Patents
Literature
33results about How to "Few optics" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
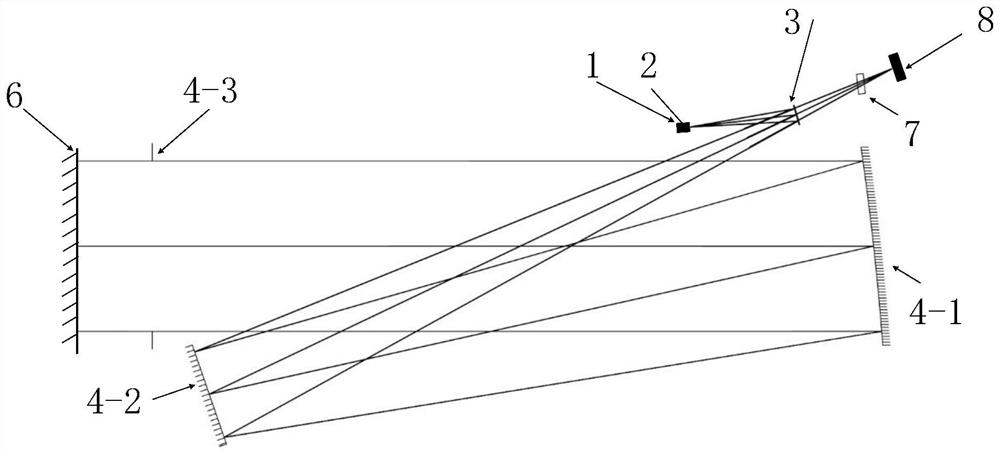
Laser measurement system and method capable of detecting 21 geometric errors
ActiveCN105492860AHighly integratedImprove detection efficiencyAngle measurementInterferometersLight beamEngineering
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
Red light semiconductor area array light source device for laser display
InactiveCN103412406ASimple structureImprove reliabilityLaser detailsProjectorsEffect lightLight beam
The invention discloses a red light semiconductor area array light source device for laser display. The red light semiconductor area array light source device for laser display comprises a VCSEL area array and a microlens array, wherein the VCSEL area array at least comprises a plurality of VCSEL units which are used for emitting circular laser beams, and the microlens array is formed by a plurality of microlens and used for performing collimation rounding on the laser beams output by the VCSEL area array and outputting the laser beams. The light source device can reduce optical elements in a projection display optical path, shorten the length of a lighting optical path, and improve the optical energy utilization rate. In addition, the VCSEL area array can reduce interference between VCSEL lasers and weaken laser speckles, and therefore projection display quality is improved. According to the red light semiconductor area array light source device, the area array light source packaging technology and VCSEL are adopted, a two-dimensional array is easy to integrate, and the defect that power transmitted by a single tube is poor can be overcome. The VCSEL is available in wafer test, reduces cost greatly and is easy in modularization and packaging.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
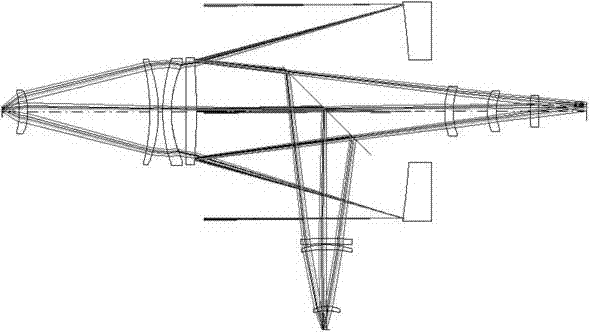
Optical imaging system for visible light waveband, medium-wave infrared waveband and long-wave infrared waveband
The invention provides an optical imaging system for visible light waveband, medium-wave infrared waveband and long-wave infrared waveband. The optical imaging system mainly solves the problem that an existing multi-spectrum camera is heavy in structure and complicated in optical system. The optical imaging system for visible light waveband, medium-wave infrared waveband and long-wave infrared waveband comprises a first reflection mirror, a second reflection mirror and a third reflection mirror, wherein the first reflection mirror is used for reflecting the visible light waveband, the medium-wave infrared waveband and the long-wave infrared waveband, the second reflection mirror is used for reflecting the visible light waveband and the medium-wave infrared waveband and transmitting the long-wave infrared waveband, and the third reflection mirror is used for transmitting the visible light waveband and the medium-wave infrared waveband and reflecting the long-wave infrared waveband. The optical imaging system for the visible light waveband, the medium-wave infrared waveband and the long-wave infrared waveband is light in structure, few in optical devices, fine in imaging quality, small and high in engineering realizability and is integrated with multi-spectrum detection.
Owner:XI'AN INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
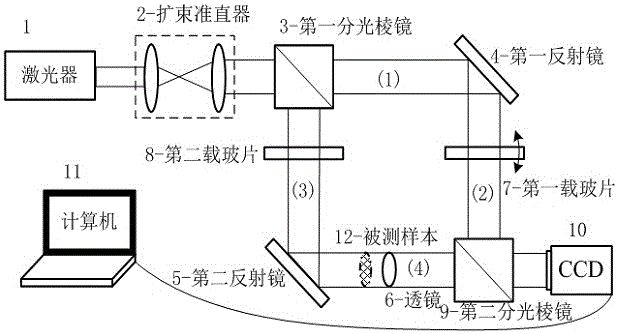
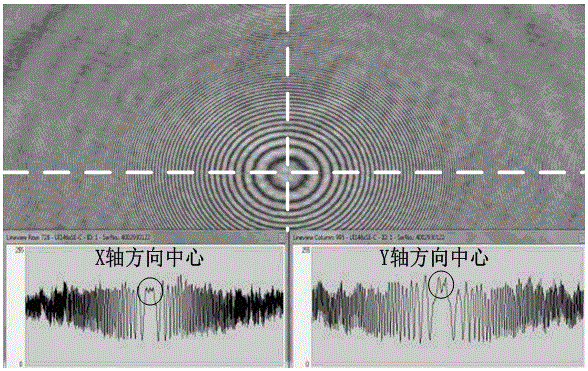
System and method of utilizing two-step phase-shifting coaxial holographic technology to realize 90 DEG phase shift and calibration
The invention relates to a system and method of utilizing the two-step phase-shifting coaxial holographic technology to realize 90 DEG phase shift and calibration. The method comprises: establishing a mach-zehnder double beam plane quasi coaxial holographic optical path system, and separately adding a standard glass slide into an object optical path and a reference light path; adding a condensing lens into the object optical path to converge with the plane of the reference light path to form spherical interference fringes; the spherical interference fringes being distributed in a Sinc function, fine tuning a rotating platform to allow the center of a Sinc function distribution curve to be a maximum value; continuing fine tuning the rotating platform, allowing the center of a sampled Sinc function distribution curve to be a minimum value; and removing the condensing lens in the object optical path, placing a tested sample, and marking according to twice scale values of the rotating platform so as to collect two holograms with 90 DEG phase shift. The recording device referred in the method has the characteristics of less optical elements, simple structure, convenient operation, high adjusting precision, and low cost, and can realize 90 DEG phase shift and calibration in the two-step phase-shifting coaxial holographic technology.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
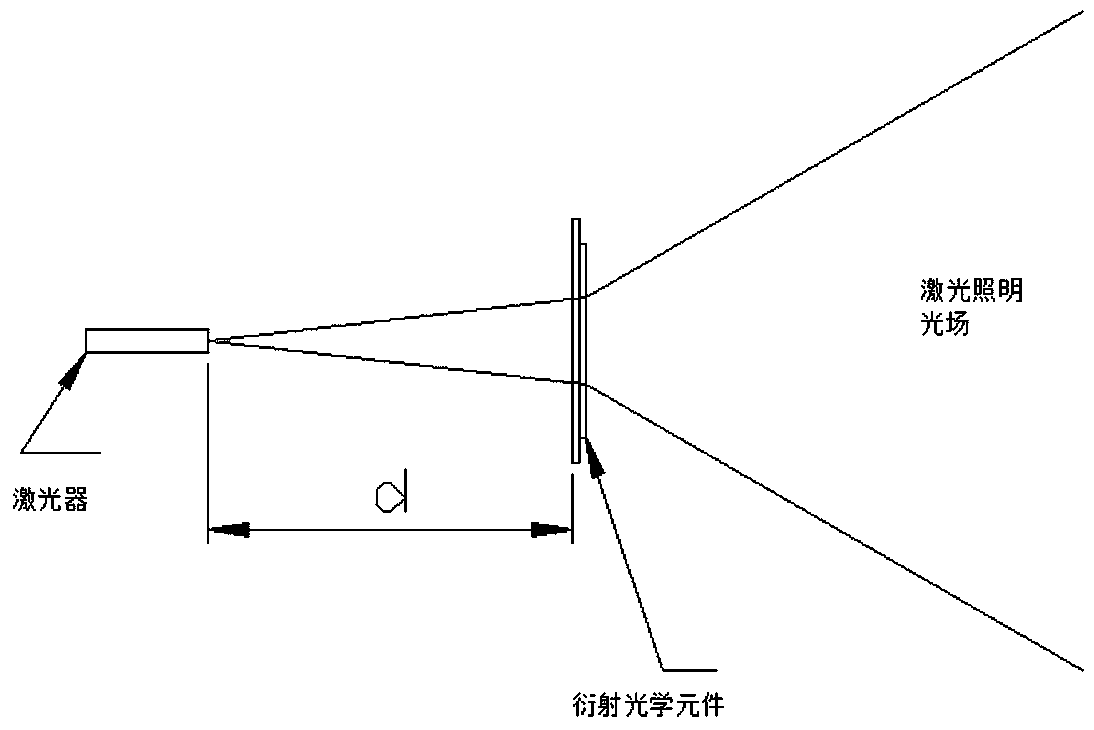
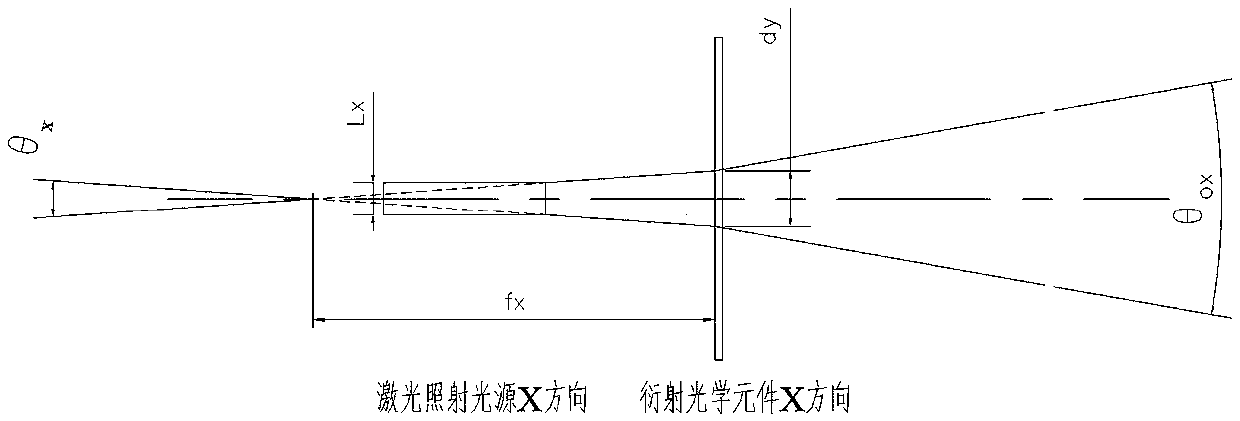
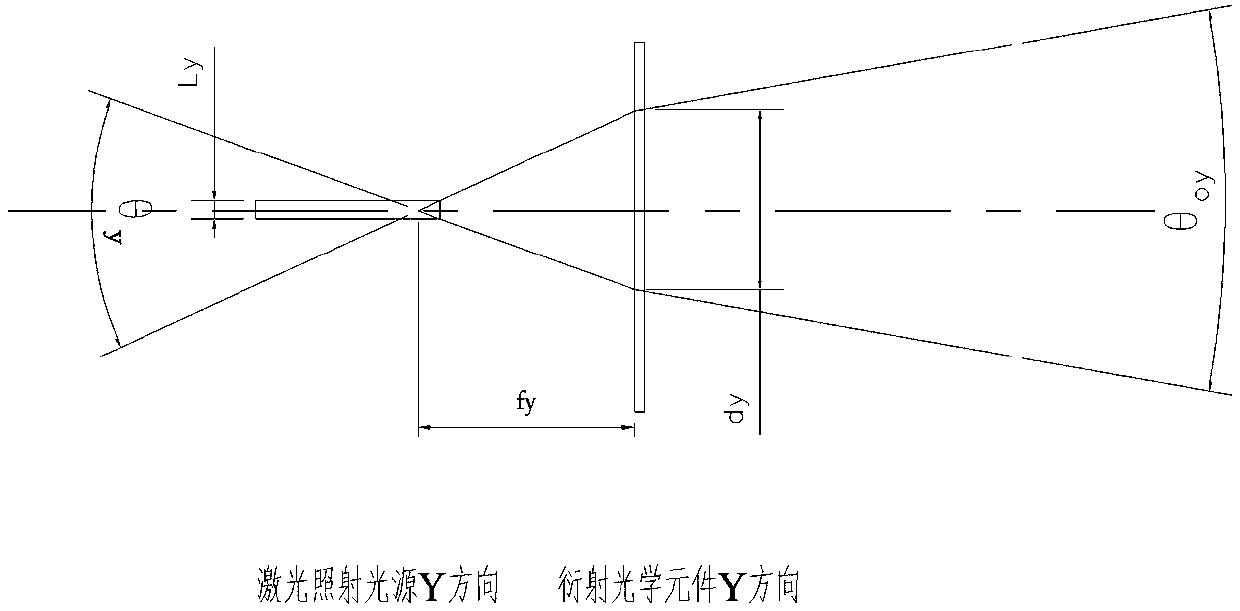
Laser illumination optical system combining diffraction optical element with laser
The invention belongs to the field of photoelectric communication, and especially relates to a laser illumination optical system combining a diffraction optical element with a laser. The laser illumination optical system comprises a laser irradiation light source and the diffraction optical element. After the laser irradiation light source is irradiated on the diffraction optical element, the optical field of the laser irradiation light source is optically modulated by the diffraction optical element, the laser optical field is spread along a specific angle area, and through design and adjustment of optical field wavefront phase modulation, micro morphology and overall dimension of the diffraction optical element, a divergence angle of a needed complex illumination optical field is designed. According to the invention, through diffraction optical design and optical modulation of optical field parameters of the laser irradiation light source are realized through the diffraction optical element, the light intensity utilization rate is high, the distribution shape of the optical field and the light intensity distribution can be flexibly controlled, and the complex illumination optical field can be realized according to needs of such application systems as monitoring shooting, human-eye observation and the like.
Owner:JIAXING UPHOTON OPTOELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
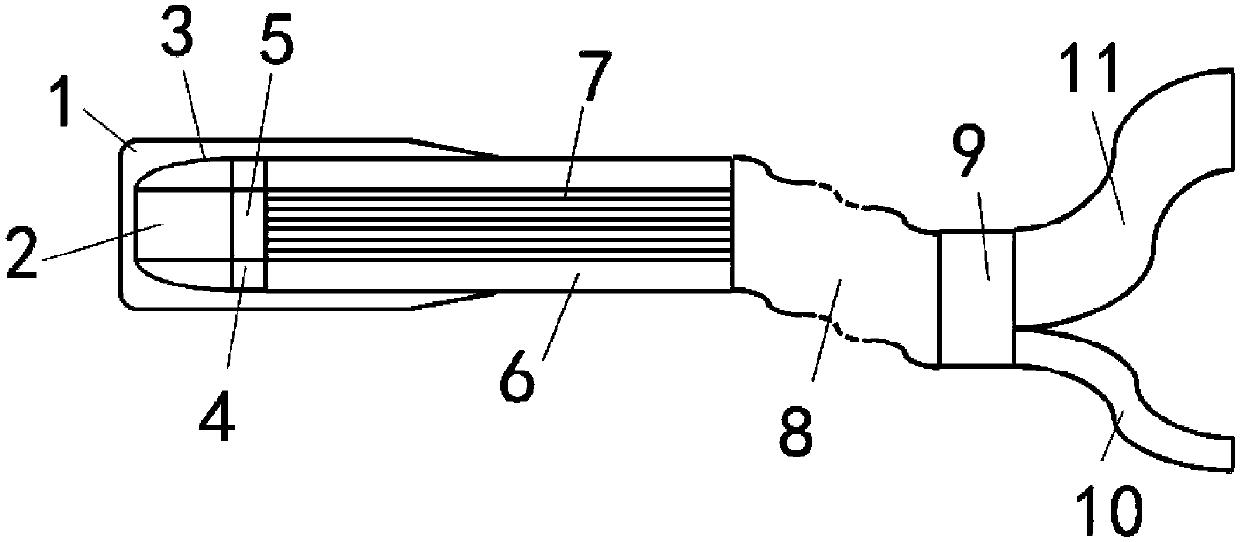
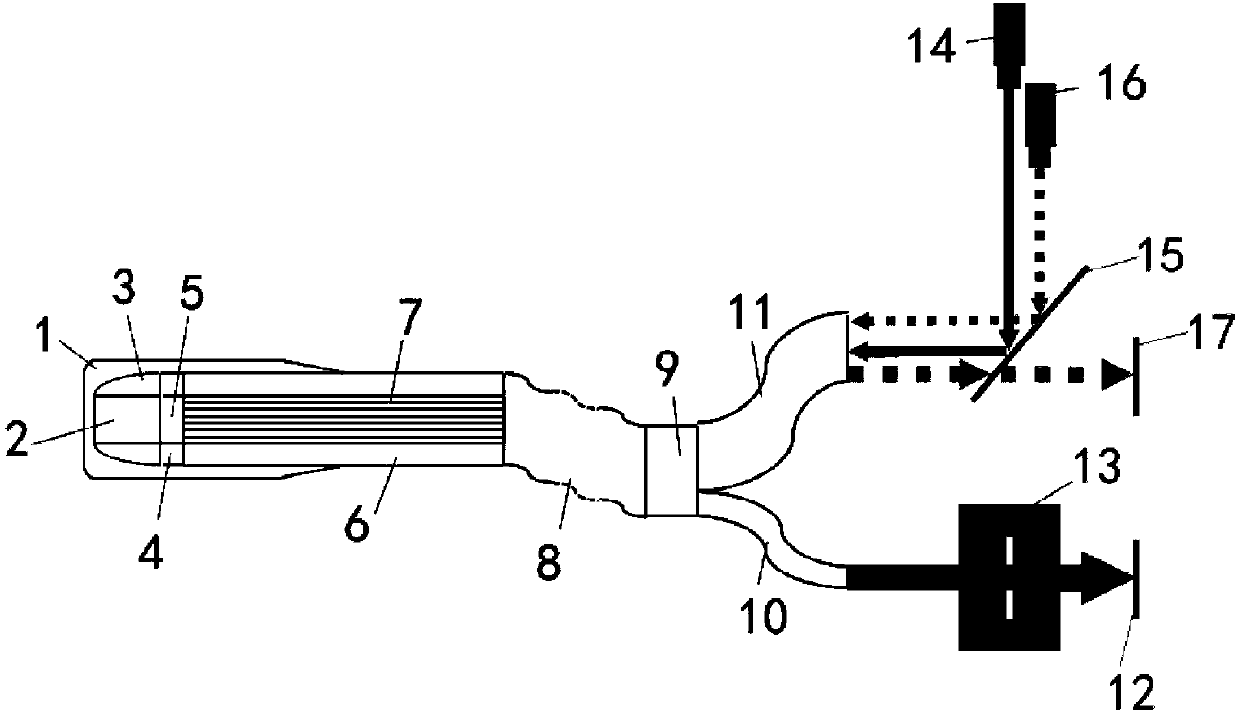
Endoscope fiber Raman probe and detection device
The invention discloses an endoscope fiber Raman probe and a detection device. The endoscope fiber Raman probe comprises a lens, a circular ring lens, a filtering layer, a circular ring filtering layer, a center optical fiber bundle, a Raman collection optical fiber, an optical fiber cable, a connecting piece, a center optical fiber bundle branch and a Raman collection optical fiber branch; the Raman collection optical fiber annually surrounds the center optical fiber bundle; the lens and the filtering layer are arranged at the front end of the center optical fiber bundle; the circular ring lens and the circular ring filtering layer are arranged at the front end of the Raman collection optical fiber; the combined optical fiber bundle of the Raman collection optical fiber and the center optical fiber bundle extends through the optical fiber cable; the other end of the optical fiber cable is divided into a Raman collection optical fiber bundle and an excitation / endoscope optical fiber bundle by the connecting piece. According to the endoscope fiber Raman probe disclosed by the invention, integrated design of optical fiber Raman and optical fiber endoscope is realized; the device hasthe advantages of small volume, low price, high flexibility and accurate detection, and is more applicable to biological in-vivo and in-situ Raman detection, and is relatively easy and convenient to maintain.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Garnet type current sensing device and manufacturing method of garnet module
InactiveCN103197118AEasy for security monitoringGood parallelism in propagation directionCurrent/voltage measurementManufacture of electrical instrumentsPhysical opticsCurrent sensor
The invention discloses a garnet type current sensor and a manufacturing method of a garnet module. The sensor is formed by a light source, an input polarization maintaining optical fiber, an input optical collimator, a polarizer, the garnet module, an analyzer, an output optical collimator, an output polarization maintaining optical fiber and a detector in a connected mode. The garnet module is a core part of the sensor, and a bias film layer capable of solidifying an initial magnetization direction of a garnet material is coated on the garnet module. The garnet type current sensor uses the detector to directly detect changes of a Faraday rotation angle of incident light caused by current changes, and current parameters can be indirectly obtained. Garnet which is provided with high Verdet constant, high transmittance, low temperature coefficient and good mechanical and physical optic performance serves as a core sensing element, and the bias film layer is coated on the garnet to correct system light paths, so that sensitivity of the garnet type current sensor is substantially improved, and system errors are reduced.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
Bidimensional small angle measuring device based on shape of interference fringe
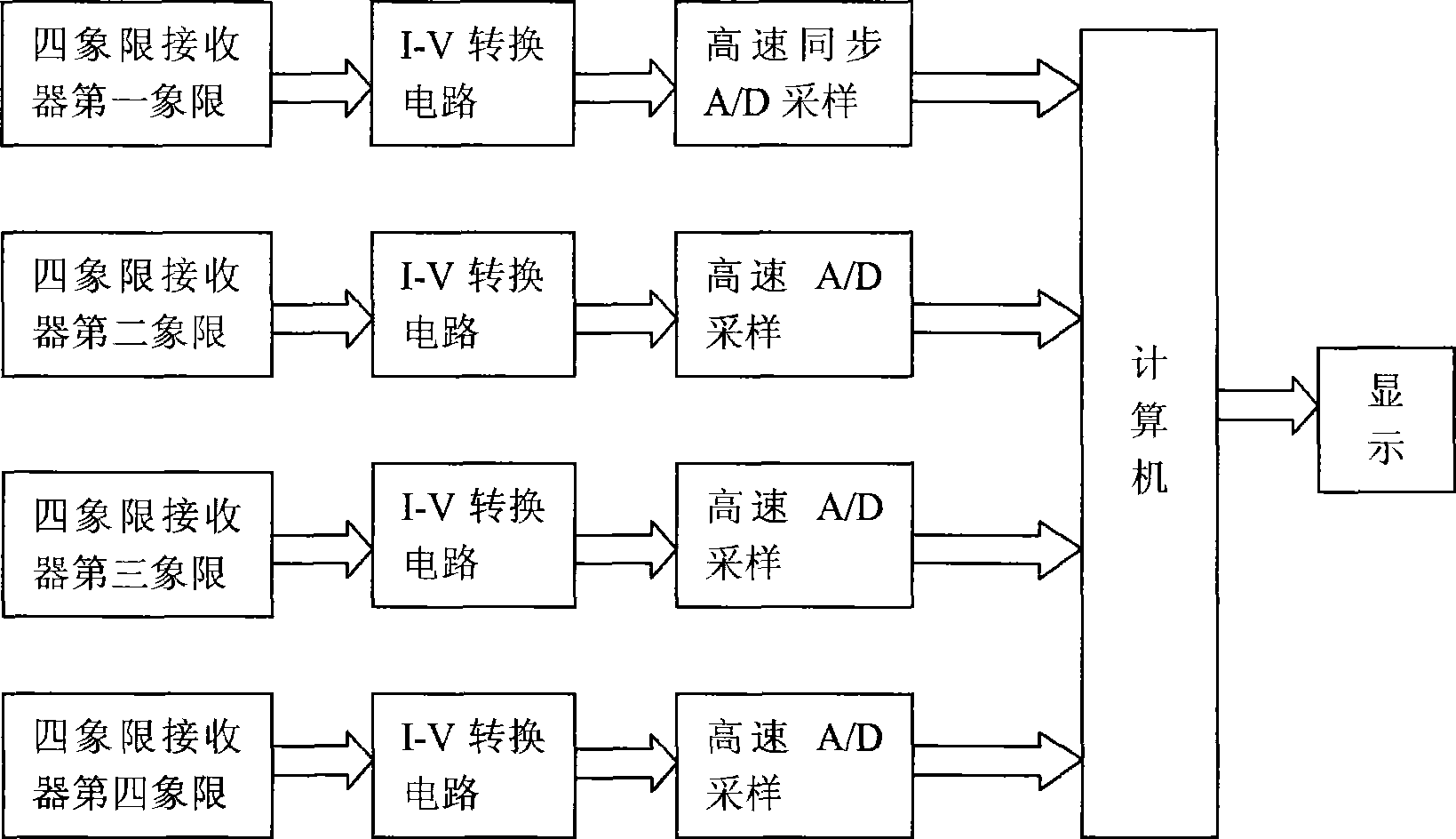
The invention discloses a bidimensional small angle measuring device based on the shape of an interference fringe and belongs to the technical field of precise measurement. The device comprises a laser, a spectroscope, a target reflector, a reference reflector and a four-quadrant receiver; and the target reflector is fixed on a measured object. A laser modulator modulates a light beam transmitted by the laser; the modulated light beam transmits the spectroscope and is divided into two beams; two beams are reflected by the target reflector and the reference reflector respectively, are returned to the spectroscope and are converged to generate the dynamic reference fringe; when the measured object has the angle change around z-axis, the width of the dynamic reference fringe is changed; and when the measured object has the angle change around x-axis, the width and the direction of the dynamic reference fringe are changed simultaneously. The dynamic reference fringe is received by the four-quadrant photoelectric receiver and converted into an electrical signal; the signal is subjected to current-voltage conversion and collected to a computer; and through the analysis of the variable quantity of the width and the direction of the fringe, the variable quantity of the angle of the measured object around the x-axis and z-axis is calculated. The bidimensional small angle measuring device has the advantages that the device adopts a wavelength modulation method and has good repeatability, good antijamming capacity, simple structure, small size and high precision which can reach 0.03 arcsec.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV OF TECH
Composite structure type tunable grating outer cavity dual-mode laser machine
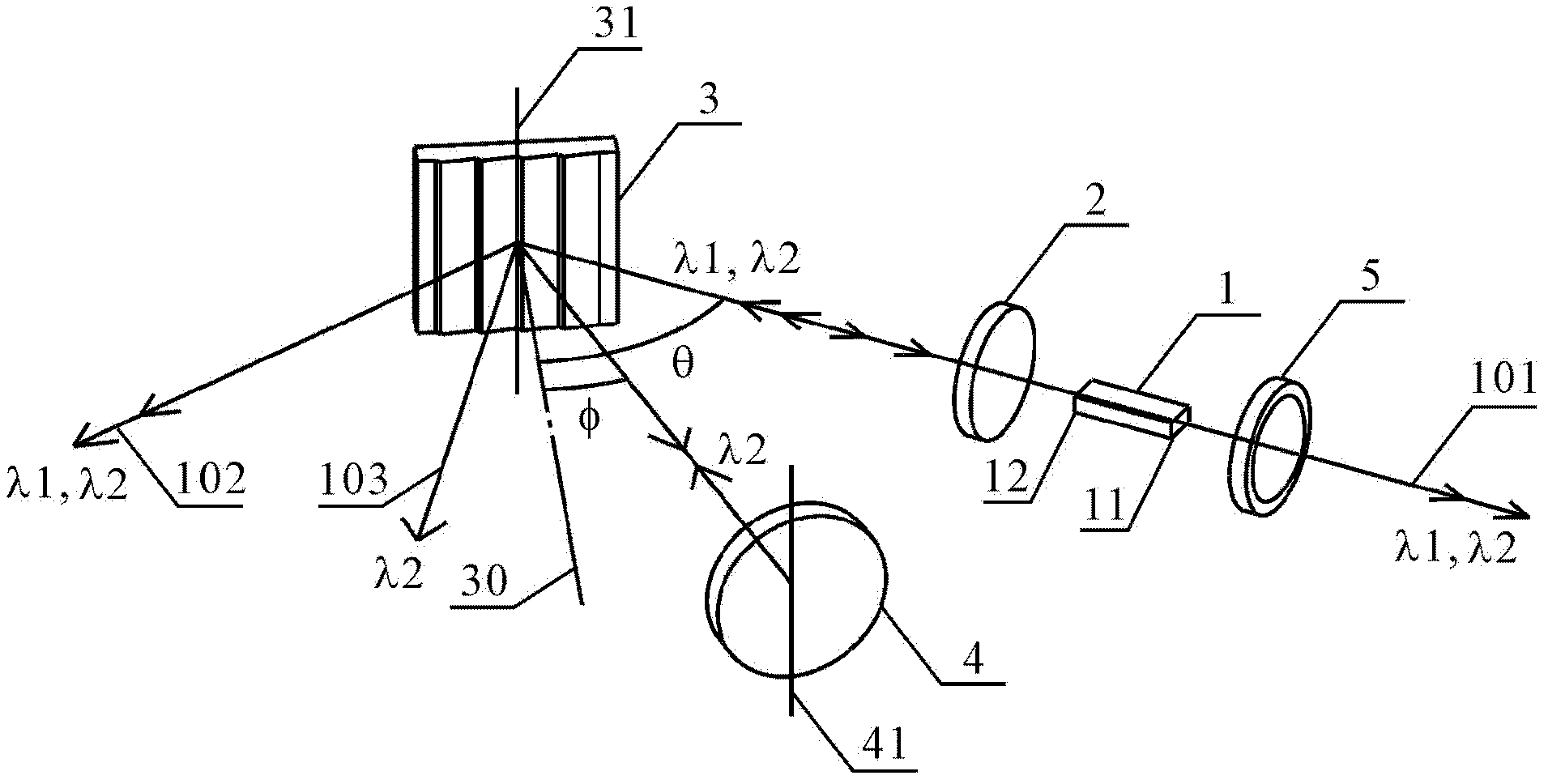
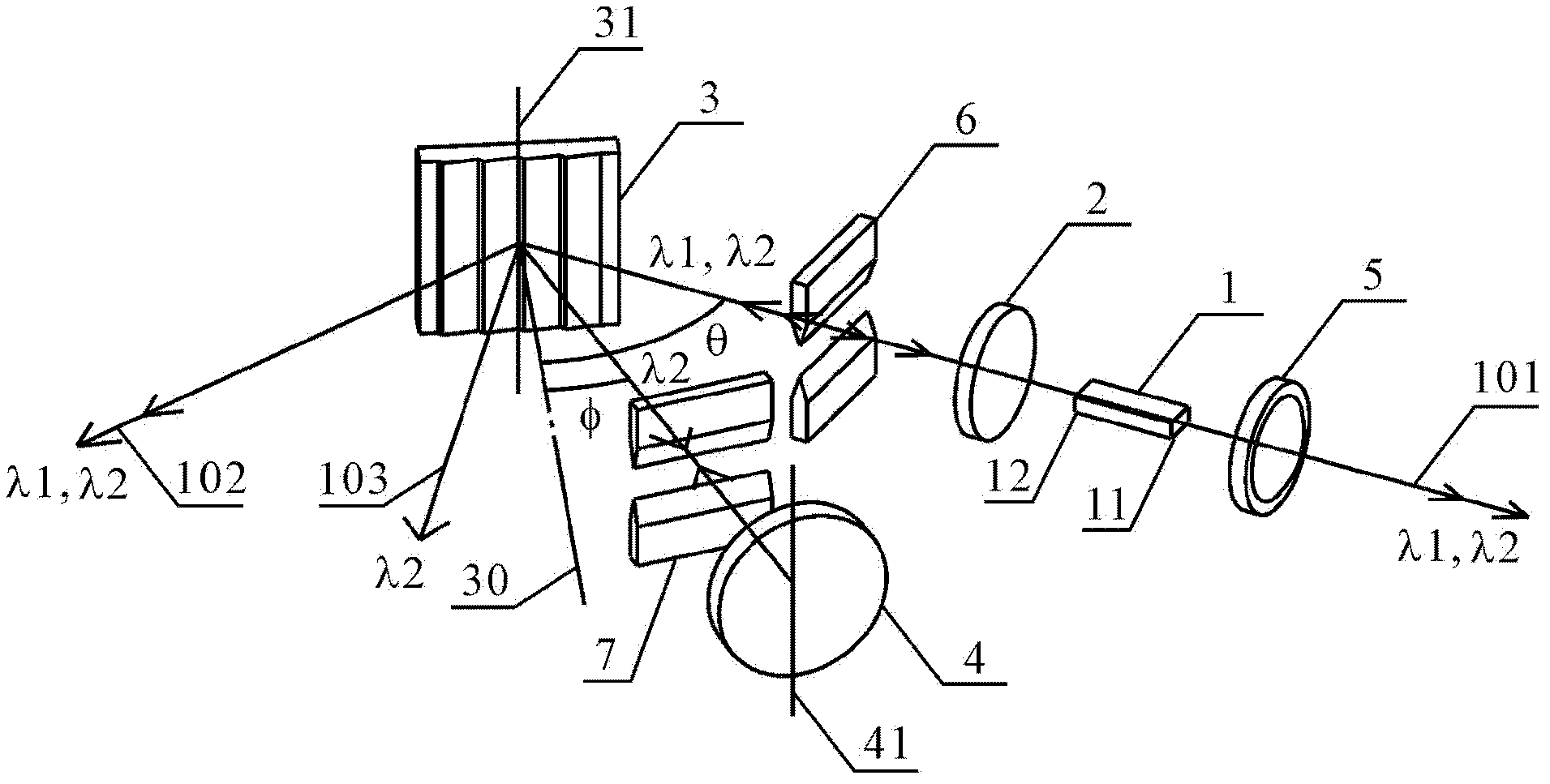
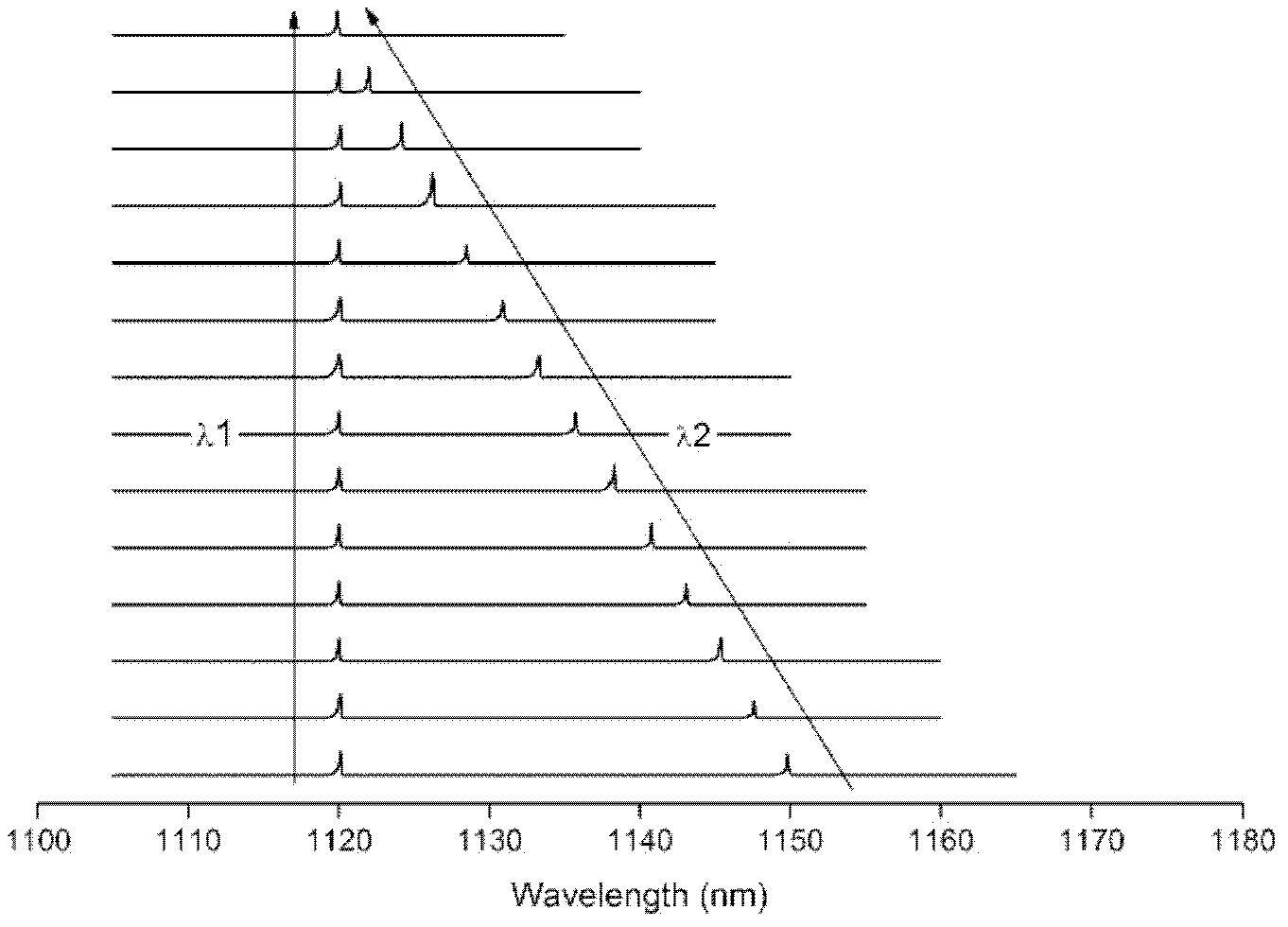
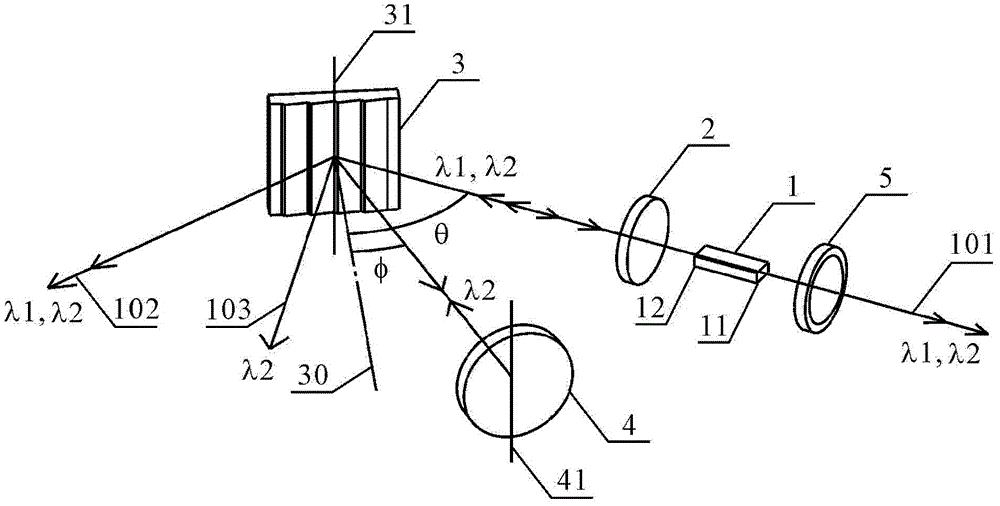
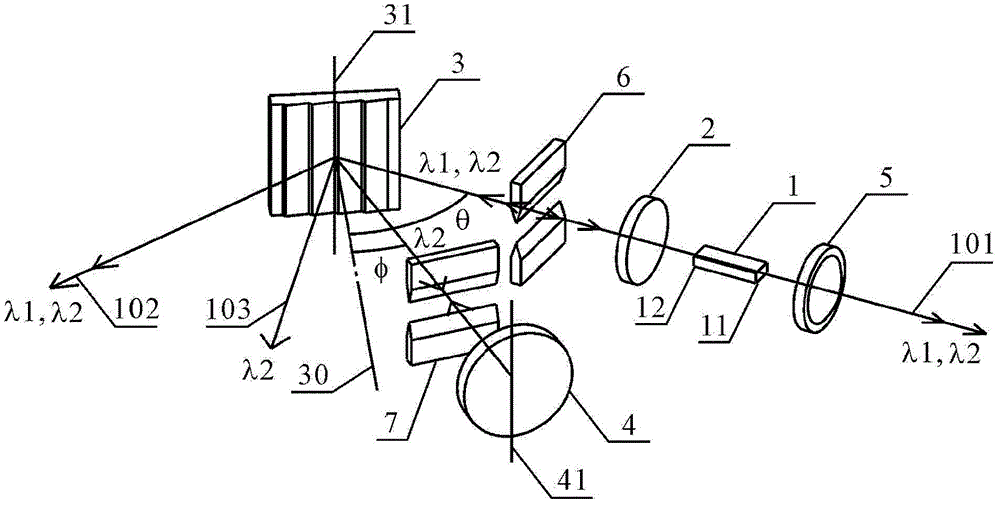
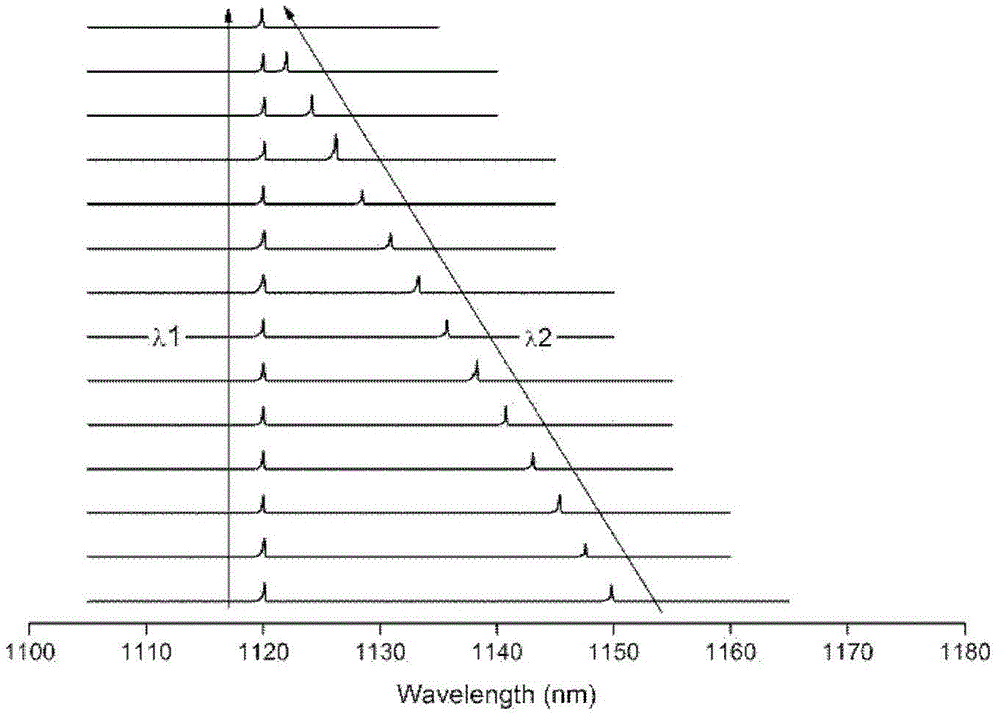
ActiveCN103326239AEasy to adjustSimple structureLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionDual modePlane mirror
The invention discloses a composite structure type tunable grating outer cavity dual-mode laser machine. The composite structure type tunable grating outer cavity dual-mode laser machine comprises a gain component, a lens, a grating and a plane mirror, wherein light emitted from the end face of one side of the gain component is collimated by the lens and then irradiated to the surface of the grating in a incident mode (the incident angle is theta), and diffraction is generated, two beams of diffraction light which are lambda 1and lambda 2 in wave length move forward along the following two paths respectively: firstly, the m level diffraction light which is lambda 1in wave length goes back to the gain component in the incident direction along the same path from which the light comes, wherein m is an integer except zero, and the diffraction angle is equal to the incident angle theta, so that a laser mode which is lambda 1in wave length is formed between the grating and the end face of the other side of the gain component, and secondly, the n level diffraction light which is lambda 2 in wave length goes back to the gain component in the incident direction along the same path from which the light comes after being reflected by the plane mirror and secondly diffracted by the grating, wherein n is an integer except zero and not equal to m, and the diffraction angle is phi, so that a laser mode which is lambda 2 in wave length is formed between the plane mirror and the end face of the other side of the gain component through the grating.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Coupling output structure of terahertz quantum cascade laser and packaging method of coupling output structure
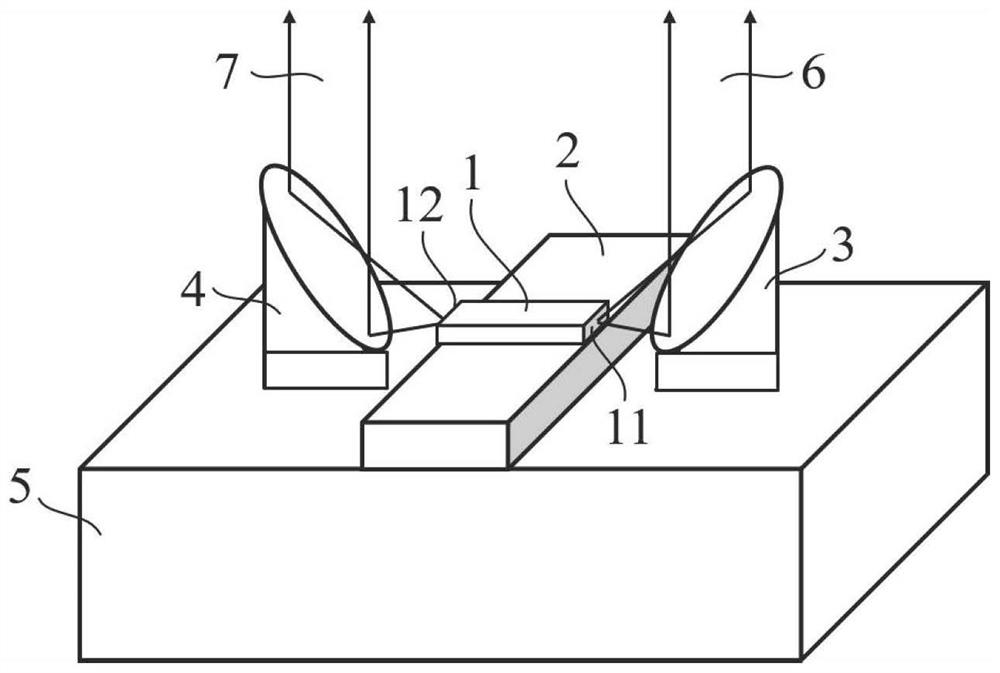
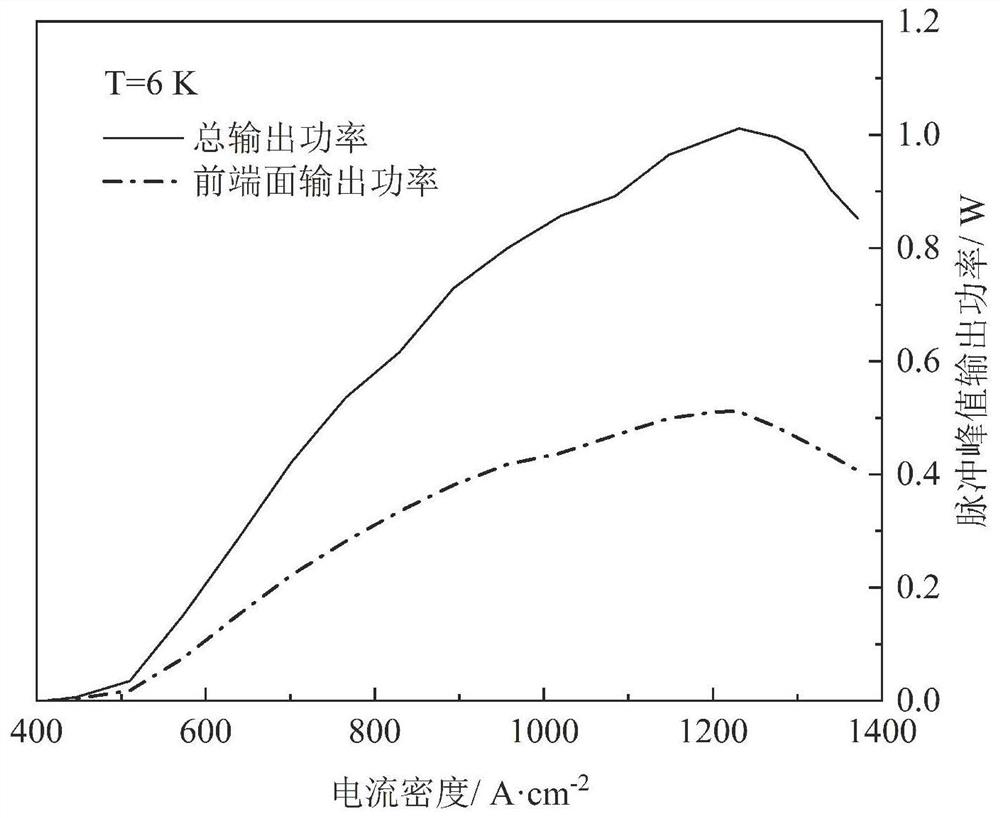
PendingCN111952837AReduce reflection lossImprove coupling efficiencyLaser detailsLaser active region structureLight beamErbium lasers
The invention relates to a coupling output structure of a terahertz quantum cascade laser, and the structure comprises a terahertz quantum cascade laser, a first off-axis parabolic mirror and a secondoff-axis parabolic mirror; the focus of the first off-axis parabolic mirror is positioned in the front end surface of the terahertz quantum cascade laser, and the collimator is used for collecting and collimating laser emitted by the terahertz quantum cascade laser and forming a first quasi-parallel light beam; the second off-axis parabolic mirror is located in the rear end face of the terahertzquantum cascade laser and used for collecting and collimating laser emitted by the terahertz quantum cascade laser and forming a second quasi-parallel light beam. The invention further relates to a packaging method of the coupling output structure of the terahertz quantum cascade laser. According to the invention, double-end-surface laser high-efficiency coupling output can be realized.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Optical isolator and laser
PendingCN111722421AReduce material costsReduce manufacturing costNon-linear opticsOptical isolatorLight beam
The invention discloses an optical isolator and a laser. According to the optical isolator, a divergence angle adjusting module used for adjusting a divergence angle of a light beam, a light beam isolation structure and a collimating lens are arranged in a light path direction so as to Implement collimated light output, optical elements needed by the collimated light output optical isolator are effectively reduced, a material and manufacturing cost of the optical isolator is reduced, a size of the optical isolator is decreased, popularization of the collimated light output optical isolator isfacilitated, and technical problems that in the prior art, an optical isolator is complex in structure, high in cost and large in size, and a use occasion is limited are solved.
Owner:光越科技(深圳)有限公司
Multipass laser amplifier and no-optical-power beam steering element
PendingUS20220131337A1Good mode qualityReduce the maximum temperaturePrismsOptical resonator shape and constructionOptical powerLight beam
A multipass laser amplifier includes a mirror, a mirror device, a gain crystal, and refractive or diffractive beam-steering element. The gain crystal is positioned on a longitudinal axis of the multipass laser amplifier between the mirror and the mirror device. The beam-steering element is positioned on the longitudinal axis between the gain crystal and the mirror device. The beam-steering element has no optical power and deflects a laser beam, by refraction or diffraction, for each of multiple passes of the laser beam between the first mirror and the mirror device, such that each pass goes through the gain crystal for amplification of the laser beam and goes through a different respective off-axis portion of the beam-steering element. The no optical power of the beam-steering element enables maintaining a large beam size in the gain crystal, thereby facilitating amplification to high average power.
Owner:COHERENT KAISERSLAUTERN
Solar blind ultraviolet imaging optical lens and system
The invention provides a solar blind ultraviolet imaging optical lens and a system. The solar blind ultraviolet imaging optical lens comprises a first meniscus lens piece and a second meniscus lens piece sequentially from an object side to an image side; the optical surfaces of the first meniscus lens piece and the second meniscus lens piece are spherical surfaces; one optical surface of the first meniscus lens piece is coated with a round ultraviolet reflection film; the rear surface of the second meniscus lens piece is coated with a round ultraviolet reflection film; and thus, to-be-detected light is outputted by the center of the second meniscus lens piece through reflection by the first meniscus lens piece and the second meniscus lens piece. As the solar blind ultraviolet imaging optical lens only comprises two spherical meniscus lens pieces, the optical elements in the solar blind ultraviolet imaging optical lens are few, and the utilization rate of light energy is high; the optical surfaces of the two meniscus lens pieces are both spherical surfaces, an aspheric surface is not needed, the manufacturing cost is low, and the technological performance is good. For the two meniscus lens pieces, hole opening in the center is not needed, and the manufacturing process is simple.
Owner:长春国科精密光学技术有限公司
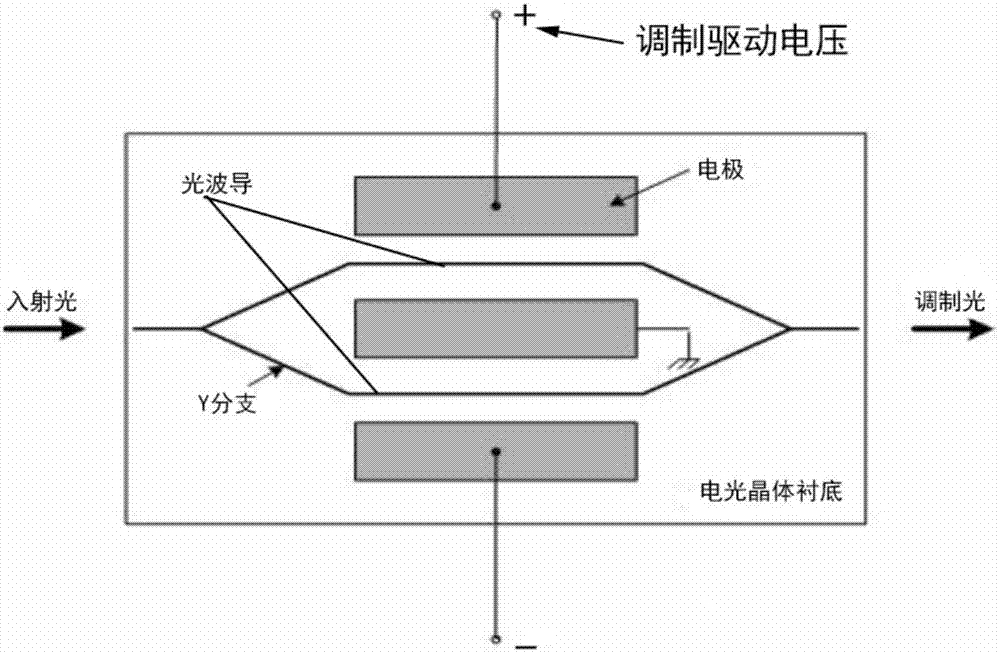
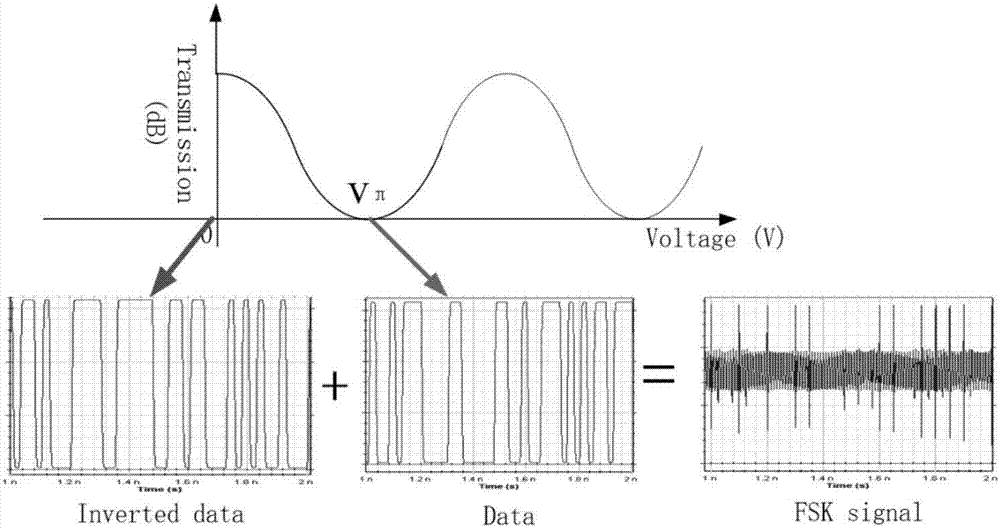
FSK signal producing apparatus, method and application
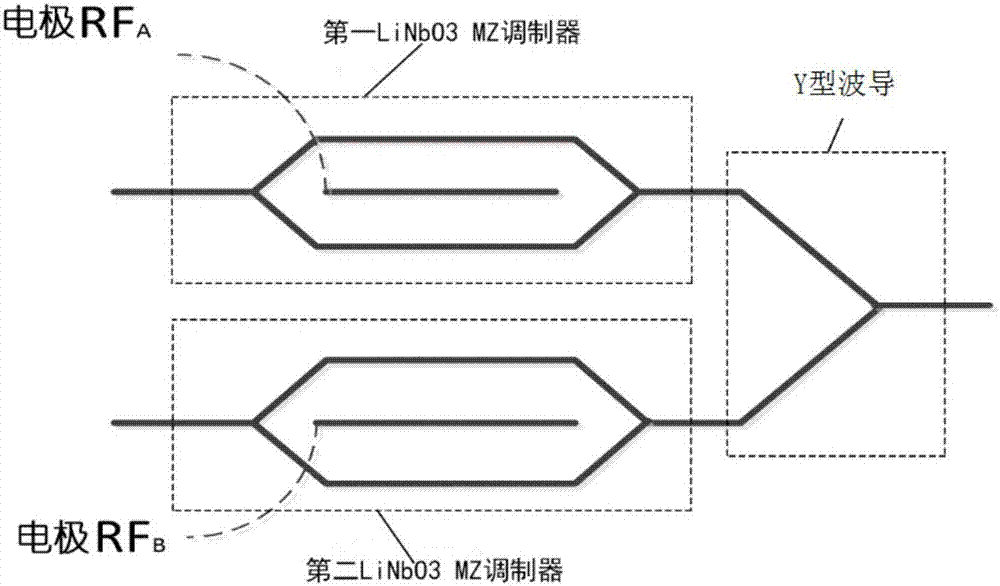
InactiveCN107017953ACompact structureFew opticsElectromagnetic transmissionVIT signalsTransmission system
Disclosed in the invention are an FSK signal producing apparatus, a method and an application. The apparatus includes a first MZ modulator, a second MZ modulator and a combination unit. By inputting a first control voltage to a control electrode of the first MZ modulator, an output end of the first MZ modulator is enabled to output an inverting modulated optical signal. By inputting a second control voltage to a control electrode of the second MZ modulator, an output end of the second MZ modulator is enabled to output a non-inverting modulated optical signal. Combination of the non-inverting modulated optical signal and the inverting modulated optical signal is realized by the combination unit, thus the output of an FSK signal is realized. The apparatus utilizes a small number of optical devices, has a compact structure and greatly simplifies the structure of an FSK modulator. In addition, the FSK signal producing apparatus is directly driven by data signals which do not include sinusoidal signals, which can avoid performance and speed limitations for transmission of the FSK signal caused by the frequency of the sinusoidal signals. The produced FSK signal has a good shape of eye pattern in the high speed optical transmission system, and can realize error-free transmission in theory with a low loss and an excellent performance.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Projection lens
The invention relates to a projection lens, which sequentially comprises a first lens group, a second lens group, a third lens group and a prism from an object end to an imaging surface along the optical axis direction. The first lens group has negative focal power; the second lens group has positive focal power; the third lens group has positive focal power. According to the invention, a reversetelephoto structure is adopted, so that the lens has a large field of view and a long back focus. The first lens group adopts negative focal power and can effectively balance off-axis aberration, andthe aperture ST is arranged between the second lens group G2 and the third lens group G3, so that the whole lens structure is symmetrical relative to the aperture ST, and coma aberration, astigmatism,vertical axis chromatic aberration, distortion and the like can be well corrected. The second lens adopts an aspheric surface design, the flat field performance of the lens can be greatly improved, the resolution power of the lens is effectively improved, and meanwhile, only one aspheric surface is adopted, so that the difficulty of adjustment is prevented from being increased. The prism is usedfor turning light, so that the layout of an optical-mechanical system is facilitated.
Owner:北京乐都展陈科技发展有限公司
Lens and automobile lamp structure
InactiveCN107435880AFew opticsReduce light lossRefractorsFixed installationOptoelectronicsLight source
A car lamp structure, the car lamp structure includes a lens and a light source, the lens includes a light-emitting surface, a fixing surface opposite to the light-emitting surface, and a total reflection surface connecting the light-emitting surface and the fixing surface; At least one light-incident structure is recessed from the fixed surface to the light-emitting surface; the light-incident structure has a first light-incident surface, the light-exit surface is flat, and the total reflection surface is composed of a plurality of curved surfaces with different radii of curvature , the first light-incident surface is located at the top of the light-incident structure opposite to the fixing surface and is a D-shaped curved surface protruding toward the fixing surface. The light source is accommodated in the light incident hole and faces the first light incident surface. The lens and the car light structure provided by the invention can directly form oval-shaped light spots that are clear and conform to car light specifications, and can also improve the utilization rate of light.
Owner:HONG FU JIN PRECISION IND (SHENZHEN) CO LTD +1
High-sensitivity and large-area laser ultrasound imaging method
ActiveCN110596009AImprove excitation efficiencyHigh sensitivityAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMaterial analysis by optical meansUltrasound imagingElectricity
The invention discloses a high-sensitivity and large-area laser ultrasound imaging method. Dorsad-mode rapid laser ultrasound imaging with the simple structure, high sensitivity and large field of view can be achieved. According to the high-sensitivity and large-area laser ultrasound imaging method, a microlens array made of a piezoelectric material with the high optical transmission rate is selected as a laser micro focusing unit and an ultrasonic signal receiving unit simultaneously, a coaxial, confocal and integrated structure of optical and acoustic paths is ingeniously achieved, an optical or acoustic multiple-reflection-type excitation or reception structure is omitted, the efficiency of laser ultrasonic excitation and sensitivity of reception are effectively improved, the signal-to-noise ratio of reception is effectively increased, miniaturization and large-area imaging of a laser ultrasonic lens are easier to achieve, and the high-sensitivity and large-area laser ultrasound imaging method is expected to be applied to the fields such as bioidentification, medical subcutaneous vascular imaging and material nondestructive testing.
Owner:南昌洋深电子科技有限公司
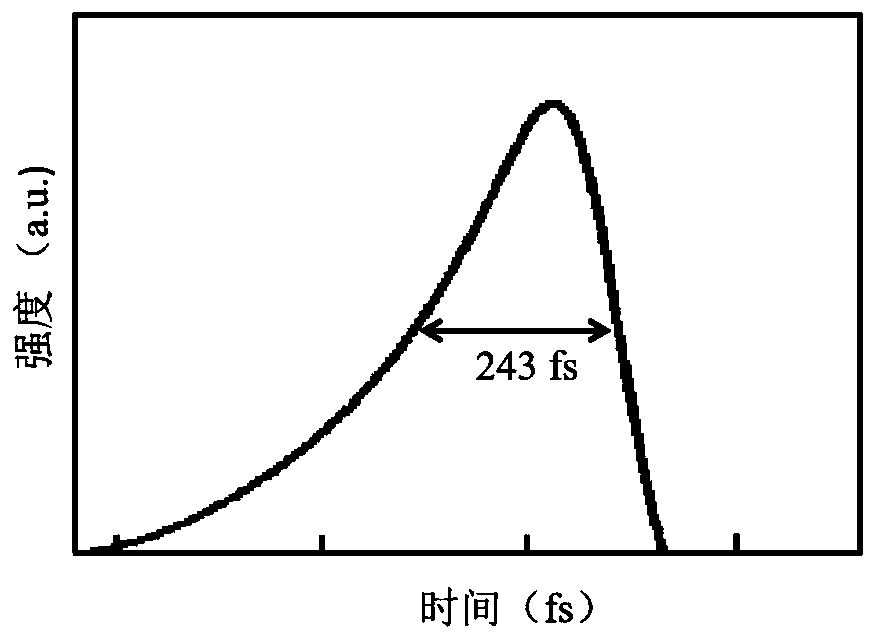
Ytterbium ion doped ABGS crystal and self-frequency-doubling ultrashort pulse laser
The invention relates to an ytterbium ion doped ABGS crystal and a self-frequency-doubling ultrashort pulse laser. The laser comprises a semiconductor laser pumping source, a focusing system, a firstresonant cavity mirror M1, a self-frequency-doubling laser crystal, a second resonant cavity mirror M2, a GTI mirror, a third resonant cavity mirror M3, a fourth resonant cavity mirror M4 and a saturable absorber, which are arranged along a light path; the self-frequency-doubling laser crystal is an ytterbium ion doped A3BGa3Si2O14 crystal, wherein A is Ca or Sr, and B is Nb or Ta. The crystal haslaser emission and nonlinear optical effects at the same time, and ultrashort pulse self-frequency-doubling green light output is realized by using a self-frequency-doubling crystal through a mode locking technology. The cost is low; one self-frequency-doubling laser crystal is used for replacing a laser crystal and a nonlinear crystal, so that the production cost is greatly reduced, and meanwhile, the machining and assembling links are simplified; and the production efficiency is improved.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
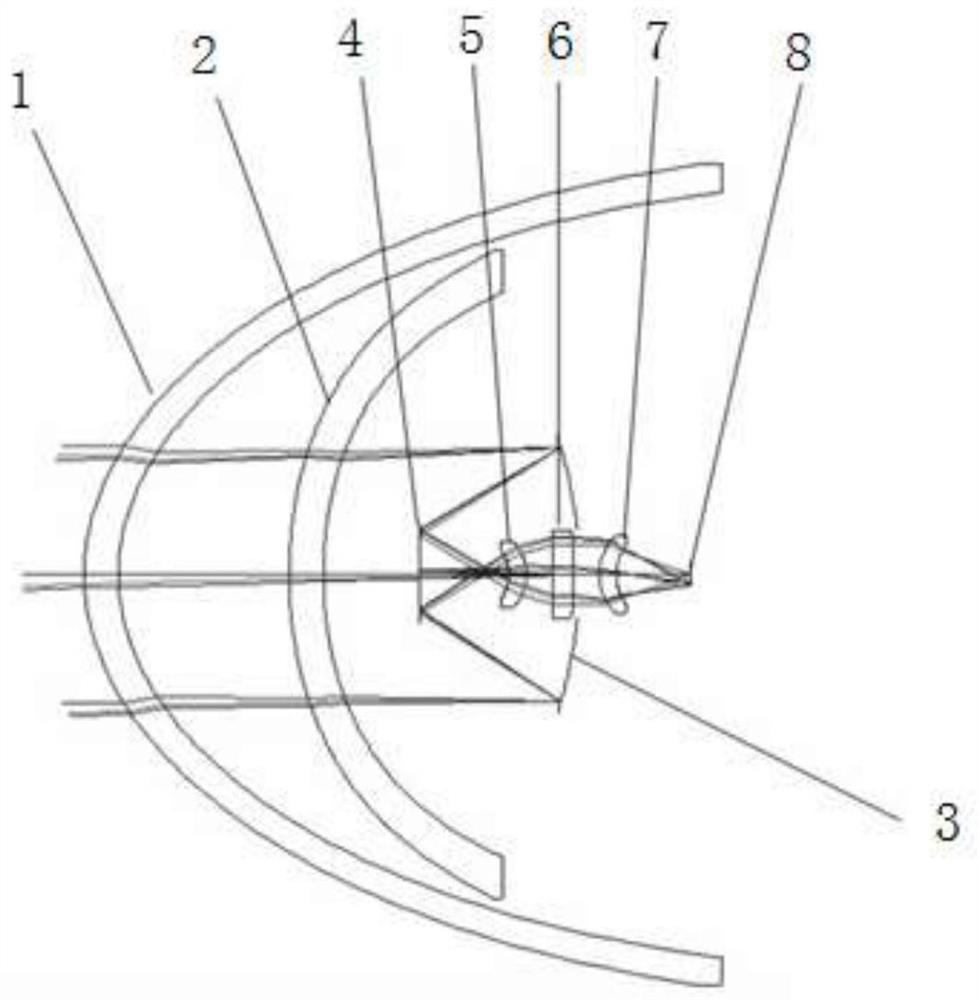
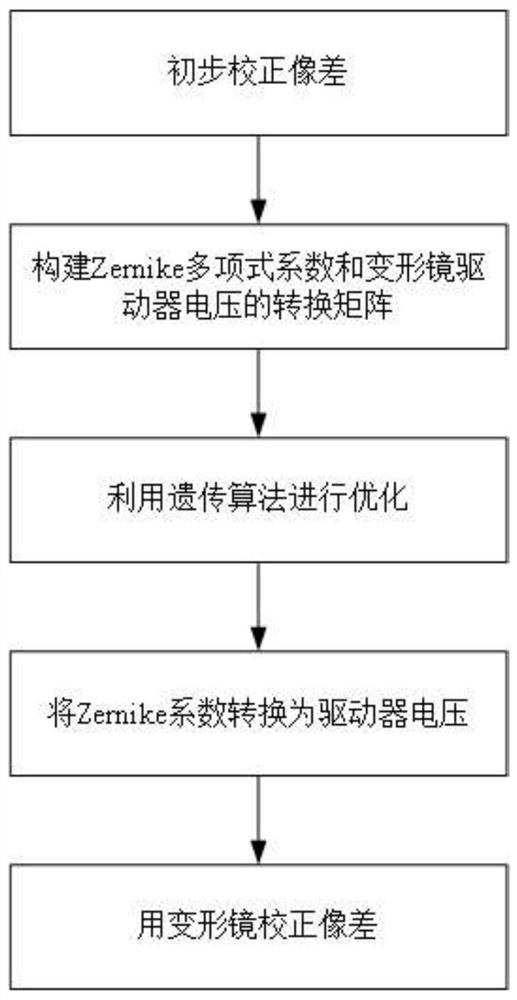
Aspheric window optical aberration correction method based on Zernike model coefficient optimization
ActiveCN112363315ASimple system structureFew opticsDesign optimisation/simulationConstraint-based CADGenetics algorithmsStrehl ratio
The invention discloses an aspheric window optical system aberration correction method based on Zernike model coefficient optimization, belongs to the technical field of aspheric window optics, and aims to overcome the defects of an existing correction method. The method comprises the steps of 1 performing optimization in optical design software CodeV, and preliminarily correcting aberration; 2 constructing a conversion matrix of a Zernike polynomial coefficient and the deformable mirror driver voltage; 3 performing optimization by utilizing a genetic algorithm: writing the genetic algorithm,taking the Strill ratio of the optical system as a fitness function of the algorithm, and taking eight coefficients of a Zernike polynomial as variables of the algorithm; 4 converting the Zernike coefficient into the driver voltage: multiplying the matrix A obtained in the step 2 by the matrix C obtained in the step 3 to obtain a deformable mirror driver voltage matrix V; and 5 correcting aberration by using a deformable mirror: changing the voltage of a deformable mirror driver into the voltage V obtained in the step 4, and enabling the deformable mirror to generate a corresponding surface shape so as to compensate the aberration.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Laser car fog lamp optical system formed by combining diffraction optical element and laser device
InactiveCN105299561AFew opticsSmall sizeOptical signallingLight fasteningsAbnormal shapedOptoelectronics
The invention discloses a laser car fog lamp optical system formed by combining a diffraction optical element and a laser device. The laser car fog lamp optical system comprises a laser illuminating light source and the diffraction optical element, wherein the laser illuminating light source is a divergency light source or a collimating parallel light source, and the diffraction optical element is designed according to parameters of the laser illuminating light source and used for achieving optical field distribution required by the optical system. The diffraction optical element has the characteristics of being small in size, easy to mount and low in cost and can greatly reduce the size of the optical system and reduce the cost of an optical product. Meanwhile, according to the diffraction optical element, the optical indicatrix allowance is large, the influence of fine dust and dirt of a light pass area on an abnormal-shaped optical field is quite small, the requirement for the application environments is low, the element can adapt to various complex application environments, an adjusting system with high light utilization efficiency of the optical field, low cost, simple optical structure design, small size and high-accuracy divergence angle is completely achieved, and the functions and applicability of the optical system are improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY +1
Spatial phase-shifting interferometer
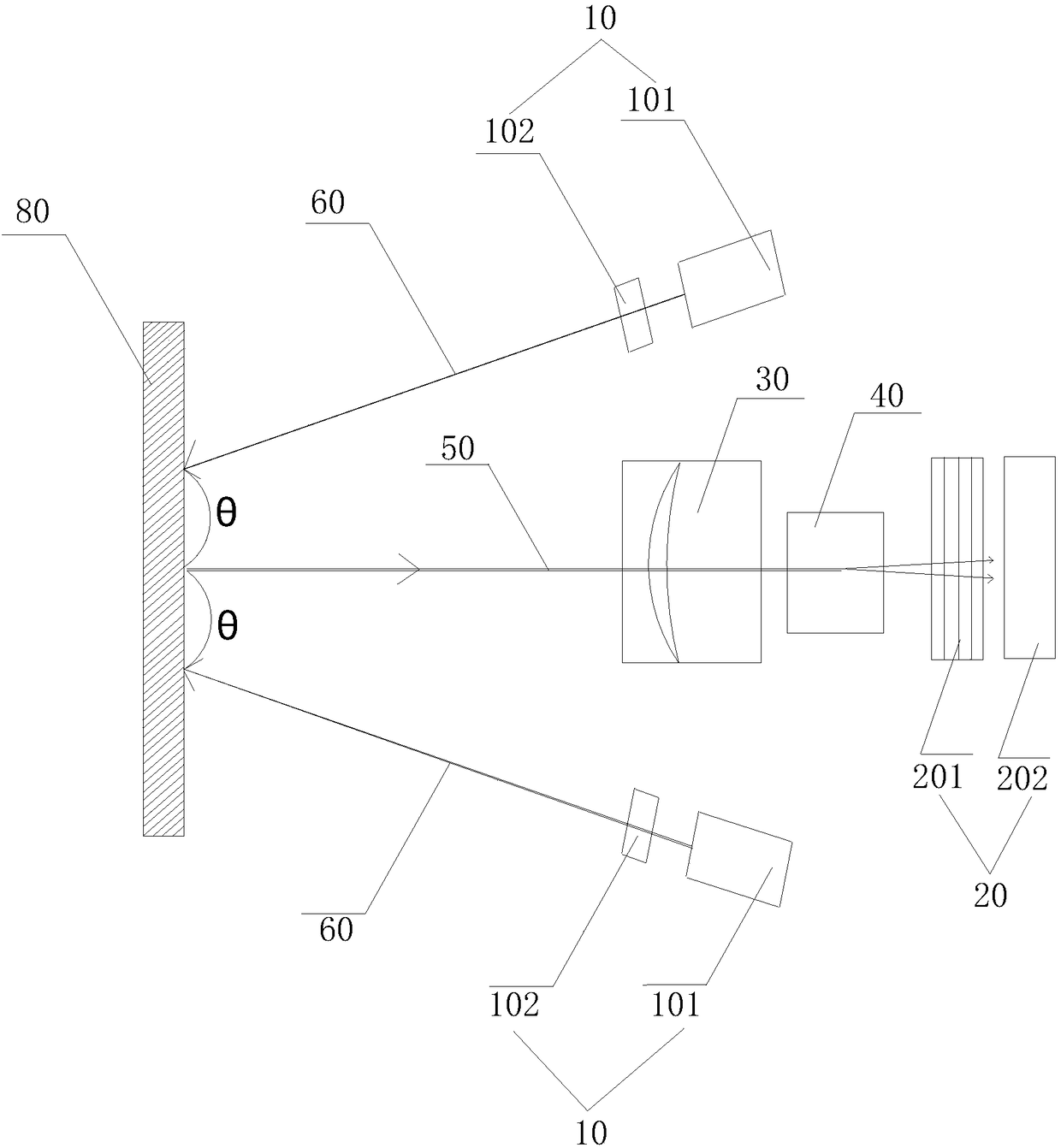
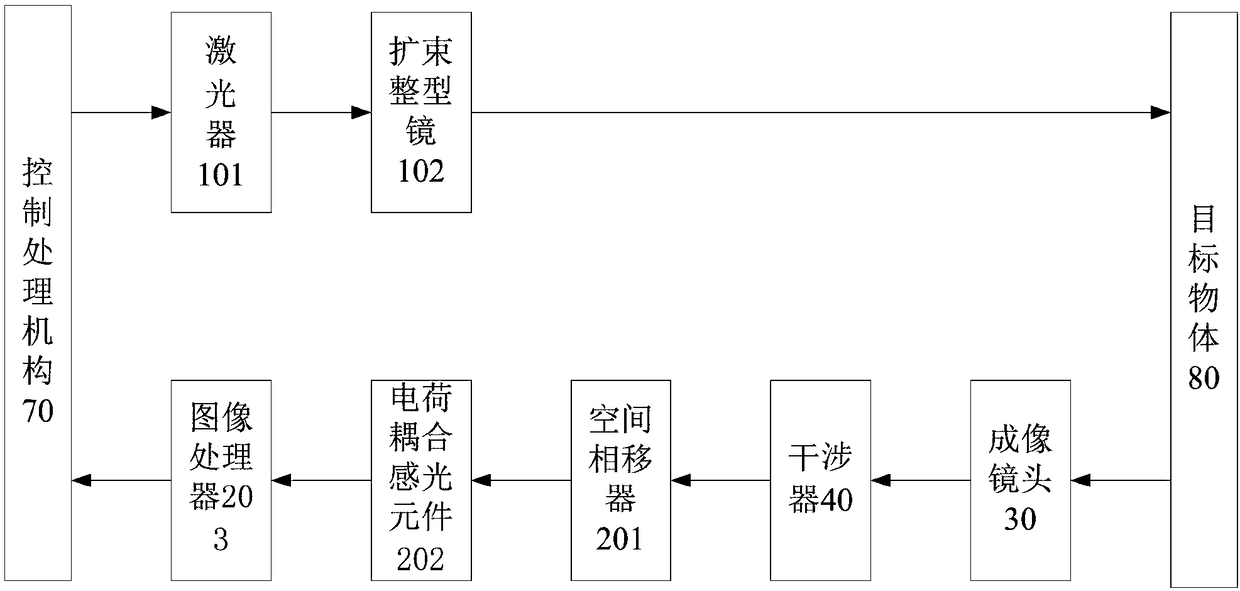
The invention provides a spatial phase-shifting interferometer. The interferometer comprises laser emission mechanisms, a laser receiving mechanism, an interference device, an imaging lens, a first coaxial line and a second coaxial line, each laser emission mechanism comprises a laser and a beam-expanding shaping prism, the laser receiving mechanism, the interference device and the imaging lens are distributed on the first coaxial line, the imaging lens and the laser receiving mechanism are arranged on the front side and the rear side of the interference device respectively, and the laser emission mechanisms are arranged on the second coaxial line and arranged on the two sides of the imaging lens respectively; when the laser emission mechanisms emit laser beams, the laser beams are reflected after shining on the surface of a target object, form two ways of light beams after passing through the imaging lens and the interference device in sequence along the first coaxial line, and then are received and treated by the laser receiving mechanism. The spatial phase-shifting interferometer is simple in structure and rapid in image information collection.
Owner:GUANGZHOU XUNZHI MACHINERY
Two path 2X2 light switch and 4X4 free space light switch composed of it
The invention is a two-way 2X2 optical switch and the 4X4 free space optical switch made up of the former one, which belongs to optical communication device, especially relates to optical passive device in full gloss communication network, the structure is compact, and it has no relation to polarization, the two-way 2X2 optical switch is only made up of polarization beam-splitting compound prism, lambda / 4 wave plate, lambda / 2 wave plate, direct angle prism, holophote and polarization light modulator, the 4X4 optical switch has light model structure, and it has no relation to the control of optical signal and the polarization state of the incidence beam. All the output ports and the input ports can interchange without obstacles. The structure is compact, and it can be widely applied to optical communication field.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Compound Configuration Tunable Grating External Cavity Dual-Mode Laser
ActiveCN103326239BSimple structureEasy to adjustLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionExternal cavity laserDual mode
The invention discloses a composite structure type tunable grating outer cavity dual-mode laser machine. The composite structure type tunable grating outer cavity dual-mode laser machine comprises a gain component, a lens, a grating and a plane mirror, wherein light emitted from the end face of one side of the gain component is collimated by the lens and then irradiated to the surface of the grating in a incident mode (the incident angle is theta), and diffraction is generated, two beams of diffraction light which are lambda 1and lambda 2 in wave length move forward along the following two paths respectively: firstly, the m level diffraction light which is lambda 1in wave length goes back to the gain component in the incident direction along the same path from which the light comes, wherein m is an integer except zero, and the diffraction angle is equal to the incident angle theta, so that a laser mode which is lambda 1in wave length is formed between the grating and the end face of the other side of the gain component, and secondly, the n level diffraction light which is lambda 2 in wave length goes back to the gain component in the incident direction along the same path from which the light comes after being reflected by the plane mirror and secondly diffracted by the grating, wherein n is an integer except zero and not equal to m, and the diffraction angle is phi, so that a laser mode which is lambda 2 in wave length is formed between the plane mirror and the end face of the other side of the gain component through the grating.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
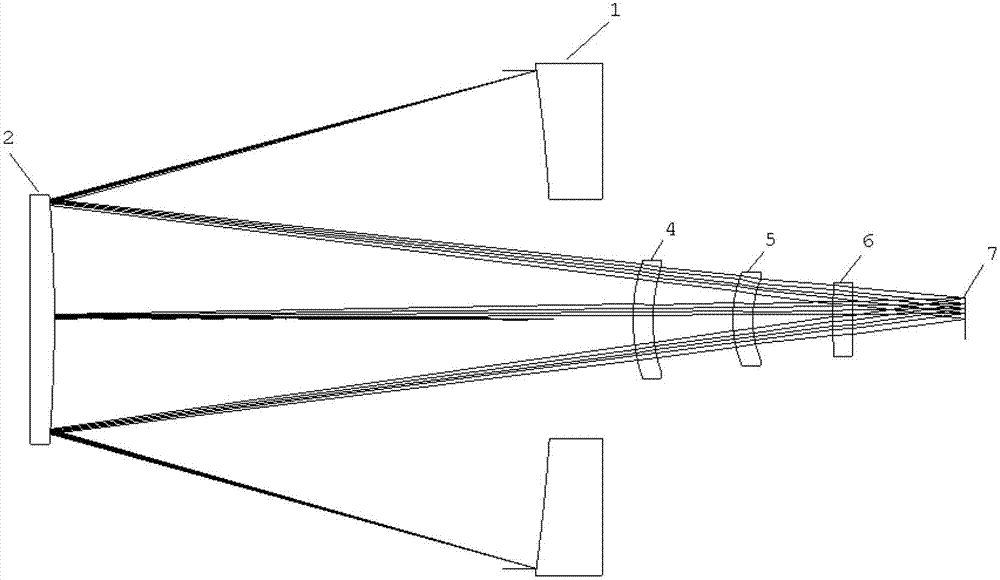
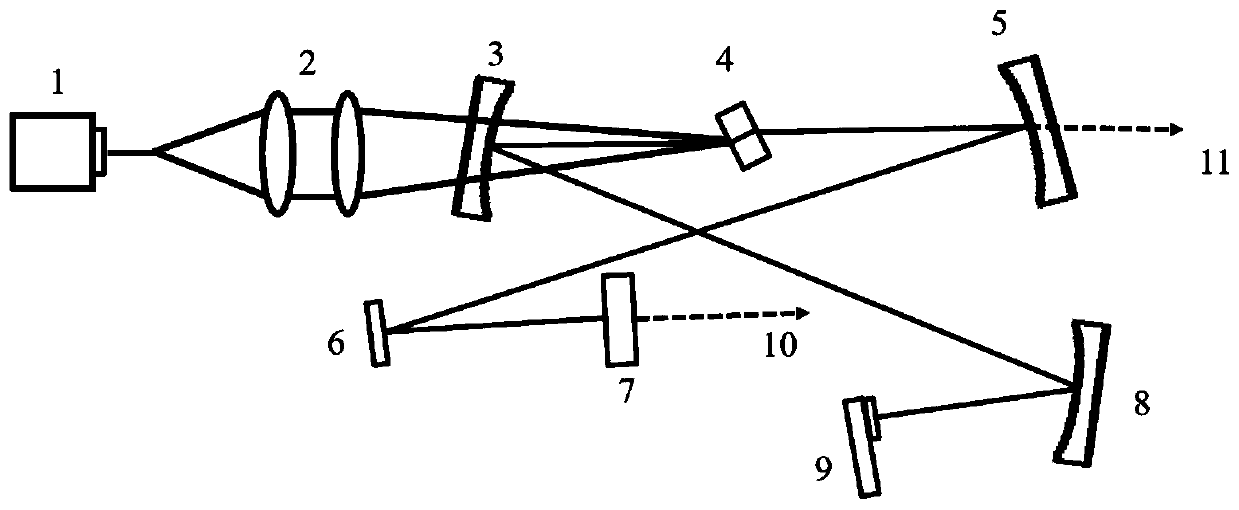
Windowless main amplification system for high power laser device
A windowless main amplification system for a high power laser device comprises a deformable mirror, a main amplifier, a first spatial filter, a polarizer, a reflector, a booster amplifier and a secondspatial filter, which are sequentially disposed along an optical path; The system is characterized in that the deformable mirror, the main amplifier, the first spatial filter, the polarizer, the reflector, the booster amplifier and the second spatial filter are closely connected with each other by a light pipe; external pollutants are isolated and deposited on the surface of components; flow field obstacles are respectively disposed on two ends of the main amplifier and the booster amplifier; airflow exchange between the light pipe and the main amplifier and the booster amplifier is blocked;an air knife A is disposed at the edge of the polarizer; and natural dust fall is isolated. The system has the advantages of ingenious design, and simple and easy operation, ensures the cleanliness ofthe main amplification system, does not bring secondary pollution, simultaneously helps to reduce B integral, makes the beam quality of a laser system improve, and helps to improve the output capability of the laser device.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Two-step phase-shift coaxial holography technology realizes 90° phase shift and calibration system and method
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
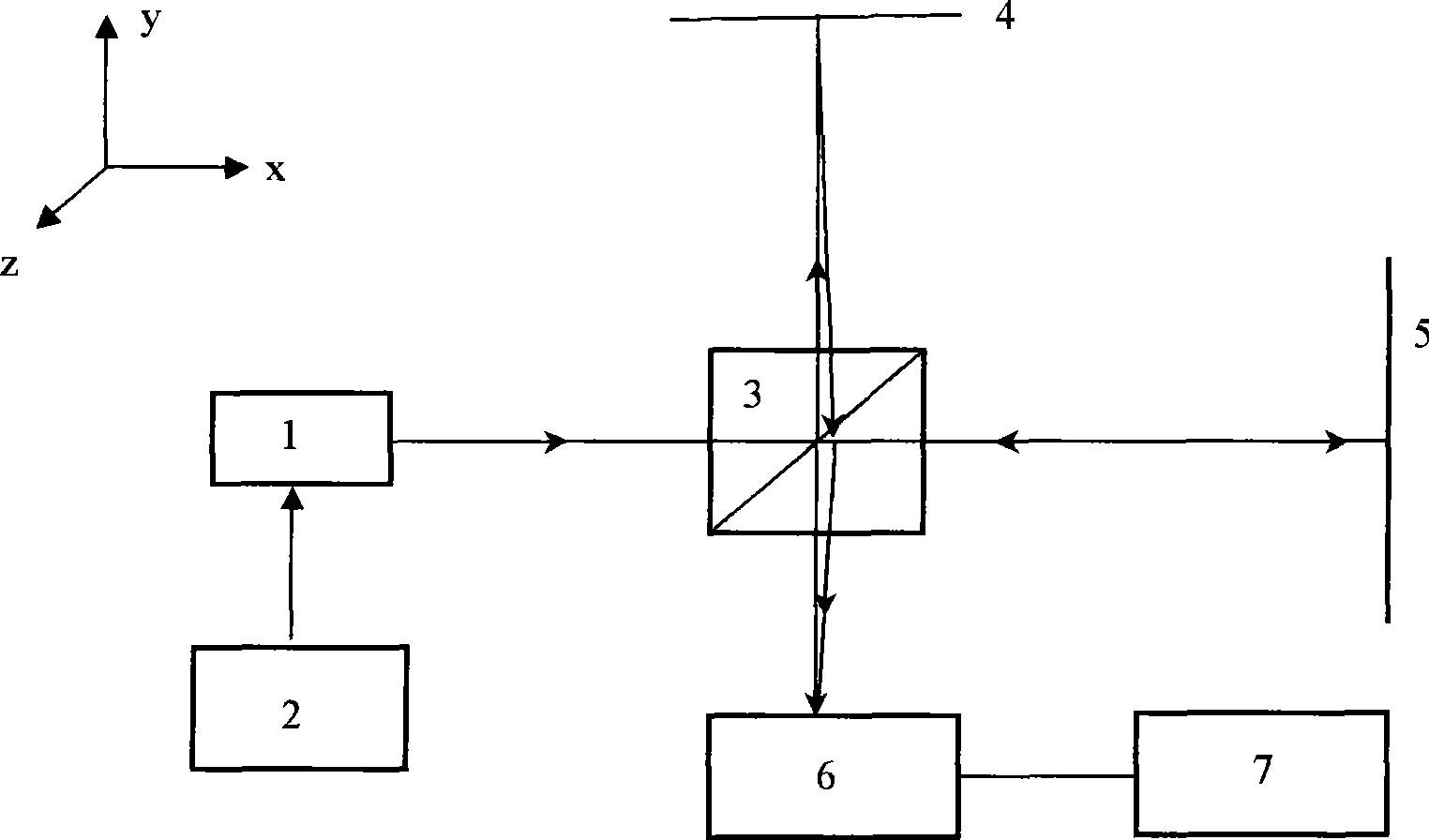
Auto-collimator
ActiveCN114111644AHigh resolutionImprove subdivision accuracyUsing optical meansOptical elementsBeam splitterPhotovoltaic detectors
The invention provides an autocollimator, which comprises a light source, a multi-slit reticle, a spectroscope and a photoelectric detector which are arranged on a base and are sequentially arranged along a light path, and also comprises a collimator and a dispersion element which are arranged on the base and are sequentially arranged along the light path, a light beam emitted by the light source enters the multi-slit reticle and is divided into N light beams through the multi-slit reticle, the N light beams enter the spectroscope, the N light beams are reflected to the collimator through the spectroscope to form N parallel light beams, the N parallel light beams enter the reflector to be measured, and the reflector to be measured is measured through the spectroscope. And a light beam reflected by the reflector to be measured is transmitted to the dispersion element through the collimator and the spectroscope in sequence, is refracted by the dispersion element and then enters the photoelectric detector for imaging, the imaging offset is obtained, and the offset angle of the reflector to be measured is further obtained.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
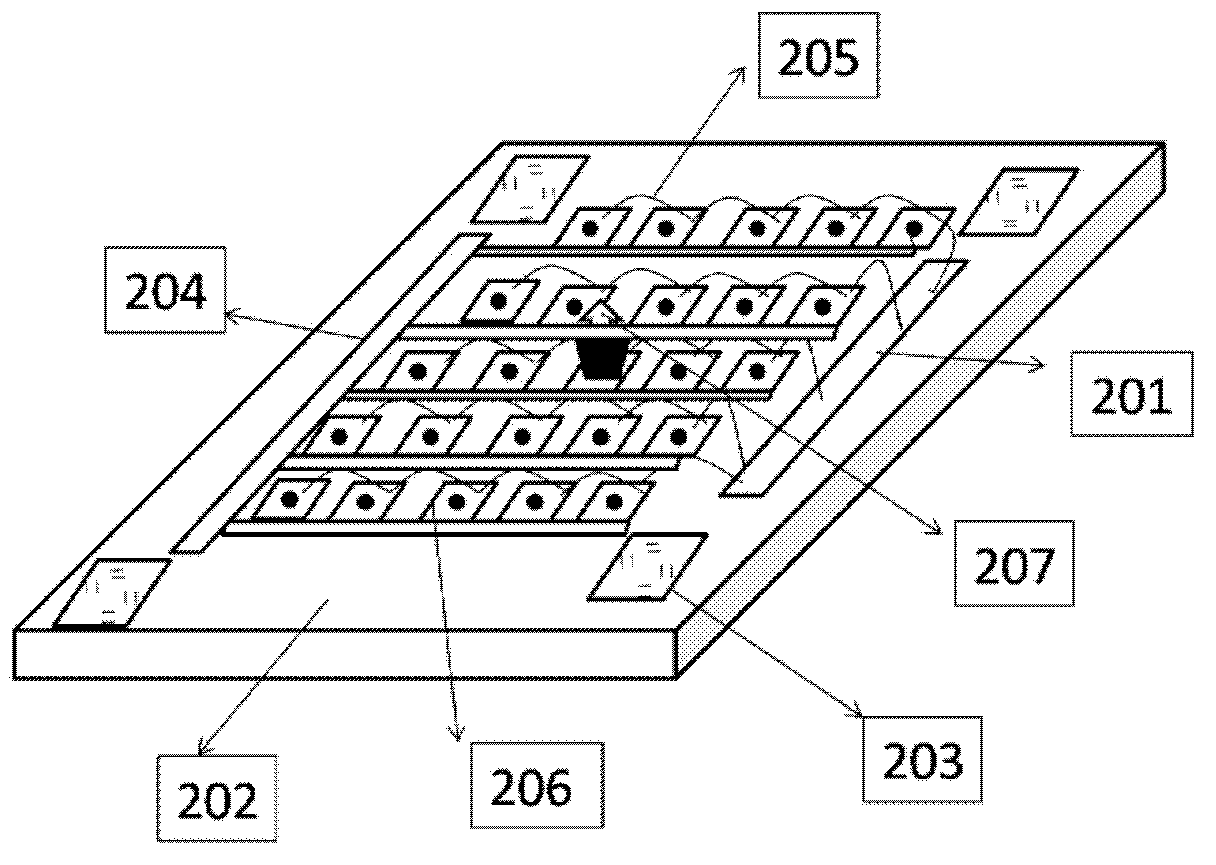
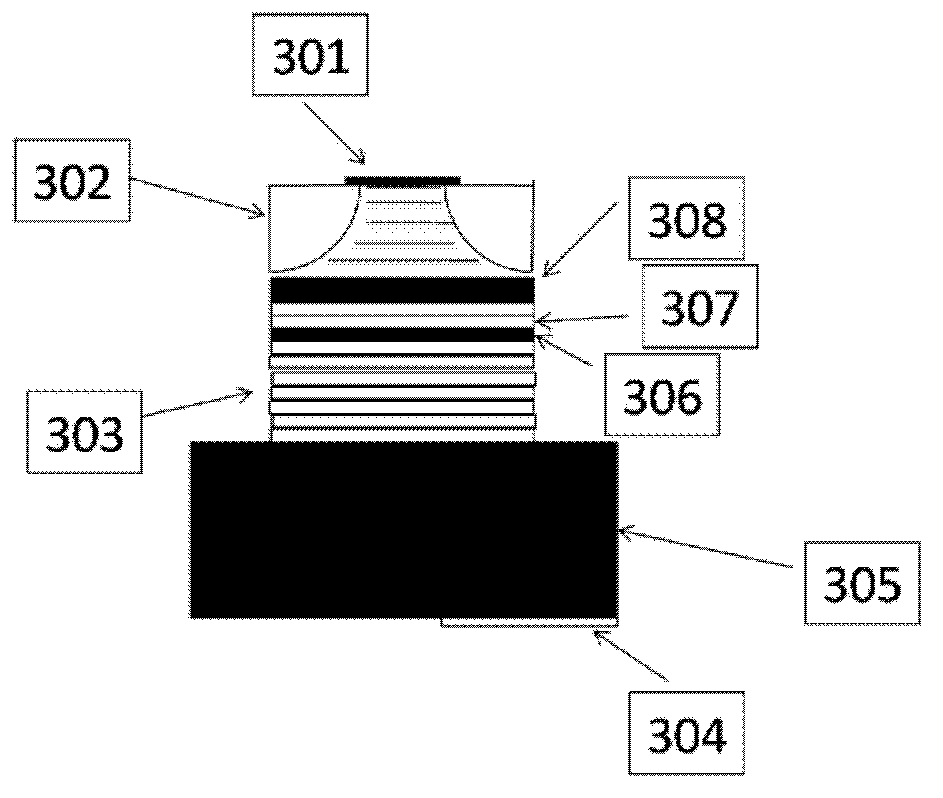
A Novel Polarized Uncooled Infrared Focal Plane Detector and Its Preparation Method
ActiveCN107128872BImprove fill factorImprove absorption efficiencyTelevision system detailsPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesGratingThermal insulation
Owner:YANTAI RAYTRON TECH
A red light semiconductor area array light source device for laser display
InactiveCN103412406BSimple structureImprove reliabilityLaser detailsProjectorsEffect lightLight beam
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
A Portable High Resolution Microscopic Imaging System
ActiveCN109061860BHigh-resolutionSimple structureMaterial analysis by optical meansMicroscopesMedicineEngineering
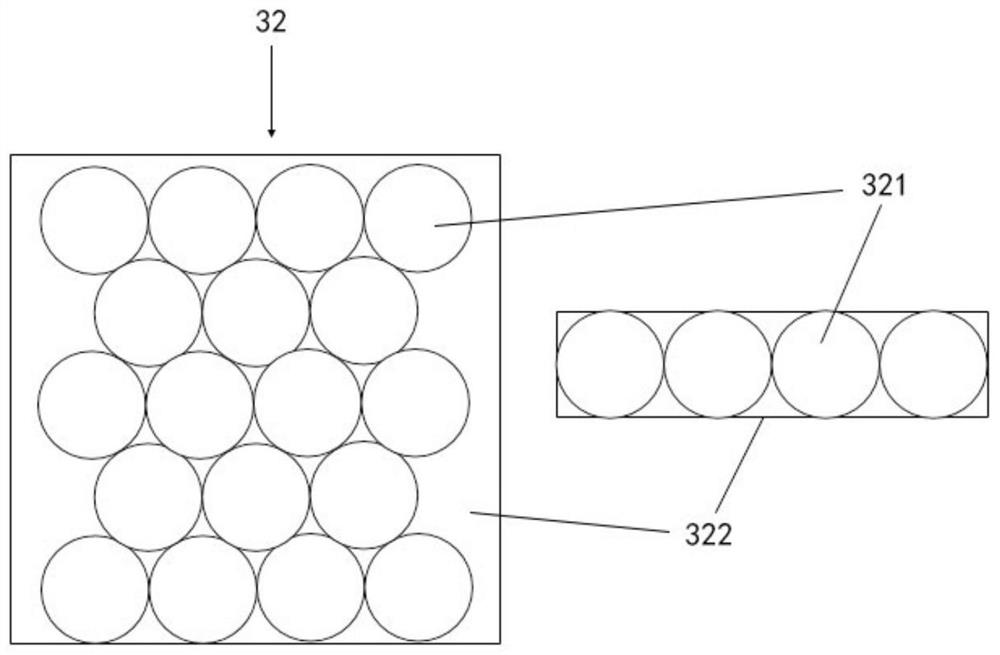
The invention provides a portable high-resolution microscopic imaging system which provides higher-resolution microscopic imaging while meeting the portability of a traditional mobile phone camera-based microscopic imaging system. The portable high-resolution microscopic imaging system is characterized by comprising a shooting device, a light source device and a high-resolution device; and the shooting device is provided with a camera and a communication module, the light source device is used for providing a light source needed for high-resolution imaging, and the high-resolution device comprises an objective lens module and a sealed microsphere array module, wherein the objective lens module is arranged on the camera and is a single objective lens with 1-4 times of magnification or an objective lens group formed by multiple objective lenses, the sealed microsphere array module is arranged on the objective lens module, the upper surface of the sealed microsphere array module serves asa specimen carrying surface, and the sealed microsphere array module is a solid immersion single-layer microsphere array sealed in a sealing material and is formed by arranging multiple microspheresalong microsphere lines arranged in a straight line in a parallel staggering mode
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
Endoscopic optical fiber Raman probe and detection device
The invention discloses an endoscope fiber Raman probe and a detection device. The endoscope fiber Raman probe comprises a lens, a circular ring lens, a filtering layer, a circular ring filtering layer, a center optical fiber bundle, a Raman collection optical fiber, an optical fiber cable, a connecting piece, a center optical fiber bundle branch and a Raman collection optical fiber branch; the Raman collection optical fiber annually surrounds the center optical fiber bundle; the lens and the filtering layer are arranged at the front end of the center optical fiber bundle; the circular ring lens and the circular ring filtering layer are arranged at the front end of the Raman collection optical fiber; the combined optical fiber bundle of the Raman collection optical fiber and the center optical fiber bundle extends through the optical fiber cable; the other end of the optical fiber cable is divided into a Raman collection optical fiber bundle and an excitation / endoscope optical fiber bundle by the connecting piece. According to the endoscope fiber Raman probe disclosed by the invention, integrated design of optical fiber Raman and optical fiber endoscope is realized; the device hasthe advantages of small volume, low price, high flexibility and accurate detection, and is more applicable to biological in-vivo and in-situ Raman detection, and is relatively easy and convenient to maintain.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com