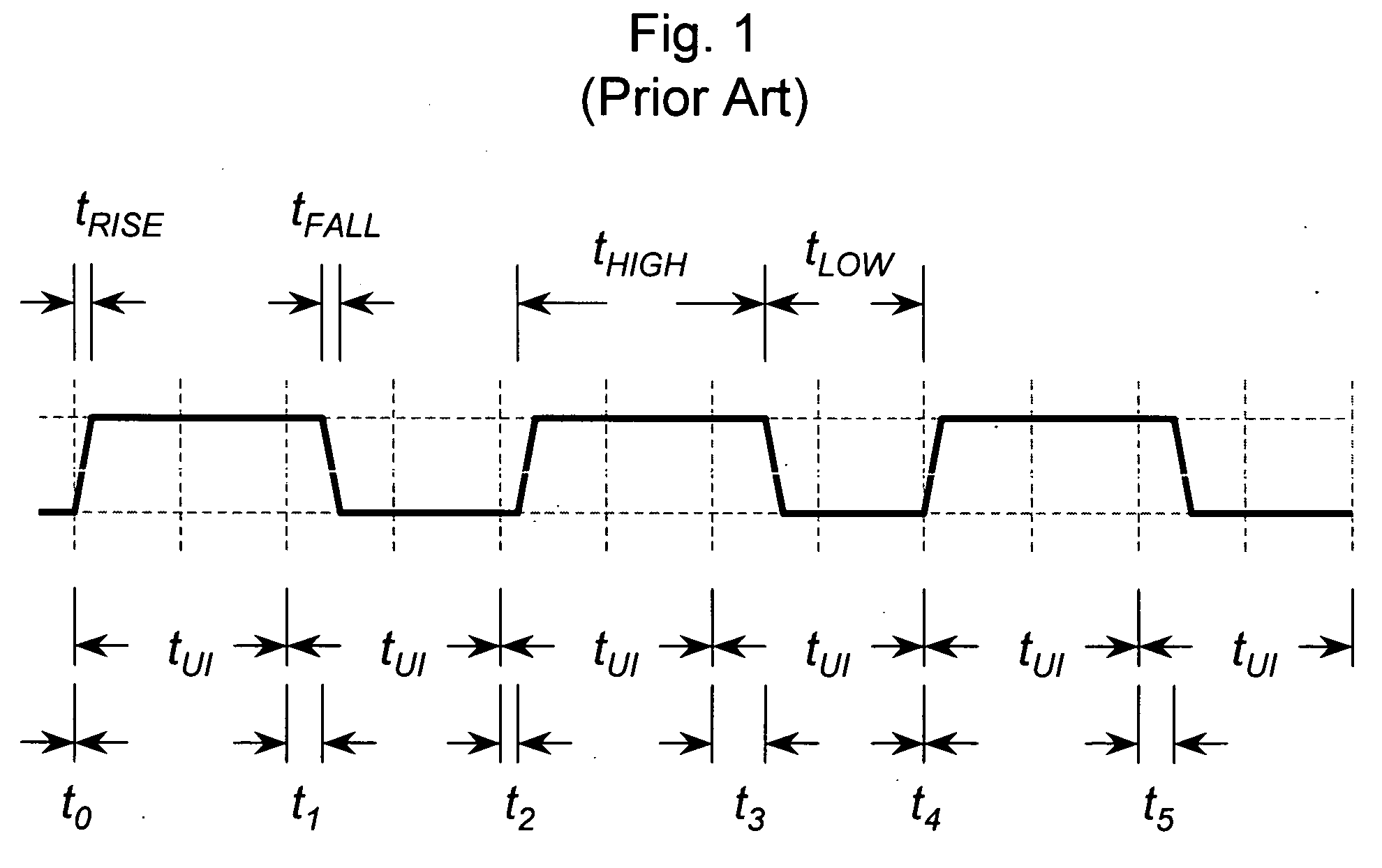
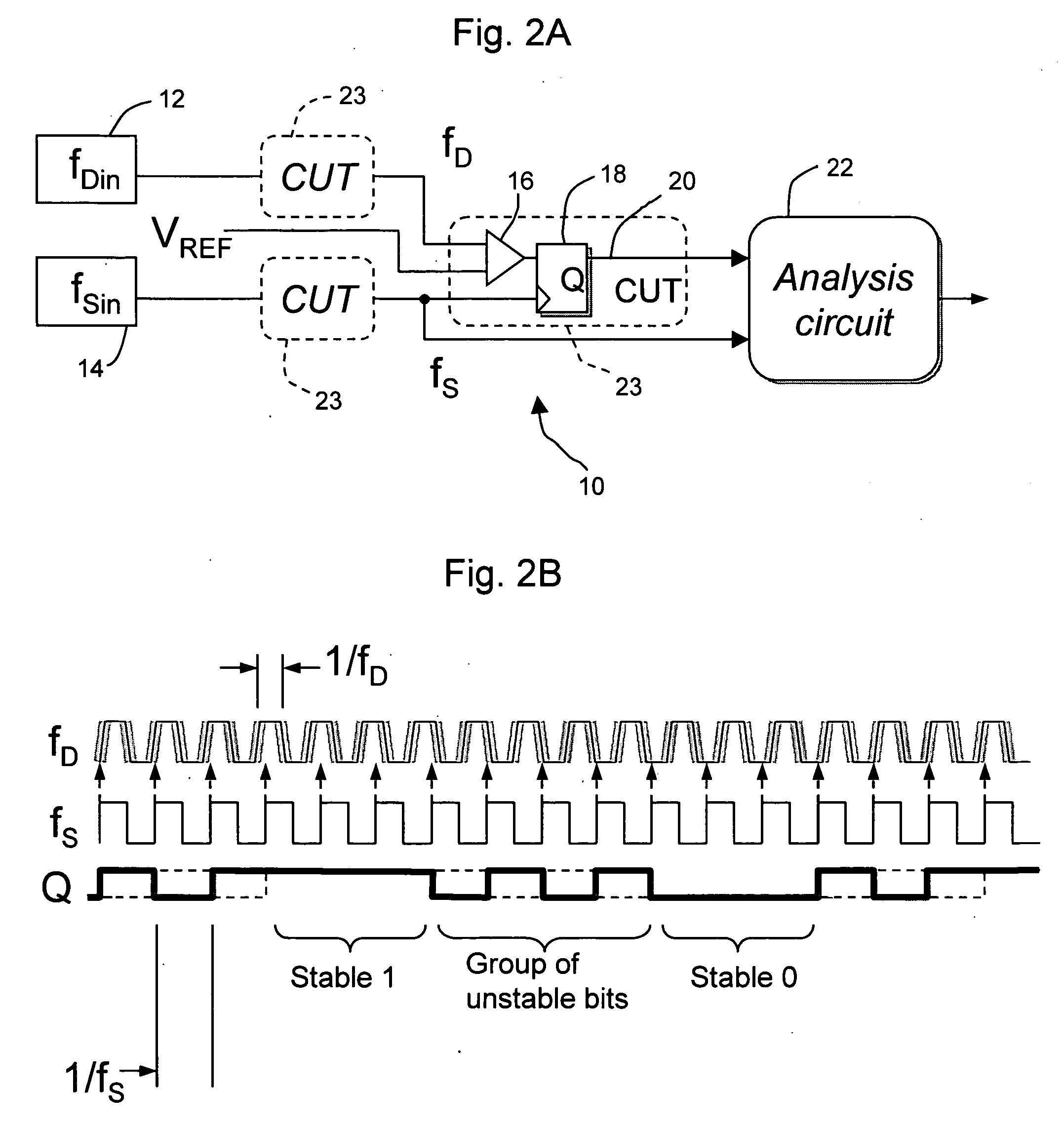
Patents
Literature
1335results about "Pulse characteristics measurements" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
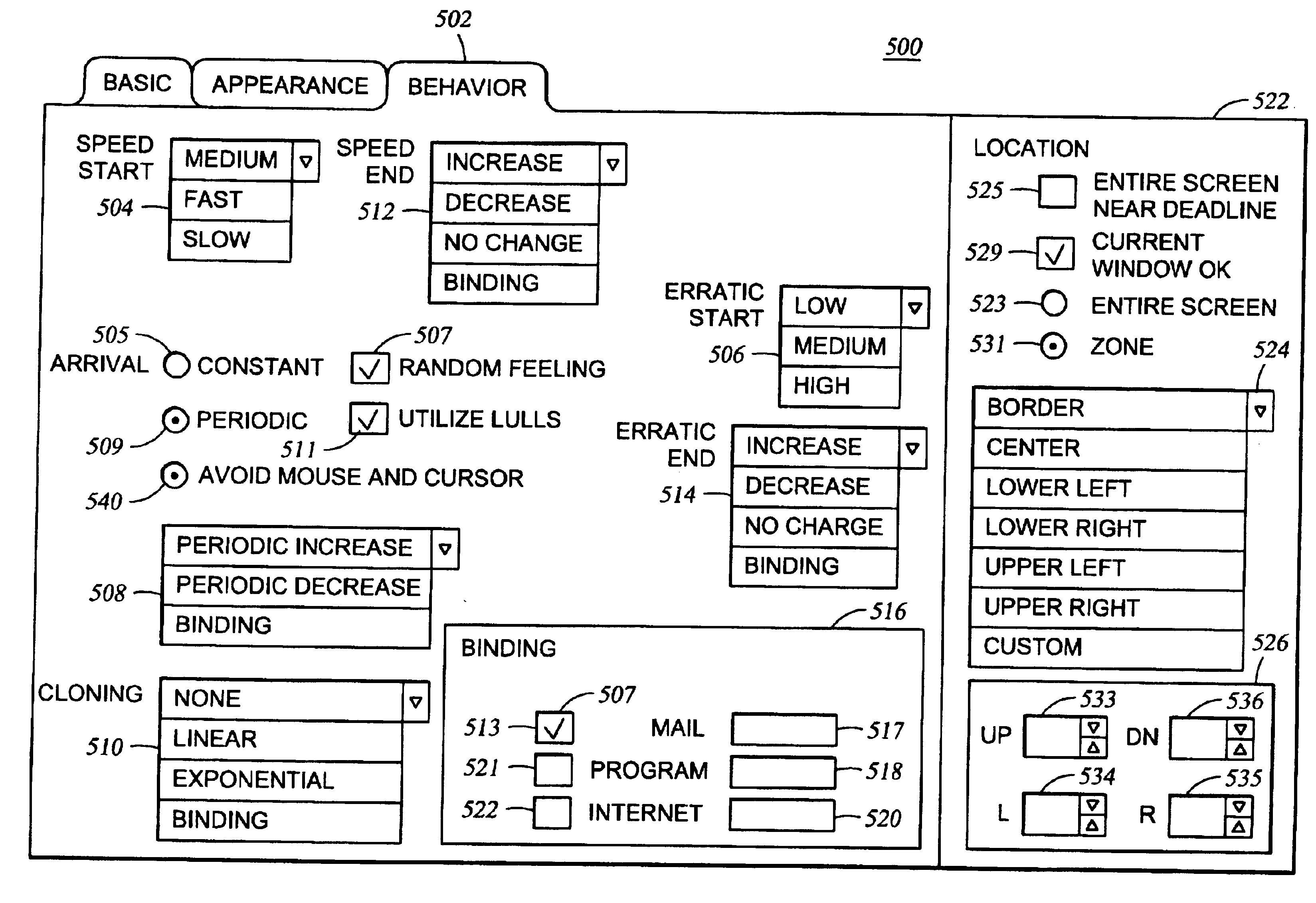
Method for software driven generation of multiple simultaneous high speed pulse width modulated signals
InactiveUS7113541B1Electroluminescent light sourcesVoltage-current phase angleTime segmentControl signal
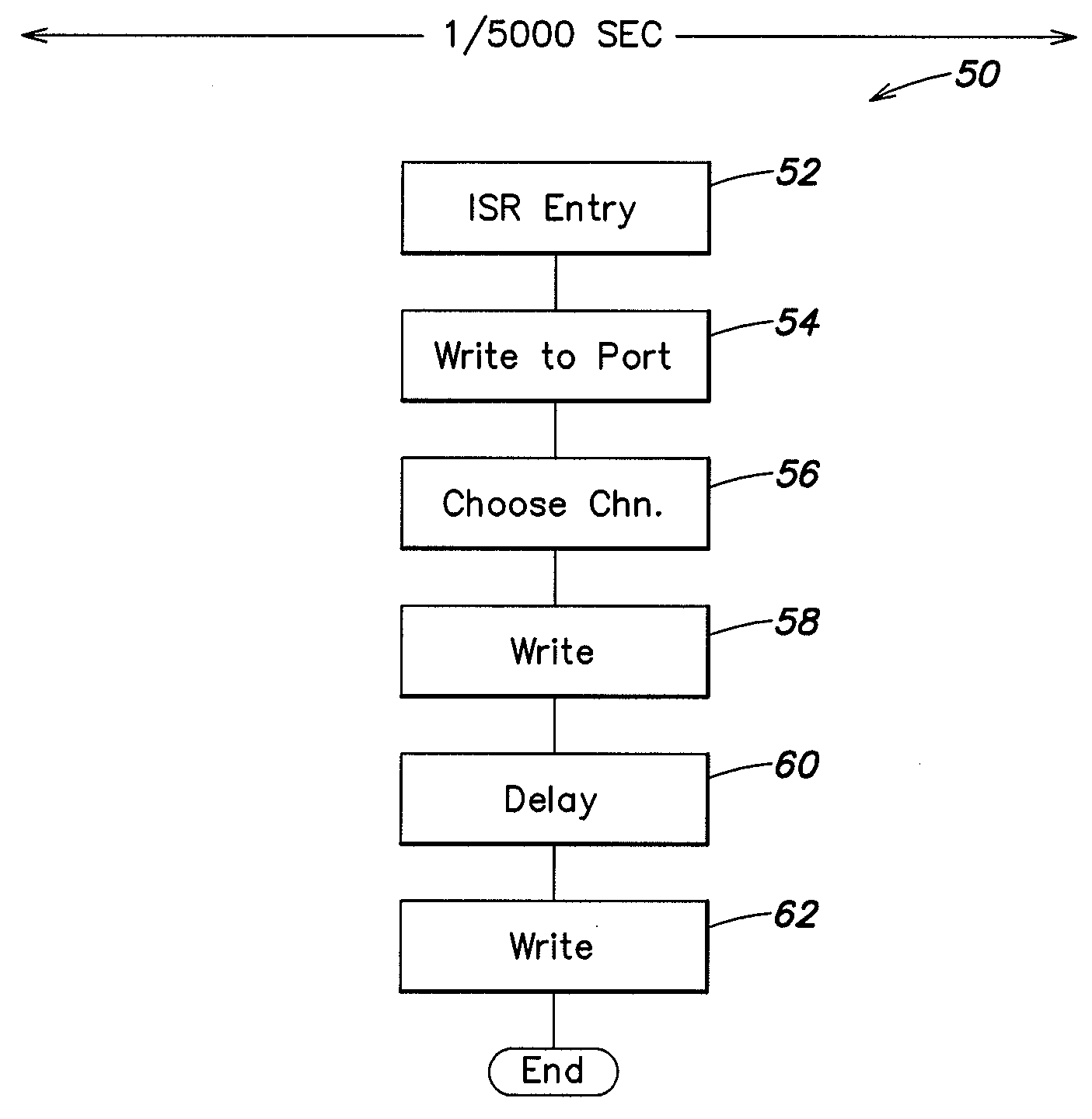
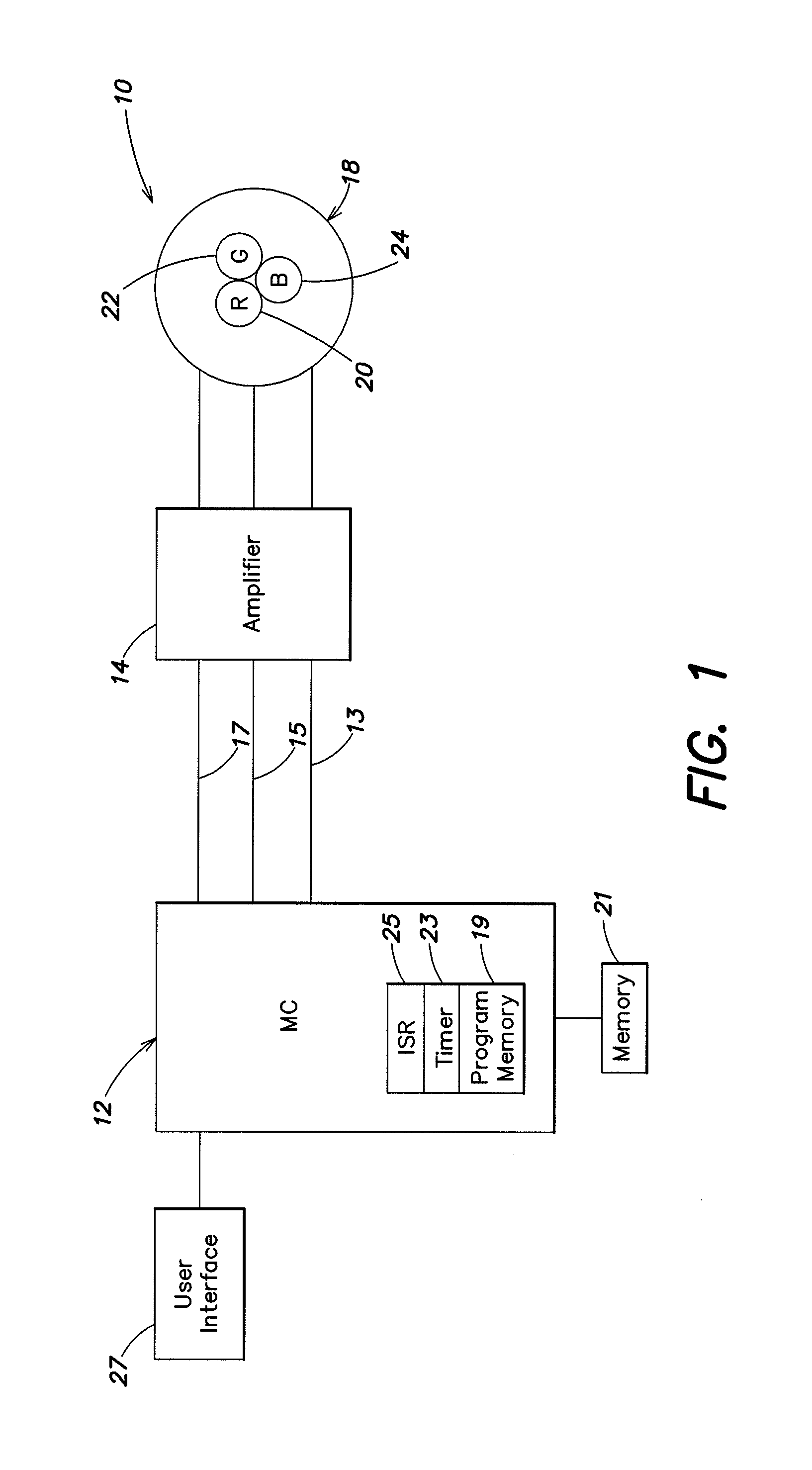
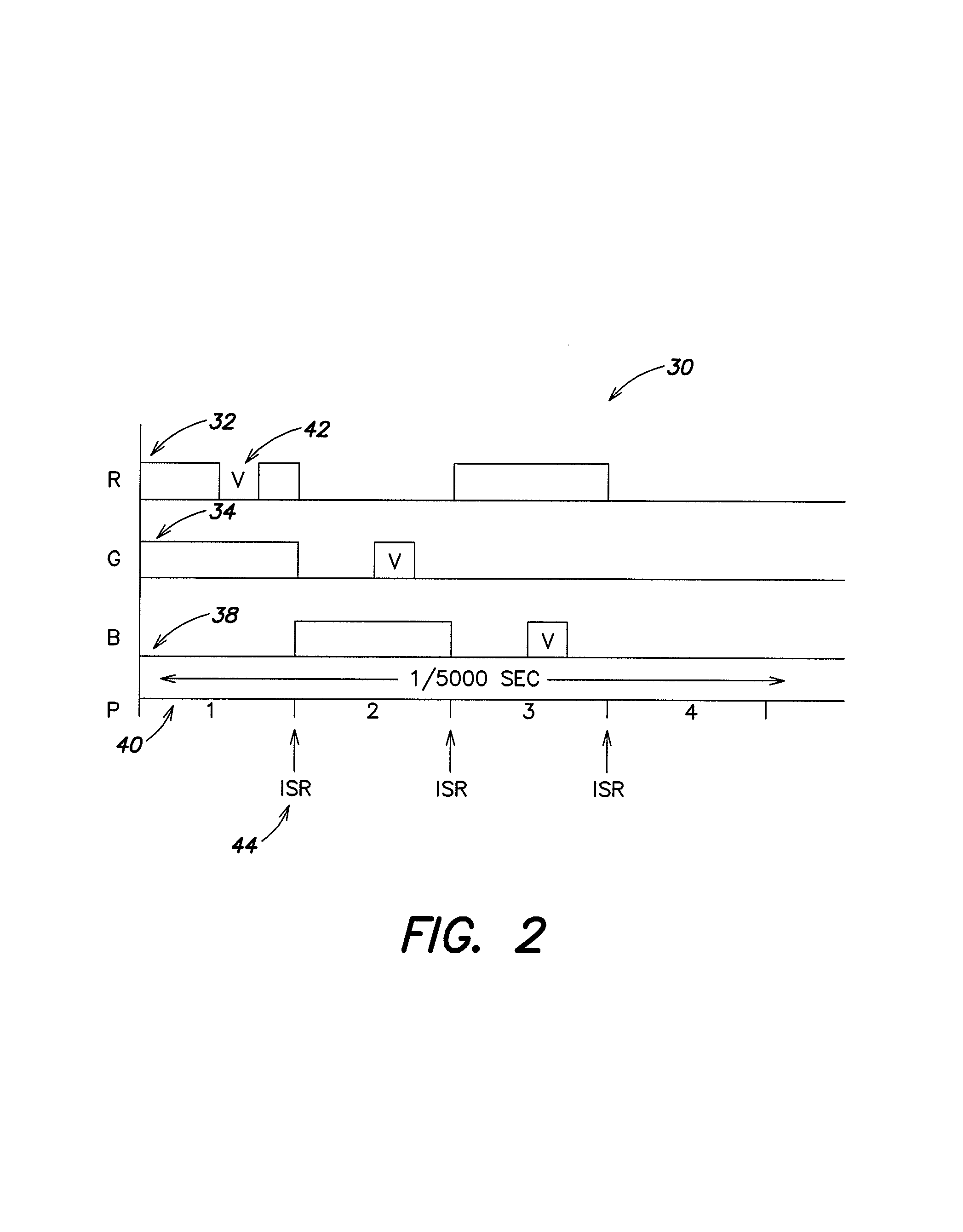
Systems and methods can provide, in one aspect, a method for modulating the pulse width of control signals generated on a plurality of separate channels. In one practice, the methods described herein are suitable for execution on a microprocessor or micro controller platform that includes a timer interrupt mechanism which will generate an interrupt in response to a timer counting down a selected time interval or time period. In one practice, the timer is set to count down a period of time that is representative of a portion, or sub period, of the PWM cycle. Upon expiration of that time period, the timer executes an interrupt that causes the micro controller to enter an interrupt service routine (ISR) that can further modulate the PWM cycle of one or more signals.
Owner:PHILIPS SOLID STATE LIGHTING SOLUTIONS
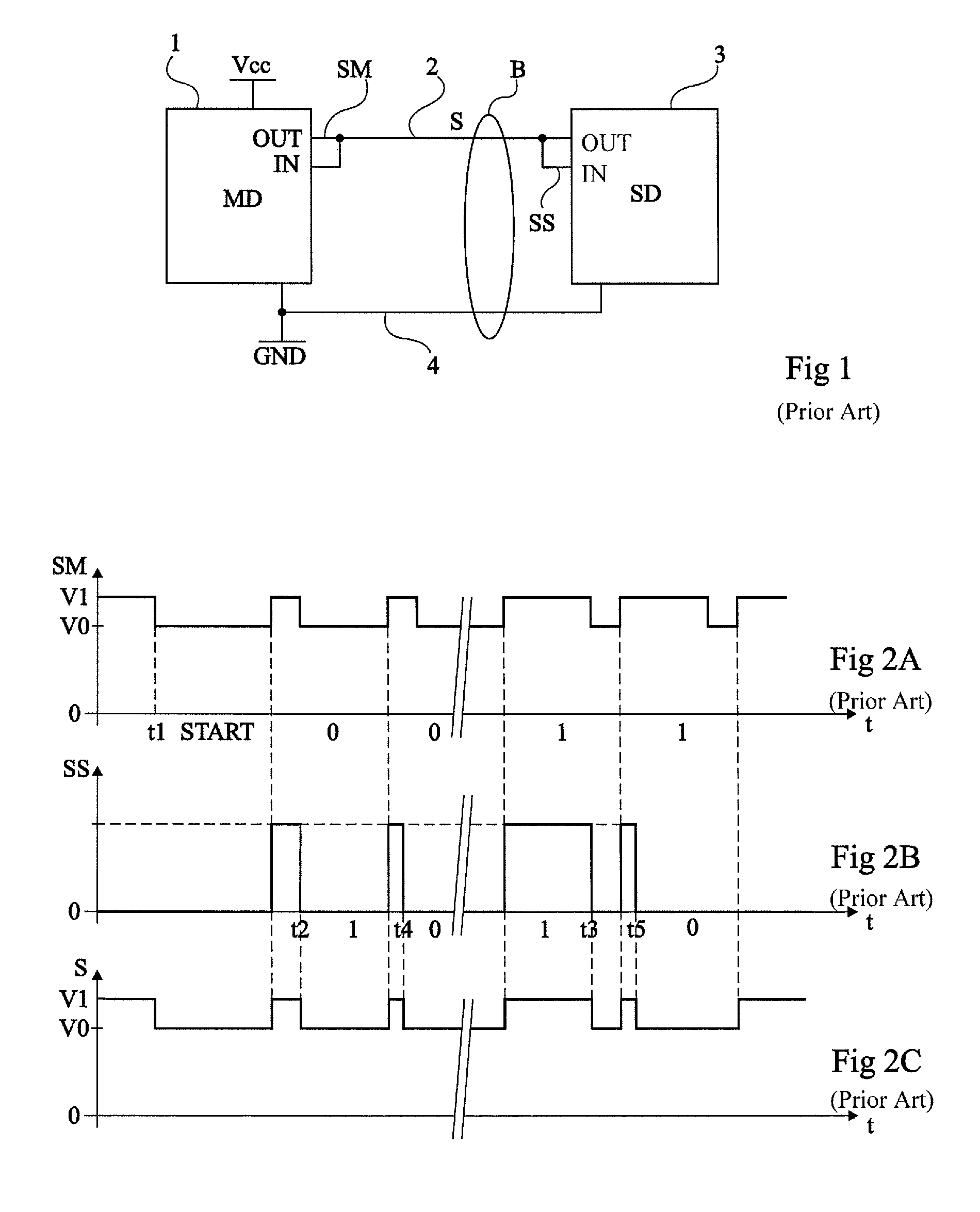
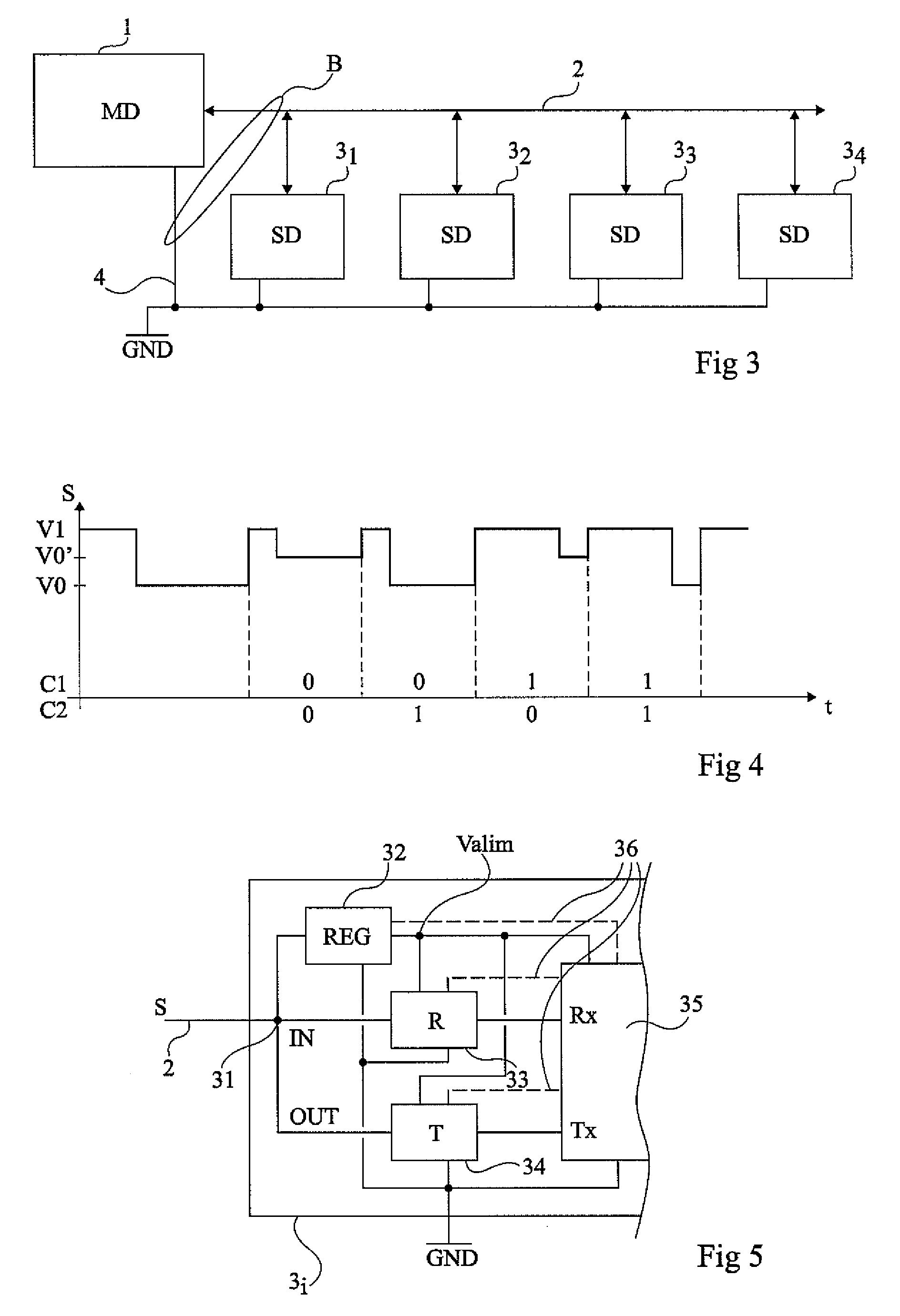
Multiple-channel transmission over a single-wire bus
ActiveUS8509318B2Batteries circuit arrangementsTransmission/receiving by adding signal to waveTransmission channelPower over
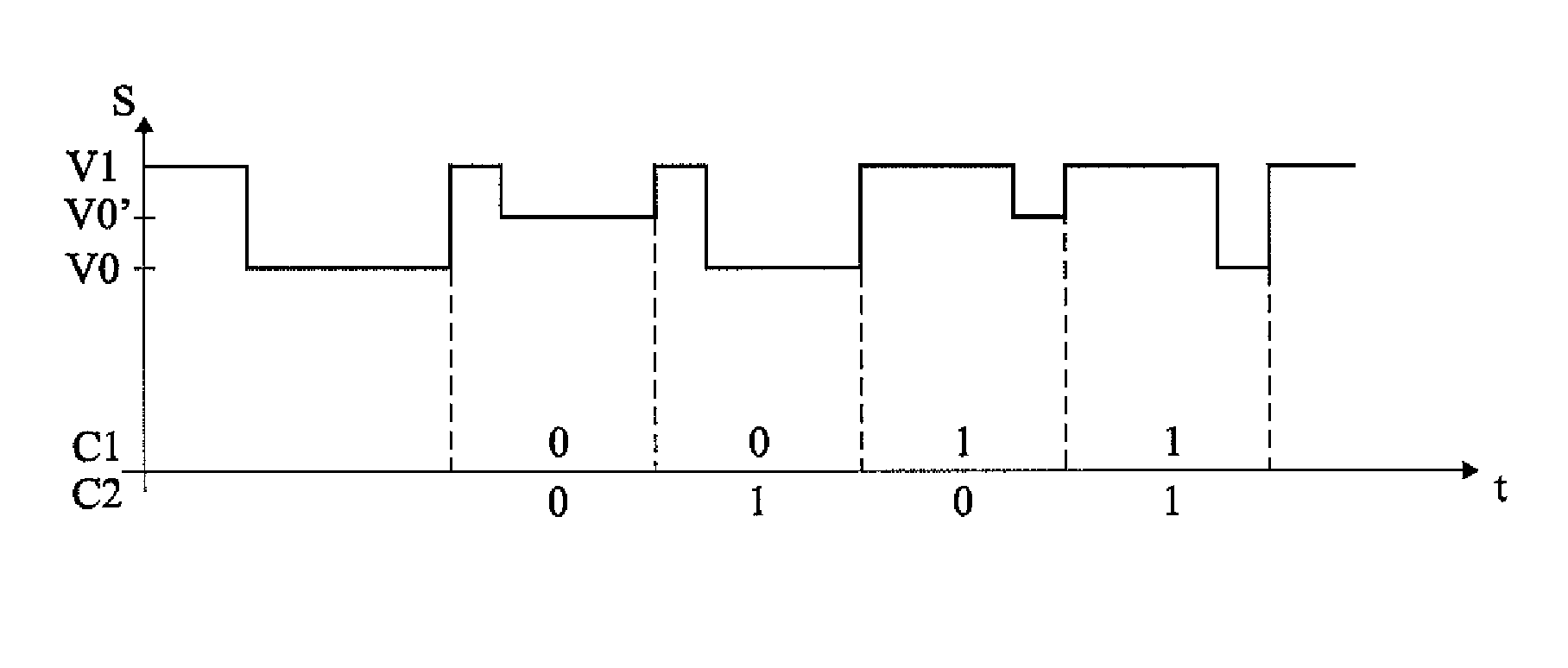
Apparatus and methods are described that enable concurrent transmission of multiple data signals including clock, synchronization, and power over a single-wire bus between a master device and one or more slave devices. A first transmission channel from the master device to the slave device may modulate the width of periodic pulses between a first voltage level and a second voltage level with respect to a reference potential. A second transmission channel may modulate the amplitude of at least one of the first and second voltage levels to at least one third voltage level. Concurrent communications between a master device and one or more slave devices over a single-wire bus can be achieved.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS (ROUSSET) SAS
Digital spread spectrum methods and apparatus for testing aircraft wiring
InactiveUS7069163B2Efficient implementationElectronic circuit testingTesting electric installations on transportOriginal dataData signal
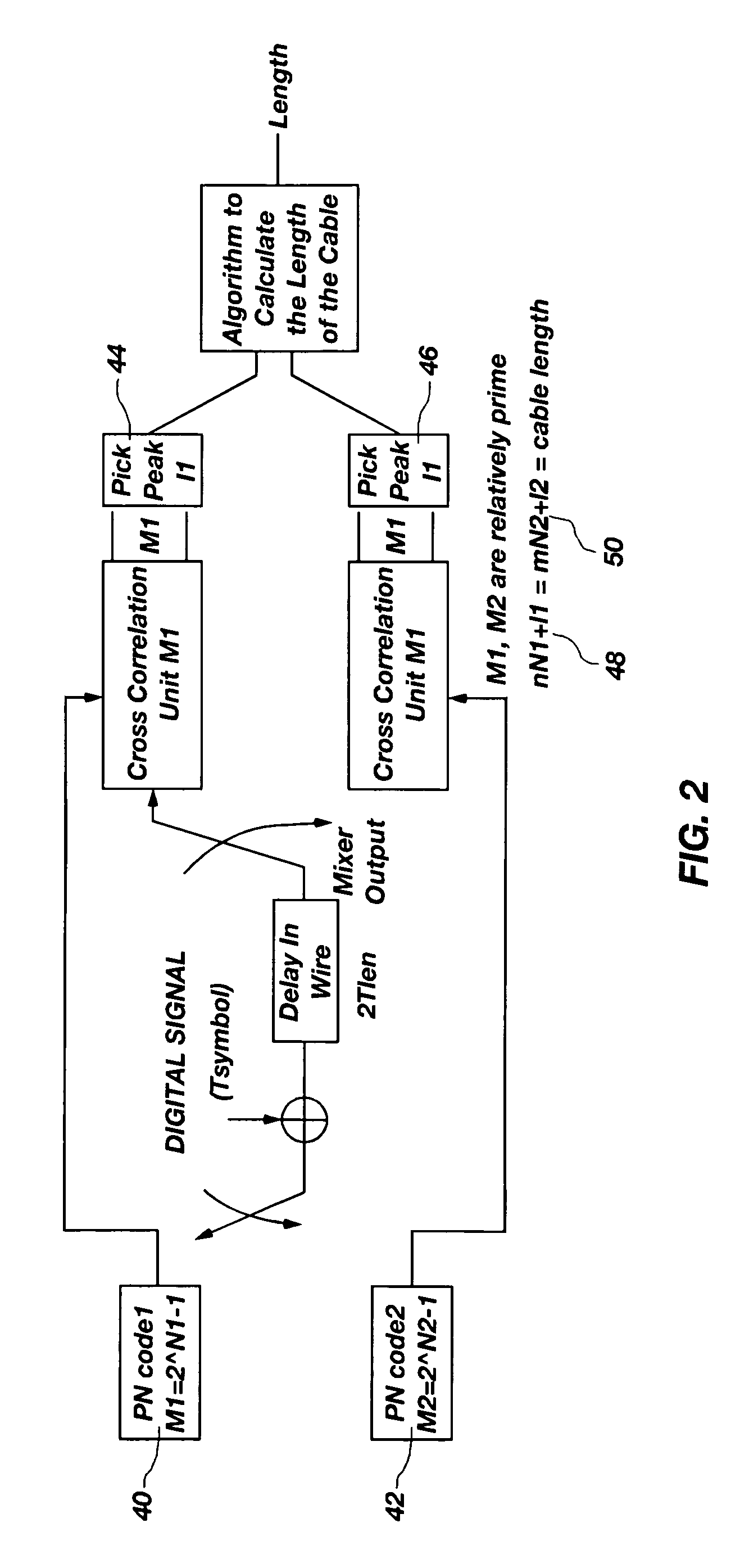
A system and method that utilizes direct sequence spread spectrum signal (DSSS) encoding to enable testing of a live wire, wherein an original data signal is modified and then transmitted along the wire, and a reflected signal is collected and analyzed using correlation techniques to determine characteristics of the live wire, including the location of a fault.
Owner:UTAH STATE UNIVERSITY
Method and apparatus for optically analyzing a surface
InactiveUS20070091317A1Quick and efficient analysisEffectively and accurately characteristicRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryCharacterization testBroadband
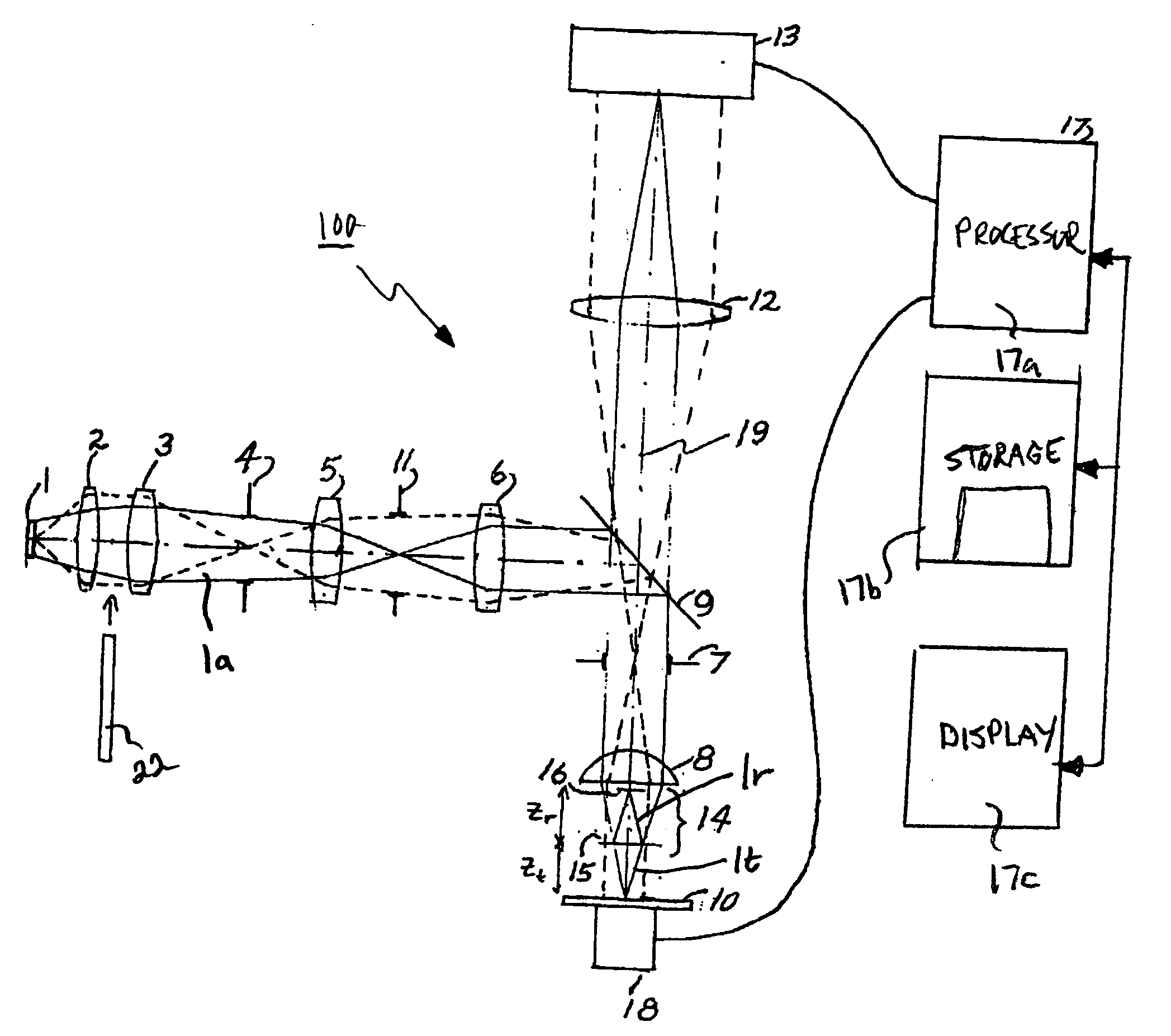
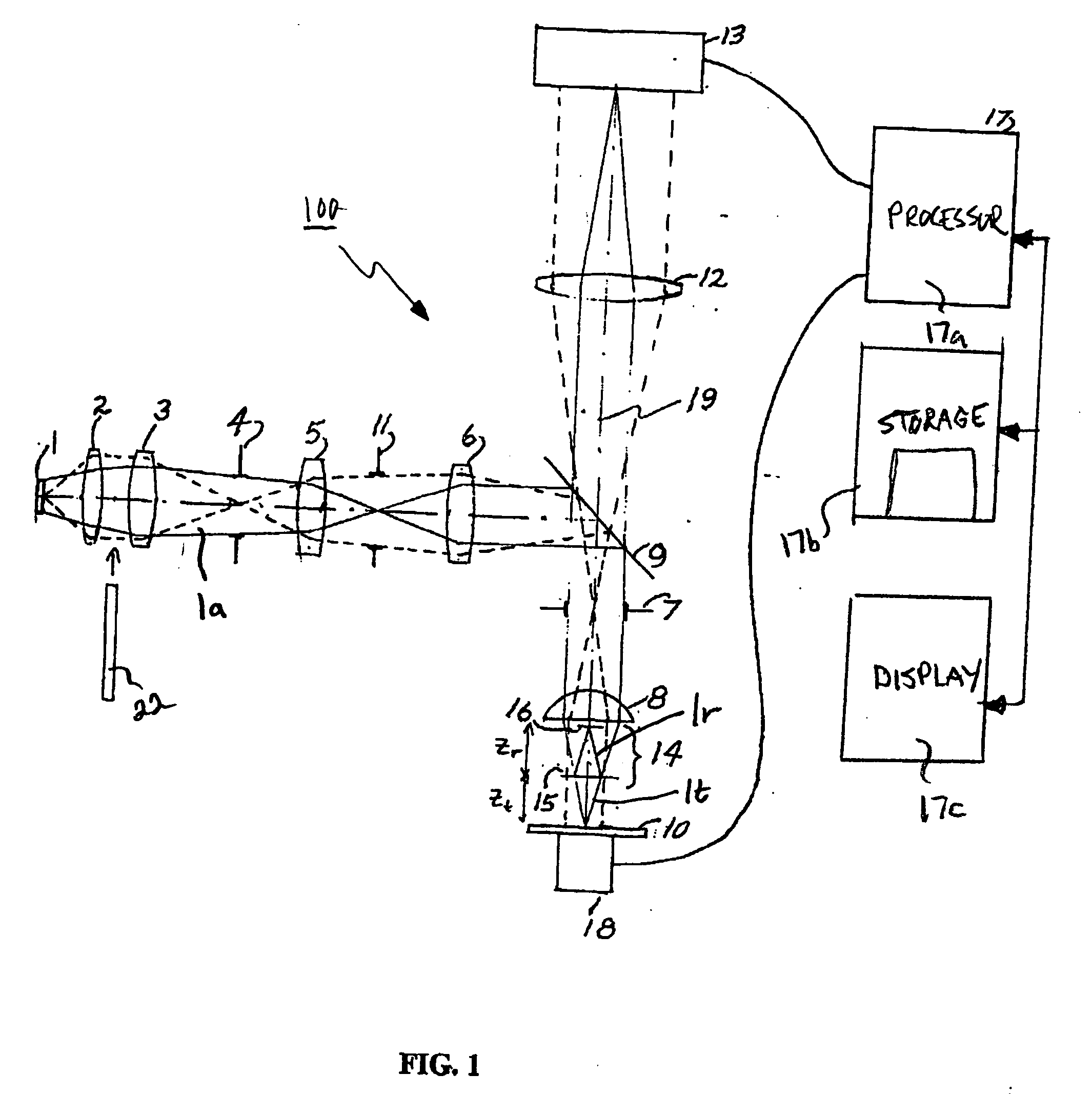
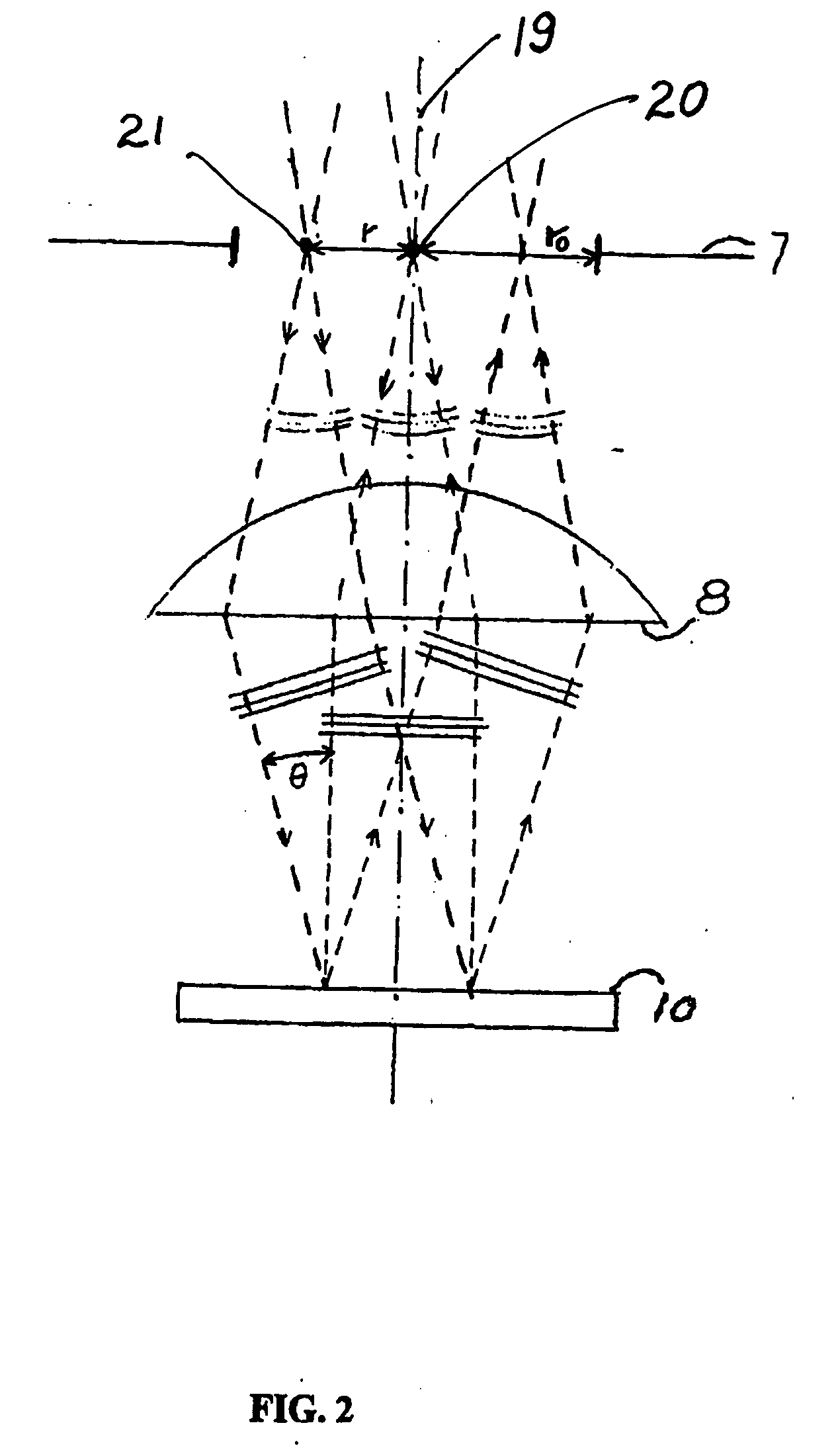
Apparatus and methods are provided for analyzing surface characteristics of a test object using broadband scanning interferometry. Test objects amenable to these apparatus and methods include but are not limited to semiconductor wafers, semiconductor devices, metallic surfaces, and the like. An interferometry system is used to obtain an interferometry signal and related to data embodied in the signal representative of the test object surface. This signal and / or data is used to construct an n-dimensional function that includes an independent frequency variable and an independent time variable, and / or an n-dimensional function that includes an independent scale variable and an independent time variable, and / or a multi-domain function. These functions are compared with various models to obtain a best match that is then used to characterize the test object surface.
Owner:PHASE SHIFT TECH
High frequency array ultrasound system
ActiveUS20070239001A1Time indicationSynchronous motors for clocksPhased array transducerLinear arrays
A system for acquiring an ultrasound signal comprises a signal processing unit adapted for acquiring a received ultrasound signal from an ultrasound transducer having a plurality of elements. The system is adapted to receive ultrasound signals having a frequency of at least 20 megahertz (MHz) with a transducer having a field of view of at least 5.0 millimeters (mm) at a frame rate of at least 20 frames per second (fps). The signal processing can further produce an ultrasound image from the acquired ultrasound signal. The transducer can be a linear array transducer, a phased array transducer, a two-dimensional (2-D) array transducer, or a curved array transducer.
Owner:SUNNYBROOK HEALTH SCI CENT +1
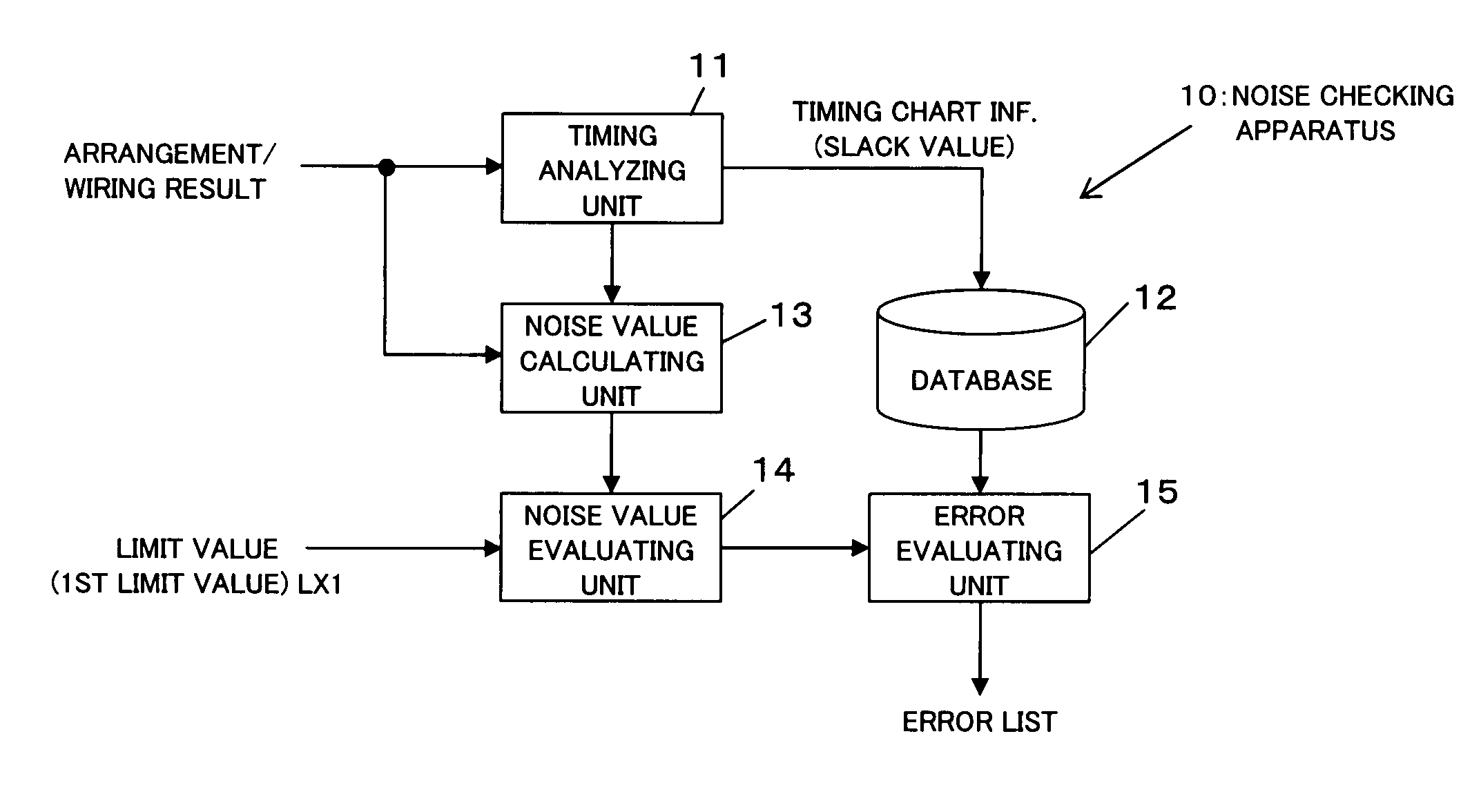
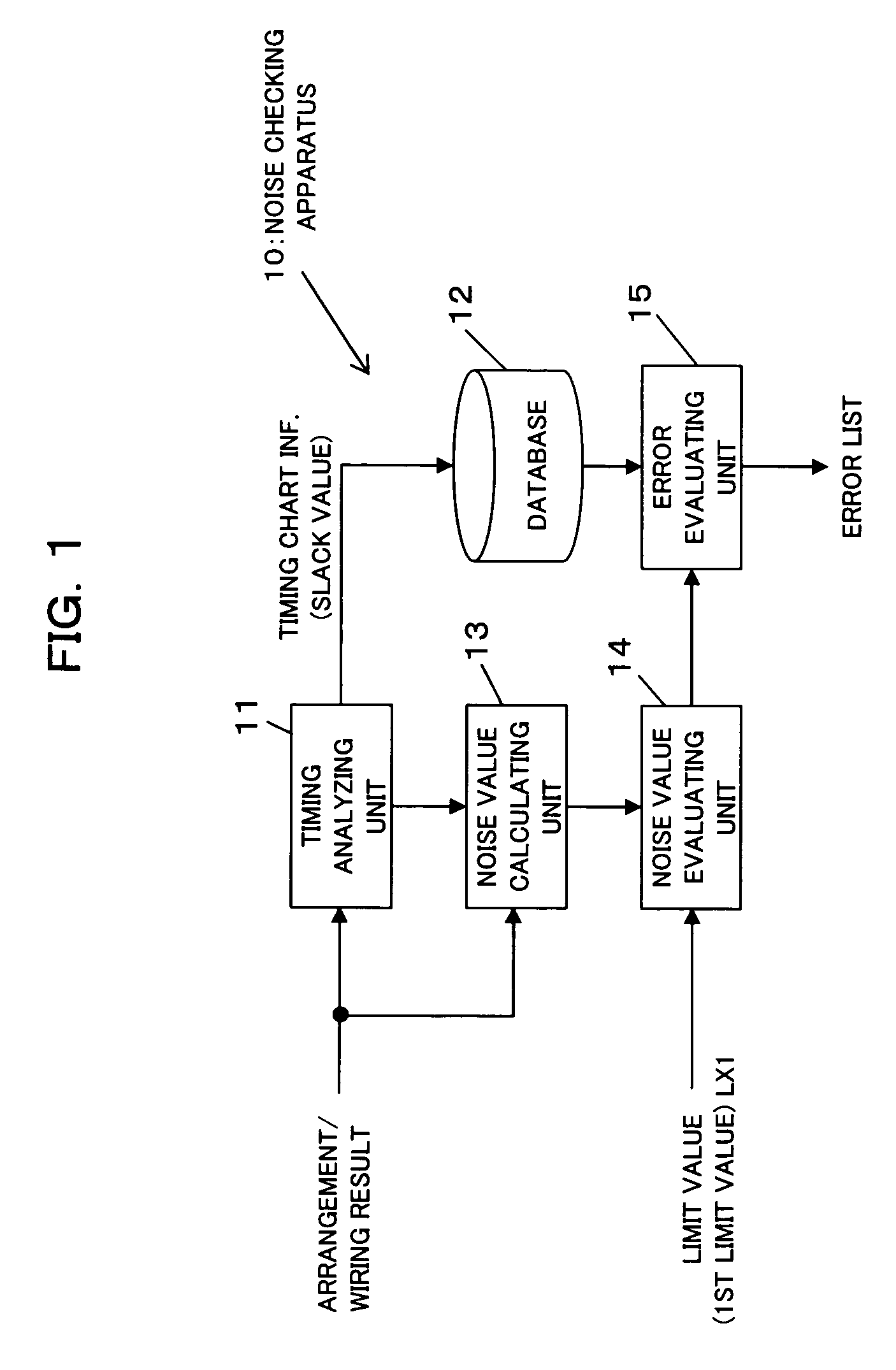
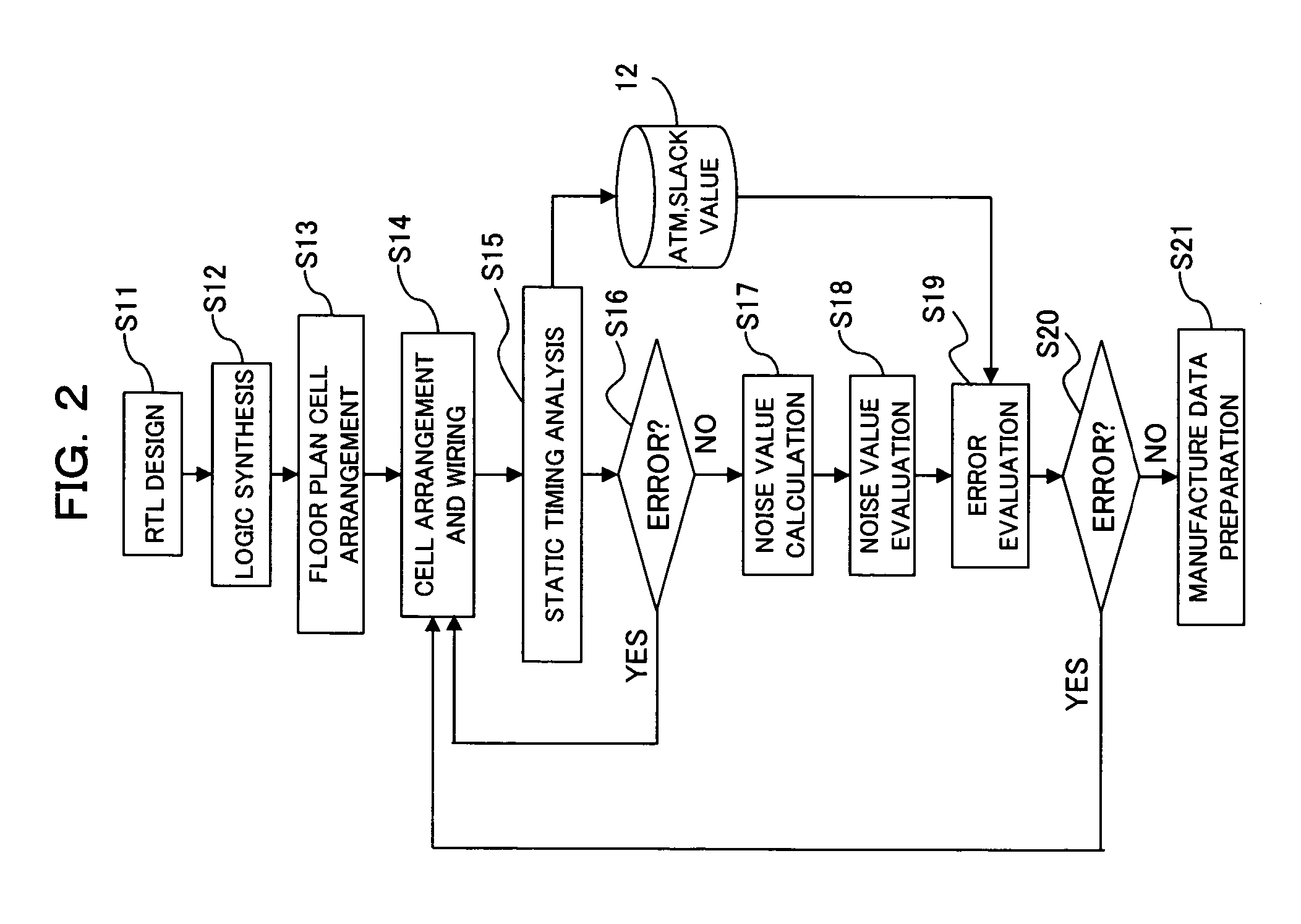
Noise checking method and apparatus and computer-readable recording medium which records a noise checking program
InactiveUS7158920B2Reduce amount and correctionWork lessSpectral/fourier analysisNoise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementLimit valueComputer science
The apparatus reduces the amount of correction for noise value error, so as to reduce work needed for correction to ensure error avoidance, and to improve the freedom of layout design, and to reduce load on DA. Based on a timing chart of signal transfer on each wire, the last edge appearance timing in the signal waveform of a victim whose noise value exceeds a limit value is compared with the last edge appearance timing in the signal waveform of an aggressor, to evaluate the noise value error in the victim. The apparatus is used in static noise checking of cell arrangement and inter-cell wiring after such cell arrangement and inter-cell wiring are performed at design of integrated circuits such as LSIs.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
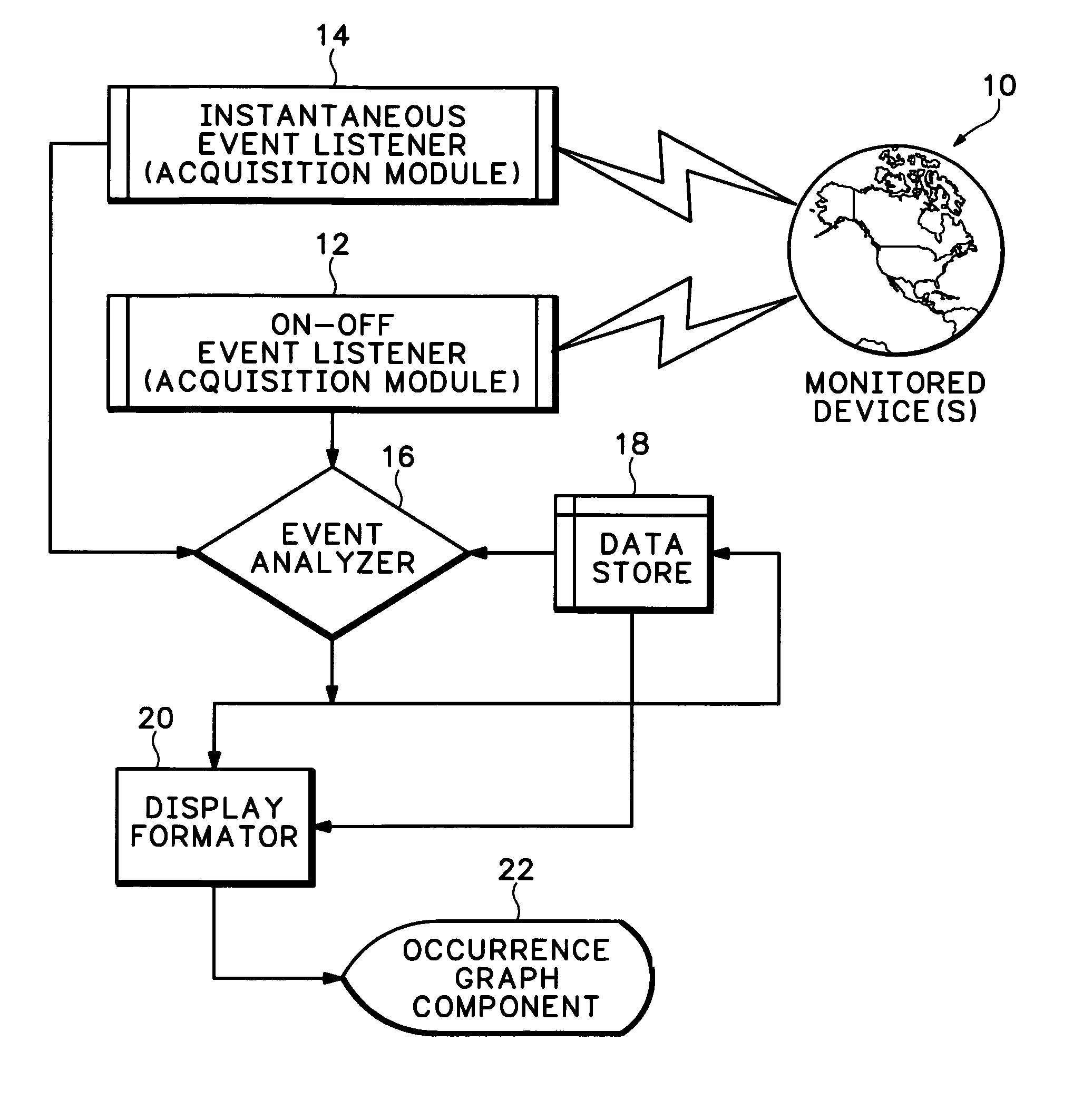
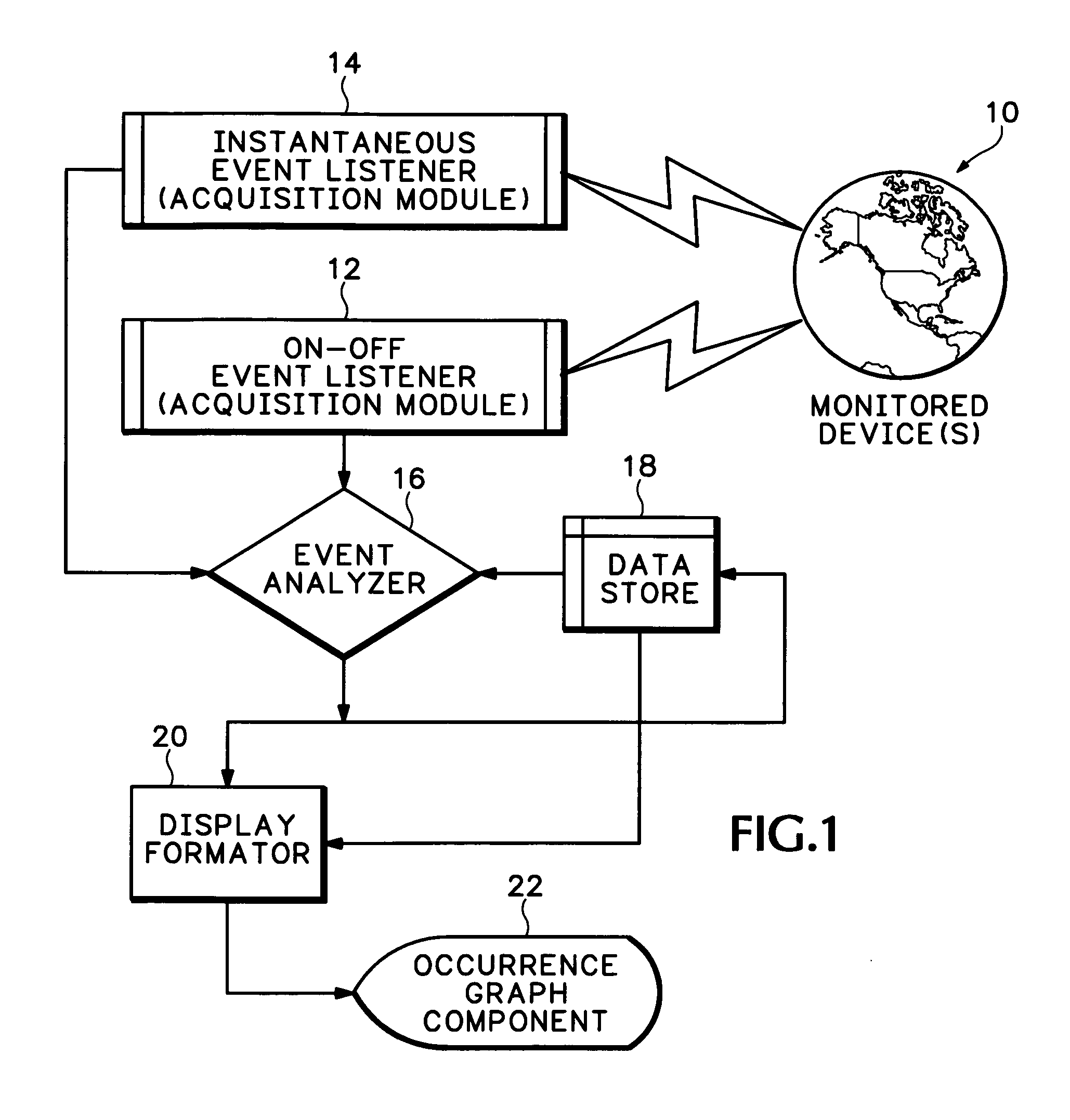
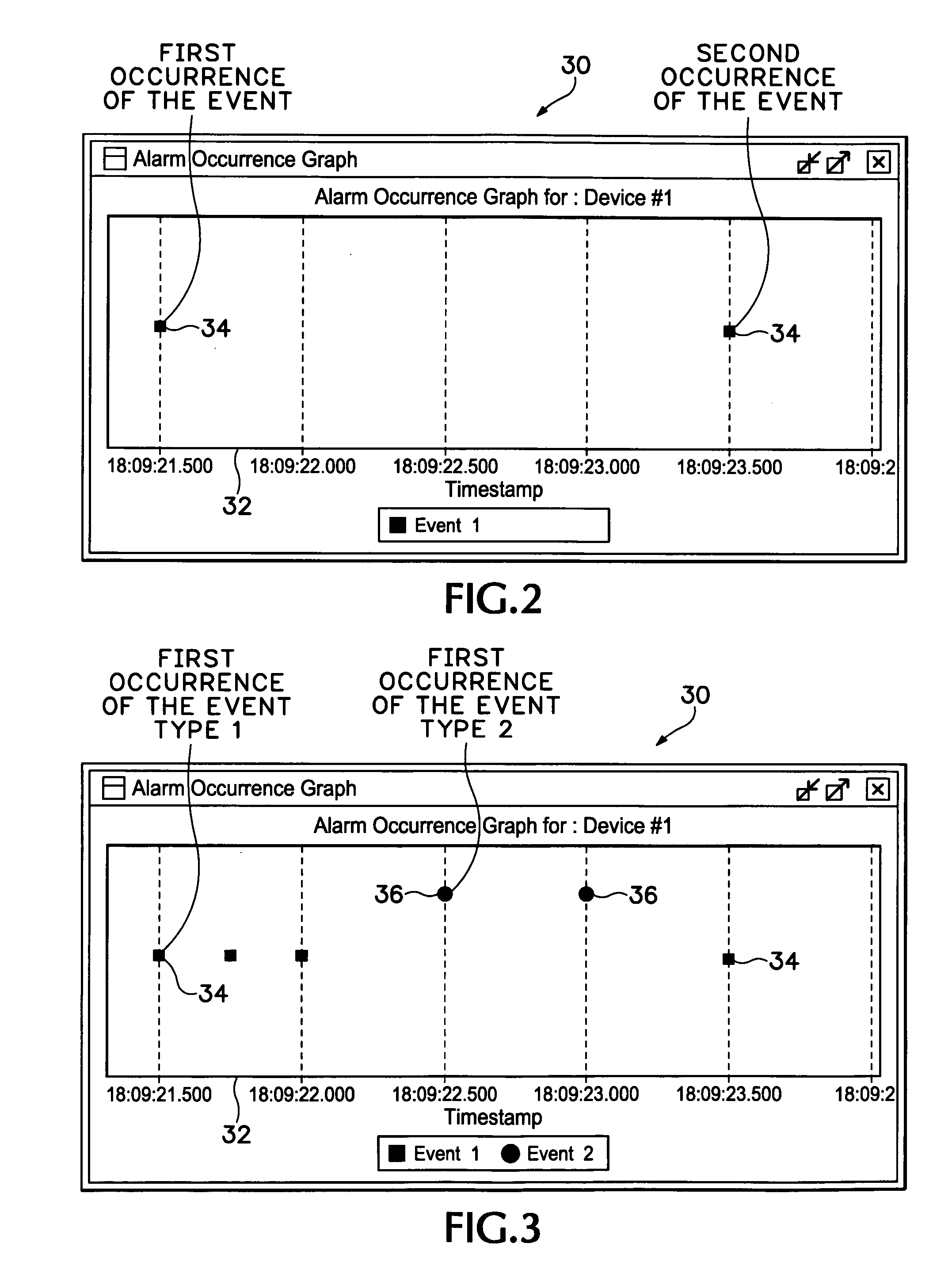
Event occurrence graph
Owner:KOODALI ANURAG T
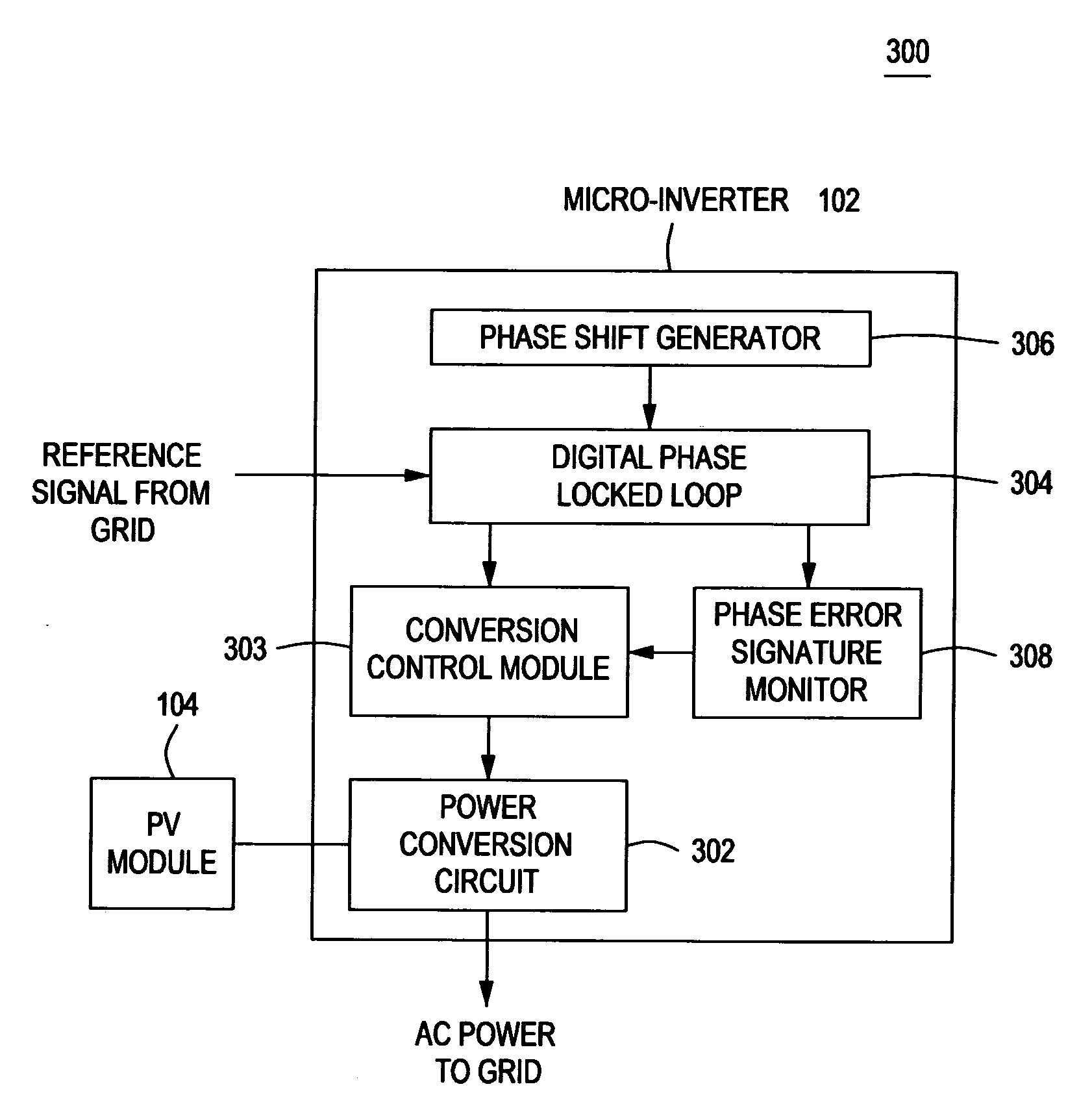
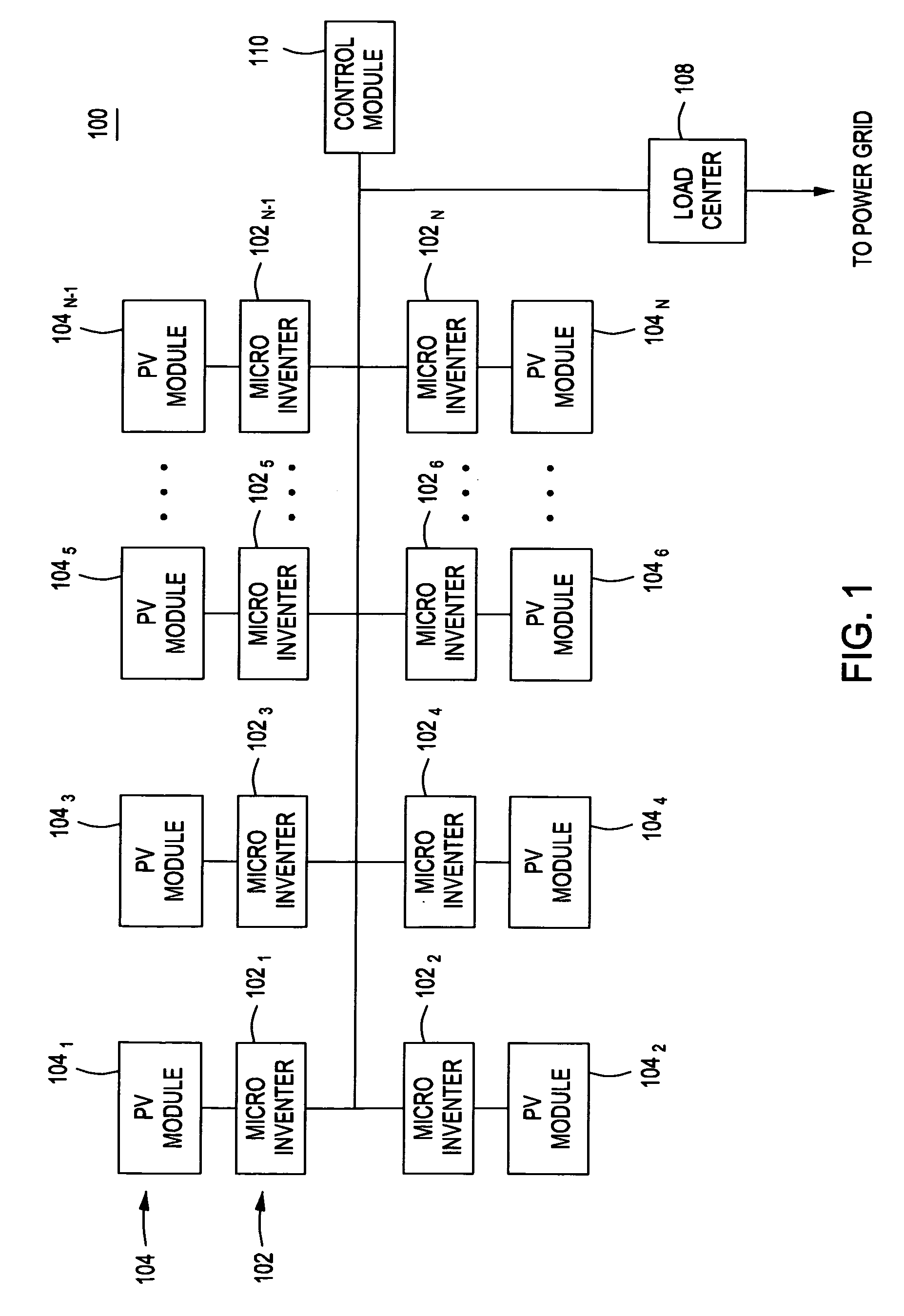
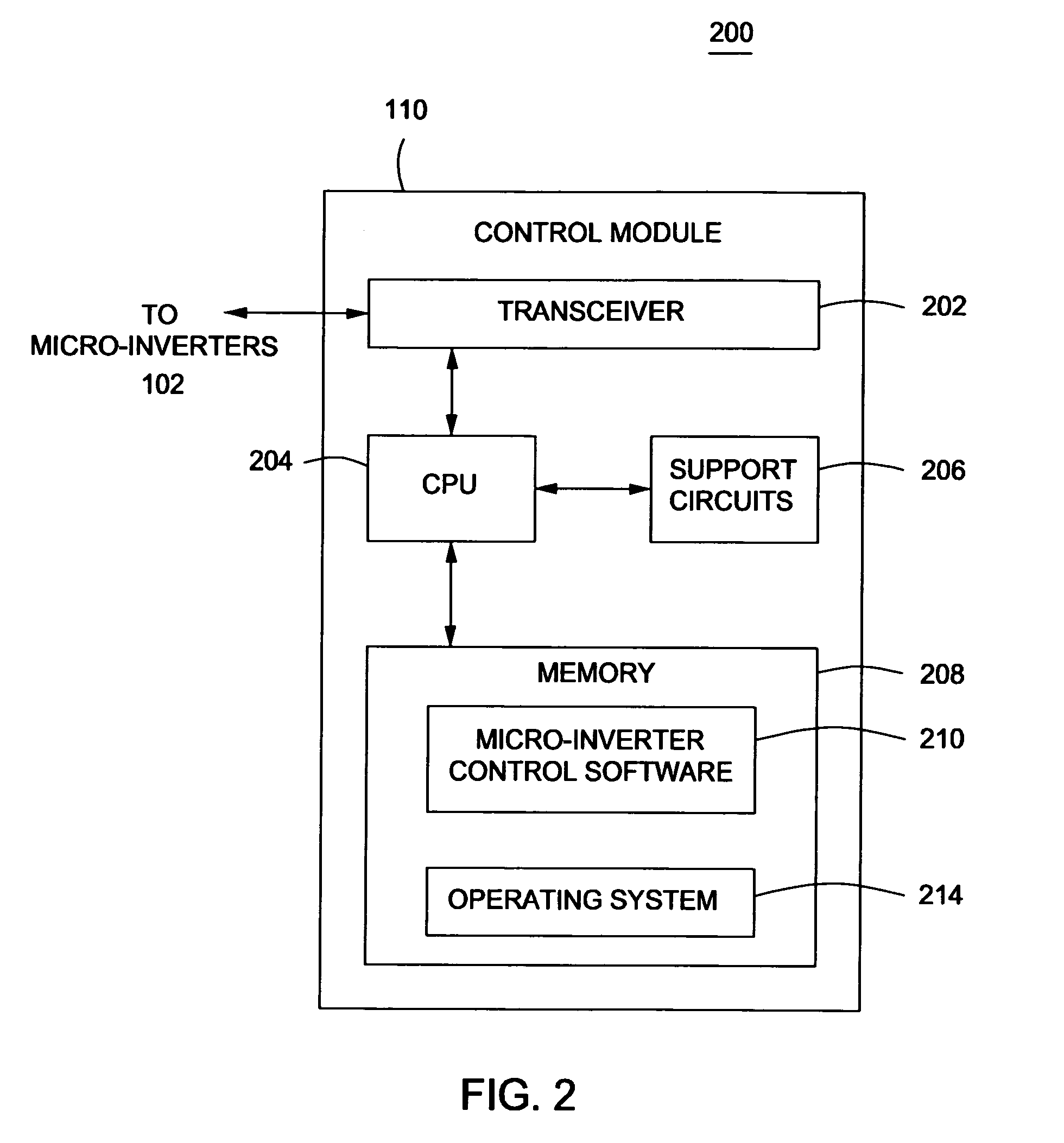
Method and apparatus for anti-islanding of distributed power generation systems
InactiveUS20090021877A1Noise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementApparatus with intermediate ac conversionIslandingPhase shifted
A method and apparatus for anti-islanding of distributed power generation systems having an inverter comprising a phase locked loop (PLL), a phase shift generator for injecting a phase shift into the PLL during at least one sample period, and a phase error signature monitor for monitoring at least one phase error response of the PLL during the at least one sample period.
Owner:ENPHASE ENERGY
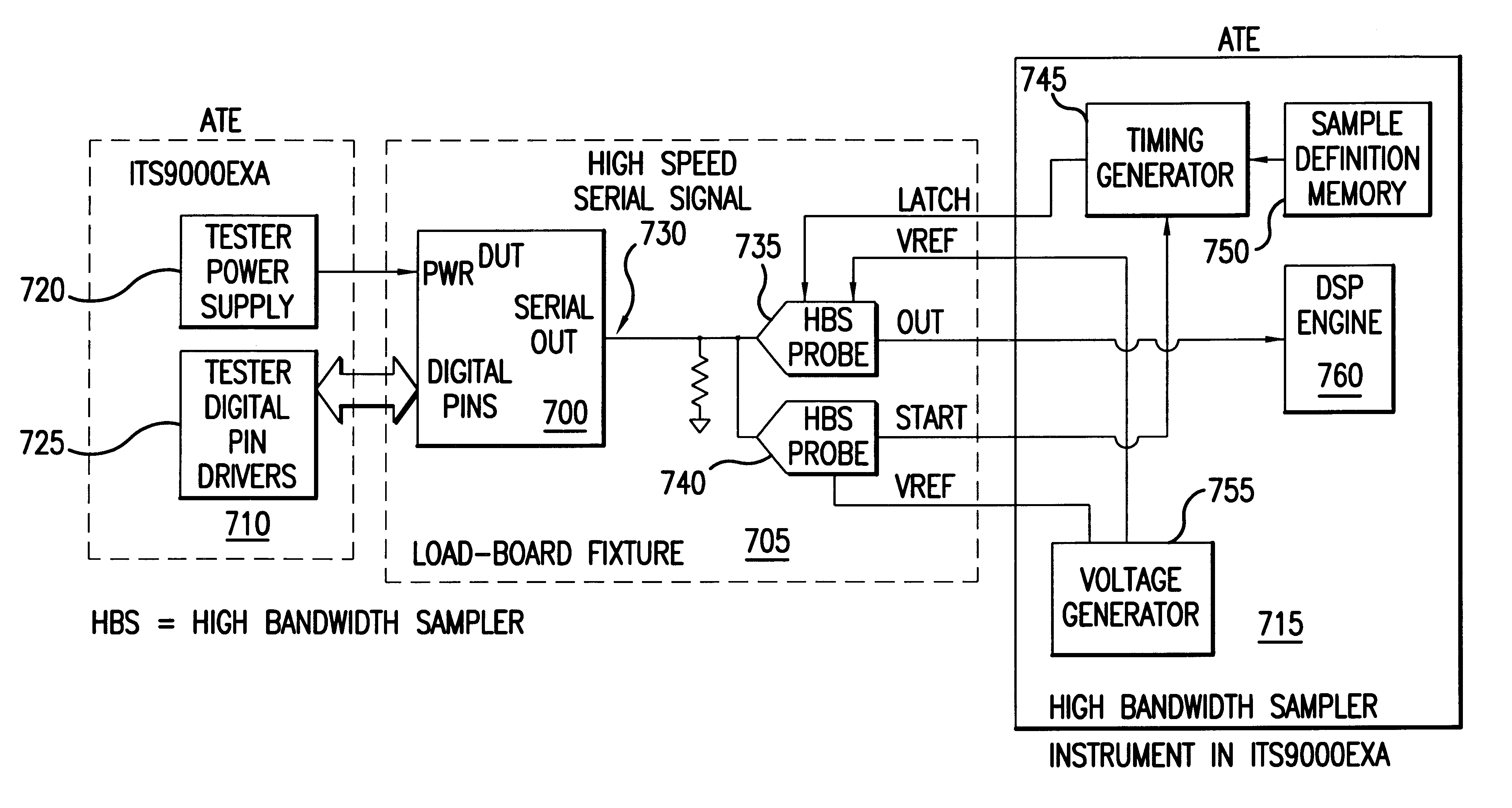
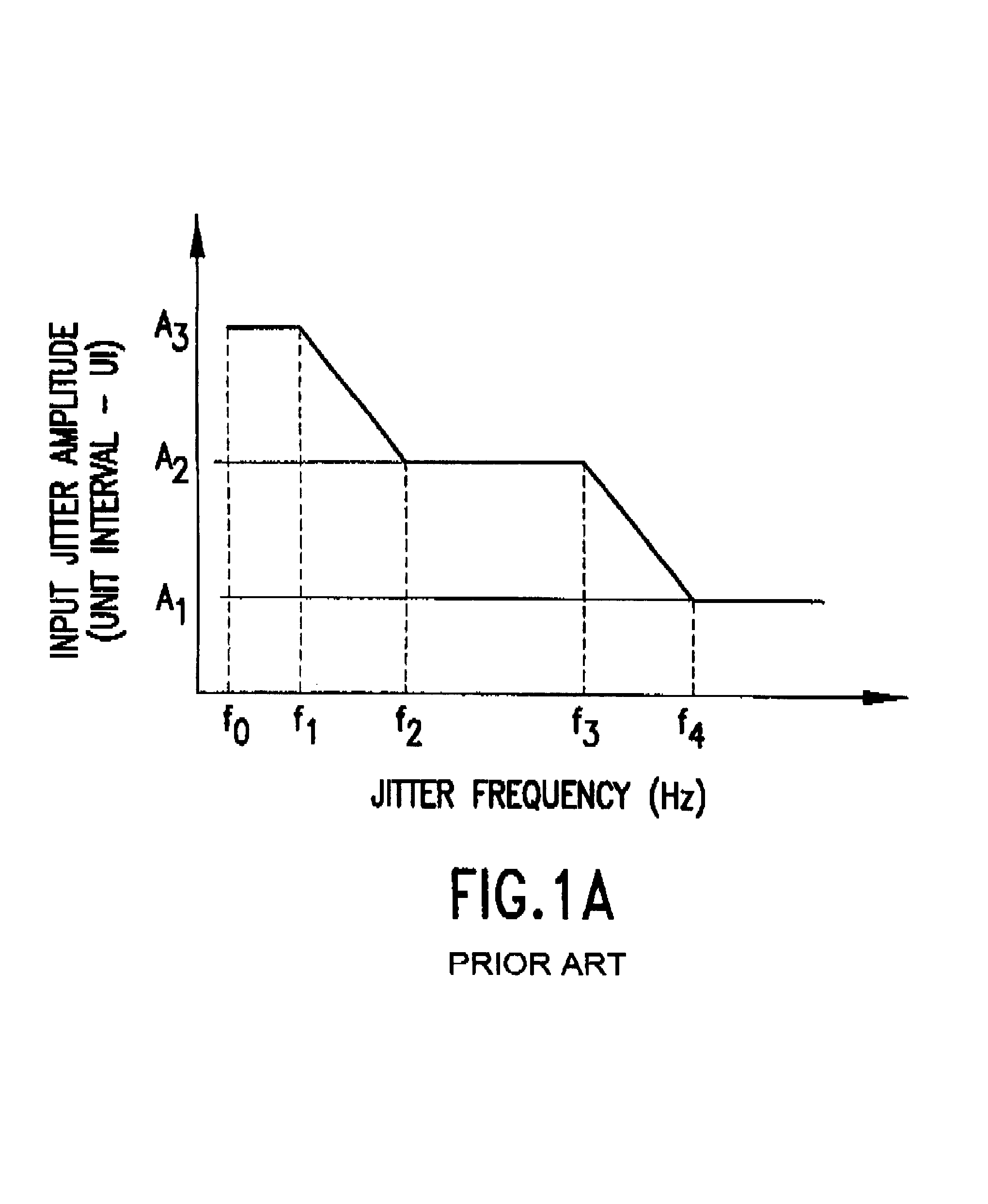
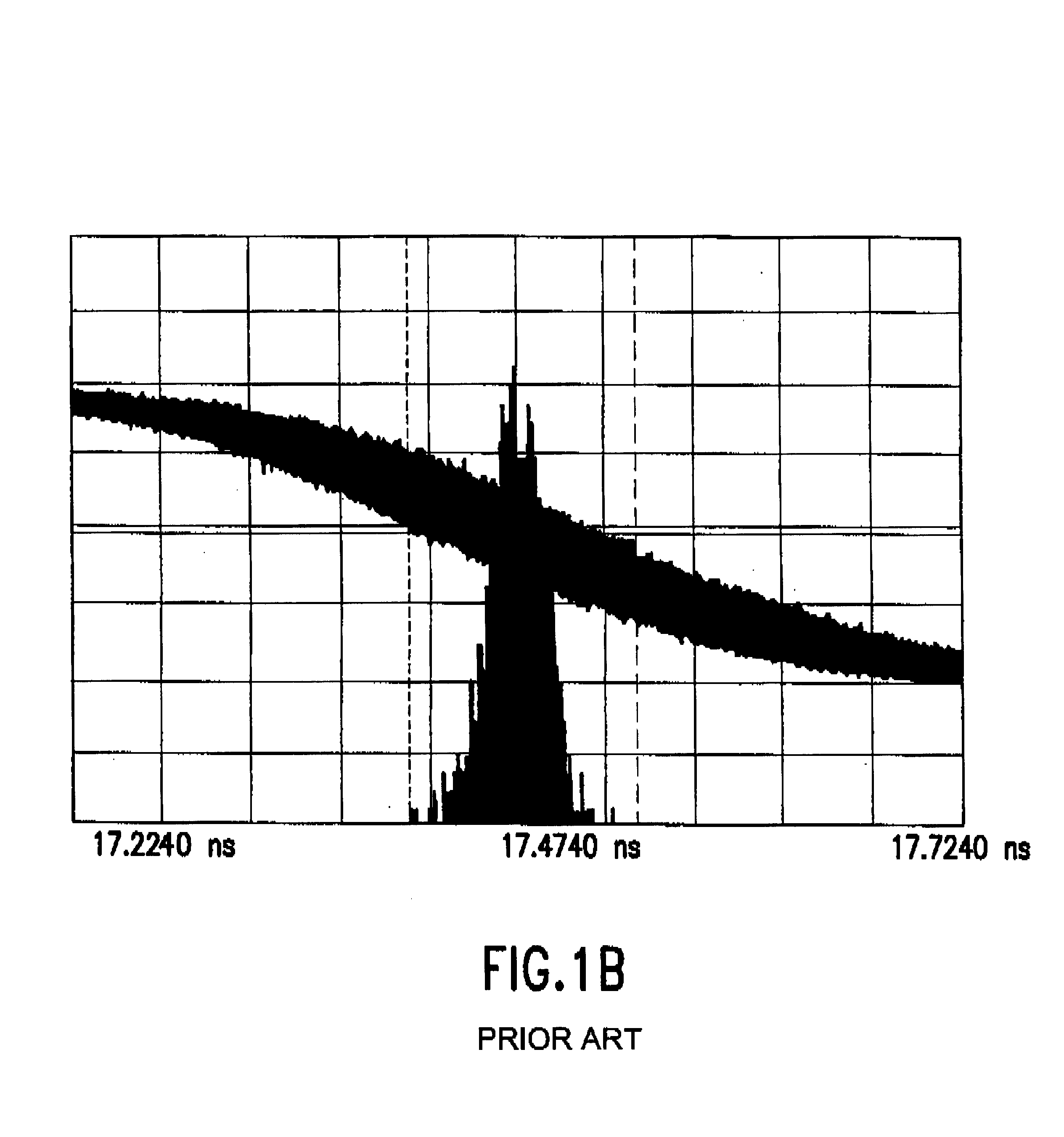
Measuring jitter of high-speed data channels
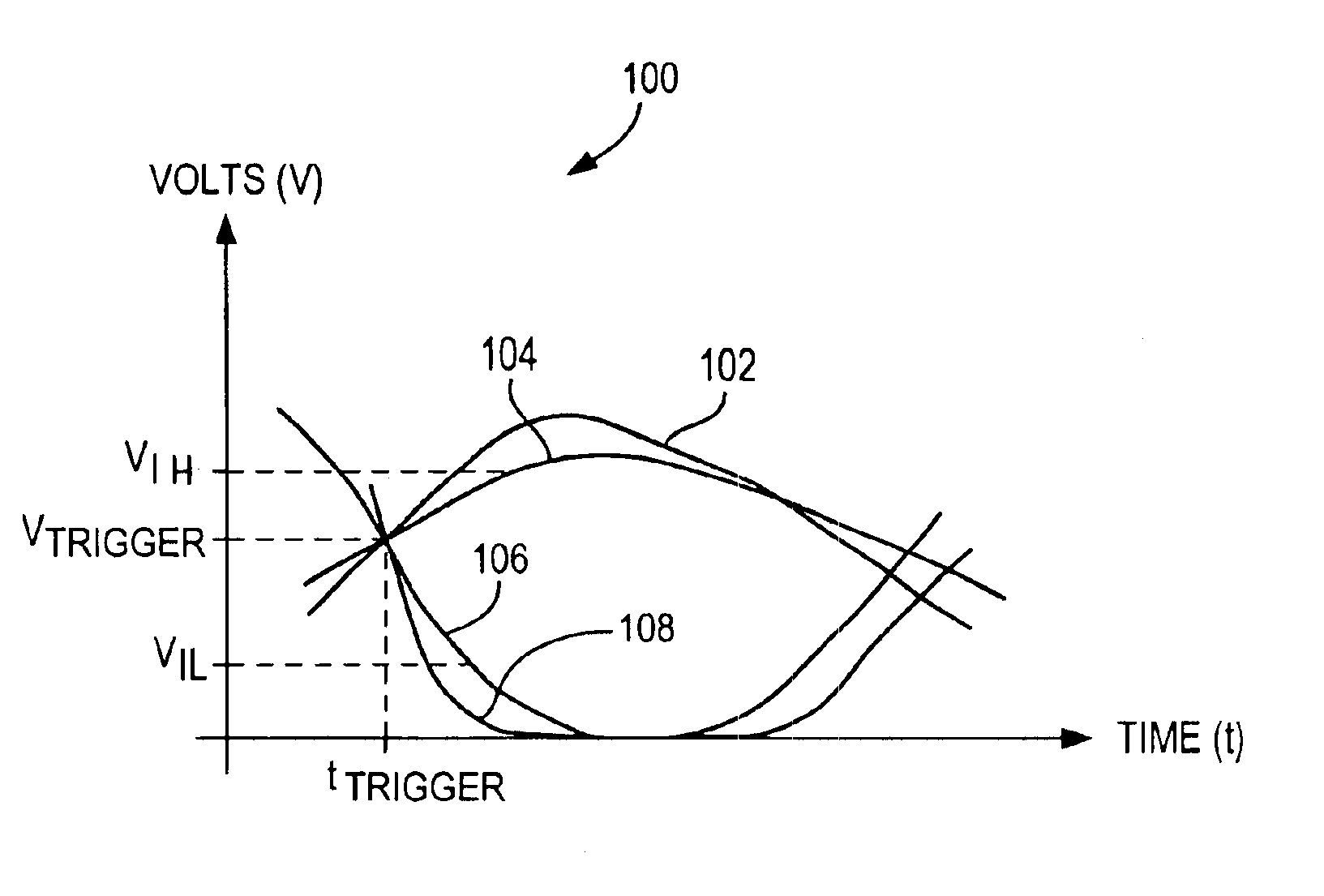
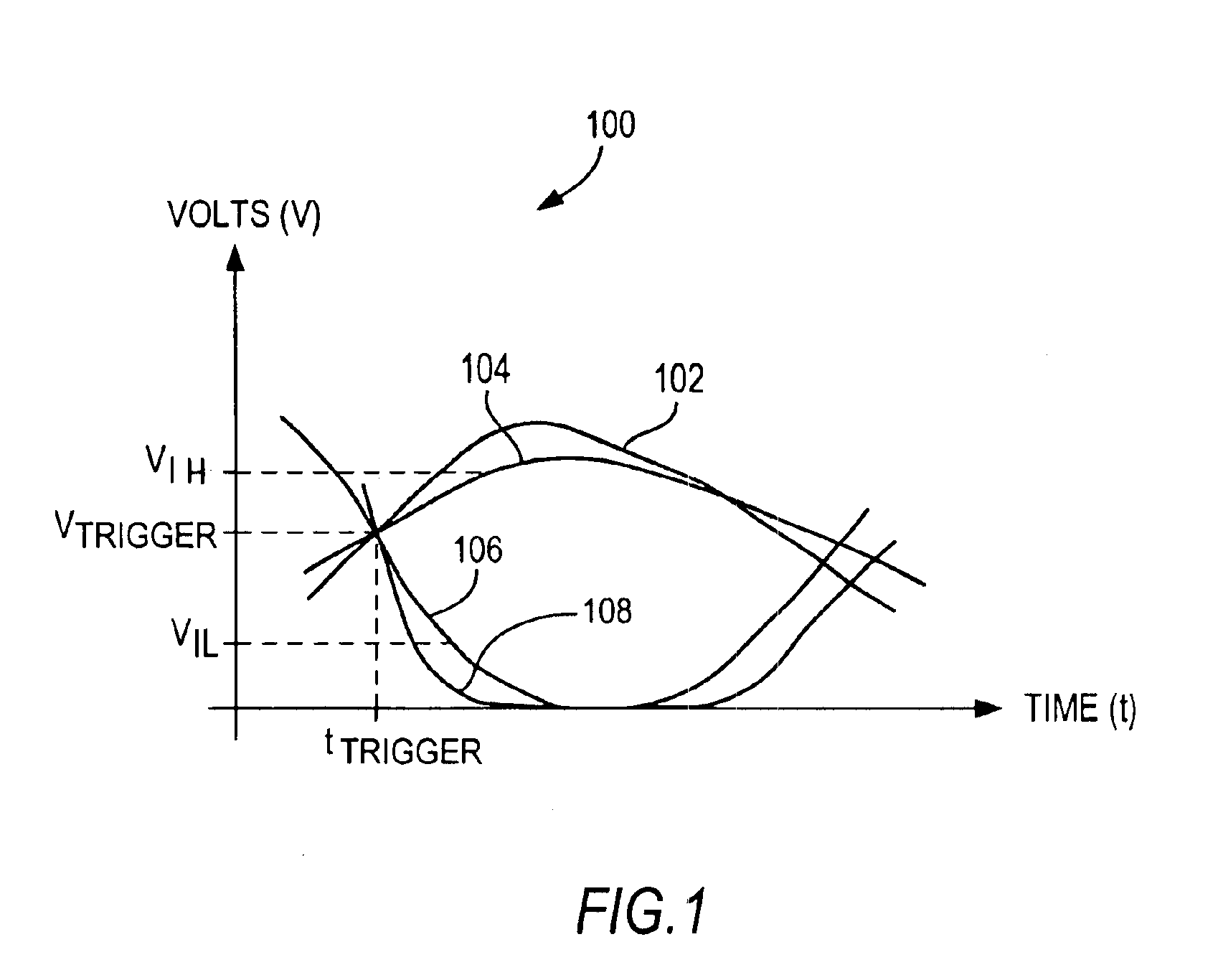
A jitter measurement technique utilizing a high-bandwidth undersampling voltage measurement instrument is presented. A trigger is derived from the a signal having a repetitive signal pattern. The signal is compared with a threshold at a plurality of times relative to the trigger during multiple repetitions of the signal pattern to produce measurement samples indicative of signal level relative to the threshold. The measurement samples are used to determine the probability of signal edge states as a function of time for the multiple repetitions. The probability of signal edge states are used to determine an edge probability density as a function of time. A histogram of signal state transition times can be prepared from the edge probability density. Mean deviation of edge transitions of the signal can be estimates, and standard deviation of edge transitions of the signal can be estimated to give the root-mean-square (rms) jitter of the signal.
Owner:CREDENCE SYSTEMS
Self-referencing communication in implantable devices
InactiveUS8055345B2Convenient treatmentReliable information transmissionElectrotherapyDuration/width modulated pulse demodulationEngineeringSelf-clocking signal
Various aspects of the present invention enable robust, reliable control functionality for effectors present on intraluminal, e.g., vascular leads, as well as other types of implantable devices. Aspects of the invention include implantable integrated circuits that have self-referencing and self-clocking signal encoding, and are capable of bidirectional communication. Also provided by the invention are effector assemblies that include the integrated circuits, as well as implantable medical devices, e.g., pulse generators that include the same, as well as systems and kits thereof and methods of using the same, e.g., in pacing applications, including cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) applications.
Owner:PROTEUS DIGITAL HEALTH INC
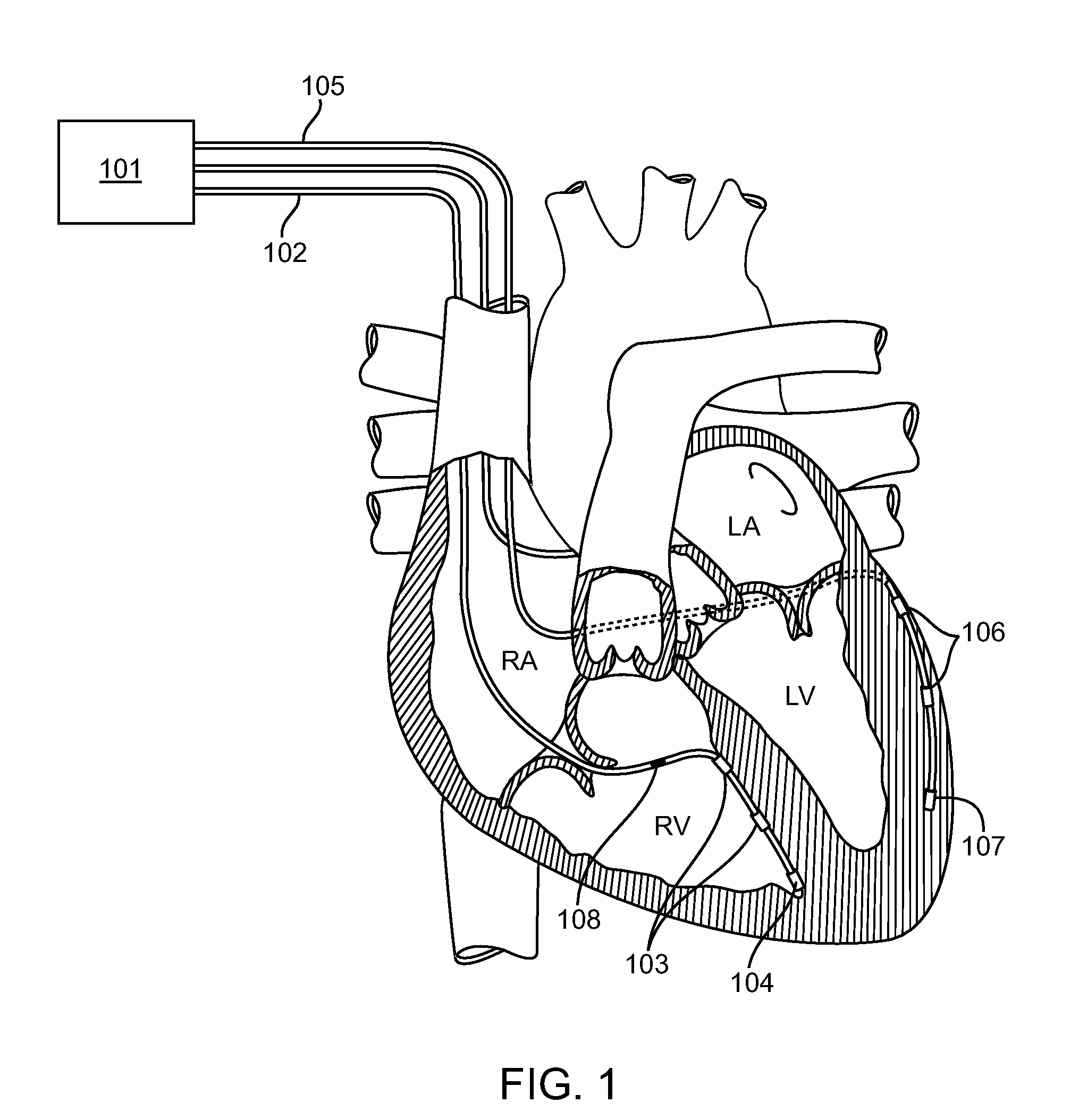
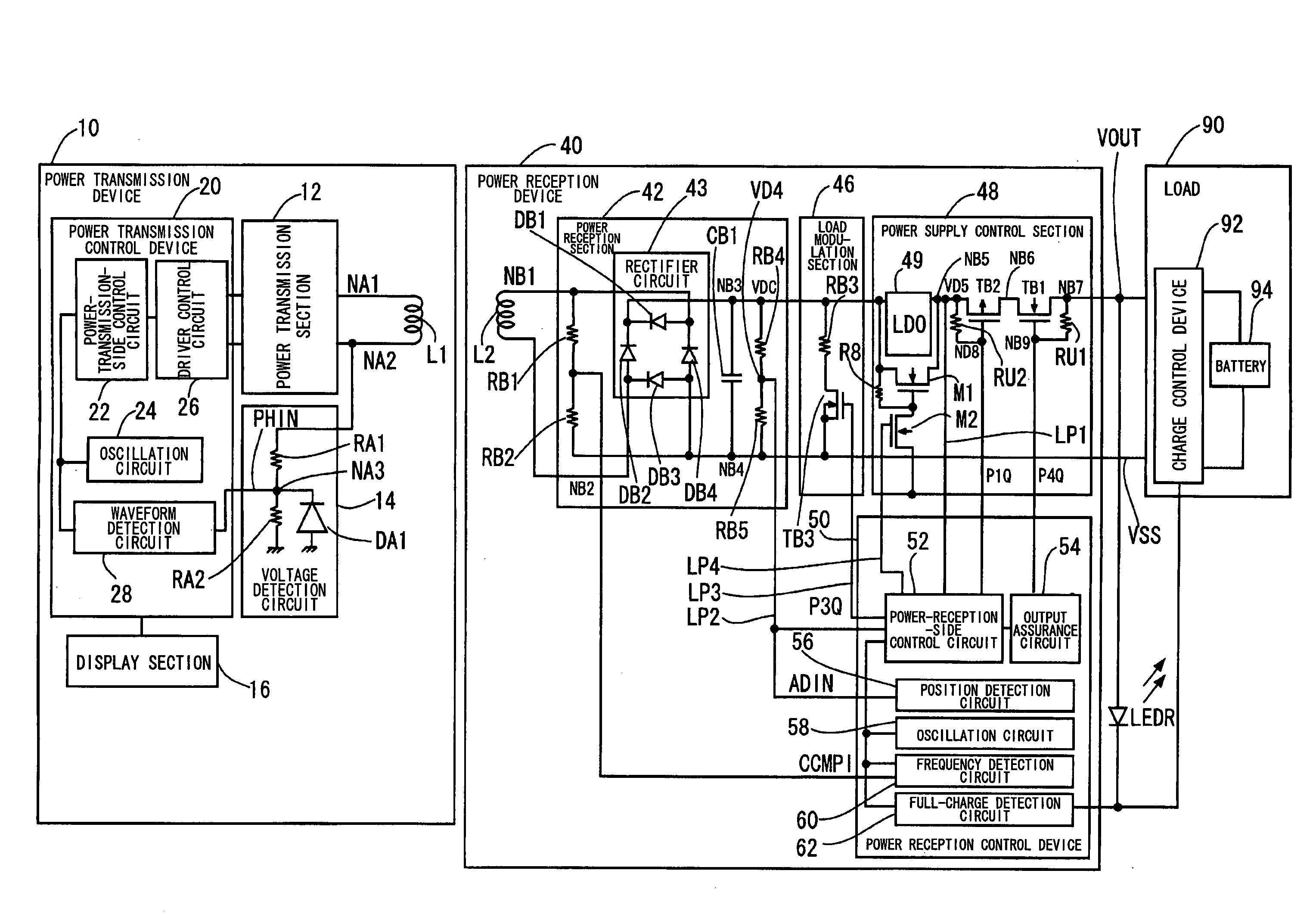
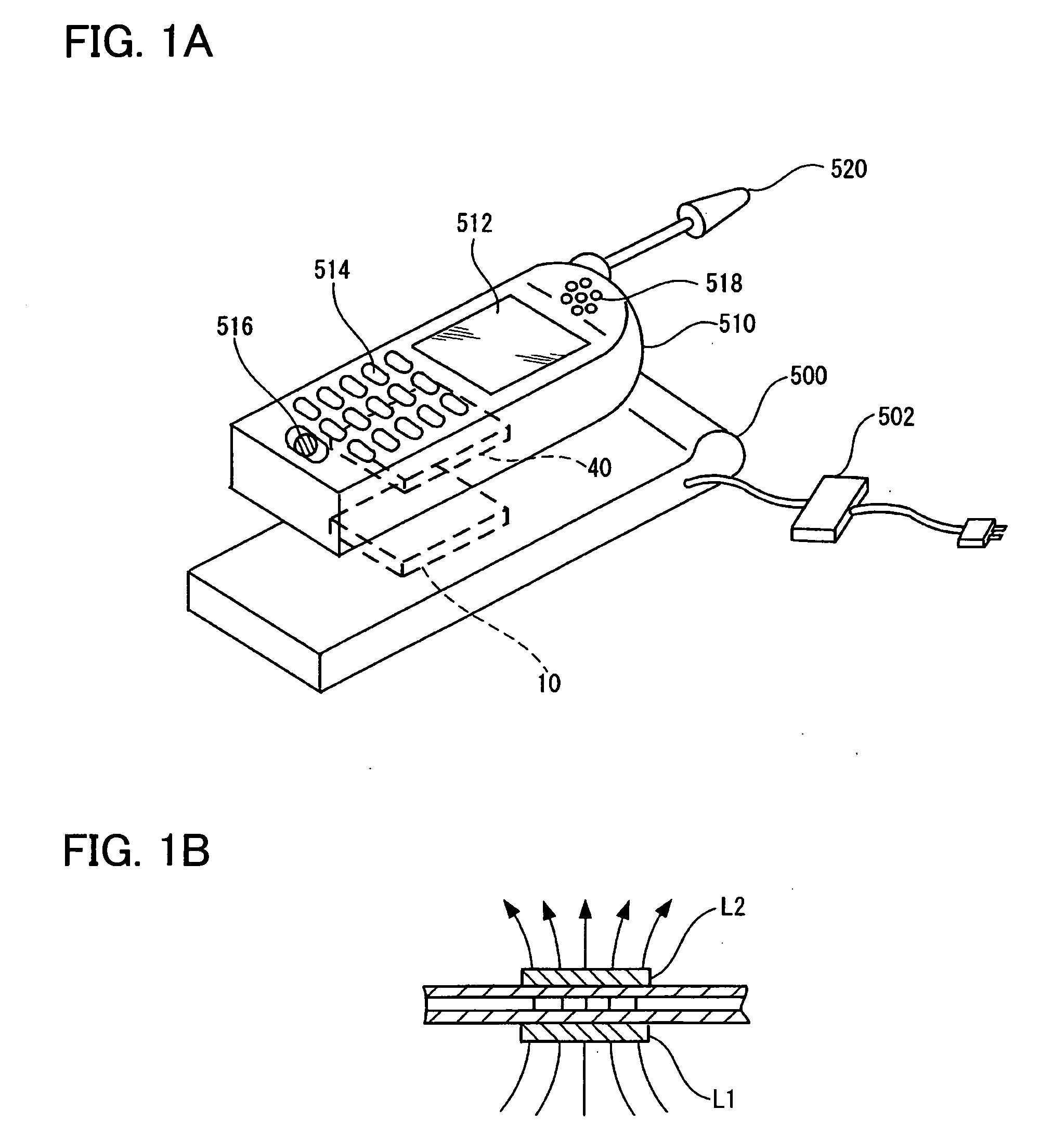
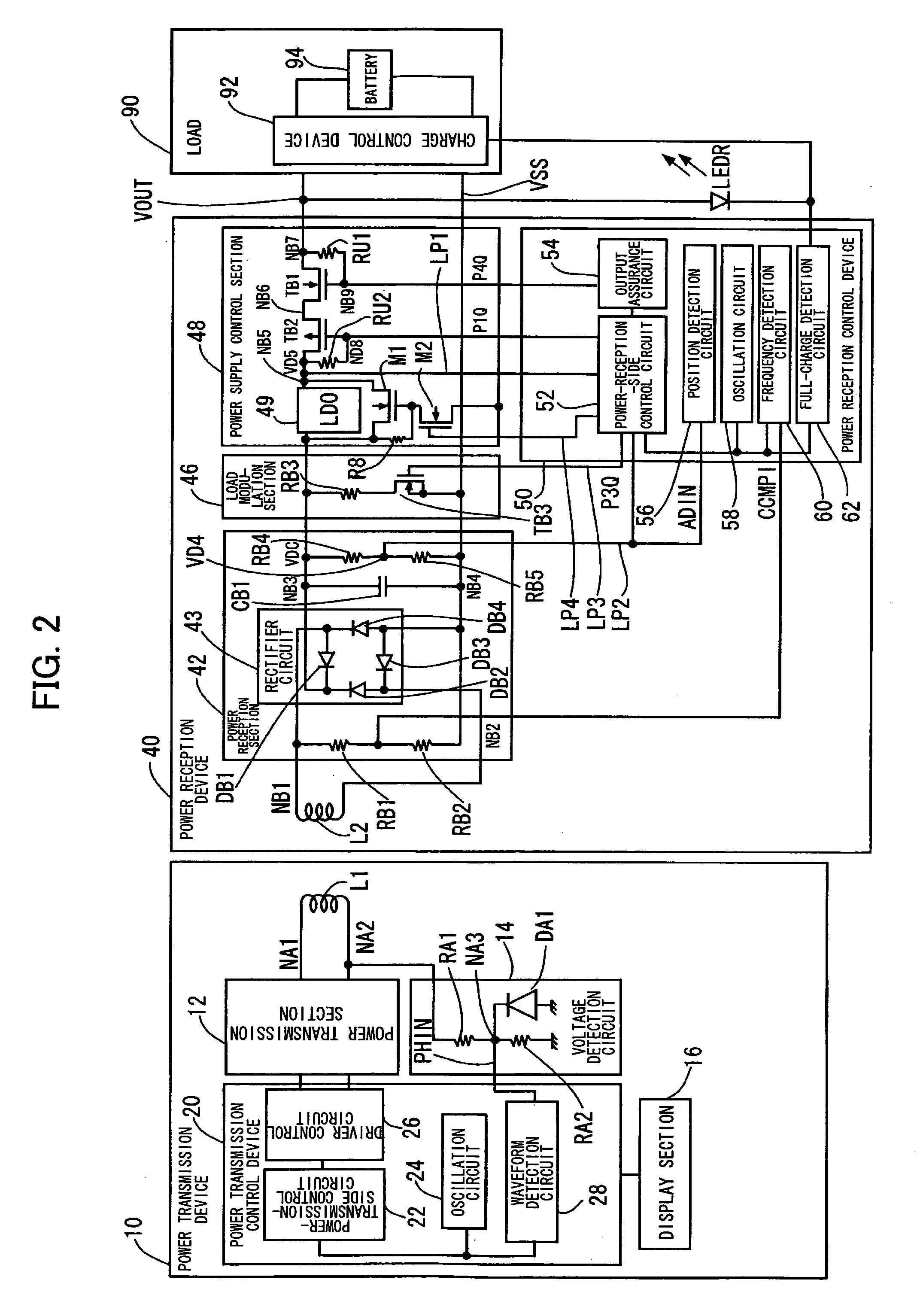
Power reception control device, power transmission control device, non-contact power transmission system, power reception device, power transmission device, and electronic instrument
ActiveUS20080200119A1Resonant long antennasNear-field transmissionElectric power transmissionTransport system
A power-receiving-side control circuit of a power reception device performs intermittent load modulation by causing an NMOS transistor to be turned ON / OFF during normal power transmission. A power-transmission-side control circuit included in a power transmission control device of a power transmission device monitors, an intermittent change in the load of the power reception device during normal power transmission. The power-transmission-side control circuit determines that a foreign object has been inserted between a primary coil and a secondary coil and stops power transmission when an intermittent change in load cannot be detected. The amount of power supplied to the load may be compulsorily reduced when the load state of the load is heavy.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP +1
Robust process identification and auto-tuning control
InactiveUS20020111758A1Accurate estimateImprove performanceAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceVoltage-current phase angleGuidelineTime delays
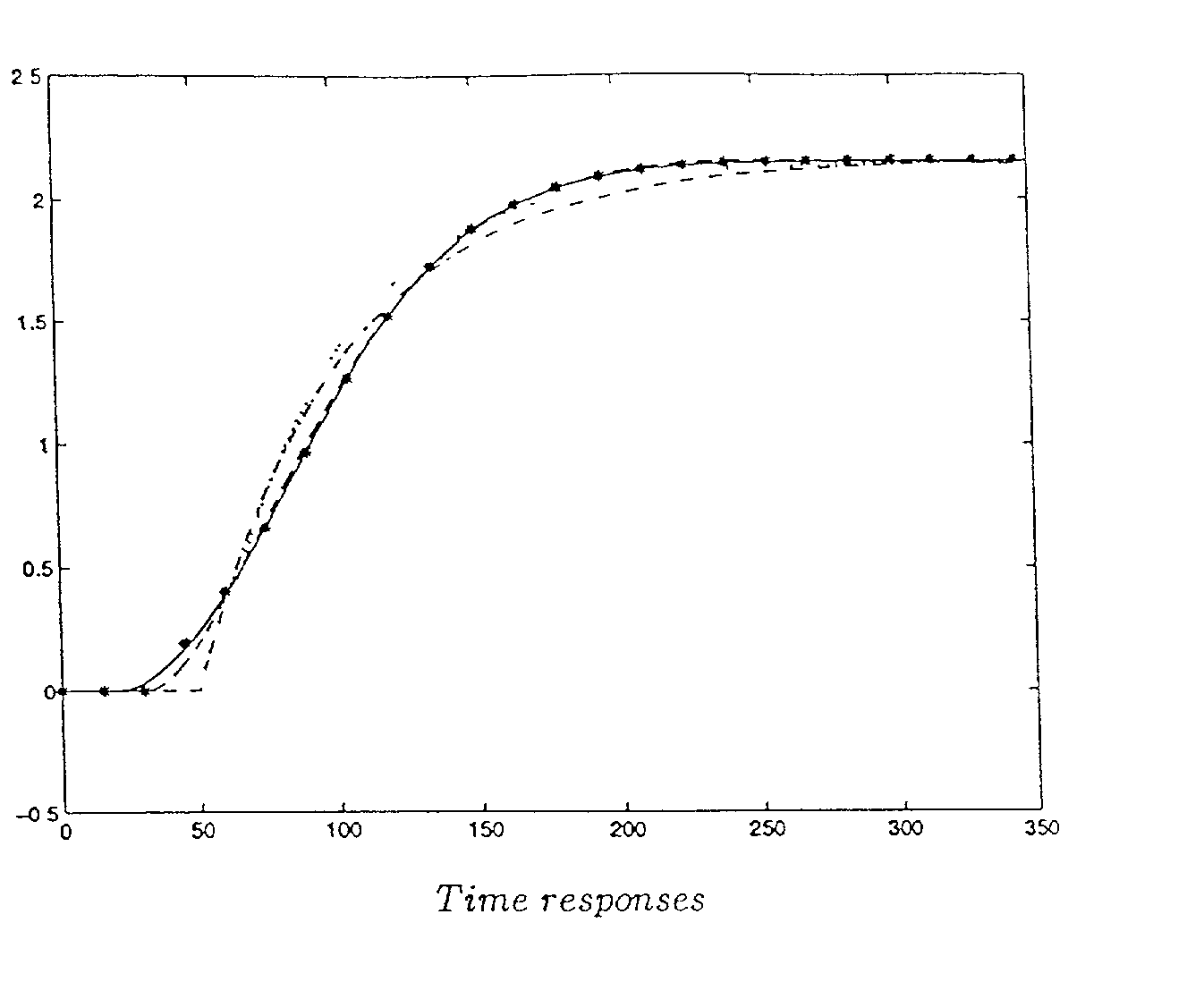
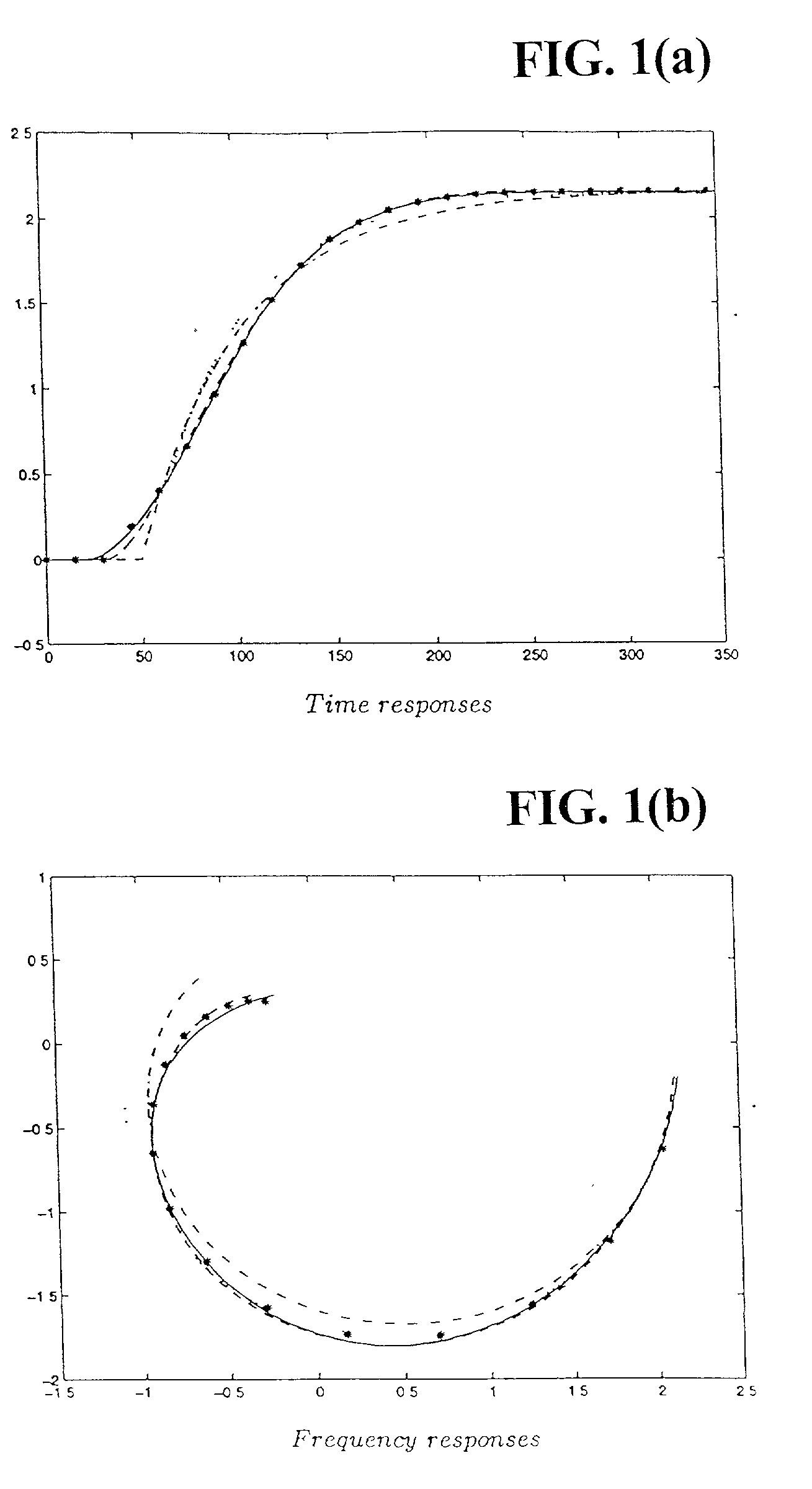
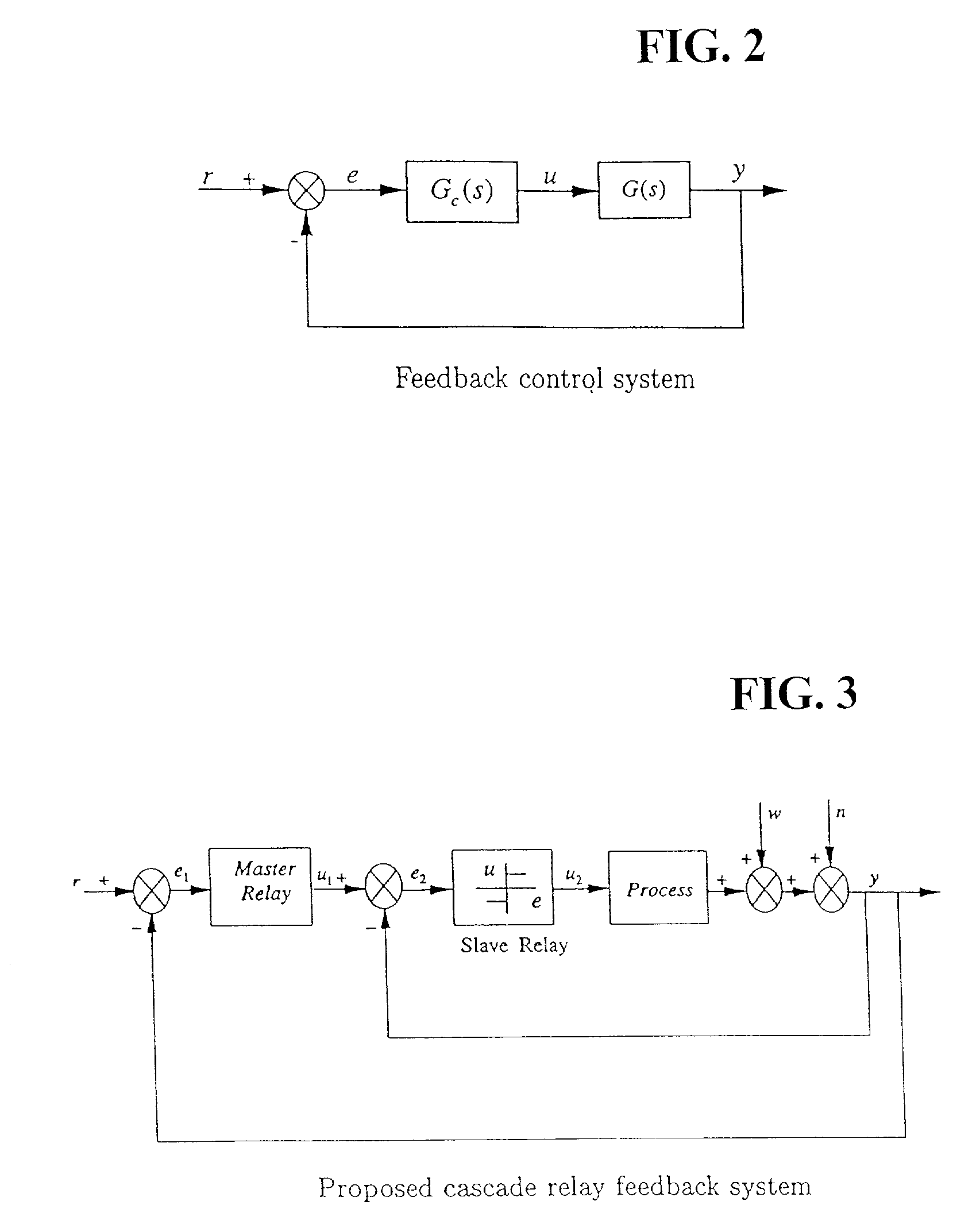
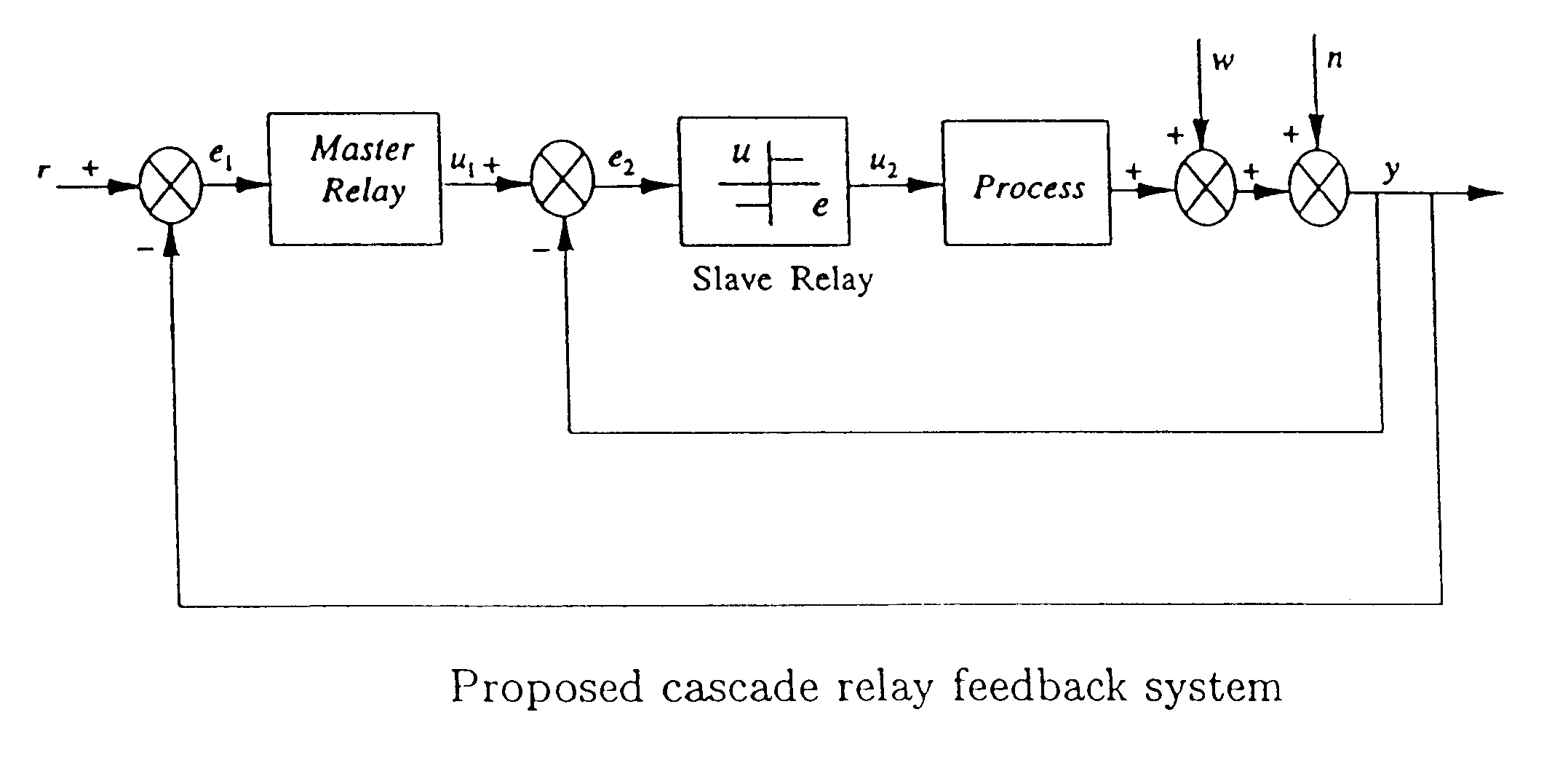
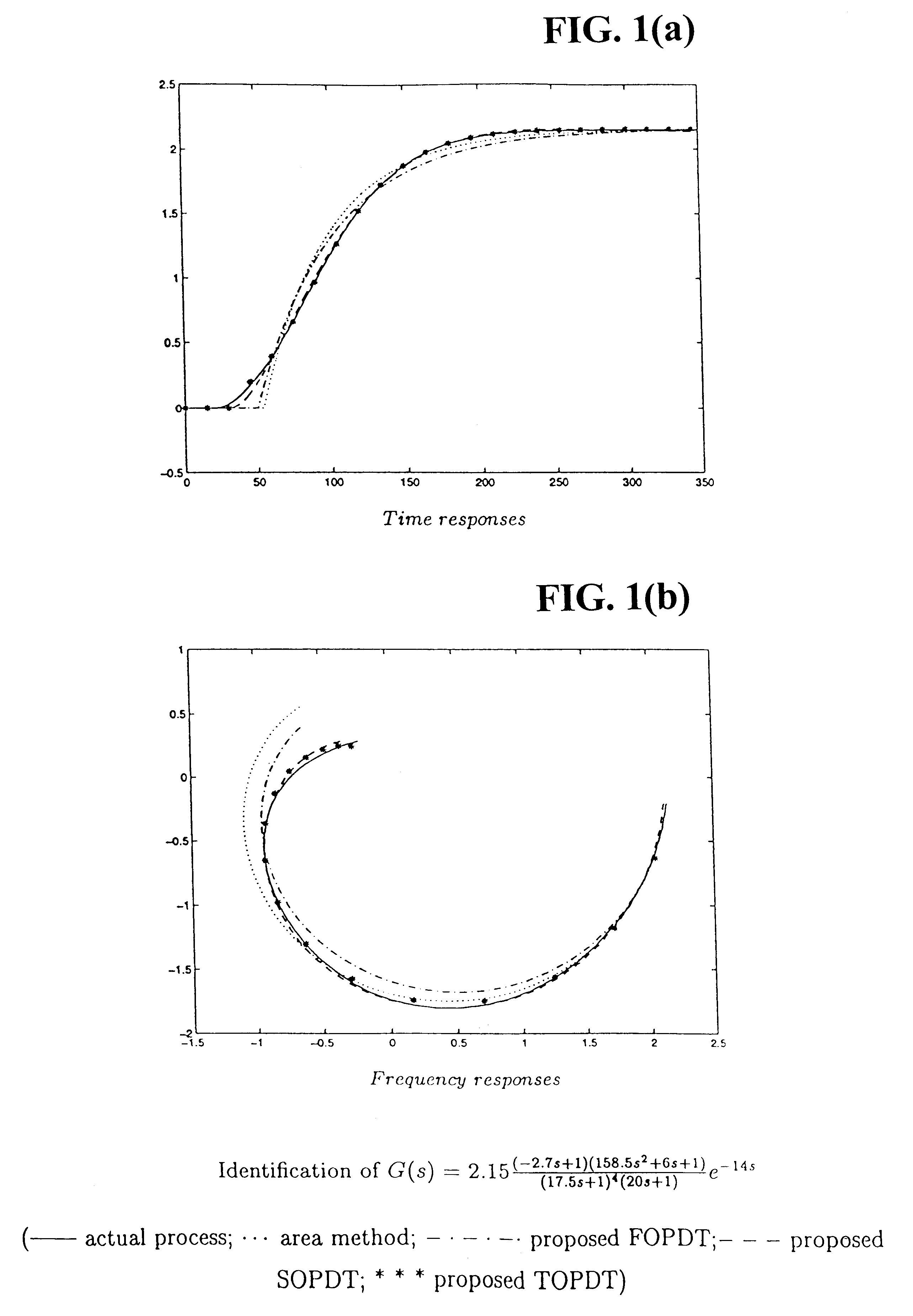
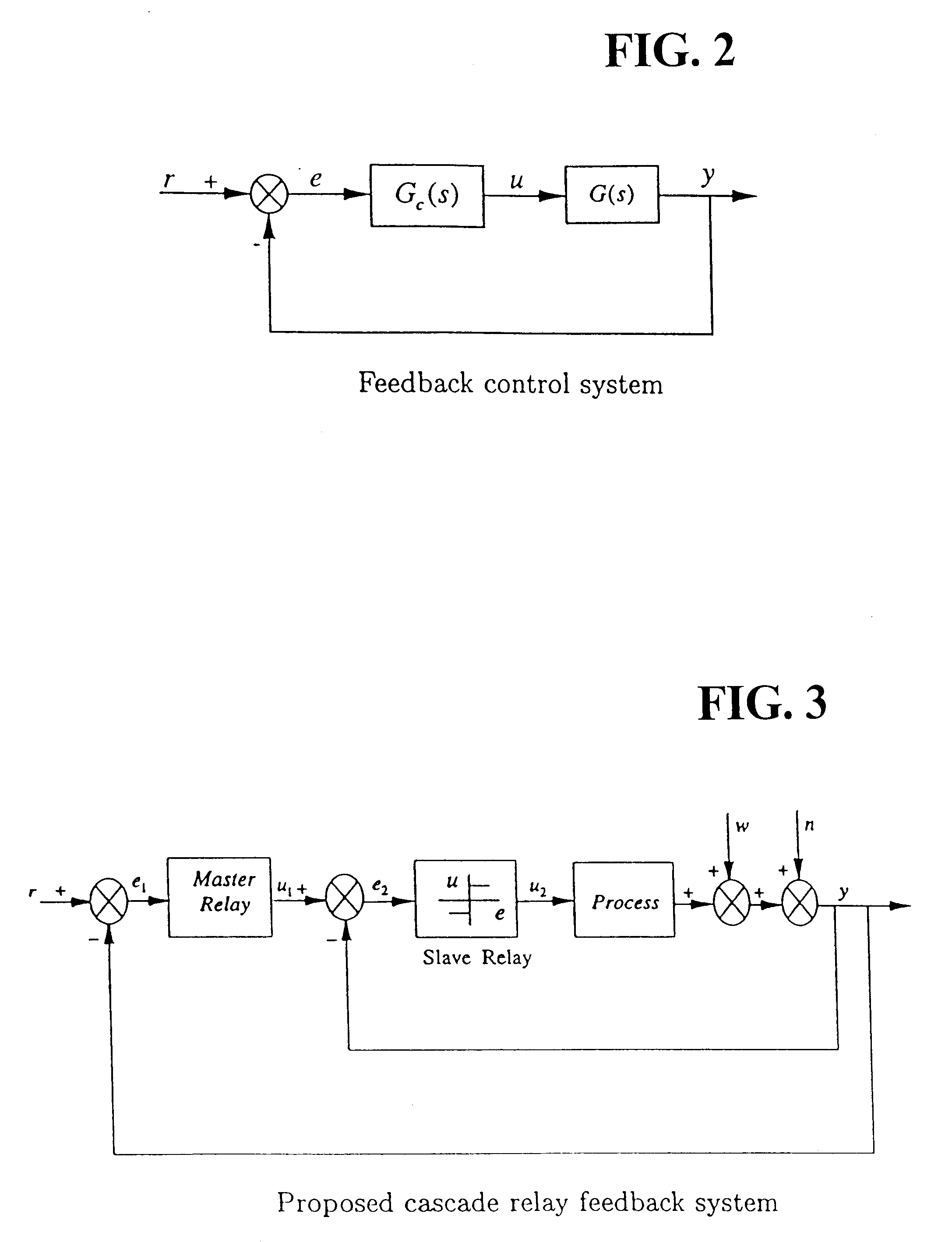
A simple yet effective and robust identification method is presented using process step responses for process identification that can provide a continuous transfer function with time-delay without iteration. A cascade relay provides accurate and reliable more points on the process frequency response. The internal model principle is employed to design single-loop controller of PID or high-order types with best achievable control performance for controller tuning, e.g. both single and multivariable cases are covered. The process identification and control design portions can be easily integrated into a control system auto-tuning package. Further, a general control scheme for disturbance rejection is given which can significantly improve disturbance rejection performance over conventional feedback systems with time delays. Practical issues such as noises, real-time implementation and tuning guidelines are also provided. The present invention provide general, systematic, effective, and applicable methods for process identification and control for a wide range of industries such as process and chemical plants, food processing, waste water treatment and environmental systems, oil refinery, servo and mechatronic systems, where a system model is needed for analysis, prediction, filtering, optimization and management, and / or where control or better control is required for their systems.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF SINGAPORE
Time delay estimation
ActiveUS7945408B2Amplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDigital computer detailsElectricityTime delays
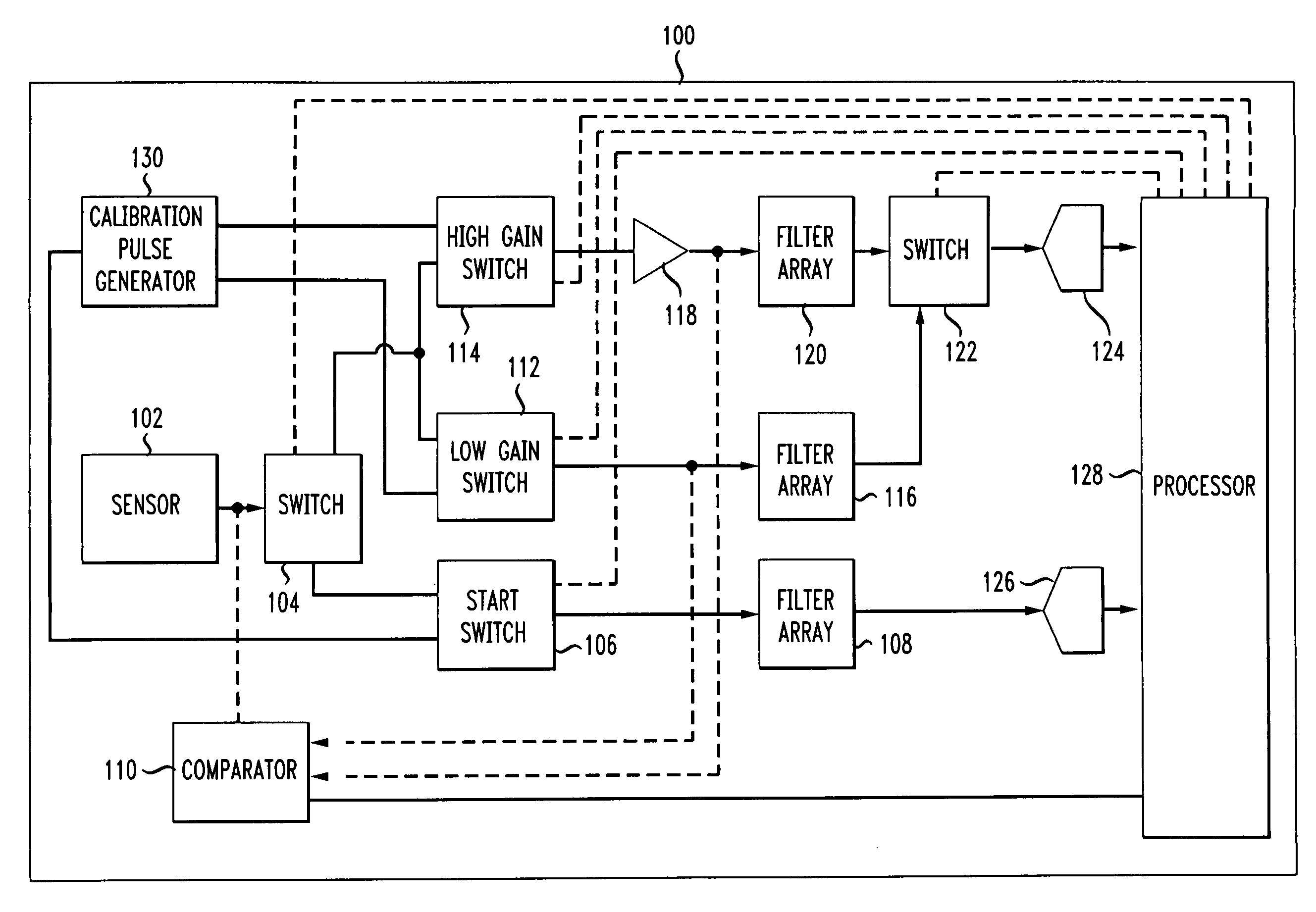
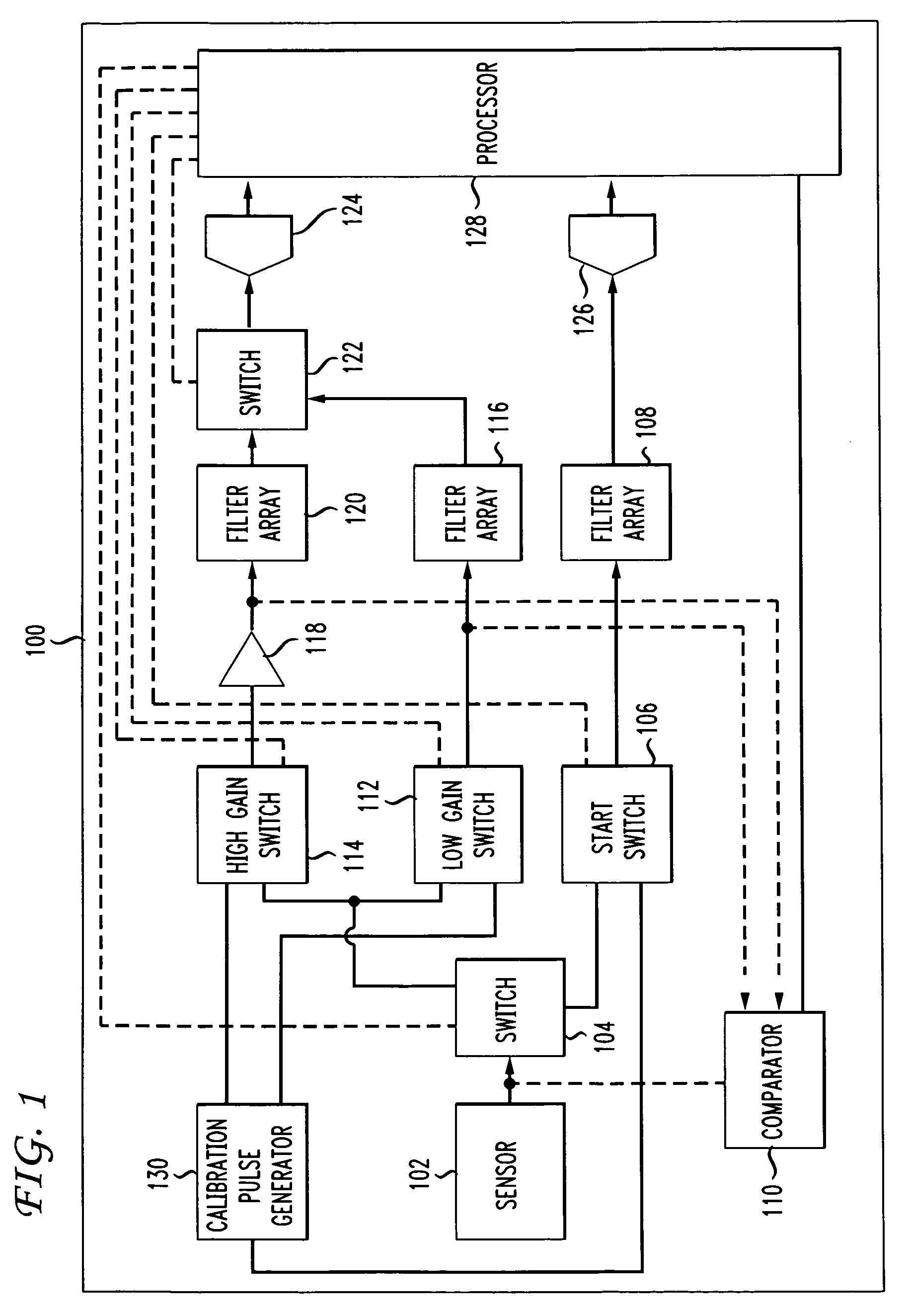
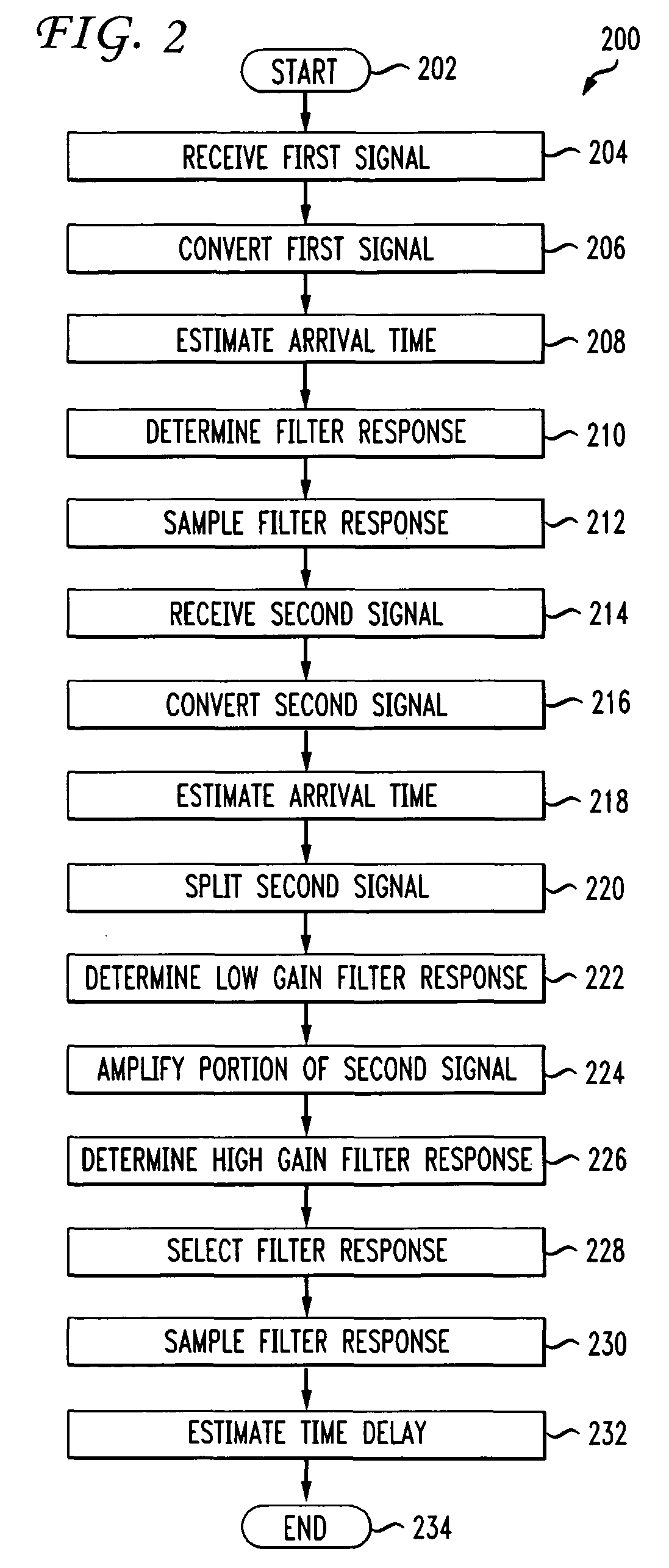
A time differential is estimated between a plurality of signals by determining a filter response of a first electrical signal with a first filter array, determining a filter response of a second electrical signal with a second filter array, and determining, based at least on the filter response of the first electrical signal and the filter response of the second electrical signal, a time differential between the first electrical signal and the second electrical signal. A first optical signal is converted into the first electrical signal and a second optical signal is converted into the second electrical signal. The filter response of the first electrical signal and the filter response of the second electrical signal are sampled and the time differential between the first electrical signal and the second electrical signal is determined based at least on the sampled filter response of the first electrical signal and the sampled filter response of the second electrical signal.
Owner:VOXIS
Circuit and method for measuring jitter of high speed signals
ActiveUS20050069031A1Accurate measurementMinimal and no impactError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorNoise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementData signalData rate
A method and circuit for measuring a statistical value of jitter for a data signal having a data rate fD, comprises digitally sampling the data signal at a sampling rate, fS, to produce sampled logic values, where fD / fS is a predetermined non-integer ratio; and analyzing the sampled values to deduce a statistical value of the jitter.
Owner:SIEMENS PROD LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE INC
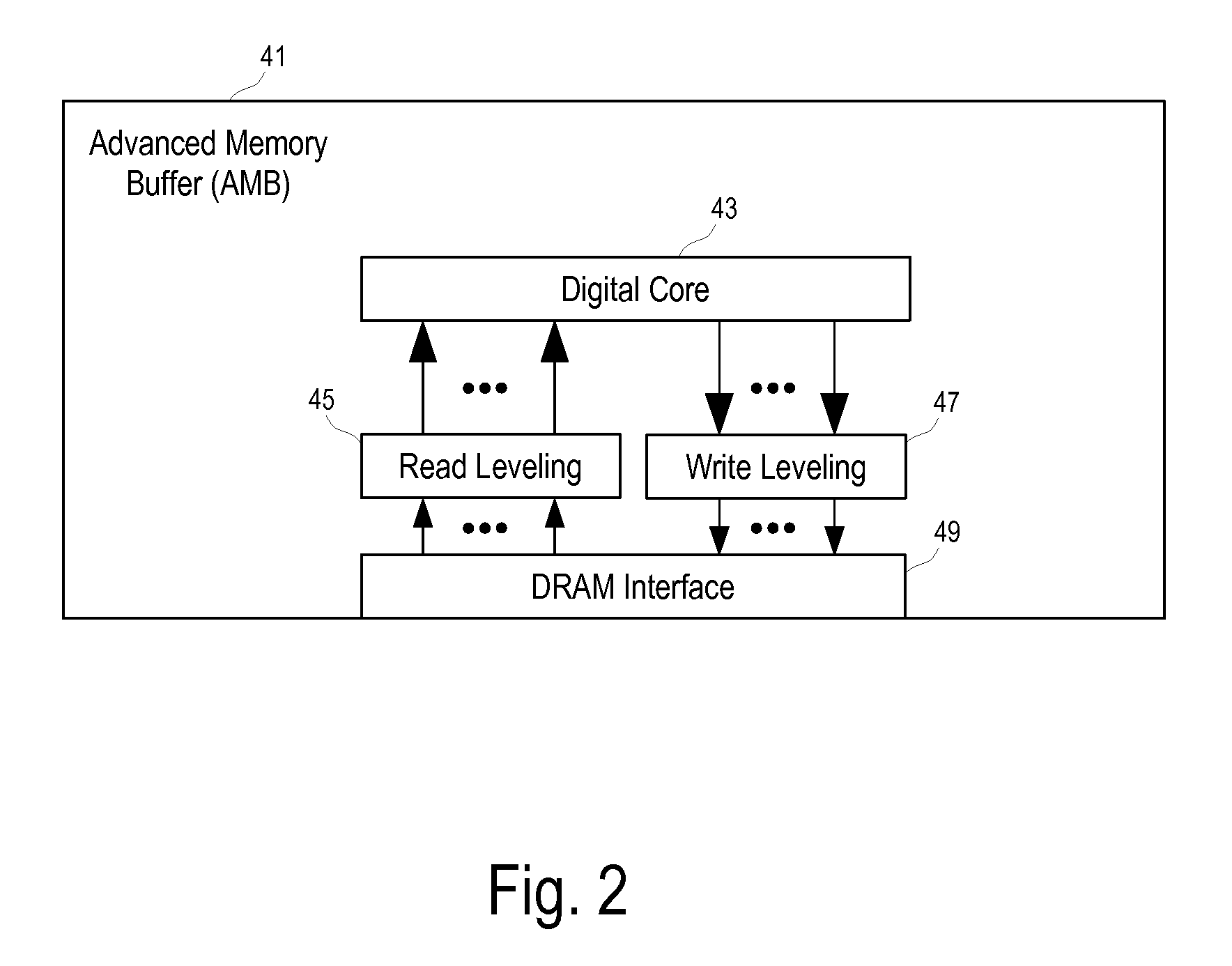
Calibration of Read/Write Memory Access via Advanced Memory Buffer
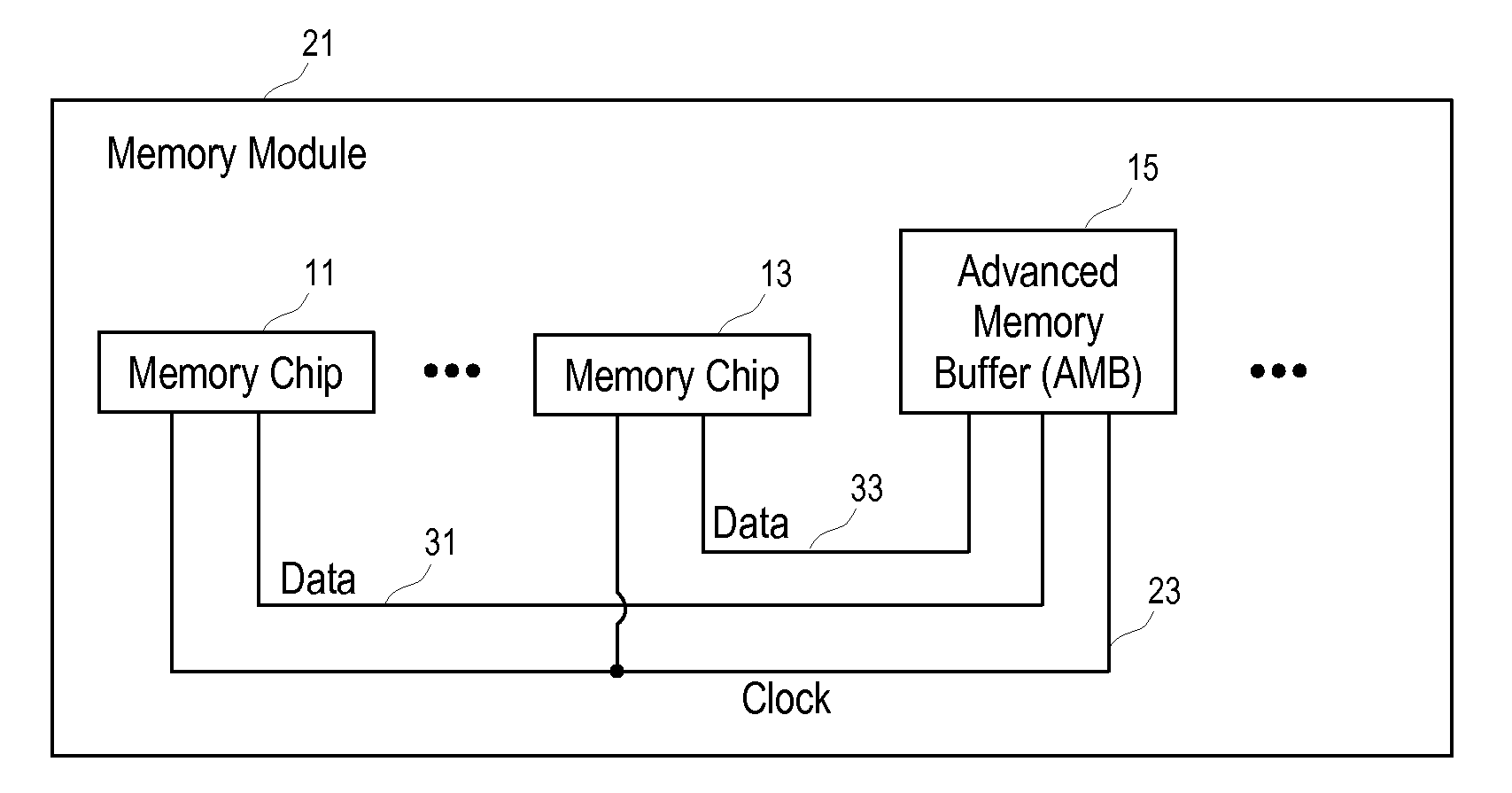
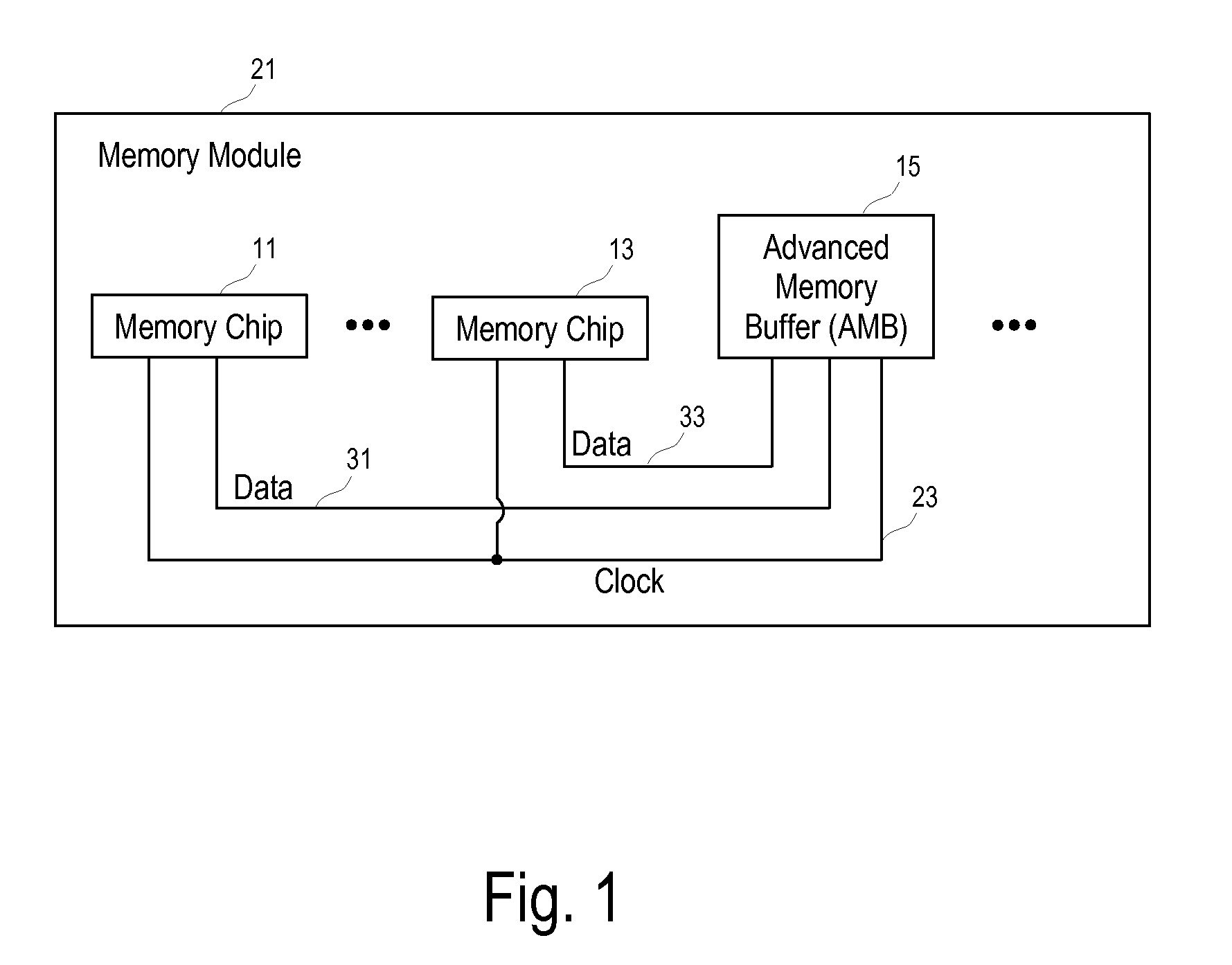
ActiveUS20080256282A1Reduce phase differenceNoise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementPulse automatic controlMemory chipParallel computing
Methods and apparatuses to calibrate read / write memory accesses through data buses of different lengths via advanced memory buffers. One embodiment includes an advanced memory buffer (AMB) having: a plurality of ports to interface respectively with a plurality of data buses; a port to interface with a common clock bus for the plurality of data buses; and an adjustable circuit coupled with the plurality of ports to level delays on the plurality of data buses. In one embodiment, the data buses have different wire lengths between the dynamic random access memory (DRAM) memory chips and the advanced memory buffer (AMB).
Owner:MONTAGE TECH HLDG CO LTD
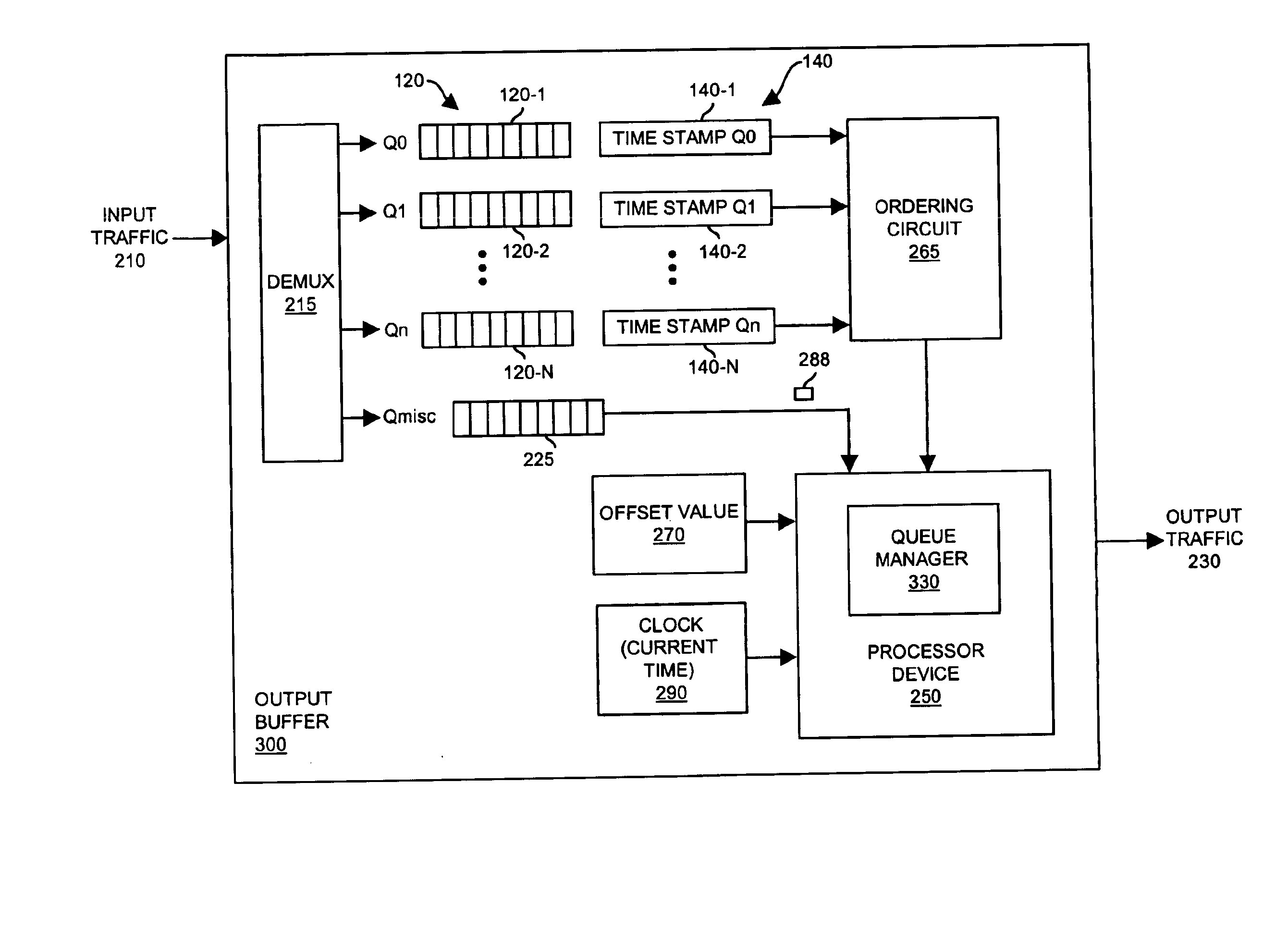
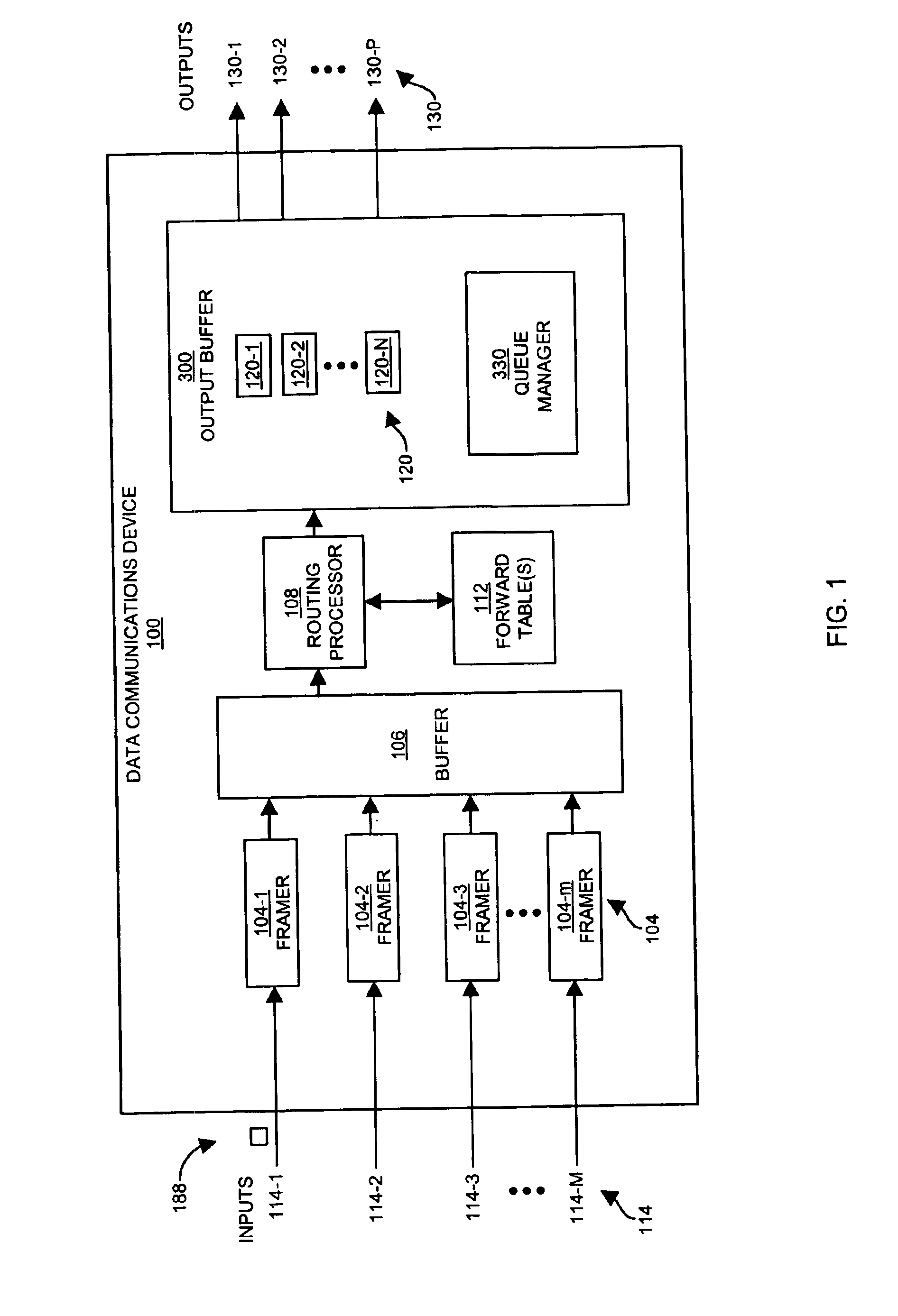
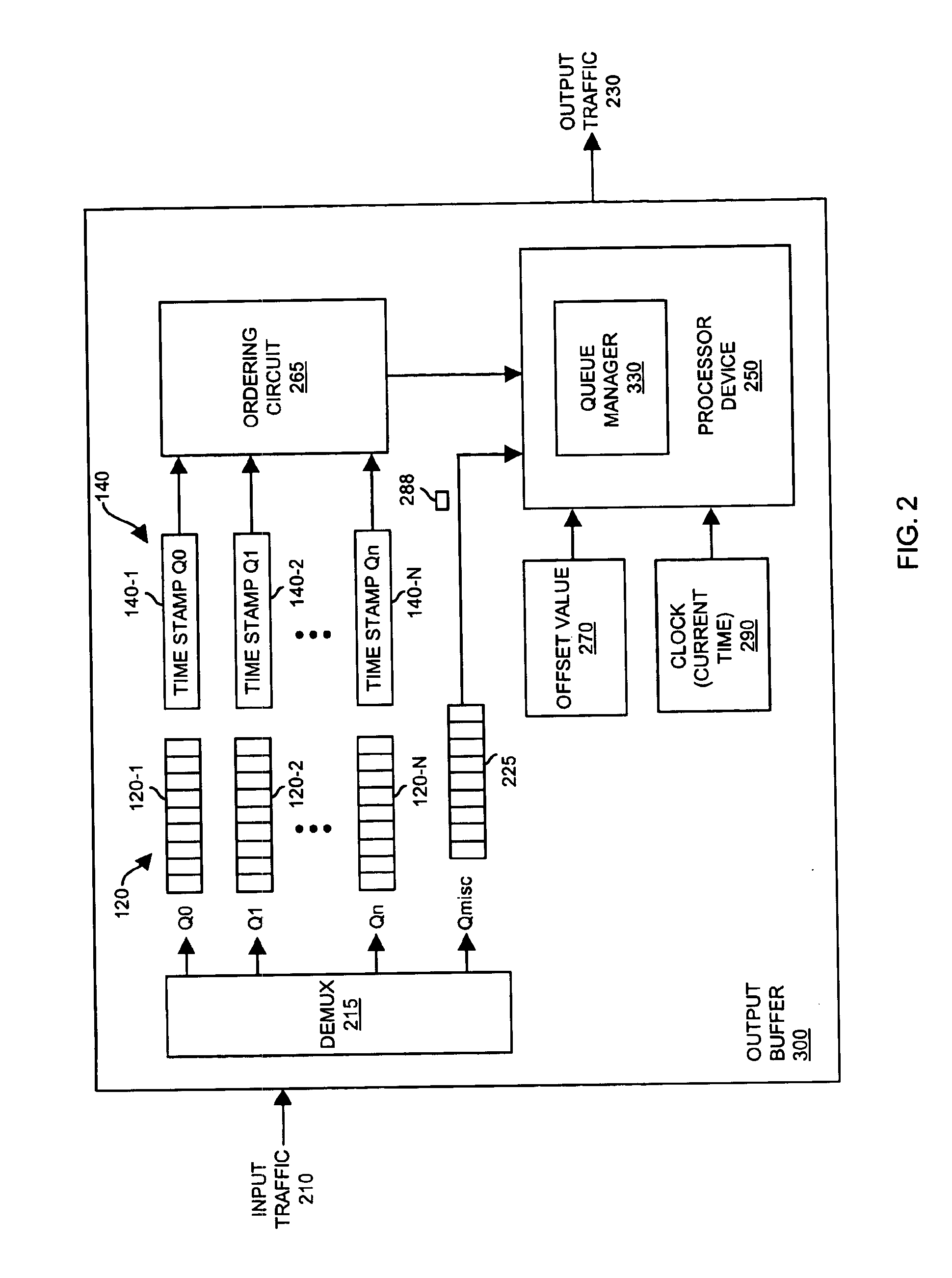
Methods and apparatus for maintaining queues
InactiveUS6876952B1Reduce circuit complexityTime indicationError preventionReal-time clockData stream
One or more queues store data information such as packets or data flows for later transmission to downstream communication devices. A real-time clock tracks current time and an advancement of a moving time reference, which is displaced with respect to the current time of the clock by an offset value. Thus, as current time advances, the moving time reference also advances in time. Upon servicing a queue, a time stamp associated with the serviced queue is also advanced in time. To monitor a rate of outputting data from the one or more queues, a processor device at least occasionally adjusts the offset value so that the moving time reference and values of the time stamps advance in relation to each other. Consequently, by tracking a relative time difference between current time of the real-time clock and a relative advancement of time stamps, a rate of outputting data information from the queue is monitored over time.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Robust process identification and auto-tuning control
InactiveUS6697767B2Accurate estimateImprove performanceAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceElectric testing/monitoringGuidelineControl system
This invention provides a novel process identification and control package for high performance. For process identification, a simple yet effective and robust identification method is presented using process step responses to give a continuous transfer function with time-delay without iteration. A new relay, called cascade relay, is devised to get more accurate and reliable points on the process frequency response. For controller tuning, the internal model principle is employed to design single-loop controller PID or high-order types with best achievable control performance. The process identification and control design parts can be easily integrated into control system auto-tuning package. Further, a general control scheme for disturbance rejection is given which can significantly improve disturbance rejection performance over conventional feedback systems with time delays. Practical issues such as noises, real-time implementation and tuning guidelines are also provided. The invention covers both open-loop and closed-loop testing, and single and multivariable cases.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF SINGAPORE
Arc fault circuit interrupter recognizing arc noise burst patterns
InactiveUS6839208B2Prevent trippingCurrent/voltage measurementProtective switchesNormal loadEngineering
An arc fault circuit interrupter (AFCI) detects arc faults by identifying the various signature patterns of arc fault noise while rejecting arc mimicking noise from normal load phenomena.
Owner:PASS SEYMOUR
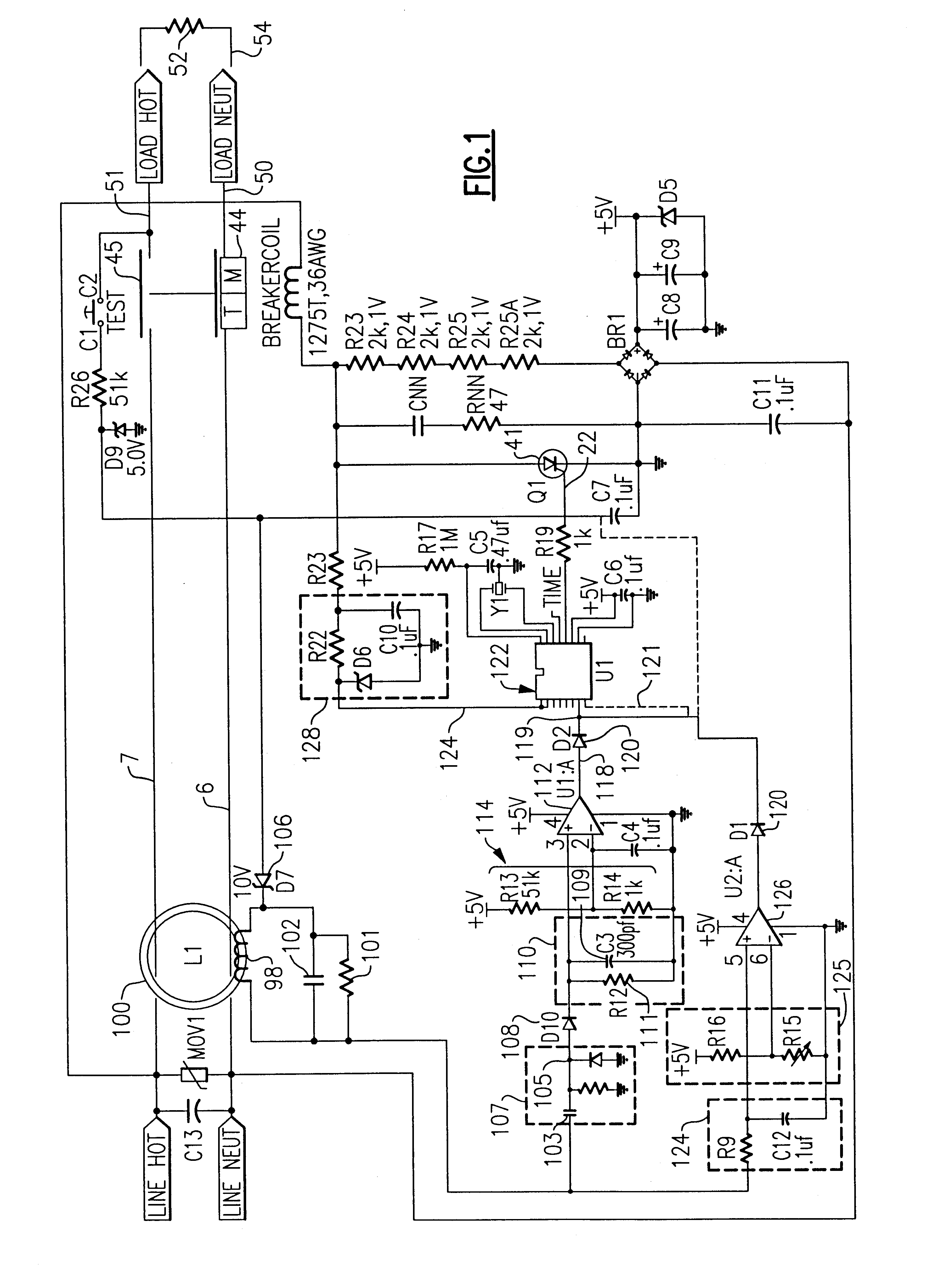
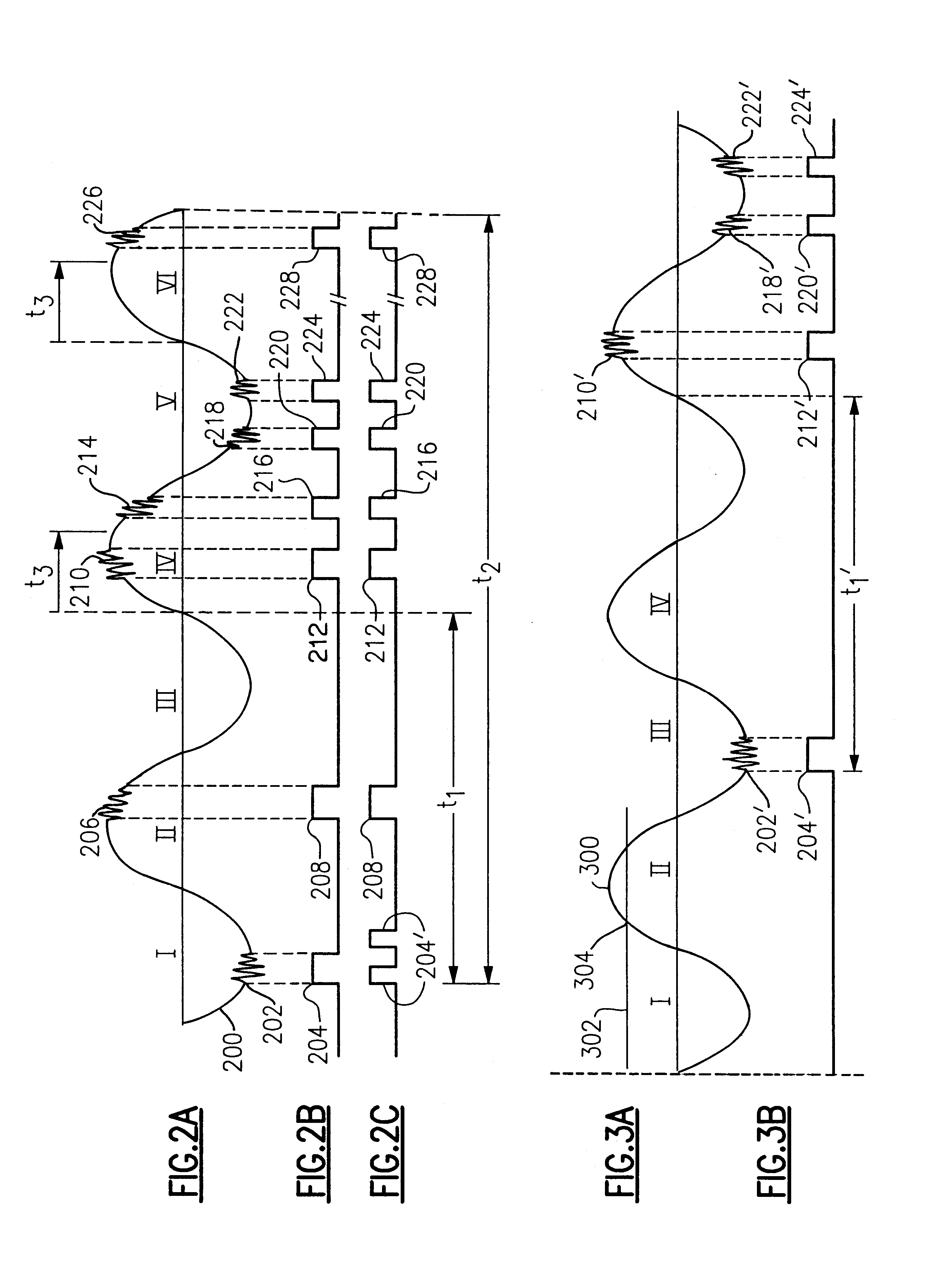
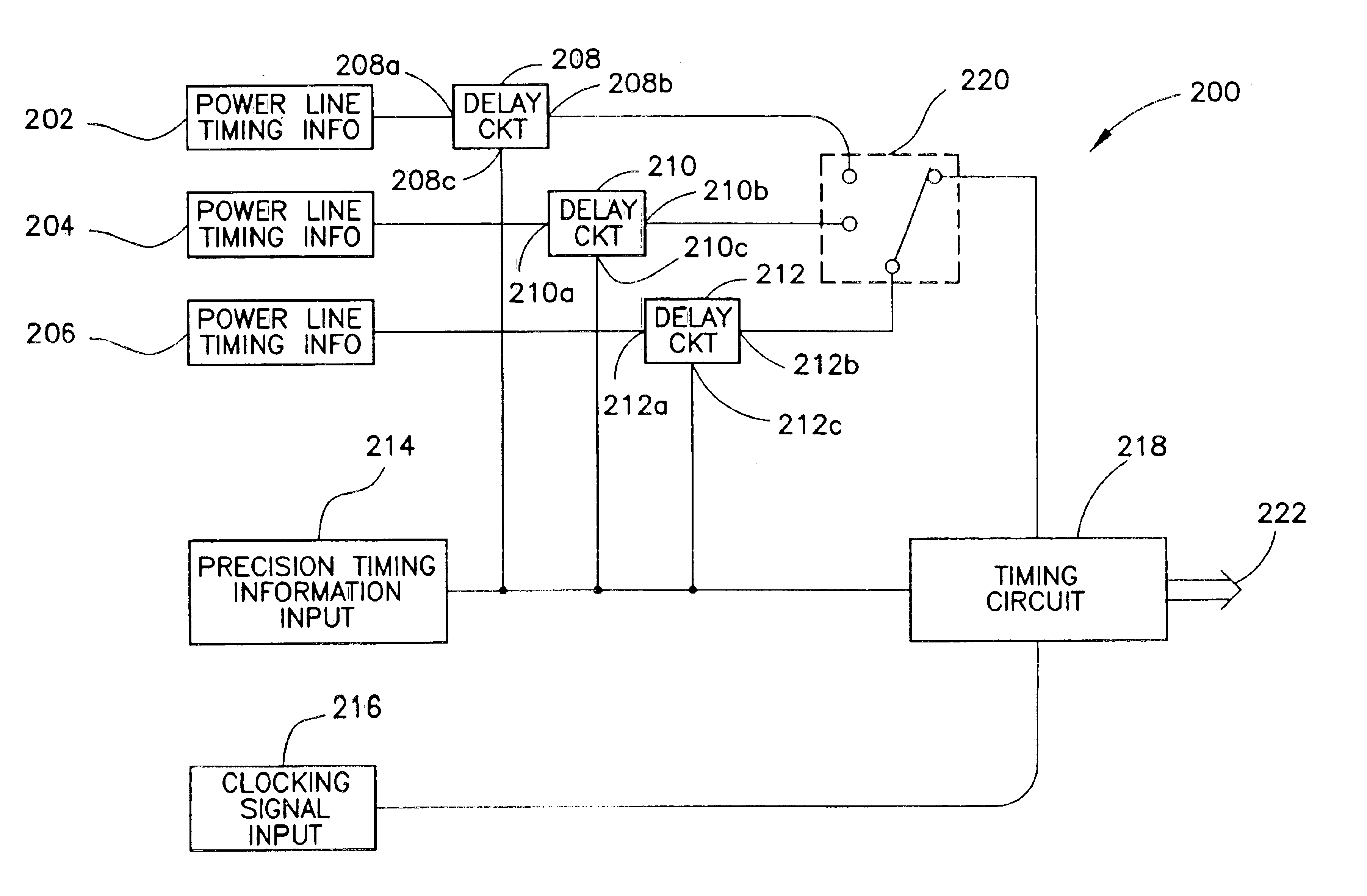
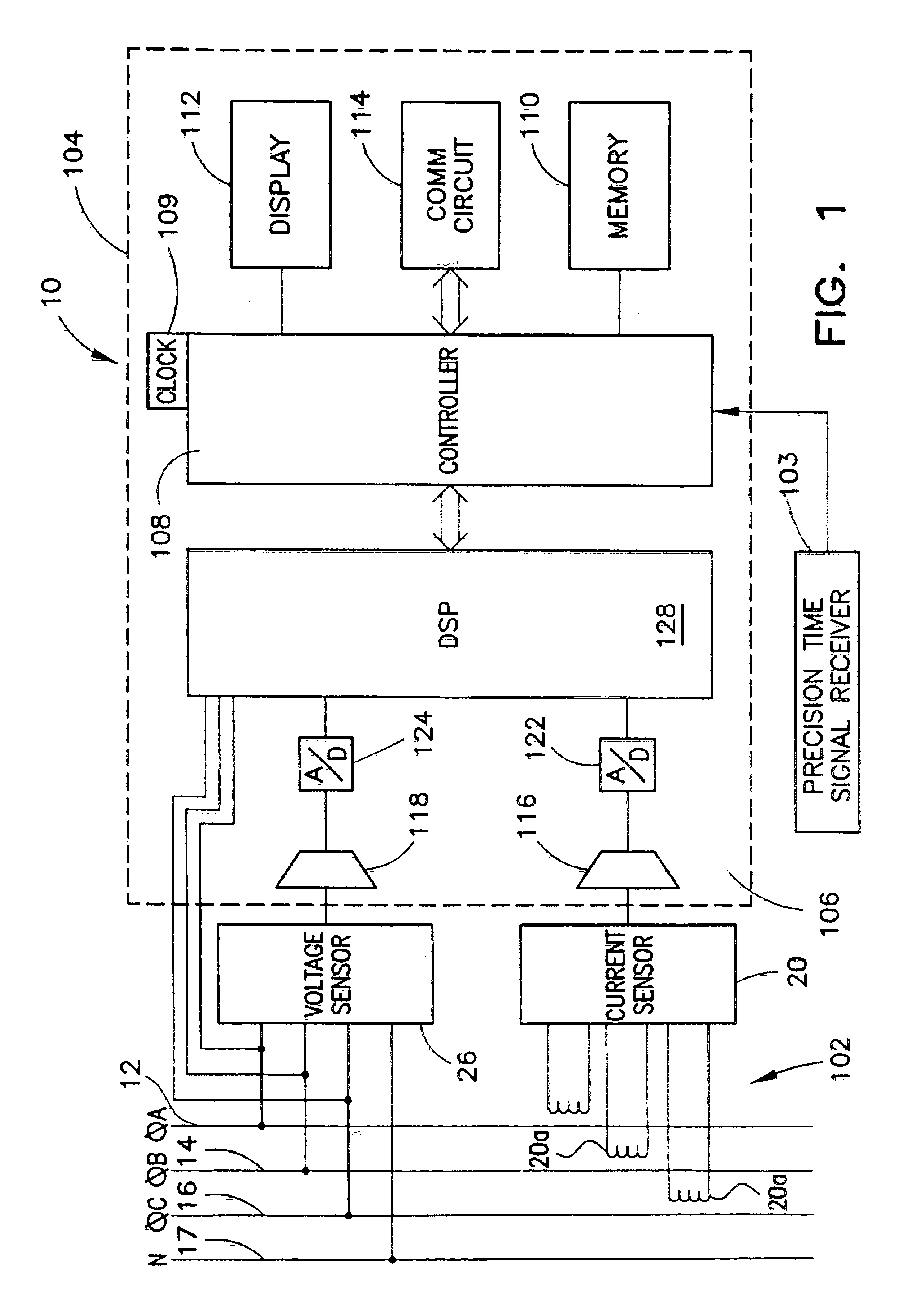
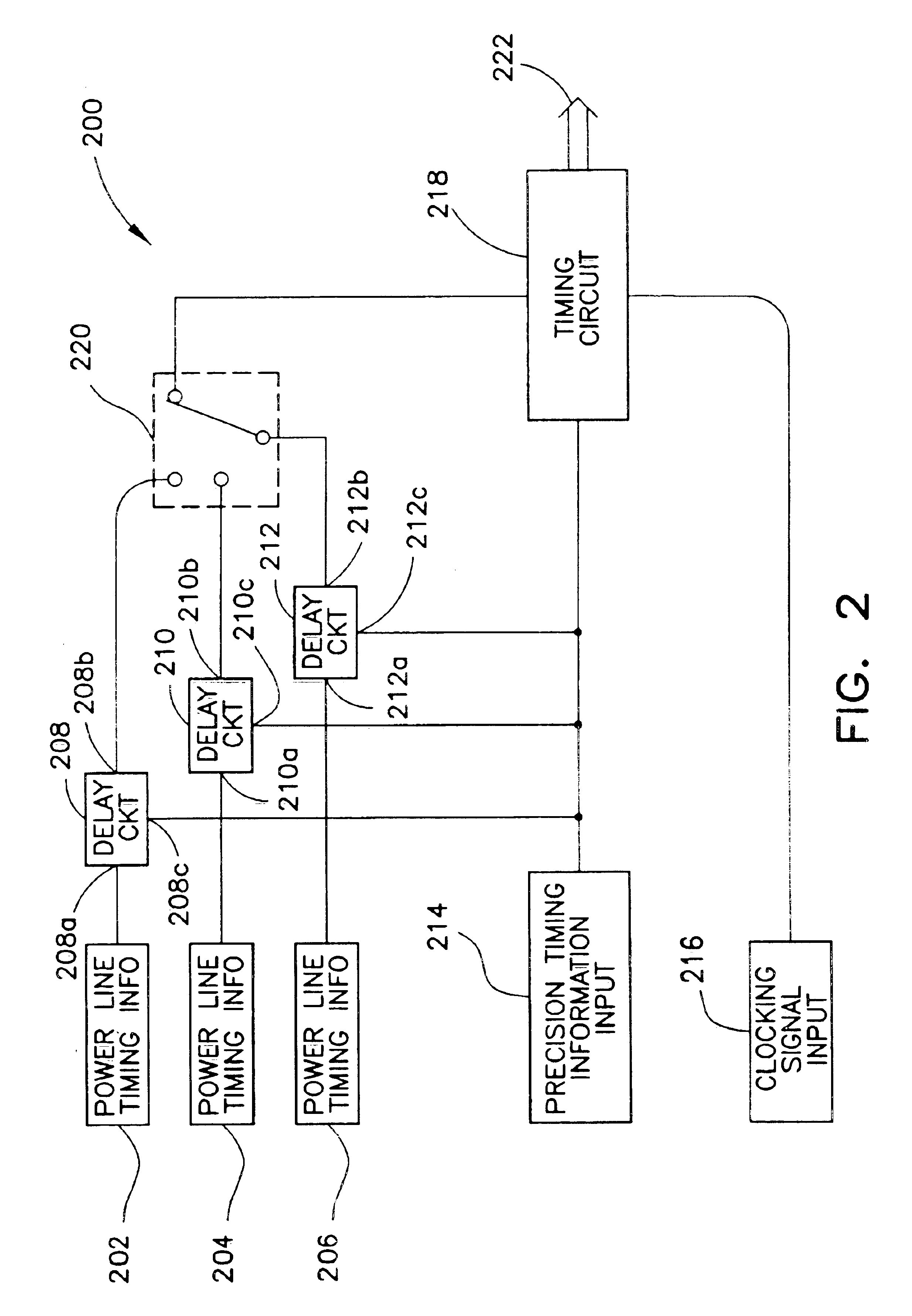
Redundant precision time keeping for utility meters
InactiveUS6859742B2Smooth transitionAccurate pictureElectric devicesDynamo-electric motor metersSignal sourceTime signal
An apparatus for generating precision time signals includes a source of power line timing information, a source of precision time signals, and a timing circuit. The timing circuit is coupled to the source of precision time signals to receive a precision time signal there from, and is operable to generate clock information based on the precision time signal. The timing circuit is further operable to generate clock information based on the power line timing information.
Owner:LANDIS GYR LLC
High frequency array ultrasound system
Owner:SUNNYBROOK HEALTH SCI CENT +1
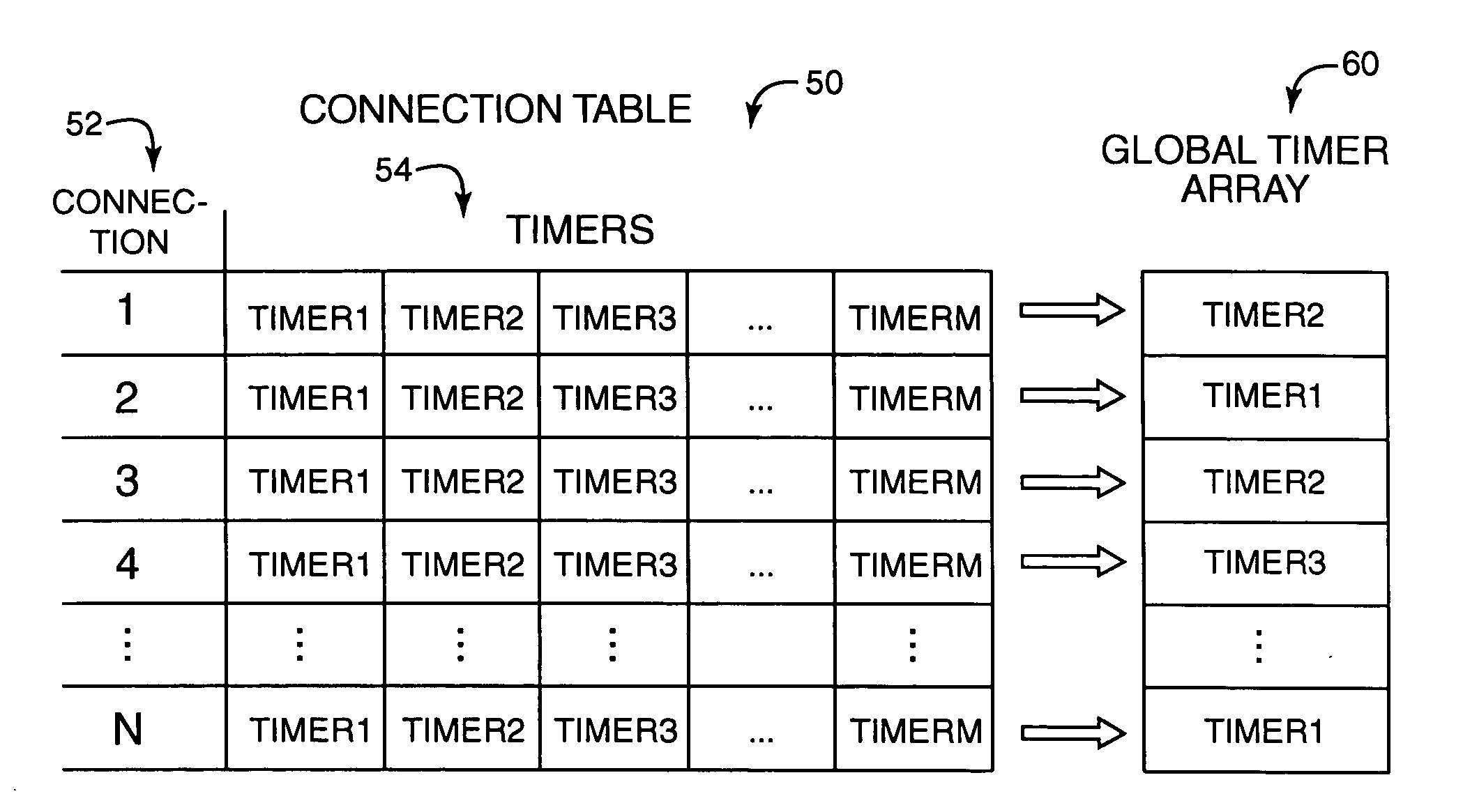
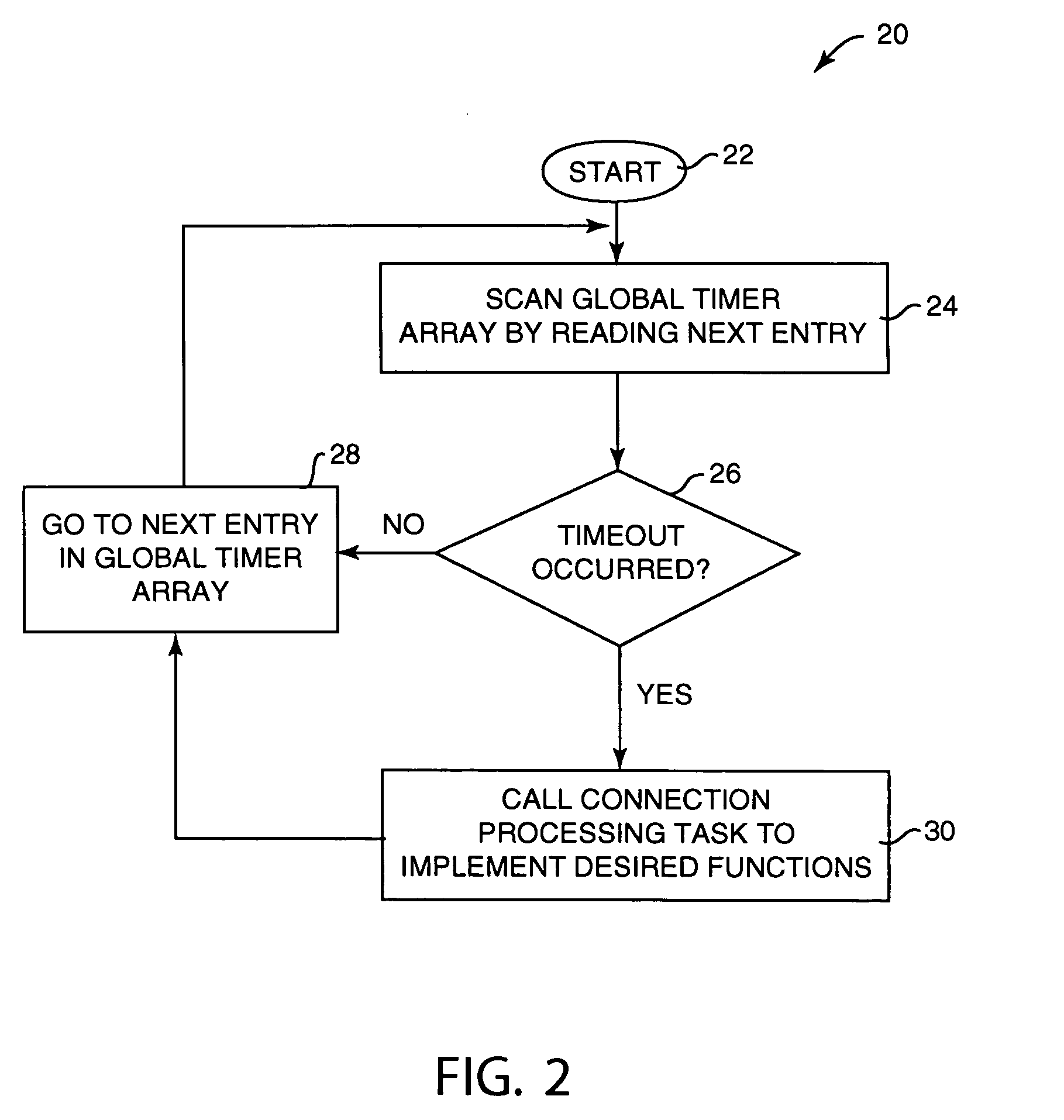
Method and system for maintaining and examining timers for network connections
InactiveUS20050209804A1Shorten the timeReduces processing resourceTime indicationDigital data processing detailsConnection tableNetwork connection
System and method for maintenance and examination of timers for a computer system having connections in a networking system. Timer values in a connection table each indicate a timeout for a timer for a connection, where each connection has multiple timers, and one of the timer values is written to a global timer array for each connection such that the global timer array can be scanned to determine when timeouts occur for active connections. Sparse restart of a timer includes restarting the timer if data is communicated with a connected computer before the timeout occurs and after a predetermined time interval after timer start, and not restarting the timer if data is communicated before the timeout occurs and within the predetermined interval after timer start.
Owner:IBM CORP
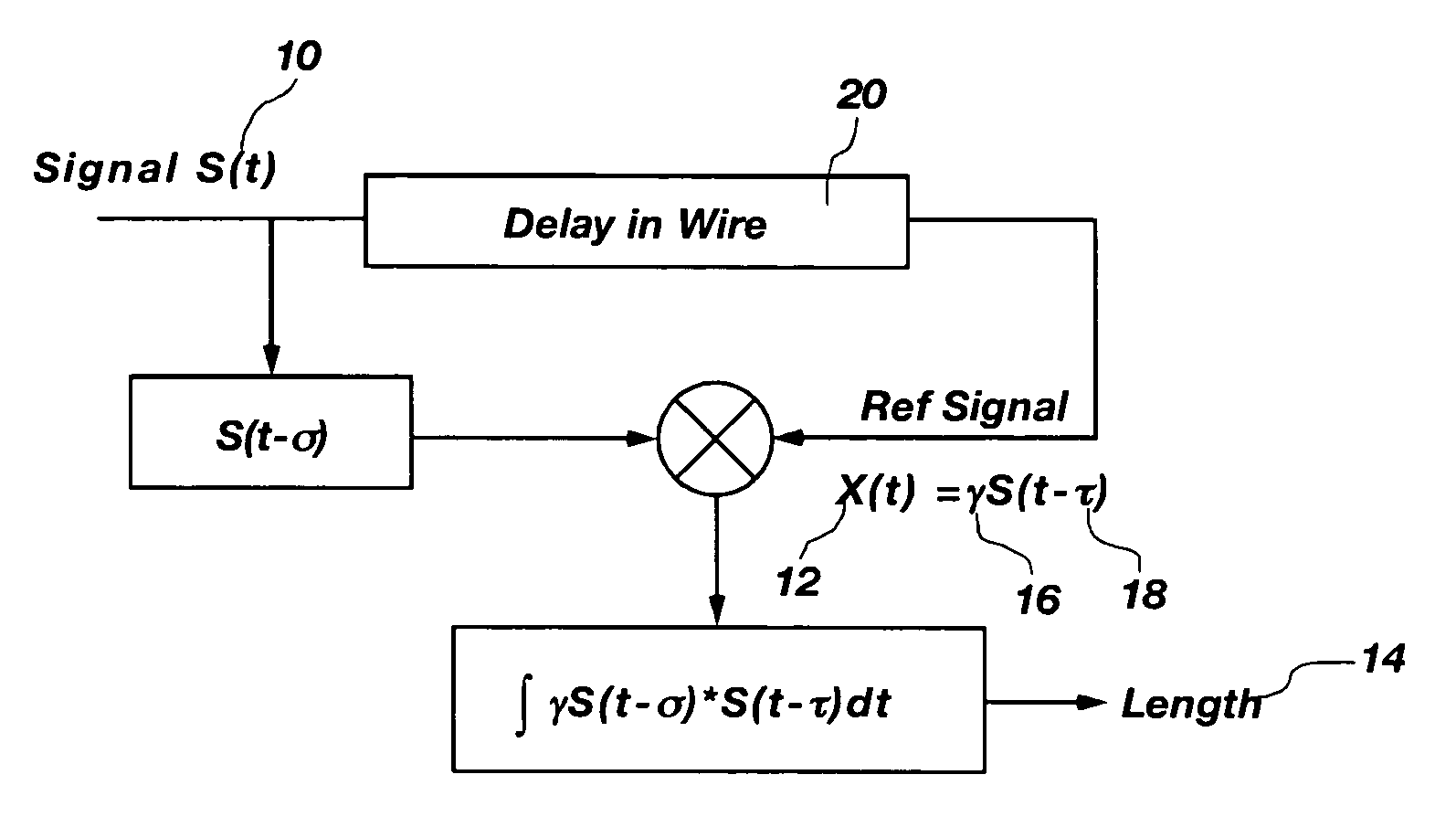
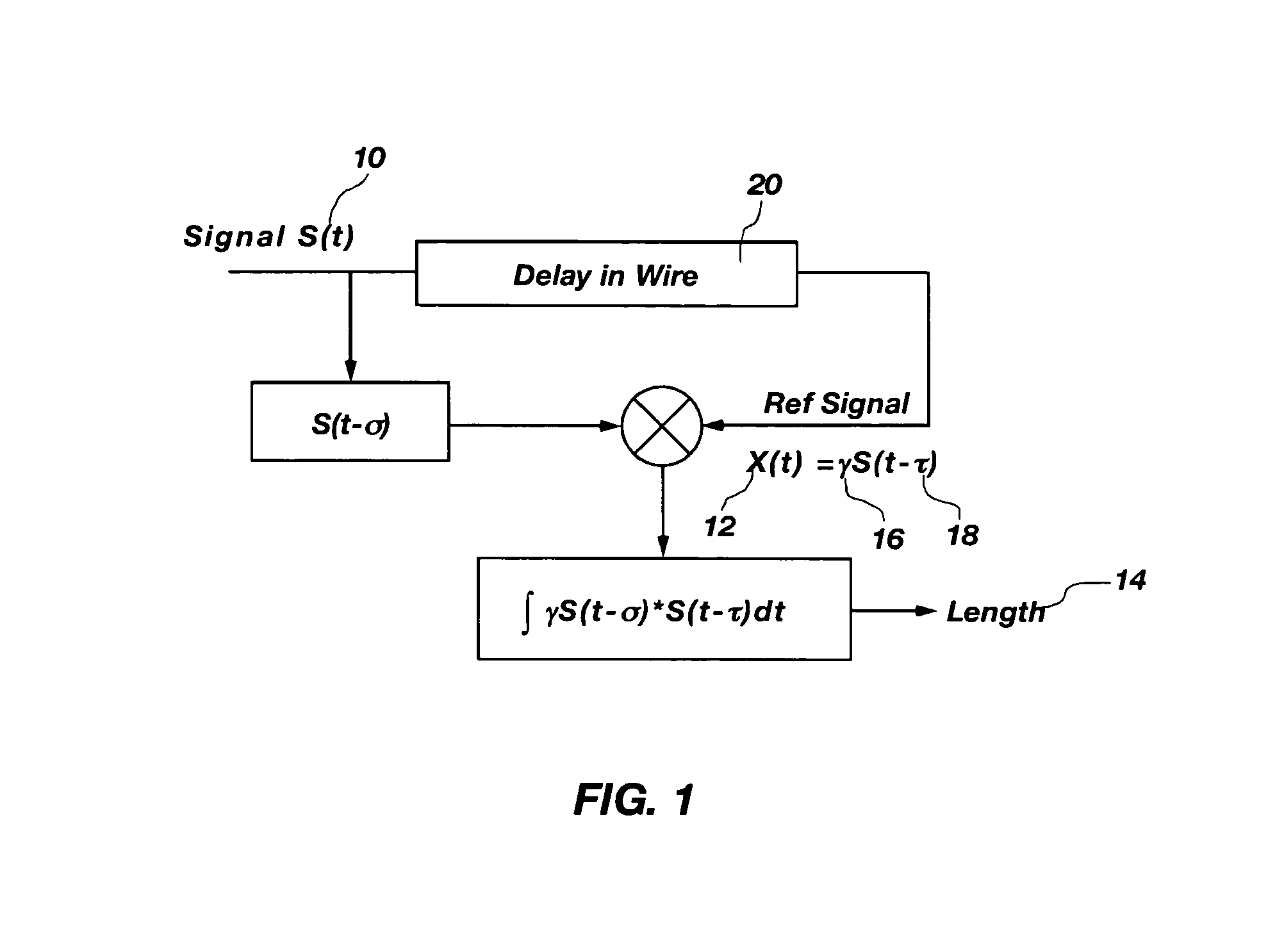
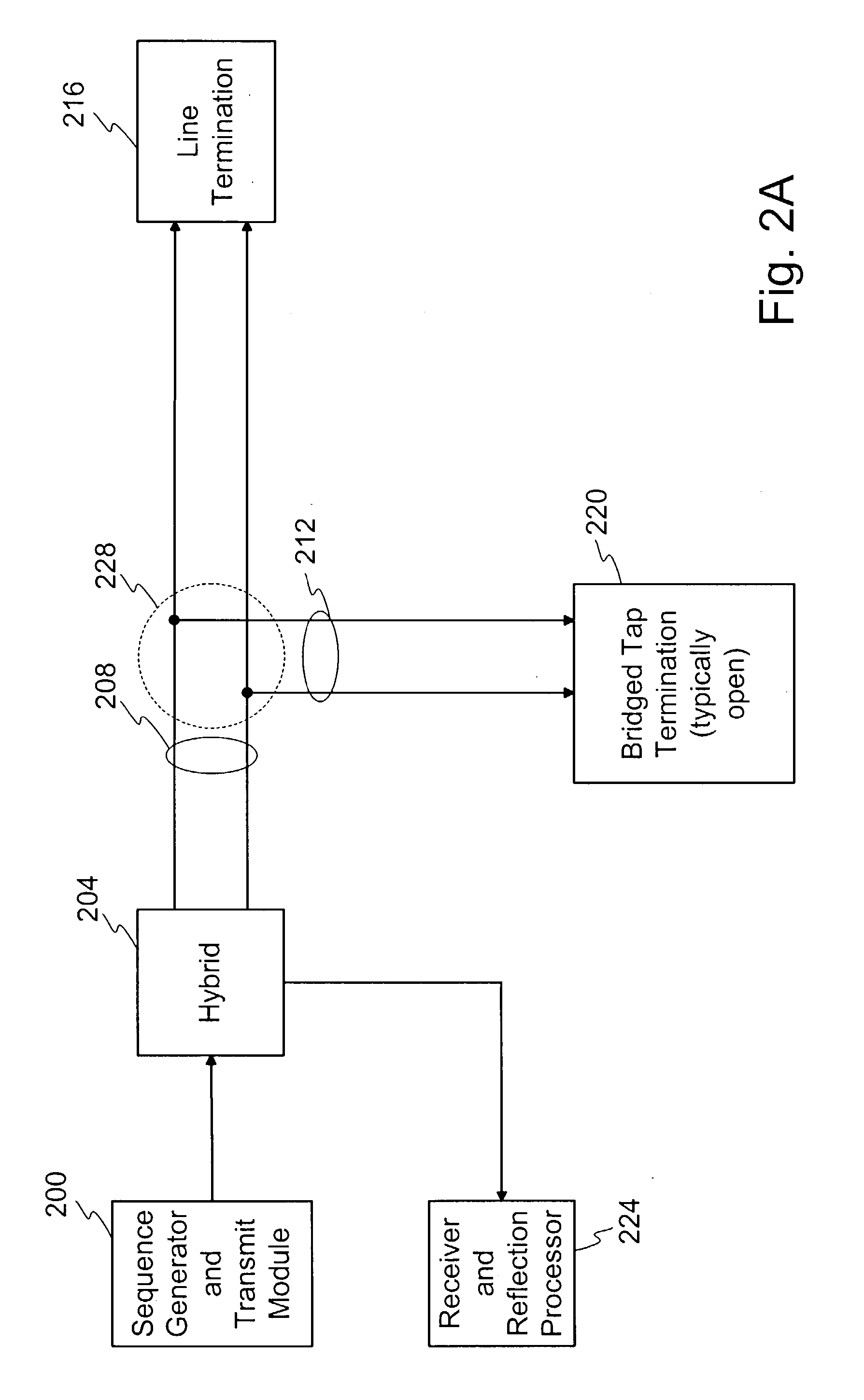
Optical sequence time domain reflectometry during data transmission
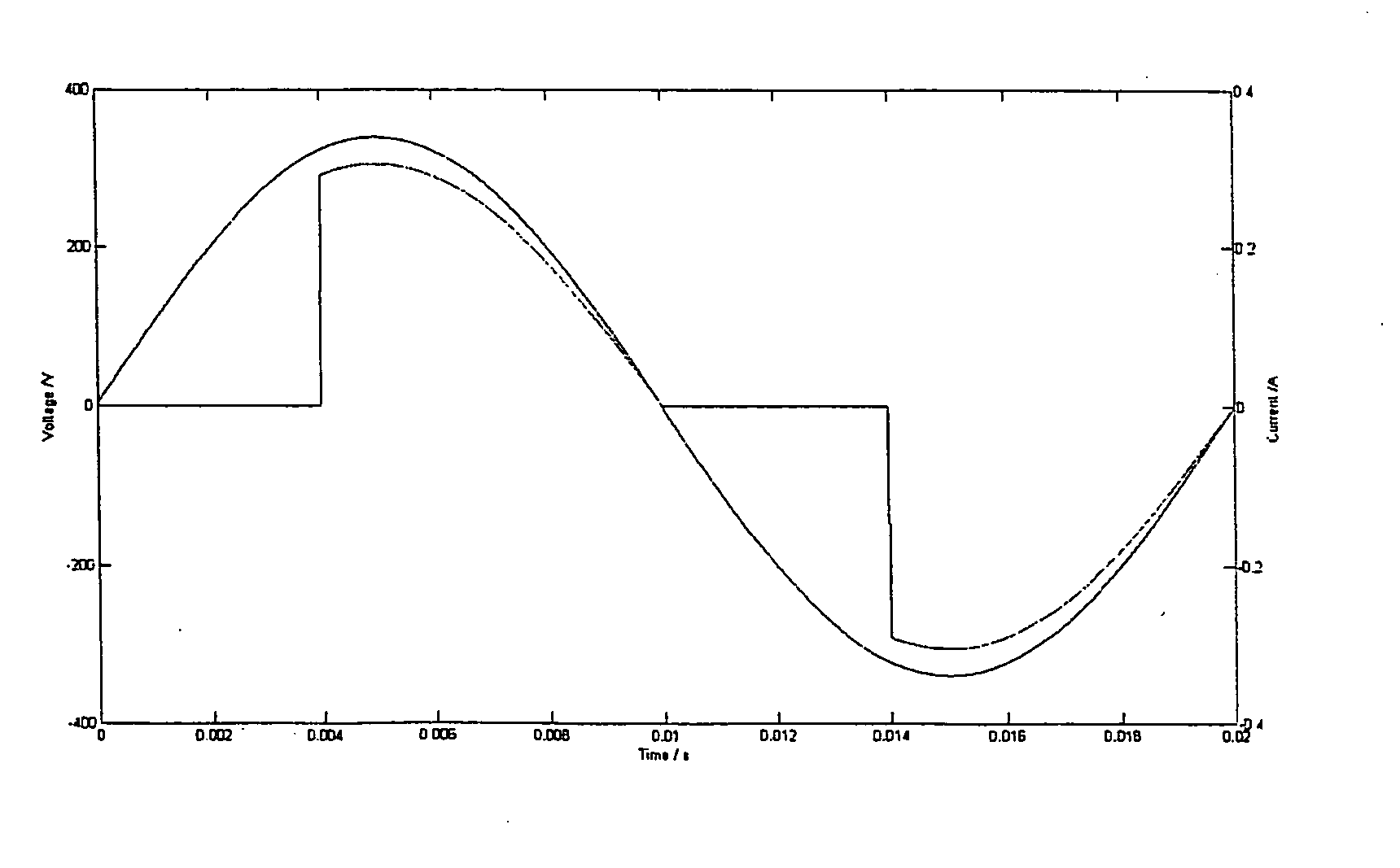
InactiveUS20040044489A1Resistance/reactance/impedenceVoltage-current phase angleOptical reflectionSequence signal
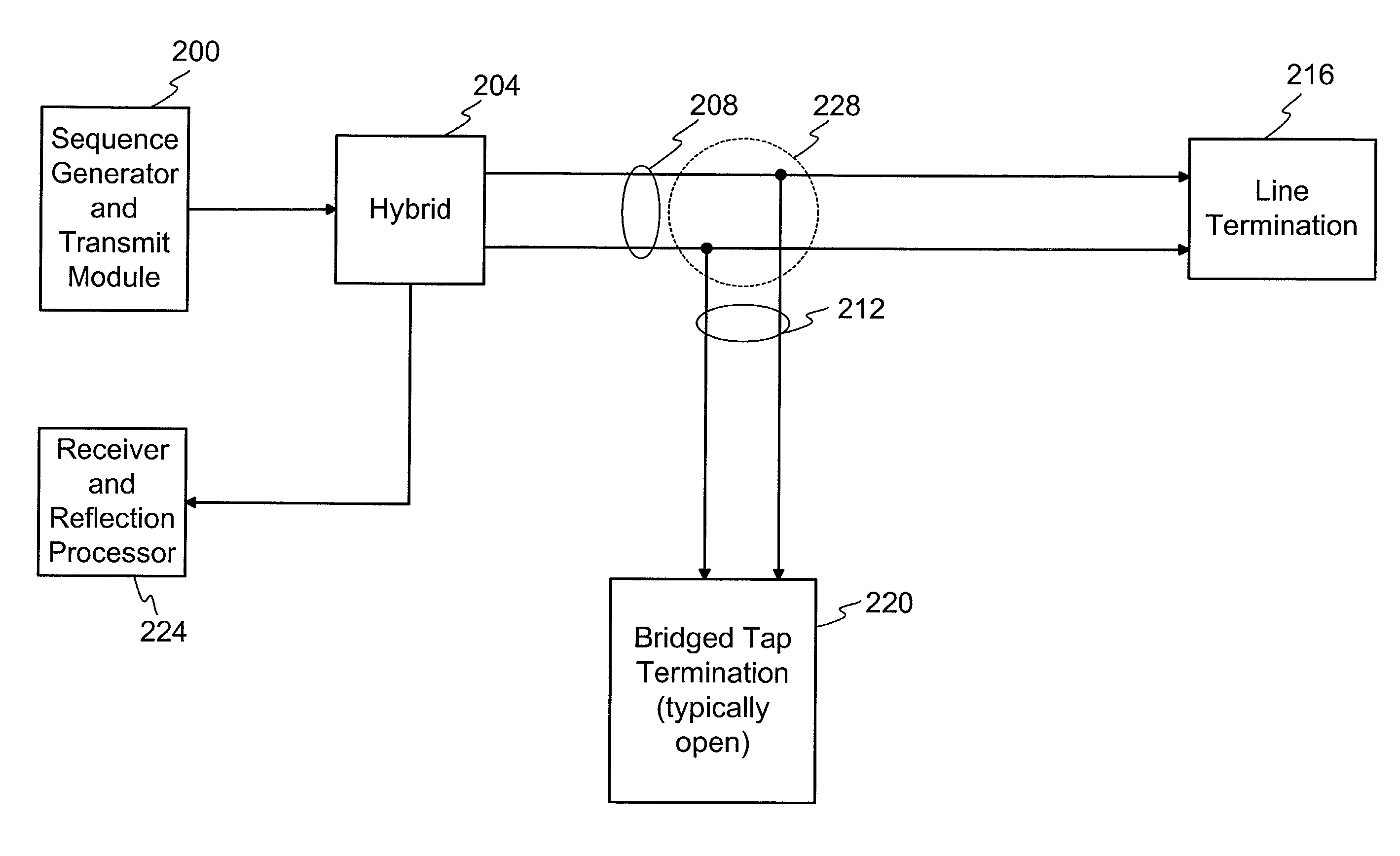
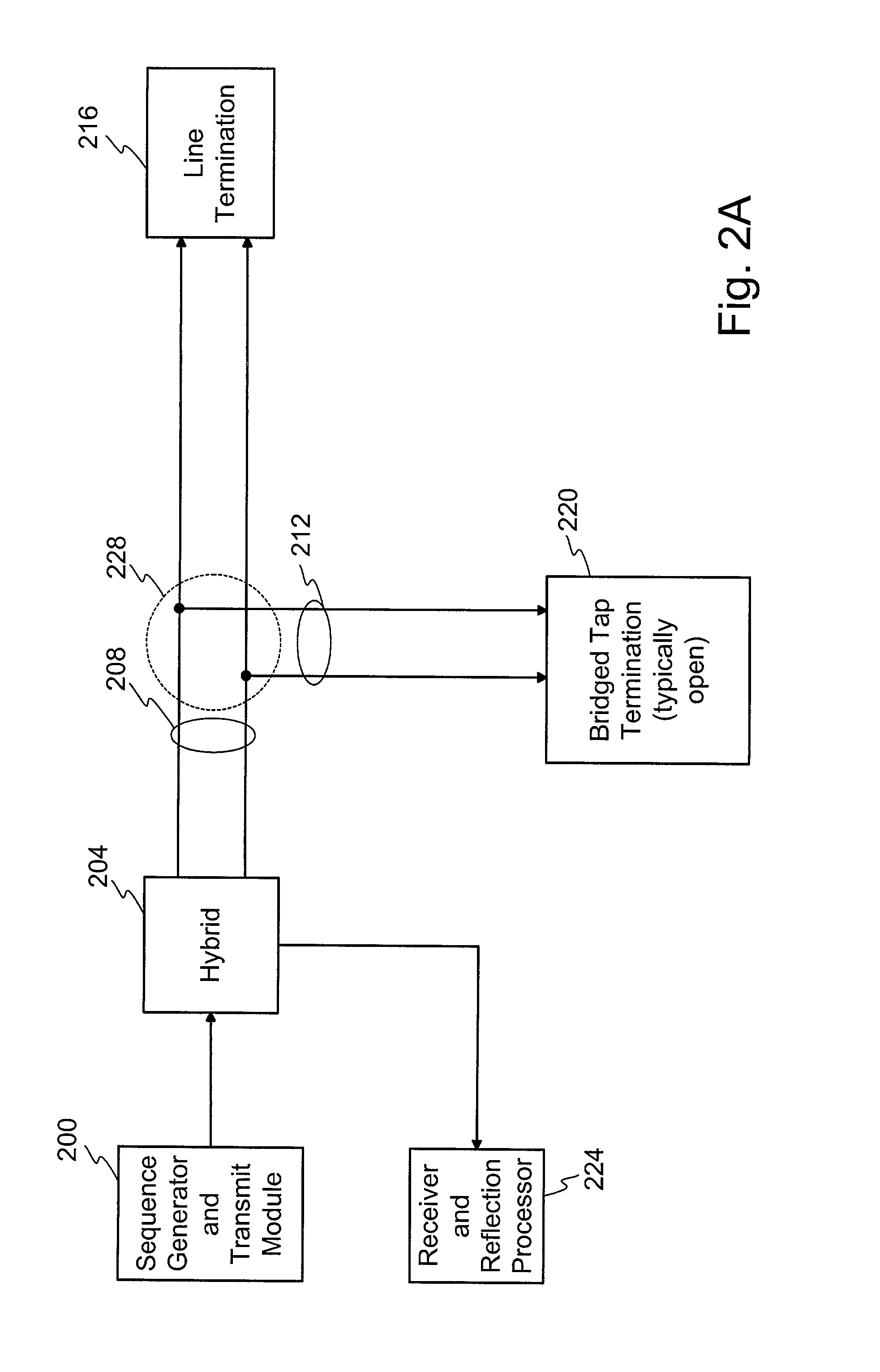
A method and system for performing sequence time domain reflectometry over a communication channel to determine the location of line anomalies in the communication channel is disclosed. In one embodiment, the system generates a sequence signal and transmits the sequence signal over an optical channel. The system receives one or more reflection signals over the optical channel and performs reflection signal processing on the reflection signal. In one embodiment, the optical reflection is transformed to an electrical signal and correlated with the original sequence signal to generate a correlated signal. The time between the start of the reflection signal and a subsequent point of correlation and the rate of propagation reveals a line anomaly location. In one or more embodiments sequence signal time domain reflectometry occurs during data transmission.
Owner:MACOM TECH SOLUTIONS HLDG INC
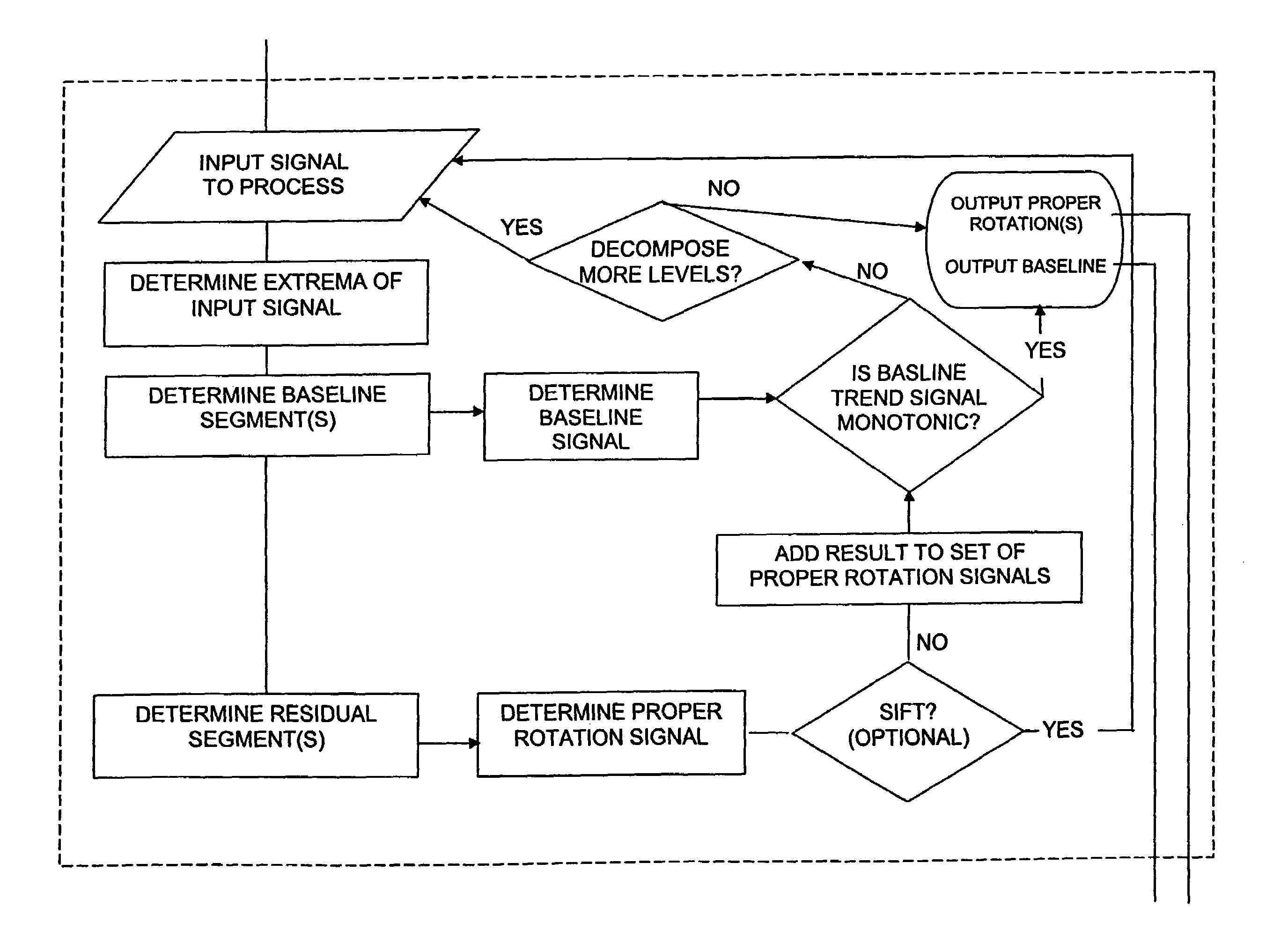
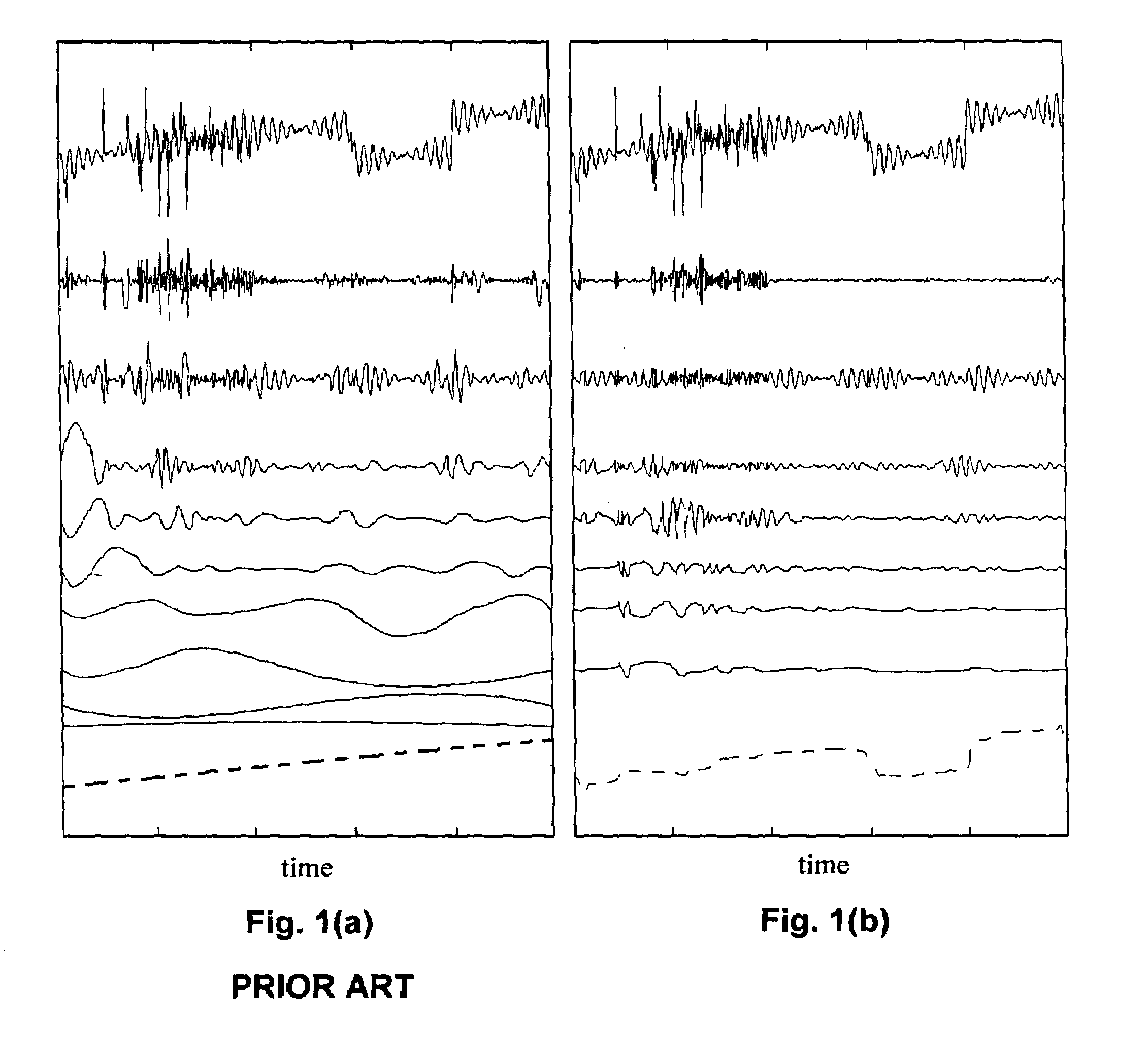
Method, computer program, and system for intrinsic timescale decomposition, filtering, and automated analysis of signals of arbitrary origin or timescale
ActiveUS7054792B2Easy to operateImprove performanceAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceTesting/monitoring control systemsTime markDecomposition
A method and system for intrinsic timescale decomposition, filtering, and automated analysis of signals of arbitrary origin or timescale including receiving an input signal, determining a baseline segment and a monotonic residual segment with strictly negative minimum and strictly positive maximum between two successive extrema of the input signal, and producing a baseline output signal and a residual output signal. The method and system also includes determining at least one instantaneous frequency estimate from a proper rotation signal, determining a zero-crossing and a local extremum of the proper rotation signal, and applying interpolation thereto to determine an instantaneous frequency estimate thereof. The method and system further includes determining at least one instantaneous frequency estimate from a proper rotation signal, extracting an amplitude-normalized half wave therefrom and applying an arc sine function to the amplitude-normalized half wave to determine an instantaneous frequency estimate of the proper rotation signal.
Owner:FLINT HILLS SCI L L C
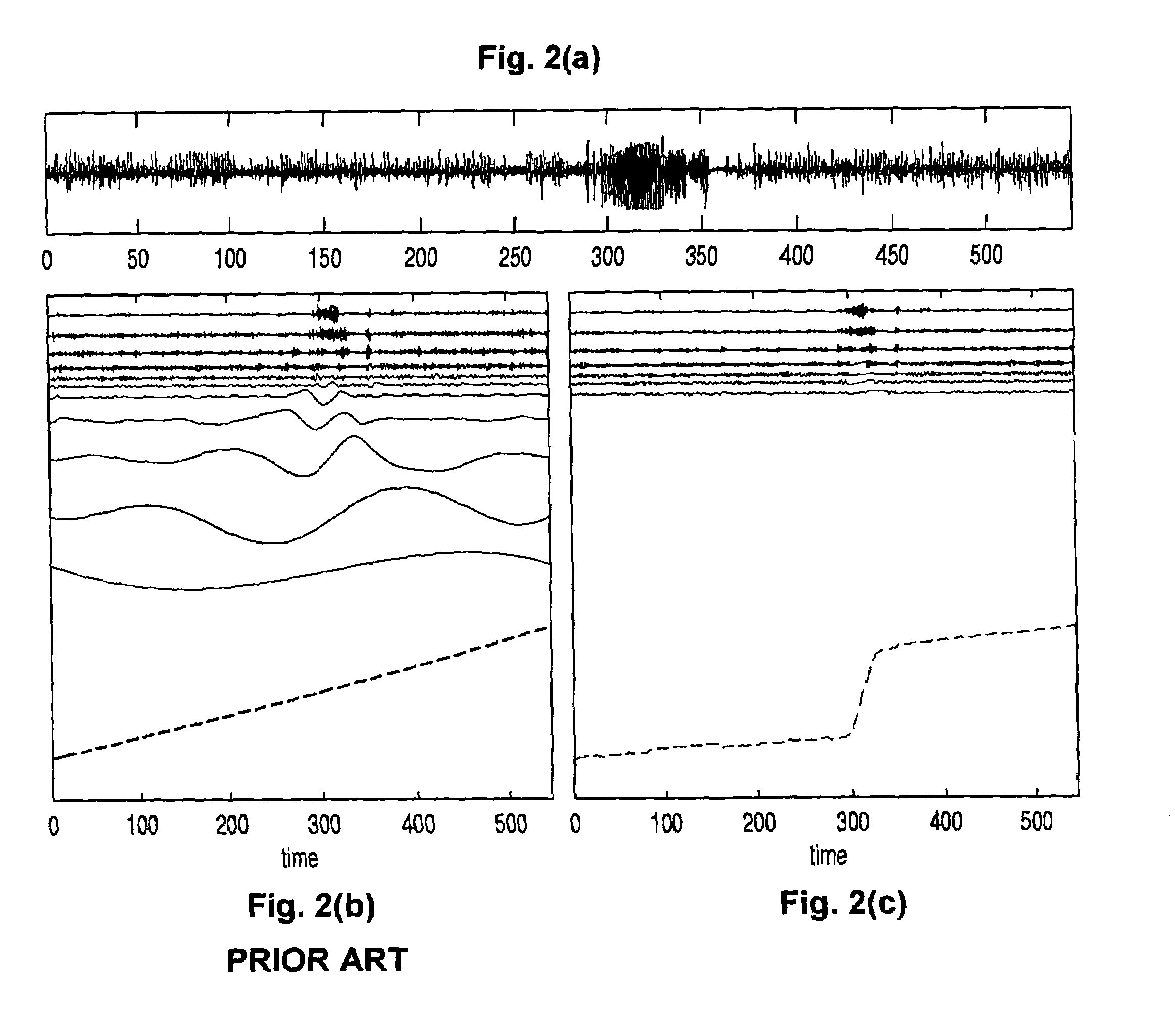
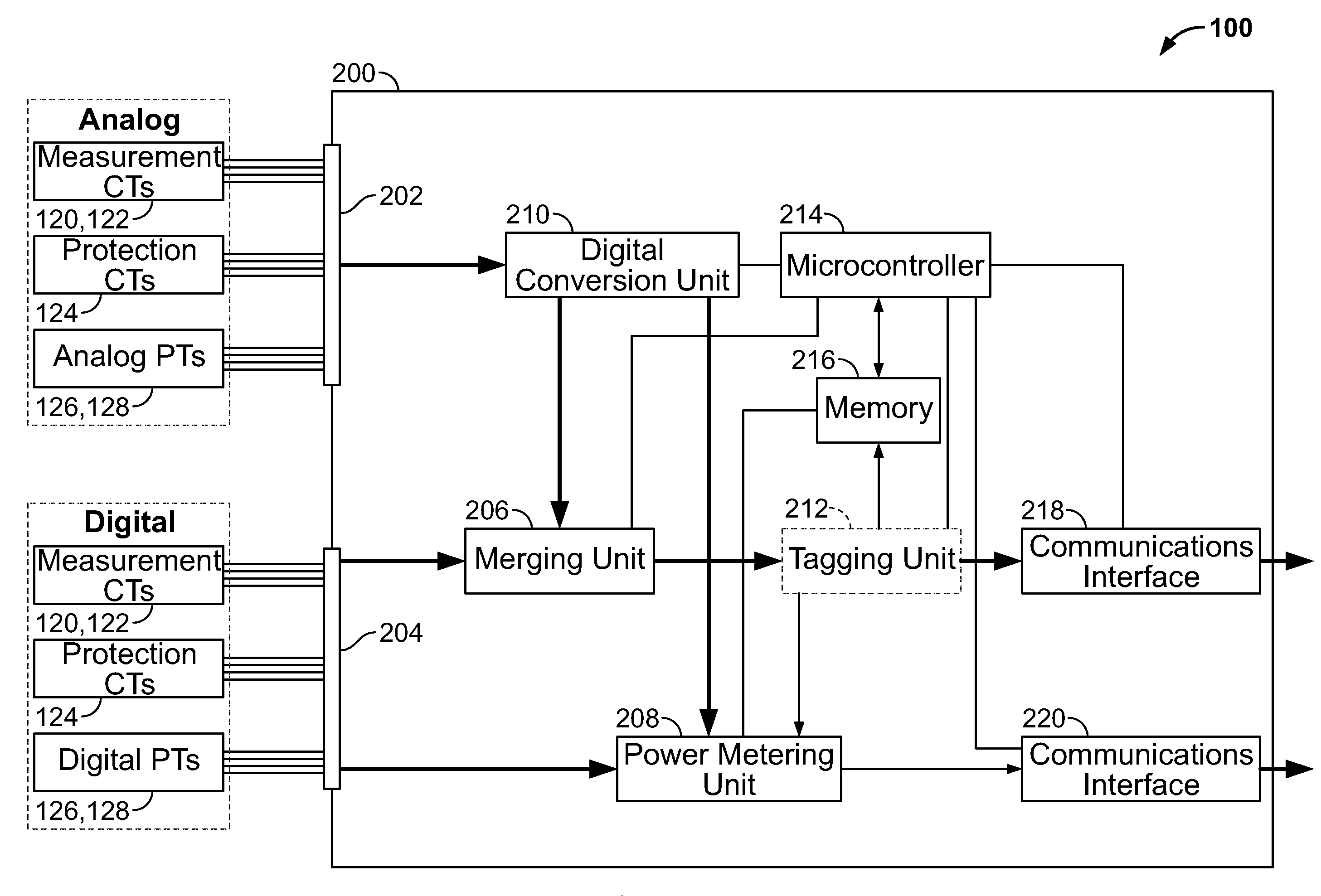
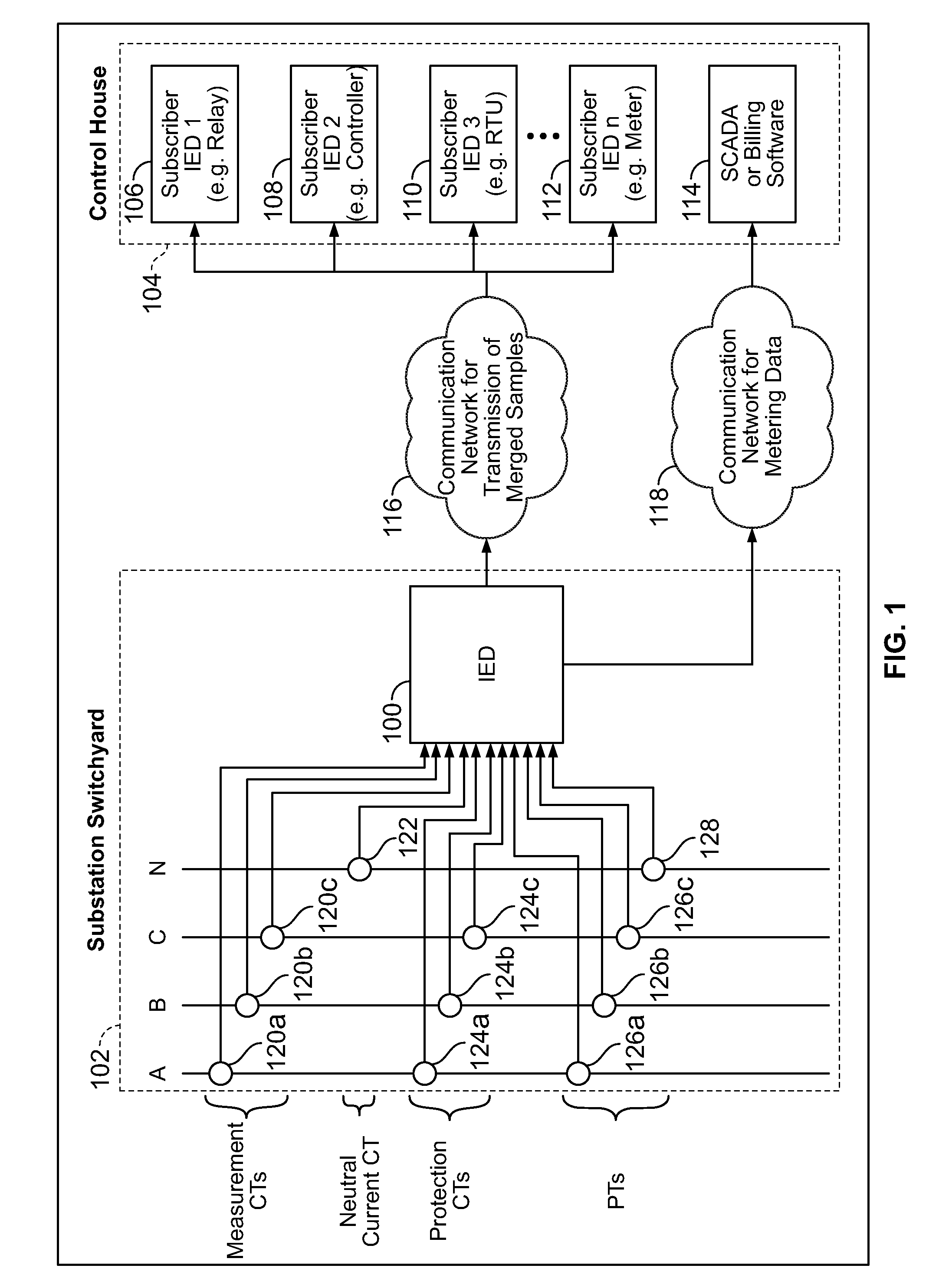
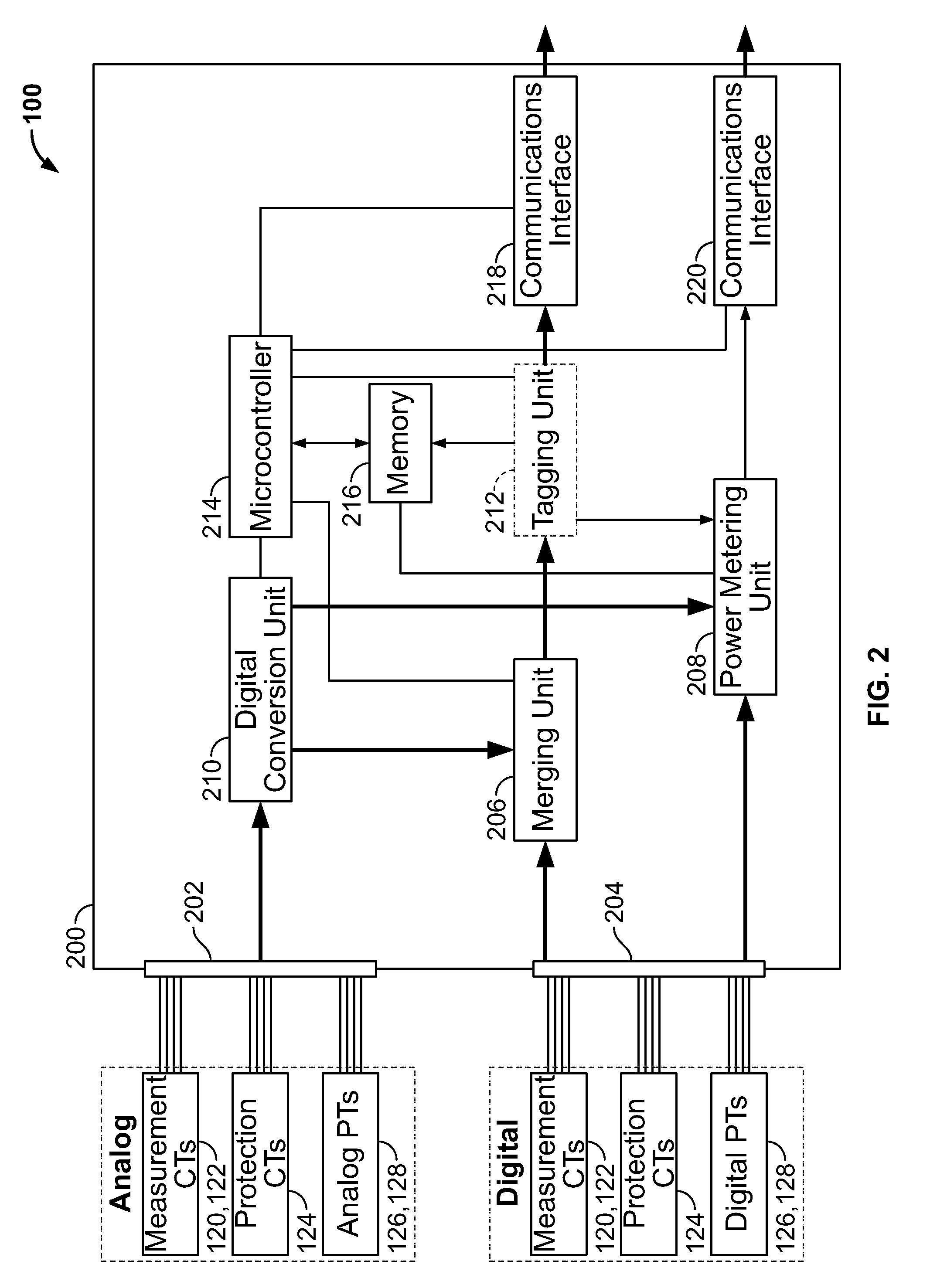
Power metering and merging unit capabilities in a single ied
An intelligent electronic device (IED) integrating a power metering unit (PMU) and a merging unit that combines signals from both analog transformers and digital transformers into a set of merged digital samples. Analog current / voltage signals from analog CTs / PTs are received at the IED's analog inputs and converted to digitized samples. Digital current / voltage samples from digital CTs / PTs are received via point-to-point connections at digital inputs of the IED. A tagging unit applies metadata tags to the digitized and digital samples. The metadata tags include the transformer providing the input signal, sampling rate, primary and / or secondary timestamps, scaling values, calibration values, and / or the location of the IED in the electrical system. The PMU performs metering and / or power quality calculations on the samples, and the calculation results are formatted and transmitted via a master-slave protocol to a requesting master. A grouping unit groups the merged samples into default or custom groupings, which are formatted and transmitted over a network via a publish-subscribe mechanism.
Owner:SQUARE D CO
Animated graphical object notification system
InactiveUS6937950B2Noise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementVoltage-current phase angleGraphicsAnimation
Owner:IBM CORP
Utility metering
InactiveUS20110153246A1Present inventionAccurate methodTariff metering apparatusResistance/reactance/impedenceElectricityElectrical resistance and conductance
An apparatus has an input section arranged to receive values representative of the total instantaneous supply of electrical current as a function of time from an alternating voltage supply. Current waveforms comprising sets of values representative of the cyclic waveform of the electric current supply are obtained. A delta waveform generator calculates the difference between a current waveform and an earlier current waveform. An edge detector is arranged to detect an edge or edges in the delta waveform. An analysis section is arranged to identify at least one appliance load based at least on information on the edge or edges detected by the edge detector, and to determine the electrical energy consumed by said appliance load. Another apparatus has an input section arranged to receive values representative of the current supplied to an installation, such as a house. A store contains appliance data characteristic of the use of electricity by each of a plurality of appliances. A processor is arranged to analyse the received values to detect when an appliance is switched on and determine the fractional change in resistance of a heating appliance from the when it is switched on until it reaches its operating temperature. This information is used to identify what the particular appliance is, and to determine the electrical energy consumption by that appliance. A utility meter for metering the use of at least one utility supplied to a plurality of appliances is also disclosed. An input section is arranged to receive values representative of the use of a first utility. A store contains appliance data characteristic of the use of utilities by each of a plurality of appliances. A processor is arranged to analyse the received values and to determine information on the use of a second utility by each appliance, based on the received values and appliance data.
Owner:ISIS INNOVATION LTD
System and method of processing a data signal
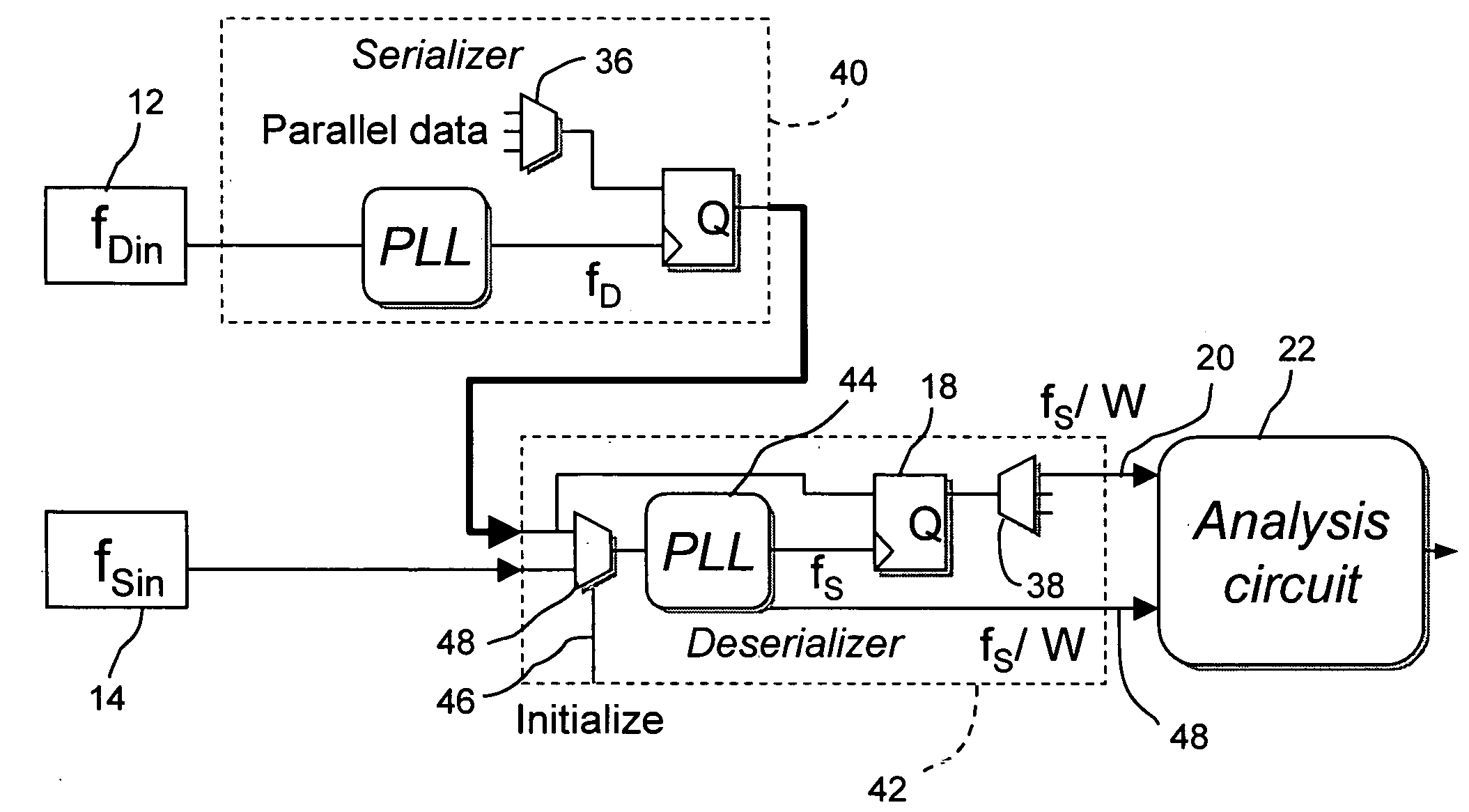
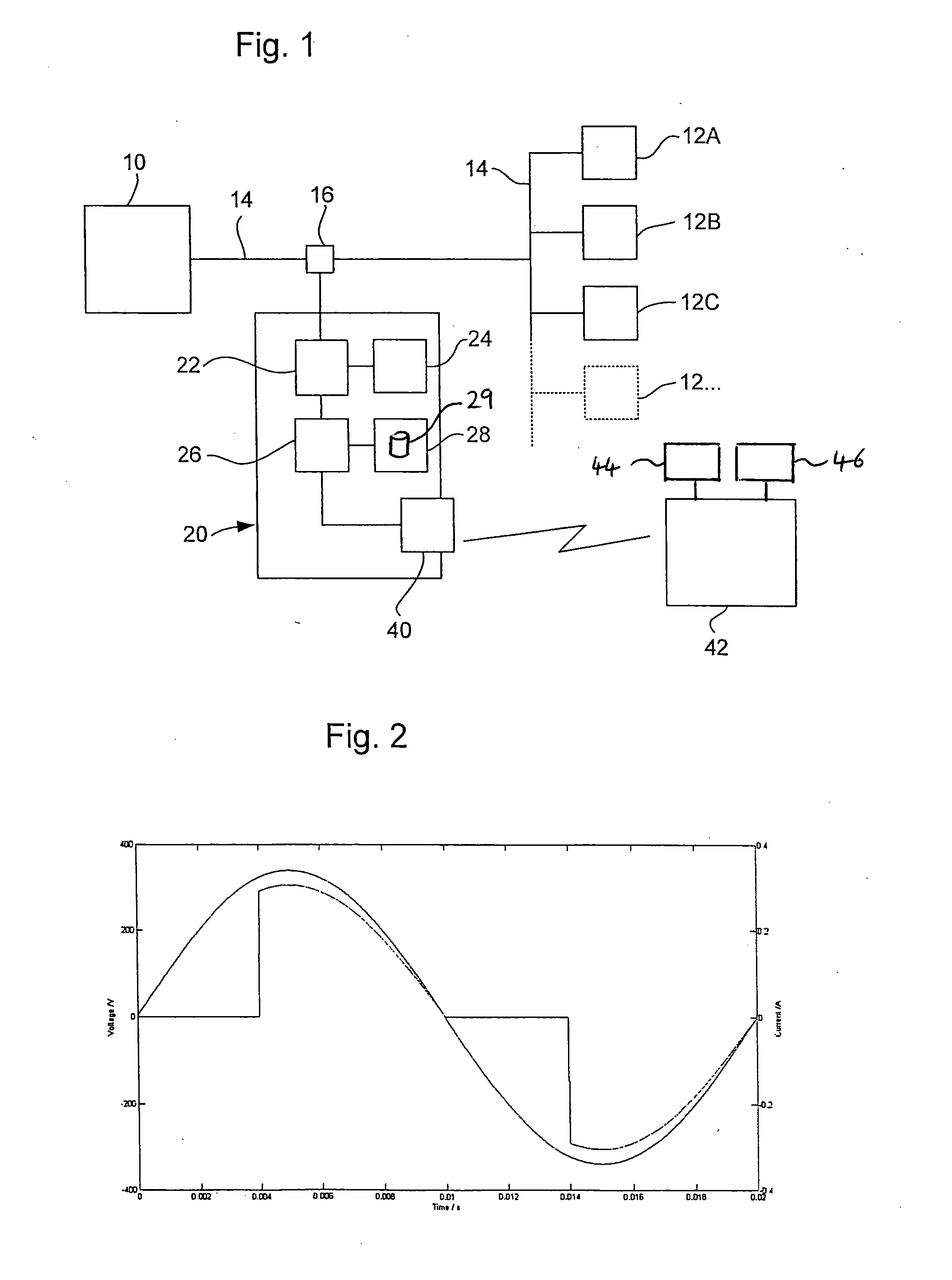
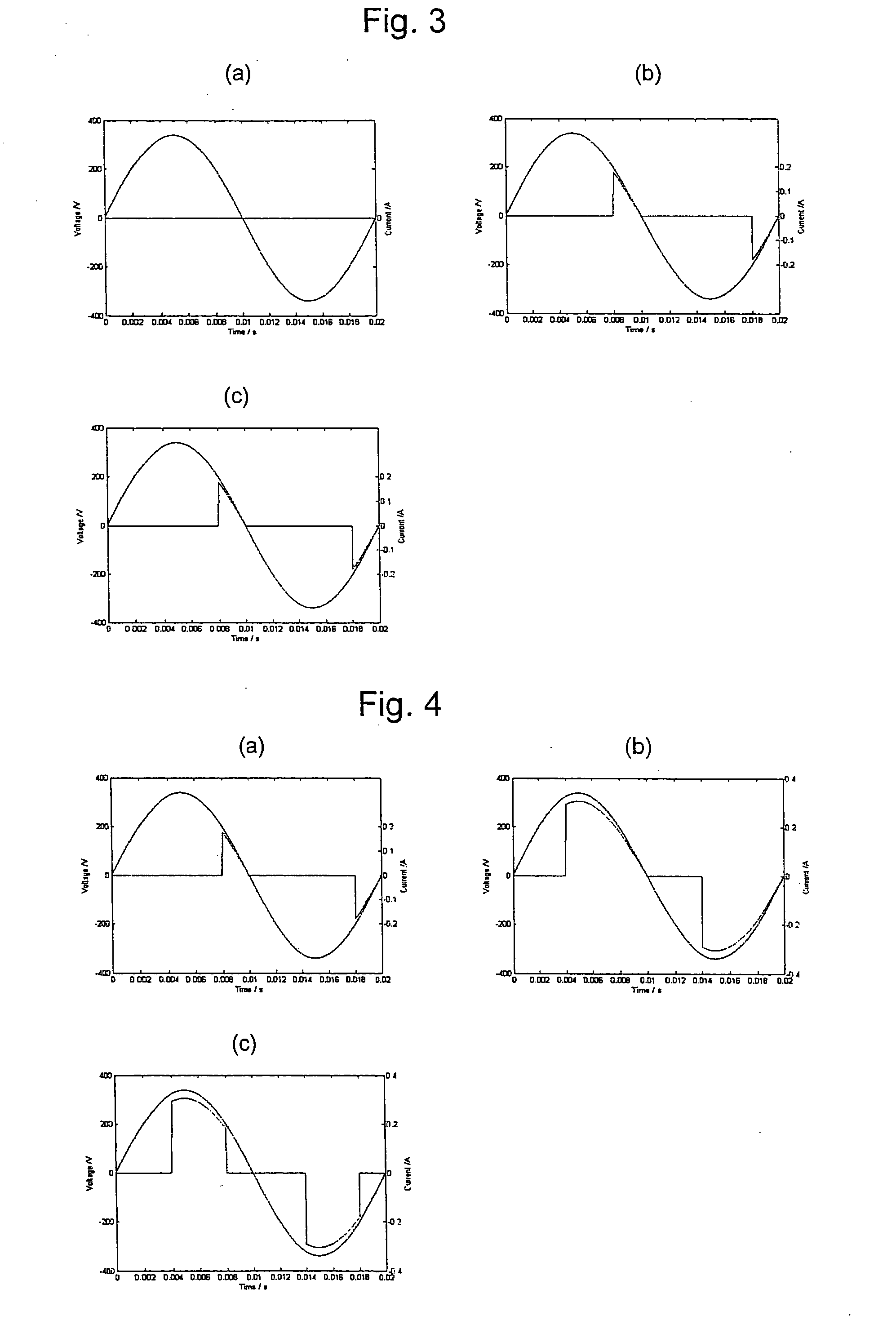
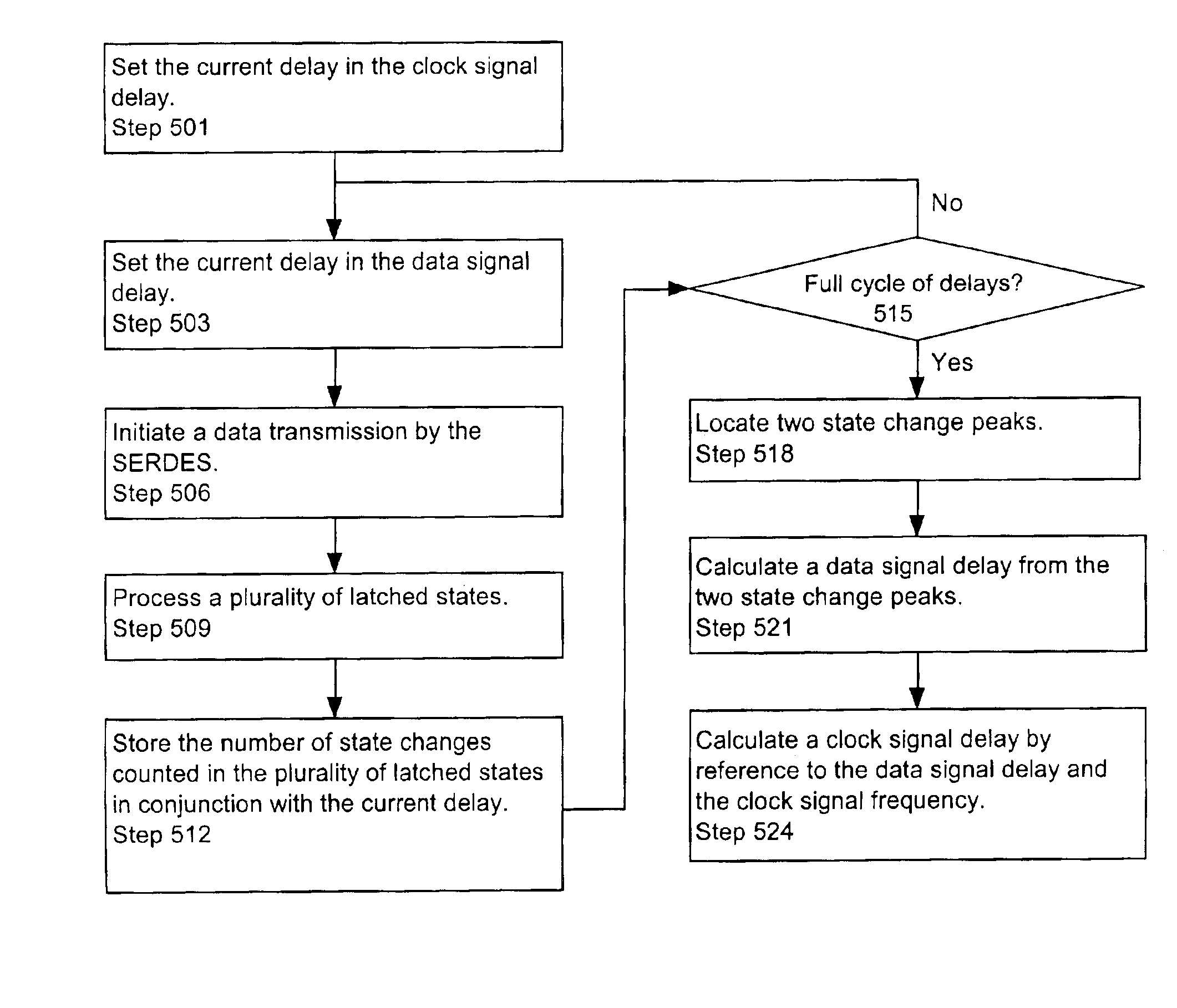
InactiveUS6937949B1Reducing and eliminating jitterDigital circuit testingNoise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementData signalSerializer
Systems and methods for testing bit processing capacities of electronic devices and for reducing or eliminating jitter that compromises the ability of electronic devices to perform this task. Embodiments include circuitry and a methodology for locating and employing a data signal delay—in conjunction with a latch—to reduce or eliminate jitter from serial encoded data generated by a serializer / deserializer. The data signal delay ensures that the latch latches a state of the serial encoded data at a position within a data signal cycle of minimum jitter.
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC
Calibration of memory circuits
A method for calibration of memory circuits is provided that adjusts memory circuit output parameters based on data eye measurements. Data eye patterns from the memory circuit outputs are measured by the memory controller for different settings of the memory circuit output parameters. Memory circuit output parameters can be adjusted to settings that correspond to widest average data eye widths, highest average data eye heights, or other suitable criteria.
Owner:ROUND ROCK RES LLC
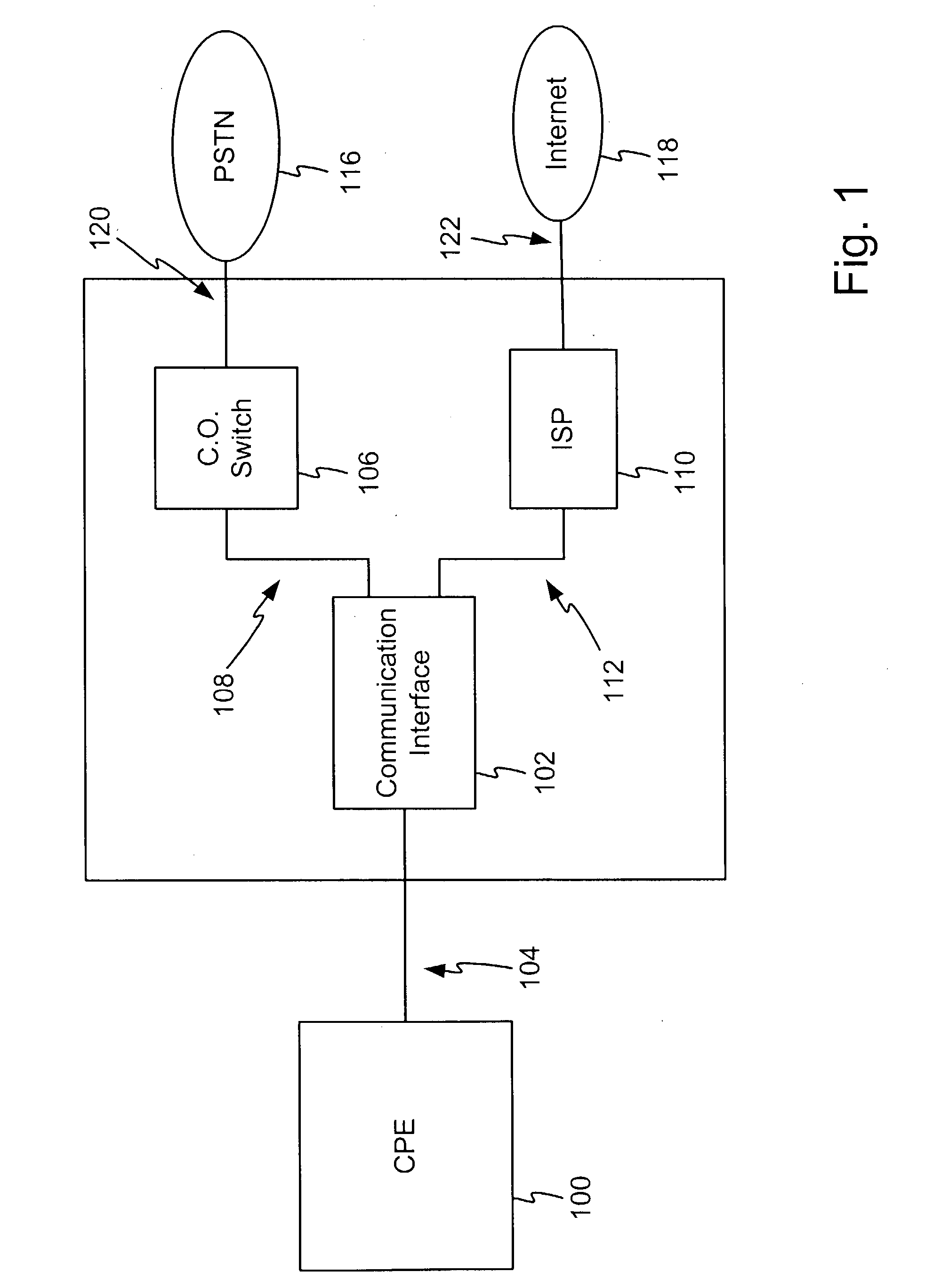
Method and apparatus for transmission line analysis
InactiveUS20020161542A1Testing/calibration of speed/acceleration/shock measurement devicesFault location by pulse reflection methodsSequence signalTime domain
A method and system for performing sequence time domain reflectometry to determine the location of line anomalies in a communication channel is disclosed. In one embodiment, the system generates a sequence signal and transmits the sequence signal over a channel that is the subject of the sequence time domain reflectometry analysis. The system monitors for and receives one or more reflections, collectively a reflection signal, and presents the reflection signal to a reflection processing module. The module also has access to the original sequence signal that was transmitted over the channel. Various methods of processing the reflection signal are available to determine the location of the line anomalies. In one embodiment, the reflection signal is correlated with the original sequence signal to generate a correlated signal. The system performs signal analysis on the correlated signal to determine a time value between the start of the reflection signal and the subsequent points of correlation. Based on the time value and the rate of propagation of the signals through the channel, the reflection processing module can determine a distance from the system to a line anomaly. In another embodiment, the original sequence signal is fed into a predictive filter and processed based on coefficient values of the predictive filter. The output of the predictive filter is compared to the reflection signal and the results of the comparison used to adjust the coefficients of the predictive filter. The reflection processing module adjusts the coefficients until the predictive filter output generally matches the reflection signal, at which point the coefficient values may be used to determine the distance from the system to a line anomaly.
Owner:MACOM TECH SOLUTIONS HLDG INC
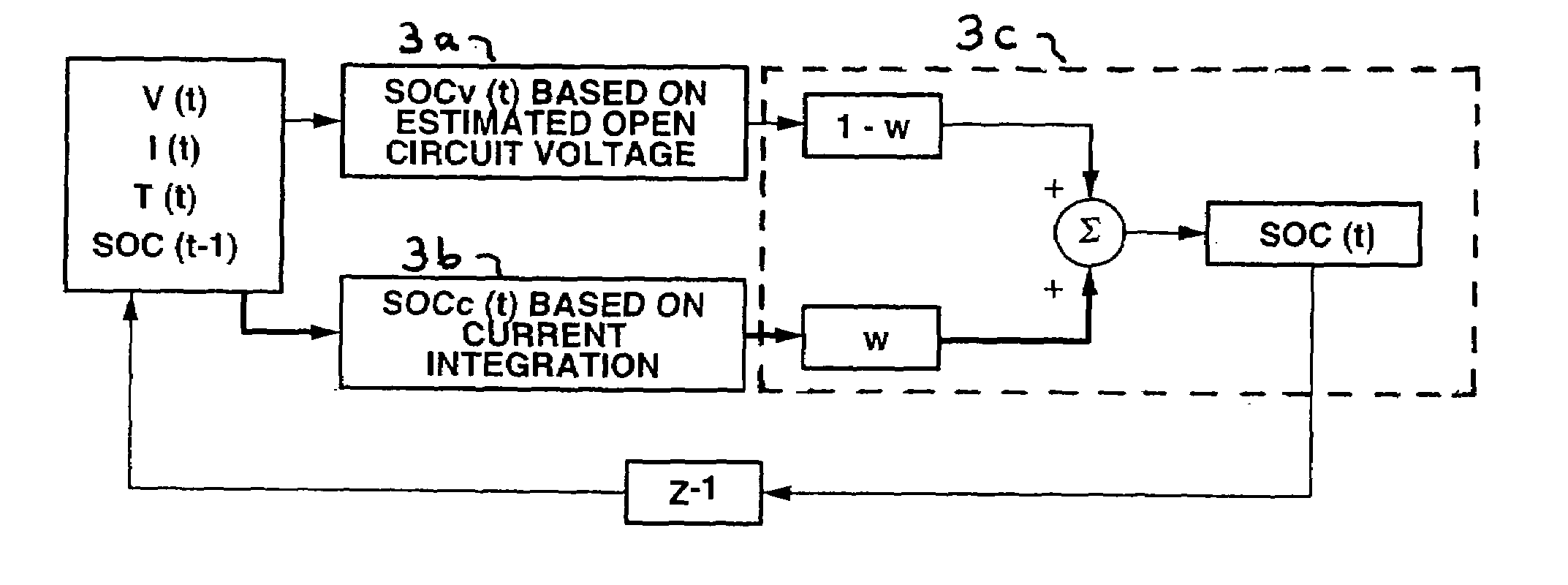
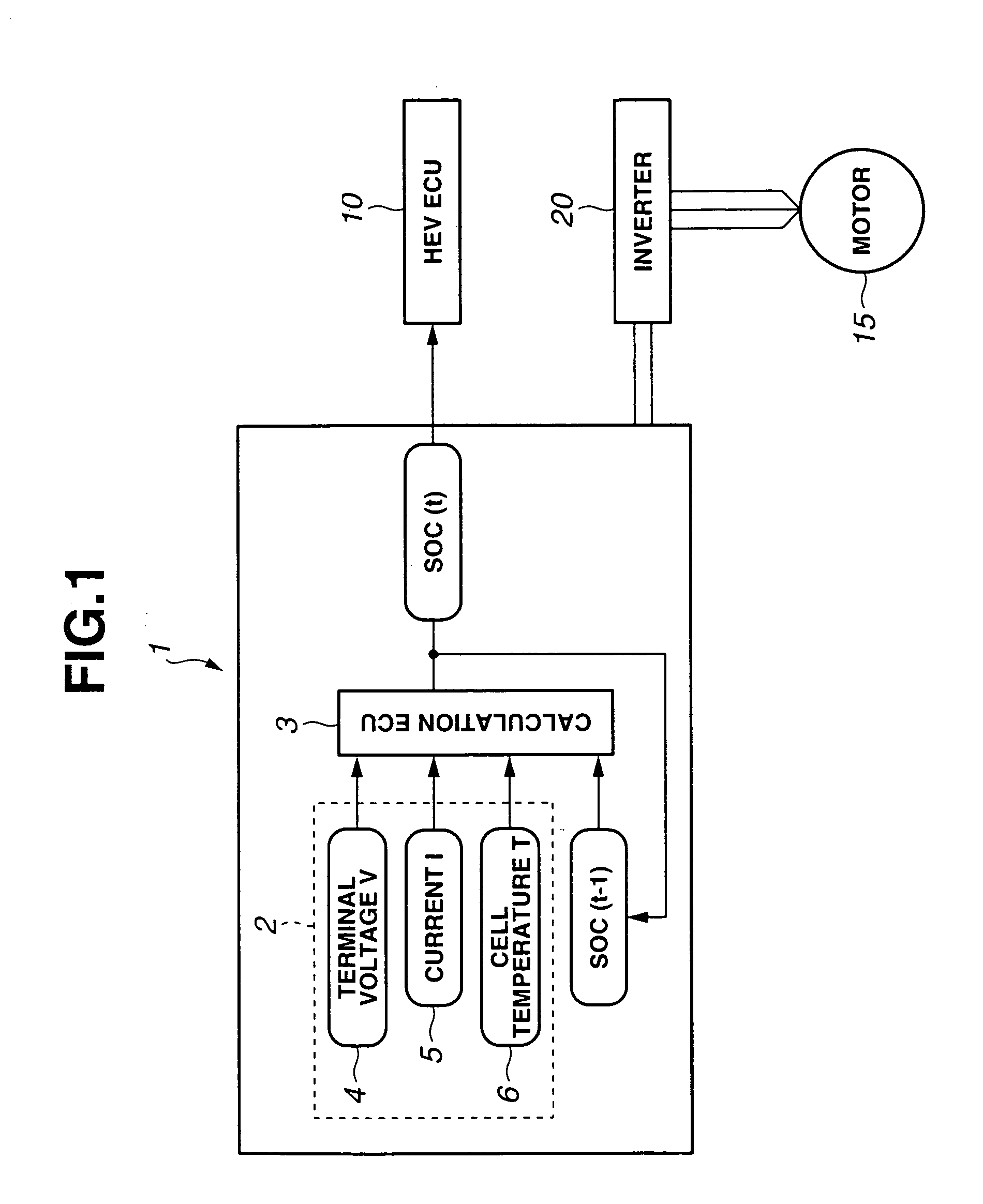
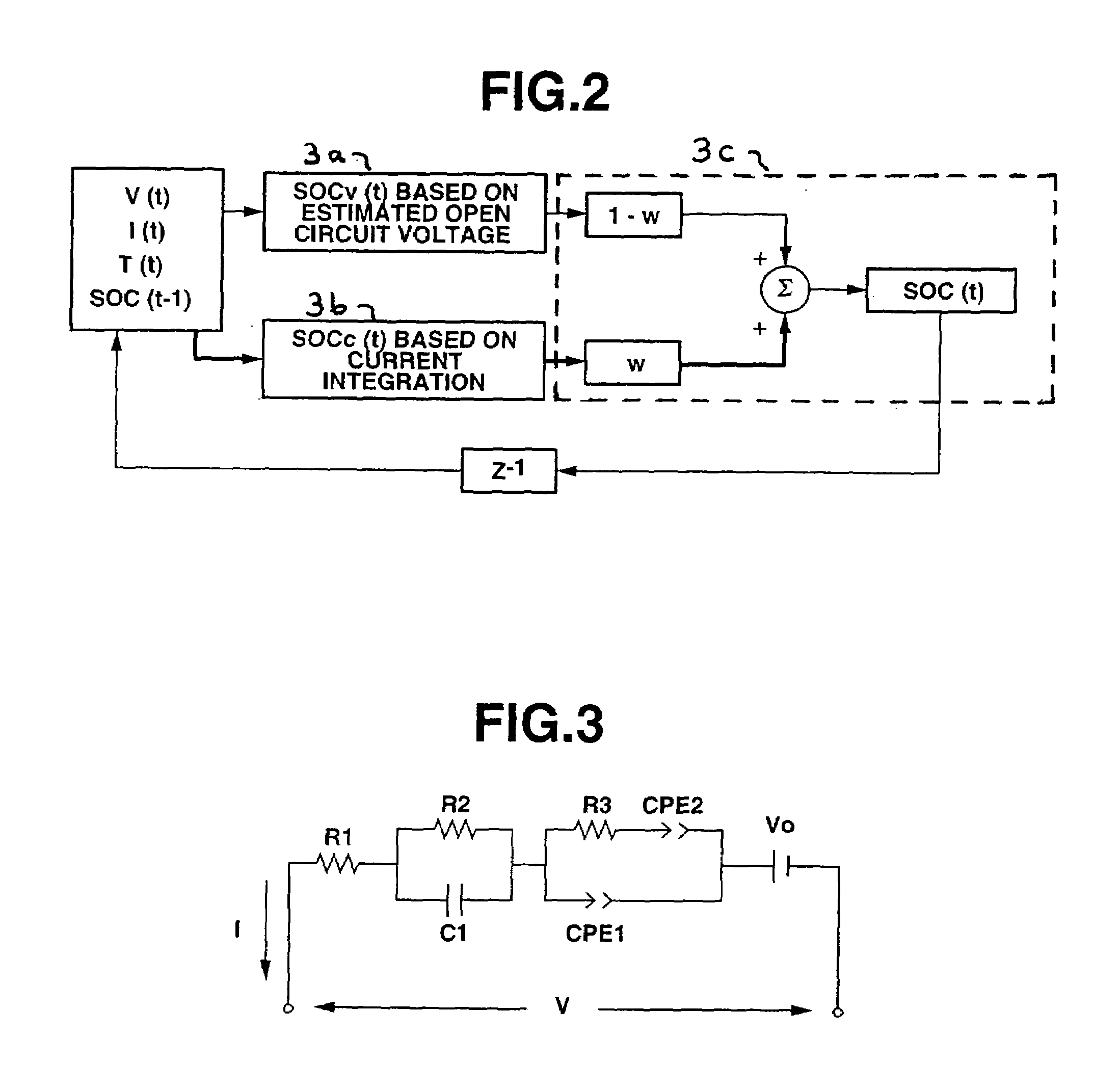
System for calculating remaining capacity of energy storage device
InactiveUS7136762B2Uniform accuracyBatteries circuit arrangementsMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansElectrical batteryEngineering
Owner:SUBARU CORP
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com