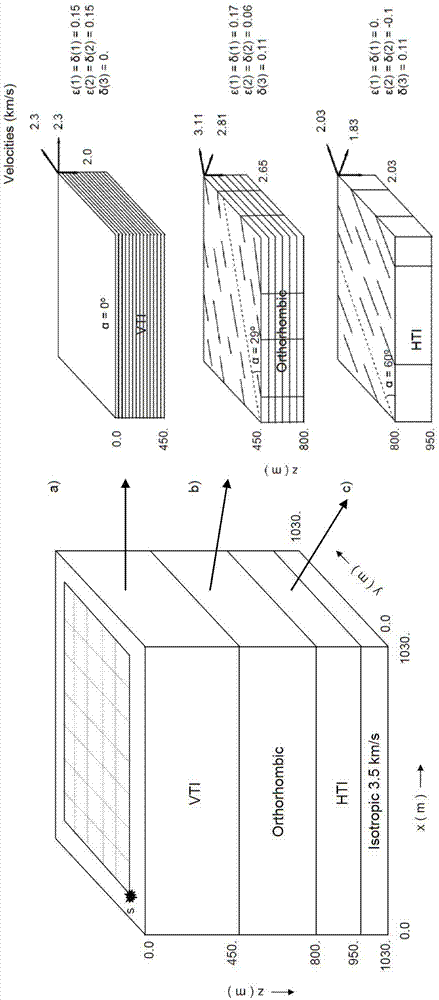
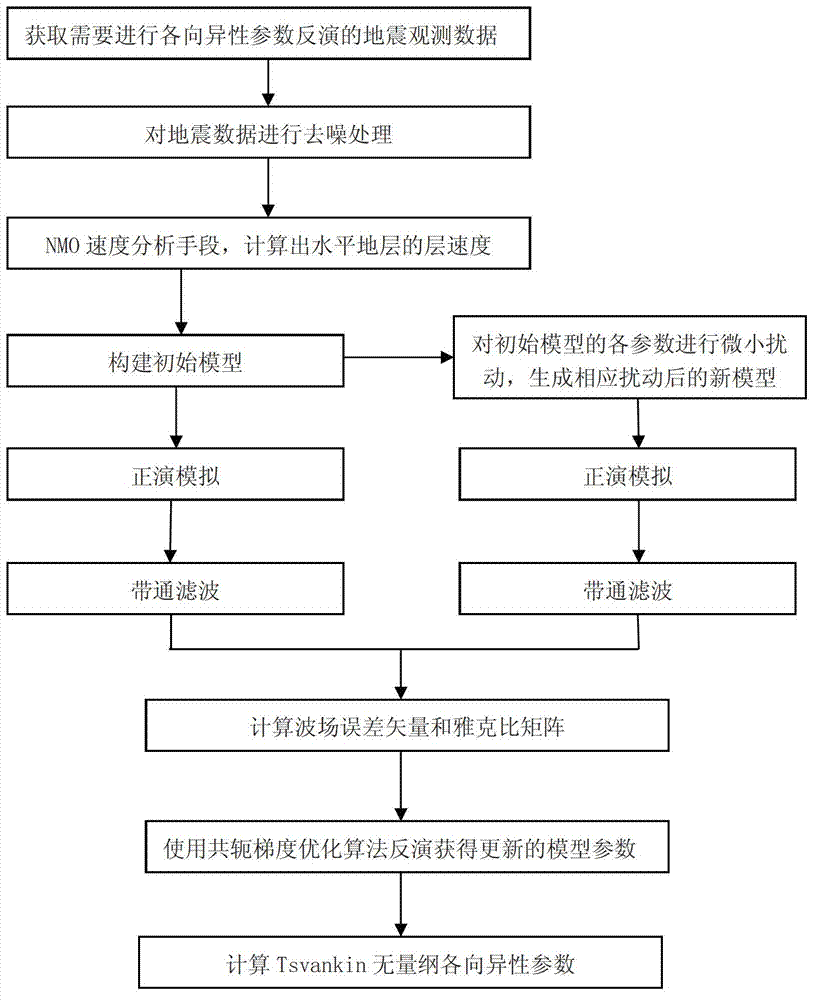
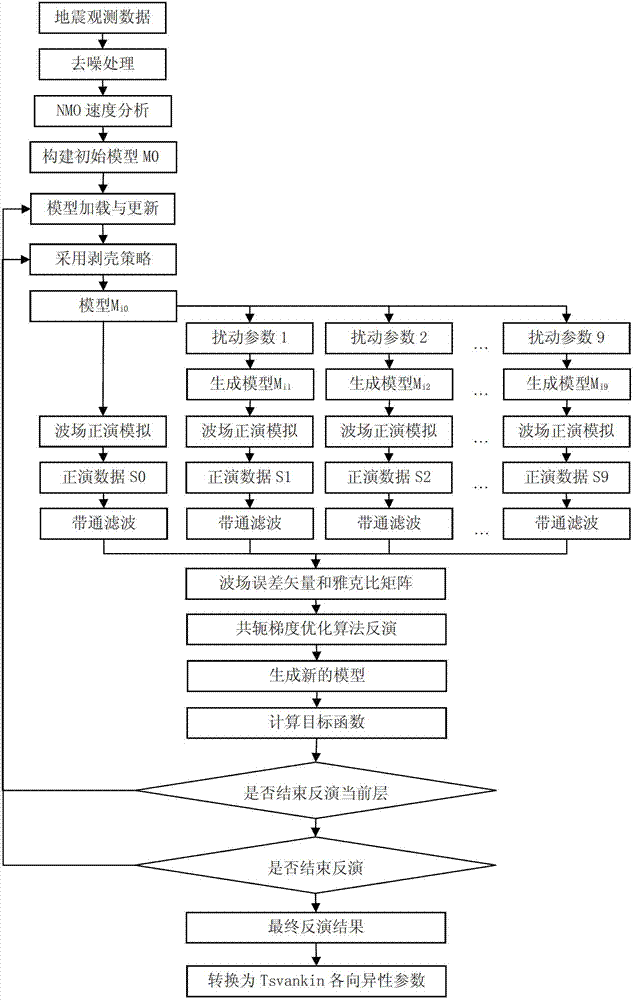
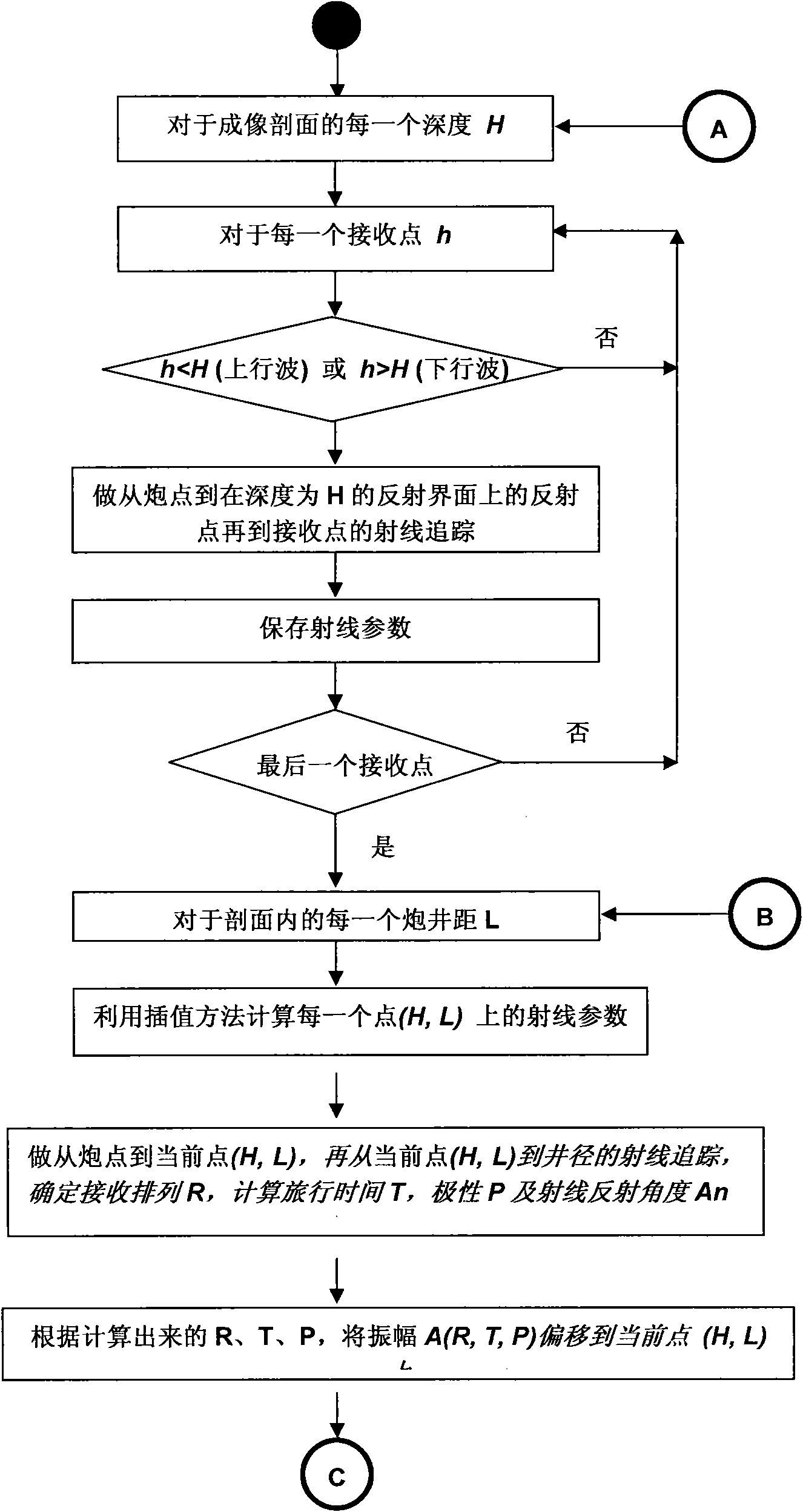
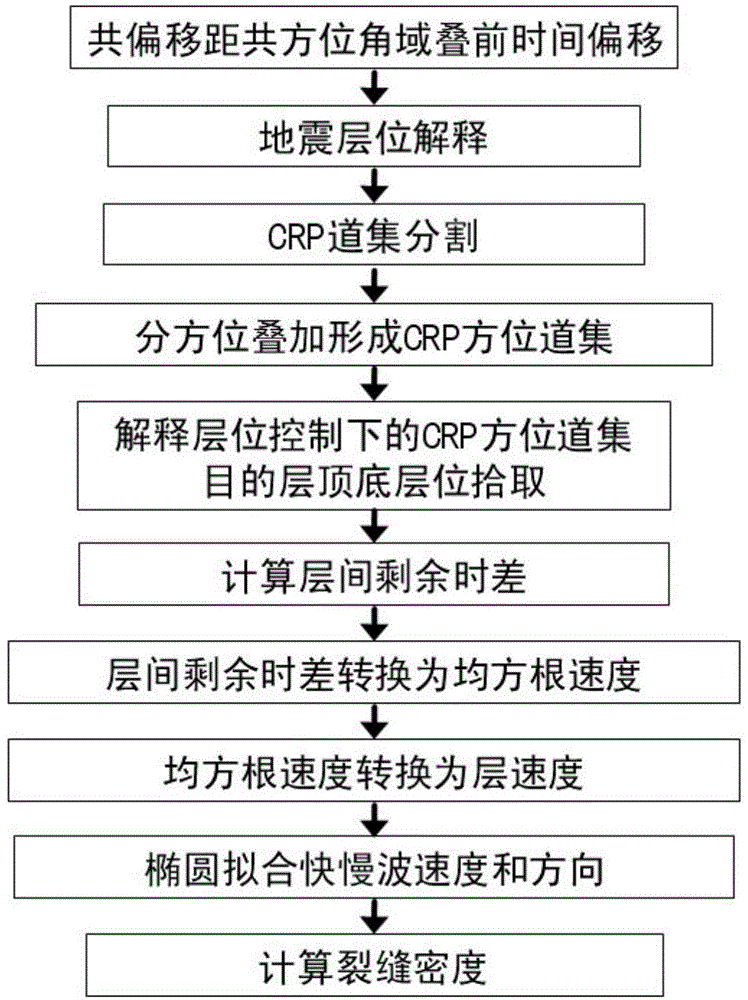
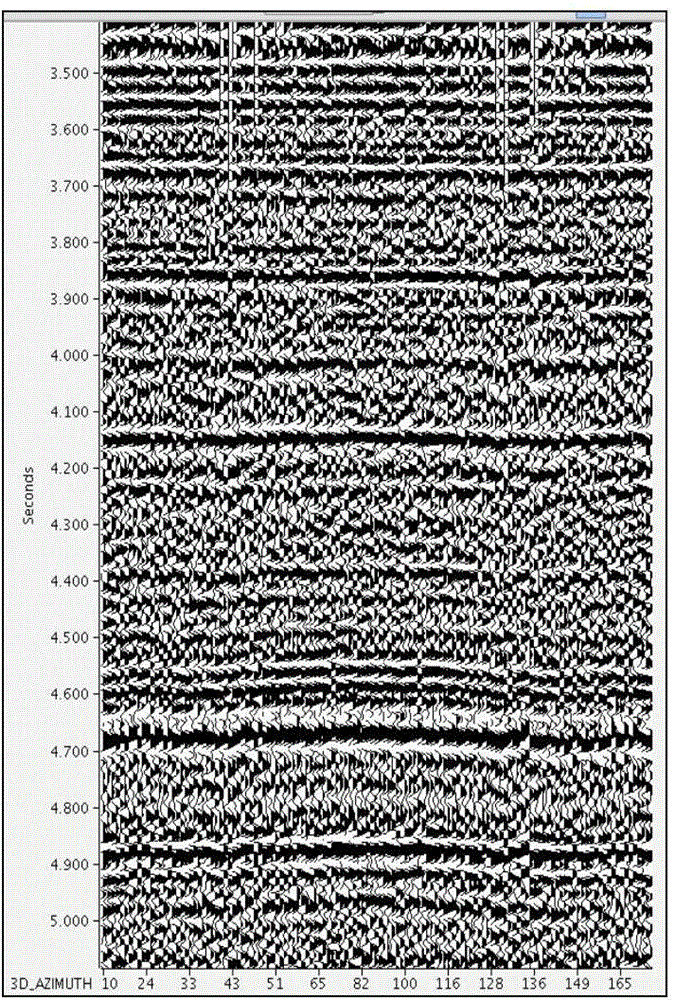
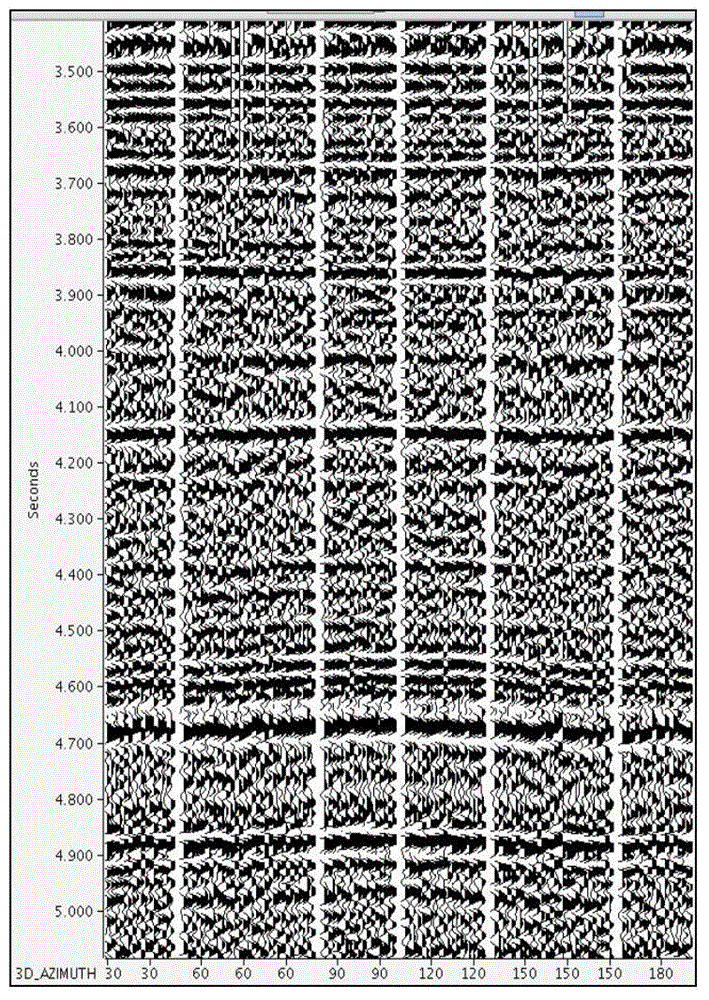
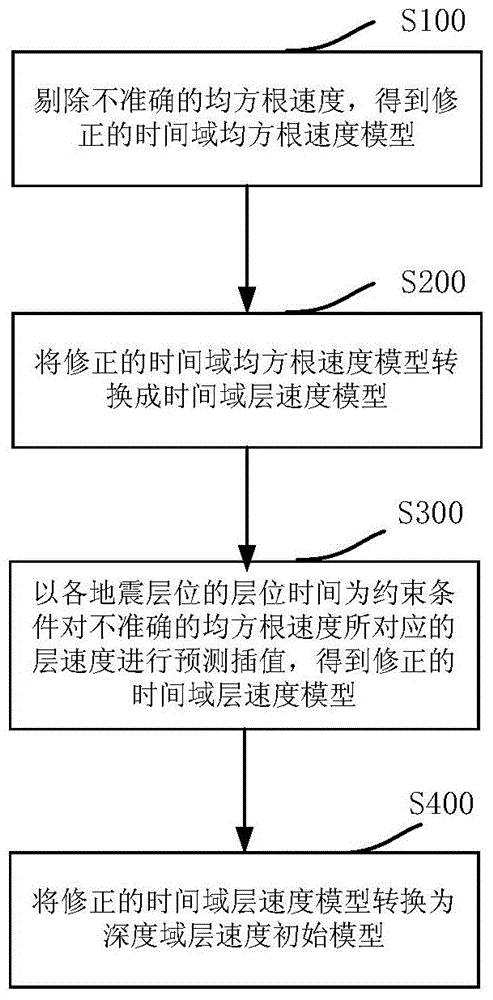
Patents
Literature
135 results about "Interval velocity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
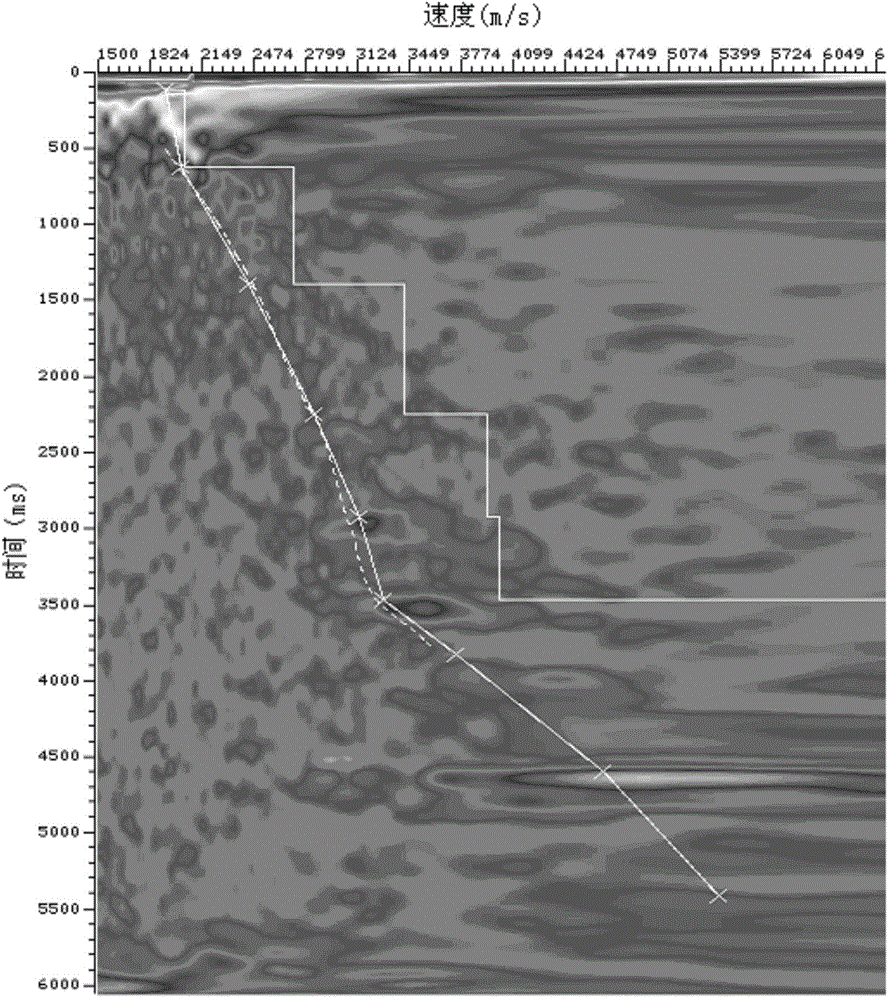
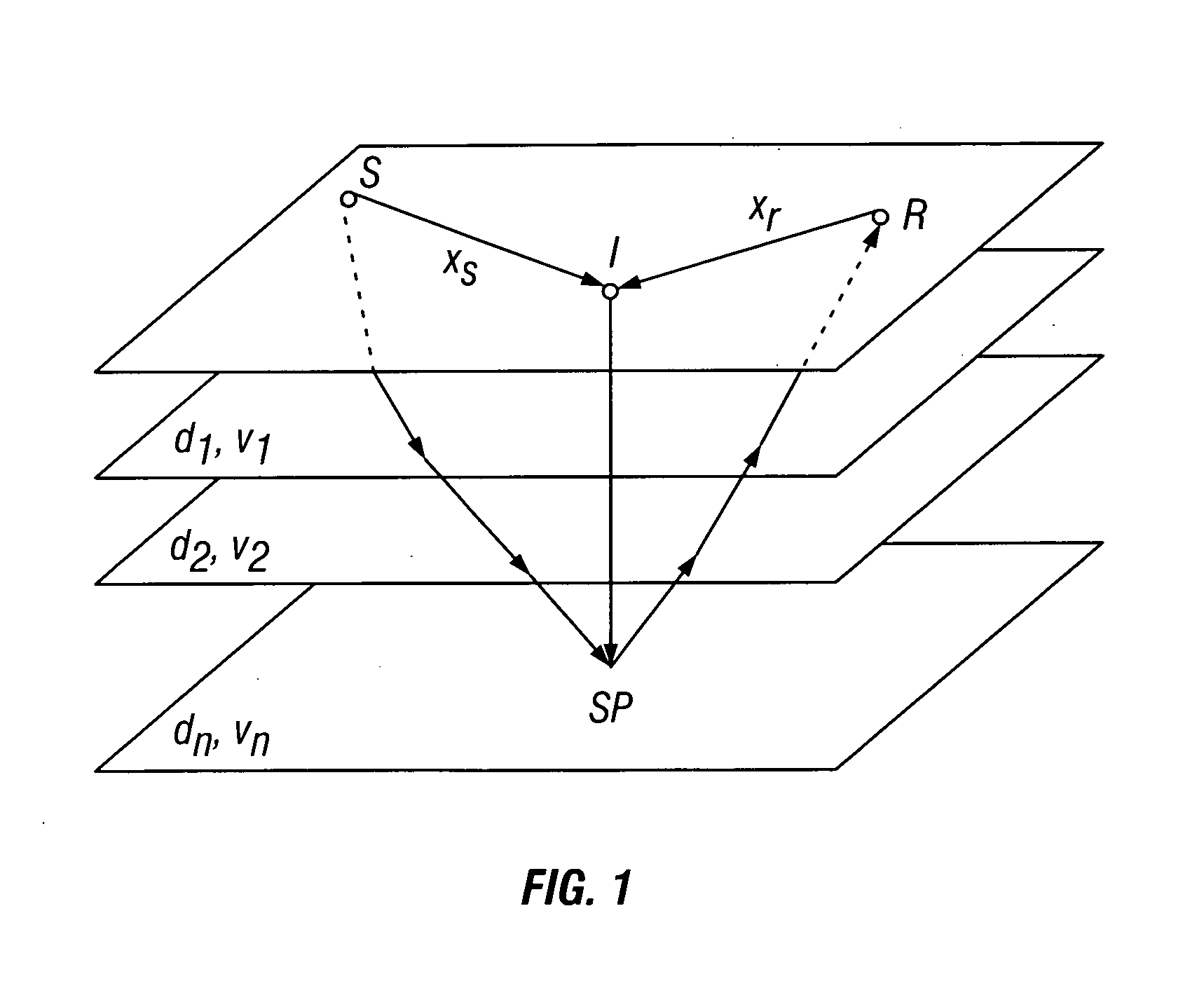
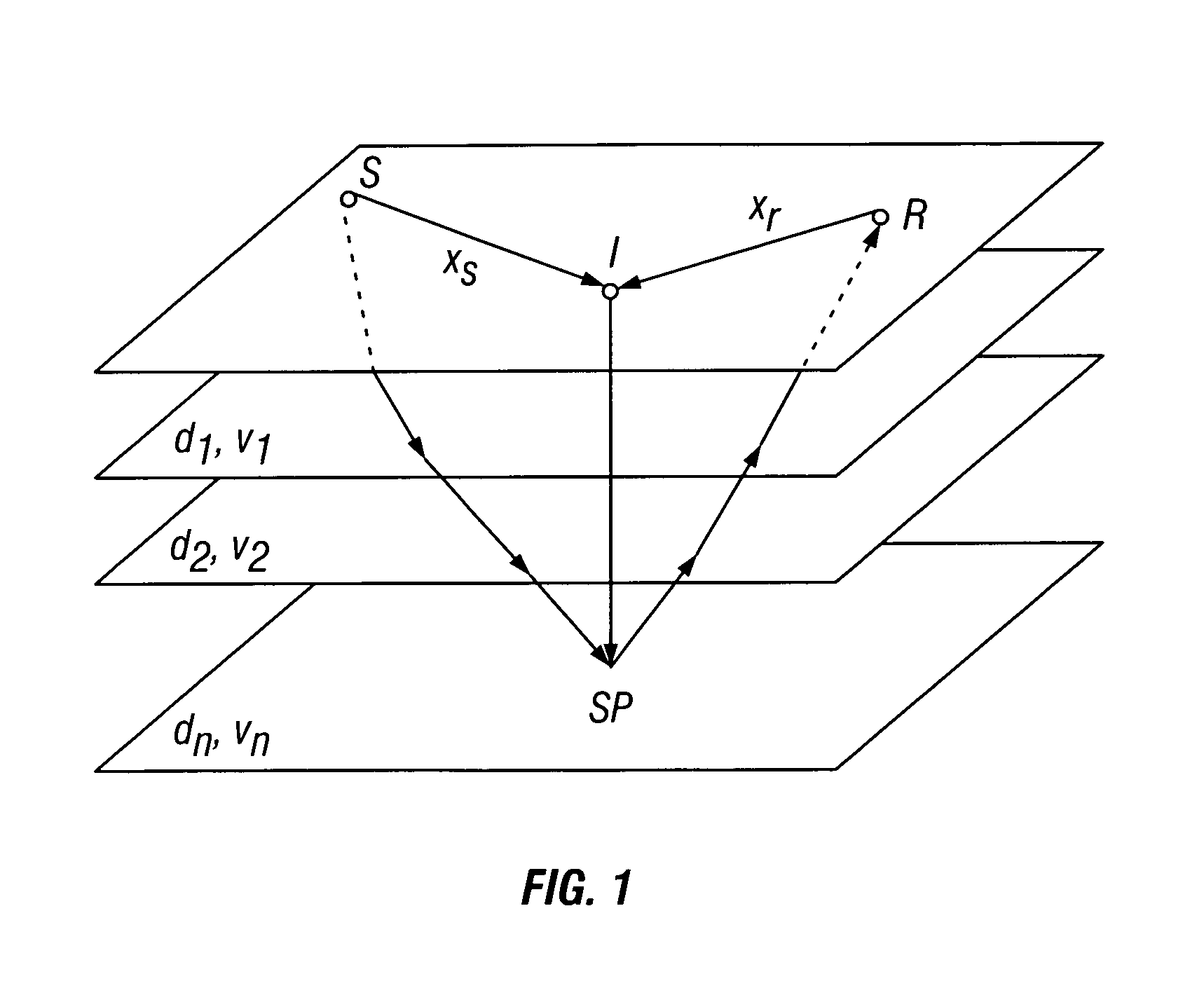
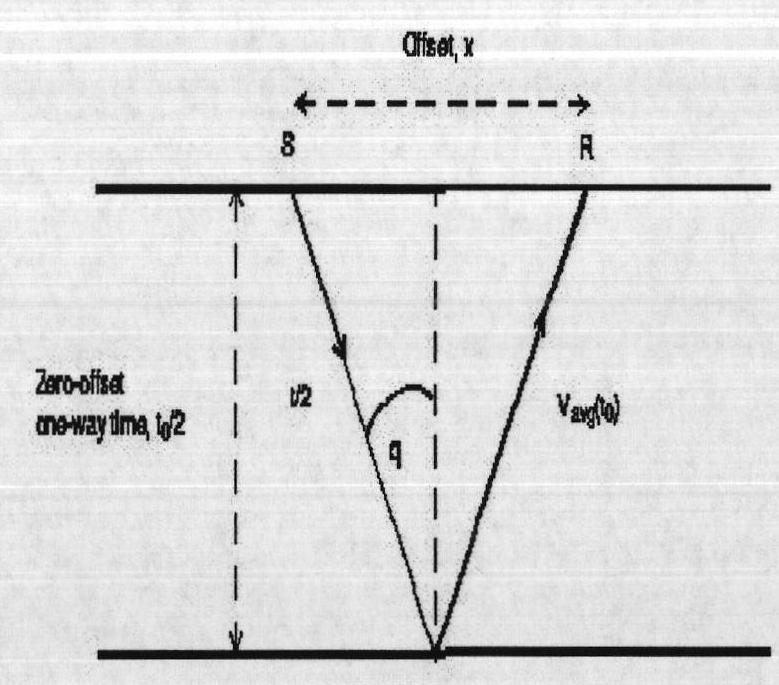
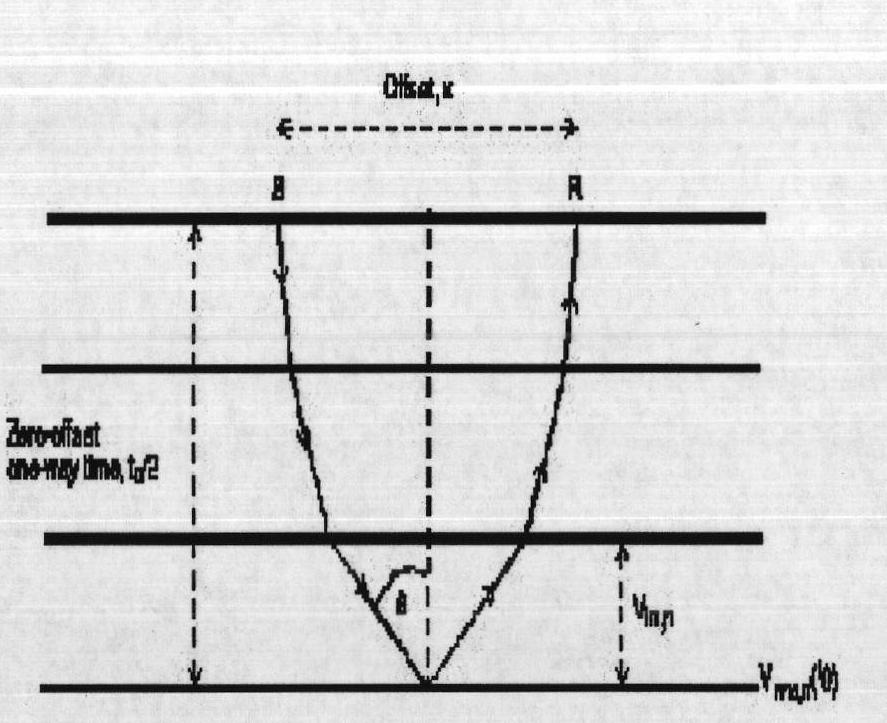
The term interval velocity is commonly used when referring to instantaneous velocity since both describe velocity variation over an interval. Remember, for a given XY (CMP) location instantaneous velocity will change with depth, in contrast, interval velocity will not change with depth within the interval.
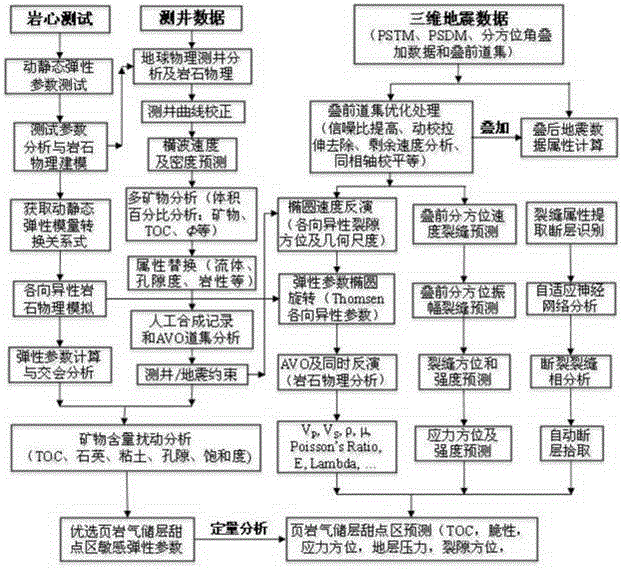
Method for evaluating shale gas reservoir and finding dessert area
ActiveCN104977618AEstimates are stable and accurateImprove fidelitySeismic signal processingSeismology for water-loggingReservoir evaluationField analysis
The invention provides a method for carrying out shale gas reservoir evaluation and finding a dessert area for shale gas exploration and development comprehensively through comprehensive application of rock physics, log data and omnibearing or wide-azimuth three-dimensional seismic data. The method is characterized by analyzing the characteristics of the dessert area in a shale reservoir by applying comprehensive geophysical exploration technologies of laboratory rock geophysical measurement, log data comprehensive analysis, rock physical modeling, vertical seismic section data, omnibearing or wide-azimuth three-dimensional seismic data high precision surface layer comprehensive modeling static correction processing, prestack de-noising processing, amplitude relative fidelity processing, resolution enhancement processing which is carried out by utilizing well constraint and well seismic data to drive ground seismic data, fine excision, iteration velocity analysis, interval velocity field analysis, prestack depth migration processing, high resolution processing, azimuth classification processing, high-precision anisotropy processing, prestack and post-stack data inversion processing, and neural network analysis and the like, and thus gas bearing characteristic prospect of the shale gas reservoir is evaluated accurately and the dessert area for shale gas exploration and development is delineated.
Owner:BGP OF CHINA NAT GASOLINEEUM CORP
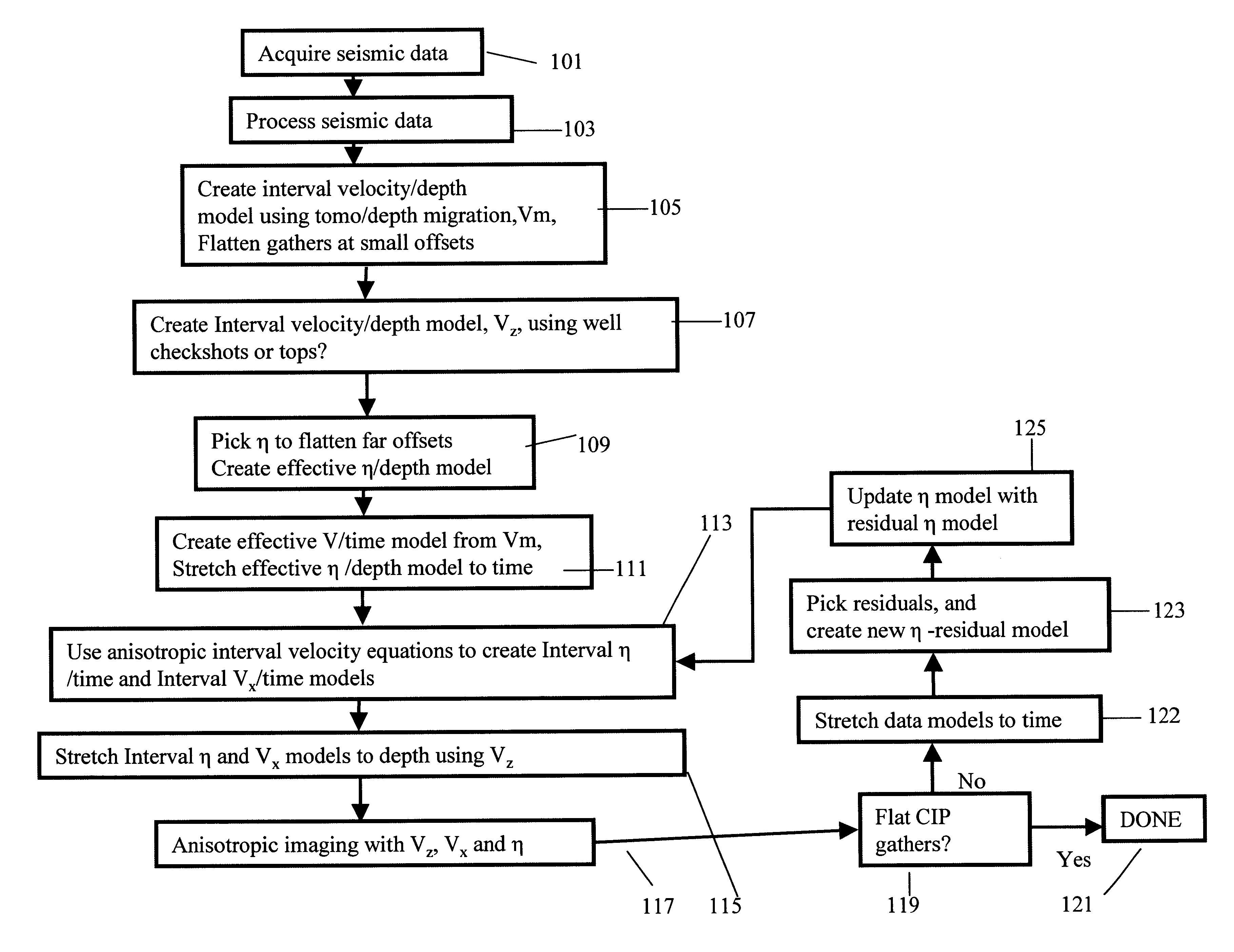
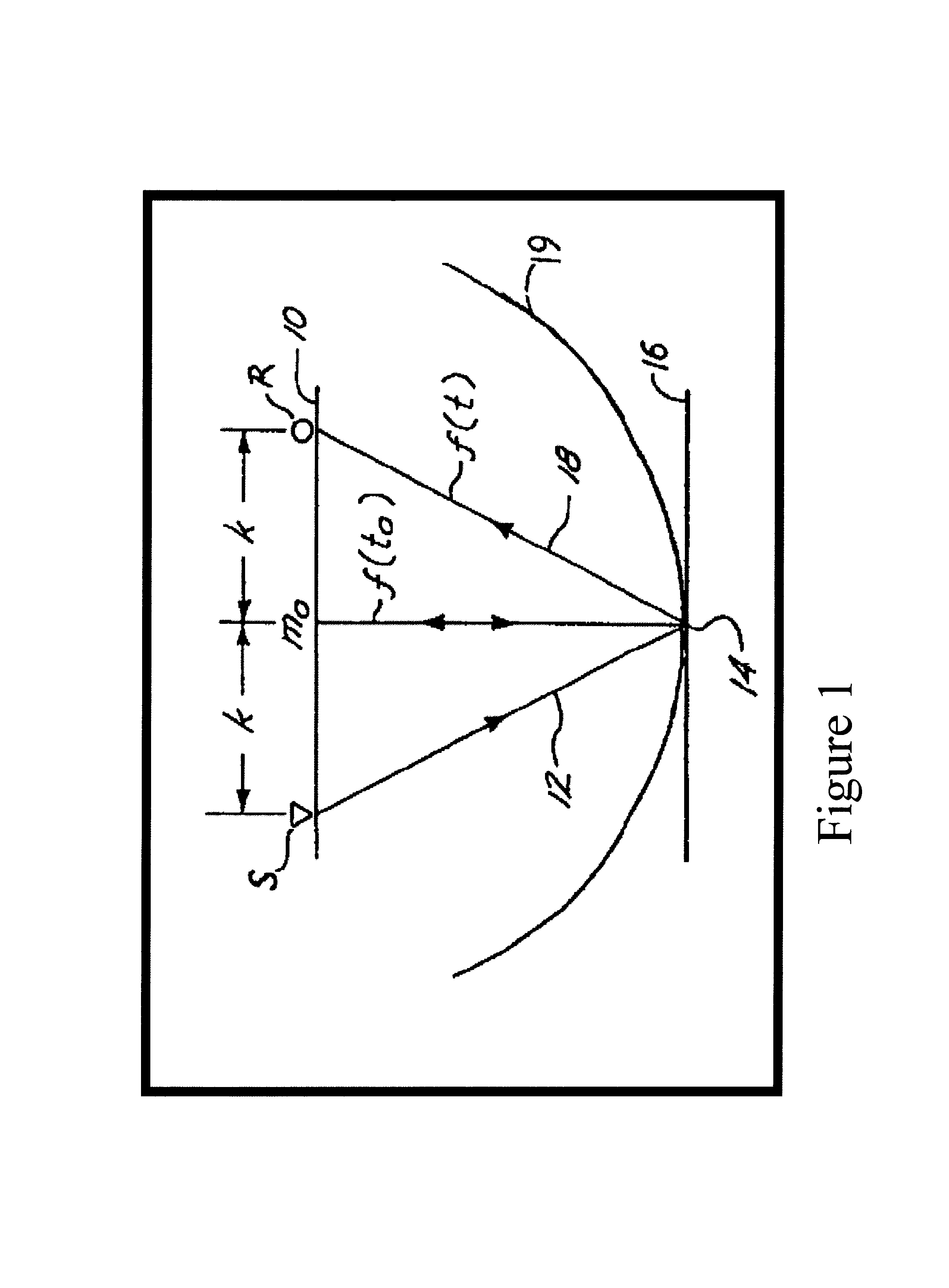
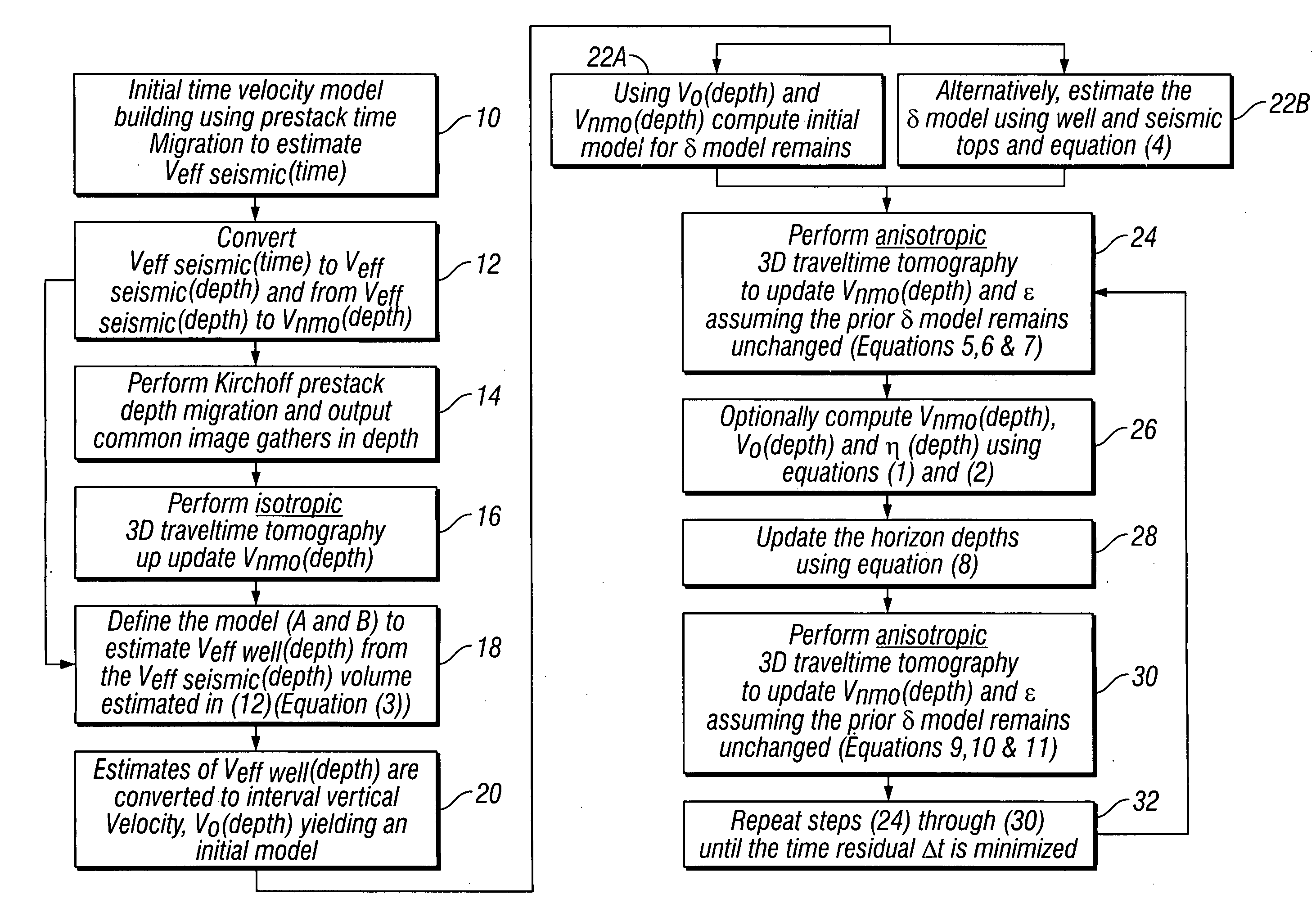
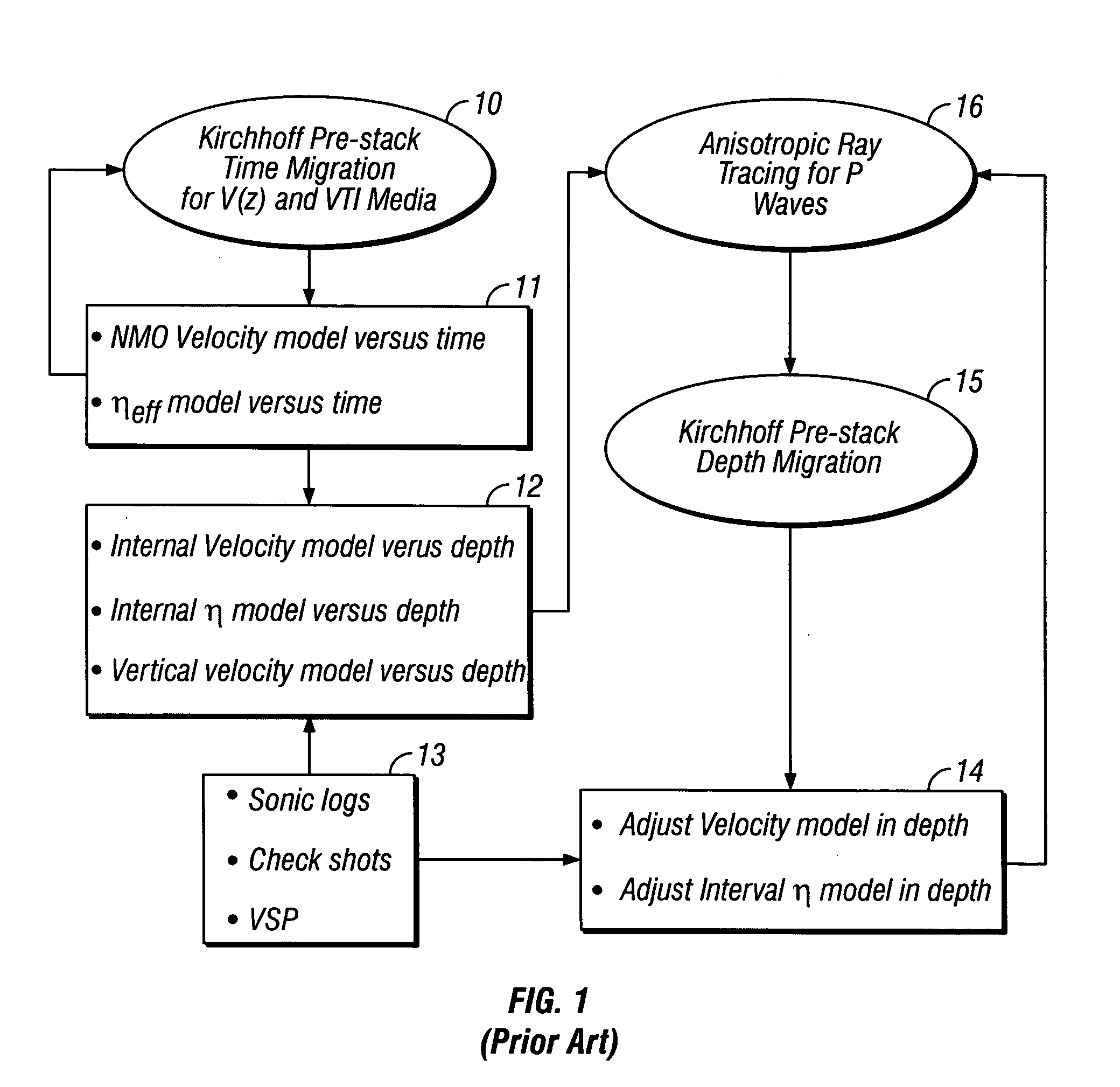
Method of building and updating an anisotropic velocity model for depth imaging of seismic data
InactiveUS6864890B2Drawing from basic elementsCathode-ray tube indicatorsDepth imagingClassical mechanics
Conventional migration of short offset seismic data is performed. An interval velocity is obtained using, for example, check shots. An initial model of effective anellipticity parameter as a function of depth is obtained by flattening long offsets within a common image point. From these, interval anellipticity and horizontal velocity are obtained as a function of time. These initial models are used for anisotropic imaging. Any remaining residuals are used to update the interval anellipticity model and the process of migration is repeated until satisfactory results are obtained.
Owner:CONOCOPHILLIPS CO
Method for updating a geologic model by seismic data
InactiveUS7400978B2Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSurveyErrors and residualsObject function
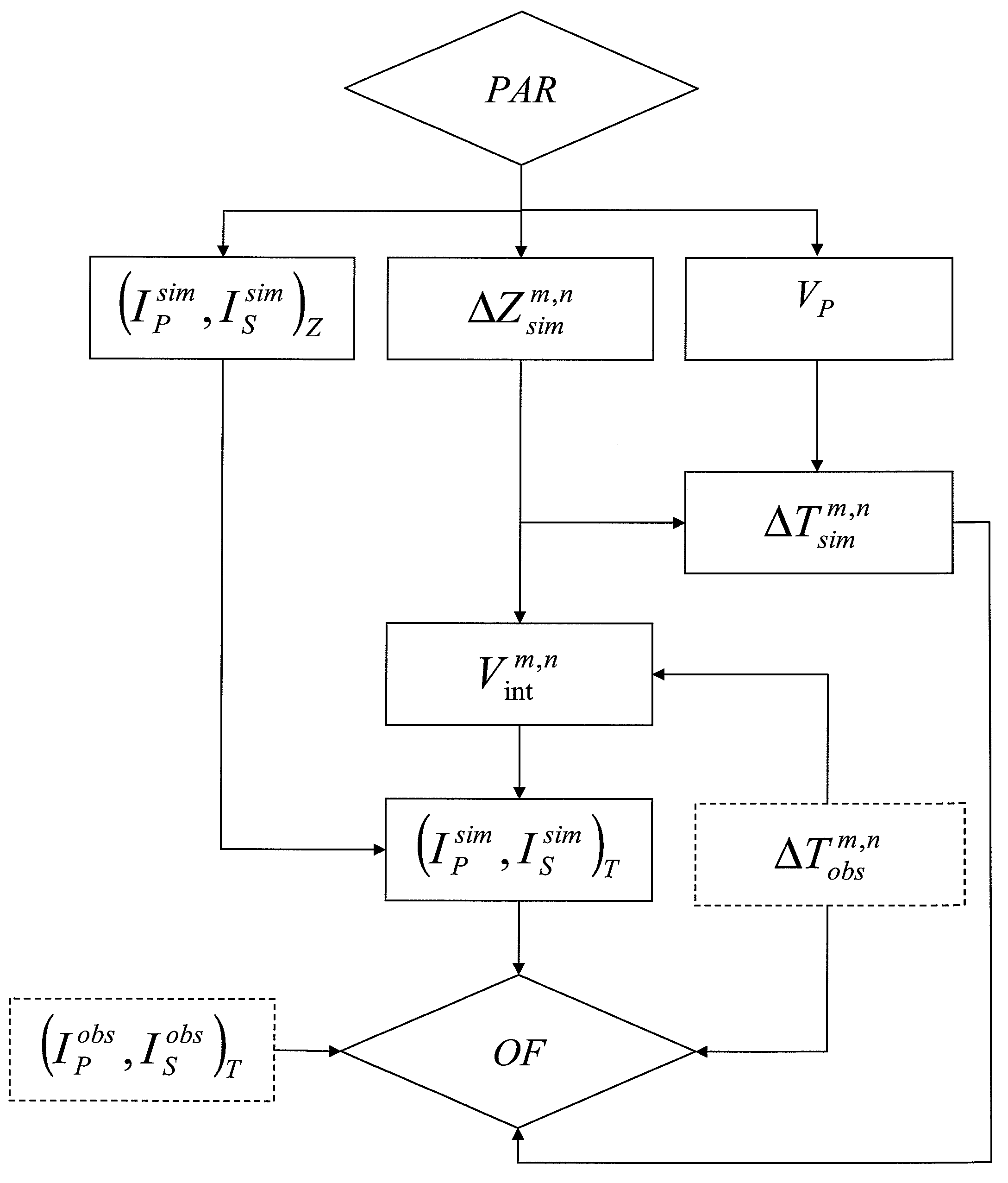
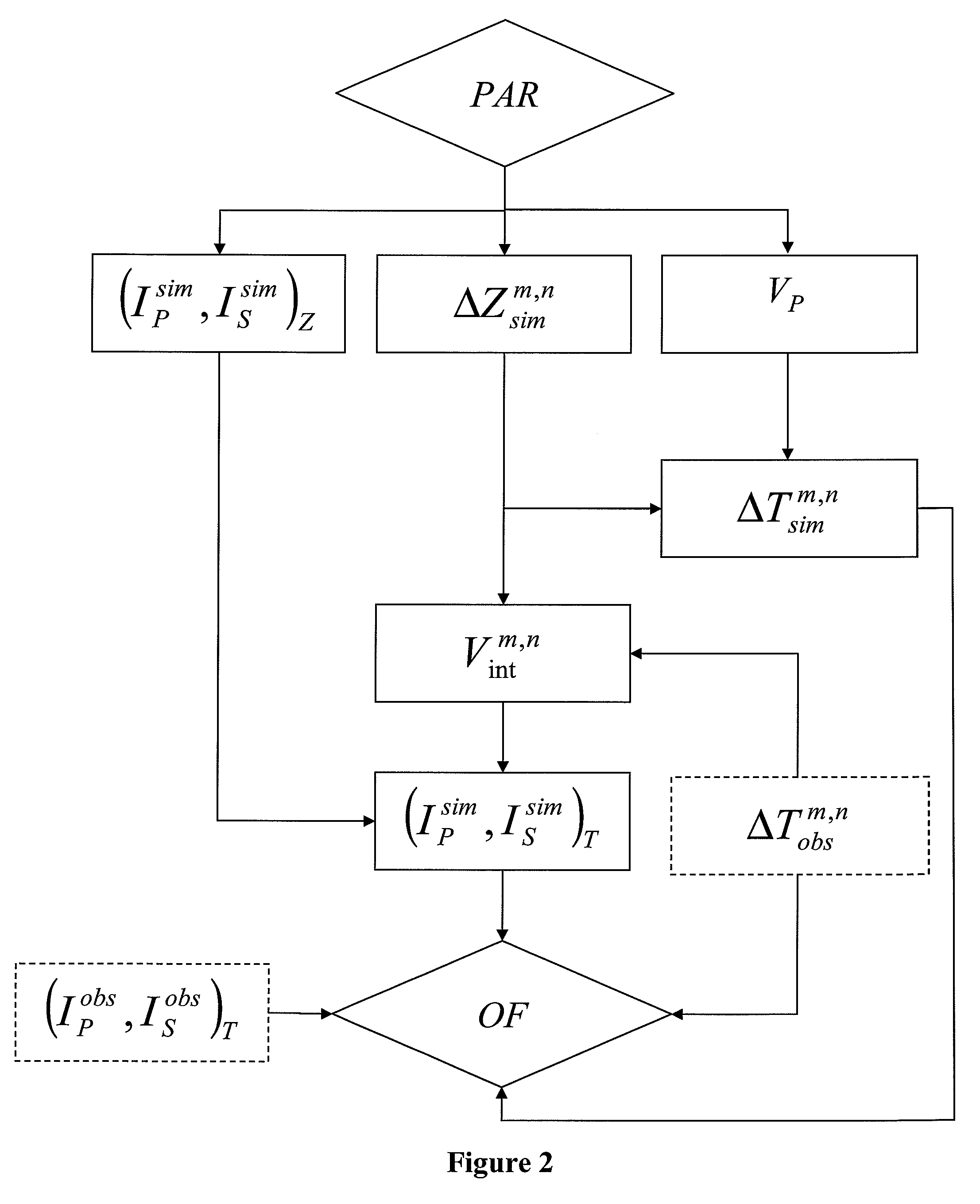
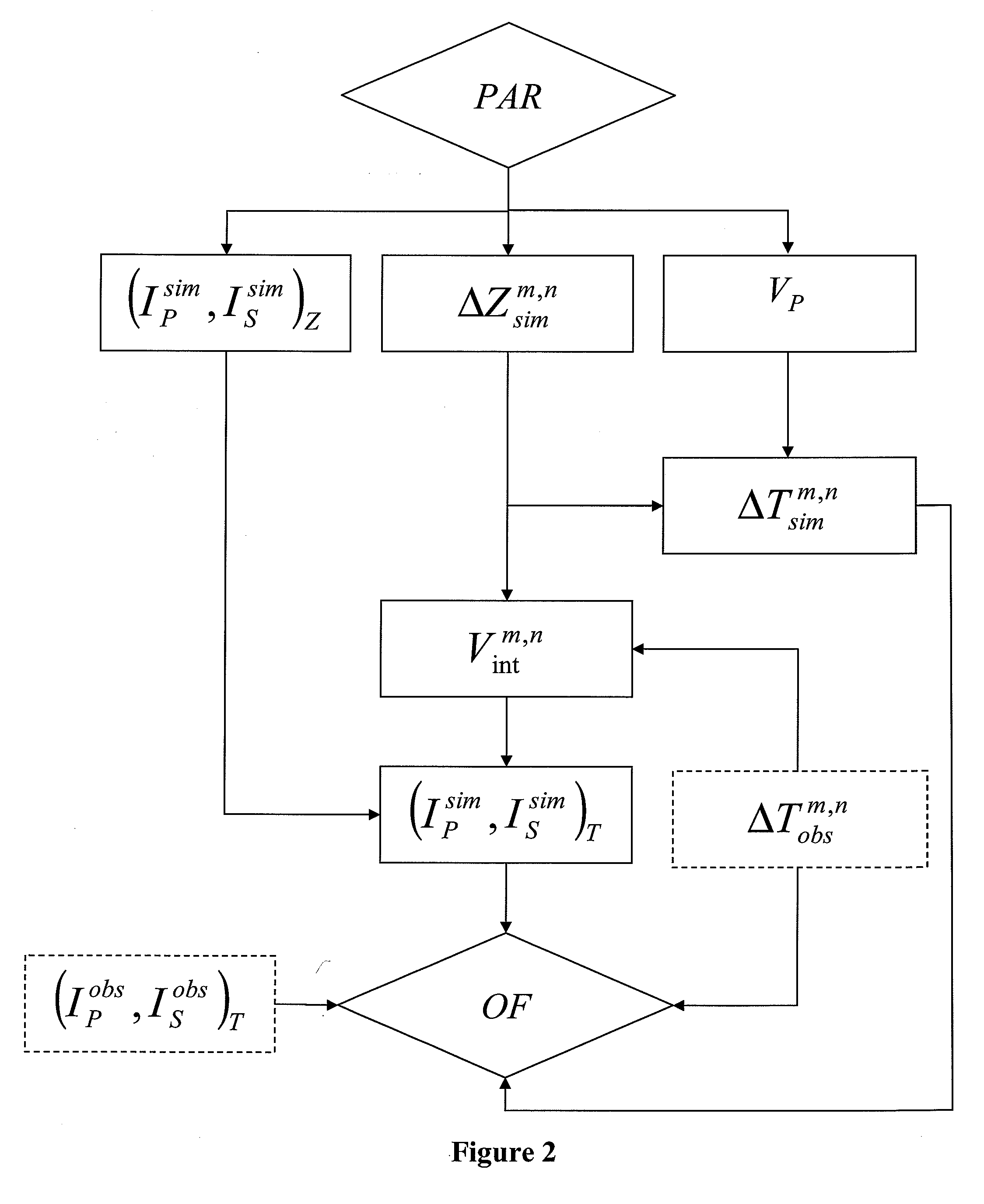
A method of predicting petrophysical characteristics of an underground reservoir by constructing a geologic model consistent with seismic measurements is disclosed which permits optimization of oil reservoir development schemes. A geologic model, from which seismic data are simulated in depth, is constructed in depth. The geologic model is made consistent with seismic measurements acquired in time by minimization of an objective function by comparing the seismic measurements with seismic data simulated from the geologic model and converted to time. During minimization, the interval velocities used for conversion are updated by comparing, within the objective function, an observed thickness in time ΔTobsm,n between two markers with a thickness in time ΔTsimm,n simulated from the seismic data, and by modifying simulation parameters such as the error εsimm,n on the thickness of the two markers estimated in depth.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
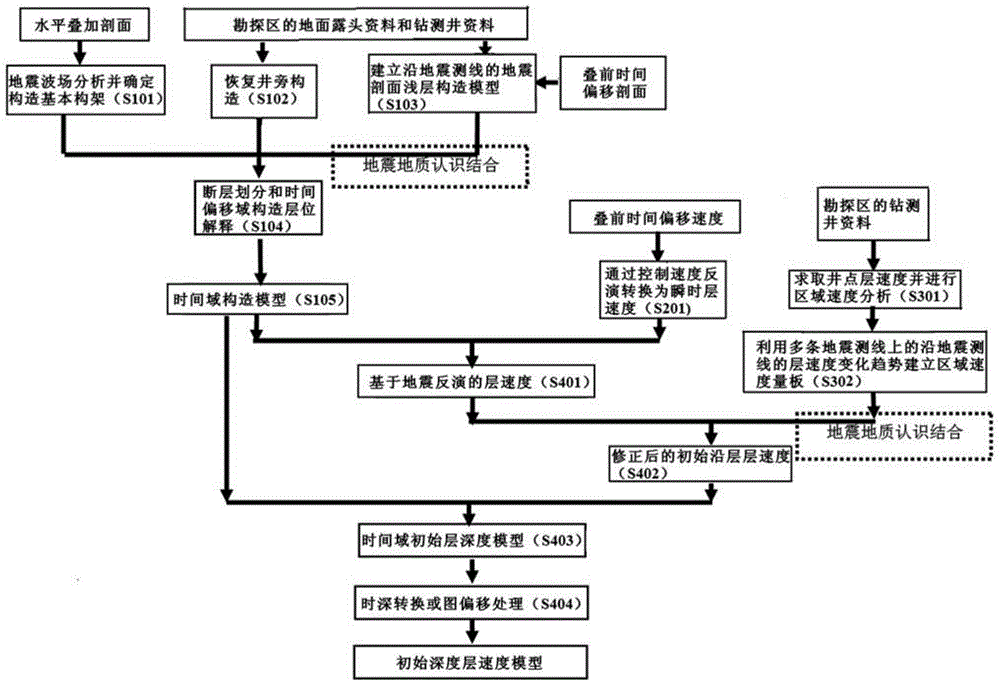
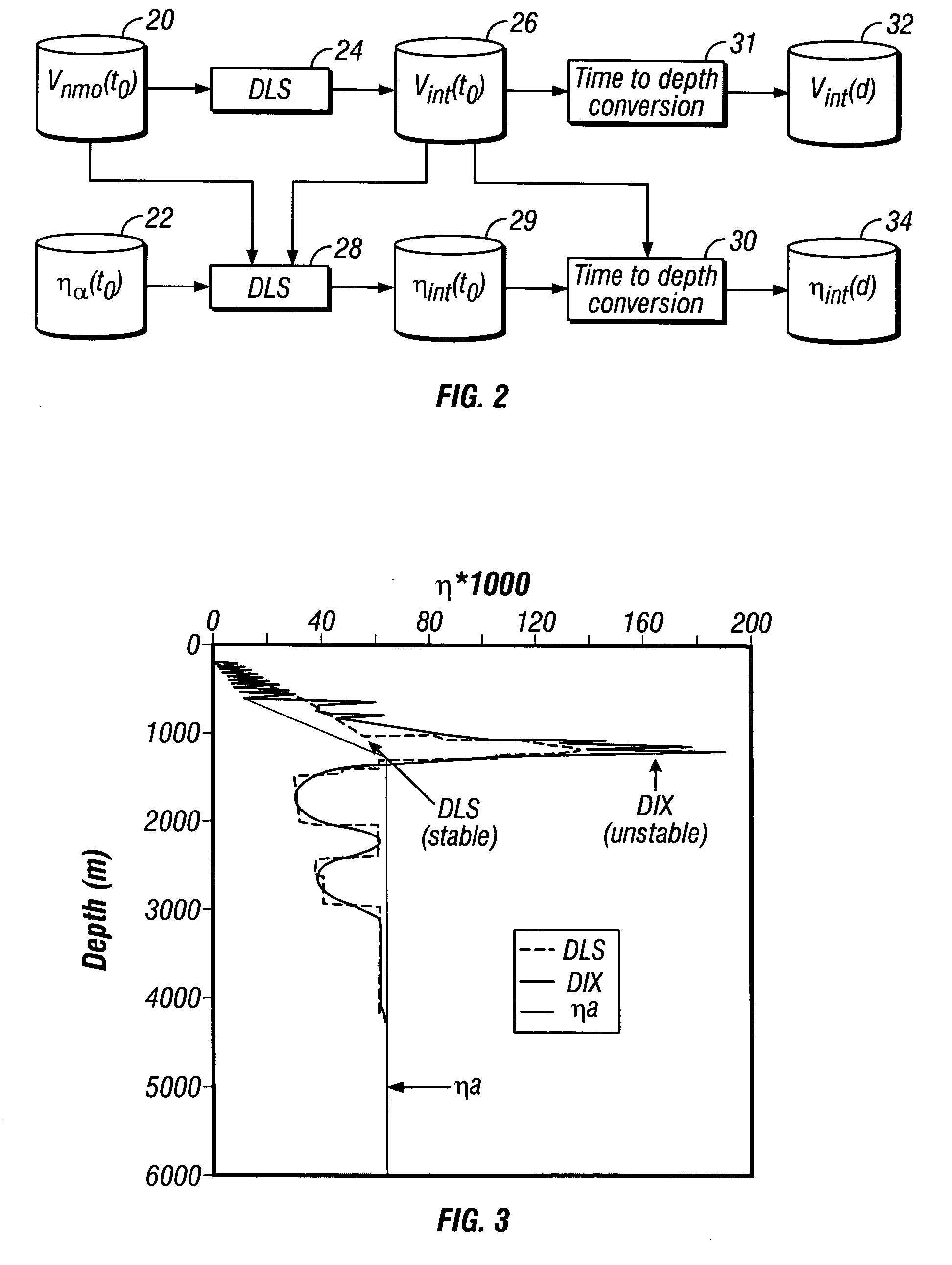
Method for comprehensively establishing initial depth interval velocity model by combining seismogeology understanding
ActiveCN104360385AAccurate initial construction modelAccurate speedSeismic signal processingInterval velocityGeophysics
The invention relates to a method for comprehensively establishing an initial depth interval velocity model by combining a seismogeology understanding. According to the method, seismic data inversion, drilling and logging information, earth surface geological outcrop data, area geological information, stratum velocity changing rules and other information are comprehensively applied to establish the initial depth interval velocity model, in other words, based on seismic data inversion, the drilling and logging information, the earth surface geological outcrop data, the area geological information and the stratum velocity changing rules serve as constraints, a relatively accurate initial structure model and the interval velocity along the stratum are obtained, and thus an enforceable initial depth interval velocity modeling process is formed. According to the method, the advantages of three existing initial depth interval velocity model establishing methods are fully absorbed; meanwhile, the concept of multiple information constraints is adopted for establishing the initial depth interval velocity model, and the initial depth interval velocity model is made to be more accurate.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +1
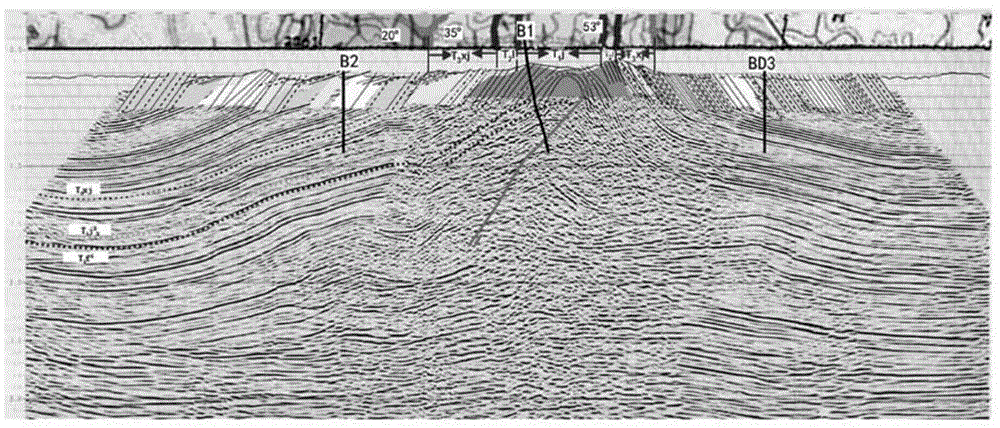
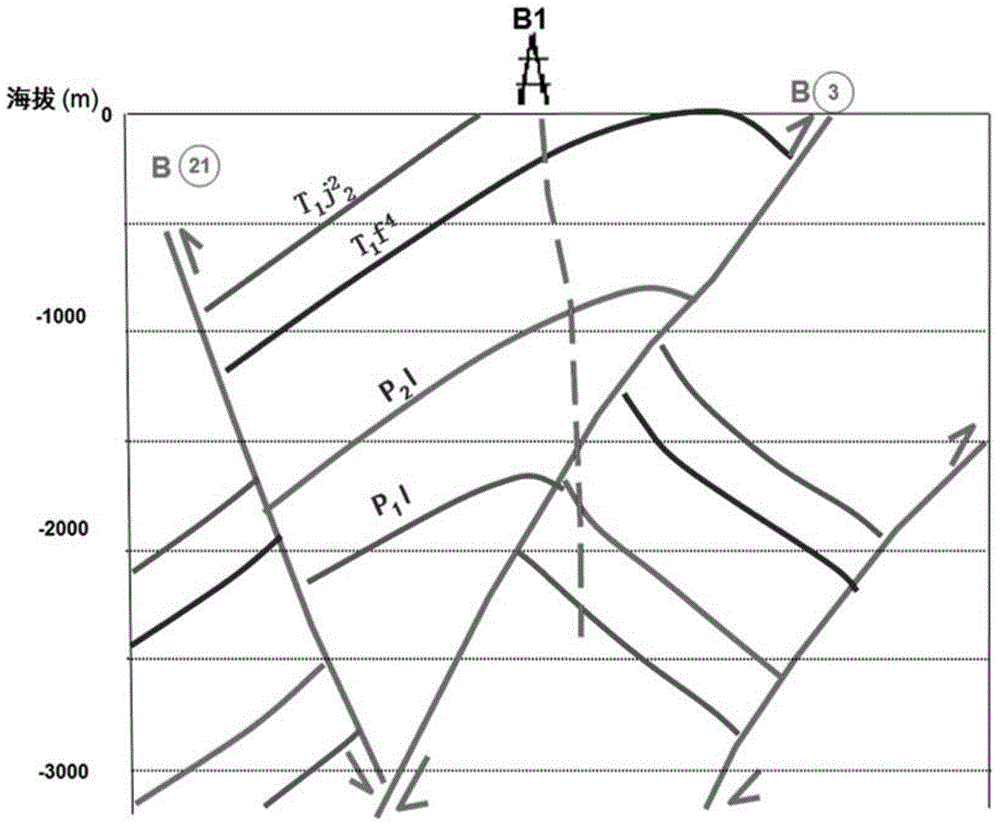
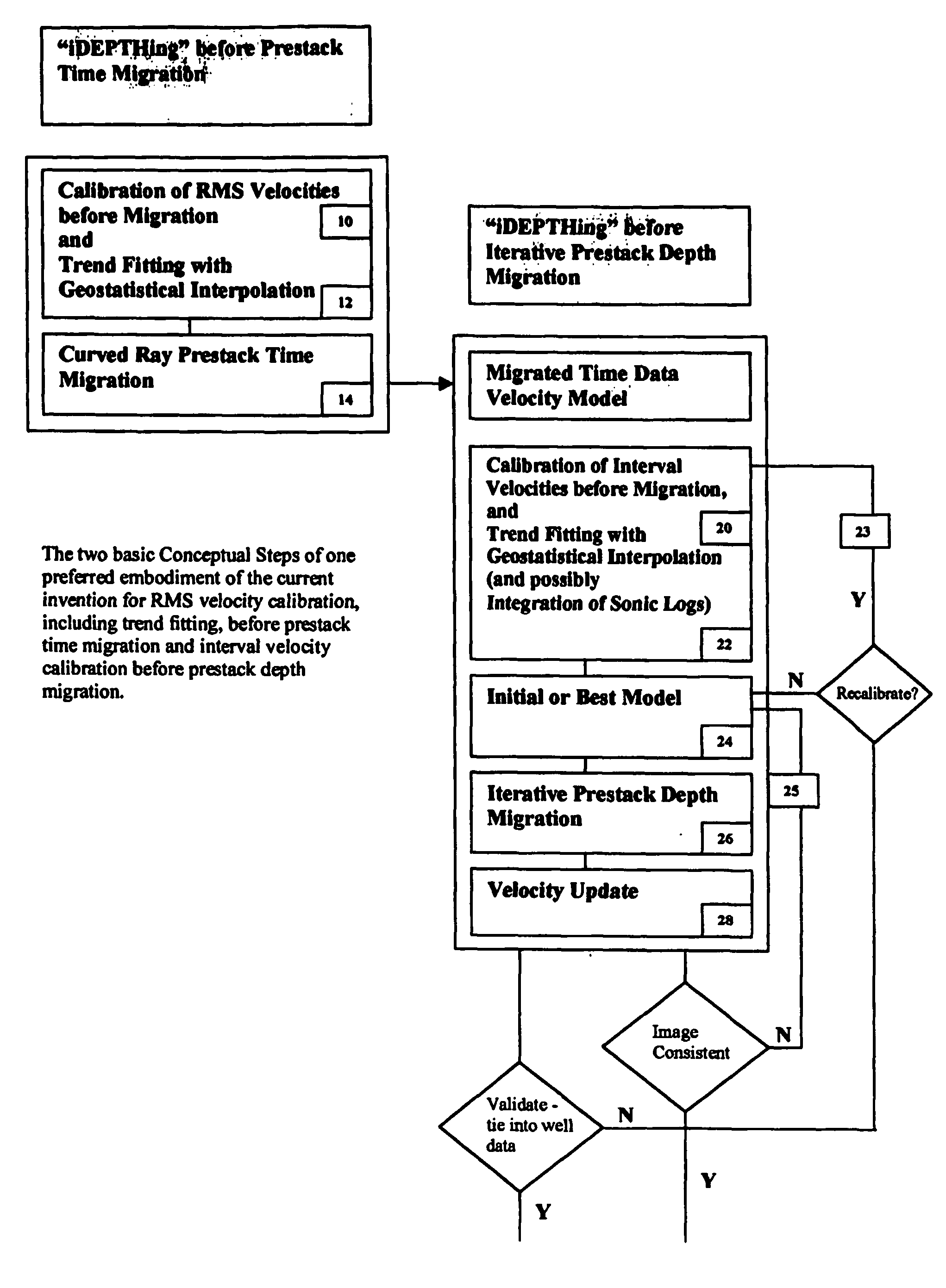
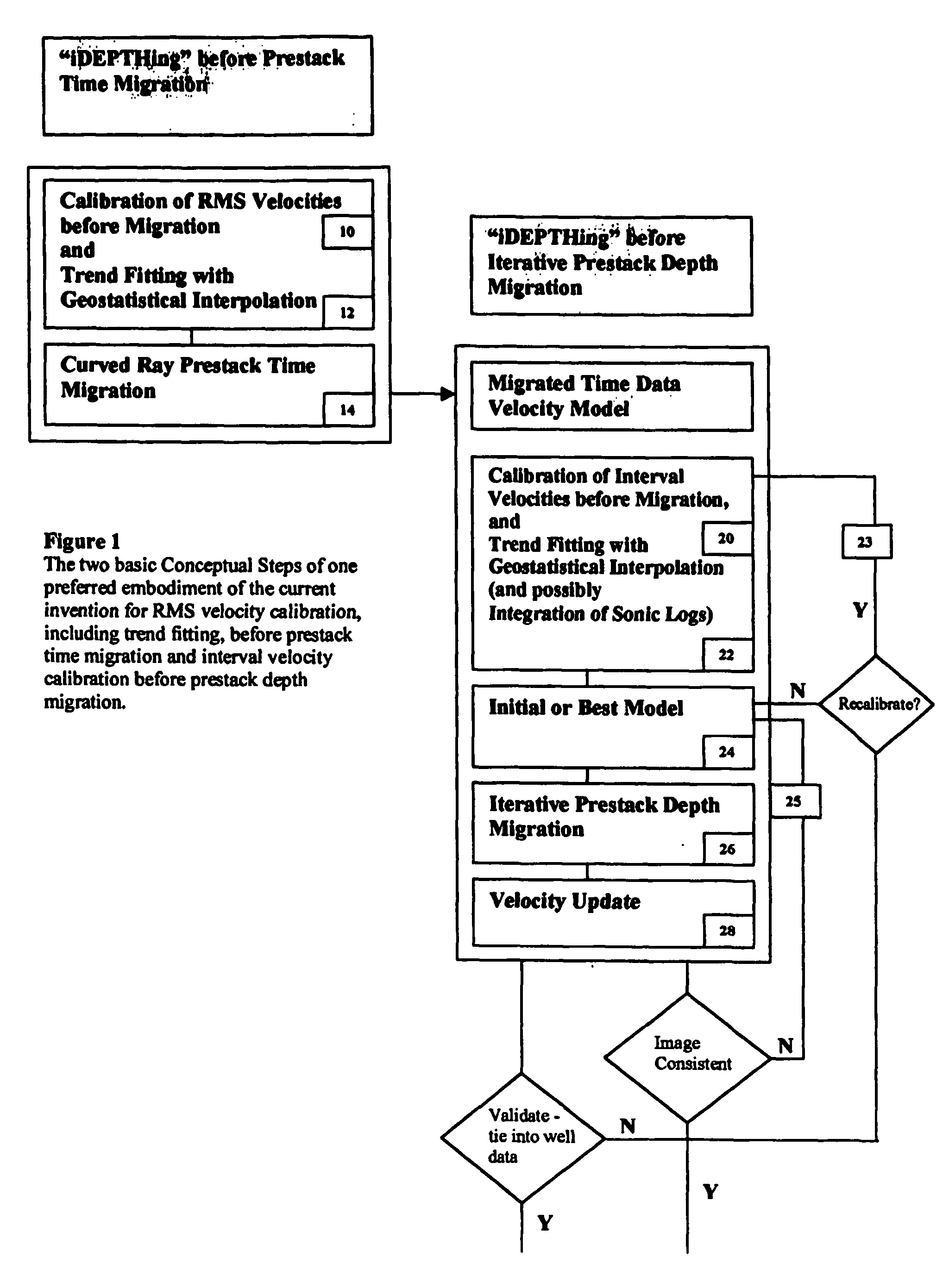
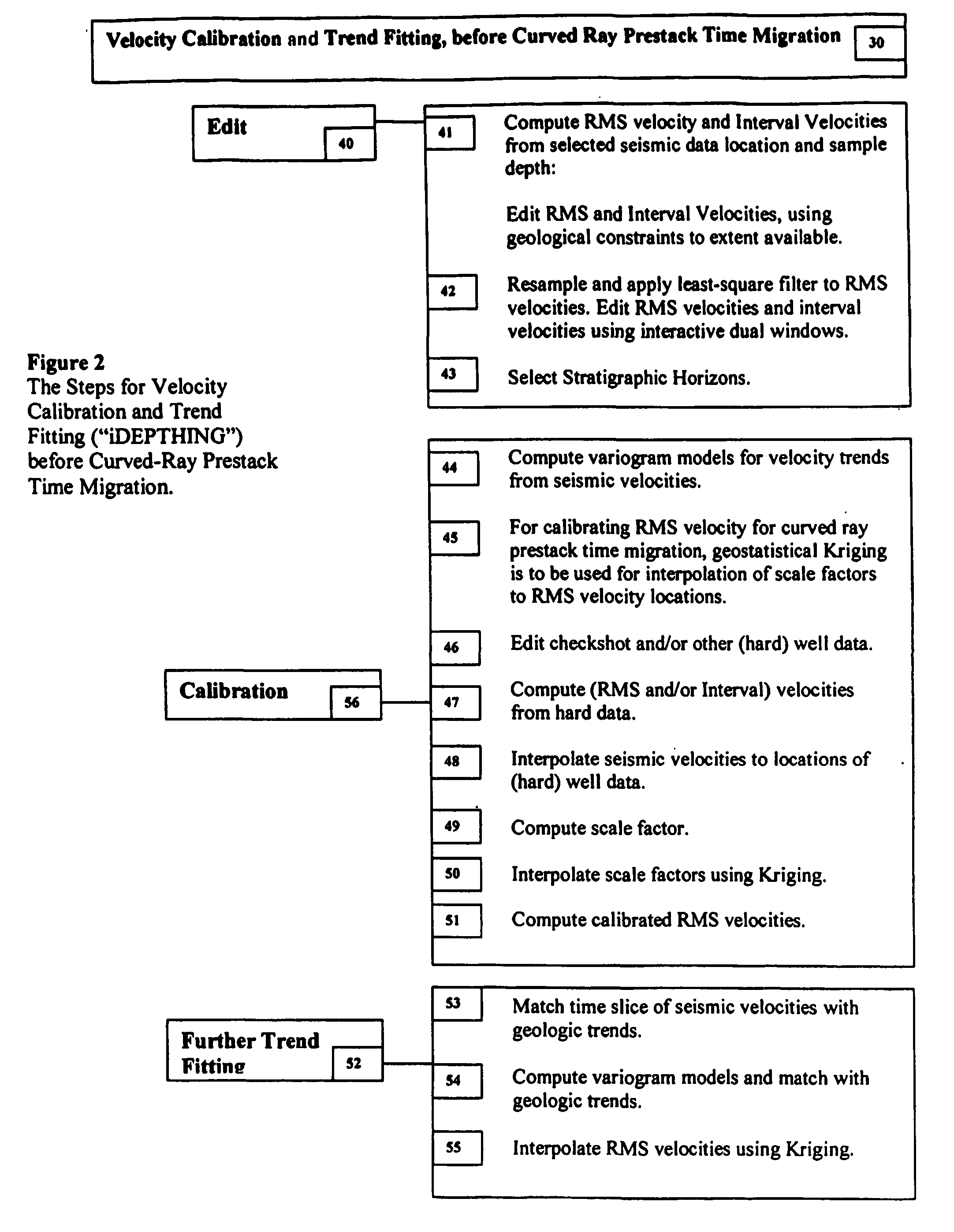
3D velocity modeling, with calibration and trend fitting using geostatistical techniques, particularly advantageous for curved for curved-ray prestack time migration and for such migration followed by prestack depth migration
InactiveUS20070021951A1Efficient and accurate prestack imagingReducing resource-intensive interpretation effortComputation using non-denominational number representationSeismic signal processingSeismic attributeVelocity function
A method of constructing a 3D geologically plausible velocity model for efficient and accurate prestack imaging wherein embodiments of the invention provide: (1) a method of calibrating velocity functions, appropriately and effectively taking into account well (hard) and seismic (soft) data as well as geological features, and trend fitting (“iDEPTHing”) RMS velocities before curved-ray prestack time migration; (2) a method of calibrating and trend fitting (“iDEPTHing”) interval velocities before prestack depth migration, appropriately and effectively taking into account well (hard) and seismic (soft) data as well as geological features; and (3) a method of constructing a geologically plausible velocity model using the previous steps of velocity calibration and trend fitting RMS and interval velocities, for efficient sequential use in prestack time migration followed by prestack depth migration. Advantages of the embodiments include providing a quick turnaround of prestack time and depth migration to interpreters and cutting back resource-intensive interpretation efforts for 3D seismic data The invention has significant implications for improving aspects of oil and gas exploration and production technologies, including pore pressure prediction, prospect evaluation and seismic attribute analysis.
Owner:LEE WOOK B
Method and device for acquiring seismic velocity in thin reservoir layer through well control
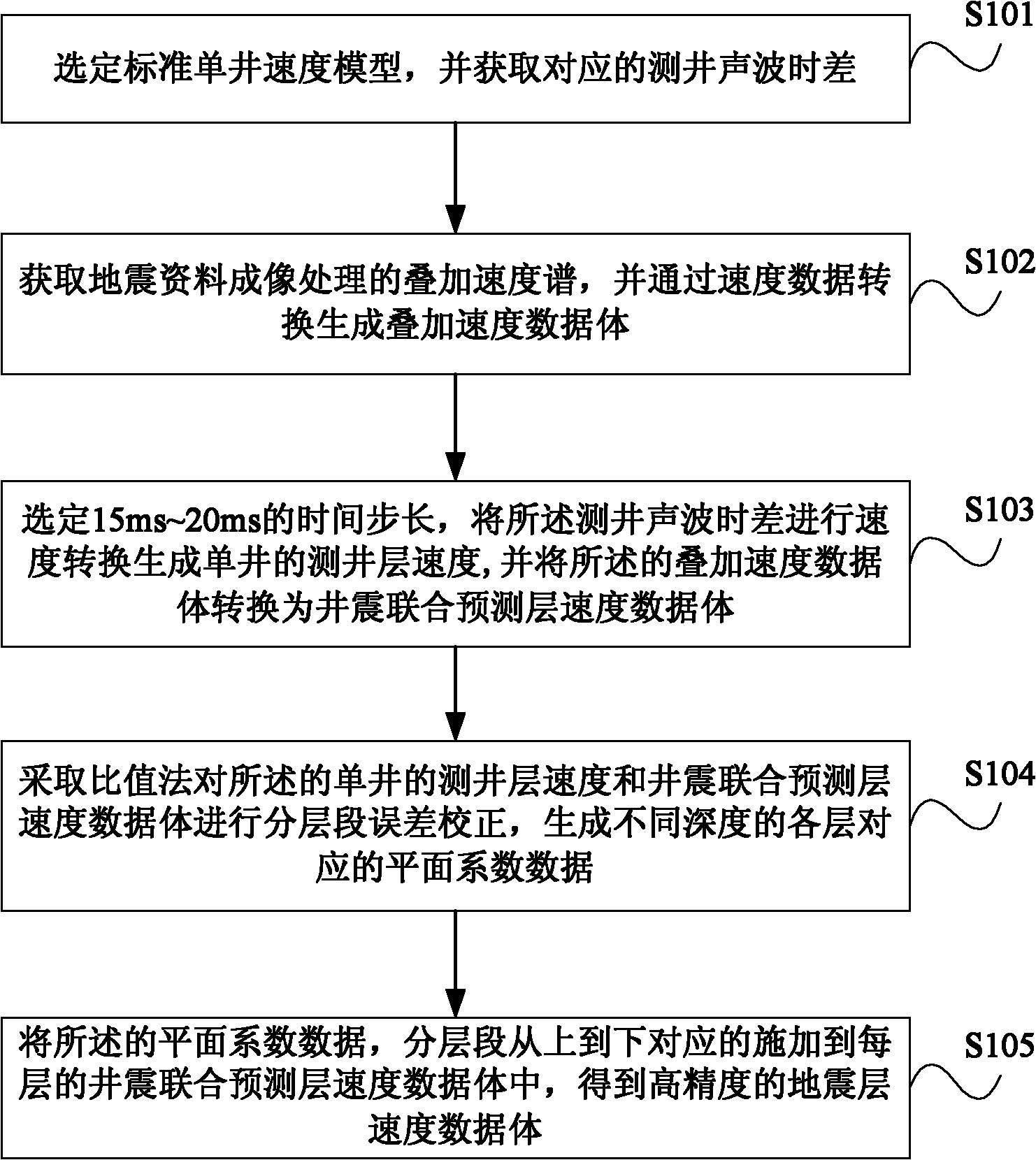
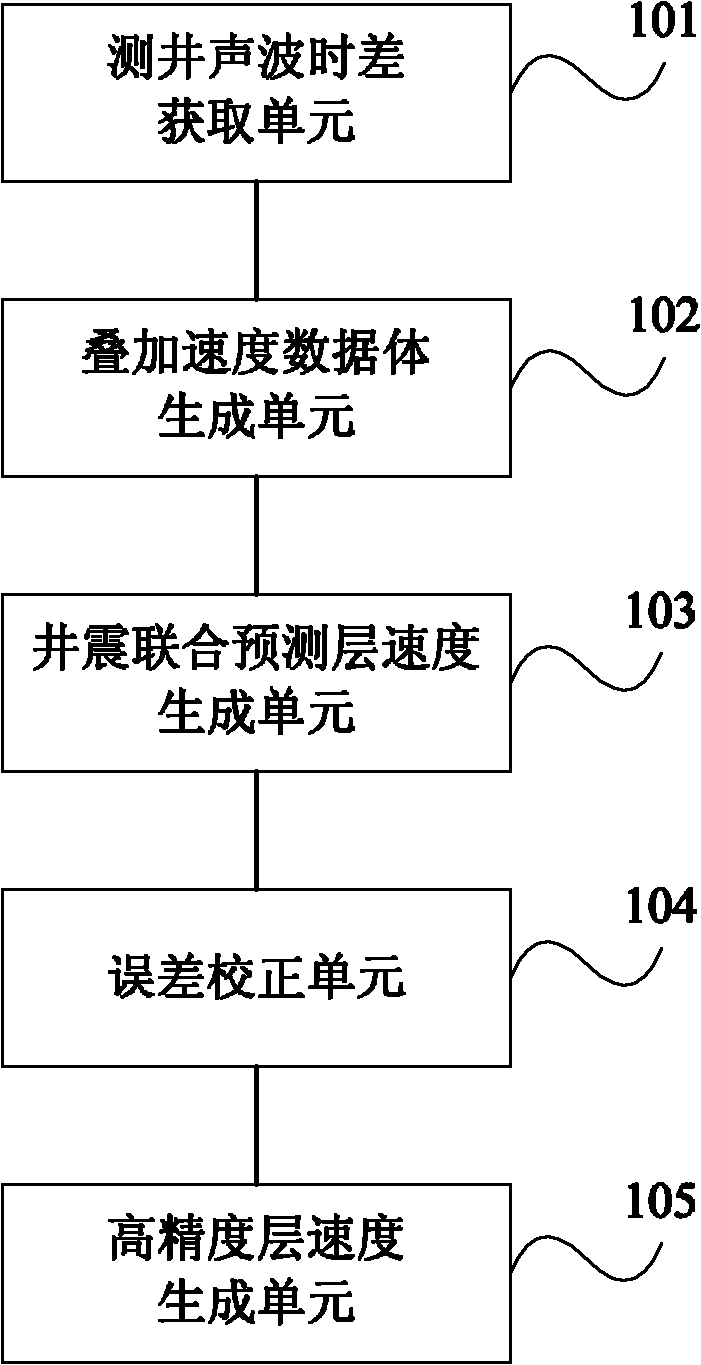
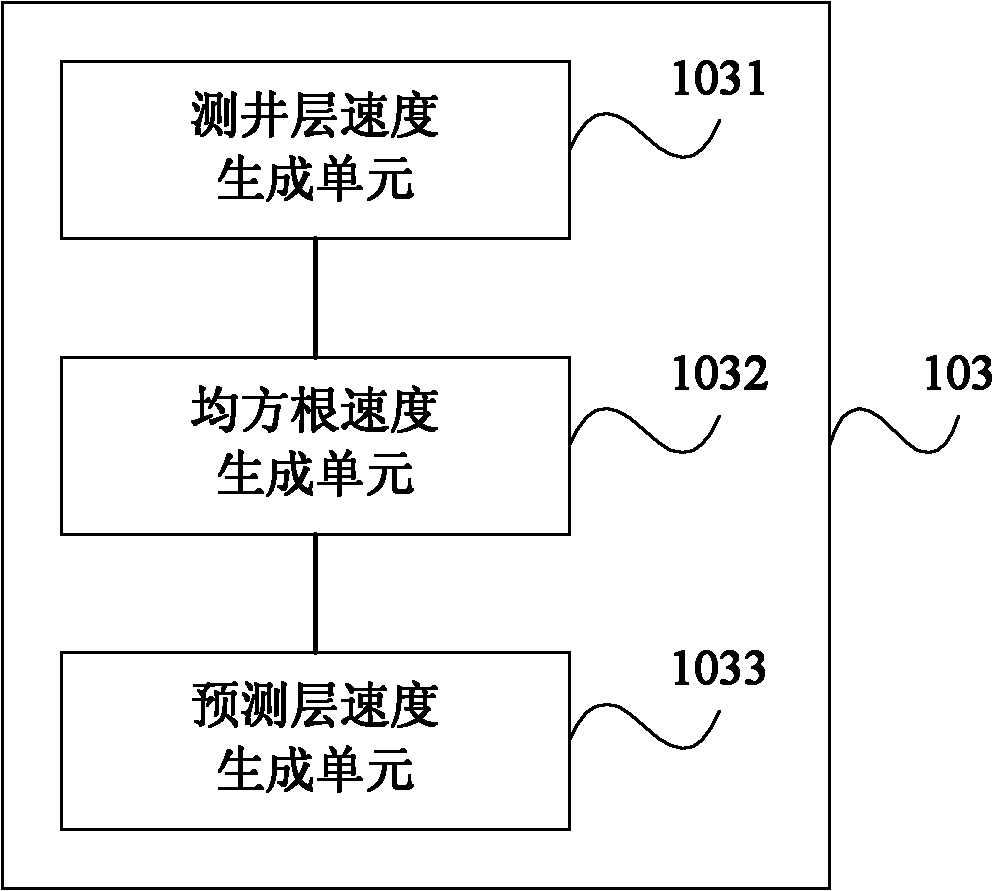
ActiveCN102129084AImprove forecast accuracyImprove reliabilitySeismic signal processingSeismic velocityVelocity spectrum
The invention discloses a method for acquiring the seismic velocity in a thin reservoir layer through well control. The method comprises the following steps of: selecting a standard single well velocity model and acquiring a corresponding logging acoustic time difference; acquiring a stacking velocity spectrum for seismic data imaging treatment and generating a stacking velocity data volume; selecting a time step length of 15-20 ms and carrying out velocity conversion on the logging acoustic time difference to obtain the velocity of a logging layer; converting the stacking velocity data volume into a logging-seismic joint forecast interval-velocity data volume; carrying out hierarchic and segmental error correction calculation on the velocity of the logging layer and the logging-seismic joint forecast interval-velocity data volume by adopting a ratio method to generate planar correction coefficients corresponding to various layers in different depths; and hierarchically and segmentally applying the planar correction coefficients to the logging-seismic joint forecast interval-velocity data volume of each layer correspondingly from top to bottom so as to obtain a high-accuracy seismic interval velocity data volume. The embodiment of the invention verifies that the method and the device for acquiring the seismic velocity in the thin reservoir layer through well control are beneficial to improvement of the forecast accuracy of the seismic velocity in the thin reservoir layer and can be used for obtaining velocity data with higher reliability.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Seismic anisotropy parameter full waveform inversion method and device
ActiveCN103713315AHigh accuracy of inversion resultsHigh precisionSeismic signal processingSeismic anisotropyWave field
The invention provides a seismic anisotropy parameter full waveform inversion method and device, and belongs to the field of seismic anisotropy parameter prediction in oil geophysical exploration. The method comprises the steps that (1) seismic data which are going to carry out anisotropy parameter inversion are acquired, namely observation wave field data; (2) denoising processing is carried out on the seismic data acquired in the step (1) to acquire denoised data; (3) by using the denoised data acquired in the step (2), and according to shot point and receiver point coordinates, a common midpoint gather is extracted to acquire seismic CMP gather information, and then the seismic CMP gather information is used to calculate the interval velocity of a horizontal stratum; (4) by using the interval velocity, which is acquired in the step (3), of the horizontal stratum, an initial model used for inversion is constructed in an interpolation mode; and (5) small perturbation is carried out on each parameter of the initial model to generate a model after parameter perturbation.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Method for imaging anisotropic medium through utilization of vertical seismic profile data
ActiveCN101630014AHigh precisionHigh resolutionSeismic signal processingVertical seismic profileThree-dimensional space
The invention relates to a method for imaging an anisotropic medium through utilization of vertical seismic profile data. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, establishing an initial depth-speed model; secondly, establishing an initial speed model through utilization of an interval velocity and an anisotropic coefficient of a Walkaway VSP or three-dimensional VSP first-arrival time inversion model; converting a plane of random normal direction of a three-dimensional space into a plane with normal parallel to the Z axis; loading information of an observation system; determining a reflecting layer of which rays run through from a shooting point to a receiving point; seeking an approximate ray parameter; determining a coordinate of the reflecting point in a reflecting interface and recording the corresponding sequence number of the receiving point; determining the traveling time from the reflecting point to the receiving point and an emergence angle of the ray in the reflecting point; and outputting imaging gather data. The method simplifies calculation, has high operation efficiency, improves the precision and the resolution of the VSP imaging result and can conveniently carry out migration imaging on Walkaway VSP or three-dimensional VSP vertical wave, transverse wave or converted wave data.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +1
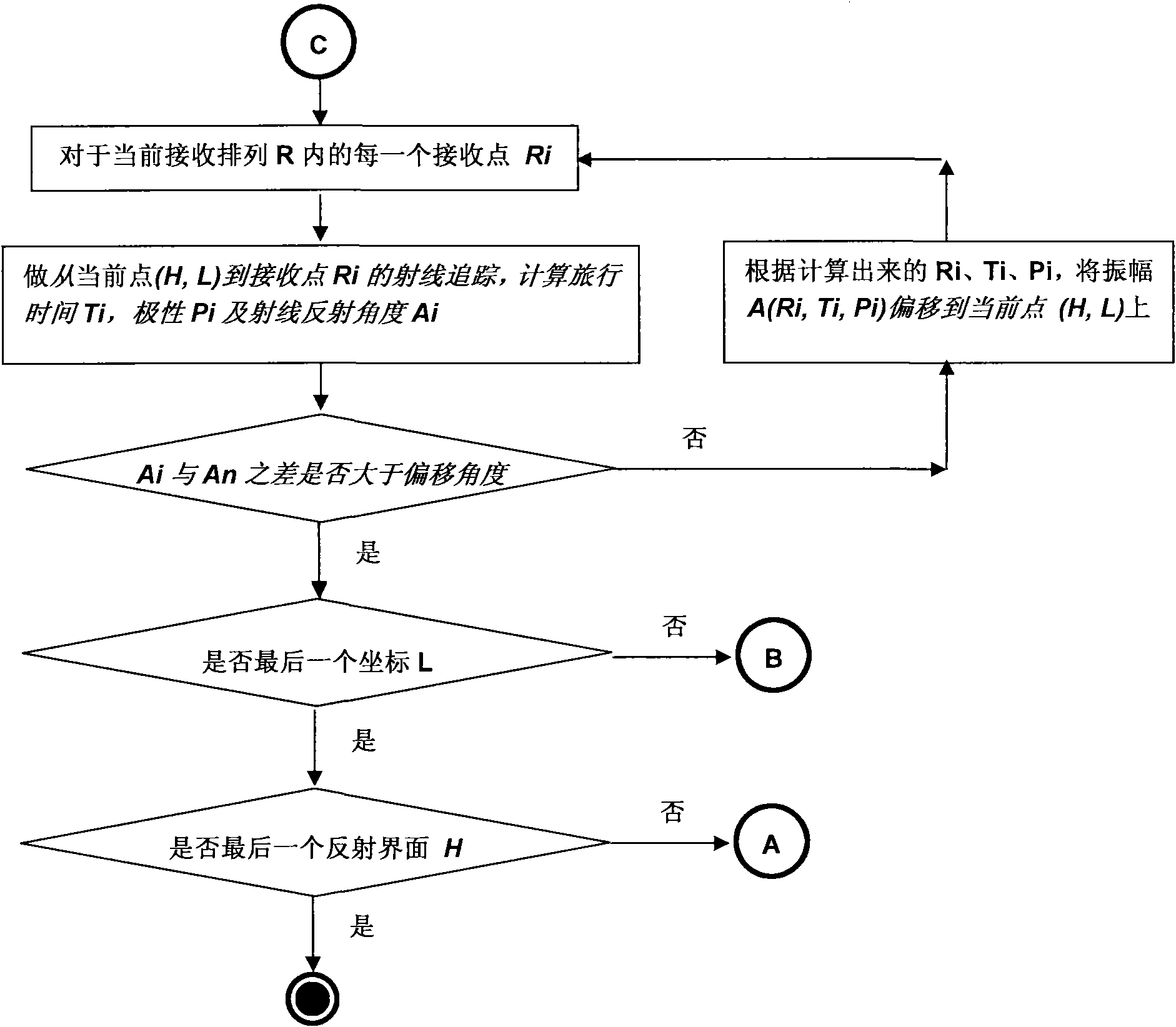
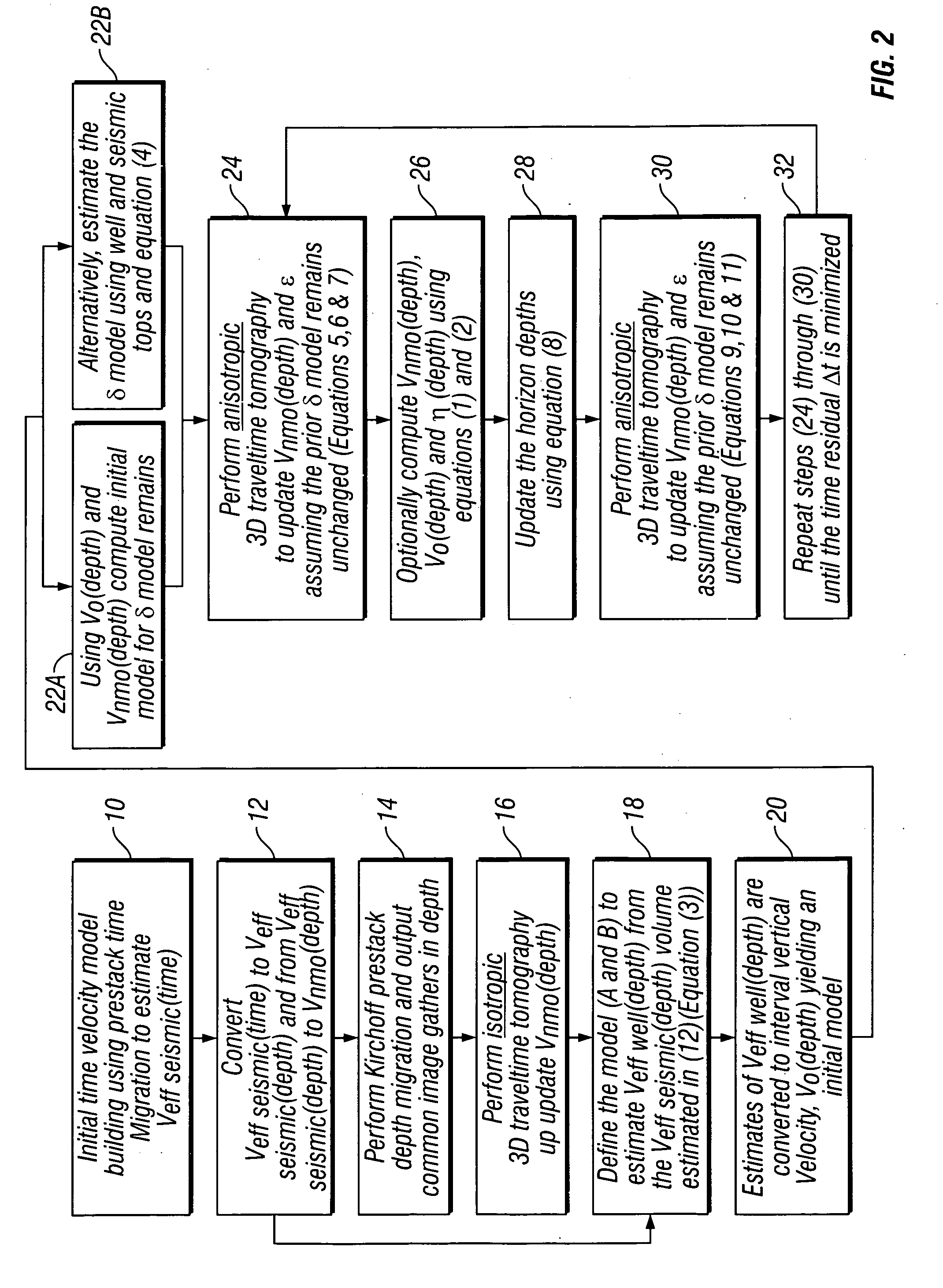
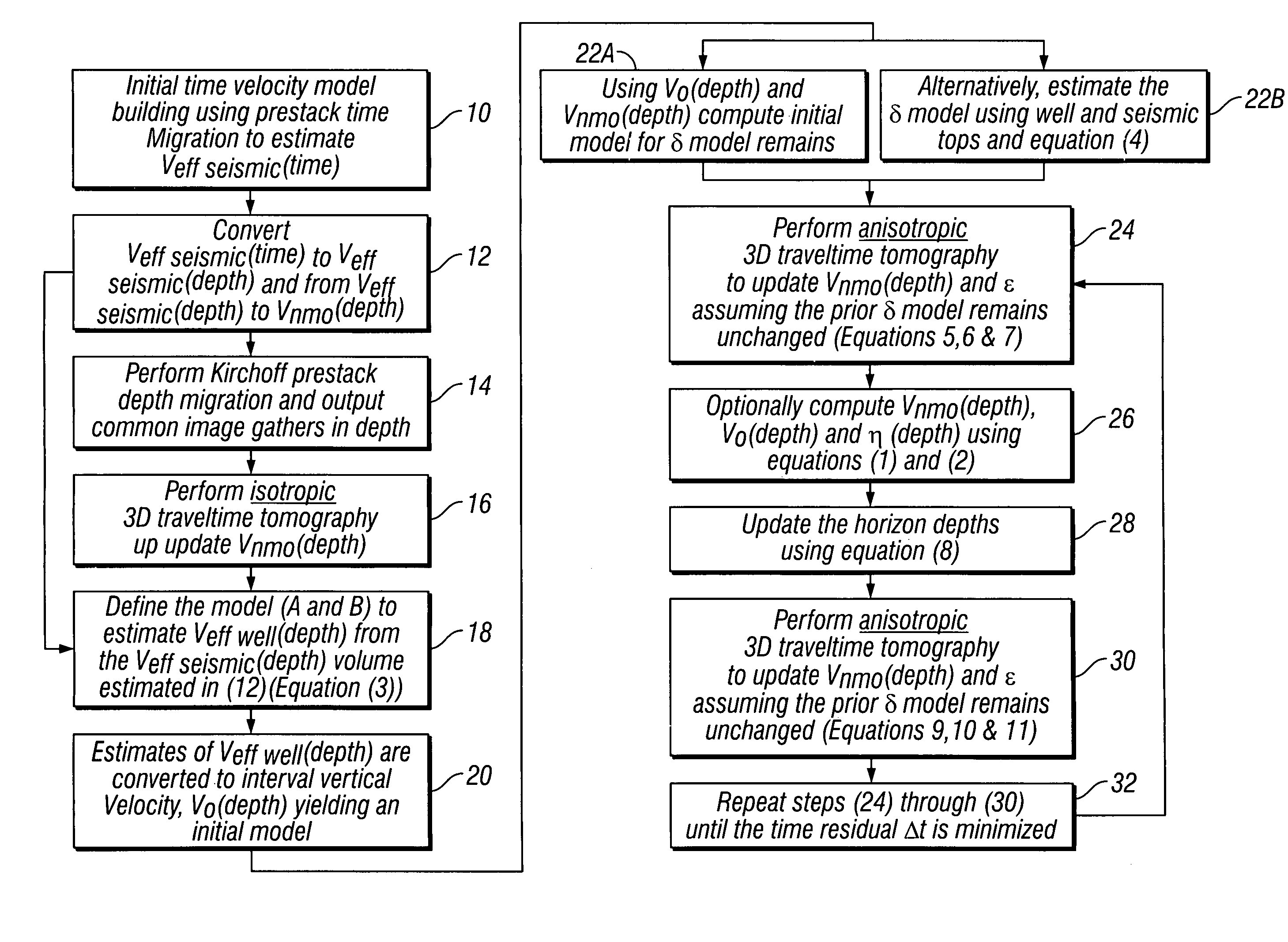
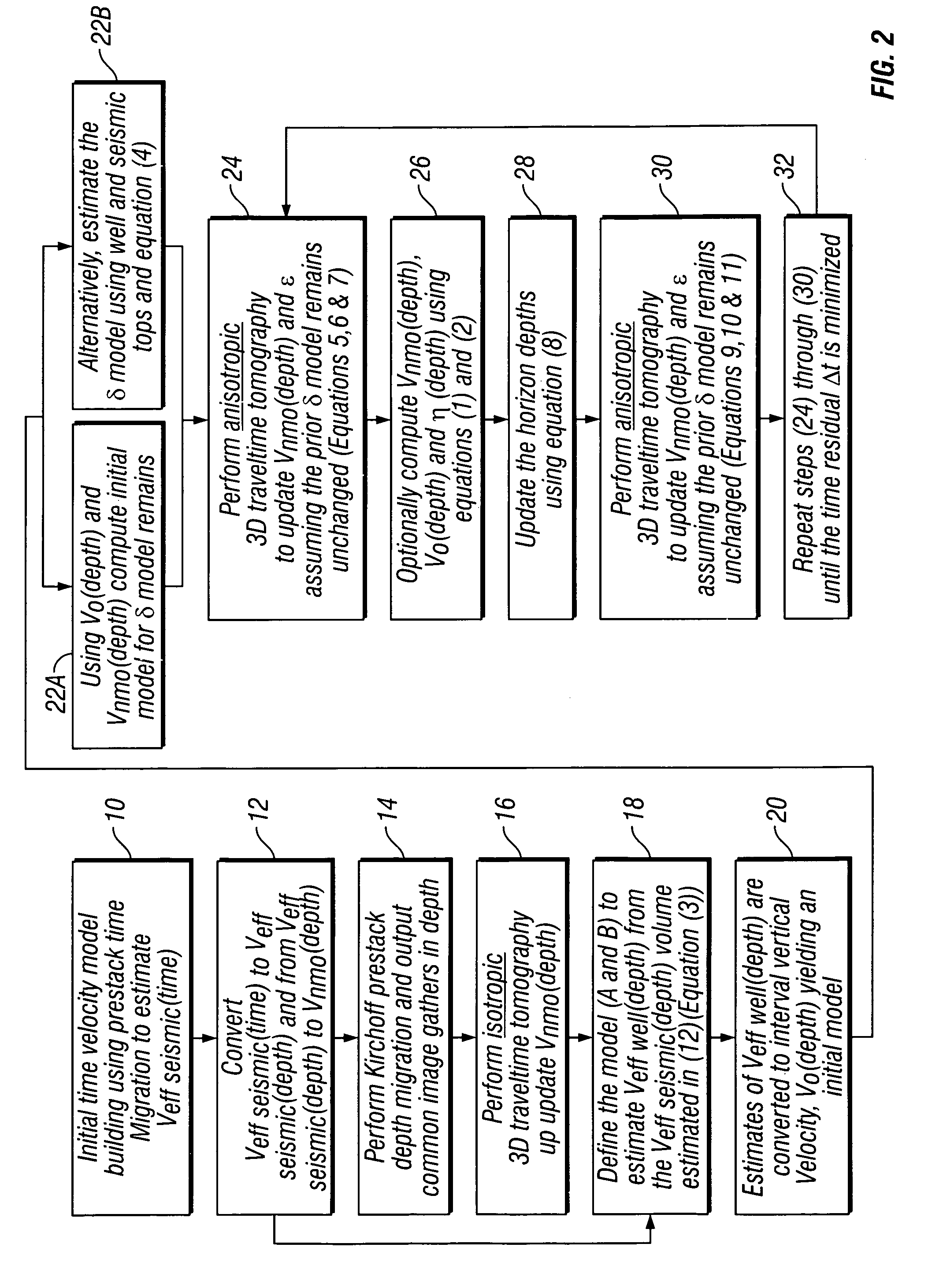
Method for three dimensional seismic travel time tomography in transversely isotropic media
A method for estimating seismic velocities in vertically transversely isotropic media includes generating an initial estimate of vertical interval velocity and interval normal moveout velocity with respect to depth from seismic data. An initial estimate is generated of a first anisotropy parameter with respect to depth. The first anisotropy parameter is related to the interval normal moveout velocity and the interval vertical velocity. An initial estimate is generated with respect to depth of a second anisotropy parameter. The second anisotropy parameter is related to the first anisotropy parameter and an interval anelliptic parameter. A first tomographic inversion is performed with respect to the interval normal moveout velocity and the second anisotropy parameter at a constant value of the first anisotropy parameter until travel time differentials reach minimum values. Layer depths are adjusted with the initial estimate of vertical interval velocity. Using values of the second anisotropy parameter determined in the first tomographic inversion, a second tomographic inversion is performed of interval normal moveout velocity and the first anisotropy parameter with respect to depth. The adjusted layer depths, interval normal moveout velocities and interval vertical velocities are again adjusted and interval anelliptic parameters are calculated from the second tomographic inversion.
Owner:PGS GEOPHYSICAL AS
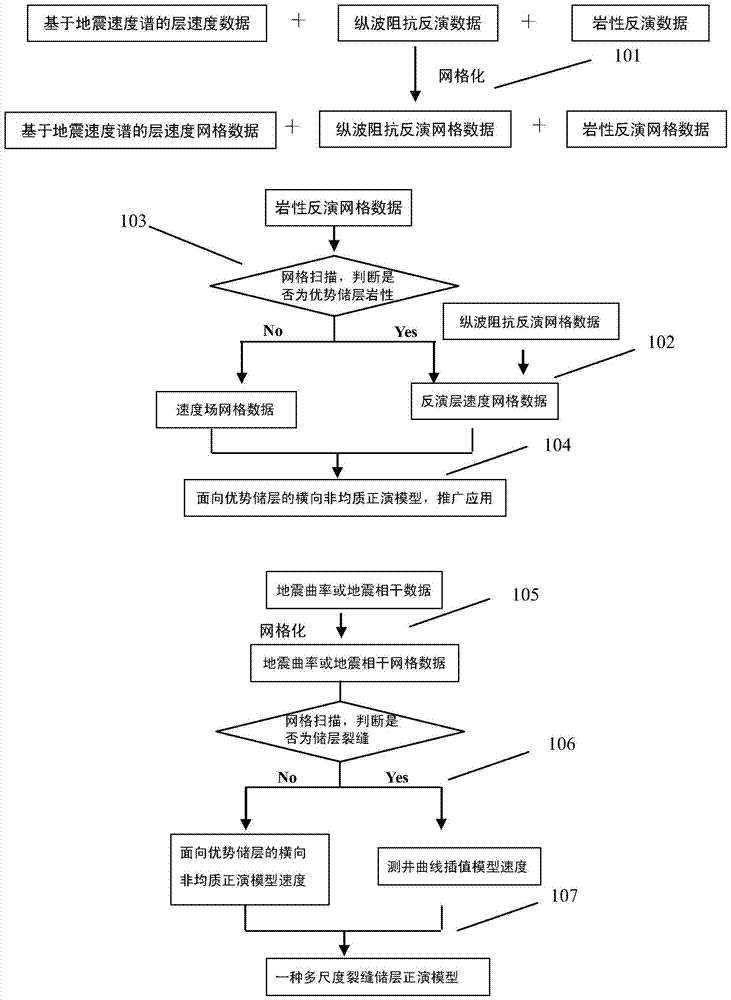
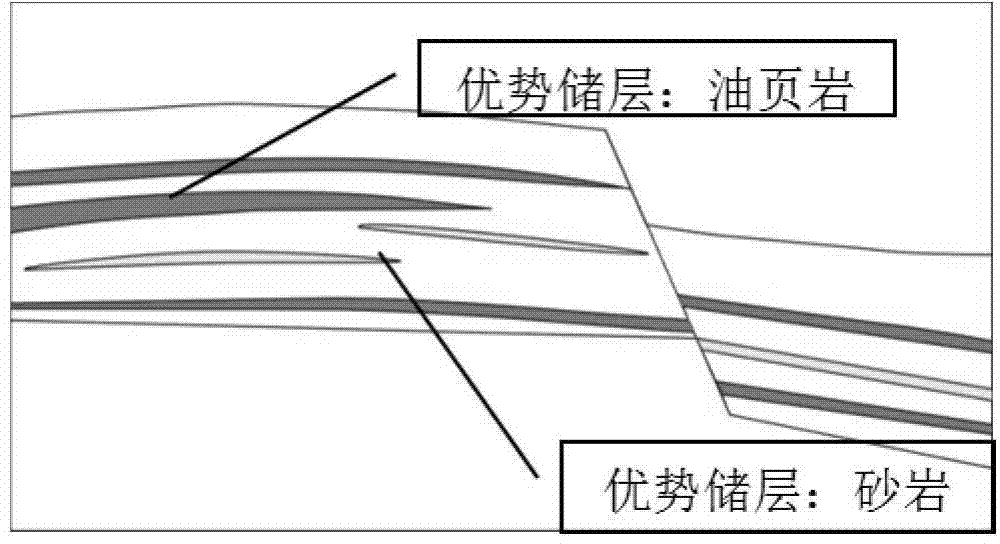
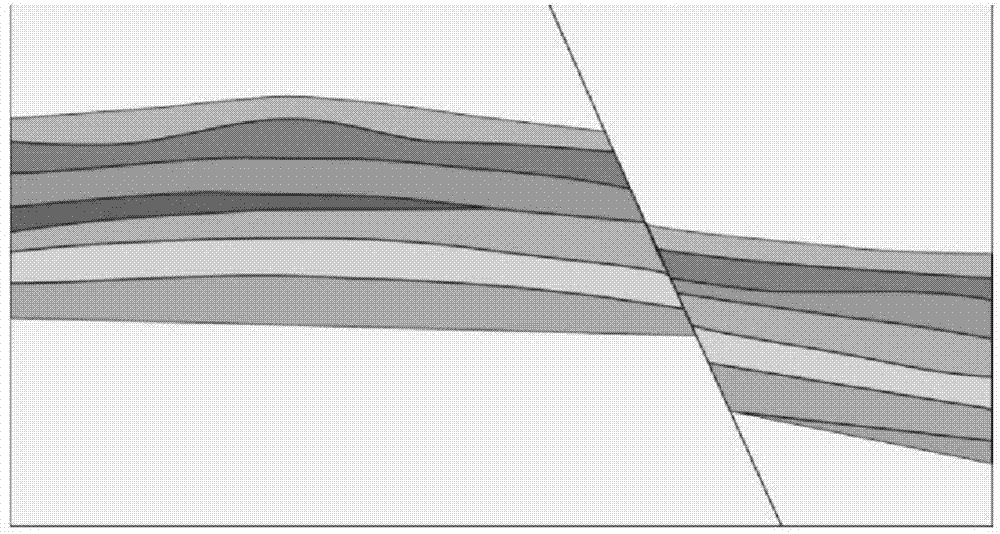
Multi-scale fractured reservoir forward model establishing method
The invention relates to the field of exploration geophysical data processing methods, and particularly relates to a multi-scale fractured reservoir forward model establishing method. First, a laterally heterogeneous model for a predominant reservoir is established by using interval velocity data based on the seismic velocity spectrum, P-wave impedance inversion data, and lithologic inversion data; then, the geometrical shape of a fracture is determined by a seismic detection method for different scales of seismic curvature or seismic coherence, and the fracture is given geophysical parameters based on well shock and is embedded to the obtained laterally heterogeneous model; and finally, a laterally and longitudinally heterogeneous multi-scale fractured reservoir model is established. The fractured reservoir model established by the method fully utilizes well shock data, truly reflects the development regularity and distribution characteristics of the fracture, and provides a basis for performing fractured reservoir forward modeling in the next step, understanding the wave field response characteristics and geophysical attributive characteristics of a fractured reservoir and improving the accuracy of reservoir prediction.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
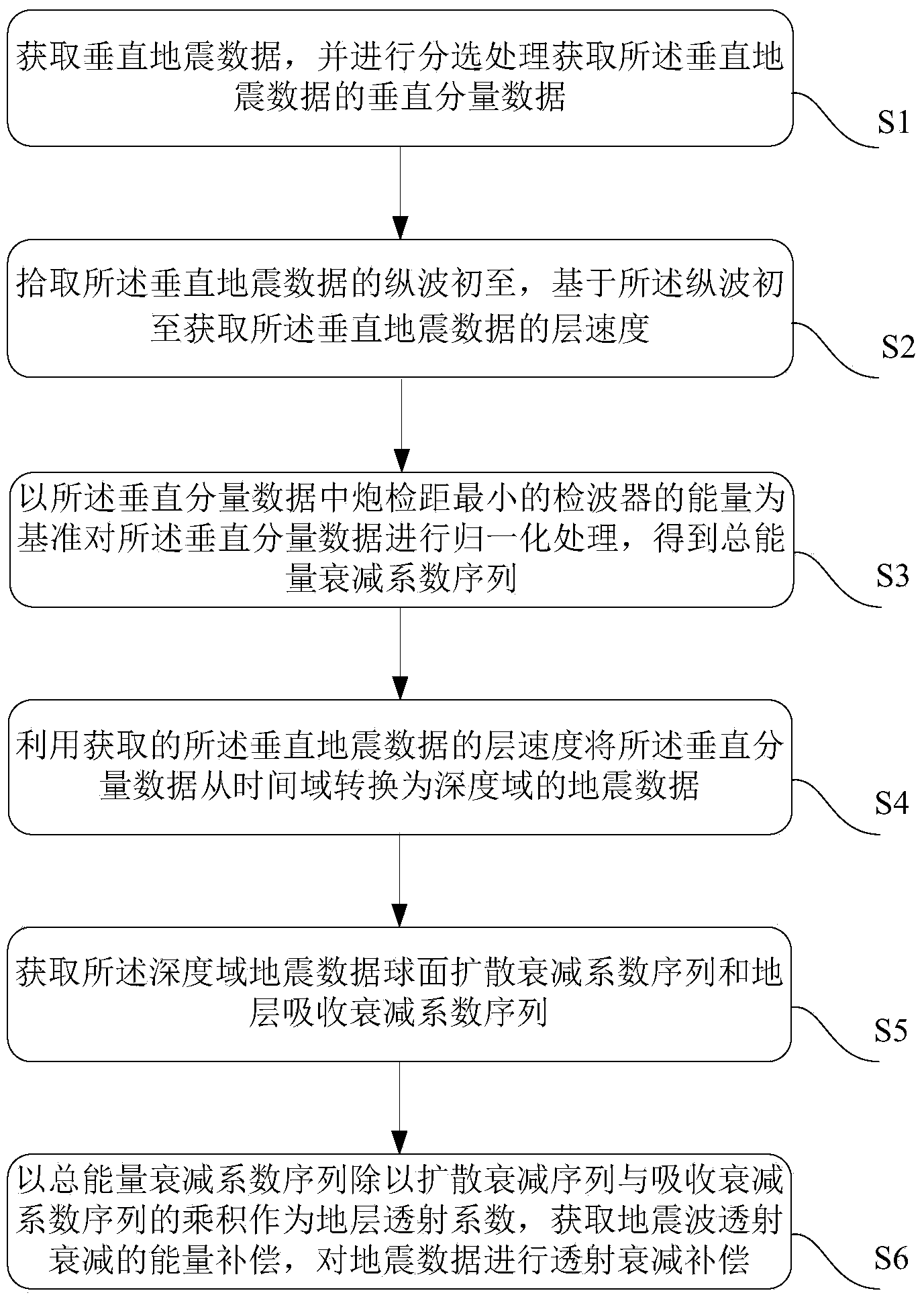
Seismic wave transmission attenuation compensation method and device
ActiveCN104375188ATransmission attenuation energy compensation results are validTransmission attenuation energy compensation results are reliableSeismic signal processingSeismology for water-loggingAttenuation coefficientTime domain
The invention provides a seismic wave transmission attenuation compensation method and device. The method comprises the first step of obtaining vertical component data of vertical seismic data, the second step of obtaining the interval velocity of the vertical seismic data based on first arrival of longitudinal waves, the third step of conducting normalization processing on the vertical component data to obtain a total energy attenuation coefficient sequence, the fourth step of converting the vertical component data in a time domain into seismic data in a depth domain, the fifth step of obtaining a spherical diffusion attenuation coefficient sequence and a stratum absorption attenuation coefficient sequence of the seismic data in the depth domain, and the sixth step of using a result obtained by dividing a total energy attenuation coefficient by the product of the spherical diffusion attenuation coefficient sequence and the stratum absorption attenuation coefficient sequence as a stratum transmission coefficient, obtaining energy compensation for seismic wave transmission attenuation according to the stratum transmission coefficient and conducting transmission attenuation compensation on the seismic data. Through utilization of all embodiments involved in the method, effective and reliable energy compensation for stratum transmission attenuation can be obtained, and the stratum transmission coefficient is used for amplitude recovery processing on the seismic data.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +1
Well-to-seismic integration paleo-formation pressure prediction method
ActiveCN104483703AEfficient use ofSeismic signal processingSpecial data processing applicationsTime domainPredictive methods
The invention relates to a well-to-seismic integration paleo-formation pressure prediction method. The method includes the steps that a velocity cube, a density cube and a porosity cube of a formation are obtained through the fine reservoir wave impedance inversion technology; time domain and depth domain conversion of a three-dimensional model is completed by means of the velocity cube; a geologic model of the geological time of a pool-forming period is obtained by subtracting the thickness of a formation needing to be eroded away in the pool-forming period from the thickness of the current formation; a paleo-porosity cube is obtained according to the erosion compaction restoration thicknesses of grids in the longitudinal direction of the geologic model of the pool-forming period and the porosity and depth relation; the paleo-density of the formation is restored by means of the density and depth linear relation; a paleo-formation interval velocity cube is obtained through the paleo-porosity cube; the rock matrix velocity and relations between pore fluid velocities with depths are obtained through logging information; ancient overlaying formation pressure is obtained through a paleo-density cube; a formation pressure cube of the ancient geological time is obtained through the ancient overlaying formation pressure, the rock matrix velocity, the relations between pore fluid velocities with depths and the paleo-formation interval velocity.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Method for improving imaging effect of wave equation prestack depth migration
InactiveCN102176053AResolve mismatchAvoid multiple offset calculationsSeismic signal processingSeismology for water-loggingSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Normal moveout
The invention provides a method for improving the imaging effect of wave equation prestack depth migration, wherein the method is used for processing seismic reflection data in seismic exploration so as to improve the application effect of the wave equation prestack depth migration. The method can be used for improving the imaging effect of the wave equation prestack depth migration by constructing the relationship of residual normal moveout between a depth domain and an angle domain and an interval velocity inversion method to directly update a migration velocity model of the wave equation prestack depth migration based on the residual normal moveout of an angle gather. Based on the relationship of residual normal moveout between the depth domain and the angle domain, the method can be used for removing the residual normal moveout, noise and stretching of a migration gather of the wave equation prestack depth migration, thereby improving the signal-to-noise ratio and resolution of a migration stack profile and improving the quality of the angle gather applied to the prestack inversion. Accordingly, the method can be used for well achieving the direct recognition of underground oil, gas or water, can be used for 2D (two-dimensional) and 3D (three-dimensional) wave equation prestack depth migration of the seismic reflection data, and has important application value for exploration of oil-gas and mineral resources.
Owner:INST OF GEOLOGY & GEOPHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
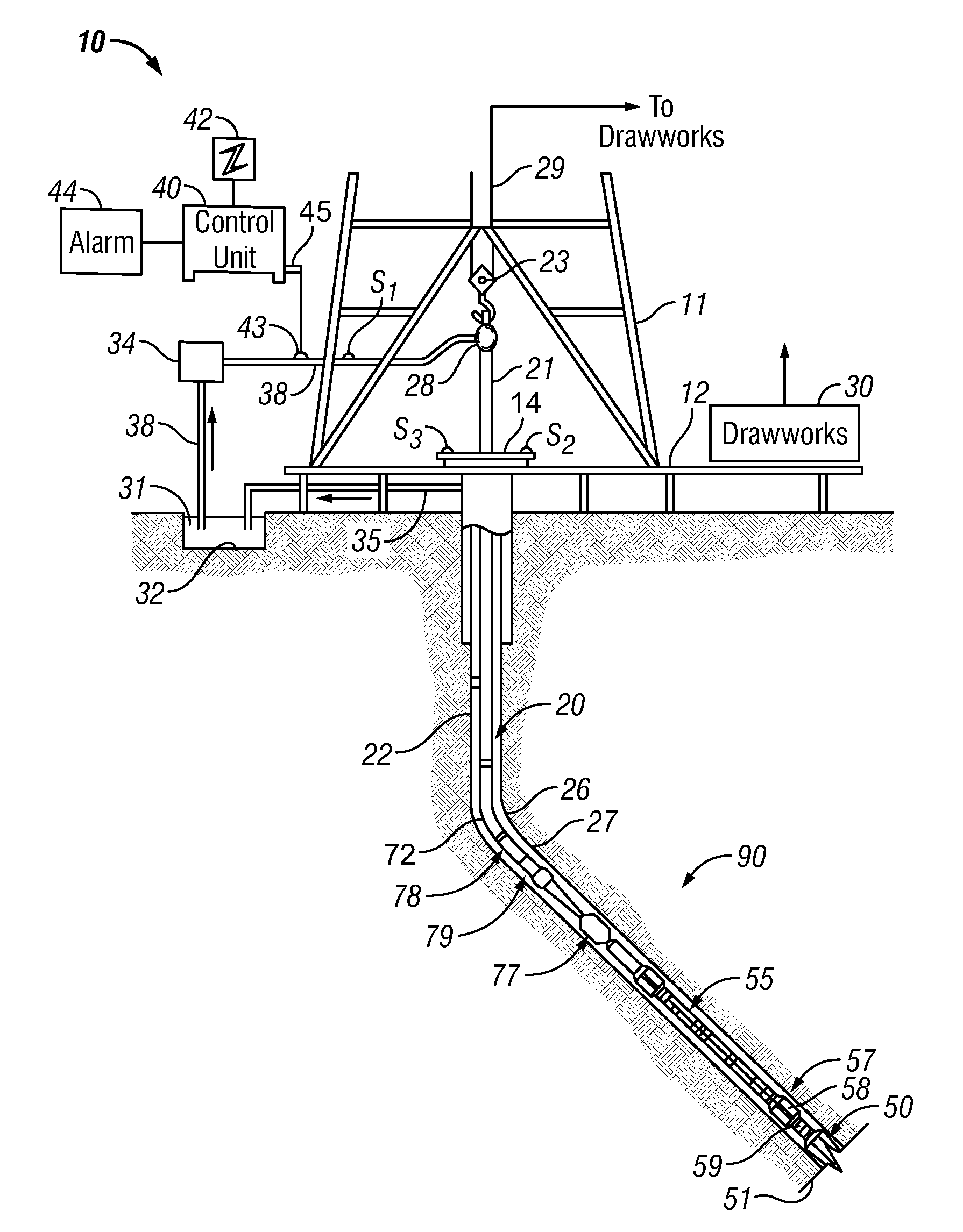
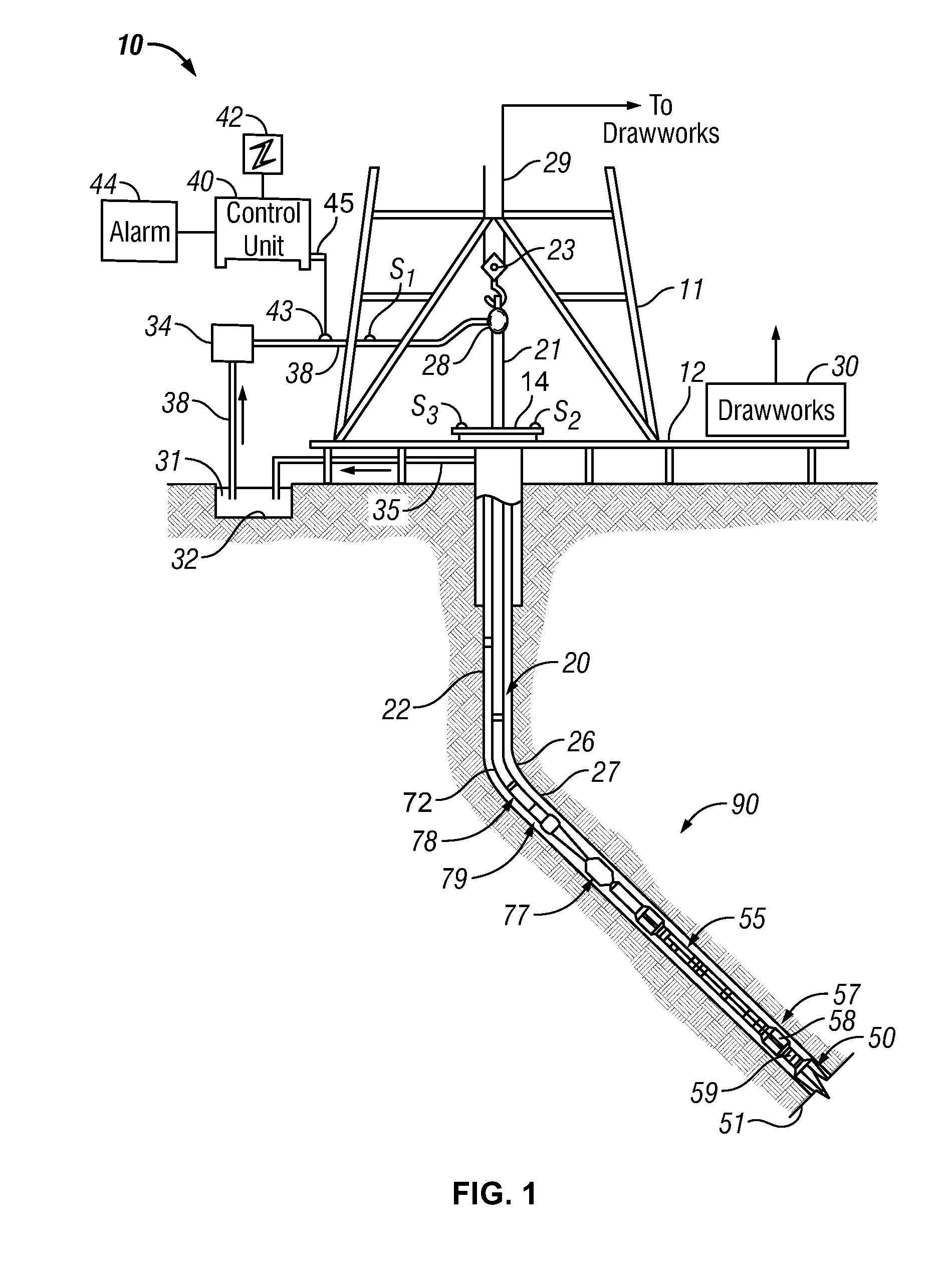
Drill-Bit Seismic With Downhole Sensors
A drill-bit seismic method where the seismic receivers are located in the BHA. The data detected by these receivers is processed by a downhole processing unit in order to estimate the interval velocity of the seismic wave between the sensors and between the bit and a sensor. Additionally, the processed data might provide the distance to a seismic reflector close to the borehole and the average seismic velocity between the well and this reflector. The processed data can be transmitted to surface location by mud-pulse telemetry. The pilot signal can be also used to process seismic data recorded by receivers located at the earth surface (or close to it).
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
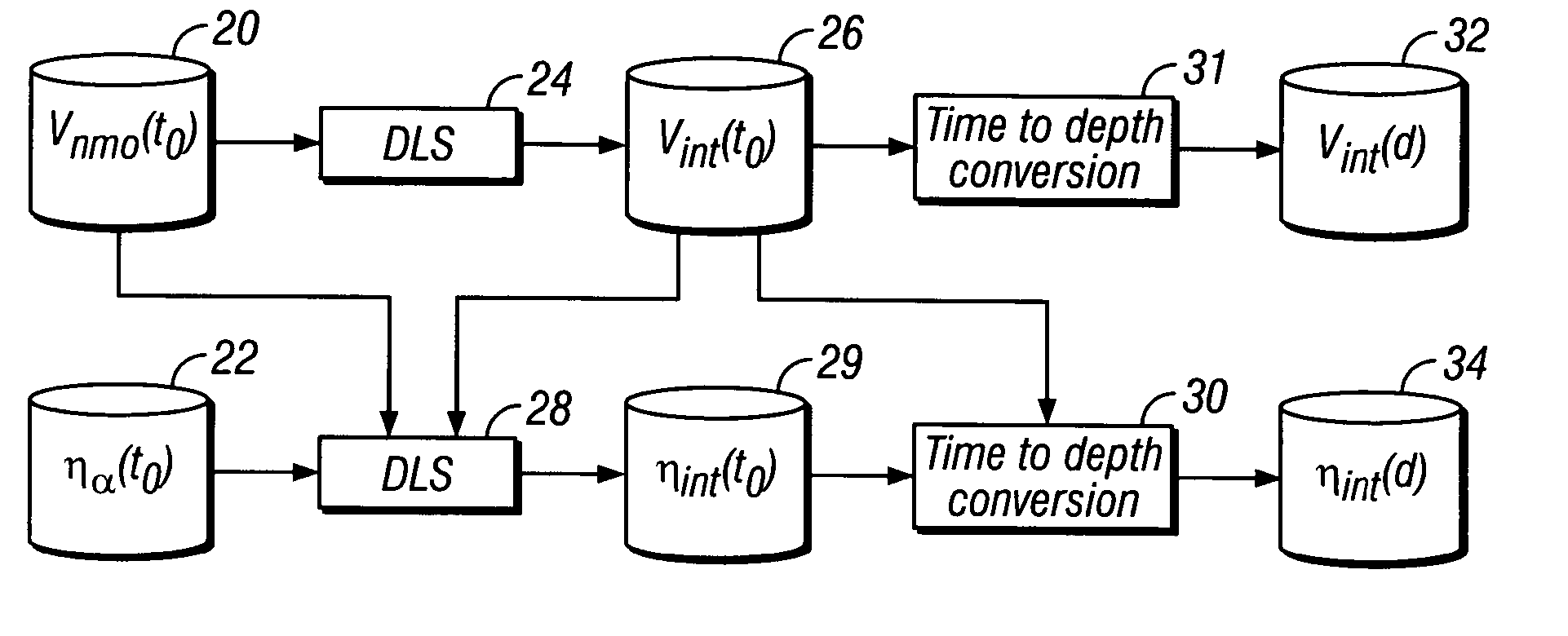
Method for stable estimation of anisotropic parameters for P-wave prestack imaging
ActiveUS20050088914A1Seismic signal processingSpecial data processing applicationsNormal moveoutVelocity inversion
A method is disclosed for determining interval anelliptical parameters. The method includes determining normal moveout velocities and effective anelliptical parameters from seismic data traces. The normal moveout velocities are processed to obtain interval velocities. The normal moveout velocities, effective anelliptical parameters and interval velocities are inverted to obtain the interval anelliptical parameters. In one embodiment, the inversion includes damped least squares. In one embodiment, the inversion is preconditioned.
Owner:PGS AMERICA INC
Method for Updating a Geologic Model by Seismic Data
InactiveUS20070156341A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSurveyErrors and residualsGeophysics
A method of predicting petrophysical characteristics of an underground reservoir by constructing a geologic model consistent with seismic measurements is disclosed which permits optimization of oil reservoir development schemes. A geologic model, from which seismic data are simulated in depth, is constructed in depth. The geologic model is made consistent with seismic measurements acquired in time by minimization of an objective function by comparing the seismic measurements with seismic data simulated from the geologic model and converted to time. During minimization, the interval velocities used for conversion are updated by comparing, within the objective function, an observed thickness in time ΔTobsm,n between two markers with a thickness in time ΔTsimm,n simulated from the seismic data, and by modifying simulation parameters such as the error εsimm,n on the thickness of the two markers estimated in depth.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Interval velocity model building method under complicated geological conditions
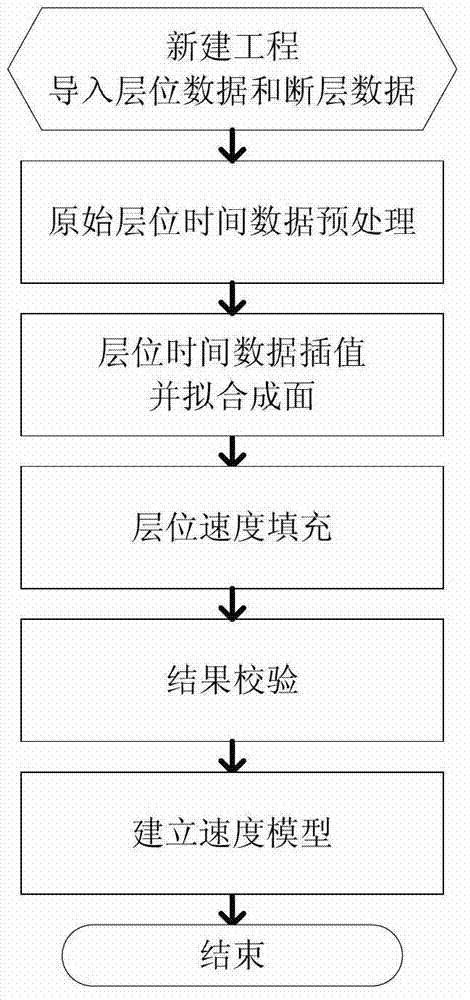
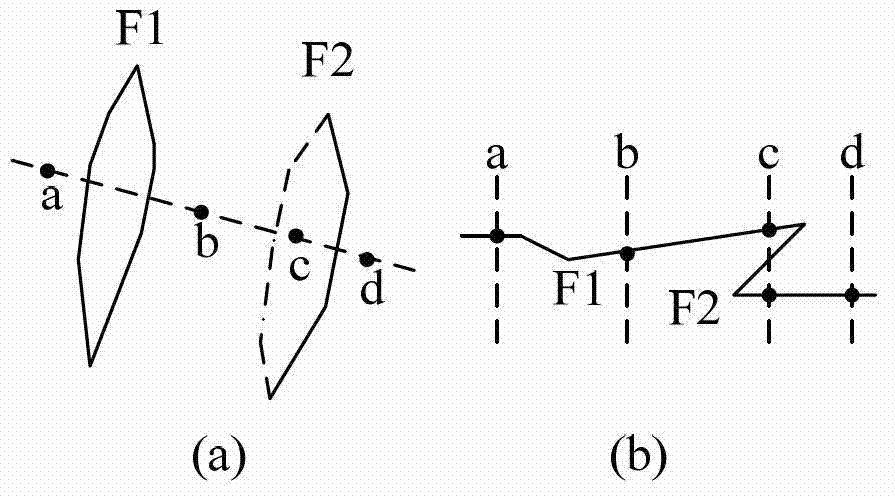
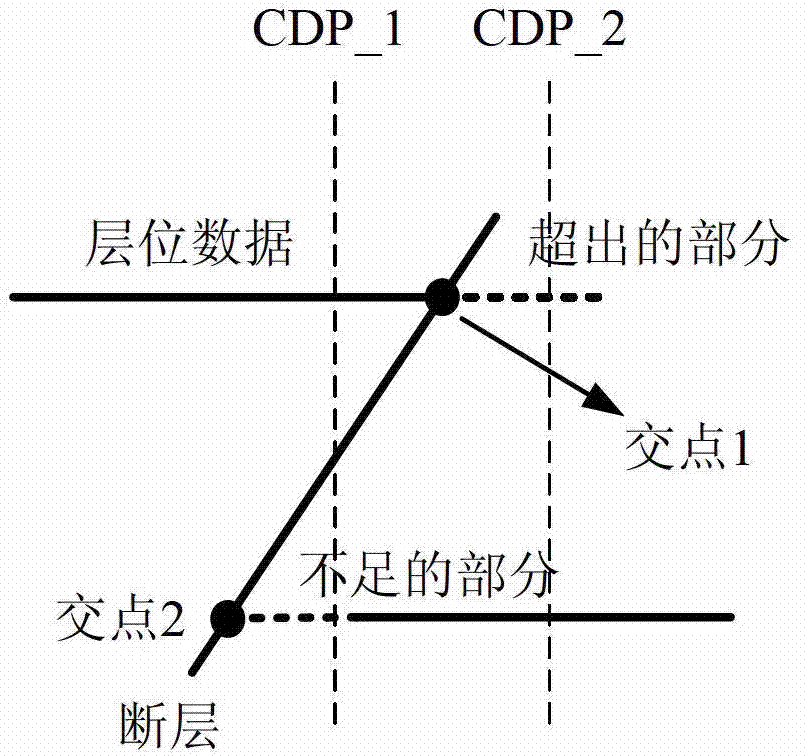
InactiveCN102819039AEfficiently buildAccurate Velocity ModelSeismic signal processingTerrainProblem of time
The invention discloses an interval velocity model building method under complicated geological conditions, firstly solves the problem of time dimension fitting under complicated terrain conditions and also solves the problems of interval velocity filling and speed modeling on the basis of the solving of the problem of time dimension fitting. The interval velocity model building method disclosed by the invention has the following positive effects: in the interval forming process, data is pretreated by utilizing the concepts of grid and hanging wall and footwall of faults, the concept of group of faults is also introduced, so that an interval time model is built more efficiently; a certain number of primary interval velocity data is utilized to fit the velocities of the hanging wall and the footwall of the faults more accurately, so that a more accurate velocity model is obtained.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
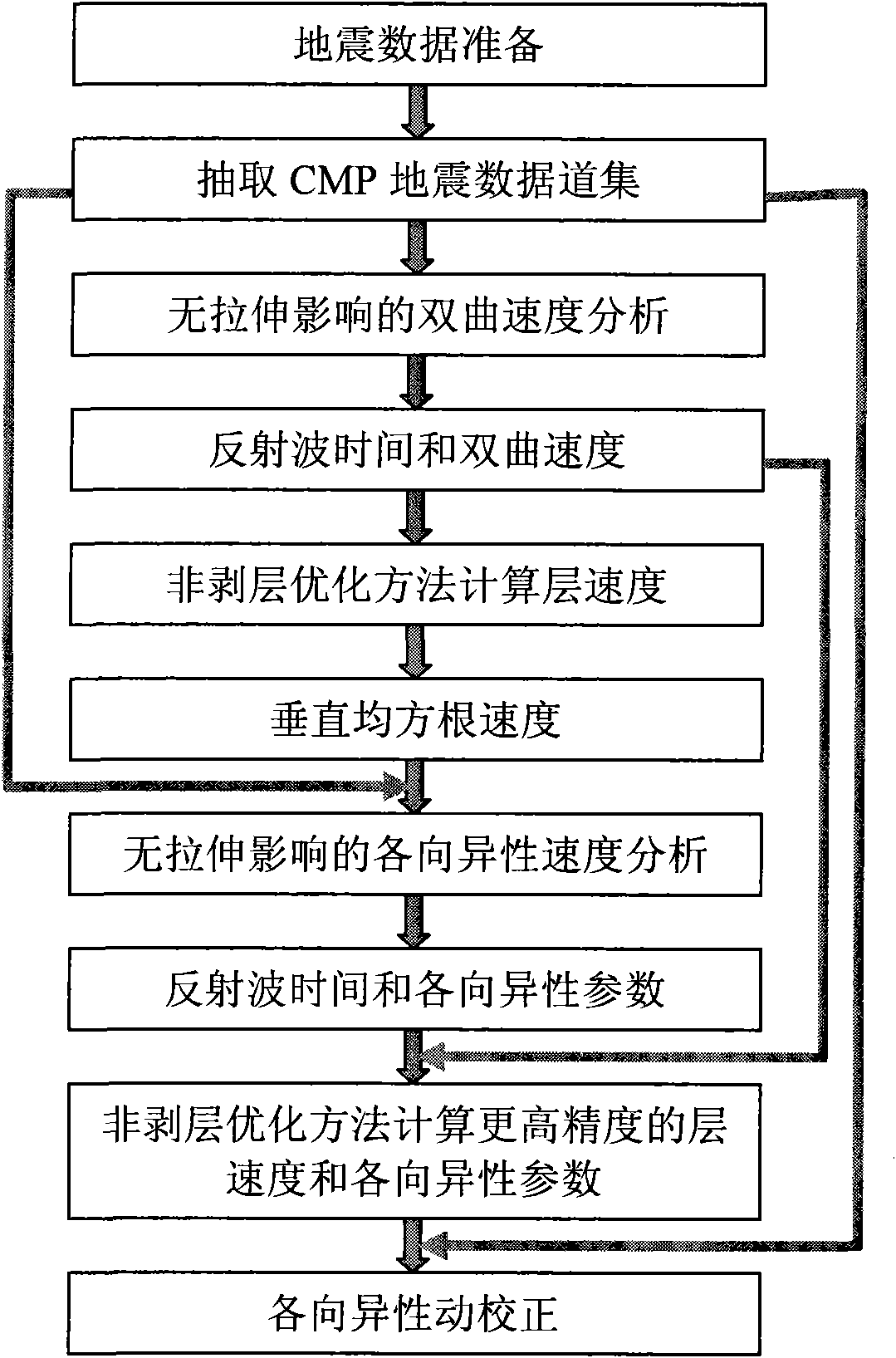
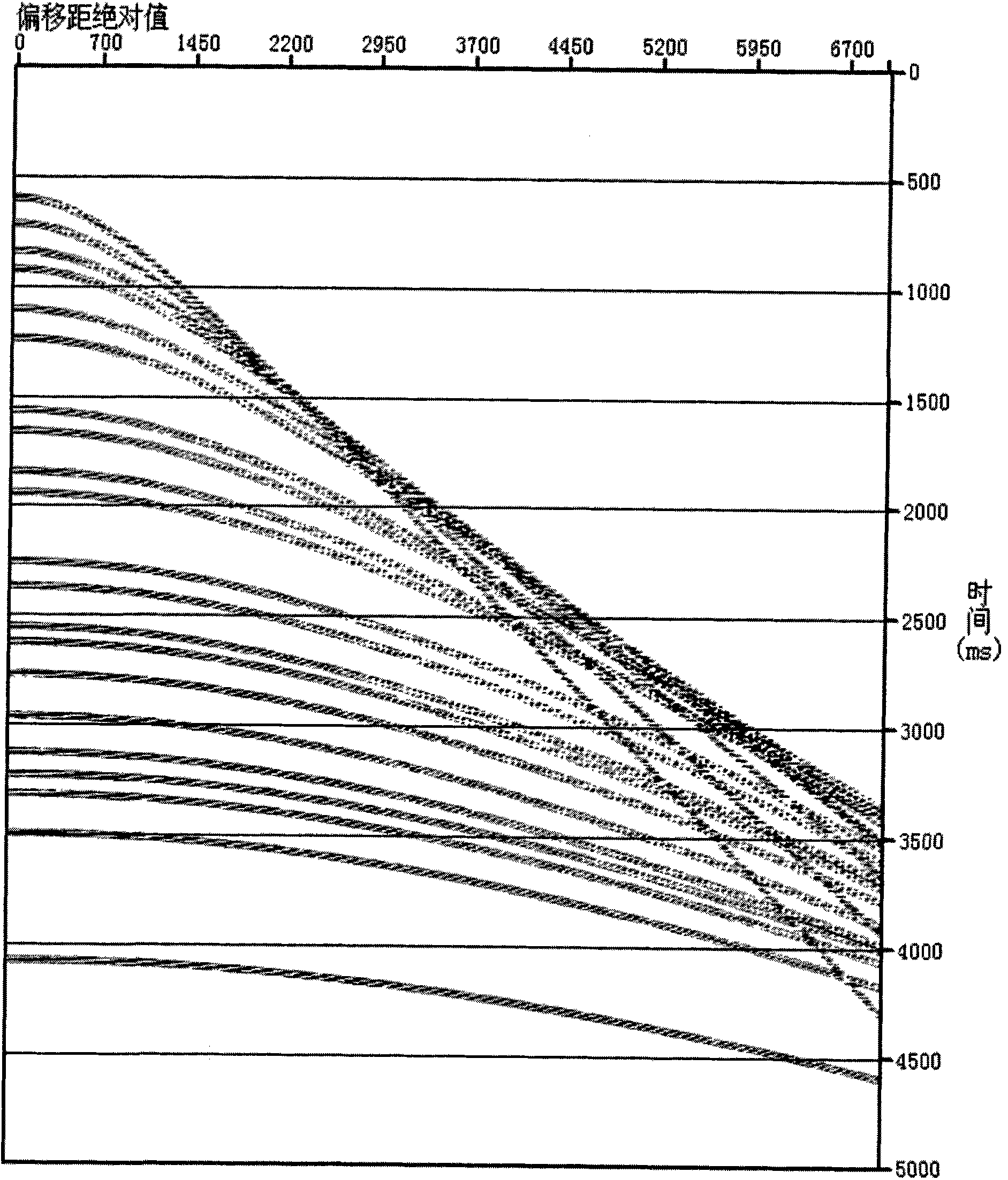
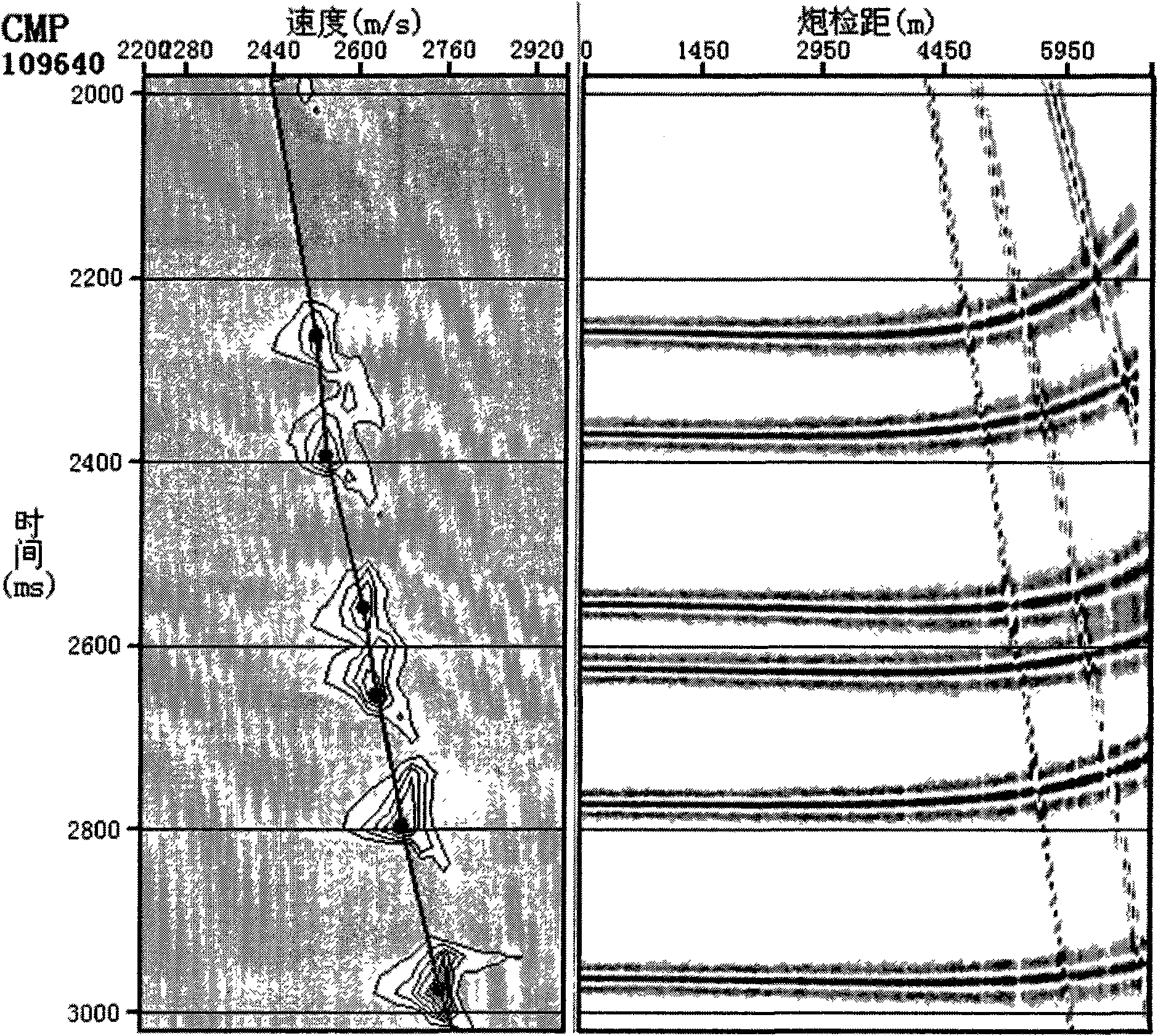
Anisotropy speed analysis and dynamic correction method
ActiveCN101776768AUnaffected by Dynamic Corrective StretchHigh precisionSeismic signal processingGeophoneVelocity spectrum
The invention relates to a high-precision anisotropy speed analysis and a dynamic correction method, which comprise the following steps: preparation of seismic data: CMP seismic data gather is sorted; hyperbolic equation is adopted to perform the speed analysis without stretching influence on the small geophone offset reflected wave data; interactive interpretation is performed for velocity spectrum so as to obtain the hyperbolic velocity of the reflected wave; interval velocity is calculated with a non-delamination optimization method according to the two-way time and the hyperbolic velocity of the reflected wave; an exclusive interval velocity is calculated according to a least squares optimization principle; a vertical root mean square velocity is calculated; all geophone offset data is used for performing the anisotropy speed analysis without the stretching influence to obtain the anisotropy parameters; higher-precision root mean square and anisotropy parameters are calculated; anisotropy dynamic correction is performed; the calculation of the vertical root mean square velocity is automatically completed according to the calculated hyperbolic velocity and the offset range so as to perform the anisotropy velocity analysis and dynamic correction. The parameters obtained by calculating are free from being influenced by the dynamic correction stretching and have the advantages of high precision and high efficiency.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD +1
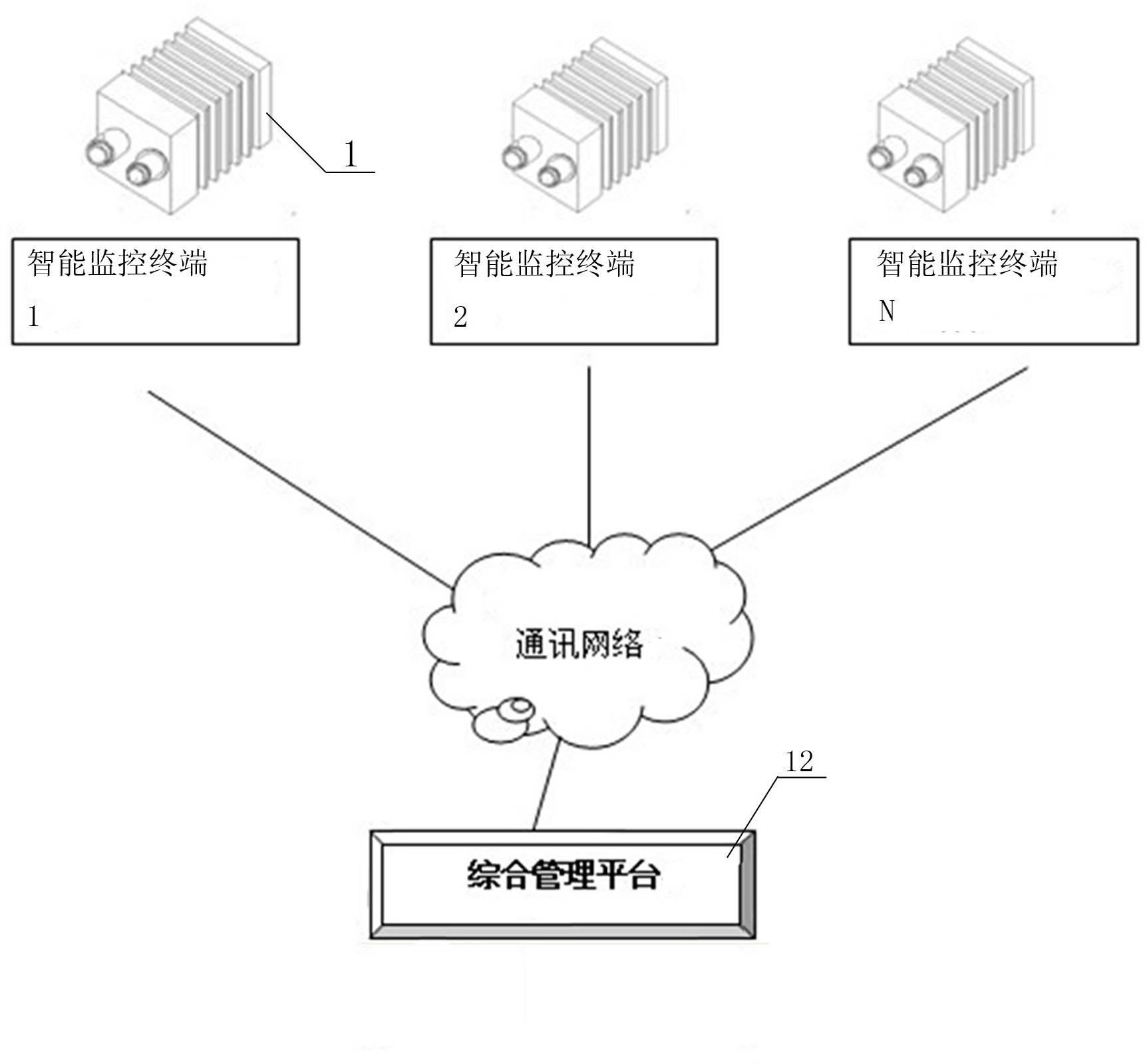
Compound type interval velocity-measuring system based on internet of things technology and method thereof
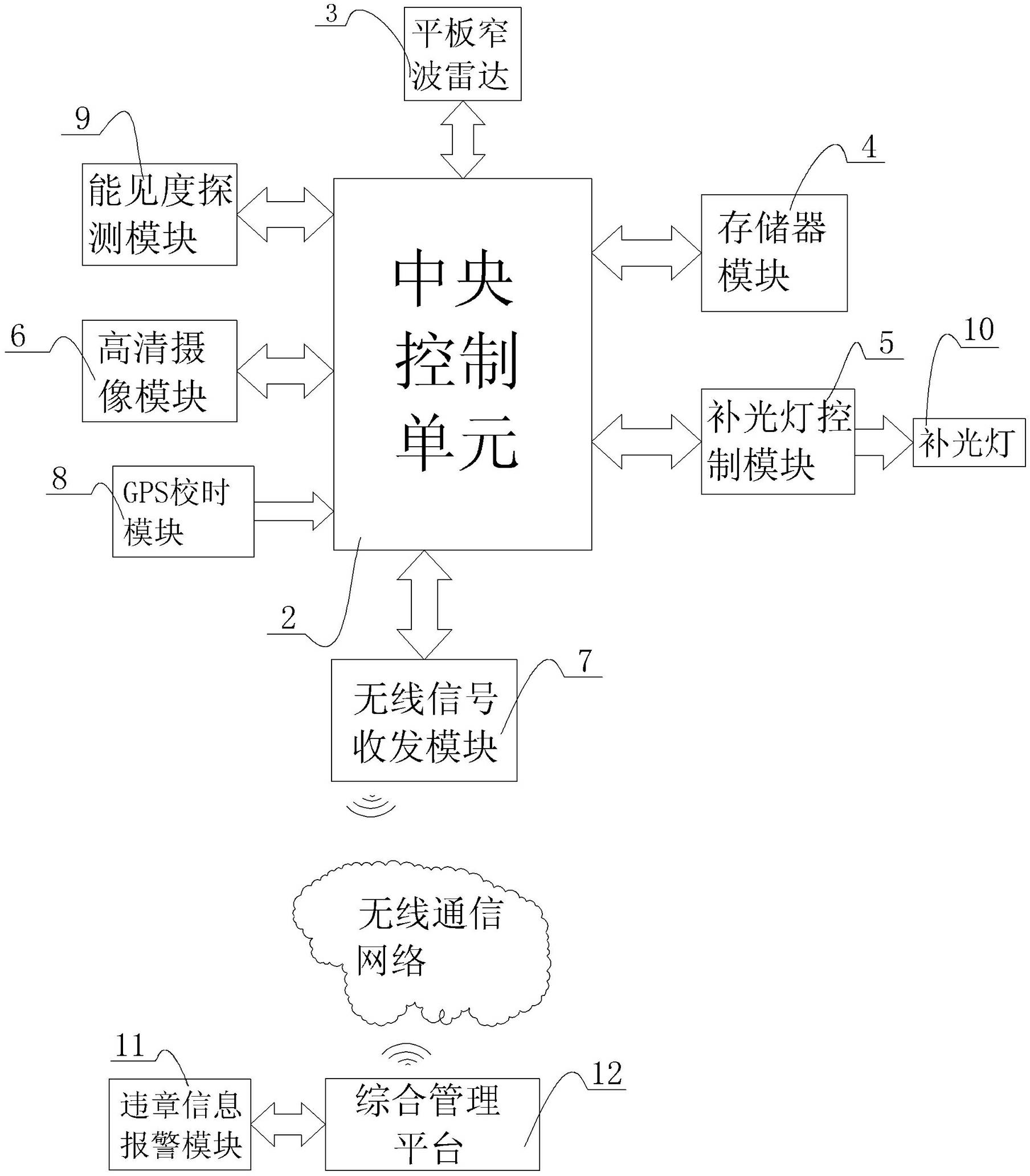
InactiveCN102592457AEffective automatic identificationRealize analysisRoad vehicles traffic controlMemory moduleControl unit
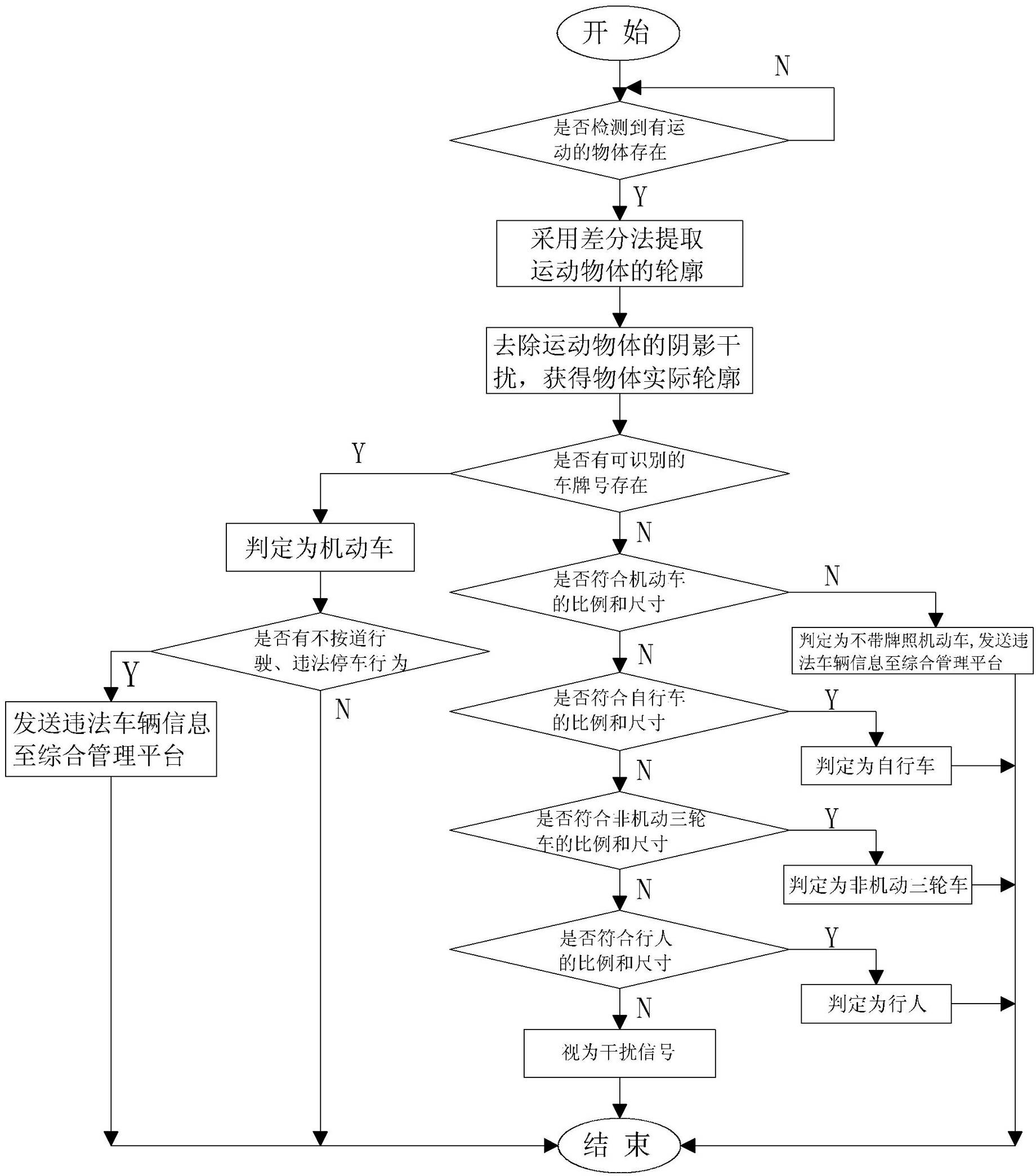
The invention relates to a compound type interval velocity-measuring system based on internet of things technology, which includes a plurality of intelligent monitor terminals, wherein each of the terminals comprises a power supply module, a central control unit with computation and control effects, a high definition camera module which is used for collecting images information and a memory module which is used for data storage. The compound type interval velocity-measuring system based on internet of things technology and a method thereof is characterized by further comprising a wireless signals transceiving module connected with the central control unit to achieve wireless communication of the intelligent monitor terminals, and flat narrow wave radar used for collecting velocity information and connected with the central control unit. An object identification method is to detect whether the license plate number exists and compare the object outline with the outlines of vehicles and pedestrians. According to the compound type interval velocity-measuring system based on internet of things technology and the method, ad hoc network and wireless transceiving functions are provided, the dependence is reduced; the object identification can effectively perform automatic identification for moving objects on road; The device can judge if the average velocity and the instantaneous velocity surpass the set value, and also can judge driving by not using correct line, illegal parking and illegal acts of non-motor vehicles and the information can be sent to management center.
Owner:山东鼎讯智能交通股份有限公司
Method of quantitative evaluation on oil and gas accumulation conditions based on seismic data
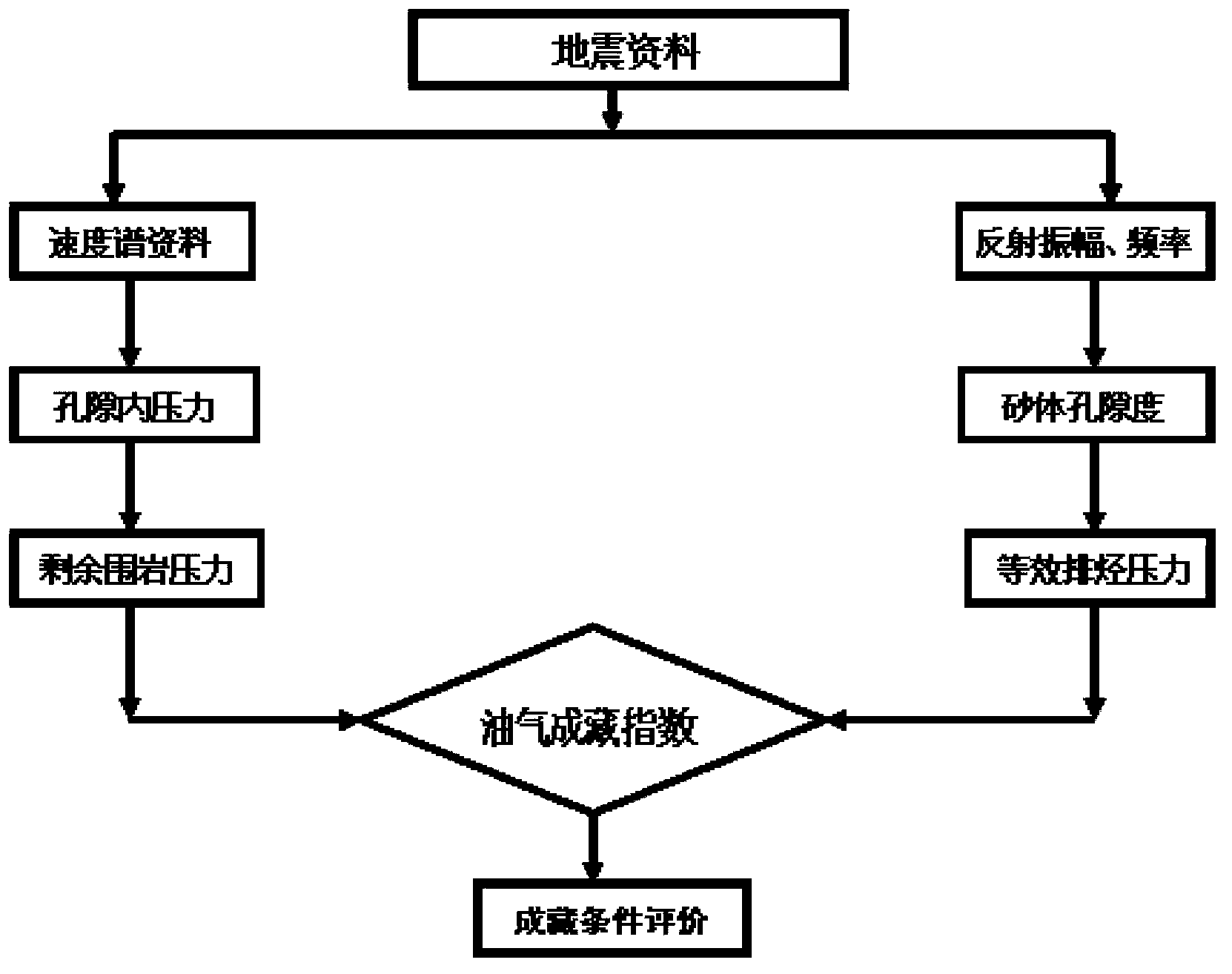
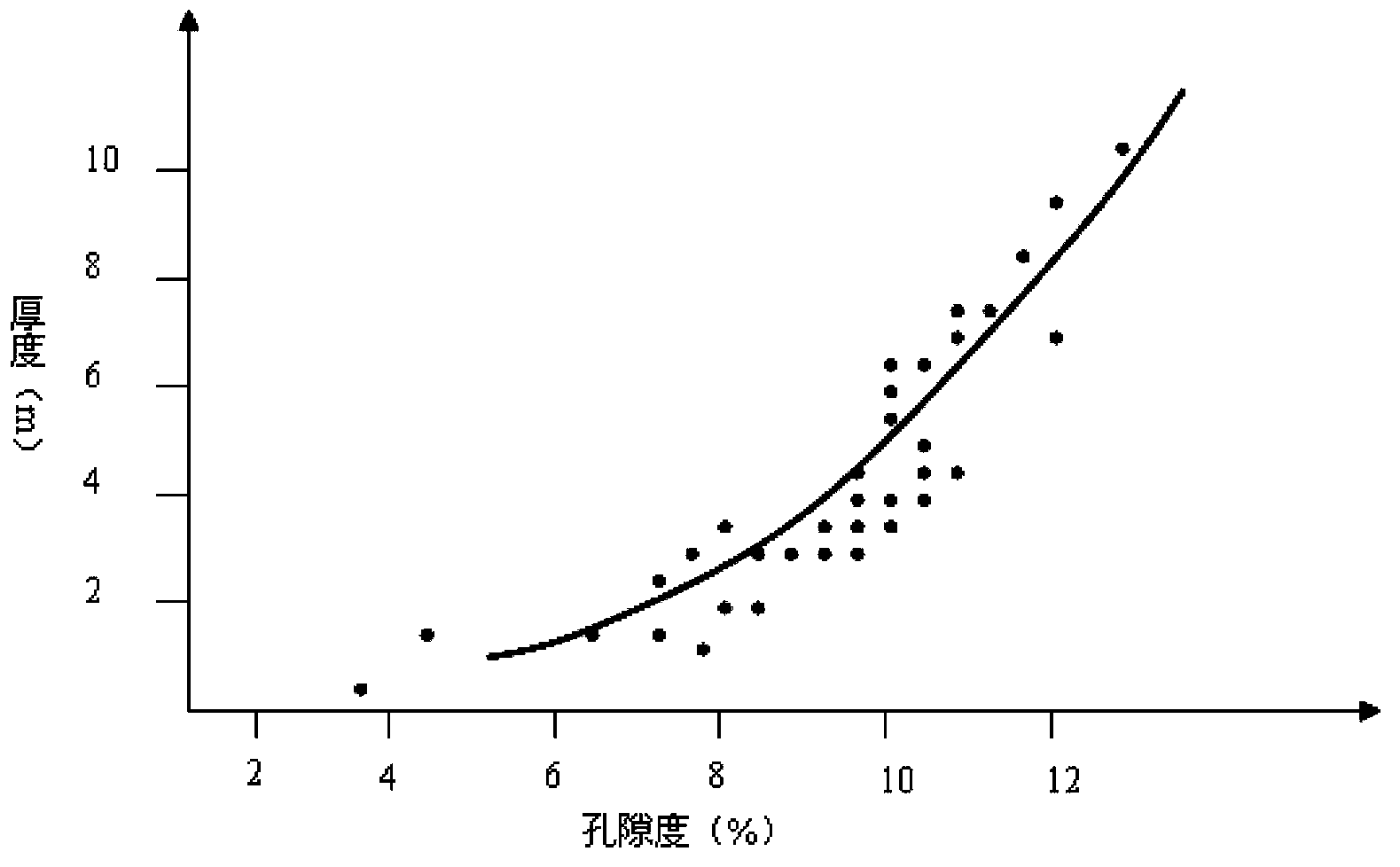
ActiveCN103777245ARealize Quantitative PredictionImprove exploration efficiencySeismic signal processingPorosityWell drilling
The invention is a method of quantitative evaluation on oil and gas accumulation conditions based on seismic data. According to the evaluation method, a mathematical model between seismic parameters such as seismic interval velocity and sandstone lens body reflection amplitude and hydrocarbon source rock residual pressure and equivalent hydrocarbon expulsion pressure is determined, the seismic interval velocity is acquired through seismic data correcting, and the hydrocarbon source rock residual pressure of a sandstone lens body is acquired according to the seismic interval velocity. Further, the sand body porosity is acquired according to the true thickness of the sandstone lens body, the equivalent hydrocarbon expulsion pressure is acquired according to the sand body porosity, and the oil and gas accumulation index of the sandstone lens body is acquired according to the hydrocarbon source rock residual pressure and the equivalent hydrocarbon expulsion pressure, thus completing quantitative evaluation on oil and gas accumulation conditions of the sandstone lens body. Quantitative evaluation on accumulation conditions of the sandstone lens body is realized with the use of the seismic parameters under the condition of lack of drilling and logging data, and the efficiency of exploration is improved.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Error checkpoint positional information automatic identification method based on big data analysis
ActiveCN105336164AImprove accuracyBig amount of dataDetection of traffic movementPath lengthData profiling
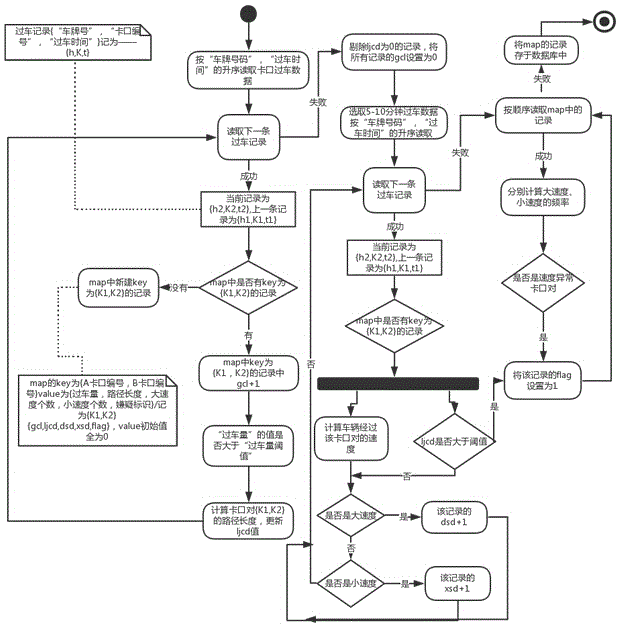
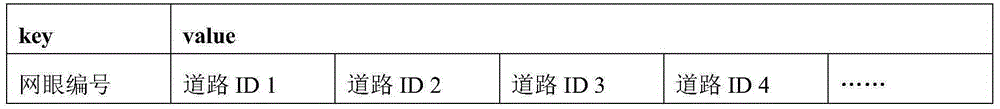
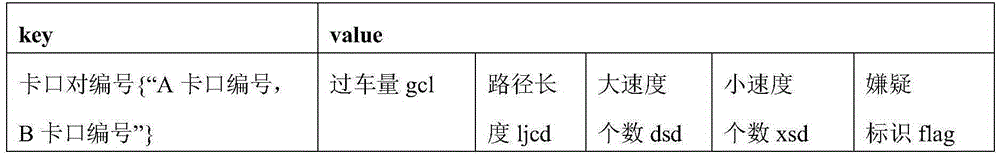
The invention discloses an error checkpoint positional information automatic identification method based on big data analysis. The method comprises the steps of: calculating adjacent checkpoint pairs according to mass historical checkpoint vehicle passing data, calculating the shortest path length of the adjacent checkpoint pairs by combining with GIS map data, and calculating passing speed of vehicles between the checkpoint pairs through vehicle data; and finding out the checkpoint with error positional information according to checkpoint shortest path abnormity, checkpoint interval velocity abnormity and abnormal frequency iteration in sequence. The error checkpoint positional information automatic identification method utilizes real checkpoint vehicle passing data, and has the advantages of large data size, high data accuracy and the like, thus the accuracy of error checkpoint positional information analyzed according to attributes of vehicle passing data is high. The error checkpoint positional information automatic identification method achieves the automatic identification of the error checkpoint positional information, has the advantages of fast execution speed, high accuracy, high efficiency and the like, and omits a great deal of manual identification.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
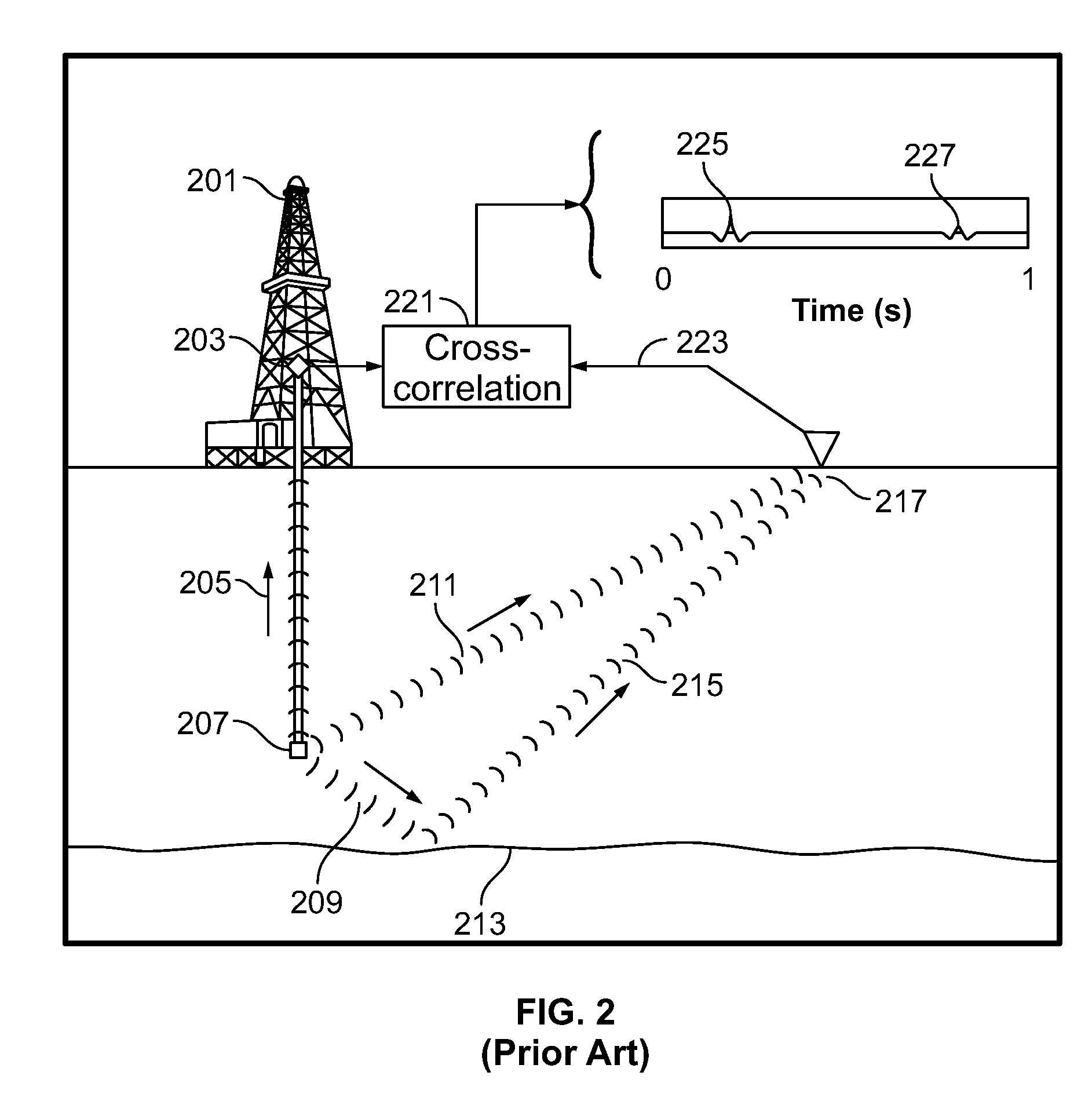
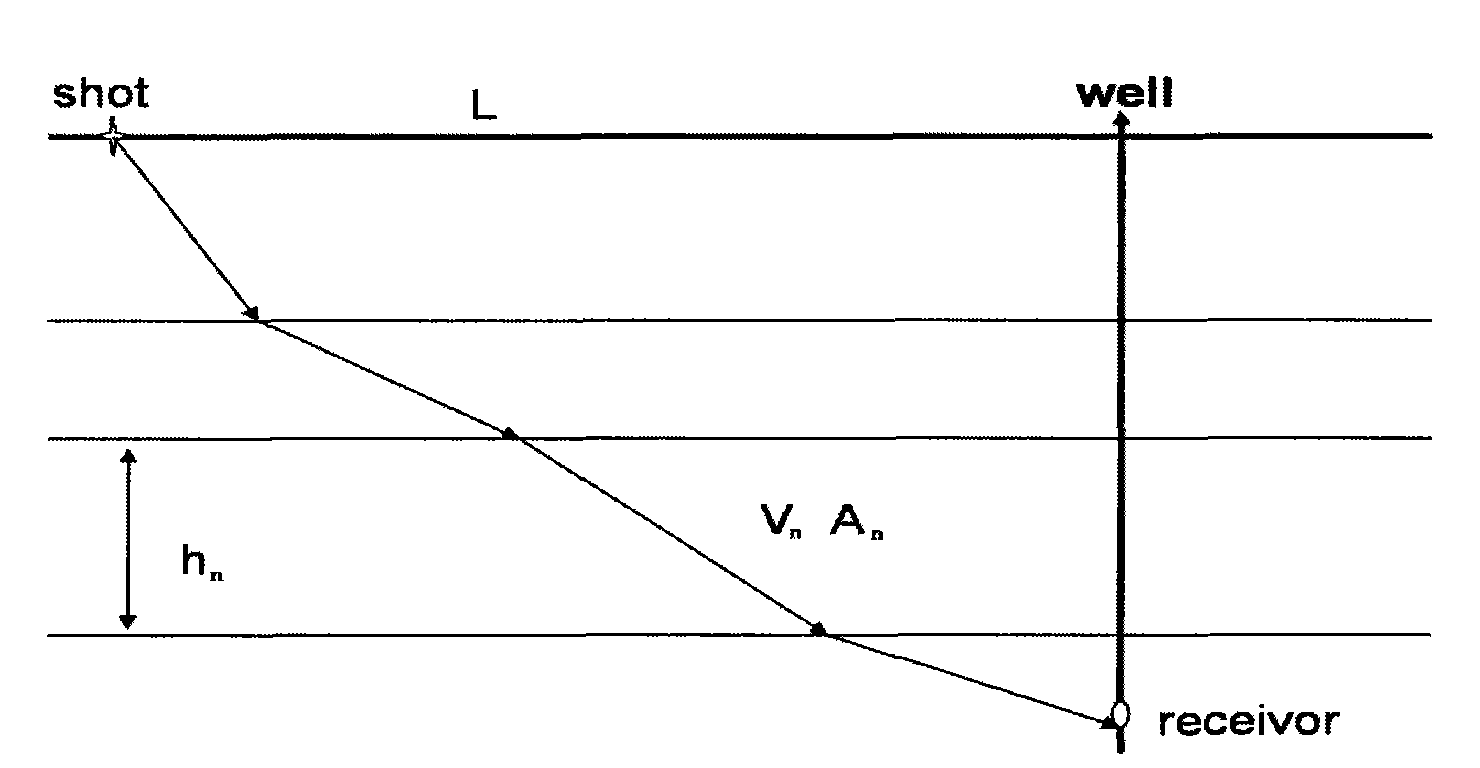
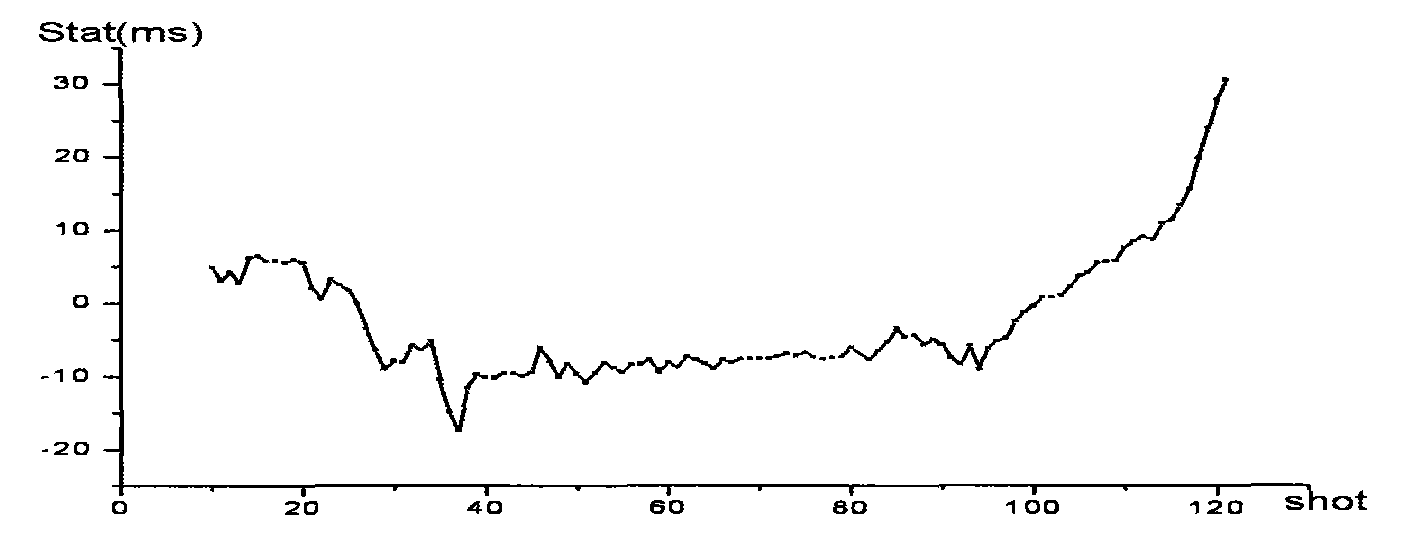
Method for calculating shot-static correction for two-dimensional vertical seismic section data
ActiveCN101598811AImprove processing qualityOvercoming the disadvantages of insufficient static correction accuracySeismic signal processingInvestigation methodsOriginal data
The invention relates to a method for calculating shot-static correction for two-dimensional vertical seismic section data in geophysical exploration. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out first arrival picking on zero-offset vertical seismic section data to obtain an interval velocity at the depth of an observation point; picking the direct wave first arrival of a longitudinal wave of the two-dimensional vertical seismic section; carrying out three-component polarimetric analysis on the original data of the two-dimensional vertical seismic section; carrying out rotation processing; back calculating the static correction amount of each shot of the two-dimensional vertical seismic section data; and moving the amplitude of each track of seismic data points to finish the static correction. The invention does not need field near-surface investigation, overcomes the defects that the field investigated points are sparse, the obtained static correction is not precise enough, and the investigated depth is shallower of the field near-surface investigation method and improves the processing quality of the vertical seismic section.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +1
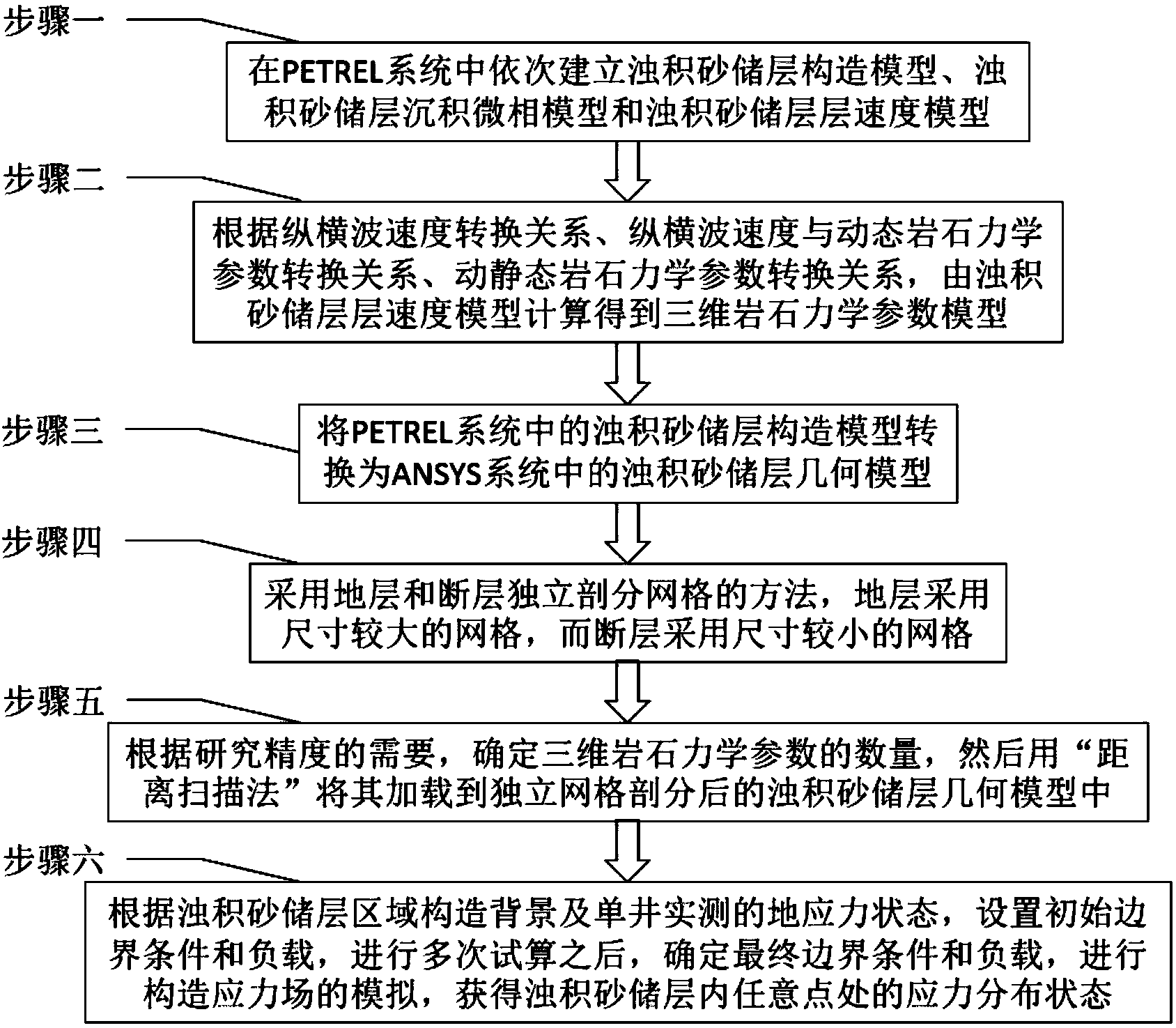
High-precision tectonic stress field simulation method applicable to turbidite sand low-permeability reservoirs
InactiveCN103838936AHigh precisionSolve rationalitySpecial data processing applicationsStress distributionTectonic stress
The invention provides a high-precision tectonic stress field simulation method applicable to turbidite sand low-permeability reservoirs and belongs to the field of tectonic stress field simulation technologies. The high-precision tectonic stress field simulation method aims at solving the problems that the high-precision simulation can not be carried out on the turbidite sand low-permeability reservoirs to direct well network deployment in the oilfield development process and improve the development effect of the low-permeability reservoirs through an existing tectonic stress field simulation method. The method includes the first step of establishing a turbidite sand reservoir tectonic model and a turbidite sand reservoir interval velocity model in a PETREL system, the second step of obtaining a three-dimensional rock mechanics parameter model through calculation on the turbidite sand reservoir interval velocity model, the third step of converting the turbidite sand reservoir tectonic model in the PETREL system to a turbidite sand reservoir geometric model in an ANSYS system, the fourth step of carrying out independent mesh subdivision on a stratum and a geologic fault; the fifth step of loading rock mechanics parameters through a range scanning mode, and the sixth step of carrying out simulation on a tectonic stress field to obtain stress distribution states of any point in the turbidite sand low-permeability reservoirs. The method is used for simulating the tectonic stress field in the turbidite sand low-permeability reservoirs.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Method for three dimensional seismic travel time tomography in transversely isotropic media
A method for estimating seismic velocities in vertically transversely isotropic media includes generating an initial estimate of vertical interval velocity and interval normal moveout velocity with respect to depth from seismic data. An initial estimate is generated of a first anisotropy parameter with respect to depth. The first anisotropy parameter is related to the interval normal moveout velocity and the interval vertical velocity. An initial estimate is generated with respect to depth of a second anisotropy parameter. The second anisotropy parameter is related to the first anisotropy parameter and an interval anelliptic parameter. A first tomographic inversion is performed with respect to the interval normal moveout velocity and the second anisotropy parameter at a constant value of the first anisotropy parameter until travel time differentials reach minimum values. Layer depths are adjusted with the initial estimate of vertical interval velocity. Using values of the second anisotropy parameter determined in the first tomographic inversion, a second tomographic inversion is performed of interval normal moveout velocity and the first anisotropy parameter with respect to depth. The adjusted layer depths, interval normal moveout velocities and interval vertical velocities are again adjusted and interval anelliptic parameters are calculated from the second tomographic inversion.
Owner:PGS GEOPHYSICAL AS
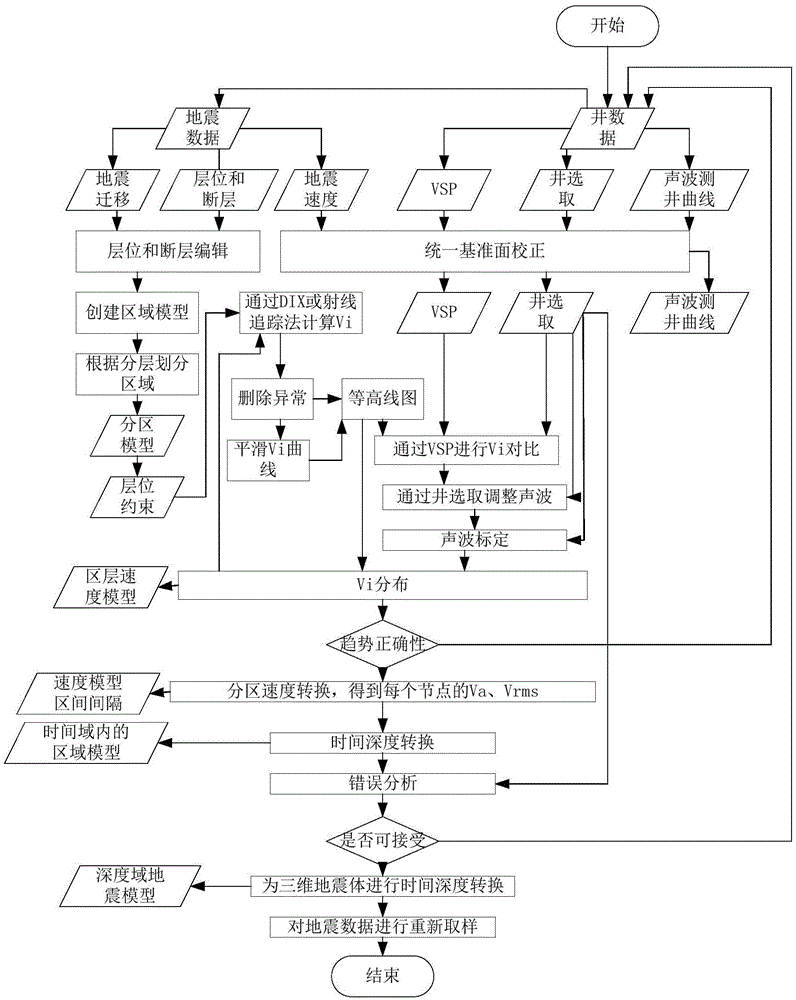
Method and system for building three-dimensional high-precision velocity model
The invention relates to the technical field of earthquake velocity model building and discloses a method for building a three-dimensional high-precision velocity model. The method comprises following steps: geological information such as sonic logging data is acquired, interval velocity Vi is calculated on the basis of a time domain framework model through interpreting and analyzing the acquired information, and the interval velocity Vi is processed and constrained; the model is interpreted in combination with the time domain construction, statistics is performed to the interval velocity Vi according to the geological information, and the distribution rule of the interval velocity Vi is analyzed; two-dimensional horizons and the interval velocity Vi are filled in the three-dimensional framework; mean square root velocity and average velocity of a certain layer are calculated by use of the interval velocity Vi inserted into the model. The method and system make the process of converting an earthquake interpretation result from a time domain to a depth domain more efficient and accurate; timely maintenance and update can be realized when the geological information changes; the cost for enlarging the scope of the model is reduced.
Owner:东营康帕斯石油科技有限公司
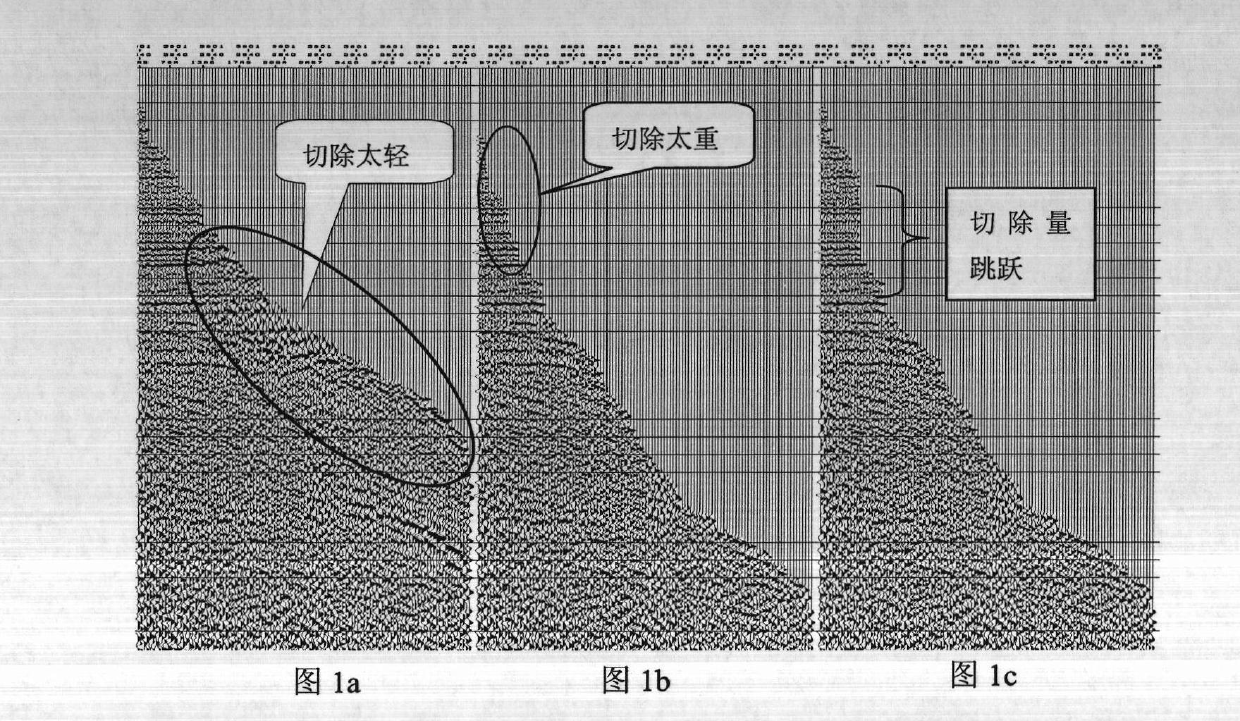
Normal moveout stretch cutting method for processing geophysical exploitation seismic data
ActiveCN102636813AHigh resolutionImprove signal-to-noise ratioSeismic signal processingGeophoneNormal moveout
The invention provides a normal moveout stretch cutting method for processing geophysical exploitation seismic data. According to the method, a stacking velocity field is utilized, average speed is calculated, or interval velocity is calculated after smoothing the average speed. Further, by using the velocity and shot-geophone distance information, approximate calculation of an incident angle is performed according to the theory of ray (straight ray or curved ray) propagated by seismic wave, and a 1D or 3D space varying incident angle threshold value reference is used as a standard of measurement to determine the cut of each seismic channel. Thus, more accurate automatic cutting of the normal moveout stretch is realized, the interference caused by net normal moveout stretch can be cut, effective wave amplitude can also be protected to the greatest extent, and finally, the resolution and the signal-noise ratio of a stacked section are improved.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Well-constrained velocity spectrum pickup method for low-SNR (signal-to-noise ratio) seismic data
ActiveCN104570103AHigh precisionReduce blindnessSeismic signal processingContinuationSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
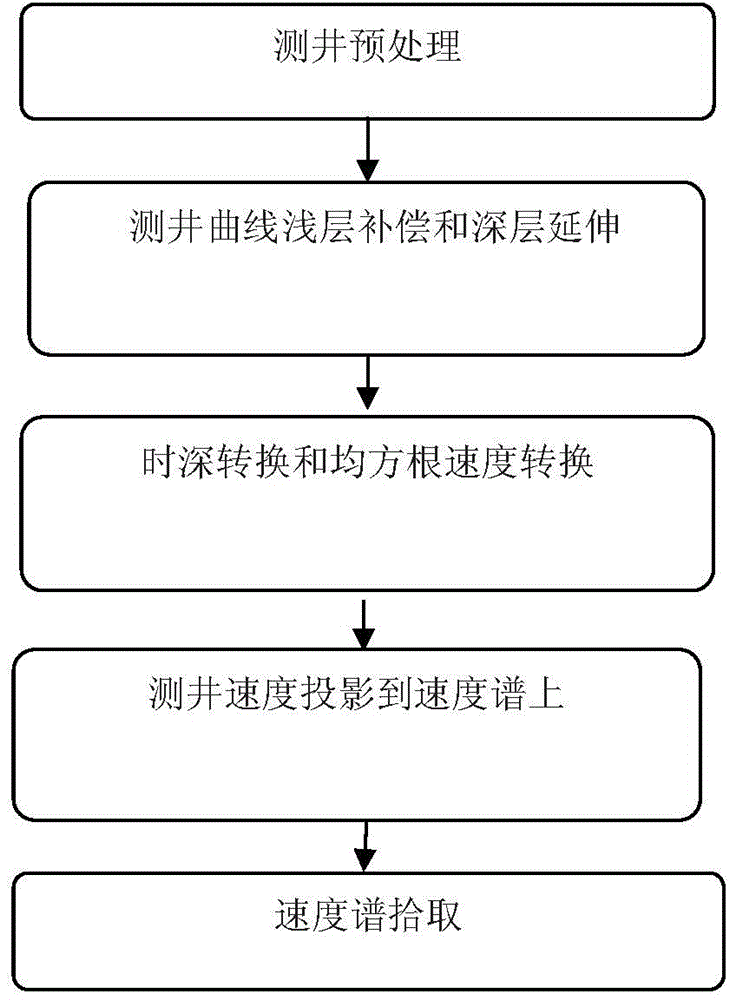
The invention provides a well-constrained velocity spectrum pickup method for low-SNR (signal-to-noise ratio) seismic data, and belongs to the field of seismic data processing. The method comprises (1), well logging preprocessing: input interval transit time or acoustic velocity is corrected, and a corrected acoustic velocity is obtained; (2), acoustic logging data shallow layer compensation and downward extension processing are performed on the corrected acoustic velocity, and the acoustic velocity subjected to shallow layer compensation and downward extension is obtained; (3), time-depth conversion is performed on the acoustic velocity subjected to shallow layer compensation and downward continuation to obtain an interval velocity, and the interval velocity is subjected to root-mean-square velocity conversion to obtain a root-mean-square velocity; (4), projection of the root-mean-square velocity on the velocity spectrum is acquired. With adoption of the method, pickup randomness is reduced, and the velocity pickup accuracy is improved.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Method for predicating pre-stack fracture within common offset and common azimuth domains
ActiveCN104570086AImprove forecast accuracyPrinciples of ScienceSeismic signal processingHorizonEllipse
The invention provides a method for predicating a pre-stack fracture within common offset and common azimuth domains, and belongs to the technical field of oil exploration fracture prediction. The method comprises the following steps: collecting seismic data; performing independent pre-stack migration on all of the common offset and common azimuth domains obtained from the seismic data; carrying out horizon interpretation, wherein obtained CRP (Common Reflection Point) gathers are stacked to obtain a result data body, and the top and the bottom of a target zone are subjected to horizon interpretation; segmenting the CRP gathers, wherein a position partition scheme is determined according to a development direction of a main fracture in a work area, and the CRP gathers are segmented into n groups of sub-CRP gathers according to azimuth information in the CRP gathers; stacking sub-positions, wherein all of the CRP gathers are stacked to obtain n seismic traces, and the n stacked seismic traces are merged together to form a new CRP position gather; converting residual interval moveout to a root-mean-square velocity; converting the new root-mean-square velocity to an interval velocity; performing ellipse fitting to obtain velocities and directions of fast and slow waves; calculating the fracture density.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
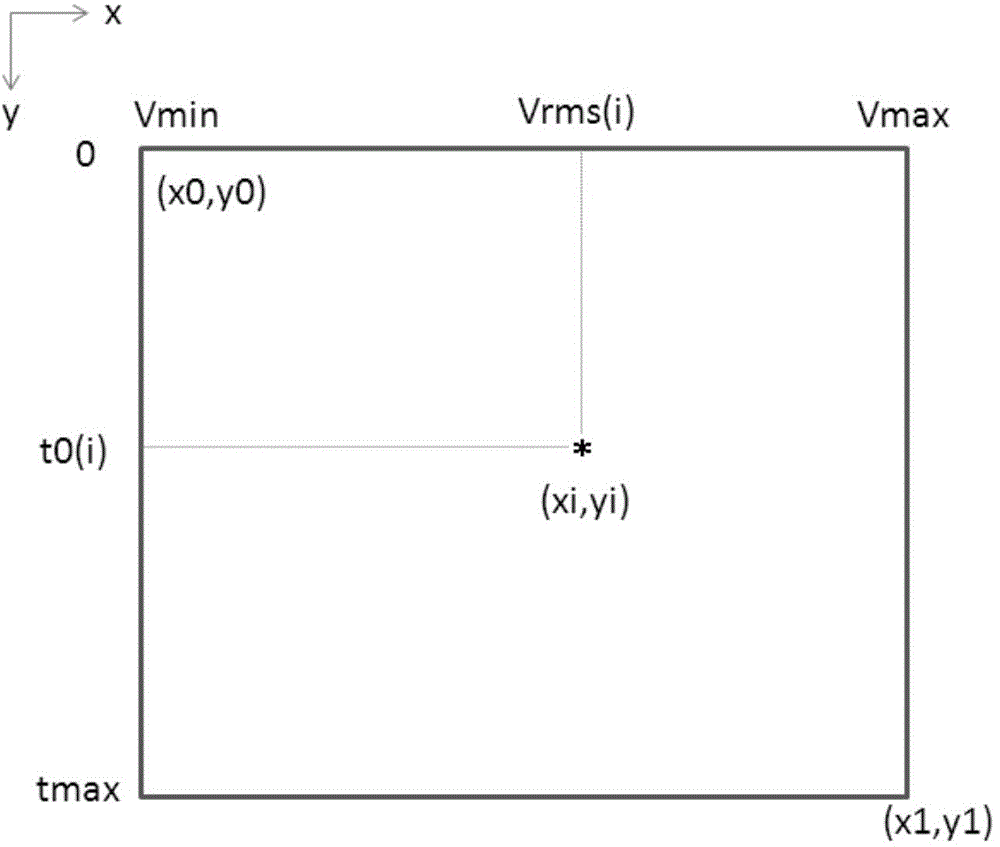
Modeling method of depth domain interval velocity initial model
The present invention discloses a modeling method of a depth domain interval velocity initial model. The method comprises the steps of rejecting the inaccurate root-mean-square velocity in a time domain root-mean-square velocity model, and obtaining a corrected time domain root-mean-square velocity model; carrying out inversion on the corrected time domain root-mean-square velocity model, and obtaining a corresponding time domain interval velocity model; carrying out the prediction interpolation on the interval velocity corresponding to the inaccurate root-mean-square velocity in the time domain interval velocity model by taking the horizon time of the seismic horizons as a constraint condition, and obtaining a corrected time domain interval velocity model; converting the corrected time domain interval velocity model from a time domain to a depth domain, and obtaining the depth domain interval velocity initial model. The modeling method provided by the present invention can eliminate an error brought by the inaccurate root-mean-square velocity during a calculation process of time domain root-mean-square velocity-to-depth domain interval velocity conversion, thereby achieving the purpose of improving the prestack depth migration imaging quality by improving the precision of the depth domain interval velocity initial model. The modeling method of the present invention can be widely used for processing the oil-gas exploration actual seismic data information.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Near-surface shear wave interval velocity model establishment method
ActiveCN107561589AImprove accuracyHigh precision dispersion dataSeismic signal processingApparent velocitySurface shear
The invention discloses a near-surface shear wave interval velocity model establishment method. The method includes: A, sorting original shot point arrangement data according to a preset spatial sampling interval and source-receiver azimuth to acquire input data; B, analyzing the input data to acquire pure surface wave data; C, calculating surface wave dispersion data of a receiving point according to the pure surface wave data; D, correcting velocity parameters of the surface wave dispersion data of the receiving point from surface azimuth apparent velocity to true velocity according to a surface inclination angle of the source-receiver azimuth; E, subjecting surface wave dispersion data of each co-receiving point to true velocity curve statistics to form unique dispersion data of each co-receiving point; F, calculating a near-surface shear wave interval velocity model according to the unique dispersion data of each co-receiving point. The near-surface shear wave interval velocity model established according to the method is high in accuracy, three-dimensional seismic data surface waves can be effectively extracted while high-precision dispersion data are acquired, and converted shear wave correction accuracy in multiwave seismic data processing is improved.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com