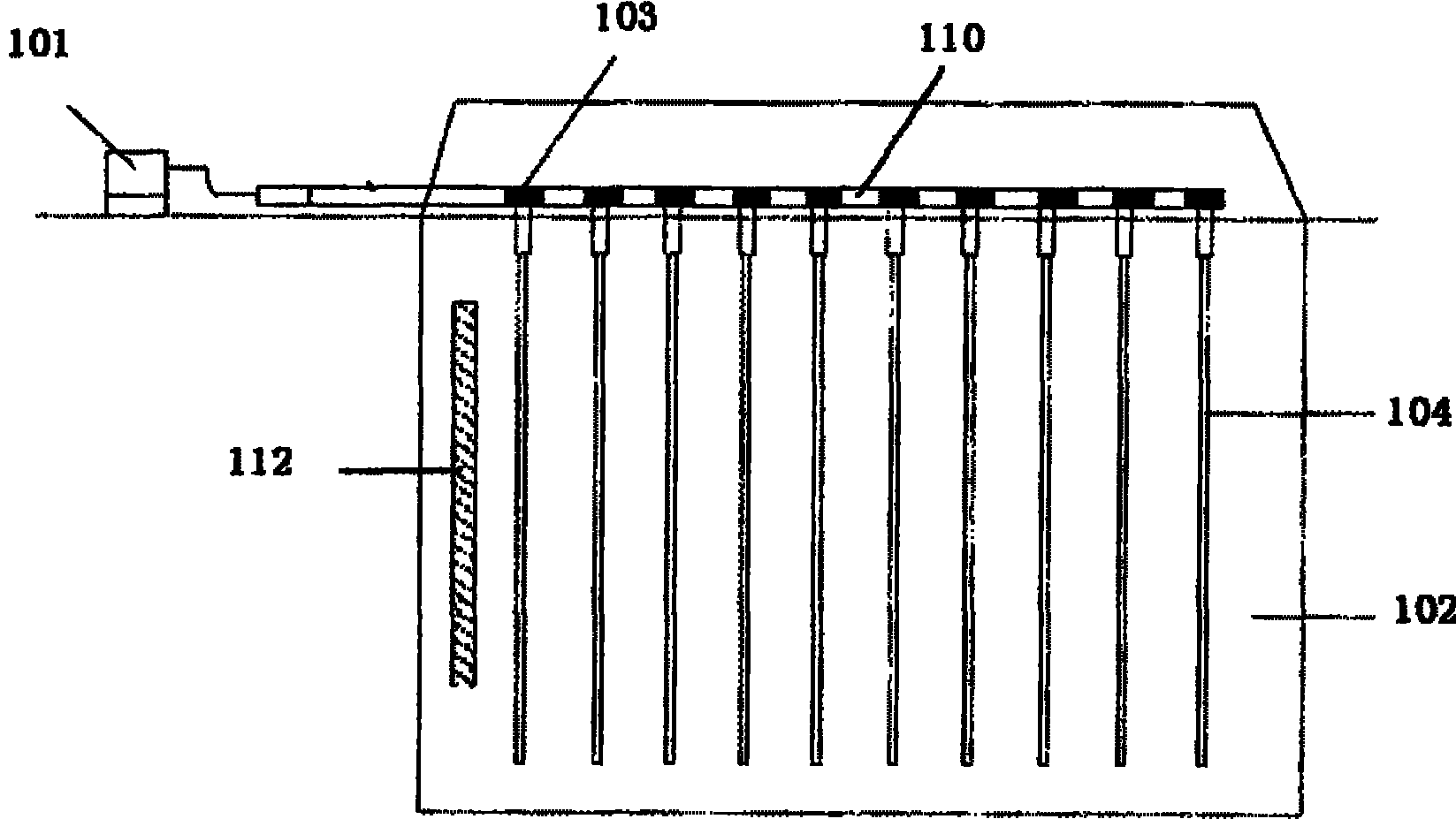
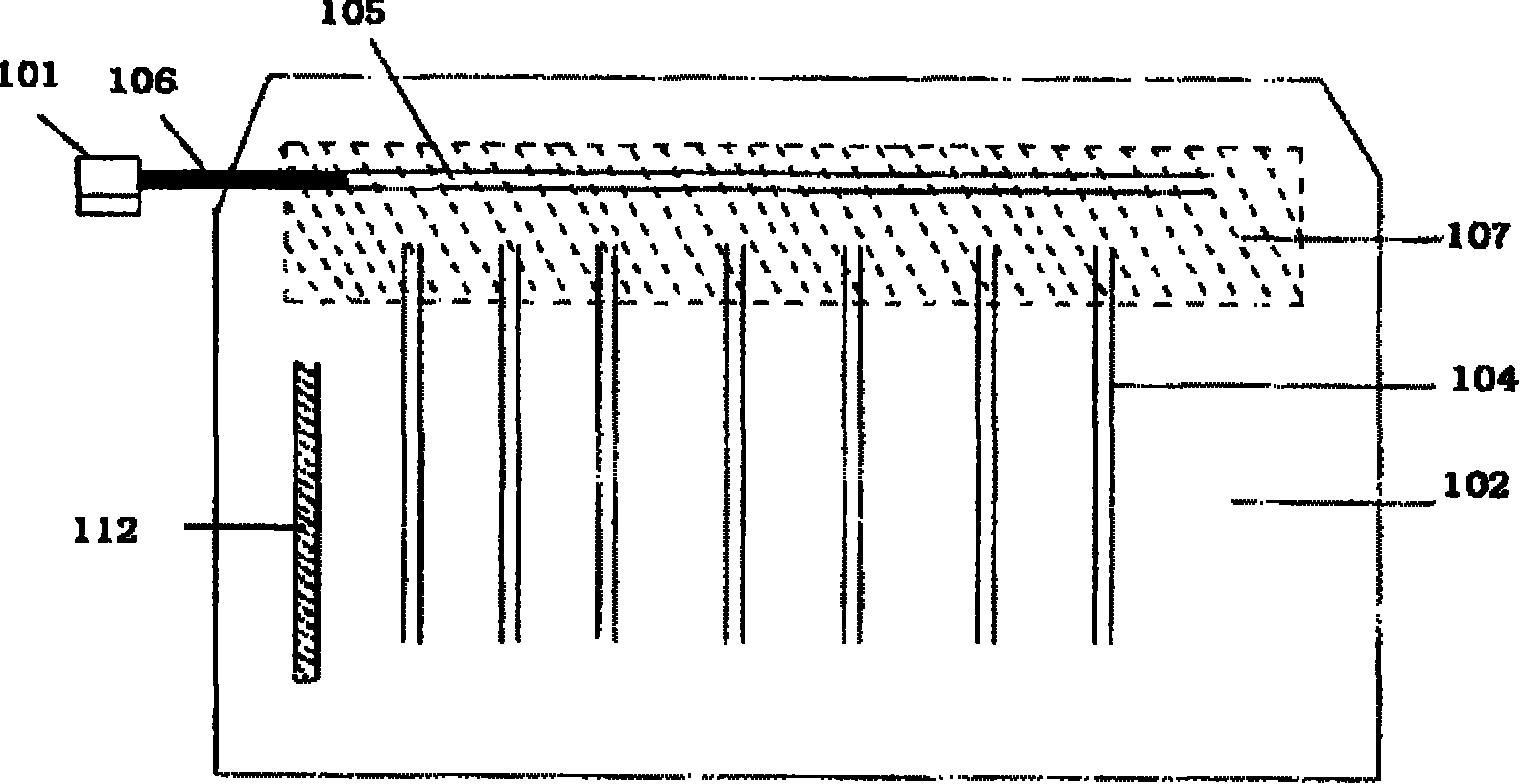
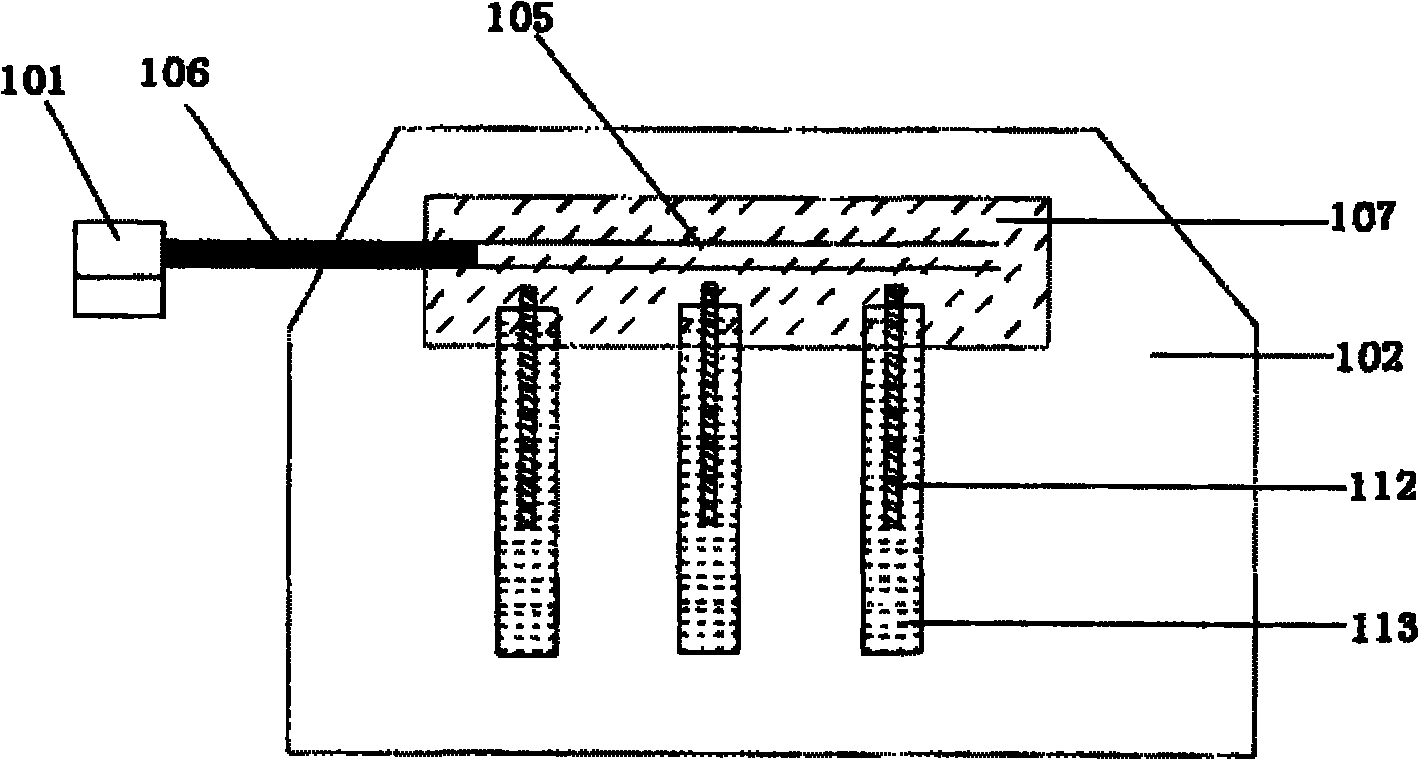
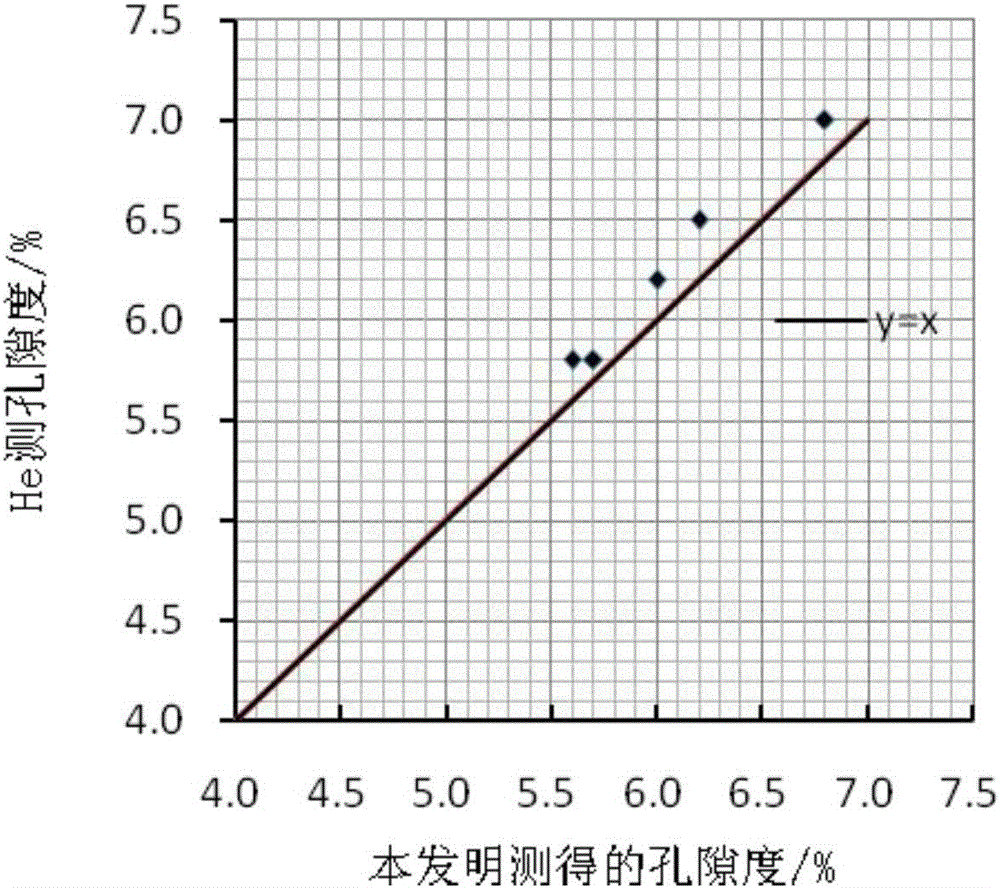
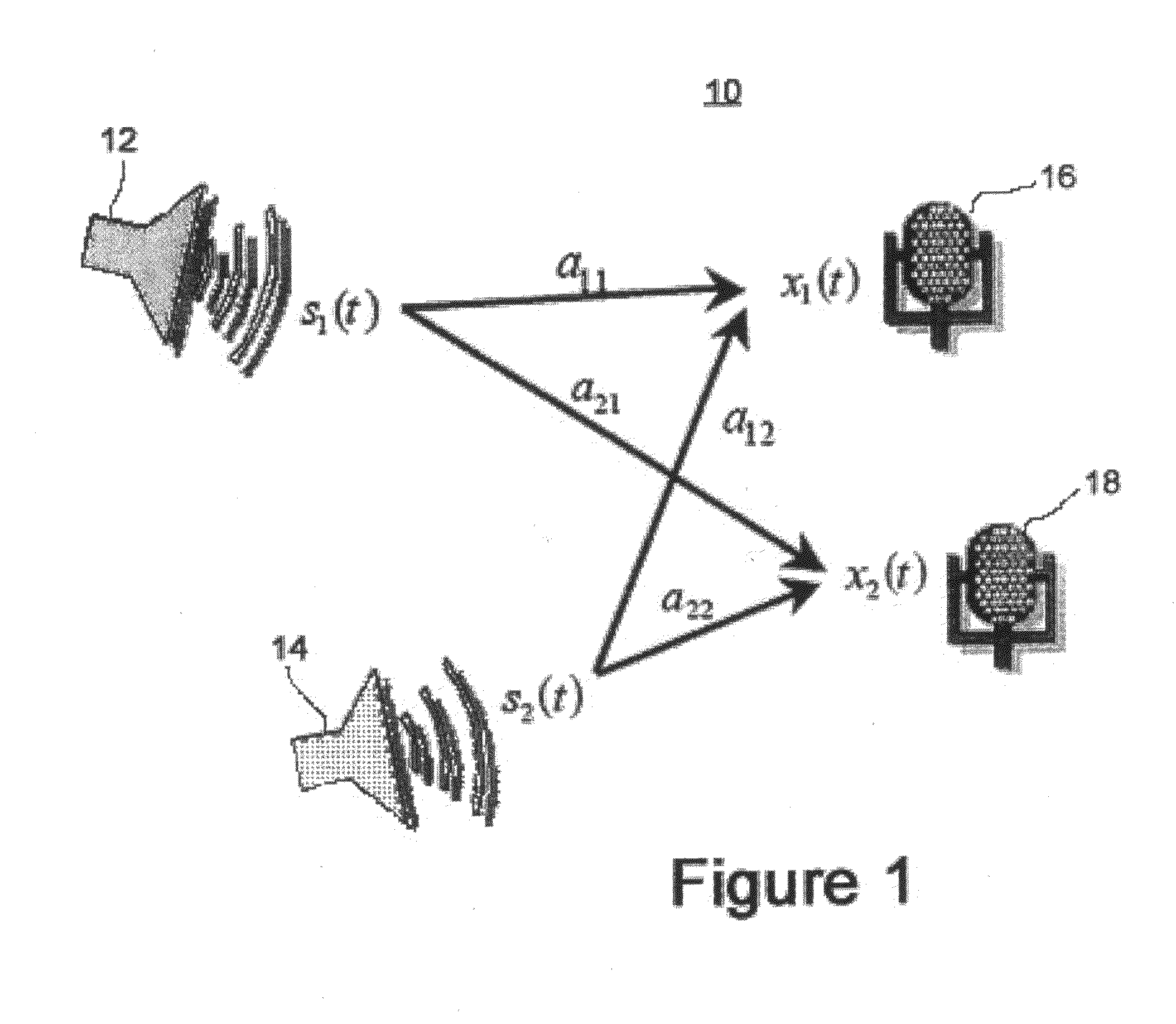
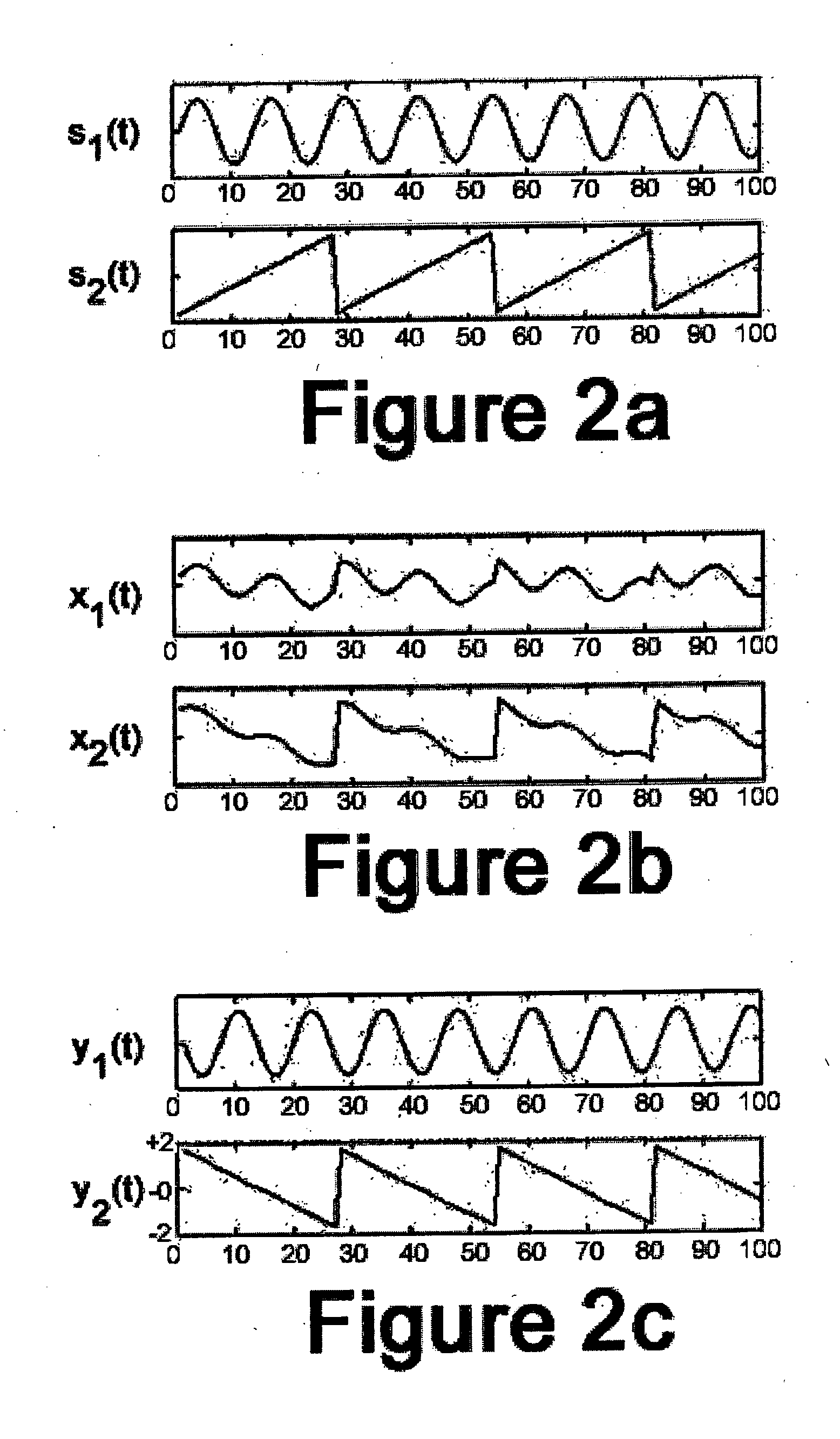
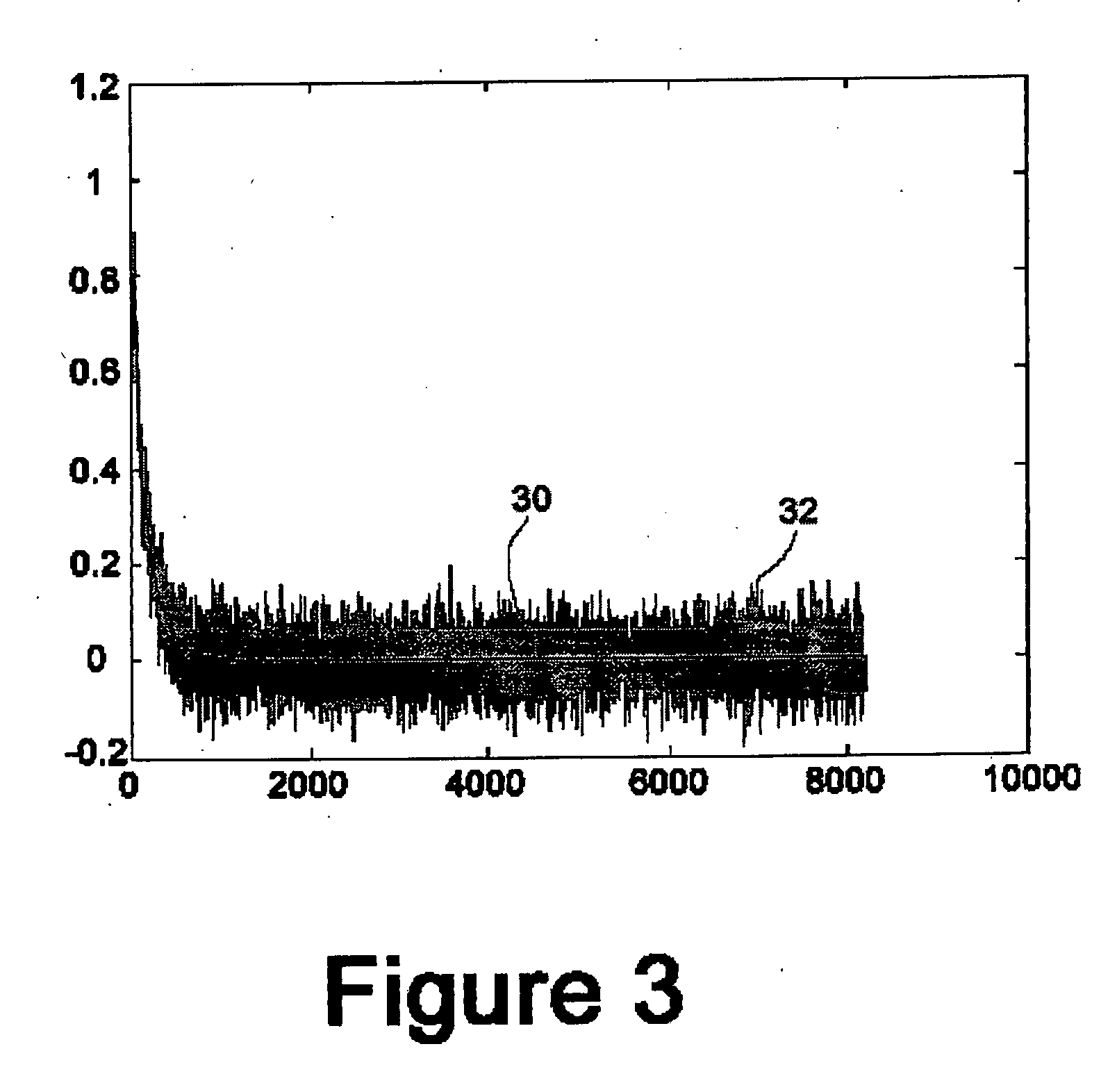
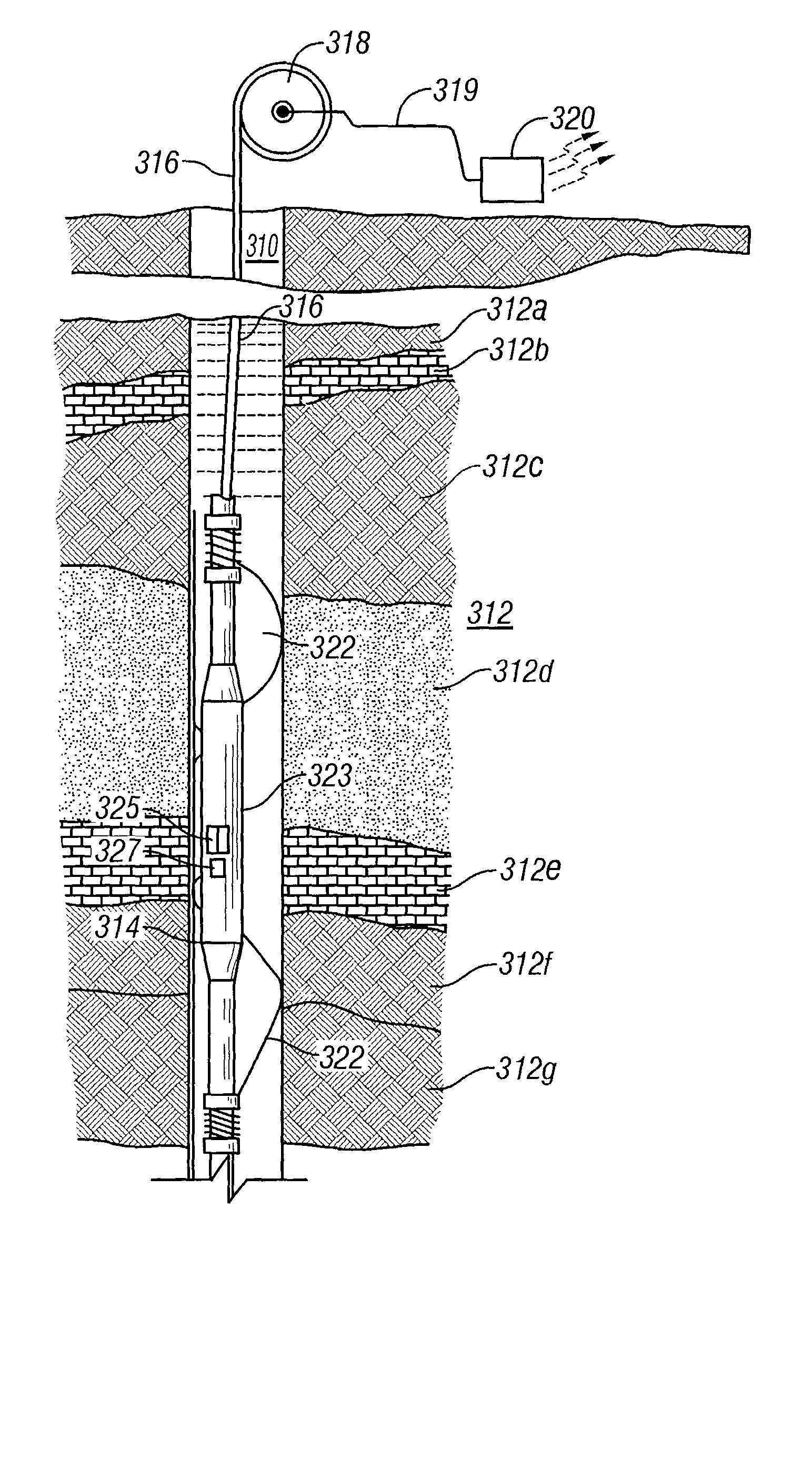
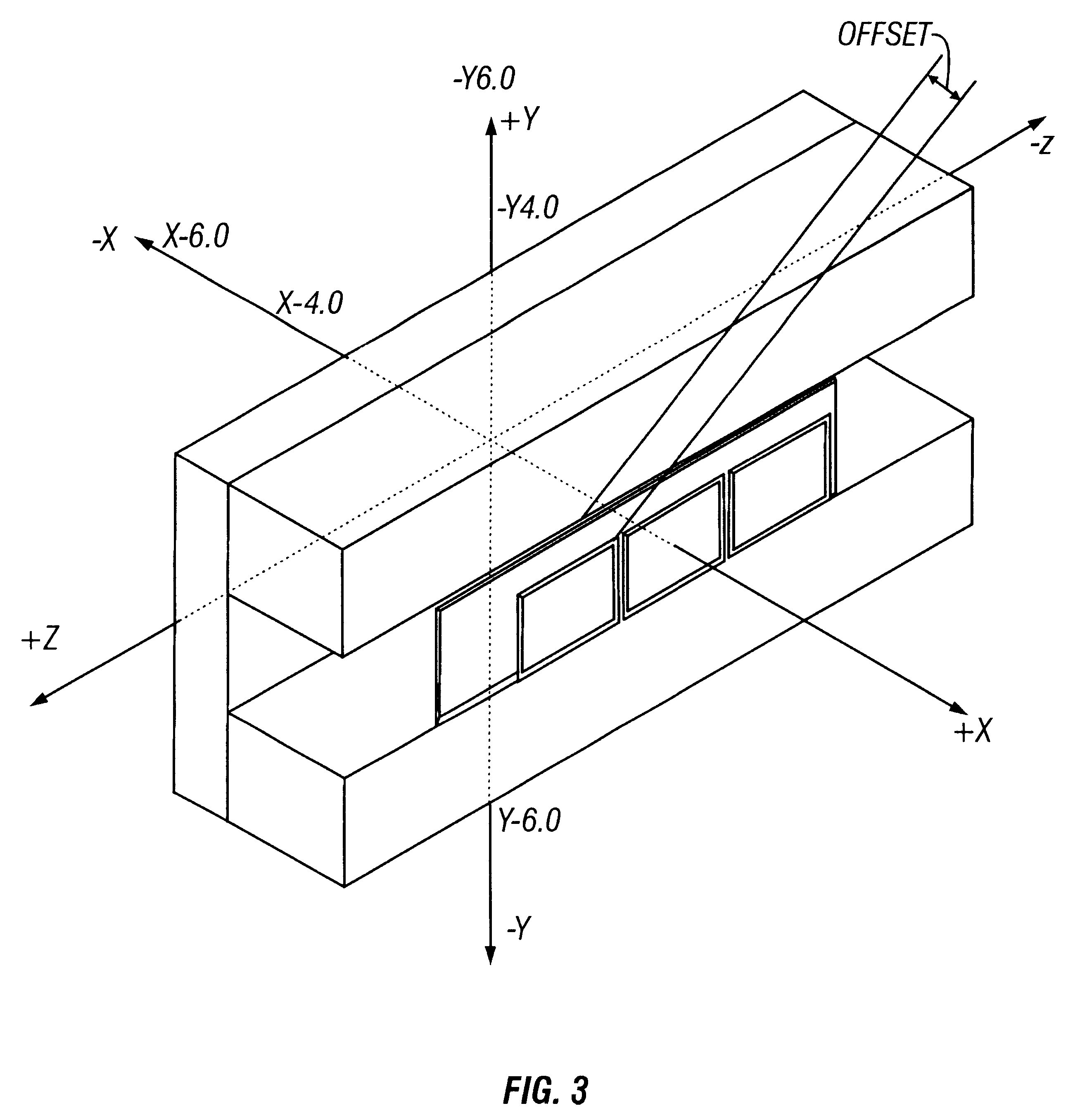
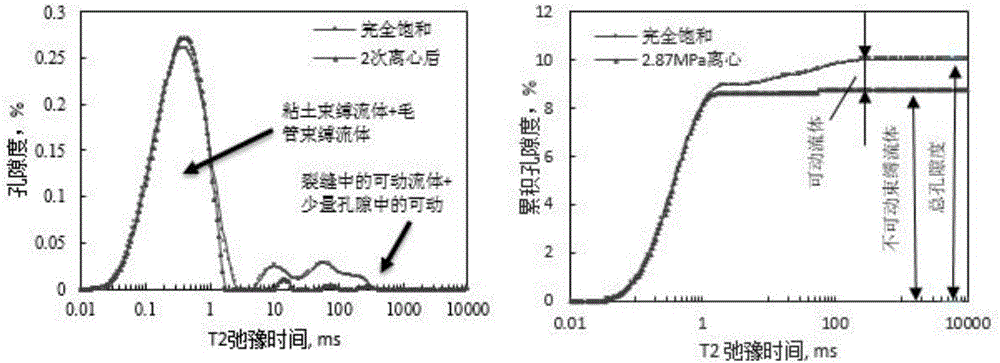
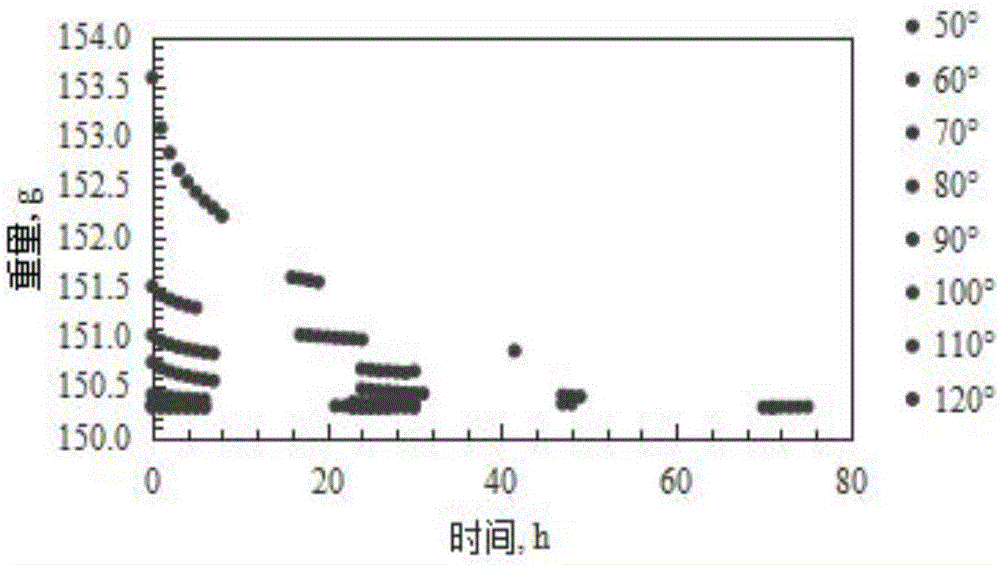
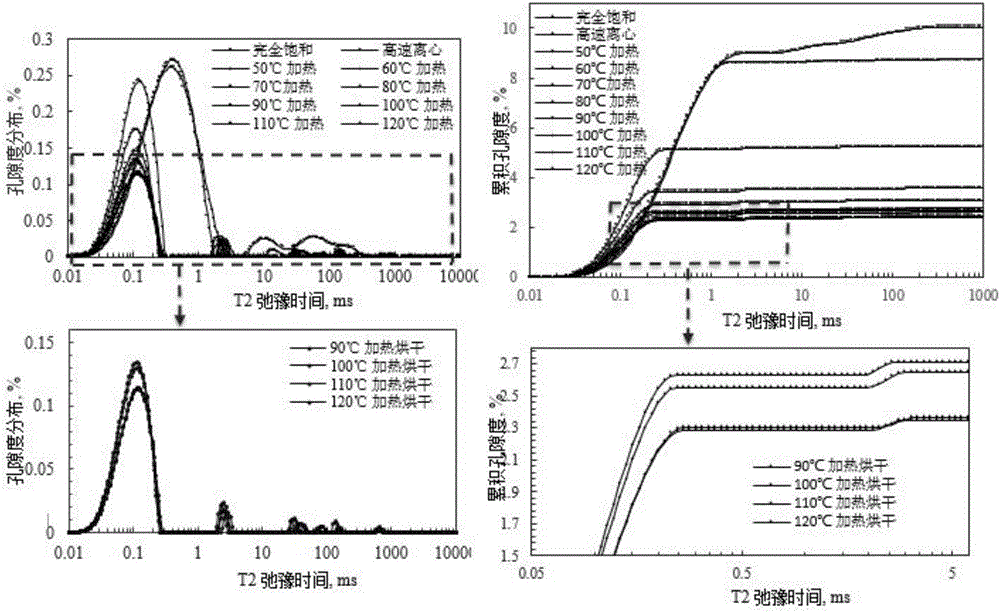
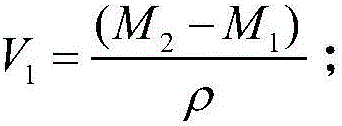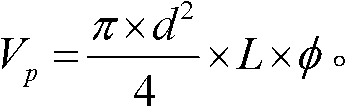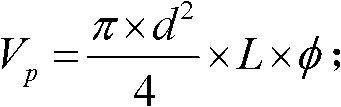Patents
Literature
472 results about "Bound water" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
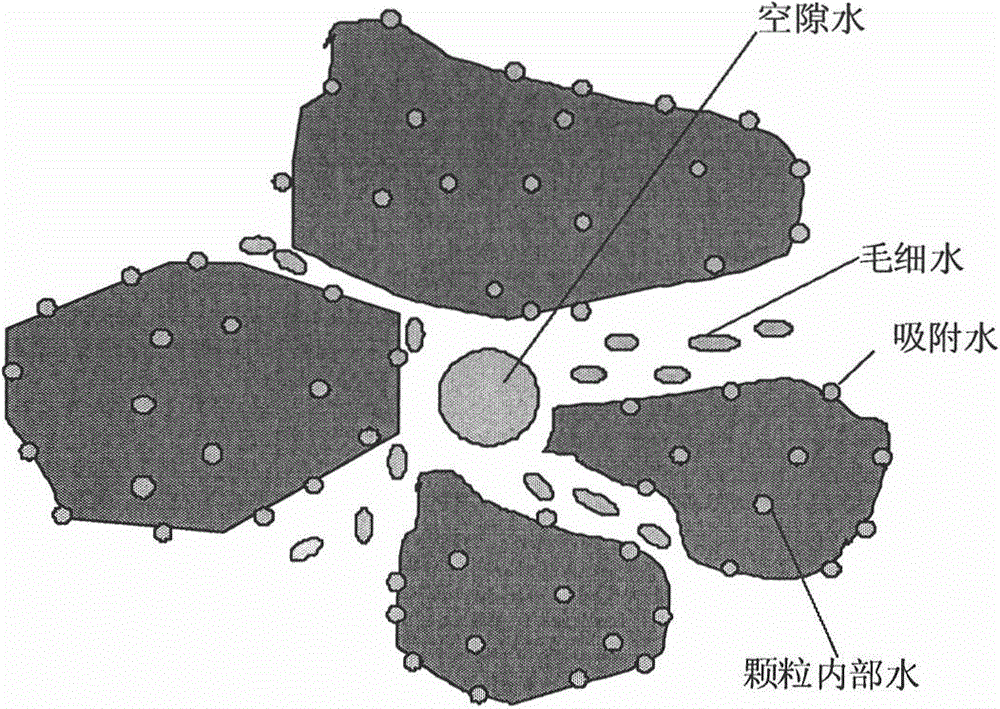
In hydrology, bound water, is an extremely thin layer of water surrounding mineral surfaces. Water molecules have a strong electrical polarity, meaning that there is a very strong positive charge on one side of the molecule and a strong negative charge on the other. This causes the water molecules to bond to each other and to other charged surfaces, such as soil minerals. Clay in particular has a high ability to bond with water molecules.
Polymer particles for delivery of macromolecules and methods of use
InactiveUS20070134332A1Slow down rate of bio-degradationImprove stabilityPowder deliveryNervous disorderPolyesterBound water
The present invention provides biodegradable polymer particle delivery compositions for delivery of macromolecular biologics, for example in crystal form, based on polymers, such as polyester amide (PEA), polyester urethane (PEUR), and polyester urea (PEU) polymers, which contain amino acids in the polymer. The polymer particle delivery compositions can be formulated either as a liquid dispersion or a lyophilized powder of polymer particles containing bound water molecules with the macromolecular biologics, for example insulin, dispersed in the particles. Bioactive agents, such as drugs, polypeptides, and polynucleotides can also be delivered by using particles sized for local, oral, mucosal or circulatory delivery. Methods of delivering a macromolecular biologic with substantial native activity to a subject, for example orally, are also included.
Owner:MEDIVAS LLC
Oil-water displacement efficiency experimental method of longitudinal and planar nonhomogeneous slab models
The invention relates to an oil-water displacement efficiency experimental method of longitudinal and planar nonhomogeneous slab models, which comprises an oil-water displacement efficiency experimental method of a longitudinal nonhomogeneous slab model and an oil-water displacement efficiency experimental method of a planar nonhomogeneous slab model. The experimental method mainly comprises the following steps: 1. applying confining pressure to the core holder of a multilayer slab model, then vacuumizing the multilayer slab model with three layers slab model, injecting simulated formation water to saturate cores, and then heating; 2. injecting simulate formation oil in a piston type container into the core holder of the multilayer slab model, and carrying out water-oil displacement to establish bound water saturation level; and 3. injecting simulate formation water in the piston type container into the core holder of the multilayer slab model, and carrying out water-oil displacement to obtain accumulated displacement oil output and wateryield under different water injection multiples, and thereby, the oil displacement efficiency is obtained. The invention not only can carry out displacement experiment research on the longitudinal nonhomogeneous slab model at high temperature and pressure but also can carry out displacement experiment research of different flooding well networks on the planar nonhomogeneous slab model under high temperature and pressure. The highest pressure reached by the experimental method is 25MPa, and the highest temperature reached by the experimental method is 100 DEG C.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
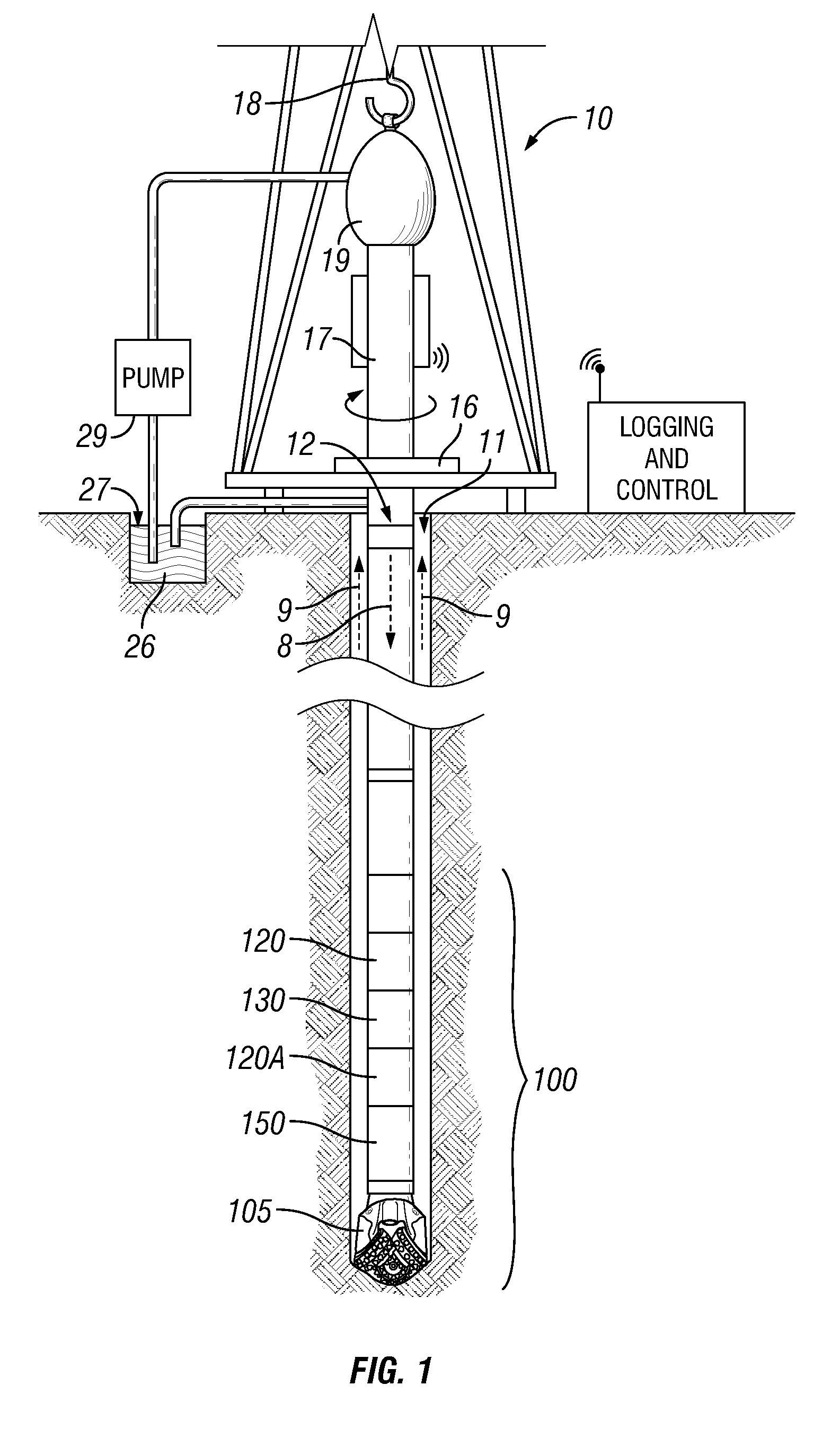
In-situ heavy-oil reservoir evaluation with artificial temperature elevation
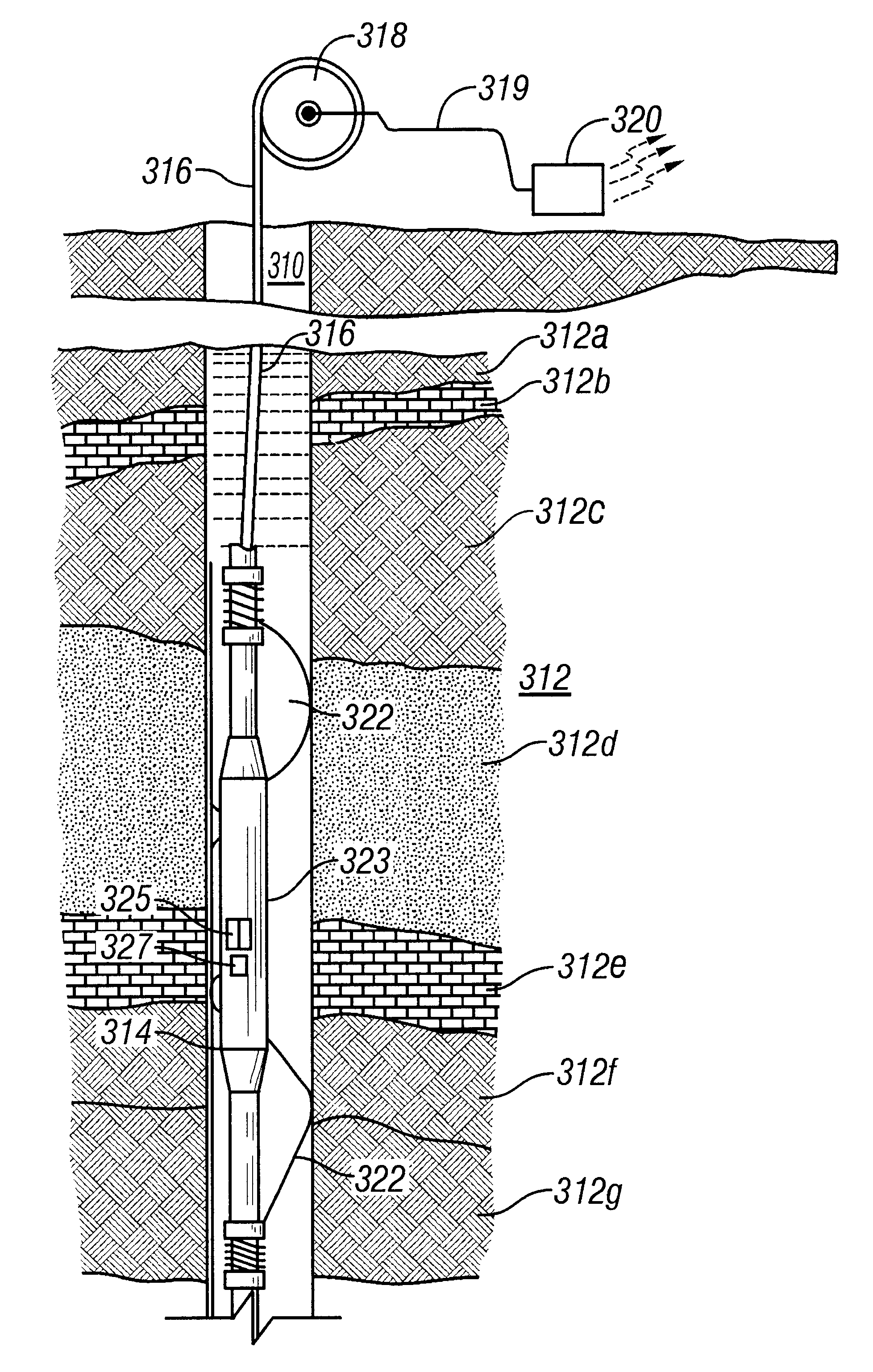
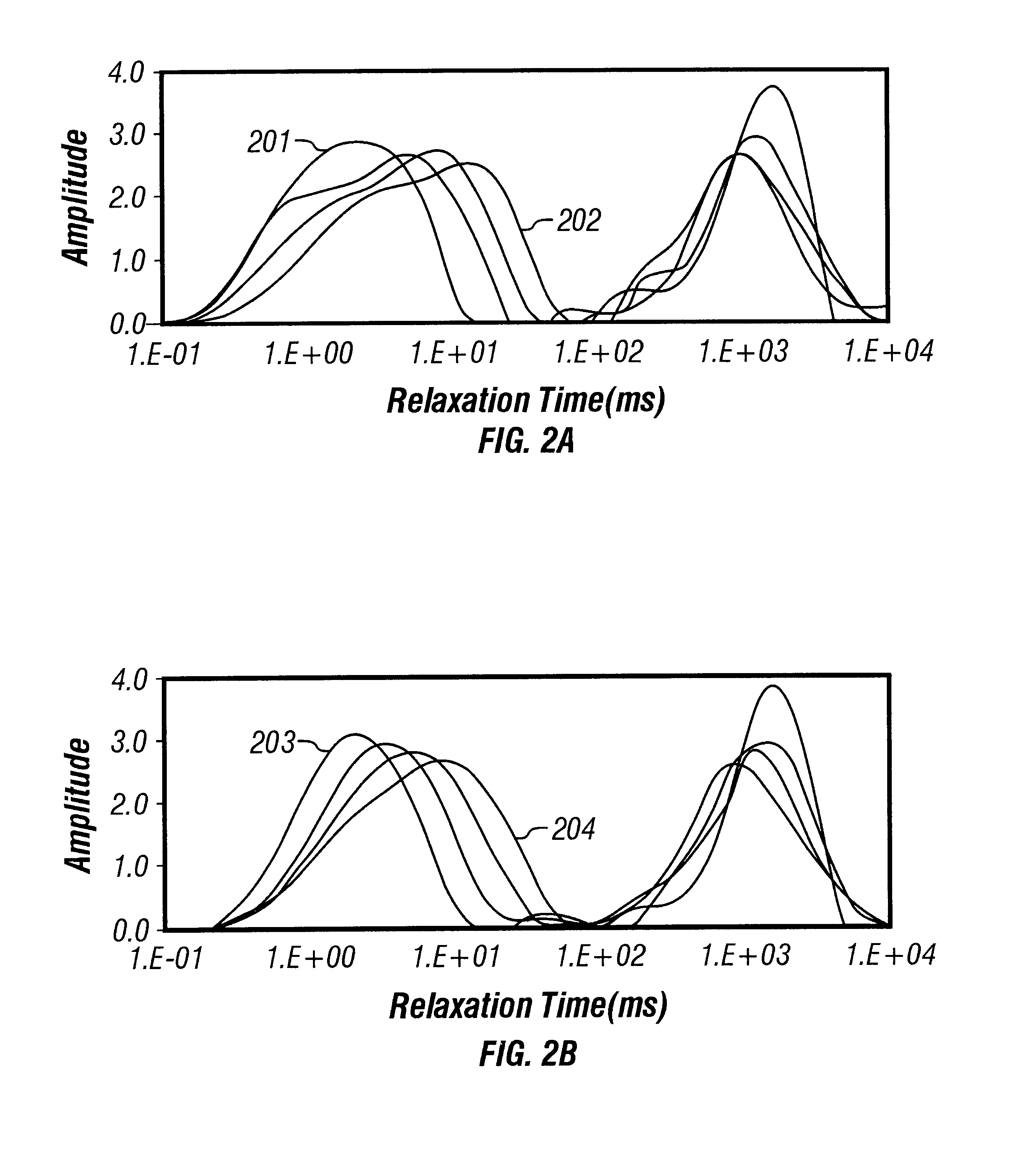
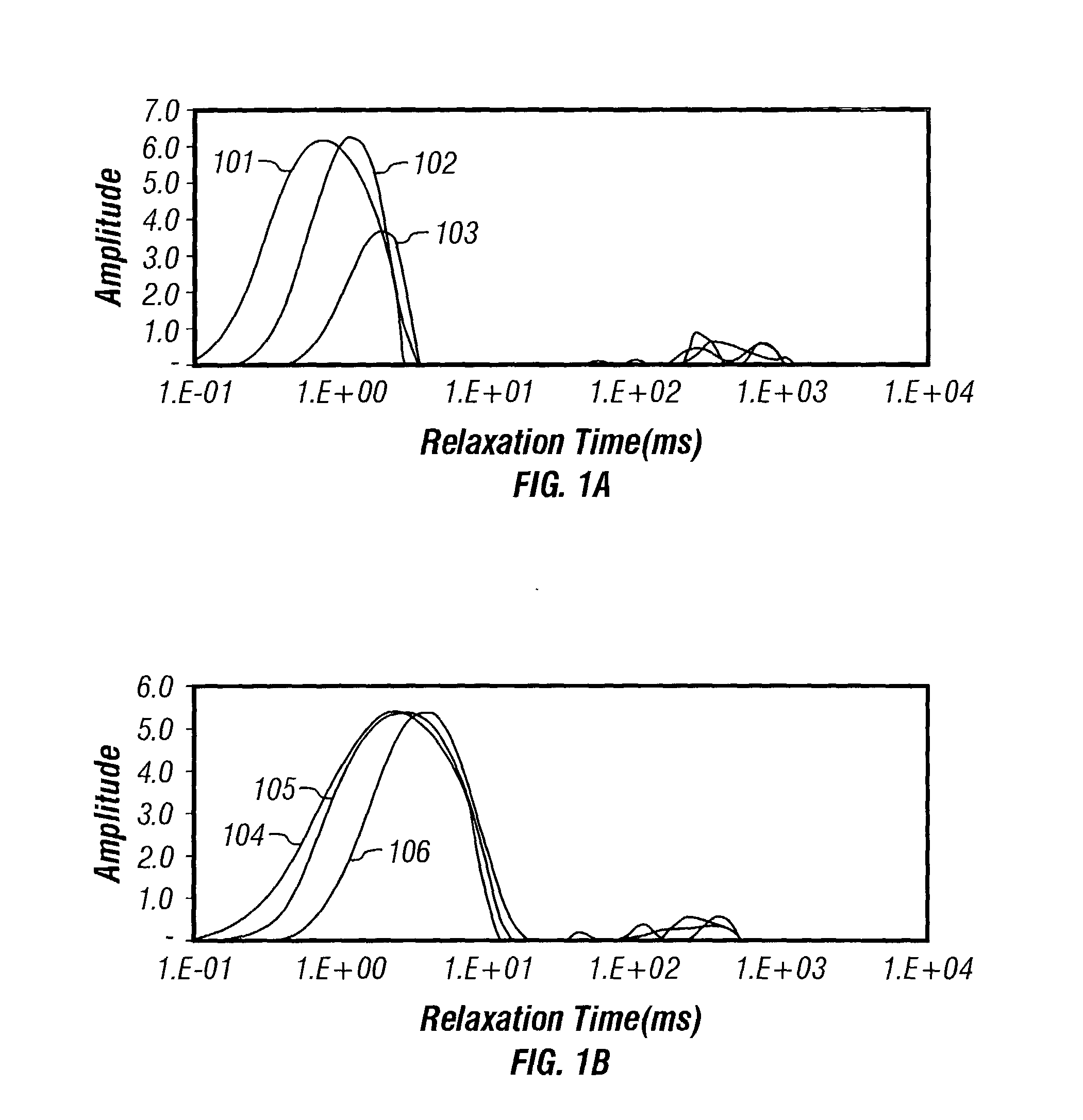
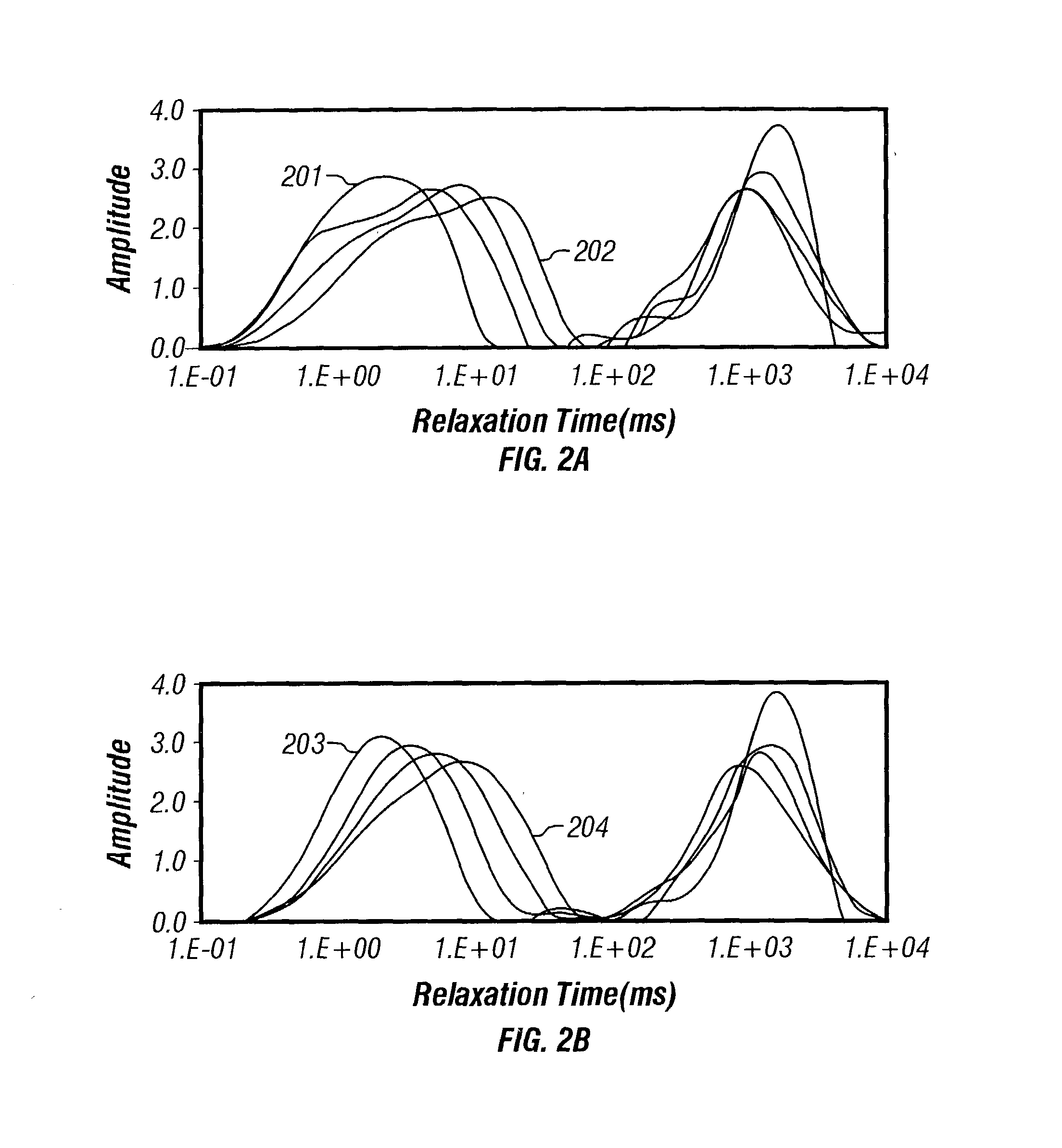
Many reservoirs of interest include heavy oil. In such reservoirs, parti at normal temperatures, many instruments commonly used for formation evaluation may not be able to distinguish between heavy oil and bound water in the formation. Passive or active heating is used to elevate the temperature of the fluids in the formation. At elevated temperatures, distinguishing between heavy oil and bound water is easier. Of particular interest is the increase in the resolvability of the transverse relaxation time T2 of NMR spin echo measurements. Additionally, the dielectric constant and the loss tangents of water and heavy oil show different temperature and frequency dependence.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES HLDG LLC
Shale micropore size and fluid distribution analysis method
ActiveCN104697915AAvoid damageGood reproducibilityWater resource assessmentAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceBound waterHydrogen
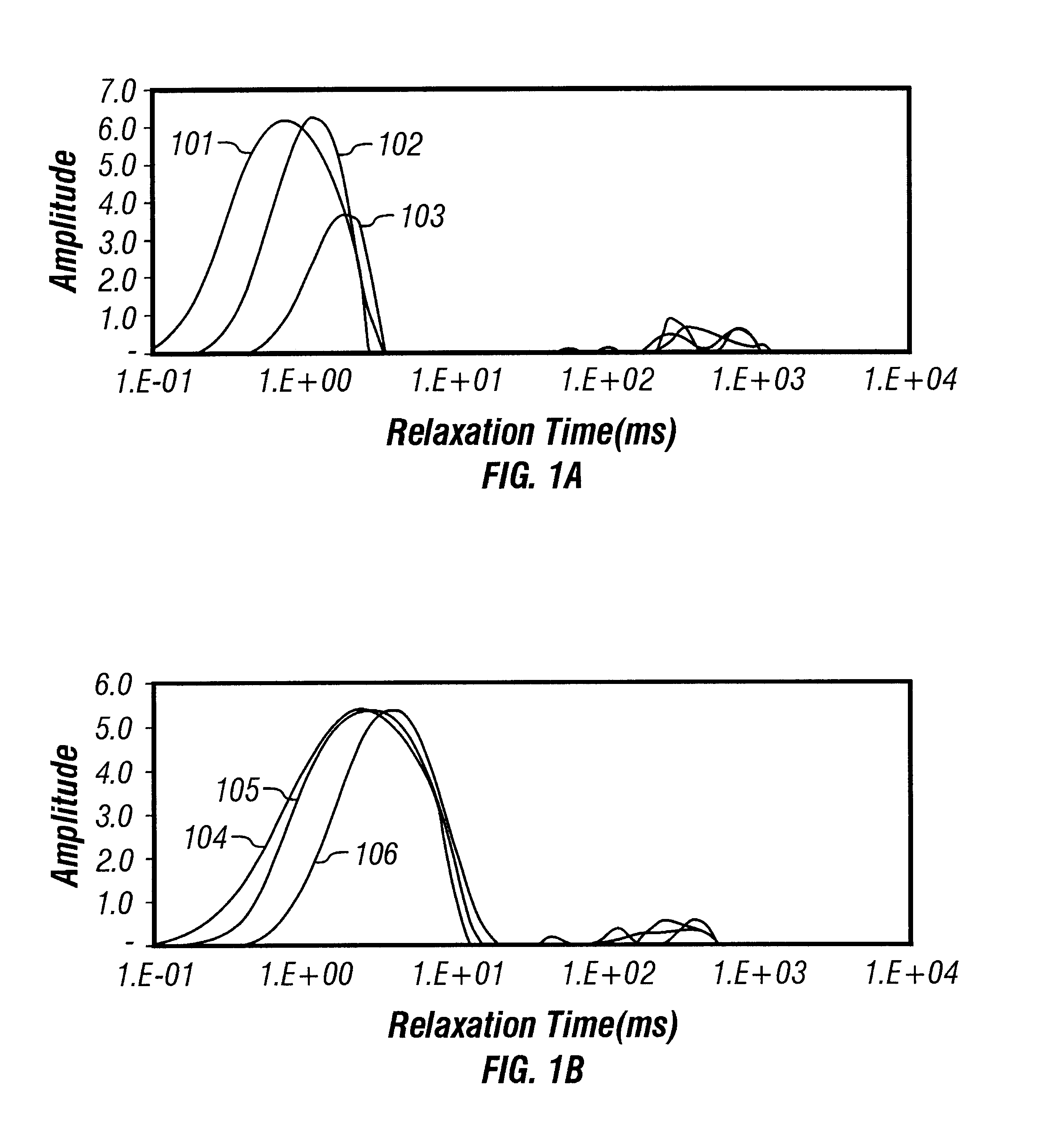
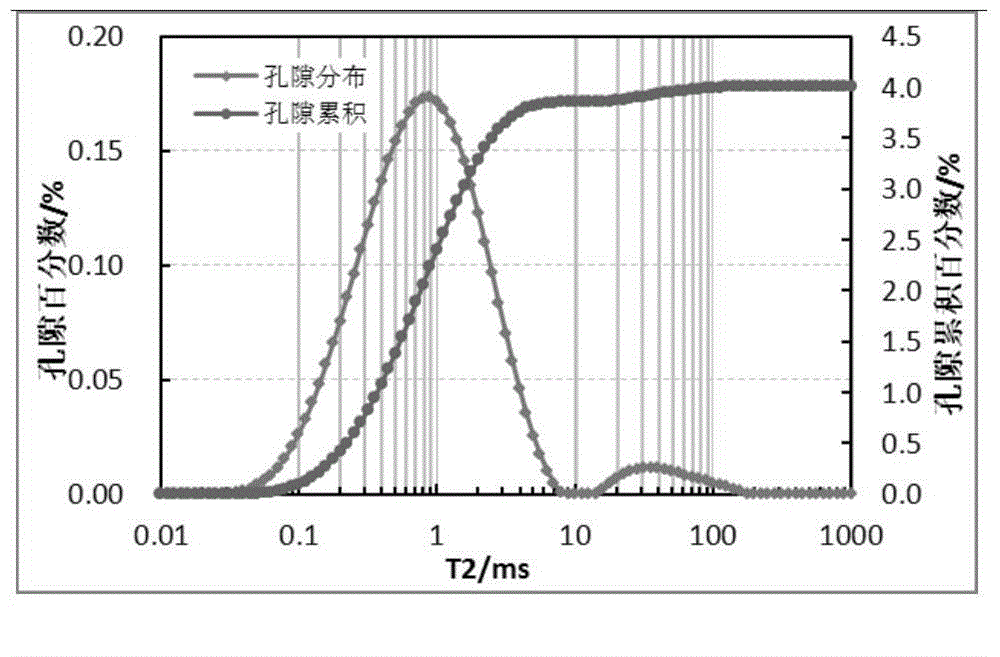
The invention discloses a shale micropore size and fluid distribution analysis method. The shale micropore size and fluid distribution analysis method comprises the following steps that shale gas reservoir rock is collected, and a natural core is manufactured; the relaxation characteristic of hydrogen-contained fluid in core pores is measured through a nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer, and a relaxation time T2 distribution map of clay water is obtained; the core is processed to obtain a saturated core, and a relaxation time T2 distribution map of saturated fluid and a summation curve are obtained; a T2 distribution map of effective fluid is obtained; a T2 distribution map of irreducible fluid and saturability Swi of bound water are obtained; a T2 distribution map of surplus water and water saturation Sw are obtained; the T2 distribution maps of the fluids are converted into a pore size distribution map, the shale clay deadline and the irreducible fluid deadline are obtained, and then the shale micropore size and fluid distribution are obtained. The nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer is adopted, the pore size and distribution of the shale and size and distribution positions of water drops in the pores are analyzed quantitatively and qualitatively, and the result is reliable.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Municipal sludge two-stage deep dehydration method combining chemical regulation strengthening preliminary mechanical dehydration and electroosmosis
ActiveCN104098250AImprove the efficiency of primary mechanical dehydrationImprove dehydration efficiencySludge treatment by de-watering/drying/thickeningSludge cakeBound water
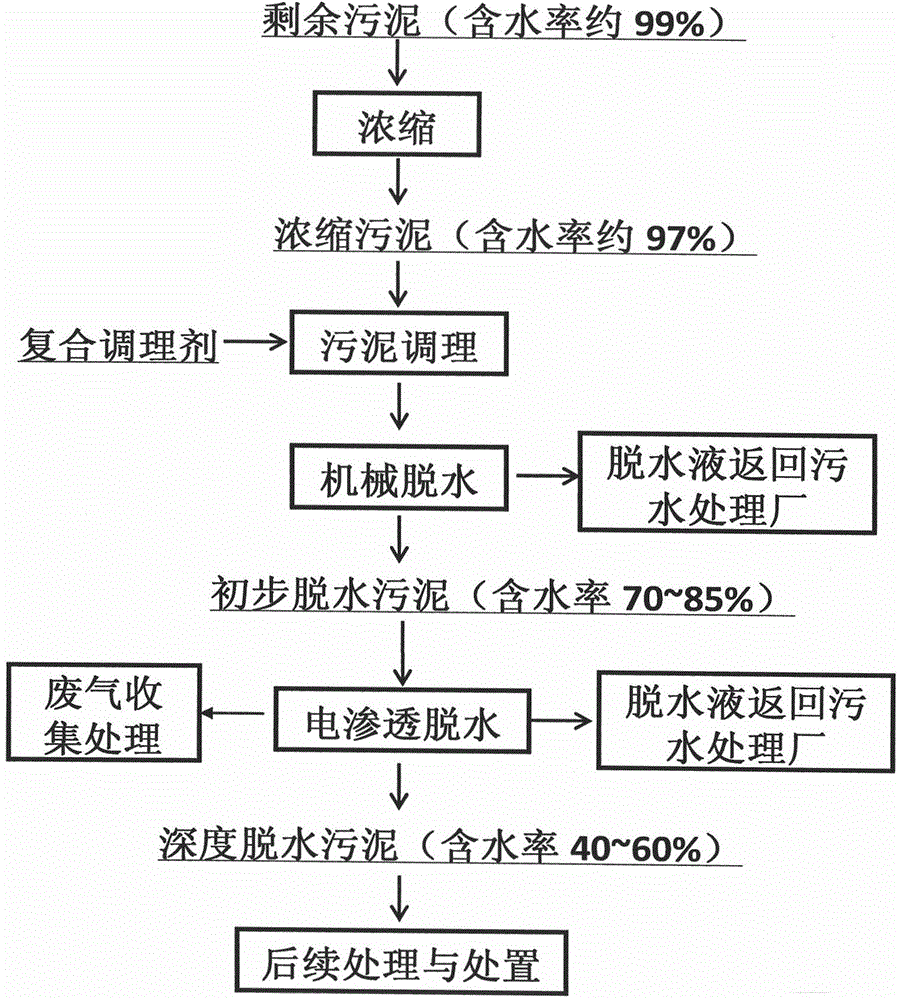
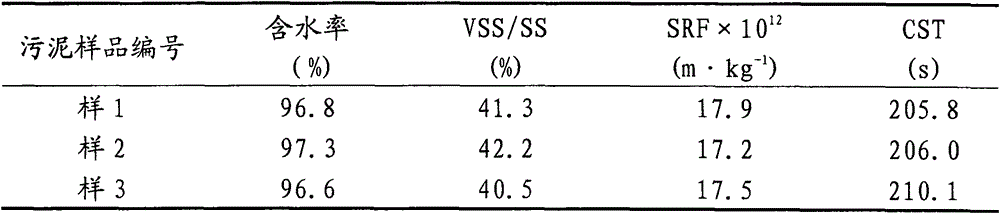
The invention relates to a municipal sludge deep dehydration composite conditioner and a dehydration method, the composite conditioner accounting for 3-30% by dry basis weight of sludge is added for conditioning modification of domestic sewage treatment plant concentrated sludge with the moisture content of about 97% to improve sludge preliminary mechanical dehydration and subsequent electroosmosis dehydration ability; the moisture content of the preliminarily dehydrated conditioned modified sludge is reduced to 70-85%; the preliminarily dehydrated sludge directly enters into electroosmosis dehydration equipment for deep dehydration, the moisture content of the sludge is reduced to 40 to 60%, landfill disposal, thermal conversion, use as building materials and other treatment, dispose and resource utilization can be directly carried out. The method can realize the continuous operation of sludge dehydration, is high in treatment efficiency, can effectively reduce the bound water content of the sludge, is good in dehydration effect, and low in moisture content of deeply dehydrated sludge cake, and is suitable for a newly-constructed sewage treatment plant and design requirements of reconstruction, expansion and contingency plans of sludge dehydration treatment of a sewage treatment plant in the prior art.
Owner:北京亿维德曼科技发展有限公司 +2
Estimating porosity and fluid volume
ActiveUS20110068788A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioEnhanced signalElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingWater resource assessmentPorosityBound water
The present disclosure relates to a method to estimate a subsurface formation property. A downhole logging tool is provided and disposed in a wellbore. Multiple measurements of various measurement types are obtained at various depths of investigation using the downhole logging tool. The multiple measurements may include natural gamma ray measurements, density measurements, resistivity measurements, nuclear measurements, and nuclear magnetic resonance measurements. The signal-to-noise ratio of the measured signals is increased using, for example, lateral stacking and multi-shell inversion. The subsurface formation property is estimated using the increased signal-to-noise ratio signals. The subsurface formation property may include porosity, adsorbed gas volume, free gas volume, bound water volume, free water volume, oil volume, and kerogen volume. A fluid analysis may be performed using a multi-dimensional nuclear magnetic resonance technique. Fluids such as water, oil, gas, and oil-based mud in the wellbore may be identified and / or evaluated.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Advanced detection system and method for TBM (Tunnel Boring Machine) tunnel construction based on forward three-dimensional induced polarization
ActiveCN103076635ACompatibleAutomatically and quickly assign jobsElectric/magnetic detectionAcoustic wave reradiationBound waterWater flow
The invention discloses an advanced detection system and method for TBM (Tunnel Boring Machine) tunnel construction based on forward three-dimensional induced polarization. By fully utilizing a narrow detection space of a full-face excavated tunnel, controlling the opening of cabin doors of a power supply and measuring electrode cabin and a shielding electrode cabin through controllers, and controlling corresponding hydraulic transmission devices to automatically and rapidly arrange power supply, measurement and shielding electrode systems onto a TBM tunneling working face and side wall bottom plates at the rear of the TBM tunneling working face, under the effect of a shielding current system, tomographic detection power supply current points to the front of the working face. By using the detection method based on the forward three-dimensional induced polarization, the three-dimensional geological information of the front of the working face can be obtained. Moreover, by using a relation between induced polarization half-time difference and water flow, the magnitude of the water flow of a water body can be quantitatively forecasted. In addition, the parameter, i.e. the half-time difference has a stronger ability of distinguishing free water and bound water.
Owner:山东百廿慧通工程科技有限公司
Method for estimating formation hydrocarbon saturation using nuclear magnetic resonance measurements
ActiveUS20090206834A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingWater resource assessmentNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceFluid saturation
A method for estimating fluid saturation in a formation penetrated by a wellbore from nuclear magnetic resonance measurements made at a plurality of lateral depths into the formation from the wellbore includes estimating a bound water volume, a total porosity and a free water volume at each of the lateral depths from the nuclear magnetic resonance measurements. A minimum water saturation is estimated at each lateral depth from the total porosity, the free water volume and the bound water volume at each lateral depth. A value of water saturation is estimated at each lateral depth from the minimum water saturation at each lateral depth. A relationship between lateral depth and water saturation is determined. Water saturation is estimated at a selected lateral depth greater than the greatest lateral depth of the nuclear magnetic resonance measurements.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Binding method of water absorbent resin
ActiveUS20110237739A1High strengthContinuously and stably carryGas treatmentDispersed particle separationParticulatesBound water
Aqueous liquid and moisture vapor are added to water absorbent resin powder so that particles of the water absorbent resin powder are bound. In forming bound particles by supplying aqueous liquid and moisture vapor to the water absorbent resin powder, the foregoing arrangement makes it possible to supply moisture to whole the powder so that a less amount of particles remains unbound (ungranulated) and increase of a concentration of the water absorbent resin bound particles allows for further improvement of a drying efficiency and makes it possible to obtain particulate water absorbent resin having excellent properties even when the bound particles are highly concentrated. The present invention provides (i) a method for binding water absorbent resin and (ii) a method for producing particulate water absorbent resin which method includes the step of binding particles of water absorbent resin powder. The foregoing effect can be obtained by these methods.
Owner:NIPPON SHOKUBAI CO LTD
Method for preparing microbial oil and fat
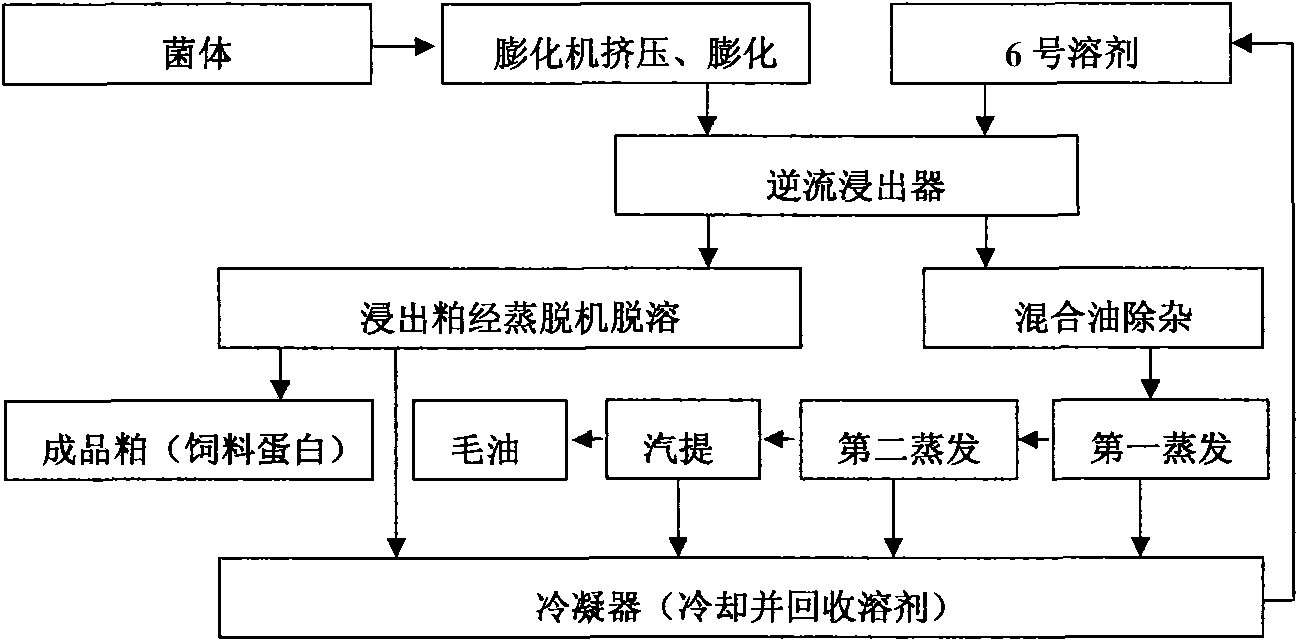
InactiveCN101560440ASimple processImprove product qualityFermentationFatty-oils/fats productionOil and greaseMicrobial oil
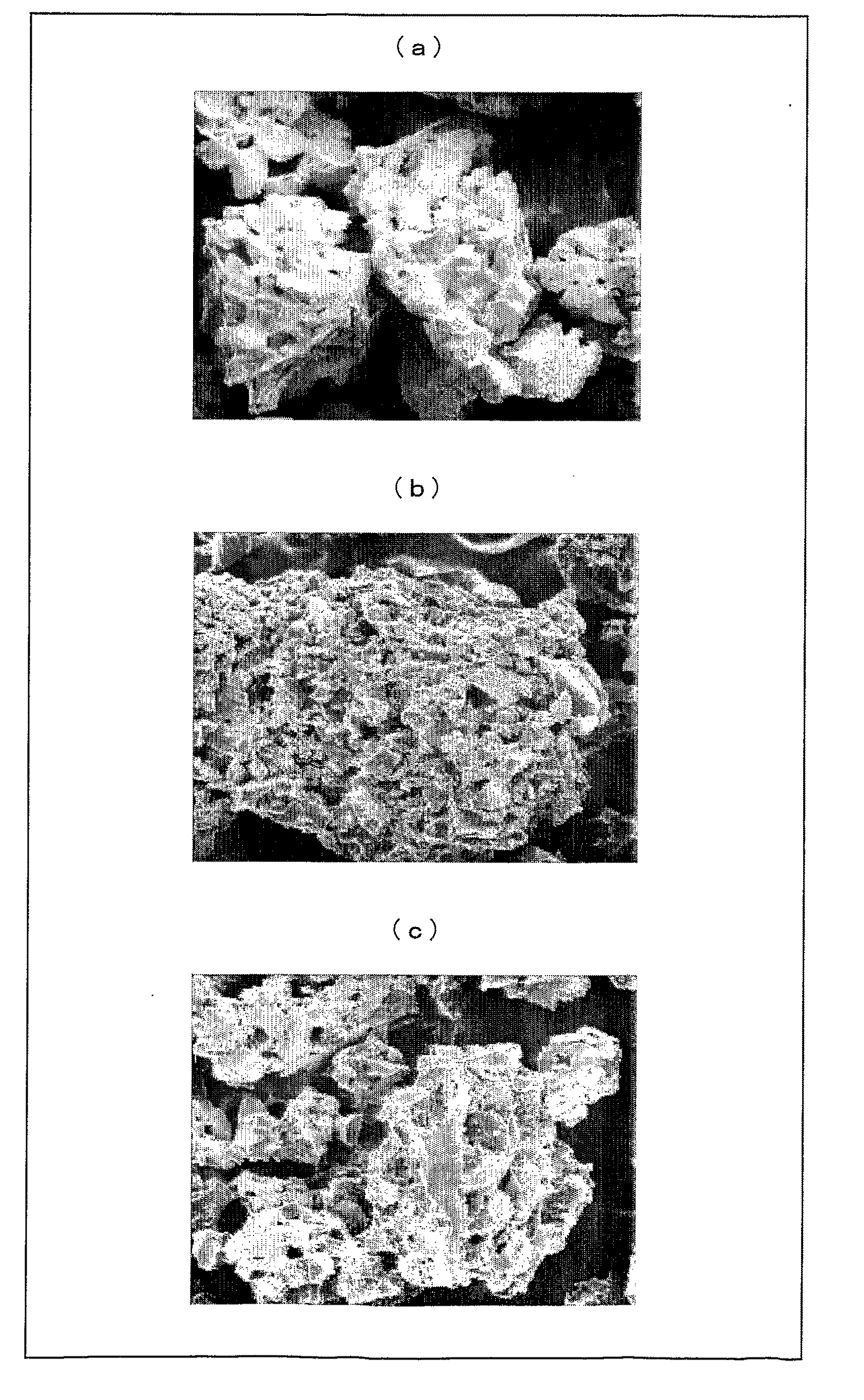
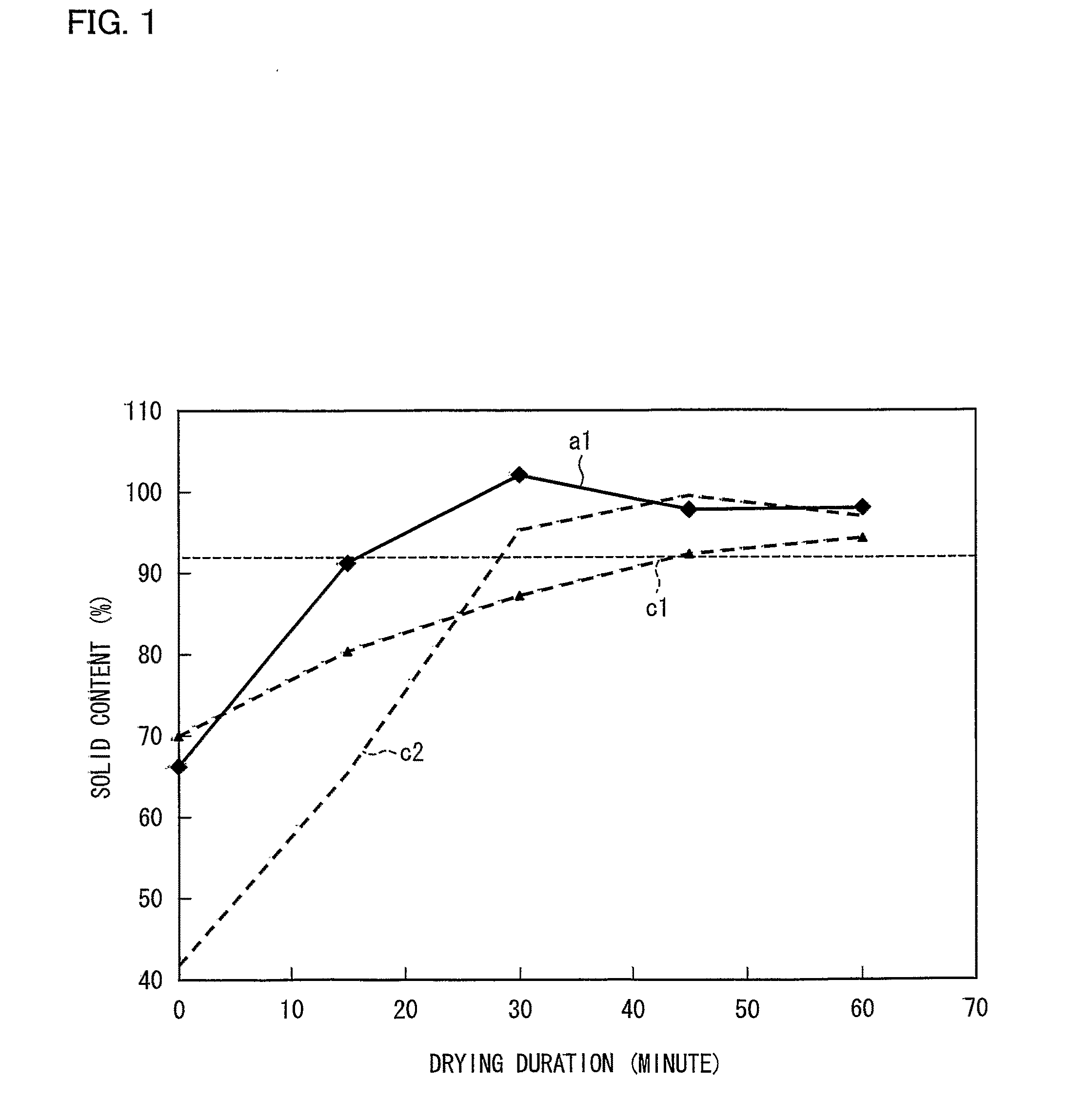
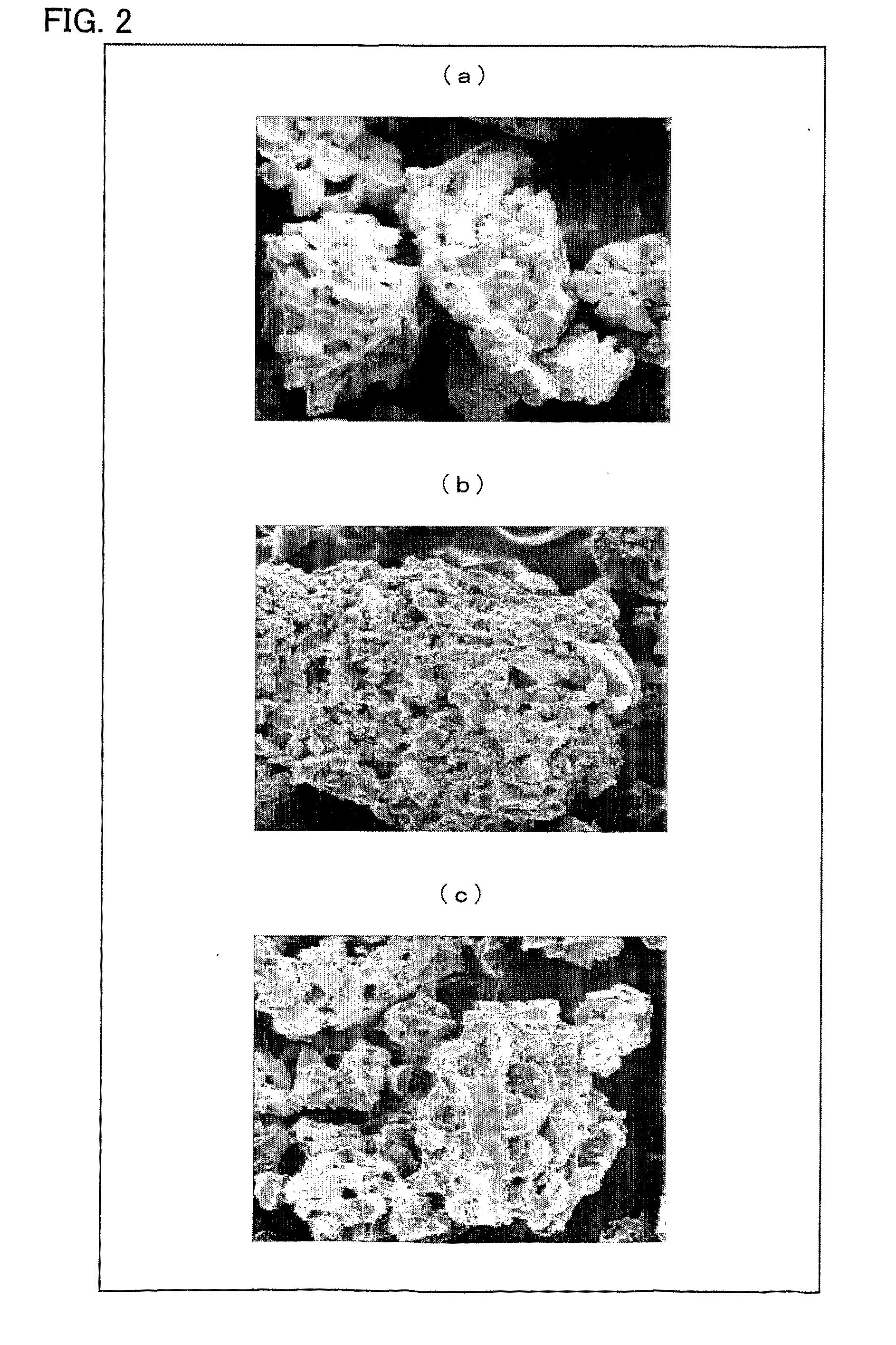
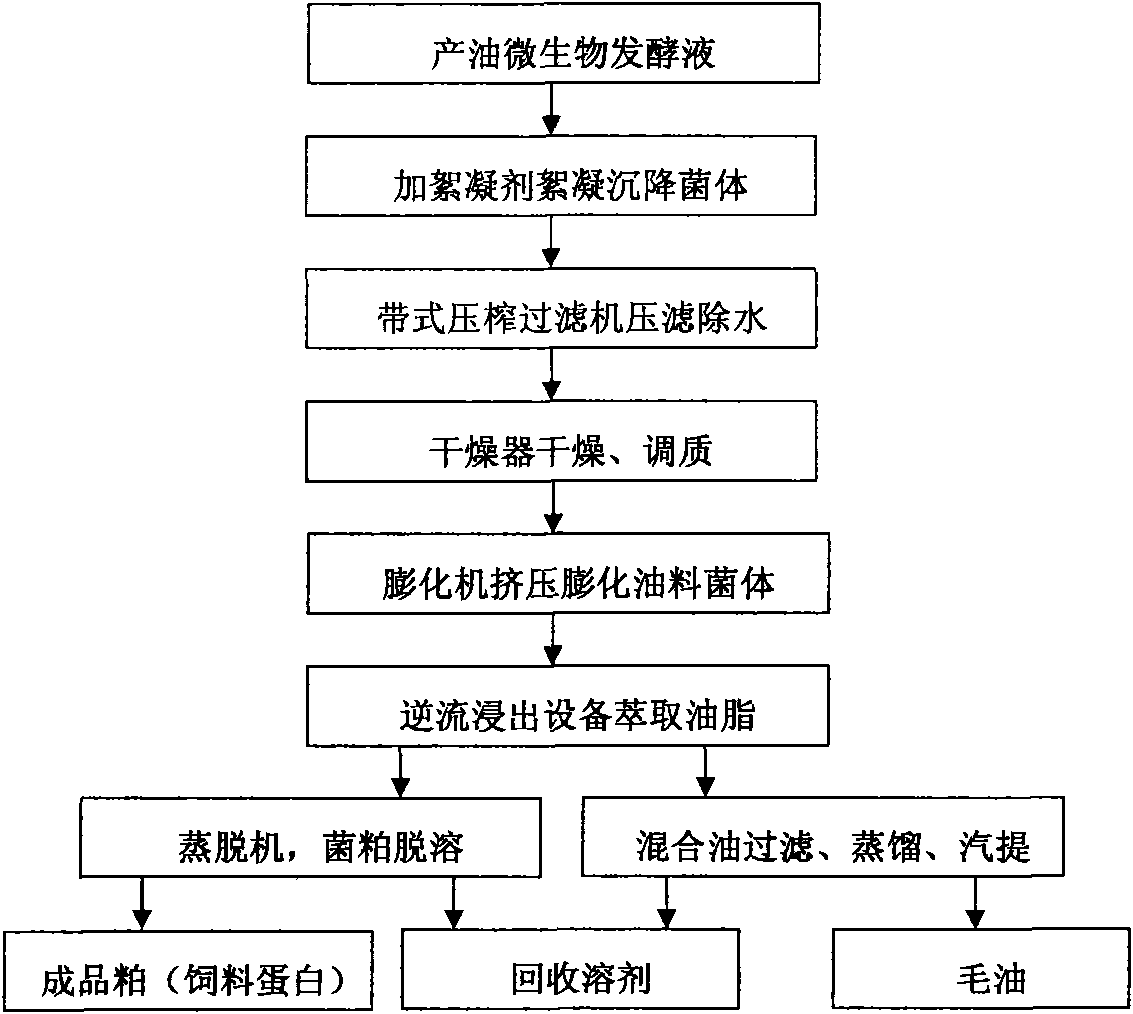
The invention discloses a method for preparing microbial oil and fat, which comprises the following steps: (1) collecting microbial thalli; (2) performing filter pressing on the thalli obtained in the step (1) to obtain wet bacterial mud; (3) performing thermal refining, namely drying the wet bacterial mud obtained in the step (2) to remove most of free moisture and partial bound water in cells, and adjusting the temperature and the moisture content of the obtained dried thalli; (4) performing extrusion swelling, namely putting the dried thalli obtained in the step (3) into an extrusion swelling machine for extrusion and swelling; and (5) extracting and soaking the oil-bearing material dried thalli obtained in the step (4) to obtain mixed oil and soaked thalli residues. The method has the advantages of simple process, large handling capacity, low energy consumption and high product quality, and belongs to the field of oil and fat preparation.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
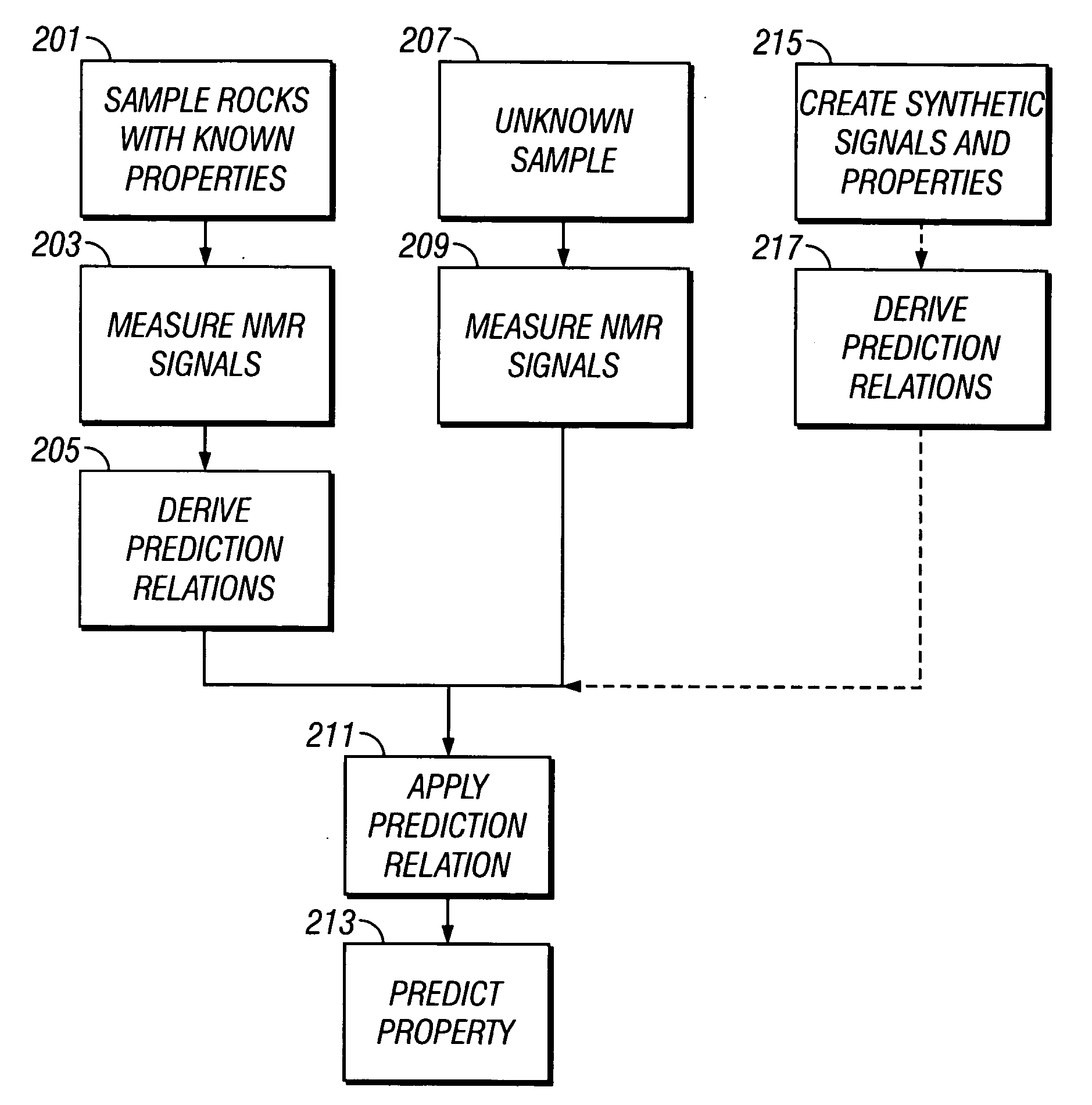
Rock properties prediction, categorization, and recognition from NMR echo-trains using linear and nonlinear regression
ActiveUS20050206378A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingWater resource assessmentBound waterComputational physics
A partial least squares (PLS) regression relates spin echo signals with samples having a known parameter such as bound water (BW), clay bound water (CBW), bound volume irreducible (BVI), porosity (PHI) and effective porosity (PHE). The regression defines a predictive model that is validated and can then be applied to spin echo signals of unknown samples to directly give an estimate of the parameter of interest. The unknown samples may include earth formations in which a NMR sensor assembly is conveyed in a borehole.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
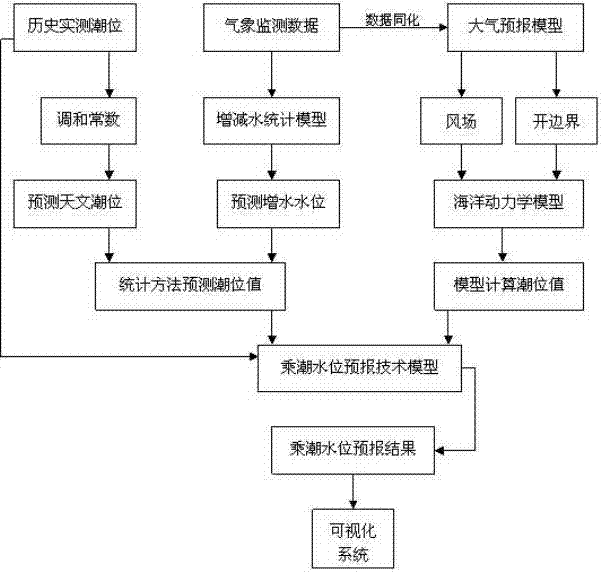
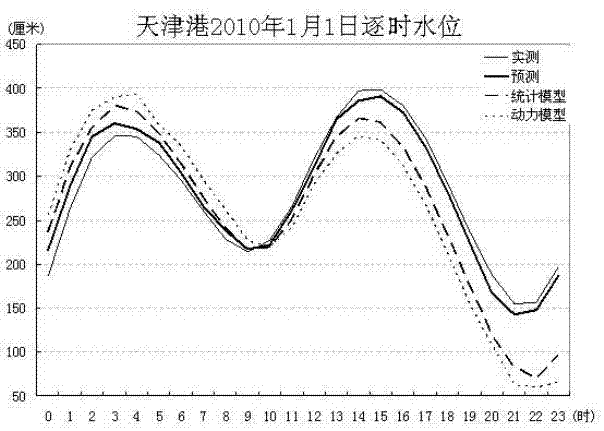
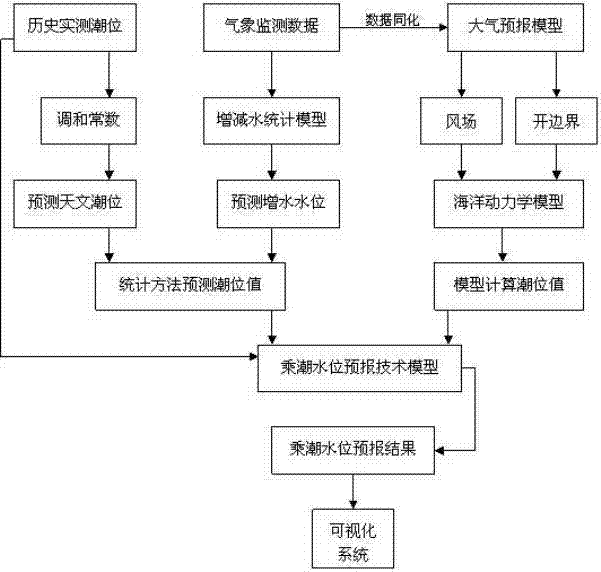
Method for predicting tide-bound water level by combining statistical model and power model
InactiveCN102221389AReal-time access to weather monitoring dataObtain tide level monitoring data in real timeMachines/enginesLevel indicatorsBound waterDynamic models
The invention provides a method for predicting tide-bound water level by combining a statistic model and a power model. The method comprises the following steps of obtaining a tidal harmonic constant; predicting the astronomical tide and water rising level; obtaining predicted tide-bound water level Ls based on the statistic model; calculating and obtaining predicted wind field results and open boundary conditions of the tide according to an atmosphere prediction model; taking the wind field results and the open boundary conditions as a forcing field; using an ocean dynamics model to calculate predicted tide-bound water level Lm containing the astronomical tide and the water rising level; establishing a best tide-bound water level prediction formula based on the veracity analysis on the prediction results of the two models under all time scale and meteorological condition; providing the prediction results on final tide-bound water level L; and displaying the prediction results in realtime by a visualized technology. The method organically couples with monitoring data of weather and sea level, the statistic prediction method of sea level values, an atmosphere and ocean dynamics model and a real-time visualized system so as to achieve the requirement of exactly and quickly predicting the tide-bound water level.
Owner:NAT MARINE DATA & INFORMATION SERVICE
Advanced detector system and method using forward three-dimensional induced polarization method for tbm construction tunnel
ActiveUS20140333308A1Improve work efficiencyLow costElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSurveyBound waterEngineering
Disclosed is an advanced detector system and method using a forward three-dimensional induced polarization method for a TBM (Tunnel Boring Machine) construction tunnel. A narrow detection space of a full-face excavated tunnel is fully used, a controller controls doors of a source and measuring electrode compartment and a shielding electrode compartment to open and controls a corresponding hydraulic delivery device to automatically and quickly arrange a source electrode system, a measuring electrode system and a shielding electrode system. Under the action of a shielding current system, tomography detection supply current is directed ahead of the working face. Three-dimensional geologic information can be obtained, and the relationship between an induced polarization half-decay time difference and a water quantity can be used to quantitatively forecast the water quantity of a water-bearing body, and meanwhile, the half-decay time difference parameter has a high capacity of distinguishing free water from bound water.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Method for conditioning and dehydrating residual sludge
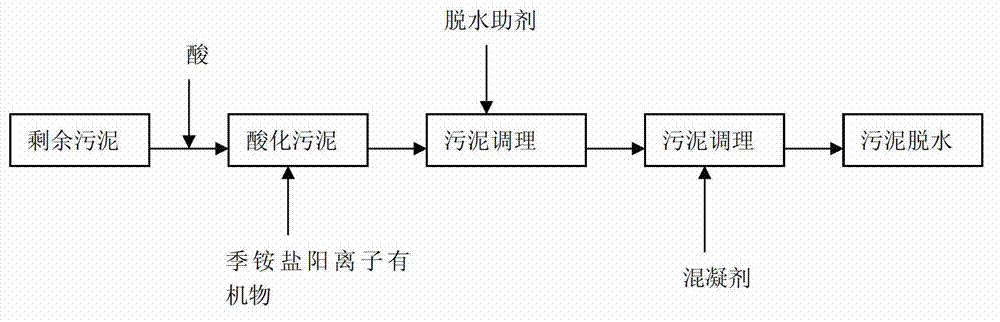
ActiveCN103030259APromote moisture penetrationImprove dehydration effectSludge treatment by de-watering/drying/thickeningPolymer dissolutionBiological cell
The invention relates to the technical field of residual sludge treatment, in particular to a process method for conditioning and dehydrating residual sludge. The method particularly comprises the following steps: (1) adding acid into the residual sludge to be treated and with the water content of 90 to 95 percent and adjusting until the pH value is between 4.0 and 6.0; (2) adding quaternary ammonium salt cationic organic matters into the conditioned sludge in the step (1) and performing hybrid reaction; (3) adding a dehydration aid into the conditioned sludge in the step (2) and stirring uniformly; and (4) adding coagulant into the conditioned sludge in the step (3) and mechanically dehydrating after mixing and stirring. The extracellular polymers on sludge flocs are stripped and partially hydrolyzed by a chemical conditioning mode, microbial cells are dissolved, a large amount of bound water is released, and the water permeability of the sludge is improved by utilizing the aid, so that the dehydration performance of the sludge is integrally improved, the water content of the sludge is reduced, the dehydration time is shortened and the dehydration cost is reduced.
Owner:北京方兴科创环境科技有限公司
Method for identifying fluid type of reservoir with complicated pore structure by using conventional logging information
ActiveCN103603659AReduce investmentImprove exploration effectBorehole/well accessoriesHigh resistanceReservoir type
The invention discloses a method for identifying a fluid type of a reservoir with a complicated pore structure by using conventional logging information and relates to the technical field of judgment of the fluid type according to logging information for oil-gas field exploration and development. The method comprises the steps of 1, distinguishing a gas layer from a non-gas layer according to a ratio of the neutron porosity to the acoustic porosity or the density porosity, wherein the non-gas layer comprises a dry layer, a gas-water layer and a water layer; 2, distinguishing an effective reservoir from an ineffective reservoir in the non-gas layer by a pore-full intersection method; and 3, based on the effective reservoir in the second step, comprehensively identifying the fluid type of the reservoir by a pore-power intersection method and gas logging. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the technical problem in evaluation of fluid type identification for a high-porosity dry layer, a middle-porosity dry layer, a high-resistance water layer and a high-resistance gas-water layer well which have high bound water characteristics under the condition that only conventional logging information is provided is effectively solved, and the difficulty in judgment of the reservoir type represented by the Majiagou formation is effectively solved.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +1
Light weight phosphate cements
A sealant having a specific gravity in the range of from about 0.7 to about 1.6 for heavy oil and / or coal bed methane fields is disclosed. The sealant has a binder including an oxide or hydroxide of Al or of Fe and a phosphoric acid solution. The binder may have MgO or an oxide of Fe and / or an acid phosphate. The binder is present from about 20 to about 50% by weight of the sealant with a lightweight additive present in the range of from about 1 to about 10% by weight of said sealant, a filler, and water sufficient to provide chemically bound water present in the range of from about 9 to about 36% by weight of the sealant when set. A porous ceramic is also disclosed.
Owner:UCHICAGO ARGONNE LLC
Method for treating soft foundation
ActiveCN101831903AReduced bound waterSolve the problem that the water content is difficult to be lower than the critical point of 35%Soil preservationThermal energyVacuum pumping
The invention relates to a method for treating a soft foundation. The method comprises the following steps of: 1, inserting electrical bars into treated soft soil; 2, reserving vertical drainage channels in the treated soft soil and communicating the vertical drainage channels with vacuum-pumping equipment; and 3, starting up the electrical bars to heat the treated soft soil and simultaneously starting up the vacuum-pumping equipment to vacuumize for quickening the drainage of bound water of the treated soft soil. The invention also relates to another method for treating the soft foundation. The method is implemented by arranging the electrical bars in sand drains. Due to the adoption of the method, the bound water in the soft soil can be gasified so that the bound water is quickly drained out of the soft soil, and the difficult problem that the water content of the soft soil is difficult to be lower than the critical point of 35 percent is solved. The method effectively reduces the bound water of the soft soil, realizes controllable improvement of mechanical properties of the soft soil, and meets the requirements of engineering construction by controlling heat energy and heating time. Due to the adoption of the technical scheme of the method, the time limit for a project can be shortened by over 50 percent, the construction cost can be saved by over 30 percent, the quality can be greatly improved, and the construction is environmentally protective.
Owner:SHANGHAI HARBOUR SOFT SOIL TREATMENT ENG CO LTD
Shale porosity measurement method
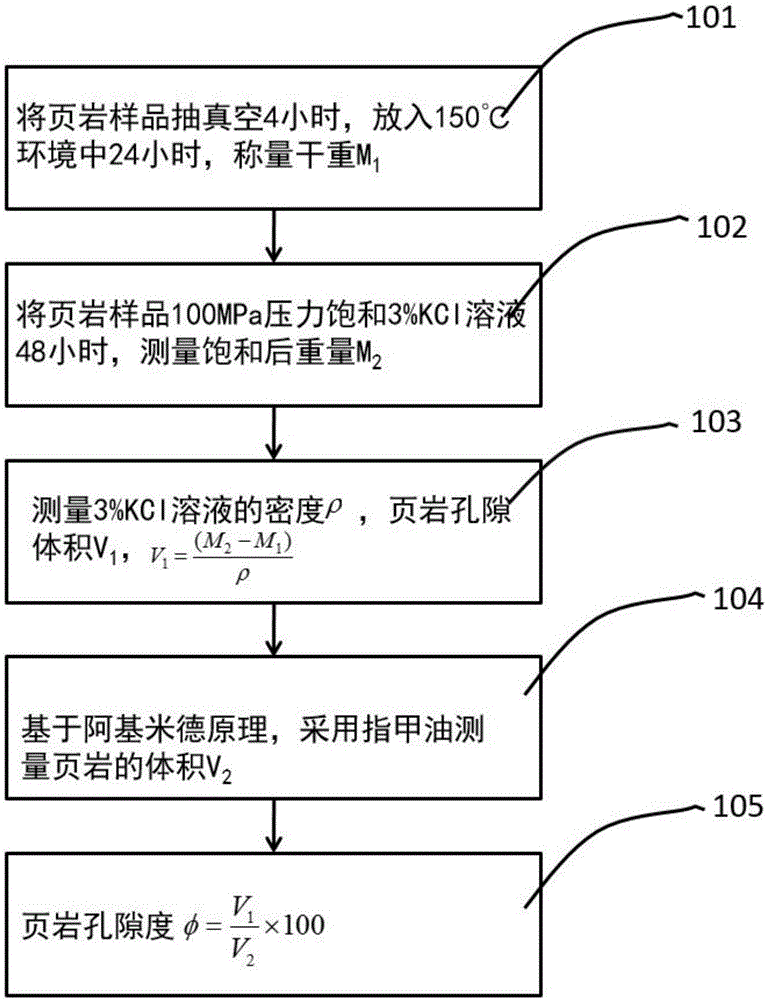
PendingCN106323840AReal volumeAvoid breakingPermeability/surface area analysisWeighing by absorbing componentVacuum pumpingPorosity
The invention discloses a shale porosity measurement method with an aim to solve problems that conventional shale porosity measurement is low in precision, long in time consumption and uneconomical. The shale porosity measurement method includes: selecting a whole-piece to-be-measured shale sample, subjecting shale to vacuum pumping for 4 hours, heating to 150DEG C under the vacuum condition, taking out after 24 hours and weighing dry weight M1; adopting 3% of a KCl solution to perform pressure saturation for 48 hours, and weighing the weight M2 with a scale after the shale is saturated; measuring 3% of the KCl solution to be p in density and calculating porosity volume V1 of the sample (as is shown in the following formula) on the premise of Archimedes principle, placing the shale sample in a container with nail polish, and measuring the volume V2 of the shale sample; calculating the porosity of the sample as is shown in the following formula. With the method, influence of clay-bound water and crystal water on measurement precision of the porosity can be removed, whether the shale sample is regular or not is not required, the method is economic and practical in measurement of the porosity and high in operability.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
Abnormal pressure determination using nuclear magnetic resonance logging
ActiveUS6954066B2Accurate porosityResolution problemElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingWater resource assessmentPorosityBound water
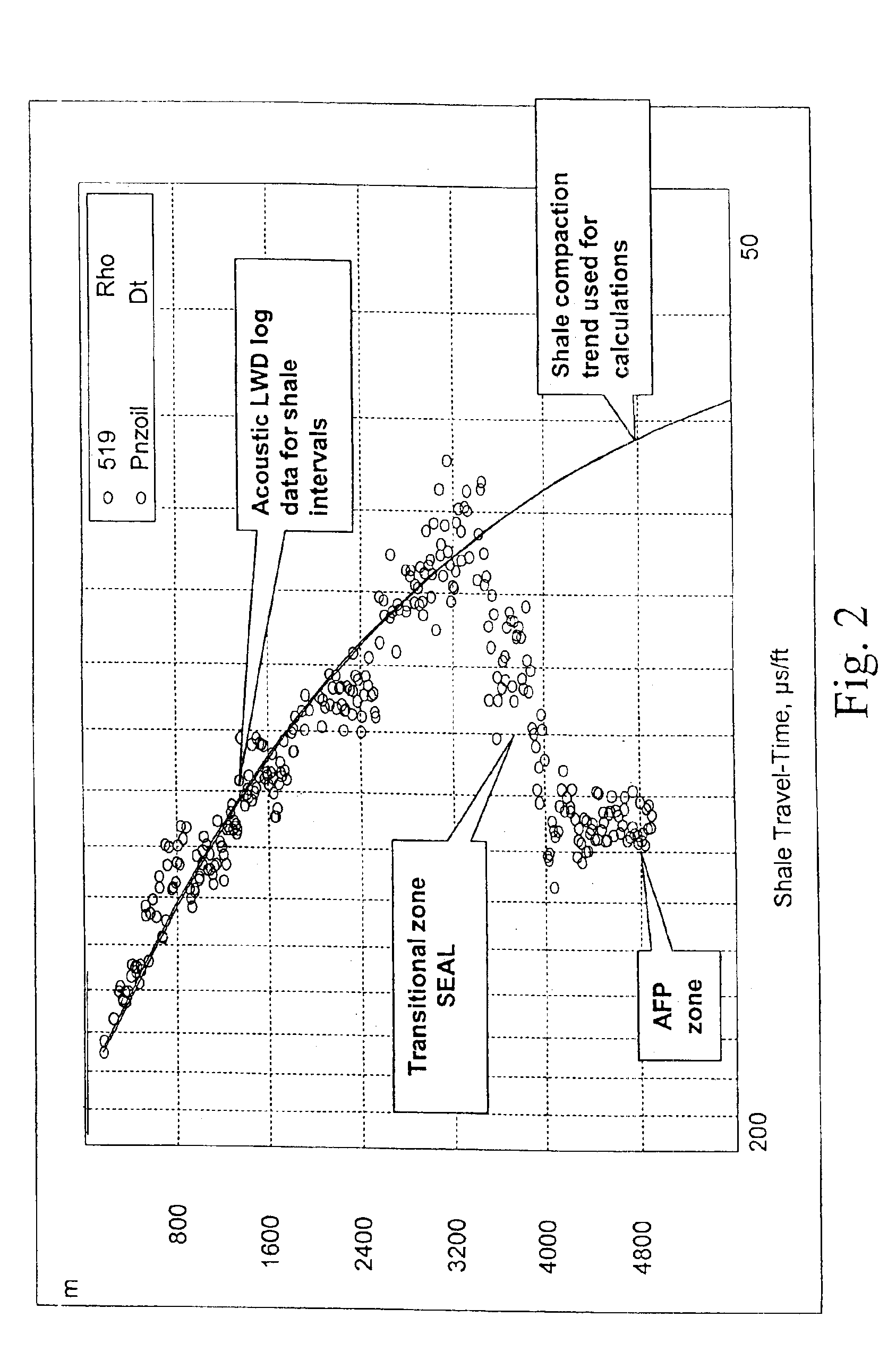
A method and apparatus for determining abnormal pressure zones of a geologic formation using NMR measurements, preferably for logging-while-drilling applications. In a preferred embodiment, a normal compaction trend is constructed using NMR-derived clay bound water volume (CBW) content for non-consolidated subsurface formations or bulk volume irreducible (BVI) and CBW for consolidated formations versus depth. Deviations from this normal compaction trend are used to indicate the presence of shale sections with higher porosity that directly corresponds to an overpressured top seal or transitional zone.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Apparatus and method for monitoring deep tissue temperature using broadband diffuse optical spectroscopy
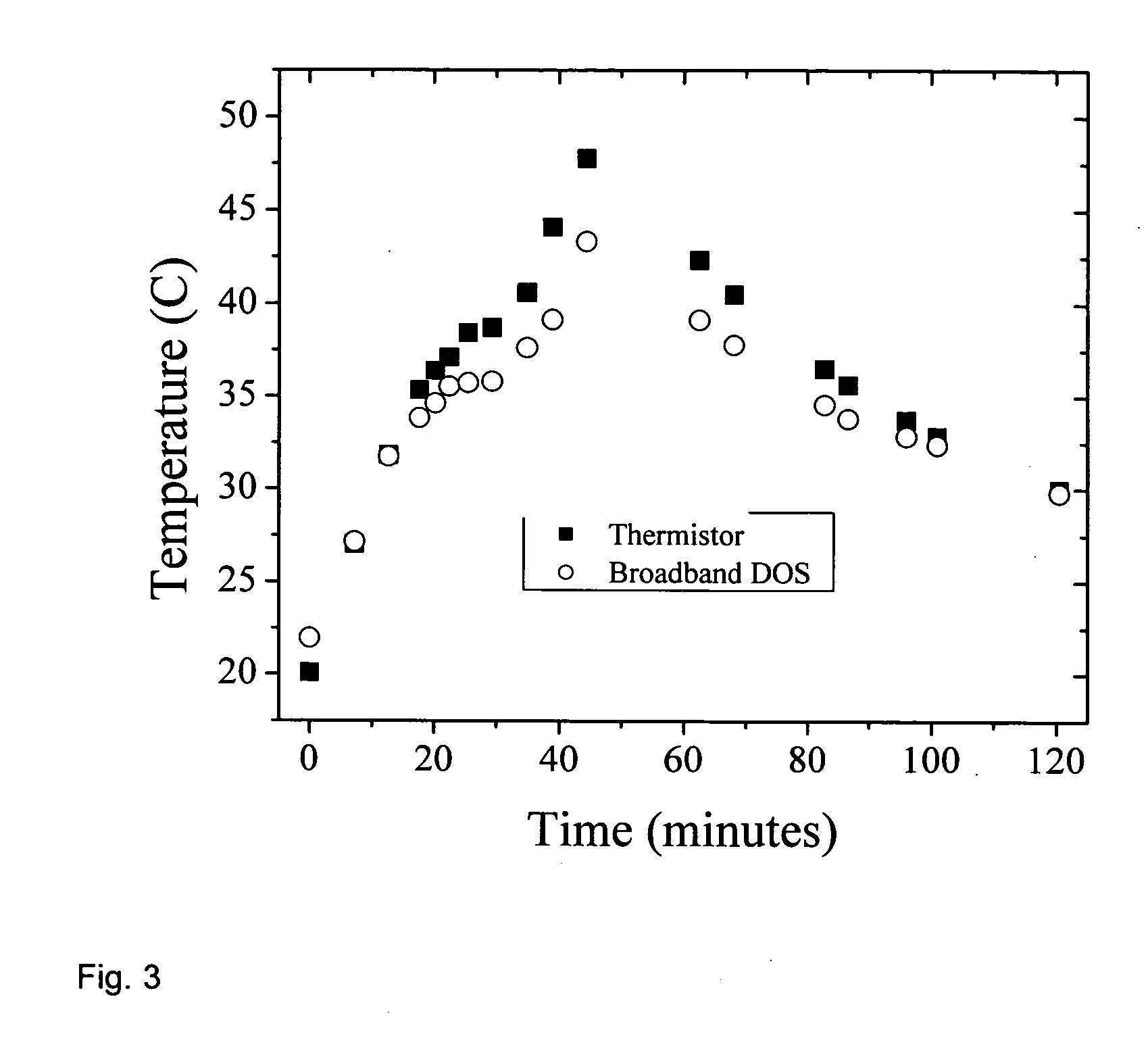
InactiveUS20060111622A1High strengthImproved chromophore fitDiagnostics using lightSensorsLipid formationBound water
A method for noninvasively determining deep tissue temperature comprises measuring data relating to spectral shifts of chromophore absorption in tissue using broadband diffuse optical spectroscopy and generating a temperature reading corresponding to the spectral shift of an absorption peak of the chromophore. A bound water correction is made to the spectral shift. A frequency domain measurement at multiple wavelengths is made to determine the absolute absorption and scattering values between 600 and 1050 nm. The measurement of an absolute absorption comprises measuring an absolute absorption coefficient of selected tissue and further comprising deducing concentrations of tissue composition including lipids, deducing information related to heterogeneity and integrity of tissue matrix, and deducing temperature heterogeneity related to vulnerable plaque in vascular tissue. The measurement comprises making a measurement in the range of 600-1100 nm to interrogate a vessel wall in the presence of blood.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
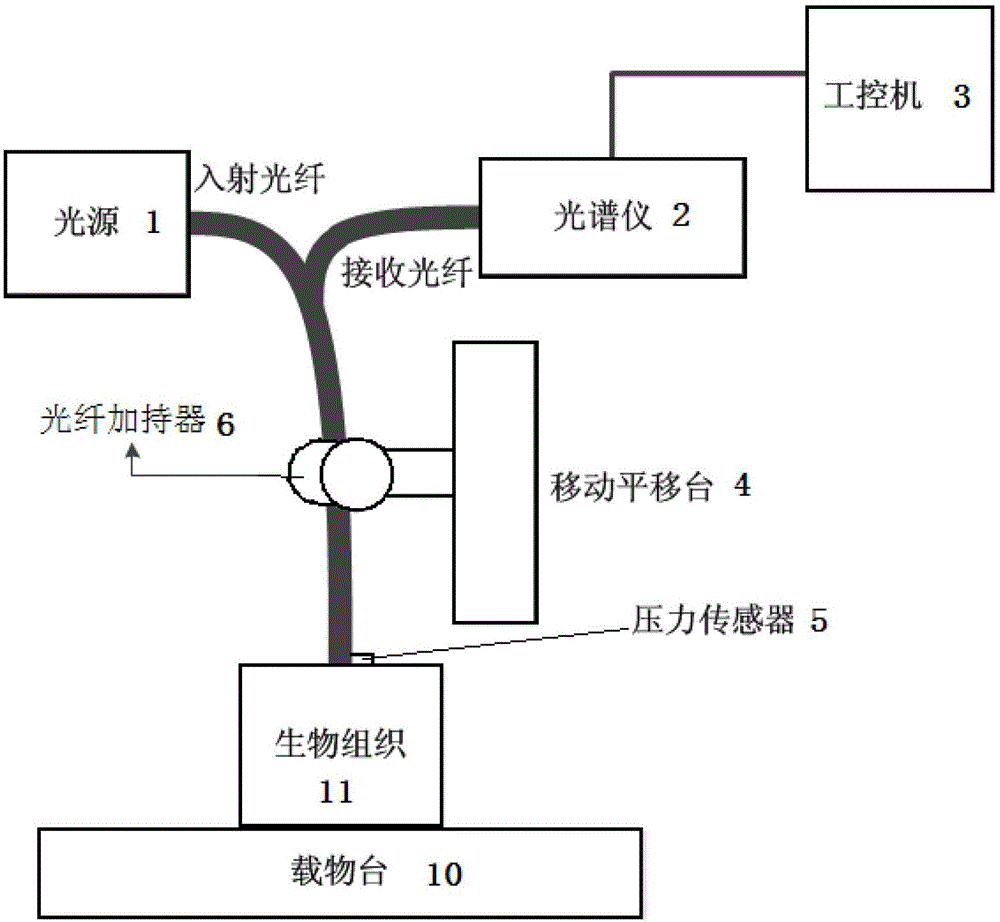
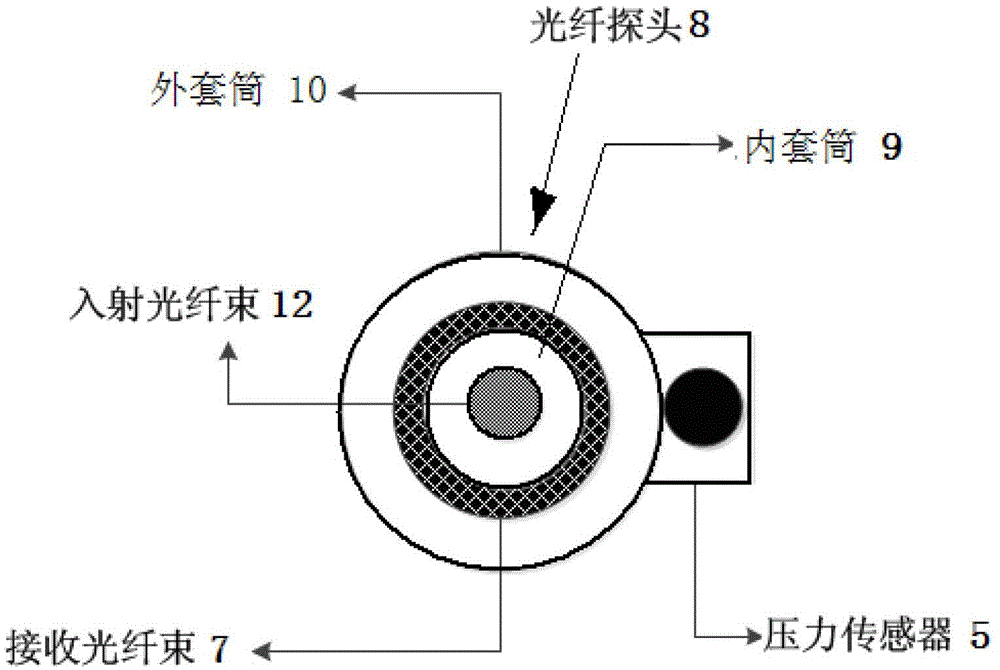
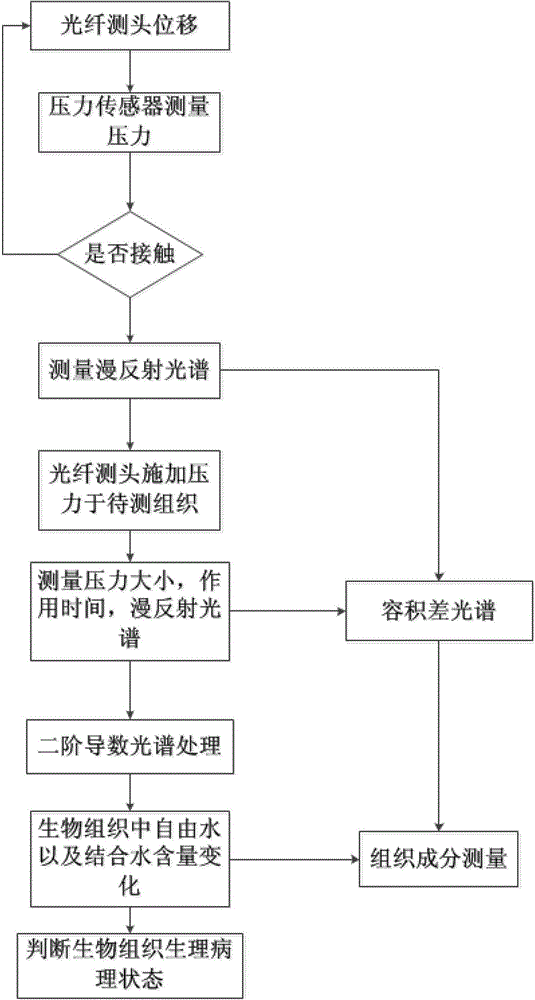
Device and method for detecting biological tissue of pressure modulation near infrared spectrum
ActiveCN103149177AImprove measurement signal-to-noise ratioBlood sugar is accurately obtainedScattering properties measurementsInfraredAnalyte
The invention discloses a device and a method for detecting biological tissue of pressure modulation near infrared spectrum. Biological tissue physiological status judgment and volume difference spectrum measurement are achieved according to pressure and spectrum measuring results in the process of deformation of the biological tissue: changing of biological tissue diffuse reflection spectrum along with the pressure and action time is respectively measured, multiplicative scatter correction and second derivative processing are conducted to the measured spectrum, content change of free water and bound water is obtained, fitting processing is conducted to the content change of the free water and the bound water, the pressure and the action time, biological tissue status is judged according to a fitting curve trend; differential treatment is conducted to diffuse reflection spectrum obtained under different pressure values, the water content change in the tissue is taken as a reference, physiological background of the tissue is deducted, and spectrum net analyte signals of tissue elements are obtained. According to method for detecting the biological tissue of the pressure modulation near infrared spectrum, rapid detecting of physiological status of the biological tissue is achieved, and spectrum detection accuracy of the tissue elements is improved.
Method for determining and building bound water for crack-pore (hole) type reservoir core
InactiveCN102608011AReduce water salinityGood effectPreparing sample for investigationPermeability/surface area analysisComing outBound water
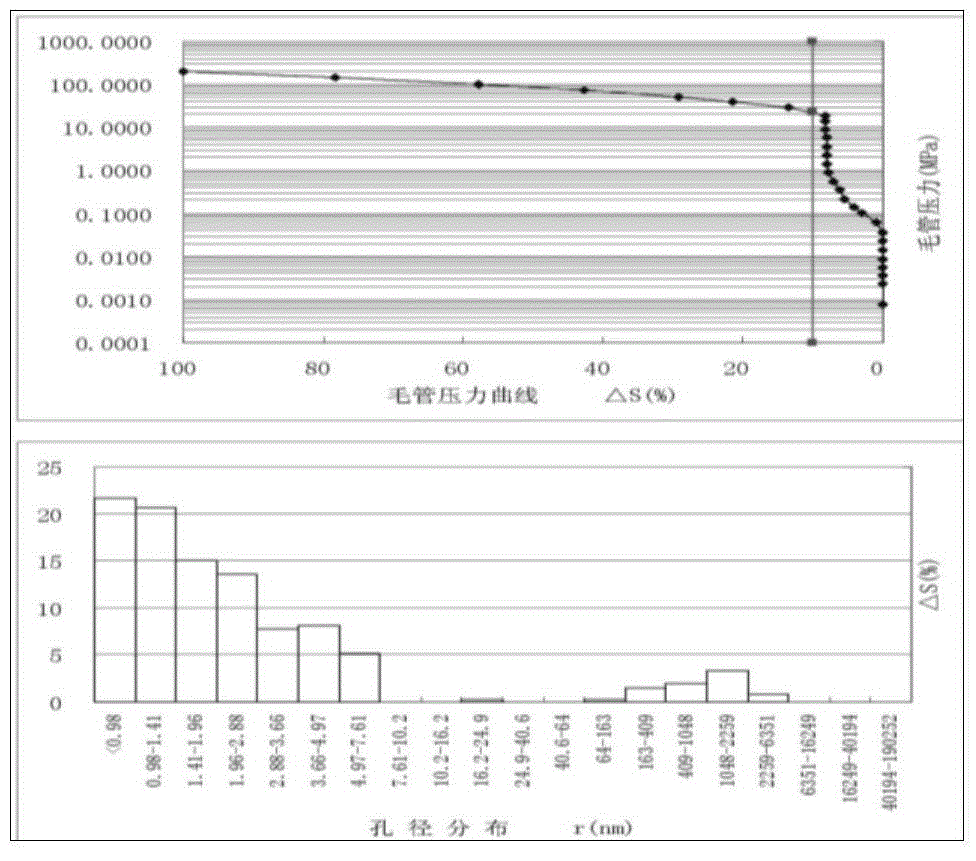
The invention relates to a method for determining and building bound water for a crack-pore (hole) type reservoir core. The method sequentially comprises the following steps of: (1) selecting a crack-free reservoir core; (2) preparing formation water and simulated oil; (3) cleaning and emptying the core, saturating the formation water, driving water by dry gas or the simulation oil until the water does not come out, and thus obtaining the saturation degree of the bound water of a basic rock; (4) perforating the core; (5) calculating the saturation degree of the bound water of the crack-pore (hole) type reservoir core; (6) putting the core into a clamp, and quantitatively saturating bound water for the core; (7) heating the clamp under negative pressure until the system temperature is 120 DEG C, so that the water becomes steam and uniformly distributed; and (8) opening an inlet of the clamp, injecting the simulated oil or the dry gas for displacement, recording a water drainage amount,and thus obtaining the actual saturation degree of the bound water of the core. According to the method, the principle is reliable, the operation is easy, and a reliable physical simulation basis is supplied to a seepage experiment of a crack-pore (hole) type reservoir.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
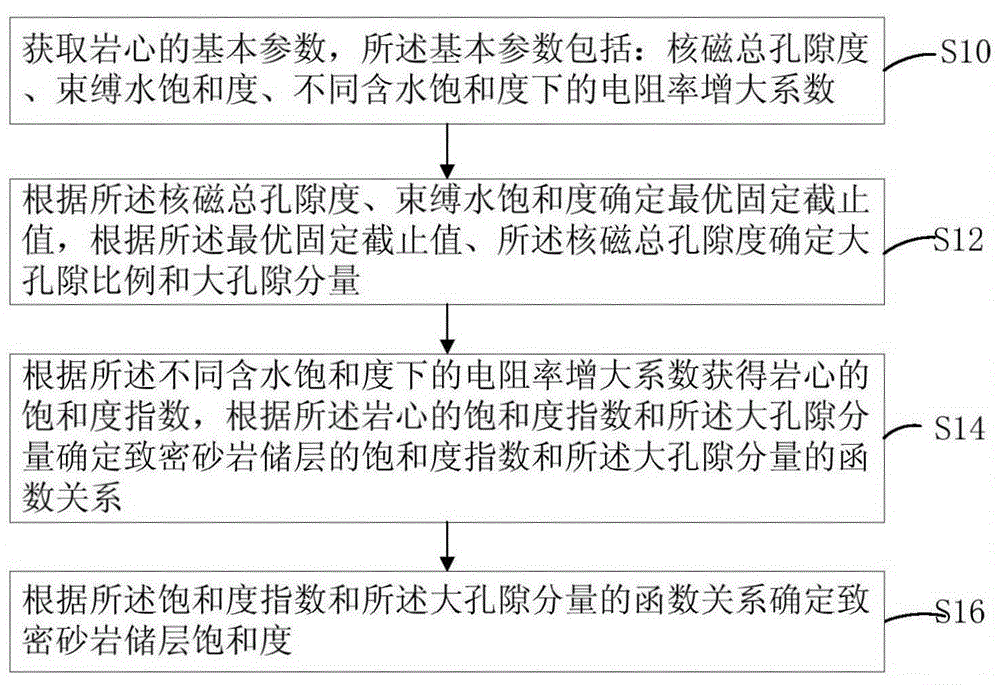
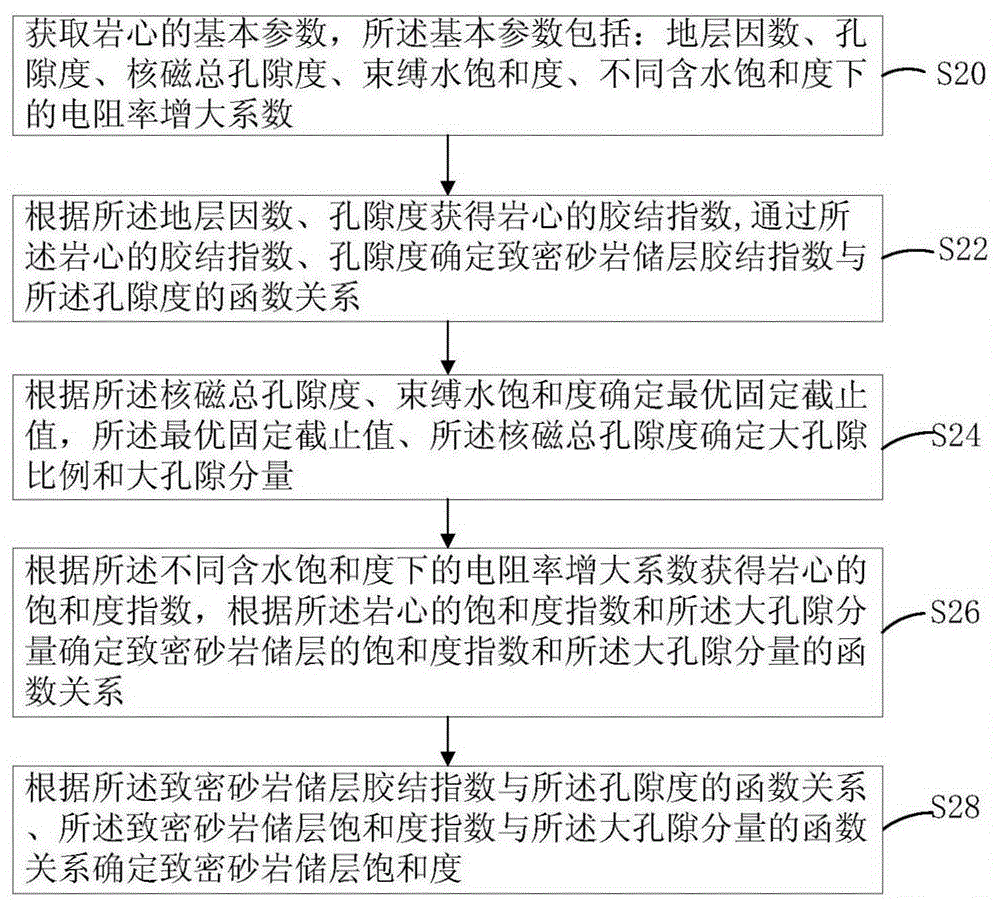
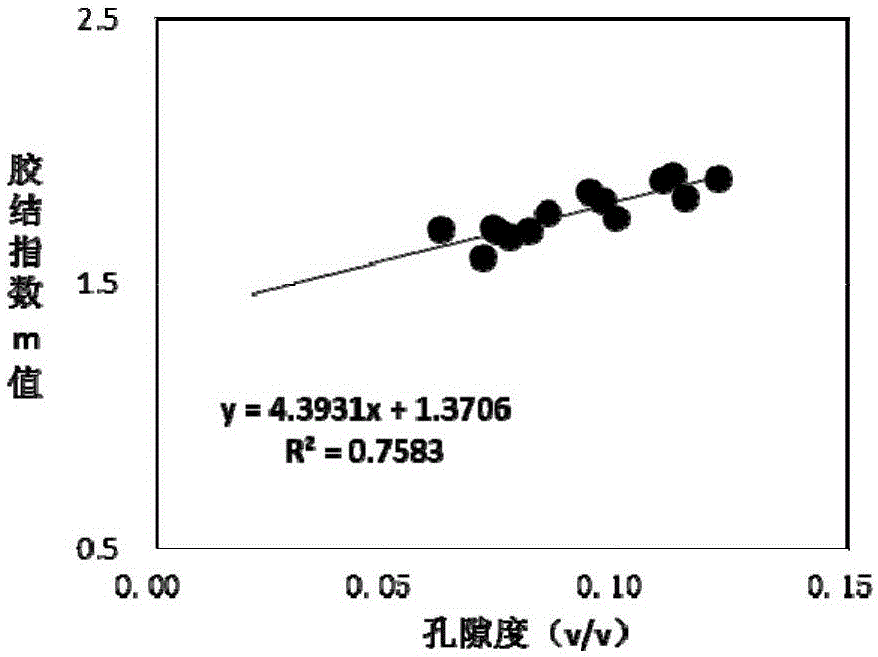
Method for determining saturation of compact sandstone reservoir
ActiveCN105114064AAccurately determineImprove saturation calculation accuracySpecial data processing applicationsBorehole/well accessoriesNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceRock core
The invention discloses a method for determining saturation of a compact sandstone reservoir. The method includes: acquiring basic parameters of a rock core, wherein the basic parameters include nuclear magnetic resonance total porosity, bound water saturation and resistivity increasing coefficient under different saturation degrees; determining an optimal fixed cutoff value according to the nuclear magnetic resonance total porosity and bound water saturation, and determining macropore ratio and macropore component according to the optimal fixed cutoff value and the nuclear magnetic resonance total porosity; acquiring saturation coefficient of the rock core according to the resistivity increasing coefficient, and determining a function relation between saturation coefficient of the compact sandstone reservoir and the macropore component according to the saturation coefficient of the rock core and the macropore component; determining saturation of the compact sandstone reservoir according to the function relation between the saturation coefficient and the macropore component. By the method, saturation of the compact sandstone reservoir can be determined accurately.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Nuclear magnetic resonance evaluation using independent component analysis (ICA)-based blind source separation
InactiveUS20090072824A1Efficient and effective in separatingElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingWater resource assessmentTime domainBound water
Disclosed is a non-lineal statistical independent component (ICA) analysis methodology for calculating T2 or T1 distributions of nuclear magnetic resonance logs. In one aspect, the invention employs a classical blind source separation (BSS) approach with the input data (T2 or T1 distributions) being considered not only horizontally (in relaxation time units), but also vertically (in depth). The statistical variations are used for separating the principal independent components and their corresponding weighting matrix. The result of such ICA based BSS is an efficient separation of T2 components correlative to the presence of particular conditions (e.g., clay bound water, heavy oil, capillary bound water, free water, mud filtrate (water and oil), and noise). Individual saturation of estimated fluids can be calculated from the weighting matrix generated in accordance with the invention. In accordance with a further feature of the invention, it is contemplated that independent component analysis techniques may be applied to the underlying time domain data prior to its transformation to a T2 distribution. This advantageously results in “de-noising” of the signal, leading to more precise and accurate results following analysis of the T2 distribution.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
In-situ heavy-oil reservoir evaluation with artificial temperature elevation
InactiveUS20030034777A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSurveyBound waterRoom temperature
Many reservoirs of interest include heavy oil. In such reservoirs, parti at normal temperatures, many instruments commonly used for formation evaluation may not be able to distinguish between heavy oil and bound water in the formation. Passive or active heating is used to elevate the temperature of the fluids in the formation. At elevated temperatures, distinguishing between heavy oil and bound water is easier. Of particular interest is the increase in the resolvability of the transverse relaxation time T2 of NMR spin echo measurements. Additionally, the dielectric constant and the loss tangents of water and heavy oil show different temperature and frequency dependence.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
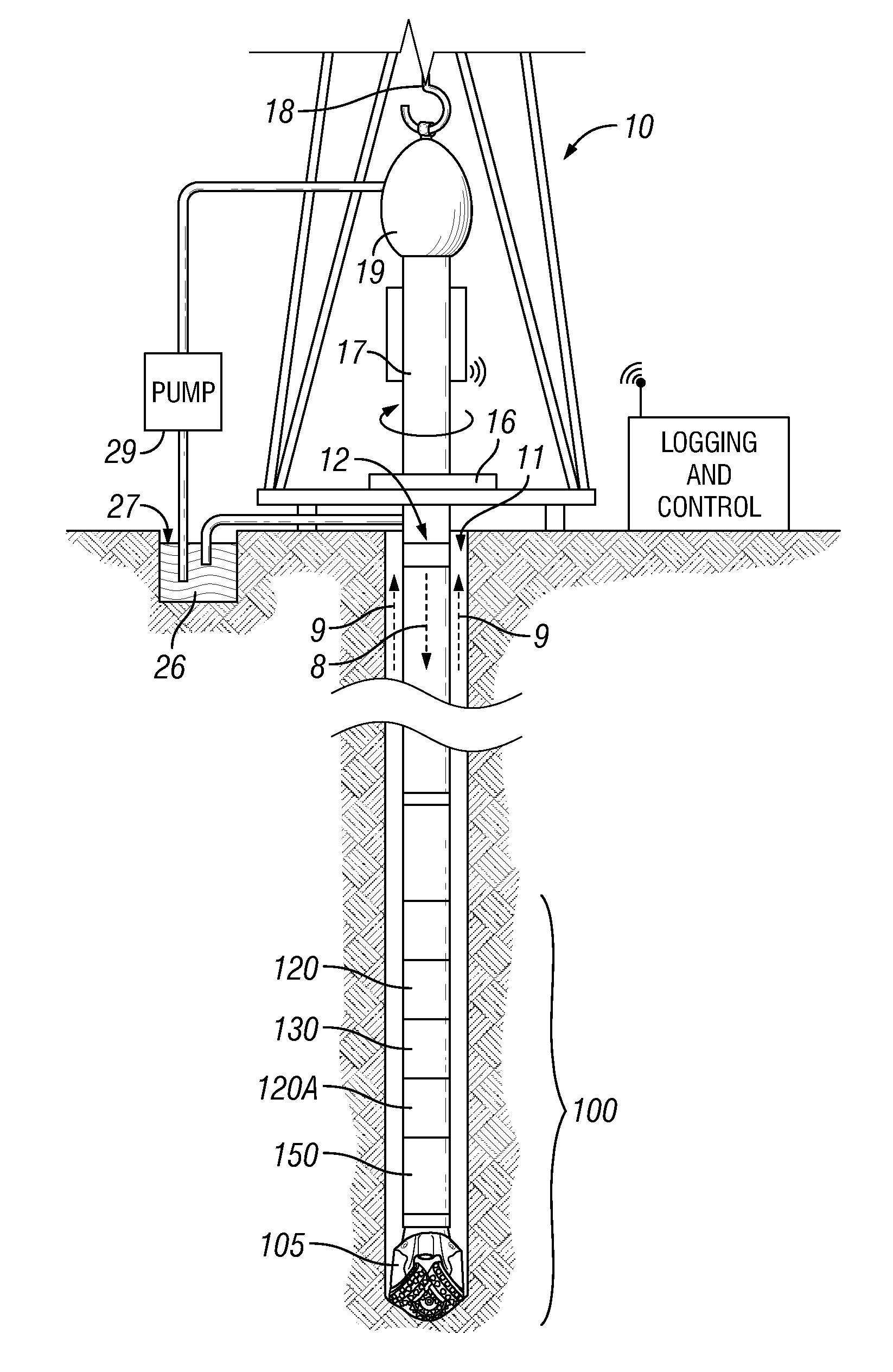
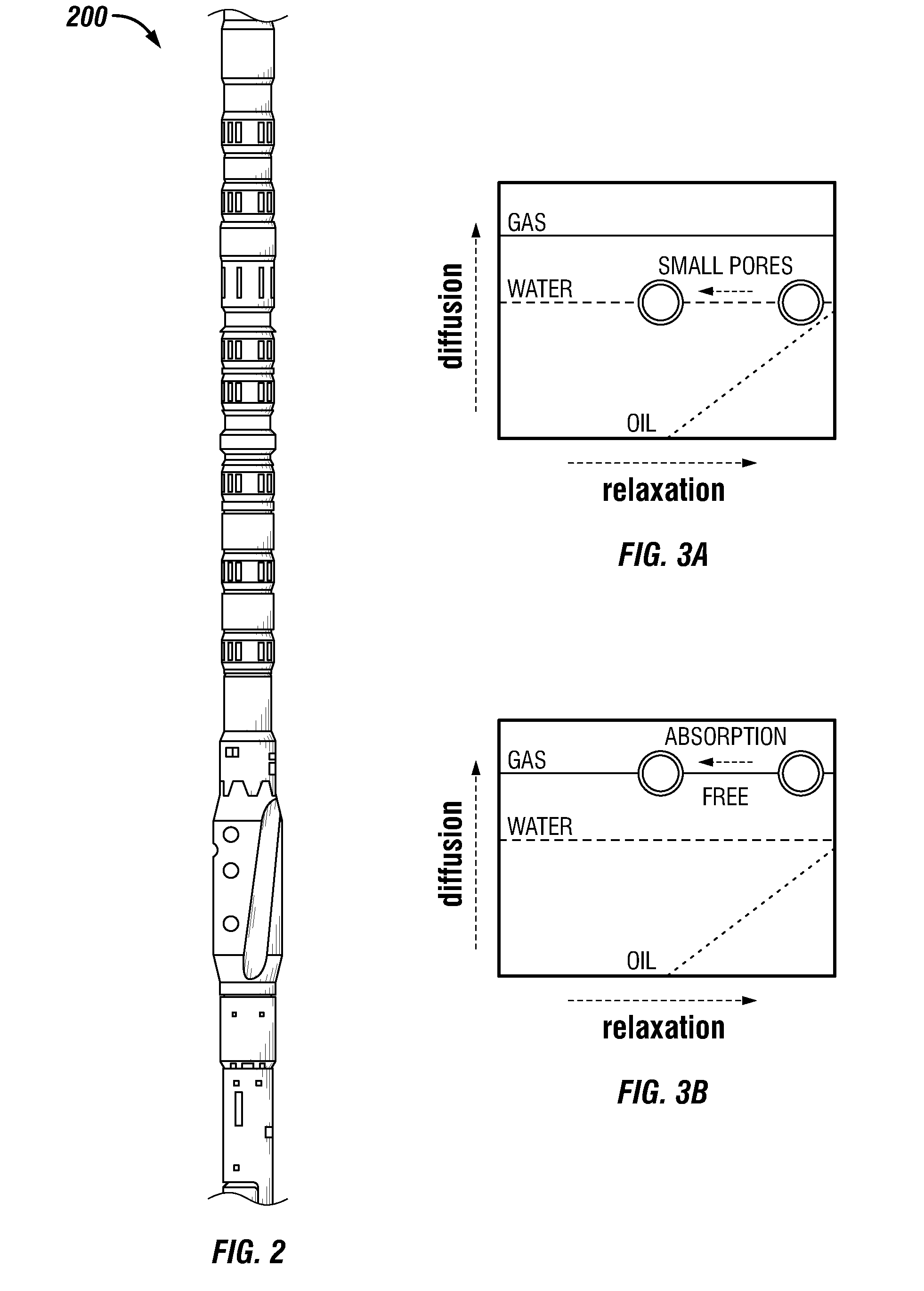
High-resolution high-speed NMR well logging device
InactiveUS6720765B2Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingWater resource assessmentBound waterNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
Wireline NMR well logging measurements suffer from disadvantages of poor vertical resolution, logging speeds less than 20 ft / min, and power consumption in excess of 200 W. In spite of these disadvantages, NMR well logging is used because it is capable of providing estimates for a number of petrophysical parameters that are difficult to obtain from other wireline data. These include estimates of the bulk volume irreducible (BVI) of fluids in the formation. The present invention targets BVI and clay bound water (CBW) measurements. Logging speeds of up to 60 ft / min are attainable with little or no loss of resolution. In one preferred embodiment, the tool has four sensors circumferentially distributed around the logging tool and in contact with the borehole wall. A horseshoe like magnet is used to generate the static magnetic field. The magnet poles are designed such that the magnetic field is uniform perpendicular tool motion, as well as provide a sufficiently large extent of the static field to provide polarization for bound water in rock formations. The RF portion of the sensor is comprised of at least one coil configured for transmission of an RF magnetic field into rock formations and at least two coils configured to separately receive the NMR signal from the formation. In another embodiment a coil is wound around the pole pieces or the iron yoke for the purpose of field shifting to enable acquisition of phase-alternated measurements.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Experimental method for saturated shale pore fluid separation and saturation degree calculation
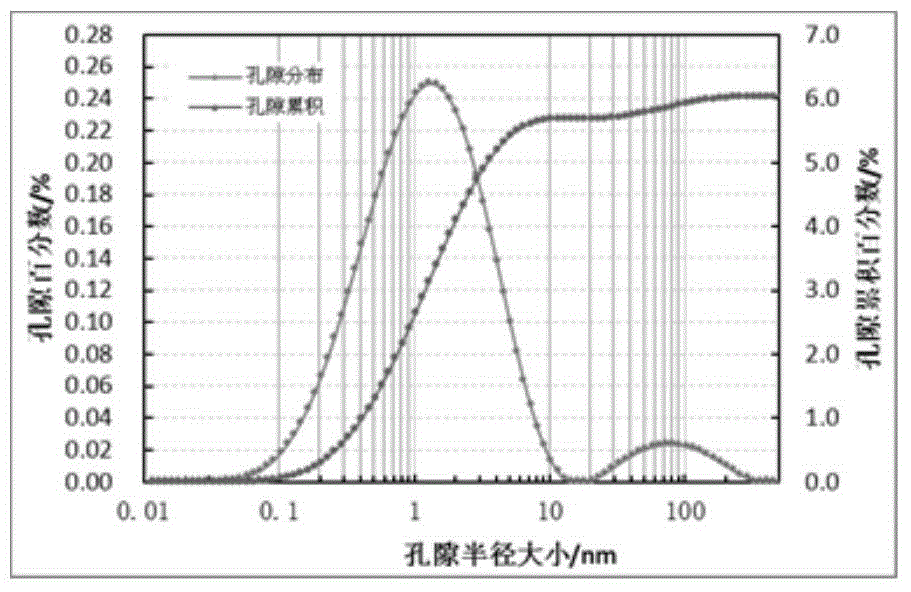
ActiveCN106525688AEfficient separationGet saturation distributionWater resource assessmentAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceChemical physics
The invention discloses an experimental method for saturated shale pore fluid separation and saturation degree calculation. The method includes the steps that firstly, separation of movable water in saturated shale is carried out through two times of a high-speed centrifugation method, and then a vacuum gradient heating experiment is added to separate capillary bound water and clay bound water in pore fluid. In the whole process, by carrying out contrastive analysis on change rules of a core weight and residual fluid nuclear magnetic resonance relaxation time T2 distribution frequency spectrum obtained after each step is completed, the saturation degrees of the movable water in saturated core pores, the capillary bound water and the clay bound water are obtained, and the saturation degree distribution of the movable water in crack space and pore space is obtained. The nuclear magnetic resonance core analysis technology is further used for calculating the storage percentage of the movable water in shale cracks and large pores, and reference is provided for evaluation of seepage space of a shale reservoir.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Prussian Blue Analogue Electrodes without Zeolitic Water Content
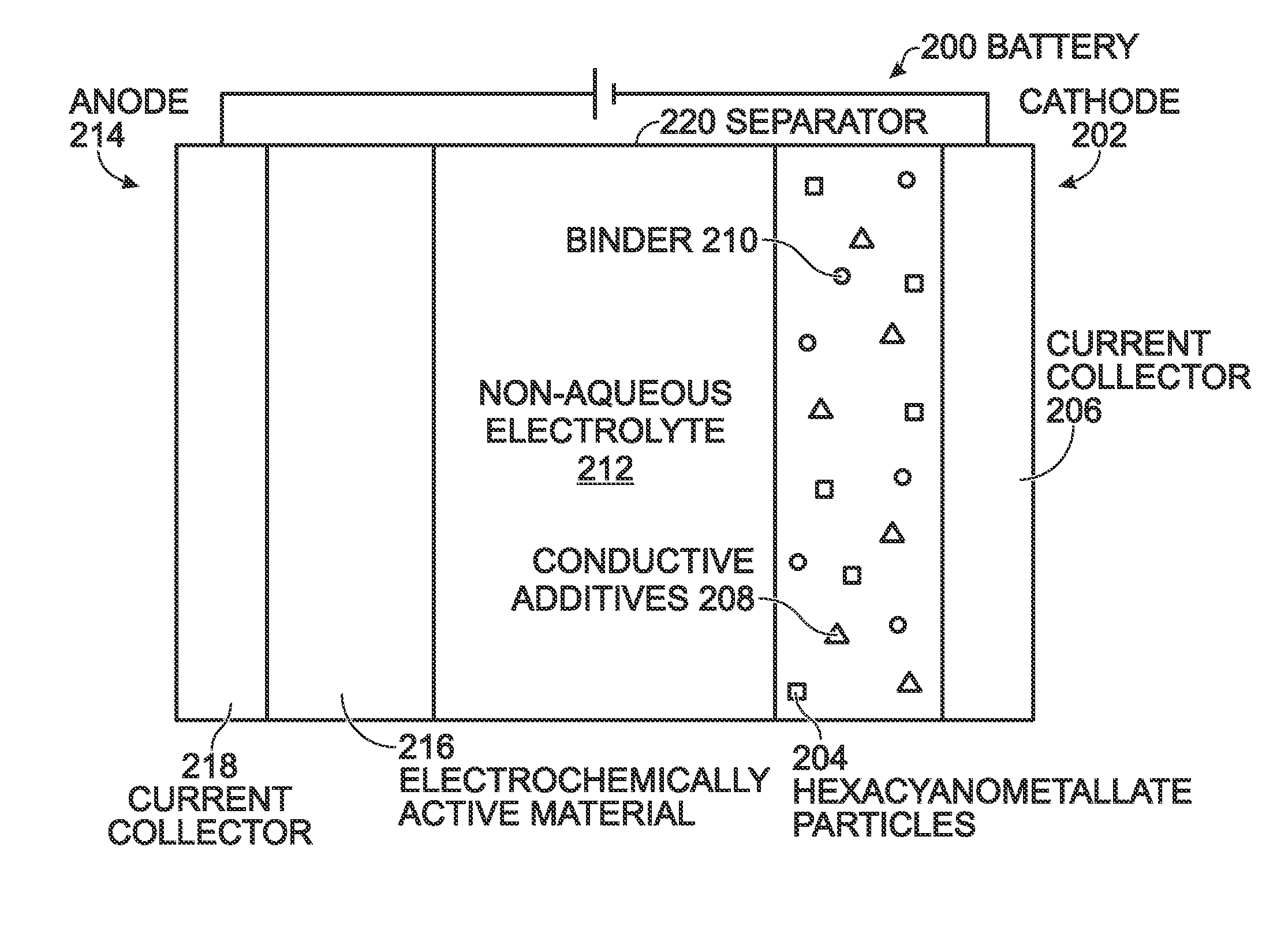
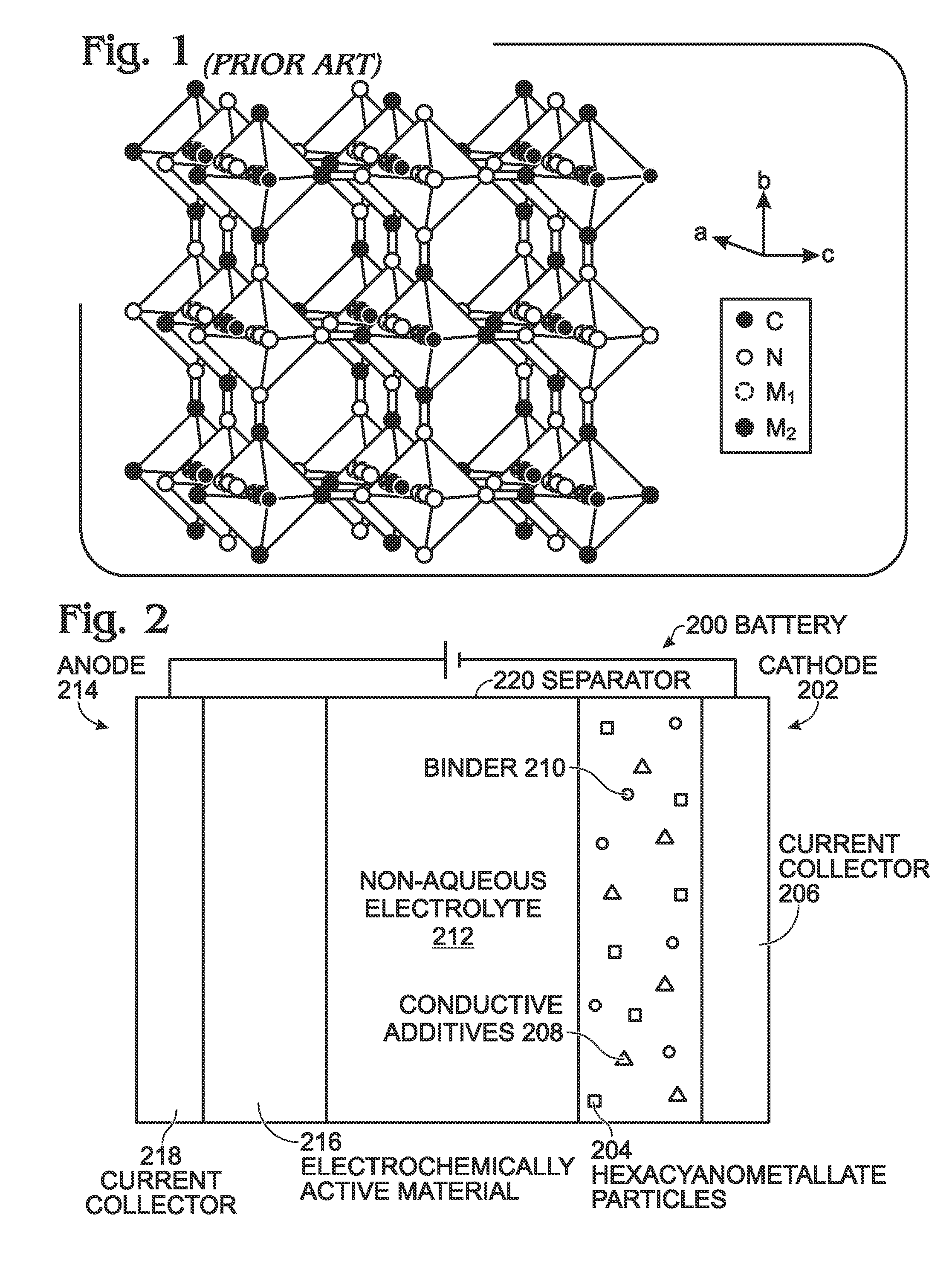
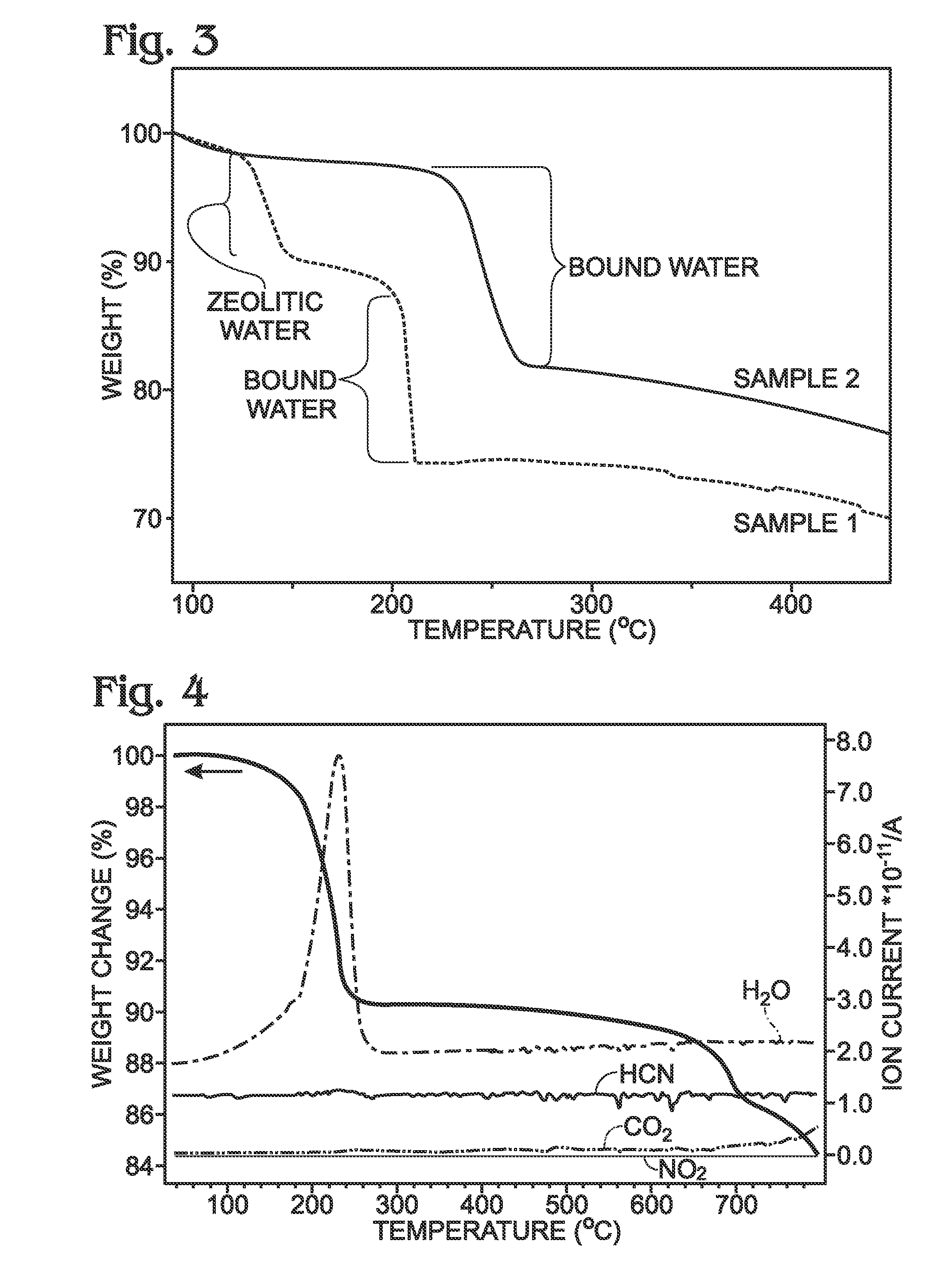
A battery is provided with a hexacyanometallate cathode. The battery cathode is made from hexacyanometallate particles overlying a current collector. The hexacyanometallate particles have the chemical formula AXM1MM2N(CN)Z.d[H2O]ZEO.e[H2O]BND. where A is a metal from Groups 1A, 2A, or 3A of the Periodic Table, where M1 and M2 are each a metal with 2+ or 3+ valance positions, where “ZEO” and “BND” indicate zeolitic and bound water, respectively, where d is 0, and e is greater than 0 and less than 8. The anode material may primarily be a material such as hard carbon, soft carbon, oxides, sulfides, nitrides, silicon, metals, or combinations thereof. The electrolyte is non-aqueous. A method is also provided for fabricating hexacyanometallate with no zeolitic water content in response to dehydration annealing at a temperature of greater than 120 degrees C. and less than 200 degrees C.
Owner:SHARP KK
Method for innocent treatment of enteromorpha and equipment using same
ActiveCN101758060ANo pollution in the processEasy to transportConveyorsSolid waste disposalLow noiseBound water
The invention provides to a method for innocent treatment of enteromorpha and equipment using the same, which is characterized by comprising the following steps: (1) with pressing dehydrogenation packing equipment, pressing and dehydrating fresh enteromorpha which is just salvaged, packing the fresh enteromorpha to form enteromorpha enclosed mass, and then transporting the mass to a disposal field; (2) sending the mass into a shearer for shearing and shattering, releasing free water in an enteromorpha tubular structure and conducting pressing and dehydrating for the second time; (3) after the second time of pressing and dehydrating, sending the enteromorpha into air dehydration equipment for drying and dehydrating through hot blast, and dehydrating most of the free water and bound water contained in the enteromorpha; (4) conducting bed cleaning and edulcoration through a cyclone dust removal system; and (5) smashing with a pulverizer. The method aims to transportation cost and pollution, and has high treatment efficiency and low energy consumption, thus the edulcoration after treatment can be put into good use. The pressing dehydrogenation packing equipment is driven by hydraulic pressure and the working force is adjustable. The equipment has low noise, is simple to operate, and convenient to feed. The equipment can feed much one time, and feeding compression can be conducted for more than one time.
Owner:青岛海大生物集团股份有限公司
Vacuum pre-compaction and electro-osmosis combined reinforcing device and method for muck foundation
InactiveCN102704463AIncrease moisture contentImprove reinforcement effectSoil preservationBound waterFree water
The invention discloses a vacuum pre-compaction and electro-osmosis combined reinforcing device and a method for a muck foundation. Sand-free cushion vacuum pre-compaction and electro-osmosis are combined to remove pore water and air under the super-soft musk foundation. Through the vacuum pre-compaction effect at the earlier stage, most of free water in the soil is removed, and part of the free water and weak bound water which cannot be removed by the vacuum pre-compaction can be further removed via the electro-osmosis, thus the reinforcing effect can be greatly improved, the manufacturing cost is increased a little on the basis of the vacuum pre-compaction, and the economical efficiency is remarkable.
Owner:南京科冠工程技术有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com