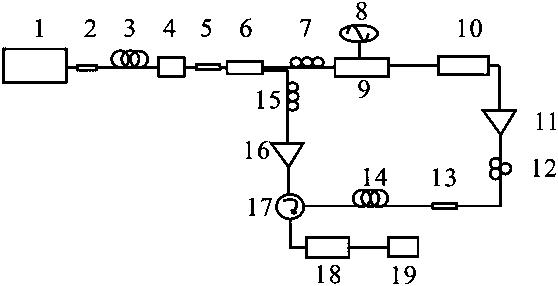
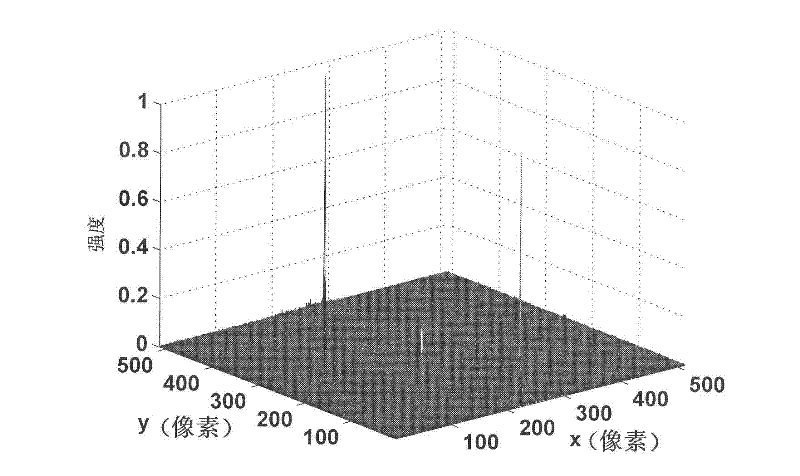
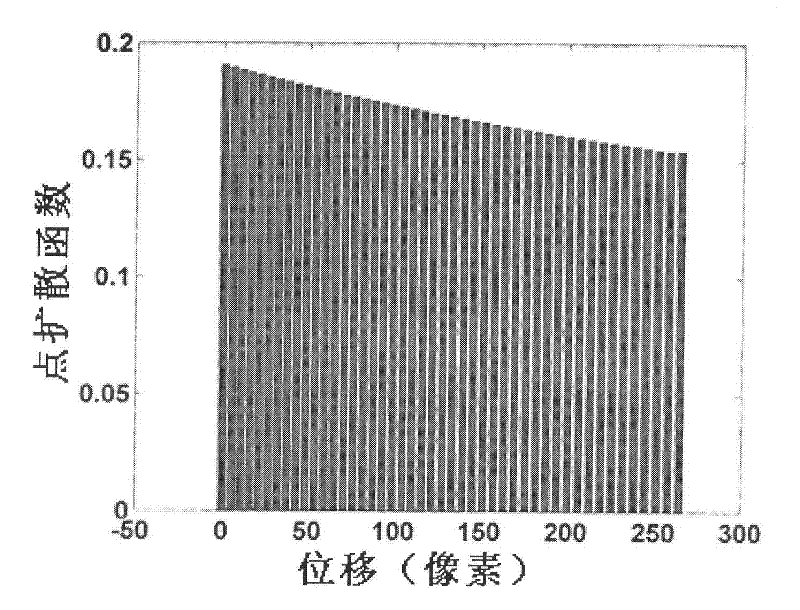
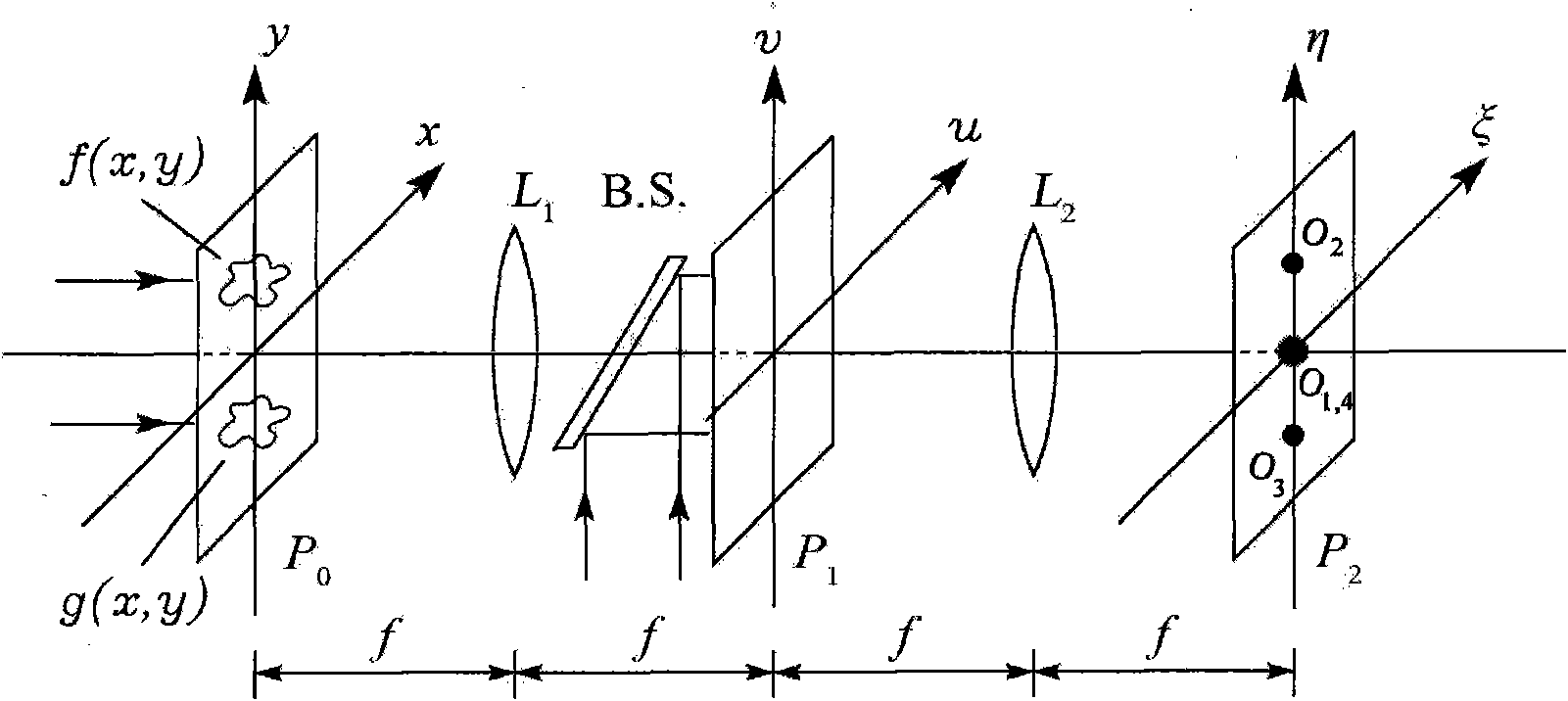
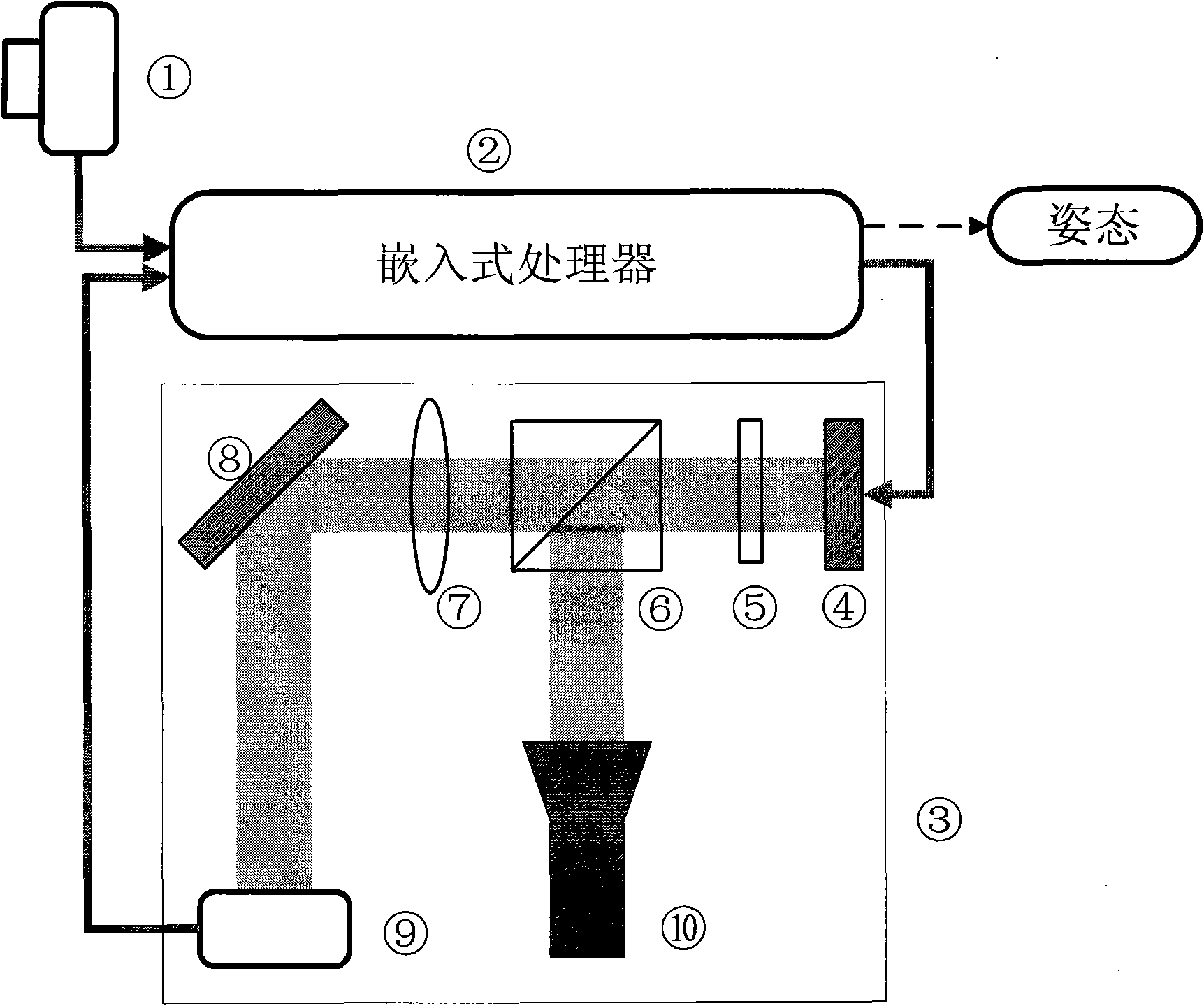
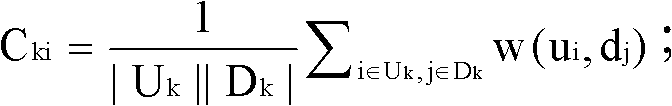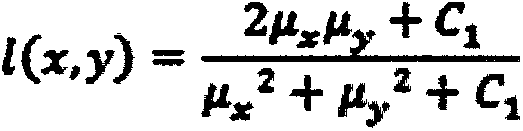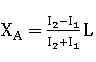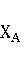Patents
Literature
62 results about "Optical correlation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
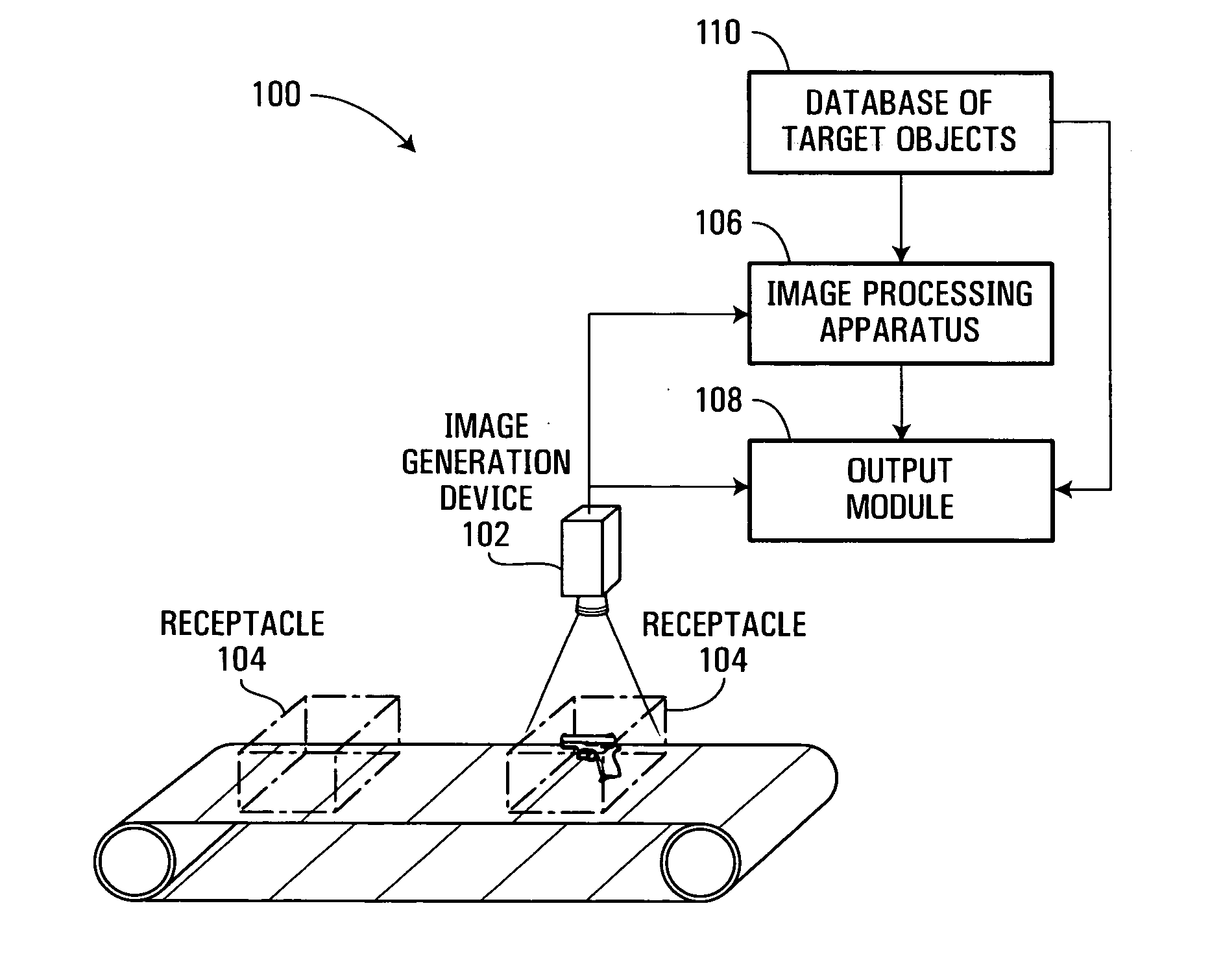
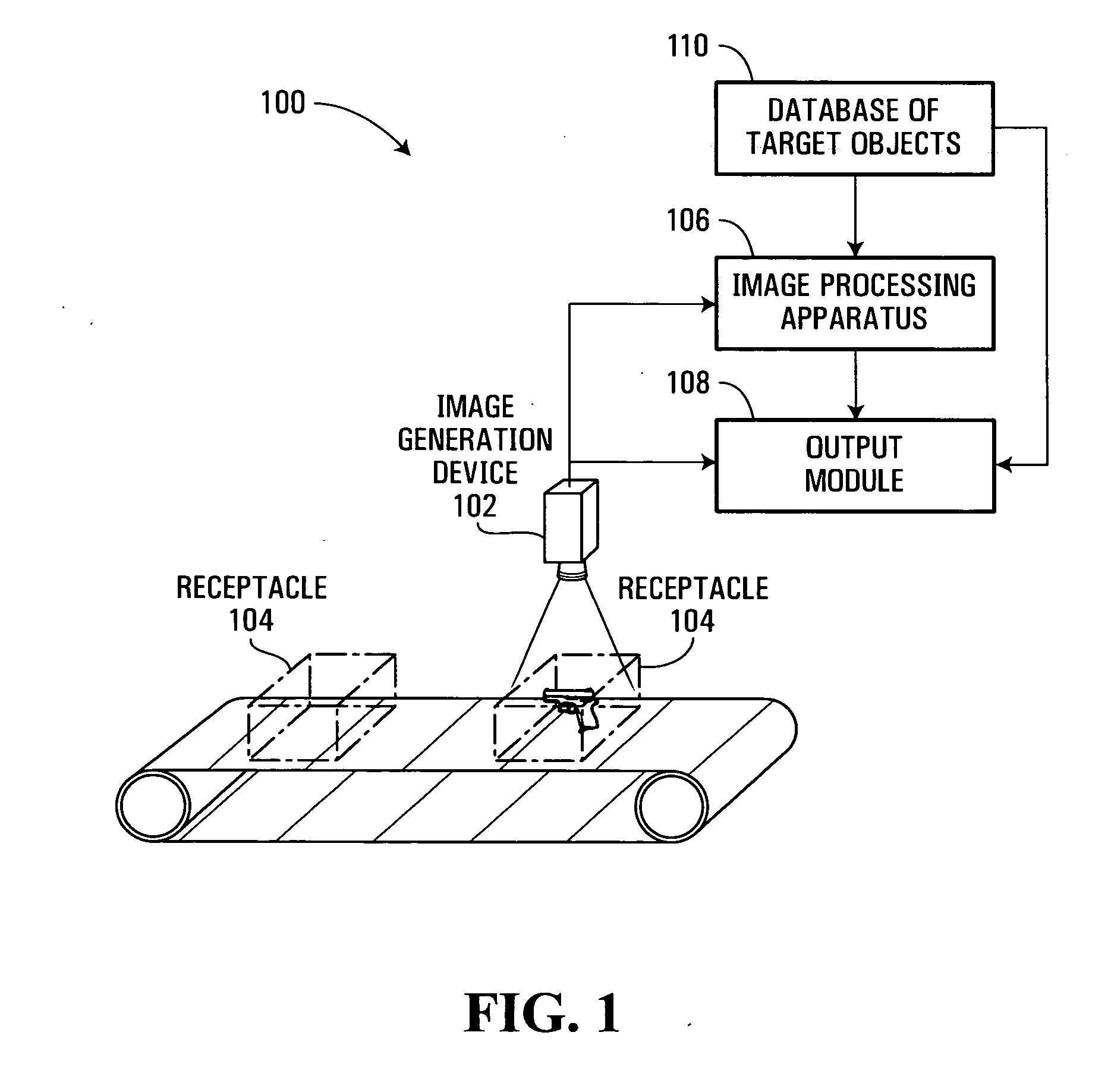
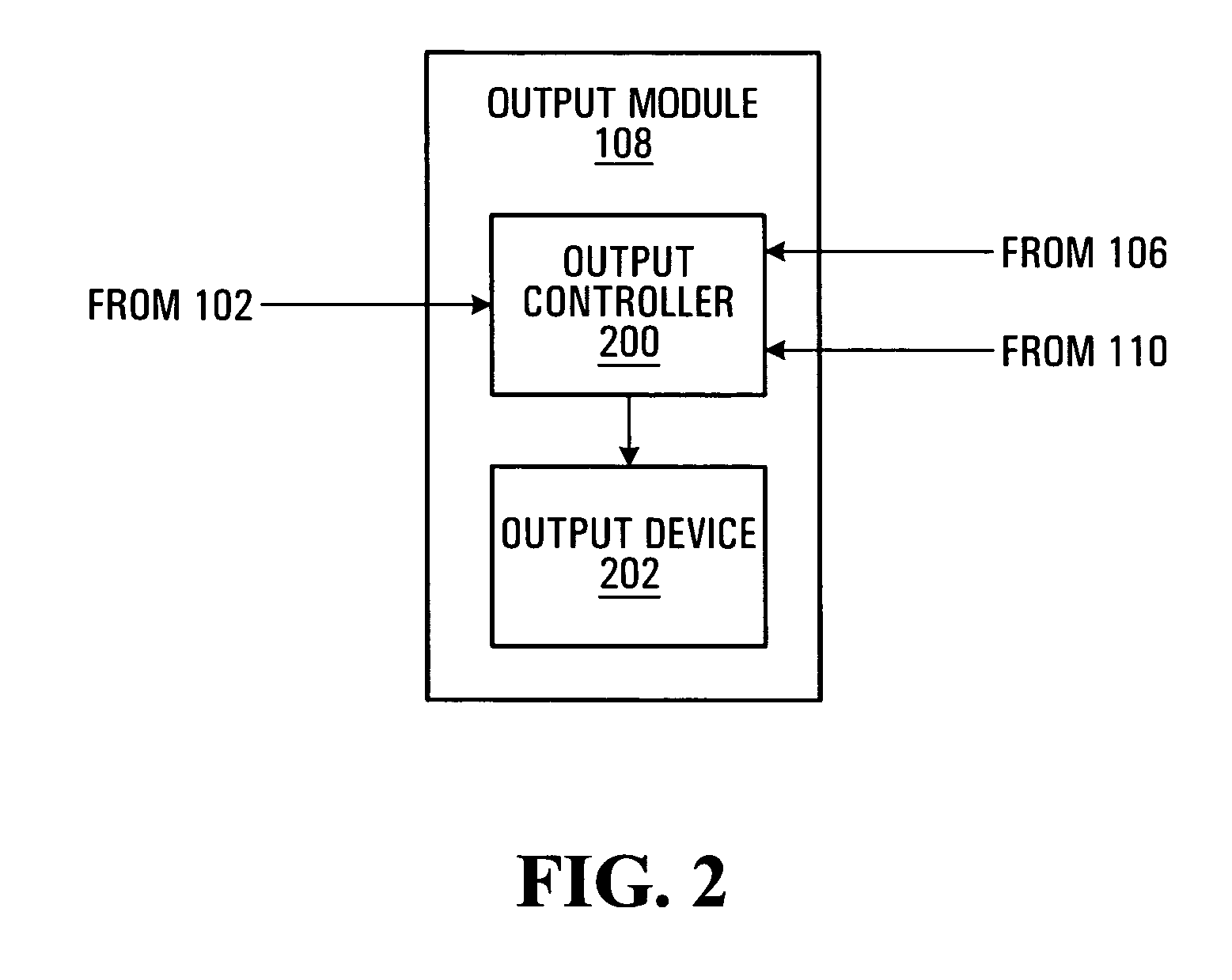
Database of target objects suitable for use in screening receptacles or people and method and apparatus for generating same
InactiveUS20070041613A1Character and pattern recognitionNuclear radiation detectionProcessing elementData mining
A database of target objects suitable for use in detecting the presence of one or more target objects in a receptacle is provided. The database of target objects comprises a plurality of entries, each entry being associated to a respective target object whose presence in a receptacle it is desirable to detect during security screening. An entry for a given target object comprises a group of sub-entries, each sub-entry being associated to the given target object in a respective orientation. At least part of each sub-entry is suitable for being processed by a processing unit implementing an optical correlation operation to attempt to detect a representation of the given target object in an image of the receptacle. A method, an apparatus and a system for generating entries for the database of target objects are also provided.
Owner:OPTOSECURITY
Apparatus and method for converting an optical image of an object into a digital representation
InactiveUS6163339AFast image generationHigh image resolutionTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsSensor arrayImage conversion
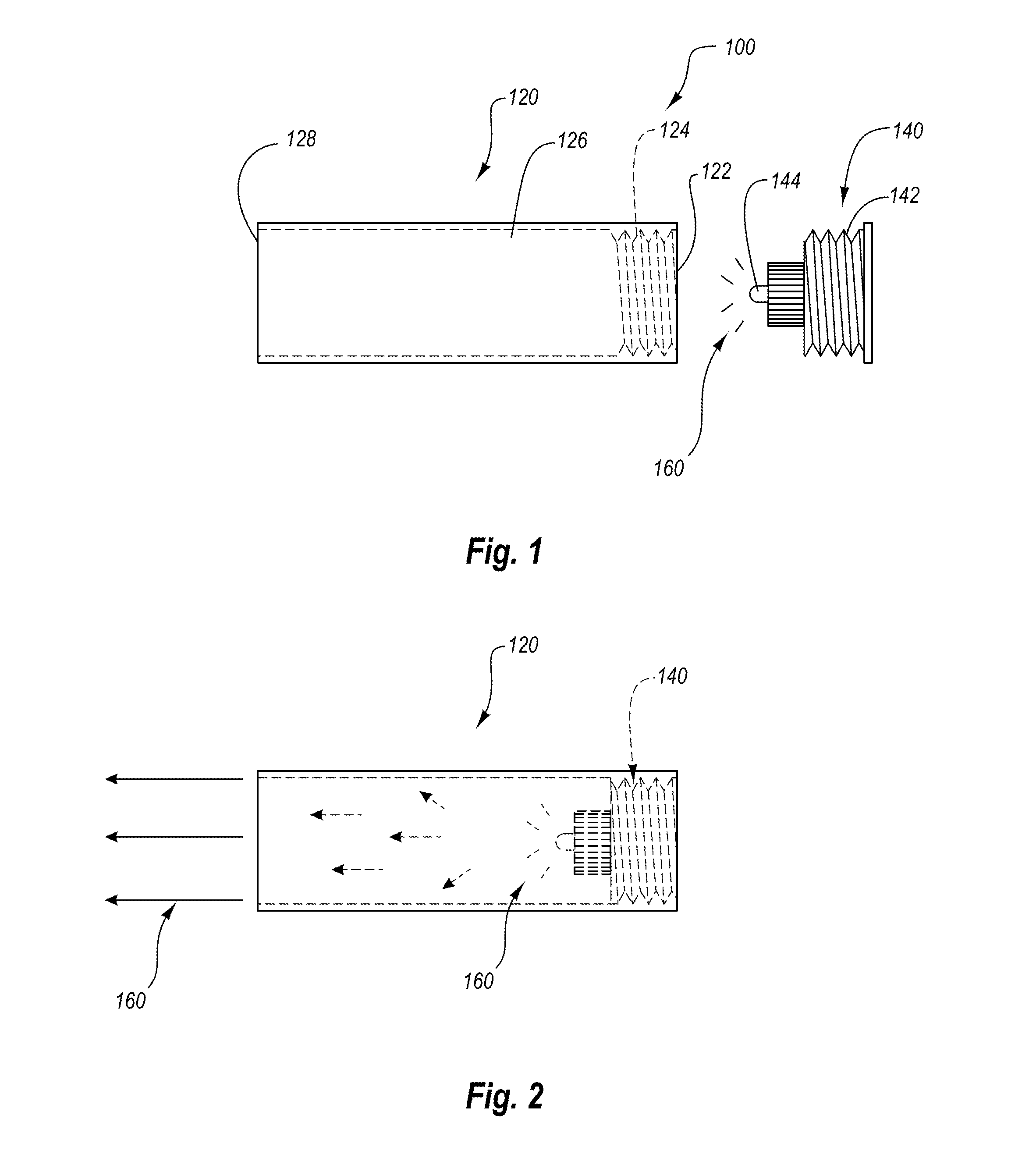
PCT No. PCT / CA94 / 00347 Sec. 371 Date Apr. 26, 1996 Sec. 102(e) Date Apr. 26, 1996 PCT Filed Jun. 17, 1994 PCT Pub. No. WO95 / 01045 PCT Pub. Date Jan. 5, 1995An electronic apparatus for converting a visible image of an object into a digital representation of this visible image is described. The apparatus comprises a cartridge having a first portion through which light emitted from a visible image of an object enters into the cartridge, which comprises an array of focusing elements, each of which having a field of vision intersecting a given area of the visible image. Adjacent ones of these focusing elements have fields of vision intersecting common portions of the visible image, whereby substantially the entirety of the visible image is covered by combined fields of vision of focusing elements. The cartridge further compised an array of optical sensors arrays, each wich is optically associated with a respective one of the focusing elements. These optical sensors arrays produce groups of analog pixel signals representing partial images associated with corresponding areas of the visible image. The apparatus further comprises a controller interface and a computer controller for converting groups of digital pixel signals into composite digital pixel signals associated with the respective points of the visible image, thereby forming a composite digital representation of the visible image.
Owner:MEUNIER JEAN FRANCOIS
Assay imaging apparatus and methods
InactiveUS20090062134A1Prevent foggingPromote disseminationHeating or cooling apparatusMicrobiological testing/measurementImaging dataPhysics
A method of conducting an assay on a plurality of samples is provided. The method includes the steps of performing an assay at each sample site in a sample array having greater than 100 sample sites simultaneously illuminating each sample site using one or more LEDs, and simultaneously imaging each of the sample sites to produce imaging data pertinent to the optical effect of each site. Each assay provides an optical effect.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Illegal domain name recognition method and device
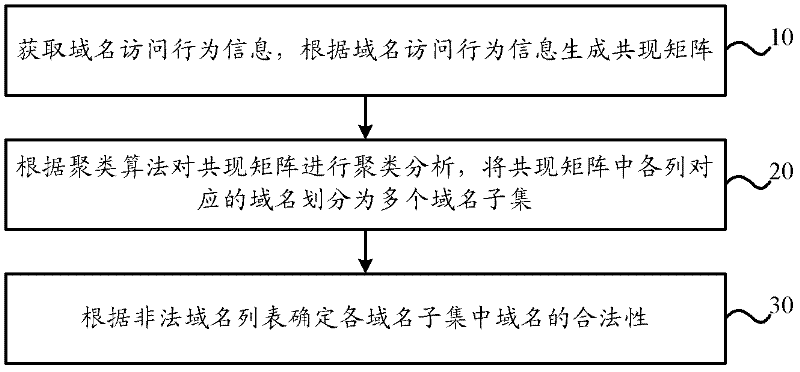
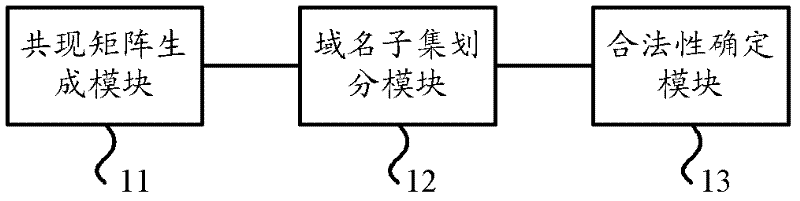
The invention provides an illegal domain name recognition method and an illegal domain name recognition device. The illegal domain name recognition method comprises the steps of: obtaining domain name access behavior information and generating a co-occurrence matrix according to the domain name access behavior information, wherein elements in the co-occurrence matrix are used for indicating times that users corresponding to the line of the elements access to domain names corresponding to the row of the elements; conducting clustering analysis to the co-occurrence matrix according to a clustering algorithm and dividing the domain names corresponding to each row in the co-occurrence matrix into a plurality of domain name subsets; and determining the legality of the domain names in each domain name subset according to an illegal domain name list. The illegal domain name recognition device comprises a co-occurrence matrix generation module, a domain name subset dividing module and a legality determining module. The illegal domain name recognition method and the illegal domain name recognition device can analyze optical correlation among the domain names aiming at the particularity of the illegal domain names to differentiate the illegal domain names from the legal domain names, and therefore the recognition efficiency of illegal websites is improved.
Owner:CHINA INTERNET NETWORK INFORMATION CENTER
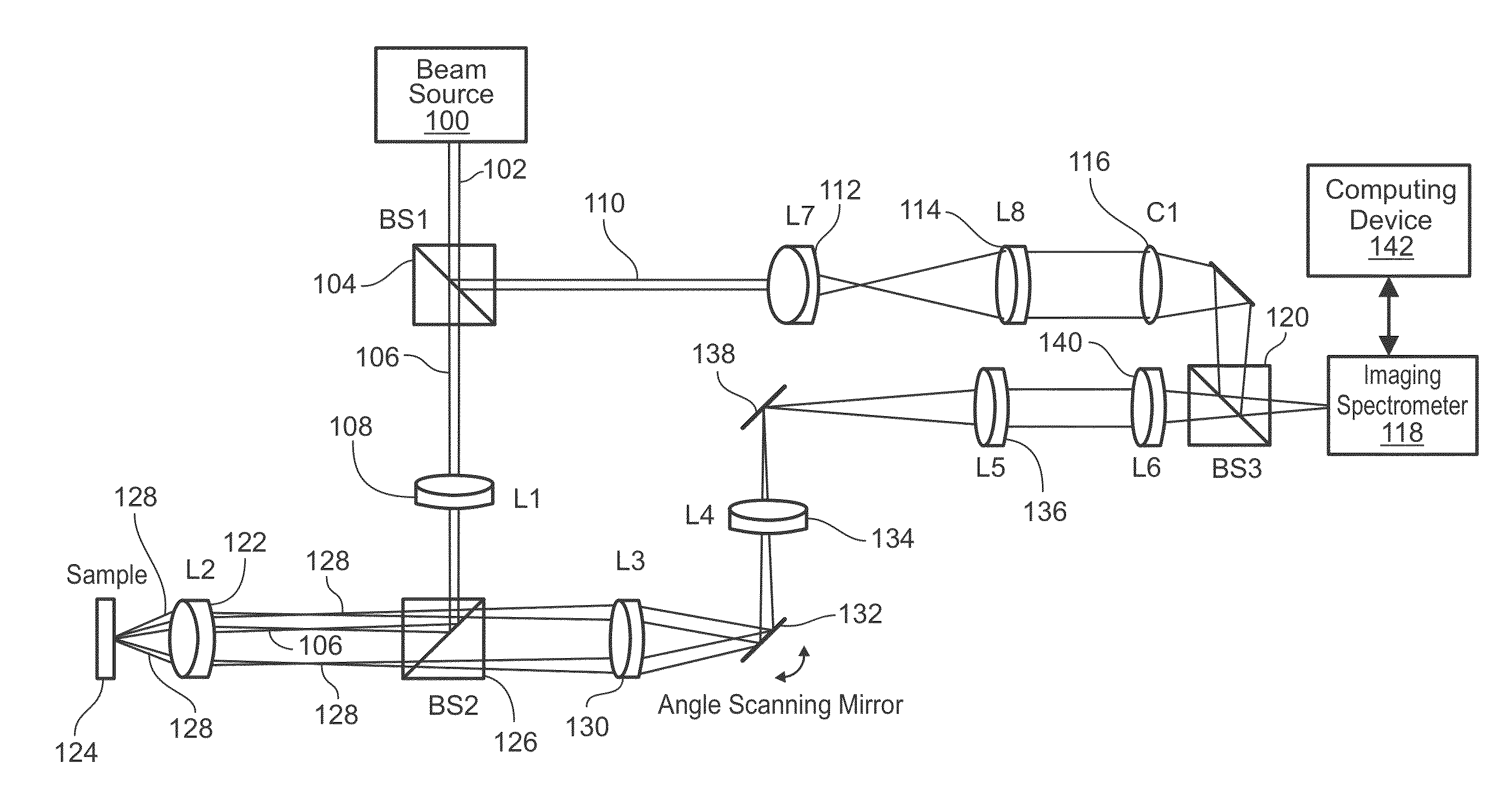
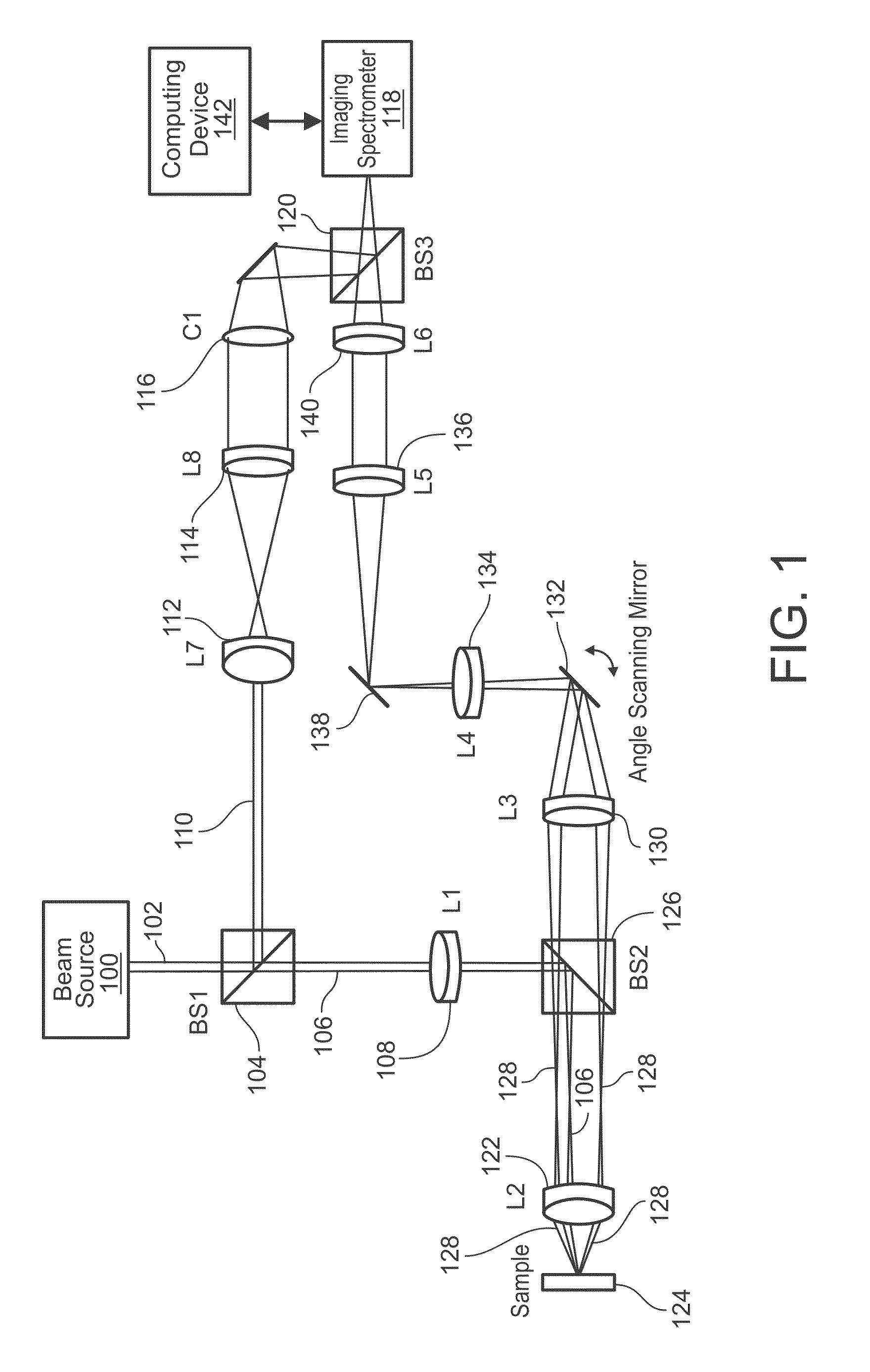
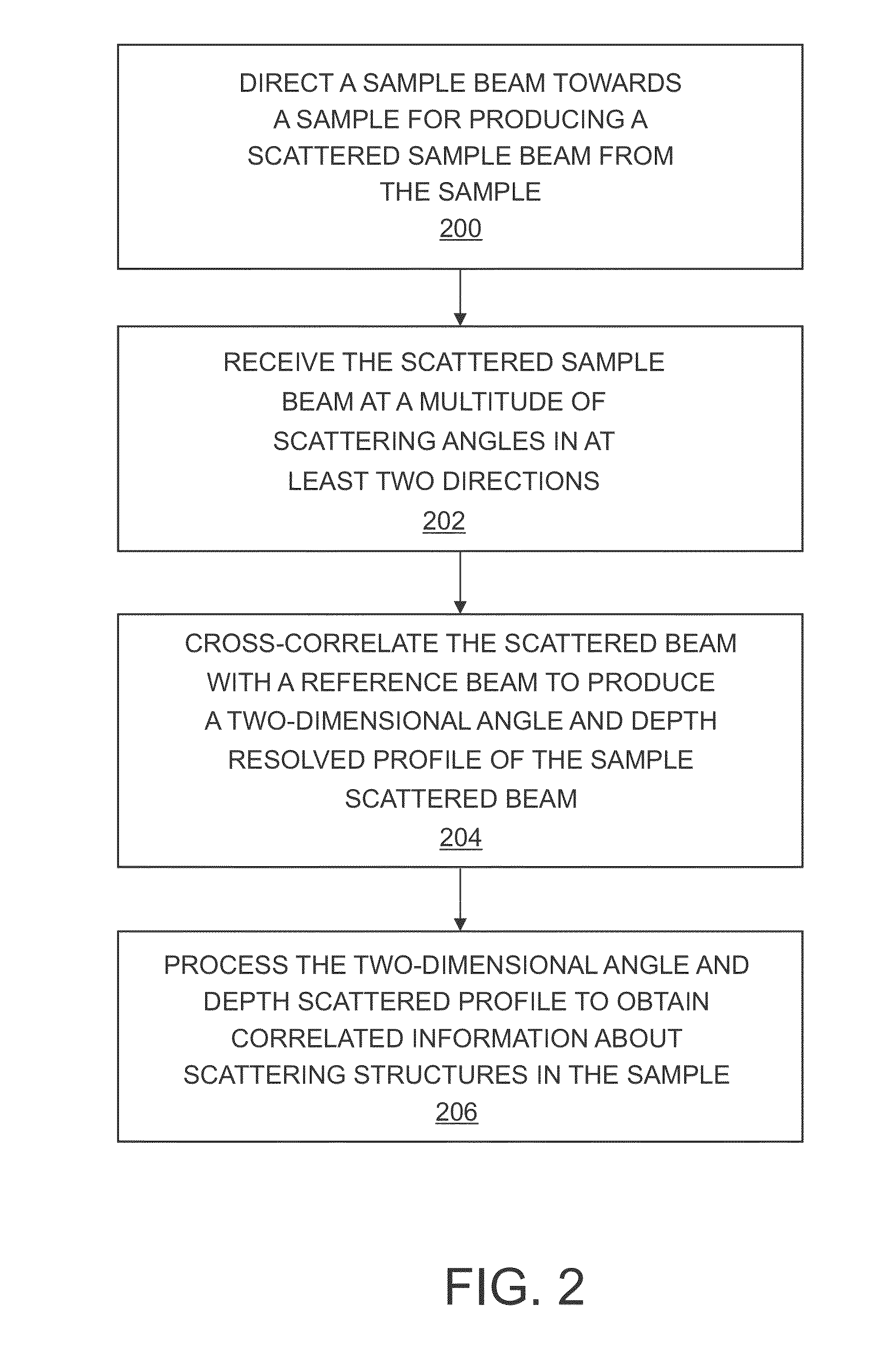
Systems and methods of angle-resolved low coherence interferometry based optical correlation
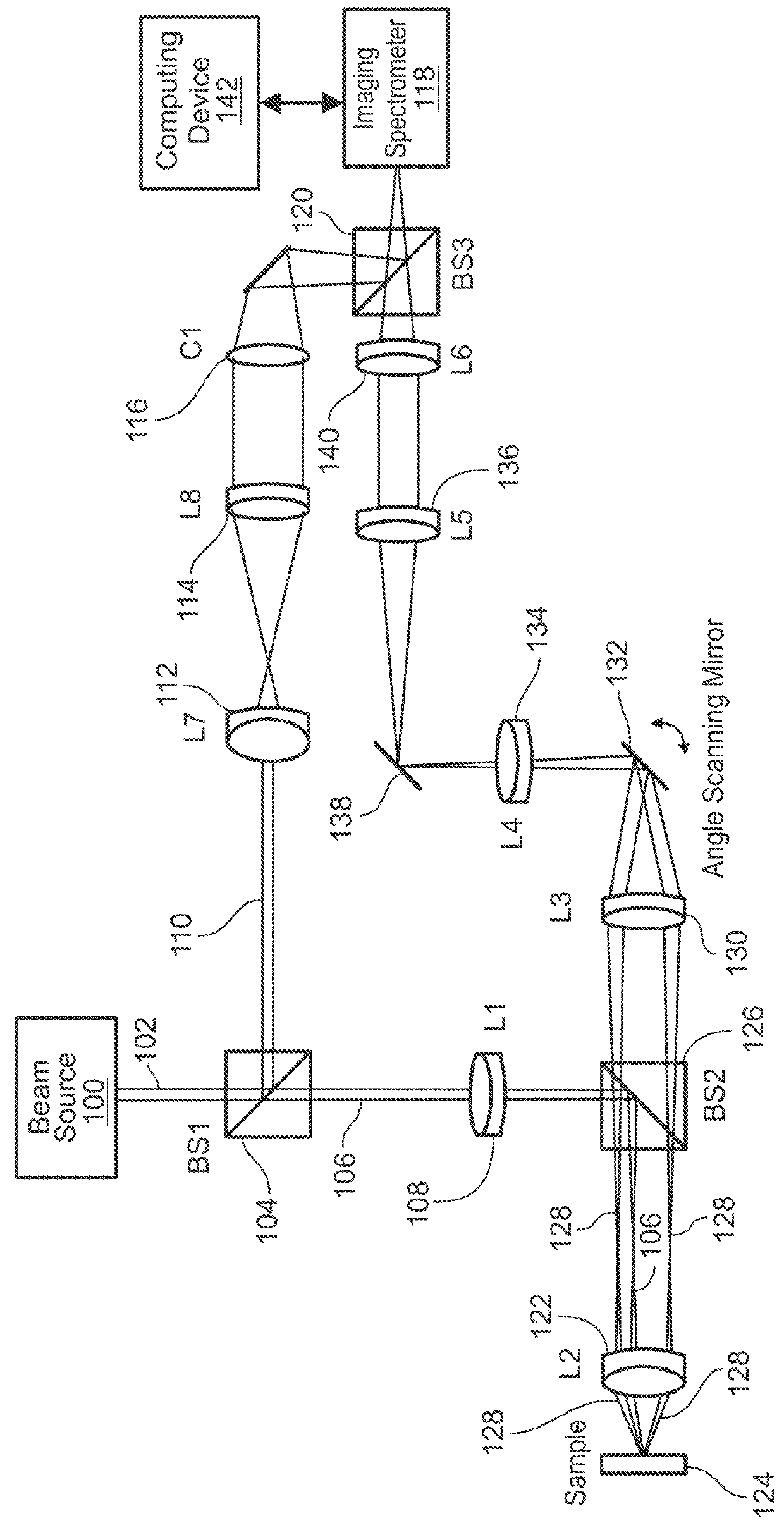
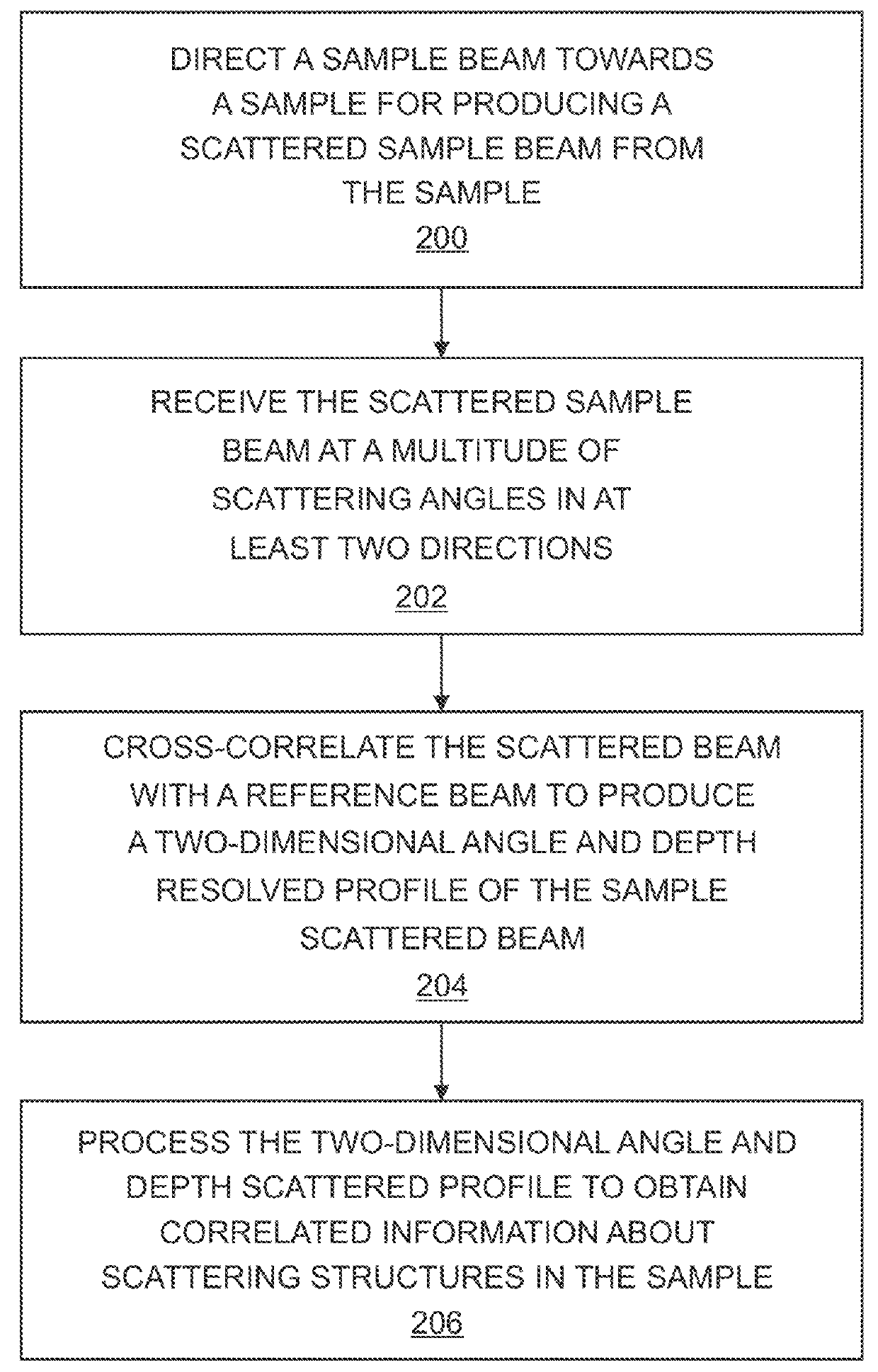
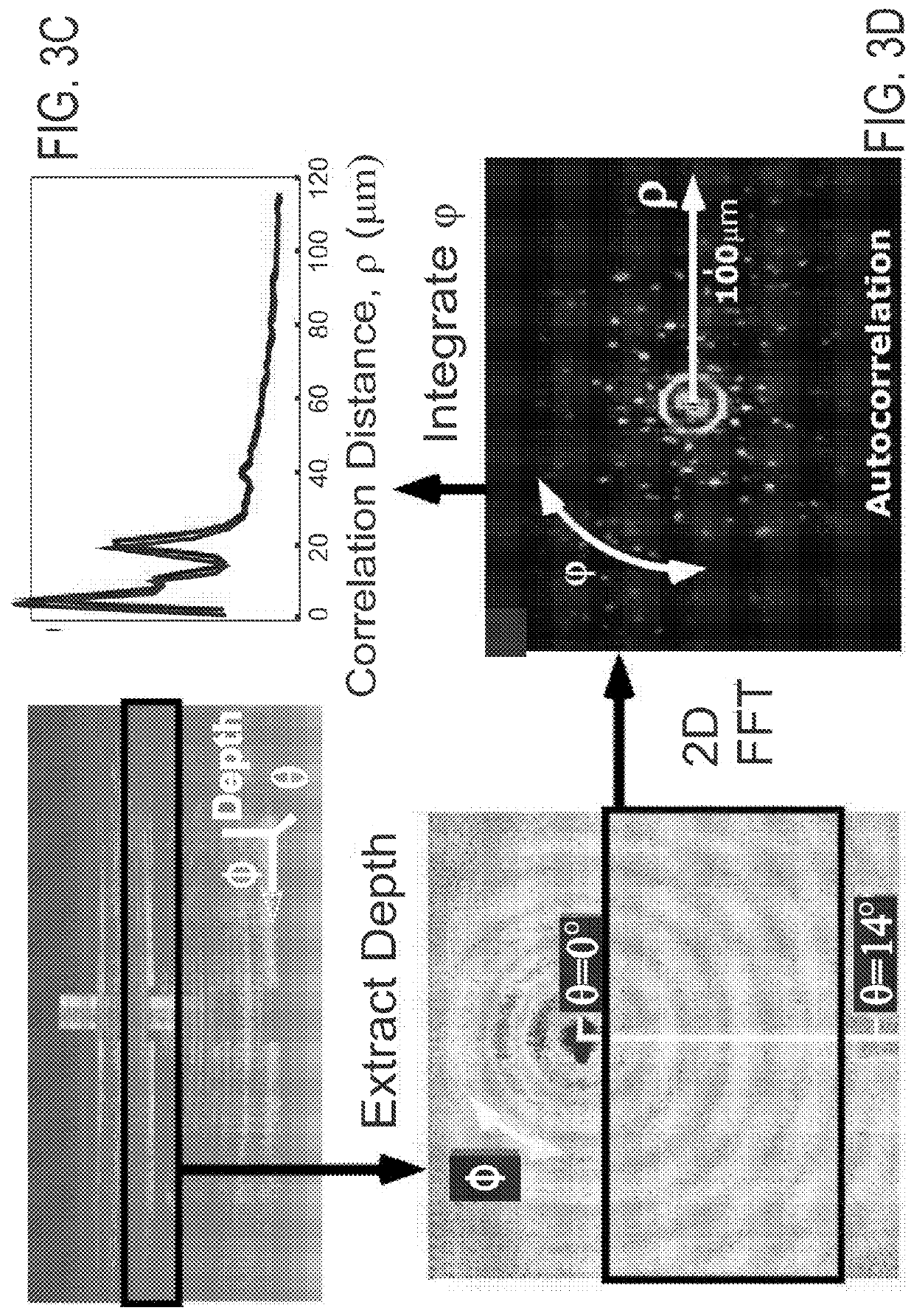
Systems and methods of angle-resolved low coherence interferometry based optical correlation are disclosed. According to an aspect, a method includes directing a sample beam towards a sample for producing a scattered sample beam from the sample. The method also includes receiving the scattered sample beam at a multitude of scattering angles in at least two directions. Further, the method includes cross-correlating the scattered sample beam with a reference beam to produce a two-dimensional angle and depth resolved profile of the sample scattered beam. The method also includes processing the two-dimensional angle and depth scattered profile to obtain correlated information about scattering structures in the sample.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
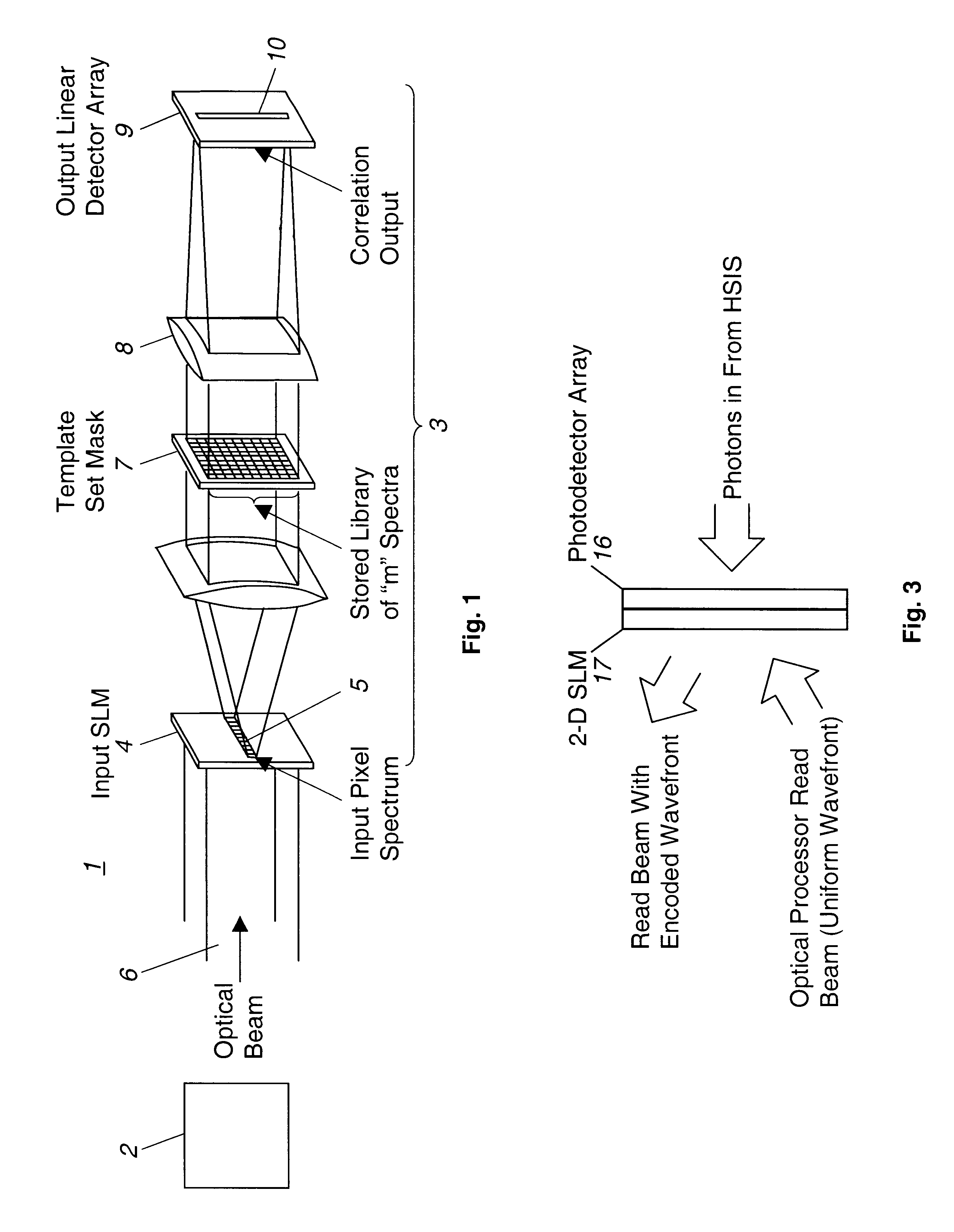
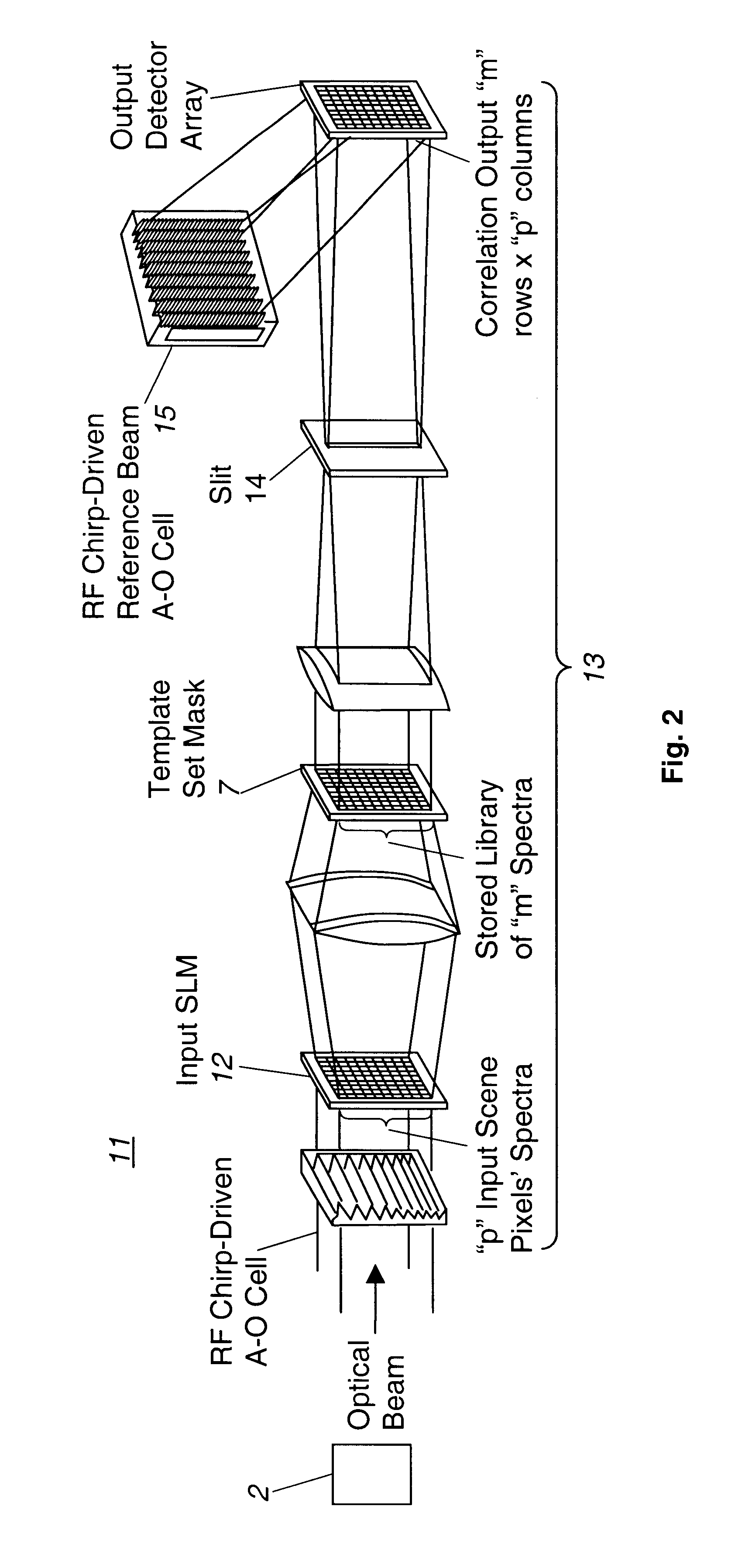
Multispectral imaging system and method
InactiveUS6480273B1Radiation pyrometryCharacter and pattern recognitionSpatial light modulatorSpectral bands
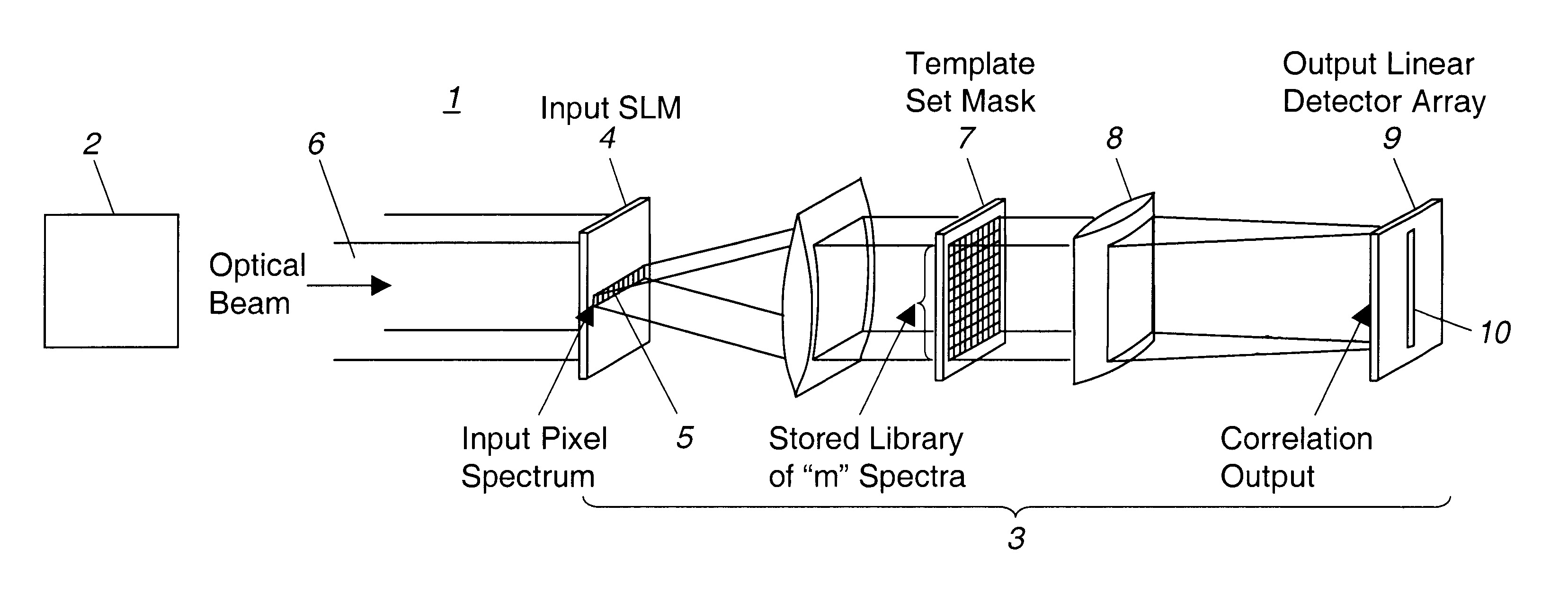
A multispectral imaging system (1) and method utilize an optical processor (3) for simultaneously comparing an input wavelength spectrum observed in a single spatial pixel in a scene image from a multispectral imager (2) with a plurality of template wavelength spectra to find a correlation. The optical processor exploits the three-dimensional attributes of optical correlation to perform massively parallel correlation processing by modulating (4) respective ones of a plurality of spectral bands of the input wavelength spectrum of an incident light beam (6) with modulating elements (5) to alter at least one property of the incident light beam by a value corresponding to the observed intensity of the input spectrum in the respective spectral band. In a disclosed embodiment, the modulated beam is expanded and transited through a spatial light modulator (7) having a two-dimensional array of modulating elements. Each row of the elements of the array alter the at least one property of the incident light by values corresponding to a particular template wavelength spectrum of a plurality of template wavelength spectra of the modulator. The values corresponding to each template spectrum are the conjugates of the representative values of the modulating elements of the template spectrum of the plurality of template spectra.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
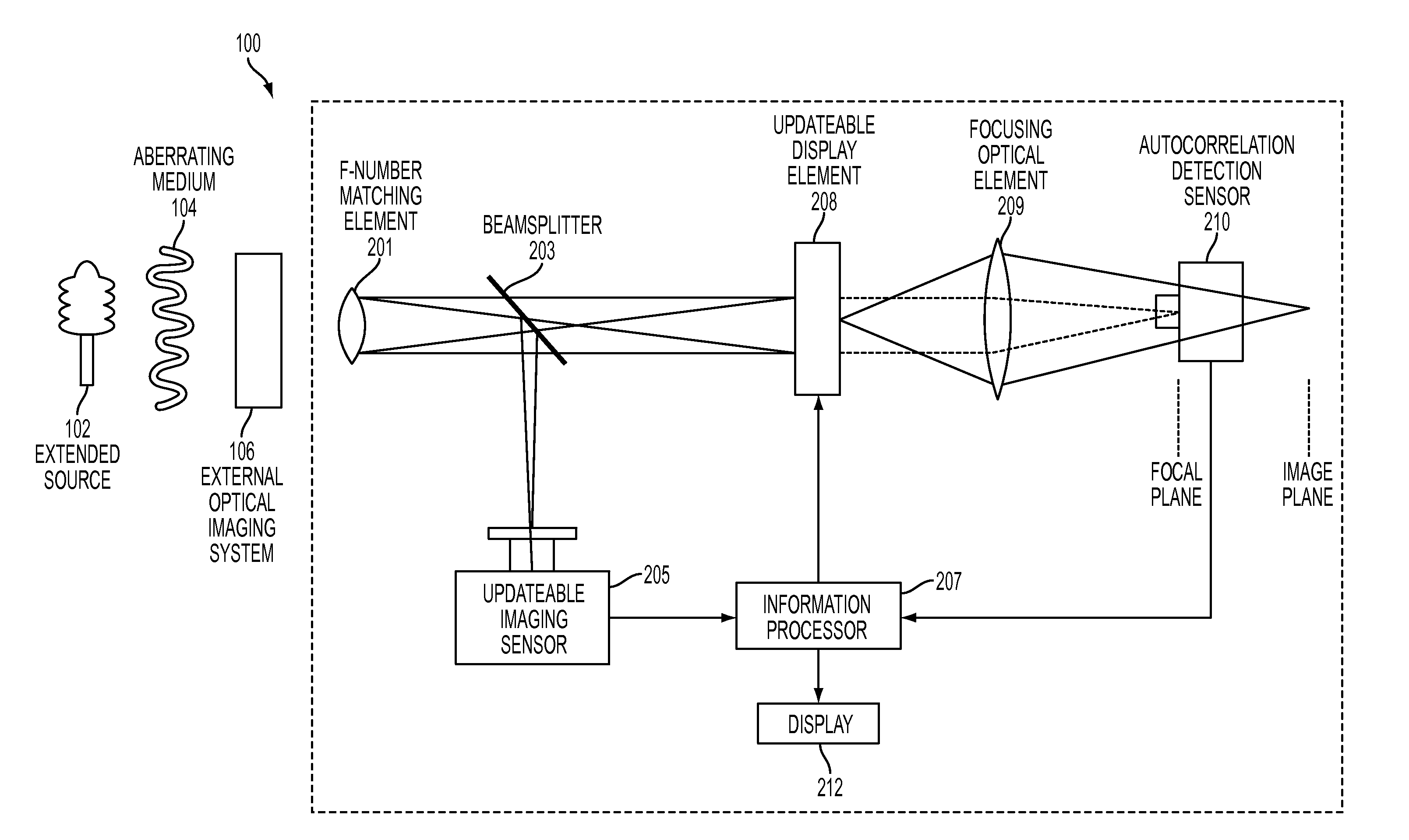
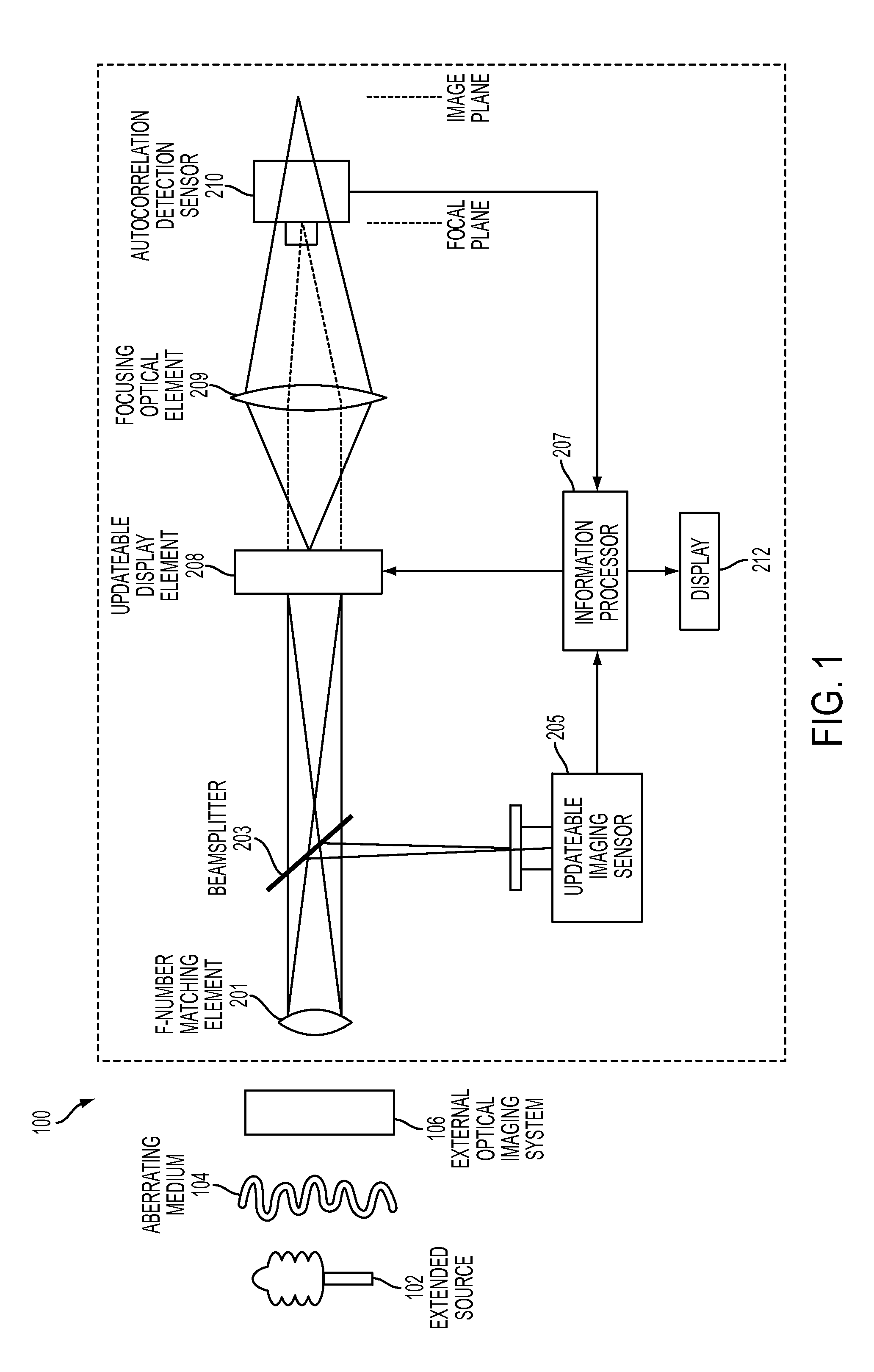
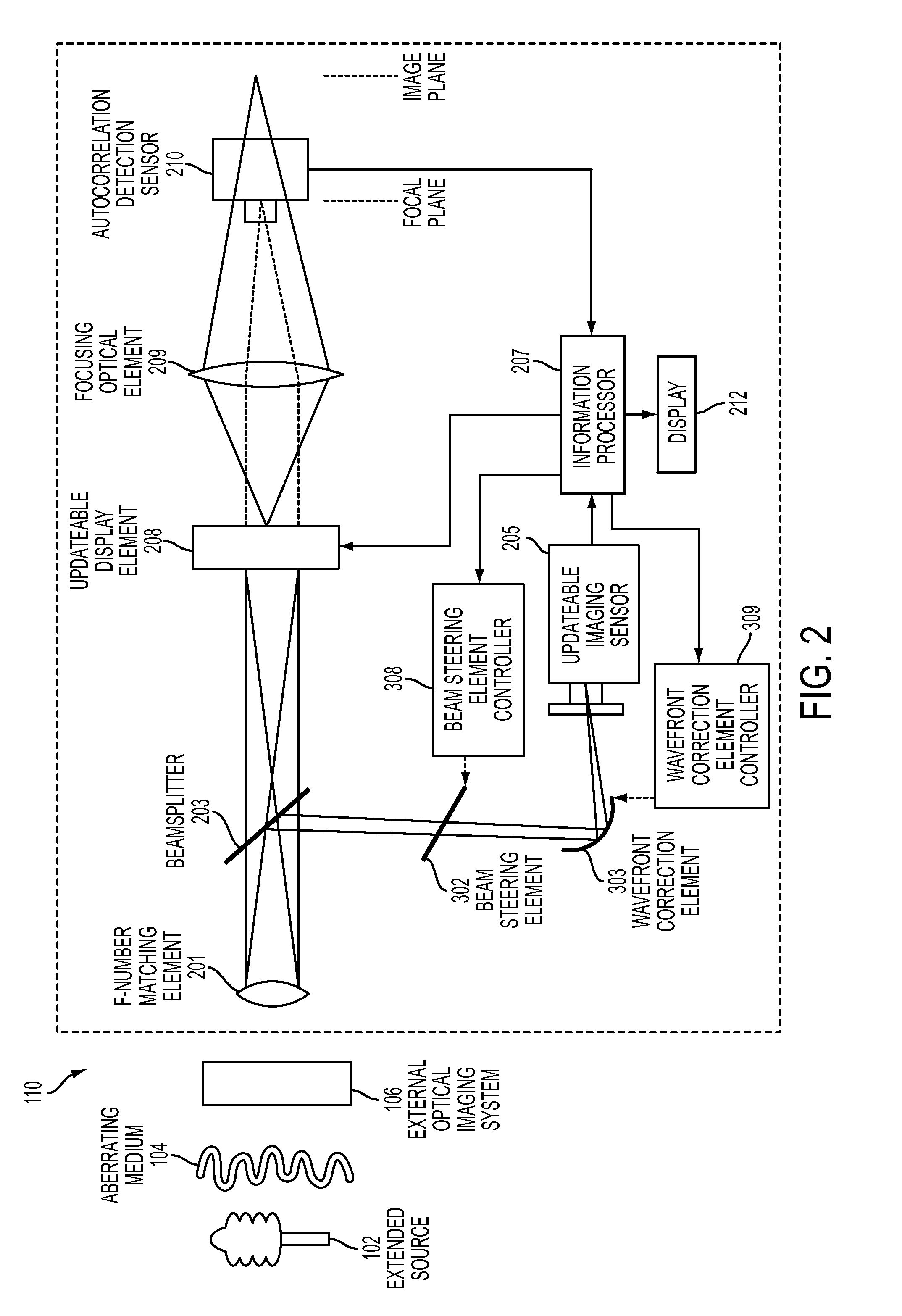
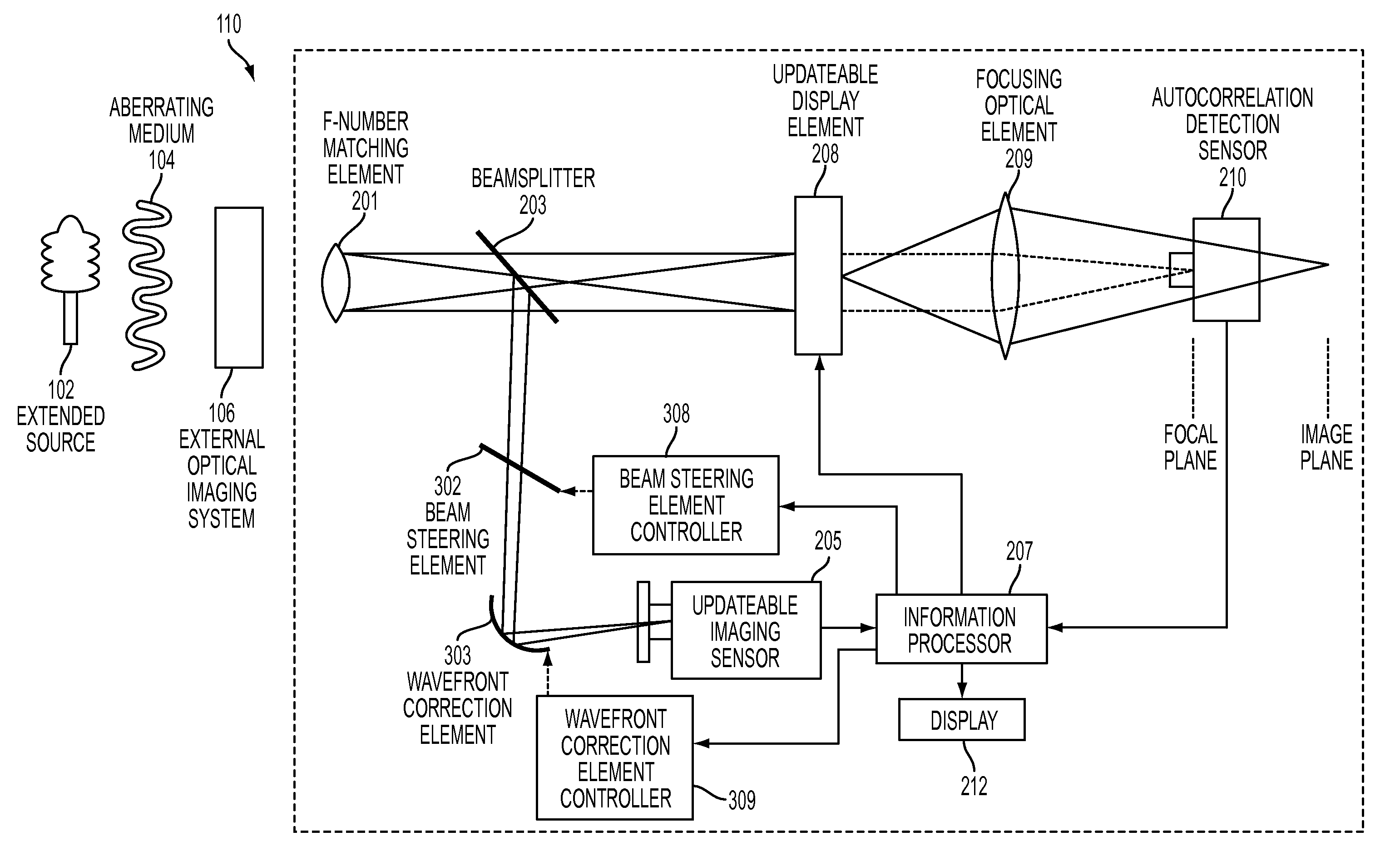
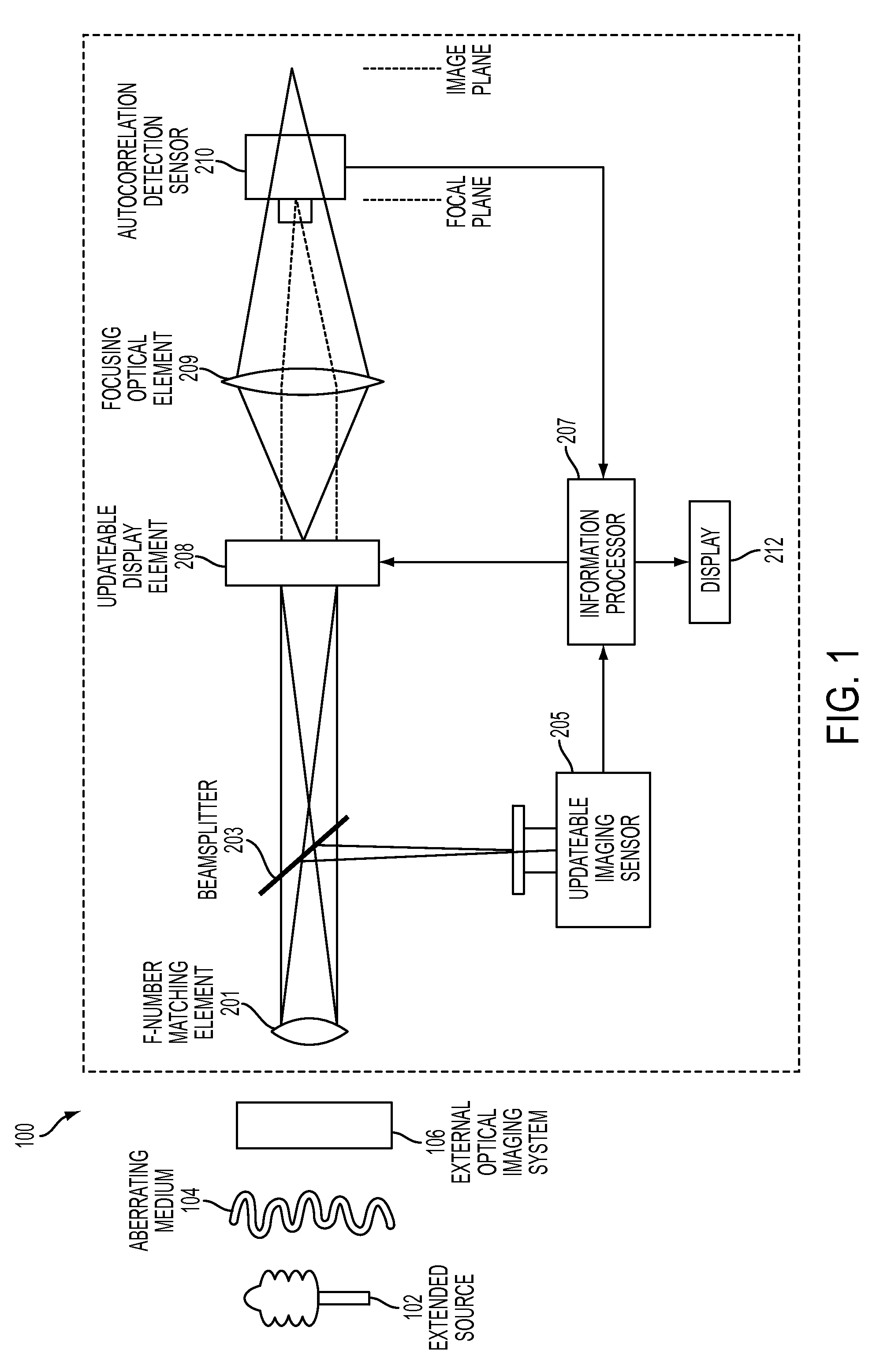
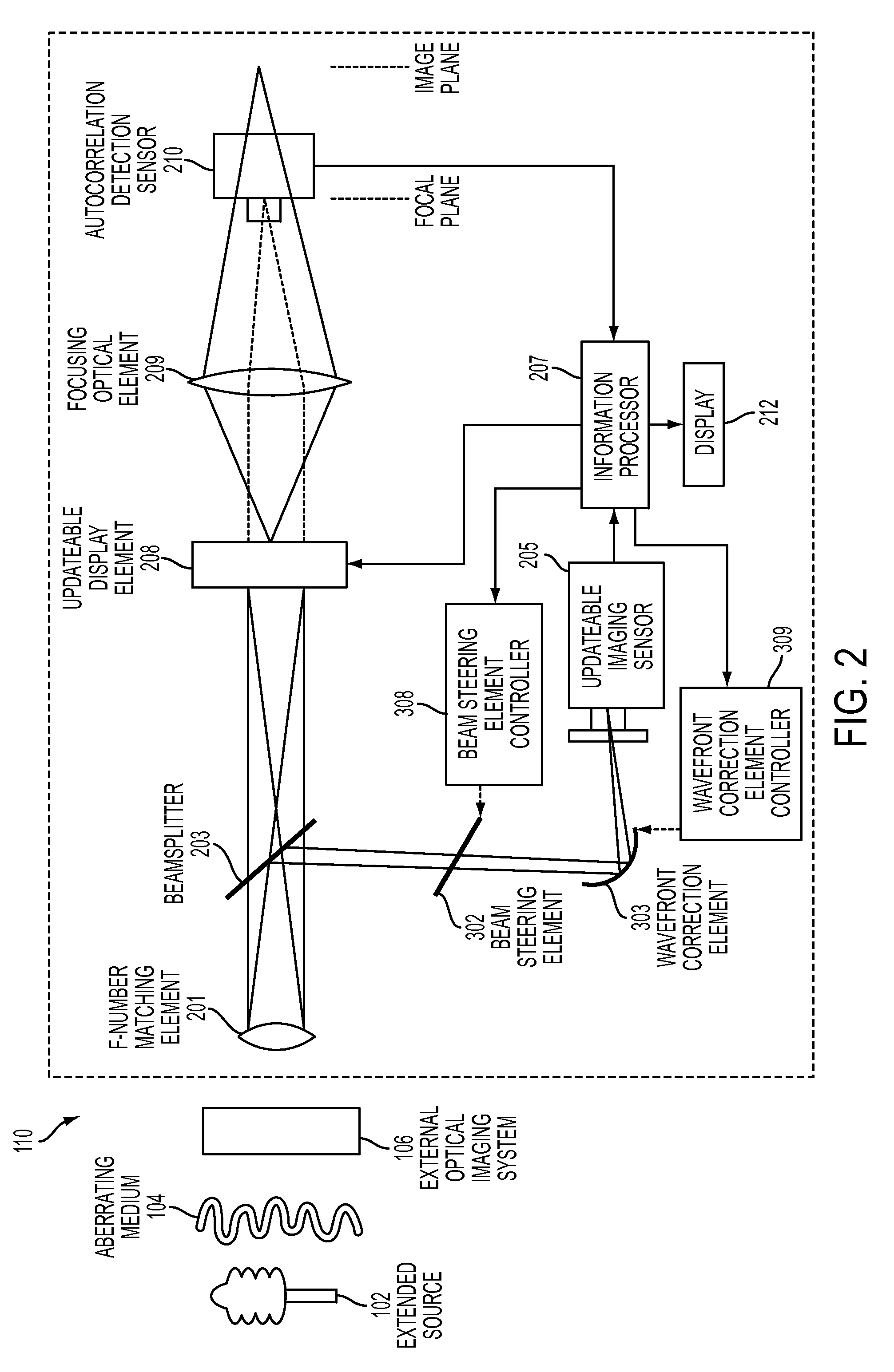
Extended Source Wavefront Sensor through Optical Correlation
InactiveUS20120242831A1Optical measurementsCharacter and pattern recognitionWavefront sensorSpatial light modulator
An atmospheric aberration sensor that uses two optically correlated images of a scene and the Fourier transform capabilities of a lens or other focusing element. The sensor receives light via an f-number matching element from a scene or from an external optical system and transmits it through a focusing optical element to an updateable display element such as a spatial light modulator or micro mirror array, which modulates the real time image from the focusing element with previous template image of the same extended scene. The modulated image is focused onto an autocorrelation detection sensor, which detects a change in centroid position corresponding to a change of the tip / tilt in the optical path. This peak shift is detected by centroid detection and corresponds to the magnitude of global wavefront tip / tilt. With a lenslet array and detector array, the system can also measure local tip / tilt and higher order aberrations.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Systems and methods of angle-resolved low coherence interferometry based optical correlation
Systems and methods of angle-resolved low coherence interferometry based optical correlation are disclosed. According to an aspect, a method includes directing a sample beam towards a sample for producing a scattered sample beam from the sample. The method also includes receiving the scattered sample beam at a multitude of scattering angles in at least two directions. Further, the method includes cross-correlating the scattered sample beam with a reference beam to produce a two-dimensional angle and depth resolved profile of the sample scattered beam. The method also includes processing the two-dimensional angle and depth scattered profile to obtain correlated information about scattering structures in the sample.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
Self-calibrating projection equation method for implementing stereo PIV method
A method for determining a conjugate distance equation for automatic calibration in the execution of stereo-PIV(Particle Image Velocimetry) is provided to execute calibration of stereo-PIV even in a closed space or micro-channel. A method for determining a conjugate distance equation includes ate least two cameras and a single light slit. The cameras observe a region of the light slit in different directions, and point-to-point correspondence between the cameras is determined by moving and measuring each interrogation field in camera images according to optical correlation. The conjugate equation is decided using an approximation method according to internal and external camera parameters.
Owner:LAVISION
Measuring arm of optical coherent tomographic eye examining instrument used together with slit lamp
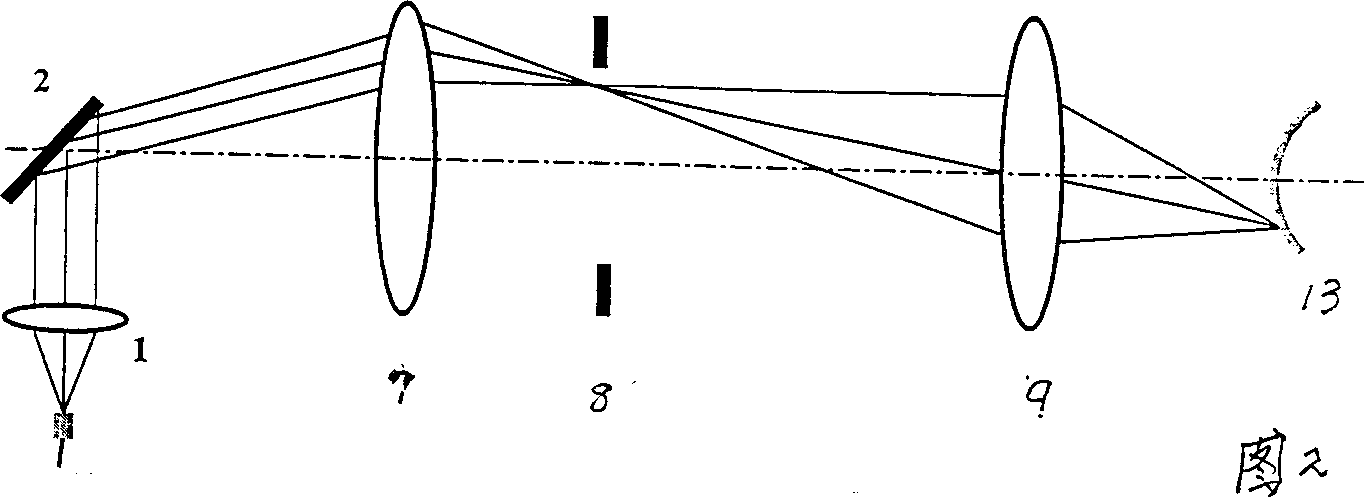
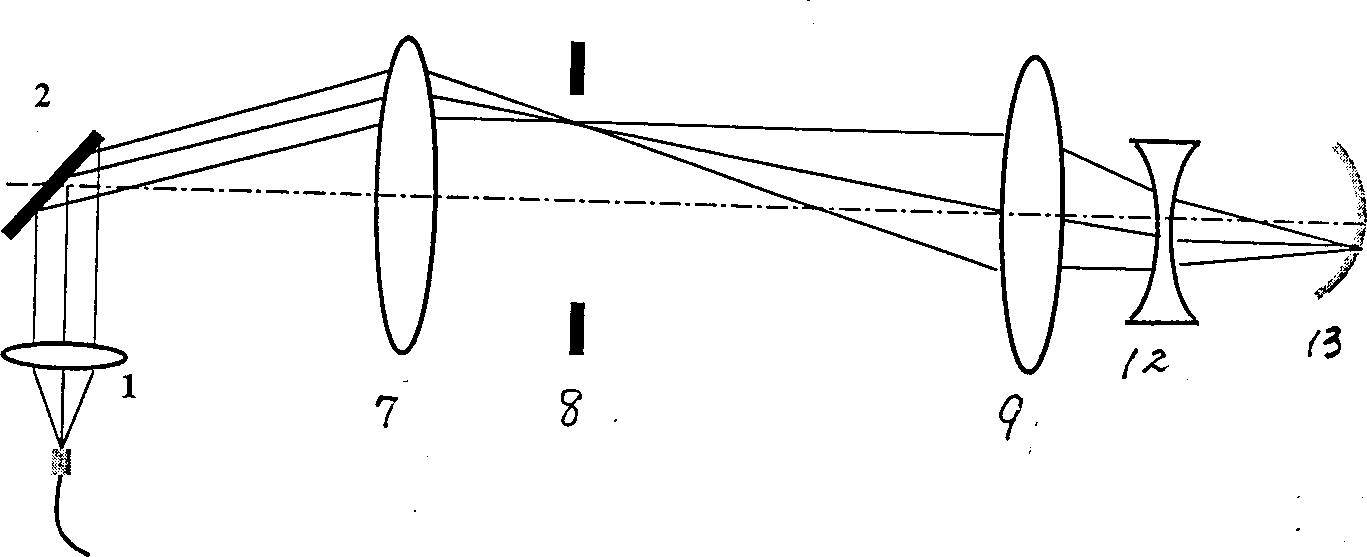
The present invention relates to measuring arm of eye axamination apparatus using slip lamp inlegrated optical correlation cromatography, it includes slip lamp system, optical fiber collimator, scan mirror, two colour lens and reflector, the white light emitted from white light source passes through collector lens and lens and narrow seam, then form image on eye through objective and reflector, then make observation to eye through telescope. The measuring arm designed by present invention not only is simple in structure but also ensures the maximum scanning range under same resolution condition or possesses maximum resolution under same scanning range.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Discrete optical correlation system
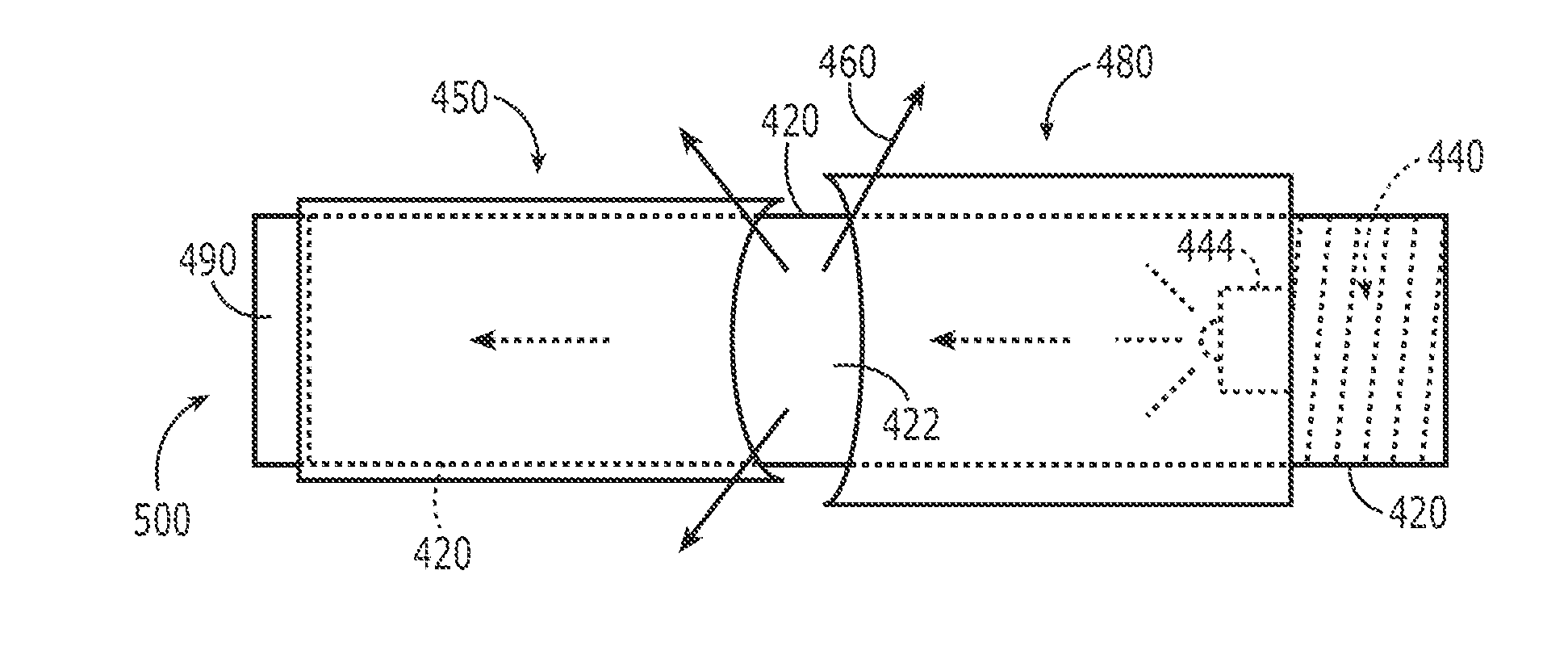
The present invention relates to a discrete optical correlation system. One embodiment of the present invention includes a portable electrical illumination system and an optically opaque hollow module, configured to releasably couple to the portable electrical illumination system in a manner such that when the portable electrical illumination system is activated, the system produces a discrete correlated or focused illumination output. The portable electrical illumination system further includes a light emitting diode, a power source, a switch, and a coupling mechanism. The optically opaque hollow module further includes at least two openings, a hollow internal region, an optically opaque outer surface, and a coupling mechanism disposed on at least one of the at least two openings.
Owner:KENNEDY GREGORY +1
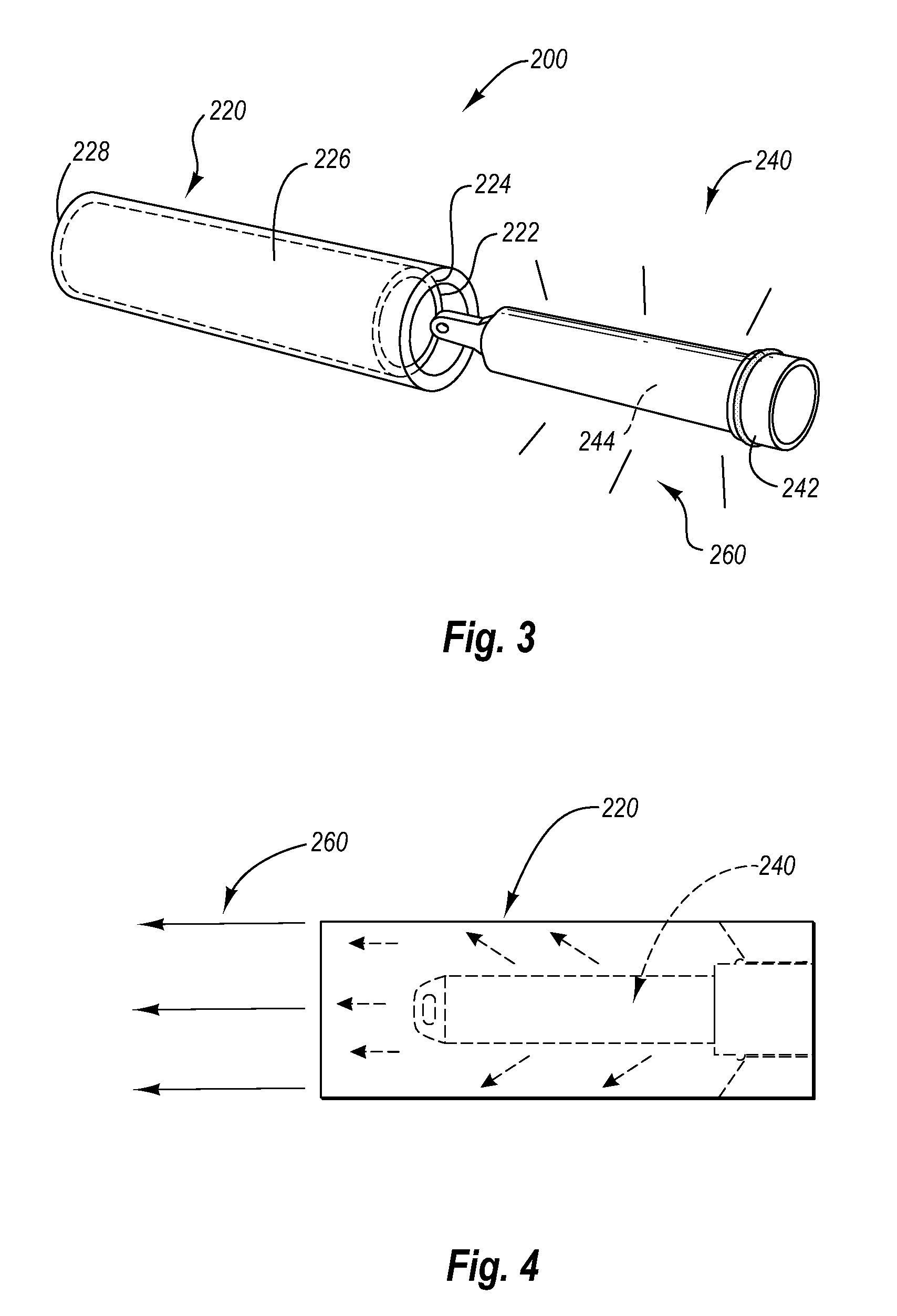
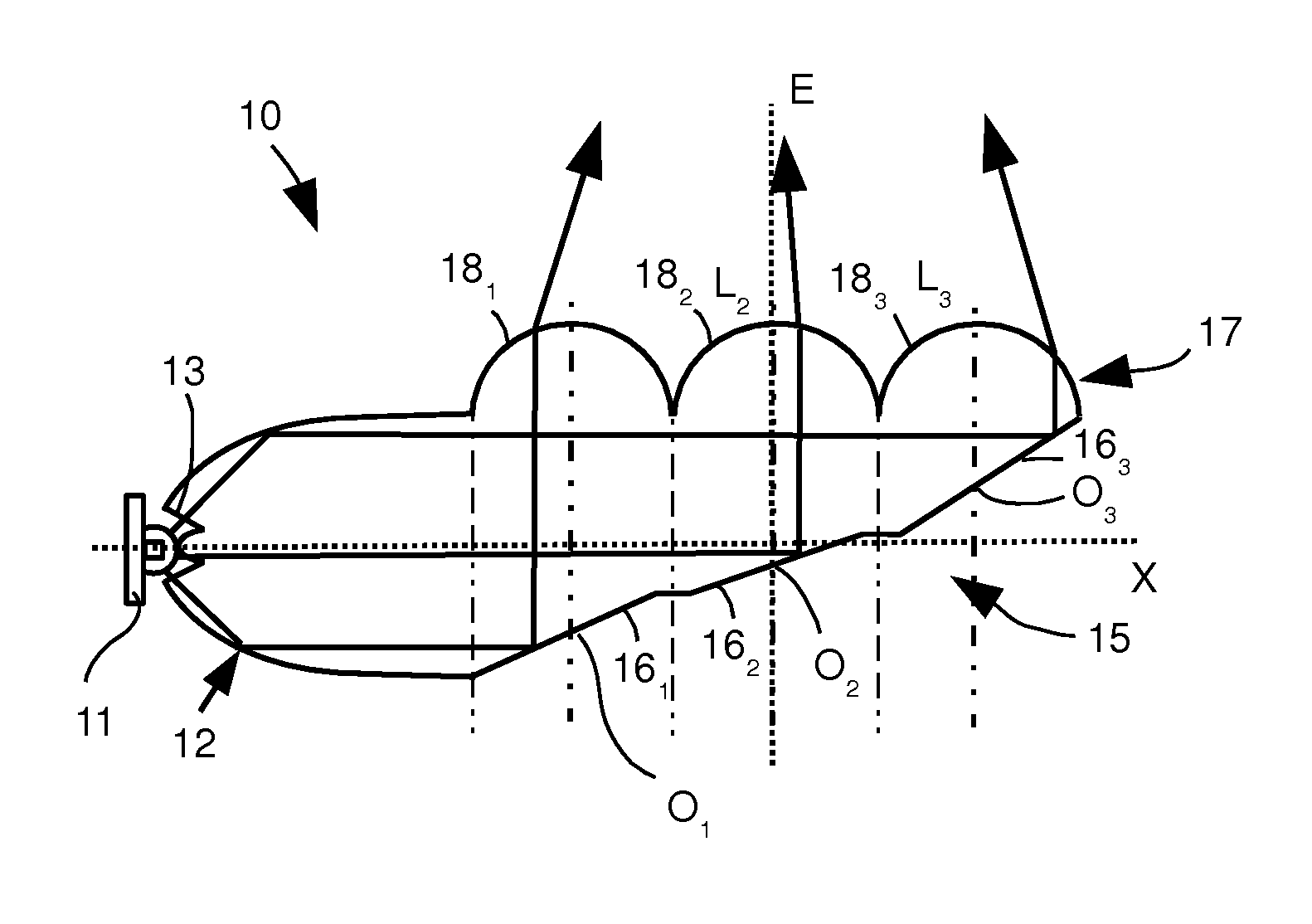
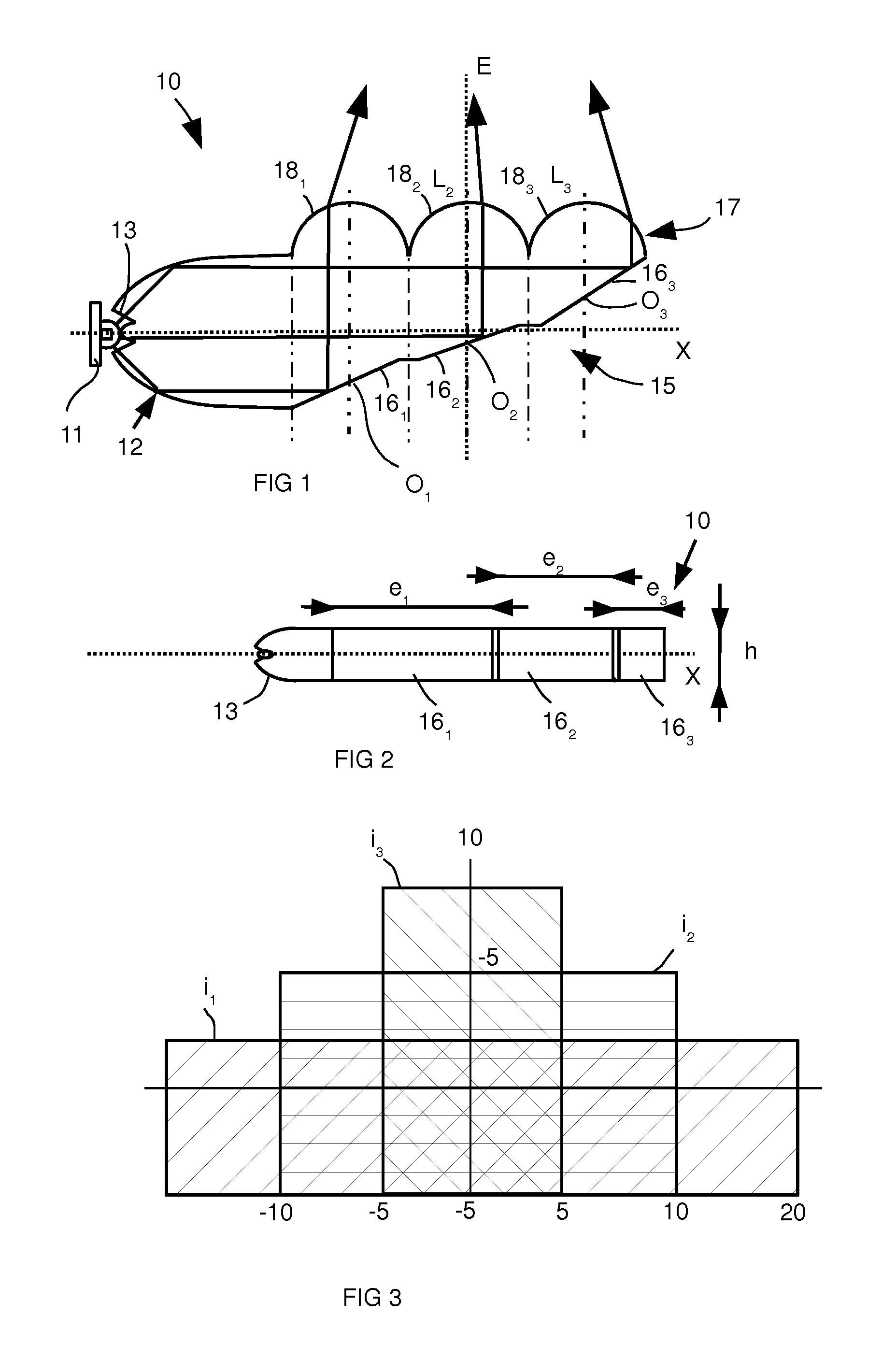
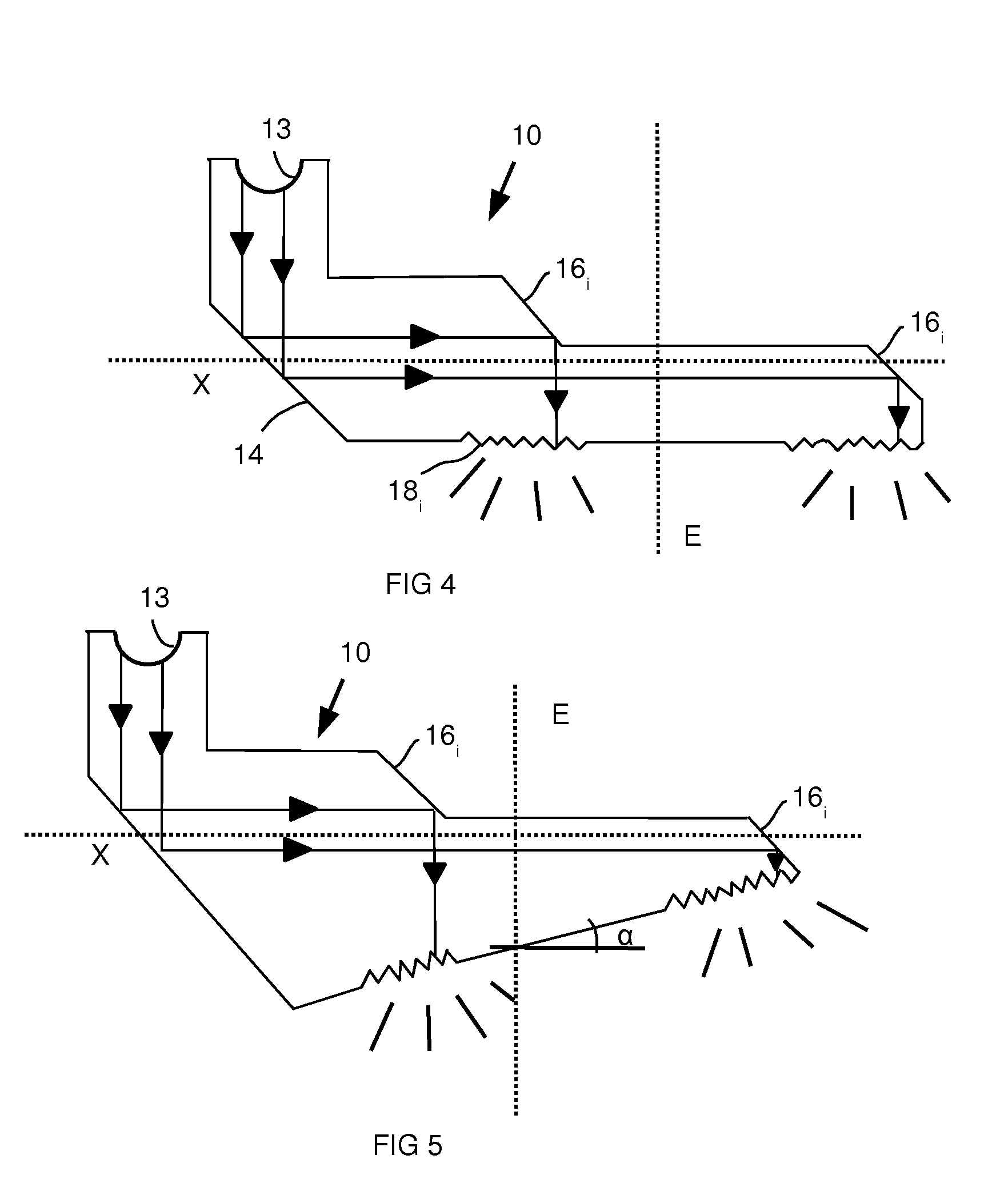
Automotive vehicle optical device having dioptric elements integrated into the light duct
An optical device of an automotive vehicle comprises a first luminous source and a light duct designed to conduct light originating from the luminous source in the form of a beam with substantially parallel rays. The light duct comprises a rear face forming at least one reflecting facet designed to return some of the beam substantially along an optical axis (E) of the light duct. It also comprises a front face fashioned as at least one dioptric element associated optically with each reflecting facet and through which the light exits the light duct after return by the associated reflecting facet. Each dioptric element is configured so as to be stigmatic between a point in the substance of the light duct situated in immediate proximity to the center (Oi) of the associated reflecting facet and a point situated at infinity.
Owner:VALEO VISION SA
Extended source wavefront sensor through optical correlation with a change in centroid position of light corresponding to a magnitude of tip/tilt aberration of optical jitter
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
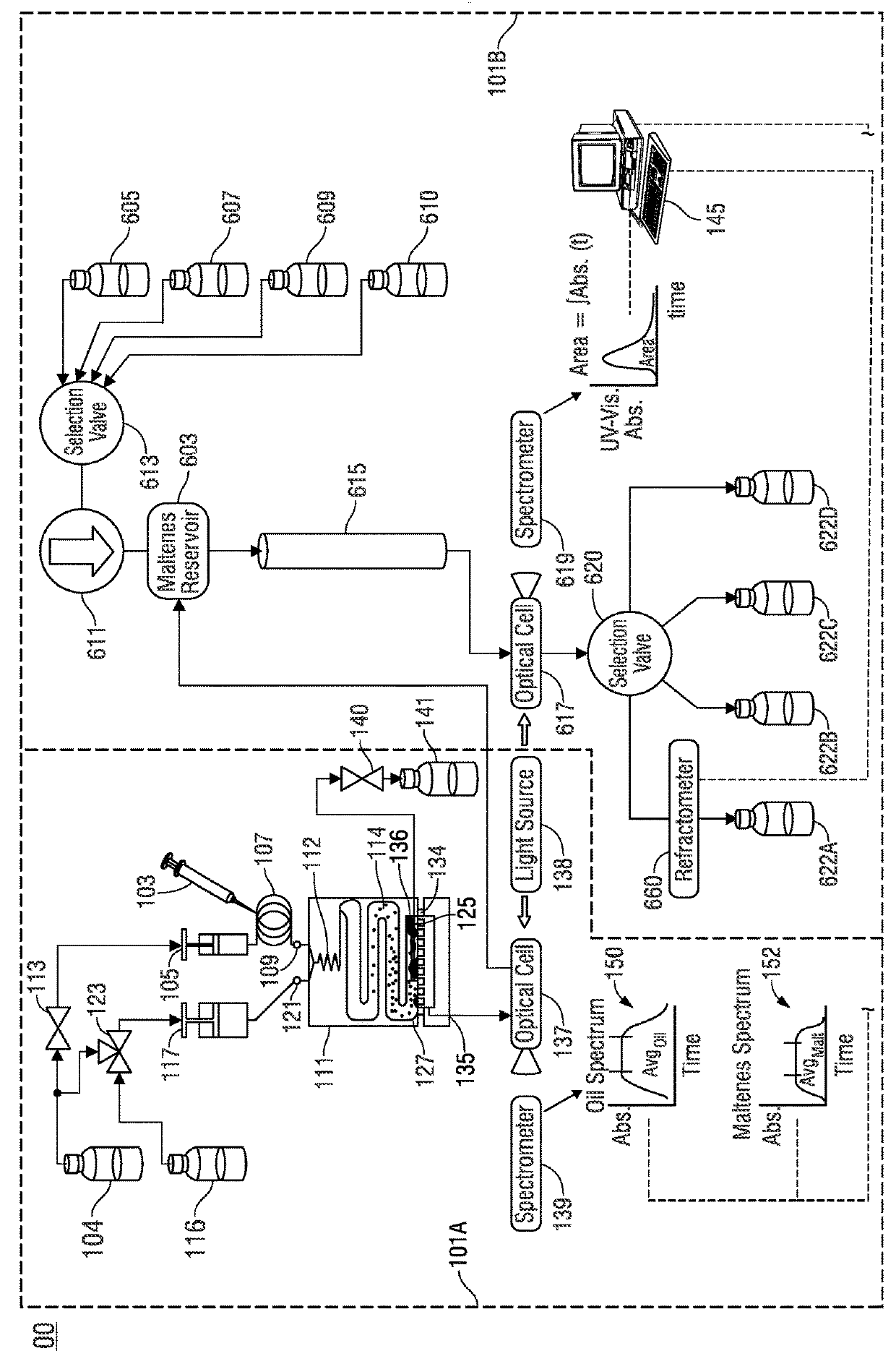
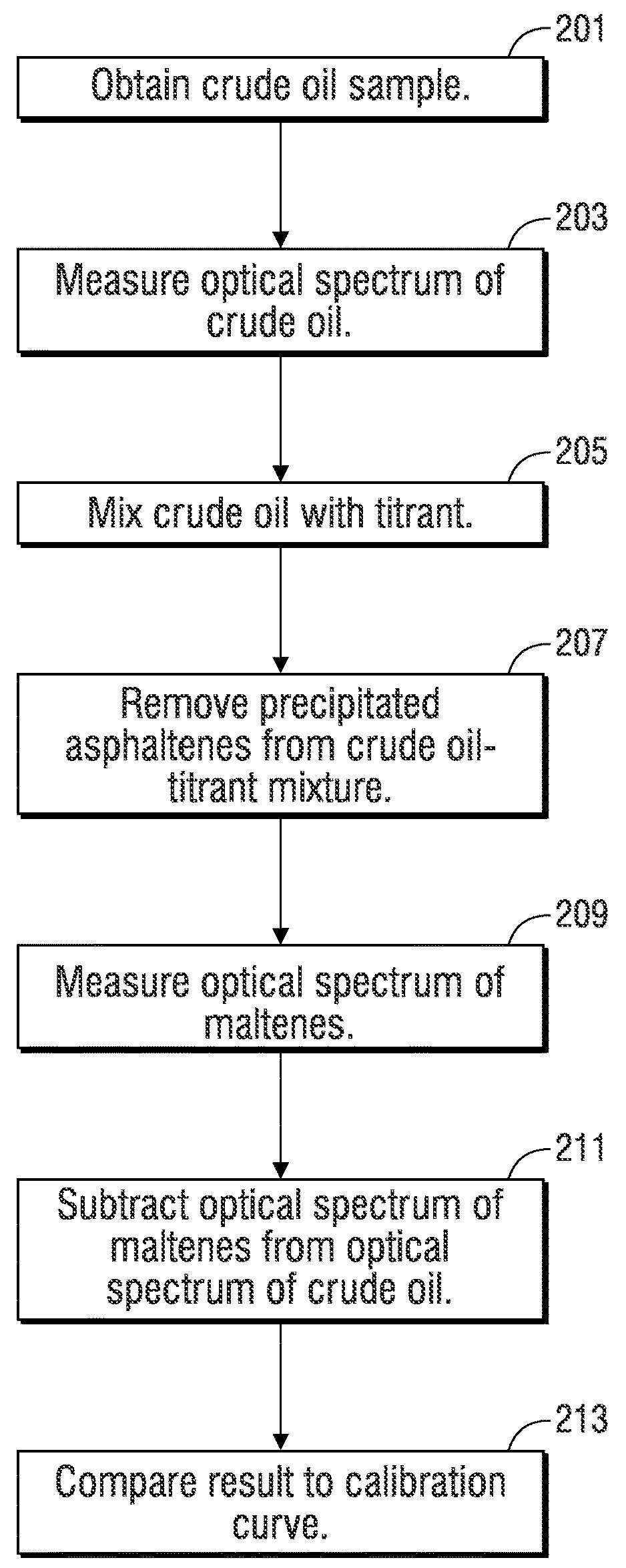
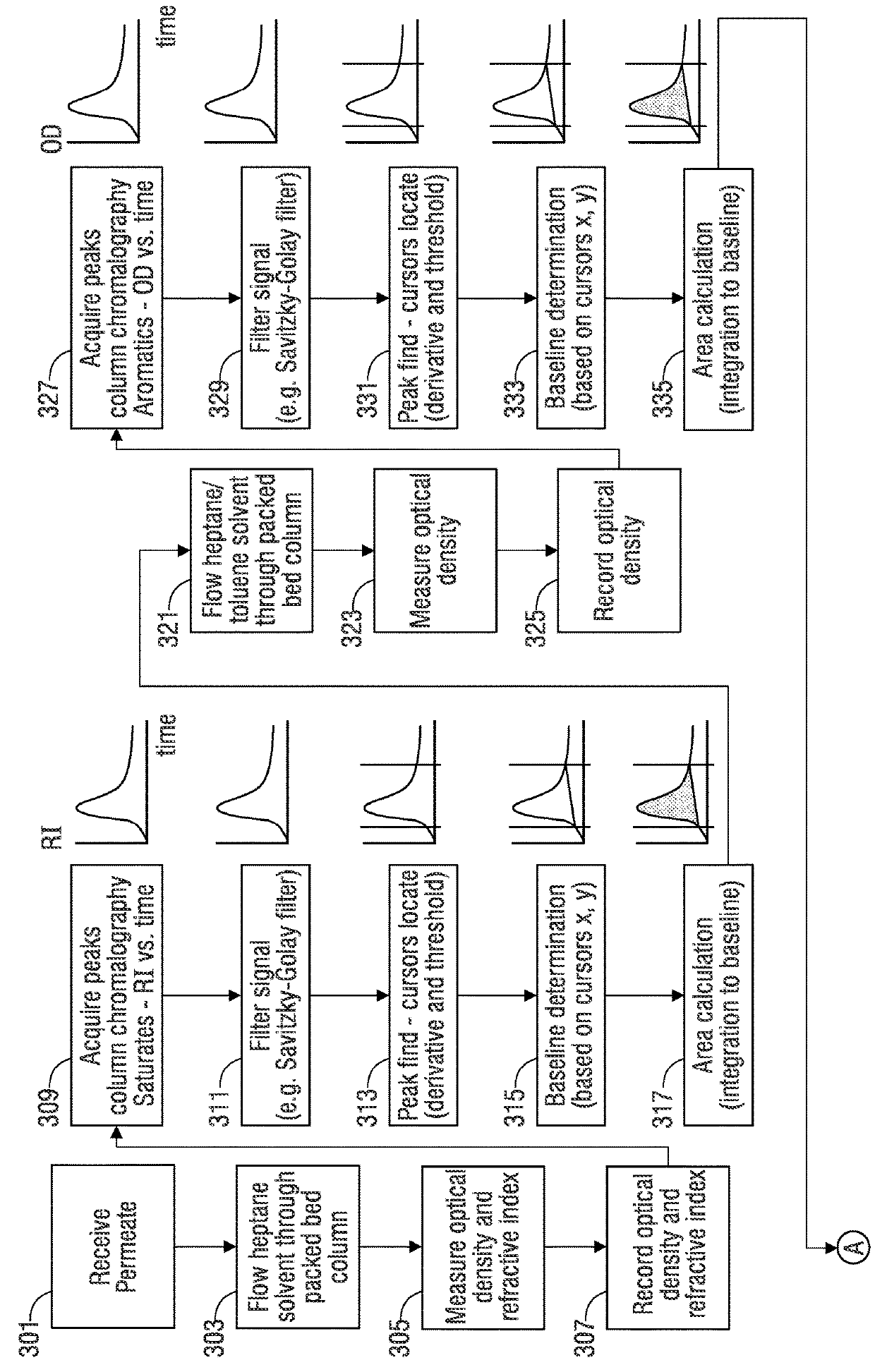
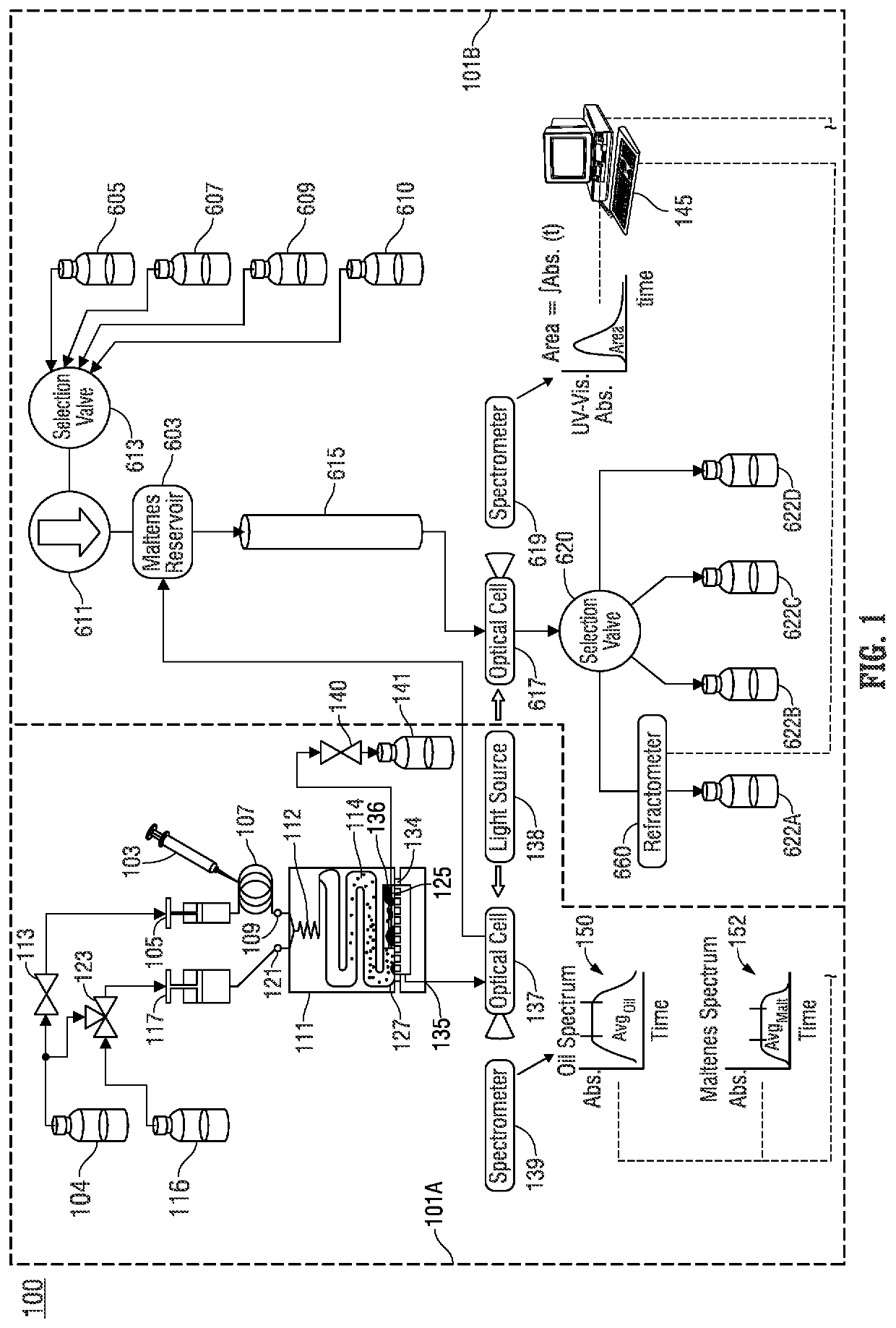
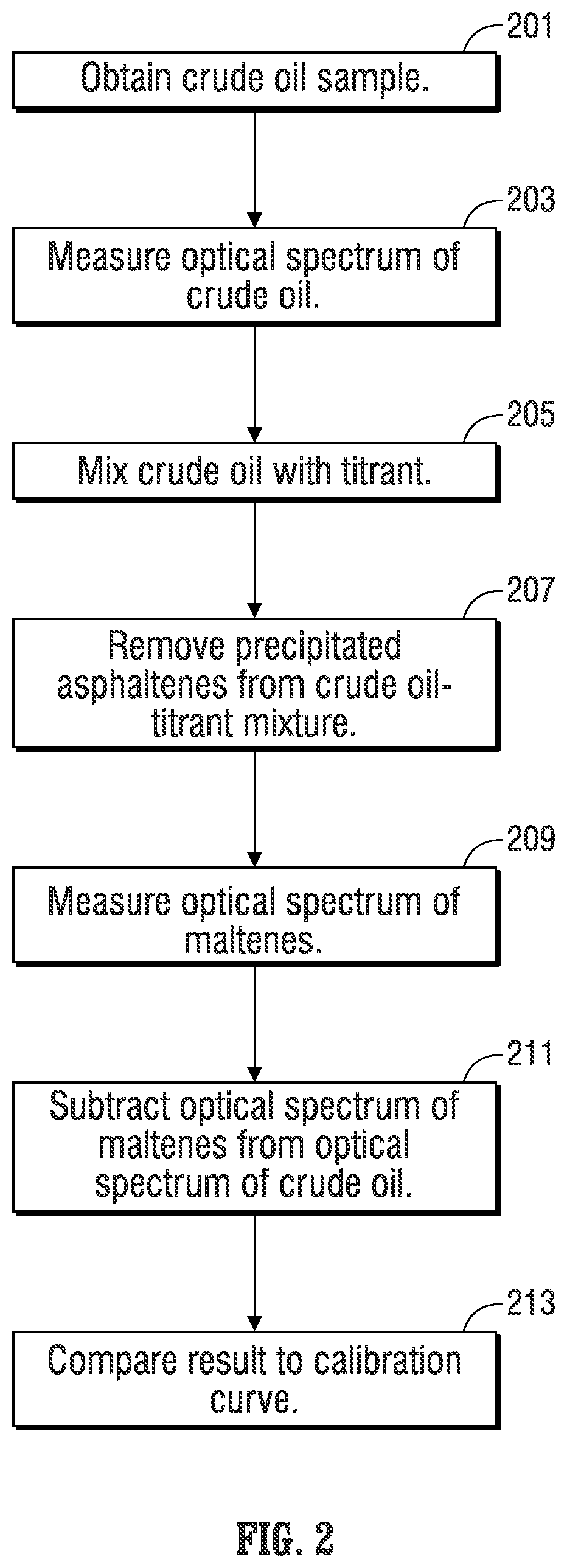
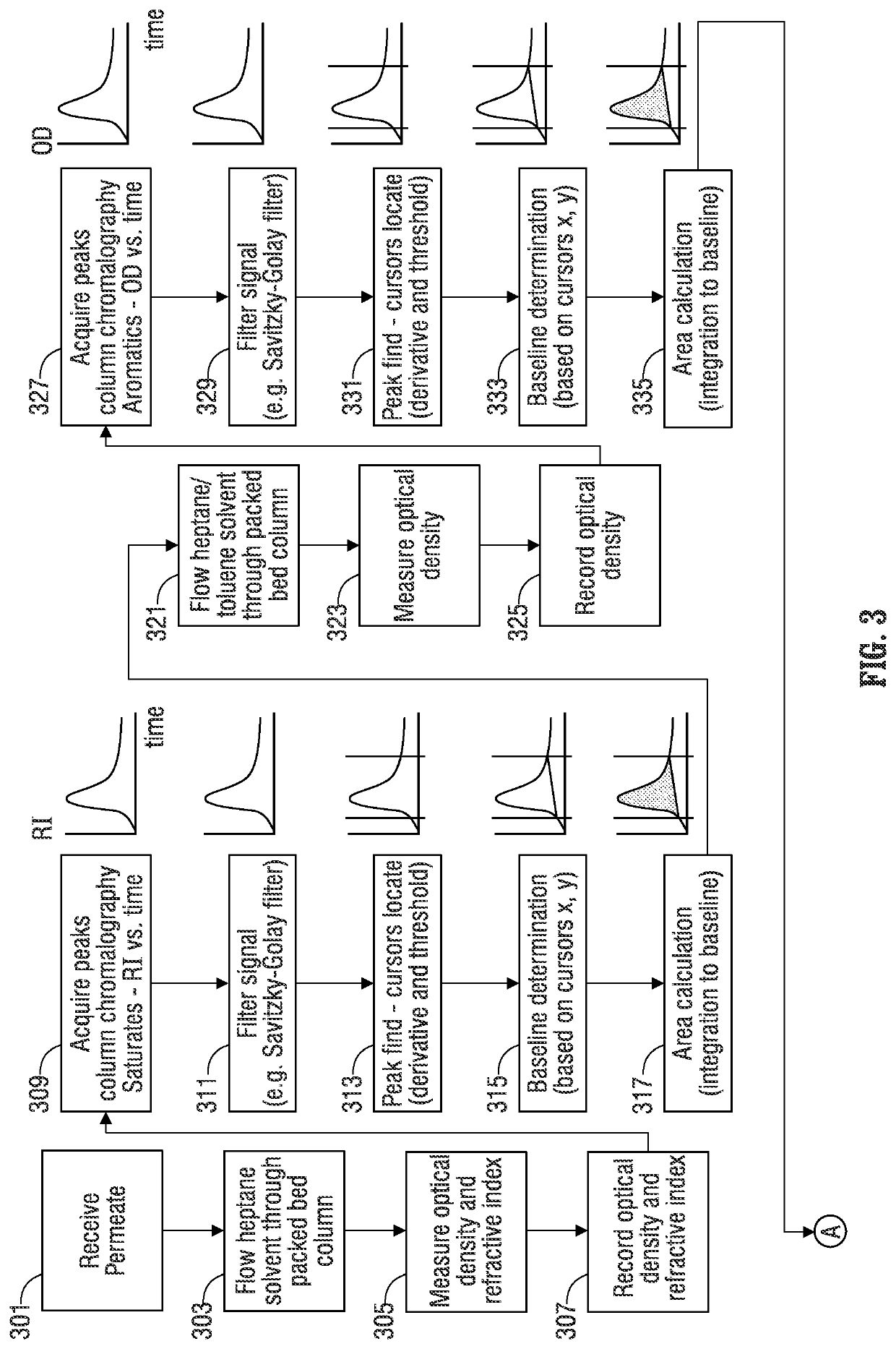
Automated method and apparatus for measuring saturate, aromatic, resin, and asphaltene fractions using microfluidics and spectroscopy
ActiveUS20180164273A1Component separationPreparing sample for investigationOptical propertyMicrofluidics
A method of determining saturate, aromatic, resin, and asphaltene (SARA) fractions of a hydrocarbon fluid sample, including: i) microfluidic mixing that forms a mixture including the hydrocarbon fluid sample and a solvent fluid that dissolves asphaltenes; ii) performing optical spectroscopy on the hydrocarbon fluid sample-solvent fluid mixture resulting from i); iii) microfluidic mixing that forms a mixture including the hydrocarbon fluid sample and a titrant fluid that precipitates asphaltenes; iv) microfluidically precipitating asphaltenes from the hydrocarbon fluid sample titrant fluid mixture resulting from iii); v) performing a microfluidic filtering operation that removes precipitated asphaltenes from the mixture resulting from iv) while outputting permeate; vi) performing optical spectroscopy on the permeate resulting from v); vii) determining an asphaltene fraction percentage of the hydrocarbon fluid sample based on the optical spectroscopy performed in ii) and vi); viii) sequentially separating saturate-, aromatic-, and resin-containing portions from the permeate from v); ix) for each separating of viii), measuring an optical property of the respective saturate-, aromatic-, and resin-containing portions over time; and x) determining fraction percentages of saturates, aromatics, and resins in the hydrocarbon fluid sample based on the measured optical properties of ix) and respective mass-to-optical correlation data.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
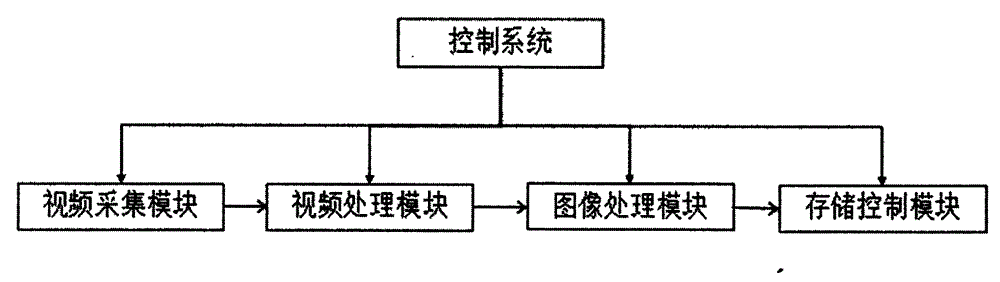
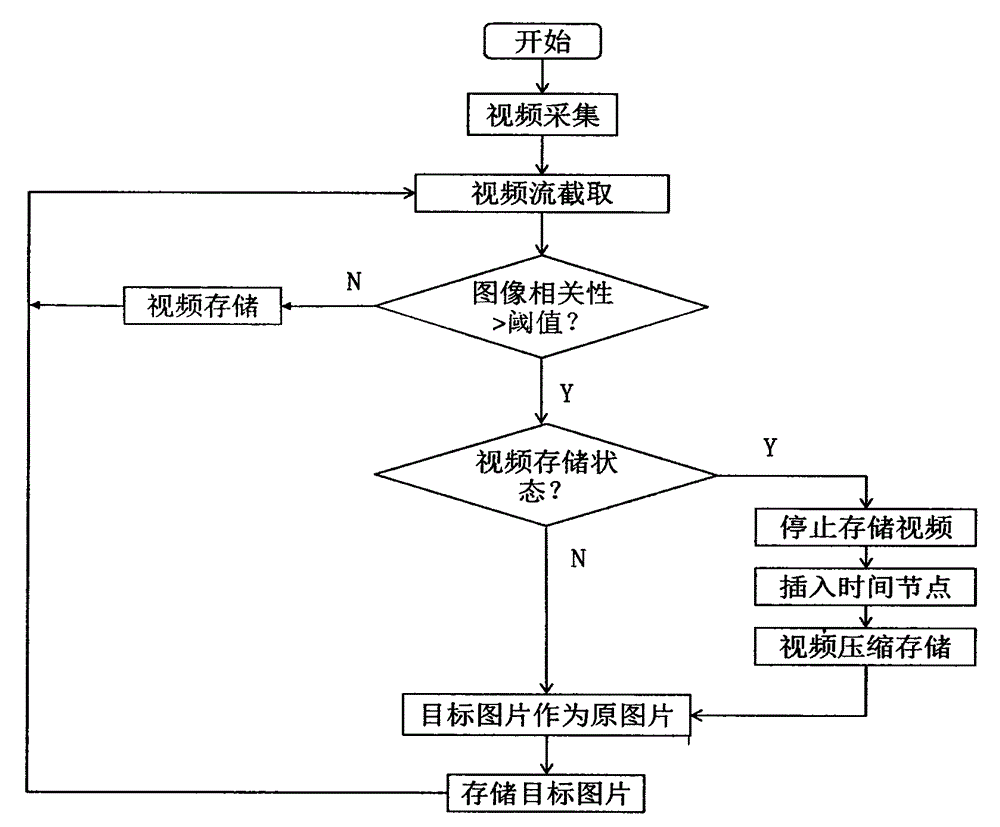
Low storage monitoring method based on optical correlation
InactiveCN104320609ASave spaceHigh densityTelevision system detailsColor television detailsInternal memoryStreaming data
The invention relates to a low storage monitoring method based on optical correlation. The low storage monitoring method is mainly technically characterized by comprising the following steps that: a video acquisition module extracts a sample image according to a certain frequency specific to video stream data; an image processing module performs image correlation computation on the sample image according to an SSIM (Structural Similarity Index Measurement System) method; the image processing module judges whether image correlation is greater than a preset threshold or not, and performs video storage if the image correlation is not greater than the preset threshold; and if the image correlation is greater than the preset threshold, the image processing module performs image storage. According to the low storage monitoring method, image correlation comparison is performed on an acquired video image, and the occurrence of a perimeter intrusion event is judged intelligently. Moreover, video data is saved selectively, so that the aim of saving internal memory can be fulfilled by not storing non-significant data when the perimeter intrusion event does not occur in an environment, and the problems of high construction cost, large occupied storage space, high energy consumption and the like in an existing video monitoring system are solved. The low storage monitoring method can be widely applied to the video monitoring occasions of security video monitoring, night security video monitoring of parking lots and dormitory areas, and the like during logistics system transportation.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Brillouin optical correlation-domain analyzer device and method based on supercontinuum
ActiveCN110243492ASolve the distance problemResolve resolutionThermometers using physical/chemical changesUsing optical meansFiber couplerOptical delay line
The invention relates to a distributed optical fiber sensing system, in particular to a Brillouin optical correlation-domain analyzer device and method based on a supercontinuum. The device comprises a quasi-continuous wave Raman fiber laser, a first optical isolator, a real wave fiber, a first tunable optical filter, a second optical isolator, a 1*2 fiber coupler, a first polarization controller, a high-speed electro-optical modulator, a microwave signal source, a variable optical delay line, a first optical amplifier, an optical scrambler, a third optical isolator, a sensing fiber, a second polarization controller, a second optical amplifier, an optical circulator, a second tunable optical filter and an optical power detector. Compared with a BOCDA (Brillouin Optical Correlation-Domain Analysis) system, the Brillouin optical correlation-domain analyzer device and method based on a supercontinuum have the higher spatial resolution and a longer distributed sensing distance; it is worth stating that the supercontinuum has a wider spectrum, meaning that the spatial resolution can reach sub-millimeter level, and the output power of the quasi-continuous Raman fiber laser is high so as to provide enough energy for long-distance sensing.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
Photoelectricity mixing correlator based on position sensitive device (PSD) position detector
InactiveCN103105887AOvercome a major bottleneck of high-speed developmentImprove photoelectric conversion rateOptical computing devicesSpatial light modulatorFourier transform on finite groups
The invention relates to a photoelectricity mixing correlator based on a position sensitive device (PSD) position detector. For the first time, the PSD position detector is introduced into a matched filtering correlator, correlation peak information is collected by a PSD, and target position information is extracted according to the correlation peak information of a target image and a template image after photology correlation conversion. Photoelectric conversion efficiency is greatly improved, and simultaneously organic combination of flexibility of electronics and high speed of optics is achieved. A matched filter is conducted in advance by an electronics method, the target image and the template image are input into a spatial light modulator, optics Fourier transformation is conducted by a Fourier transformation lens, and related computing results are collected by the PSD position detector. The photoelectricity mixing correlator based on the PSD position detector can be applied to high-speed image stabilizing of video, high-speed identification and tracking of a target and the like.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Object tracking using optical correlation and feedback
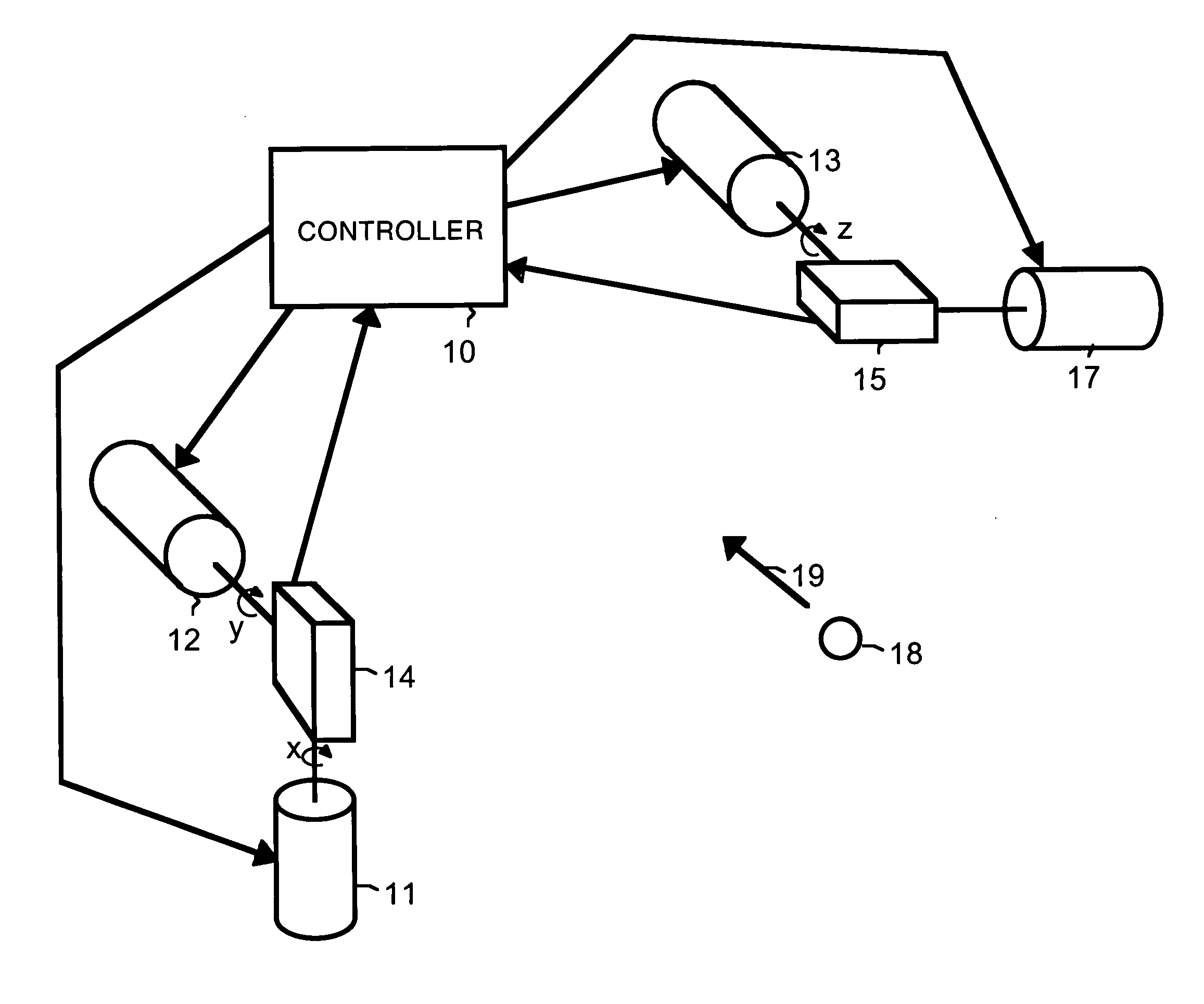
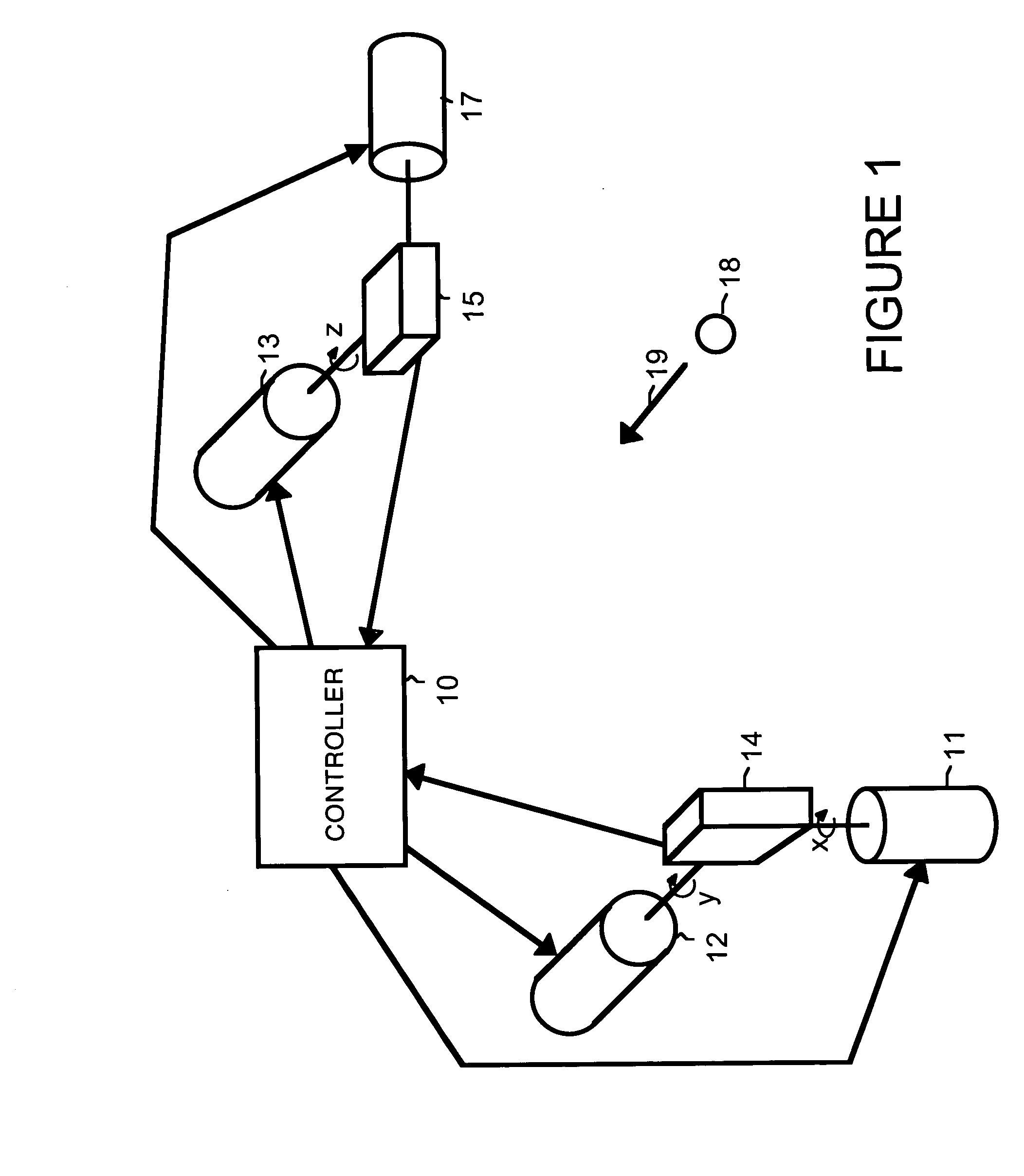
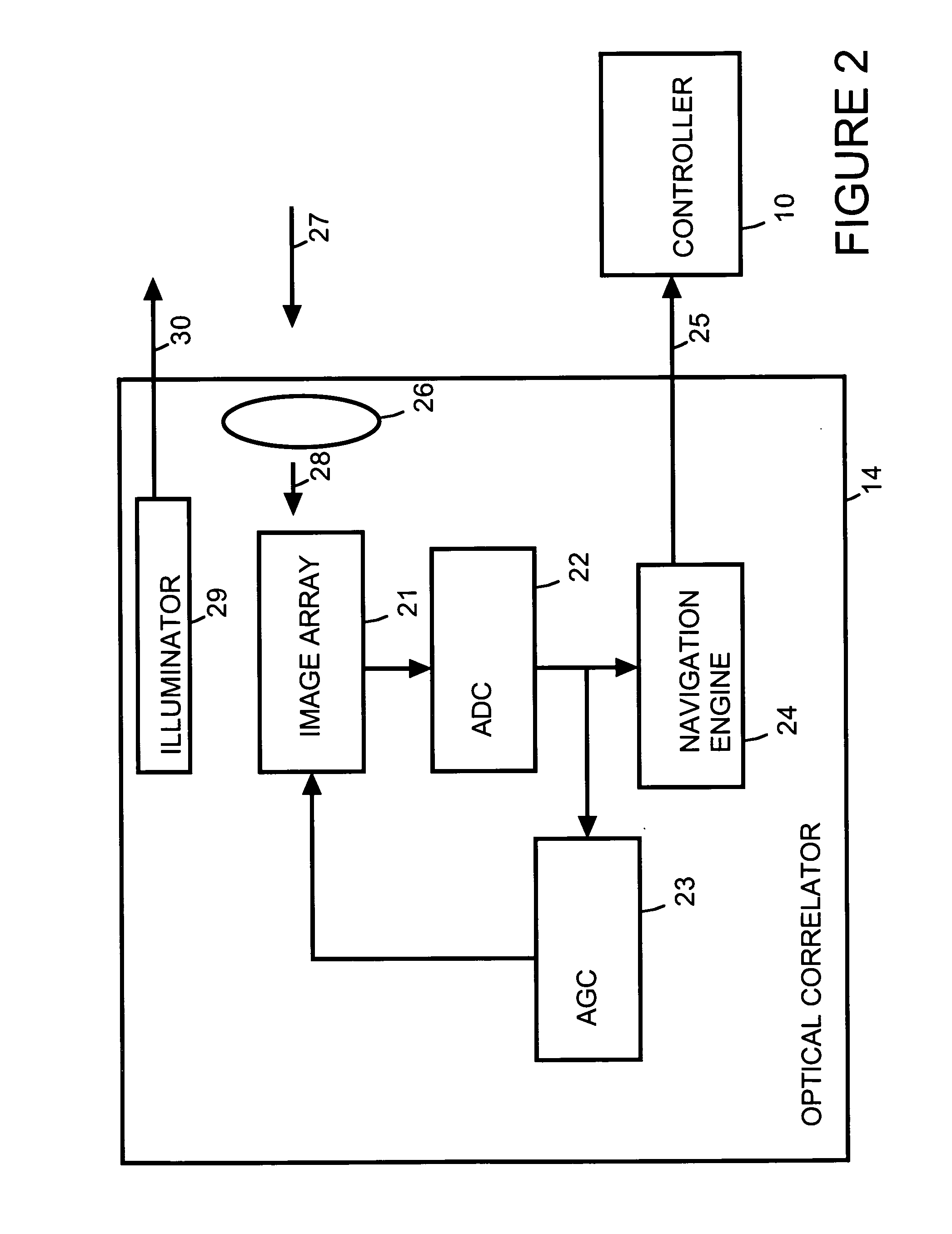
A motion-sensing device is used to track motion of an object. The motion-sensing device includes an optical correlator, a motor system and a controller. The optical correlator has an imager. The optical correlator provides a feedback signal that indicates motion of the object in at least one dimension based on detected movement of an image of the object from a first location within the imager to a second location within the imager. The motor system can move the imager. The controller receives the feedback signal from the optical correlator and uses the feedback signal to calculate motion of the object and to control the motor system to move the imager so that the image of the object is returned to the first location within the imager.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Discrete optical correlation system with adjustable aperture
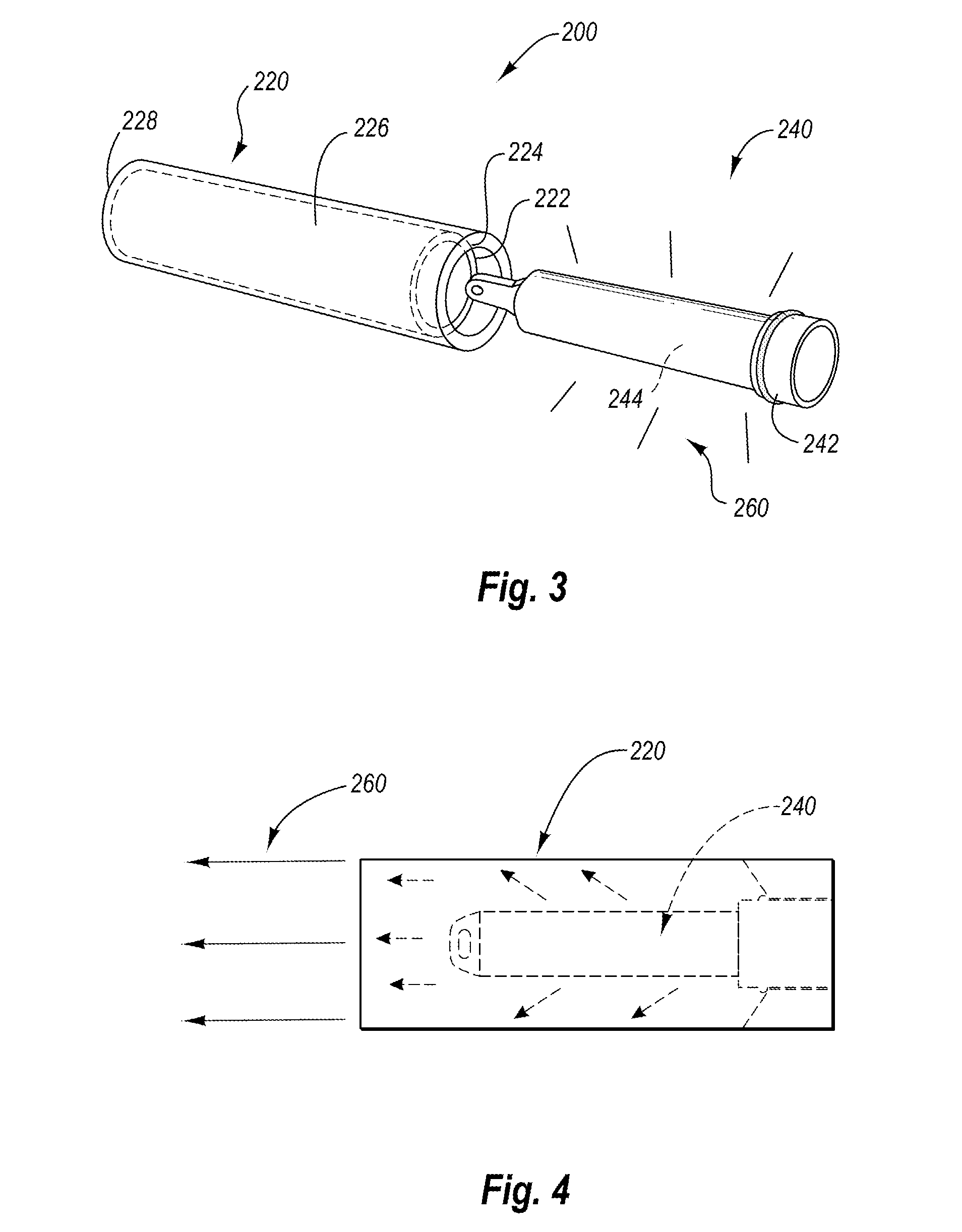
The present invention relates to a discrete optical correlation system. One embodiment of the present invention includes a portable electrical illumination system and an optically opaque hollow module, configured to releasably couple to the portable electrical illumination system in a manner such that when the portable electrical illumination system is activated, the system produces a discrete correlated or focused illumination output. The portable electrical illumination system further includes a light emitting diode, a power source, a switch, and a coupling mechanism. The optically opaque hollow module further includes at least two openings, a hollow internal region, an optically opaque outer surface, and a coupling mechanism disposed on at least one of the at least two openings. A fourth embodiment relates creating an adjustable aperture between two optically opaque sleeves sliding over an optically transparent module coupled to the portable electrical illumination system.
Owner:KENNEDY DOUGLAS BRIAN +1
Real-time motion blurred image restoration method for photoelectric hybrid joint transform correlation
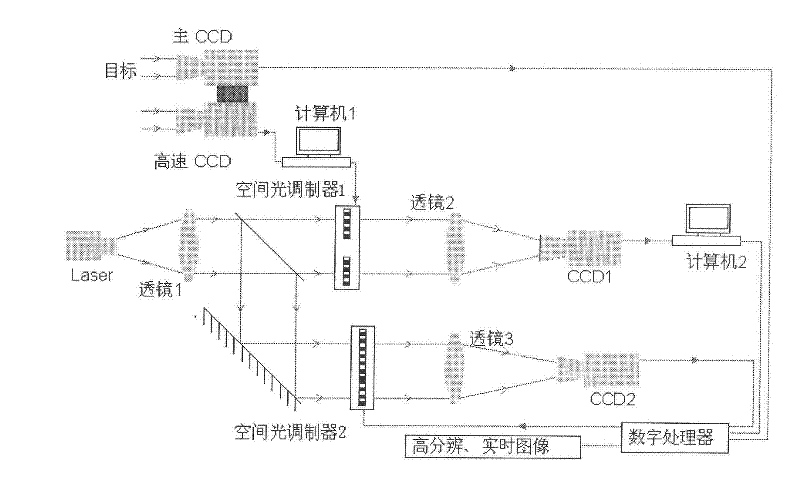
The invention belongs to the field of image processing, in particular to a restoration method for a real-time motion blurred image of photoelectric hybrid joint transform correlation. The method comprises the following steps of: performing optical correlation computation on an image sequence acquired by using a high-speed CCD (Charge Coupled Device) according to a quick real-time optical correlation principle, so that correlation detection of an image motion displacement vector is realized, wherein a processing speed is increased by hundreds of times than that of digital-electronic processing; and establishing an accurate model of a point spread function (PSF), and determining an image restoration algorithm through the model, so that high-resolution real-time motion image restoration is performed on a blurred image obtained by using a main imaging CCD system. The method has high displacement vector detection accuracy and accurate PSF modeling, so that image restoration accuracy is high; and meanwhile, the method has the advantages of high speed, large volume and parallel processing of optical image processing and flexibility, accuracy and programmability of a digital processing technology, so that image instantaneity is high.
Owner:ZHEJIANG NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Optical correlation object identification and tracking system based on genetic algorithm
InactiveCN101598795AEasy accessSimple compositionGenetic modelsControl using feedbackAlgorithmPhotodetector
The invention relates to an optical correlation object identification and tracking system based on genetic algorithm. The genetic algorithm is used to control location / angle controller to make system evaluation functions of location control voltage information and angle control voltage information functioning on location / angle controller obtain the global extremum. The invention uses ordinary photodetector to replace image acquisition equipment in the current system to simplify system composition, uses genetic algorithm to process optical correlation operation result to acquire all-dimensional location information of object quickly without any special requirement for system operation environment and apparatus and greatly improves the response speed and dynamic range of optical correlation objection identification and tracking system.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Method for environment-friendly preparation of fluorescent silicon nanoparticles
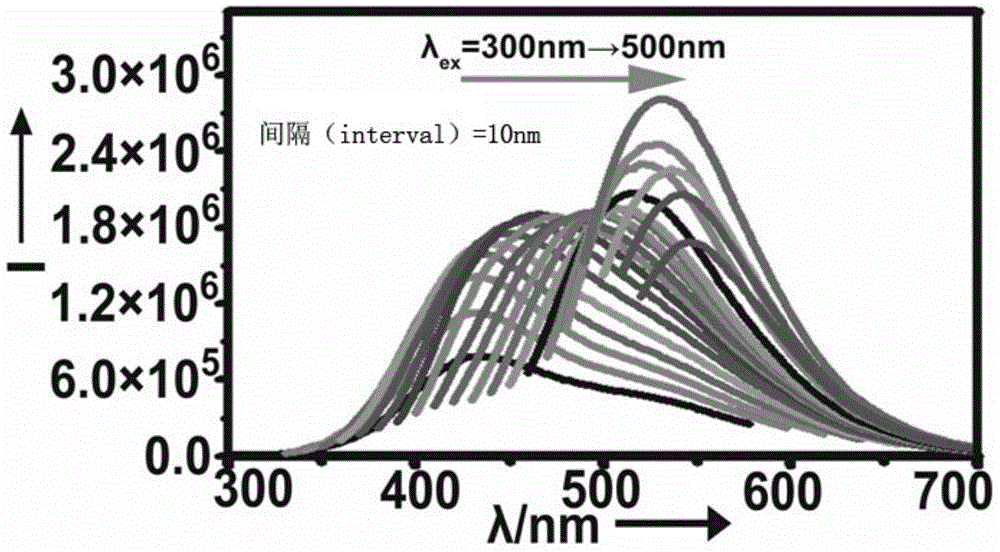
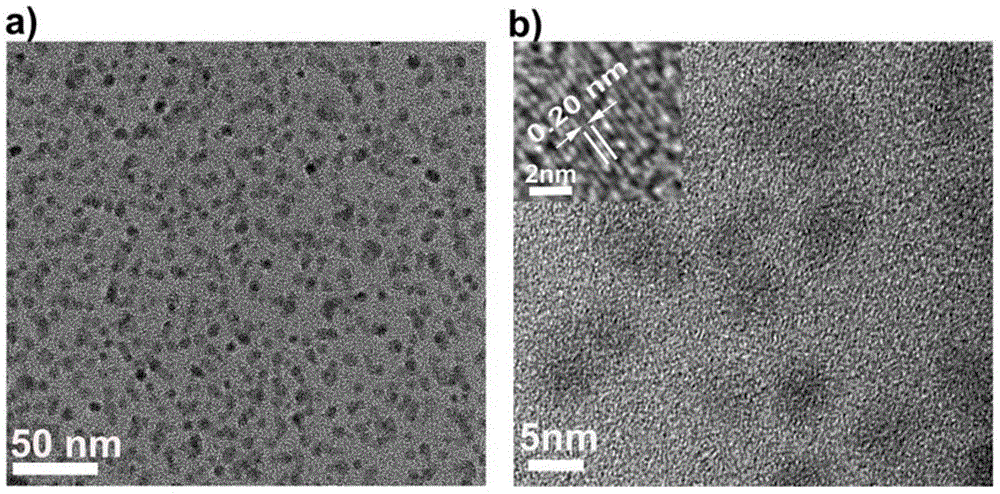
ActiveCN104560030AGood dispersionExcellent fluorescence propertiesNanoopticsLuminescent compositionsQuantum yieldWater baths
The invention discloses a method for environment-friendly preparation of fluorescent silicon nanoparticles. The method comprises the following steps: cutting a plant with high silicon content into pieces, cleaning with deionized water, adding into acid liquor, and heating in a water bath; washing a sample subjected to acid treatment to be neutral by using deionized water, putting the sample into a crucible, and heating until the sample becomes white powder; and adding the white powder into an alkali solution, and performing microwave radiation heating to obtain the fluorescent silicon nanoparticles. The method for environment-friendly preparation of the fluorescent silicon nanoparticles is completely implemented in a water phase, is cheap in raw material, is environmentally friendly, is safe in operation, is quick, simple and convenient, and is small in toxicity, and the obtained fluorescent silicon nanoparticles have very good monodispersity and fluorescent property, are high in quantum yield, good in storage stability and good in water solubility, and can be widely applied to various optical correlation fields as a fluorescent marker.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
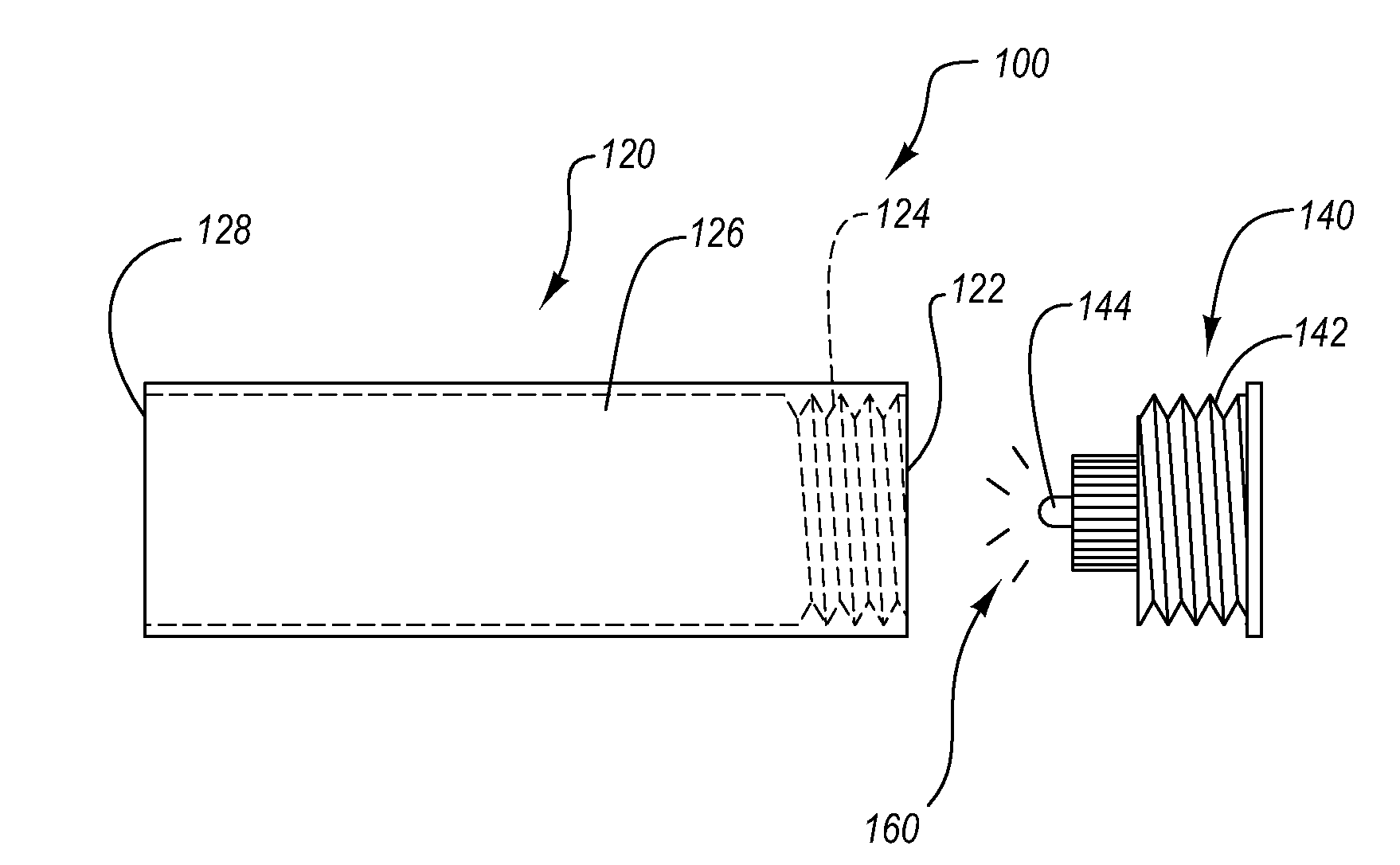
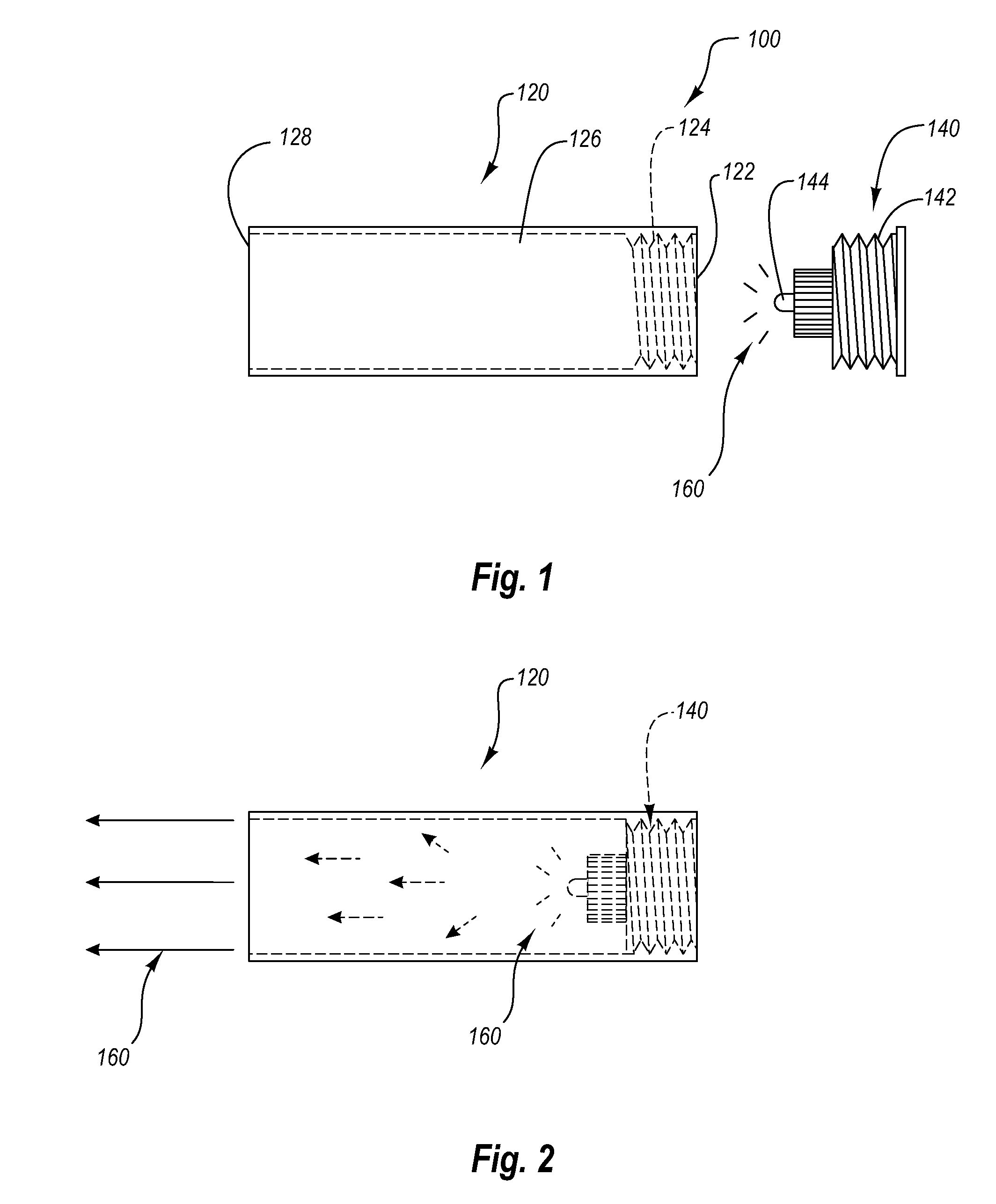
Optical correlation type oil smoke detection device with sheath gas protection
The invention provides an optical correlation type oil smoke detection device with sheath gas protection. The device consists of a fixing flange plate, a light source generating cavity, a light sourcesignal cavity and a connecting beam, wherein the fixing flange plate, the light source signal cavity and the light source generating cavity are hollow cylinders which are coaxially arranged from leftto right at a circle center in sequence; the fixing flange plate and the light source signal cavity are connected together; a gap is arranged between the light source signal cavity and the light source generating cavity; and the connecting beam is arranged between the light source generating cavity and the light source signal cavity. A sheath air supplementing system is added to the whole device,so that the inaccuracy of data caused by oil smock adhering to a detection lens is avoided, the service life of the equipment is greatly prolonged, and the maintenance frequency of operation and maintenance personnel on the equipment is reduced.
Owner:苏州源慧达智能科技有限公司
Integrated photonic microwave sampling system
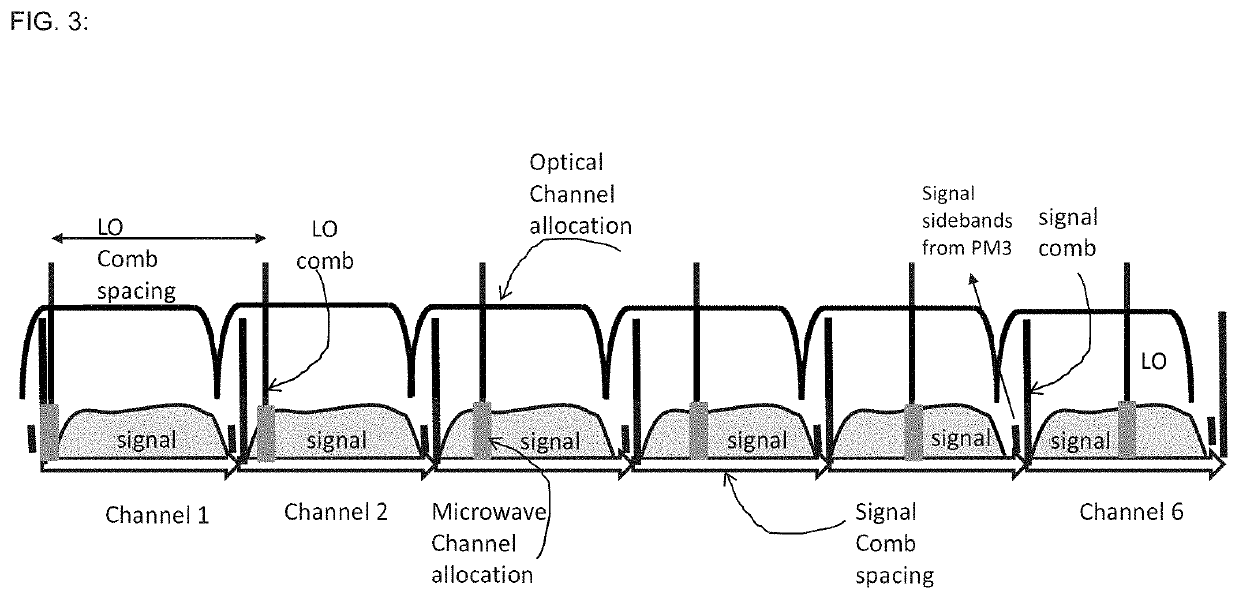
InactiveUS20210266063A1Wavelength-division multiplex systemsOptical transmission for RF signal generation/processingTransceiverFrequency spectrum
Examples of systems and methods for integrated photonic broadband microwave receivers and transceivers are disclosed based on integrated coherent dual optical frequency combs. In some cases, when the system is configured as a receiver, the microwave spectrum of the input signal can be sliced into several spectral segments for low-bandwidth detection and analysis. In some cases, when the system is configured as a transmitter, multiple radio frequency (RF) carriers can be generated, which can be coherently added or encoded independently for transmission of individual microwave bands. In some systems, the optics-related functionalities can be achieved via integrated optic technology, for example, based on silicon photonics, providing tremendous possibilities for mass-production with significantly reduced system footprint.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
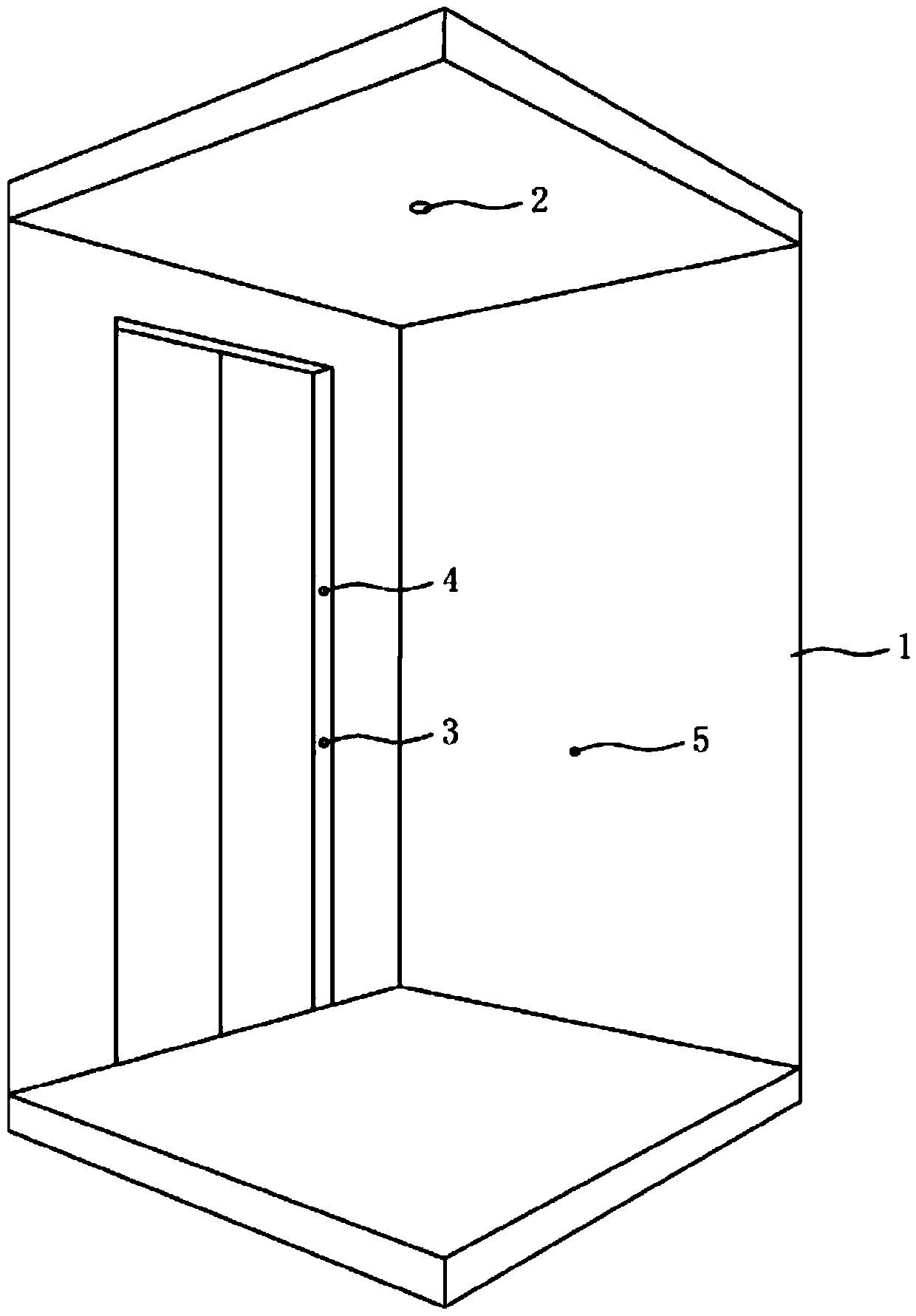
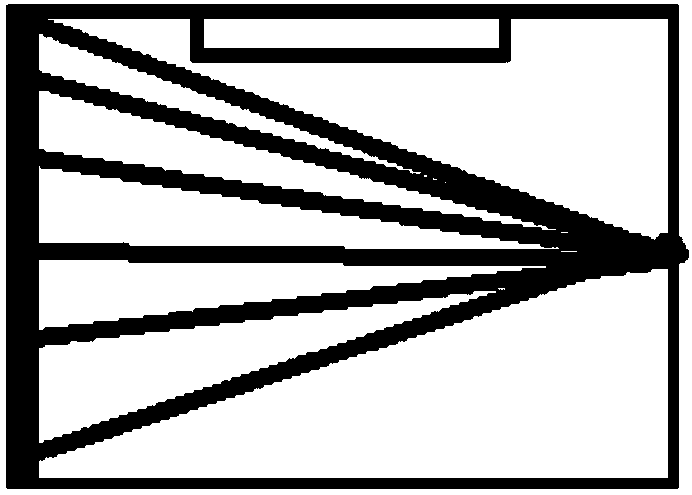
In-car monitoring system
The invention discloses an in-car monitoring system. The system comprises a first group of optical correlation sensors, a second group of optical correlation sensors and a processor; a light beam projector and a light beam receiver of the same group of light correlation sensors are respectively arranged on the left side wall and the right side wall of a car; when no light blocking object exists ona light beam path between the light beam projector and the light beam receiver of one group of light correlation sensors, a non-blocking signal is output to the processor, and when the light blockingobject exists, a light blocking signal is output to the processor; the distance between a light beam projector and a light beam receiver of the first group of light correlation sensors and the car ground is a first height; the distance between a light beam projector and a light beam receiver of the second group of light correlation sensors and the car ground is a second height, and the second height is greater than the first height; and when the first group of optical correlation sensors output the optical blocking signal and the second group of optical correlation sensors output no blockingsignal, the processor outputs a falling signal in the car.
Owner:SHANGHAI MITSUBISHI ELEVATOR CO LTD
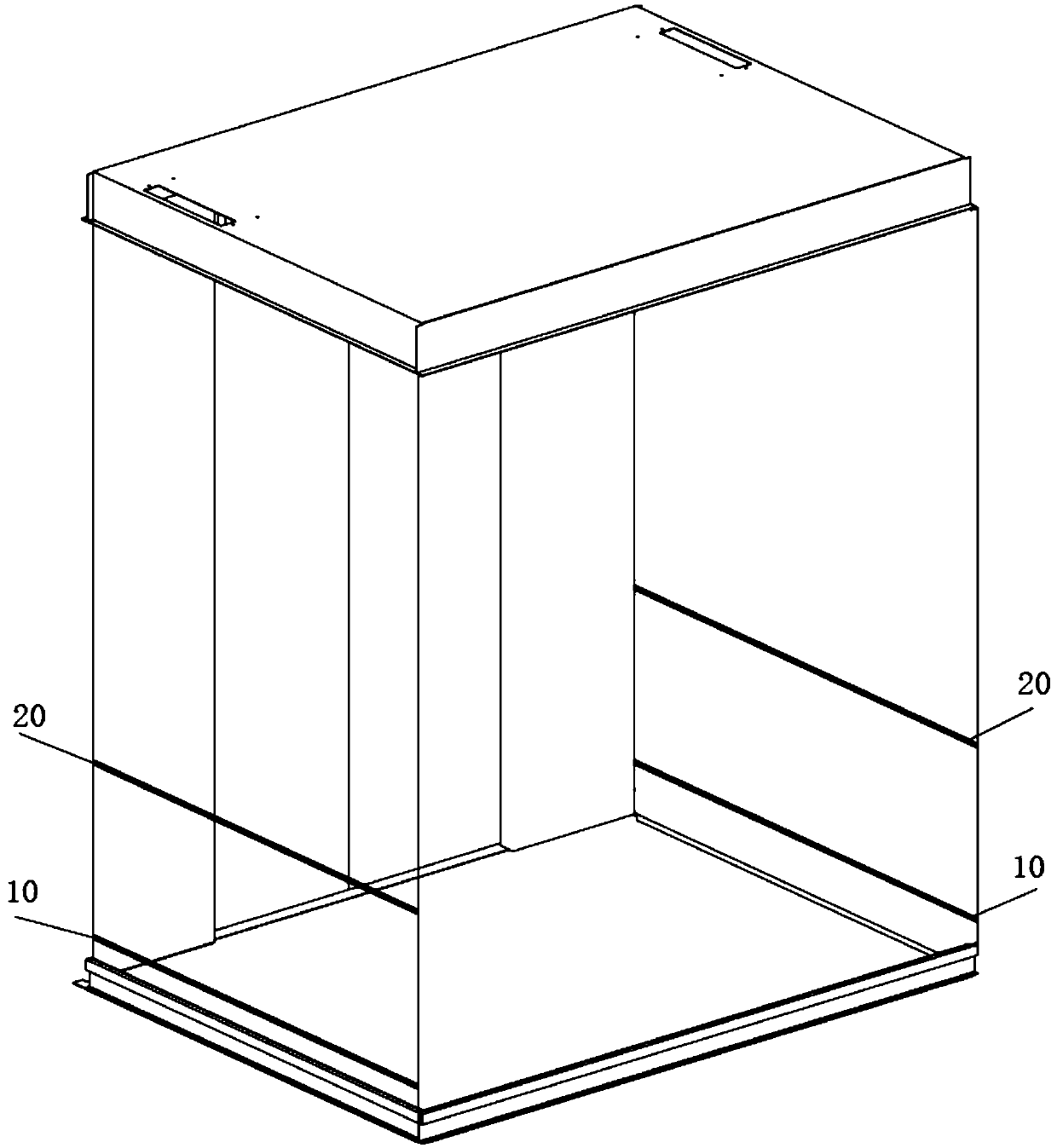
Automatic optical identification system for vehicle profile
ActiveCN113781797AEliminate joint fraudImplement automatic detectionDetection of traffic movementWeighing auxillary devicesStructural engineeringMechanical engineering
An automatic optical identification system for a vehicle profile comprises an identification room, lanes, a driving unit, a wheel axle identification unit and optical identification units. The lanes are arranged at two ends of the identification room. The driving unit is arranged in the identification room. The upper end face of an identification table is provided with a wagon balance. The axle recognition unit comprises a C-shaped frame, whereina plurality of laser axle identifiers arranged on one side face of the C-shaped frame. The optical identification units are arranged on the two sides of the driving unit, one end of an output shaft of the third linear mechanism is provided with an optical mechanism, and one end of an output shaft of the fourth linear mechanism is also provided with an optical mechanism.The optical mechanism comprises a rotating mechanism which is vertically arranged; two second optical correlation assemblies on one side of a right-angle plate and two second optical correlation assemblies on the other side of the right-angle plate have a preset height difference so that light paths on the two sides can be staggered. According to the invention, automatic and accurate detection is realized, joint cheating of detection personnel and drivers is avoided, overload hidden dangers are avoided, the influence of weather on detection is reduced, the universality of equipment is improved, and traceability of related records is realized.
Owner:成都古河云科技有限公司
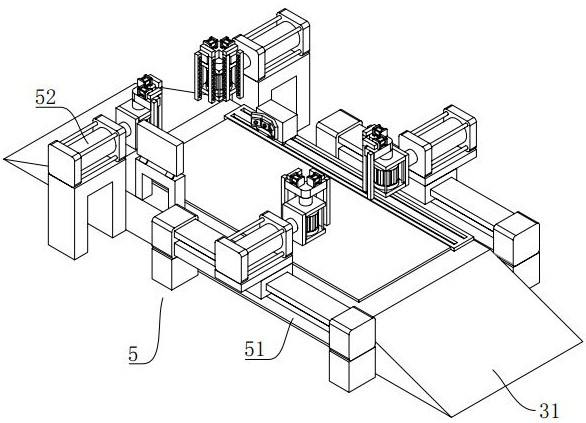
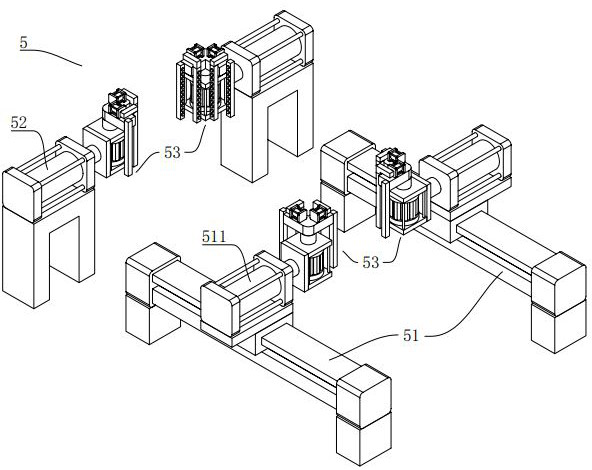
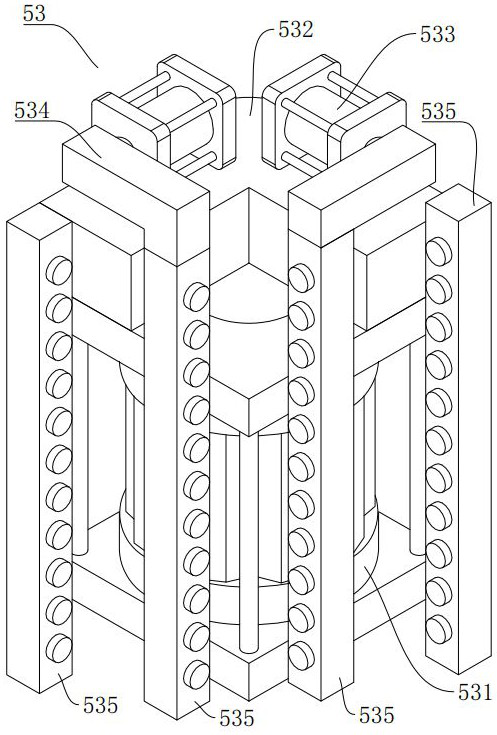
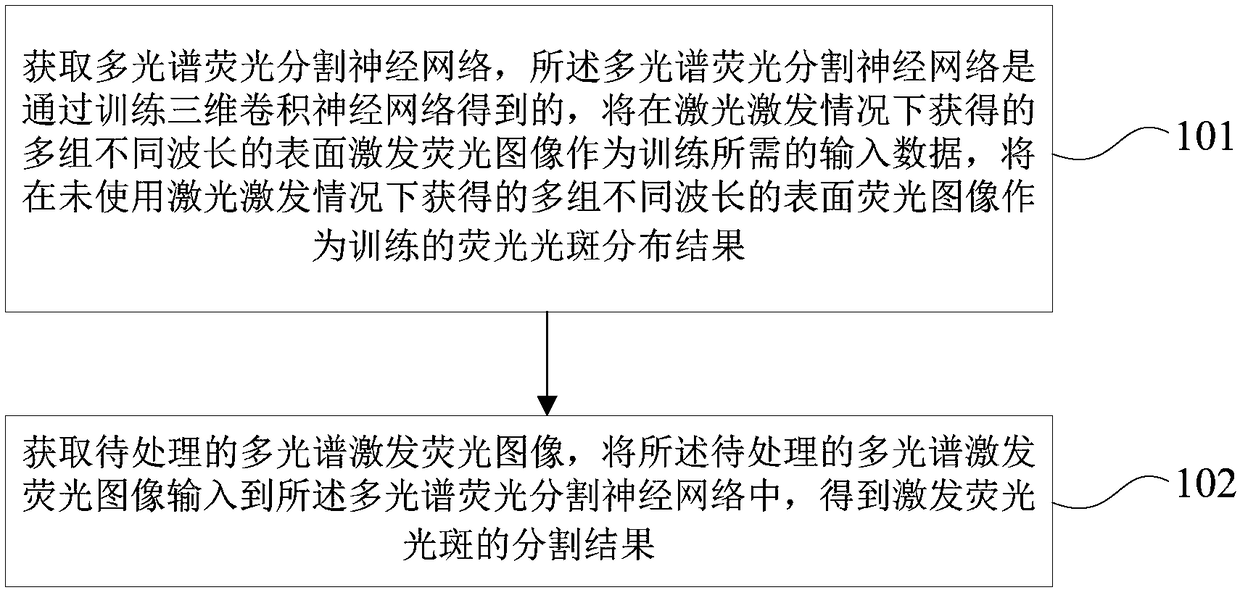
Multispectral fluorescence segmentation method and apparatus
ActiveCN108230335AImprove relevanceAccurate divisionImage enhancementImage analysisFluorescenceLength wave
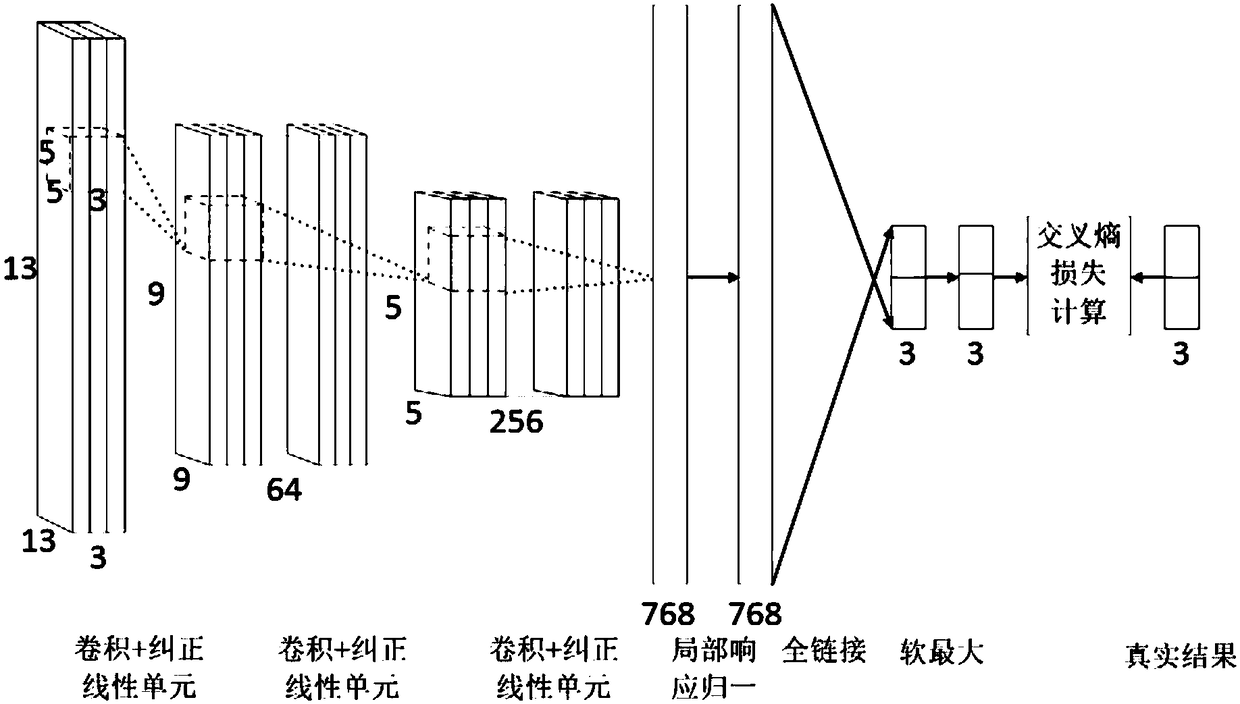
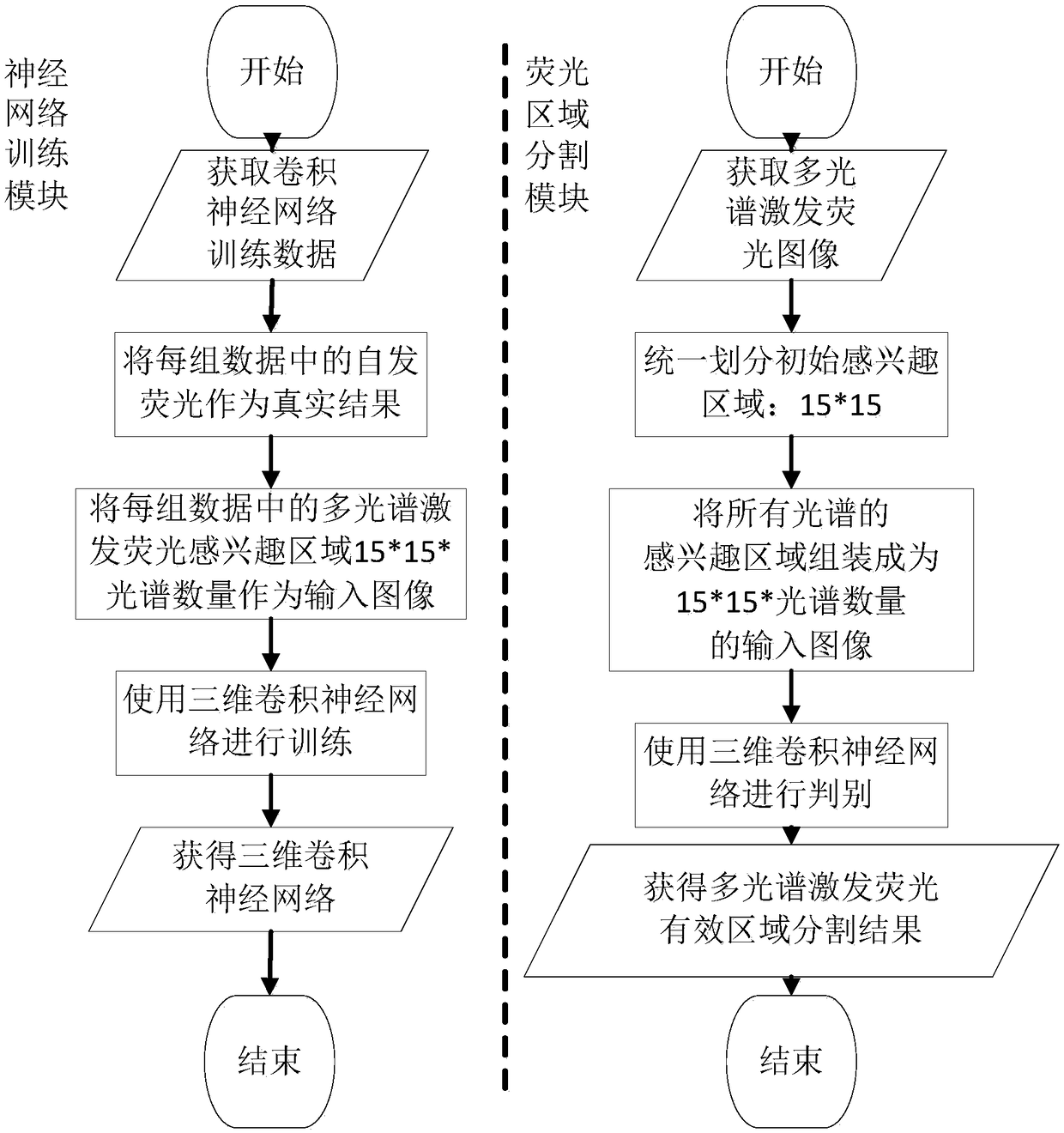
Embodiments of the invention provide a multispectral fluorescence segmentation method and apparatus. The method comprises the steps of obtaining a multispectral fluorescence segmentation neural network, wherein the multispectral fluorescence segmentation network is obtained by training a three-dimensional convolutional neural network; taking multiple groups of surface excitation fluorescence images of different wavelengths obtained under a laser excitation condition as input data required for training, and taking multiple groups of surface fluorescence images of different wavelengths obtainedunder no laser excitation condition as a fluorescence spot distribution result of training; and obtaining to-be-processed multispectral excitation fluorescence images, and inputting the to-be-processed multispectral excitation fluorescence images to the multispectral fluorescence segmentation neural network, thereby obtaining a segmentation result of excitation fluorescence spots. According to thescheme, the situation that the fluorescence images of the different fluorescence wavelengths have optical correlation, so that an effective fluorescence region can be accurately divided and the accuracy of the segmentation result of the excitation fluorescence spots can be improved.
Owner:BEIJING DIGITAL PRECISION MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Object tracking using optical correlation and feedback
A motion-sensing device is used to track motion of an object. The motion-sensing device includes an optical correlator, a motor system and a controller. The optical correlator has an imager. The optical correlator provides a feedback signal that indicates motion of the object in at least one dimension based on detected movement of an image of the object from a first location within the imager to a second location within the imager. The motor system can move the imager. The controller receives the feedback signal from the optical correlator and uses the feedback signal to calculate motion of the object and to control the motor system to move the imager so that the image of the object is returned to the first location within the imager.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
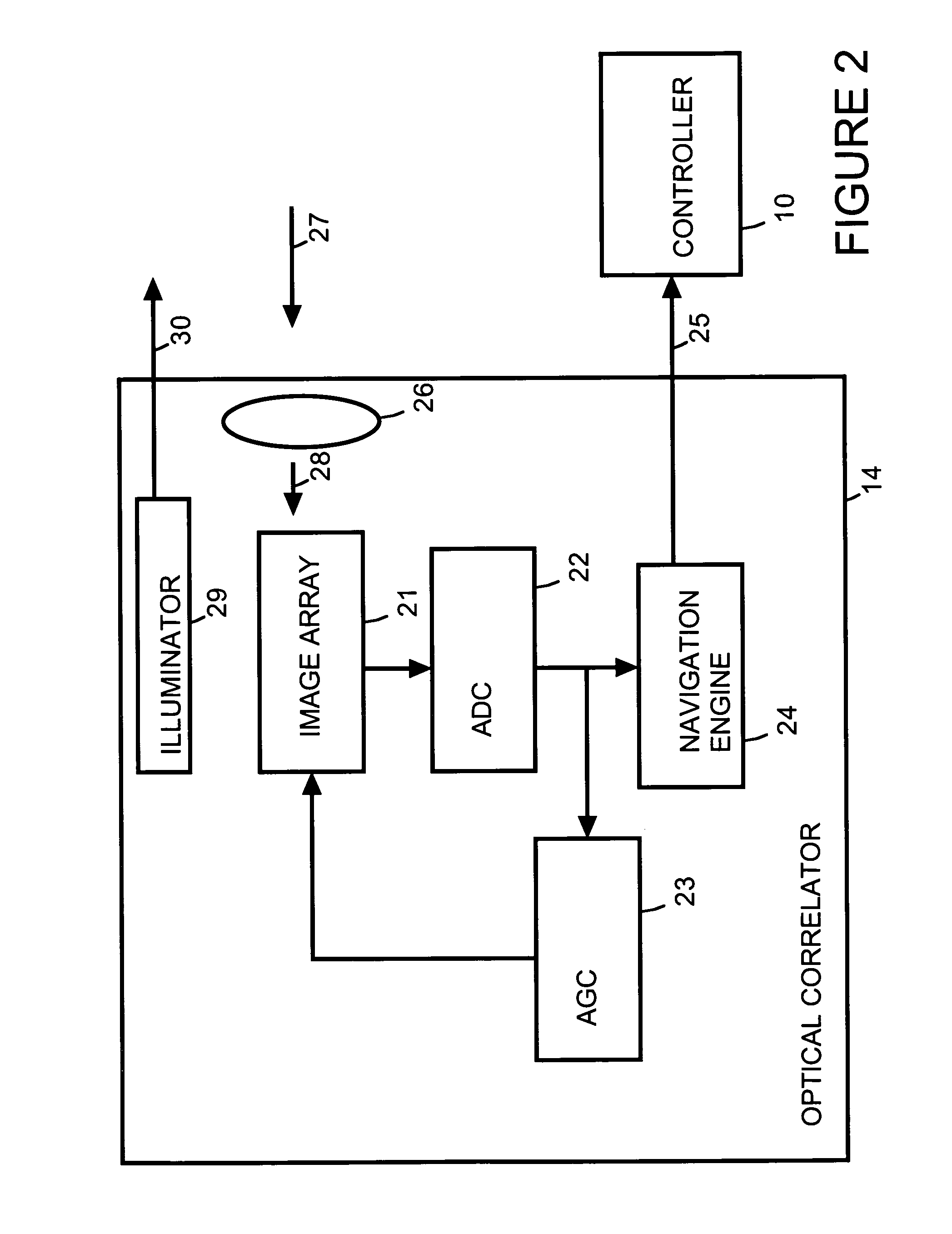
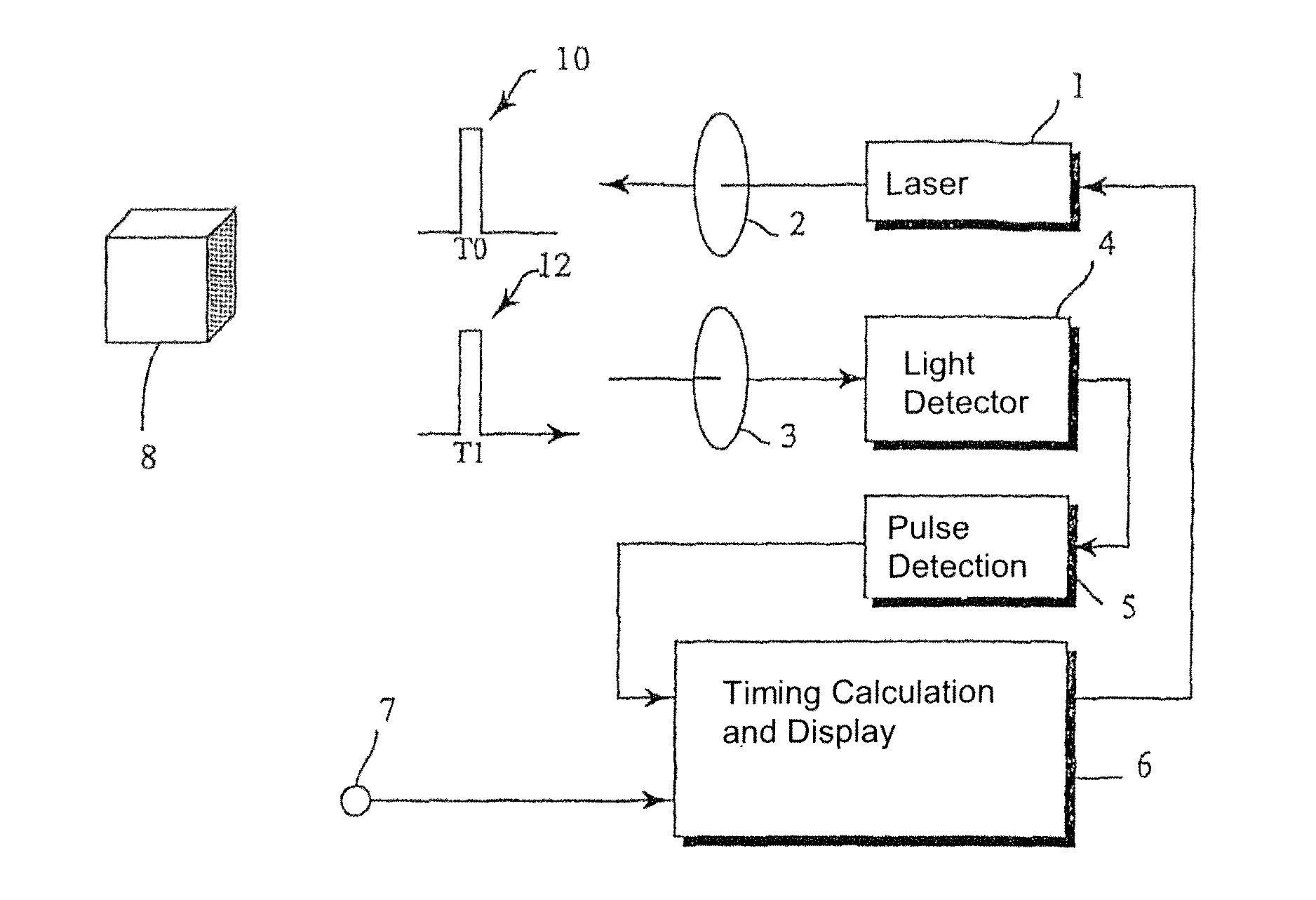
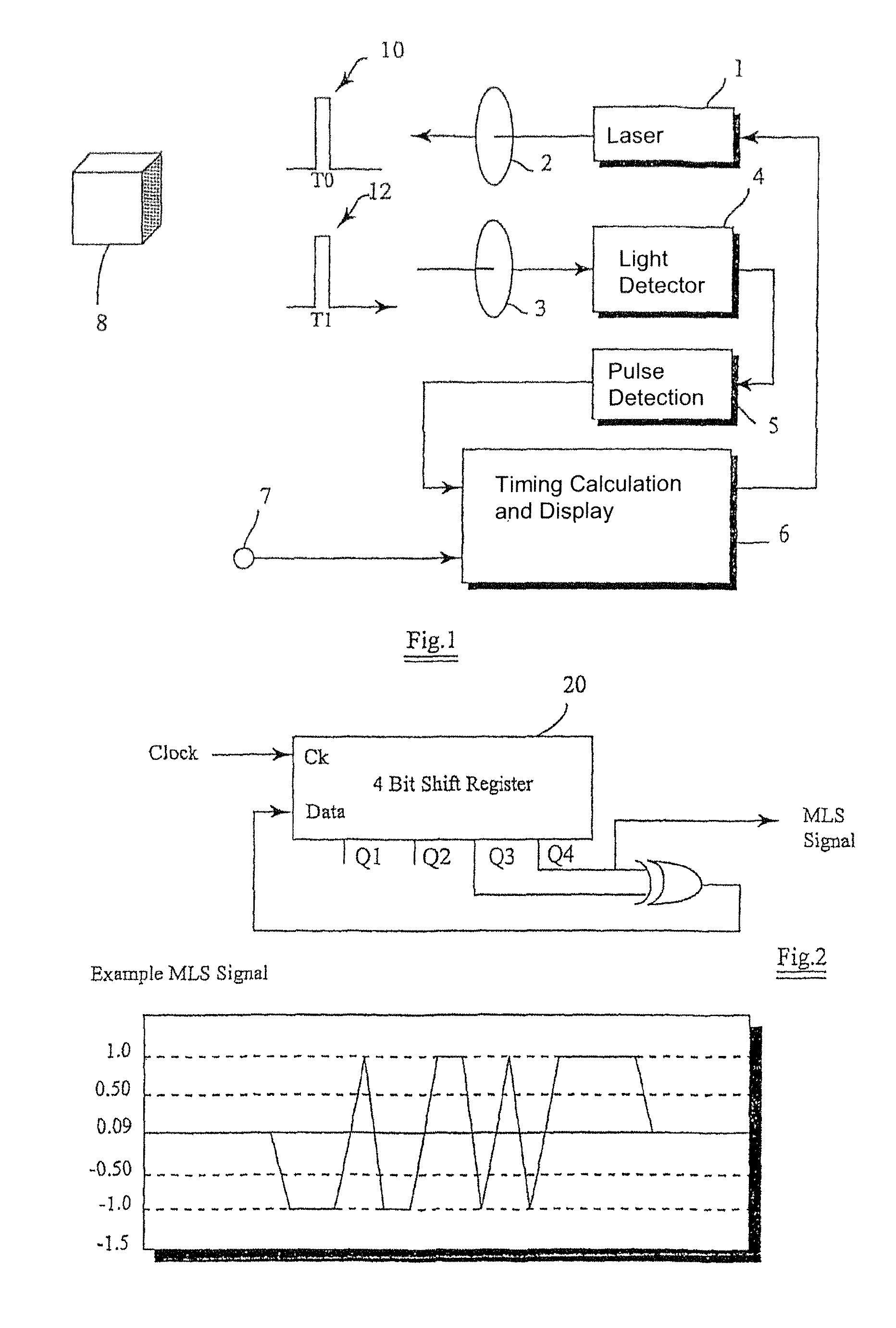
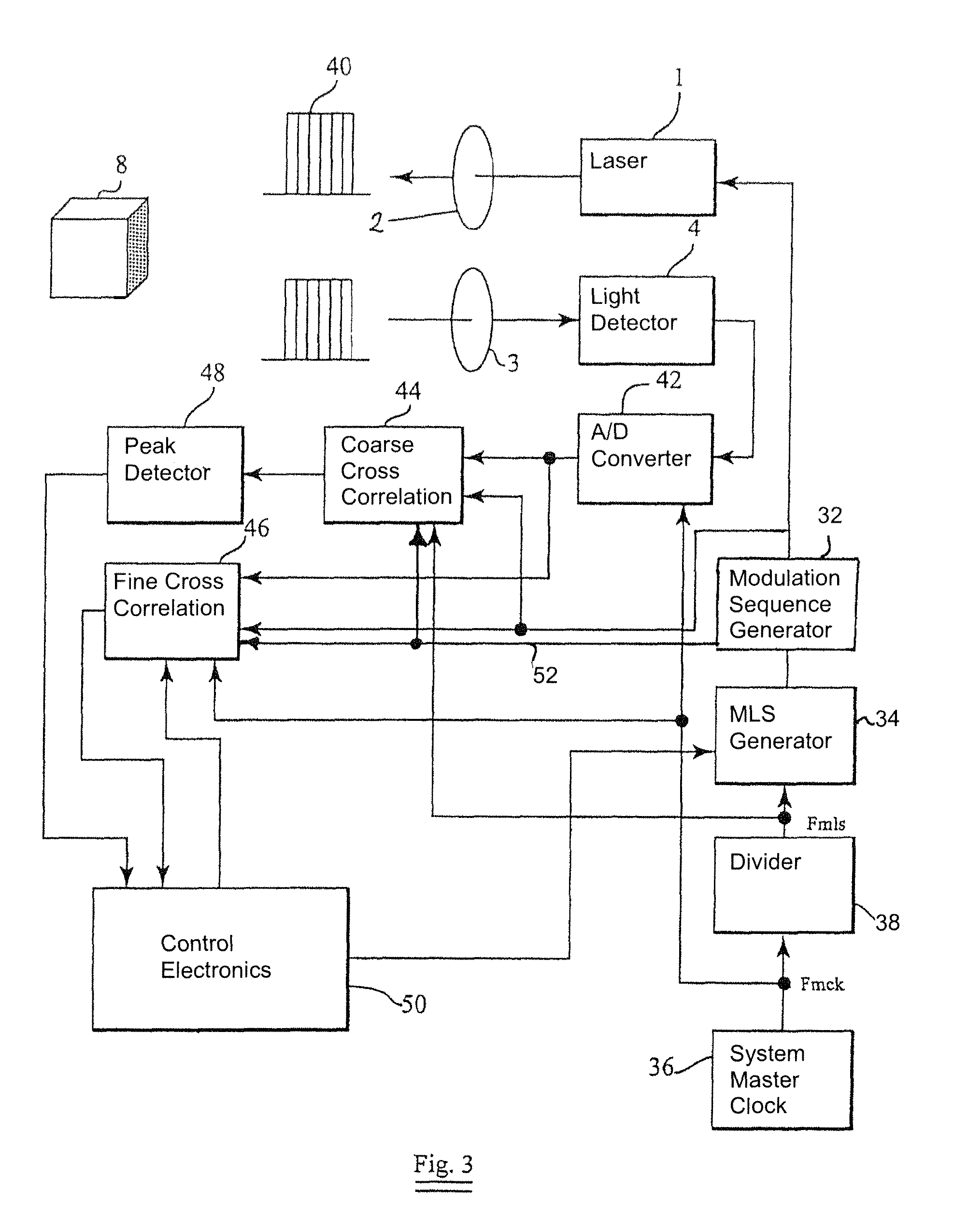
Optical correlation apparatus and method
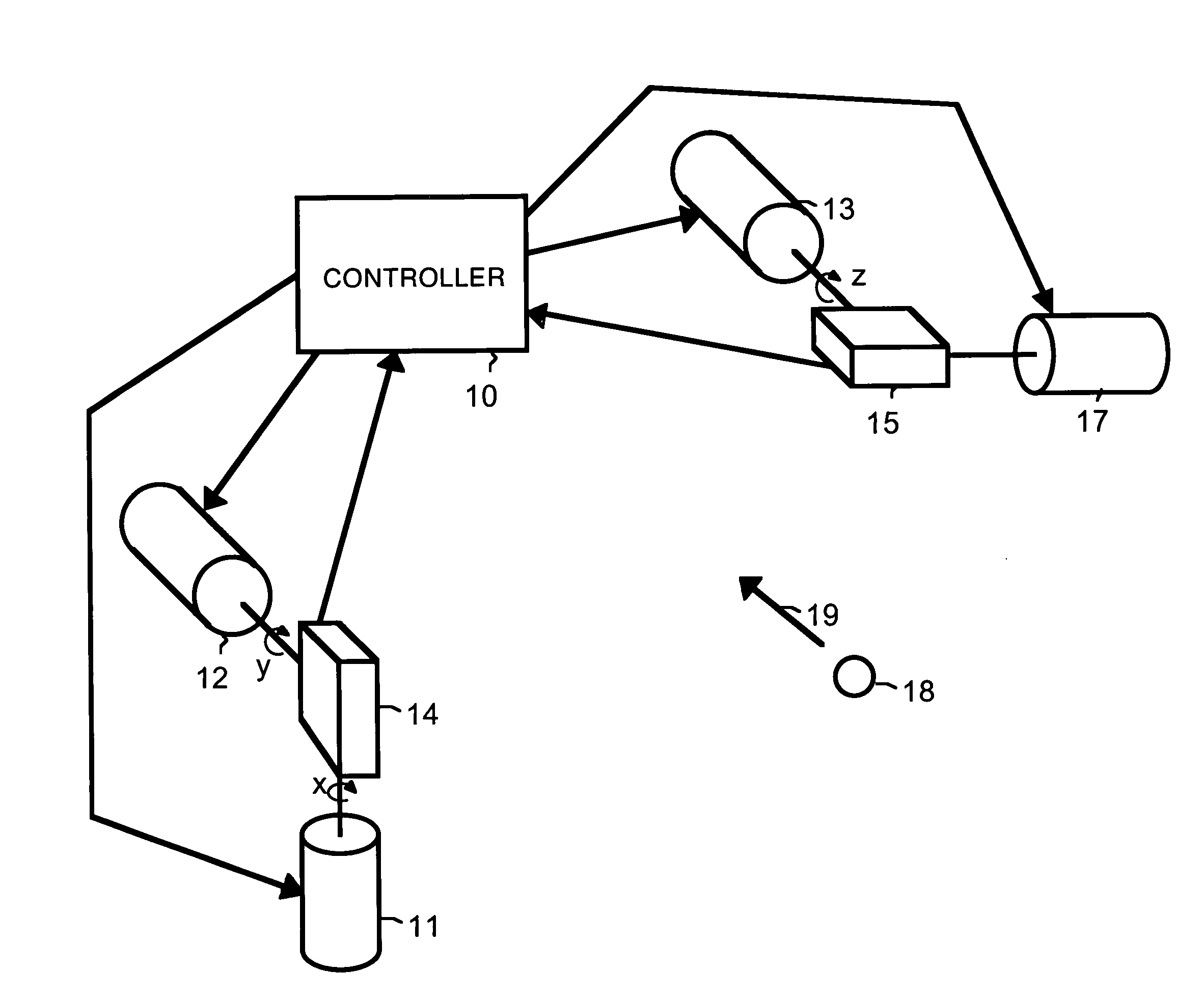
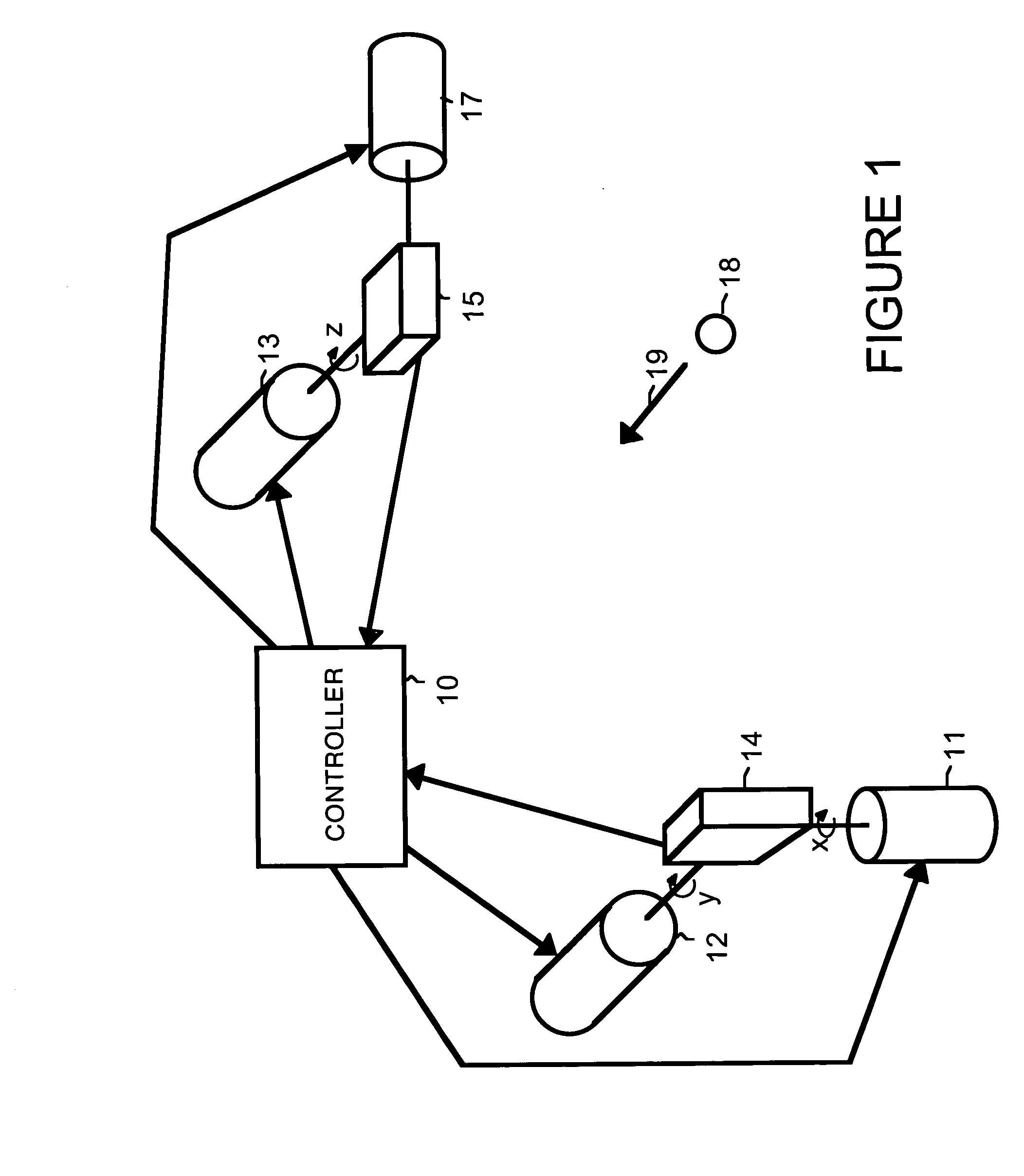
InactiveUS8098712B2Reduce cross-correlationHigh autocorrelationTransmissionElectromagnetic wave reradiationIn vehicleDistance measurement
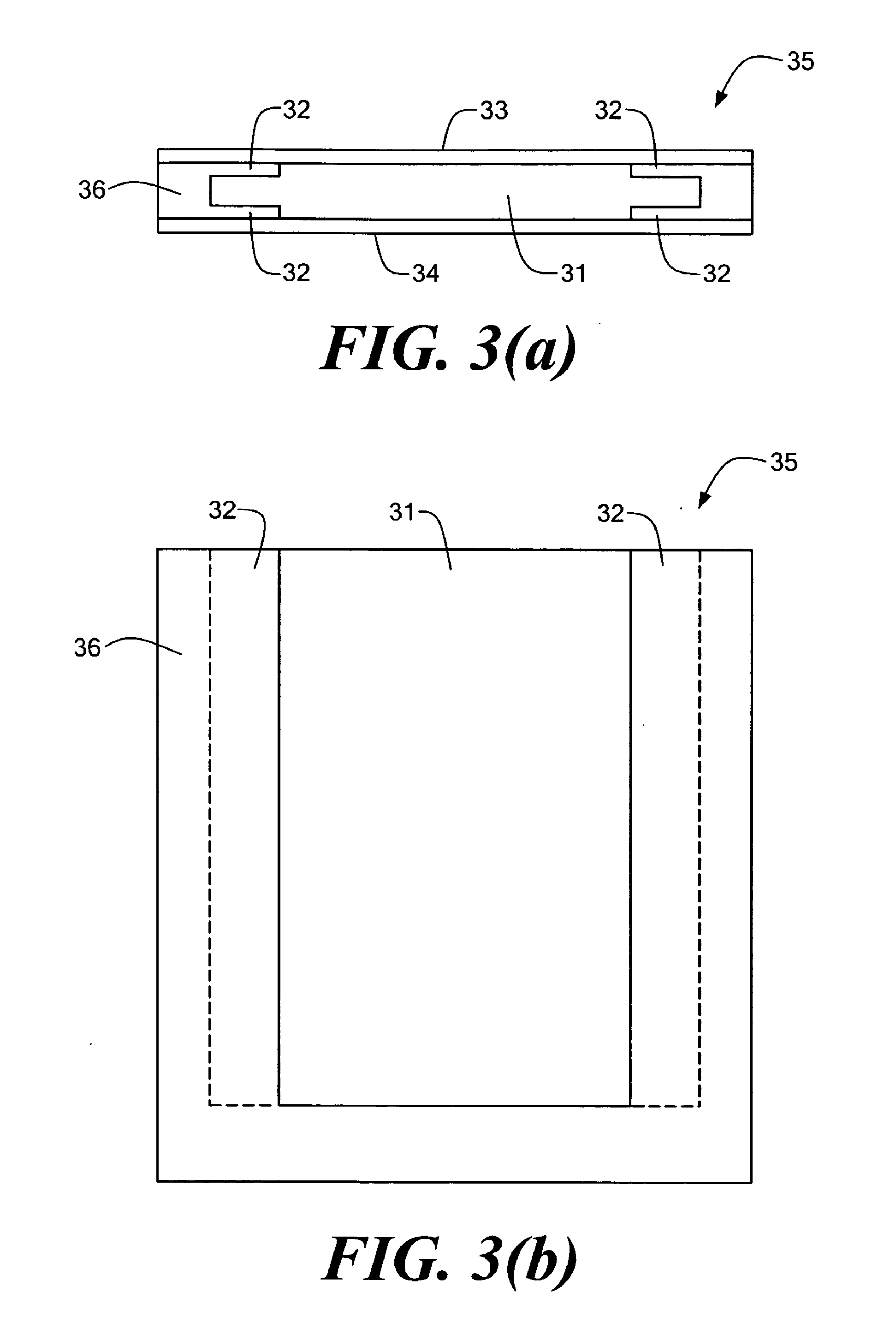
Optical correlators are discussed, suitable for in-vehicle distance measurement. The correlators use modulation sequences based on maximal length sequences. A number of different modulation sequences are obtained by generator (32) from a single maximal length sequence, either by adding a variable number of cycles to the end of the maximal length sequence or by starting the maximal length sequence at different points in the sequence.
Owner:INSTRO PREC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com