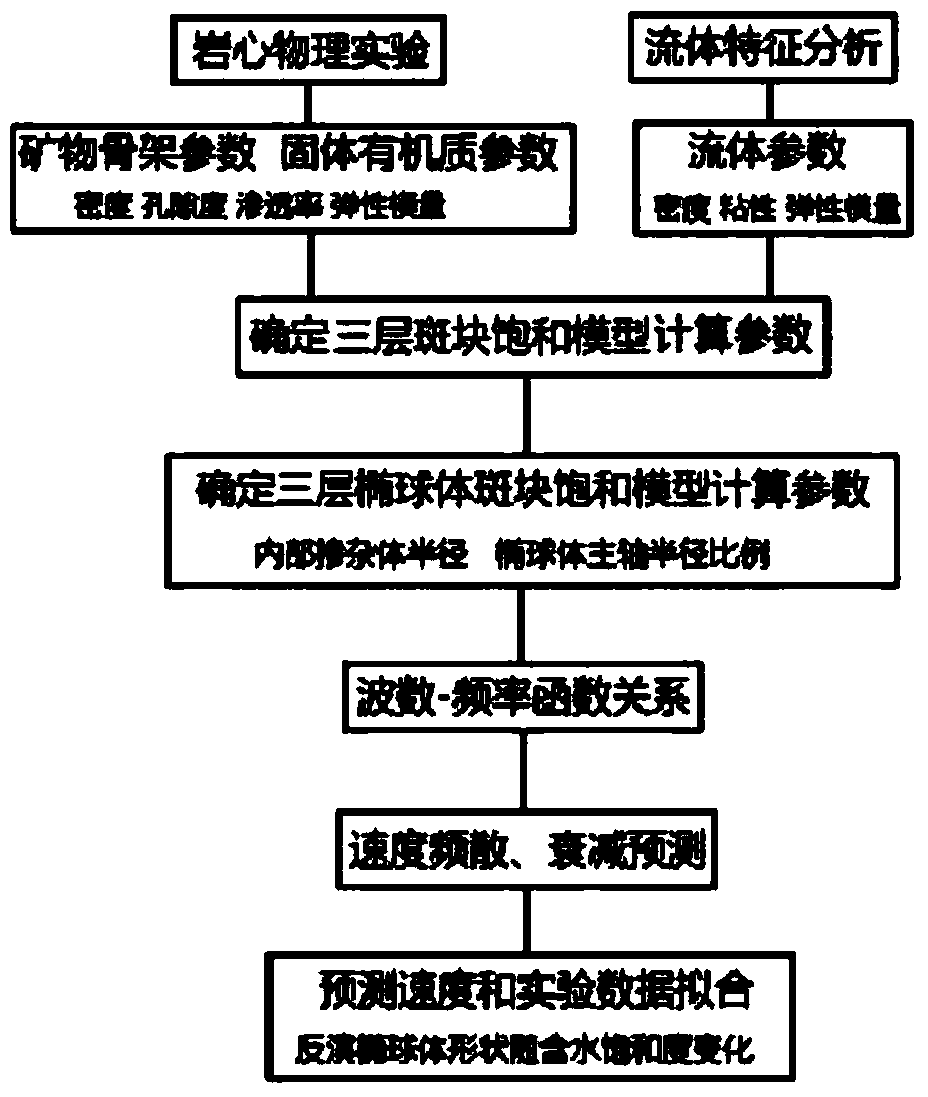
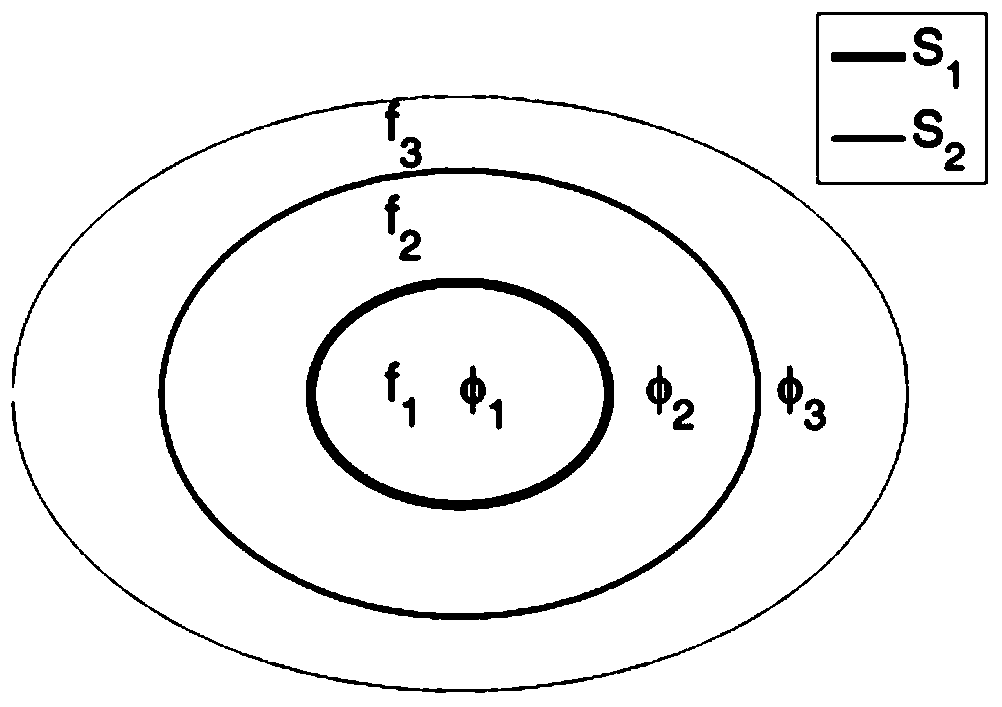
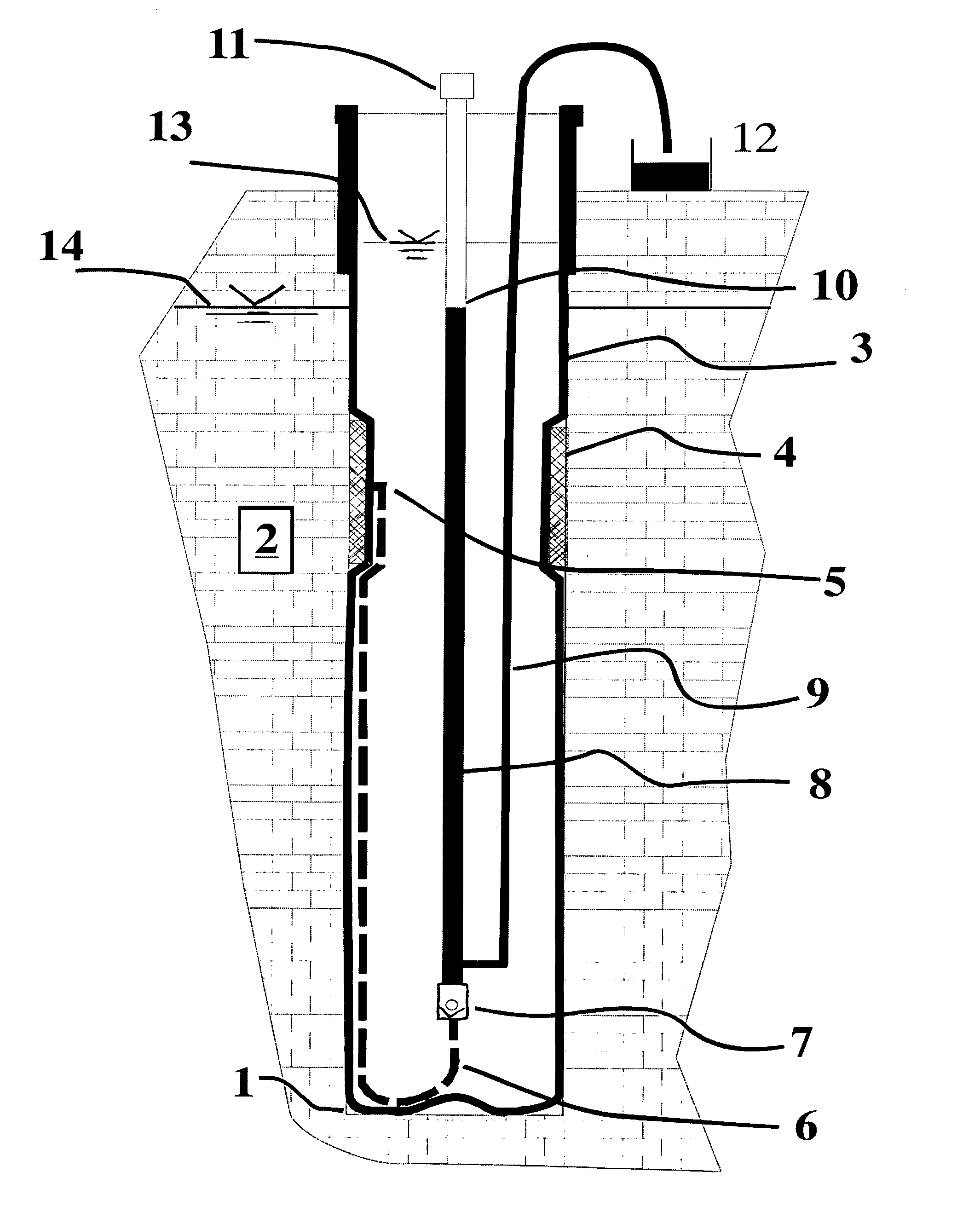
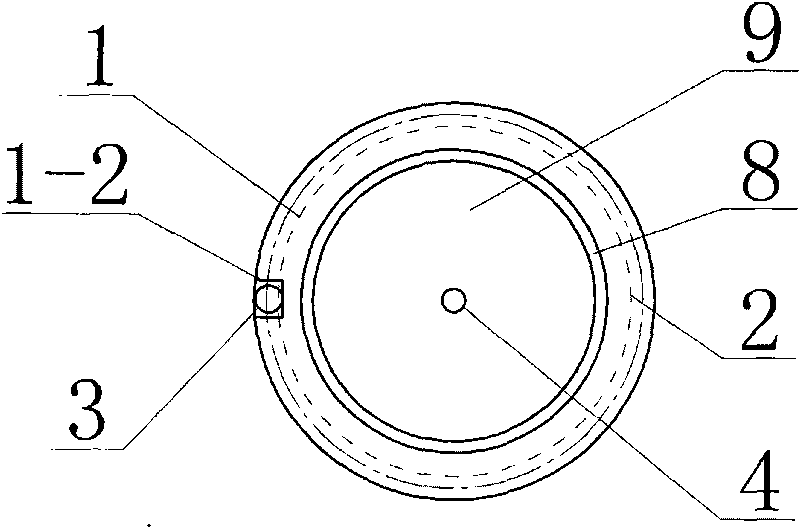
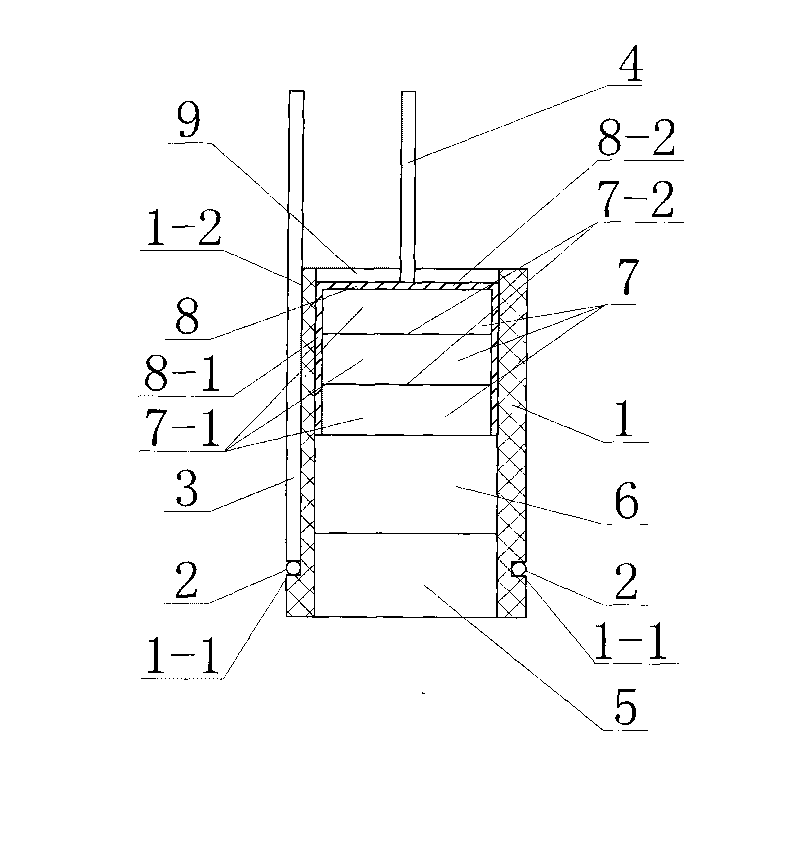
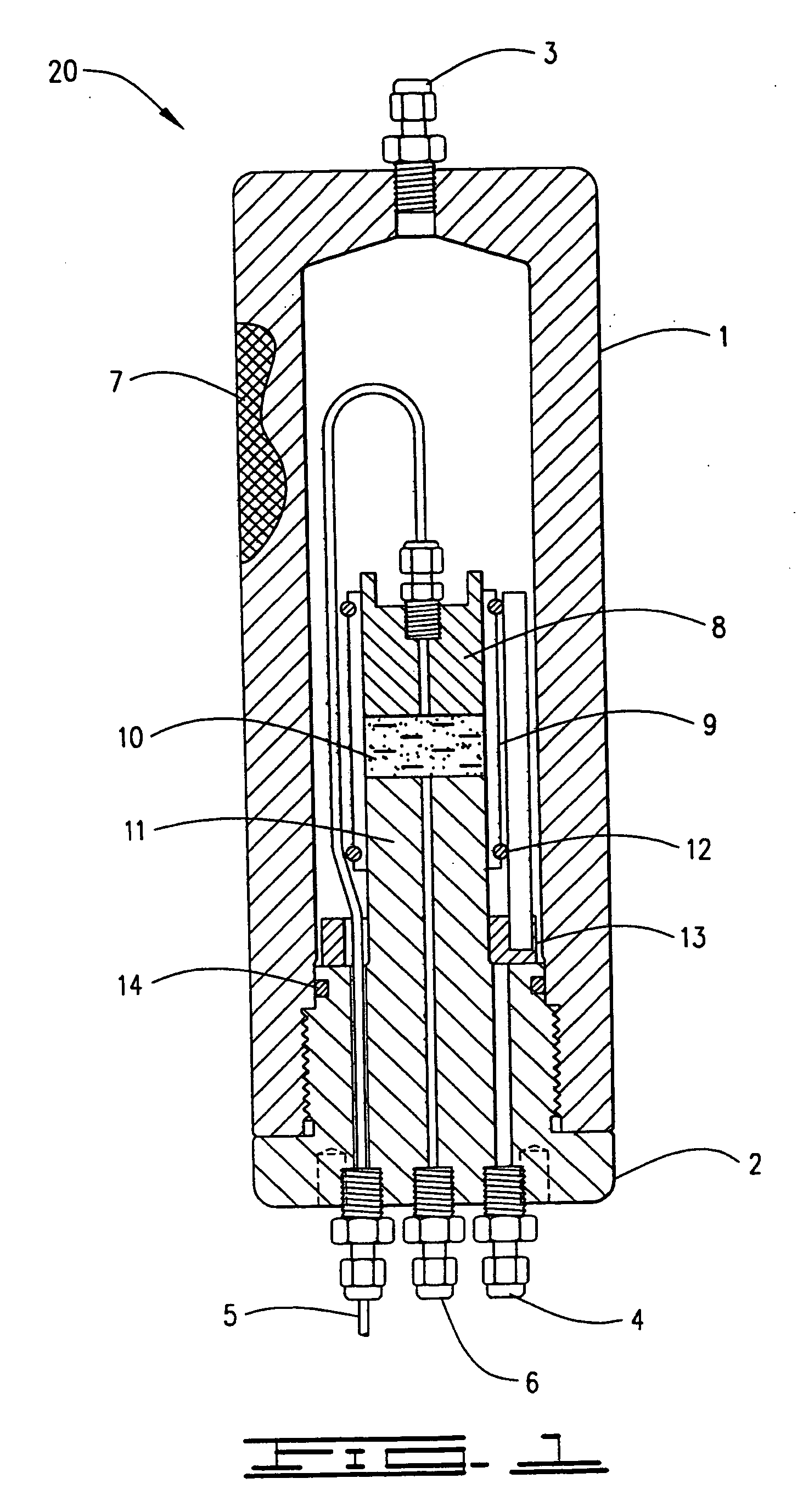
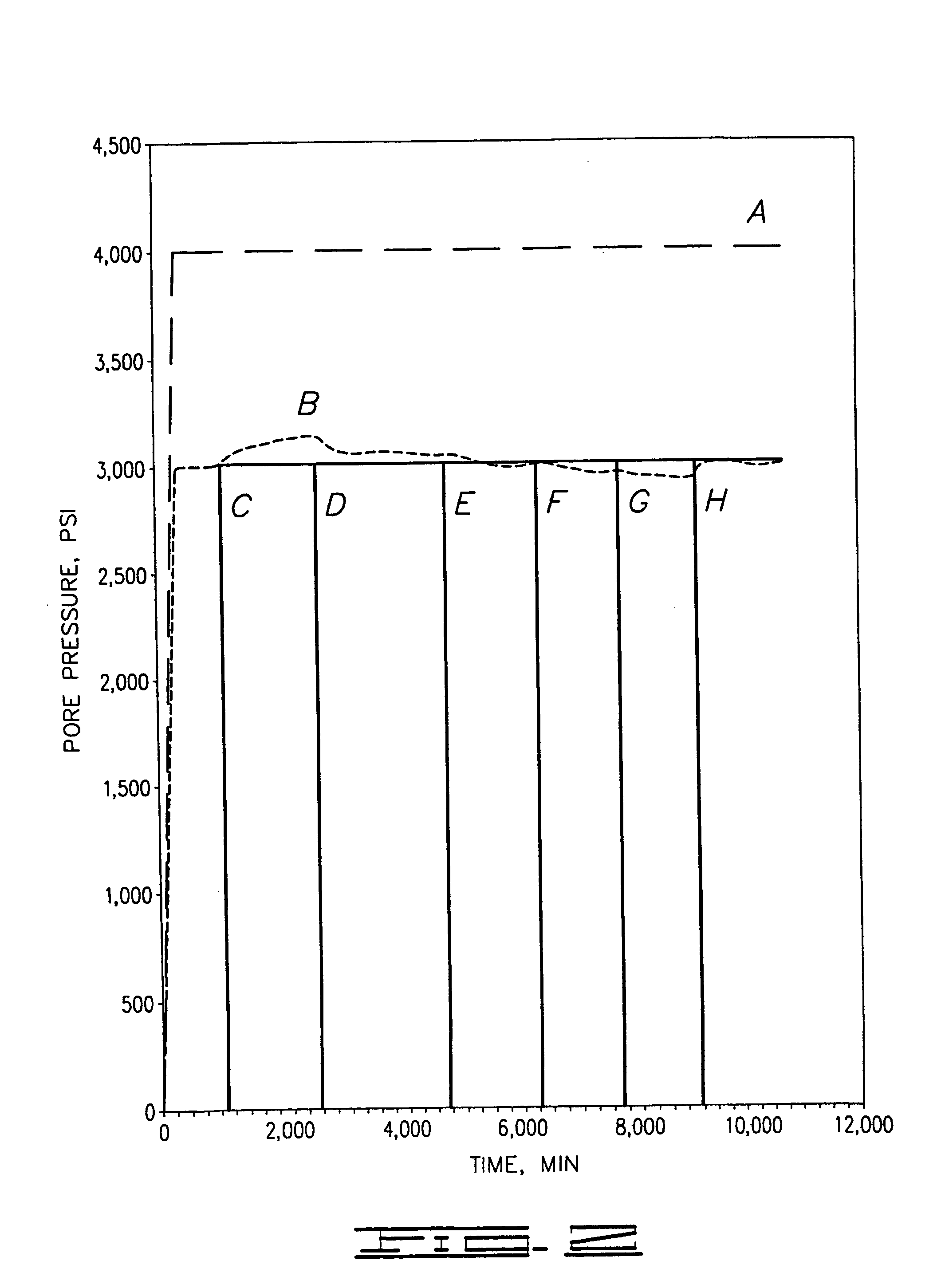
Patents
Literature
146 results about "Pore fluid" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Pore fluid properties. Hydrocarbons occur in a variety of conditions, in different phases, and with widely varying properties, This page will cover the important geophysical properties of pore fluids. Pore fluids are fluids that occupy pore spaces in a soil or rock.
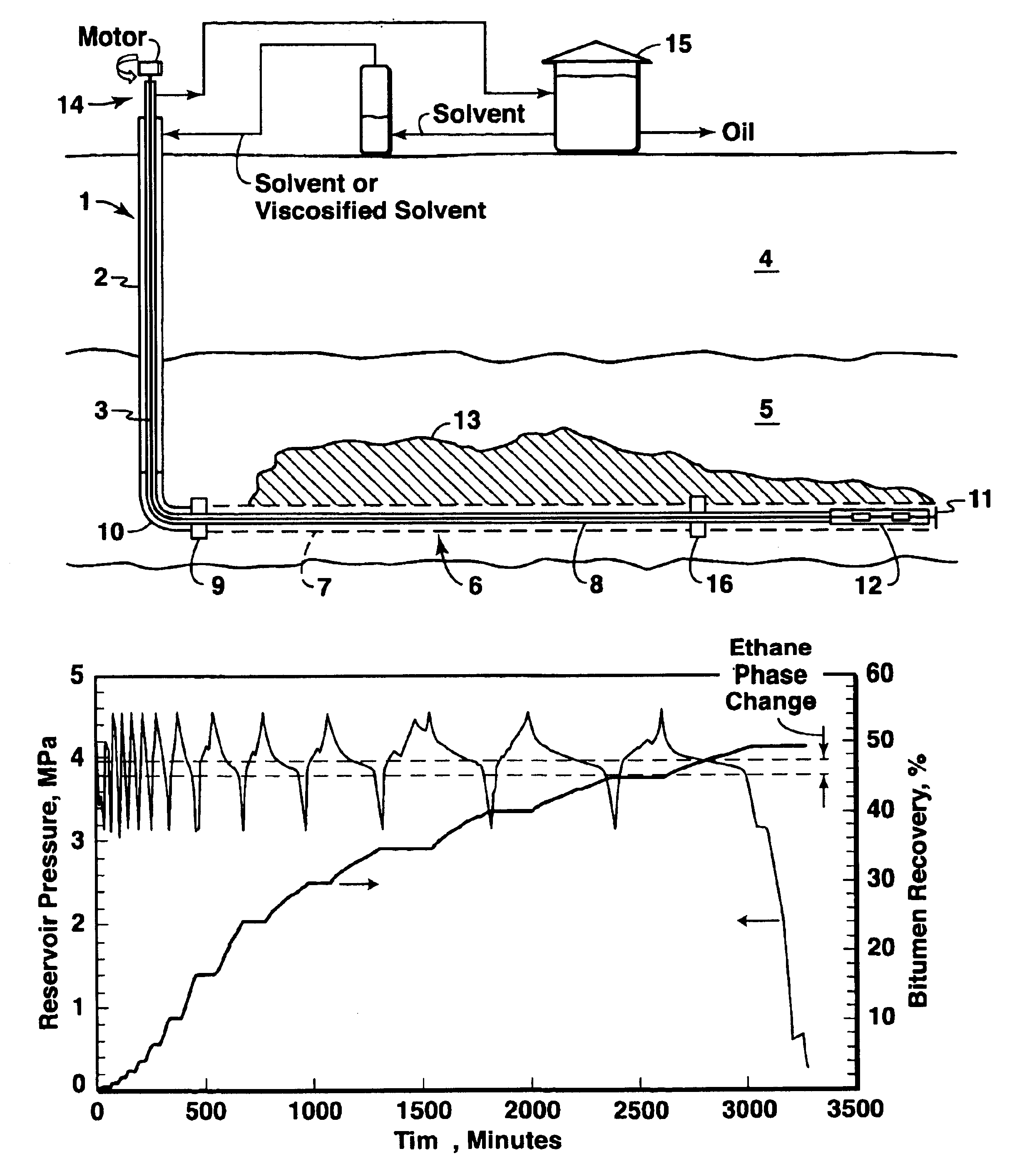
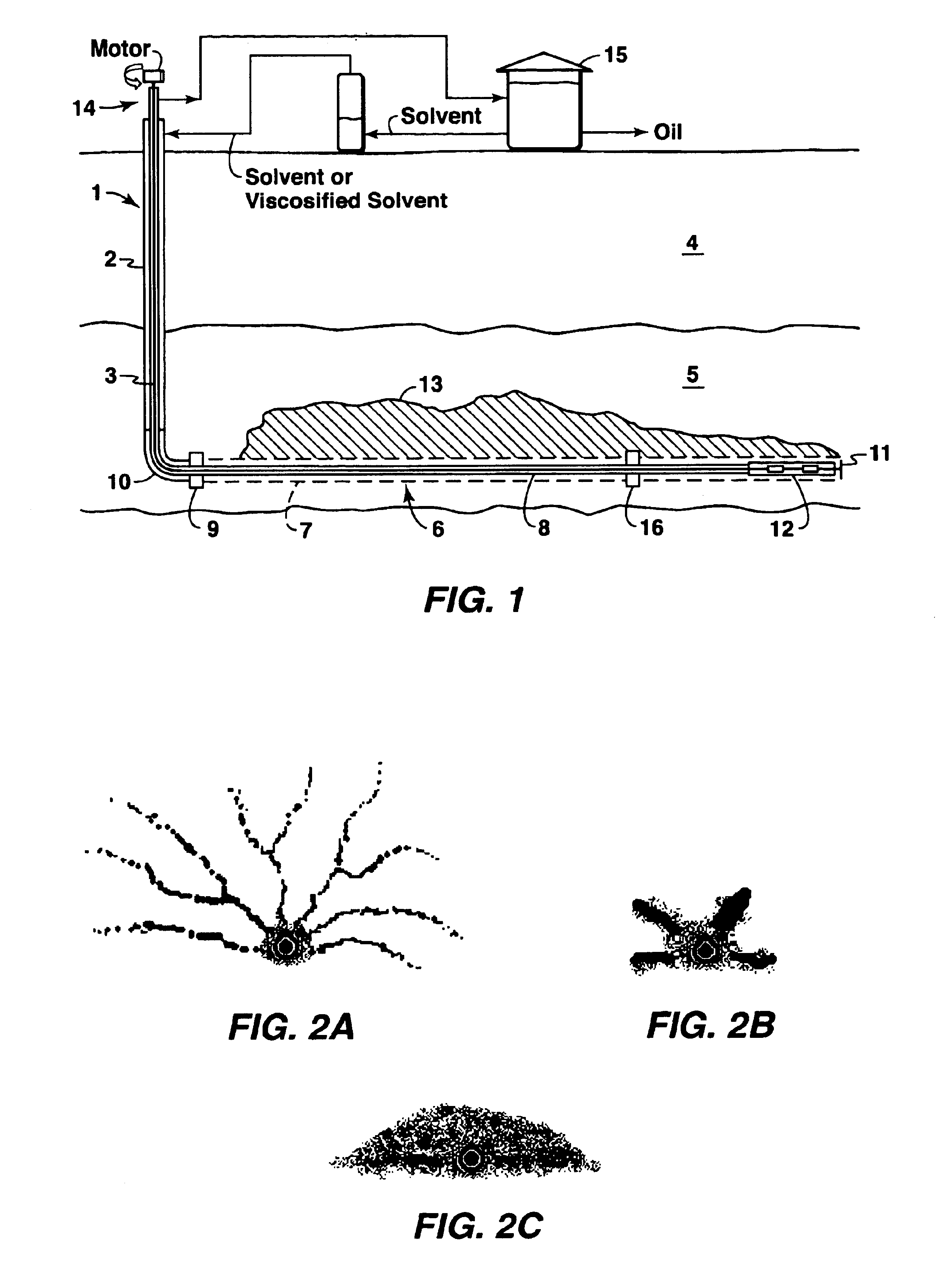
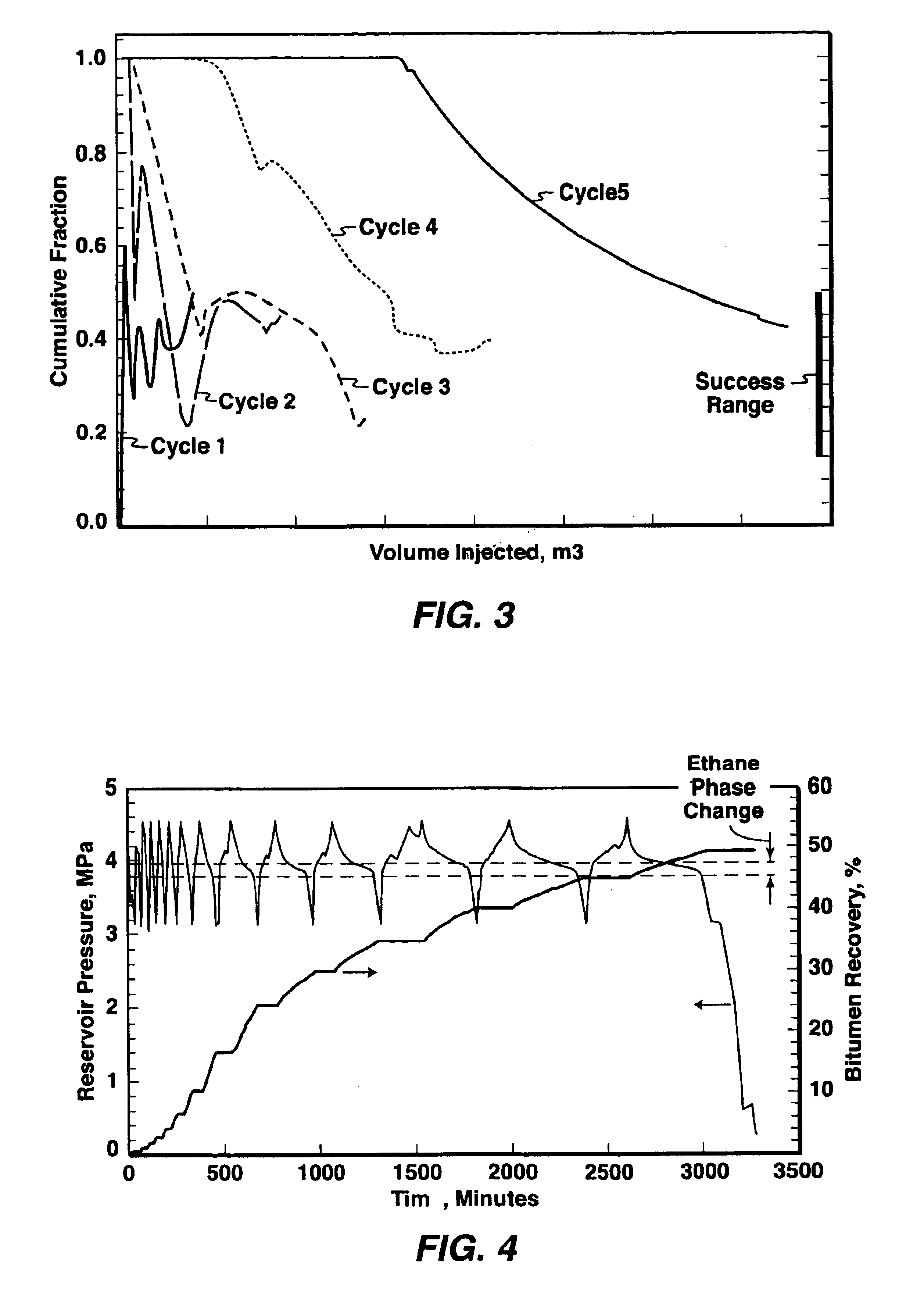
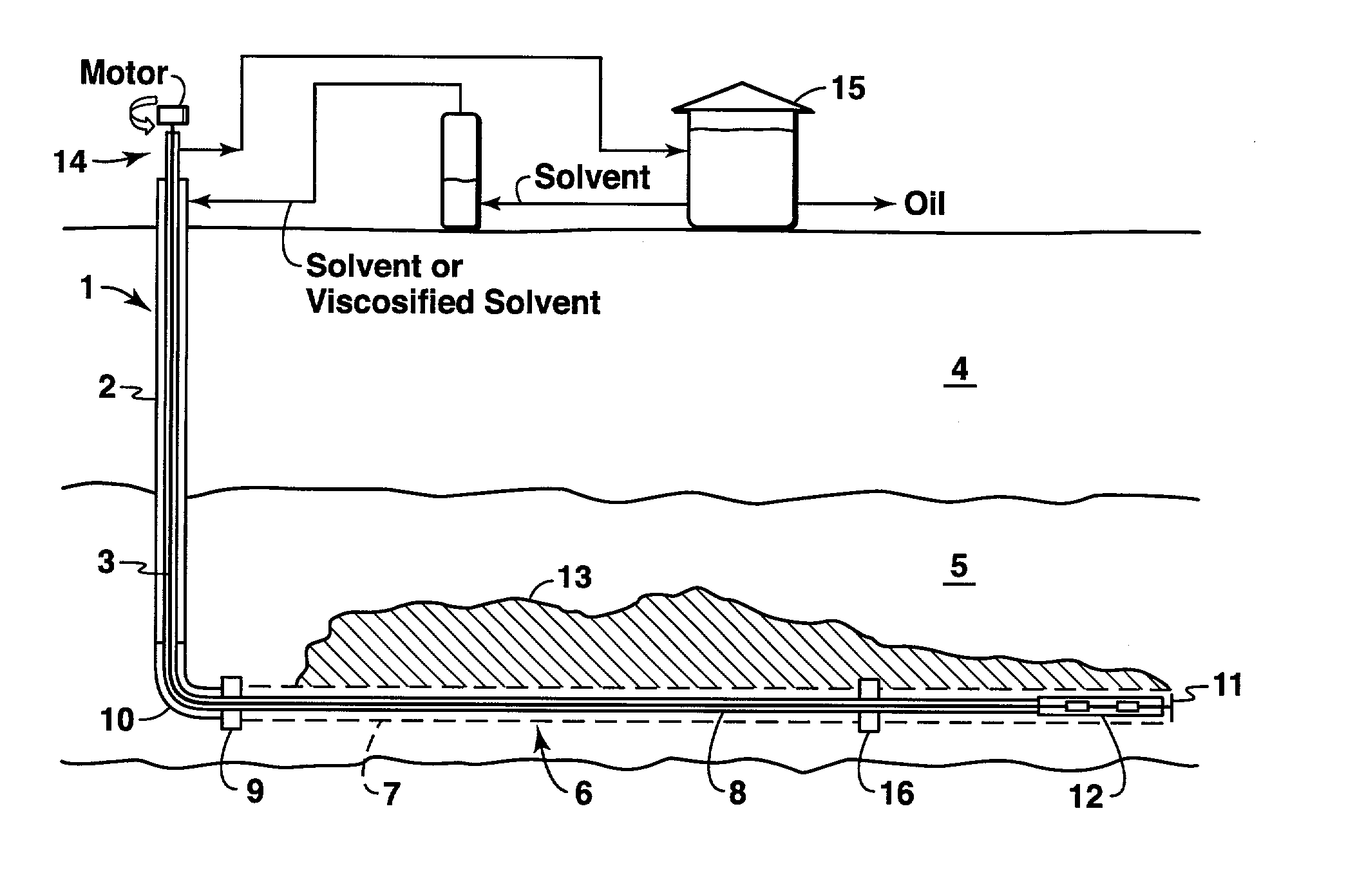
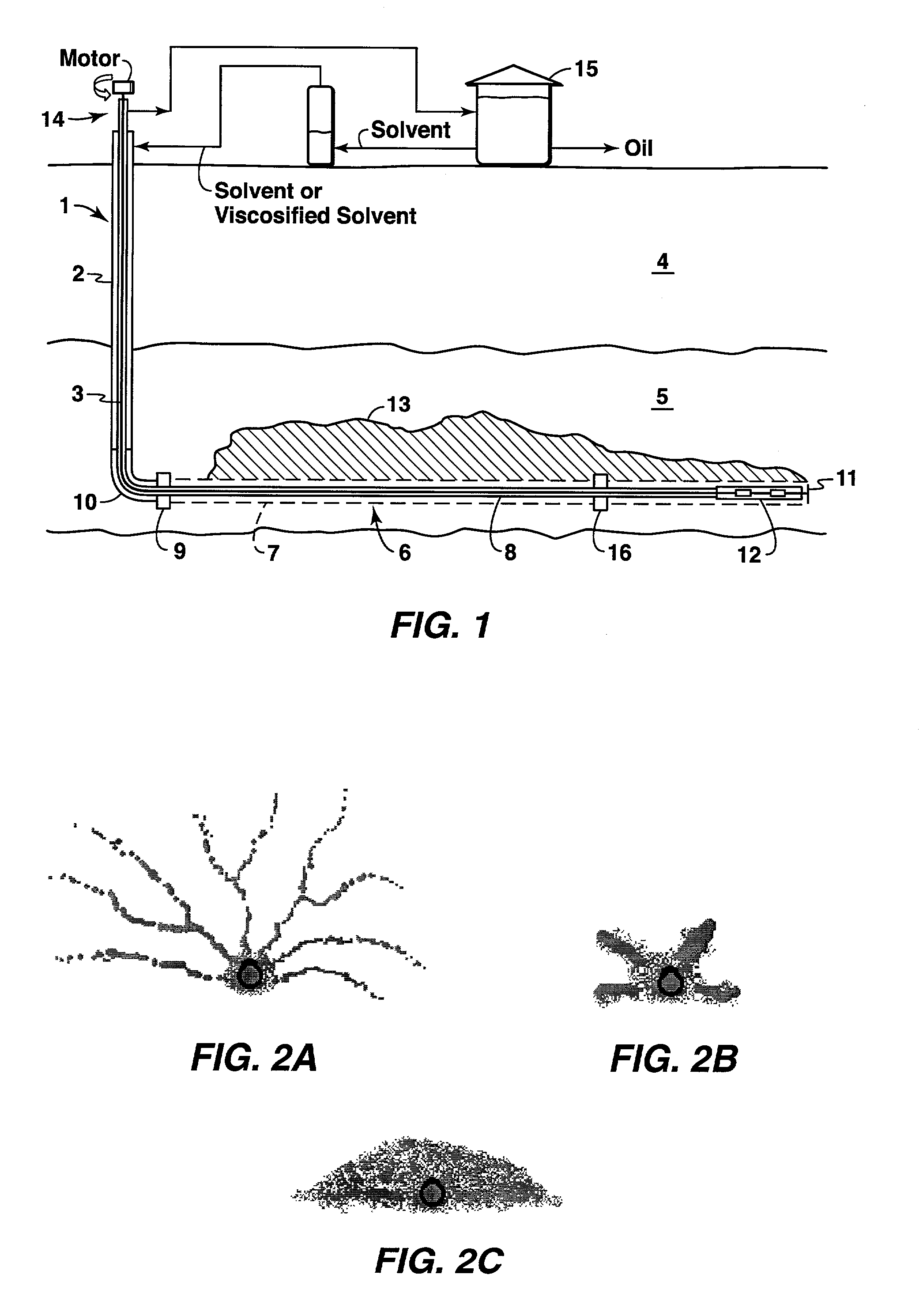
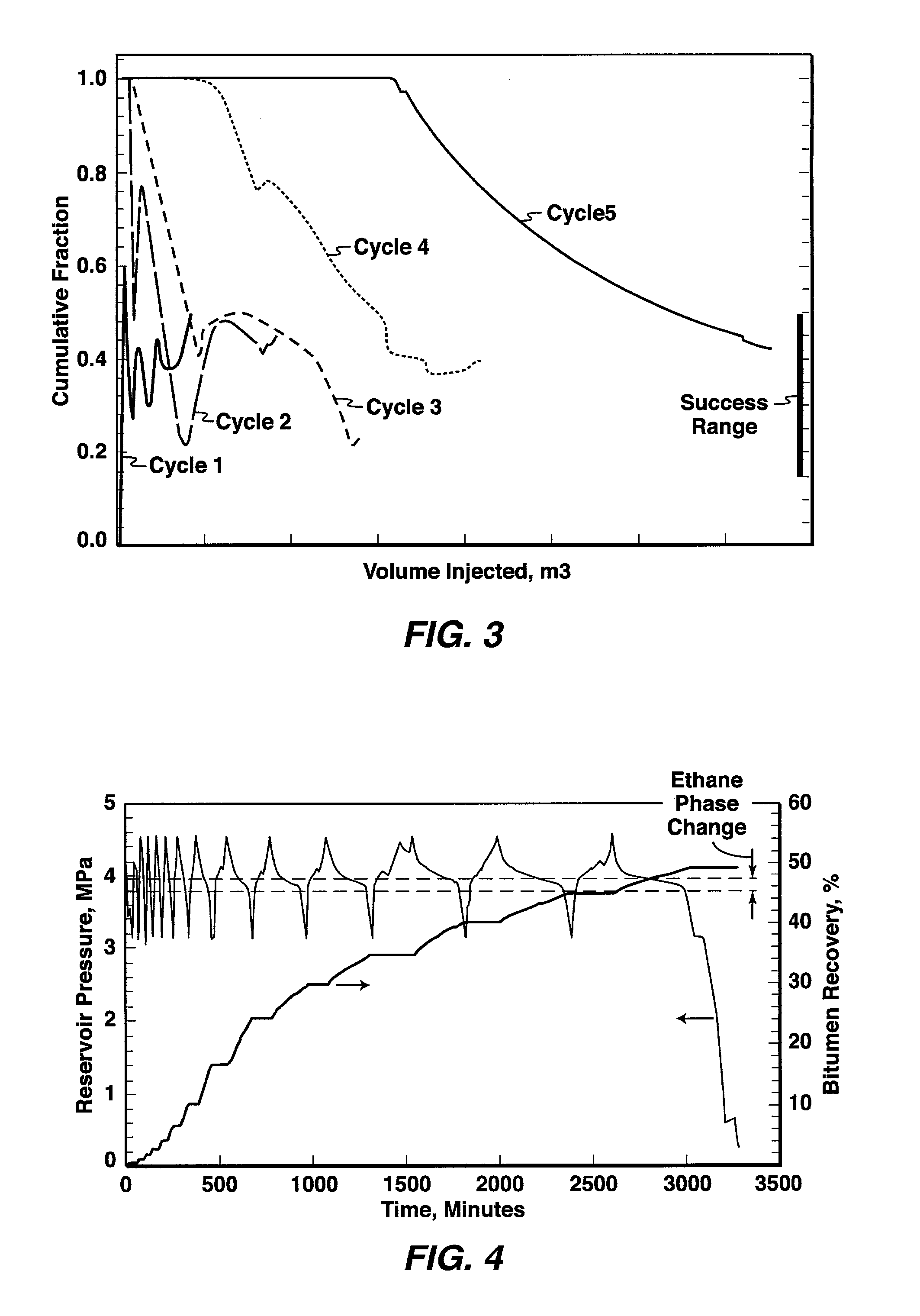
Cyclic solvent process for in-situ bitumen and heavy oil production
A process for recovery of hydrocarbons in a production fluid from an underground reservoir of said hydrocarbons, the process comprising of: (a) injecting a viscosity reducing solvent of a fraction of said hydrocarbons into said reservoir at a pressure in the reservoir of above a liquid / vapor phase change pressure of a fraction of said solvent; said pressure in said reservoir also being sufficient to cause geomechanical formation dilation or pore fluid compression, and then, (b) allowing said solvent to mix with said hydrocarbons under pore dilation conditions, and then, (c) reducing the pressure in said reservoir to below said liquid / vapor phase change pressure of at least said fraction of said solvent thereby evincing solvent gas drive of said fraction of said hydrocarbons from said reservoir; and then, (d) repeating steps (a) to (c) as required.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
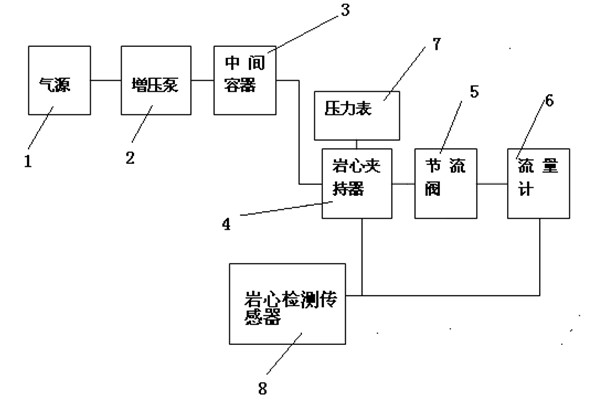
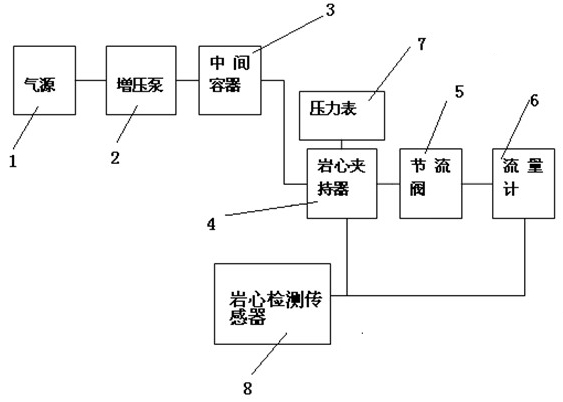
Formation core sample holder assembly and testing method
InactiveUS20100126266A1Earth material testingPermeability/surface area analysisPore fluidEngineering
A core sample holder assembly for performing laboratory core flooding experiments with a core sample:a pressure chamber provided by a tubular hull made of a carbon fiber composite material and an aluminum liner, and a pair of disk-shaped flanges;a flexible core sample holder sleeve within the pressure chamber, which sleeve comprises a tubular steel sheet with a plastic inner lining;an opening for injecting oil into an annular space between the hull and the sleeve;pressure control means for maintaining the oil at a predetermined pressure;an fluid injection port for injecting a fluid into a cylindrical core sample within the sleeve;a fluid outlet port arranged in the other flange for discharge of fluid from the core sample; andmeans for monitoring the migration of injected and / or pore fluid through the pores of the core sample.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
Cyclic solvent process for in-situ bitumen and heavy oil production
A process for recovery of hydrocarbons in a production fluid from an underground reservoir of said hydrocarbons, the process comprising of: (a) injecting a viscosity reducing solvent of a fraction of said hydrocarbons into said reservoir at a pressure in the reservoir of above a liquid / vapor phase change pressure of a fraction of said solvent; said pressure in said reservoir also being sufficient to cause geomechanical formation dilation or pore fluid compression, and then, (b) allowing said solvent to mix with said hydrocarbons under pore dilation conditions, and then, (c) reducing the pressure in said reservoir to below said liquid / vapor phase change pressure of at least said fraction of said solvent thereby evincing solvent gas drive of said fraction of said hydrocarbons from said reservoir; and then, (d) repeating steps (a) to (c) as required.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
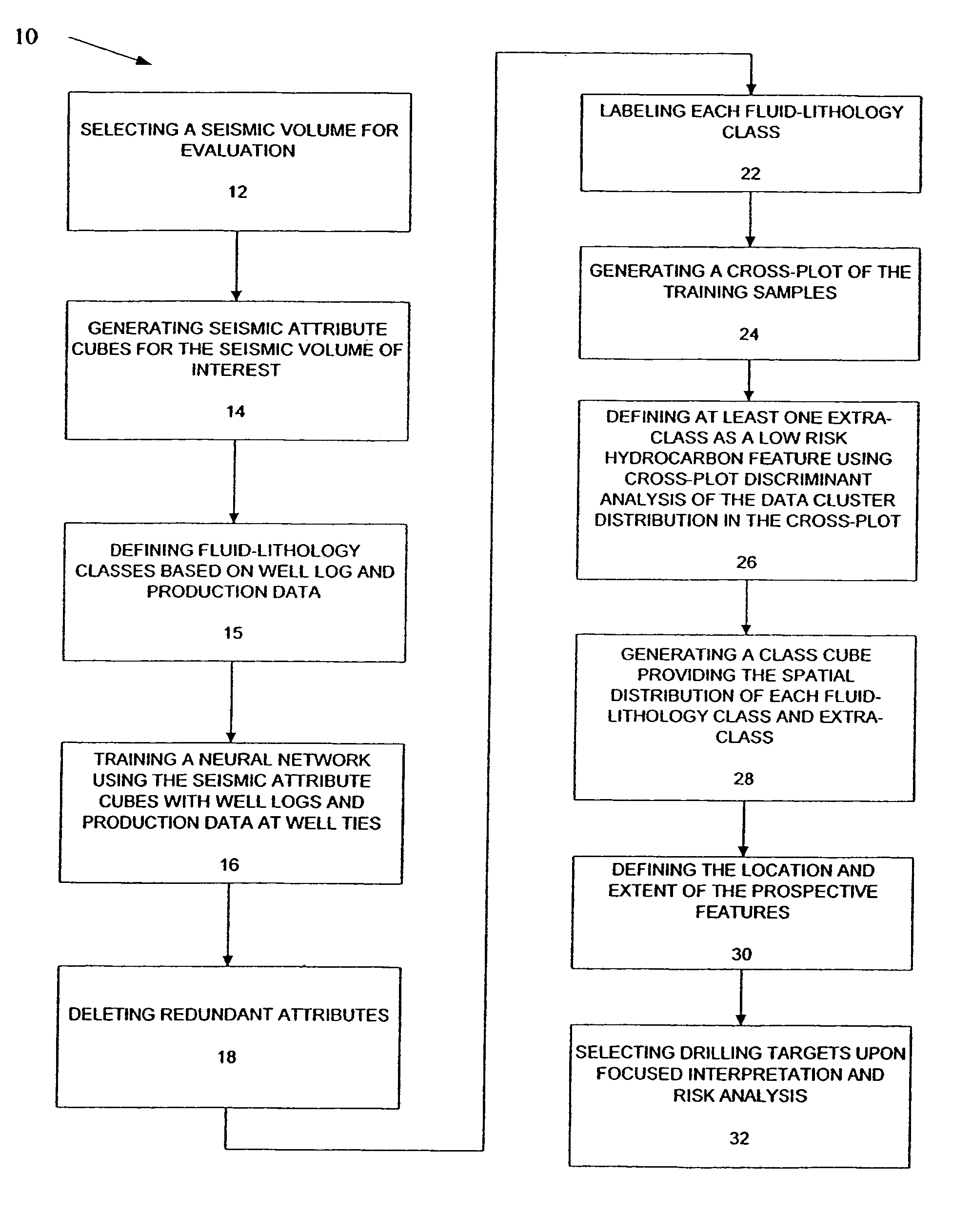
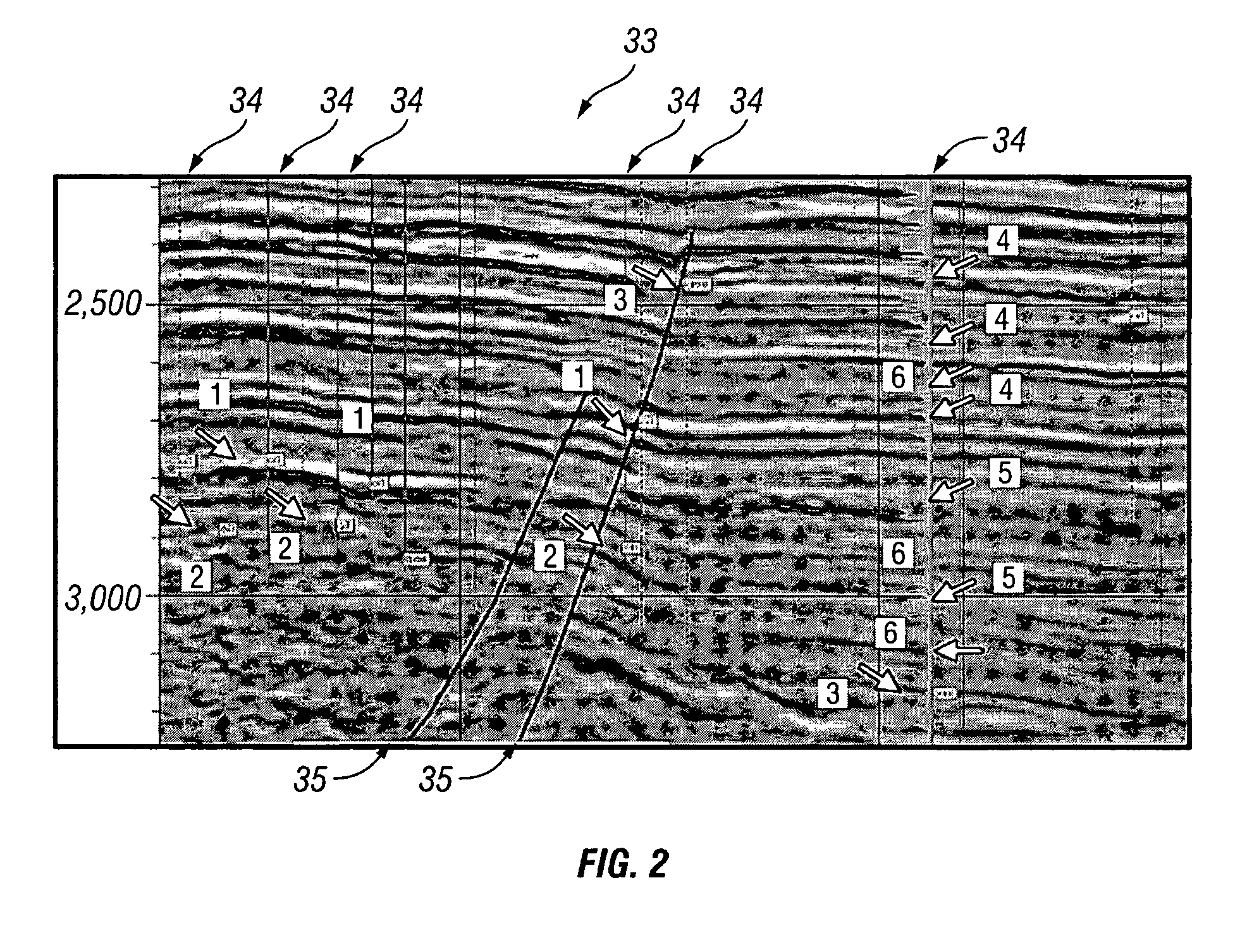
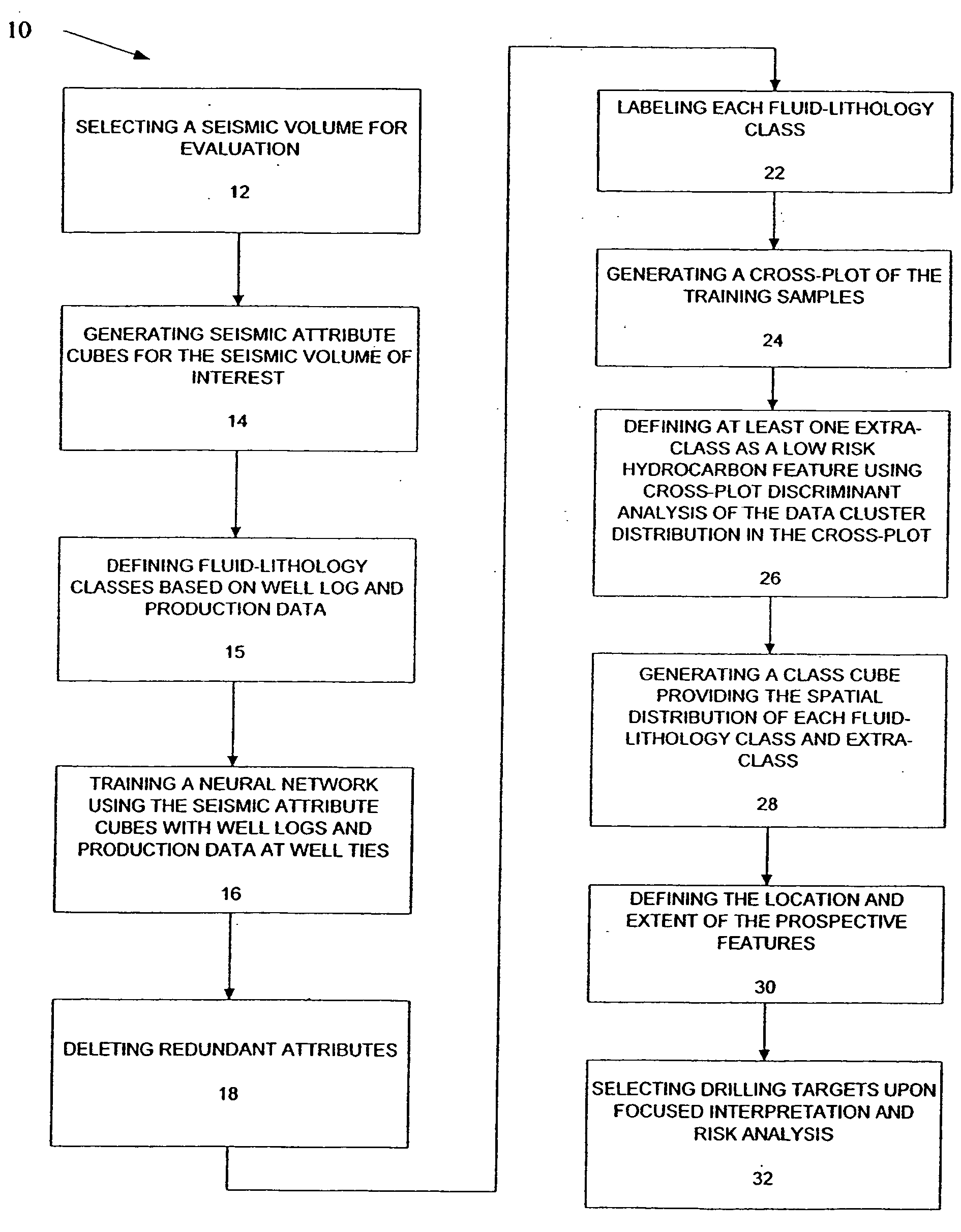
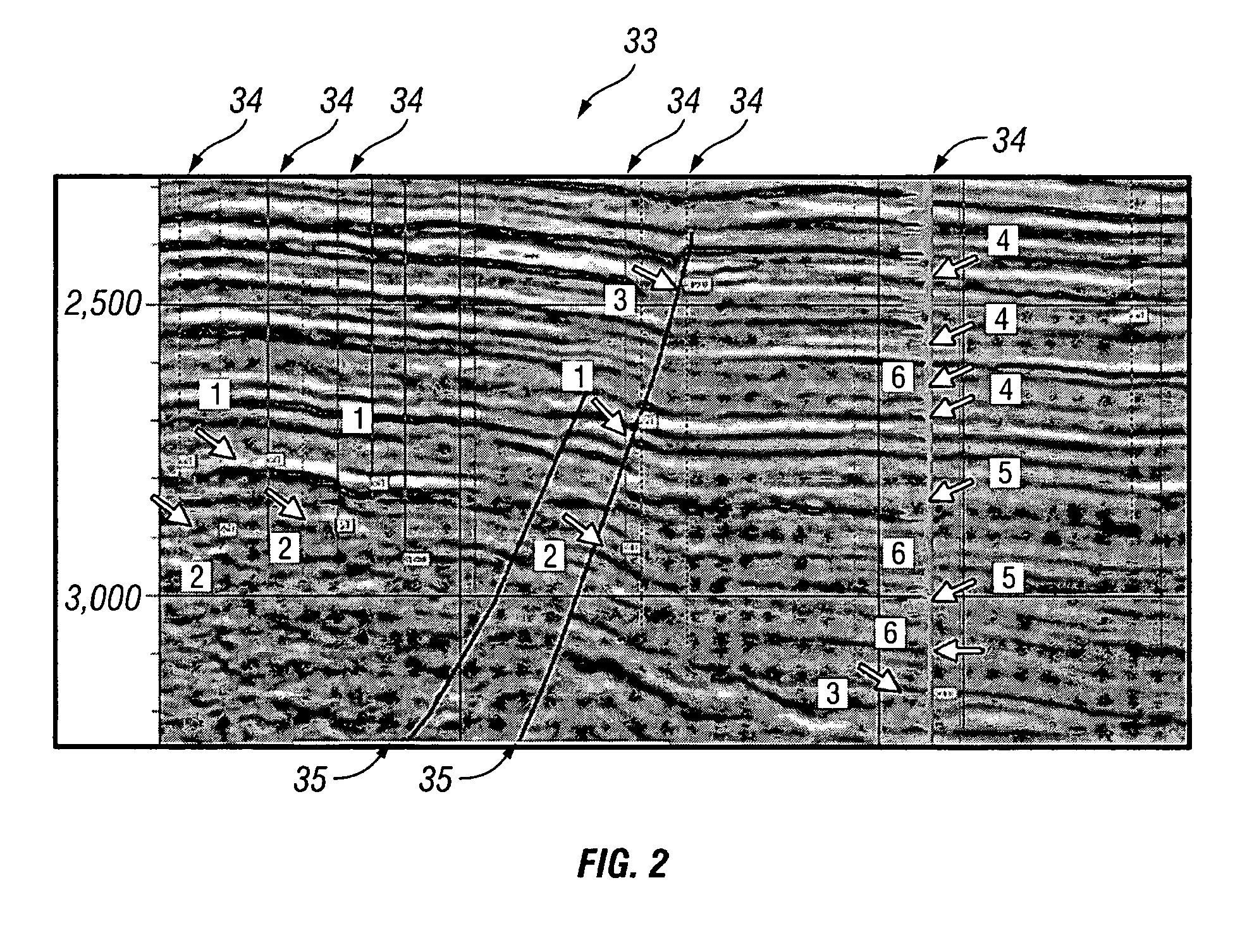
Method for prospect identification in asset evaluation
InactiveUS7113869B2Effective wayPowerful toolElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSeismic signal processingLithologyPore fluid
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Simple method of multi-parameter seismic inversion
ActiveCN101329405AImprove computing efficiencyImprove instabilitySeismic energy generationSeismic signal processingLithologyDensity ratio
The invention relates to a simple multi-parameter seismic inversion method for improving the precision and the reliability of the conventional pre-stack seismic inversion with the help of the seismic wave elastic impedance, thereby simultaneously extracting a variety of formation parameters. The steps are as follows: full wave logging information is utilized; an acoustic impedance AI and an elastic wave impedance EI are determined; a CMP gather is converted into an angle gather, and part of the angles are stacked; the conventional pre-stack elastic impedance inversion process is utilized to respectively carry out the AI and the EI inversion of cross-well measuring line of small angle stacked data and part of the stacked data of the middle incident angles; the channel calculation of the EI and the AI data which are obtained by inversion is carried out, thereby obtaining the seismic attributes which are closely related to the elastic density ratio, the lithology changes and the pore fluid ingredients; the reservoir lithology and the properties of the pore fluid are determined. The simple multi-parameter seismic inversion method only needs the seismic data of near and middle angles, and other parameters are obtained through the channel calculation of the relationship between the elastic density ratio and the acoustic impedance, thereby improving the calculation efficiency and being used in the pre-stack inversion of the seismic data obtained by the vast majority of the collection conditions.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +1
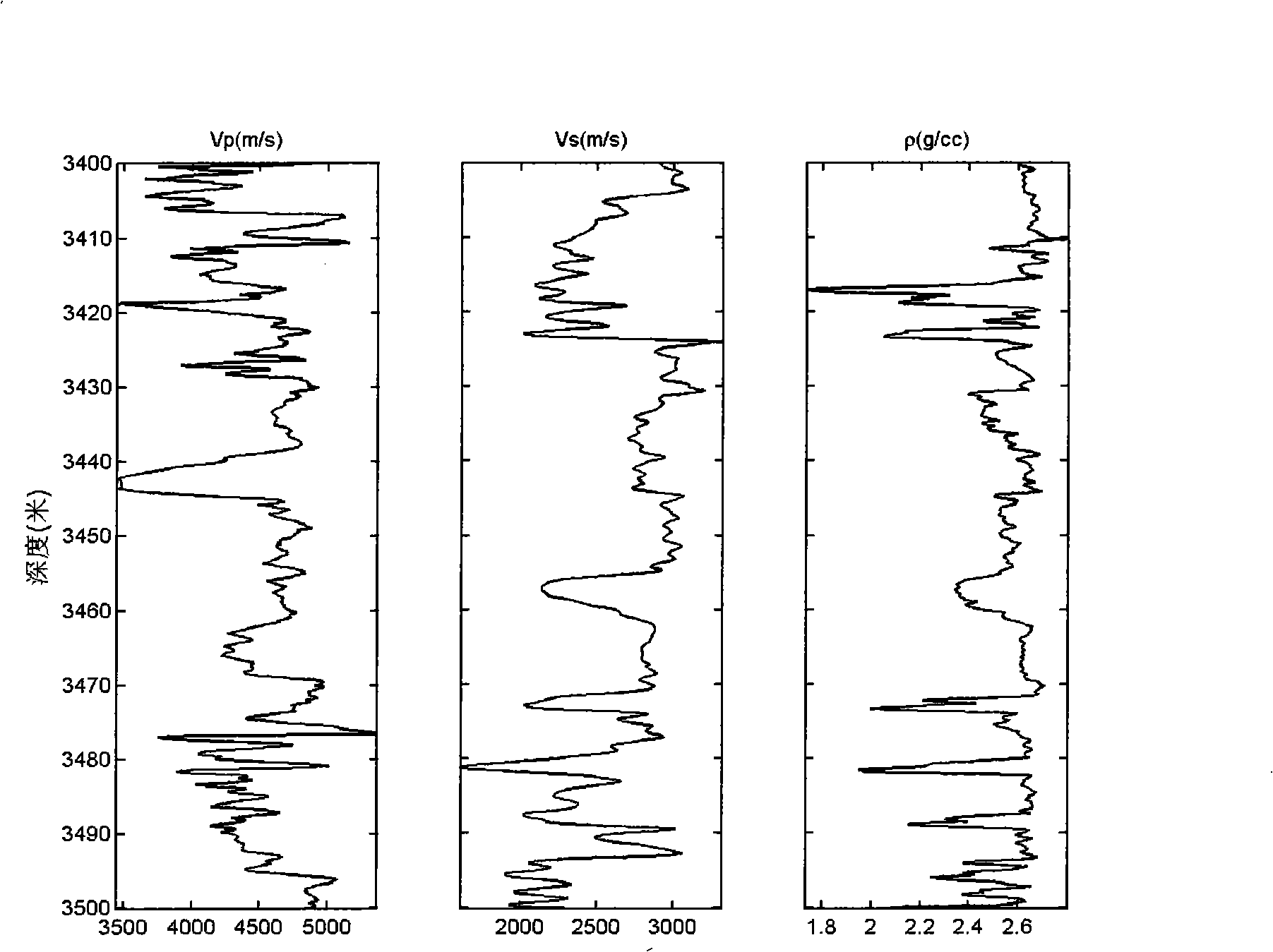
Method for predicting carbonate formation pore pressure by using log information
The invention discloses a method for predicting carbonate formation pore pressure by using log information. The method for predicting the carbonate formation pore pressure by using the log information is based on the effective stress theorem; and by establishing a framework longitudinal wave velocity and pore fluid longitudinal wave velocity equation, a carbonate formation pore pressure equation is established, so that the carbonate formation pore pressure is detected according to the measured log information, scientific evidences are provided for determining safety drilling fluid density during drilling design, and carbonate formation underground complex accidents in the construction process are effectively prevented.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (BEIJING)
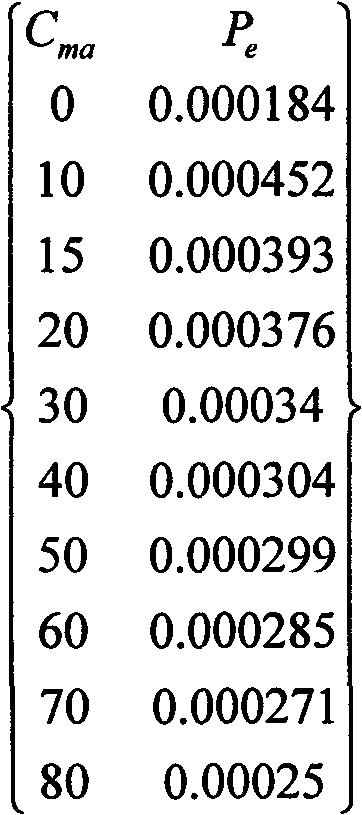
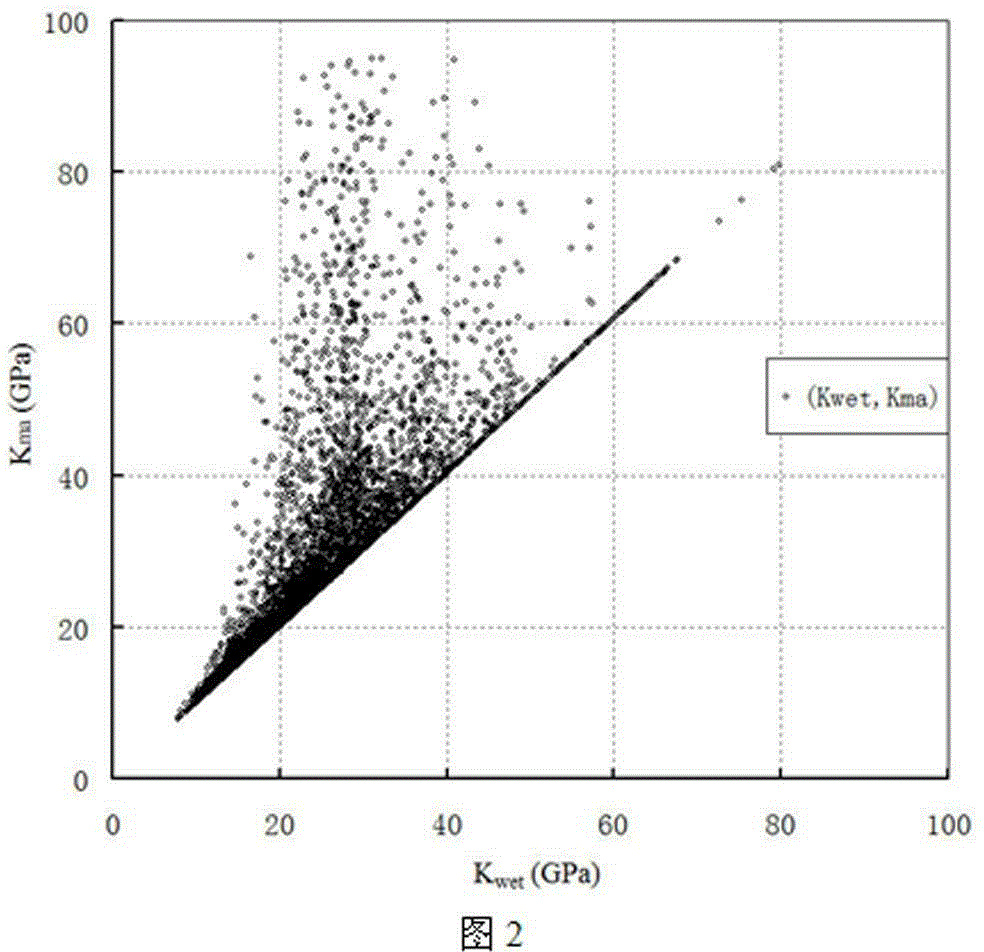
Method for calculating formation pressure based on petrophysical parameters
The invention discloses a method for calculating formation pressure based on petrophysical parameters, and uses well measurement data of a velocity of a P-wave VP, a velocity of a shear wave VS, a density Rho and a porosity Phi of formation. The method comprises the following steps: deriving a ratio value between a bulk modulus Kdry of a dry rock and a bulk modulus Kma of a rock matrix material by using a Gassmann equation; calculating an effective bulk modulus Kma of a mineral component according to a V-G-H model, calculating a bulk modulus Kf of a pore fluid according to a Wood model to calculate an effective stress coefficient Alpha and an Skempton coefficient B; and estimating the formation pressure according to an effective stress between the Skempton coefficient B and a porous media, the effective stress coefficient Alpha and the Skempton coefficient B. The method is suitable for a mixed lithology and a single lithology, the formation pressure is estimated without relying on a conventional under compaction theory of a mudstone or a shale, so that the calculated formation pressure is more close to real formation pressure.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
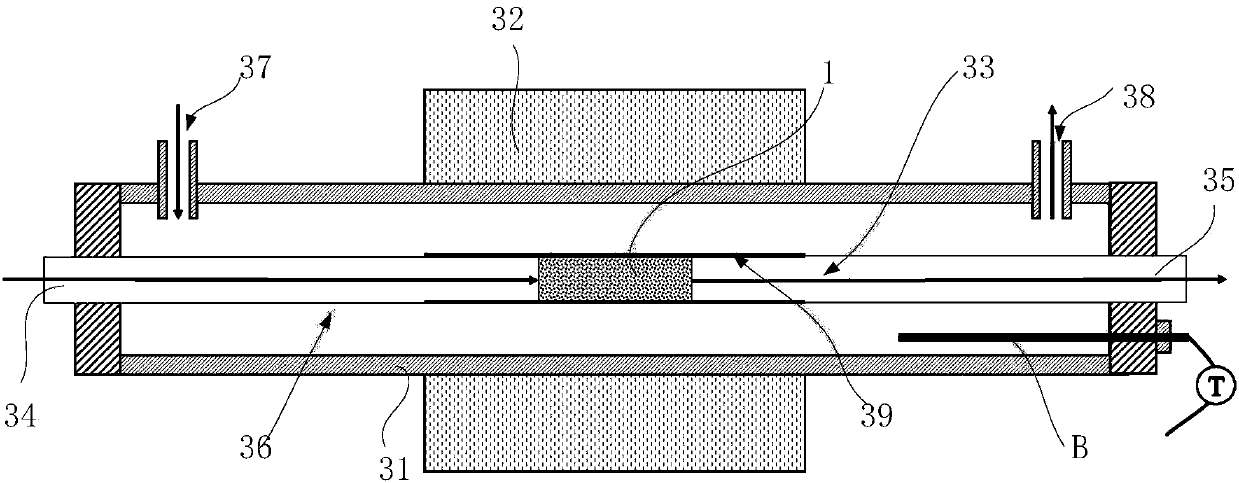
Device and method for testing rock permeability under different pore fluid pressure
InactiveCN102156087AMature processing and production technologyLow costPermeability/surface area analysisRock corePore fluid
The invention belongs to the field of rock permeability test, and discloses a device for testing rock permeability under different pore fluid pressure. The device is characterized by comprising a high-pressure gas source generating device, a back pressure control device and a data detection and display device, wherein the high-pressure gas source generating device is connected with the back pressure control device, and the data detection and display device is connected with the back pressure control device; and the back pressure control device comprises a needle-shaped throttling valve and a rock core holder, wherein the needle-shaped throttling valve is arranged at the outlet end of the rock core holder. The invention also discloses a method for testing the rock permeability under different pore fluid pressure. A back pressure valve in the prior art is replaced by using the needle-shaped throttling valve to adjust the pressure of the rock core in the rock core holder under different pore fluid, the device has good back pressure stabilizing effect, and meanwhile, the processing production technology for the throttling valve is mature and has low cost and strong adaptability.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
Low-field nuclear magnetic resonance multi-probe quantitative test system and method special for hydrate
PendingCN107807143ARealize the integration of testing and analysisRealize integrationAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceWater resource assessmentPore fluidLow field nuclear magnetic resonance
The invention discloses a low-field nuclear magnetic resonance multi-probe quantitative test system and a low-field nuclear magnetic resonance multi-probe quantitative test method special for hydrate.The test system comprises a low-field nuclear magnetic resonance analyzer, a confining pressure-adding low-temperature high-pressure probe, a confining pressure-free low-temperature high-pressure probe, a confining pressure-free normal-temperature normal-pressure probe, a temperature confining pressure control module, a pore fluid supply module and an industrial personal computer. Through combined use of the confining pressure-adding low-temperature high-pressure probe, the confining pressure-free low-temperature high-pressure probe and the confining pressure-free normal-temperature normal-pressure probe and the improved design of the structure as well as by adoption of a multi-probe combined use mode, research on integration of hydrate-containing deposit low-field nuclear magnetic resonance measuring signal quantitative calibration and hydrate-containing deposit pore scale behavior measuring analysis is realized, research on the hydrate-containing deposit pore scale behavior featureis facilitated, and foundation is laid for discussion on hydrate-containing deposit basic physical property parameter change micromechanism.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF MARINE GEOLOGY
Preparation method for artificially synthesized transparent soil material
InactiveCN103969099AHigh purityWide range of gradingPreparing sample for investigationAlkaneVisual observation
The invention discloses a preparation method for an artificially synthesized transparent soil material. The transparent soil material comprises baked silica sand particles and colorless pore fluids which have the same refractive index, wherein the pore fluids are mixed fluids of 12, alkane and 15# white oil; during preparation, a glass bar is used to stir constantly so as to ensure intensive mixing; a vacuum chamber is adopted for vacuumizing so as to remove residual air in a mixture until the mixture is transparent; finally, a consolidometer is adopted for consolidation. According to the invention, the preparation method is simple and convenient to operate and easy to implement; compared with other preparation methods, the preparation method is wide in material sources, low in cost, pollution-free and non-hazardous and can achieve a better transparent effect; the prepared transparent soil can be effectively used for model tests, and metabolic un-embedding visual observation in soil bodies can be realized.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Mapping permeable reservoir formations by measuring the elastic nonlinear interactions of a seismic wave as it propagates through the reservoir rock matrix and its pore fluids
Owner:NONLINEAR SEISMIC IMAGING
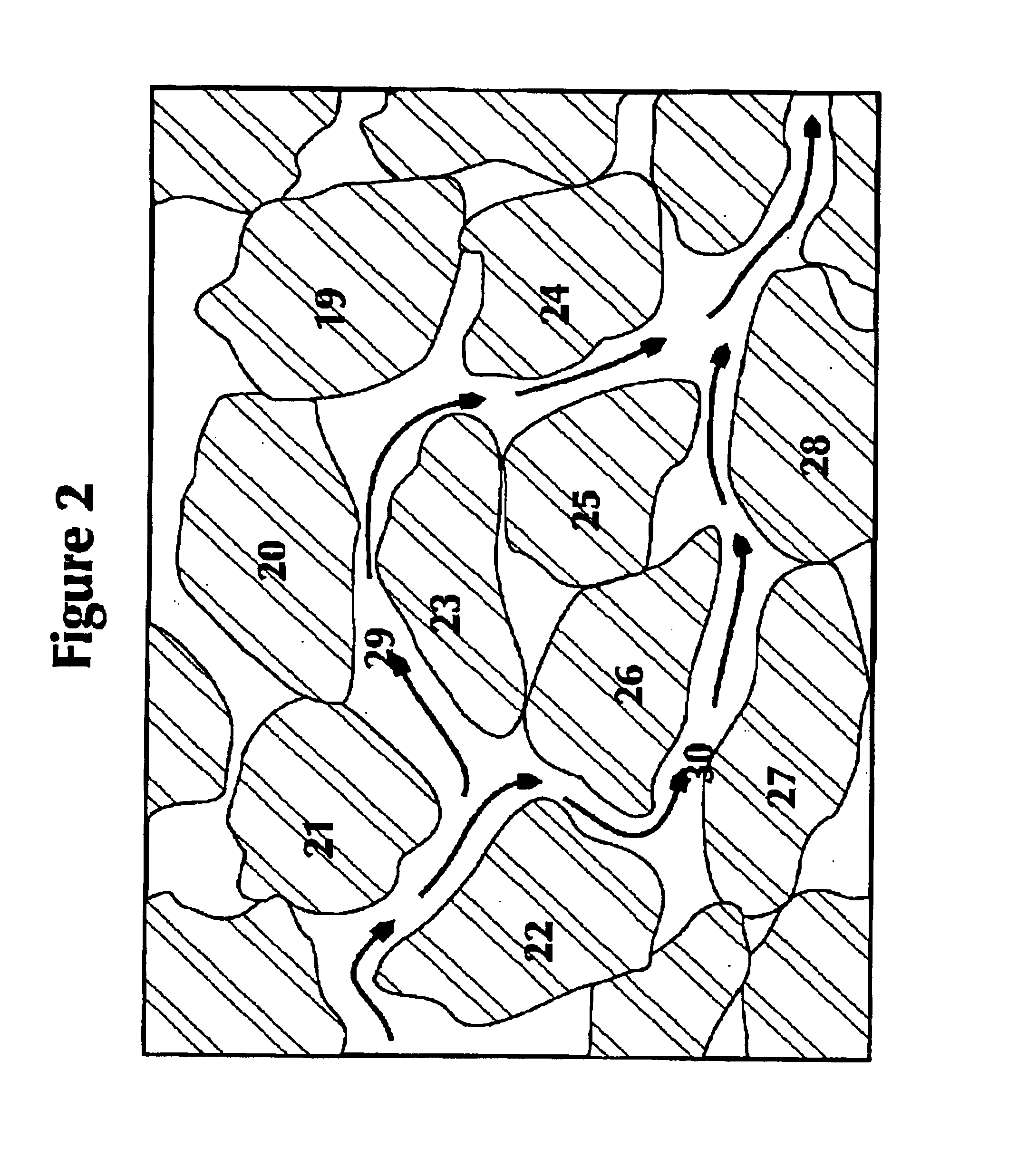
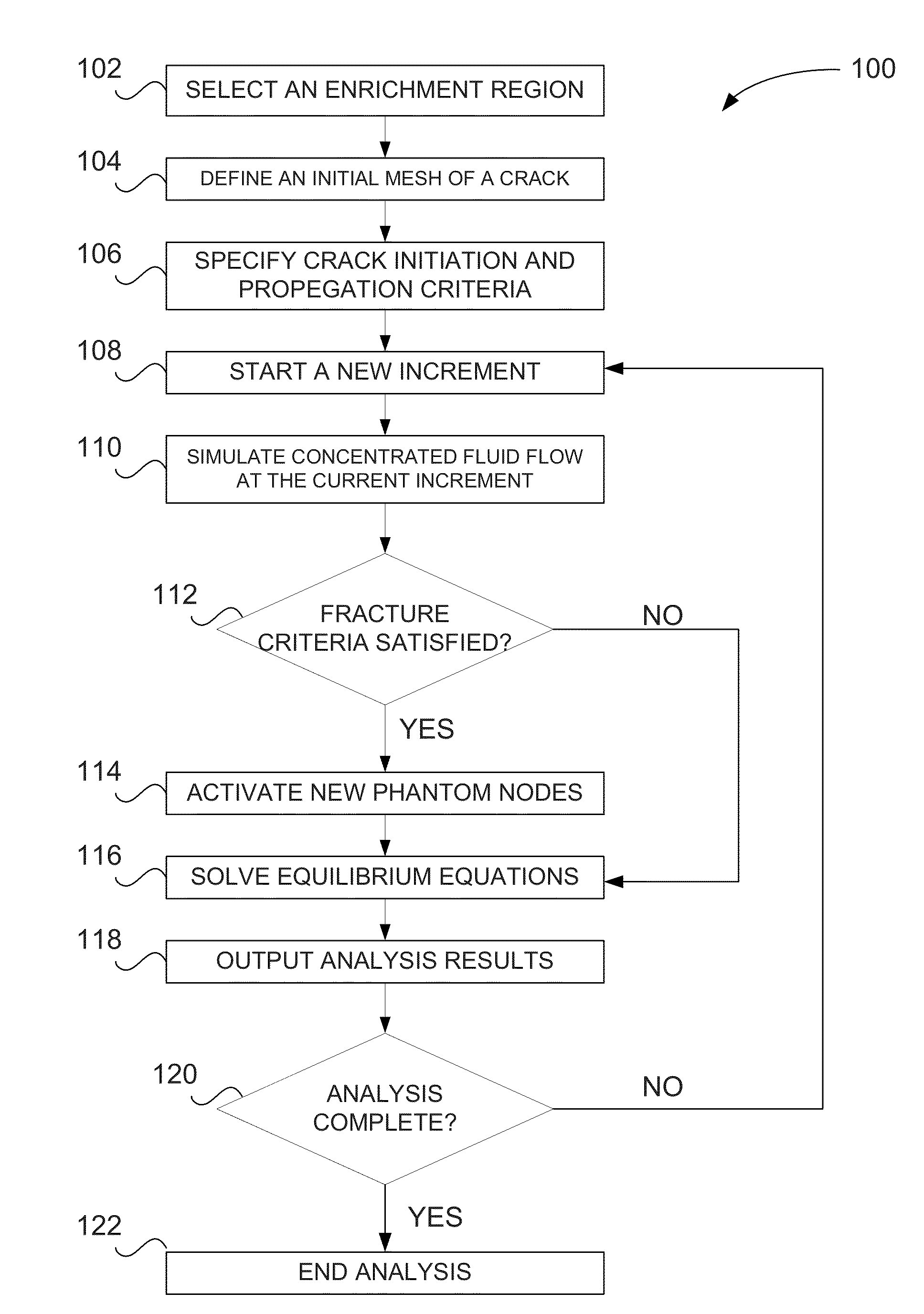
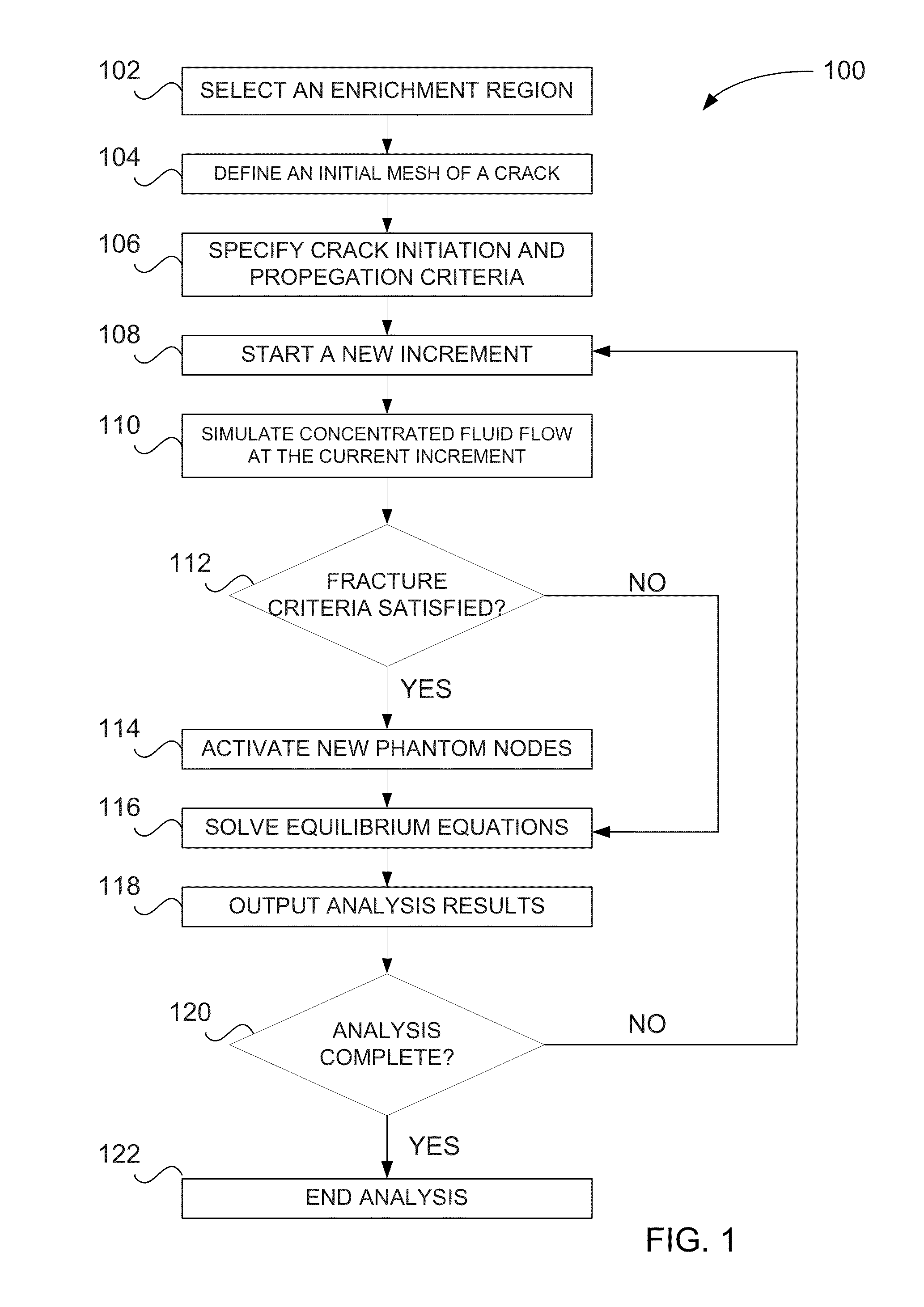
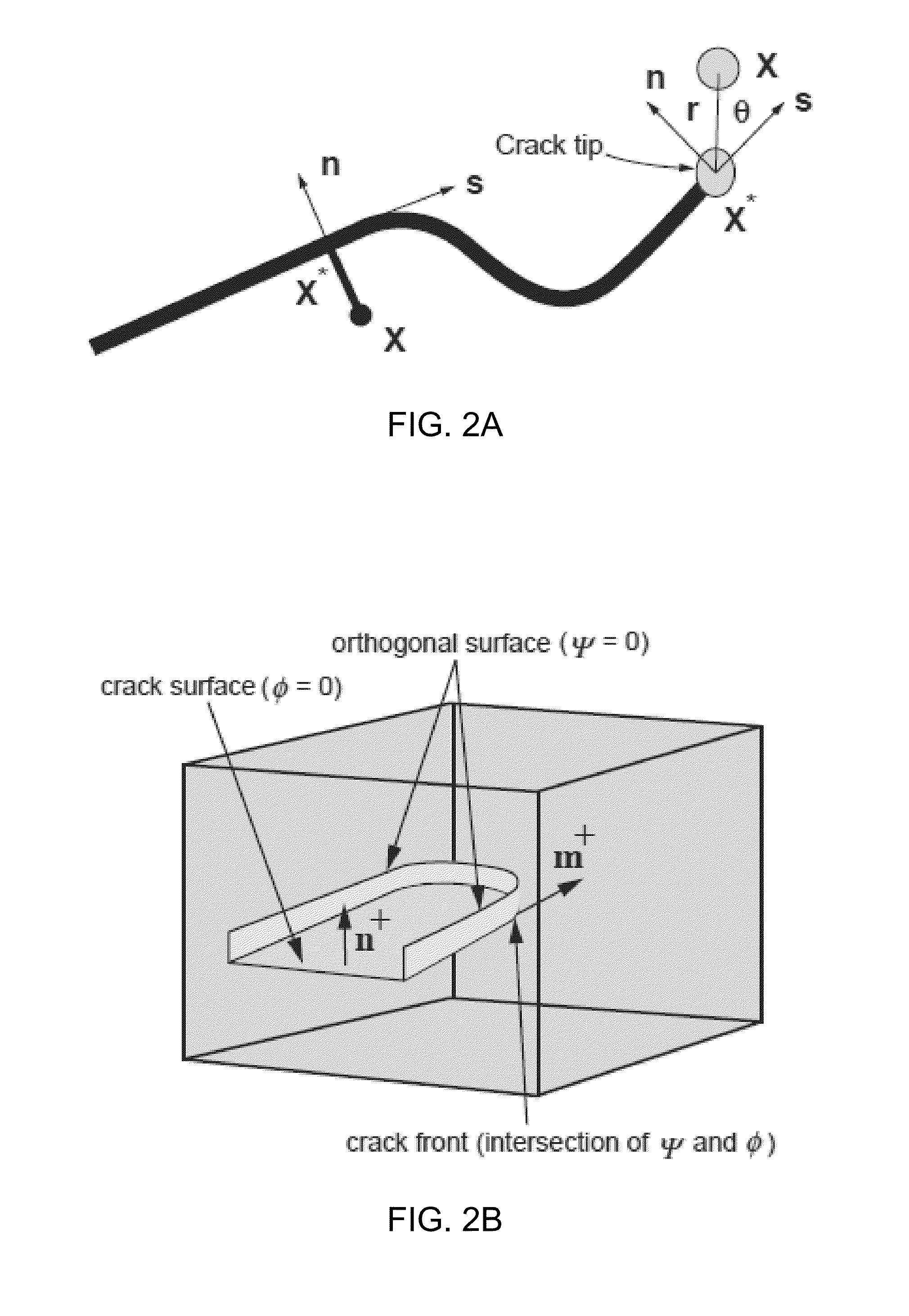
Hydraulic fracture simulation with an extended finite element method
A computer-implemented method includes defining respective positions of a first set of nodes and a second set of nodes in an enrichment region, and performing a coupled pore fluid diffusion and stress analysis on the enrichment region at the first set of nodes. It is then determined whether the second set of nodes is activated—representing a fracture—as a result of the analysis, and the results are visually output to a user.
Owner:DASSAULT SYSTEMES SIMULIA CORP
Rock longitudinal wave speed prediction method based on ellipsoid double porosity model
ActiveCN103984027ASolving the longitudinal wave prediction problemSeismic signal processingSeismology for water-loggingPorosityWave equation
The invention provides a rock longitudinal wave speed prediction method based on an ellipsoid double porosity model. The method comprises the following steps: rock physical parameters are obtained by acquiring well-logging data and experimental observation data, and a dry skeleton model and a porosity fluid model of the rock are generated; a double porosity medium ellipsoid plaque saturation model is established, the potential energy / kinetic energy of the porosity medium and kinetic energy and dissipative equation of the fluid in an inner embedded body are calculation, an Lagrange equation system is derived, and the longitudinal wave and transverse wave speeds are solved; according to the plane wave analysis method, the dispersion relationship of the wave equations is obtained, and the longitudinal wave speed dispersion and attenuation computational formula is obtained. According to the invention, the rock longitudinal wave speed prediction accuracy can be improved.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
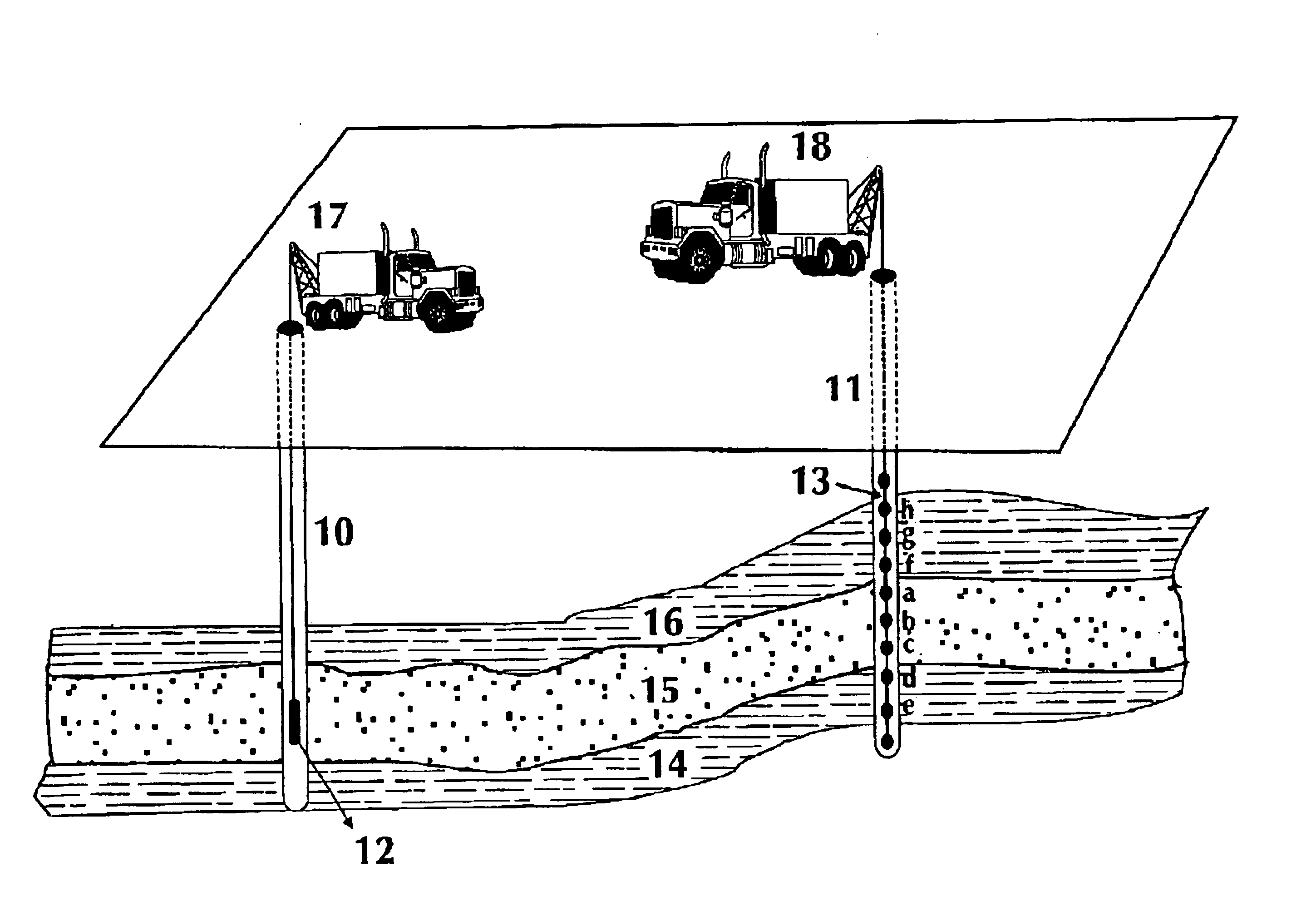
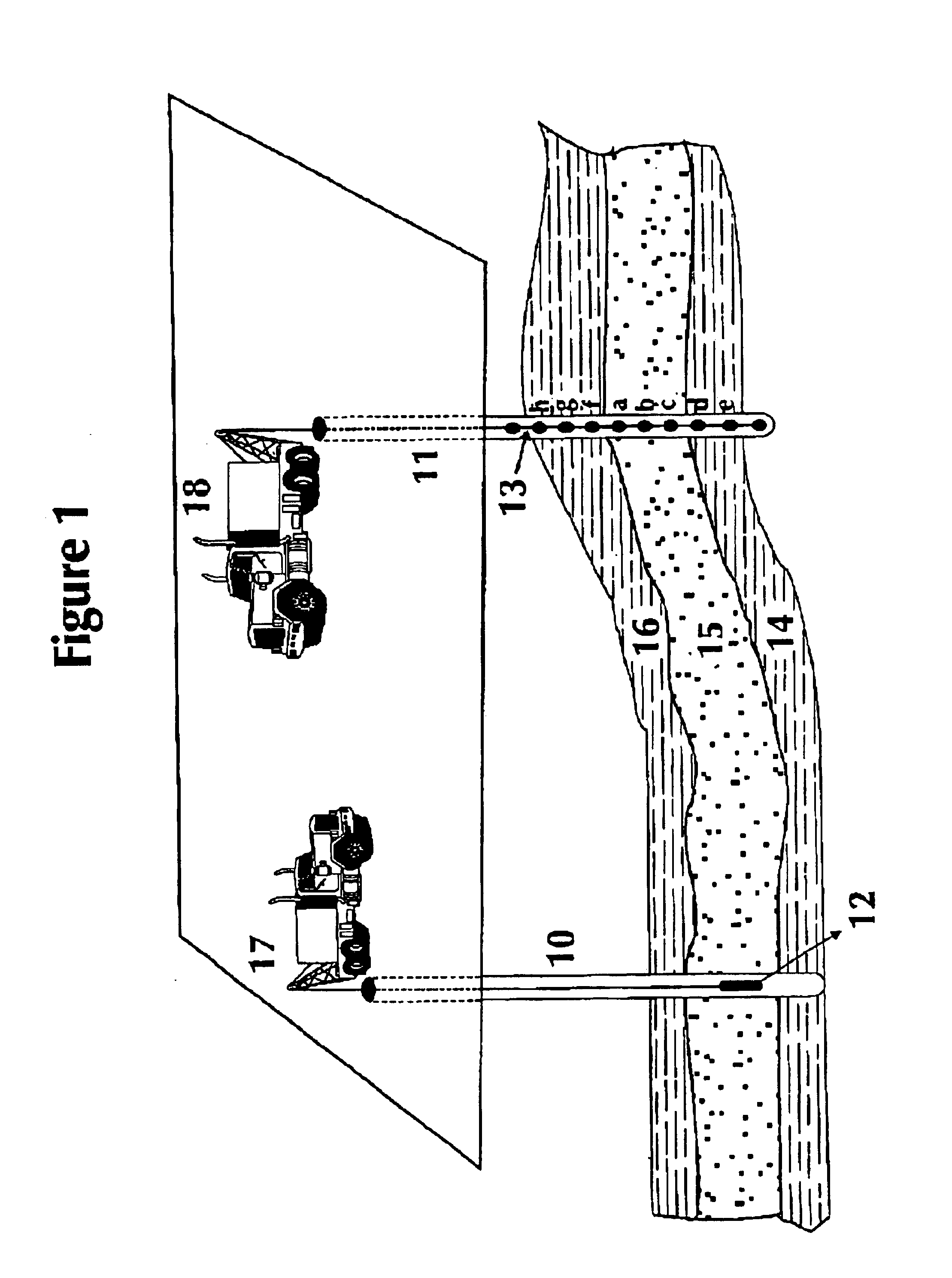
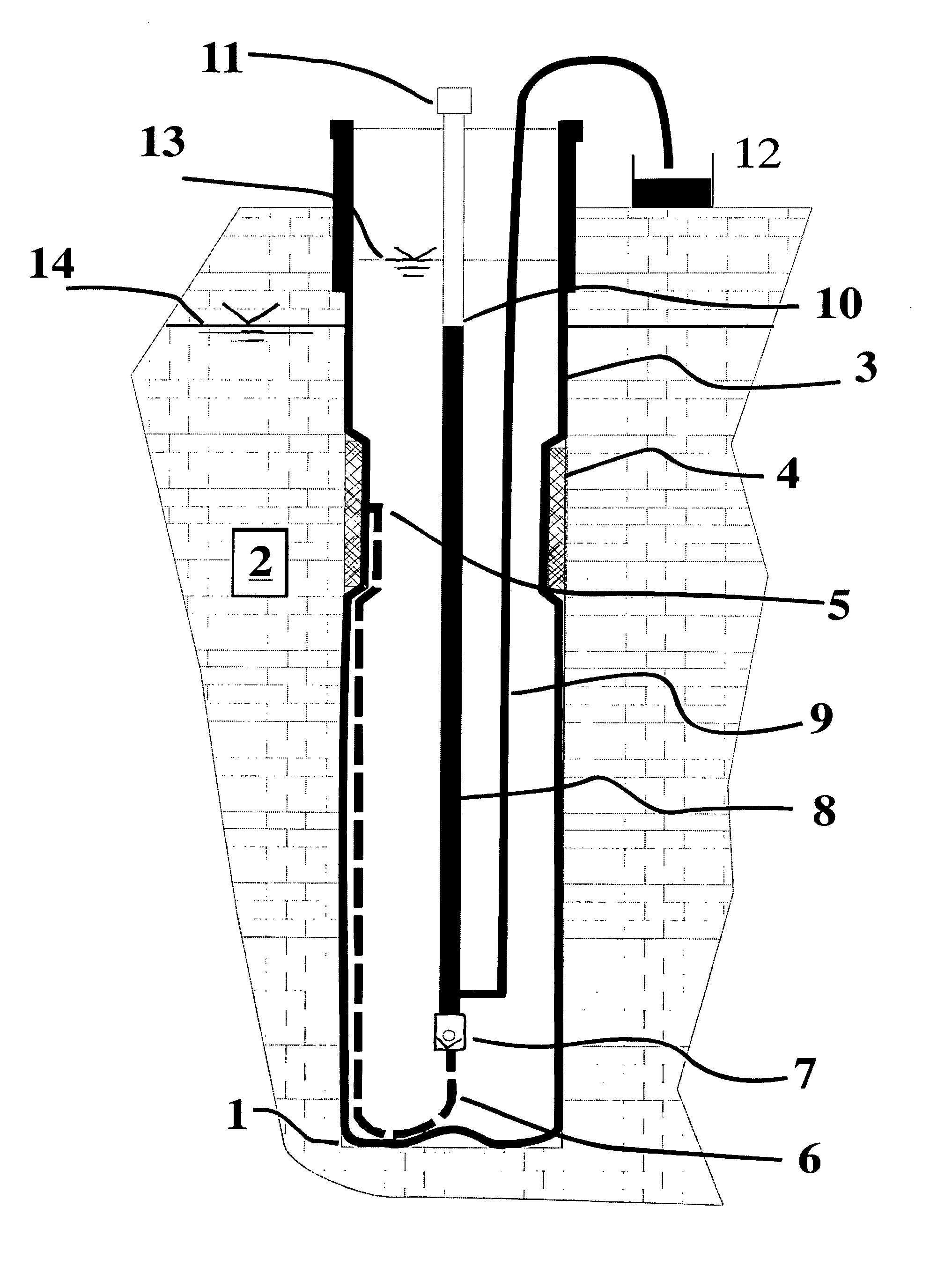
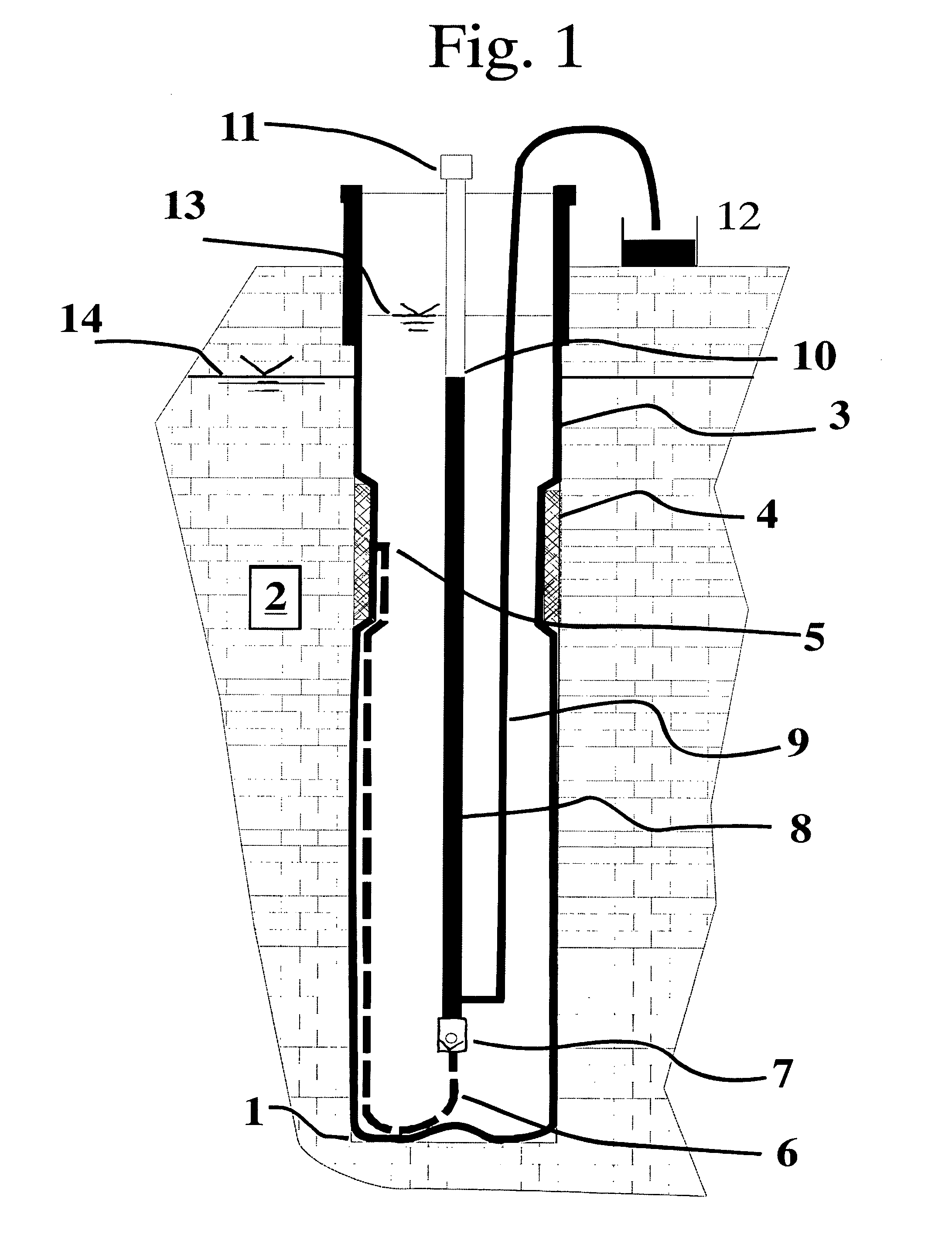
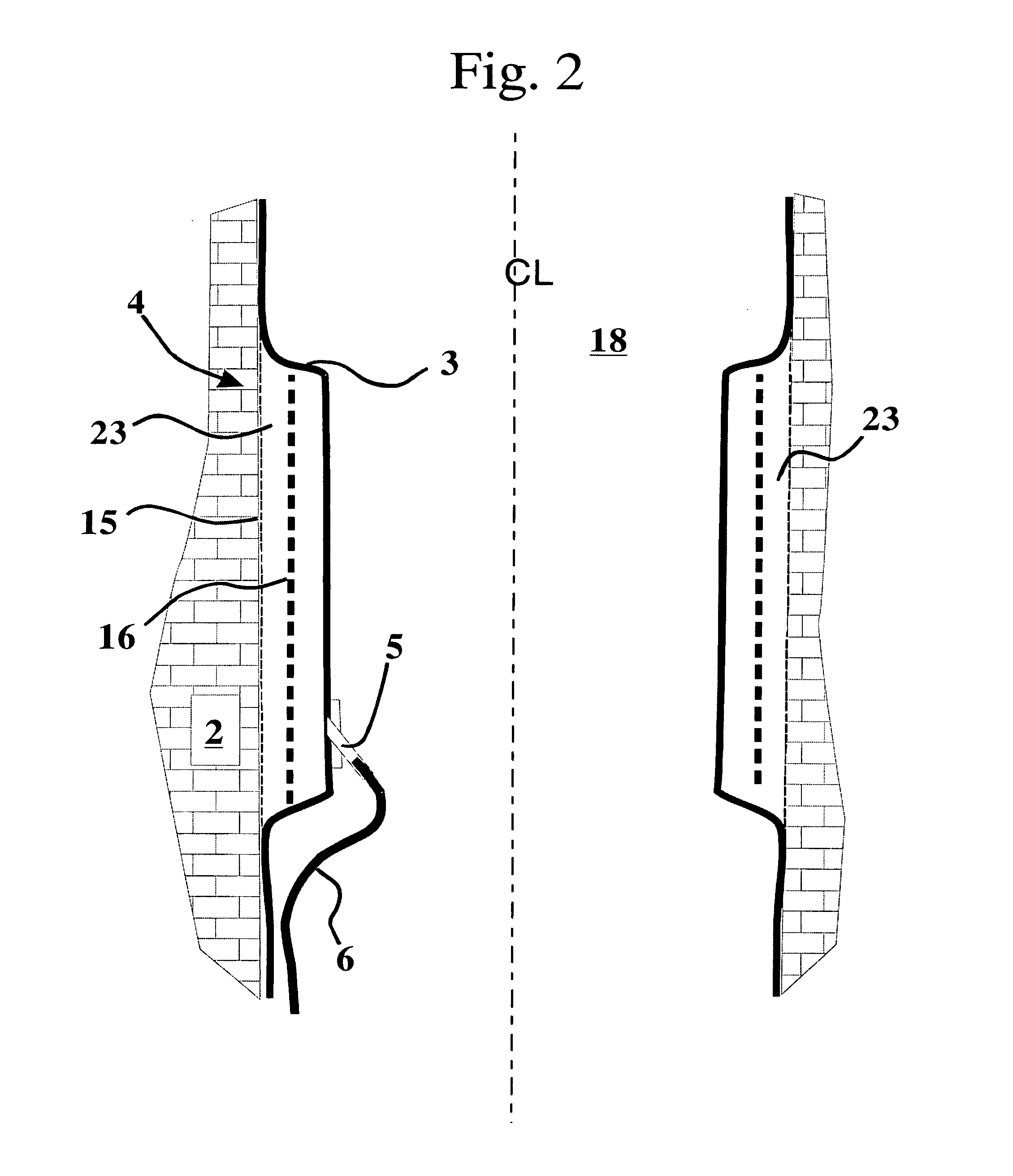
Pore fluid sampling system with diffusion barrier
A sampling system and method for use in pipes or in boreholes beneath the earth's surface, including the use of flexible borehole liners, the liners provided with a diffusion barrier to prevent contamination of fluid samples obtained by the system and method. There is provided a flexible diffusion barrier in the construction of a flexible fluid sampling liner, so as to nearly eliminate concern for diffusion transport into or out of the liner. The flexible diffusion barrier may be incorporated into and constructed with known devices, called spacers, in use with flexible borehole liners. The diffusion barrier according to the present disclosure is attached or secured by a suitable means to the interior surface, or the exterior surface, or both surfaces, of the flexible borehole liner. In one embodiment, a spacer with a diffusion barrier prevents both the diffusion into the liner, and the diffusion out of the liner, in the interval subtended by the spacer length.
Owner:KELLER CARL
Method for predicting velocity of longitudinal wave of rock system in heterogeneous reservoir
ActiveCN103412336APrediction of compressional and shear wave velocity capabilitiesPredict heterogeneitySeismic signal processingSeismology for water-loggingLongitudinal wavePore fluid
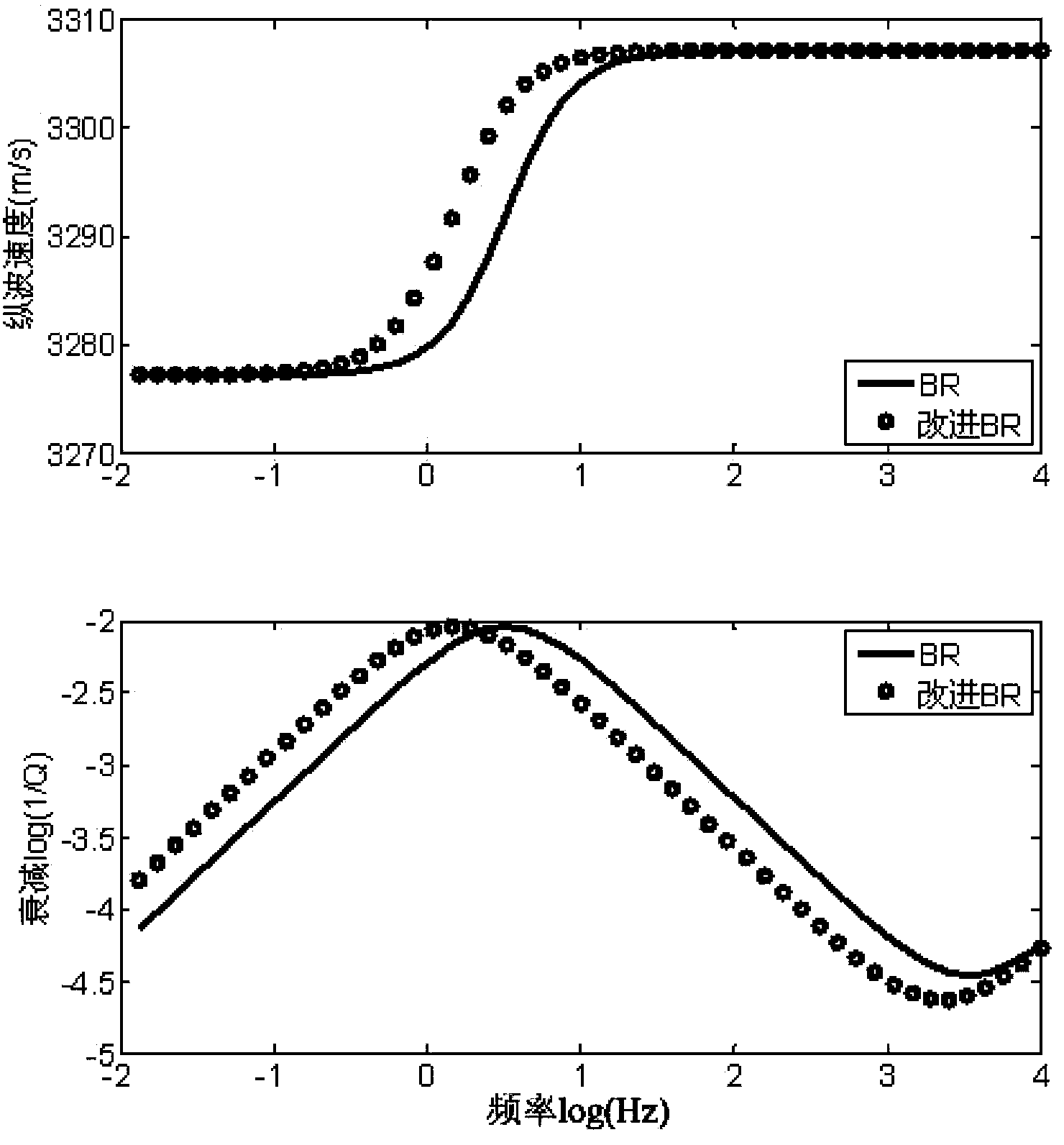
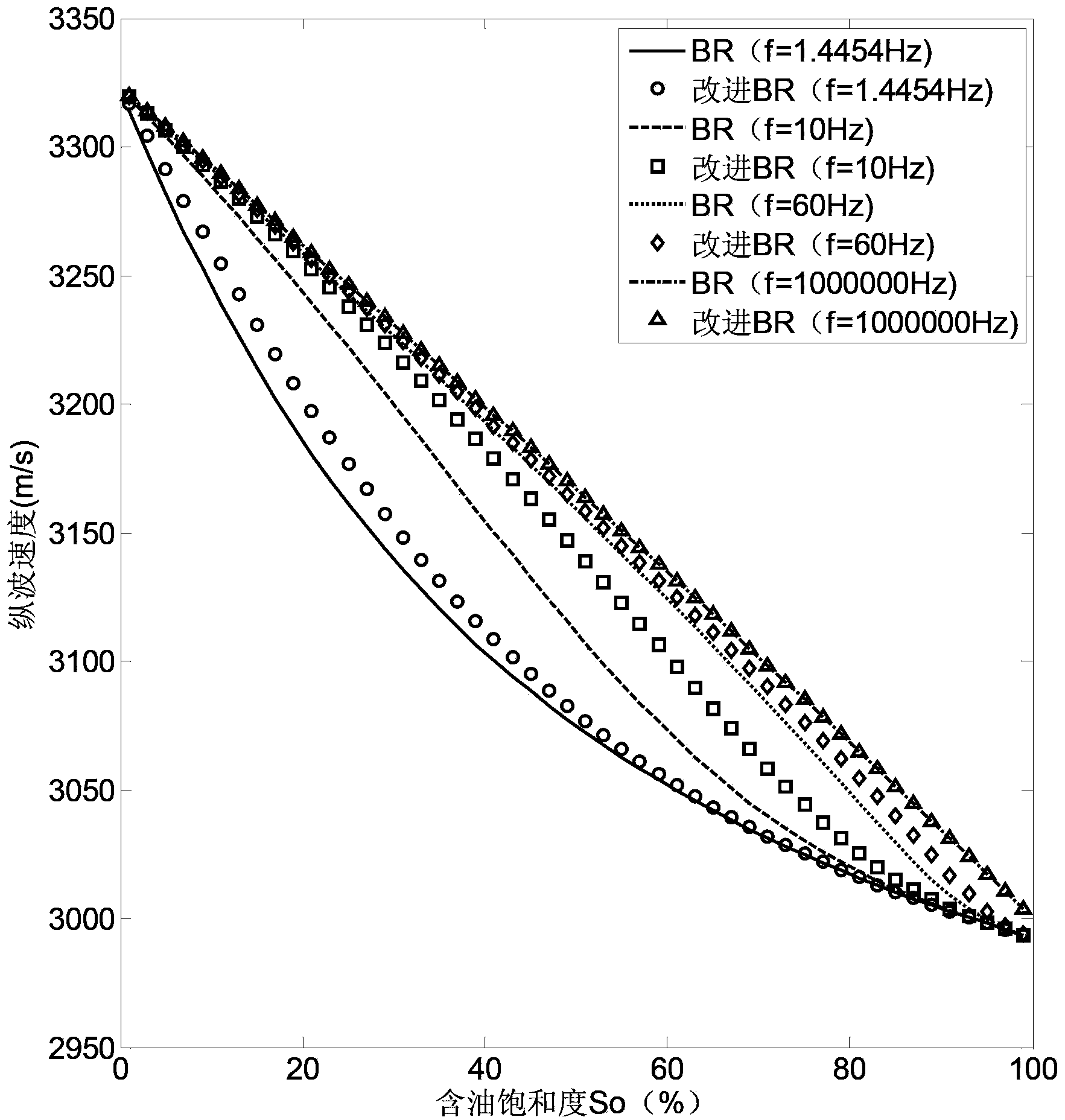
The invention provides a method for predicting the velocity of a longitudinal wave of a rock system in a heterogeneous reservoir. The method for predicting the velocity of the longitudinal wave of the rock system in the heterogeneous reservoir comprises the steps of (1) obtaining the permeability, the porosity, the shale content, mineral constituents, mineral volume rates and pore fluid data, (2) building a rock bare-skeleton model and an embedded body fluid model, (3) calculating the velocity of fluid inside an embedded body according to the embedded body fluid model, (4) calculating the kinetic energy function and the dissipative energy function of a double-pore medium according to the velocity of the fluid inside the embedded body, (5) using the kinetic energy function and the dissipative energy function of the double-pore medium to export an improved Biot-Rayleigh equation set according to the Hamilton principle and the Lagrange equation, and (6) predicting the velocity of the longitudinal wave of rock in the heterogeneous reservoir through plane wave analysis and the improved Biot-Rayleigh equation set. The method for predicting the velocity of the longitudinal wave of the rock system in the heterogeneous reservoir takes full consideration of anisotropism of the rock system and fluid kinetic energy caused by a fluid velocity field inside the embedded body and dissipative energy caused by the fluid velocity field inside the embedded body, can predict the velocity of the longitudinal wave of the oil-in-water double-pore rock system, overcome the defects of an original Biot-Rayleigh equation set, and retain the advantage, of the original Biot-Rayleigh equation set, of being simple in format.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Mapping permeable reservoir formations by measuring the elastic nonlinear interactions of a seismic wave as it propagates through the reservoir rock matrix and its pore fluids
InactiveUS20020188407A1Seismic signal processingSeismology for water-loggingPore fluidInterconnection
Permeability is one of the most important factors in influencing the commercial viability of a hydrocarbon reservoir. So far, permeability cannot be measured directly in-situ in reservoir formations. This invention relates to the field of estimating in-situ permeability of the reservoir rock formations. The measurements can be made across two wells or in a single well. Due to the morphology of their pore interconnections and the pore fluids in the rock, permeable rocks are elastically nonlinear. In a permeable rock, which is elastically nonlinear, the interactions between two elastic waves can be used in a unique way to map its physical properties. In this invention, the interaction of an elastic wave generated within the permeable rock with an externally generated seismic signal is used to determine the bulk tortuosity and bulk permeability of a reservoir rock formation.
Owner:NONLINEAR SEISMIC IMAGING
Method for calculating water saturation of porous medium
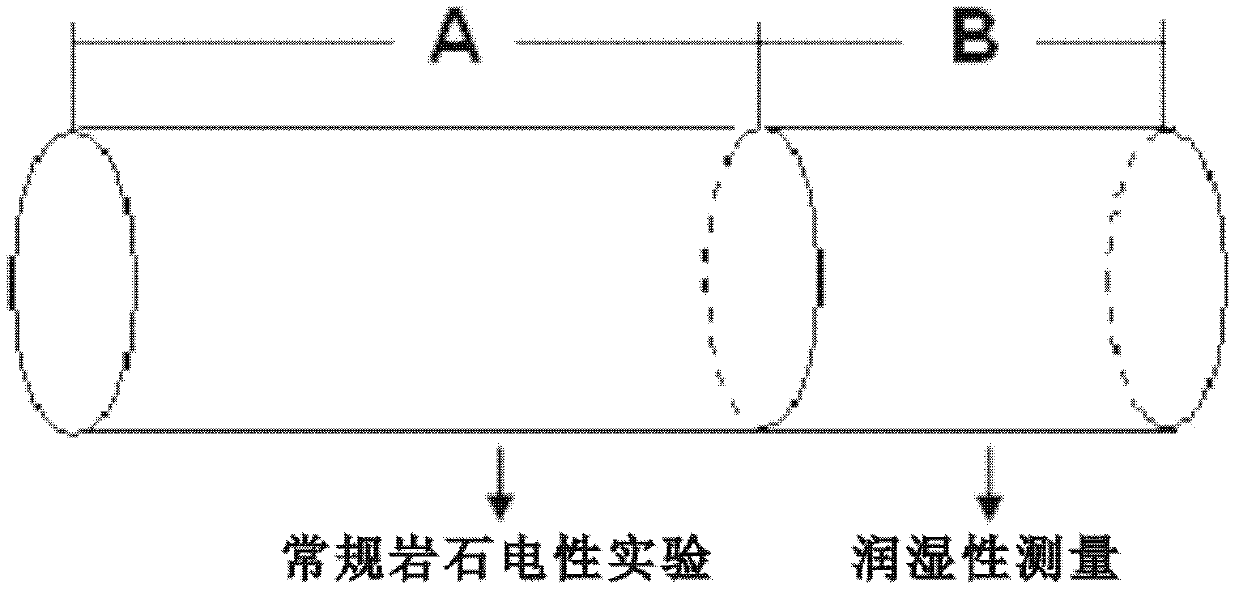
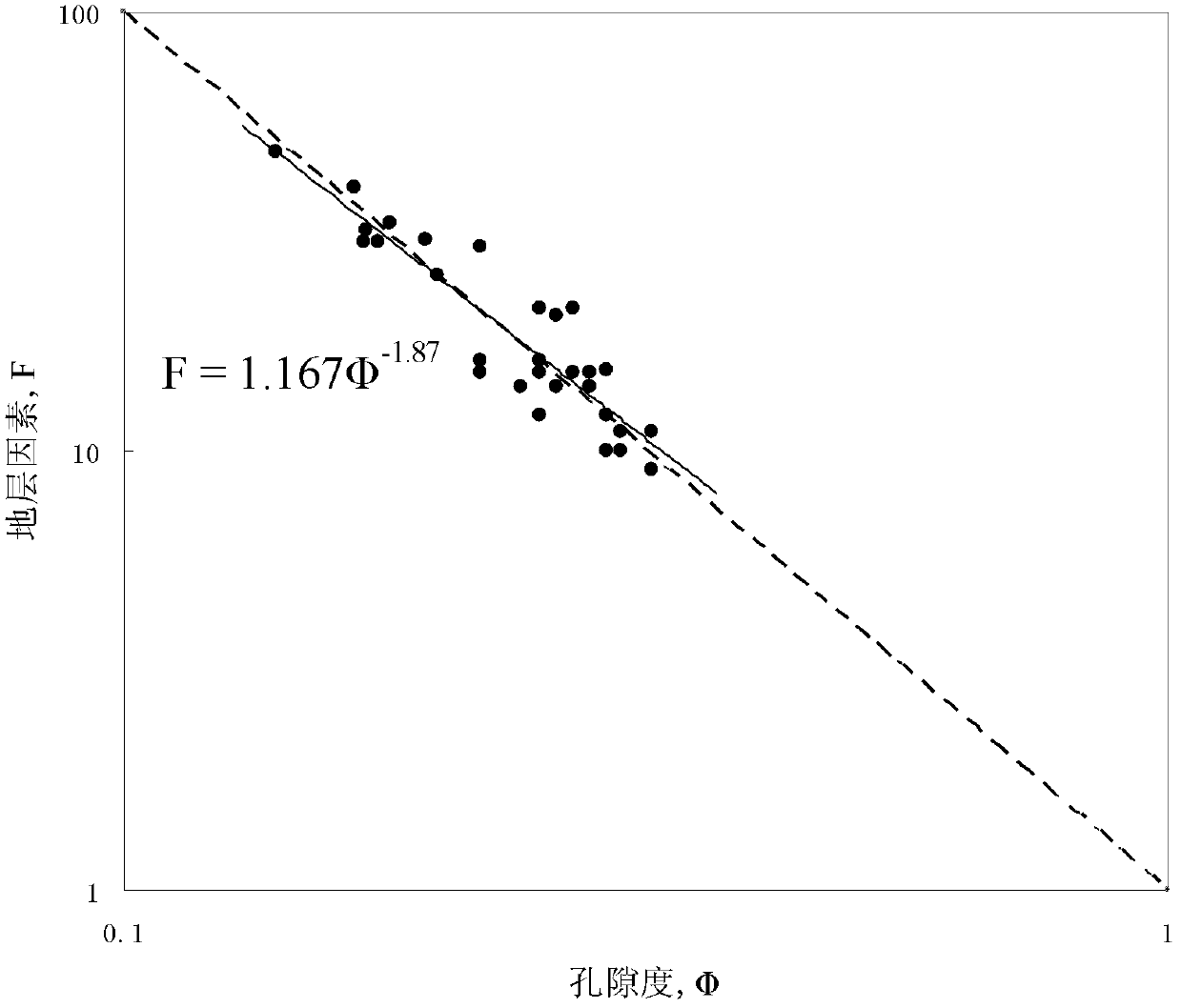
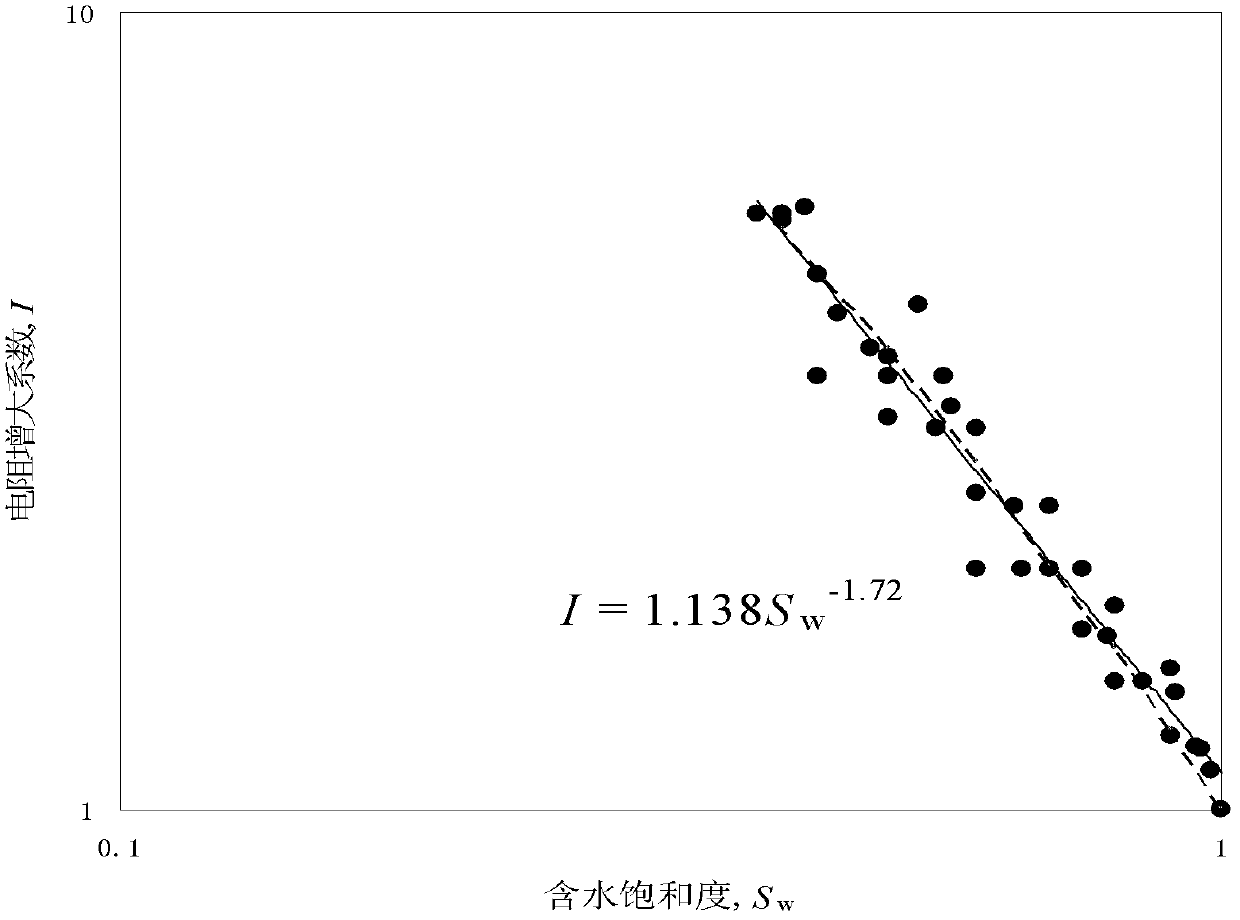
InactiveCN102565858AVarious methodsPerfect technologySeismology for water-loggingSpecial data processing applicationsElectrical resistance and conductancePore fluid
The invention relates to a method for calculating water saturation of a porous medium, which is an explanation method of geophysical electrical logging data and sequentially comprises the steps of (1) selecting and cutting a rock sample, performing an rock electrical experiment on an A section rock sample, and applying a B section rock sample to wettability measurement; (2) calculating a formation factor F; (3) calculating a parameter a' and fitting change relation of the a' along with Sw; and (4) calculating the water saturation Sw. The parameter a' has clear physical significance, describes influence of the distribution of a pore structure and the pore fluid of the porous medium on a resistance increase coefficient, and changes along with the changes of the water saturation. Due to the fact that a water saturation calculation formula in the method defines the influence of the distribution pattern of the pore structure and the pore fluid in pores on the resistance increase coefficient I, calculating results are accurate, the explanation method and the technique of geophysical electrical logging are perfected, and a basis and a means are provided for quantitative calculation of the water saturation of a reservoir stratum.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
Methods of decoupling diffusion effects from relaxation times to determine properties of porous media containing fluids
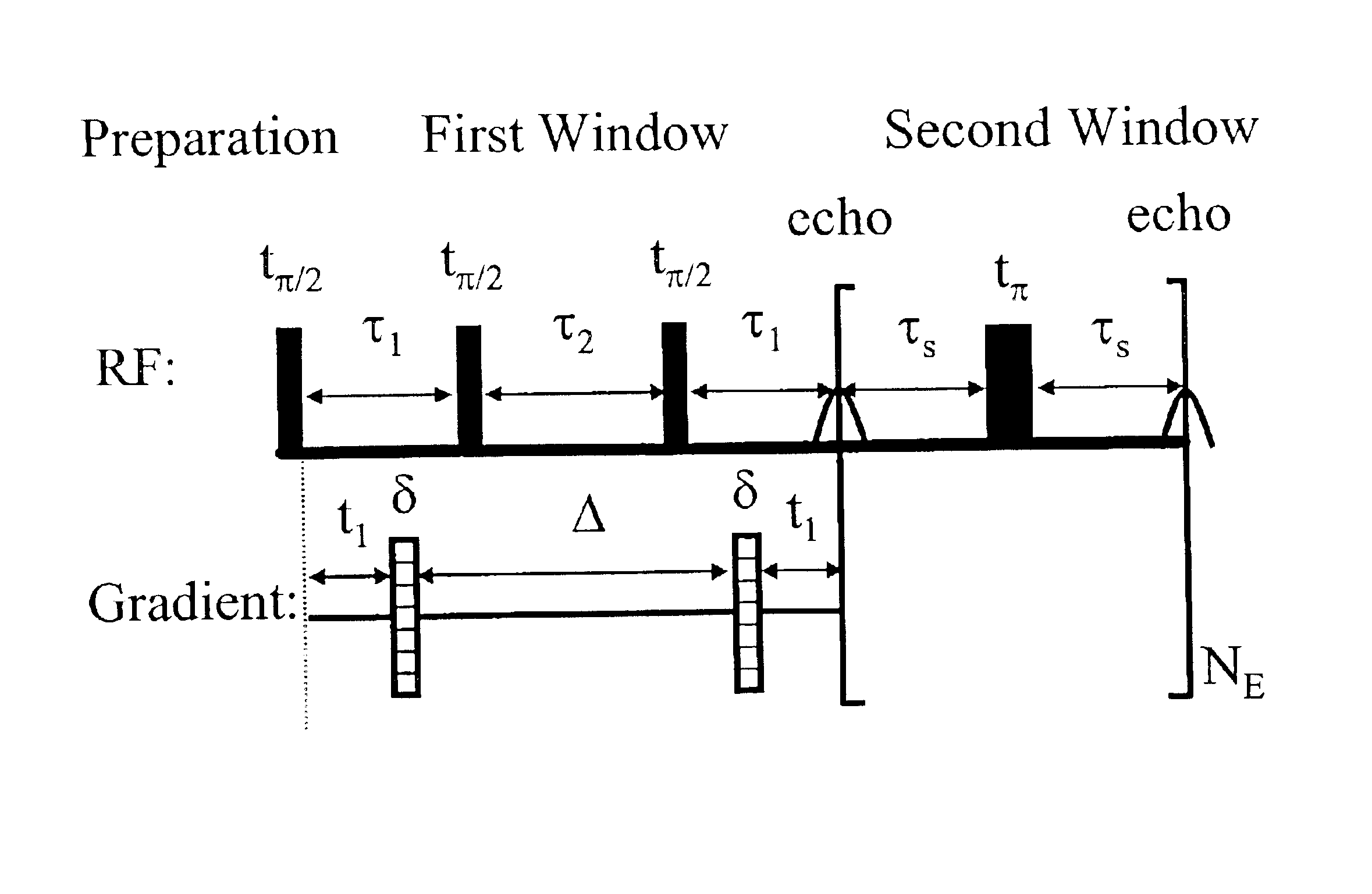
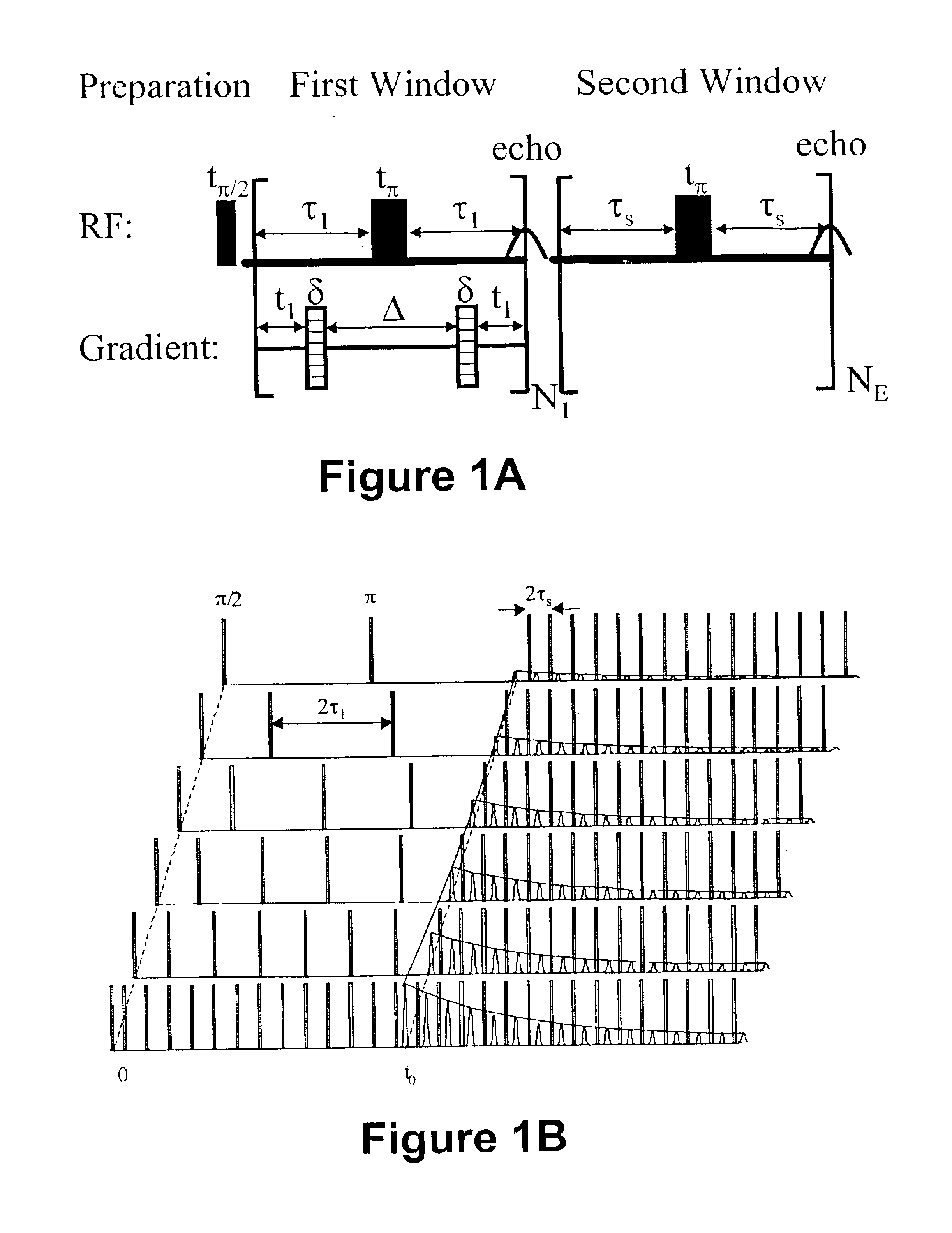
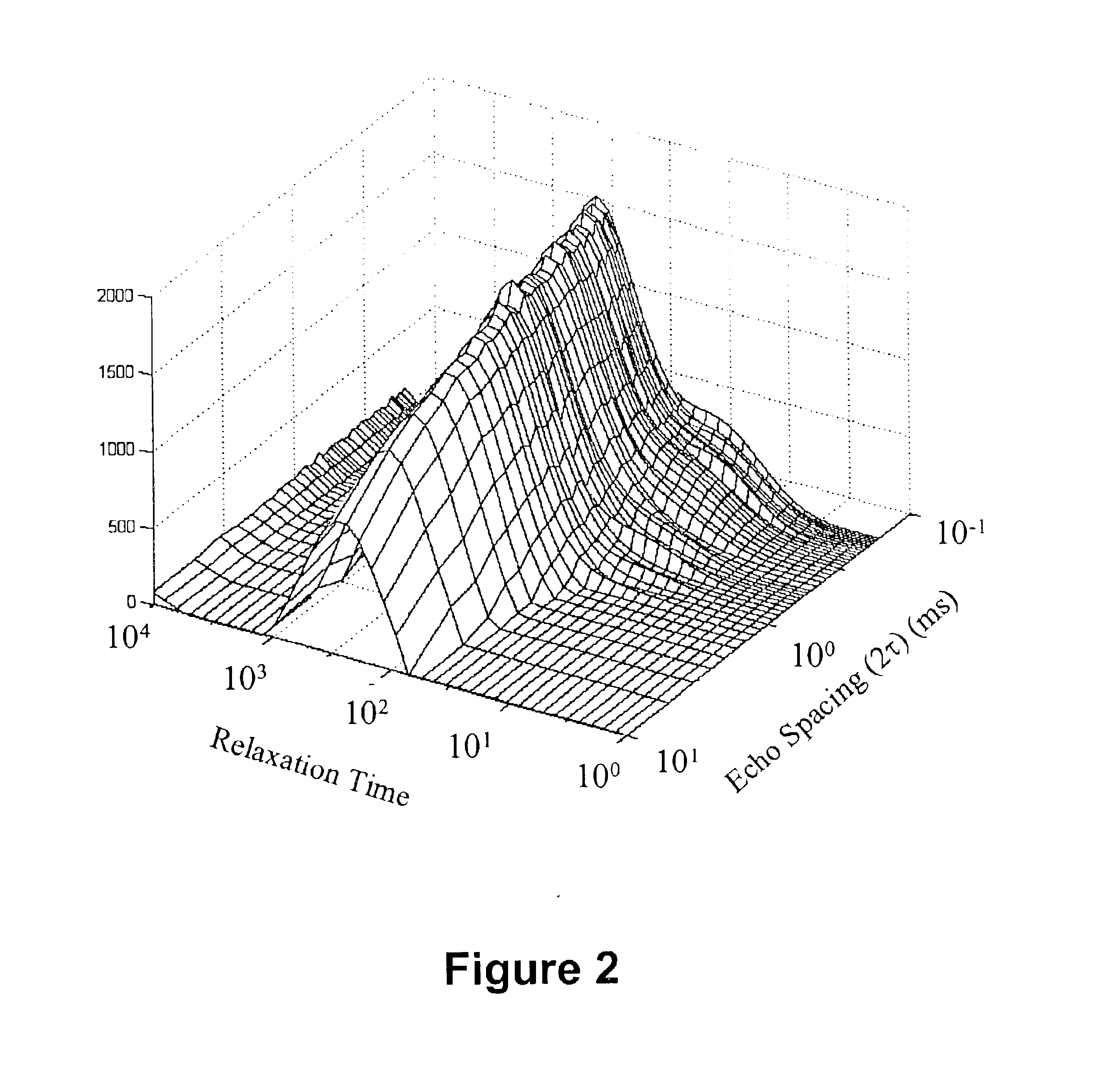
InactiveUS6833698B2Remove and minimizes effectElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingMaterial analysis by using resonancePore fluidPorous medium
Novel pulse sequences are used to probe the properties of porous media, such as are found in subterranean formations and core samples. This use allows diffusion effects to be uncoupled from the overall T2 relaxation time of the sample. Properties such as internal field gradient and distribution of diffusion coefficients may be determined. A series of pulse sequences are applied to the media to be evaluated. The series of pulse sequences include first and second windows. The first windows include pulse sequences have varying characteristics, such as increasing echo spacing, while the second windows preferably utilize similar pulse sequences which have very small echo spacing. Apparent internal field gradient distribution and apparent diffusion coefficient may be determined as a function of T2 relaxation time. These properties are readily visualized in a two-dimensional map with a first axis being the apparent internal field gradient or alternatively the diffusion coefficient of pore fluids, a second axis being the T2 relaxation times, and the vertical amplitudes being proportional to the proton population. Other properties which may be determined from use of this method include porosity, pore size distribution, oil and water saturation, oil viscosity, oil wettability, and permeability. Also, a method for determining and plotting a T1-MAS 2D spectrum is provided where T1 relaxation time and chemical shift are plotted on x,y axes while intensity of proton population is displayed along a third axis.
Owner:CHEVRONTEXACO US
Well-to-seismic integration paleo-formation pressure prediction method
ActiveCN104483703AEfficient use ofSeismic signal processingSpecial data processing applicationsTime domainPredictive methods
The invention relates to a well-to-seismic integration paleo-formation pressure prediction method. The method includes the steps that a velocity cube, a density cube and a porosity cube of a formation are obtained through the fine reservoir wave impedance inversion technology; time domain and depth domain conversion of a three-dimensional model is completed by means of the velocity cube; a geologic model of the geological time of a pool-forming period is obtained by subtracting the thickness of a formation needing to be eroded away in the pool-forming period from the thickness of the current formation; a paleo-porosity cube is obtained according to the erosion compaction restoration thicknesses of grids in the longitudinal direction of the geologic model of the pool-forming period and the porosity and depth relation; the paleo-density of the formation is restored by means of the density and depth linear relation; a paleo-formation interval velocity cube is obtained through the paleo-porosity cube; the rock matrix velocity and relations between pore fluid velocities with depths are obtained through logging information; ancient overlaying formation pressure is obtained through a paleo-density cube; a formation pressure cube of the ancient geological time is obtained through the ancient overlaying formation pressure, the rock matrix velocity, the relations between pore fluid velocities with depths and the paleo-formation interval velocity.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Method for determining formation lithologic character and pore fluid
ActiveCN101354444AAvoid ambiguityHigh resolutionSeismic signal processingSeismology for water-loggingLithologyPore fluid
The invention relates to a method which uses geophysical exploration to determine stratum lithology and pore-fluid. The method of the invention adopts recorded three-component VSP seismic wave field, obtains zero offset seismic wave field, calculates the transmission longitudinal wave P of the seismic wave field of sampling points of different depths, then calculates the reflecting coefficients and wave resistances of the longitudinal wave and the transverse wave; according to the obtain stratum wave resistance changing curve, compared with the known logging data, the lithology and the pore-fluid property of the stratum can be determined. The method of the invention can provide directly the wave resistance changing curve of deep domain, avoids the problems of multiplicity of the speed-depth, limited wideband and low resolution, has high resolution, sufficiently uses the advantages of three-component VSP, can provide resistance longitudinal wave and transverse wave and azimuth and inclined angle of the stratum simultaneously under a situation without transverse wave seismic source excitation, and provides beneficial bases for determining the change of the stratum lithology and the pore-fluid property.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +1
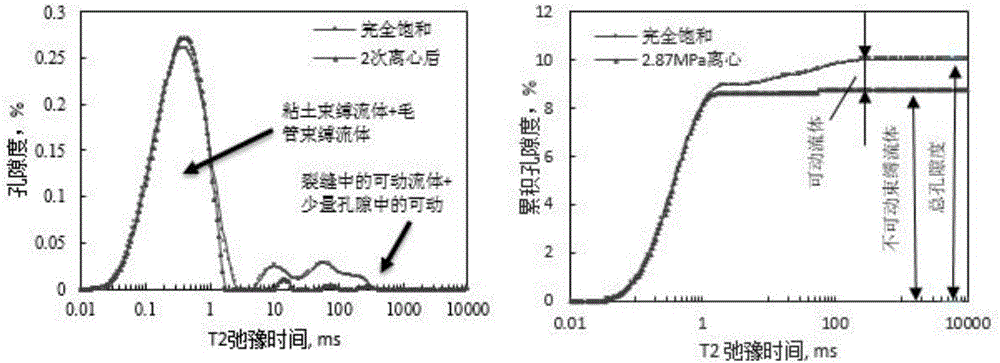
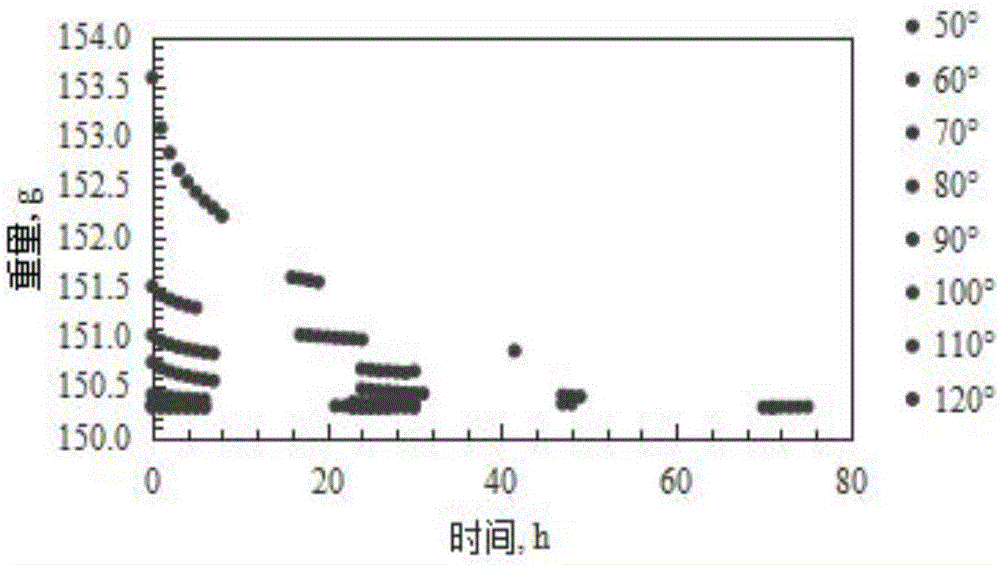
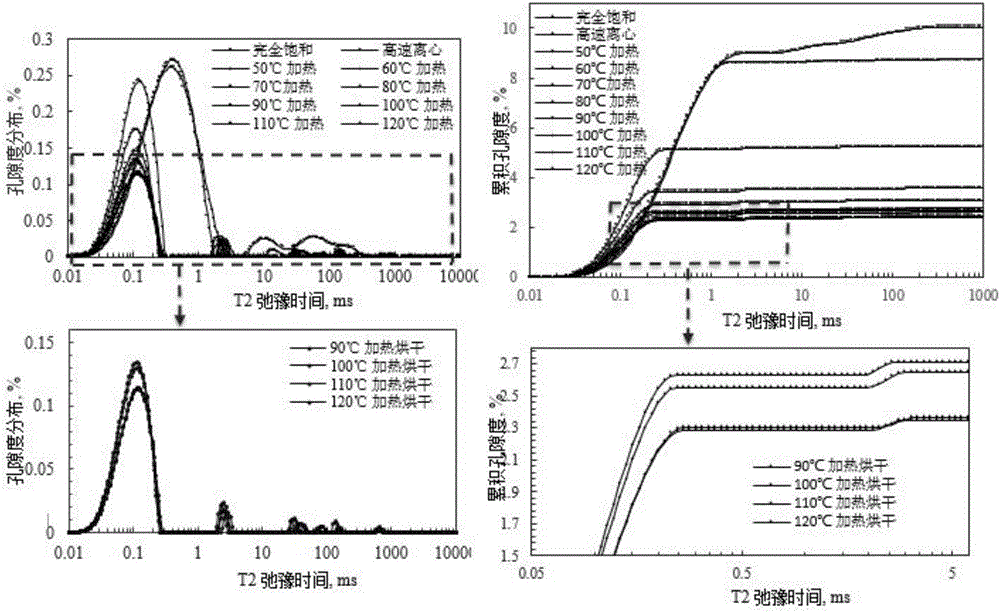
Experimental method for saturated shale pore fluid separation and saturation degree calculation
ActiveCN106525688AEfficient separationGet saturation distributionWater resource assessmentAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceChemical physics
The invention discloses an experimental method for saturated shale pore fluid separation and saturation degree calculation. The method includes the steps that firstly, separation of movable water in saturated shale is carried out through two times of a high-speed centrifugation method, and then a vacuum gradient heating experiment is added to separate capillary bound water and clay bound water in pore fluid. In the whole process, by carrying out contrastive analysis on change rules of a core weight and residual fluid nuclear magnetic resonance relaxation time T2 distribution frequency spectrum obtained after each step is completed, the saturation degrees of the movable water in saturated core pores, the capillary bound water and the clay bound water are obtained, and the saturation degree distribution of the movable water in crack space and pore space is obtained. The nuclear magnetic resonance core analysis technology is further used for calculating the storage percentage of the movable water in shale cracks and large pores, and reference is provided for evaluation of seepage space of a shale reservoir.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Method for predicting volume content of corrosion pores in carbonate reservoir
InactiveCN106290105AMake up for the inability to describe the pore type of the reservoirAvoid non-promotable flawsPermeability/surface area analysisShear modulusPore fluid
The invention discloses a method for predicting the volume content of corrosion pores in a carbonate reservoir. The method comprises the following steps: step 1, obtaining physical parameters of the carbonate reservoir; step 2, based on the physical parameters obtained in the step 1, calculating the bulk modulus and shear modulus of saturated rock of an actually-measured carbonate reservoir; step 3, calculating the bulk modulus and shear modulus of a rock matrix of the carbonate reservoir and the bulk modulus of a pore fluid; step 4, establishing a dual-pore-medium critical porosity model, and calculating the bulk modulus and shear modulus of a rock framework of the carbonate reservoir; step 5, calculating the bulk modulus and shear modulus of saturated rock of the carbonate reservoir through a Geissmann equation; step 6, comparing the bulk modulus and shear modulus of saturated rock of the carbonate reservoir with the bulk modulus and shear modulus of saturated rock of the actually-measured carbonate reservoir, and calculating an error; and step 7, modifying the set volume content of corrosion pores, performing the step 4 to the step 6 in sequence, calculating an error corresponding to the set corrosion pore condition, and obtaining an optimal volume content of corrosion pores.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD +1
Method for processing formation data based on lithologic parameter of reservoir rock
ActiveCN102174888AImprove calculation accuracyEliminate systematic errorsElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSurveyLithologyWell logging
The invention provides a method for processing formation data based on the lithologic parameter of a reservoir rock, which belongs to the field of geophysical exploration and well logging evaluation and development of lithologic parameters of reservoir rocks and the formation data. The method comprises the following steps of: acquiring formation lithology and fluid information by using geological exploration and development equipment; analyzing the acquired formation lithology and fluid information by using analytical equipment to acquire a basic parameter required by the calculation of pore fluid volume of the reservoir rock; and establishing a petroleum volume and petroleum geological reserve calculation equation by selecting reservoir parameters such as corresponding porosity, oil saturation and the like. The method is suitable for evaluating reservoir rock petroleum resources with proved reserves, controlled reserves and predicted reserves, which belongs to the field of reserve calculation by a volume method. By a volume method reserve calculation equation established in the method, system errors caused by the original volume method reserve calculation formula are eliminated, so that the calculation accuracy of petroleum geological reserves is improved by 6 to 21 percent.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Method for prospect identification in asset evaluation
InactiveUS20050015204A1Powerful toolDeveloped solutionElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSeismic signal processingLithologyPore fluid
3D seismic classification is a breakthrough technology to determine the three-dimensional distribution of pore fluid, lithology, and faults / fractures from multiple seismic attribute volumes. This method provides an innovative, timesaving solution for identification and definition of drilling targets, especially in areas with multiple pay zones and complex geology.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Embedded-type sensor for detecting concrete chloride ion content and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101726525AAvoid damageEffective protectionMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansFiberIon content
The invention discloses an embedded-type sensor for detecting concrete chloride ion content and a preparation method thereof, relating to a sensor and a preparation method. The invention solves the problems that the existing sensor can not detect concrete chloride ion content in real time and has larger voltage drop, poor sturdiness and poor stability, and the sensor manufactured with the existing method can not continuously detect changed chloride ion concentration and has inaccurate detection result. A micro-expansion fiber cement semipermeable membrane layer, an alkaline gel layer and a manganese dioxide layer are successively arranged in a sensor barrel from bottom to top. The method is as follows: successively arranging the manufactured micro-expansion fiber cement semipermeable membrane layer, the alkaline gel layer and the manganese dioxide layer from bottom to top in the sensor barrel; and dipping the lower part of the manufactured sensor into simulative concrete pore fluid. The sensor of the invention can detect concrete chloride ion content in real time, has favourable sturdiness and favourable long-term stability; the sensor manufactured by the invention can continuously detect changed chloride ion concentration and has accurate detection result.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Cementing fluid for enhancing the stability of a water sensitive, reactive subterranean formation
InactiveUS20050080161A1Enhancing of formationImprove stabilityFlushingDrilling compositionWater activityPore fluid
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
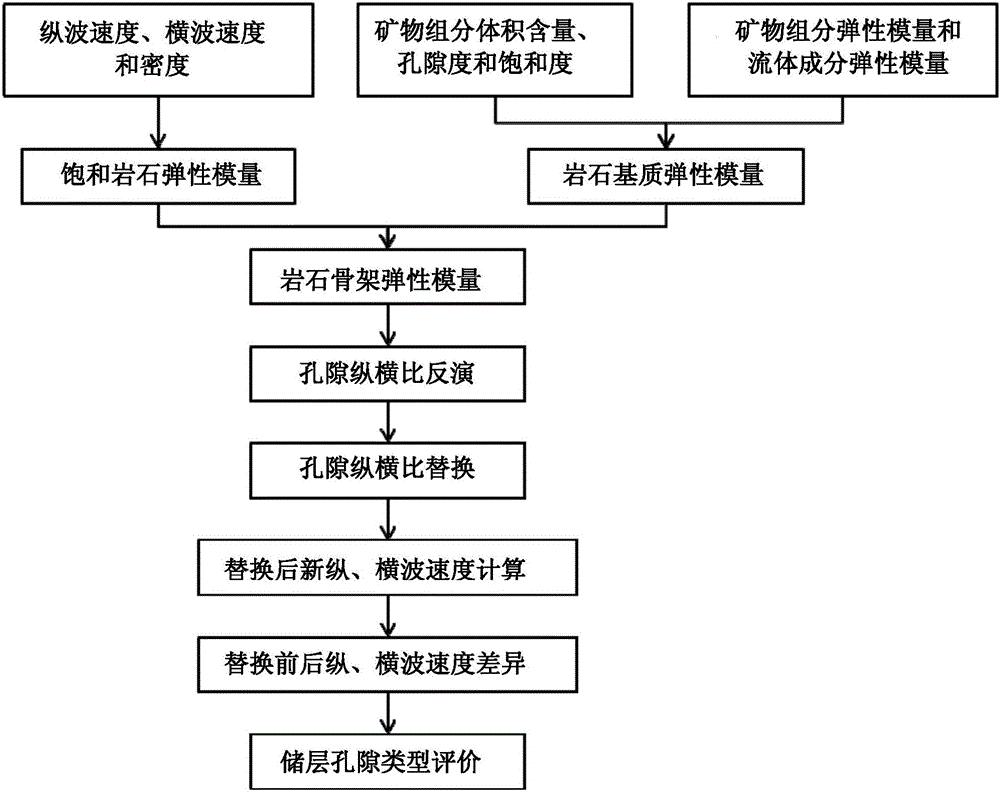
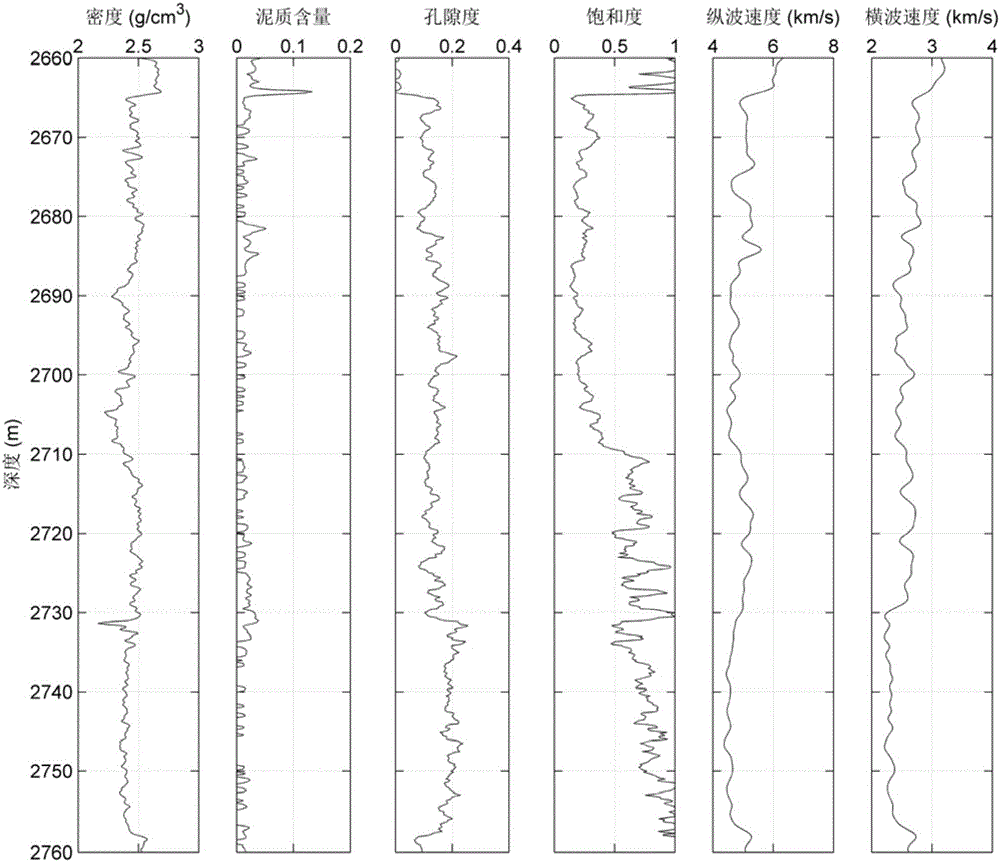
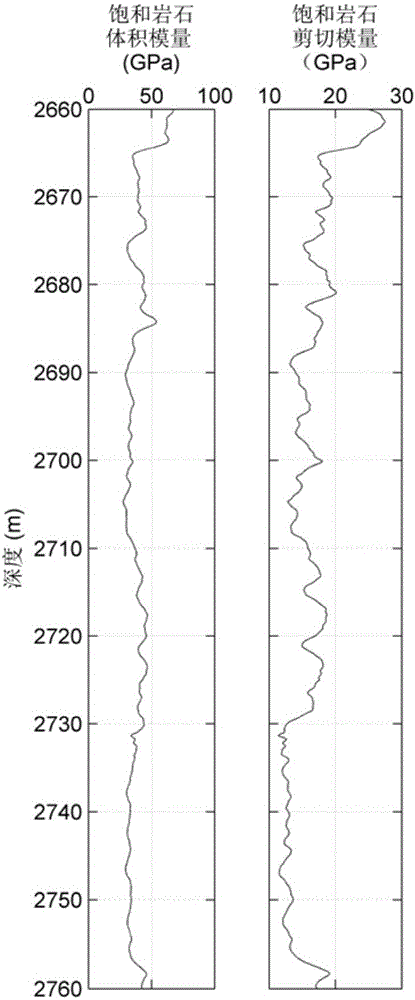
Method for evaluating reservoir pore type based on pore replacement
ActiveCN105974474AMake up for the inability to describe the pore type of the reservoirAvoid non-promotable flawsSeismic signal processingSoil scienceLongitudinal wave
The invention relates to a method for evaluating reservoir pore type based on pore replacement. The method includes the following steps: based on longitudinal wave speed, transverse wave speed, and density of a known reservoir stratum, calculating saturated rock elastic modulus of an original pore type 1 contained in the reservoir stratum; selecting the elastic modulus of a reservoir rock matrix mineral component and the elastic modulus of a pore fluid composition component, in combination with porosity, saturation and mineral component volume content, calculating the elastic modulus of the reservoir rock matrix; calculating a rock skeleton elastic modulus of the original pore type 1 contained in the reservoir stratum; conducting inversion on a pore aspect ratio of the reservoir stratum when the pore type 1 is contained; replacing the original pore type 1 with a pore type 2 through a given new pore aspect ratio; calculating the new longitudinal wave speed and transverse wave speed of the replaced reservoir stratum; comparing the longitudinal wave speed and transverse wave speed of the original reservoir stratum and the replaced reservoir stratum, and conducting reservoir pore type evaluation. According to the invention, the method can depict reservoir pore type and is more suitable for actual reservoir stratum.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Pore fluid sampling system with diffusion barrier and method of use thereof
A sampling system and method for use in pipes or in boreholes beneath the earth's surface, including the use of flexible borehole liners, the liners provided with a diffusion barrier to prevent contamination of fluid samples obtained by the system and method. There is provided a flexible diffusion barrier in the construction of a flexible fluid sampling liner, so as to nearly eliminate concern for diffusion transport into or out of the liner. The flexible diffusion barrier may be incorporated into and constructed with known devices, called spacers, in use with flexible borehole liners. The diffusion barrier according to the present disclosure is attached or secured by a suitable means to the interior surface, or the exterior surface, or both surfaces, of the flexible borehole liner. In one embodiment, a spacer with a diffusion barrier prevents both the diffusion into the liner, and the diffusion out of the liner, in the interval subtended by the spacer length.
Owner:KELLER CARL
Transparent frozen soil and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveUS20160216247A1Preparing sample for investigationFoundation testingPore fluidRefractive index
The present invention discloses a transparent frozen soil, which is prepared from a fluorine-containing polymer, cube ice and a colorless pore fluid by steps of preparing materials, blending, vacuuming, and freezing. The fluorine-containing polymer is Teflon AF 1600 produced by American DuPont Company, with the refractive index of 1.31, and are particles with the particle diameter of 0.25-2.0 mm, and the density of 2.1-2.3 g / cm3. The present invention also provides the application of the above transparent frozen soil in the frozen soil directional blasting model test and the frozen soil road embankment model thaw-slumping test. The transparent frozen soil prepared by the present invention can well simulate the properties of natural transparent frozen sandy soil, is effectively used in model tests in the geotechnical engineering, with accurate measurement results, and can realize the visualization of the internal deformation of the soil body, and it is low in the expense, and simple in the operation.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Predicting method for longitudinal wave speed and attenuation in pore fracture medium
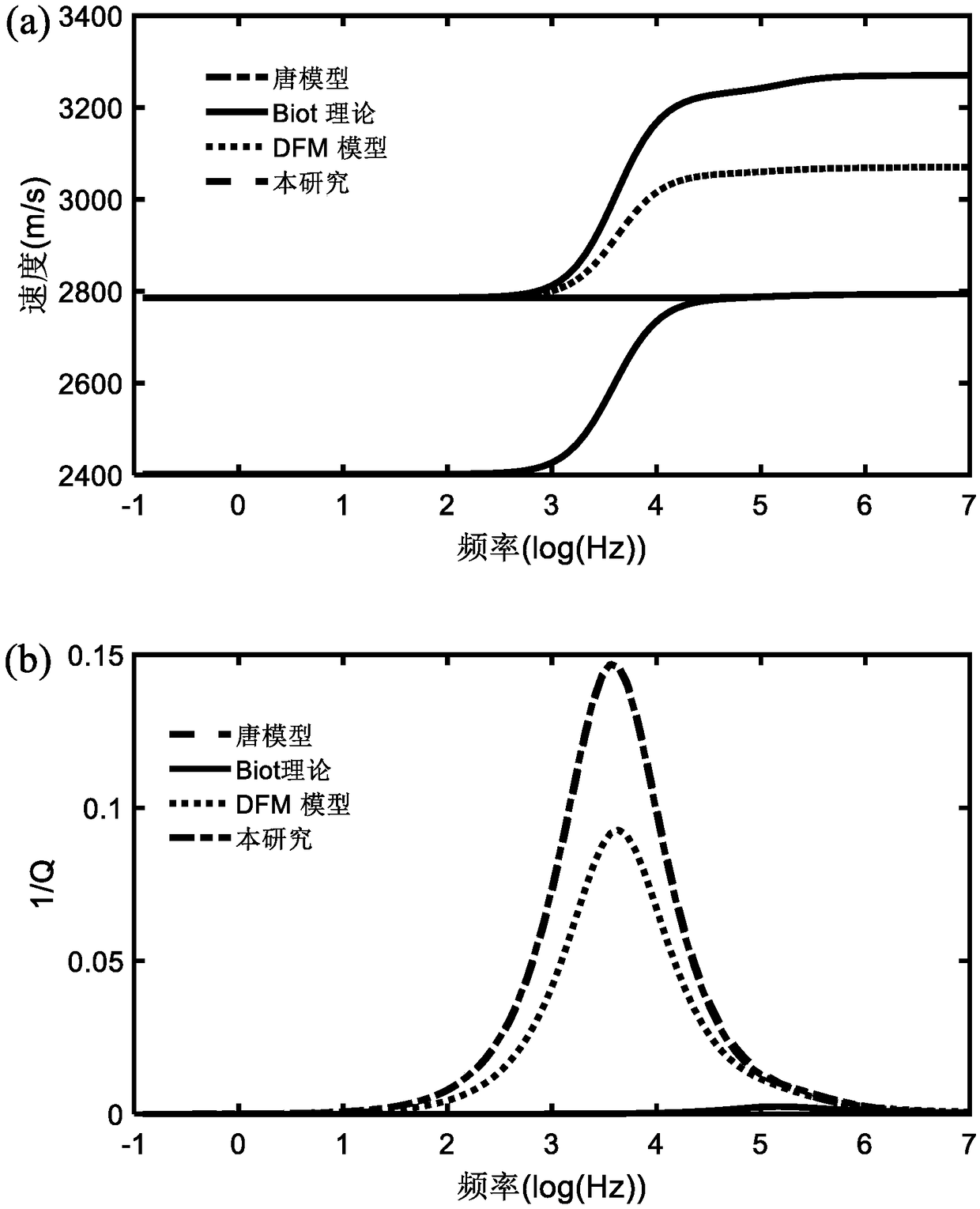
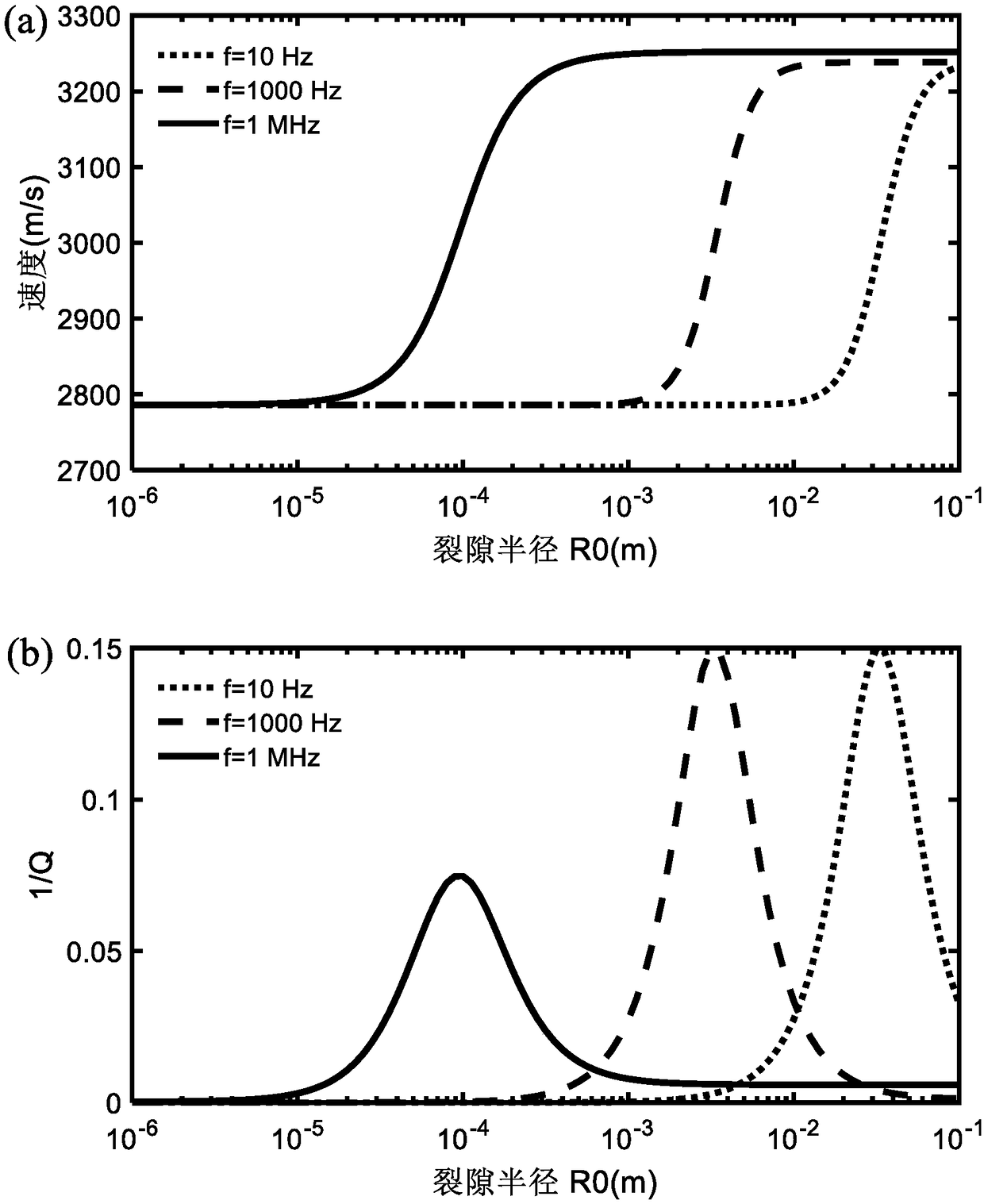
The invention discloses a predicting method for longitudinal wave speed and attenuation in a pore fracture medium. The predicting method comprises the following steps of 1 obtaining ultrasonic speed experimental data of change along with pressure; 2, building an effective medium theory conforming to microcosmic pore structure characteristics of a pore fracture reservoir, and solving microcosmic pore structure characteristics inside rock in combination with the obtained experimental data; 3, deriving a stress strain relationship of the pore fracture medium; 4, deriving a motion equation of thepore fracture medium; 5, simulating the fractures as a coin-shaped embedding body to simulate flow of pore fluid among the pore fractures, and deriving a local area flow control equation of the pore fracture medium; 6, utilizing planar wave analysis for predicting longitudinal wave speed and attenuation of the pore fracture medium; 7, further guiding exploration and development of underground oiland gas reservoirs through the obtained longitudinal wave speed and attenuation of the pore fracture medium. According to the predicting method, the coin-shaped embedding body is utilized for simulating flow of the pore fluid among the pore fractures, and then transmission characteristics of seismic waves in the pore fracture medium are studied.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com