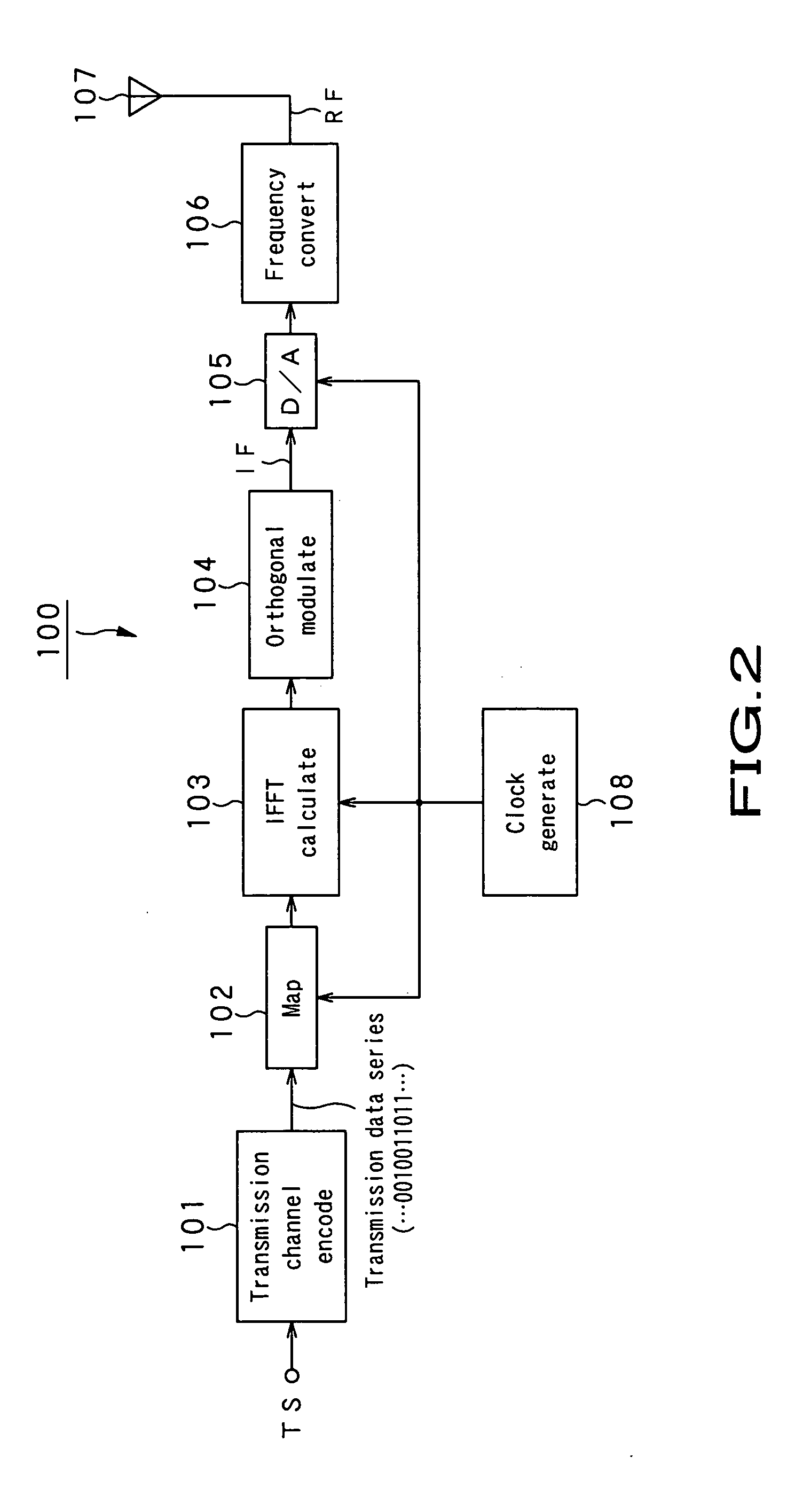
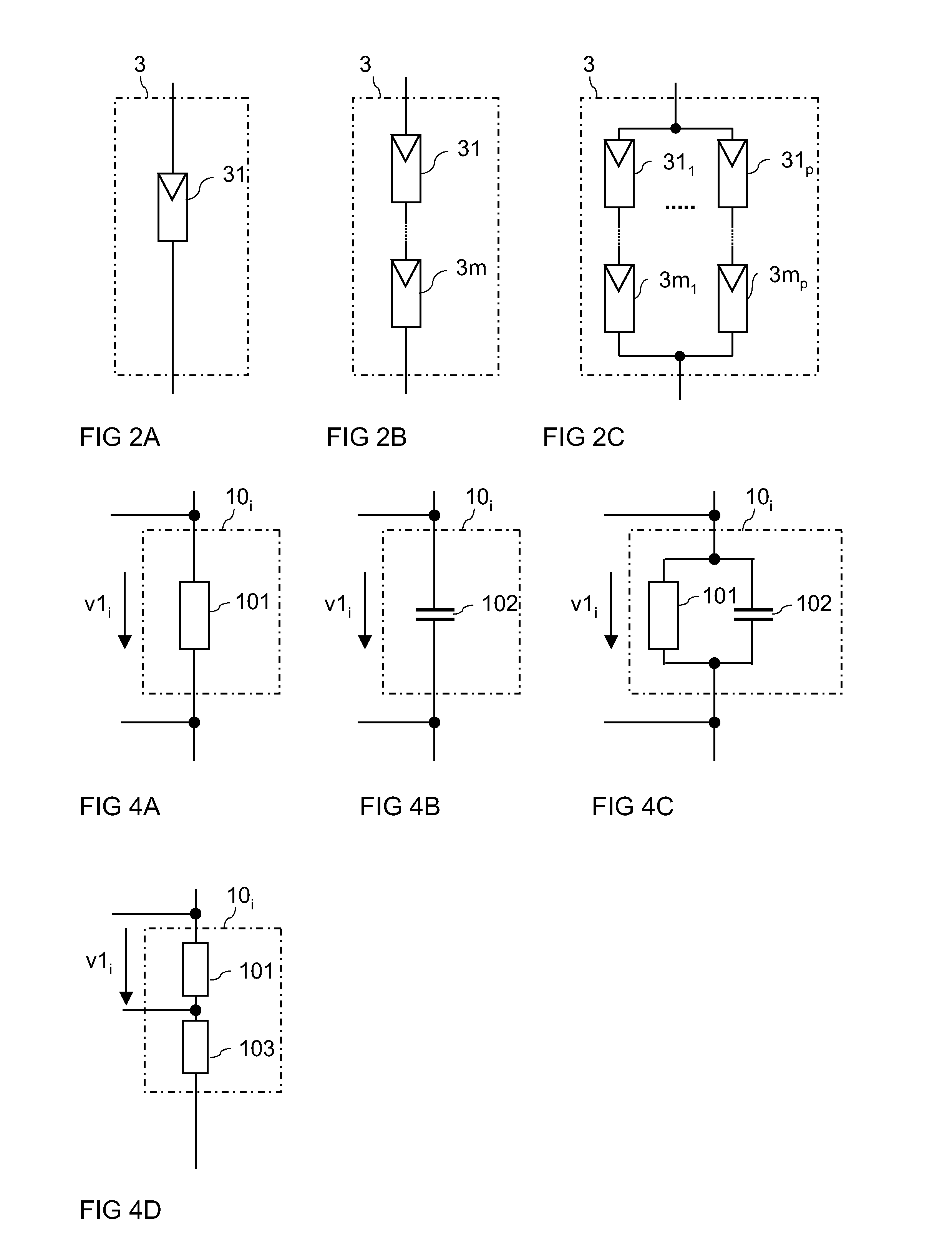
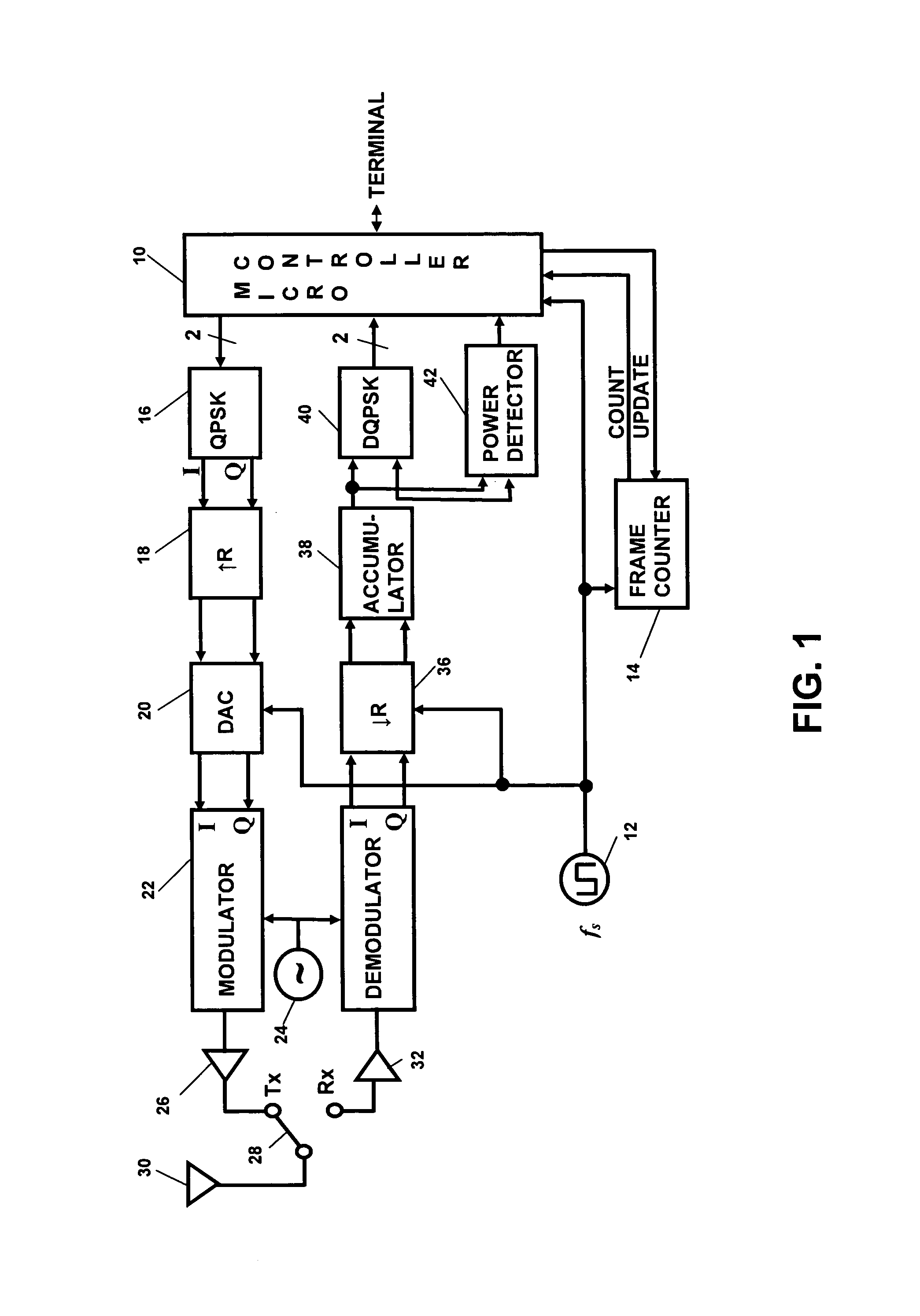
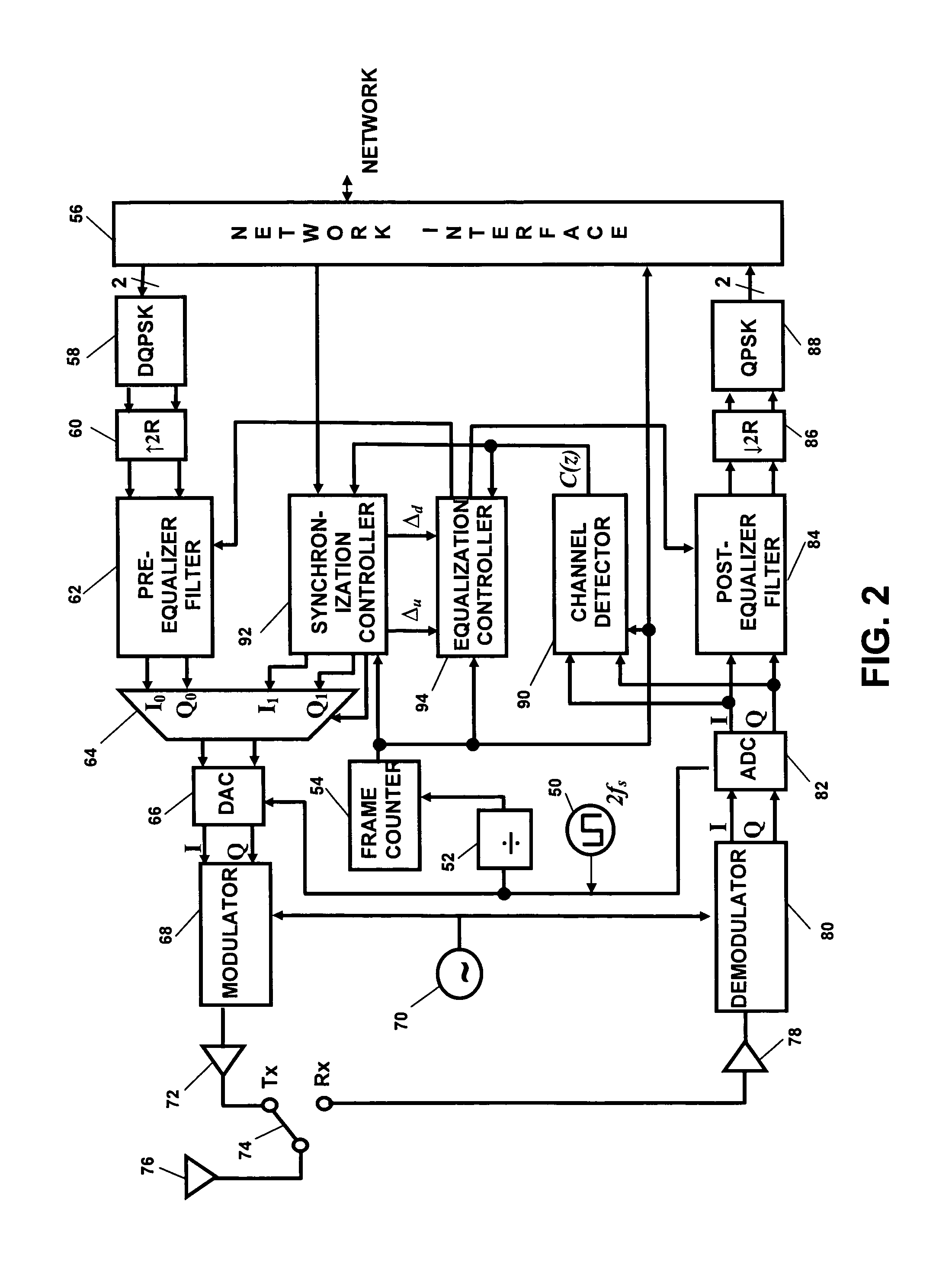
Patents
Literature
1075 results about "Synchronous circuit" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
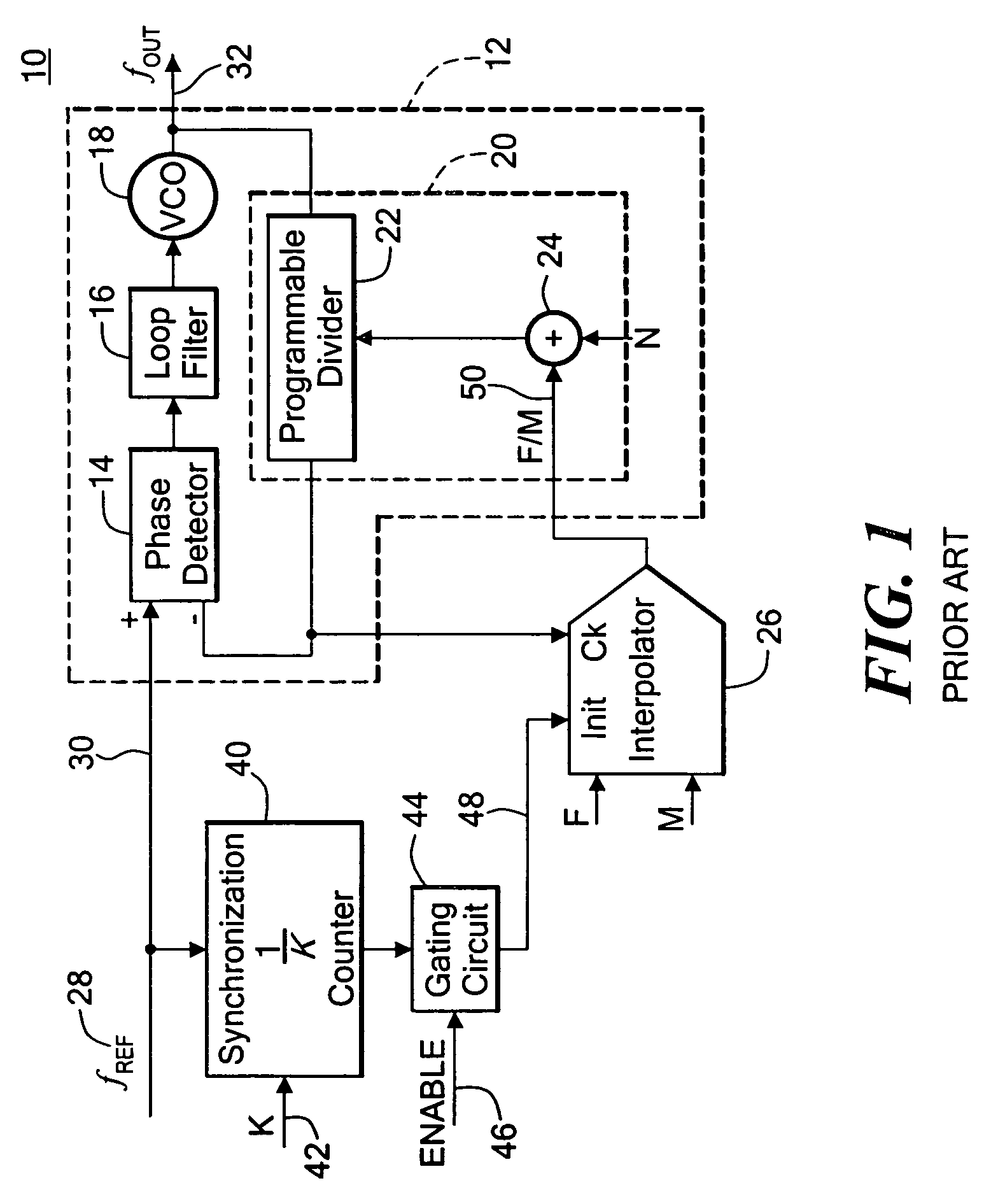
A synchronous circuit is a digital circuit in which the changes in the state of memory elements are synchronized by a clock signal. In a sequential digital logic circuit, data is stored in memory devices called flip-flops or latches. The output of a flip-flop is constant until a pulse is applied to its "clock" input, upon which the input of the flip-flop is latched into its output. In a synchronous logic circuit, an electronic oscillator called the clock generates a string of pulses, the "clock signal". This clock signal is applied to every storage element, so in an ideal synchronous circuit, every change in the logical levels of its storage components is simultaneous. Ideally, the input to each storage element has reached its final value before the next clock occurs, so the behaviour of the whole circuit can be predicted exactly. Practically, some delay is required for each logical operation, resulting in a maximum speed at which each synchronous system can run.
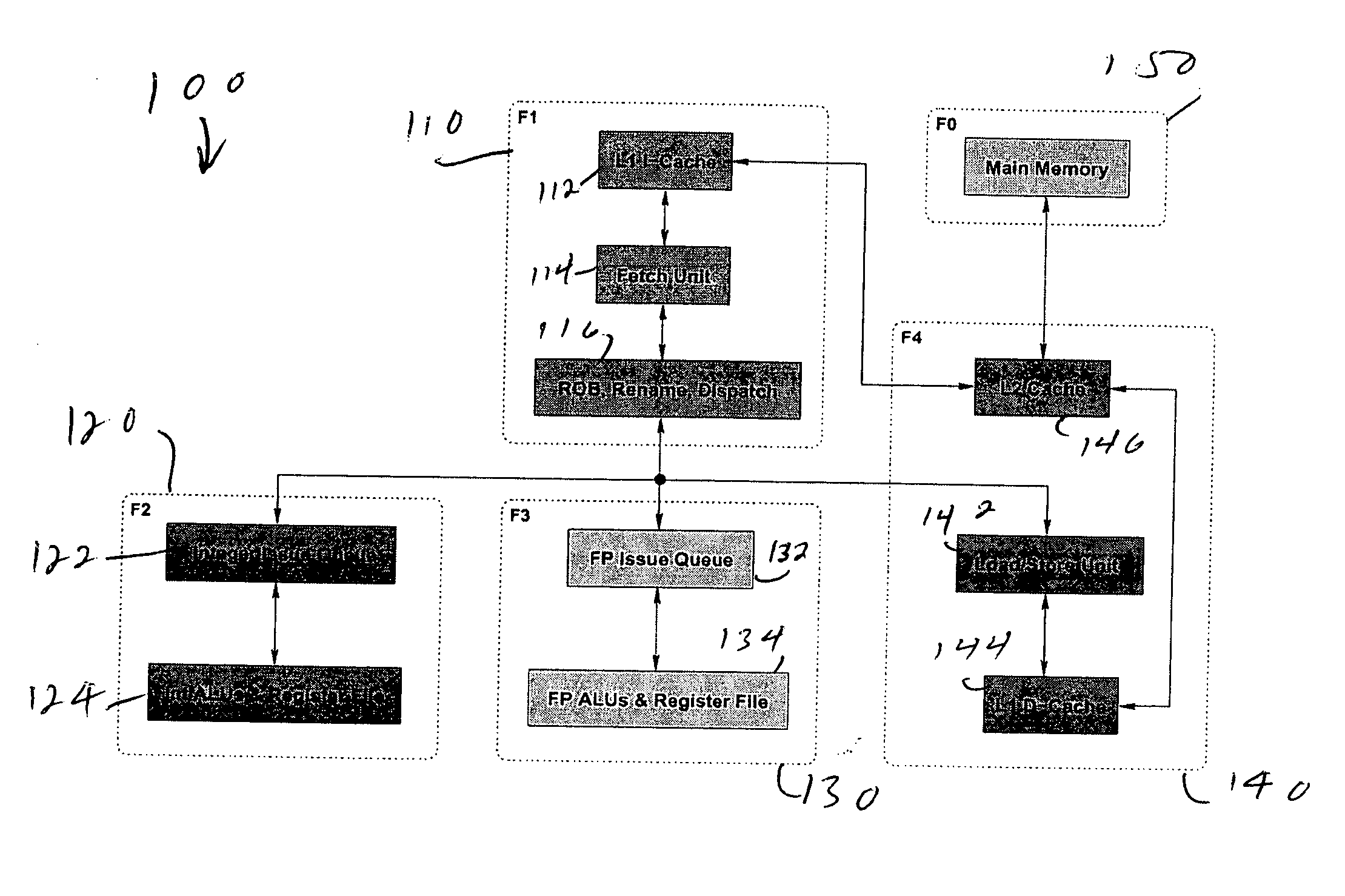
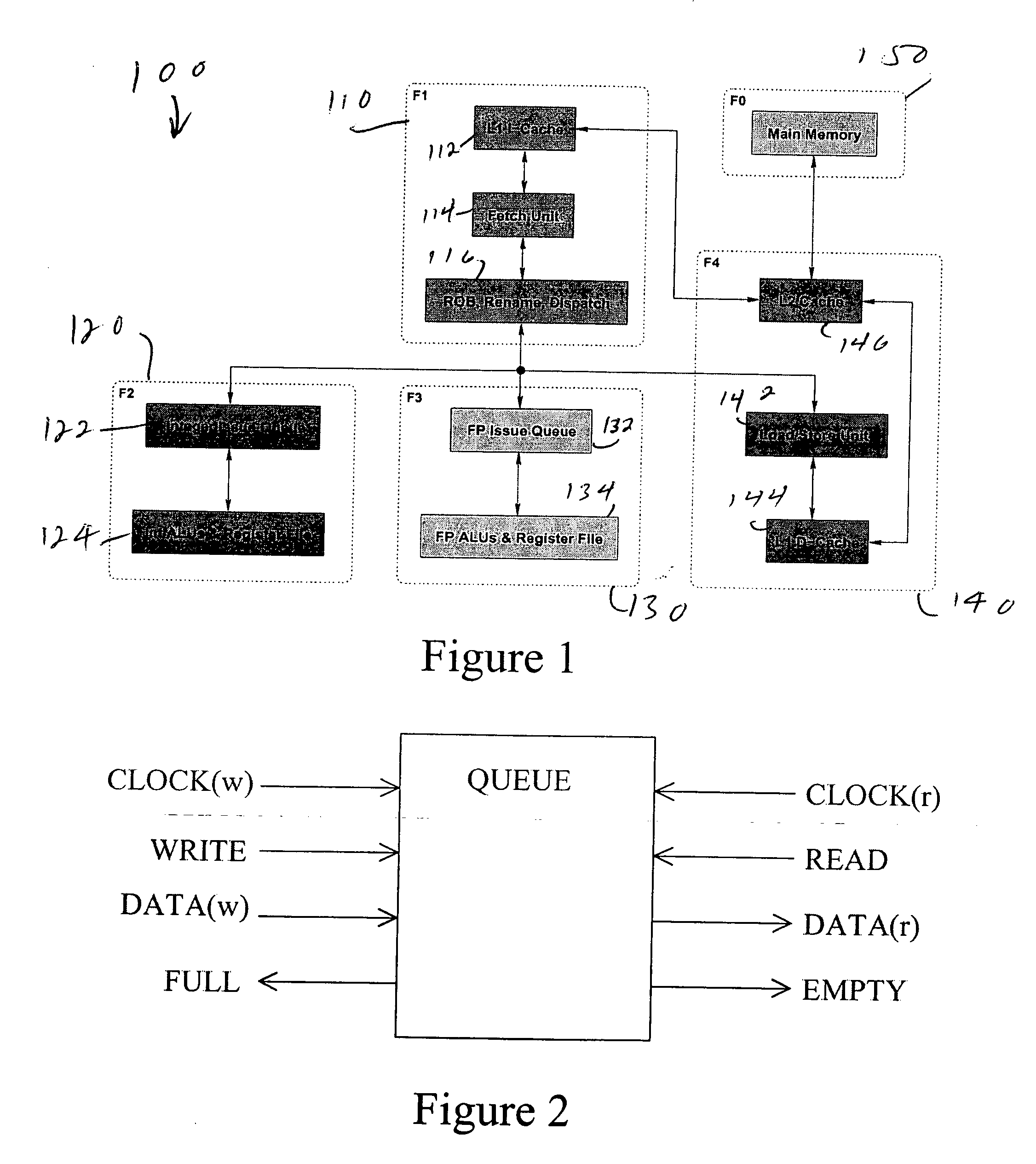
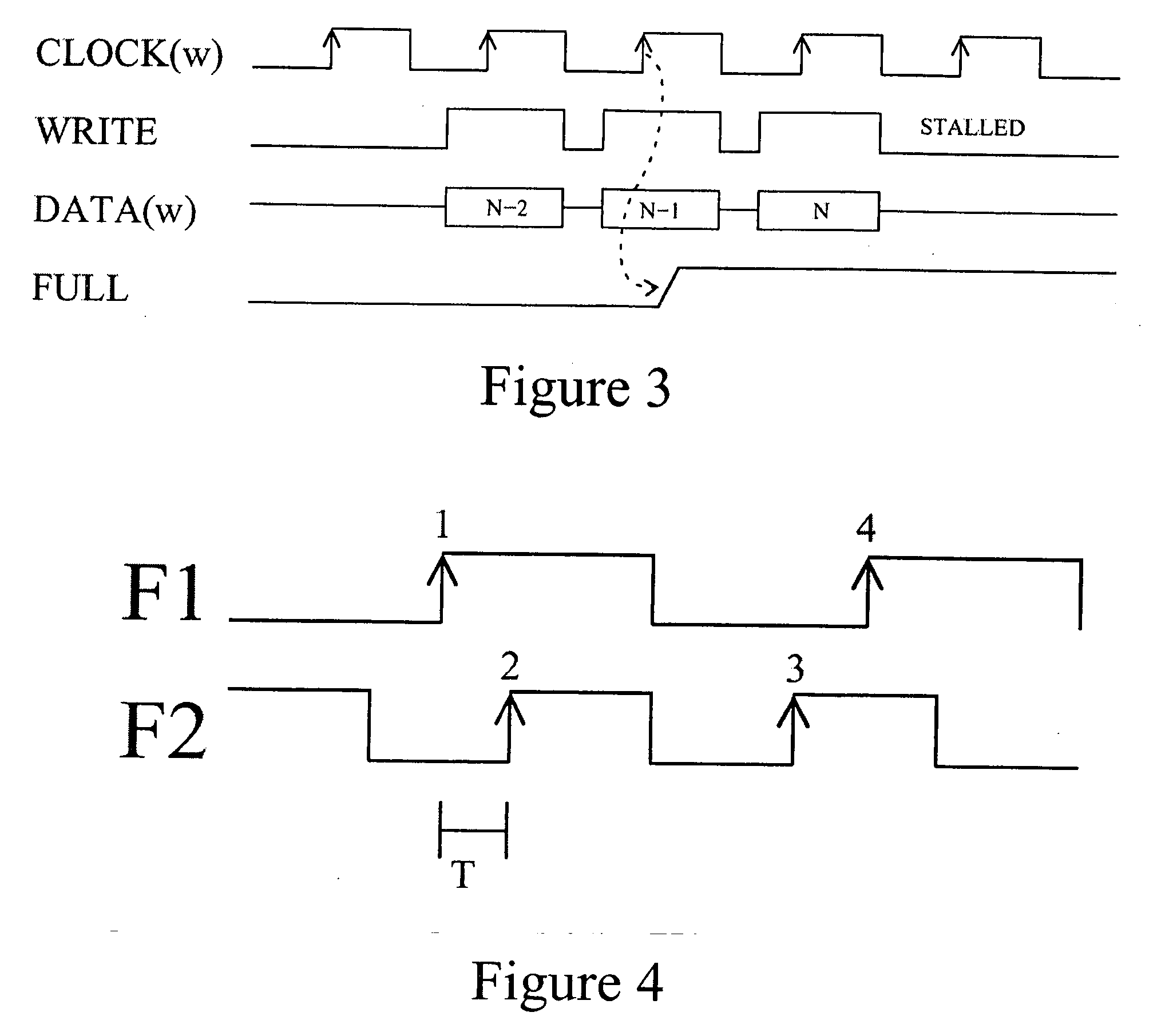
Multiple clock domain microprocessor
ActiveUS20070016817A1High frequencyImprove good performanceEnergy efficient ICTPower supply for data processingComputer scienceInter-domain
A multiple clock domain (MCD) microarchitecture uses a globally-asynchronous, locally-synchronous (GALS) clocking style. In an MCD microprocessor each functional block operates with a separately generated clock, and synchronizing circuits ensure reliable inter-domain communication. Thus, fully synchronous design practices are used in the design of each domain.
Owner:ALBONESI DAVID +5
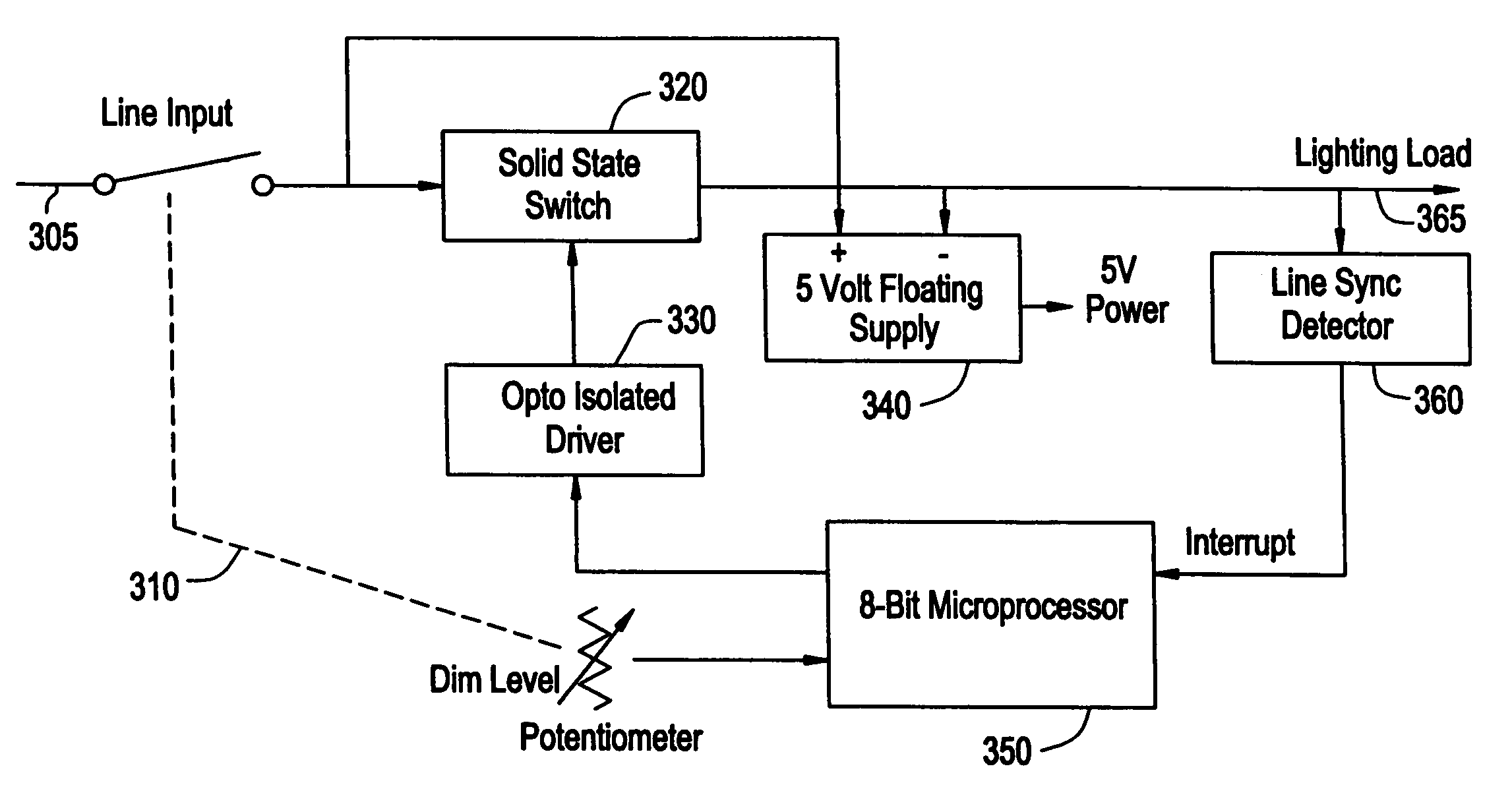
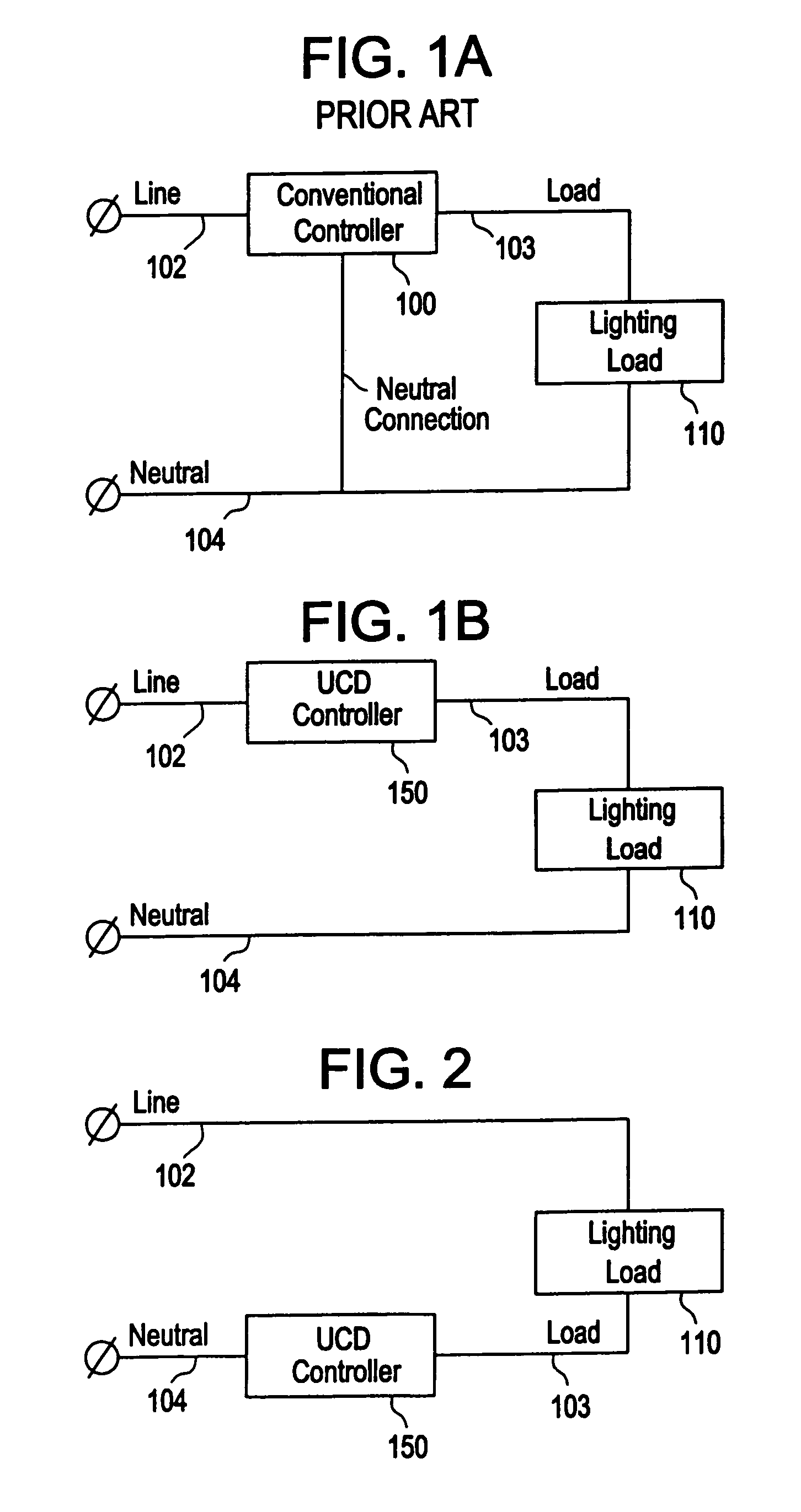
Energy savings device and method for a resistive and/or an inductive load and/or a capacitive load
InactiveUS7164238B2Save energyElectrical apparatusElectric ignition installationElectrical resistance and conductanceCapacitance
An energy savings device for an inductive, a resistive or a capacitive load, such as a fluorescent light fixture having a magnetic ballast or an electronic ballast, which is powered by an AC voltage waveform. The energy savings device includes a setting unit for setting a desired power operating level for the load. The energy savings device also includes a processor configured to receive a signal from the setting unit indicative of the desired power operating level for the load, to determine a phase delay to be provided to an output AC voltage waveform that is to be provided to the load, and to output a control signal as a result thereof. The energy savings device further includes an active element provided between a line that provides the input AC voltage waveform and the load, the active element receiving the control signal and turning off and on at predetermined times in accordance with the control signal, so as to create the output AC voltage waveform from the AC voltage waveform. The processor includes a synchronization circuit that synchronizes to the Green Safety ground line.
Owner:ASTRAL COMM
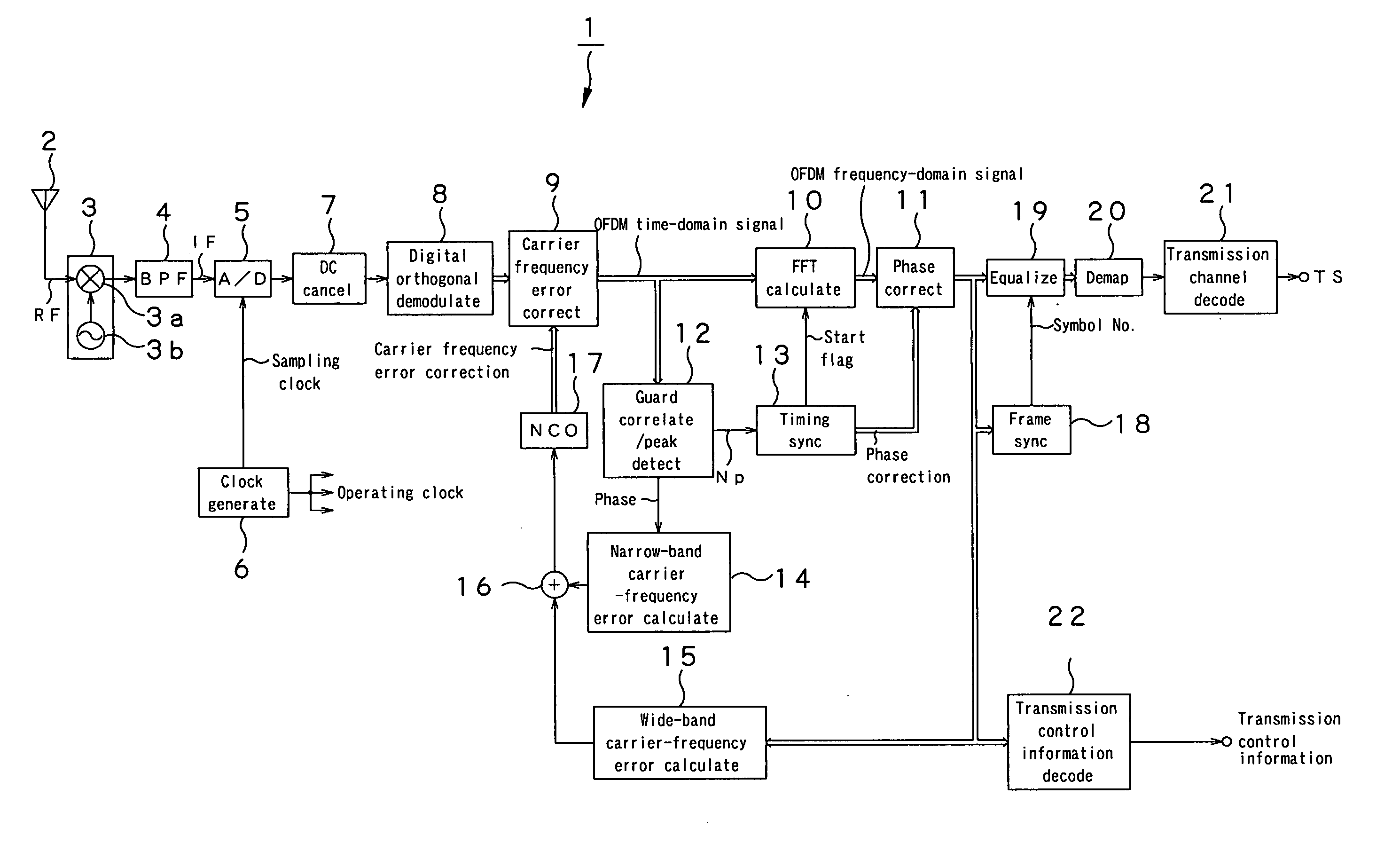
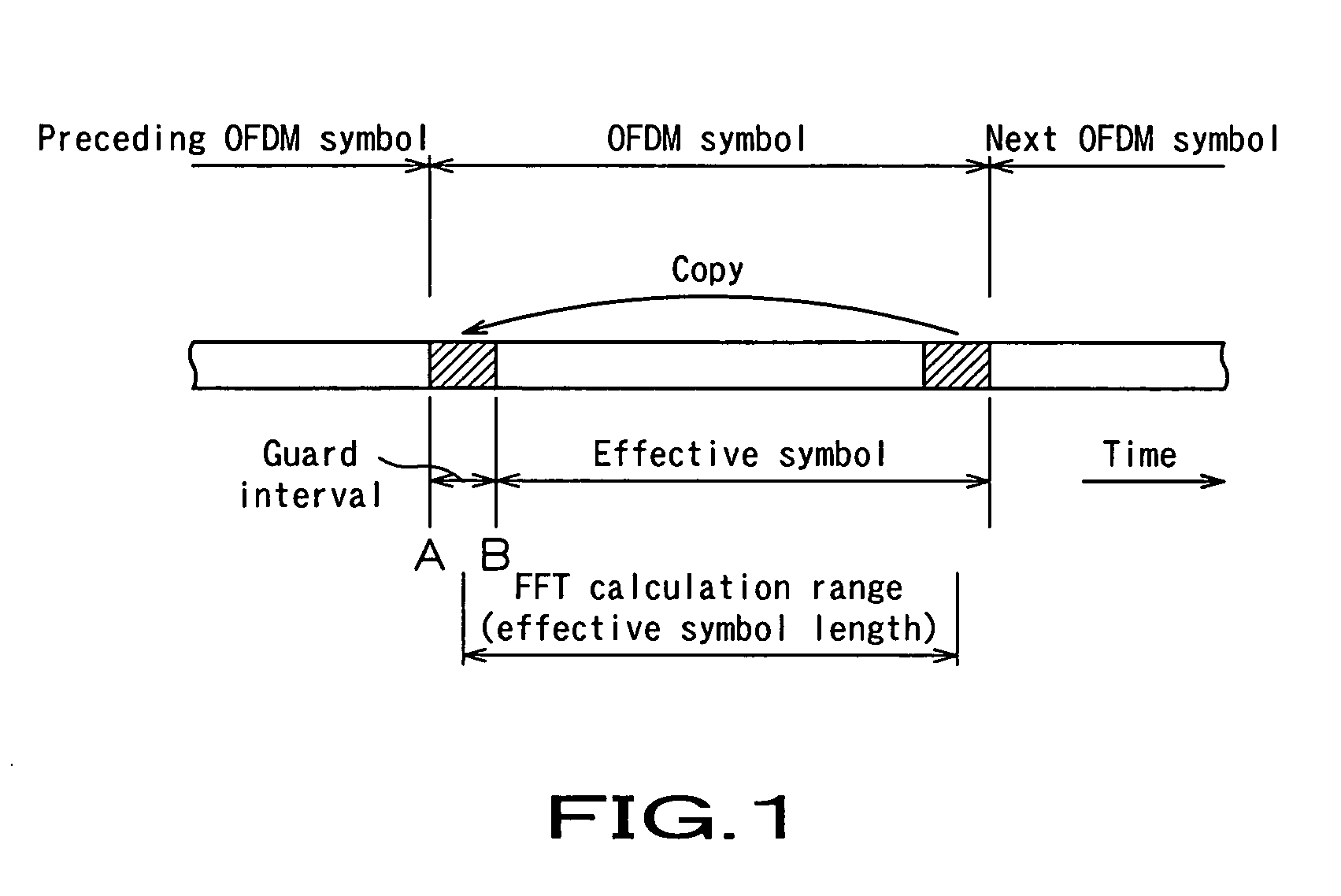
Ofdm demodulation apparatus
InactiveUS20050147186A1Improve accuracySynchronisation signal speed/phase controlFrequency-modulated carrier systemsGuard intervalDelay-locked loop
An OFDM demodulation (1) is provided which includes a guard correlation / peak time detection circuit (12) to generate a peak timing Np of a guard interval correlation value, and a timing synchronization circuit (13) to estimate a symbol-boundary time Nx from the peak timing Np. The timing synchronization circuit (13) calculates the symbol-boundary time Nx by filtering the peak time Np by a DLL (delay locked loop) filter (43). Further, the DLL filter (43) includes a limiter (52) to limit the range of phase-error component and an asymmetric gain circuit (53) to change the magnitude of the gain correspondingly to the polarity of the phase error to prevent the timing from being pulled out due to a fading or multipath.
Owner:SONY CORP
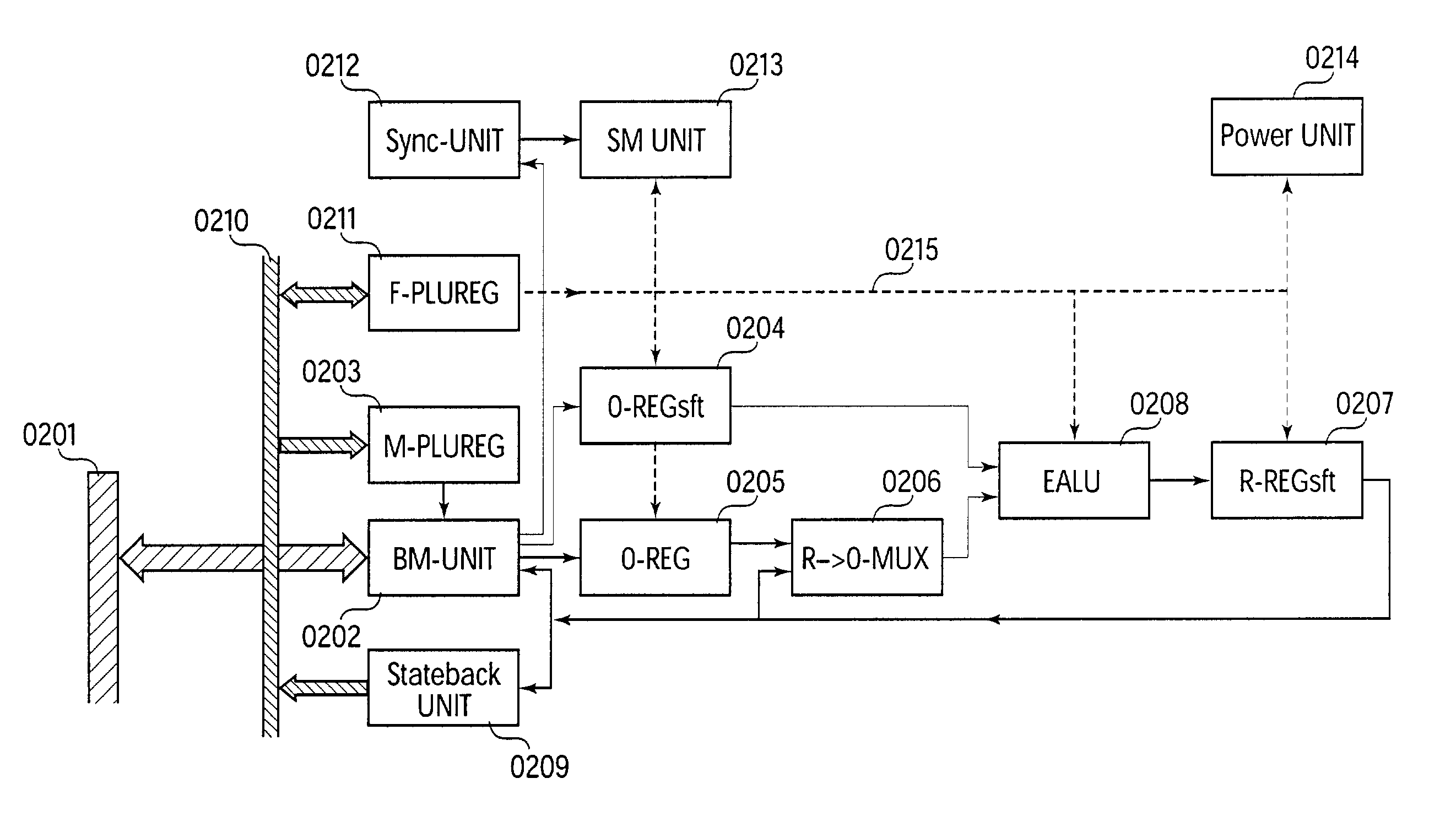
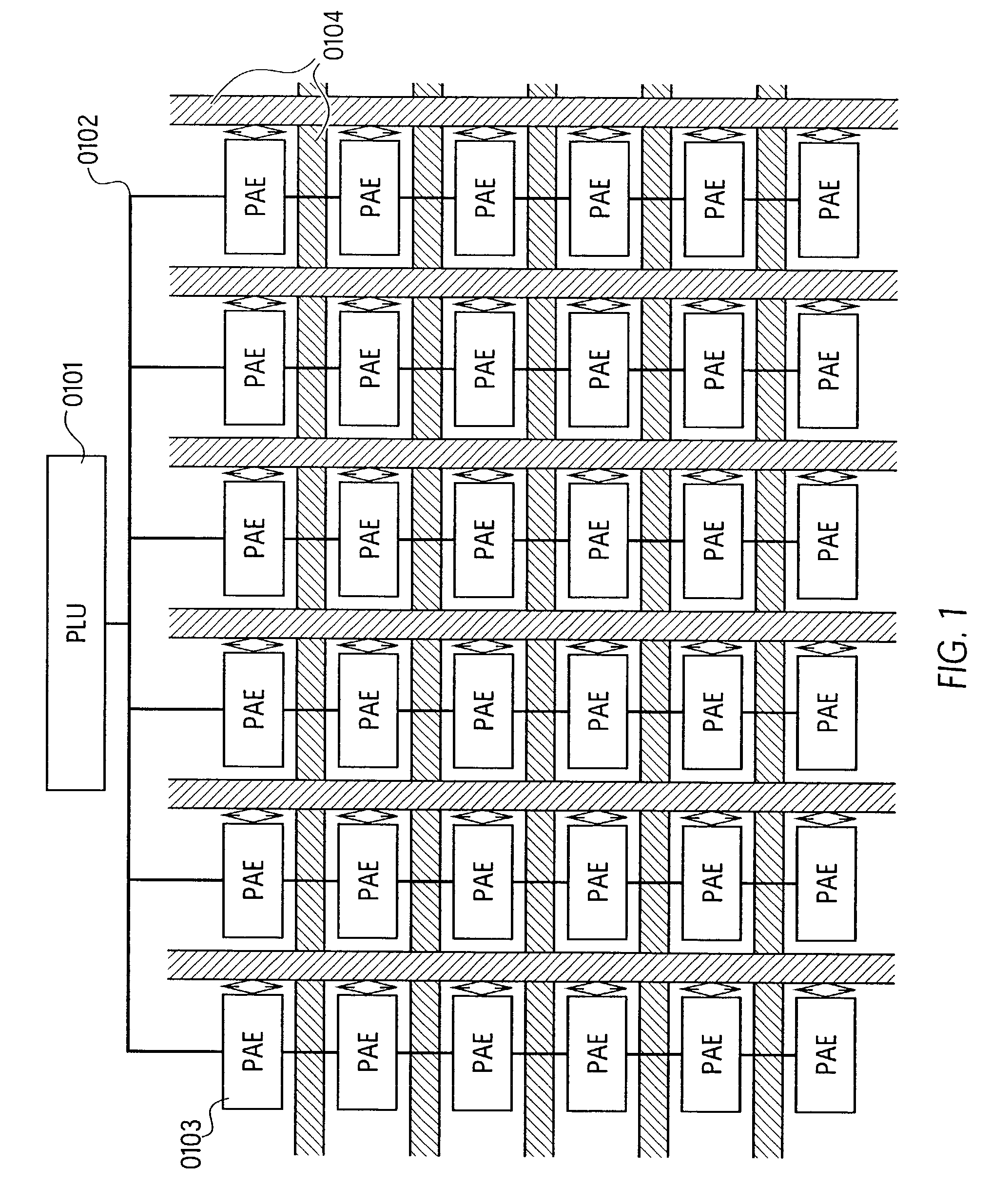
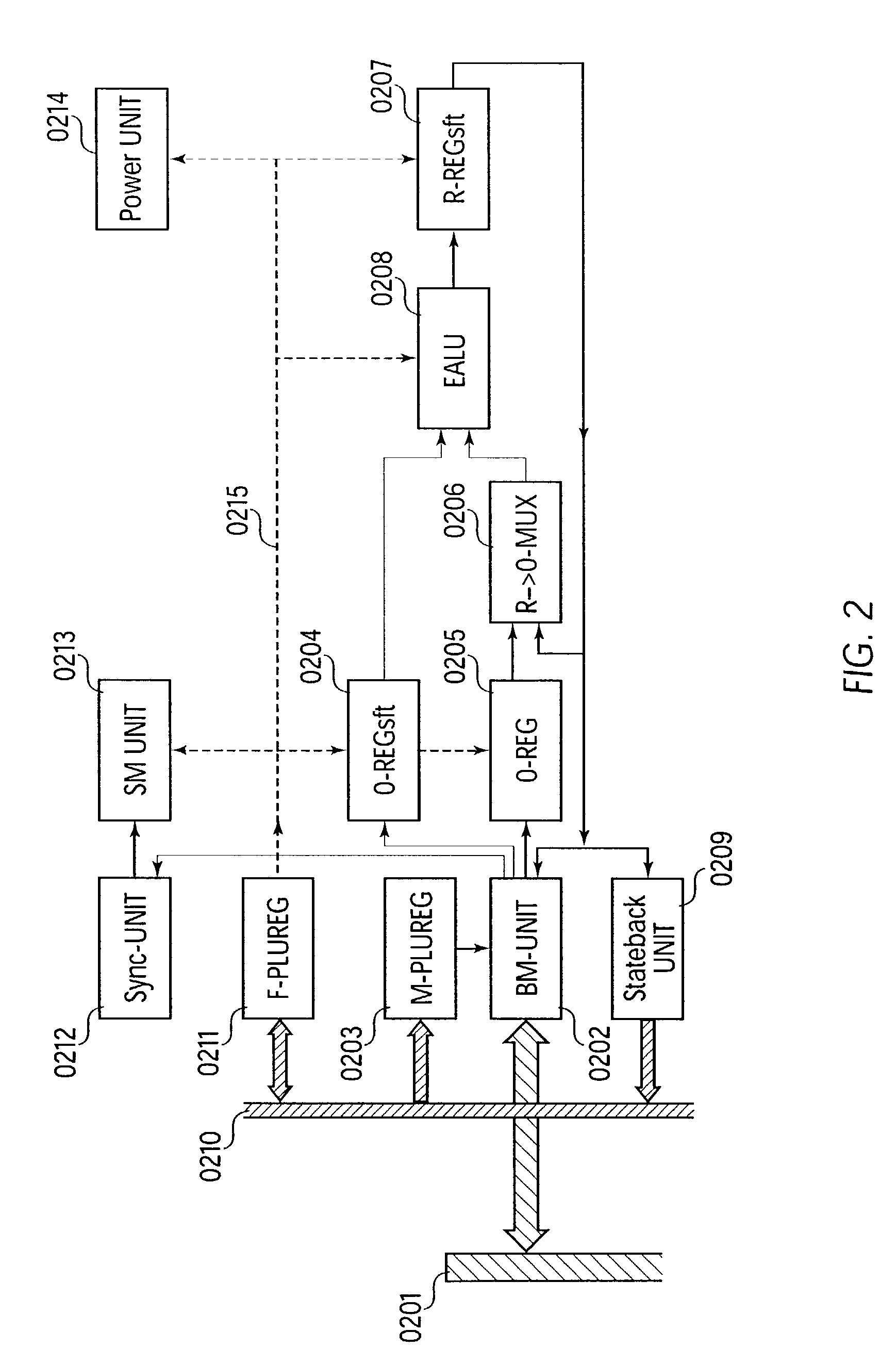
Unit for processing numeric and logic operations for use in central processing units (CPUS), multiprocessor systems, data-flow processors (DSPS), systolic processors and field programmable gate arrays (FPGAS)
InactiveUS20030056085A1The process is convenient and fastSimplifies (re)configurationEnergy efficient ICTMultiple digital computer combinationsBus masteringBroadcasting
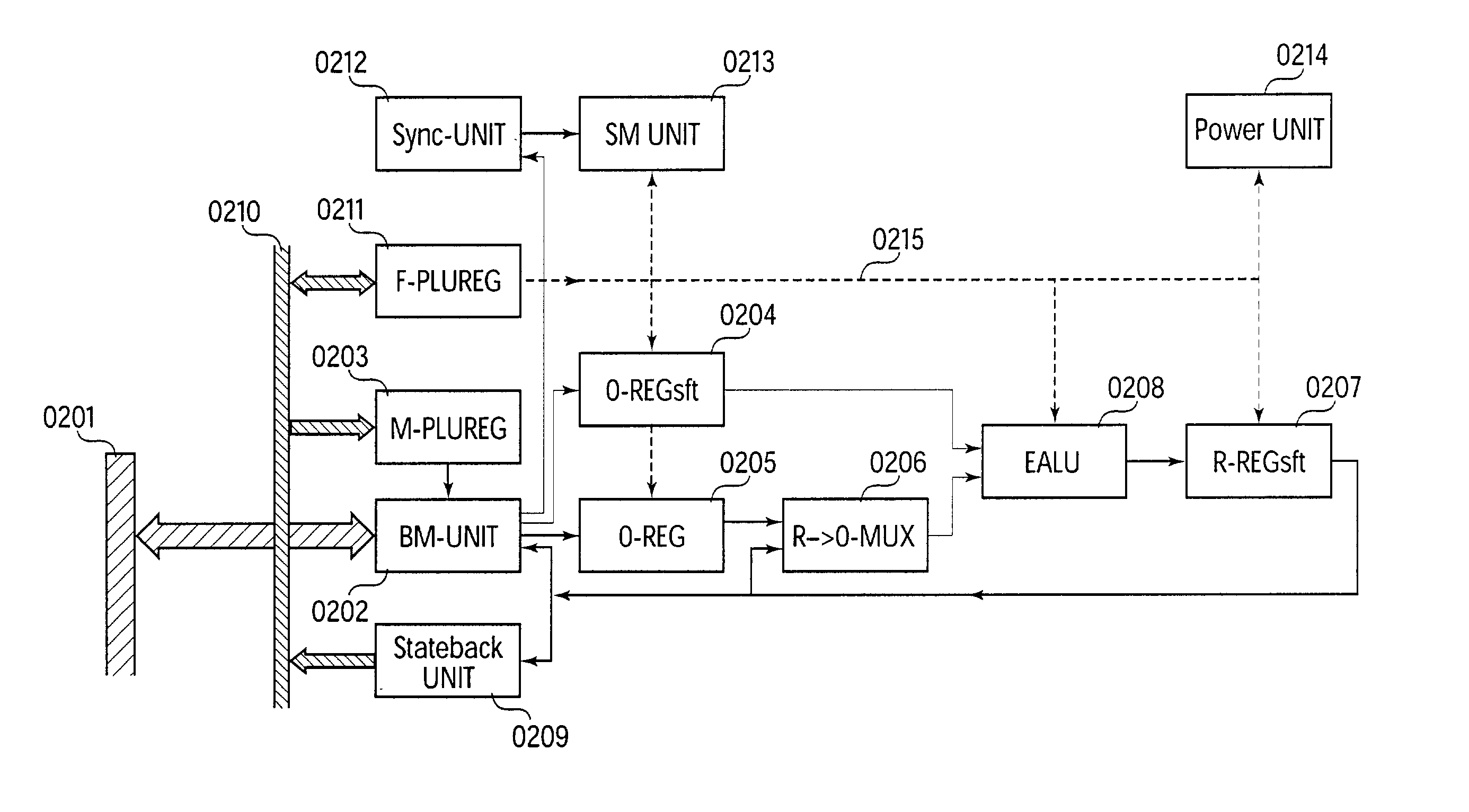
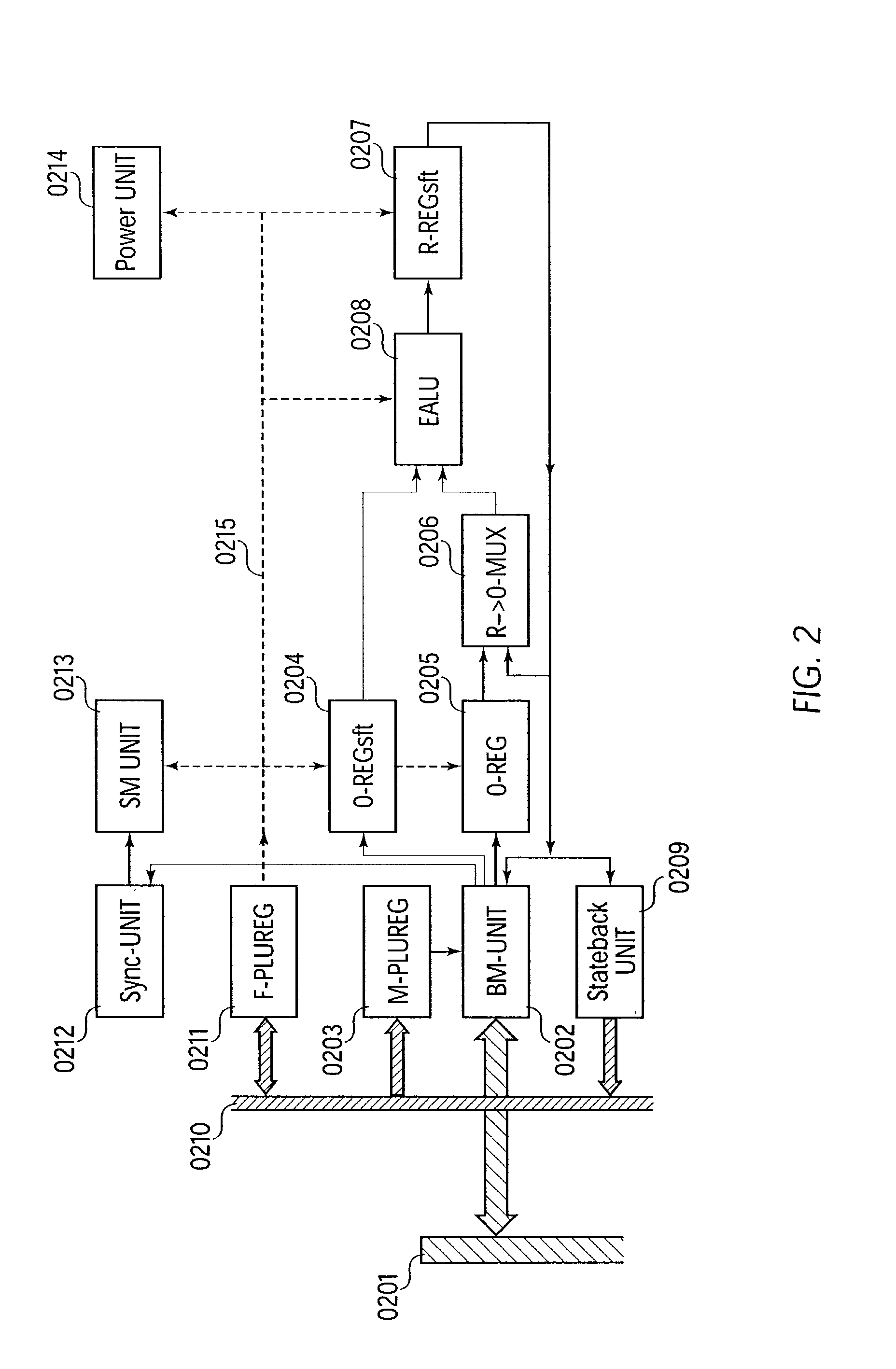
An expanded arithmetic and logic unit (EALU) with special extra functions is integrated into a configurable unit for performing data processing operations. The EALU is configured by a function register, which greatly reduces the volume of data required for configuration. The cell can be cascaded freely over a bus system, the EALU being decoupled from the bus system over input and output registers. The output registers are connected to the input of the EALU to permit serial operations. A bus control unit is responsible for the connection to the bus, which it connects according to the bus register. The unit is designed so that distribution of data to multiple receivers (broadcasting) is possible. A synchronization circuit controls the data exchange between multiple cells over the bus system. The EALU, the synchronization circuit, the bus control unit, and registers are designed so that a cell can be reconfigured on site independently of the cells surrounding it. A power-saving mode which shuts down the cell can be configured through the function register; clock rate dividers which reduce the working frequency can also be set.
Owner:PACT +1
Liquid crystal display apparatus, driving method for same, and driving circuit for same
ActiveUS20060145978A1Easy to displayQuick responseStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsElectrode potentialLiquid-crystal display
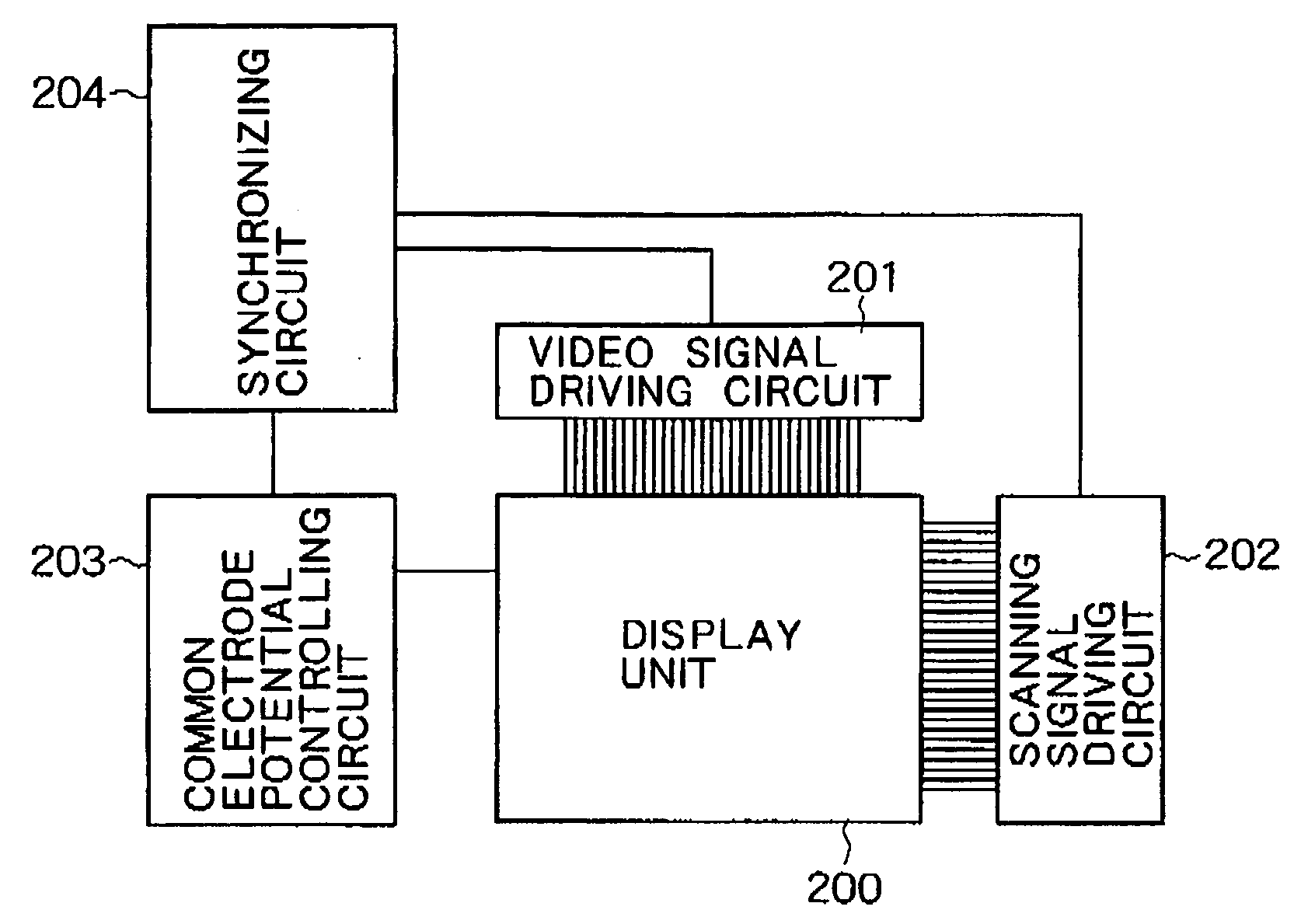
The liquid crystal display apparatus is provided with a display unit, a video signal driving circuit, a scanning signal driving circuit, a common electrode potential controlling circuit, and a synchronizing circuit. The display unit has a scanning electrode, a video signal electrode, a plurality of pixel electrodes arranged in matrix form, a plurality of switching elements which transmit video signals to the pixel electrodes, and a common electrode. After the scanning signal driving circuit scans the entire scanning electrodes and transmits video signals to the pixel electrodes, the common electrode potential controlling circuit changes the potential of the common electrode into a pulse shape, overdrives video signals, or increases a torque required to return to a state in which no voltage is applied.
Owner:NEC LCD TECH CORP
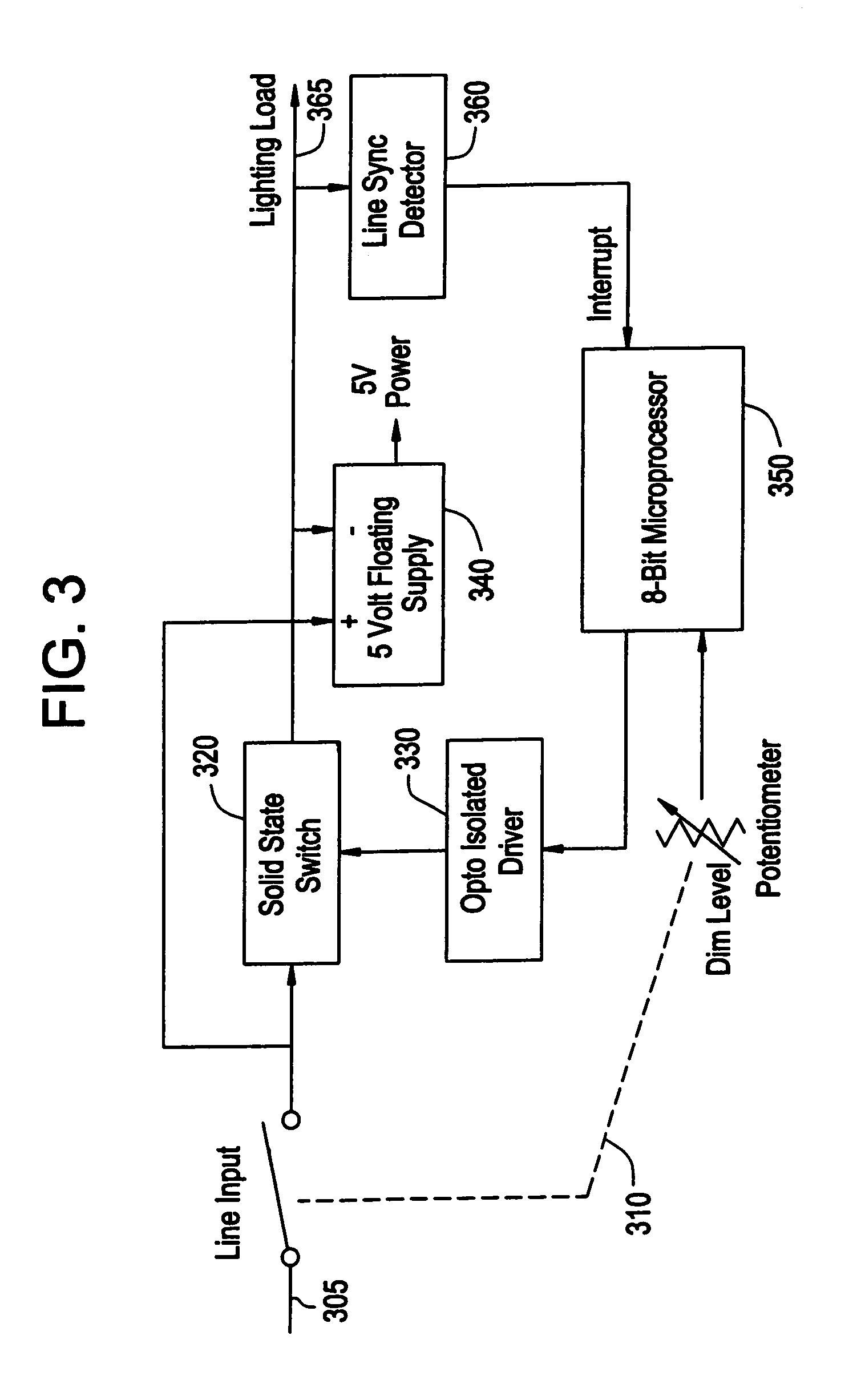
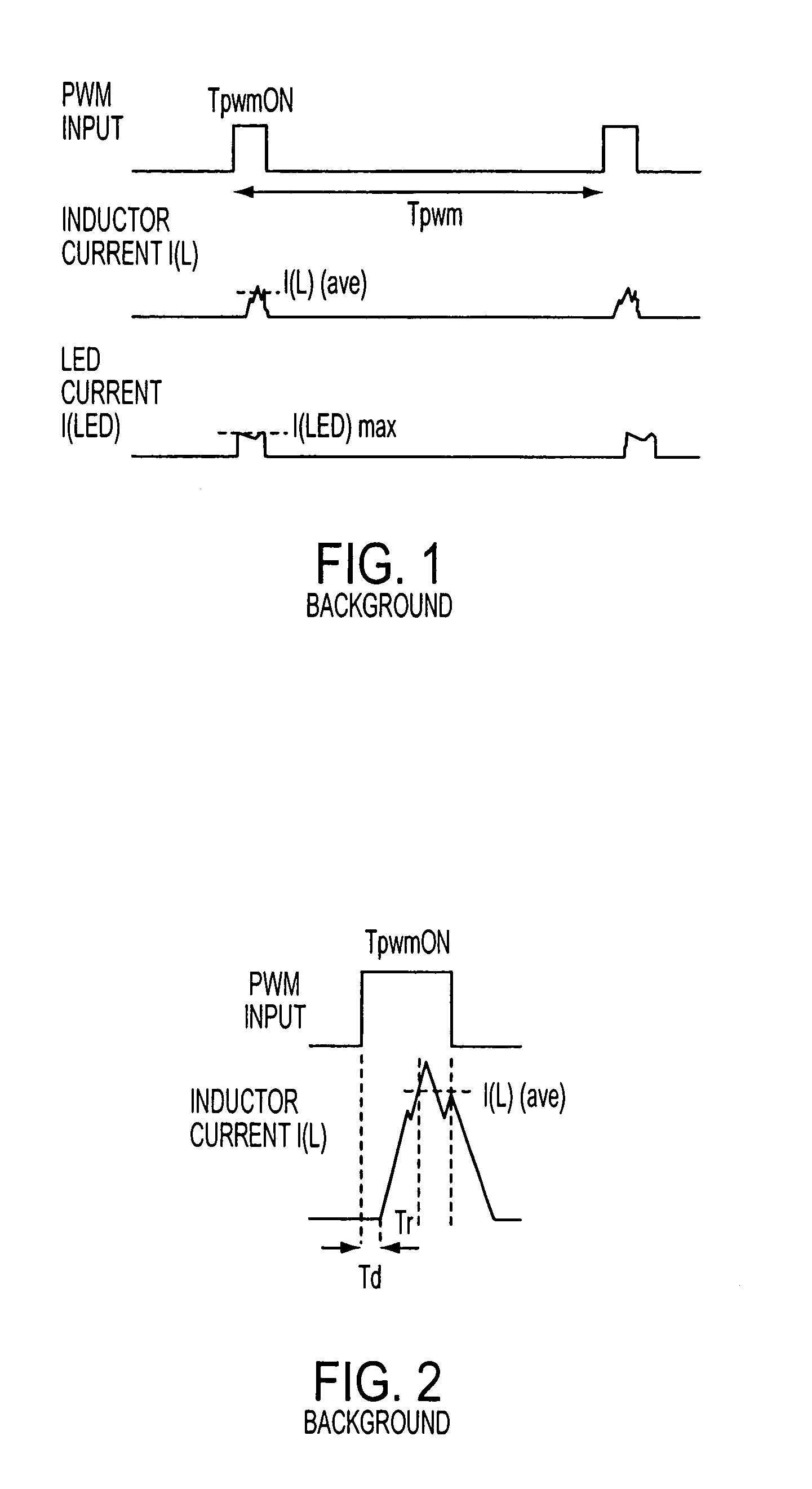
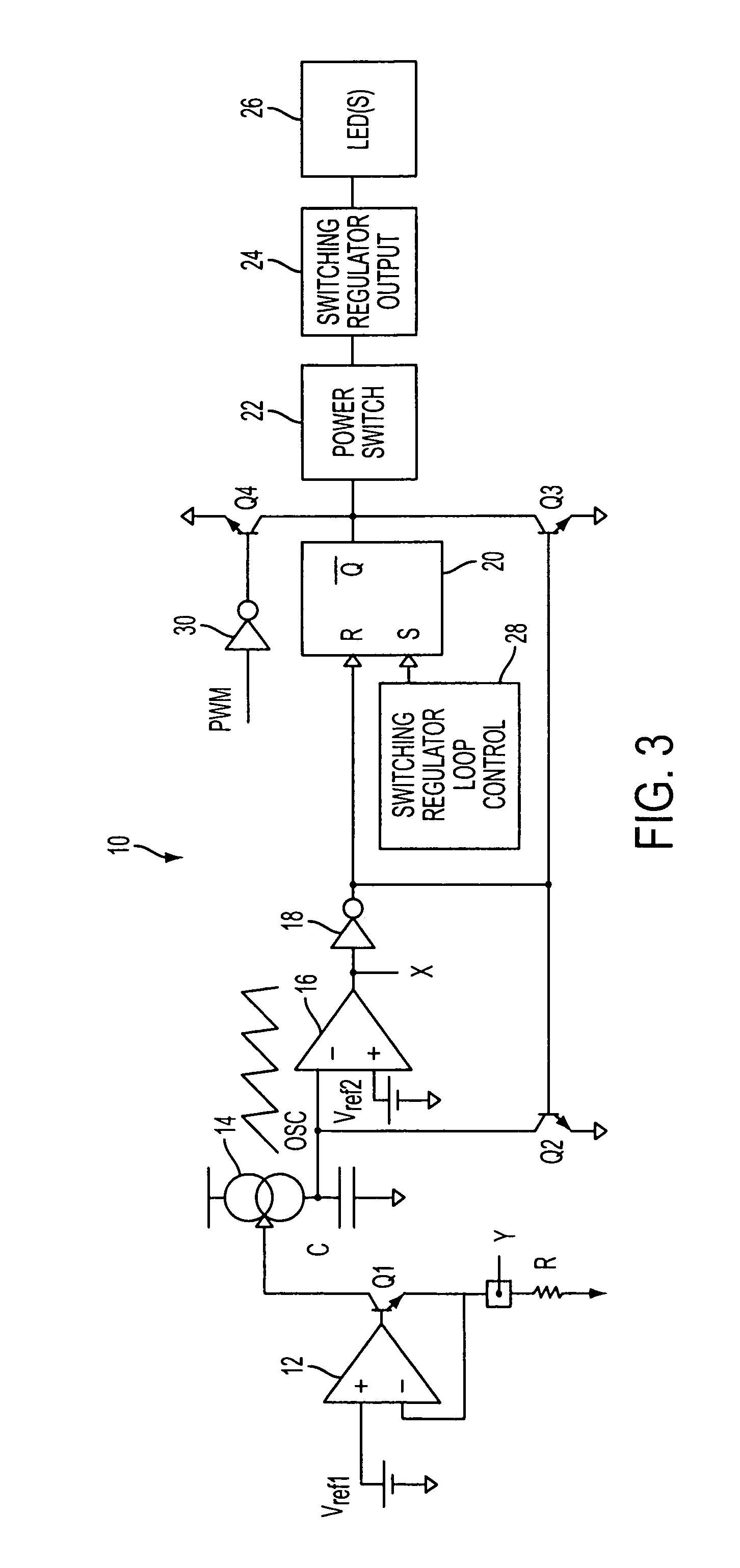
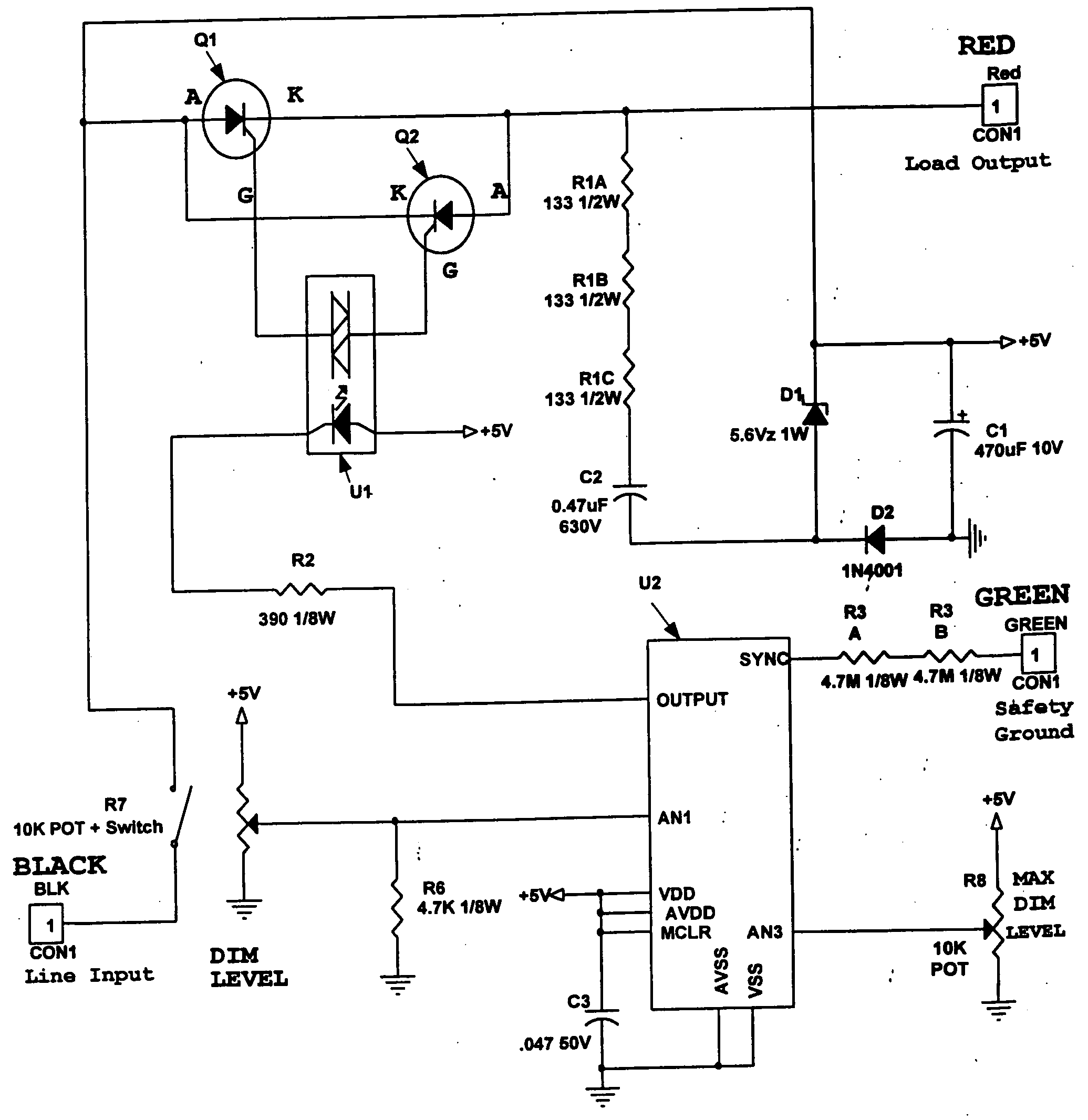
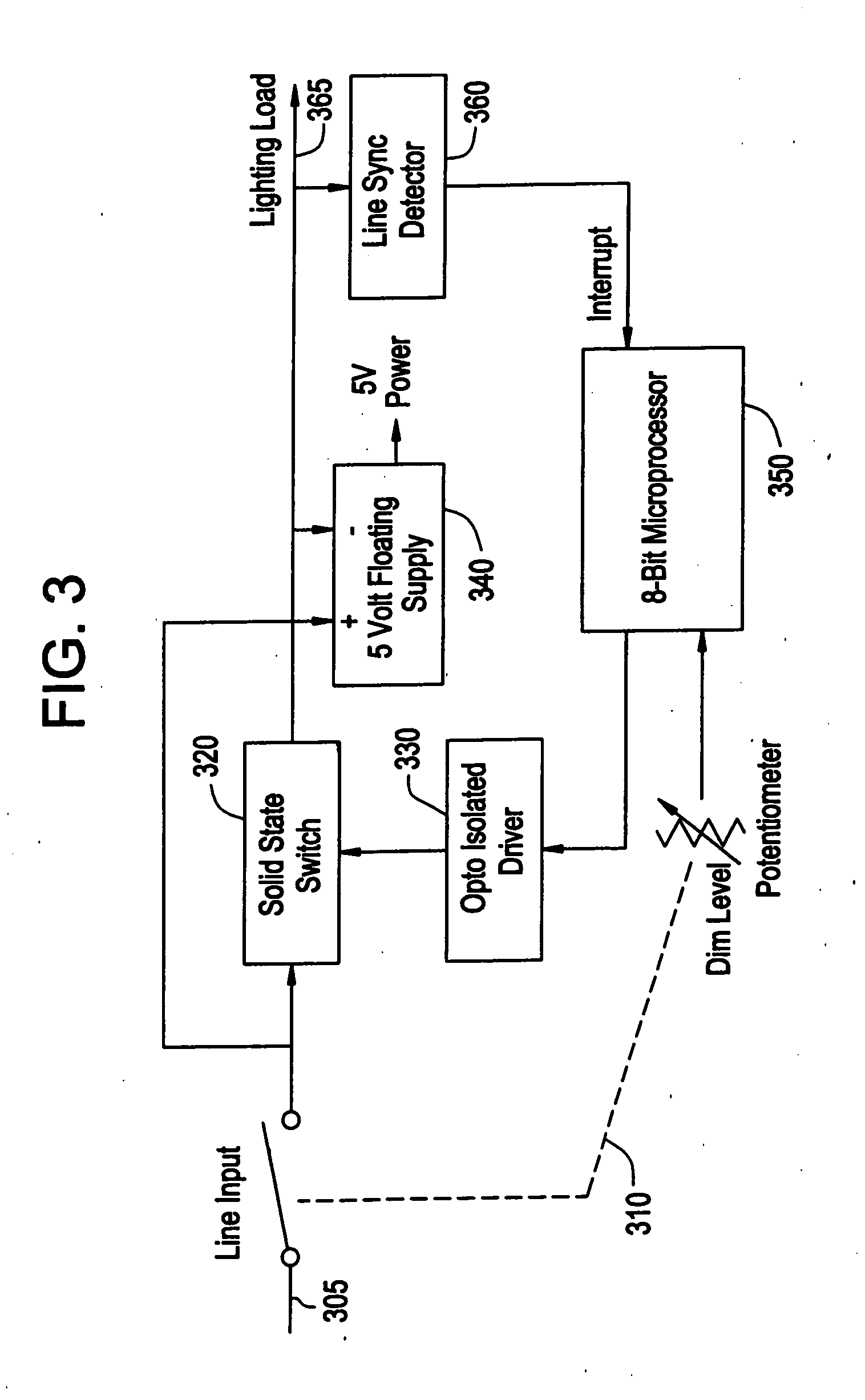
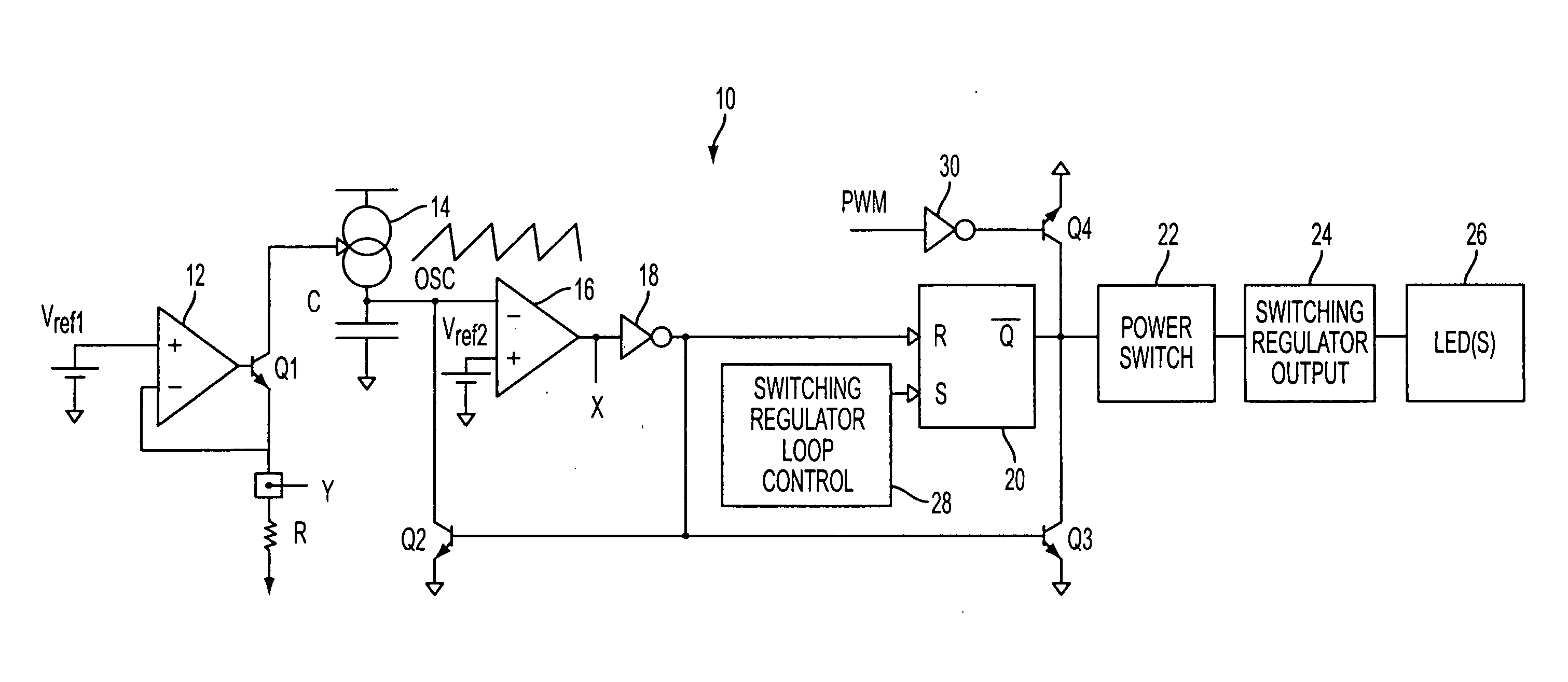
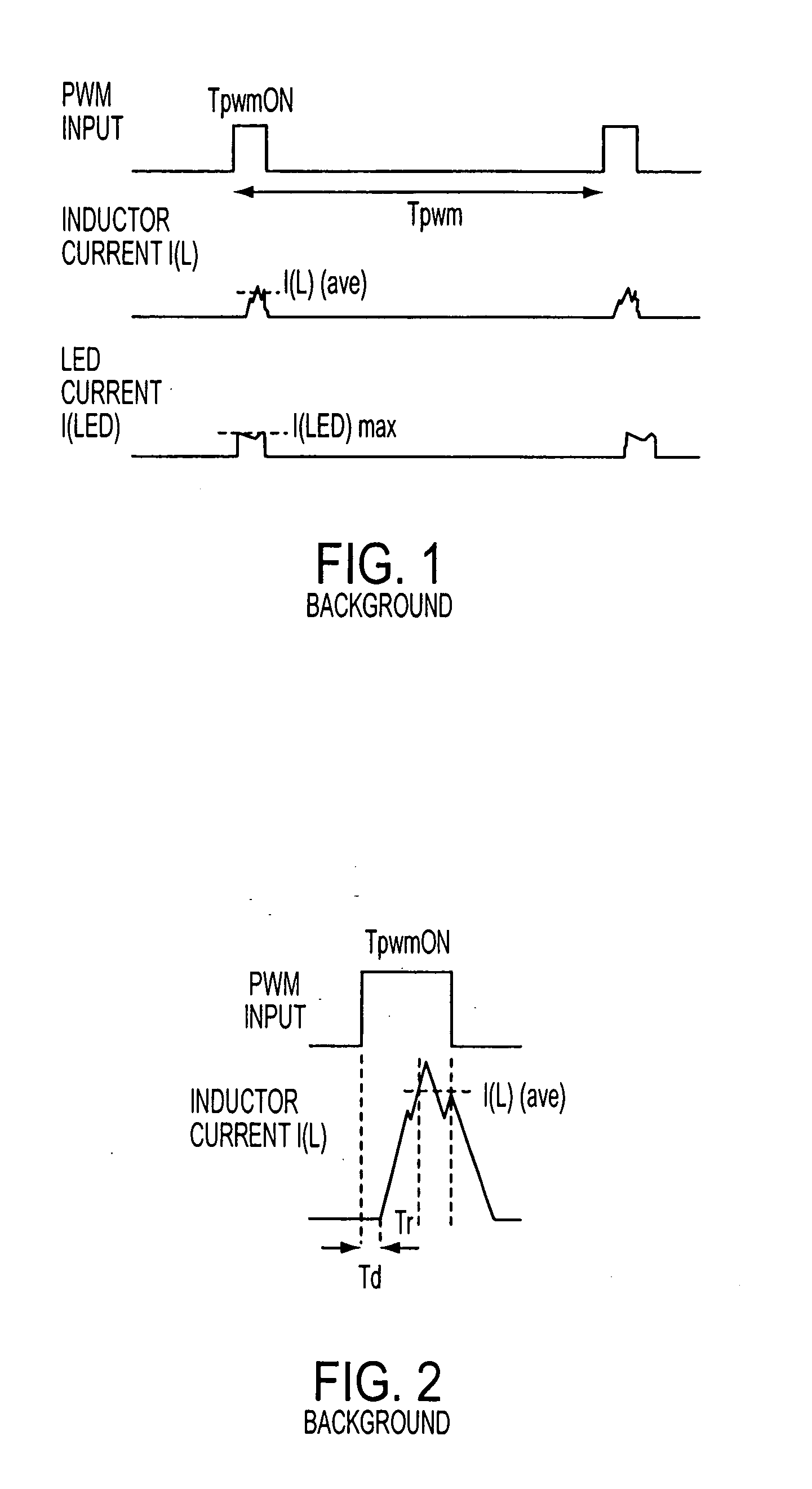
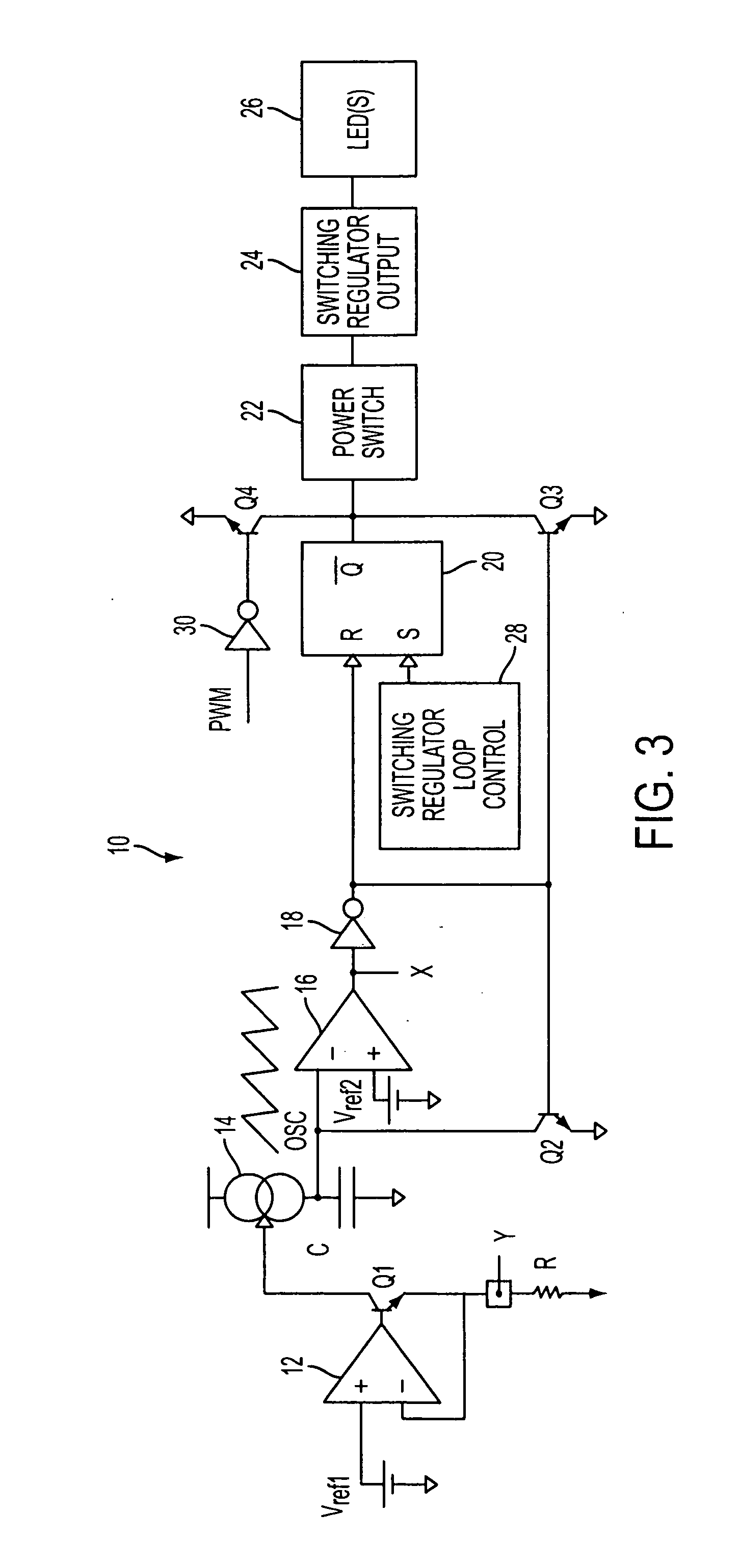
LED dimming control technique for increasing the maximum PWM dimming ratio and avoiding LED flicker
ActiveUS7321203B2Electroluminescent light sourcesSemiconductor lamp usageControl signalControl theory
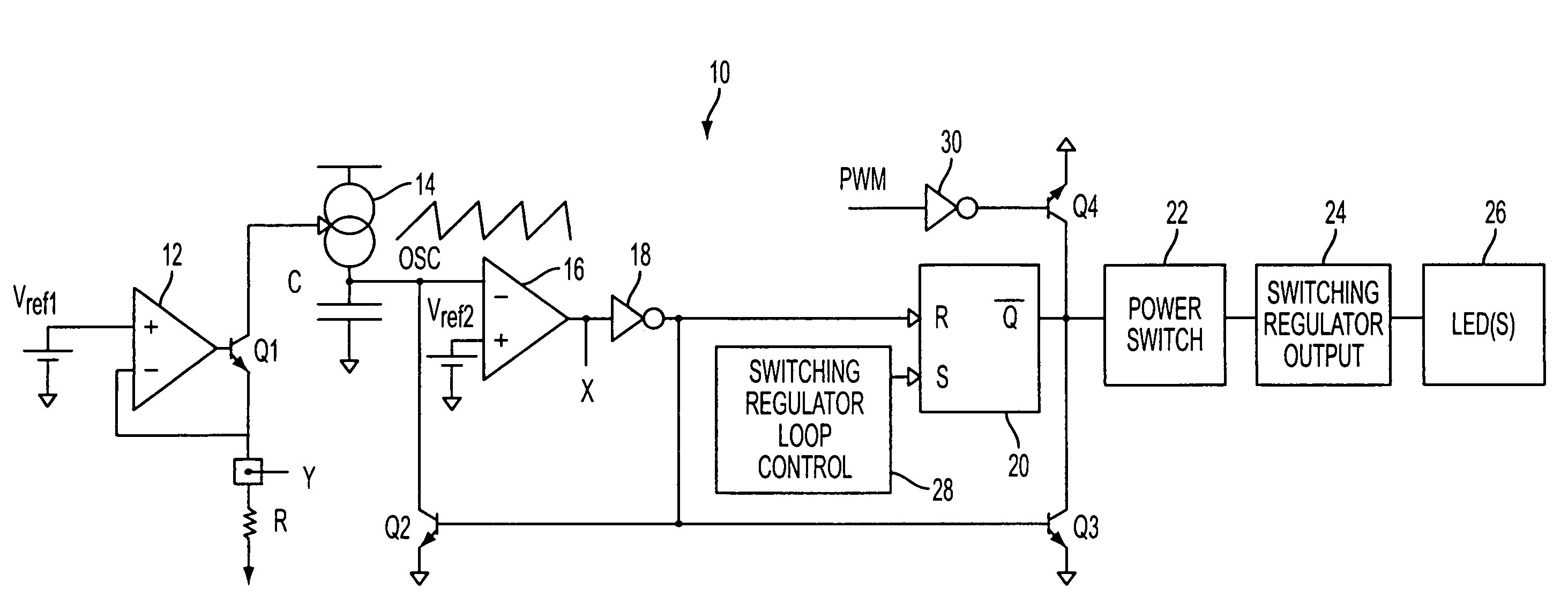
Circuitry and methodology for providing LED dimming control in a LED driving system having a switching regulator for providing power supply to drive the LED. The switching regulator includes a switching circuit to which an oscillation signal is applied to control switching of the switching circuit. A dimming control input is supplied with a pulse-width modulation (PWM) dimming control signal to provide PWM dimming control of the LED. The dimming control input applies the PWM dimming control signal to control switching of the switching circuit. A synchronizing circuit is provided for synchronizing the oscillation signal to the PWM dimming control signal.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INT UNLTD
Energy savings device and method for a resistive and/or an inductive load and/or a capacitive load
InactiveUS20050104543A1Provide energy savingSave energyElectrical apparatusElectric light circuit arrangementCapacitanceElectrical resistance and conductance
An energy savings device for an inductive, a resistive or a capacitive load, such as a fluorescent light fixture having a magnetic ballast or an electronic ballast, which is powered by an AC voltage waveform. The energy savings device includes a setting unit for setting a desired power operating level for the load. The energy savings device also includes a processor configured to receive a signal from the setting unit indicative of the desired power operating level for the load, to determine a phase delay to be provided to an output AC voltage waveform that is to be provided to the load, and to output a control signal as a result thereof. The energy savings device further includes an active element provided between a line that provides the input AC voltage waveform and the load, the active element receiving the control signal and turning off and on at predetermined times in accordance with the control signal, so as to create the output AC voltage waveform from the AC voltage waveform. The processor includes a synchronization circuit that synchronizes to the Green Safety ground line.
Owner:ASTRAL COMM
Reconfigurable multidimensional array processor allowing runtime reconfiguration of selected individual array cells
InactiveUS7237087B2Small volumeEffects spaceEnergy efficient ICTMultiple digital computer combinationsClock rateAnd logic unit
An expanded arithmetic and logic unit (EALU) with special extra functions is integrated into a configurable unit for performing data processing operations. The EALU is configured by a function register, which greatly reduces the volume of data required for configuration. The cell can be cascaded freely over a bus system, the EALU being decoupled from the bus system over input and output registers. The output registers are connected to the input of the EALU to permit serial operations. A bus control unit is responsible for the connection to the bus, which it connects according to the bus register. The unit is designed so that distribution of data to multiple receivers (broadcasting) is possible. A synchronization circuit controls the data exchange between multiple cells over the bus system. The EALU, the synchronization circuit, the bus control unit, and registers are designed so that a cell can be reconfigured on site independently of the cells surrounding it. A power-saving mode which shuts down the cell can be configured through the function register; clock rate dividers which reduce the working frequency can also be set.
Owner:PACT +1
Electronic endoscope apparatus adaptable to endoscopes equipped with imaging device with different pixel density
InactiveUS6992694B2Low costAvoid wastingTelevision system detailsSurgeryPixel densitySignal processing circuits
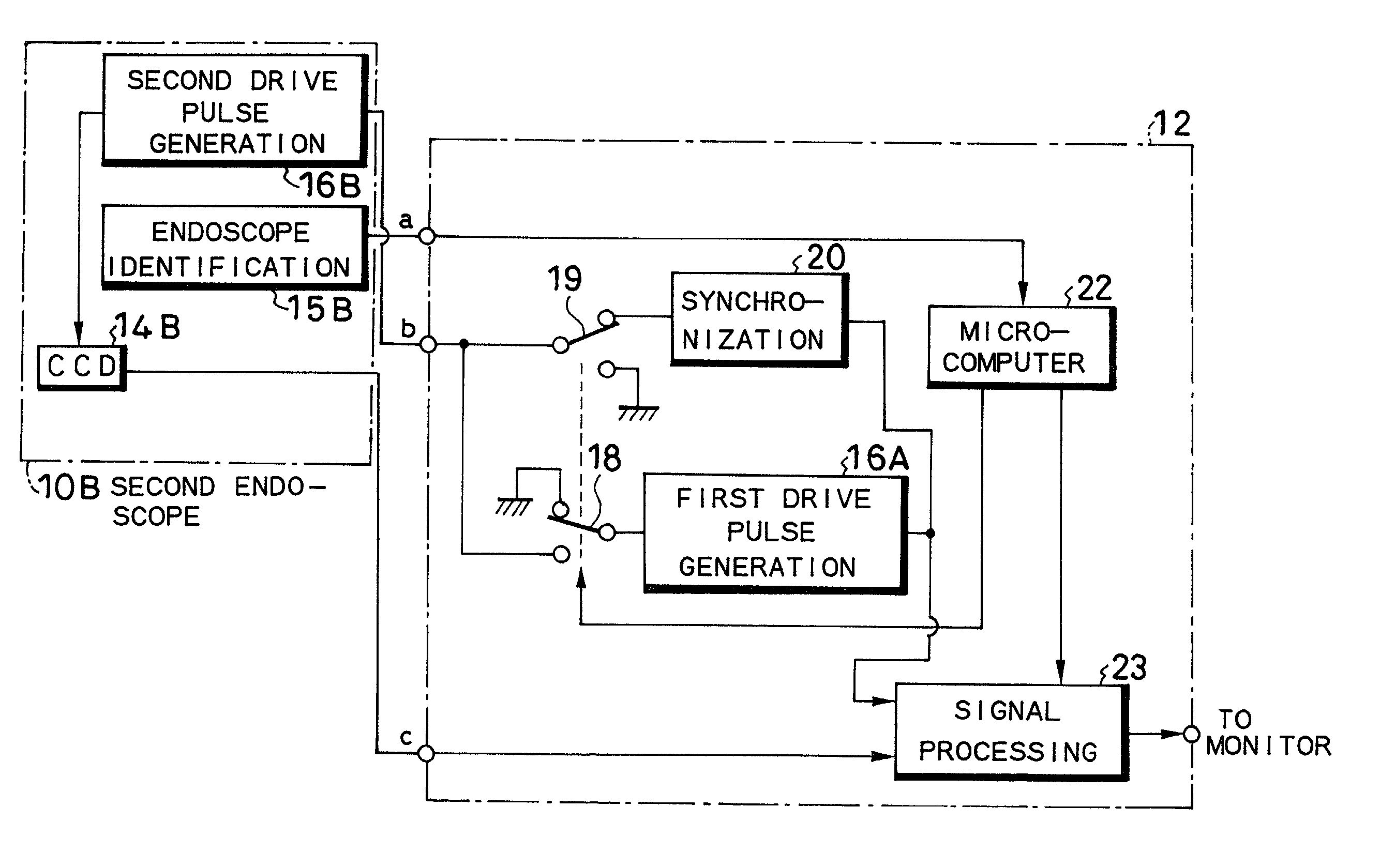
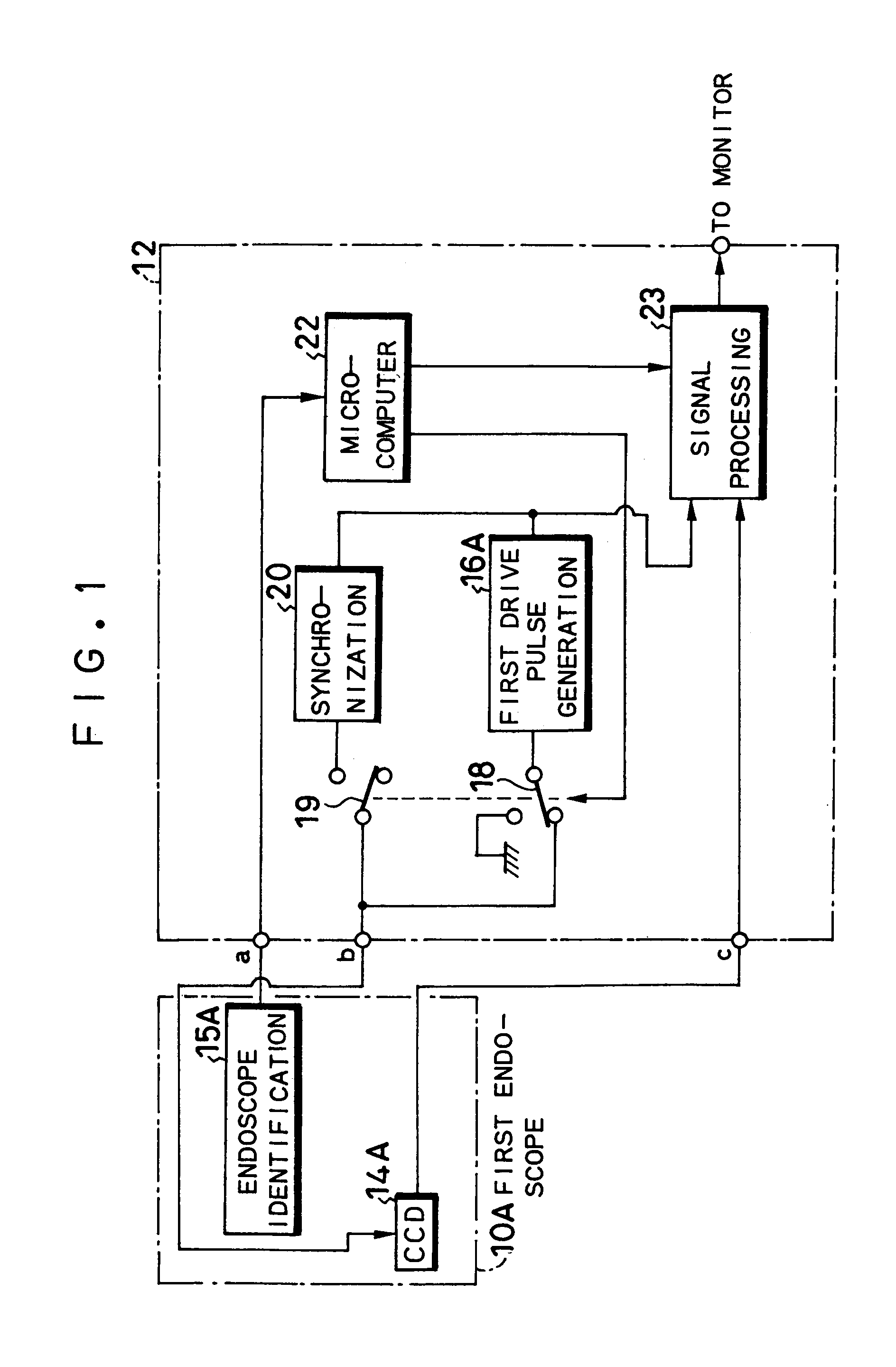
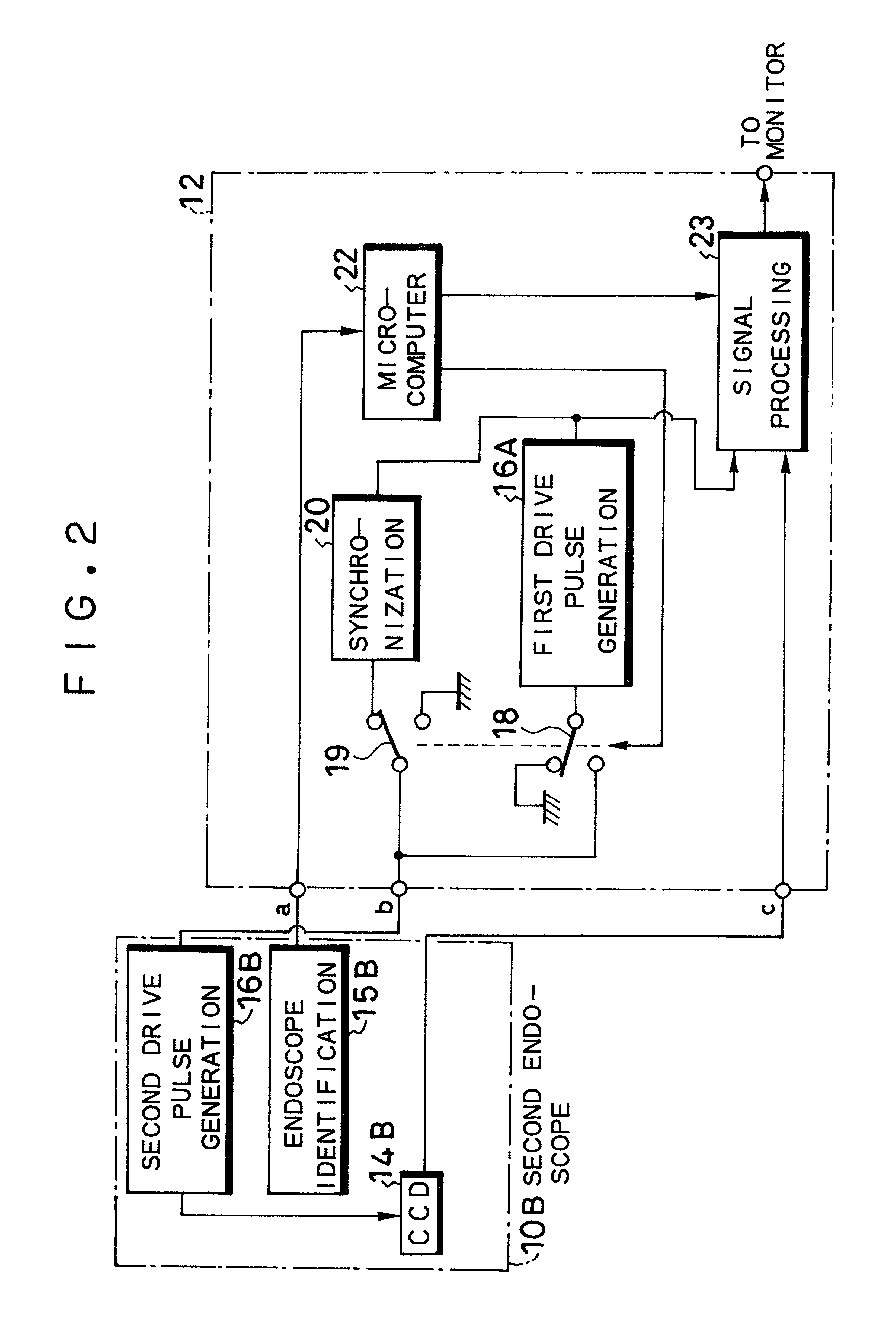
An electronic endoscope apparatus including: a first endoscope having a first imaging device; and a second endoscope having a second imaging device with a different pixel density and a second drive pulse generation circuit, wherein a processor unit, which connects the two endoscopes, comprises: a first drive pulse generation circuit for driving the first imaging device, a synchronization circuit for generating a synchronizing signal synchronous with the signal of the second drive pulse generation circuit, a switching circuit for activating the synchronization circuit when the second endoscope is connected, and a signal processing circuit for processing the signals obtained by the first imaging device and for processing the signals obtained by the second imaging device based on the synchronizing signal. By this configuration, a single processor unit will suffice even when employing an imaging device with a different pixel density.
Owner:FUJI PHOTO OPTICAL CO LTD
Video processor for endoscopy
InactiveUS20050018042A1Improve immunityEndoscopesColor television detailsFlexible endoscopeEndoscopic camera
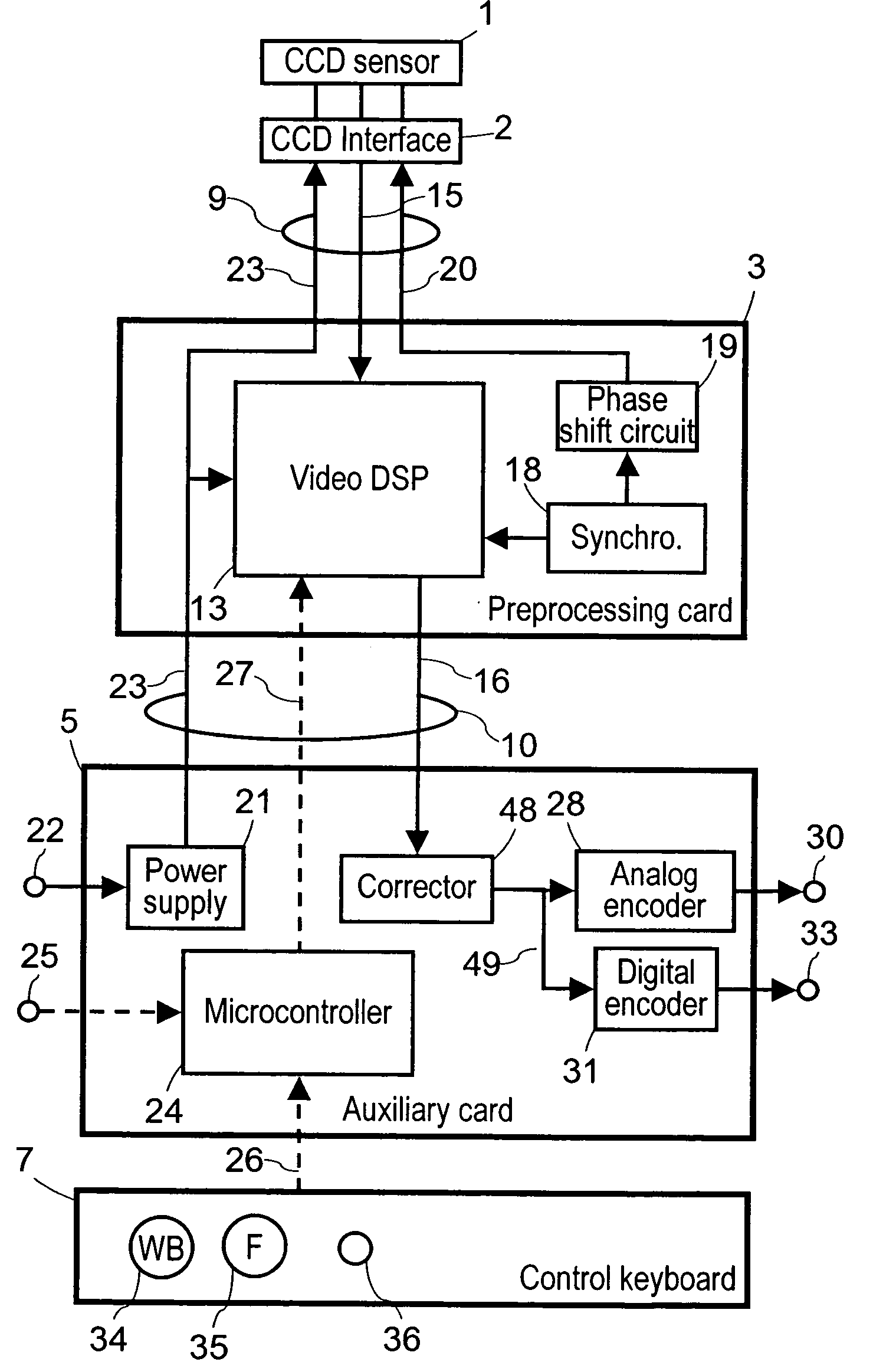
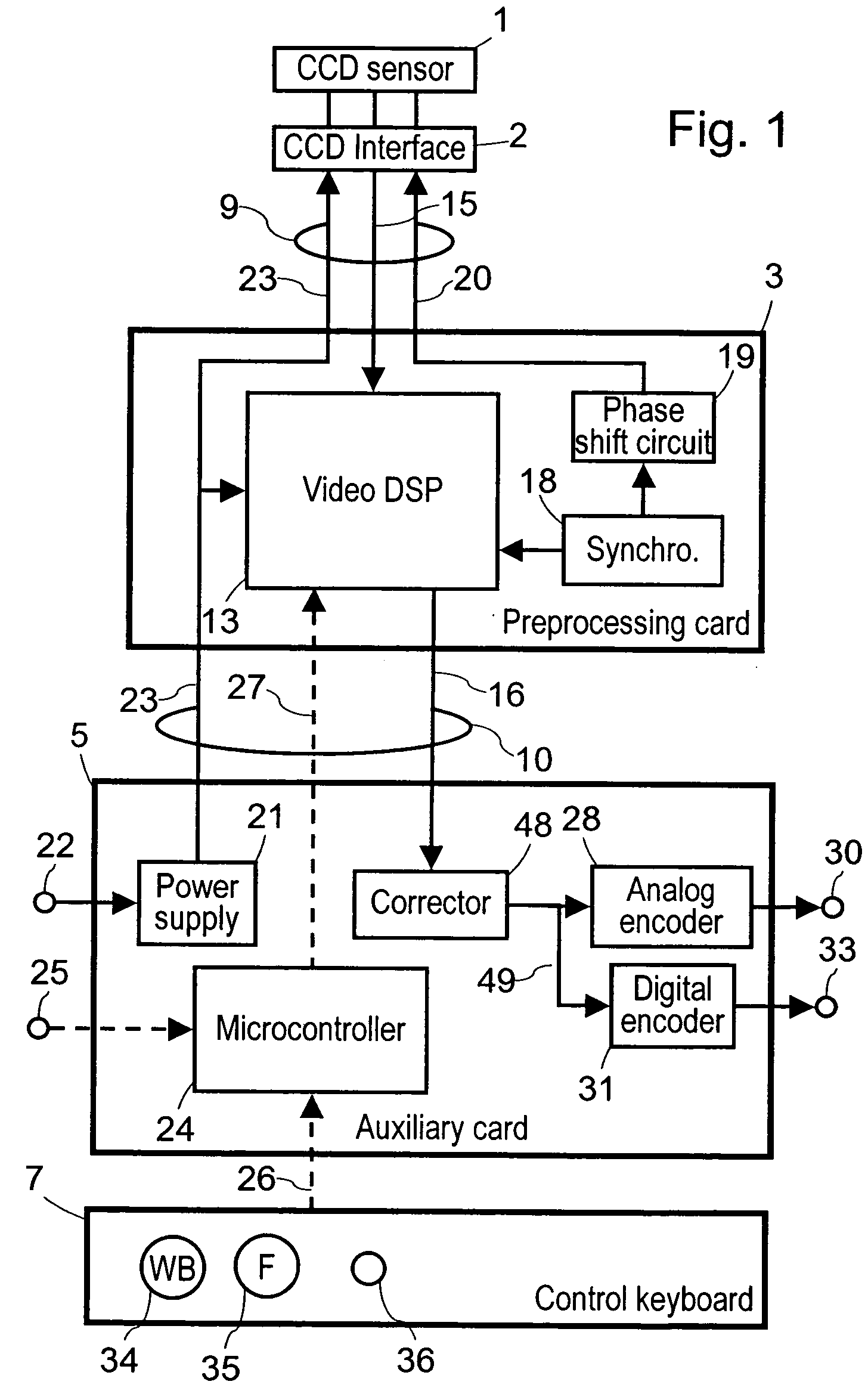
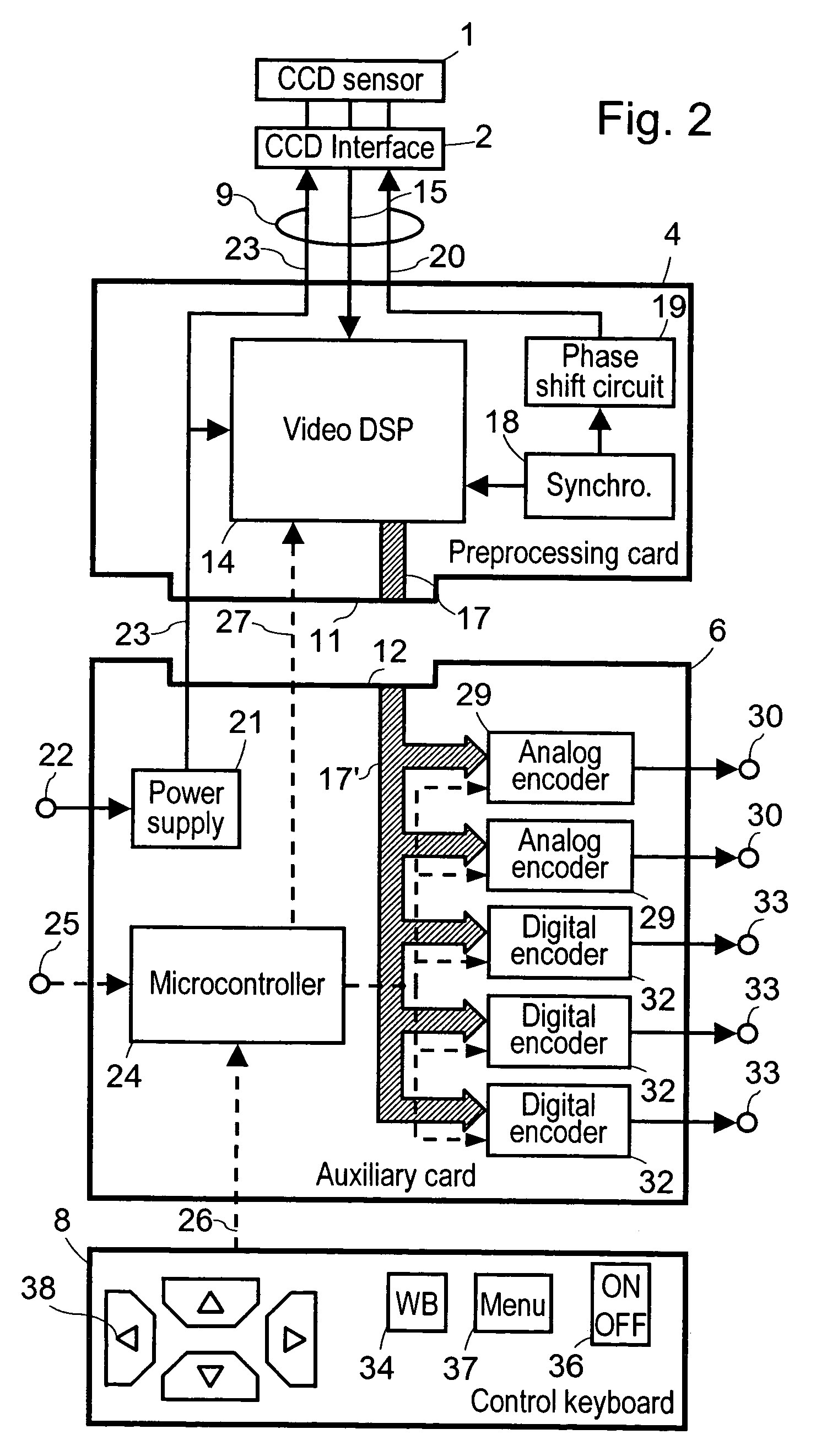
A video processor for endoscopic camera or for videoendoscopic probe associated with a color video sensor, the video processor comprising: a signal preprocessing circuit designed to be remotely connected to the video sensor through an electrical link without any intermediate connection device, the preprocessing circuit comprising a first signal processor for generating from image signals output by the video sensor raw video signals comprising a brightness signal and a color signal, these signals being not usable directly because they are phase shifted and are noisy due to synchronization residues, and a synchronizing circuit for synchronizing the video sensor and the first signal processor; and a remote auxiliary circuit comprising a second signal processor connected to the first signal processor through a low impedance electrical link providing good immunity to interference, the second signal processor generating from said raw video brightness and color signals at least one useful video signal according to an international video standard.
Owner:TOKENDO
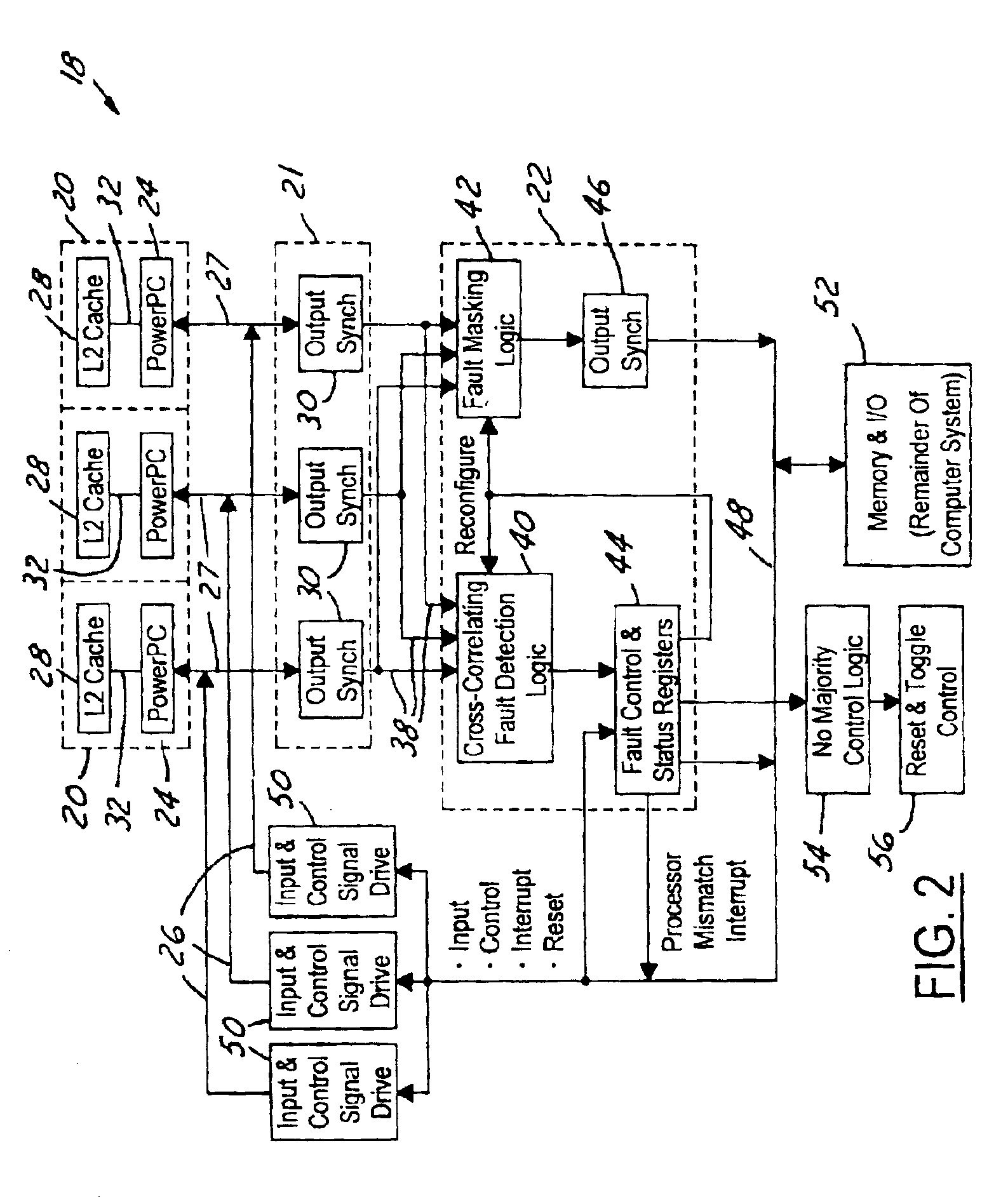
Fault tolerant processing architecture
InactiveUS6938183B2Hinders its propagationRestoring normal computational behaviorError preventionRedundant data error correctionComputer scienceLogic circuitry
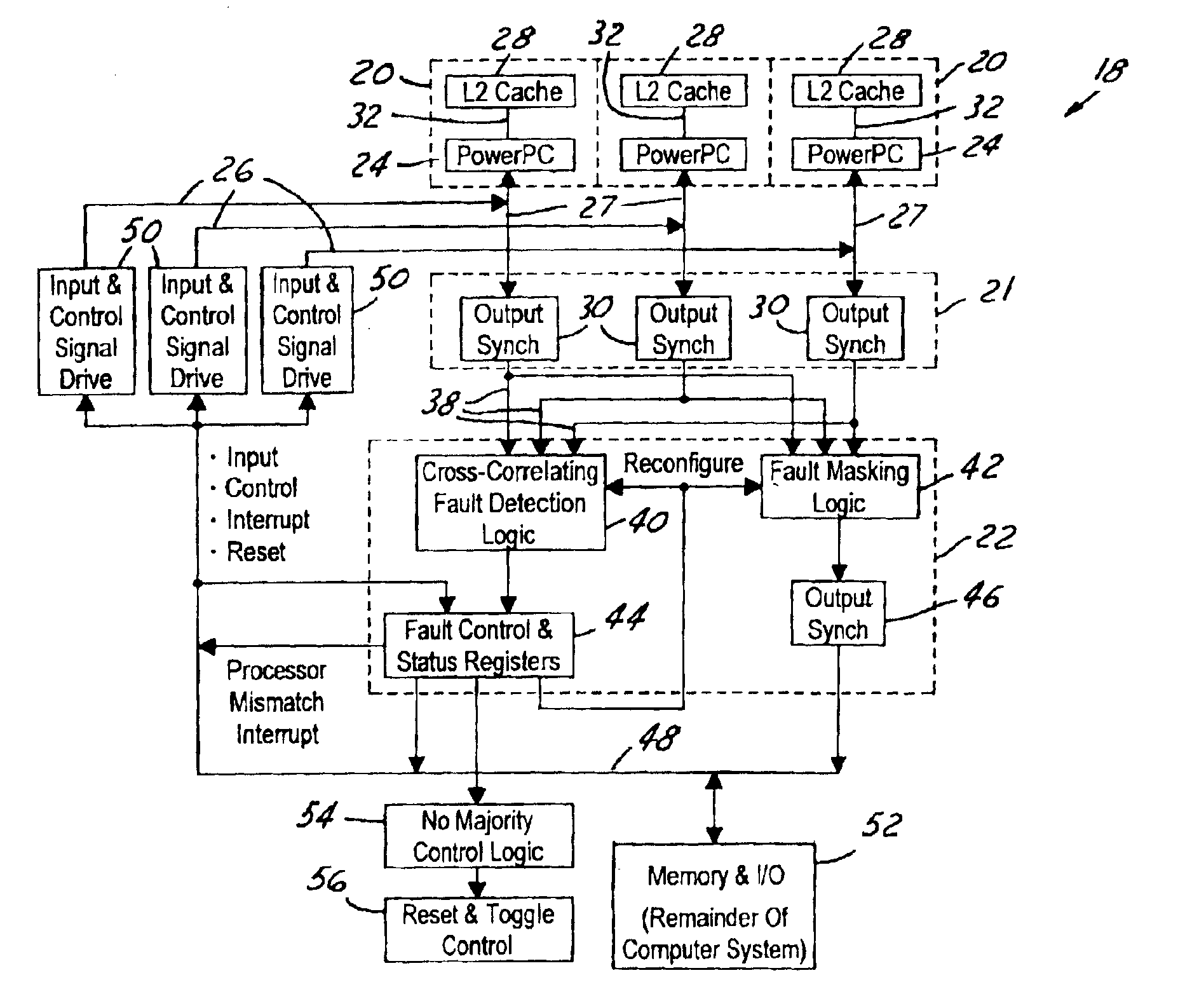
A fault tolerant processing circuit comprising at least three processor groupings, a synchronizing circuit and a fault logic circuit. Each of the processor groupings have a plurality of processor grouping inputs and a plurality of processor grouping outputs. The synchronizing circuit comprises a plurality of output synchronizers, wherein each output synchronizer communicates with a corresponding respective processor grouping for synchronizing the output of each processor grouping. A fault logic circuit communicates with the synchronizing circuit. The fault logic circuit comprises a fault detection circuit and a fault mask circuit. The fault logic circuit compares the plurality of processor group outputs to detect errors in any one of the plurality of processor group outputs. An error is detected when none of the at least three processor groups is in a majority of the processor groups. Upon a detected fault, the fault mask circuit masks the output of the respective processor grouping associated with a detected error and signals a detected error. The error signal latch is then used to reset the processor groupings.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
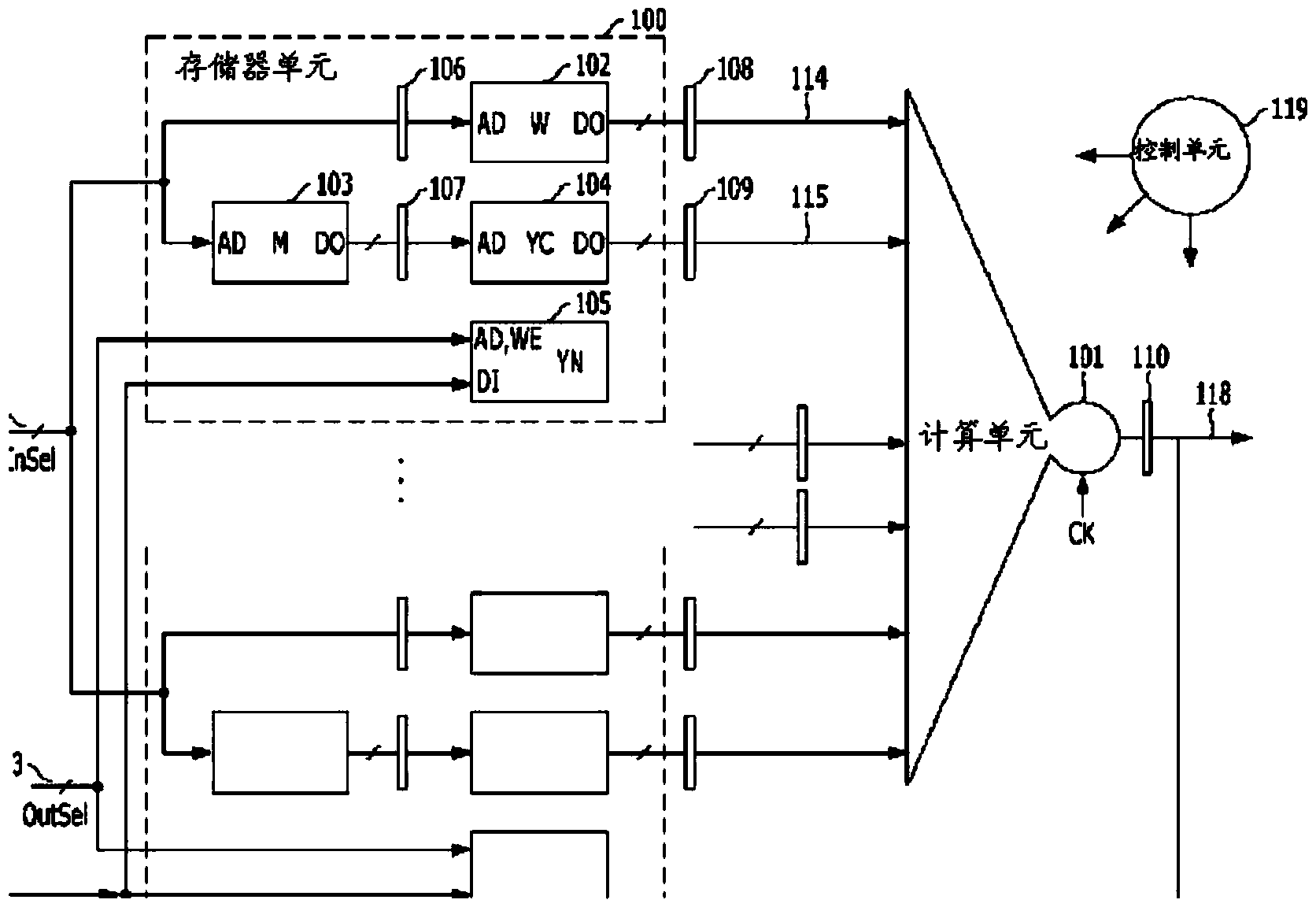
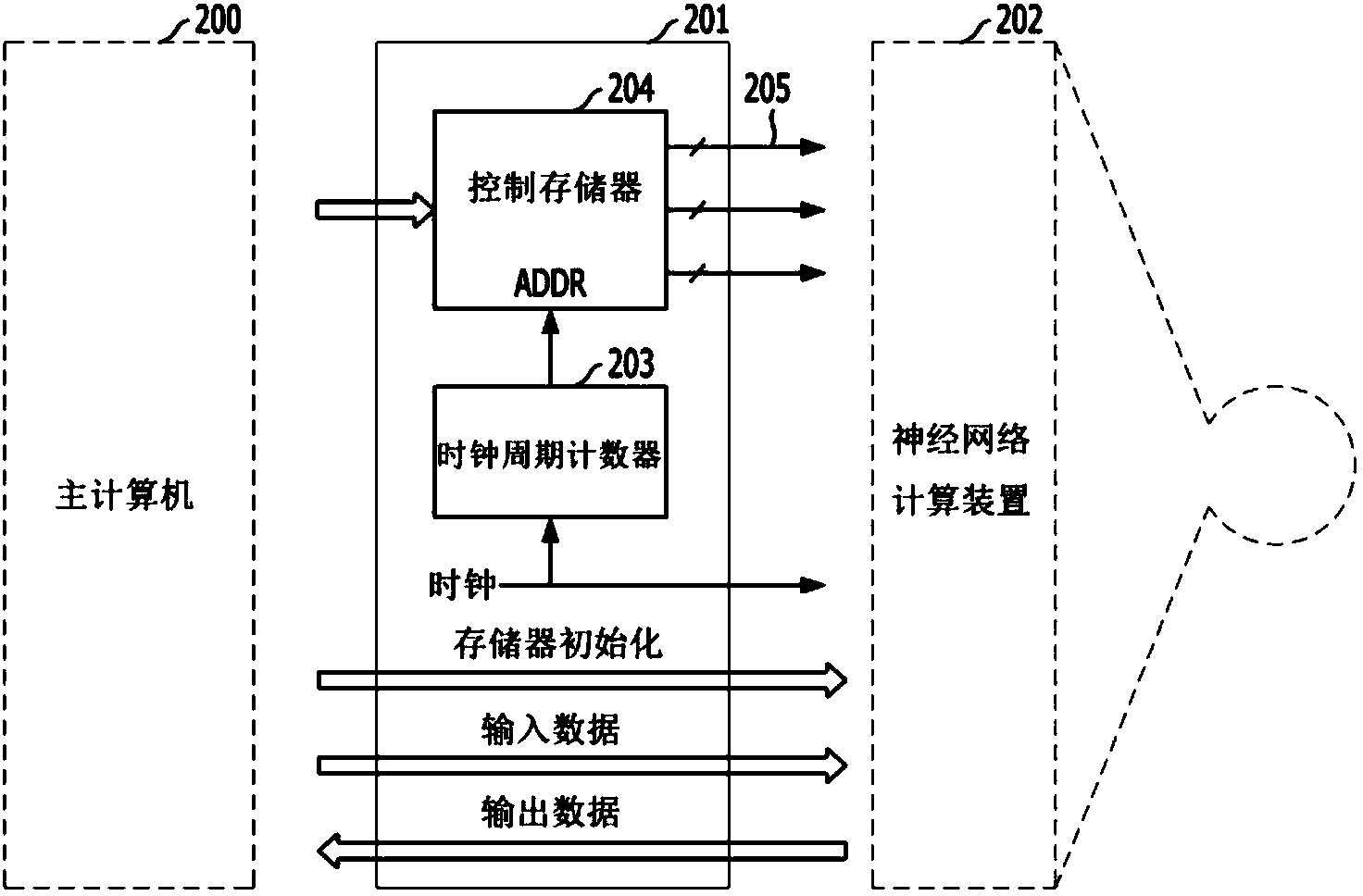
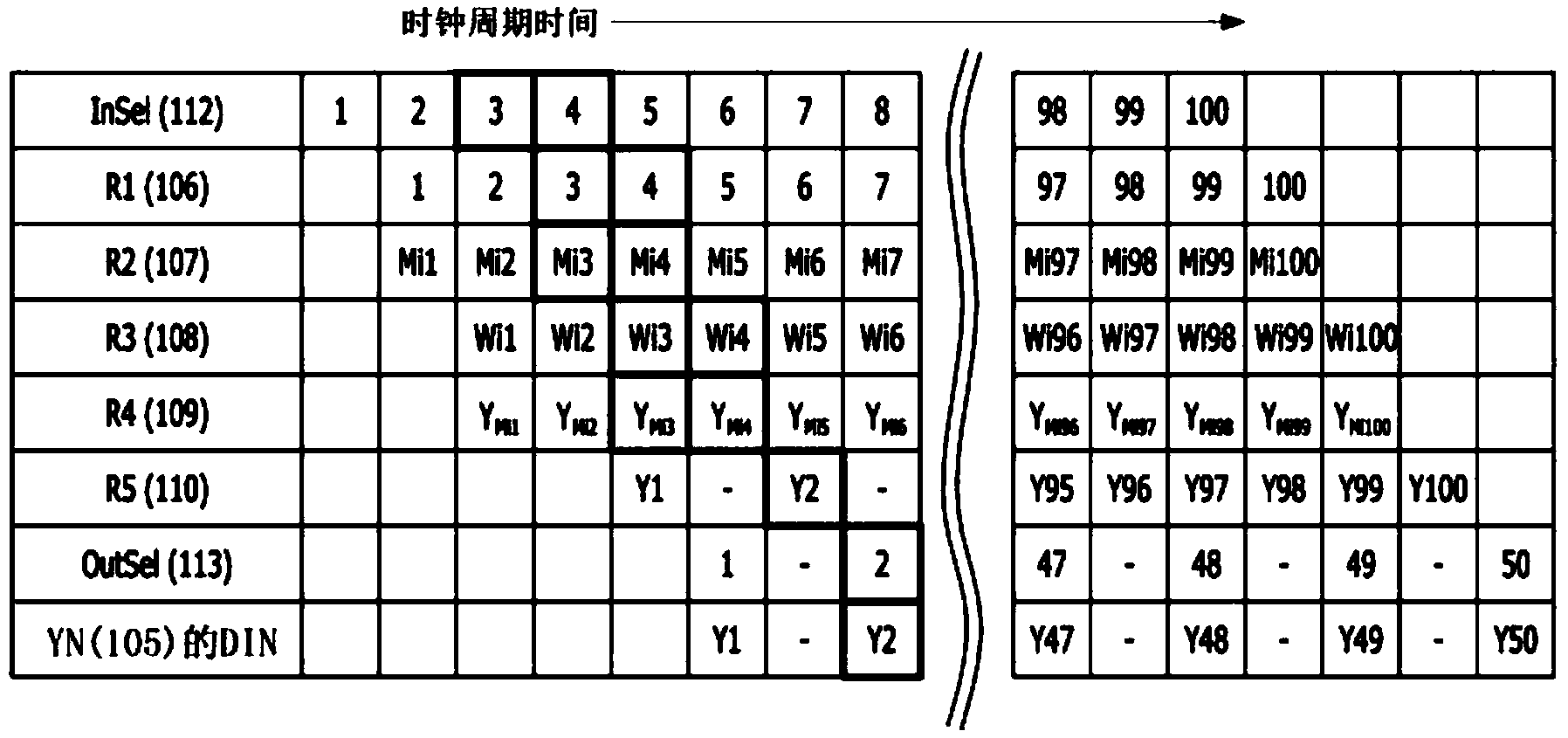
Neural network computing apparatus and system, and method therefor
InactiveCN104145281AReduce connectionsProcessing speedPhysical realisationNeural learning methodsNerve networkTime-sharing
In order to provide a neural network computing apparatus and system, as well as a method therefor, which operate via a synchronization circuit in which all components are synchronized with one system clock, and which include a dispersion-type memory structure for storing artificial neural network data, and a calculating structure for processing all neurons through time-sharing in a pipeline circuit, the present invention comprises: a control unit for controlling the neural network computing apparatus; a plurality of memory units for outputting both a connecting line attribute value and a neuron attribute value; and one calculating unit for using the connecting line attribute value and neuron attribute value inputted from the plurality of memory units so as to calculate a new neuron attribute value and provide feedback to each of the plurality of memory units.
Owner:安秉益
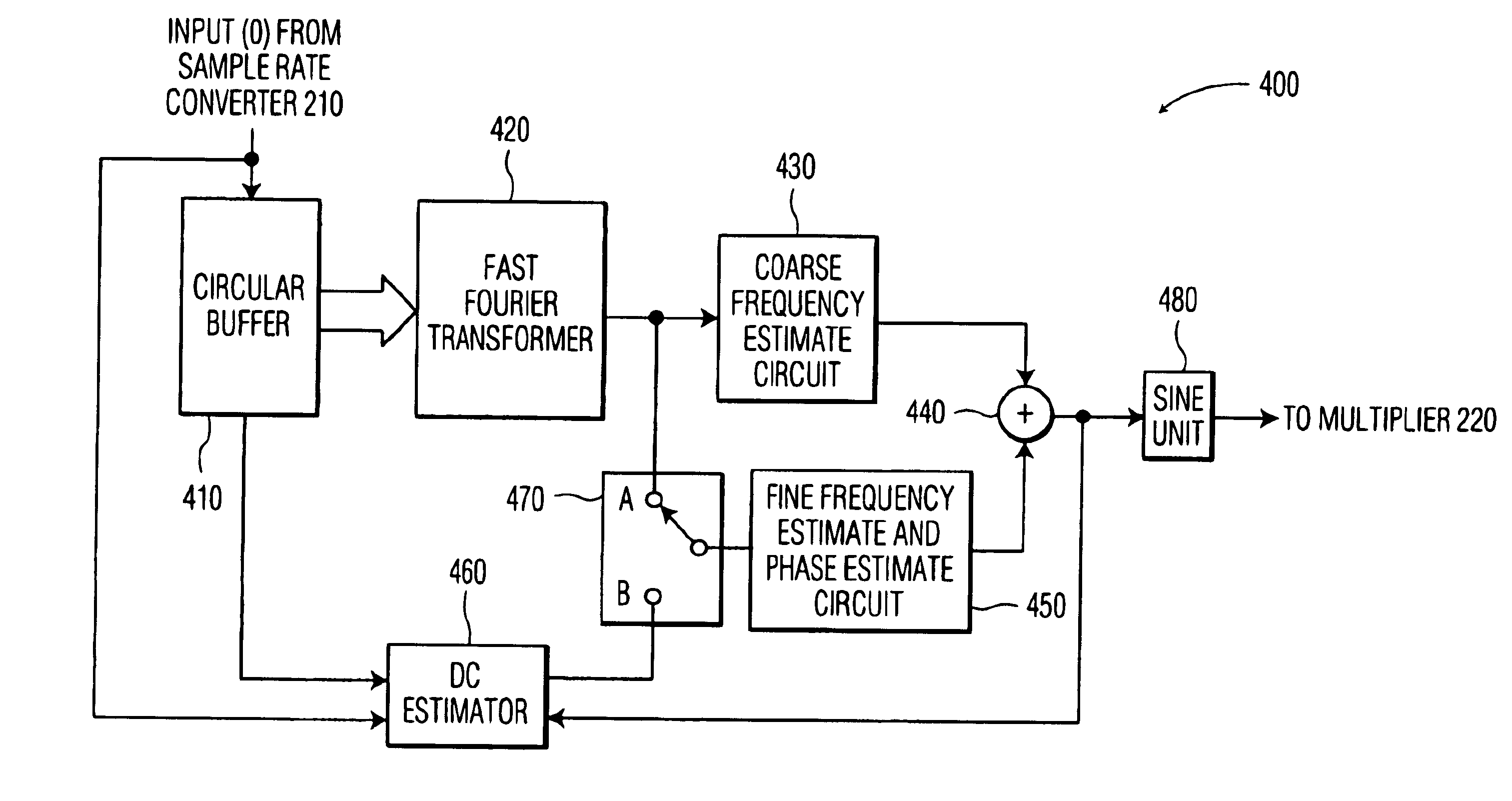
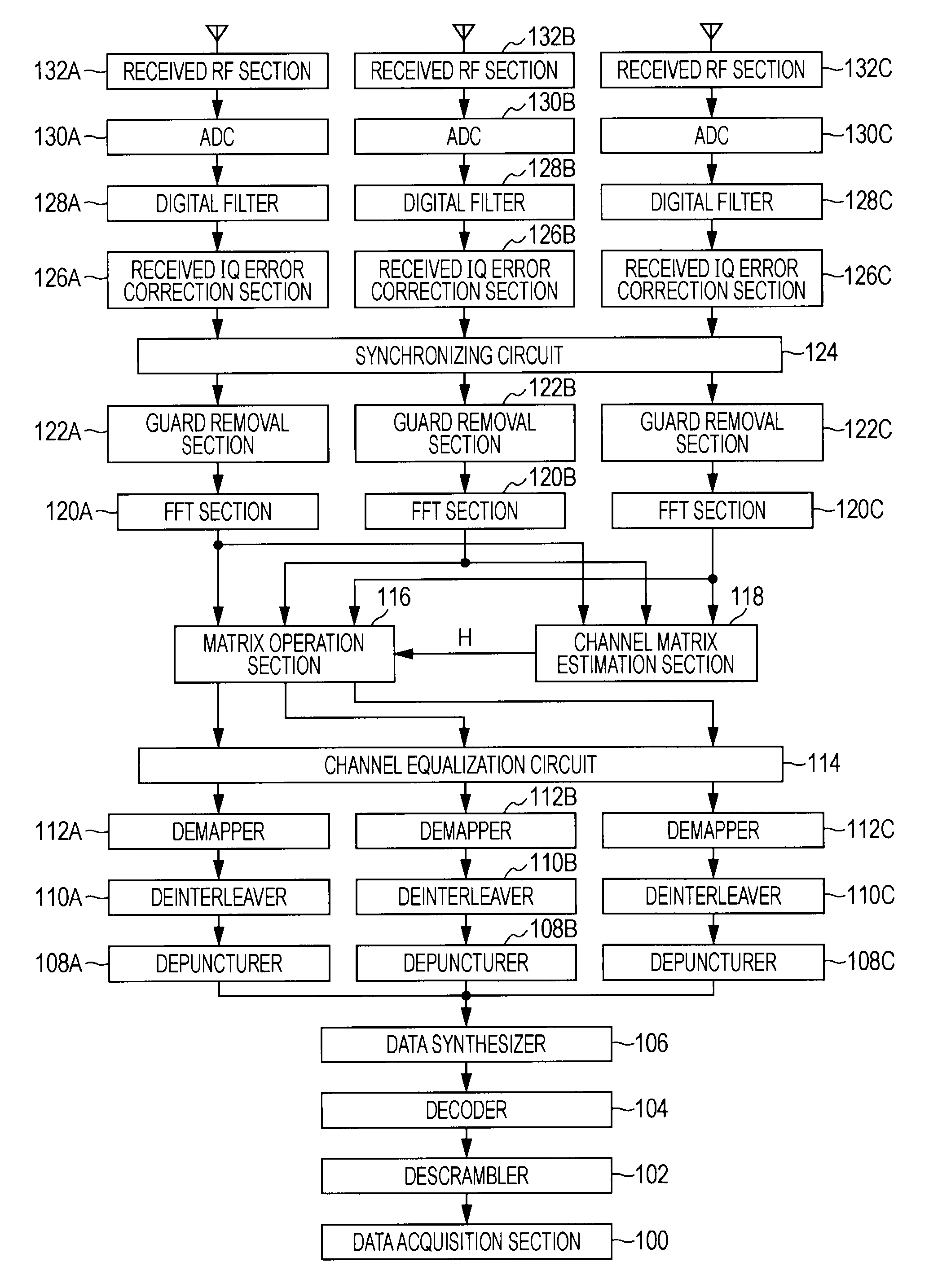
System and method for providing frequency domain synchronization for single carrier signals
InactiveUS6839388B2Fine frequency estimationTelevision system detailsCarrier regulationTime domainSideband
There is disclosed an improved system and method for providing frequency domain synchronization for a single carrier signal such as a vestigial sideband signal. The system comprises a synchronization circuit that is capable of obtaining a coarse frequency estimate of the single carrier signal and a fine frequency estimate of the single carrier signal. The system also comprises a three state machine for obtaining an accurate frequency estimate from three separately obtained frequency estimates. The system also comprises a DC estimator circuit that is capable of providing a time domain DC estimate. The system provides a pilot carrier recovery circuit for single carrier signals that has a linear transfer function.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Method and apparatus for metadata synchronization
InactiveUS7333725B1Accurate time informationHigh precisionTelevision system detailsProjectorsTime informationGps receiver
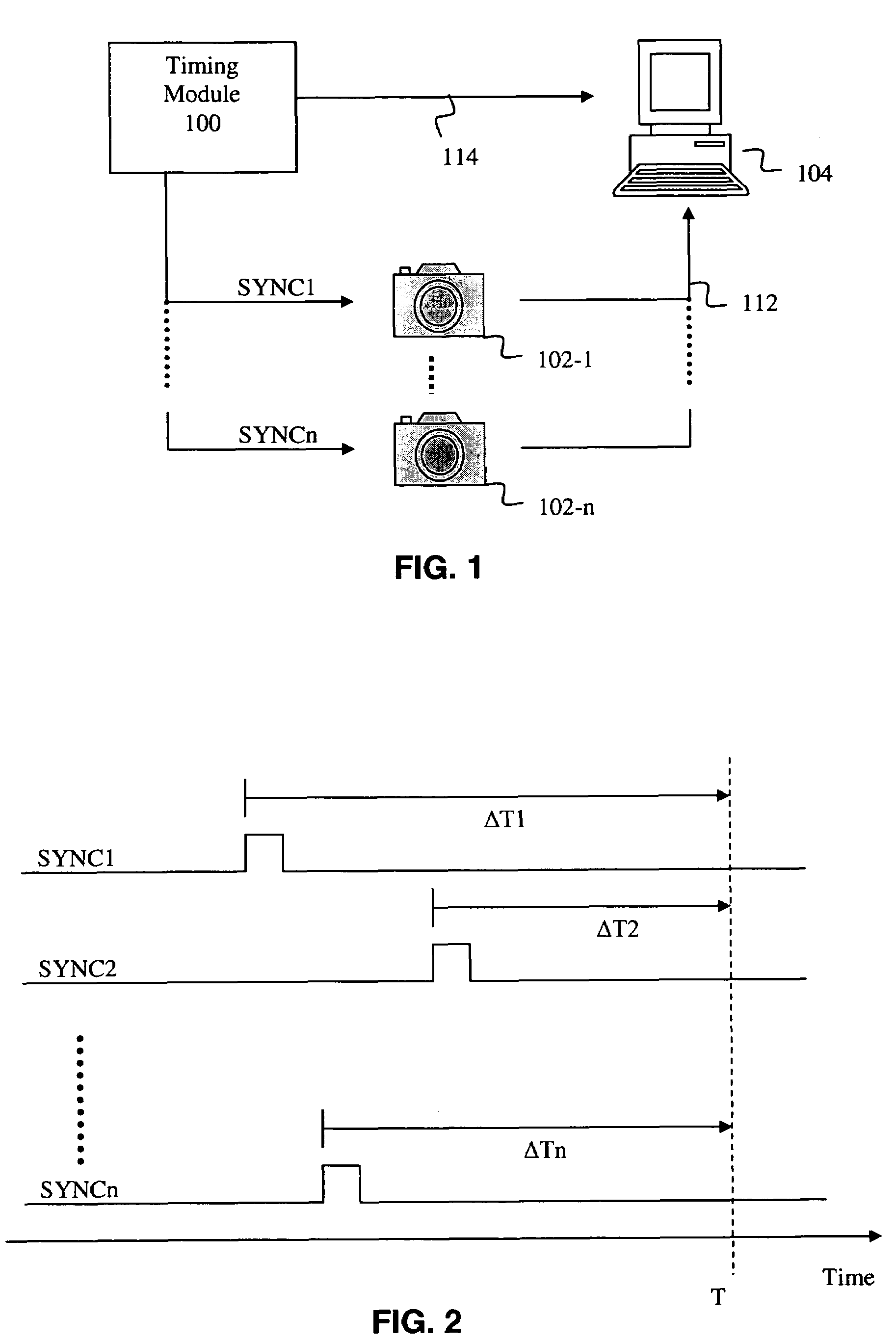
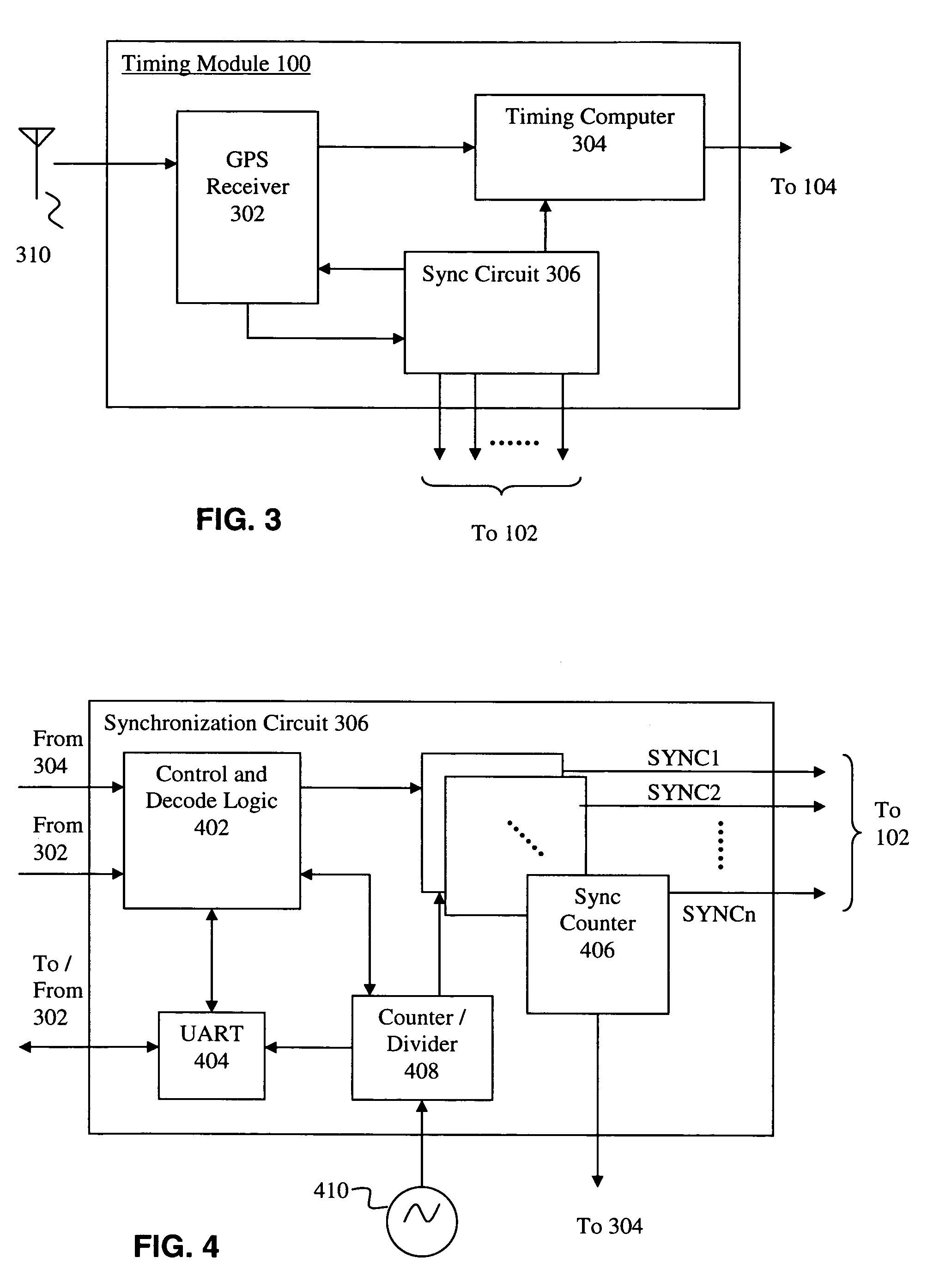
A method and apparatus provides for accurately synchronizing a plurality of sensors, as well as for providing accurate timing information (e.g. timing metadata) associated with the synchronized data capture. According to one aspect of the invention, an apparatus includes a synchronization circuit that stores a counter having a value corresponding to the delay characteristics of an associated sensor. The counter is used to provide a synchronization pulse to the associated sensor which is offset from a desired synchronization time by an amount that will compensate for the delay characteristics. In one example, one counter is provided for each associated sensor, allowing a high degree of accuracy in synchronization among a plurality of sensors. According to another aspect of the invention, the synchronization pulses are locked onto and derived from a pulse received from a GPS receiver. The GPS receiver is also used to mark time associated with the generated synchronization pulses, and thus obtain highly accurate time information (e.g. metadata) associated with the synchronization pulses provided to the sensors.
Owner:L 3 COMM CORP
Multiphase Power Converter Circuit and Method
ActiveUS20150016159A1Efficient power electronics conversionPhotovoltaicsPower flowElectrical current
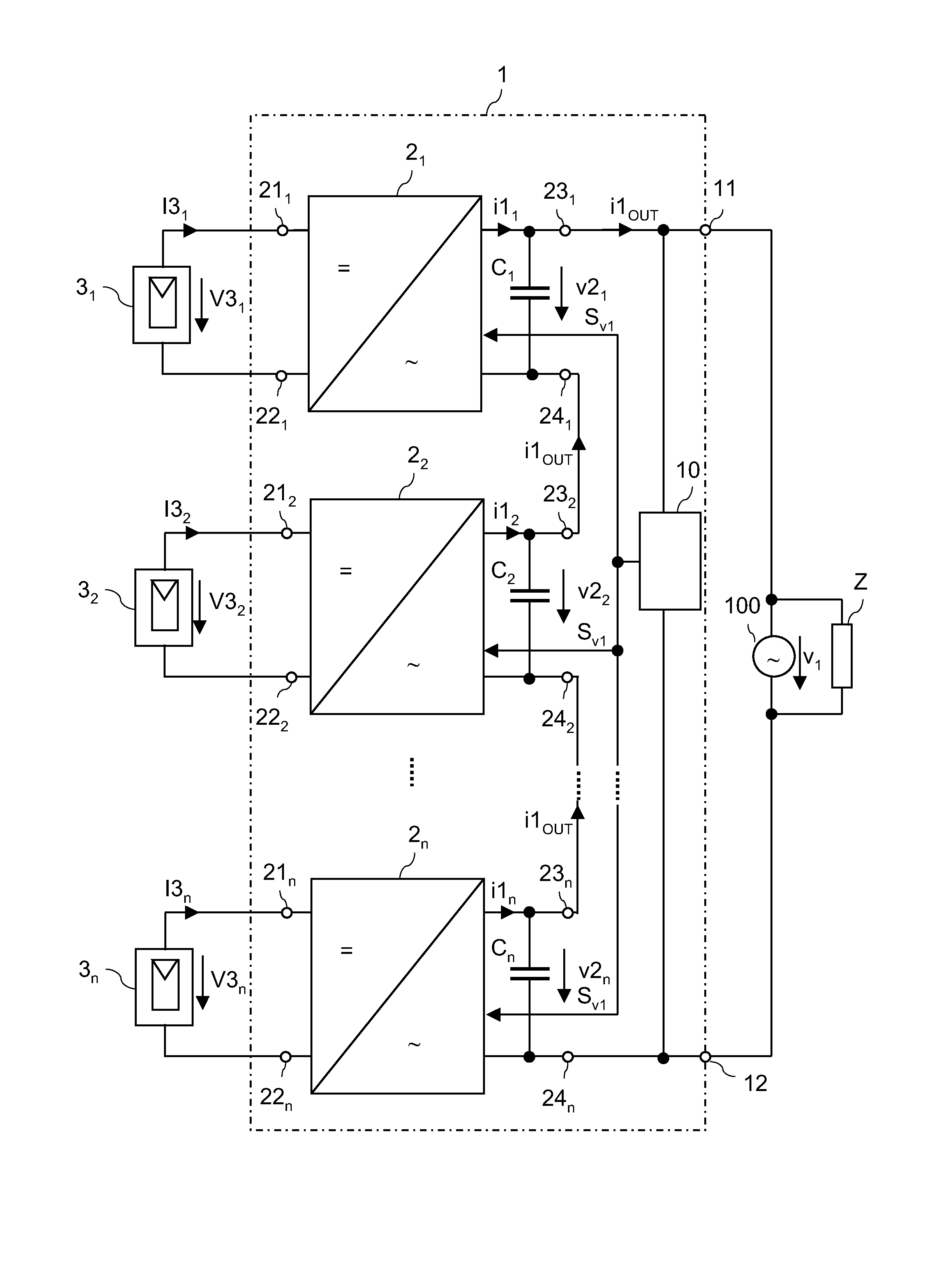
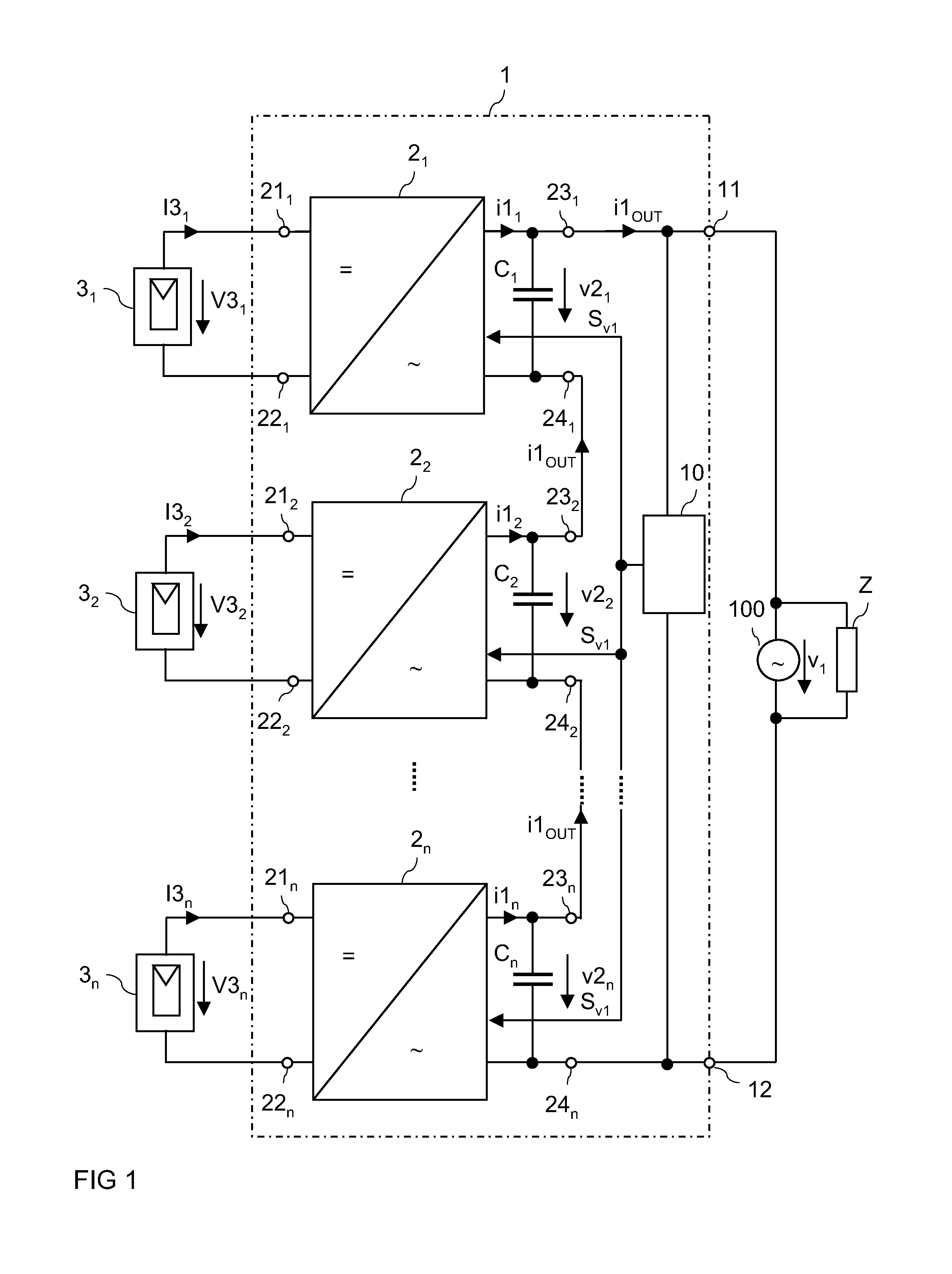
A multiphase power converter circuit includes at least two single phase power converter circuits. Each single phase power converter circuit includes at least one converter series circuit with a number of converter units. The converter series circuit is configured to output a series circuit output current. A synchronization circuit is configured to generate at least one synchronization signal. At least one of the converter units is configured to generate an output current such that at least one of a frequency and a phase of the output current is dependent on the synchronization signal.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AUSTRIA AG
Centralized synchronization for wireless networks
InactiveUS7324559B2Undo distortion effectAccurate samplingSynchronisation arrangementFrequency-division multiplex detailsRadio networksDigital radio
This invention synchronizes the sample clocks of an entire wireless network from a single central base station. Unlike a conventional digital radio network where every terminal must have a synchronization circuit in its receiver to adjust the sample clock, each of the radio terminals in this network is clocked from an independent free-running oscillator. For each terminal, the base station learns the frequency and phase of the oscillator by exchanging a special set of signals: first a vernier signal to determine the initial time and frequency offset, and then an early-late signal to track changes in the oscillator. Once the base station is synchronized to the terminal's oscillator, it can determine the absolute path delay between itself and the terminal and correct for the delay using an equalizer. Signals received from the terminal are corrected after the signal arrives at the base station. Signals sent to the terminal are corrected within the base station before they are transmitted so they arrive at the terminal at the precise time that the terminal's free running oscillator takes a sample.
Owner:TELECOMM RES LAB
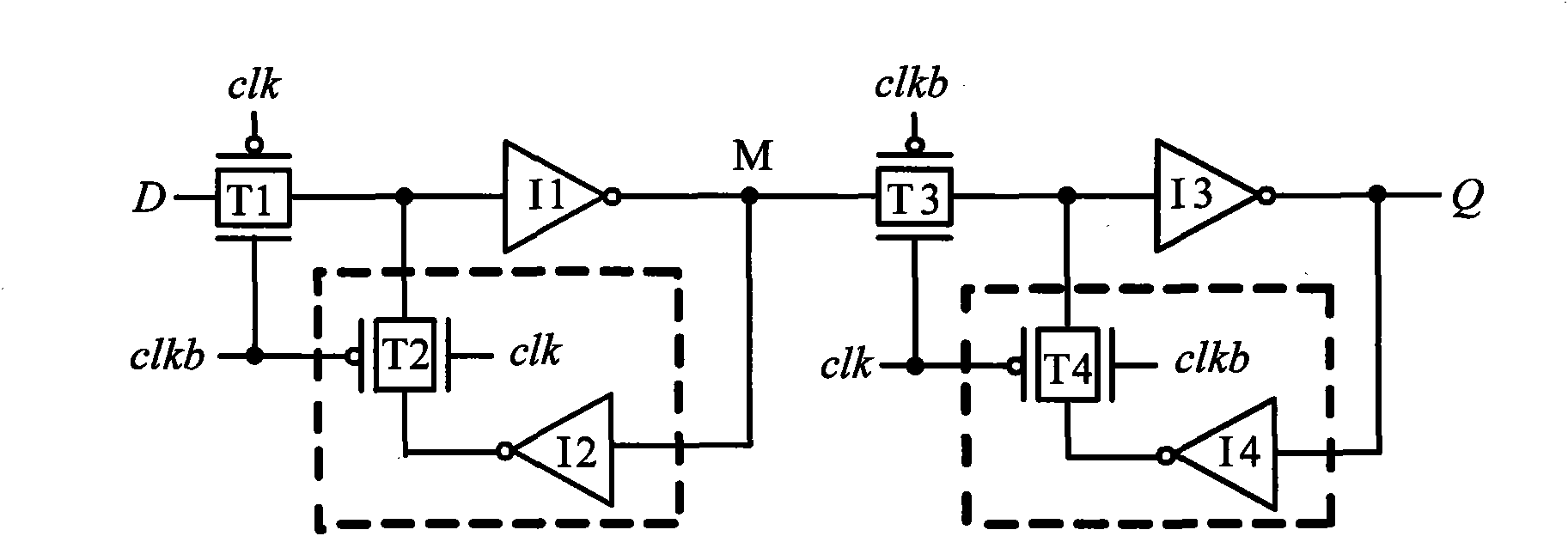
Low-power dissipation RS latch unit and low-power dissipation master-slave D flip-flop
InactiveCN101777907ASimple and completely symmetrical structureGood leakage power suppression performanceElectric pulse generatorLogic circuitsHemt circuitsControl theory
The invention discloses a low-power dissipation RS latch unit and a low-power dissipation master-slave D flip-flop, which is characterized in that the low-power dissipation RS latch unit comprises an input driving and synchronizing circuit, a pull-down circuit, a function control circuit, a first phase inverter and a second phase inverter, wherein the first phase inverter and the second phase inverter are mutually overlapped and coupled. The low power dissipation master-slave D flip-flop is composed of an input phase inverter, a clock phase inverter, a first low-power dissipation RS latch unit and a second low-power dissipation RS latch unit, wherein the first low power dissipation RS latch unit and the second low power dissipation RS latch unit have the same inner structure and are cascaded. The low power dissipation master-slave D flip-flop has the advantages that the low-power dissipation RS latch units use three kinds of leaked power consumption lowering technology, i.e. P-type logic technology, function control technology and double-threshold technology, so that the low-power dissipation RS latch units have better leaked power consumption inhibiting performance. The low-power dissipation master-slave D flip-flop has simple and totally symmetrical circuit structure. Compared with the traditional single-threshold transmission gate D trigger circuit, the invention can save 80% of leaked power consumption and 40% of total power consumption in the 90 nm process, so that the invention is suitable to serve as a digital circuit unit to the design of low-power consumption integrated circuits in the deep sub-micron CMOS process.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
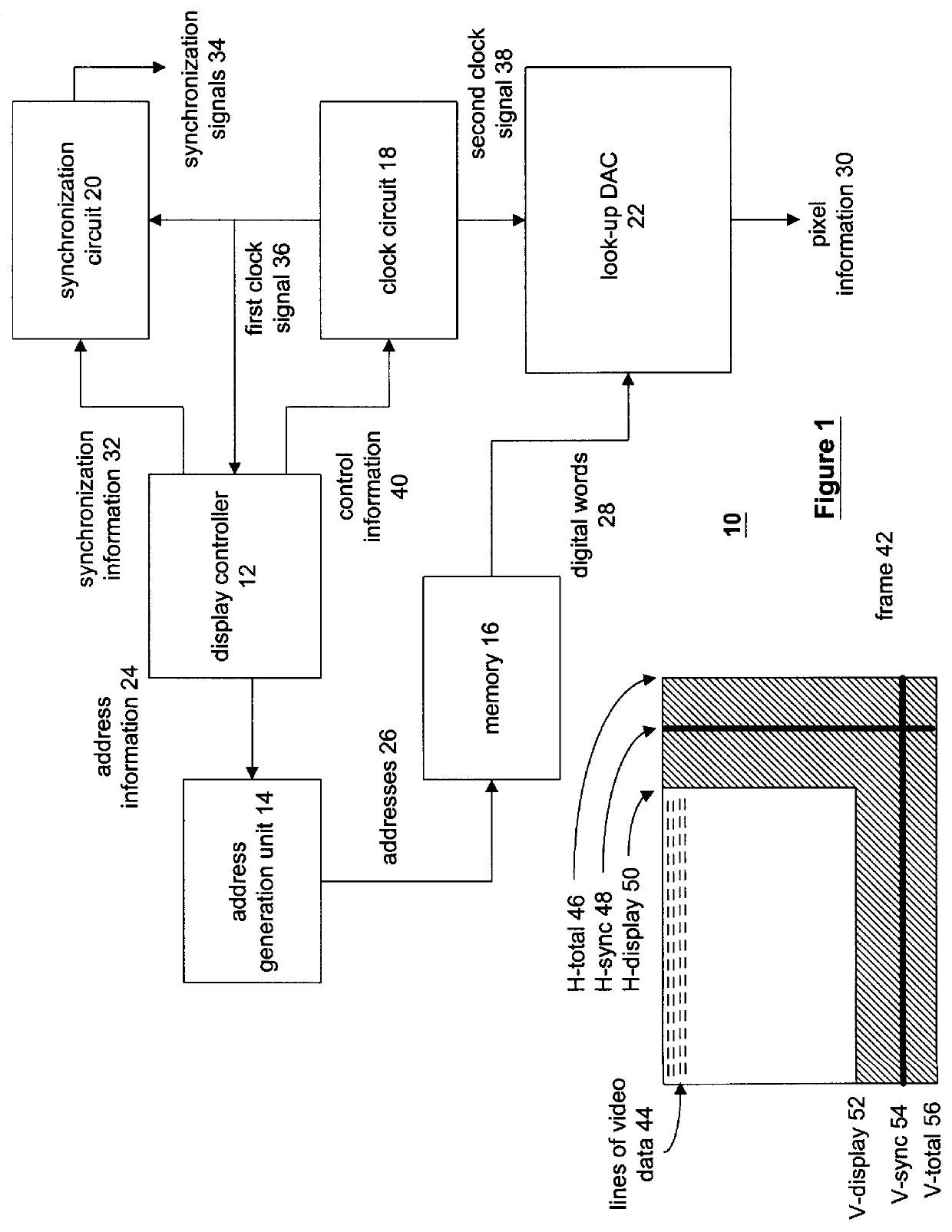
Method and apparatus for processing video data utilizing a palette digital to analog converter
InactiveUS6067083ALess powerDisabling itCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingGraphicsDigital analog converter
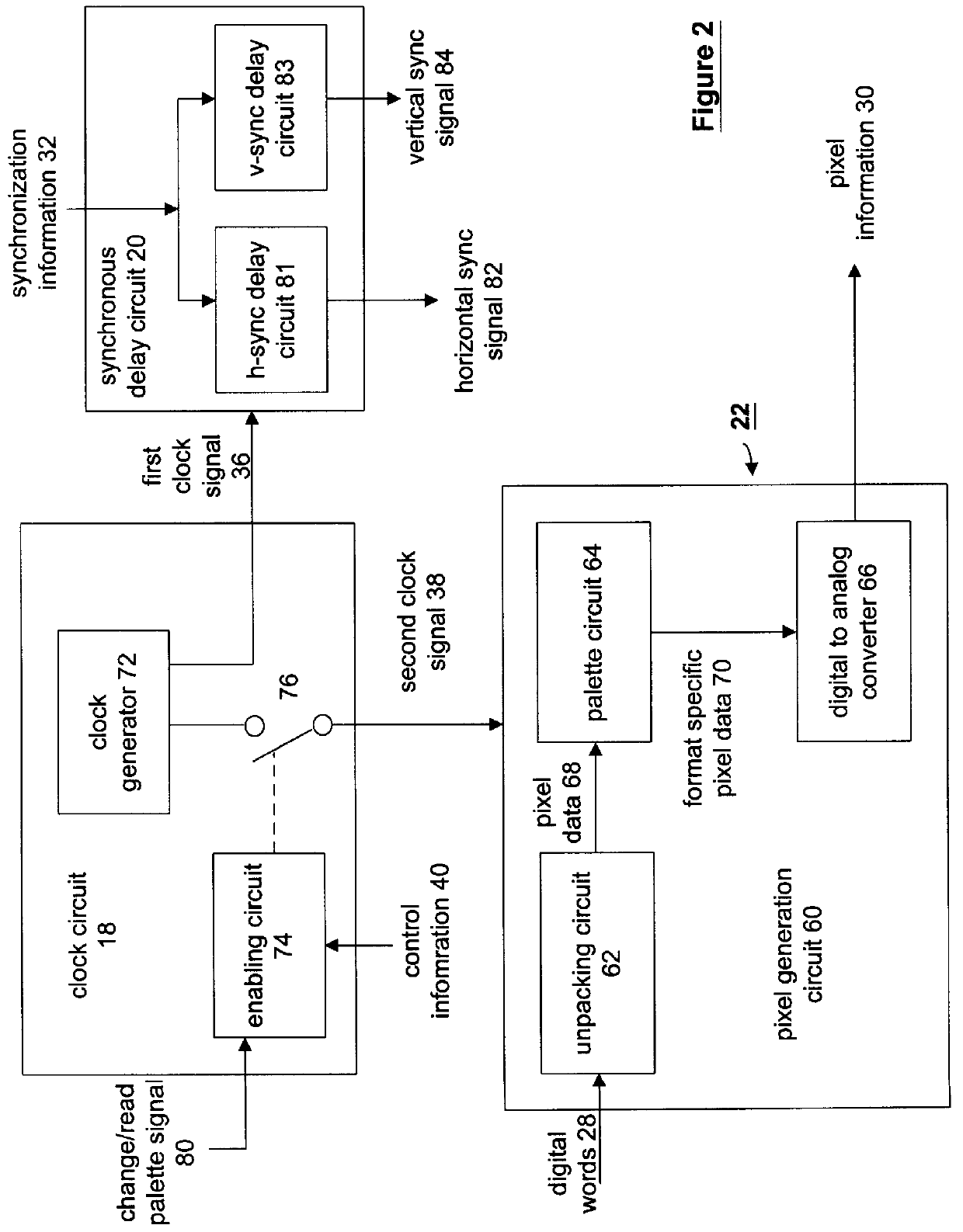
A method and apparatus for processing video graphics utilizing less power is accomplished by providing a clock circuit that generates a clock signal. The clock signal is fed to a synchronization circuit that generates horizontal and vertical retrace. The clock signal is also provided to a look-up table DAC (digital to analog converter), or a palette DAC. While the video graphics circuit is processing data for display, the clock circuit provides the clock signal to the both the look-up table DAC and the synchronization circuit. When the data being processed is non-video data (i.e., the horizontal and vertical synchronization information), the clock circuit ceases to provide the clock signal to the look-up table DAC, which disables the look-up table DAC. Thus, it is not consuming power. The clock circuit again provides the clock signal to the look-up table DAC when the data being processed is video data (i.e., the data that is to be displayed).
Owner:ATI TECH INC
Pseudo-synchronization of the transportation of data across asynchronous clock domains
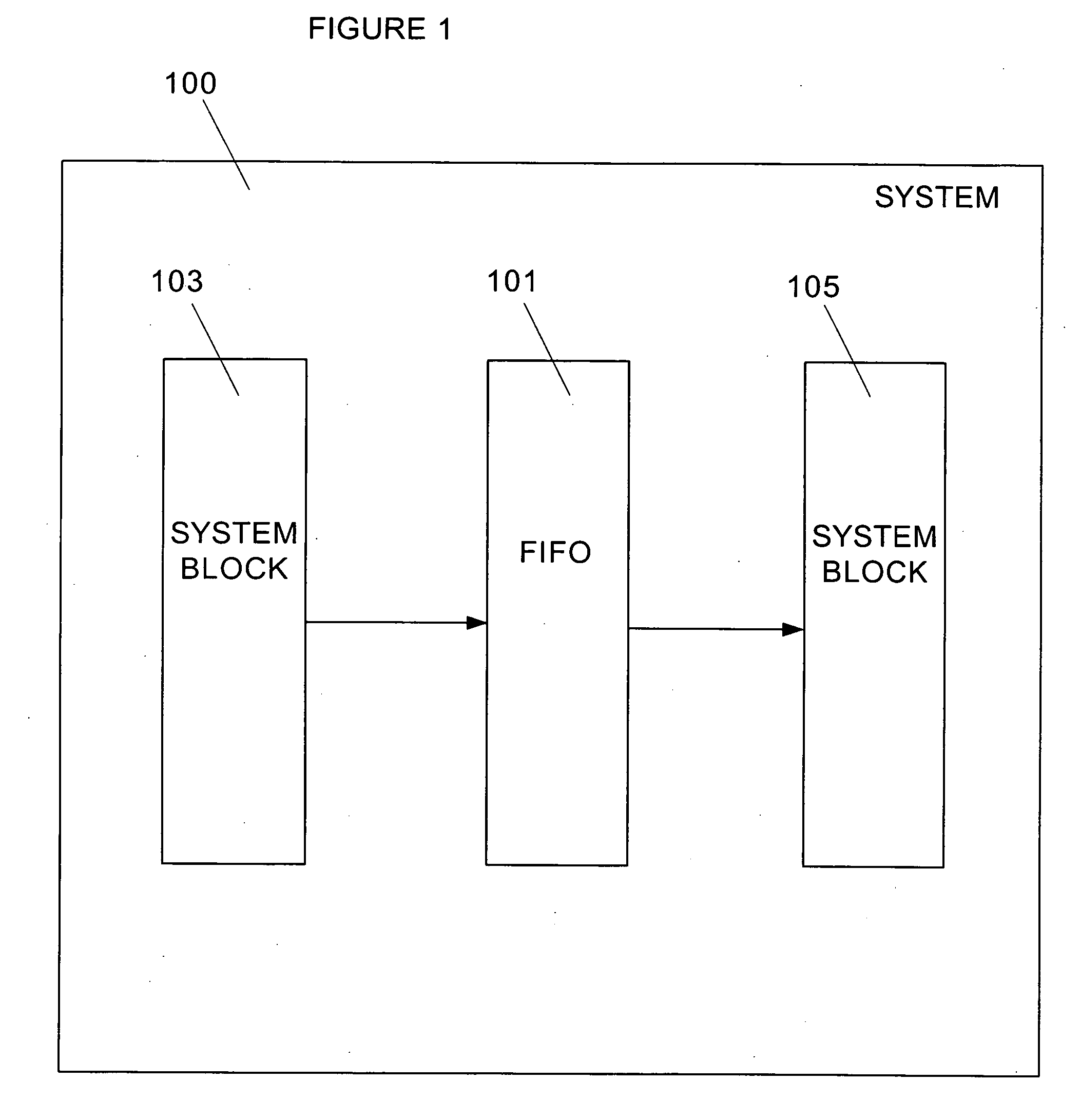
A pseudo-synchronous temporary storage element transports data between two system blocks with different clock systems by pseudo-synchronizing the clock edges of the two clock signals. The pseudo-synchronization circuit may be an integral part of a storage element, a separate pseudo-synchronization device, or a discrete add-on circuit to an off the shelf storage element device.
Owner:VIA TECH INC
Interface circuit
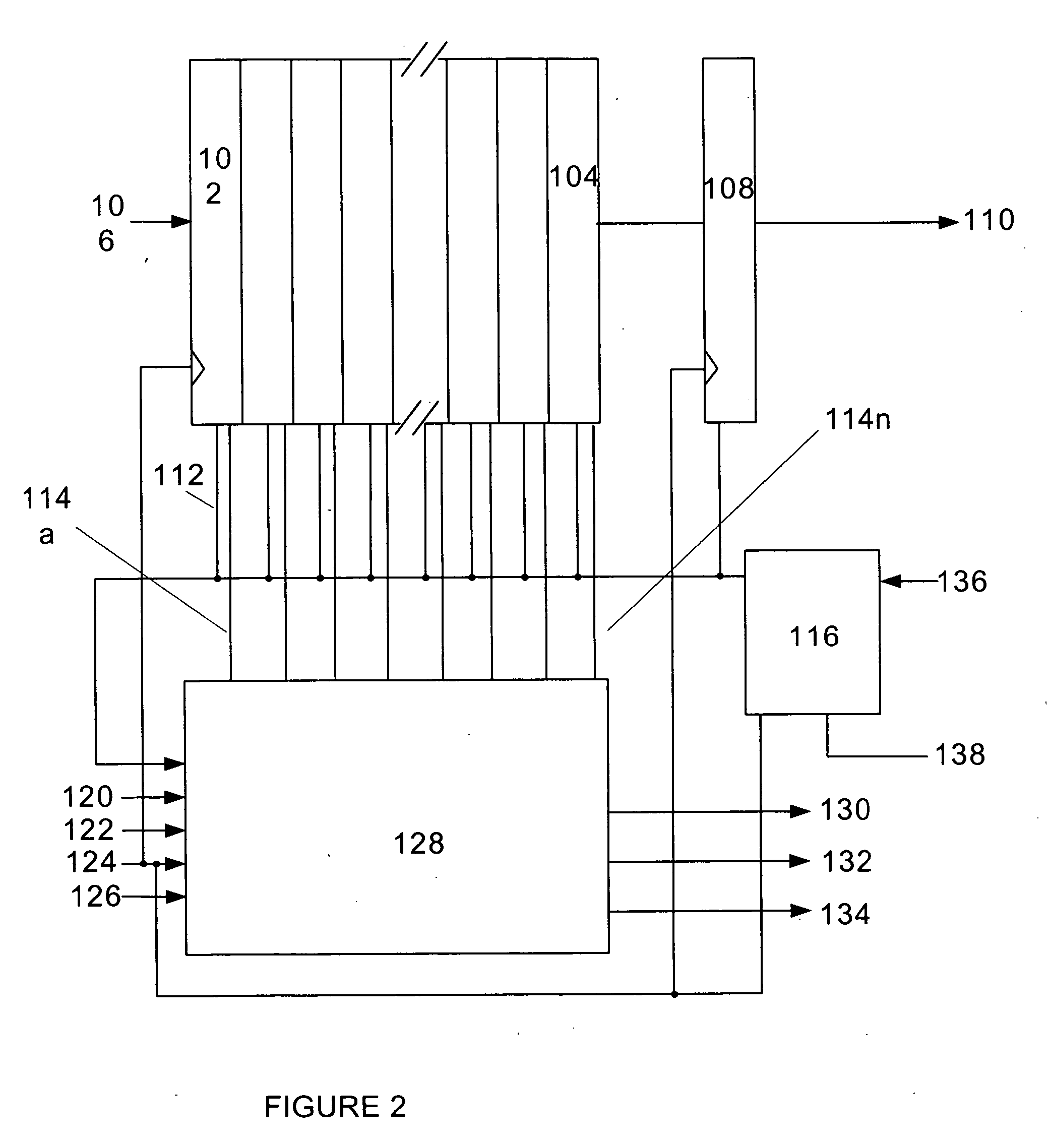
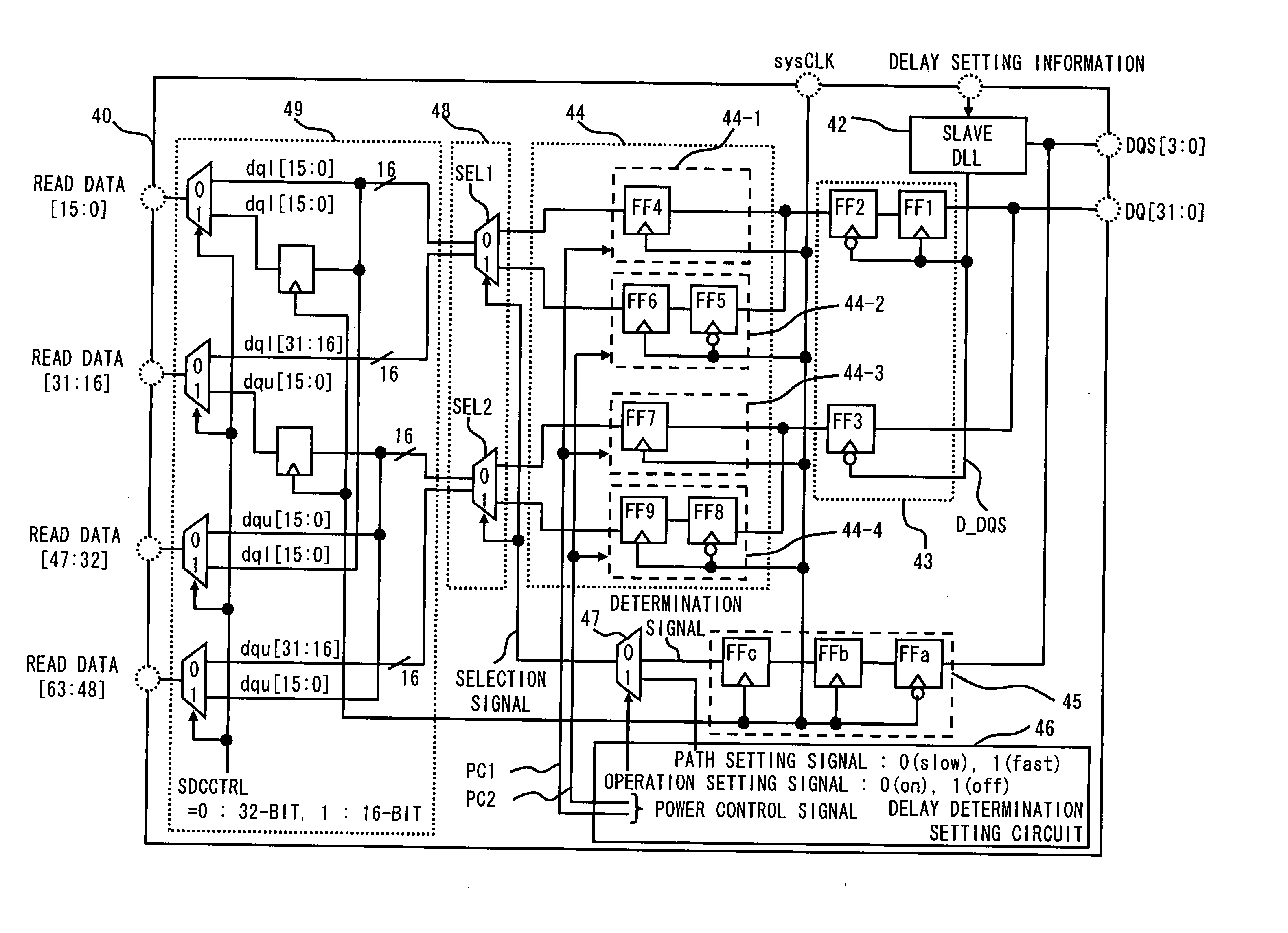
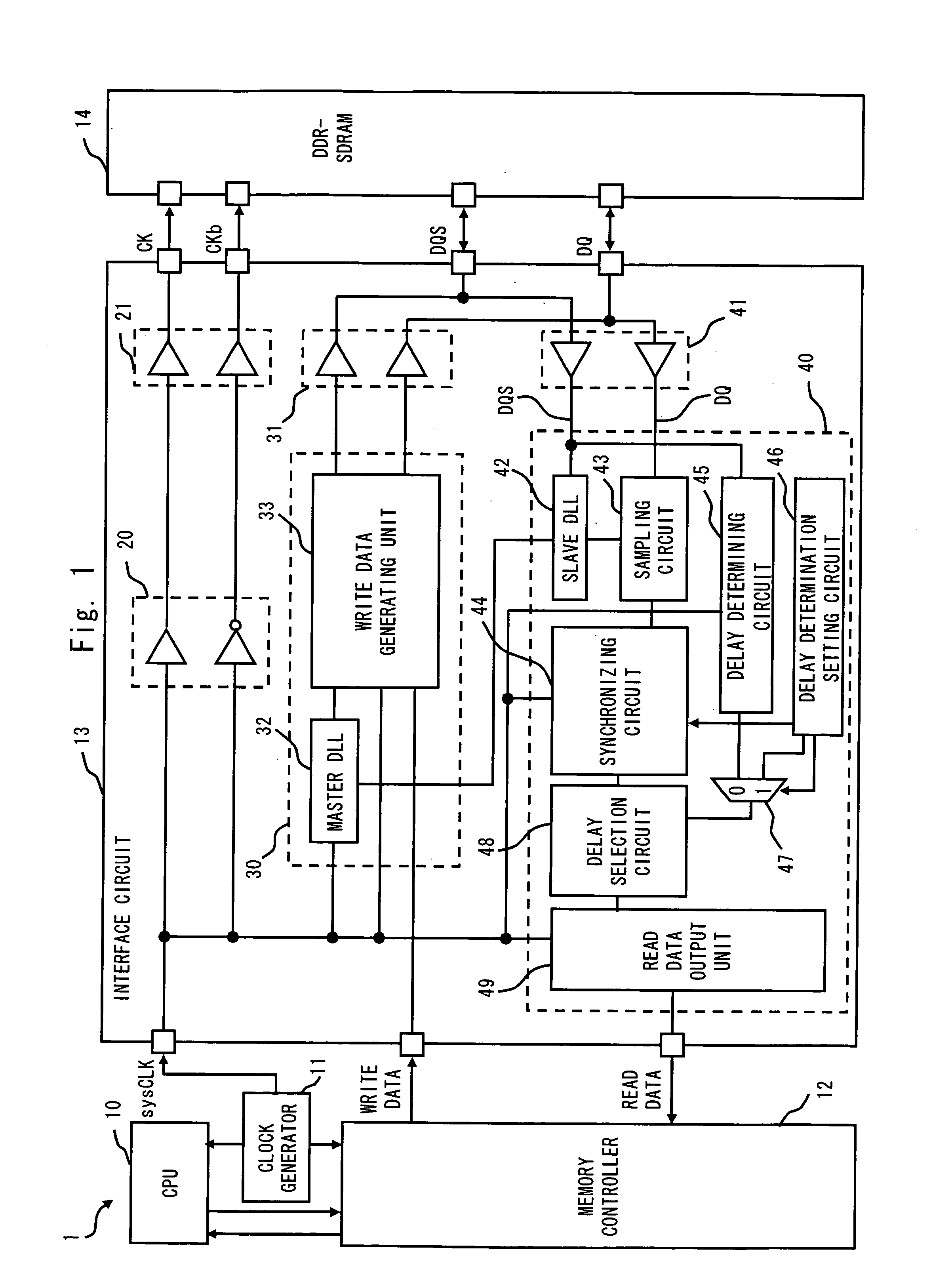
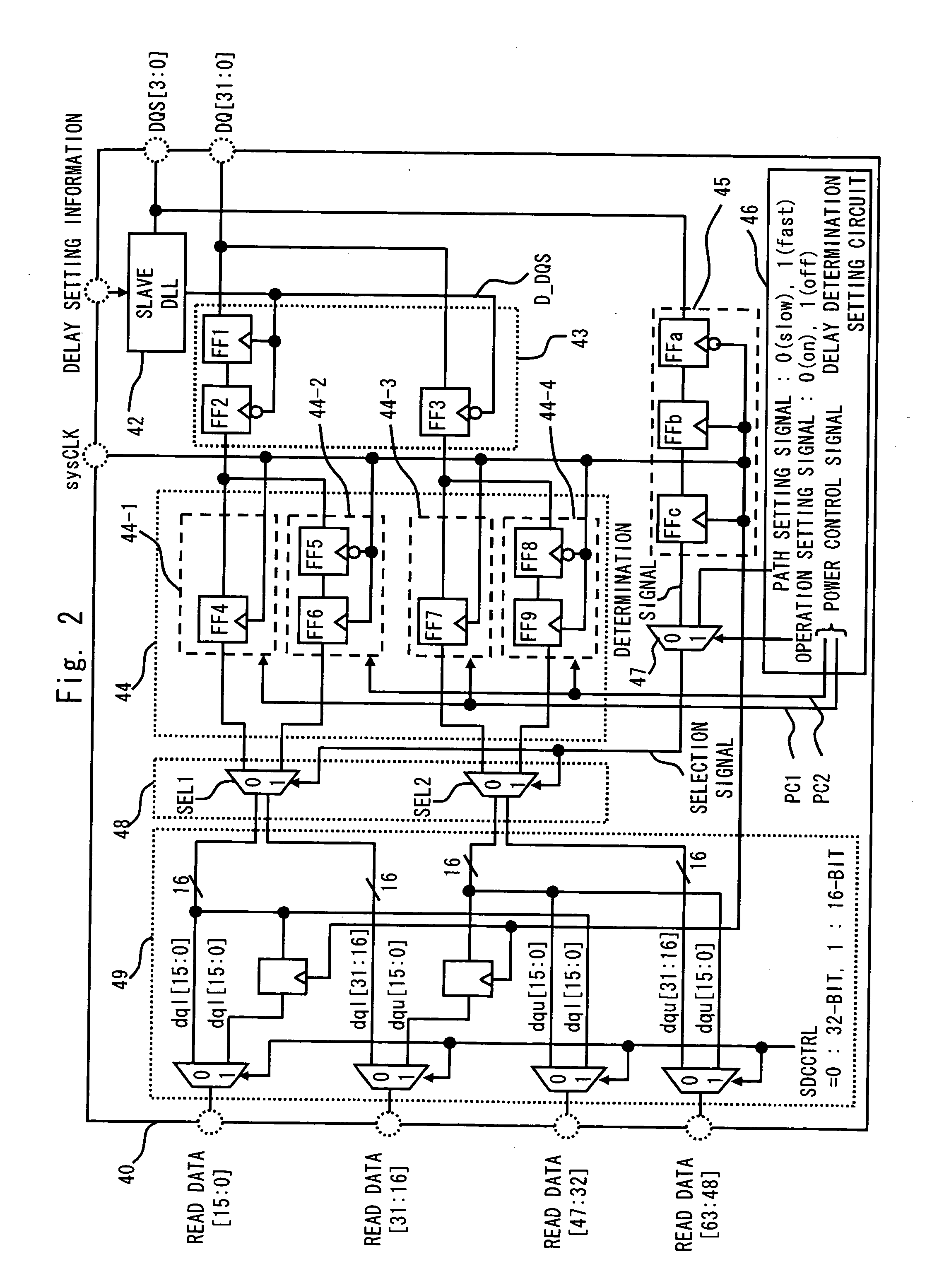
InactiveUS20070058478A1Easy to masterReduce power consumptionDigital storageComputer scienceInterface circuits
An interface circuit includes: a first synchronizing circuit for synchronizing a signal having a delay equal to or more than a predetermined period with respect to a reference clock, with the reference clock; a second synchronizing circuit for synchronizing a signal having a delay less than the predetermined period with respect to the reference clock, with the reference clock; a delay determining circuit for outputting a determination signal based on a delay of the signal relative to the reference clock; a delay determination setting circuit for outputting a path setting signal that designates an output value of one of the first synchronizing circuit and the second synchronizing circuit based on a preset value; and a delay selecting circuit for selecting and outputting an output value of one of the first synchronizing circuit and the second synchronizing circuit based on one of the determination signal and the path setting signal.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
LED dimming control technique for increasing the maximum PWM dimming ratio and avoiding LED flicker
ActiveUS20070210725A1Electroluminescent light sourcesSemiconductor lamp usageControl signalControl theory
Circuitry and methodology for providing LED dimming control in a LED driving system having a switching regulator for providing power supply to drive the LED. The switching regulator includes a switching circuit to which an oscillation signal is applied to control switching of the switching circuit. A dimming control input is supplied with a pulse-width modulation (PWM) dimming control signal to provide PWM dimming control of the LED. The dimming control input applies the PWM dimming control signal to control switching of the switching circuit. A synchronizing circuit is provided for synchronizing the oscillation signal to the PWM dimming control signal.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INT UNLTD
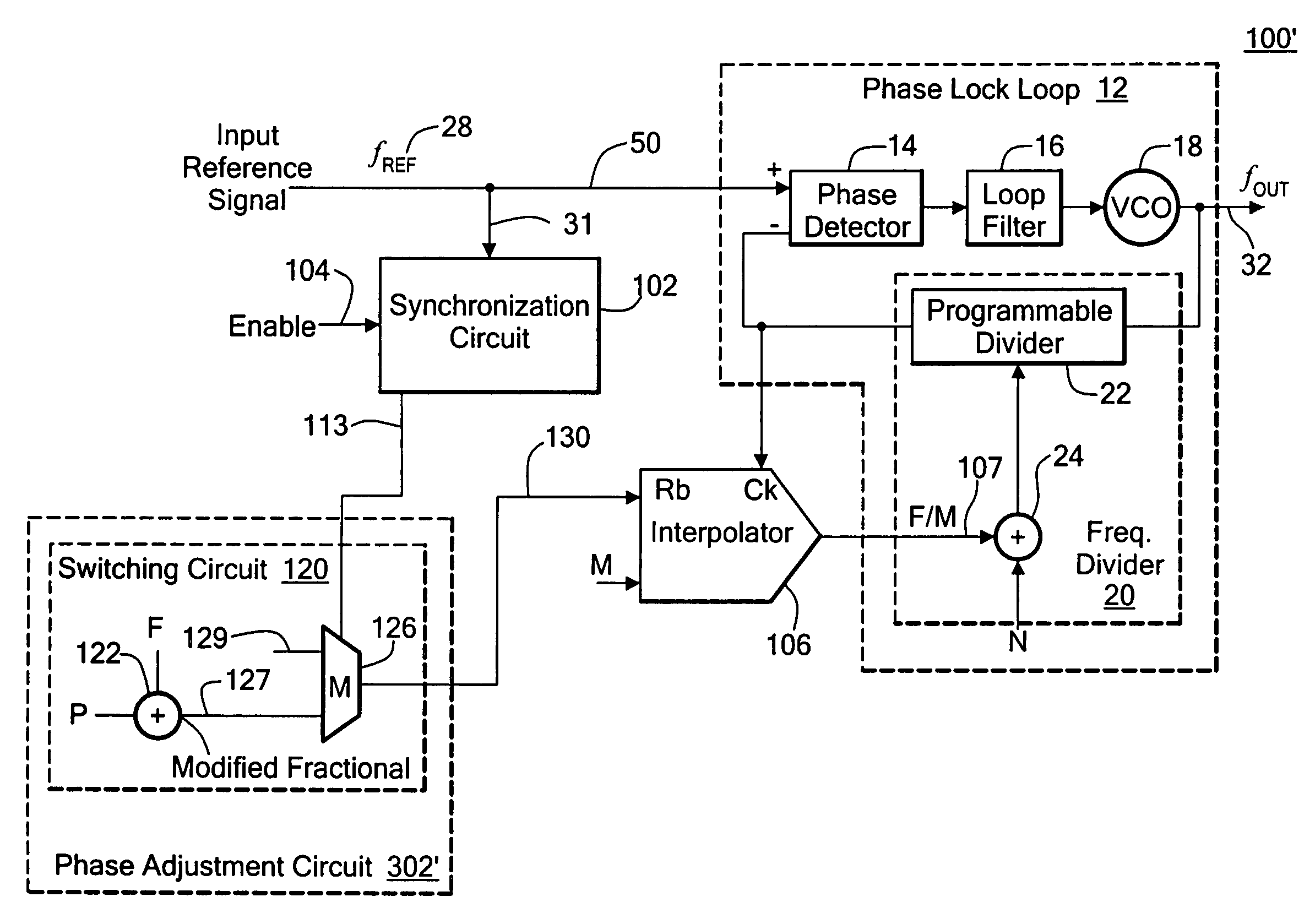
Fractional-N synthesizer and method of programming the output phase
ActiveUS7463710B2Simple and effective fractional-NPulse automatic controlAngle demodulation by phase difference detectionPhase-locked loopPhase adjustment
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
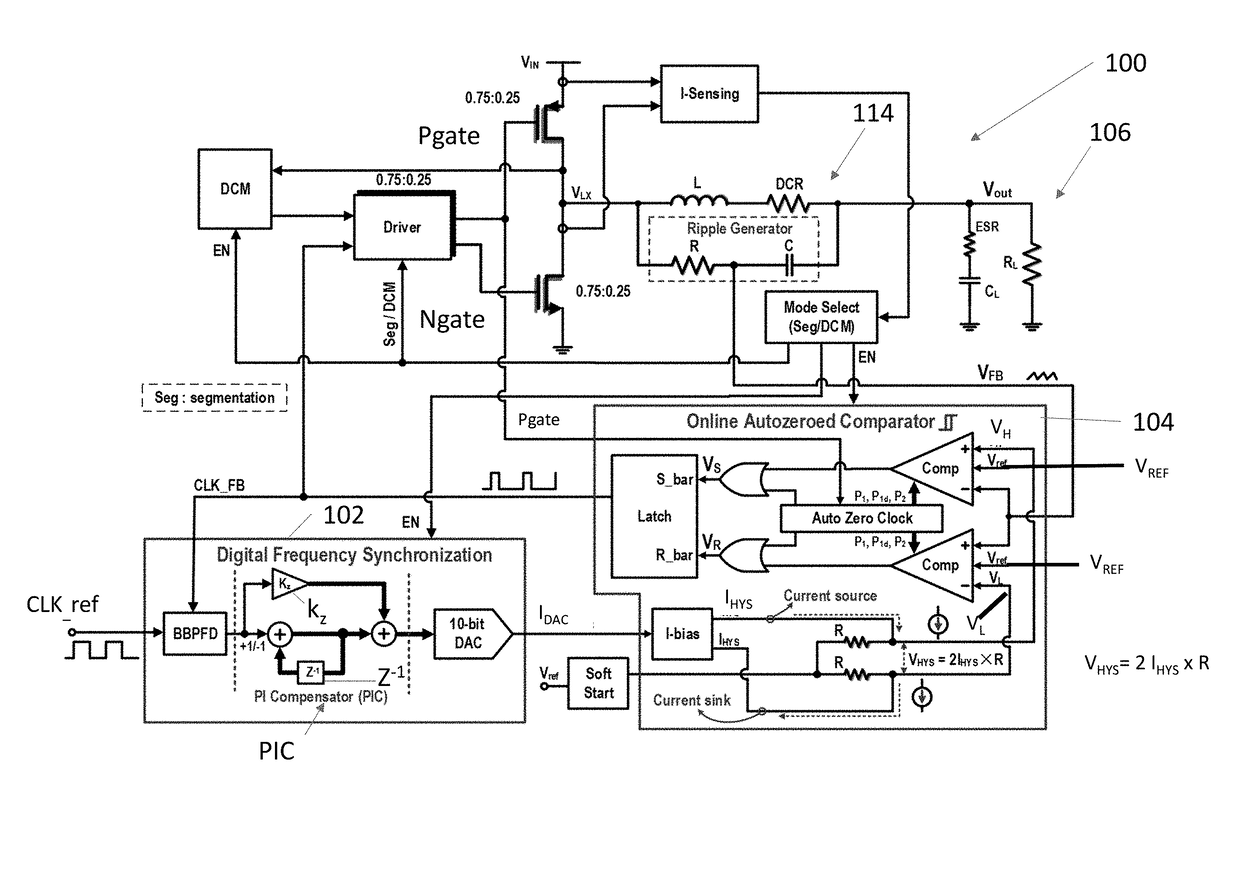
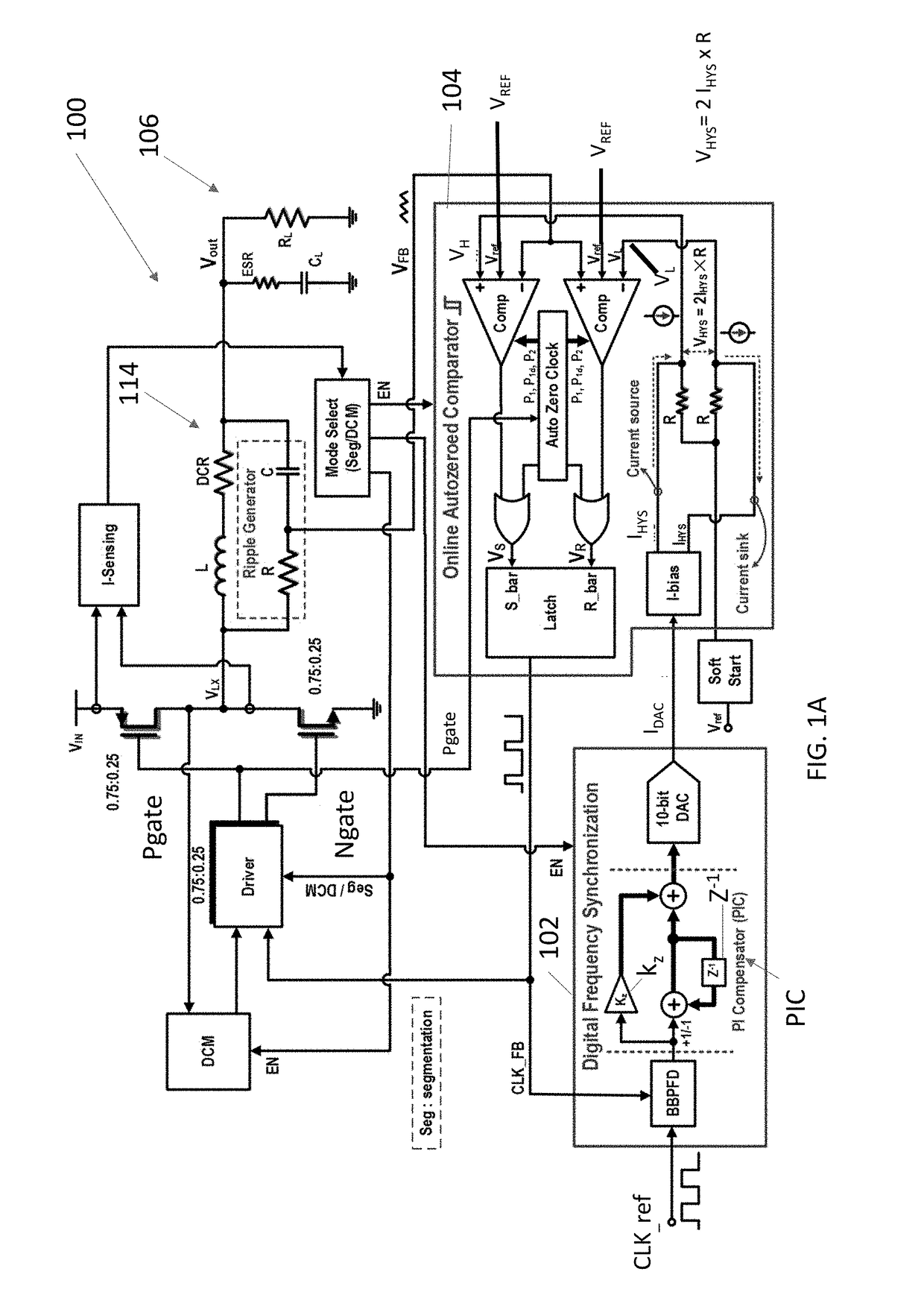
Digital multiphase hysteretic point-of-load dc/dc converter
ActiveUS20180048232A1Improve transient responseOptimal recovery timePulse automatic controlDc-dc conversionPoint of loadConstant frequency
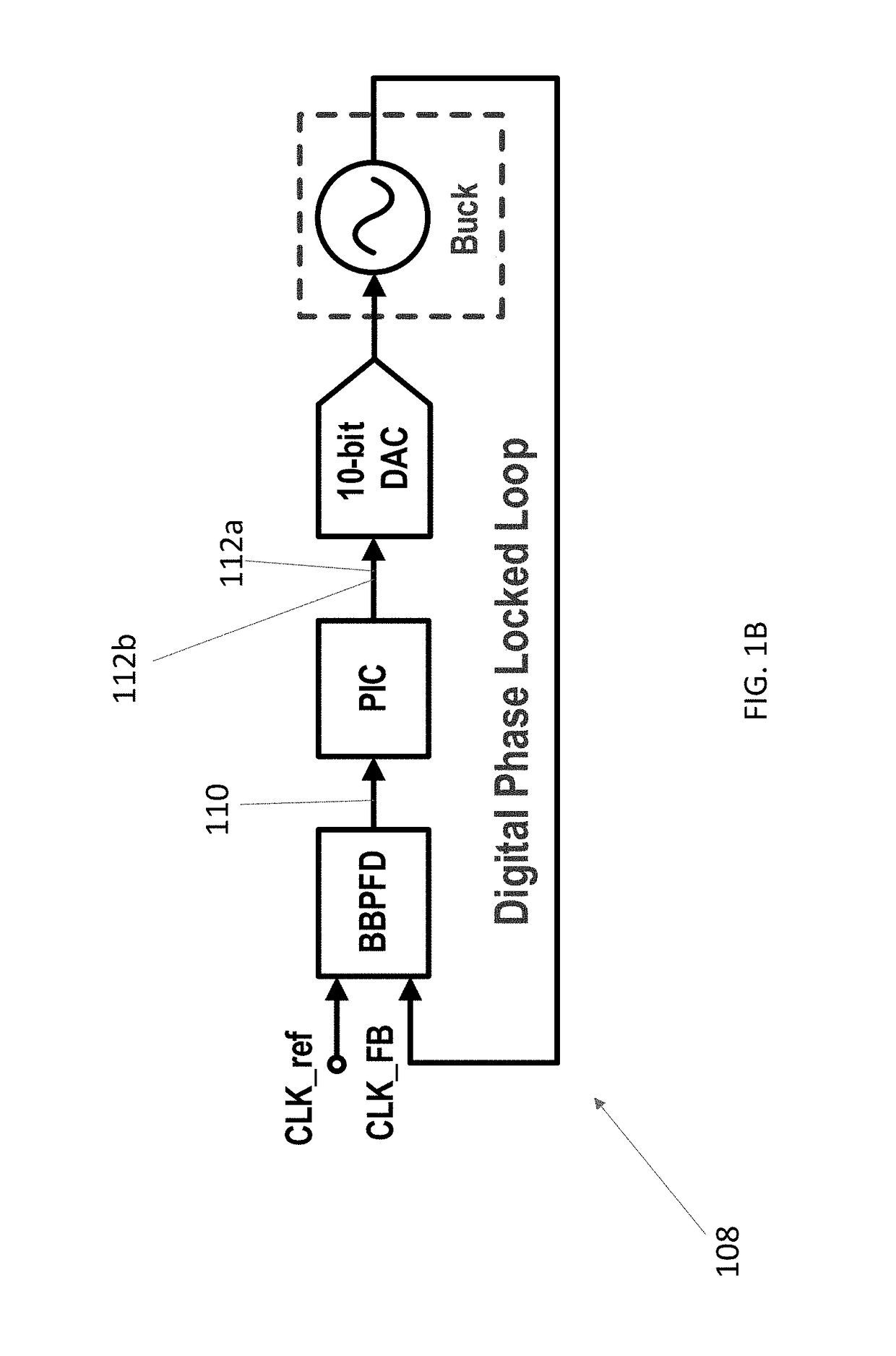
An autozeroed comparator controls a frequency fsw of the input voltage inputted to a DC / DC converter. A digital frequency synchronization circuit is connected to the autozeroed comparator so as to form a phase locked loop, wherein the DES circuit controls the hysteretic window of the autozeroed comparator so as to lock fsw to a clock reference frequency. A plurality of slave phase circuits may be connected to the master phase circuit including the DFS circuit and the autozeroed comparator. Duty cycle calibration circuits adjust a duty cycle signal applied to each of the slave phase circuits, in response to average current measured in the slave phase circuits, so that each slave phase circuit is synchronized with the master phase circuit. A 6 A 90.5% peak efficiency 4-phase hysteretic quasi-current-mode buck converter is provided with constant frequency and maximum ±1.5% current mismatch between the slave phases and the master phase.
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY +1
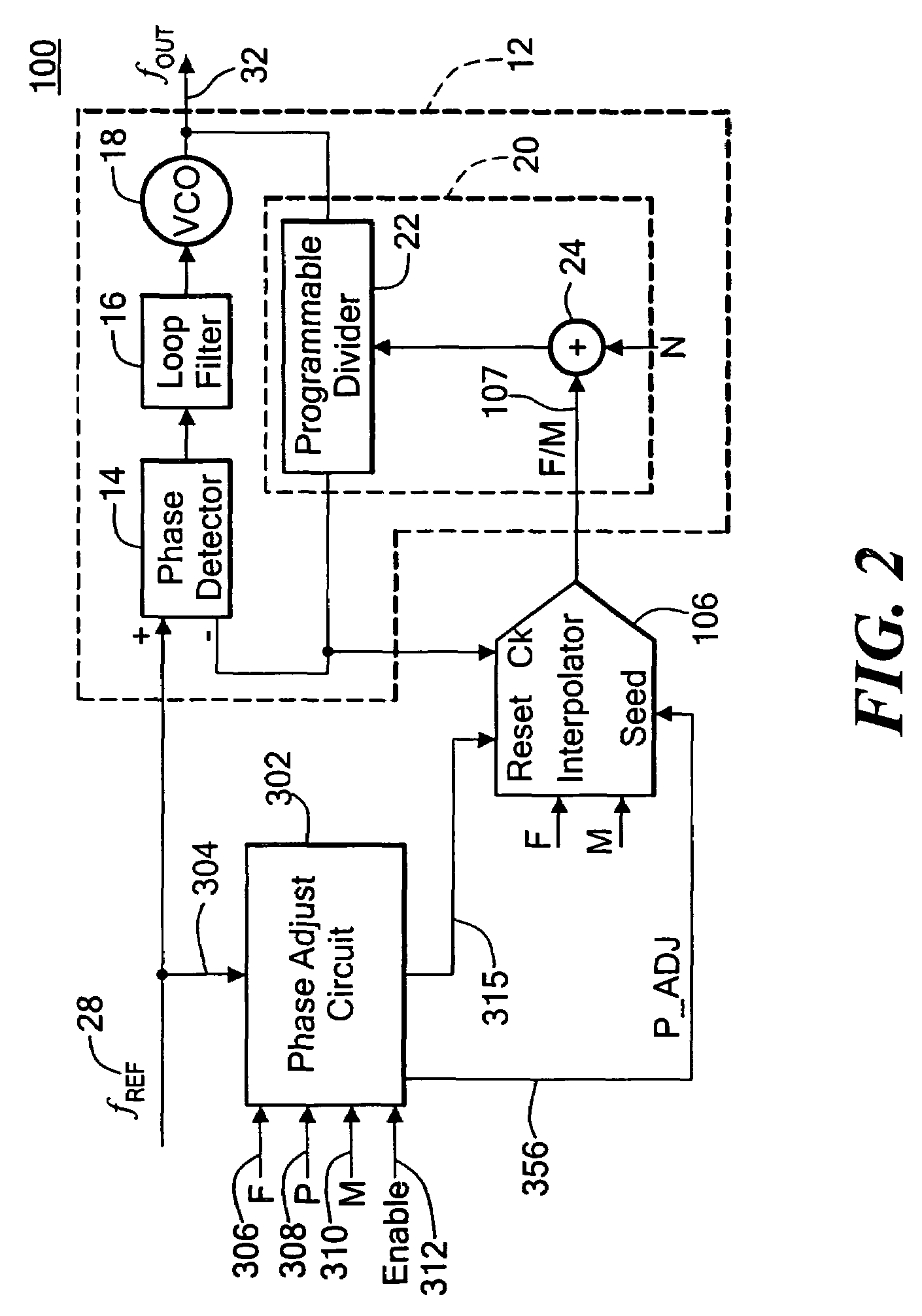
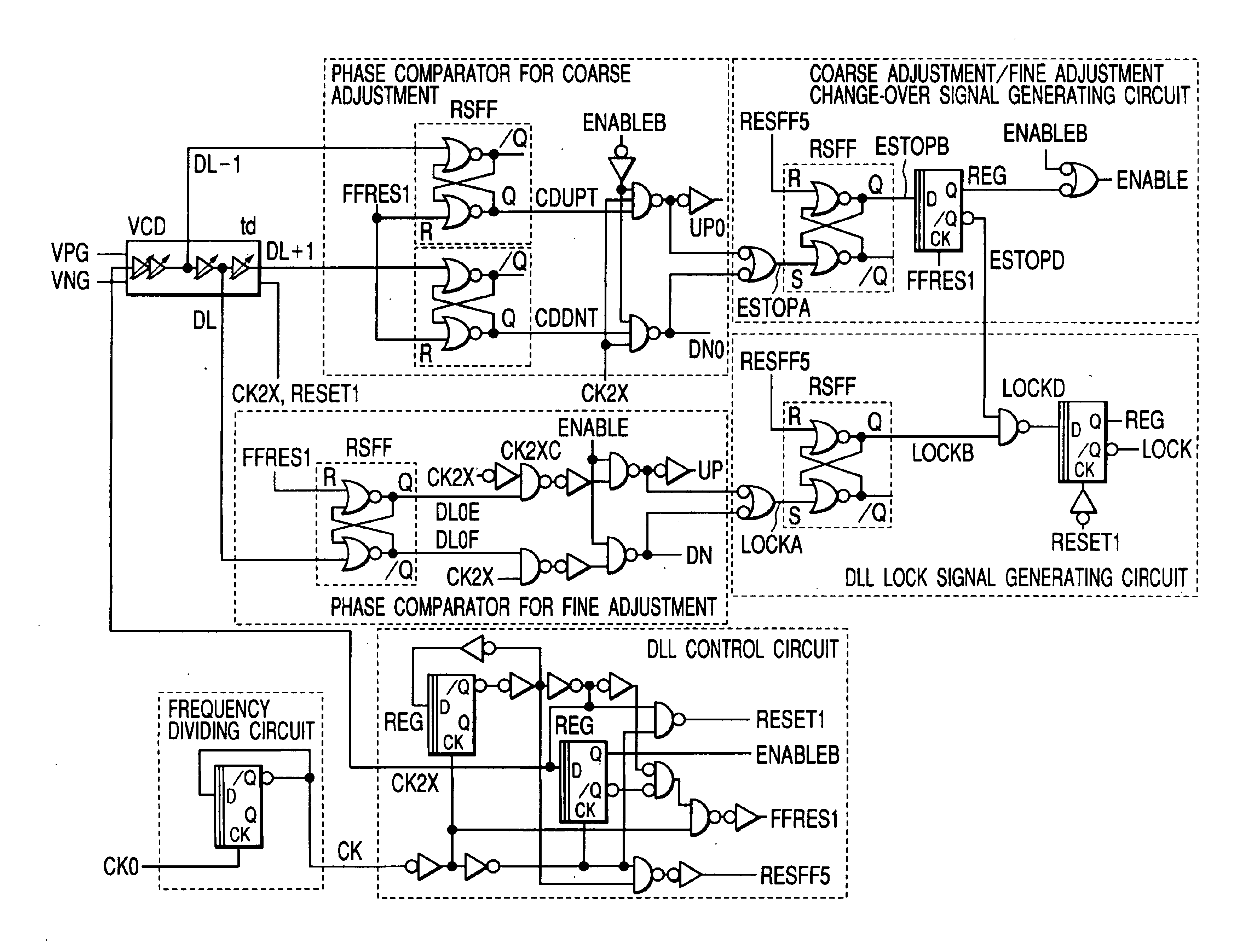
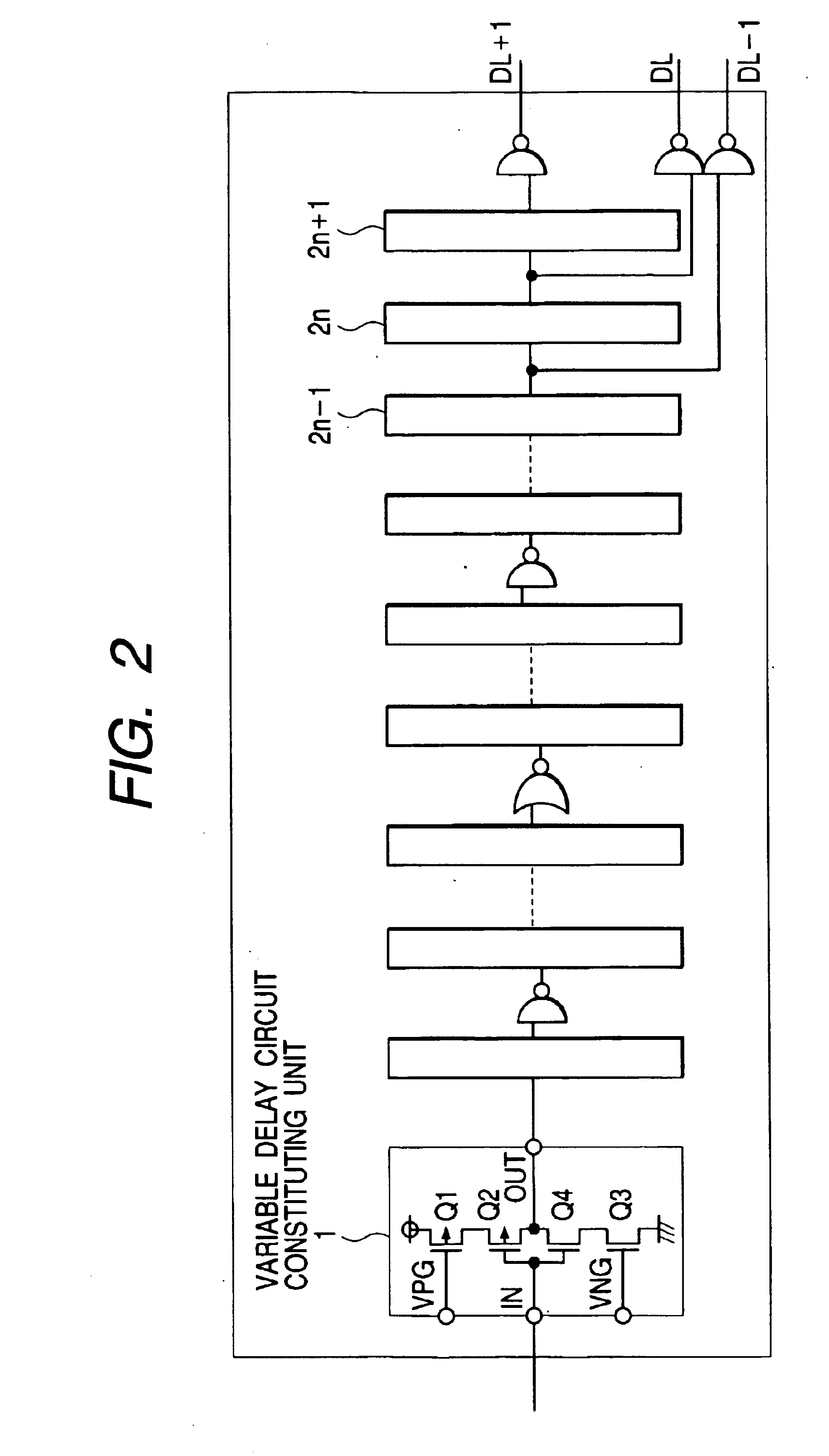
Centralizing the lock point of a synchronous circuit
InactiveUS20050122153A1CentralizationIncrease tuning rangePulse automatic controlElectric pulse generatorMostly TruePhase relationship
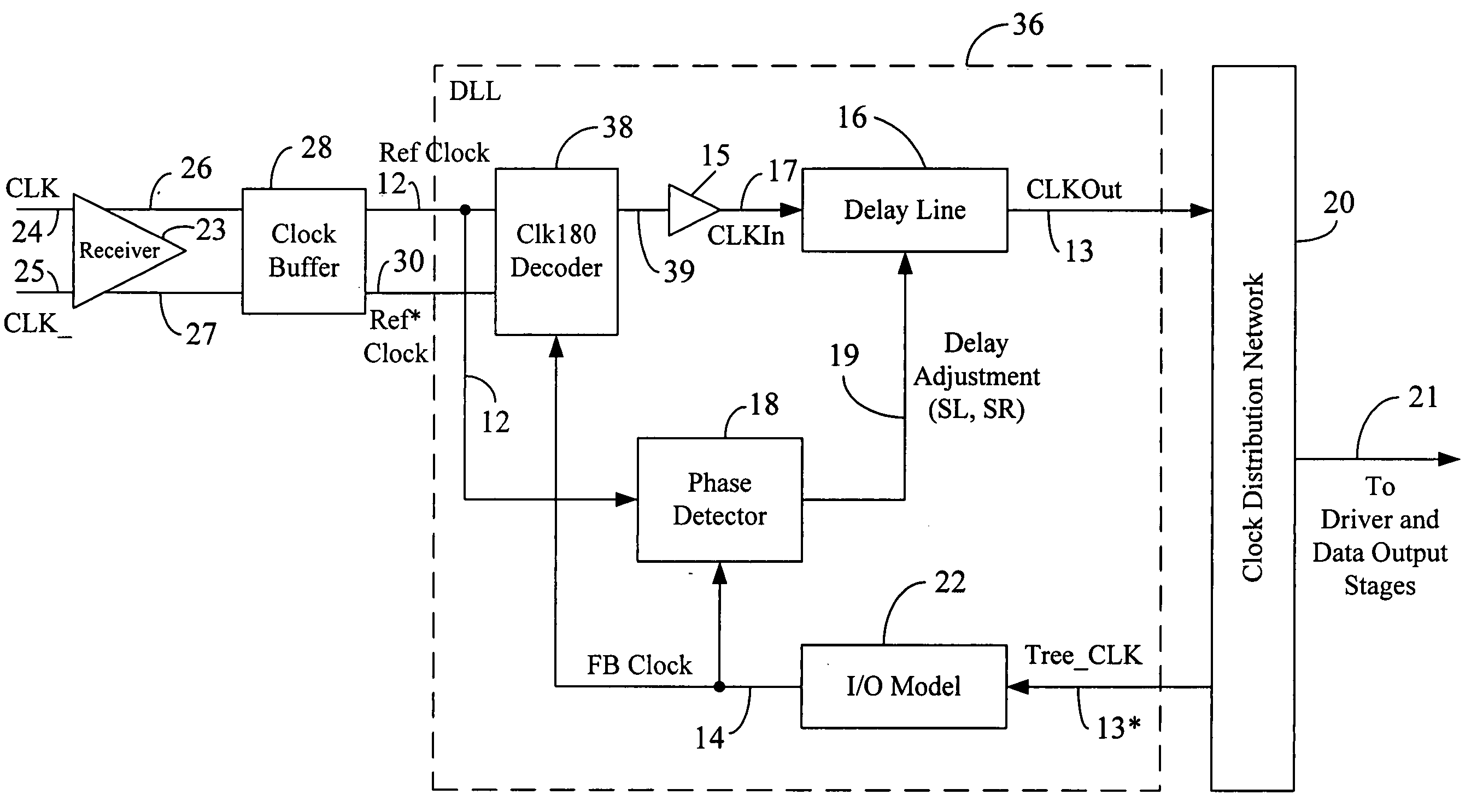
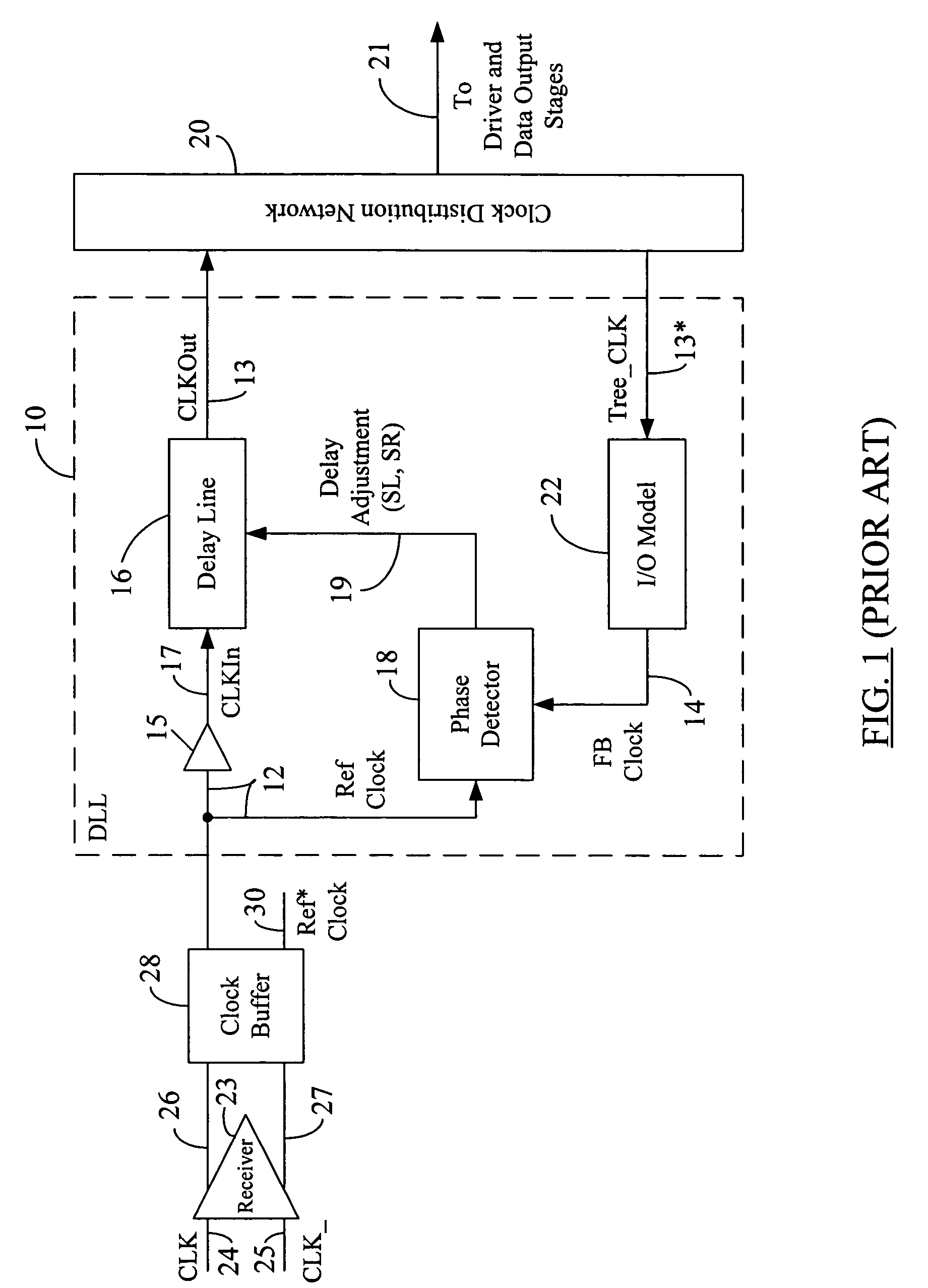
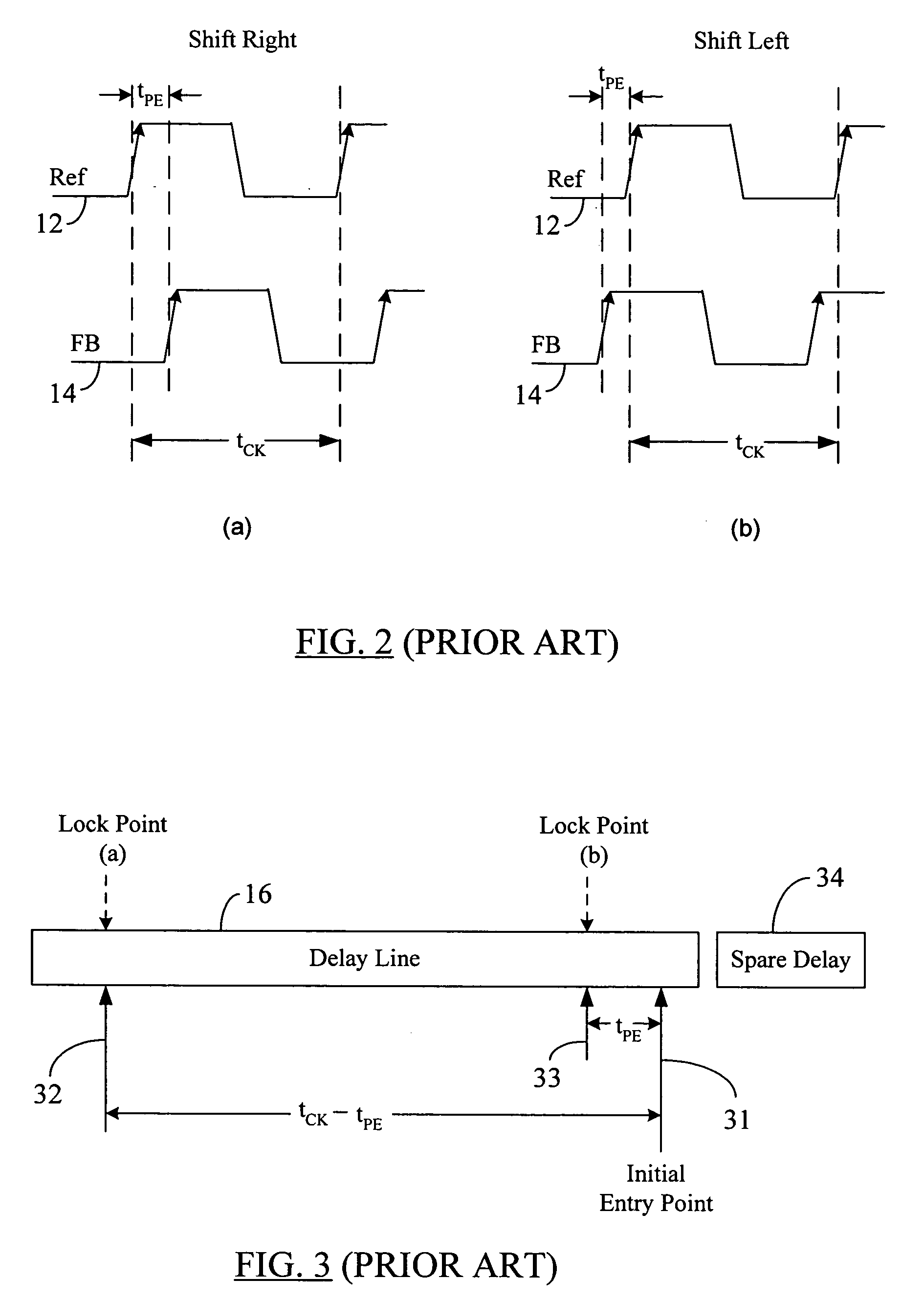
A system and method to establish the lock point of a digital synchronous circuit (e.g., a DLL) at the center of or close to the center of its delay line to provide for extra tuning range in the event of voltage, temperature and frequency changes after the initial lock is established. The delay line receives a clock signal as its input and imparts a given delay to the clock signal to generate a feedback clock that is synchronized or “locked” with the clock signal. The synchronous circuit is configured to selectively use either a reference clock or its inverted version (an inverted reference clock) as the clock signal input to the delay line based on a relationship among the phases of the reference clock, the inverted reference clock, and the feedback clock. A delayed version of the feedback clock may be used during determination of the phase relationship. The selective use of the opposite phase of the reference clock for the input of the delay line results in centralization of the lock point for most cases as well as improvement in the tuning range and the time to establish the initial lock, without requiring an additional delay line or without increasing the size or changing the configuration of the existing delay line.
Owner:ROUND ROCK RES LLC
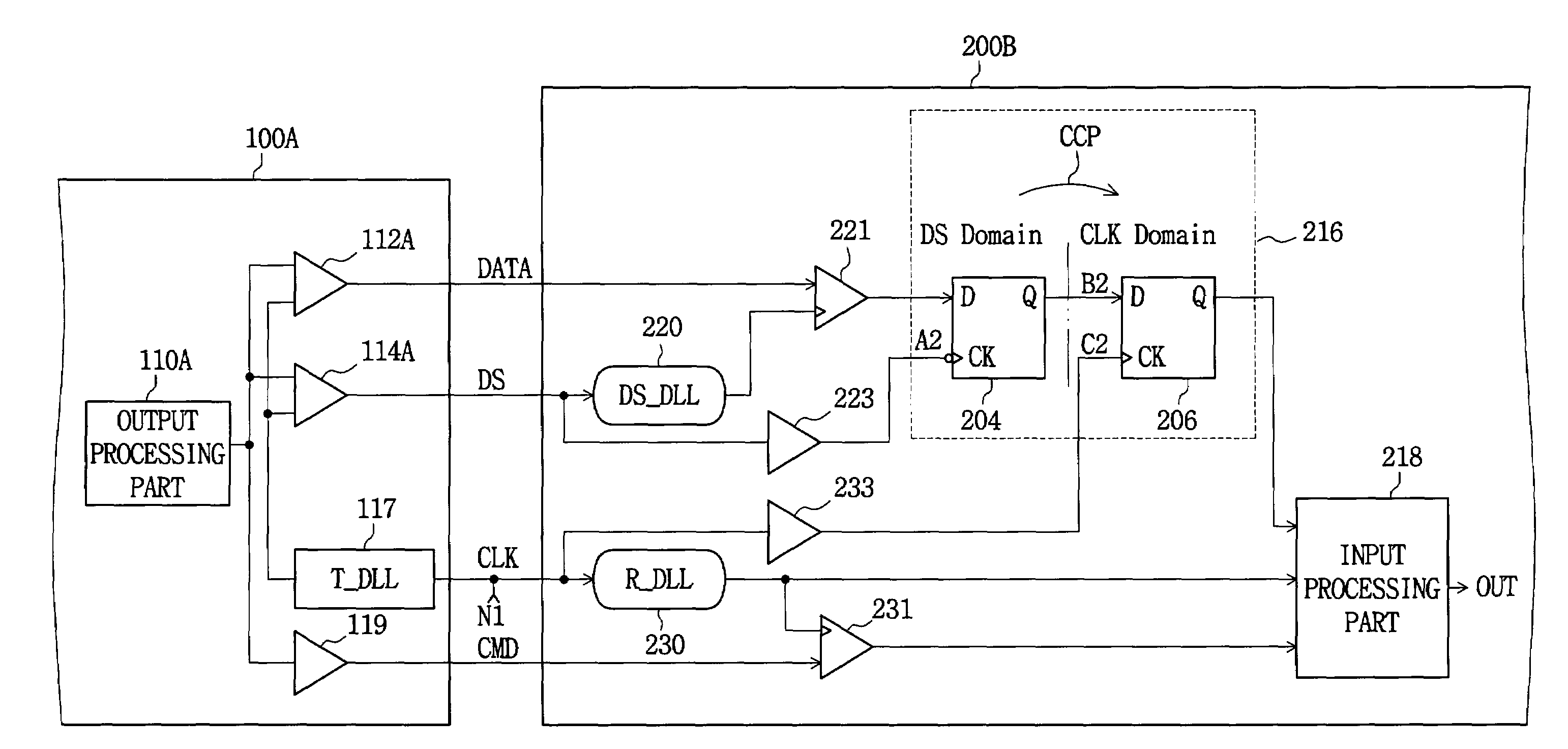
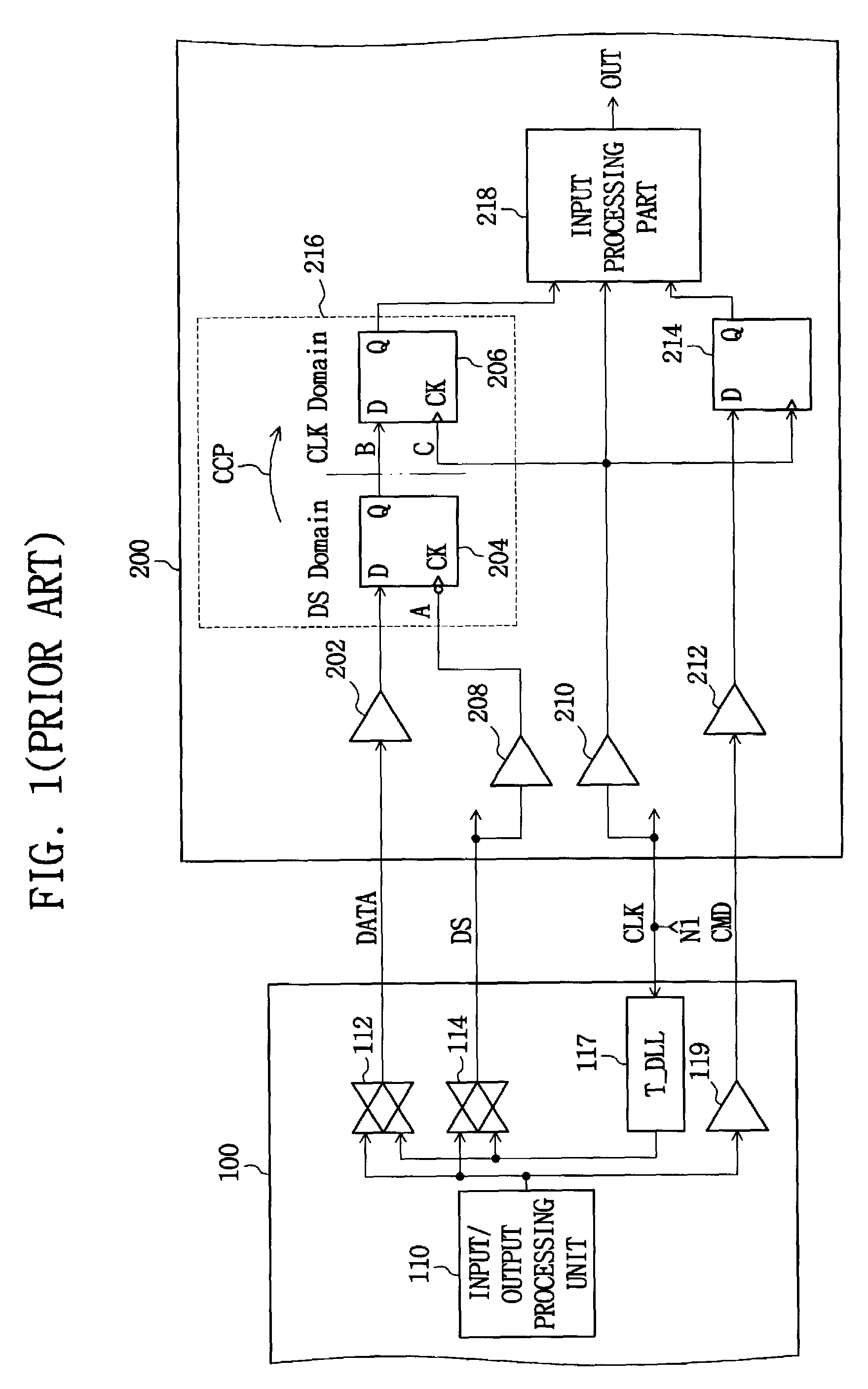
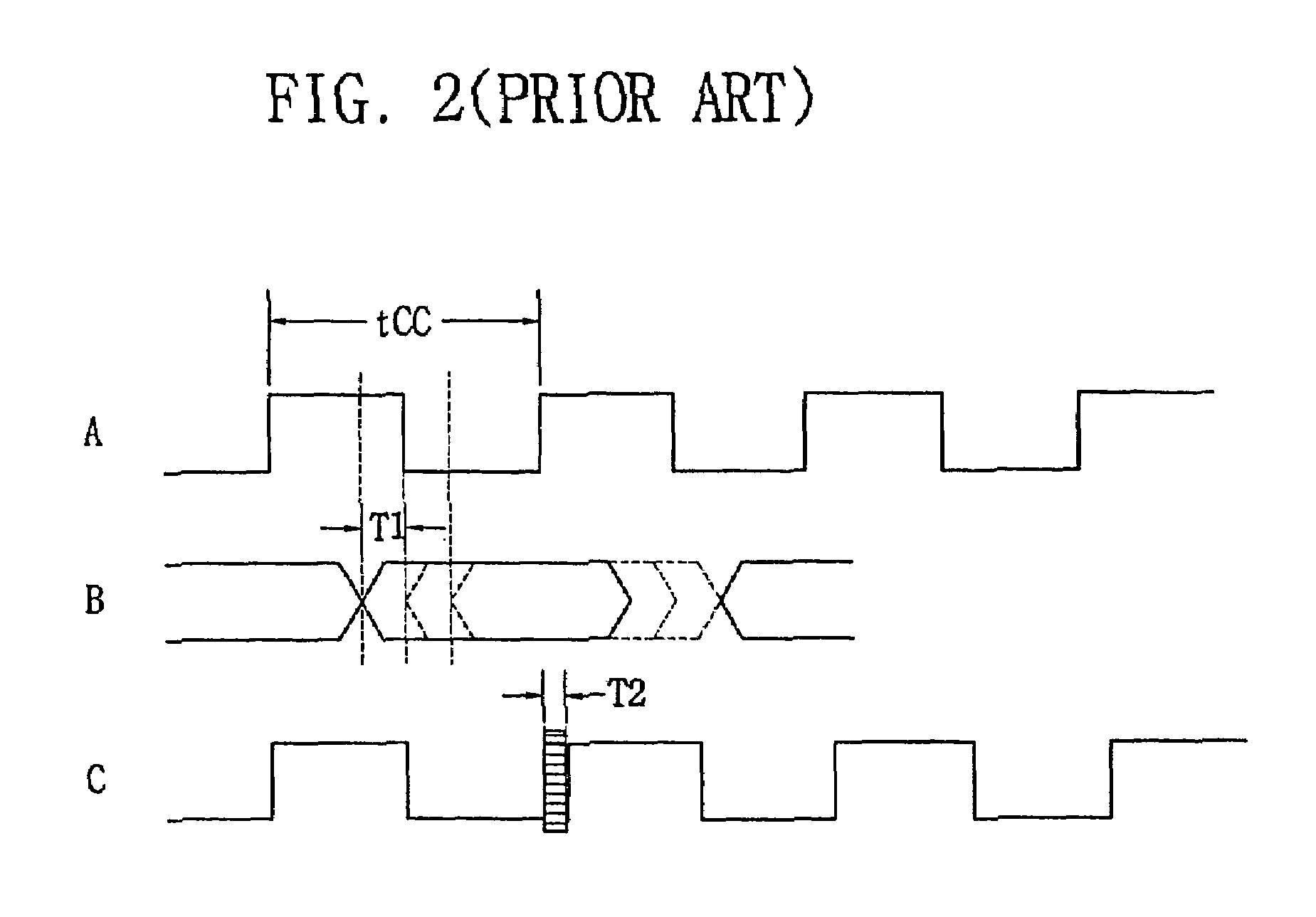
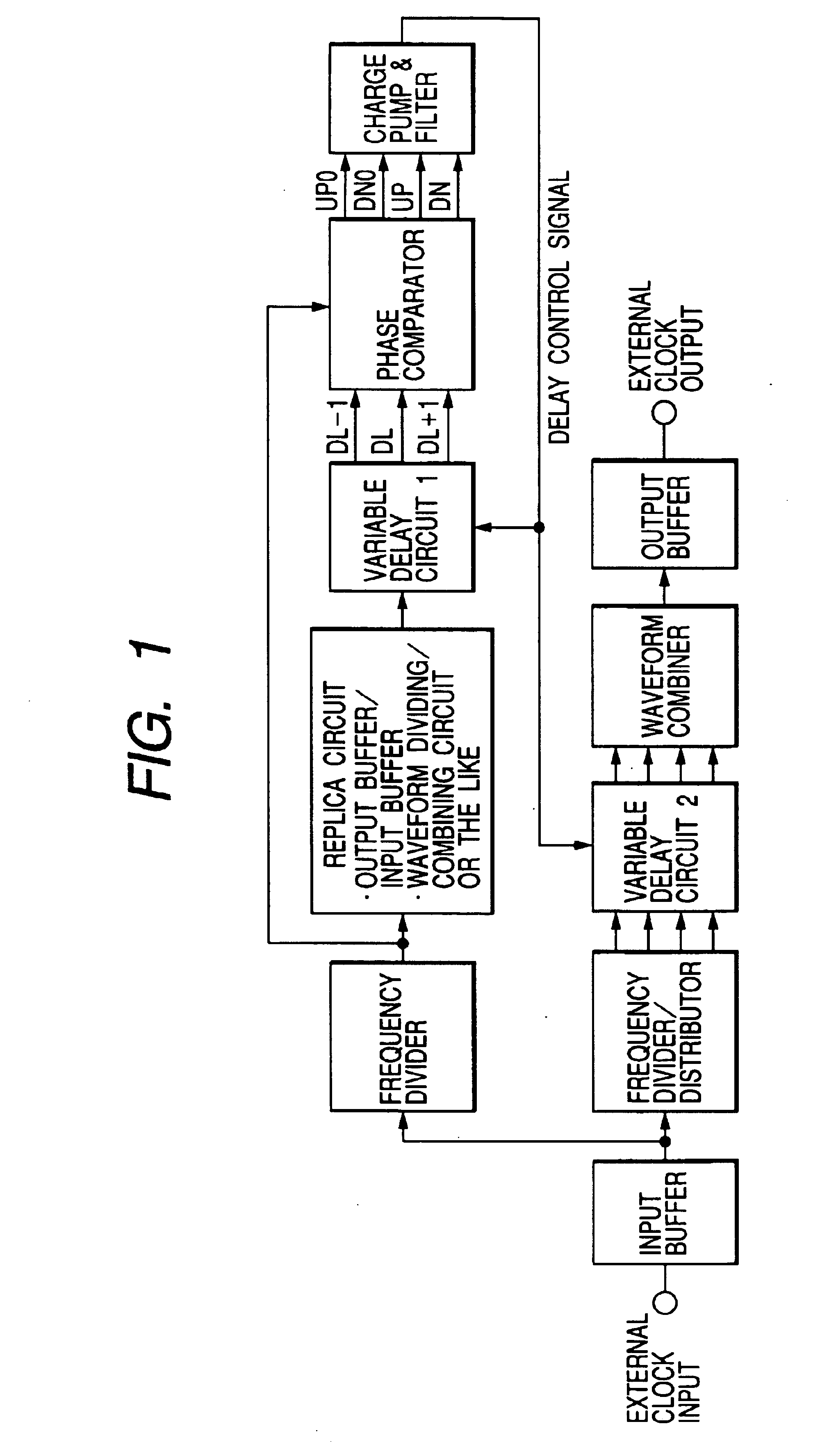
Multi-clock domain data input-processing device having clock-receiving locked loop and clock signal input method thereof
InactiveUS7038971B2Reduce restrictionsMaximizes timing marginSynchronisation information channelsPulse automatic controlDelay-locked loopClock transition
A multi-clock-domain data input processing device preferably includes: a clock-signal-receiving synchronous circuit that generates an output clocking signal by phase-delaying a first clock signal; a data input part having a delay locked loop (DLL); and an input-processing part. The data input part preferably inputs data in response to the first clock signal and the input-processing part transfers data in response to a second clock signal having a timing different from that of the first clock signal. A clock-signal applying method for operating the multi-clock-domain data input-processing device preferably includes the steps of: applying a plurality of clock signals to a signal-receiving clock conversion part; and applying a delayed clocking signal outputted from the DLL to the remaining parts of the data input-processing device.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
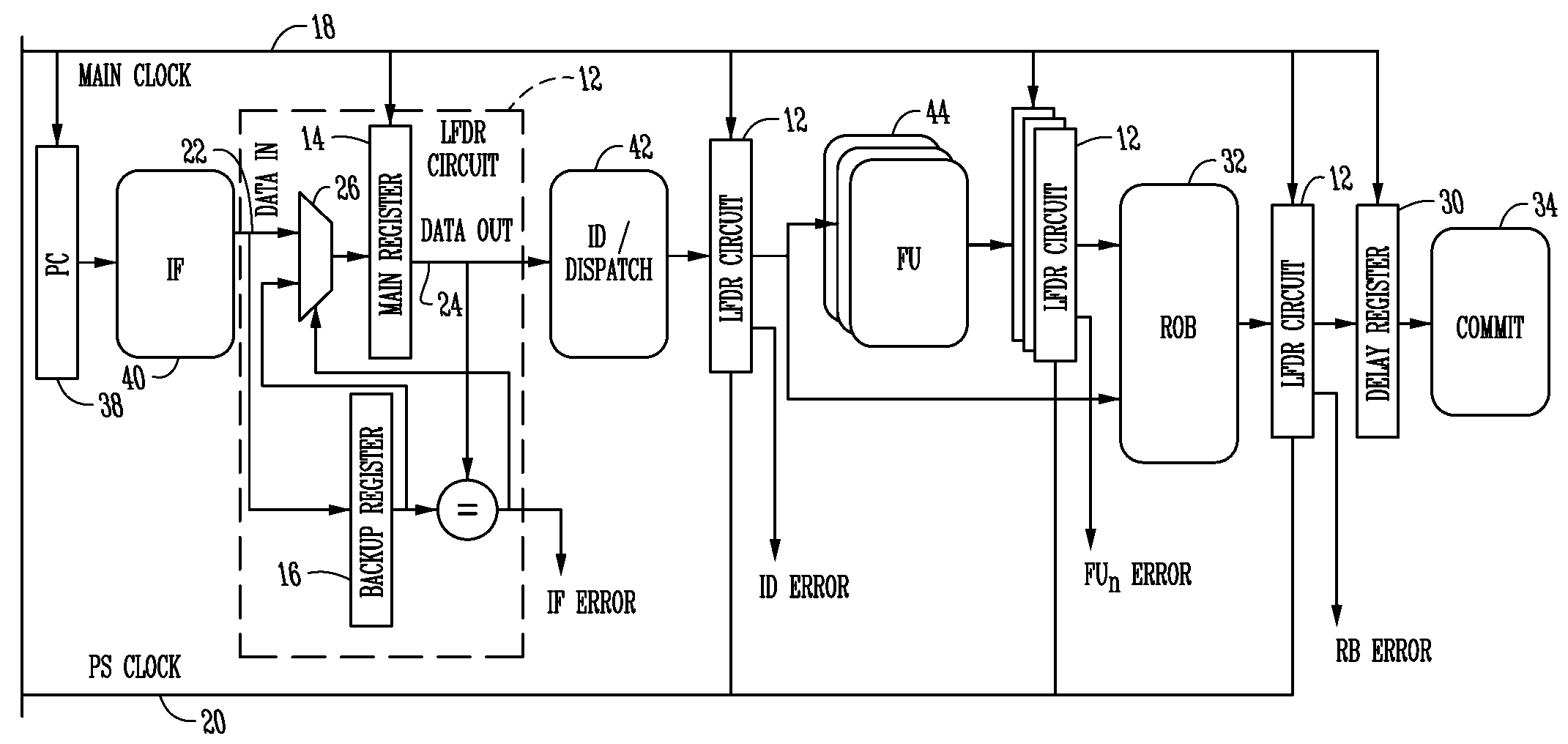
Superscale processor performance enhancement through reliable dynamic clock frequency tuning
InactiveUS7671627B1Easy to optimizeGuaranteed uptimeElectronic circuit testingError detection/correctionPhase shiftedPerformance enhancement
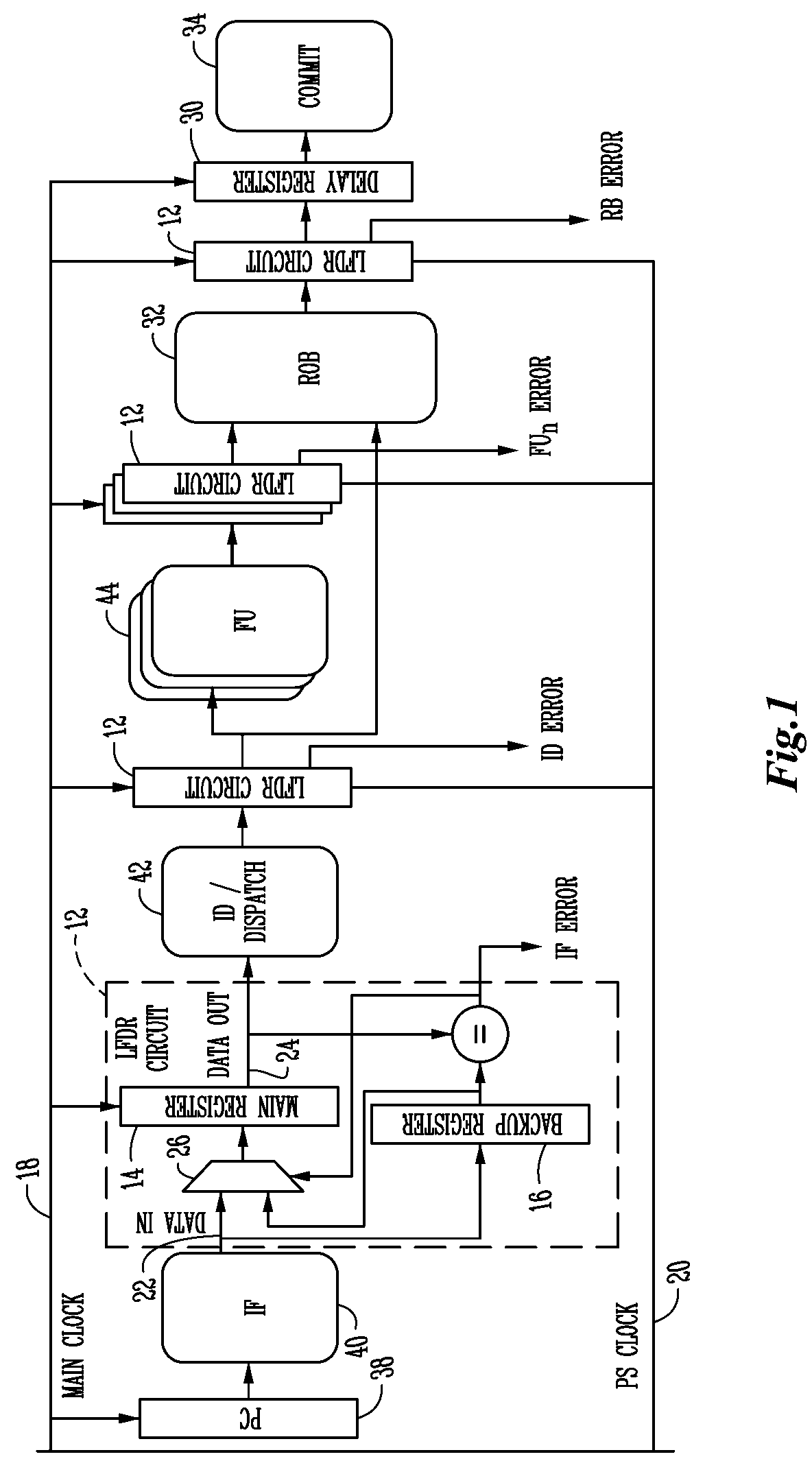
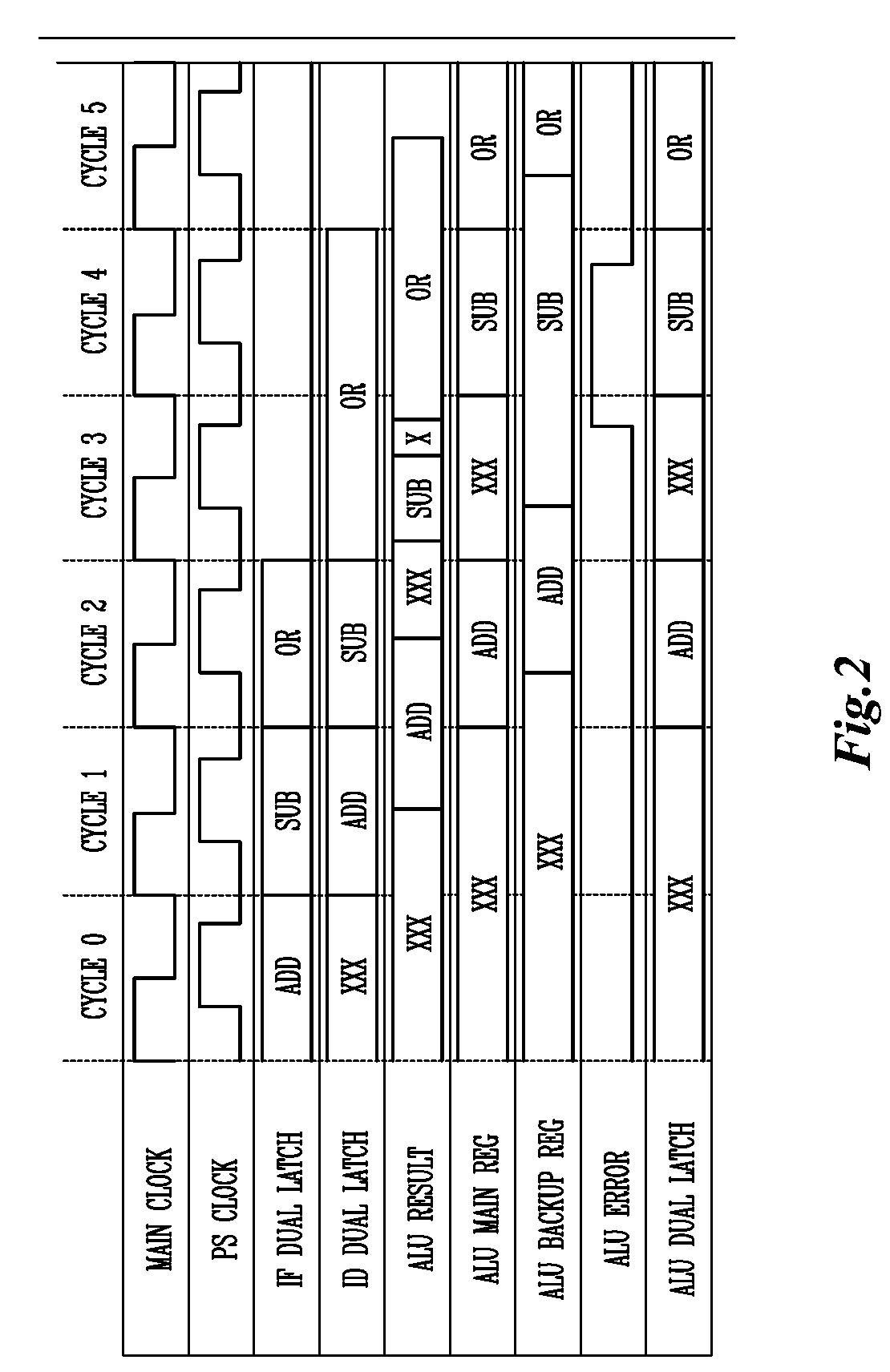
In the case of a pipelined processor, a performance gain is achievable through dynamically generating a main clock signal associated with a synchronous logic circuit and generating at least one backup register clock signal, the backup register clock signal at the same frequency as the main clock signal and phase shifted from the main clock signal to thereby provide additional time for one or more of the logic stages to execute. Error detection or error recovery may be performed using the backup registers. The methodology can further be extended, to design a system with cheaper technology and simple design tools that initially operates at slower speed, and then dynamically overclocks itself to achieve improved performance, while guaranteeing reliable execution.
Owner:IOWA STATE UNIV RES FOUND
Circuit for synchronizing CDMA mobile phones
InactiveUS6028855AAccurately reacquireReduce power consumptionPower managementSynchronisation arrangementNetwork clockEngineering
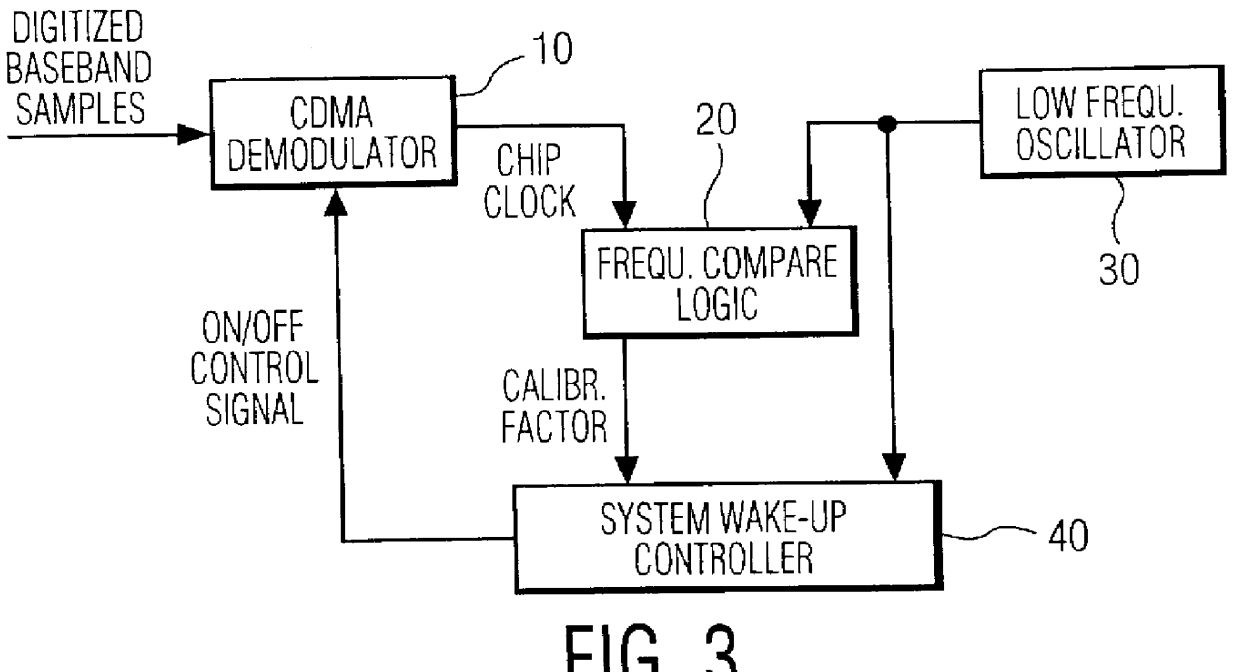
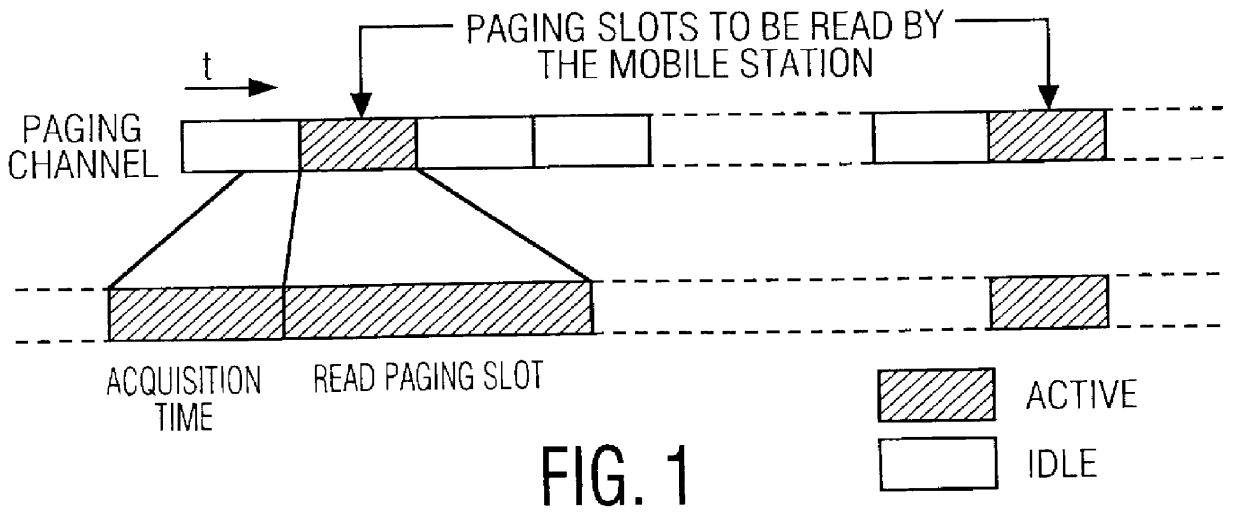
A frequency calibration circuit for use in a spread spectrum receiver. The receiver includes circuitry for receiving a spread spectrum signal from a base station and for recovering a network clock signal therefrom, a low frequency oscillator for producing an oscillator clock signal, and a frequency comparator that takes as inputs the network clock signal and the oscillator clock signal and produces a calibration factor based on the difference between the clock signals. A controller coupled to the low frequency oscillator amd the frequency comparator utilizes the calibration factor together with the low frequency oscillator clock signal to output a accurate and precision timed signal thereby being able to accurately require the timing of the paging channel.
Owner:ST ERICSSON SA
Fault injection system and method for verifying anti-single particle effect capability
InactiveCN101281555AHigh fault injection coverageHigh performance reference valueSpecial data processing applicationsControl signalStatistical analysis
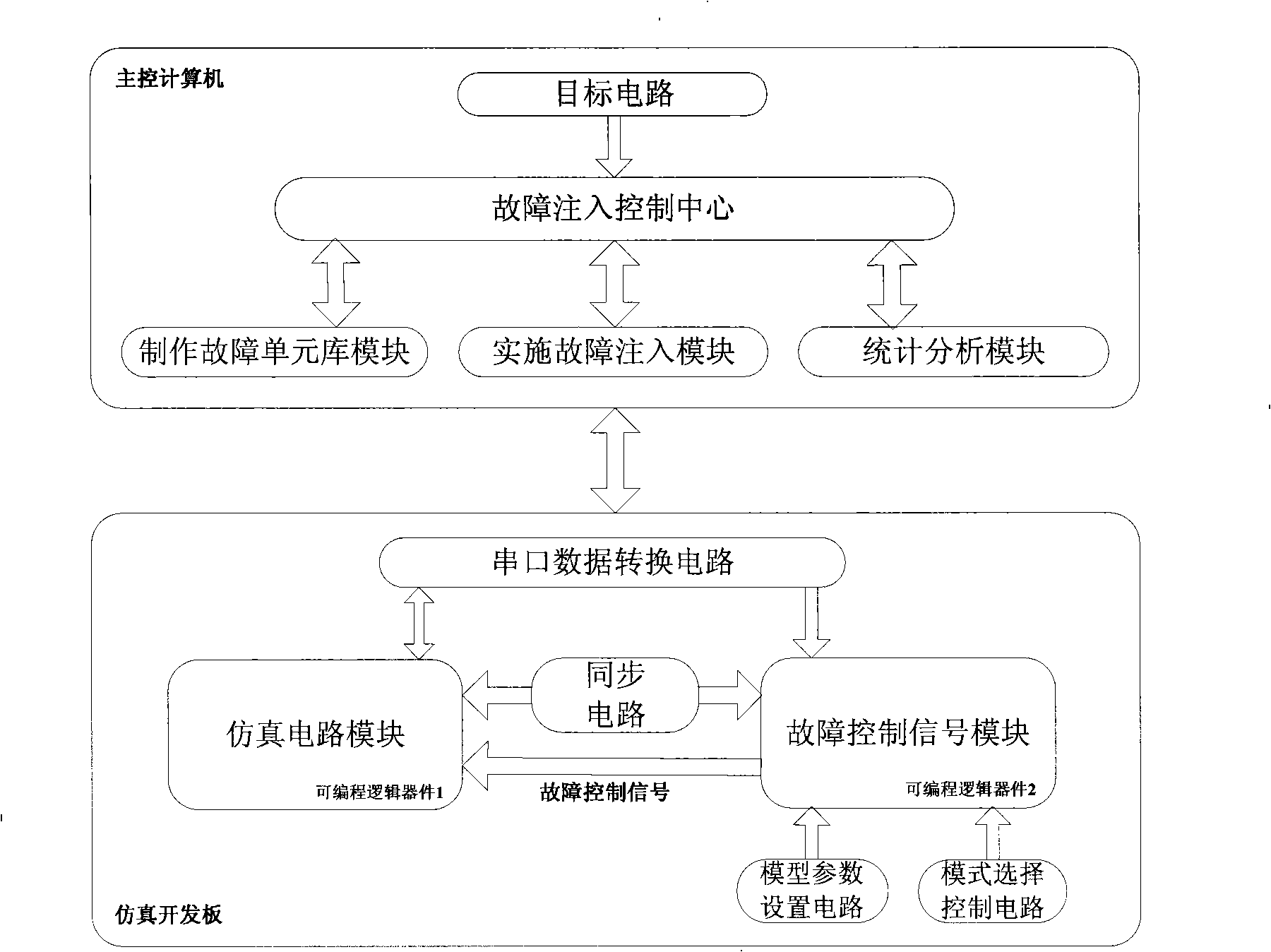
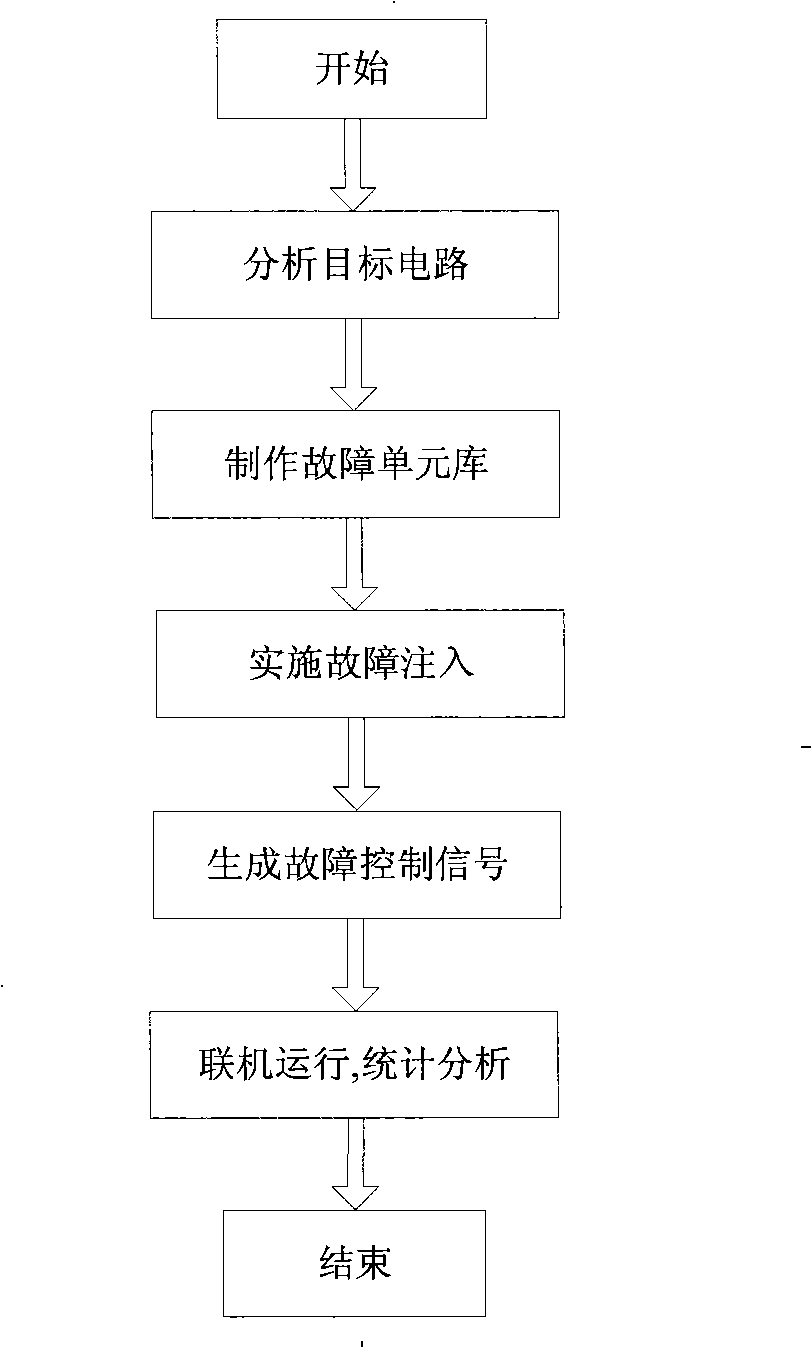
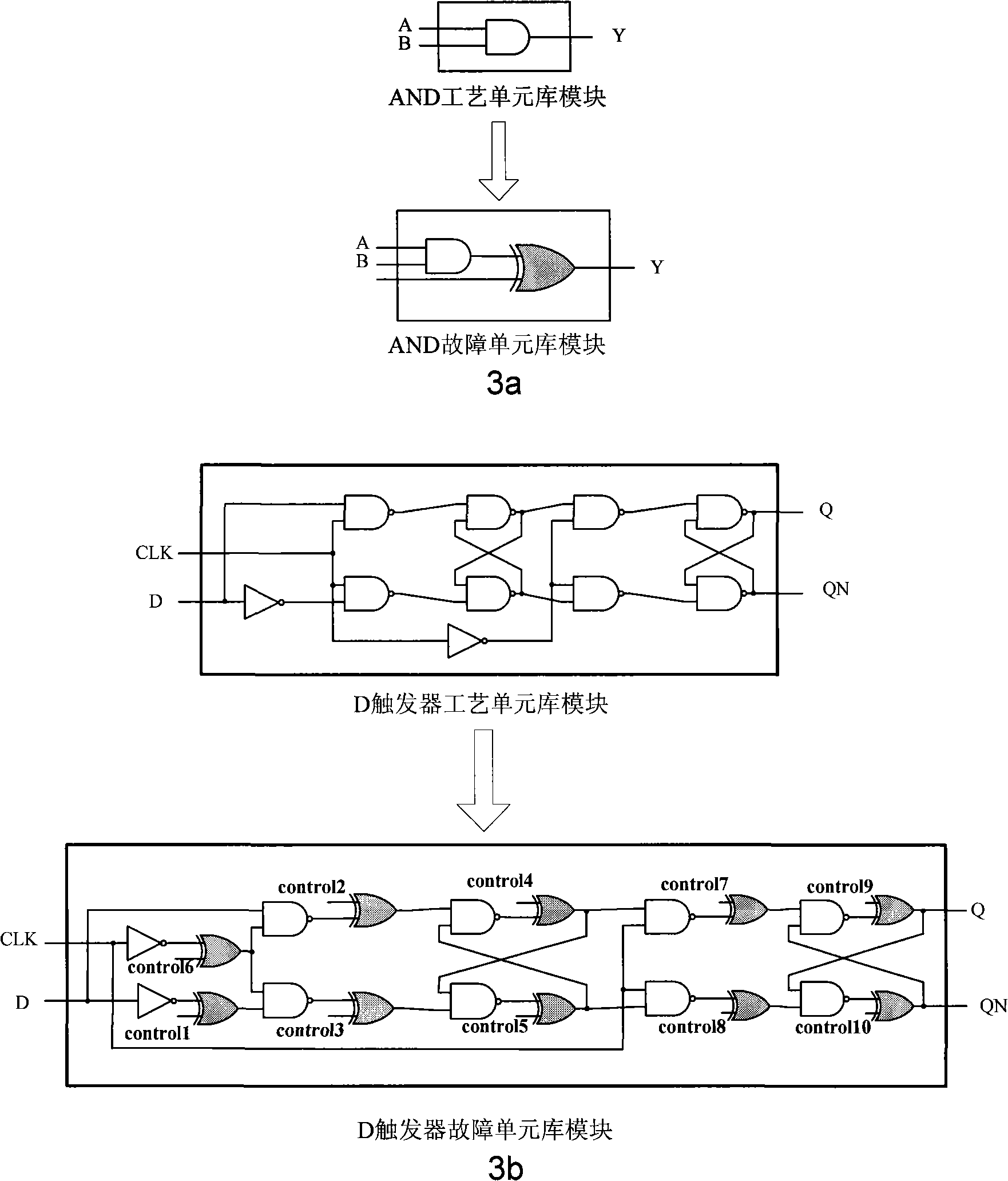
The invention relates to a fault injection system for verifying anti-single-particle-effect ability. A fault unit library fabrication module modifies a process unit library of an objective circuit to a fault unit library of the objective circuit; a fault injection implementation module modifies the gate level HDL codes of the objective circuit, generates a non-fault circuit and a fault circuit, maps the modified codes to the fault unit library, counts the number of the fault terminals of the codes and sends to a fault control signal module; a synchronous circuit realizes clock synchronization of a simulation circuit module and a fault control signal module; the fault control signal module generates a fault control signal and sends to the fault circuit of the simulation circuit module; the simulation circuit module loads the non-fault circuit and the fault circuit, provides input signals to the two circuits, provides the control signal to the non-fault circuit, compares the outputs of the two circuits and sends the comparison result and the fault control signal to a statistical analysis module to record, the statistical analysis module calculates the error rate and sensitivity of each node.
Owner:BEIJING MXTRONICS CORP +1
Synchronization circuit and synchronization method
InactiveUS6909312B2Simple structurePulse automatic controlSingle output arrangementsPhase synchronizationPulse delay
Phase synchronization is achieved by forming a first pulse to be synchronized with a reference pulse, a second pulse leading in phase for a certain period relative to said first pulse and a third pulse delayed in phase for a certain period from said first pulse; comparing said reference pulse with said first pulse in a first comparing; comparing said reference pulse with said second pulse and said third pulse in a second comparing; and forming a control voltage by giving priority to a comparison output of said second comparing with respect to a comparison output of said first comparing, matching the phase of said reference pulse with the phrase of said second pulse or said third pulse, and matching, after said matching of phases, the phrase of said reference pulse with the phase of said first pulse by forming said control, voltage from the comparison output of said first comparing.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
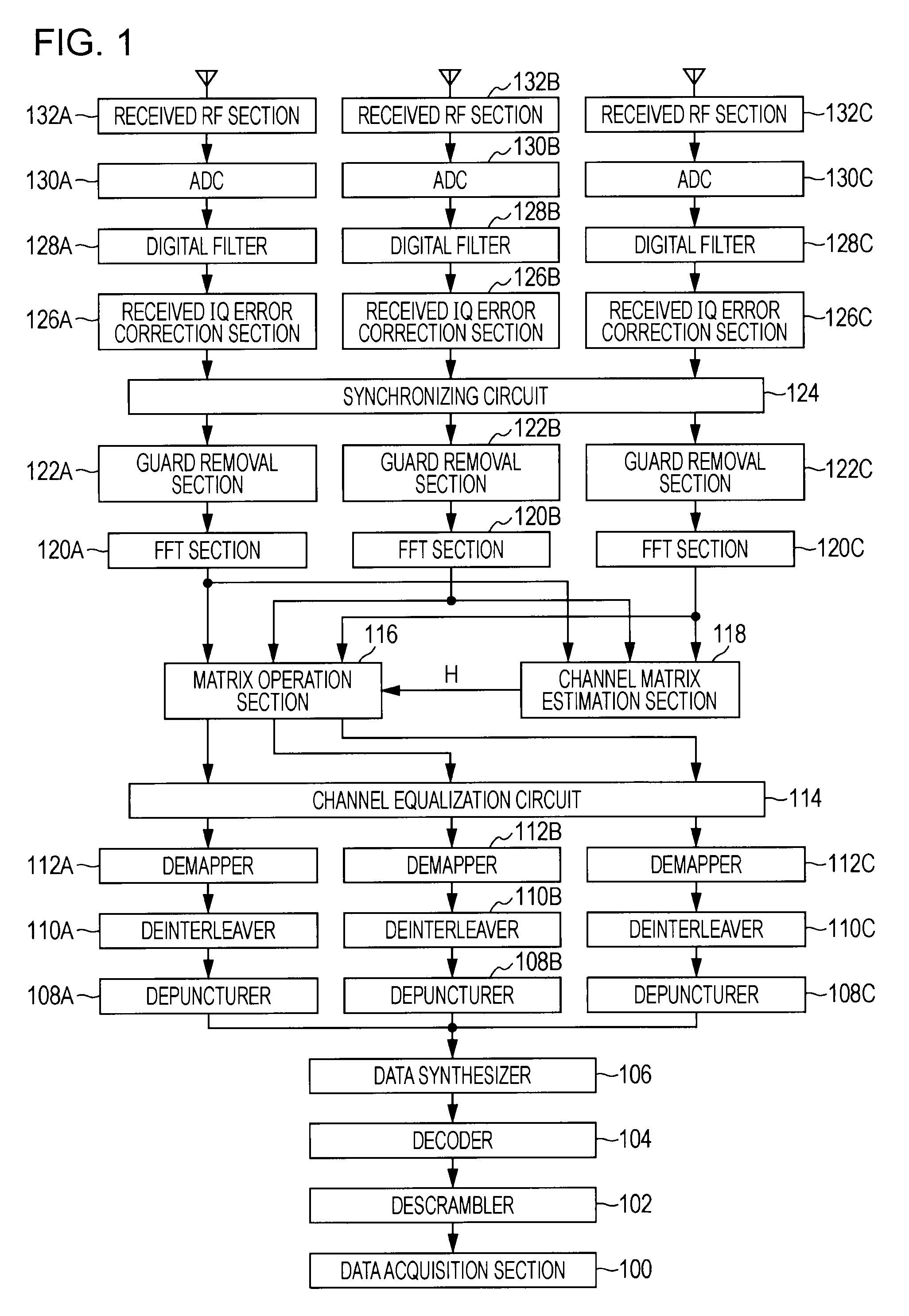
Synchronization circuit and synchronization method, wireless communication device and wireless communication method, and computer program
InactiveUS20100061493A1Improve accuracyImproved time detectionTime-division multiplexAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsSignal qualityTime control
A synchronizing circuit comprising: a coarse synchronizing circuit which determines temporary reception timing using a preamble consisting of a repetition of known training signals added to a reception packet; a synchronization candidate timing control section which sets up multiple synchronization candidates based on the temporary reception timing and controls synchronization of received signal s in each of the multiple synchronization candidates; a signal quality monitoring section which monitors signal quality of the received signal s synchronized in each of the multiple synchronization candidates; and a synchronization candidate selecting section which selects one of the synchronization candidates as a final reception timing based on a monitoring result of the signal quality in the signal quality monitoring section.
Owner:SONY CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com