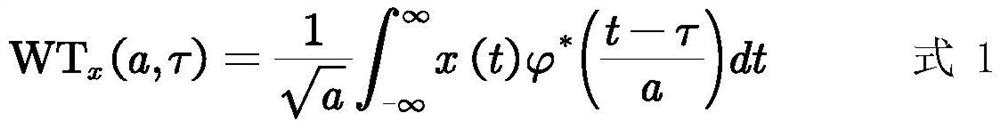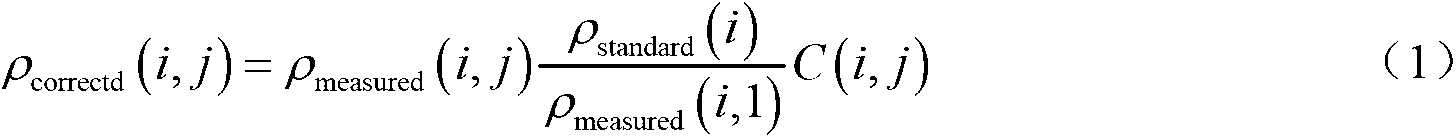Patents
Literature
96 results about "Time domain electromagnetics" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In physics and mathematics, time domain electromagnetics refers to one of two general groups of techniques (in mathematics, often called ansätze) that describe electromagnetic wave motion. In contrast with frequency domain electromagnetics, which are based on the Fourier or Laplace transform, time domain keeps time as an explicit independent variable in descriptive equations or wave motion.
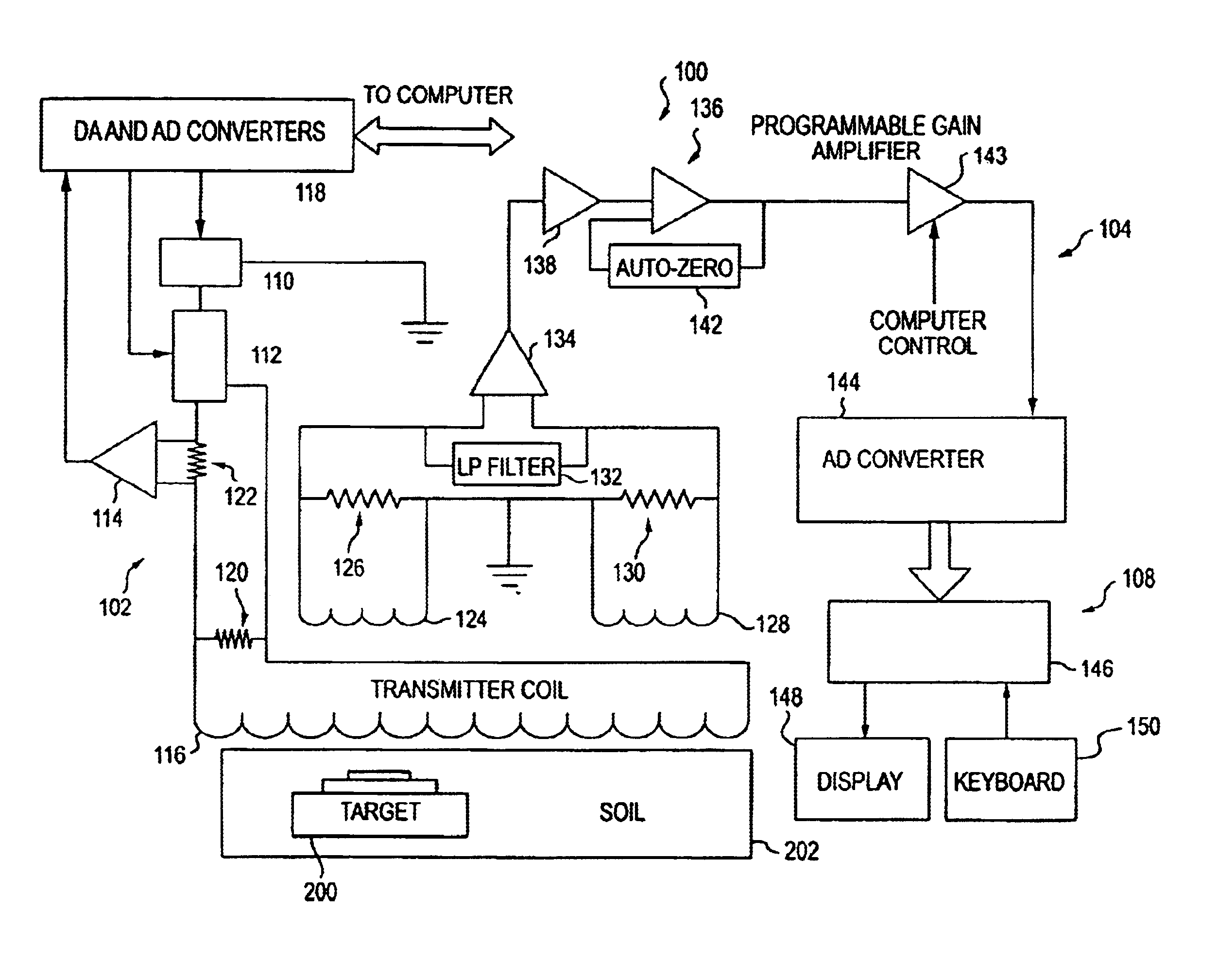
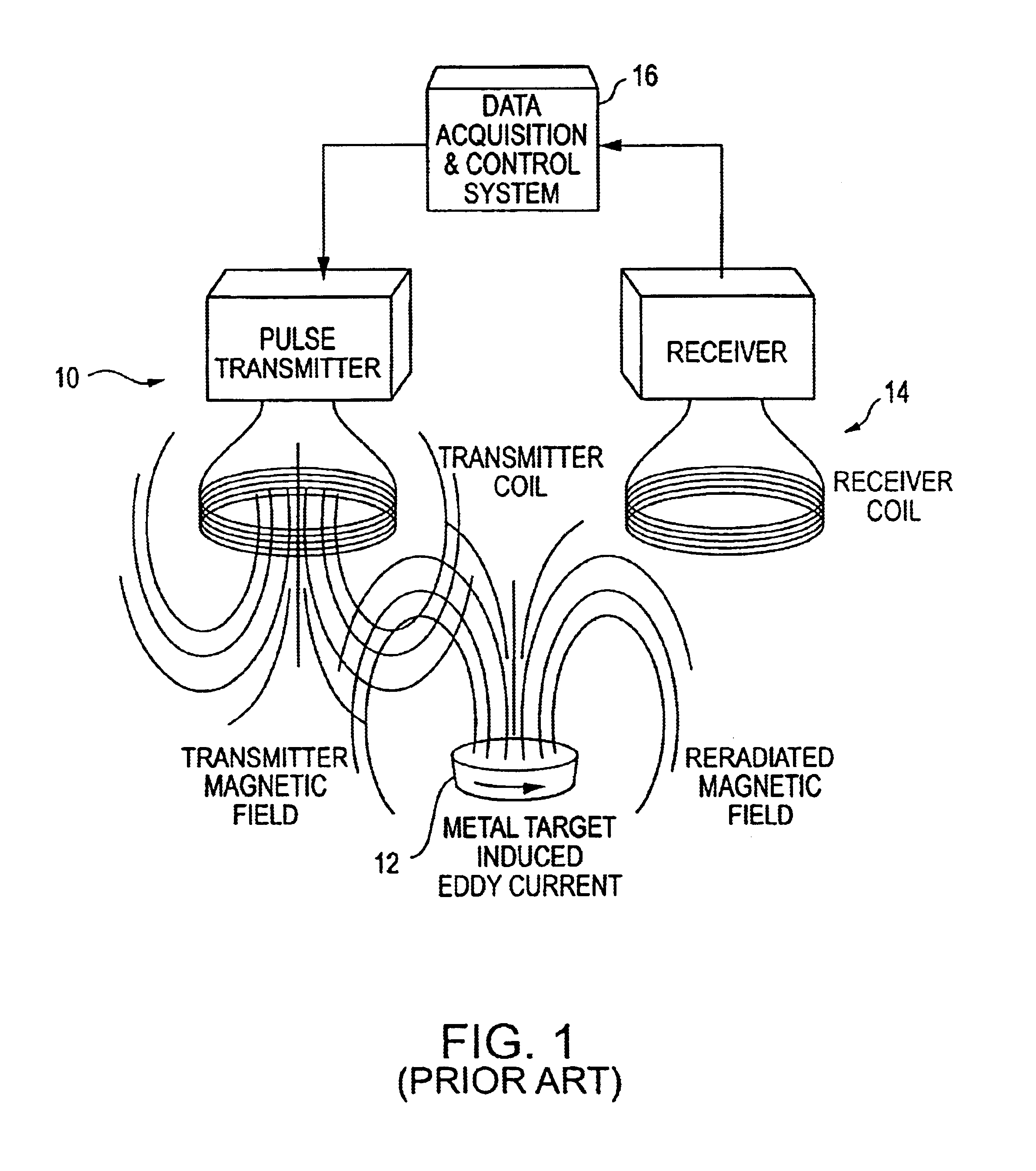
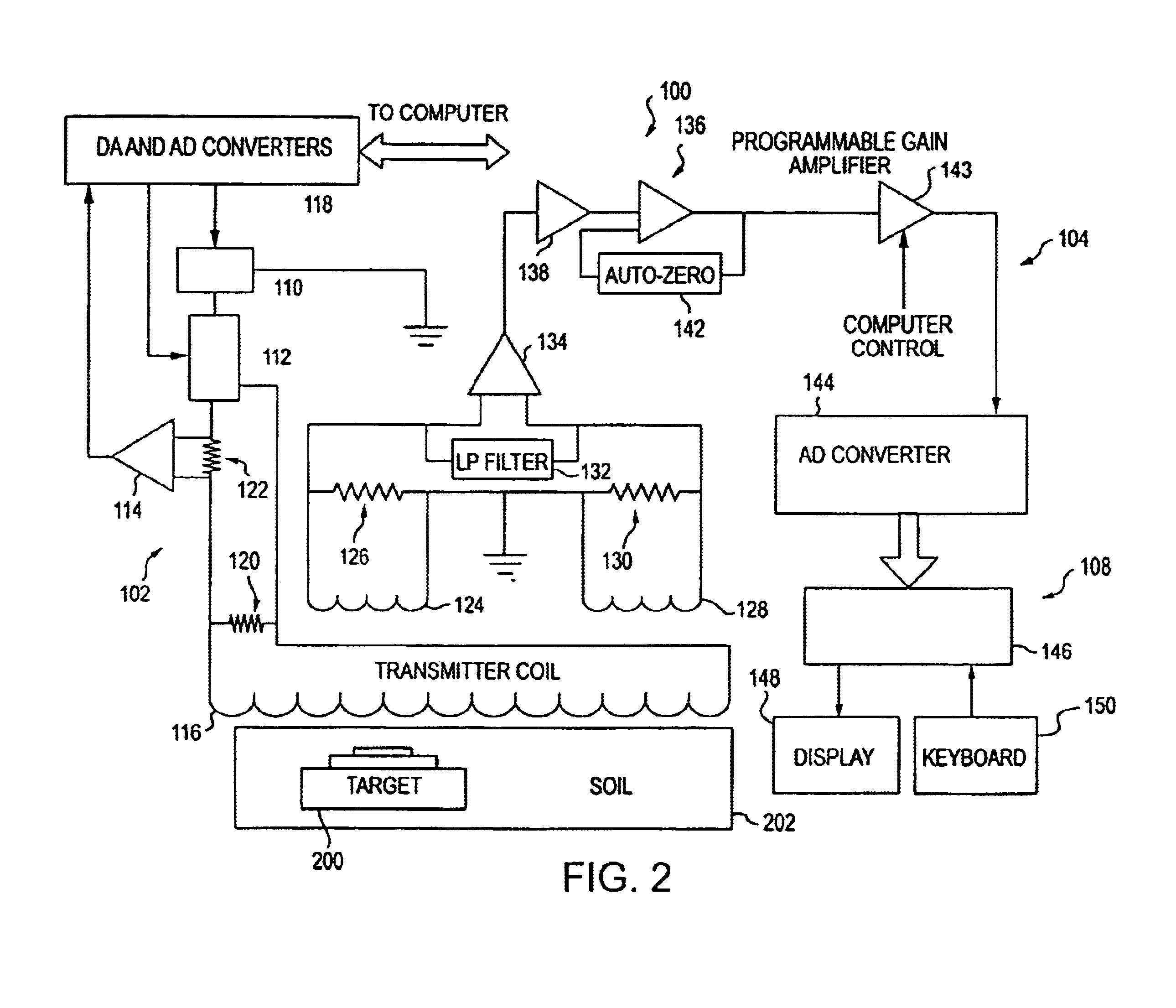
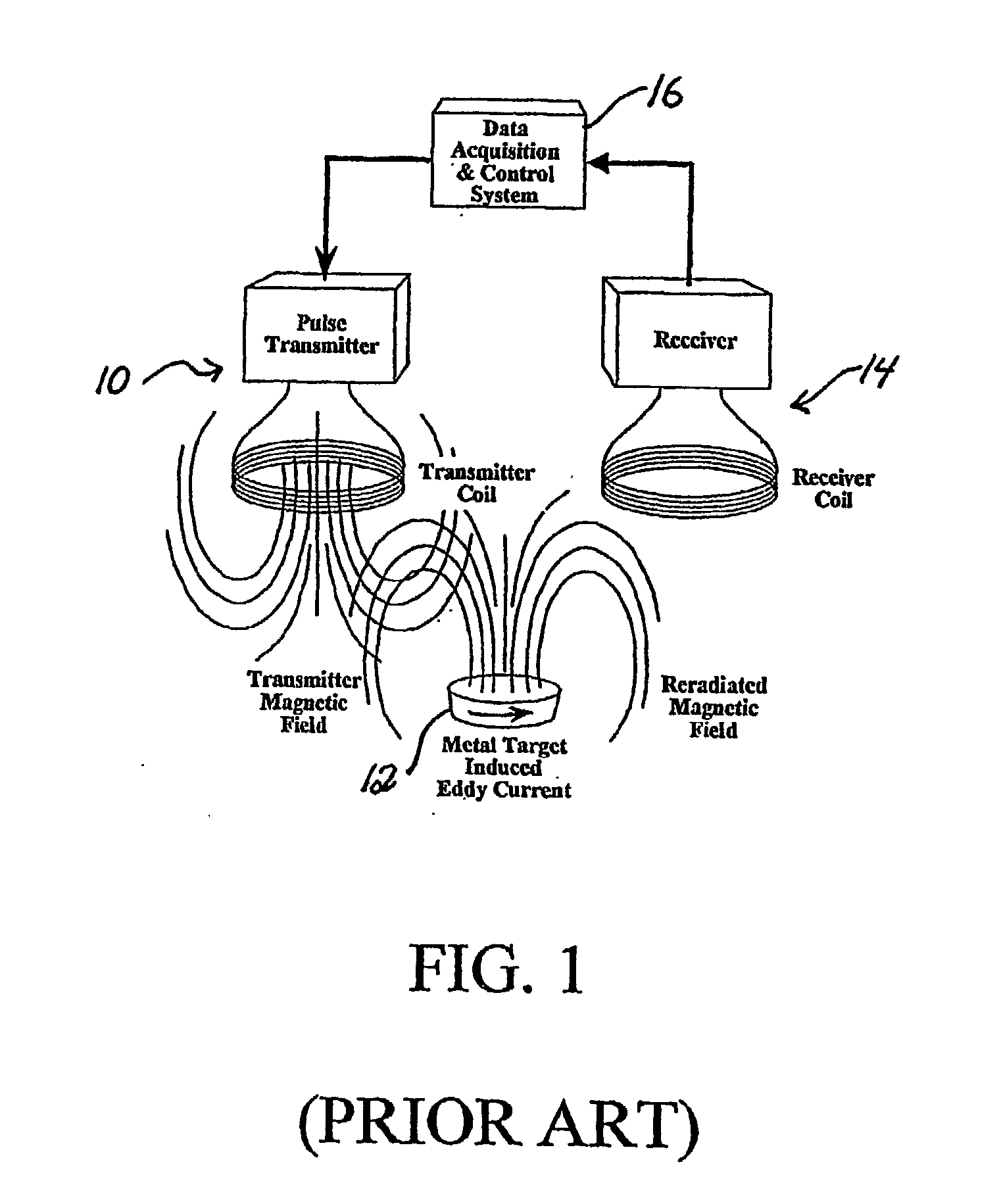
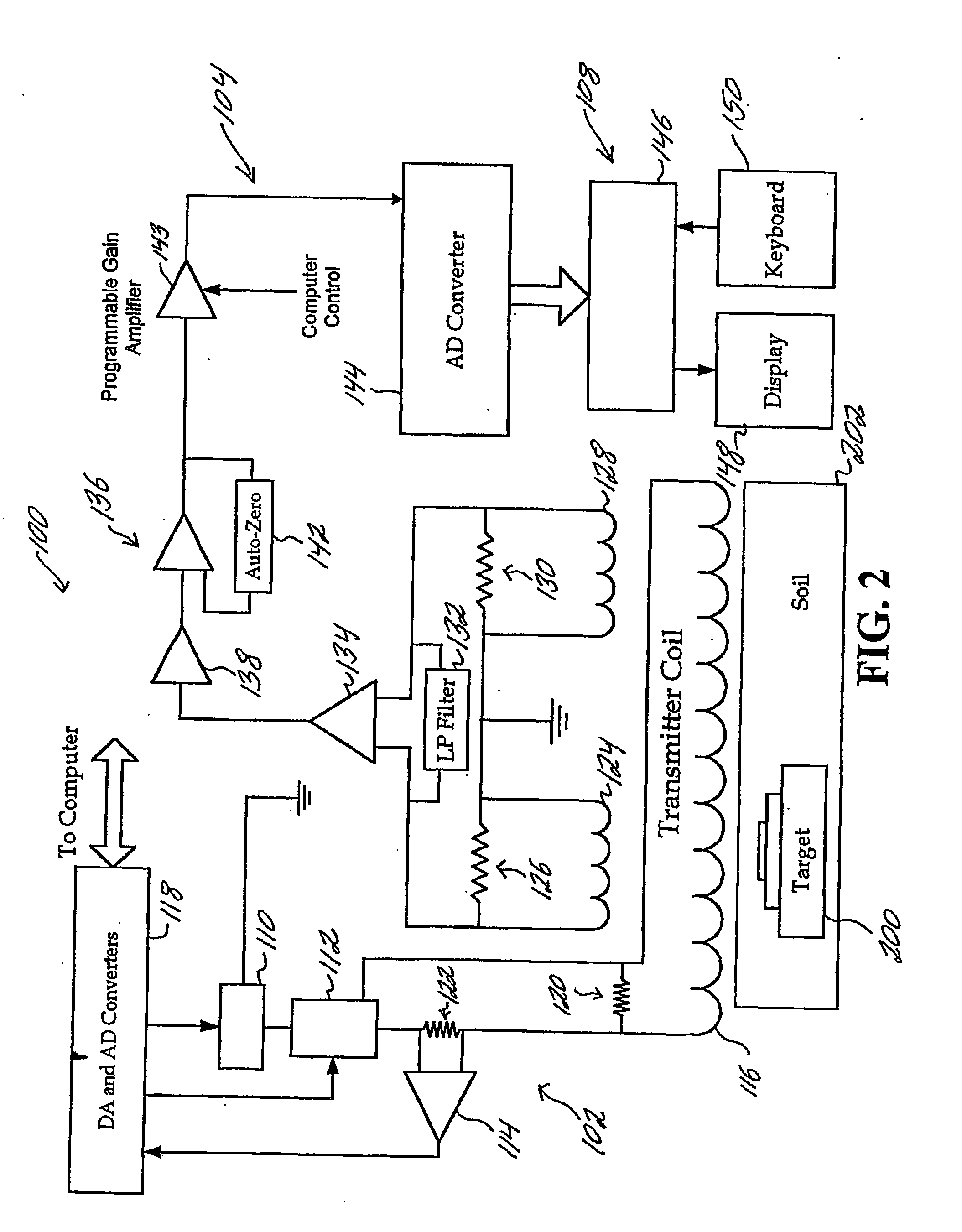
Electromagnetic target discriminator sensor system and method for detecting and identifying metal targets
InactiveUS6853194B2Character and pattern recognitionElectric/magnetic detection for transportDiscriminatorControl system
A time-domain electromagnetic target discriminator (ETD) sensor system and method are provided capable of measuring a metal target's time decay response based on the physical parameters of the metal target and its environment and for identifying the metal target. The ETD sensor system includes a pulse transmitter connected to a receiver via a data acquisition and control system. The transmitter and receiver include coil configurations for placement in proximity to a visually obscured, e.g., buried, metal target (or underground void) for inducing eddy currents within the metal target. The ETD sensor system measures the eddy current time decay response of the metal target in order to perform target recognition and classification. The identification process entails comparing the metal target's (or, underground void or other object's) time decay response with a library of normalized object signatures, e.g., time decay responses and other characteristics.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
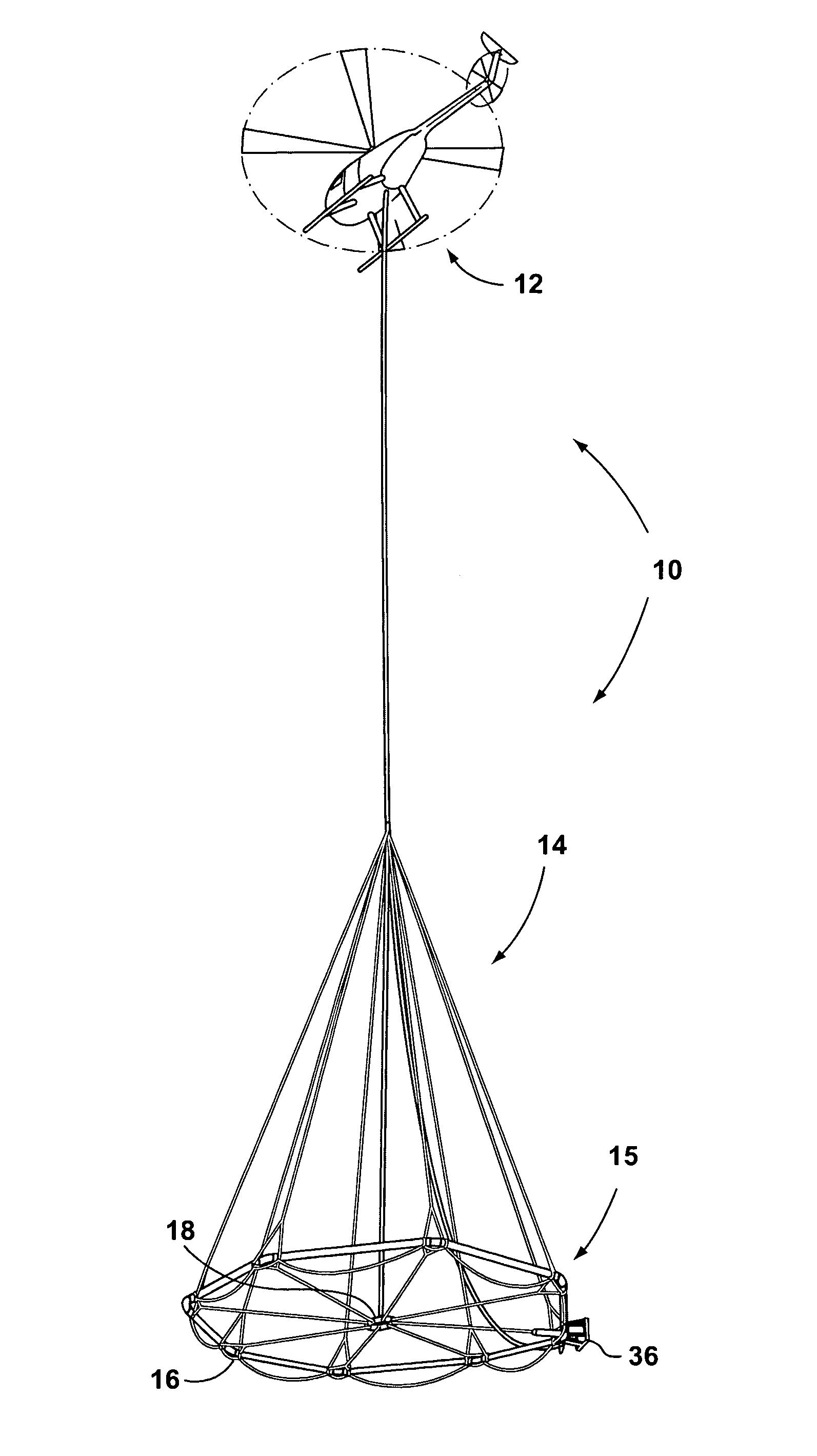
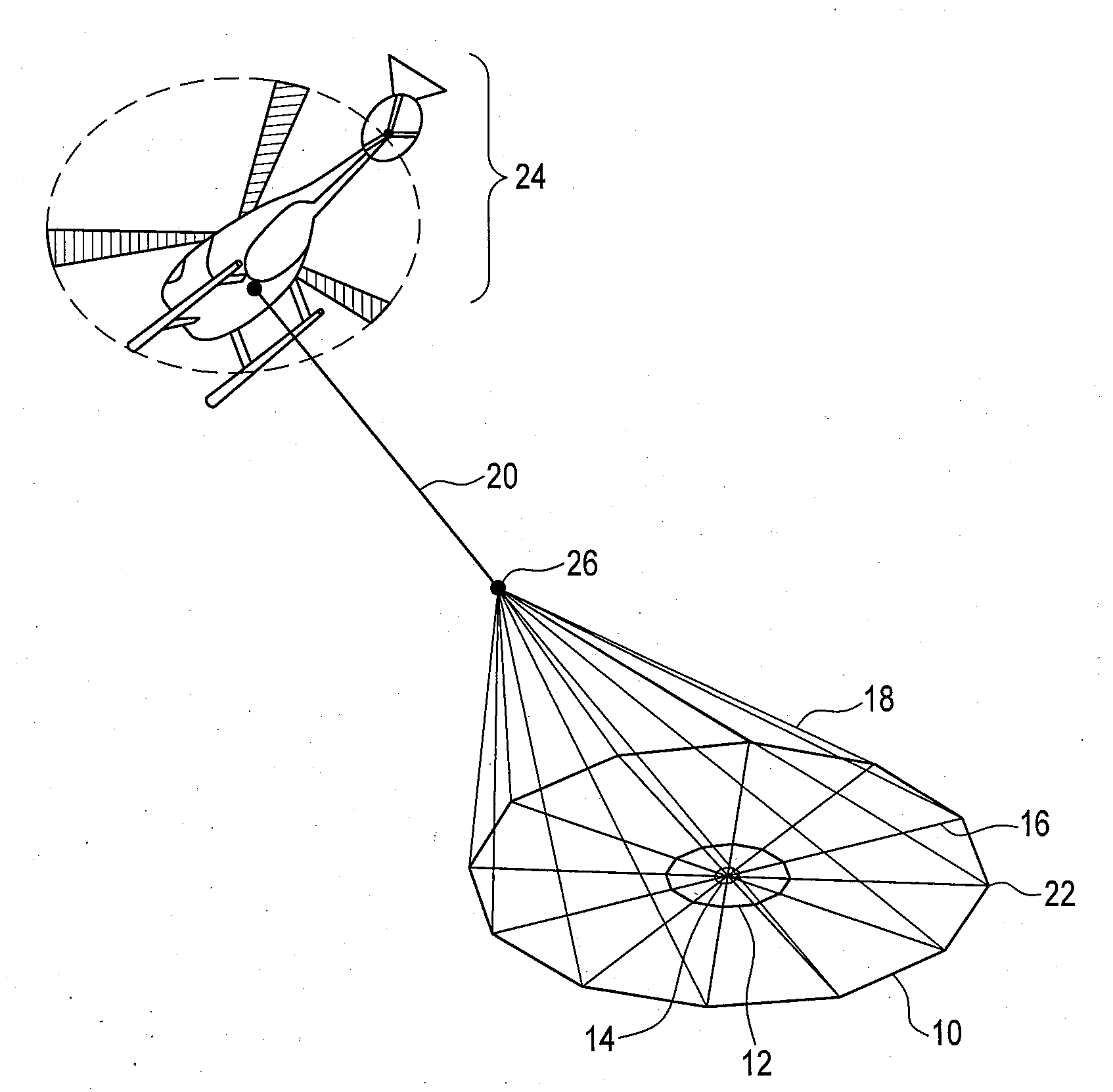
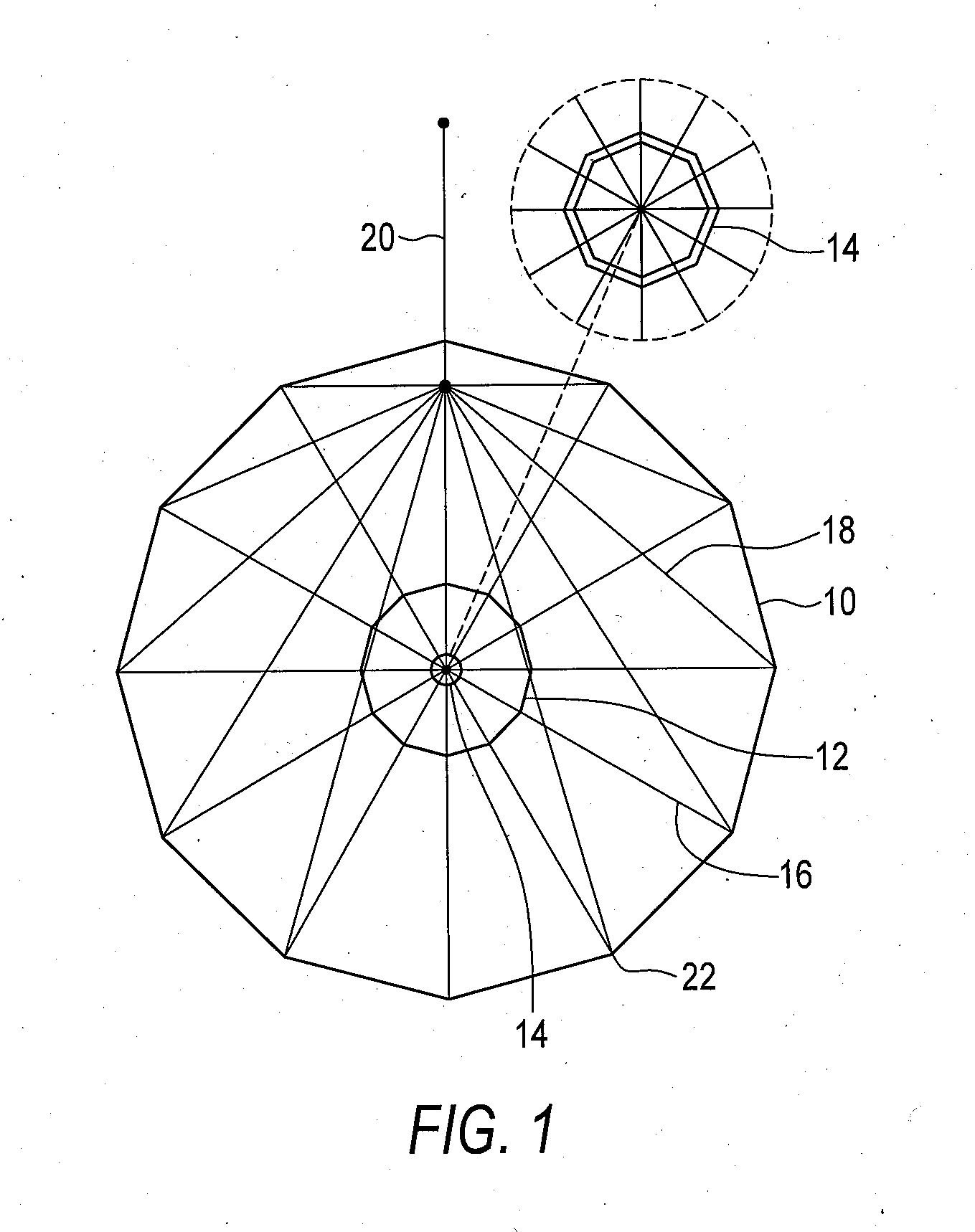
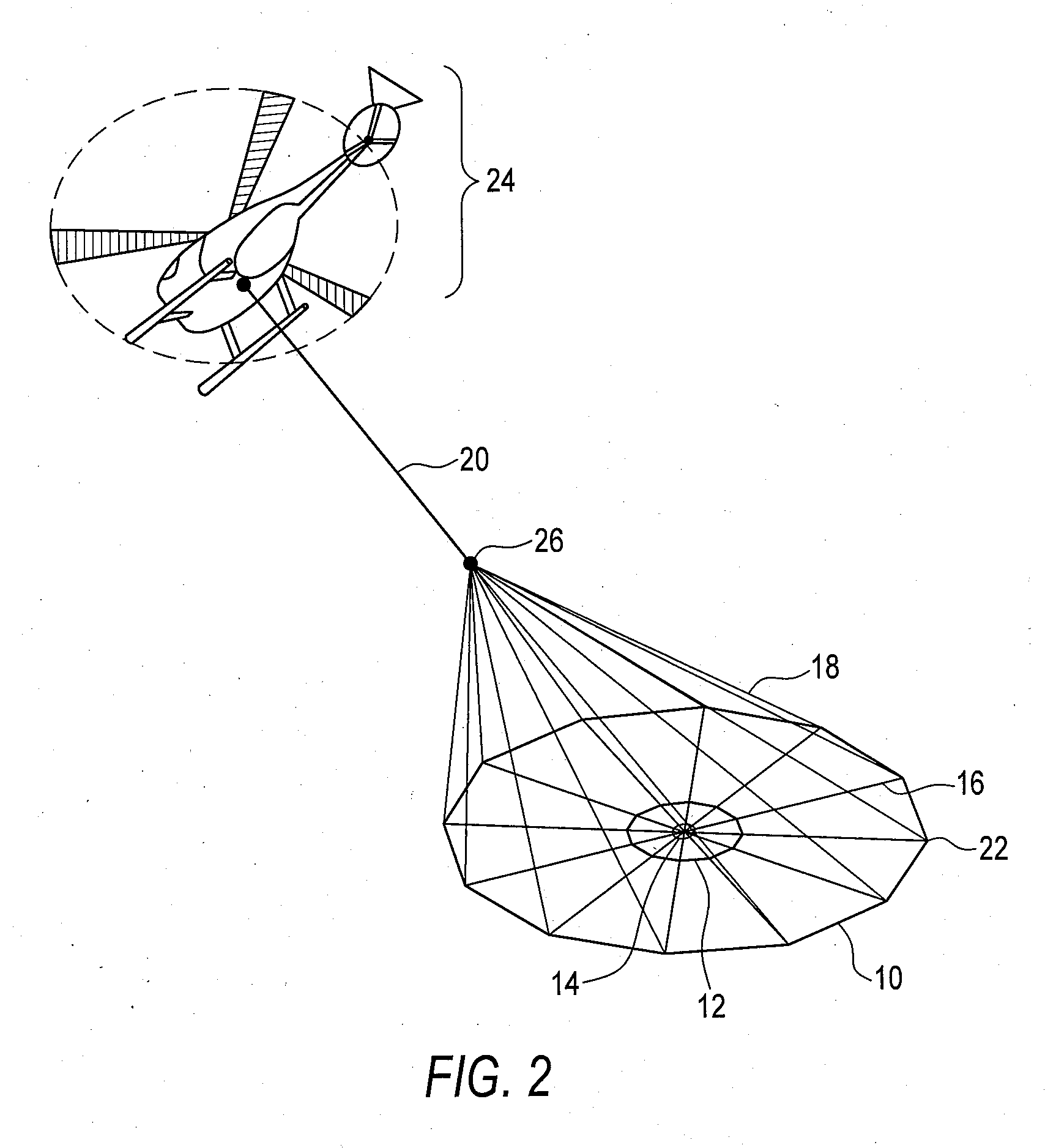
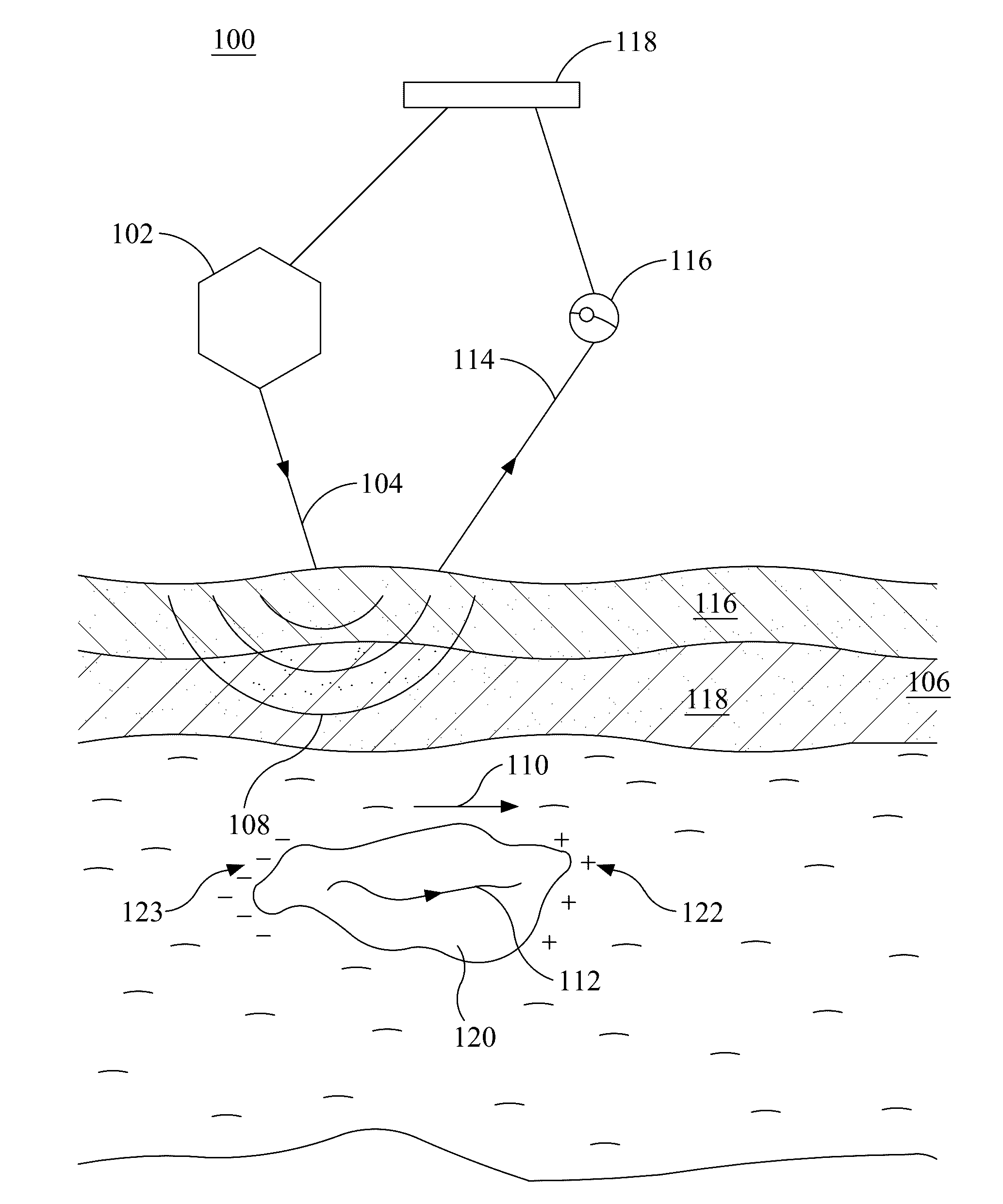
Airborne electromagnetic time domain system, computer product and method
ActiveUS7157914B2Improved sensor resolutionAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesWater resource assessmentEngineeringTime domain electromagnetics
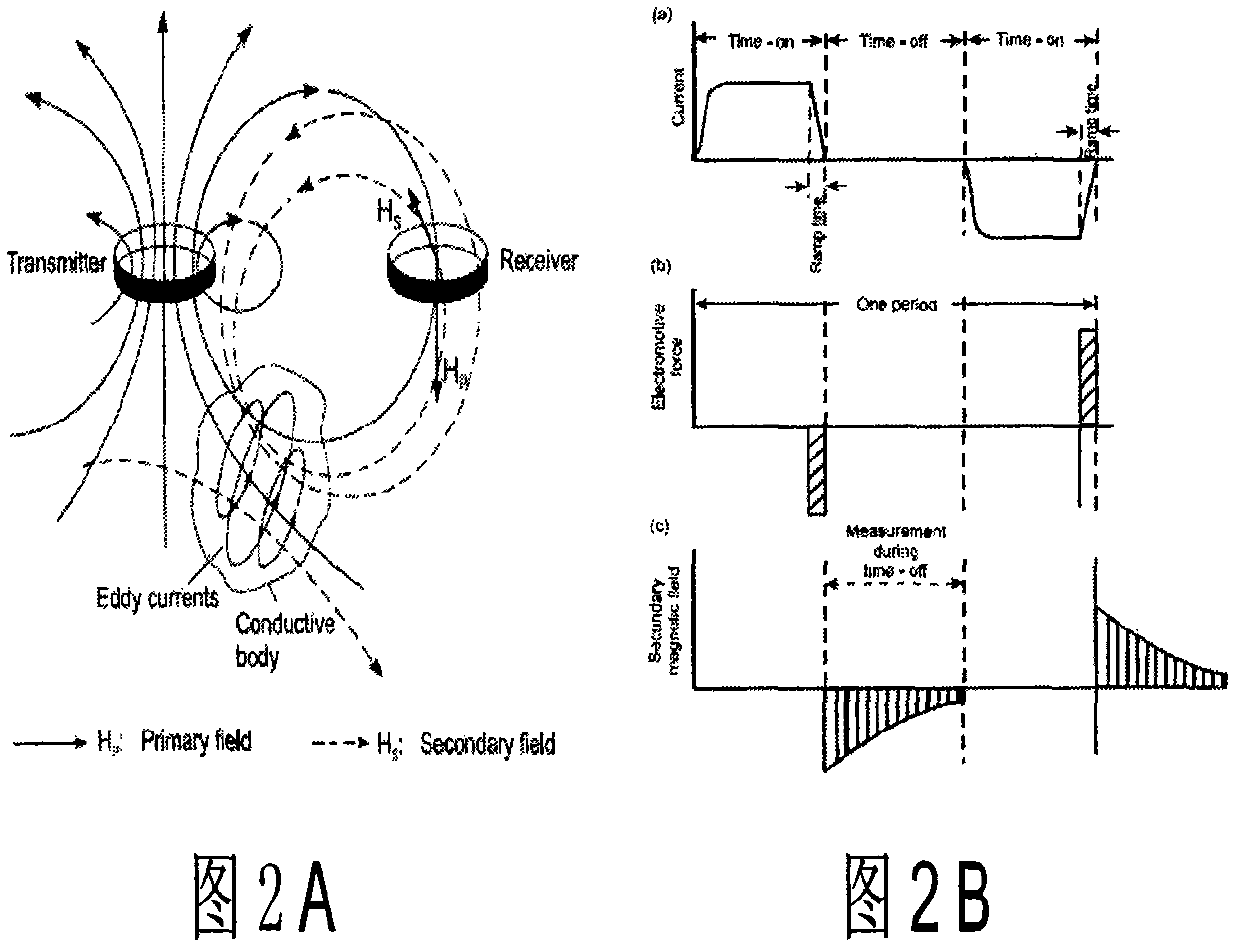
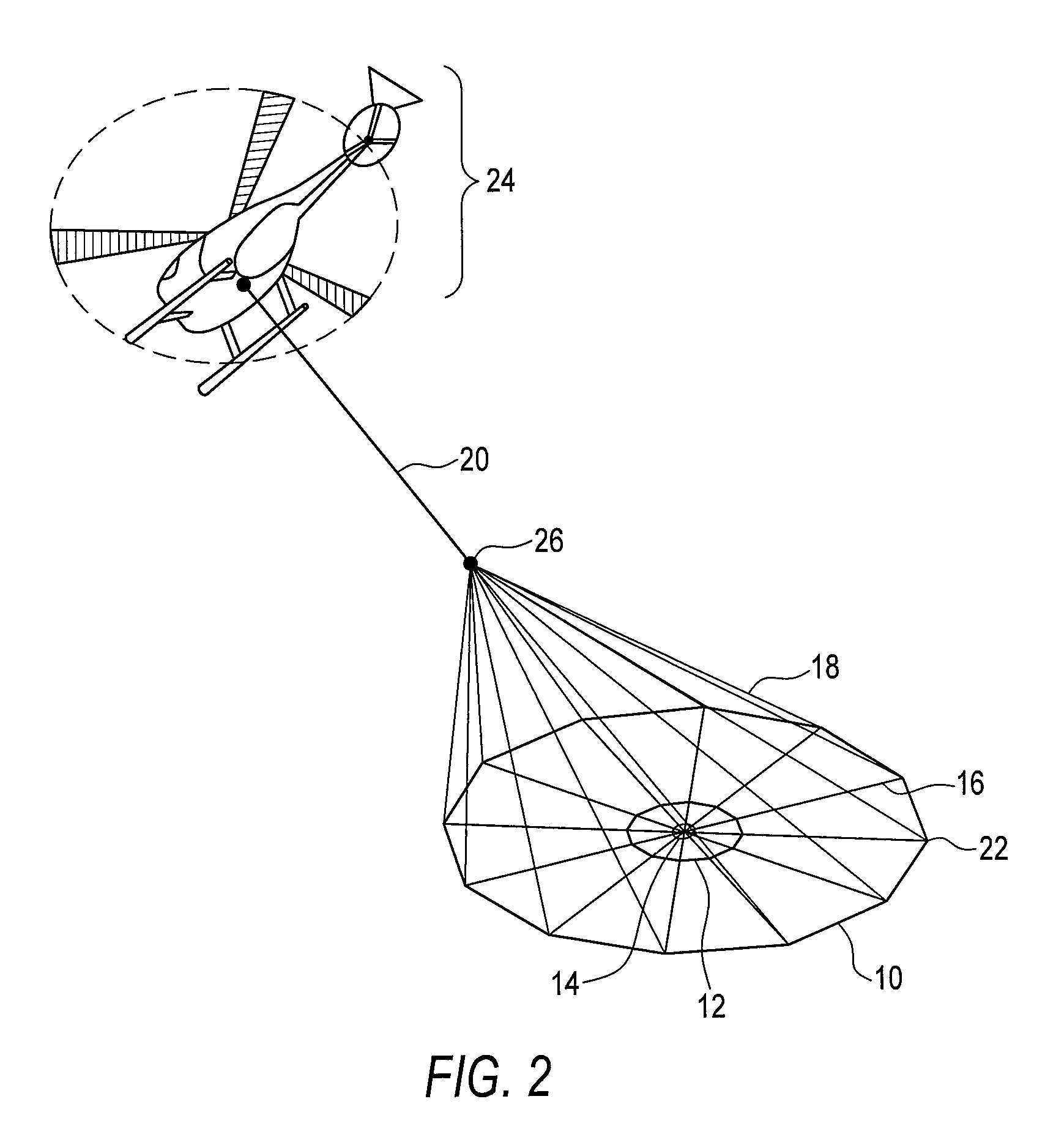
An airborne time domain electromagnetic surveying system is provided. The system includes a tow assembly with a flexible support frame. The flexible support frame spaced apart from the aircraft includes a transmitter section with a transmitter loop and a receiver section with a sensor aligned with the central axis of the transmitter section. The flexible support frame has a lightweight modular structure that enables the surface area of the transmitter section to be increased and decreased to suit particular survey applications. The transmitter loop sends a pulse in an “ON” interval, and in an “OFF” interval the sensor measures the earth response to the pulse. The tow assembly also includes a sensor for generating selected survey data in the “ON” interval. A transmitter driver enables the creation of earthbound pulse. The system components are linked to a computer and control computer program linked thereto for controlling the functions thereof. The invention also includes a method for producing survey data using the tow assembly of the invention.
Owner:EDWARD BEVERLY MORRISON +1
Electromagnetic target discriminator sensor system and method for detecting and identifying metal targets
InactiveUS20030052684A1Character and pattern recognitionElectric/magnetic detection for transportDiscriminatorControl system
A time-domain electromagnetic target discriminator (ETD) sensor system and method are provided capable of measuring a metal target's time decay response based on the physical parameters of the metal target and its environment and for identifying the metal target. The ETD sensor system includes a pulse transmitter connected to a receiver via a data acquisition and control system. The transmitter and receiver include coil configurations for placement in proximity to a visually obscured, e.g., buried, metal target (or underground void) for inducing eddy currents within the metal target. The ETD sensor system measures the eddy current time decay response of the metal target in order to perform target recognition and classification. The identification process entails comparing the metal target's (or, underground void or other object's) time decay response with a library of normalized object signatures, e.g., time decay responses and other characteristics.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Airborne electromagnetic time domain system, computer product and method
ActiveUS20050001622A1Improved sensor resolutionAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesWater resource assessmentEngineeringTime domain electromagnetics
An airborne time domain electromagnetic surveying system is provided. The system includes a tow assembly with a flexible support frame. The flexible support frame spaced apart from the aircraft includes a transmitter section with a transmitter loop and a receiver section with a sensor aligned with the central axis of the transmitter section. The flexible support frame has a lightweight modular structure that enables the surface area of the transmitter section to be increased and decreased to suit particular survey applications. The transmitter loop sends a pulse in an “ON” interval, and in an “OFF” interval the sensor measures the earth response to the pulse. The tow assembly also includes a sensor for generating selected survey data in the “ON” interval. A transmitter driver enables the creation of earthbound pulse. The system components are linked to a computer and control computer program linked thereto for controlling the functions thereof. The invention also includes a method for producing survey data using the tow assembly of the invention.
Owner:EDWARD BEVERLY MORRISON +1
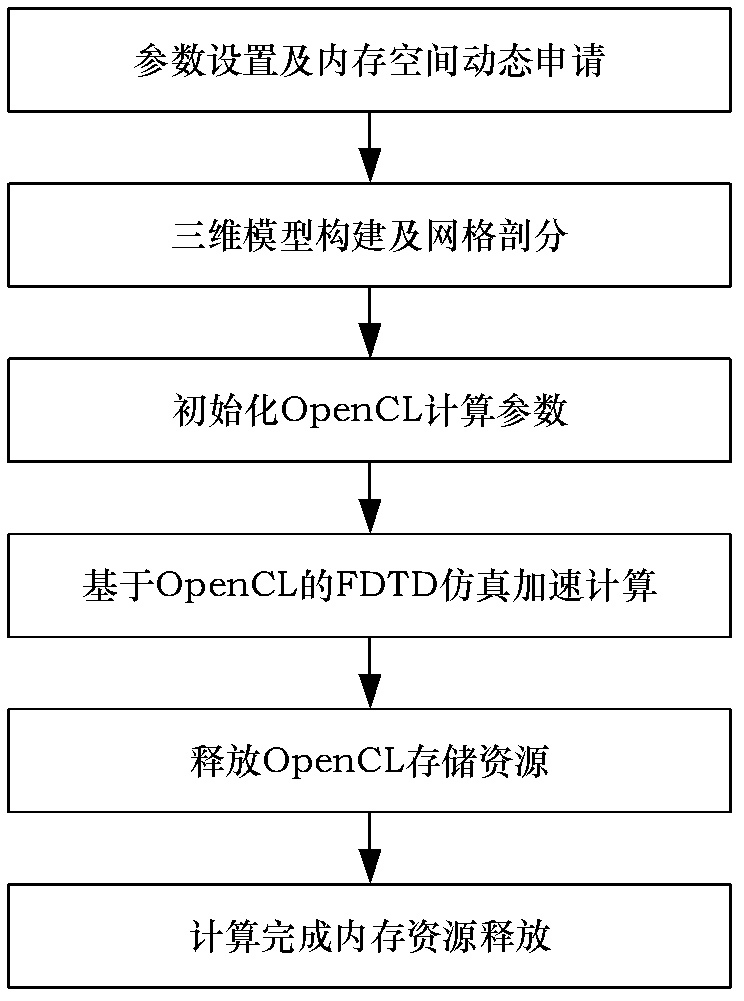
Method for accelerating three-dimensional finite-difference time-domain electromagnetic field simulation by using graphic processing unit (GPU) based on Open computer language (OpenCL)
ActiveCN102207987ASpeed up electromagnetic field simulationsPopularization of electromagnetic field simulationSpecial data processing applicationsPerfect matched layerTime domain electromagnetics
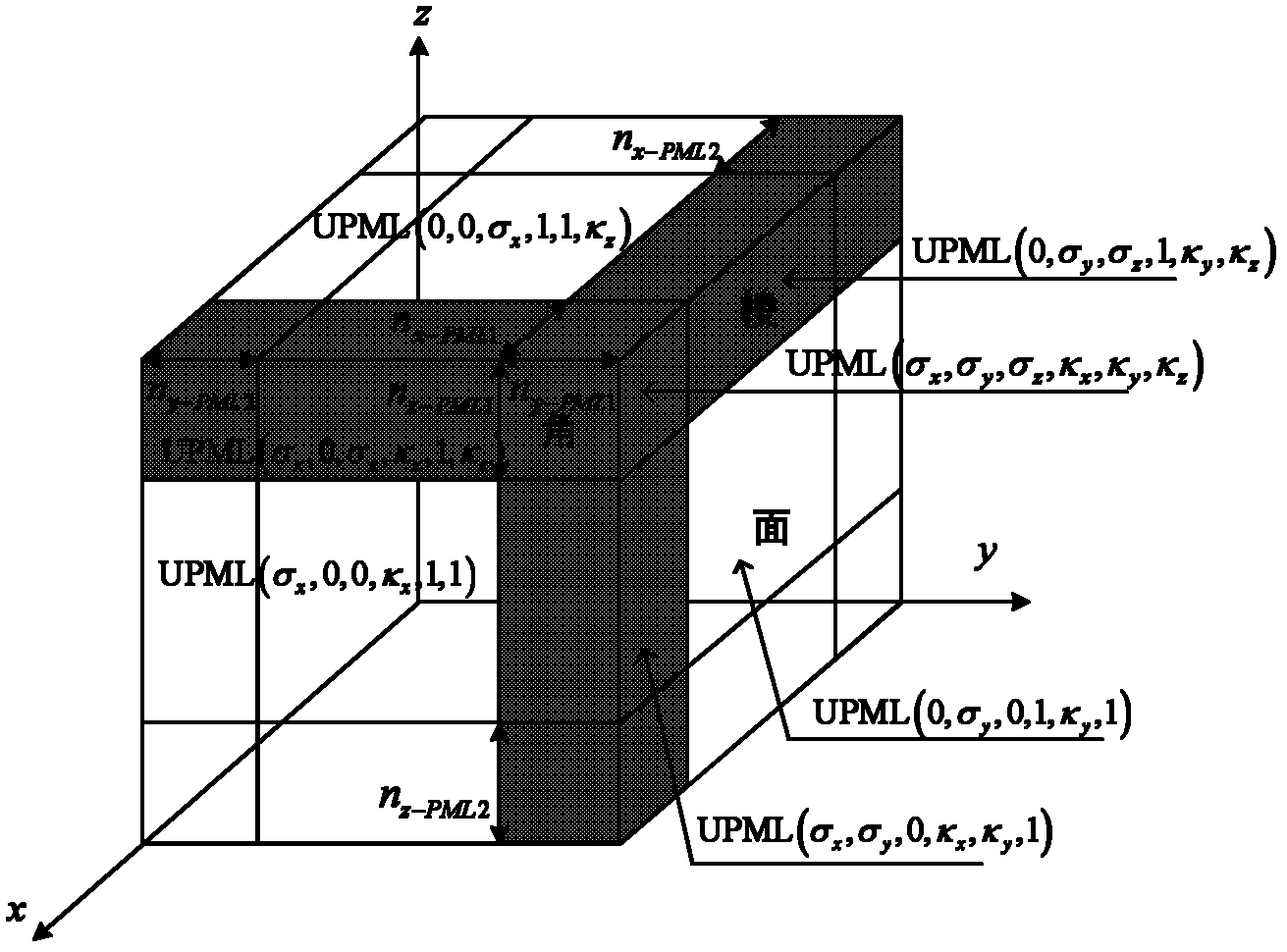
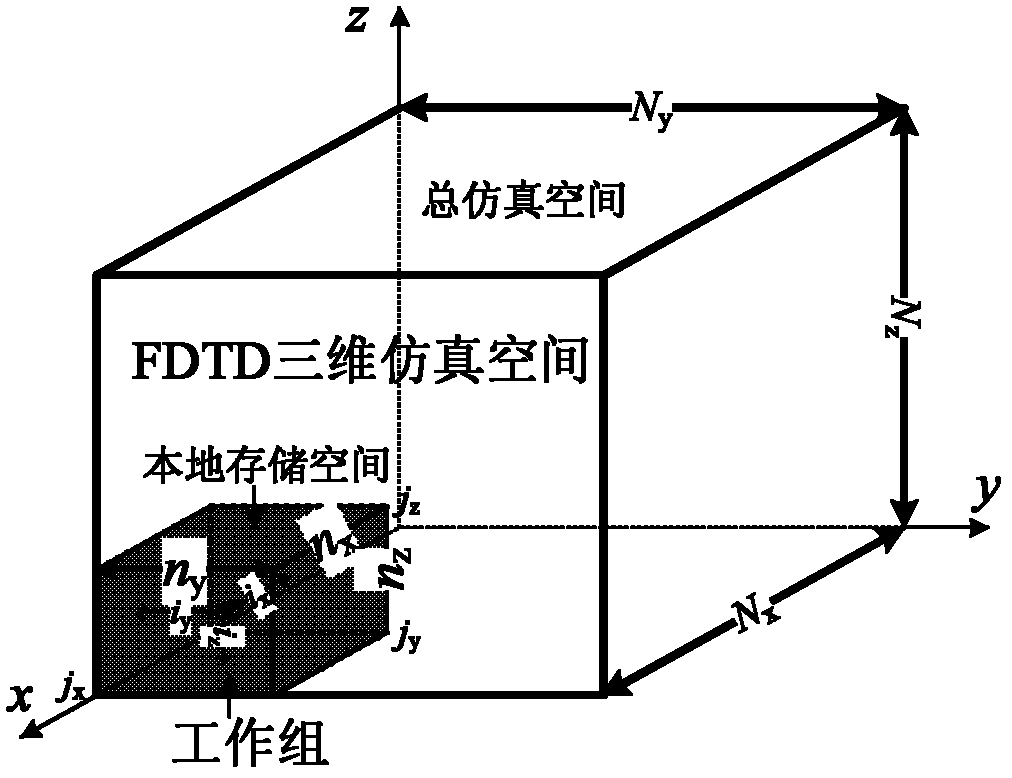
The invention provides a method for accelerating three-dimensional finite-difference time-domain (FDTD) electromagnetic field simulation by using a graphic processing unit (GPU) based on an Open computer language (OpenCL). The method is applied to the field of electromagnetic simulation and analysis; and design and realization of electromagnetic simulation are simplified by the OpenCL in an FDTD method. The method comprises the following steps of: setting an FDTD simulation parameter at first and dynamically applying a memory space; constructing a three-dimensional electromagnetic model and performing grid subdivision; initializing a calculation parameter of the OpenCL and performing FDTD accelerated simulation on the three-dimensional electromagnetic model based on the OpenCL; and finally releasing data stored in the memory by using a function in an OpenCL standard base and releasing central processing unit (CPU) memory resources. By the method, the FDTD electromagnetic field simulation speed is increased obviously; compared with a CPU calculation method, the method increases the speed by 5 to 10 times; a uniaxial perfect matched layer (UPML) absorbing boundary condition can be obtained, and the transmission of electromagnetic waves in a free space can be simulated; therefore, the FDTD electromagnetic field simulation can be applied widely and actually.
Owner:CHINA AEROSPACE STANDARDIZATION INST
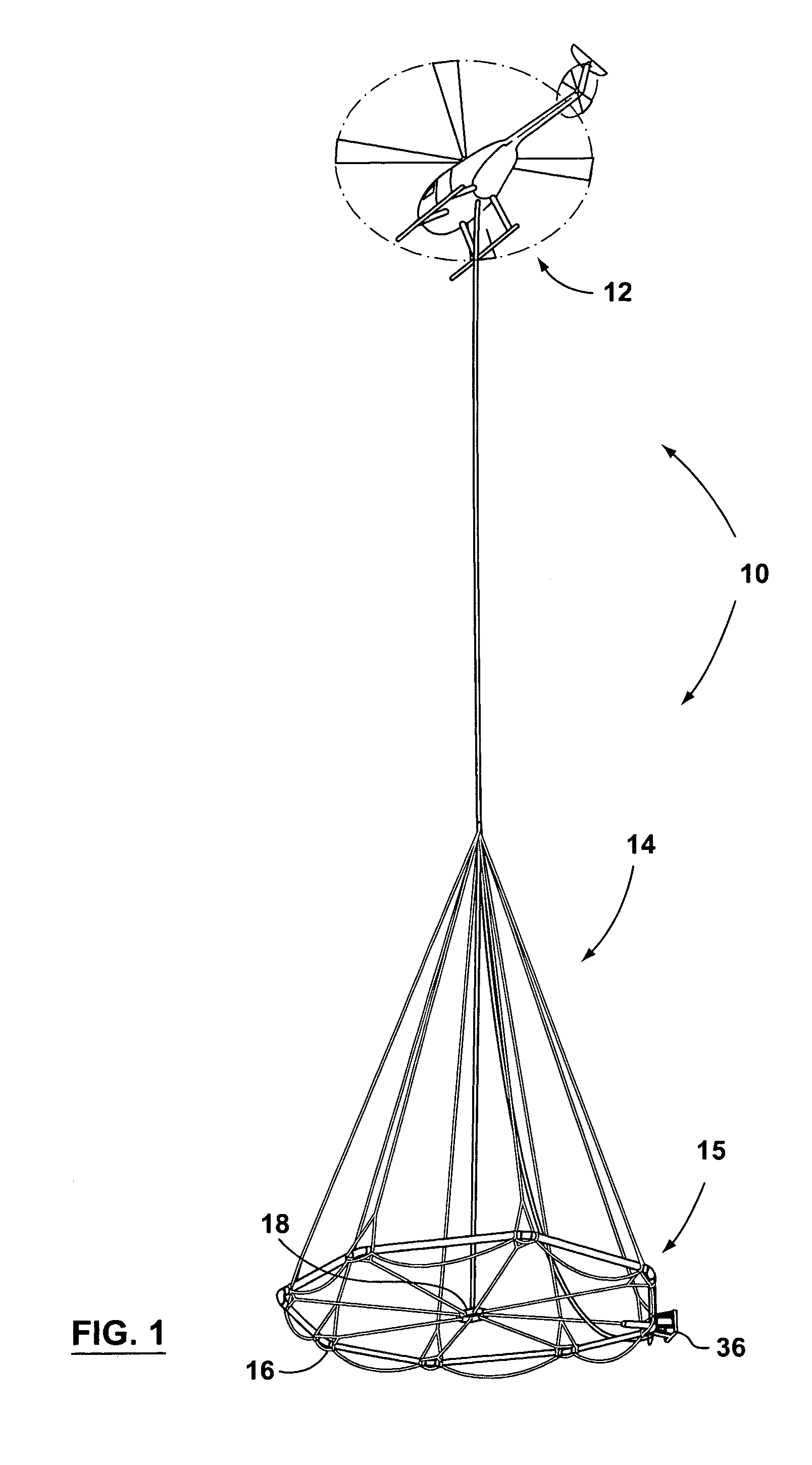
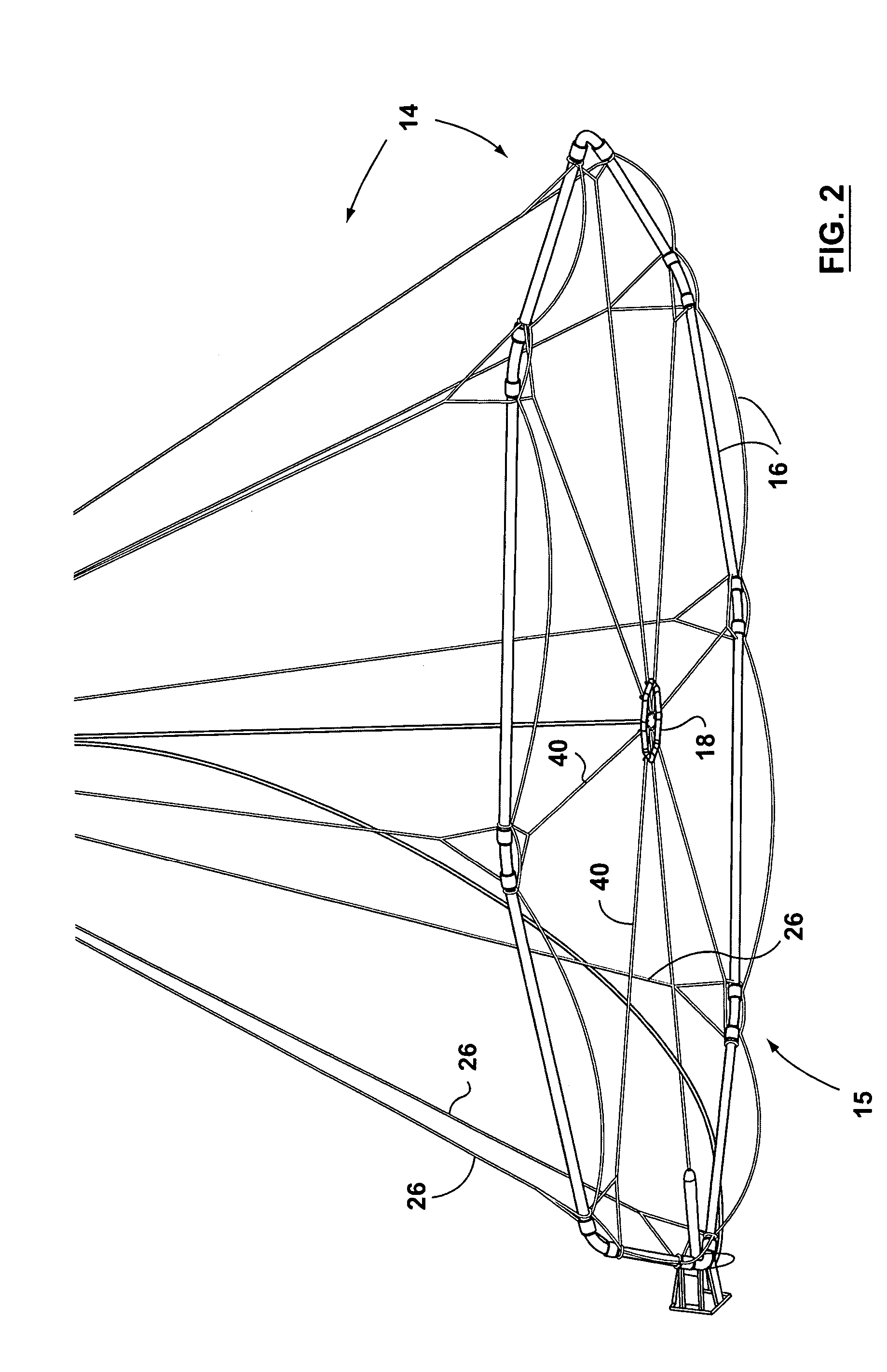
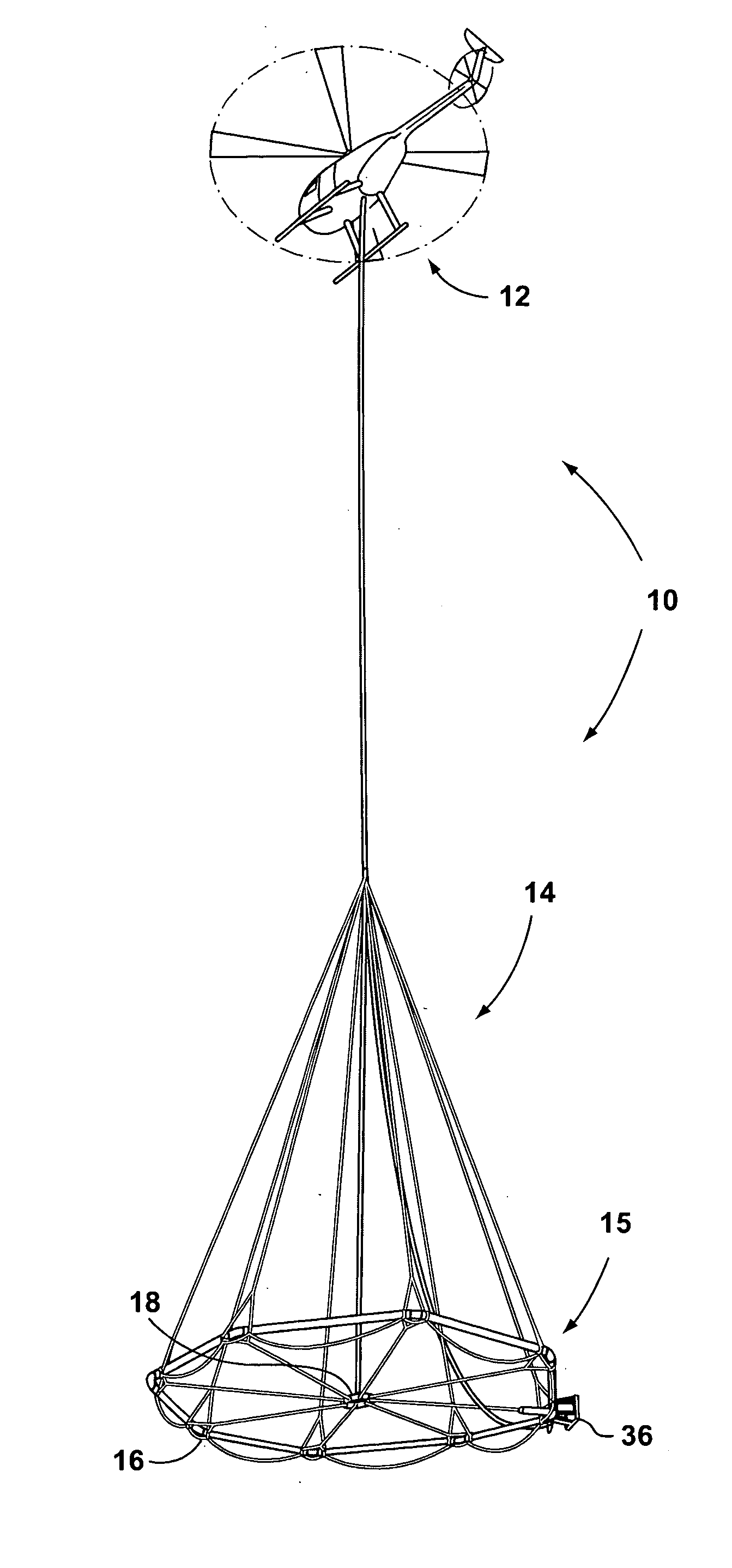
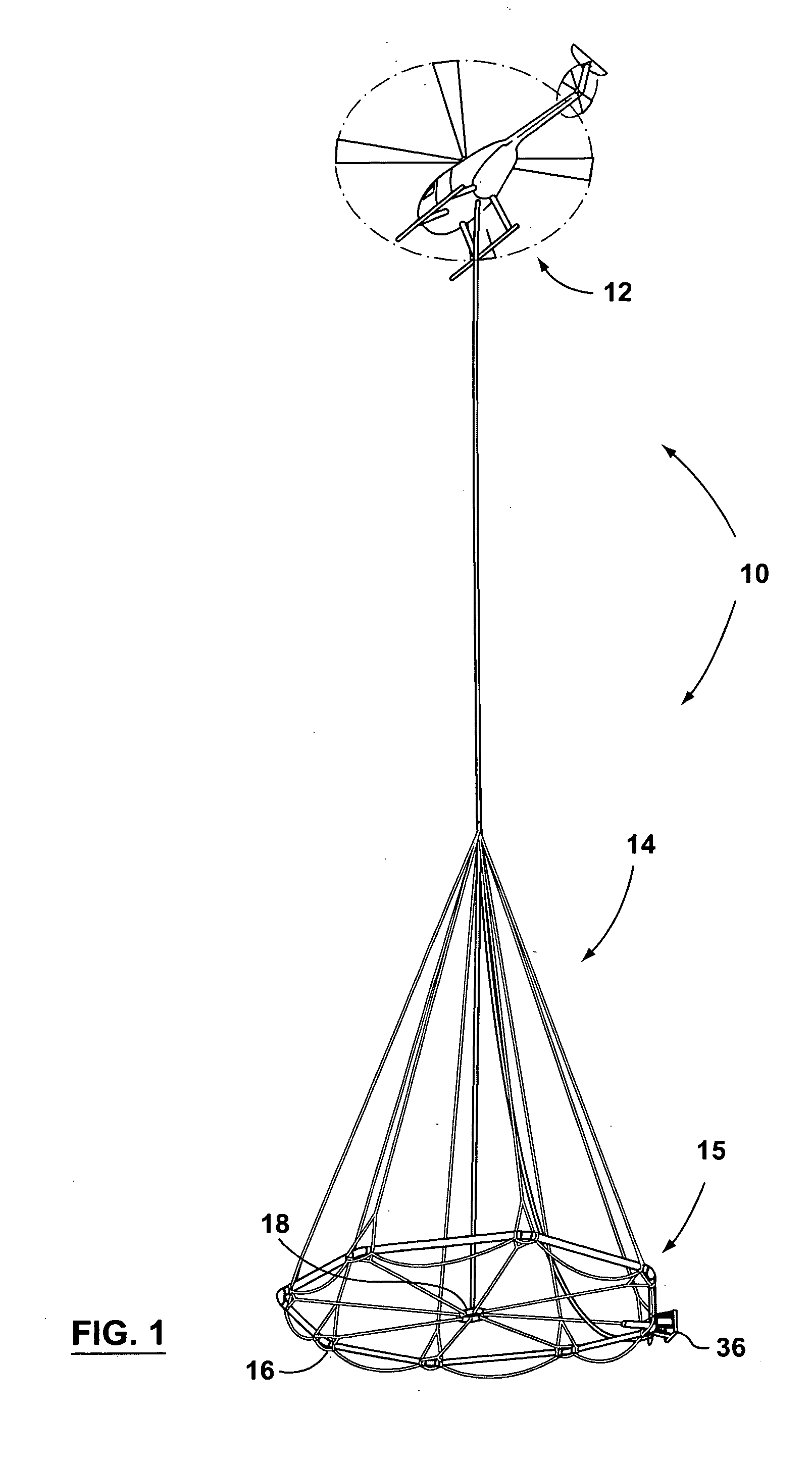
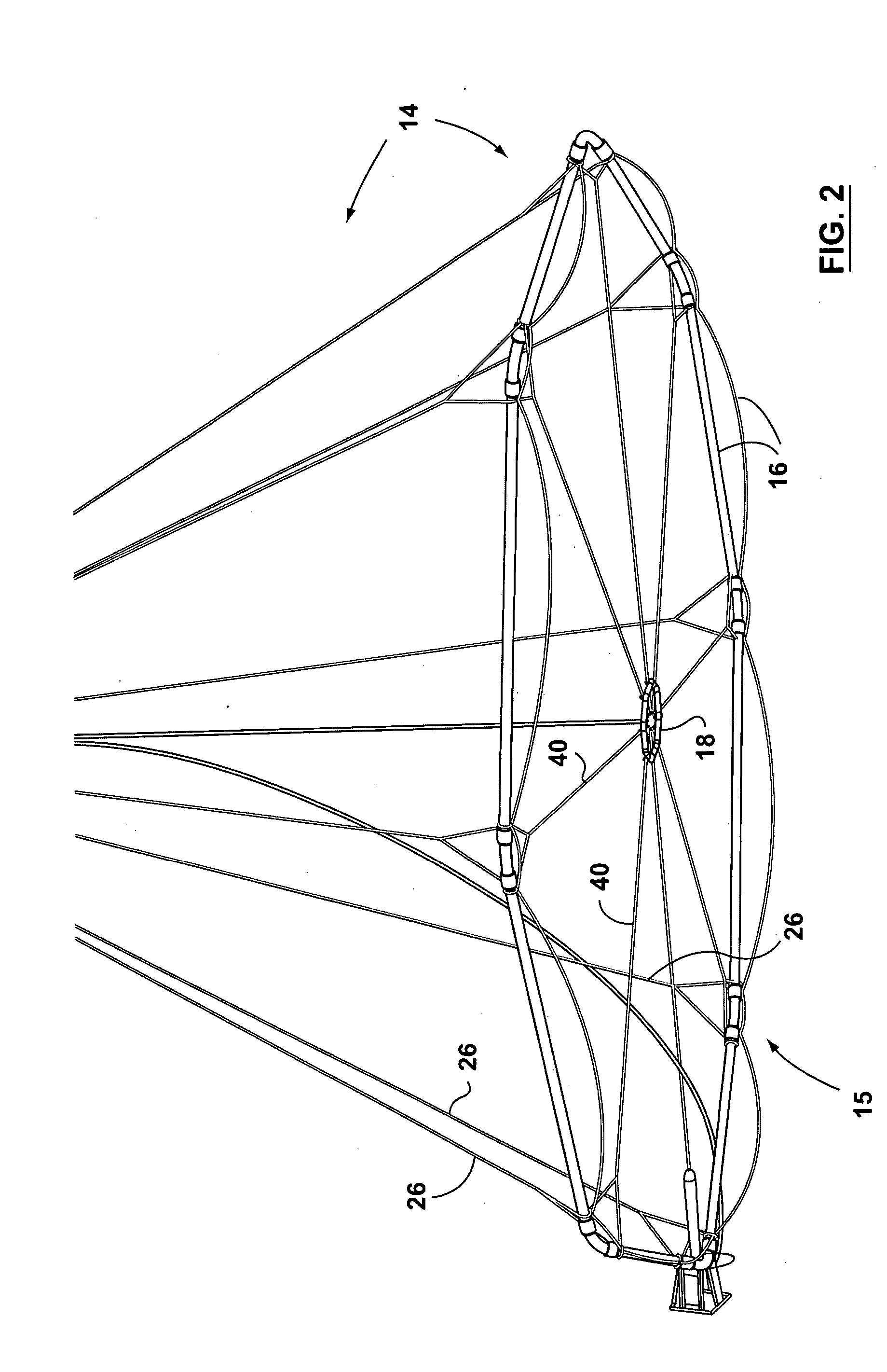
Large airborne time-domain electromagnetic transmitter coil system and apparatus
ActiveUS7948237B2Acoustic wave reradiationElectric/magnetic detection for transportElectromagnetic launchTransmitter coil
An airborne time domain electromagnetic survey system is provided. The system and apparatus of the present invention are able to address the interest in exploring base metals and uranium deposits at depths approaching 1 kilometer. It encompasses a transmitter coil having a large magnetic dipole moment, flight stability, which is light weight, compatible with small helicopters, and can be transported, setup and repaired in the field. It is of a semi-rigid modular structure that can decrease the incidence of damage or breakage during take-off or landing in rough terrain.
Owner:GEOTECH
High-efficiency time domain electromagnetic simulation method based on H matrix algorithm
InactiveCN102033985AQuick solveDiscrete Fit ExactSpecial data processing applicationsComputation complexityDecomposition
The invention discloses a high-efficiency time domain electromagnetic simulation method based on an H matrix algorithm, which can realize electromagnetic simulation on a large three-dimensional target. In the method, a time domain finite element method (TDFEM) is used as a background, a low-rank compression technique is used as a core, and a tree structure is used as a basis for carrying out logical unit (LU) decomposition on a sparse matrix generated by the TDFEM by a four arithmetic algorithm corresponding to the H matrix. The acquired upper and lower triangular factors have low-rank compressible characteristics, and the compressed matrix equation can realize quick solution of high-efficiency time domain electromagnetic simulation by the H matrix algorithm. The high-efficiency time domain electromagnetic simulation method has the advantages of fast computation speed, low memory consumption, controllable computation accuracy, good stability and the like, can reduce the complexity of computation to O(Nlog<2>N) and reduce the memory consumption to O(NlogN), can be widely applied to the solution of a large sparse linear system of equations during high-efficiency time domain electromagnetic simulation, and can provide important reference for analyzing the electromagnetic property of the large three-dimensional target.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
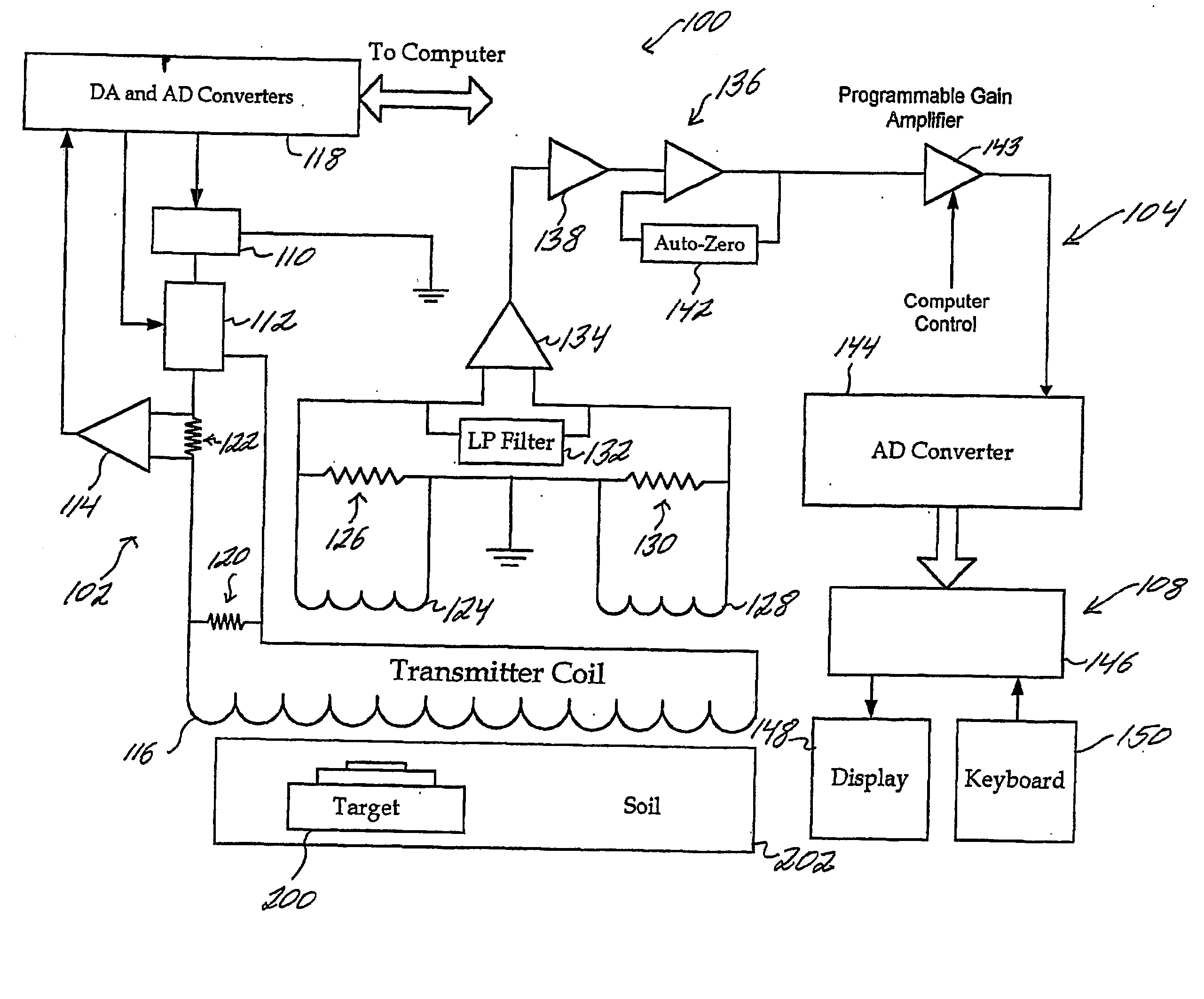
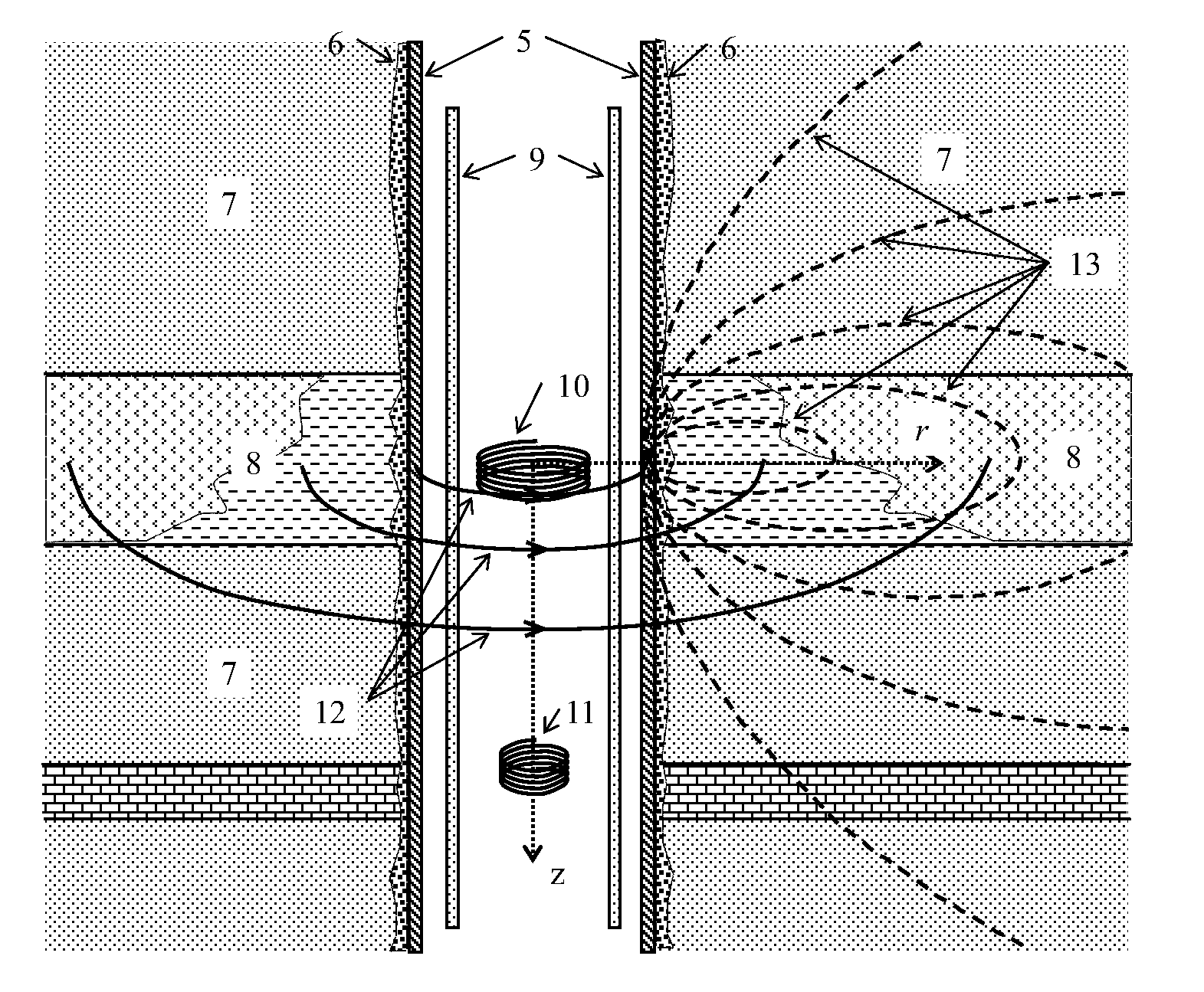
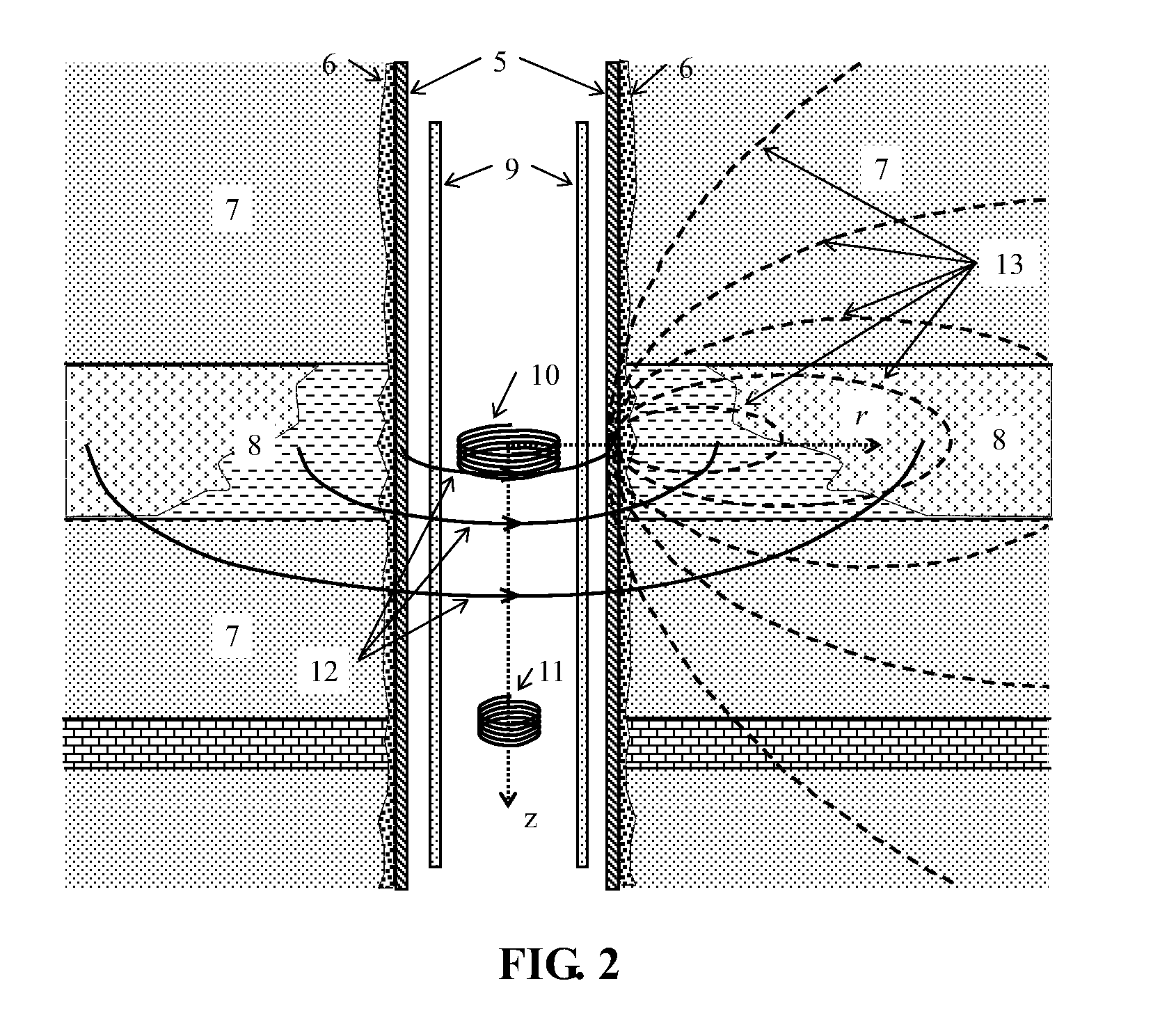
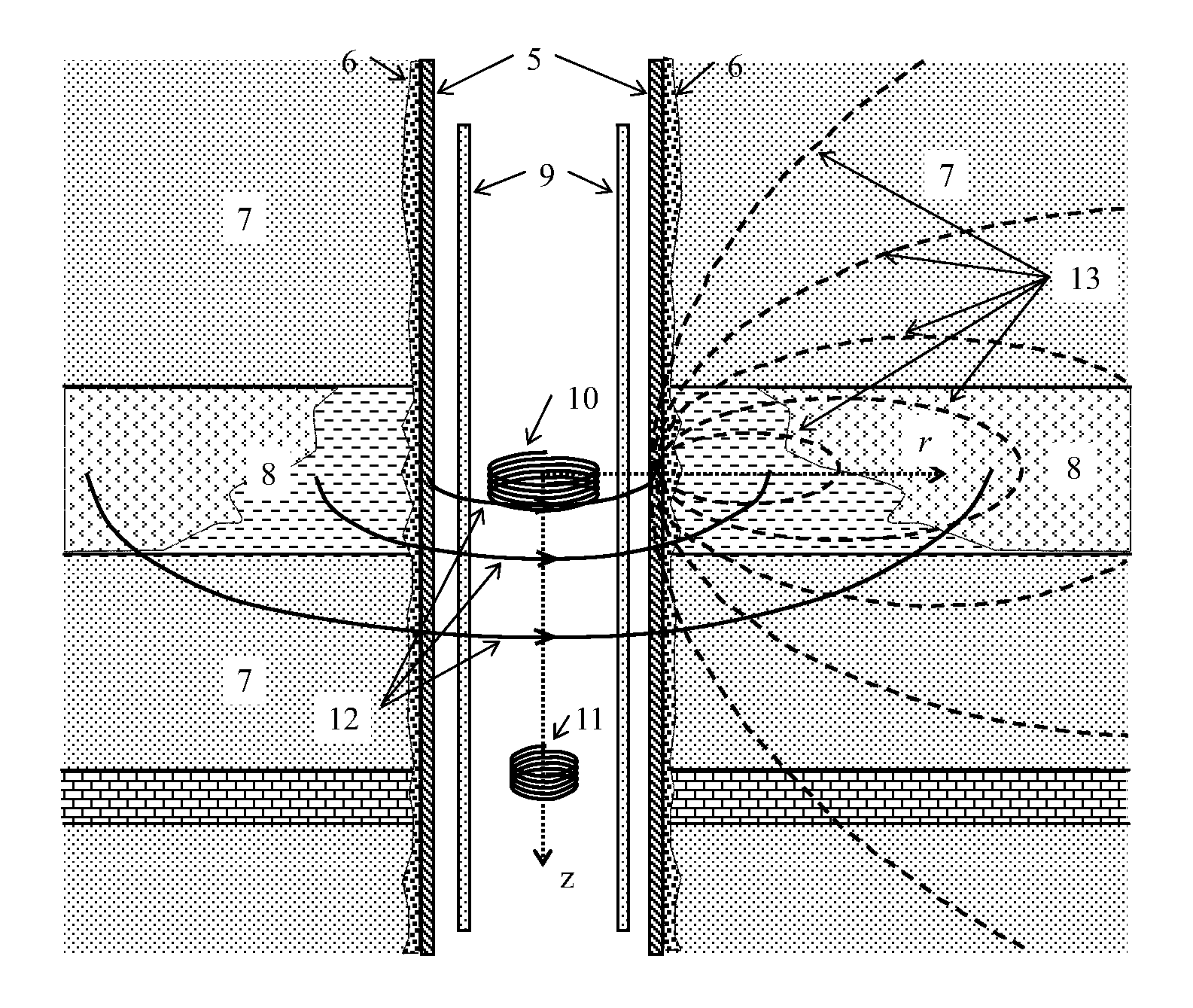
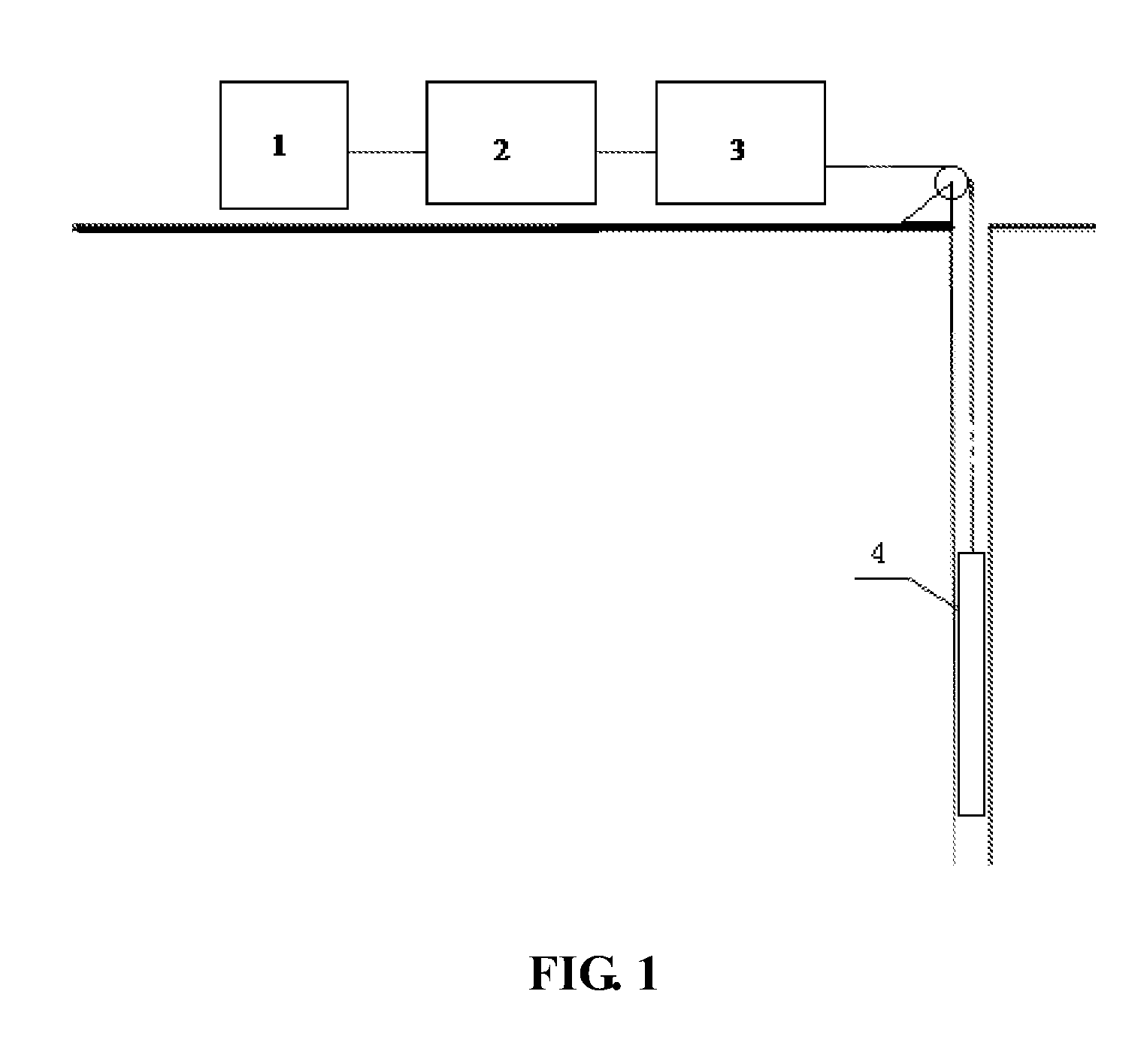
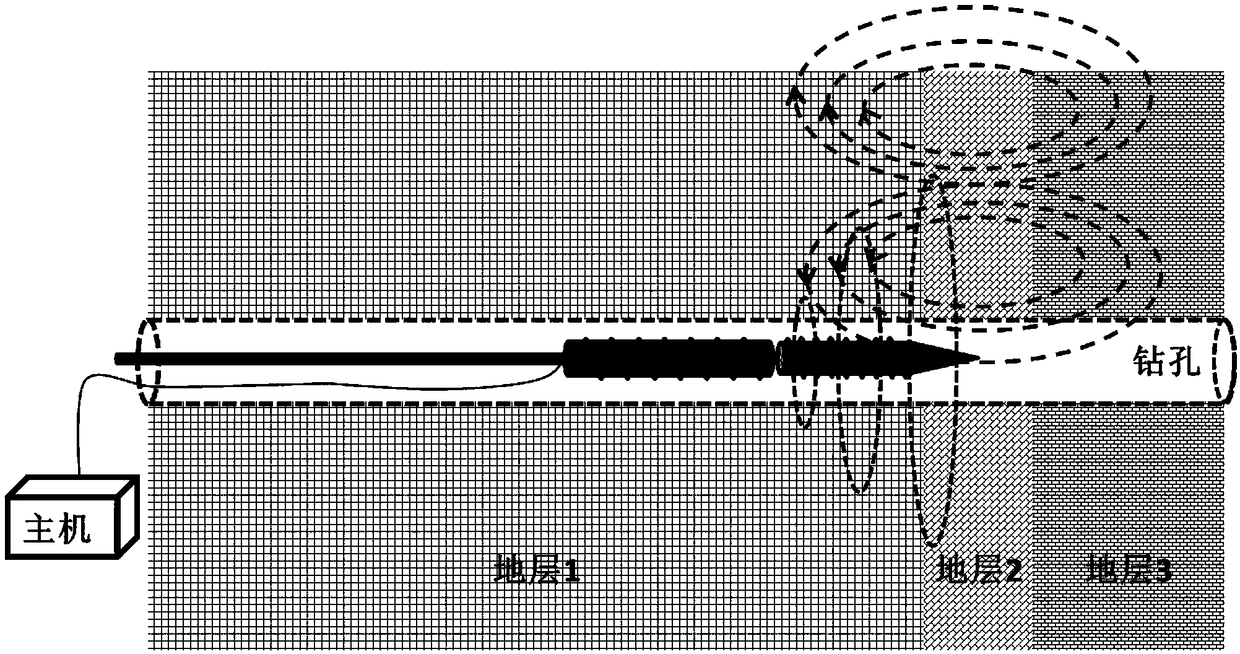
Method for detecting formation resistivity outside of metal casing using time-domain electromagnetic pulse in well
InactiveUS20120215448A1Power consumption of power supply is notReduce use costElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSeismology for water-loggingDigital recordingElectromagnetic pulse
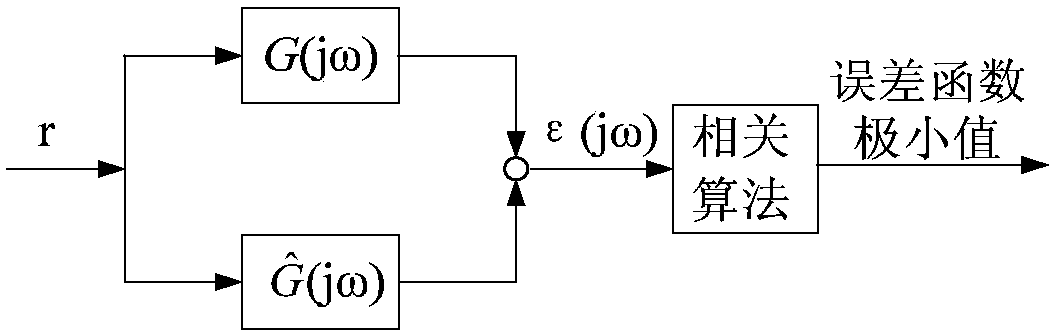
A method for detecting formation resistivity outside of metal casing using time-domain electromagnetic pulse in a borehole, the method including steps of a) providing a borehole large power pulse transmitting source, recording an induced electromotive force ε, and full time digital recording a transmitted waveform and a received signal; b) conducting transmission-reception and superimposing received signals to improve signal to noise ratio; c) calculating corresponding casing response according to known casing parameters and recorded current waveform of the transmitting source to obtain a relative induced electromotive force Δεf; d) correcting relative induced electromotive force value; e) carrying out one-dimensional inversion and converting the observation signal into radial variation information of the formation resistivity; f) obtaining a two-dimensional image of the longitudinal and radial resistivity distribution of outer cased formation resistivity for measured well sections; and g) determining residual oil distribution in a reservoir from outer cased reservoir resistivity distribution.
Owner:YANGTZE UNIVERSITY
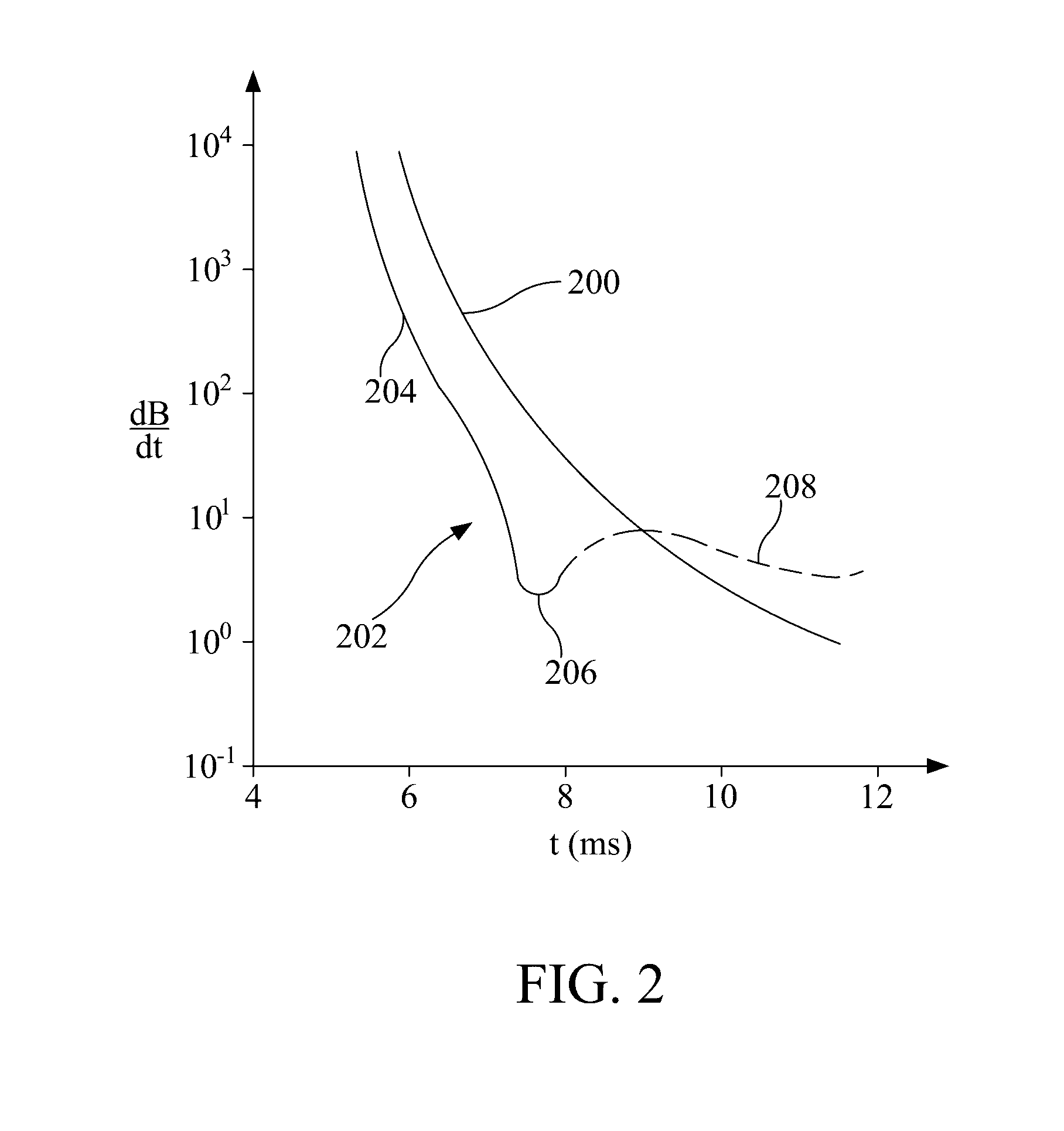
Bucking coil and b-field measurement system and apparatus for time domain electromagnetic measurements
ActiveUS20100052685A1Eliminating pre-amplifier set-offEliminating temperature-dependent driftElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSeismology for water-loggingTransmitter coilData acquisition
The present invention relates to a HTEM system that includes a semi-rigid bucking coil and an algorithm to determine the magnetic field B from the measured signal dB / dt. The bucking coil may be positioned in a concentric coplanar manner relative to a transmitter coil and receiver coil, in order to minimize spurious signals at the receiver coil during data acquisition time. Signals gathered by the system may be further processed by a signal processing means. Moreover, measurements performed upon data generated by the system may be performed upon the entire period of a current waveform applied to the transmitter and bucking coils.
Owner:GEOTECH
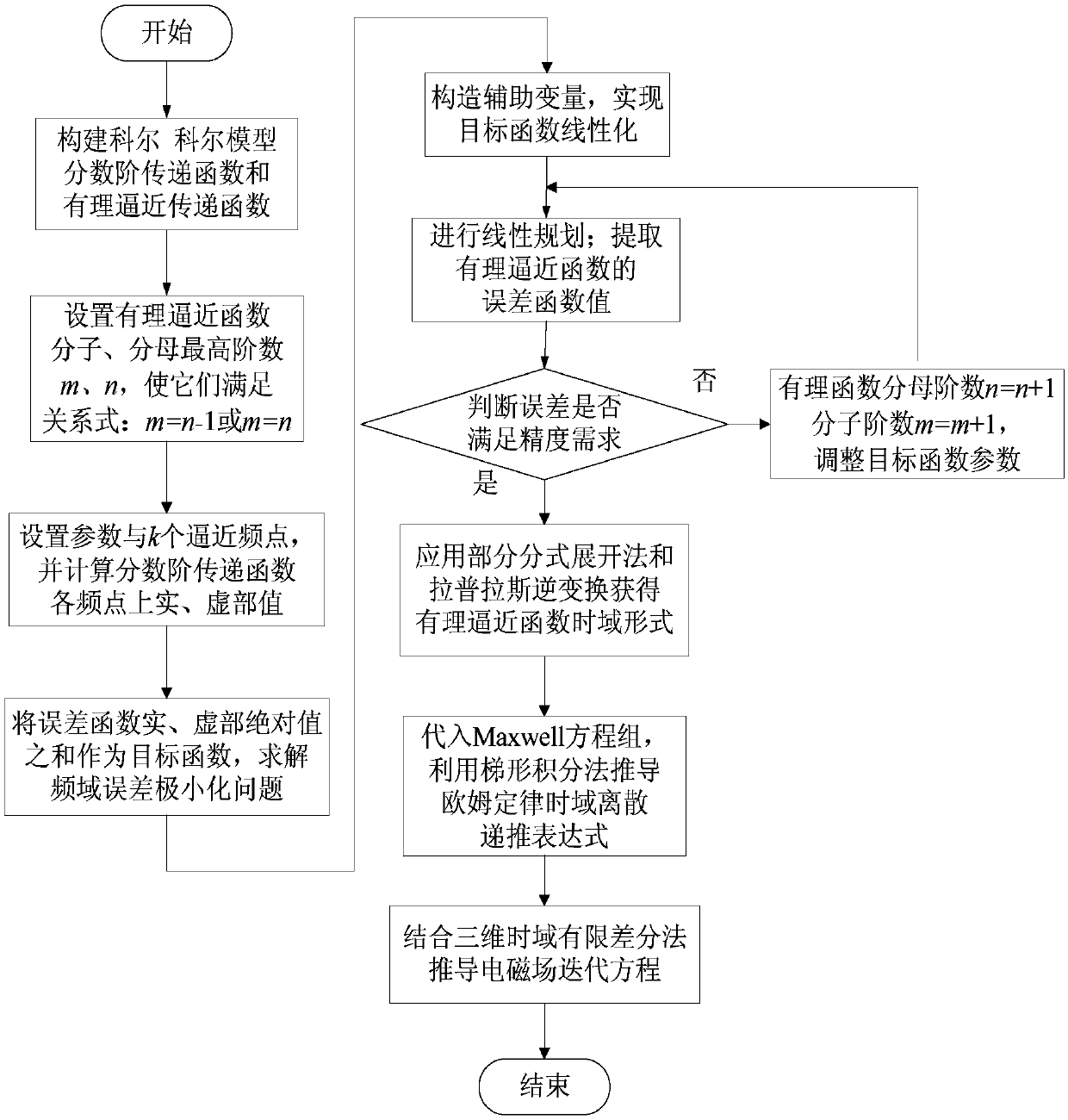
Fractional order electromagnetic anomalous diffusion three-dimensional simulation method of rational function approximation
ActiveCN107657137AQuick calculationMeet the dispersion characteristicsDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsThree dimensional simulationElectromagnetic response
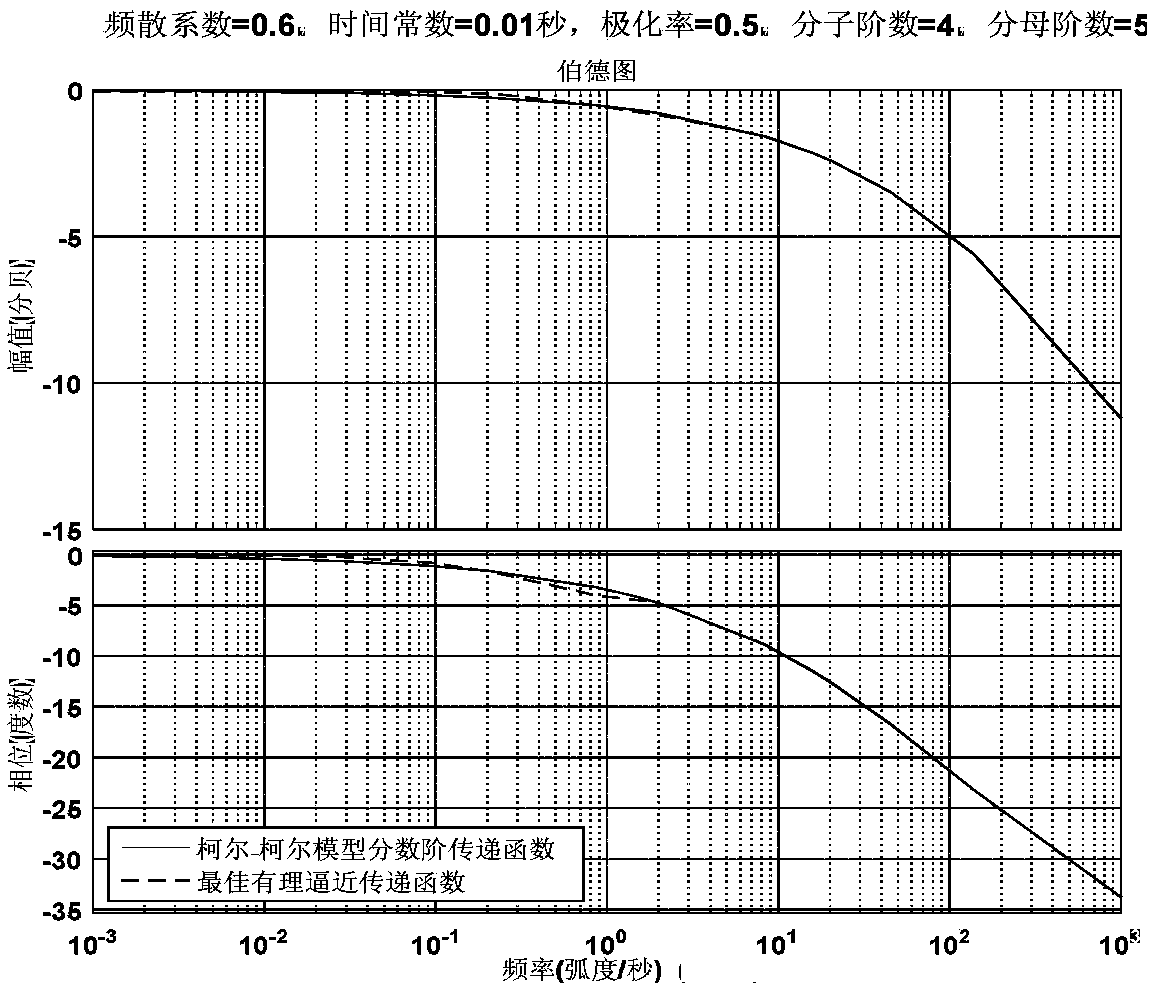
The invention relates to a fractional order electromagnetic anomalous diffusion three-dimensional simulation method of rational function approximation, and aims at calculating three-dimensional time-domain induction-polarization double field response of a fractional order Cole-Cole model. The method mainly comprises the steps of establishing a Cole-Cole model fractional order transfer function andan n-odrer rational approximation function based on a frequency domain rational function approximation method, and making the sum of the real part and the imaginary part of an error function as a target function; achieving linearization of the target function through an instrumental variable technique, and obtaining an optimal approximation rational function by adopting a linear programming approach; obtaining a time-domain mode of a conductivity by adopting a partial fraction expansion method and inverse laplace transformation; putting the time-domain mode in a Maxwell equation, deducing aniterative equation of an electromagnetic field based on a finite difference method, and achieving fractional order Cole-Cole model three-dimensional electromagnetic response value calculation. The fractional order electromagnetic anomalous diffusion three-dimensional simulation method of the rational function approximation has the advantages of fast and accurately simulating the fractional order Cole-Cole model three-dimensional time-domain electromagnetic response and providing theoretical foundation for research on abnormal electromagnetic diffusion in a polarization medium.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Unmanned aerial vehicle semi-aviation time domain electromagnetic detection data analysis and interpretation method
InactiveCN112068212ACancel motion noiseExploration fastHeight/levelling measurementElectric/magnetic detectionAviationEngineering
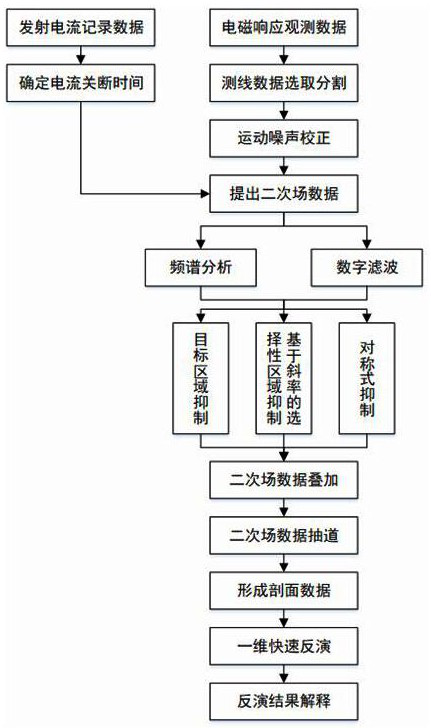
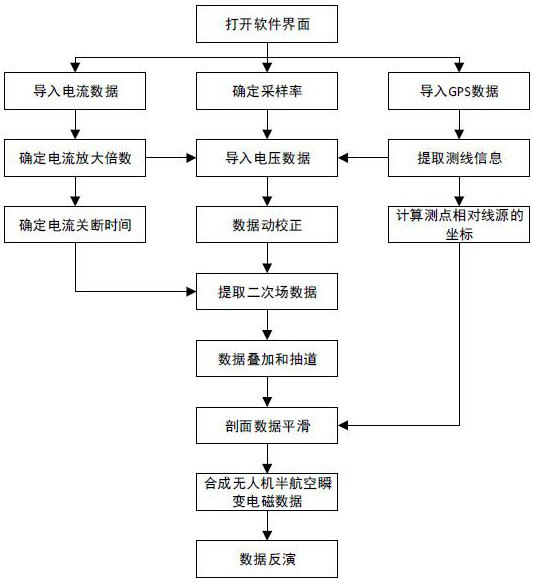
The invention discloses an unmanned aerial vehicle semi-aviation time domain electromagnetic detection data analysis and interpretation method, and belongs to the technical field of geophysical aviation electromagnetic exploration. The method comprises the following steps of a, preprocessing survey line data to eliminate a motion noise; b, performing spectral analysis and digital filtering processing on secondary field data; c, forming data to be imaged or inversely interpreted; and d, performing one-dimensional rapid inversion on the superimposed and lane-drawn secondary field data, establishing an underground electrical structure profile, and performing geological interpretation on an inversion imaging result in combination with geological data to form a comprehensive interpretation result. On the basis of ground grounding long wire source emission, an aerial unmanned aerial vehicle receives semi-aviation time domain electromagnetic detection data of an observation mode, and the method can quickly complete processing, analysis and explanation work while guaranteeing higher detection precision, and can realize quick exploration in a smaller area range.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
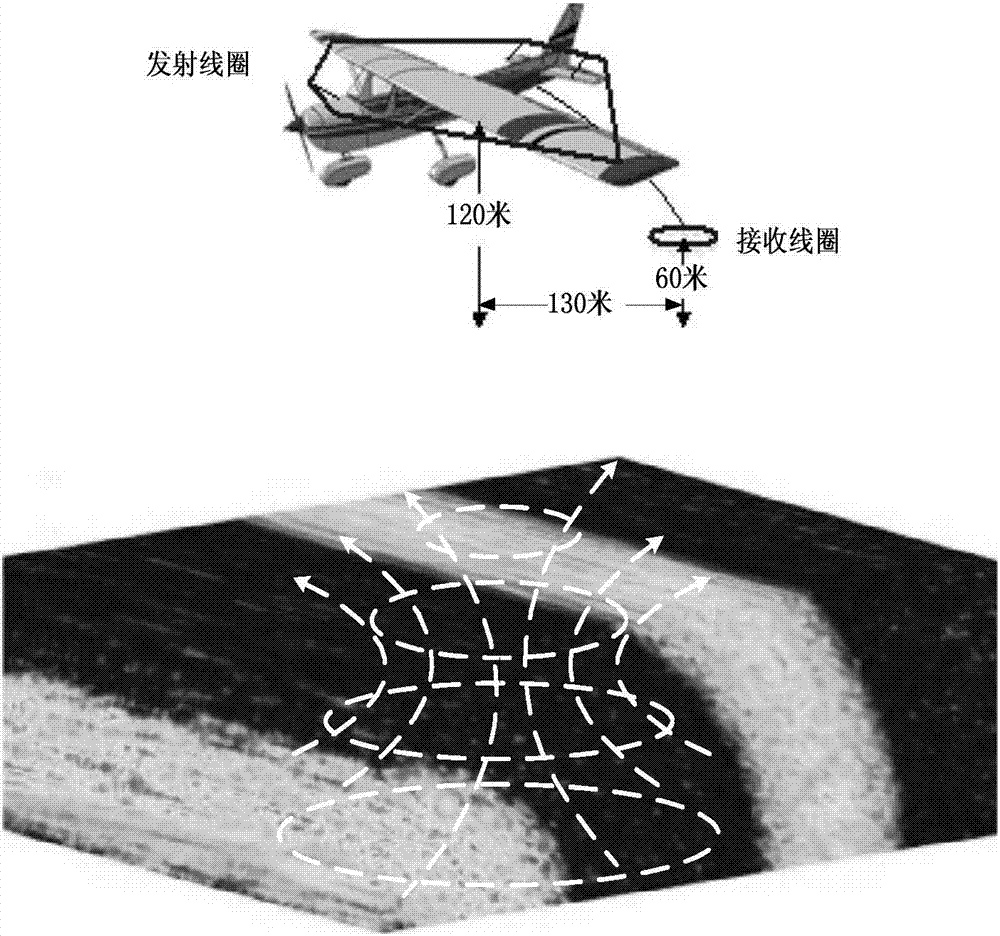
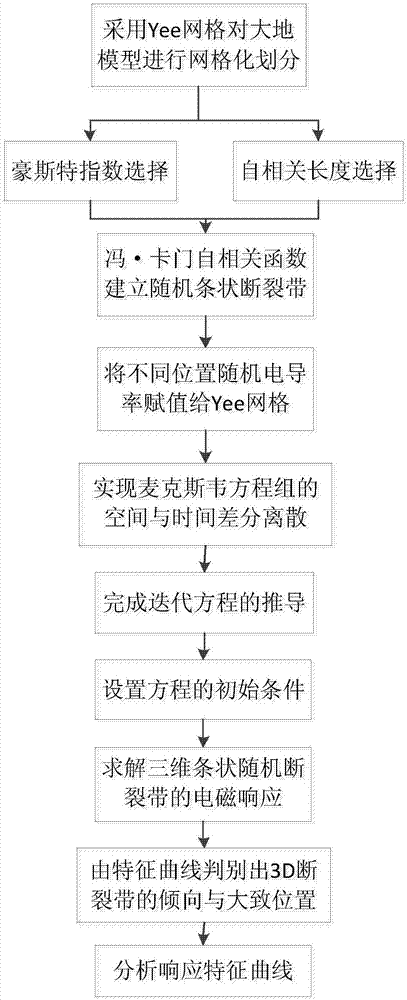
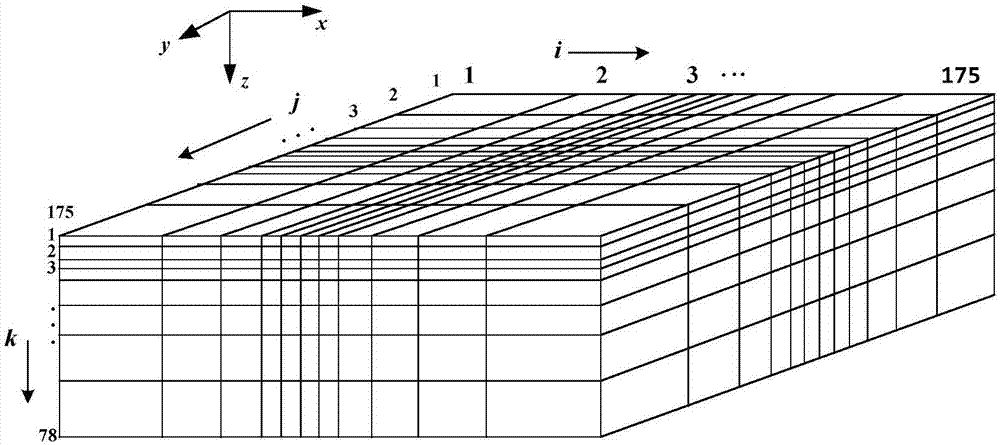
Method for building and judging three-dimensional strip-shaped random fault zone model in aviation time domain
ActiveCN107991711AImprove accuracyImprove reliabilityElectric/magnetic detectionAcoustic wave reradiationAviationTime domain electromagnetics
The invention discloses a method for building and judging a three-dimensional strip-shaped random fault zone model in the aviation time domain. The method comprises the steps of step 1, performing gridding subdivision on a geodetic model by adopting Yee grids; step 2, conducting a random strip-shaped fault zone model by adopting the statistical method; step 3, determining the number and the widthof random fault zones; step 4, deducing a explicit differential iterative formula in six direction magnetic fields and electric fields; step 5, endowing a corresponding random electric conductivity value to a geodetic grid model; step 6, judging the tendency and the position of the model through a response curve and a slicing diagram. By adopting the method, the blank of the time domain electromagnetic method in the exploration of fault zones can be made up. The accuracy and the reliability of the electromagnetic method in the exploration of oil and gas reservoirs are greatly improved. The efficiency of related work is improved, and the exploration cost is greatly reduced.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Line source time domain electromagnetic response numerical calculation method based on meshless method
ActiveCN105426339AGet rid of dependenceImprove smoothnessComplex mathematical operationsTerrainElectromagnetic response
The invention relates to a line source time domain electromagnetic response numerical calculation method based on meshless method, particularly a numerical simulation which can overcome dependence on mesh in the conventional numerical calculation method and is suitable for time domain electromagnetic surveying under complex terrain. In the line source time domain electromagnetic response numerical calculation method based on meshless method, based on a governing equation and a definite condition which the transient electromagnetic method satisfies, a generic function of a two-dimensional line source boundary value problem is established, essential boundary conditions are loaded through a penalty method, a paraxial approximate equation is provided to eliminate reflected waves at truncated boundaries, time discretization is carried out through a Crack-Nicolson format, and a recurrence equation is obtained. Based on an isoparametric element thought, units with regular shape in local coordinates are discretized to be irregular solving objects of which nodes are distributed at random. The recurrence equation is solved through a LU decomposition method, and finally, a field value of each node in a solving region is obtained. Calculation result shows that, with the method provided by the invention, a shape function has good smoothness, simulation precision is high, maximum error is not more than 1*10<-3>, and electromagnetic method high-accuracy numerical calculation is realized.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
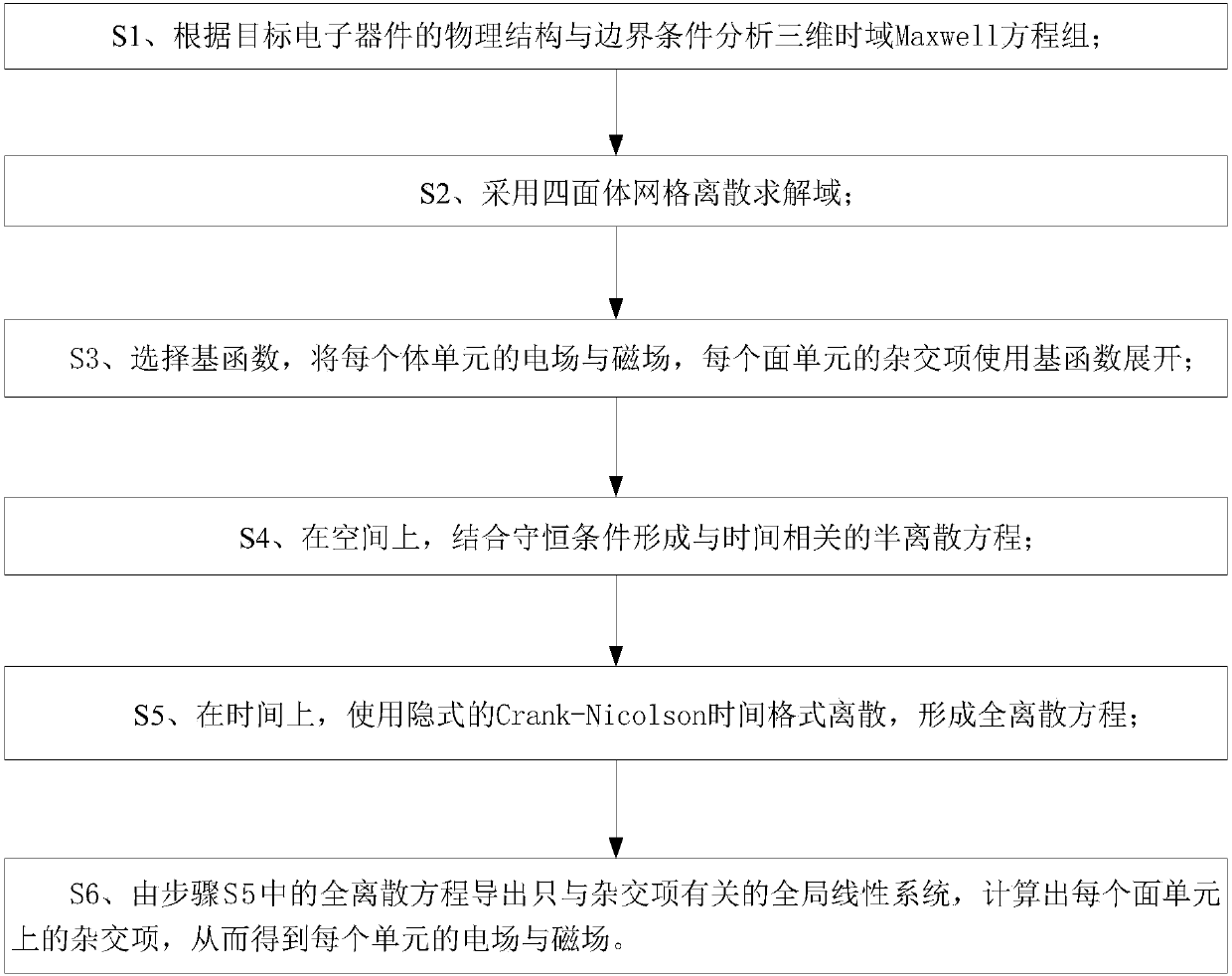
Hybrid time-domain discontinuous-Galerkin-method-based numerical method of time-domain computational-electromagnetics
InactiveCN107944141AObtaining Electromagnetic Response CharacteristicsImprove parallelismDesign optimisation/simulationComplex mathematical operationsElectromagnetic environmentTime domain electromagnetics
The invention discloses a hybrid time-domain discontinuous-Galerkin-method-based numerical method of time-domain computational-electromagnetics. The method is applied to the numerical-solving field oftime-domain computational-electromagnetics. A hybrid term is introduced on interface units of adjacent body units, and is used to define numerical flux of electromagnetic fields, an implicit Crank-Nicolson time format is used to disperse three-dimensional time-domain Maxwell equations, after introducing the hybrid term, to obtain a global linear system related only to the hybrid term, and the electromagnetic fields of all the units are obtained through solving for the hybrid term. Therefore, the deficiency of calculation time, memory and precision of existing time-domain electromagnetic-fieldnumerical-methods in processing multi-scale equipment under complex electromagnetic environments can be effectively avoided.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
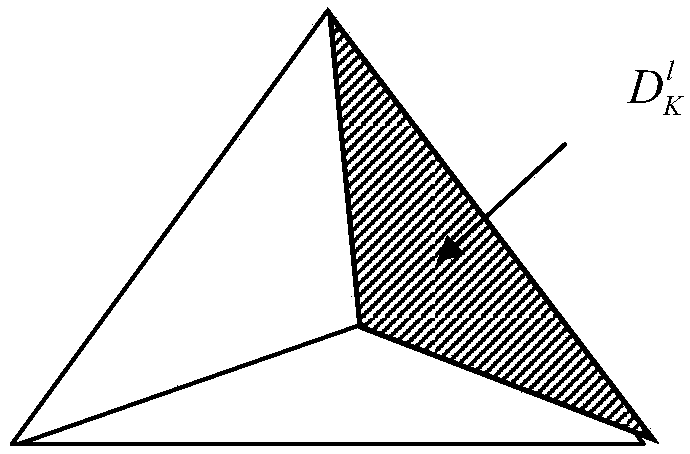
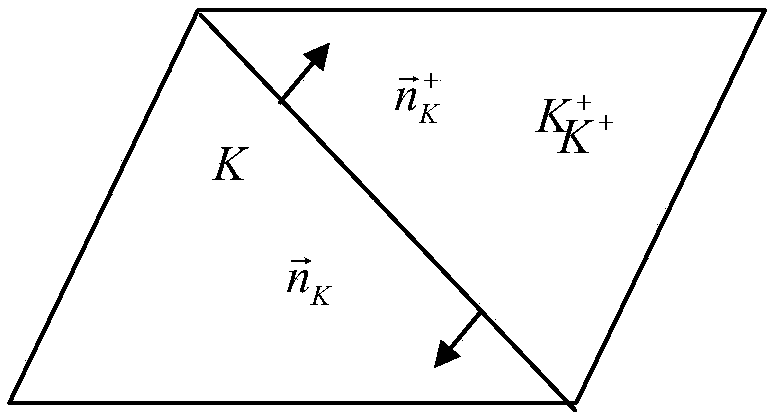
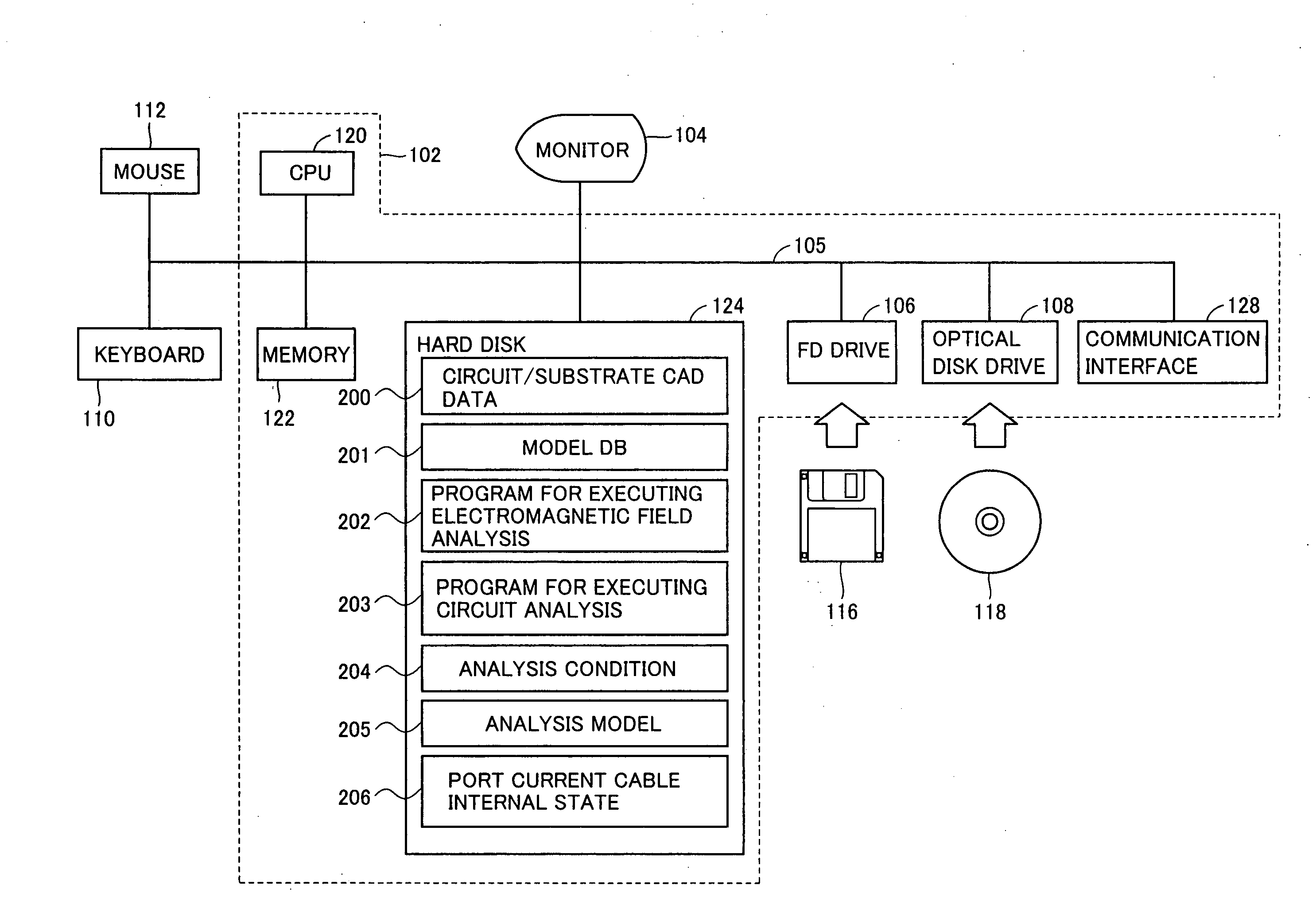
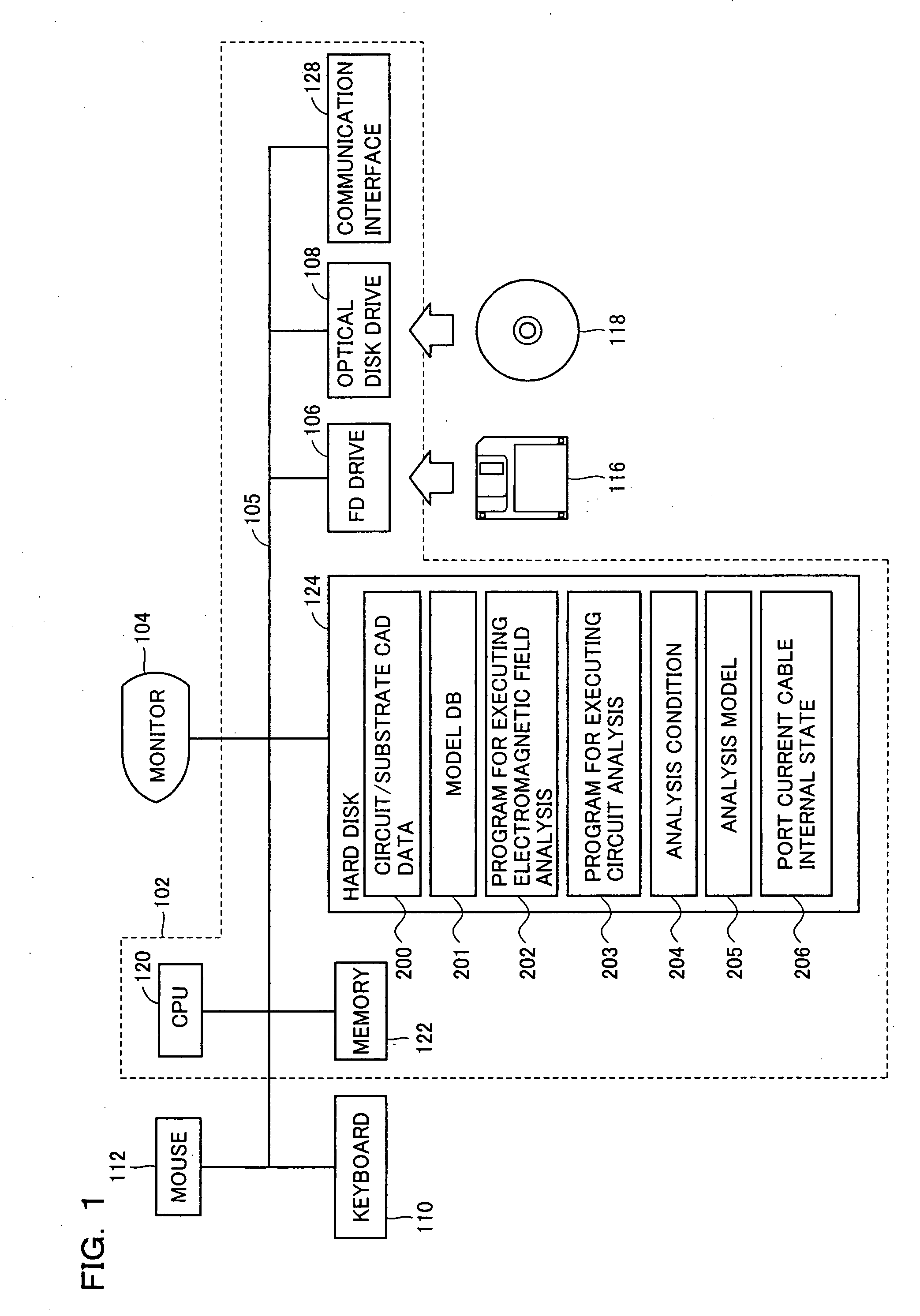
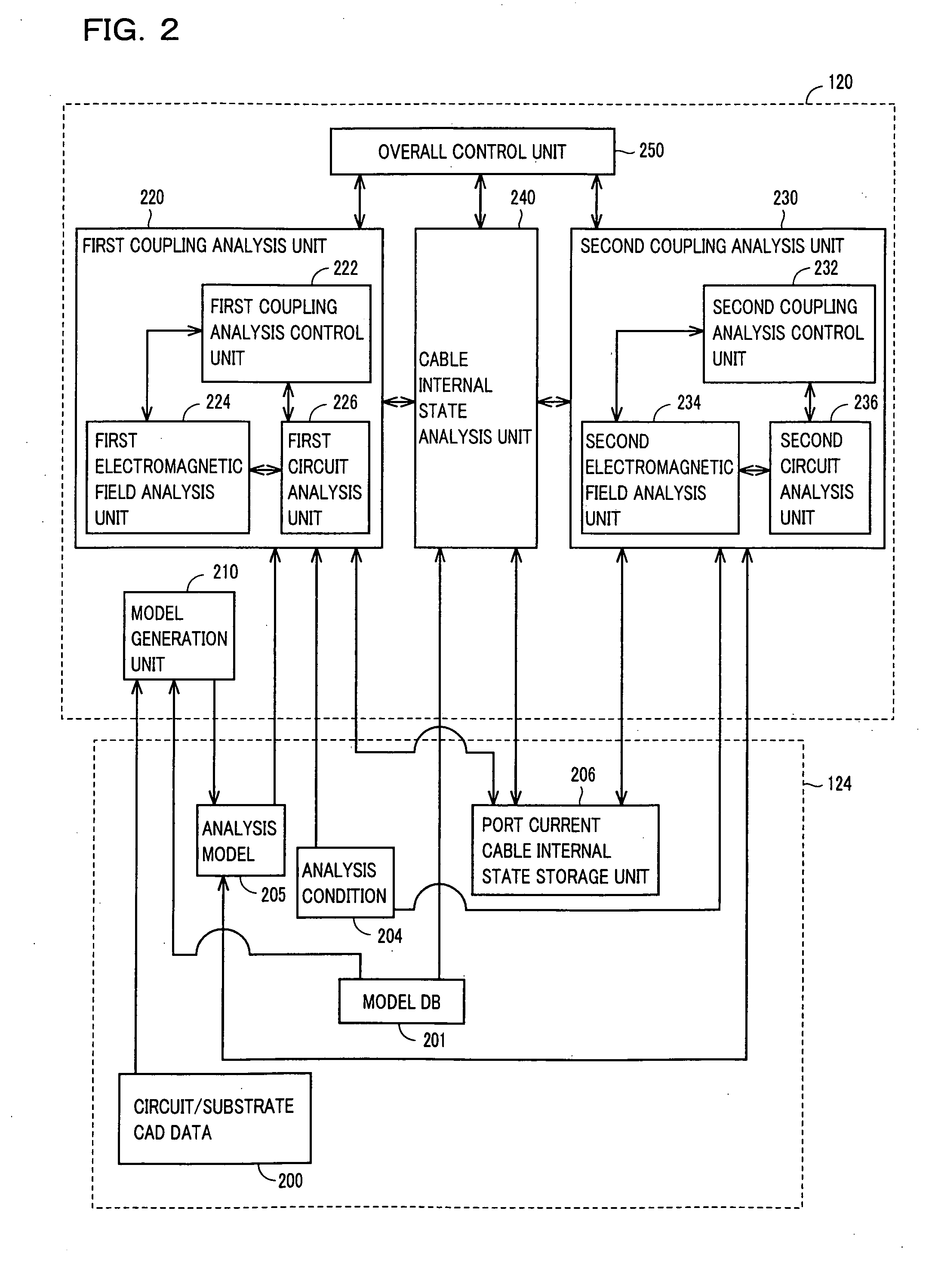
Simulation method implemented by coupling electromagnetic field analysis method and circuit analysis method together, simulation apparatus, and computer-readable medium storing simulation program
ActiveUS20090102470A1Efficient executionEfficient analysisComputation using non-denominational number representationComputer aided designElectricityCoupling
A simulation apparatus according to an embodiment performs an electromagnetic field circuit coupling analysis on a first substrate and a second substrate electrically coupled via a circuit element having a finite delay time. A first coupling analysis unit carries out a time domain electromagnetic field analysis and also a circuit analysis on a circuit element at a first analytical domain including the first substrate. The second coupling analysis unit carries out a time domain electromagnetic field analysis and also a circuit analysis on a circuit element at a second analytical domain including the second substrate. A cable internal state analysis unit carries out a circuit analysis on a circuit element, employing an electromagnetic field value obtained at the first coupling analysis unit at one terminal of the circuit element connecting the first substrate and the circuit element, and an electromagnetic field value obtained at the second coupling analysis unit at another terminal of the circuit element connecting the second substrate and the circuit element.
Owner:SHARP KK
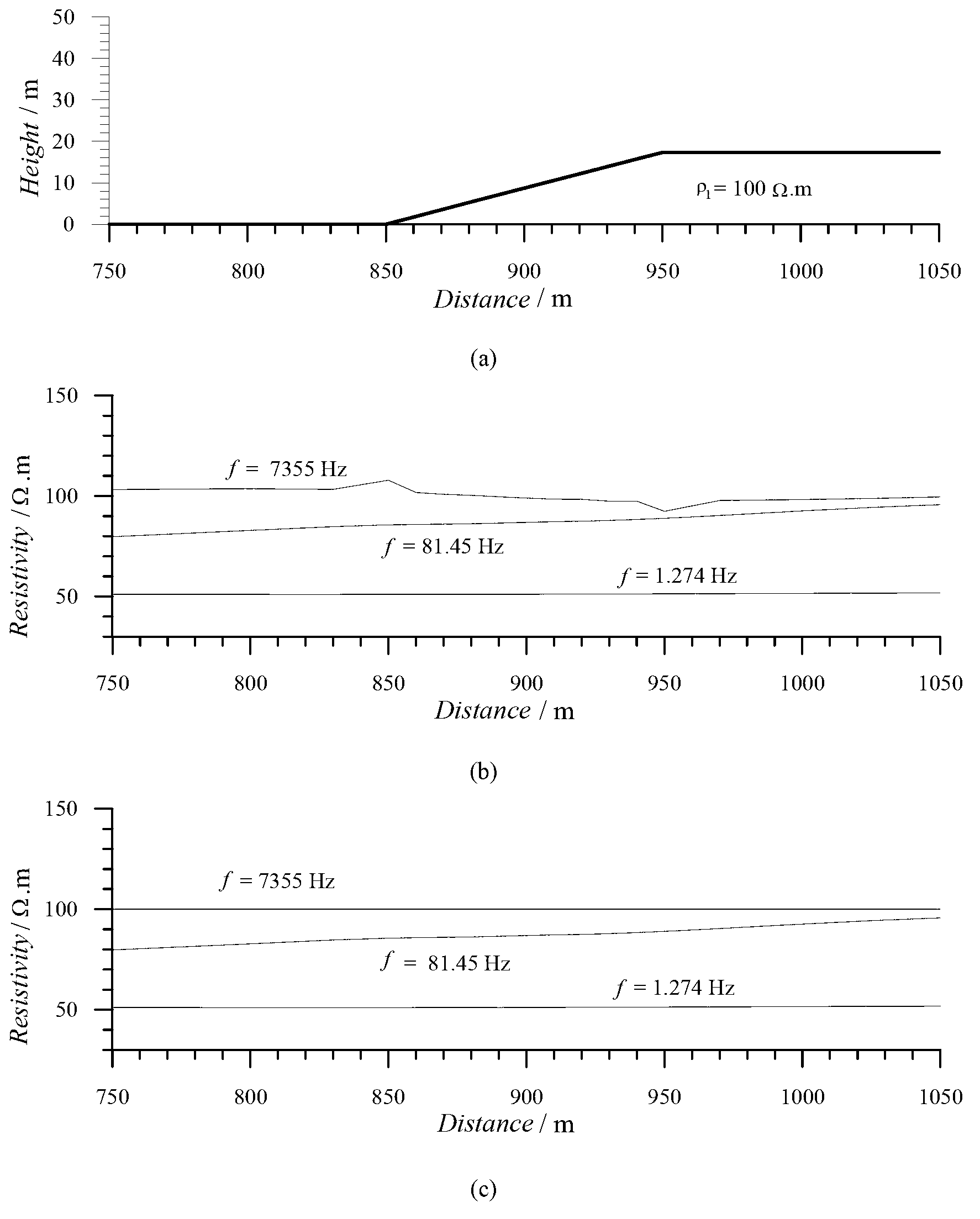
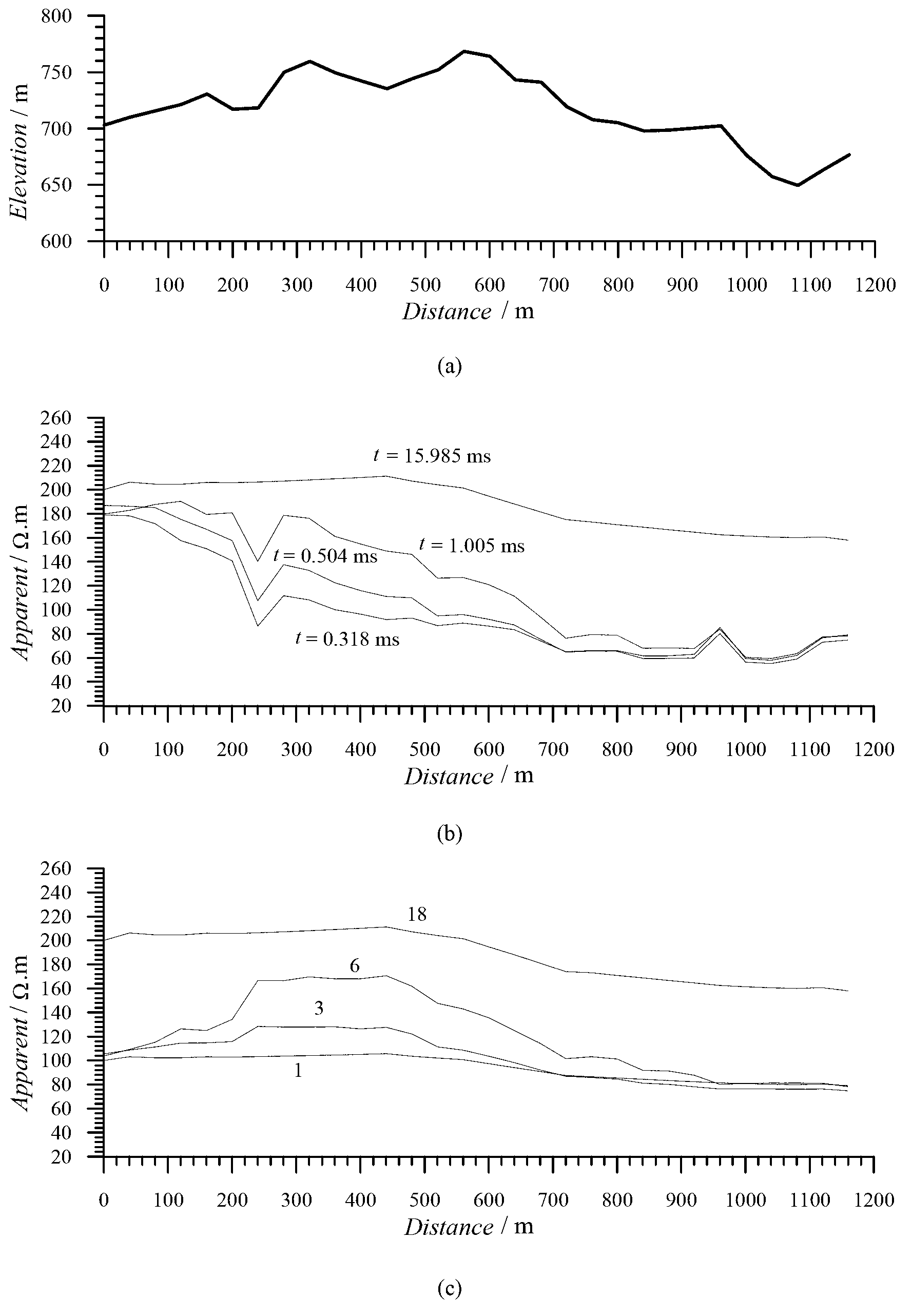
Ratio method for correcting topographic influence in electromagnetic prospecting
ActiveCN103064124AHold responseAvoid introducing errorsElectric/magnetic detectionAcoustic wave reradiationTopographic profileElectromagnetic shielding
The invention discloses a ratio method for correcting topographic influence in electromagnetic prospecting. The ratio method comprises the steps of acquiring a surface layer resistivity value without topographic influence to serve as a standard resistivity of topographic correction; drawing an in-line topographic profile, respectively comparing the topographic profile with a frequency point profile of a frequency domain electromagnetic method and a time channel profile of a time domain electromagnetic method, and judging the topographic influence suffered by the actually measured data according to the influence rule of the topography on the resistivity in the frequency domain and the time domain electromagnetic field; observing from the highest frequency point of the frequency domain electromagnetic method and the earliest time channel of the time domain electromagnetic method so as to obtain the topographic response which is closest to the surface layer until the absence of low-frequency frequency point of the topographic influence is observed in the frequency domain electromagnetic method and the absence of the late time channel of the topographic influence is observed in the time domain electromagnetic method, and acquiring the observation data without topographic influence; and performing topographic correction according to a ratio formula of pcorrected(i,j)=pmeasured(i,j) [pstandard(i) / pmeasured(i,l)]C(i,j). The ratio method is good in correction effect in the process of correcting the topographic influence, is high in feasibility and can be widely applied to topographic influence correction in electromagnetic prospecting.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
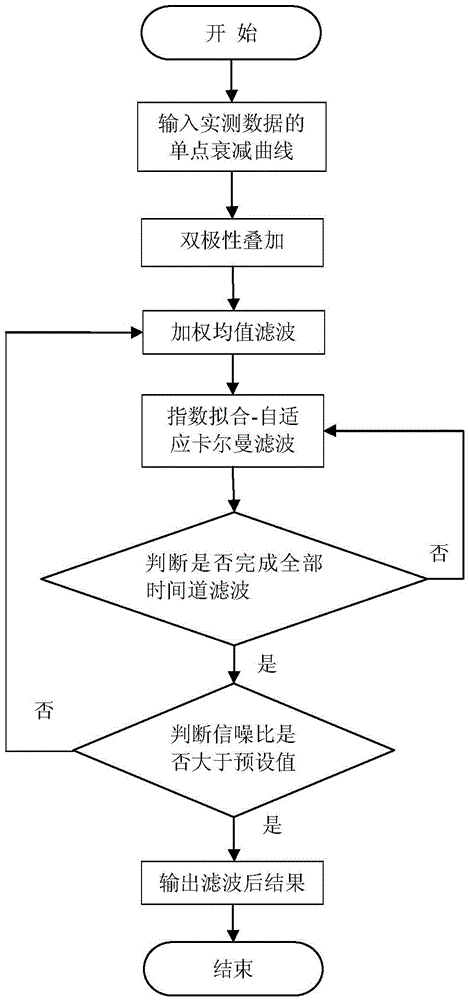
Direct time domain processing method for transient electromagnetic sounding data
ActiveCN102419456AAccurate locationThe right sizeElectric/magnetic detectionAcoustic wave reradiationEngineeringTime domain electromagnetics
The invention provides a direct time domain processing method for transient electromagnetic sounding data. The direct time domain processing method comprises the following step of: deducing a large fixed-source loop and long grounding lead analytic expression by using time varying point charge as a basic microelement to obtain a large fixed source loop and long grounding lead analytic solution. The direct time domain processing method for the transient electromagnetic sounding data based on the time varying point charge is used for replacing the traditional processing method for the transientelectromagnetic sounding data based on dipoles, and therefore, errors generated in the process from frequency domain deduction to time domain switching in the traditional method can be reduced, the inherent characteristic of a time domain electromagnetic field is highlighted, and the surveying accuracy of a transient electromagnetic method is greatly improved.
Owner:INST OF GEOLOGY & GEOPHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Ground-airborne time-domain electromagnetic data height correction method
ActiveCN105487129ASolving Long Offset Transient Electromagnetic MethodSimple calculationElectric/magnetic detectionAcoustic wave reradiationFlight testFlight height
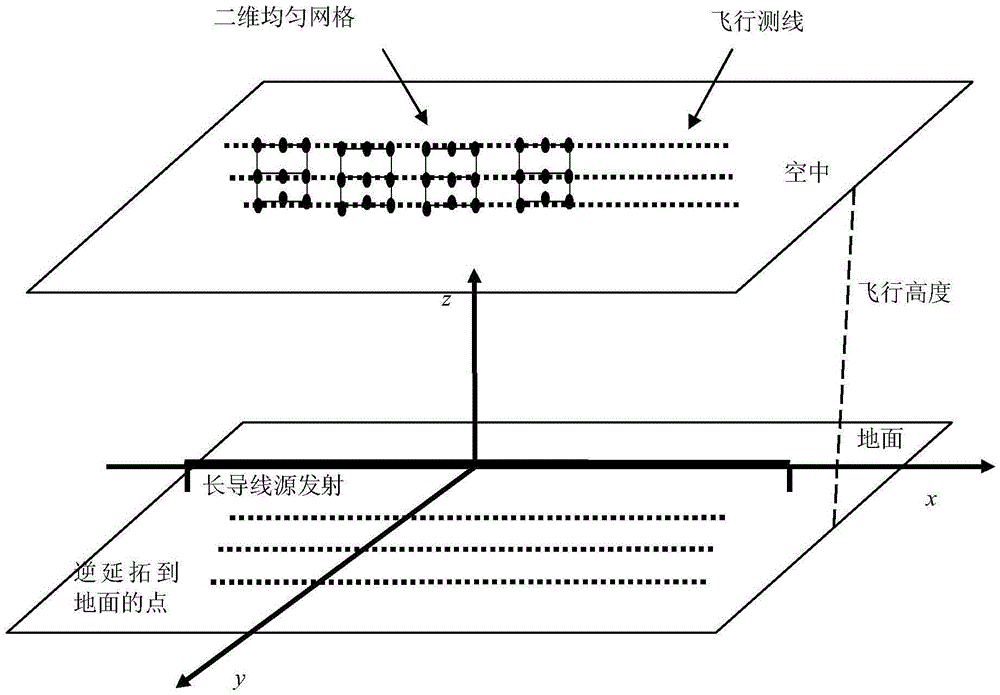
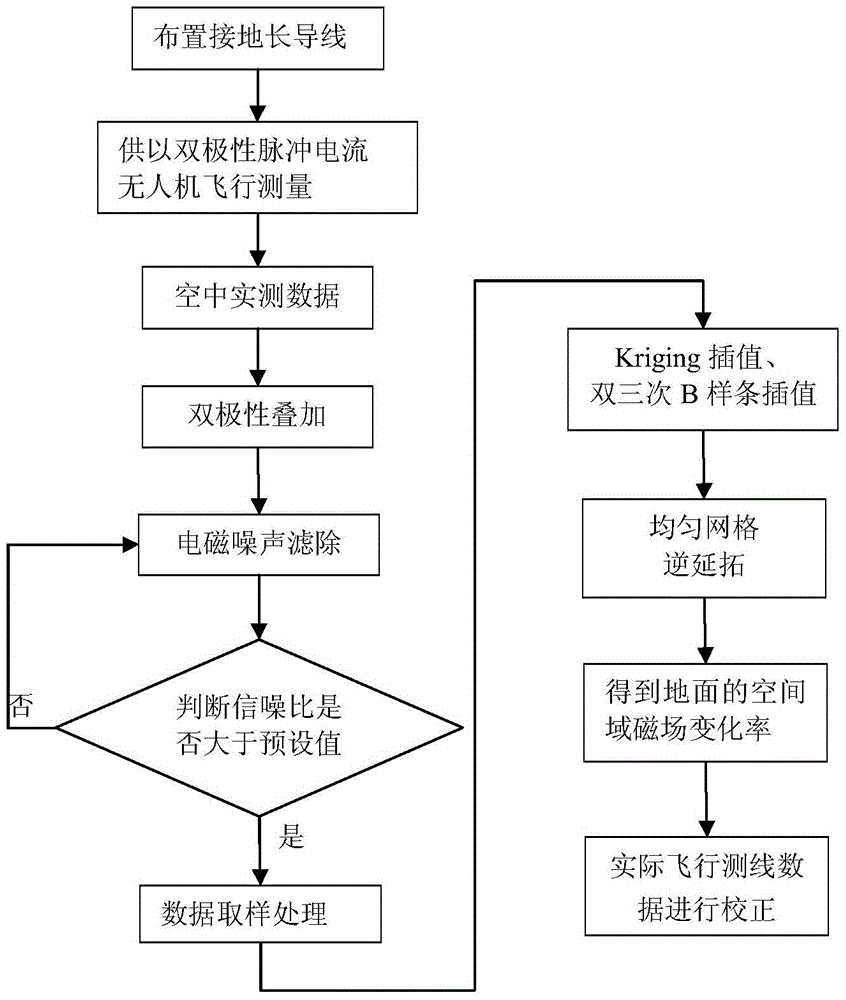
The invention relates to a ground-airborne time-domain electromagnetic data height correction method. The method mainly comprises the following steps that: an unmanned aerial vehicle or an airship is adopted to perform flight measurement in the air; electromagnetic noise removal and bipolar overlay sampling are performed on measured data; Kriging interpolation and double-cubic B spline interpolation are adopted to perform uniform interpolation on the magnetic field change rate of each measuring point in flight measurement, wherein the magnetic field change rate is expressed by a formula mentioned in the descriptions in the invention, so that magnetic field change rates in two-dimensional uniform grids can be obtained; and an inverse continuation theory is adopted to perform continuation calculation on a magnetic field change rate measured at a height where z=-h in the air, so that the magnetic field change rate data of a site on the ground where z=0 can be obtained, and therefore, flight height correction is realized. With the ground-airborne time-domain electromagnetic data height correction method adopted, the problem of ignoring of height in the prior art in which an LOTEM method is adopted to interpret ground-airborne time-domain electromagnetic data can be solved; the magnetic field change rate data can be directly used to perform correction, and the magnetic field change rate is not required to be converted into a magnetic field to perform correction, and only three flight test lines are just required, so that height correction can be carried out, and a calculation process only involves interpolation and Fourier transform. The ground-airborne time-domain electromagnetic data height correction method has the advantages of simple calculation and high computing speed.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
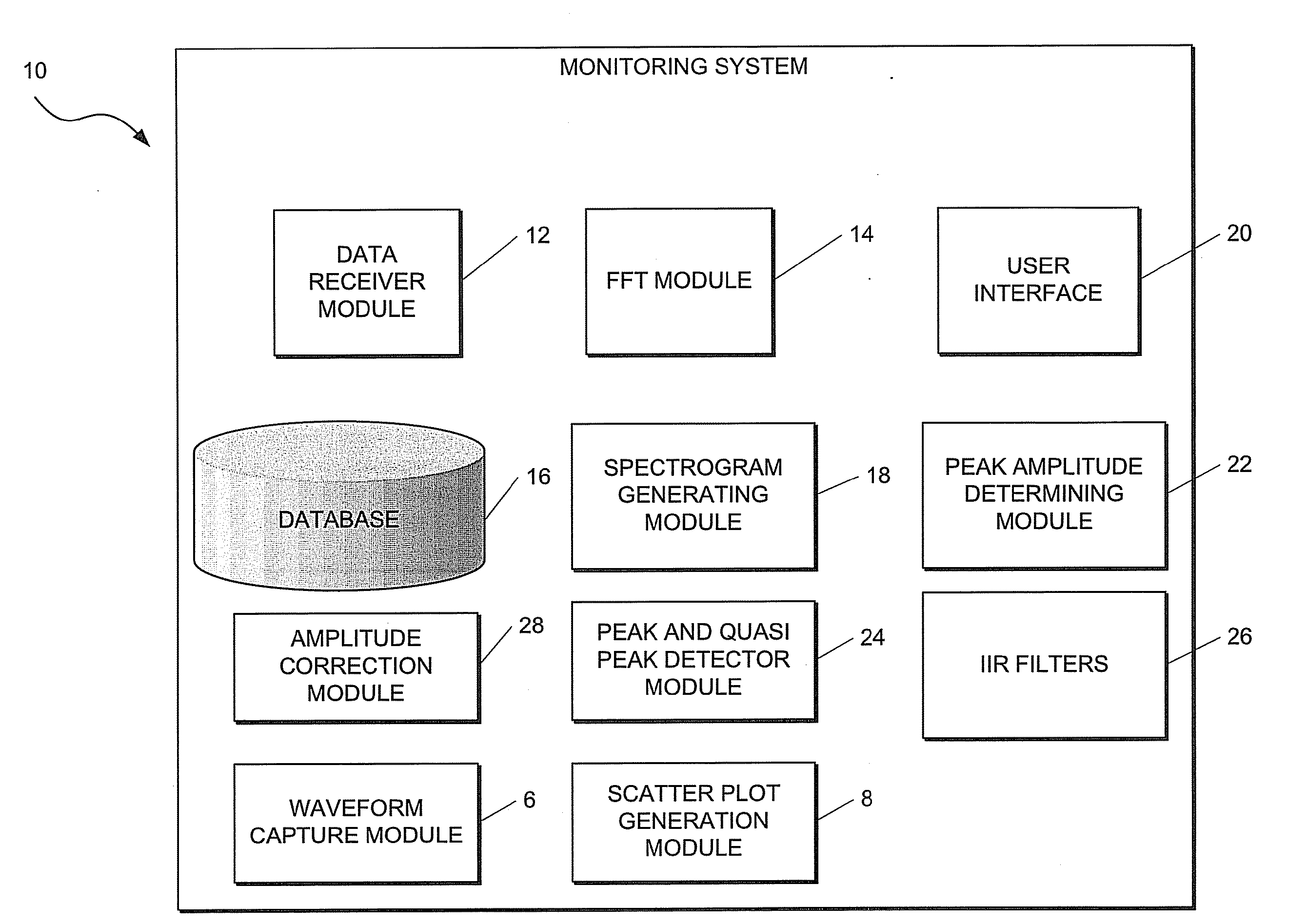
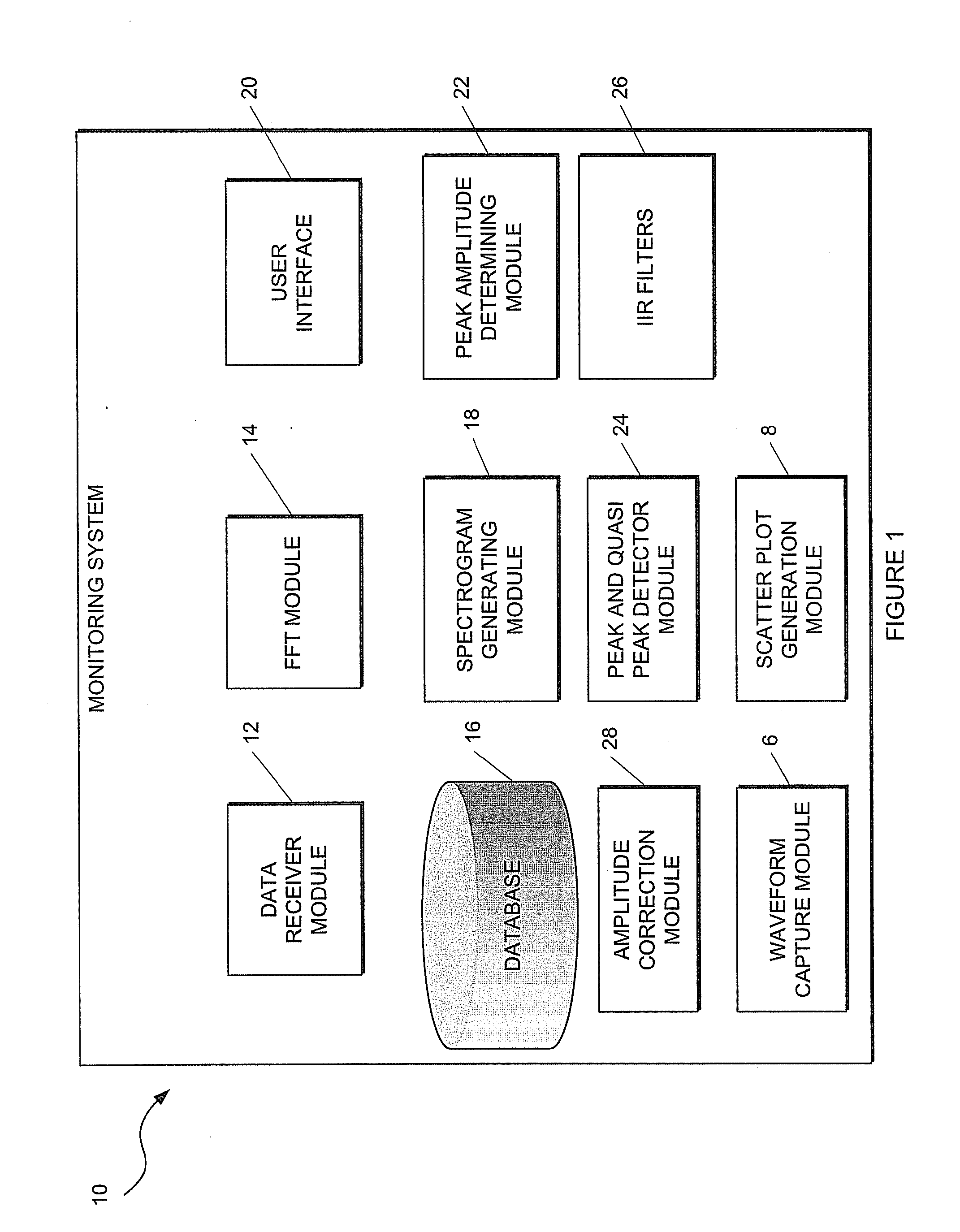
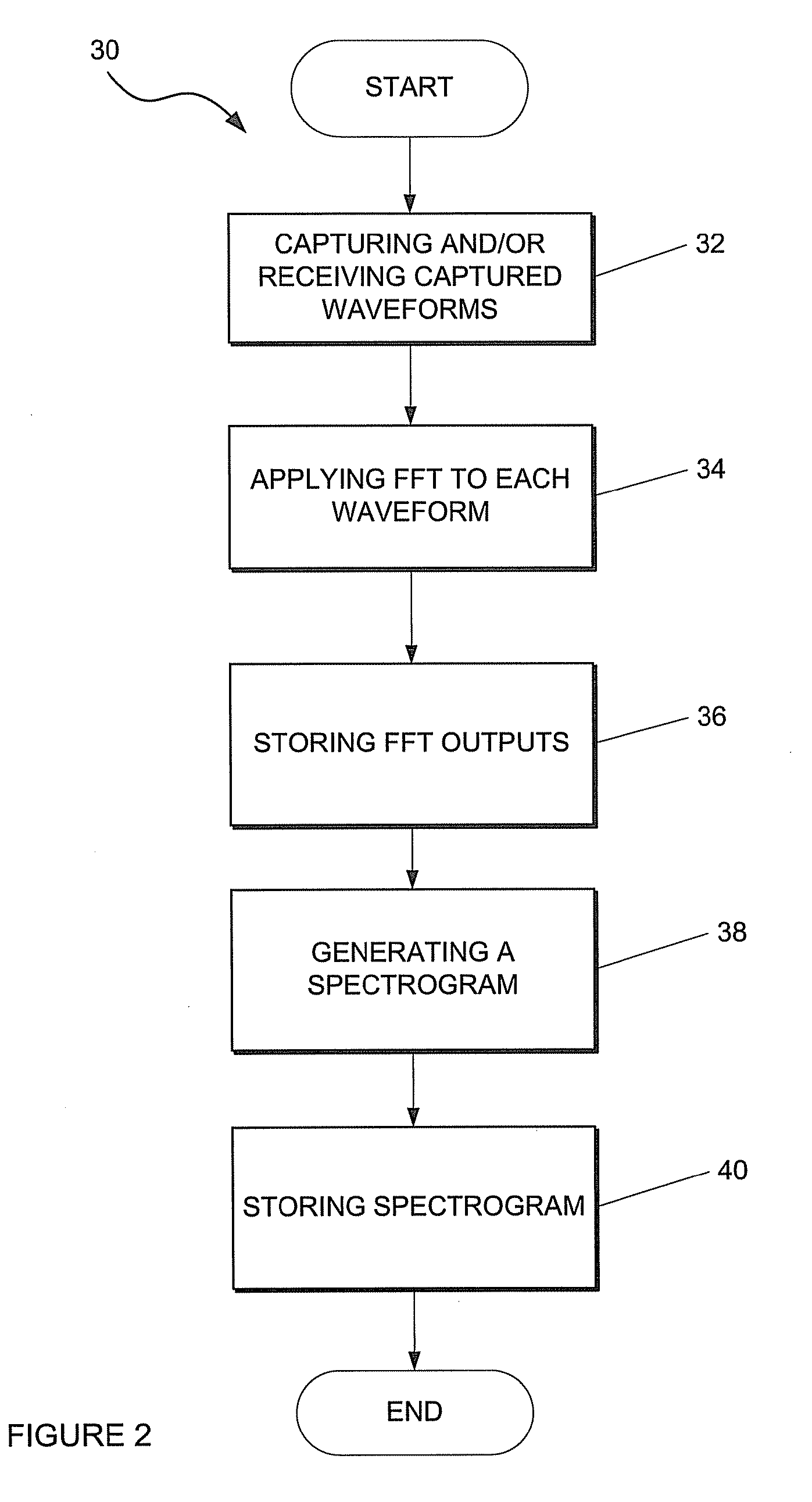
Time domain electromagnetic interference monitoring method and system
ActiveUS20120130665A1Wide bandwidthSpectral/fourier analysisSpecial data processing applicationsSpectrum analyzerSpectrograph
This invention relates to a method of, and a system for, monitoring electromagnetic interference. The method comprising capturing a plurality of time domain waveforms, and a plurality of scatter plots; receiving the plurality of captured time domain waveforms and scatter plots; applying a fast fourier transform (FFT) to each of the received time domain waveforms as it is received thereby to receive FFT outputs; storing the FFT outputs in a database; generating a statistically representative spectrograph or spectrogram in the frequency domain based on at least the stored FFT outputs and scatter plots or data associated with the scatter plots, combining constituent FFTs of the statistically representative spectrograph or spectrogram in such a manner as to emulate the result that would be produced by an EMI (Electromagnetic Interference) receiver or spectrum analyser; and combining resultant outputs from a number of iterations of this process to produce a final result (EMI spectrum).
Owner:ESKOM HLDG
Apparatus and method for calculating earth's polarization properties from airborne time-domain electromagnetic data
InactiveUS20160282498A1Electric/magnetic detection for transportAcoustic wave reradiationTotal responseTime domain electromagnetics
A device and method for estimating an apparent chargeability of a surveyed underground formation. The method includes receiving a total response of the underground formation from an airborne time domain electromagnetic (TDEM) survey system; separating, in two stages, the total response into an inductive response and an induced polarization response; and calculating (308) the apparent chargeability based on the induced polarization response.
Owner:CGG SERVICES SA
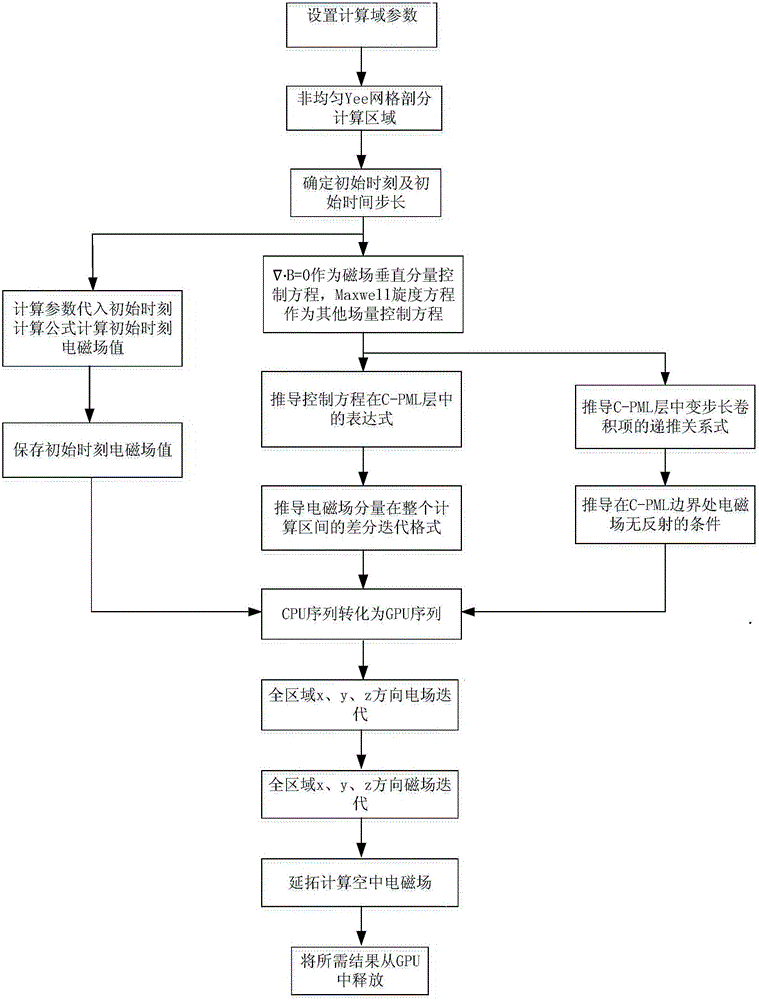
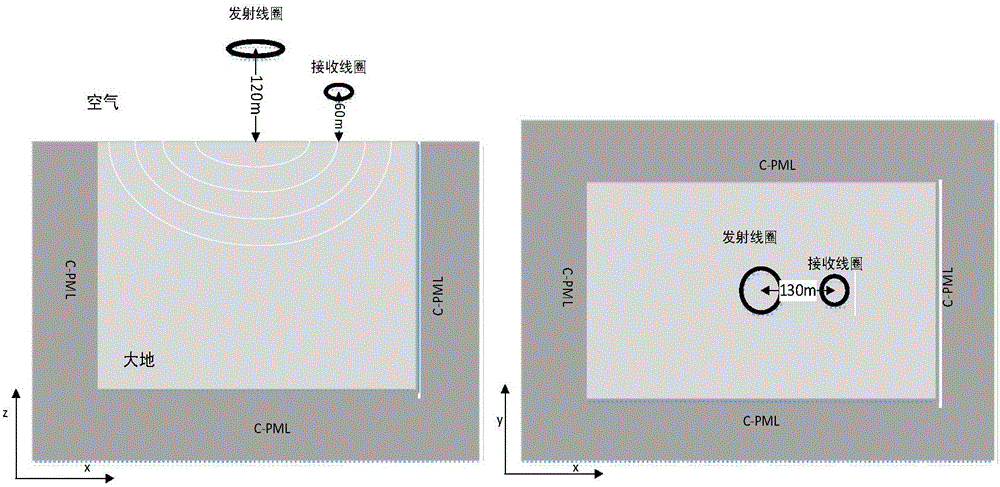
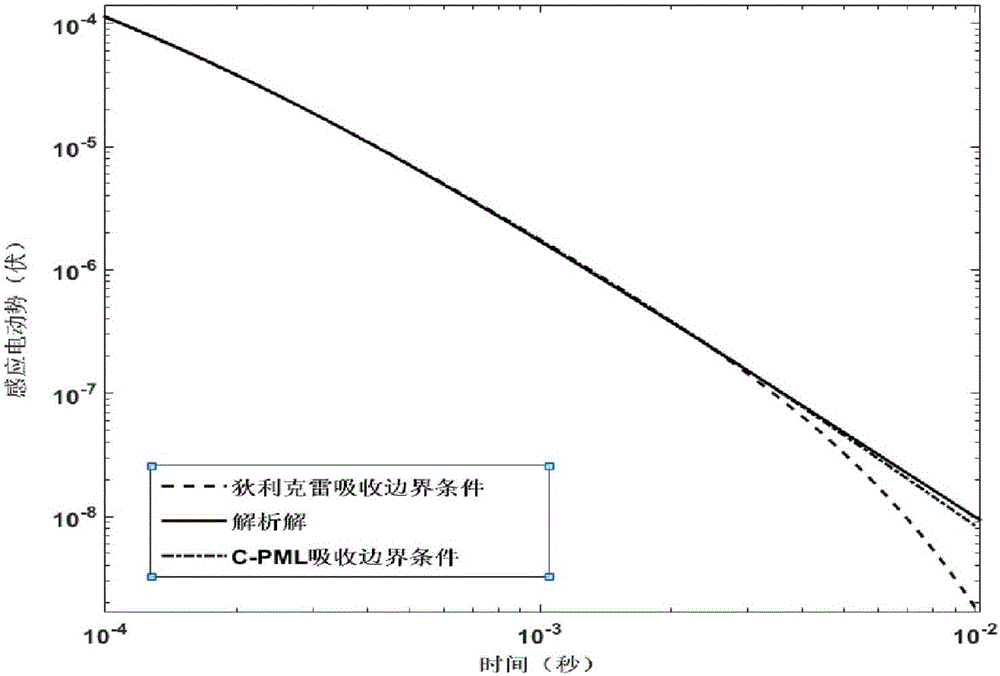
Loading method of C-PML boundary conditions during time-domain airborne electromagnetic numerical simulation
ActiveCN105808968AAvoid storageQuick calculationInformaticsSpecial data processing applicationsAviationTime domain electromagnetics
The invention relates to a loading method of C-PML boundary conditions during time-domain airborne electromagnetic numerical simulation.By introducing a divergence equation (please see the formula in the description) as a control equation of a magnetic field vertical component, electric field and magnetic field expressions in a C-PML layer are deduced, and electromagnetic field no-reflection conditions on an interface of the C-PML layer are determined.A time-domain convolution variable-step-size recursive algorithm in the C-PML layer is constructed through a range-variation integral method, storage of electromagnetic field values at each moment is avoided, a corresponding electric field and magnetic field difference-iteration form is deduced based on a finite difference method, and finally time-domain airborne three-dimensional later period high-precision and long-time-window calculation is achieved.The loading method of the C-PML boundary conditions during time-domain airborne electromagnetic numerical simulation aims at overcoming the truncation error problem of a calculation area in time-domain airborne electromagnetic numerical simulation and can more efficiently and accurately calculate the three-dimensional time-domain electromagnetic responses.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Method for detecting formation resistivity outside of metal casing using time-domain electromagnetic pulse in well
InactiveUS8756017B2Enhanced signalProbe radius is largeElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSeismology for water-loggingDigital recordingElectromagnetic pulse
A method for detecting formation resistivity outside of metal casing using time-domain electromagnetic pulse in a borehole, the method including steps of a) providing a borehole large power pulse transmitting source, recording an induced electromotive force ε, and full time digital recording a transmitted waveform and a received signal; b) conducting transmission-reception and superimposing received signals to improve signal to noise ratio; c) calculating corresponding casing response according to known casing parameters and recorded current waveform of the transmitting source to obtain a relative induced electromotive force Δεf; d) correcting relative induced electromotive force value; e) carrying out one-dimensional inversion and converting the observation signal into radial variation information of the formation resistivity; f) obtaining a two-dimensional image of the longitudinal and radial resistivity distribution of outer cased formation resistivity for measured well sections; and g) determining residual oil distribution in a reservoir from outer cased reservoir resistivity distribution.
Owner:YANGTZE UNIVERSITY
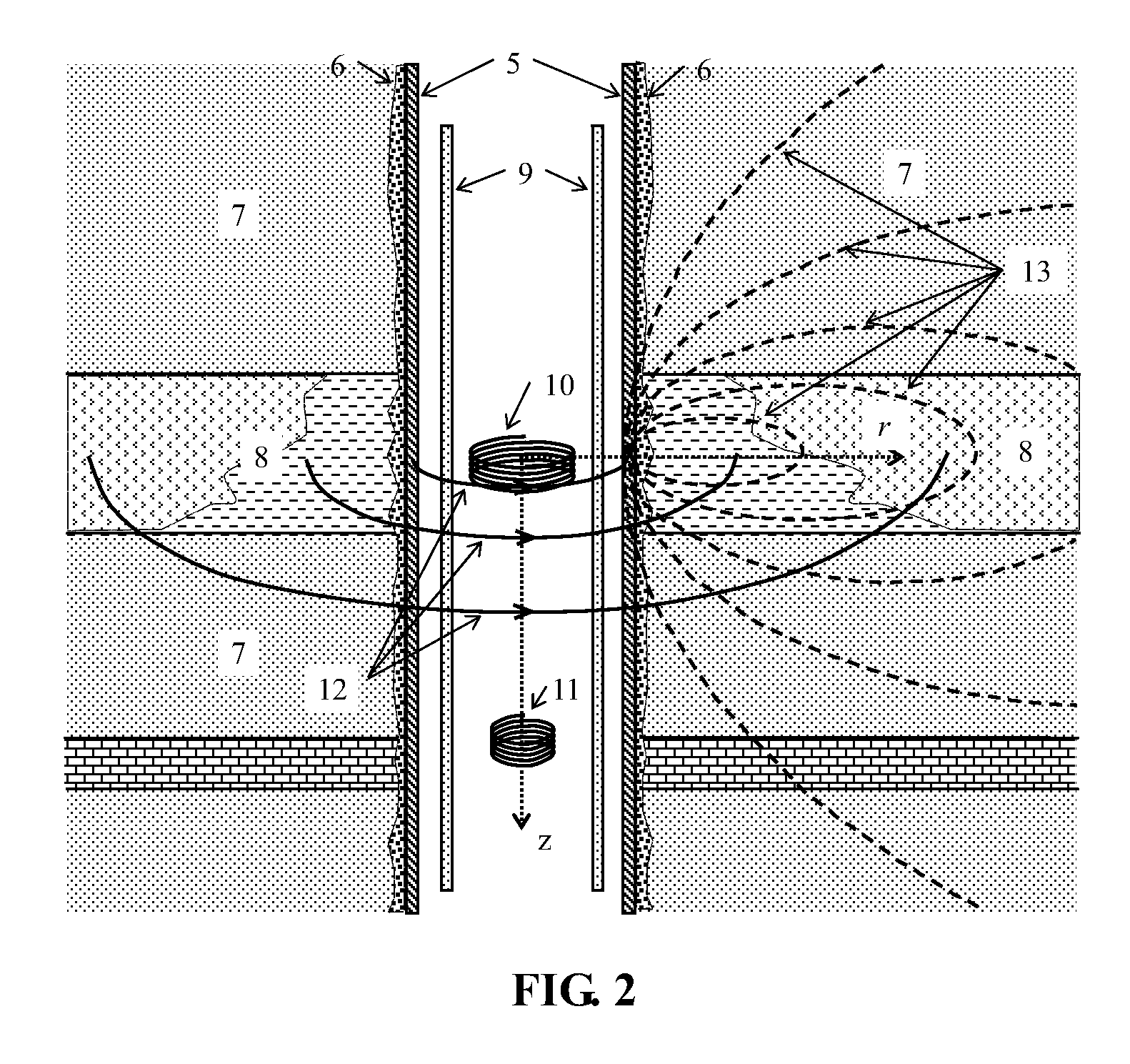
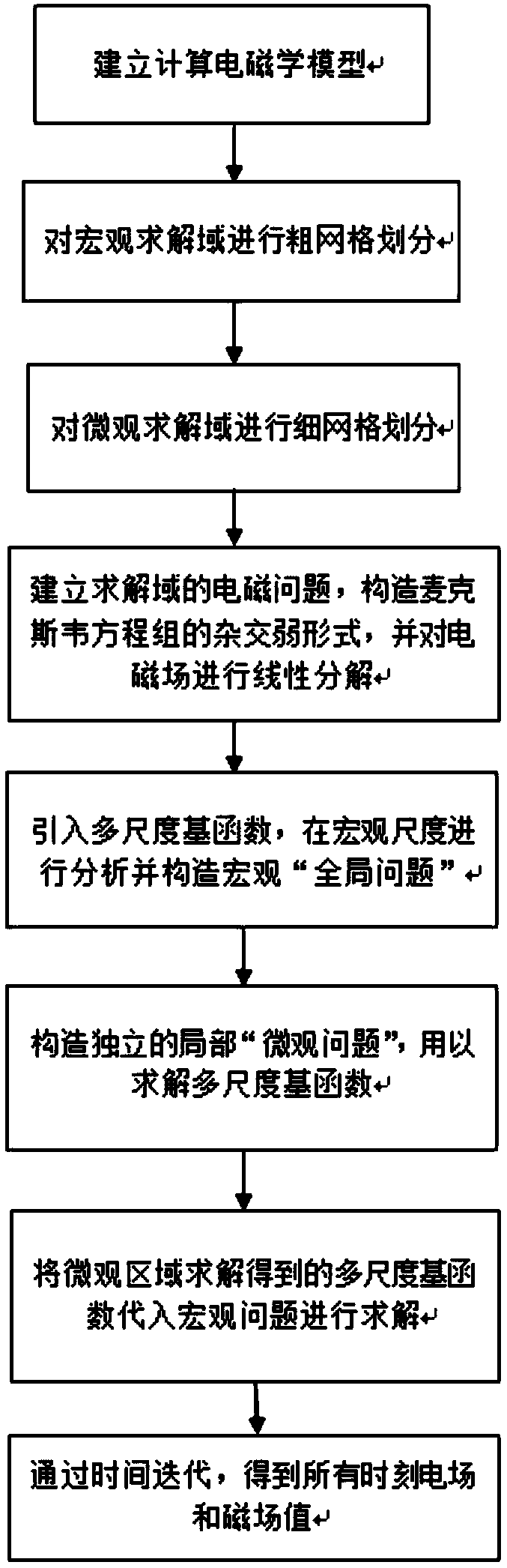
An electromagnetic multi-scale calculation method based on a hybrid grid and a time step length
ActiveCN109684740AAchieve couplingAvoid the disadvantage of too many time iterationsDesign optimisation/simulationComplex mathematical operationsMicrogridMacroscopic scale
The invention belongs to the field of time domain calculation electromagnetism, and relates to an electromagnetism multi-scale calculation method based on a hybrid grid and a time step length. According to the method, a multi-scale time domain electromagnetic problem is decomposed into a macro scale part and a micro scale part, scale separation is achieved, the solving scale of an original problemis effectively reduced, a mixed grid suitable for the characteristics of a micro unit is adopted in the micro unit for discretization, and the solving freedom degree of the micro unit is further reduced. And in the aspect of time iteration, independent time step lengths are adopted for different microcosmic units for time discretization, so that the defect of too many times of time iteration caused by too small local microgrid size is effectively avoided. After the microscopic information is solved through the microscopic problem, coupling between the macroscopic problem and the microscopic problem is achieved, the macroscopic problem is substituted into the macroscopic problem, iteration solving is conducted through the macroscopic time step length, and finally the technical effect of efficiently solving the multi-scale time domain electromagnetic problem is achieved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Arbitrary high-order hybrid grid time domain discontinuous Galerkin method based on multi-stage local time stepping technology
ActiveCN111639447AQuick analysisReduce computing timeDesign optimisation/simulationComplex mathematical operationsEngineeringNumerical models
The invention discloses an arbitrary high-order hybrid grid time domain discontinuous Galerkin method based on a multistage local time stepping technology. According to the method, a Maxwell equationset is selected as a basic numerical model; an arbitrary high-order derivative (ADER) time stepping scheme is combined; a computational domain is divided by adopting a reasonable tetrahedron / hexahedron hybrid grid; each subdivision cell respectively and automatically determines a proper time iteration step length according to a stability condition; iteration updating can be carried out on a plurality of time iteration step lengths and each cellular electromagnetic field quantity in any proportion according to the own time iteration step length until all cellular field quantities are iterated to a specified time point, and the obtained time-varying electromagnetic field quantity is post-processed to obtain a corresponding S parameter, a radar scattering sectional area and electromagnetic field spatial distribution. According to the method, the problem that the calculation efficiency is low due to the fact that the time step length of a time domain electromagnetic analysis method is limited by the minimum discrete grid size is solved, the calculation precision is improved, the calculation time is shortened, and the method is particularly suitable for rapid analysis of the space multi-scale electromagnetic problem.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Tensor apparent conductivity measurement method
ActiveCN105204073AFlexible layoutVarious forms of applicationElectric/magnetic detectionAcoustic wave reradiationObservation matrixTime domain electromagnetics
The invention provides a tensor apparent conductivity measurement method. The tensor apparent conductivity measurement method comprises the following steps that 1, an orthogonal electric field E and a curl M of a magnetic field are simultaneously measured on the surface of ground or underground; 2, the tensor apparent conductivity is calculated according to observation data through a formula (please see the formula in the specification), wherein E and M represents observation matrices containing multiple sets of the E and the M. According to the tensor apparent conductivity measurement method, a measured electromagnetic field can adopt a natural electromagnetic field, and also can adopt an electromagnetic field generated through motivation of an artificial field source; the electromagnetic field can be measured at a frequency domain, changes of the tensor apparent conductivity along with the frequency are obtained, and frequency domain sounding is performed; the electromagnetic field also can be measured at a time domain, changes of the tensor apparent conductivity along with time are obtained, and time domain electromagnetic sounding is performed; the calculation formula does not need to make plane wave hypothesis, is also set up on the condition of a non-plane wave field source and is not limited by the field source conditions; the apparent conductivity calculation formula is simple and does not need iteration or parameters such as a field source position and a sending and receiving distance.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
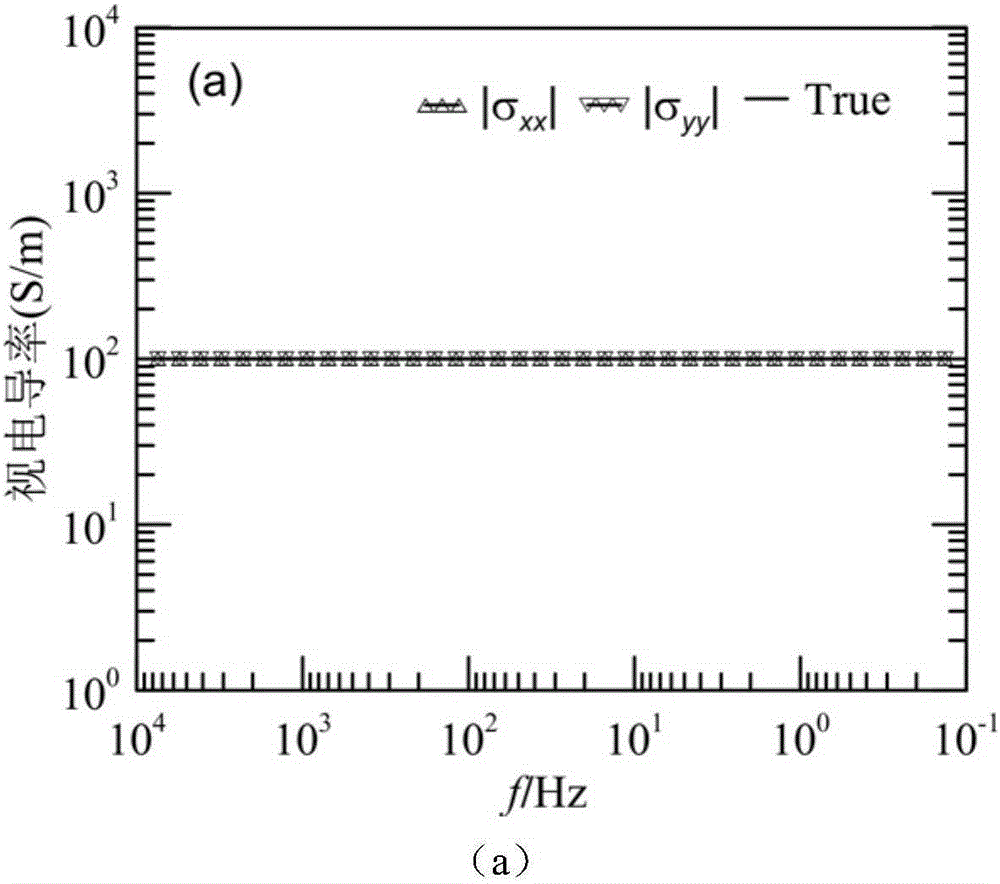
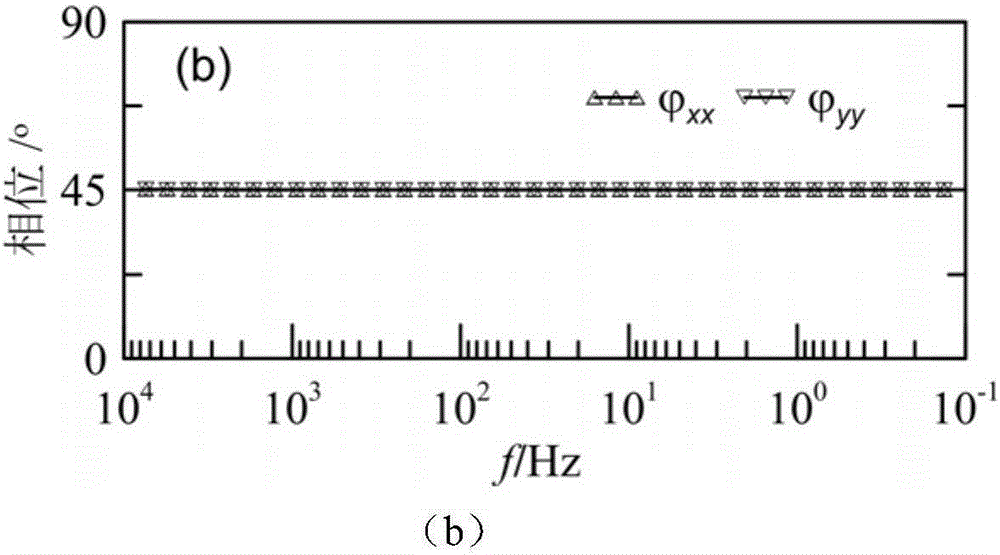
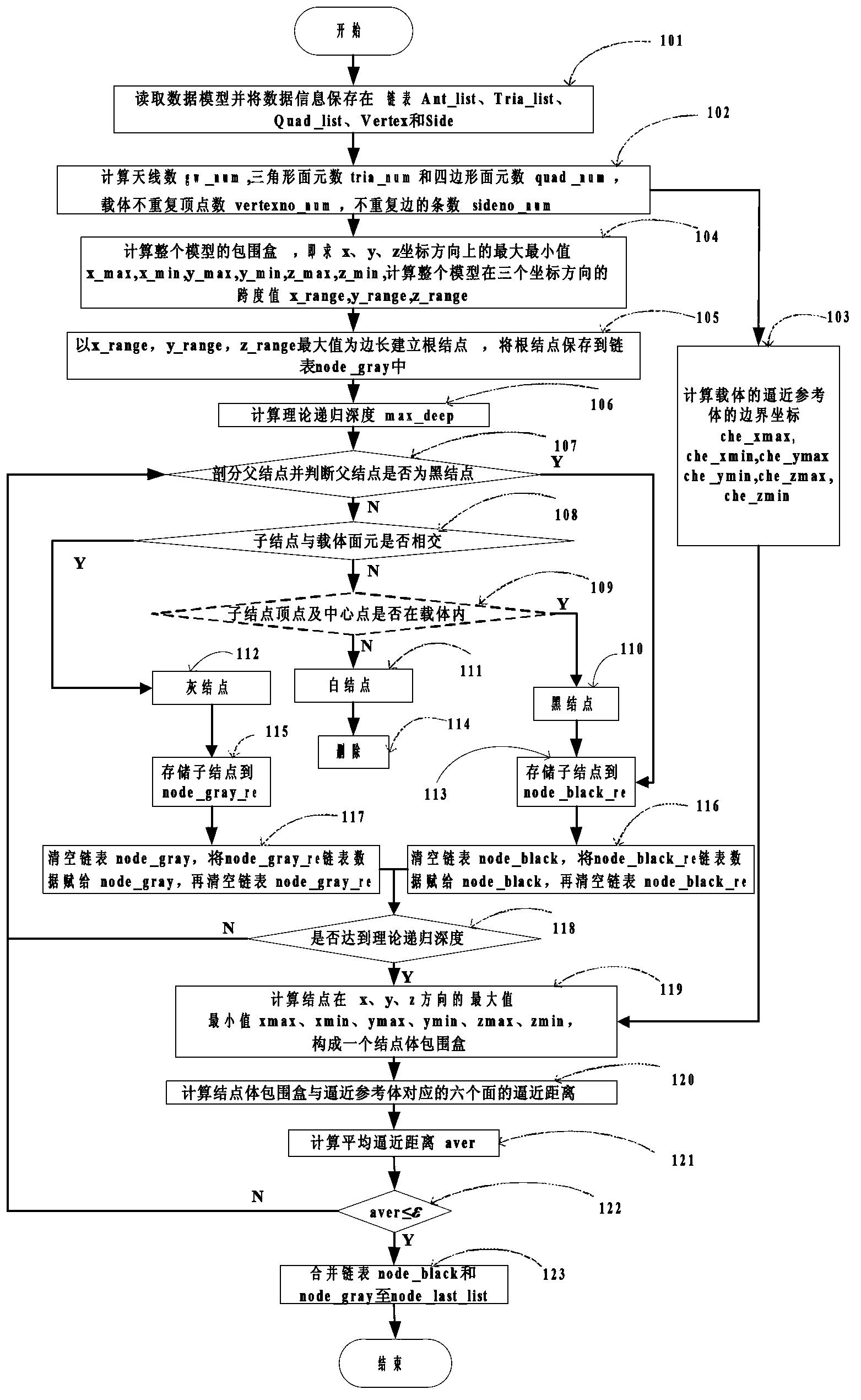
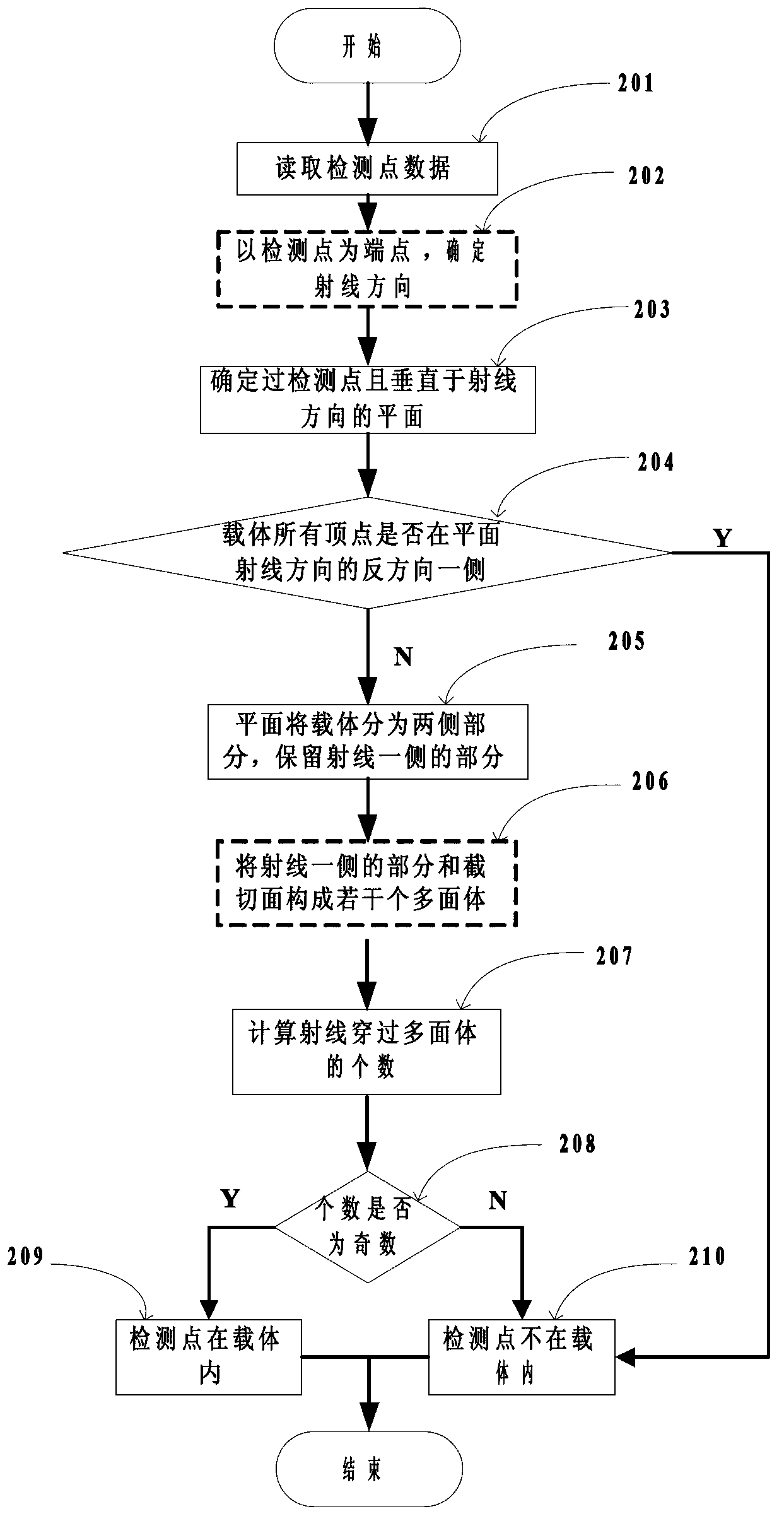
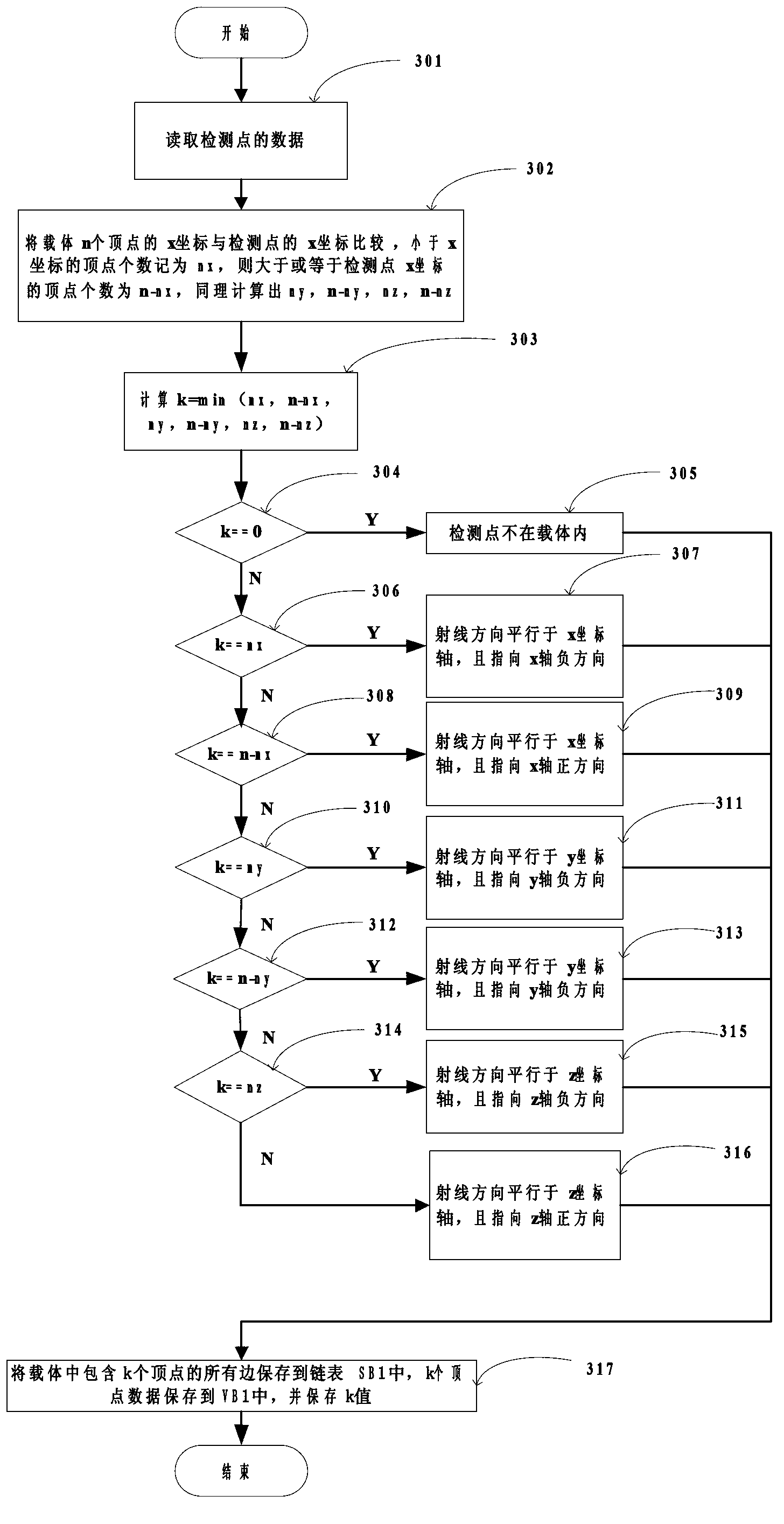
Finite difference time domain electromagnetic calculation carrier meshing method
InactiveCN103310069AHigh degree of geometric approximationThe calculation result is accurateSpecial data processing applicationsTime domain electromagneticsGrid partition
The invention discloses a finite difference time domain electromagnetic calculation carrier meshing method. According to the method, the mesh size is jointly controlled by the discrete electrical dimensional accuracy and the carrier surface approximation accuracy, the geometrical approximation degree between the divided mesh model and the carrier model is high especially under the situation of low frequency with large wavelength, finite difference time domain electromagnetic calculation is performed on the basis of the mesh model, and the calculation result is relatively accurate; surface approximation accuracy controlling parameters for meshing the mesh model are provided, the blindness of meshing precision control of the conventional direct subdivision method is avoided, and the calculated amount for meshing can be effectively controlled; when mesh refinement is required, all that is needed is to perform octree recursive subdivision to the black nodes in the bottommost layer, and mesh refinement is easy to realize.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
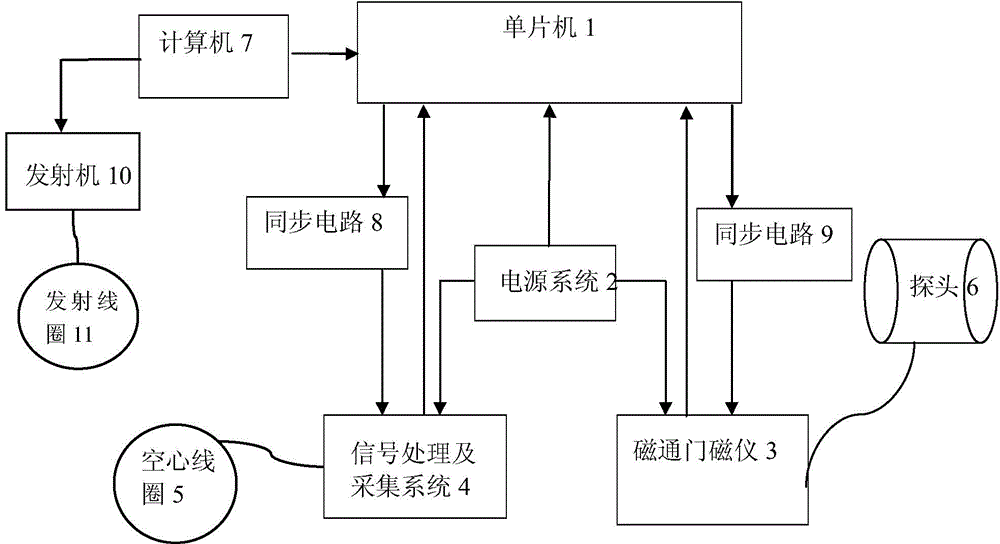
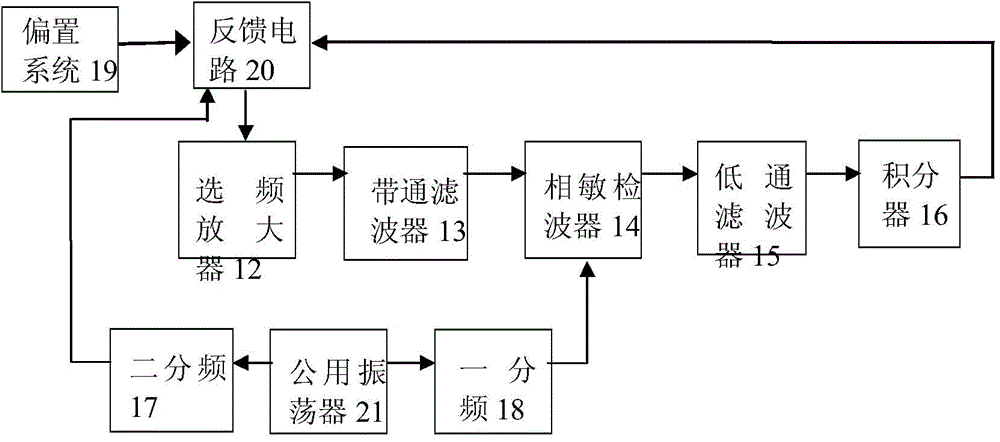
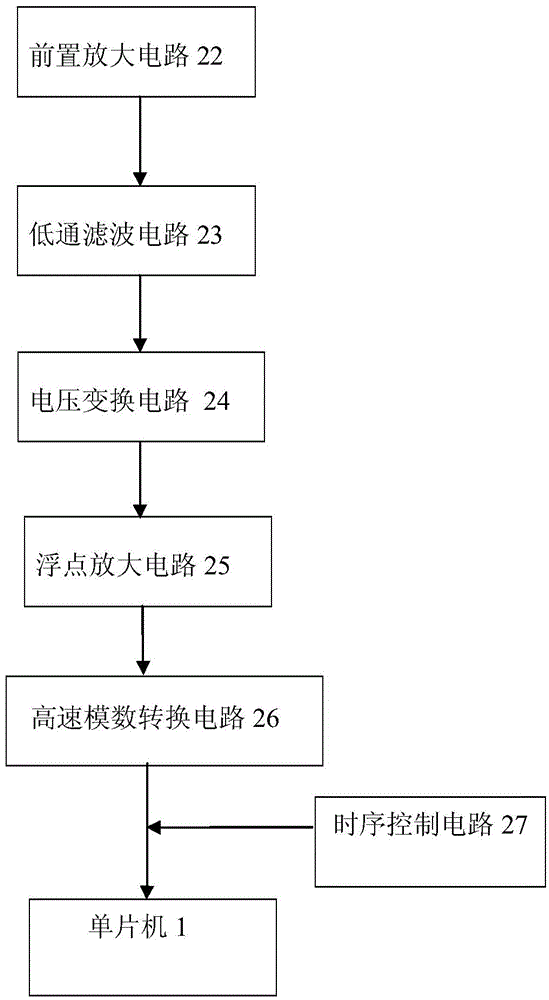
Device and method for measuring magnetic induction intensity B through time domain electromagnetic method
InactiveCN104535943AImprove accuracyImprove reliabilityMagnetic field measurement using flux-gate principleElectric/magnetic detectionMicrocomputerMicrocontroller
The invention relates to a device and method for measuring a magnetic induction intensity B through a time domain electromagnetic method. The device is formed in the mode that a single-chip microcomputer is connected with a flux-gate magnetometer and a signal processing and collecting system through a power supply system, the single-chip microcomputer is connected with an open gate magnetometer through a synchronous circuit, a probe is connected with the single-chip microcomputer through the open gate magnetometer, the single-chip microcomputer is connected with the signal processing and collecting system through the synchronous circuit, a hollow coil is connected with the single-chip microcomputer through the signal processing and collecting system, and a transmitting coil is connected with the single-chip microcomputer through a transmitter and a computer. By means of combined application of the hollow coil and the flux-gate magnetometer, the flux-gate magnetometer with a good low-frequency characteristic is used for measuring a relatively stable magnetic field, the hollow coil with a good high-frequency characteristic, interpolation and integral computation are used for measuring magnetic fields which change quickly, a change relation curve of the magnetic induction intensity B along with the time can be precisely measured, good inversion model data are obtained, and accuracy and reliability of inverse interpretation are improved.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Hand push type device and method for time domain electromagnetic logging in coal mine underground borehole
InactiveCN108594313AImprove strata divisionImprove the accuracy of lithology identificationElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingFiberTime domain electromagnetics
The invention belongs to the technical field of geophysical prospecting and relates to an electromagnetic logging device and method, in particular to a hand push type device and method for time domainelectromagnetic logging in a coal mine underground borehole. In-hole transmitting and receiving devices with identical-diameter transmitting coils are wound on the rear portion of a probe, a multi-joint carbon fiber rod is used for pushing the device into the coal mine underground borehole, time domain rectangular wave current in a duty ratio of 50% is supplied into the transmitting coils to realize measurement of borehole radial rock electrical property variation. By adoption of the method, one-dimensional electrical property variation curves of rocks can be obtained while borehole radial two-dimensional apparent restivity distribution can be obtained through a data processing technique, and stratigraphic division and lithologic identification accuracy of the borehole can be remarkably improved by natural gamma-ray logging.
Owner:XIAN RES INST OF CHINA COAL TECH& ENG GROUP CORP
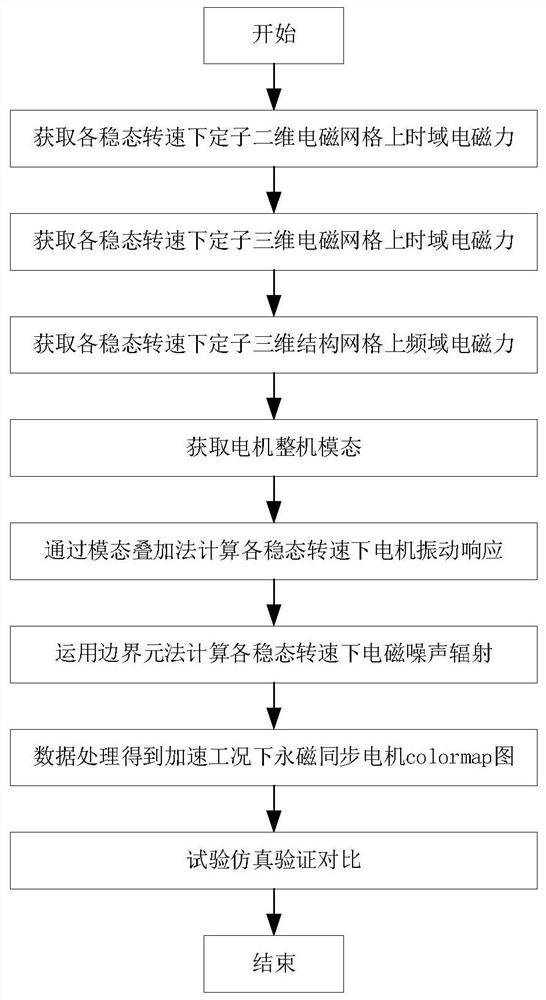
Electromagnetic noise simulation calculation method for permanent magnet synchronous motor under acceleration condition
PendingCN112560302ADesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsData setPermanent magnet synchronous motor
The invention provides an electromagnetic noise simulation calculation method for a permanent magnet synchronous motor under an acceleration working condition. The method includes obtaining a time domain electromagnetic force on a corresponding rotating speed two-dimensional stator in a steady state; obtaining a time domain electromagnetic force on the three-dimensional stator electromagnetic gridat a corresponding rotating speed at a steady-state rotating speed; obtaining a frequency domain electromagnetic force on the stator three-dimensional structure grid at a corresponding rotating speedat a steady-state rotating speed; obtaining the mode of the whole motor; obtaining a motor vibration response at the rotating speed through a modal superposition method; obtaining an electromagneticnoise sound pressure level at a corresponding rotating speed in a steady state by using a boundary element method; and constructing a matrix through the steady-state rotating speed data set and the electromagnetic noise radiation sound pressure level data set, and performing data processing on the electromagnetic noise radiation sound pressure level data set and the corresponding rotating speed data set in the steady state to obtain an electromagnetic radiation colomap of the permanent magnet synchronous motor under the acceleration working condition. The method provided by the invention is suitable for prediction of electromagnetic noise radiation and diagnosis of fault noise under the acceleration condition of the permanent magnet synchronous motor.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Bucking coil and B-field measurement system and apparatus for time domain electromagnetic measurements
ActiveUS8400157B2Eliminating pre-amplifier set-off and temperature-dependent driftsElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSeismology for water-loggingTransmitter coilData acquisition
Owner:GEOTECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com