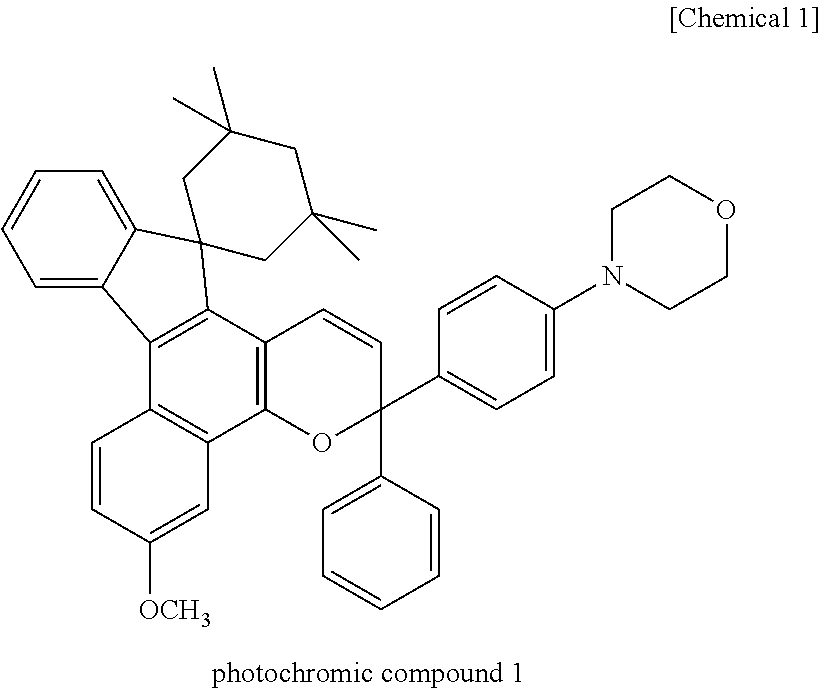
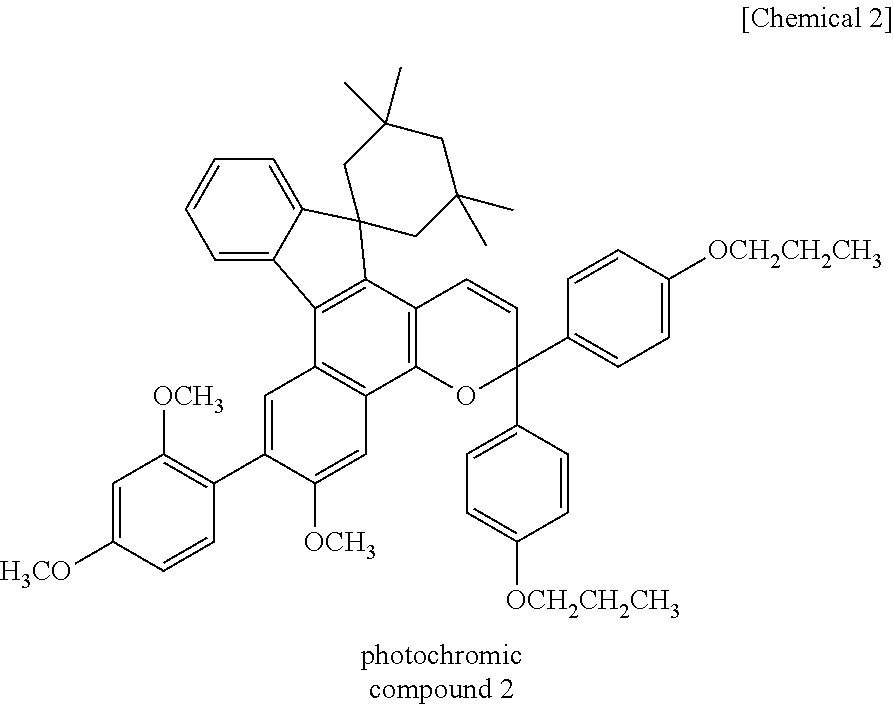
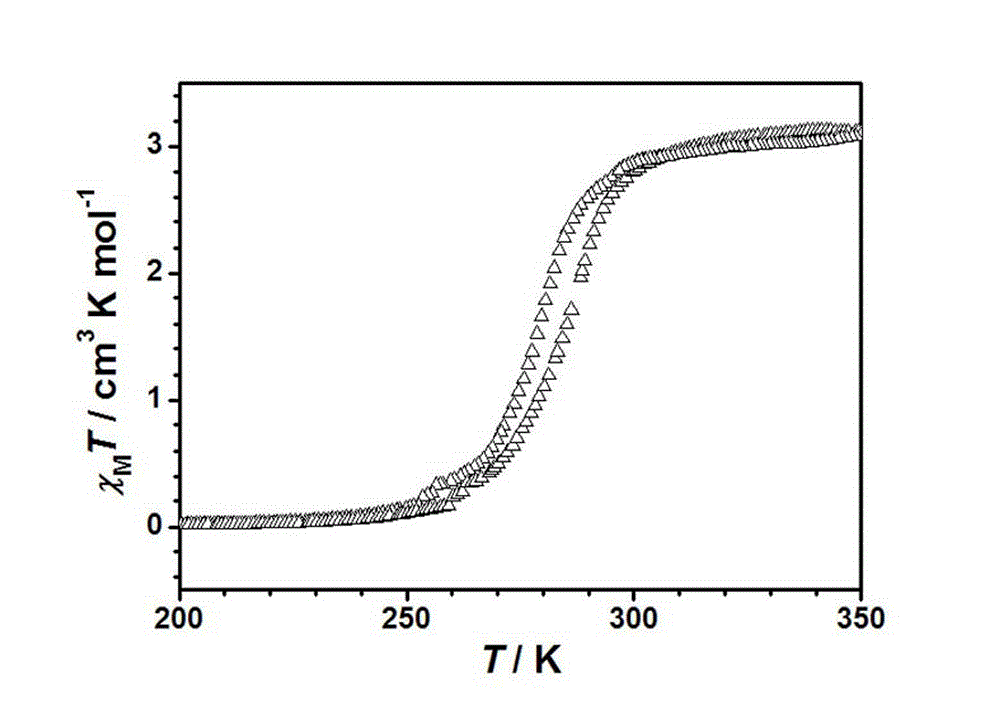
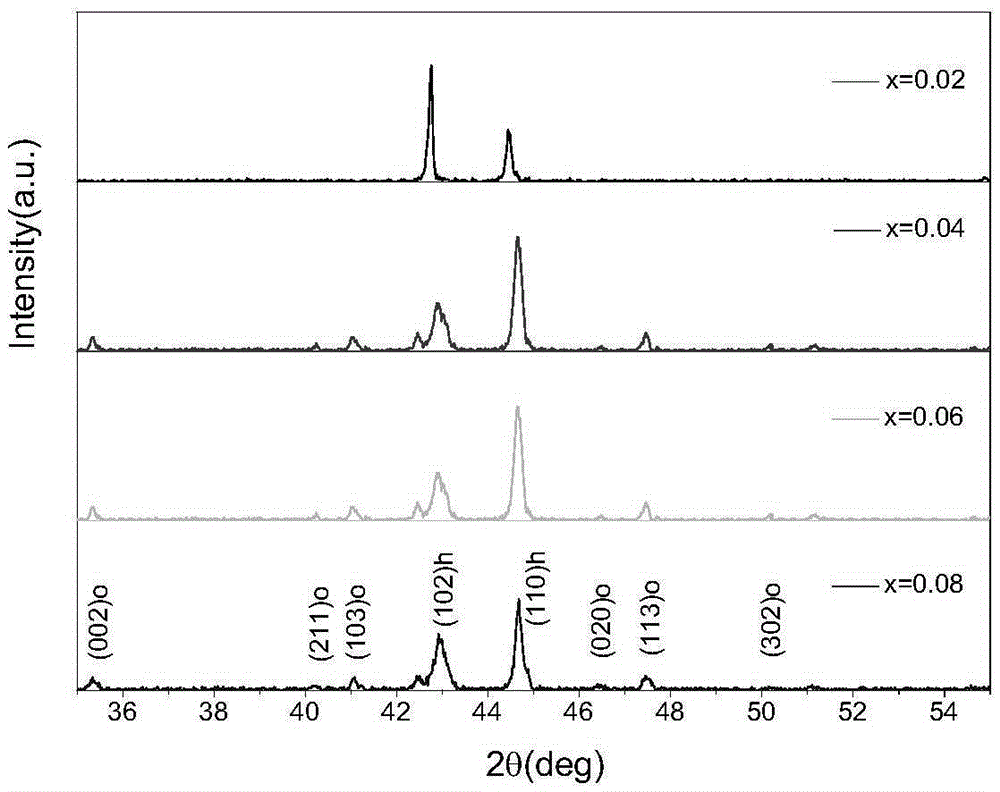
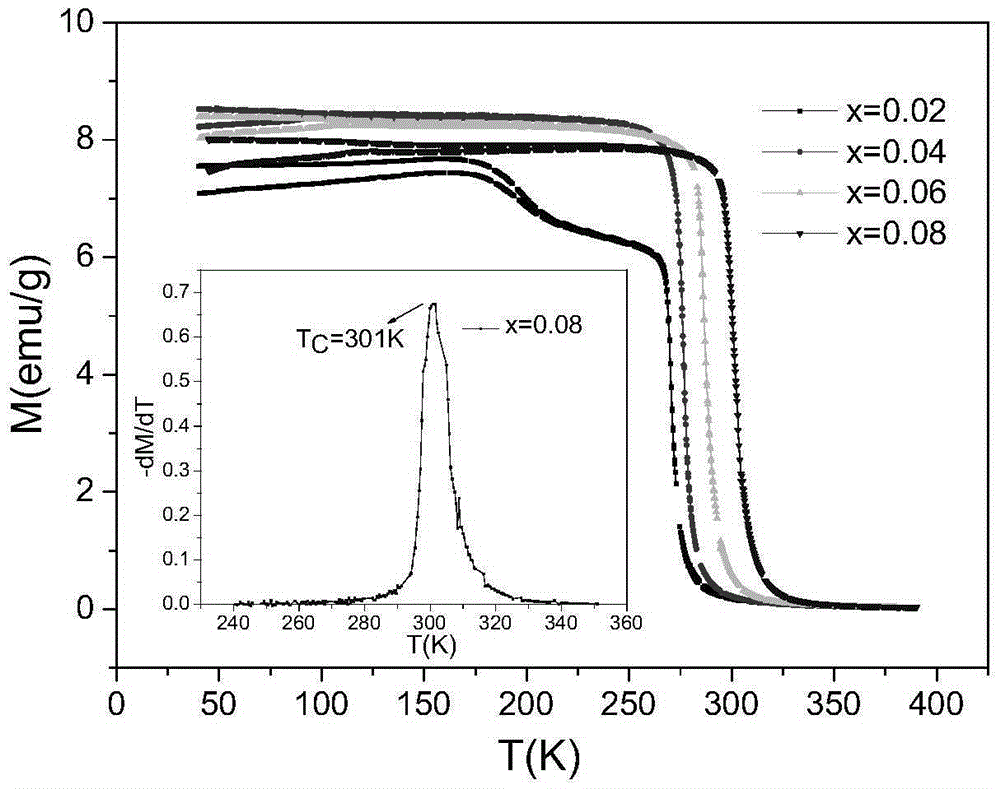
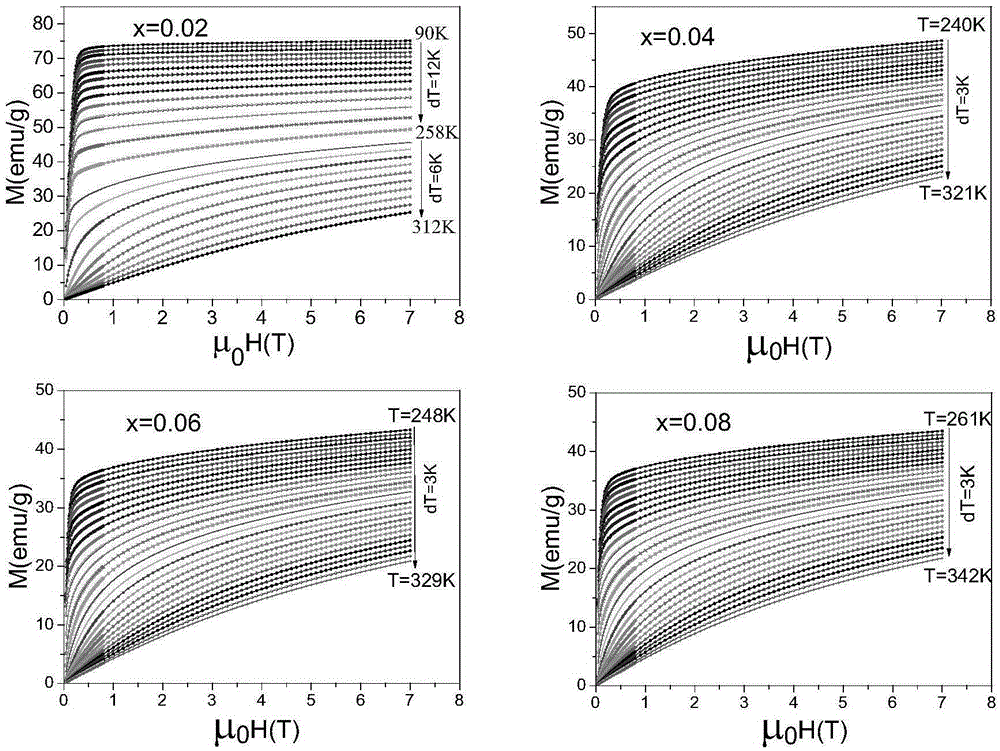
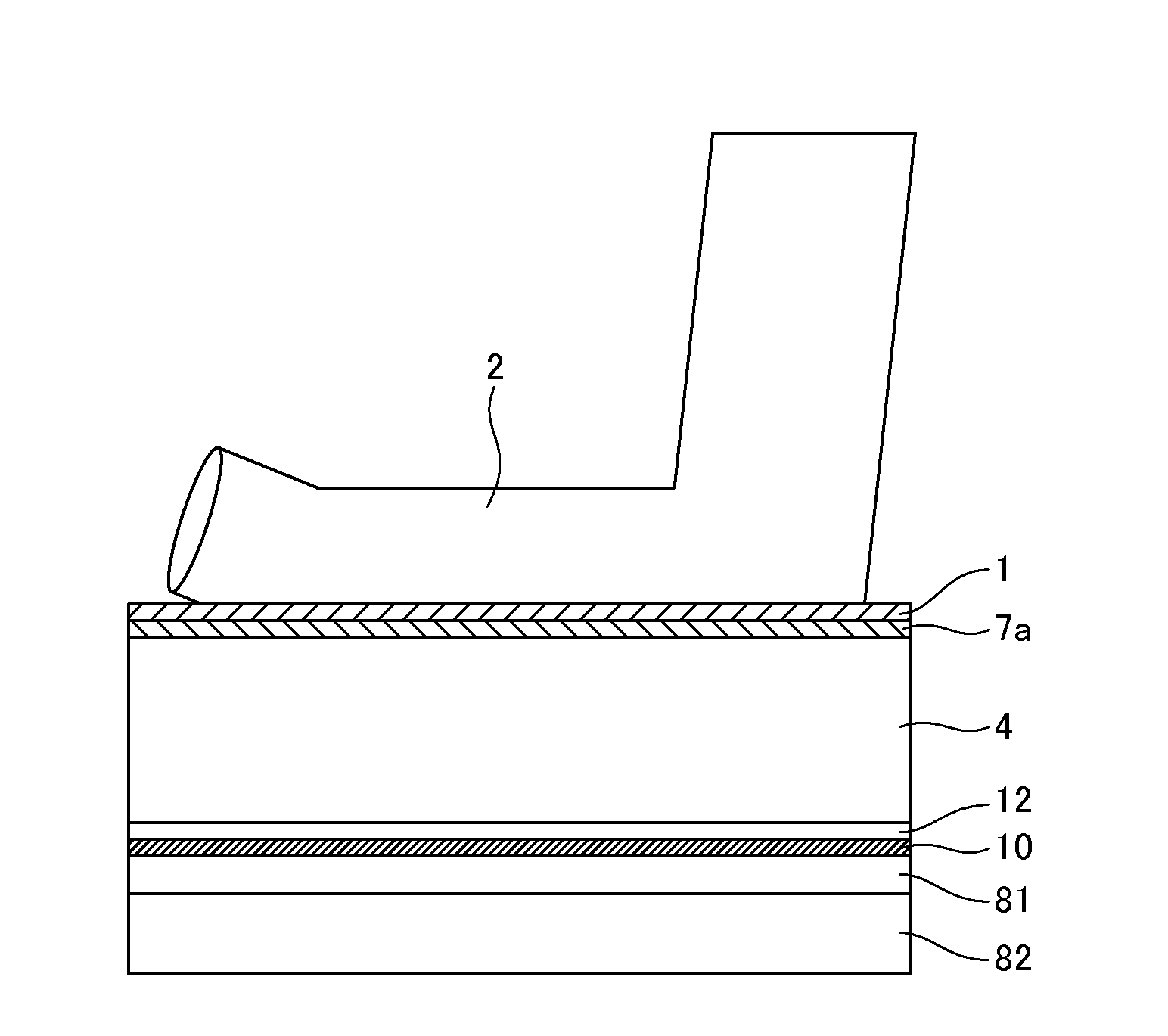
Patents
Literature
100 results about "Thermal hysteresis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
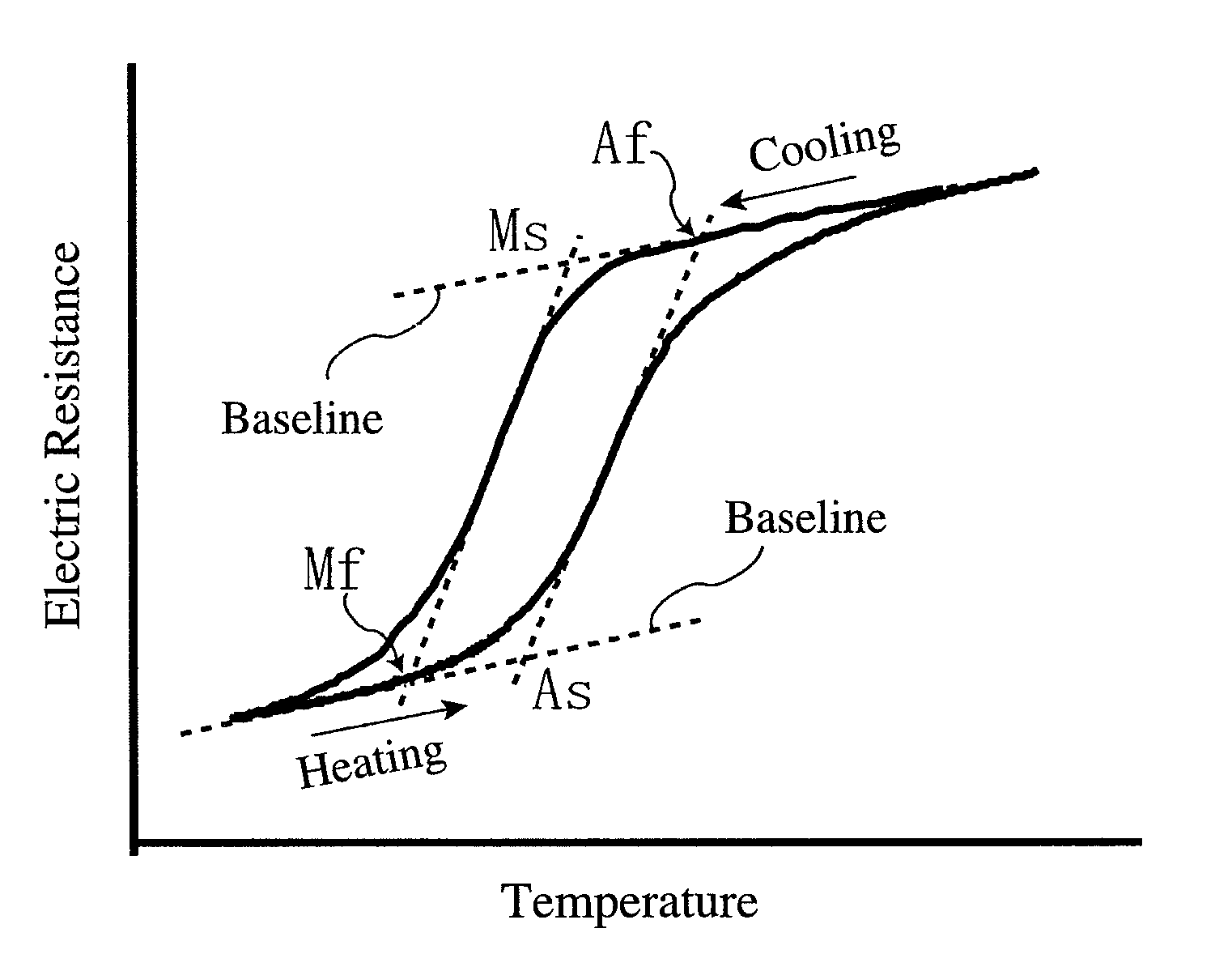
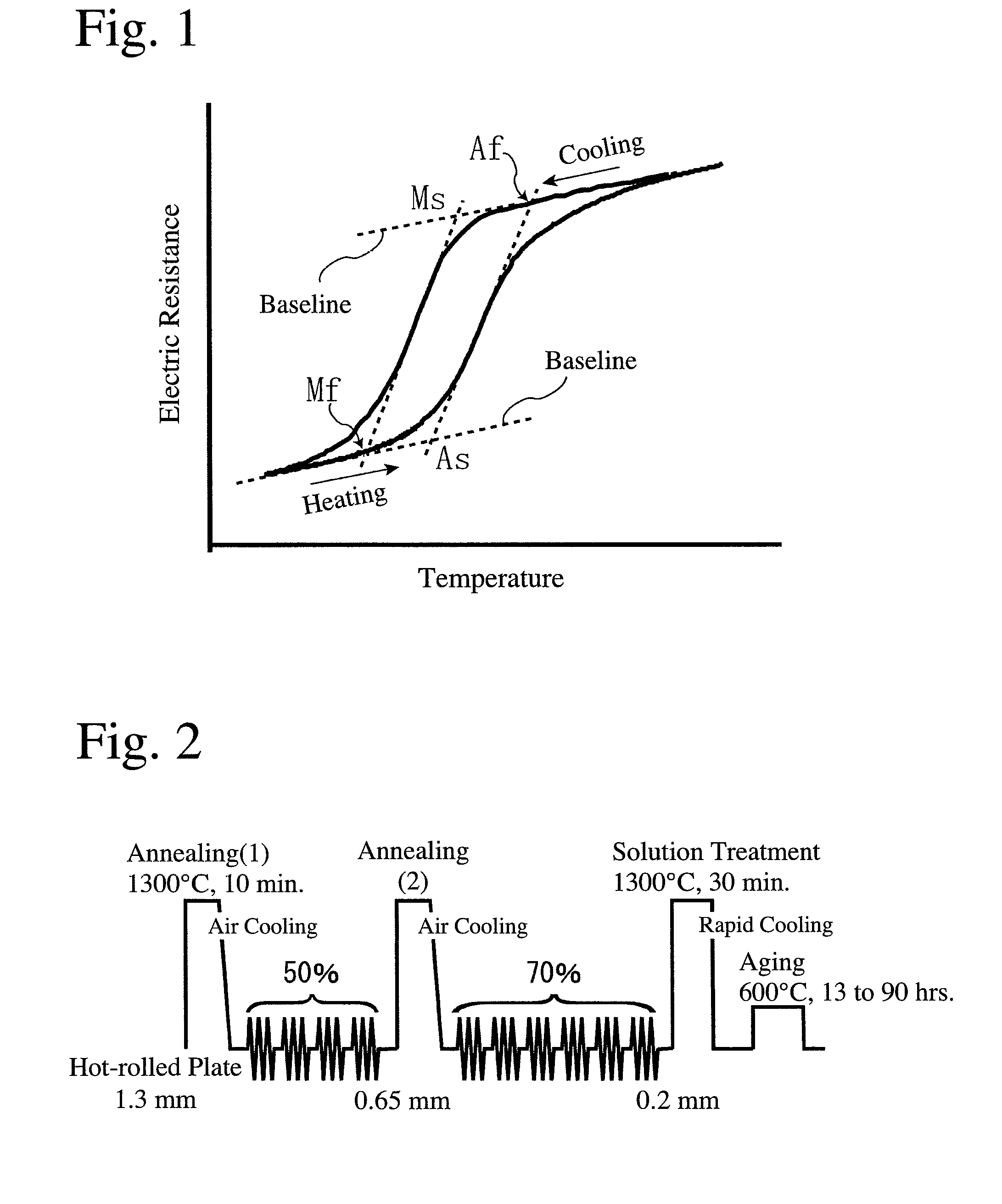
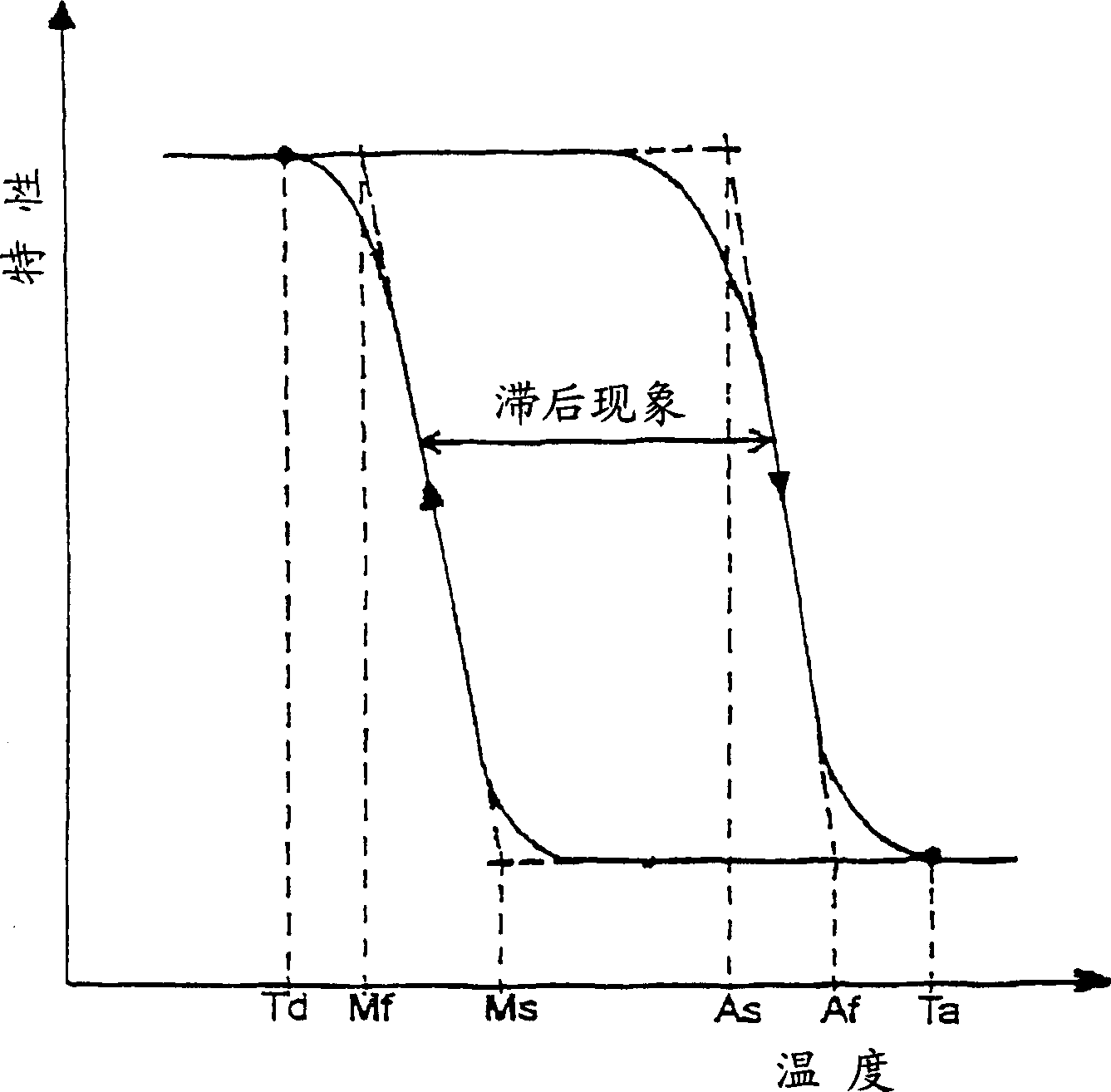
Thermal Hysteresis. Hysteresis [his-tuh-ree-sis] is defined as the lag in response exhibited by a body reacting to changes in the forces affecting it.[ a] Relating this idea to building failures, thermal hysteresis is the term used to describe the long-term response that certain types of marble display after years of thermal cycling.
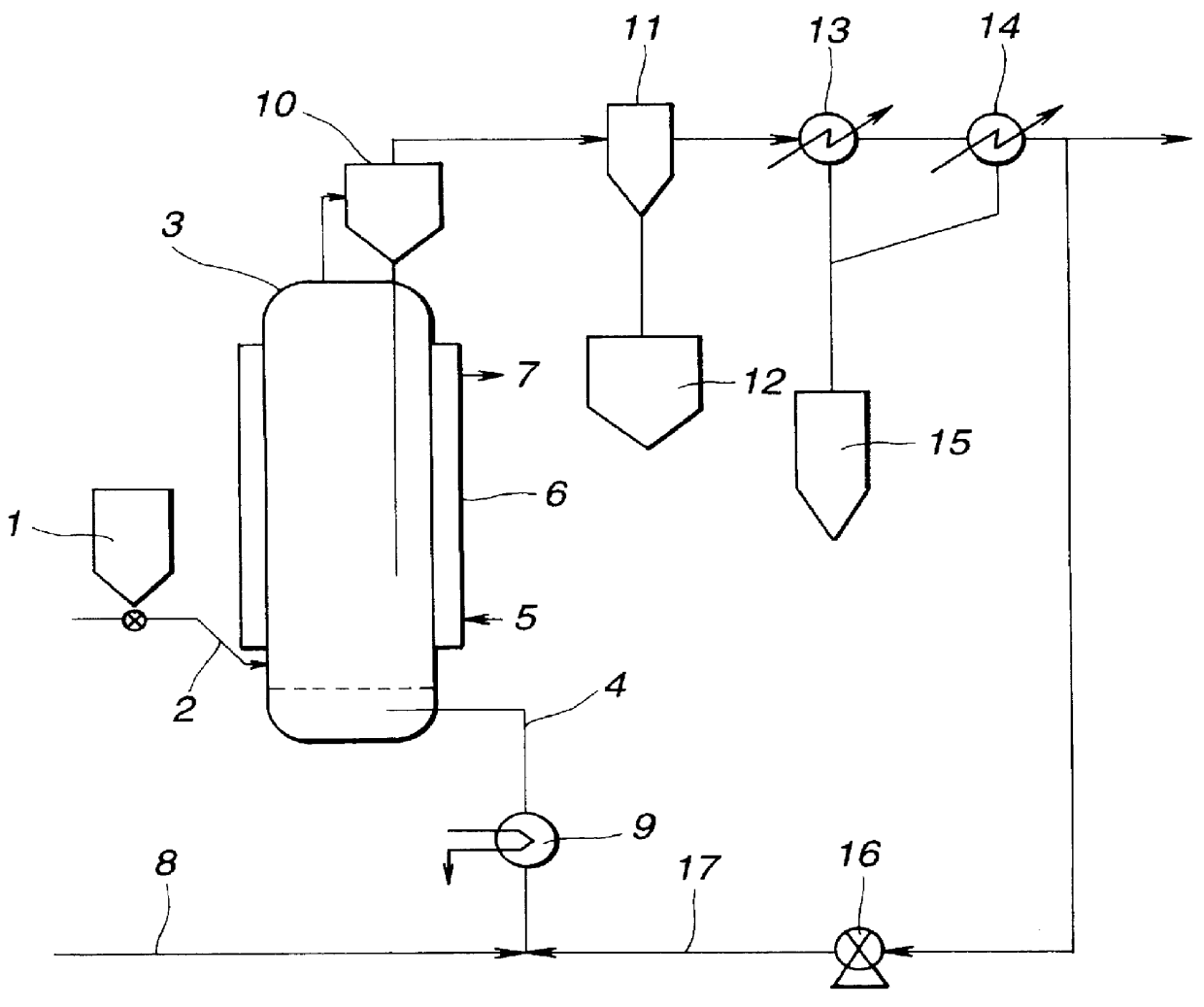
Magnetic material for magnetic refrigeration and method for producing thereof
ActiveUS7063754B2Stable magnetic refrigeration cycleLow costCompression machinesInorganic material magnetismHydrogenRoom temperature
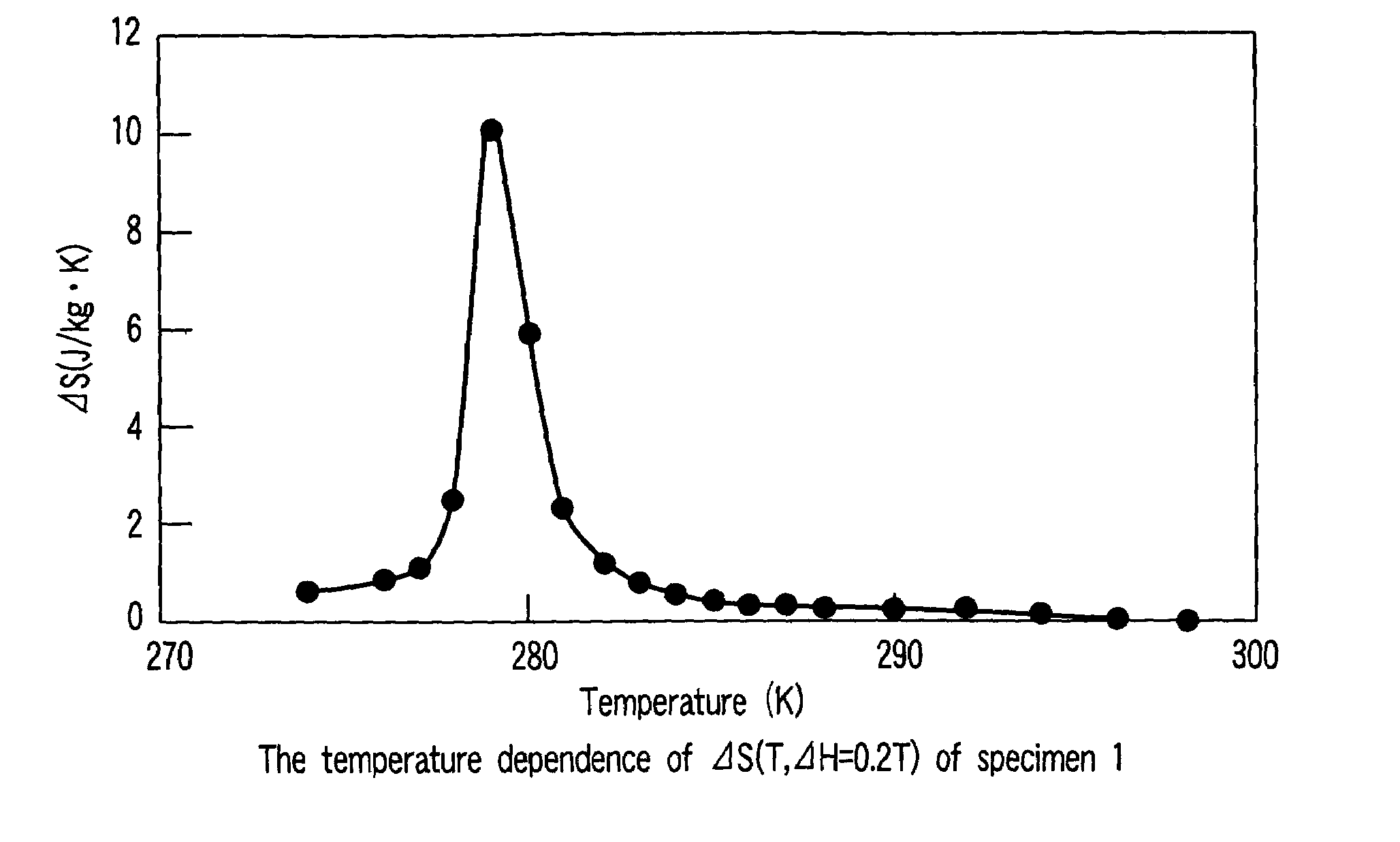
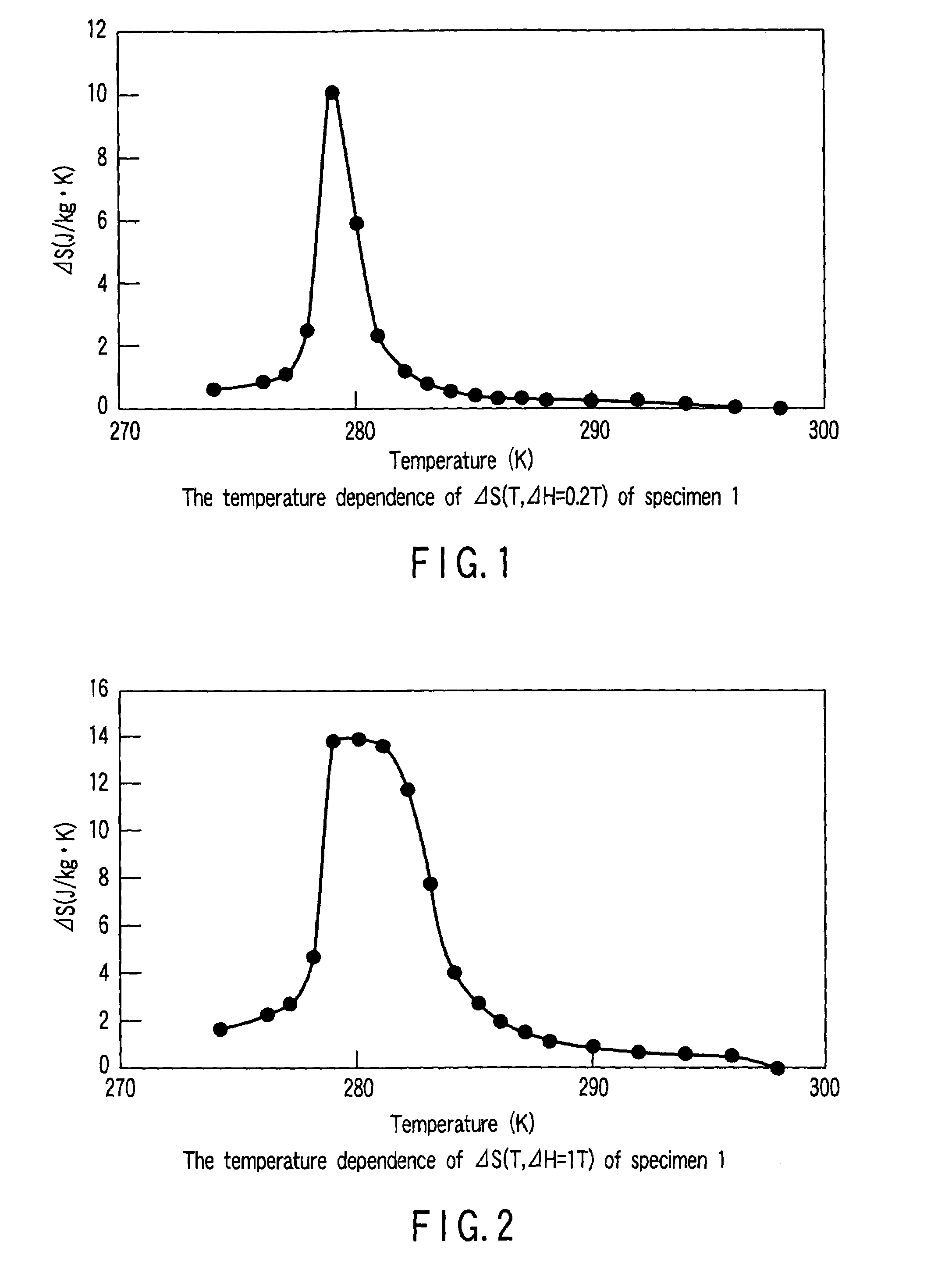
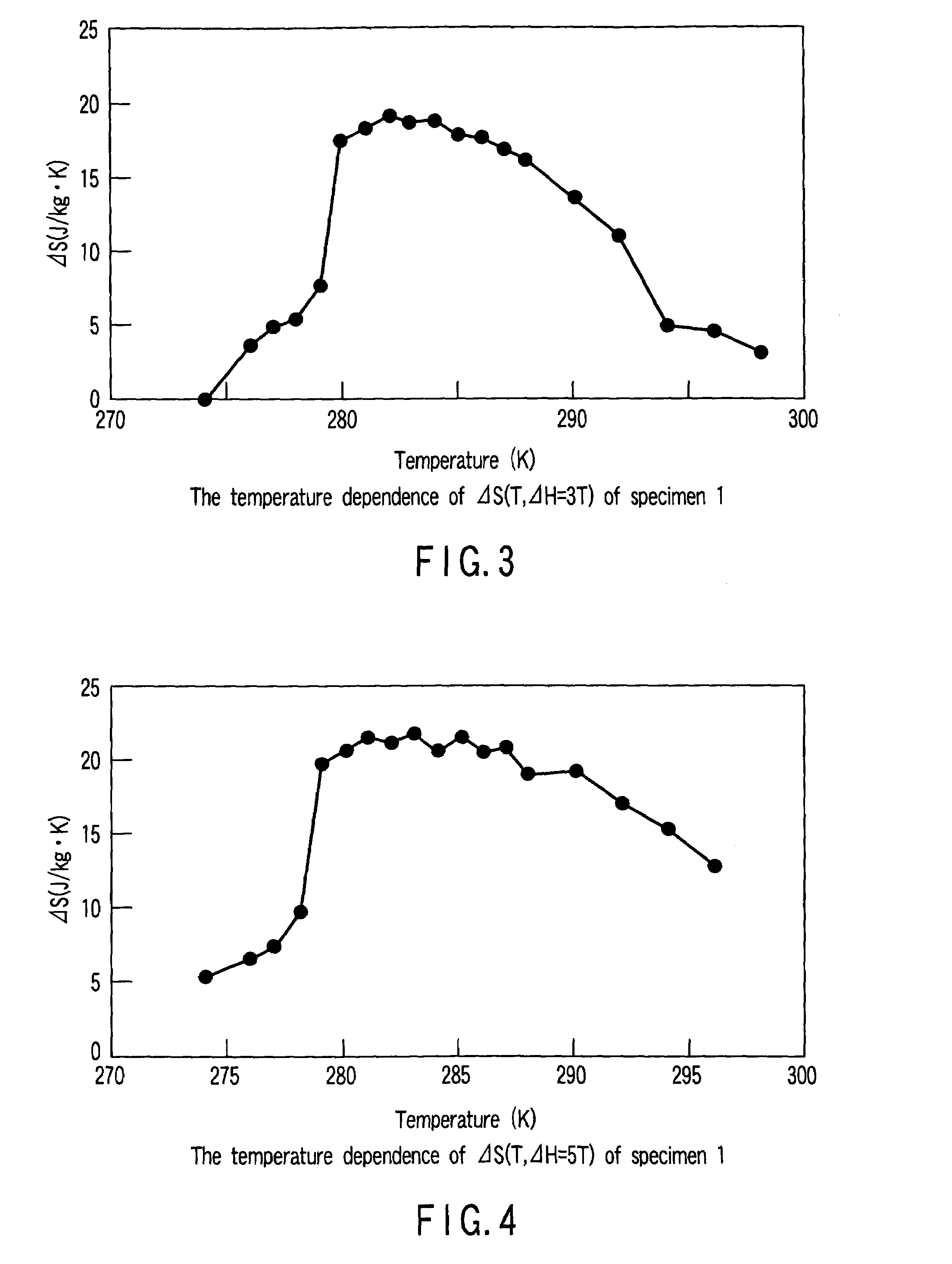
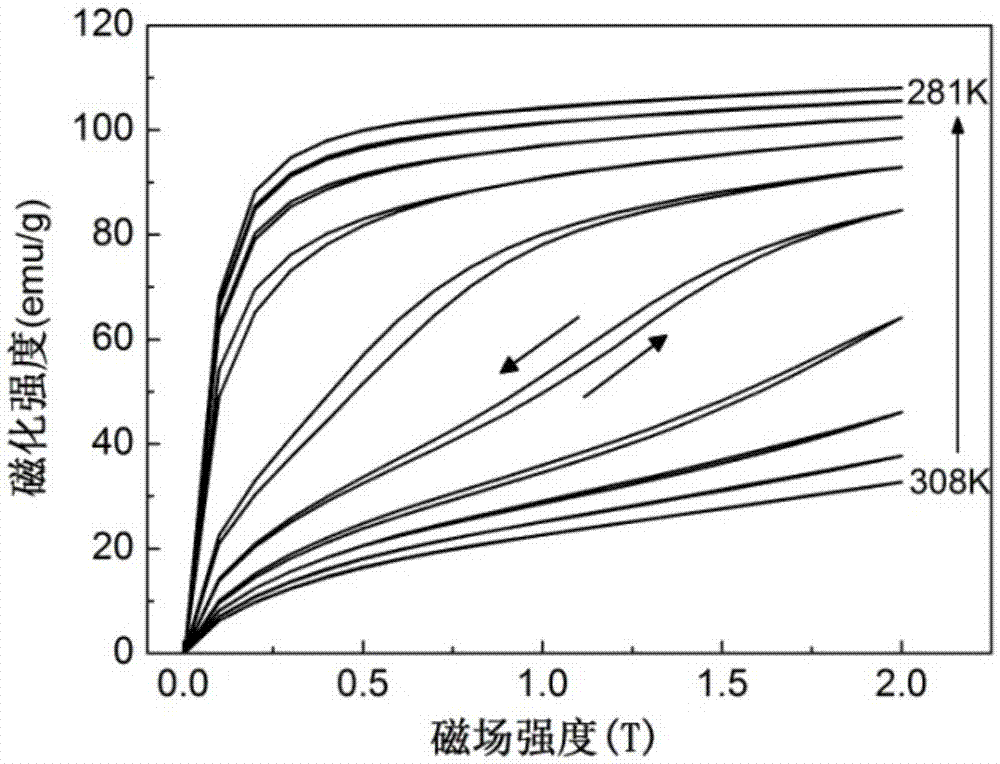
The magnetic material for magnetic refrigeration according to the present invention has an NaZn13-type crystalline structure and comprises iron (Fe) as a principal element (more specifically, Fe is substituted for the position of “Zn”) and hydrogen (H) in an amount of 2 to 18 atomic % based on all constitutional elements. Preferably, the magnetic material for magnetic refrigeration preferably contains 61 to 87 atomic % of Fe, 4 to 18 atomic % of a total amount of Si and Al, 5 to 7 atomic % of La. The magnetic material for magnetic refrigeration exhibits a large entropy change in a room temperature region and no thermal hysteresis in a magnetic phase transition. Therefore, when a magnetic refrigeration cycle is configured using the magnetic material for magnetic refrigeration, a stable operation can be performed.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Temperature controlling method for satellite-borne rubidium clock temperature-control cabin
ActiveCN103279157AHigh precisionImprove stabilityAuxillary controllers with auxillary heating devicesTemperature controlRubidium
The invention discloses a temperature controlling method for a satellite-borne rubidium clock temperature-control cabin and belongs to the technical field of spacecraft thermal control. Firstly, the maximum power needed by additional heating of a heater is detached, so that multiple one-way heaters with low power are formed. Secondly, thermal hysteresis time of the one-way heaters is calculated so as to design a control time interval of each one-way heater, after control of all the heaters is finished according to the time intervals, a complete heating and control period is formed. A system is provided with a backup temperature sensor and the heaters, when a main temperature sensor is effective or the main heater incorrectly responds to a controller switch order, primary backup switch is finished. The method for controlling the temperature and automatically dealing with a fault can provide high-precision and high-stability temperature control for the working environment of a rubidium clock. The control method is simple, high-efficiency, reliable and capable of meeting the requirement for long-time orbital continuous and stable work.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF SPACECRAFT SYST ENG
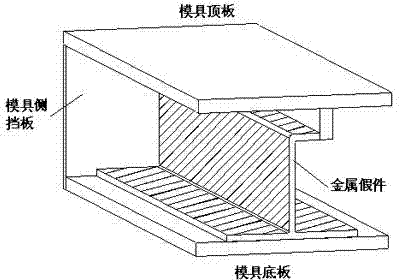
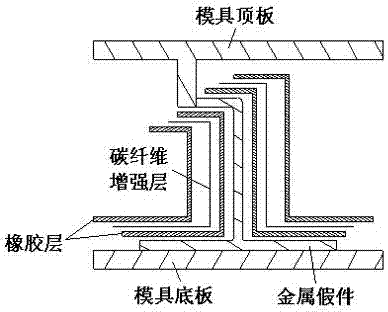
Method for forming J-shaped beam structure composite workpiece by open type soft tooling
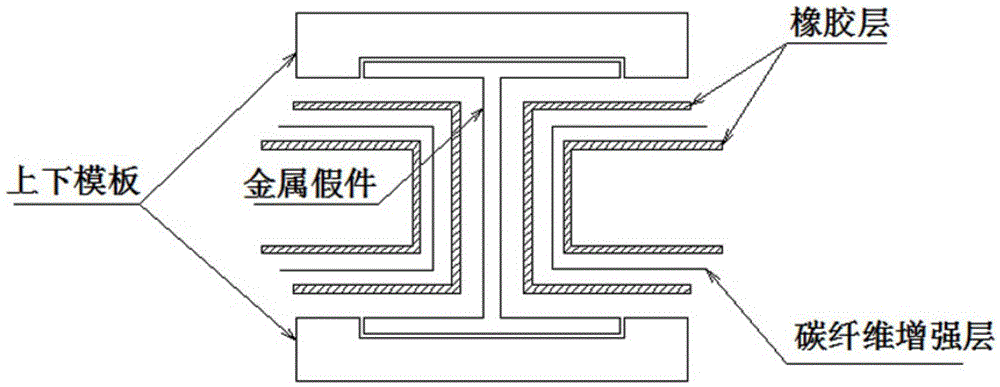
The invention discloses a method for forming a J-shaped beam structure composite workpiece by open type soft tooling; fiber-reinforced rubber open type soft tooling can be formed by a metal mold, the formed soft tooling can be one part of a formed mold for completing the forming process of the composite produced part. Compared with a traditional core mold forming method, the soft tooling can uniformly and accurately transmits pressure applied by an autoclave, out-of-tolerance of thickness of the composite workpiece can be avoided, the soft tooling is thinner in wall thickness, thermal hysteresis effect can be avoided, the forming quality of the workpiece can be effectively guaranteed by the above two points, and the qualified rate and the efficiency of production can be improved. The soft tooling can be used repeatedly, the reproduction is also more convenient, and the production cost and the manufacturing cycle are effectively reduced, and the production efficiency is improved.
Owner:航天海鹰(镇江)特种材料有限公司
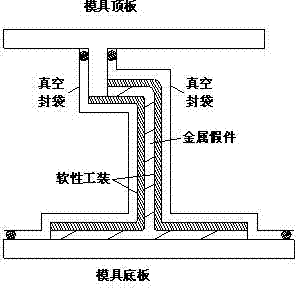
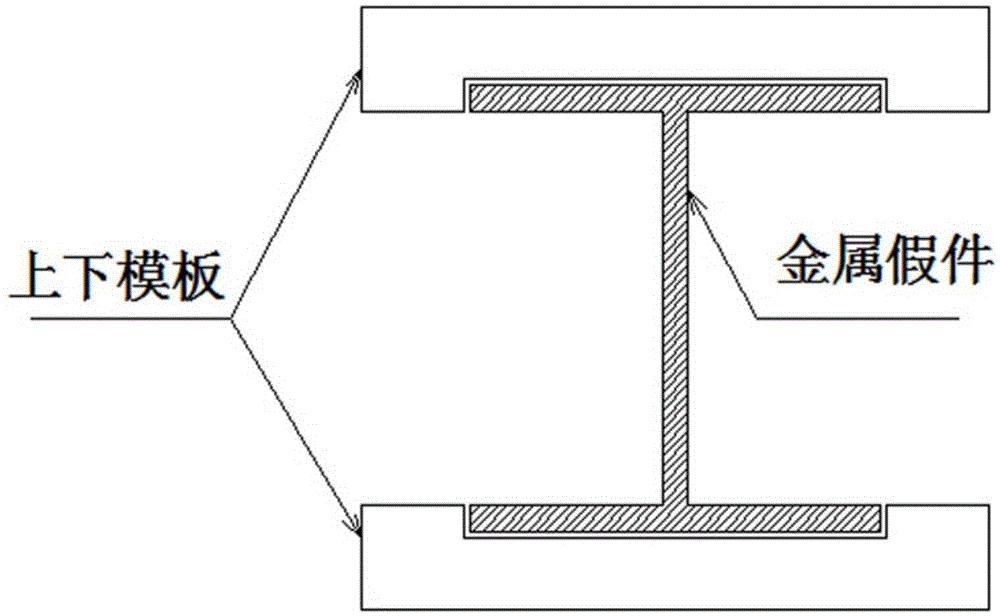
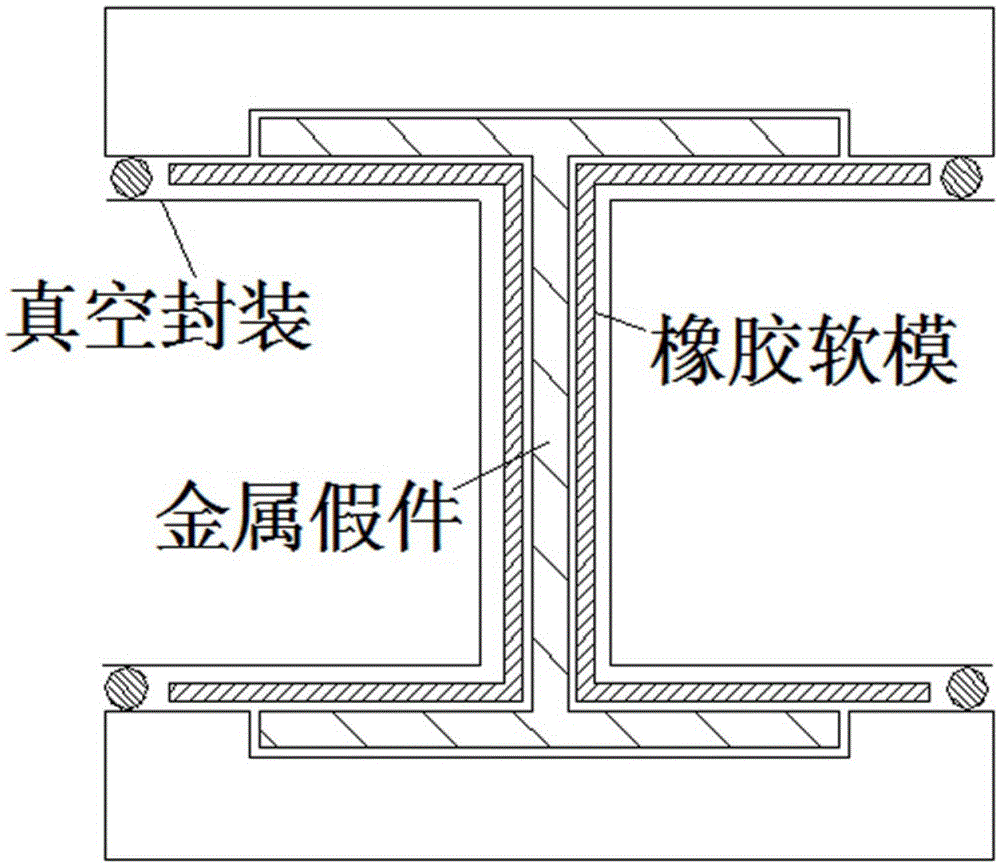
Method for using open-type rubber soft die for realization of thin-wall I-beam structure composite material part
The present invention discloses a method for using an open-type rubber soft die for realization of a thin-wall I-beam structure composite material part, by a machine manufacturing method, a metal false part with a boundary dimension which is entirely consistent with the boundary dimension of the composite material part is processed, a rubber soft die molding mold with a baffle is also processed, a rubber soft die is paved and pasted in a cavity formed by the metal false part and upper and lower templates, the external part of the rubber soft die is vacuum-sealed with a vacuum bag, and the rubber soft die is molded in a hot-pressing tank; after the rubber soft die is molded, the vacuum bag is removed, the metal false part is taken out, and filled with a composite material, then the external part of the rubber soft die is vacuum-sealed with the vacuum bag, and thee rubber soft die is molded in the hot-pressing tank to obtain the I-beam structure composite material part. The method can avoid the thickness over-deviation phenomenon of the composite material part, avoids the thermal hysteresis phenomenon, effectively guarantees the molding quality of the part, and improves the passing rate and efficiency of production.
Owner:航天海鹰(镇江)特种材料有限公司
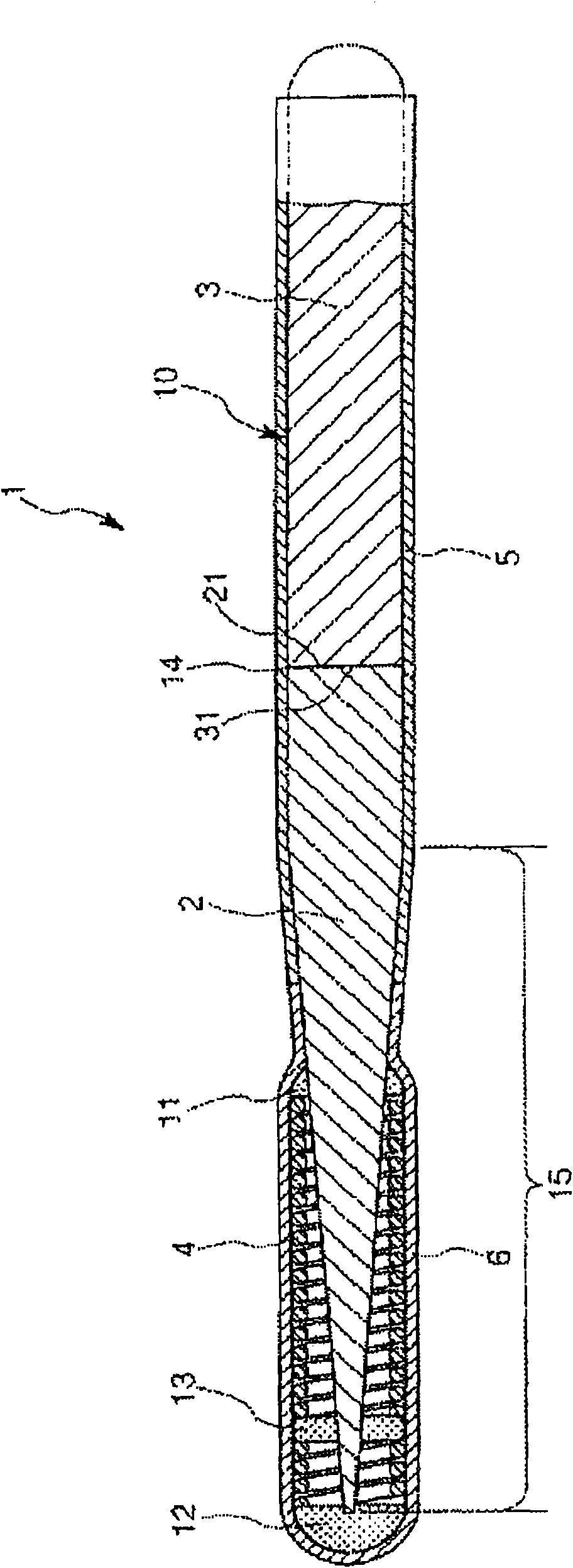
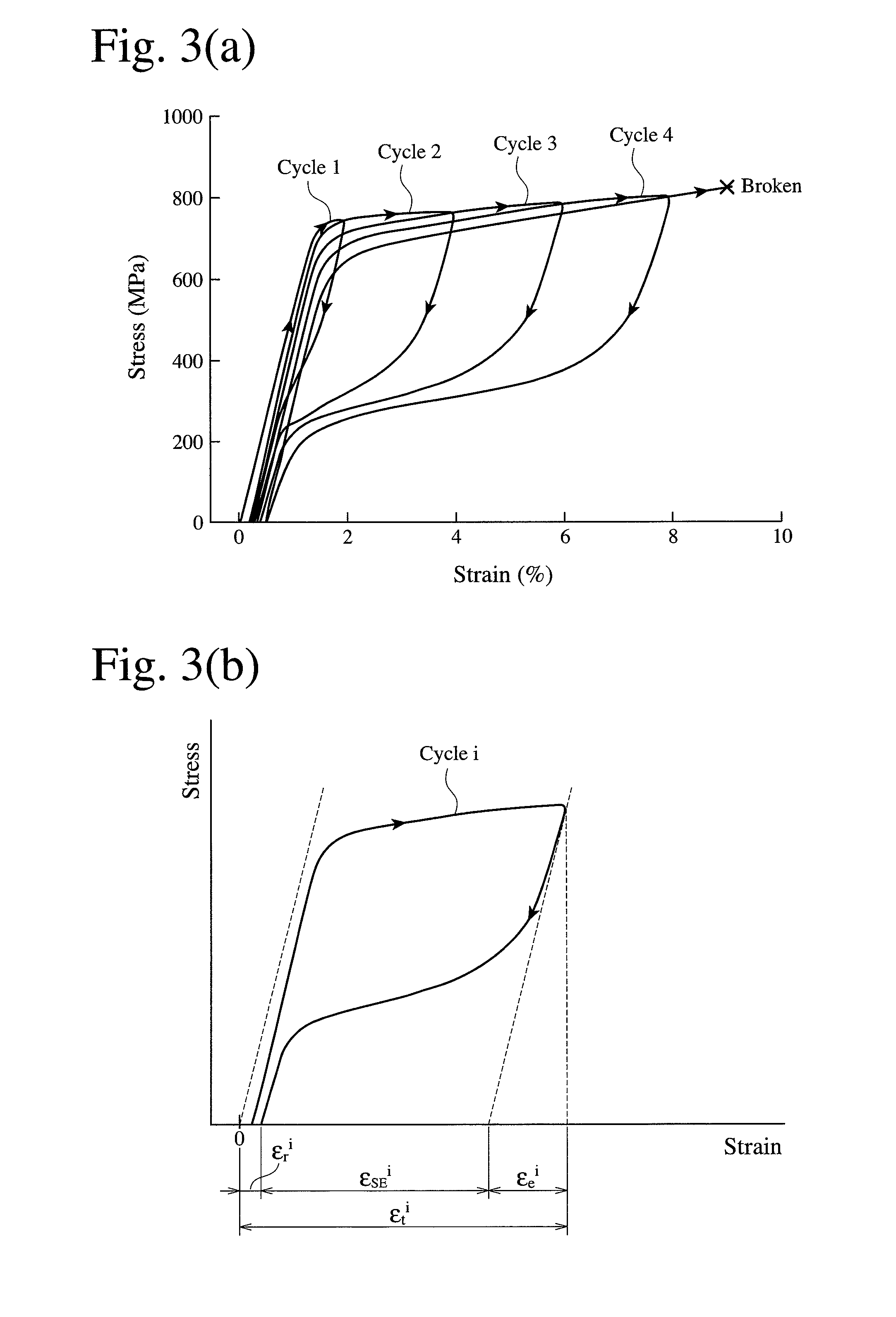
Guide wire and stent
ActiveCN101674861AEasy to slideExcellent X-ray contrastStentsGuide wiresPlastic materialsYoung's modulus
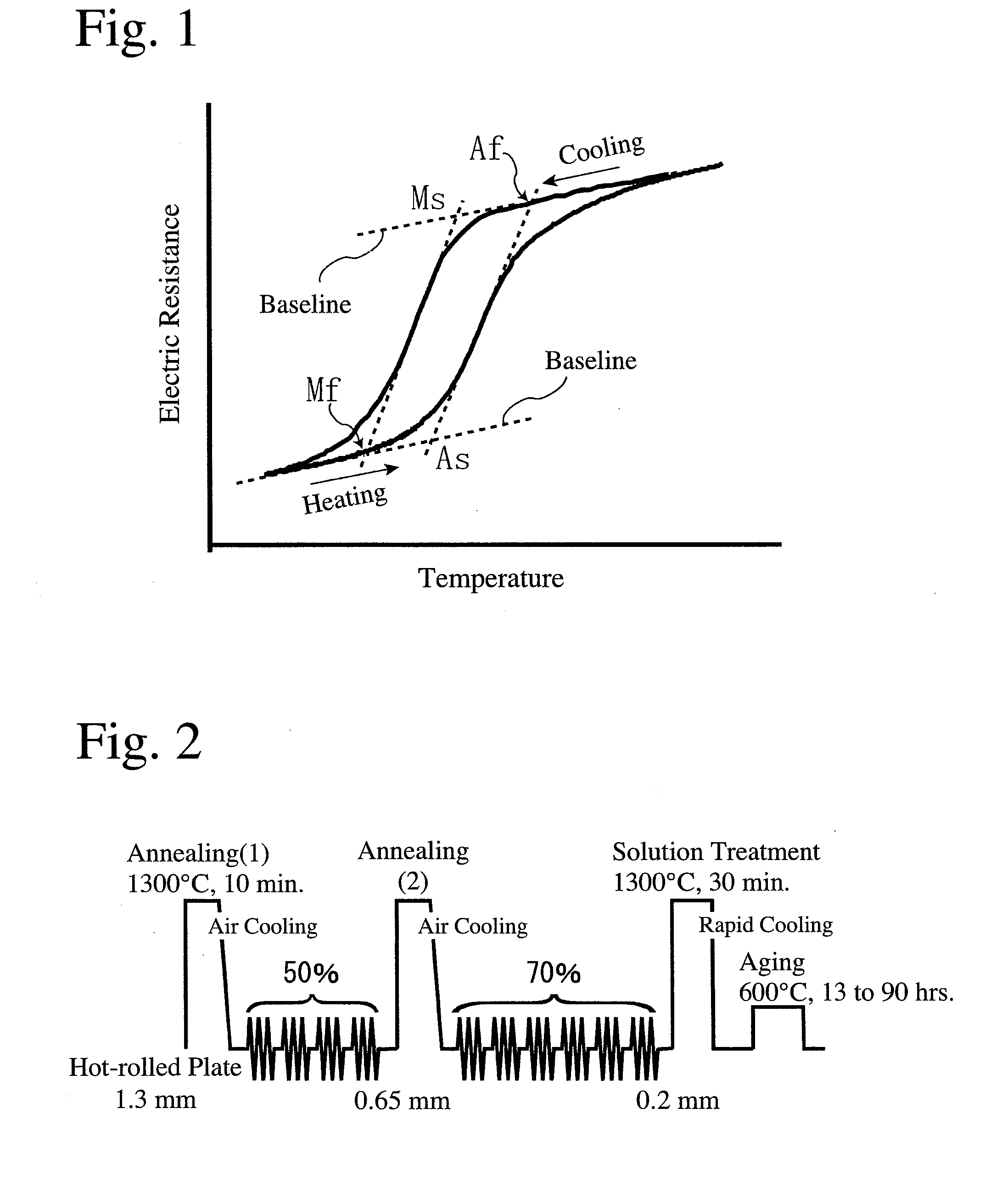
A guide wire that due to its wide elastic region and high Young's modulus, simultaneously has pliability and pushability, and that even when its surface is coated with a plastic material of high melting point, is highly impervious to influences of heat treatment, and that has excellent slidability and excels in weldability between a distal-end-side base material and a proximal-end-side core material. The guide wire has a core material comprising a distal-end-side core material and a proximal-end-side core material. The distal-end-side core material is made of an iron alloy having shape memorycapability and superelasticity, consisting essentially of two phases of gamma-phase and gamma'-phase and exhibiting, in a thermal hysteresis of martensite transformation and reverse transformation, adifference between reverse transformation completion temperature (Af-point) and martensite transformation starting temperature (Ms-point) of 100 DEG C or below. The proximal-end-side core material ismade of an alloy containing iron and has an elastic modulus higher than that of the distal-end-side core material. The distal-end-side core material and the proximal-end-side core material are weldedtogether.
Owner:TERUMO KK
Preparation of contract mass for alkylhalosilane production and process for producing alkylhalosilanes
InactiveUS6090966AHigh selectivityEliminate the problemGroup 4/14 element organic compoundsSilicon halogen compoundsReaction temperatureCopper
Alkylhalosilanes are produced by first fluidizing a metallic silicon powder with an inert gas, preheating the silicon powder at a temperature between 200 DEG C. and a steady reaction temperature while keeping the silicon powder fluidized, adding a copper catalyst to the preheated silicon powder to form a contact mass, and feeding an alkyl halide into the contact mass whereby the alkylhalosilanes are formed by direct synthesis. This process prevents the copper catalyst from being sintered by thermal hysteresis and activates a high catalysis on the contact mass at the start of reaction. The desired dialkyldihalosilane can be produced at a high selectivity.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
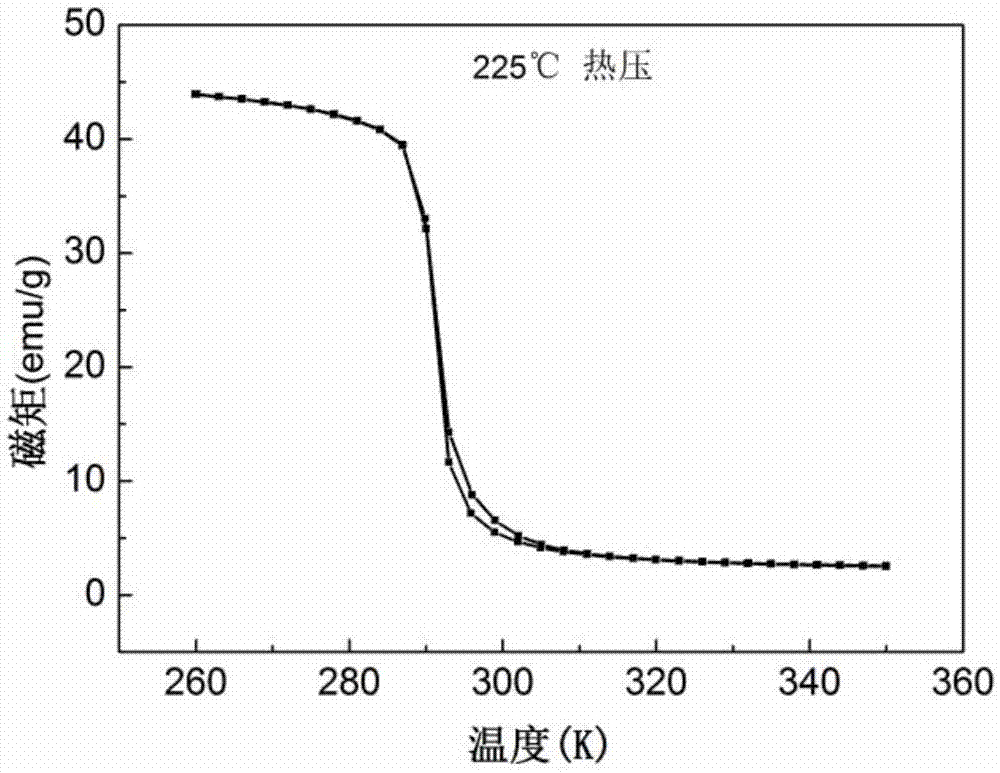
LaFeSi based magnetic refrigeration composite material and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN106906408ARaw materials are cheap and easy to getHigh thermal conductivityHeat-exchange elementsAlloyThermal hysteresis
The invention discloses a LaFeSi based magnetic refrigeration composite material and a preparation method and application thereof. The LaFeSi based magnetic refrigeration composite material comprises functional body components such as LaFeSi based alloy particles and matrix components such as low-melting-point metal or alloy, and the LaFeSi based alloy particles are bonded and coated by the matrix components to form a bulk material; and the LaFeSi based alloy particles are of a NaZn13 type structure. According to the LaFeSi based magnetic refrigeration composite material and the preparation method and application thereof, composite hot pressing is conducted between the cheap and easily-obtained low-melting-point metal or alloy and the LaFeSi based alloy particles, the appropriate low-melting-point components are selected, the pressing pressure, the hot pressing temperature, the pressure maintaining time and the like are adjusted, and thus the high-thermal-conductivity LaFeSi based magnetic refrigeration composite material can be obtained; the magnetic entropy change of the LaFeSi based magnetic refrigeration composite material is less reduced compared with that before hot pressing, the magnetic hysteresis loss is low, and thermal hysteresis is avoided; and in addition, the process is simple and easy to operate, the process conditions are relatively mild, energy consumption is little, the cost is low, the repeatability is good, and the preparation method can be widely used in preparation of magnetic refrigeration materials.
Owner:NINGBO INST OF MATERIALS TECH & ENG CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Iron-based alloy having shape memory properties and superelasticity and its production method
ActiveUS20090242083A1Good shape memory propertiesGood superelasticityMagnetic materialsHeat treatment process controlMartensite transformationCrystal orientation
An iron-based alloy having shape memory properties and superelasticity, which has a composition comprising 25-35% by mass of Ni, 13-25% by mass of Co, 2-8% by mass of Al, and 1-20% by mass in total of at least one selected from the group consisting of 1-5% by mass of Ti, 2-10% by mass of Nb and 3-20% by mass of Ta, the balance being substantially Fe and inevitable impurities, and a recrystallization texture substantially comprising a γ phase and a γ′ phase, particular crystal orientations of the γ phase being aligned, and the difference between a reverse transformation-finishing temperature and a martensitic transformation-starting temperature being 100° C. or less in the thermal hysteresis of martensitic transformation and reverse transformation.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
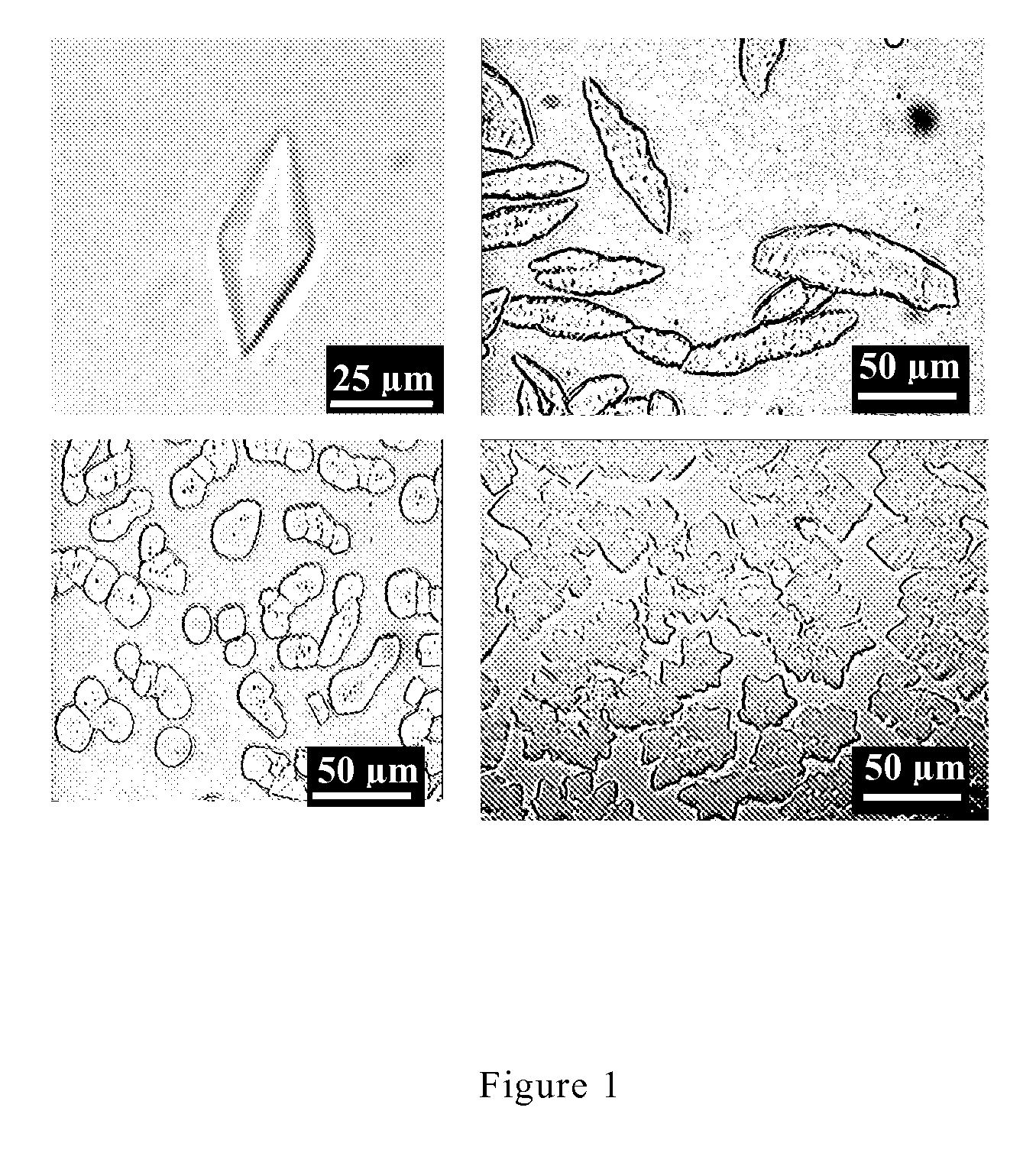
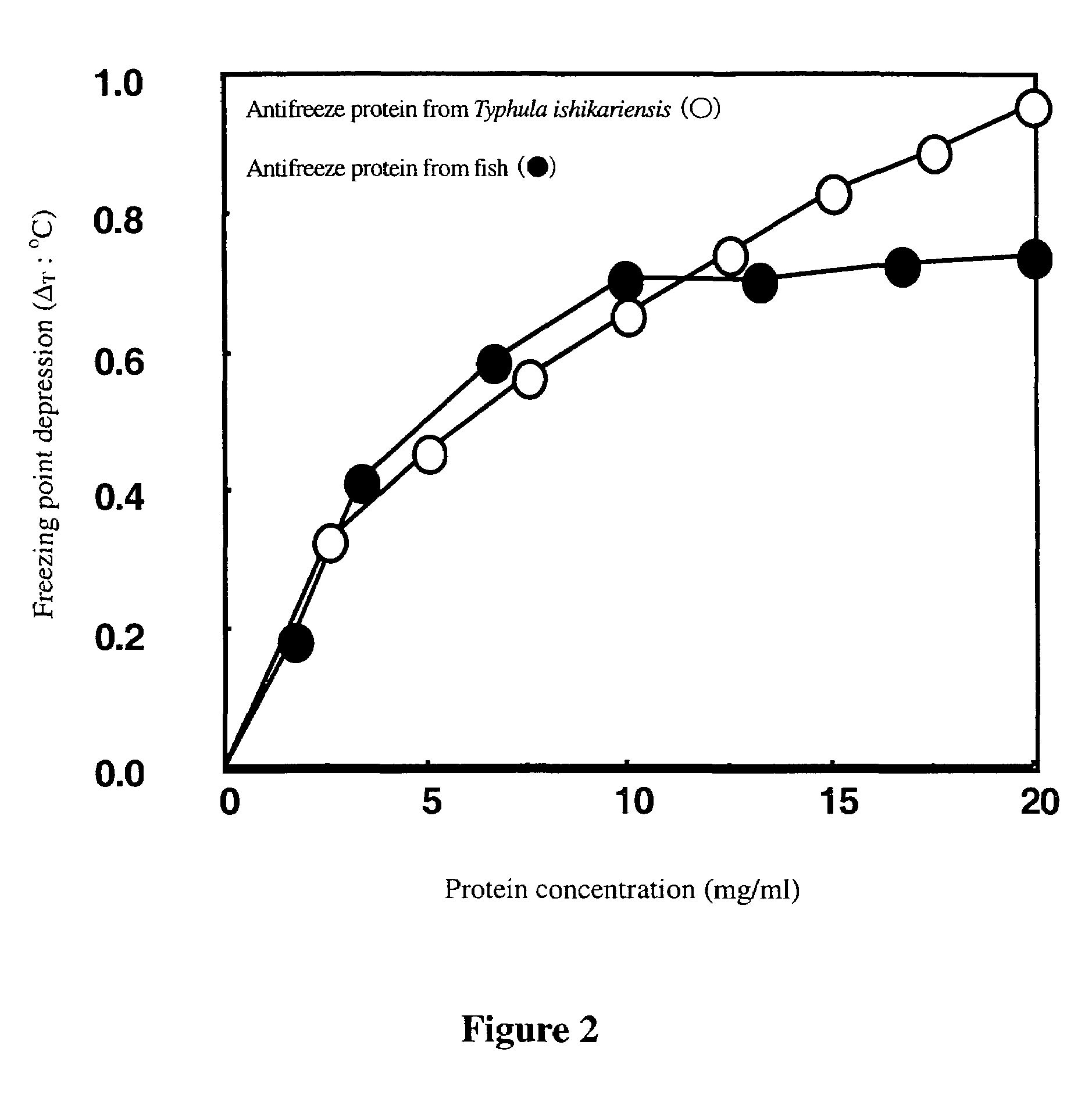
Antifreeze proteins from basidiomy cetes
The present invention provides antifreeze proteins produced by a basidiomycete. The antifreeze protein has a high antifreeze activity such as a thermal hysteresis activity or an ice-recrystallization inhibition activity.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
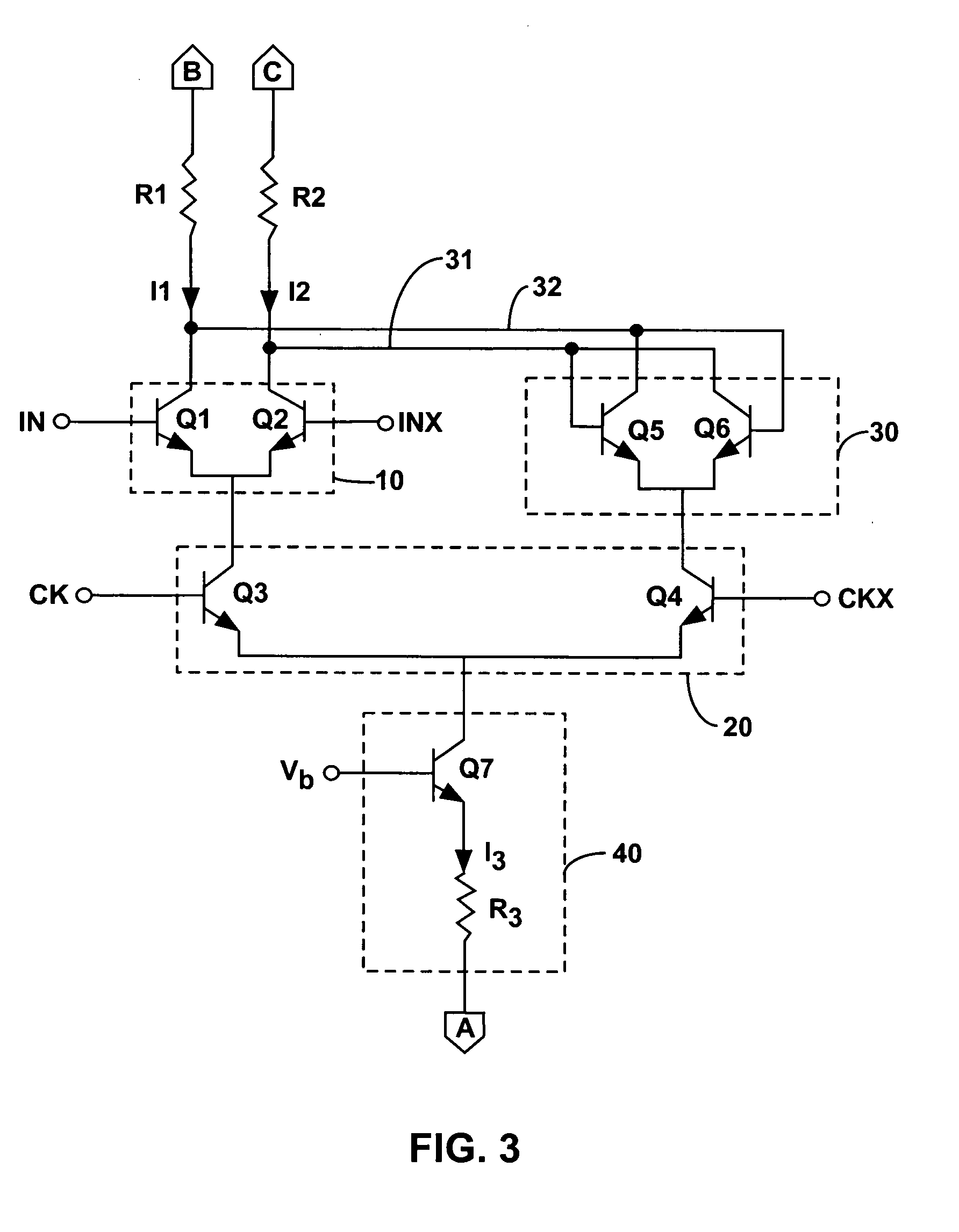
Clocked D/A converter
InactiveUS20050156765A1TransistorElectric signal transmission systemsBistable circuitsClock transition
A digital-to-analog converter is disclosed, comprising an input / output circuit, a bistable circuit connected with the input / output circuit, a clock circuit connected with the input / output circuit and the bistable circuit, and a current generator circuit connected with the clock circuit. The clock circuit acts as a switch, providing current from the current generator either to the input / output circuit or to the bistable circuit. The digital input signal switches when the current generator provides current to the bistable circuit, and switching of the input signal is asserted at the output of the converter when the current generator provides current to the input / output circuit. Therefore, switching of a clock circuit signal, rather than switching of the digital input signal determines switching of the output signal, in order to reduce intersymbol interference of the converter associated with thermal hysteresis of some of the components of the converter.
Owner:HRL LAB
Wide thermal hysteresis tininb shape memory alloy memory ring and its preparation method and application
InactiveCN102296224AImprove mechanical propertiesGood high-frequency electronic performanceShape-memory alloySmall footprint
A wide thermal hysteresis TiNiNb shape memory alloy memory ring and its preparation method and application, characterized in that the alloy components of the memory ring are Ti: 42-47; Ni: 44-49; Nb: 6-14; the preparation method is : 1) Melting: Melting by vacuum ultra-pure smelting technology; 2) Homogenization treatment: 700-1000°C, time 3-6h; 3) Forging at 700-900°C; 4) Hot drawing at 400-750°C Wire is required; 5) The wire is wound into a ring and welded by micro-beam plasma welding technology; 6) The diameter is expanded under the condition of -60°C. The memory ring prepared by the present invention has the characteristics of high connection strength, small space occupation, light weight, and convenient installation. It can be used for storage and transportation at -190°C-+60°C ambient temperature, and can be used at -60°C-+ after fastening. Keep fastening without loosening in the range of 200°C.
Owner:沈阳天贺新材料开发有限公司
Iron-based alloy having shape memory properties and superelasticity and its production method
ActiveUS8083990B2Maintain good propertiesGood superelasticityMagnetic materialsHeat treatment process controlMartensite transformationCrystal orientation
An iron-based alloy having shape memory properties and superelasticity, which has a composition comprising 25-35% by mass of Ni, 13-25% by mass of Co, 2-8% by mass of Al, and 1-20% by mass in total of at least one selected from the group consisting of 1-5% by mass of Ti, 2-10% by mass of Nb and 3-20% by mass of Ta, the balance being substantially Fe and inevitable impurities, and a recrystallization texture substantially comprising a γ phase and a γ′ phase, particular crystal orientations of the γ phase being aligned, and the difference between a reverse transformation-finishing temperature and a martensitic transformation-starting temperature being 100° C. or less in the thermal hysteresis of martensitic transformation and reverse transformation.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Coating composition
InactiveUS20110304817A1Avoid crackingImprove hot water resistanceCoatingsOptical partsOrganic solventMicroparticle
[Problem] To provide a coating composition for forming a hard coating which, by itself, favorably adheres to a plastic optical substrate, and effectively prevents the occurrence of cracks caused by the thermal hysteresis at the time of curing.[Means for Solution] The coating composition for forming a hard coating, contains a fine inorganic oxide particle, a hydrolyzable organosilicon compound, water, a curing catalyst and an organic solvent, wherein cyclic ketone is contained in an amount of 0.10 parts by mass to 30.00 parts by mass per 100 parts by mass of the total of the fine inorganic oxide particle and the hydrolyzable organosilicon compound.
Owner:TOKUYAMA CORP
Preparation method of spin-crossover nanometer materials of mononuclear Fe (II) complexes
The invention relates to the preparation of novel spin-crossover nanometer materials, and in particular relates to a preparation method of spin-crossover nanometer materials of mononuclear Fe (II) complexes. According to the method, the nanometer mononuclear spin-crossover materials are prepared through introducing surfactant i.e. polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP). The method is simple to operate, low in cost and has the advantages that the prepared Fe (AP-MeSAL) 2 nanometer materials still have the near room-temperature spin-crossover properties and are accompanied by 7K of thermal hysteresis loops.
Owner:XINJIANG UNIVERSITY
Method for separating and purifying plant ice structural protein
InactiveCN101579036AActive influenceHigh yieldProteins working-up by texturisingFood preservationFood additiveFreeze-drying
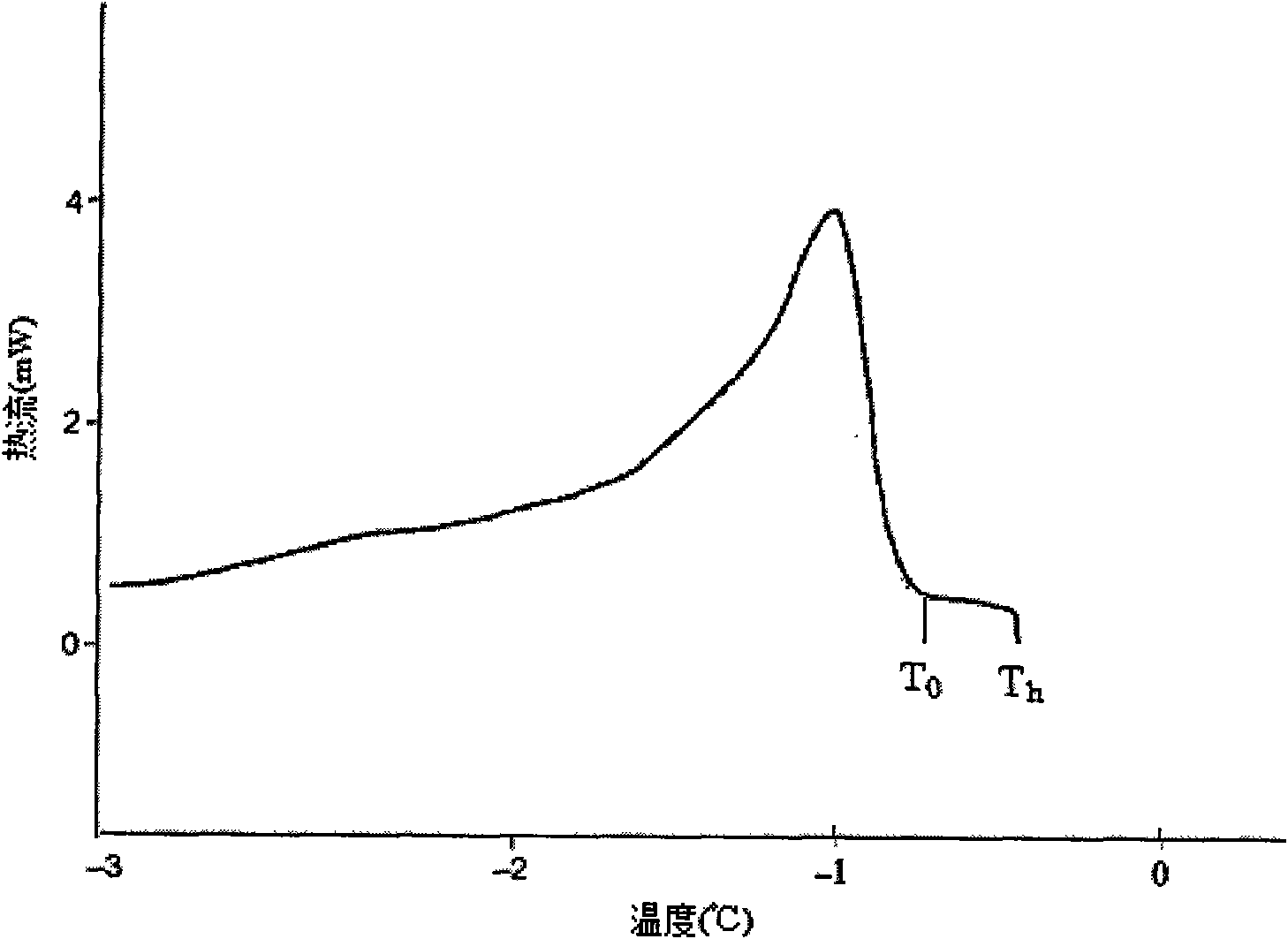
The invention relates to a method for separating and purifying plant ice structural protein, which belongs to the field of food additive separation. The method uses cold-stress plants as raw materials to separate and purify the ice structural protein by leaching and adopting a cloud point extraction method, and comprises the following steps: firstly, adopting buffer solution containing a non-ionic surfactant to leach out the ice structural protein from the plant raw materials; secondly, performing cloud point extraction by adopting a micellar solution formed by the non-ionic surfactant, wherein the mixture is divided into a water phase and a micellar phase after being heated to the cloud point temperature, hydrophobic impurities are enriched at the micellar phase, while the hydrophilic ice structural protein is kept at the water phase; and finally, performing dialysis concentration and freeze drying to obtain a white ice structural protein mixture. A differential scanning calorimetry is adopted to perform thermal hysteresis activity detection on a separated and purified sample to prove that the product has high thermal hysteresis activity. The method has the advantages of simple separation process, low production cost, no volatile organic solvent in the process of extraction and high purification efficiency, and is advantageous for producing the ice structural protein industrially and making full use of plant resources.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Adhesive film or sheet
InactiveUS20100255302A1Increase forceHigh transparencyMonocarboxylic acid ester polymer adhesivesFilm/foil adhesivesPolymer sciencePropylene Polymers
[Problem] To provide an adhesive film or sheet for protecting the surfaces of articles having proper initial adhesive force, sufficiently suppressing an increase in the adhesive force after aged, maintaining a suitable adhesive force in a proper range despite of being subjected to thermal hysteresis to some extent or even after preserved for extended periods of time and, as desired, being capable of imparting a high degree of transparency to the adhesive film or sheet.[Means for Solution] An adhesive film or sheet comprising a mixed resin of an ethylene / unsaturated ester copolymer resin (A) and a highly crystalline ethylene or propylene polymer or copolymer resin (B) having a melting point of not lower than 115° C.
Owner:MITSUI LTD
Over-temperature protection circuit used for power module
ActiveCN103840434AAccurate detectionWith thermal hysteresisEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionStopped workControl signal
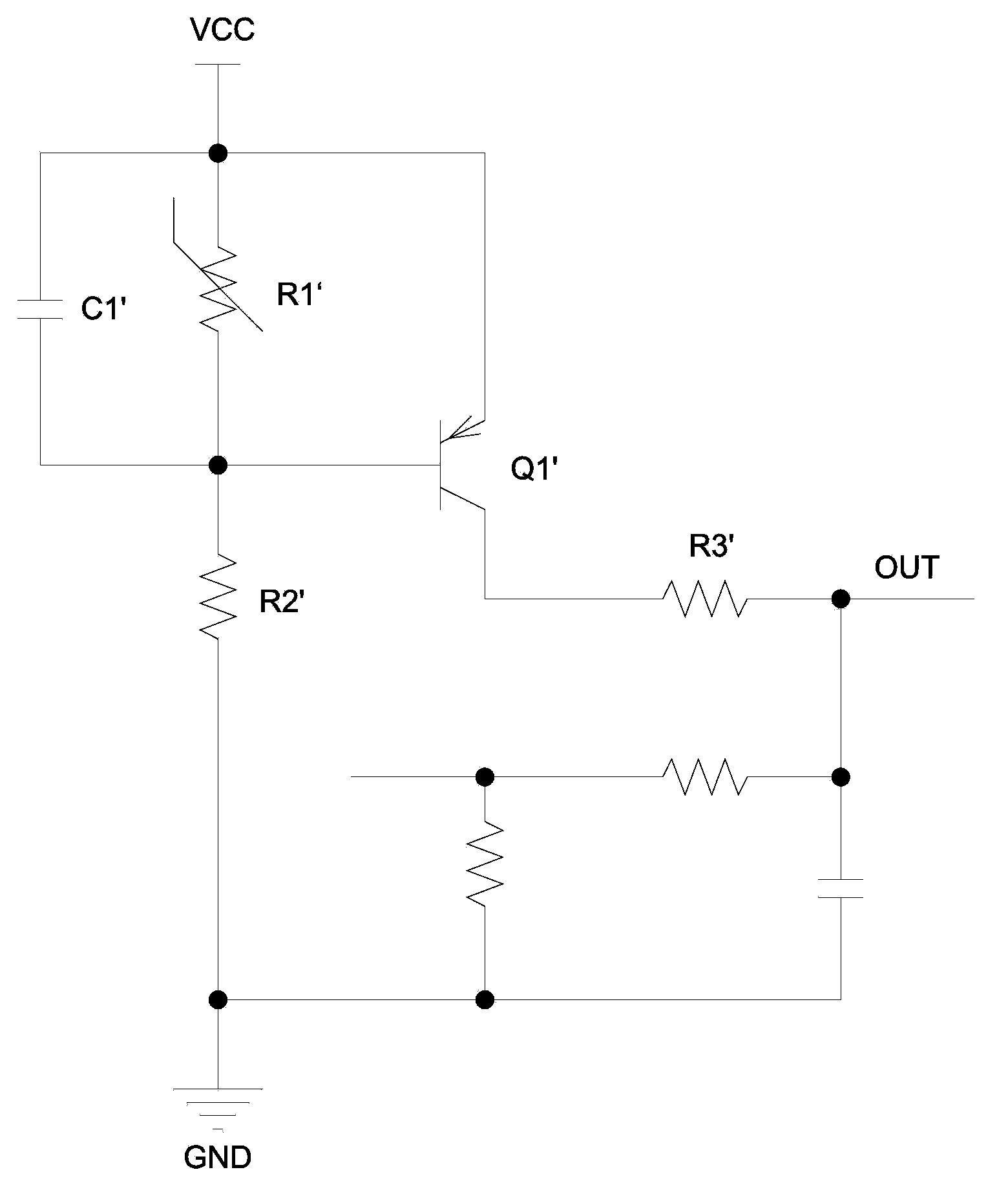
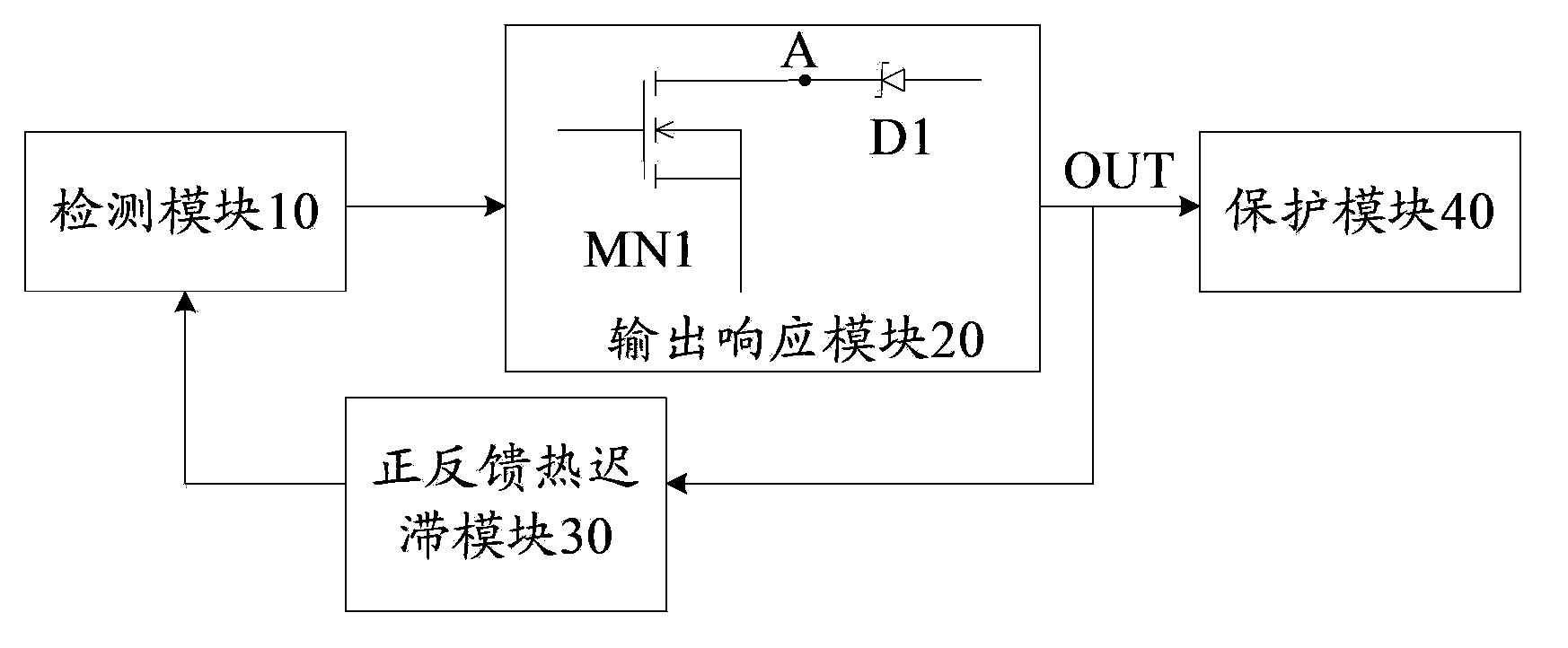
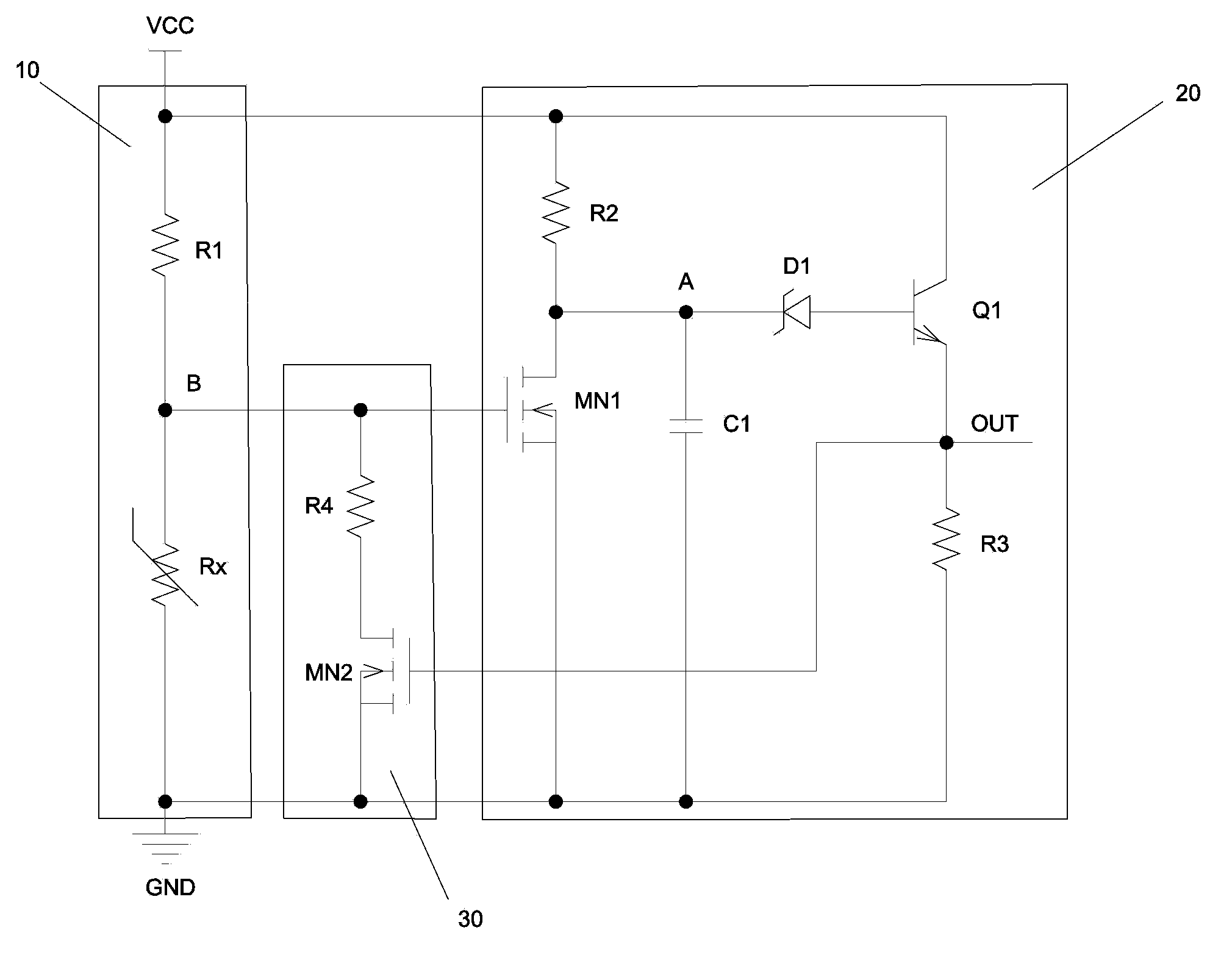
The invention discloses an over-temperature protection circuit used for a power module. The circuit includes a detection module used for detecting the temperature of the power module so as to generate detection signals; an output response module connected with the detection module; a positive and negative thermal-feed hysteresis module which is connected with the output response module and the detection module and used for adjusting detection signals according to control signals so as to realize thermal hysteresis; and a protection module which is connected with the output response module and used for controlling the power module to stop work according to the control signals so as to realize protection of the power module. The output response module includes a first NMOS tube and a Zener diode, and a first node is arranged between the first NMOS tube and the Zener diode. The voltage of the first node changes according to the detection signals and the output response module outputs the control signals according to the voltage of the first node. The over-temperature protection circuit used for the power module is capable of detecting accurately the temperature of the power module and has a thermal hysteresis function and capable of effectively preventing happening of a thermal oscillation phenomenon.
Owner:GD MIDEA AIR-CONDITIONING EQUIP CO LTD
Room temperature magnetic cooling material
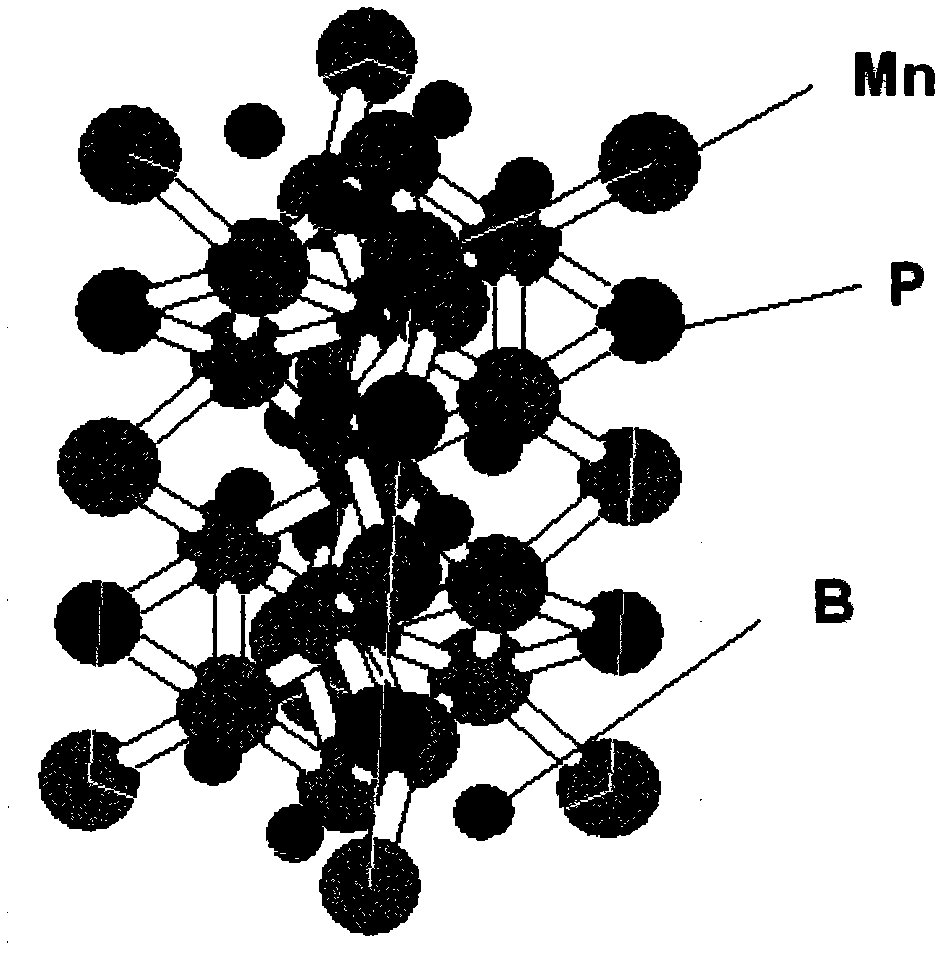
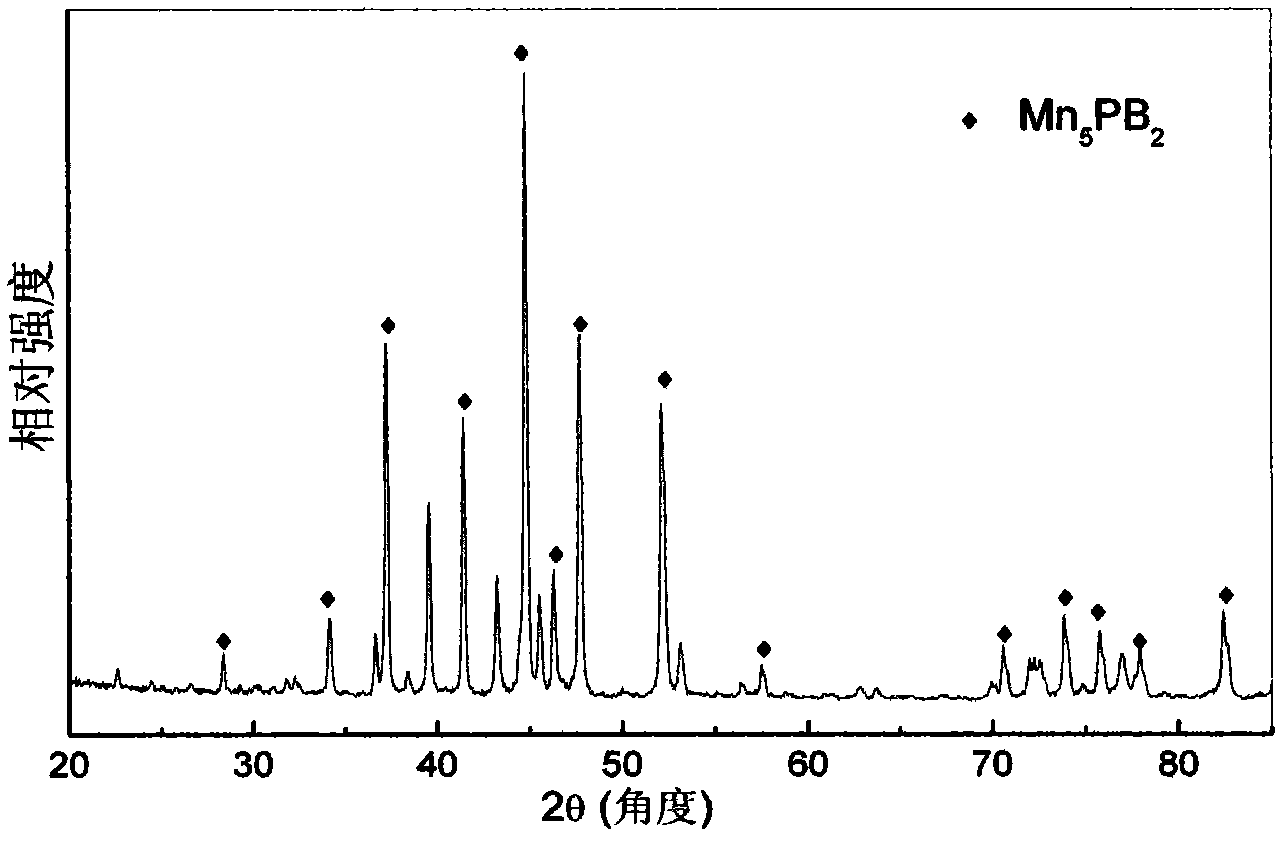
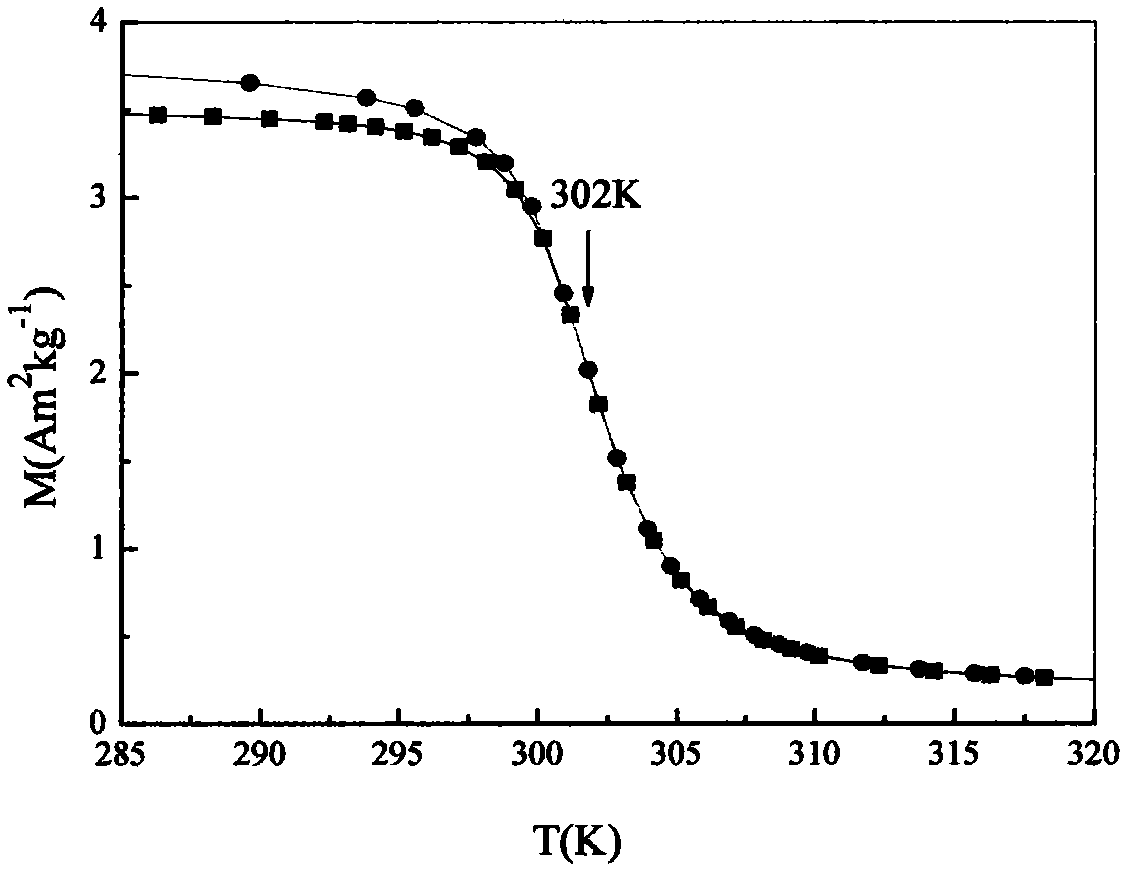
The invention provides a room temperature magnetic cooling material, which is characterized by containing Mn, P and B elements simultaneously, with Mn5PB2 as the main phase, a space group of I4 / mcm and a quadrangle structure. Specifically, the main phase Mn5PB2 accounts for 60-100 wt% of the magnetic cooling material. The material of the invention has the advantages of small thermal hysteresis, small magnetic hysteresis, no rare earth, and proper Curie point. In a 3000 Oe magnetic field, the magnetic intensity of Mn5PB2 can be 80% of a saturation value, so that Mn5PB2 can be applied in a 3000 Oe magnetic field established by a relatively low permanent magnet NdFeB, thus making the volume of a magnetic cooling machine small.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
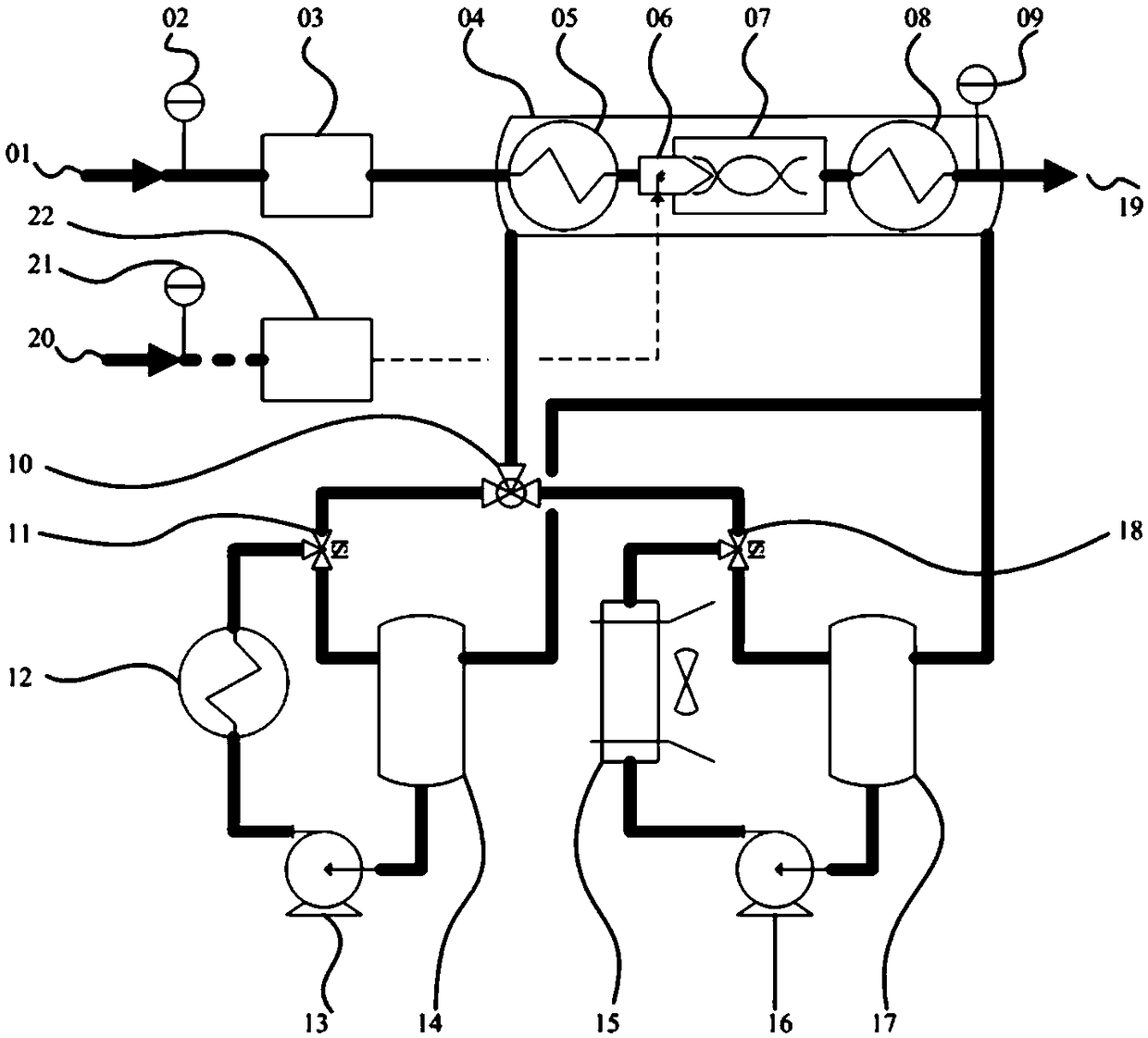
An apparatus and method for quickly regulating temperature and humidity of pipeline gas
ActiveCN109004250AQuick responseSmall thermal hysteresisFuel cell heat exchangeInternal combustion piston enginesFuel cellsChange control
The invention relates to an apparatus and a method for regulating pipeline gas, in particular to a technology for quickly regulating temperature and humidity of pipeline gas, belonging to the field offuel cells. The device comprises a gas and steam mixing system and a temperature regulating system, wherein the gas and steam mixing system is respectively provided with two pipelines of gas and steam, the two pipelines are confluent at the nozzle, after spraying-out through the nozzle, mixed temperature regulation is continued and then output is performed, and the temperature regulating system regulates the temperature inside a jacket by regulating the proportion of a heat agent and a refrigerant entering the jacket. The invention can improve the response speed, and in particular provide thequick change control of the temperature and humidity flow in the rated range for the humidifying device after thermal hysteresis is reduced.
Owner:大连锐格新能源科技有限公司
Sensing steering axis inclination and camber with an accelerometer
Method and apparatus for measuring and calculating wheel alignment angles. During the alignment process, lightweight and mechanically robust accelerometers in the measuring head are attached to the wheels of the vehicle. The output of the accelerometer can be compensated for temperature or thermal hysteresis effects through a memory lookup or a temperature based feedback control loop.
Owner:SNAP ON INC (US)
Clocked D/A converter
A digital-to-analog converter is disclosed, comprising an input / output circuit, a bistable circuit connected with the input / output circuit, a clock circuit connected with the input / output circuit and the bistable circuit, and a current generator circuit connected with the clock circuit. The clock circuit acts as a switch, providing current from the current generator either to the input / output circuit or to the bistable circuit. The digital input signal switches when the current generator provides current to the bistable circuit, and switching of the input signal is asserted at the output of the converter when the current generator provides current to the input / output circuit. Therefore, switching of a clock circuit signal, rather than switching of the digital input signal determines switching of the output signal, in order to reduce intersymbol interference of the converter associated with thermal hysteresis of some of the components of the converter.
Owner:HRL LAB
Shape memory device for changing shape at small temperature changes
With the use of shape memory elements a series of devices can be made which change shape at small changes of the environmental temperature. The devices may be composed of a shape memory element and a bias element, in such a way that the thermal hysteresis of the device becomes lower than the intrinsic thermal hysteresis of the shape memory element. The devices may be used in jewelry that is adapted to change shape or configuration when subjected to temperatures in the region of the body of a wearer.
Owner:菲利普·巴萨米安 +1
Fastening ring made of wide thermal hysteresis Ti-Ni-based shape-memory alloy, preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN1763233AFasten the connectionImprove connection strengthOther manufacturing equipments/toolsHose connectionsElectrical resistance and conductanceShape-memory alloy
The present invention discloses one kind of fastening ring of wide heat hysteresis TiNi-base shape memory alloy and its preparation and apply. The alloy consists of in atom% Ti 42-47, Ni 44-49, Nb 6-13 and Zr 0.1-3. The preparation process includes smelting in vacuum MF inducing electric furnace and casting ingot; homogenizing at 800-1000 deg.c for 3-5 hr; forging at 800-900 deg.c; hot rolling at 800-900 deg.c; annealing at 800-900 deg.c for 10-60 min and cooling inside the furnace to room temperature; and machining to obtain finished product. The present invention realizes fastening and connection by means of the recovering characteristic of shape memory alloy, and the fastening and connection method has the advantages of high strength, small connection resistance, etc.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Semiconductor device and method of fabrication thereof
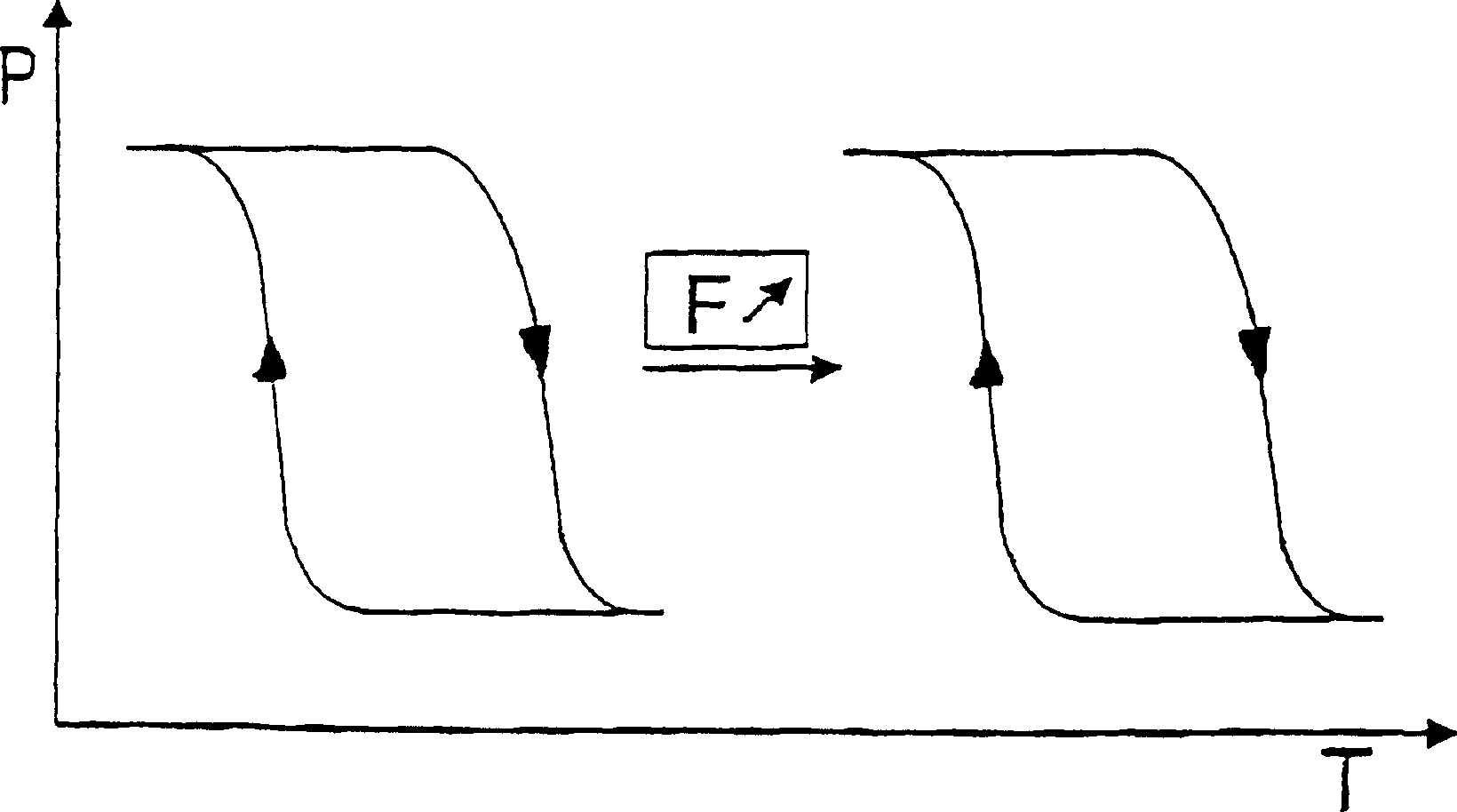
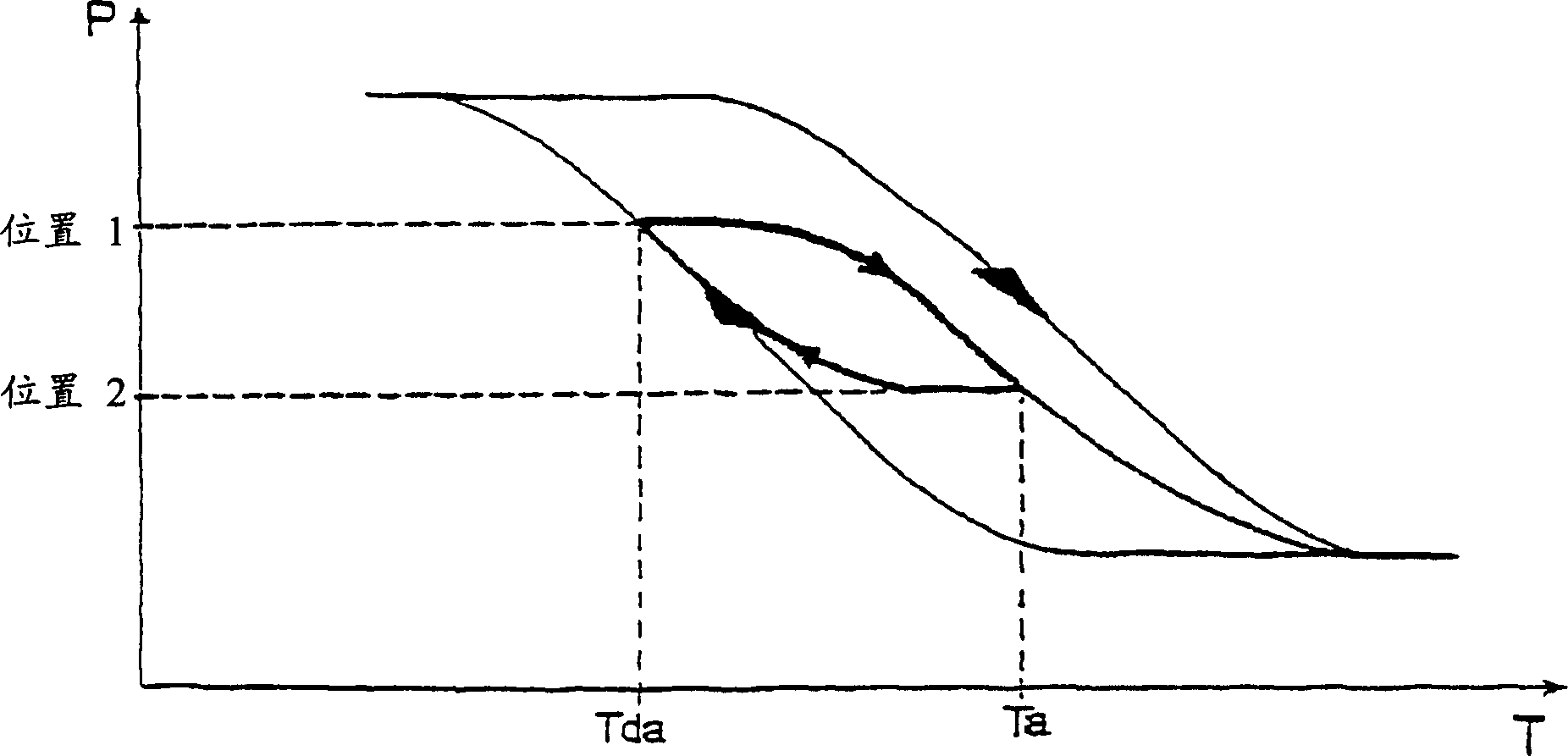
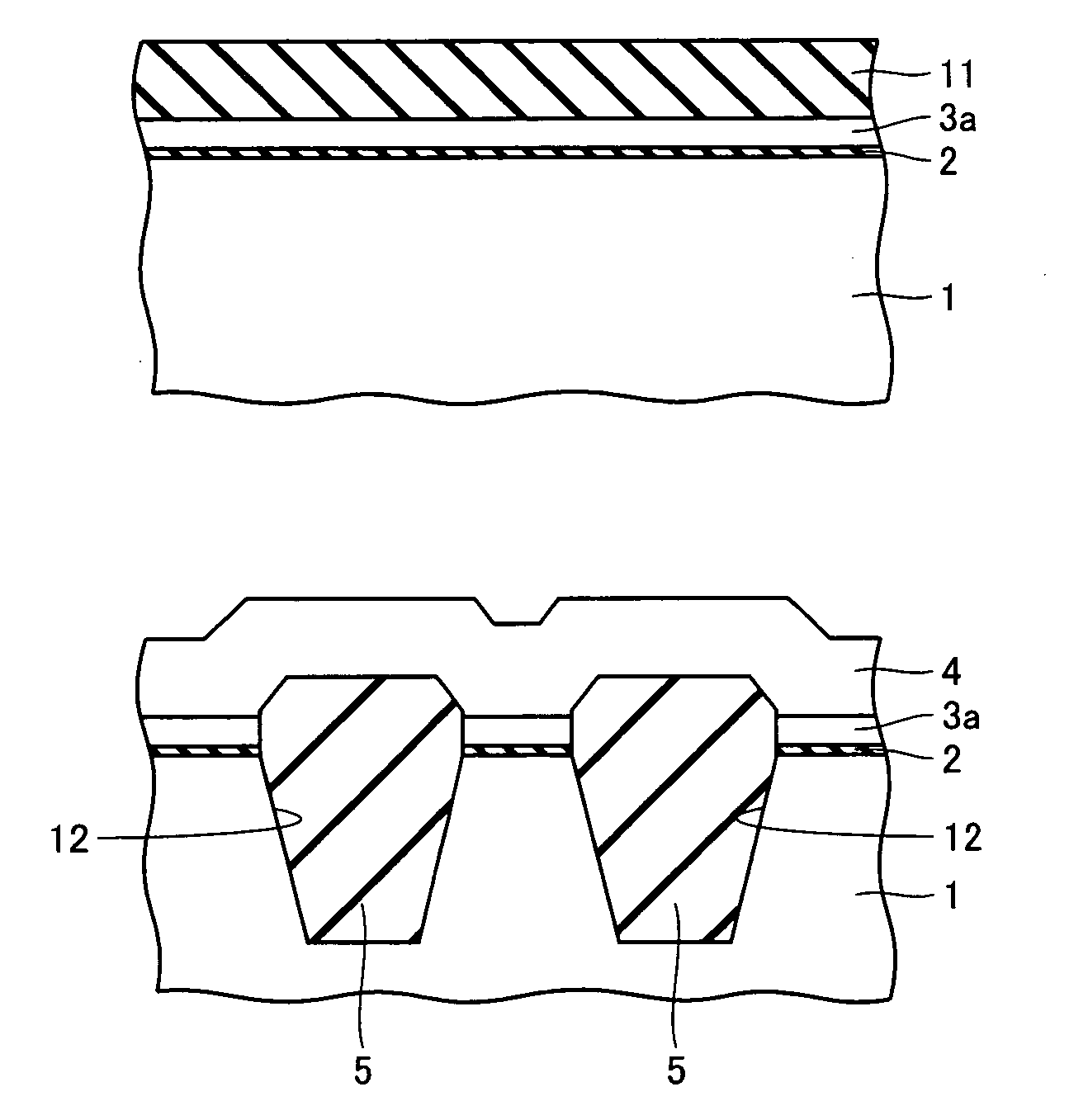
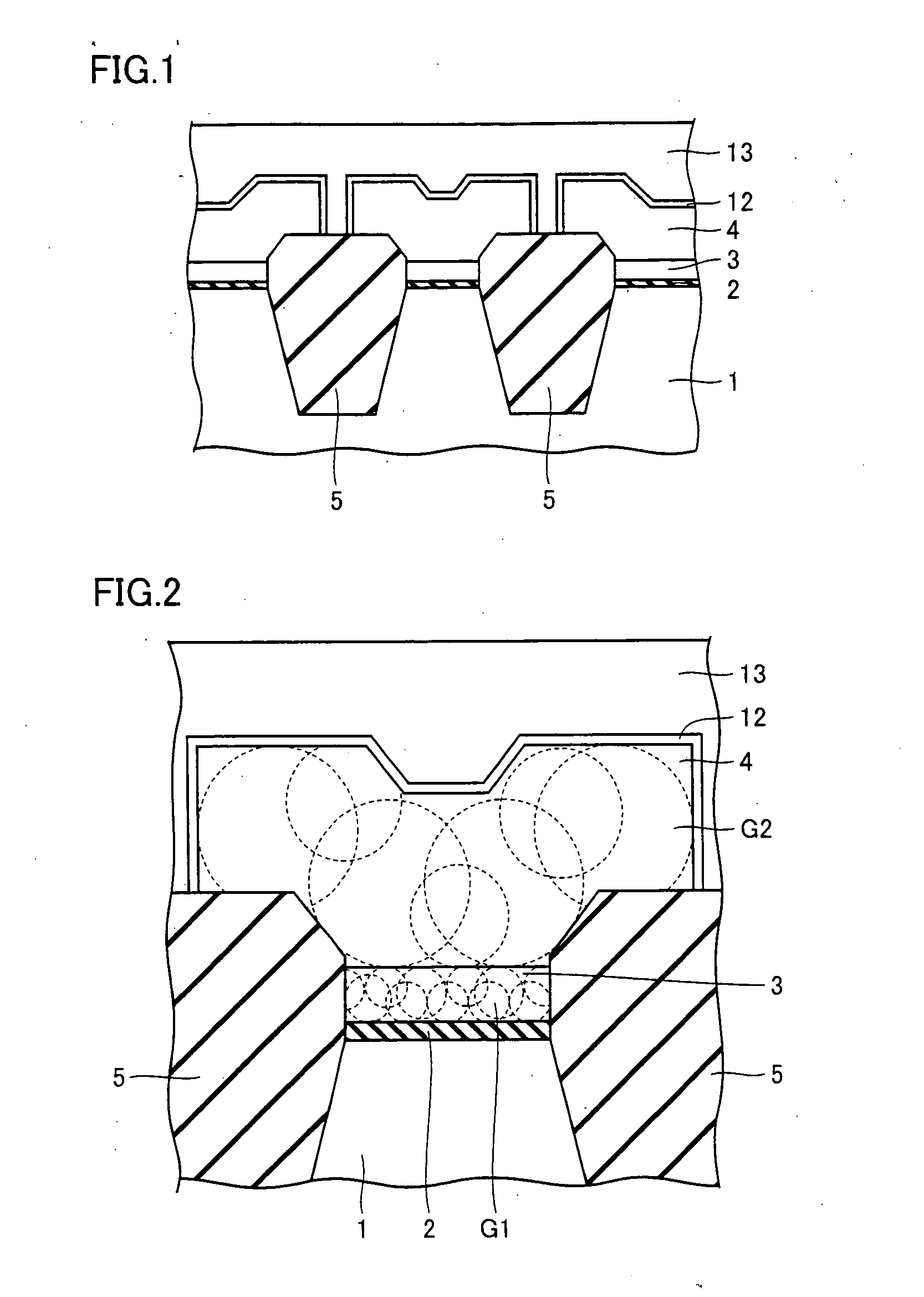
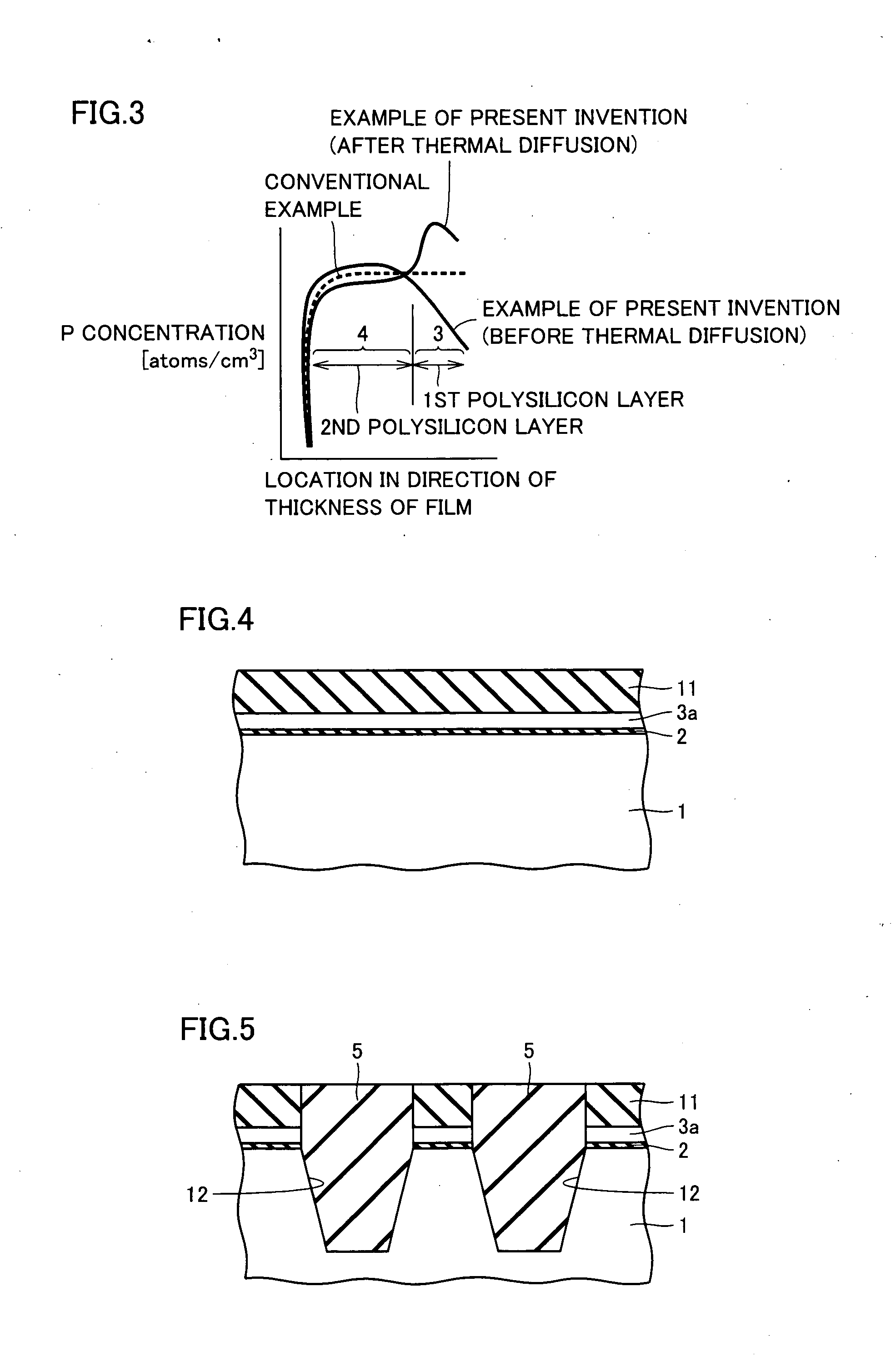
InactiveUS20050287777A1Improve equipment performanceAvoid distributingSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDevice materialThermal hysteresis
A method includes the steps of: introducing insulation film into a trench to provide a trench isolation; planarizing the trench isolation to expose a passivation film; and removing the passivation film and depositing a second silicon layer on a first silicon layer and the trench isolation; and in the step of depositing the first silicon layer the first silicon layer is an undoped silicon layer and in the step of depositing the second silicon layer the second silicon layer is a doped silicon layer or an undoped silicon layer subsequently having an impurity introduced thereinto or the like and thermally diffused through subsequent thermal hysteresis into the first silicon layer.
Owner:RENESAS TECH CORP
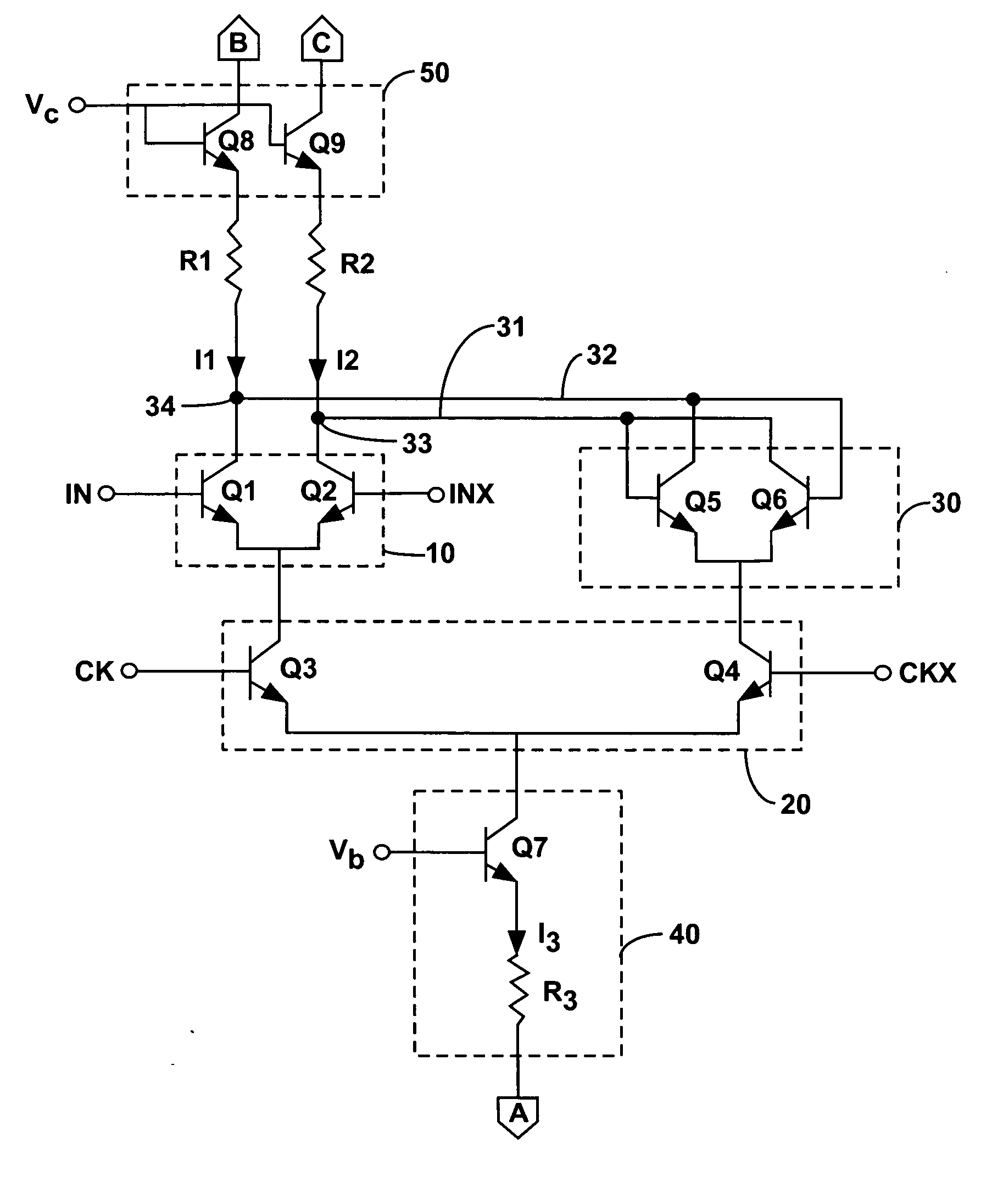
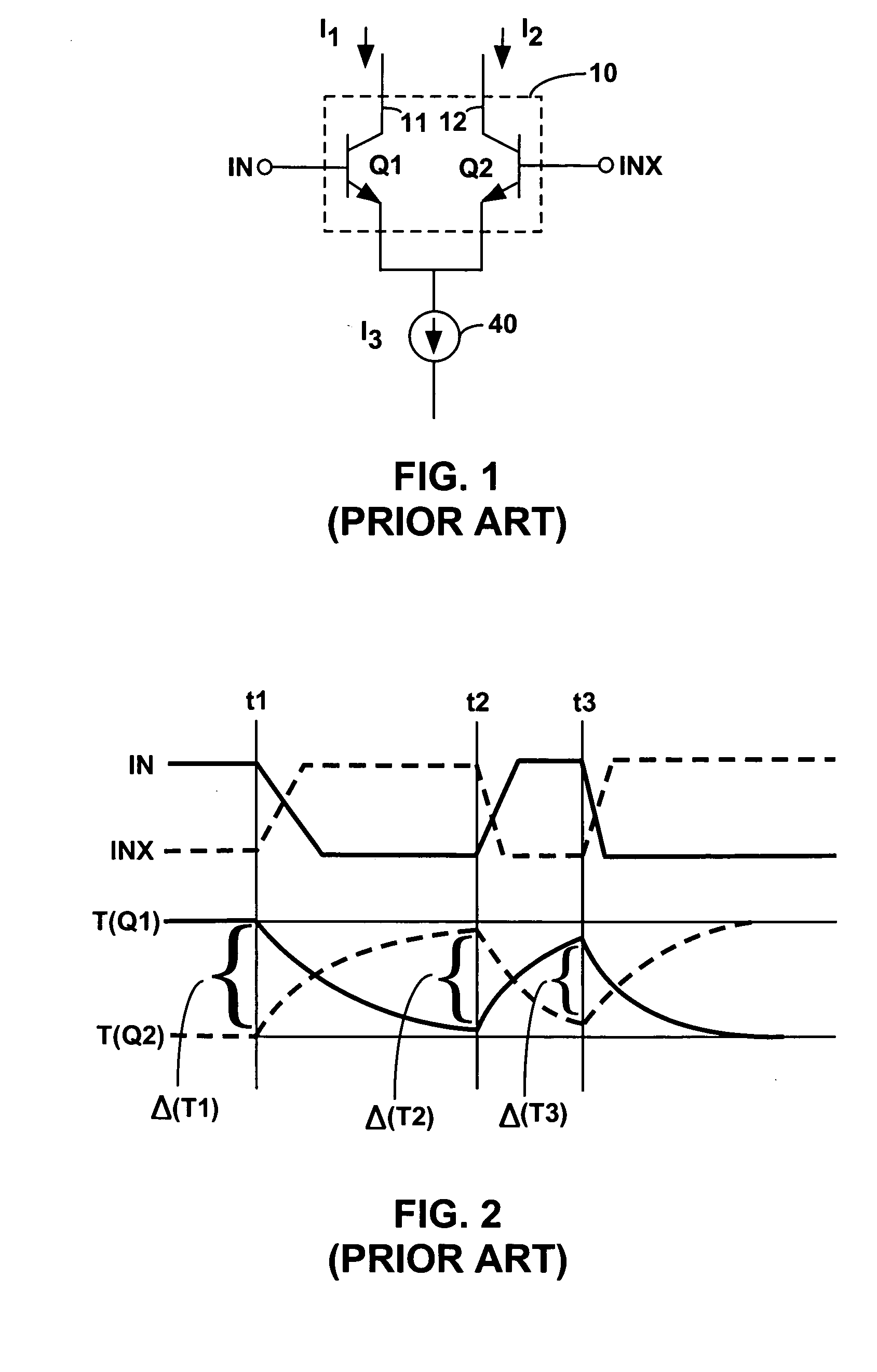
Low thermal hysteresis bandgap voltage reference
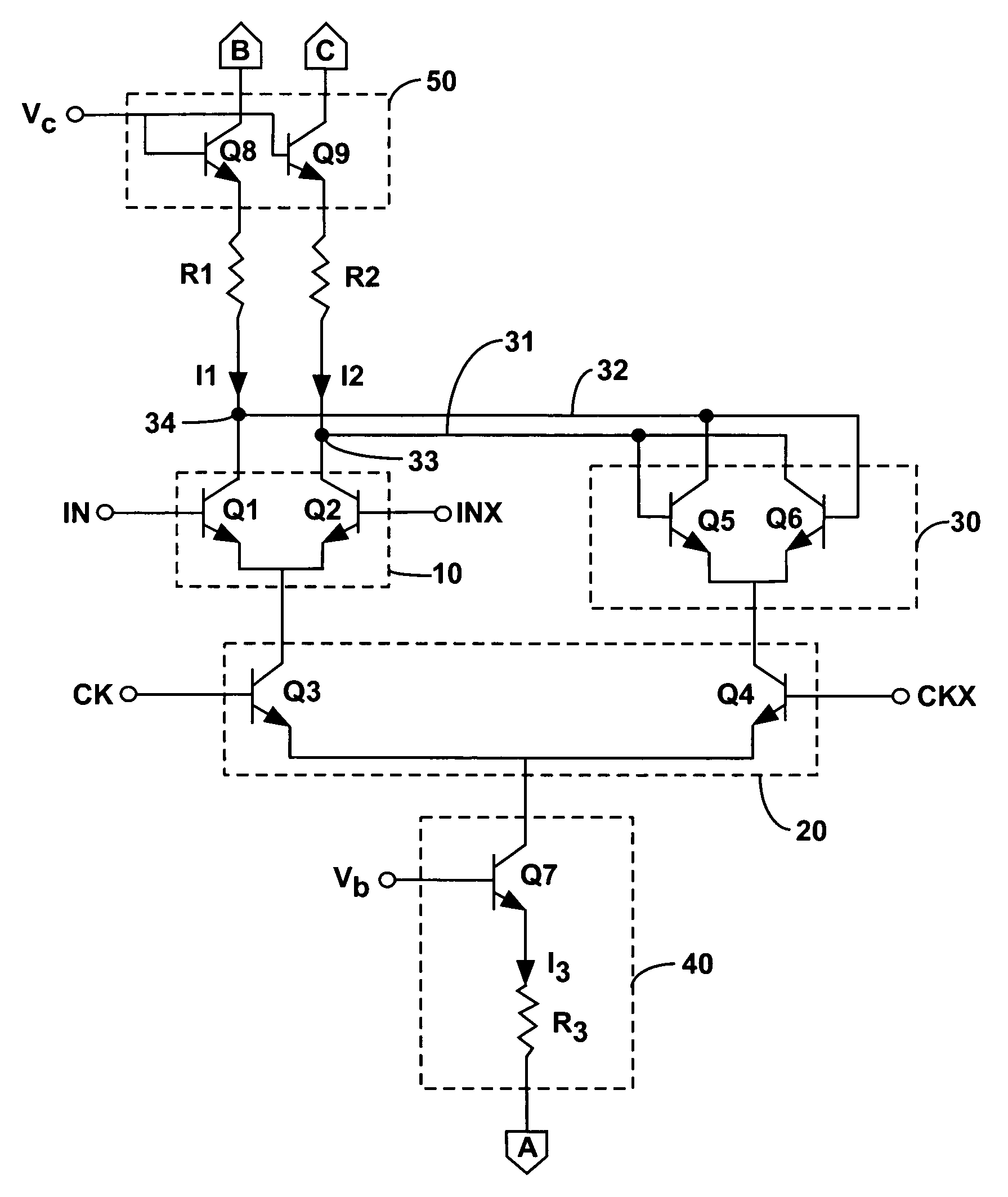
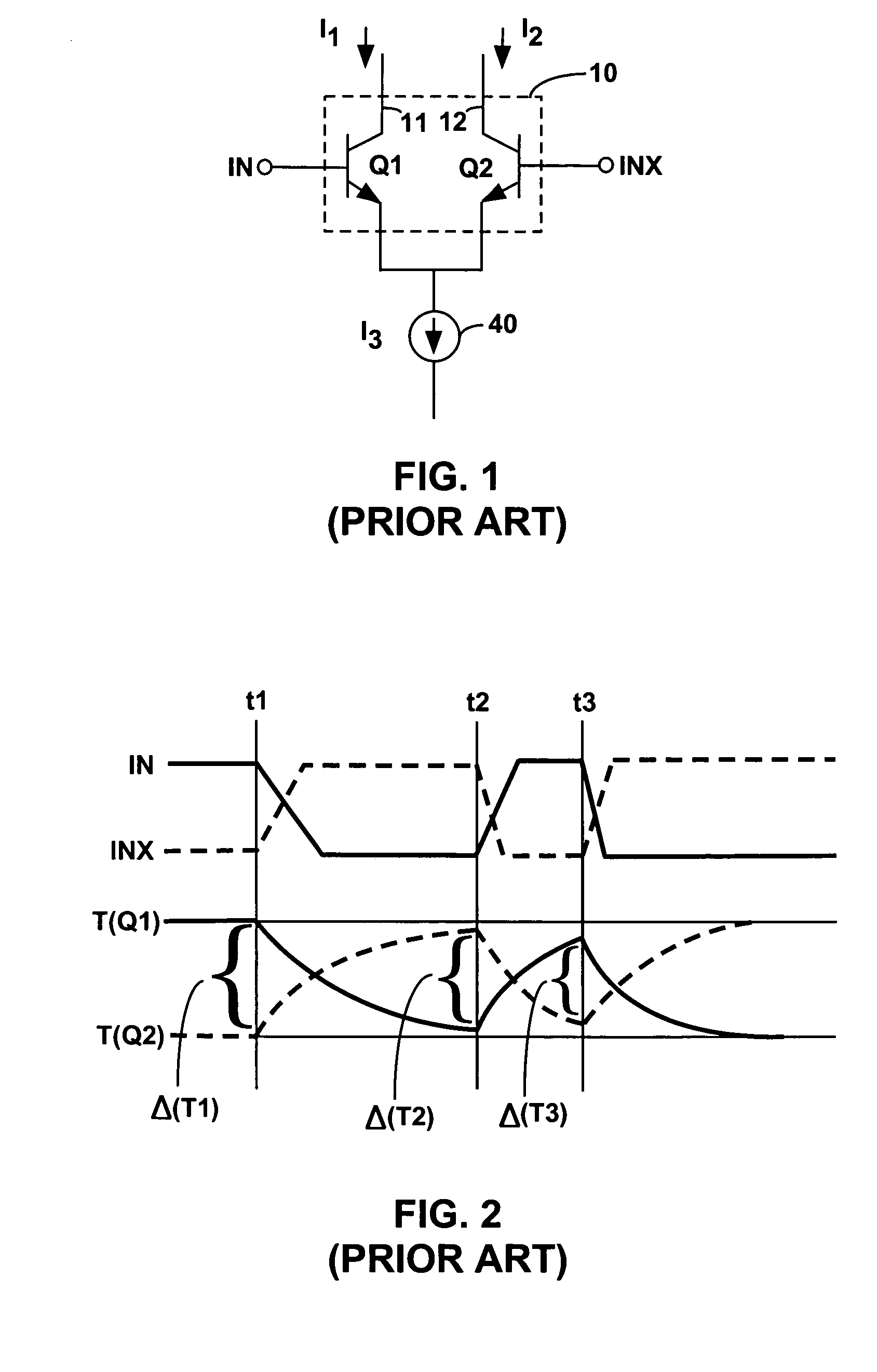
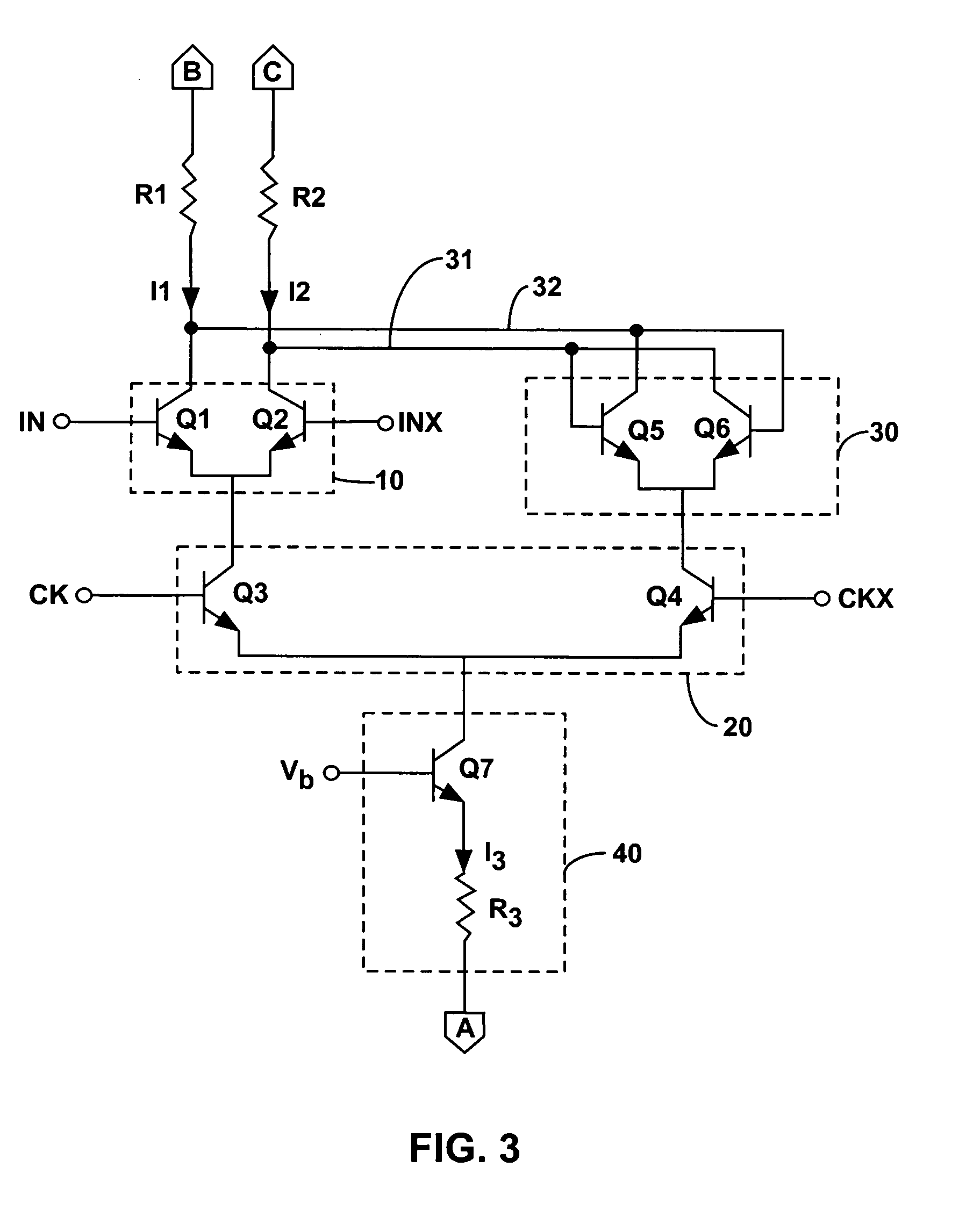
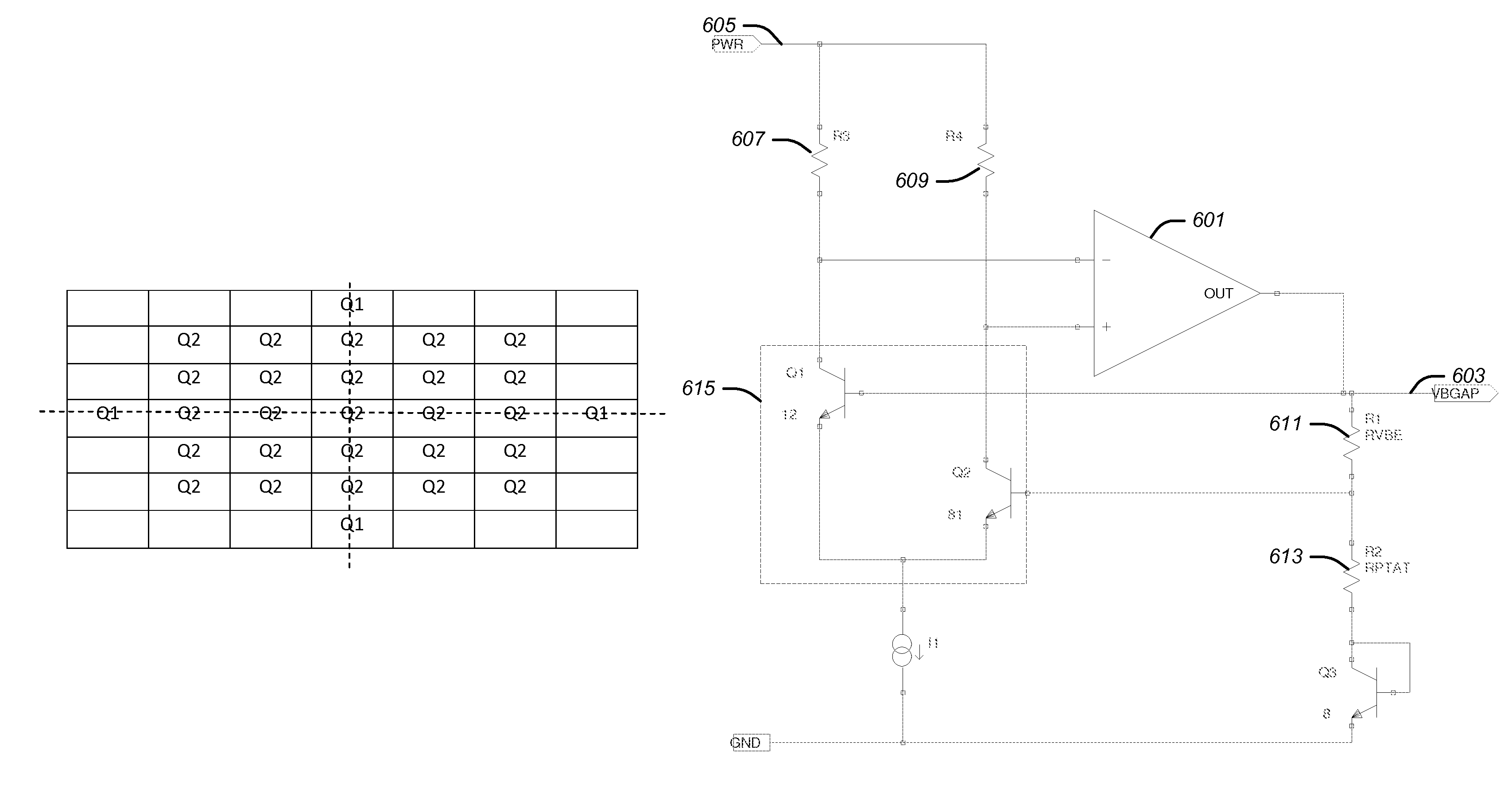
ActiveUS7772920B1Electronic switchingGenerating/distributing signalsThermal hysteresisVoltage reference
A first and a second group of individual transistors in a voltage reference may collectively function as a first and a second composite transistor with a first and a second emitter area equal to the combined areas of the emitters of the first and the second groups of individual transistors, respectively. The second emitter area may be larger than the first emitter area. The stability of the reference voltage may depend upon the stability of the ratio between the first emitter area and the second emitter area. The first group of individual transistors may not be at the center of an arrangement of the second group of individual transistors. The constant reference voltage may vary due to thermal hysteresis by less than 200 parts per million over a 40 degree centigrade temperature range.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INT UNLTD
Soft tooling forming method used for reinforcing rib and web plate co-bonding and application
InactiveCN110815857AAvoid the phenomenon of excessive thicknessAvoid Thermal HysteresisDomestic articlesFiberThermal hysteresis
The invention discloses a soft tooling forming method used for reinforcing rib and web plate co-bonding and application. Rubber and reinforced fiber prepreg are paved on a reinforcing rib metal fake part and a positioning device part to make soft tooling, and the soft tooling is used for reinforcing rib and web plate co-bonding. Compared with a traditional core mold forming method, the soft tooling can evenly and precisely transmit pressure applied by a hot pressure tank, the phenomenon of thickness overproof appearing in a composite part is avoided, meanwhile, the soft tooling is thin, and the thermal hysteresis effect of the reinforcing rib portion can be avoided. The forming quality of the composite product can be effectively ensured, the production yield and efficiency can be improved,meanwhile, the positioning device ensures the reinforcing rib and web plate relative position precision of the composite product obtained through reinforcing rib and web plate co-bonding, and the product quality is ensured.
Owner:航天海鹰(镇江)特种材料有限公司
Air supply type energy-saving electric heater
PendingCN107084423AHeating up fastHeat radiation transfer distanceLighting and heating apparatusElectric heating systemThermal hysteresisAirflow
The invention discloses an air supply type energy-saving electric heater which comprises a shell, wherein an air outlet is formed in the side surface of the shell; air feeding holes are formed in the bottom of the shell; an inner cavity of the shell is divided into a lower air flow circulating cavity and an upper heat isolation cavity; a cross flow fan, carbon fiber heating pipes and a hot air flow guide plate tilting towards the air outlet direction are arranged in the air flow circulating cavity in sequence from bottom to top; the cross flow fan and the carbon fiber heating pipes are connected with a controller; and the heat isolation cavity is filled with a heat isolation material. By the adoption of the carbon fiber heating pipes, the air supply type energy-saving electric heater disclosed by the invention has the advantages of high heating speed, low thermal hysteresis, uniform heating, long heat radiation transmission distance, high heat exchange speed and the like.
Owner:于宝军
Process for producing glass optical element and method for determining glass component of glass blank
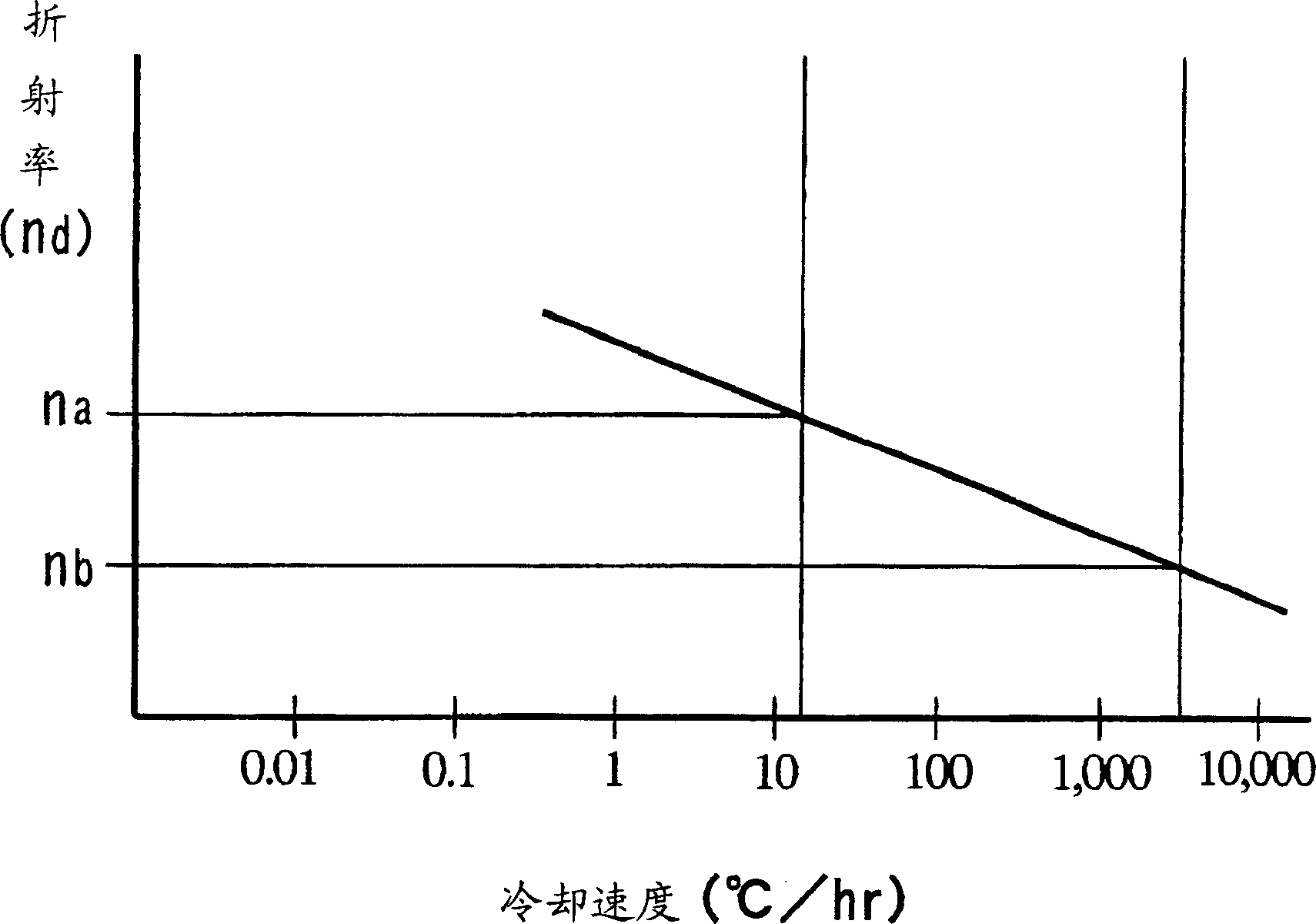
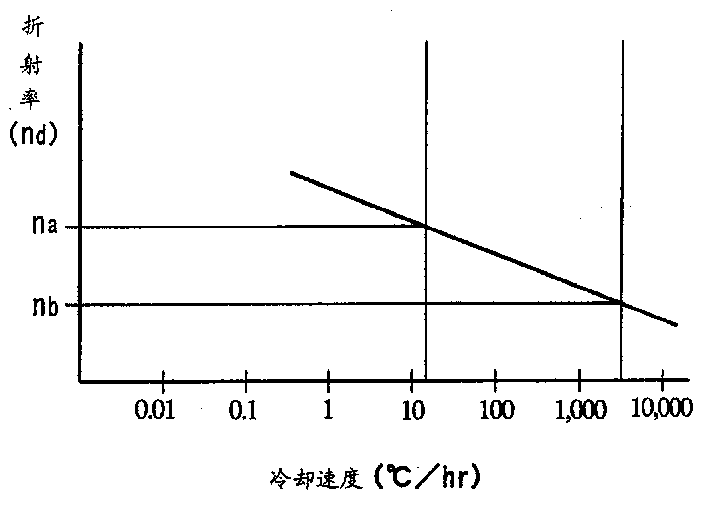
InactiveCN1440942AHigh precision manufacturingThe annealing process is omitted or shortenedGlass pressing apparatusLensComposition processRefractive index
Owner:HOYA CORP
Room temperature magnetic refrigeration alloy material and preparation method therefor
ActiveCN105390223AControl crystal structureLarge adjustable temperature widthInorganic material magnetismInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureElectric arc furnaceManganese
The invention discloses a room temperature magnetic refrigeration alloy material. The room temperature magnetic refrigeration alloy material is represented by the molecular formula of Mn1-XAlXCoGe; and the alloy material comprises 33.3-34.4% of manganese element, 0.6-2.7% of aluminum element, 32.8-33.3% of cobalt element, and 30.2-32.7% of germanium element in percentage by mass. The invention also provides a preparation method for the room temperature magnetic refrigeration alloy material. The preparation method comprises the steps of adding reactive materials into a vacuum arc furnace, vacuumizing until the pressure is lower than 10<-4>Pa, and pumping argon gas in; smelting the sample repeatedly; and taking out the sample and cooling the sample, putting the sample into a high-temperature-resistant quartz glass tube, vacuumizing, inflating the high-temperature-resistant quartz glass tube with high-purity argon for performing gas washing, then putting the high-temperature-resistant quartz glass tube into a furnace type box, taking the sample out and performing annealing to obtain the room temperature magnetic refrigeration alloy material. According to the preparation method, the Curie temperature of the alloy is obviously reduced to the temperature close to the room temperature, the thermal hysteresis phenomenon occurring close to phase change is effectively avoided, and a relatively wide adjustable temperature range close to the room temperature is obtained.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIVERSITY OF ELECTRIC POWER
Semiconductor device and method for manufacturing the semiconductor device
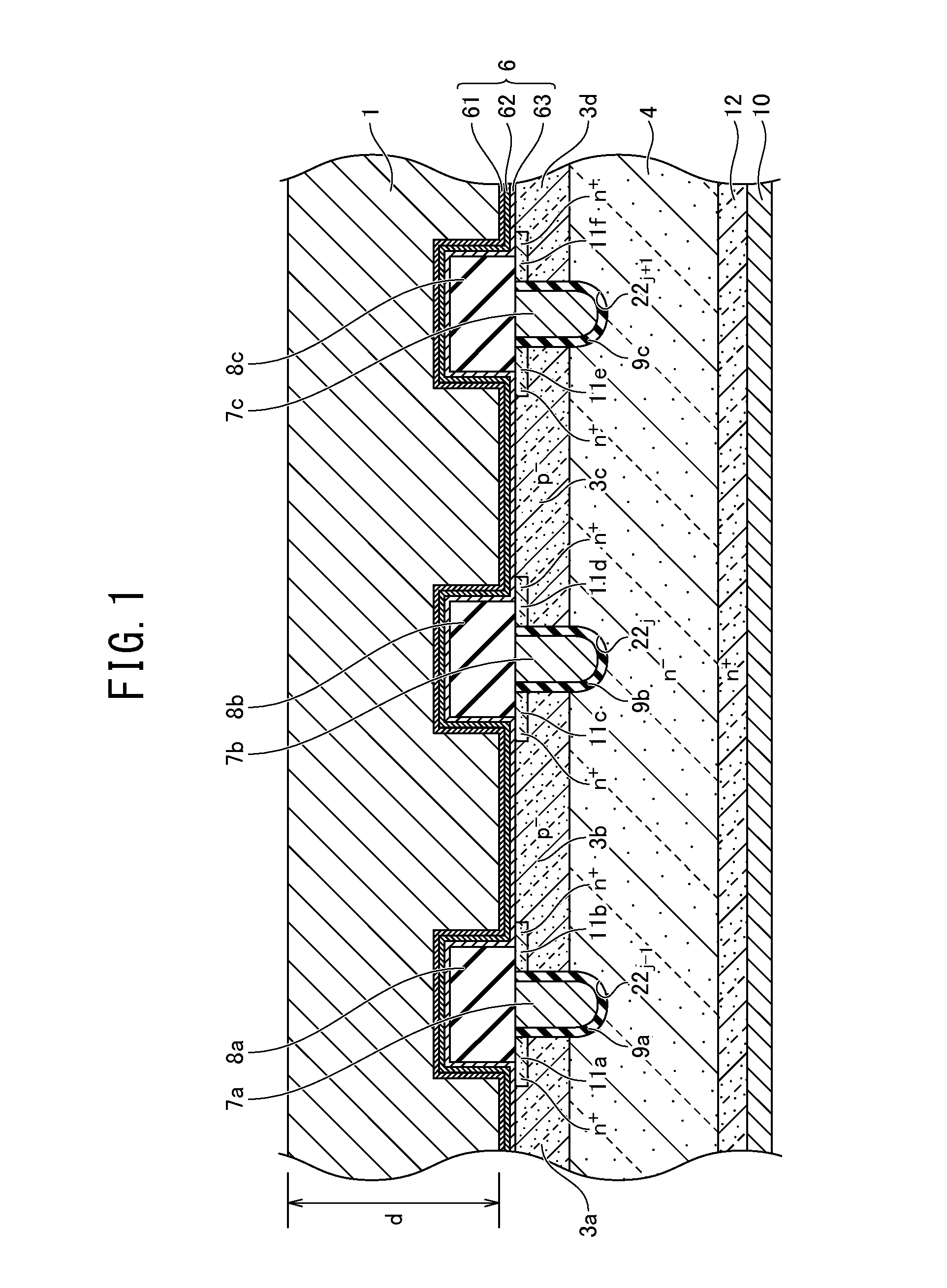
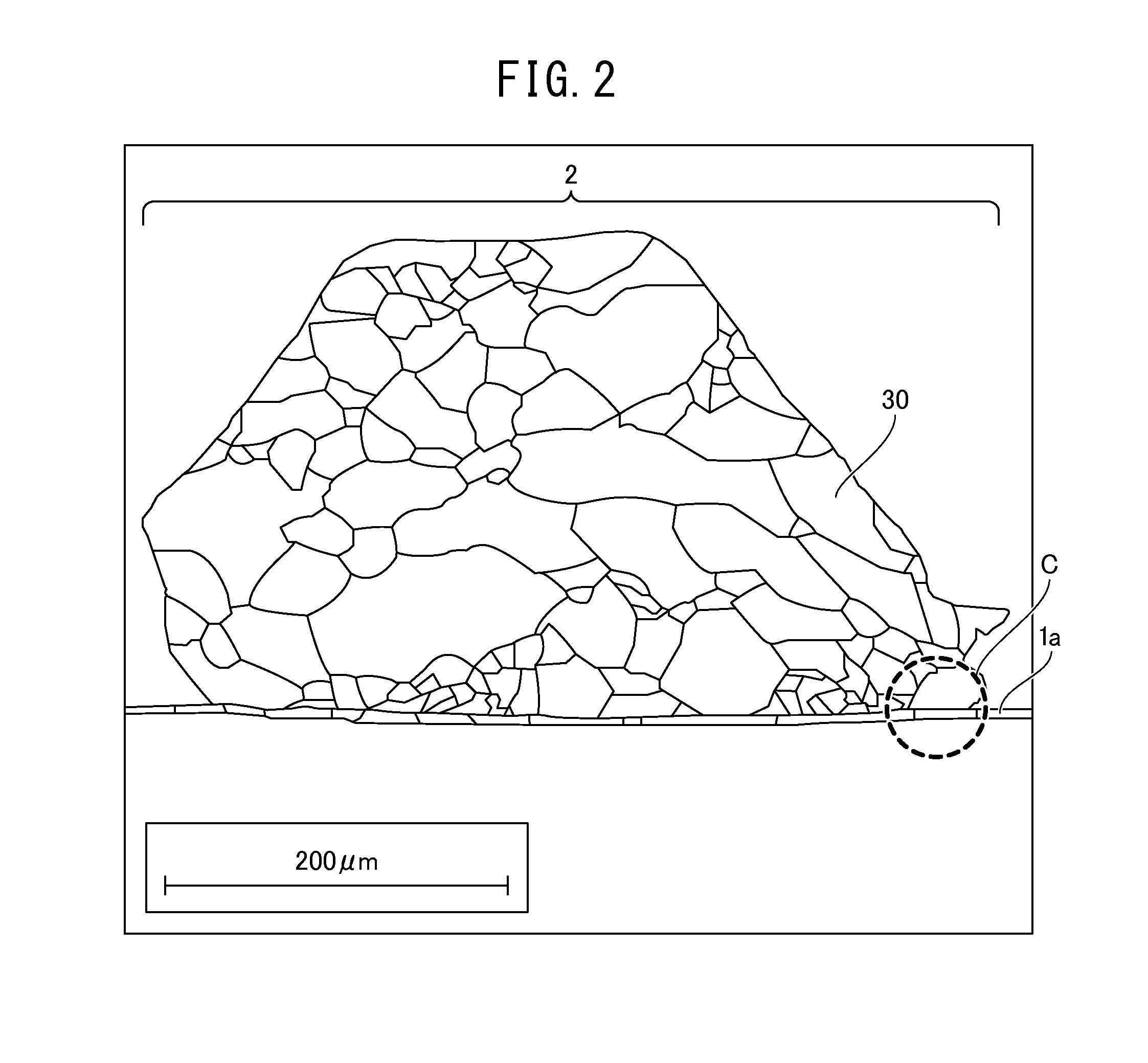
ActiveUS20160163806A1Suppressing deterioration of gate threshold voltageThyristorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSemiconductor chipThermal hysteresis
A deterioration of a gate threshold voltage, which is caused by a stress and a thermal hysteresis when wire bonding for a surface of an electrode layer of a semiconductor device is performed, can be suppressed. The semiconductor device includes a metallic film provided at a surface of a semiconductor chip, and a wire bonded to an upper surface of the metallic film. The metallic film has a plurality of grains, particle diameters of the grains are substantially equal to or more than a thickness of the metallic film.
Owner:FUJI ELECTRIC CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com