Patents
Literature
122 results about "Clock transition" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
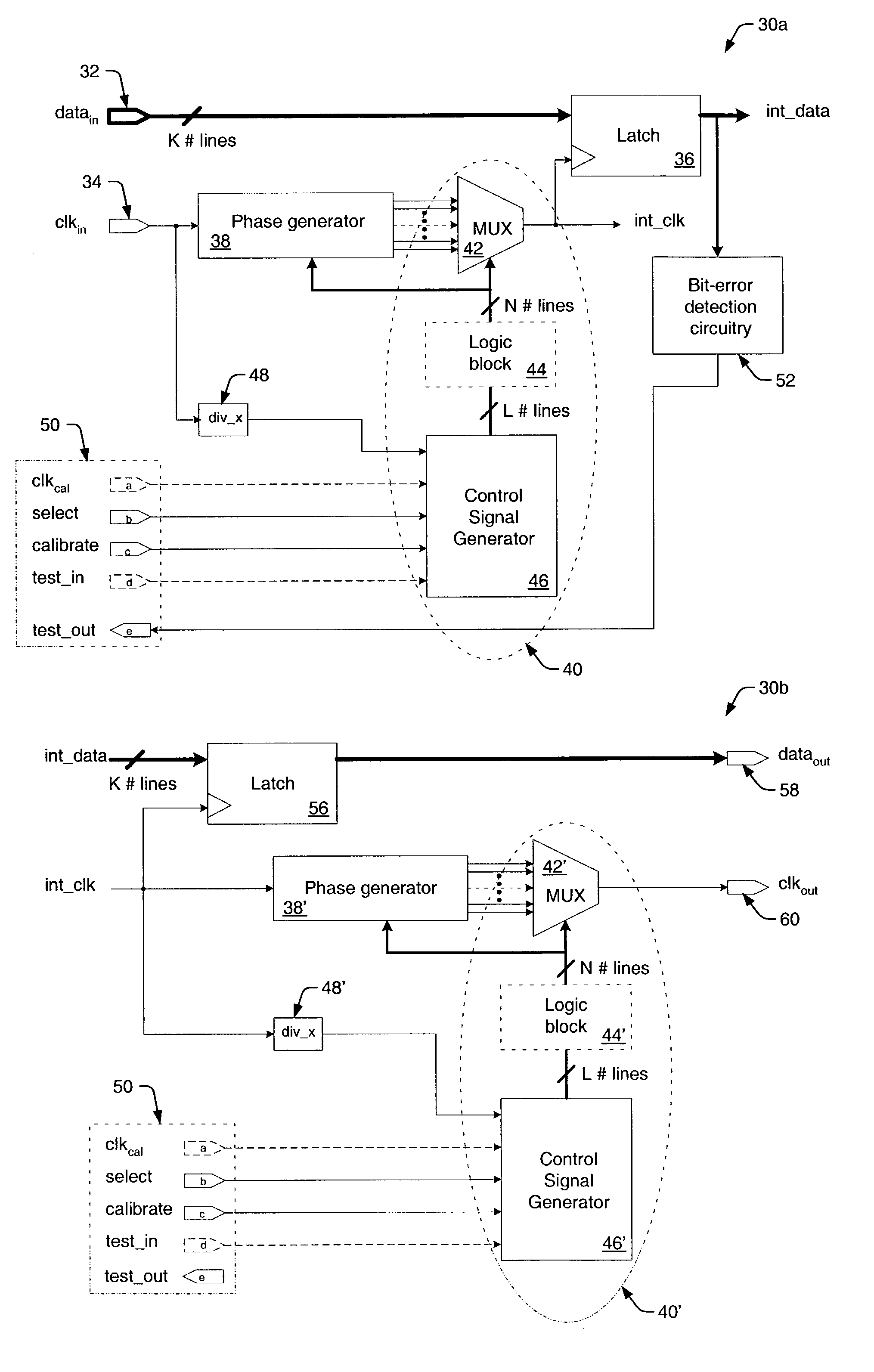
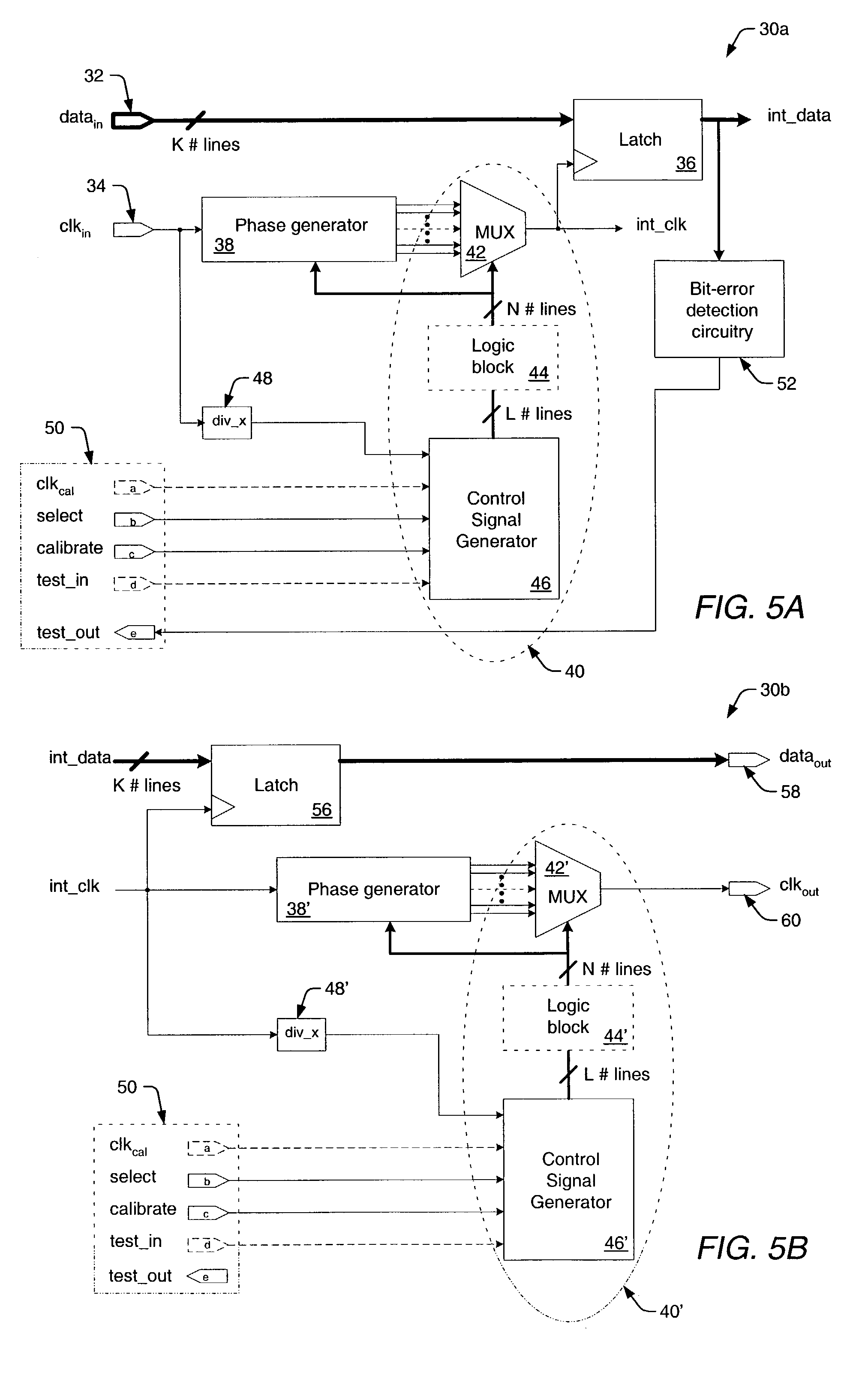
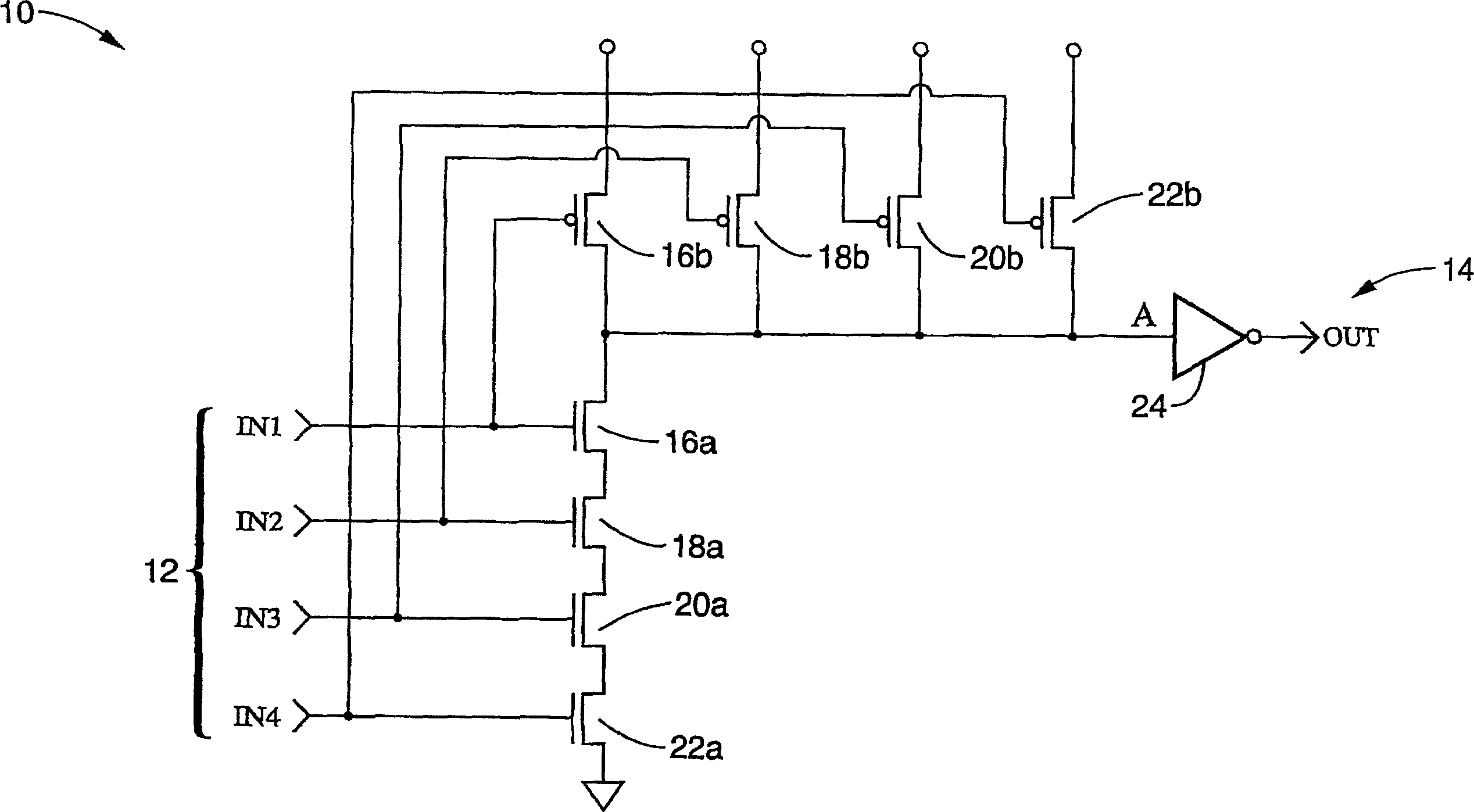
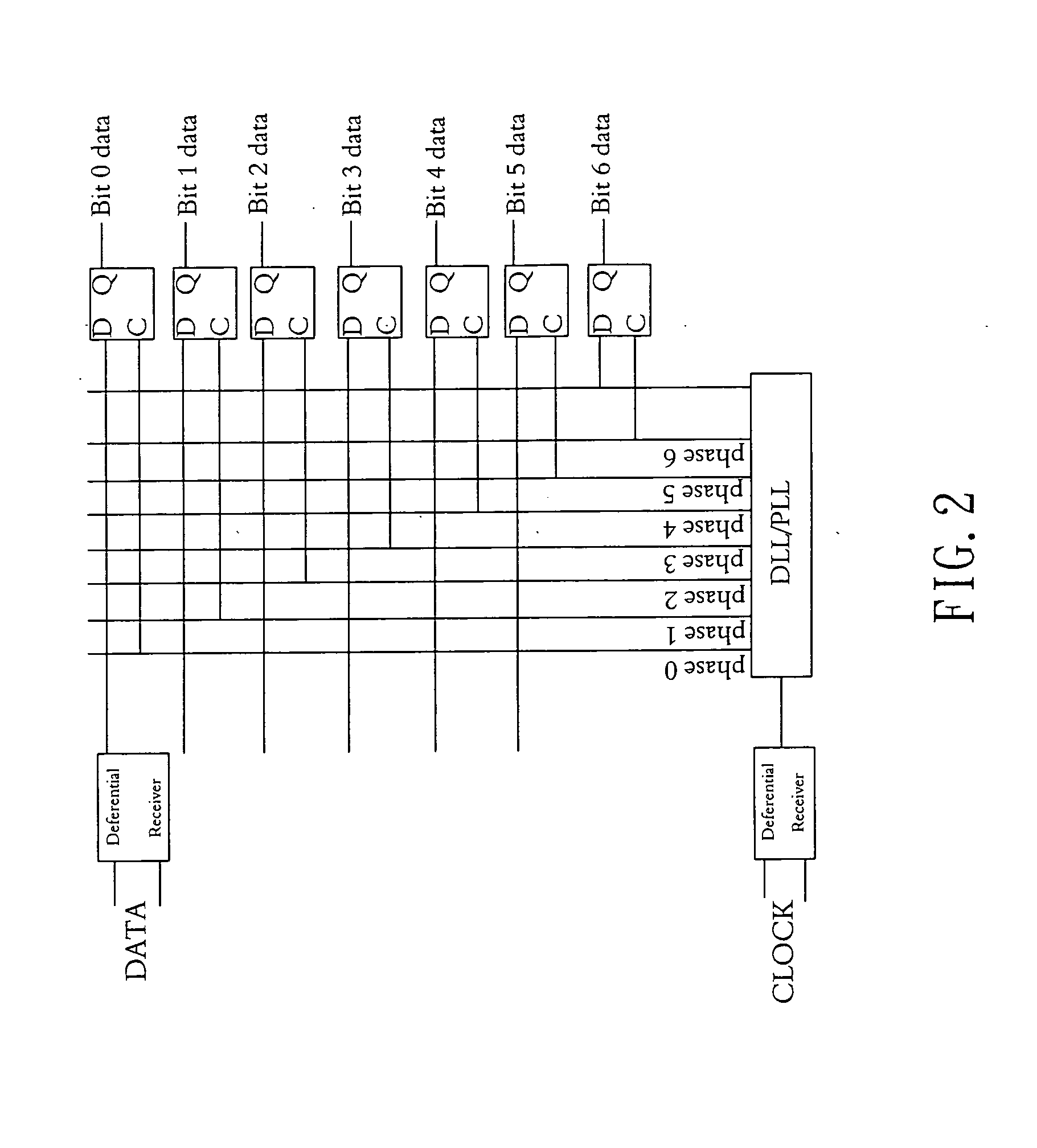
Parallel data interface and method for high-speed timing adjustment
InactiveUS7069458B1Accurate samplingMinimize clock skewPulse automatic controlElectronic circuit testingAccess timeTime delays
A parallel data interface and method is provided herein, which adjusts a timing relationship of a clock signal to not only minimize clock skew, but to also compensate for noise components that may affect one or more paths of a parallel data bus. In some embodiments, the parallel data interface includes a first phase generator coupled to generate a first plurality of time delay pulses, and a first phase selector adapted to select one of the first plurality of time delay pulses to adjust the timing of a clock signal to sample each and every one of the plurality of data signals between minimum setup and hold time thresholds. In some embodiments, the parallel data interface includes a second phase generator coupled to generate a second plurality of time delay pulses, and a second phase selector adapted to select one of the second plurality of time delay pulses to adjust the timing of the clock signal to output the plurality of data signals from the data interface at least an amount of time (i.e., an access time) after the adjusted clock transition is output from the data interface.
Owner:RPX CORP
Low noise charge pump method and apparatus
ActiveUS20050052220A1Reduce noiseSimple designAc-dc conversionApparatus without intermediate ac conversionCapacitanceLow noise
A charge pump method and apparatus is described having various aspects. Noise injection from a charge pump to other circuits may be reduced by limiting both positive and negative clock transition rates, as well as by limiting drive currents within clock generator driver circuits, and also by increasing a control node AC impedance of certain transfer capacitor coupling switches. A single-phase clock may be used to control as many as all active switches within a charge pump, and capacitive coupling may simplify biasing and timing for clock signals controlling transfer capacitor coupling switches. Any combination of such aspects of the method or apparatus may be employed to quiet and / or simplify charge pump designs over a wide range of charge pump architectures.
Owner:PSEMI CORP
Low noise charge pump method and apparatus
ActiveUS7719343B2Reduce noiseSimple designAc-dc conversionApparatus without intermediate ac conversionCapacitanceLow noise
A charge pump method and apparatus is described having various aspects. Noise injection from a charge pump to other circuits may be reduced by limiting both positive and negative clock transition rates, as well as by limiting drive currents within clock generator driver circuits, and also by increasing a control node AC impedance of certain transfer capacitor coupling switches. A single-phase clock may be used to control as many as all active switches within a charge pump, and capacitive coupling may simplify biasing and timing for clock signals controlling transfer capacitor coupling switches. Any combination of such aspects of the method or apparatus may be employed to quiet and / or simplify charge pump designs over a wide range of charge pump architectures.
Owner:PSEMI CORP
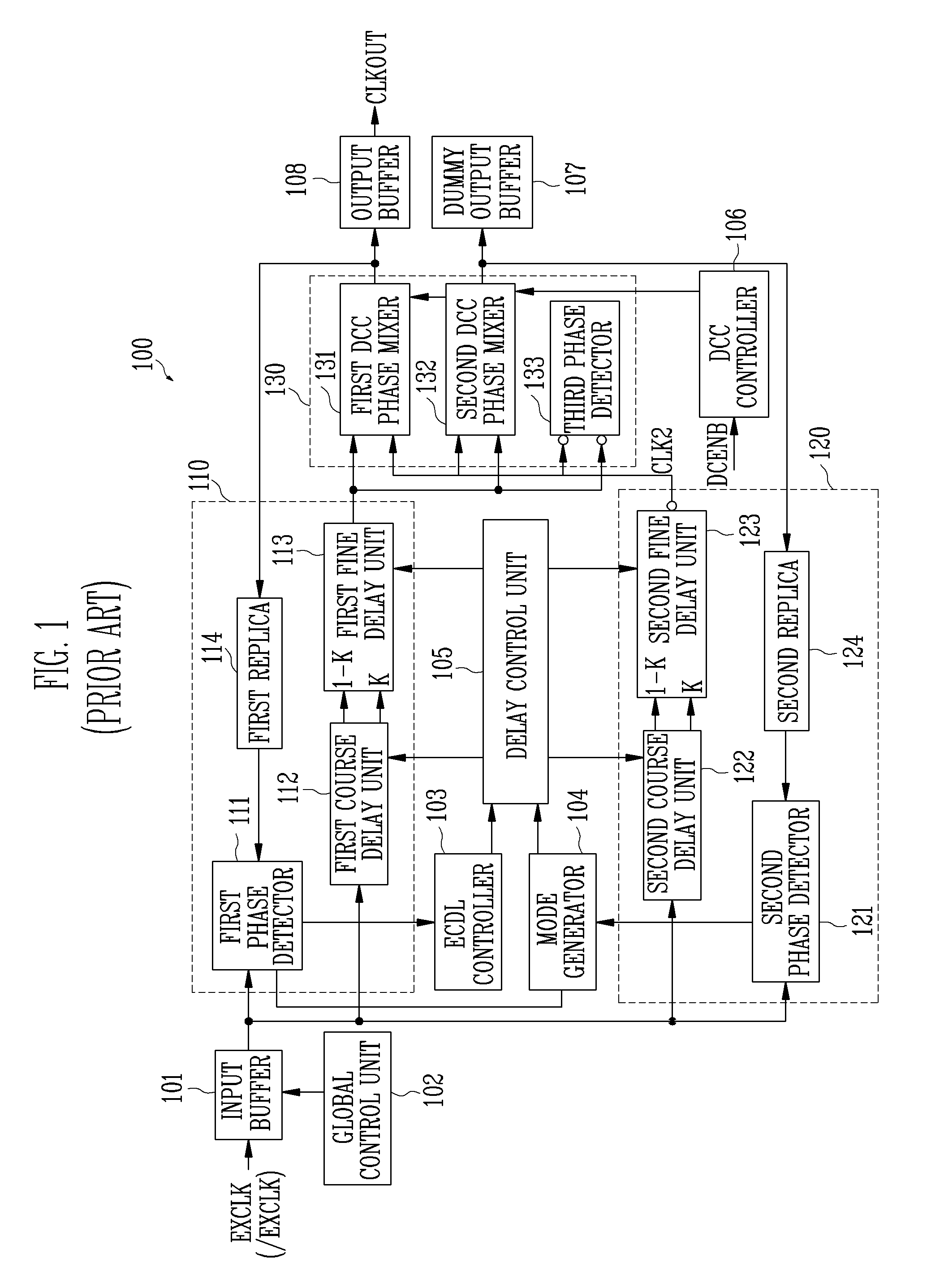
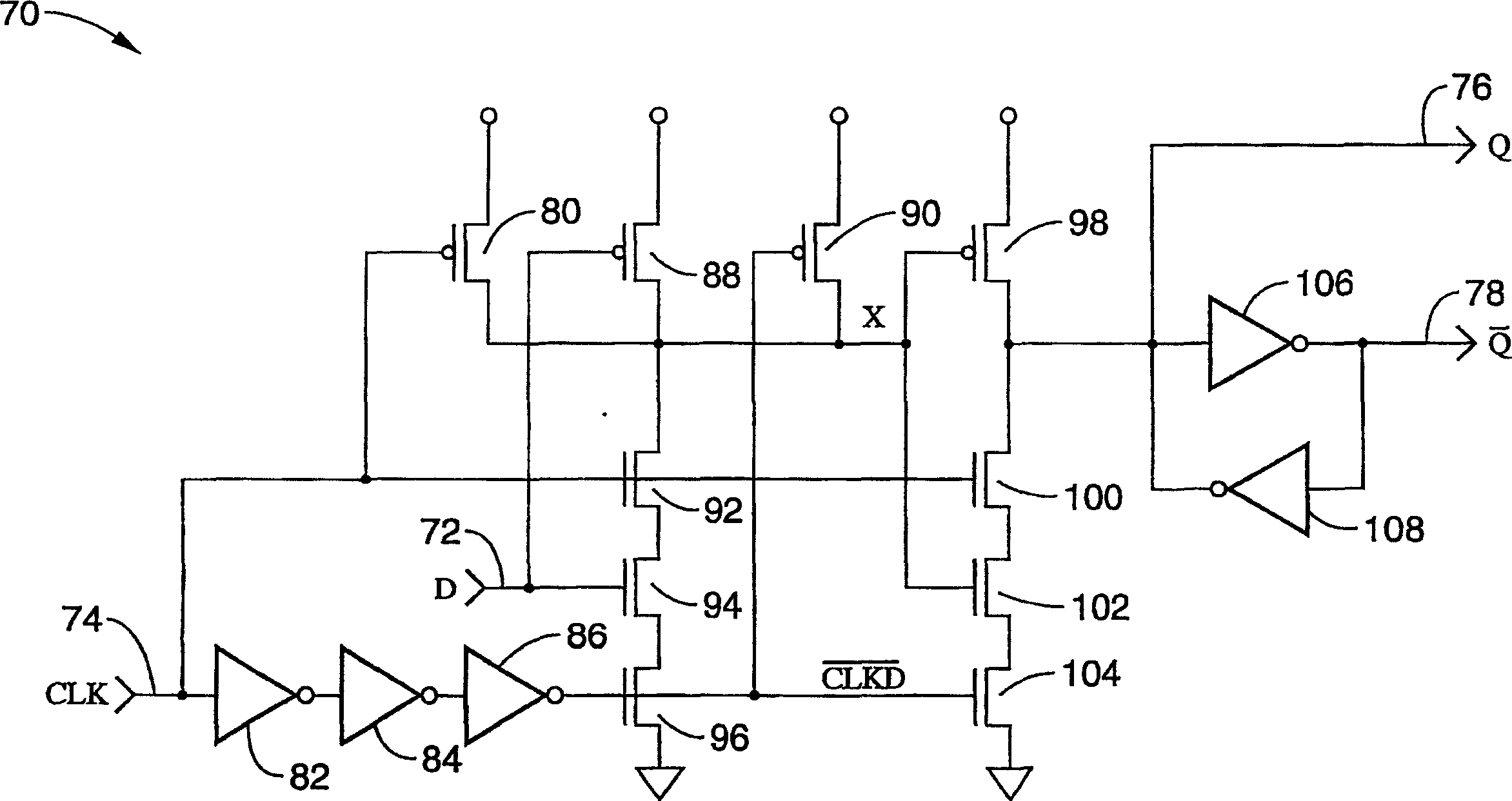
Multi-clock domain data input-processing device having clock-receiving locked loop and clock signal input method thereof
InactiveUS7038971B2Reduce restrictionsMaximizes timing marginSynchronisation information channelsPulse automatic controlDelay-locked loopClock transition
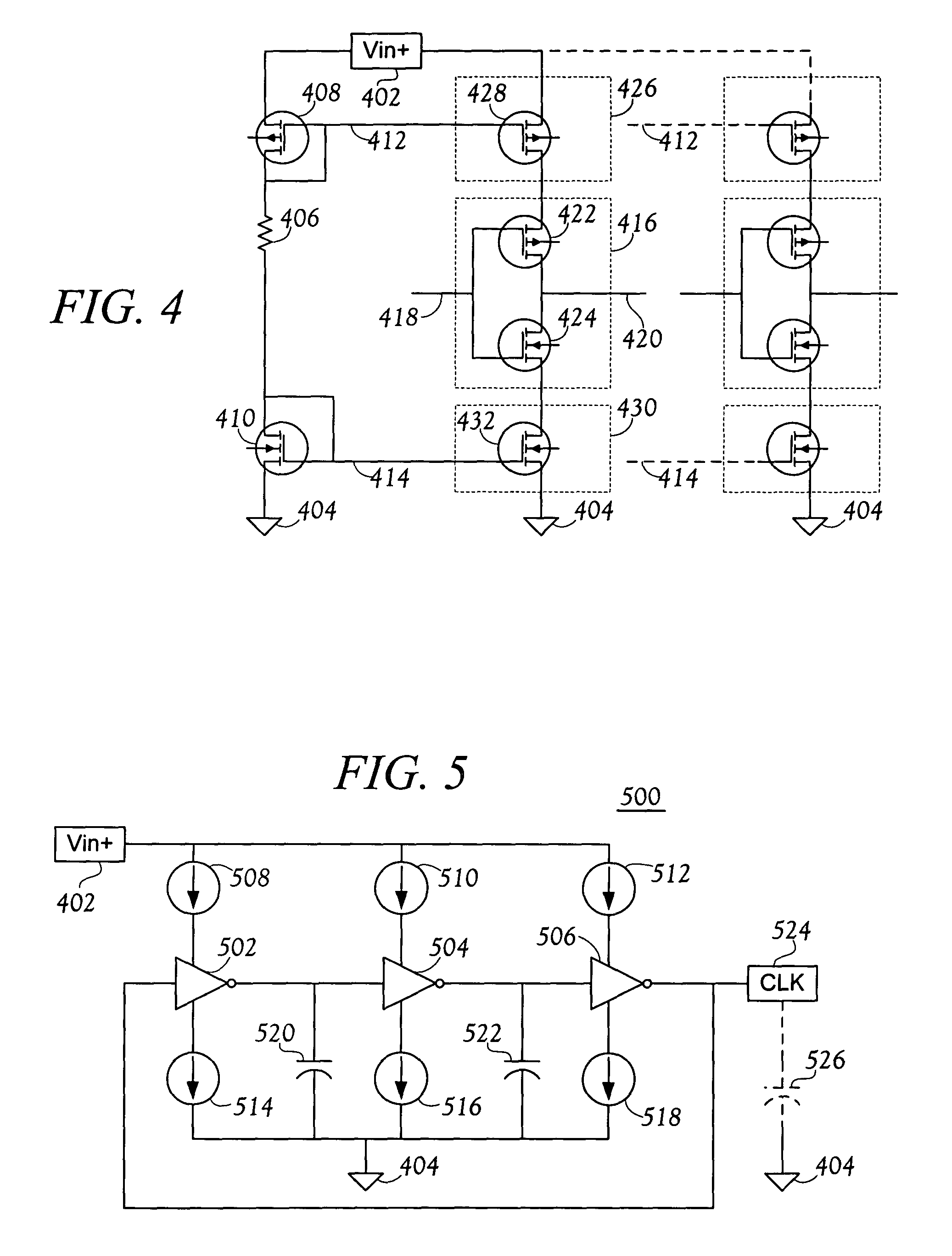
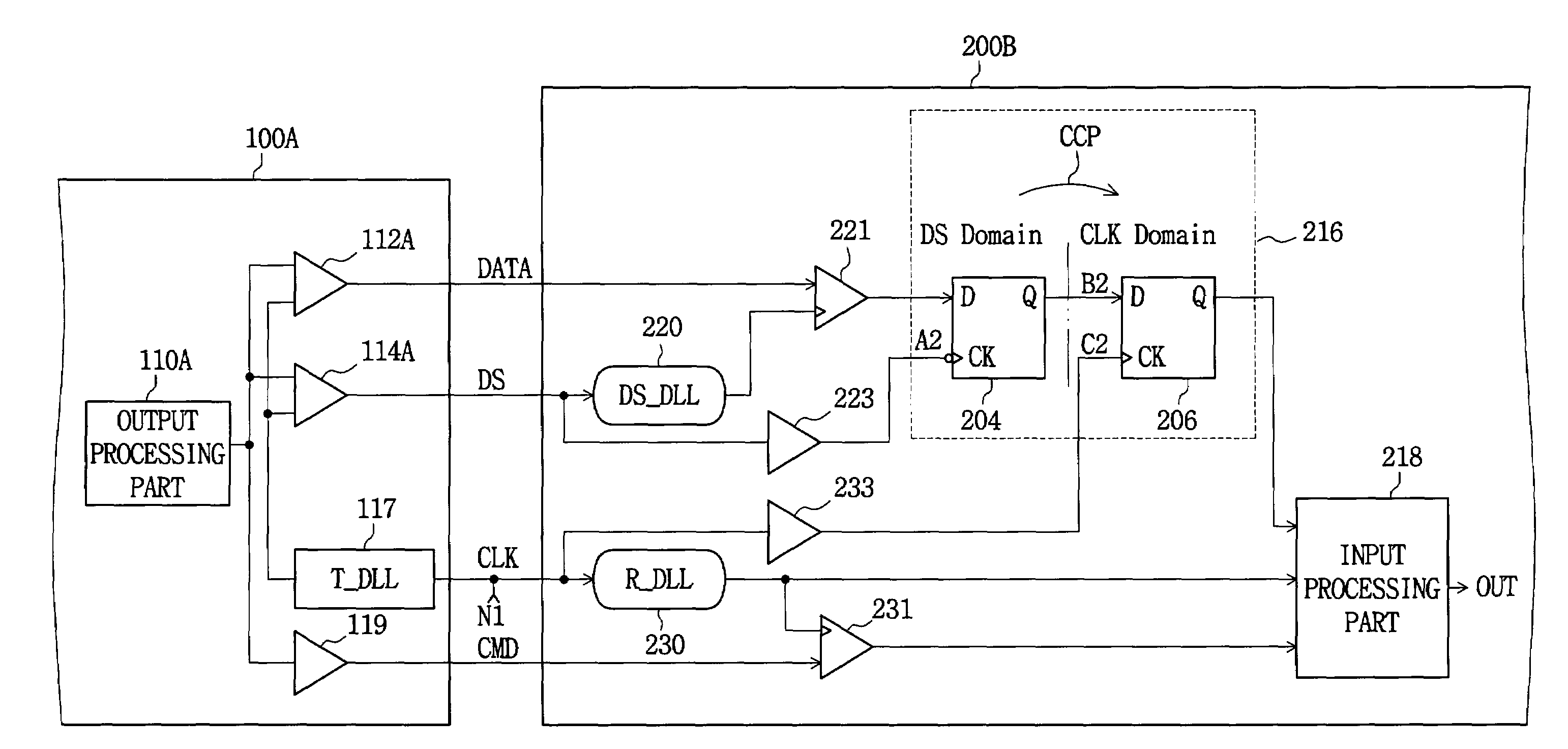
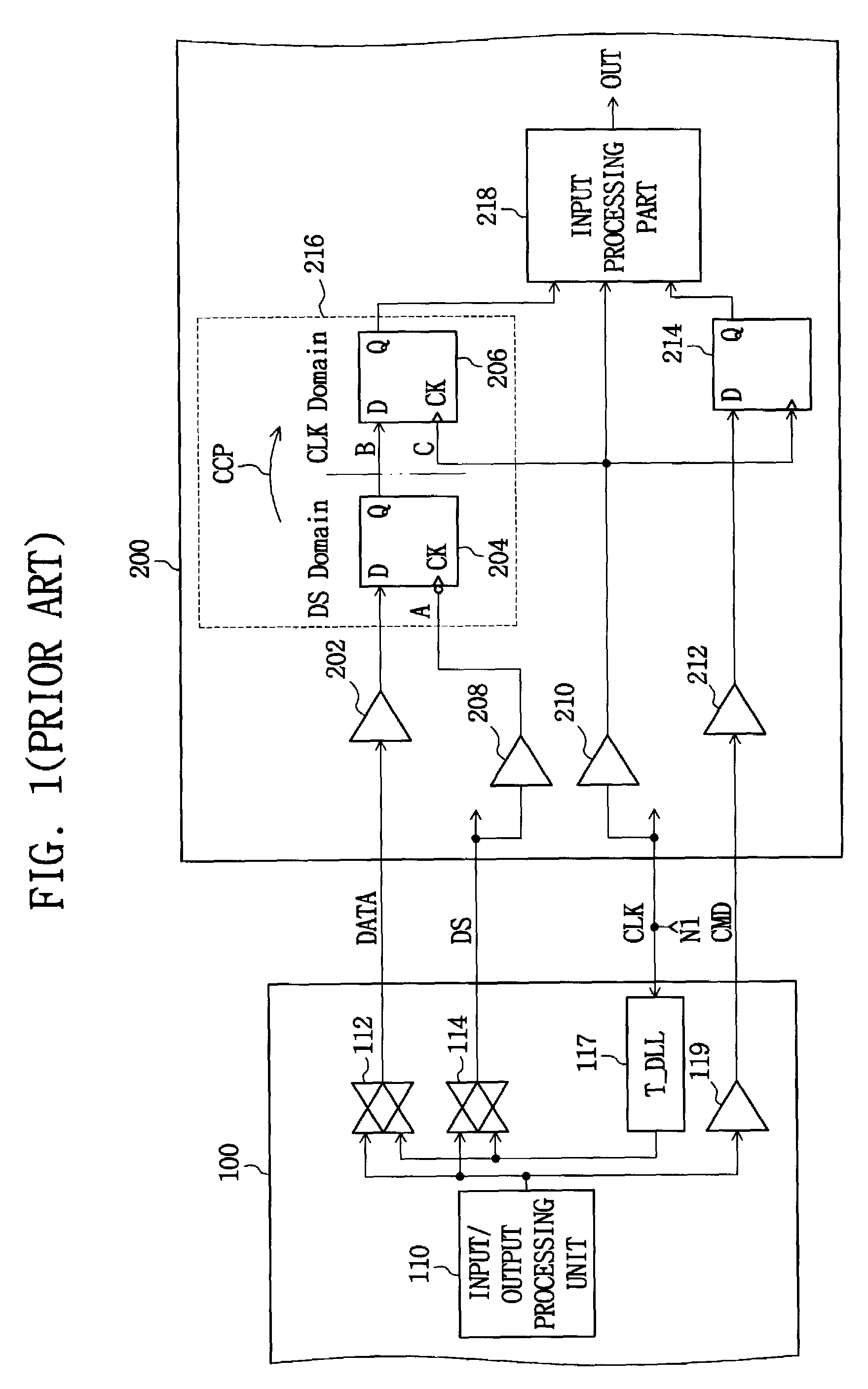
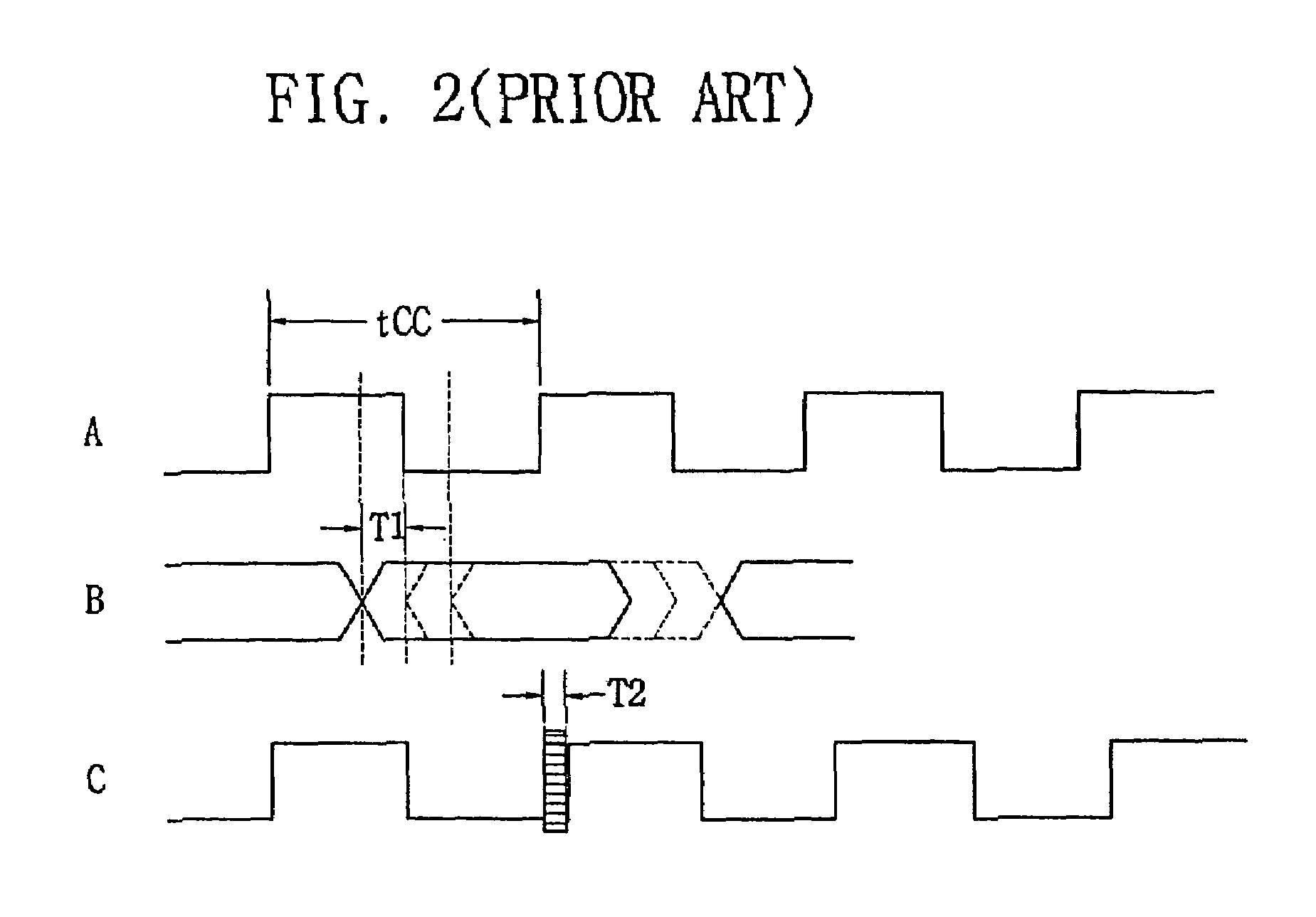
A multi-clock-domain data input processing device preferably includes: a clock-signal-receiving synchronous circuit that generates an output clocking signal by phase-delaying a first clock signal; a data input part having a delay locked loop (DLL); and an input-processing part. The data input part preferably inputs data in response to the first clock signal and the input-processing part transfers data in response to a second clock signal having a timing different from that of the first clock signal. A clock-signal applying method for operating the multi-clock-domain data input-processing device preferably includes the steps of: applying a plurality of clock signals to a signal-receiving clock conversion part; and applying a delayed clocking signal outputted from the DLL to the remaining parts of the data input-processing device.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
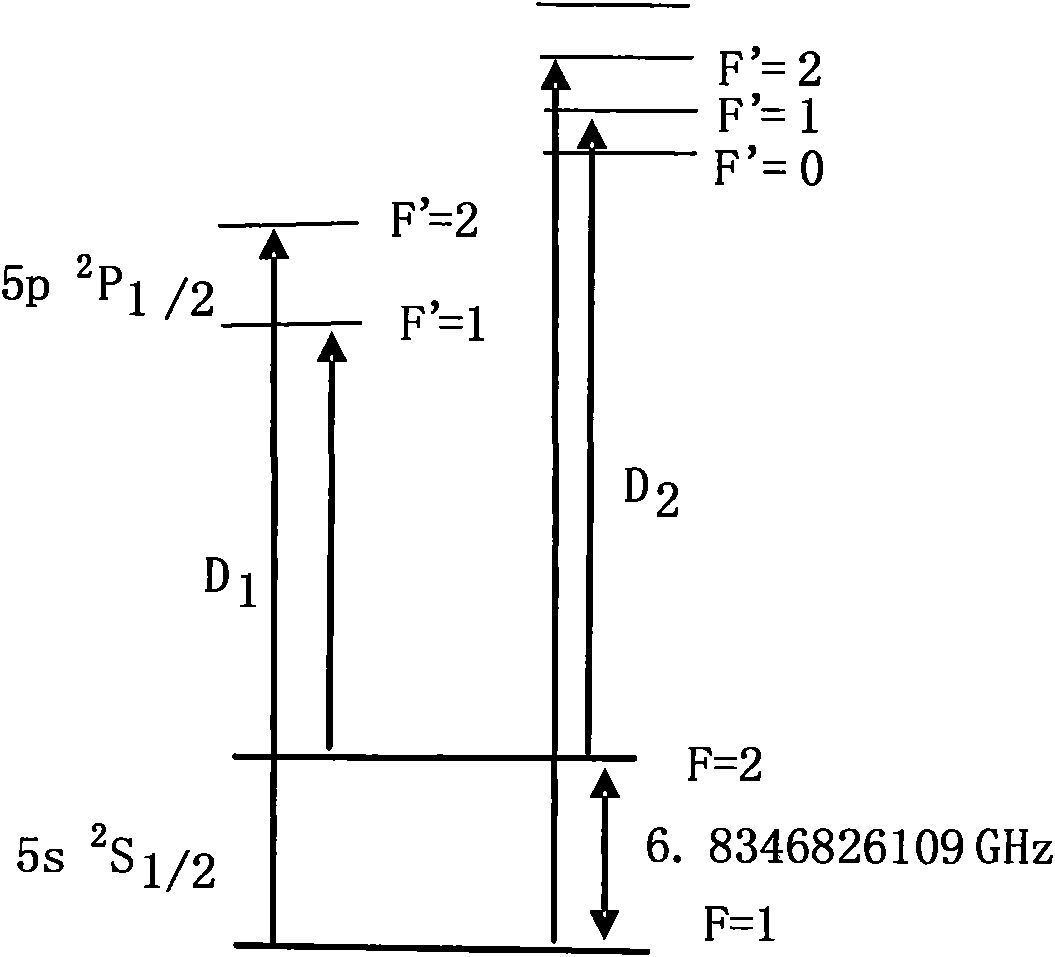
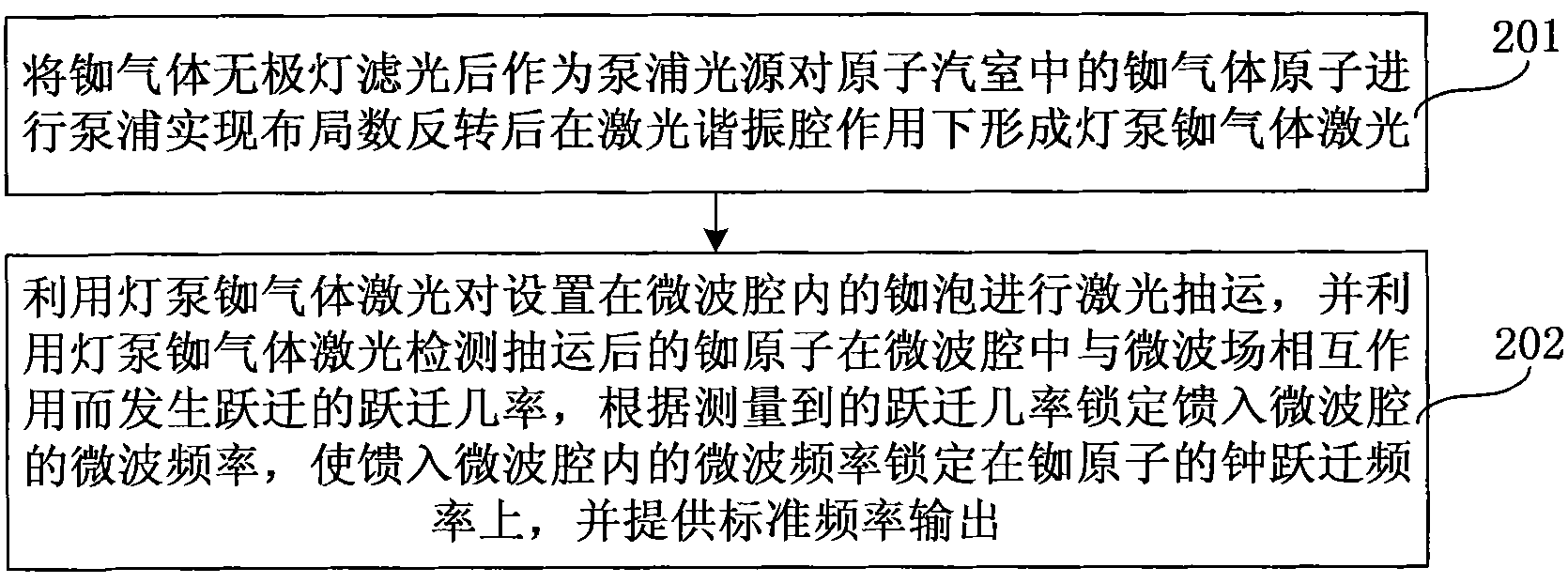
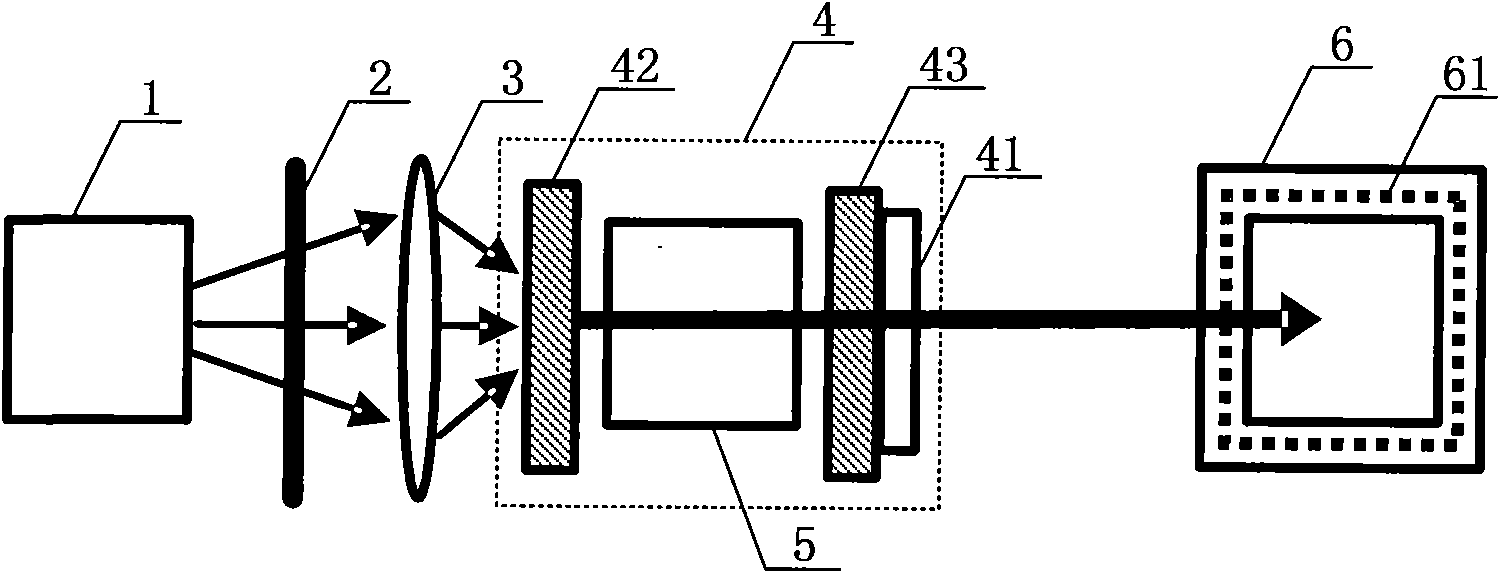
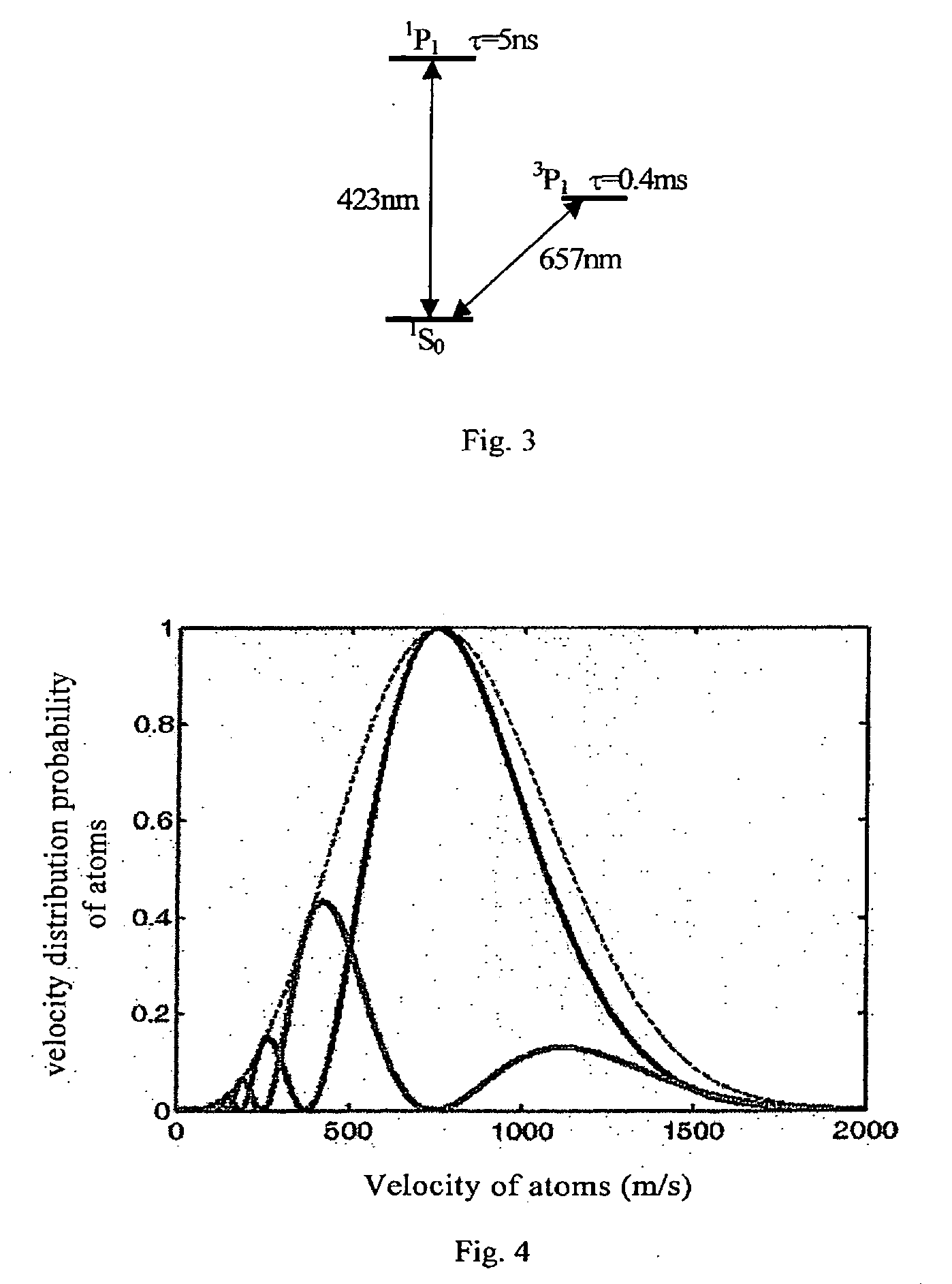
Method for pumping rubidium bubble for outputting standard frequency by lamp pump rubidium gas laser and rubidium atomic clock
ActiveCN101846965AEasy to lockQuick lockPulse automatic controlApparatus using atomic clocksMicrowave cavityResonant cavity
The invention relates to a method for pumping a rubidium bubble for outputting standard frequency by a lamp pump rubidium gas laser and a rubidium atomic clock. The method comprises the following steps of: adopting a filtered rubidium gas electrodeless lamp as a pumping light source for pumping a rubidium gas atom in an atom steam chamber, realizing distribution quantity conversion and then forming a lamp pump rubidium gas laser under the action of a laser resonant cavity; carrying out laser pumping on the rubidium bubble arranged in a microwave cavity by utilizing the lamp pump rubidium gas laser and detecting the transition probability of the pumped rubidium atom for generating transition by generating interaction with a microwave field in the microwave cavity by utilizing the lamp pump rubidium gas laser; and locking microwave frequency fed in the microwave cavity according to the detected transition probability and locking the microwave frequency fed in the microwave cavity on clock transition frequency of the atom. In the embodiment of the invention, because the frequency of the lamp pump rubidium gas laser still operates on a rubidium transition spectral line broadening spectrum in an unlocking state, even if the frequency of the lamp pump rubidium gas laser is unlocked, the lamp pump rubidium gas laser can be rapidly locked on needed laser frequency.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
System and method for reducing skew in complementary signals that can be used to synchronously clock a double data rate output
Owner:MONTEREY RES LLC
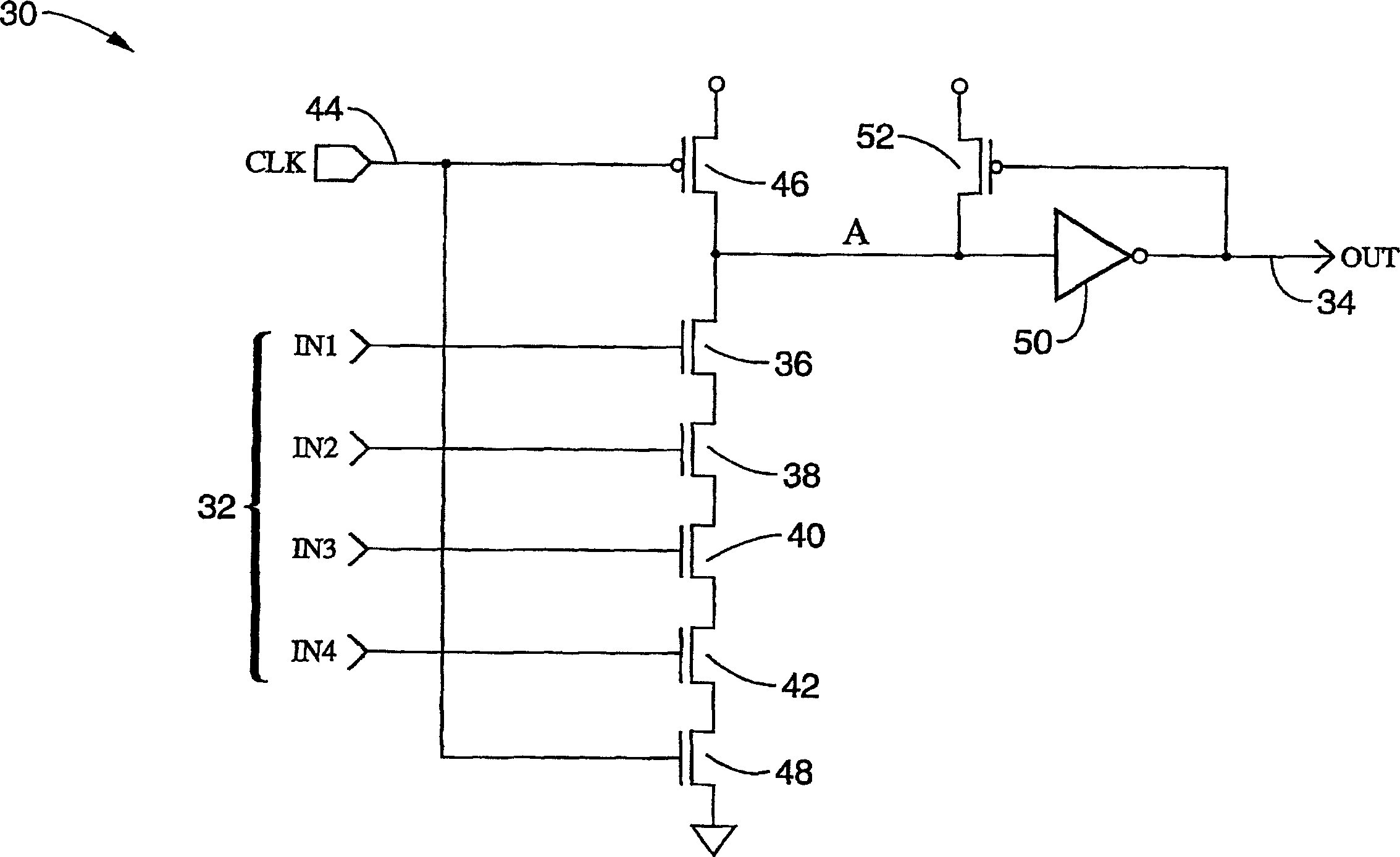
Event driven dynamic logic for reducing power consumption
InactiveUS6977528B2Reduce power consumptionReduce capacitive loadReliability increasing modificationsPower reduction by control/clock signalCapacitanceState variation
Methods and circuits are described for reducing power consumption within digital logic circuits by blocking the passage of clock signal transitions to the logic circuits when the clock signal would not produce a desired change of state within the logic circuit, such as at inputs, intermediary nodes, outputs, or combinations. By way of example, the incoming clock is blocked if a given set of logic inputs will not result in an output change of state if a clock signal transition were to be received. By way of further example, the incoming clock is blocked in a data flip-flop if the input signal matches the output signal, such that receipt of a clock transition would not produce a desired change of state in the latched output. The invention may be utilized for creating lower power combinatorial and / or sequential logic circuit stages subject to less unproductive charging and discharging of gate capacitances.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Digital pulse width modulation
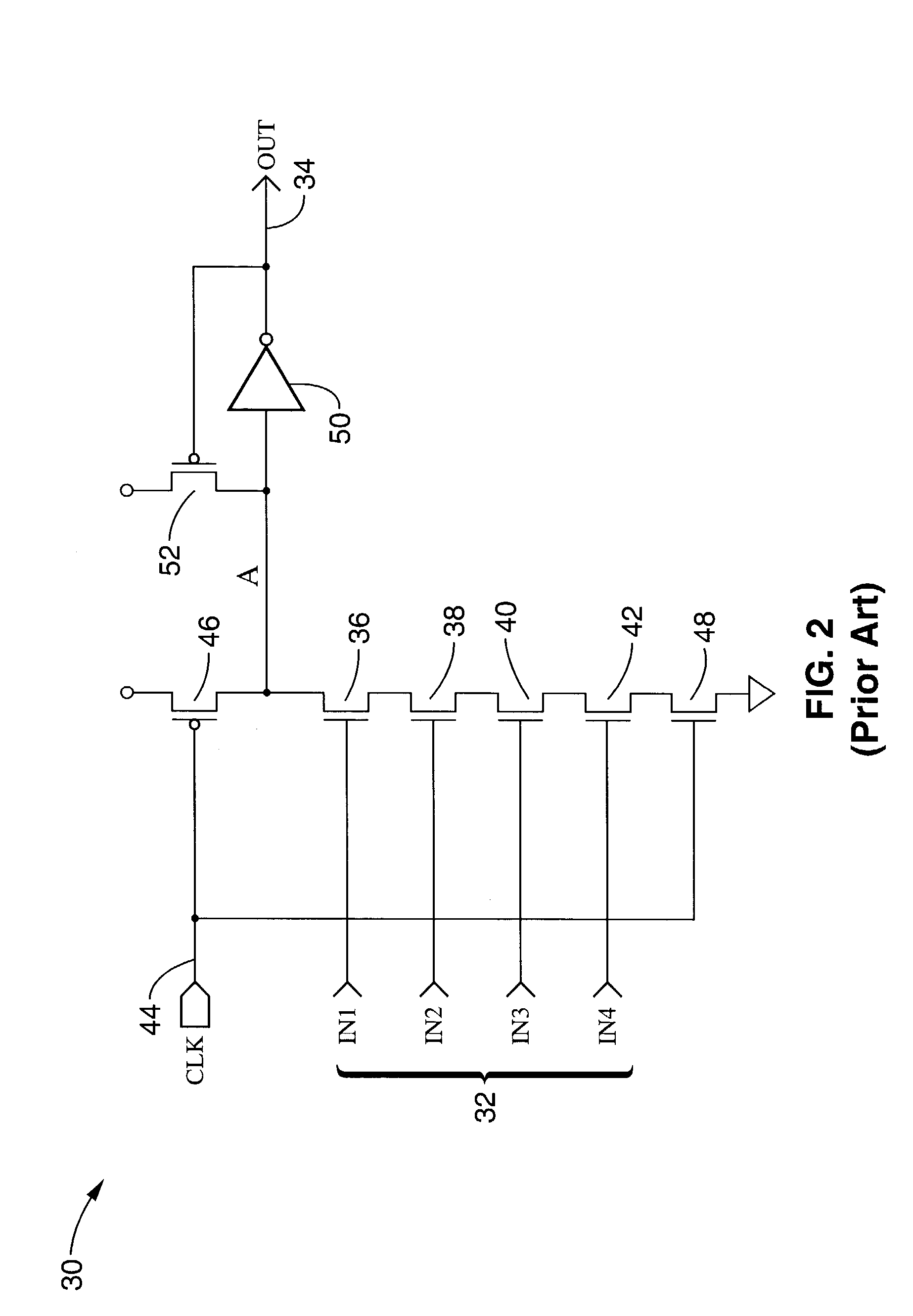
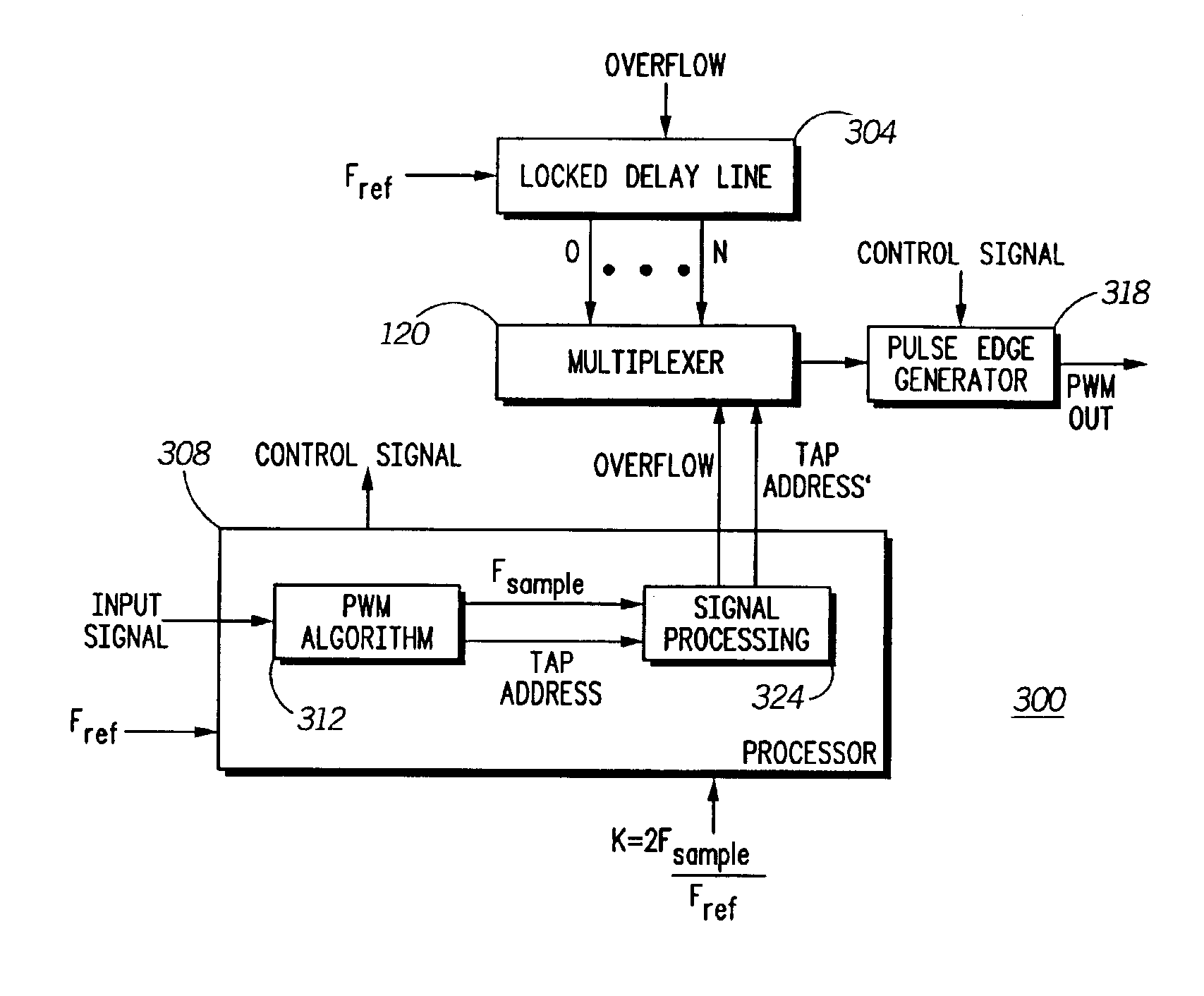
A digital technique for pulse width modulation (PWM) utilizes a tapped delay line 304 receiving a reference clock and generating a plurality of time delayed reference clock transitions having finer time resolution than the reference clock signal. A multiplexer 120 receives the plurality of time delayed reference clock transitions as an input thereto and producing an output when one of the plurality of time delayed reference clock transitions is addressed. An accumulator circuit 524 generates control timing signals associated with the input signal sampling rate Fsample that are used to select outputs from the delay line 304 representing a pulse width modulated output signal.
Owner:MOTOROLA SOLUTIONS INC
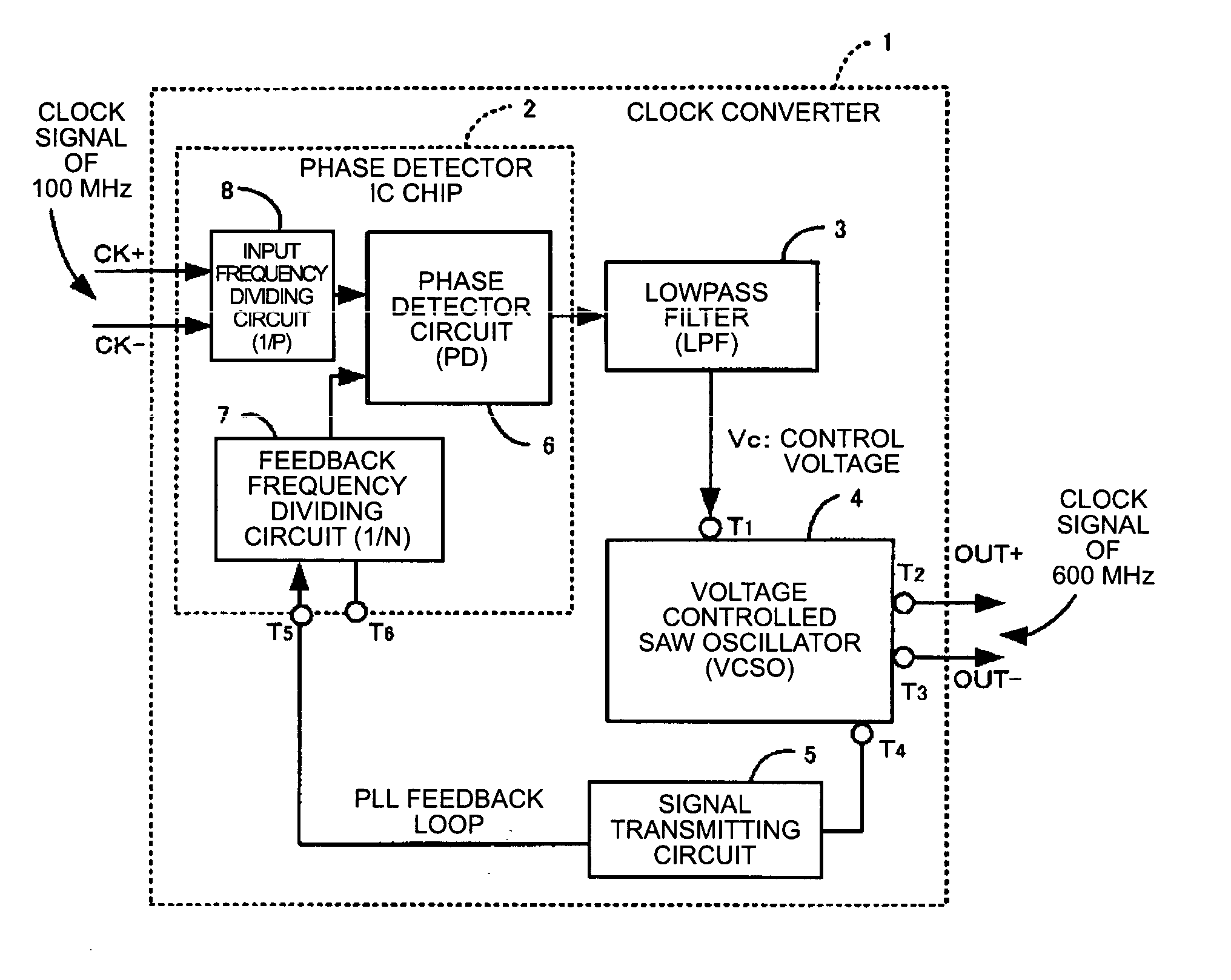
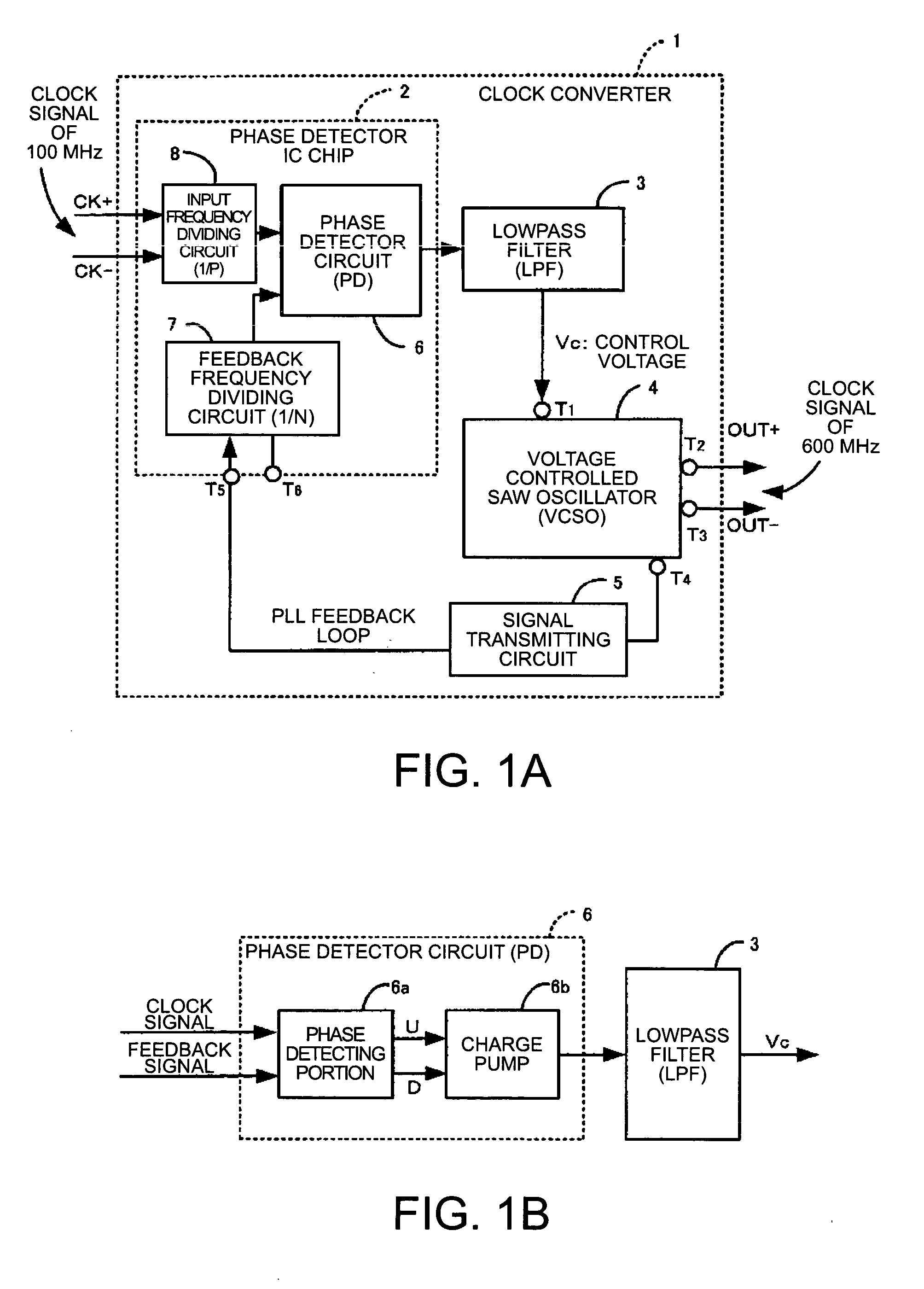
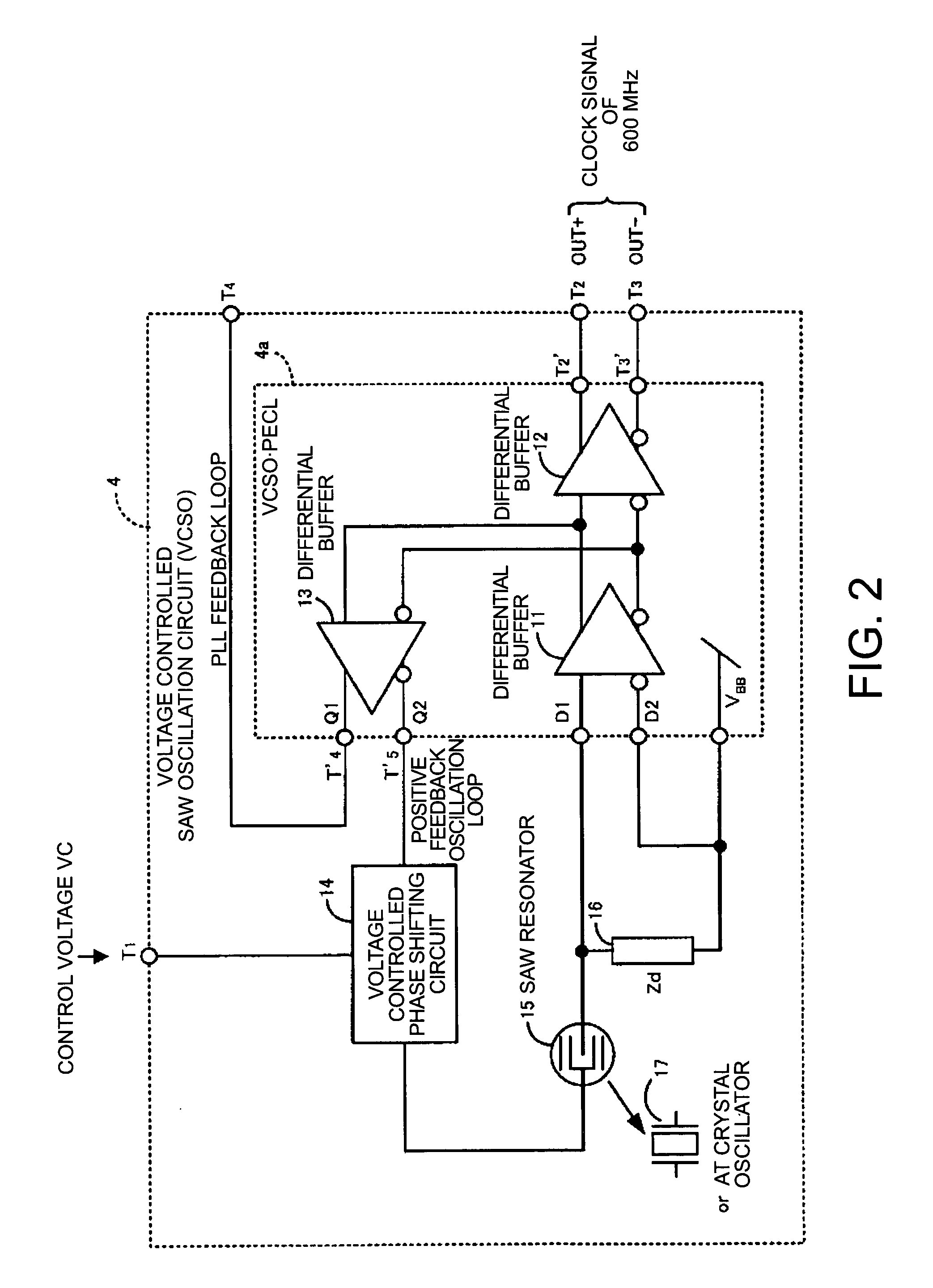
Voltage-controlled oscillator, clock converter, and electronic device
InactiveUS7012476B2Excellent frequency temperature characteristicsStable receptionRadiation pyrometryPulse automatic controlVoltage controlVoltage-controlled oscillator
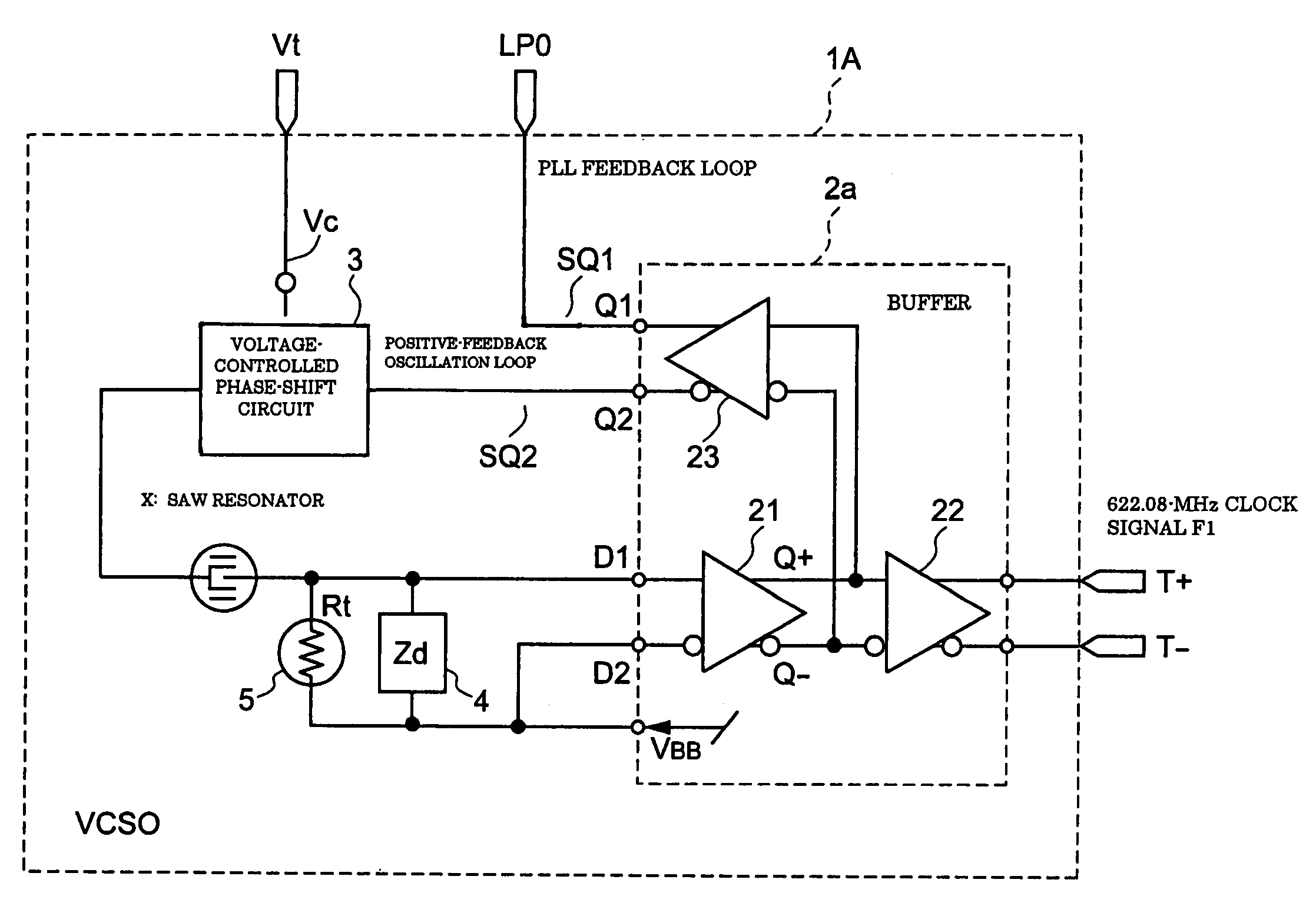
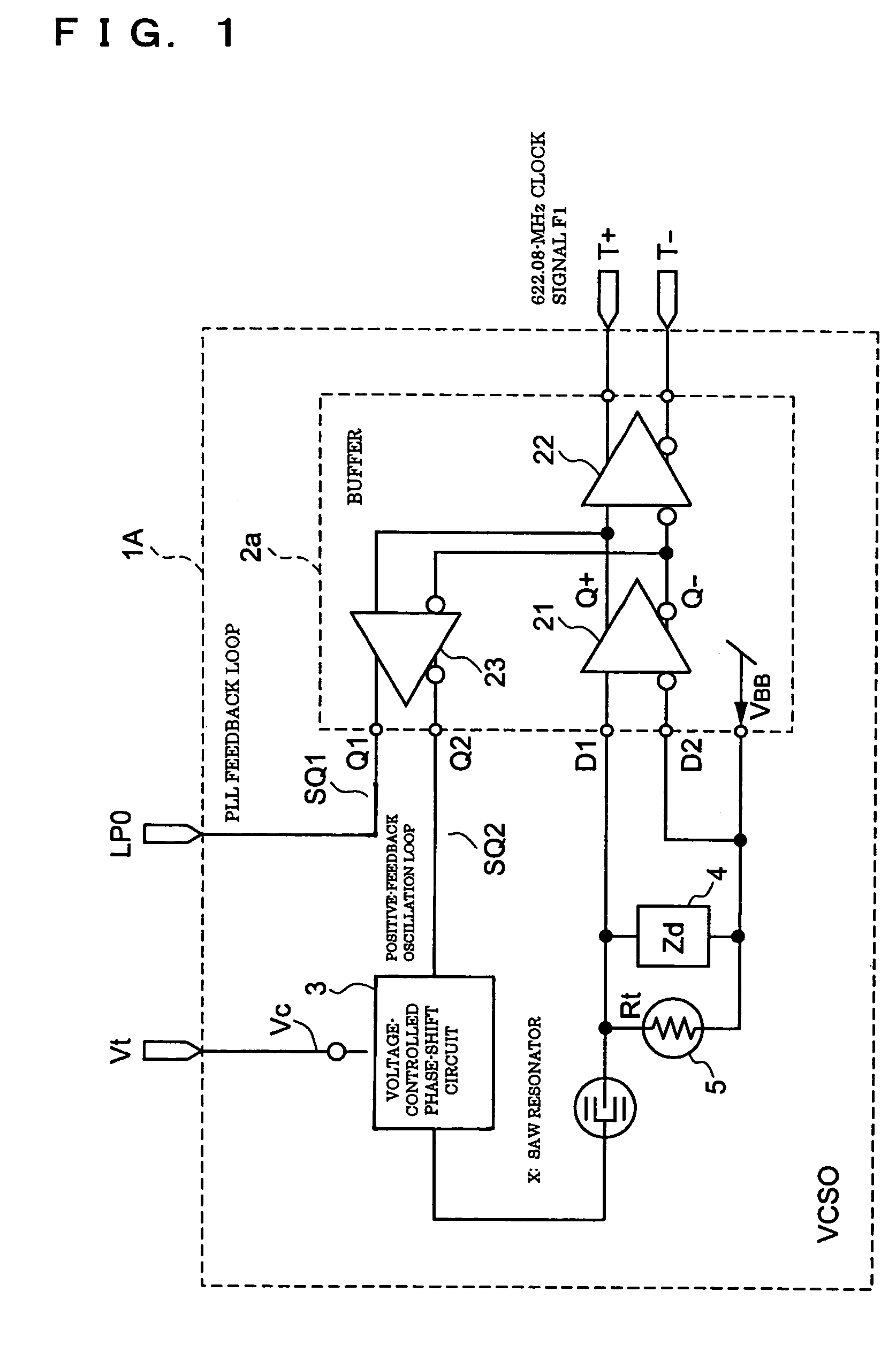
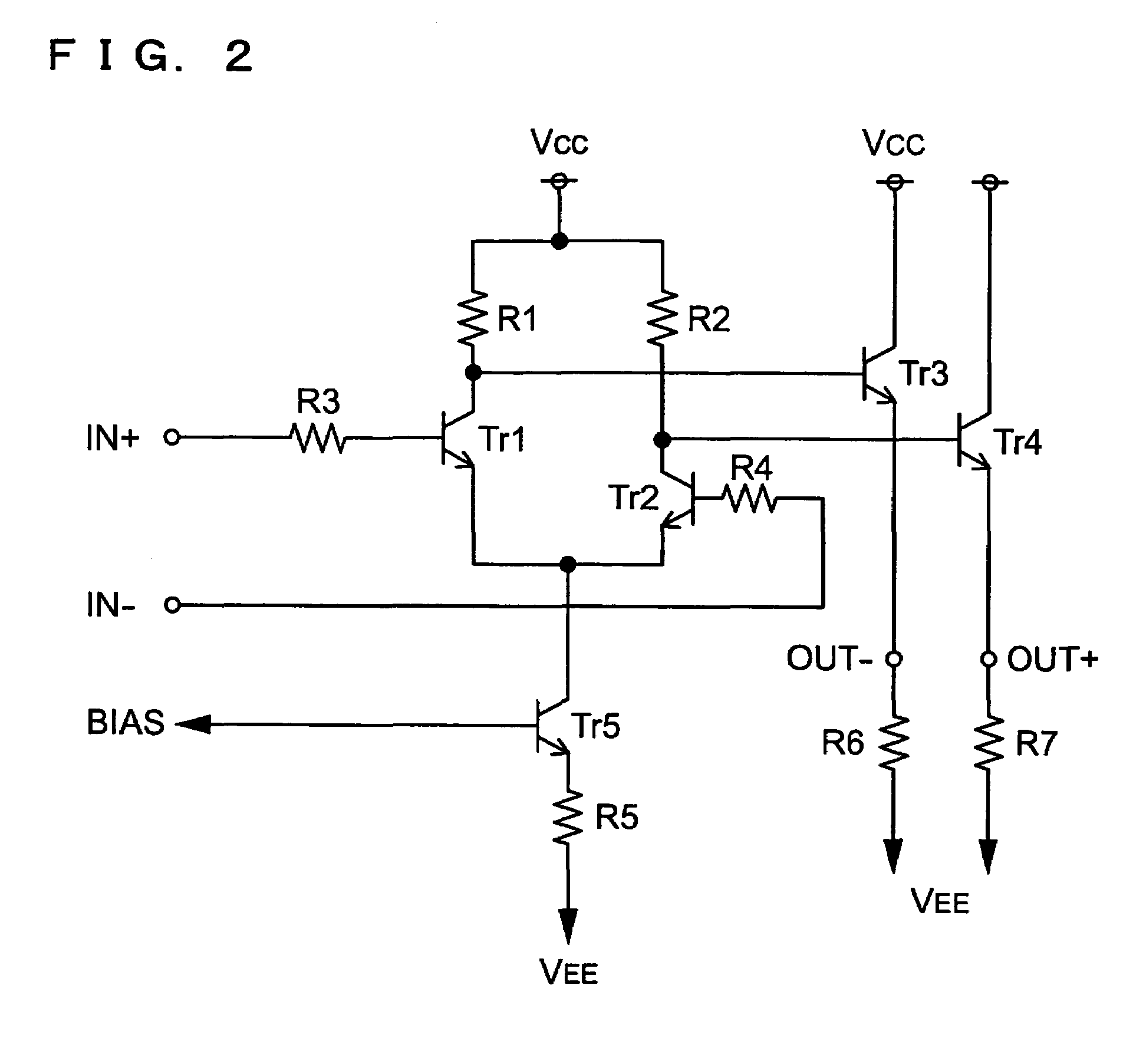
A voltage-controlled oscillator includes a voltage-controlled phase-shift circuit, outputting a signal with the shift deviated from an input signal by a specified amount with an external control voltage Vt, a SAW resonator, a buffer, inputting a resonance signal having a specified resonance frequency from the SAW resonator, outputting a clock signal with a desired frequency, and outputting a positive-feedback-oscillation-loop output signal, wherein the voltage-controlled phase-shift circuit, the SAW resonator, and the buffer construct a positive-feedback oscillation loop, in which the frequency temperature characteristic of the SAW resonator is rotated by a specified amount using the temperature characteristic of the propagation delay time of the buffer to correct the frequency temperature characteristic of the SAW resonator.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
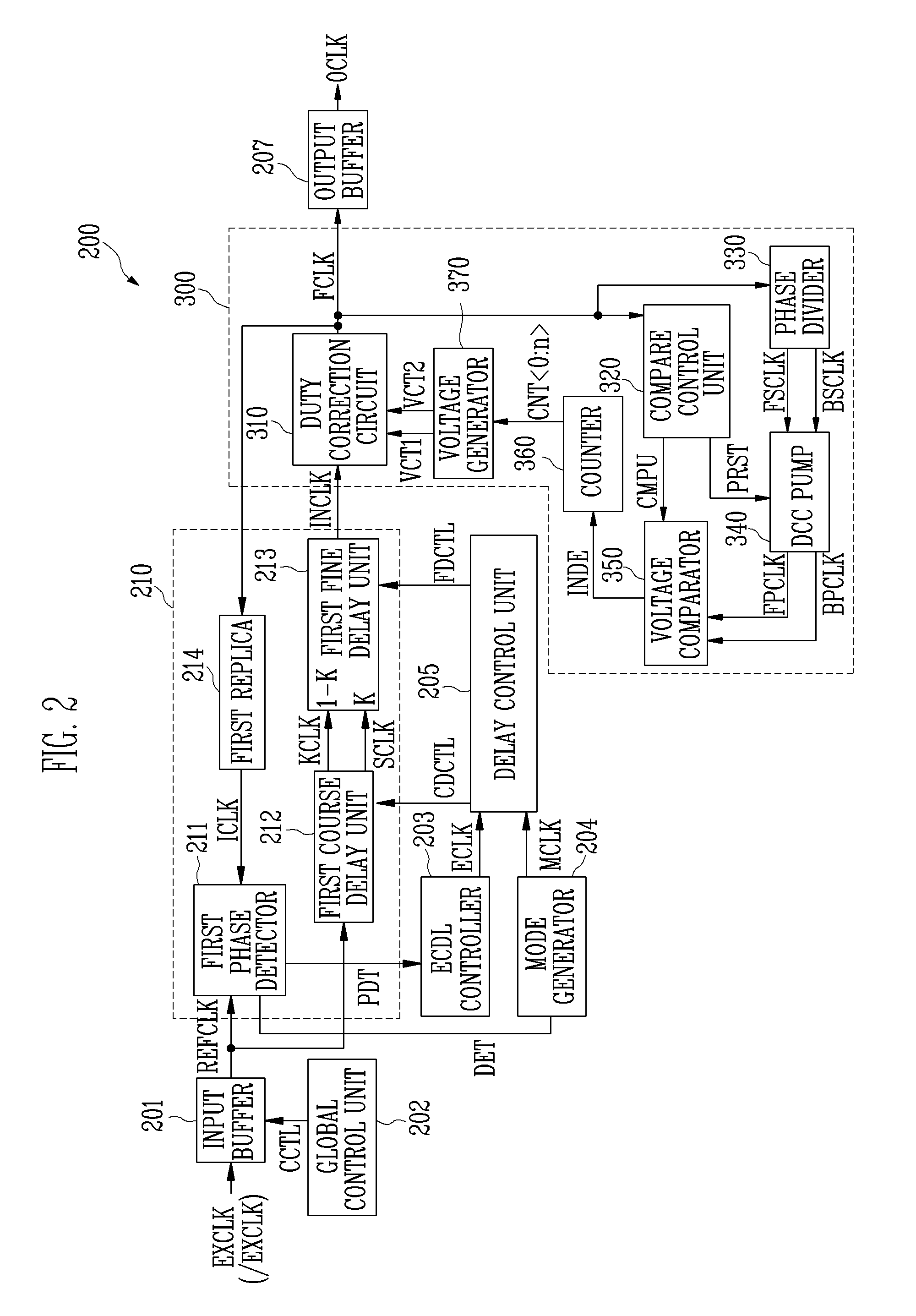
Delay locked loop
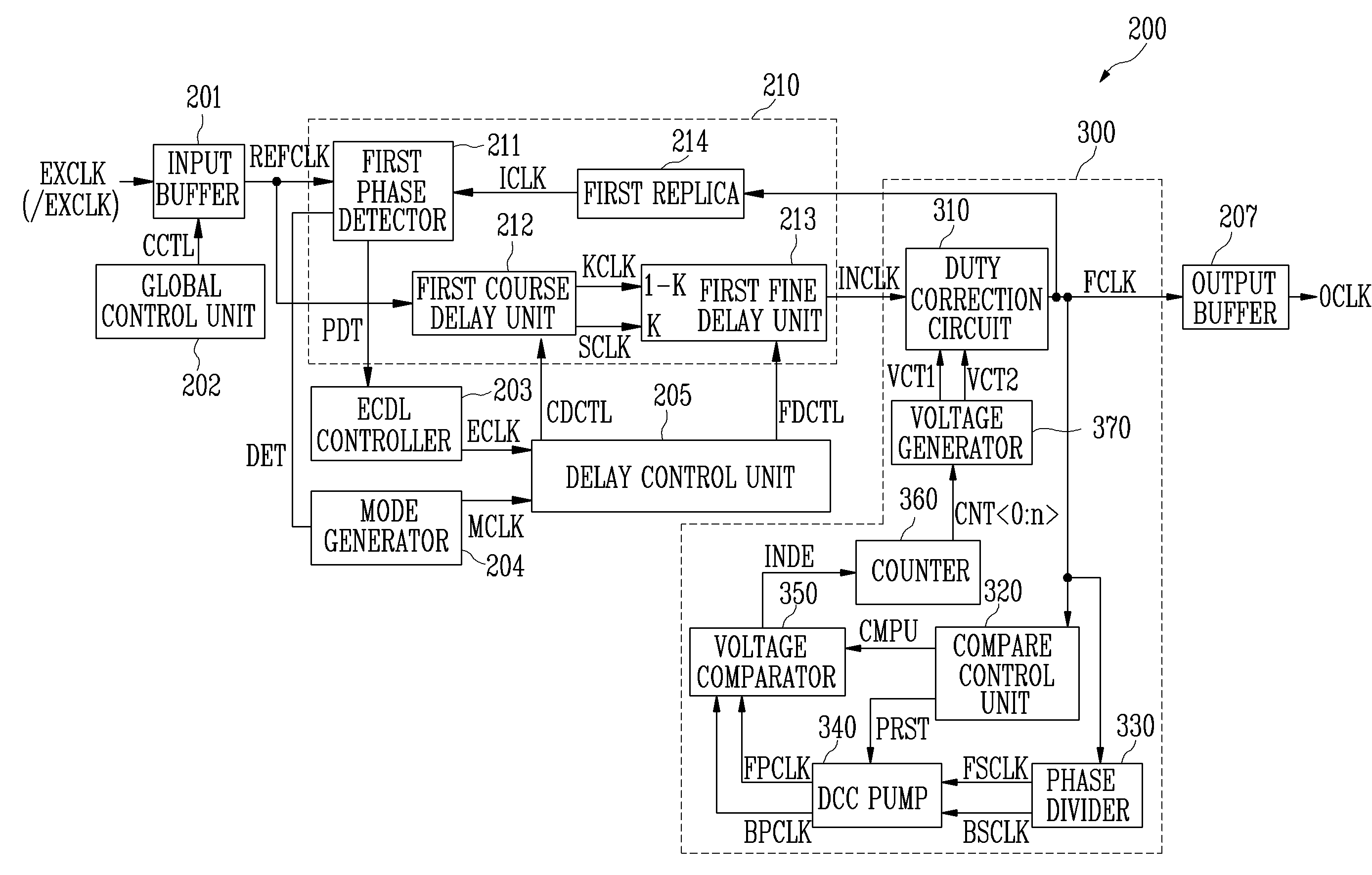
ActiveUS20070247203A1Area minimizationMinimize power consumptionPulse automatic controlDigital storageDelay-locked loopClock transition
The digital duty cycle correction circuit according to the present invention includes a first conversion circuit for buffering an internal clock output from a delay locked loop (DLL), converting the buffered internal clock into first and second clocks through first and second terminals, delaying the second clock according to voltage supplied to the second terminal through a capacitor, converting the delayed second clock into a first signal, and converting the first clock into a third clock, which rises at a falling edge of the first clock and falls at a rising edge of the first signal; and a second conversion circuit for converting the third clock into an output clock, which rises at a falling edge of the third clock and falls at a rising edge of the third clock.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
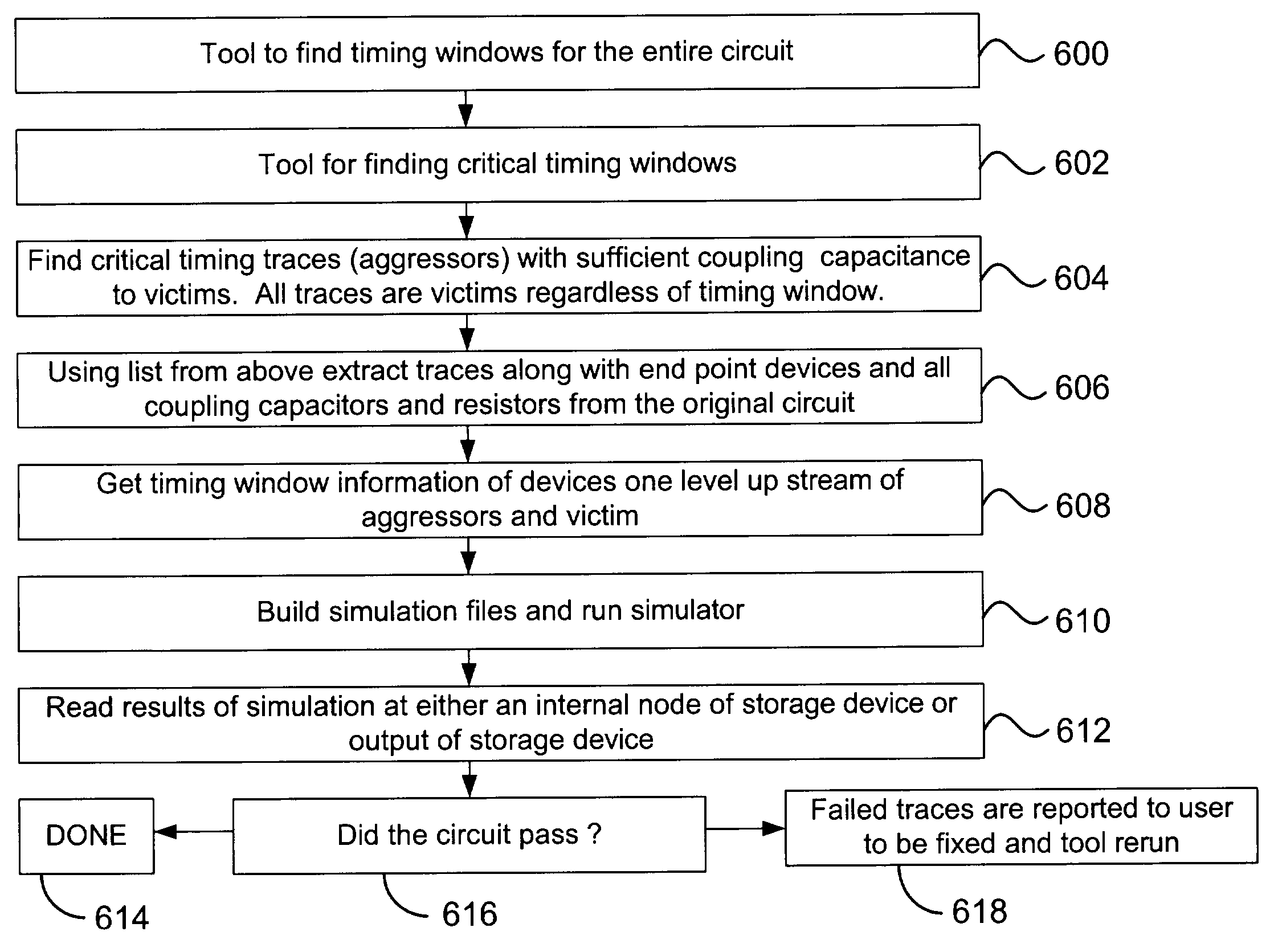
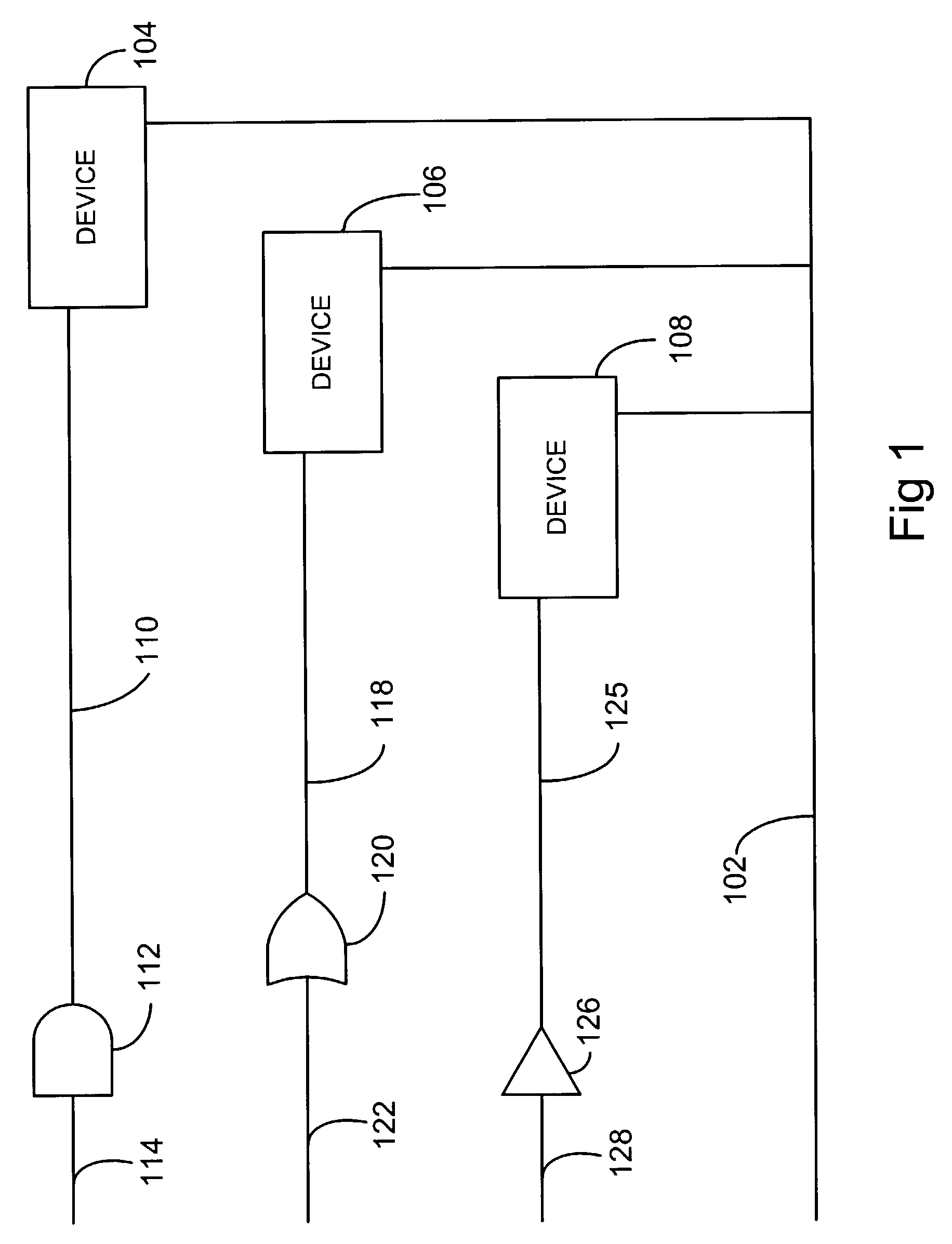
Method and apparatus for automated signal integrity checking
InactiveUS20040015338A1Analogue computers for electric apparatusElectrical testingElectronic systemsCoupling
The present invention is directed to a method and apparatus for simulating digital electronic systems. The signal integrity of a digital electronic system is assessed by analyzing traces (e.g. wires between components) for cross coupling. Problem areas are identified by monitoring storage components or output ports of the electronic system. Wires (traces), which carry signal transitions to the storage component or output ports are analyzed and quantified based on timing windows associated with the wires (traces). The clock transitions into a storage device are analyzed and vulnerability windows are identified for the storage device. The vulnerability windows are time periods when cross coupling may occur on a storage device. If a timing window overlaps a vulnerability window the timing window is considered a critical timing window. Devices driving the transition on wires with critical timing windows are then analyzed. Adjustments are made to the parameters of the driving devices to create a worse case scenario. The worse case scenario is simulated and analyzed for cross-coupling.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Zero-delay buffer with common-mode equalizer for input and feedback differential clocks into a phase-locked loop (PLL)
ActiveUS20090134923A1Pulse automatic controlElectric pulse generatorClock transitionVoltage regulation
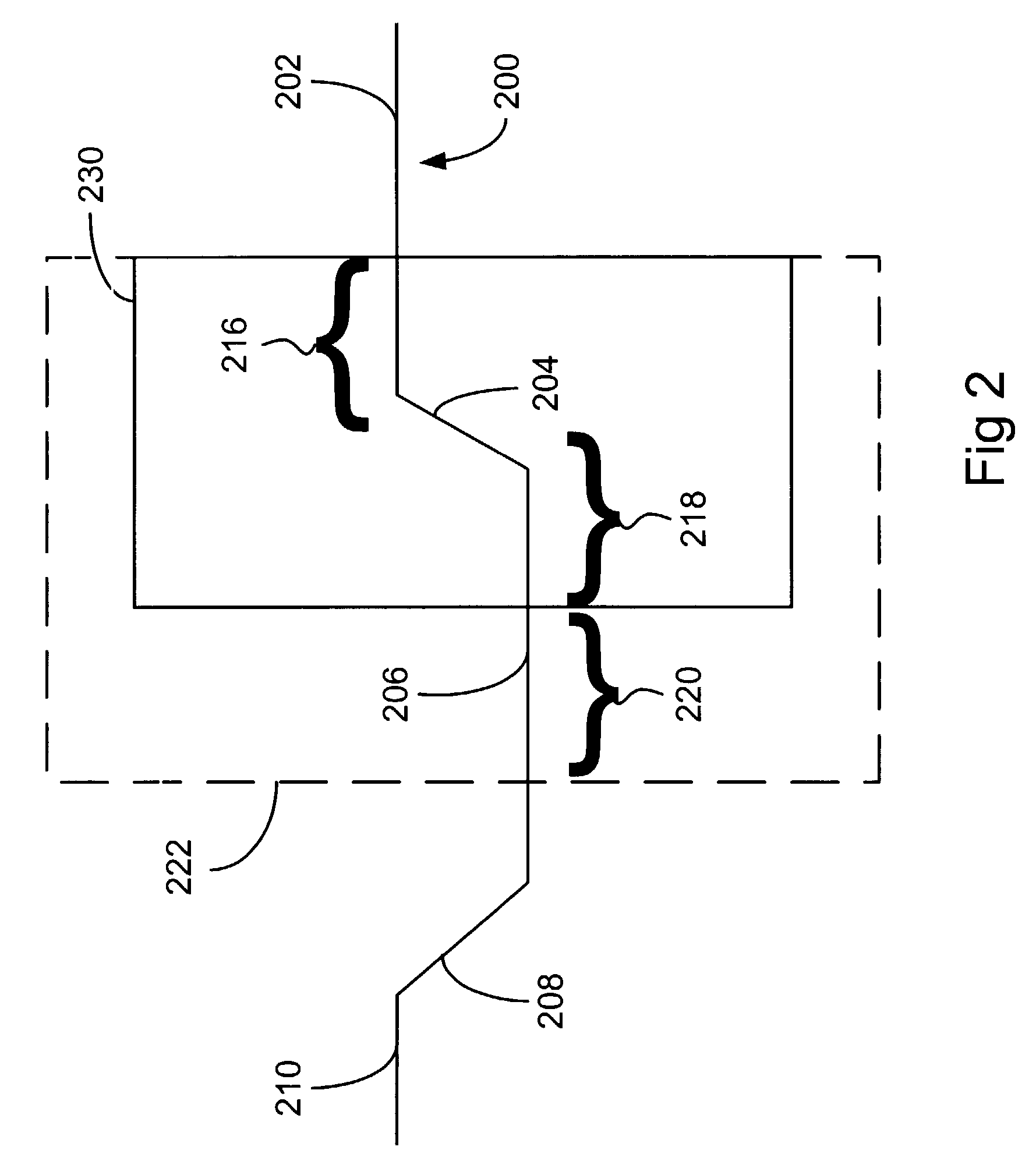
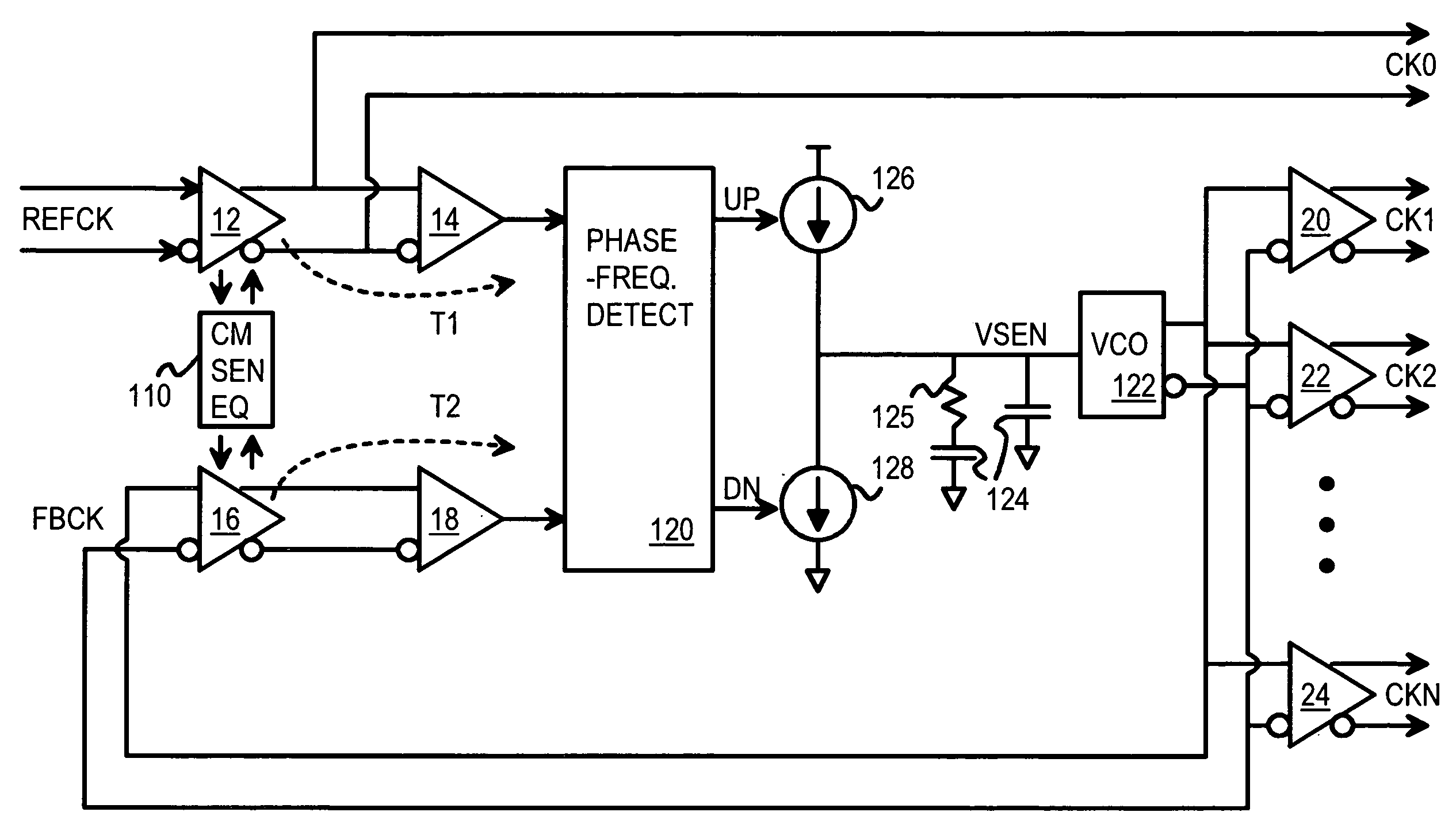
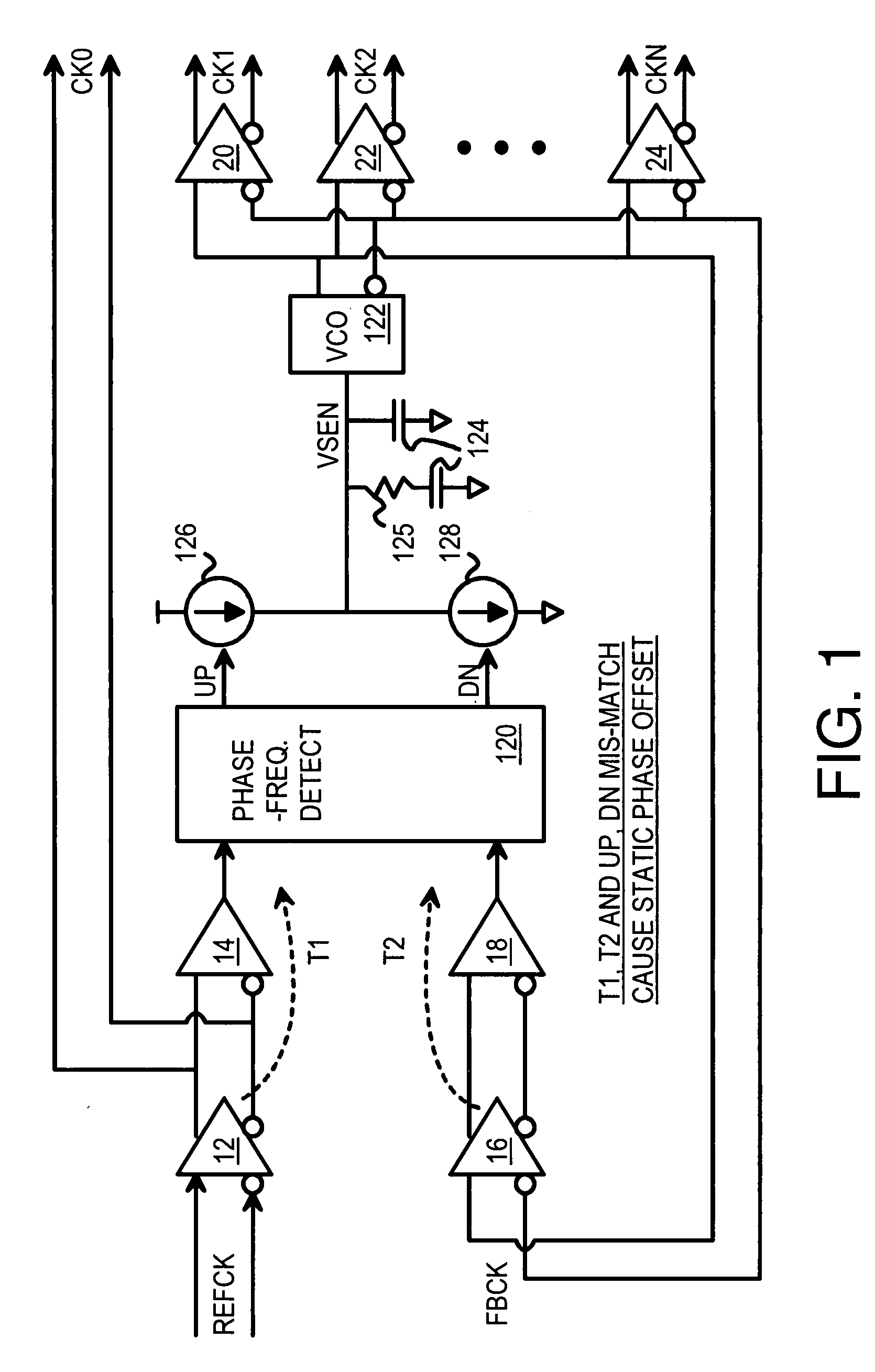
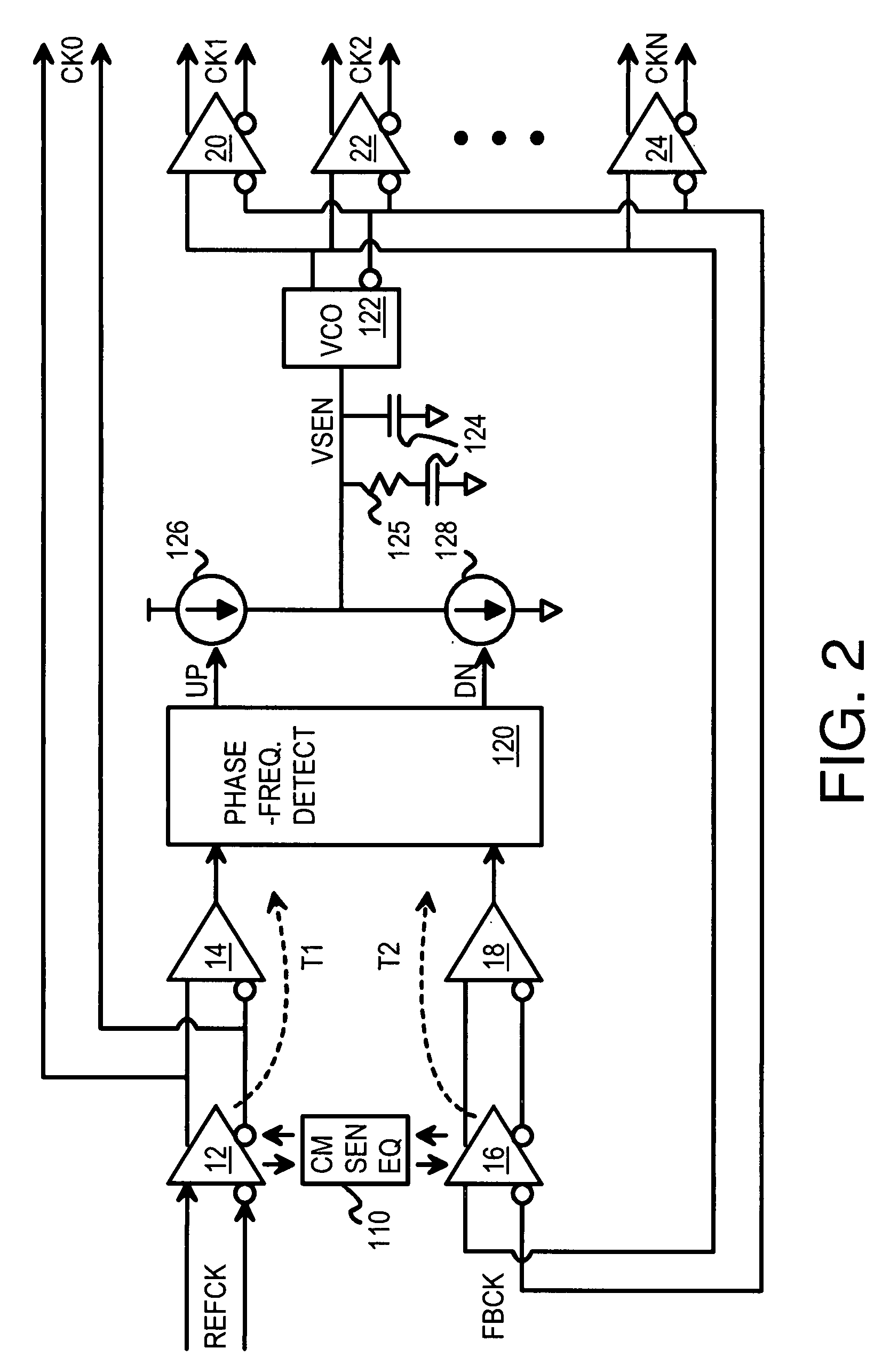
A zero-delay clock generator has a phase-locked loop (PLL) that generates a feedback clock and receives a reference clocks. All clocks are differential and have a common-mode voltage. The common-mode voltage of an externally-generated reference clock can vary from the common-mode voltage of the internally-generated feedback clock. Differences in common-mode voltage of the reference clock and feedback clock cause delay variations resulting in static phase offsets of generated clocks. A common-mode sense and equalizer senses the common-mode voltages of the buffered reference and feedback clocks, and generates control voltages. The control voltages adjust the common-mode voltage and delay of differential buffers that receive the reference and feedback clocks. The control voltages adjust the differential buffers to match the common-mode voltages of the buffered reference and feedback clocks. The buffered clocks are then applied to a phase and frequency detector of the PLL.
Owner:HONG KONG APPLIED SCI & TECH RES INST
Event driven dynamic logic for reducing power consumption
InactiveCN1679237AReduced power dissipation levelsReduce power lossPower reduction by control/clock signalLogic circuits characterised by logic functionCapacitanceState variation
Methods and circuits are described for reducing power consumption within digital logic circuits by blocking the passage of clock signal transitions to the logic circuits when the clock signal would not produce a desired change of state within the logic circuit, such as at inputs, intermediary nodes, outputs, or combinations. By way of example, the incoming clock is blocked if a given set of logic inputs will not result in an output change of state if a clock signal transition were to be received. By way of further example, the incoming clock is blocked in a data flip-flop if the input signal matches the output signal, such that receipt of a clock transition would not produce a desired change of state in the latched output. The invention may be utilized for creating lower power combinatorial and / or sequential logic circuit stages subject to less unproductive charging and discharging of gate capacitances.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
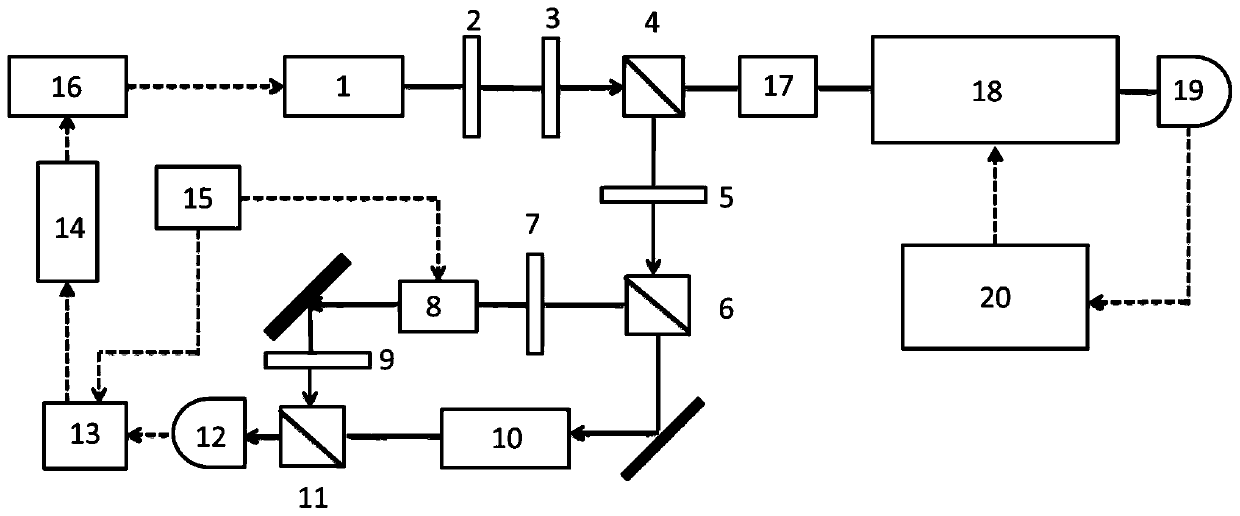
Optical pumping rubidium atomic clock based on modulation transfer spectrum frequency stabilization laser, and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN110768097AHigh-speed full-bandwidth lockingImprove performanceLaser detailsApparatus using atomic clocksFrequency stabilizationBeam splitting
The invention discloses an optical pumping rubidium atomic clock based on modulation transfer spectrum frequency stabilization laser, and a preparation method thereof. The optical pumping rubidium atomic clock comprises a narrow linewidth laser, a beam expander, a half wave plate, a polarization beam splitting prism, a phase modulator, a rubidium atomic bubble for laser frequency stabilization, ahigh-speed photoelectric detector, a mixer, a high-speed servo feedback circuit, a radio frequency signal source, a laser driving power supply, a convex lens, an acoustic optical modulator, a rubidiumatomic bubble for obtaining a clock transition spectral line, a crystal oscillator frequency synthesizer and a control circuit part; the radio frequency signal source generates a modulation signal, the modulation signal is input into the phase modulator to perform phase modulation on pumping laser, meanwhile, a demodulation signal is generated to perform mixing demodulation with the signal from the photoelectric detector to obtain an error signal, and the laser driving power supply is controlled by the high-speed servo feedback circuit to realize high-stability narrow linewidth laser based ona modulation transfer spectrum. The laser subjected to frequency stabilization is used as the pumping laser of the optical pumping rubidium atomic clock to obtain a high-performance optical pumping rubidium atomic clock.
Owner:WENZHOU COLLABORATIVE INNOVATION CENT OF LASER & OPTOELECTRONICS
Low distortion digital to analog converter and digital signal synthesizer systems
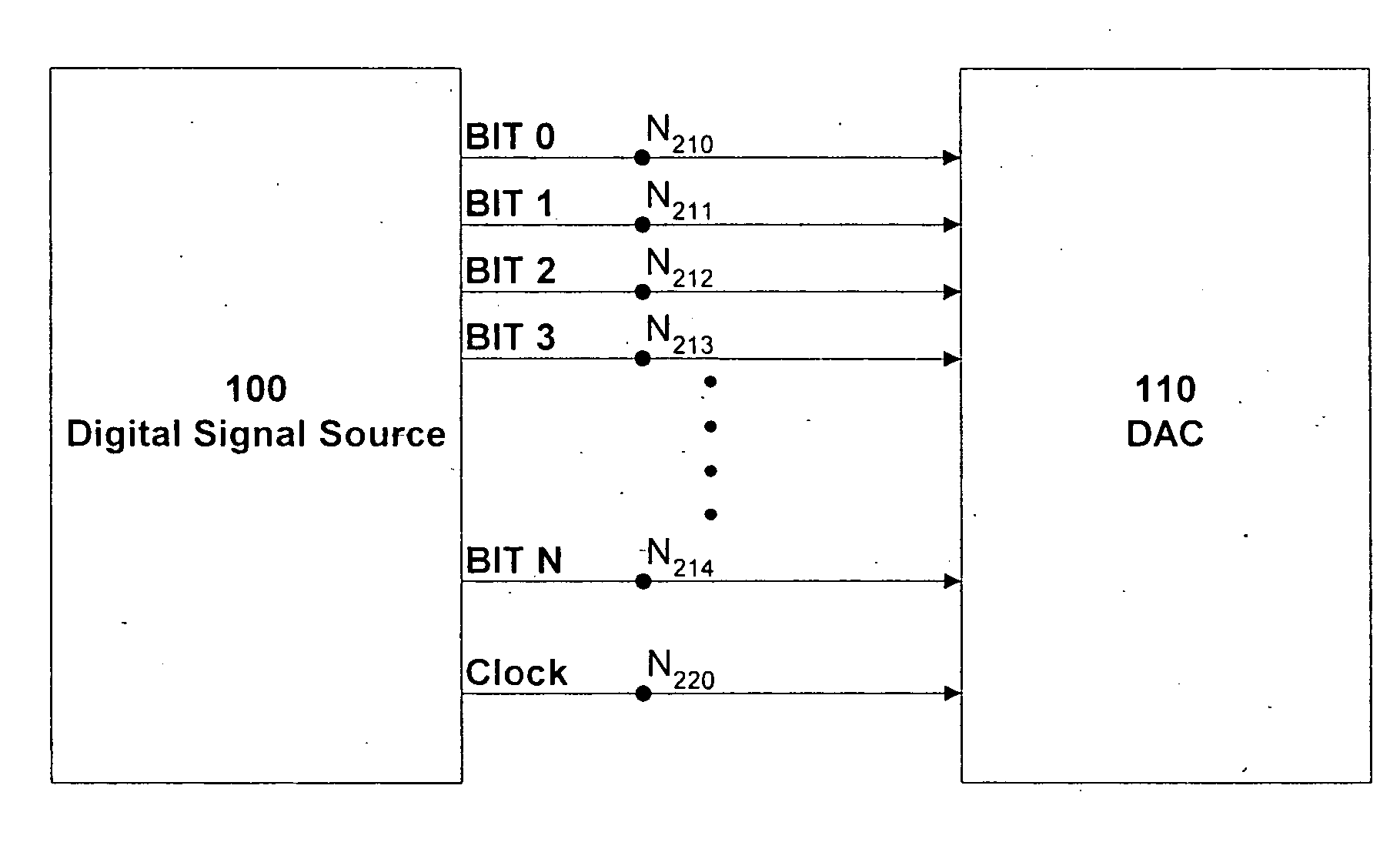
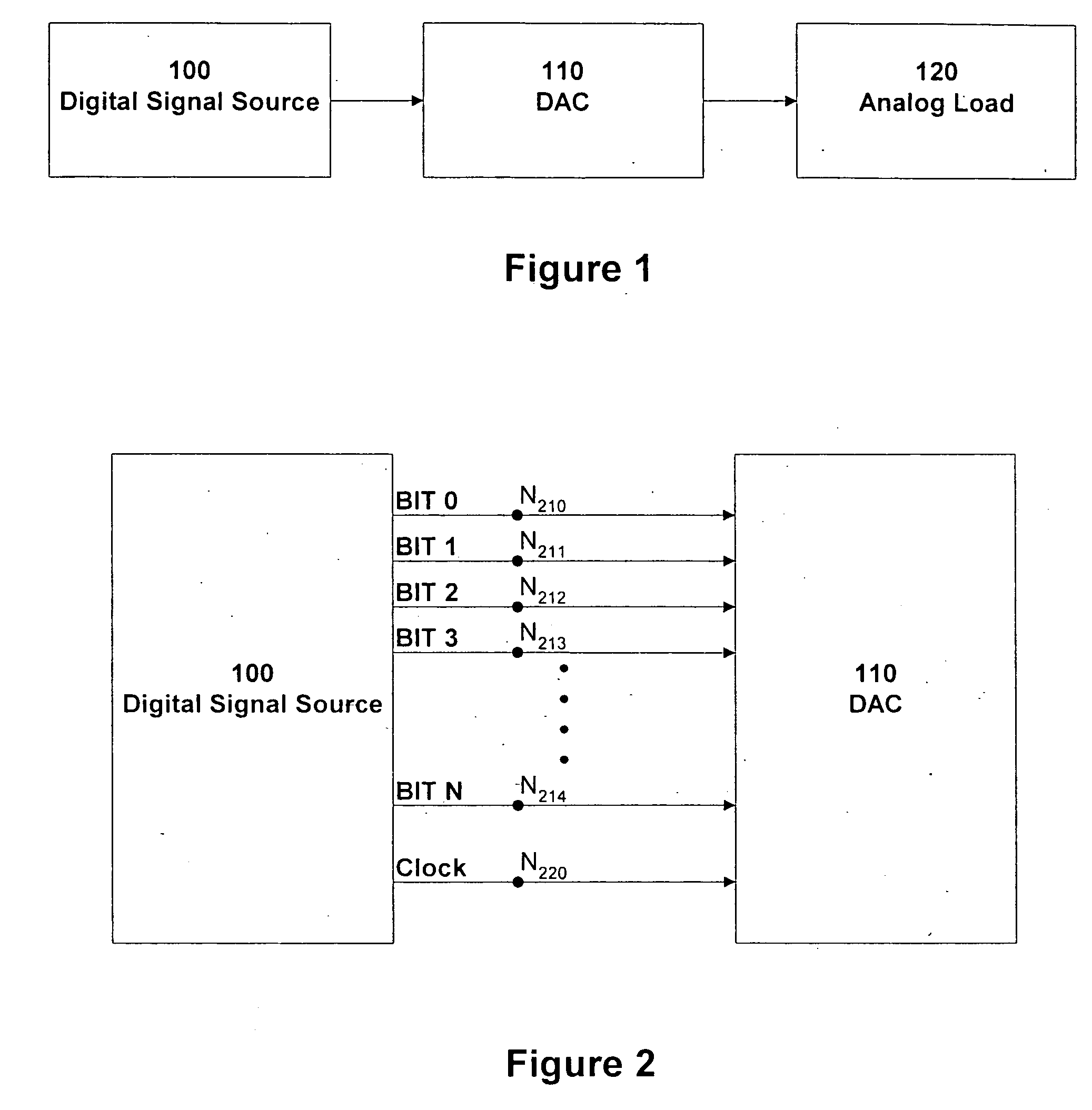
InactiveUS20050062631A1Increase sampling rateReduce output signalElectric signal transmission systemsDigital variable displayLow distortion24-bit
The present invention is a digital to analog converter circuit that provides significantly lower distortion than achieved by digital to analog converter circuits having comparable speed and resolution utilizing the present art. The present invention provides linear or higher order transitions between clock transition time points rather than step transitions used in the present art. Distortion reduction can exceed 30 dB in the embodiment with linear sample-to-sample transitions and greater in alternate embodiments with non-linear transitions. In other embodiments, the present invention can provide low distortion at resolutions from 16 to 24 bits or more at sample rates typical of high-speed 8-bit devices of the present art.
Owner:MASHHOON HAMID R
Timing skew error correction apparatus and methods
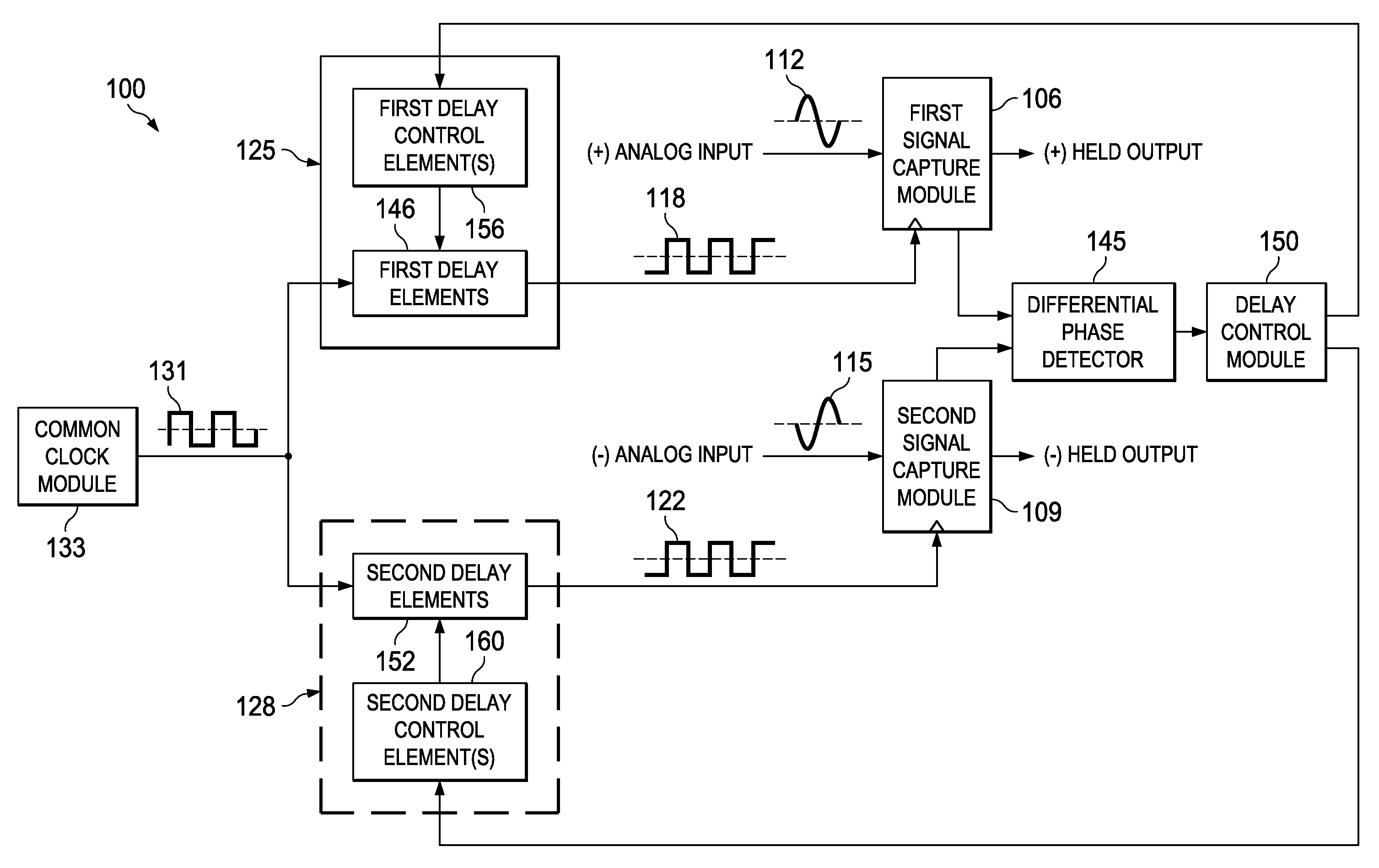
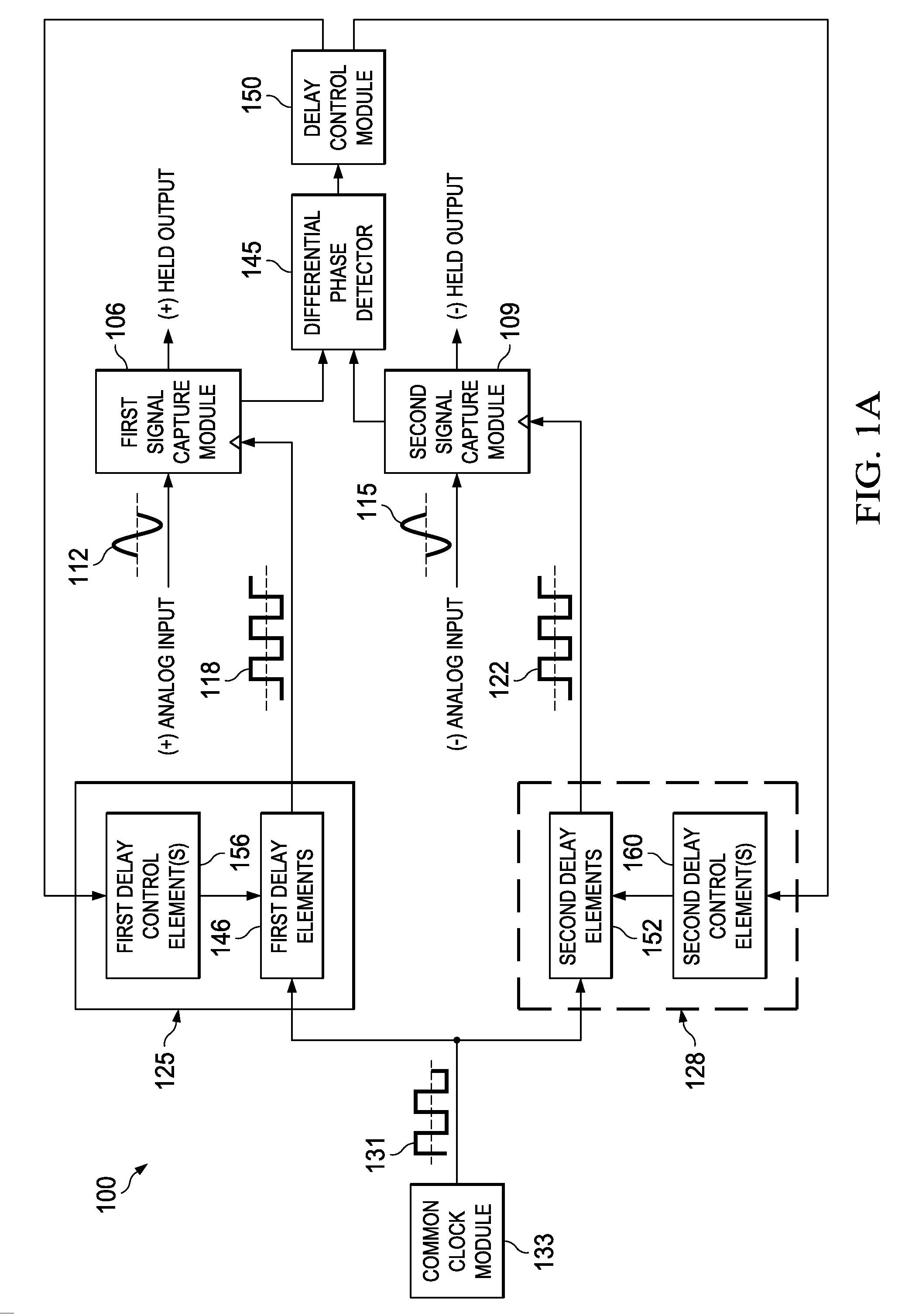
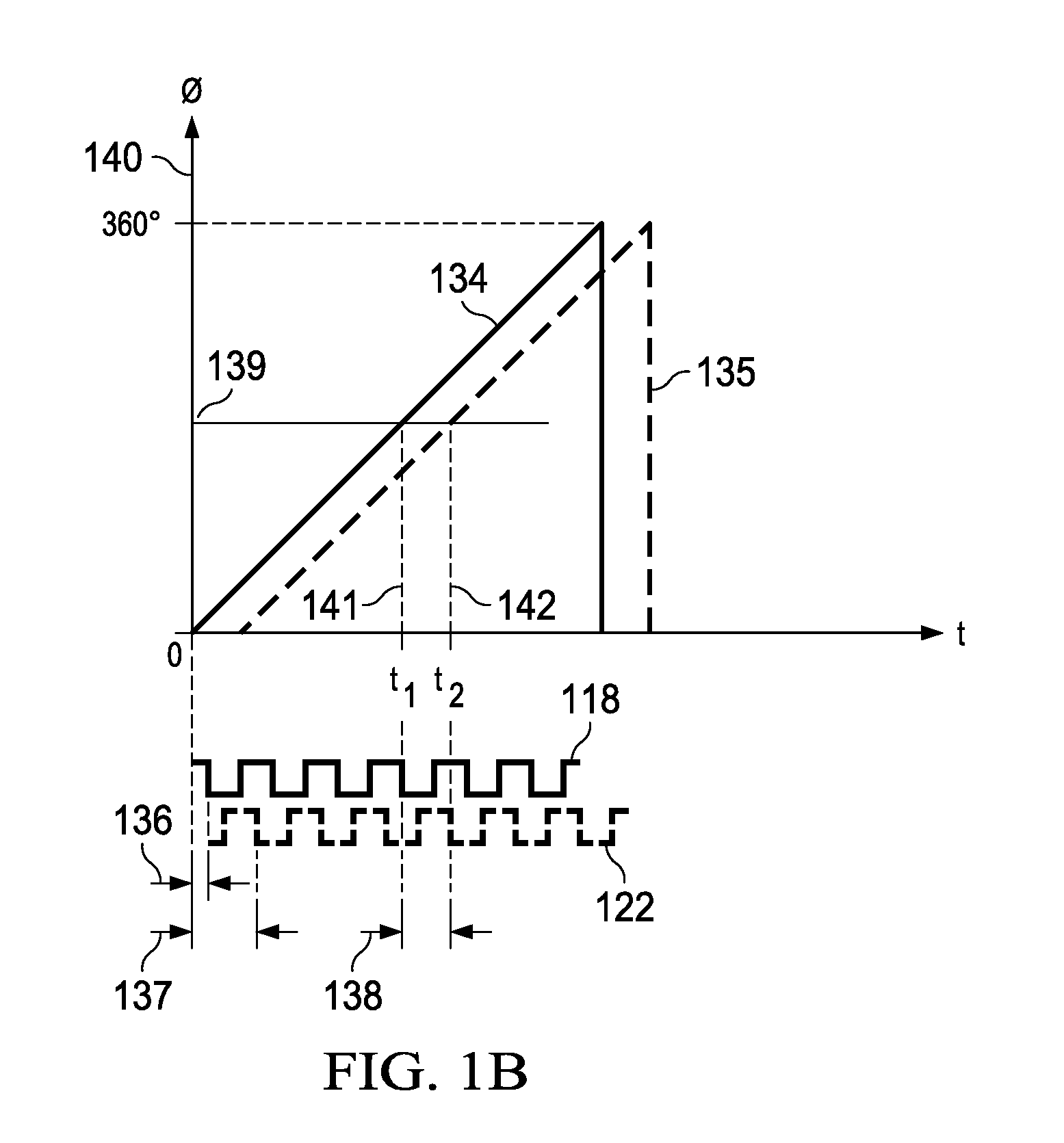
ActiveUS20120126869A1Efficient samplingAnalogue/digital conversionElectric signal transmission systemsElectricityDifferential phase
Apparatus and methods disclosed herein operate to compensate for skew between inverse phases (e.g., differential phases) of an analog signal appearing at the inputs of an analog signal capture circuit such as a track-and-hold or sample-and-hold circuit associated with an ADC or similar device. Each of two capture clocks is used to capture one of the inverse phases. One or more delay circuits are configured to create a differential delay between clock transitions associated with the two capture clocks. The differential delay is proportional to the input skew between the inverse phases. The phases are consequently sampled at substantially identical points on a phase domain axis. Embodiments operate to create phase sampling synchronicity and to thereby decrease the amplitude of a common-mode signal component that results from the skew. Increased linearity and decreased distortion may result.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Method and apparatus for reducing power consumption
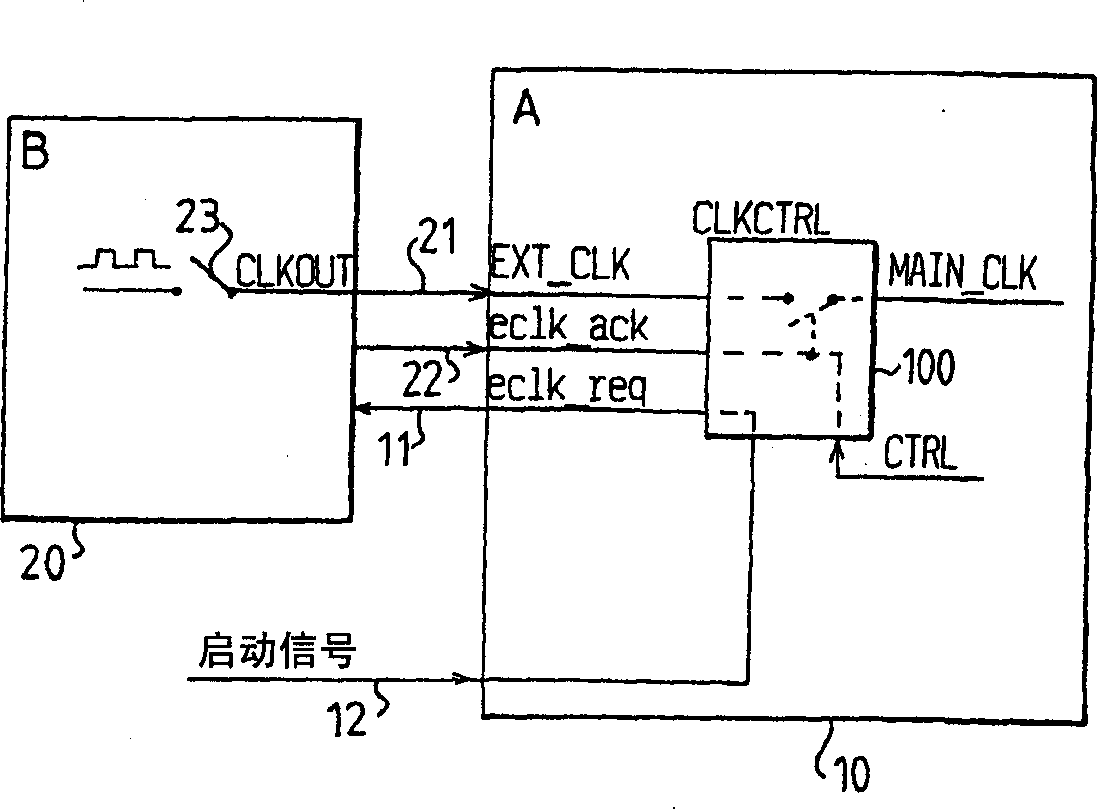
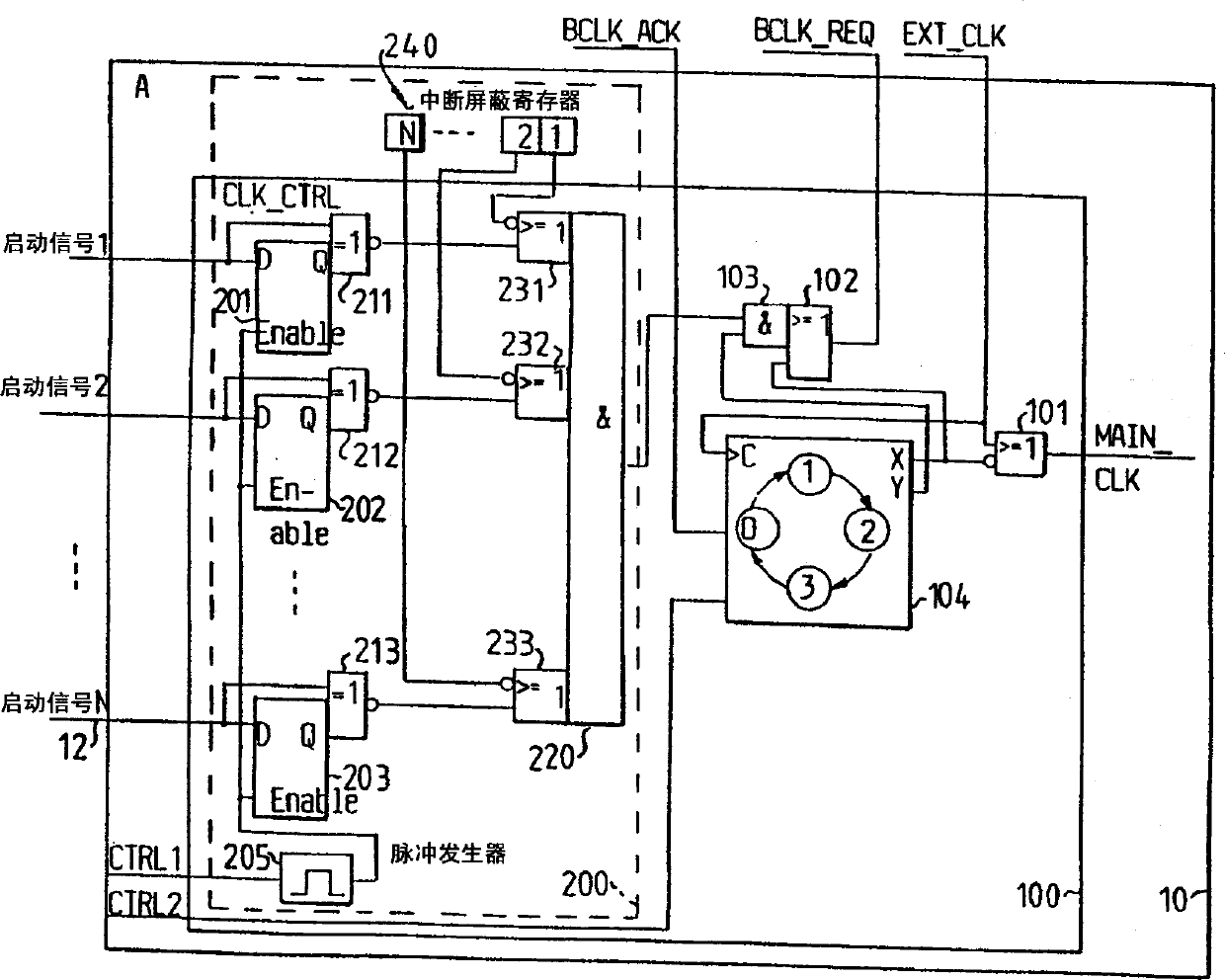
InactiveCN1348558AReliable stopReliable restartEnergy efficient ICTPower managementClock transitionComputer module
An arrangement for clock control in a device receiving a clock from an external source includes switching means (101) for switching an external clock through to the device as an internal clock, and clock request generation means (102, 103), adapted to switch clock signal through to the external clock controller as requests for suppressing and restarting the external clock. Control means (104) are provided in the form of a state machine to control the generation of the internal clock through the switching means, and to control the clock request generation means in accordance with a predetermined state of two signals, one generated internally by the device, the other by the external clock controller (20). The clock request generation means are also coupled to a clock start module adapted to receive several input signals (12) for signalling an event requiring the clocked operation of the device.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
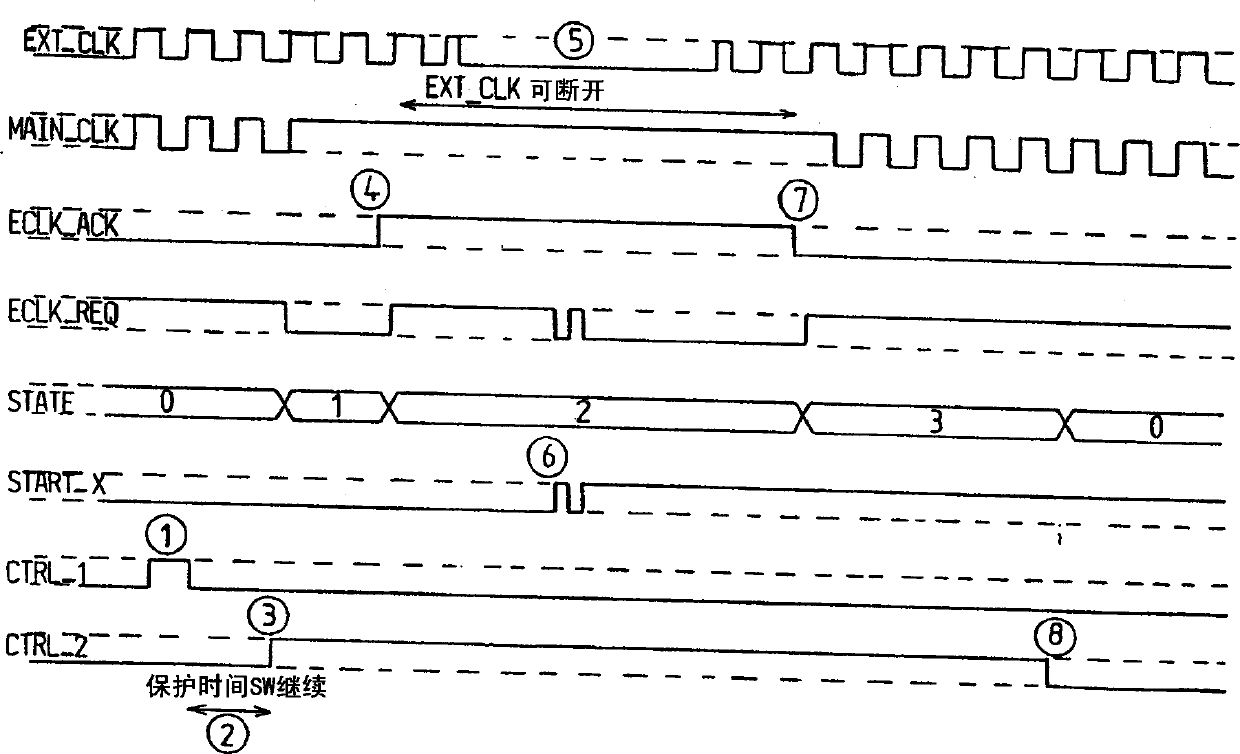
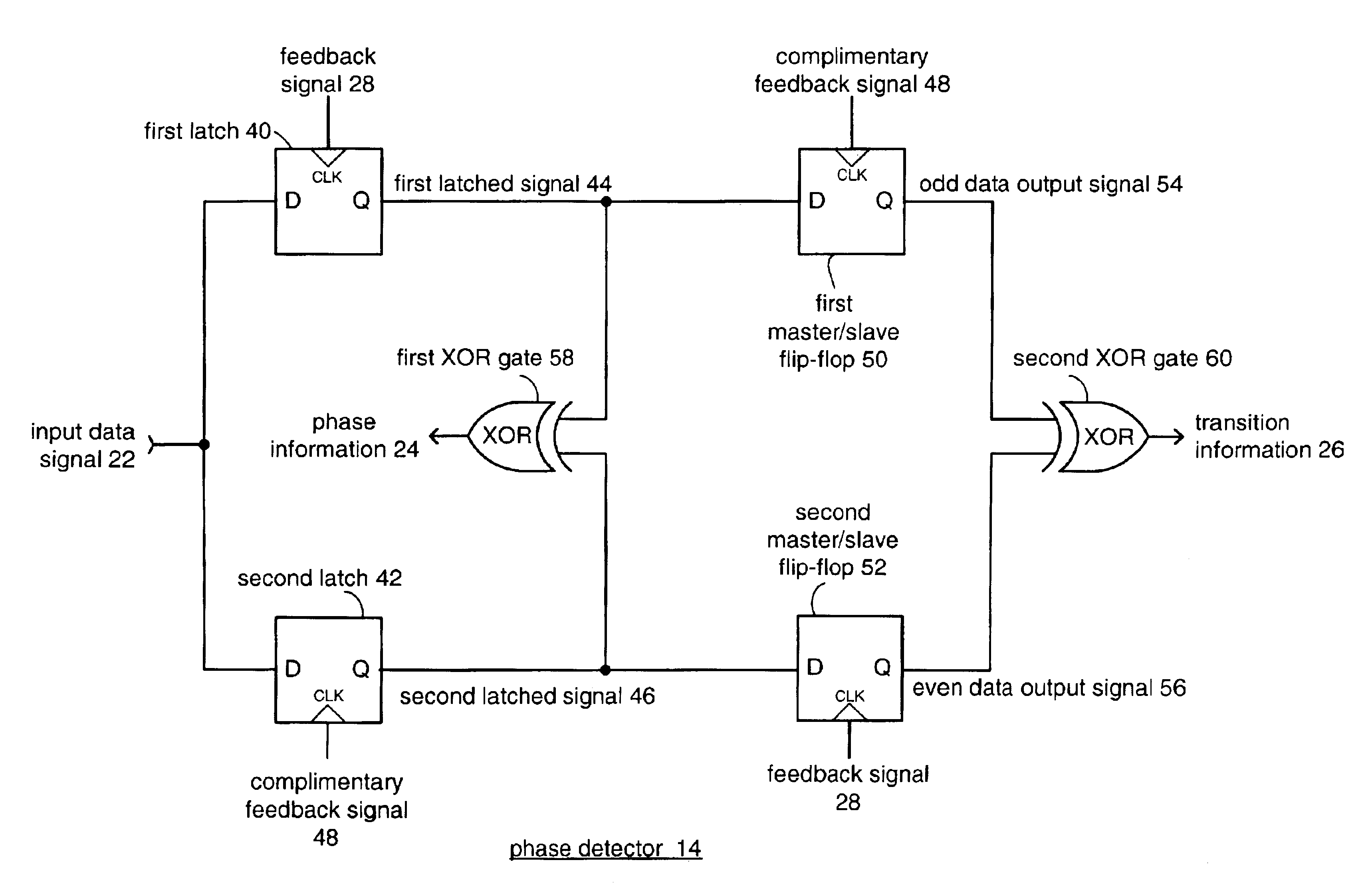
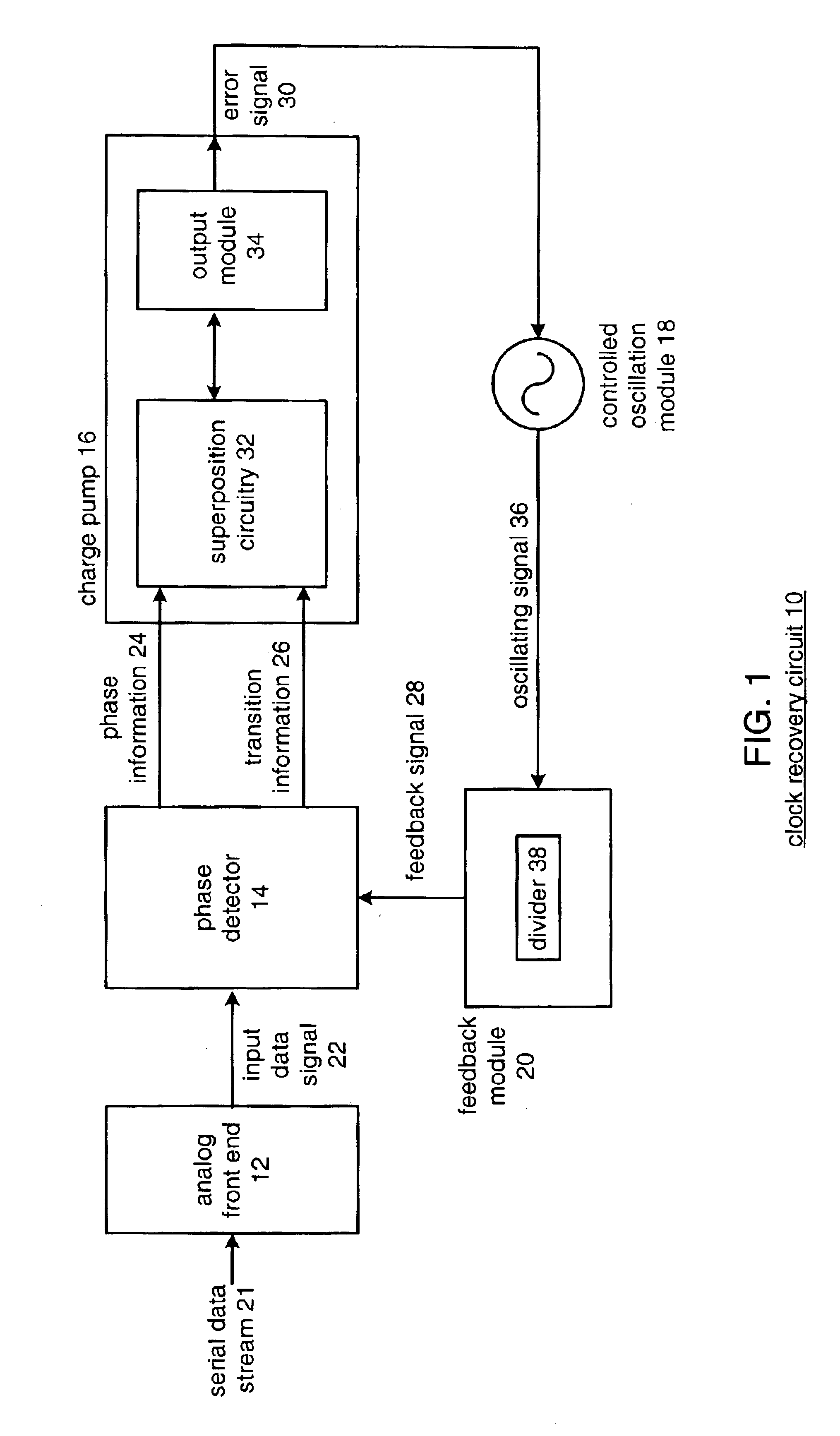
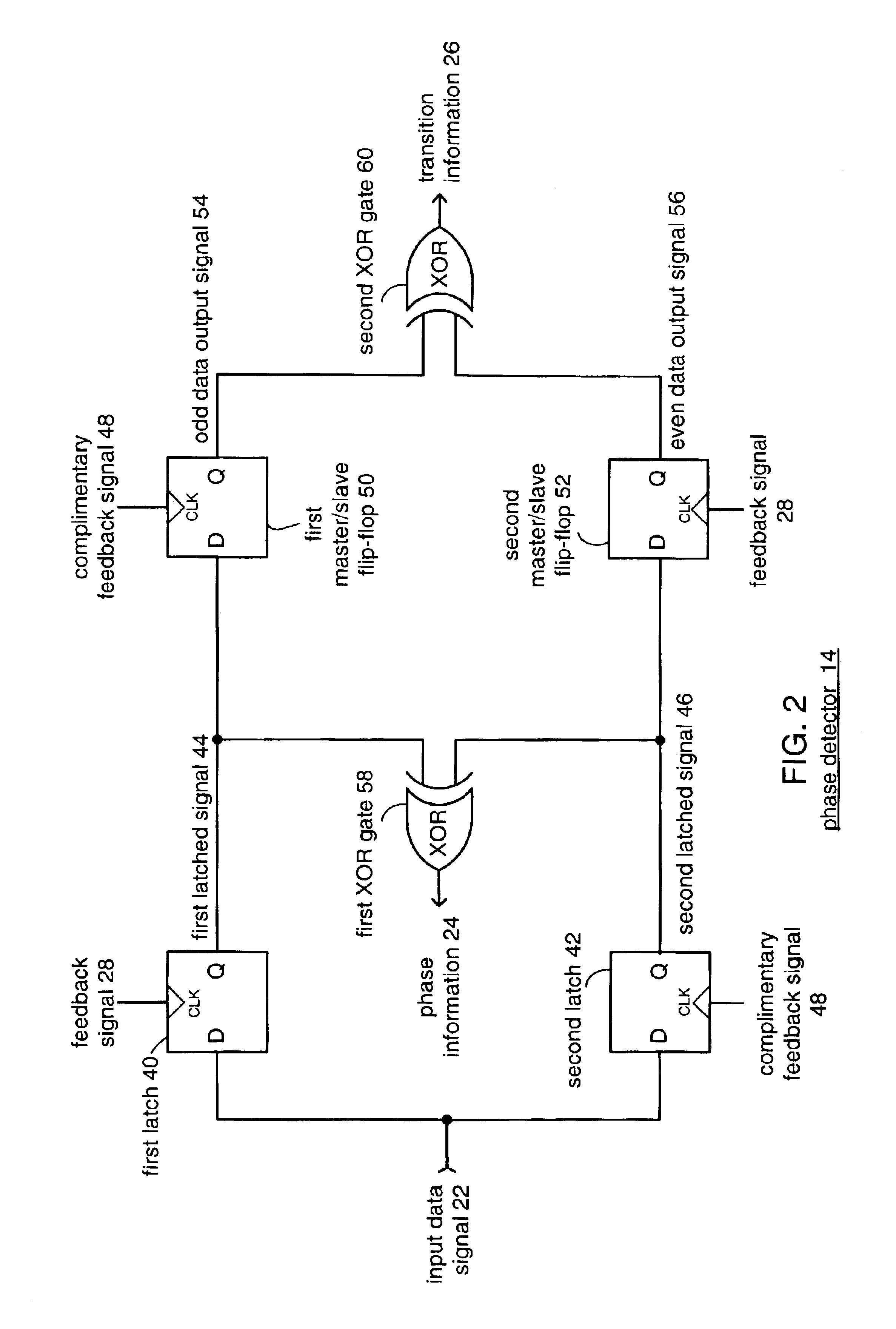
Clock and data recovery phase-locked loop
A clock recovery circuit that operates at a clock speed equal to one-half the input data rate is presented. The clock recovery circuit uses dual input latches to sample the incoming serial data on both the rising edge and falling edge of a half-rate clock signal to provide equivalent full data rate clock recovery. The clock recovery circuit functions to maintain the half-rate clock transitions in the center of the incoming serial data bits. The clock recovery circuit includes a phase detector, charge pump, controlled oscillation module and a feedback module. The phase detector produces information on the phase and data transitions in the incoming data signal to the charge pump. Generally, the circuit is delay insensitive and receives phase and transition information staggered relative to each other.
Owner:XILINX INC
Device for programmable frequency divider
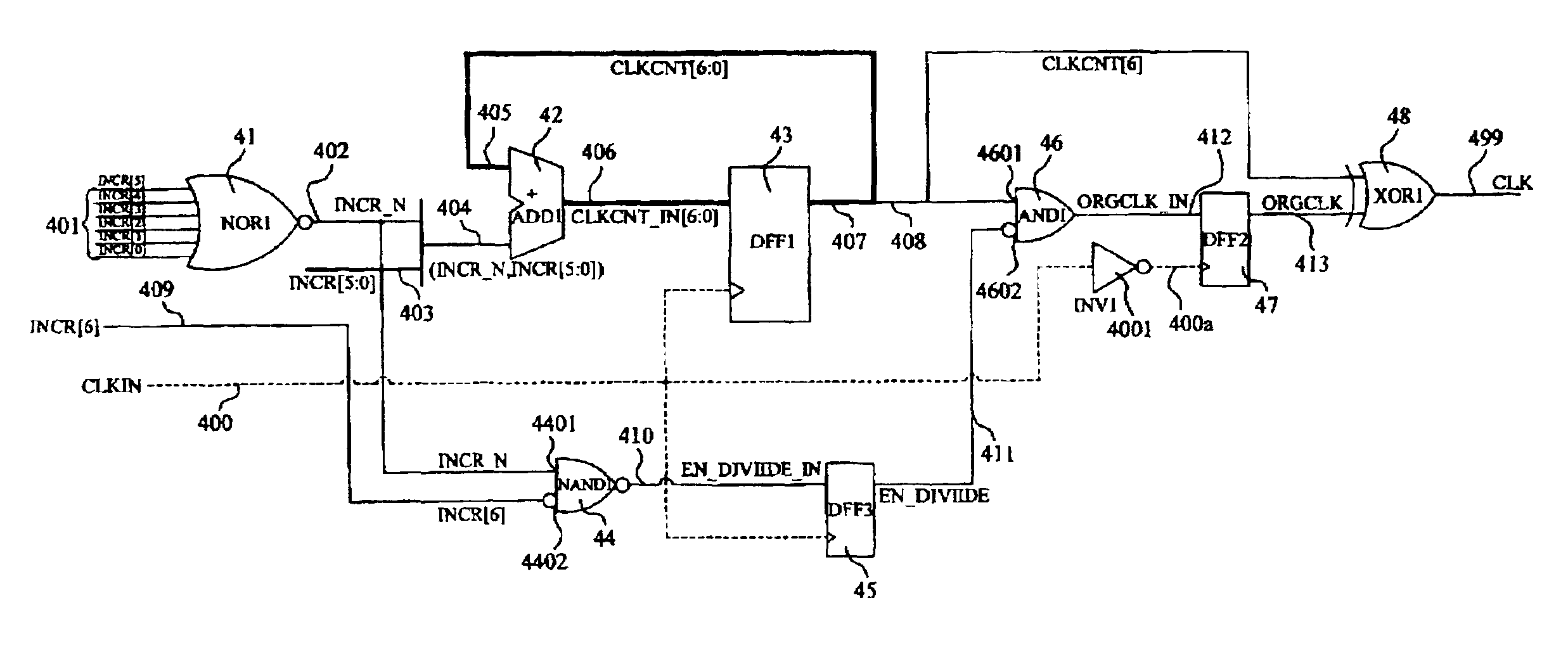
InactiveUS6959066B2Rule out the possibilityStable conditionCounting chain pulse countersPulse counters with static storageTarget signalClock transition
The present invention relates to a programmable frequency divider having one n-bit adder and one n-bit D Flip Flop. These are used to transform the import clock to the target clock. The adder takes one adjustment parameter and one return signal as a basis to create the first output signal, with the possibility to program the adjustment parameter. The D Flip Flop and the adder create a cycle, which is used to receive the first output signal and its import clock to create the second output signal. The second output signal is separated into a return signal and the target signal. The D Flip Flop sends the return signal back to the adder, which will make addition calculations under the adjustment parameter, finally giving out the target clock with the target signal as a calculation basis.
Owner:ELAN MICROELECTRONICS CORPORATION
Digital lock detector for phase-locked loop
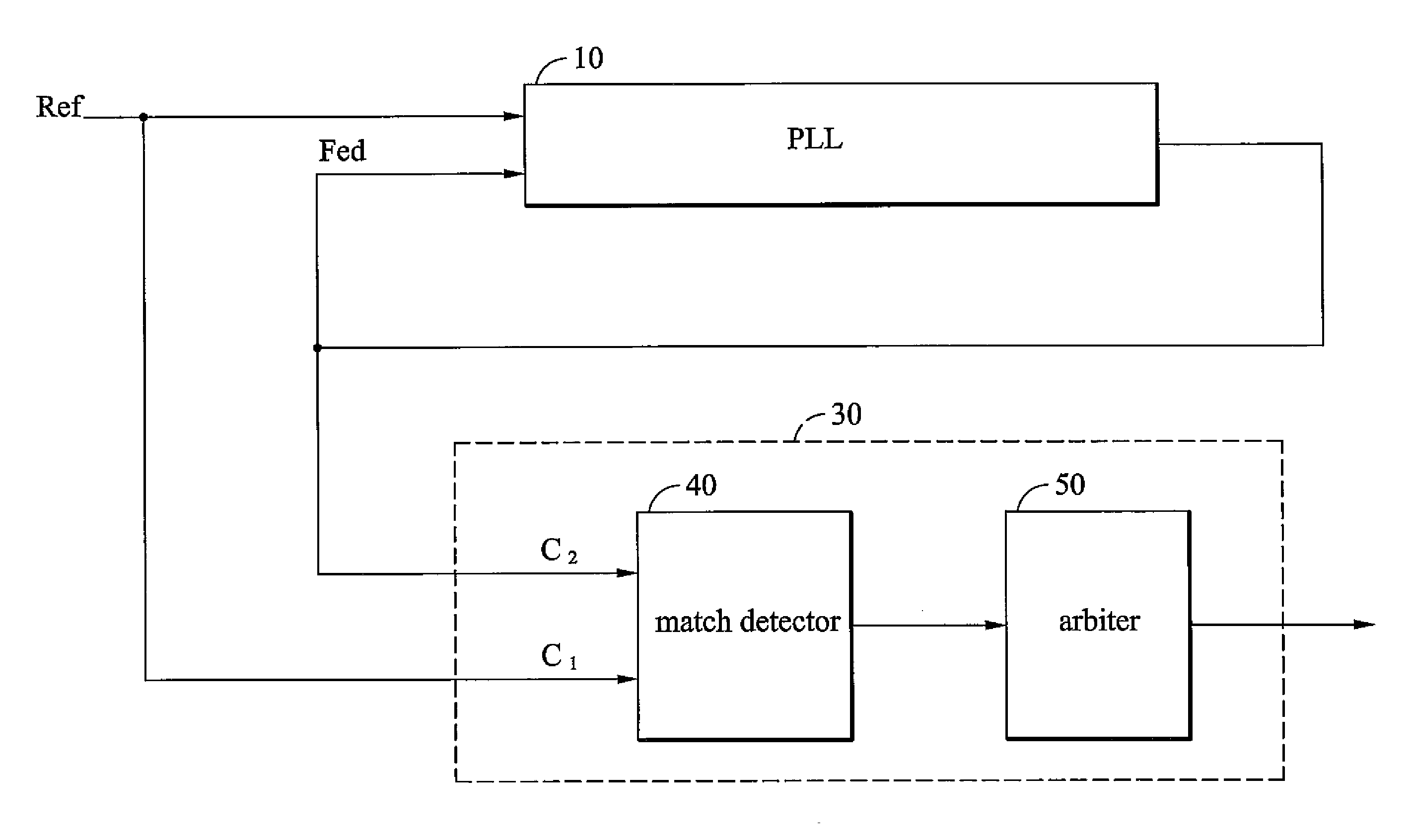
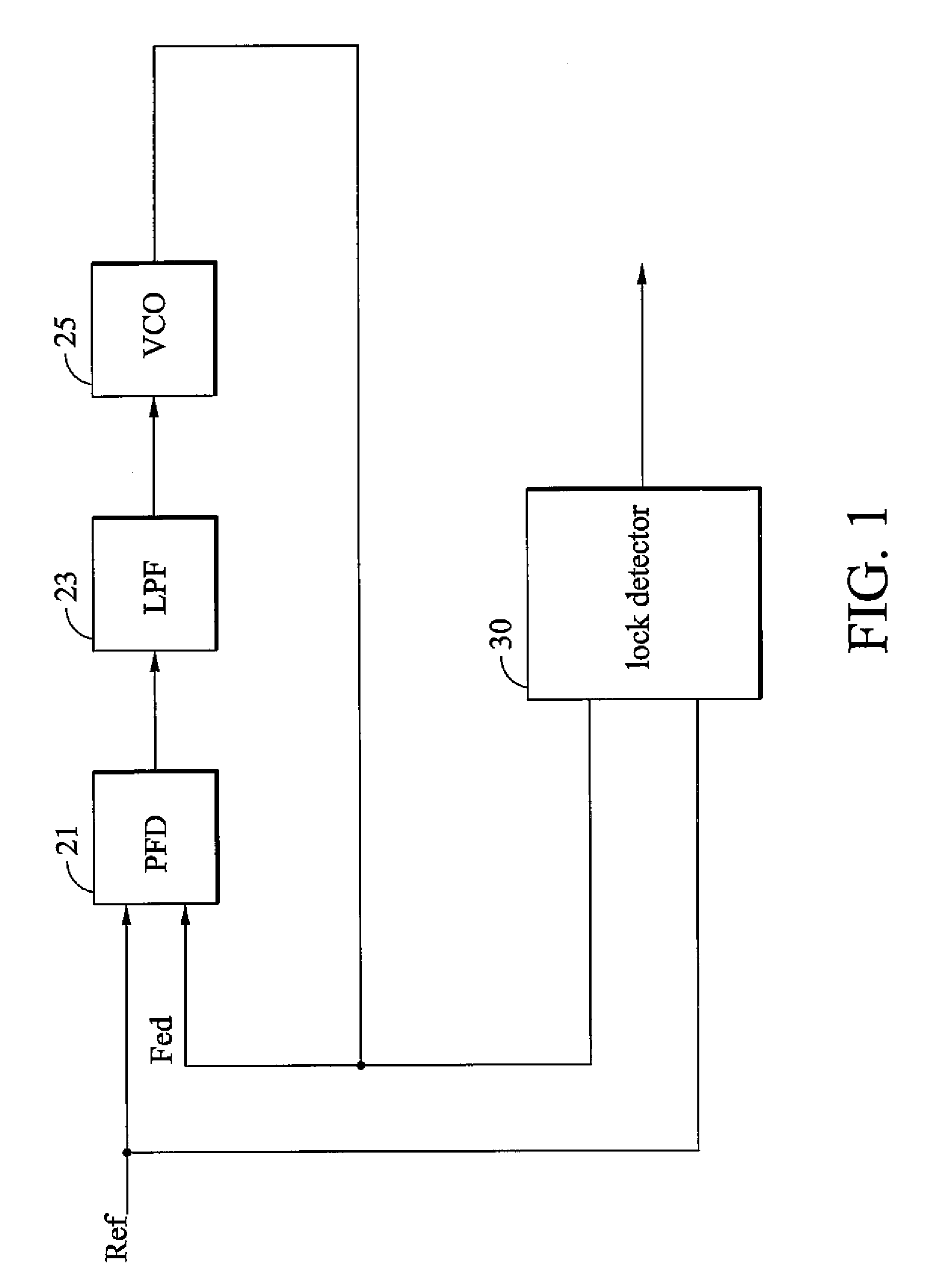
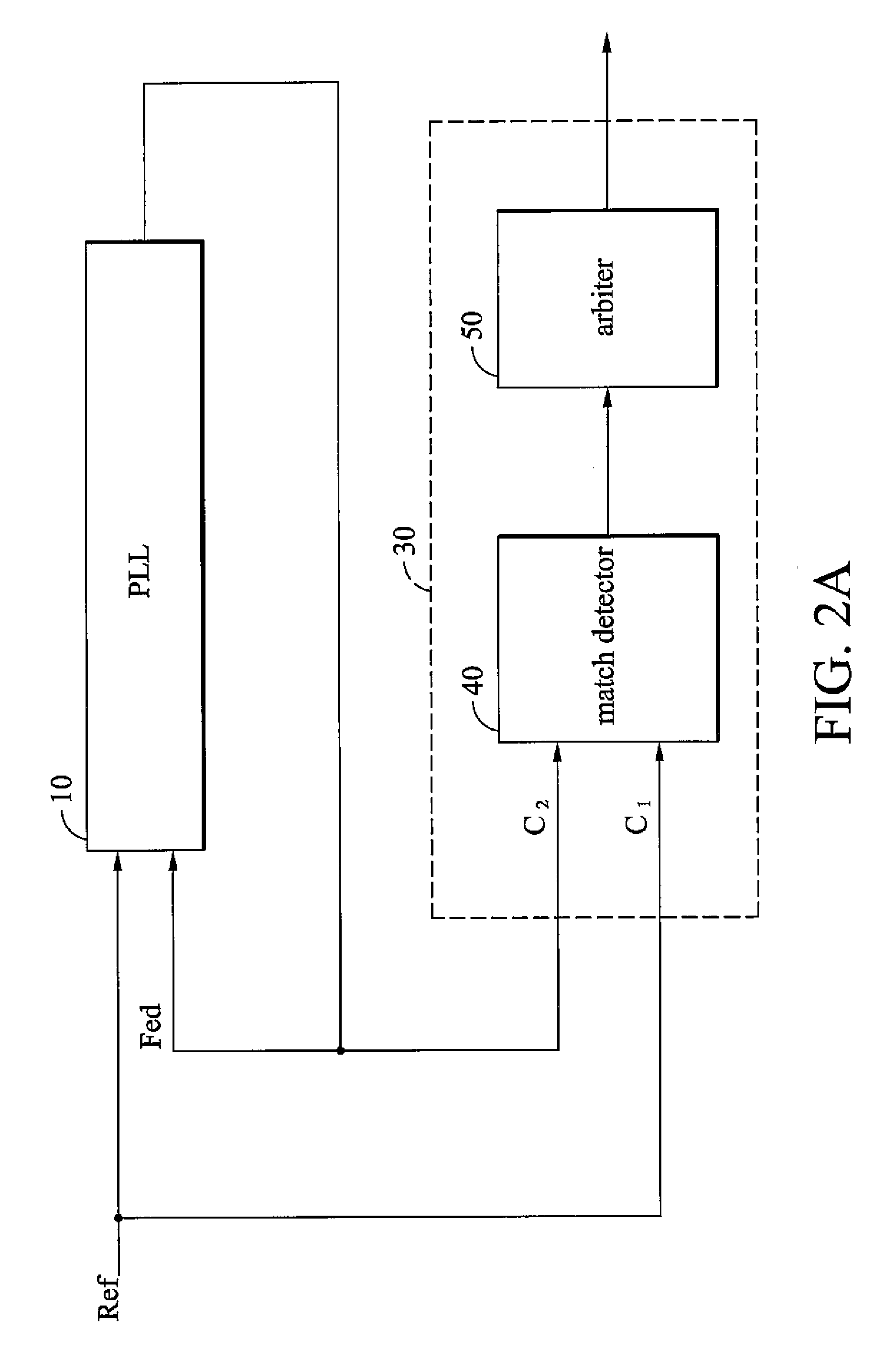
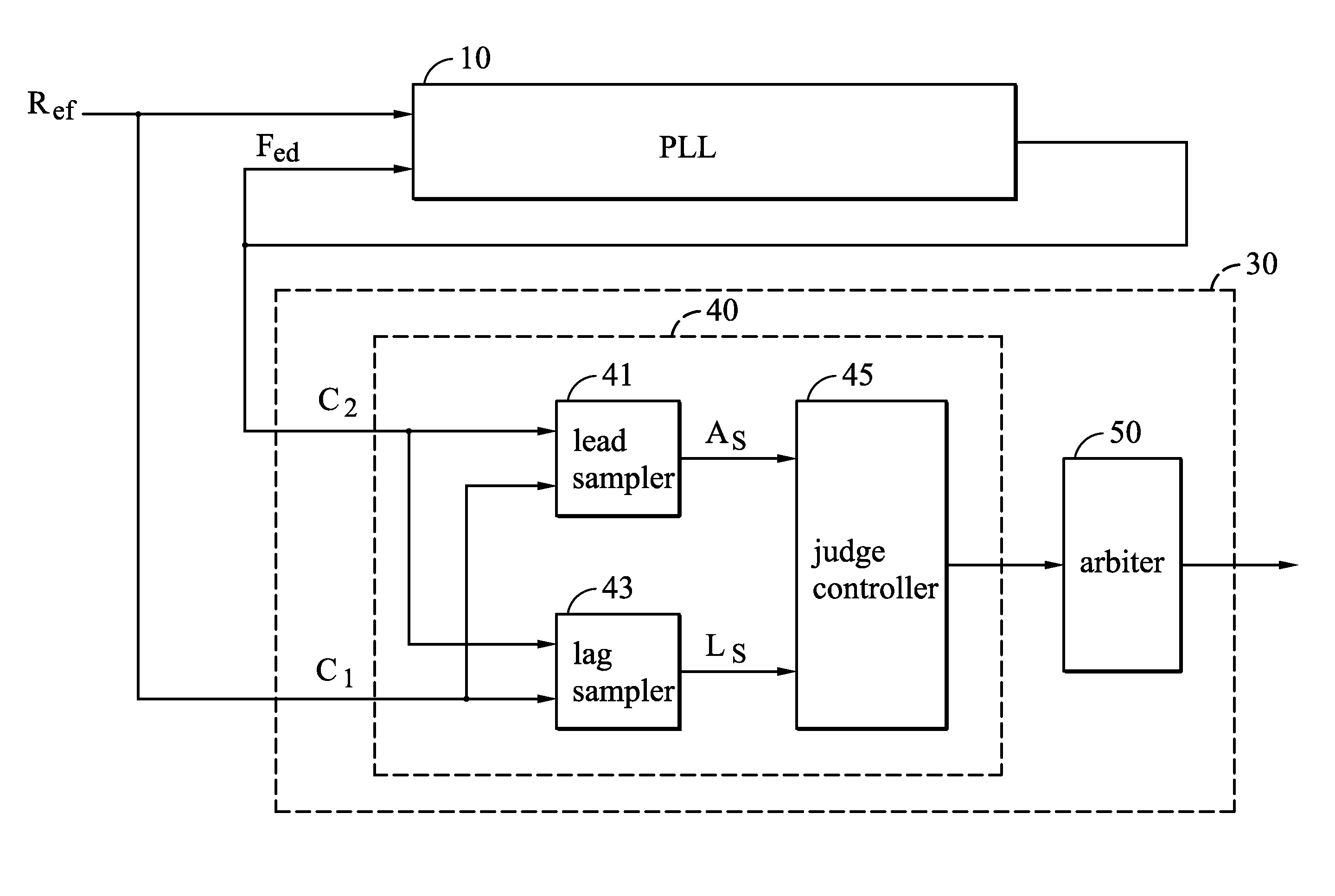
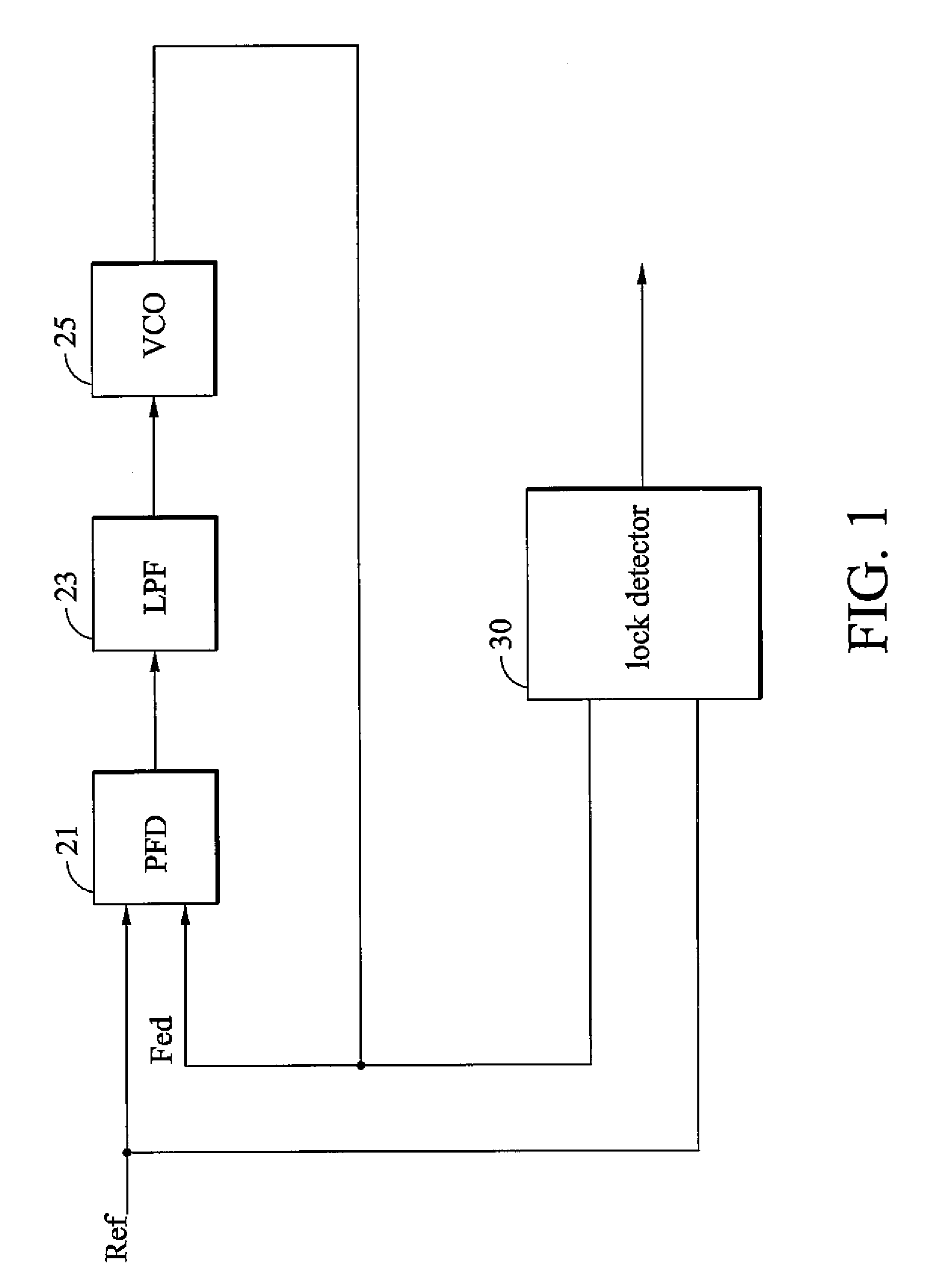
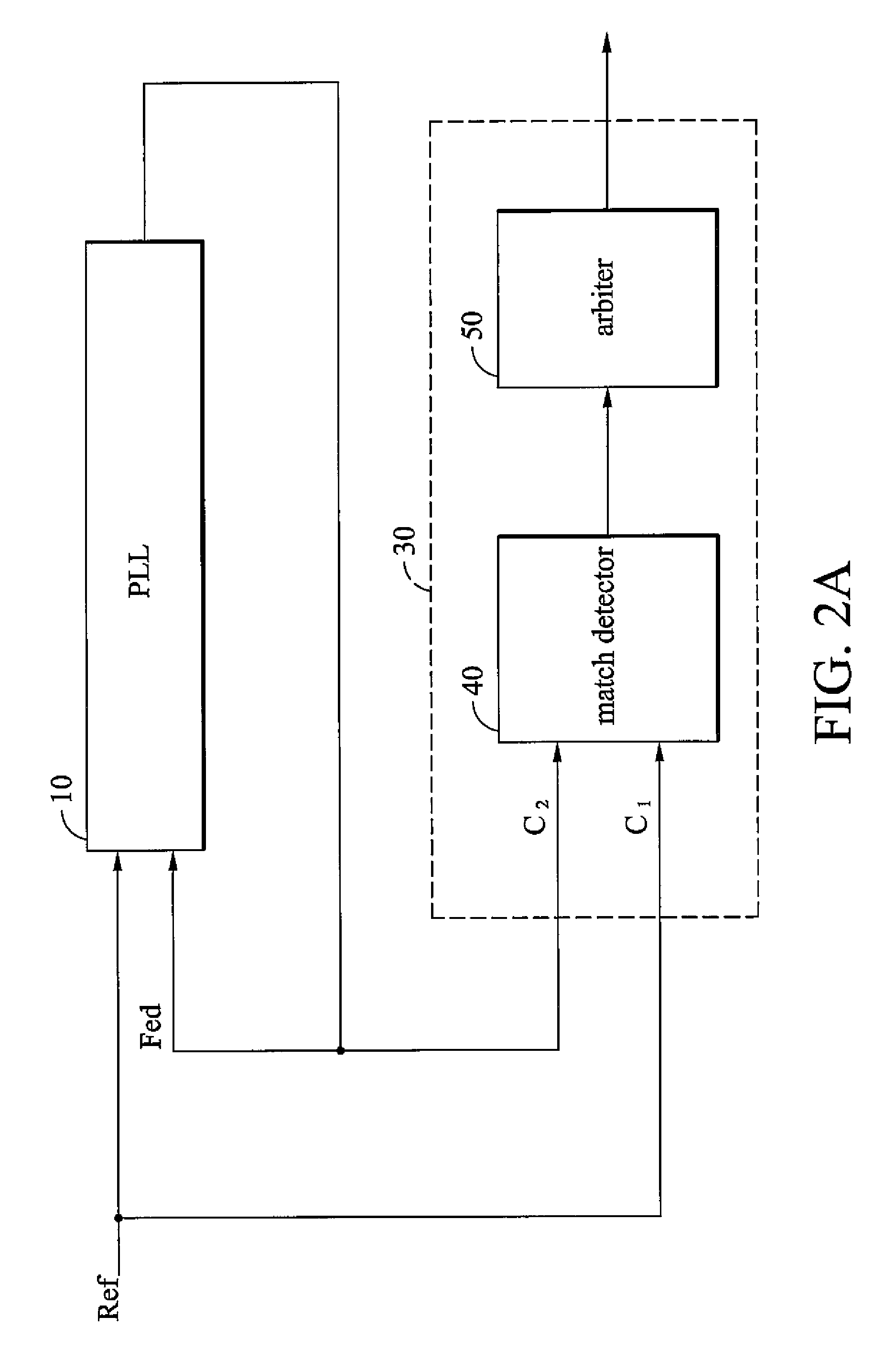
ActiveUS20060280276A1High precisionSaving circuit areaPulse automatic controlAngle demodulation by phase difference detectionClock transitionComputer science
A digital lock detector for a phase-locked loop. The PLL generates a feedback clock according to a reference clock. The digital lock detector includes a match detector and an arbiter. When a first clock transitions, the match detector checks that whether a second clock transitions in a predetermined time window or not. The match detector generates a match signal if the second clock transitions in the predetermined time window. The arbiter counts a number of the successive match signals and generates a lock signal to indicate a lock state when the number exceeds a first predetermined number.
Owner:VIA TECH INC
Low voltage differential signal receiving device
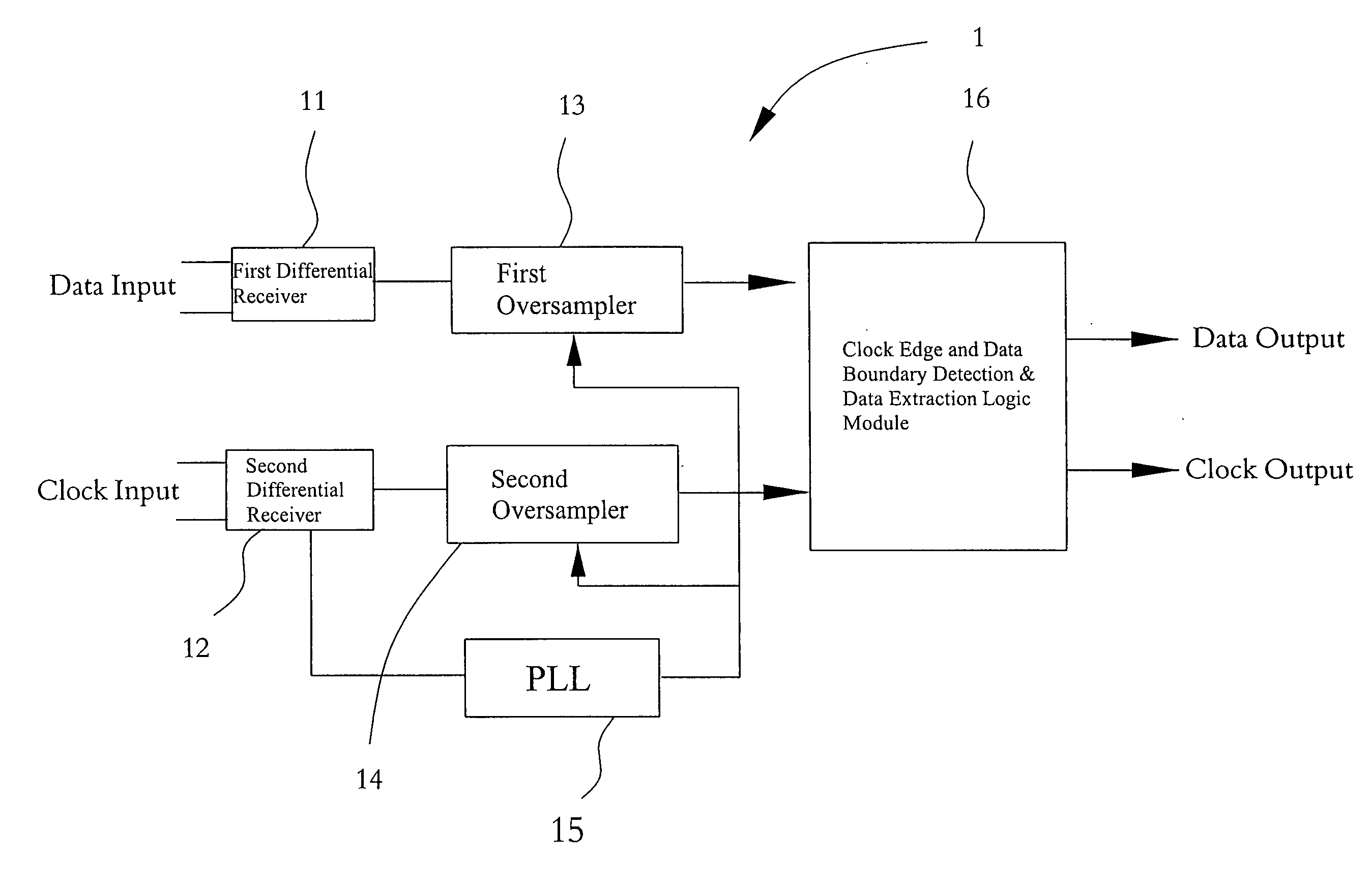
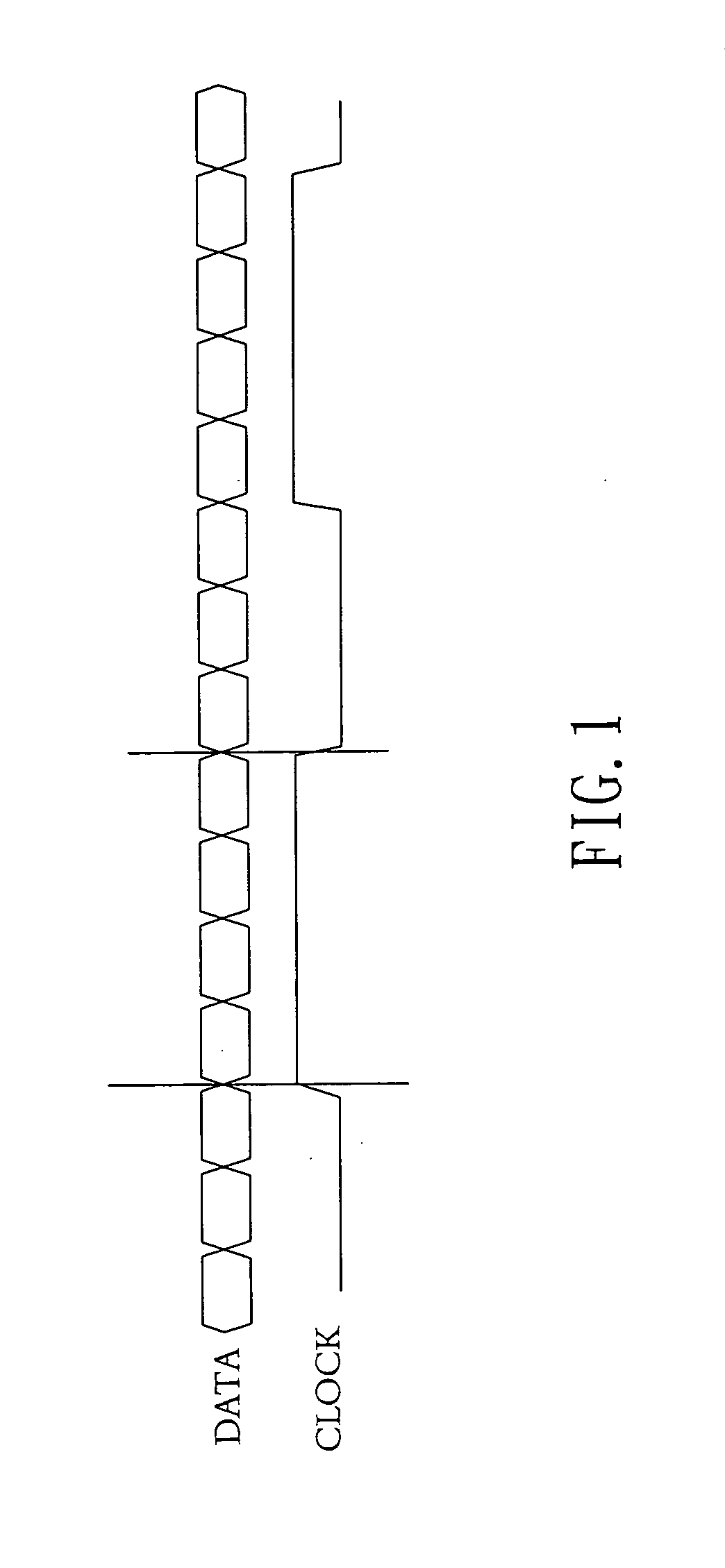
InactiveUS20080068355A1Smooth transmissionEasy to useCathode-ray tube indicatorsGenerating/distributing signalsLow voltageDelayed time
A low voltage differential signal receiving device includes two differential receivers, two oversamplers, a phase locked loop, and a clock edge and data boundary detection & data extraction logic module. Clock and data signals are transmitted via channels having the same circuit layout, so that the clock signal is treated as another type of data signal. A frequency of sampling input clock and data is increased via asynchronous clock, clock transition is detected, and data bytes are extracted from clock and data samples. Therefore, the clock signal and the data signal have the same delay time to avoid any sampling error due to a difference in time sequence between the clock and the data. Meanwhile, due to the accurately increased sampling frequency, the sampled clock and the data signals are not adversely affected by different factors to enable upgraded data transmission efficiency and quality at the same time.
Owner:EXPLORE SEMICON
Mixed signal processor with noise management
ActiveUS6950044B1Inhibition transitionAvoid noiseElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue-digital convertersDigital dataClock rate
Mixed signal processor with noise management. A method for noise management in a mixed signal processor integrated circuit having a digital processing section and an analog section The digital processing section is clocked at a first clock rate to process digital data. When a conversion operation is to be carried out by the analog section, the clocking of the digital processing section is inhibited during at least a portion of the data conversion operation by the analog section to prevent noise from clock transitions in the digital processing section from being injected into the analog section during the at least a portion of th data conversion operation.
Owner:SILICON LAB INC
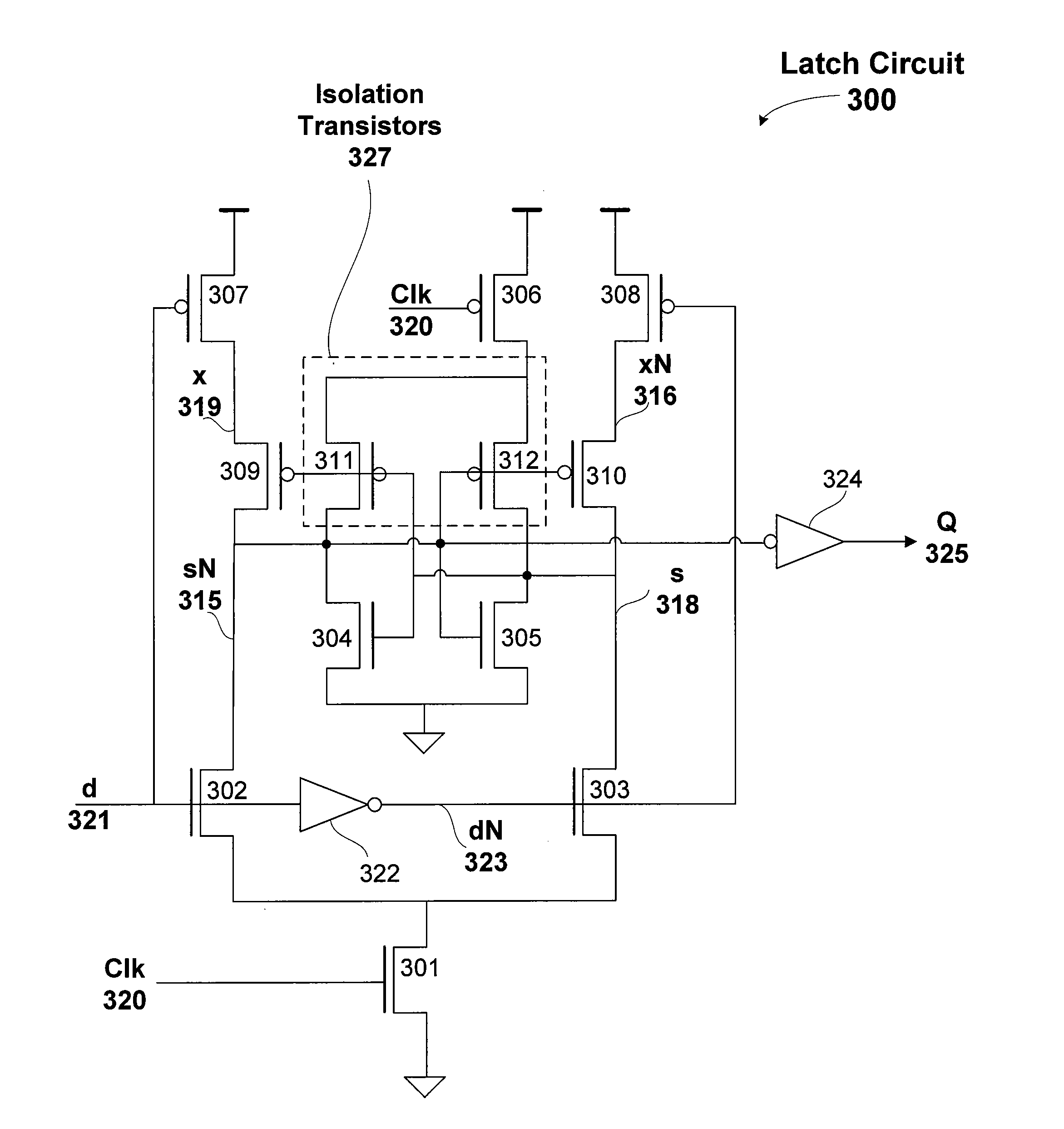
Low-Clock-Energy, Fully-Static Latch Circuit
One embodiment of the present invention sets forth a technique for capturing and holding a level of an input signal using a low-clock-energy latch circuit that is fully static. The clock is only coupled to a first clock-activated pull-up or pull-down transistor and a second clock-activated pull-down or pull-up transistor. The level of the input signal is captured by a storage sub-circuit on one of the rising or the falling clock edge and stored to generate an output signal until the clock transitions. The level of the input signal is propagated to the output signal when the storage sub-circuit is not enabled. The storage sub-circuit is enabled and disabled by the first clock-activated transistor and a propagation sub-circuit is activated and deactivated by the second clock-activated transistor.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
Method and apparatus for writing data between fast and slow clock domains
InactiveUS7085952B2Energy consumptionReduce needEnergy efficient ICTElectrotherapyProcessor registerClock transition
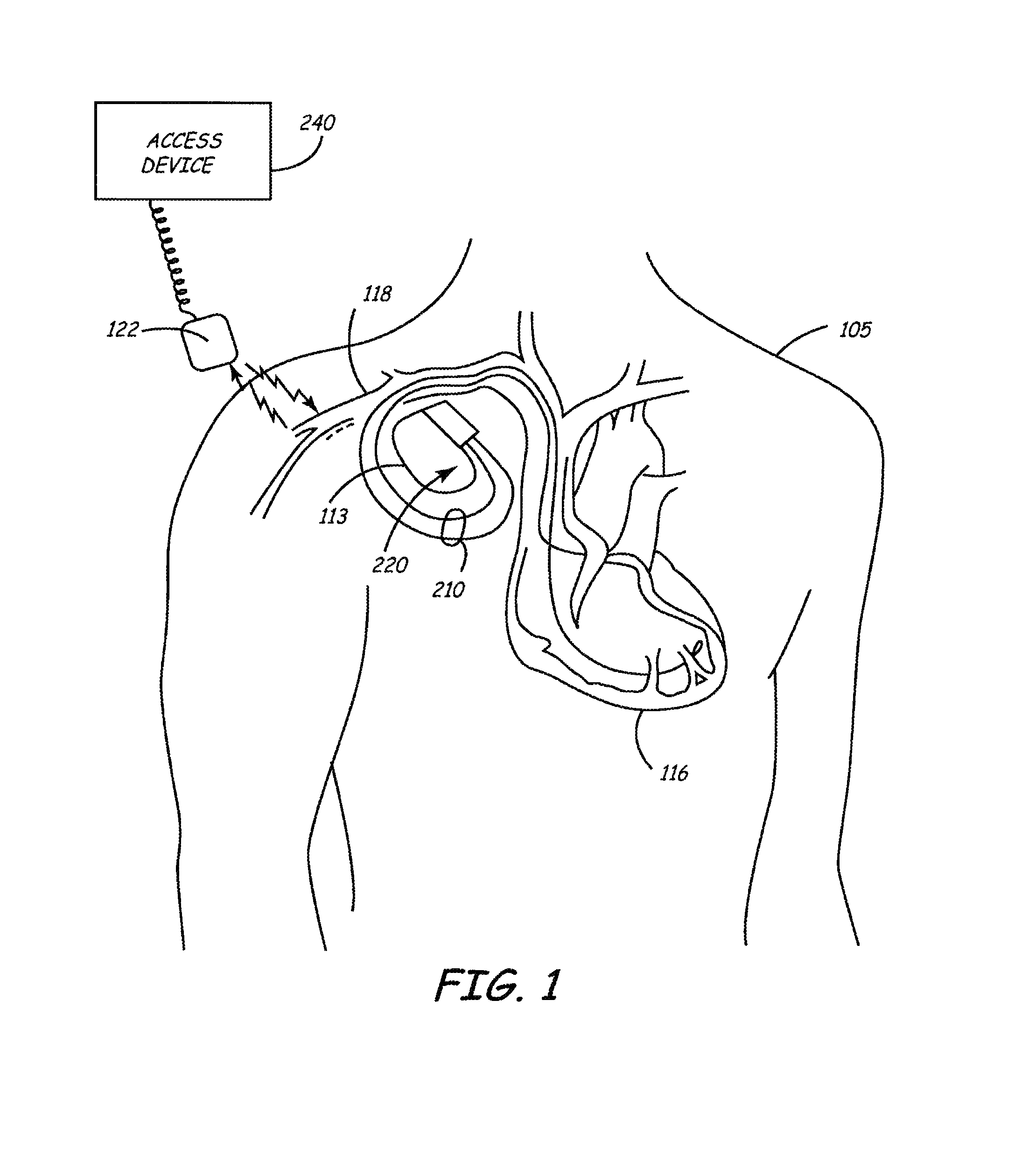
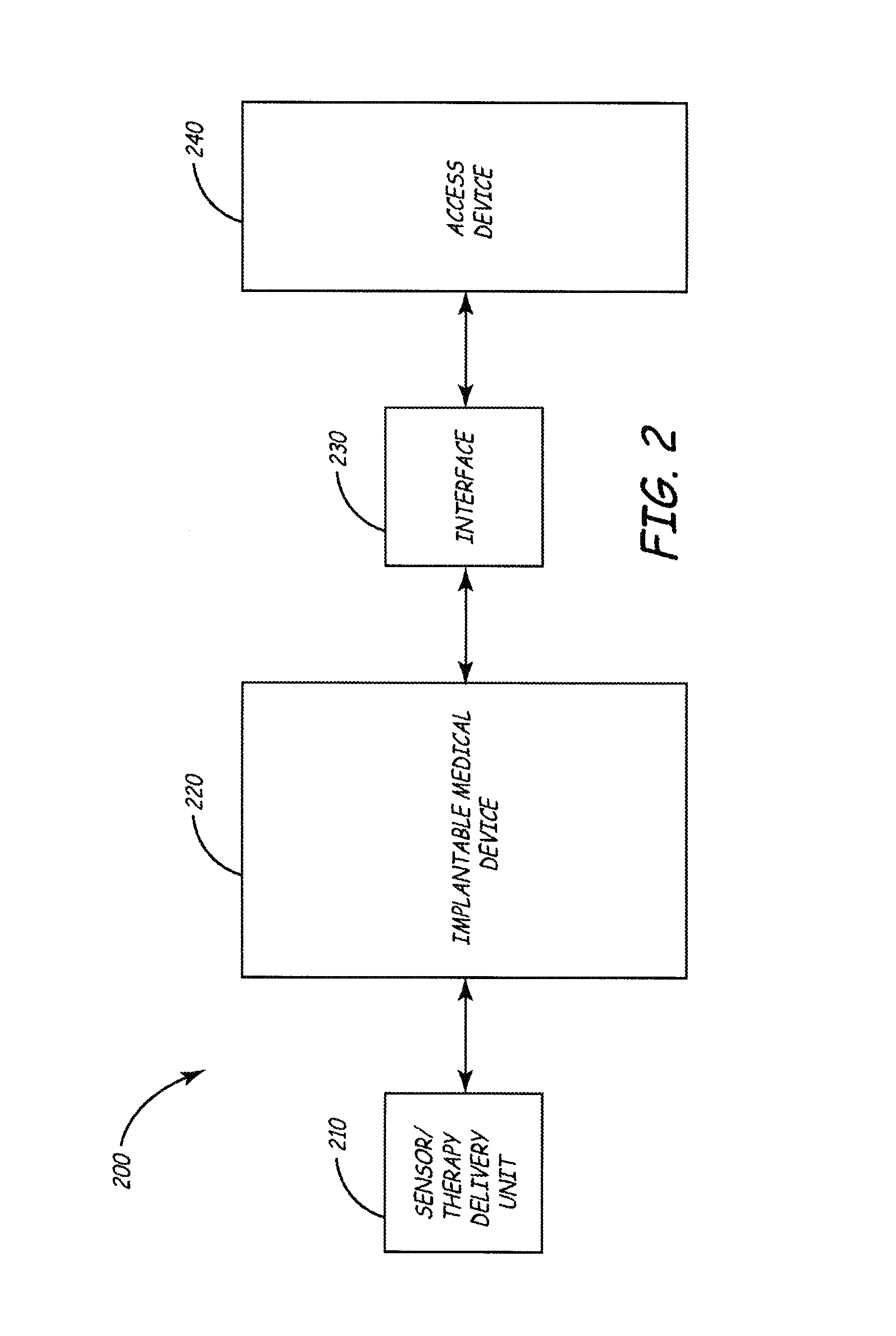
A system for writing data efficiently between a fast clock domain and a slow clock domain. In one embodiment, a processor that performs firmware routines is clocked by a fast clock that is turned on when a prescribed event occurs to operate in the fast clock domain in conjunction with hardware that performs certain device operations that is clocked by a slow clock that is always on to operate in a slow clock domain. Writing data from the processor to the hardware involves determining if a bit is to be written to a register of the slow clock domain in synchrony with a transition of the slow clock, stopping the fast clock to pause operation of the processor, writing the bit to the register of the slow clock domain upon a succeeding slow clock transition, and starting the fast clock to resume operation of the processor.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Clocked D/A converter
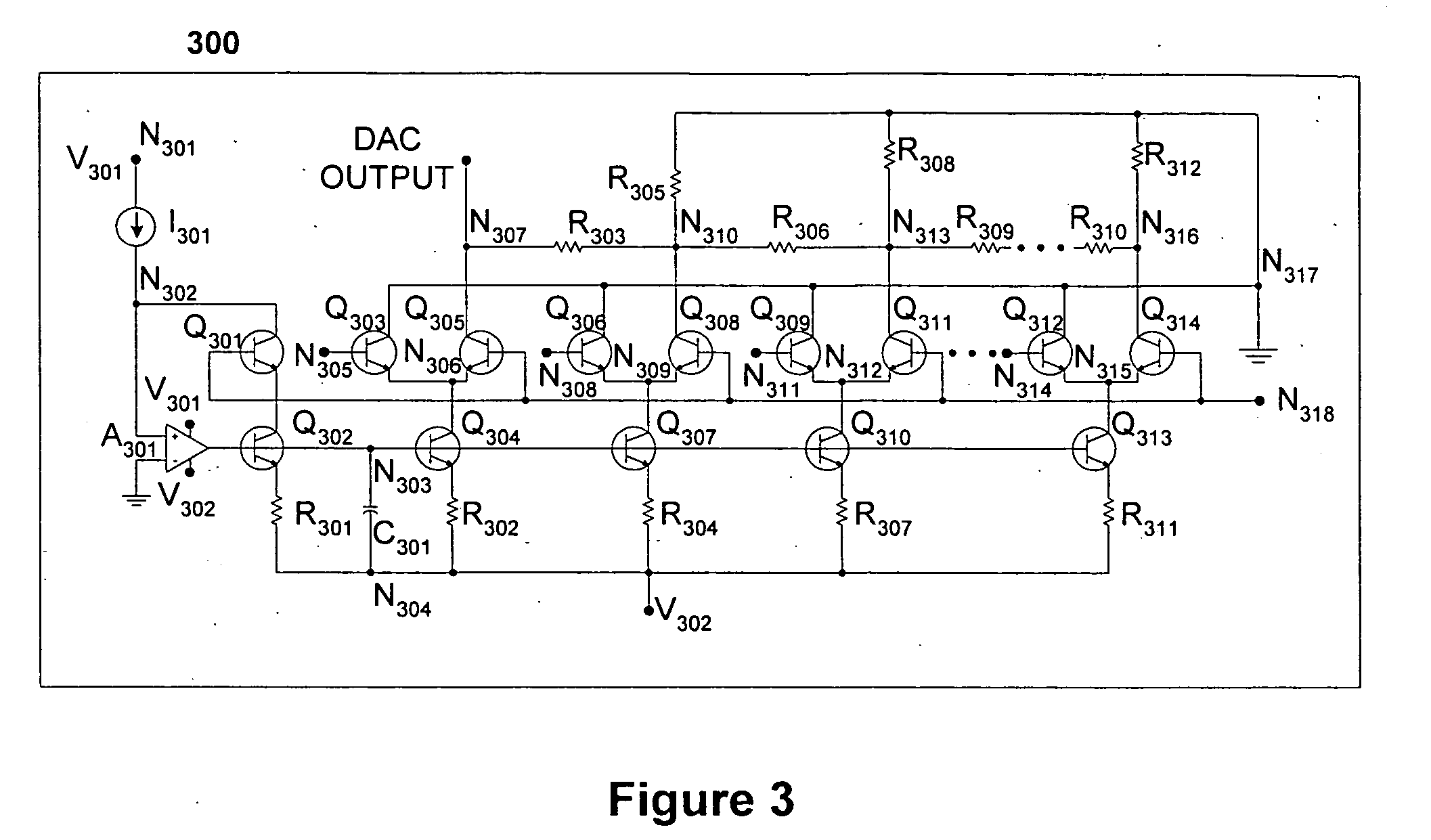
InactiveUS20050156765A1TransistorElectric signal transmission systemsBistable circuitsClock transition
A digital-to-analog converter is disclosed, comprising an input / output circuit, a bistable circuit connected with the input / output circuit, a clock circuit connected with the input / output circuit and the bistable circuit, and a current generator circuit connected with the clock circuit. The clock circuit acts as a switch, providing current from the current generator either to the input / output circuit or to the bistable circuit. The digital input signal switches when the current generator provides current to the bistable circuit, and switching of the input signal is asserted at the output of the converter when the current generator provides current to the input / output circuit. Therefore, switching of a clock circuit signal, rather than switching of the digital input signal determines switching of the output signal, in order to reduce intersymbol interference of the converter associated with thermal hysteresis of some of the components of the converter.
Owner:HRL LAB
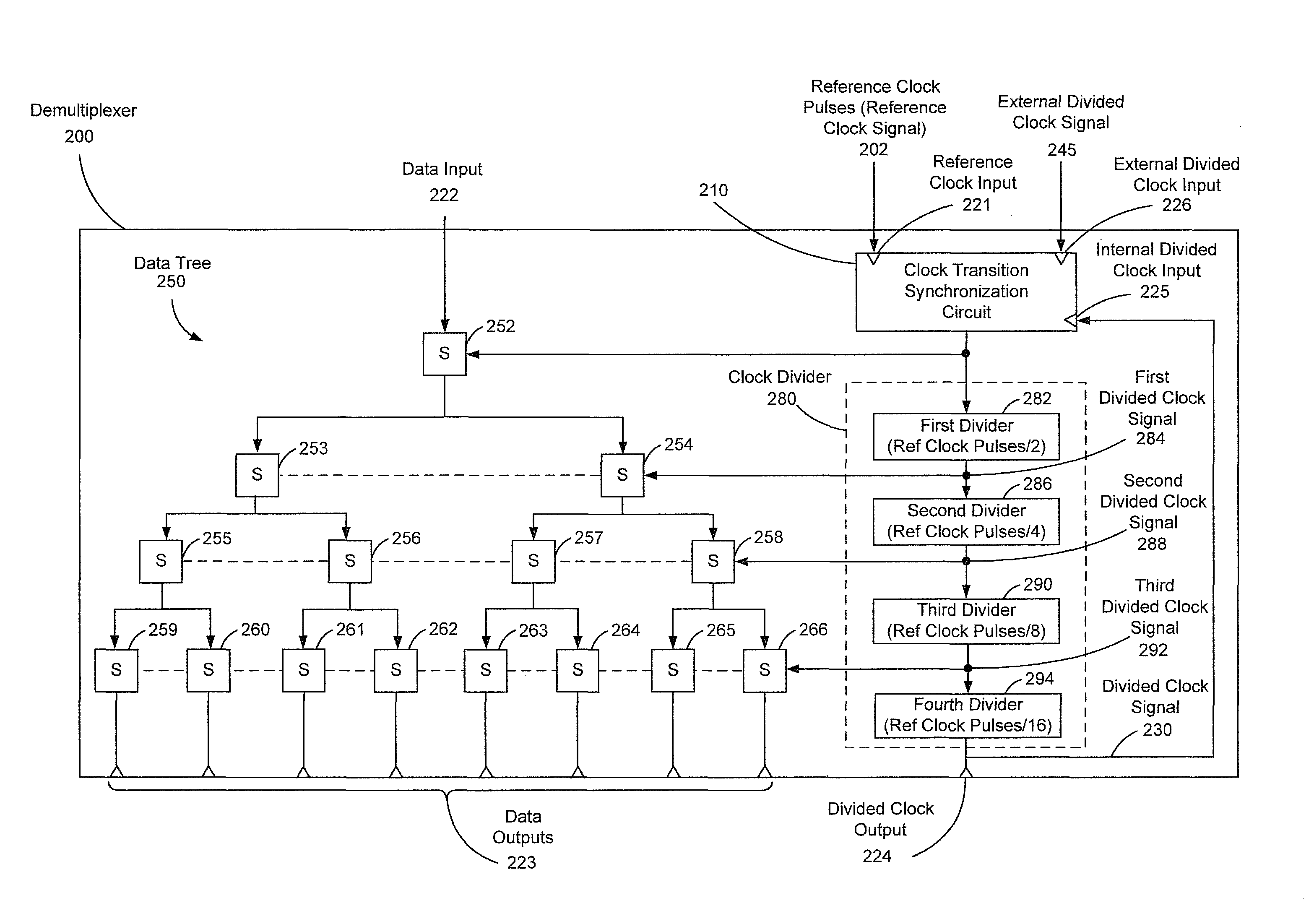
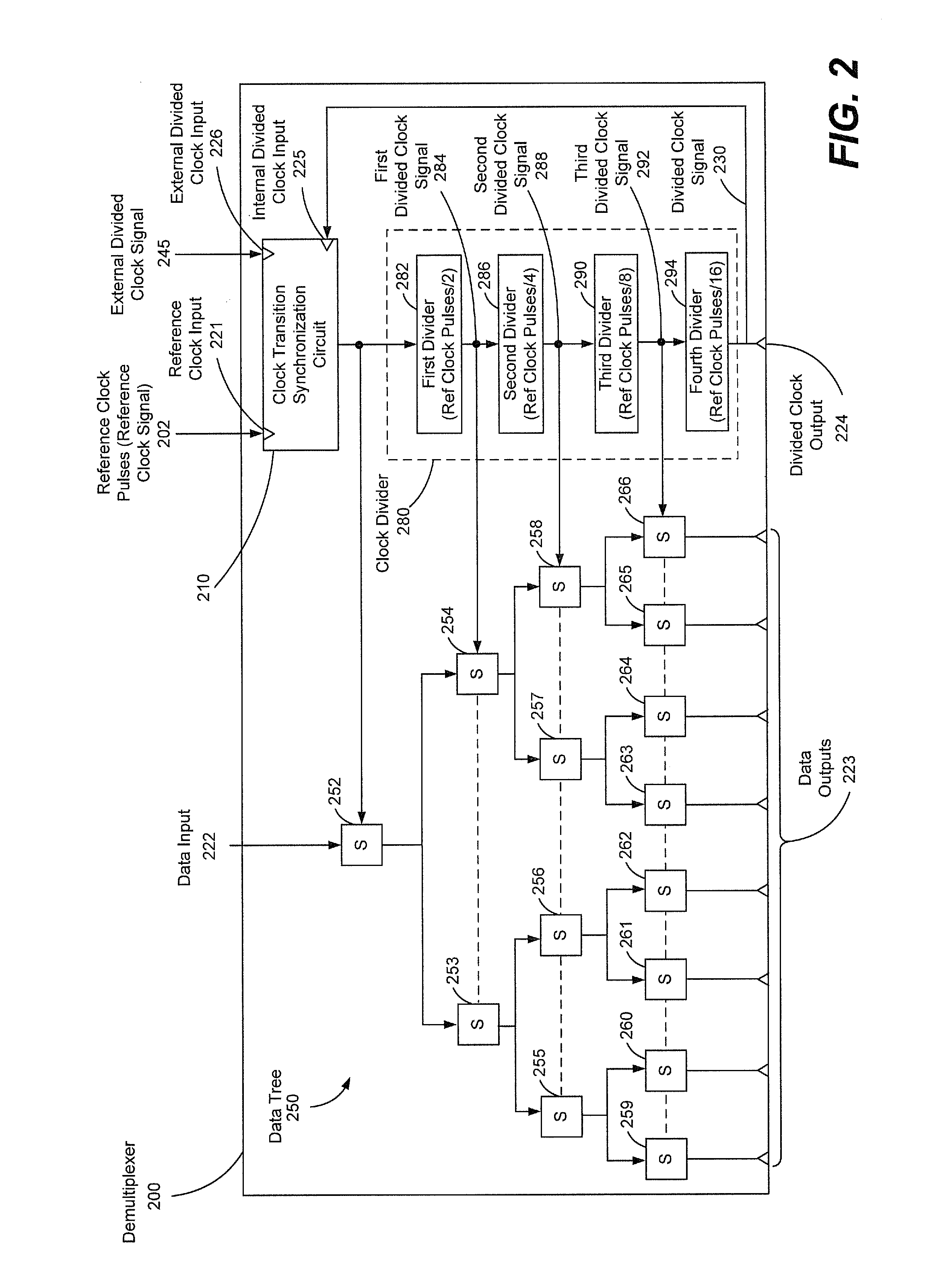
Divided clock synchronization
Circuits, demultiplexers, and methods are disclosed. A circuit includes a reference clock input to receive clock pulses at a reference clock speed. An internal divided clock input receives a divided clock signal from a clock divider that is driven by the clock pulses. The clock divider generates the divided clock signal at a second clock speed that is a fraction of the reference clock speed. An external divided clock input receives an external divided clock signal. The external divided clock signal is driven by the clock pulses and operates at the second clock speed. A clock transition synchronization circuit suppresses application of one or more of the clock pulses to the clock divider when the divided clock signal transitions between clock states out of synchronization with the external divided clock signal.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Digital lock detector for phase-locked loop
ActiveUS7676014B2High precisionSave areaPulse automatic controlAngle demodulation by phase difference detectionClock transitionComputer science
Owner:VIA TECH INC
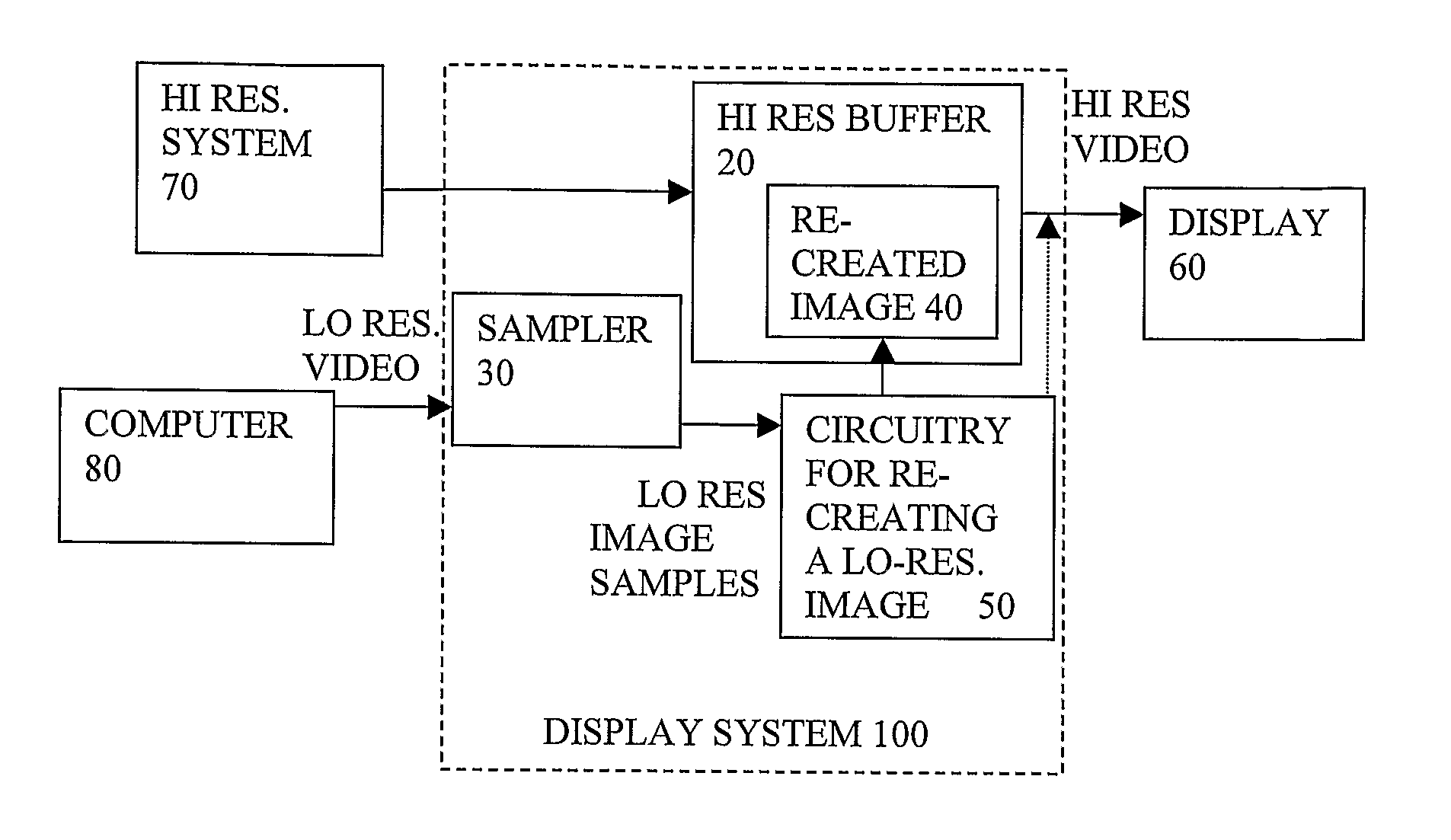
Asynchronous Video Capture for Insertion Into High Resolution Image
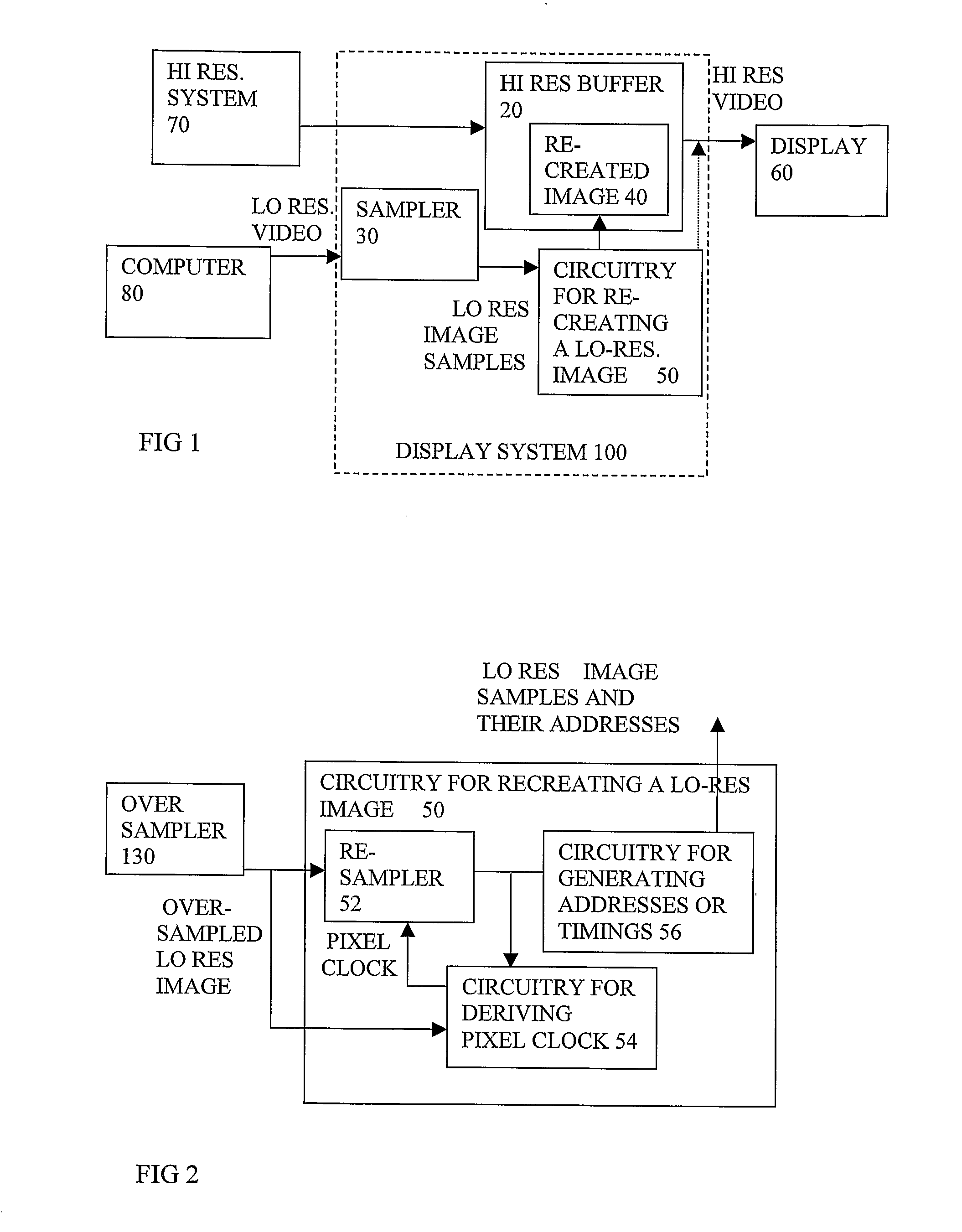
InactiveUS20080094427A1Minimize and avoid sampling clockImproved jitter suppressionCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingImage resolutionClock transition
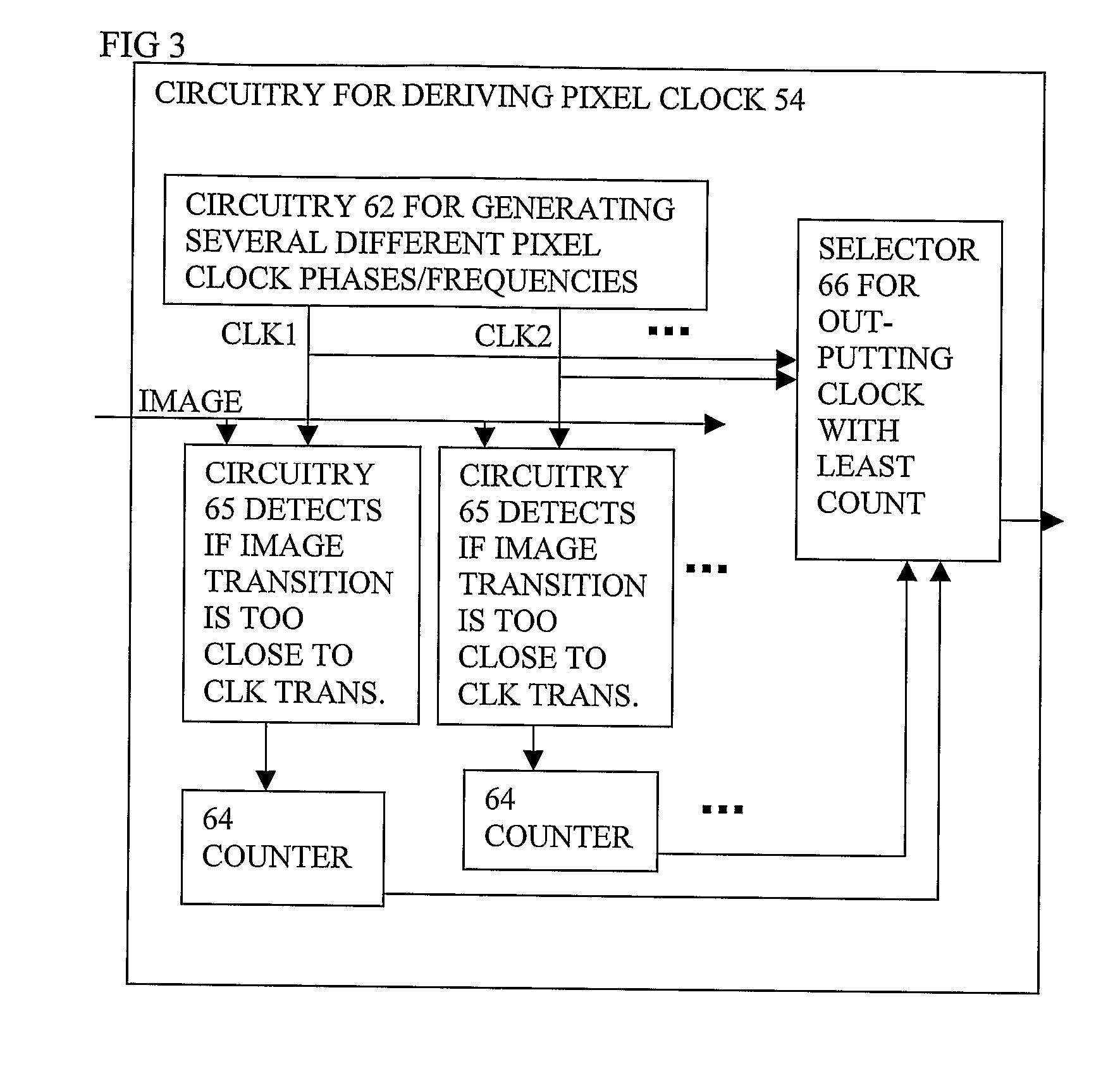
A display system has a first resolution video buffer 20, and can insert a second resolution analog video signal, the first resolution being higher than the second resolution. It can sample the second resolution video signal and insert it 50 without substantially reducing the resolution of the image. An advantage over software solution is more independence from software standards. The sampling can involve asynchronous over-sampling 130 to two or more states, adequate for recreating text or attributes. Then a re-sampler 52 uses a pixel clock derived 54 by counting coincidences of image and clock transitions, and adjusting a clock phase or frequency to minimize the count.
Owner:BARCO NV
Atomic beam optical frequency atomic clock and a producing method thereof
ActiveUS20090180357A1Improves atom detection efficiencyImprove signal-to-noise ratioLaser detailsApparatus using atomic clocksFrequency spectrumExcited state
An atomic clock at optical frequency based on atomic beam and a method for generating the atomic clock comprises: The atomic beam (8) is ejected from a pile mouth after heating an atomic pile (1) in a vacuum chamber (2); A laser (4) corresponding to frequency of a clock transition transfers the atomic beam (8) from a ground state of the clock transition to an excited state of the clock transition in a adiabatic passing mode; After interaction with the laser corresponding to the frequency of a clock transition, the atomic beam (8) passes a signal detection region with a detection laser (5), and after the interaction with the detection laser (5), each of the atoms gives off a photon of spontaneous emission; An emitted fluorescence photon signal from atoms which is excited by the detection laser (5) is explored; A clock laser (4) for exploring transition frequency of an atomic clock is modulated. The signal which is detected performs frequency locking for the frequency of the clock laser which is locked on the clock transition spectrum of the atoms so as to implement the atomic clock.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Clock converter and electronic apparatus with the same
InactiveUS20040119545A1Pulse automatic controlPulse generation by logic circuitsPhase detectorLine width
A voltage controlled oscillating means in a clock converter outputs a positive feedback signal for a positive feedback loop from one output terminal of buffer means forming a portion of a positive feedback loop using voltage controlled phase shifting means and outputs a PLL feedback signal from the other output terminal of the buffer means. The PLL feedback signal is fed back to phase detector means through a signal transmitting circuit. As a result, it is possible to form a PLL feedback loop, which is not affected by the load to thus output a stable clock signal of high frequency. Furthermore, it is possible to realize a small clock converter by narrowing the line width of a wiring pattern in the signal transmitting circuit.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com