Patents
Literature
94 results about "Optical processor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
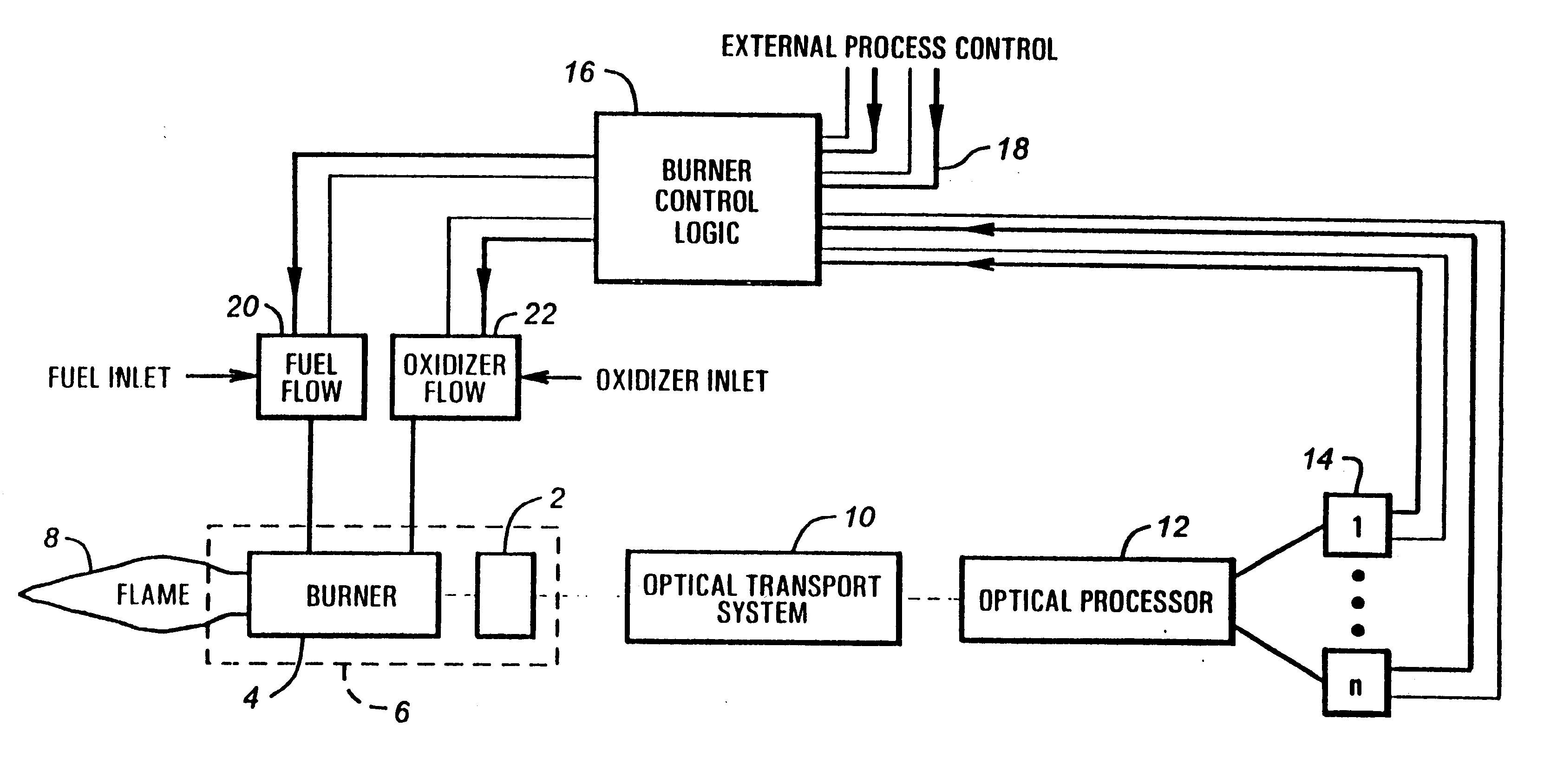
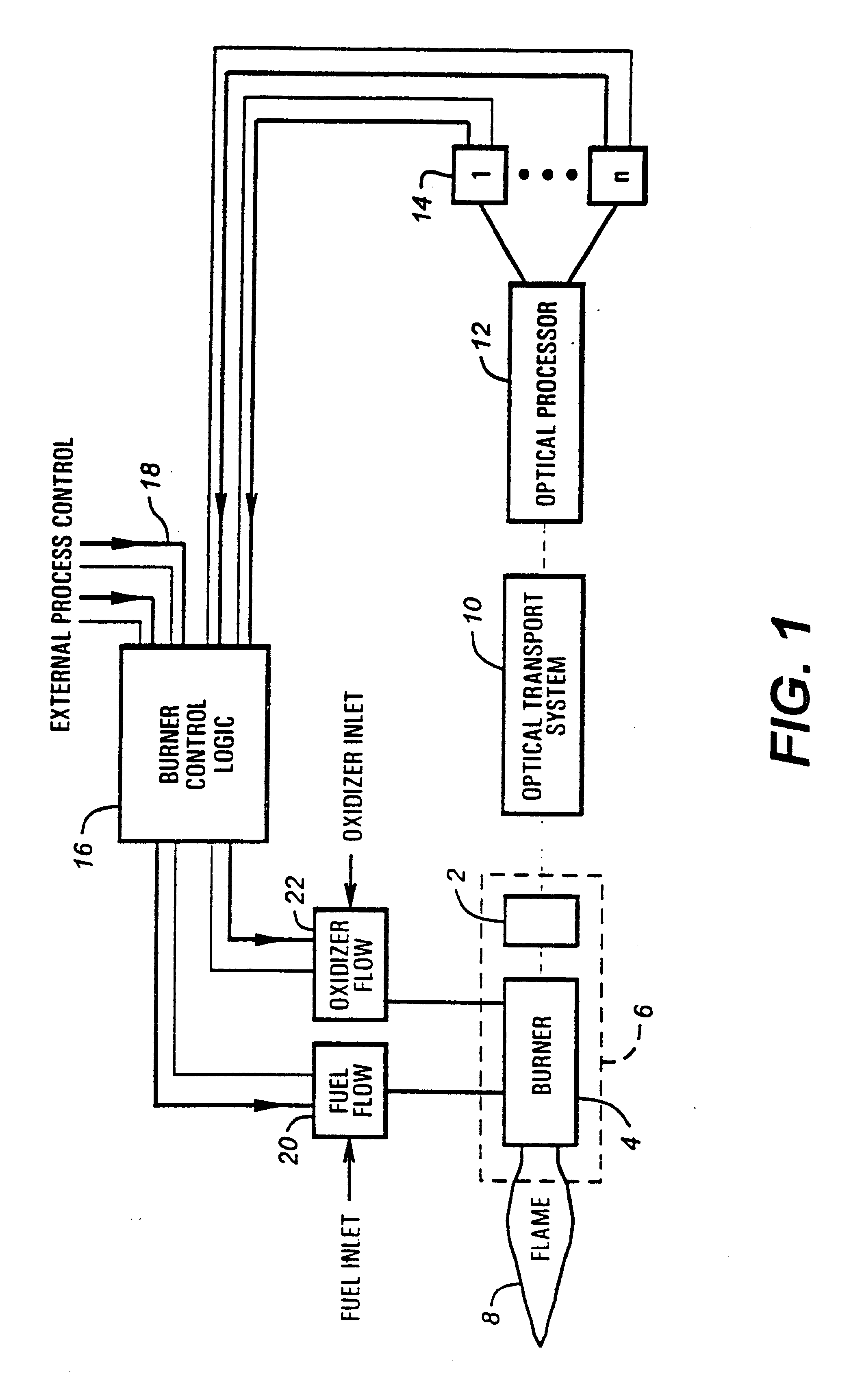
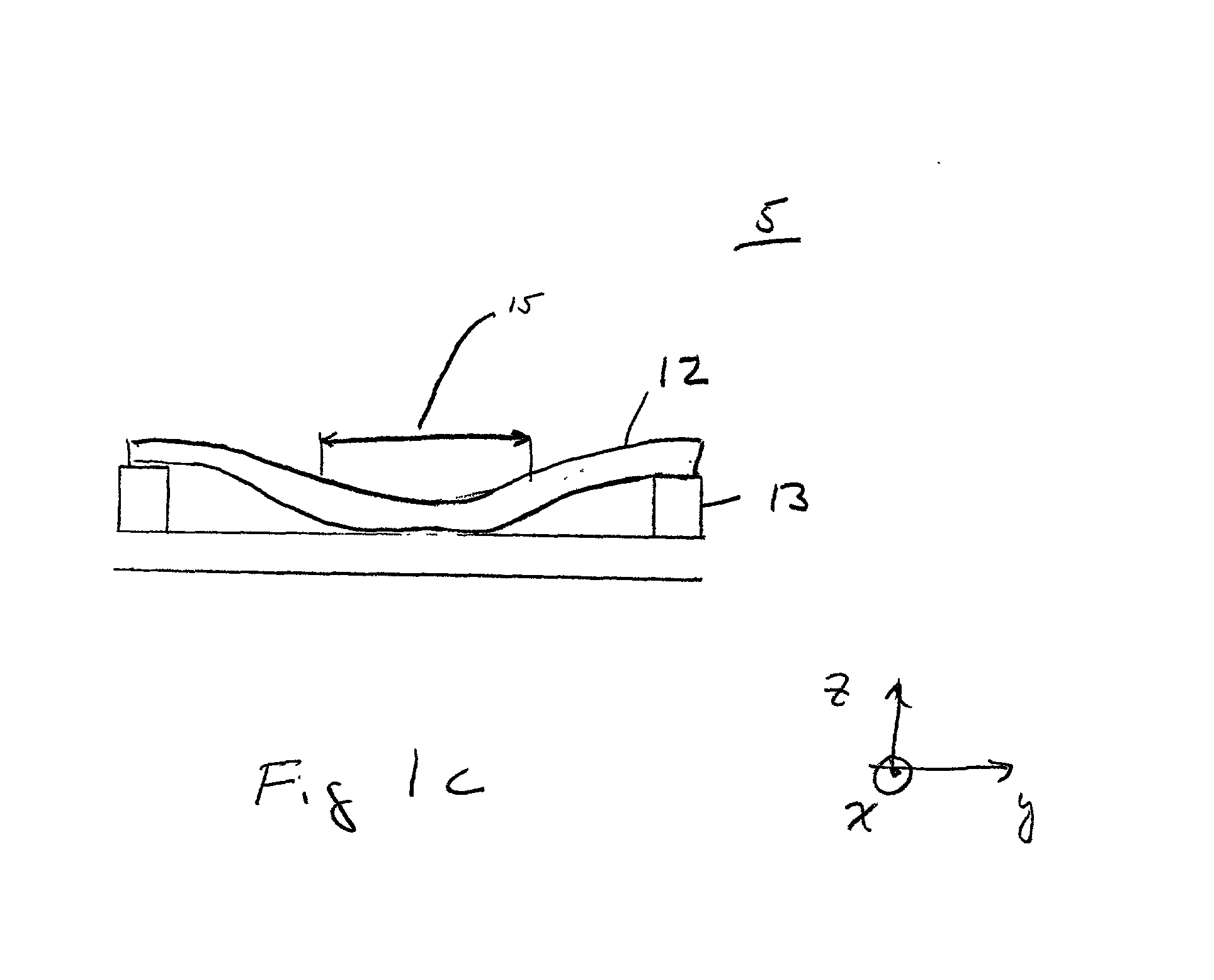
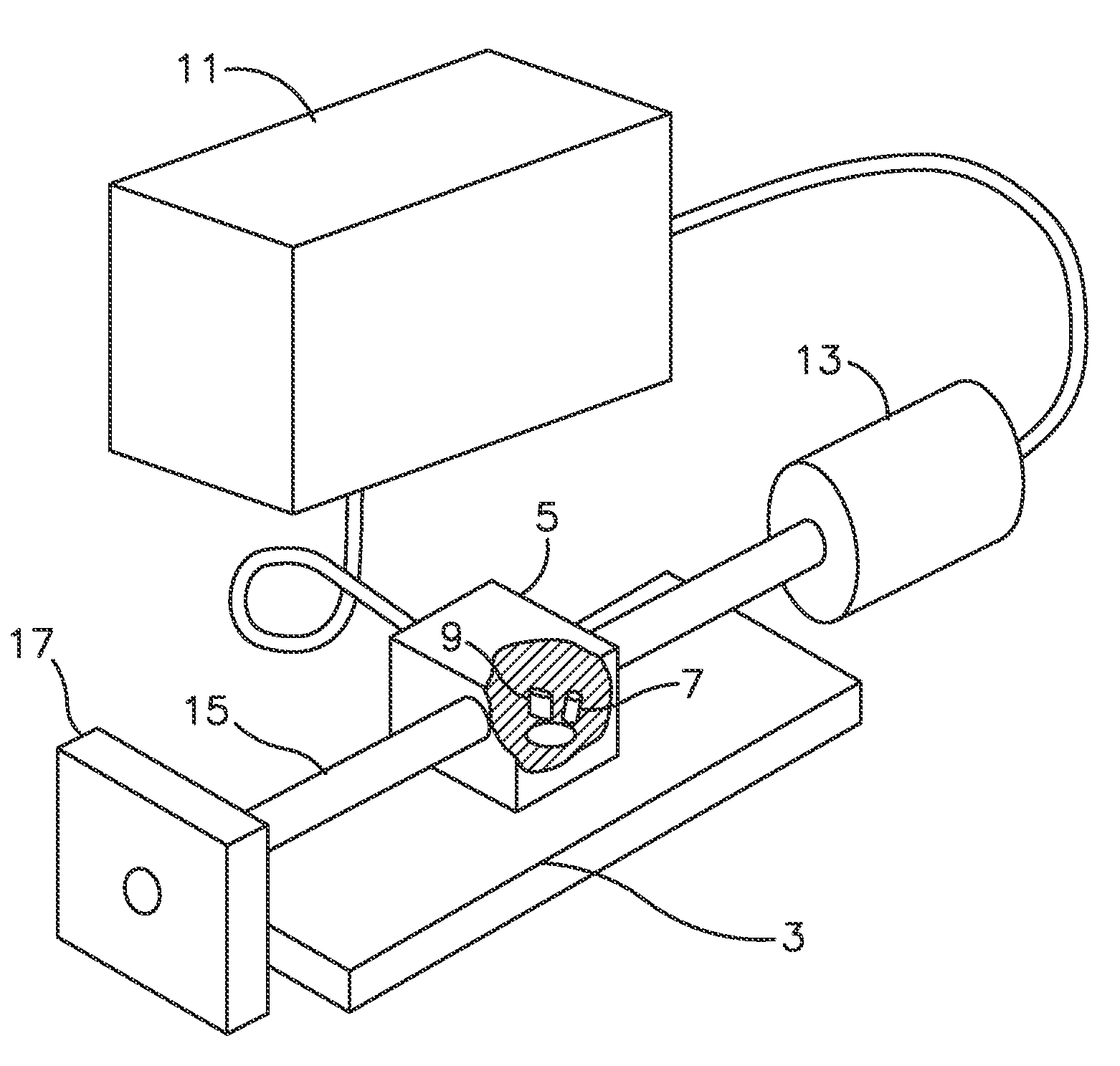
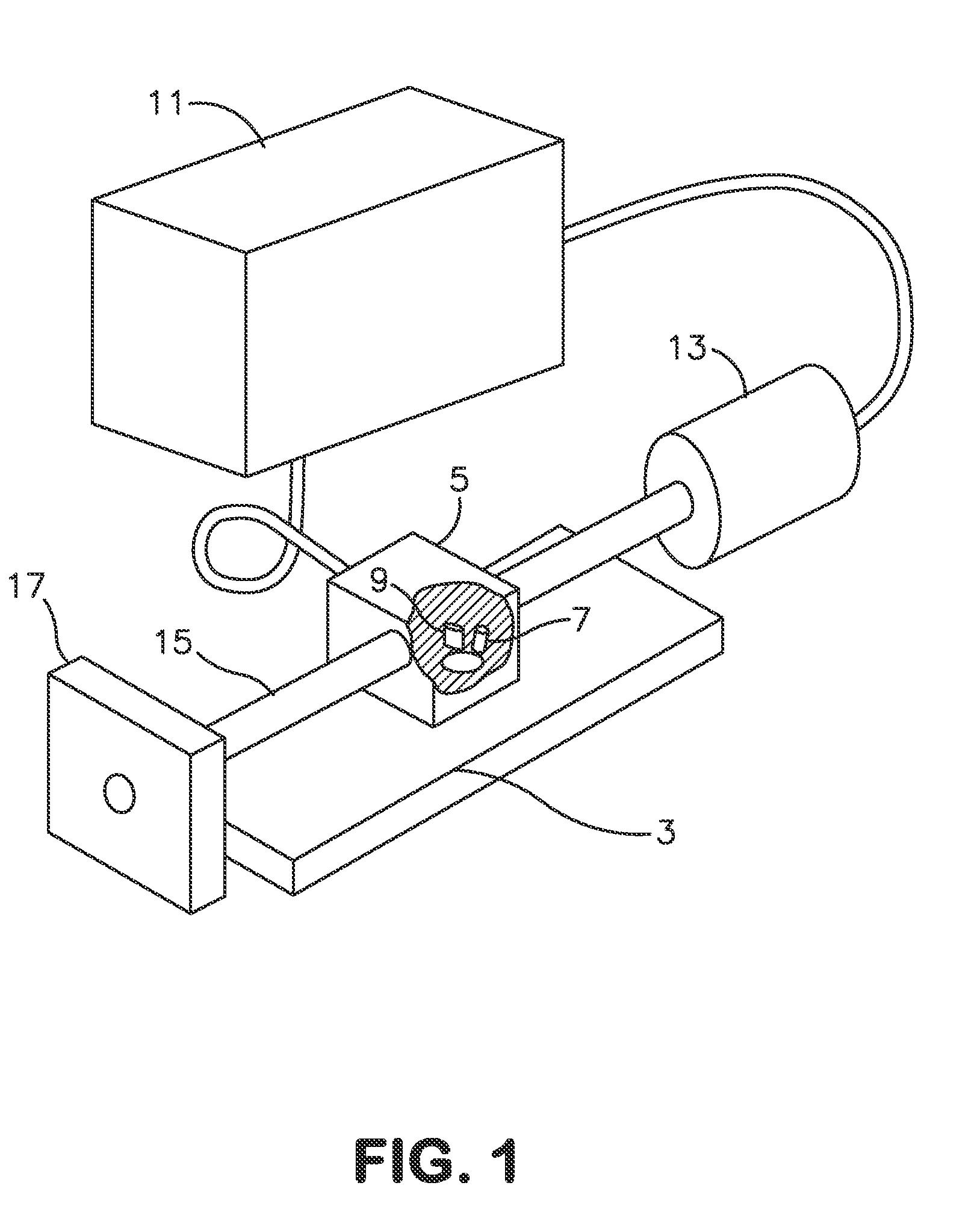
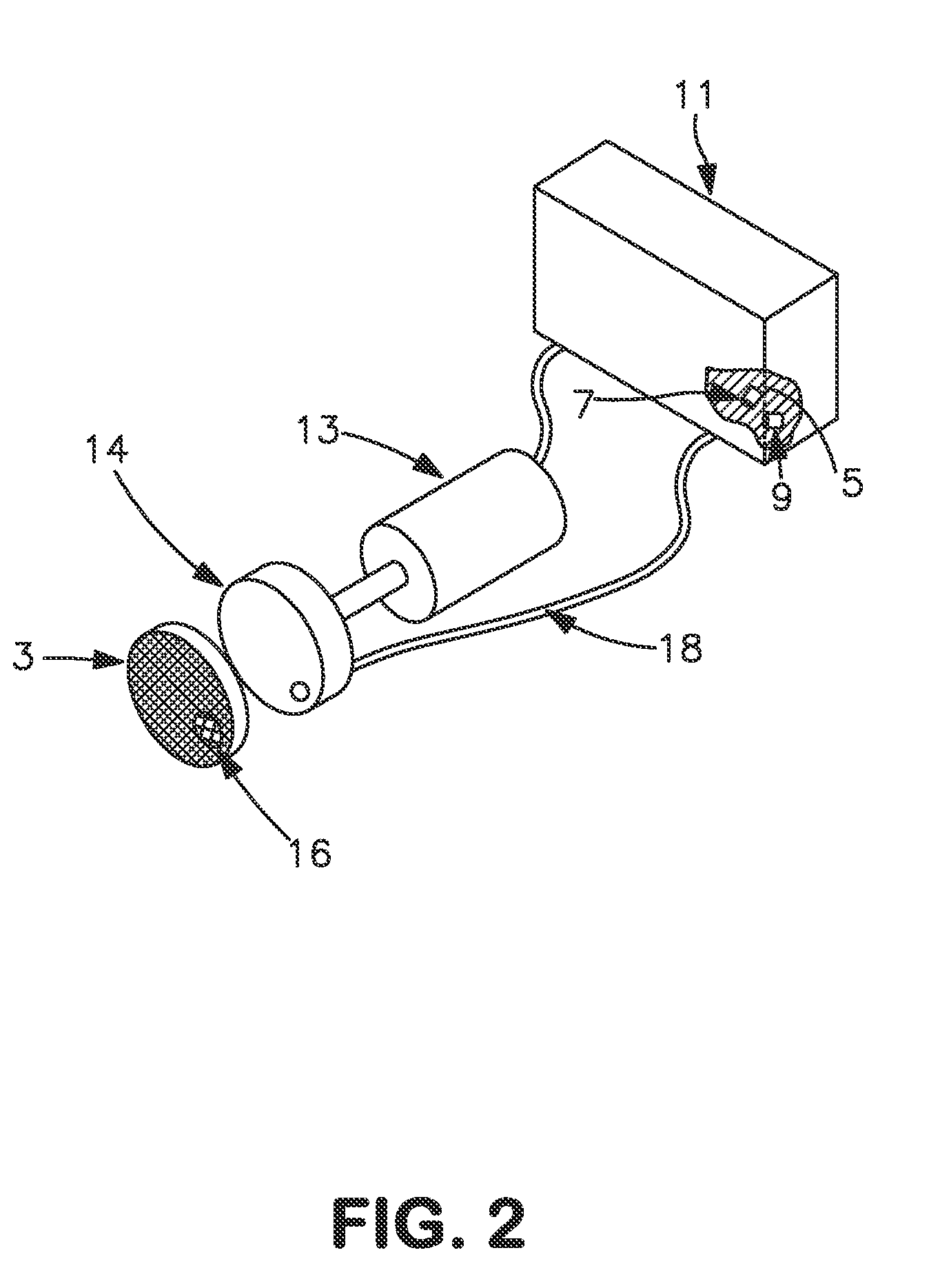
Method and apparatus for optical flame control of combustion burners
In accordance with the present invention, methods and apparatus to control the combustion of a burner are presented which overcome many of the problems of the prior art. One aspect of the invention comprises a burner control apparatus including a device for viewing light emitted by a flame from a burner, a device for optically transporting the viewed light into an optical processor, an optical processor for processing the optical spectrum into electrical signals, a signal processing for processing the electrical signals obtained from the optical spectrum, and a control device which accepts the electrical signals and produces an output acceptable to one or more oxidant or fuel flow control devices. The control device, which may be referred to as a "burner computer," functions to control the oxidant flow and / or the fuel flow to the burner. In a particularly preferred apparatus embodiment of the invention, a burner and the burner control apparatus are integrated into a single unit, which may be referred to as a "smart" burner.
Owner:AIR LIQUIDE AMERICA INC
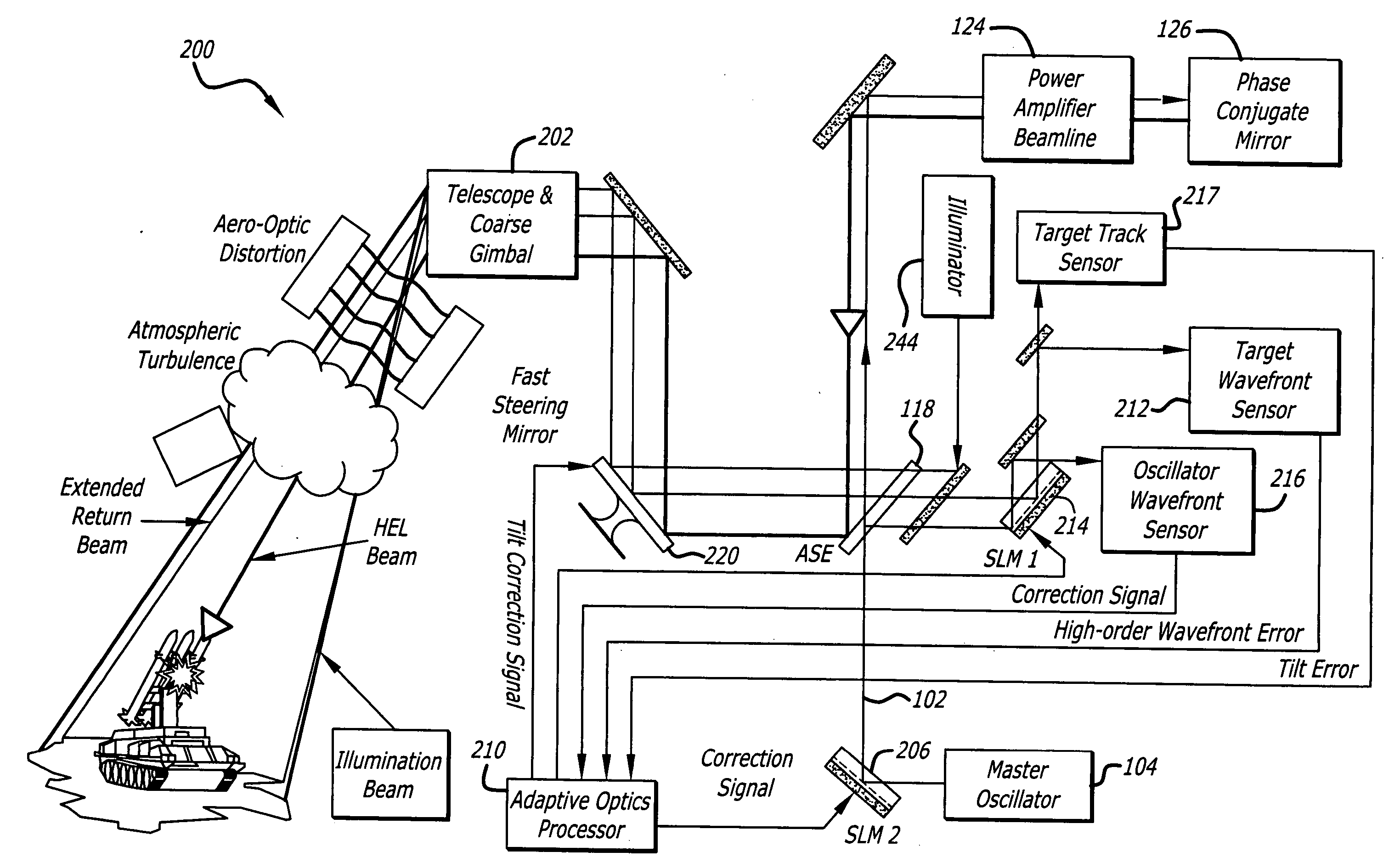
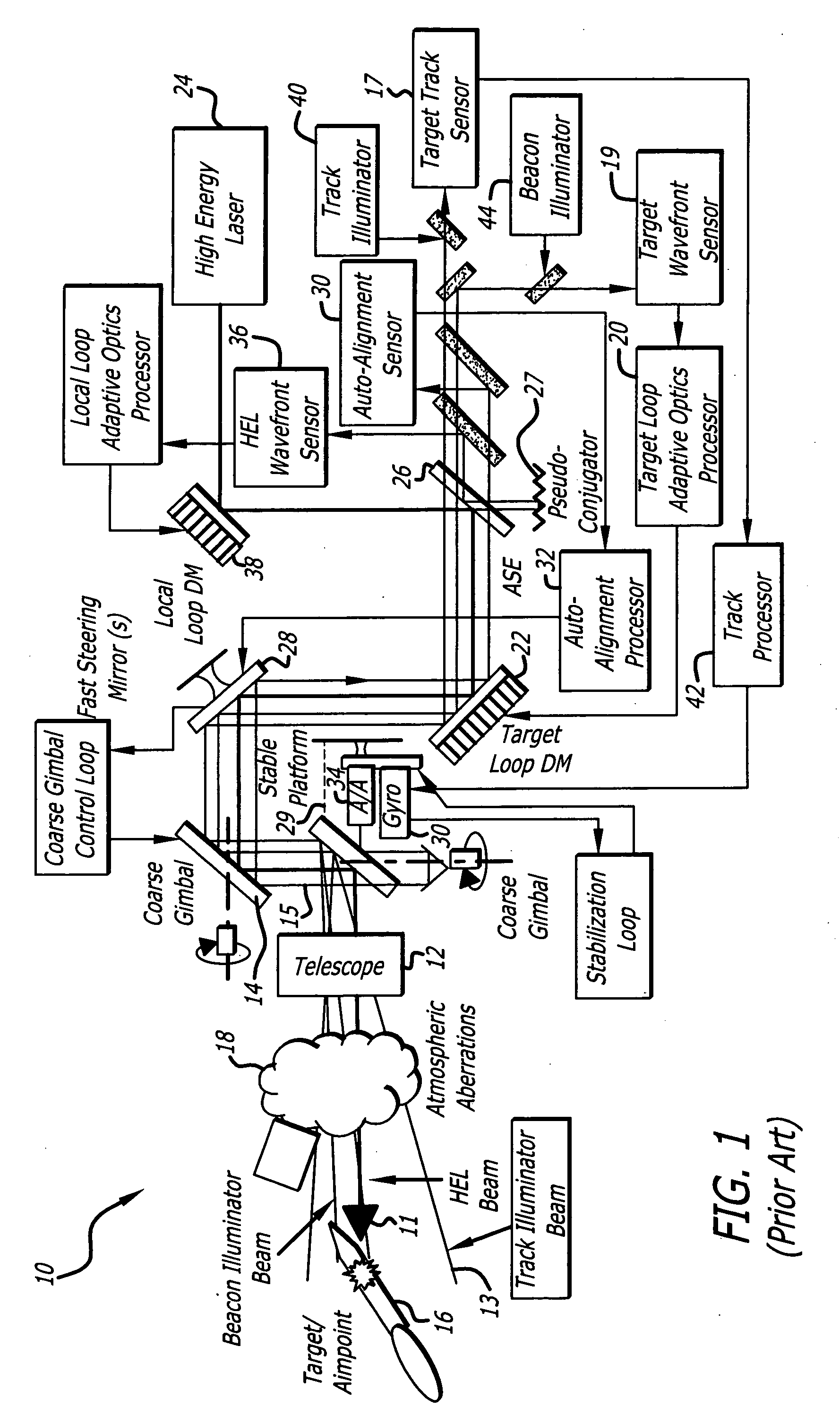
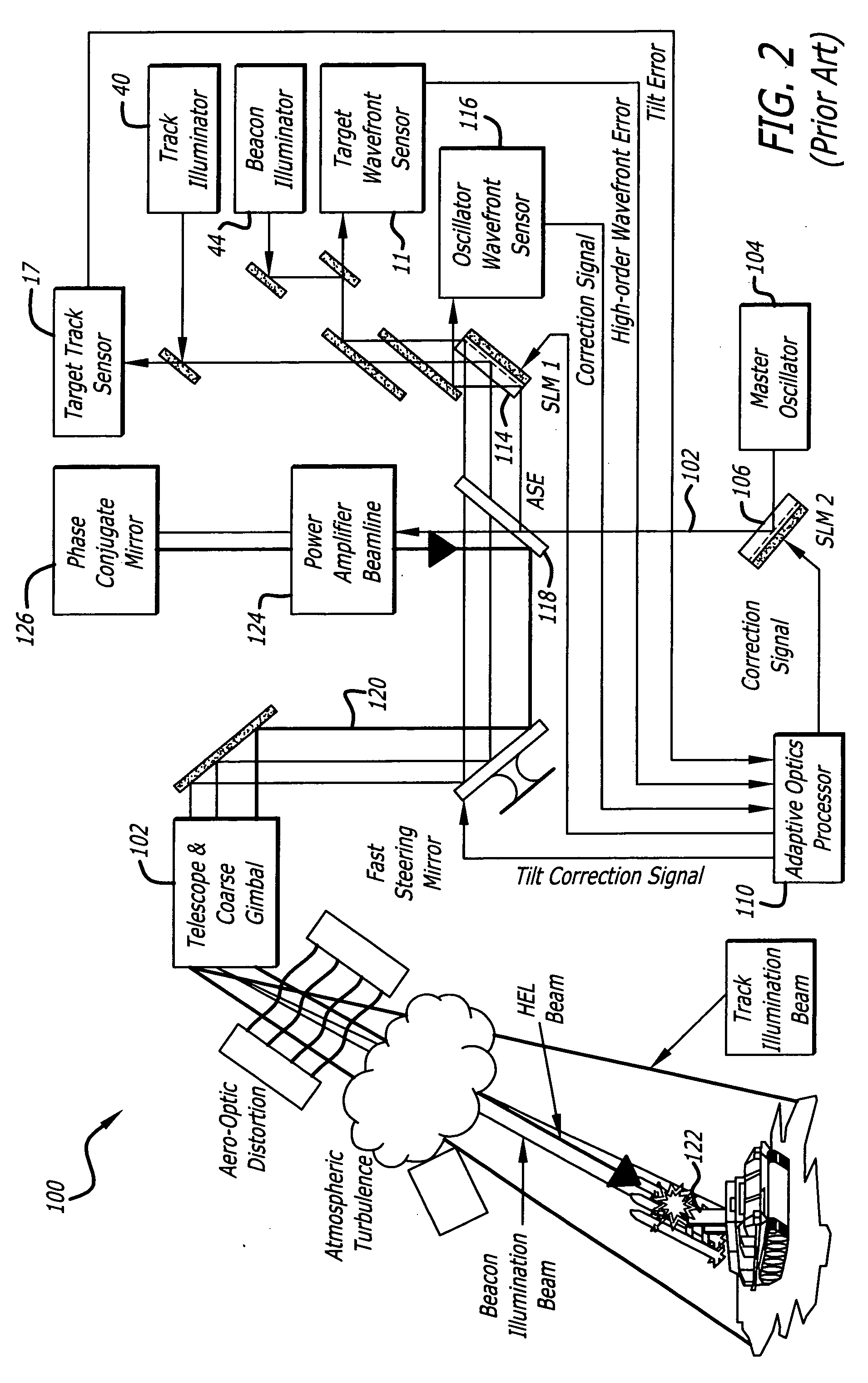
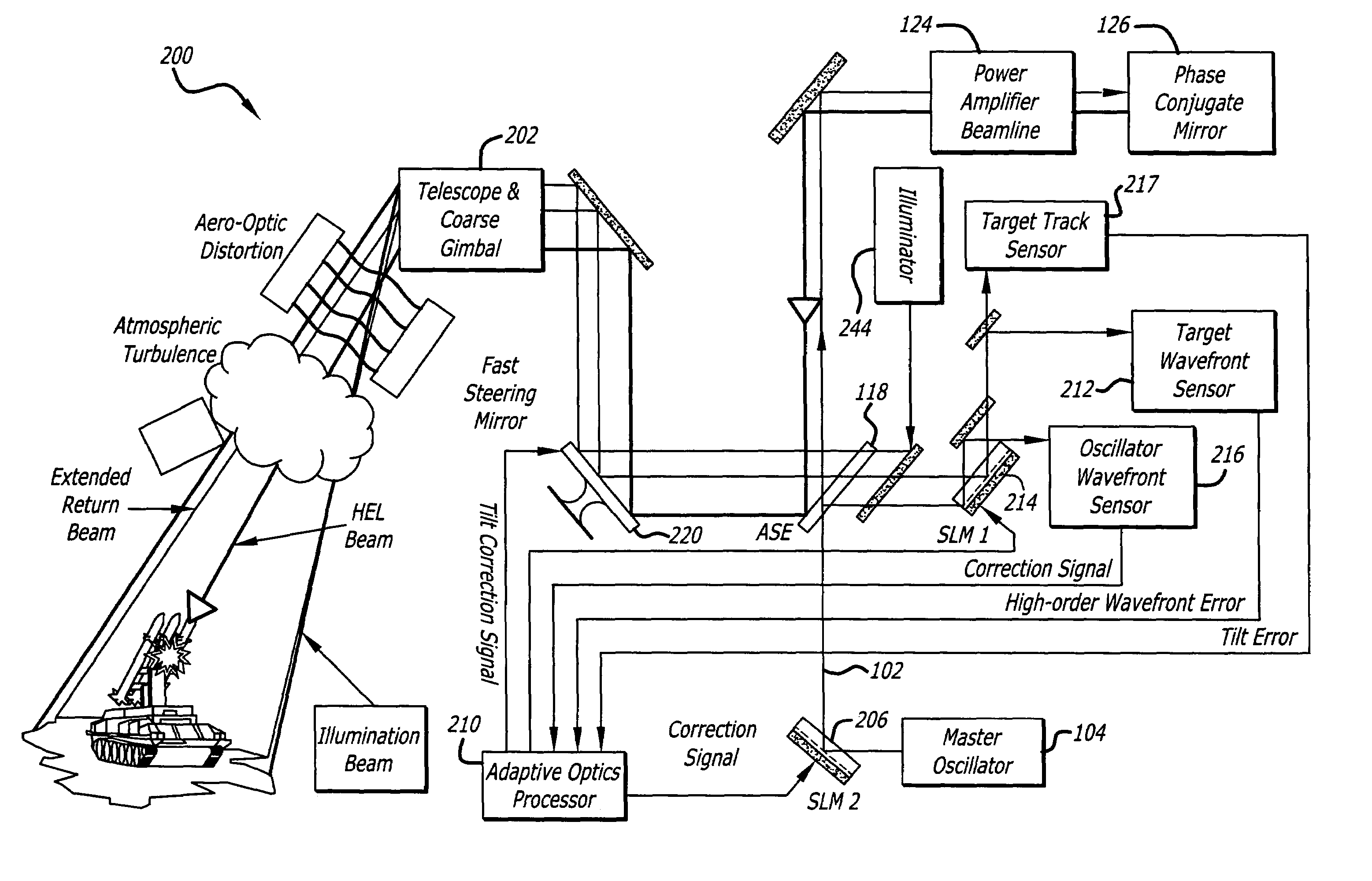
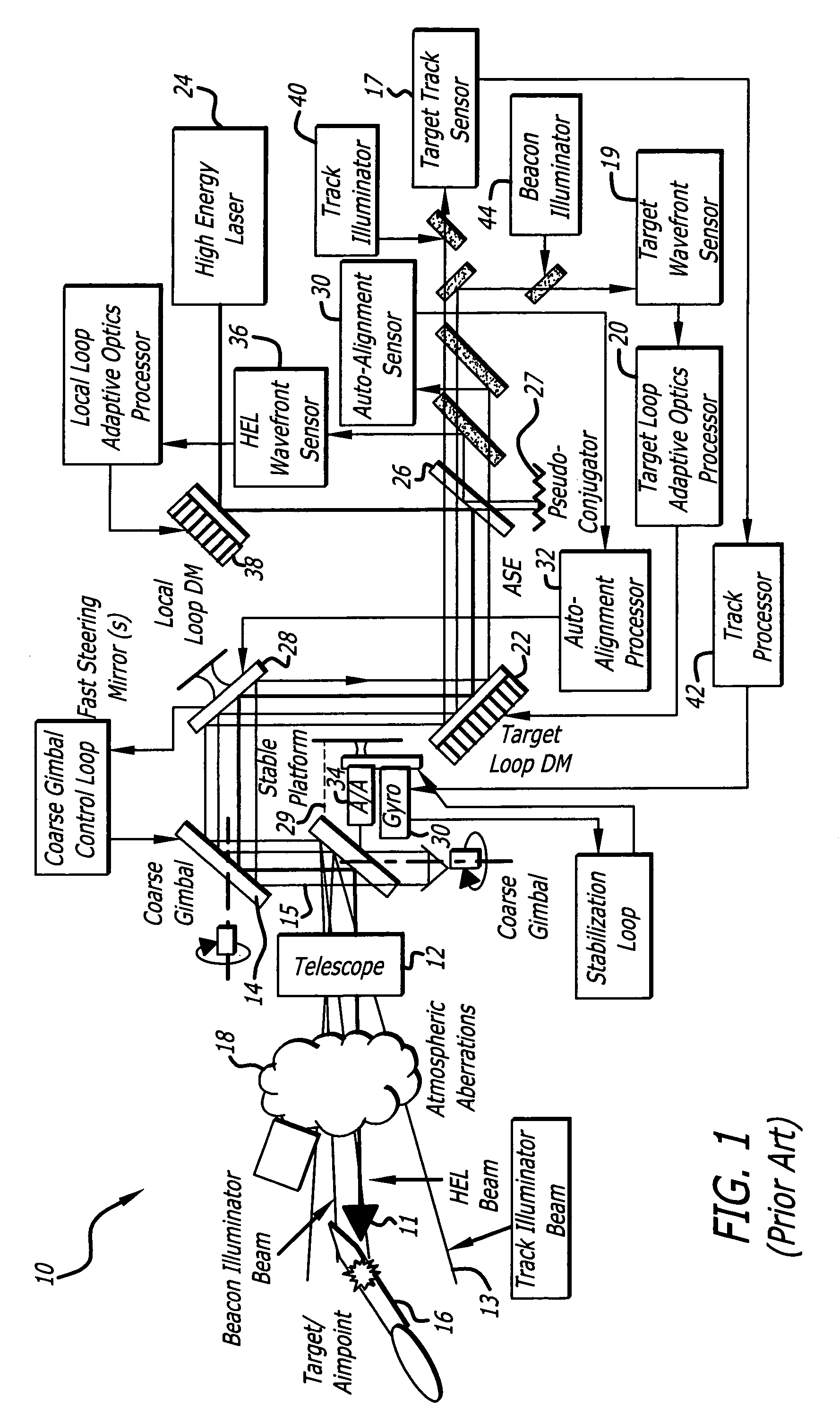
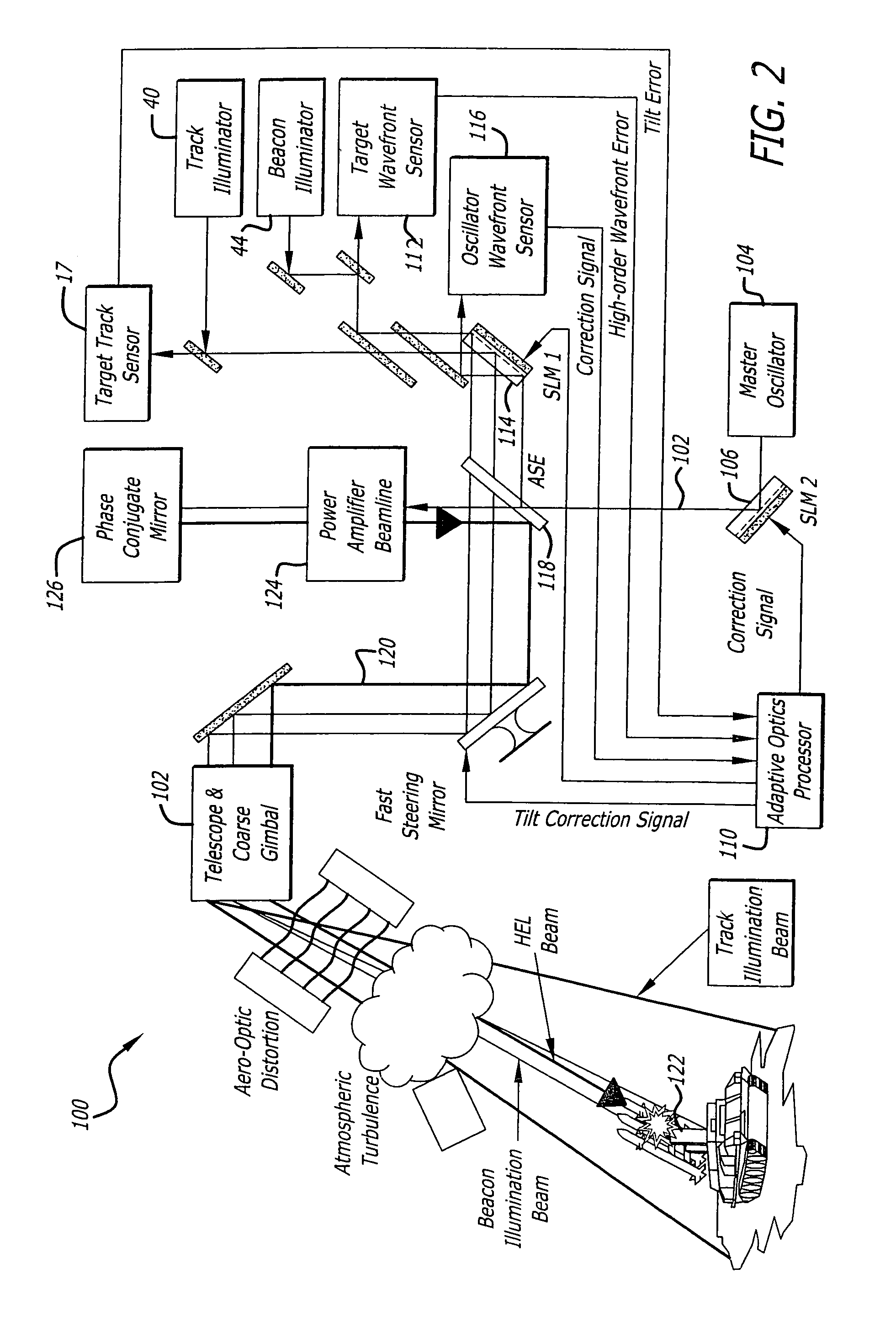
Beam control system with extended beacon and method
ActiveUS20060022115A1High error rateOptical measurementsPhotometry using reference valueSpatial light modulatorWavefront aberration
A beam control system and method: The inventive system includes, an arrangement for receiving a first beam of electromagnetic energy; measuring wavefront aberrations in the first beam with a wavefront sensor; and removing global tilt from the measured wavefront aberrations to provide higher order aberrations for beam control. In the illustrative embodiment, the invention uses a traditional (quad-cell) Shack-Hartmann wavefront sensor to measure wavefront aberrations. An adaptive optics processor electronically removes the global tilt (angular jitter) from this measurement leaving only the higher-order Zernike components. These higher-order aberrations are then applied to wavefront control elements, such as deformable mirrors or spatial light modulators that correct the tracker image and apply a conjugate distortion to the wavefront of the outgoing HEL beam. A track error (angular jitter) component is supplied by a separate fine track sensor. This jitter error is then applied by the adaptive optics processor to a fast steering mirror, which corrects jitter in the tracker image and applies a compensating distortion to the LOS of the HEL beam.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
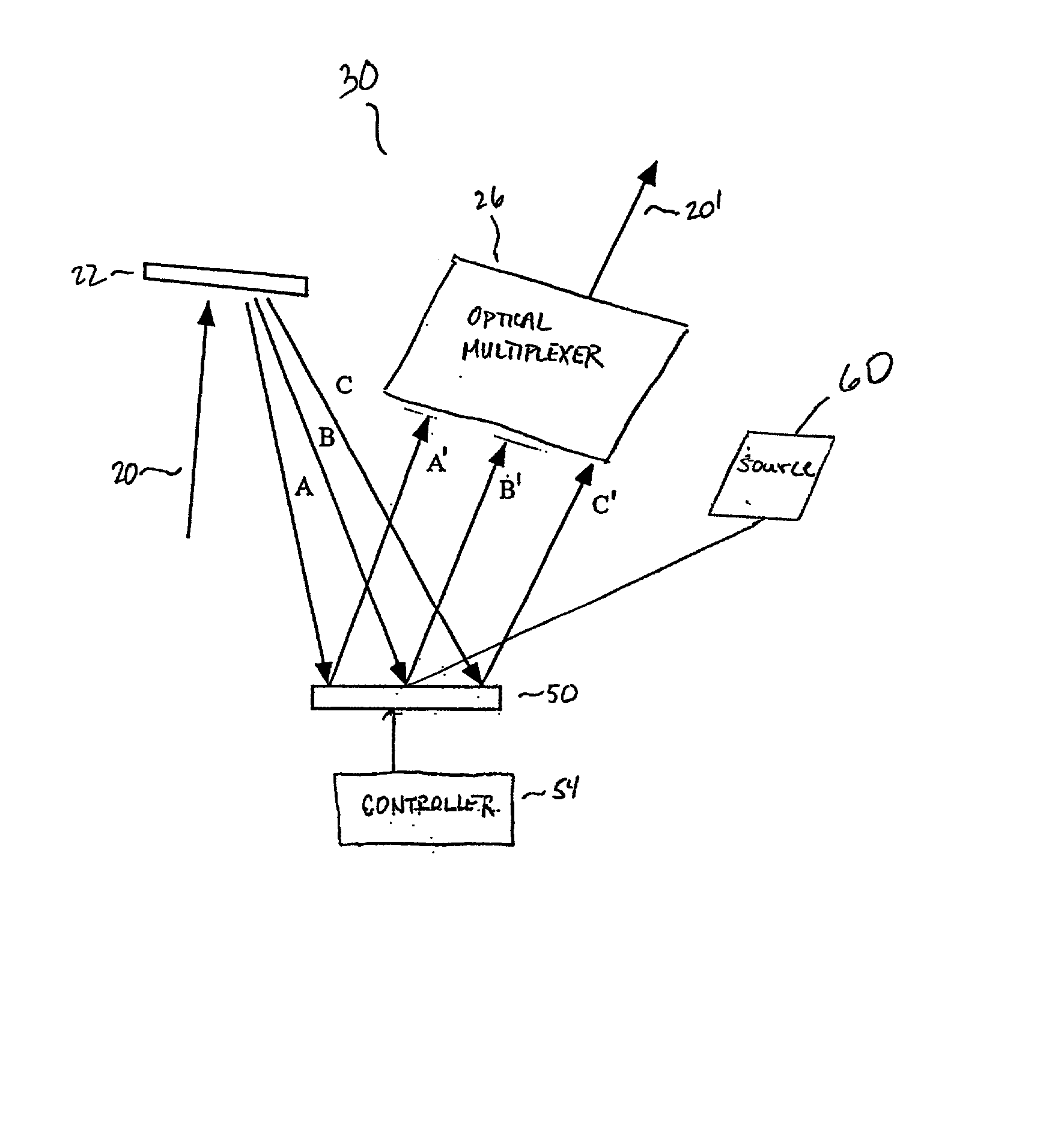
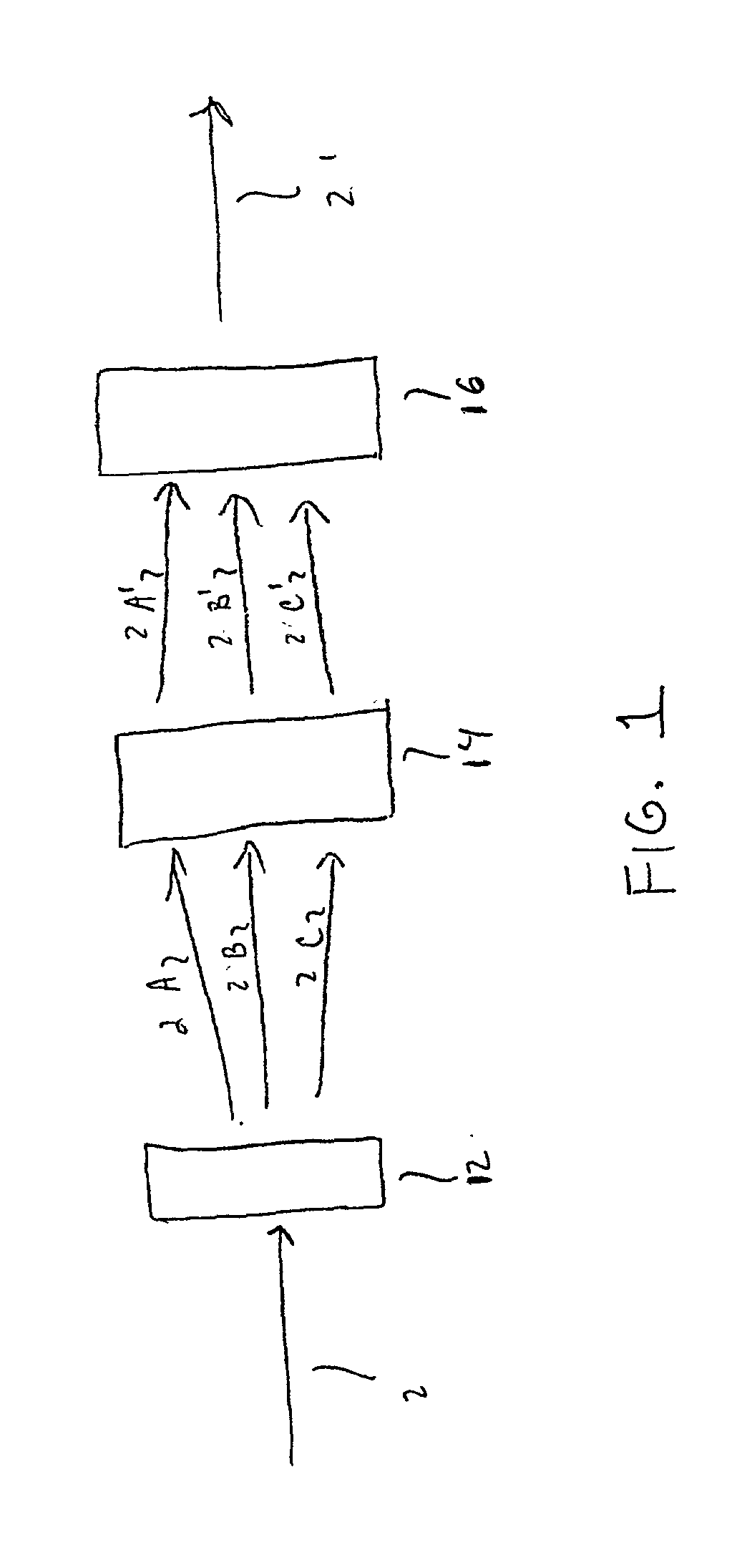
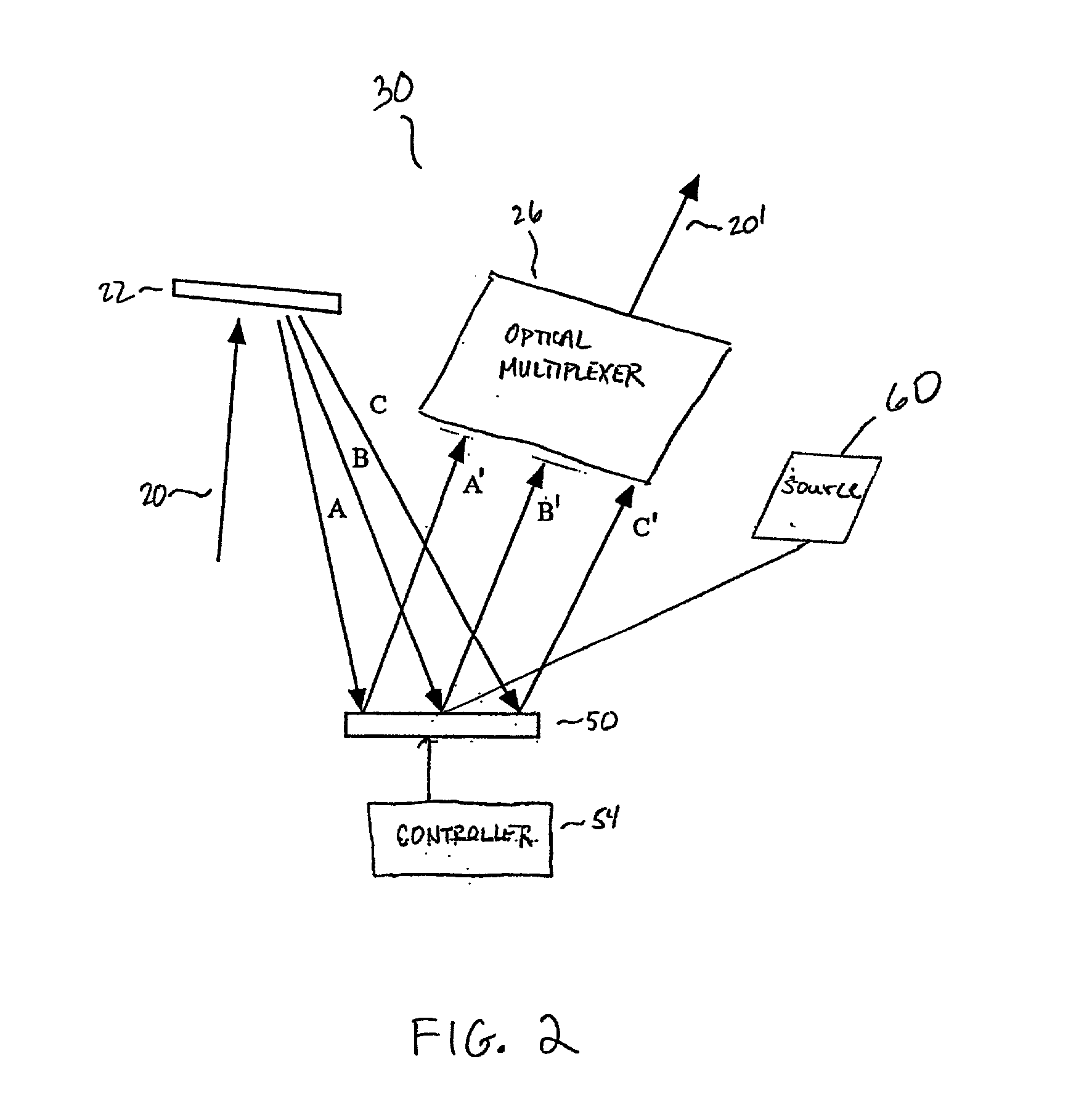
Optical processor
Method and apparatus are disclosed for optical packet decoding, waveform generation and wavelength multiplexing / demultiplexing using a programmed holographic structure. A configurable programmed holographic structure is disclosed. A configurable programmed holographic structure may be dynamically re-configured through the application of control mechanisms which alter operative holographic structures.
Owner:OL SECURITY LIABILITY CO
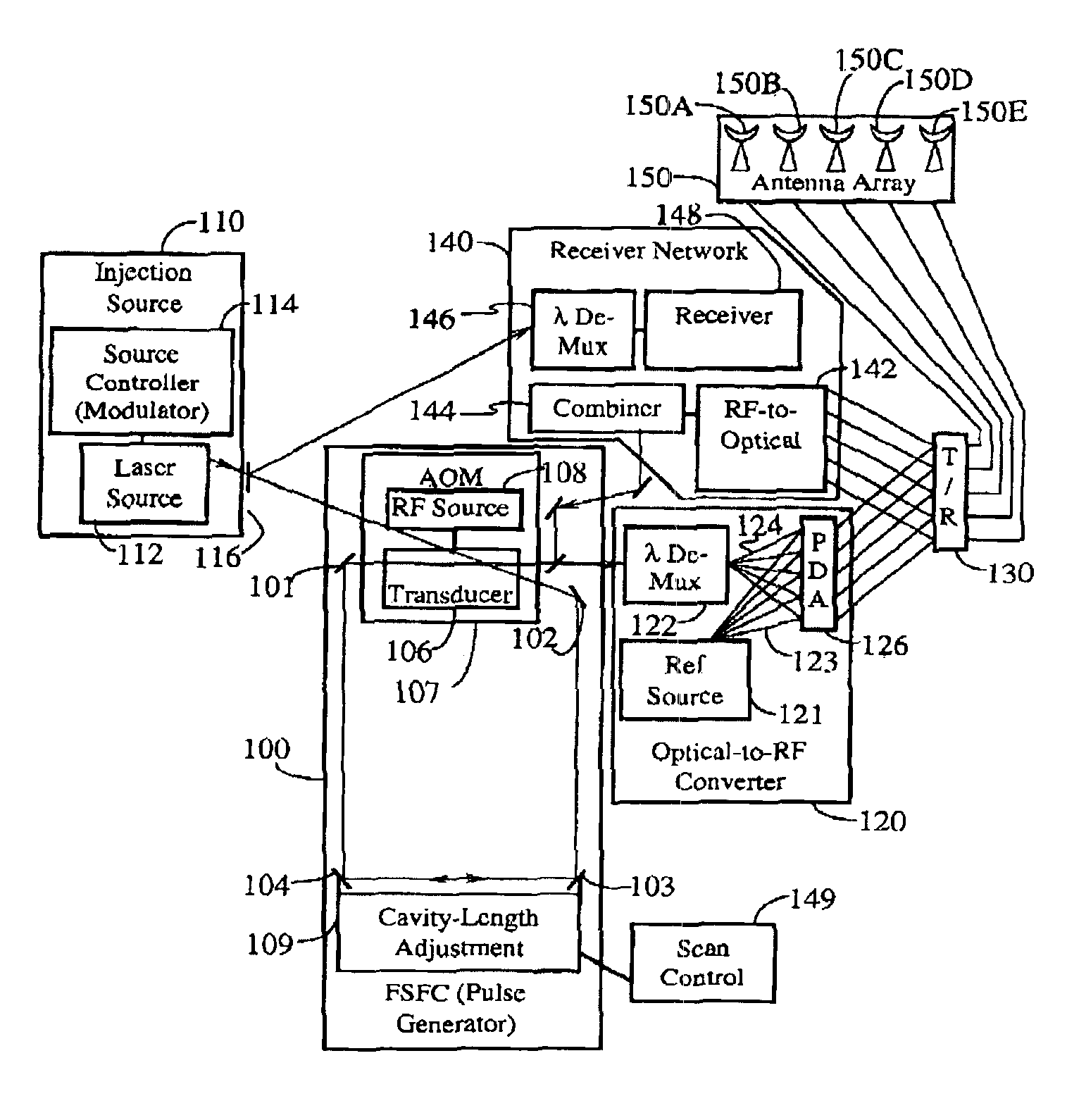
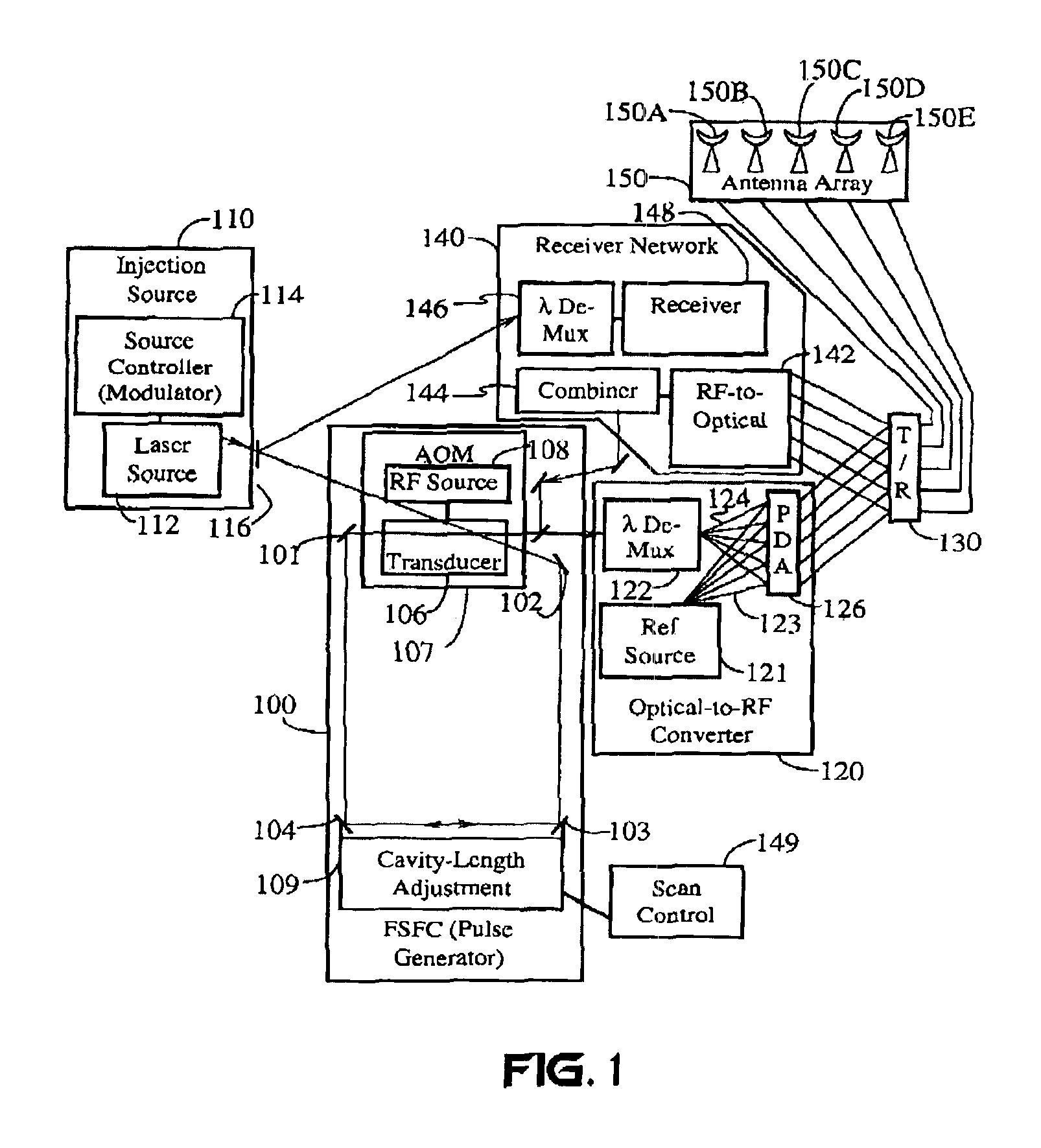
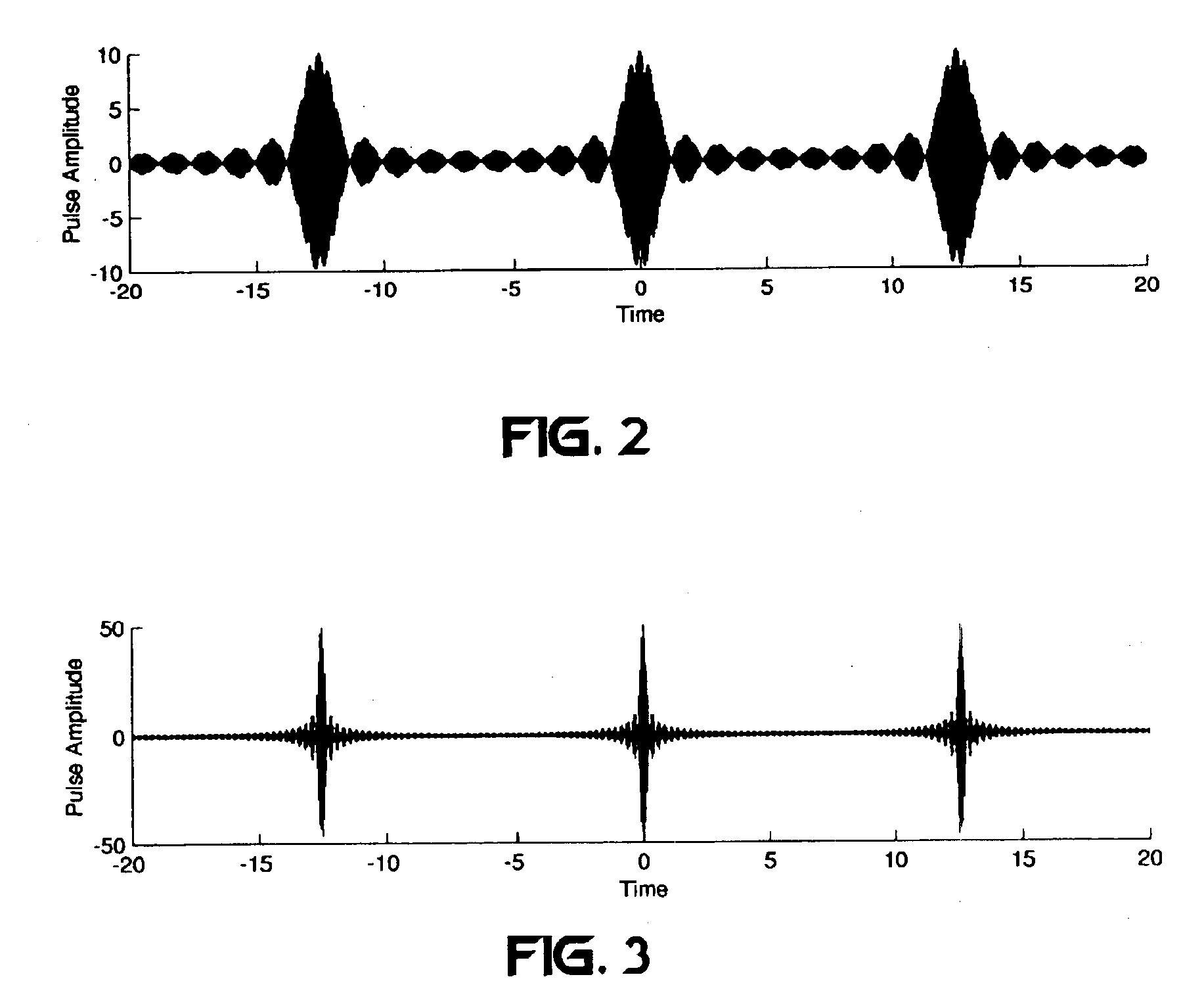
Frequency-shifted feedback cavity used as a phased array antenna controller and carrier interference multiple access spread-spectrum transmitter
InactiveUS20050232182A1Easy to adaptFrequency diversityWavelength-division multiplex systemsTime domainCarrier signal
An optical processor for controlling a phased antenna array uses a frequency-shifted feedback cavity (FSFC), which includes a traveling-wave cavity. The FSFC incrementally delays and incrementally frequency shifts optical signals circulating in the traveling-wave cavity. Optical signals coupled out of the FSFC are separated by frequency, hence by delay, and processed to control either or both transmit and receive beam-forming operations. The FSFC provides a receiver with multiple receive signals which have incremental values of frequency. Each frequency corresponds to an incremental time sampling of optical signals input into the FSFC. Transmit signals coupled out of the FSFC have frequency and phase relationships that result in short time-domain pulses when combined. Controlling modulation and frequency of the transmit signals achieves carrier interference multiple access, a new type of spread-spectrum communications.
Owner:DEPARTMENT 13 INC
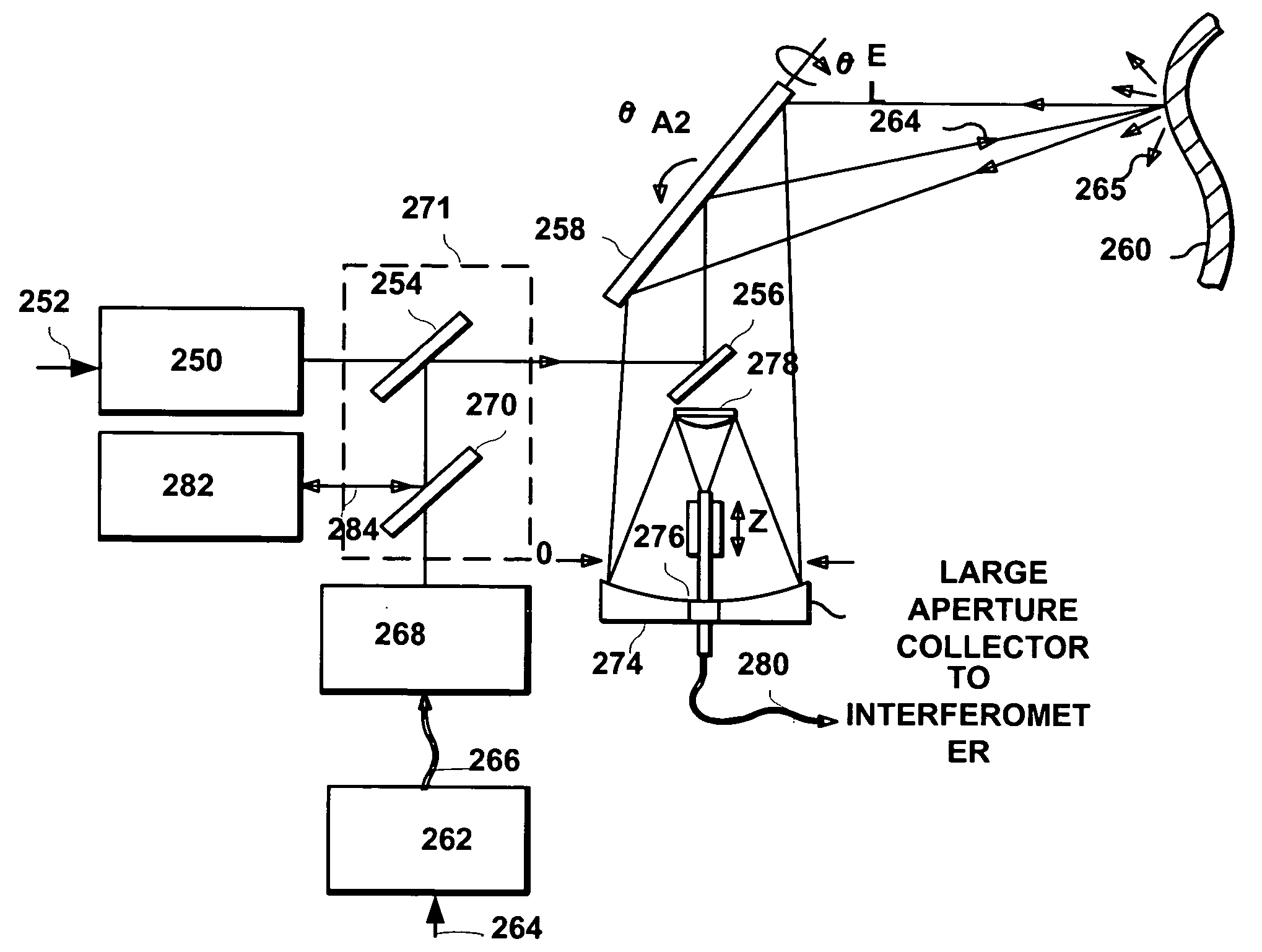
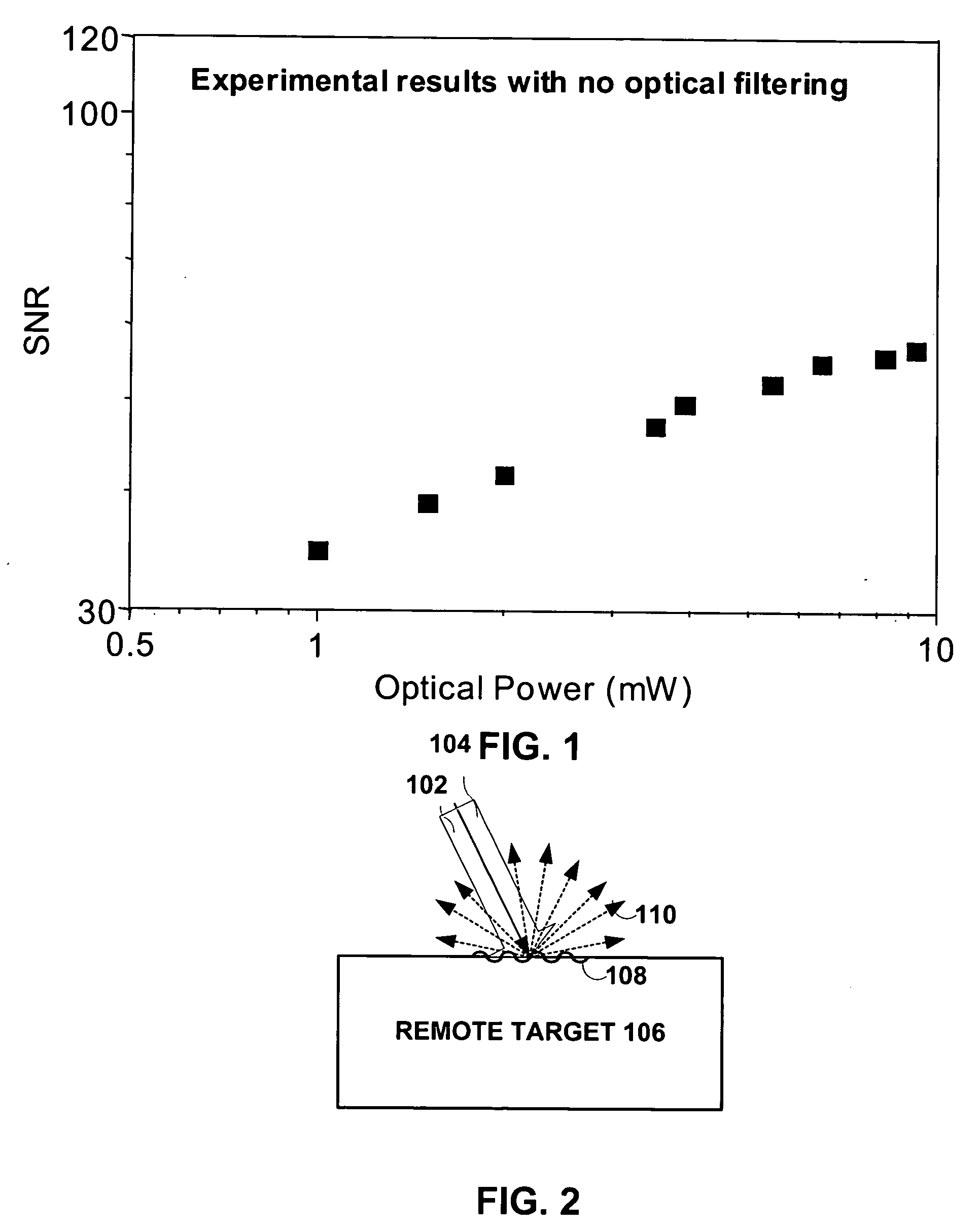
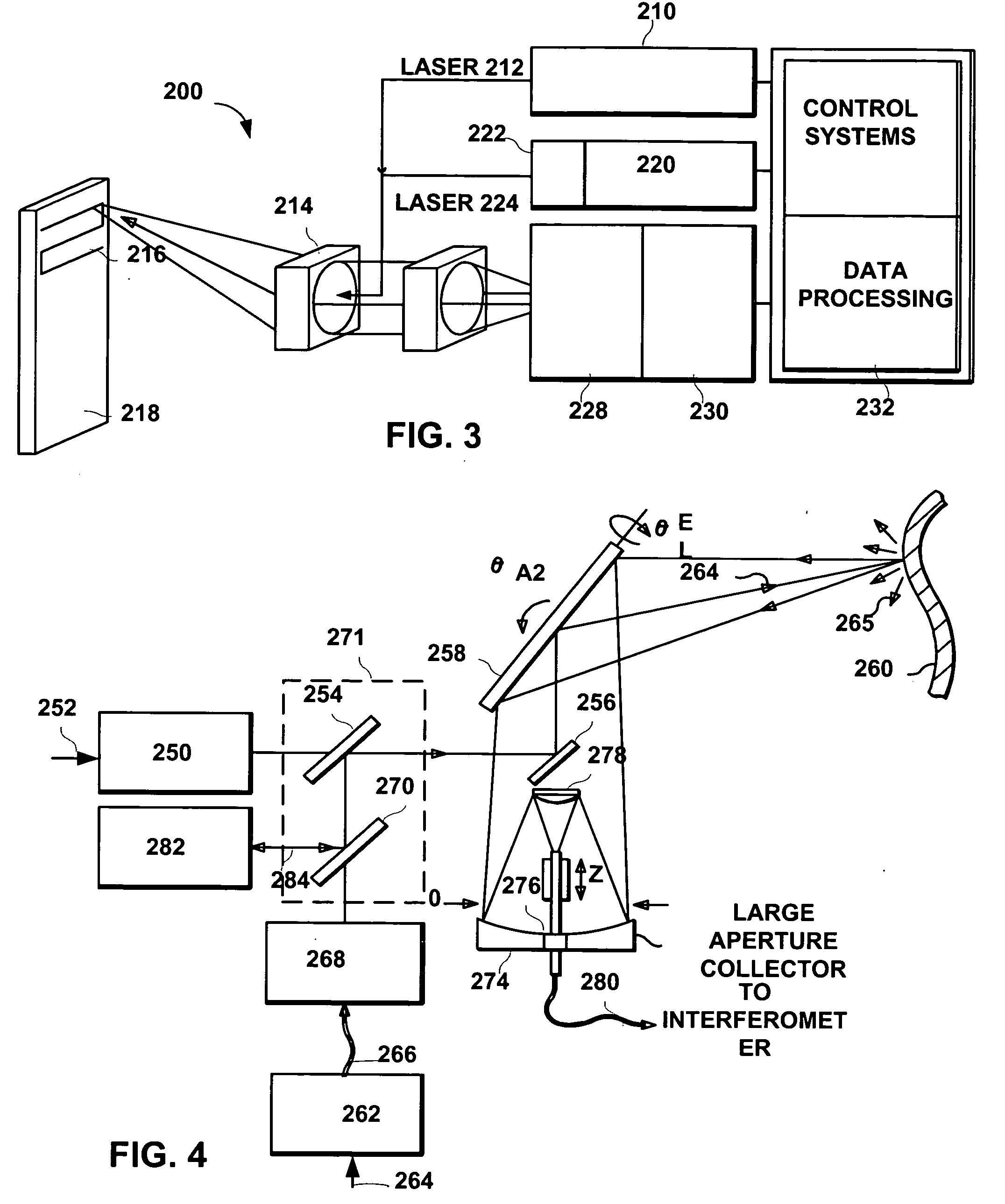
System and method to reduce laser noise for improved interferometric laser ultrasound detection
ActiveUS20050099634A1Eliminates and reduces disadvantage and problemReduce noiseSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementUsing optical meansSonificationLaser noise
The present invention provides an optical filter assembly that reduces the phase and amplitude noise of a detection laser used to detect ultrasonic displacements. The filtered detection laser is directed to the surface of a remote target. Ultrasonic displacements at the surface scatter the filtered detection laser. Collection optics then gather phase modulated light scattered by the surface and direct the phase modulated light to an optical processor to produce a signal representative of the ultrasonic displacements with an improved SNR. Additional processors may determine the structure of the remote target.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Frequency-shifted feedback cavity used as a phased array antenna controller and carrier interference multiple access spread-spectrum transmitter
InactiveUS6888887B1Easy to adaptFrequency diversityFrequency/rate-modulated pulse demodulationTime domainCarrier signal
An optical processor for controlling a phased antenna array uses a frequency-shifted feedback cavity (FSFC), which includes a traveling-wave cavity. The FSFC incrementally delays and incrementally frequency shifts optical signals circulating in the traveling-wave cavity. Optical signals coupled out of the FSFC are separated by frequency, hence by delay, and processed to control either or both transmit and receive beam-forming operations. The FSFC provides a receiver with multiple receive signals which have incremental values of frequency. Each frequency corresponds to an incremental time sampling of optical signals input into the FSFC. Transmit signals coupled out of the FSFC have frequency and phase relationships that result in short time-domain pulses when combined. Controlling modulation and frequency of the transmit signals achieves carrier interference multiple access, a new type of spread-spectrum communications.
Owner:DEPARTMENT 13 INC
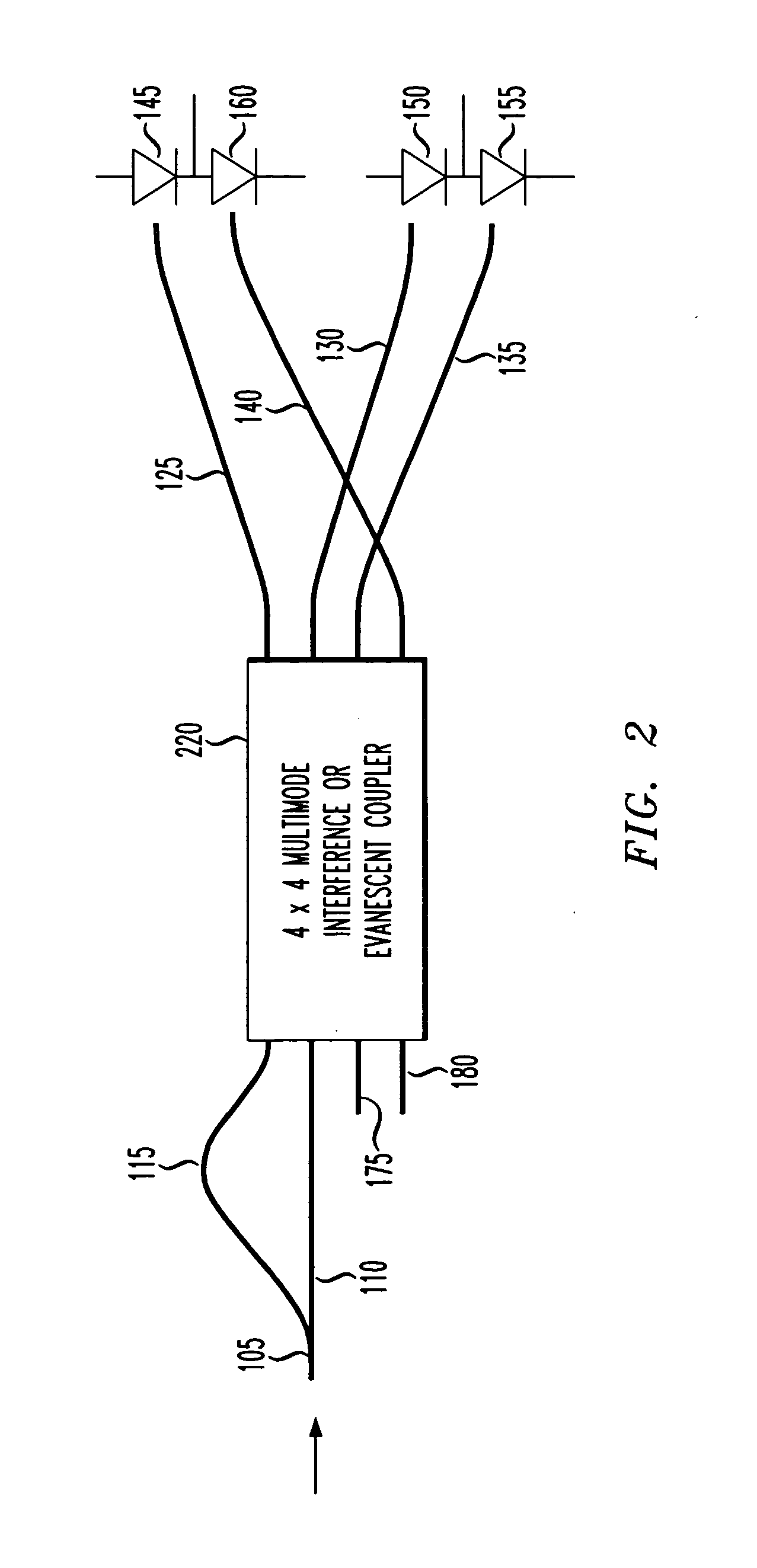
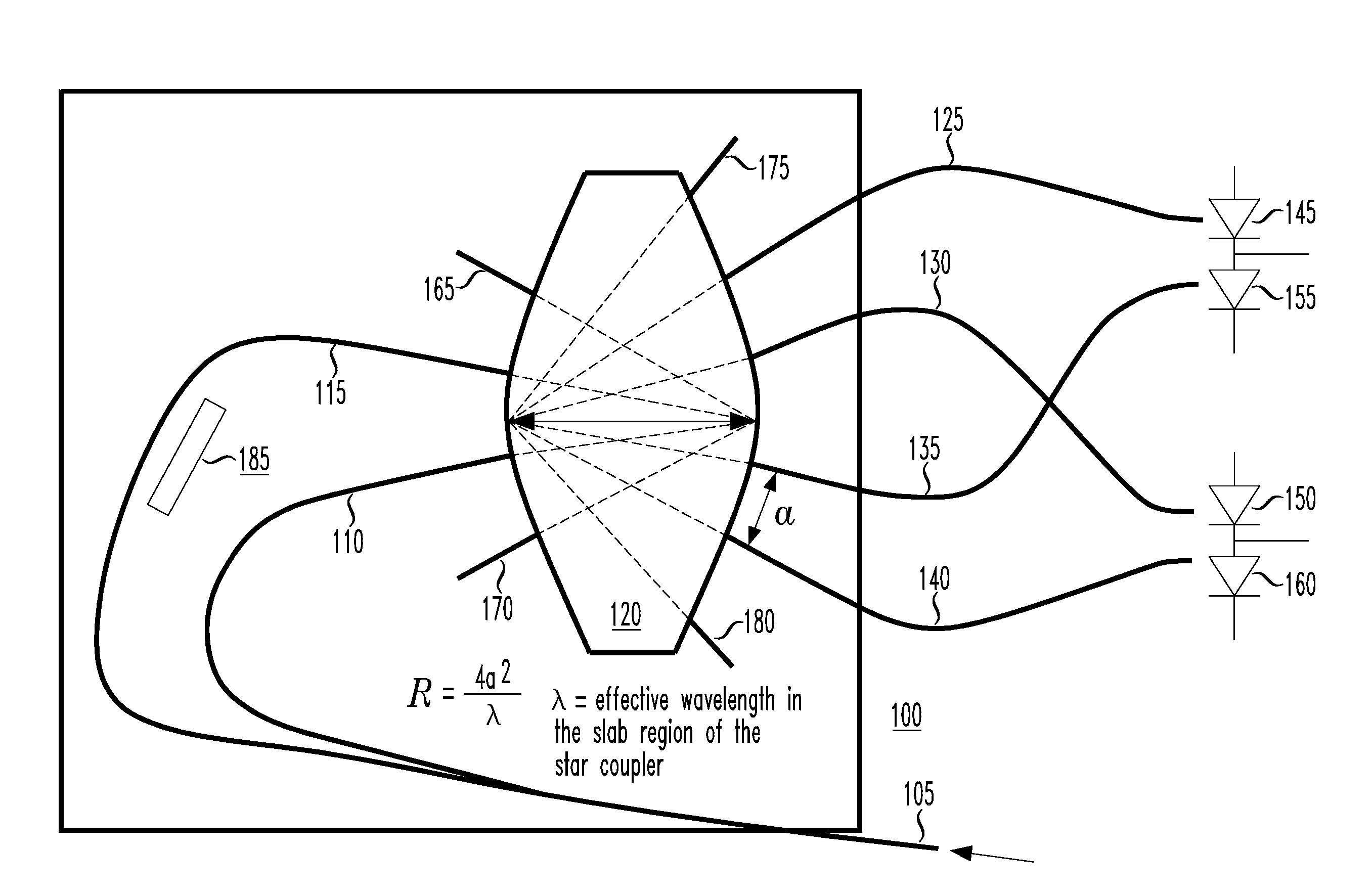
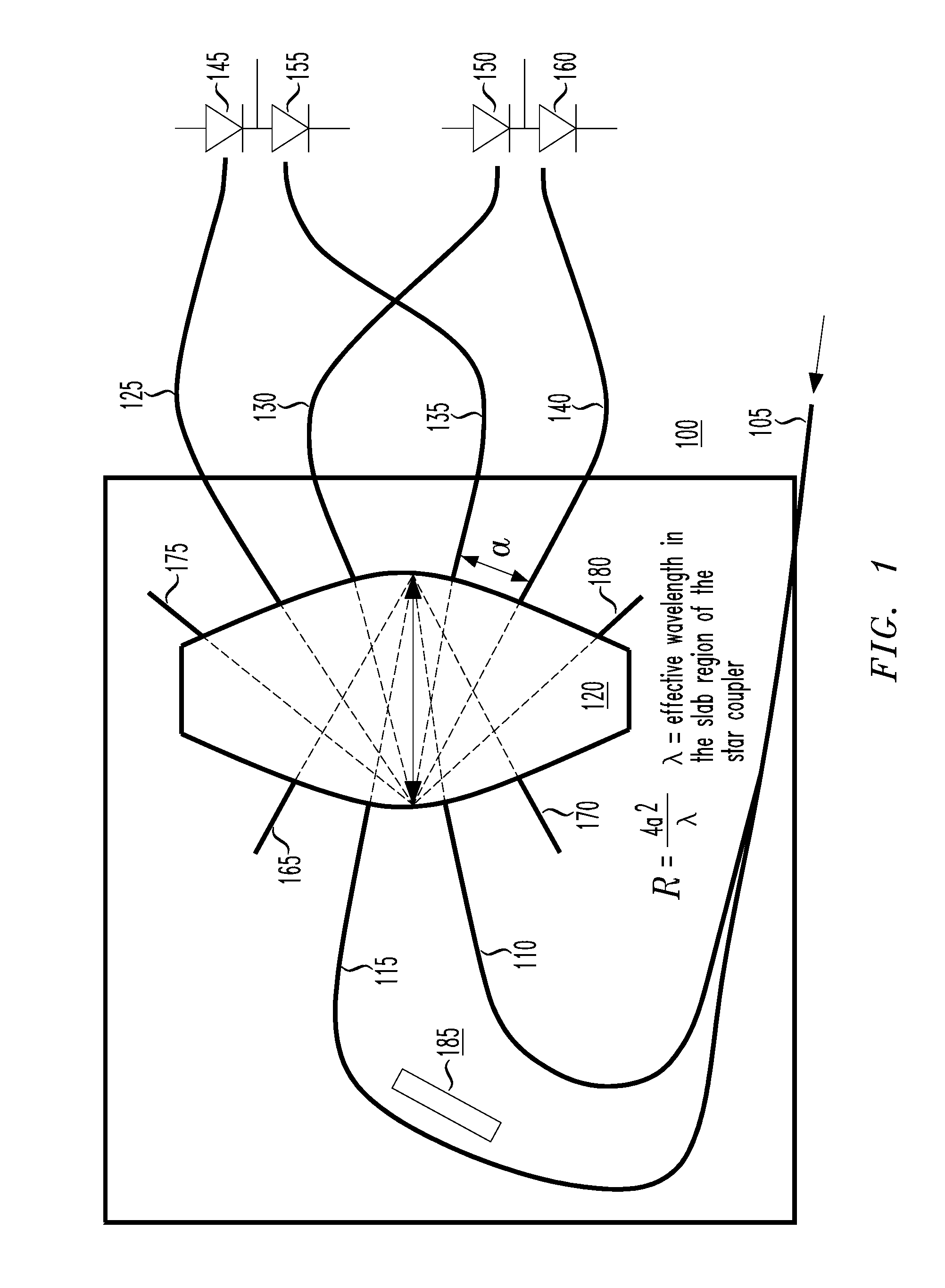
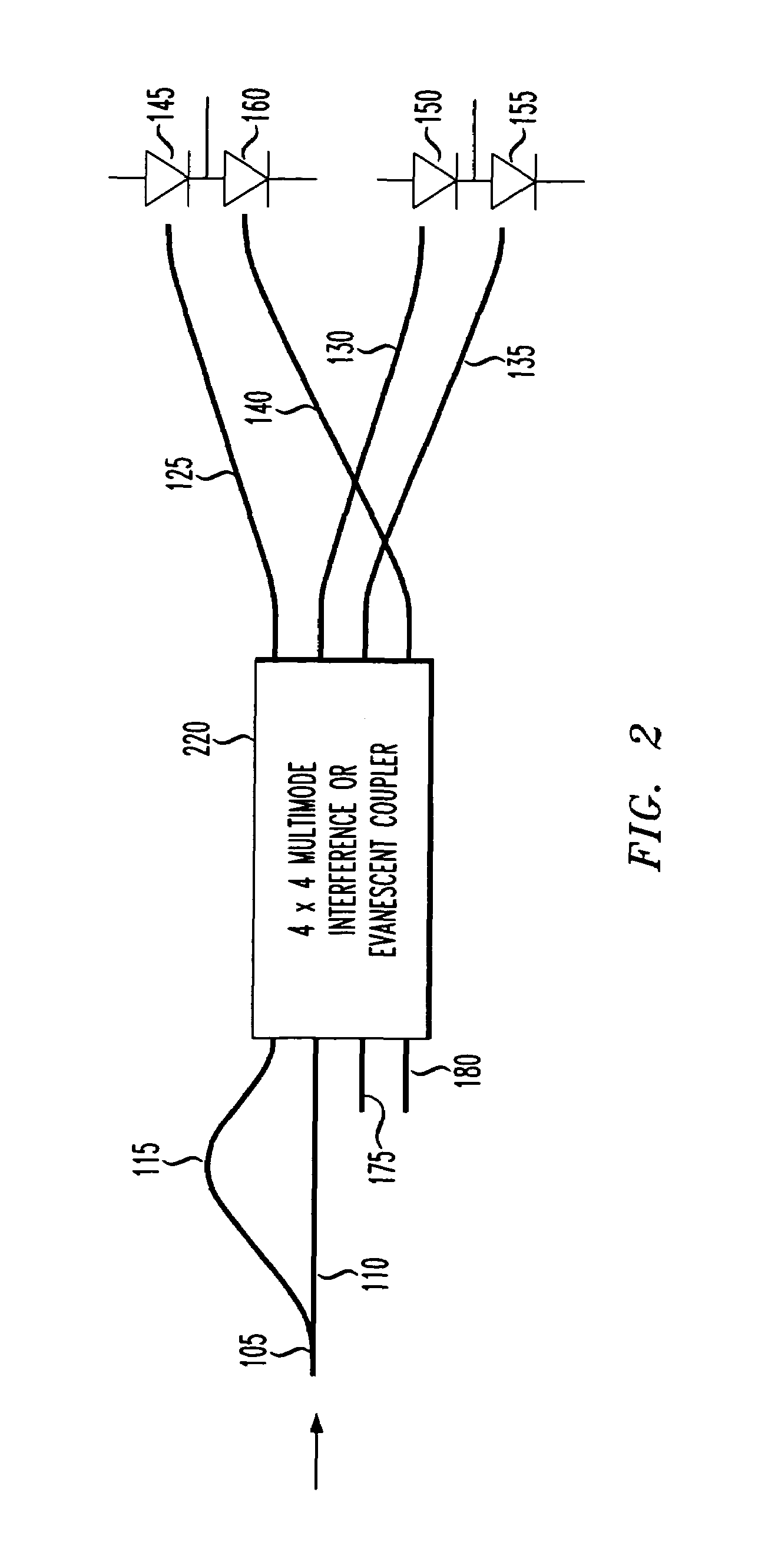
Apparatus and method for receiving a quadrature differential phase shift key modulated optical pulsetrain
InactiveUS20050286911A1Consumes less powerFew opticsElectromagnetic receiversDigital dataDifferential phase
An optical differential phase shift key (DPSK) receiver, a method of demodulating an optical DPSK modulated signal and an optical processor capable of operating as either a DPSK receiver or DPSK transmitter. In one embodiment, the DPSK receiver includes: (1) an optical waveguide and a delay line associated therewith configured to receive simultaneously an optical DPSK modulated signal, (2) a coupler having at least two inputs and at least four outputs, the at least two inputs configured to terminate the optical waveguide and the delay line, the delay line having a path length difference that delays the optical DPSK modulated signal by at least one timeslot relative to the optical waveguide and (3) photodetectors associated with the at least four outputs and configured to provide signals indicative of digital data contained in components of the optical DPSK modulated signal.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
Apparatus and method for receiving a quadrature differential phase shift key modulated optical pulsetrain
An optical differential phase shift key (DPSK) receiver, a method of demodulating an optical DPSK modulated signal and an optical processor capable of operating as either a DPSK receiver or DPSK transmitter. In one embodiment, the DPSK receiver includes: (1) an optical waveguide and a delay line associated therewith configured to receive simultaneously an optical DPSK modulated signal, (2) a coupler having at least two inputs and at least four outputs, the at least two inputs configured to terminate the optical waveguide and the delay line, the delay line having a path length difference that delays the optical DPSK modulated signal by at least one timeslot relative to the optical waveguide and (3) photodetectors associated with the at least four outputs and configured to provide signals indicative of digital data contained in components of the optical DPSK modulated signal.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
Optical processor enhanced receiver architecture (opera)
InactiveUS20020126644A1Improve performanceIncrease capacityMirrorsTime-division optical multiplex systemsTime delaysReceiver function
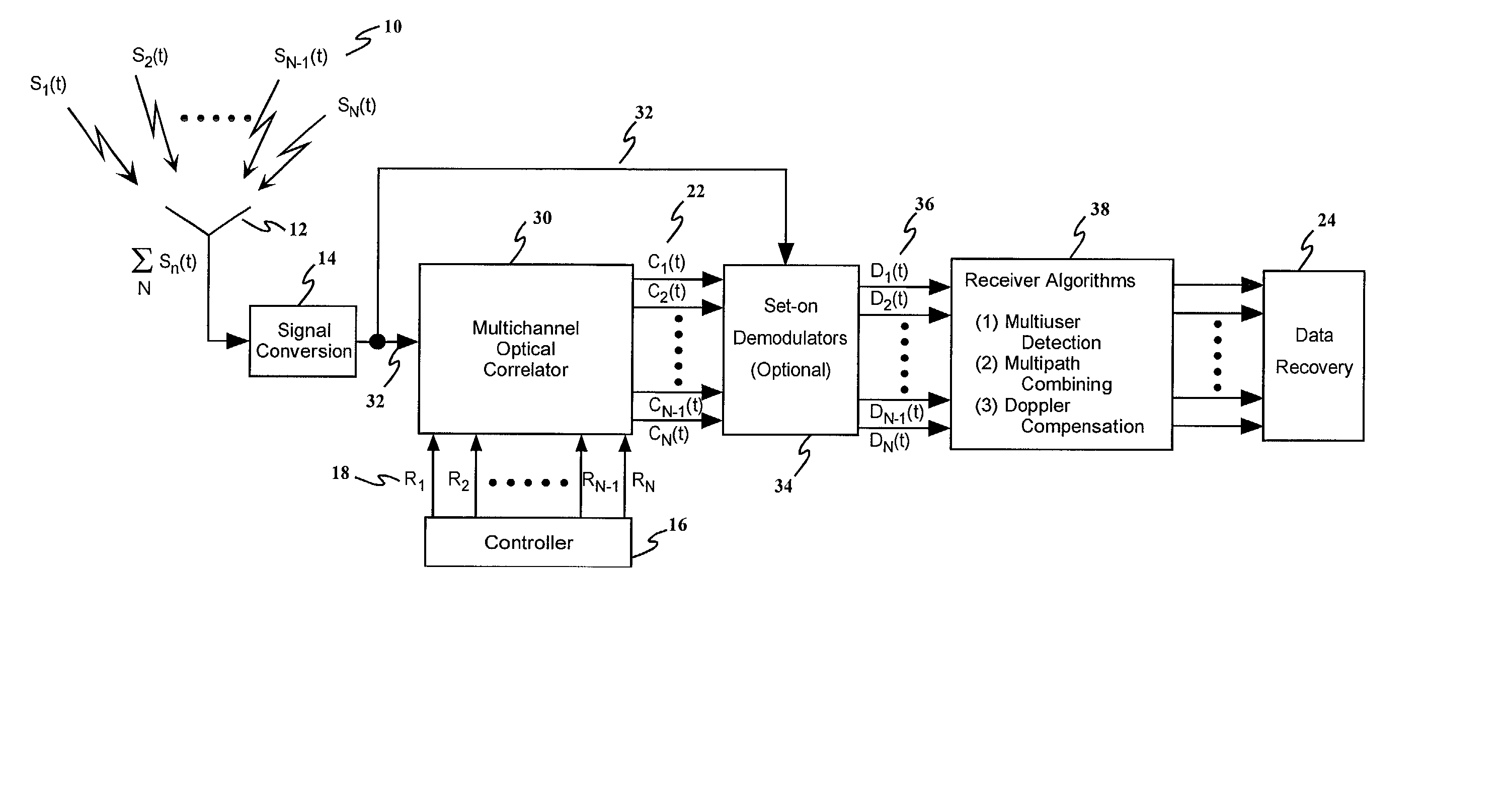
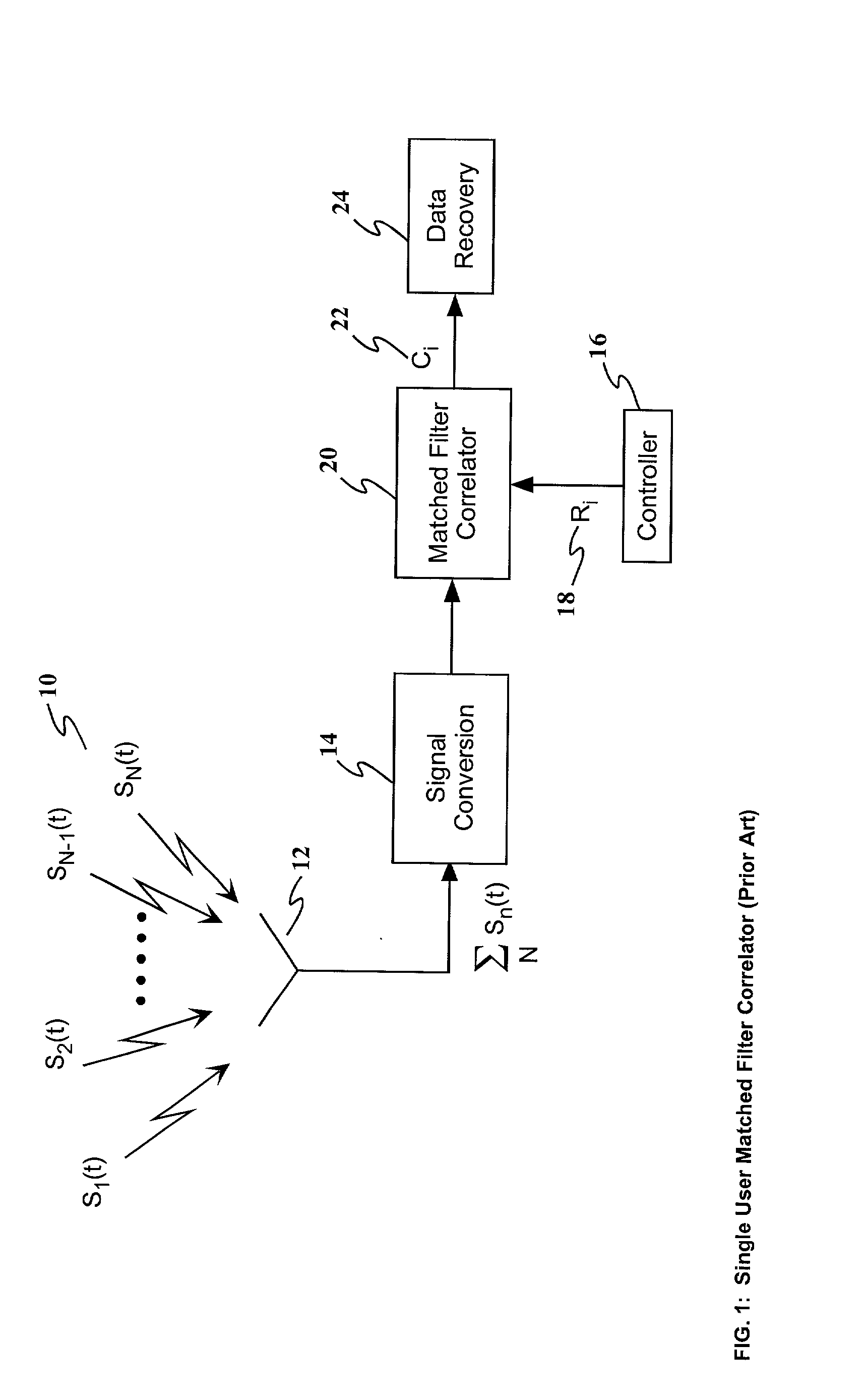
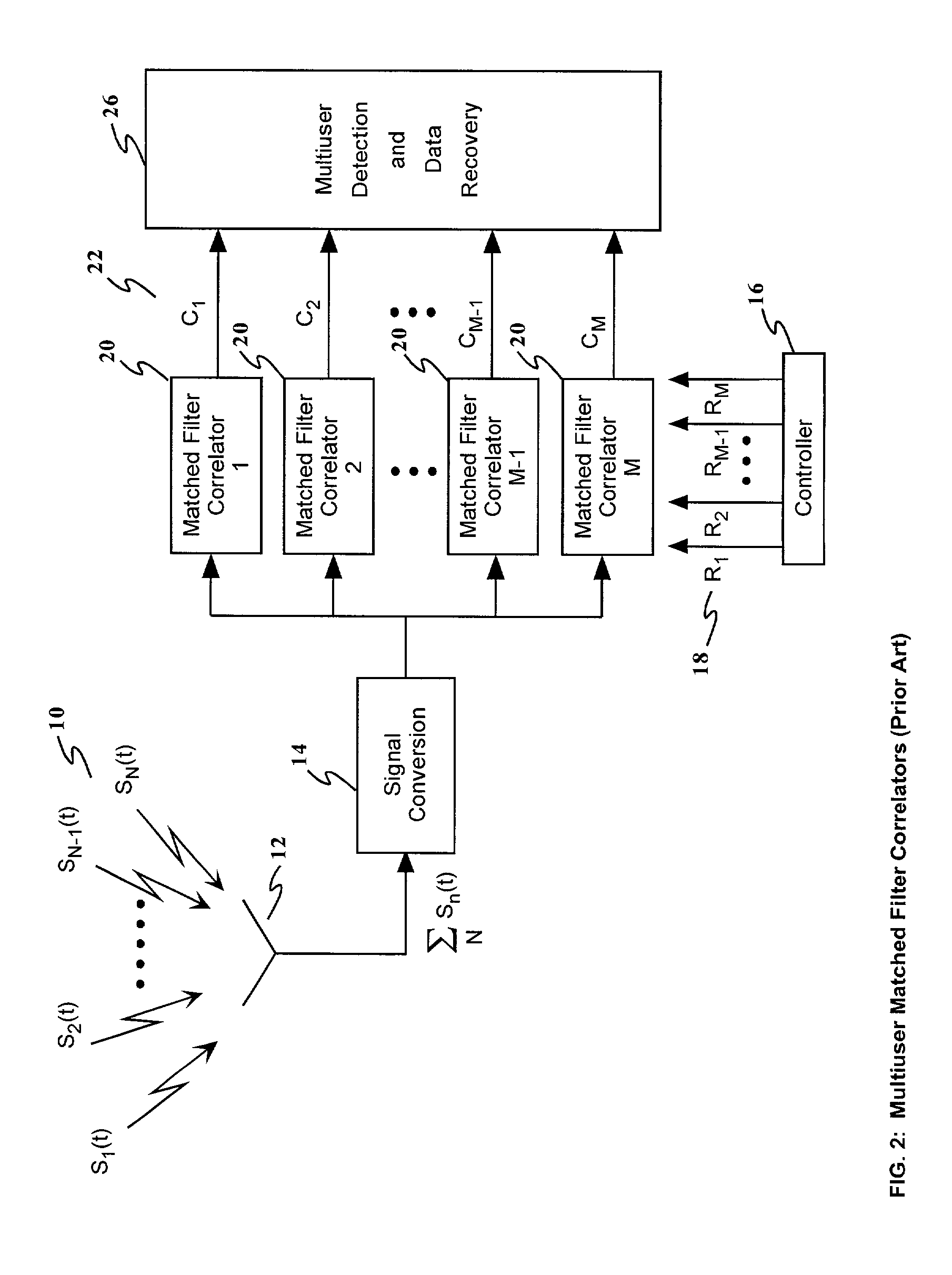
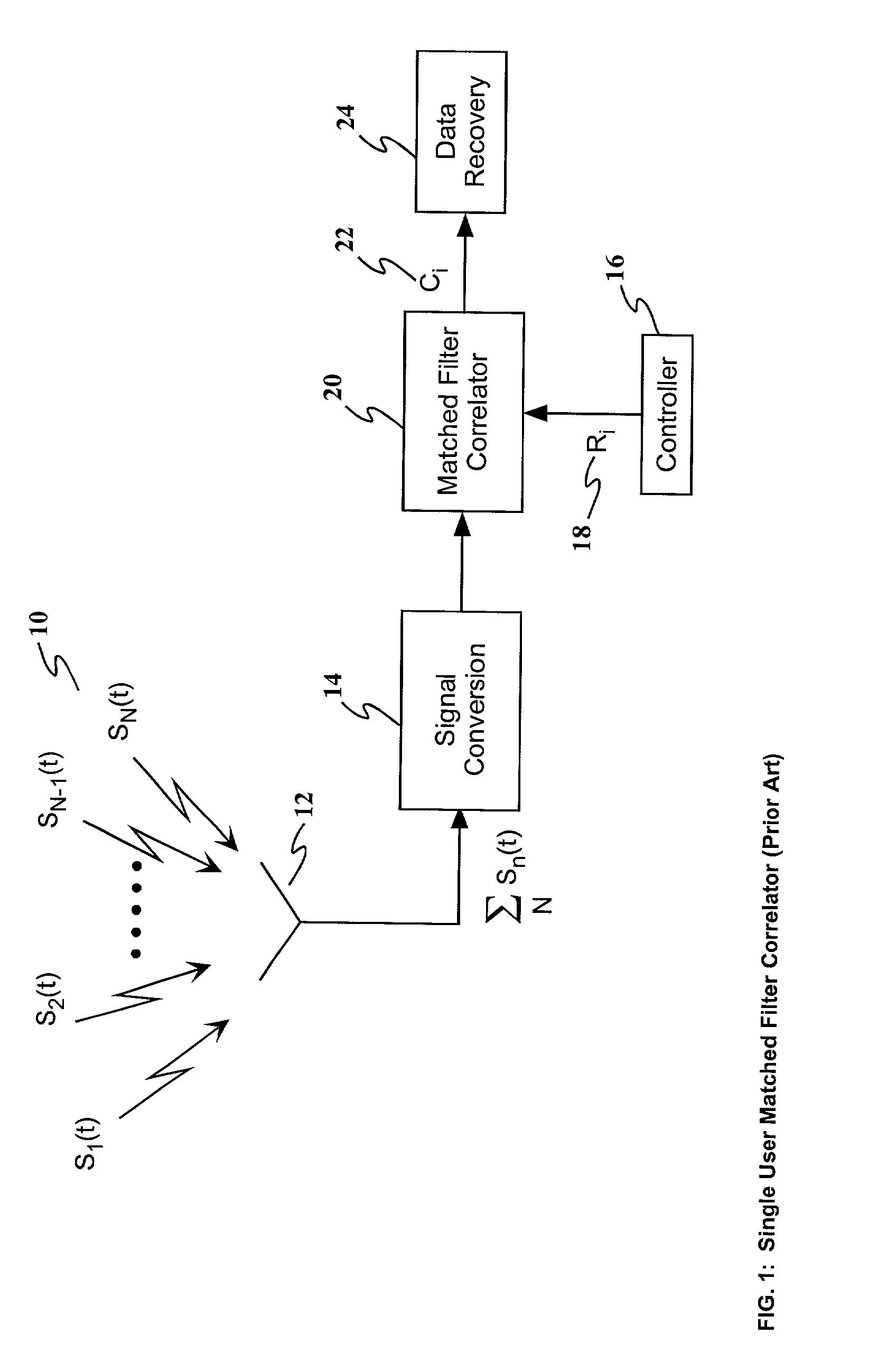
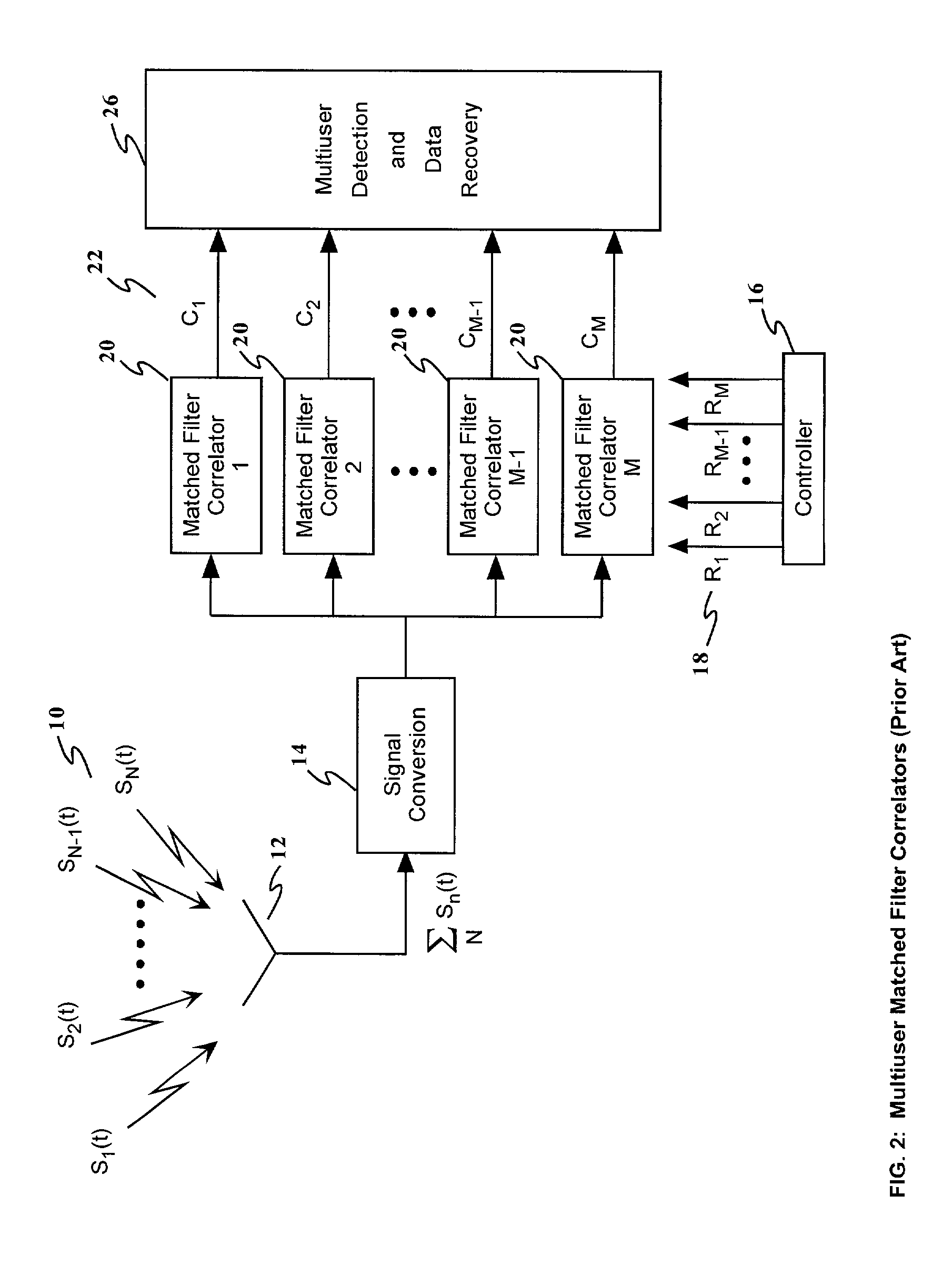
A method and apparatus for enhancing the receiving and information identification functions of multiple access communications systems by employing one or more optical processors configured as a bank of 1-D correlators. The present invention is particularly useful in a DS / SS CDMA communications system, resulting in a multiuser CDMA system that approaches carrier to noise performance (C / N) as opposed to being limited by multiple access interference (MAI). The correlators are arranged in parallel to detect and / or demodulate the received signal, in conjunction with one or more complex algorithms to perform near-optimum multiuser detection, perform multipath combining and / or perform carrier Doppler compensation. An improved receiver in accordance with the present invention comprises means for receiving a plurality of signals transmitted through a communications channel; signal conversion means for converting the received signals into a form suitable for input to the multichannel correlator; a multichannel optical correlator for identifying the presence of particular waveforms and estimating the relative time delay or delays, carrier frequency offset from expected, RF amplitude and RF phase for each received spread spectrum waveform present in the received plurality of signals; a controller for determining and providing to the optical correlator the appropriate set of reference hypotheses; and one or more receiver algorithms depending on the exact receiver function to be performed.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
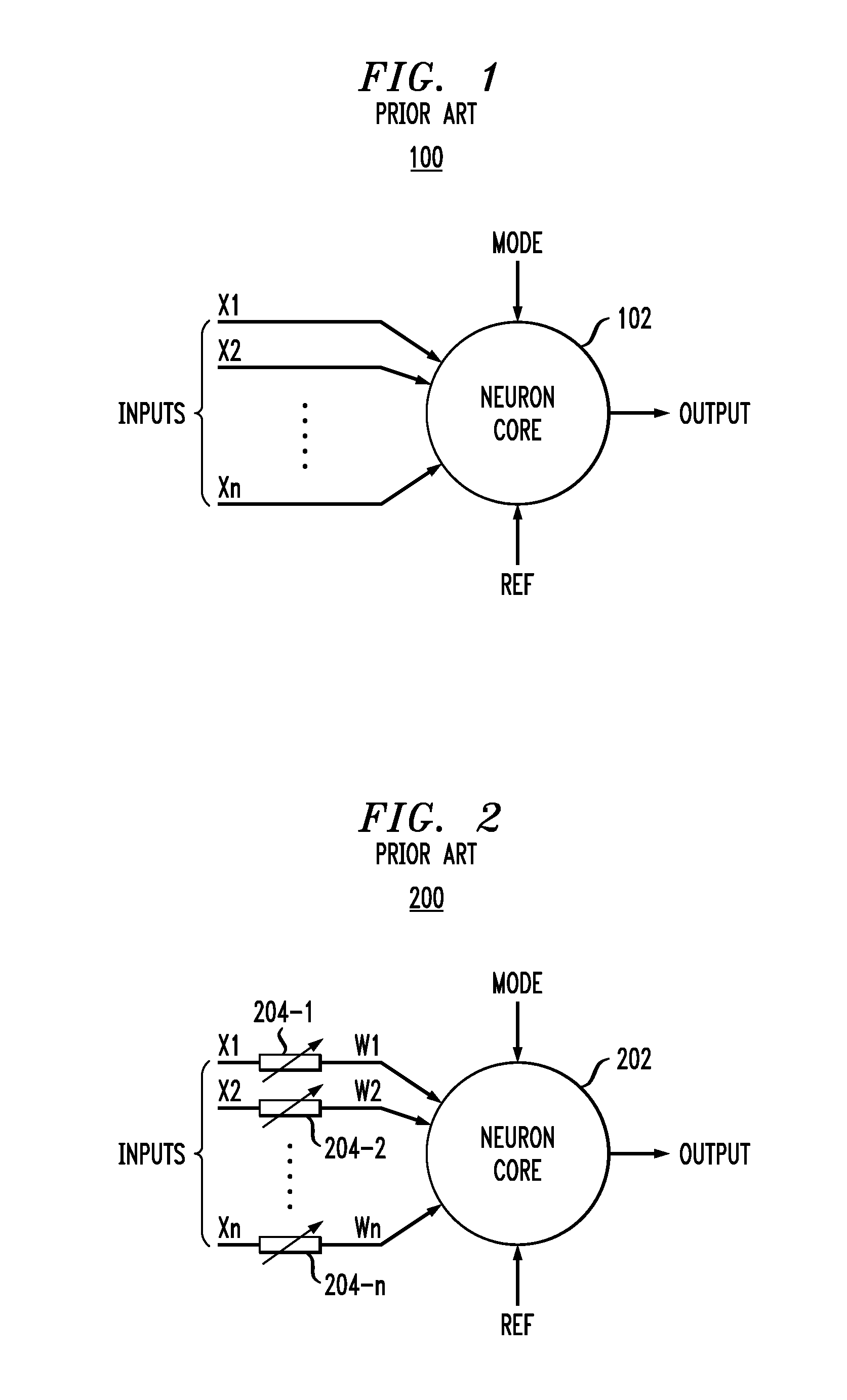
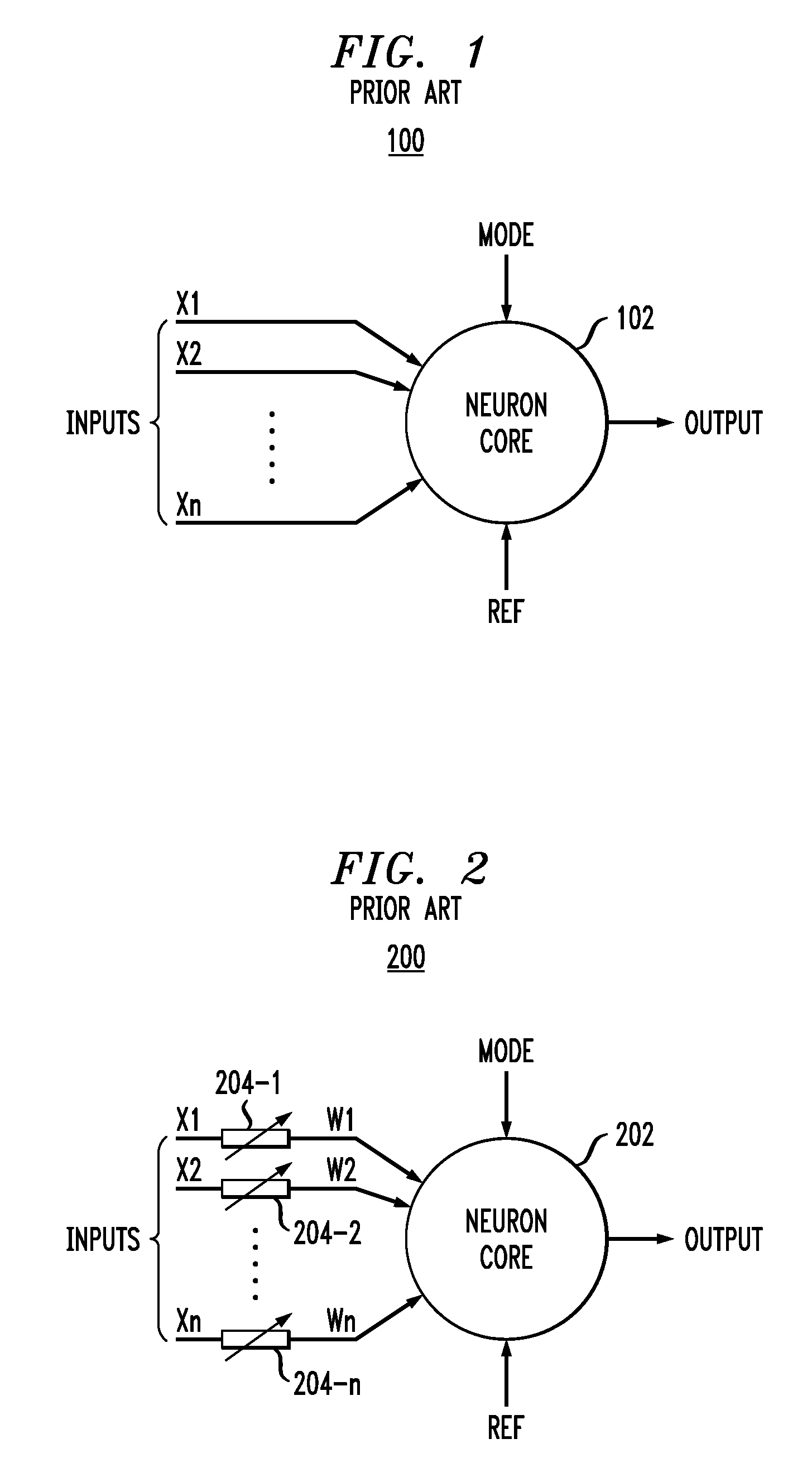
Optical processor for an artificial neural network
InactiveUS20080154815A1Improve processing speedDigital computer detailsDigital dataPattern recognitionSpatially resolved
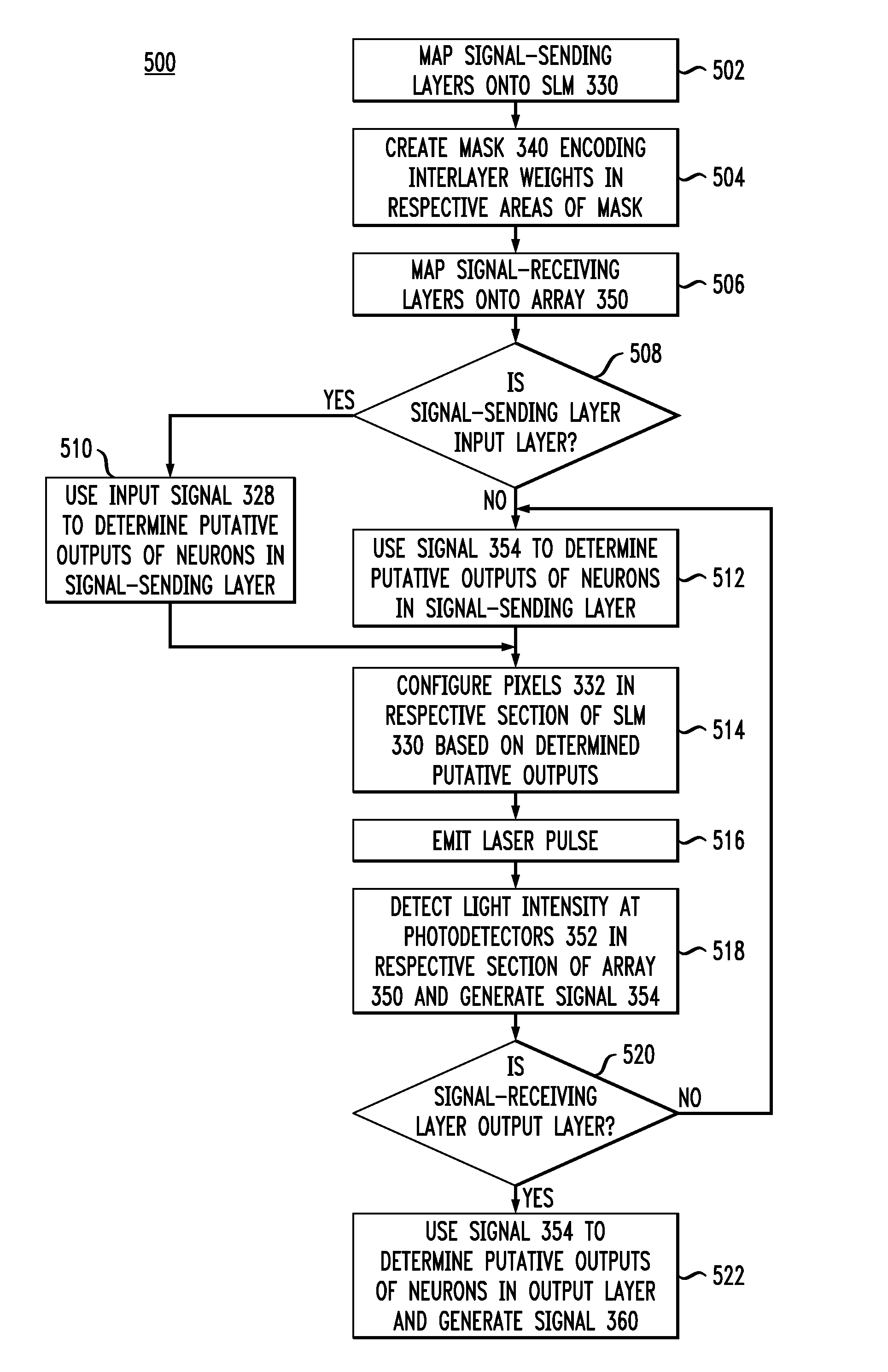
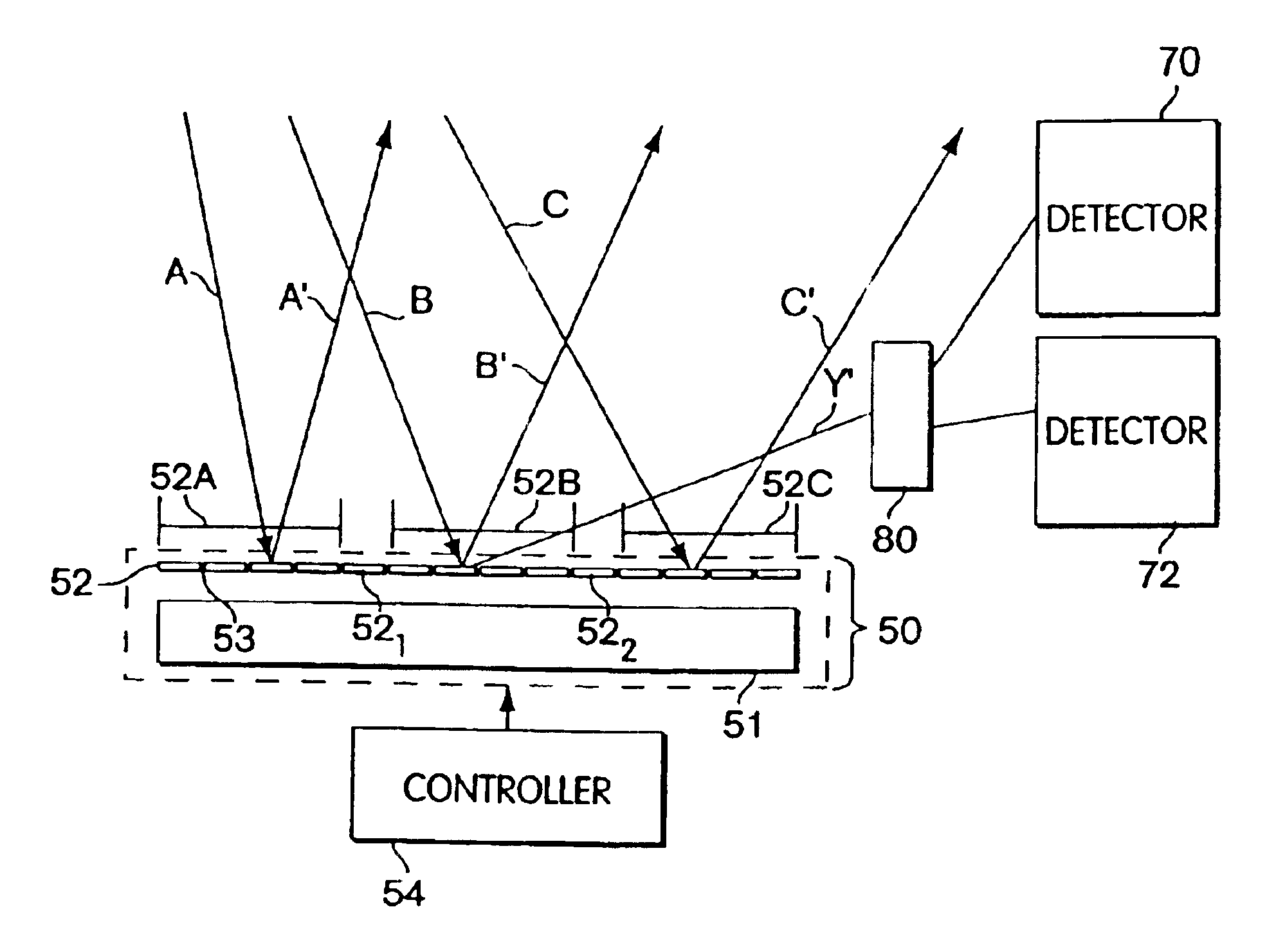
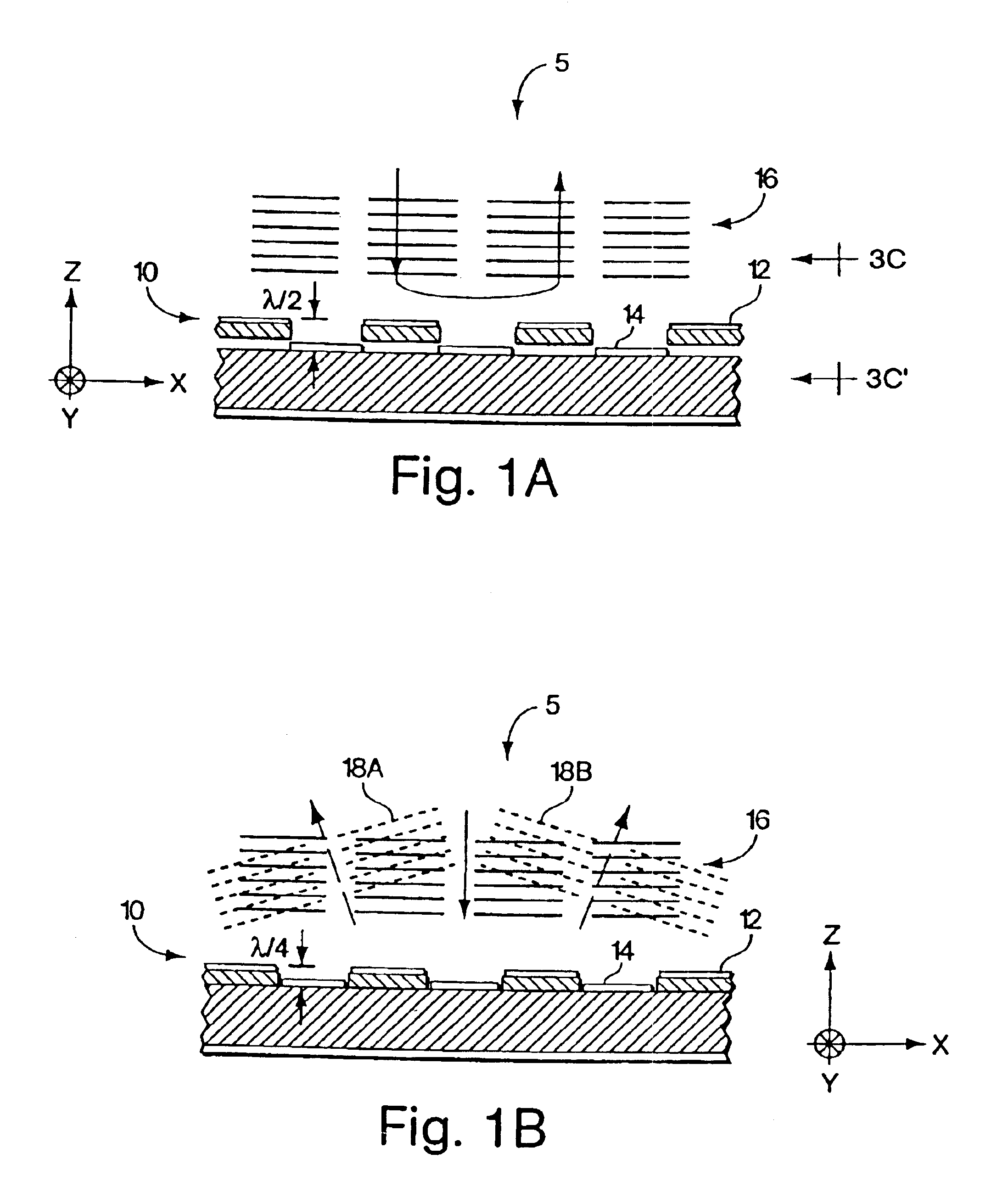
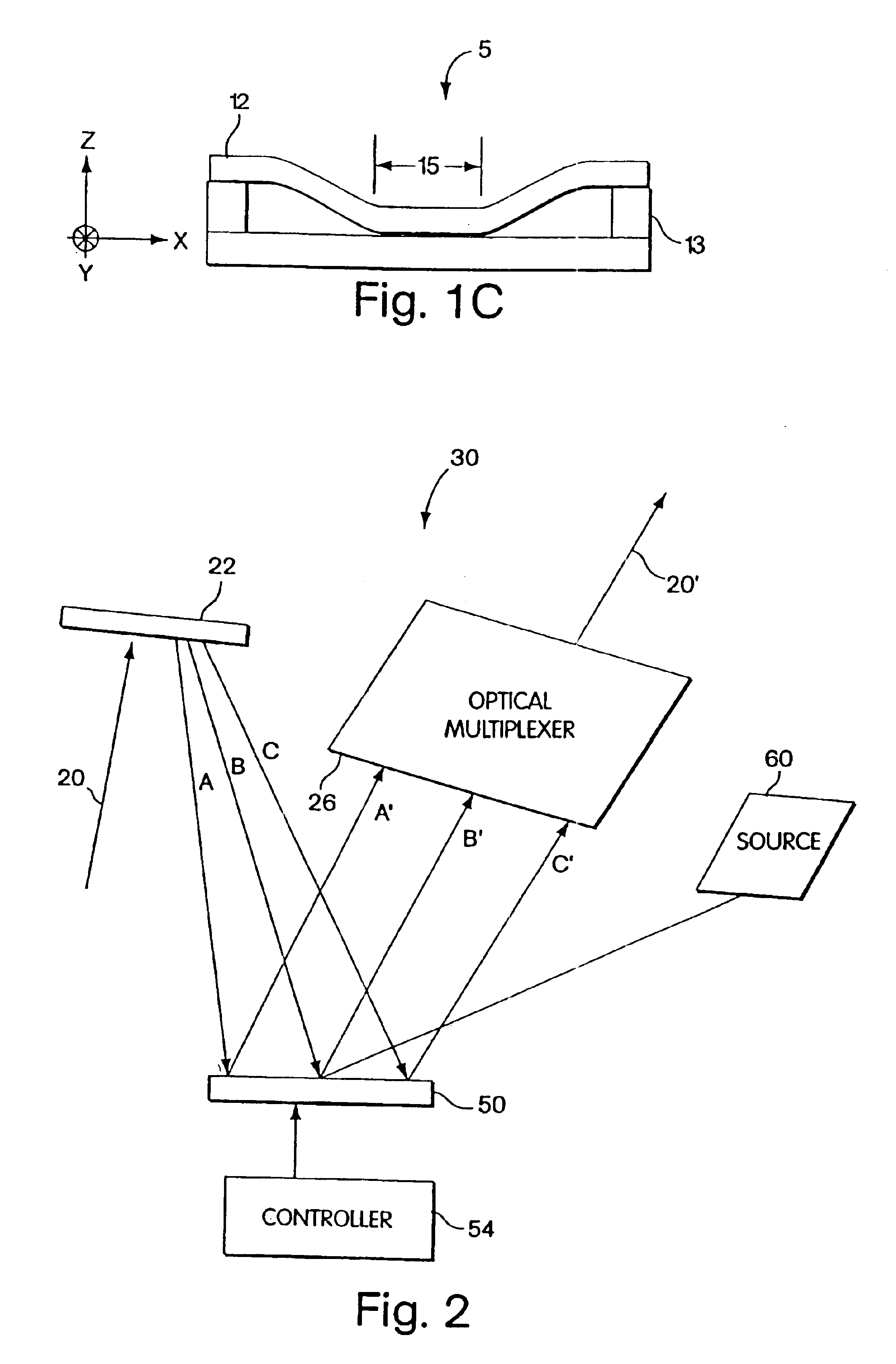
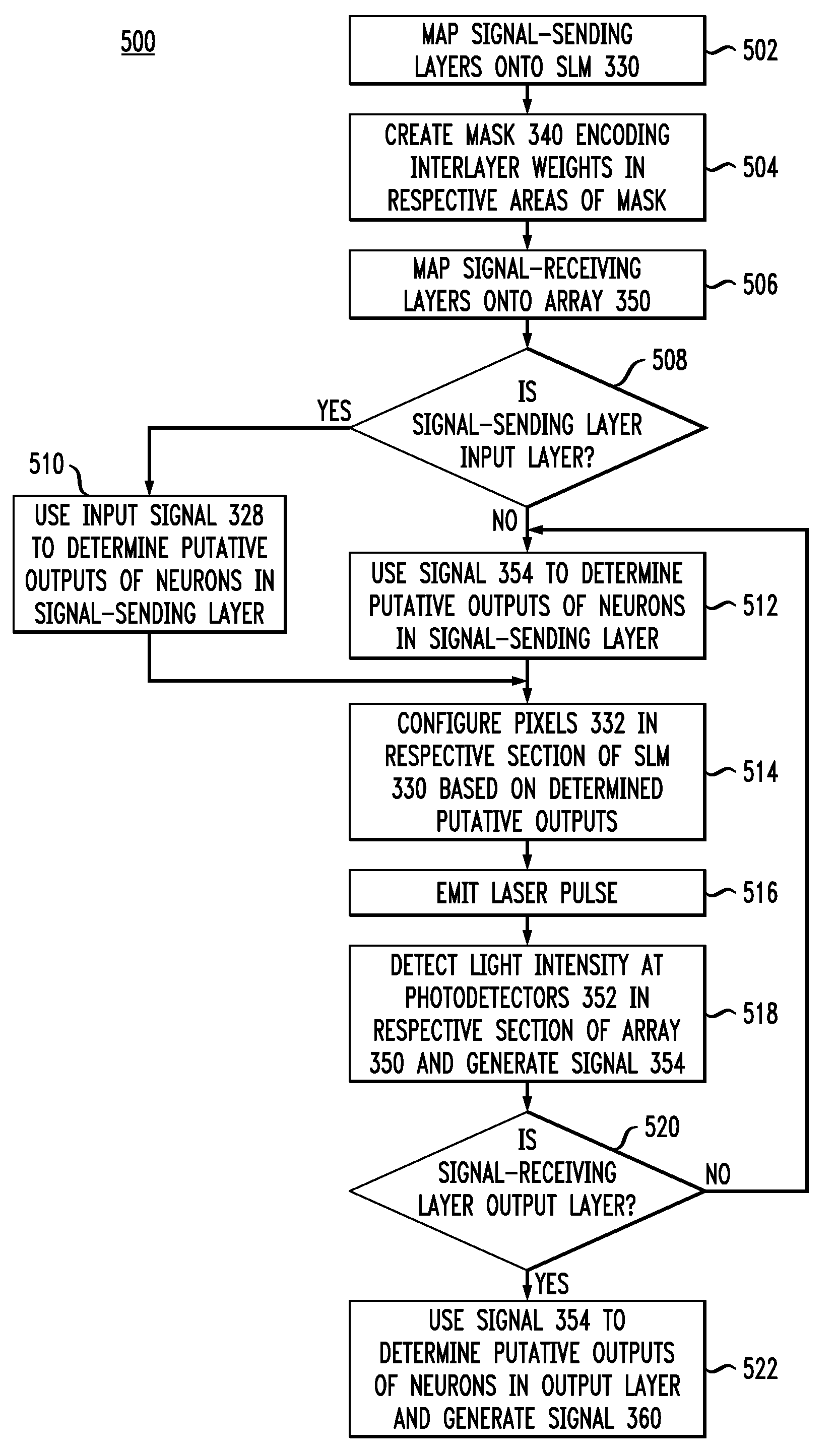
An optical processor adapted to emulate an artificial neural network (ANN) having a plurality of interconnected layers, each layer having one or more artificial neurons, the processor having a spatial light modulator (SLM) optically coupled, via an optical mask, to a photodetector array. In one embodiment, the SLM has a plurality of pixels, each pixel being configurable to emulate an output portion of a corresponding artificial neuron in a signal-sending ANN layer. The optical mask has a hologram that encodes the weights corresponding to interlayer connections in the ANN and spatially modulates the light transmitted by the SLM. The photodetectors of the array spatially resolve the interference pattern produced by the spatially modulated light, with each photodetector being configurable to emulate an input portion of a corresponding artificial neuron in a signal-receiving ANN layer.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC
Methods and apparatus for diffractive optical processing using an actuatable structure
InactiveUS20020167245A1Wavelength-division multiplex systemsCoupling light guidesLength waveOptical processor
A method of redirecting light using an actuatable two-layer diffraction grating structure, the method having applications in wavelength-division multiplexed systems. An optical add / drop modulator (OADM) including an actuatable diffraction grating, for use with a wavelength-division multiplexed signal. An OADM having an optical source located off the main pathway to direct a optical carrier to be added onto the actuatable diffraction grating such that the carrier is diffracted into the main pathway. A detector to measure signal strength for use with an optical processor, the optical processor having an actuatable structure having gaps between the actuated portion of the structure. The detector detecting the portions of light diffracted by the gaps.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Optical Chemical Sensor Feedback Control System
InactiveUS20100032583A1Eliminating and minimizing disturbancePhotometry using reference valueMaterial analysis by optical meansPhase shiftedOptical processor
An optical chemical sensor feedback control system is provided comprised of a luminescent sensing film, an optical processor adjacent the sensing film capable of sinusoidally photoexciting the luminescent sensing film and detecting the luminescent emission resulting therefrom, and a computer control means executing a computer program, in communication with the optical processor. The computer control means is operable to control the magnitude of the photoexcitation of the luminescent sensing film, wherein the computer control means receives data regarding the luminescent emission resulting therefrom, analyzes same, and determines the magnitude and phase shift of the luminescence relative to the photoexcitation. Further, the system herein is operable to determine the status of the sensing film, and adjust the magnitude of photoexcitation thereof based on same. In addition, the system, via the optical processor positioning means, is operable to adjust the physical position of the optical processor and / or light source in relation to the sensing film, based on data received from the computer control means.
Owner:POLESTAR TECH
Beam control system with extended beacon and method
ActiveUS7041953B2Optical measurementsPhotometry using reference valueSpatial light modulatorWavefront aberration
A beam control system and method: The inventive system includes, an arrangement for receiving a first beam of electromagnetic energy; measuring wavefront aberrations in the first beam with a wavefront sensor; and removing global tilt from the measured wavefront aberrations to provide higher order aberrations for beam control. In the illustrative embodiment, the invention uses a traditional (quad-cell) Shack-Hartmann wavefront sensor to measure wavefront aberrations. An adaptive optics processor electronically removes the global tilt (angular jitter) from this measurement leaving only the higher-order Zernike components. These higher-order aberrations are then applied to wavefront control elements, such as deformable mirrors or spatial light modulators that correct the tracker image and apply a conjugate distortion to the wavefront of the outgoing HEL beam. A track error (angular jitter) component is supplied by a separate fine track sensor. This jitter error is then applied by the adaptive optics processor to a fast steering mirror, which corrects jitter in the tracker image and applies a compensating distortion to the LOS of the HEL beam.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
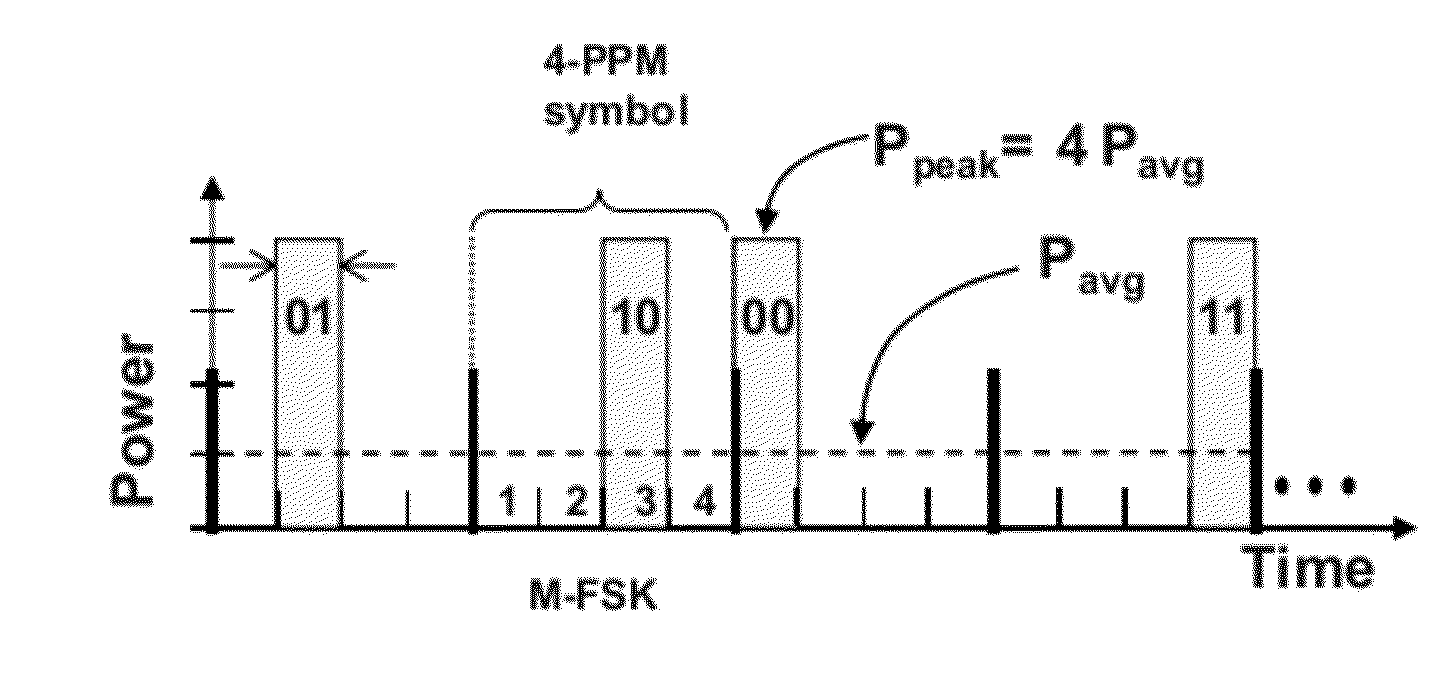
Optical receiver configurable to accommodate a variety of modulation formats
ActiveUS20120281990A1Improve receiver sensitivityAttenuation bandwidthElectromagnetic receiversFiberBandwidth requirement
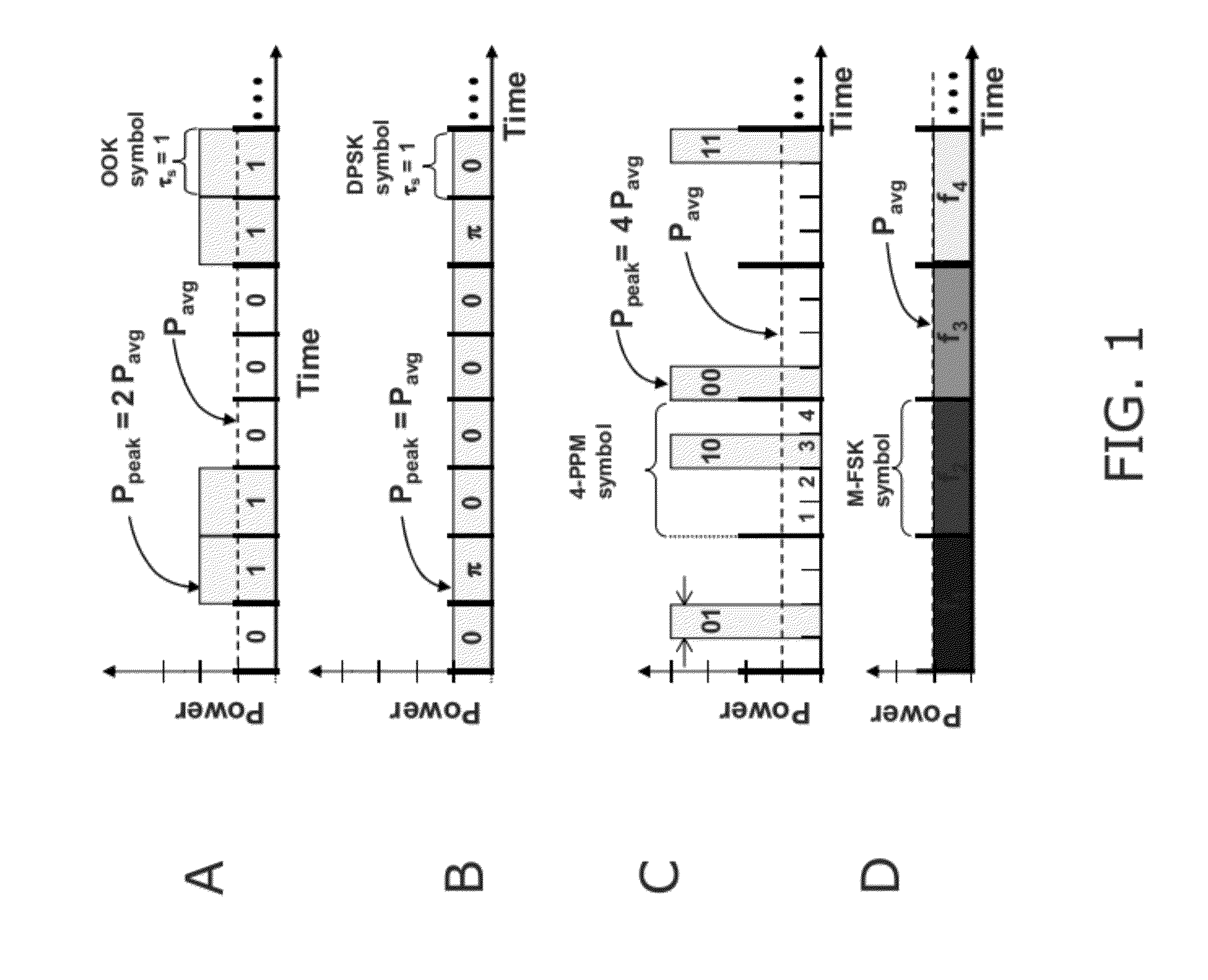
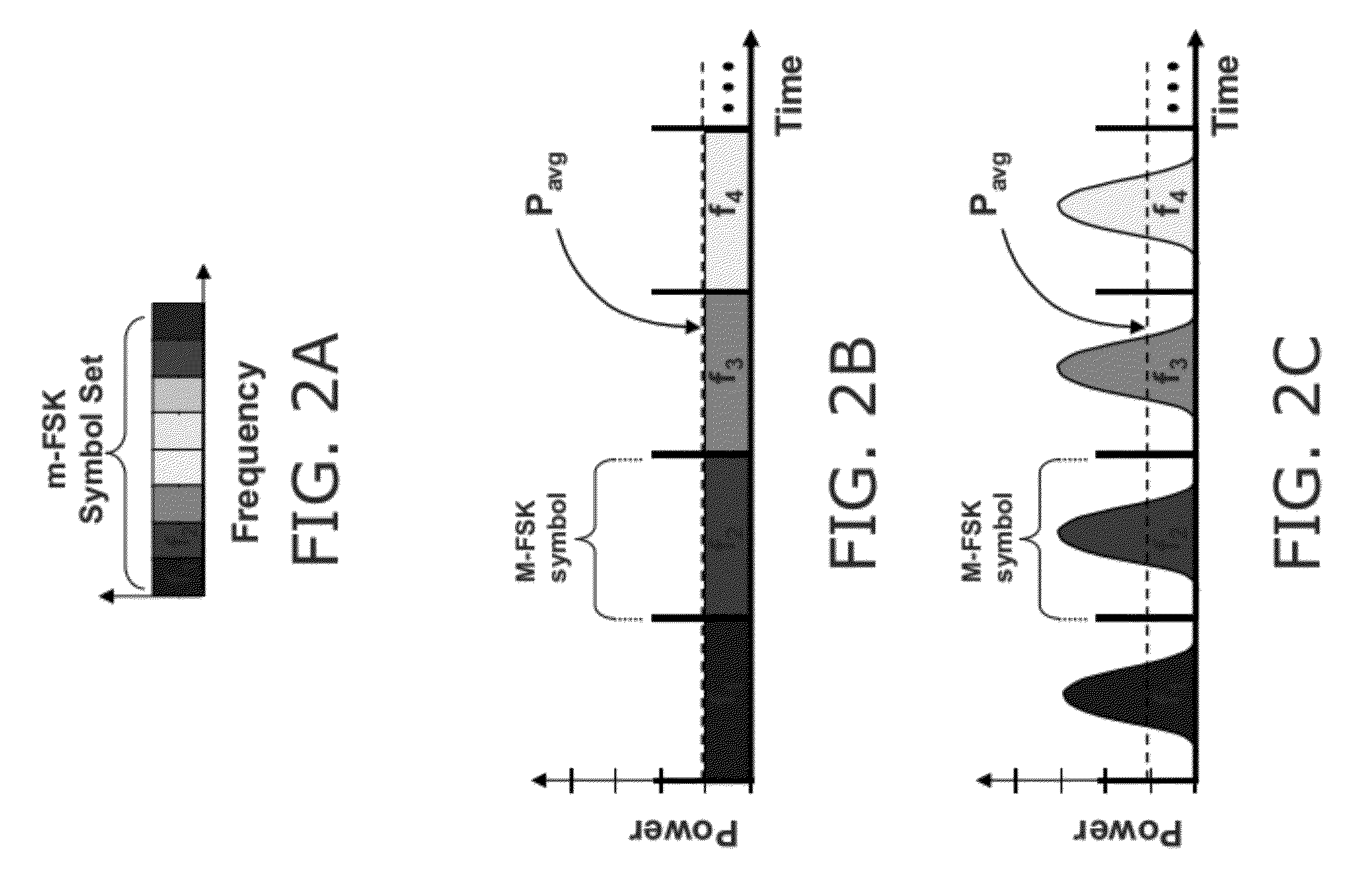
The present invention provides a simple means of demodulating optical signals, e.g. wideband M-ary orthogonal. The demodulator comprises an optical processor and a comparison module. The optical processor transforms M input optical signals into 2 log2(M) intermediary optical signals and the comparison module determines the logical representation of the input data based on log2(M) binary comparisons of the optical power of the intermediary signals. Example embodiments may be reconfigurable to receive optical signals using M-FSK, M-PPM, M-PolSK, and hybrid M-ary orthogonal modulation formats. Example embodiments also offer small size, weight and power consumption for both free-space and fiber optic environments as well as improved receiver sensitivity and reduced electron bandwidth requirements.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
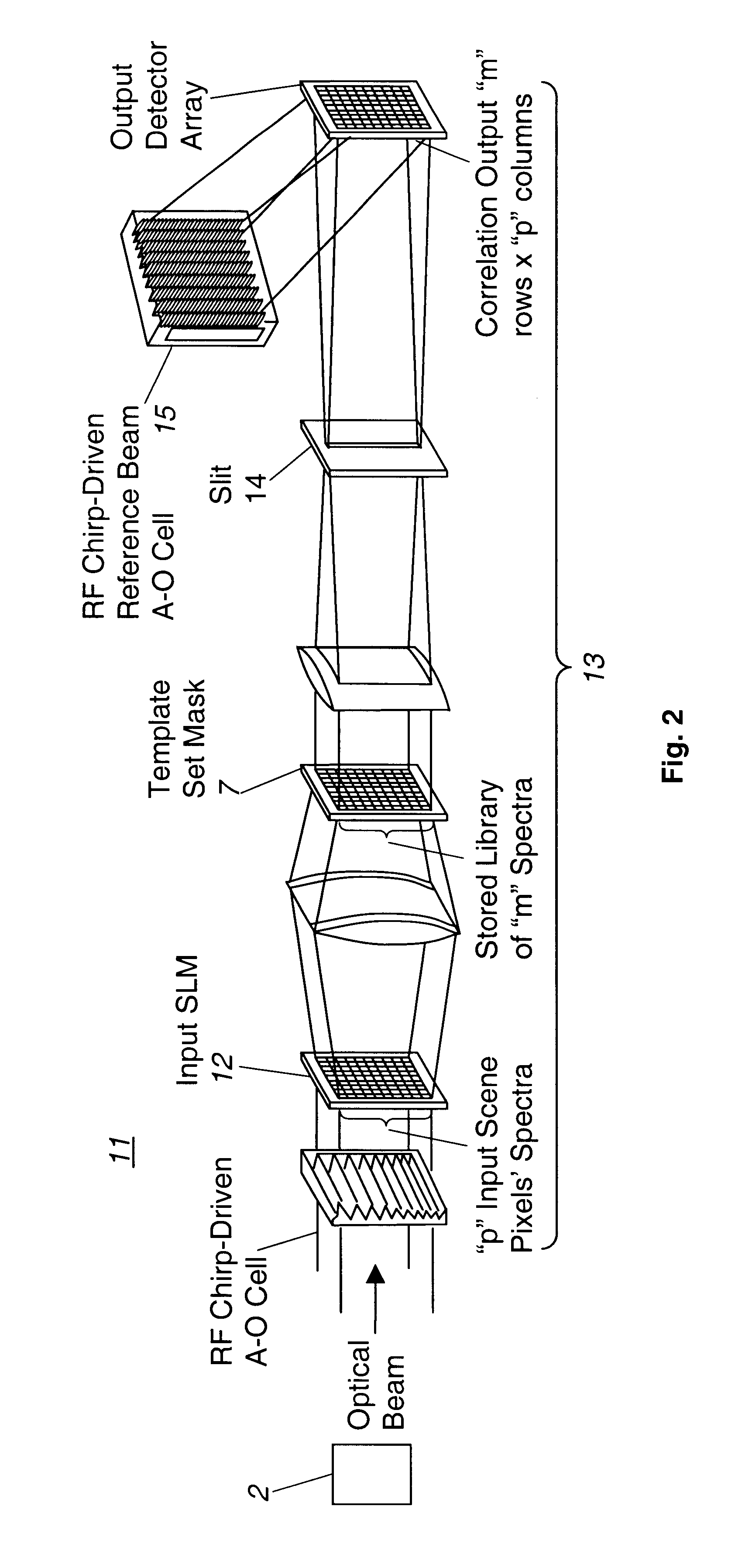
Multispectral imaging system and method
InactiveUS6480273B1Radiation pyrometryCharacter and pattern recognitionSpatial light modulatorSpectral bands
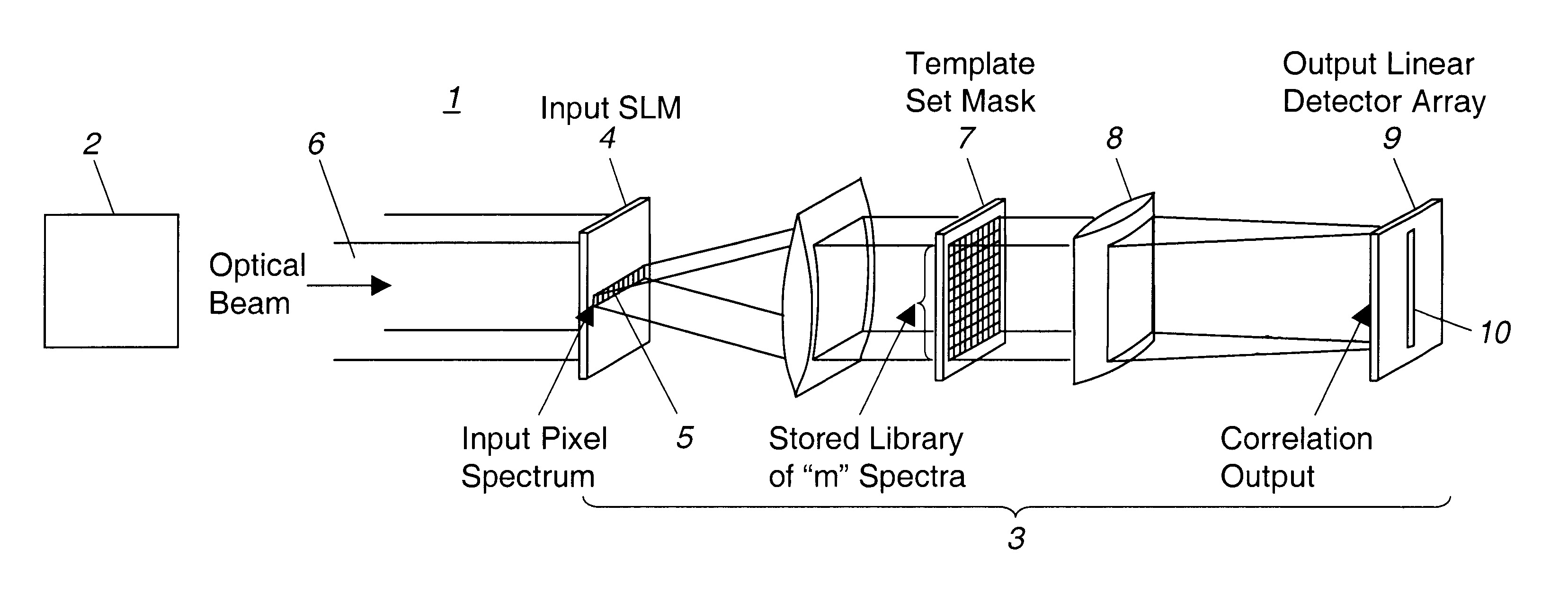
A multispectral imaging system (1) and method utilize an optical processor (3) for simultaneously comparing an input wavelength spectrum observed in a single spatial pixel in a scene image from a multispectral imager (2) with a plurality of template wavelength spectra to find a correlation. The optical processor exploits the three-dimensional attributes of optical correlation to perform massively parallel correlation processing by modulating (4) respective ones of a plurality of spectral bands of the input wavelength spectrum of an incident light beam (6) with modulating elements (5) to alter at least one property of the incident light beam by a value corresponding to the observed intensity of the input spectrum in the respective spectral band. In a disclosed embodiment, the modulated beam is expanded and transited through a spatial light modulator (7) having a two-dimensional array of modulating elements. Each row of the elements of the array alter the at least one property of the incident light by values corresponding to a particular template wavelength spectrum of a plurality of template wavelength spectra of the modulator. The values corresponding to each template spectrum are the conjugates of the representative values of the modulating elements of the template spectrum of the plurality of template spectra.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
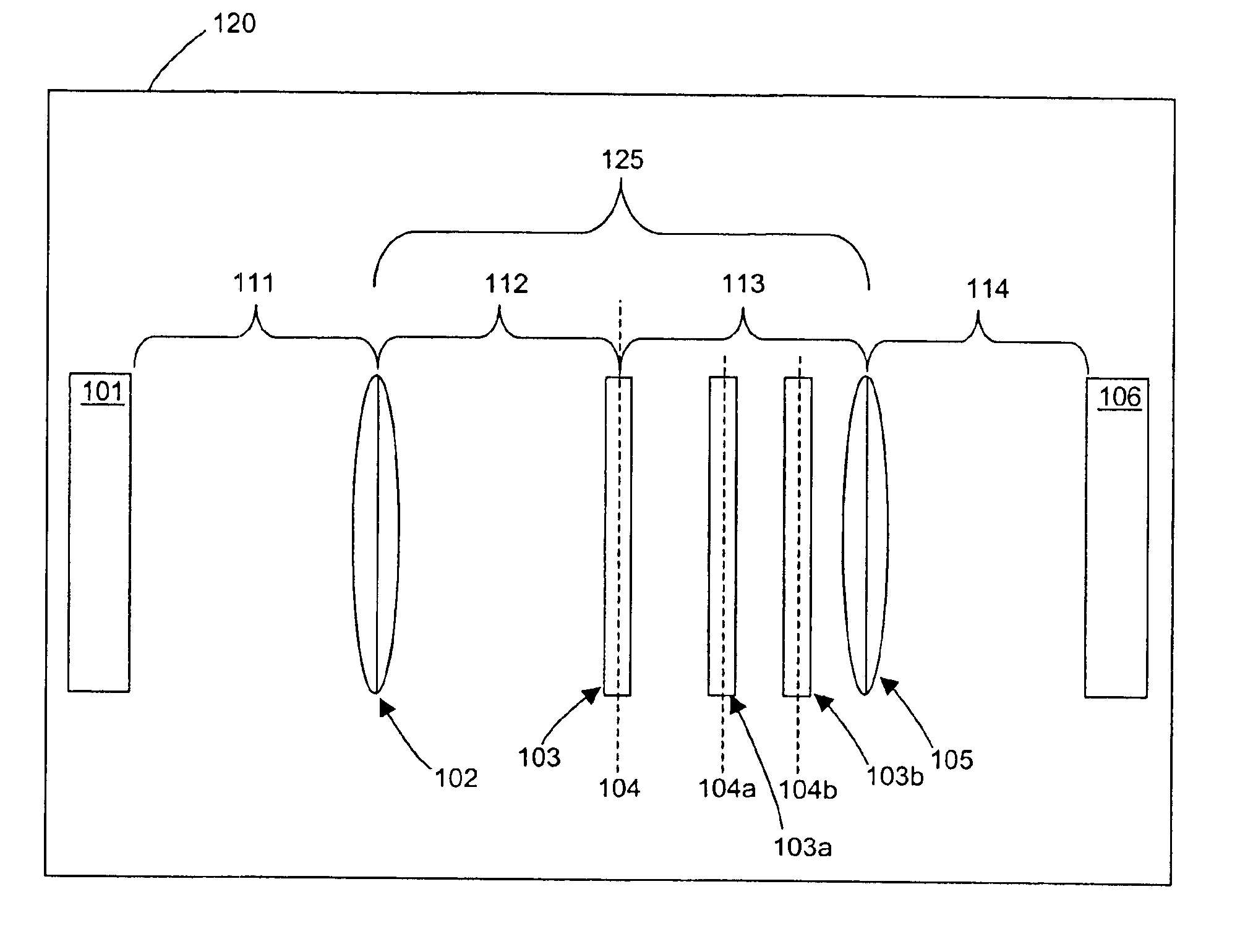
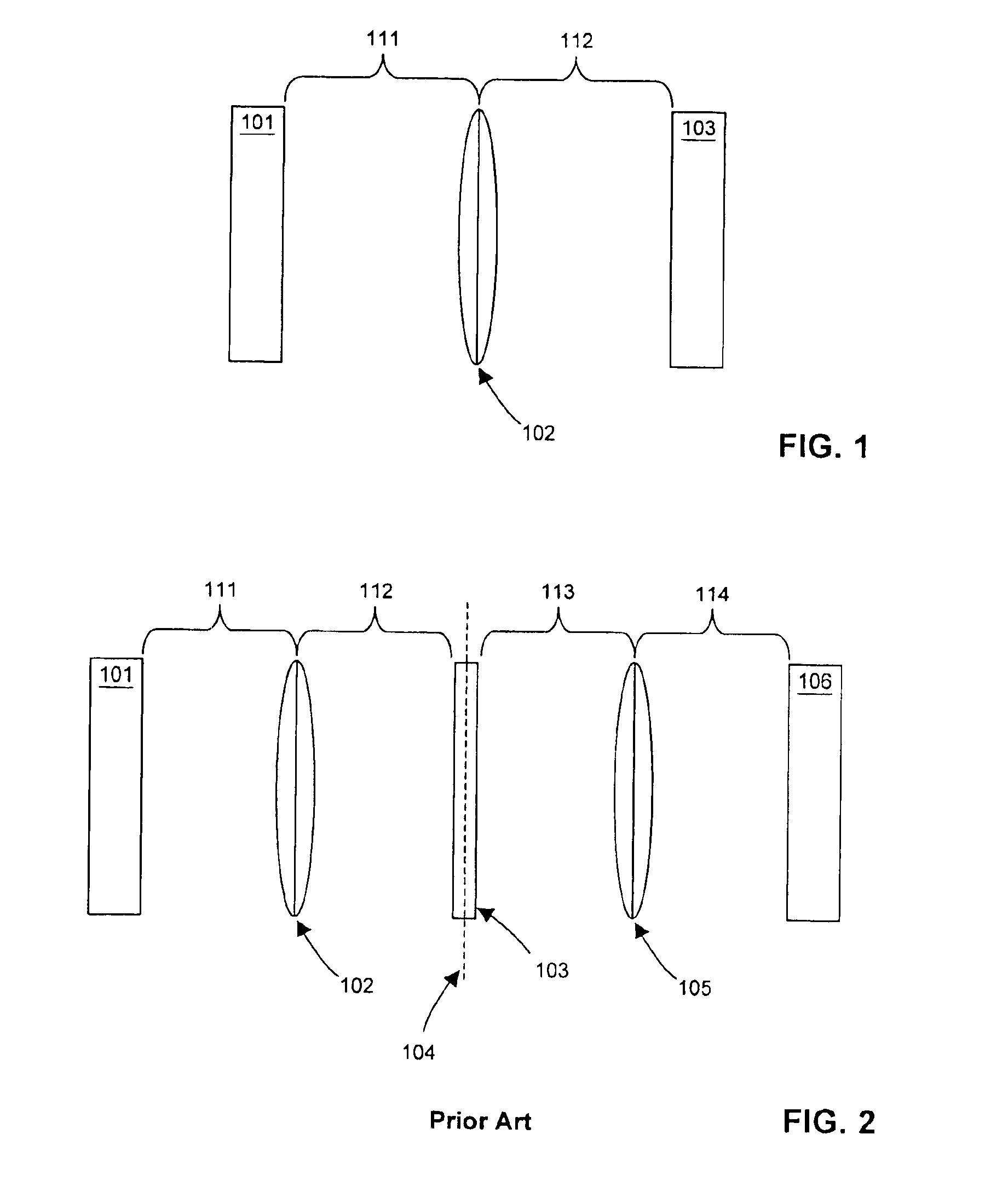
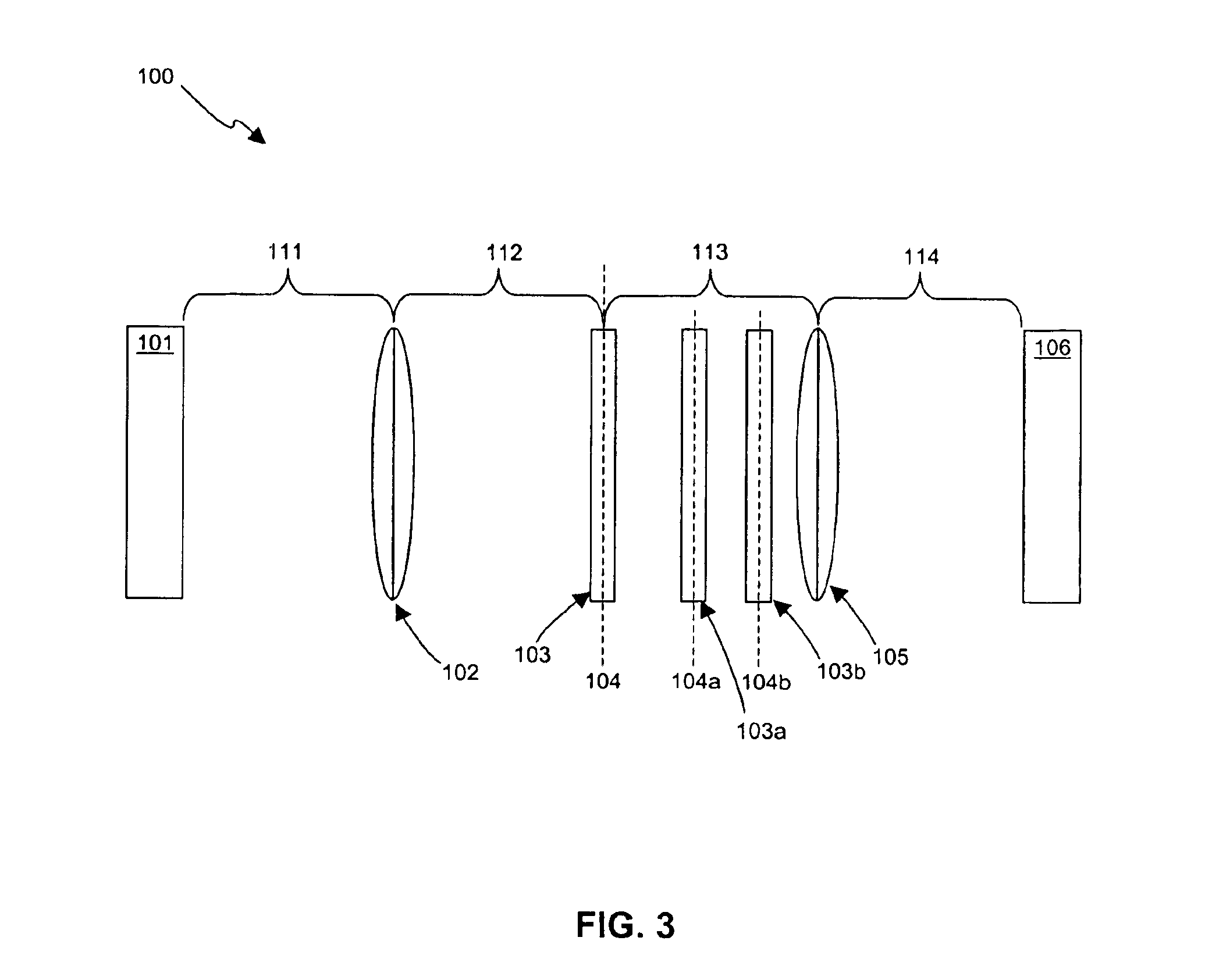
Non-positive-definite optical filtering from positive-definite transfer functions
Fractional Fourier transform properties of lenses or other optical environments are applied to one or more positive-definite optical transfer functions at locations outside the Fourier plane to realize or closely approximate arbitrary non-positive-definite transfer functions varying in both amplitude and phase. Controllable filter elements can be employed to create controllable optical processors which may be used for image filtering and optical computations using complex-valued arithmetic for monochromatic, color, and wide-spectrum optical signals. Applications include integrated optics, optical computing systems, particle beam systems, radiation accelerators, astronomical observation systems, and controllable lens systems.
Owner:NRI R&D PATENT LICENSING LLC
Method and apparatus for measuring stress in semiconductor wafers
InactiveCN1618004ASemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementElectronic circuit testingLayer thicknessTotal measurement
Integral measurement apparatus (50) and method for measuring layer thickness and bow in a wafer. The device comprises: a monochromatic light source (52), a white light source (100), a first switch (102) for switching between the white light source and the monochromatic light source, a switch for directing light from the switched light source to the semiconductor wafer A plurality of optical heads (56) at different locations on the surface (54), a first optical processor (104) for spectrally processing reflected light from the wafer, a second optical processor (104) for processing the reflected light to determine the degree of curvature in the wafer Two optical processors (58), and a second optical switch (106) for switching the reflected light from the wafer between the first optical processor and the second optical processor for spectral processing of white light to determine layer thickness , processes monochromatic light to determine the bend.
Owner:TEVET PROCESS CONTROL TECH
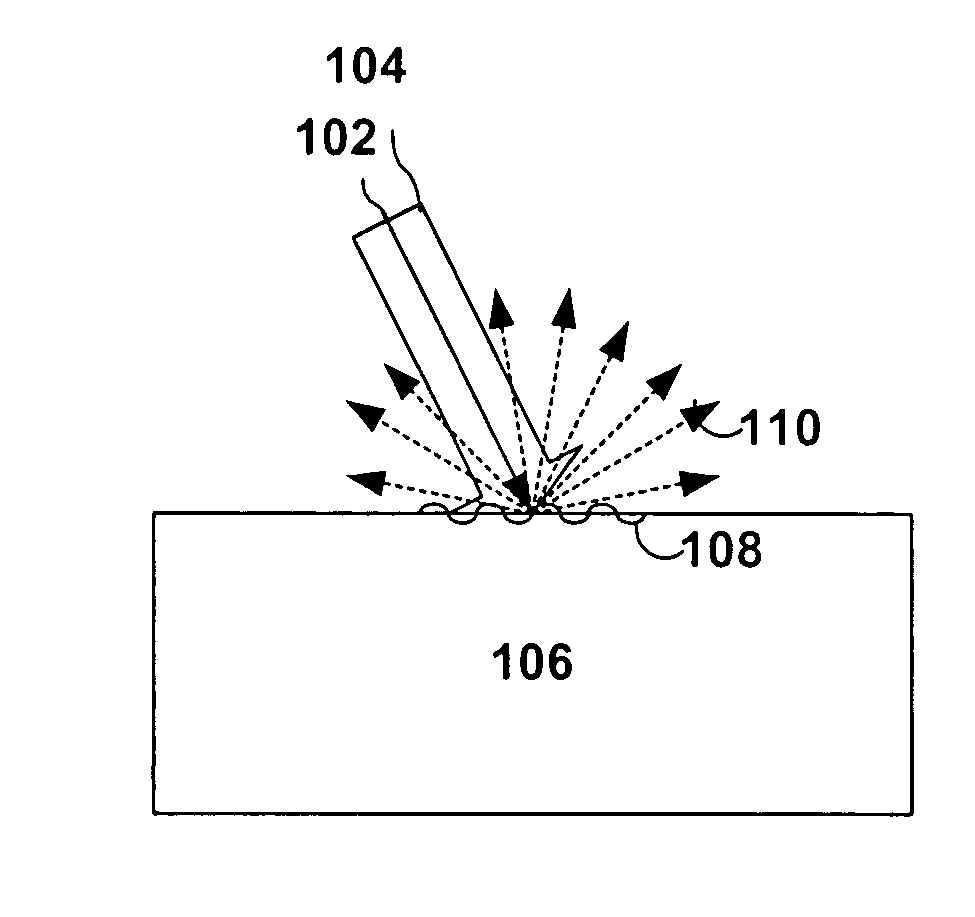
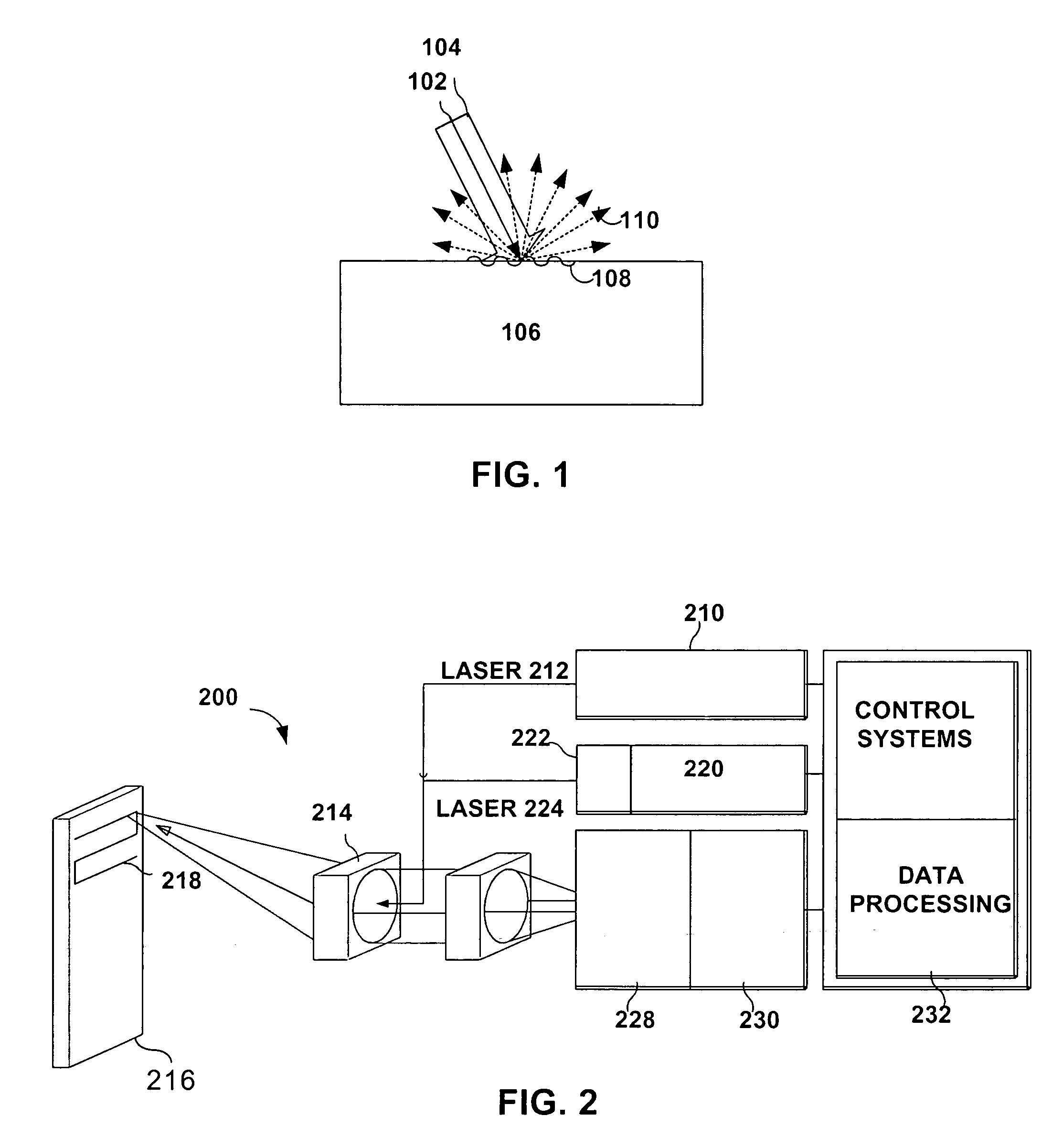
System and method to decrease probe size for improved laser ultrasound detection
InactiveUS20060132804A1Improve efficiencyEasy and fastMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMaterial analysis by optical meansDirect illuminationLight beam
The present invention provides a compact optical probe assembly that measures ultrasound in materials. The probe uses angle-terminated optical fiber to direct illumination laser light at the surface of a remote target. Ultrasonic displacements at the surface scatter the illumination laser light. Angle-terminated optical fibers collect phase modulated light and direct the phase modulated light to an optical processor to produce a signal representative of the ultrasonic surface displacements. The probe may also incorporate angle-terminated optical fibers to direct generation laser light to the surface of a remote target to generate ultrasonic surface displacements. Optional shared beam forming element(s) may optically act on the illumination laser and collected phase modulated light.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Methods and apparatus for diffractive optical processing using an actuatable structure
InactiveUS20020167695A1Easy to separateWavelength-division multiplex systemsDiffraction gratingsOptical processingLength wave
A method of redirecting light using an actuatable two-layer diffraction grating structure, the method having applications in wavelength-division multiplexed systems. An optical add / drop modulator (OADM) including an actuatable diffraction grating, for use with a wavelength-division multiplexed signal. An OADM having an optical source located off the main pathway to direct a optical carrier to be added onto the actuatable diffraction grating such that the carrier is diffracted into the main pathway. A detector to measure signal strength for use with an optical processor, the optical processor having an actuatable structure having gaps between the actuated portion of the structure. The detector detecting the portions of light diffracted by the gaps.
Owner:POLYCHROMIX
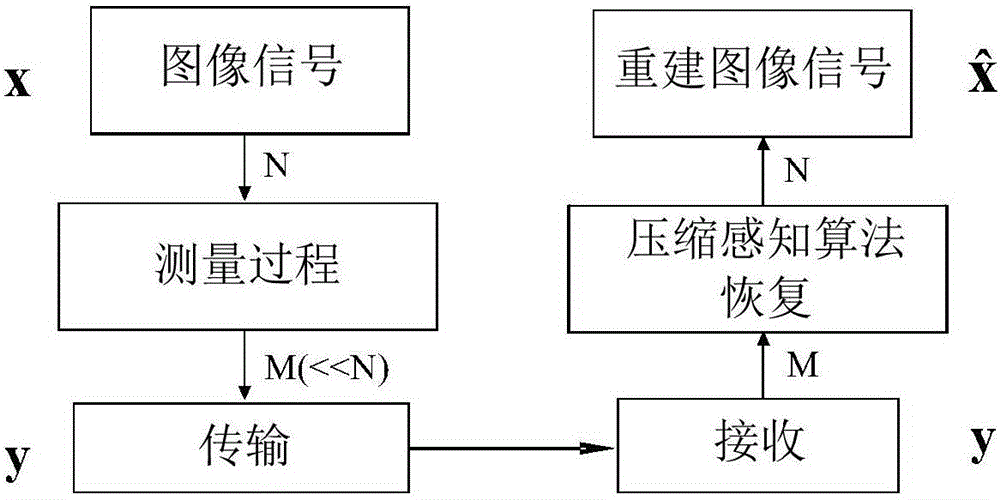
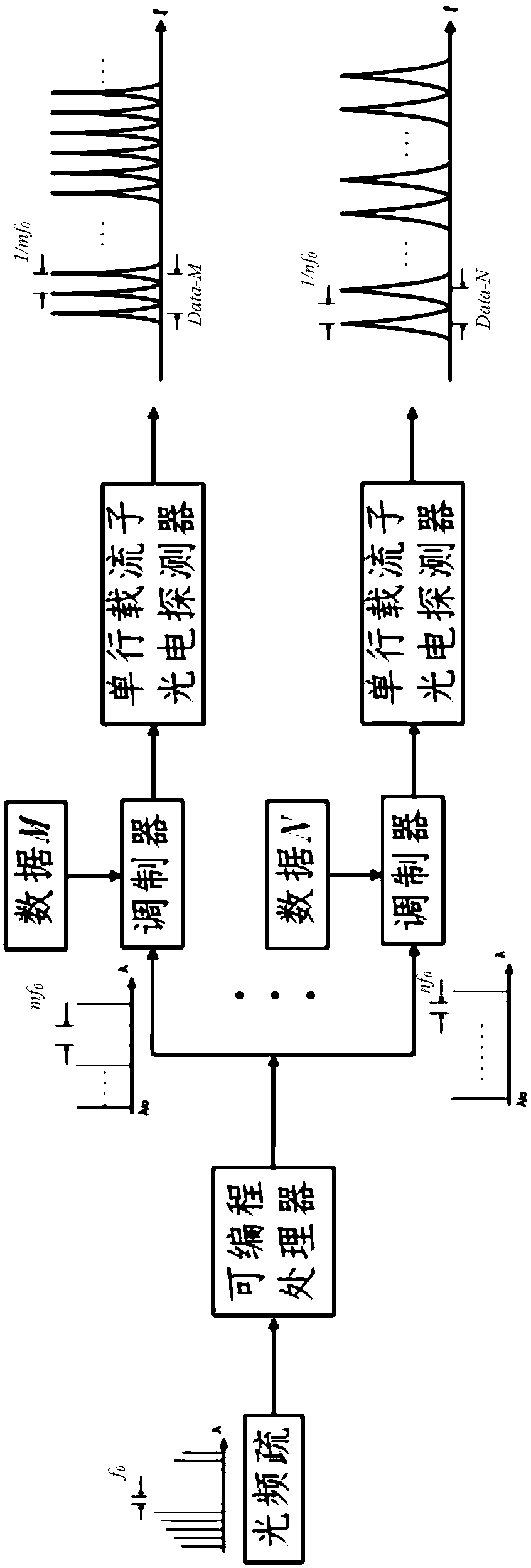
Single-pixel two-dimensional imaging system and method using light frequency domain random frequency mixing
InactiveCN105897344AIncrease frame rateSave spaceFibre transmissionElectromagnetic transmittersErbium dopingPeak value
The invention discloses a single-pixel two-dimensional imaging system and method using light frequency domain random frequency mixing. The single-pixel two-dimensional imaging system and method are characterized in that a mode-locked laser is utilized to provide a pulse light source which is amplified through an erbium doped fiber amplifier; the amplified pulse light source enters a collimating mirror through a circulator, and then irradiates to images requiring to be collected through a reflector, a semi-cylindrical lens, a virtual image phase array, a reflective diffraction grating and a cylindrical mirror and is reflected; optical signals return to the circulator along the original path; mixing of the optical signals and the pseudo random sequence frequency is implemented in a programmable optical processor; photoelectric conversion is performed through a photoelectric detector, and then sampling is performed through a digital sampling oscilloscope; and the oscilloscope samples each pulse peak value, and utilizes a compressed sensing algorithm to reconstruct the image signal. The single-pixel two-dimensional imaging system using light frequency domain random frequency mixing utilizes the programmable optical processor to implement mixing of signals and random sequence in a frequency domain to avoid the complicated process that a Mach-Zehnder modulator is used to modulate the random sequence after broadening of the fiber, and then the random sequence is compressed through the fiber for mixing in the time domain, thus having the advantages of being simple and compact in structure, and being easy to integrate.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Tunable multi-band terahertz pulse wireless communication transmitting device
ActiveCN108712214ARealize high-speed communicationUltra short cycleElectromagnetic transmittersMulti bandPhotodetector
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
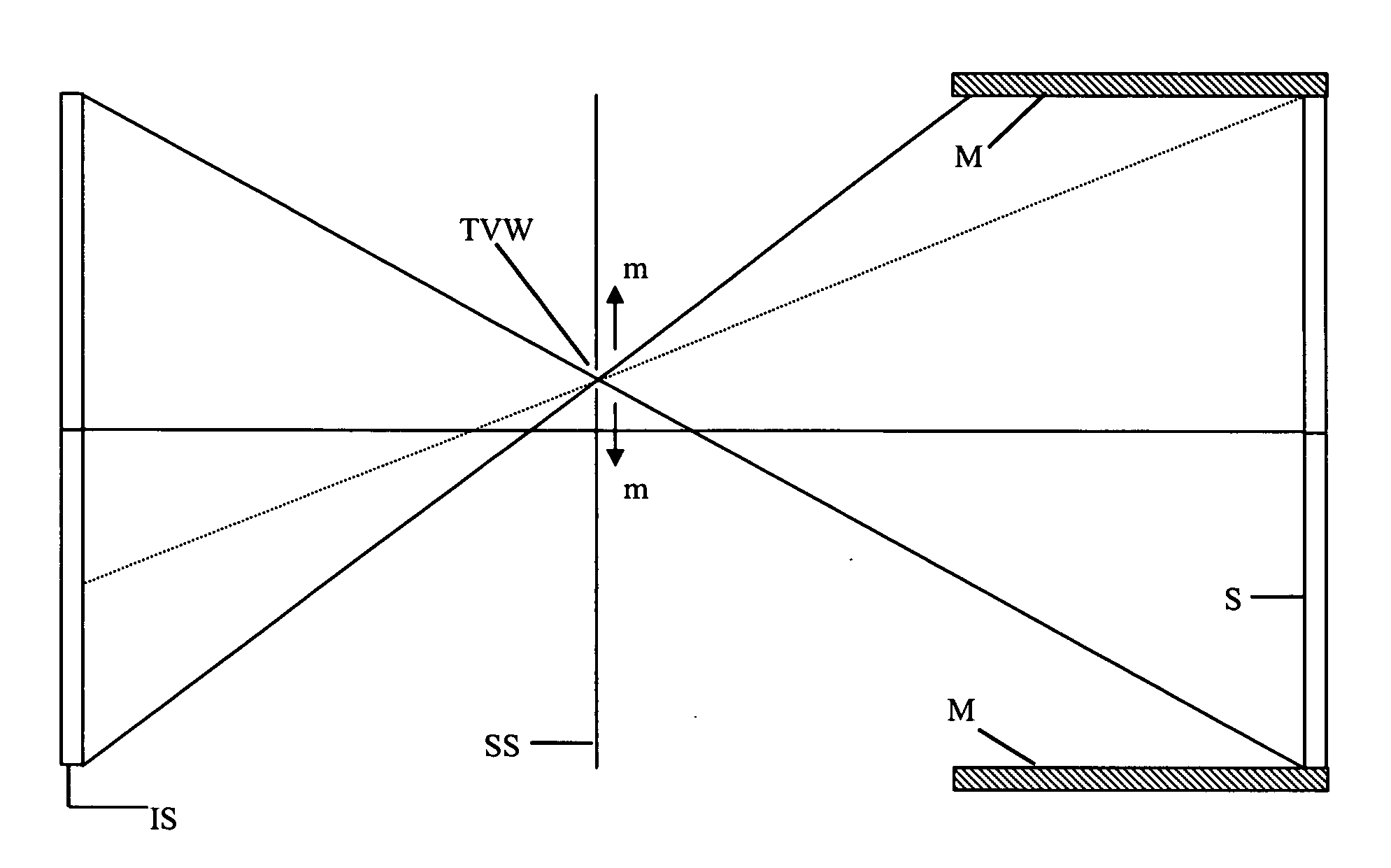
Three-dimensional autostereoscopic display and method for reducing crosstalk in three-dimensional displays and in other similar electro-optical devices
InactiveUS20070121028A1Reduce resolutionSmall sizeNon-linear opticsOptical elementsImaging qualityComputer science
This Patent Application describes invention in form of a design of three-dimensional (3D) autostereoscopic displays and other similar electro-optical devices, and also describes a method for reducing crosstalk in said 3D displays and in other similar electro-optical devices, such as in the electro-optical devices that perform optical switching, optical processors, optical data storage, etc. The improvement of the image quality as a result of the decrease of the size of the samples of Holographic / Diffractive Optical Element without increased crosstalk and / or superposition of extraneous images in the image reconstruction is also achieved by the use of the invention described in this Patent Application.
Owner:MIHAJLOVIC ZORAN
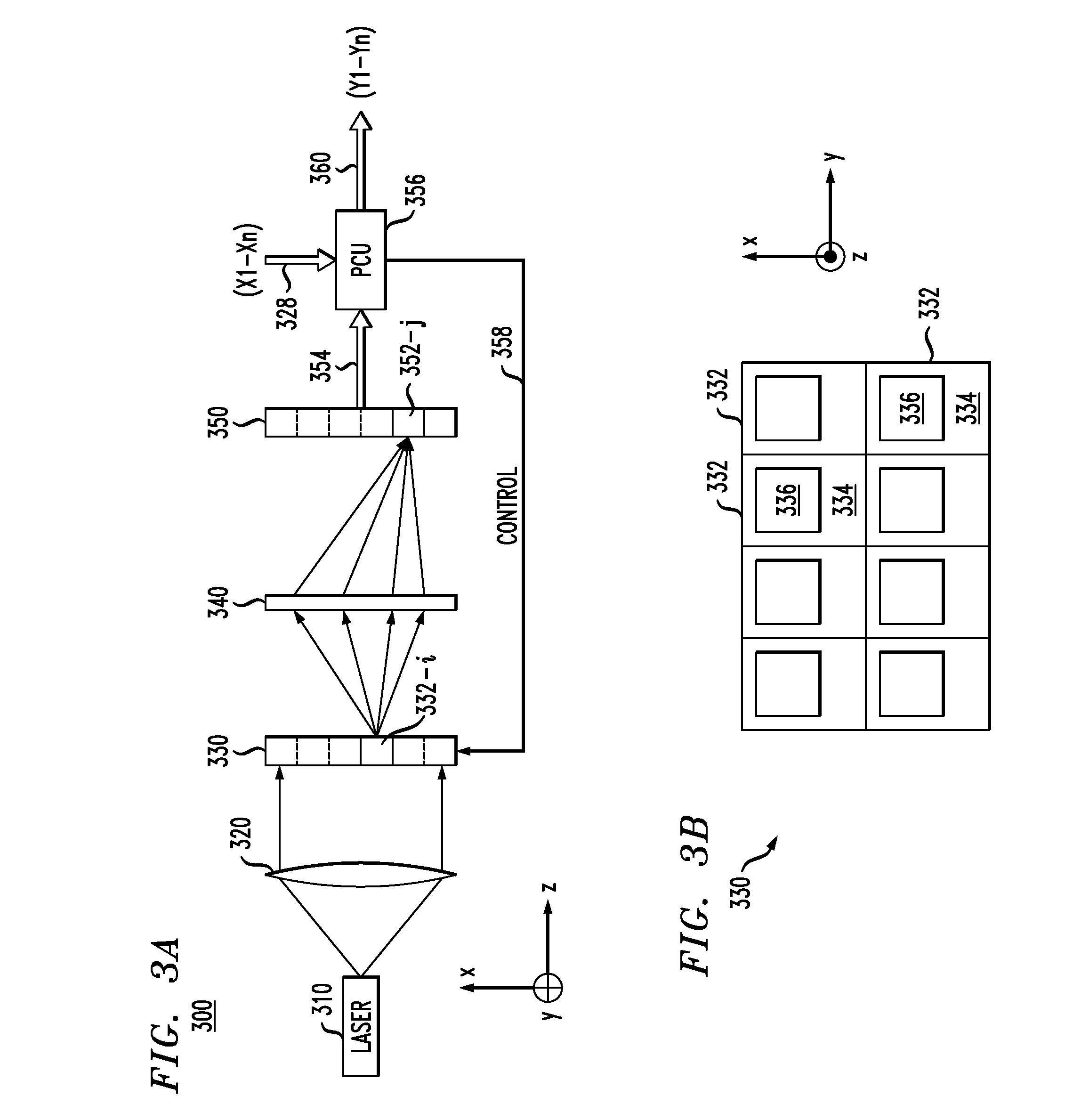
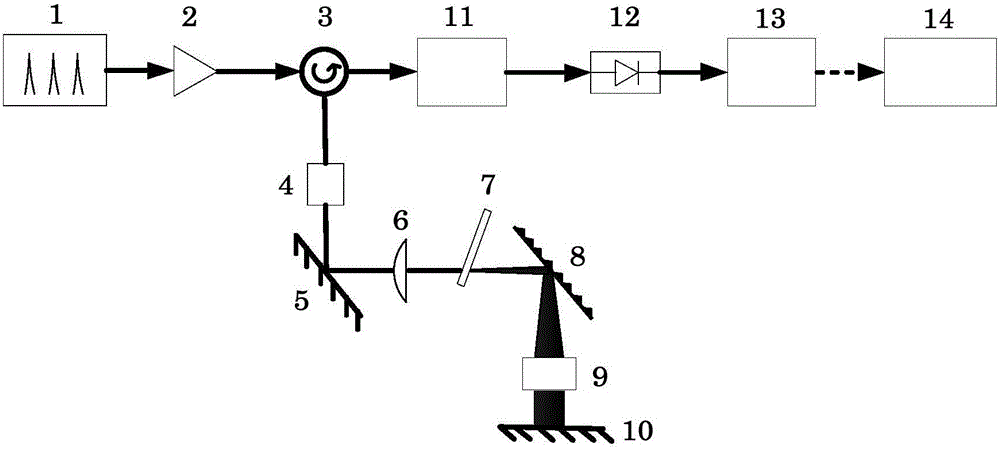
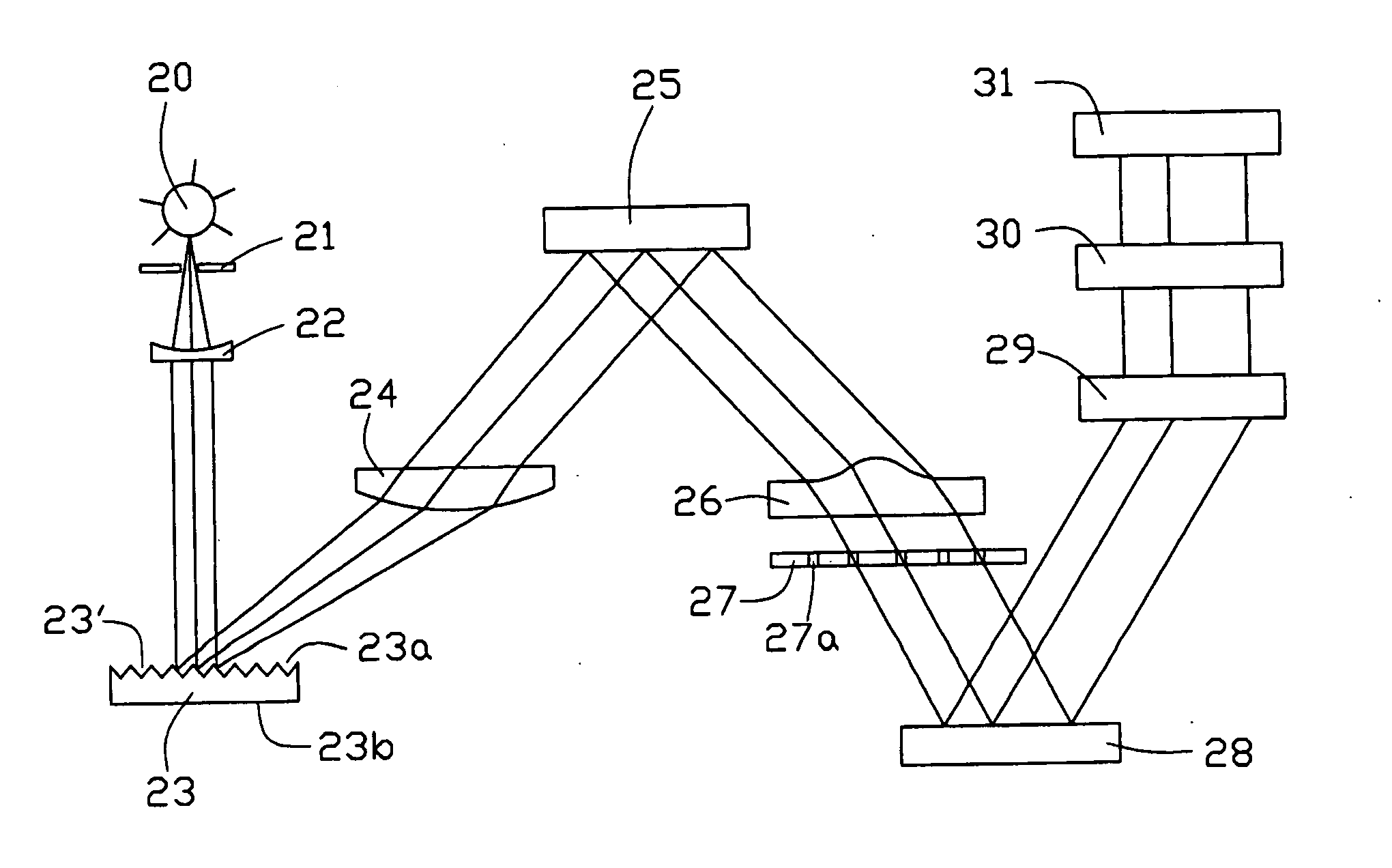
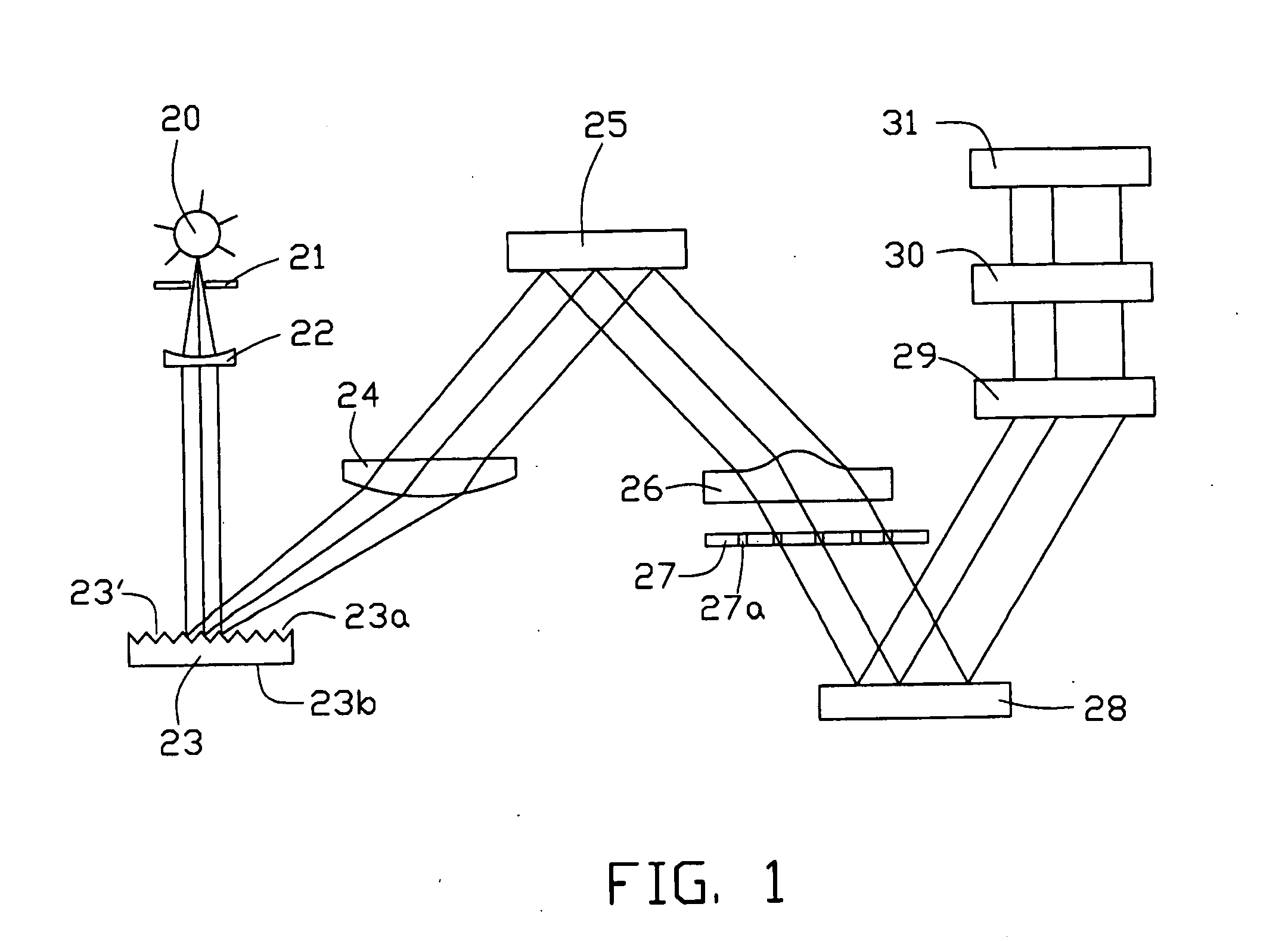
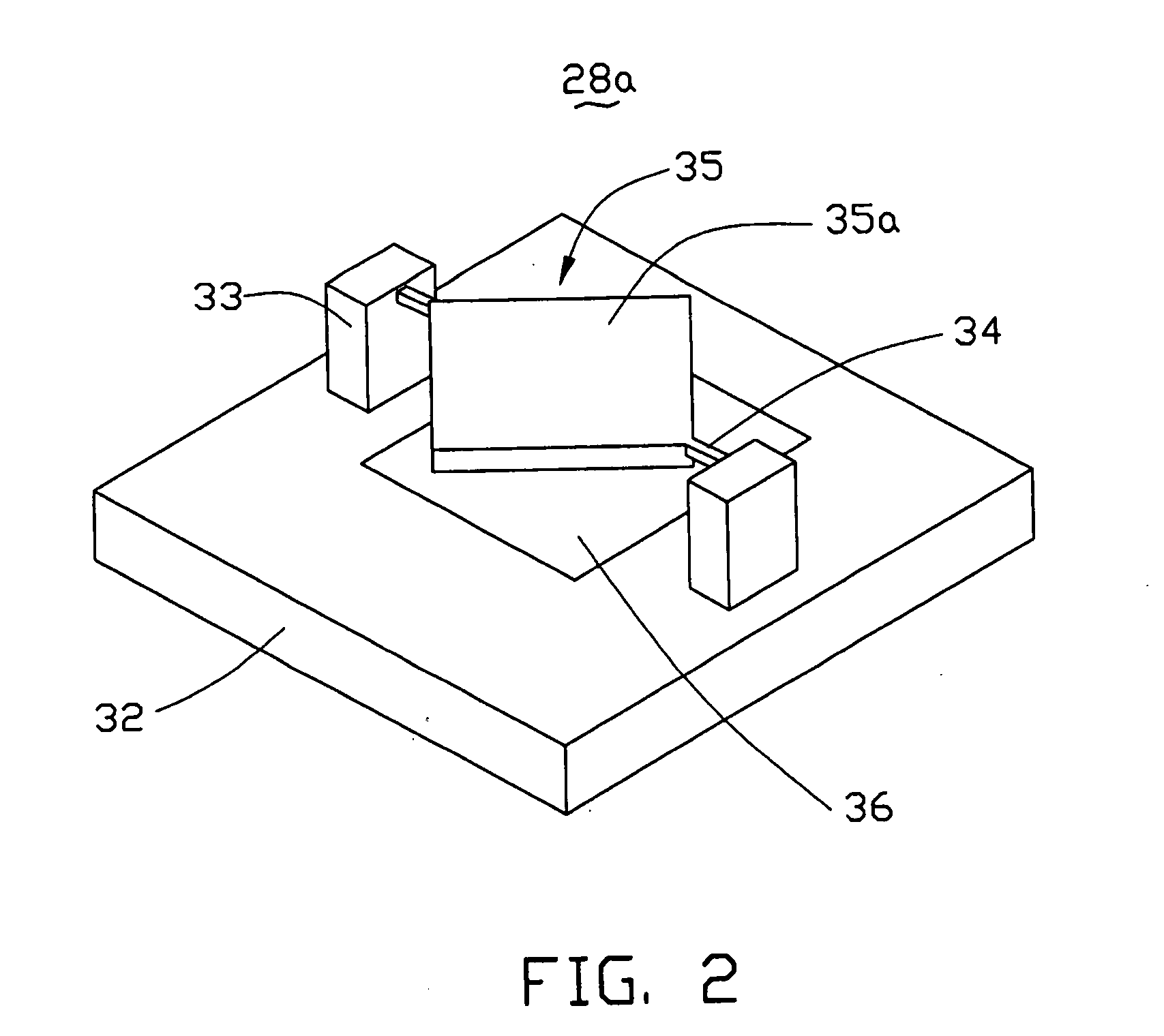
Optical processor using detecting assembly and method using same
An optical processor includes a light source (20), a grating device (23), a first lens (24), a reflector (25), a second lens (26), an array of mirror cells (28), a color wheel (29), and a third lens (30). The light source is for generating a number of light beams. The grating device is for reflecting and dispersing the generated light beams. The first lens is for imaging the reflected and dispersed light beams. The reflector is for reflecting the imaged light beams. The second lens is for correcting any aberration of the reflected light beams. The array of mirror cells is for reflecting the light beams received from the second lens. The color wheel is for coloring the reflected light beams. The third lens is for projecting the colored light beams onto a display.
Owner:HON HAI PRECISION IND CO LTD
Image processing utilizing non-positive-definite transfer functions via fractional fourier transform
InactiveUS6650476B1Implementation processSignificant synergistic valueCharacter and pattern recognitionDiffraction gratingsComplex valuedObservation method
Fractional Fourier transform properties of lenses or other elements or optical environments are used to introduce one or more positive-definite optical transfer functions outside the Fourier plane so as to realize or closely approximate arbitrary non-positive-definite transfer functions. Designs can be straightforwardly obtained by methods of approximation. The invention provides for single and multiple channel controllable optical processors which may be used for image or other types of computation, including computation with complex-valued arithmetic, visual color, and wide-spectrum optical signals. The invention also provides for synthesis of Fractional Fourier transforms, extensions to non-Hermite basis functions, phase-shifting filter elements and non-quadratic graded-index materials (which do not naturally invoke the Fractional Fourier transform operation). Applications include integrated optics, optical computing systems, particle beam systems, radiation accelerators, astronomical observation methods, and controllable lens systems.
Owner:NRI R&D PATENT LICENSING LLC
Methods and apparatus for diffractive optical processing using an actuatable structure
InactiveUS6724125B2Impedence networksWavelength-division multiplex systemsLength waveOptical processor
A method of redirecting light using an actuatable two-layer diffraction grating structure, the method having applications in wavelength-division multiplexed systems. An optical add / drop modulator (OADM) including an actuatable diffraction grating, for use with a wavelength-division multiplexed signal. An OADM having an optical source located off the main pathway to direct a optical carrier to be added onto the actuatable diffraction grating such that the carrier is diffracted into the main pathway. A detector to measure signal strength for use with an optical processor, the optical processor having an actuatable structure having gaps between the actuated portion of the structure. The detector detecting the portions of light diffracted by the gaps.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Optical processor for an artificial neural network
InactiveUS7512573B2Improve processing speedDigital computer detailsDigital dataPattern recognitionSpatially resolved
An optical processor adapted to emulate an artificial neural network (ANN) having a plurality of interconnected layers, each layer having one or more artificial neurons, the processor having a spatial light modulator (SLM) optically coupled, via an optical mask, to a photodetector array. In one embodiment, the SLM has a plurality of pixels, each pixel being configurable to emulate an output portion of a corresponding artificial neuron in a signal-sending ANN layer. The optical mask has a hologram that encodes the weights corresponding to interlayer connections in the ANN and spatially modulates the light transmitted by the SLM. The photodetectors of the array spatially resolve the interference pattern produced by the spatially modulated light, with each photodetector being configurable to emulate an input portion of a corresponding artificial neuron in a signal-receiving ANN layer.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC
Optical multi-gate device and method
InactiveUS20050211881A1Reduce necessityOvercome disadvantagesRadiation pyrometryMaterial analysis by optical meansLogical elementPhase shifted
A logical element including an optical junction coupled to at least two optical inlets and to at least one optical outlet. Incoming light beams of coherent monochromatic light beams and the same uniform frequency are applied to the optical inlets, and their super-positioning is provided as an outgoing light beam(s) via the optical outlet to another logical element or to a light intensity gauge. The light intensity gauge measures light intensity in specific zone(s) of an interference pattern created by the outgoing light beam, dependent on phase shift difference between the components of the incoming light beams, and the measured intensity is correlated with intensity ranges predetermined to conjugate to logical integer values, such as Boolean or other integer numeric values. A multiplicity of logical elements can be installed to provide an optical processor. Parallel use of the same logical element is provided by the simultaneous application of sets of light beams. The sets do not interact with each other by means of differing characteristics, such as different frequencies, or polarizations of the sets. A corresponding method is also provided.
Owner:DMITRY PONOMARENKO
Nanophotonic integrated circuit and fabrication thereof
InactiveUS20060158230A1Multiple input and output pulse circuitsInstant pulse delivery arrangementsDendrimerAdditive ingredient
A class of nanophotonic integrated circuit (nPIC) has been disclosed that is a platform technology for fiberoptic communication and computing, that is fabricated from waveguides that are based on natural index contrast (NIC) principle. A multifunctional nPIC and its fabrication details have been described. The nPIC is also known as an “optical processor”. A novel nanomaterial “dendrimer” is highlighted as the key ingredient that enables the fabrication of the nPICs and its multifunctionality from the same basic process. Other nanomaterials such as spin-on glass, nano-silica sol, and a combination of any of these materials can also be used via the natural index contrast method. Several preferred embodiments of the nPIC are described.
Owner:APPLIED RES & PHOTONICS
Actuatable diffractive optical processor
InactiveUS7046410B2Improve flatnessReduced insertion lossMaterial nanotechnologyOptical elementsGratingDiffraction optics
A programmable MEMS diffractive optical processor having actuatable grating elements that are optically adjacent and supported at points intermediate the ends of the grating elements. The grating elements are maintained substantially flat during actuation of the grating elements.
Owner:AHURA SCI +1
Optical processor enhanced receiver architecture (opera)
InactiveUS7130292B2Enhance performance and capacityEliminate distractionsMirrorsTime-division optical multiplex systemsTime delaysReceiver function
A method and apparatus for enhancing the receiving and information identification functions of multiple access communications systems by employing one or more optical processors configured as a bank of 1-D correlators. The present invention is particularly useful in a DS / SS CDMA communications system, resulting in a multiuser CDMA system that approaches carrier to noise performance (C / N) as opposed to being limited by multiple access interference (MAI). The correlators are arranged in parallel to detect and / or demodulate the received signal, in conjunction with one or more complex algorithms to perform near-optimum multiuser detection, perform multipath combining and / or perform carrier Doppler compensation. An improved receiver in accordance with the present invention comprises means for receiving a plurality of signals transmitted through a communications channel; signal conversion means for converting the received signals into a form suitable for input to the multichannel correlator; a multichannel optical correlator for identifying the presence of particular waveforms and estimating the relative time delay or delays, carrier frequency offset from expected, RF amplitude and RF phase for each received spread spectrum waveform present in the received plurality of signals; a controller for determining and providing to the optical correlator the appropriate set of reference hypotheses; and one or more receiver algorithms depending on the exact receiver function to be performed.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com