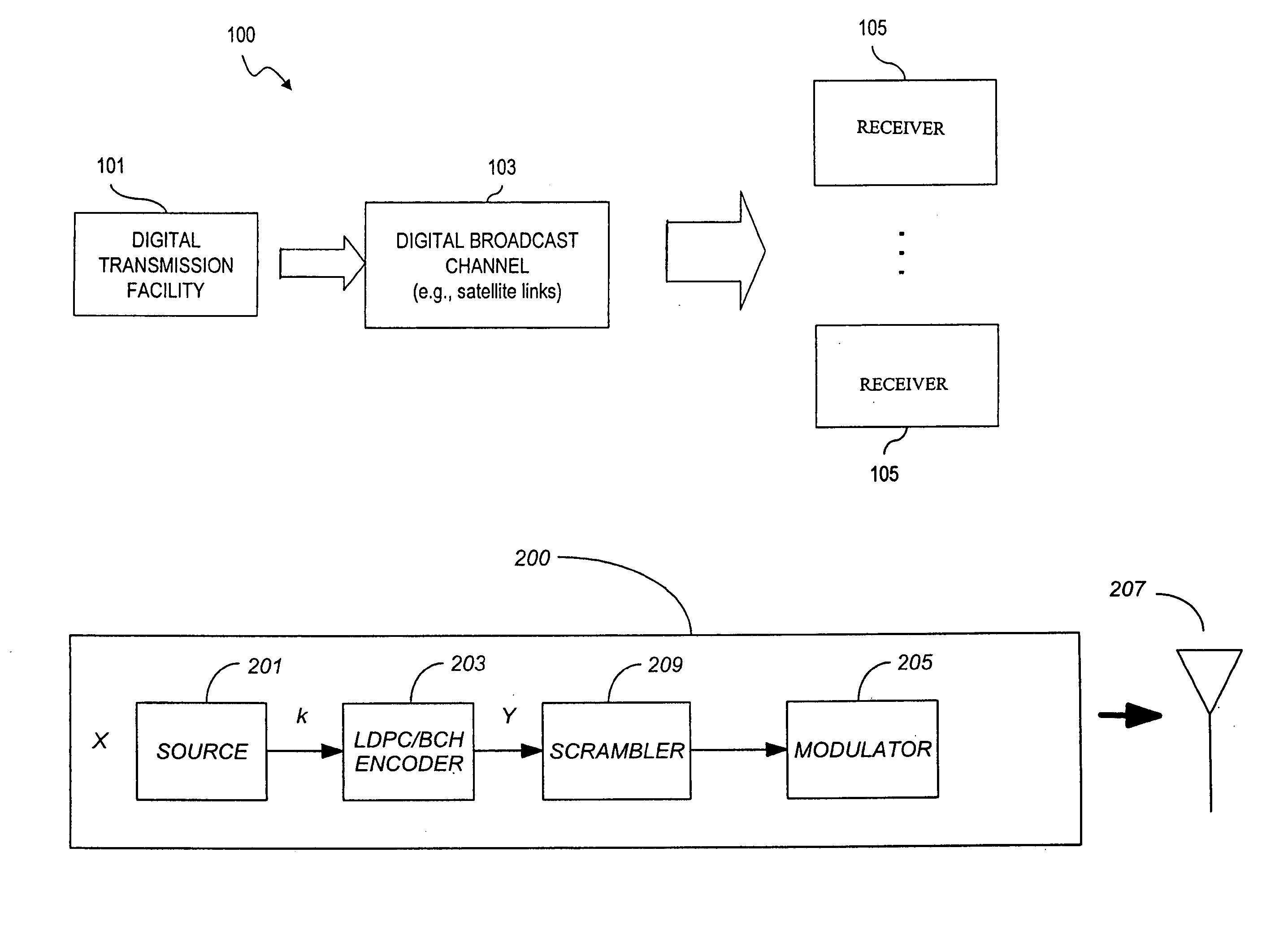
Patents
Literature
339results about "Pulse amplitude modulation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
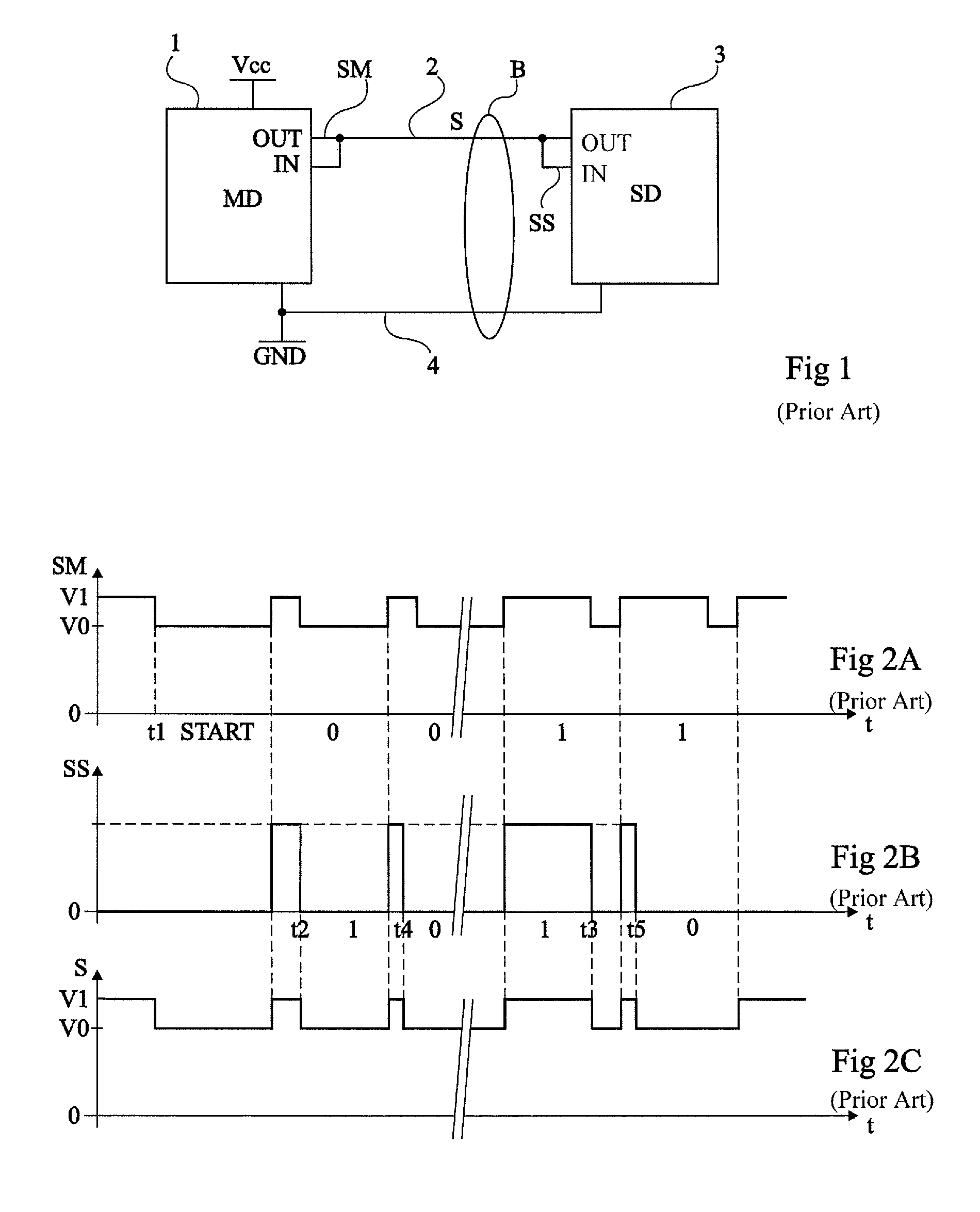
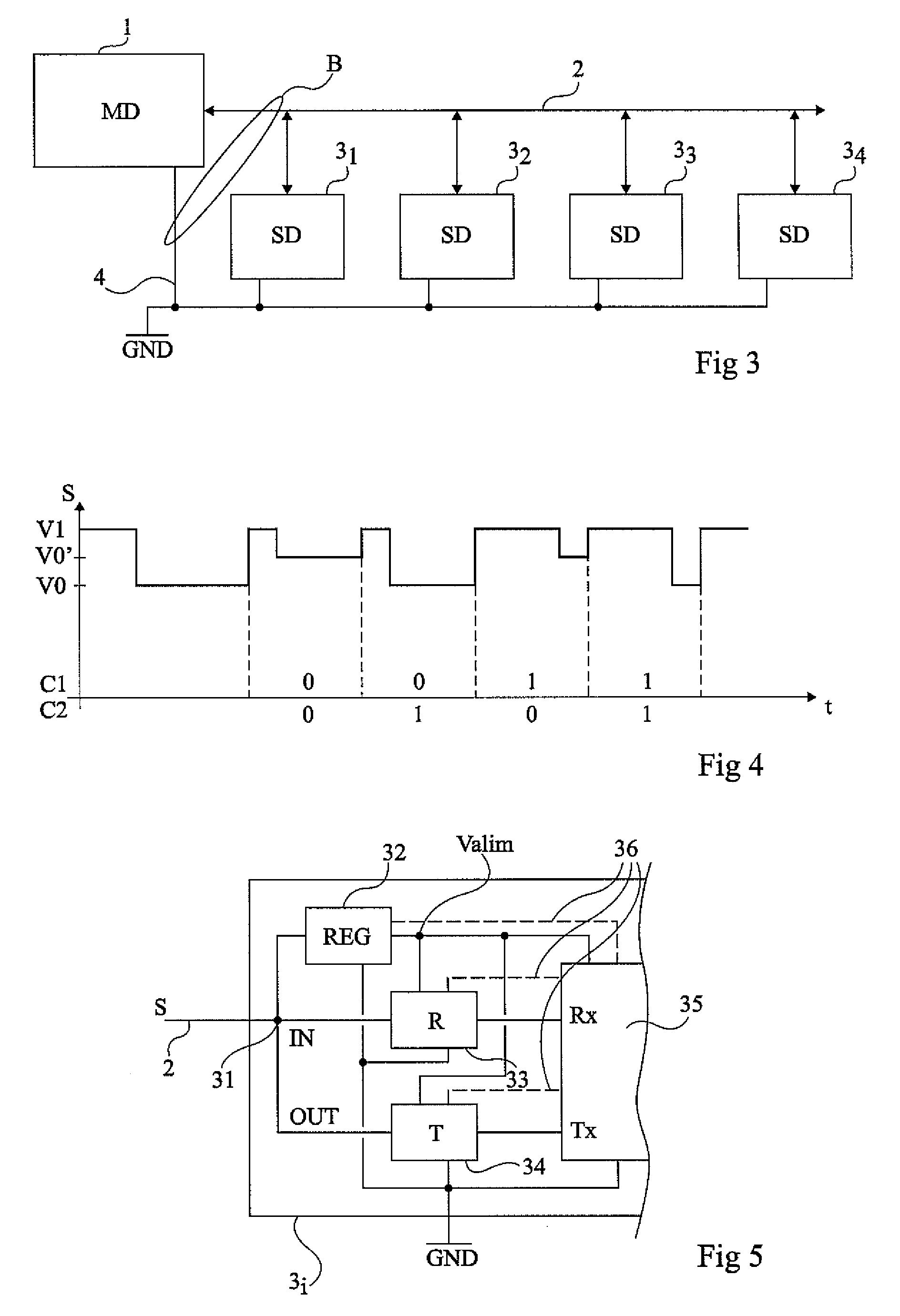
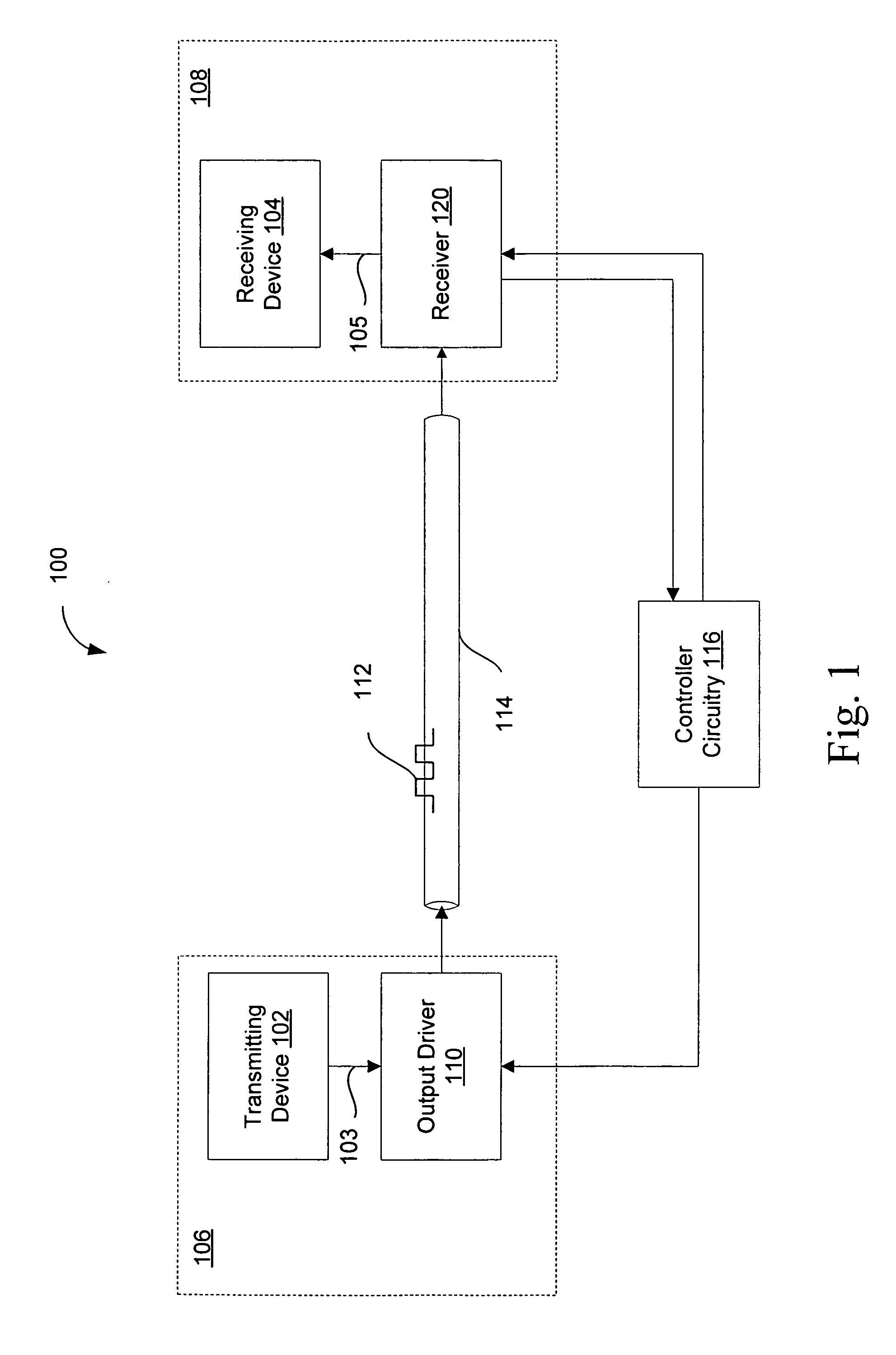
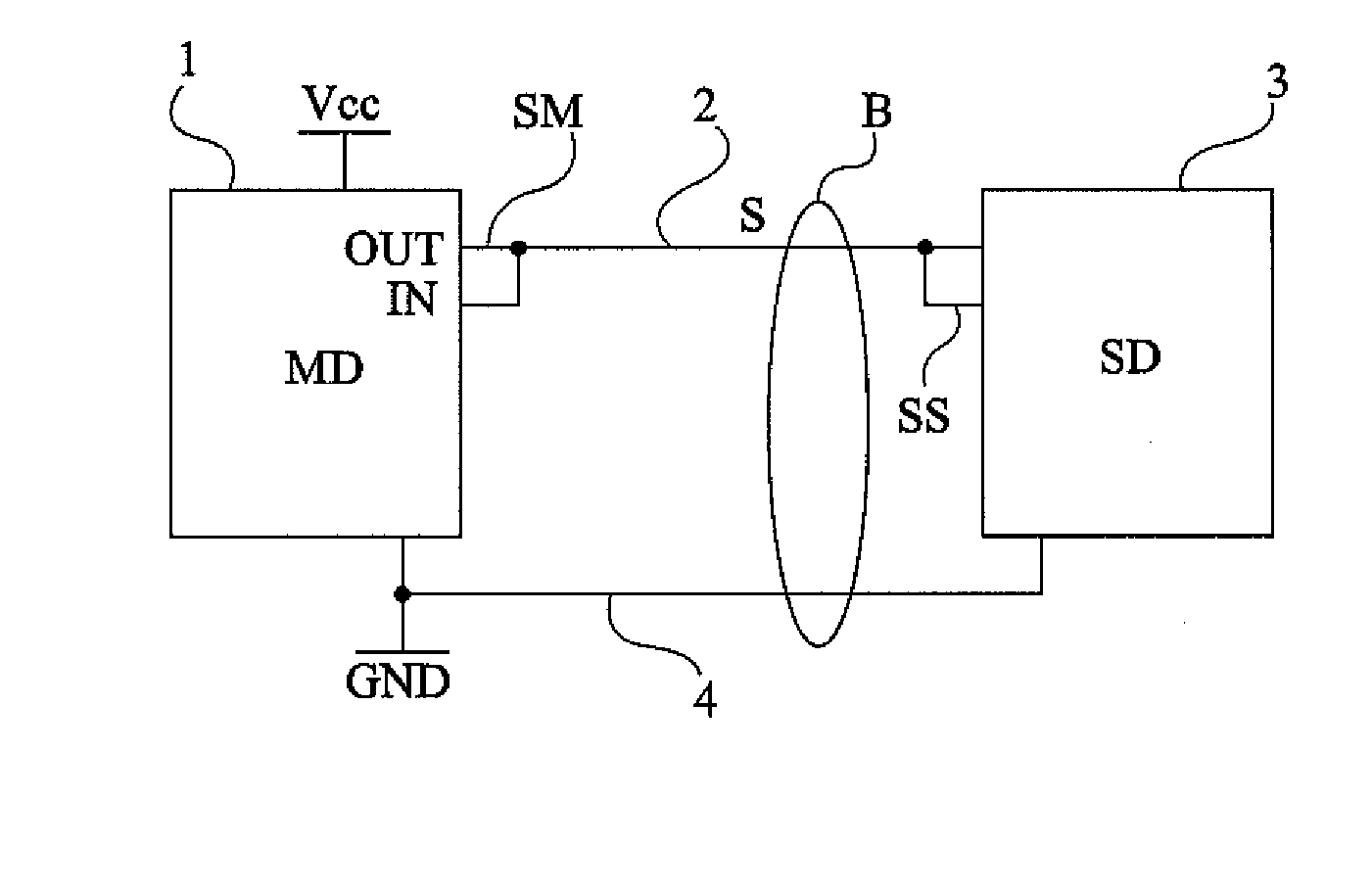
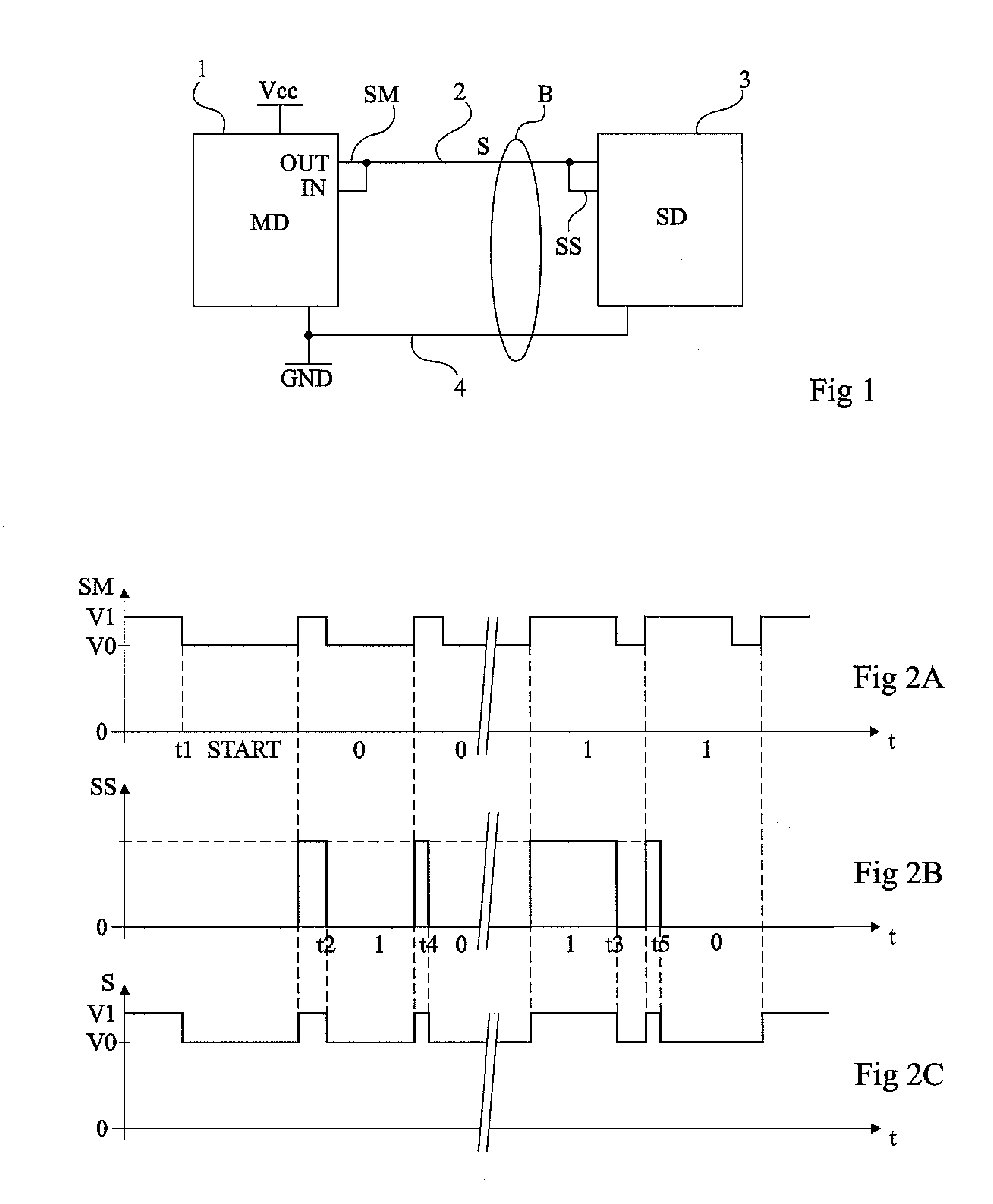
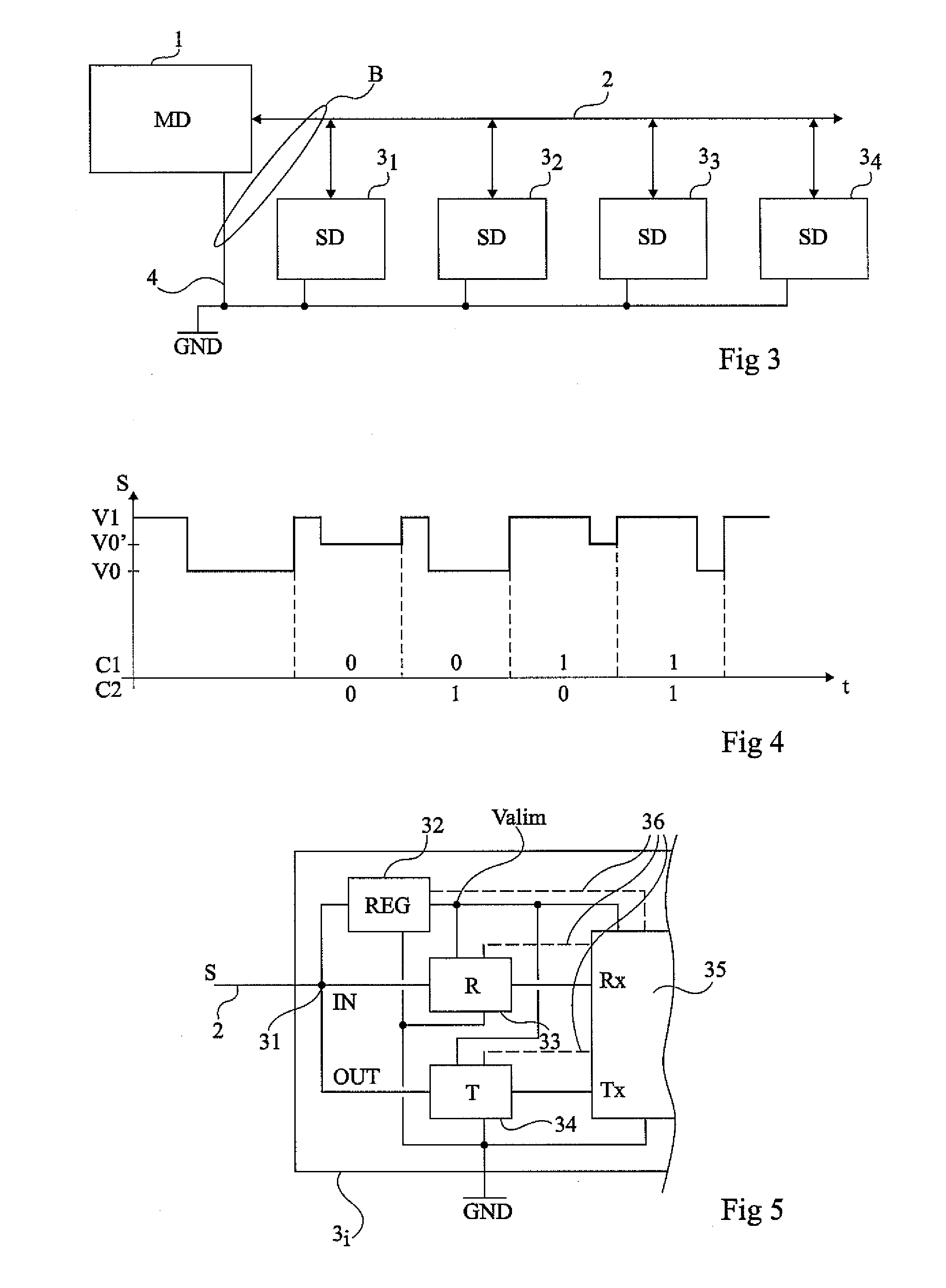
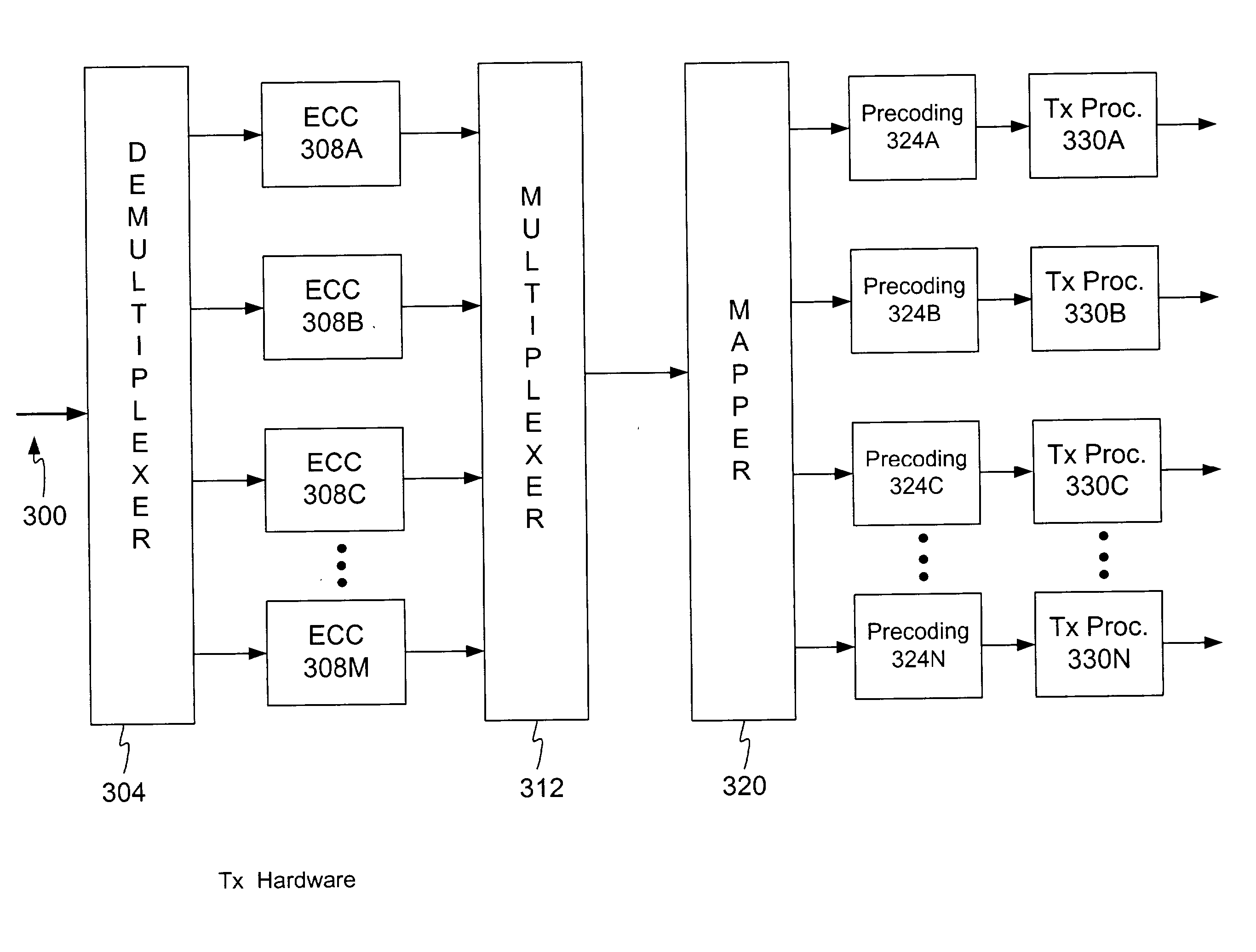
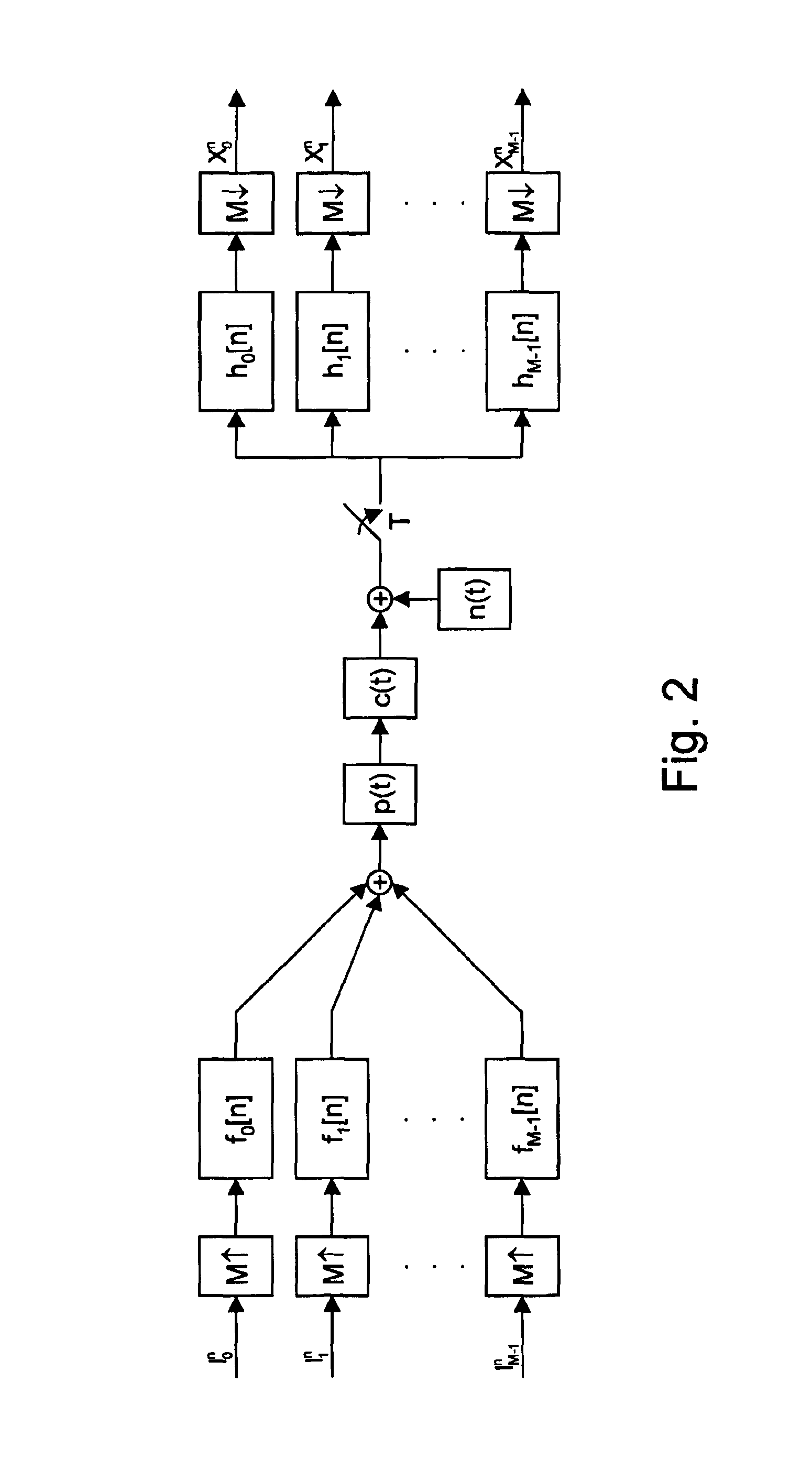
Multiple-channel transmission over a single-wire bus
ActiveUS8509318B2Batteries circuit arrangementsTransmission/receiving by adding signal to waveTransmission channelPower over
Apparatus and methods are described that enable concurrent transmission of multiple data signals including clock, synchronization, and power over a single-wire bus between a master device and one or more slave devices. A first transmission channel from the master device to the slave device may modulate the width of periodic pulses between a first voltage level and a second voltage level with respect to a reference potential. A second transmission channel may modulate the amplitude of at least one of the first and second voltage levels to at least one third voltage level. Concurrent communications between a master device and one or more slave devices over a single-wire bus can be achieved.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS (ROUSSET) SAS
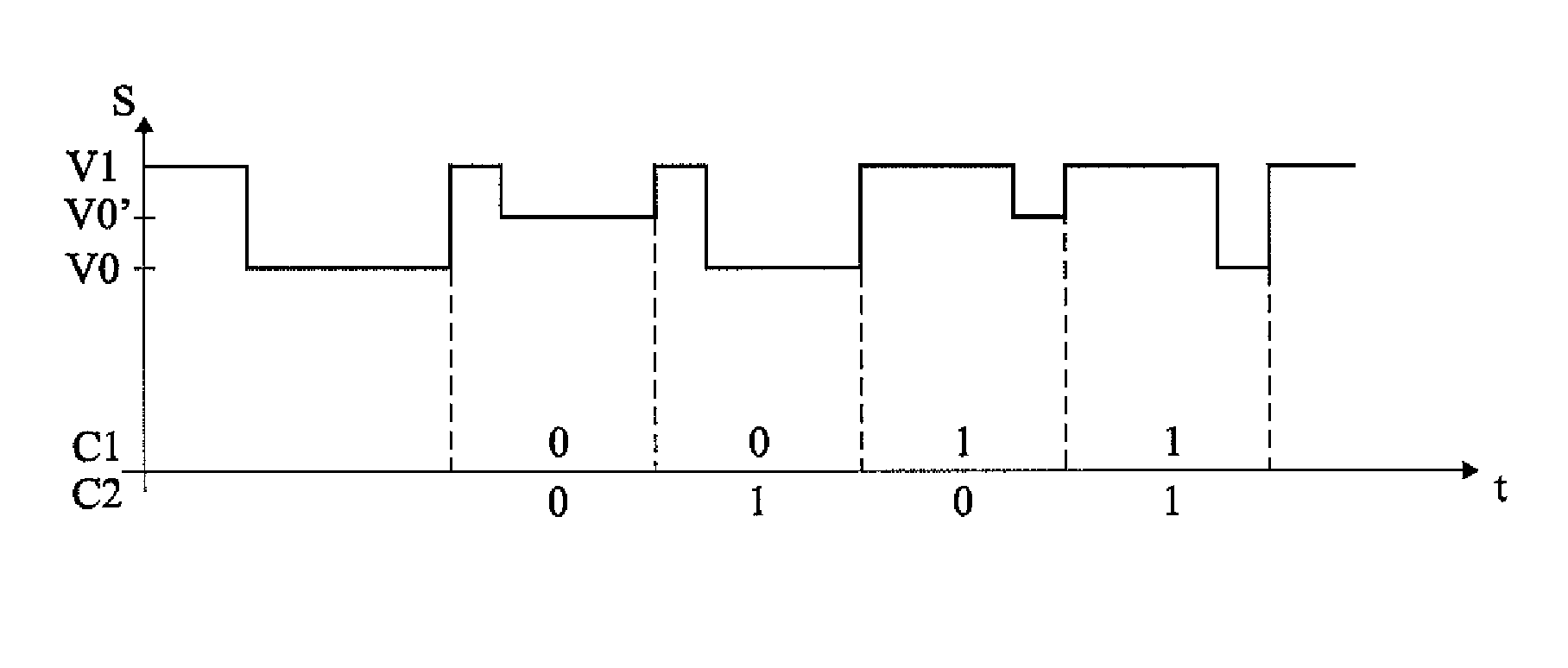
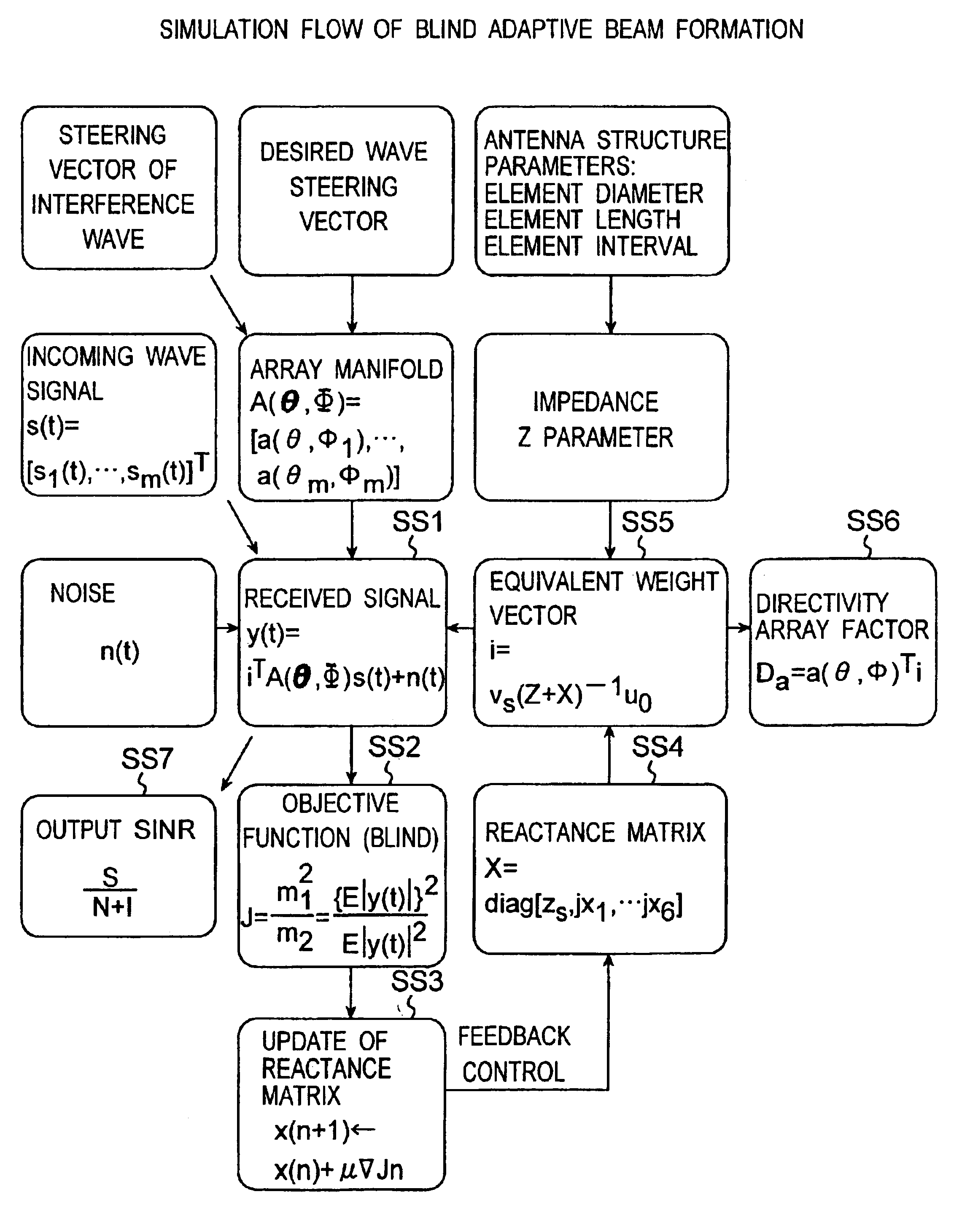
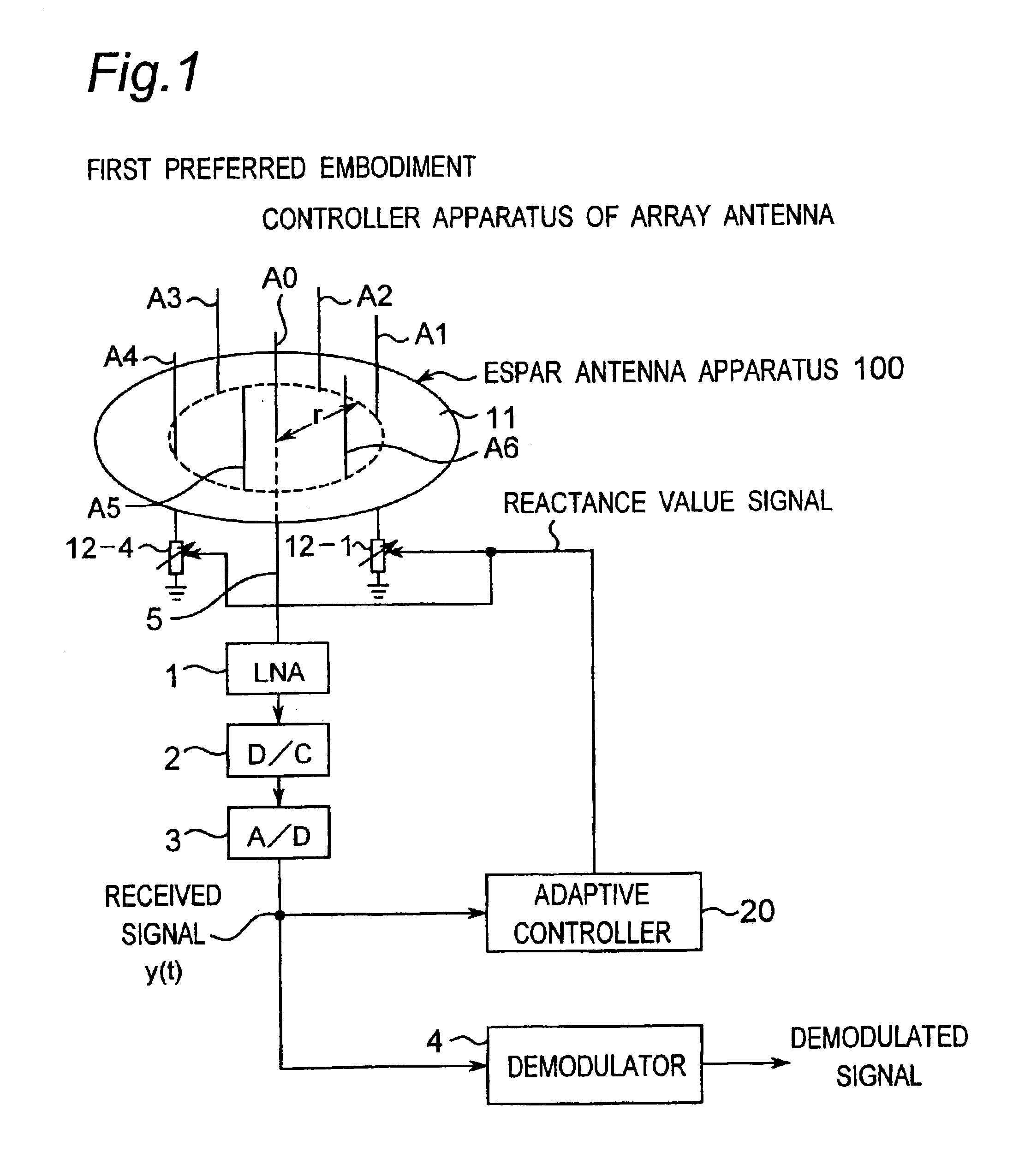
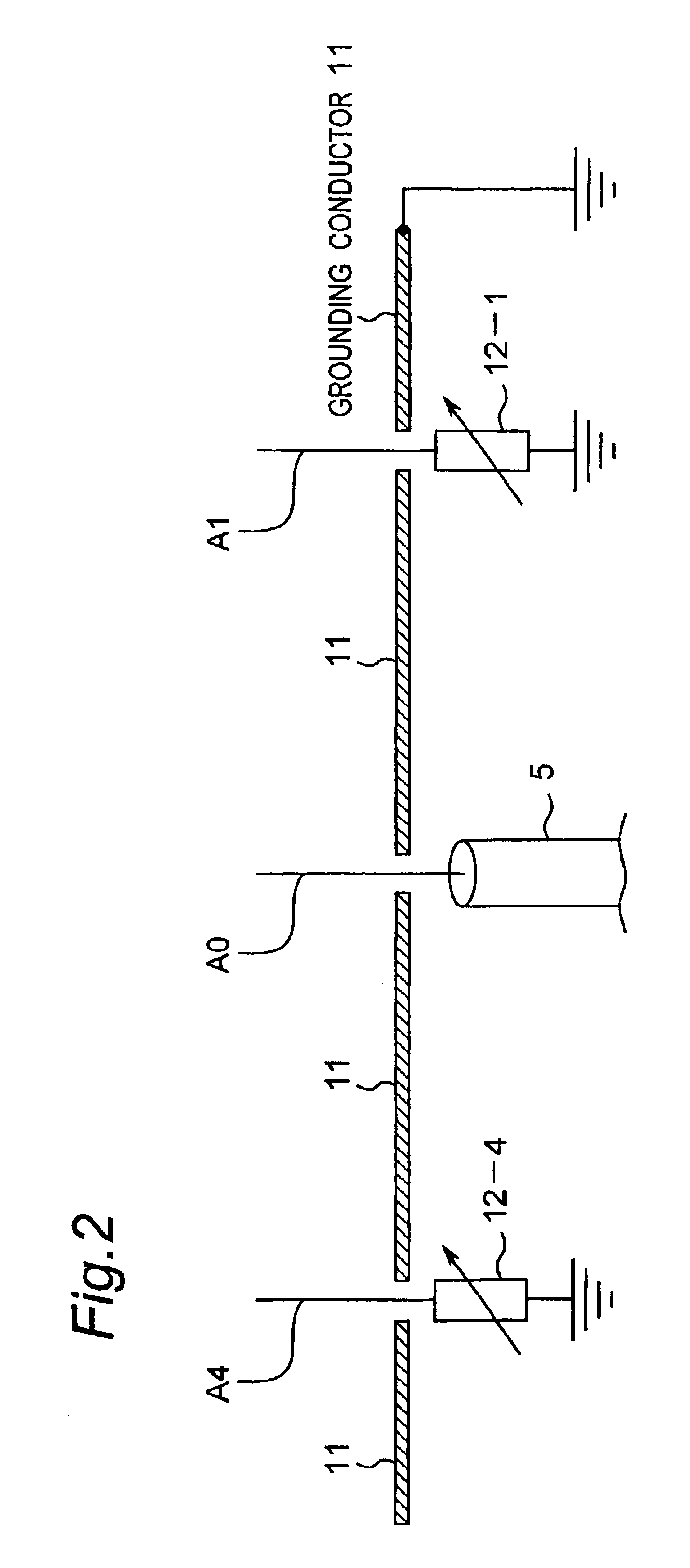
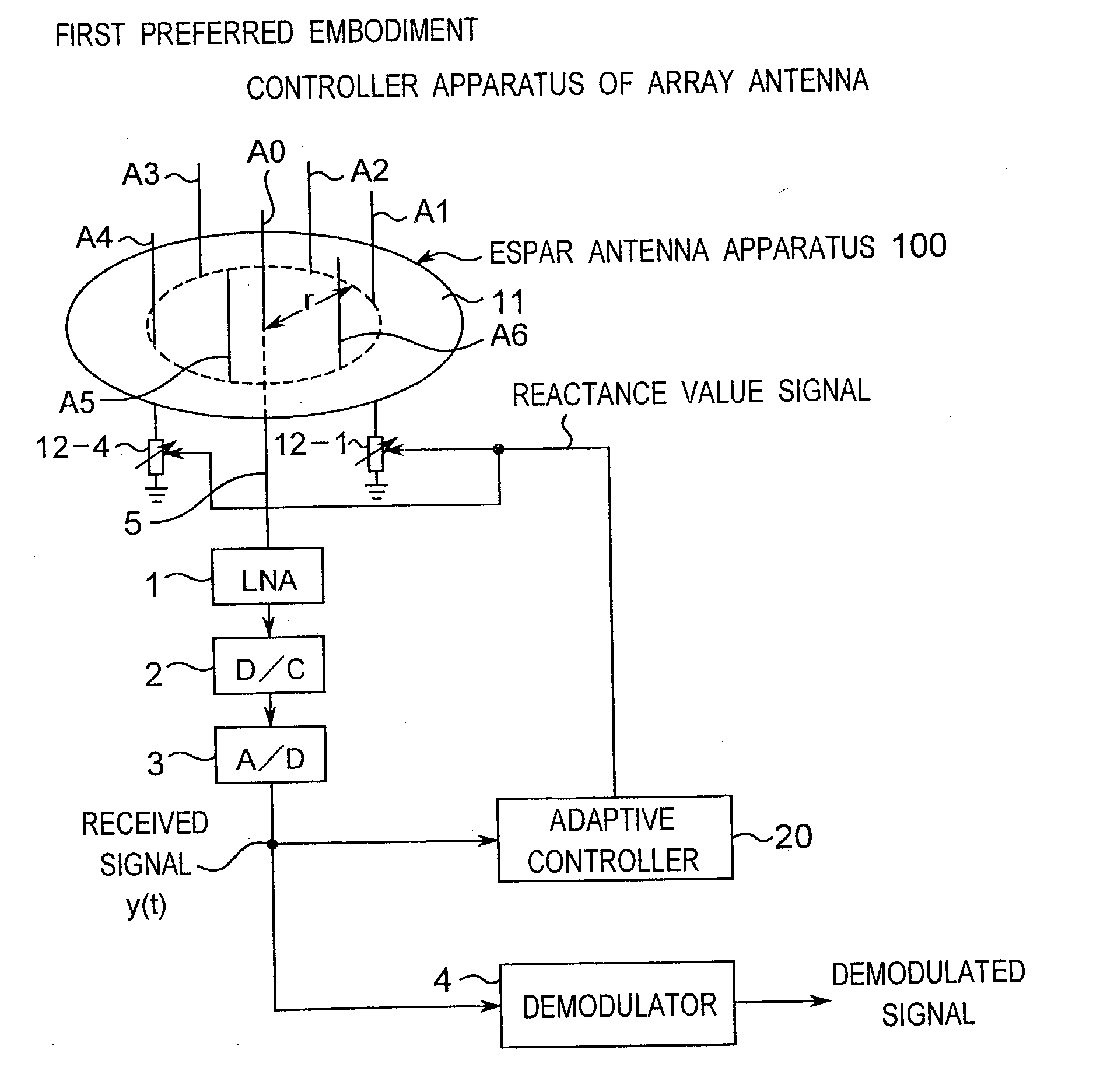
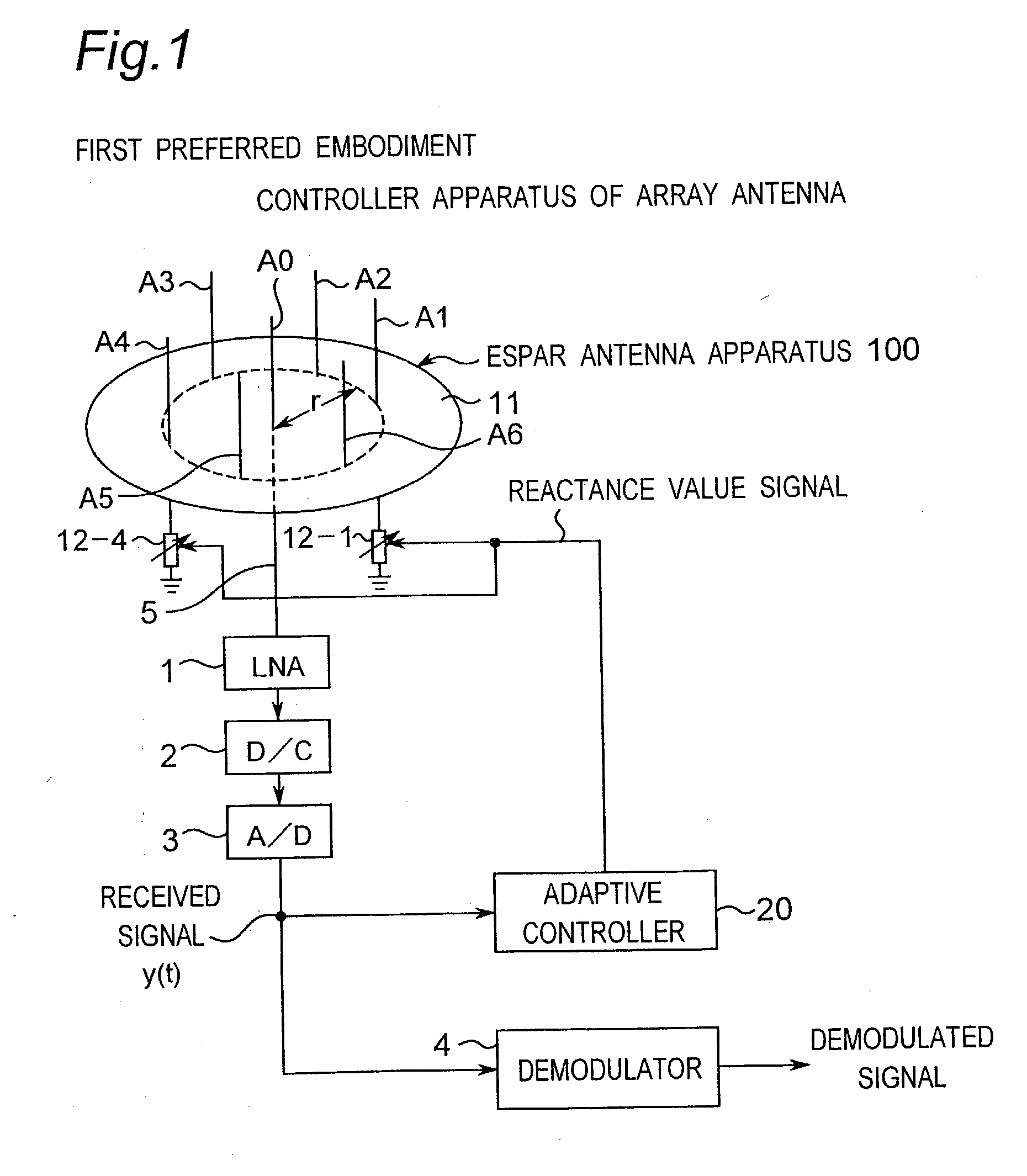
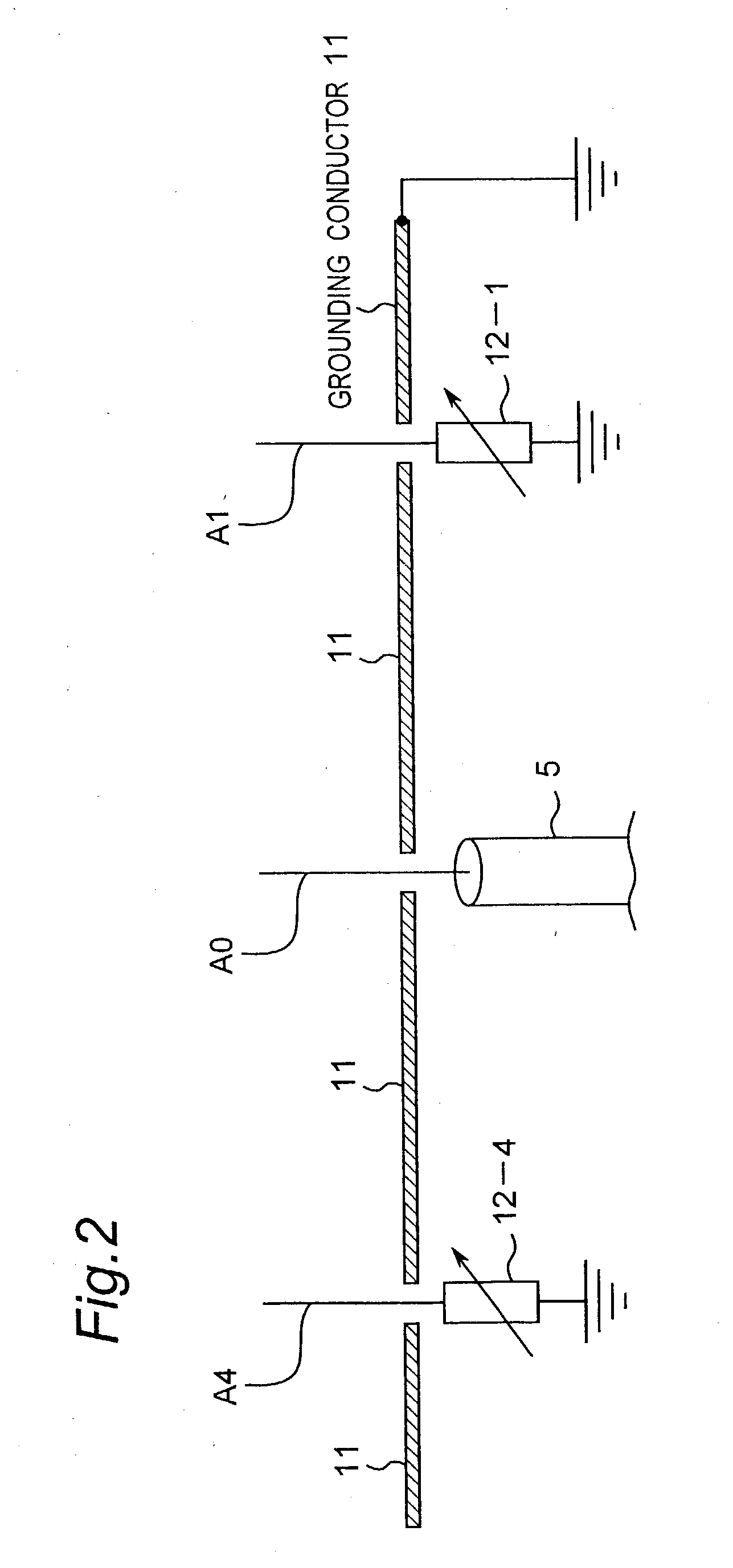
Method for controlling array antenna equipped with a plurality of antenna elements, method for calculating signal to noise ratio of received signal, and method for adaptively controlling radio receiver
InactiveUS7057573B2Radio wave direction/deviation determination systemsAmplitude-modulated pulse demodulationSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Radio reception
Based on a received signal y(t) received by a radiating element of an array antenna including the single radiating element and a plurality of parasitic elements, an adaptive controller calculates and sets a reactance value of a variable reactance element for directing a main beam of the array antenna in a direction of a desired wave and directing nulls in directions of interference waves so that a value of an objective function expressed by only the received signal y(t) becomes either one of the maximum and the minimum by using an iterative numerical solution of a nonlinear programming method.
Owner:ATR ADVANCED TELECOMM RES INST INT
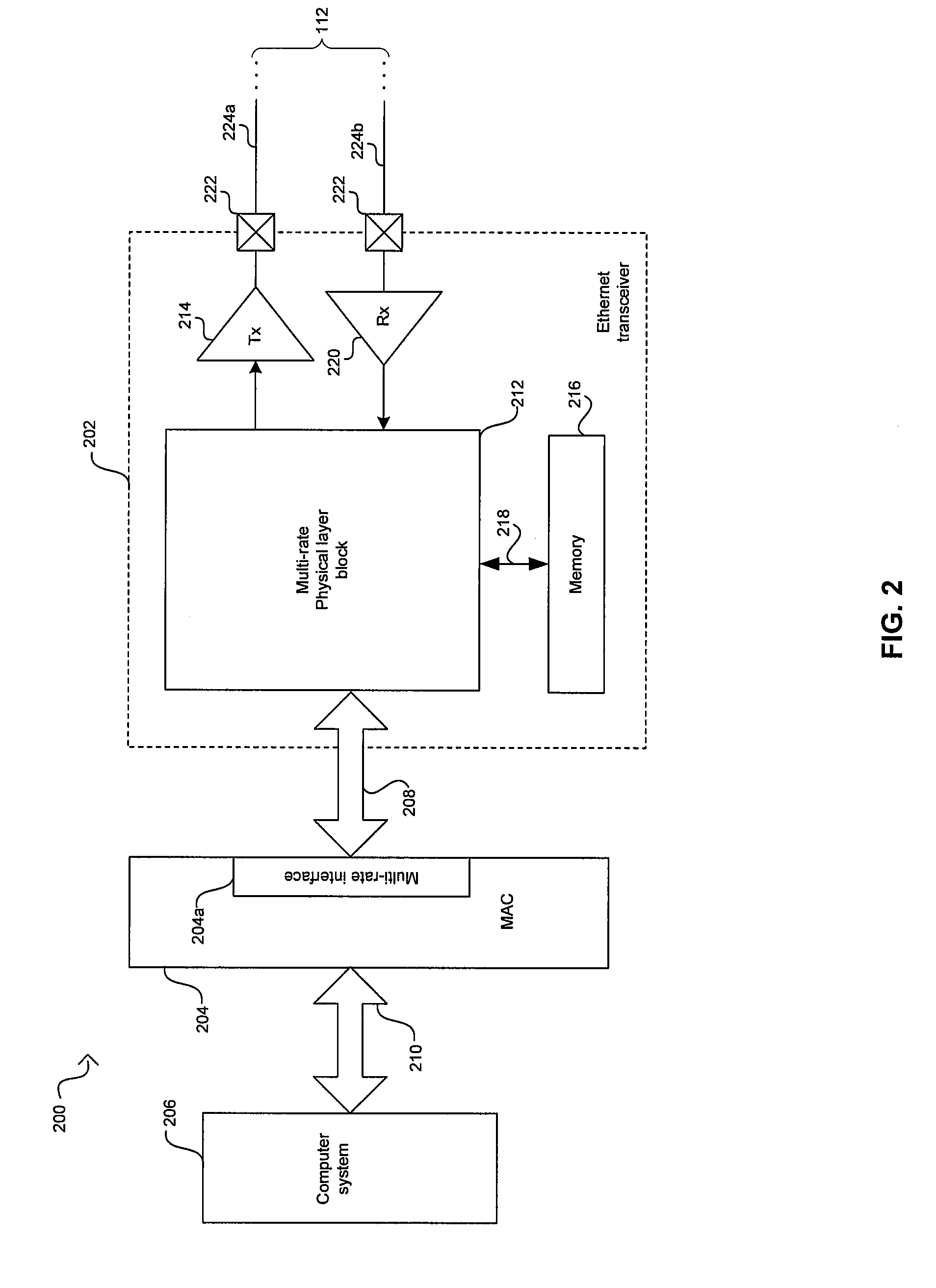
Method and system for low power idle signal transmission in ethernet networks
ActiveUS20080225841A1Reduce power consumptionEnergy efficient ICTError preventionNetwork linkSymbol rate
Aspects of a method and system for low power IDLE signal transmission in Ethernet networks are provided. In this regard, during time periods between transmissions of actual data by a local Ethernet link partner, the local Ethernet Link partner may generate one or more signals, in place of a standard Ethernet IDLE signal, that enable synchronization between Ethernet link partners. In this manner, the generated signals may enable reducing power consumption as compared to standard Ethernet IDLE signals. Accordingly, link activity may be monitored to enable detecting periods when there may be no actual data for transmission and the generated signals may be transmitted. The generated signals may be transmitted at a reduced symbol rate as compared to standard Ethernet IDLE signals. The generated signals may be transmitted via fewer network links as compared to standard Ethernet IDLE signals.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
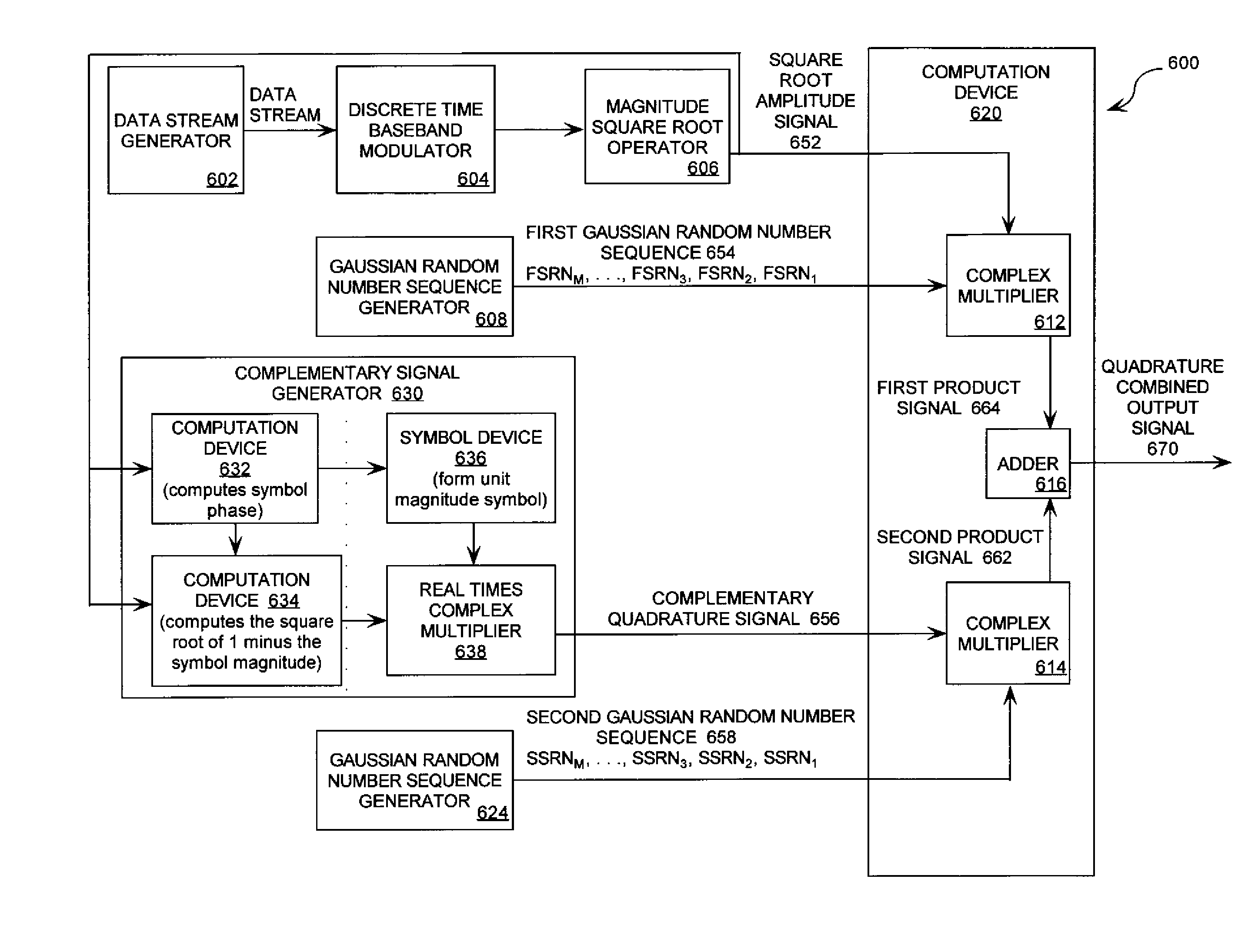
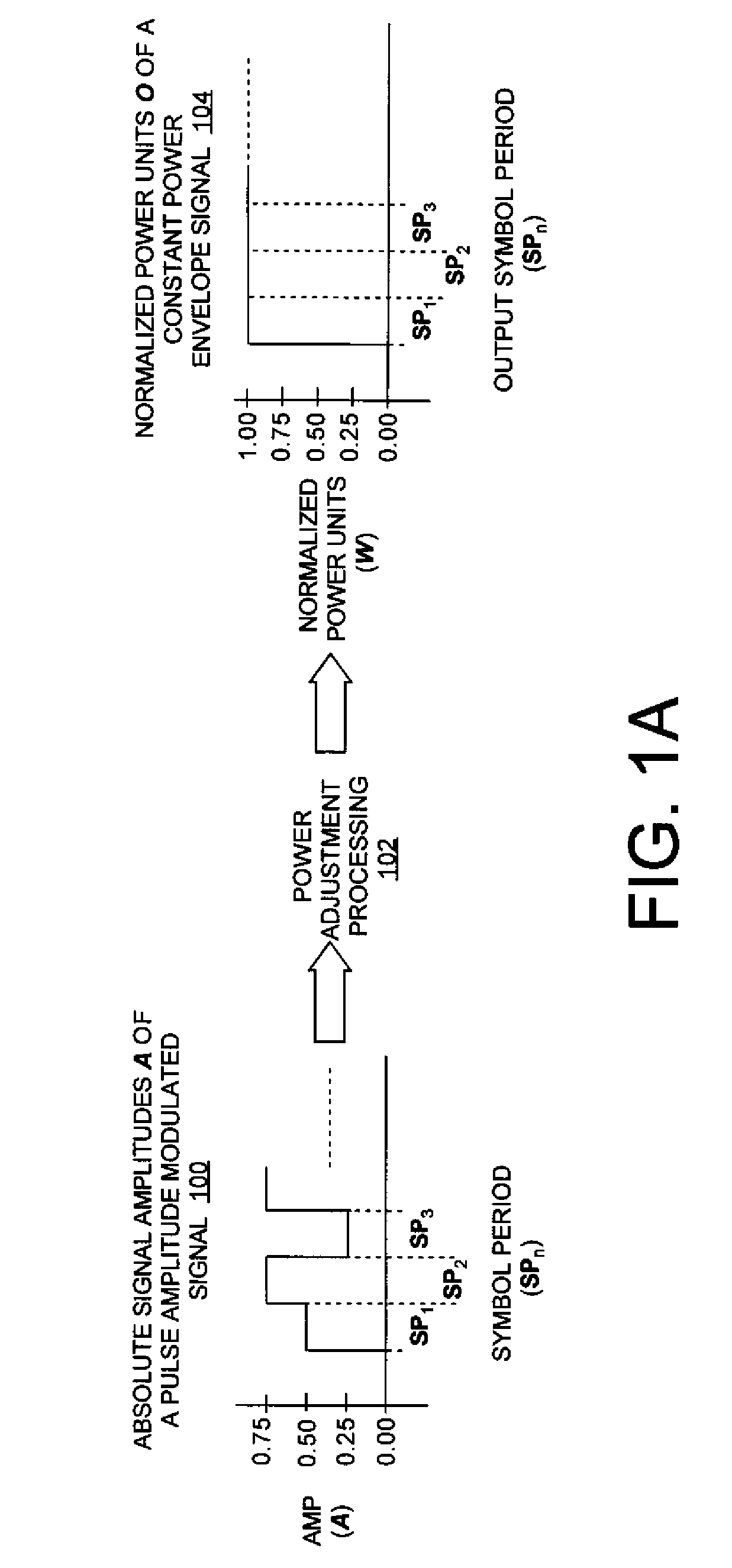
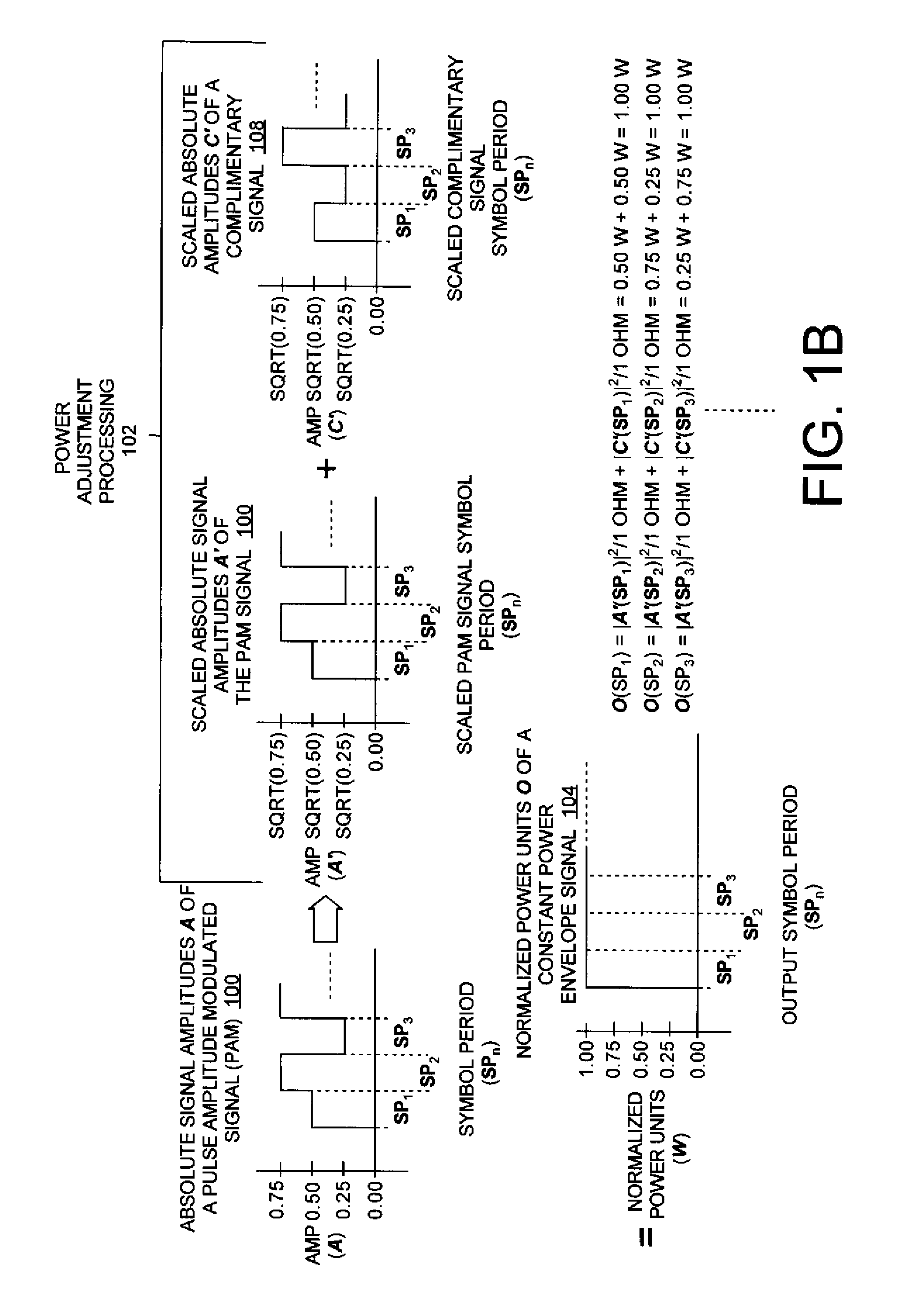
Featureless coherent chaotic amplitude modulation
ActiveUS20090310650A1Time-division multiplexAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsConstant powerPulse-code modulation
Systems (400, 500, 600) and methods (300) for generating a chaotic amplitude modulated signal absent of cyclostationary features by preserving a constant variance. The methods involve: generating a PAM signal including pulse amplitude modulation having a periodically changing amplitude; generating a first part of a constant power envelope signal (FPCPES) by dividing the PAM signal by a square root of a magnitude of the PAM signal; generating a second part of the constant power envelope signal (SPCPES) having a magnitude equal to a square root of one minus the magnitude of the PAM signal; and generating first and second spreading sequences (FSS and SSS). The methods also involve combining the FPCPES with the FSS to generate a first product signal (FPS) and combining the SPCPES with the SSS to generate a second product signal (SPS). A constant power envelope signal is generated using the FPS and SPS.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
Transparent multi-mode PAM interface
ActiveUS20050089126A1Amplitude-modulated carrier systemsAmplitude-modulated pulse demodulationState variationData rate
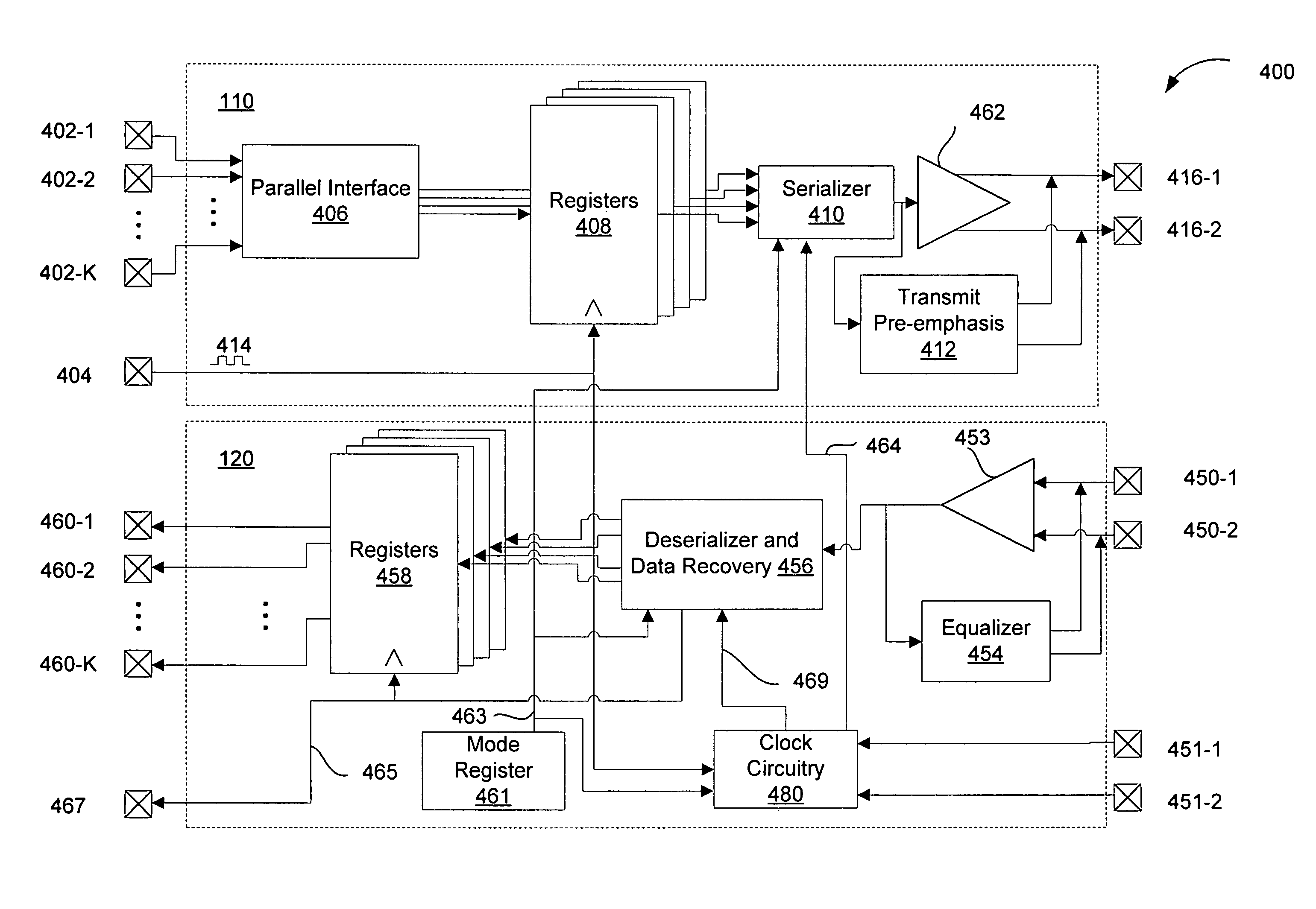
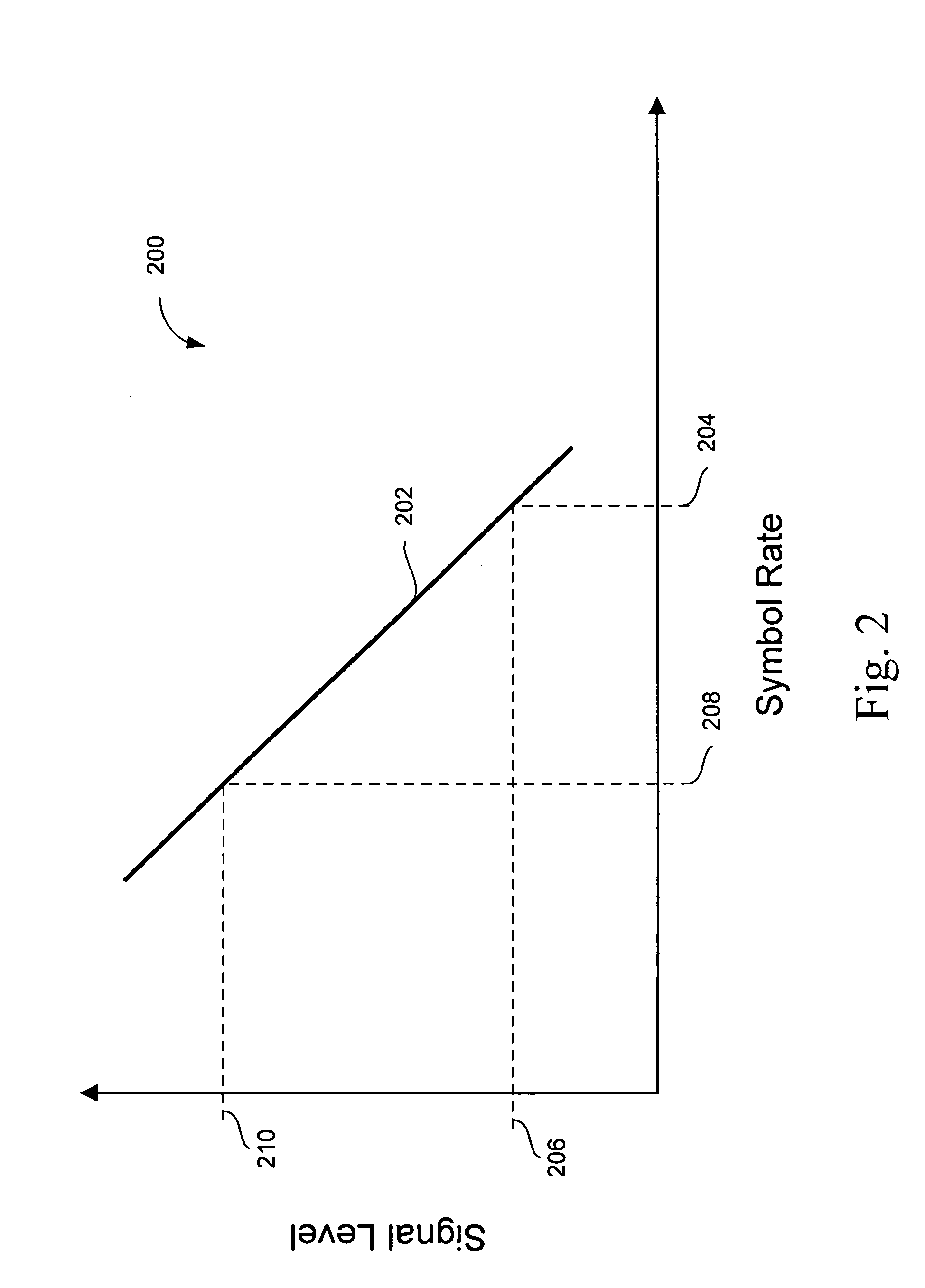
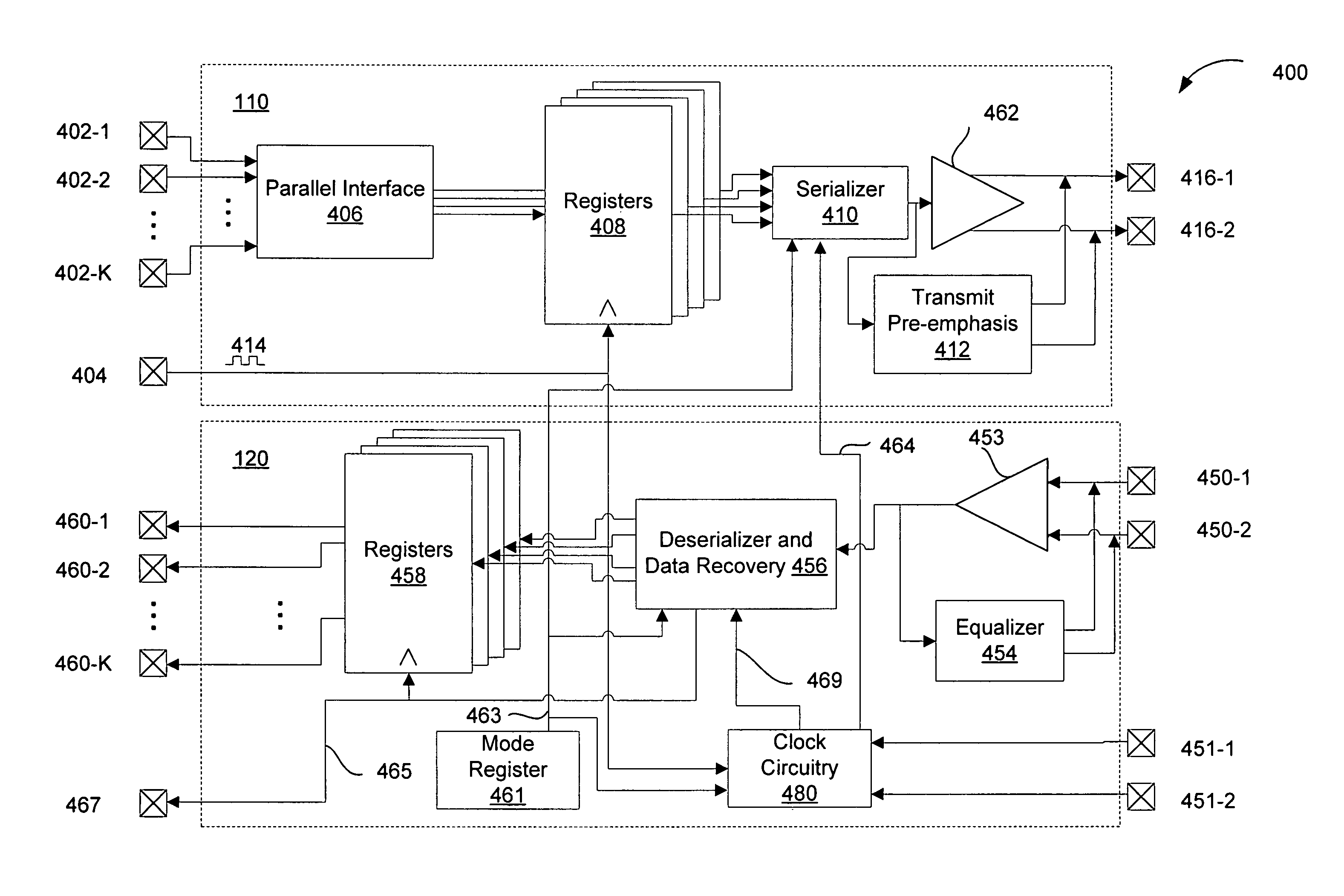
Provided are a method and apparatus for high-speed, multi-mode PAM symbol transmission. A multi-mode PAM output driver drives one or more symbols, the number of levels used in the PAM modulation of the one or more symbols depending on the state of a PAM mode signal. Additionally, the one or more symbols are driven at a symbol rate, the symbol rate selected in accordance with the PAM mode signal so that a data rate of the driven symbols in constant with respect to changes in the state of the PAM mode signal. Further provided are methods for determining the optimal number of PAM levels for symbol transmission and reception in a given physical environment.
Owner:RAMBUS INC
Transparent multi-mode PAM interface
ActiveUS7308058B2Amplitude-modulated carrier systemsAmplitude-modulated pulse demodulationData rateEngineering
Provided are a method and apparatus for high-speed, multi-mode PAM symbol transmission. A multi-mode PAM output driver drives one or more symbols, the number of levels used in the PAM modulation of the one or more symbols depending on the state of a PAM mode signal. Additionally, the one or more symbols are driven at a symbol rate, the symbol rate selected in accordance with the PAM mode signal so that a data rate of the driven symbols is constant with respect to changes in the state of the PAM mode signal. Further provided are methods for determining the optimal number of PAM levels for symbol transmission and reception in a given physical environment.
Owner:RAMBUS INC
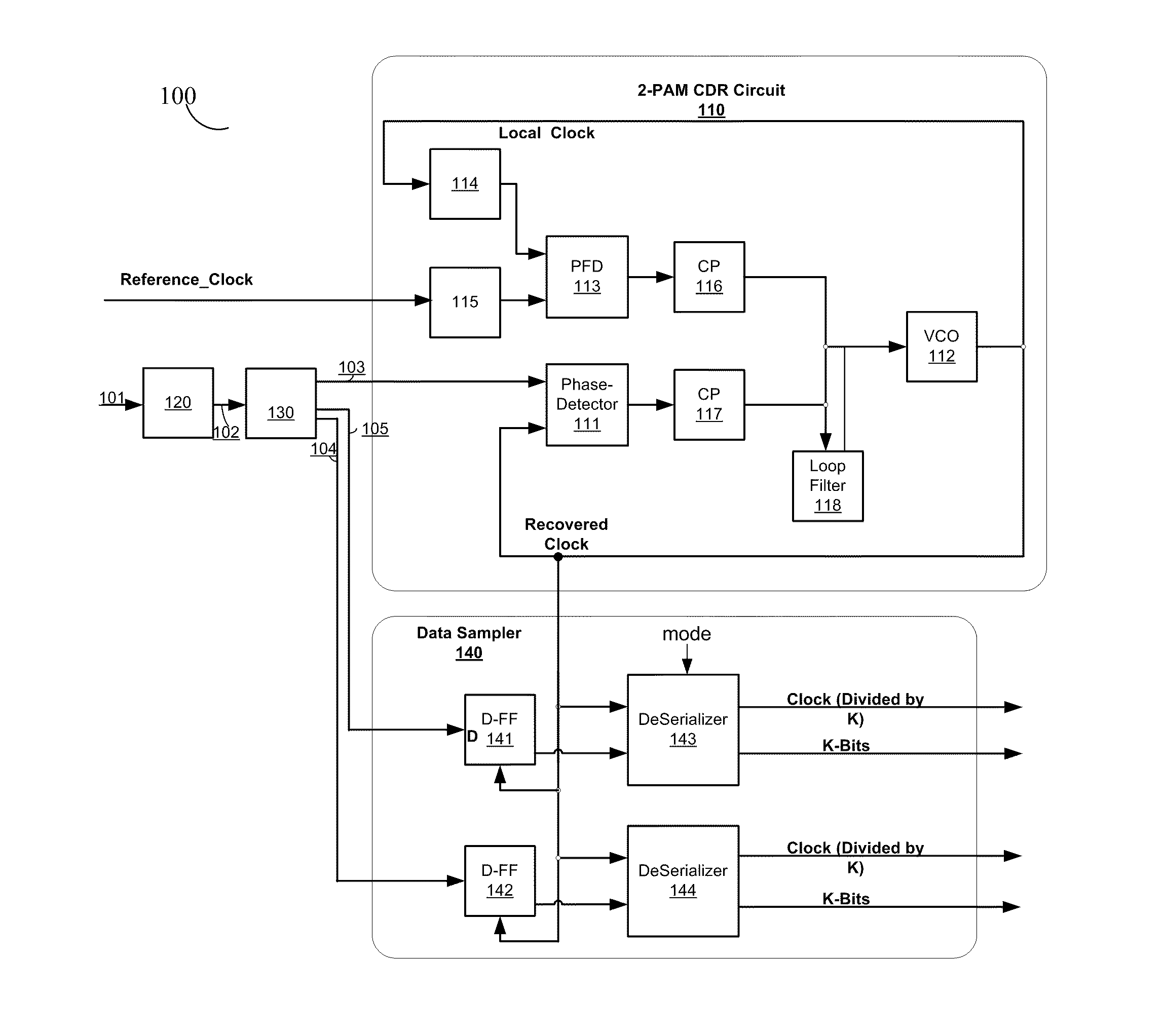
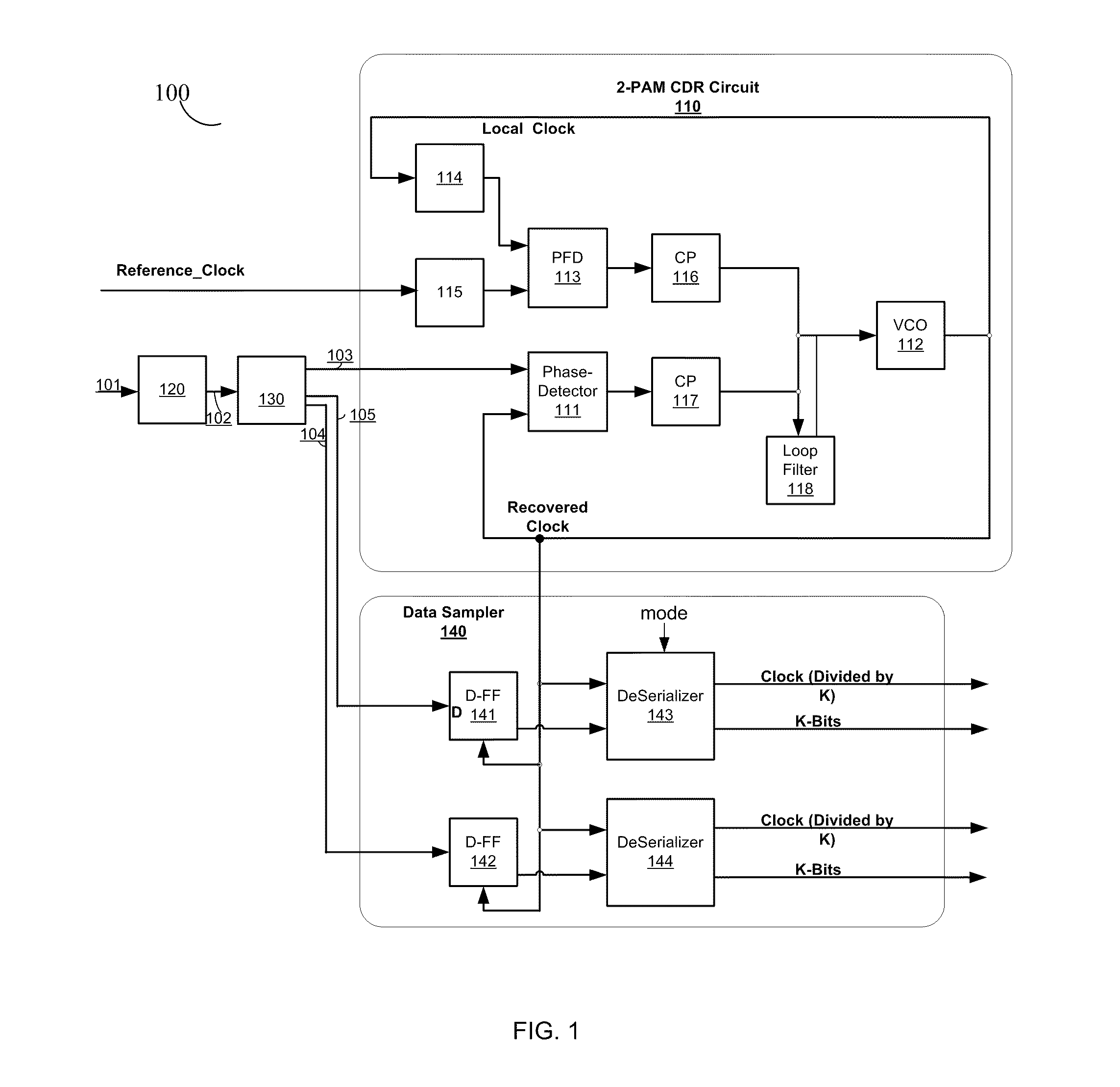
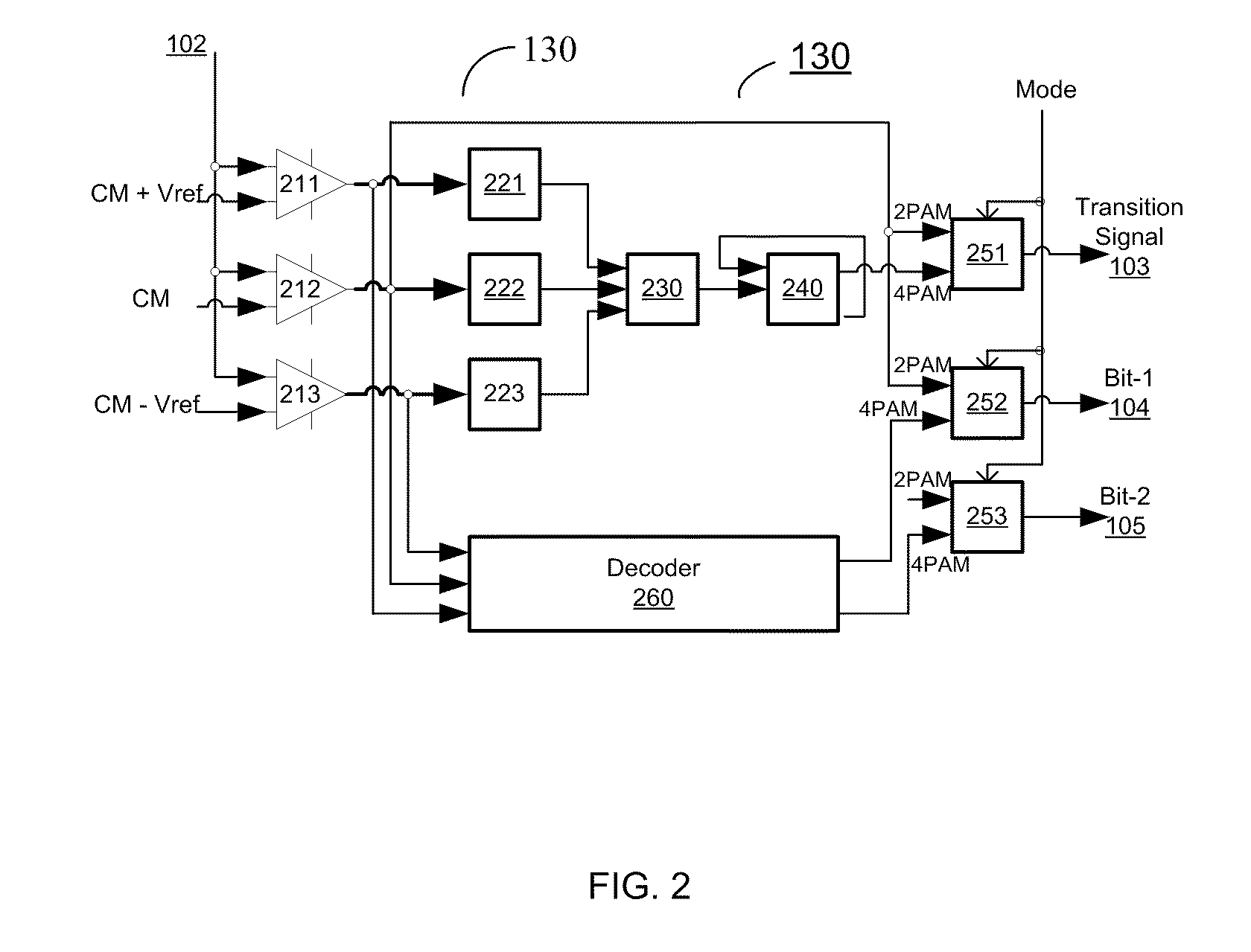
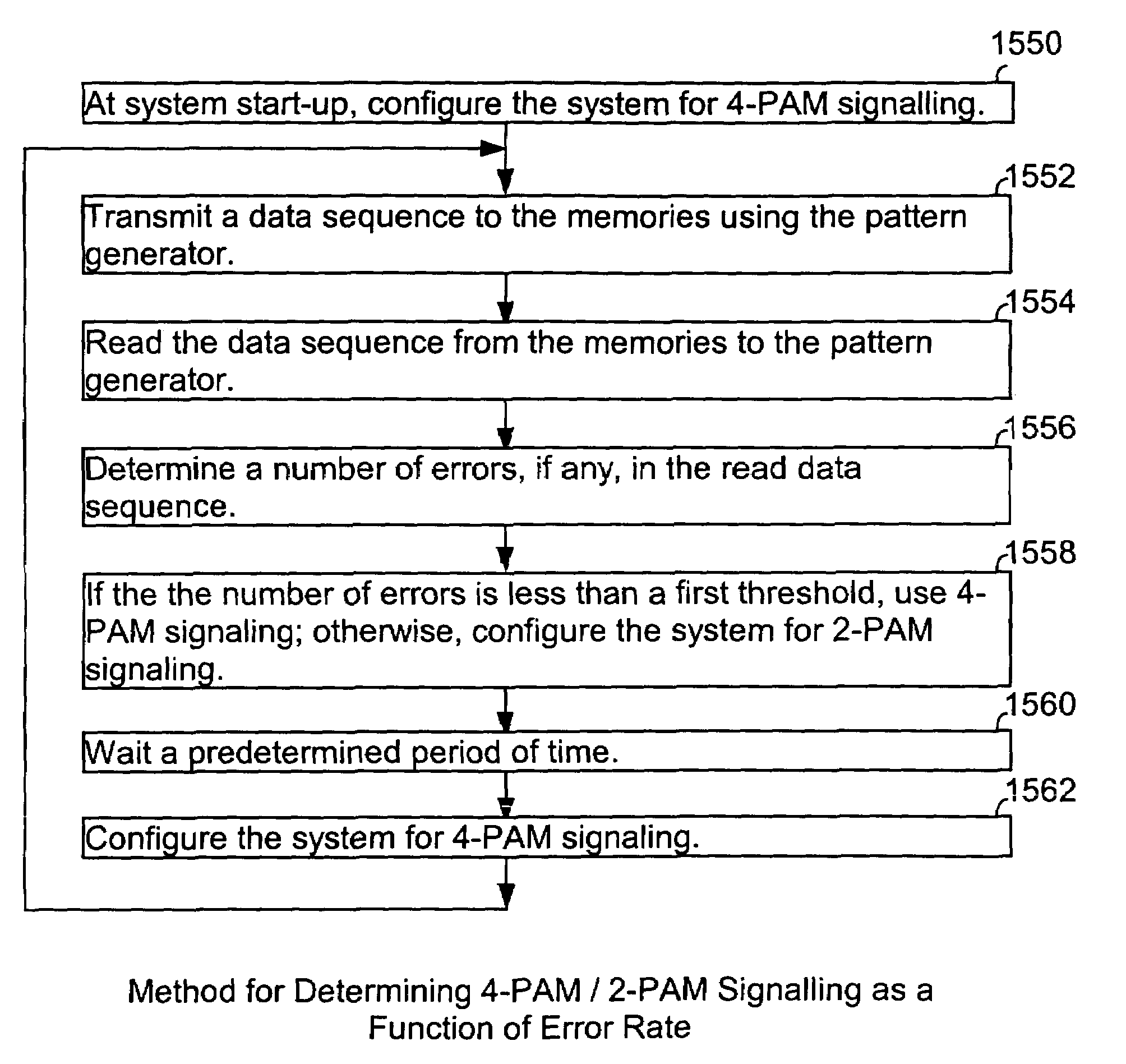
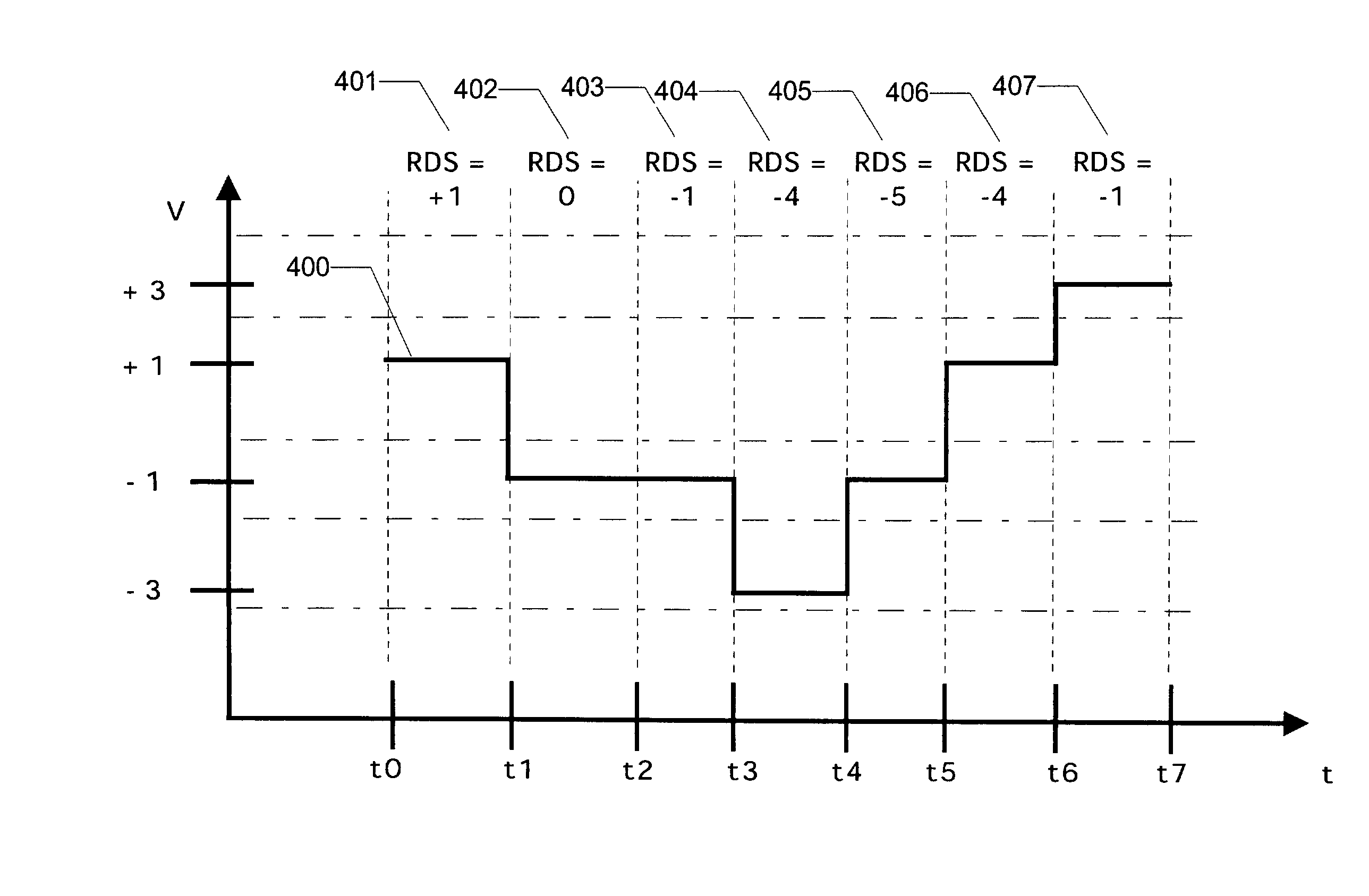
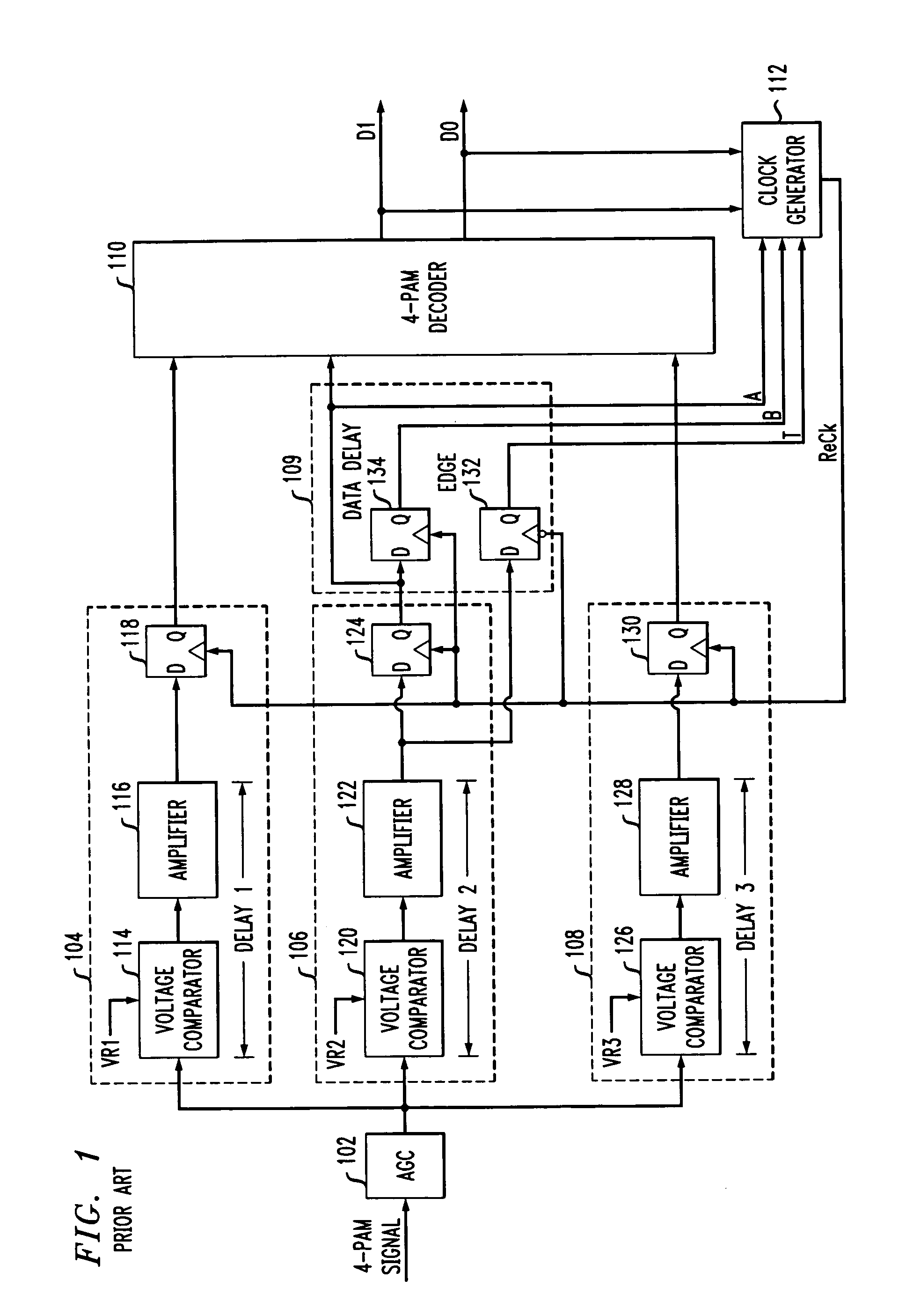
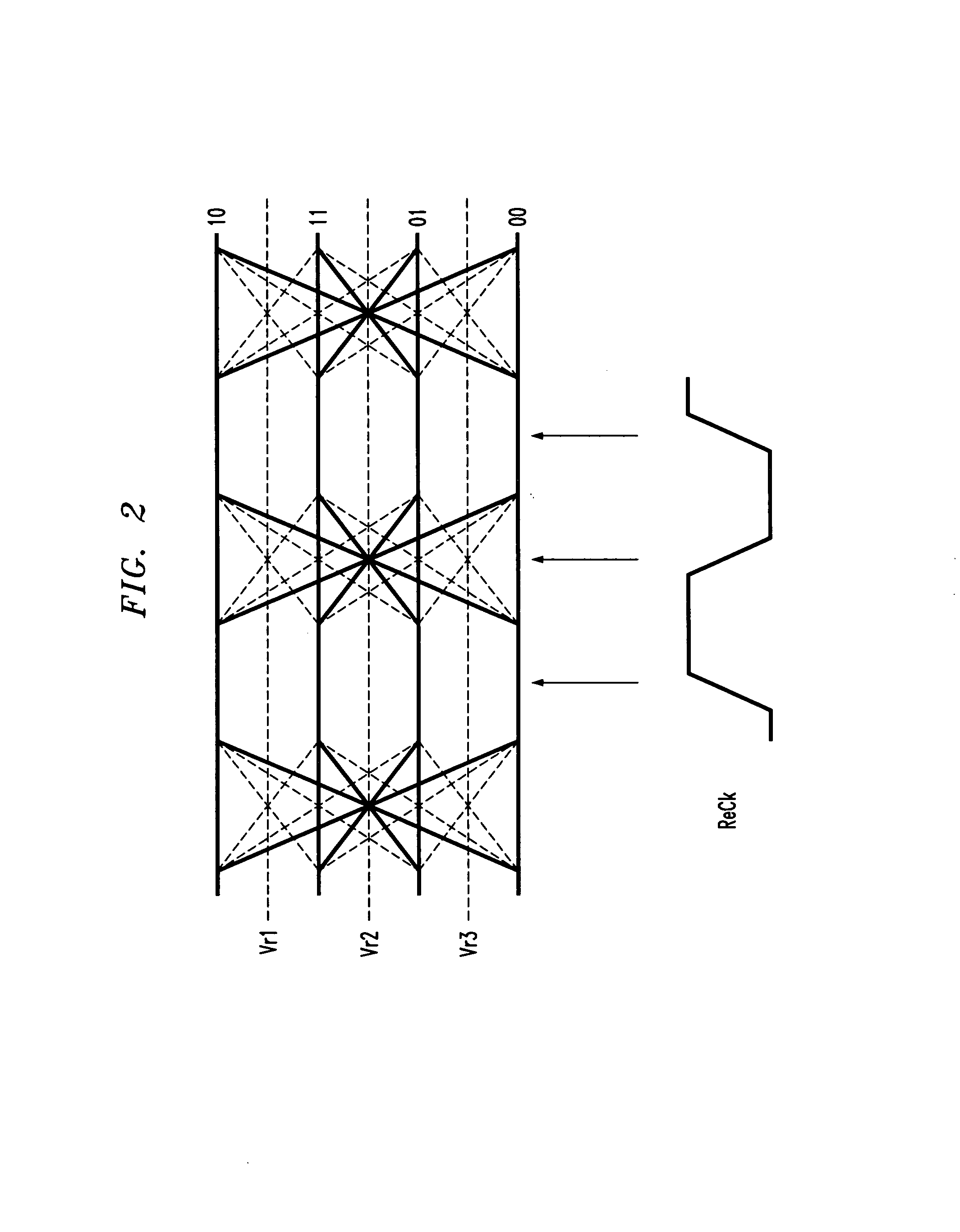
Apparatus and method thereof for clock and data recovery of n-PAM encoded signals using a conventional 2-PAM CDR circuit
An interface circuit for enabling clock and data recovery (CDR) of N-level pulse amplitude modulation (N-PAM) modulated data streams using a 2-PAM CDR circuit. The circuit comprises a number of N−1 comparators for comparing an input data stream to N−1 configurable thresholds, the input data stream is N-PAM modulated and the N−1 configurable thresholds are N−1 different voltage levels; a number of N−1 of edge detectors respectively connected to the N−1 comparators for detecting transitions from one logic value to another logic value, N is a discrete number greater than two; and a determination unit for determining if the detected transitions is any one of a major transition and a minor transition and asserting a transition signal if only a major transition or a minor transition has occurred, the transition signal is fed into a 2-PAM CDR circuit and utilized for recovering a clock signal of the input data stream.
Owner:CADENCE DESIGN SYST INC
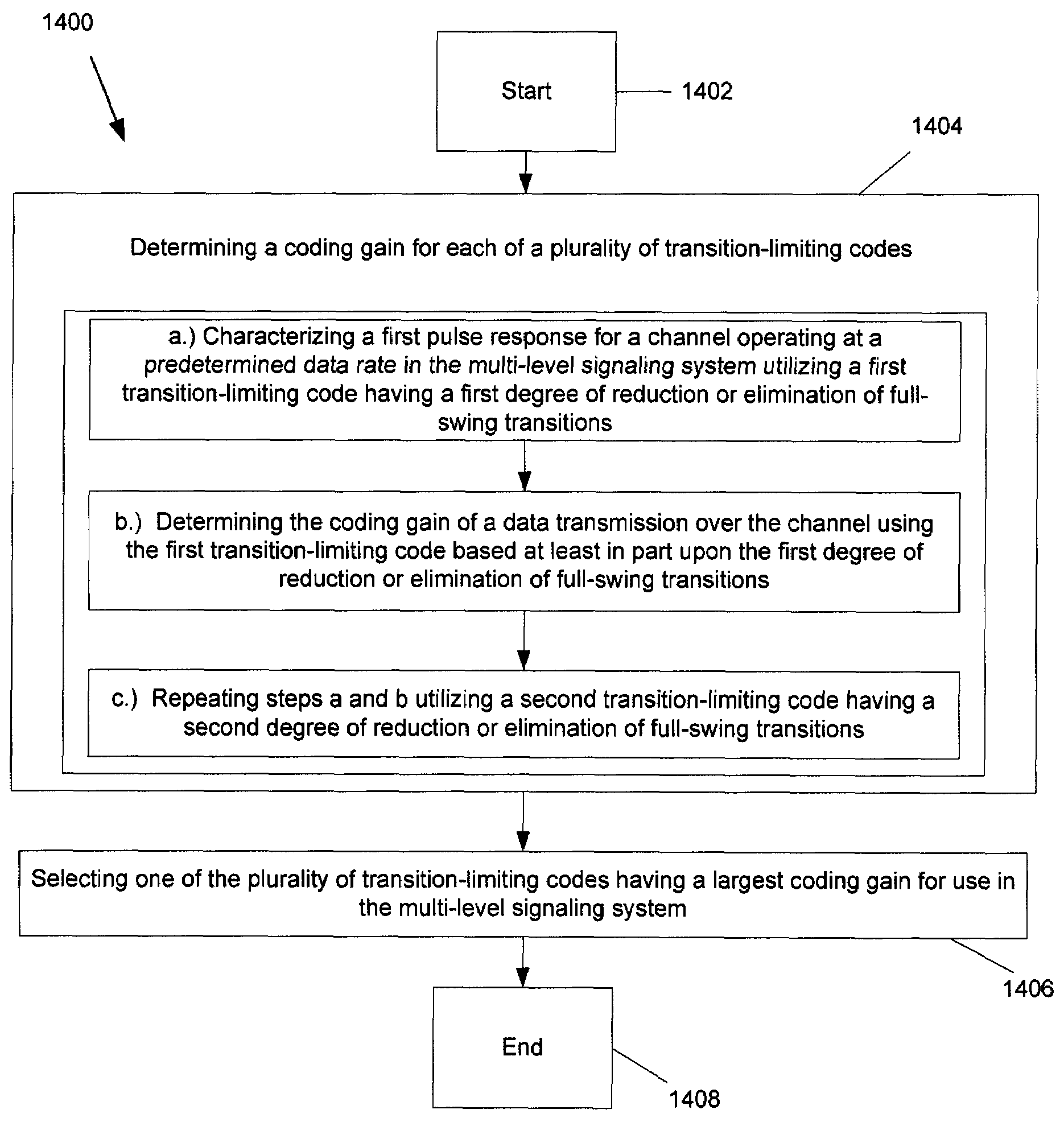
Technique for determining an optimal transition-limiting code for use in a multi-level signaling system
InactiveUS7620116B2Guaranteed maximum utilizationReduce eliminateModulated-carrier systemsIndividual digits conversionEngineeringSignaling system
A technique for determining an optimal transition-limiting code for use in a multi-level signaling system is disclosed. In one particular exemplary embodiment, the technique may be realized as a method for determining an optimal transition-limiting code for use in a multi-level signaling system. Such a method comprises determining a coding gain for each of a plurality of transition-limiting codes, and selecting one of the plurality of transition-limiting codes having a largest coding gain for use in the multi-level signaling system.
Owner:RAMBUS INC
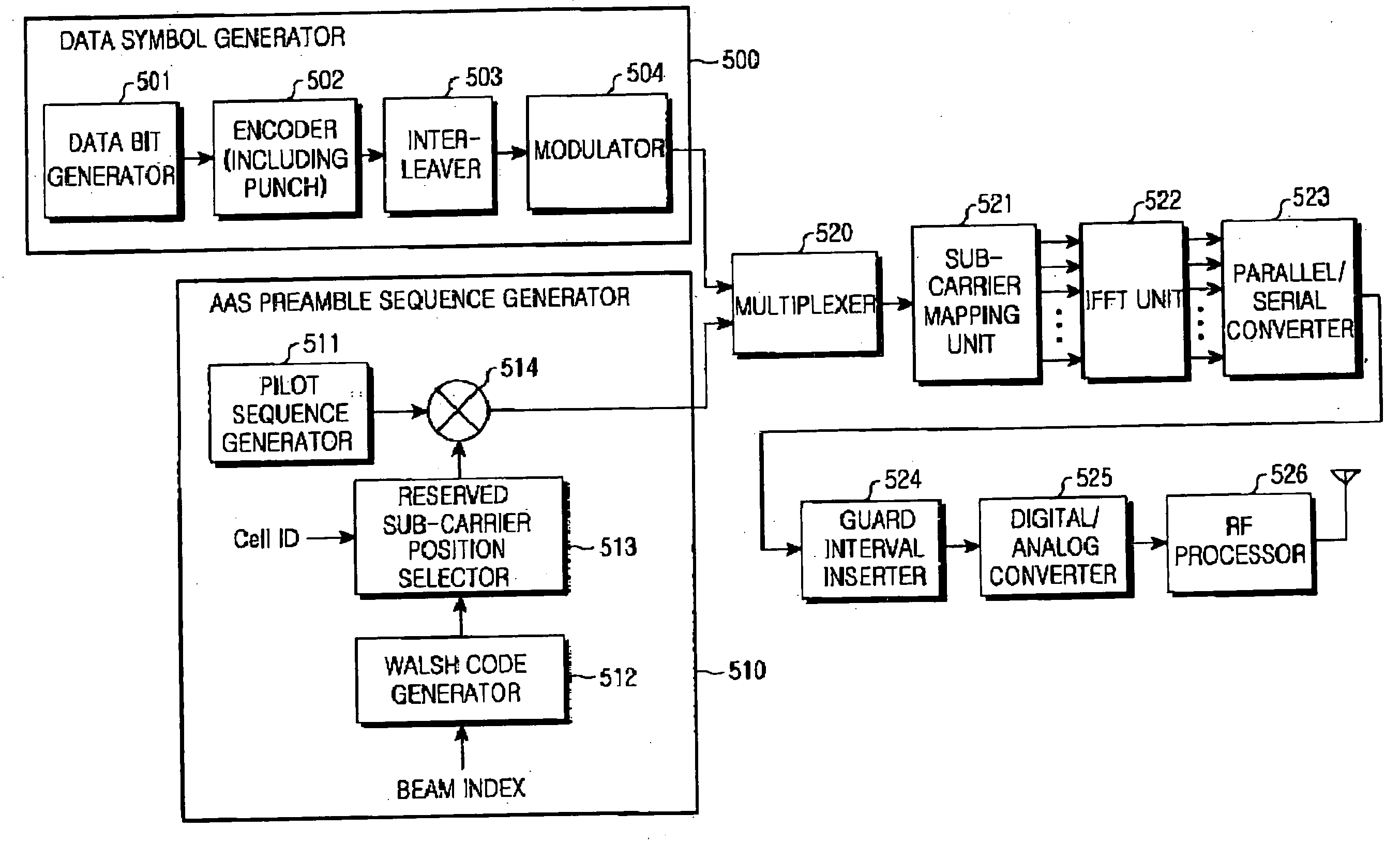
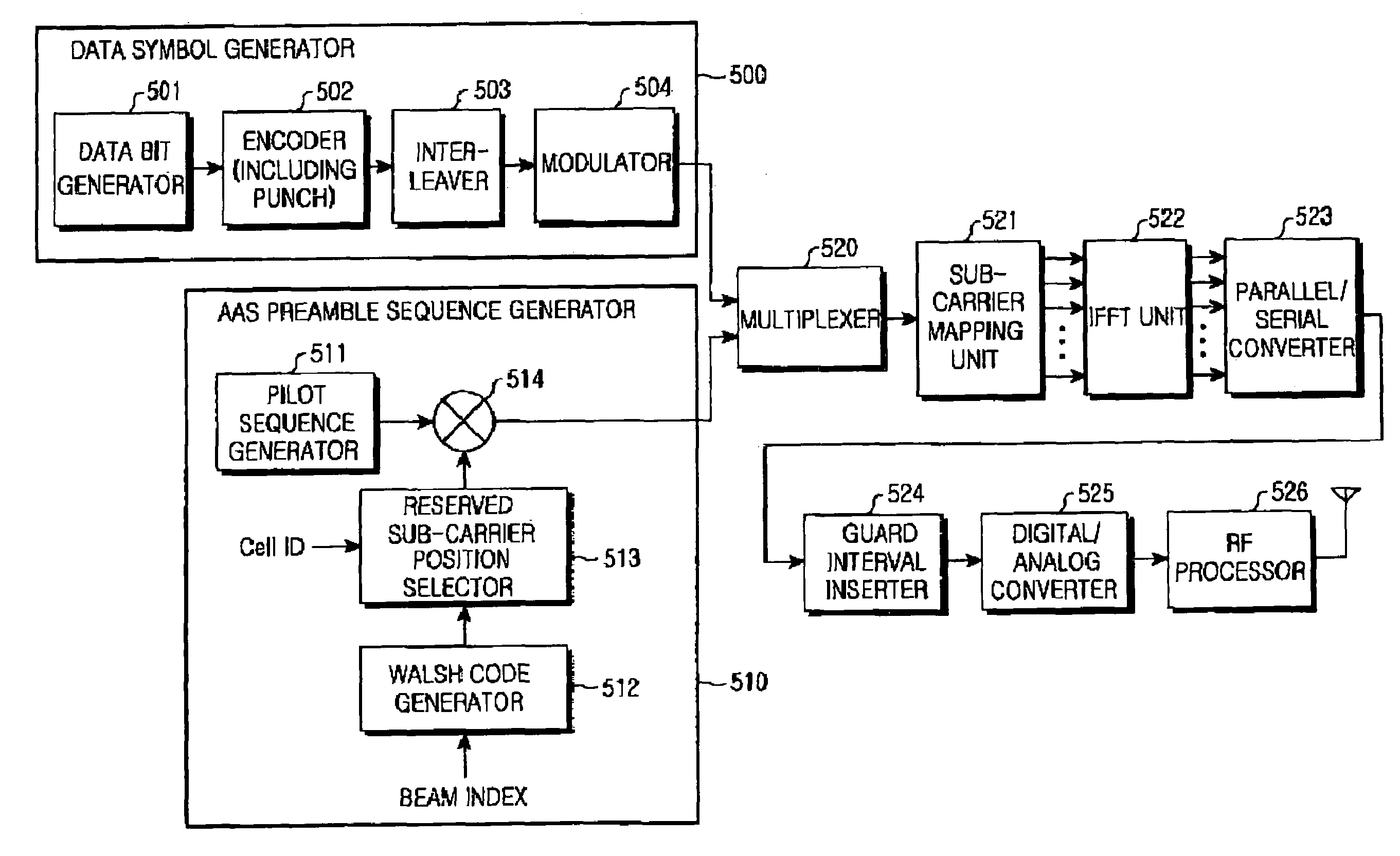
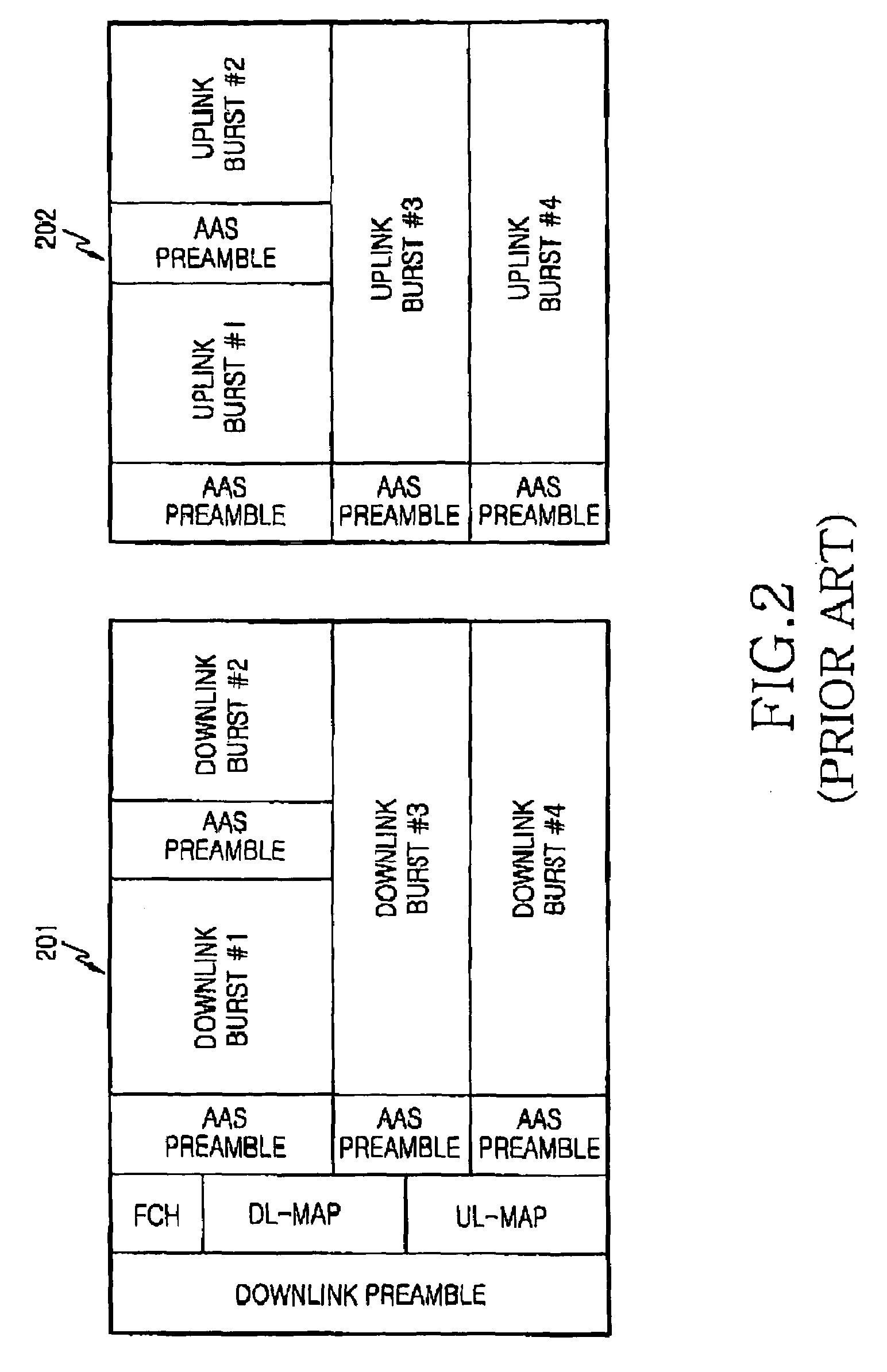
Method and apparatus for generating preamble sequence for adaptive antenna system in orthogonal frequency division multiple access communication system
ActiveUS20050243940A1Network traffic/resource managementCode division multiplexTelecommunicationsCommunications system
Disclosed is a method and an apparatus for generating a preamble sequence for an adaptive antenna system supporting a space division multiple access in an OFDMA communication system. Particularly, disclosed is a method for forming a preamble sequence identifying each of a plurality of mobile subscriber stations located within a cell or a sector of a communication system which includes a plurality of sub-channels assigned to the mobile subscriber stations, each of the sub-channels including a plurality of bins each of which includes n number of contiguous subcarriers in a frequency domain, the preamble sequence being transmitted before each of the sub-channels is transmitted, the method including the step of generating a preamble sequence by phase-shifting a predetermined sequence according to a predetermined phase shift sequence in the frequency domain.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
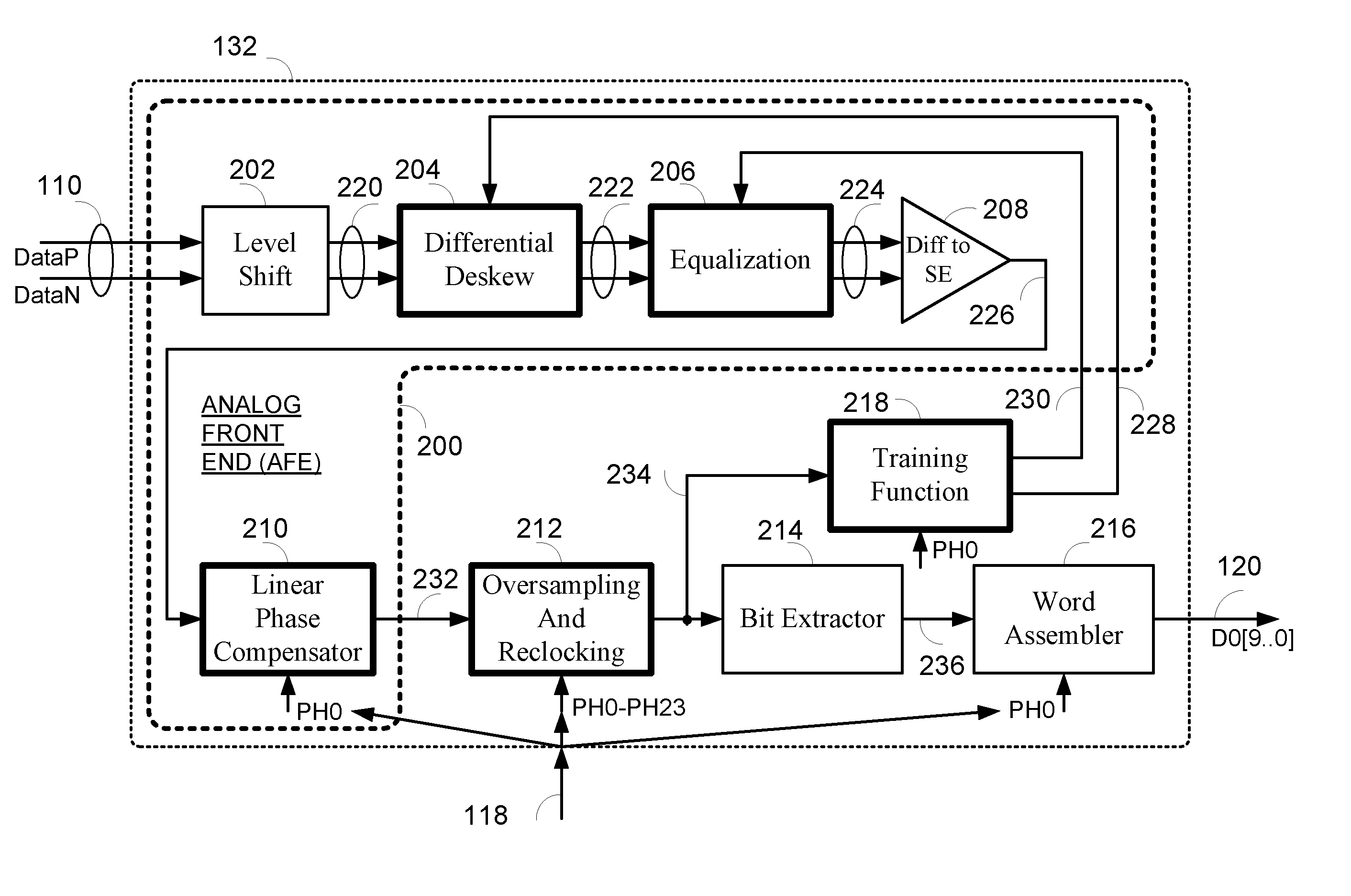
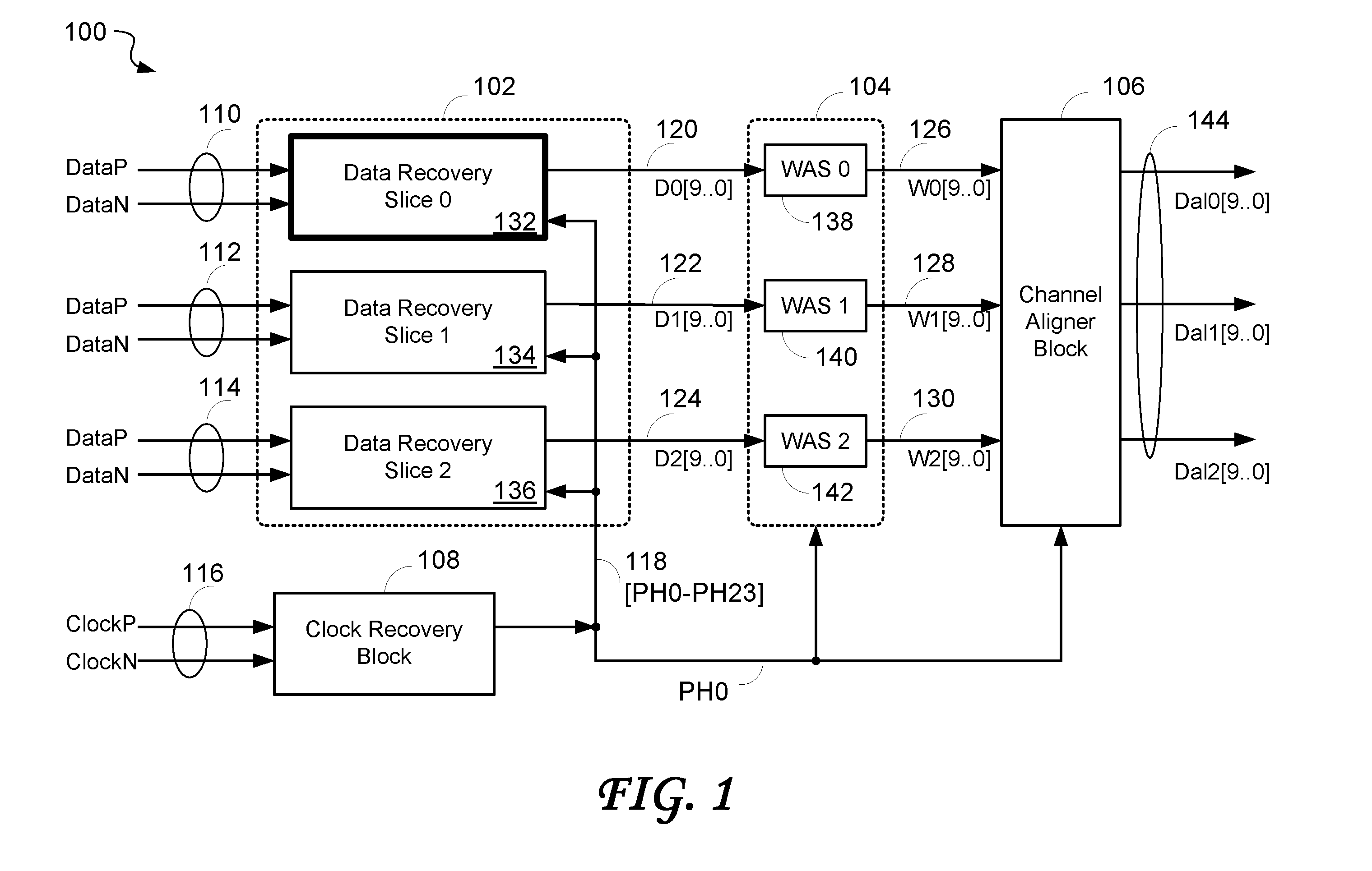
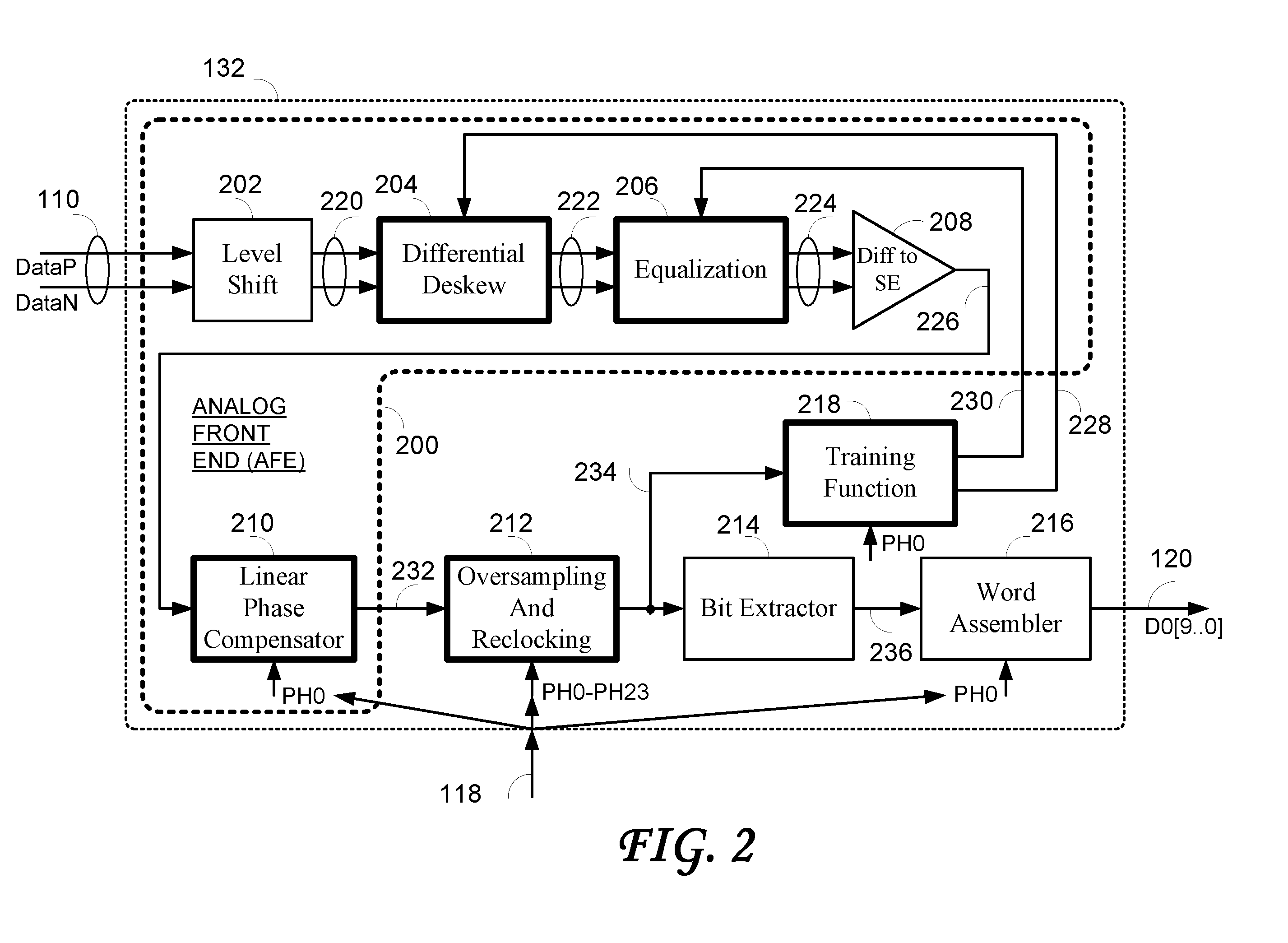
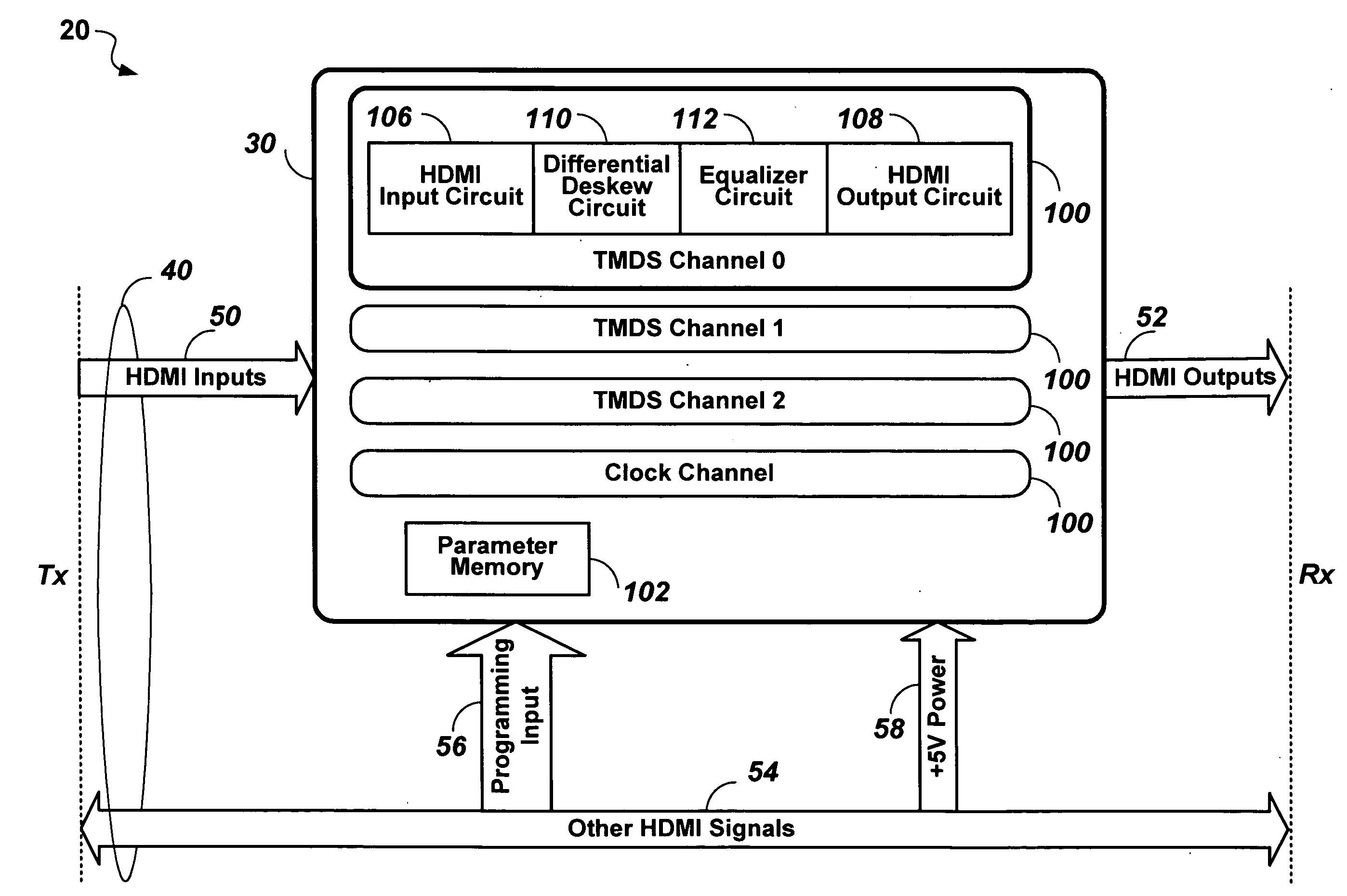
Data recovery system for source synchronous data channels
ActiveUS20070164802A1Easy Data RecoveryReduce distortion problemsModulated-carrier systemsPulse demodulator24-bitAnalog signal
A high-definition multimedia interface (HDMI) receiver recovers high speed encoded data which are transmitted differentially over data channels of a lossy cable, along with a clock. Inter symbol interference, high-frequency loss, skew between the clock and data channels, and differential skew within a differential signal are compensated by analog circuits which are automatically tuned for best performance by observing the quality of the recovered analog signal. Oversampling is used to provide a 24-bit digital representation of the analog signal for determining the quality of the signal. A corresponding method of deskewing a differential signal and a system and circuit therefor are also provided.
Owner:REDMERE TECH
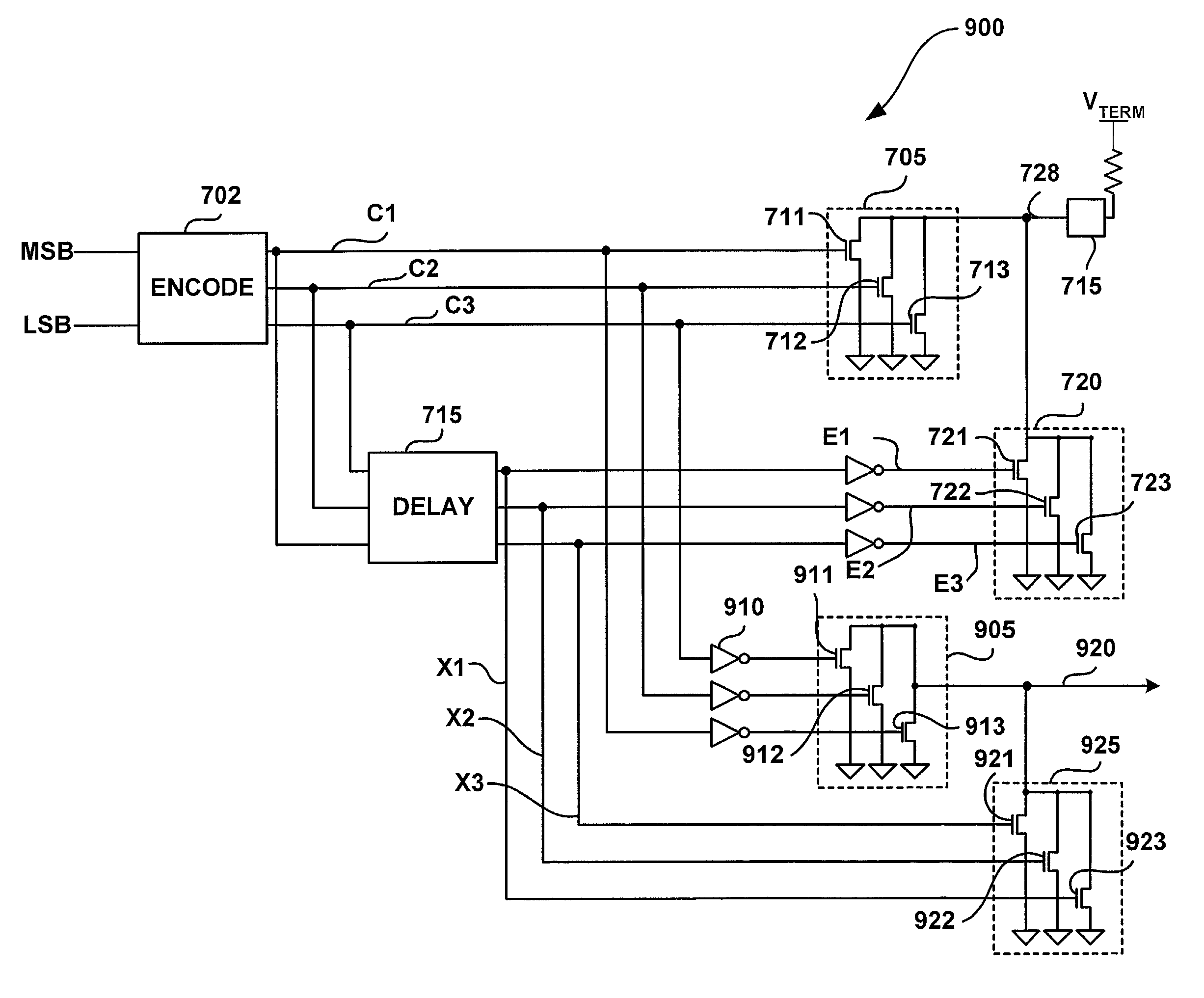
Low latency multi-level communication interface
InactiveUS7124221B1Reduce static power consumptionWide input common mode rangePulse modulation television signal transmissionElectric analogue storesCommunication interfaceLeast significant bit
A memory system uses multiple pulse amplitude modulation (multi-PAM) output drivers and receivers to send and receive multi-PAM sigsnals. A multi-PAM signal has more than two voltage levels, with each data interval now transmitting a “symbol” at one of the valid voltage levels. In one embodiment, a symbol represents two or more bits. The multi-PAM output driver drives an output symbol onto a signal line. The output symbol represents at least two bits that include a most significant bit (MSB) and a least significant bit (LSB). The multi-PAM receiver receives the output symbol from the signal line and determines the MSB and the LSB.
Owner:RAMBUS INC
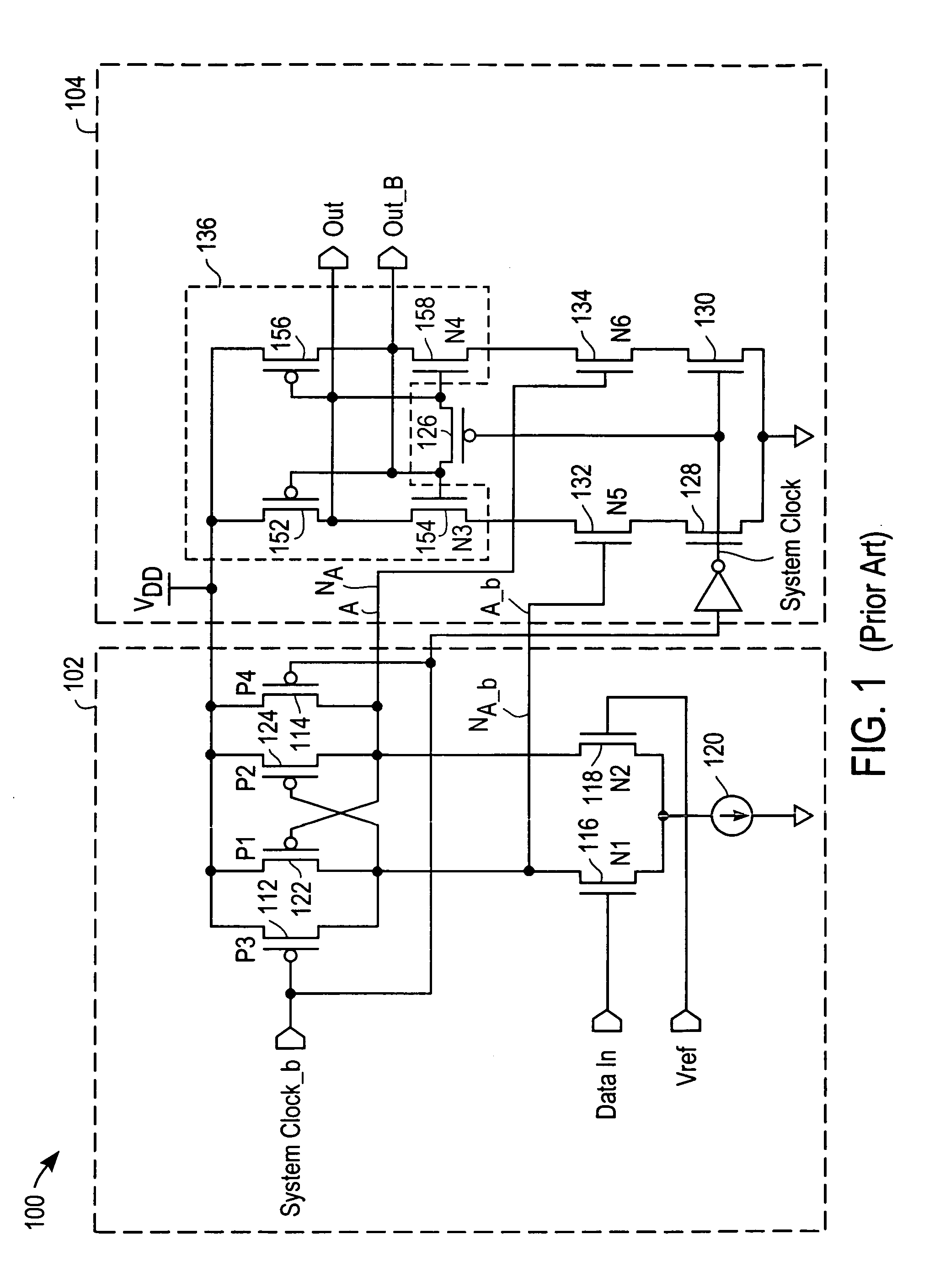
Method and system for a generation of a two-level signal
InactiveUS6975177B2Improve linearityImprove power efficiencyModulation with suppressed carrierFrequency/rate-modulated pulse demodulationAudio power amplifierControl signal
In a modulation system, in order to provide a two-level signal with a desired modulation which is suited to be amplified by a switching mode power amplifier, the modulation system may include a first constant envelope modulator modulating a signal according to a first control signal, a second constant envelope modulator modulating a signal according to a second control signal, and a combining portion combining the output signal of the first and said second constant envelope modulator to a single, two-level pulse-width-modulated signal. The information which is to be represented by the modulation of the single, two-level pulse-width-modulated signal is coded in the first and the second control signals. The invention relates equally to a corresponding method for generating a modulated signal.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Method and apparatus for encoding and decoding digital communications data
ActiveUS7260155B2Improve robustnessEliminate and minimize and reduce and limit transitionCross-talk reductionAmplitude-modulated pulse demodulationEngineeringSlew rate
In one aspect, the present invention is a system and technique that provides for the systematic development or implementation of codes that increase the robustness of systems employing, for example, PAM-n transmission techniques. The system and technique of this aspect of the invention eliminate, minimize, reduce or limit transitions between extreme signaling levels. As a result, the slew rate employed and / or required by the transmitter may reduce crosstalk and intersymbol interference, and provide for wider “eye” openings from the perspective of the receiver.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
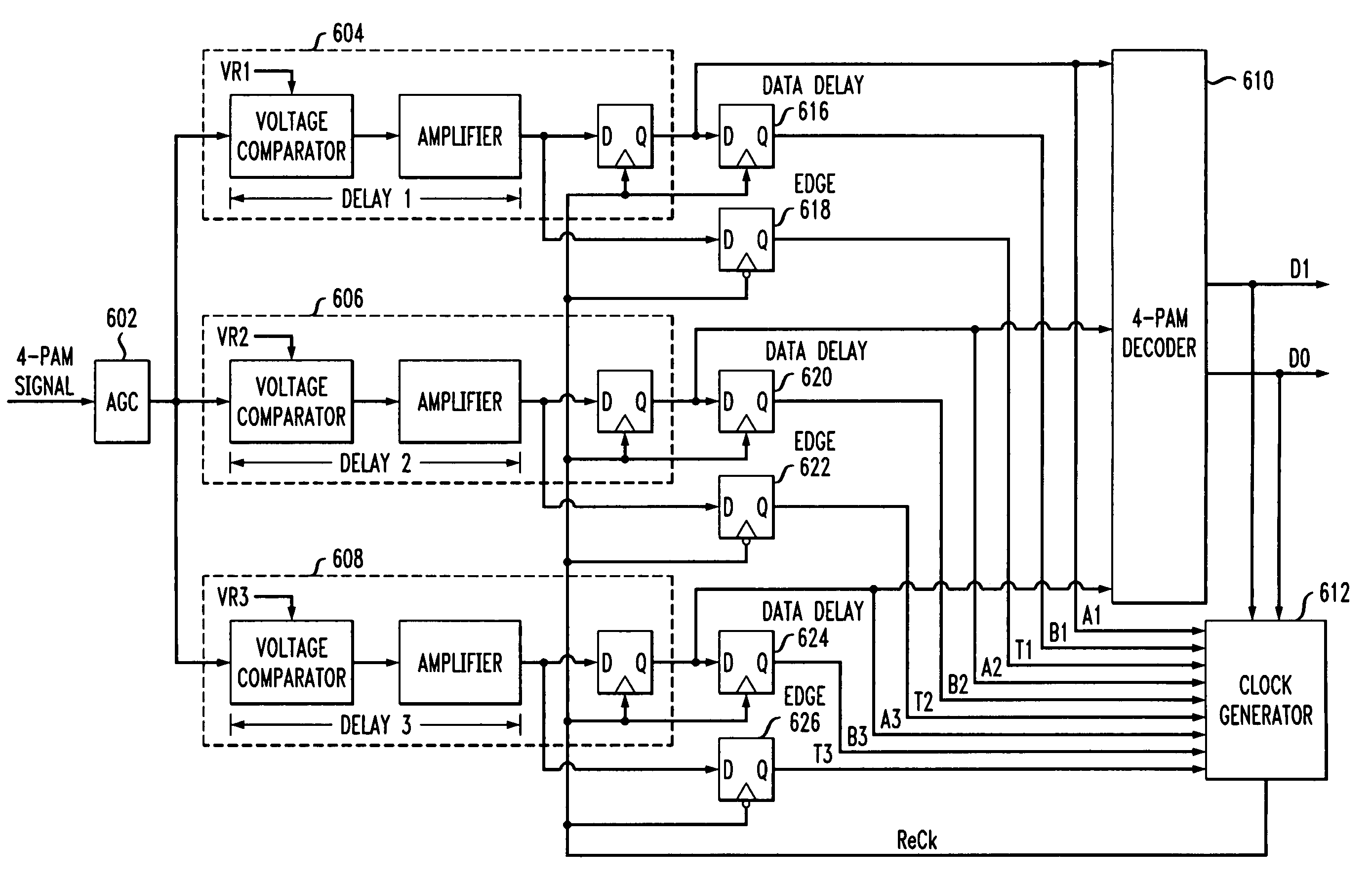
Multi-level pulse amplitude modulation receiver
InactiveUS7099400B2Pulse automatic controlDc level restoring means or bias distort correctionPhase detectorComputer science
Multiple-level phase amplitude (M-PAM) clock and data recovery circuitry uses information from multiple phase detectors to generate one or more data sampling clocks that are optimized for each of the data slicers. One possible 4-PAM implementation includes 3 data slicers, 3 edge slicers, 3 phase detectors, and a single VCO. The phase detector outputs are combined (e.g., via weighted voting, weighted average, minimum error, and / or minimum variance) to determine an optimized phase estimate for the clock used to sample the data at all three data slicers. Another 4-PAM implementation similarly includes 3 data slicers, 3 edge slicers, 3 phase detectors, and a single VCO. The mid-amplitude edge slicer and phase detector are used in combination with the VCO to generate a central phase while a multiple-tap delay line provides N phase variants before and after the central phase. Information from the non-mid-amplitude edge slicers and phase detectors is used to choose a phase from among the phase variants that best suits the other data slicers. In yet another implementation, a single edge slicer, single phase detector, and single VCO is used to generate a key clock which is used by the edge slicer to track the symbol timing. A clock generator provides a single optimized clock (that is offset from the key clock) that is used by the data slicers. Bit error rates from the data slicers are used to adjust the offset until the data slicer clock is optimized with respect to all the slicers. Alternatively, multiple clocks are generated via offsets from the key clock, each being optimized to the data slicer group that it drives.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Methods and apparatuses for minimizing co-channel interference
ActiveUS20050226414A1Minimizing co-channel interferenceInterference minimizationTelevision system detailsError preventionComputer hardwareCommunications system
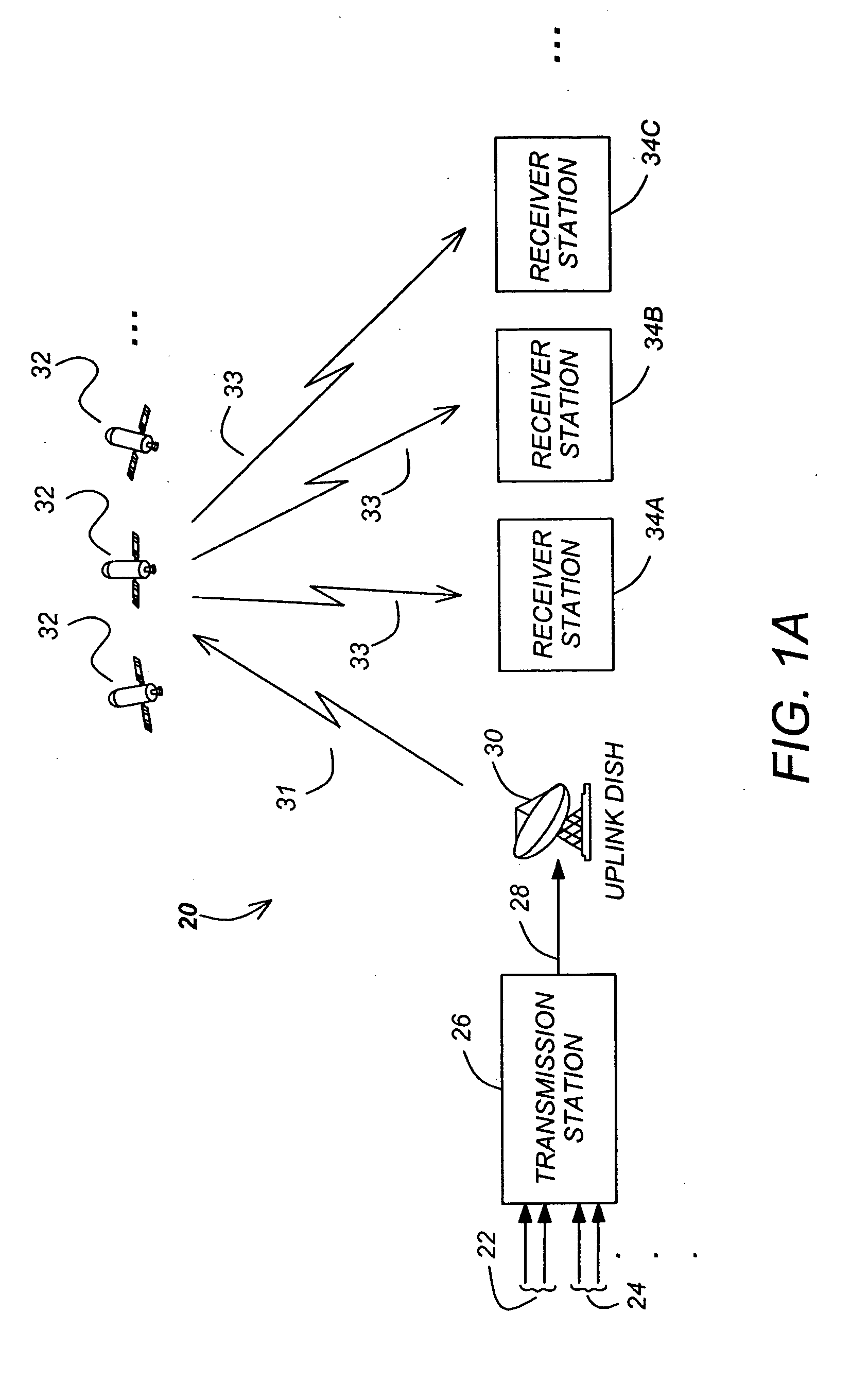
Methods and apparatuses for minimizing co-channel interference in communications systems are disclosed. A method in accordance with the present invention comprises scrambling a first frame using a first scrambling code, attaching a first header to the first frame to create the first signal, scrambling a second frame using a second scrambling code, attaching a second header to the second frame to create the second signal, and transmitting the first signal and the second signal over different channels of the communication system.
Owner:DTVG LICENSING INC
Multiple-channel transmission over a single-wire bus
ActiveUS20110150065A1Improve transfer rateBatteries circuit arrangementsTransmission/receiving by adding signal to waveData signalTransmission channel
A method for transmitting at least a synchronization and a data signal on a single-wire bus between a master device and at least one slave device, wherein a first transmission channel from the master device to the slave device modulates the periodic pulse width between a first level and second level of a same sign voltage relative to a reference potential, and a second transmission channel amplitude modulates at least one of the voltage levels between the level and at least one third level different from the two others and from the reference potential.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS (ROUSSET) SAS
Method and apparatus for generating preamble sequence for adaptive antenna system in orthogonal frequency division multiple access communication system
ActiveUS7567639B2Network traffic/resource managementAmplitude-modulated pulse demodulationPhase shiftedCommunications system
Disclosed is a method and an apparatus for generating a preamble sequence for an adaptive antenna system supporting a space division multiple access in an OFDMA communication system. Particularly, disclosed is a method for forming a preamble sequence identifying each of a plurality of mobile subscriber stations located within a cell or a sector of a communication system which includes a plurality of sub-channels assigned to the mobile subscriber stations, each of the sub-channels including a plurality of bins each of which includes n number of contiguous subcarriers in a frequency domain, the preamble sequence being transmitted before each of the sub-channels is transmitted, the method including the step of generating a preamble sequence by phase-shifting a predetermined sequence according to a predetermined phase shift sequence in the frequency domain.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
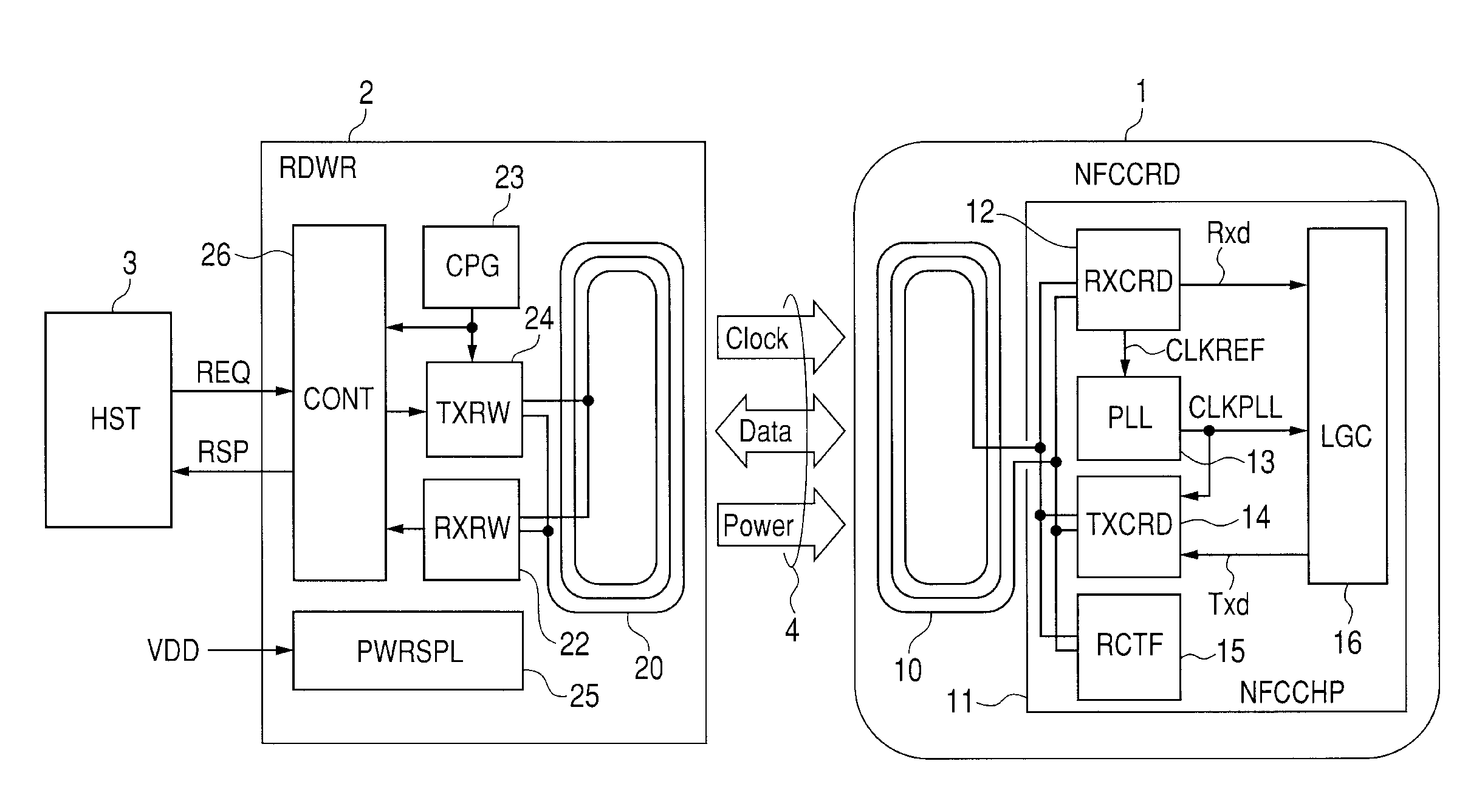
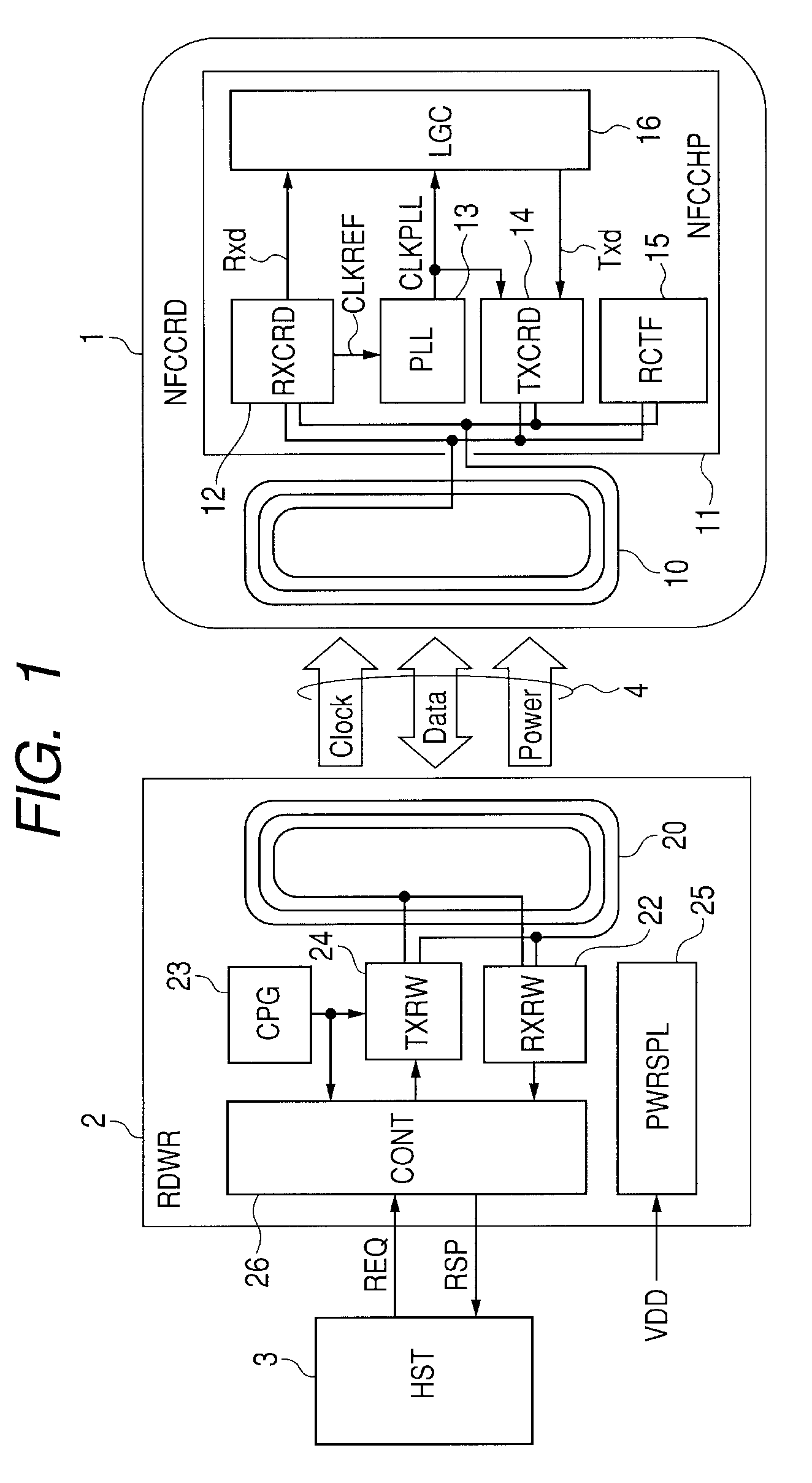
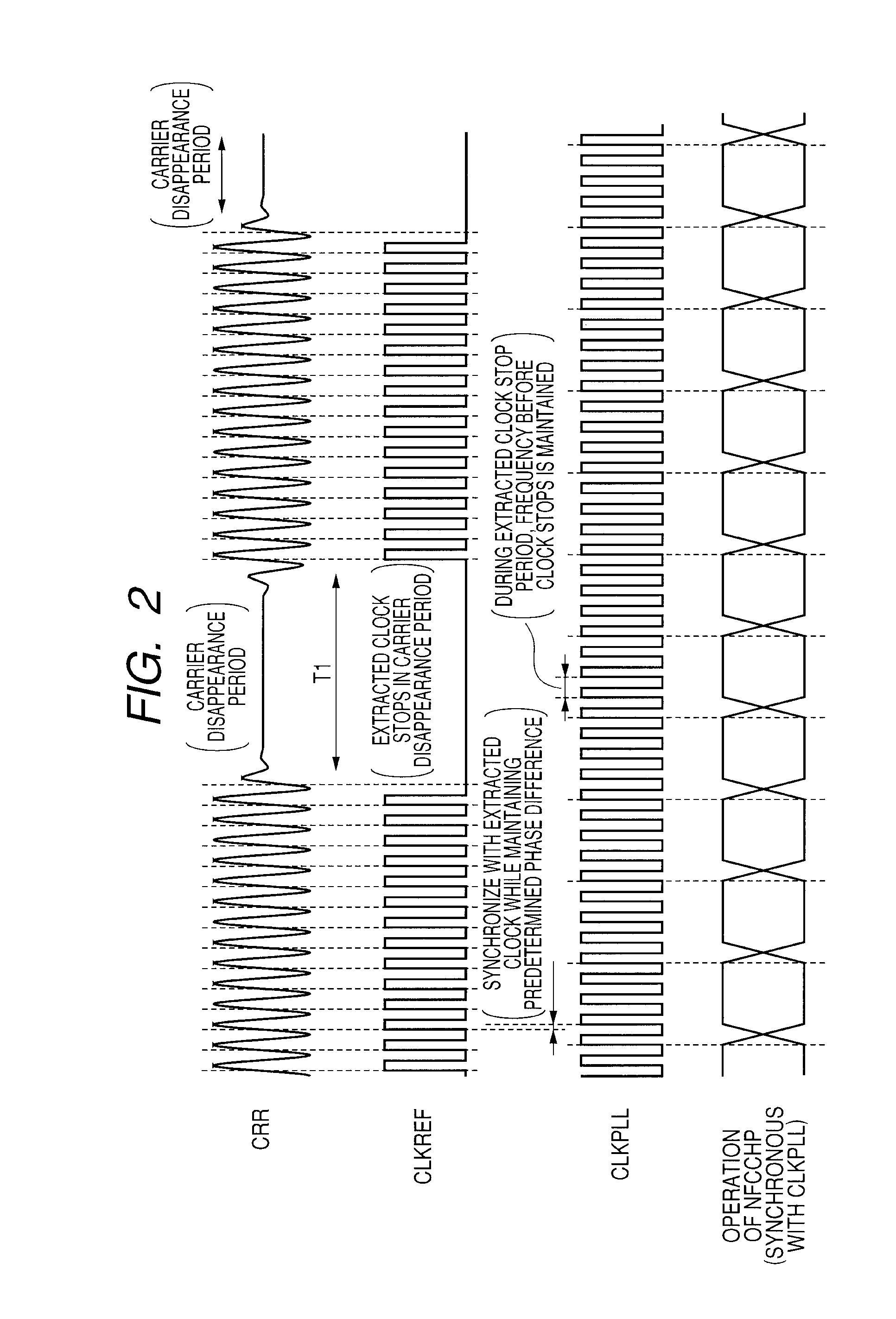
Semiconductor device, portable communication terminal, IC card, and microcomputer
ActiveUS20100197349A1Pulse automatic controlAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsMicrocomputerCarrier signal
The present invention provides a noncontact interface technique capable of performing communication operation without stopping an internal operation even when a clock signal cannot be extracted from a carrier wave. In a semiconductor device that receives a modulated carrier wave from an antenna, generates an internal clock signal on the basis of a clock signal extracted from the received carrier wave, and performs operation synchronously with the internal clock signal, a PLL circuit that receives the extracted clock signal and generates the internal clock signal is provided with a voltage control oscillation function. In the case where the clock signal extracted from the carrier wave is discretely interrupted, the function makes the internal clock signal maintained at a frequency immediately before the interruption. With the configuration, even when the clock signal extracted from the carrier wave is interrupted, internal data processes such as decoding and bus interfacing can be continued.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
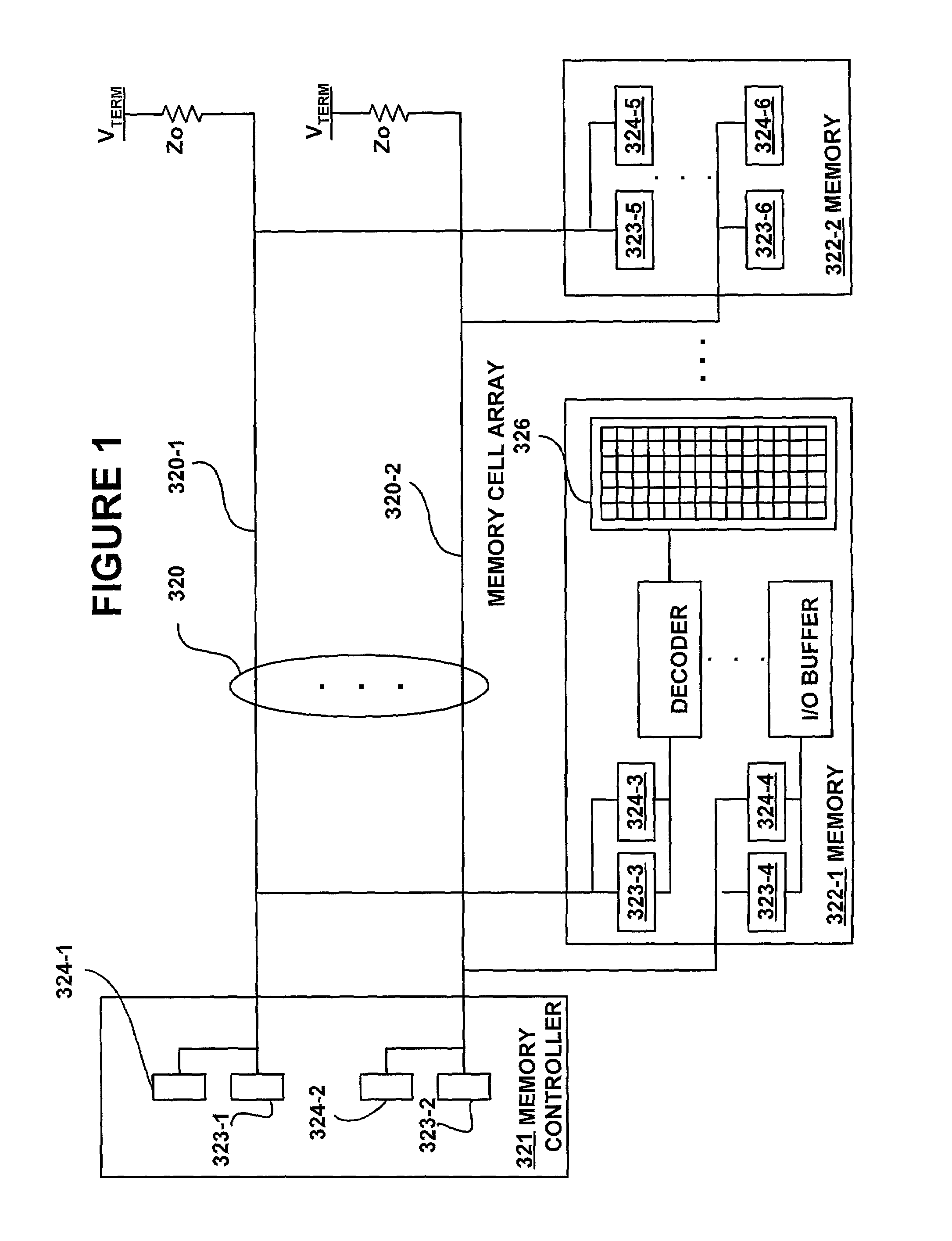
Method and apparatus for generating multi-level reference voltage in systems using equalization or crosstalk cancellation
InactiveUS7072415B2Line-faulsts/interference reductionDigital storageVoltage generatorCrosstalk cancellation
A system and method are shown for generation of at least one reference voltage level in a bus system. A reference voltage generator on a current driver includes at least one reference voltage level, at least one control signal, and an active device. The active device is coupled to the at least one control signal, such as a current control signal, and a selected reference voltage of the at least one reference voltage level. The active device is arranged to shift the at least one reference voltage level based on the at least one current control signal such as an equalization signal, a crosstalk signal, or the combination thereof, employed on the current driver.
Owner:RAMBUS INC
Technique for improving the quality of digital signals in a multi-level signaling system
InactiveUS7113550B2Quality improvementPulse conversionAmplitude-modulated pulse demodulationSignaling systemComputer science
A technique for improving the quality of digital signals in a multi-level signaling system is disclosed. In one particular exemplary embodiment, the technique may be realized as a method for improving the quality of transmitted digital signals in a multi-level signaling system wherein digital signals representing more than one bit of information may be transmitted at more than two signal levels on a single transmission medium. The method comprises encoding digital values represented by sets of N bits to provide corresponding sets of P symbols, wherein each set of P symbols is selected to eliminate full-swing transitions between successive digital signal transmissions. The method also comprises transmitting the sets of P symbols.
Owner:RAMBUS INC
Method for controlling array antenna equipped with a plurality of antenna elements, method for calculating signal to noise ratio of received signal, and method for adaptively controlling radio receiver
InactiveUS20030156061A1Radio wave direction/deviation determination systemsAmplitude-modulated pulse demodulationSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Radio reception
Based on a received signal y(t) received by a radiating element of an array antenna including the single radiating element and a plurality of parasitic elements, an adaptive controller calculates and sets a reactance value of a variable reactance element for directing a main beam of the array antenna in a direction of a desired wave and directing nulls in directions of interference waves so that a value of an objective function expressed by only the received signal y(t) becomes either one of the maximum and the minimum by using an iterative numerical solution of a nonlinear programming method.
Owner:ATR ADVANCED TELECOMM RES INST INT
High-speed cable with embedded power control
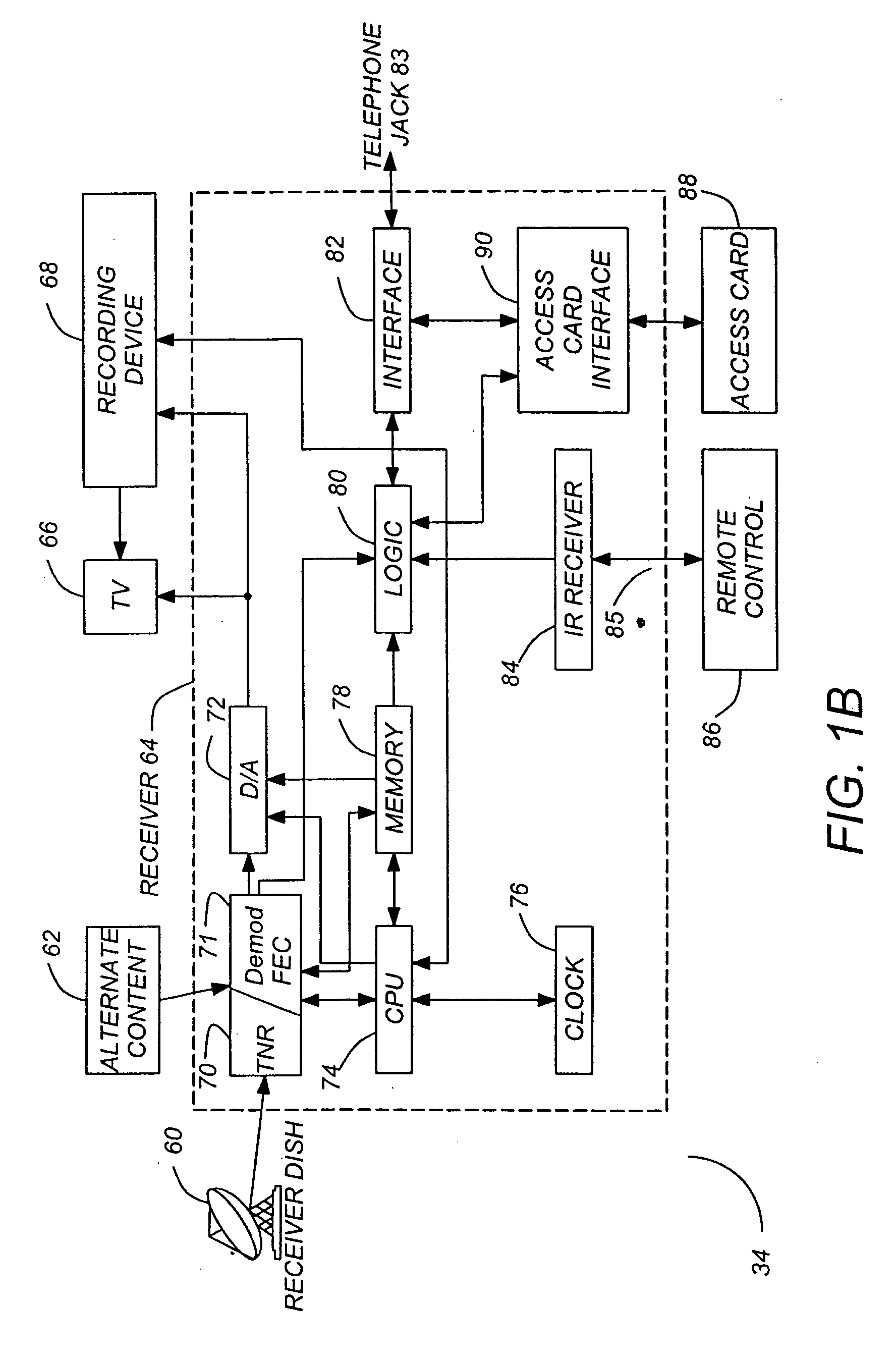
ActiveUS20080106313A1Quality improvementBaseband system detailsElectric pulse generatorDifferential signalingEngineering
An HDMI cable carries high speed encoded data which are transmitted differentially over data channels, along with a clock. High-frequency loss and differential skew within a differential signal may be compensated by analog circuits embedded in the cable. These embedded circuits are tuned at production for best performance by observing the quality of the recovered analog signal. The embedded circuits are powered by a combination of power sources, both carried within the cable, and harvested from the high-speed signals themselves.
Owner:REDMERE TECH
System and Method for Scheduling Users on a Wireless Network
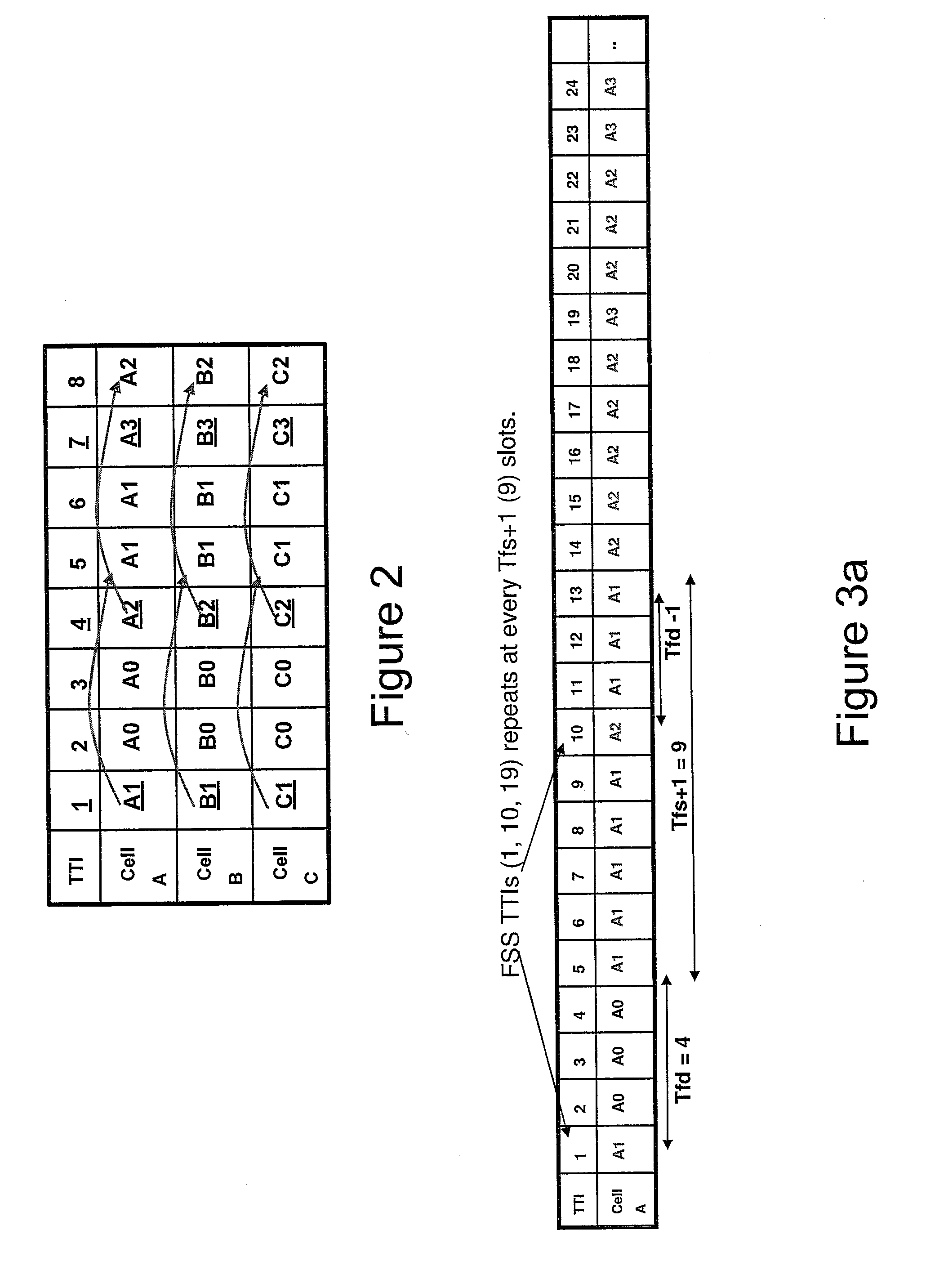
ActiveUS20110177821A1Easy to useModulated-carrier systemsBroadcast transmission systemsResource blockWireless network
In accordance with an embodiment, a method of operating a base station configured to operate with user devices includes scheduling a first user device in a first slot, scheduling the first user device for at least one further slot, and transmitting an assignment for the at least one further slot to the first user device. The first slot has a first resource block (RB) and a first transmission time interval (TTI) and the at least one further slot has the first RB and a second TTI.
Owner:HONOR DEVICE CO LTD
Automatic gain control apparatus and method in an orthogonal frequency division multiple access sytem
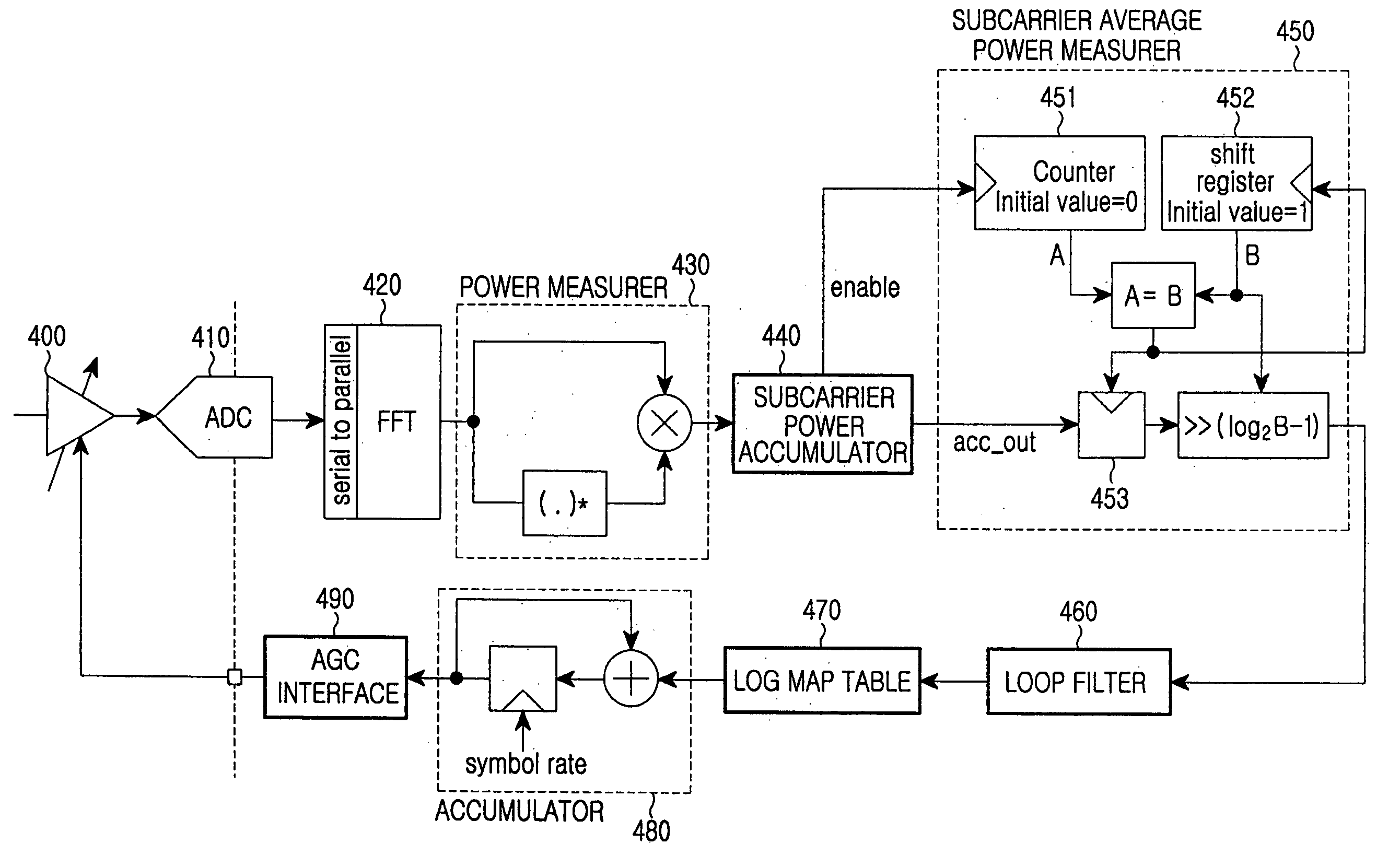
InactiveUS20060176093A1Accurately reflectEffective precisionGain controlAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsControl signalCarrier signal
An automatic gain control (AGC) apparatus of a wireless mobile terminal, and method, in an orthogonal frequency division multiple access (OFDMA) system. A gain amplifier controls an amplification gain of received analog symbols. An analog-to-digital converter converts the received analog symbols into a digital signal. A fast Fourier transform (FFT) unit converts the digital signal into a frequency-domain signal. A power measurer measures power in the frequency domain in units of sub-carriers. A sub-carrier power accumulator detects a sub-carrier carrying a signal, and accumulates its power value. A sub-carrier average power measurer estimates an average power value transmitted per sub-carrier from the accumulated power value. A control means compares the estimated average power value with a reference power value, and generates a control signal used for controlling a gain of the gain amplifier according to the comparison result.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and apparatus for constellation shaping
ActiveUS20040008794A1Time-division multiplexAmplitude-modulated pulse demodulationComputer hardwareTransmitted power
A method and apparatus is disclosed for facilitating high-speed data communication. In one embodiment a receiver is configured to include error correction coding in an interleaved environment to increase data transmission rates. In one embodiment the signal mapping scheme includes constellation shaping to reduce transmit power levels. In one embodiment 8-state Ungerboeck trellis coding is implemented with 4-dimensional PAM 10 signal mapping.
Owner:MARVELL INT LTD
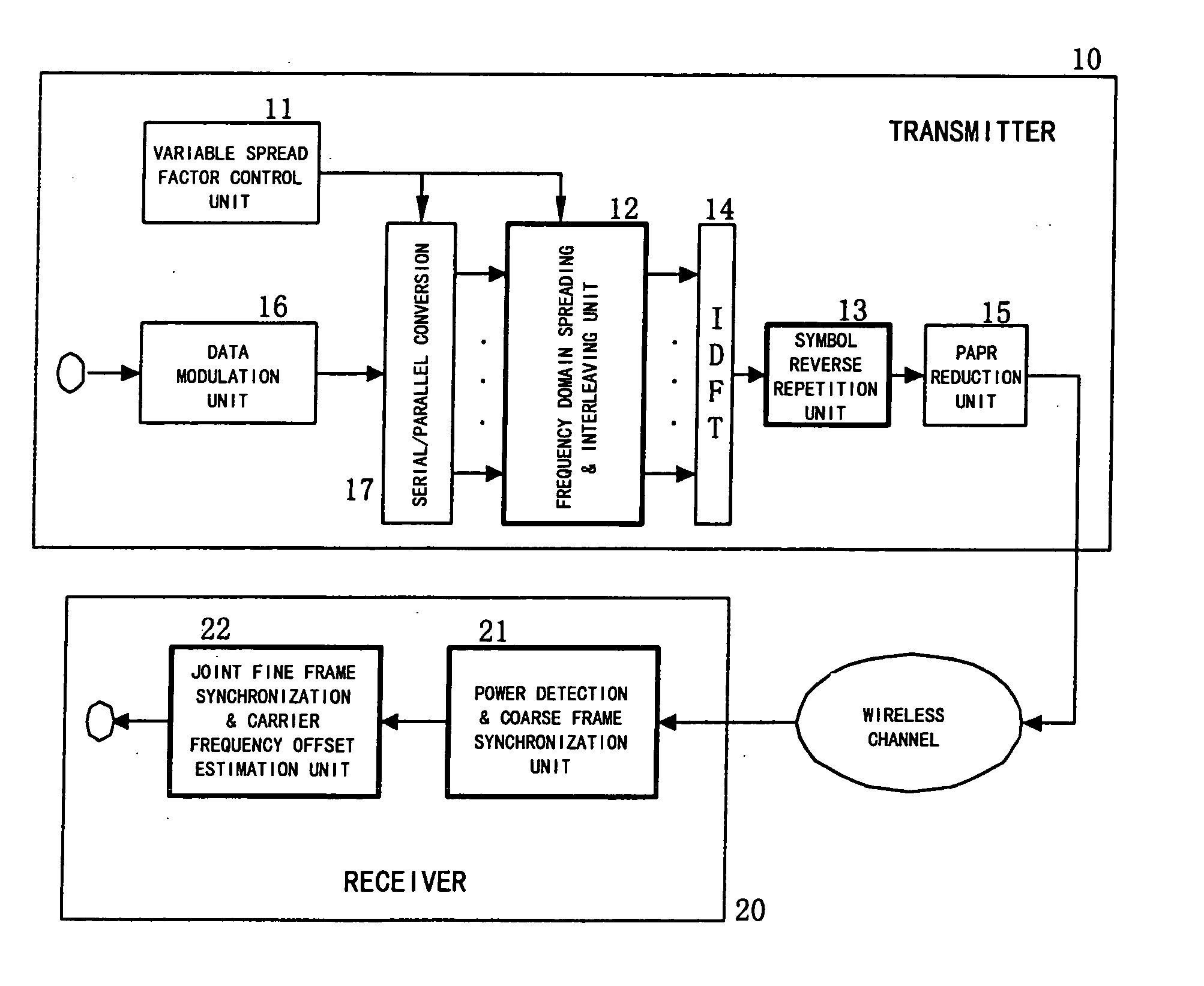
Method for joint time synchronization and frequency offset estimation in OFDM system and apparatus of the same
InactiveUS20060133526A1Improve accuracyReduce loss rateAmplitude-modulated pulse demodulationSecret communicationCarrier frequency offsetSpreading factor
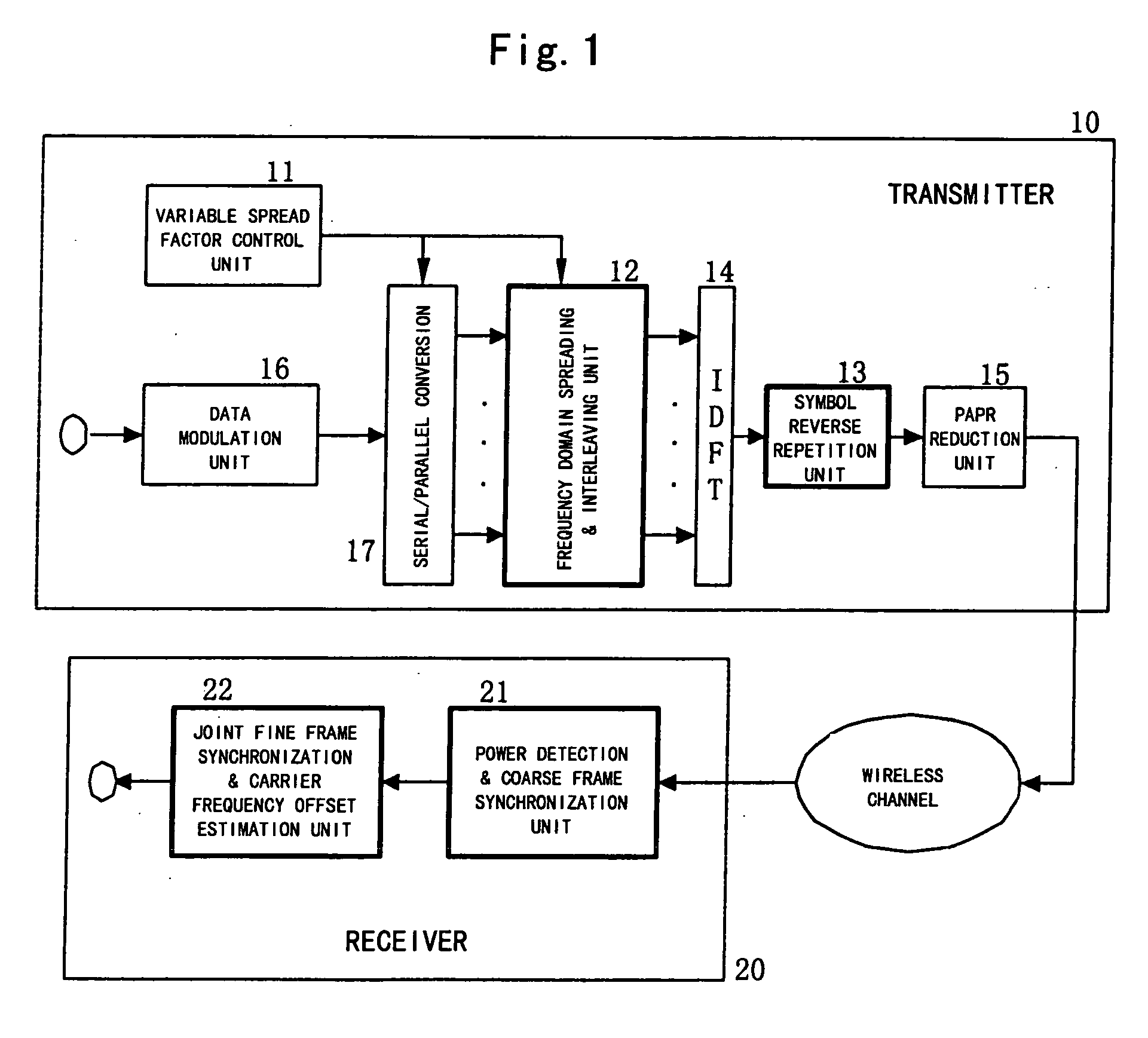
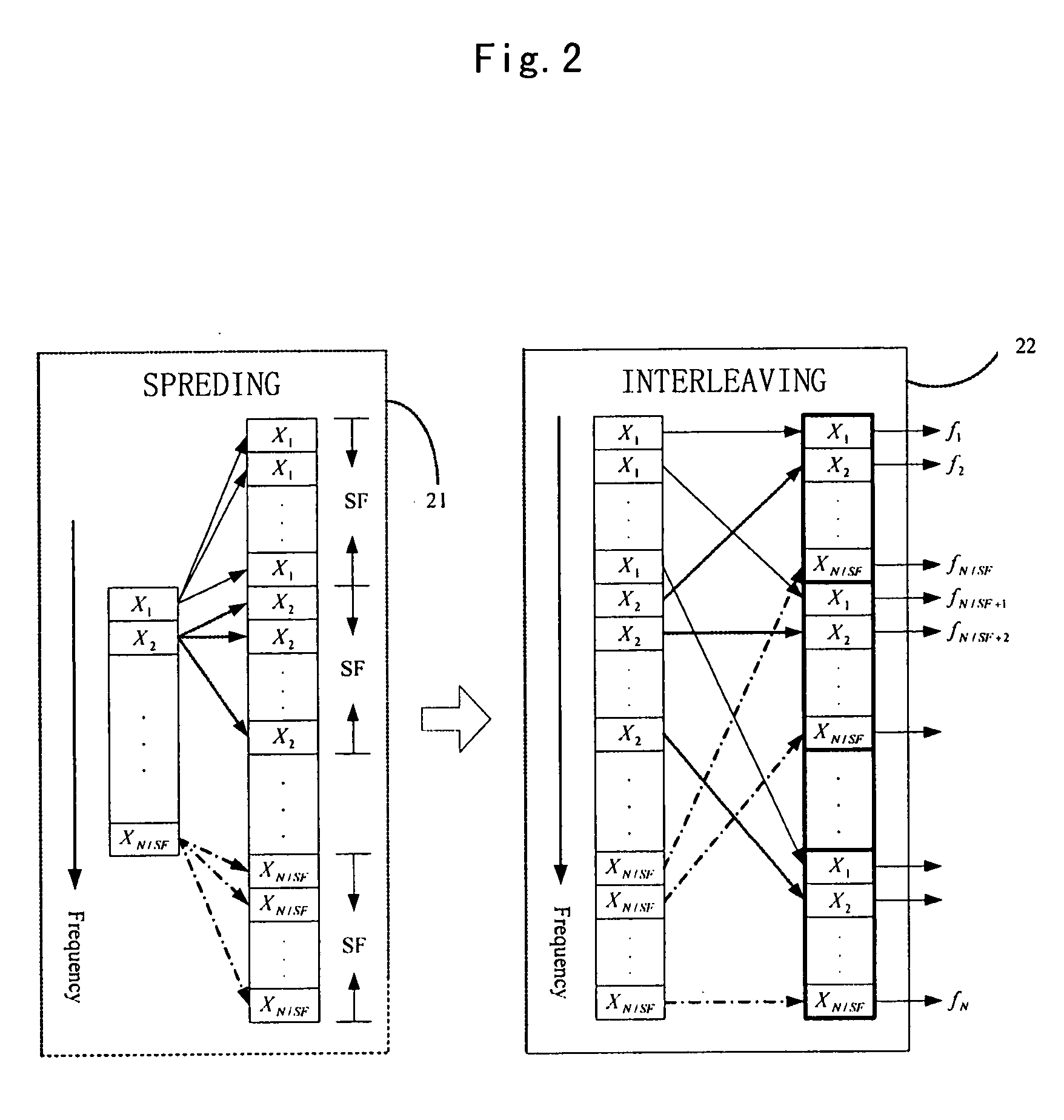
Embodiments of the present invention include a method for performing joint time synchronization and carrier frequency offset estimation in a wireless communication system, comprising steps of: on a transmitter: performing frequency domain spreading and interleaving on input data by using a predetermined spreading factor (SF) to generate a frequency domain training symbol; performing Inverse Discrete Fourier Transformation (IDFT) on the generated frequency domain training symbol to generate a first time domain training symbol; reversely copying the generated first time domain training symbol to a second time domain training symbol such that a complete training sequence is formed; and on a receiver: detecting an average power of received signals to judge the coming of a training sequence, and performing coarse frame synchronization; performing joint fine frame synchronization and carrier frequency offset estimation based on a received training sequence; and compensating for the carrier frequency offset based on the carrier frequency offset estimation result so as to eliminate the carrier frequency offset. In addition, embodiments of the present invention also include an apparatus for performing joint time synchronization and carrier frequency offset estimation and a method for generating a training sequence.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY +1
Method to determine a channel characteristic, and discrete wavelet transmitter and receiver to perform the method
InactiveUS6952441B2Modulated carrier system with waveletsBaseband system detailsEngineeringFilter bank
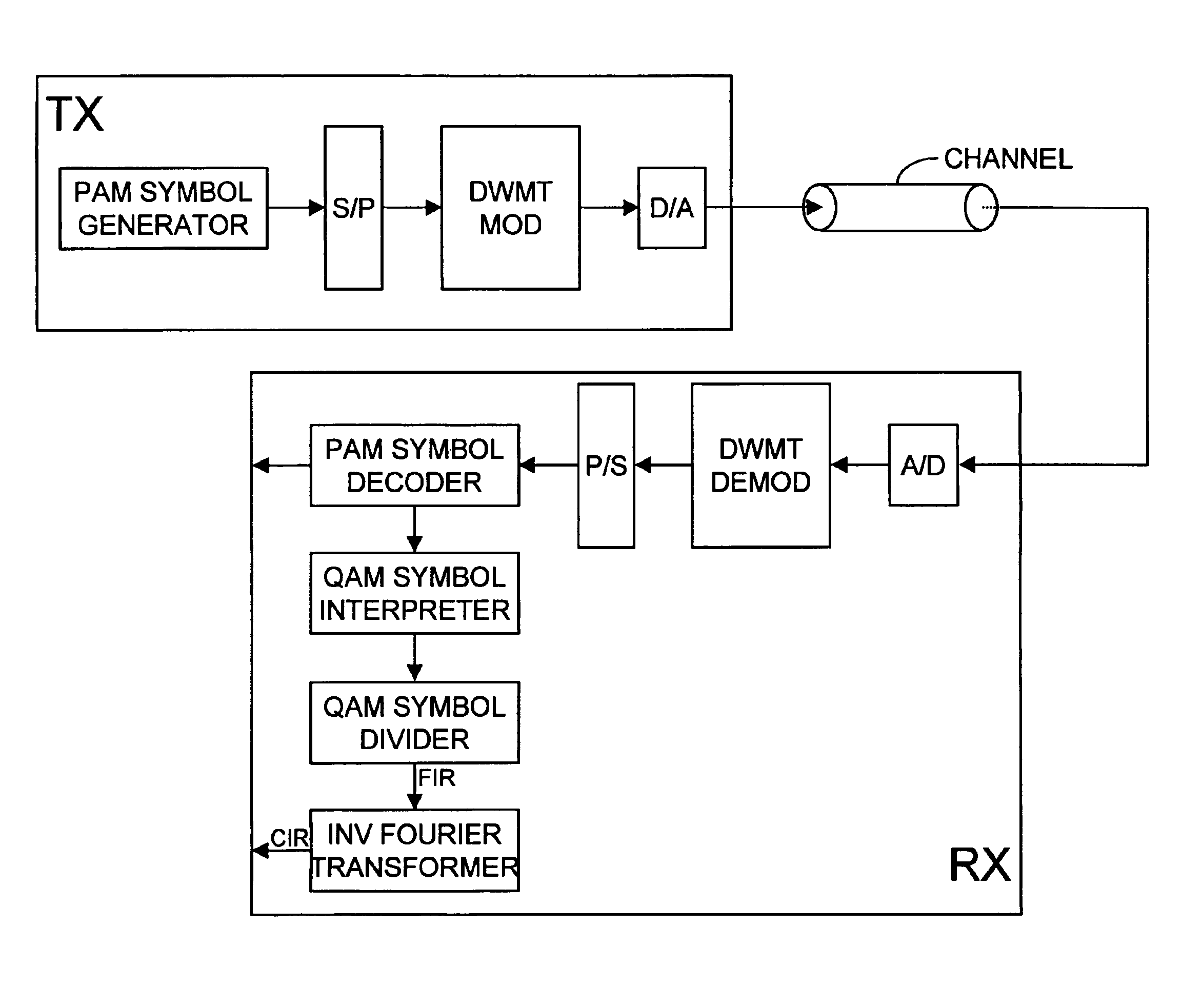
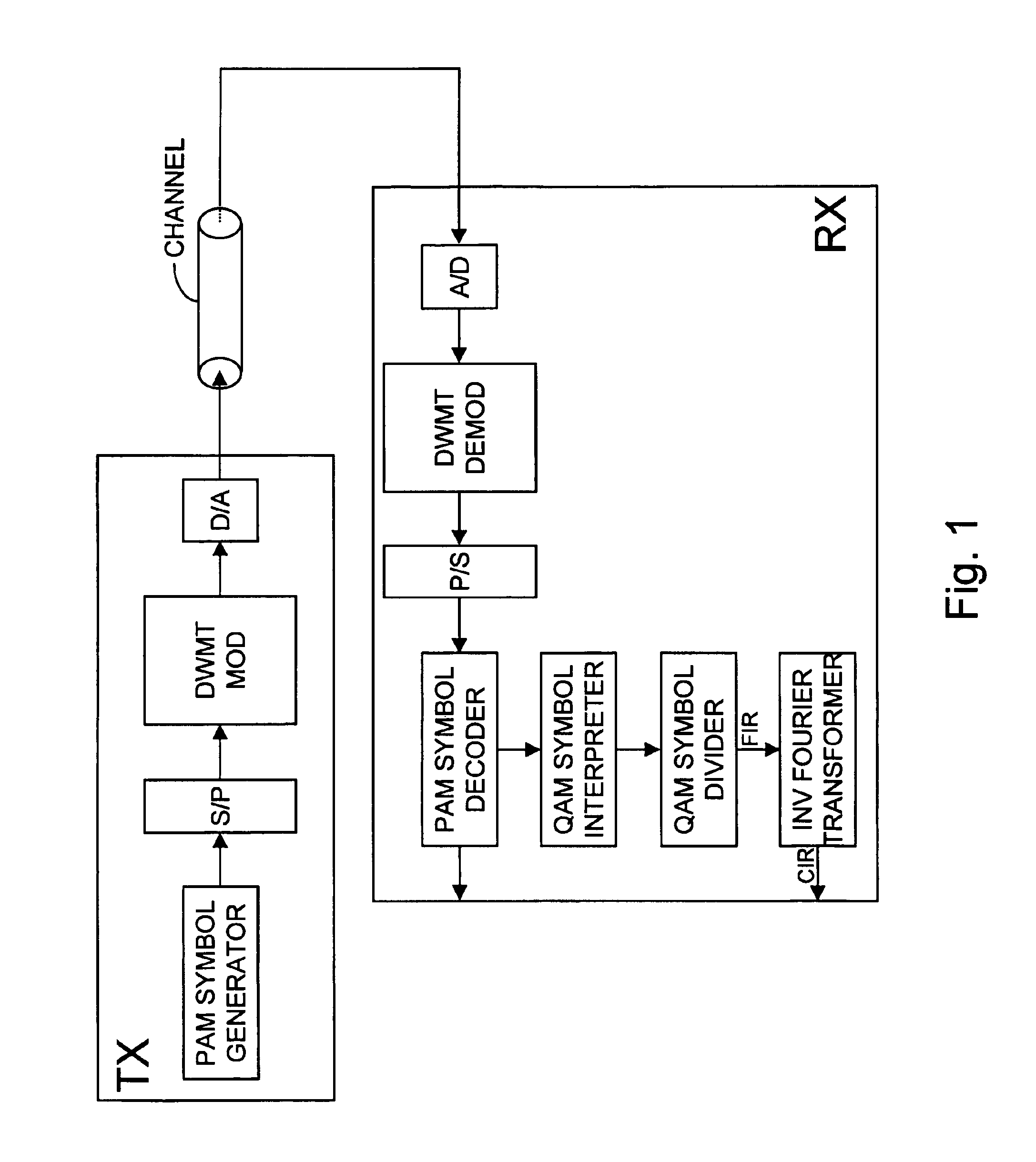
To determine the channel characteristic of a channel (CHANNEL) between a transmitter (TX) and a receiver (RX), a predetermined periodic signal of pulse amplitude modulated symbols is modulated on waveforms by a cosine modulated filter bank (DWMT MOD) in the transmitter (TX), and the waveforms are transmitted over the channel (CHANNEL). In the receiver (RX), the received pulse amplitude modulated symbols are demodulated from the waveforms by a cosine modulated filter bank (DWMT DEMOD), pairs of the received pulse amplitude modulated symbols are combined to form received quadrature amplitude modulated symbols, and the received quadrature amplitude modulated symbols are divided by the transmitted predetermined pulse amplitude modulated symbols considered pairwise as transmit quadrature amplitude modulated symbols. So, samples of the channel characteristic are generated.
Owner:RPX CORP
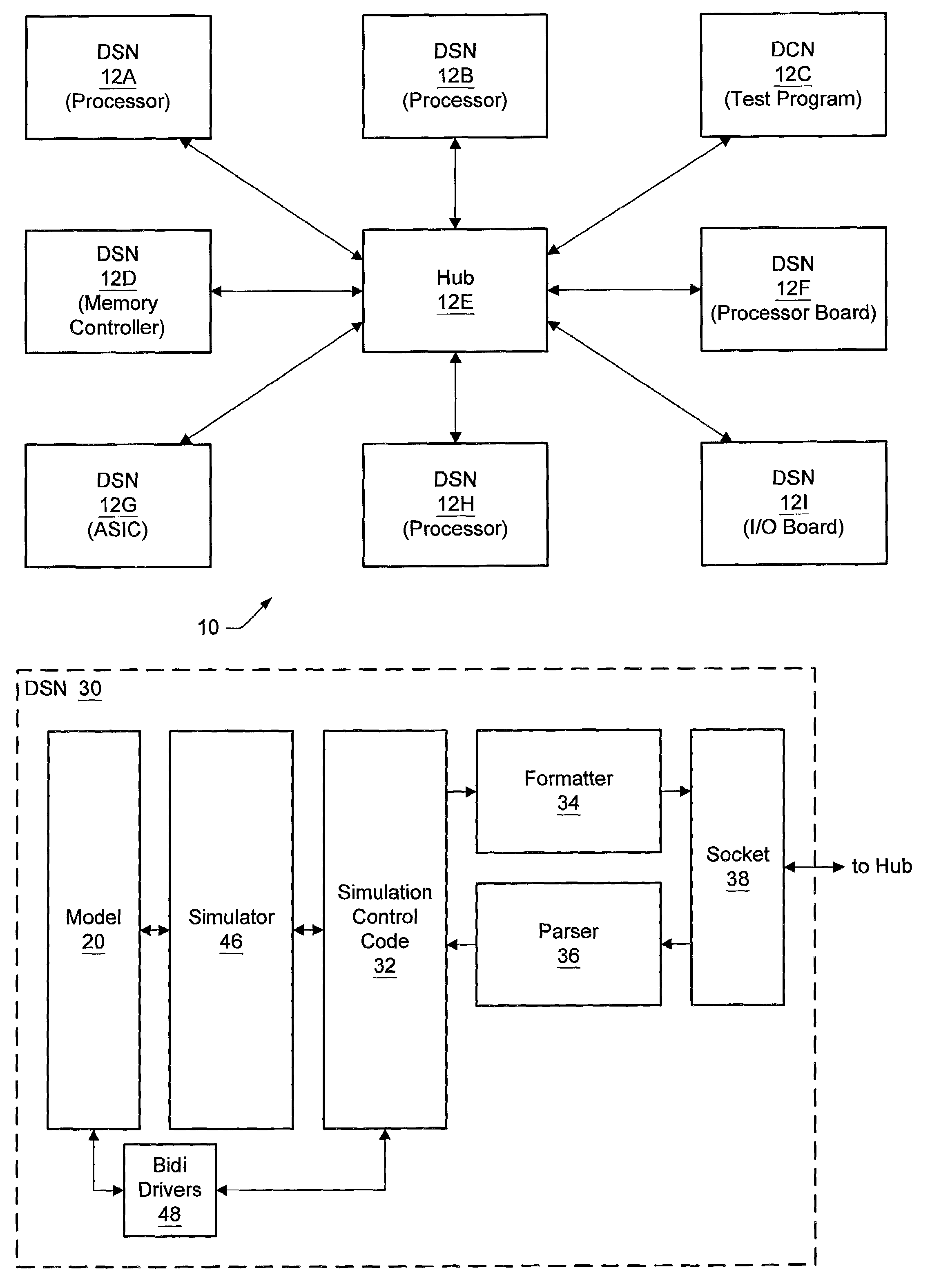
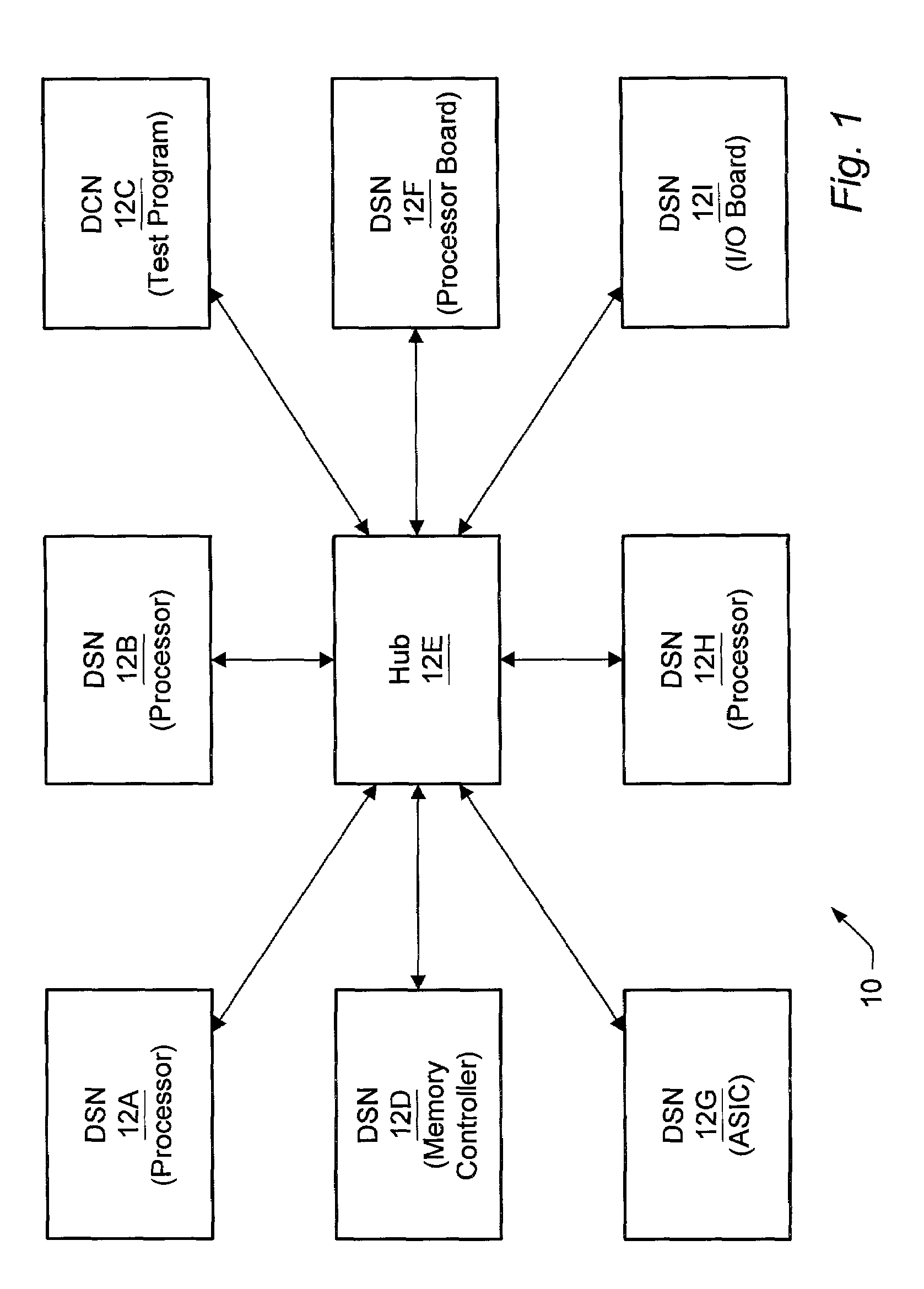
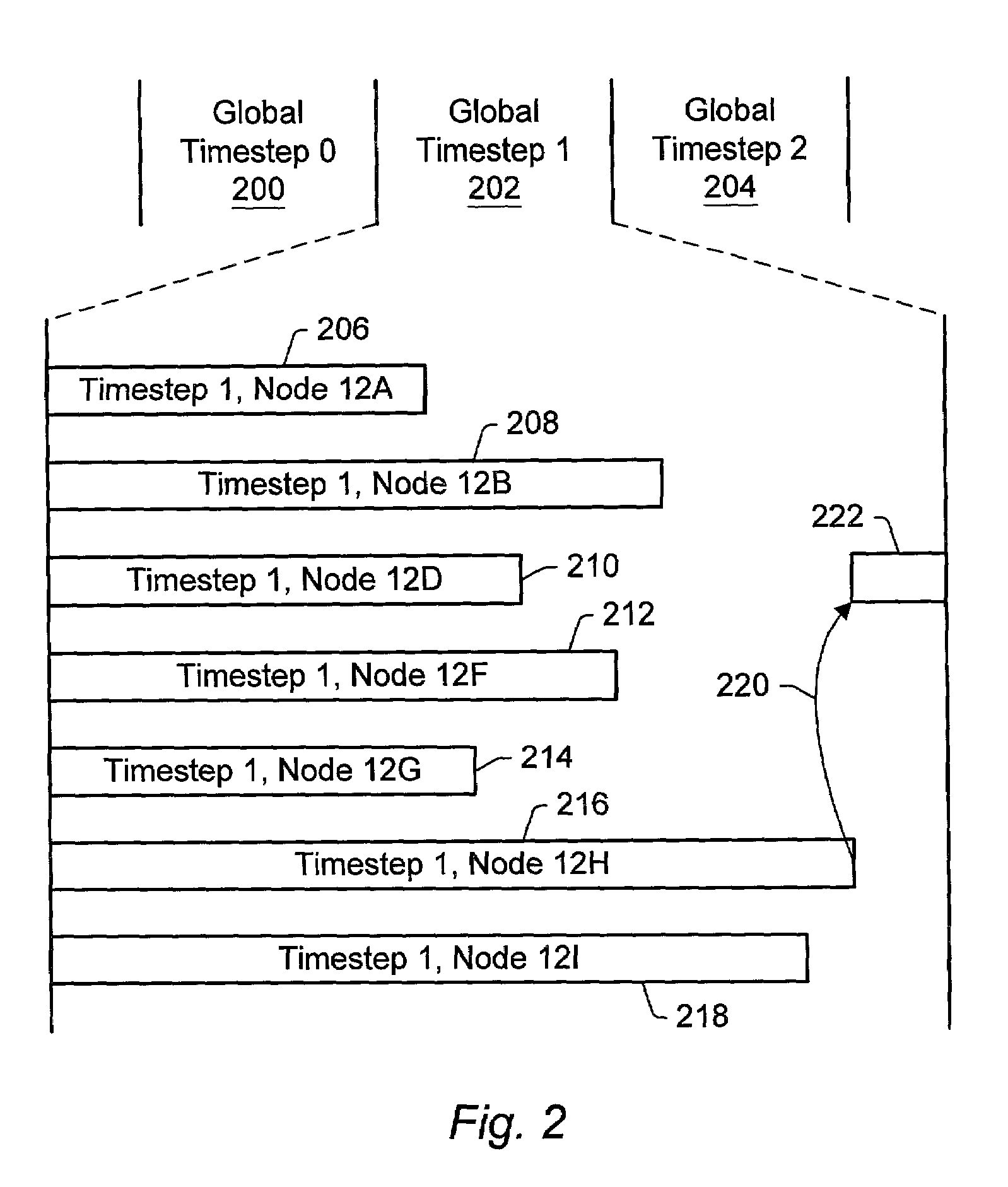
Synchronization of distributed simulation nodes by keeping timestep schedulers in lockstep
InactiveUS7020722B2Multiple digital computer combinationsCAD circuit designSystem under testReal-time computing
A distributed simulation system includes a plurality of nodes. Each node is configured to simulate a portion of a system under test. The simulation is performed as a series of timesteps. The transition between timesteps is synchronized in the plurality of nodes. In one implementation, the distributed simulation system includes a hub which is configured to synchronize the transition between timesteps in the plurality of nodes. For example, in one embodiment, the hub may receive commands from each of the plurality of nodes. If each command indicates that the corresponding node is capable of completing the timestep, the hub transmits a command to each node indicating that the timestep is complete. The nodes may begin processing the next timestep in response to the command. In other embodiments, a hub may not be included.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
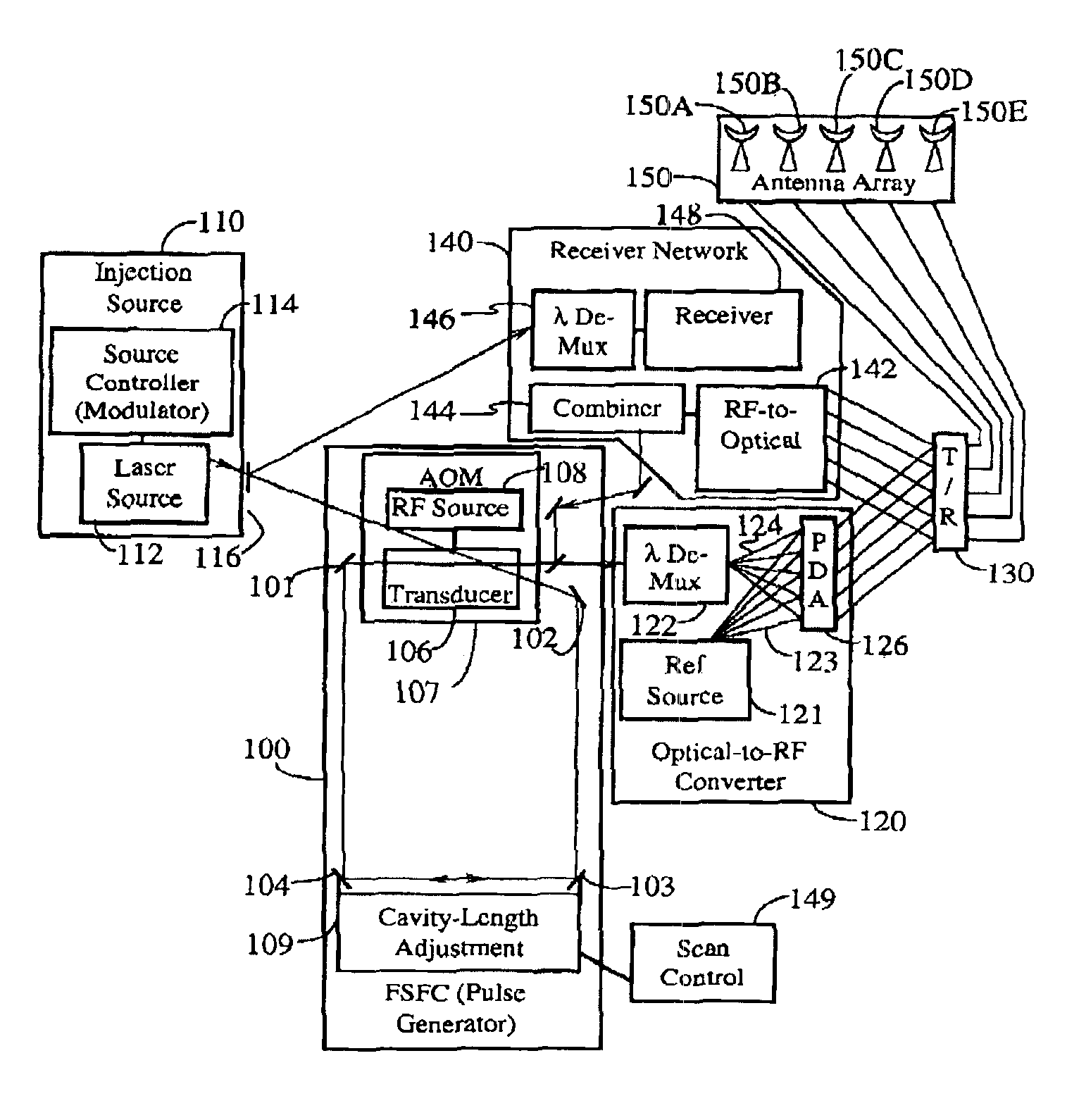
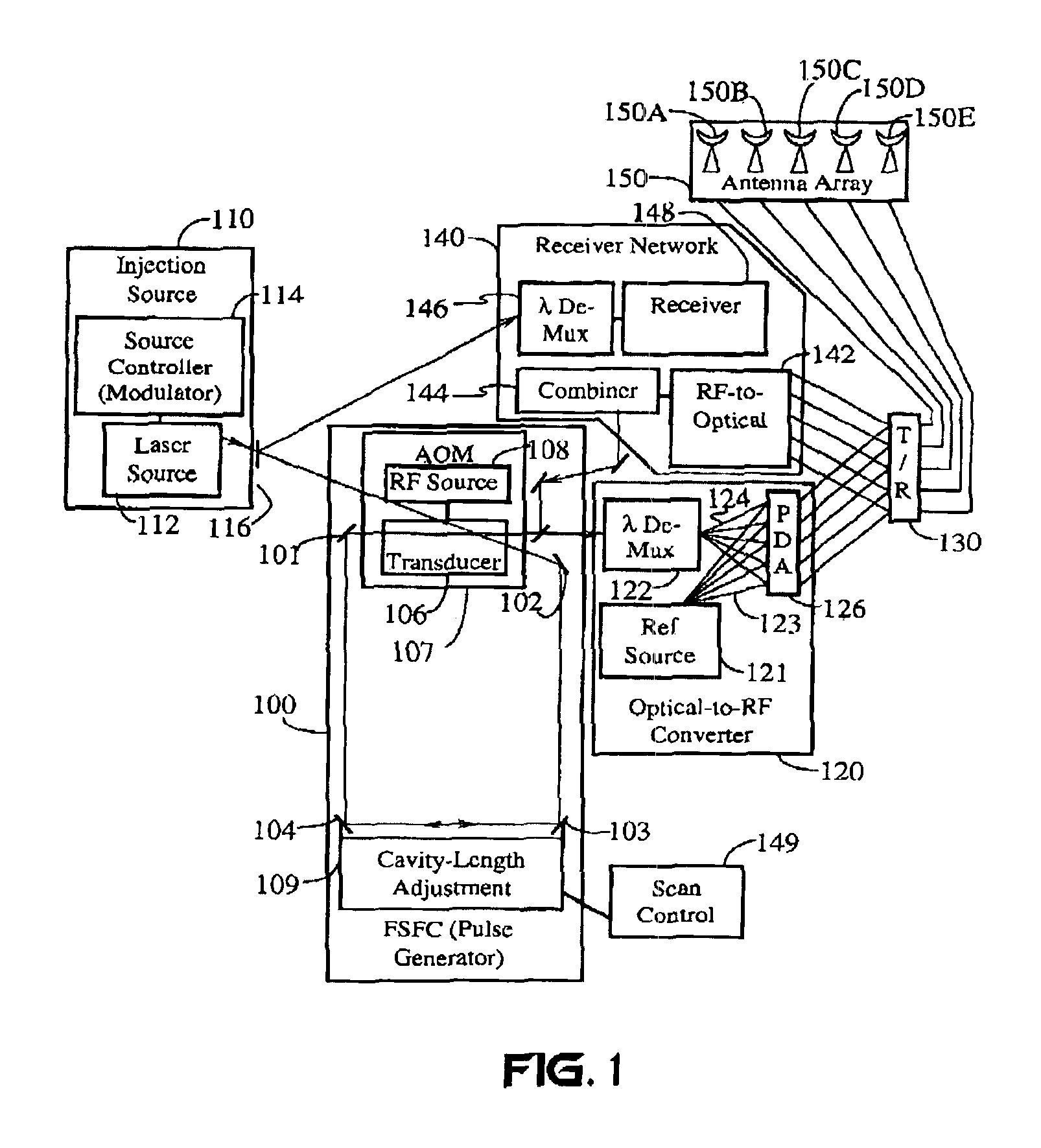
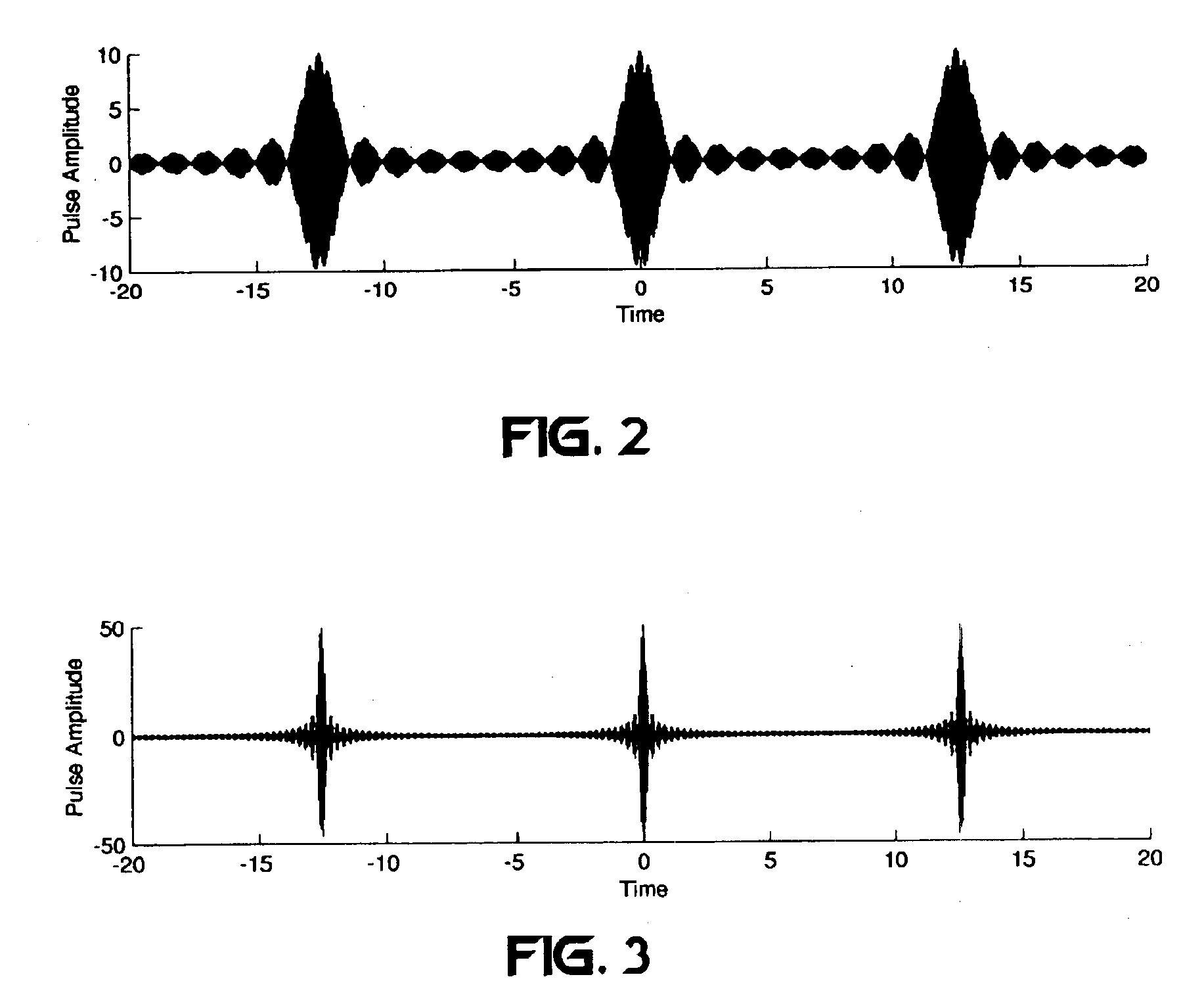
Frequency-shifted feedback cavity used as a phased array antenna controller and carrier interference multiple access spread-spectrum transmitter
InactiveUS6888887B1Easy to adaptFrequency diversityFrequency/rate-modulated pulse demodulationTime domainCarrier signal
An optical processor for controlling a phased antenna array uses a frequency-shifted feedback cavity (FSFC), which includes a traveling-wave cavity. The FSFC incrementally delays and incrementally frequency shifts optical signals circulating in the traveling-wave cavity. Optical signals coupled out of the FSFC are separated by frequency, hence by delay, and processed to control either or both transmit and receive beam-forming operations. The FSFC provides a receiver with multiple receive signals which have incremental values of frequency. Each frequency corresponds to an incremental time sampling of optical signals input into the FSFC. Transmit signals coupled out of the FSFC have frequency and phase relationships that result in short time-domain pulses when combined. Controlling modulation and frequency of the transmit signals achieves carrier interference multiple access, a new type of spread-spectrum communications.
Owner:DEPARTMENT 13 INC
Shifted channel characteristics for mitigating co-channel interference
ActiveUS20050229230A1Interference minimizationMinimize limitationTelevision system detailsError preventionCommunications systemEngineering
Methods and apparatuses for minimizing co-channel interference in communications systems are disclosed. A method in accordance with the present invention comprises shifting a characteristic of the first signal with respect to a like characteristic of the second signal to mitigate co-channel interference, and transmitting the first signal and the second signal over different channels of the communication system.
Owner:DTVG LICENSING INC
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com