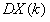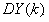Patents
Literature
181 results about "Grid size" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Grid Size. Under normal usage, your application should set the width and height of the grid using CSS styles. The grid will then fit the width you provide and use scrolling inside the grid to allowing viewing all rows and columns.
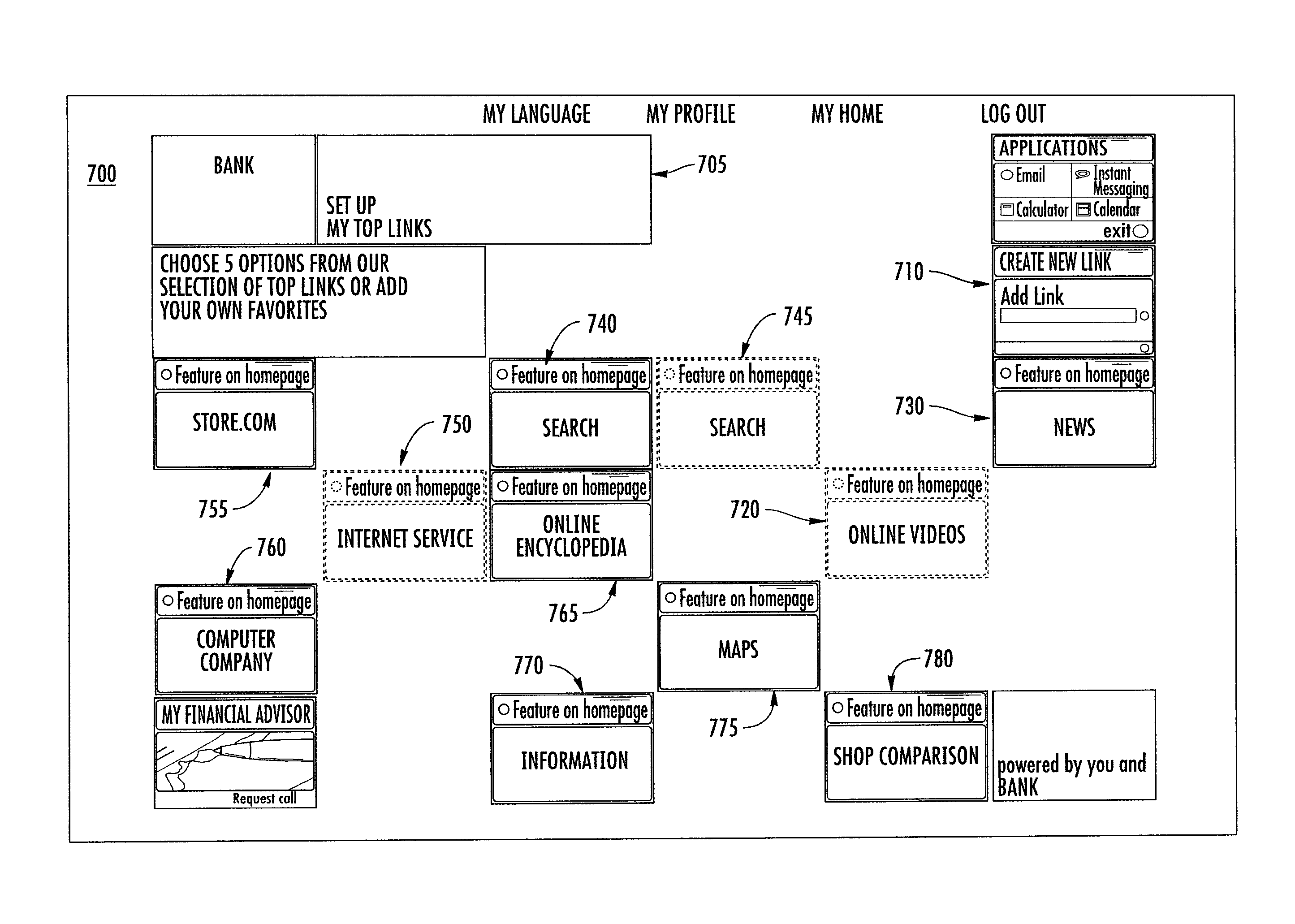
Customizable graphical user interface
InactiveUS20110107265A1Improve customer serviceGood serviceFinanceMarketingGraphicsCommunication interface
An apparatus is provided having a processor configured to generate a graphical user interface, the graphical user interface having: (a) one or more rectangular base icons of a first size, (b) a grid where the cells of the grid are of the first size, and (c) one or more content fields having a size that is a multiple of the first size and being aligned with the grid. The apparatus further includes a communication interface configured to communicate the graphical user interface to a user terminal for display on the user terminal. The graphical user interface is further configured such that the user can move the one or more base icons and the one or more content fields to other locations within the grid provided that the one or more base icons and one or more content fields are aligned with the grid at the other locations.
Owner:BANK OF AMERICA CORP
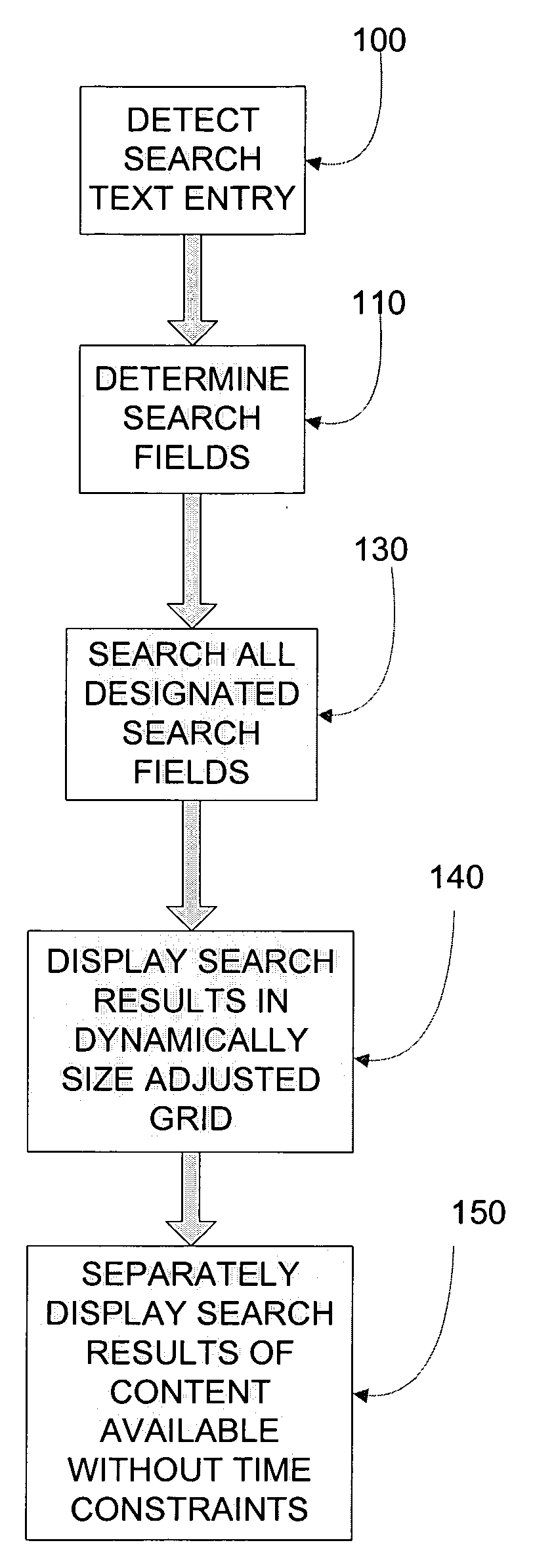
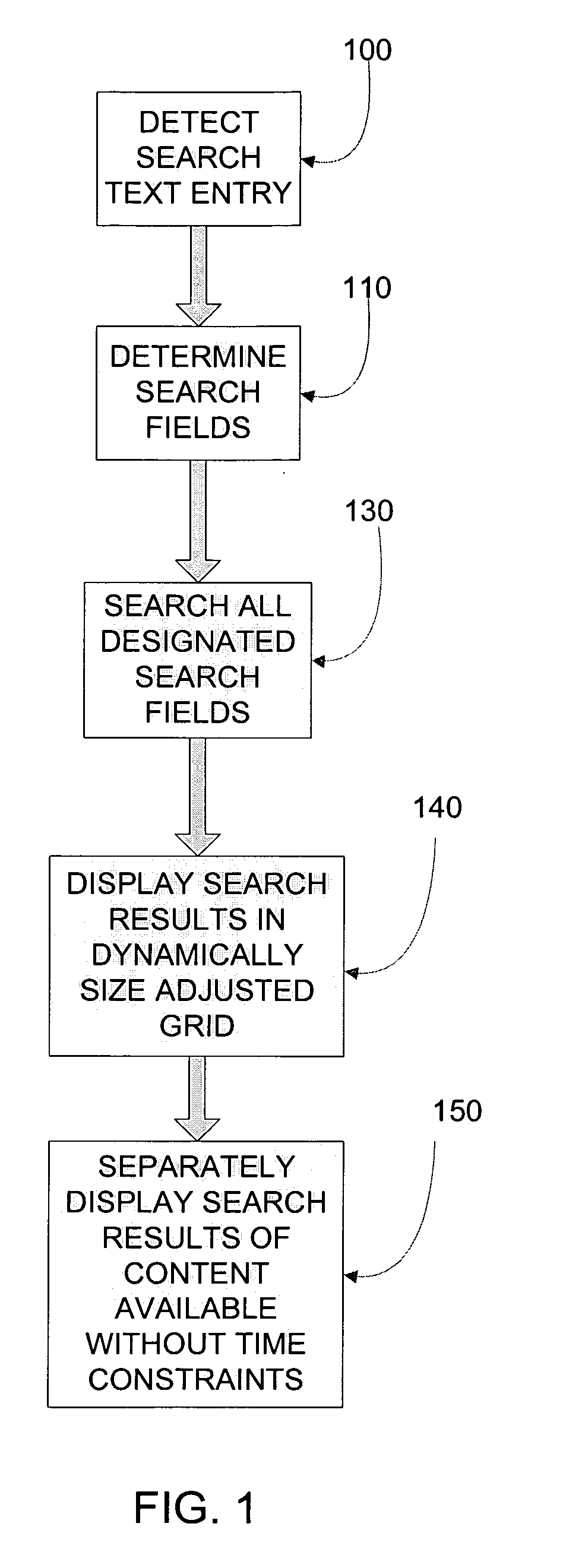
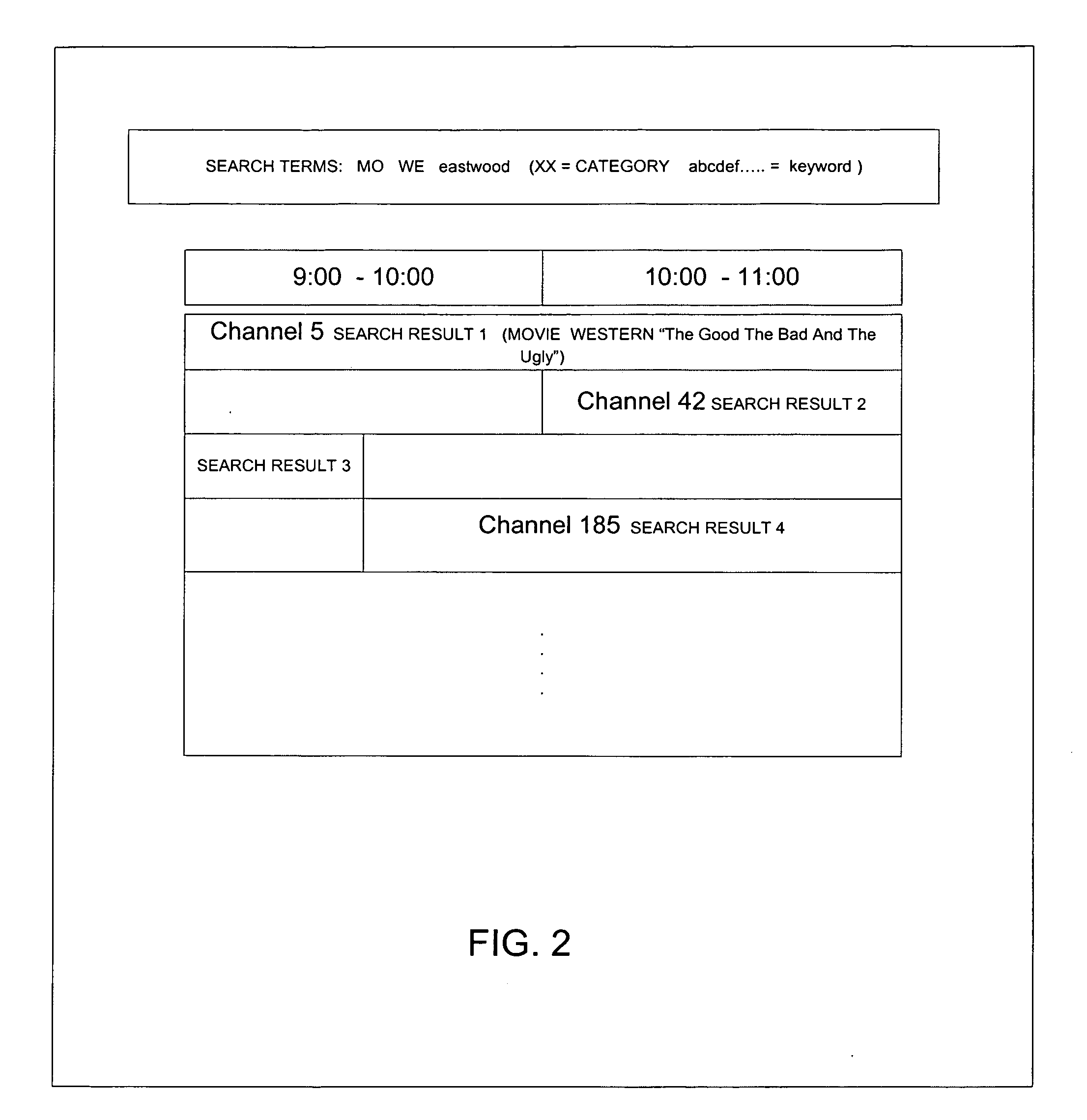
TV content search system and method with multi-field search and display
InactiveUS20080282291A1Television system detailsDigital data information retrievalMulti fieldTime dynamics
A search based TV interface system and method is disclosed. Search results are dynamically displayed based on search parameters and / or time. A dynamically adjusted grid may be provided which collapses to a list if a minimum grid size is not met. Search results may also be dynamically displayed organized by category.
Owner:I INTERACTIVE LLC
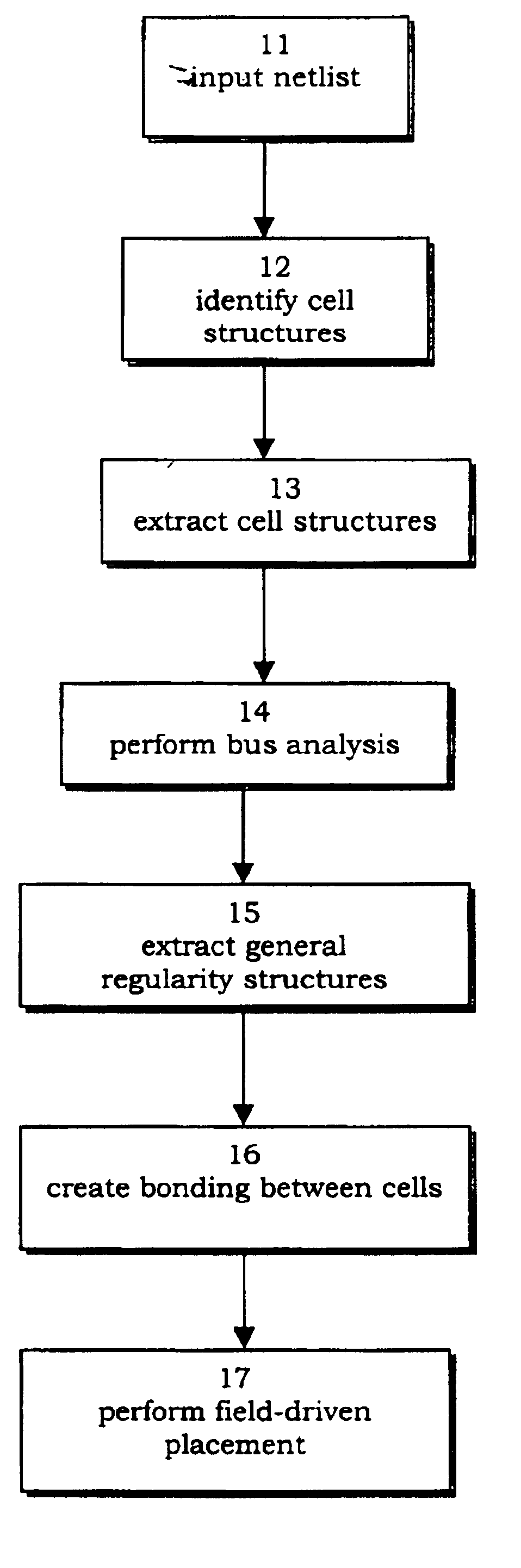
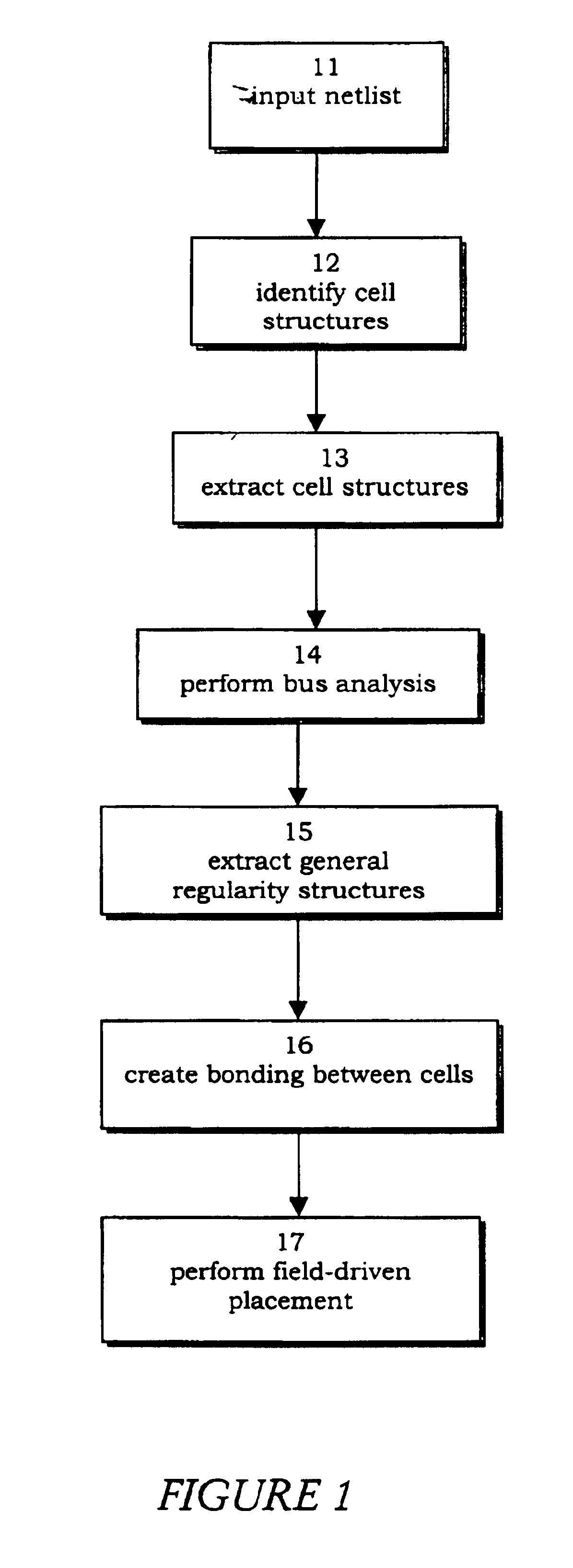
Method and apparatus of relative datapath cell placement with structure bonding
The invention discloses a relative structure placement of datapath of cell instances in a column structure, a row structure, or an array structure. To encourage placement of a desirable structure, pseudo cells, pseudo pins, and pseudo nets are selected to be placed at certain locations with respect to real cell instances. The end result produces a cluster of real cell instances that form a desirable structure while minimizing the length of nets. The invention further discloses a non-uniform partitioning of a density map for calculating a force update vector. The partitioning is taken over a region A to compute Riemann sum approximations of a function F over the region A. A force update vector is calculated for a given cell instance within the region A where neighboring cell instances have an exponentially larger grid size as cell instances extend further away from the given cell instance.
Owner:ARCADIA DESIGN SYST
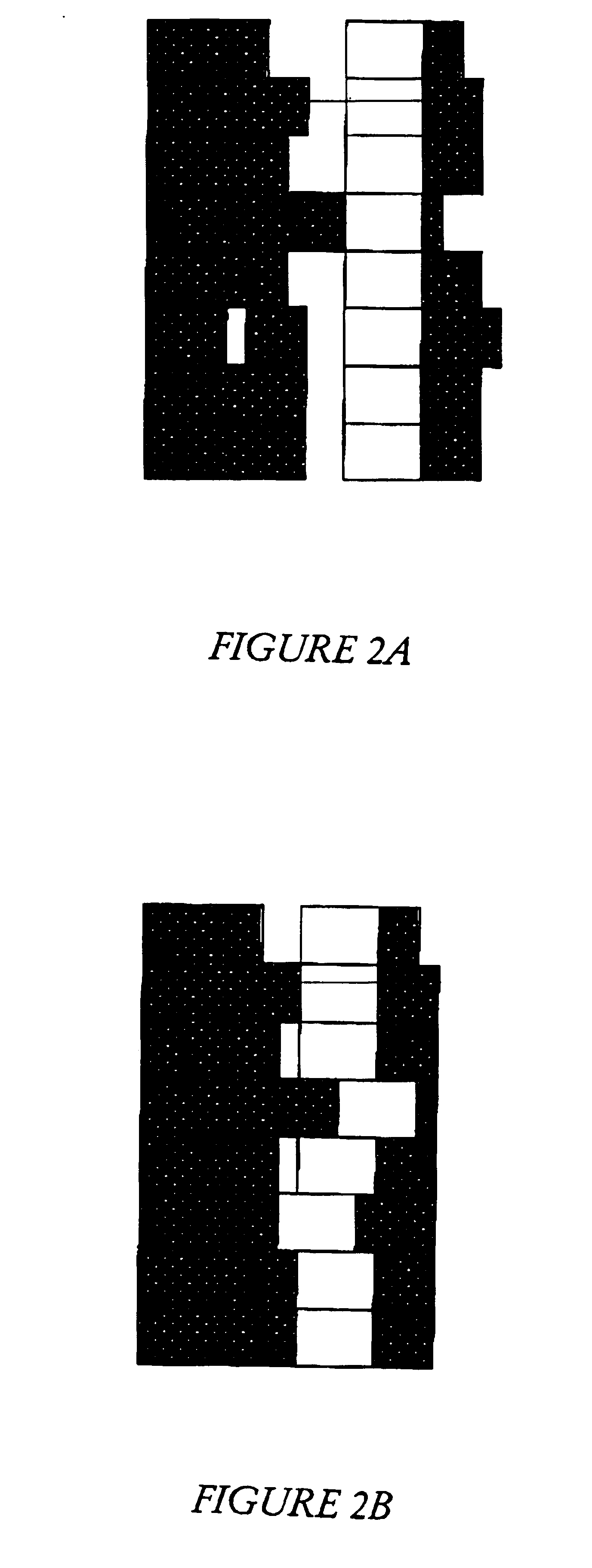
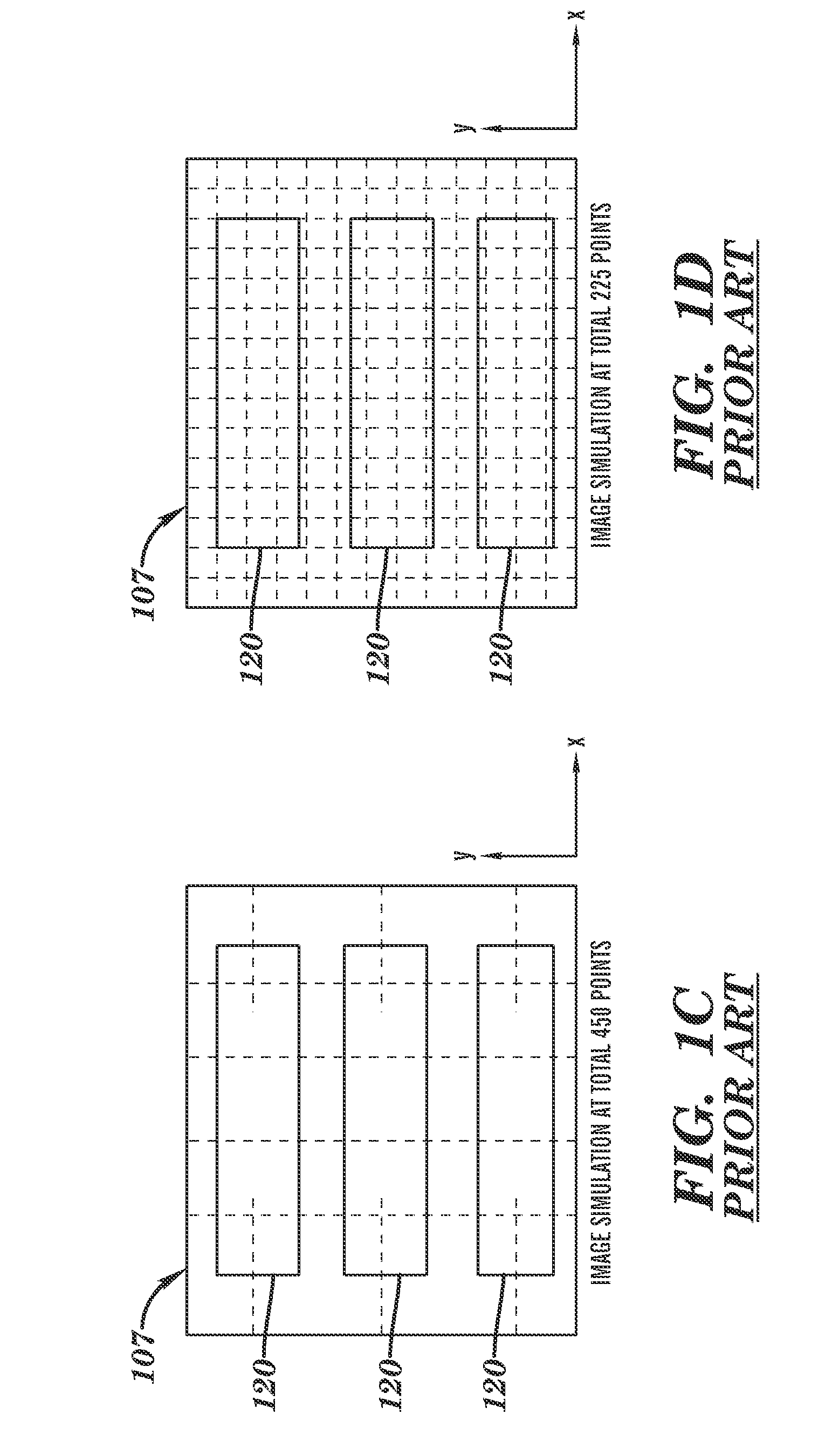
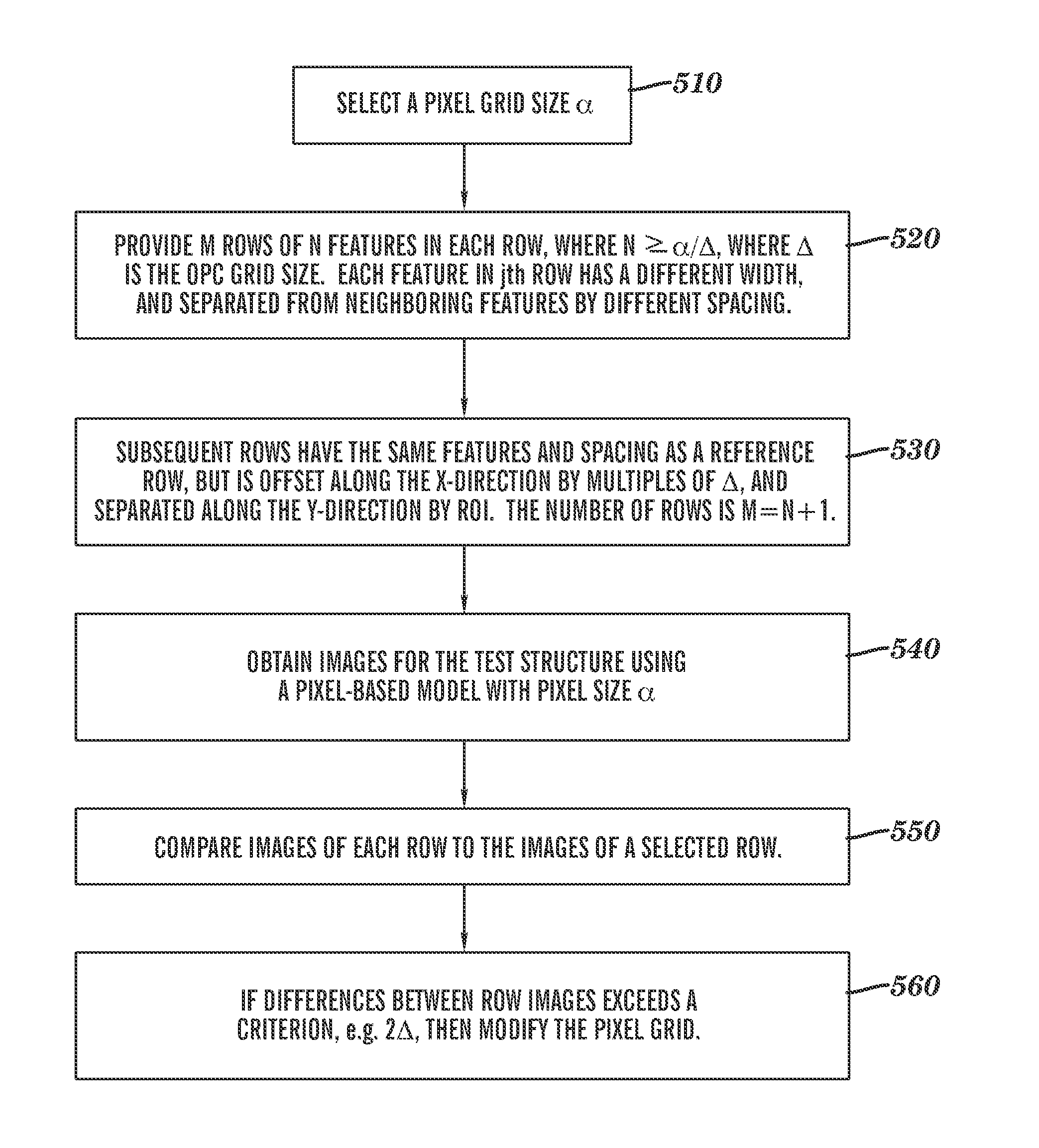
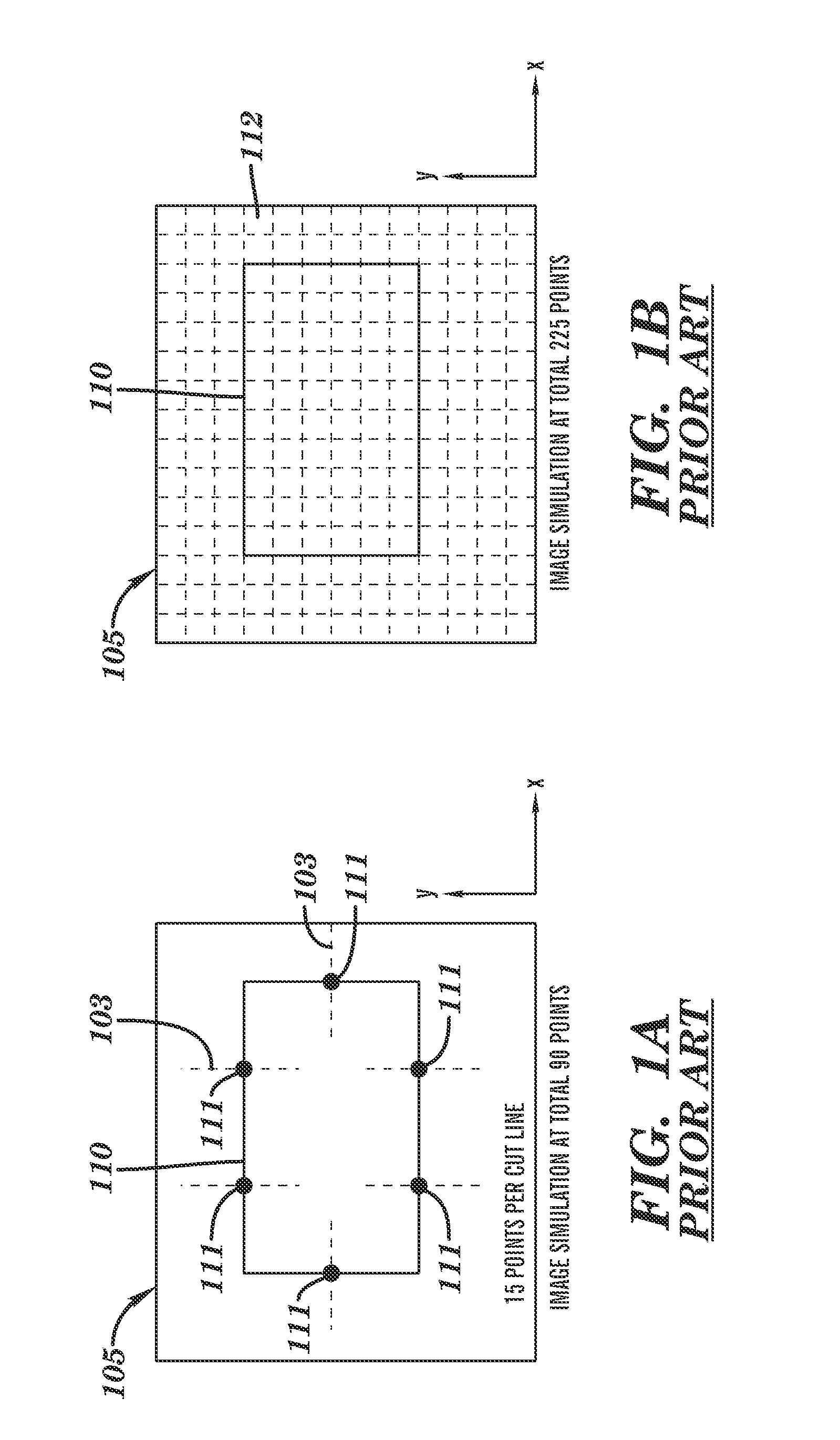
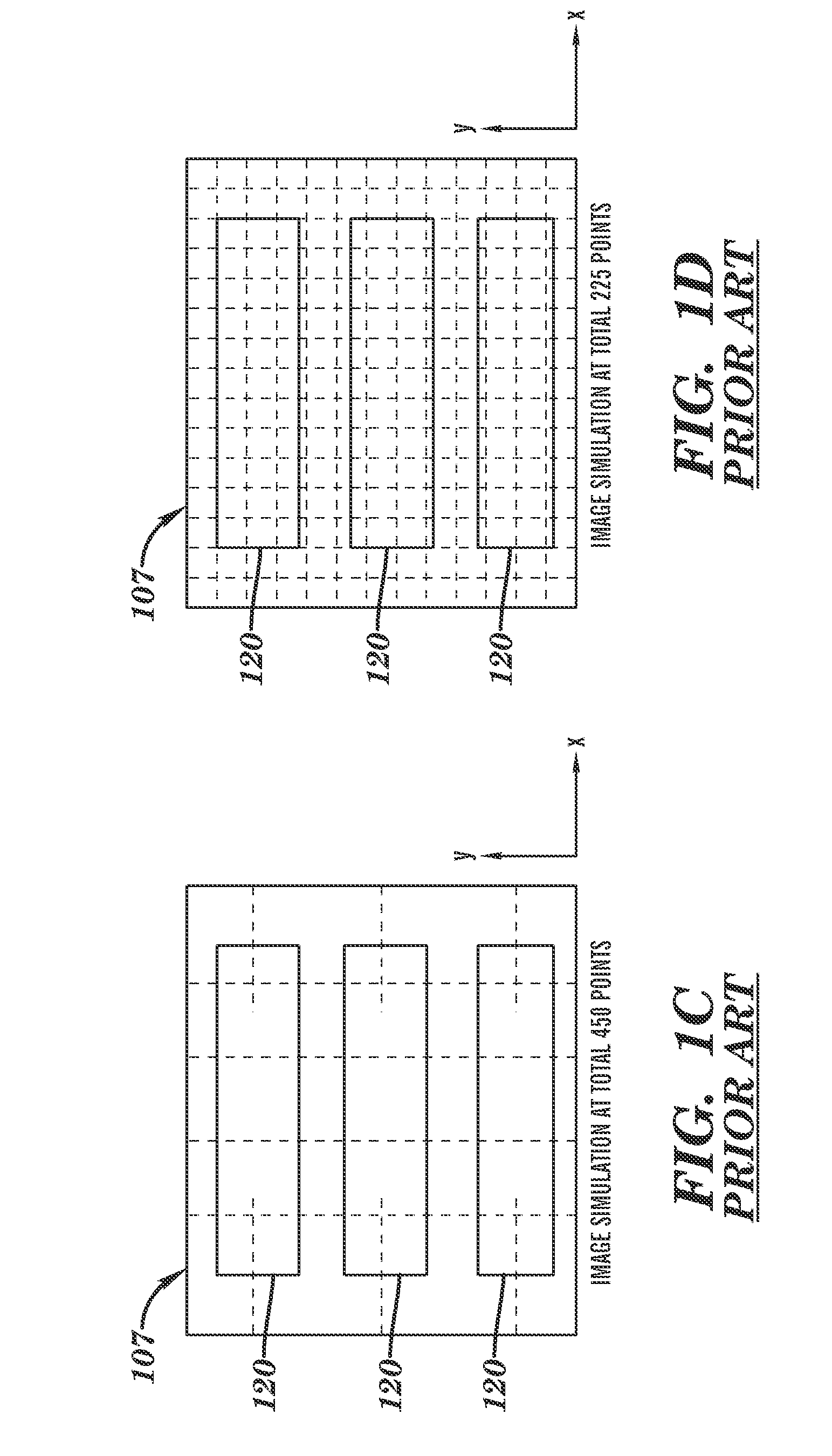
Methodology and system for determining numerical errors in pixel-based imaging simulation in designing lithographic masks
InactiveUS20090193387A1Originals for photomechanical treatmentSpecial data processing applicationsPixel basedErrors and residuals
A method is provided for designing a mask that includes the use of a pixel-based simulation of a lithographic process model, in which test structures are designed for determining numerical and discretization errors associated with the pixel grid as opposed to other model inaccuracies. The test structure has a plurality of rows of the same sequence of features, but each row is offset from other rows along an x-direction by a multiple of a minimum step size, such as used in modifying masks during optical proximity correction. The images for each row are simulated with a lithographic model that uses the selected pixel-grid size and the differences between row images are compared. If the differences between rows exceed or violate a predetermined criterion, the pixel grid size may be modified to minimize discretization and / or numerical errors due to the choice of pixel grid size.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Generation method of quadrilateral grid of geometric model with any internal feature constraints
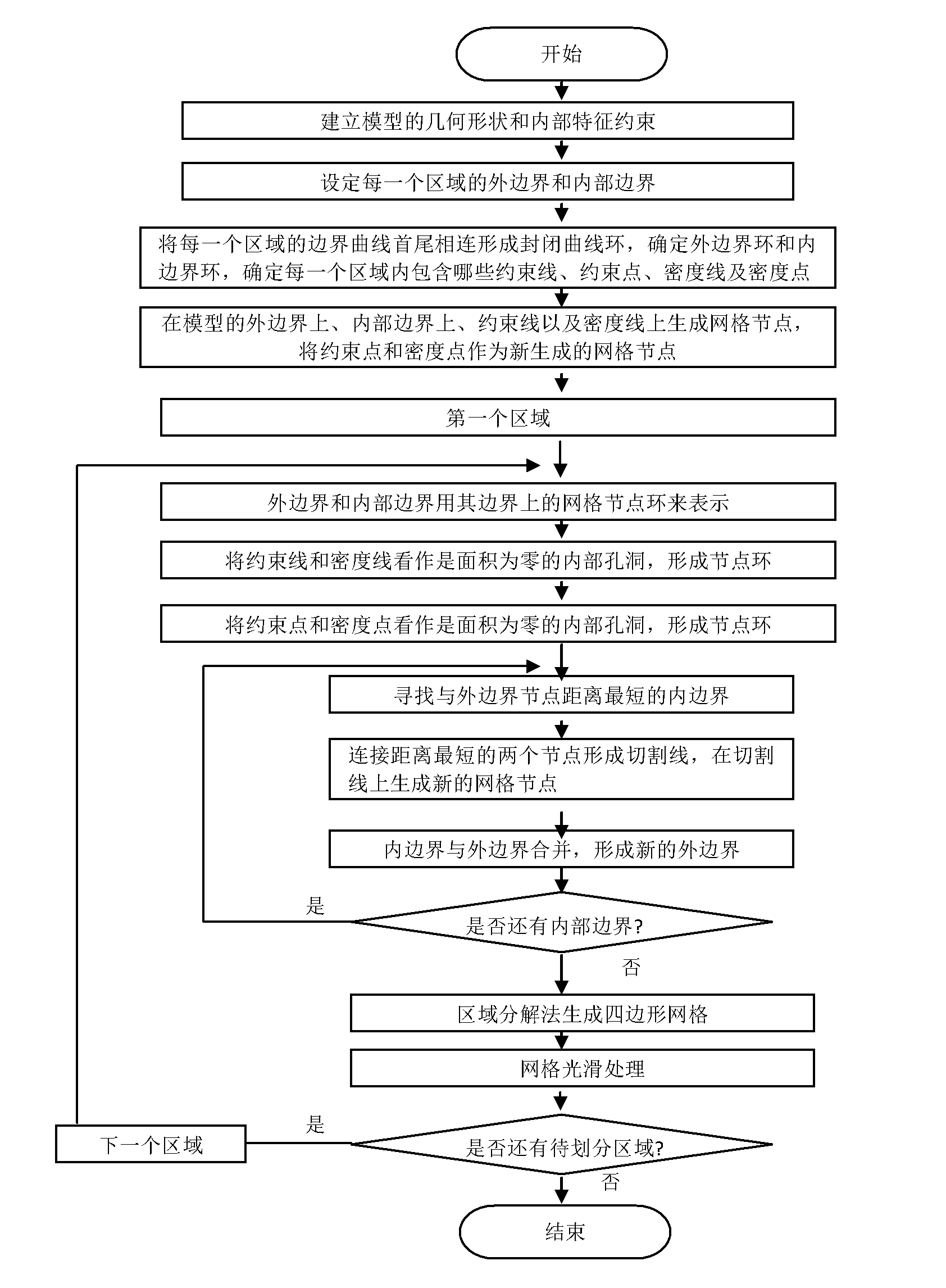
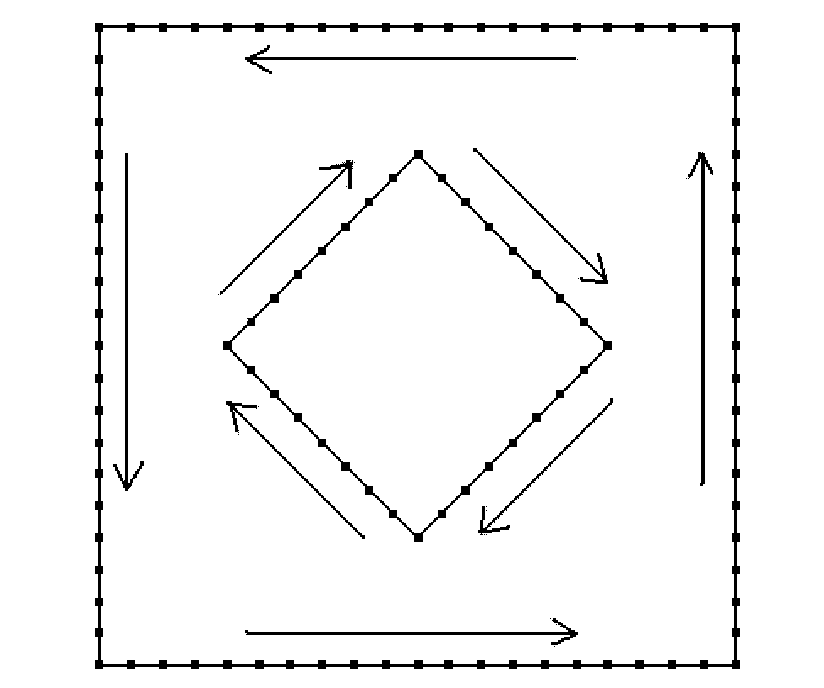
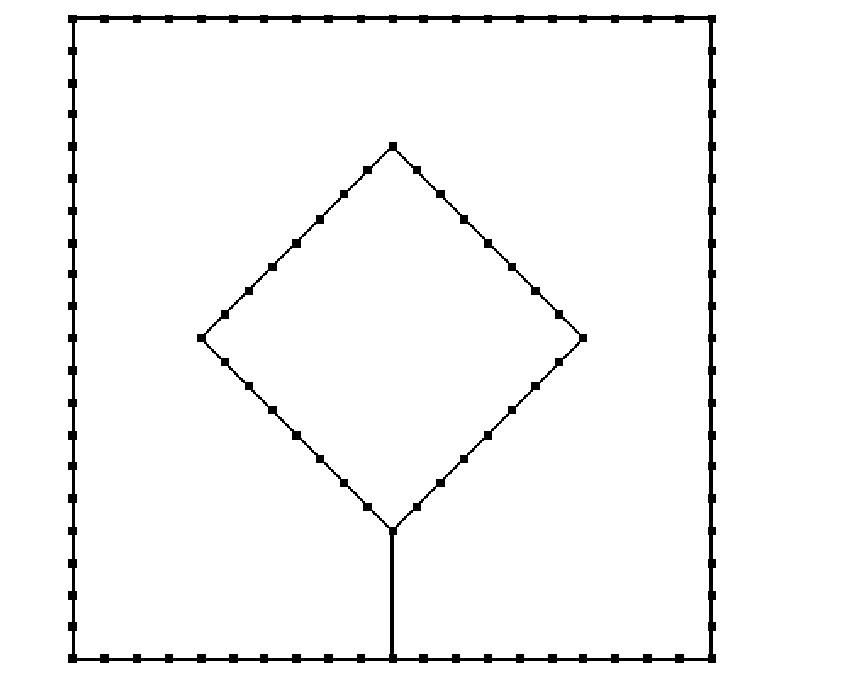
The invention relates to a generation method of quadrilateral grids of a geometric model with any internal feature constraints, which outstandingly enhances the generation quality and efficiency of the quadrilateral grids and has convenience and practicability. The generation method comprises the following steps of: (1.1) building an entitative geometric model according to an entity to be analyzed by utilizing a computer; and determining the shapes and the positions of constraint lines and density lines of the entitative geometric model, the positions of constraint points and density points and the range and the inner and outer boundaries of each region; (1.2) generating grid nodes on the inner and outer boundaries, the constraint lines and the density lines of the entitative geometric model according to grid size information set by a user, and numbering the grid nodes; viewing the constraint points and the density points as newly generated grid nodes, and numbering the newly generated grid nodes; (1.3) viewing the constraint lines, the density lines, the constraint points and the density points as internal cavities with areas of zero, generating node rings on the inner and outer boundaries of each region, and transforming a multiply connected region with the internal feature constraints into a simply connected region; (1.4) dividing the quadrilateral grids in each region; and finally generating the quadrilateral grids with the internal feature constraints.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Method of image segmentation
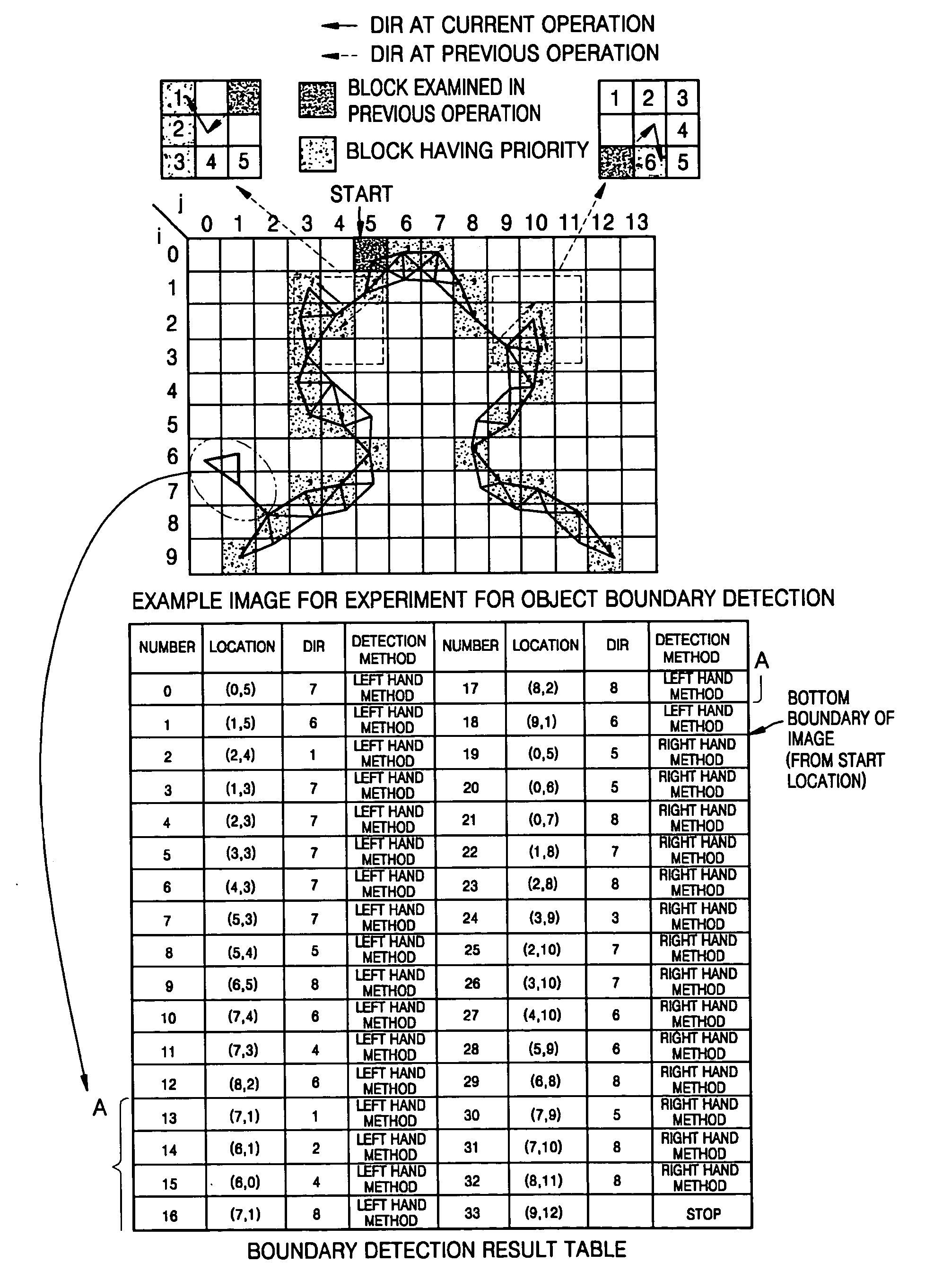
InactiveUS20060045336A1Accurate and continuous object boundaryReduce the amount of calculationImage enhancementImage analysisImage segmentationMethod of images
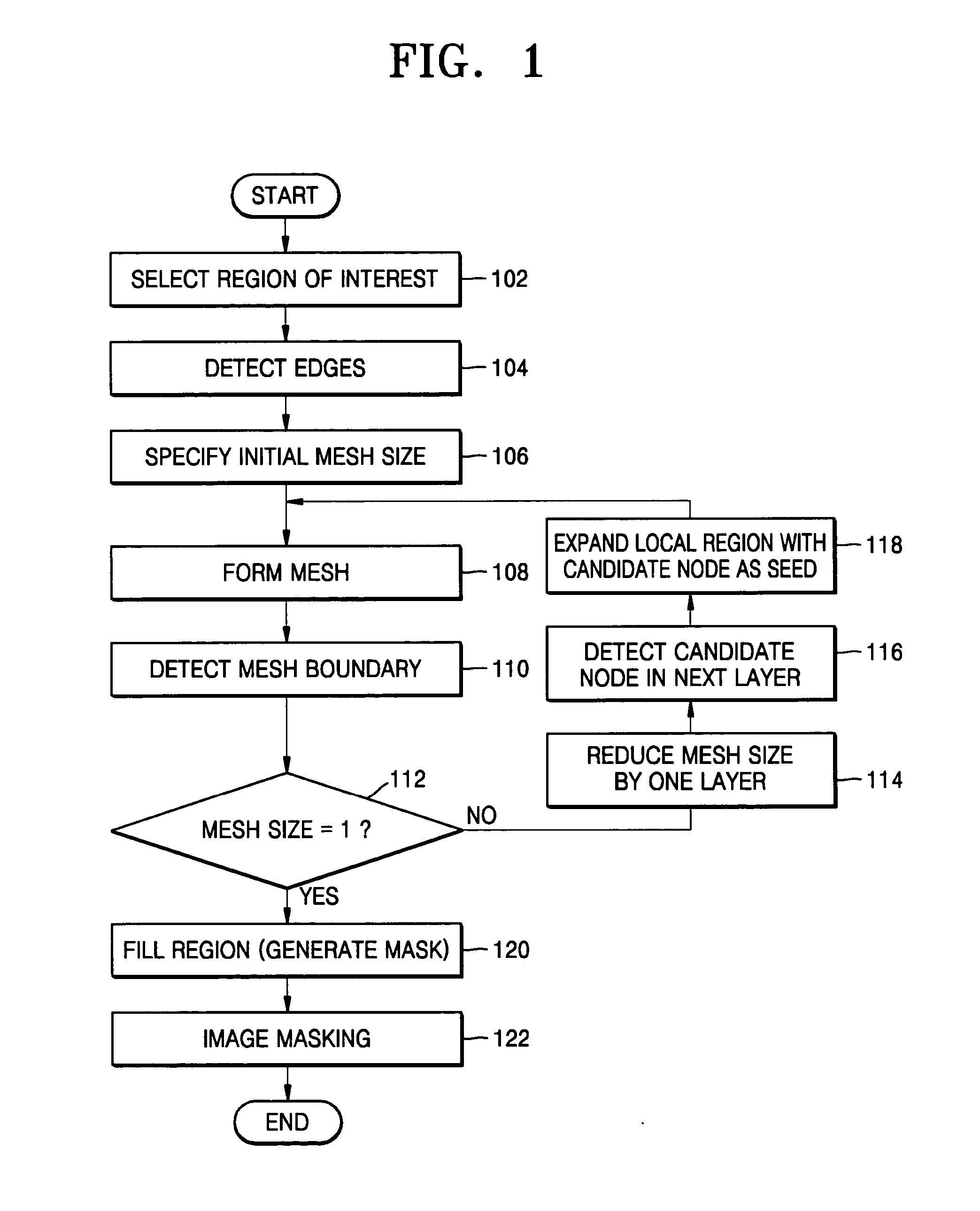
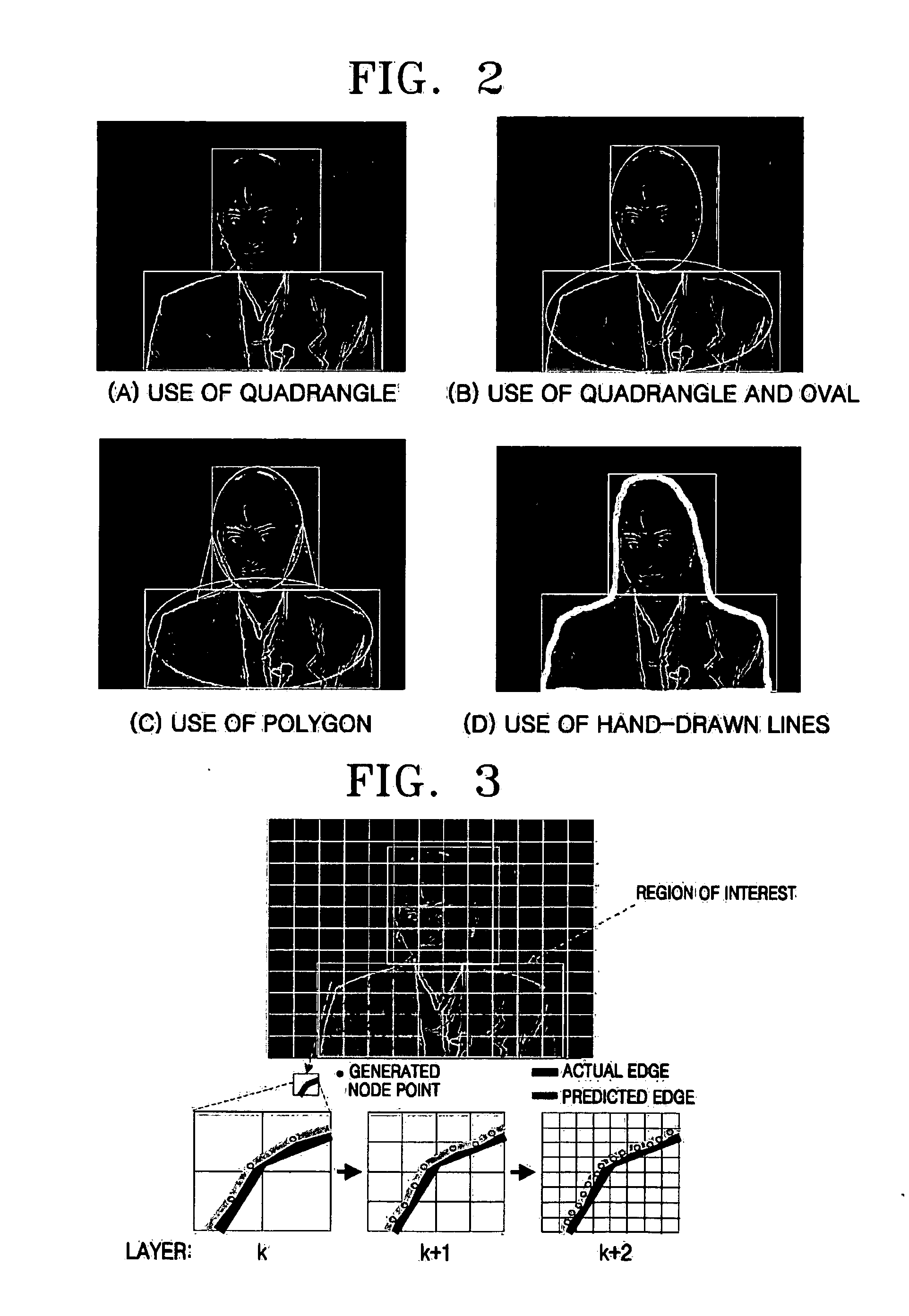
An image segmentation method including: selecting a region of interest including an object whose image is to be segmented; detecting the edge of the object; repeatedly performing, until a specified precision is obtained, a process in which by using a layered mesh structure based on the detected edge, a mesh boundary of the object is detected, a mesh size is reduced by one layer, and then by using areas adjacent to the detected mesh boundary, correcting the mesh boundary; and generating a mask to fill a inside area of the correcting mesh boundary and masking the object.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
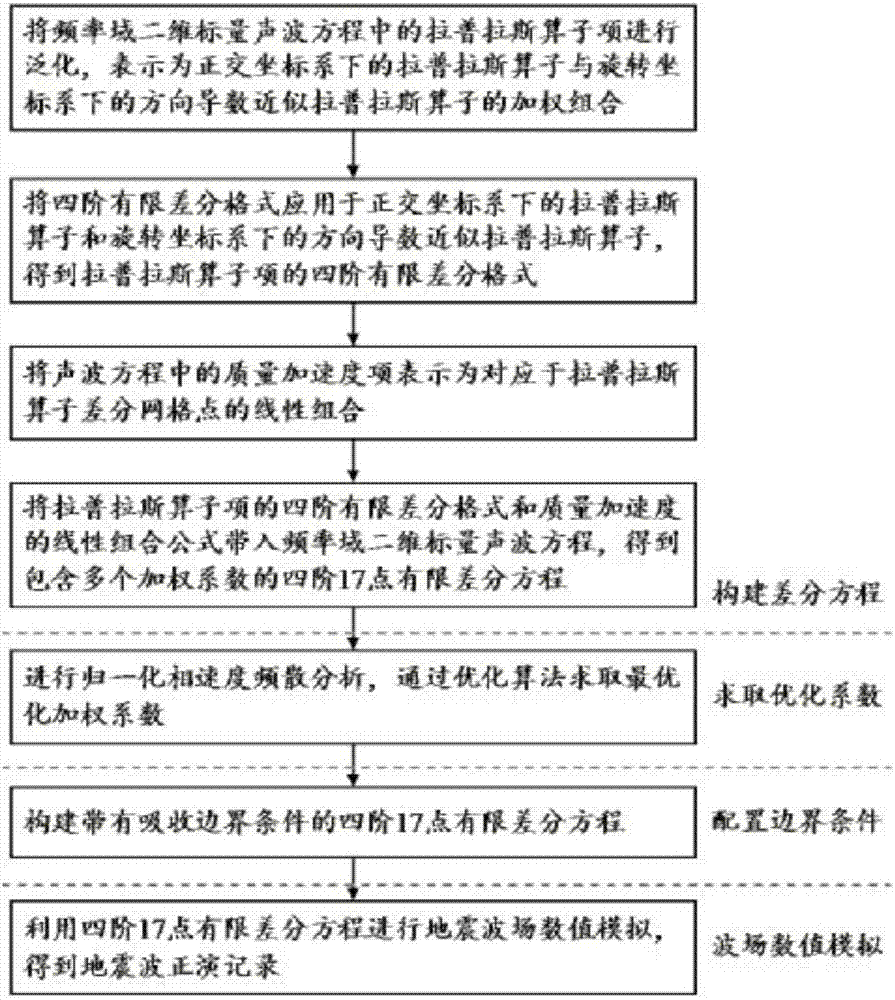
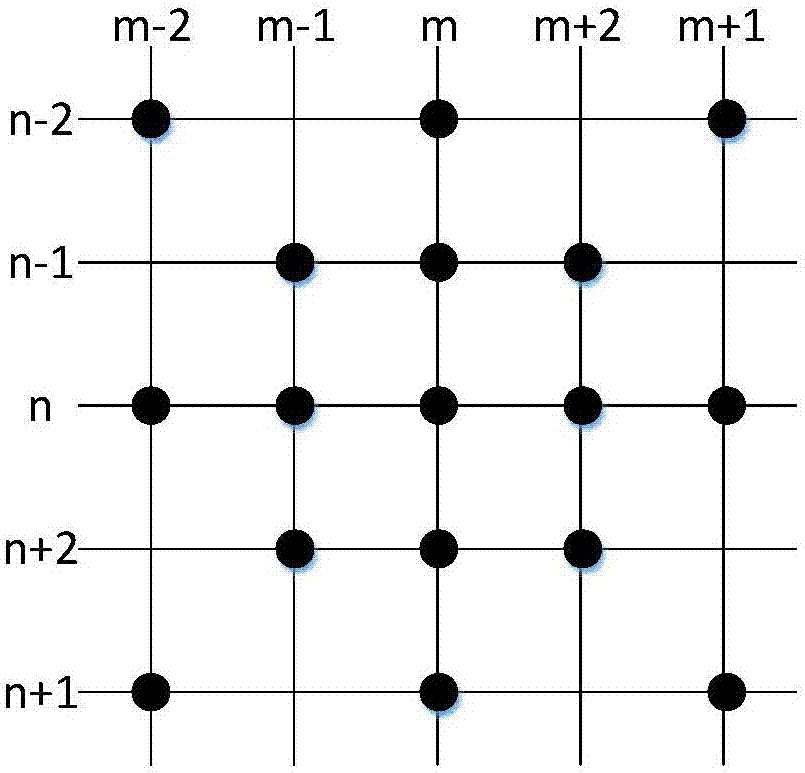
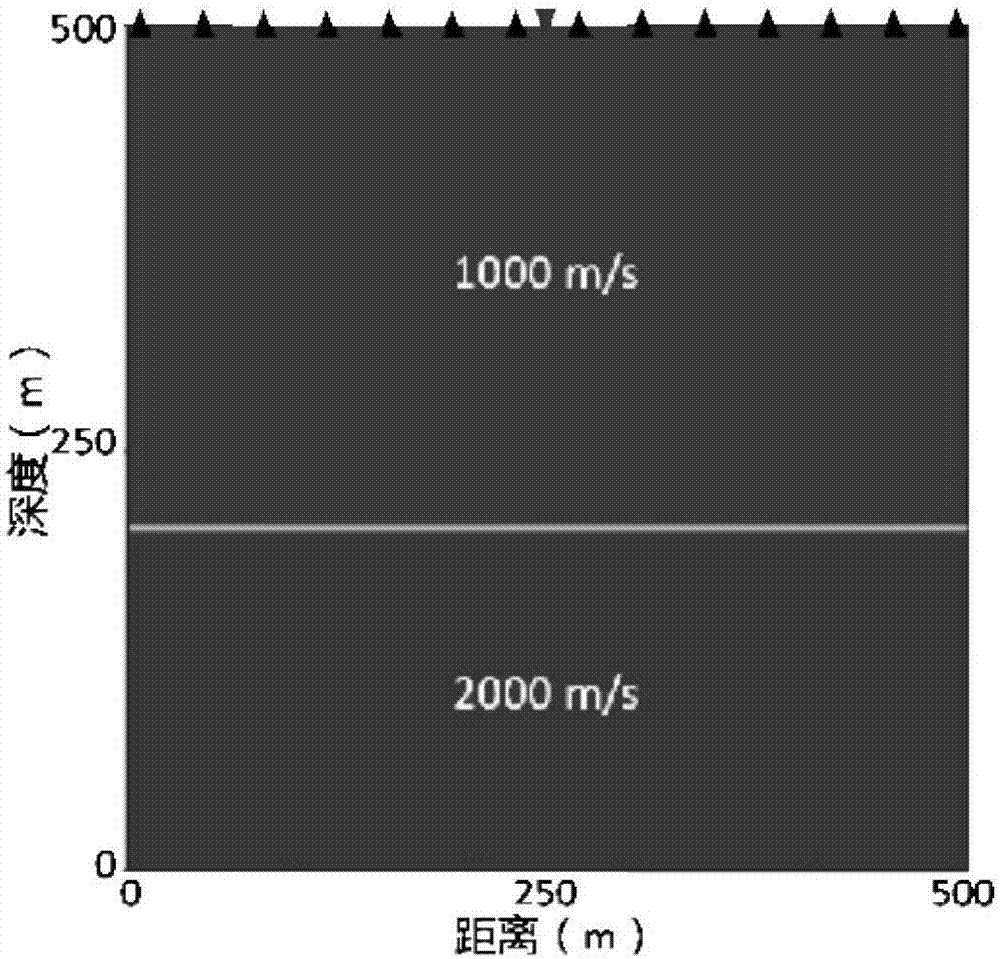
Frequency-domain higher-order sound wave equation forward modeling method based on directional derivative
ActiveCN107479092ADispersion suppressionHigh precisionSeismic signal processingData simulationWeight coefficient
The invention discloses a frequency-domain higher-order sound wave equation forward modeling method based on directional derivative, belongs to the technical field of seismic exploration, and aims at providing a frequency domain two-dimensional scalar sound wave equation forward modeling simulation method with the higher simulation precision. The method comprises the steps: building a fourth-order 17-point finite difference equation comprising a plurality of weighting coefficients according to a frequency domain scalar sound wave equation through the directional derivative; carrying out the normalized phase velocity frequency dispersion analysis, and solving an optimal weighting coefficient through an optimization algorithm; constructing a finite difference equation with the absorbing boundary condition; carrying out the seismic wave field data simulation through the fourth-order 17-point finite difference equation, and obtaining a seismic wave forward modeling record. The method can inhibit the frequency dispersion to the greatest extent, improves the simulation precision of the seismic wave field data, and also can adapt to a condition that the longitudinal and lateral grid sizes are not equal. The method is mainly used in the technical field of seismic exploration, and provides basic data and technological support for the simulation and analysis of a seismic wave field, the seismic inversion imaging, and geologic modeling.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
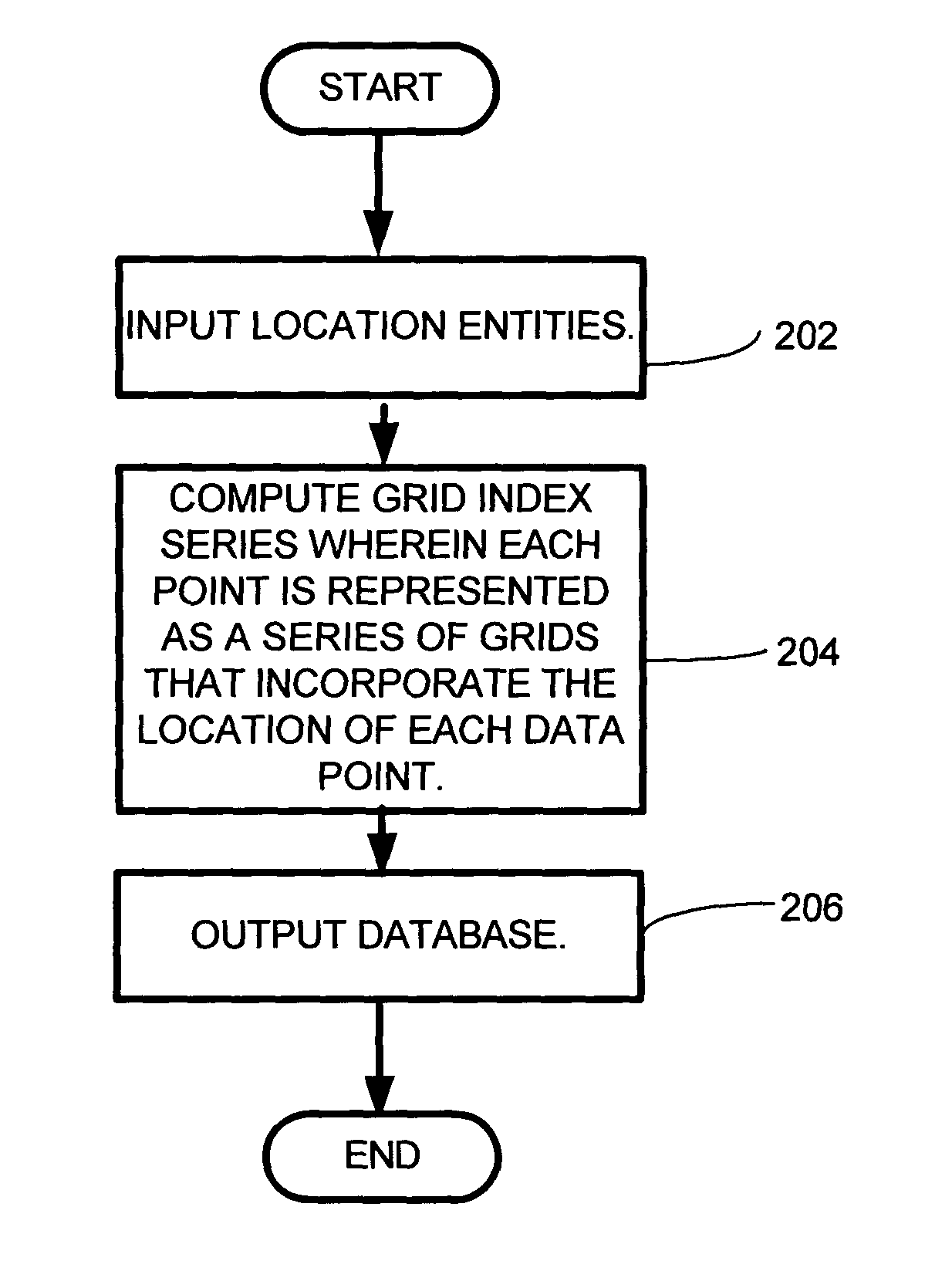
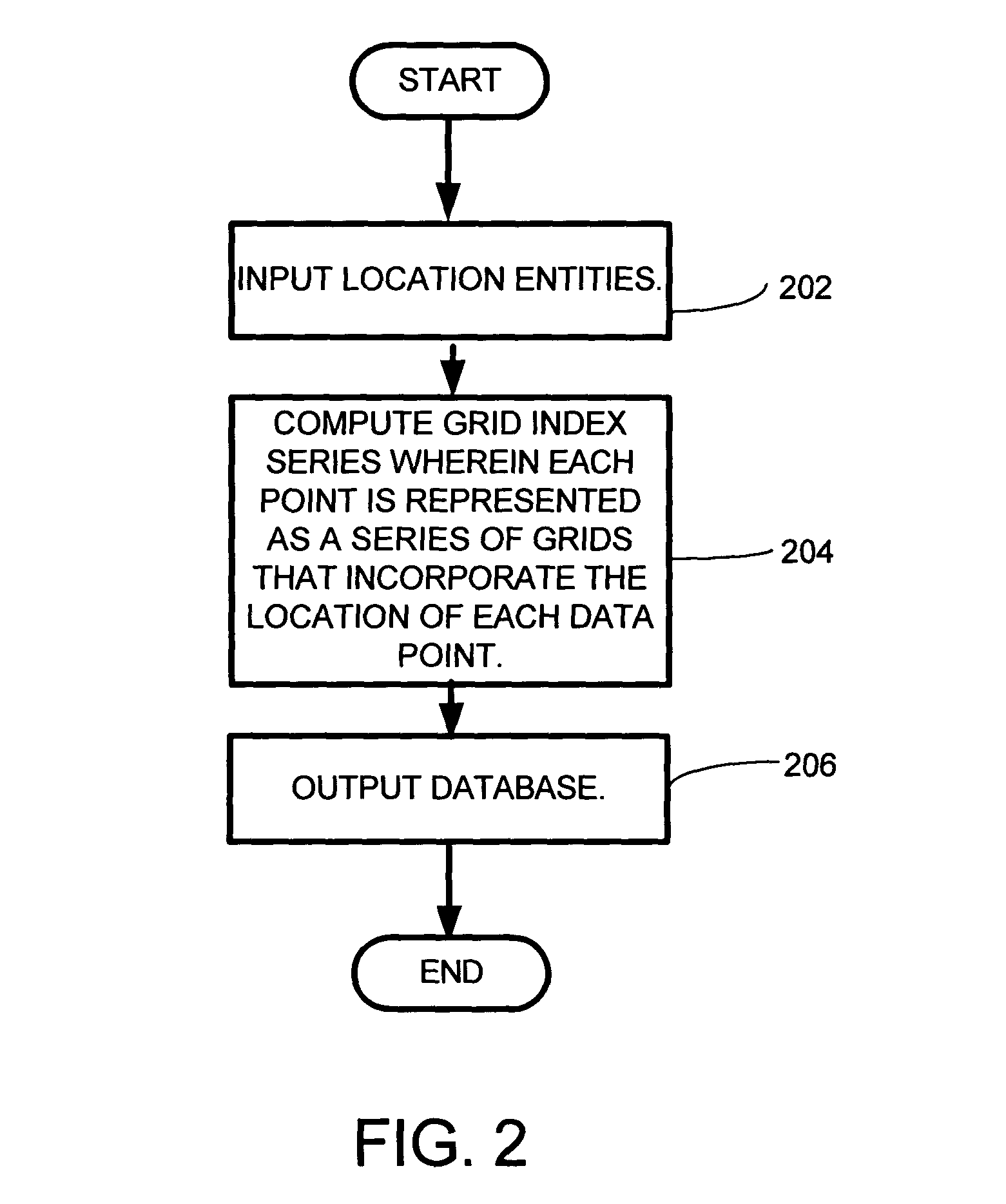
System and method for employing a grid index for location and precision encoding
InactiveUS7966301B2Heavy calculationConvenient and accurateDigital data processing detailsDevices with sensorDatabase queryGrid cell
A system and method for combining the precision estimate of a database entry's coordinate value such that the precision information is included as part of the one-dimensional index. This is done by constructing a hierarchical index in which the size of the grid is related to the precision of the coordinate value. A grid index is a gridding of an n-dimensional space into a regular partition of the grid space into grid units, for which for a point in space, x, there is a function index (x), which retrieves a unique integer value for the grid that contains Point x, and a function coordinate (y, s), which returns a point associated with the index y at scale s. A hierarchical grid index is effectively a number of grid indices overlaid on the same space, with grid units of different sizes. In this case, each of the functions employs an additional argument that specifies the size of the grid unit to use. Thus, assuming that the grid size, s, is drawn from a set of grid sizes, S, Index (x,s) returns a unique integer value for the grid of size s that contains Point x. Hierarchical indexes may be used to enhance the performance of database queries. A query that seeks results from a small grid size, ssmall, does not seek matches at a large grid size, slarge. Similar calculations can be performed for a finite area A.
Owner:MICROSOFT CORP +1
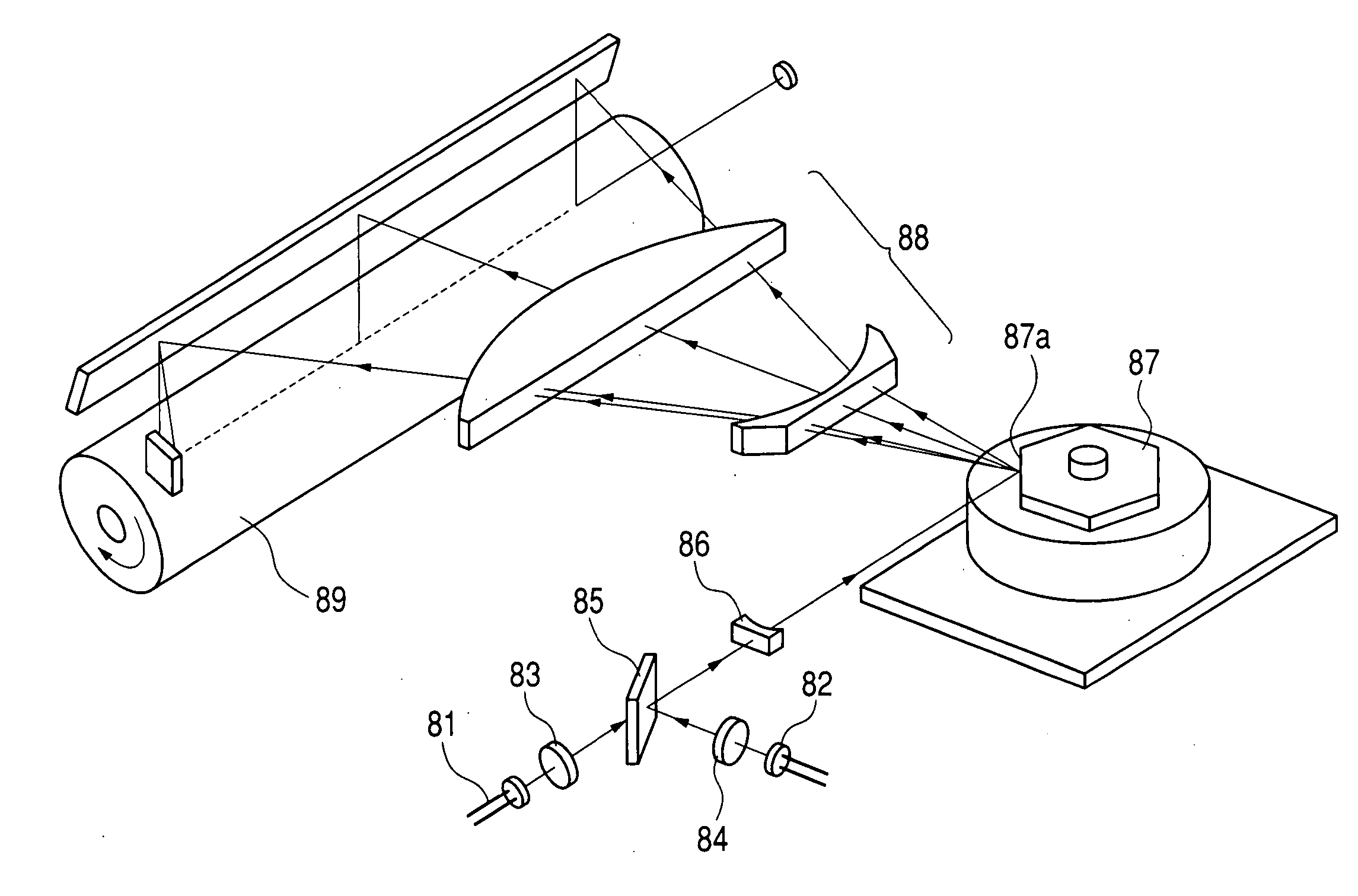
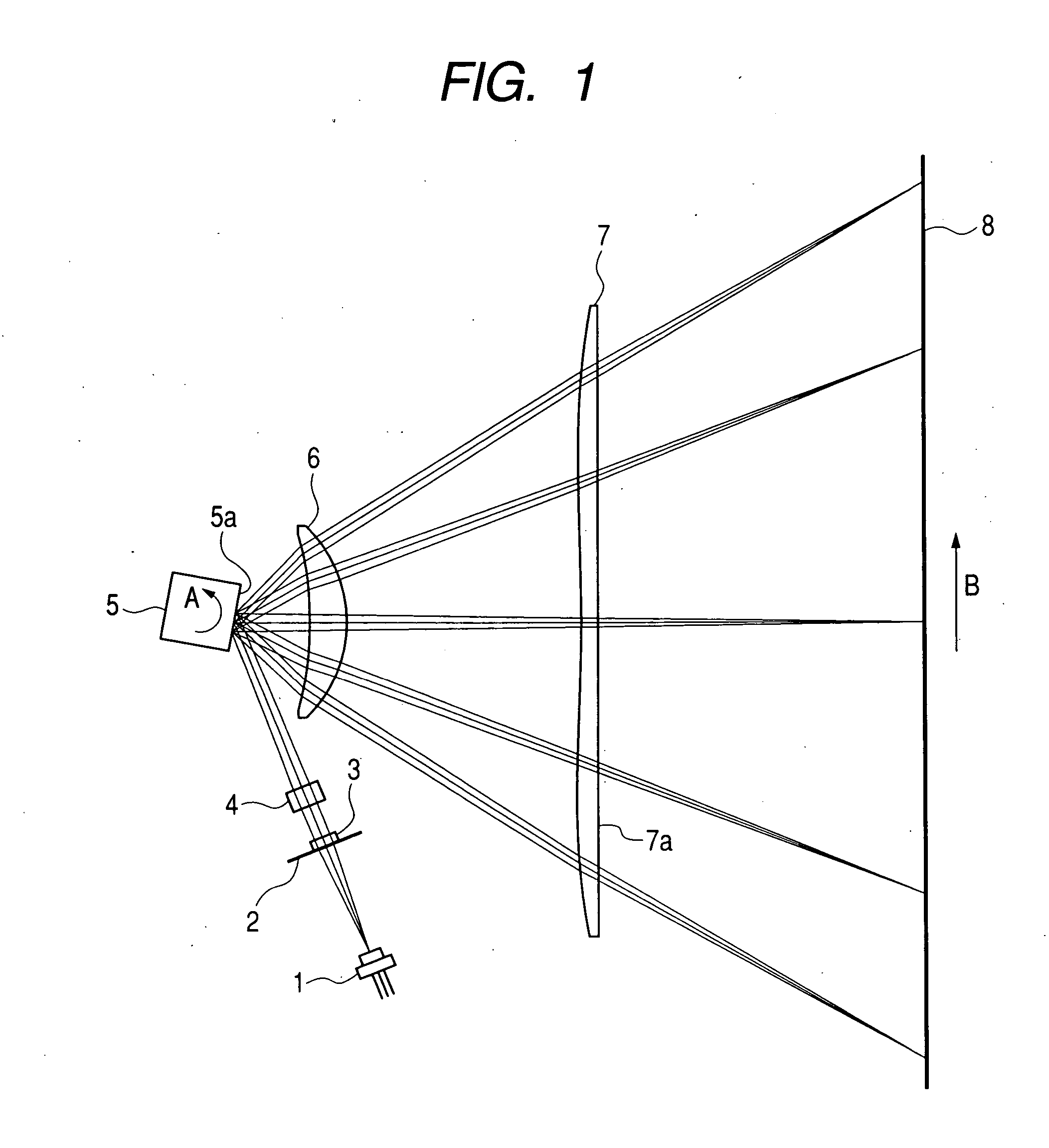
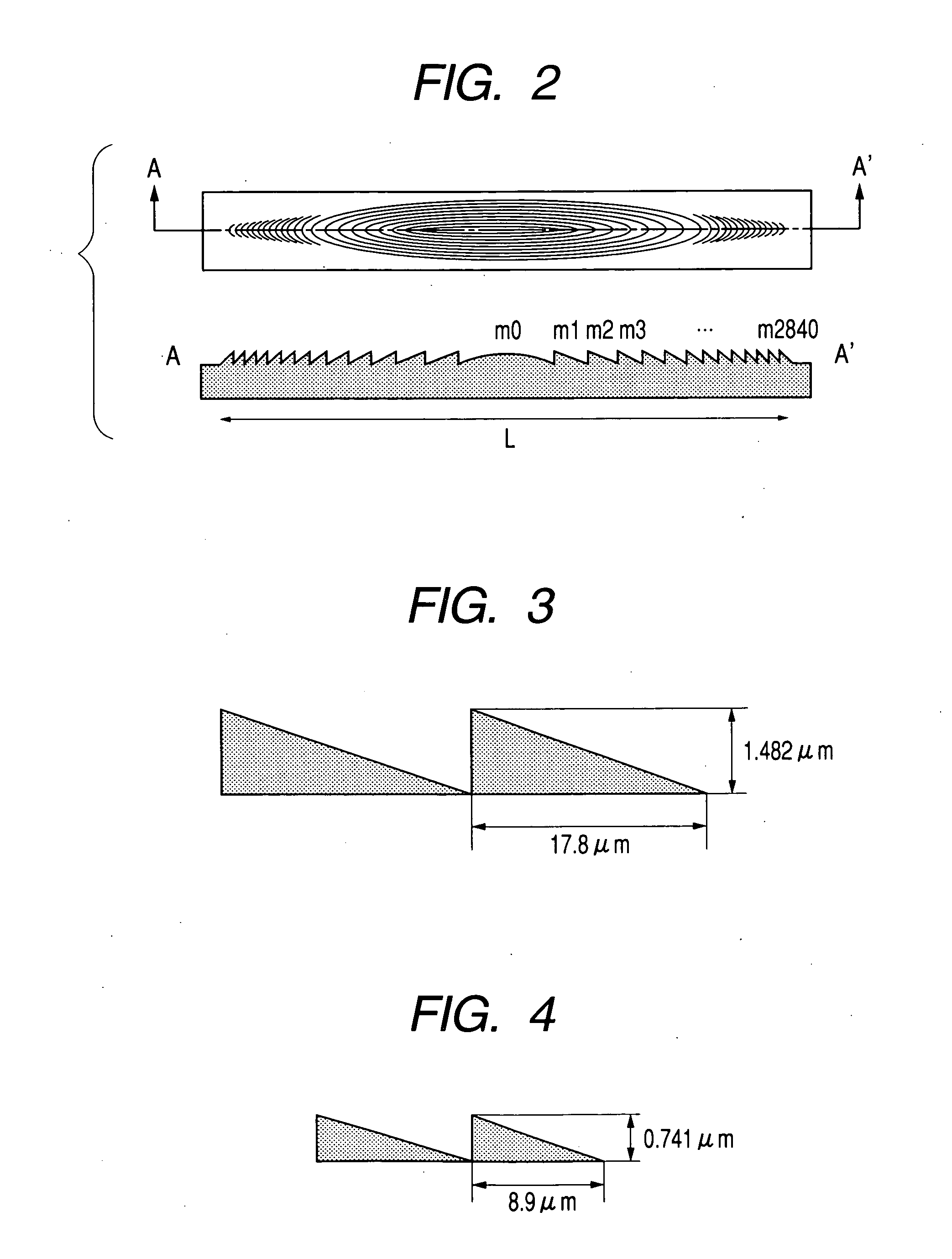
Optical scanning device and image forming apparatus using the same
InactiveUS20050045814A1Easy to producePreferable performanceInking apparatusBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsDiffraction orderImage formation
There is provided a diffraction grid which is easily produced without reducing a grid size. There is provided an optical scanning device having effects such as a chromatic aberration correction and a temperature compensation even when a short wavelength light source having a wavelength of 500 nm or less is used, and an image forming apparatus using the optical scanning device. In the optical scanning device having the diffraction grid, for which the short wavelength light source having a wavelength of 500 nm or less is used, a design order of the diffraction grid is set to a diffraction order equal to or larger than a second order to obtain a grid shape which is easily formed.
Owner:CANON KK
Method for testing residual stress of welding joint based on three-dimensional optical measurement technology and contour method
ActiveCN109186836AAccurate and efficient measurementGuarantee the sameDesign optimisation/simulationApparatus for force/torque/work measurementMeasurement pointEngineering
Disclosed is a method for testing a residual stress of a welding joint based on a three-dimensional optical measurement technology and a contour method. The method comprises the following steps: performing pre-processing before welding; after welding, performing cutting perpendicular to a cross section of a weld on a welding test plate, and performing XJTU-OM capturing on the cut test plate to obtain calculated measurement point cloud data; marking two cut planes as cutting faces A and B; performing preliminary de-noising fitting on the measurement point cloud data by adopting a Geomagic-qualify extruded scanning data band width to obtain an primary de-noised point cloud; performing de-noising on the primary de-noised point cloud obtained in the step3 according to a mean value of grid sizes by MATLAB, interpolating contour data between points to obtain fitting contours of the cutting faces A and B; performing mirroring on a fitting profile of the cutting face A measured by XJTU-OM, then performing point-by-point averaging on the two cutting faces A and B, generating a model with a displacement deviation by MATLAB for final elasticity calculation; and performing stress calculation and analyzing. The present invention has advantages of having important theoretical and engineering values for testing the residual stress of a weldment.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
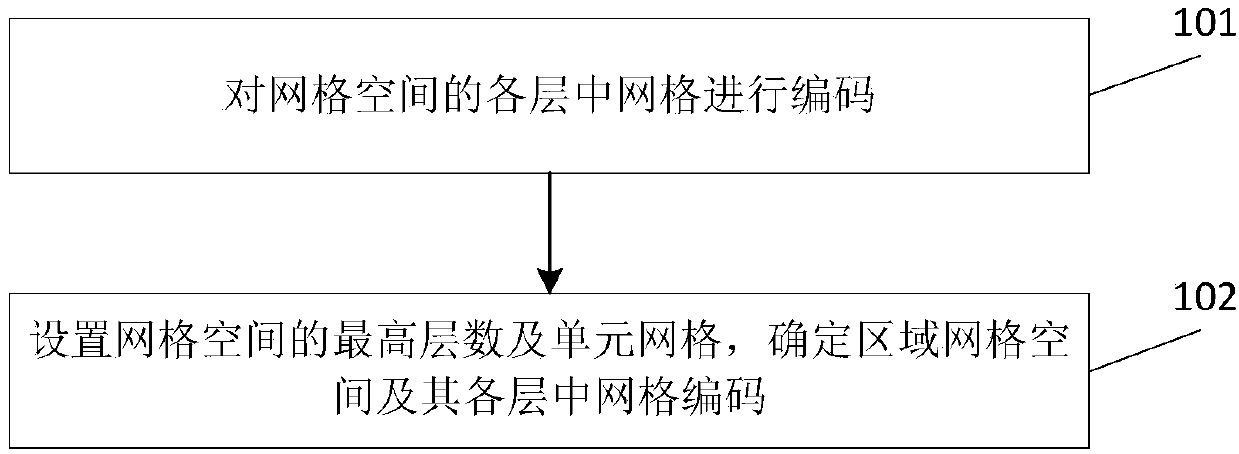
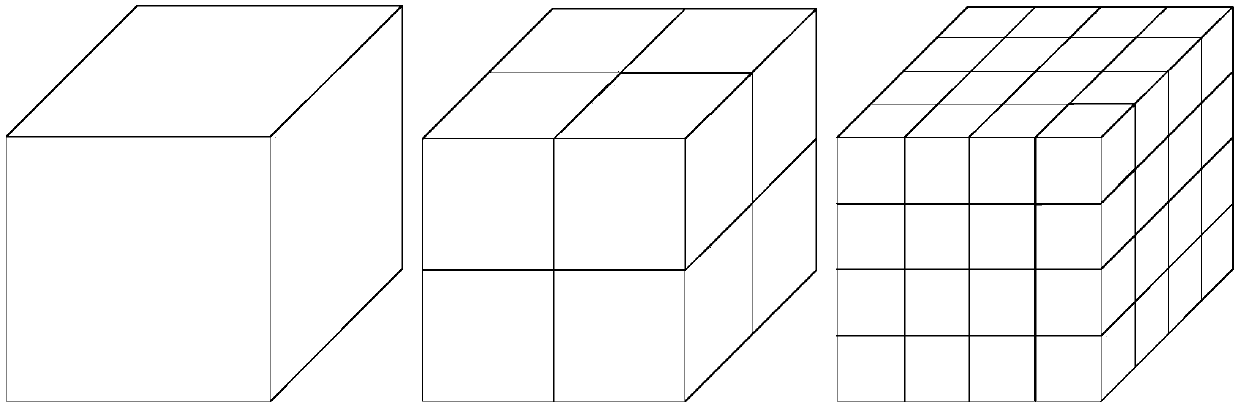
Area space multi-dimension grid encoding method and device
PendingCN107665242AOvercome the disadvantages of different sizesEasy to codeGeographical information databasesSpecial data processing applicationsGrid cellComputer science
The invention relates to an area space multi-dimension grid encoding method and device. The method comprises the steps of encoding grids in all layers of a grid space; setting the largest number of the layers of the grid space and unit grids and determining an area grid space and grid codes in all layers of the area grid space; adopting an eight division method to obtain a model of the grid space,starting from the smallest grid unit, through aggregation of the different layers, a larger grid unit is formed, namely the area grid space, further, aiming at the east-west direction, the south-north direction and the vertical direction, a binary system method is applied for encoding, through sequence combination in combination with an identification code, a complement code and the like, a complete code is formed, the characteristics can be guaranteed that in the aggregation process, the sizes of the grids in all the layers are the same, layering can be flexible in the vertical direction, binary system characteristics of a computer are conformed to, the multiple dimensions on multiple meanings are achieved, and therefore the method and device can be conveniently applicable to various occasions when space position management and services are needed.
Owner:南京王师大数据有限公司
Unconditional stability and conditional stability mixed time domain spectral element electromagnetic analyzing method
ActiveCN104951580AFit closelyFast solutionSpecial data processing applicationsTime domainAnalysis method
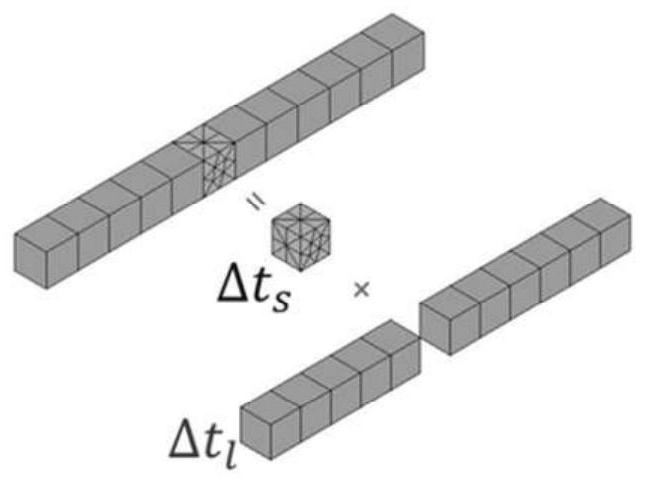
The invention discloses an unconditional stability and conditional stability mixed time domain spectral element electromagnetic analyzing method. In a traditional time domain spectral element method, for complex models, especially under the condition of containing multiscale problems, the sizes of meshes obtained through hexahedral subdivision are not uniform. In the subsequent time iteration, in order to ensure that an algorithm is stable and not diverging, the time step is set according to the size of the minimum subdivision mesh, and therefore the whole solution process wastes a large amount of time. The invention provides the self-adapting unconditional stability and conditional stability mixed time domain spectral element method. Small meshes and large meshes are automatically found out through the self-adapting method, an ordinary central difference format is used for the large mesh area, and a Newmark-beta difference format is used for the small mesh area, so that the unconditionally stable iteration format is obtained, the whole time step can be very large, and the solution time is greatly shortened.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
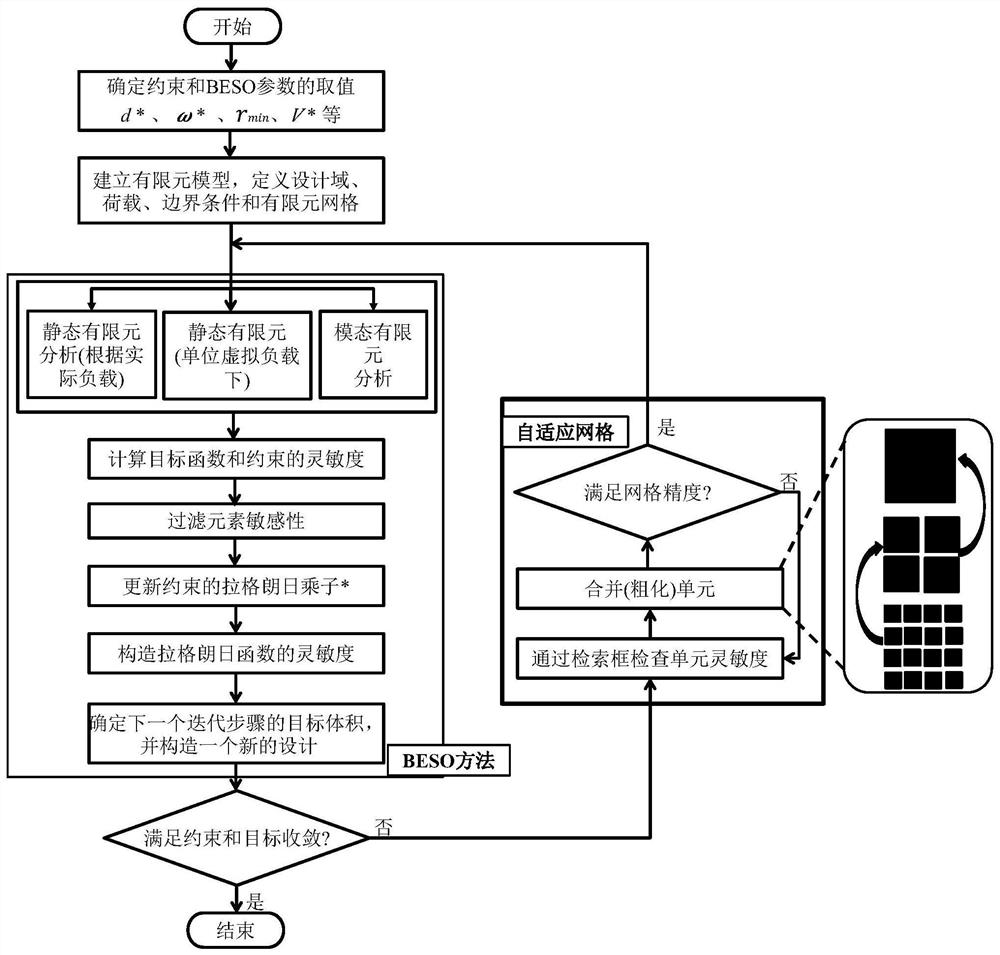
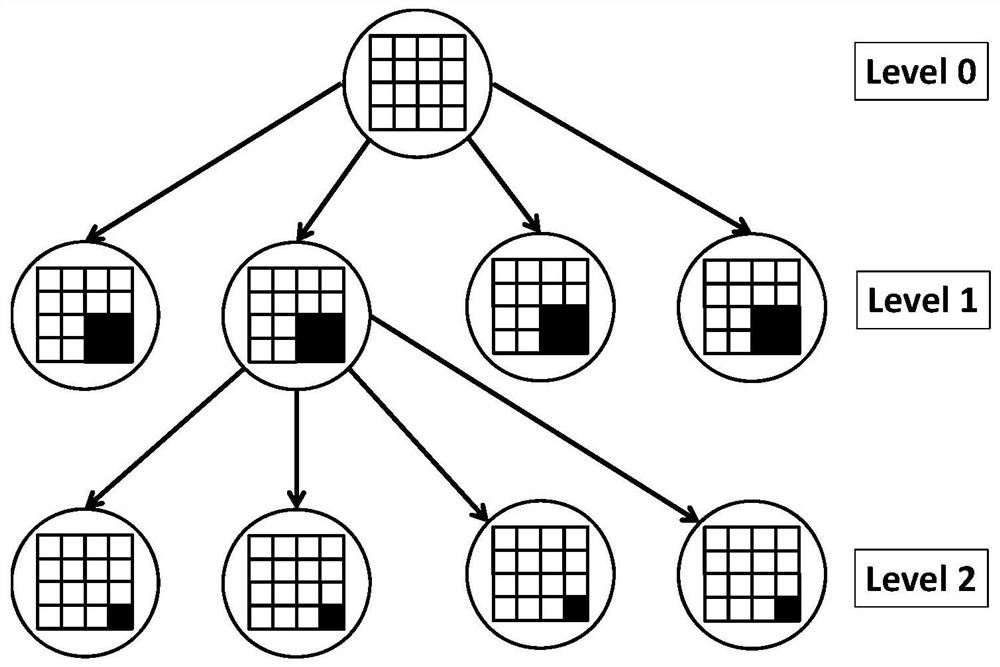
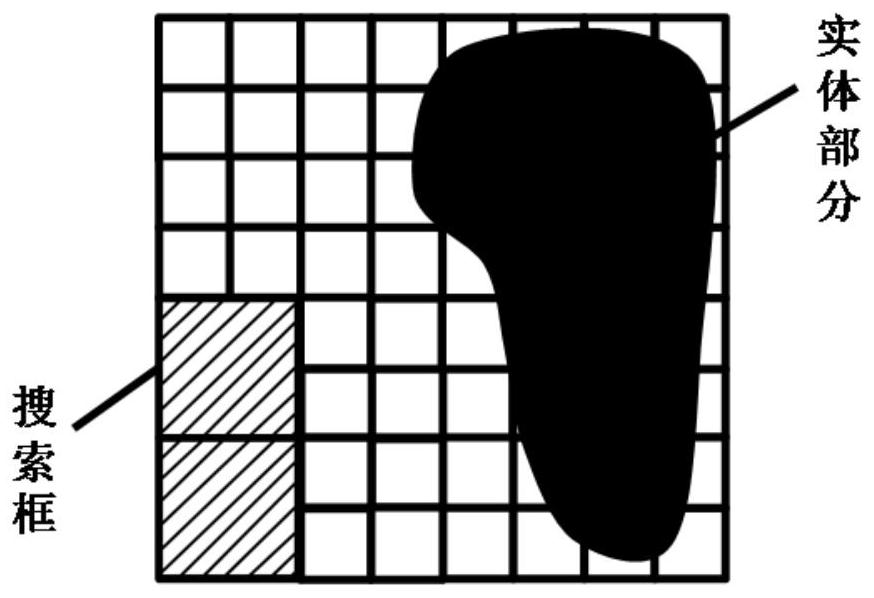
BESO topological optimization method based on dynamic evolution rate and adaptive grid and application of BESO topological optimization method
ActiveCN111737839ASmall amount of calculationImprove calculation accuracyGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationElement modelElement analysis
The invention discloses a BESO topological optimization method based on a dynamic evolution rate and an adaptive grid and application thereof, and the method comprises the steps: building a finite element model for a to-be-topologically optimized basic structure, and defining a design domain, a load, a boundary condition and a grid size; determining a constraint value and BESO necessary parameters; performing finite element analysis on the structure after mesh division, and calculating unit sensitivity under a target function and a constraint condition; filtering the unit sensitivity and updating the constrained Lagrange multiplier, and constructing the sensitivity of a Lagrange function; determining an evolution rate of the current iterative step based on a dynamic evolution rate functionof a Logistic function according to the volume rate of the current iterative step; and updating a design variable according to a set constraint function, judging whether constraint conditions and convergence conditions are met or not, if not, performing grid adaptive updating, then performing unit updating, and stopping iteration until the constraint conditions and the convergence conditions aremet. According to the invention, the calculation amount of single finite element analysis and the number of iterations required by topological optimization are effectively reduced while high calculation precision is ensured, so that the total calculation time consumption of topological optimization is greatly reduced.
Owner:GUANGZHOU UNIVERSITY
Method for reconstituting sea surface temperature remote sensing dataset in same latitude
InactiveCN103400022AReduce initial value estimation errorImprove reconstruction accuracyImage analysisSpecial data processing applicationsSensing dataMissing data
The invention discloses a method for reconstituting a sea surface temperature remote sensing dataset in the same latitude. The method comprises the following steps that first, the spatial position of the dataset is matched with grids in size; second, a same latitude dataset is extracted and processed; third, the DINEOF method for reconstituting the same latitude SST sensing data is implemented. The method for reconstituting the sea surface temperature remote sensing dataset in the same latitude can achieve the reconstitution of the missing data of sea temperature sensing products, based on the fact that the variation of temperature distribution on a latitude line is smaller than longitude variation, initial value estimation errors of the missing data are lowered, and a practical operation method for improving the reconstitution precision is achieved.
Owner:HANGZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
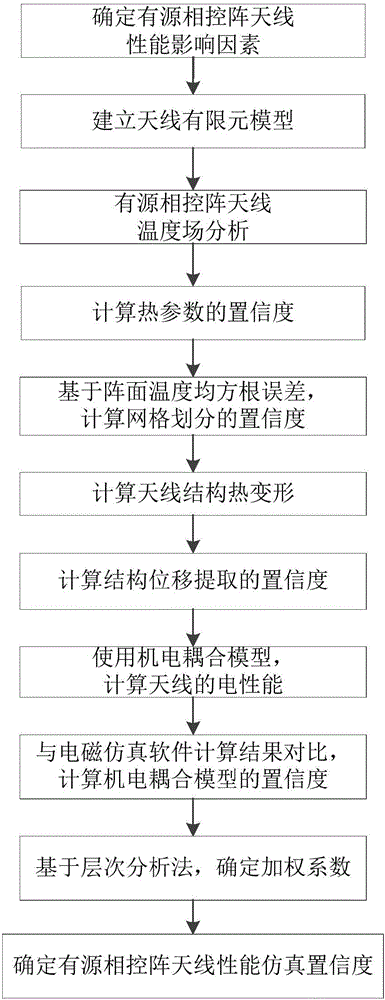
Electromechanical-coupling-oriented calculation method for performance simulation confidence degree of active phased array antenna
ActiveCN106021764AGood engineering application valueDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsElement modelThermal deformation
The invention discloses an electromechanical-coupling-oriented calculation method for the performance simulation confidence degree of an active phased array antenna. The method comprises the steps that influence factors of the performance of the active phased array antenna are determined; an antenna finite element model is established; temperature field analysis is conducted, and the confidence degree of thermal parameters is calculated; the confidence degree of the grid size is calculated based on a root-mean-square error of array surface temperature; antenna structural thermal deformation is calculated, and position offset of geometric center nodes of antenna units is extracted; the confidence degree of structural displacement extraction is calculated; an electromechanical coupling model is used for calculating electric performance of the antenna; the calculation result is compared with a calculation result obtained through electromagnetic simulation software, and the confidence degree of the electromechanical coupling model is calculated; the weighting coefficient is determined based on an analytic hierarchy process; a confidence degree calculation formula is established, and the performance simulation confidence degree of the active phased array antenna is calculated and finally determined. The antenna performance simulation confidence degree calculation method is established, and a judgment criterion is provided for the simulating calculation result of influences of structural thermal deformation of the active phased array antenna on electrical properties.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
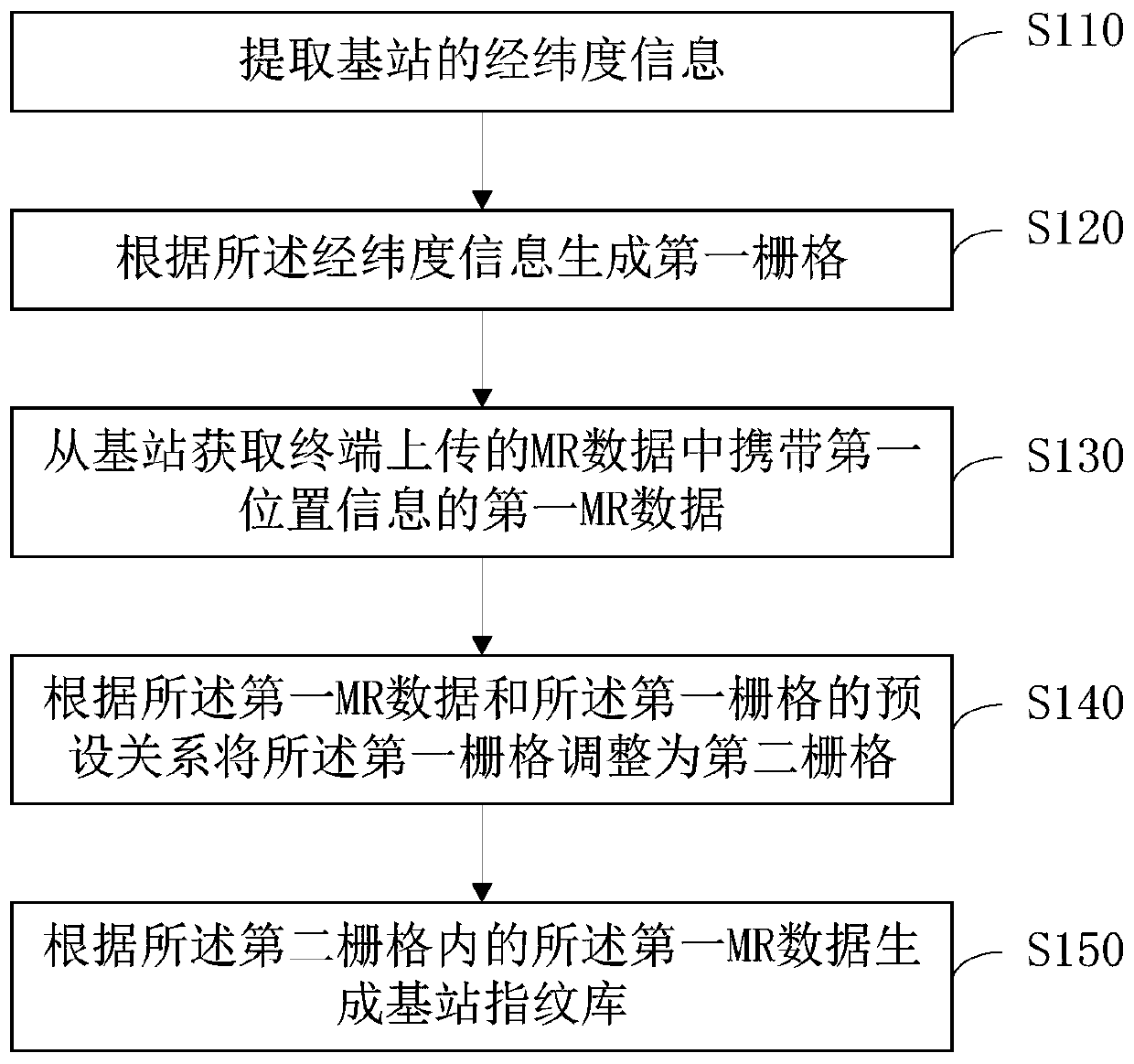
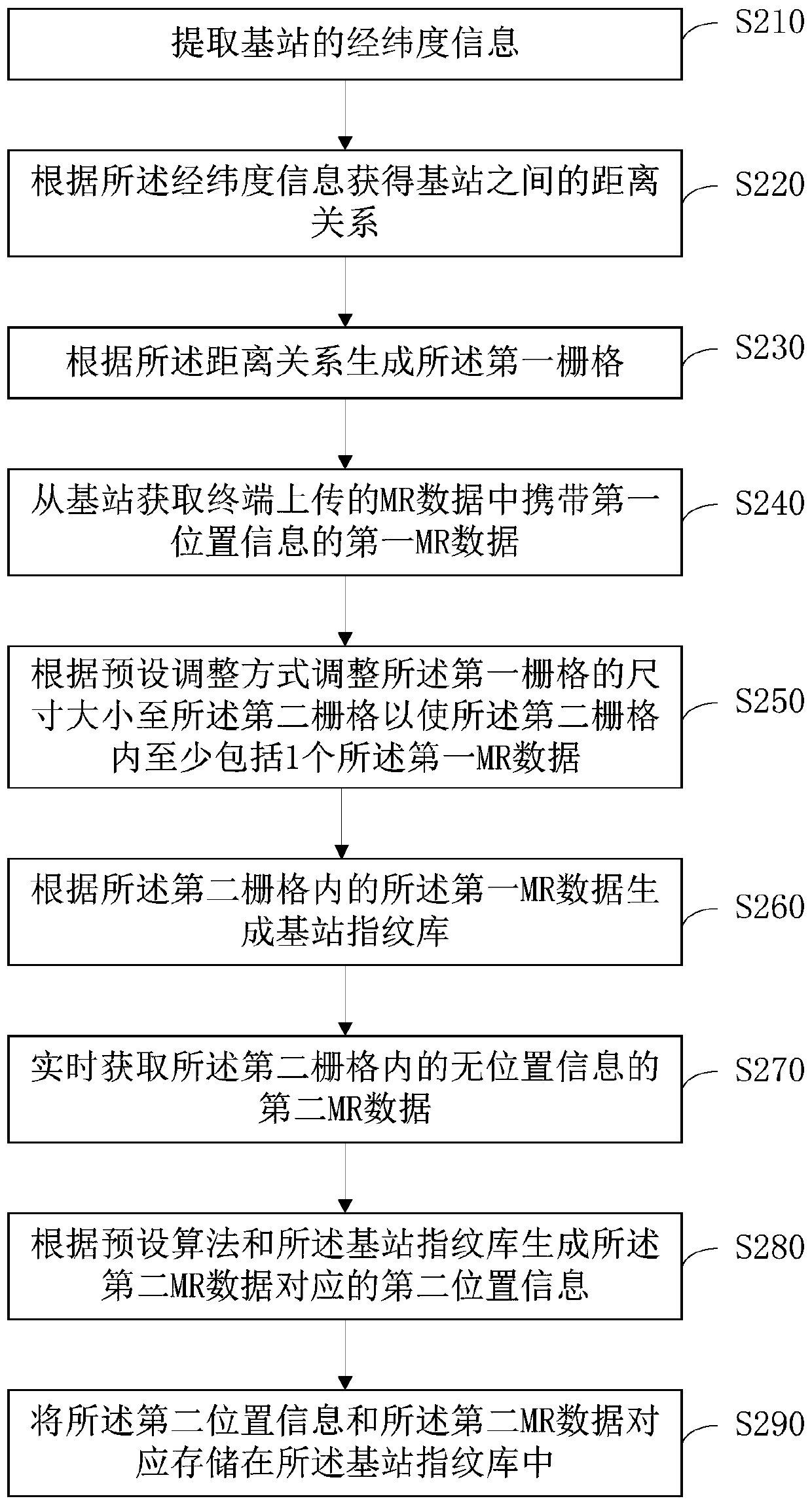
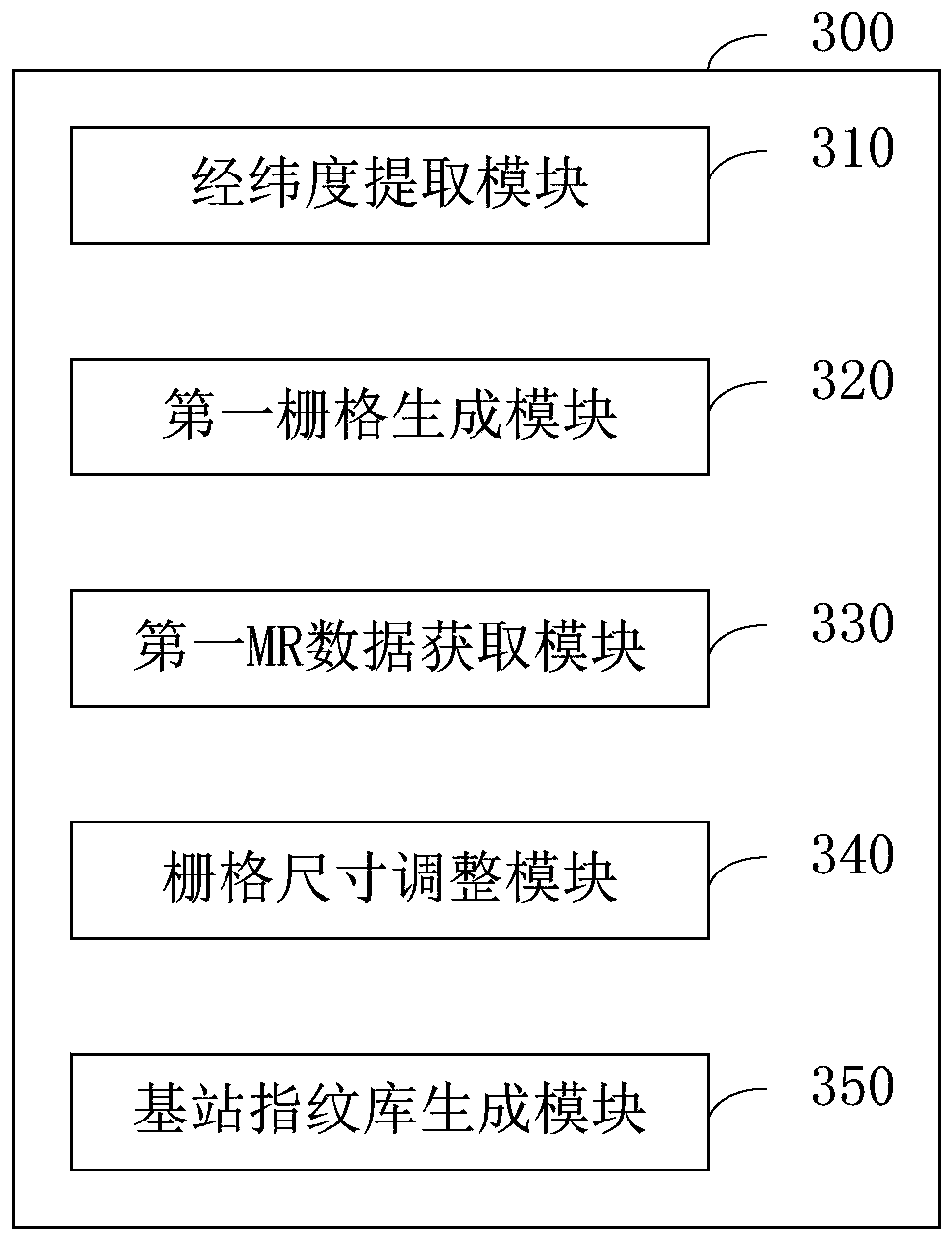
Base station fingerprint database establishment method and device, server and storage medium
InactiveCN110972261ASolve the problem of difficult selectionLocation information based serviceEngineeringData mining
The invention discloses a base station fingerprint database establishment method and device, a server and a storage medium. The method comprises the following steps: extracting longitude and latitudeinformation of a base station; generating a first grid according to the longitude and latitude information; obtaining first MR data carrying first position information in MR data uploaded by a terminal from the base station; adjusting a first grid into a second grid according to a preset relationship between the first MR data and the first grid; and generating a base station fingerprint database according to the first MR data in the second grid. According to the technical scheme, the effect of generating the grid size in a self-adaptive mode is achieved.
Owner:北京红山信息科技研究院有限公司
Method for estimating spatio-temporal change of remote sensing image, device and storage medium
ActiveCN109241846AImprove efficiencyAutomate processingCharacter and pattern recognitionGeographical information databasesModel extractionData set
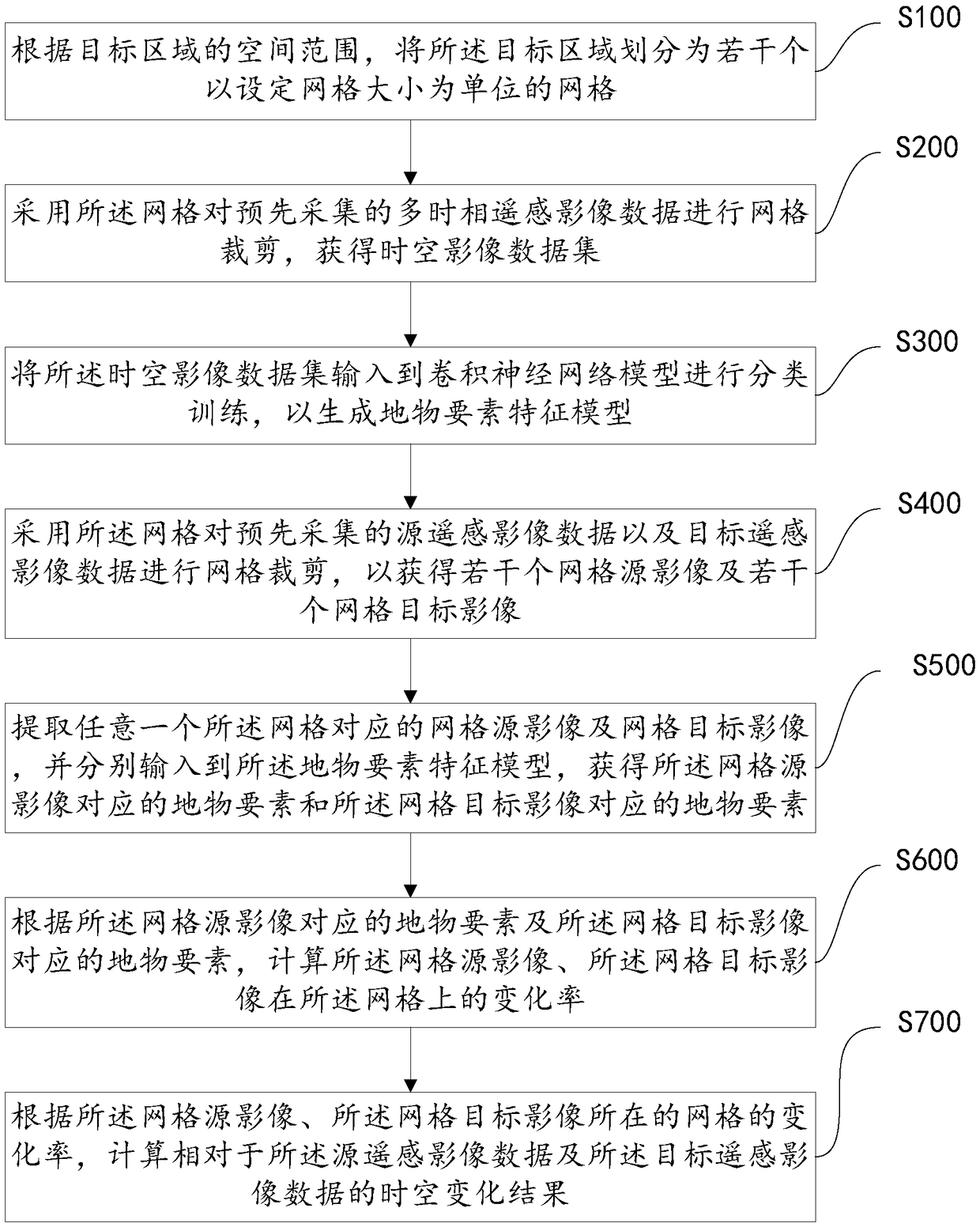
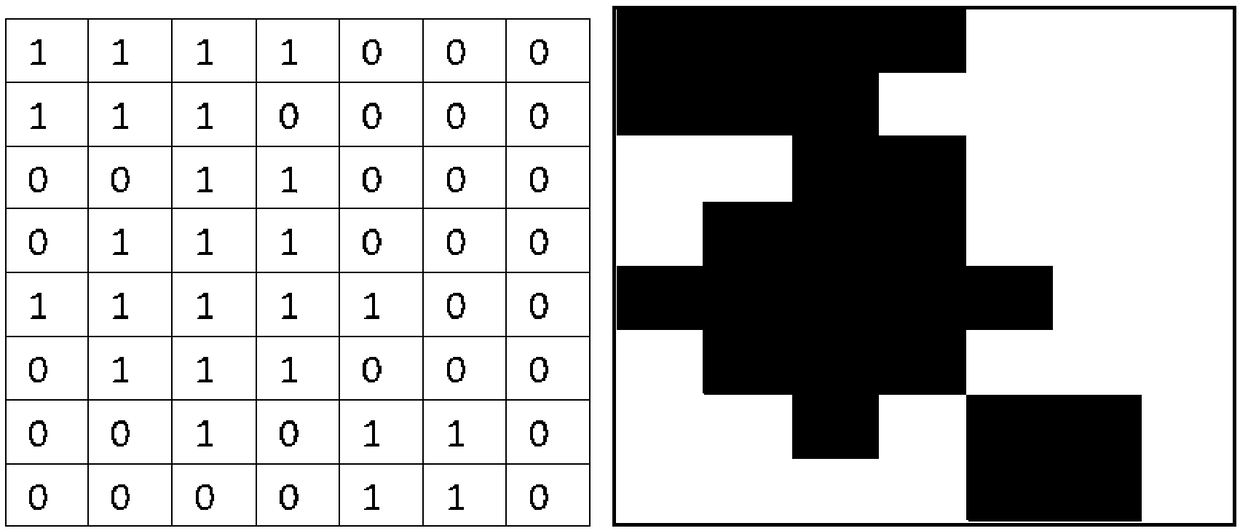
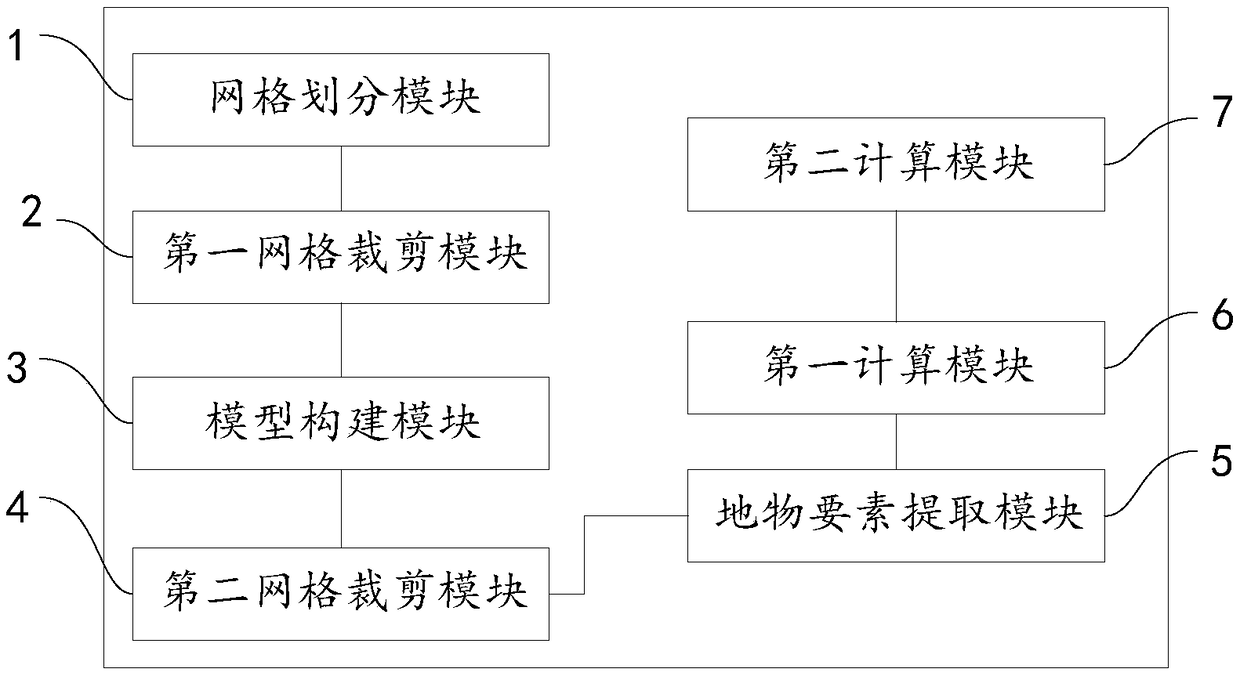
The invention discloses a method for estimating temporal and spatial change of remote sensing image, a device and a storage medium. The method includes: a target area is divided into a plurality of grids with a set grid size as a unit; the multi-temporal remote sensing image data are clipped by the grid, and the spatio-temporal image data set is obtained; CNN model is used to classify and train the spatio-temporal image dataset to generate feature model of surface features; the grid is used to cut the source remote sensing image data and the target remote sensing image data so as to obtain aplurality of grid source images and a plurality of grid target images; the features of the grid source image and the grid target image are extracted by the feature model of the features, and the differences are compared and analyzed to obtain the spatio-temporal change results of the target region. Through this method, the CNN and GIS technology can be highly integrated, and the automatic processing of urban spatial and temporal change estimation based on the massive urban remote sensing image data is realized, which has high efficiency.
Owner:GUANGZHOU URBAN PLANNING & DESIGN SURVEY RES INST
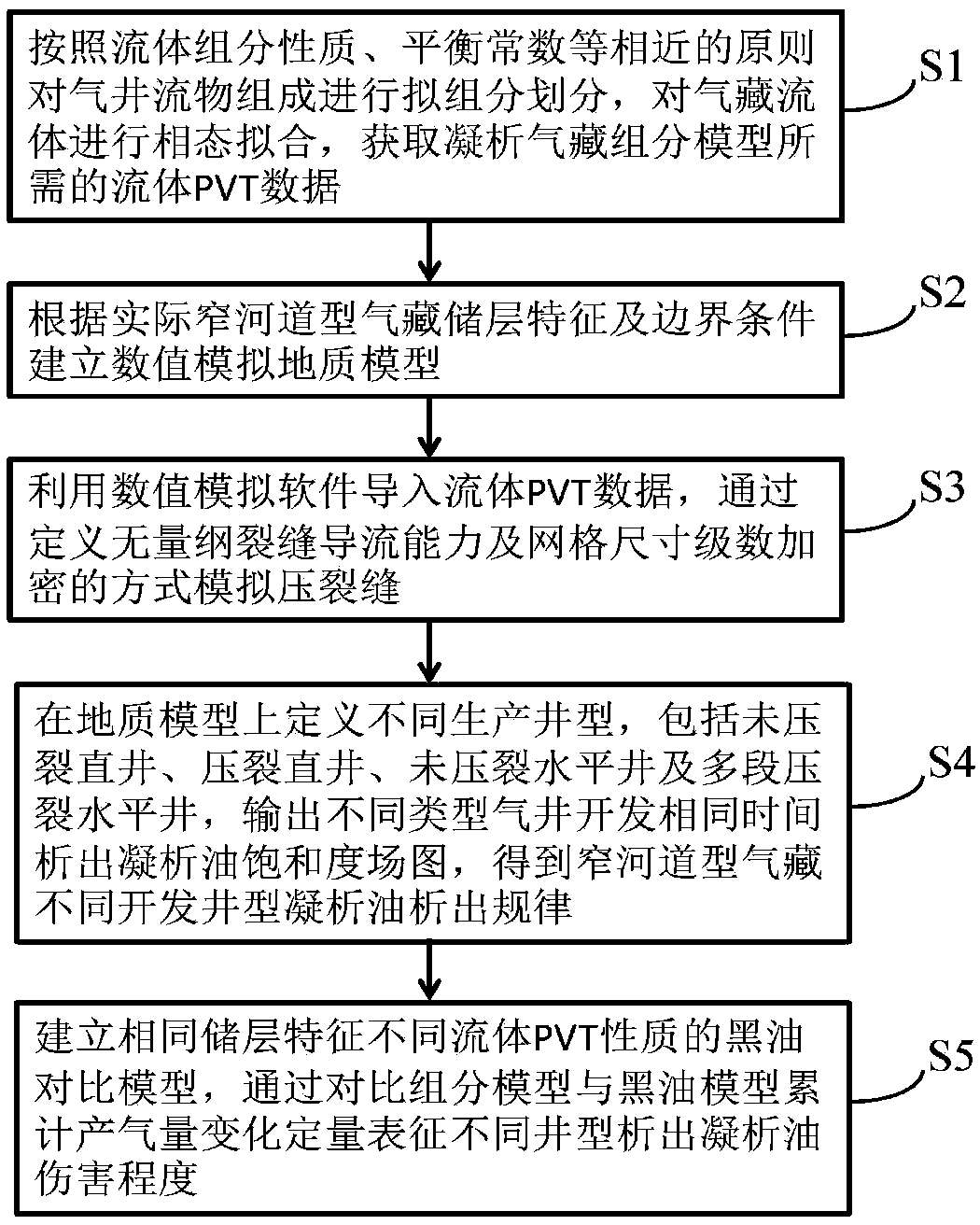
A method for numerical simulation of condensate oil damage of different well type of narrow channel gas reservoir
ActiveCN108959767AImprove development efficiencySimple methodDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsPhase stateBlack oil
A method for numerical simulation of condensate oil damage of different well types in a narrow channel gas reservoir includes such steps as dividing pseudo-component of gas well flow and phase state fitting to obtain fluid PVT data required by component model of gas reservoir; establishing a numerical simulation geological model according to the reservoir characteristics and boundary conditions ofnarrow channel gas reservoirs; by defining dimensionless fracture conductivity and grid size series refinement, simulating the fractures and importing the PVT data by numerical simulation software;by simulating the distribution of condensate saturation in different development wells, obtaining the law of condensate precipitation in different development wells of narrow channel gas reservoirs; establishing a black oil model to quantitatively characterize the condensate oil damage of different well types by comparing the cumulative gas production reduction range of gas wells. The invention can finely simulate hydraulic fracturing fractures, and can qualitatively and quantitatively evaluate the influence of condensate oil precipitation of different development well types on gas well productivity of narrow channel gas reservoirs.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (BEIJING)
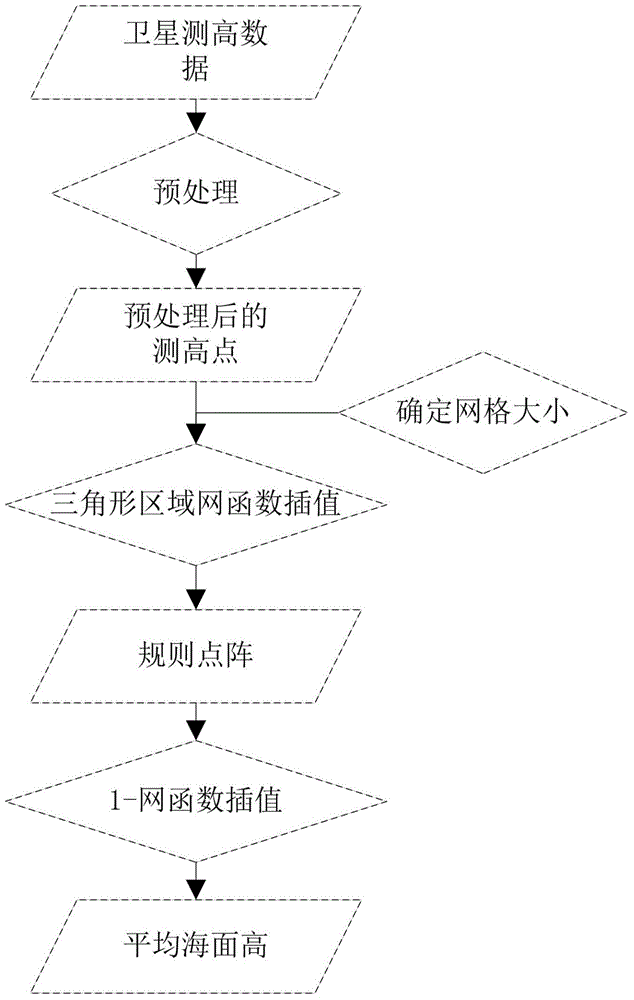
Method for the production of mean sea surface height products based on satellite altimeter data network function interpolation
InactiveCN104933291AFacilitate automatic divisionThe derivation is rigorous and accurateSpecial data processing applicationsImage resolutionSea-surface height
The present invention discloses a method for the production of mean sea height products based on satellite altimeter data network function interpolation, which comprises the steps of: data preprocessing, determination of grid size and central point, grid interpolation, and refined interpolation. The method according to the present invention facilitates automatic grid segmentation on the computer, has obvious statistical characteristics, reflect the spatial distribution of the marine gravity field on the physical properties, wherein the marine gravity field is in a positive proportion to mean sea surface height, gives full consideration to the physical characteristics of sea level, and can improve mean sea height products of high accuracy and spatial resolution.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
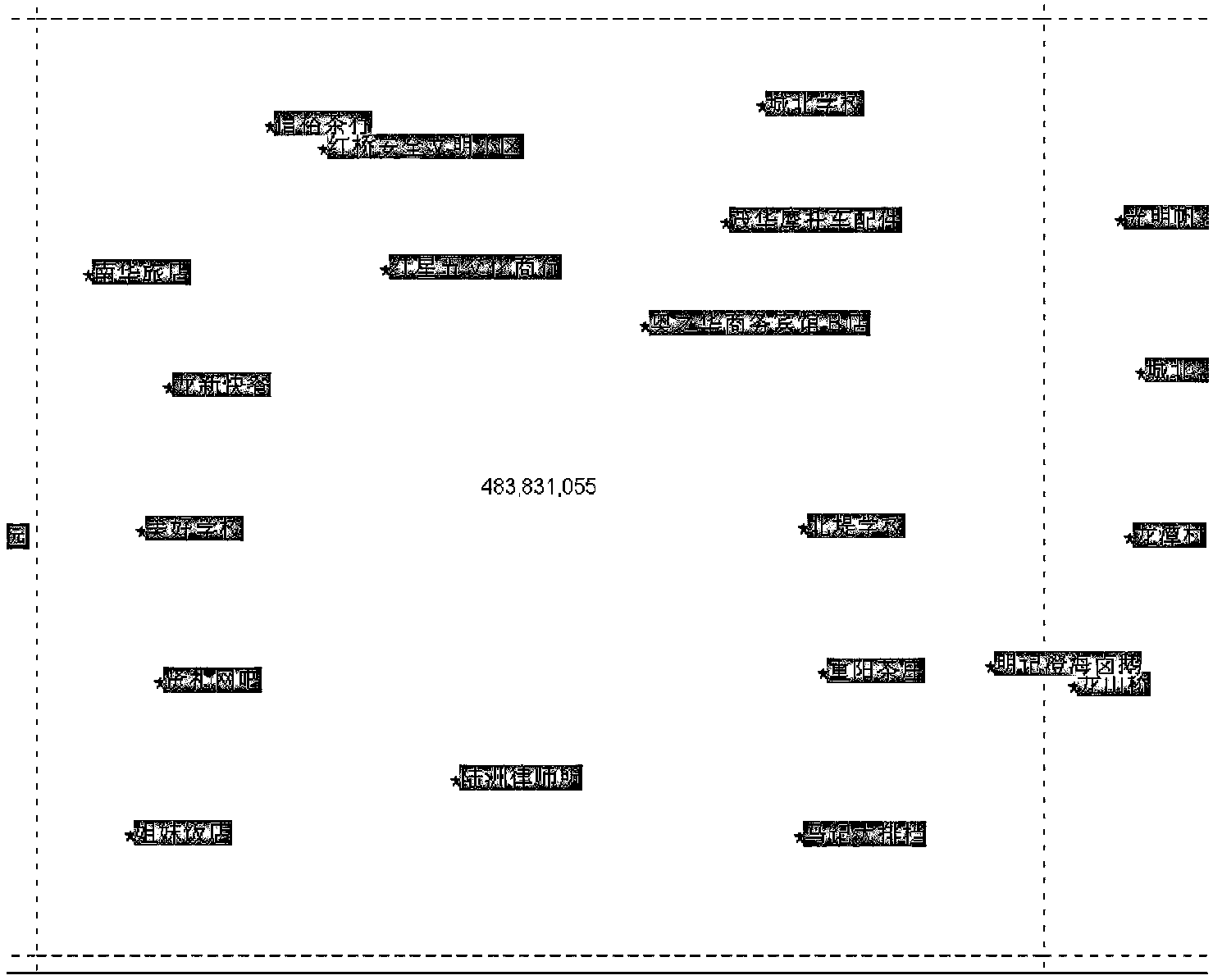
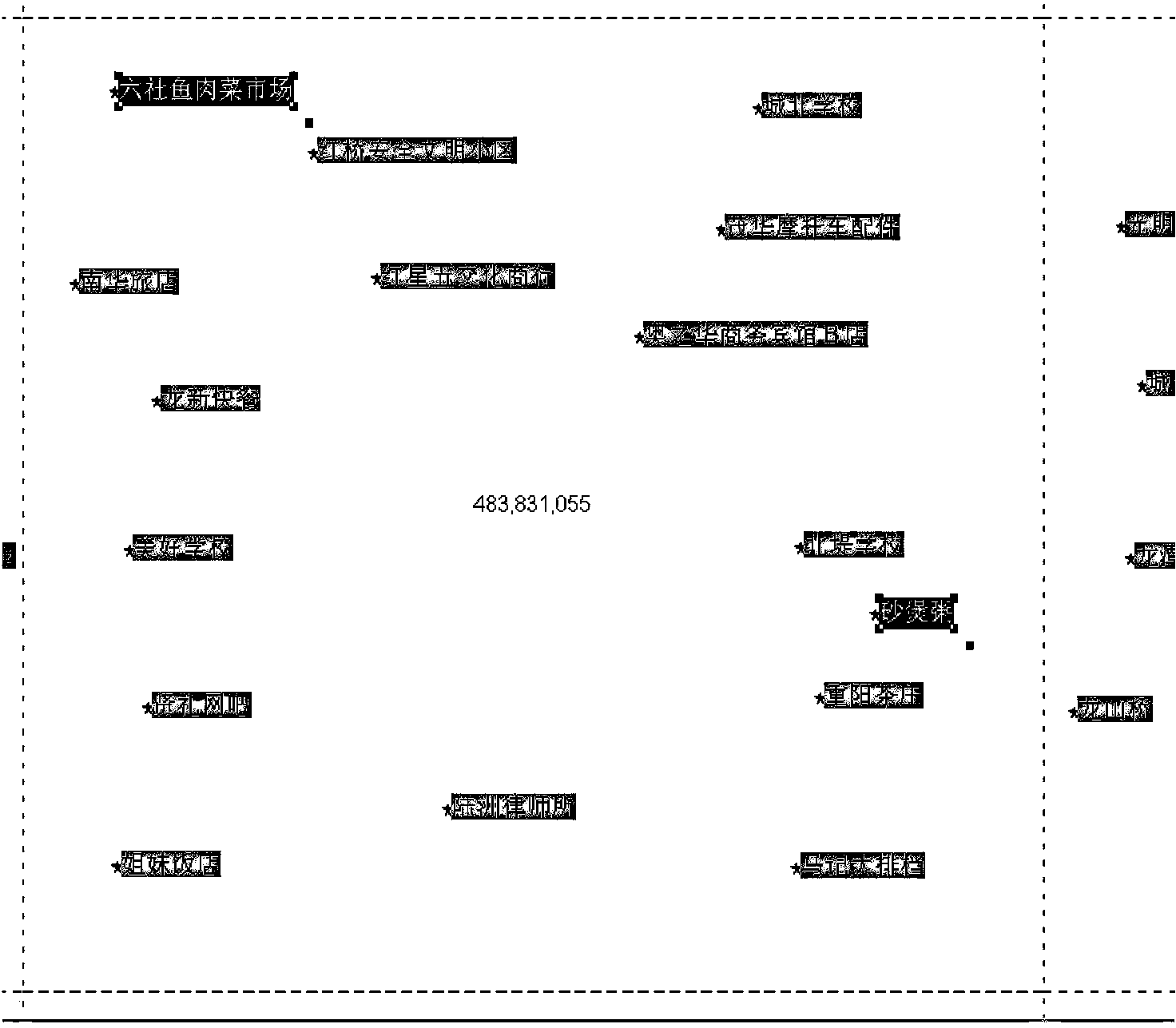
Map load based method for dynamically screening electronic map point elements
ActiveCN104036688ADoes not affect visibilityDoes not affect comprehensionMaps/plans/chartsGrid partitionComputer science
The invention provides a map load based method for dynamically screening electronic map point elements. The map load based method for dynamically screening the electronic map point elements comprises 1, performing mesh dividing on point sets of POI (Point of Information) on a map, wherein the size of meshes is identical; 2, dividing the POI in different types to be in different display levels according to the map purpose; 3, confirming pre-reserved points in an electronic map according to the display levels of the POI and the largest area load under the electronic map scale; 4, screening the point set of reserved POI of every mesh and achieving screening of the electronic map point elements. According to the map load based method for dynamically screening the electronic map point elements, the reserved point elements can display the information amount of the point elements in the map maximally, meanwhile mutual covering is avoided, and accordingly cognitive difficulties caused by too much or too little map information amount are avoided.
Owner:XIAMEN YAXON NETWORKS CO LTD
Arbitrary high-order hybrid grid time domain discontinuous Galerkin method based on multi-stage local time stepping technology
ActiveCN111639447AQuick analysisReduce computing timeDesign optimisation/simulationComplex mathematical operationsEngineeringNumerical models
The invention discloses an arbitrary high-order hybrid grid time domain discontinuous Galerkin method based on a multistage local time stepping technology. According to the method, a Maxwell equationset is selected as a basic numerical model; an arbitrary high-order derivative (ADER) time stepping scheme is combined; a computational domain is divided by adopting a reasonable tetrahedron / hexahedron hybrid grid; each subdivision cell respectively and automatically determines a proper time iteration step length according to a stability condition; iteration updating can be carried out on a plurality of time iteration step lengths and each cellular electromagnetic field quantity in any proportion according to the own time iteration step length until all cellular field quantities are iterated to a specified time point, and the obtained time-varying electromagnetic field quantity is post-processed to obtain a corresponding S parameter, a radar scattering sectional area and electromagnetic field spatial distribution. According to the method, the problem that the calculation efficiency is low due to the fact that the time step length of a time domain electromagnetic analysis method is limited by the minimum discrete grid size is solved, the calculation precision is improved, the calculation time is shortened, and the method is particularly suitable for rapid analysis of the space multi-scale electromagnetic problem.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
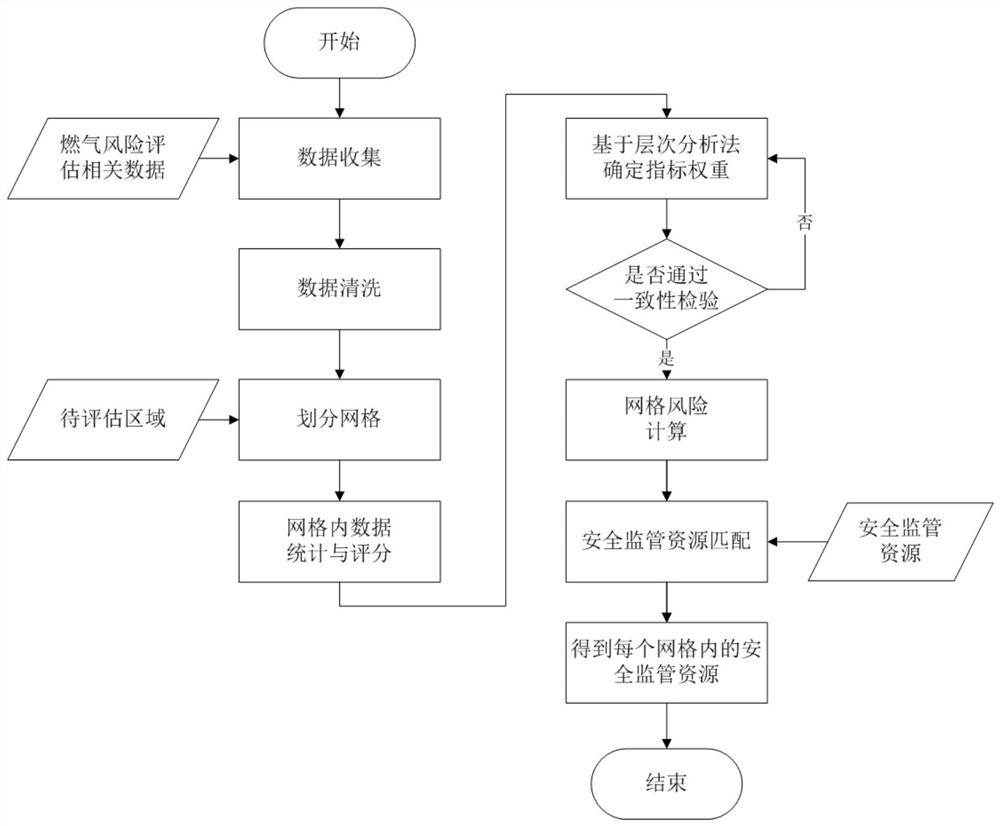
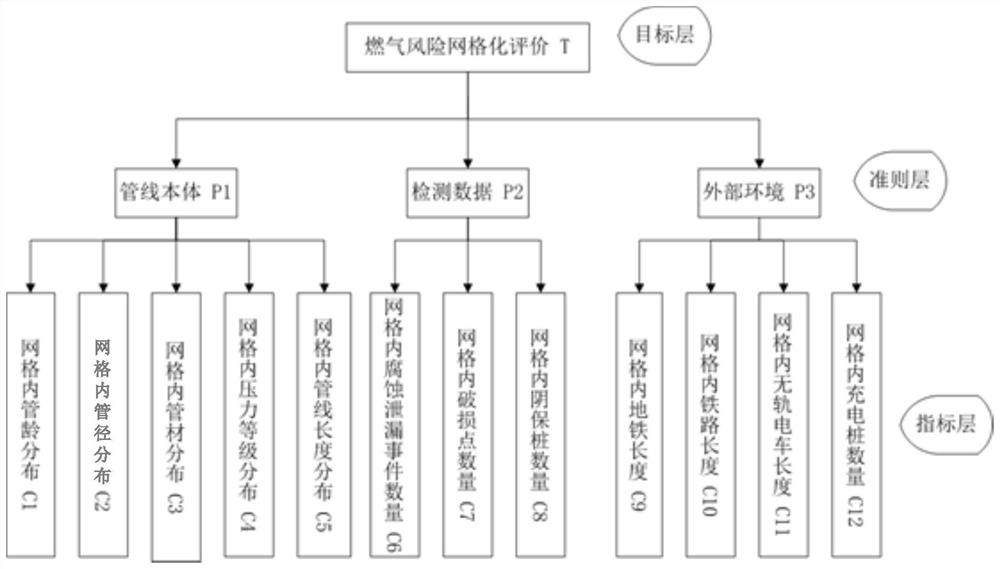
Fuel gas risk assessment and safety supervision resource matching method and device
PendingCN111611524AAvoid reasonable controlAvoid wastingResourcesComplex mathematical operationsAssessment dataGrid partition
The invention provides a fuel gas risk assessment and safety supervision resource matching method and device. The method comprises the steps: collecting fuel gas risk assessment data; performing datacleaning on the collected gas risk assessment to obtain cleaned data; determining a risk assessment area, and performing grid division on the risk assessment area according to a preset grid size; obtaining scores of the cleaned data in the grids; determining an index weight based on an analytic hierarchy process, judging whether consistency verification is passed or not, and if the consistency verification is passed, performing grid risk calculation; and acquiring safety supervision resources, and matching the safety supervision resources to obtain the safety supervision resources in each grid.
Owner:BEIJING GAS GRP
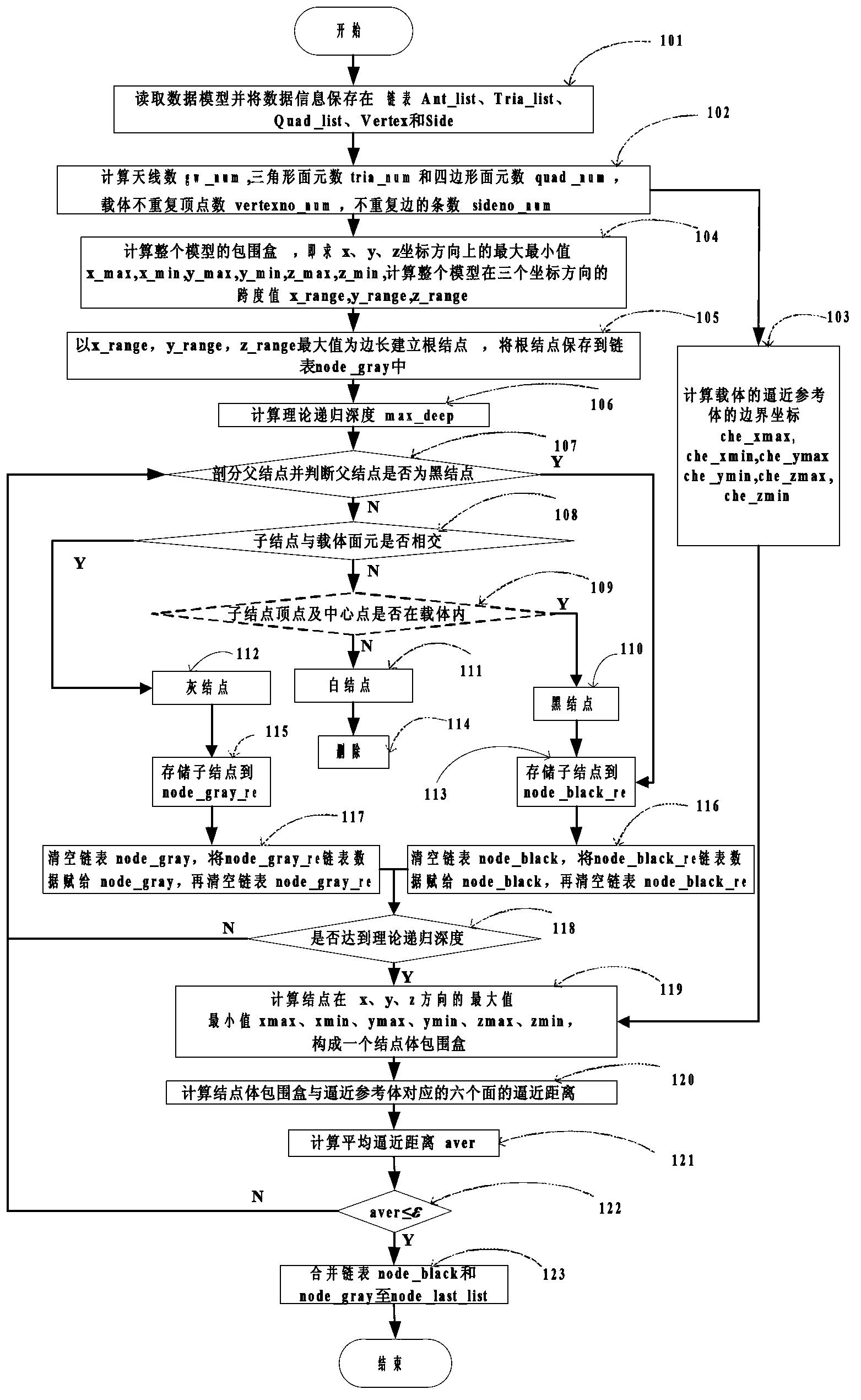
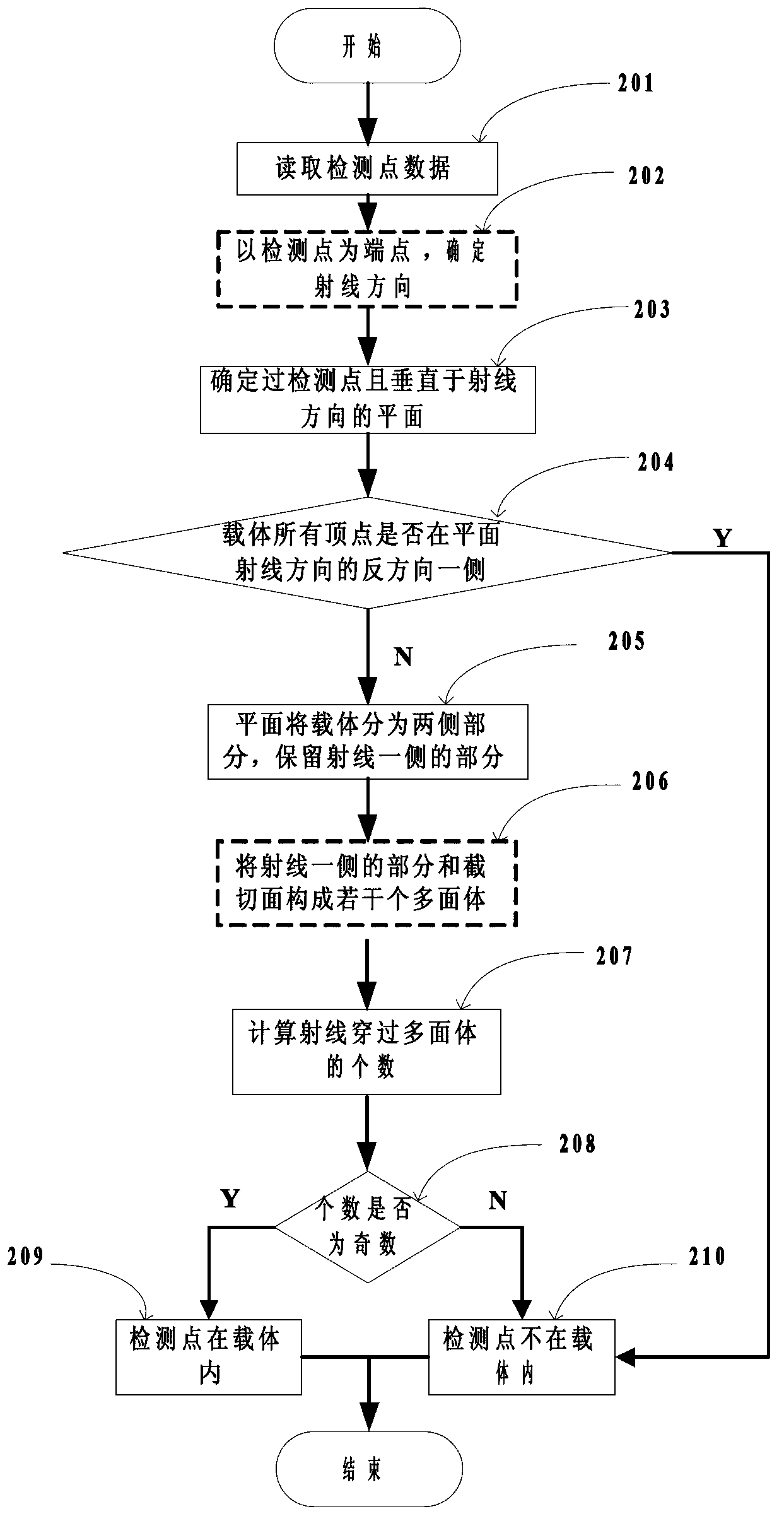
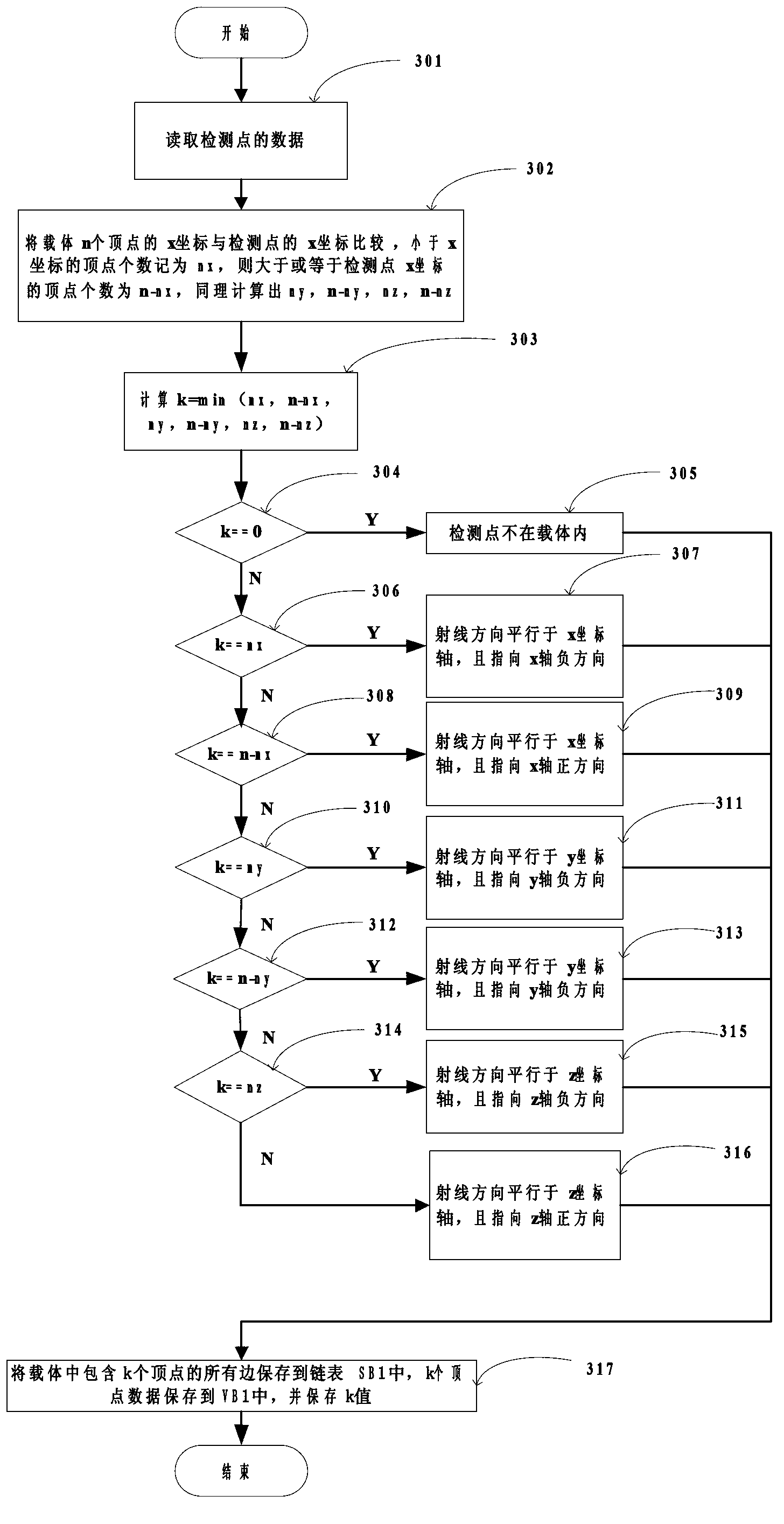
Finite difference time domain electromagnetic calculation carrier meshing method
InactiveCN103310069AHigh degree of geometric approximationThe calculation result is accurateSpecial data processing applicationsTime domain electromagneticsGrid partition
The invention discloses a finite difference time domain electromagnetic calculation carrier meshing method. According to the method, the mesh size is jointly controlled by the discrete electrical dimensional accuracy and the carrier surface approximation accuracy, the geometrical approximation degree between the divided mesh model and the carrier model is high especially under the situation of low frequency with large wavelength, finite difference time domain electromagnetic calculation is performed on the basis of the mesh model, and the calculation result is relatively accurate; surface approximation accuracy controlling parameters for meshing the mesh model are provided, the blindness of meshing precision control of the conventional direct subdivision method is avoided, and the calculated amount for meshing can be effectively controlled; when mesh refinement is required, all that is needed is to perform octree recursive subdivision to the black nodes in the bottommost layer, and mesh refinement is easy to realize.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
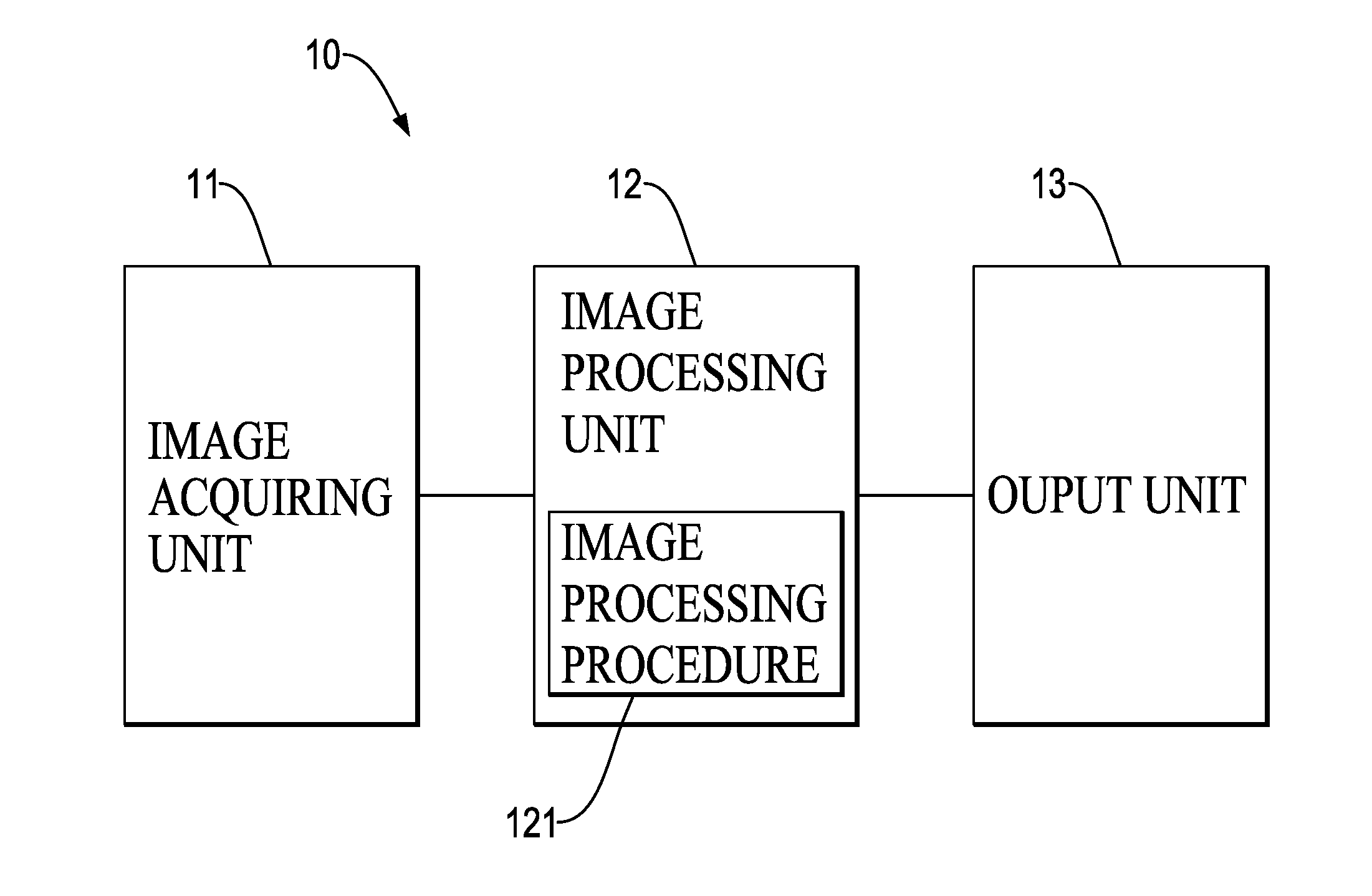
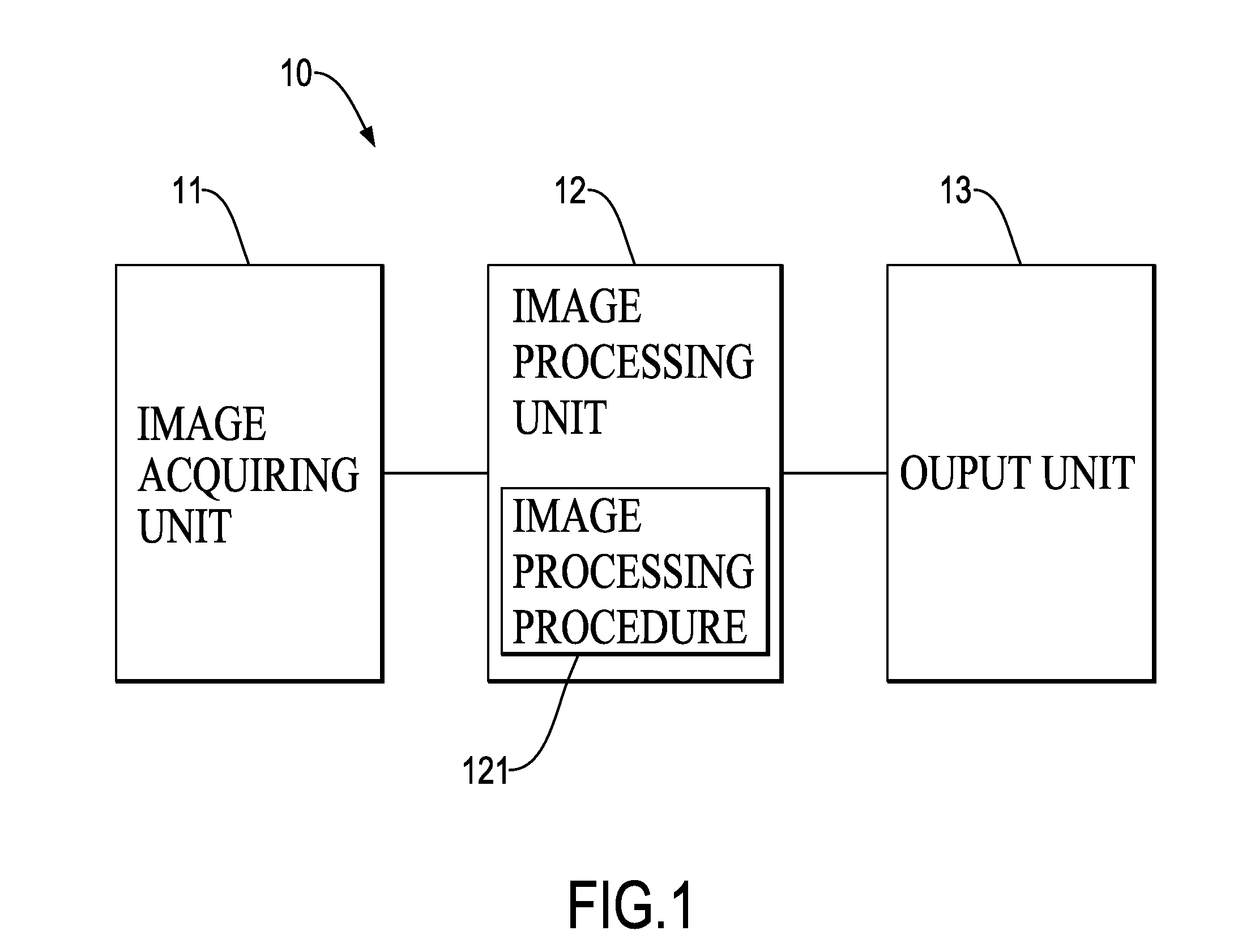
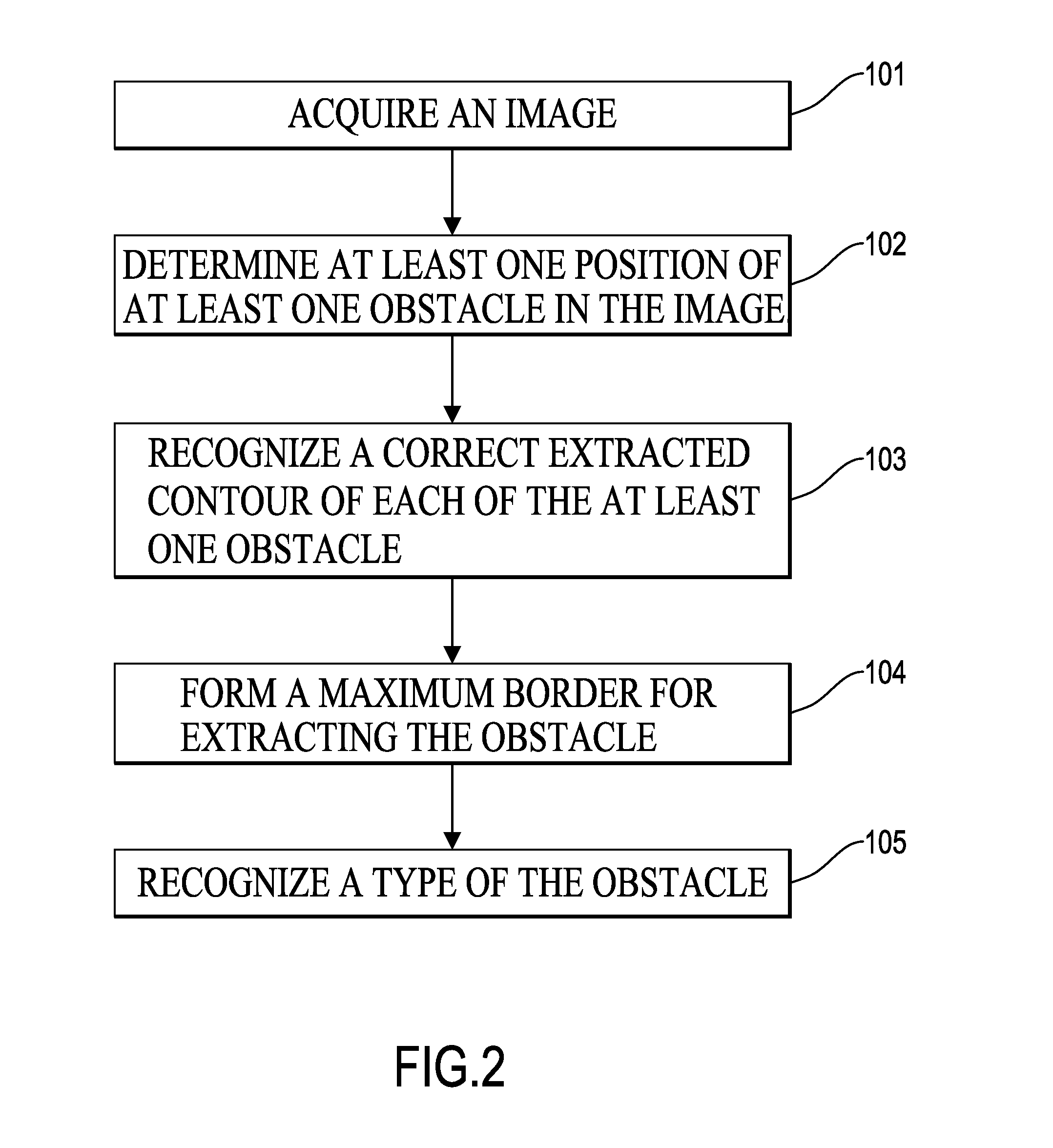
Object detection method with a rising classifier effect and object detection device with the same
An object detection method with a rising classifier effect is embedded in an object detection device and has steps of acquiring image information; determining a position of an obstacle in the image information, wherein the image information is detected for generation of an extracted range corresponding to the obstacle; recognizing an extracted contour of the obstacle, wherein the extracted contour of the obstacle associated with the extracted range is obtained by using an algorithm for Poisson gradient vector flow based active deformable contour model and a multi-mesh algorithm with different grid sizes; and forming a maximum border of the extracted contour of the obstacle for a classifier to recognize a type of the obstacle according to the maximum border of the obstacle. Accordingly, the object detection method is advantageous in complete extraction, higher recognition rate, faster computation and feasibility to be integrated with vehicle systems.
Owner:AUTOMOTIVE RES & TESTING CENT
Intelligent POS interface layout method and system
ActiveCN106775614AFlexible and dynamic adjustment of layoutExecution for user interfacesImage resolutionInterface design
The invention discloses an intelligent POS interface layout method and system. The method comprises the steps that parameters of the screen direction of equipment are acquired through a desktop launcher, and a mesh layout direction is judged according to the screen direction and a preset rule; parameters of the resolution and screen size of the equipment are acquired through the desktop launcher, and the grid size is obtained according to the resolution parameter, the screen size parameter and a preset rule; a basic network layout is obtained according to the grid layout direction and the grid size; the number of built-in applications of the equipment and the display priorities of the applications are acquired; the number of grids is obtained according to the number of the applications, the basic network layout and a preset rule; the applications are sequentially displayed according to the display priorities of the applications, and then the interface layout is completed. According to the interface design method, the layout can be flexibly and dynamically adjusted according to requirements in response to interaction.
Owner:深圳市云刷科技有限公司
Firing target automatic score apparatus
InactiveCN1955632ARealize automatic scoringImprove practicalityTarget detectorsTarget arrayDisplay device
An automatic point-recording device of shooting target consist of frame of automatic point-recording device, horizontal target array, vertical target array, control module, radio emission module, radio receiving module and display. It is feature as utilizing two said target arrays to form a grid, setting grid size to be less than diameter of bullet to let bullet contact with steel wire of grid when grid is hit by bullet in order to obtain coordinate of hitting point then to obtain ring number of the shoot.
Owner:揭雪强
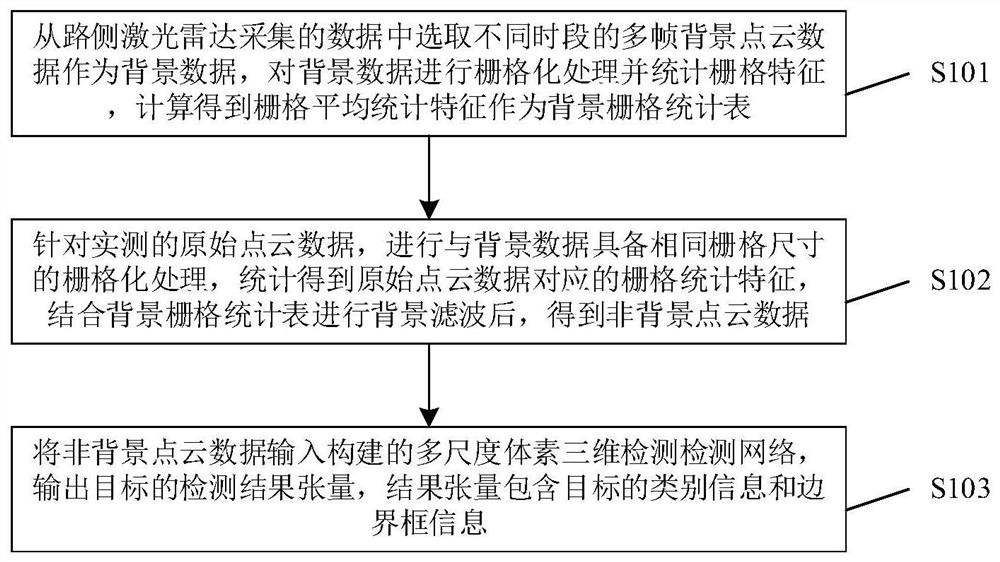
Roadside laser radar target detection method and device
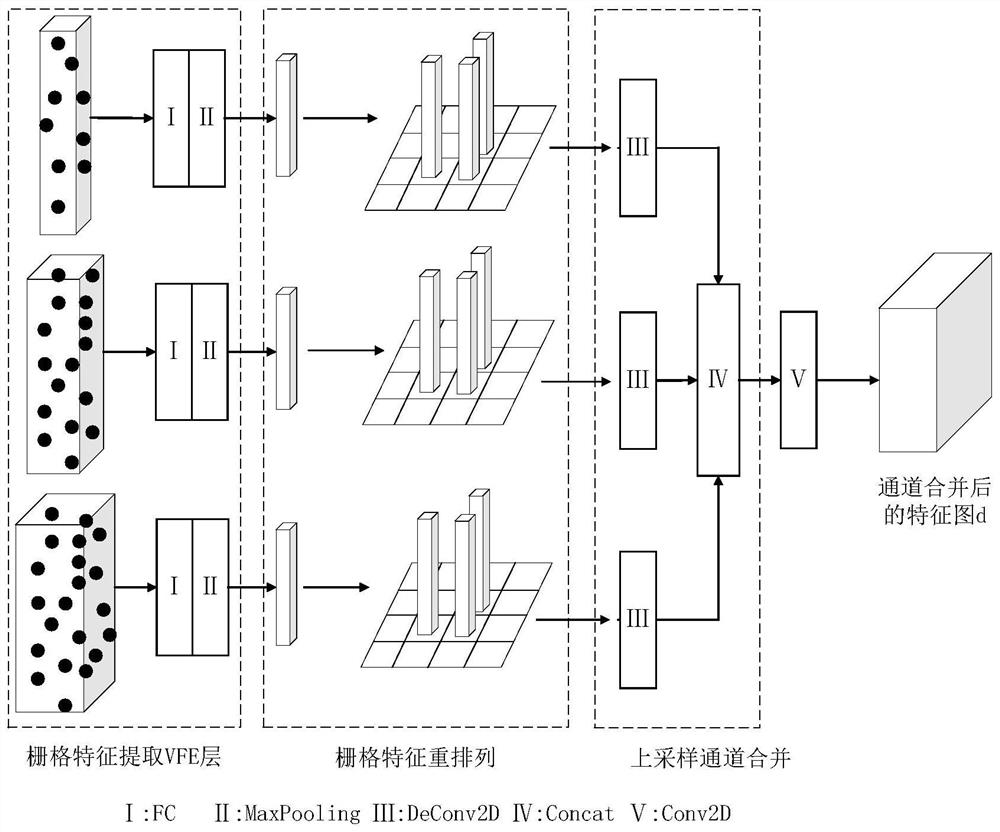
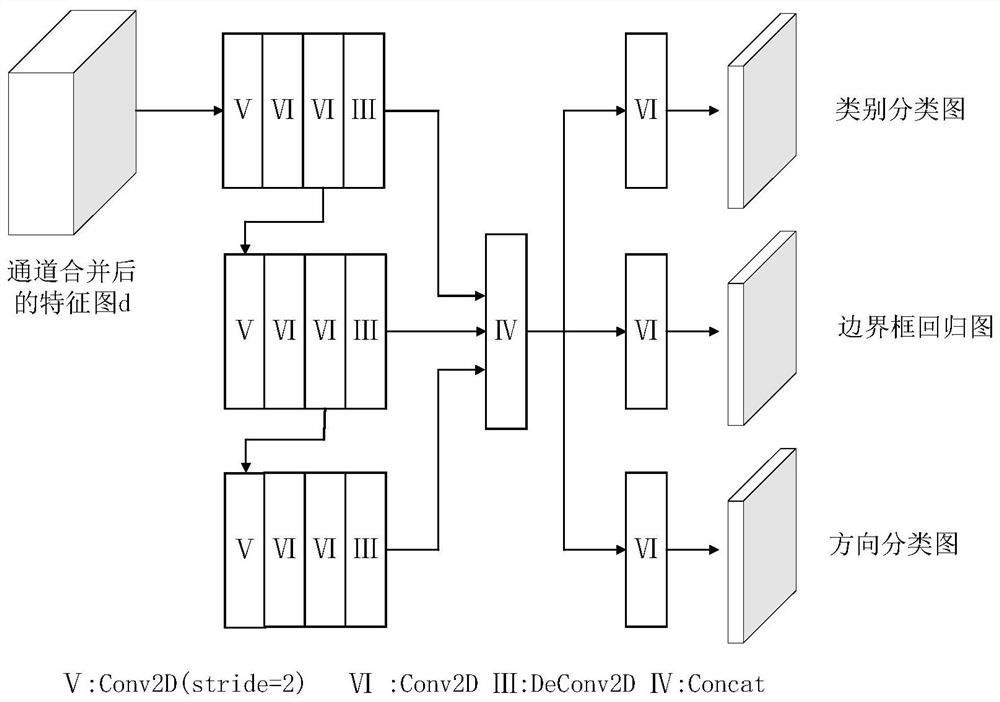
ActiveCN111999741AReduce distractionsImprove inference speedElectromagnetic wave reradiationICT adaptationVoxelPoint cloud
The invention provides a roadside laser radar target detection method, which comprises the steps: selecting multiple frames of background point cloud data in different time periods from data acquiredby a roadside laser radar as background data, performing rasterization processing on the background data, performing statistics on grid features, and performing calculation to obtain grid average statistical features as a background grid statistical table; for the actually measured original point cloud data, carrying out rasterization processing with the same grid size as the background data, performing statistics to obtain grid statistical features corresponding to the original point cloud data, and carrying out background filtering in combination with the background grid statistical table to obtain non-background point cloud data; and inputting the non-background point cloud data into a constructed multi-scale voxel three-dimensional detection network, and outputting a detection resulttensor of the target, the result tensor comprising category information and bounding box information of the target. According to the method, a large number of invalid points are filtered through background filtering, the training and reasoning time of the network is remarkably shortened, interference of a large number of background points is avoided, and the precision of a detection result is improved.
Owner:QINGDAO VEHICLE INTELLIGENCE PIONEERS INC
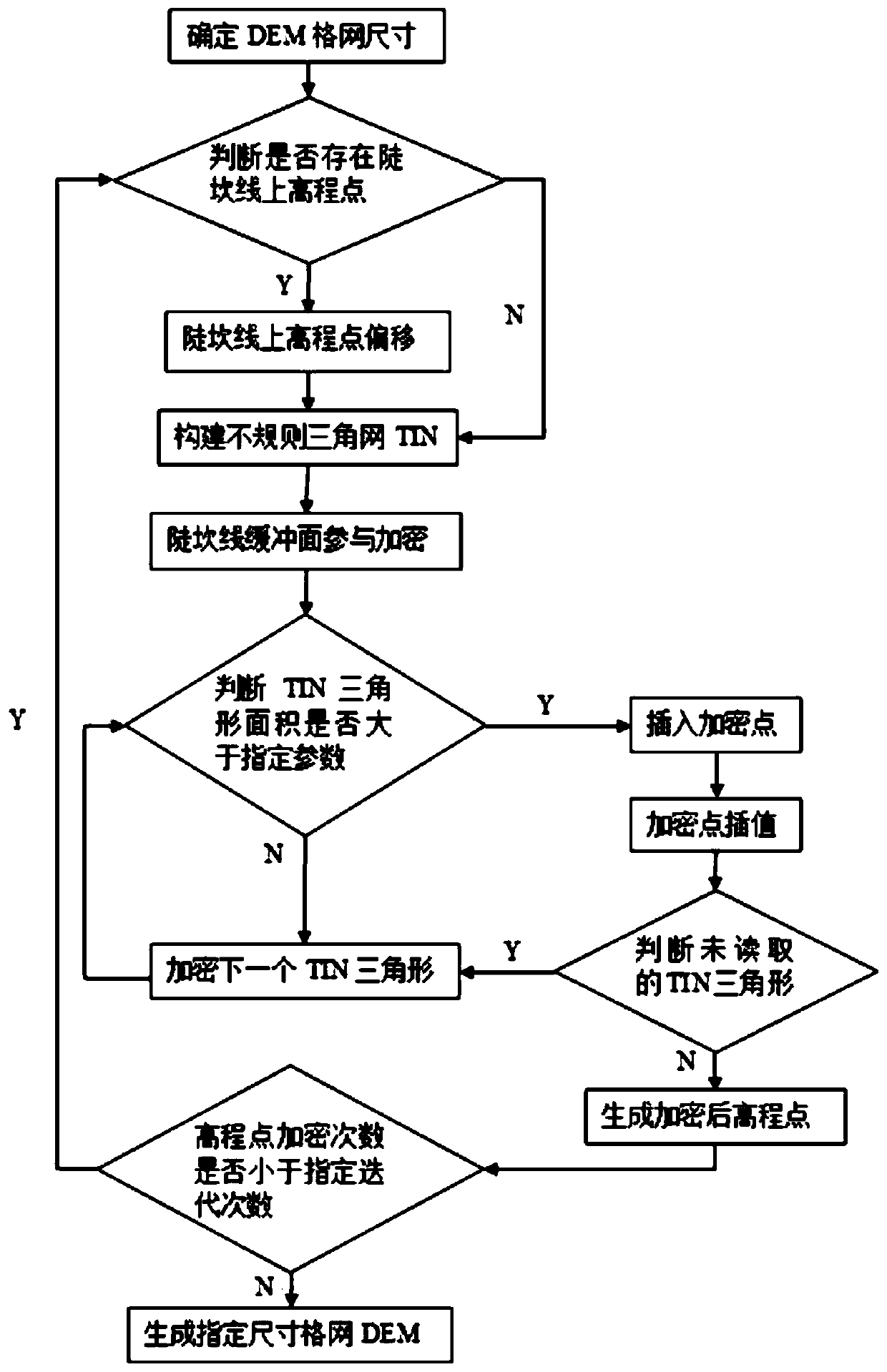
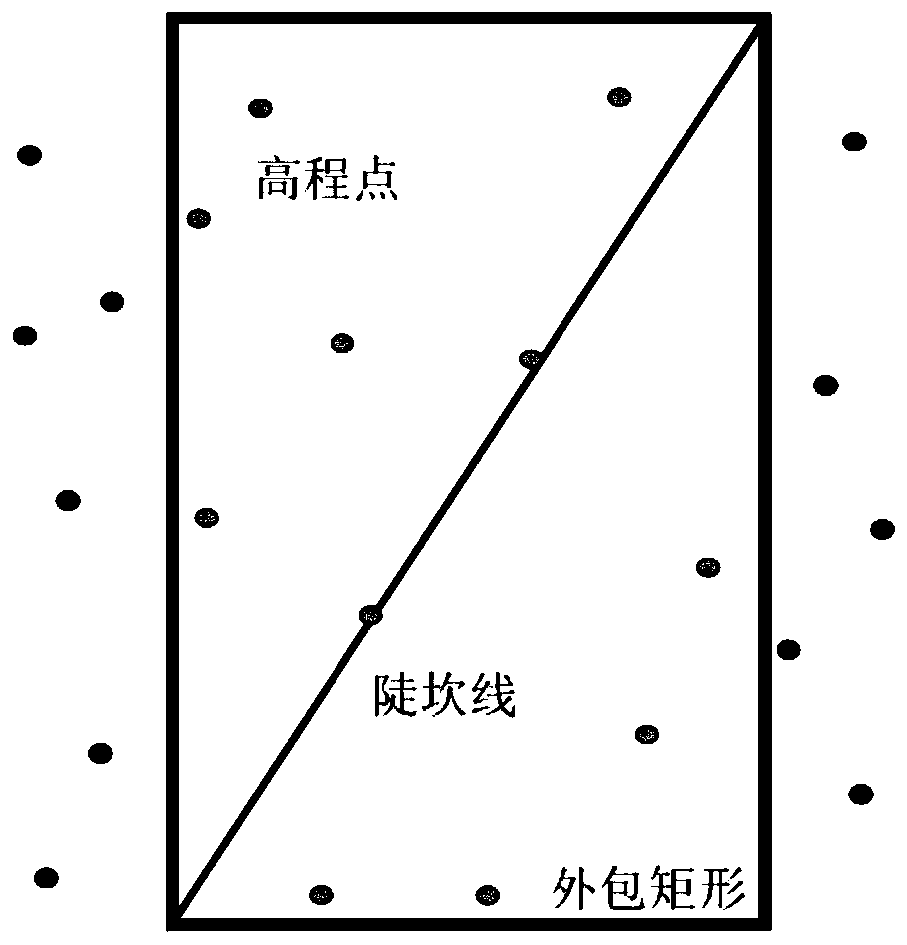
Terrain steep ridge line information fusion method for regular grid DEM construction
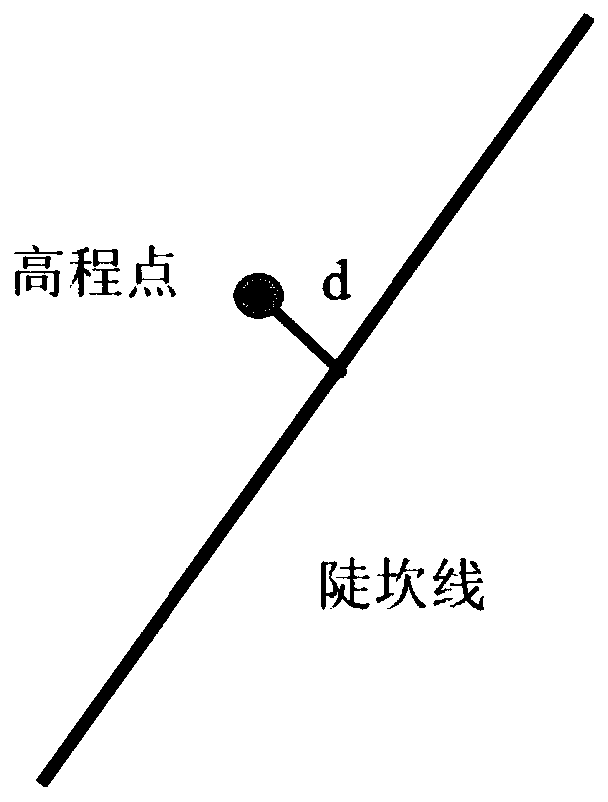
ActiveCN110544305AGuaranteed terrain featuresGood shaping effectICT adaptation3D modellingRegular gridInformation integration
The invention discloses a terrain steep ridge line information fusion method for regular grid DEM construction. The method comprises the following steps: S1, determining the minimum height differenceof regional steep ridge lines, and then determining the grid size of a target regular grid DEM; S2, deviating an elevation point on the steep ridge line, namely, deviating the elevation point fallingon the steep ridge line by a certain distance towards one side of the steep ridge line; S3, performing iterative encryption in a certain range of the steep ridge line to generate elevation points; andS4, constructing a regular grid DEM. According to the method, two key technical links of terrain steep ridge line elevation node offset and encryption generation considering virtual elevation sampling points around the steep ridge line are adopted, and the problem of form distortion caused by the terrain steep ridge line in high-precision terrain modeling can be effectively solved.
Owner:CHUZHOU UNIV
Methodology and system for determining numerical errors in pixel-based imaging simulation in designing lithographic masks
InactiveUS7975244B2Originals for photomechanical treatmentSpecial data processing applicationsErrors and residualsPixel based
A method is provided for designing a mask that includes the use of a pixel-based simulation of a lithographic process model, in which test structures are designed for determining numerical and discretization errors associated with the pixel grid as opposed to other model inaccuracies. The test structure has a plurality of rows of the same sequence of features, but each row is offset from other rows along an x-direction by a multiple of a minimum step size, such as used in modifying masks during optical proximity correction. The images for each row are simulated with a lithographic model that uses the selected pixel-grid size and the differences between row images are compared. If the differences between rows exceed or violate a predetermined criterion, the pixel grid size may be modified to minimize discretization and / or numerical errors due to the choice of pixel grid size.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
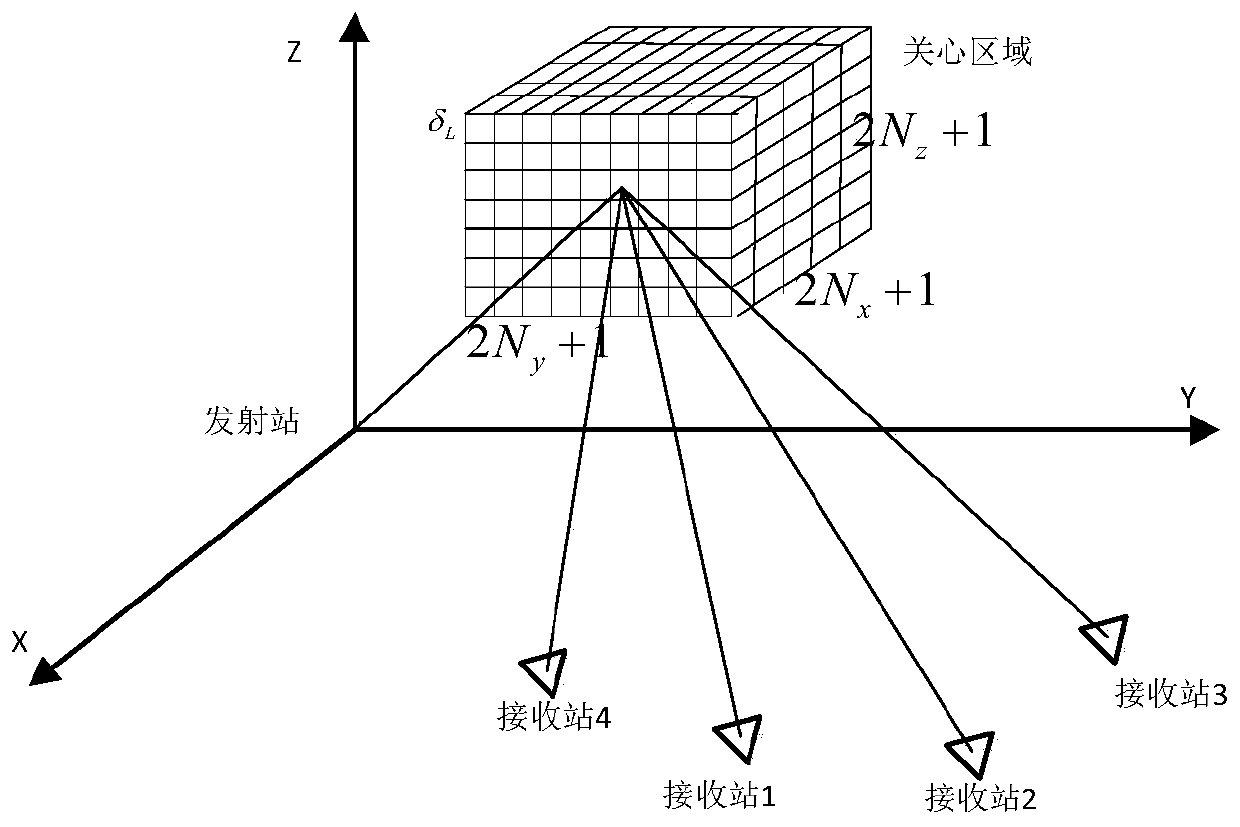
Multi-base radar target positioning method based on grid division
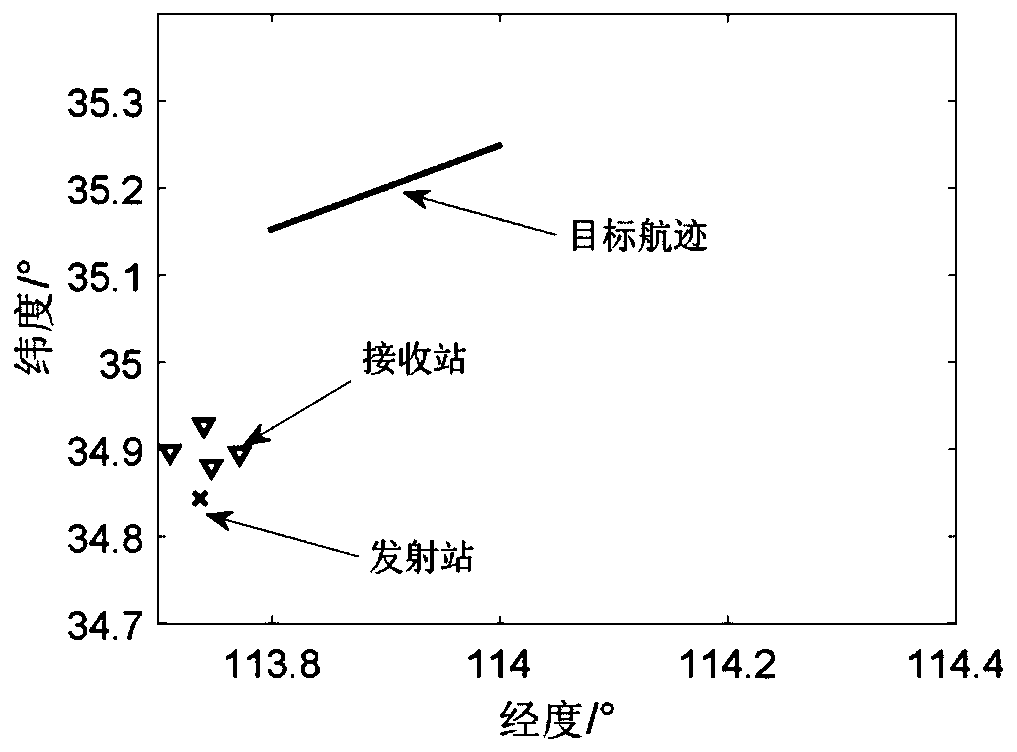
InactiveCN111142096AImprove real-time positioning efficiencyReduce false positioning resultsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRectangular coordinatesRadar
The invention discloses a multi-base radar target positioning method based on grid division. The method comprises the following steps: 1, defining a geodetic coordinate system, a geocentric rectangular coordinate system and a radar station rectangular coordinate system; 2, determining the positions of a radar transmitting station and a radar receiving station; 3, setting the central position of aregion of interest; 4, transferring the position of the receiving station and the central position of the region of interest to a radar rectangular coordinate system; 5, setting the size of divided grids and calculating the central position of each grid; 6, calculating the corresponding distance sum of each grid center relative to each receiving station; 7, obtaining the sum of distances measuredby the plurality of receiving stations at the same moment; 8, associating the sum of the distances obtained in the step 7 and the step 6; and 9, obtaining a target positioning result at a certain moment according to the association result. The method can be applied to cooperative / non-cooperative multi-base radar target detection; the real-time positioning efficiency in multi-base radar target detection can be improved; and false positioning results in multi-base radar target detection are reduced.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com