Patents
Literature
1901results about How to "Excellent mechanical properties" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
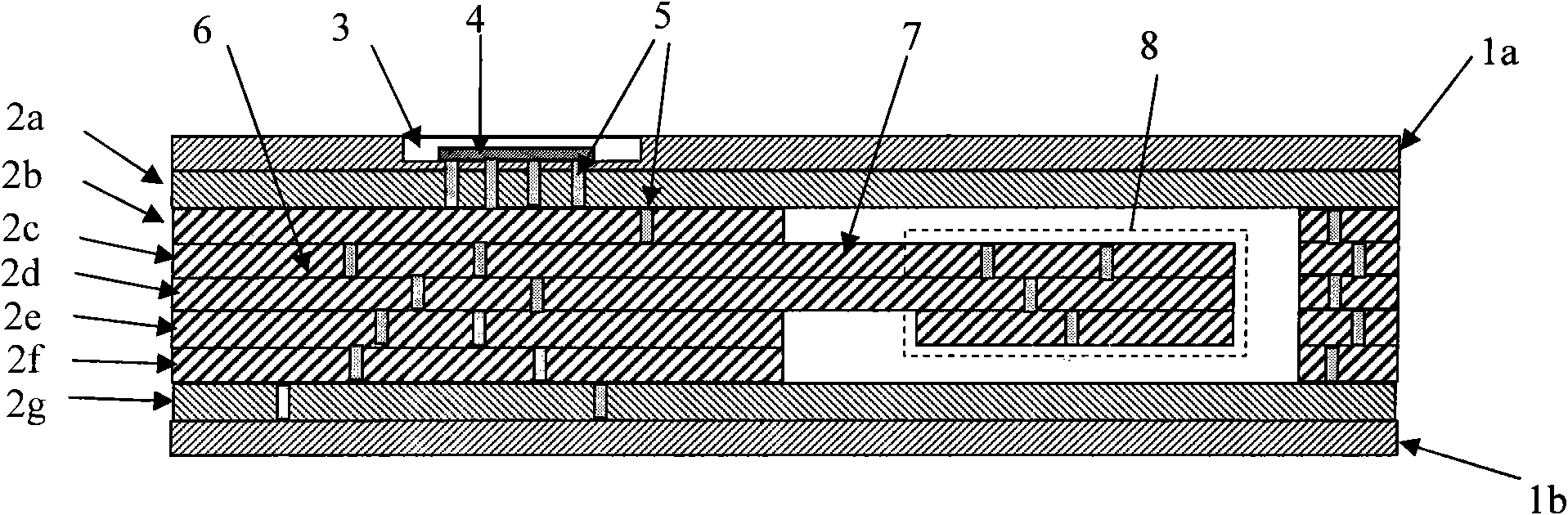
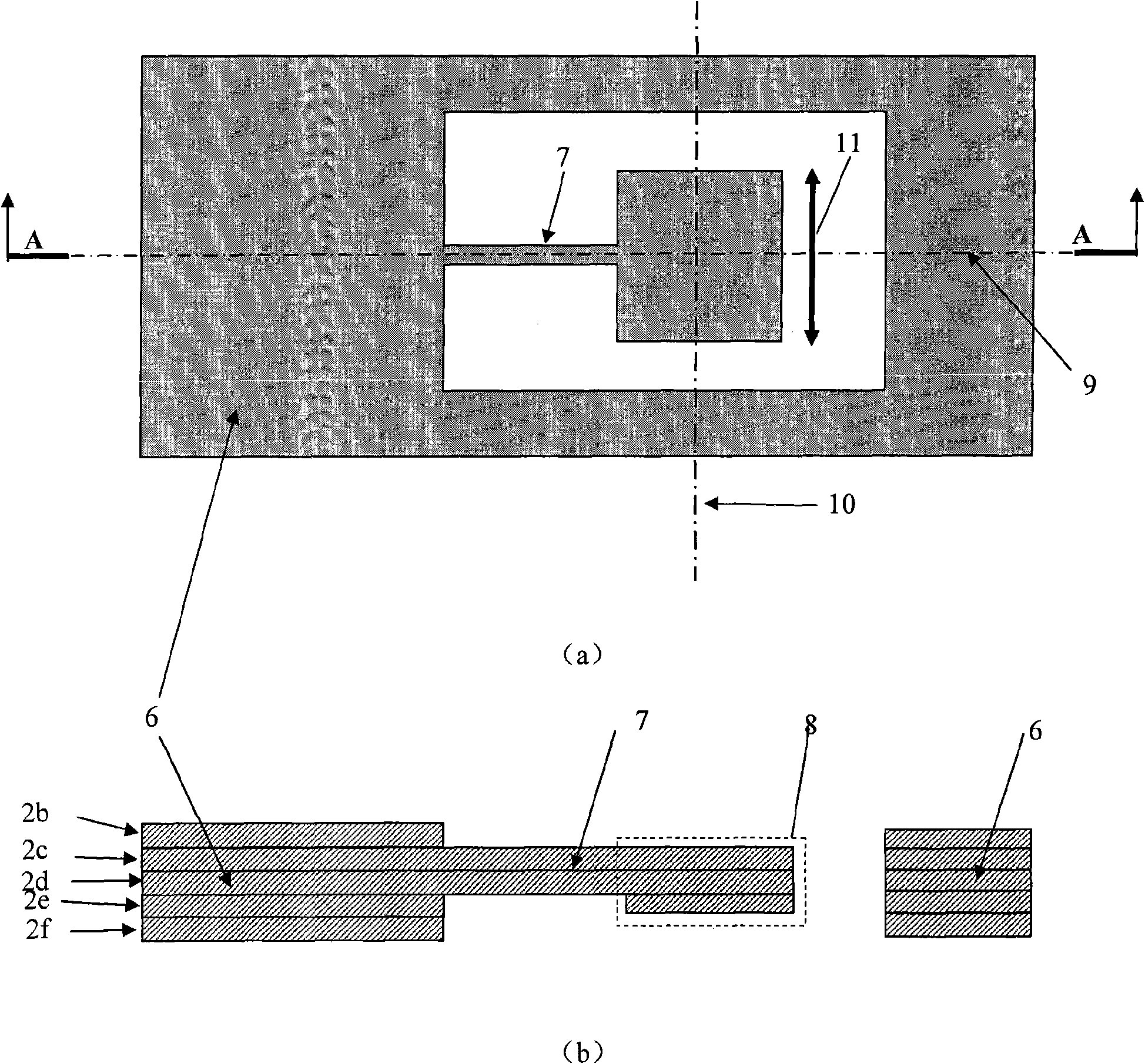
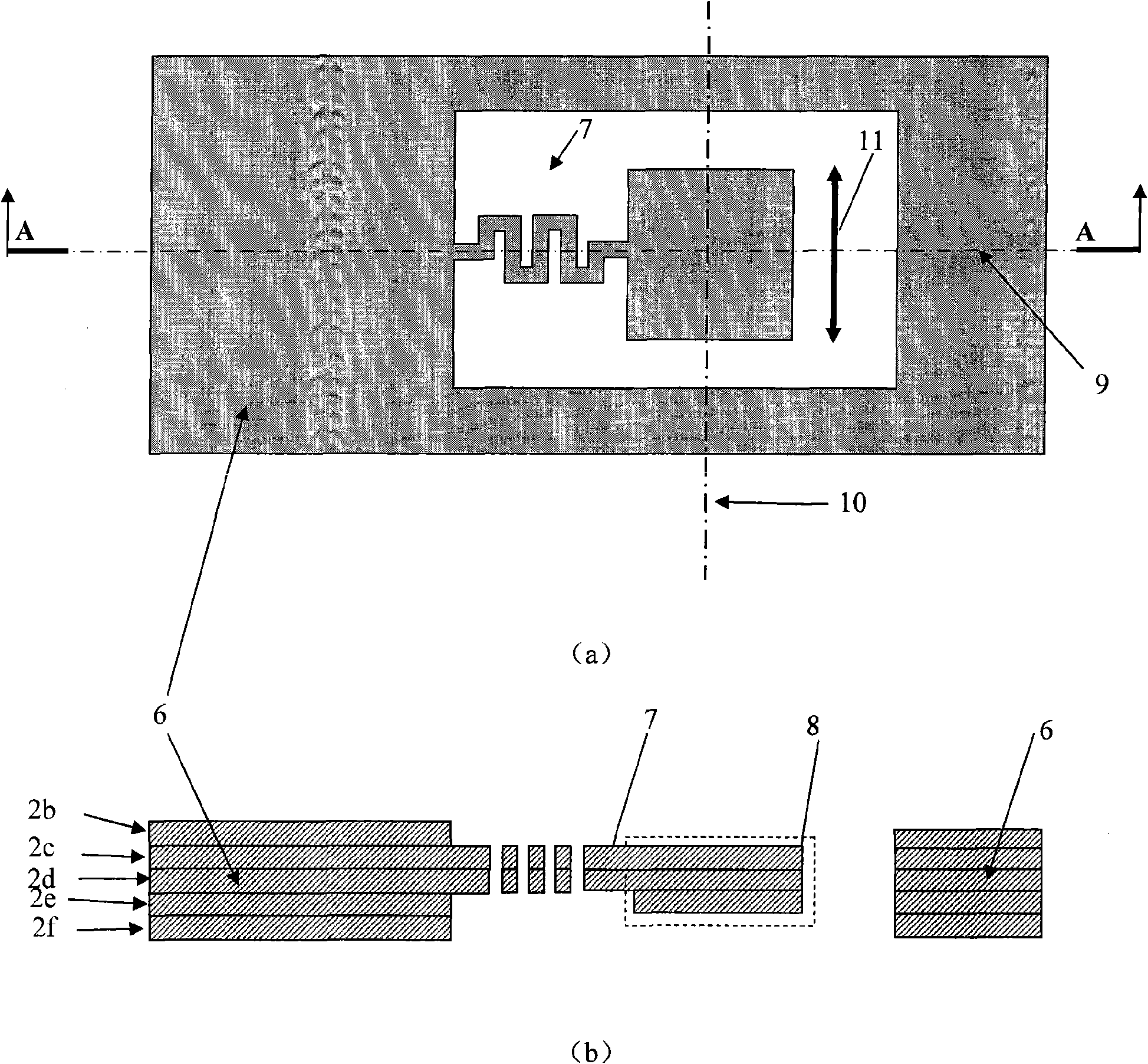
Fiber-reinforced thermoplastic vehicle cell
InactiveUS6854791B1Good long-term stabilityExcellent mechanical propertiesVehicle seatsUnderstructuresEngineeringThermoplastic matrix
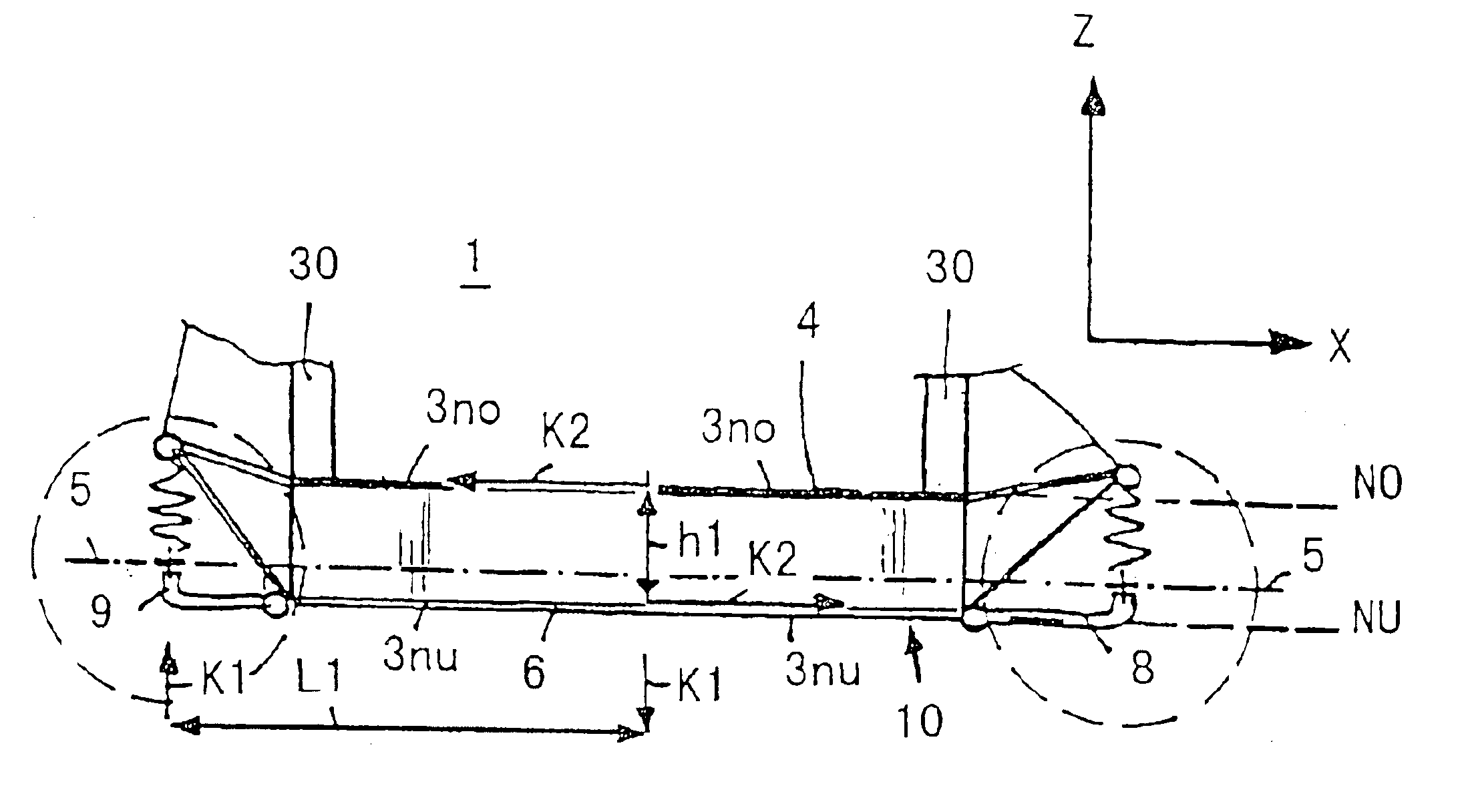
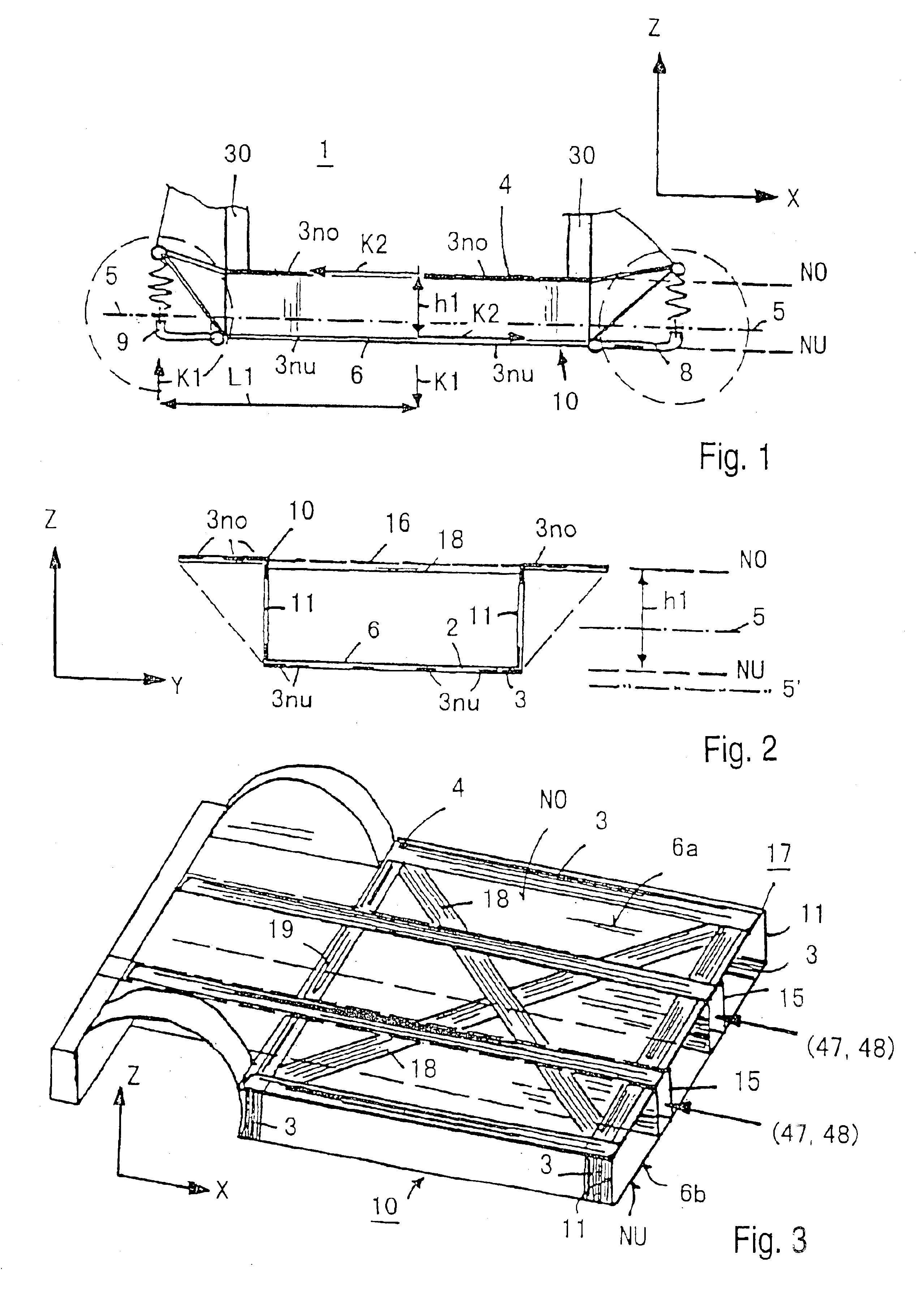
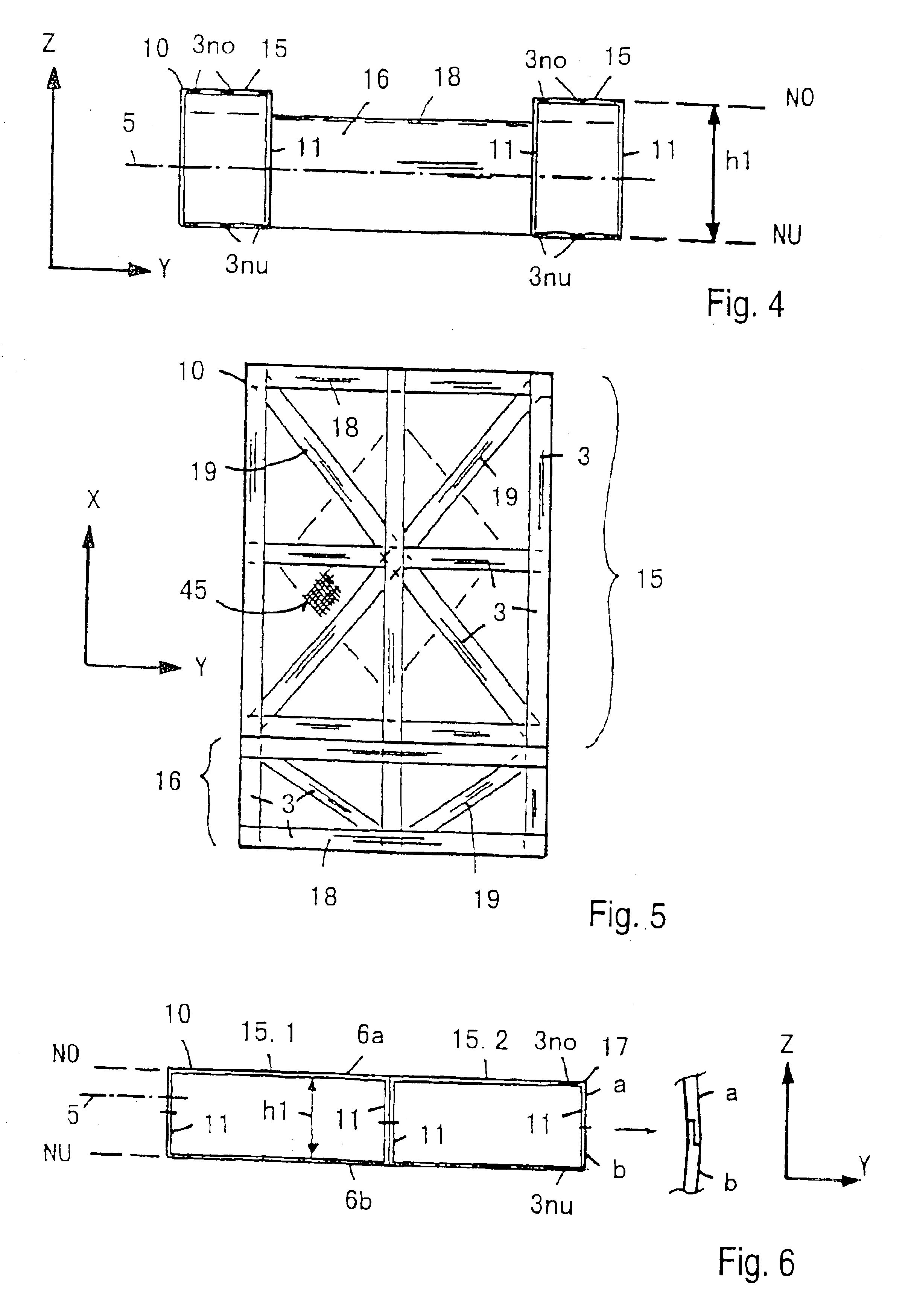
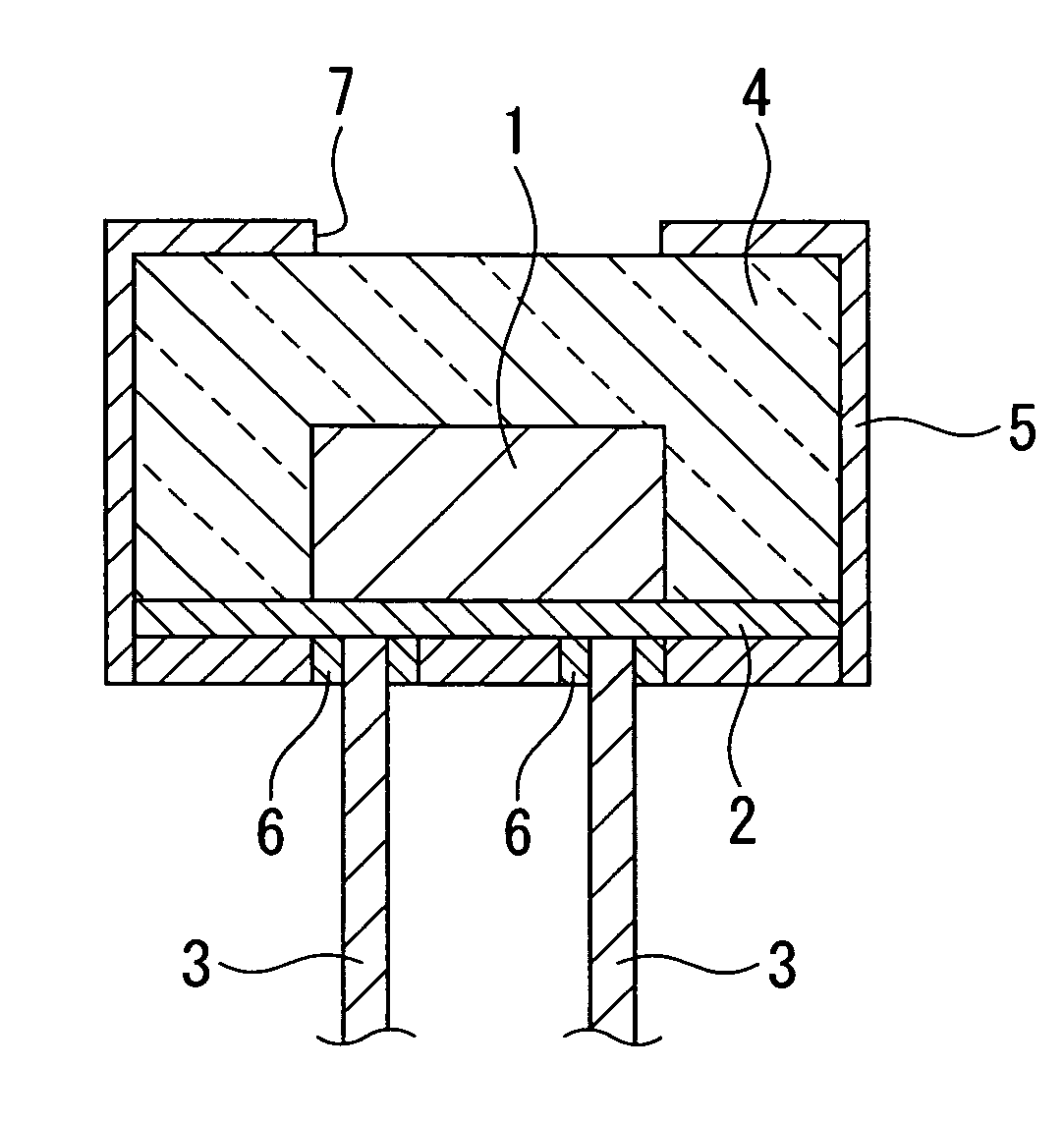
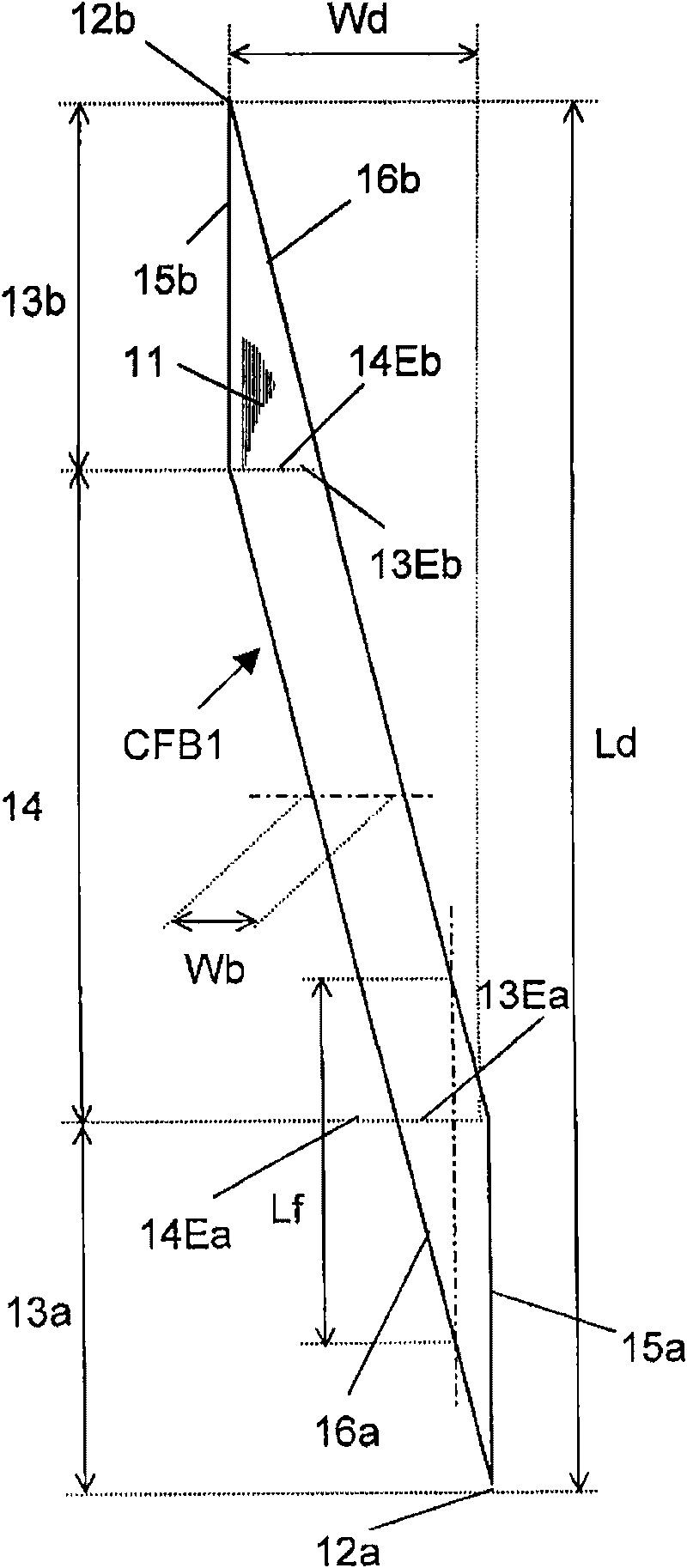
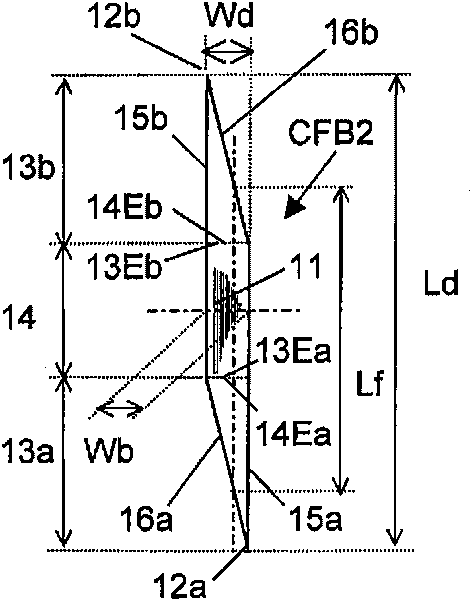
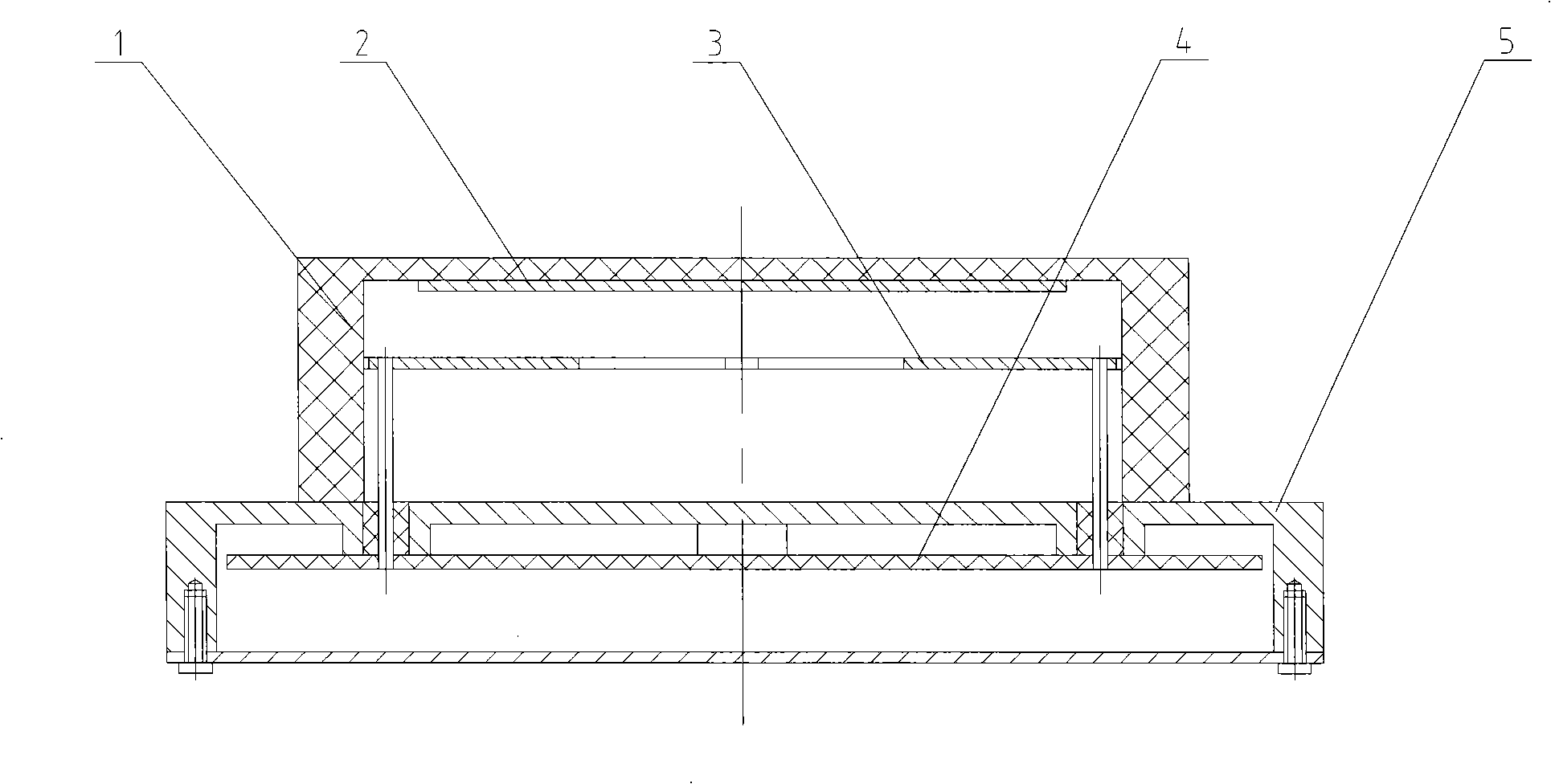
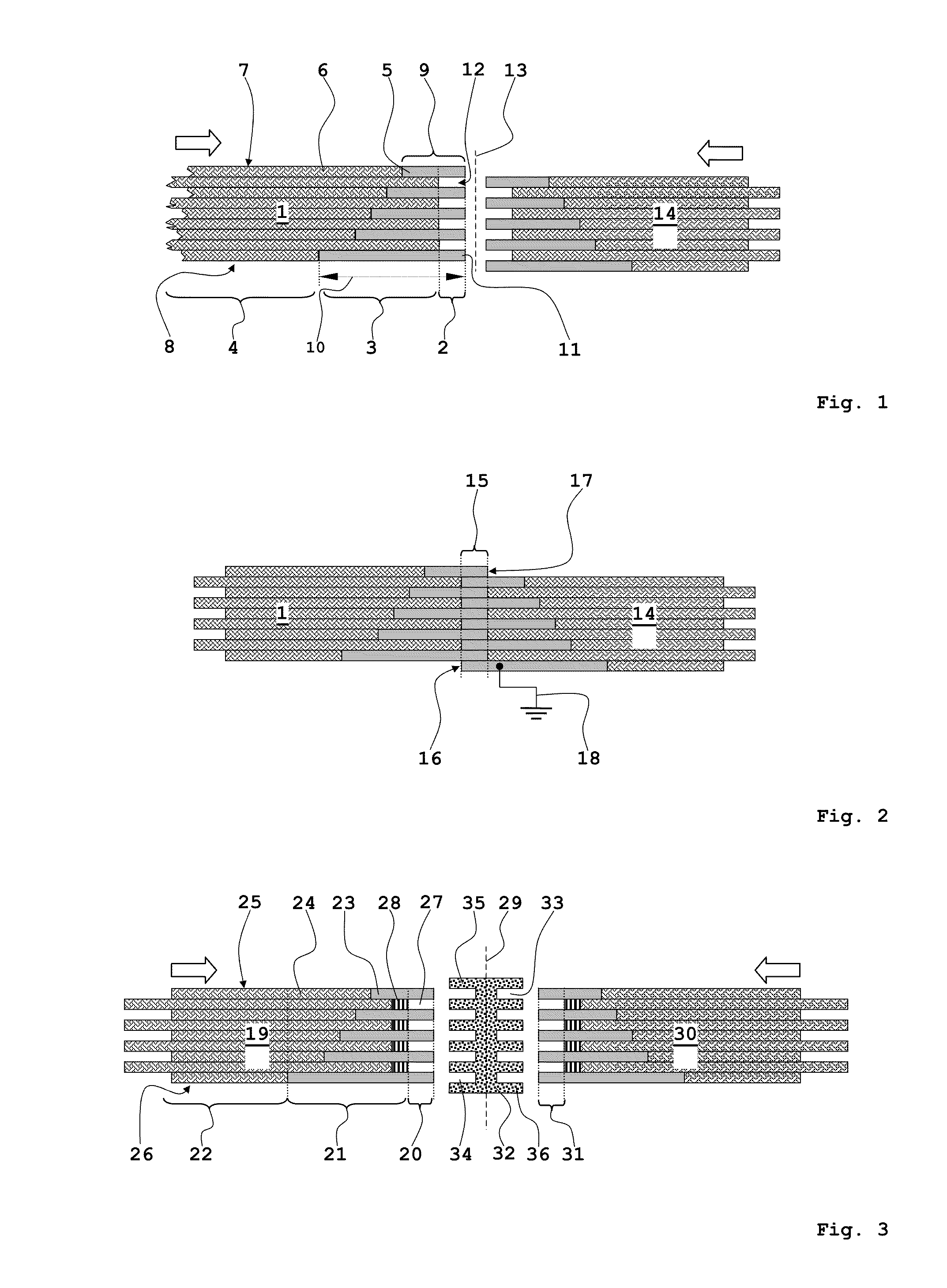
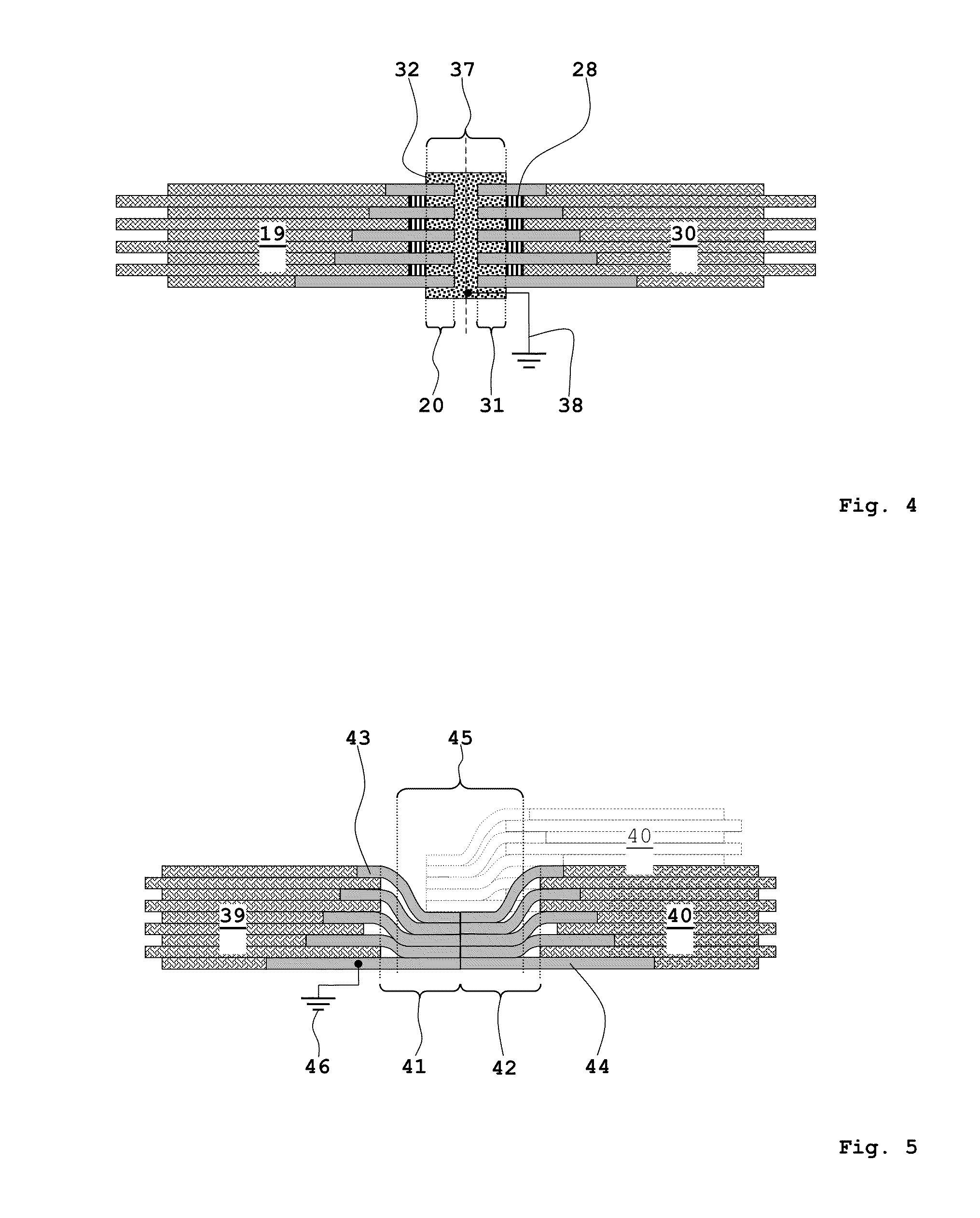
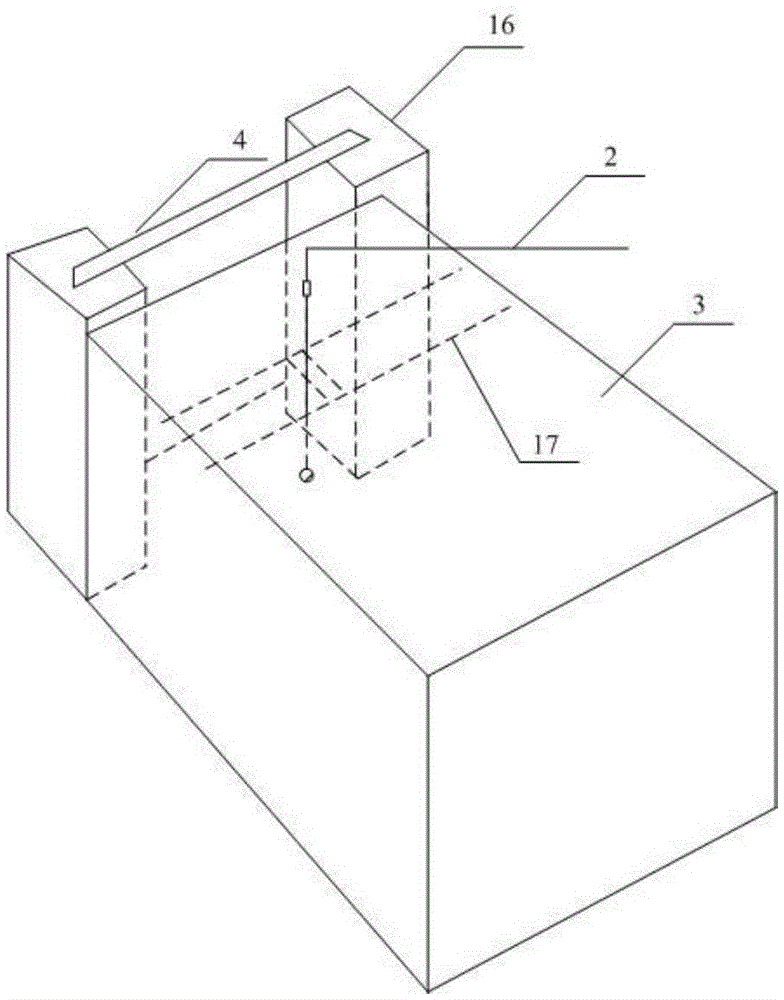
A vehicle cell made of reinforced—reinforced thermoplastic material includes a shape-defining, long-reinforced-reinforced thermoplastic matrix (2) with integrated continuos fiber strands or strips (3). In a base structure (10), which includes a base plate (6), uninterrupted continuous fiber strands running longitudinally (3no) in an upper base area (NO) and continuous fiber strands running longitudinally (3nu) in a lower base area (NU). The upper and the lower base areas are connected with vertical walls (11). This results in an economically manufacturable, light-weight, rigid and safe vehicle cell.
Owner:RCC REGIONAL COMPACT CAR
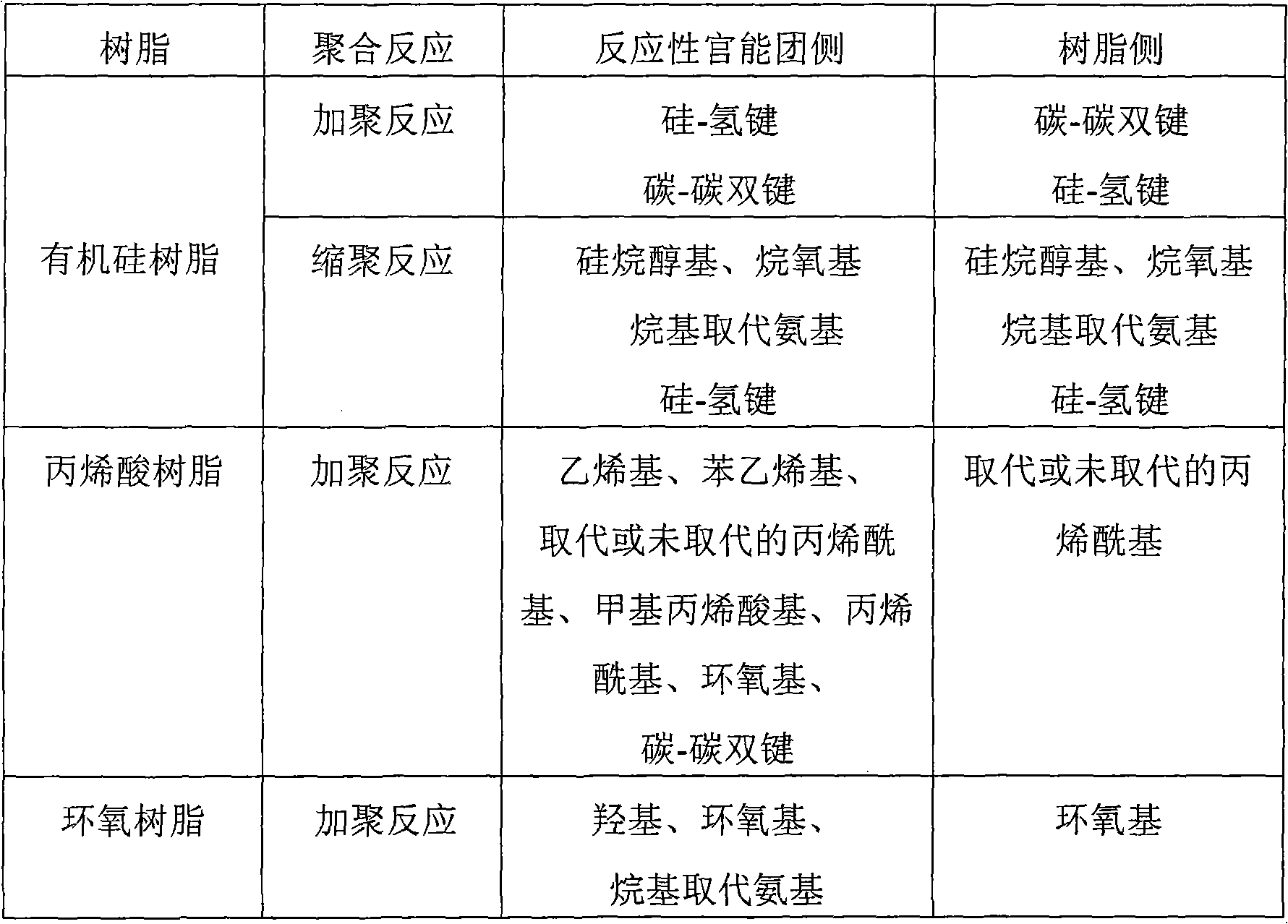
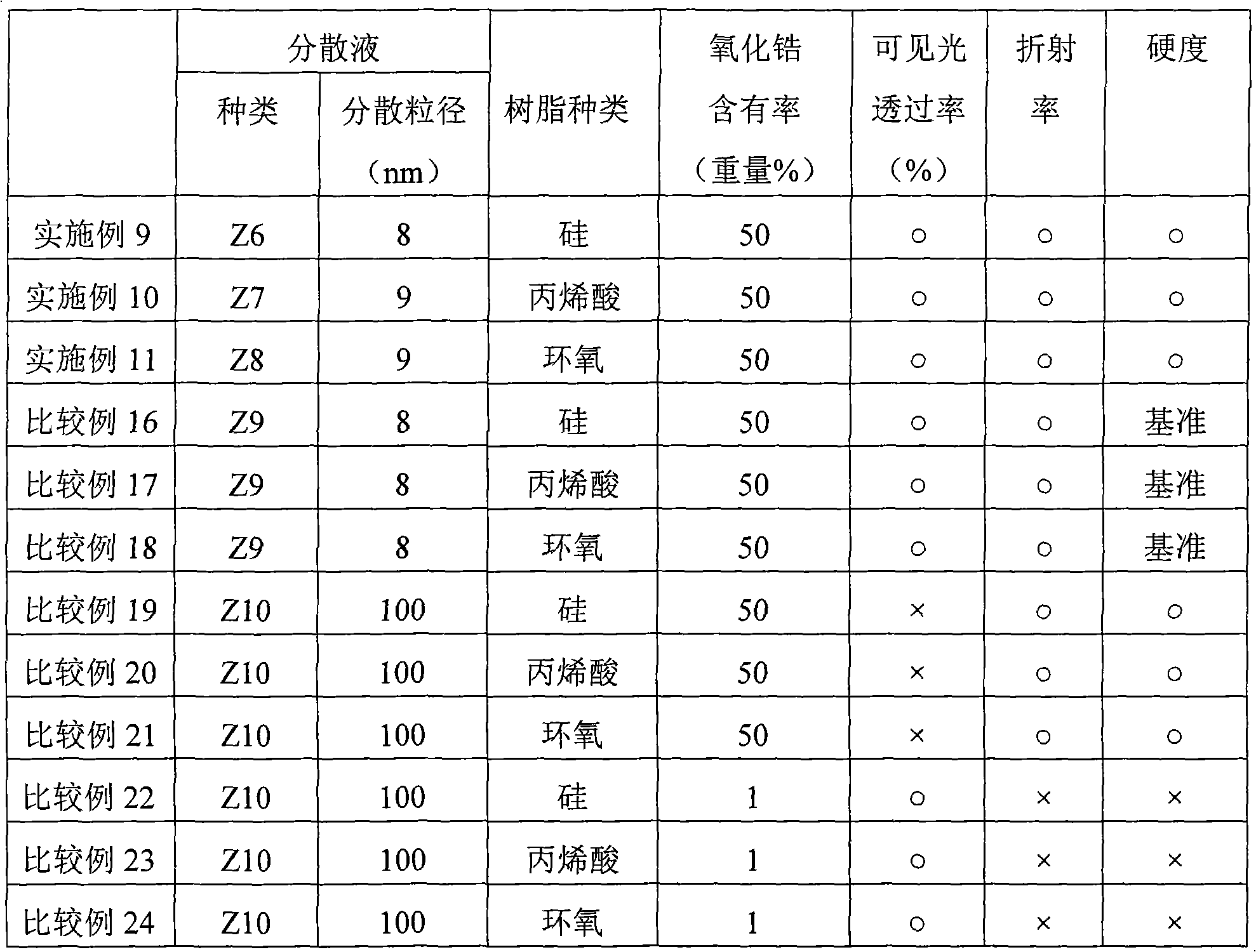
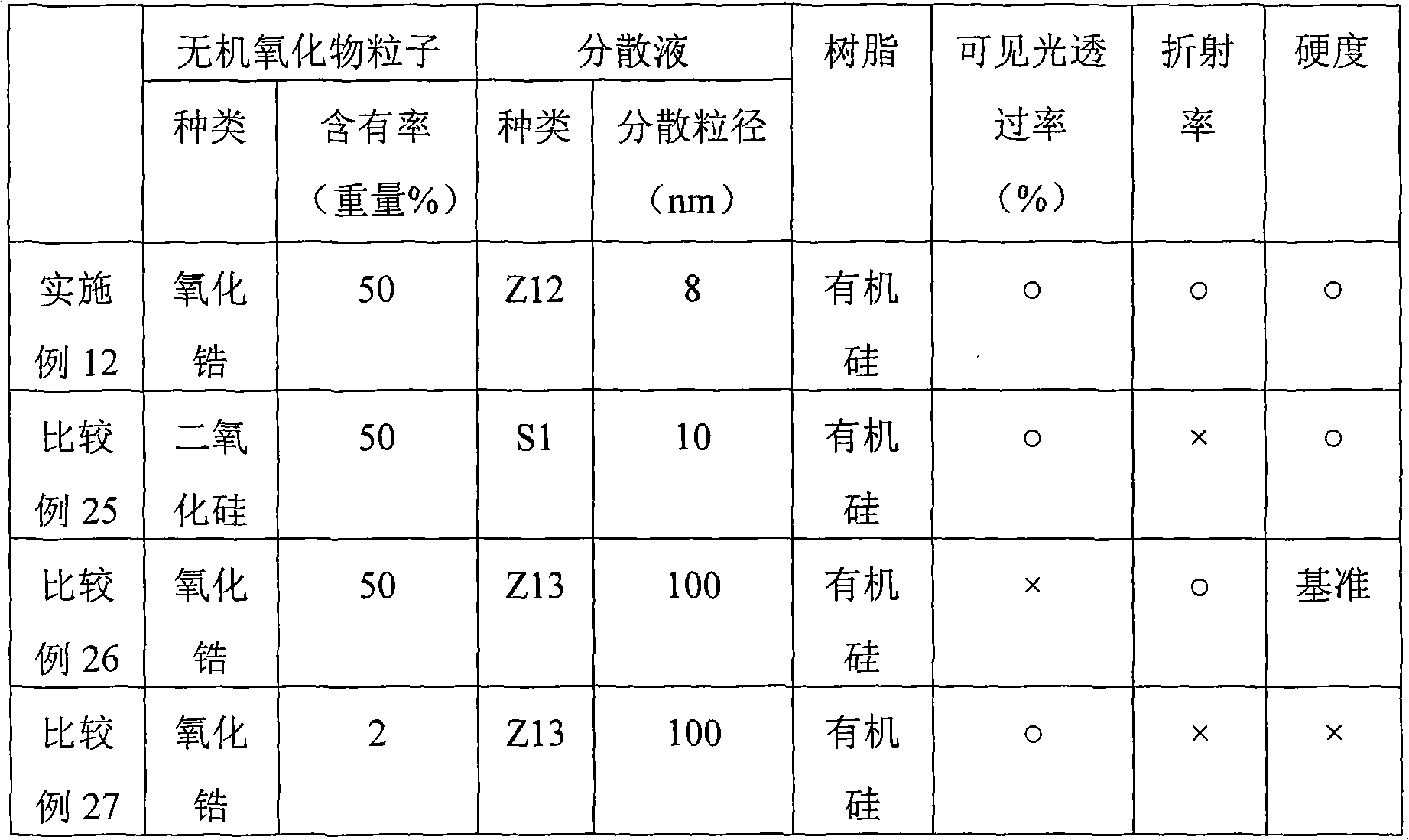
Transparent Inorganic Oxide Dispersion and Iorganic Oxide Particle-Containing Resin Composition, Composition for Sealing Light Emitting Element and Light Emitting element, Hard Coat Film and Optical Functional Film and Optical Component, and Method for Producing Inorganic Oxide Pariticle-Containing Resin
InactiveUS20090140284A1High refractive indexExcellent mechanical propertiesMixing methodsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsDispersed mediaOrganic Oxide
The present invention provides a transparent inorganic oxide dispersion which makes it possible to improve the refractive index and mechanical characteristics and to maintain transparency by modifying the surface of inorganic oxide particles with a surface modifier having one or more reactive functional groups; and an inorganic oxide particle-containing resin composition in which the transparent inorganic oxide dispersion and a resin are compositely integrated by the polymerization reaction, a composition for sealing a light emitting element, a light emitting element, and a method for producing an inorganic oxide particle-containing resin composition; and a hard coat film which has high transparency and makes it possible to improve a refractive index and tenacity, an optical functional film, an optical lens and an optical component. The transparent inorganic oxide dispersion of the present invention comprises inorganic oxide particles which have a surface modified with a surface modifier having one or more reactive functional groups and have a disperse particle diameter of 1 nm or more and 20 nm or less, and a disperse medium, wherein the surface modifier is one or more kinds selected from the group consisting of a silane coupling agent, a modified silicone, and a surfactant.
Owner:SUMITOMO OSAKA CEMENT CO LTD
Method and apparatus for granulating by mixing powder and liquid continuously
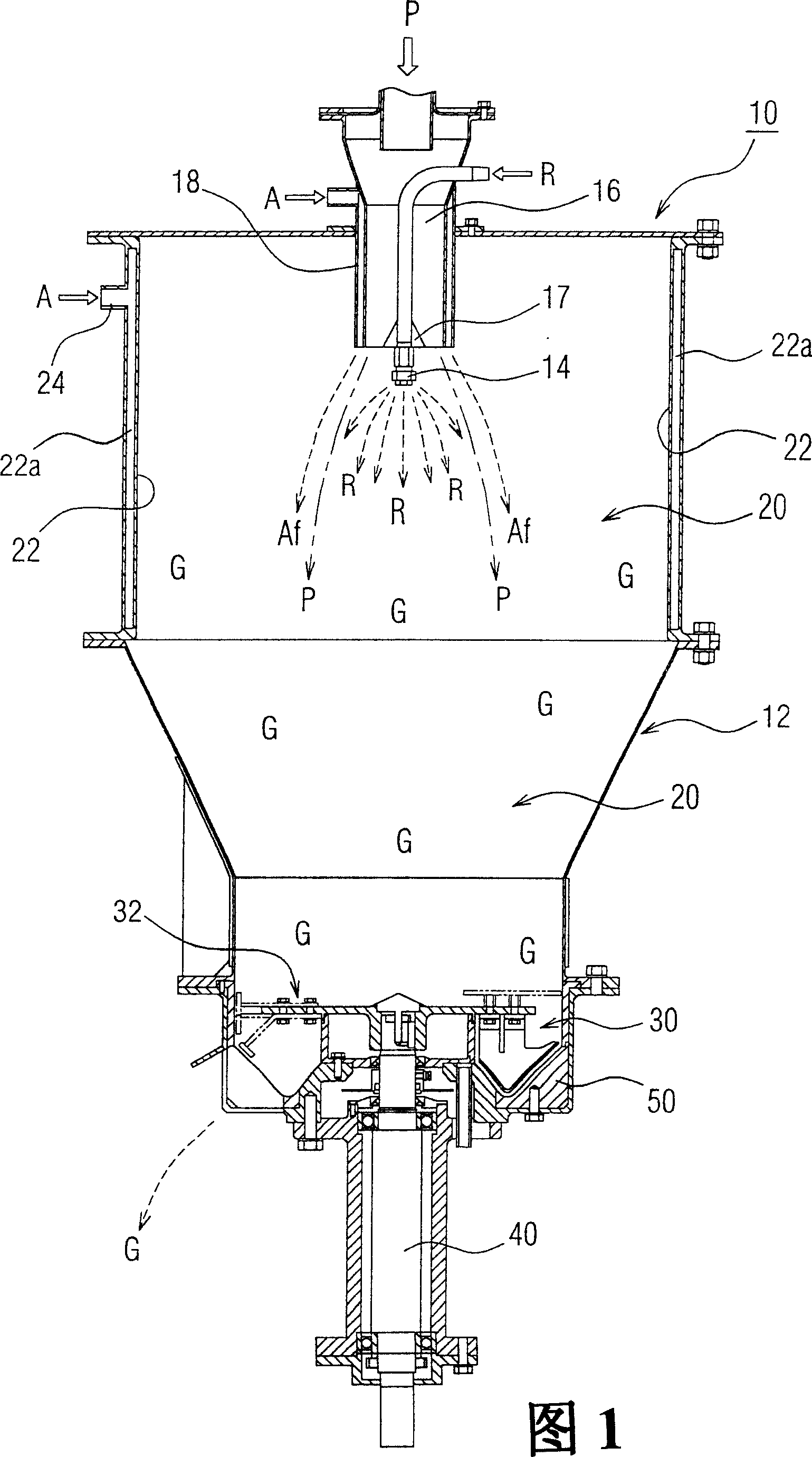
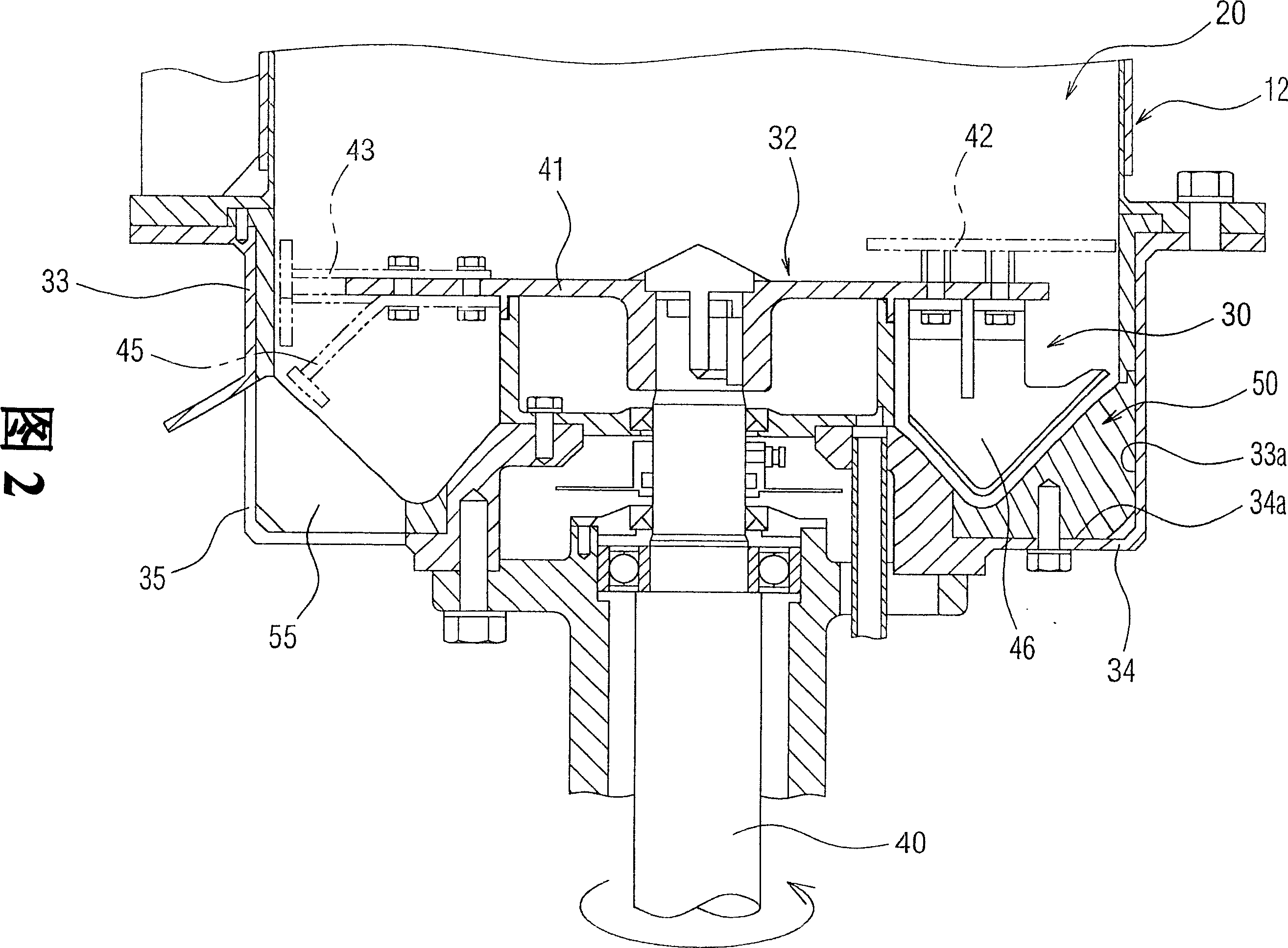
ActiveCN1927437AImprove yieldWide applicabilityFlow mixersGranulation in rotating dishes/pansManufacturing cost reductionEngineering
The invention relates to a method of powder / liquid continuous mixing particle production. Wherein, said method comprises that sealing the top of hopper mixed particle producing room (12); the center at the top uses ejector (14) to continuously eject liquid downwards; the powder outlet (16) at the circumference of ejector disperses the atomized liquid to the powder; and the gas ejector (18) at the circumference of powder outlet feeds gas as the protective air film (Af) that avoiding dispersing the fed powder; therefore, the powder and liquid can continuously contact to form mixed particle (G); and the bottom of room (12) via the rotation of mixing disc (32) can make the air passive pressure, to generate eddy flow, to accelerate the particle (G) generation, and shear or mix the particle (G), to form and discharge uniform particles (G).
Owner:FUNKEN POWTECHS
Preparation method of high-performance carbon nanotube fiber
ActiveCN101967699AExcellent mechanical propertiesReduce dosageYarnArtificial filament chemical after-treatmentYarnMechanical properties of carbon nanotubes
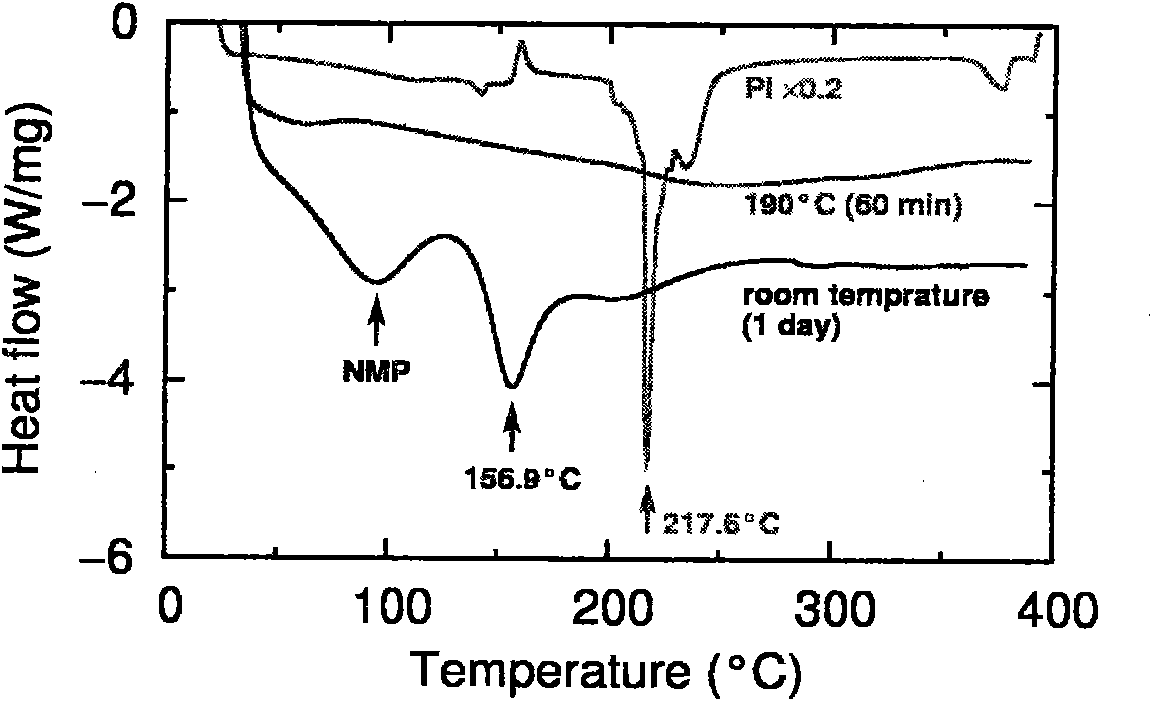
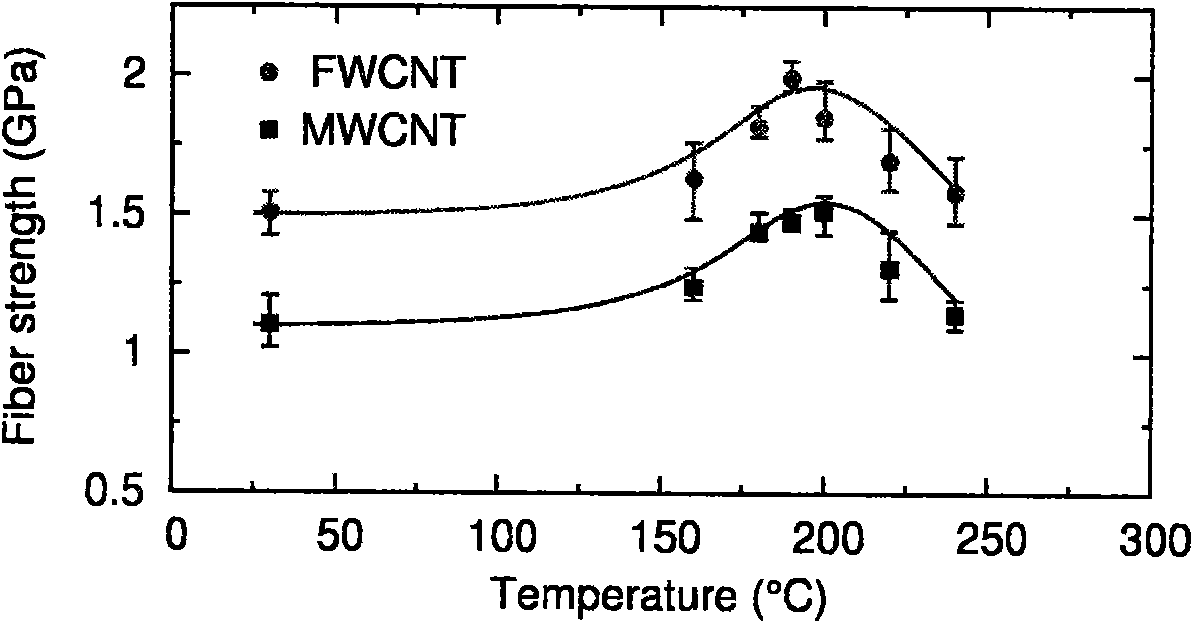
The invention relates to a preparation method of a high-performance carbon nanotube fiber, which comprises the following specific steps of: drawing a carbon nanotube film from a spinning carbon nanotube array; then, immersing the carbon nanotube film in a thermosetting polyamic acid / N-methyl pyrrolidone solution, and twisting to form a carbon nanotube / polyamic acid composite fiber; subsequently, curing the carbon nanotube / polyamic acid composite fiber so that polyamic acid in the composite fiber forms polyimide with a net type crosslinking structure; and finally preparing the carbon nanotube / polyimide composite fiber. The invention has the advantages of simple and easy process, low cost and easy realization of large-scale production; moreover, the prepared carbon nanotube composite fiber has excellent mechanical performance, the strength can reach 2.06 GPa, the tenacity is superior to that of carbon fiber, and the conducting property is maintained unchanged as compared with that of pure carbon nanotube fiber; meanwhile, the carbon nanotube composite fiber also has the operability of common yarn, so that the requirements on subsequent treatment processes of stretching, stranding, weaving and the like can be satisfied.
Owner:SUZHOU CREATIVE CARBON NANOTECH
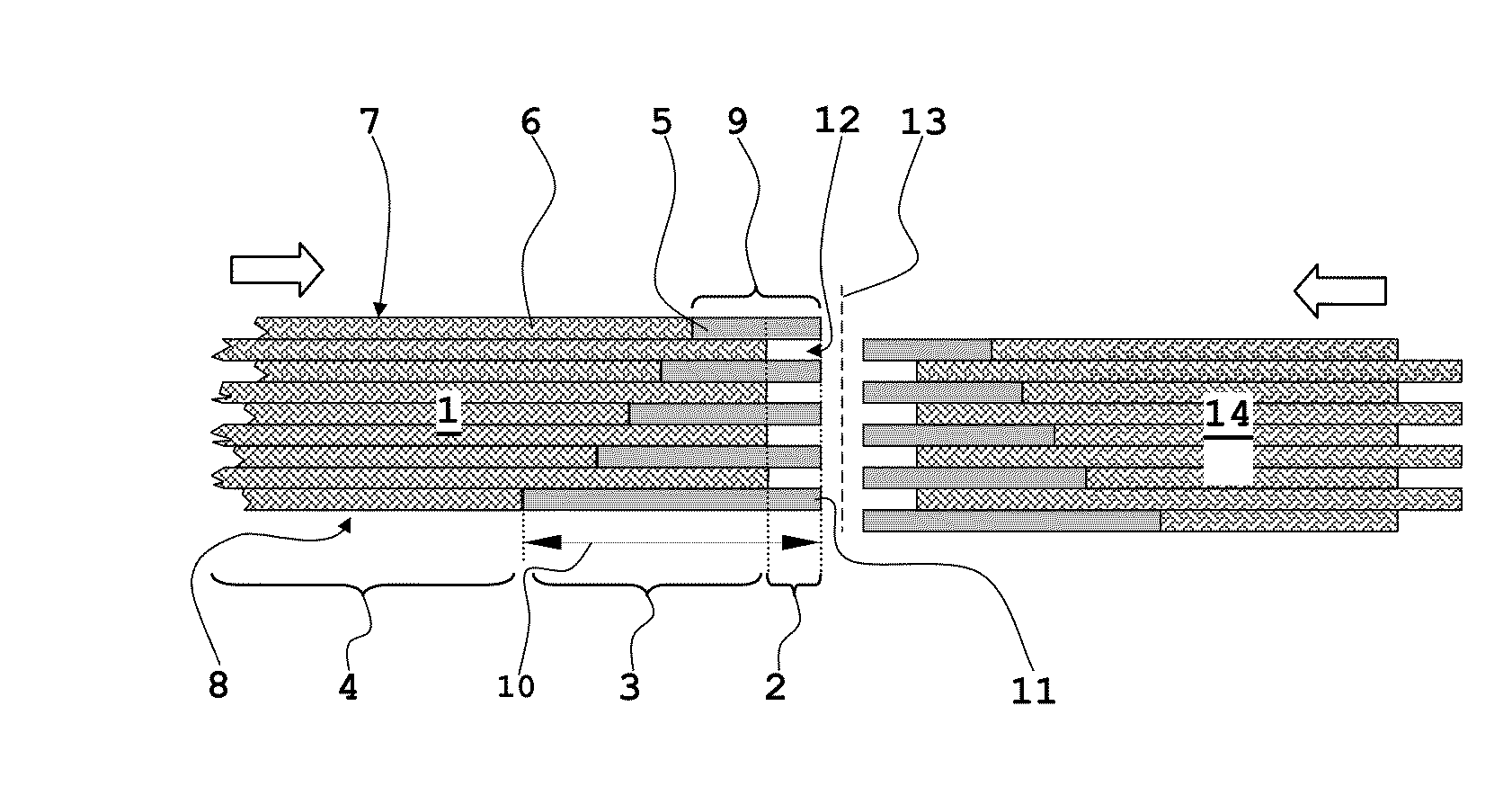
Chopped fiber bundle, molding material, and fiber reinforced plastic, and process for producing them
ActiveCN101711230AImprove liquidityGood molding followabilityGlass making apparatusFibre treatmentFiber bundleFiber reinforcement
This invention provides a chopped fiber bundle comprising a large number of unidirectionally arranged reinforced fibers. The length of each of the reinforced fibers is in the range of 5 to 100 mm. The chopped fiber bundle has a transition segment in which the number of the reinforced fibers increases toward the central part of the chopped fiber bundle in the aligned direction of the reinforced fibers with both ends in the aligned direction of the reinforced fibers in the chopped fiber bundle being a starting point. The level of a change in total sectional area of the large number of reinforced fibers is not more than 0.05 mm2 per mm in the aligned direction of the reinforced fibers over the whole area in the longitudinal direction of the chopped fiber bundle.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
Low-roughness and low-square-resistance flexible transparent conductive composite thin film and preparation method therefor
ActiveCN106782769AReduce roughnessImprove conductivityConductive layers on insulating-supportsApparatus for manufacturing conducting/semi-conducting layersPolymer thin filmsSolar battery
The invention belongs to the technical field of photo-electronics, and more specifically relates to a low-roughness and low-square-resistance flexible transparent conductive composite thin film, wherein the thin film adopts a three-layer composite structure; the lowest bottom layer is provided with a transparent polymer thin film; the middle layer is provided with a conductive network formed by metal nanowires; the topmost layer is a provided with a transparent conductive layer which uniformly covers the transparent polymer thin film and the conductive network; the flexible transparent conductive composite thin film is less than 20-nanometer in average roughness, less than 30-ohm / square meter in square resistance, and greater than 80% of light transmittance within a visible light range; and the transparent conductive thin film can bear bending with radius of curvature of 2mm. The invention also discloses a preparation method for the flexible transparent conductive composite thin film. The flexible transparent conductive composite thin film provided by the invention has low roughness, high conductivity, high light transmittance, simple preparation method and low cost, and is particularly suitable for flexible display and illumination, a flexible solar battery and flexible touch equipment.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Transparent inorganic-oxide dispersion, resin composition containing inorganic oxide particles, composition for encapsulating luminescent element, luminescent element, hard coat, optical functional fi
ActiveCN101296982AHigh refractive indexExcellent mechanical propertiesInorganic pigment treatmentZirconium oxidesSilane couplingChemistry
A transparent inorganic-oxide dispersion which contains inorganic oxide particles whose surface has been modified with a surface modifier having one or more reactive functional groups and, due to this, enables improvements in refractive index and mechanical properties and retention of transparency; and an inorganic-oxide-particle-containing resin composition obtained by combining and uniting this transparent inorganic-oxide dispersion with a resin through a polymerization reaction. Also provided are: a composition for encapsulating luminescent elements; a luminescent element; a process for producing the resin composition containing inorganic oxide particles; a hard coat and an optical functional film which have high transparency and can attain improvements in refractive index and toughness; an optical lens; and an optical part. The transparent inorganic-oxide dispersion is characterized by comprising a dispersion medium and inorganic oxide particles the surface of which has been modified with a surface modifier having one or more reactive functional groups and which have a dispersed-particle diameter of 1 to 20 nm. It is further characterized in that the surface modifier is one or more members selected from the group consisting of silane coupling agents, modified silicones, and surfactants.
Owner:SUMITOMO OSAKA CEMENT CO LTD
Epoxy resin composition for carbon-fiber-reinforced composite material, prepreg, integrated molding, sheet of fiber-reinforced composite material and cabinet for electrical/electronic equipment
ActiveCN1946780AIncrease flame retardancyExcellent mechanical propertiesPigmenting treatmentLayered productsCombustionHalogen
A lightweight fiber-reinforced composite material that exhibits excellent flame resistance and mechanical properties and does not emit any halogen gas at combustion; an epoxy resin composition and prepreg suitable for obtaining the above fiber-reinforced composite material; and an integrated molding suitable to electrical / electronic equipment cabinet, in which use is made of the above fiber-reinforced composite material. There is provided an epoxy resin composition for carbon-fiber-reinforced composite material, comprising: [A] epoxy resin, [B] amine curing agent, and [C] phosphorus compound, the component [C] contained in an amount, in terms of concentration of phosphorus atoms, of 0.2 to 15 wt.%.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
Polyethylene multilayer microporous membrane, battery separator using same, and battery
InactiveCN101208198AImprove permeabilityExcellent mechanical propertiesSynthetic resin layered productsSecondary cellsVitrificationSurface layer
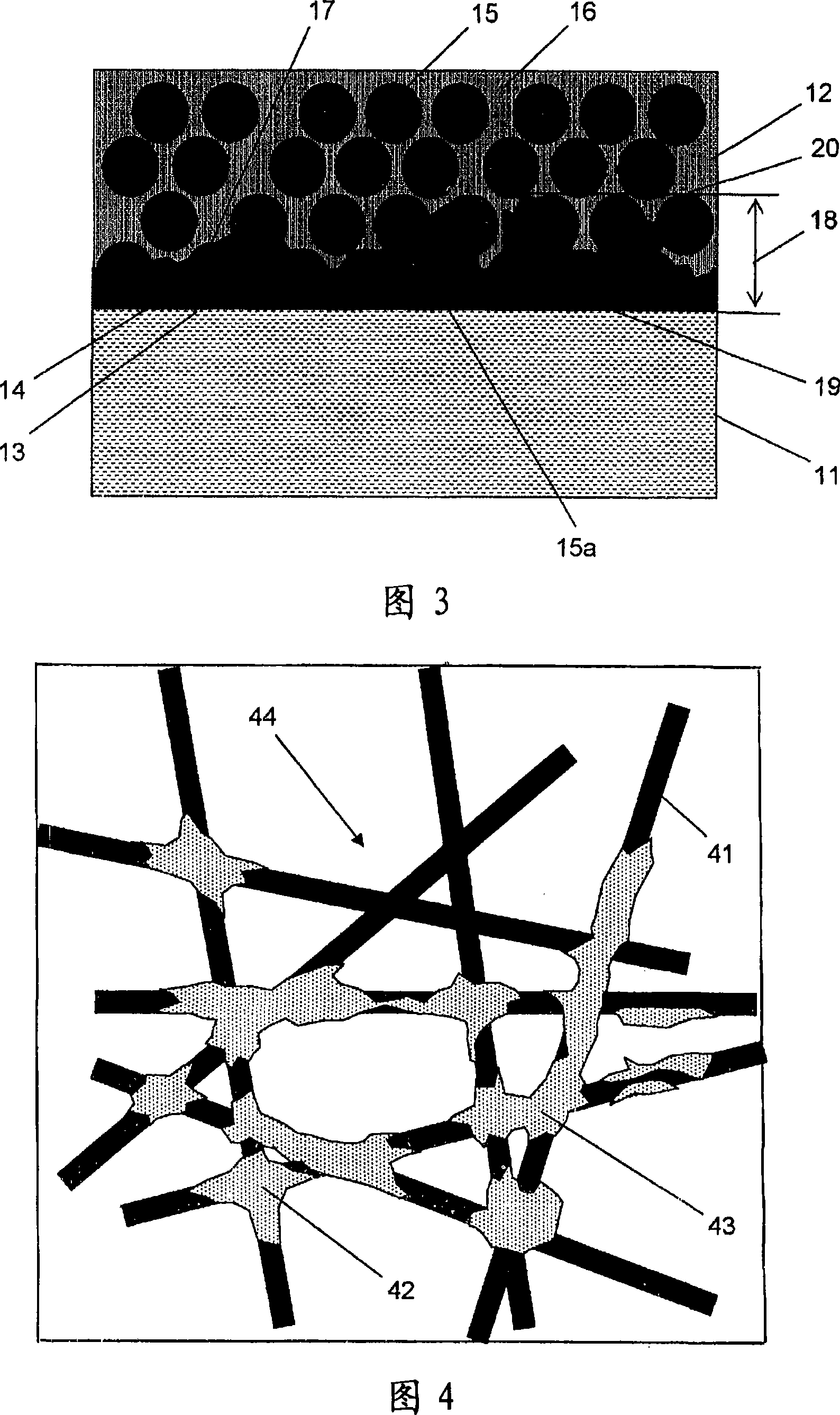
A multi-layer, microporous polyethylene membrane having at least three layers comprising (a) a first microporous layer amount of a polyethylene resin and constituting at least both surface layers, and (b) at least one second microporous layer made of a polyethylene resin, a heat-resistant resin having a melting point or glass transition temperature of 150°C or higher and a filler, and sandwiched by both surface layers.
Owner:东丽东燃机能膜合同会社
Method for preparing epoxy sheet mould plastic
The invention provides a method for preparing an epoxy sheet-like mold plastic, which comprises the following steps: thickening the mixed epoxide resin system with diisocyanate compound; strengthening the chopped strand; making the tectorial into non-stick hand and shear epoxy sheet-like mold plastic, that is, preparing the epoxide resin paste and the epoxy sheet-like mold plastic; ripening. The epoxy sheet-like mold plastic comprises the following parts: 100 quetient mixed epoxide resin, 4-10 quetient deflocculating agent, 15-80 quetient curing agent, 5-20 quetient thickener, 1-4 quetient internal releasing agent, 80-180 filler and 50-150 fiber, wherein the intermediate core material of the epoxy sheet-like mold plastic comprises fiber which is dipped epoxide resin paste, and the up-down surface is covered by PE thin film. The epoxy sheet-like mold plastic is provided with the good heat flow property, the short curing time, the long saving time and the corrosion resistant, which can be made high strength epoxide composite material part.
Owner:SHANGHAI MANSDA INDAL
Wood-plastic formwork for construction engineering
InactiveCN1987018AExcellent mechanical propertiesFlat and smooth appearanceSolid waste managementLaminationFiberGlass fiber
A wood-plastics shuttering board for building engineering is composed of at least two basic wood-plastic ply layers made of the filler (vegetative fibers, glass fibers and plastics) and assistant (calcium carbonate, modifier, coupling agent and lubricant), and at least one lattice material layer between two basic wood-plastic ply layers and with two adhesive layers coated on its both surfaces. Its manufacture technology is also disclosed.
Owner:徐肖虎
Negative electrode material used for lithium battery and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN103474632AStable structureImprove performanceMaterial nanotechnologyCell electrodesPorosityMicro nano
The invention relates to a negative electrode material used for a lithium battery and a preparation method and application thereof, the negative electrode material includes a conductive substrate material layer and a silicon based thin film material layer, the silicon based thin film material layer contains one or more components selected from the group consisting of silicon element, SiOX and silicon alloy, wherein, 0 < X =< 2; in the silicon based thin film material layer, silicon accounts for 10-100% of the weight of the silicon based thin film material layer; the silicon based thin film material layer is a thin film formed by regular and / or irregular columnar and / or fibrous micro nano naps, wherein the micro nano naps are connected with each other by root parts, and the root parts of the micro nano naps are connected with the conductive substrate material layer; gaps are existed among the micro nano naps, and the porosity among the micro nano naps is 2%-98%; the diameter size of the micro nano naps is 1 nm to 10 mum, and the thickness of the silicon based thin film material layer is 50 nm-10 mum.
Owner:LIYANG TIANMU PILOT BATTERY MATERIAL TECH CO LTD
Molding material, prepreg, fiber-reinforced composite material, fiber-reinforced composite material laminate, and process for production of fiber-reinforced molding base material
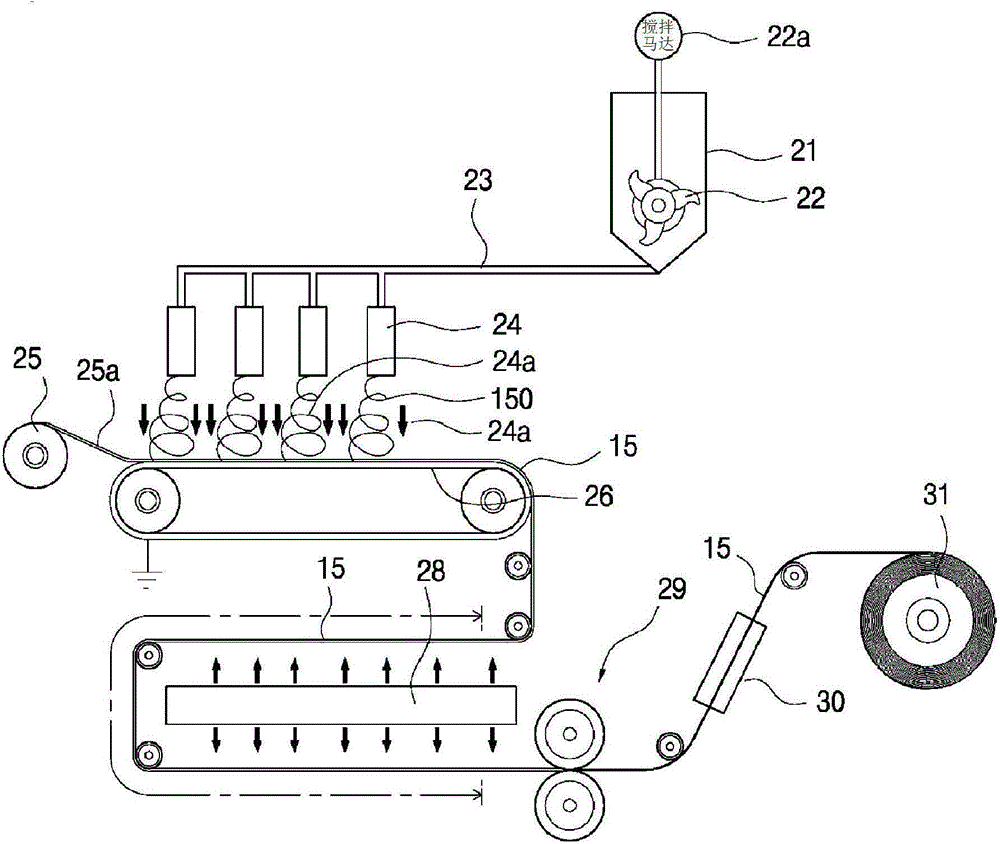
InactiveUS20130295806A1Economical efficiencyEconomical productivityPretreated surfacesWoven fabricsProduction rateFiber-reinforced composite
A molding material is provided including a composite having 1 to 50 wt % of (A) a bundle of continuous reinforcing fibers and 0.1 to 40 wt % of (B) a polyarylene sulfide prepolymer or (B′) a polyarylene sulfide; and 10 to 98.9 wt % of (C) a thermoplastic resin adhered to the composite; wherein the composite further has (D) a zero-valent transition metal compound or (E) a low-valent iron compound in an amount of 0.001 to 20 mol % based on the amount of sulfur atoms contained in the component (B) or (B′). A prepreg and a method of producing a fiber-reinforced molding base material is also provided. By using the molding material according to the present invention which exhibits excellent economic efficiency and productivity, a molded article having excellent mechanical characteristics can be easily produced.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
Multimodal satellite navigation terminal antennae with wide-band circular polarized wide wave beam
ActiveCN101286592AIncrease inductanceSmall sizeElongated active element feedPolarised antenna unit combinationsWide beamAntenna feed
Owner:SPACE STAR TECH CO LTD
Sandwich structure and integrated formed article using the same
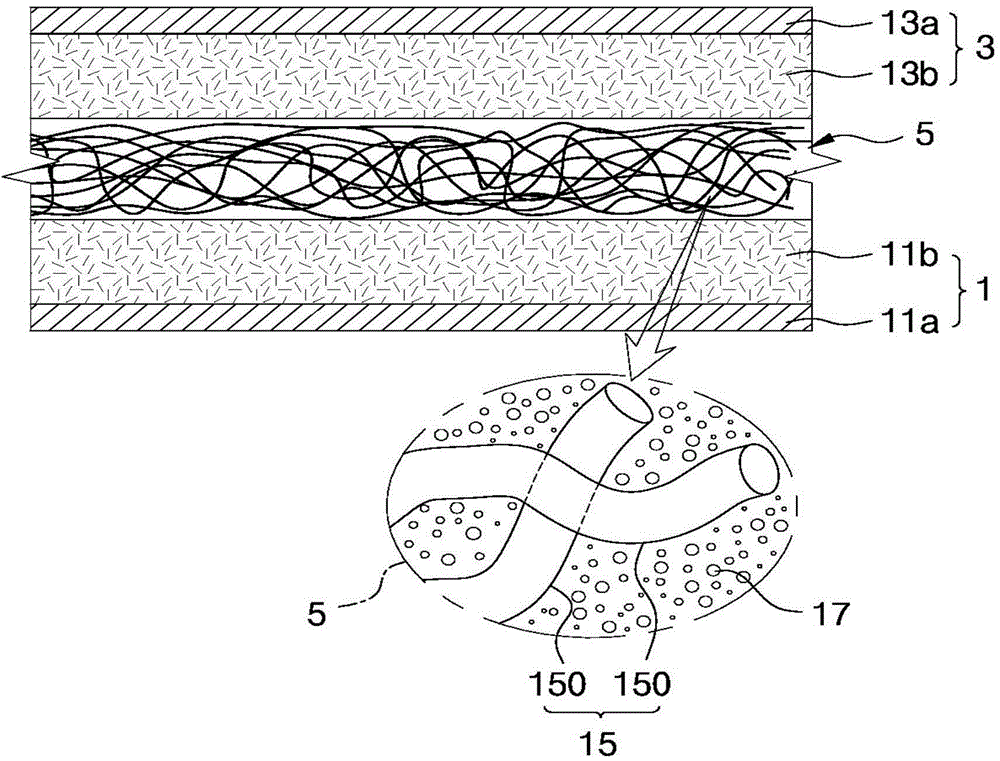
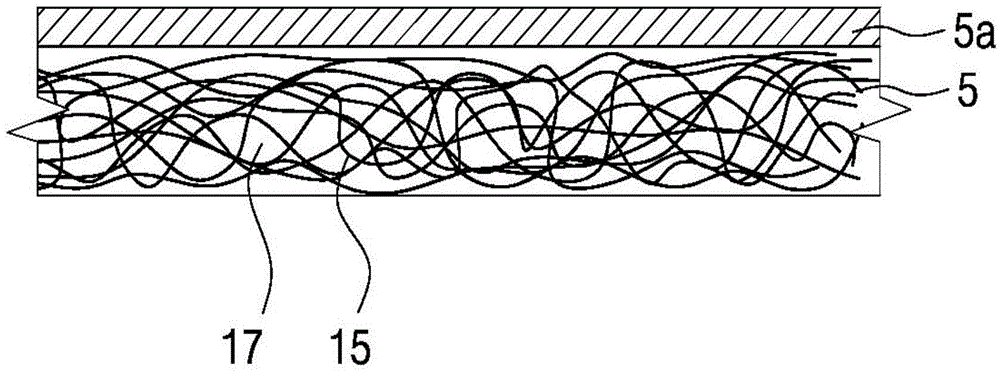
ActiveCN101010188AExcellent mechanical propertiesImprove lightnessSynthetic resin layered productsThin material handlingFiberPolymer science
A sandwich structure (III) which has a core material (I) and, arranged on the both surfaces of said core material (I), a fiber-reinforced material (II) composed of a continuous reinforcing fiber (A) and a matrix fiber (B), wherein the above core material (I) comprises a void. The void is formed by bubbles of a foamed material or, the core is composed of a discontinuous reinforcing fiber and a thermoplastic resin and the void is formed by interstices formed at crossings of filaments of said reinforcing fiber.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
Flame retardant polycarbonate resin composition and light reflection member
InactiveCN101585961AAchieve high concentration mixingGuaranteed flame retardant performanceMirrorsMass ratioPolycarbonate
Provided is a flame retardant polycarbonate resin composition, a light reflecting plate formed from the same and peripheral members thereof. The flame retardant polycarbonate resin composition is characterized by comprising (a) aromatic polycarbonate resin, (b) white pigment and (c) talcum treated by the alkali neutralizing treatment and the surface treating of a silane coupling agent, the sum of the (a), (b) and (c) is 100 mass parts, wherein the mass ratio of the (a) to (b) to (C) is (91 to 40) to (4 to 40) to (4 to 20). The formed product has no combustion inhibitor containing halogen or phosphor, with high light reflectivity and fire-retardancy, as well as favorable appearance and light index of reflection, shading performance, thermal conductivity (exothermicity ), mechanical characteristic(rigidity) and dimension stability.
Owner:IDEMITSU KOSAN CO LTD
Micro-accelerometer and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101634662ALow acceleration measurement sensitivity limitLarge measurement dynamic rangeTelevision system detailsAcceleration measurement using interia forcesAccelerometerEngineering
The invention discloses a micro-accelerometer and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the technical field of processing micro inertia devices. The micro-accelerometer is arranged on a package substrate which is formed by stacking an upper surface plate, a lower surface plate and a plurality of middle substrates, wherein a signal detection circuit of the micro-accelerometer is attached on the upper surface plate; a sensitive element of the micro-accelerometer is embedded in the middle substrates, i.e. the middle substrates with cavities form a frame of the sensitive element; a flexible hanger and a sensitive mass block of the sensitive element are arranged in the cavities, and one end of the flexible hanger is connected with the sensitive element, while the other end is fixed on the frame; metal electrodes are respectively sputtered on the sensitive mass block and the surface of the frame corresponding to the sensitive mass block so as to form a flat plate sensitive capacitor, or a metal piezoresistive thick-film pattern is deposited at a connecting part of the flexible hanger and the inner side surface of the frame so as to form a metal piezoresistive strain gauge. The micro-accelerometer has high sensitivity and high-temperature resistance and can be fused into a whole with a system level package substrate, thus the micro-accelerometer has low processing difficulty and cost.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Componet, in particular a shell component, which can be joined thermally and/or mechanically, for building a fuselage section of an aircraft
InactiveUS20110031350A1Reduce weightEliminate needFuselage framesElectric power distributionFuselageComposite structure
A component for building a fuselage section of an aircraft includes a border area connectable to a corresponding further border area of a further component so as to form an electrically conductive joint, wherein the component includes a composite structure
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS GMBH
Graphene masterbatch
InactiveCN105017742AExcellent mechanical propertiesImprove antioxidant capacityNon-conductive material with dispersed conductive materialChemical LinkageMasterbatch
Disclosed is a graphene masterbatch including a base resin, electrically conductive carbon black, graphene nanoplatelets with modified surface and a dispersant. The modified surface of graphene nanoplatelet is formed by a modifying agent containing a coupling compound so as to possess hydrophobic and hydrophilic functional groups, which help graphene nanoplatelets form chemical bonding with carbon black and the base resin. Since the modified surface makes graphene nanoplatelets evenly dispersed in the base resin, the graphene masterbatch of the present invention is suitably melt blended with a polymer material to form a composite material such that graphene nanoplatelets are evenly dispersed in the polymer material, thereby enhancing junction strength, increasing mechanical properties, and improving anti-oxidation, acid / base resistance, and thermal conductivity.
Owner:北京烯创科技有限合伙企业(有限合伙)
Nonaqueous dispersion containing fluorine-based resin, polyimide precursor solution composition containing fluorine-based resin, polyimide, polyimide film and adhesive composition for circuit boards, each using said polyimide precursor solution composition containing fluorine-based resin; and production methods thereof
ActiveCN107429028ALow viscosityLow storage stabilityMacromolecular adhesive additivesEpoxy resin adhesivesPolymer scienceDielectric loss
In order to provide a dispersion wherein the dispersed state of a fluorine-based resin is uniformly controlled, a polyimide precursor solution composition using this dispersion, an adhesive composition, a polyimide and polyimide film obtained from this polyimide precursor solution composition and having excellent heat resistance, excellent mechanical characteristics, excellent electrical characteristics such as lower dielectric constant and lower dielectric loss tangent, and excellent processability, a method for producing the polyimide, a method for producing the polyimide film, and a circuit board and coverlay film using the polyimide film, the present invention provides: a polyimide precursor solution composition containing a fluorine-based resin, which is characterized by containing a polyimide precursor solution and a nonaqueous dispersion of a fluorine-based resin containing a micropowder of a fluorine-based resin and a butyral resin or a fluorine-based additive containing at least a fluorine-containing group and a lipophilic group; and an adhesive composition.
Owner:MITSUBISHI PENCIL CO LTD
Acrylate grafted aqueous polyurethane emulsion and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102558460AImprove stabilitySmall particle sizeFibre treatmentCoatingsHydrophilic monomerPolymer science
The invention discloses acrylate grafted aqueous polyurethane emulsion and a preparation method thereof. The emulsion is characterized is prepared from polyether polyol, dimethylol propionic acid, isophorone diisocyanate, ethylenediamine, hydroxyethyl acrylate and the like. The preparation method comprises the following steps: carrying out prepolymerization on polyether polyol, dimethylol propionic acid and isophorone diisocyanate so as to introduce a hydrophilic monomer; adding ethylenediamine and hydroxyethyl acrylate to carry out chain extension so as to introduce a functional monomer; adding an acrylate mixed monomer so as to reduce system viscosity; adding triethylamine for neutralization; adding deionized water for emulsification and dispersion under the condition of high-speed shearing to obtain emulsion; then dropwise adding the acrylate mixed monomer and an initiator, raising the temperature and carrying out reaction; and cooling to obtain the PUA (polyurethane-acrylate) emulsion. The emulsion prepared by the method has small grain size and excellent performances such as mechanical performance, is narrowly distributed and can be widely applied to industry fields such as leather finish, coatings, adhesives and fabric coatings.
Owner:顶立新材料科技股份有限公司
Deep sea bionic pressureproof shell
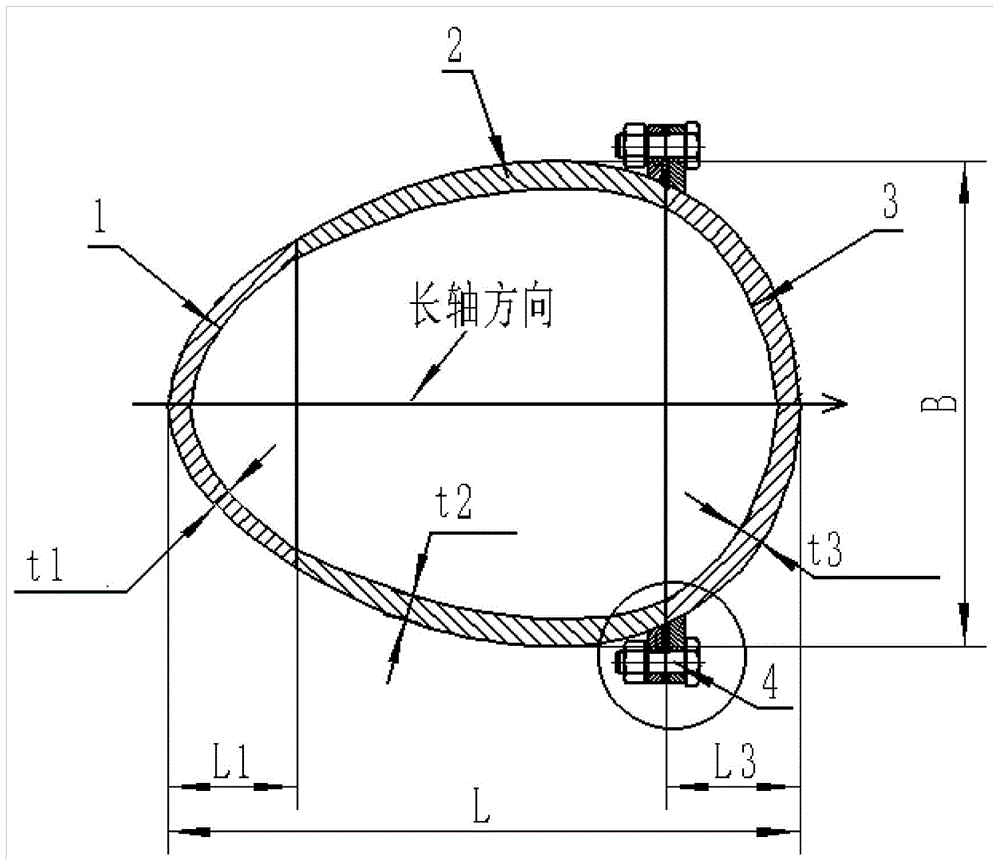
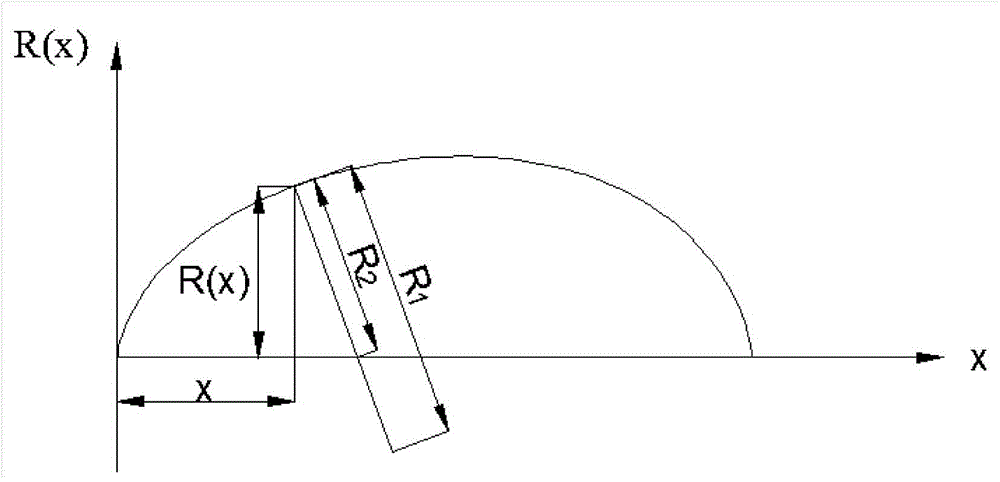
ActiveCN104648638AGood pressure resistanceStreamlinedUnderwater vesselsUnderwater equipmentVariable thicknessCarrying capacity
The invention discloses a deep sea bionic pressureproof shell. An axial-symmetry eggshell-shaped structure with the length of L, the width of B and the turning radius of R(x) is formed by a left end socket, a right end socket and a middle shell, wherein the thickness t2 of the middle shell is of an equal-strength variable-thickness structure, the thickness t1 of the left end socket and the thickness t3 of the right end socket are respectively of an equal-thickness structure, the left end socket and the middle shell are fixedly connected, and the right end socket and the middle shell are connected by a flange bolt or a movable hatch cover with a seal ring. The deep sea bionic pressureproof shell has good mechanical properties, in-shell space utilization rate, hydrodynamic characteristics and passenger comfort, and comprehensive improvement on safety, carrying capacity, mobility and diving time of a diving device is facilitated; meanwhile, the weight of the pressureproof shell is lightened, the reserve buoyancy of the pressureproof shell is increased, and the processing and manufacturing difficulty and cost are reduced.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Aluminum alloy for compression casting and casting of aluminum alloy
The invention provides aluminum alloy for compression casting and a high-toughness aluminum alloy casting formed of the alloy through compression casting. The aluminum alloy has the advantages of superior yield strength and extensibility, low probability of sintering and superior thermal conductivity. The aluminum alloy is characterized by comprising the following components in percentage by weight: 5.5-11.0 percent of Si, 0.3-0.7 percent of Mg, 0.05-0.3 percent of Cu, 0.2-0.8 percent of Fe, 0.2-0.5 percent of Mn, 0.05-0.3 percent of Ti, 0.05-0.1 percent of Cr, 0.05-0.3 percent of V and the balance of Al and inevitable impurities. The aluminum alloy for compression casting and the casting of the aluminum alloy provided by the invention have the advantages of high yield strength and extensibility, superior thermal conductivity and low probability of sintering.
Owner:东莞市闻誉实业有限公司
Prosthetic Spinal Disc Replacement and Methods Thereof
ActiveUS20140296985A1Easy to insertImprove stabilitySurgerySpinal implantsProsthesisSecondary Stability
Owner:GLOBUS MEDICAL INC
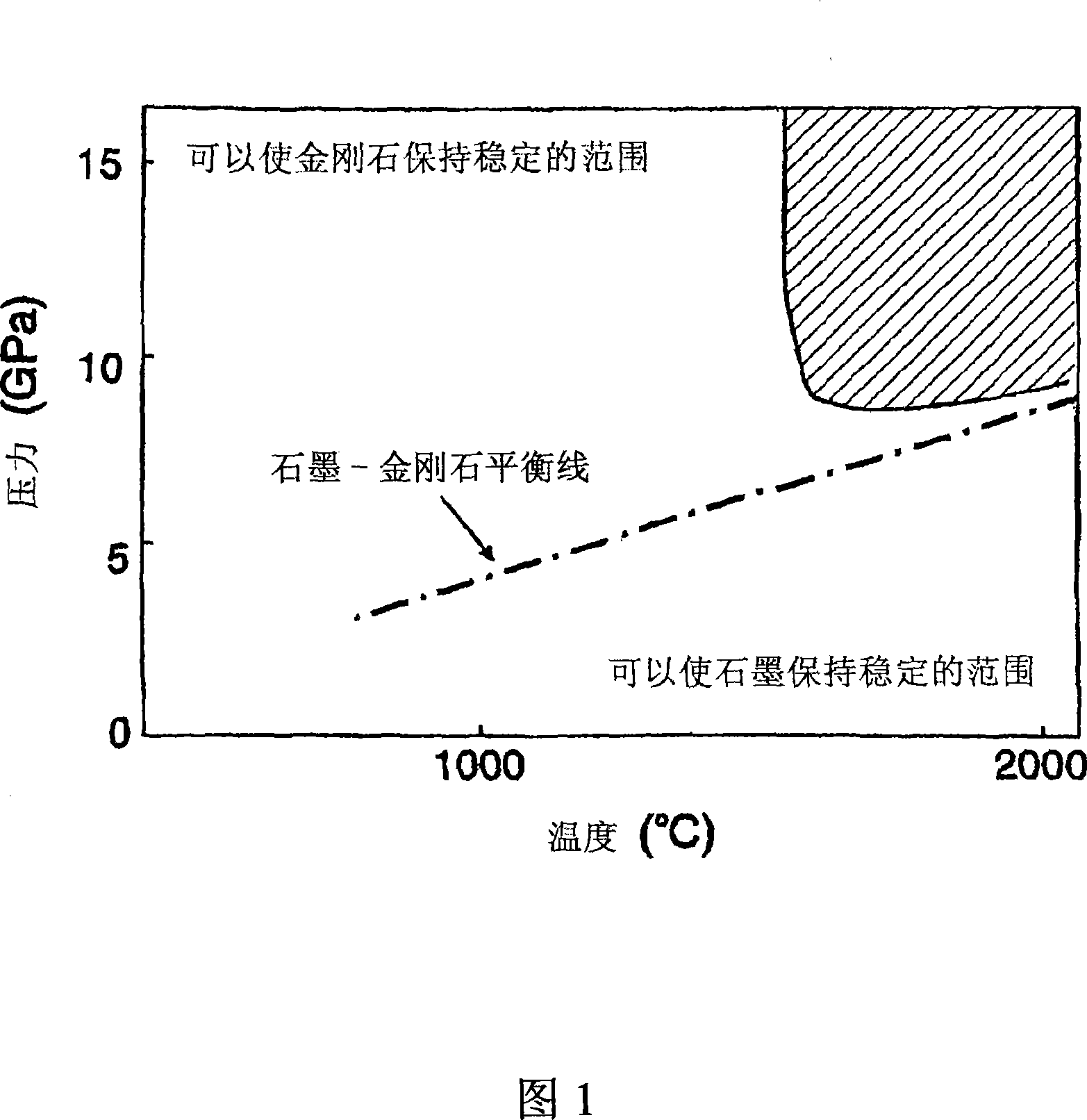
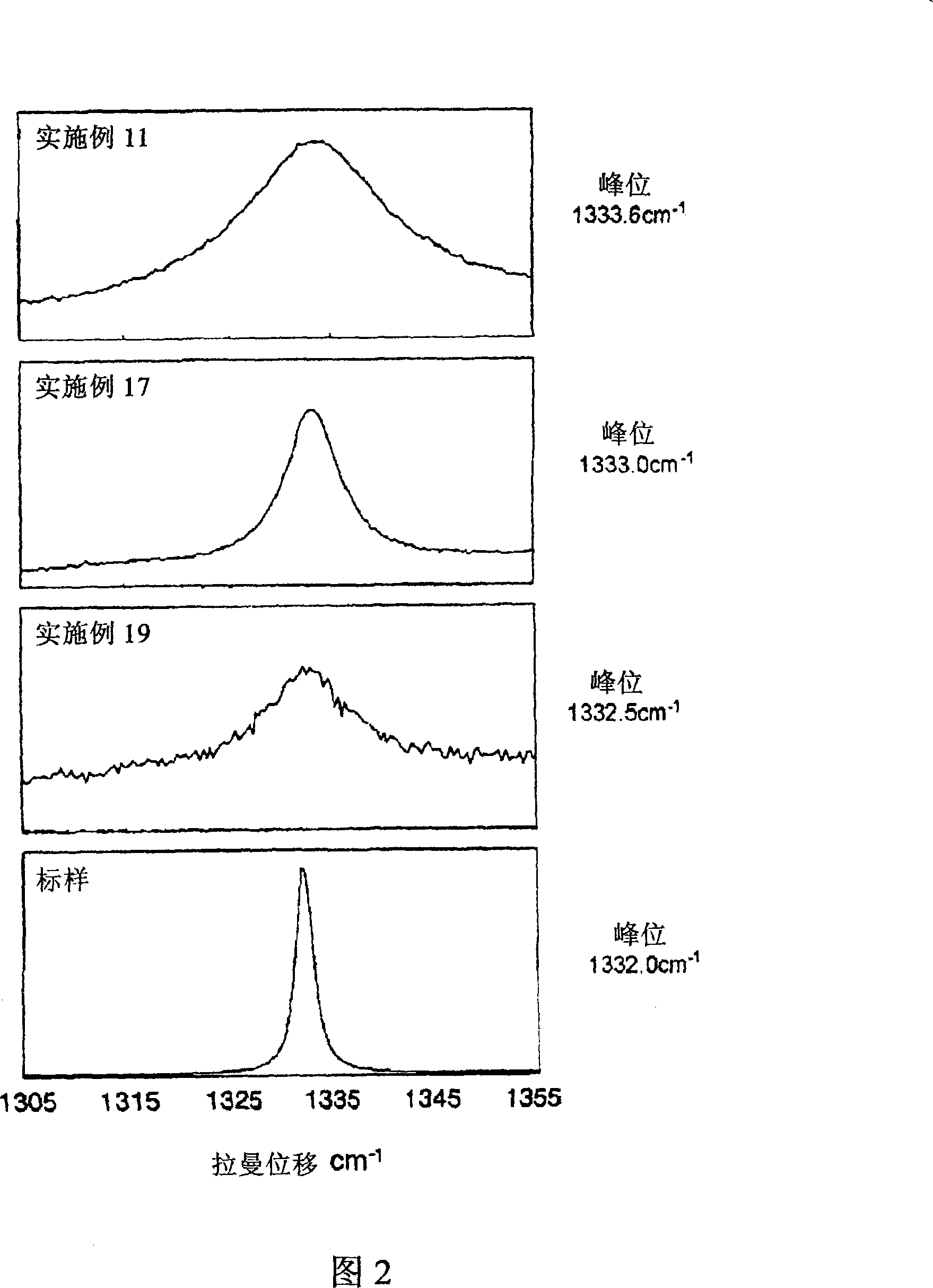
High-hardness polycrystalline diamond and process for producing the same
ActiveCN101228095AStable and cheap offerSolve the hardnessUltra-high pressure processesTurning toolsParticulatesUltra high pressure
The present invention provides a dense and homogeneous polycrystalline diamond having sufficient strength, hardness and heat resistance, which can be used in cutting tools, shapers, dies and other machining tools, excavation bits, etc., and a polycrystalline diamond made of the polycrystalline diamond A cutting tool that forms a cutting edge. The polycrystalline diamond consists essentially of only diamond, and is directly converted into diamond and sintered from a raw material composition containing non-diamond-type carbon material under ultra-high pressure and ultra-high temperature and without the use of sintering aids or catalysts formed, wherein the polycrystalline diamond has a mixed microstructure comprising diamond fine grains with a maximum grain size of 100 nm or less and an average grain size of 50 nm or less and a grain size of 50 nm to 10,000 nm Flake or granular diamond coarse grains.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Low-temperature SCR (Selective Catalytic Reduction) catalyst based on active coke loaded manganese-cerium composite oxide and preparation method of low-temperature SCR catalyst
ActiveCN103433034AHigh catalytic activityEnhance oxygen circulationDispersed particle separationMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsPtru catalystNitrogen oxides
The invention provides a low-temperature SCR (Selective Catalytic Reduction) catalyst based on an active coke loaded active component and a preparation method of the low-temperature SCR catalyst. The catalyst is suitable for SCR reaction of nitrogen oxides under the condition of low temperature. A Mn and Ce composite oxide is loaded on an active coke particle with a relatively high special surface area and mechanical strength, so that the SCR reaction temperature is reduced, the adsorption capability and mechanical wear resistance of the catalyst are improved, and the whole sulfate resistance and regeneration capability of the catalyst are improved. The preparation method provided by the invention is simple in step, artful in process design and convenient for industrial production. The catalyst provided by the invention takes the active coke particle as a carrier on which the Mn and Ce composite oxide is loaded. Oxides of modified elements can also be loaded on the carrier of the catalyst, wherein the modified elements are selected from one or more of the following elements: Fe, Zr, Si, Ti, V, Mo, W, Cr, Au, Ag, Pt, Pd, Rh and Co.
Owner:GUODIAN ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION RES INST CO LTD
Ceramic composite material and method for producing same
InactiveUS20070129233A1Excellent mechanical propertiesGood release effectMaterial nanotechnologyCeramic compositeWear resistant
Highly wear-resistant, low-friction ceramic composites suited for machining-tool, sliding-component, and mold-die materials are made available. The ceramic composites characterized are constituted from a phase having carbon of 3 μm or less, preferably 30 nm or less, average crystal-grain size as the principal component, and a ceramic phase (with the proviso that carbon is excluded). The ceramic phase is at least one selected from the group made up of nitrides, carbides, oxides, composite nitrides, composite carbides, composite oxides, carbonitrides, oxynitrides, oxycarbonitrides, and oxycarbides of Al, Si, Ti, Zr, Hf, V, Nb, Ta, Cr, Mo and W. The ceramic composites are produced by sintering the source-material powders at a sintering temperature of 800 to 1500° C. and a sintering pressure of 200 MPa or greater.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Model test device for carrying out underwater explosion research on centrifuge platform
InactiveCN105486525AIncrease rangeHigh sensitivityStructural/machines measurementDetonationUnderwater explosion
The invention discloses a model test device for carrying out underwater explosion research on a centrifuge platform. The model test device comprises a model box, a data acquisition and analysis unit and a synchronous control unit. The model box is internally equipped with a test medium; an explosion device is arranged in the test medium; the bottom of the model box is fixedly provided with a target body; the model box is internally provided with a data receiving unit; the data receiving unit is connected with a data transmission unit; and the data transmission unit is connected with the data acquisition and analysis unit. When the explosion device is detonated, the data receiving unit receives various test data; the test data is transmitted to the data acquisition and analysis unit for processing through the data transmission unit; and the processed data is uploaded to the synchronous control unit. The model test device for carrying out underwater explosion research on a centrifuge platform can be suitable for centrifuge high-speed rotation special mechanical environment, and realizes precise and safe detonation of the explosion device in the centrifugal model test and signal synchronous acquisition and transmission.
Owner:CHINA INST OF WATER RESOURCES & HYDROPOWER RES +1
Polymer electrolyte, lithium secondary battery using same, and method for manufacturing lithium secondary battery
ActiveCN104919639AAvoid short circuitAchieve securityFinal product manufactureConductive materialPolymer electrolytesLithium
The present invention relates to a polymer electrolyte, a lithium secondary battery using the same, and a method for manufacturing the lithium secondary battery, wherein: an electrode assembly is formed by using a porous nanofiber web as an electrolyte matrix; an organic electrolyte having a mixture of a gel polymer-forming monomer and a polymerization initiator is injected, and a gel polymer electrolyte is formed by polymerization; and the porous nanofiber web is maintained in a web form such that stability can be increased by preventing a short circuit between a cathode and an anode. The polymer electrolyte, according to the present invention, comprises: the porous nanofiber web which is provided with a plurality of nanofibers; and a gel polymer portion which is impregnated into the porous nanofiber web, wherein the gel polymer portion is formed by polymerizing the gel polymer-forming monomer after a non-aqueous organic solvent, a solute of lithium salt, and the organic electrolyte having the gel polymer-forming monomer and the polymerization initiator have been impregnated into the porous nanofiber web.
Owner:AMOGREENTECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com