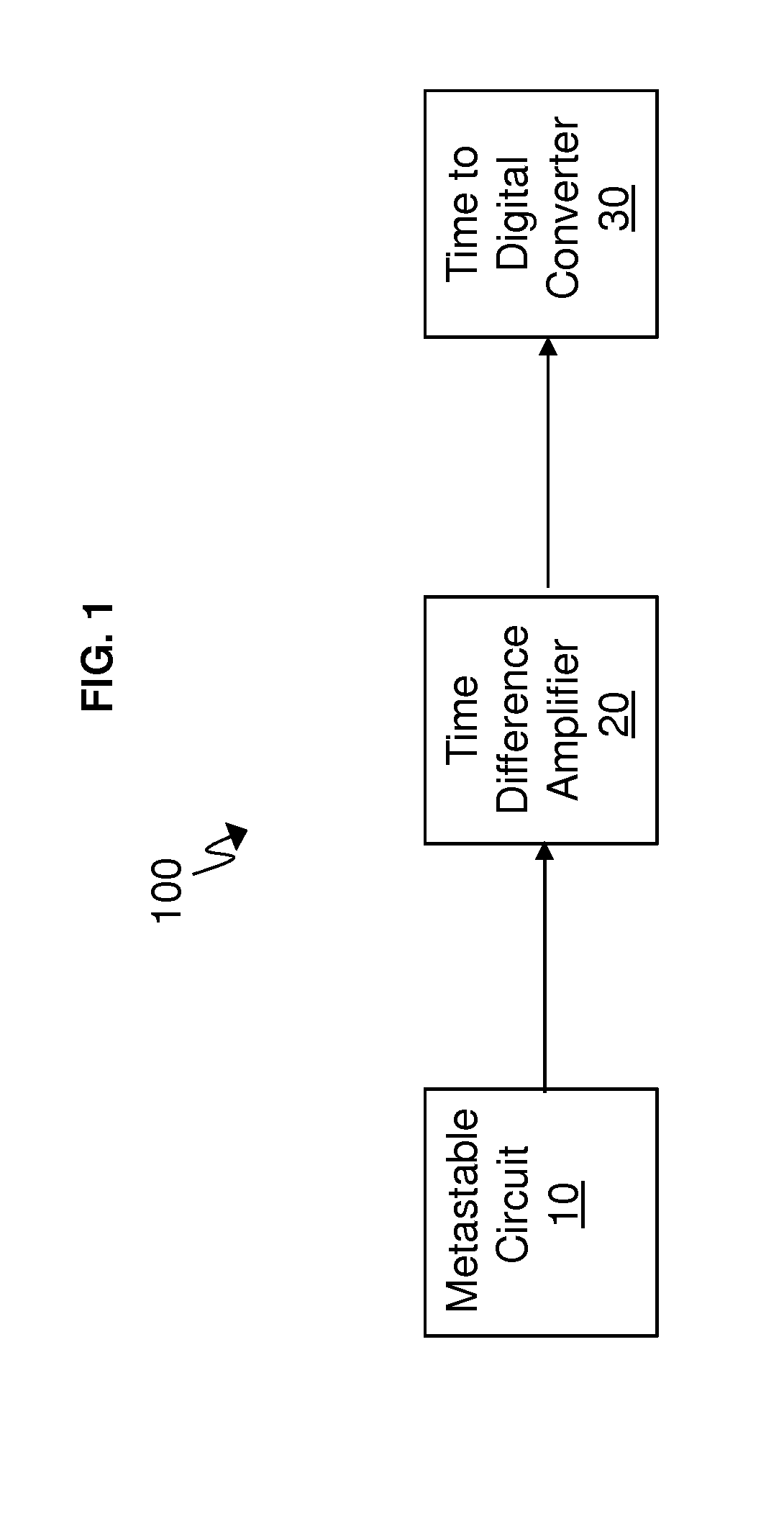
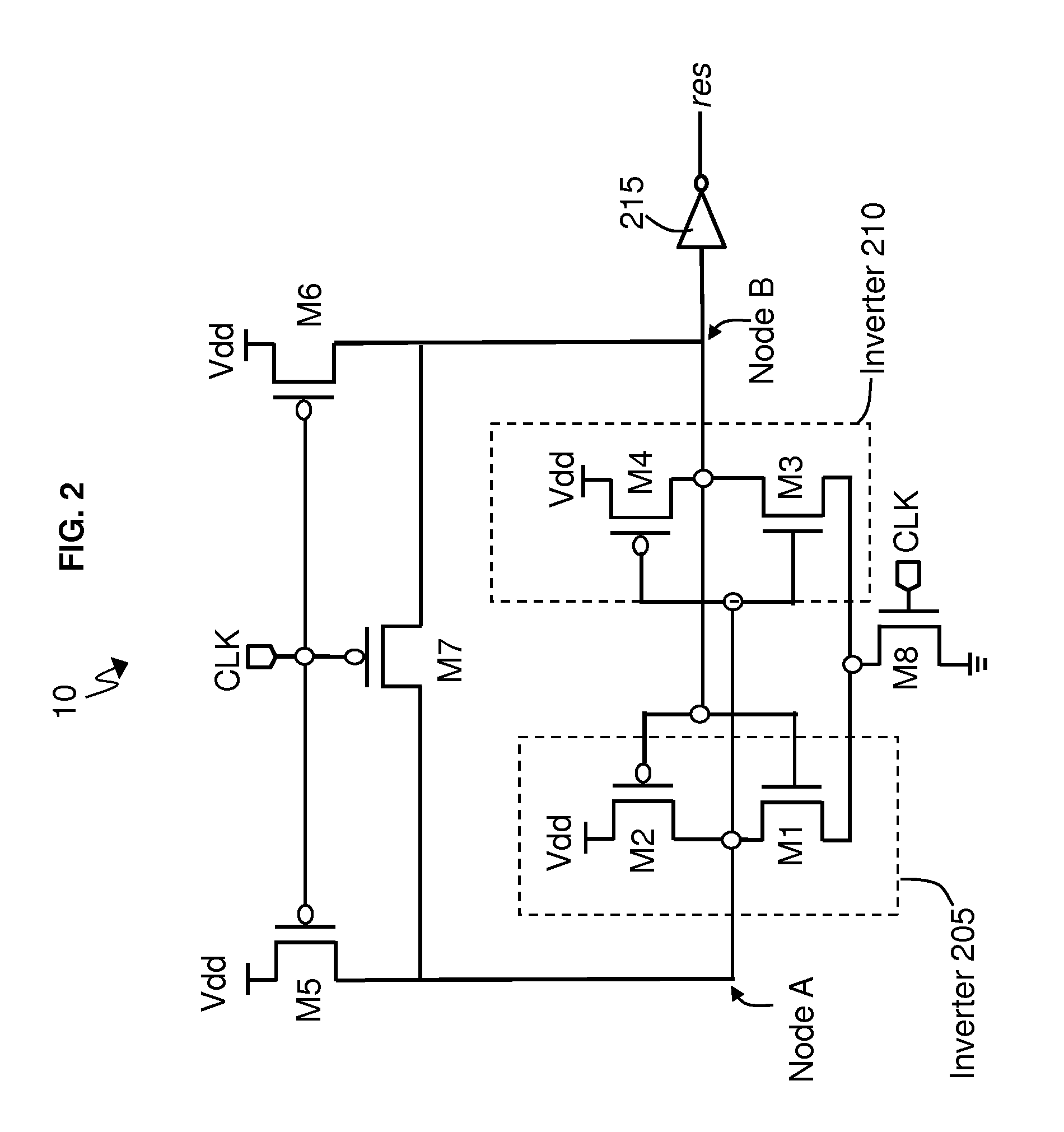
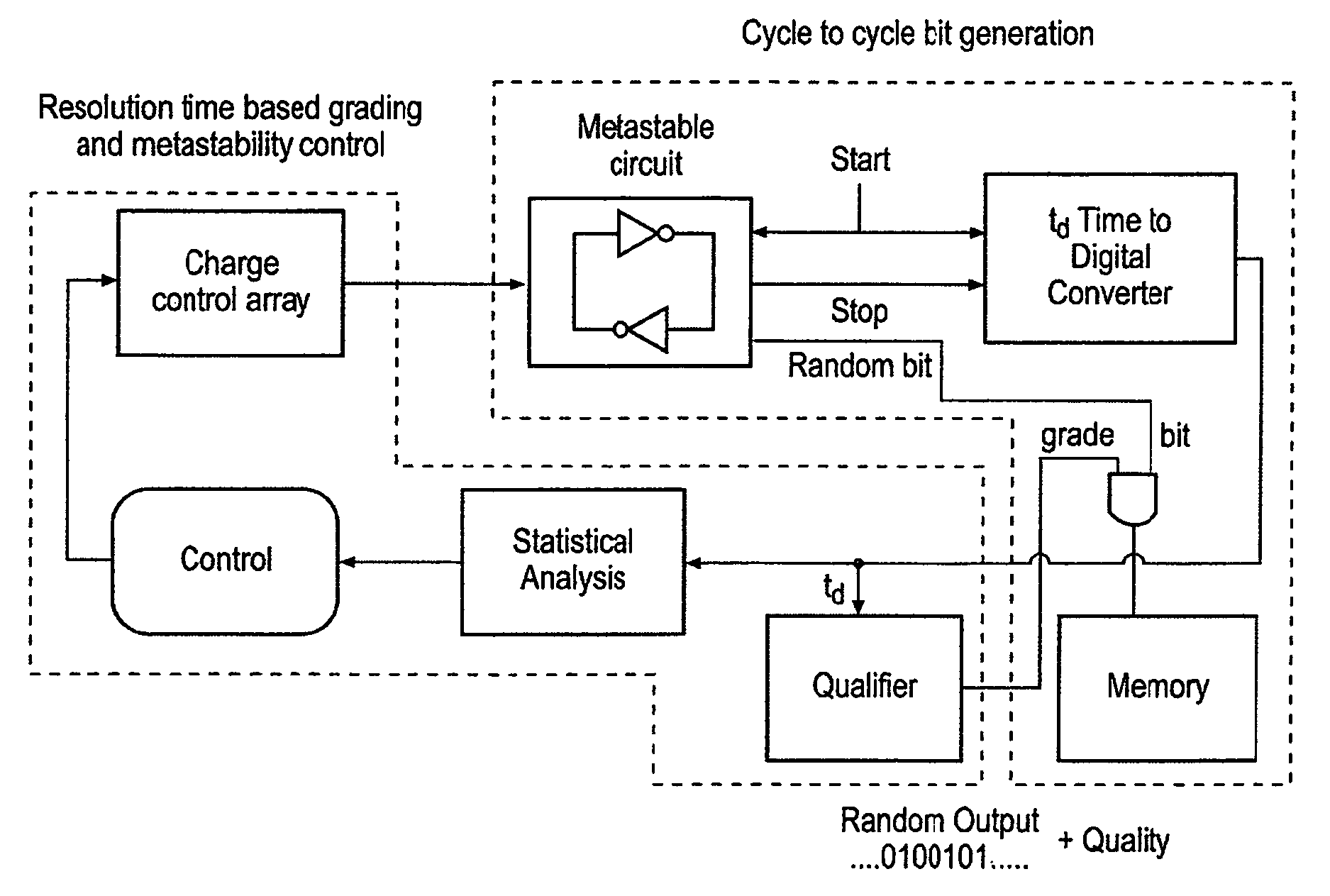
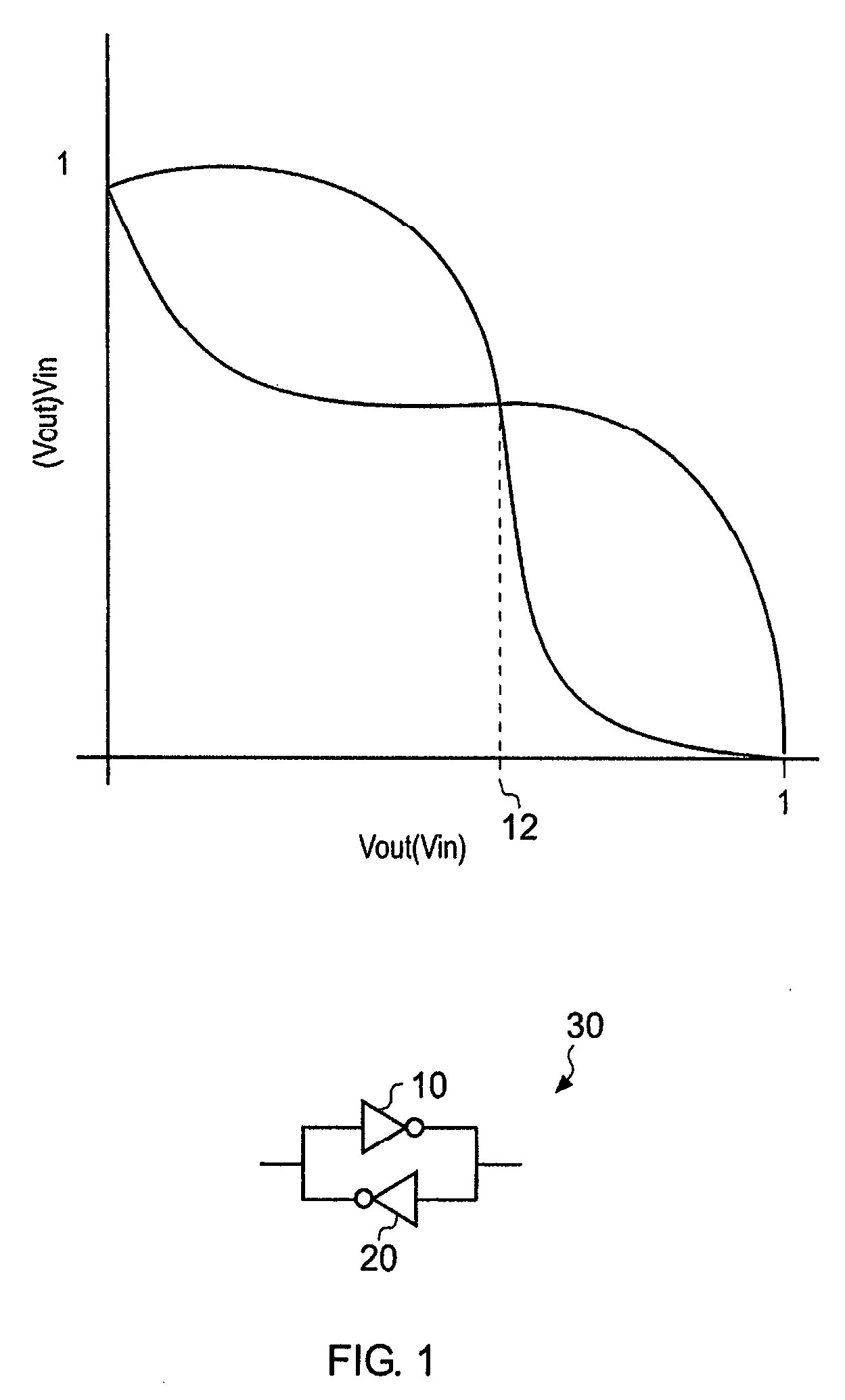
Patents
Literature
175 results about "Bistable circuits" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
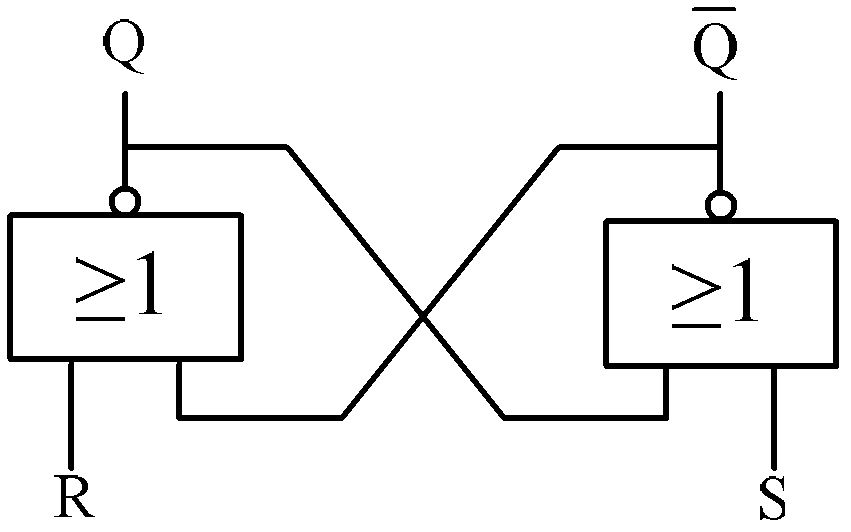
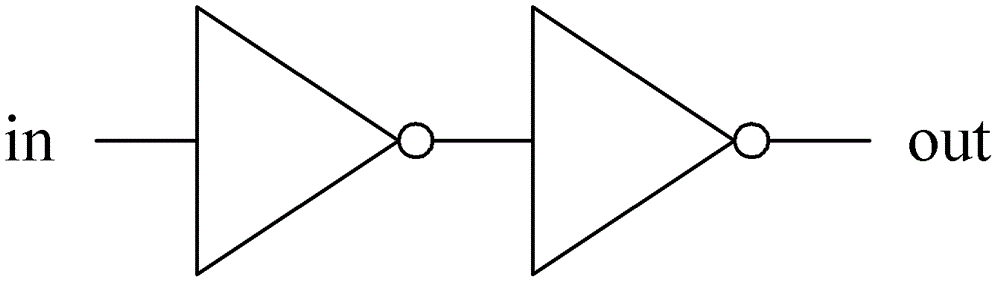
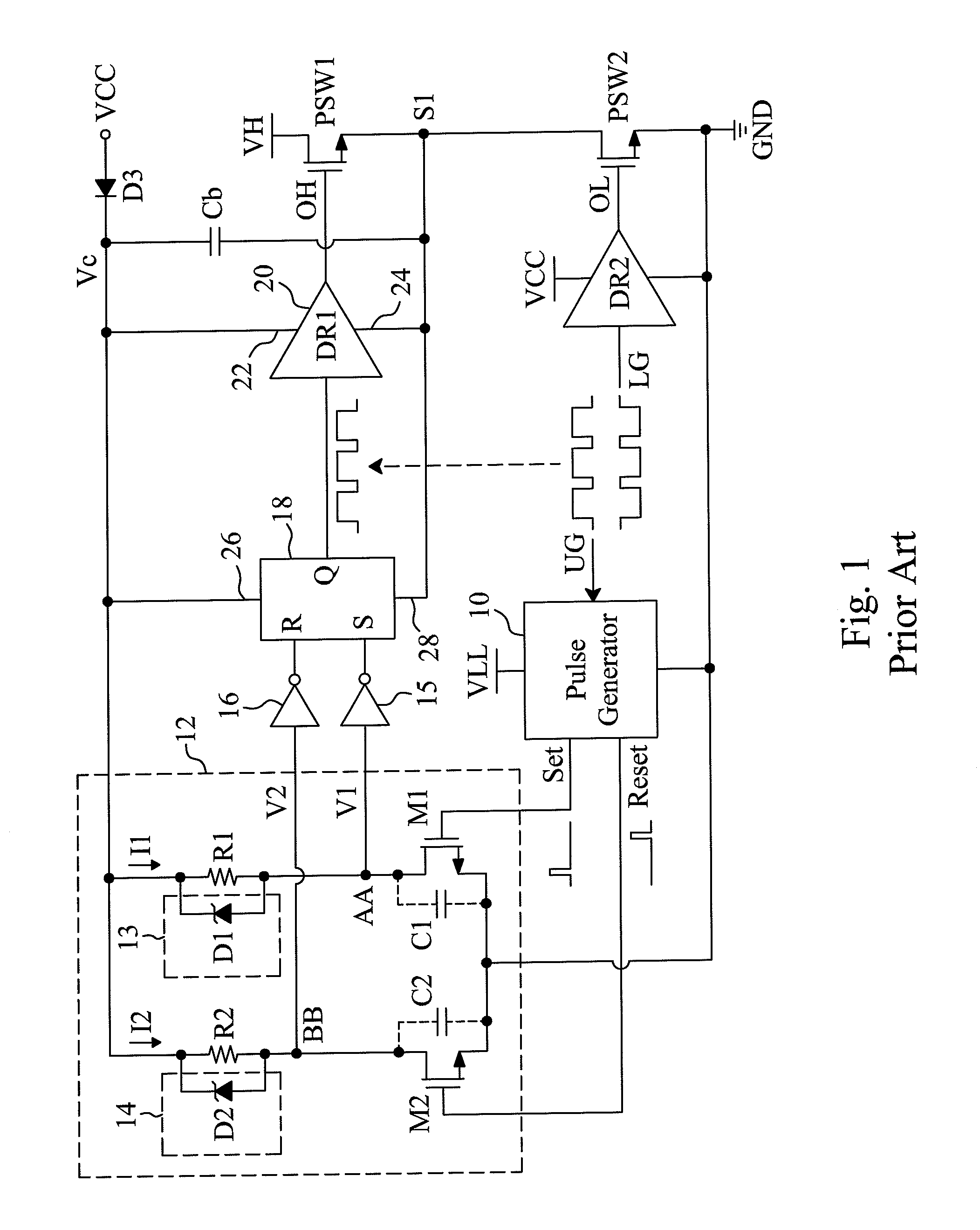
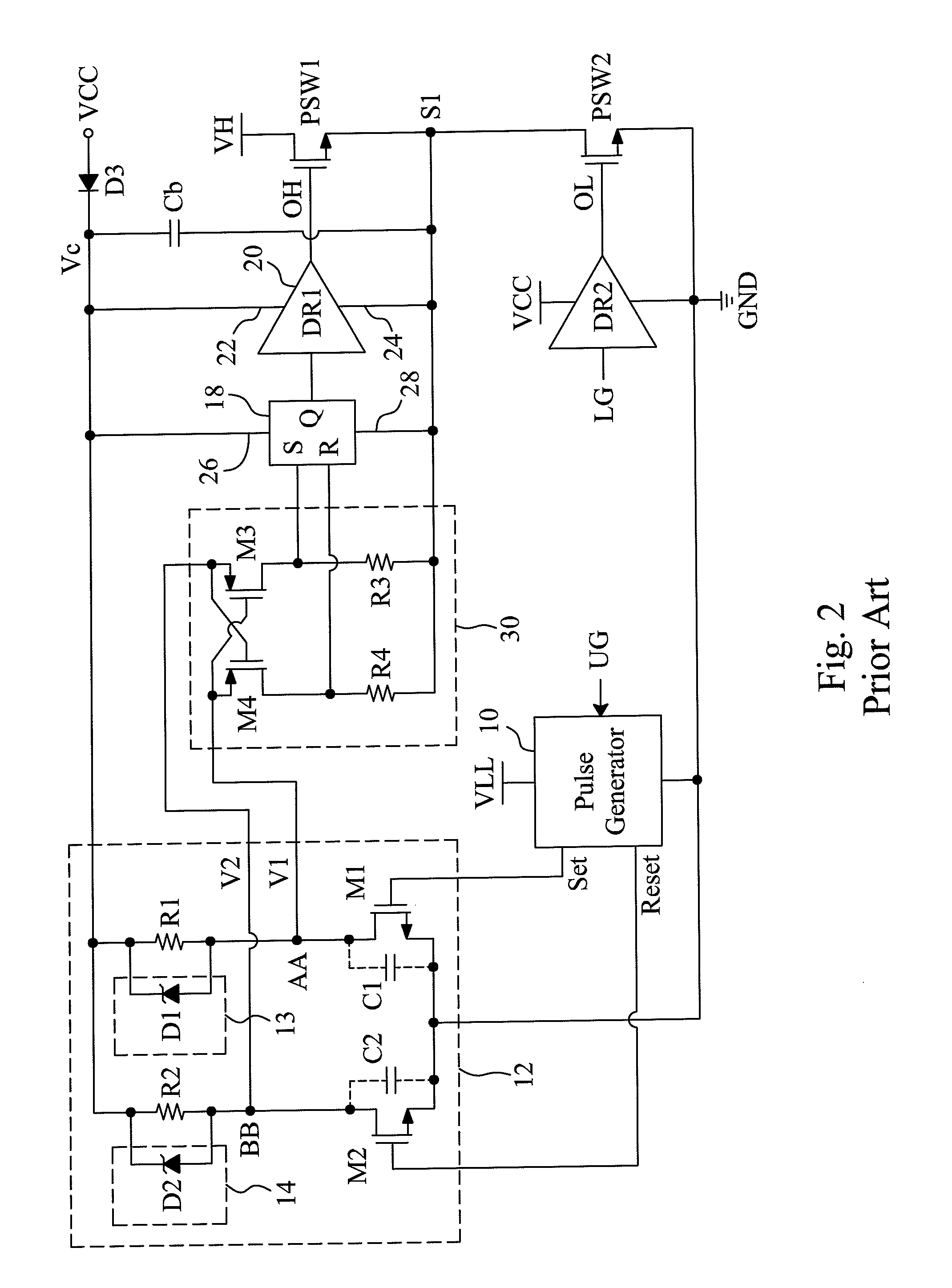
The bistable circuit is a function of a flip flop. It's able to store bits indefinitely unless desired to be changed. It can be used basically for any circuit in where you want manual control over outputs which you want to keep stable states unless you trigger it to change.
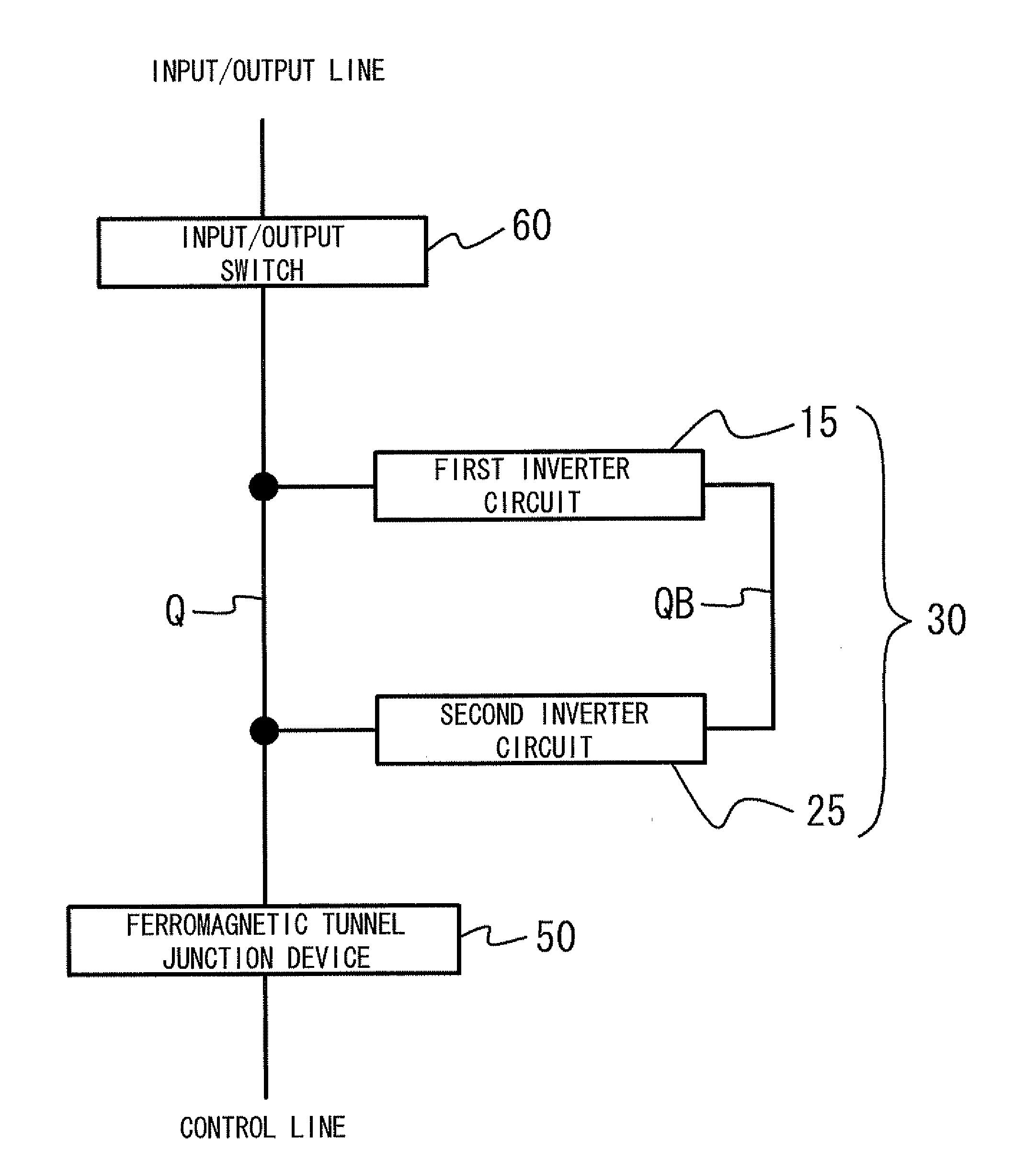
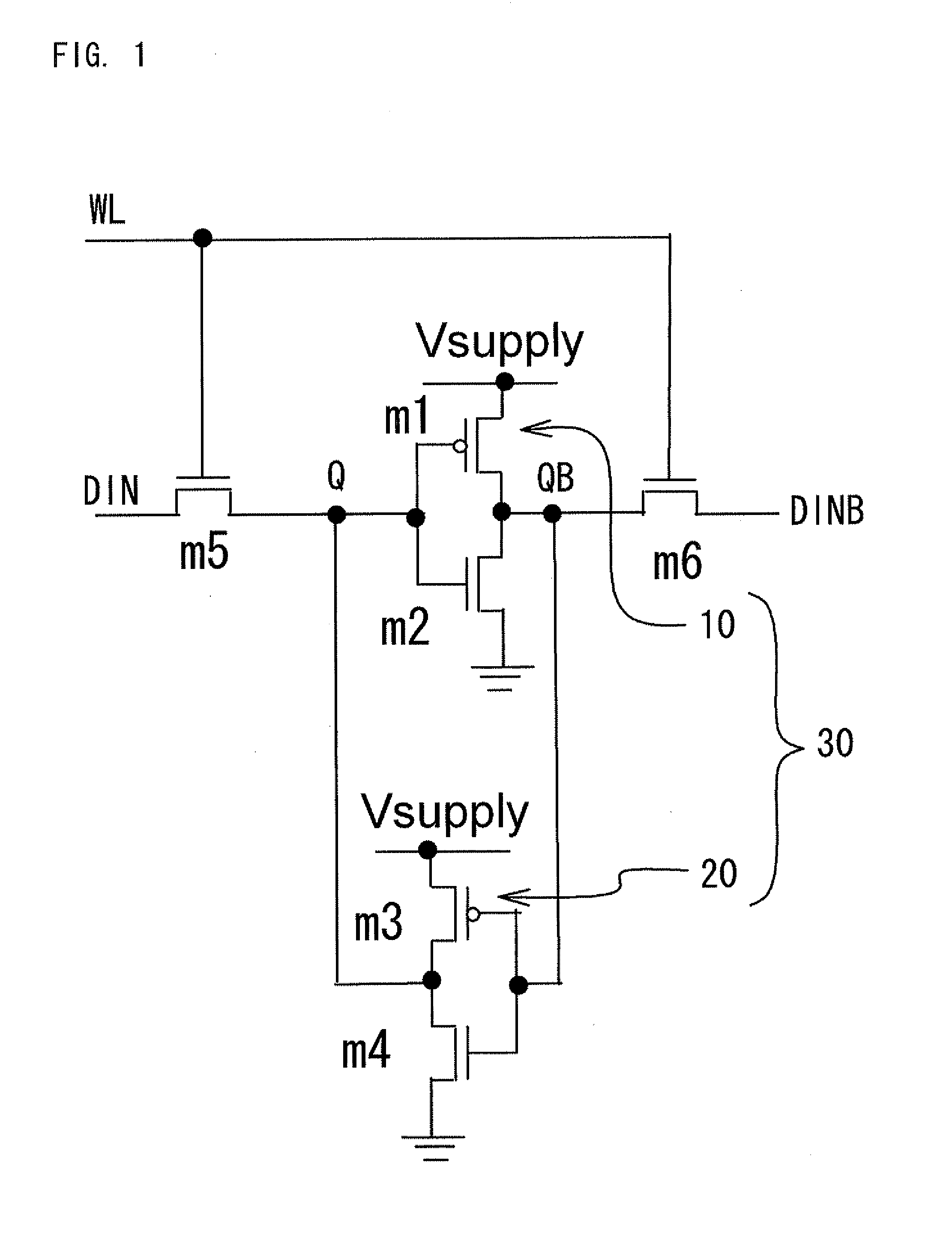
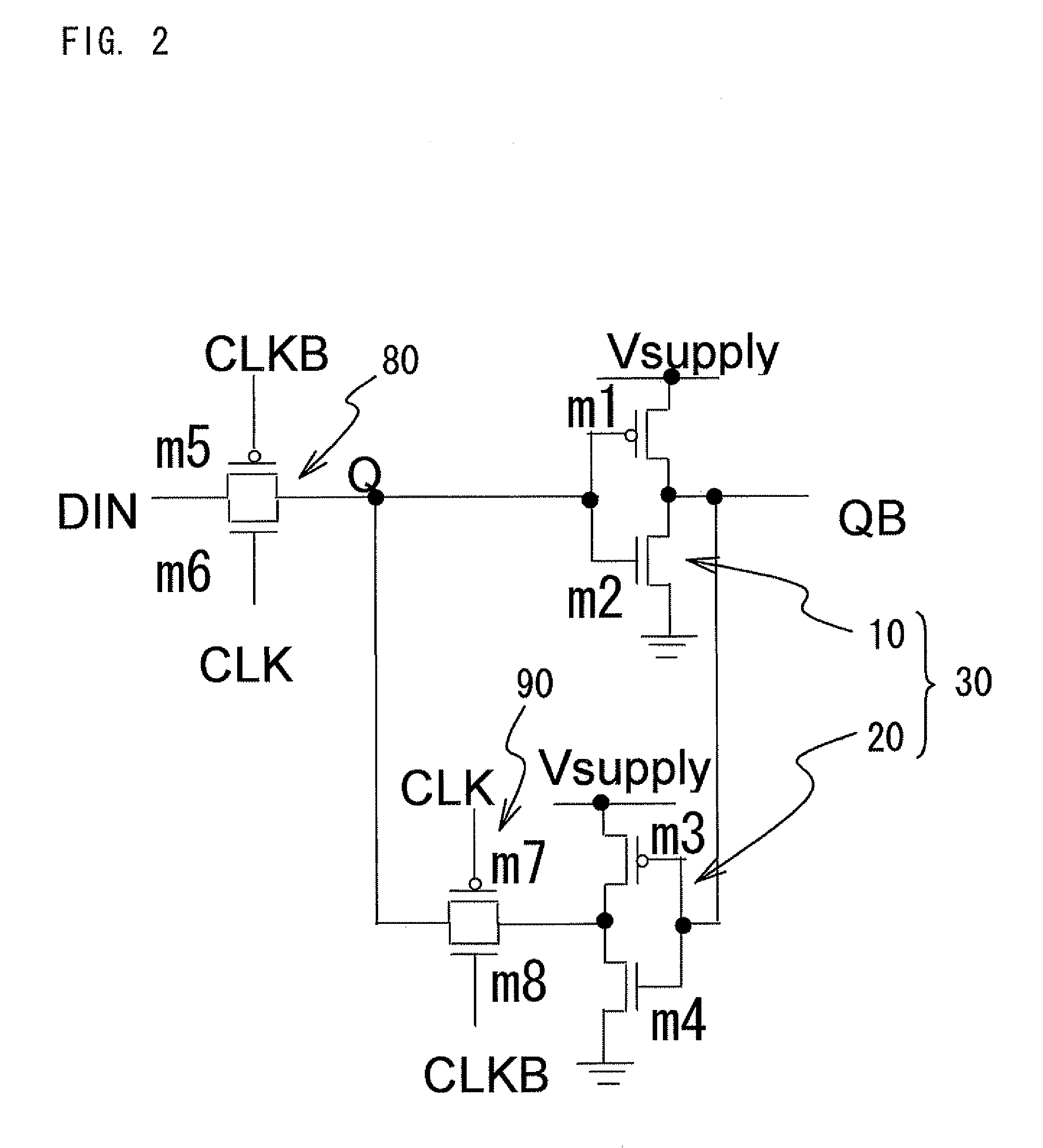
Nonvolatile sram/latch circuit using current-induced magnetization reversal mtj
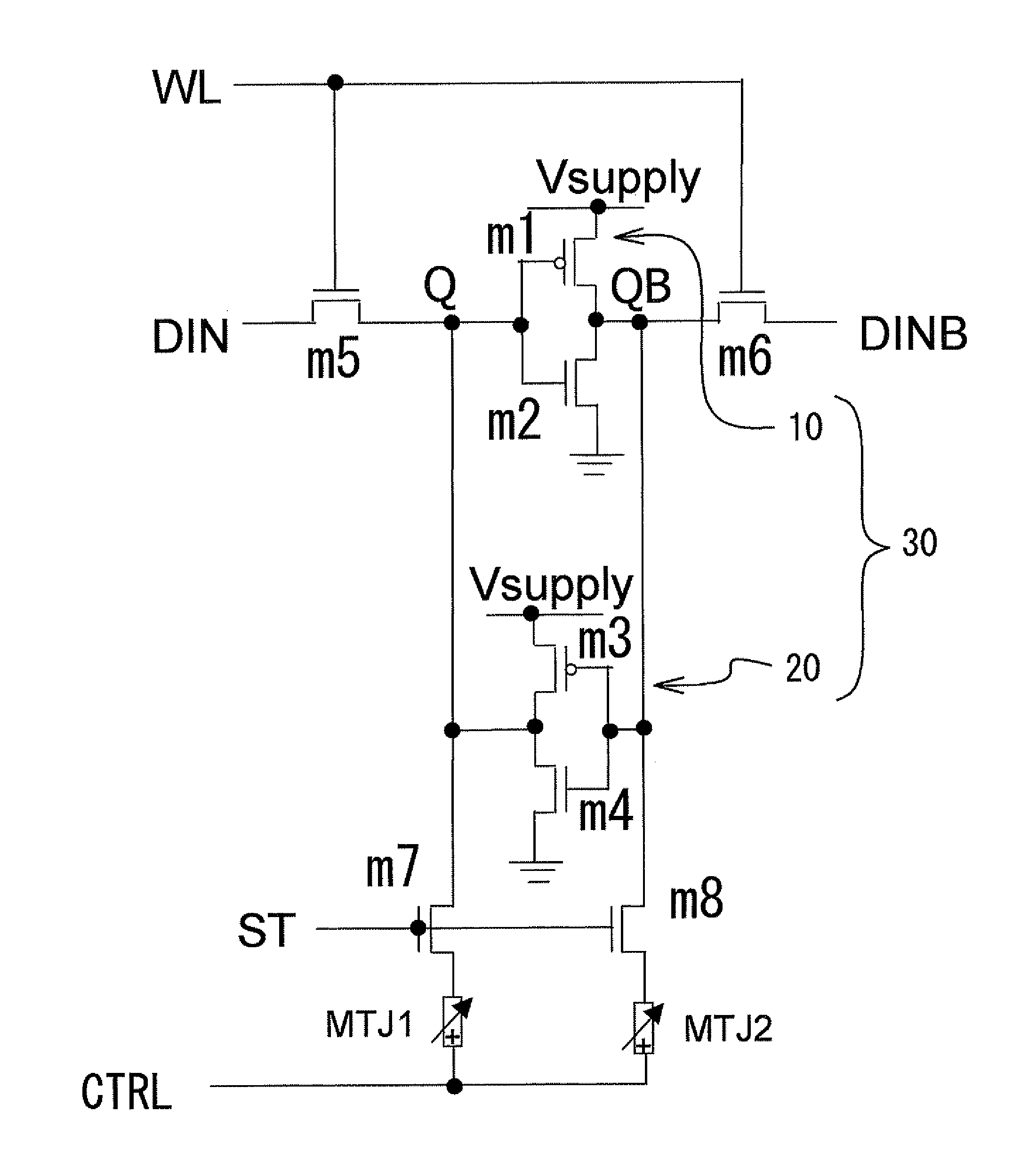
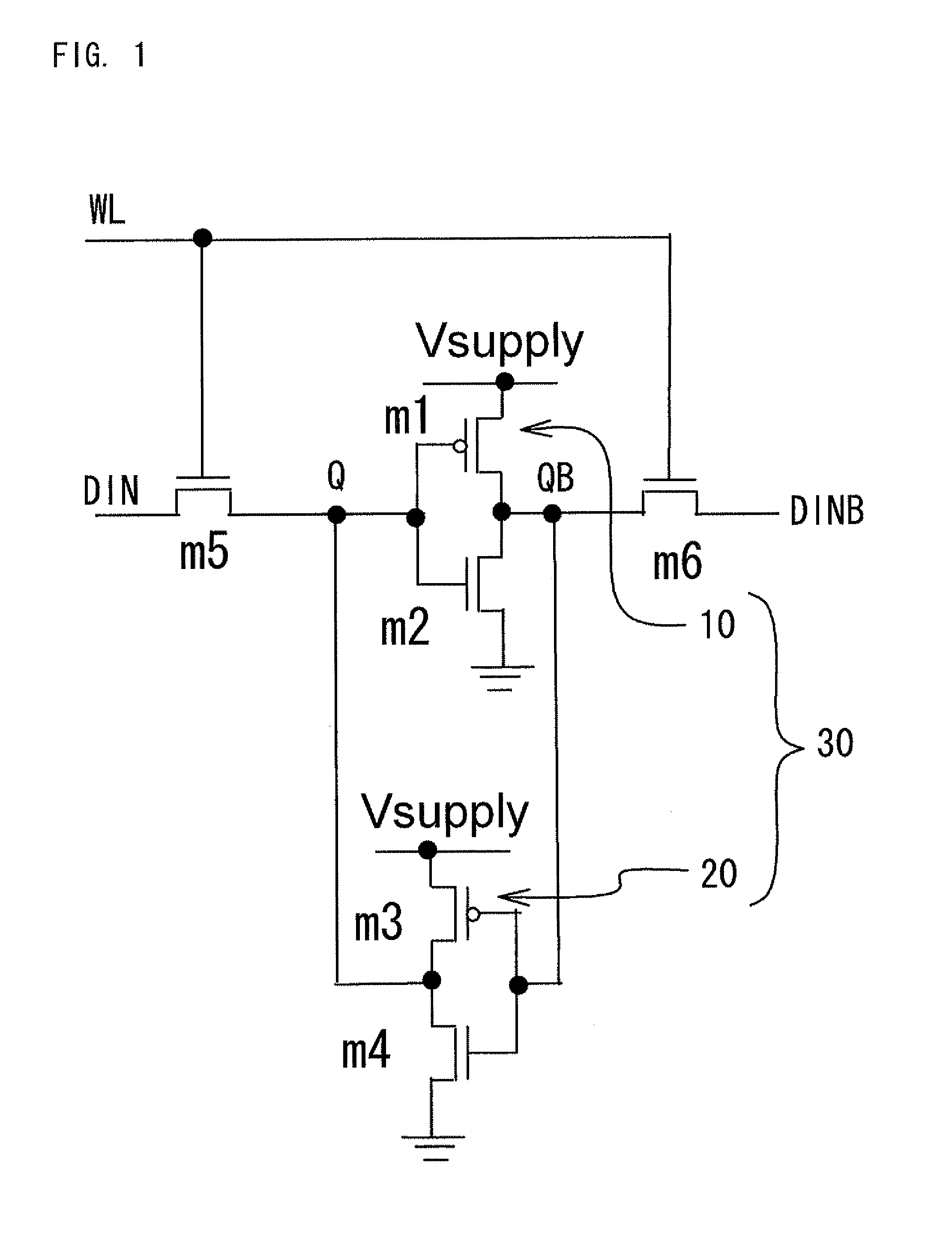
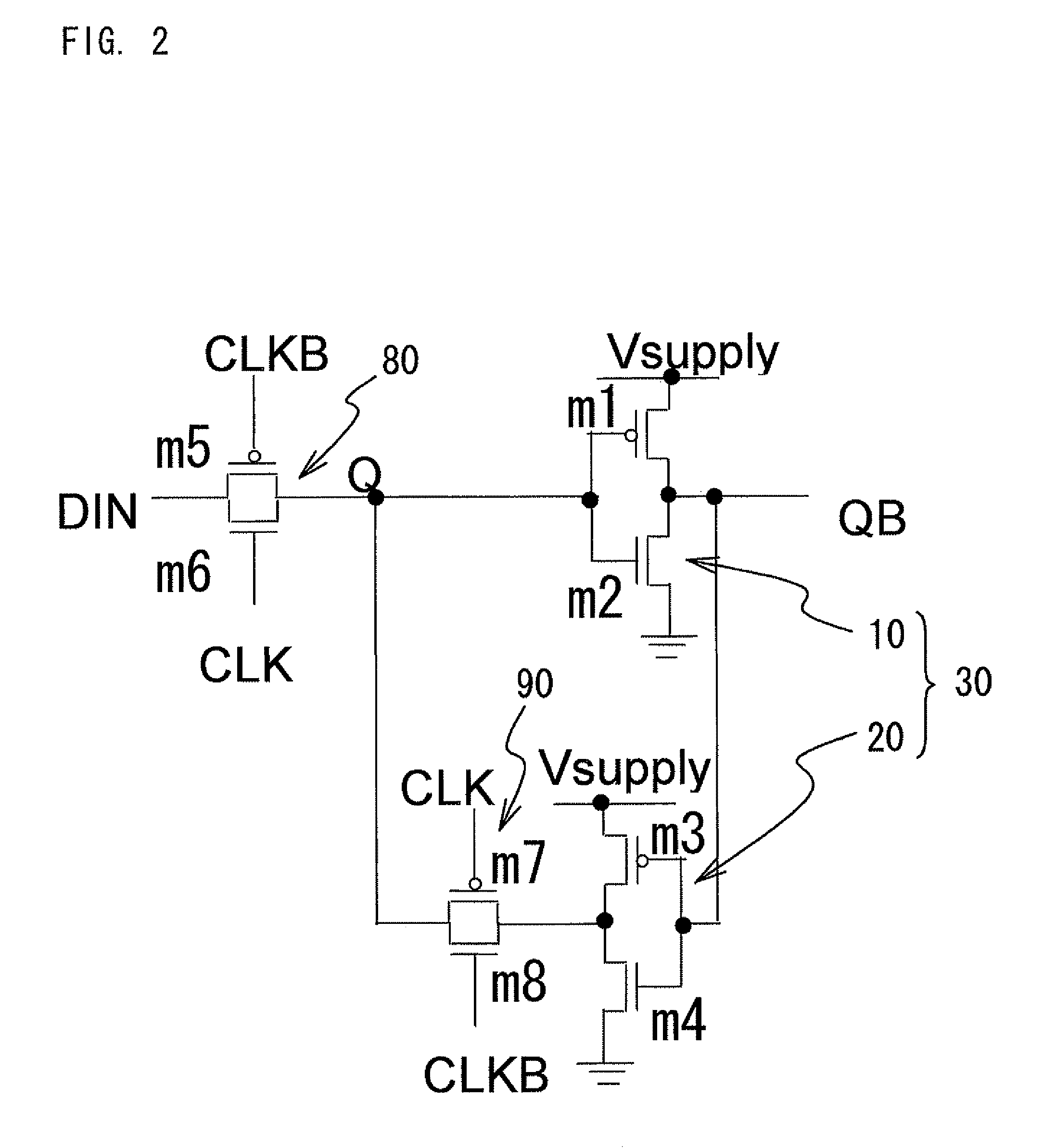
The present invention is a memory circuit that includes a bistable circuit that stores data, and a ferromagnetic tunnel junction device that nonvolatilely stores the data in the bistable circuit according to a magnetization direction of a ferromagnetic electrode free layer, the data nonvolatilely stored in the ferromagnetic tunnel junction device being able to be restored in the bistable circuit. According to the present invention, writing data to and reading data from the bistable circuit can be performed at high speed. In addition, even though a power source is shut down, it is possible to restore data nonvolatilely stored in the ferromagnetic tunnel junction devices to the bistable circuit.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
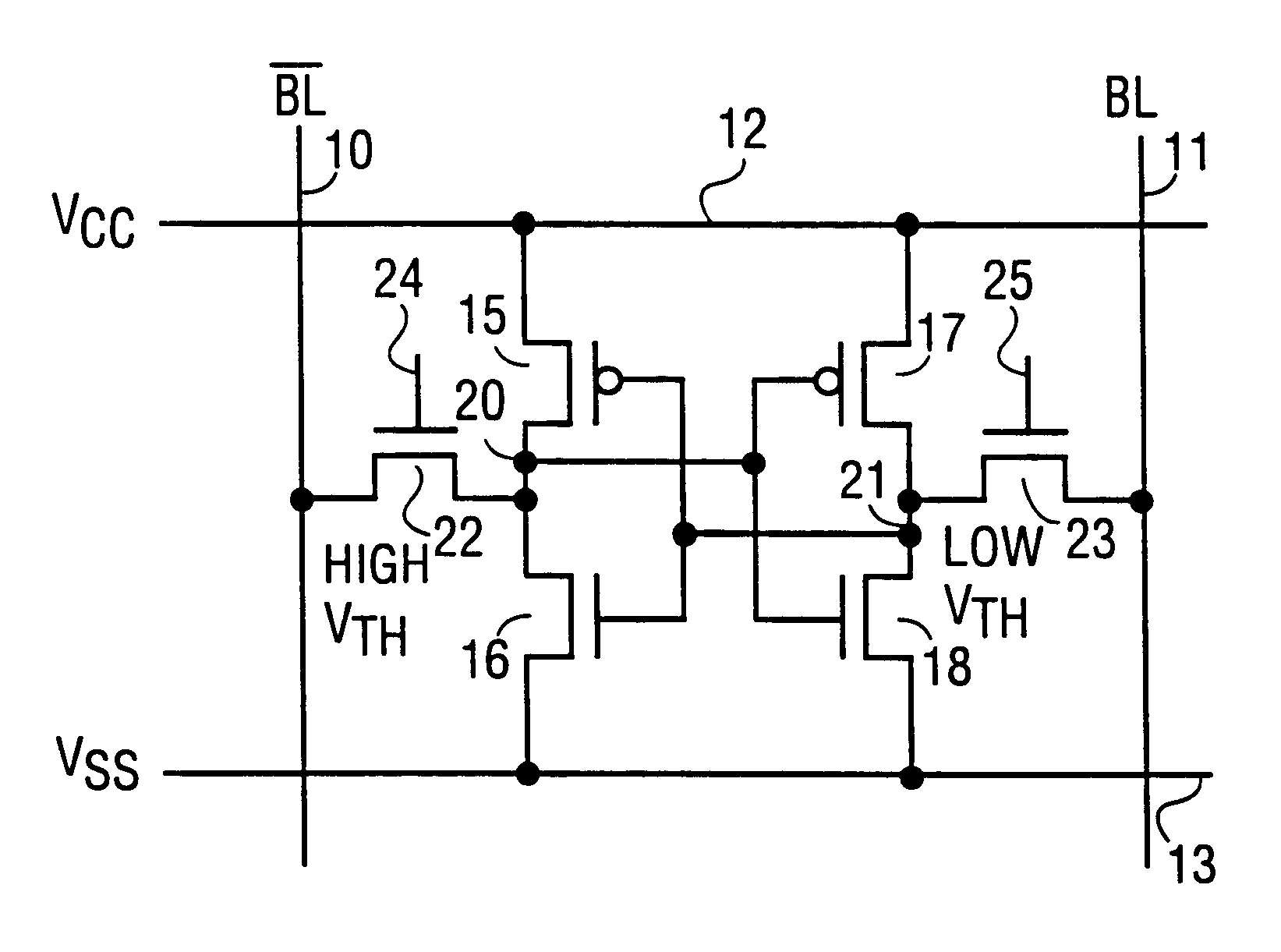
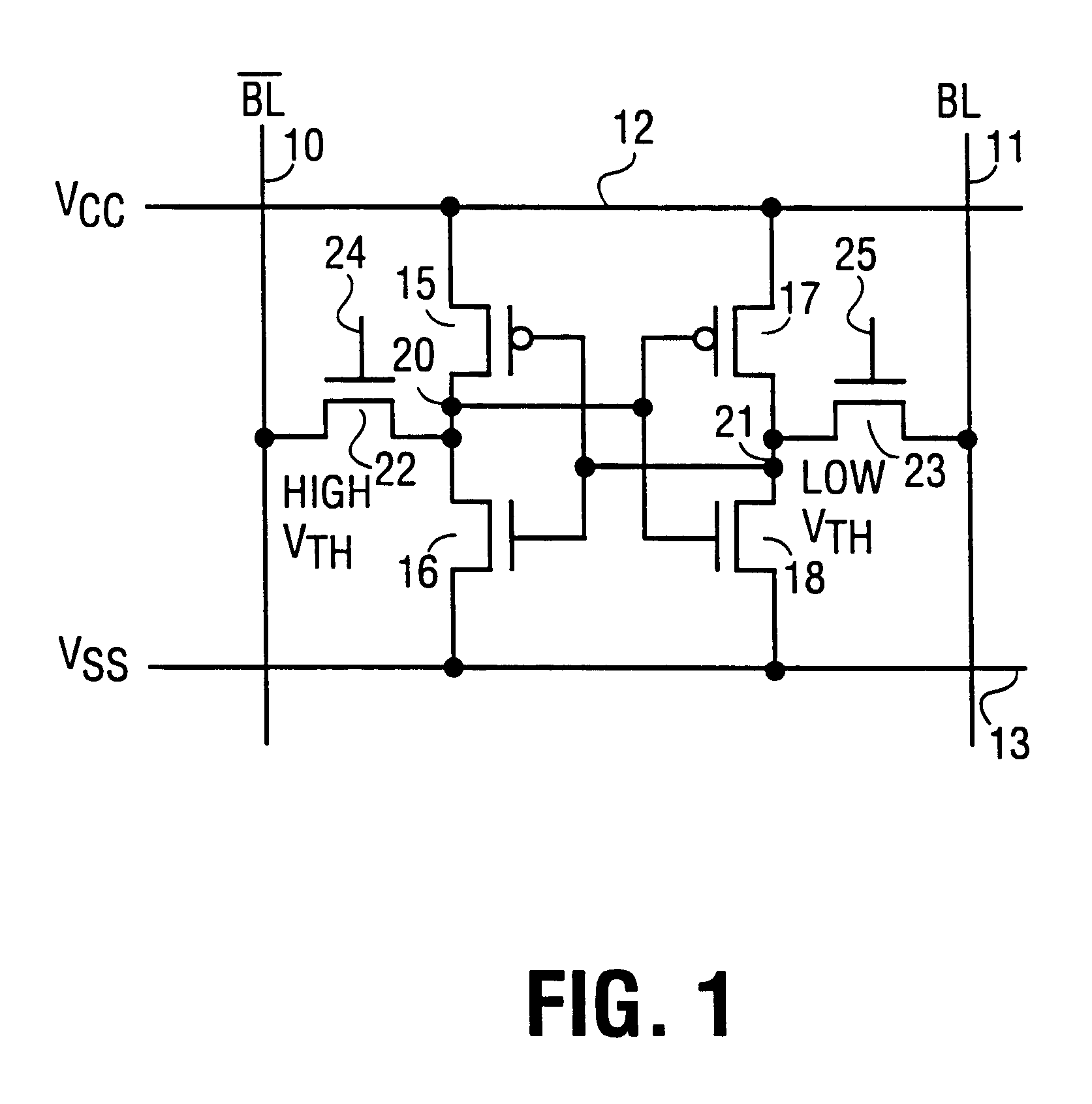
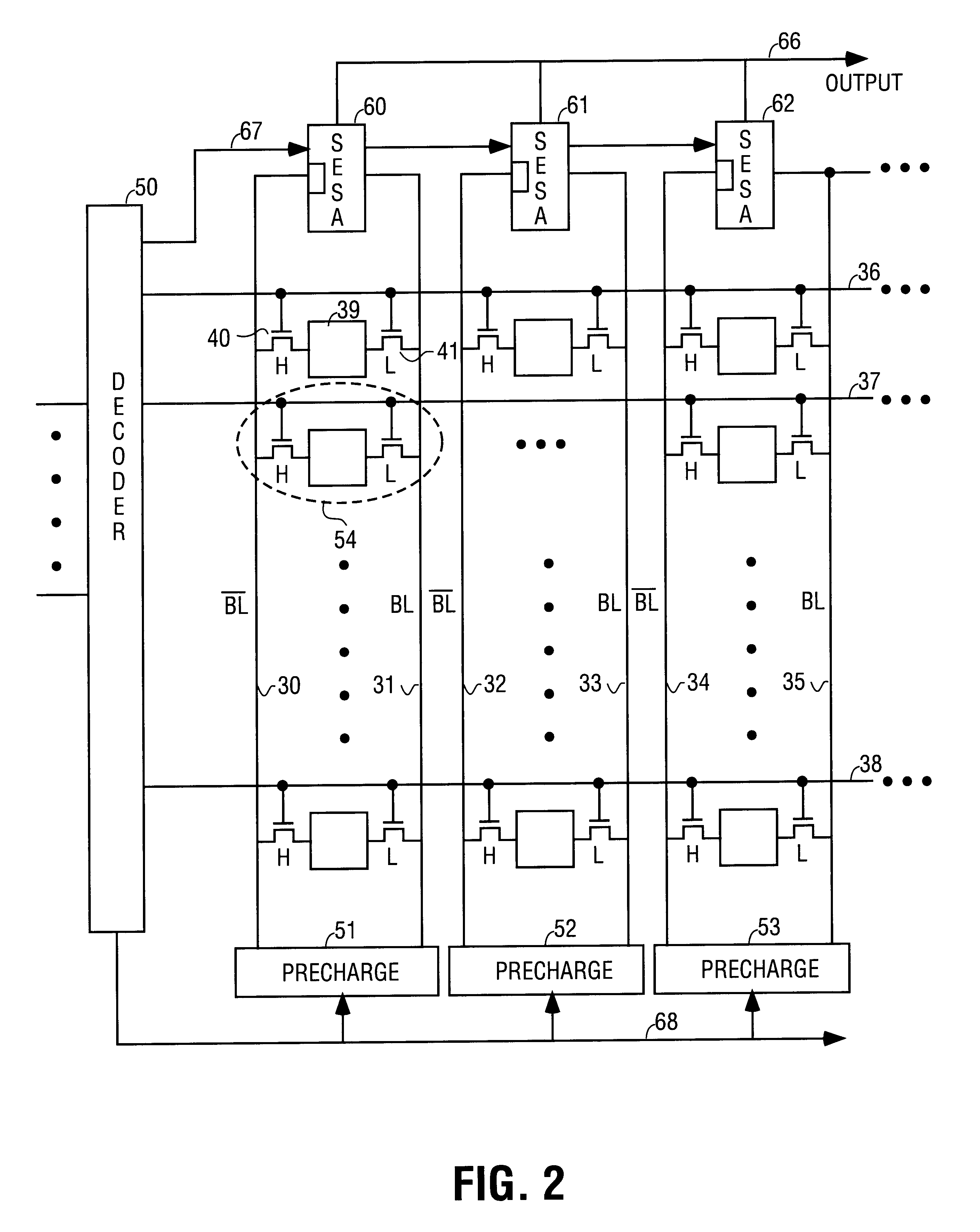
Dual threshold SRAM cell for single-ended sensing
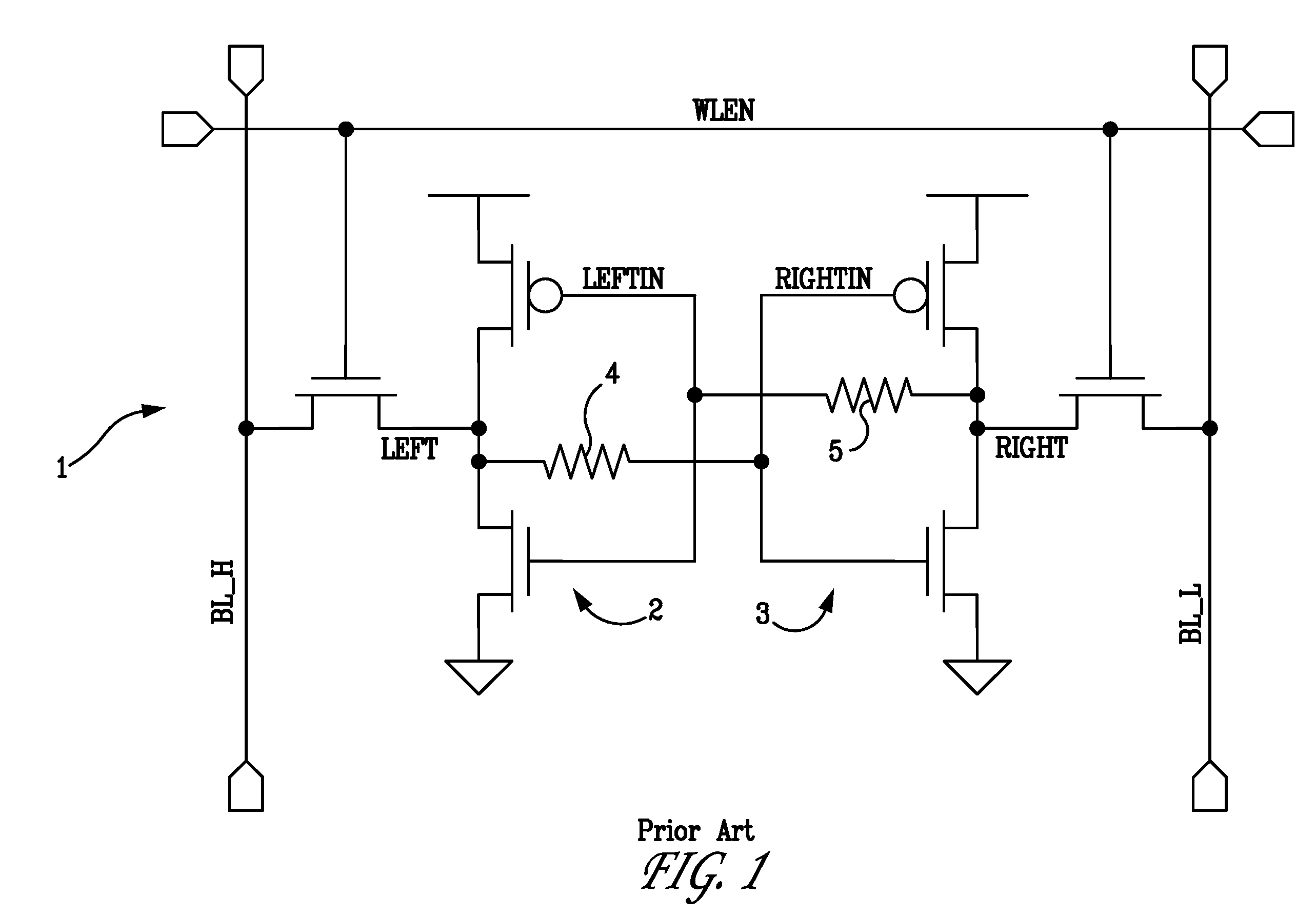
A six transistor SRAM cell for single-ended sensing is described along with related memory architecture. The cell comprises a bistable circuit connected to complementary bit lines through a pair of passgate transistors. One of the passgate transistors has a lower threshold voltage than the other transistor. The lower threshold voltage is used to couple the cell to a single-ended sense amplifier through one of the bit lines. In one embodiment fewer than all the bit lines in an array are precharged in order to reduce power consumption in the array.
Owner:INTEL CORP
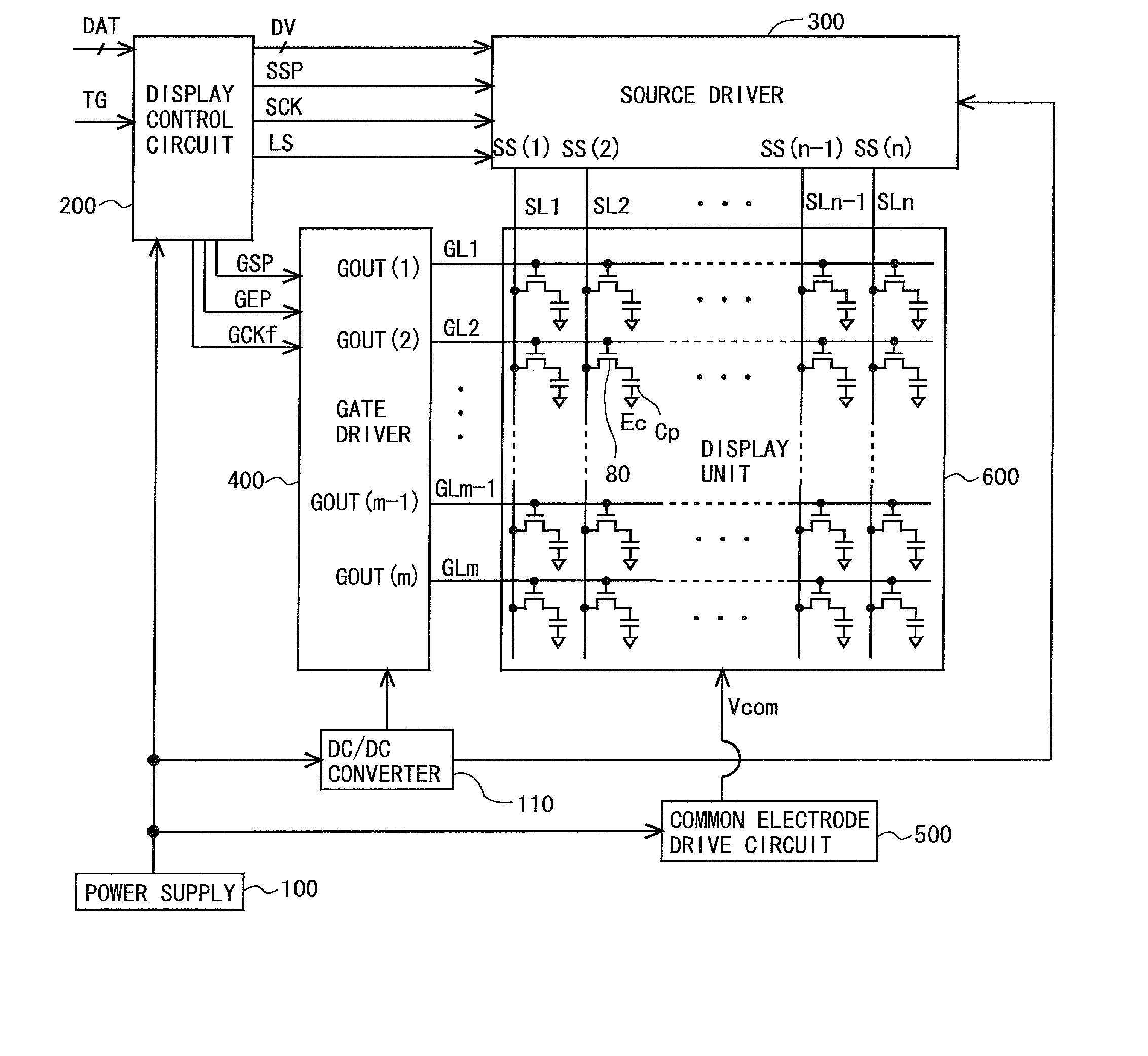
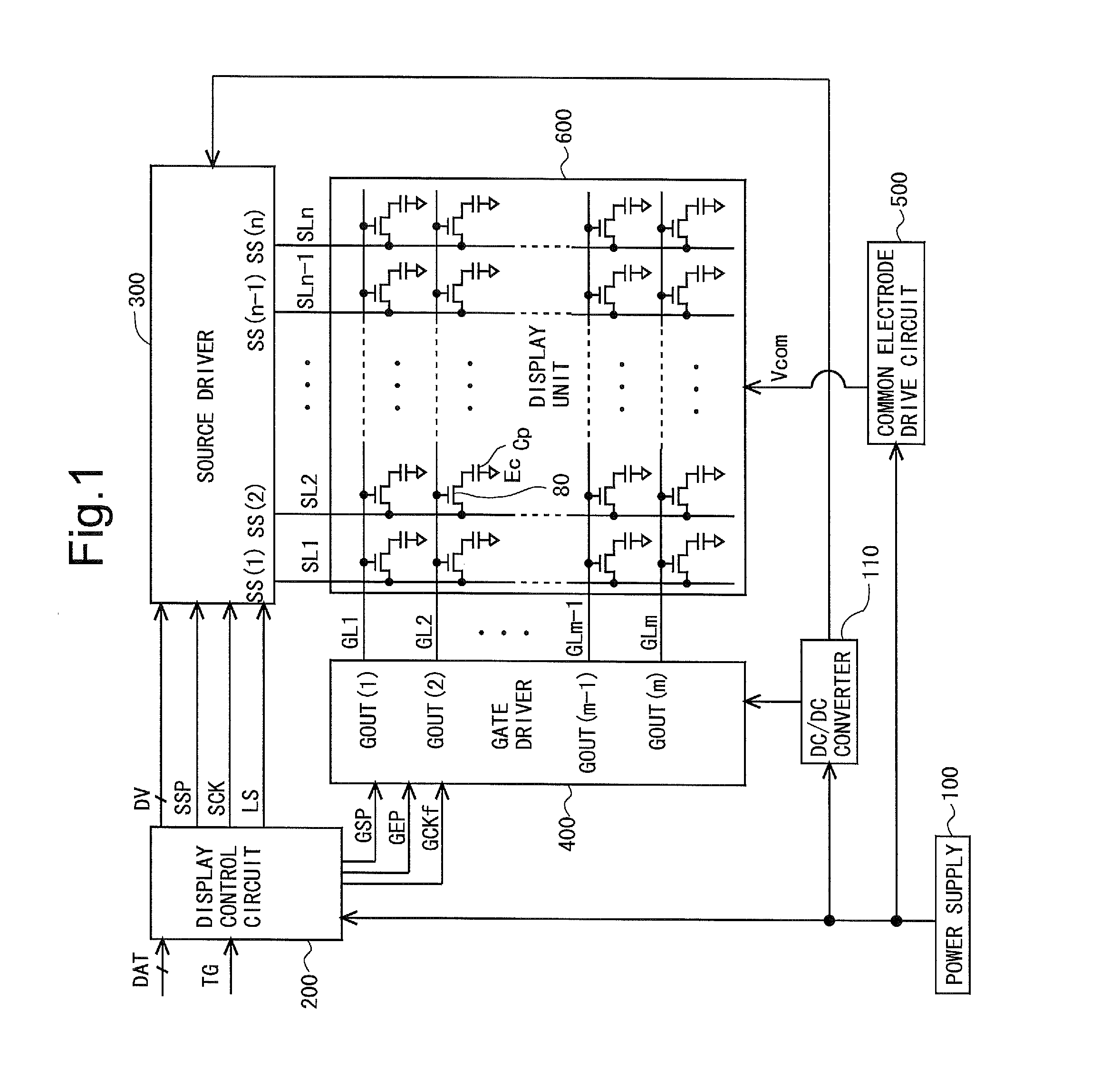
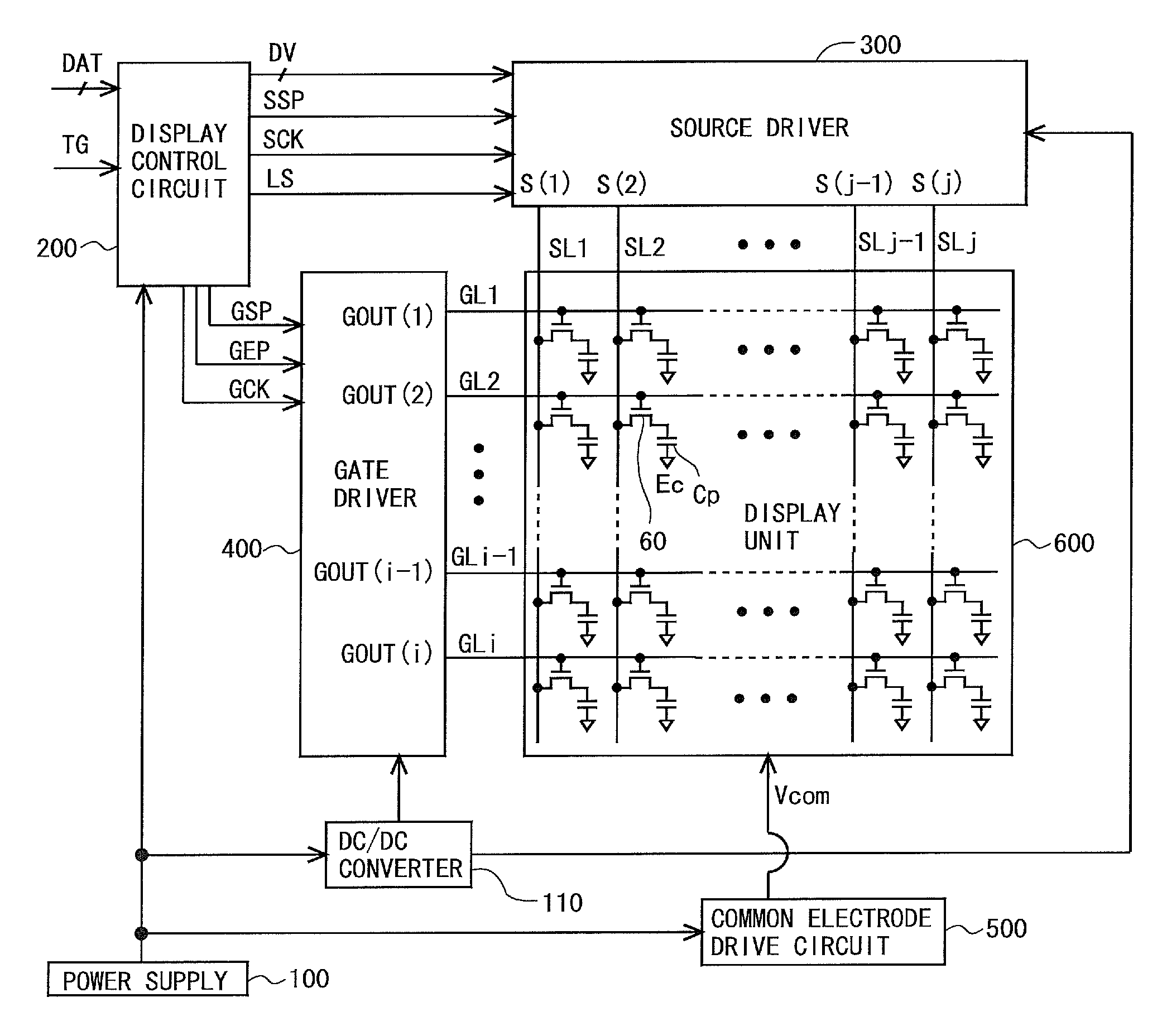
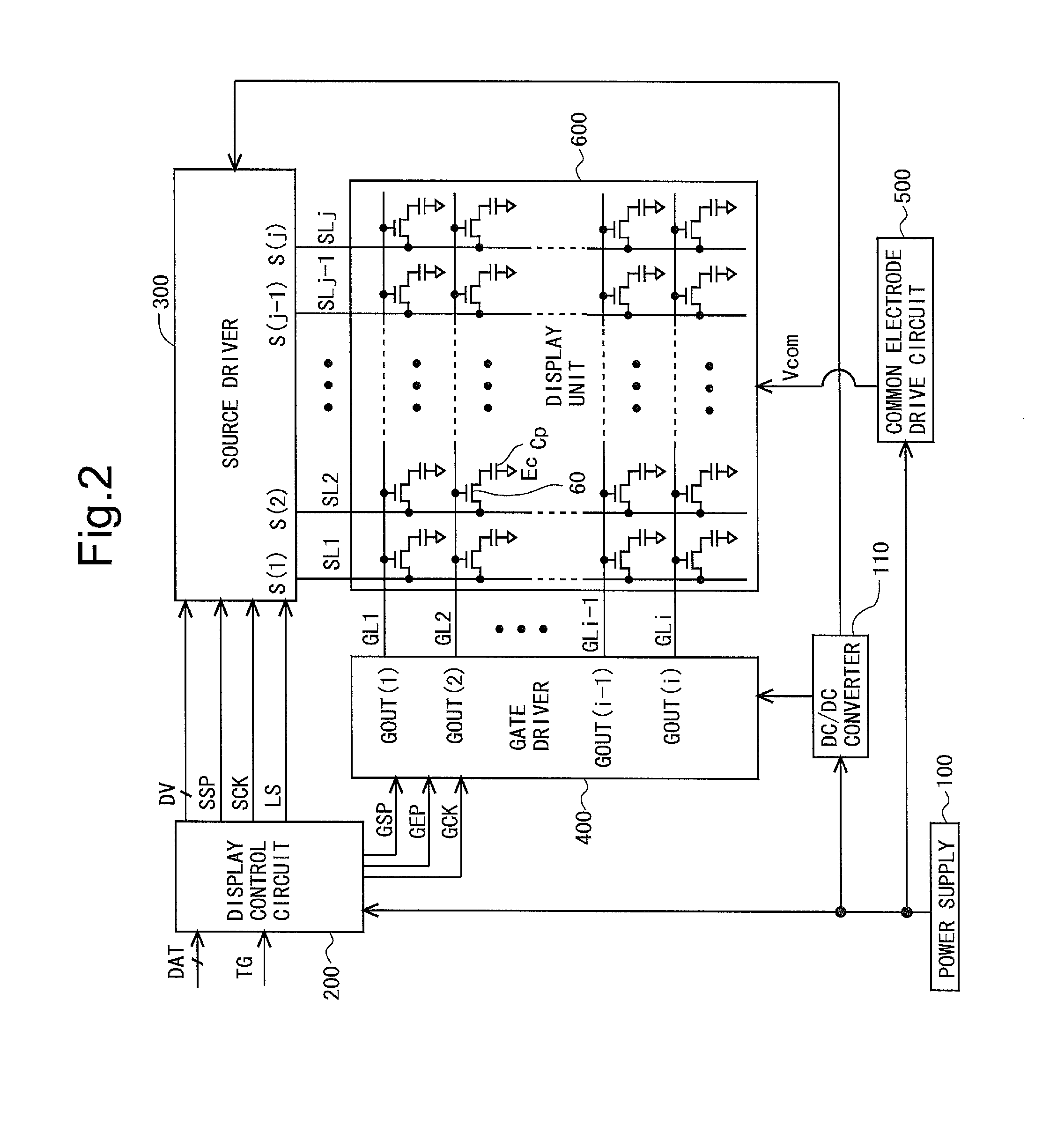
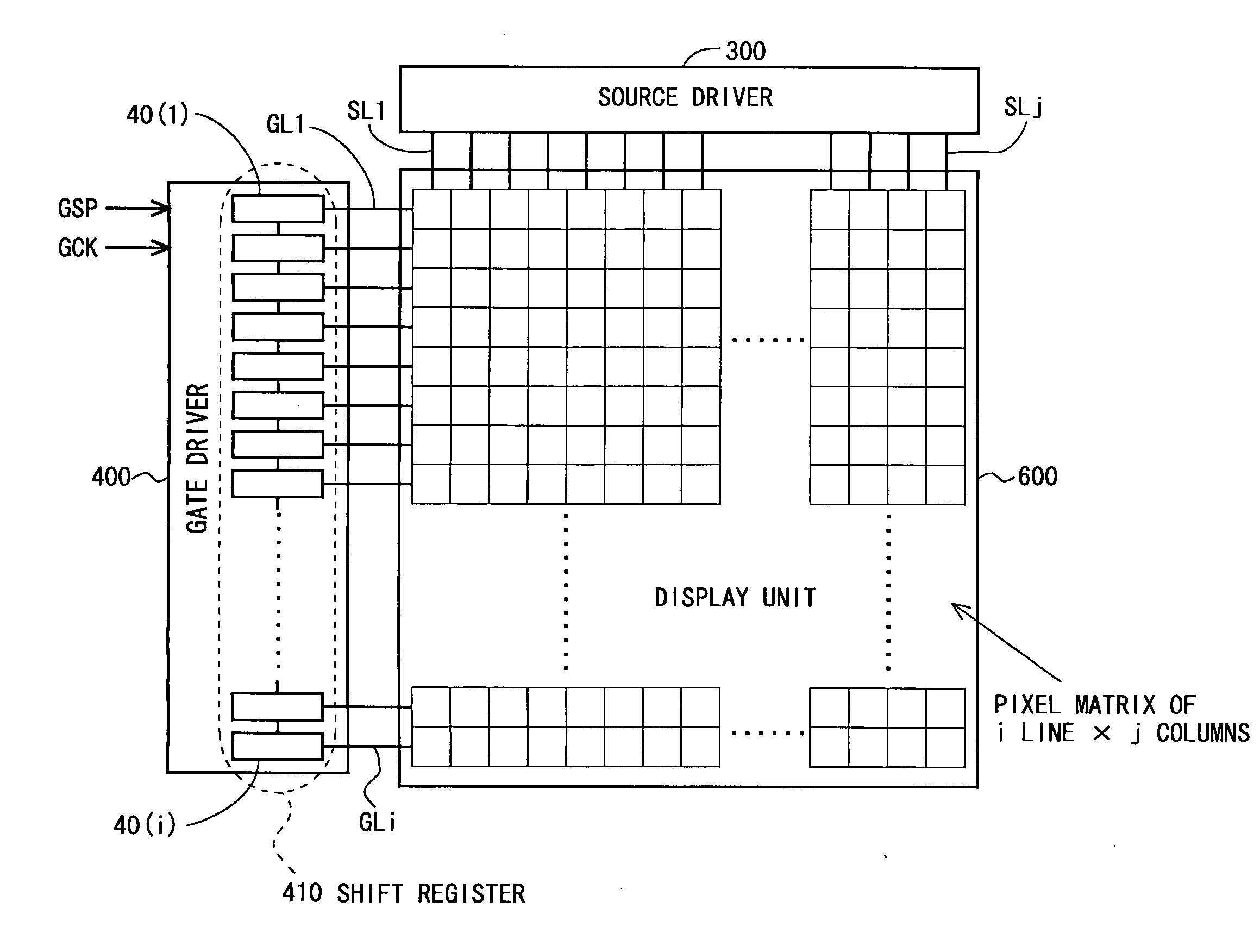
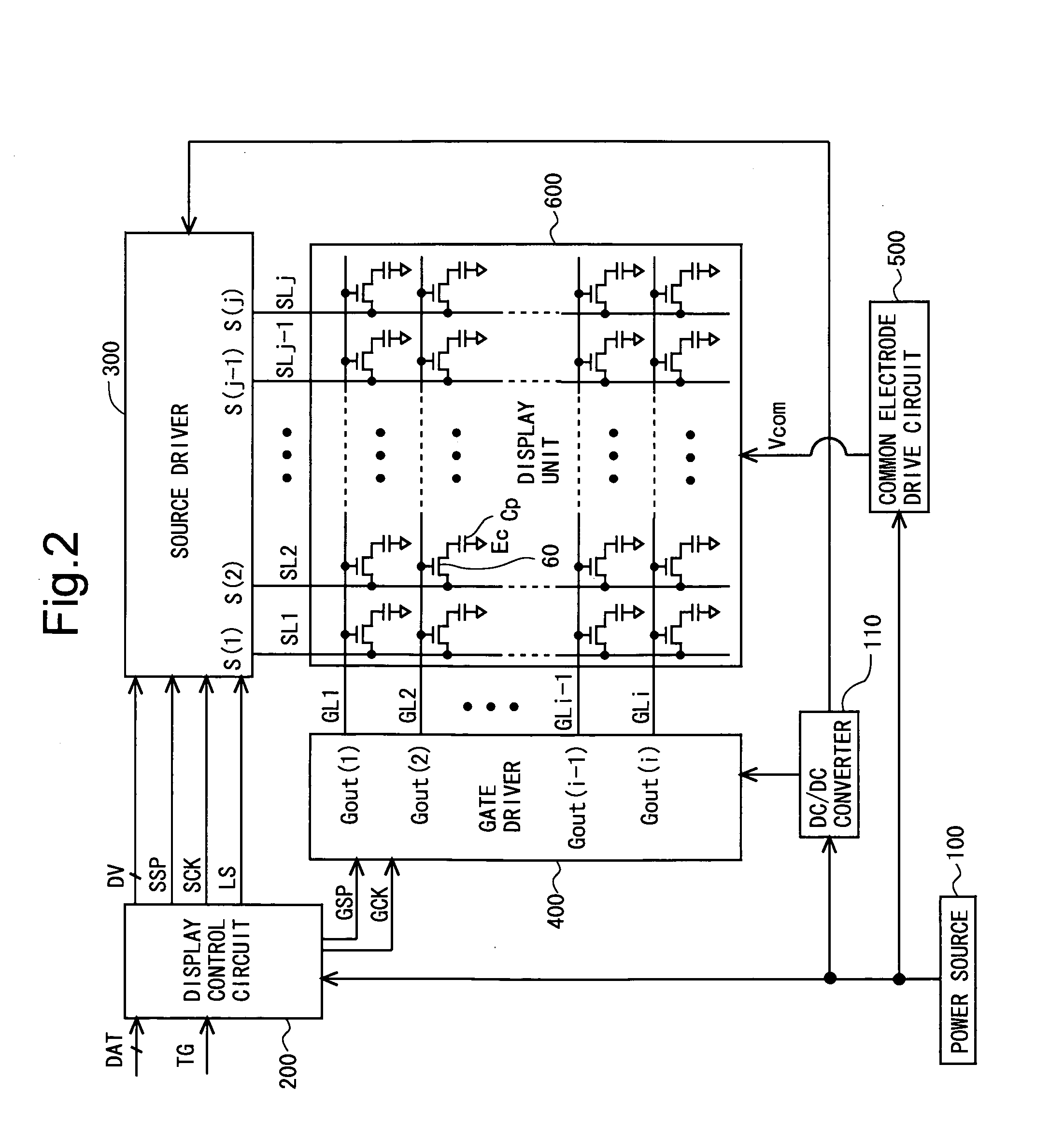
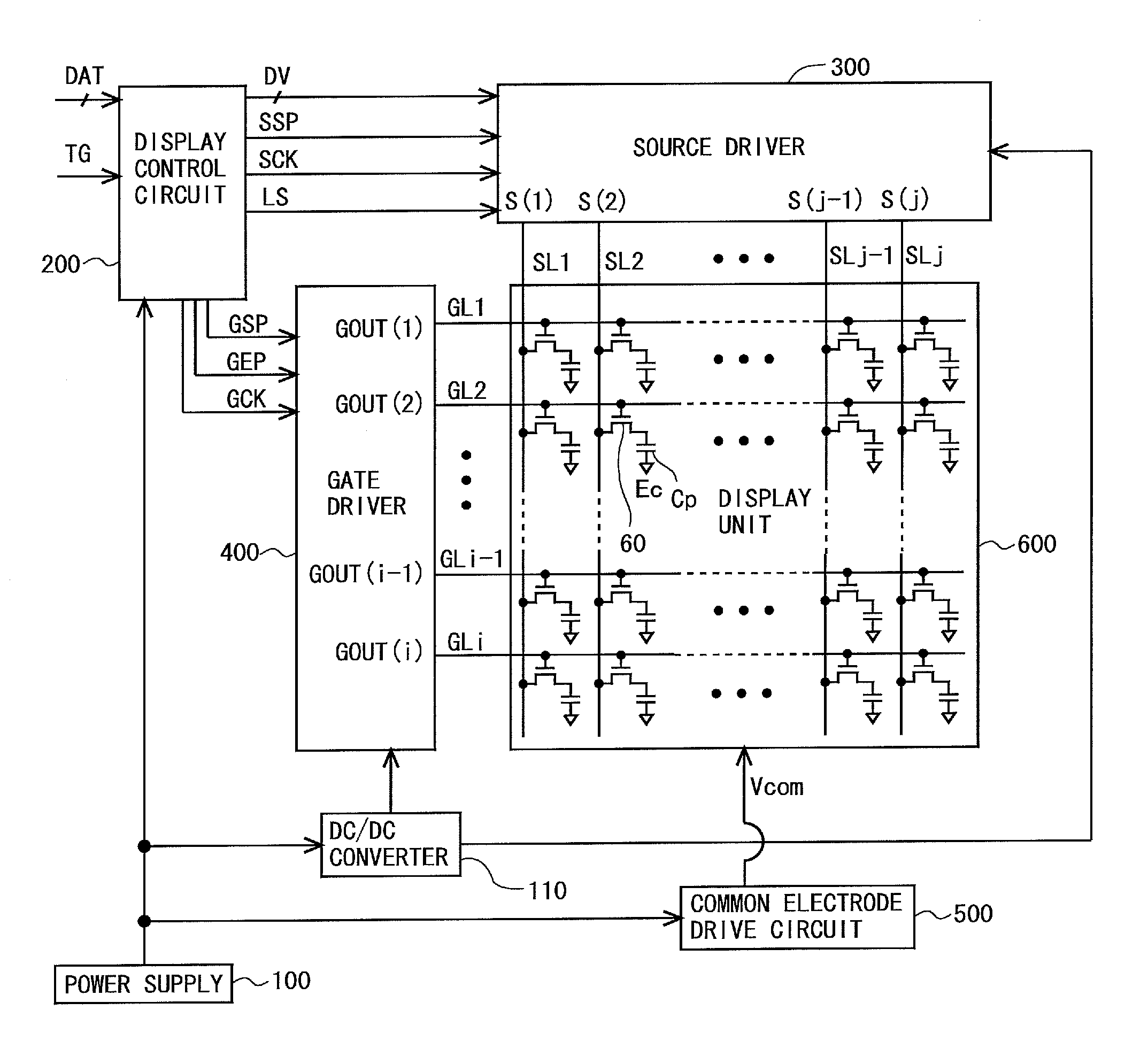
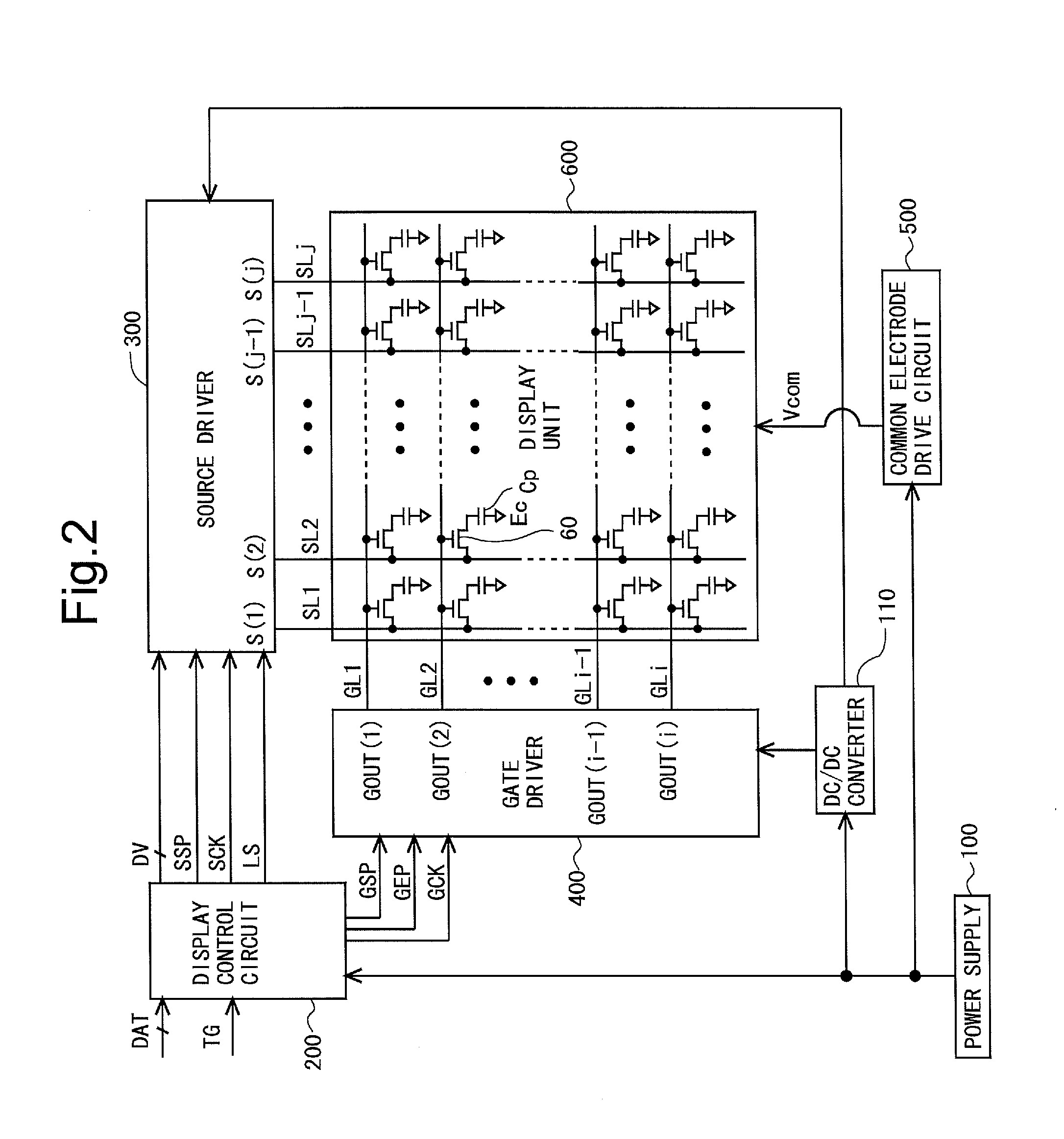
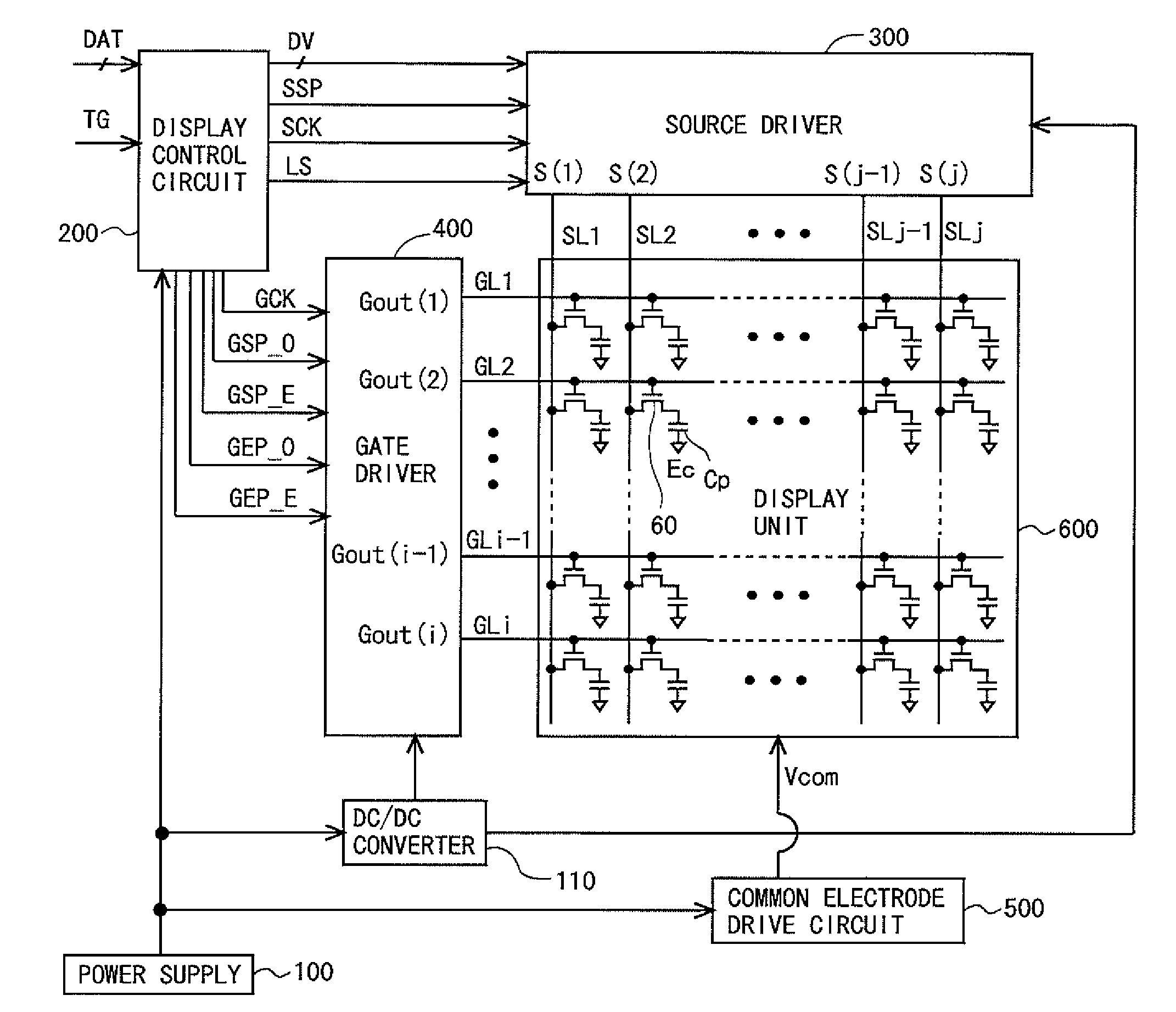
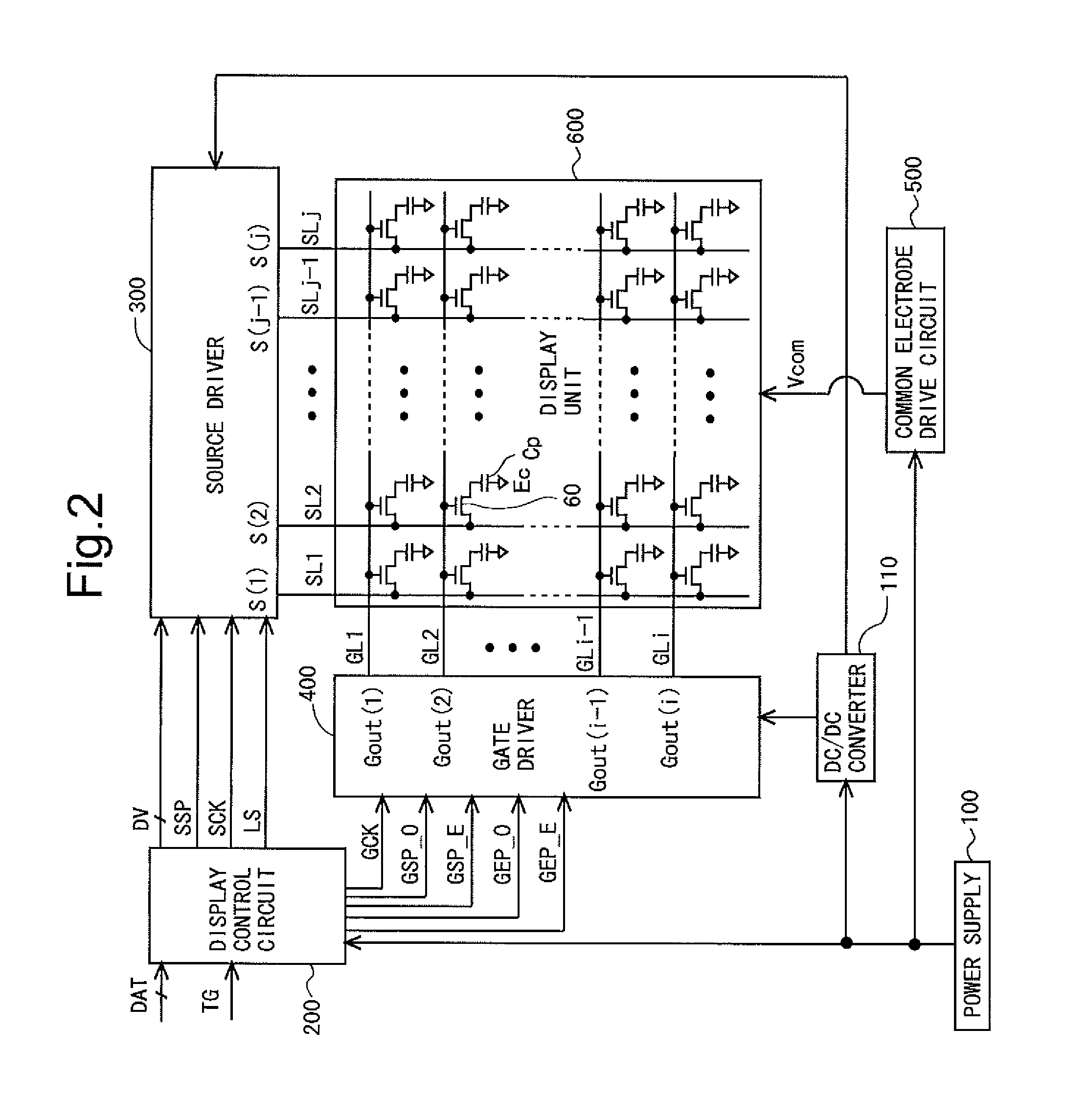
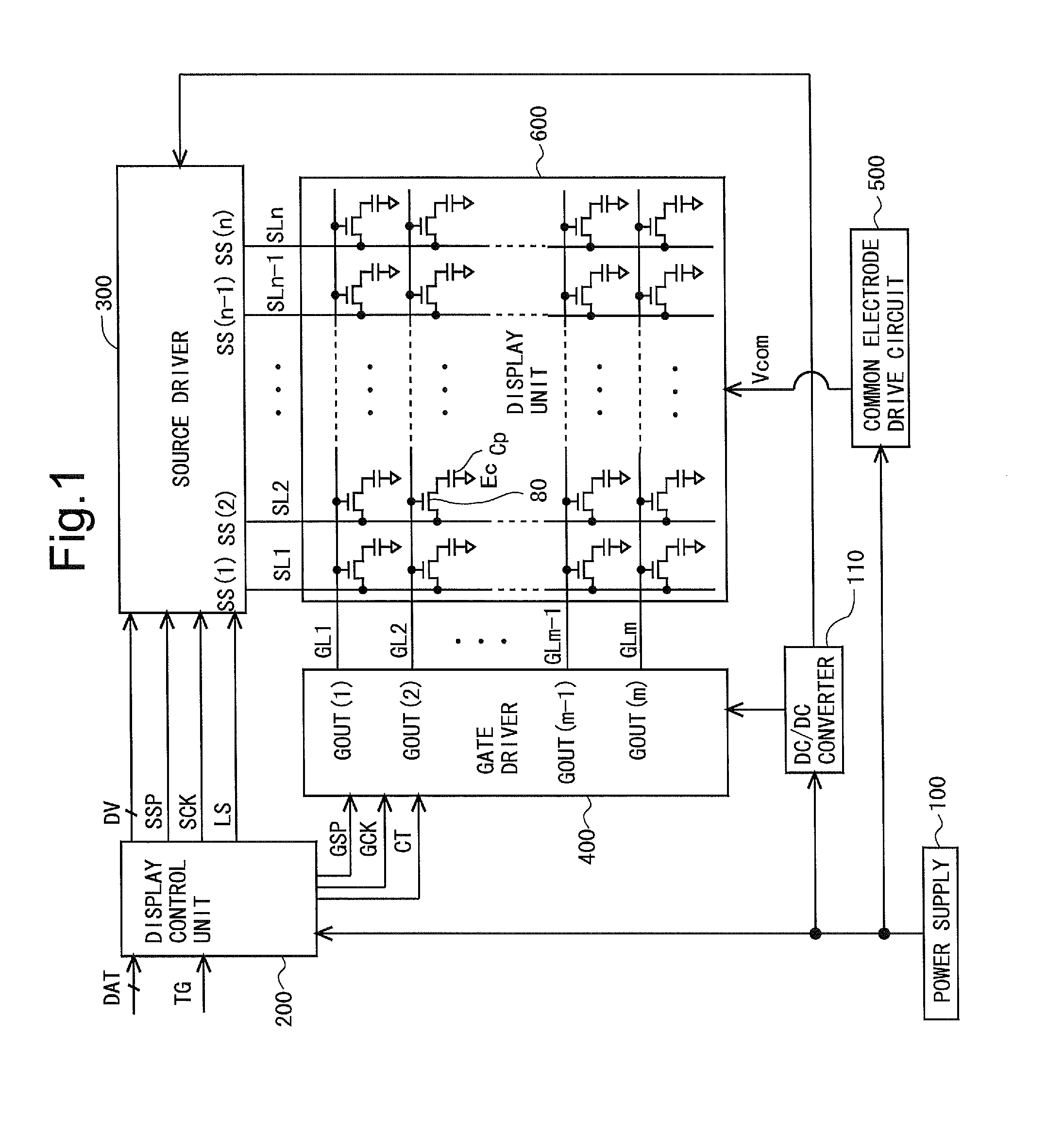
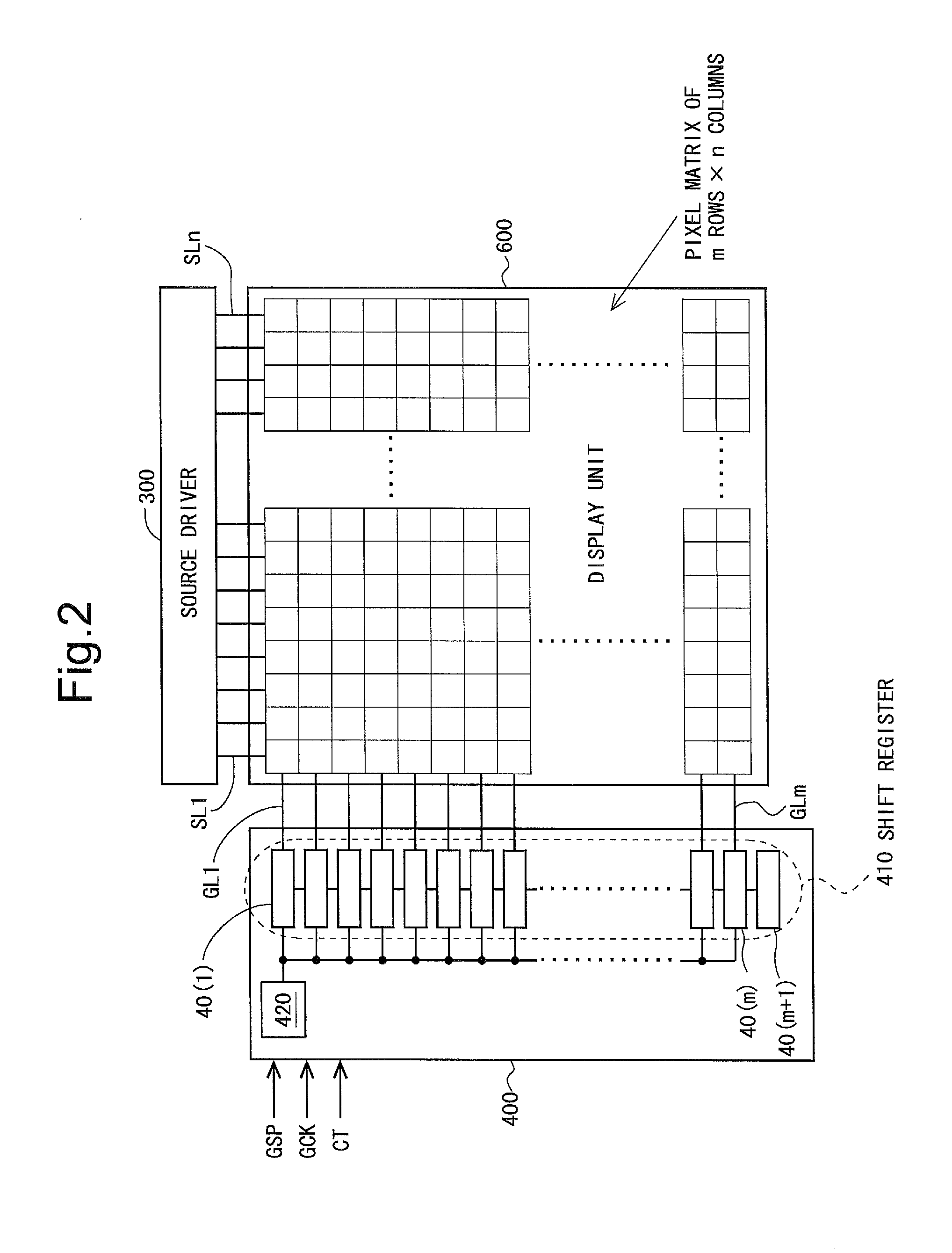
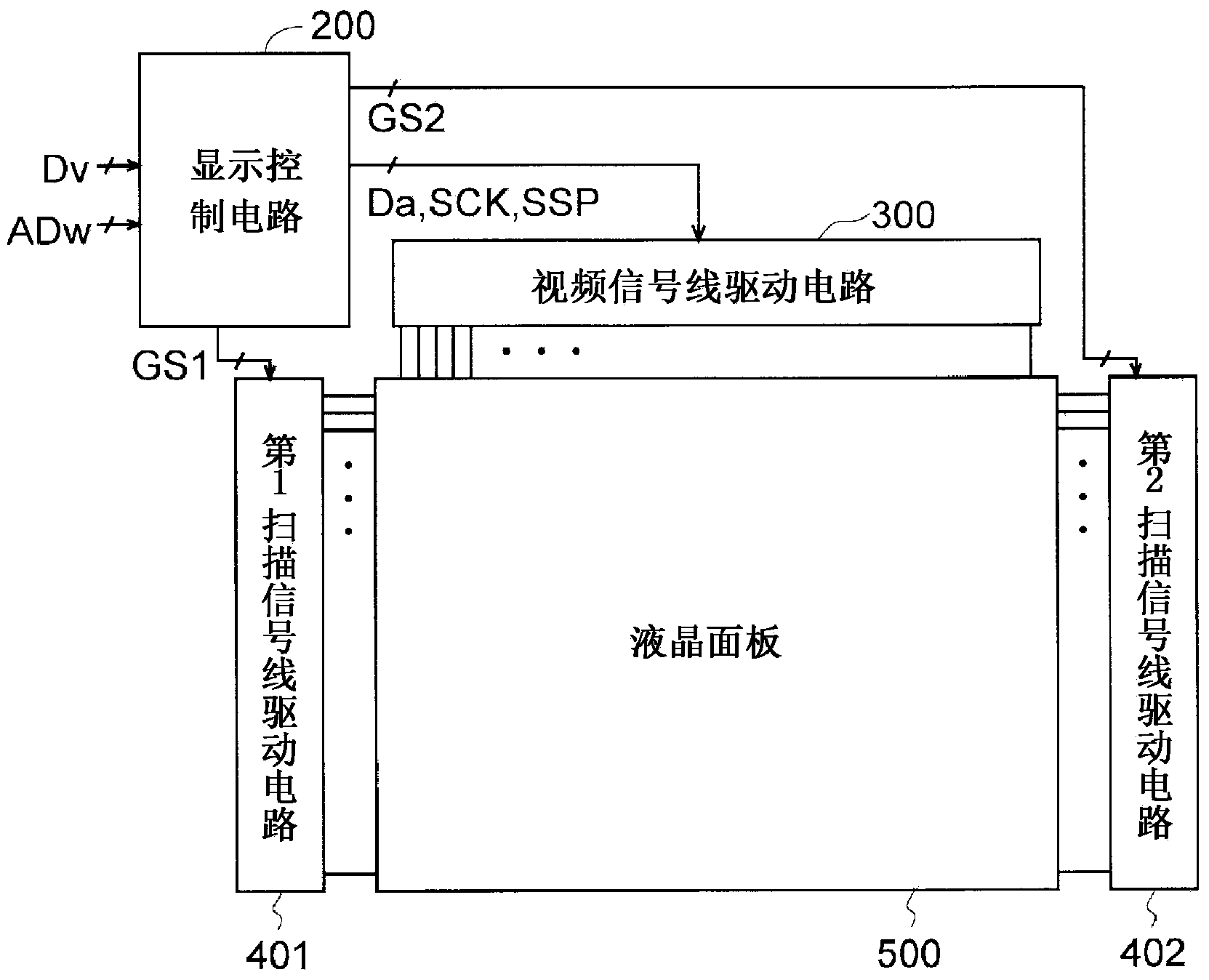
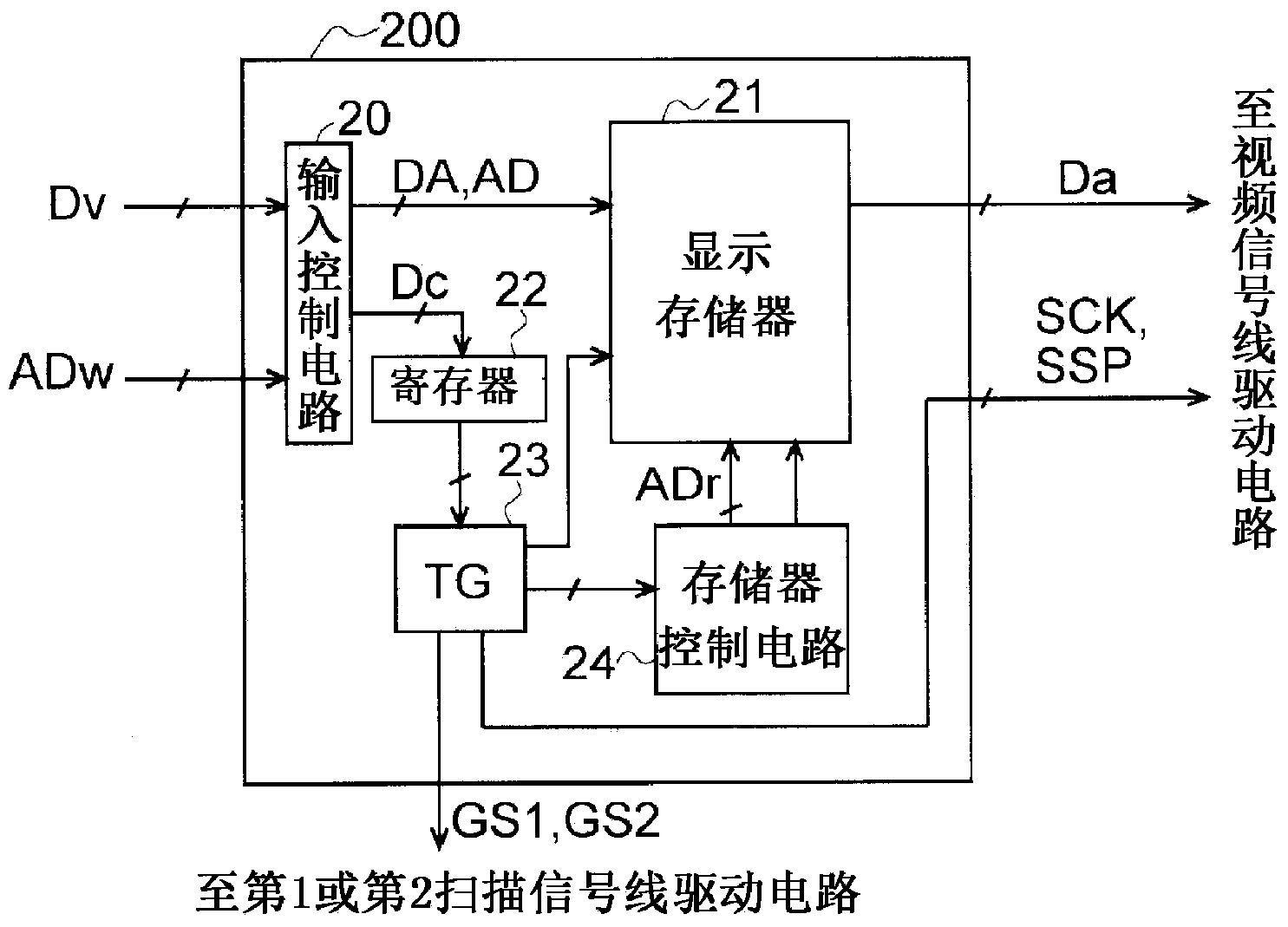
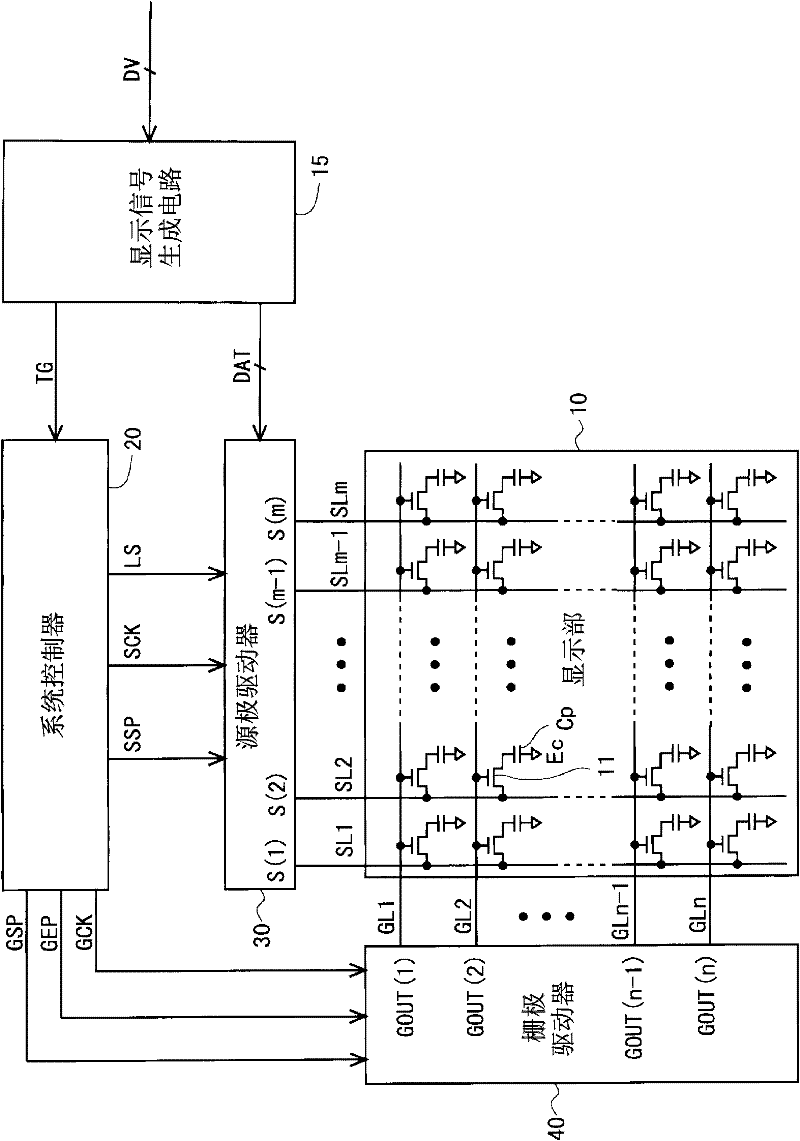
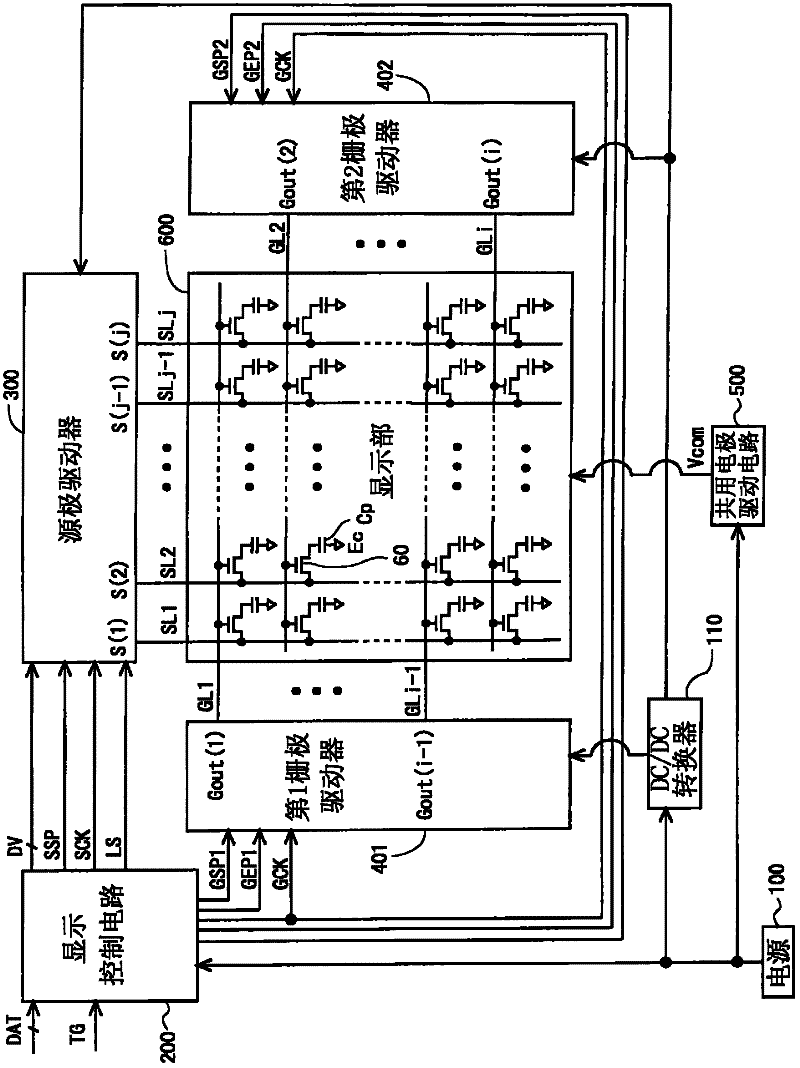
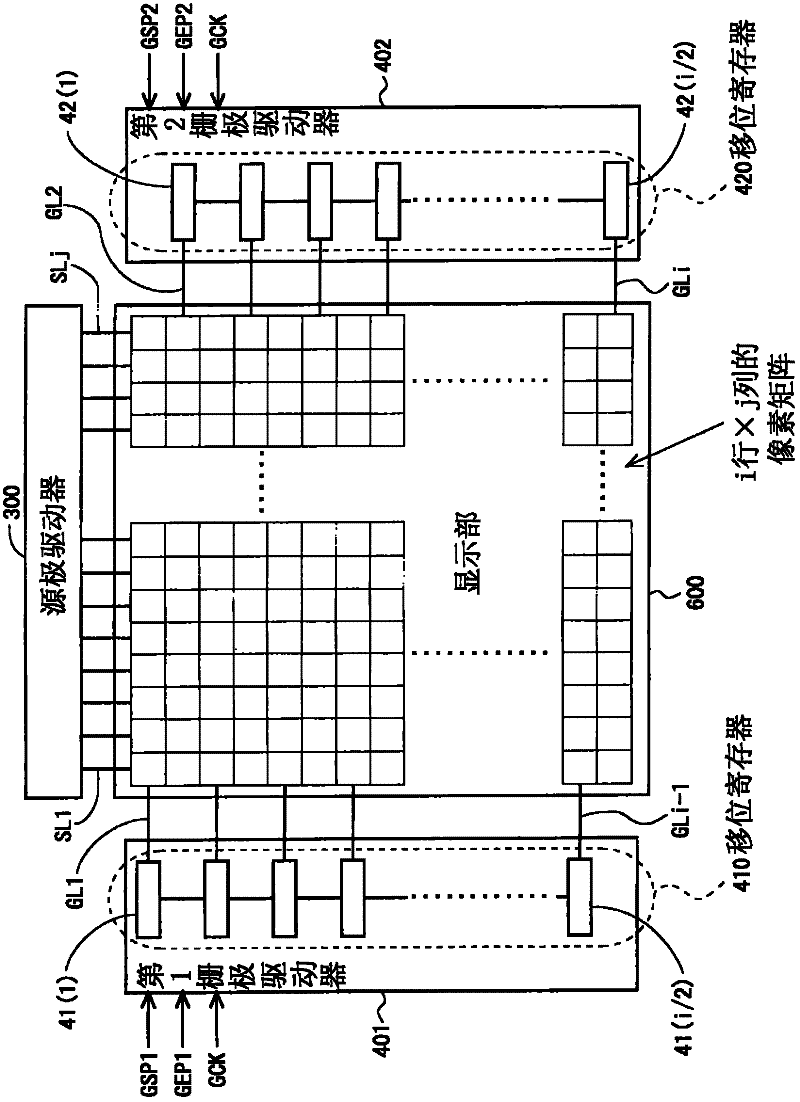
Scanning signal line drive circuit, display device having the same, and driving method for scanning signal line
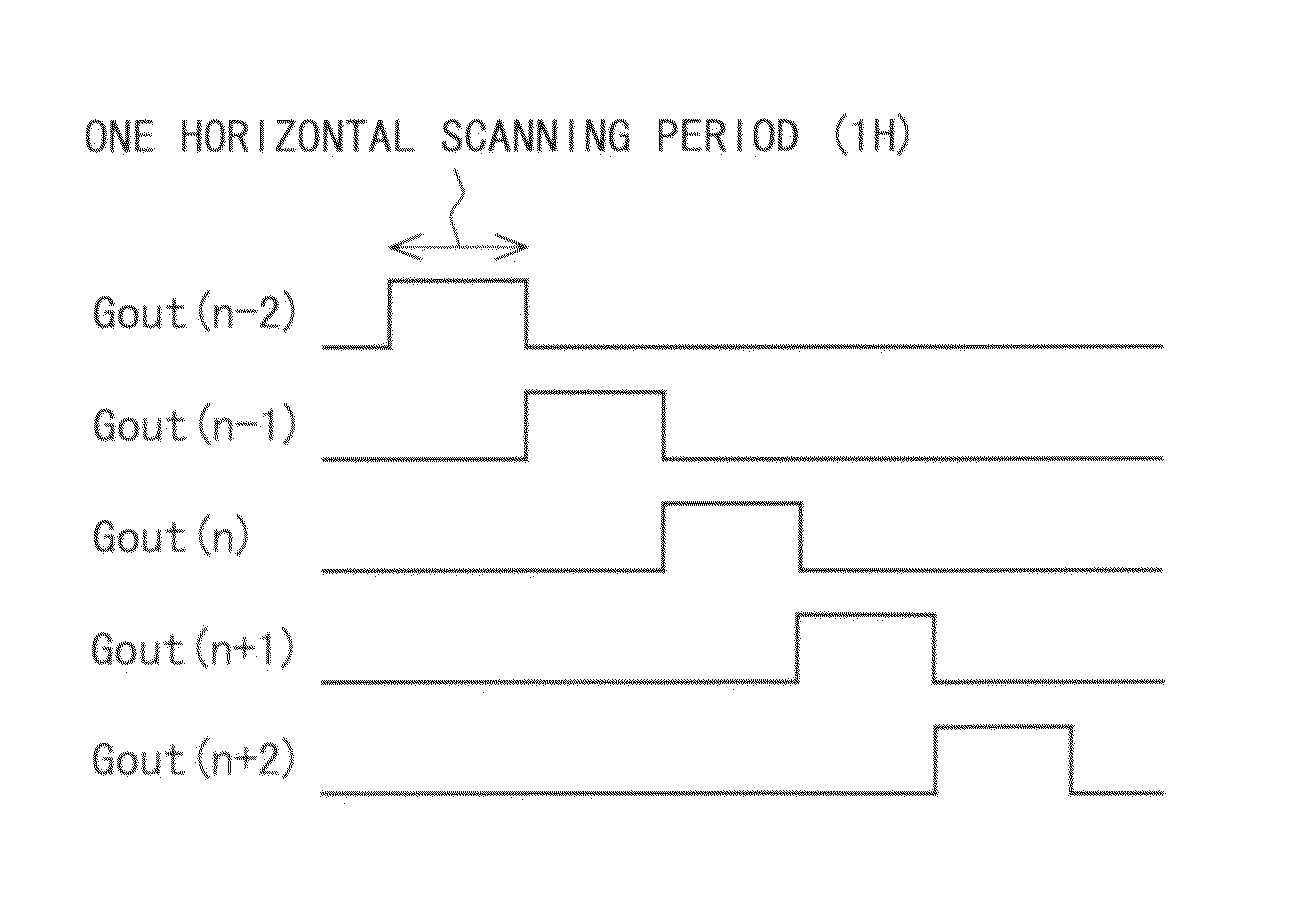
InactiveUS20140111495A1Small sizeReduce power consumptionCathode-ray tube indicatorsDigital storageShift registerBistable circuits
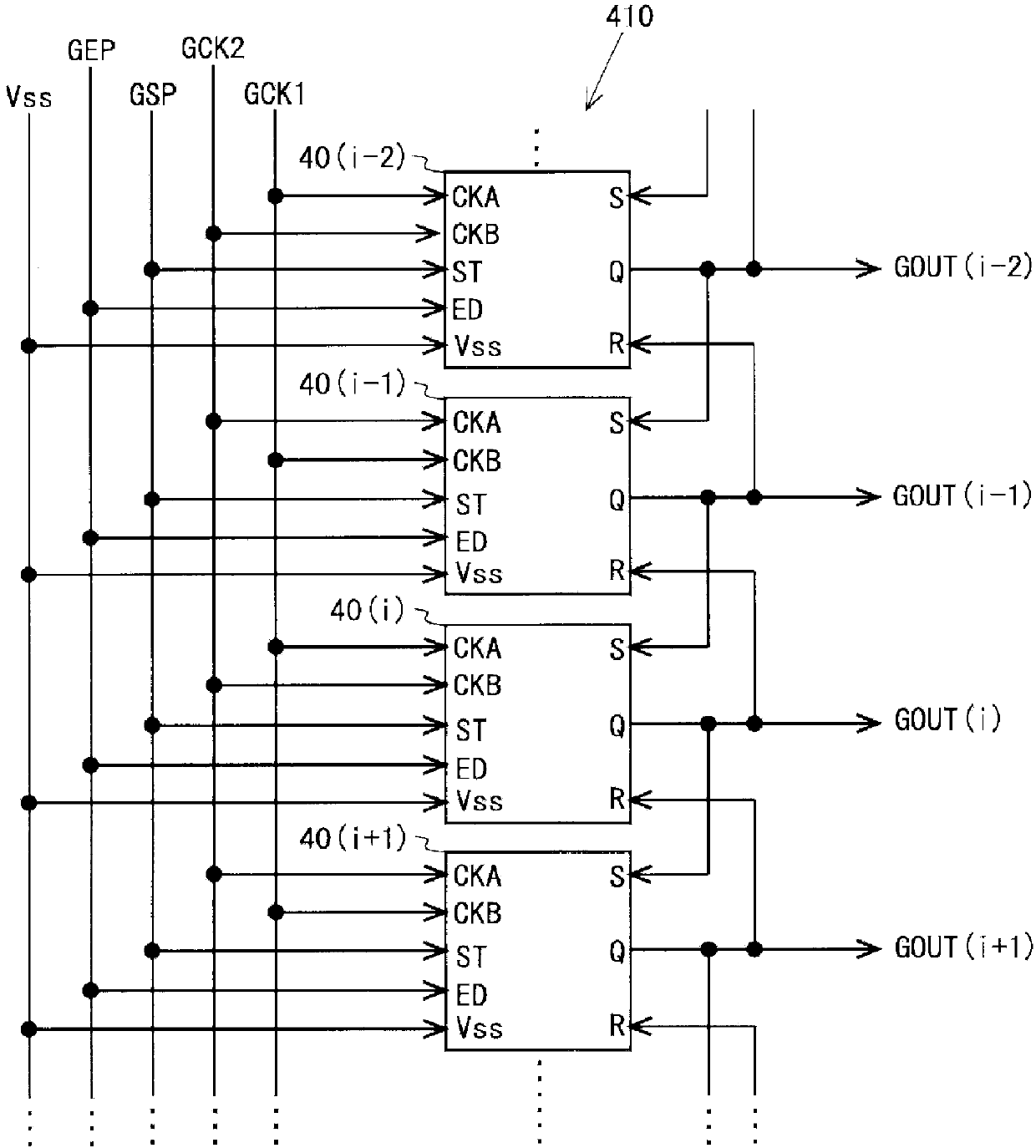
The purpose of this invention is to increase reliability of a switching element while reducing consumption power. In the vertical blanking period, an end pulse signal (ED) changes from the low level to the high level. The potential of first nodes (N1) in the first stage to (m−1)th stage of cascade-connected m-stage bistable circuits included in a shift register of the scanning signal drive circuit is reliably maintained at the low level, and the potential of second nodes (N2) in the first stage to the (m−1)th stage changes from the high level to the low level. In a bistable circuit in the m-th stage, the potential of the first node (N1) in the m-th stage changes from the high level to the low level, and the potential of the second node (N2) in the m-th stage is maintained at the low level. The supply to a bistable circuit of clock signals (CKA, CKB) is stopped. Until a write period in the subsequent vertical scanning period, the potential of the first node (N1) and the potential of the second node (N2) in each stage are maintained at the low level.
Owner:SHARP KK
Scanning signal line drive circuit, shift register, and drive method of shift register
ActiveUS20110199354A1Reduce power consumptionRaise the potentialCathode-ray tube indicatorsDigital storageBistable circuitsShift register
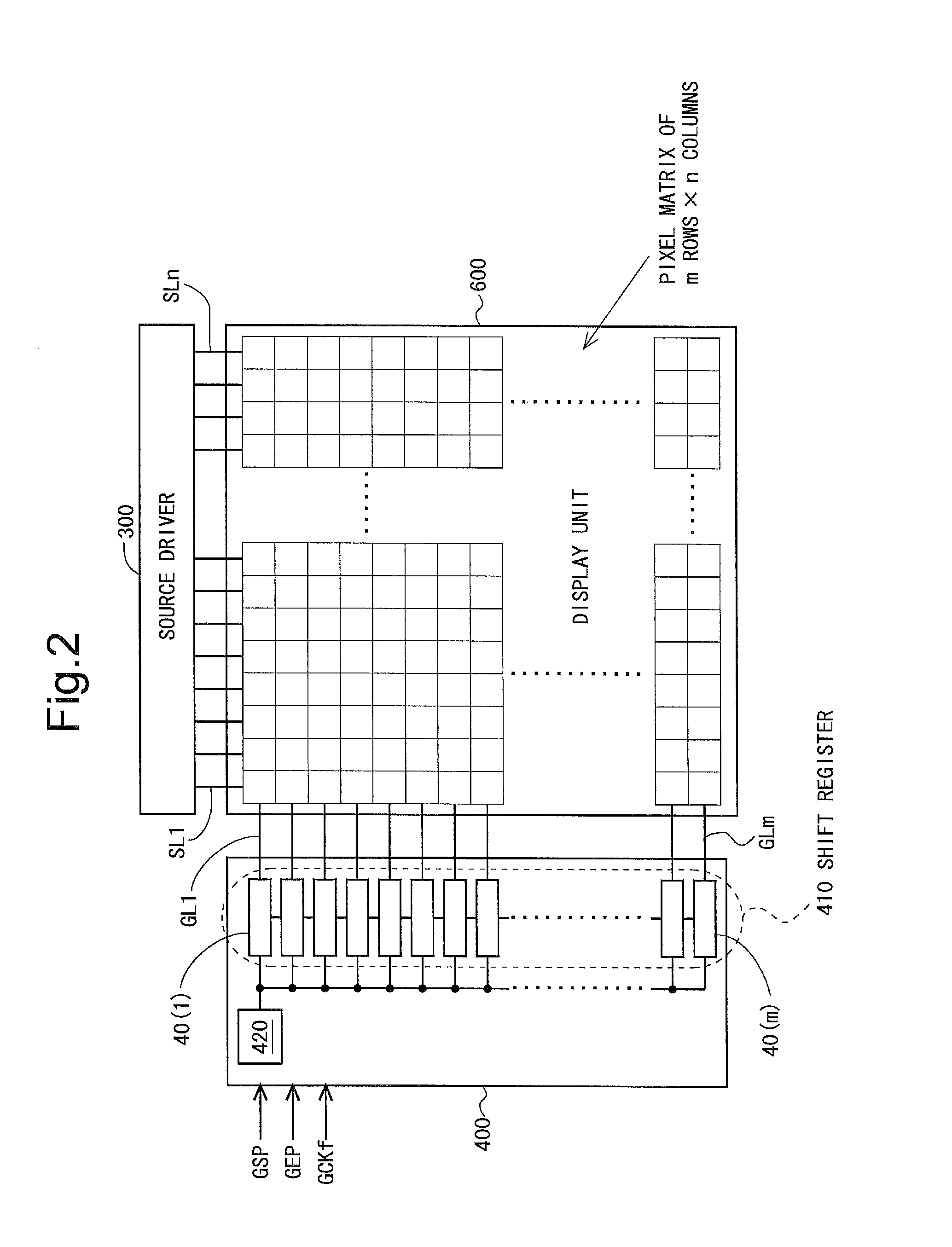
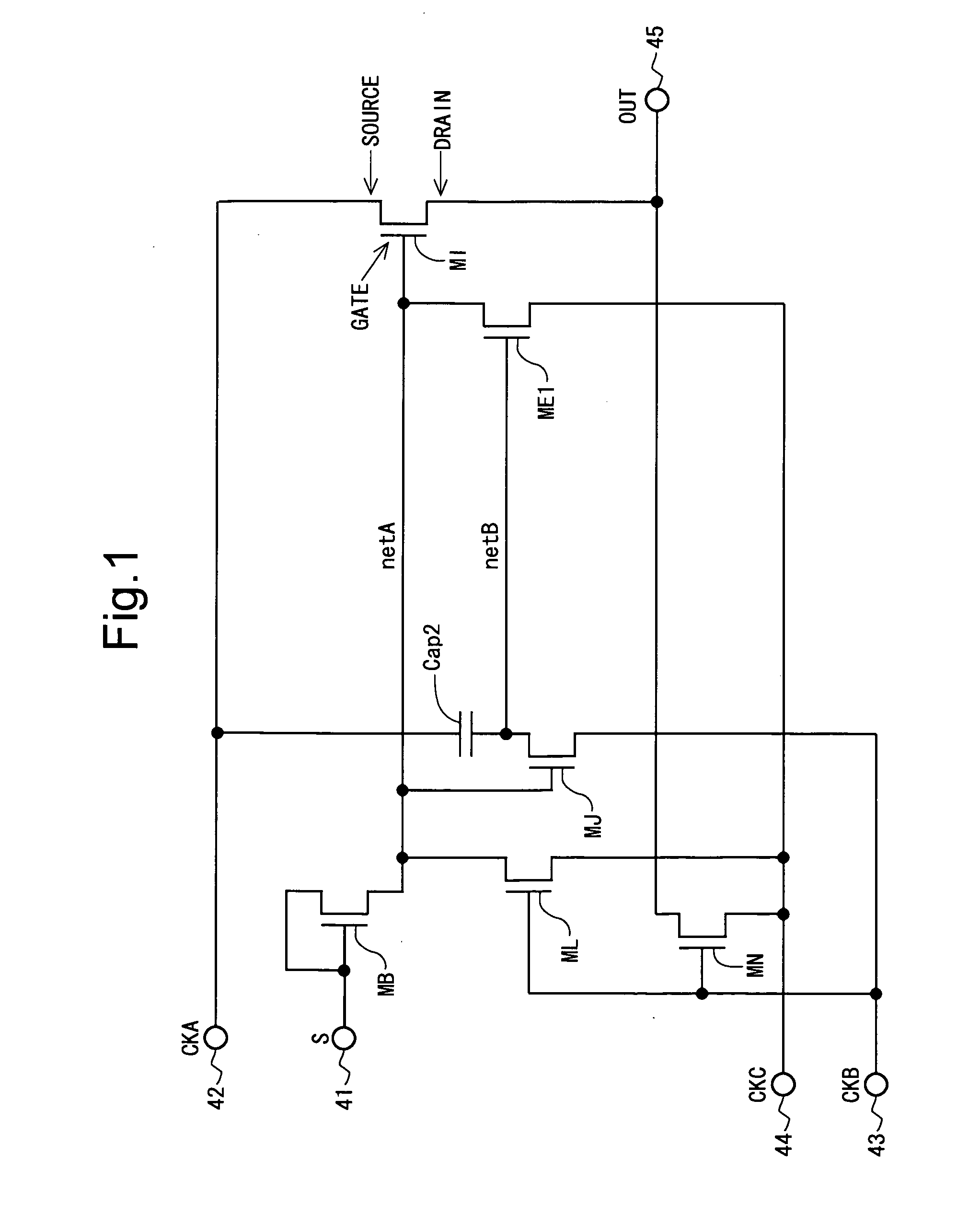
There is realized a scanning signal line drive circuit (in a display device) capable of, even in a case where a circuit in a shift register is formed using a thin-film transistor which is relatively large in off leakage, suppressing unnecessary power consumption due to a leakage current in the thin-film transistor. In at least one embodiment, bistable circuit that forms the shift register includes a thin-film transistor for raising a potential of an output terminal based on a first dock, a region netA connected to a gate terminal of the thin-film transistor, another thin-film transistor for lowering a potential of the region netA, and a region netB connected to a gate terminal of the other thin-film transistor. With this configuration, the potential of the region netB is raised based on a third clock which is advanced in phase by 90 degrees with respect to the first clock and is lowered based on a fourth clock which is delayed in phase by 90 degrees with respect to the first clock.
Owner:SHARP KK
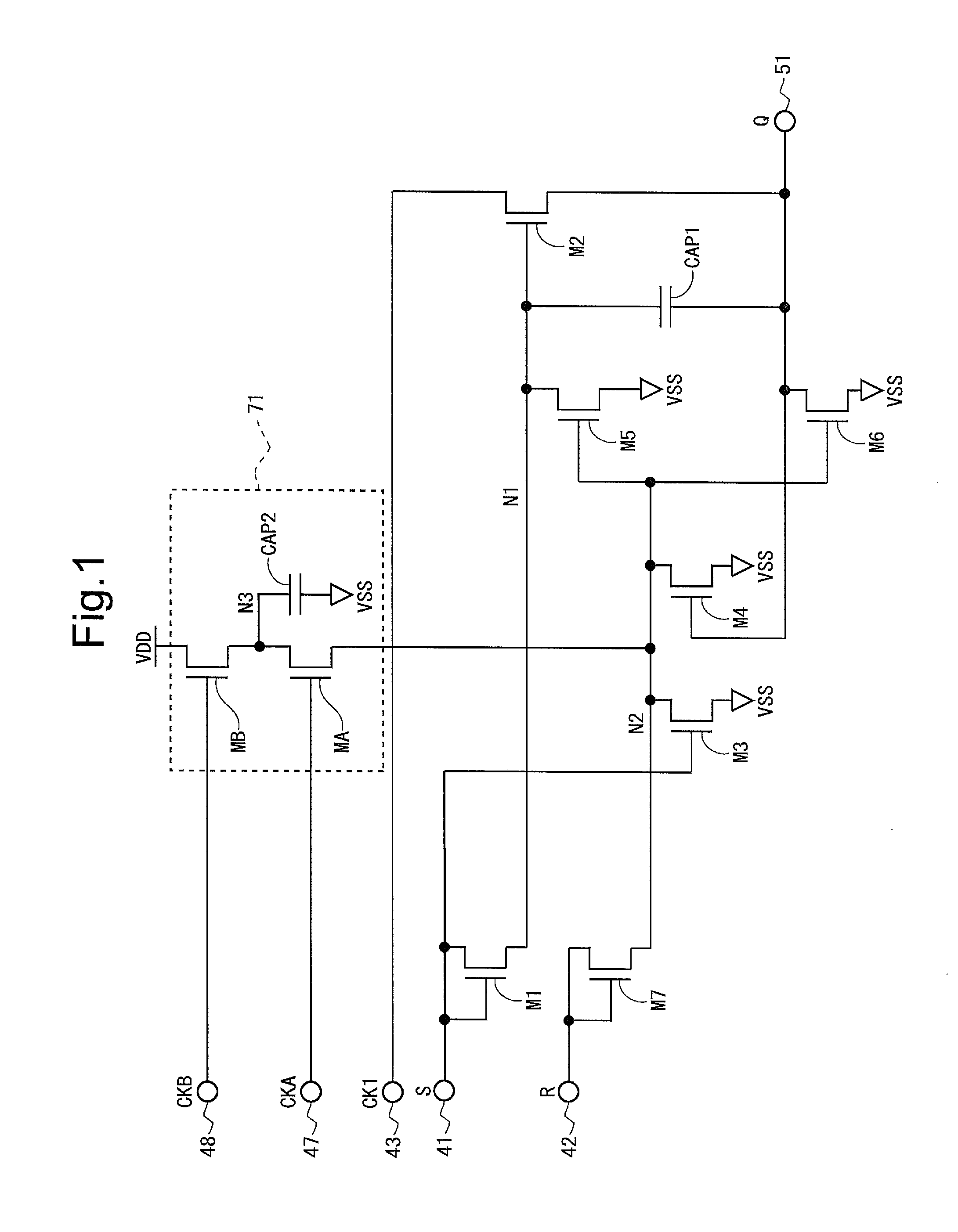
Scanning signal line drive circuit and display device having the same
InactiveUS20130009856A1Improve circuit stabilityImprove stabilityStatic indicating devicesSolid-state devicesBistable circuitsDisplay device
Stability of a circuit operation in a monolithic gate driver is improved. A bistable circuit is provided with a charge replenishment circuit (71) including: a capacitor (CAP2); a thin-film transistor (MA) having a first electrode supplied with a first clock for charge replenishment (CKA), a second electrode connected to a third-node (N3) connected to one end of the capacitor (CAP2), and a third electrode connected to a second-node (N2) to be maintained at the high level during a normal operation period; and a thin-film transistor (MB) having a first electrode supplied with a second clock for charge replenishment (CKB), a second electrode supplied with a high-level DC power supply potential (VDD), and a third electrode connected to the third-node (N3). The first clock for charge replenishment (CKA) and the second clock for charge replenishment (CKB) are alternately driven to the high level so as to eliminate a period in which “the first clock for charge replenishment (CKA) is at the high level and the second clock for charge replenishment (CKB) is at the high level”.
Owner:SHARP KK
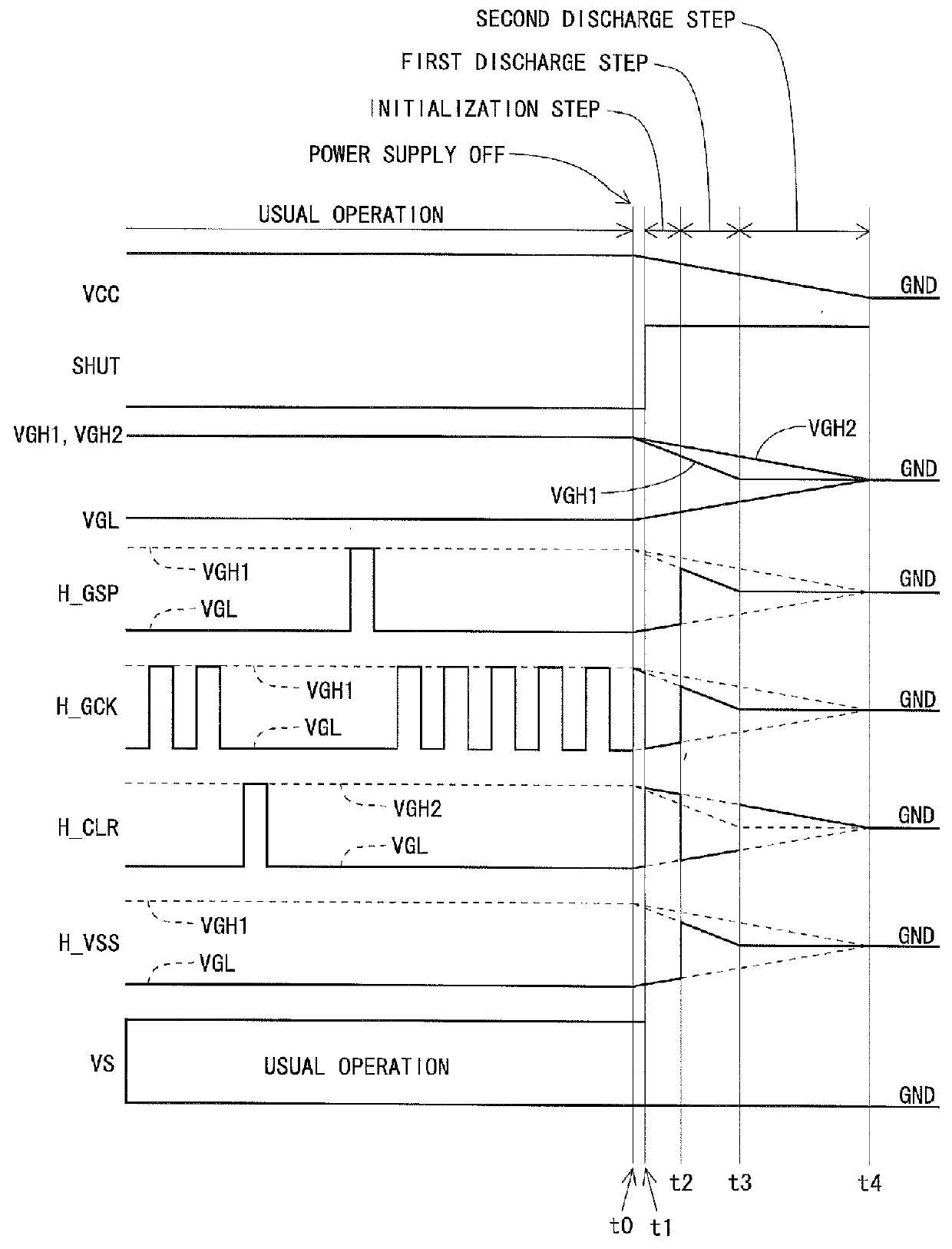
Liquid crystal display device and drive method for same
InactiveUS20140306948A1Lower potentialPotential variationCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingShift registerBistable circuits
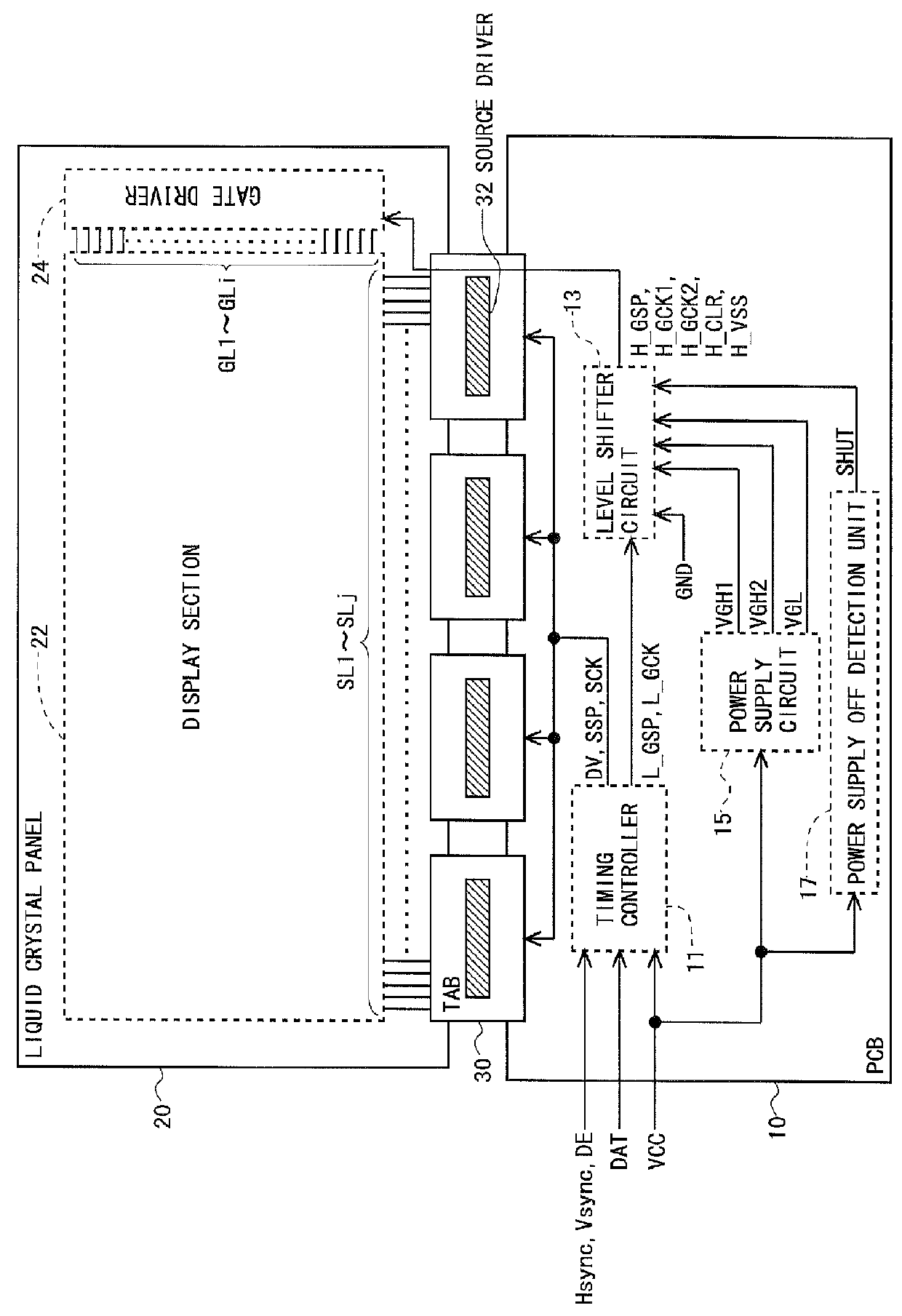
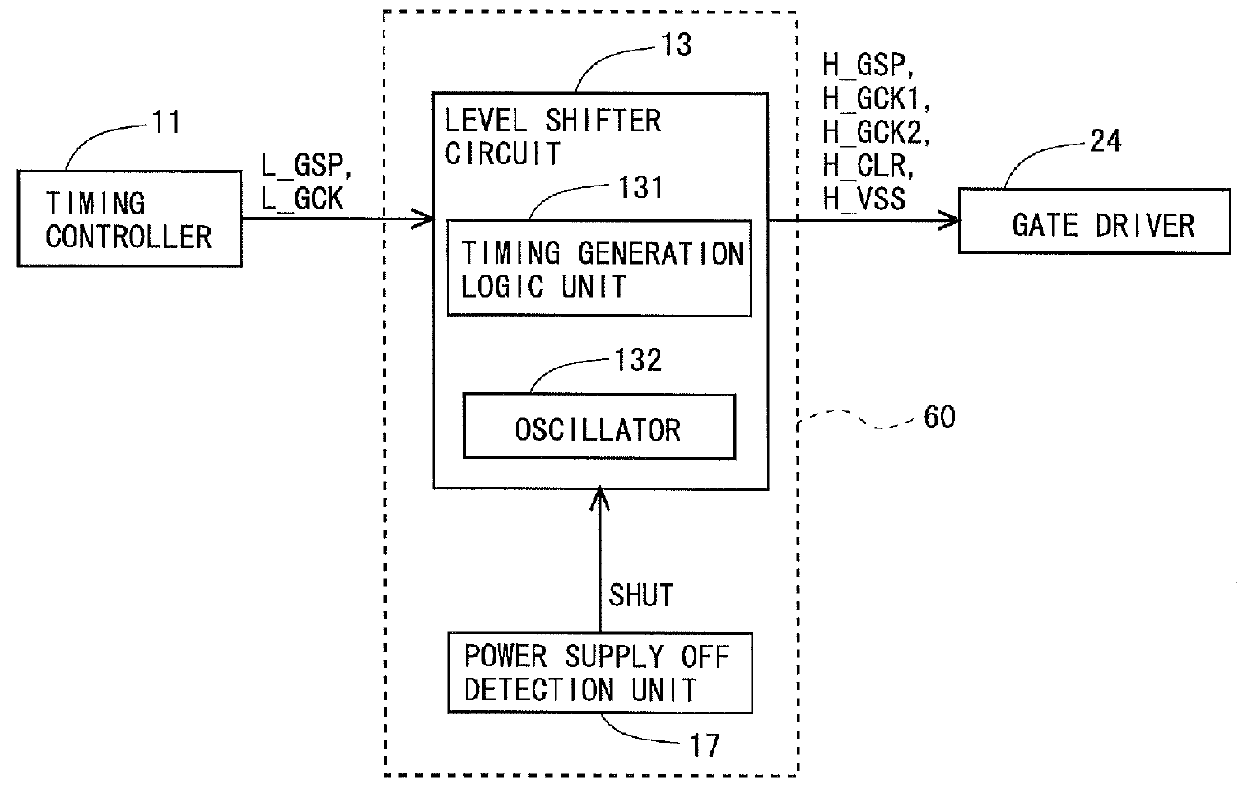
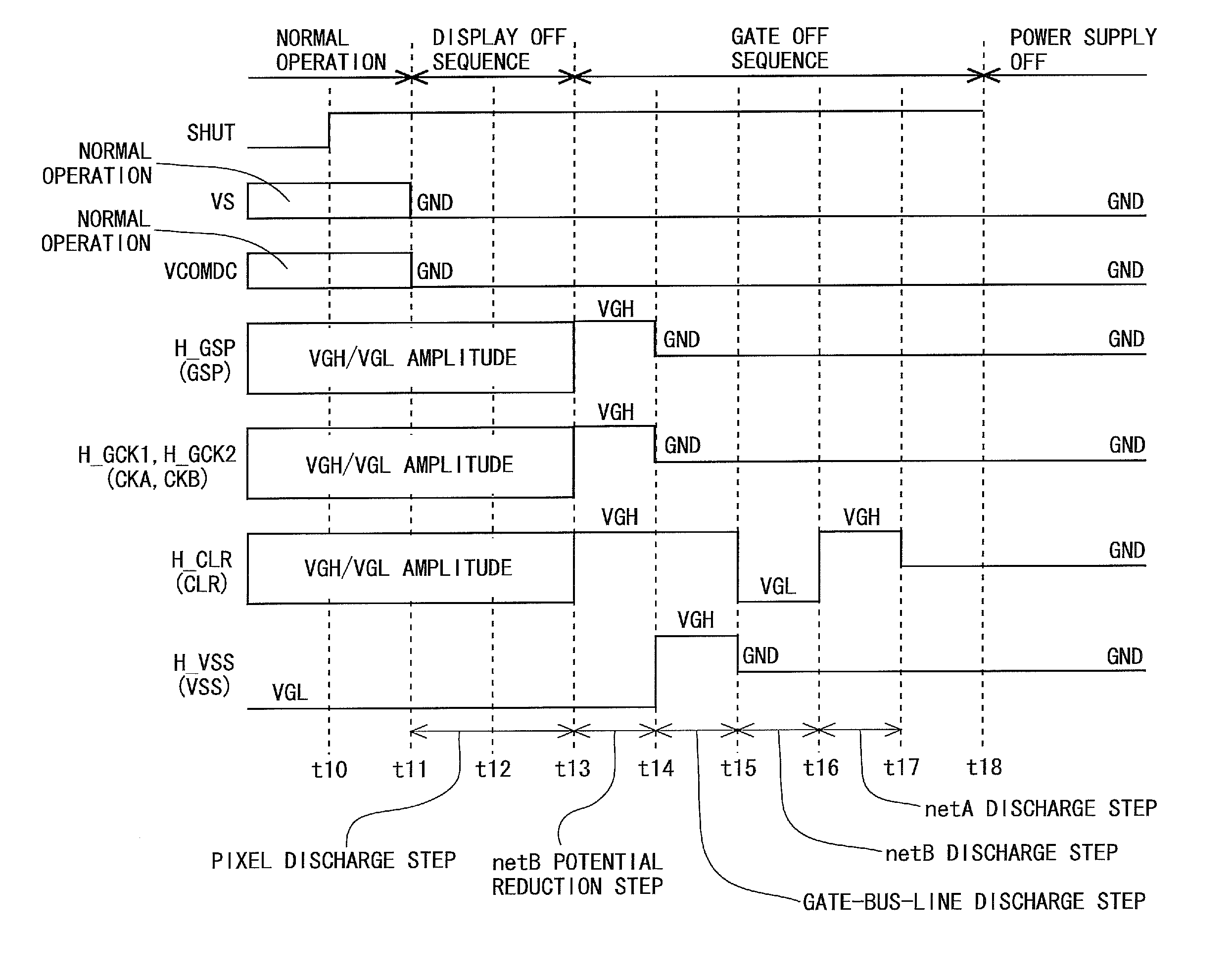
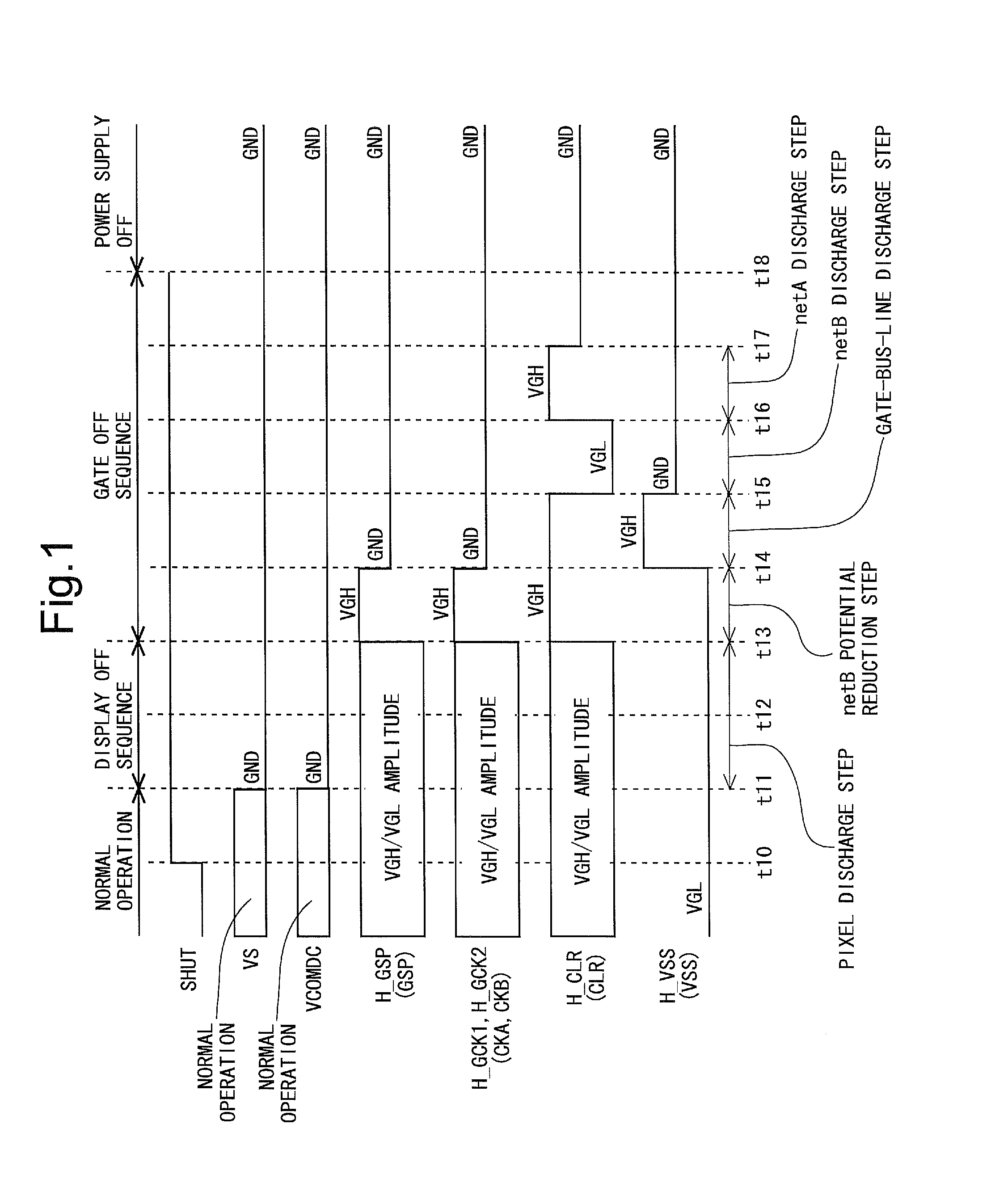
Provided are: a liquid crystal display device capable of rapidly removing residual electric charges in a panel when a power supply is turned off, and in particular, suitable for a case where IGZO-GDM is adopted; and a driving method of the liquid crystal display device.In the liquid crystal display device, when an OFF state of the power supply is detected, a power supply OFF sequence including an initialization step, a first discharge step and a second discharge step is executed. In the initialization step, only a clear signal (H_CLR) among GDM signals is set at a high level, and a state of each of bistable circuits which constitute a shift register is initialized. In the first discharge step, only the clear signal (H_CLR) among the GDM signals is set at a low level, all of gate bus lines are turned to a selected state, and electric charges in pixel formation portions are discharged. In the second discharge step, the clear signal (H_CLR) is set at the high level, and electric charges on floating nodes in each of the bistable circuits are discharged.
Owner:SHARP KK
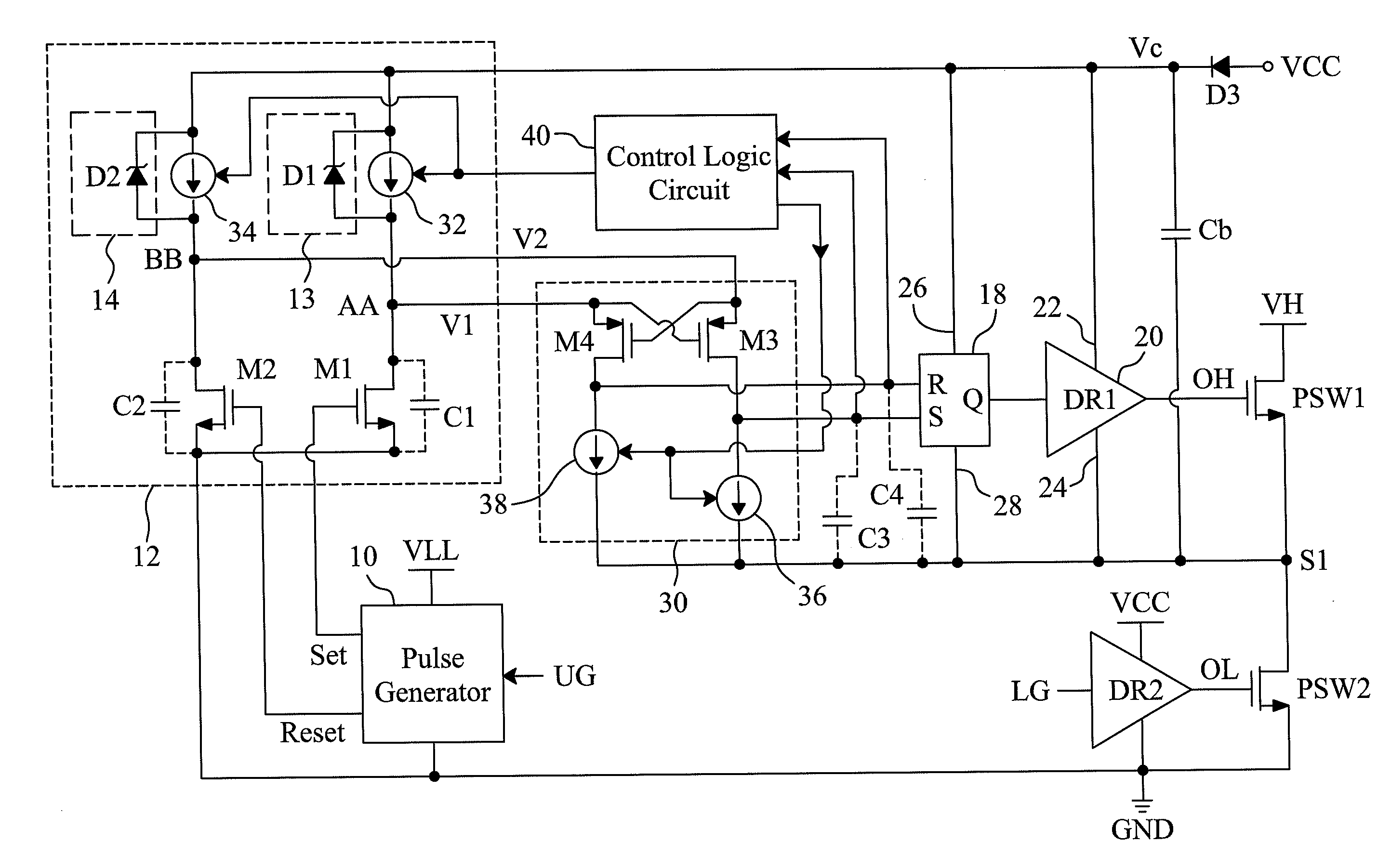
System and shadow bistable circuits coupled to output joining circuit
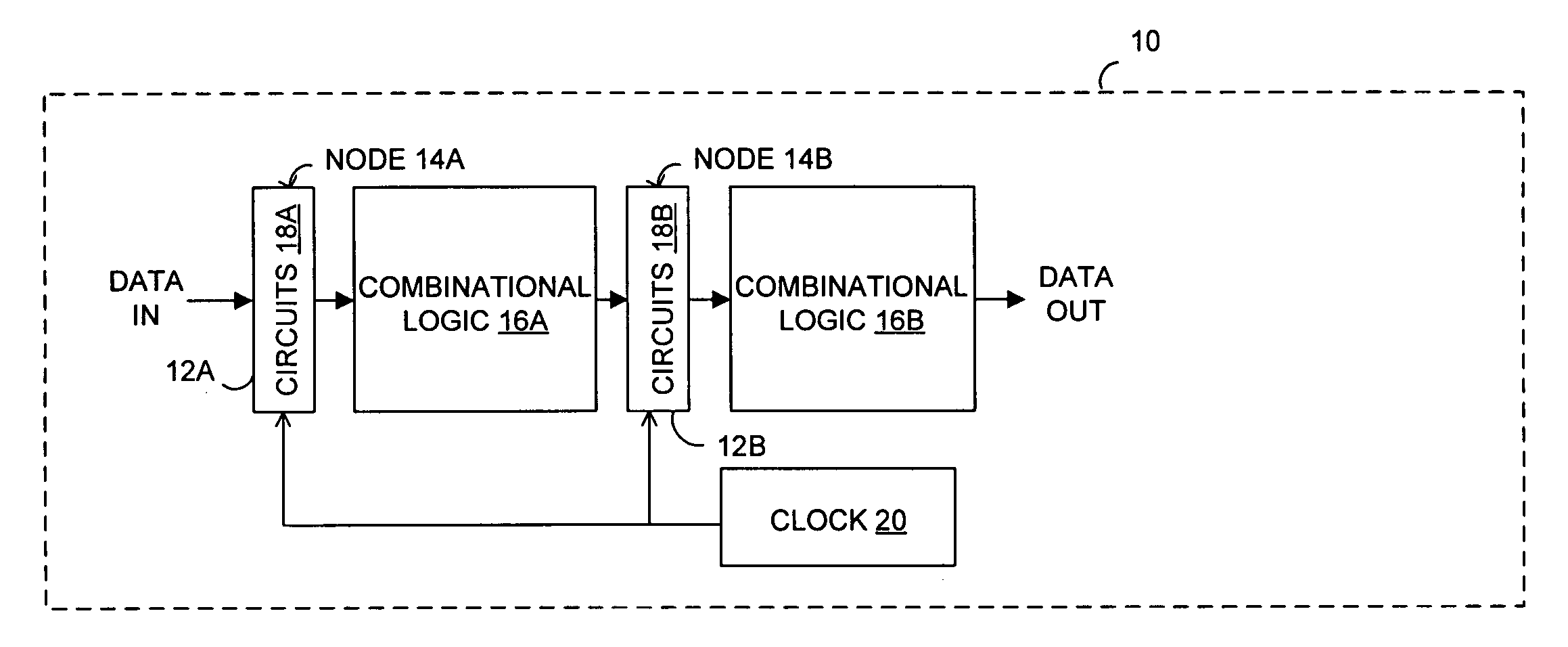
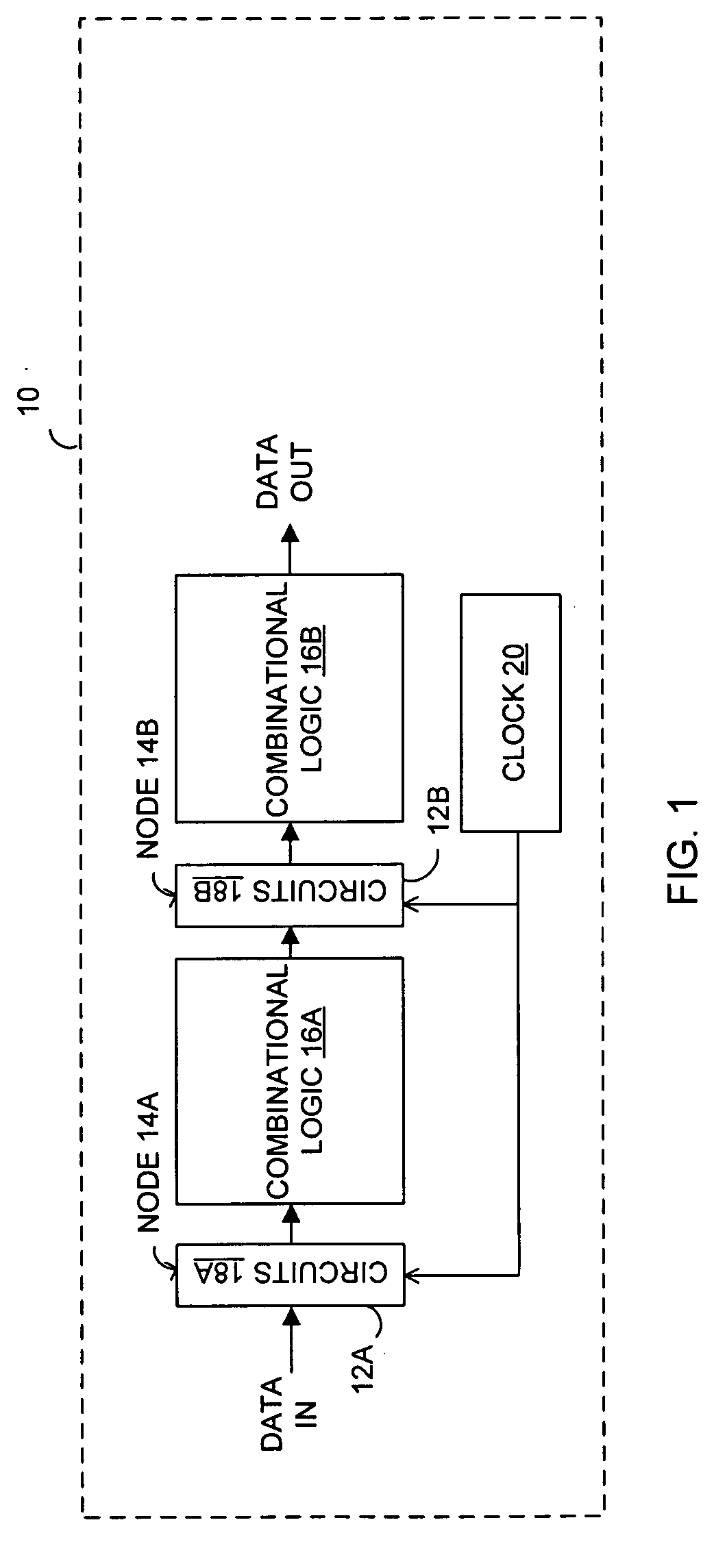
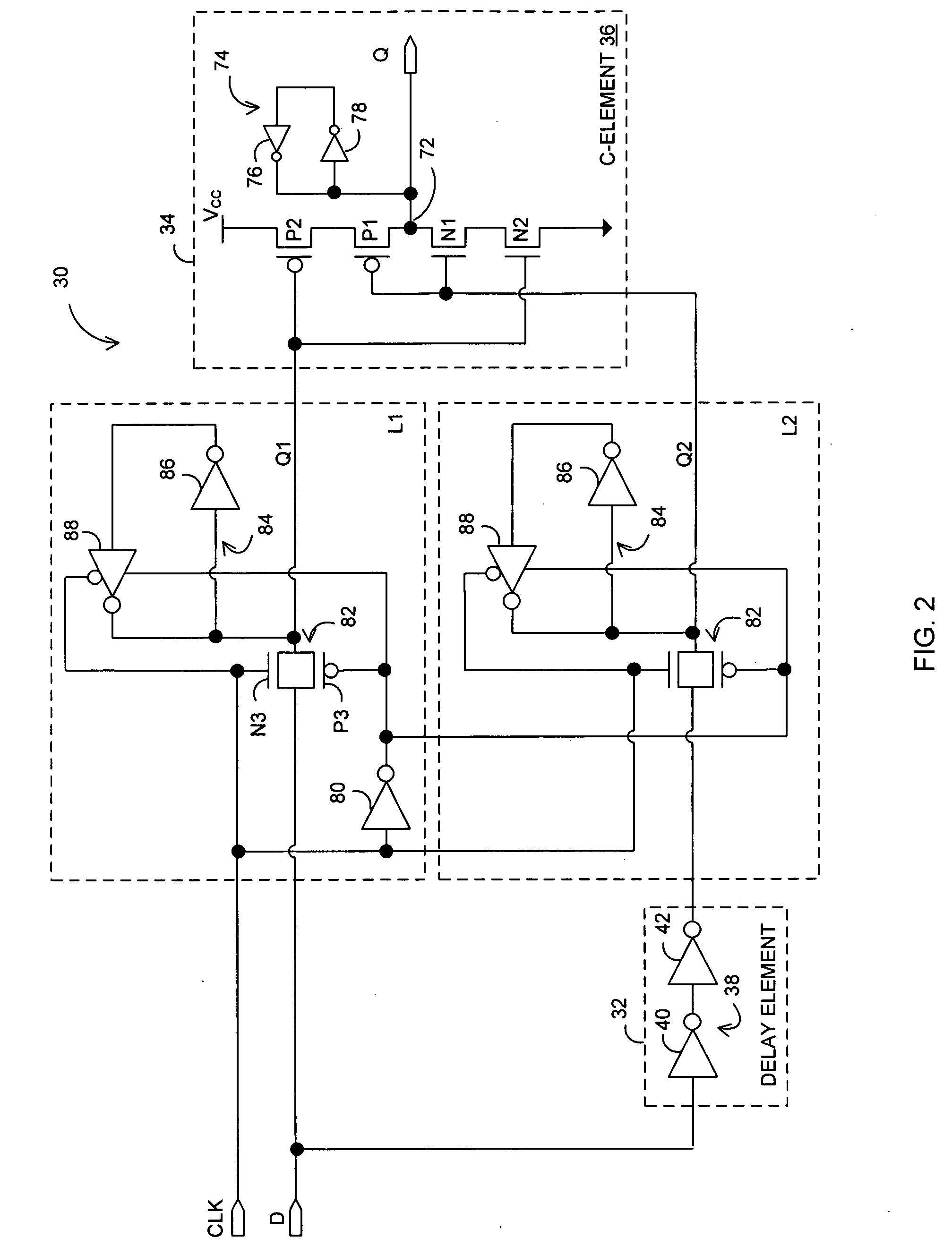
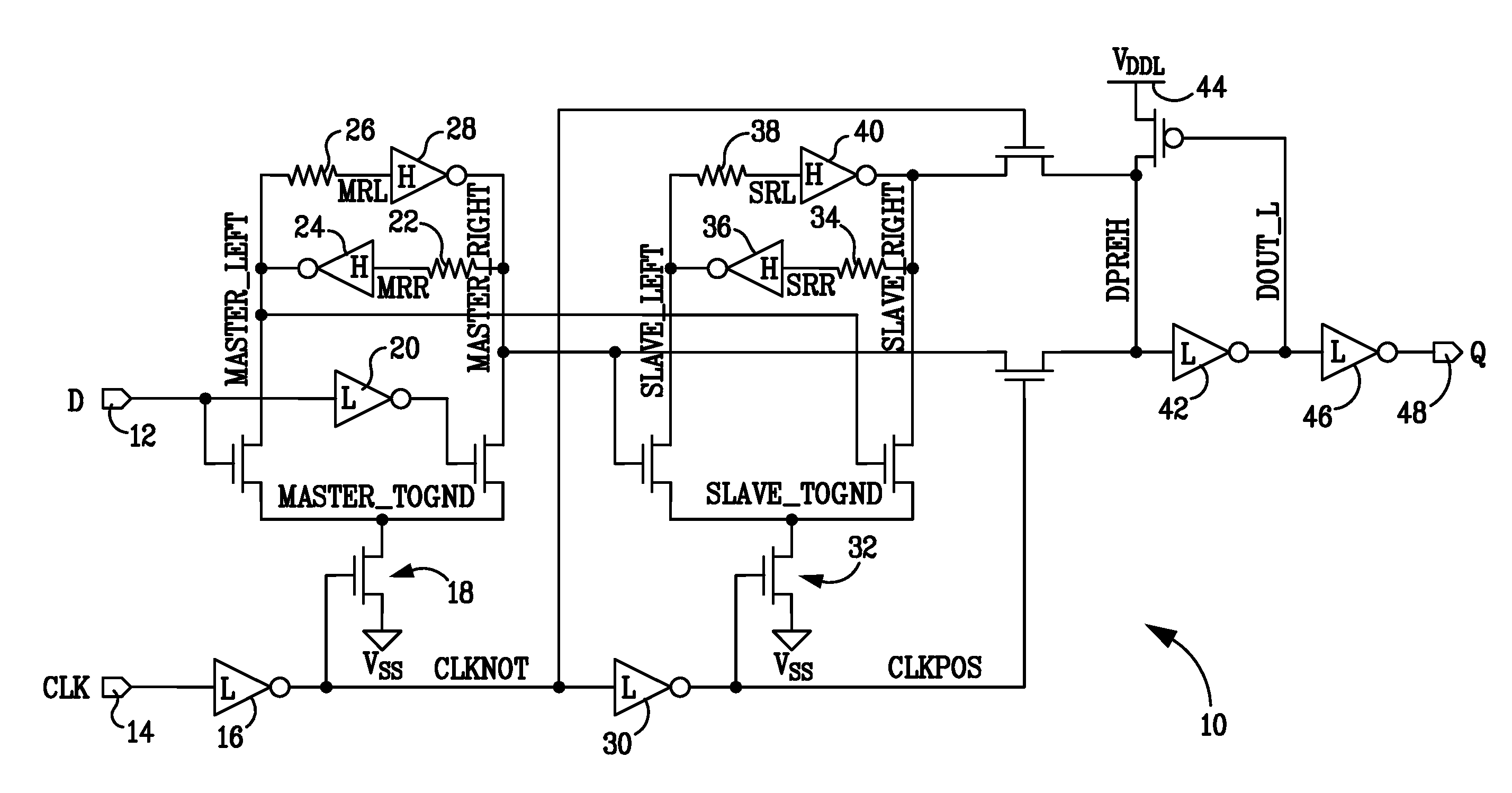
In one embodiment, an apparatus is provide with a combinational logic circuit to generate a data input signal; a delay element, coupled to the combinational logic circuit, to provide a delayed data input signal in response to the data input signal. Additionally, the apparatus is provided with a system bistable circuit, coupled to the combinational logic circuit, to generate a system bistable signal in response to at least the data input signal; a shadow bistable circuit, coupled to the delay element, to generate a shadow bistable signal in response to at least the delayed data input signal. Further, the apparatus is provided with an output joining circuit, coupled to the system and the shadow bistable circuits, to provide a data output signal in response to the system and the shadow bistable signals.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Nonvolatile SRAM/latch circuit using current-induced magnetization reversal MTJ
The present invention is a memory circuit that includes a bistable circuit that stores data; and a ferromagnetic tunnel junction device that nonvolatilely stores the data stored in the bistable circuit according to a magnetization direction of a ferromagnetic electrode free layer, the data nonvolatilely stored in the ferromagnetic tunnel junction device being able to be restored in the bistable circuit. According to the present invention, writing data to and reading data from the bistable circuit can be performed at high speed. In addition, even though a power source is shut down, it is possible to restore data nonvolatilely stored in the ferromagnetic tunnel junction devices to the bistable circuit.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Scanning signal line drive circuit, shift register and display device
InactiveUS20110193853A1Raise the potentialLower potentialCathode-ray tube indicatorsDigital storageBistable circuitsShift register
There is provided a display device capable of preventing a malfunction and a display defect due to an off-leak from occurring even when a circuit in a shift register is configured utilizing thin film transistors of relatively large off-leaks. In at least one embodiment, each of bistable circuits that constitute the shift register includes: a thin film transistor for increasing a potential of an output terminal based on a first clock; a thin film transistor for decreasing the potential of the output terminal; a thin film transistor for increasing a potential of a range netA connected to a gate terminal of the thin film transistor based on a start signal; thin film transistors for decreasing the potential of the range netA; a capacitor for increasing the potential of a range netB connected to a gate terminal of the thin film transistor; and a thin film transistor for decreasing the potential of the range netB.
Owner:SHARP KK
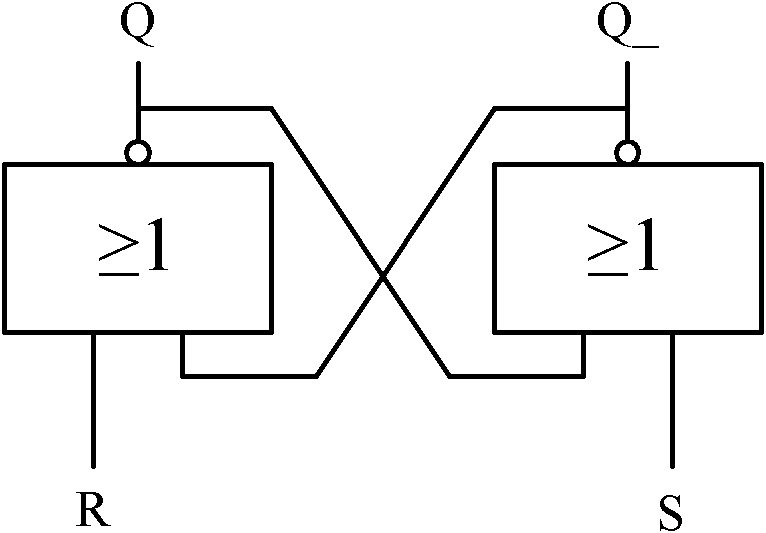
Generate random numbers using metastability resolution time
ActiveUS20150178048A1Random number generatorsDigital function generatorsStable stateBistable circuits
A mechanism is provided for a circuit for generation of a random output. A bistable circuit has two stable states as an output and a clock signal as an input. The bistable circuit includes a first logic circuit and a second logic circuit cross-coupled connected together, which transition into a metastable state before resolving to the two stable states. The second logic circuit resolves to a stable state at a resolution time. A digitization circuit is configured to generate random bits corresponding to a variance of the resolution time of the second logic circuit resolving from the metastable state to the stable state for cycles of the clock signal. The resolution time randomly varies according to noise. An actual value of the stable state is eliminated as factor in generating the random bits.
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS
Random number generator
InactiveUS20080091755A1Avoid the needRandom number generatorsSecuring communicationStable stateBistable circuits
A circuit for generating a random output value is disclosed that comprises: a bistable circuit having two stable states in which a 0 or a 1 is output and having a balanced metastable state in which a floating value between 0 and 1 is output, said bistable circuit resolving from said metastable state to one of said stable states on being switched on, said state depending on a voltage level at a port on said bistable circuit; a voltage level control circuit for controlling a voltage level at said port on said bistable circuit; a time measuring circuit for measuring a switching time taken for said bistable circuit to switch from said metastable state to one of said stable states following switch on; and control logic for controlling said time measuring circuit, said voltage level control circuit and a switching off and on of said bistable circuit, said control logic being adapted to perform a following sequence: control said voltage level control circuit to set a predetermined voltage level at said port on said bistable circuit, switch said bistable circuit on, detect a measured switching time, and turn said bistable circuit off and if said measured switching time is longer than a predetermined value, output said resolved stable state of said bistable circuit as said random output value.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Scanning signal line drive circuit and display device having the same
ActiveUS20120320008A1Improve circuit stabilityImprove stabilityCathode-ray tube indicatorsDigital storageBistable circuitsDisplay device
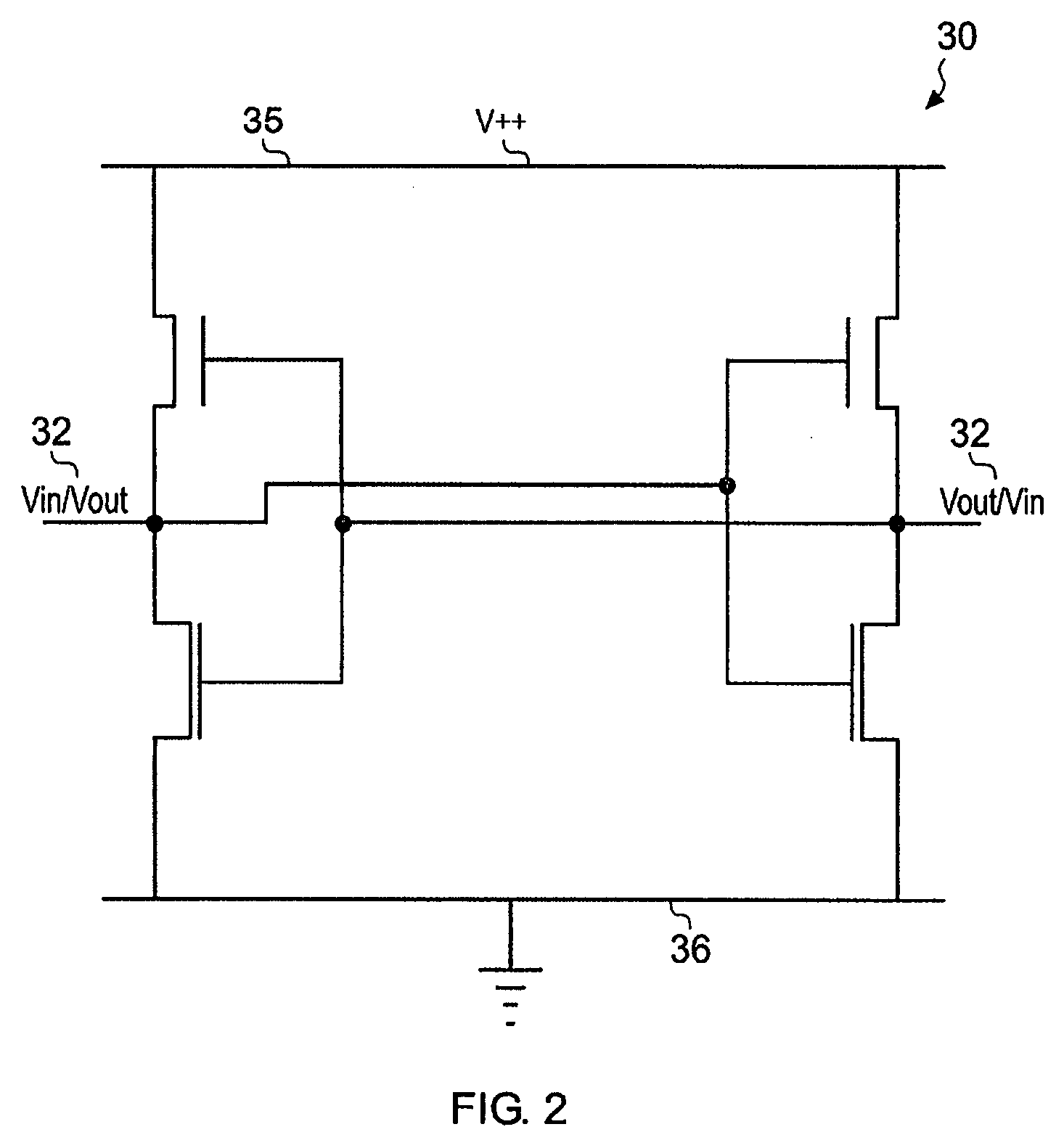
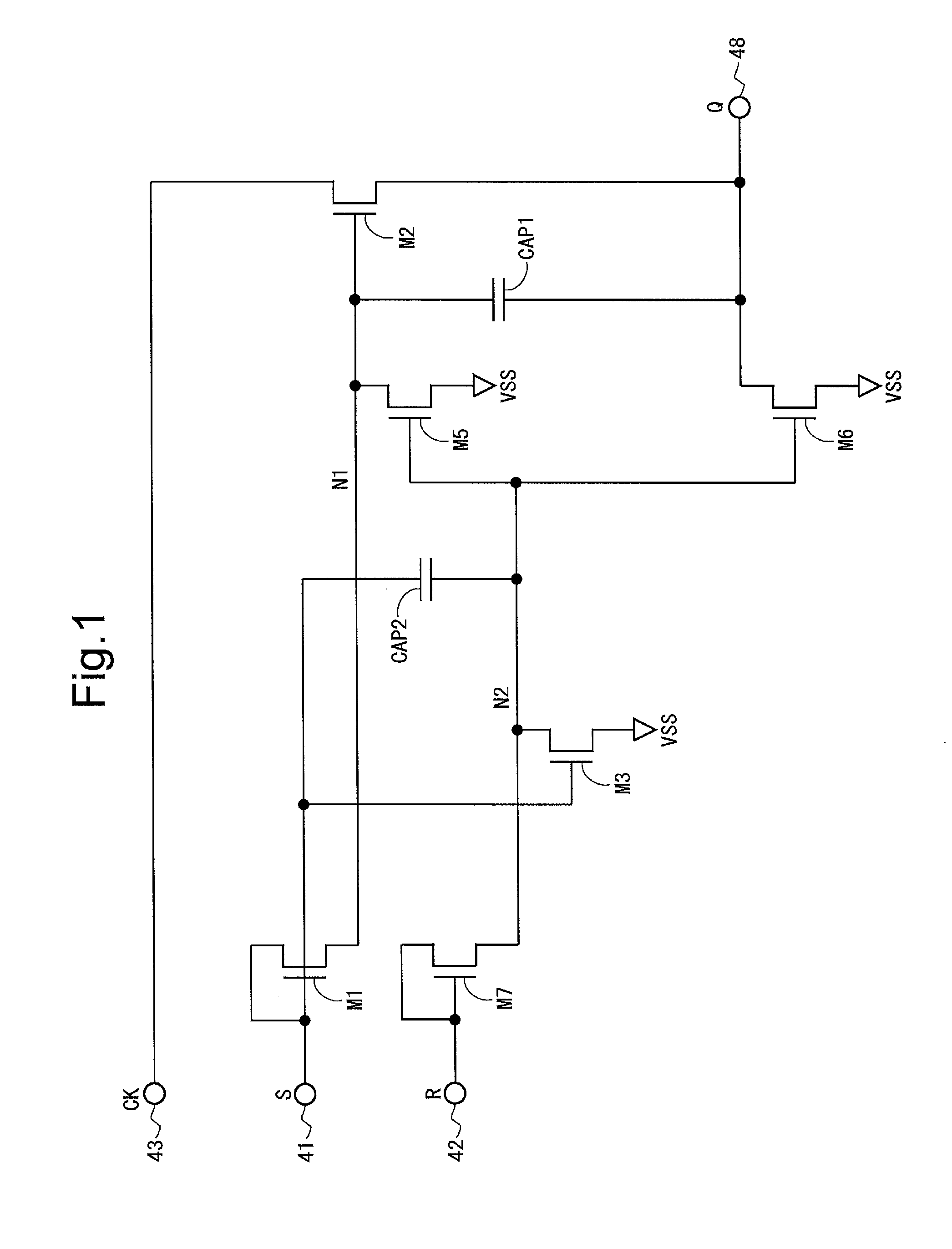
A bistable circuit includes an input terminal (41) for a set signal, an input terminal (42) for a reset signal, an output terminal (48) for a state signal, a thin-film transistor (M2) for increasing a potential of the output terminal (48) based on a first clock, a thin-film transistor (M1) for increasing a potential of a first-node connected to a gate terminal of the thin-film transistor (M2) based on the set signal, a thin-film transistor (M5) for decreasing the potential of the first-node, a thin-film transistor (M7) for increasing a potential of a second-node connected to a gate terminal of the thin-film transistor (M5) based on the reset signal, a thin-film transistor (M6) for decreasing the potential of the output terminal (48) based on the potential of the second-node, a thin-film transistor (M3) for increasing the potential of the second-node based on the set signal, and a capacitor (CAP2) having one end connected to the second-node and the other end connected to the input terminal (41).
Owner:SHARP KK
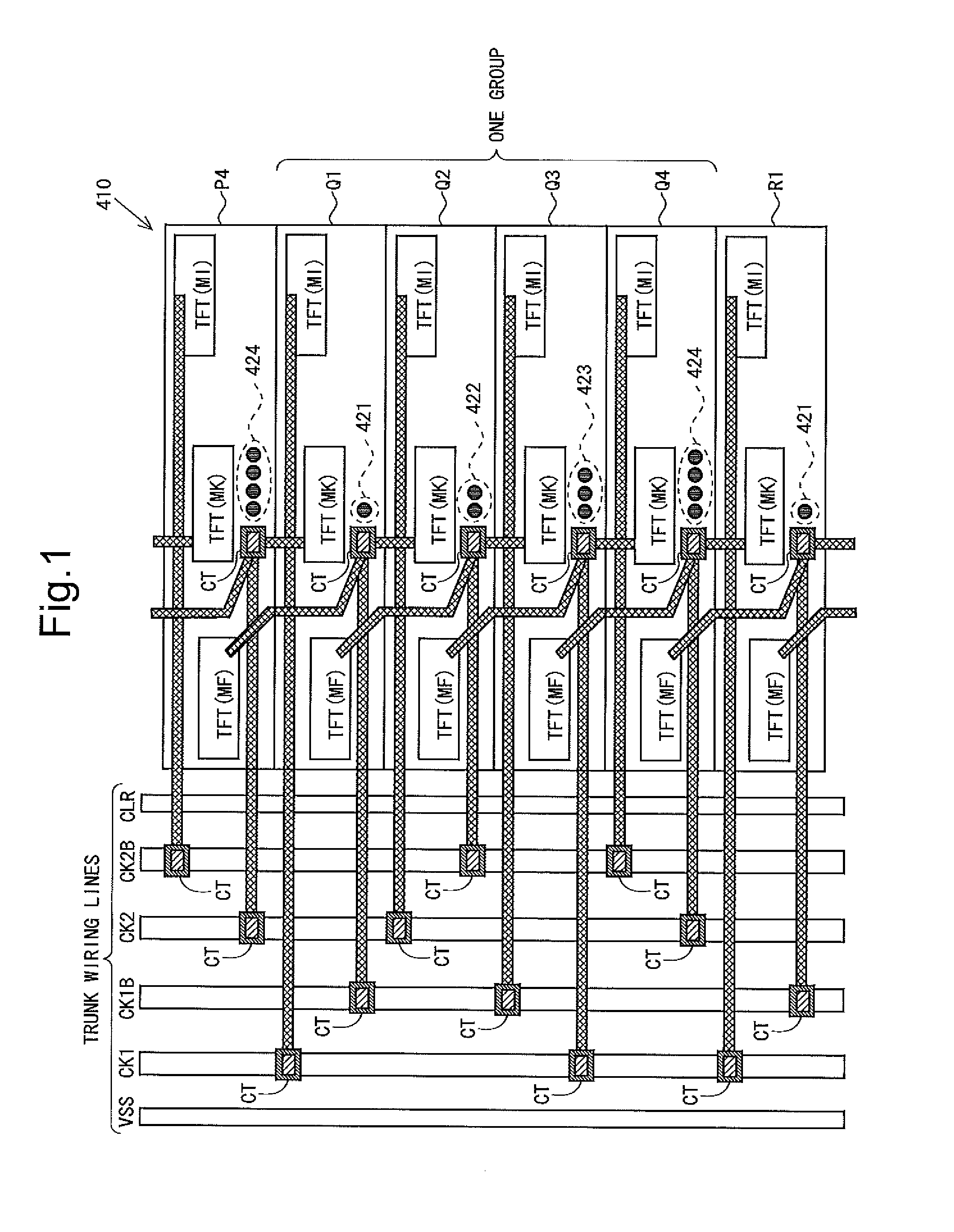
Scanning signal line drive circuit and display device including same
InactiveUS20120146969A1Improving panel yieldEasy to testSolid-state devicesCathode-ray tube indicatorsBistable circuitsShift register
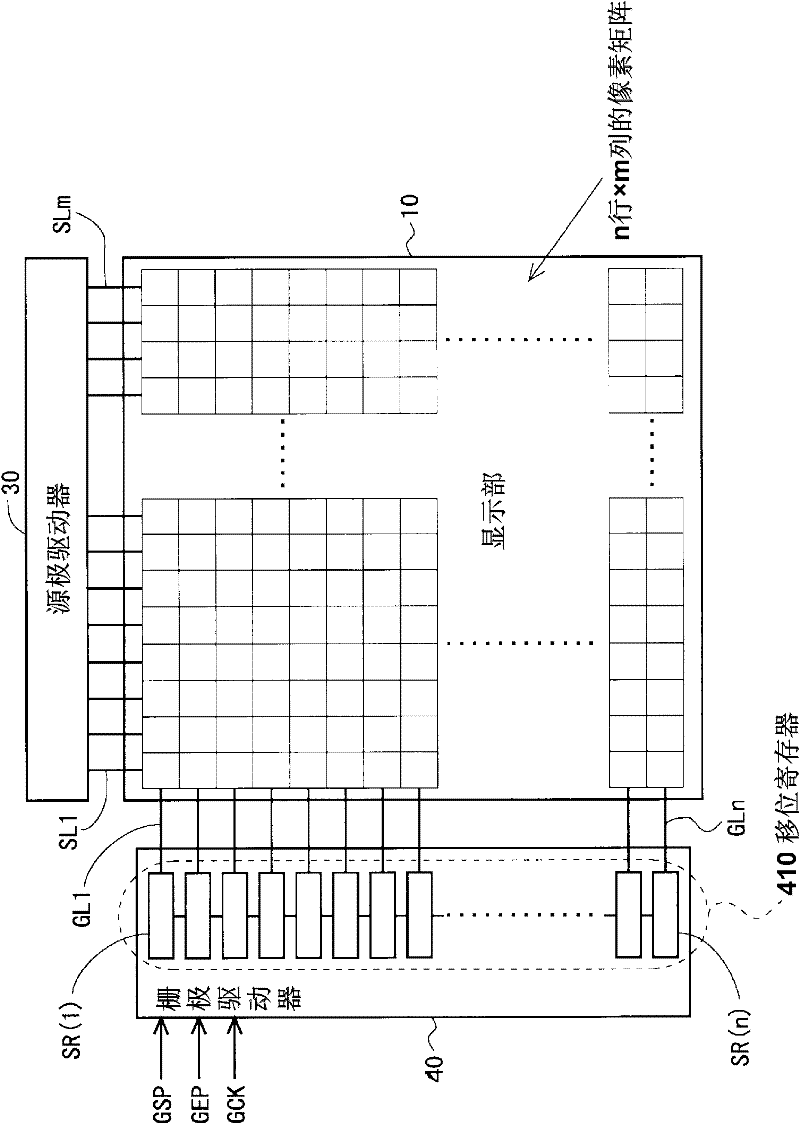
A gate driver is implemented that includes an easily testable shift register to improve panel yields. In a monolithic gate driver including a shift register that operates based on 4-phase clock signals, each stage of the shift register is provided with an inter-stage connecting wiring line for receiving a clock signal other than clock signals received from a clock signal trunk wiring line, from a different stage than the stage; and a contact that connects a wiring line formed on the stage to the inter-stage connecting wiring line. The shift register is grouped every four consecutive stages. Markings formed of different numbers of planar-view circular-shaped structures are formed on bistable circuits of four stages included in each group such that the same type of marking appears every four stages.
Owner:SHARP KK
Scanning signal line drive circuit, display device having the same, and drive method for scanning signal line
ActiveUS20140035891A1Reduce controlGuaranteed uptimeCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingBistable circuitsControl signal
The present invention is directed to suppress dullness of a scanning signal in a scanning signal line drive circuit. A bistable circuit is provided with an input terminal (43) for receiving a first clock signal (CK), an input terminal (48) for receiving a control signal (CT), an input terminal (49) for receiving a level down signal (LD), an output terminal (51), a thin film transistor (T2), and a thin film transistor (TA). The thin film transistor (T2) has a gate terminal connected to a first node (N1), a drain terminal connected to the input terminal (43), and a source terminal connected to the output terminal (51). The thin film transistor (TA) has a gate terminal connected to the input terminal (48), a drain terminal connected to the first node (N1), and a source terminal connected to the input terminal (49). The potential of the control signal (CT) becomes the high level in a control period as a period except for the first one horizontal scanning period in a vertical blanking period. The level down signal (LD) is a potential lower than DC power supply potential (Vss).
Owner:SHARP KK
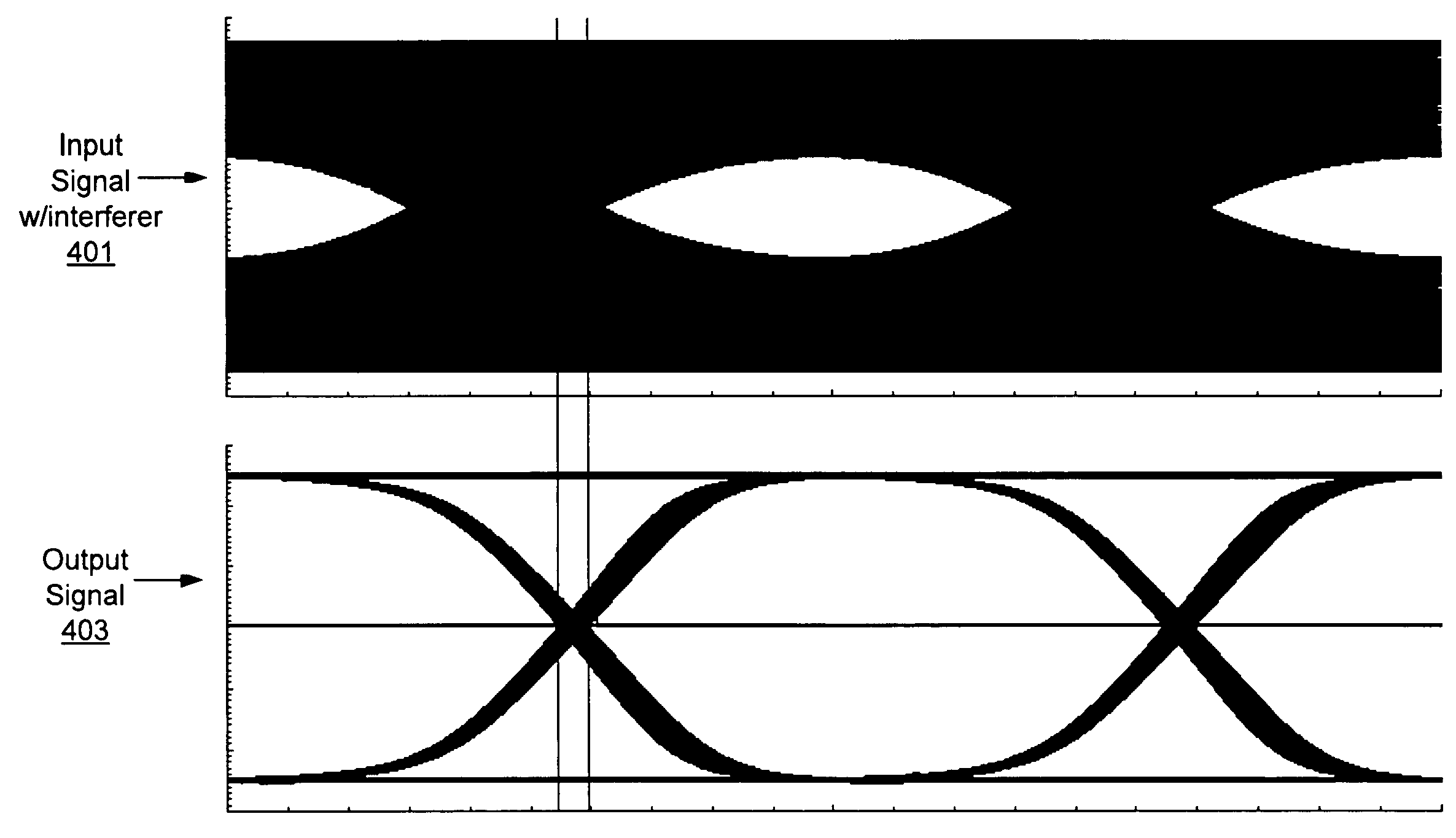
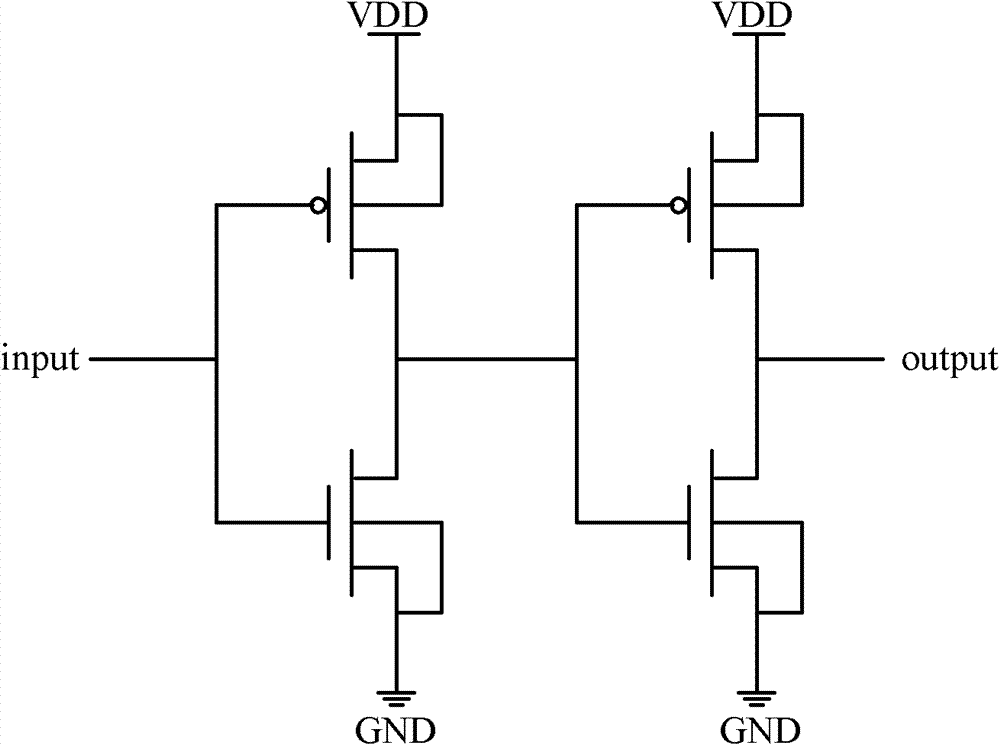
Method and system for a narrowband, non-linear optoelectronic receiver
Methods and systems for a narrowband, non-linear optoelectronic receiver are disclosed and may include amplifying a received signal, limiting a bandwidth of the received signal, and restoring the signal utilizing a level restorer, which may include a non-return to zero (NRZ) level restorer. The NRZ level restorer may include a pulse-triggered bistable circuit, which may include two parallel inverters, with one being a feedback path for the other. The inverters may be single-ended or differential. A photogenerated signal may be amplified in the receiver utilizing a transimpedance amplifier and programmable gain amplifiers (PGAs). A received electrical signal may be amplified via PGAs. The bandwidth of the received signal may be limited utilizing one or more of: a low pass filter, a bandpass filter, a high pass filter, a differentiator, or a series capacitance on the chip. The signal may be received from a photodiode integrated on the chip.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Liquid crystal display device and driving method therefor
InactiveCN102598105AEasy dischargeSuppresses degradation of display qualityStatic indicating devicesShift registerBistable circuits
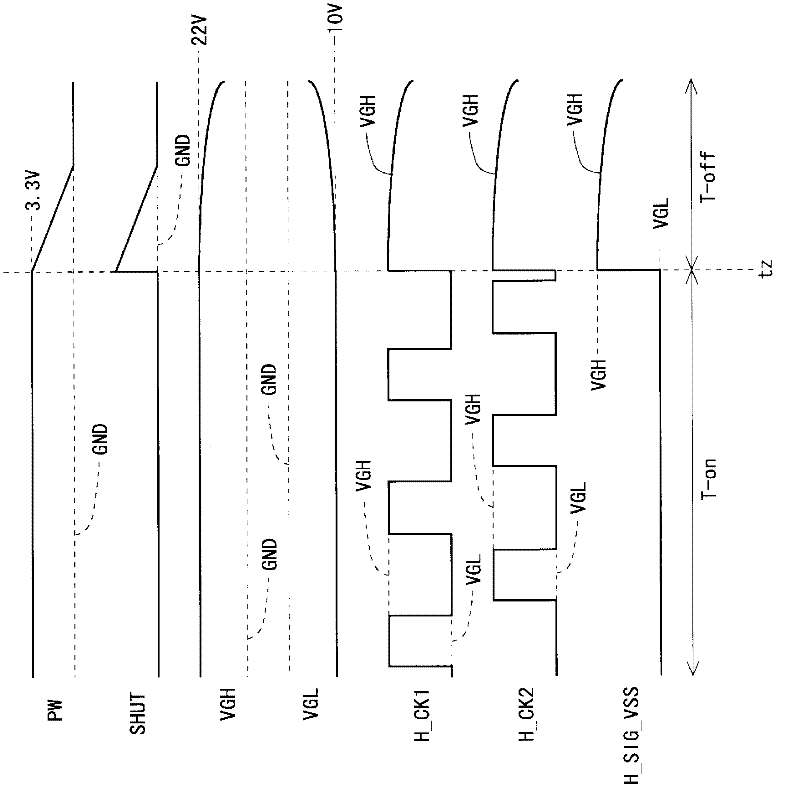
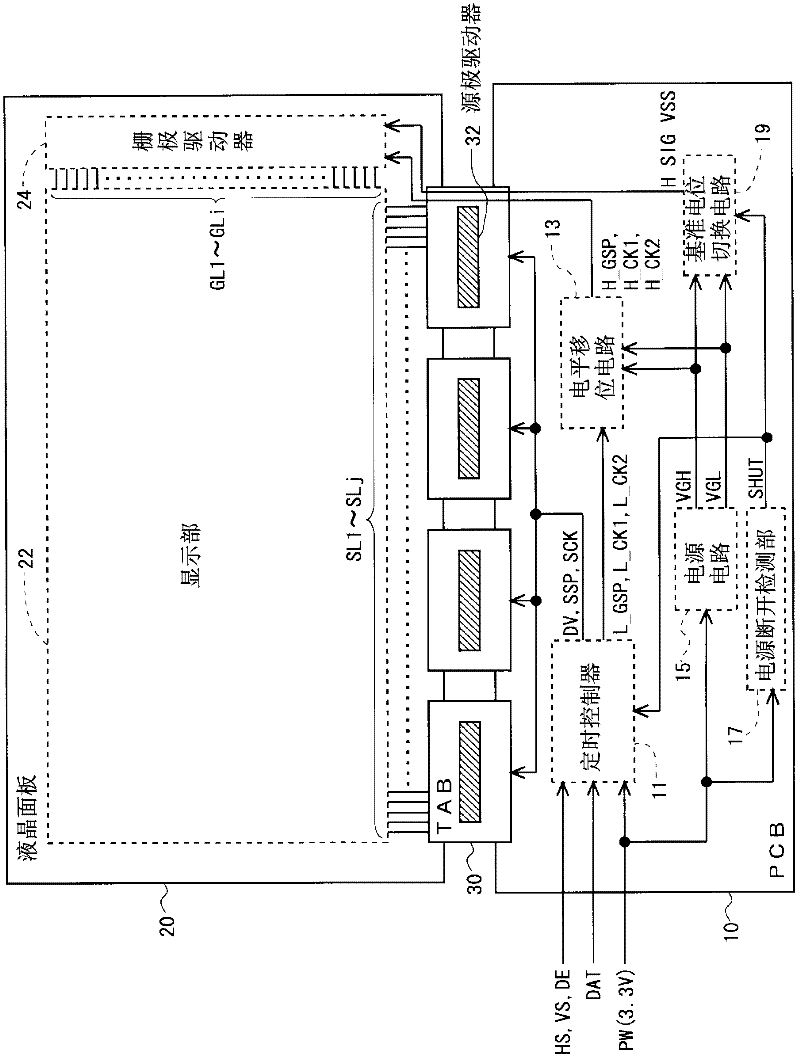
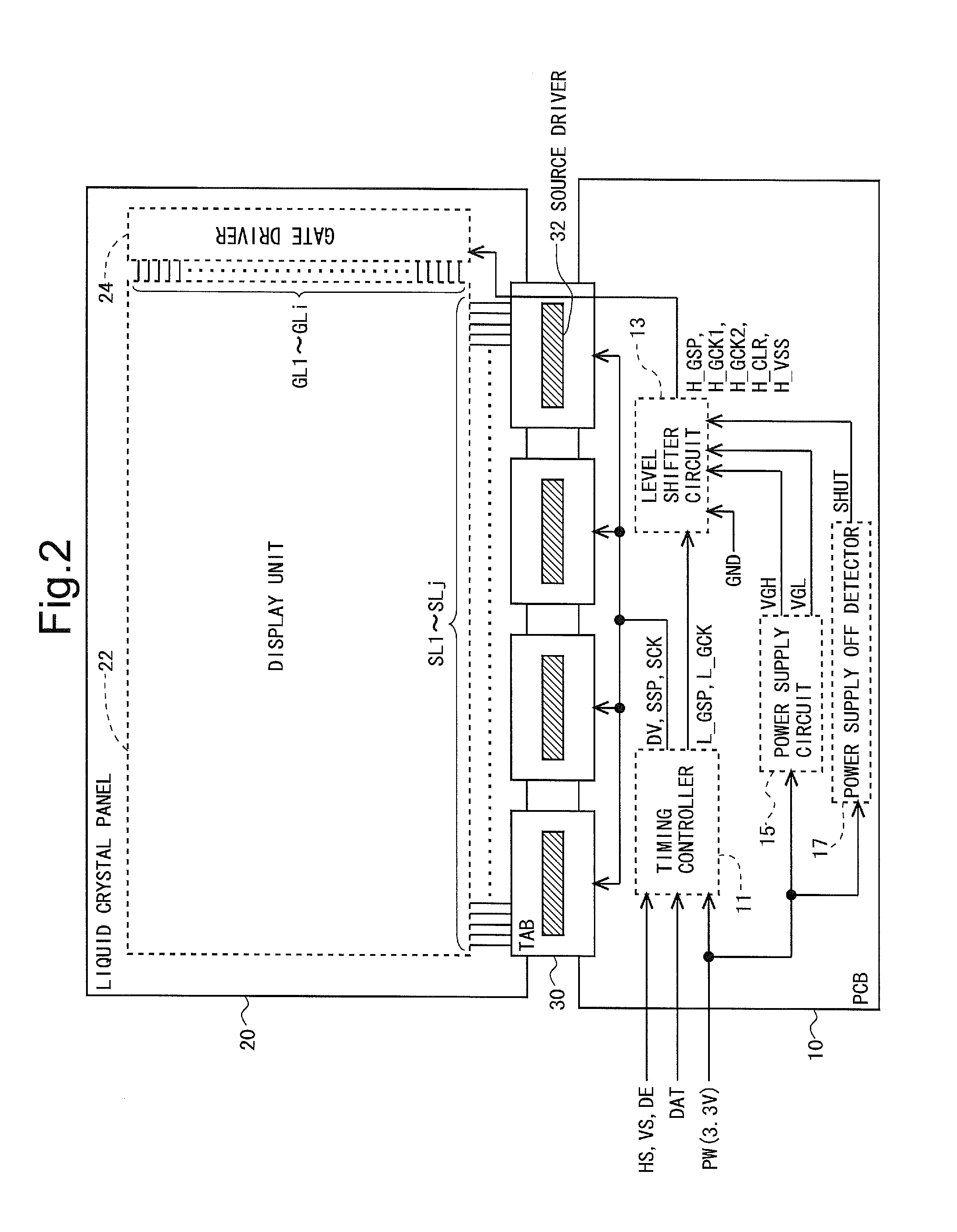
Disclosed is a liquid crystal display device provided with a monolithic gate driver, wherein residual charge in a pixel formation portion can be rapidly eliminated when the power is turned off. In a bistable circuit which constitutes a shift register in a gate driver (24), a thin-film transistor having a drain terminal connected to a gate bus line, a source terminal connected to a reference potential line for transmitting a reference potential (H_SIG_VSS), and a gate terminal to which a clock signal (HCK_1, HCK_2) for operating the shift register is given is provided. When a power OFF detection unit (17) detects the cutoff of the supply of power-supply voltage (PW) from the outside, the clock signal (HCK_1, HCK_2) is driven high to turn the thin-film transistor on, and a reference potential switching circuit (19) switches the reference potential (H_SIG_VSS) from a gate off potential (VGL) to a gate on potential (VGH).
Owner:SHARP KK
Clock generator with duty cycle control and method
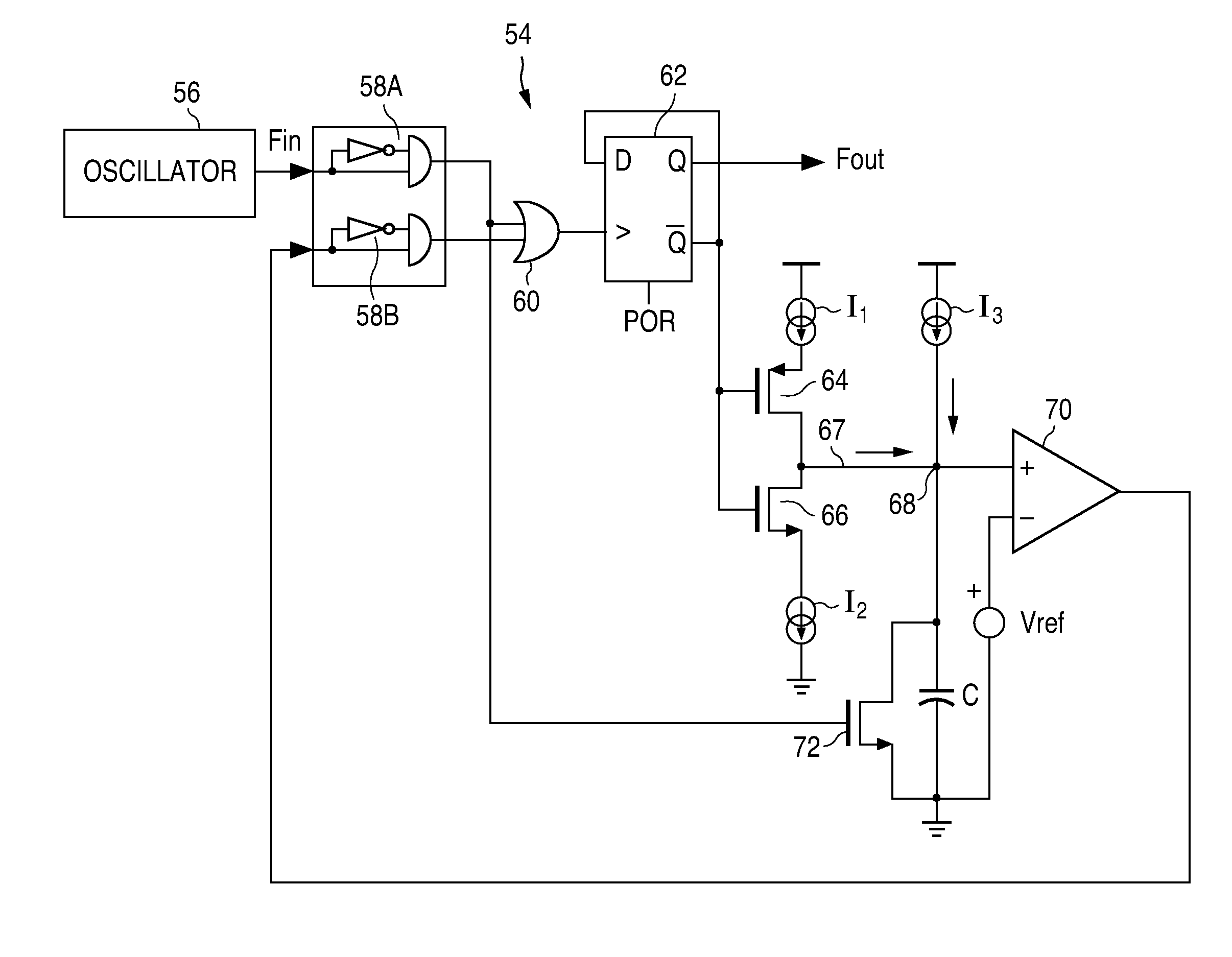
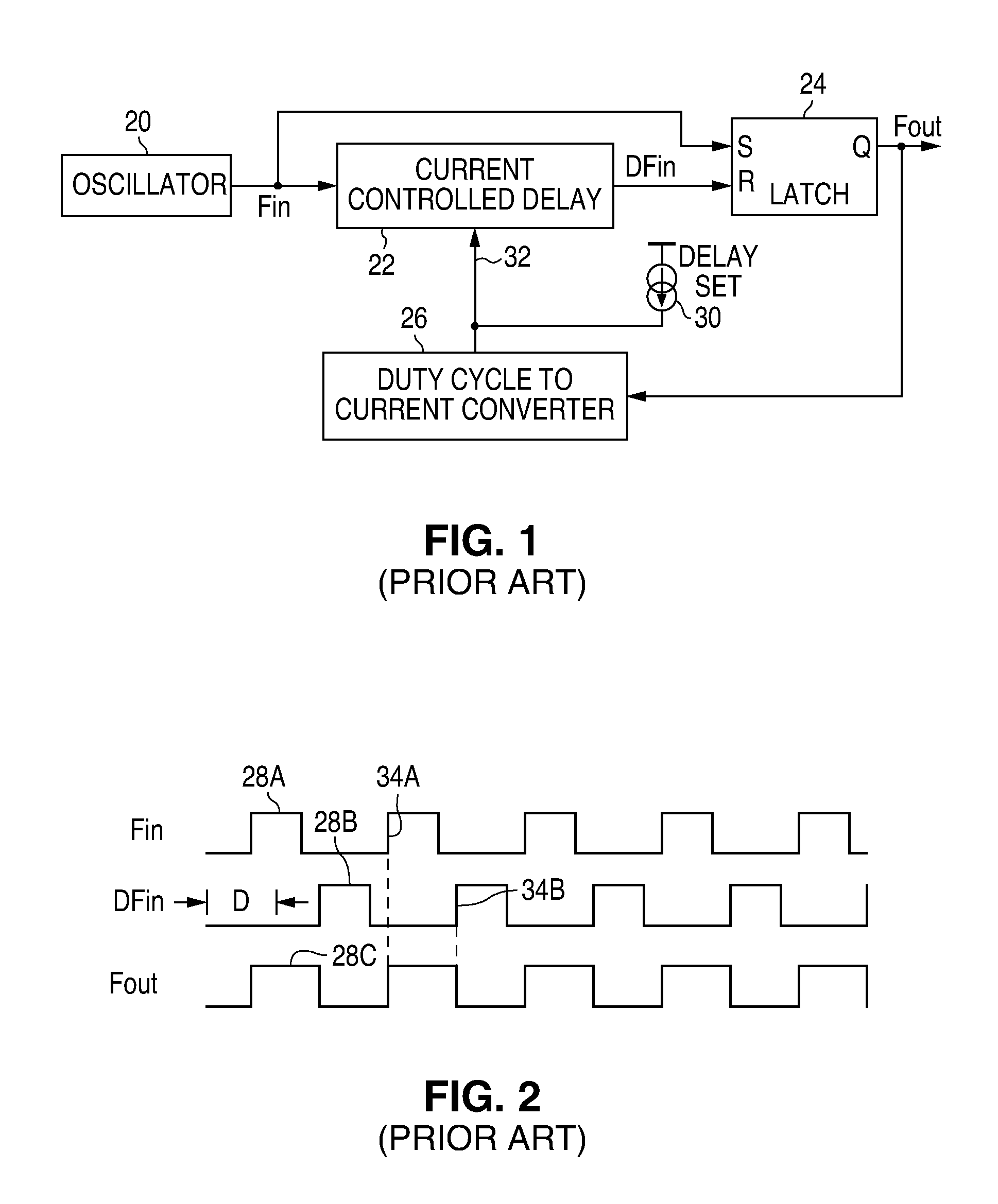
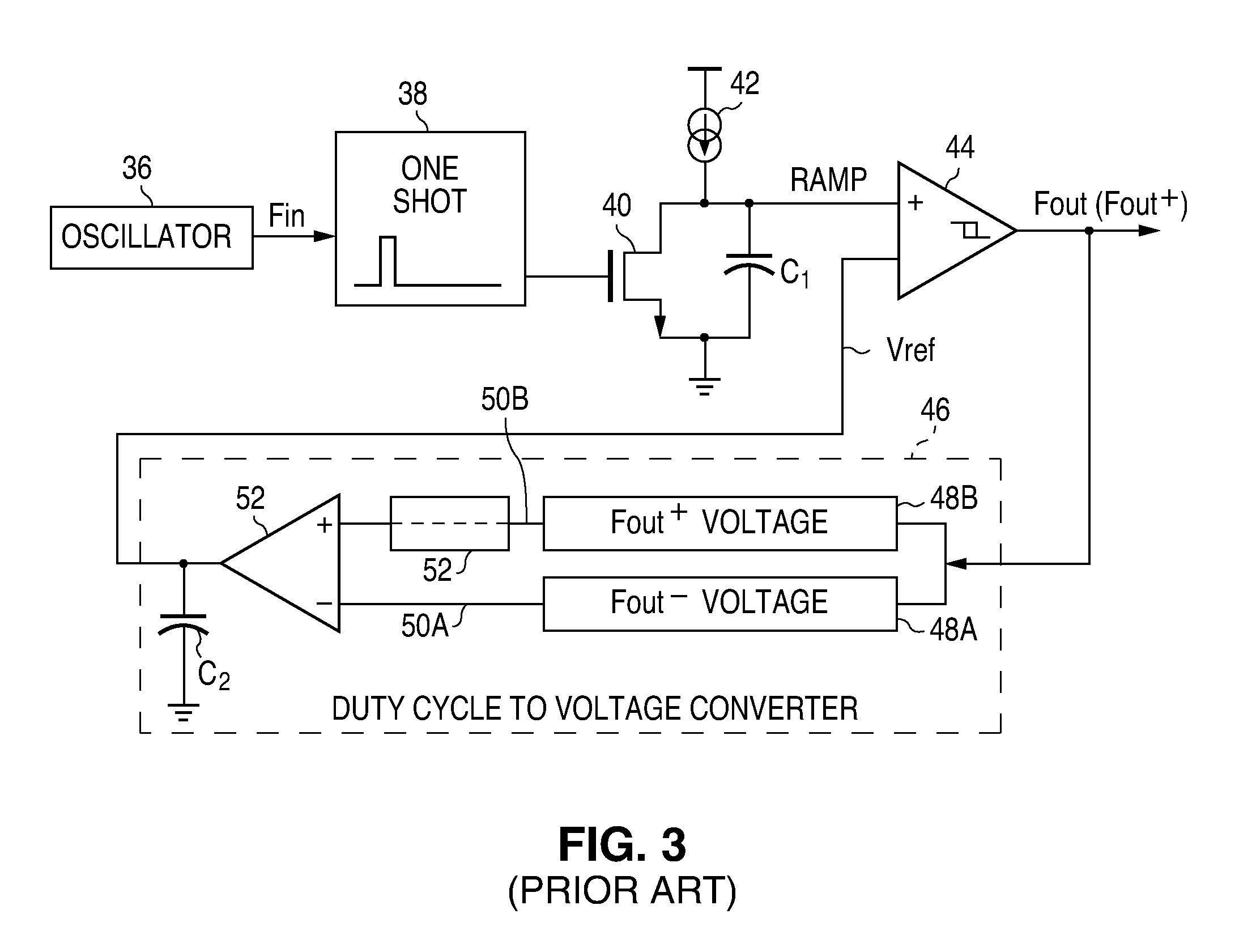
A clock generator circuit for producing a clock output having a controlled duty cycle is disclosed. A bi-stable circuit provides the clock output which is switchable to a first state in response to an edge of the input clock signal and to a second state in response to a feedback signal. A duty cycle detection circuit is configured to source a current to a node and to sink a current from the node depending upon the output clock state. A capacitor is connected to receive a duty cycle current relating to the current at the node, with a comparator circuit being configured to sense a voltage on the capacitor and to produce the feedback signal when the voltage is at a selected level.
Owner:NAT SEMICON CORP
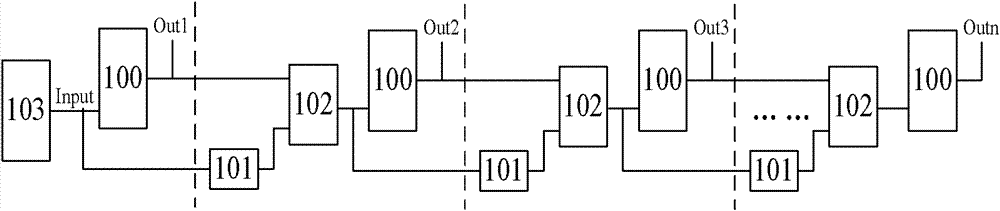
Measuring circuit of single-particle pulse width
ActiveCN103063933AAdjust the test rangeHigh measurement accuracyPulse characteristics measurementsBistable circuitsVIT signals
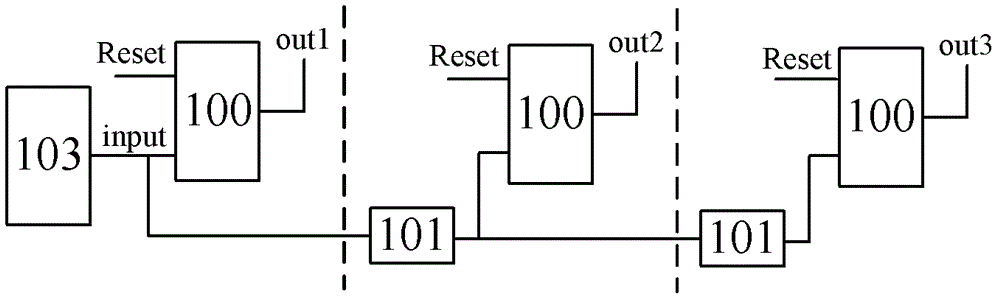
The invention discloses a measuring circuit of single-particle pulse width. The measuring circuit comprises a single-particle pulse signal generating circuit and at least one stage of a measuring circuit. The single-particle pulse signal generating circuit generates a single-particle pulse signal to be measured. A bistable circuit directly driven by the single-particle pulse signal to be measured forms a first stage of the measuring circuit. From a second stage of the measuring circuit on, each stage of circuit is composed of a pulse attenuator circuit and a bistable circuit. The input ends of the pulse attenuator circuits are connected with the signal input ends of the bistable circuits of former stages, and output ends of the pulse attenuator circuits are connected with the signal input ends of the bistable circuits of identical stage circuit. The output ends of a stage of preset bistable circuit or multiple stages of preset bistable circuits form the output result of the measuring circuit together, and the output result corresponds to the single-particle pulse width. The measuring circuit of the single-particle pulse width can improve the measuring accuracy of the single-particle pulse width, and reduce equipment cost.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
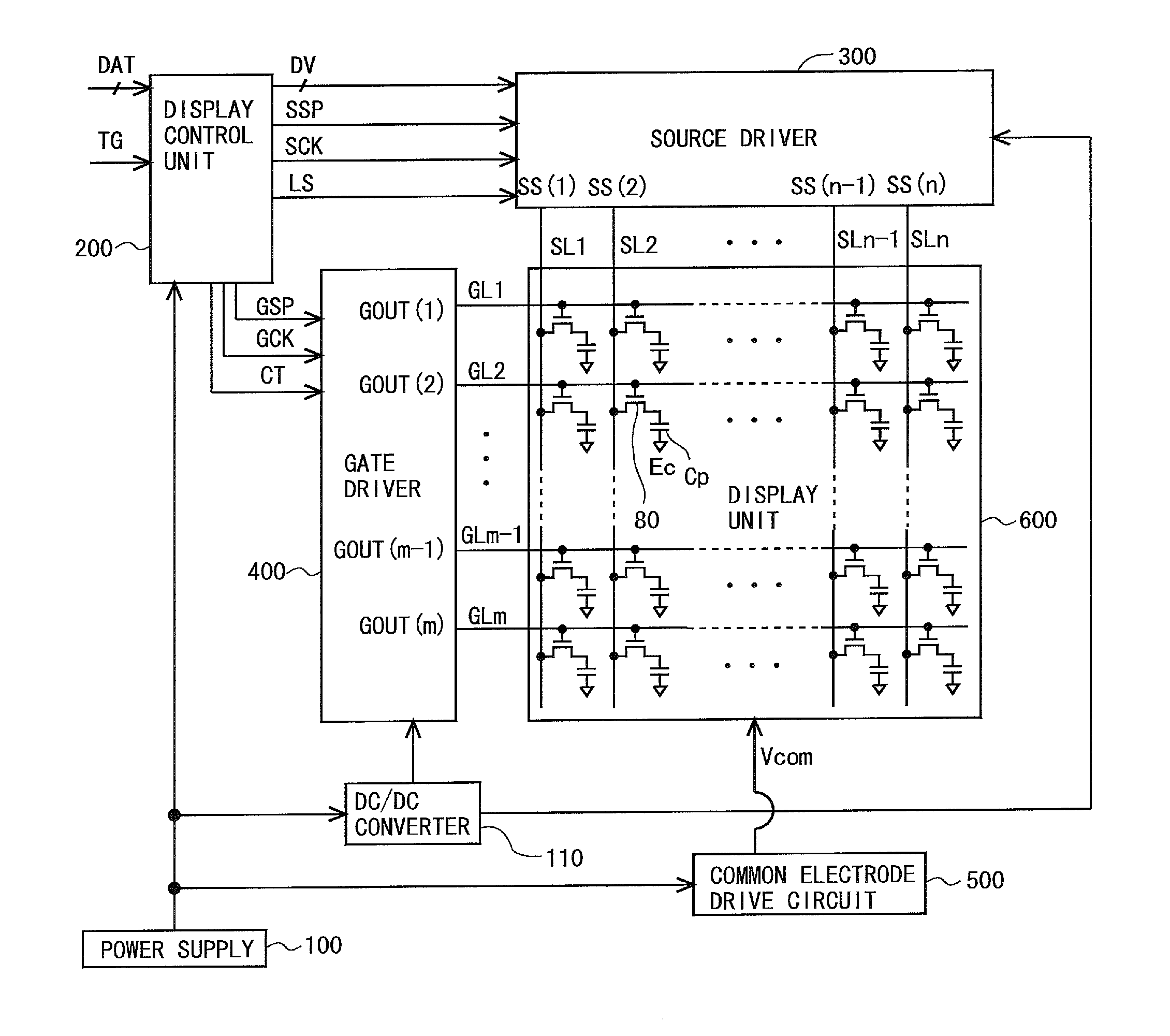
Scanning signal line drive circuit and display device provided with same
InactiveCN104246862AReduce in quantityReduce frequencyStatic indicating devicesBistable circuitsShift register
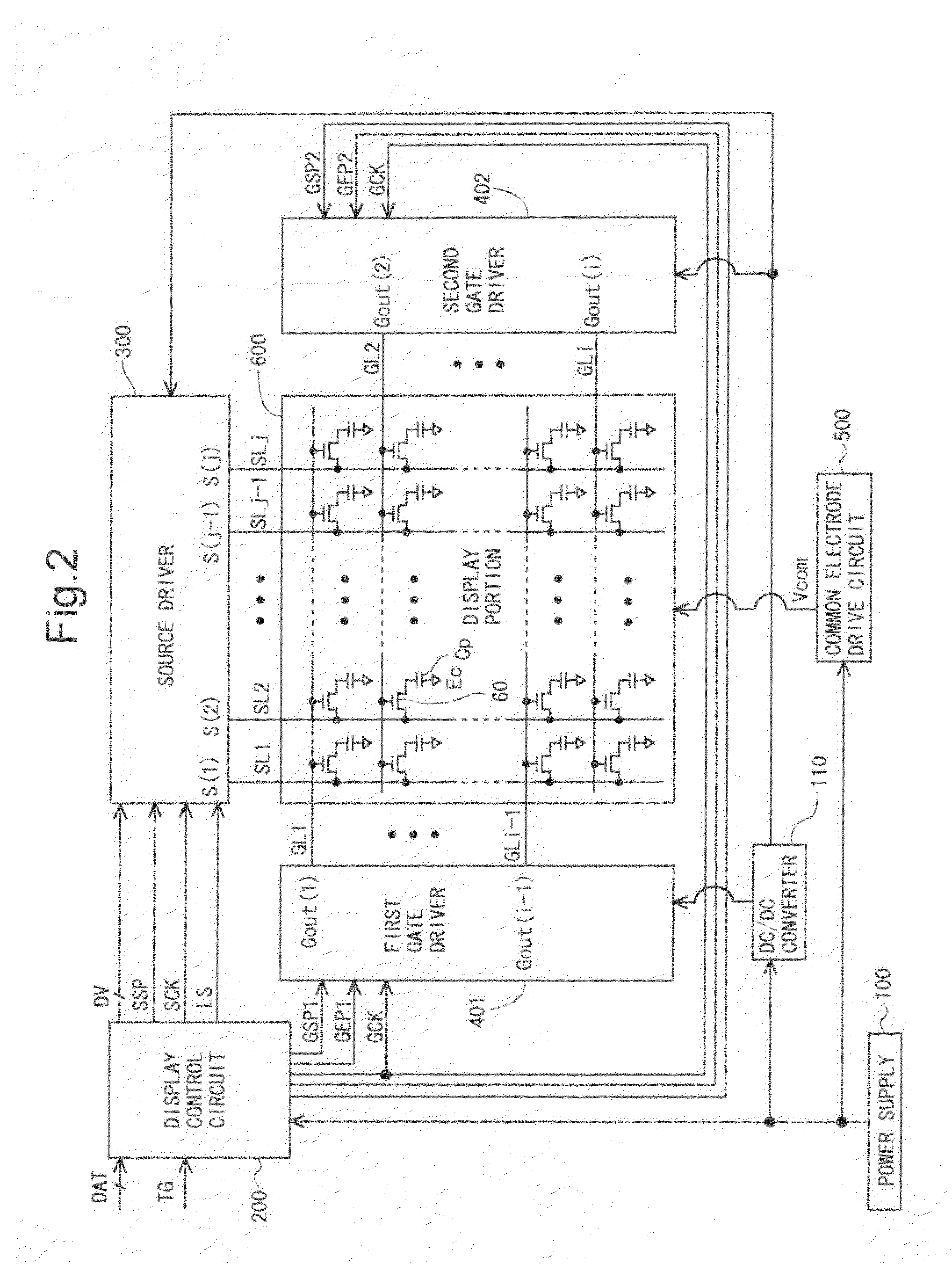
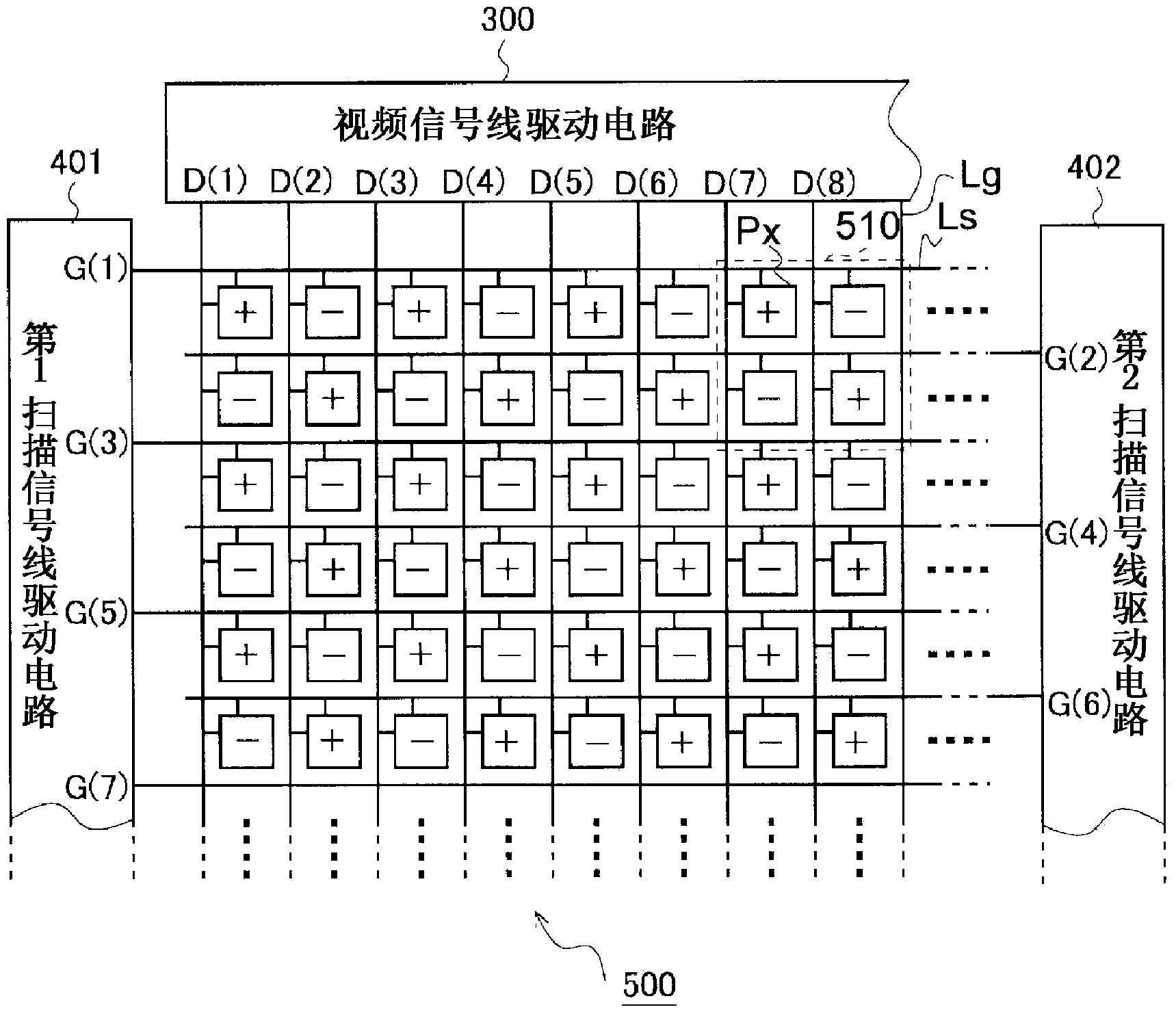
First and second scanning signal line drive circuits (401, 402) provided to this liquid crystal display device perform interlaced driving. A gate clock signal, a gate start pulse signal, and a clear signal which are presented to these circuits are presented by sets of two trunk lines each, which correspond to the two shift register circuits respectively included therein. Consequently, the number of bistable circuits connected to a single trunk line is half that in a typical conventional scanning signal line drive circuit comprising a single shift register circuit, and moreover the clock signal frequency is lower, thereby further reducing power consumption.
Owner:SHARP KK
Shift register circuit, display device provided with same, and shift register circuit driving method
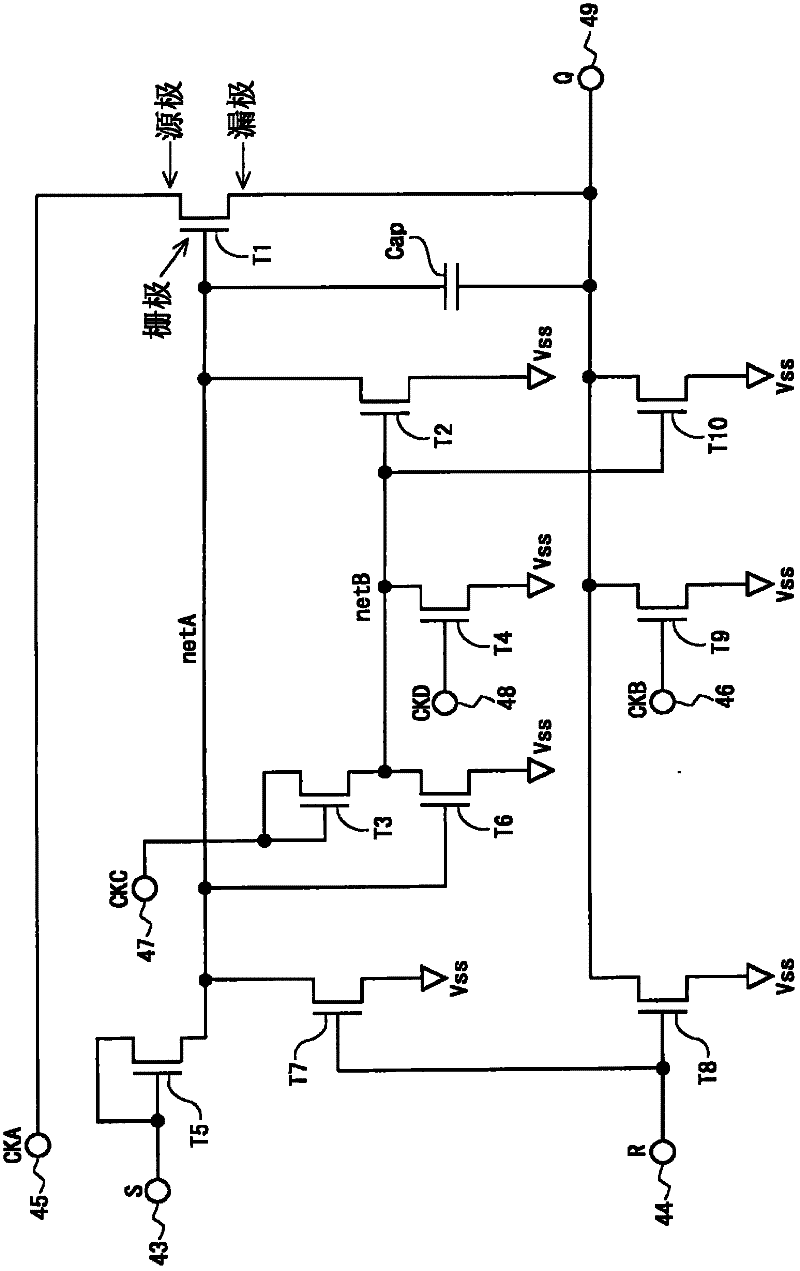
InactiveCN102460587ADisplay quality degradedSuppress crosstalkStatic indicating devicesDigital storageBistable circuitsShift register
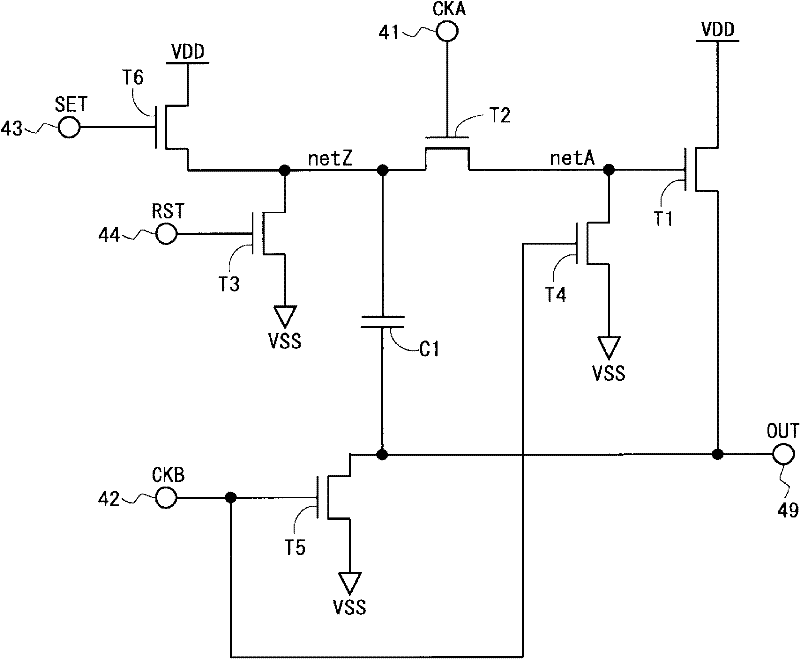
Disclosed is a display device capable of inhibiting degradation of visual quality that has been caused by crosstalk, without causing an increase in frame size or an increase in power consumption. Each bistable circuit is provided with an output terminal (49) that outputs a state signal; a thin-film transistor (T1), the drain terminal of which is given a high-level potential (VDD), and the source terminal of which is connected to the output terminal (49); a thin-film transistor (T2), the source terminal of which is connected to an area netA that is connected to the gate terminal of the thin-film transistor (T1), and the gate terminal of which is given a clock (CKA); a thin-film transistor (T6) for increasing a potential of an area netZ that is connected to the drain terminal of the thin-film transistor (T2); and thin-film transistors (T4, T5, T3) for lowering each of the potentials of netA, netC, and the output terminal (49). A channel area of the thin-film transistor (T1) is made to be larger than a channel area of the thin-film transistor (T2).
Owner:SHARP KK
Liquid crystal display device and driving method thereof
ActiveUS20140191935A1Easy to removeLower potentialStatic indicating devicesShift registerBistable circuits
The invention provides a liquid crystal display device that includes an IGZO-GDM which can quickly remove a residual charge in a panel when the power supply is turned off, and a driving method of the liquid crystal display device. Each bistable circuit that configures a shift register includes a thin film transistor TI for increasing a potential of an output terminal based on a first clock, a region netA connected to a gate terminal of the thin film transistor TI, a thin film transistor TC for lowering a potential of the region netA, and a region netB connected to a gate terminal of the thin film transistor TC. In such a configuration, a power supply off sequence includes a display off sequence and a gate off sequence. The gate off sequence includes at least a gate-bus-line discharge step (t14 to t15), a netB discharge step (t15 to t16), and a netA discharge step (t16 to t17).
Owner:SHARP KK
Radiation sensors and single-event-effects suppression devices
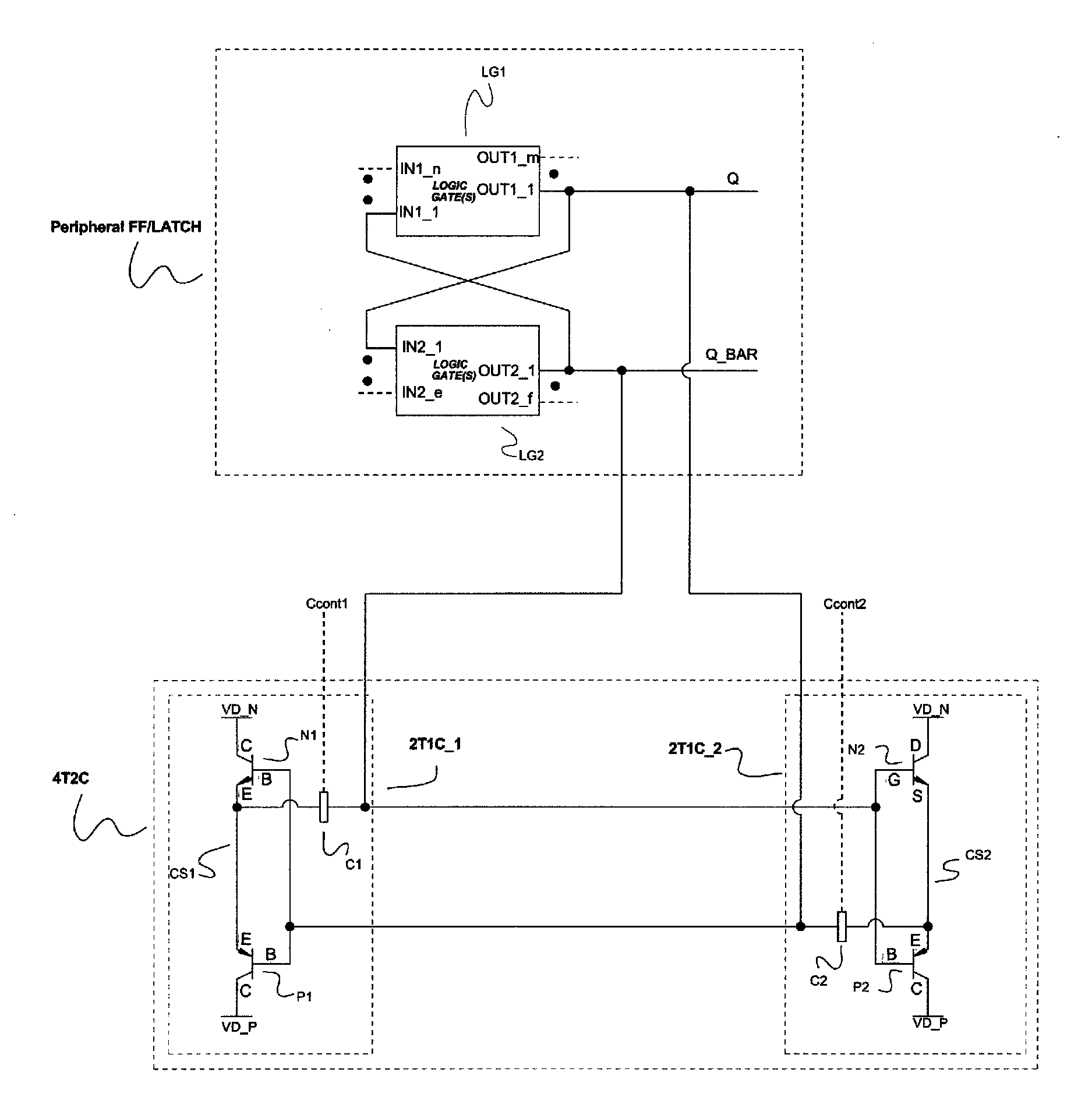
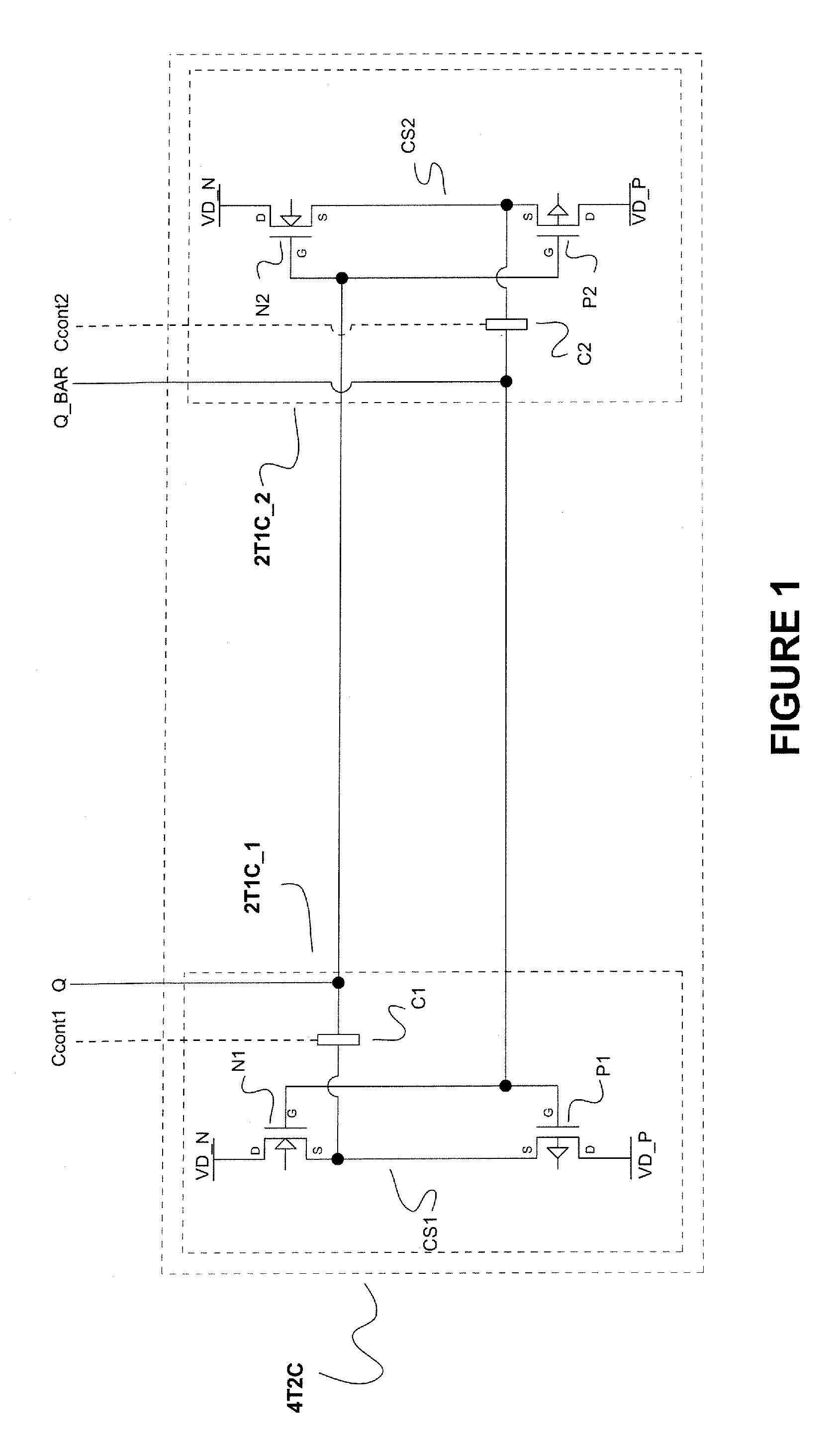
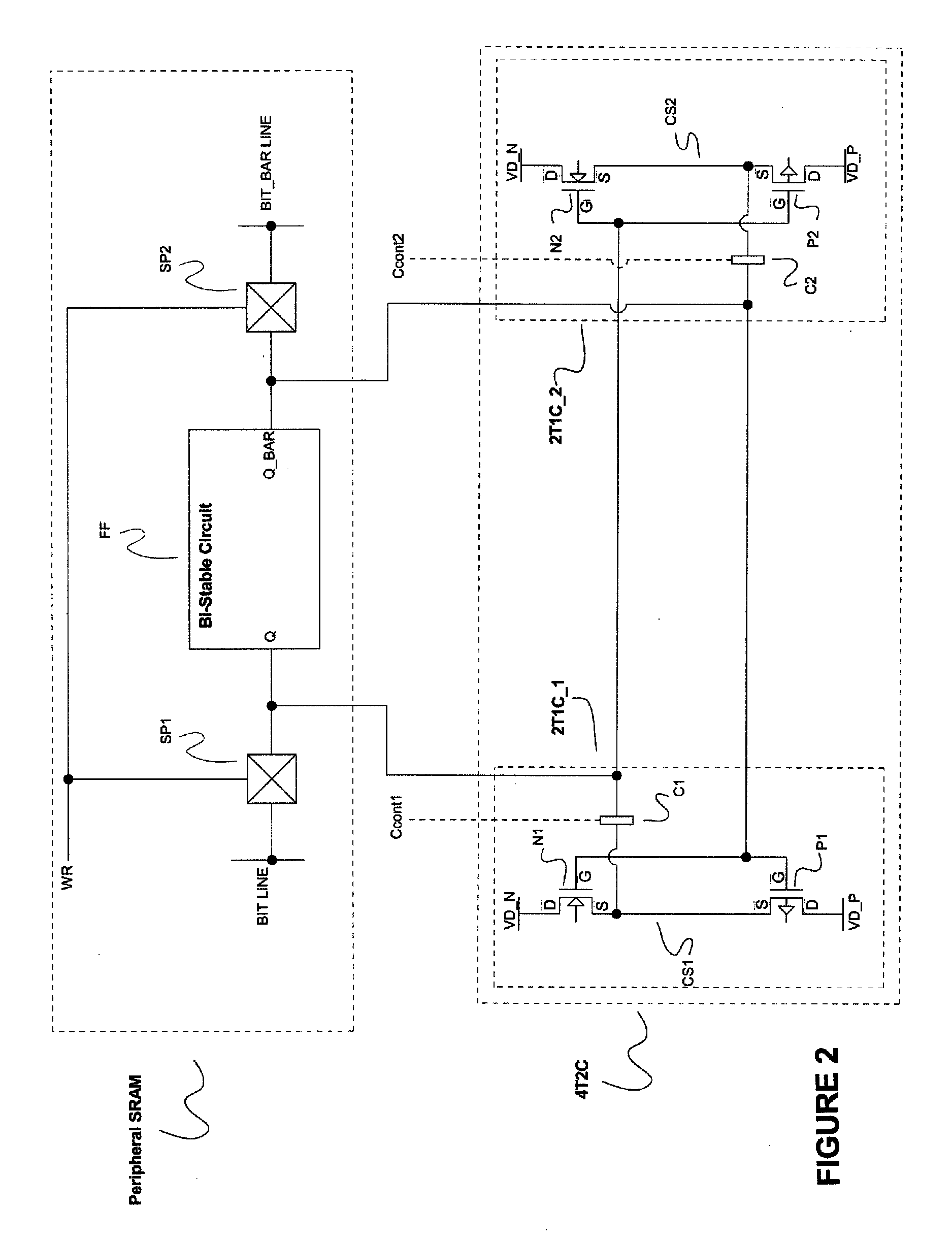
The present invention provides a Single-Event-Upset (SEU) and Single-Event-Gate-Rupture (SEGR) protection against incident radiation for any bi-stable circuit either in one state, having a 2 transistor, 1 capacitor integrated circuit coupled to a bi-stable circuit's outputs, or in both states, having a 4 transistor, 2 capacitor integrated circuit coupled to the bi-stable circuit's outputs. The protection against SEU and SEGR is achieved by the 2T1C or the 4T2C circuits, by providing the opposite drive to the SEU or SEGR event through capacitive coupling, and shunting electron-hole pair current, created by an ion tracking through the bi-stable circuit, into the power supplies. The 2T1C integrated circuit architecture, which only protects bi-stable circuits in one state, is to allow the bi-stable circuit to be a Single-Event-Upset (SEU) detector by capturing the effect of an incident ion and store that state. The 2T1C architecture, while protecting the bi-stable circuit after it has been affected by incident radiation, can alert the system the bi-stable integrated circuit is embedded in, to compensate or at be aware that an Single-Event-Upset has occurred. The purpose of the 4T2C integrated circuit architecture, which protects bi-stable circuits in both stable states, is to allow for critical data / state retention in any radiation environment, while not effecting speed of operation.
Owner:RYAN TECH
Scanning signal line driving circuit, display device provided therewith, and scanning signal line driving method
ActiveCN103503057AImprove reliabilityLow reliabilityStatic indicating devicesDigital storageShift registerBistable circuits
The purpose of this invention is to provide a scanning signal line driving circuit with increased reliability of switching elements while reducing power consumption. In the vertical blanking interval, an end signal (ED) changes from the low level to the high level. The potential of the 1st through (m-1)st stage first nodes (N1) of cascade-connected m-stage bistable circuits contained in a shift register of the scanning signal line driving circuit is reliably maintained at the low level, and the potential of 1st through (m-1)st stage second nodes (N2) changes from the high level to the low level. In the mth stage bistable circuit, the potential of the mth stage first node (N1) changes from the high level to the low level, and the potential of the mth stage second node (N2) is maintained at the low level. Further, supply of the clock signal (CKA, CKB) to the bistable circuit is stopped. Until the write period in the subsequent vertical scanning period, the potential of the first nodes (N1) and the potential of the second nodes (N2) in each stage is maintained at the low level.
Owner:SHARP KK
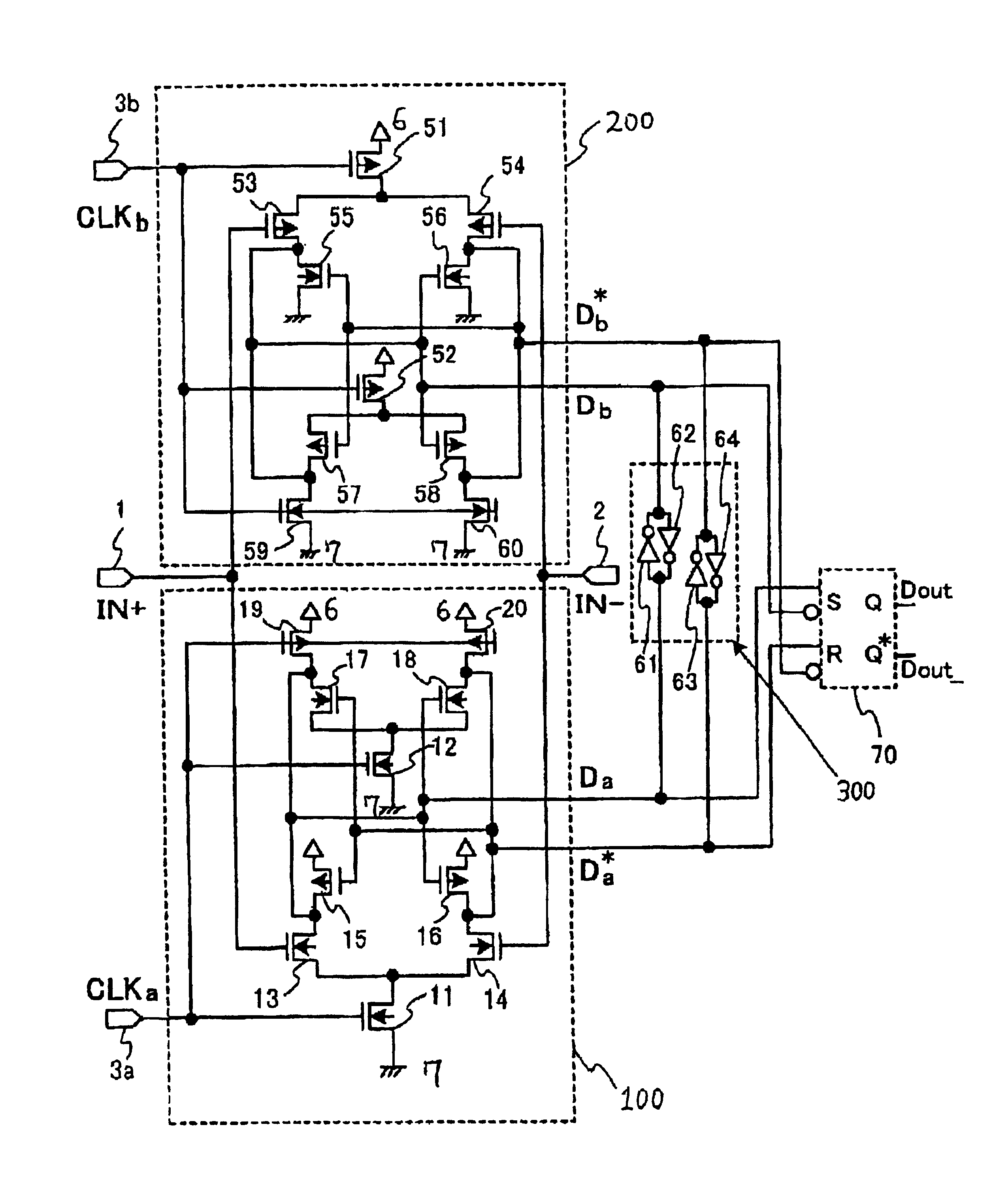
High speed sampling receiver with reduced output impedance
InactiveUS6922083B2Enlarged common mode levelHigh latch operationCurrent/voltage measurementLogic circuits coupling/interface using field-effect transistorsBistable circuitsEngineering
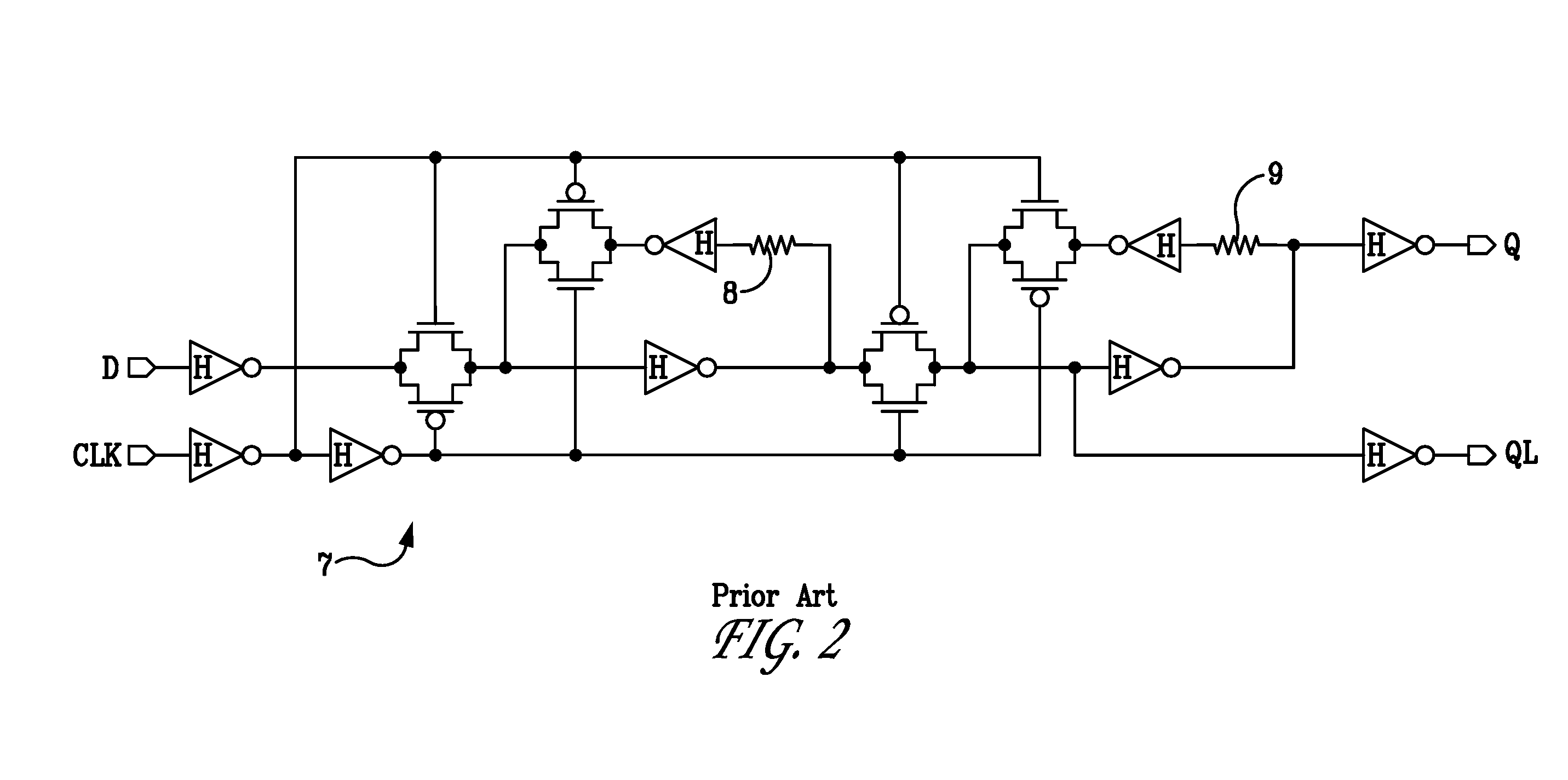
A sampling receiver includes: at least one slave latch circuit; and at least one master latch circuit which further includes: at least one differential input transistor pair, and at least one bistable circuit. Output terminals of the at least one differential input transistor pair and output terminals of the at least one bistable circuit are coupled to the at least one slave latch circuit but in parallel to each other with reference to the at least one slave latch circuit for the purpose of reducing an output impedance to allow the sampling receiver to exhibit a high speed latch operation.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Sequential circuit design for radiation hardened multiple voltage integrated circuits
ActiveUS20080007312A1Solve high hardnessReduce power consumptionElectric pulse generatorBistable circuitsLow voltage
The present invention includes a radiation hardened sequential circuit, such as a bistable circuit, flip-flop or other suitable design that presents substantial immunity to ionizing radiation while simultaneously maintaining a low operating voltage. In one embodiment, the circuit includes a plurality of logic elements that operate on relatively low voltage, and a master and slave latches each having storage elements that operate on a relatively high voltage.
Owner:STC UNM
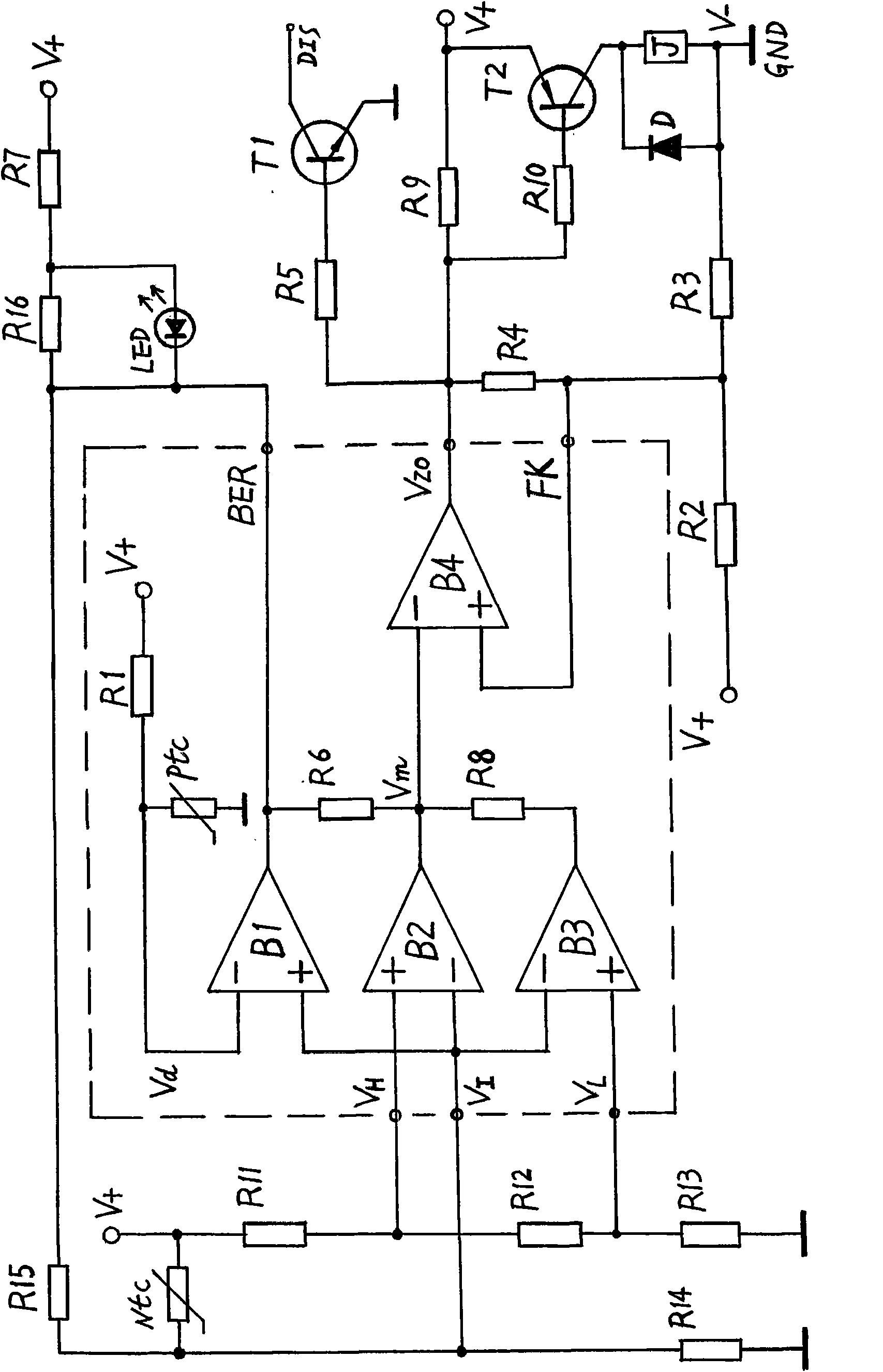
Three-limit time-base circuit
InactiveCN101656527AIncrease the monitoring function of exceeding the bottom limitTimely displayMultiple input and output pulse circuitsElectronIntegrated circuit
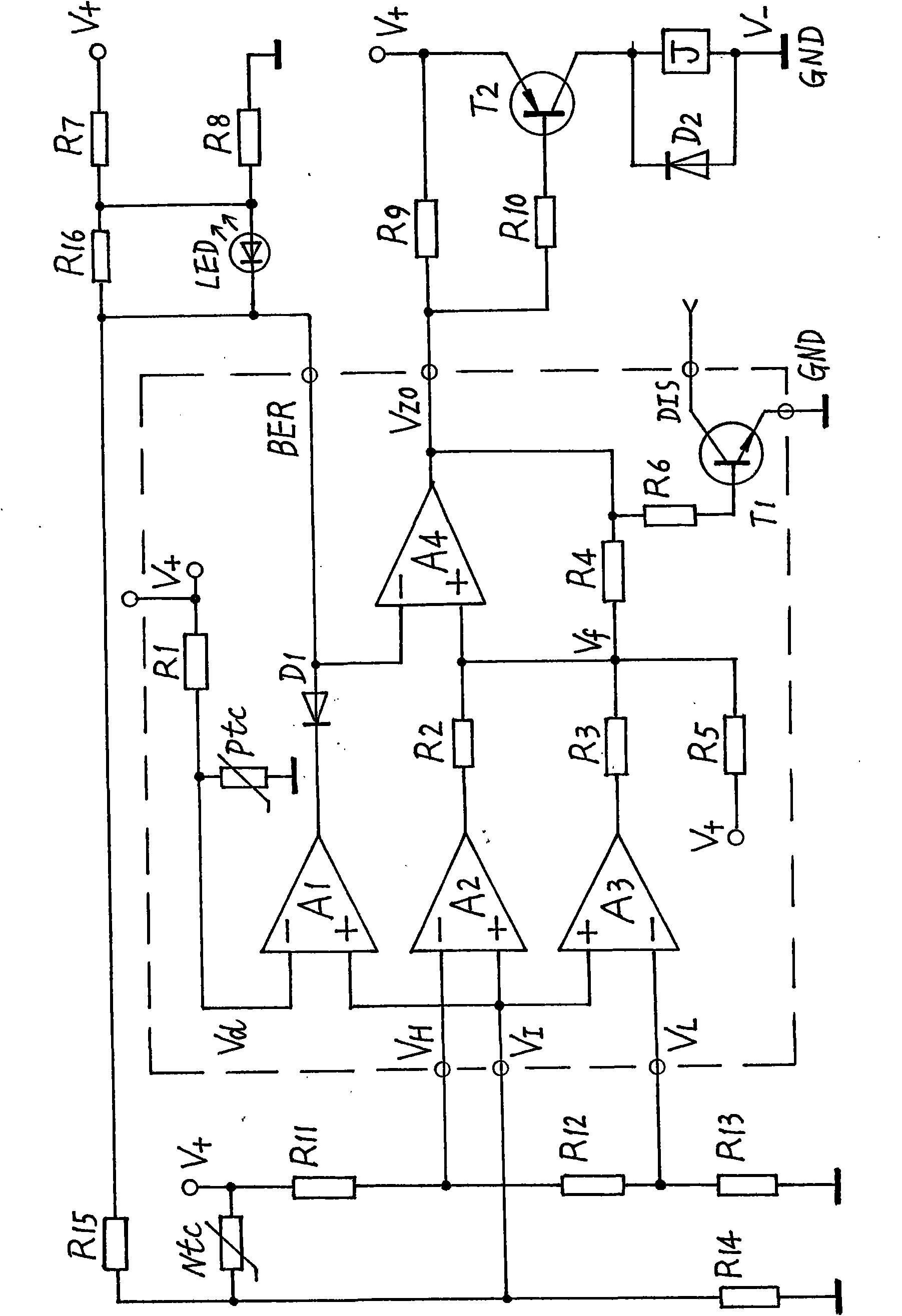
The invention provide a three-limit time-base circuit composed of analogue integrated circuit operational amplifier A (or voltage comparator B), few separate electronic elements by using new principleand ingenious connection mode. The three-limit time-base circuit has top and bottom limit main control functions completely compatible to all functions of classic 555 time-base circuit can be used asultra-top and bottom limit control circuit and astable, monostable and bistable circuit. The invention increases exceed bottom limit protection and control function, when inputted sensing circuit hasfault, fault display and protection control can be executed in time to prevent the main control circuit from being out of control. The invention, used in control circuits for temperature, pressure, water level etc., may improve security, and prevent severe accidents (such as fire hazard). So, the invention has wide use in electronic application field such as household electrical appliances, simple controllers, and high cost performance of products are provided.
Owner:刘圣平
Scanning signal line driving circuit, shift register, and method of driving shift register
ActiveCN102224539ALower potentialInhibitory dip potentialStatic indicating devicesDigital storageShift registerBistable circuits
Owner:SHARP KK
Measuring circuit for single-event transient pulse width
ActiveCN102818939AWide rangeImprove test accuracyPulse characteristics measurementsBistable circuitsLogic gate
The invention discloses a measuring circuit for single-event transient pulse width. The measuring circuit for single-event transient pulse width comprises a single-event pulse signal generating circuit (103) and at least one measuring circuit. Primary stage of the measuring circuit consists of a bistable circuit. From the second stage, each stage of the measuring circuit comprises a delay circuit, a logic gate circuit and a bistable circuit. In the second stage, input signal of the delay circuit is signal to be measured, input signal of the logic gate circuit serves as output signal of the delay circuit and output signal of the first-stage bistable circuit, and output signal of the logic gate circuit serves as input signal of the bistable circuit in the second stage. From the third stage, the input signal of the delay circuit in each stage serves as the output signal of the logic gate circuit in the previous stage, the input signal of the logic gate circuit serves as the output signal of the current-stage delay circuit and the output signal of the previous bistable circuit, and the output signal of the current-stage logic gate circuit serves as the input signal of the current-stage bistable circuit. The measuring circuit is capable of measuring within a wide pulse width range and is high in measuring precision.
Owner:BEIJING ZHONGKE XINWEITE SCI & TECH DEV
Configuration and method for improving noise immunity of a floating gate driver circuit
ActiveUS20120229165A1Minimize time of influencePrevent erroneous triggering of control signalVoltage/current interference eliminationLogic circuit coupling/interface arrangementsDriver circuitBistable circuits
A floating gate driver circuit includes a level shifter, a pass element, a bistable circuit and a control logic circuit, to shift the voltage level of a control signal from a lower one to a higher one. The level shifter or the pass element has loads dynamically controlled by the control logic circuit to filter malfunction caused by dv / dt noise induced by a floating node.
Owner:RICHTEK TECH
DC-AC Frequency Converter Type Nose Cleaner
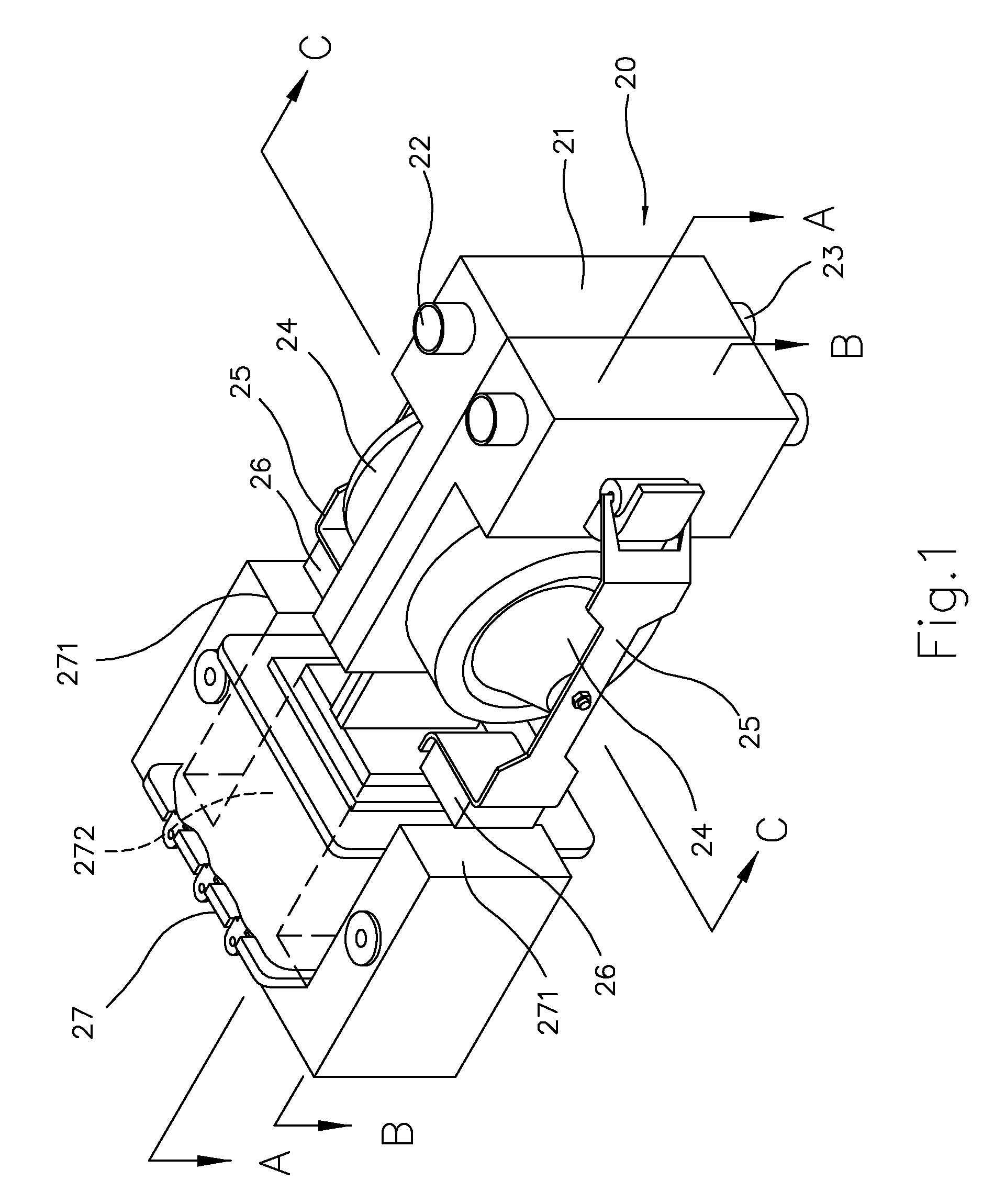
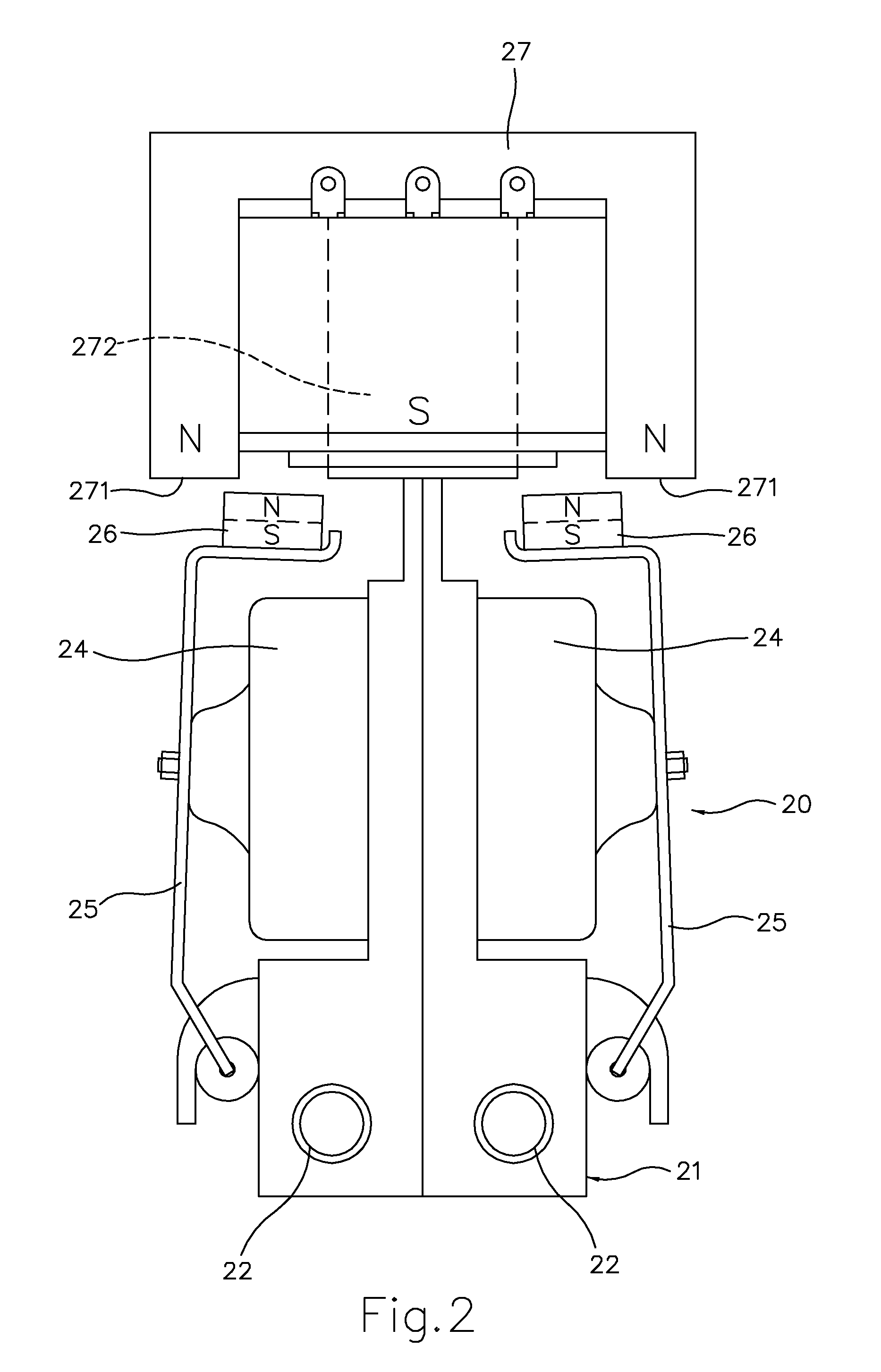
InactiveUS20120053519A1Easy to useOvercomes splashing out defectCannulasMedical devicesFrequency changerBistable circuits
A DC-AC frequency converter type nose cleaner includes an electromagnetic pump, a container storing a cleaning solution, a nose-washing tool and a frequency converter circuit driving the electromagnetic pump. The frequency converter circuit at least includes an oscillator circuit, a bistable circuit and a push-pull circuit. The electromagnetic pump is supplied with AC obtained from the oscillation of DC in the frequency converter circuit. The swing speed, the swing frequency and the swing amplitude of the swing arms vary with the change of the oscillation frequency of the oscillator circuit. Thereby, the discharge pressure and the discharge flow of the electromagnetic pump could further be changed to obtain the most appropriate discharge pressure and discharge flow of the nose cleaner. In other words, the DC-AC frequency converter type nose cleaner can change the pressure and the flow generated by the electromagnetic pump so as to satisfy the requirement of the discharge pressure and flow of the nose cleaner so as to overcome the defect of the discharge pressure of the conventional nose cleaner that is too big to hurt the user.
Owner:CHIOU JACKEY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com