Patents
Literature
172 results about "Seismic velocity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
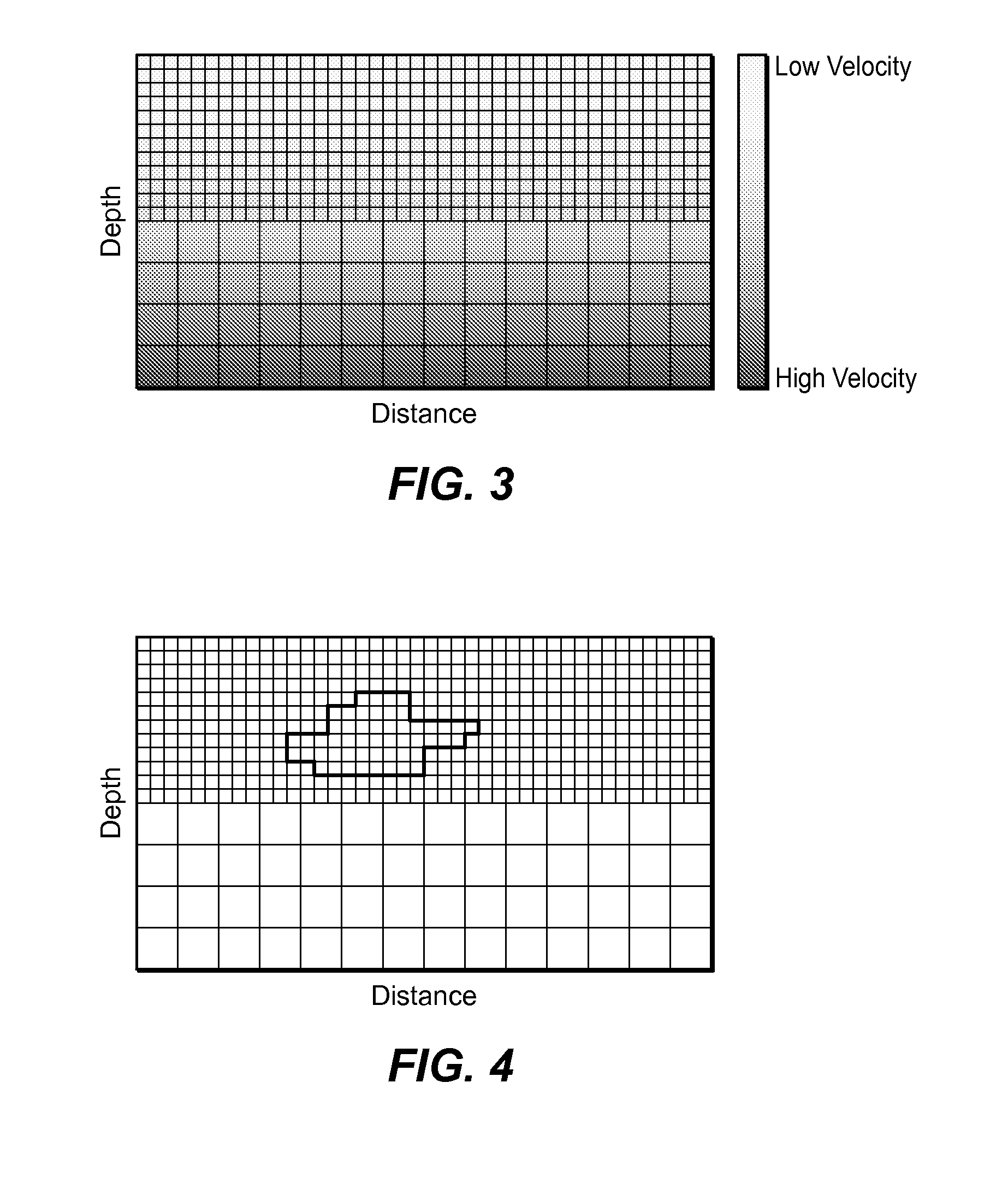
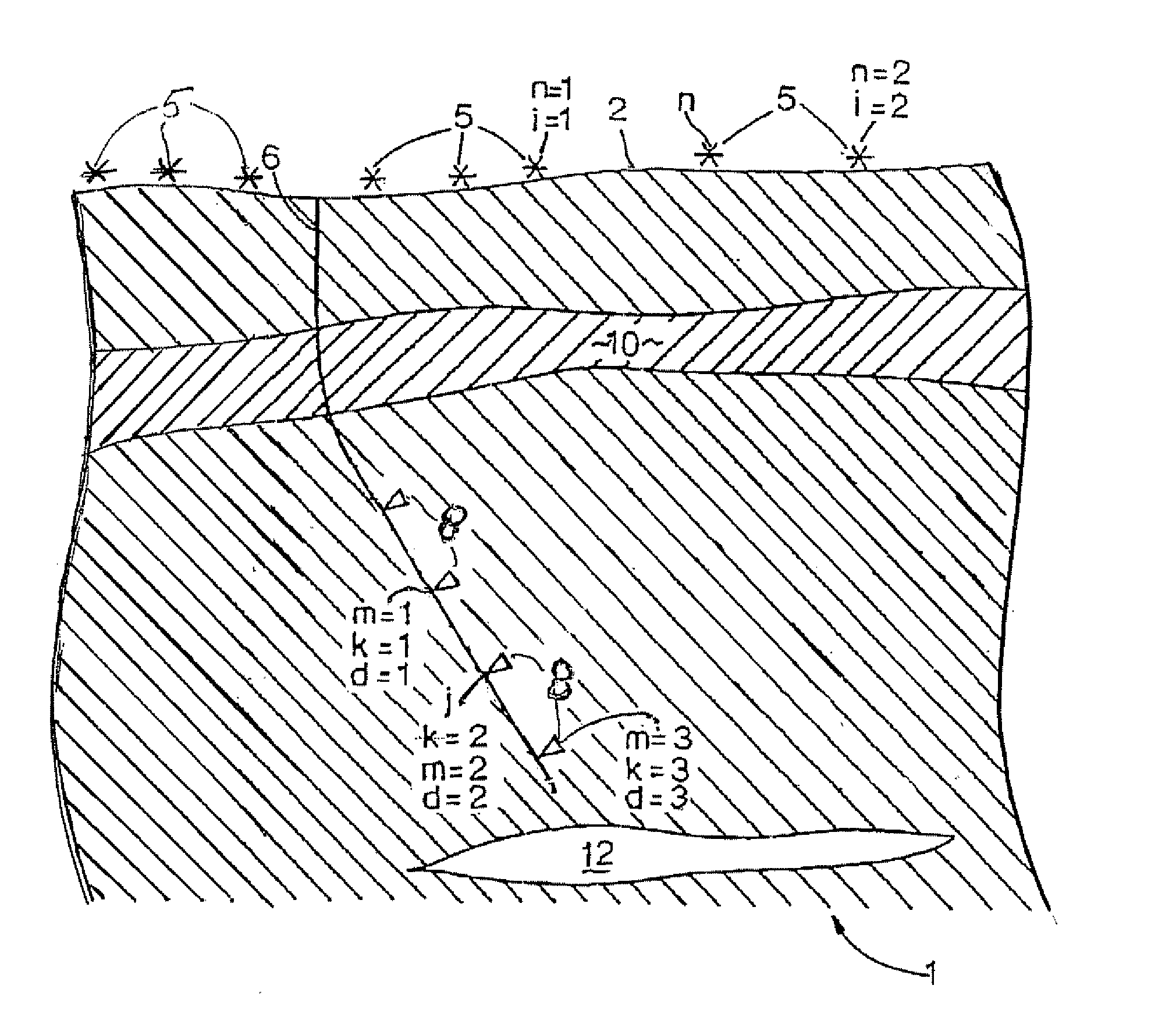
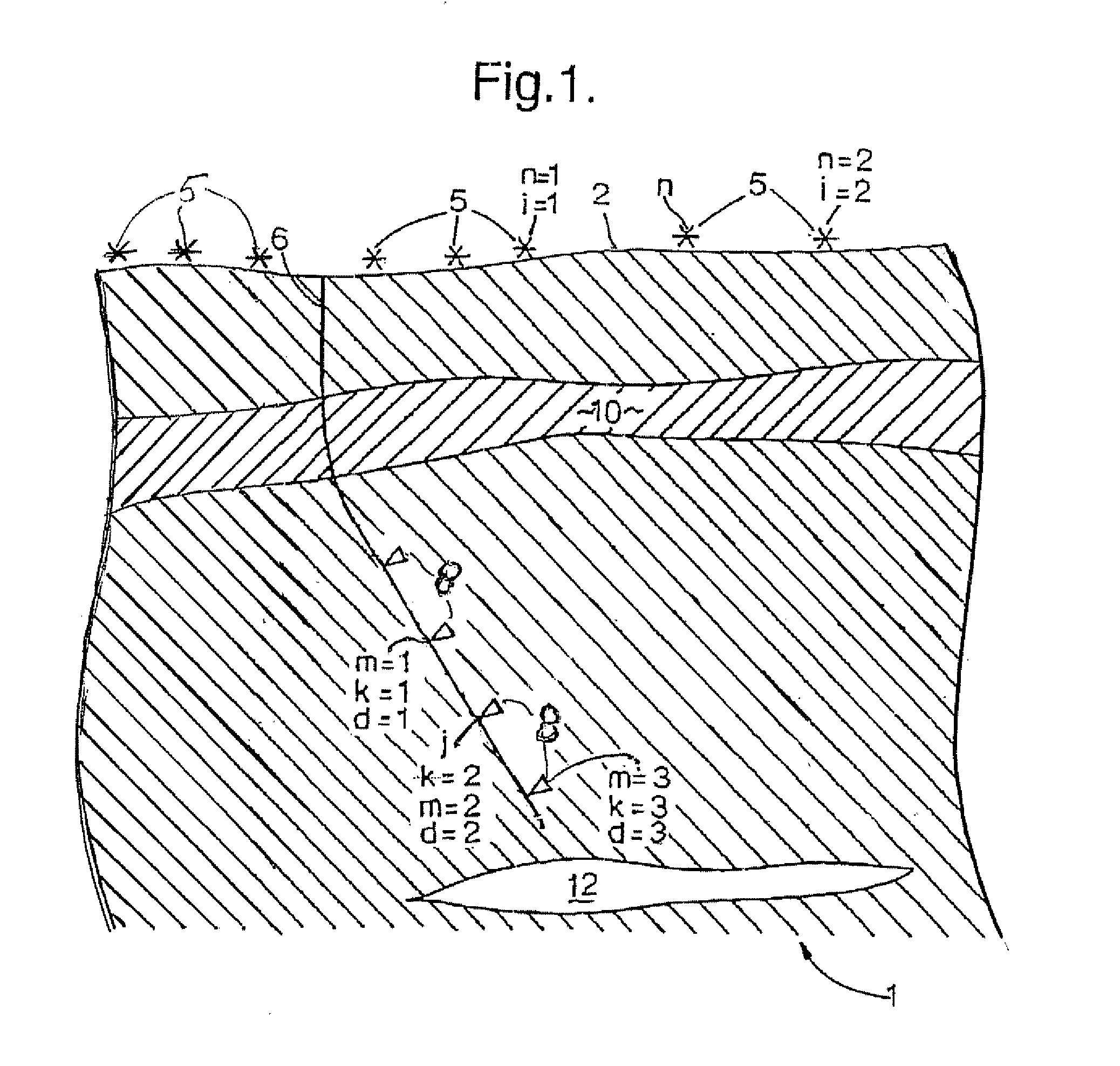
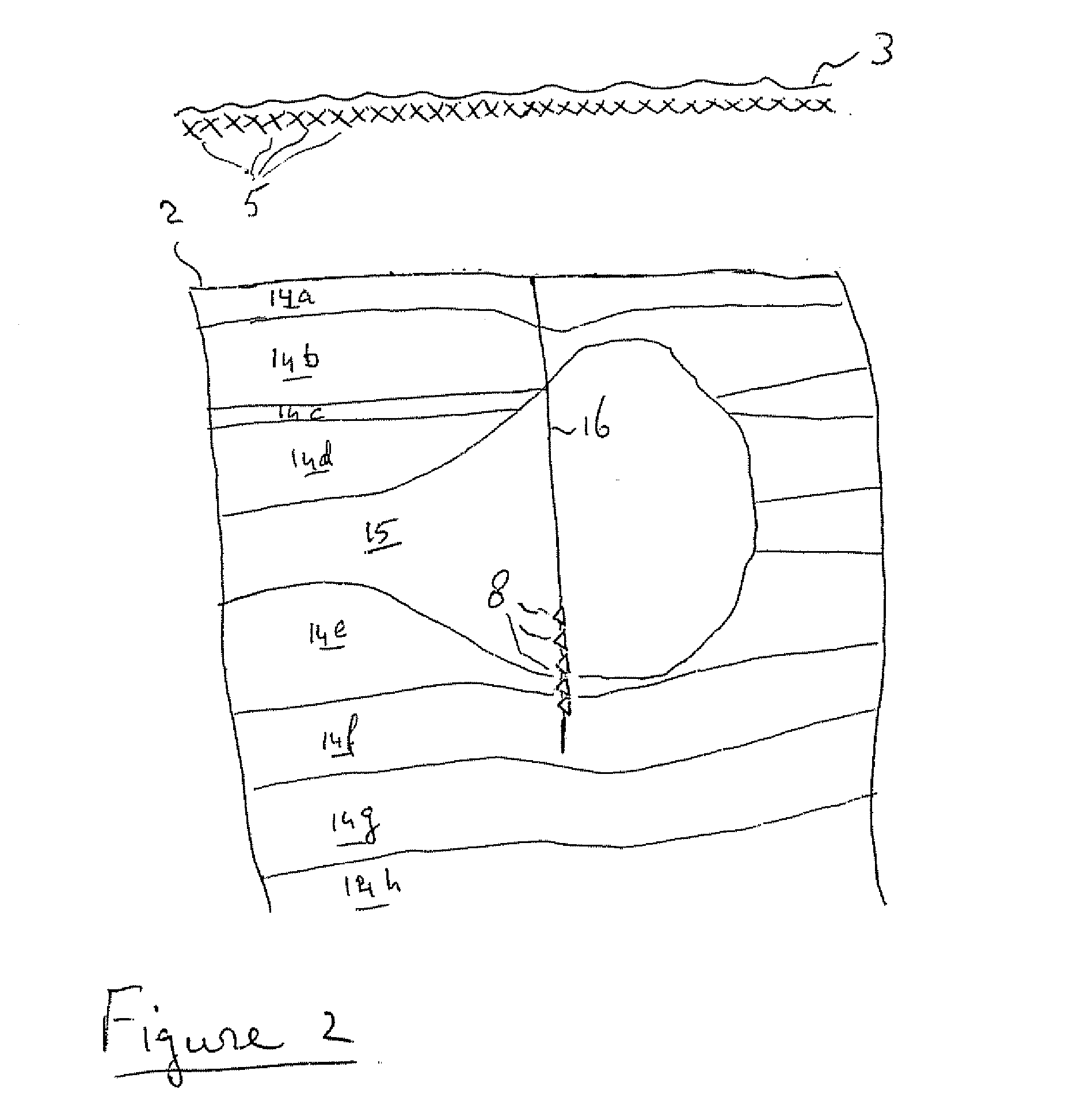
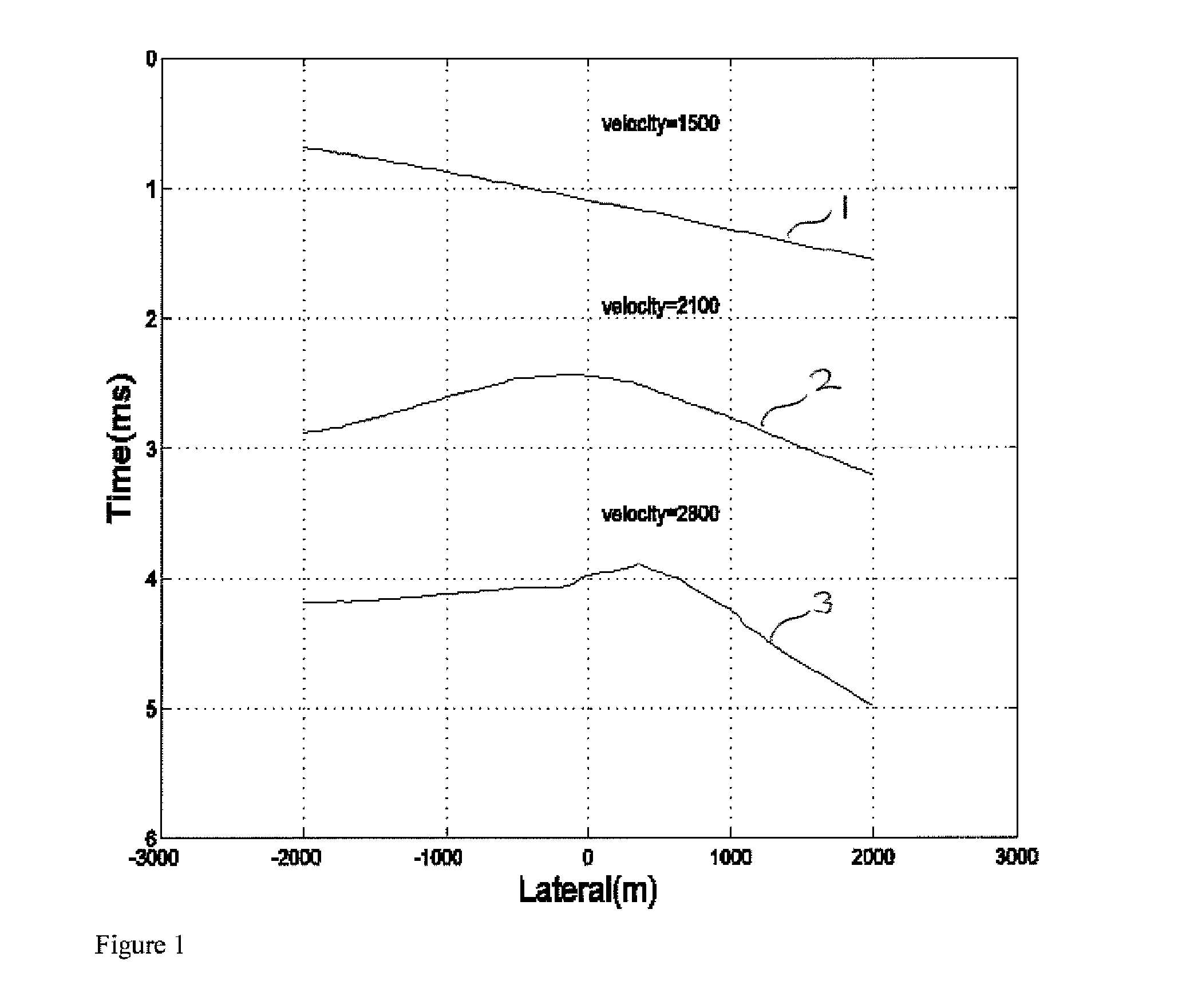
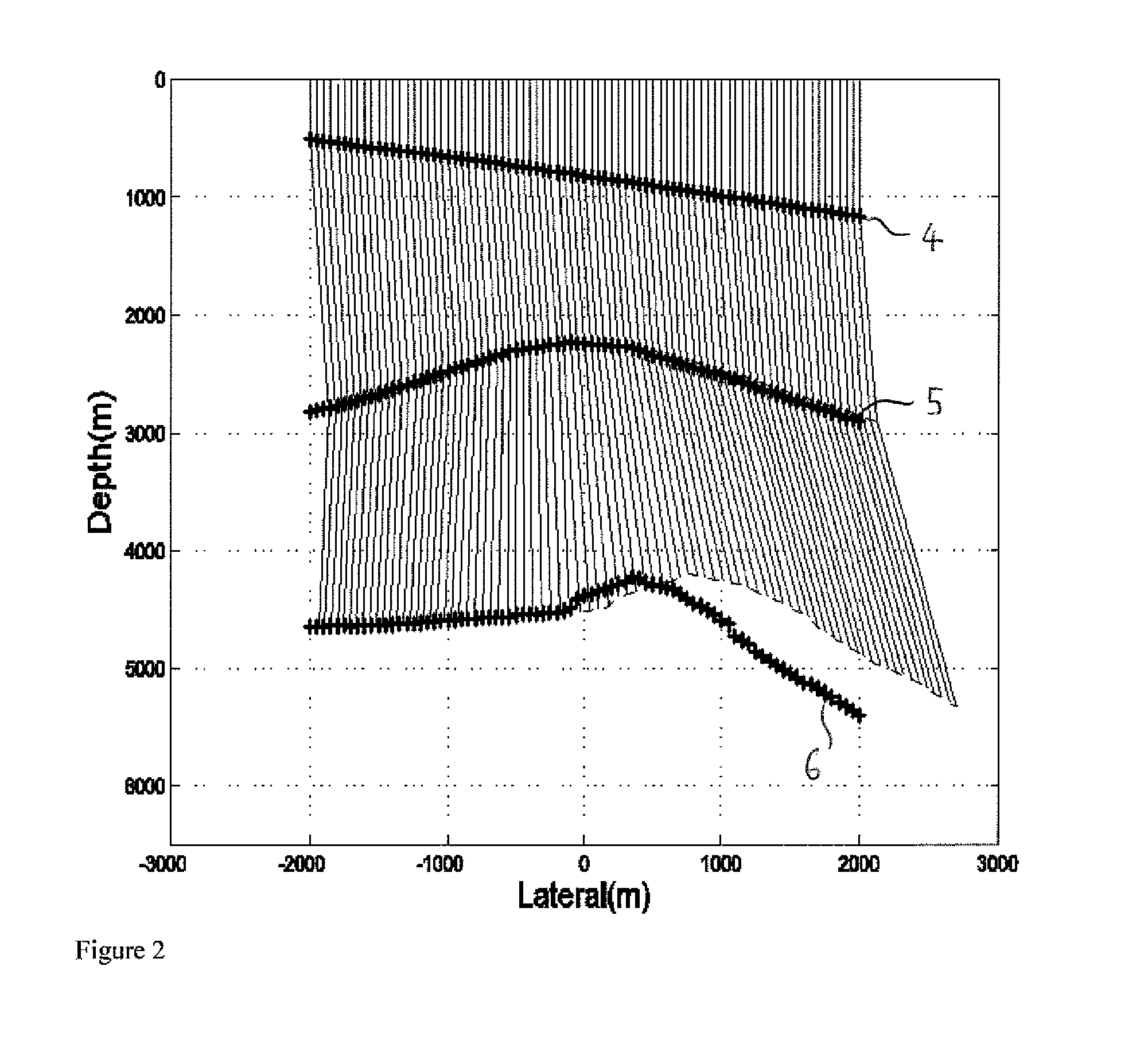
Seismic velocity is a vector magnitude which varies laterally, vertically and azimuthally in an anisotropic (property dependable of the direction in which it is measured) medium. It is directly proportional to depth in the Earth.
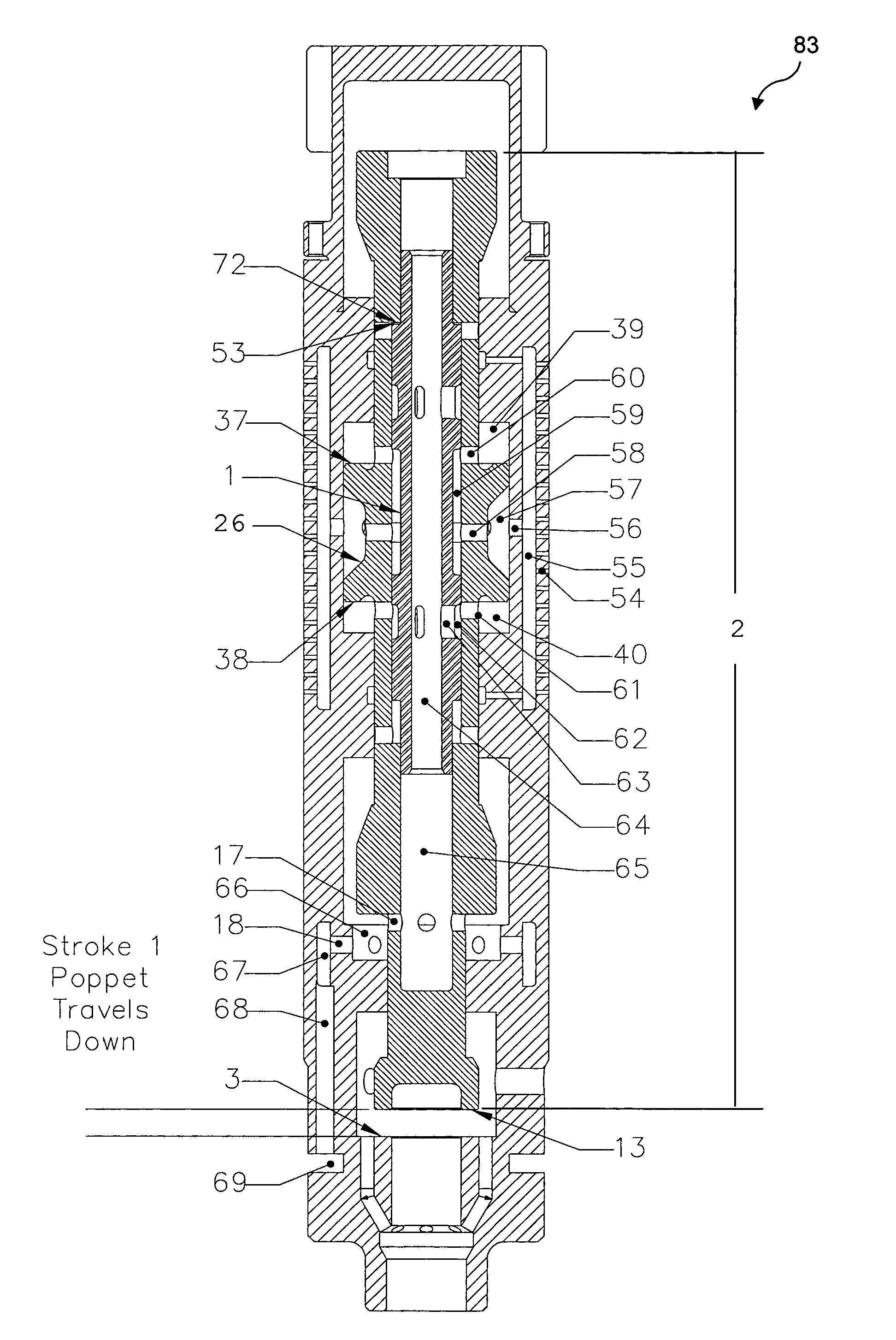
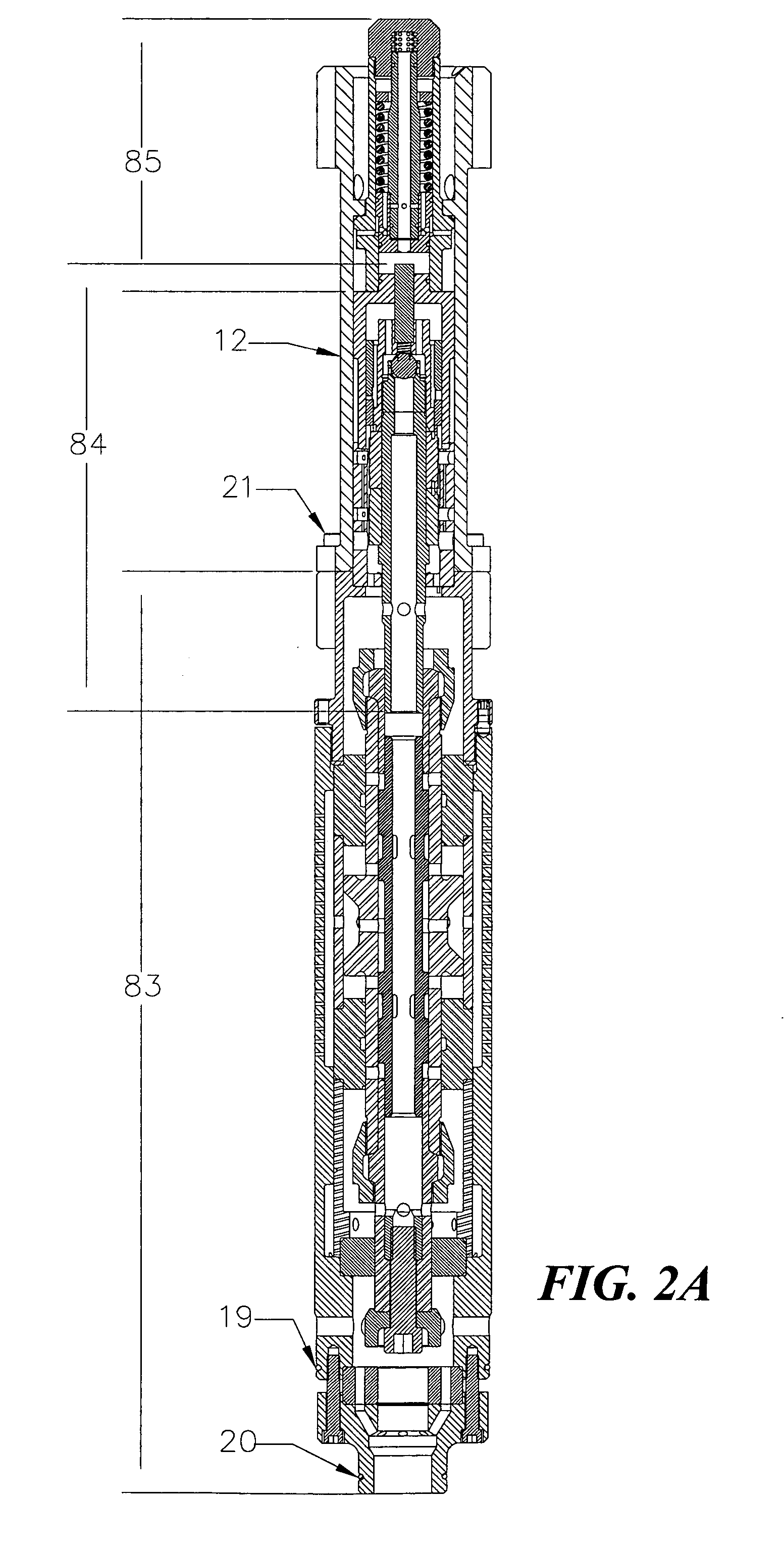
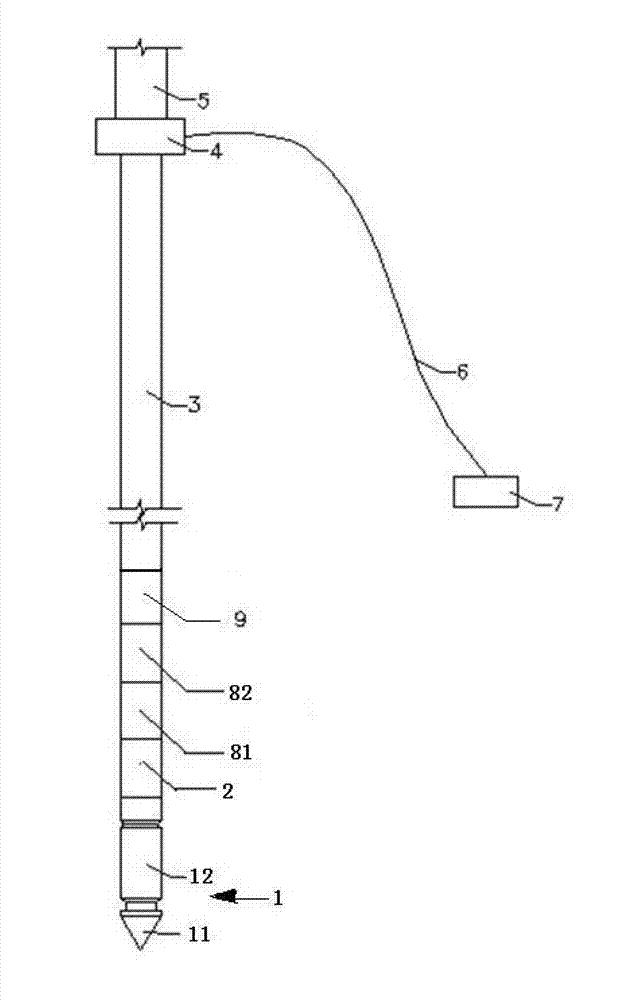
Hydraulic impulse generator and frequency sweep mechanism for borehole applications
This invention discloses a valve that generates a hydraulic negative pressure pulse and a frequency modulator for the creation of a powerful, broadband swept impulse seismic signal at the drill bit during drilling operations. The signal can be received at monitoring points on the surface or underground locations using geophones. The time required for the seismic signal to travel from the source to the receiver directly and via reflections is used to calculate seismic velocity and other formation properties near the source and between the source and receiver. This information can be used for vertical seismic profiling of formations drilled, to check the location of the bit, or to detect the presence of abnormal pore pressure ahead of the bit. The hydraulic negative pressure pulse can also be used to enhance drilling and production of wells.
Owner:WELLS FARGO BANK NAT ASSOC +1
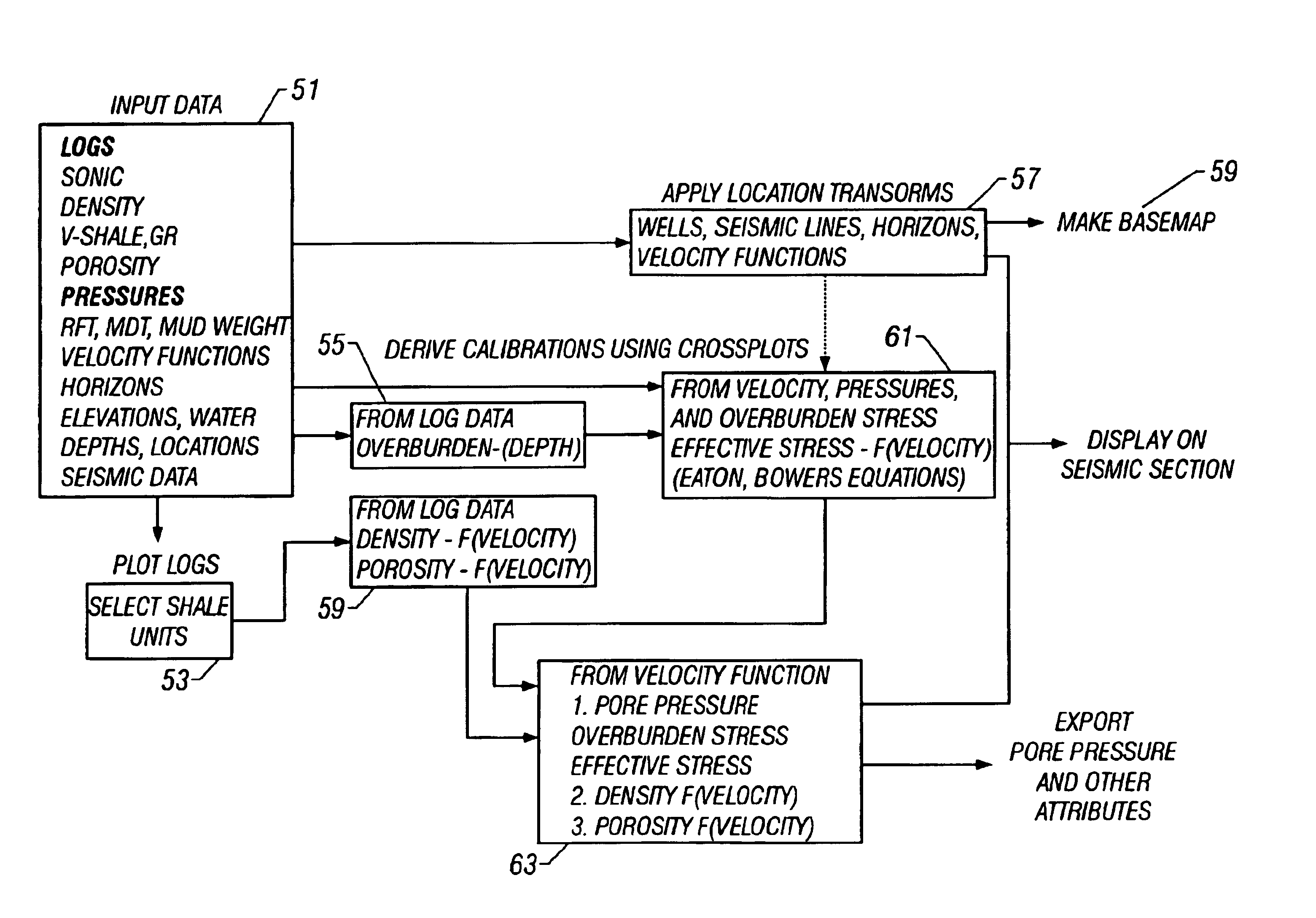
Method and process for prediction of subsurface fluid and rock pressures in the earth
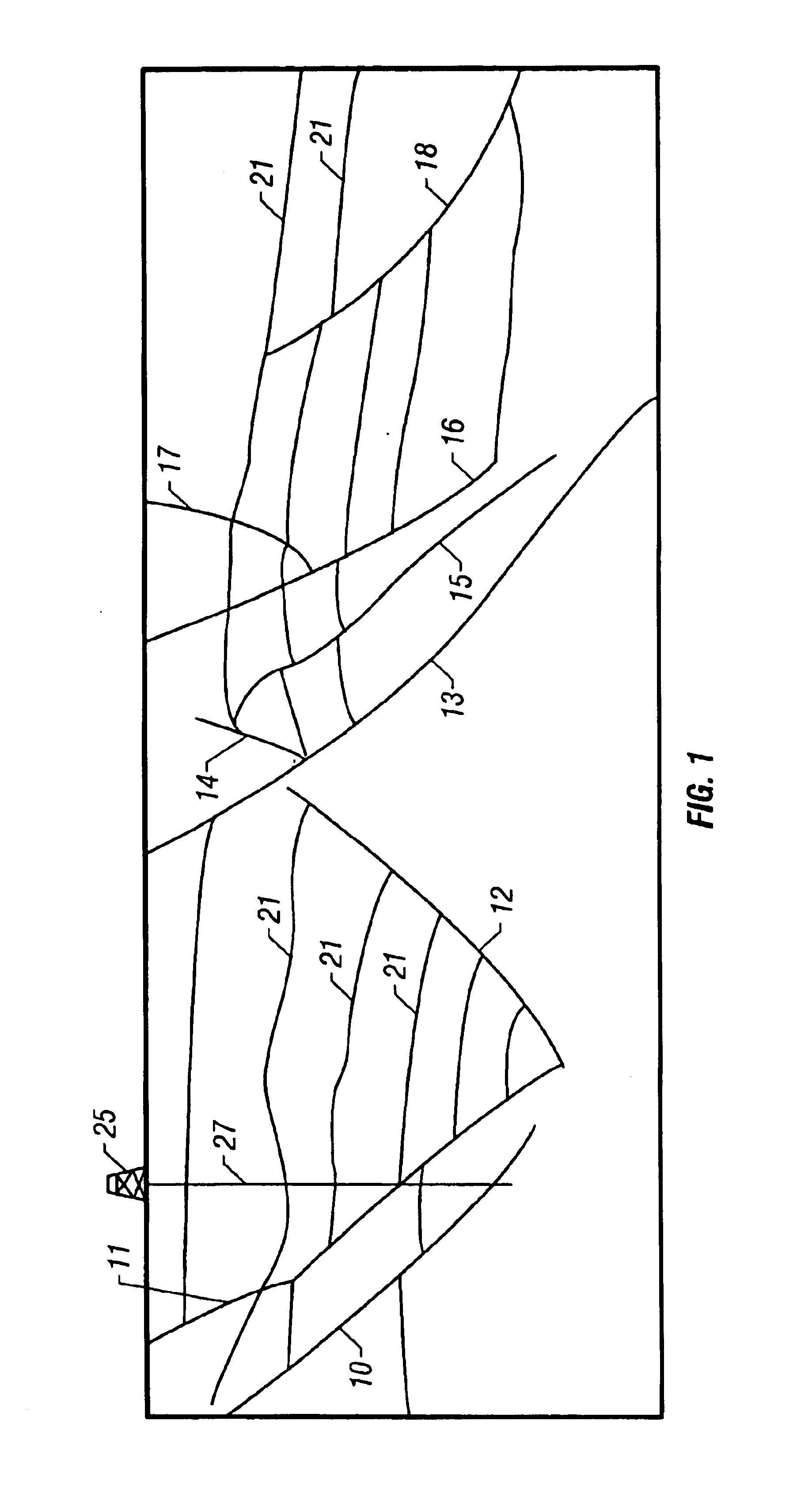
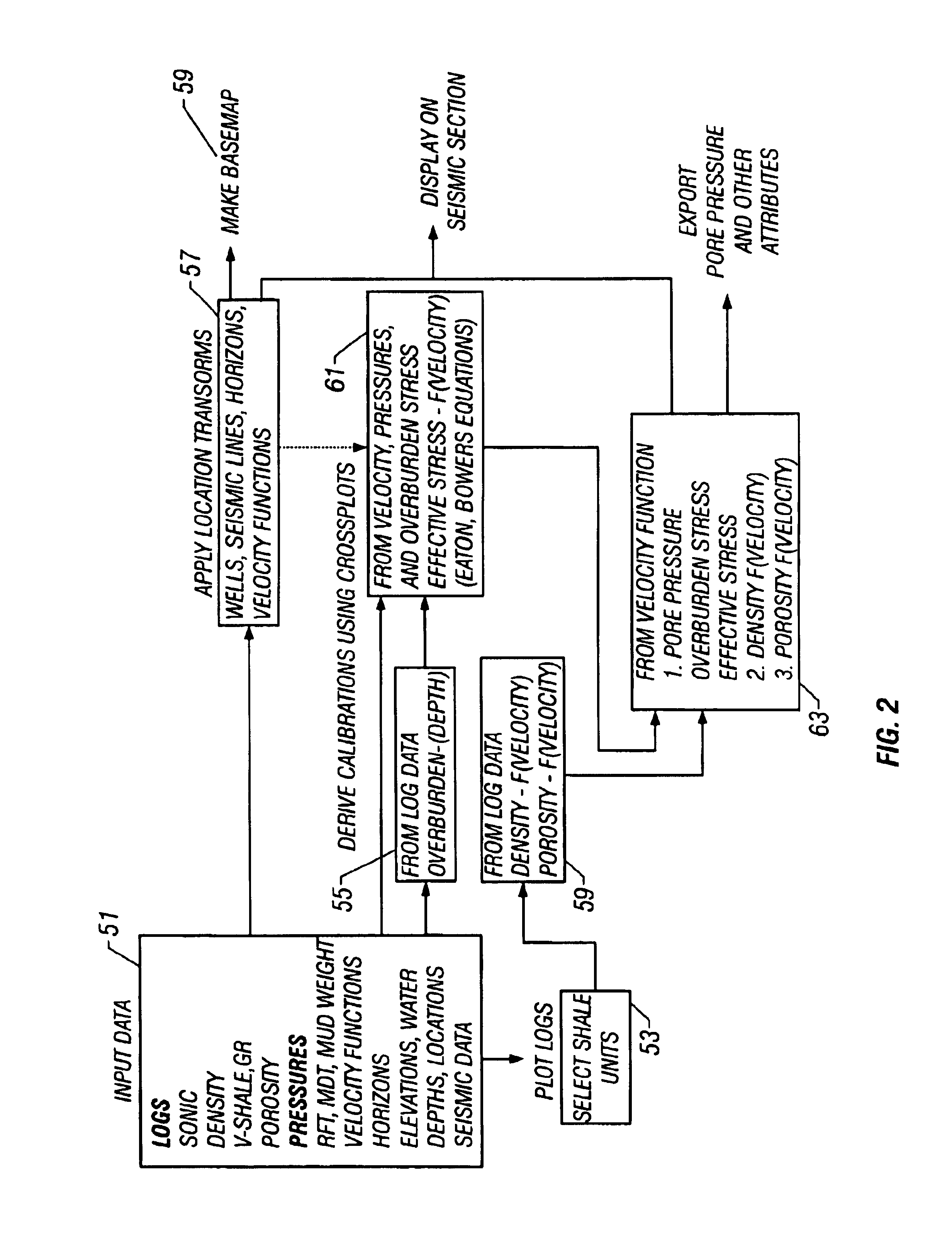
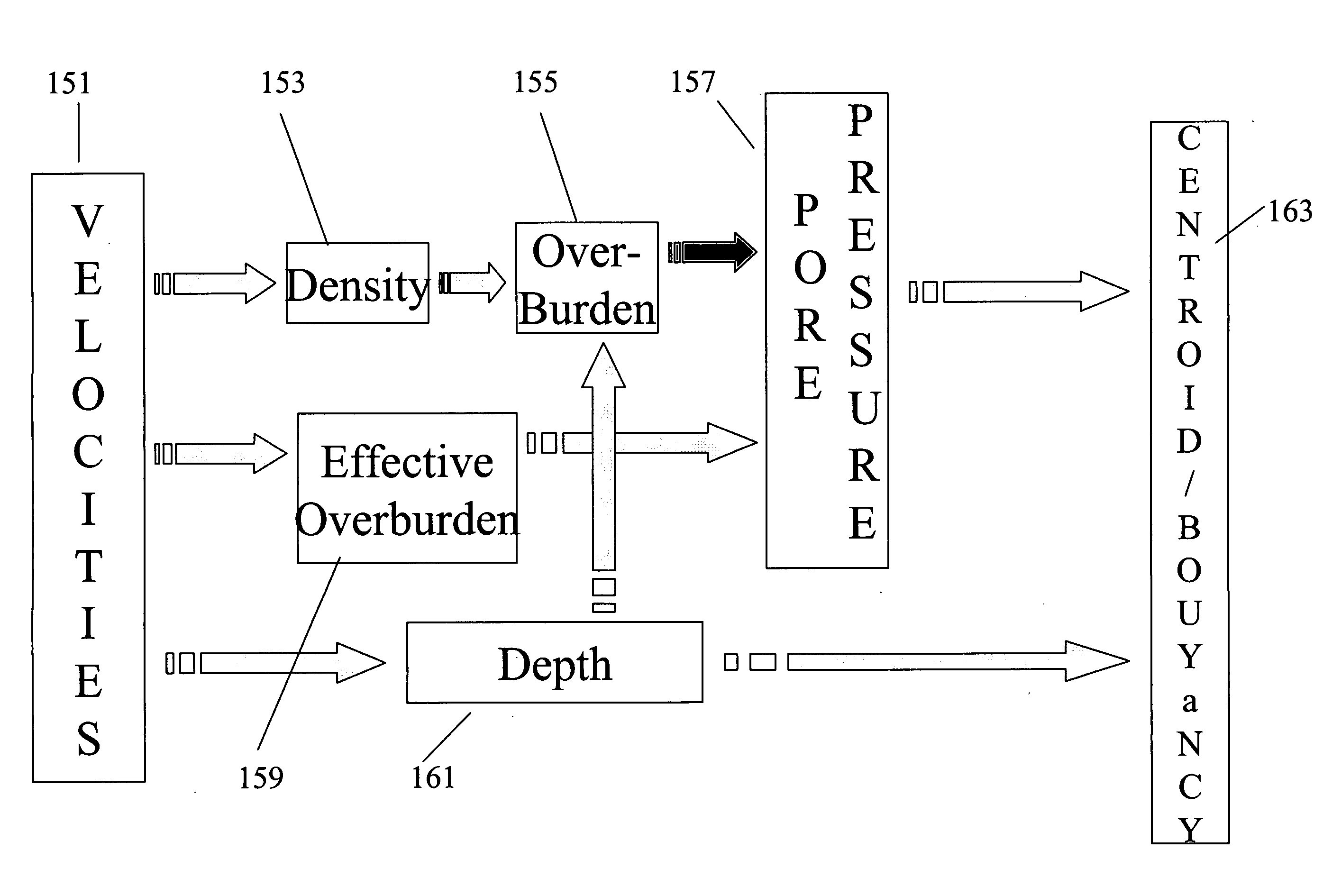
A method of determination of fluid pressures in a subsurface region of the earth uses seismic velocities and calibrations relating the seismic velocities to the effective stress on the subsurface sediments. The seismic velocities may be keyed to defined seismic horizons and may be obtained from many methods, including velocity spectra, post-stack inversion, pre-stack inversion, VSP or tomography. Overburden stresses may be obtained from density logs, relations between density and velocity, or from inversion of potential fields data. The seismic data may be P-P, P-S, or S-S data. The calibrations may be predetermined or may be derived from well information including well logs and well pressure measurements. The calibrations may also include the effect of unloading. The determined pressures may be used in the analysis of fluid flow in reservoirs, basin and prospect modeling and in fault integrity analysis.
Owner:CONOCOPHILLIPS CO
Hydraulic impulse generator and frequency sweep mechanism for borehole applications
ActiveUS20050178558A1Travel can be limitedEliminate water hammer effectSurveyOperating means/releasing devices for valvesGeophoneSeismic velocity
This invention discloses a valve that generates a hydraulic negative pressure pulse and a frequency modulator for the creation of a powerful, broadband swept impulse seismic signal at the drill bit during drilling operations. The signal can be received at monitoring points on the surface or underground locations using geophones. The time required for the seismic signal to travel from the source to the receiver directly and via reflections is used to calculate seismic velocity and other formation properties near the source and between the source and receiver. This information can be used for vertical seismic profiling of formations drilled, to check the location of the bit, or to detect the presence of abnormal pore pressure ahead of the bit. The hydraulic negative pressure pulse can also be used to enhance drilling and production of wells.
Owner:WELLS FARGO BANK NAT ASSOC +1
Forming a geological model
ActiveUS20100332139A1Seismic signal processingSpecial data processing applicationsSeismic velocityGeophysics
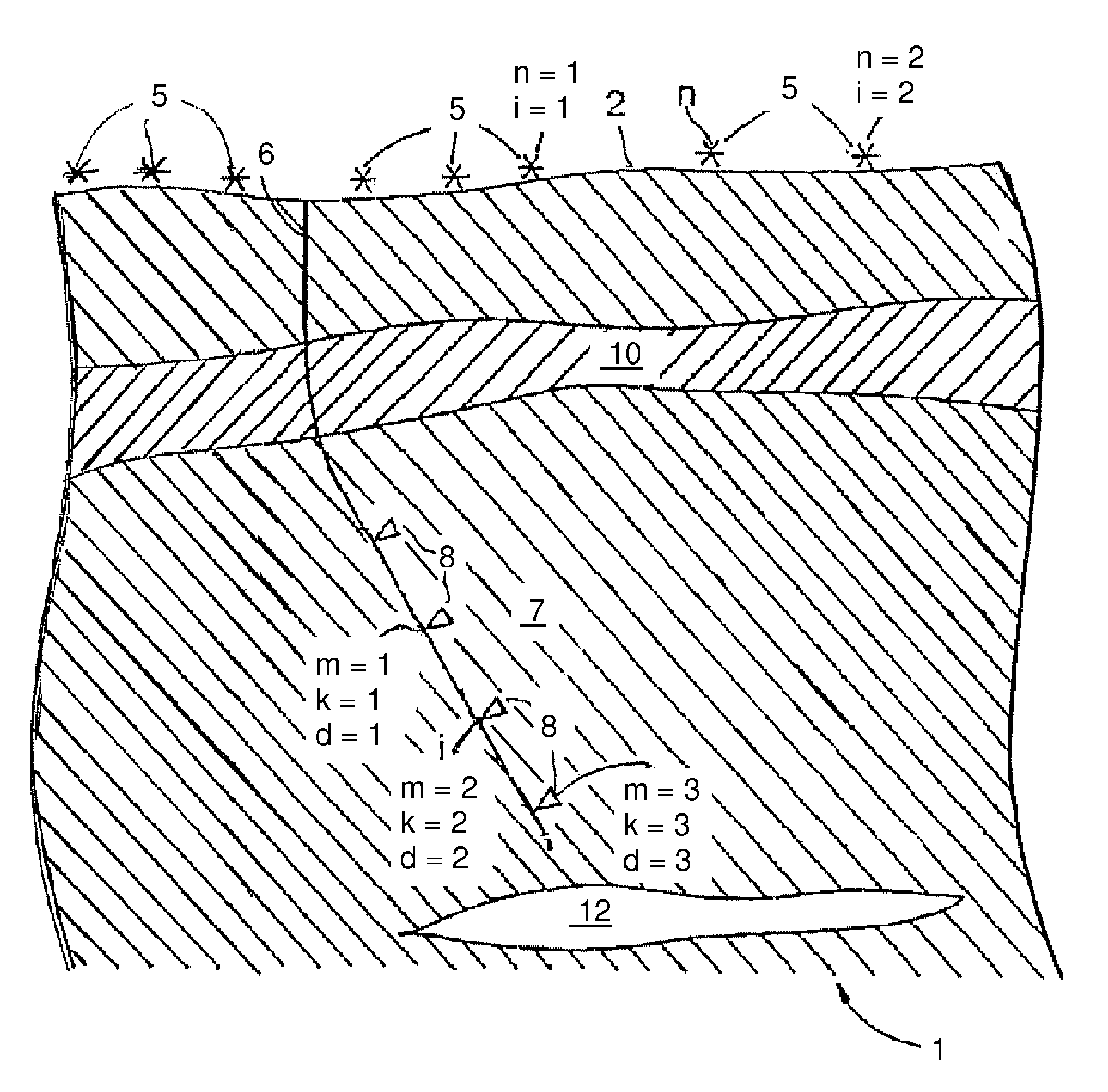
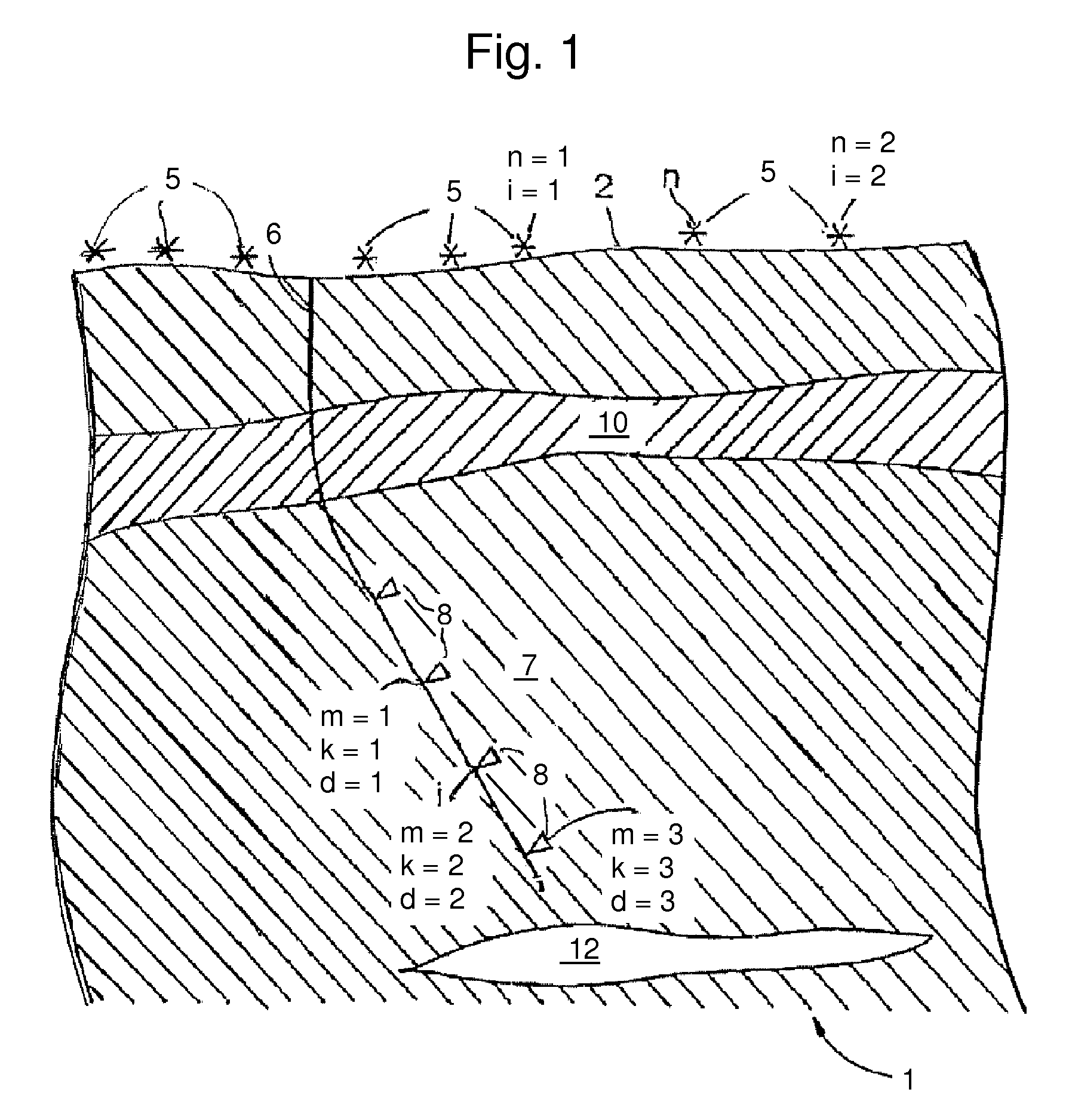
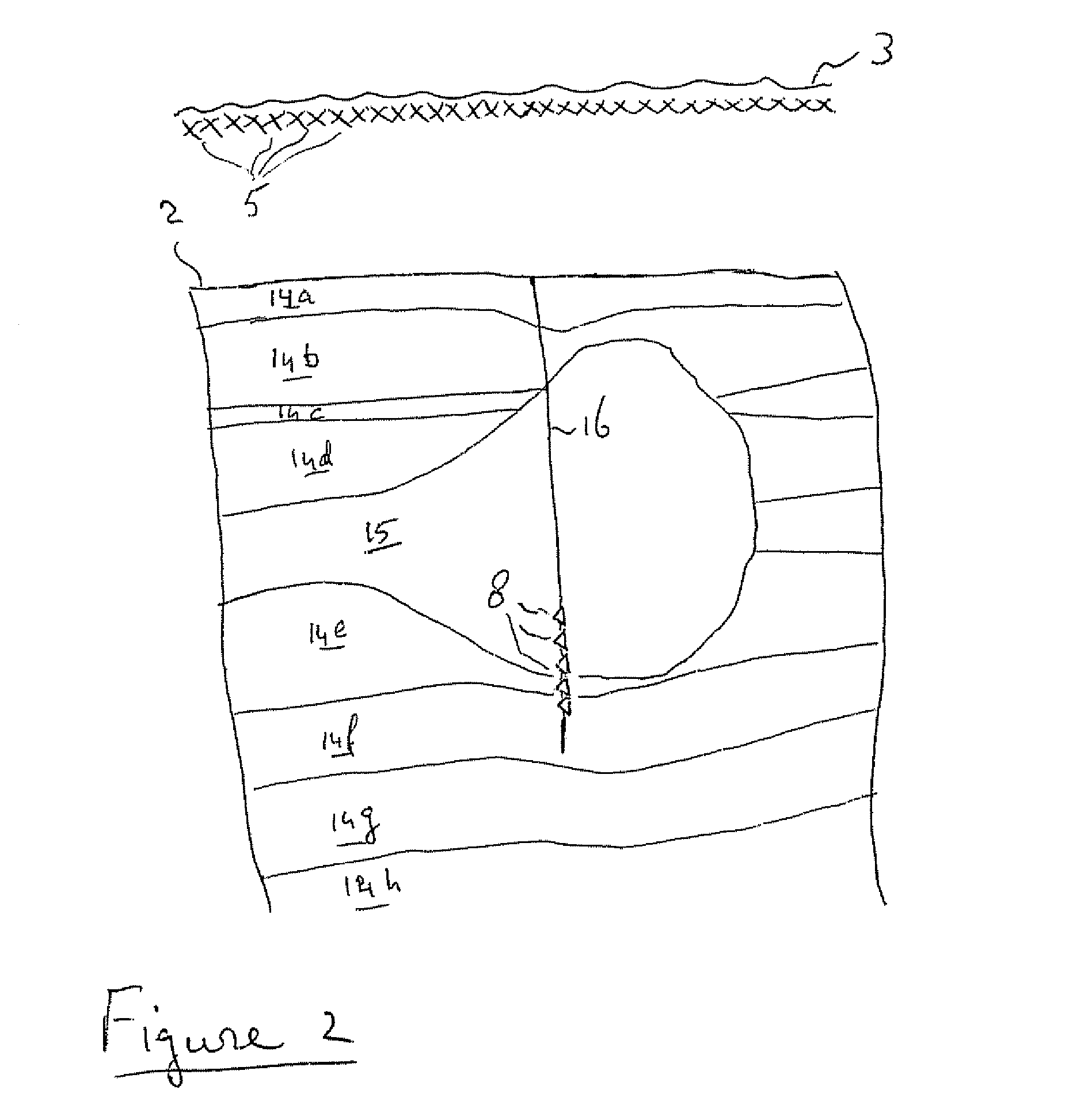
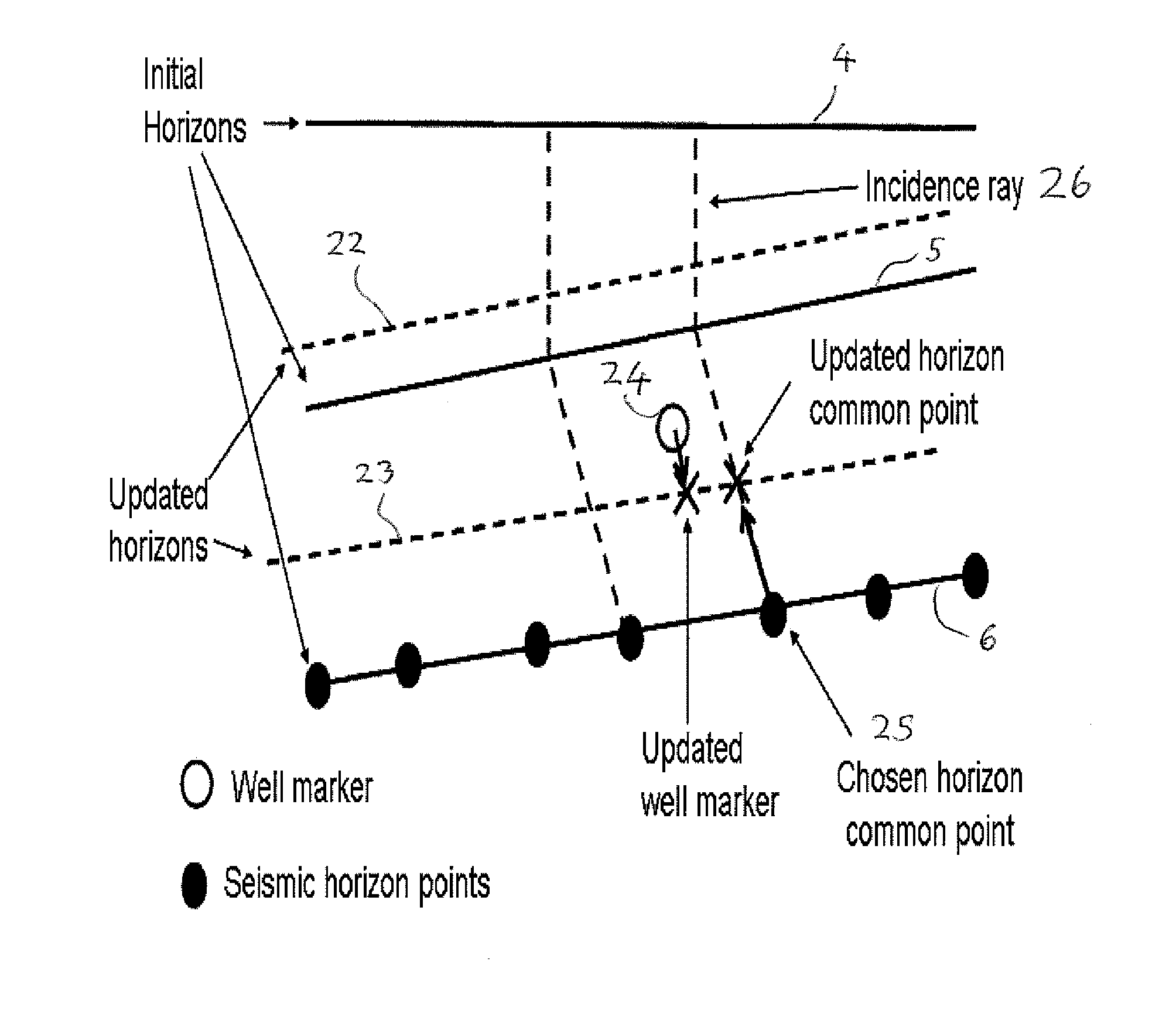
A method of forming a geological model of a region of the earth includes obtaining seismic data relating to the region, the seismic data including seismic traveltime uncertainty. A seismic velocity model of the region may also be provided and includes velocity uncertainty. Ray tracing may be performed on the seismic data using the velocity model to determine the three dimensional positions of a plurality of points of the region. The three dimensional positional uncertainties (7-12) of at least some of the points can be calculated from the traveltime uncertainty, the velocity uncertainty, and uncertainty in the ray propagation direction. This can be combined with the positions determined by the ray tracing to form a geological model.
Owner:EQUINOR ENERGY AS
Quantitative risk assessment applied to pore pressure prediction
ActiveUS20050197780A1Reduce uncertaintyAvoiding well cave-inElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSeismic signal processingSeismic velocityClassical mechanics
Pre-drill pore pressure and fracture gradient predictions obtained from seismic velocity data are used in well design taking into account uncertainties in the velocity estimation and in the models that use the velocities to determine pore pressure. Using geological constraints, limits are established on hydrocarbon column height. It is also possible to predict the relative number of casings required to reach target reservoirs.
Owner:GEOMECHANICS INT
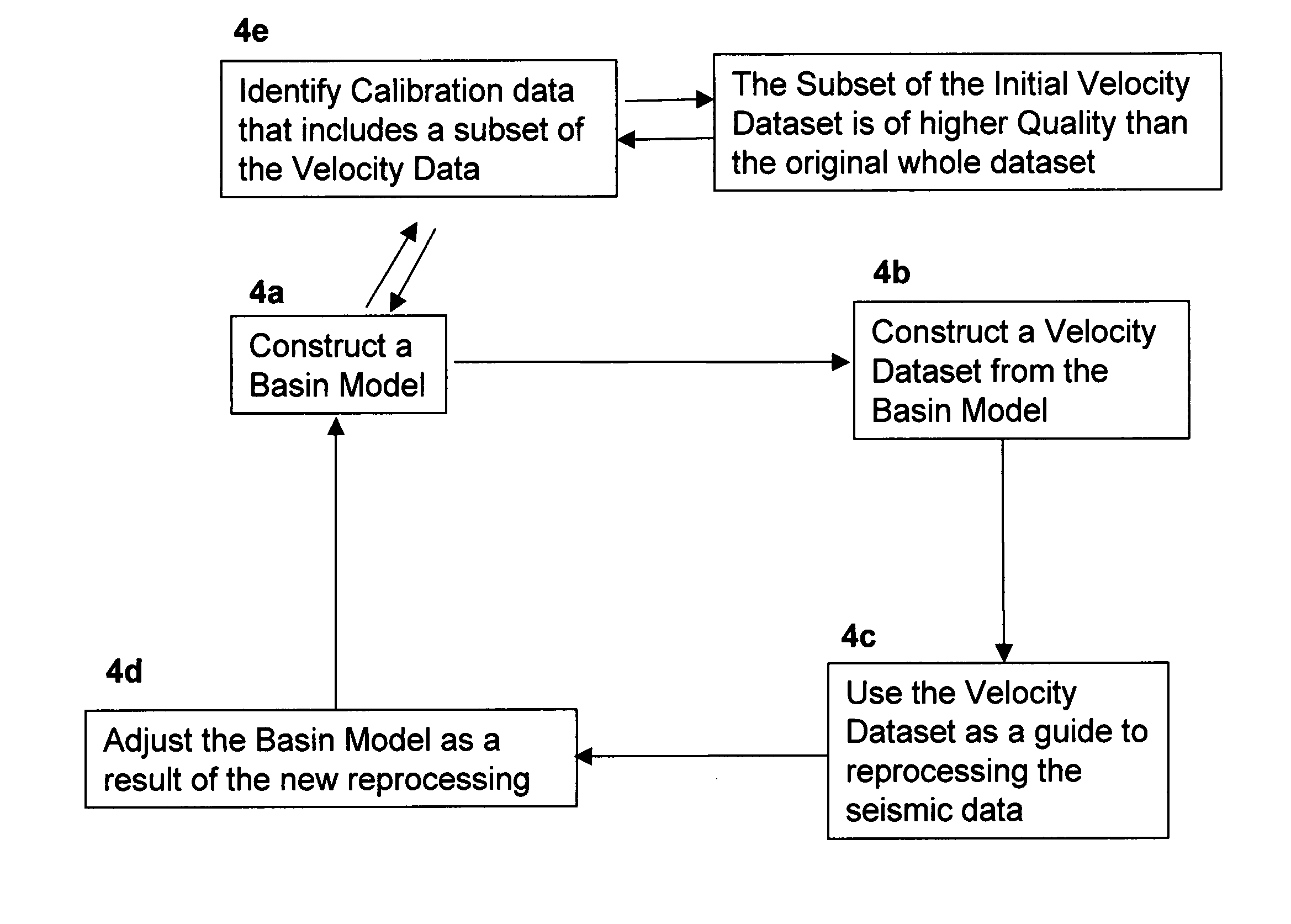
Method and system for combining seismic data and basin modeling
ActiveUS7280918B2Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSeismic signal processingSeismic velocityData set
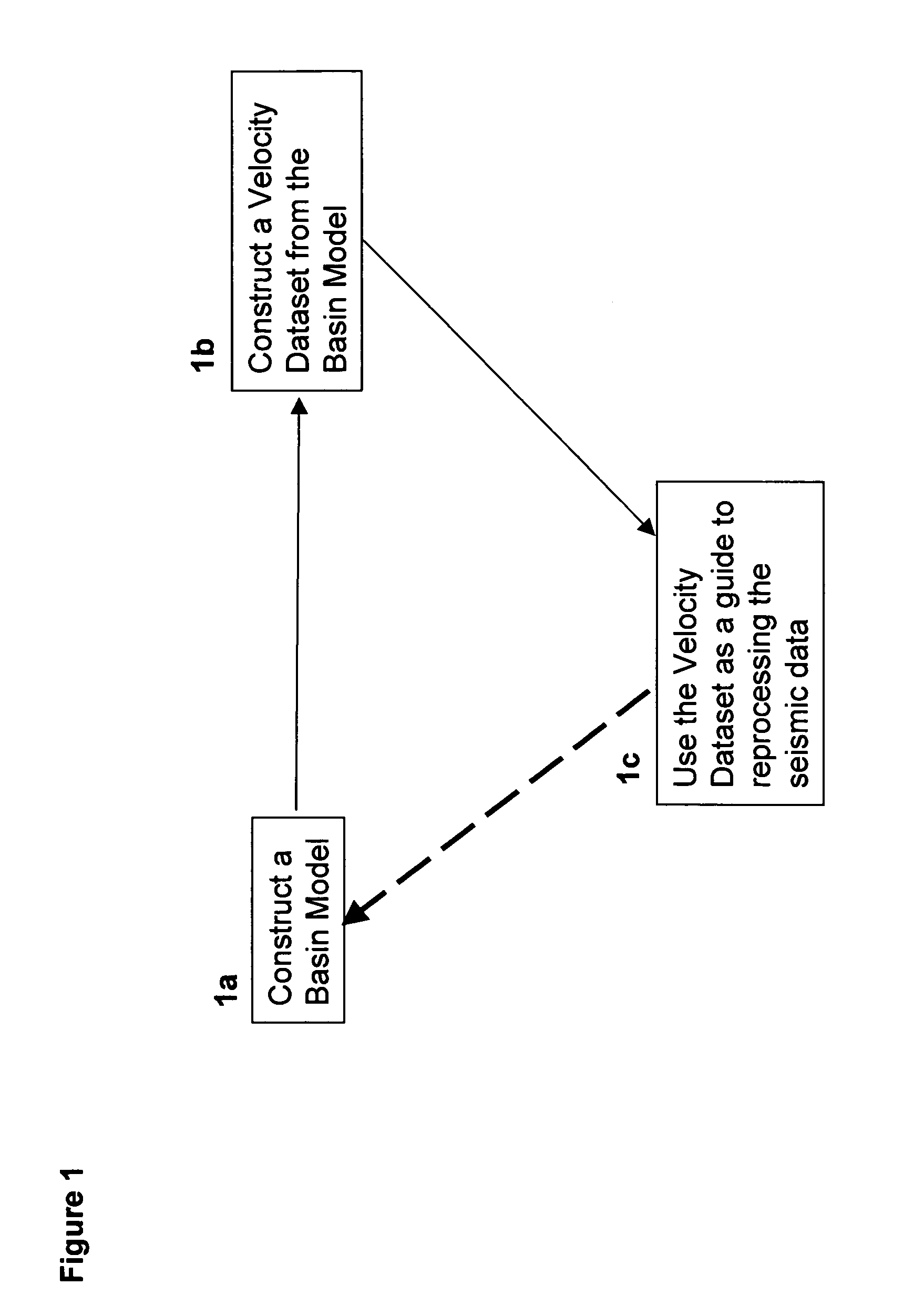
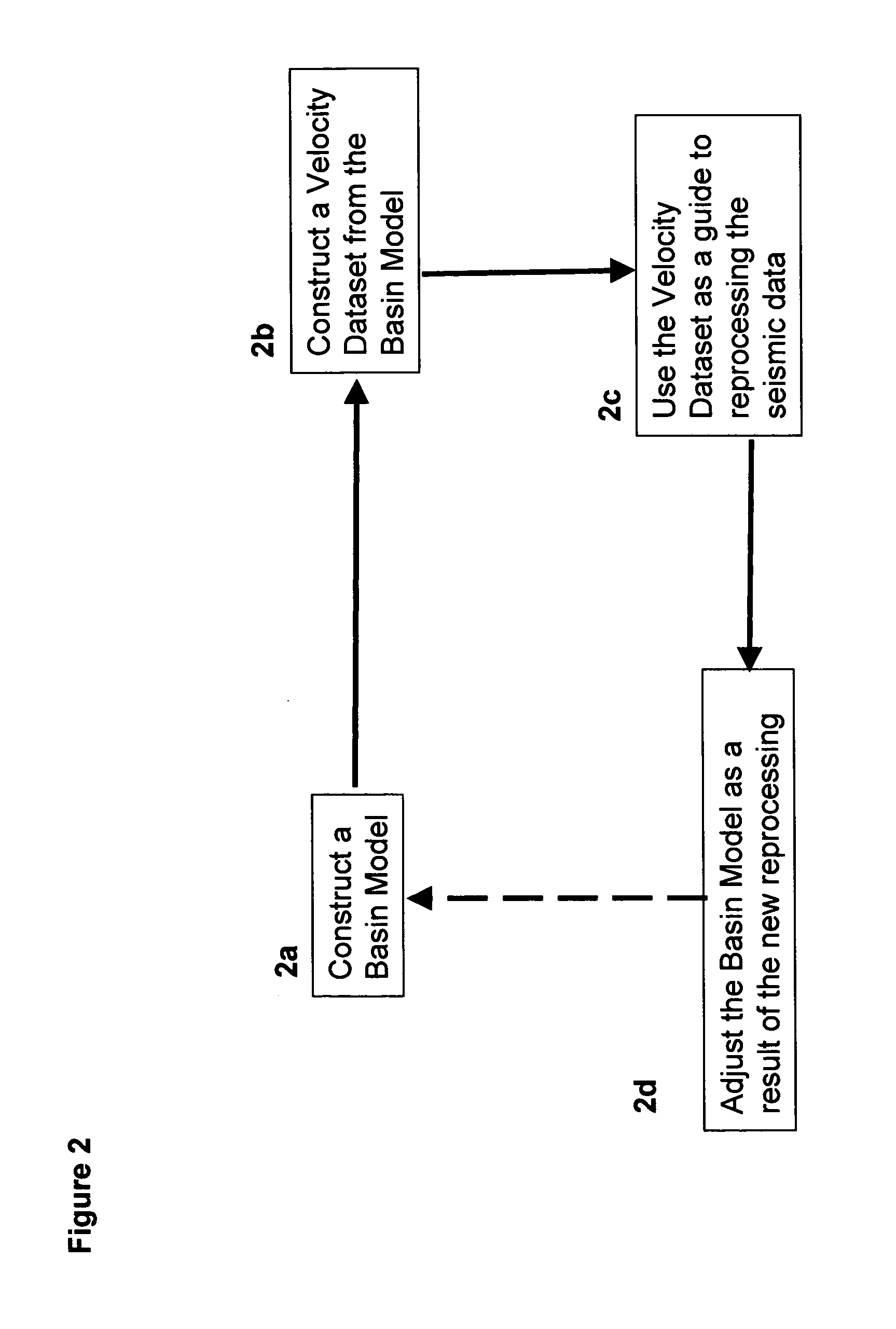
Methods and computer-based systems are provided for processing seismic data through the use of information provided by basin modeling. Provided are methods and systems for providing an improved seismic dataset by means of providing an initial basin model constructed using an initially-available dataset including seismic velocity data; constructing a velocity dataset from the initial basin model; and reprocessing the initially available seismic data using the velocity dataset from the initial basin model as a guide. Also provided are methods and systems for predicting fluid pressure in a subsurface region of interest.
Owner:LANDMARK GRAPHICS CORP
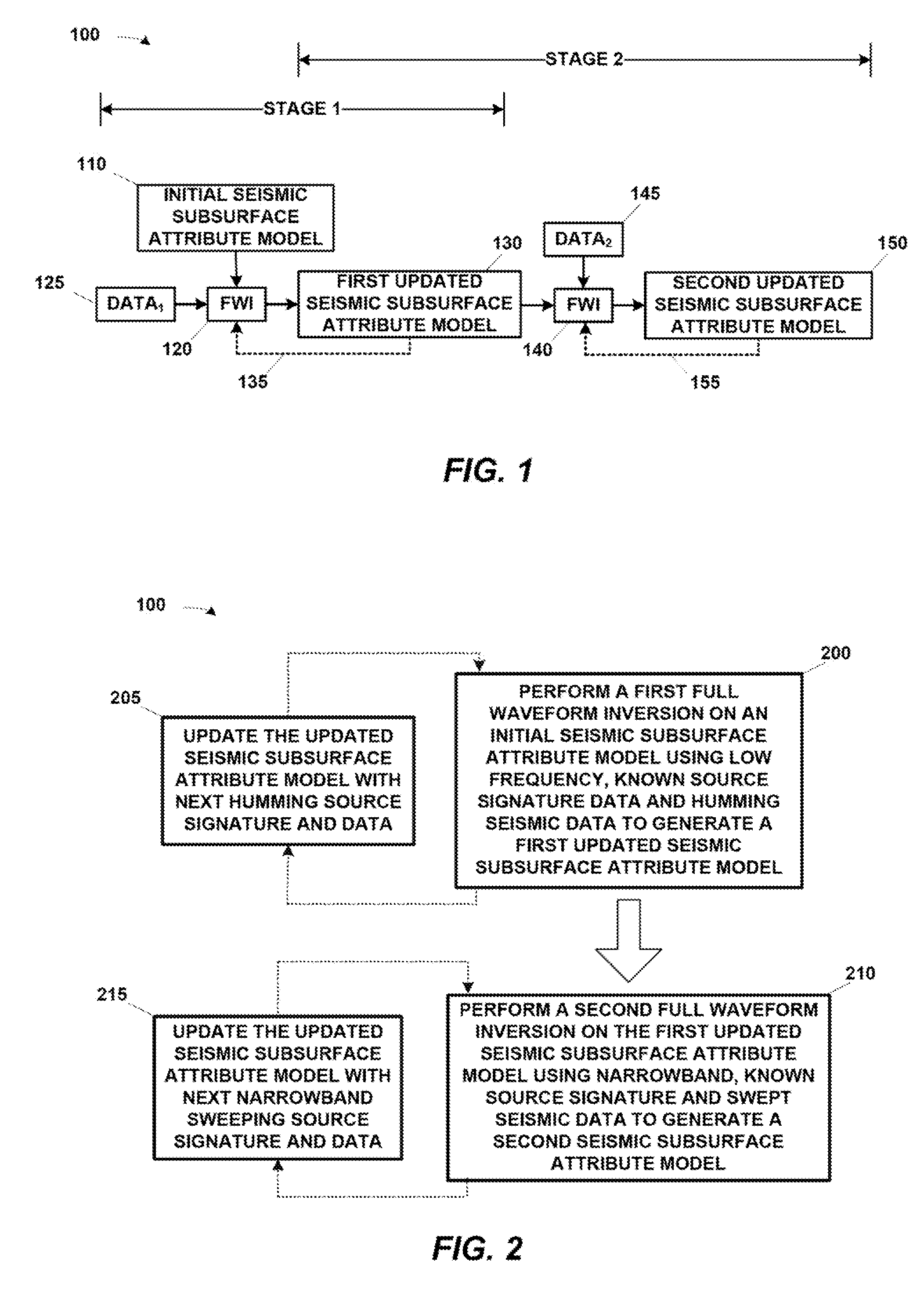
Two stage seismic velocity model generation
InactiveUS20150120200A1Seismic data acquisitionSeismic signal processingSeismic velocityFeature data
A computer-implemented process includes: performing a first foil waveform inversion on an initial subsurface attribute model using low frequency, known source-signature data and low frequency humming seismic data to generate a first updated subsurface attribute model; and performing a second full waveform inversion on the first updated subsurface attribute model using low-frequency, narrowband sweeping known source-signature data and low-frequency, swept seismic data to generate a second updated subsurface attribute model. The process may be performed by a suitably programmed computing apparatus, the program residing on some form of non-transitory program storage medium.
Owner:BP CORP NORTH AMERICA INC
Method and device for acquiring seismic velocity in thin reservoir layer through well control
ActiveCN102129084AImprove forecast accuracyImprove reliabilitySeismic signal processingSeismic velocityVelocity spectrum
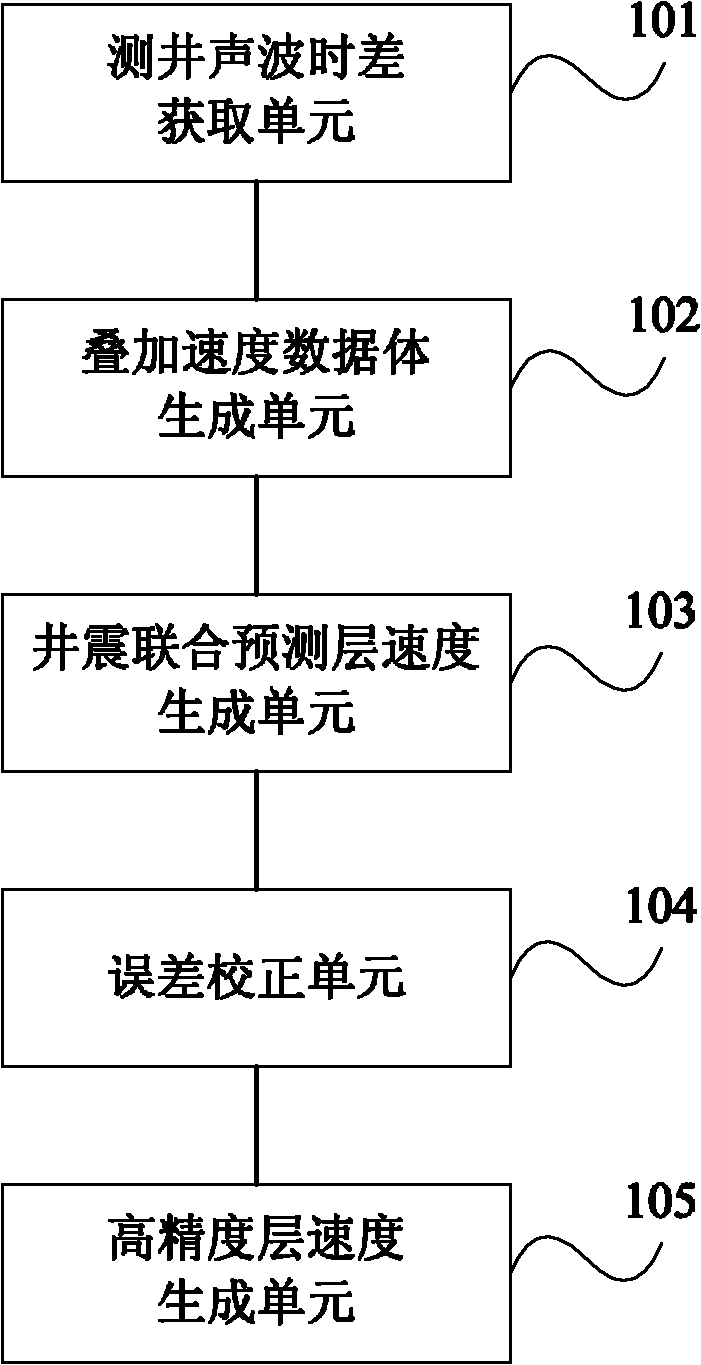
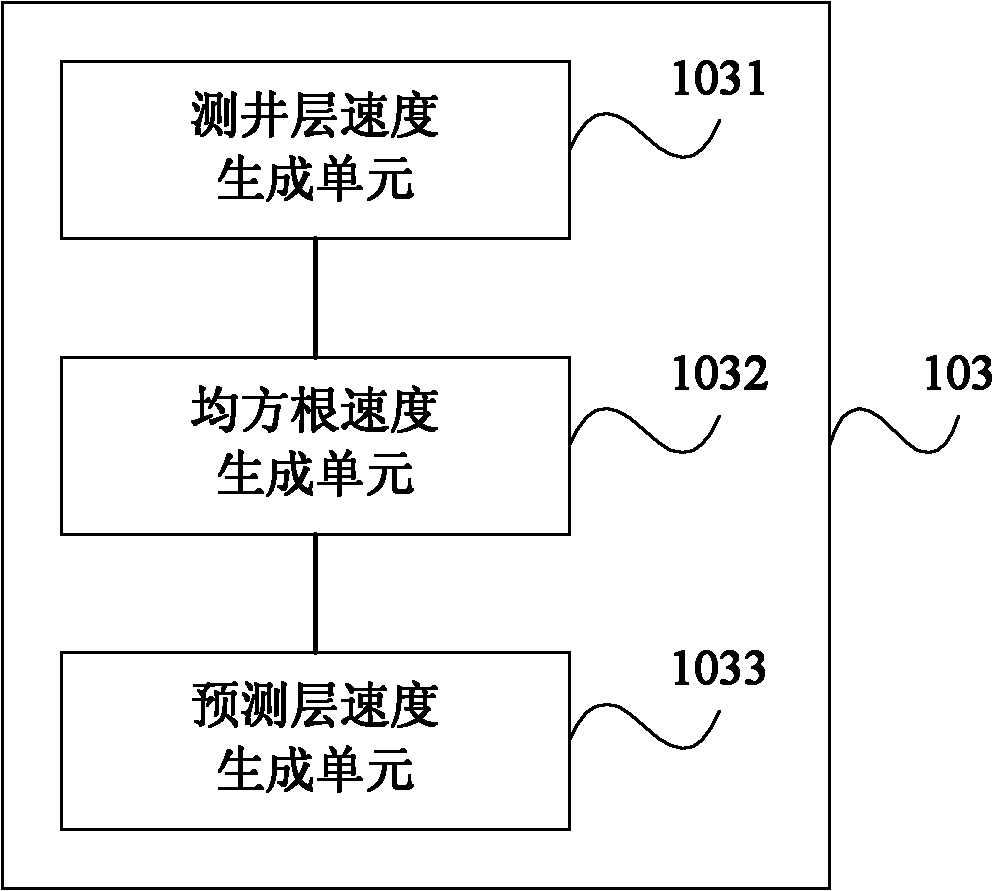
The invention discloses a method for acquiring the seismic velocity in a thin reservoir layer through well control. The method comprises the following steps of: selecting a standard single well velocity model and acquiring a corresponding logging acoustic time difference; acquiring a stacking velocity spectrum for seismic data imaging treatment and generating a stacking velocity data volume; selecting a time step length of 15-20 ms and carrying out velocity conversion on the logging acoustic time difference to obtain the velocity of a logging layer; converting the stacking velocity data volume into a logging-seismic joint forecast interval-velocity data volume; carrying out hierarchic and segmental error correction calculation on the velocity of the logging layer and the logging-seismic joint forecast interval-velocity data volume by adopting a ratio method to generate planar correction coefficients corresponding to various layers in different depths; and hierarchically and segmentally applying the planar correction coefficients to the logging-seismic joint forecast interval-velocity data volume of each layer correspondingly from top to bottom so as to obtain a high-accuracy seismic interval velocity data volume. The embodiment of the invention verifies that the method and the device for acquiring the seismic velocity in the thin reservoir layer through well control are beneficial to improvement of the forecast accuracy of the seismic velocity in the thin reservoir layer and can be used for obtaining velocity data with higher reliability.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Frequency domain full-waveform inversion seismic velocity modeling method
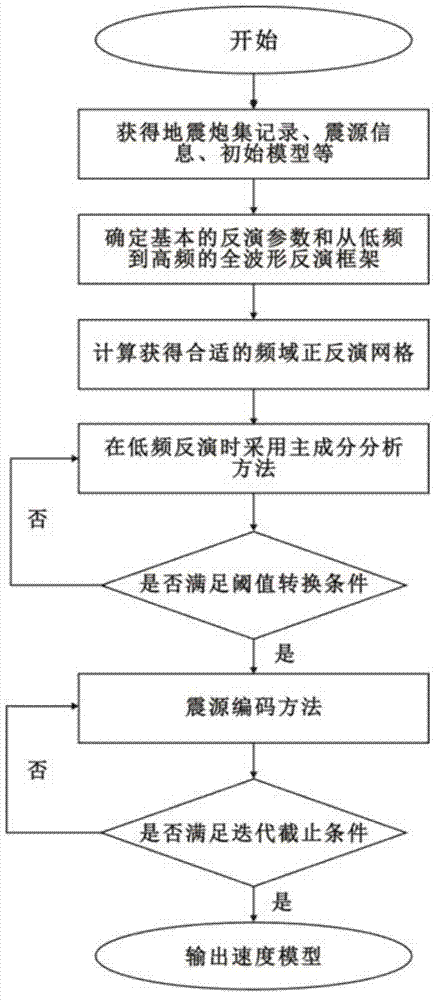
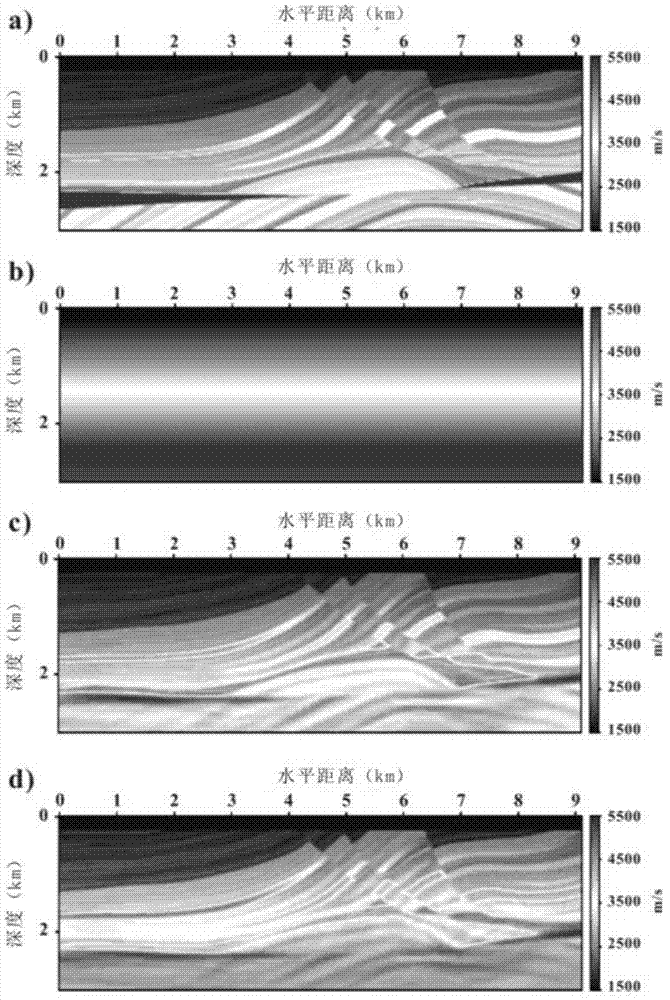
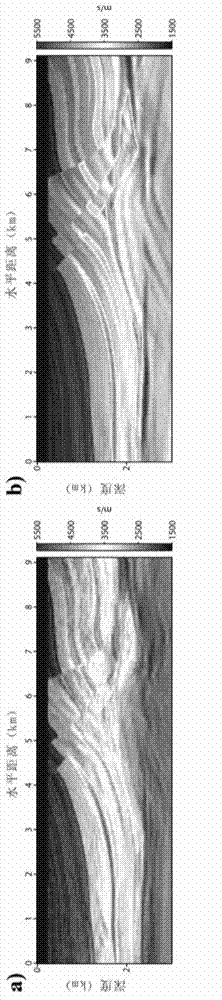
The invention relates to a frequency domain full-waveform inversion seismic velocity modeling method. The method comprises the following steps of: 1) acquiring an original seismic shot gather record, focus wavelet information and an initial model used by inversion; 2) analyzing information acquired in the step 1), and determining basic inversion parameters and a full-waveform inversion frame from low frequency to high frequency based on a forward modeling algorithm and an optimization algorithm; 3) calculating to acquire the most appropriate forward and inversion model network for different frequencies; 4) compressing data dimensions which participate in inversion by a principal component analysis method during low-frequency inversion; 5) judging whether projection matrix dimensions corresponding to different frequencies meet the threshold value conversion standard, if the conversion standard is met, performing a next step, and if the conversion standard is not met, returning to the step 4); 6) introducing a focus encoding method, and pressing crosstalk noise by a random phase encoding method; 7) judging whether an iteration stopping condition is met, if the iteration stopping condition is met, performing a next step, and if the iteration stopping condition is not met, returning to the step 6); and 8) if the inversion of all the frequencies is not finished, returning to the step 3) until the inversion of all the frequencies is finished, acquiring the final velocity model, and outputting the velocity model.
Owner:CHINA NAT OFFSHORE OIL CORP +1
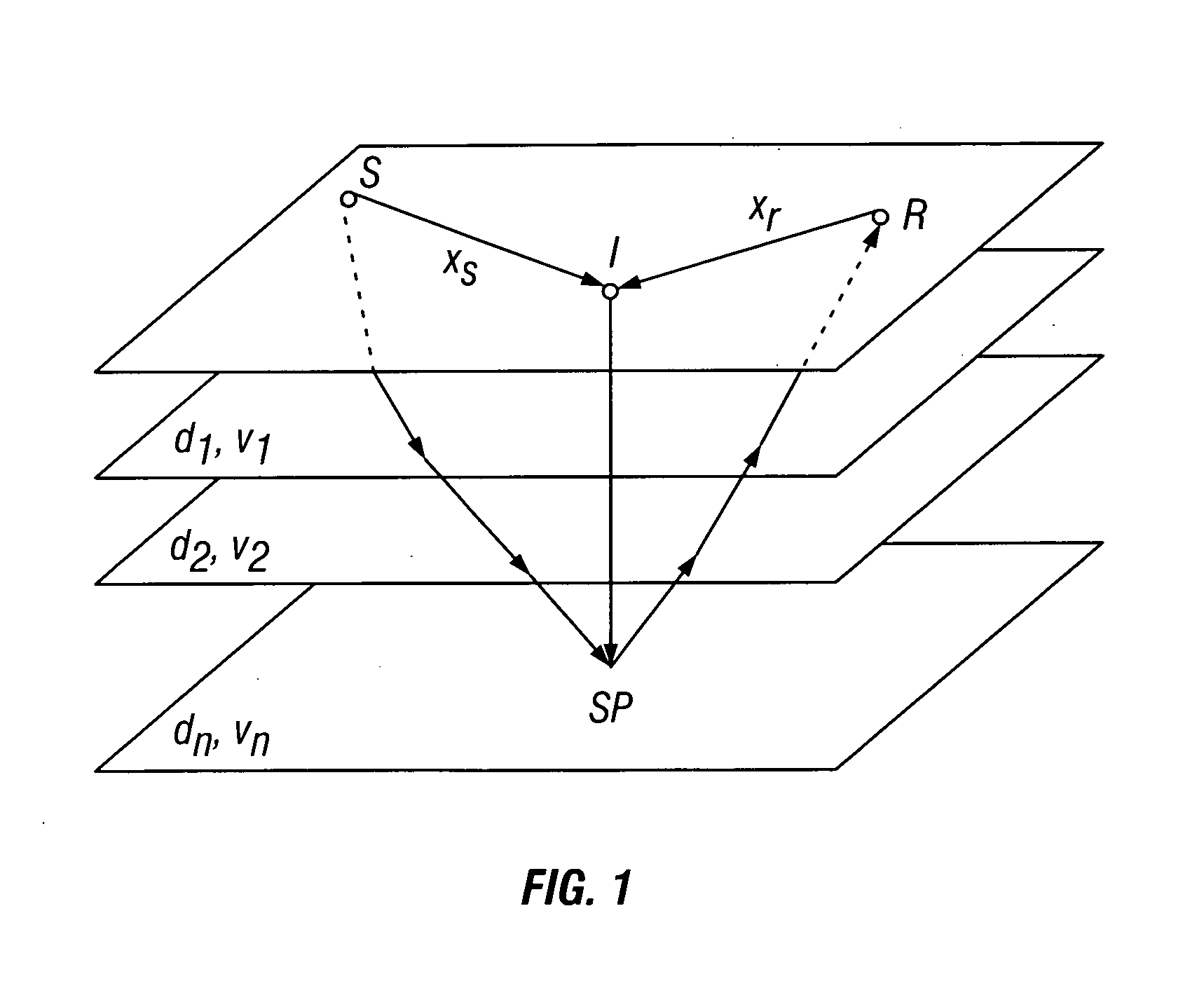
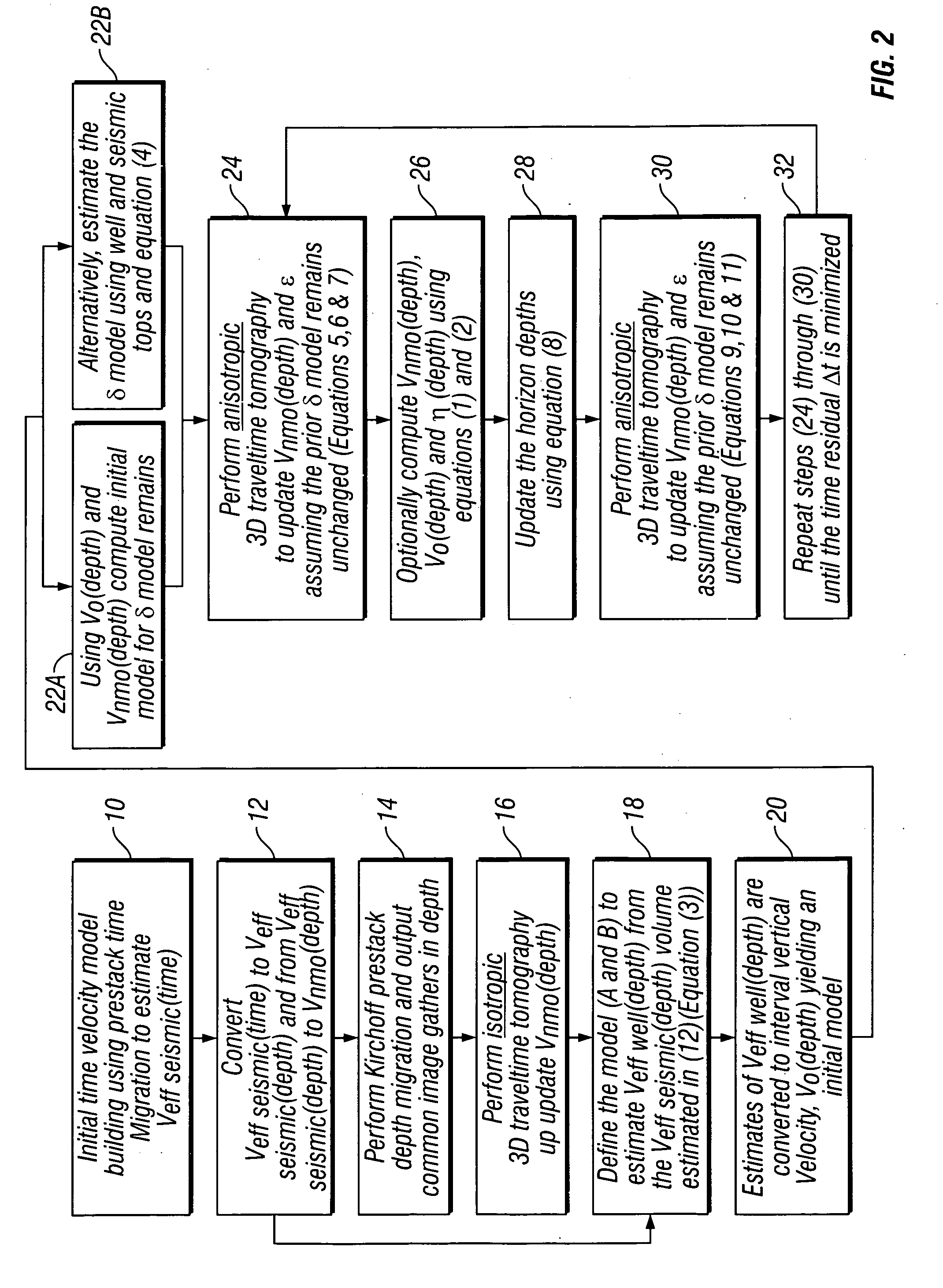
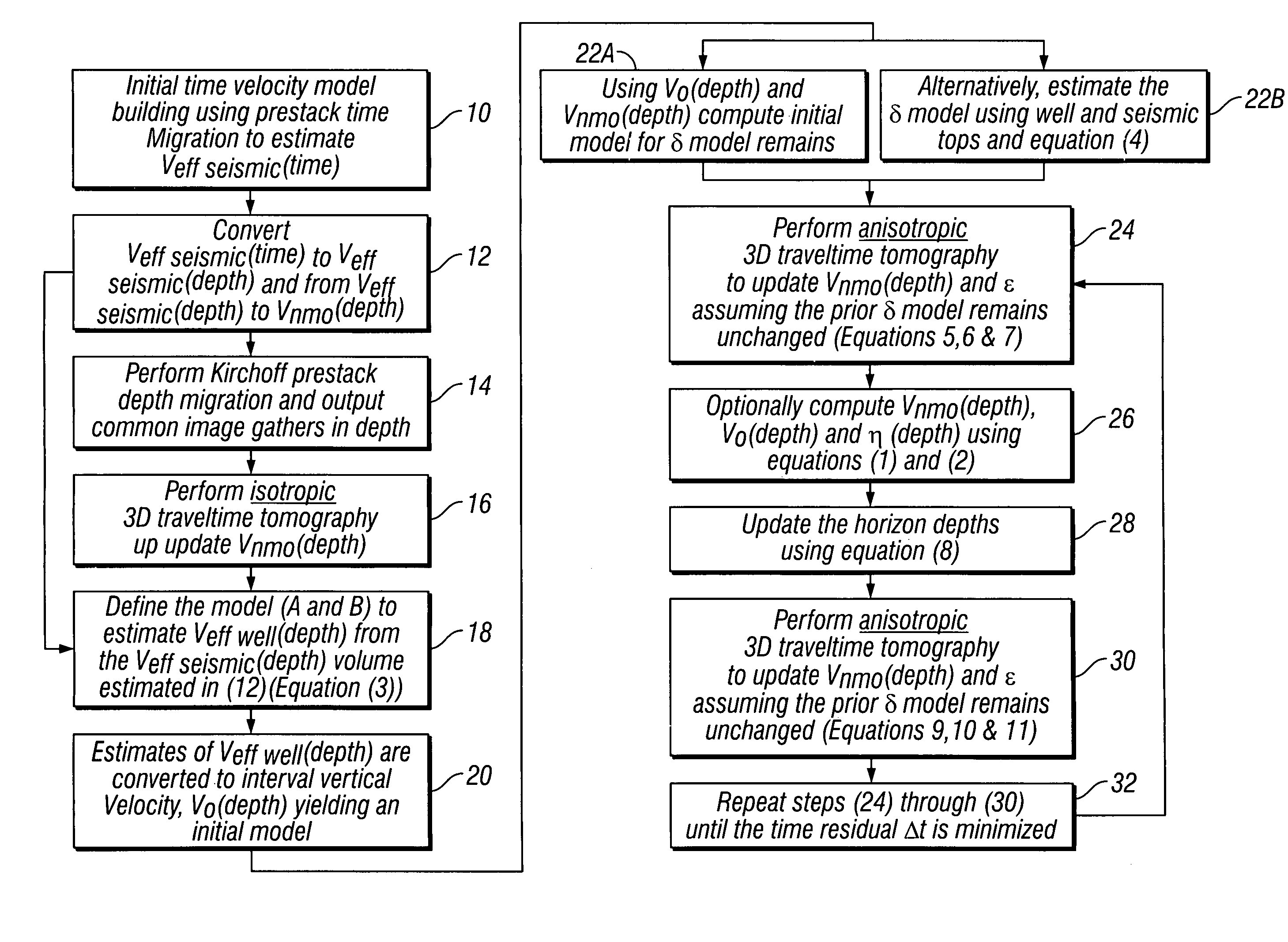
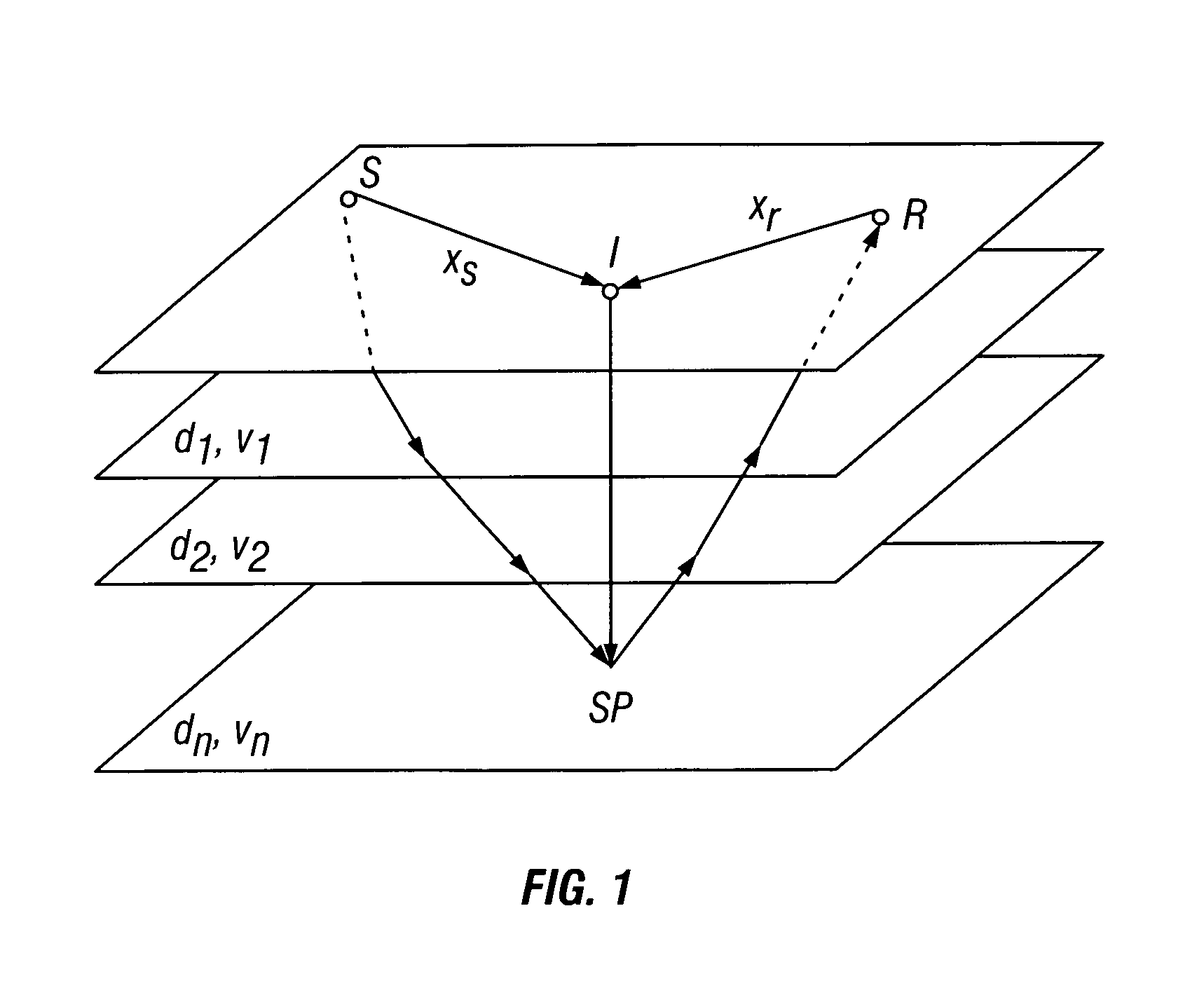
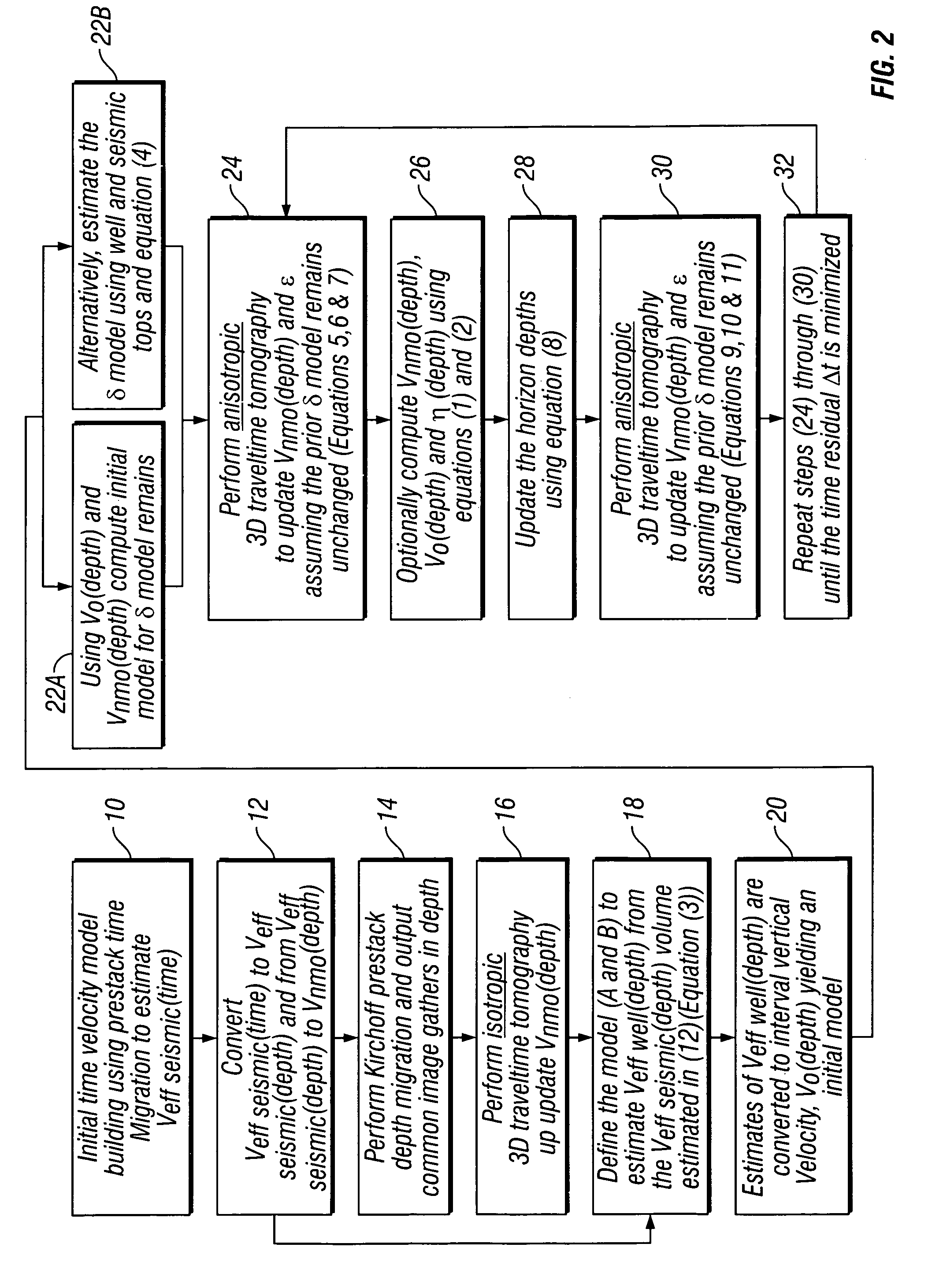
Method for three dimensional seismic travel time tomography in transversely isotropic media
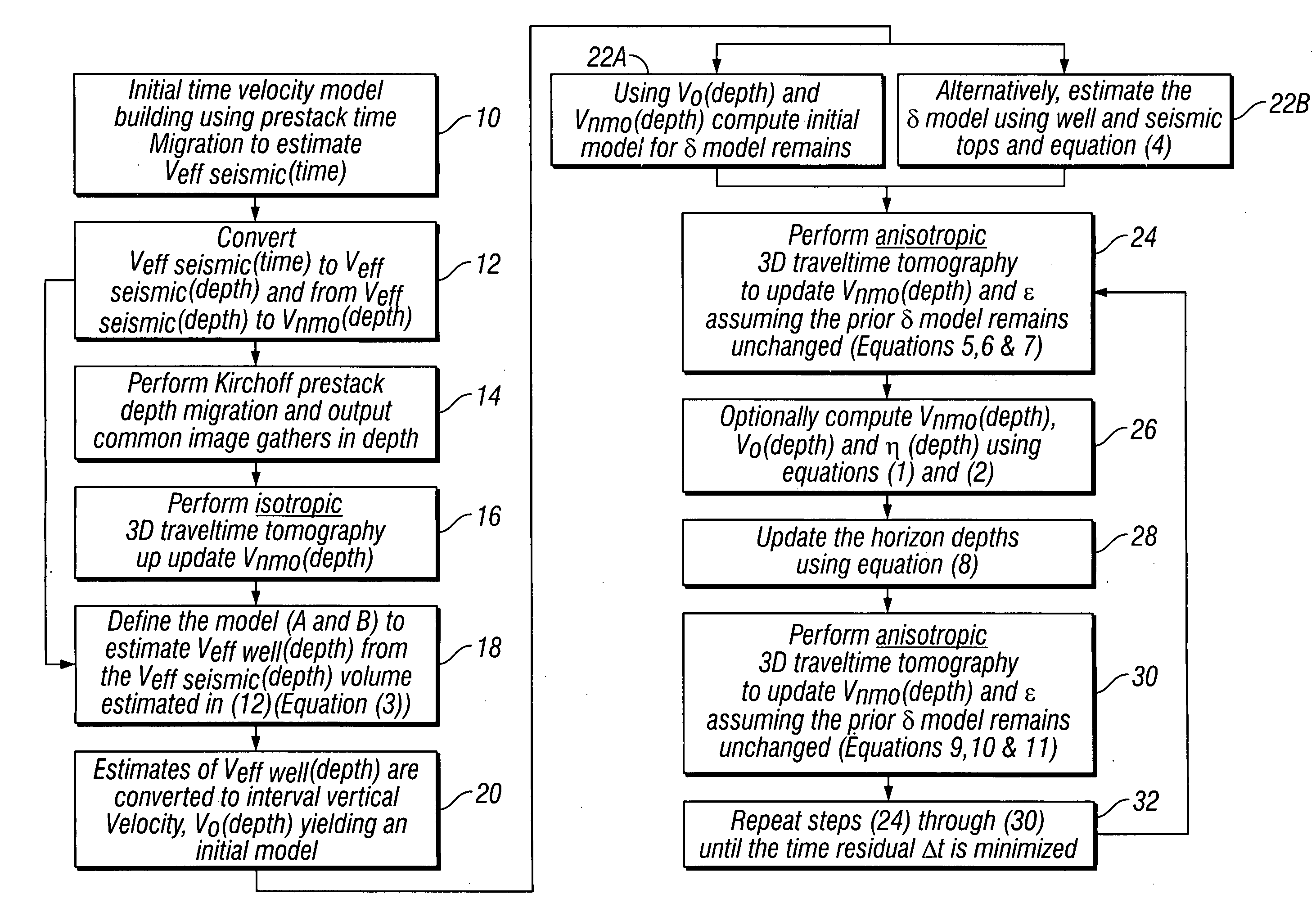
A method for estimating seismic velocities in vertically transversely isotropic media includes generating an initial estimate of vertical interval velocity and interval normal moveout velocity with respect to depth from seismic data. An initial estimate is generated of a first anisotropy parameter with respect to depth. The first anisotropy parameter is related to the interval normal moveout velocity and the interval vertical velocity. An initial estimate is generated with respect to depth of a second anisotropy parameter. The second anisotropy parameter is related to the first anisotropy parameter and an interval anelliptic parameter. A first tomographic inversion is performed with respect to the interval normal moveout velocity and the second anisotropy parameter at a constant value of the first anisotropy parameter until travel time differentials reach minimum values. Layer depths are adjusted with the initial estimate of vertical interval velocity. Using values of the second anisotropy parameter determined in the first tomographic inversion, a second tomographic inversion is performed of interval normal moveout velocity and the first anisotropy parameter with respect to depth. The adjusted layer depths, interval normal moveout velocities and interval vertical velocities are again adjusted and interval anelliptic parameters are calculated from the second tomographic inversion.
Owner:PGS GEOPHYSICAL AS
Full Waveform Inversion Using Perfectly Reflectionless Subgridding
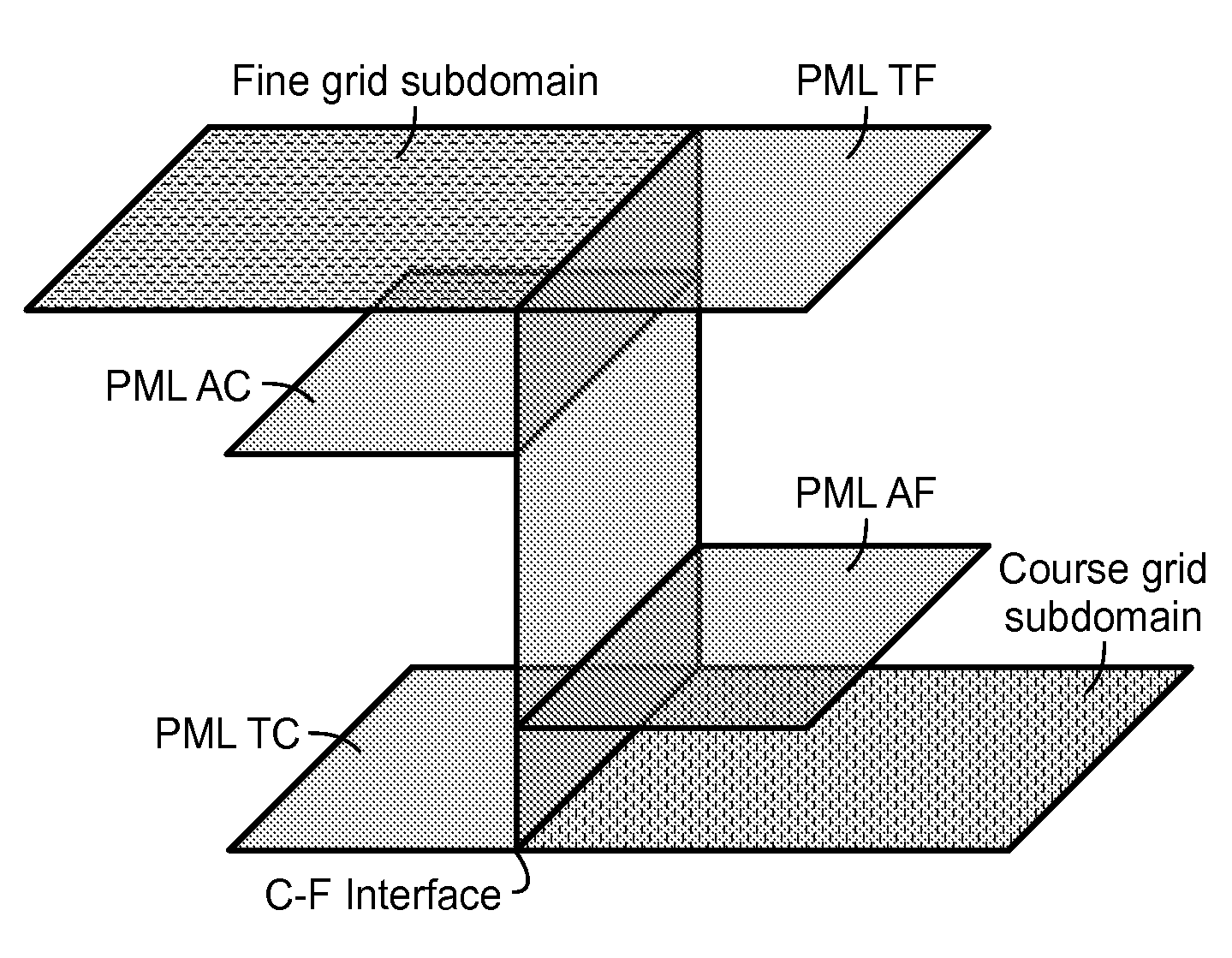
InactiveUS20140372043A1Improve efficiencySignificant computational expenseSeismic signal processingSpecial data processing applicationsSeismic velocityPerfectly matched layer
Method for reconstructing subsurface profiles for seismic velocity or other geophysical properties from recorded seismic data. In one embodiment, a starting model of seismic velocity is assumed (10). The computational domain is divided into two (or more) subdomains by horizontal planes based on an analysis of velocity model (30), and the allowed maximum grid size for each subdomain is determined (50). Auxiliary perfectly matched layers (PML's) are attached to each planar interface between subdomains (80), e.g. two PML's on each side of the interface between the coarse and fine subdomains. Simulated seismic data are computed using the SG-DO technique (100-230). The simulated seismic data are compared to the recorded seismic data, then the residual is calculated (240) and used to update the model (320). The method may be iterated until the model is suitably converged (260).
Owner:HU WENYI +3
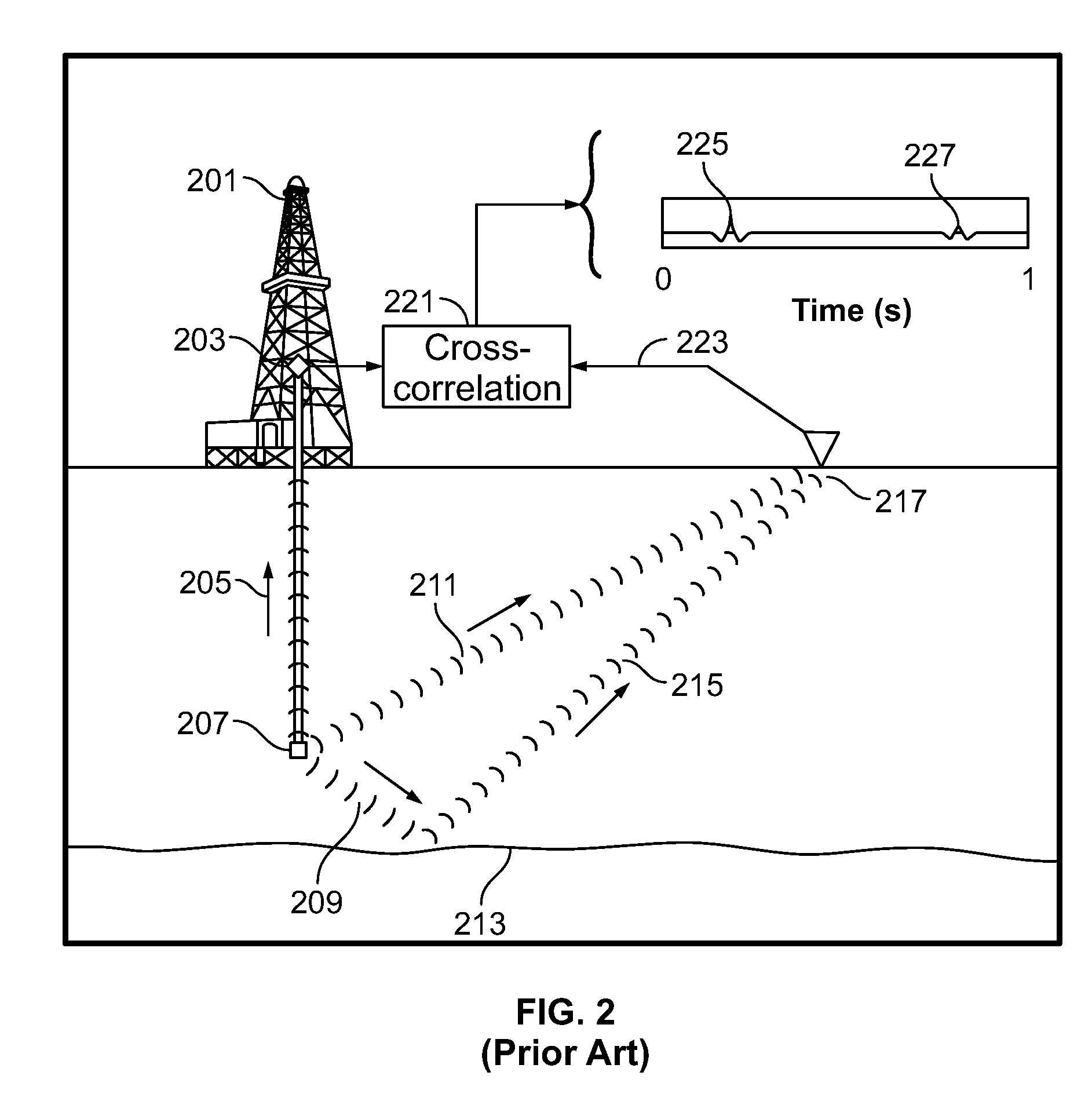
Method of determining a seismic velocity profile
ActiveUS20070195643A1Seismic signal processingSeismology for water-loggingSeismic velocitySignal trace
A seismic velocity profile in a region of interest in a subsurface formation is determined using at least the following steps. (a) Activating a seismic source at a location n, thereby exciting a wave in the subsurface formation. (b) Recording a wave signal trace unm(t) against time t, at a seismic receiver m. (c) Recording a wave signal trace unk(t) against time t at a seismic receiver k. (d) Cross correlating the wave signal traces unm(t) and unk(t) to obtain uconvnmnk(t). (e) Repeating these steps, for different locations n; (f) Summing uconvnmnk(t) over all locations n, to obtain a signal trace uvsmk(t) which corresponds to the signal received by the seismic receiver k from the virtual source at the position of seismic receiver m; (g) Deriving the seismic velocity based on the time of first arrival of the wave in uvsmk(t) and the predetermined distance between the seismic receiver m and the seismic receiver k.
Owner:SHELL USA INC
Comprehensive underground test method for deformation and damage of terranes of mining top plate and mining bottom plate of coal bed
ActiveCN101581234AGood for fine graspAccurate determination of damage depth valuesMining devicesSeismology for water-loggingSeismic velocityEngineering
The invention discloses a comprehensive underground test method for deformation and damage of terranes of mining top plate and mining bottom plate of a coal bed, comprising the following steps of: (1) constructing a comprehensive test system; (2) utilizing a network parallel electrical method to synchronously collect test electrode supply current and potential signal in boreholes of the top plate and the bottom plate, thus obtaining the electric field distribution situation between the top plate and the bottom plate of the working face in a control area; (3) respectively extracting the electric field parameter distribution situation of rock masses, the seismic velocity distribution situation and the displacement variation of terranes at different places in the borehole in the control area according to the collected data characteristics of various geophysical fields; (4) dynamically obtaining the parameter change of the geophysical fields in a detected area at different time along with the advancing state of the working face; and (5) completing the installation and sealing of facilities in the tested borehole before the stoping of the coal face. The method precisely masters the damage situation of the rock masses, thus not only delimitating the deformation and damage distribution situation of rock masses in the control area, but also precisely determining the water-guiding fissure zone height of the covered rock masses of the top plate and the damage depth value of the bottom plate.
Owner:张平松 +1
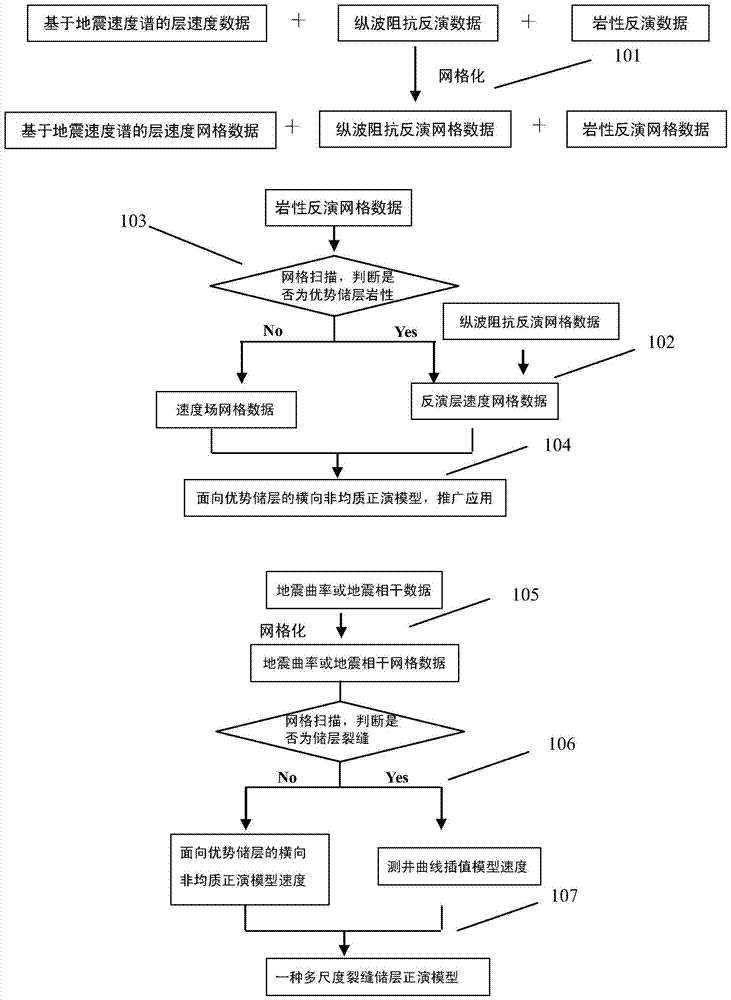
Multi-scale fractured reservoir forward model establishing method
The invention relates to the field of exploration geophysical data processing methods, and particularly relates to a multi-scale fractured reservoir forward model establishing method. First, a laterally heterogeneous model for a predominant reservoir is established by using interval velocity data based on the seismic velocity spectrum, P-wave impedance inversion data, and lithologic inversion data; then, the geometrical shape of a fracture is determined by a seismic detection method for different scales of seismic curvature or seismic coherence, and the fracture is given geophysical parameters based on well shock and is embedded to the obtained laterally heterogeneous model; and finally, a laterally and longitudinally heterogeneous multi-scale fractured reservoir model is established. The fractured reservoir model established by the method fully utilizes well shock data, truly reflects the development regularity and distribution characteristics of the fracture, and provides a basis for performing fractured reservoir forward modeling in the next step, understanding the wave field response characteristics and geophysical attributive characteristics of a fractured reservoir and improving the accuracy of reservoir prediction.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Mine working face inter-lane seismic wave CT detection method
InactiveCN101581789AImprove detection accuracyAvoid causing ray-sparse areas or even blind spotsSeismic energy generationSeismology for water-loggingSeismic velocityResearch Object
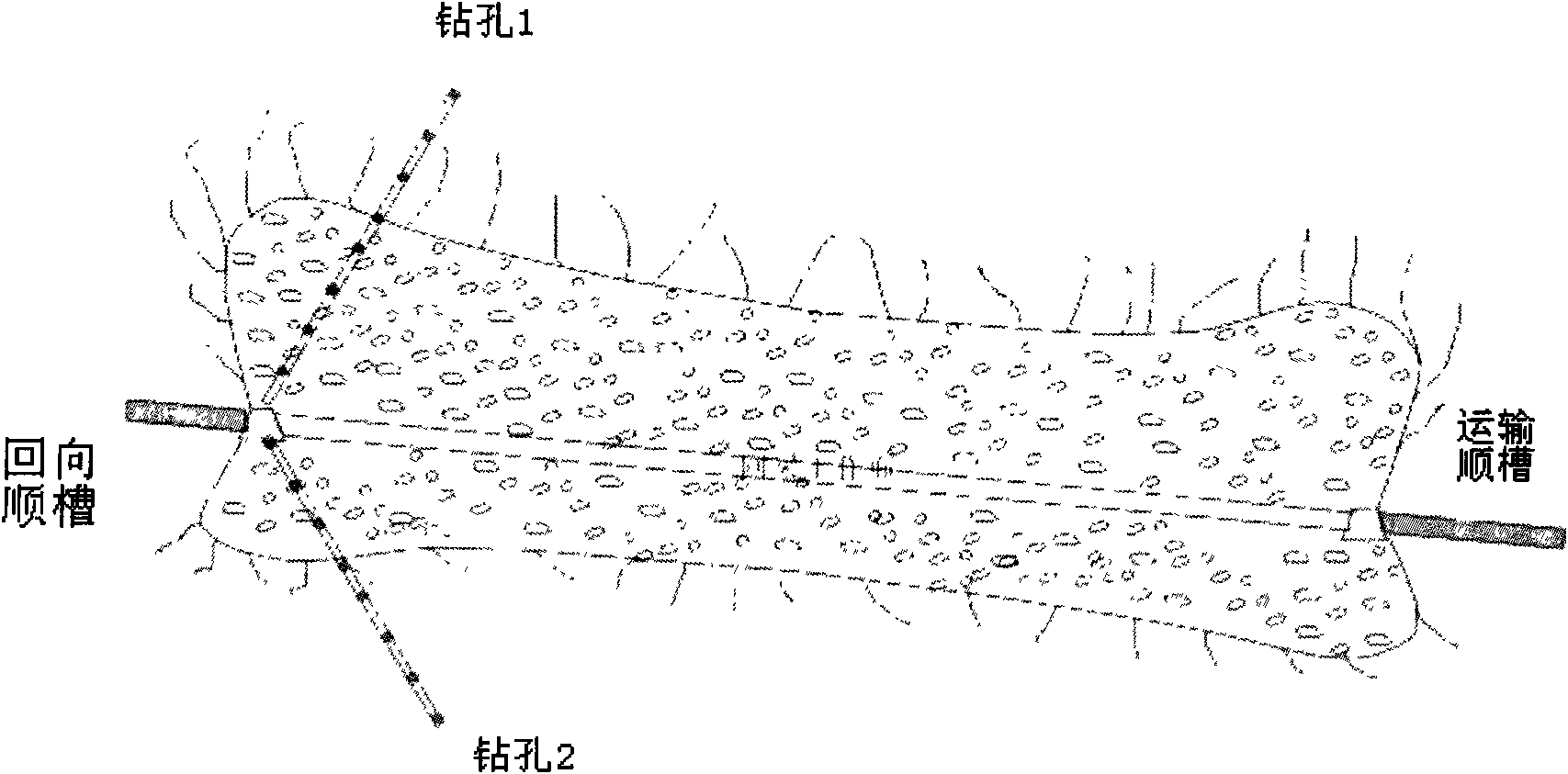
The invention discloses a mine working face inter-lane seismic wave CT detection method which is a highly precise detection method for a geologic anomalous body in the mine working face, namely, seismic wave CT detection which is similar to medical CT and relates to a practical technique by taking the coal mine coal face as a research object and utilizing an upper lane and a lower lane for CT detection. An observation system relates to the relative relationship between a trigger point and a receiving point in space, and generally, the trigger point (adopting mining explosive as a seismic focus) is arranged at one lane, and the receiving point is arranged at another lane, and the observation mode of 'one-trigger, multi-receiving, and one-explosion, one-release' is adopted. After a coordinate system is established, the coordinate parameters of each point of the observation system are determined, and inversion calculation is conducted by utilizing an inter-lane seismic wave CT tomography technique, thus obtaining seismic velocity equal CT inversion slice in the working face so as to accurately and effectively judge the geological structure and the anomalous body trace in the working face. The method has better pertinence to the geological structure and the interpretation of anomaly thereof, and can provide reliable technical parameters for safe production in mines. The method broadens the application scope of the seismic wave CT detection technique and improves the accuracy for geologic anomalous body detection in the mine working face.
Owner:刘盛东
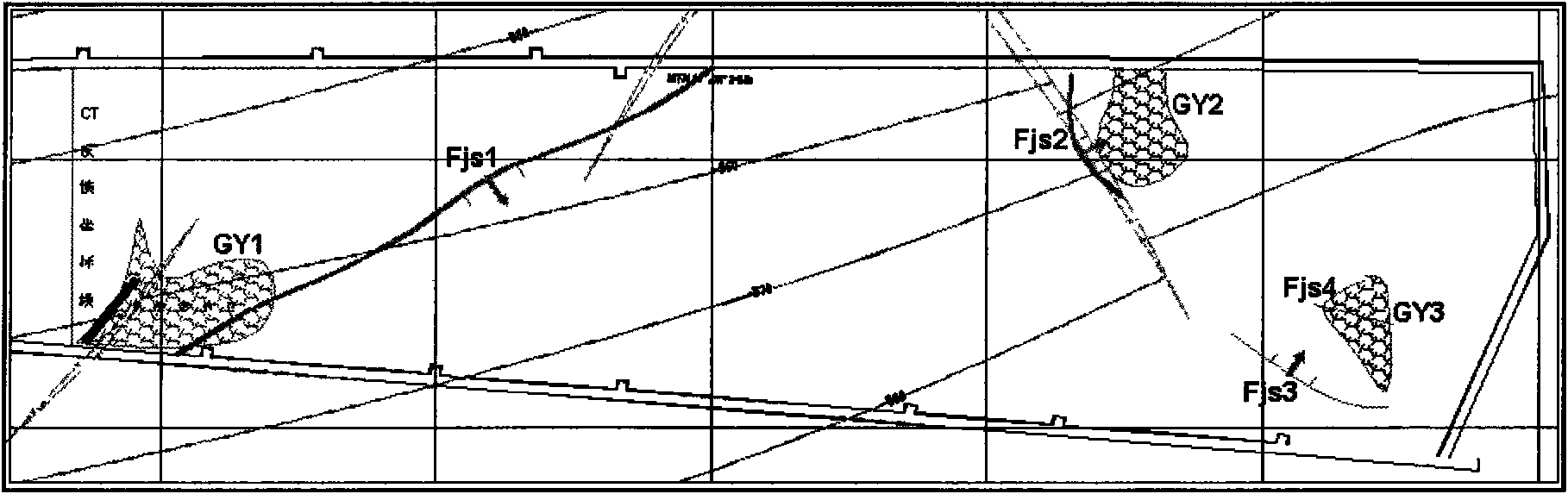
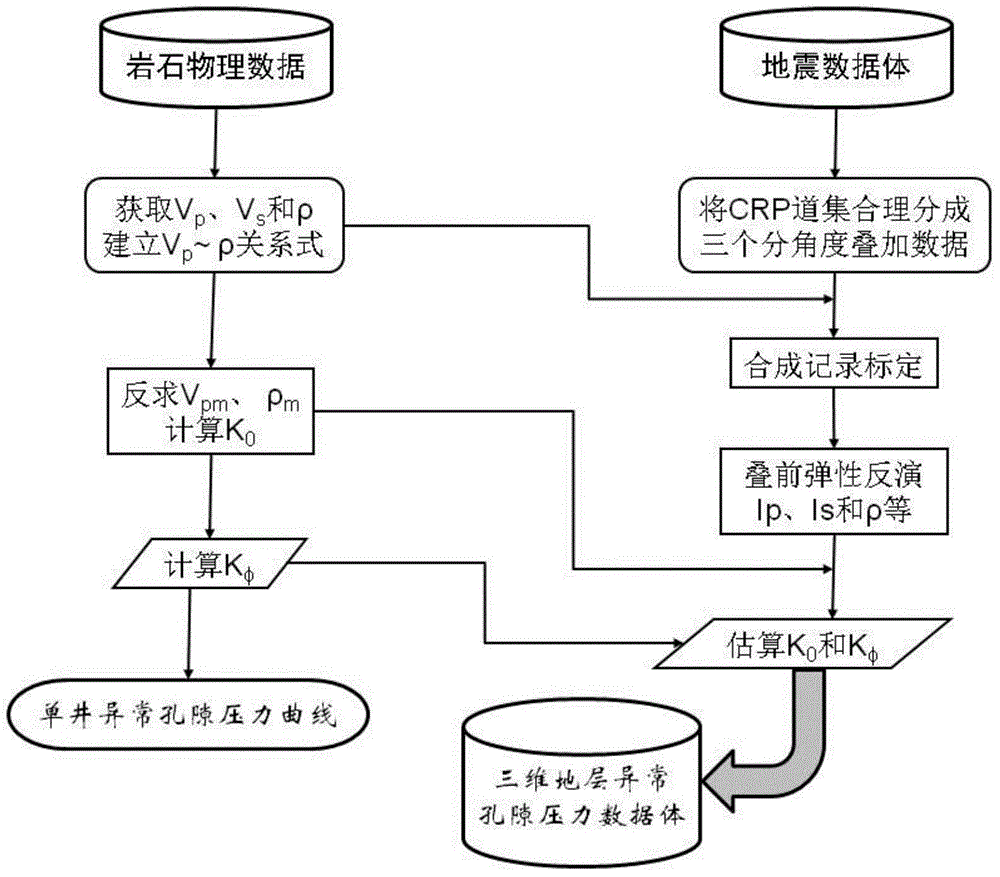
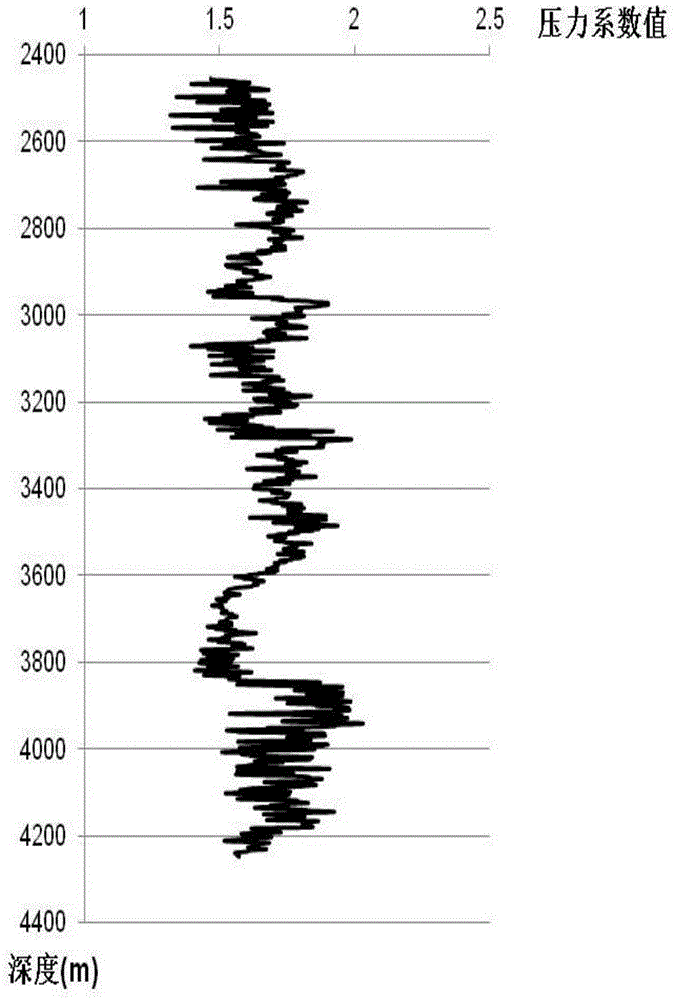
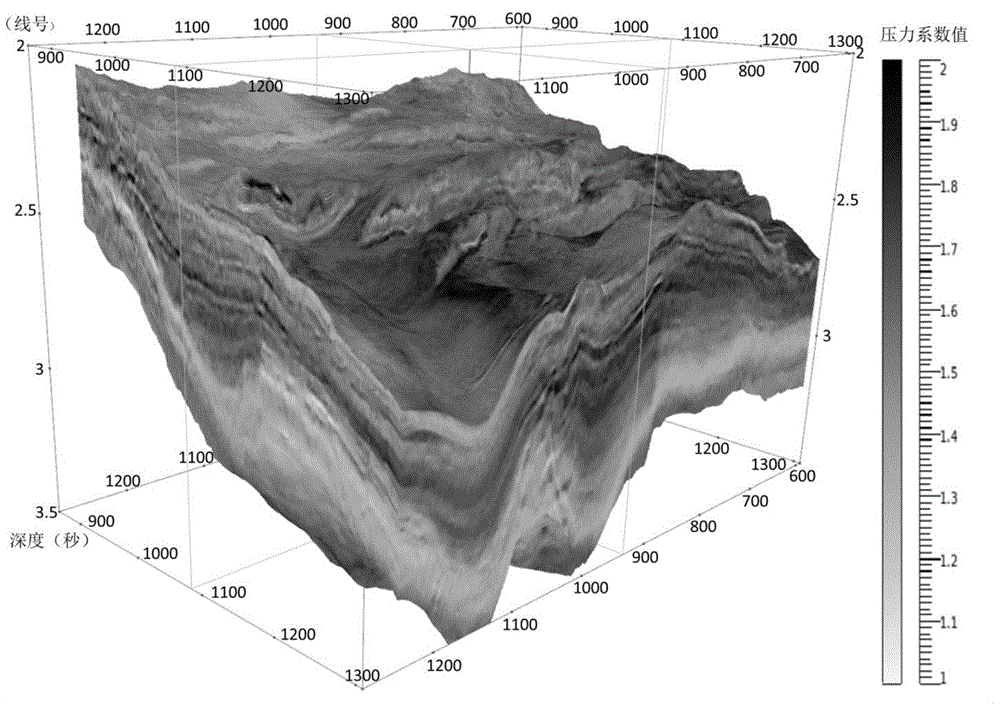
Method for predicting three-dimensional abnormal pore pressure based on rock physical seismic information
The invention relates to a method for predicting three-dimensional abnormal pore pressure based on rock physical seismic information. The method comprises the steps that the lithologic stratum matrix bulk modulus is calculated by applying parameters of the rock physical longitudinal wave velocity, transverse wave velocity and density, rock core geological analysis is additionally conducted so as to calculate the dry pore spatial rigidity, the pore pressure coefficient is obtained accordingly, and the single-well stratum abnormal pore pressure is calculated; and secondly, a three-dimensional data cube of the longitudinal wave impedance, the transverse wave impedance, Poisson ratio and the density is obtained by applying a three-dimensional seismic reflection data cube and three-dimensional prestack elastic wave impedance retrieval method, and the three-dimensional stratum abnormal pore pressure is predicted by reference to the single-well stratum abnormal pore pressure calculation method and an obtained empirical formula. According to the method for predicting the three-dimensional abnormal pore pressure based on the rock physical seismic information, rock physical parameters obtained indirectly through logging and seismic geophysical methods are applied to prediction of the abnormal stratum pore pressure, and the practice is easier compared with direct measuring of rock physical parameters in a laboratory, more scientific compared with subjective parameter presetting, and finer compared with calculation separately through post-stack seismic velocity.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Multi-bridge static sounding equipment and multi-bridge static sounding test method
InactiveCN102966086AIncrease the amount of test informationLow costIn situ soil foundationSeismic velocityPore water pressure
The invention discloses multi-bridge static sounding equipment which comprises a static sounding rod and a force applying device, wherein a probe is arranged at the bottom end of a rod body; the force applying device is positioned above the static sounding rod and applies force to the static sounding rod; and a conical tip resistance sensor for measuring the resistance of a conical tip and a side wall friction resistance sensor for measuring the side wall friction resistance are arranged on the probe. The multi-bridge static sounding equipment is characterized in that the static sounding rod further comprises a microcamera for underground shooting and a plurality of sensors; the sensors are respectively used for measuring the pore water pressure, the temperature, the side pressure, the inclination, water content, the seismic velocity and seismic acceleration; and the sensors can be arranged in a connector and can be sequentially connected according to the requirement of test projects or can be directly and fixedly arranged inside the rod body of the static sounding rod or can be integrated on the probe to form the multifunctional probe. Due to the adoption of the technical scheme provided by the invention, one test process can be used for testing a large amount of projects so as to obtain abundant underground geotechnical information. The invention further discloses a multi-bridge static sounding test method.
Owner:广东永基建筑基础股份有限公司
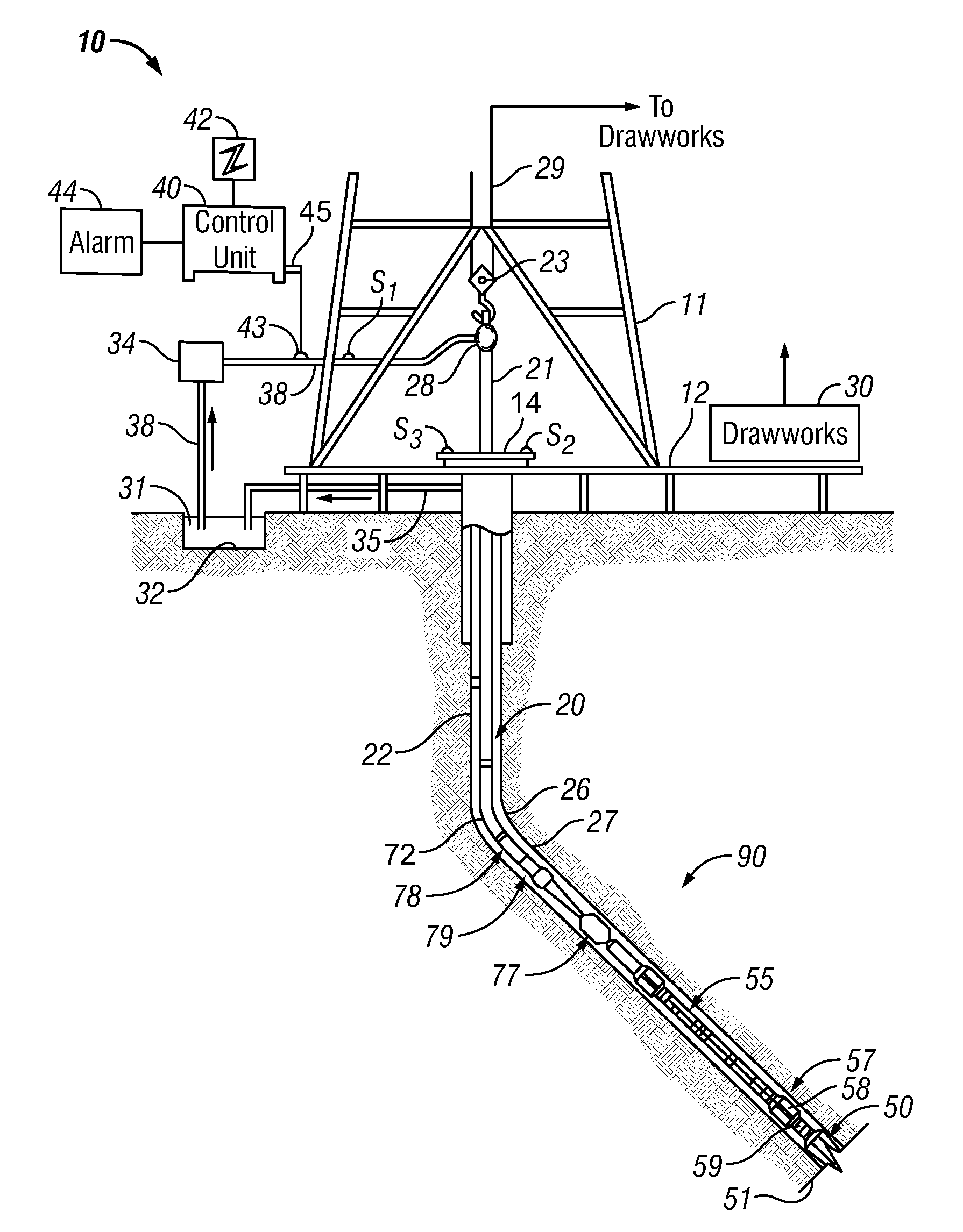
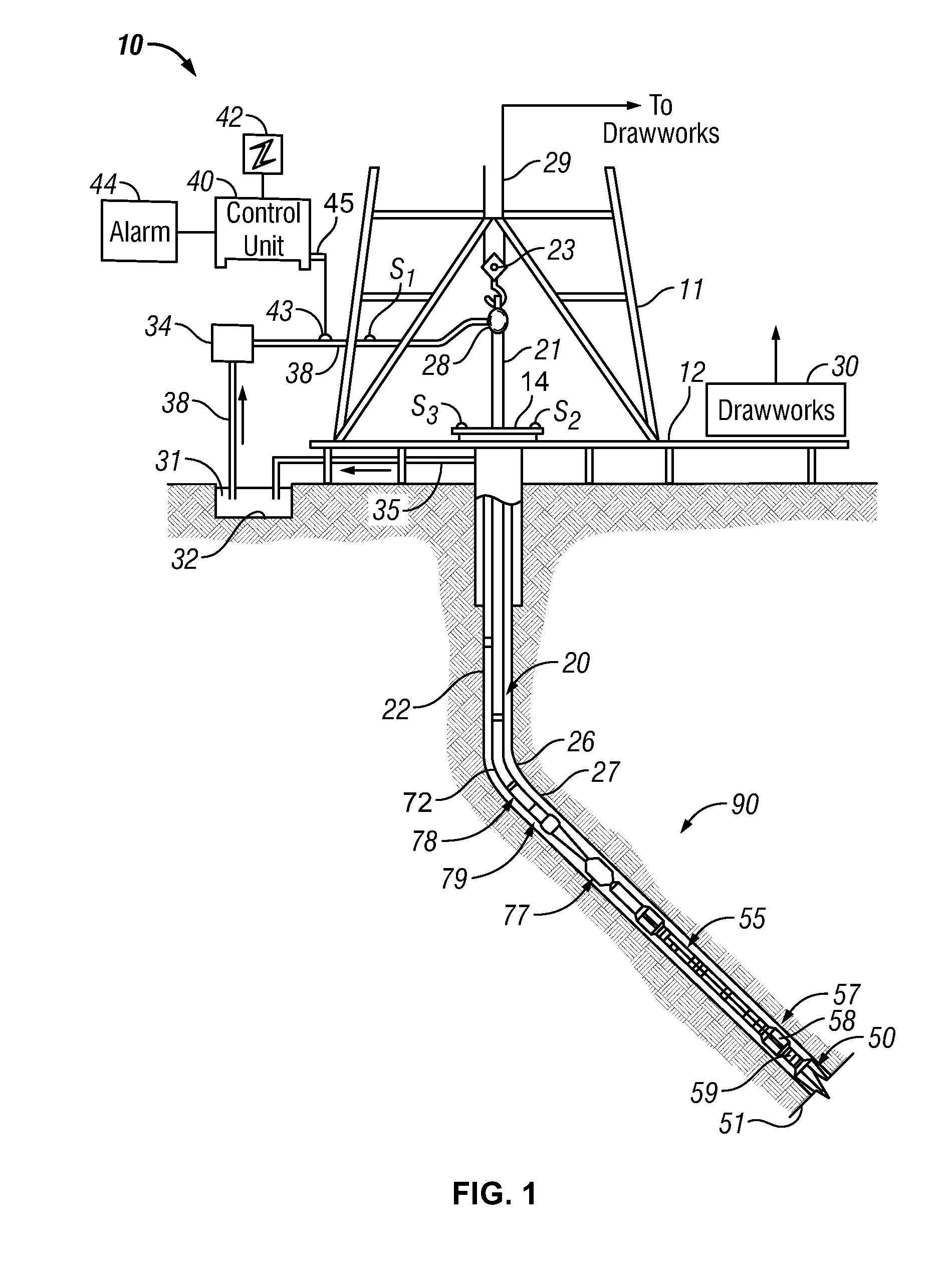
Drill-Bit Seismic With Downhole Sensors
A drill-bit seismic method where the seismic receivers are located in the BHA. The data detected by these receivers is processed by a downhole processing unit in order to estimate the interval velocity of the seismic wave between the sensors and between the bit and a sensor. Additionally, the processed data might provide the distance to a seismic reflector close to the borehole and the average seismic velocity between the well and this reflector. The processed data can be transmitted to surface location by mud-pulse telemetry. The pilot signal can be also used to process seismic data recorded by receivers located at the earth surface (or close to it).
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Method for optimizing seismic velocity analysis data in oil and gas exploration
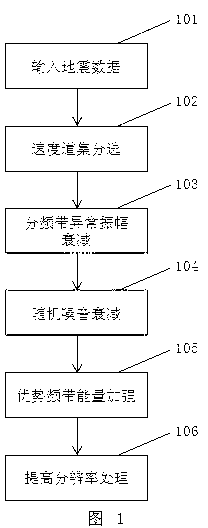
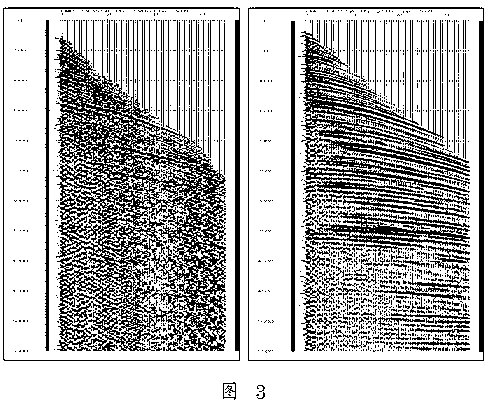
ActiveCN103217713AImprove signal-to-noise ratioImprove qualitySeismic signal processingSeismic velocityAnalysis data
The invention provides a method for optimizing seismic velocity analysis data in oil and gas exploration. The method for optimizing the seismic velocity analysis data in the oil and gas exploration includes the following steps: velocity trace gather sorting is carried out on the seismic data, and an ultra trace gather used for velocity analysis is sorted out; sub-band abnormal amplitude attenuation is carried out; F-X-Y domain three-dimensional prestack random noise attenuation is carried out; frequency filtering is carried out, so that energy of a superiority frequency band of reflection waves can be enhanced; and wavelet shaping deconvolution processing is carried out to improve resolution. The method for optimizing the seismic velocity analysis data in the oil and gas exploration solves the problems that in the prior art, focusing of an energy group in velocity analysis is poor and precision is low, and has the advantages that effective reflection energy can be enhanced, the quality of the velocity analysis data is improved, the signal-to-noise ratio and the resolution of the velocity analysis trace gather are improved, and the focusing property of a velocity spectrum can be improved.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
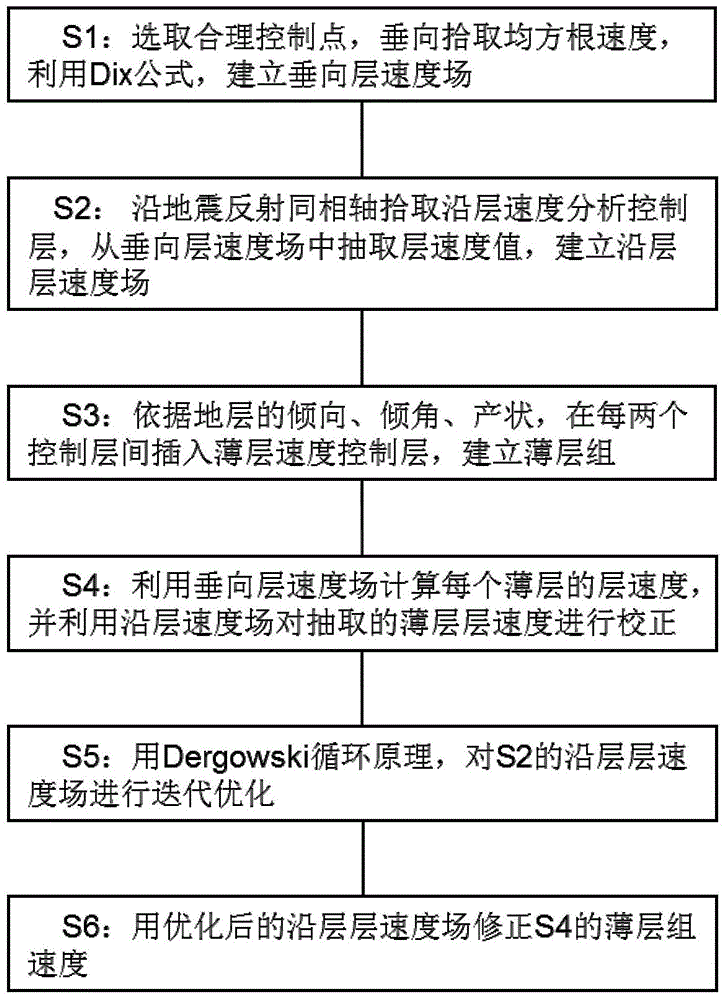
Horizon chromatography inversion earthquake speed modeling method with thin layers used and modeling unit
The invention discloses a horizon chromatography inversion earthquake speed modeling method with thin layers used and a modeling unit. The use of the thin layers is introduced in a horizon chromatography inversion method so that the precision of a speed field can be improved. The method includes the following steps that a perpendicular layer speed field is set up; earthquake reflecting interfaces are picked to serve as control layers for horizon speed analysis, and a horizon layer speed field is set up; a thin layer speed control layer is inserted between every two control layers, and a thin layer set is set up; the perpendicular layer speed field is used for calculating the layer speed of each thin layer, and the horizon layer speed field is used for correcting the picked thin layer speed; iterative optimization is conducted on the horizon layer speed field; the obtained optimized speed field is used for correcting the thin layer set speed. According to the horizon chromatography inversion earthquake speed modeling method with the thin layers used and the modeling unit, due to the linked application of the perpendicular speed modeling method and the horizon speed modeling method, the layer interior constant speed of the horizon speed field is replaced by the perpendicular speed detail characteristics of the perpendicular speed field, and the precision of earthquake speed modeling is improved.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Method of predicting the pressure sensitivity of seismic velocity within reservoir rocks
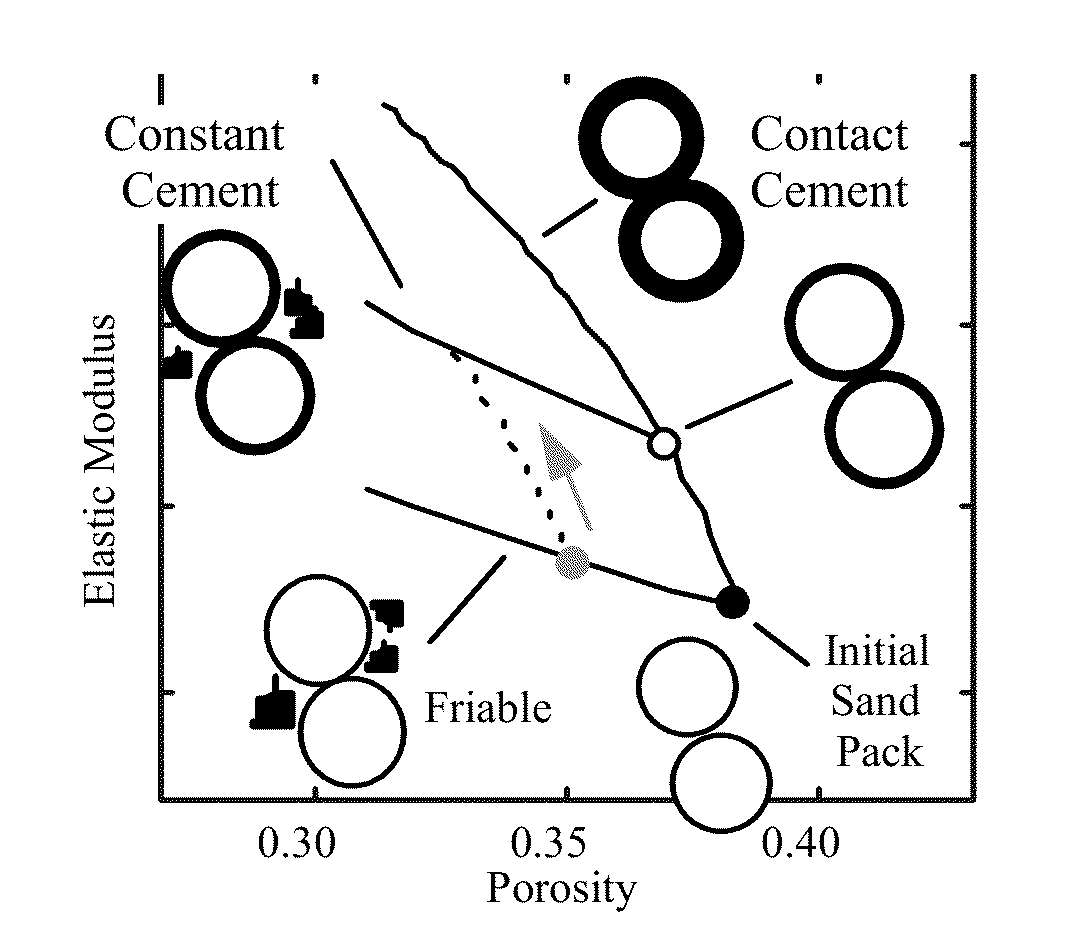
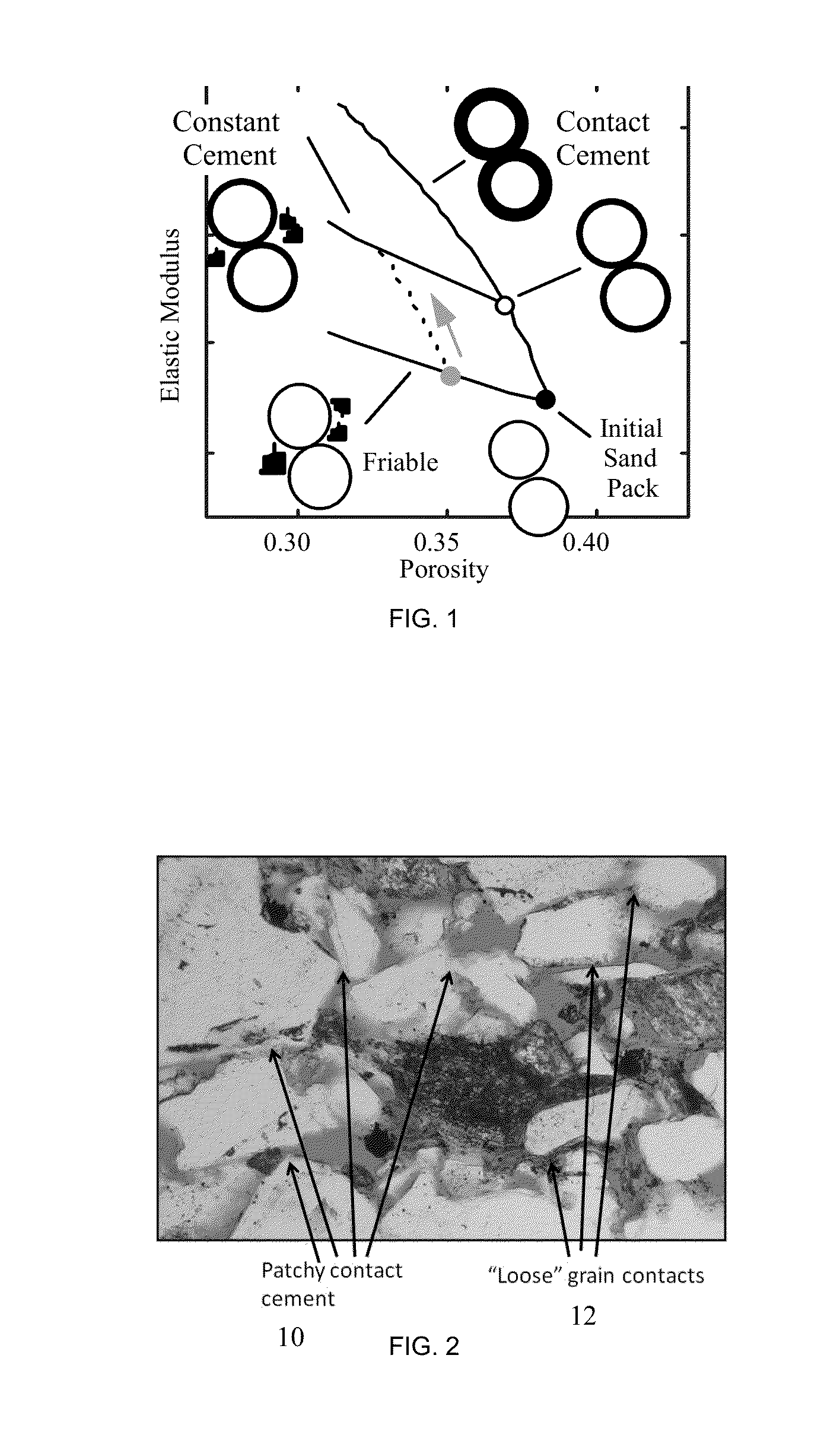
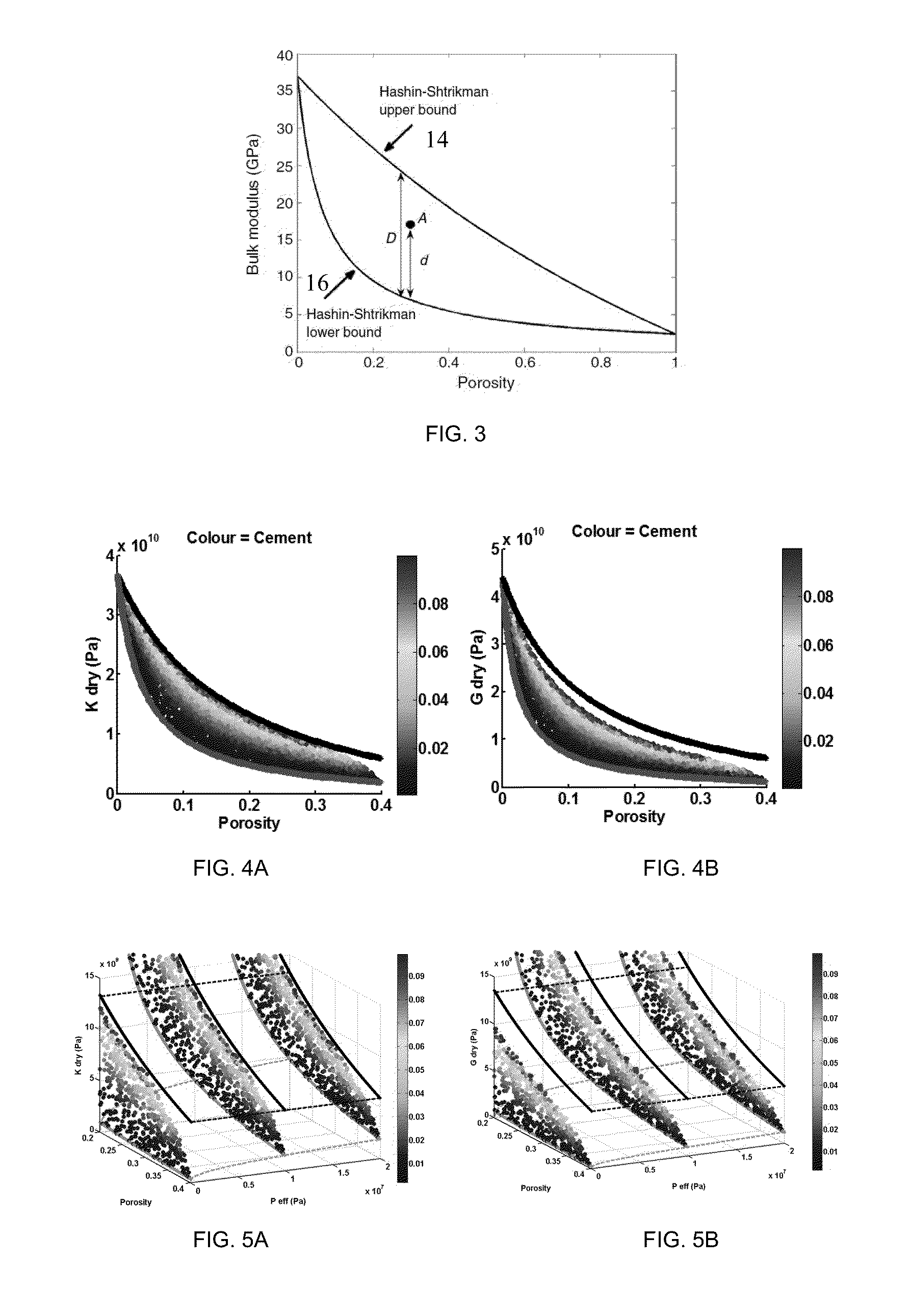
A method of predicting the pressure sensitivity of seismic velocity within reservoir rocks includes defining the degree of cementation of rock as at least one of friable sand, partially cemented rock and cemented rock. For rock including friable sand, a first model specifying a dependence of seismic velocity upon pressure is defined. For rock including partially cemented rock, a second model specifying a dependence of seismic velocity upon pressure and a weighting function accounting for a degree of cementation of the rock is defined. For rock including cemented rock, a third model demonstrating an insensitivity of seismic velocity to pressure is defined. For a given dry rock moduli and porosity, the method includes determining a degree of cementation, selecting the appropriate model, and using the selected model to predict the sensitivity of seismic velocity to pressure.
Owner:DEN NORSKE STATS OLJESELSKAP AS
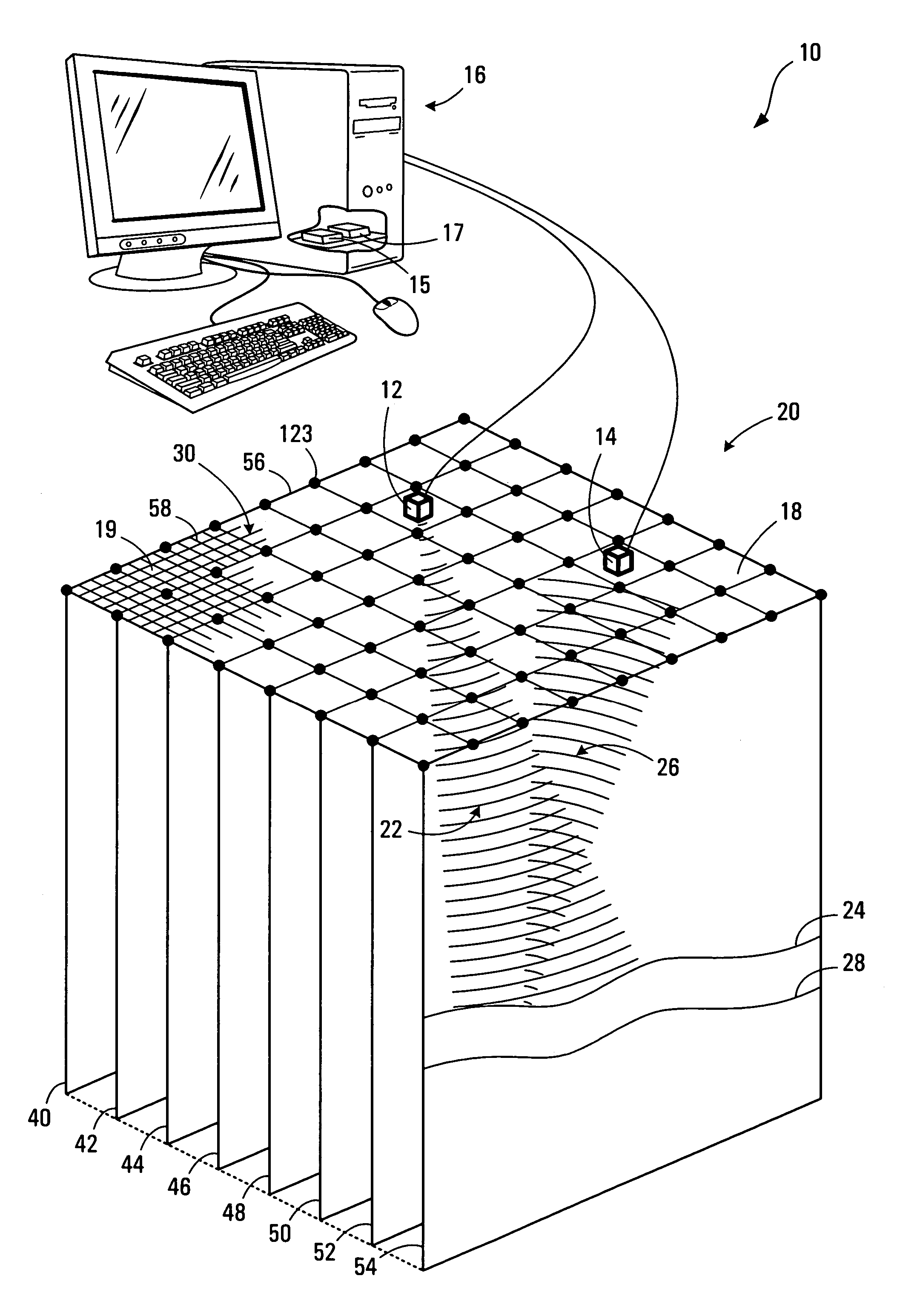
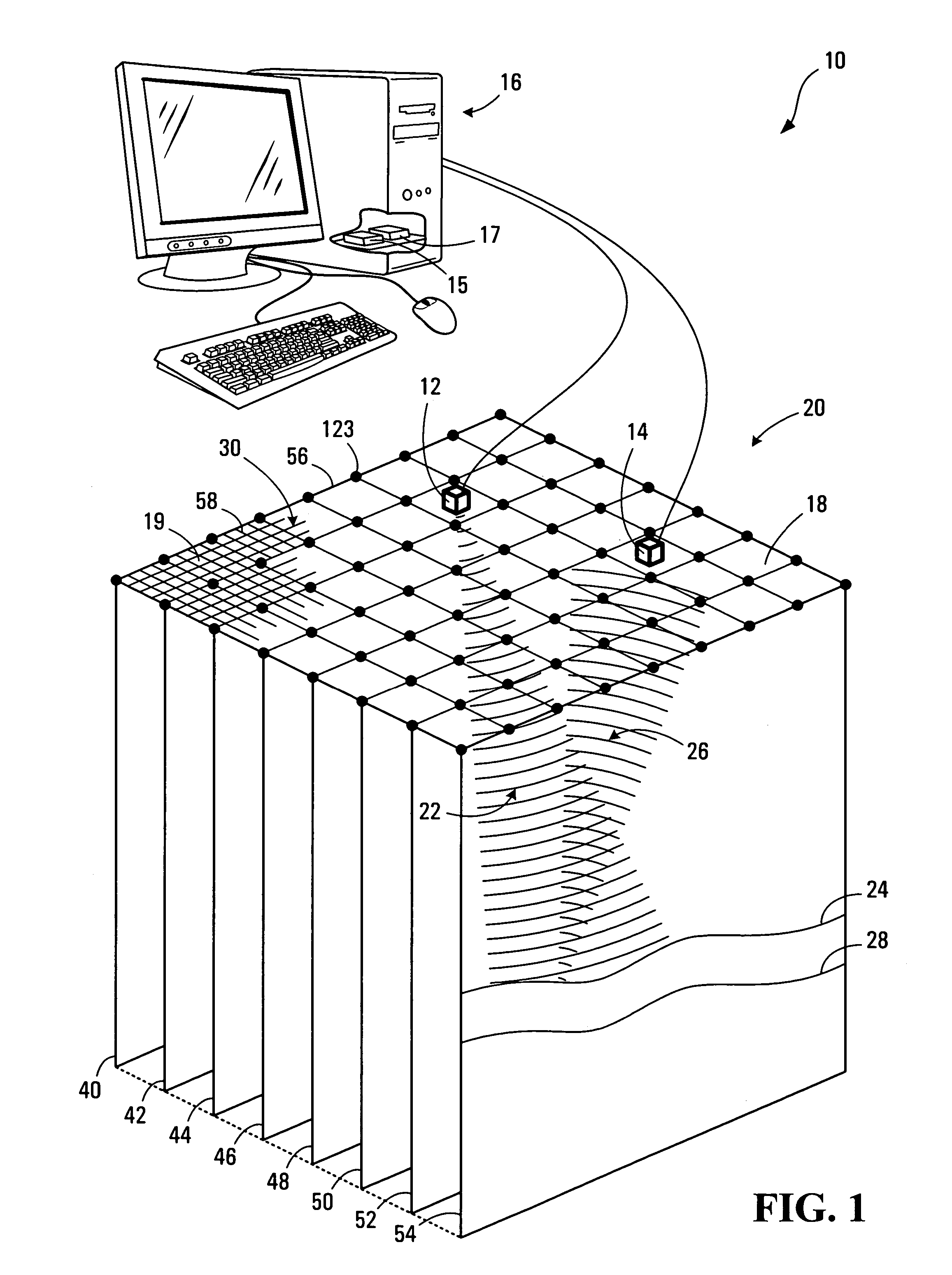
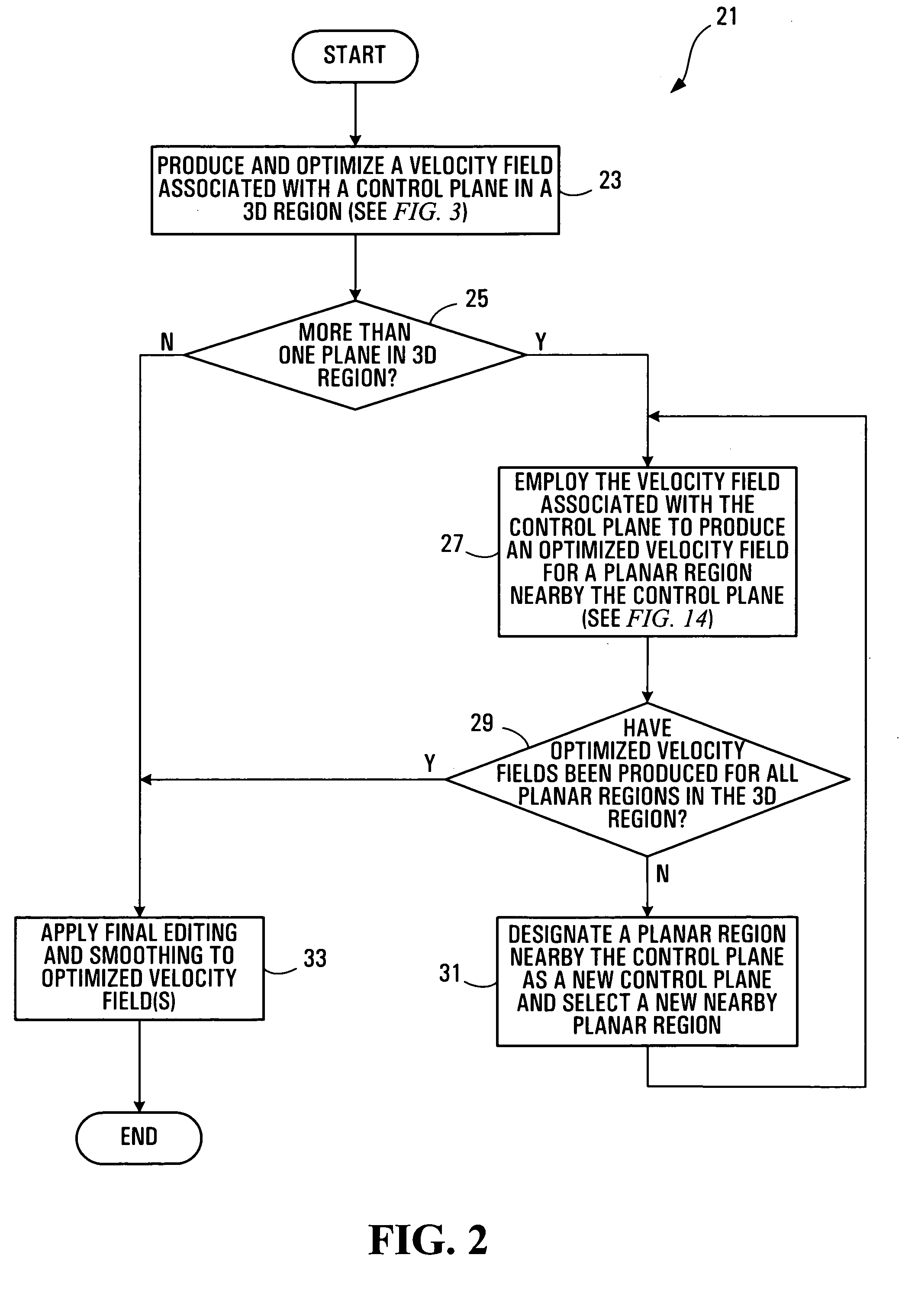
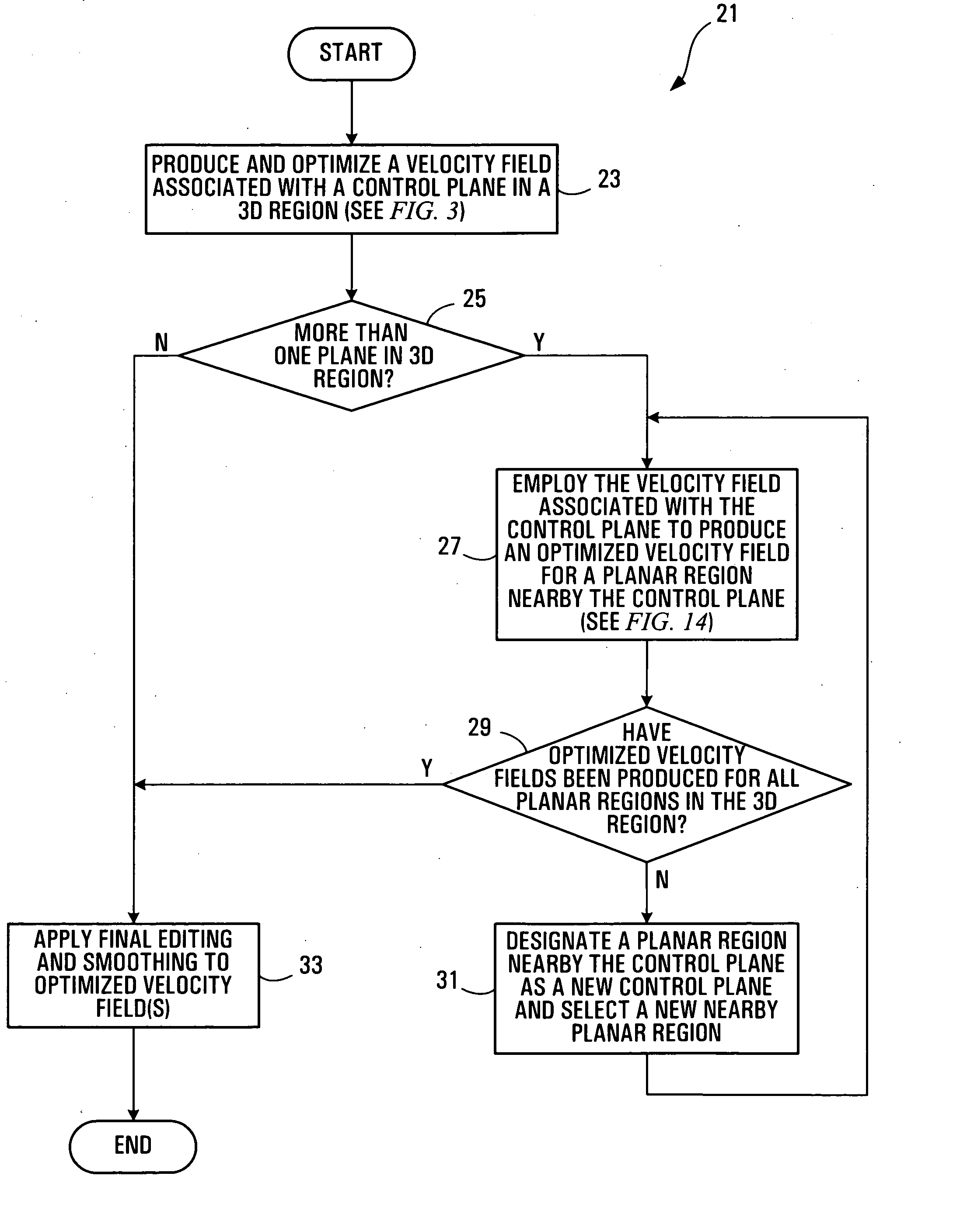
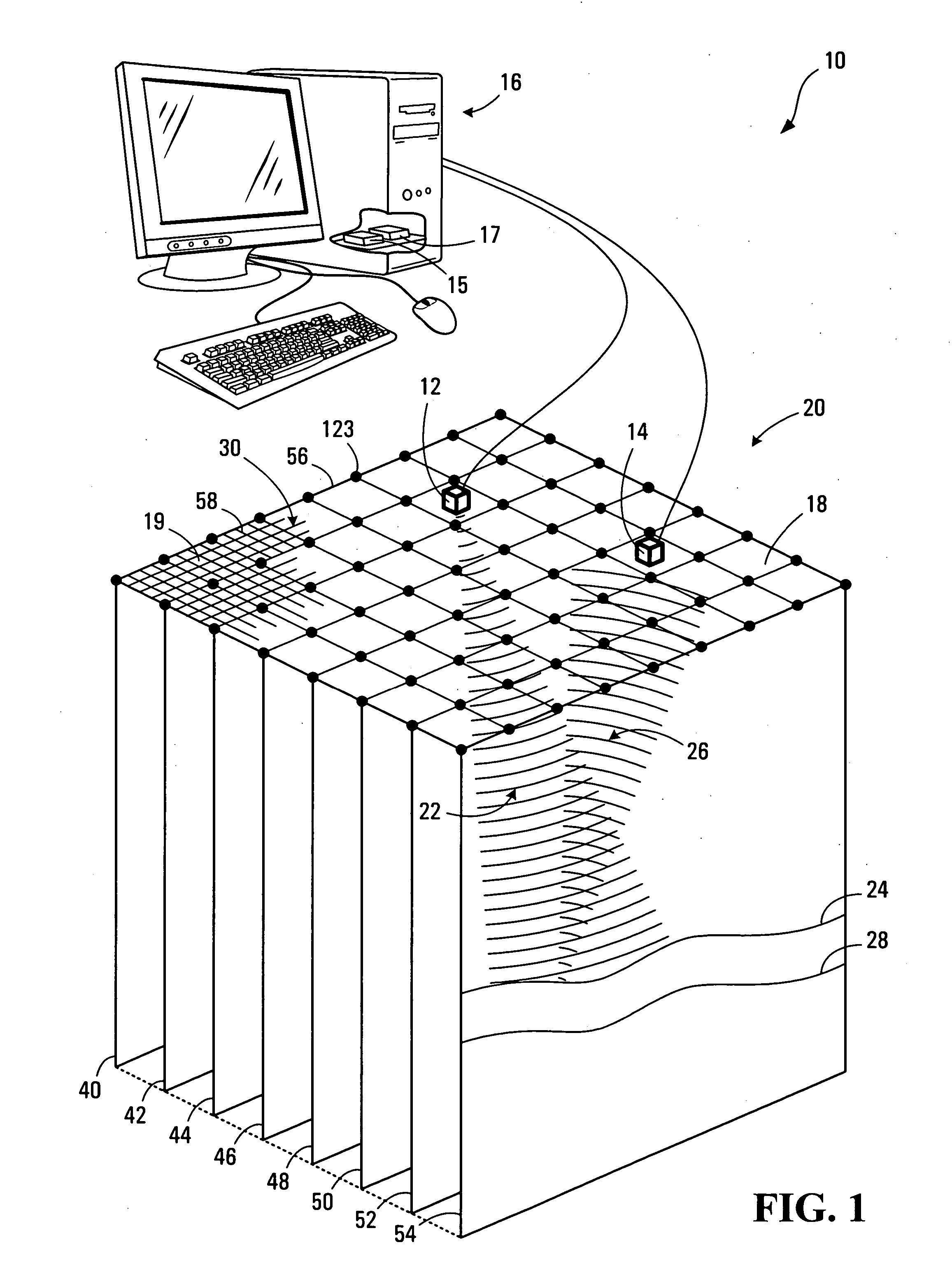
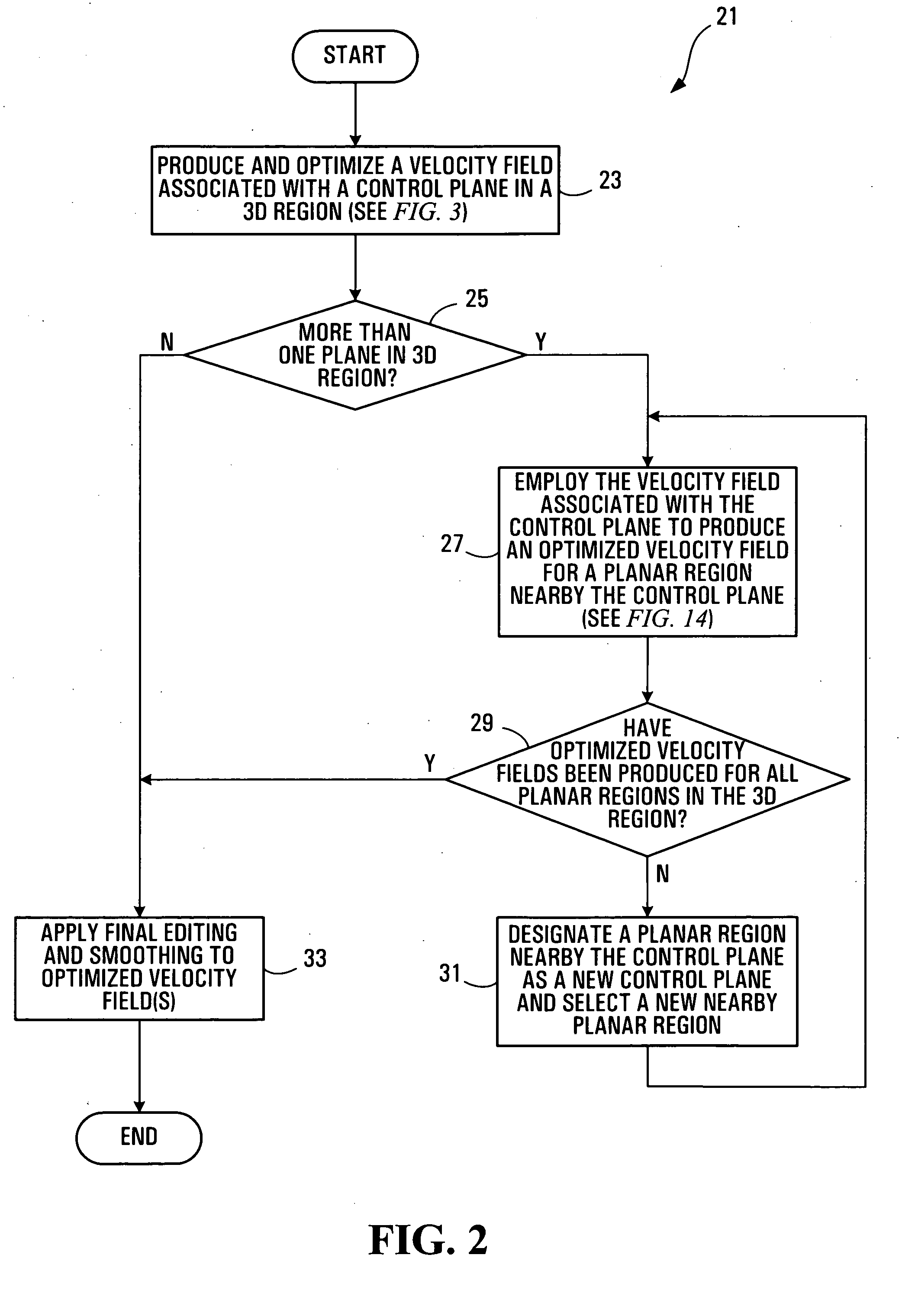
Method, media, and signals for processing seismic data to obtain a velocity field
ActiveUS7117093B2Seismic signal processingAnalogue computers for heat flowSeismic velocityOffset distance
A method and apparatus for estimating a seismic velocity field from seismic data including time-amplitude representations associated with source-receiver locations spaced apart by an offset distance and having a midpoint therebetween, the seismic data being arranged into common midpoint (CMP) gathers associated with respective CMP locations. A control plane having an edge intersecting a plurality of the CMP locations is defined, an initial velocity field for the control plane is produced, the initial velocity field including a plurality of time-velocity values for each of the CMP locations; and an optimized velocity field for the control plane is produced by adjusting the time-velocity values for each of the CMP locations in response to trends, relative to offset distance, in time values, associated with common seismic events, until said optimized velocity field satisfies a condition.
Owner:DATA MODELING
High-precision speed locker for multi-span bridge anti-seismic
InactiveCN102296528AHigh sensitivityGood reversibilityBridge structural detailsShock proofingSeismic velocityThickened fluids
The invention relates to a high-precision speed locker for anti-seismic use of multi-span bridges. Including the cylinder part, the piston part and the working material; the piston part and the cylinder part are assembled to form a whole, and the working material is located in the cylinder; the working material is a shear thickening liquid or a shear thickening gel; the cylinder body The end cover is a cylindrical sealing cover, and the bottom of the sealing cover is provided with a boss matching the inner diameter of the cylinder; the outer side of the sealing cover is provided with a dust cover; the piston rod and the connecting rod are threaded ; A liquid injection hole is opened on the side wall of the cylinder body, and a plunger is arranged in the liquid injection hole. The shear thickening liquid and shear thickening gel used in the present invention are very soft at ordinary times and have easy flowability under normal conditions. Once the critical shear rate is reached, the viscosity increases rapidly and finally becomes a hard solid. Return to the soft state; make the speed locker have the characteristics of precision, high sensitivity, and good reversibility.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Method for three dimensional seismic travel time tomography in transversely isotropic media
A method for estimating seismic velocities in vertically transversely isotropic media includes generating an initial estimate of vertical interval velocity and interval normal moveout velocity with respect to depth from seismic data. An initial estimate is generated of a first anisotropy parameter with respect to depth. The first anisotropy parameter is related to the interval normal moveout velocity and the interval vertical velocity. An initial estimate is generated with respect to depth of a second anisotropy parameter. The second anisotropy parameter is related to the first anisotropy parameter and an interval anelliptic parameter. A first tomographic inversion is performed with respect to the interval normal moveout velocity and the second anisotropy parameter at a constant value of the first anisotropy parameter until travel time differentials reach minimum values. Layer depths are adjusted with the initial estimate of vertical interval velocity. Using values of the second anisotropy parameter determined in the first tomographic inversion, a second tomographic inversion is performed of interval normal moveout velocity and the first anisotropy parameter with respect to depth. The adjusted layer depths, interval normal moveout velocities and interval vertical velocities are again adjusted and interval anelliptic parameters are calculated from the second tomographic inversion.
Owner:PGS GEOPHYSICAL AS
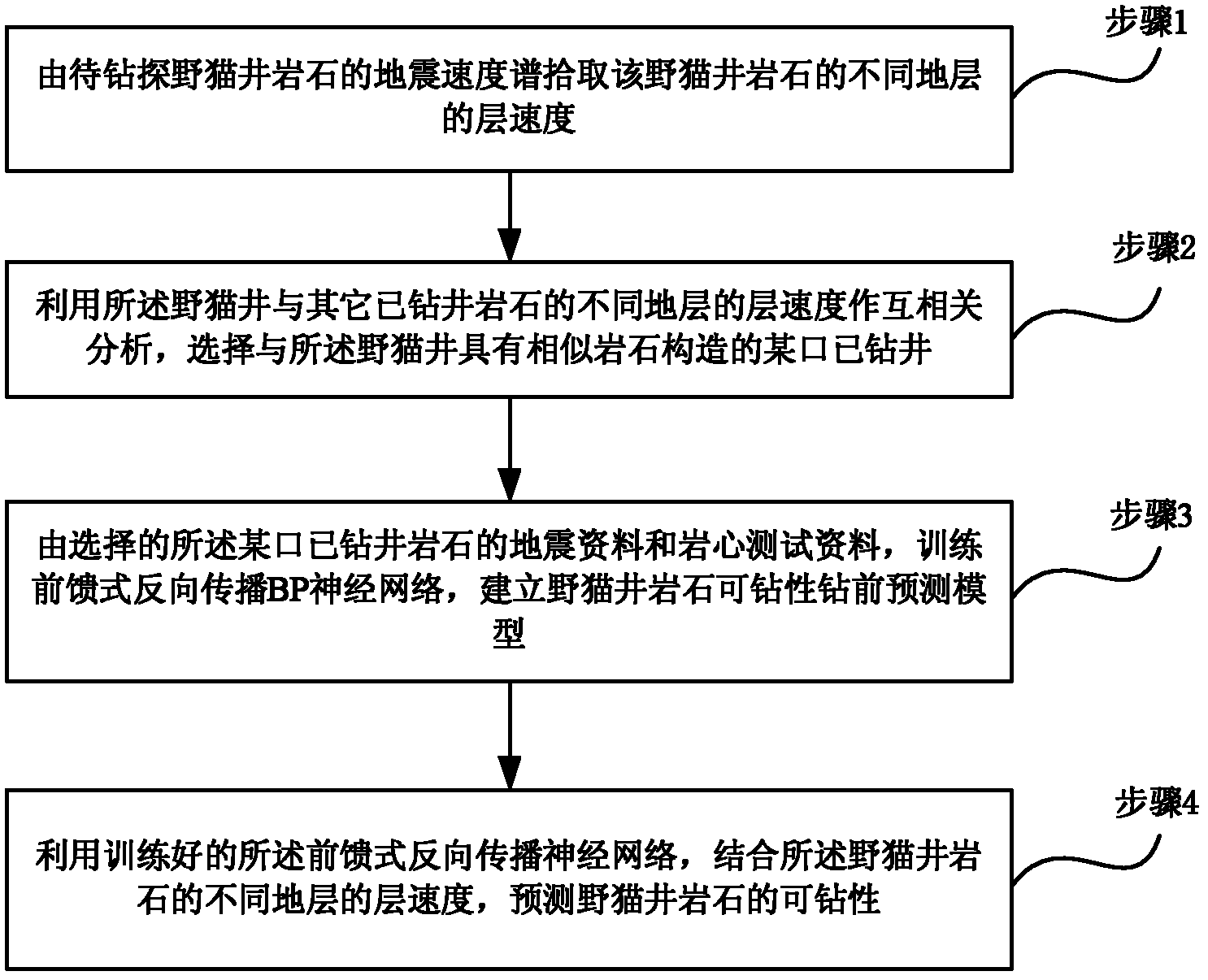
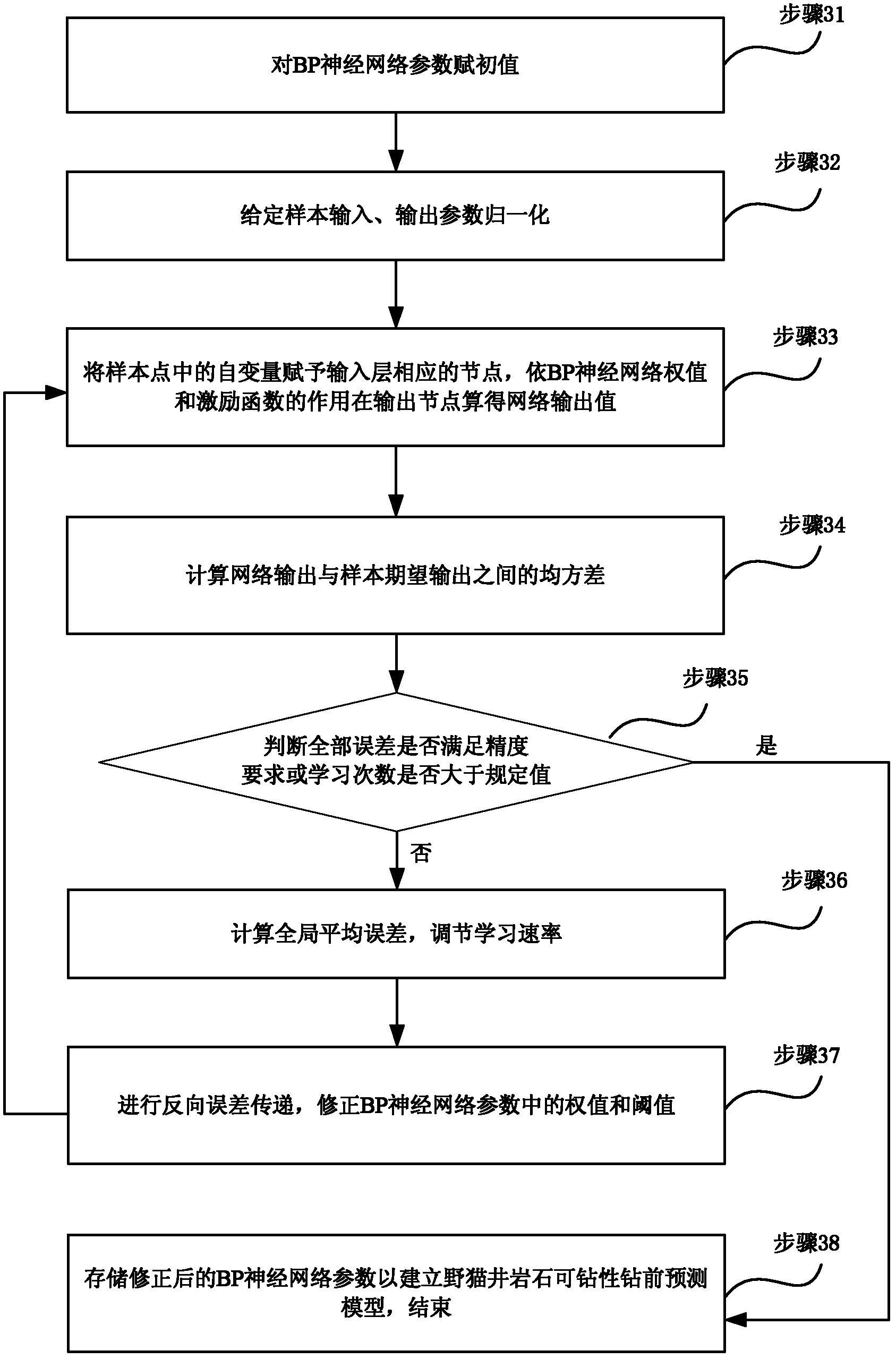
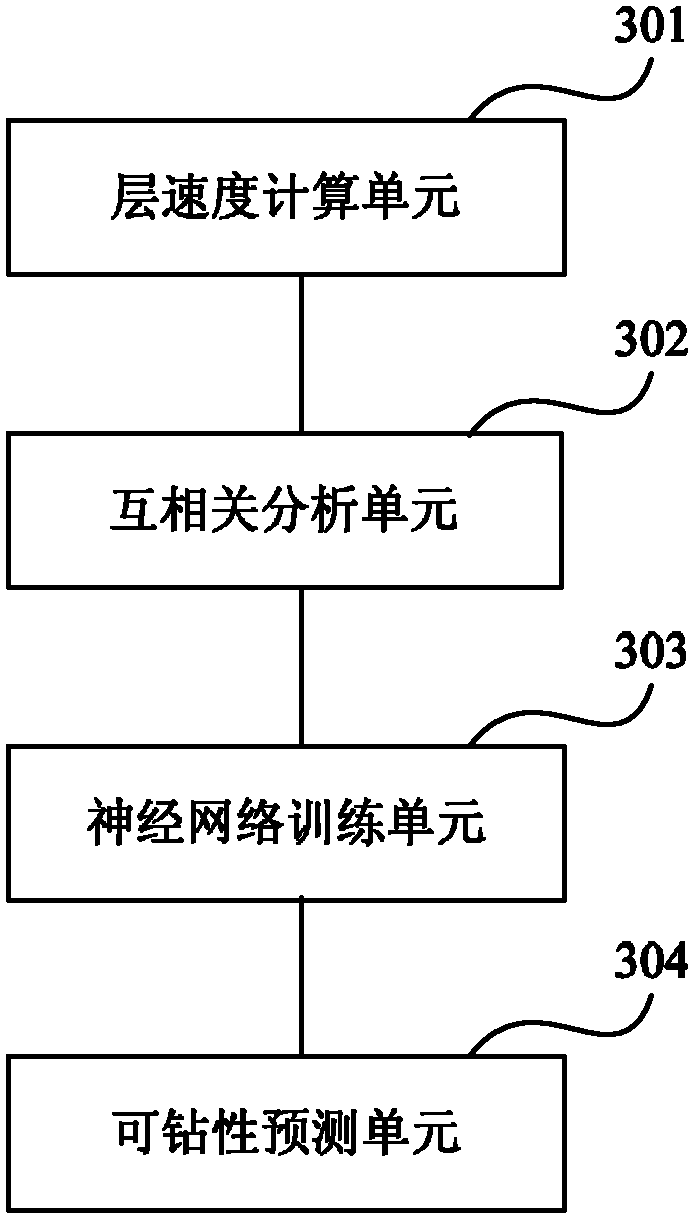
Method and device for predicting rock drillability of wildcat well before drilling
InactiveCN102606151AIncrease drilling speedLower Drilling CostsBiological neural network modelsBorehole/well accessoriesCross correlation analysisSeismic velocity
The invention provides a method and a device for predicting rock drillability of a wildcat well before drilling. The method includes: picking up layer velocities of different layers of wildcat well rocks by the aid of a seismic velocity spectrum for the wildcat well rocks to be drilled; performing correlation analysis by the aid of the layer velocities of the different layers of the wildcat well and other drilled rocks, and selecting a certain drilled well with a rock structure similar to the wildcat well; training a feedforward BP (back-propagation) neural network according to seismic data and core test data of rocks of the selected drilled well to establish a model for predicting the rock drillability of the wildcat well before drilling; and predicting the rock drillability of the wildcat well by the aid of the trained feedforward BP neural network and the layer velocities of the different layers of the wildcat well rocks. By the aid of the method and the device, the relationship between each layer velocity and the rock drillability can be found, important data can be provided for reasonably selecting drilling modes, drill bit types and designed drilling parameters, drilling speed can be increased, and drilling cost can be reduced.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (BEIJING)
Method of determining a seismic velocity profile
A seismic velocity profile in a region of interest in a subsurface formation is determined using at least the following steps.(a) Activating a seismic source at a location n, thereby exciting a wave in the subsurface formation.(b) Recording a wave signal trace unm(t) against time t, at a seismic receiver m.(c) Recording a wave signal trace unk(t) against time t at a seismic receiver k.(d) Cross correlating the wave signal traces unm(t) and unk(t) to obtain uconvnmnk(t).(e) Repeating these steps, for different locations n;(f) Summing uconvnmnk(t) over all locations n, to obtain a signal trace uvsmk(t) which corresponds to the signal received by the seismic receiver k from the virtual source at the position of seismic receiver m;(g) Deriving the seismic velocity based on the time of first arrival of the wave in uvsmk(t) and the predetermined distance between the seismic receiver m and the seismic receiver k.
Owner:SHELL USA INC
Forming a geological model
ActiveUS8442770B2Preparing sample for investigationSeismic signal processingSeismic velocityGeophysics
A method of forming a geological model of a region of the earth includes obtaining seismic data relating to the region, the seismic data including seismic traveltime uncertainty. A seismic velocity model of the region may also be provided and includes velocity uncertainty. Ray tracing may be performed on the seismic data using the velocity model to determine the three dimensional positions of a plurality of points of the region. The three dimensional positional uncertainties (7-12) of at least some of the points can be calculated from the traveltime uncertainty, the velocity uncertainty, and uncertainty in the ray propagation direction. This can be combined with the positions determined by the ray tracing to form a geological model.
Owner:EQUINOR ENERGY AS
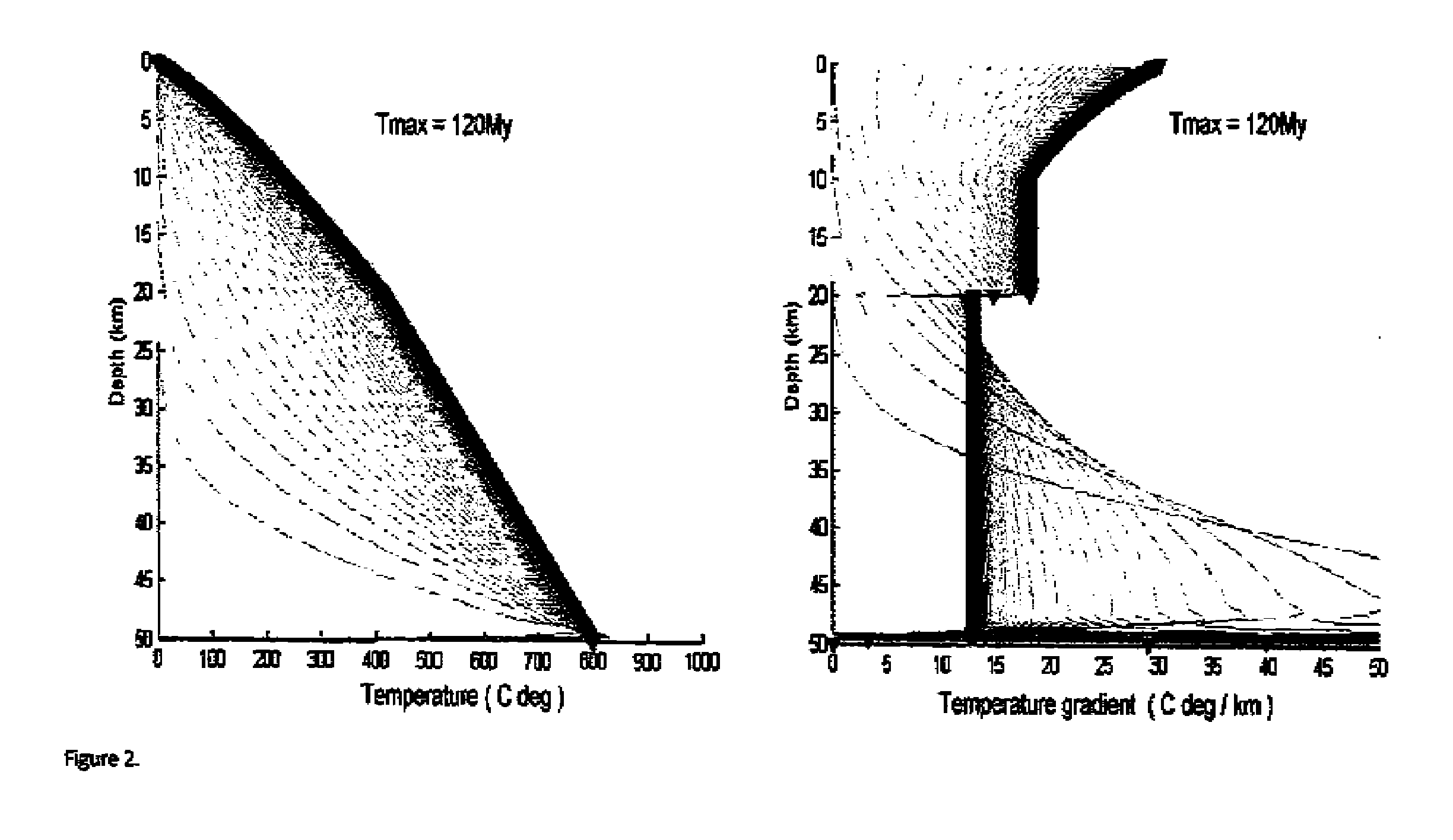
Temperature modeling constrained on geophysical data and kinematic restoration
ActiveUS20150242362A1Reduce uncertaintyAccurate kinematic restorationGeomodellingComputation using non-denominational number representationPorosityOcean bottom
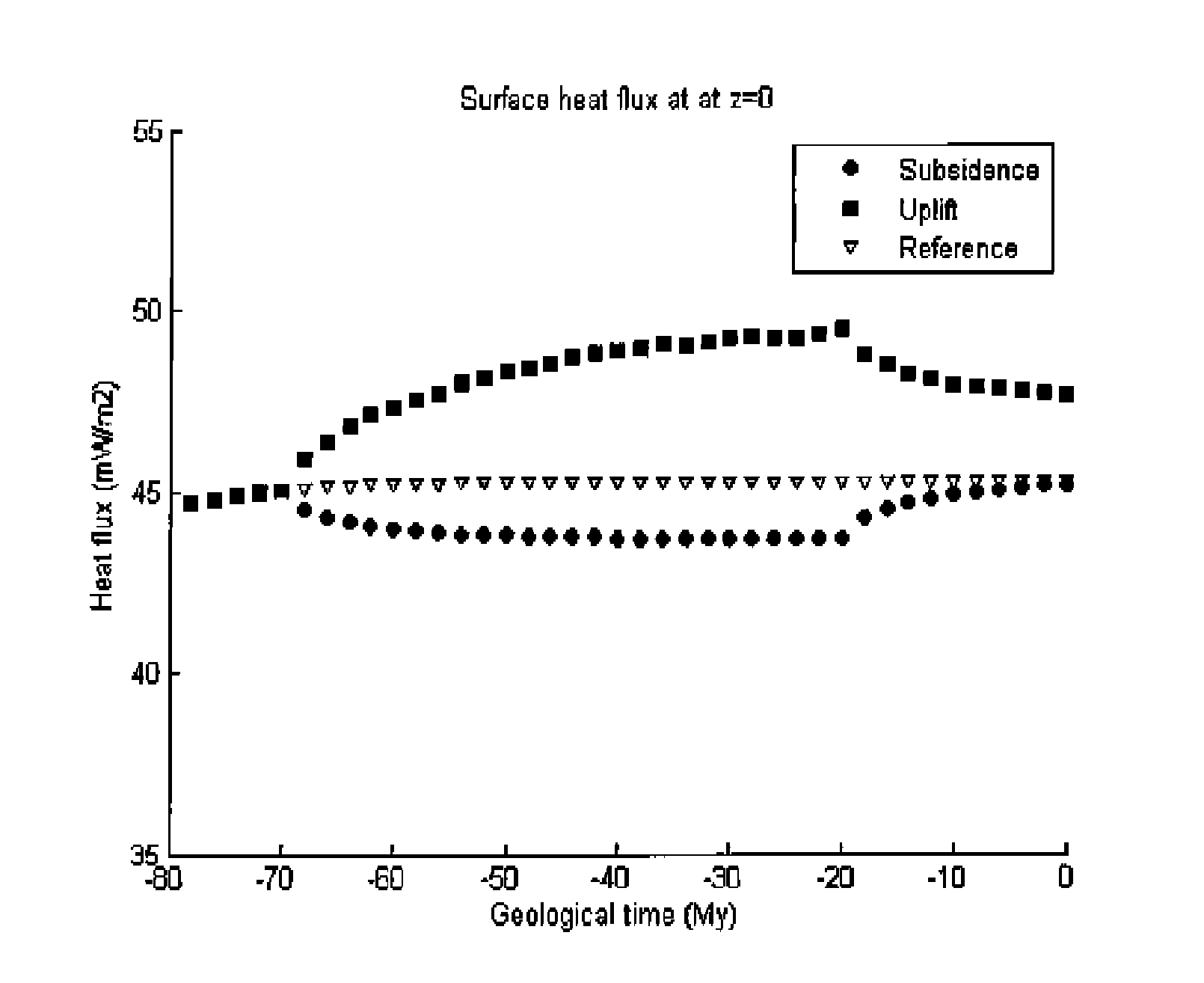
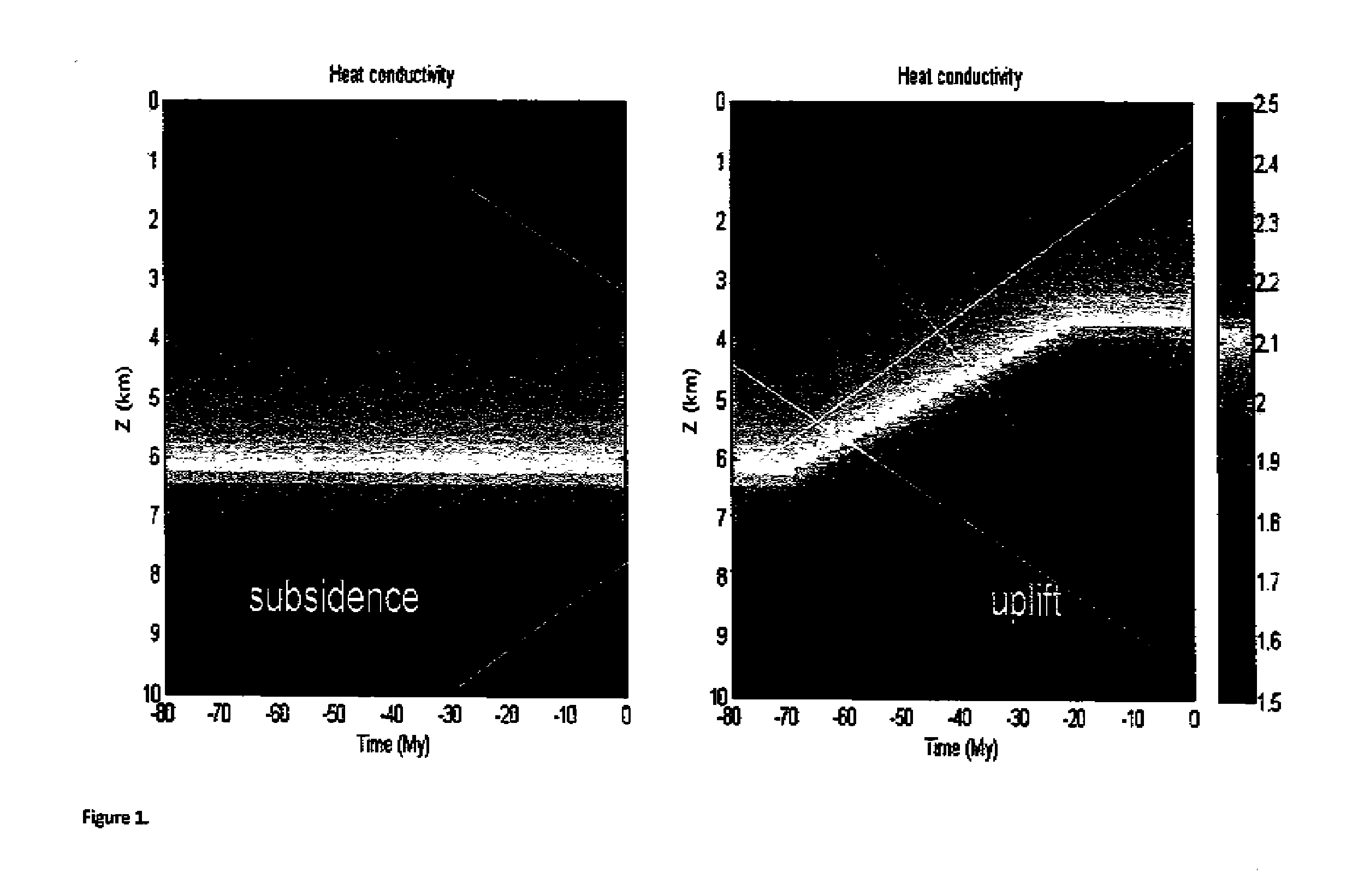
A method is disclosed for the estimation of subsurface temperature distributions from a 3-dimensional heat conductivity model for a geological formation. The method may be characterized by the following steps: (a) obtaining measured data corresponding to a geological subsurface formation of interest including seismic survey data, in-well temperature, seafloor or surface heat flux measurements and laboratory-based measurements of core porosity, (b) estimating a relationship between seismic velocity and heat conductivity, wherein seismic velocity is linearly dependent on porosity and heat conductivity is exponentially or linearly dependent on porosity, and (c) calibrating the model to the measured in-well data and laboratory-based measurements of core porosity.
Owner:DEN NORSKE STATS OLJESELSKAP AS
Method, media, and signals for processing seismic data to obtain a velocity field
ActiveUS20050197779A1Seismic signal processingAnalogue computers for heat flowOffset distanceSeismic velocity
A method and apparatus for estimating a seismic velocity field from seismic data including time-amplitude representations associated with source-receiver locations spaced apart by an offset distance and having a midpoint therebetween, the seismic data being arranged into common midpoint (CMP) gathers associated with respective CMP locations. A control plane having an edge intersecting a plurality of the CMP locations is defined, an initial velocity field for the control plane is produced, the initial velocity field including a plurality of time-velocity values for each of the CMP locations; and an optimized velocity field for the control plane is produced by adjusting the time-velocity values for each of the CMP locations in response to trends, relative to offset distance, in time values, associated with common seismic events, until said optimized velocity field satisfies a condition.
Owner:DATA MODELING
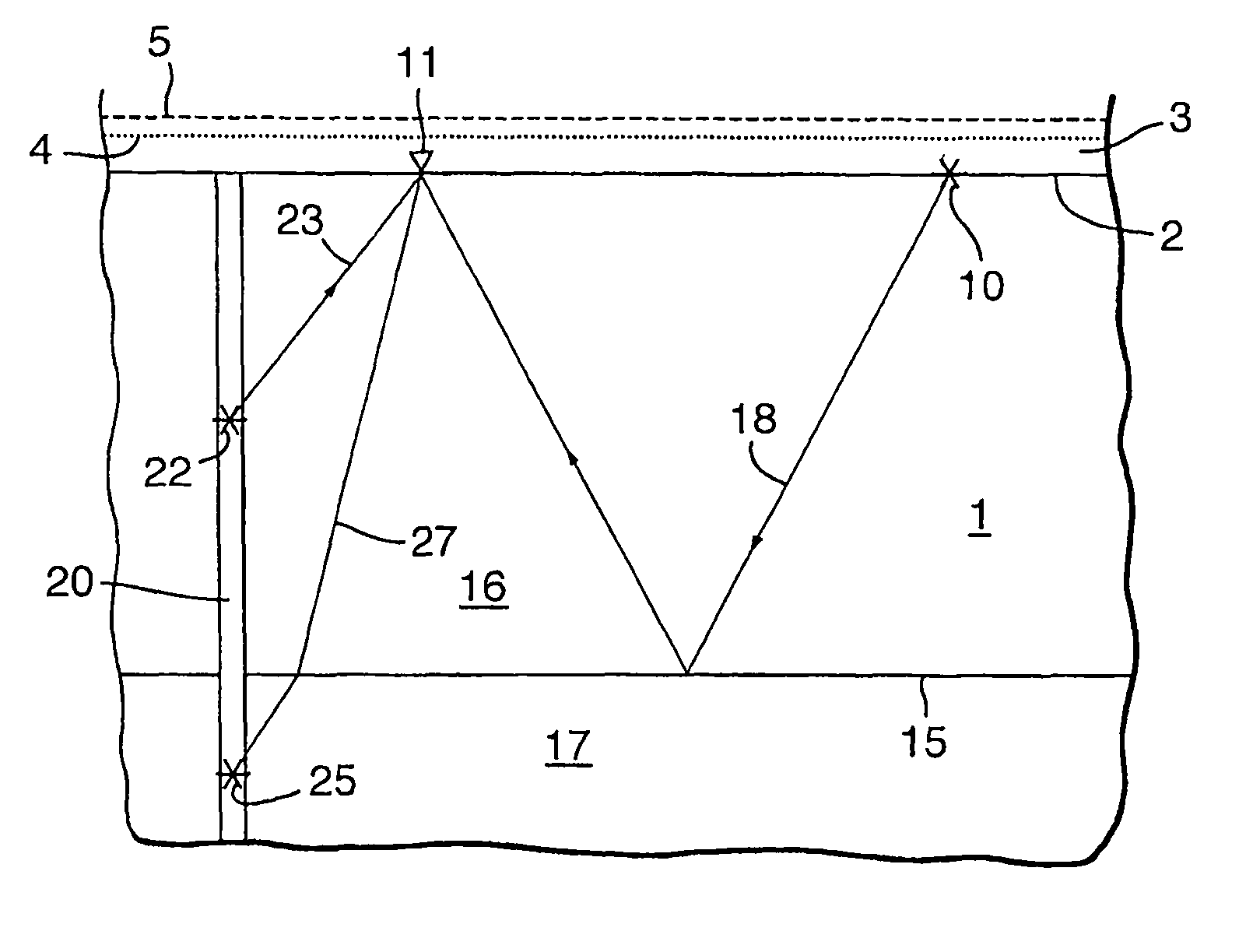
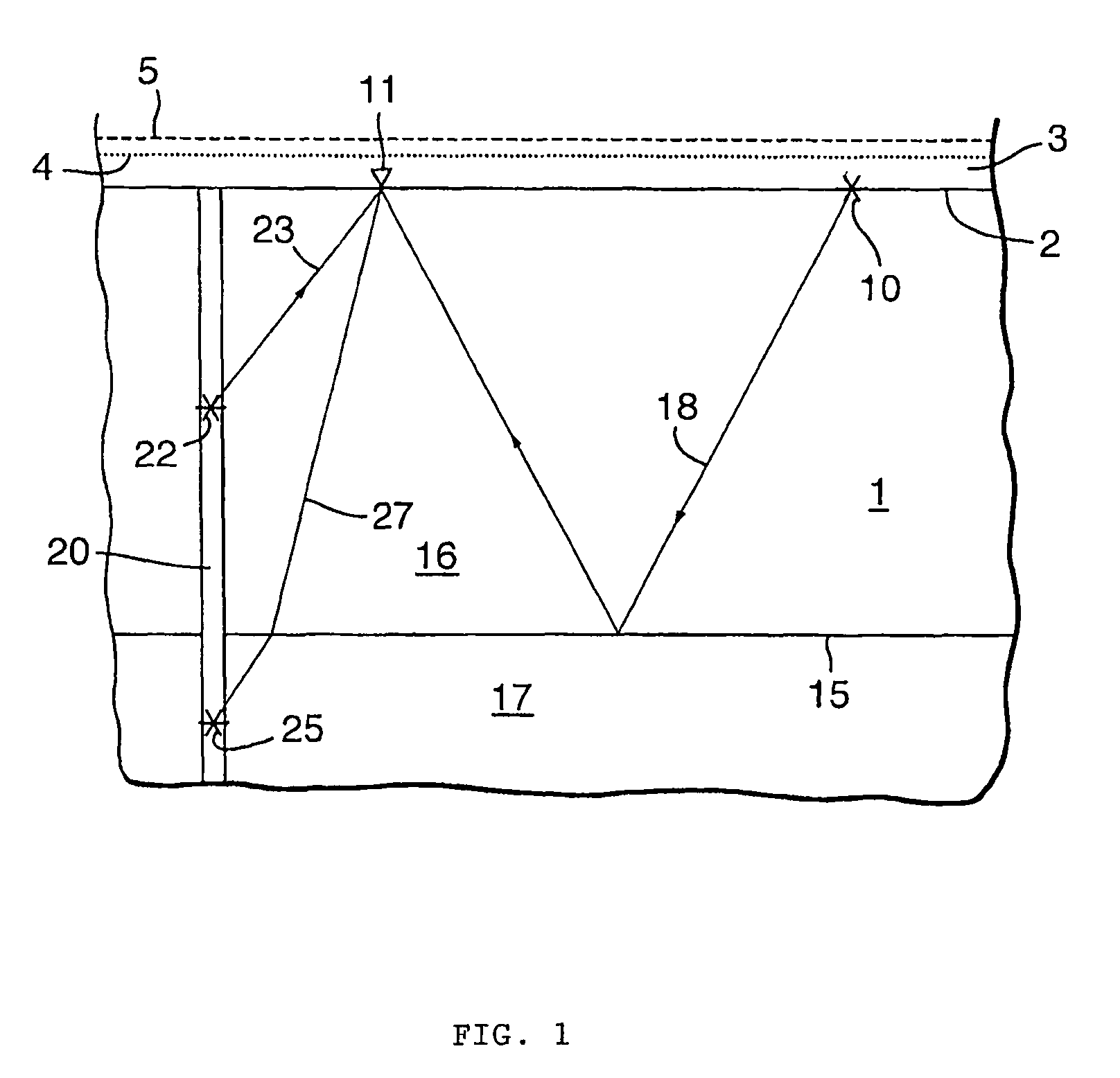
Determining in-situ the relation between seismic velocity and state of stress in an underground formation
ActiveUS7751979B2Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSeismic signal processingSeismic velocityTime changes
A method of determining in-situ a relation between the seismic velocity and the state of stress in an underground formation located under a surface subjected to time-changing surface loading conditions. A relation is selected between the seismic velocity and the state of stress containing at least one unknown parameter. A seismic source is arranged at surface or in a borehole penetrating the underground formation, and a seismic receiver is arranged at a distance from the seismic source at surface or in a second borehole. At two different times the seismic velocity of the formation along a path from the seismic source to the seismic receiver is determined. The difference in surface loading conditions at the two times is converted in a difference in states of stress in the underground formation. The unknown parameter(s) are calculated to obtain the relation between the seismic velocity and the state of stress in the underground formation.
Owner:SHELL USA INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com