprove adsorption capacityOther chemical processesWater contaminantsAcetic acidSorbent
The invention provides a composite modified montmorillonite chitosan cross-linking adsorbent, a preparation method and an application. The present invention prepares tetrabutyl titanate columnizer with tetrabutyl titanate, glacial acetic acid, dehydrated ethanol, nitric acid, sodium hydroxide and water; Disodium ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid columning agent; prepare montmorillonite-chitosan aqueous suspension with montmorillonite, chitosan and water, and add the above two columnizing agents to montmorillonite-chitosan water suspension The composite modified montmorillonite-chitosan cross-linked adsorbent as mentioned above was prepared in the solution. The invention also provides a composite modified montmorillonite chitosan cross-linking adsorbent used for waste water treatment of waste water containing Cr(VI) and rhodamine B. The composite modified montmorillonite chitosan cross-linked adsorbent of the present invention can effectively remove Cr(Ⅵ) and rhodamine B in the waste water during the application process, so that the remaining amount is less, the adsorption capacity is higher, and the removal effect is better. Obvious and good removal efficiency.
Owner:陕西聚泰新材料科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com