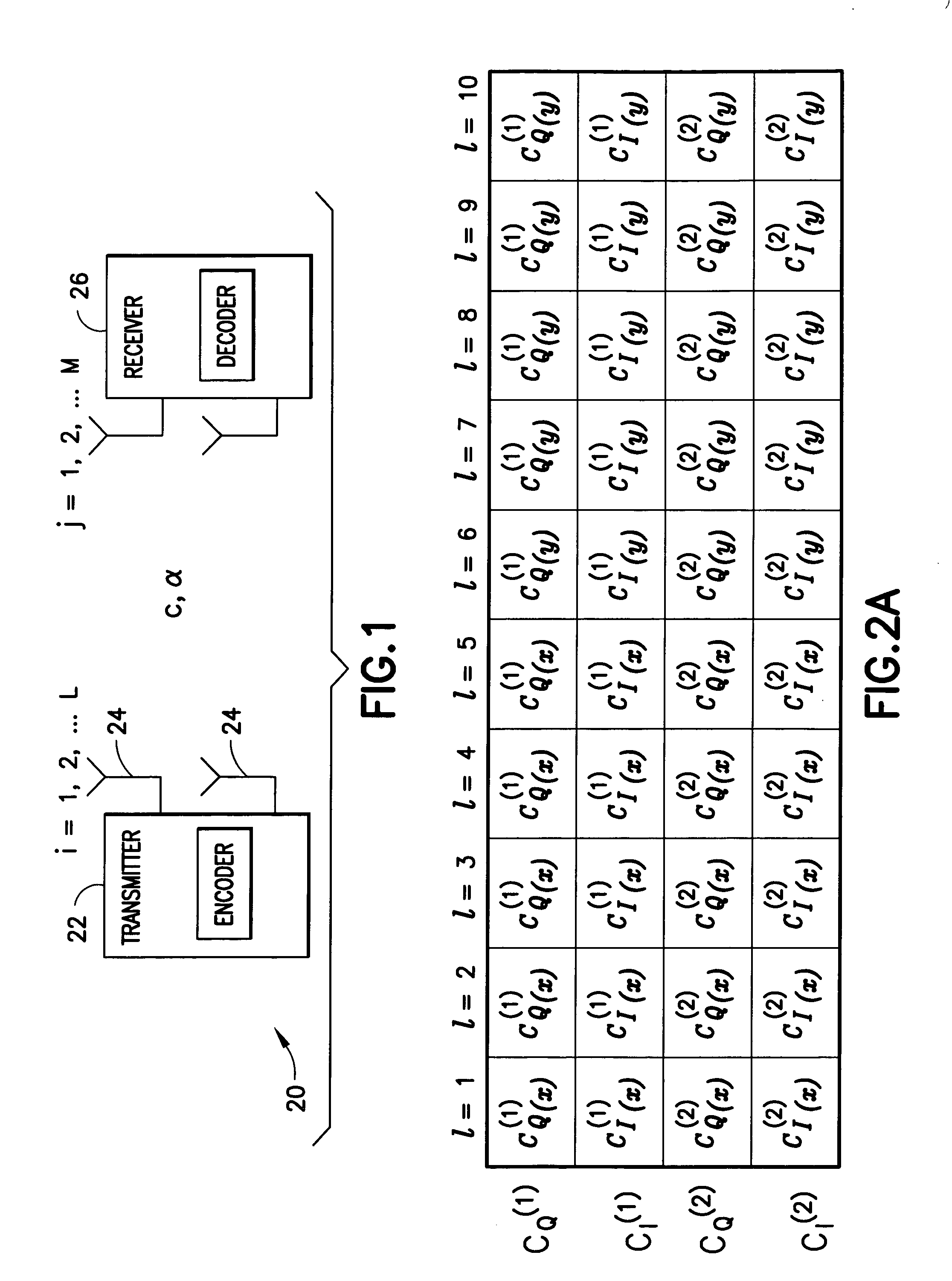
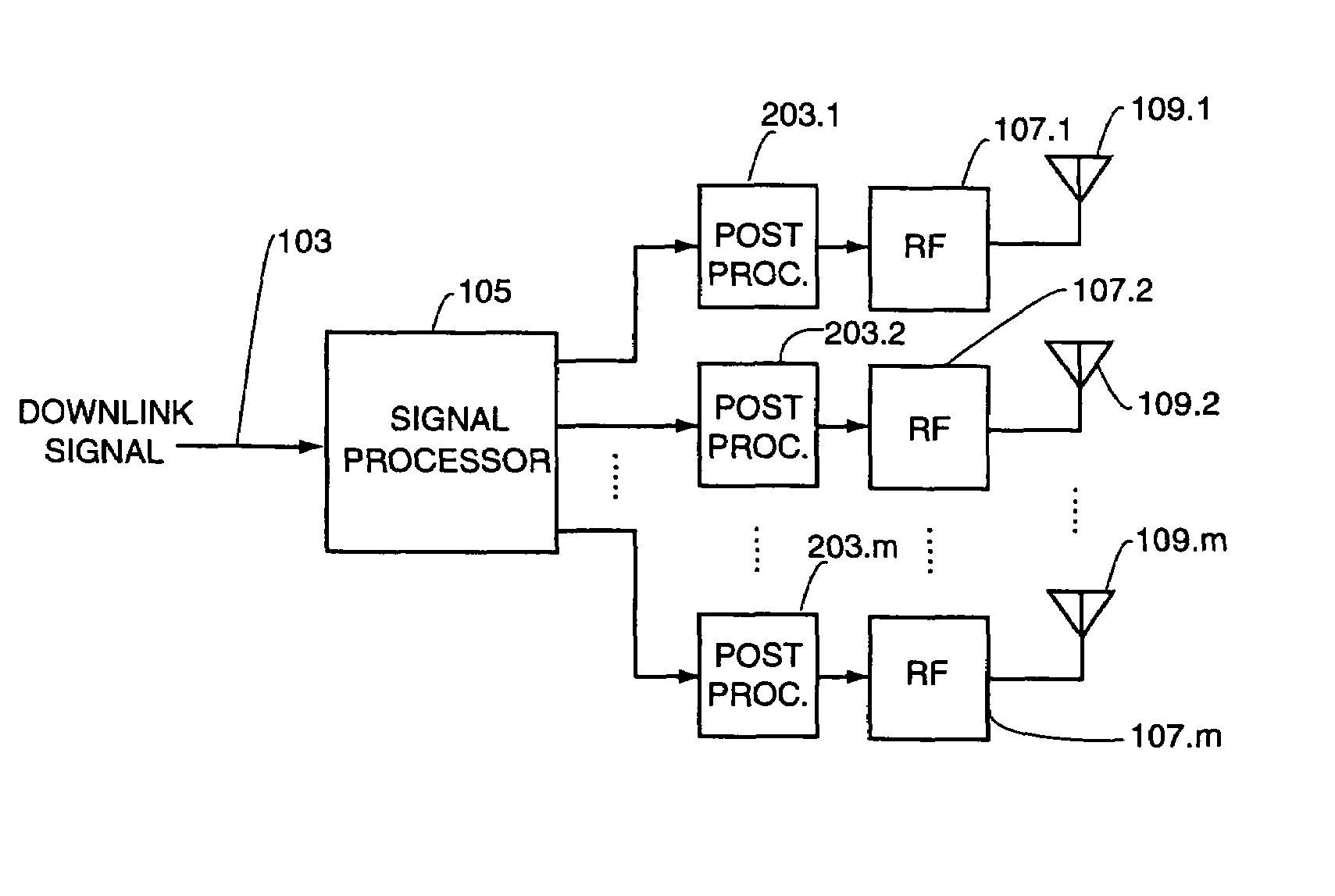
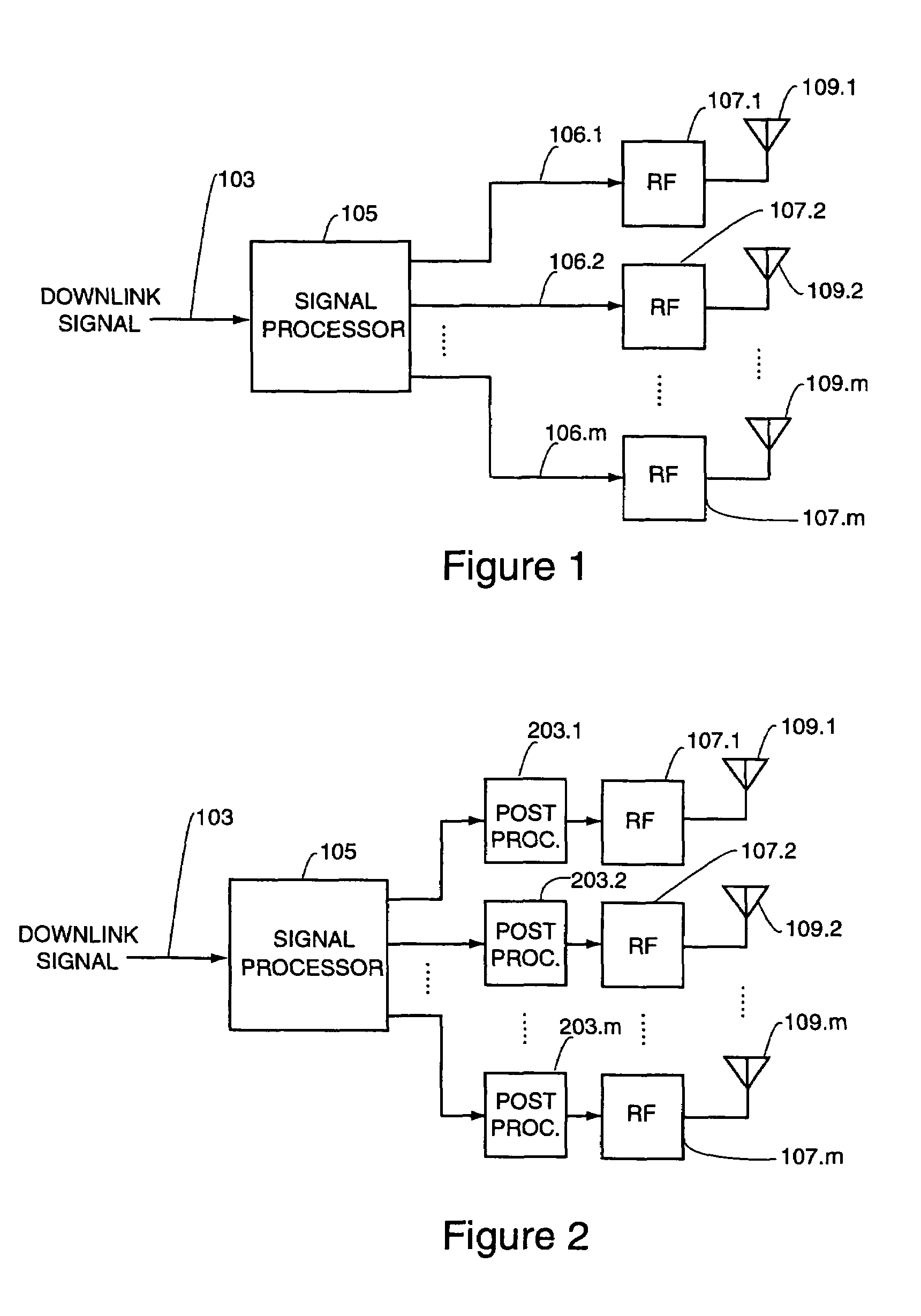
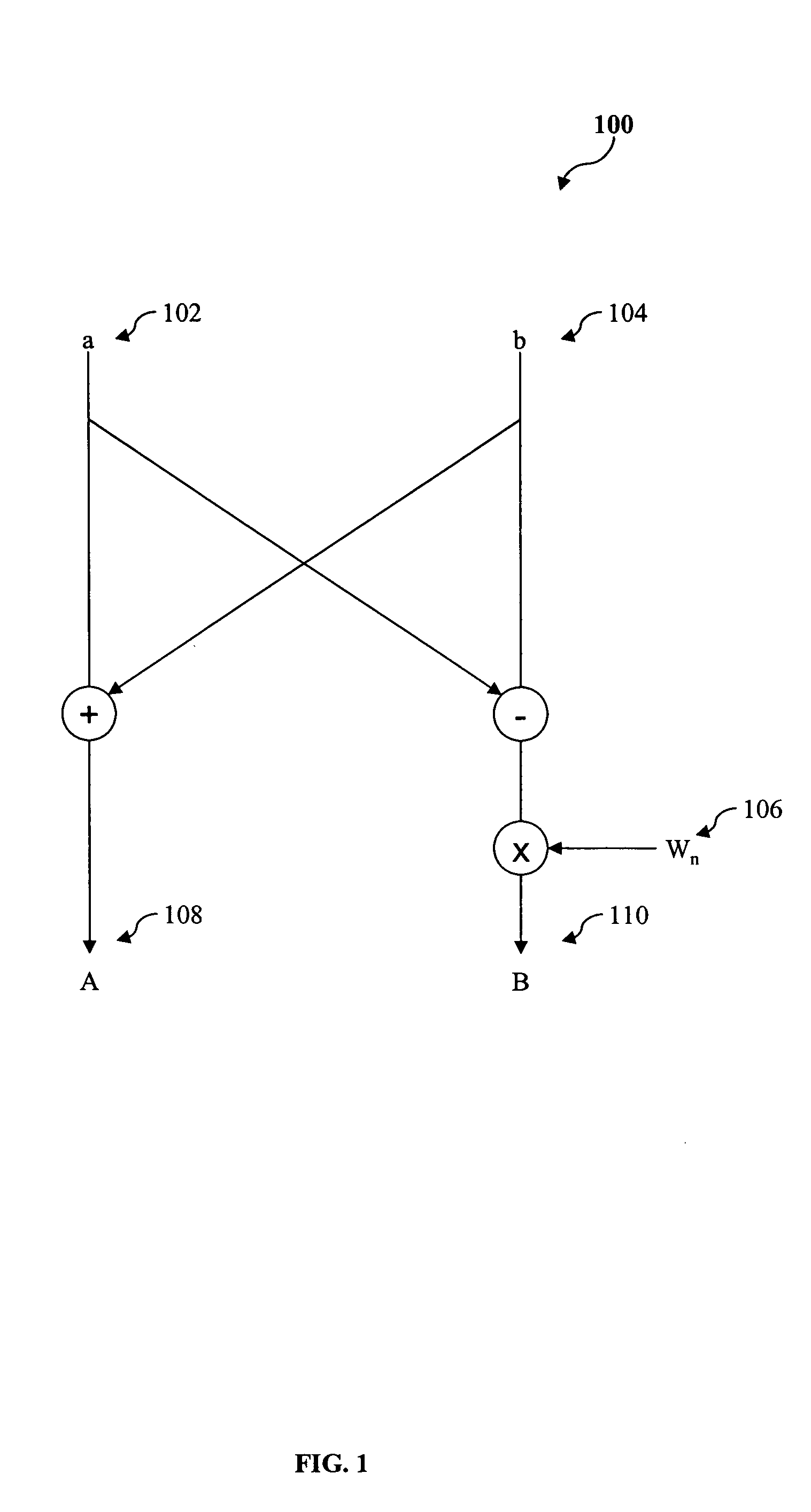
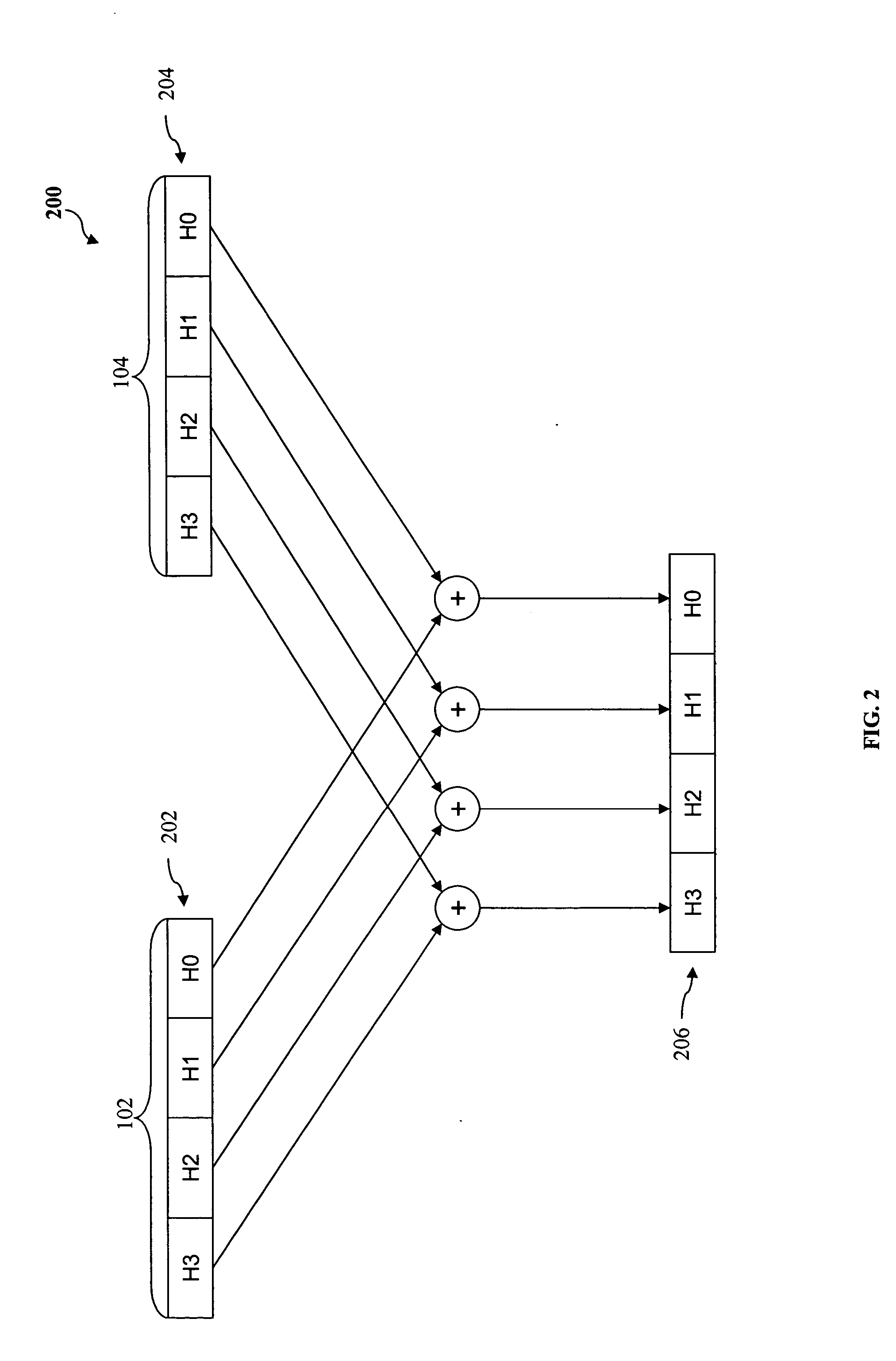
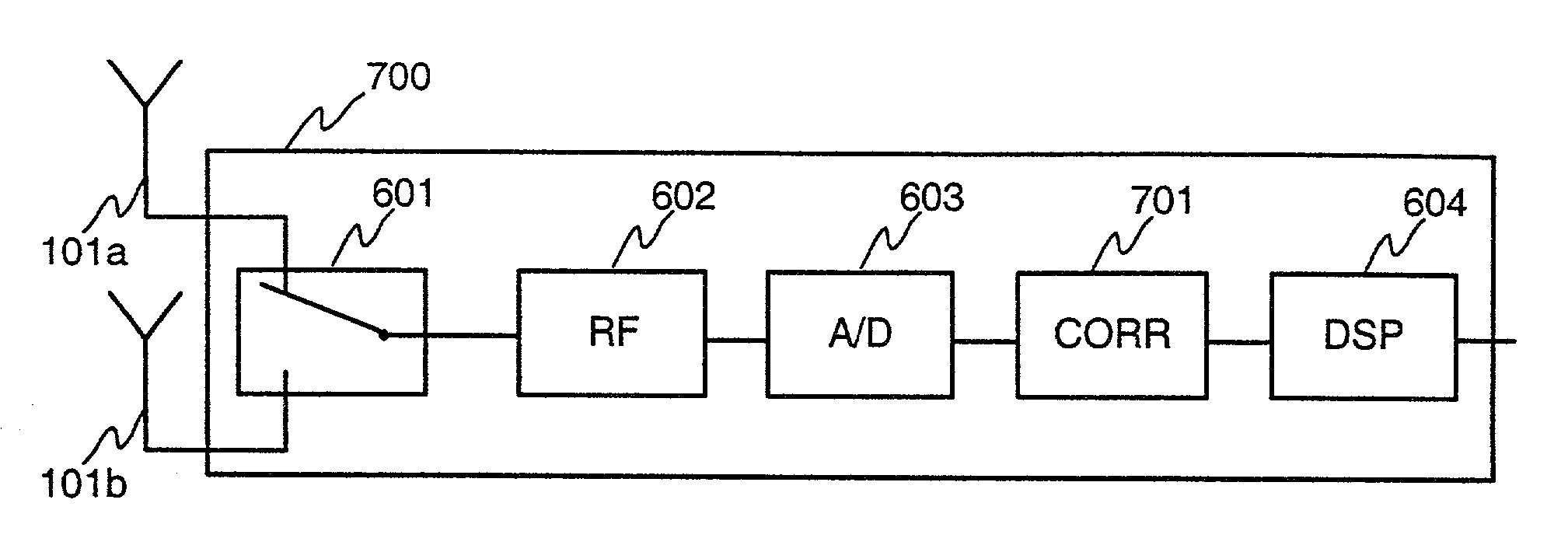
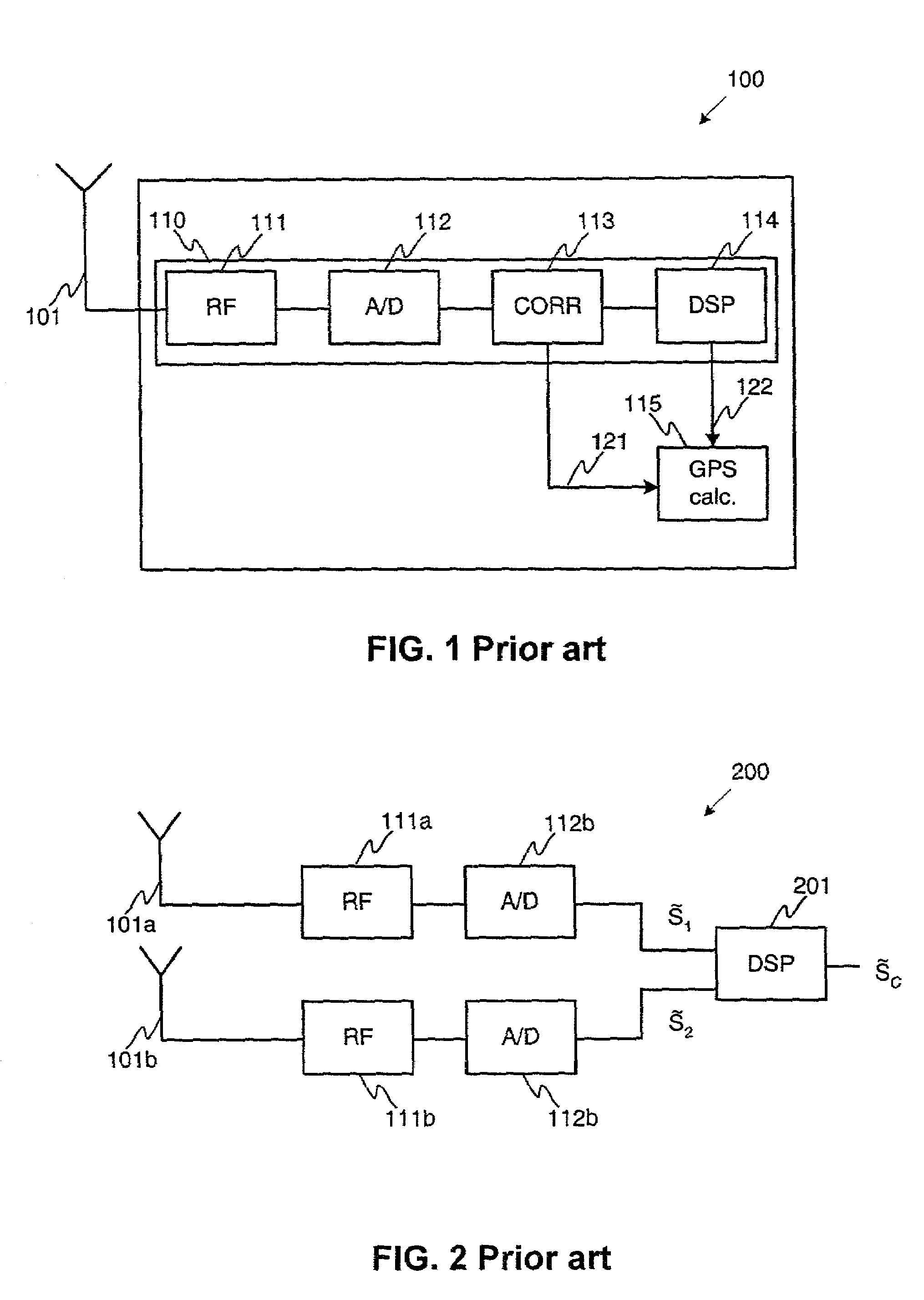
Patents
Literature
329 results about "Complex valued" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
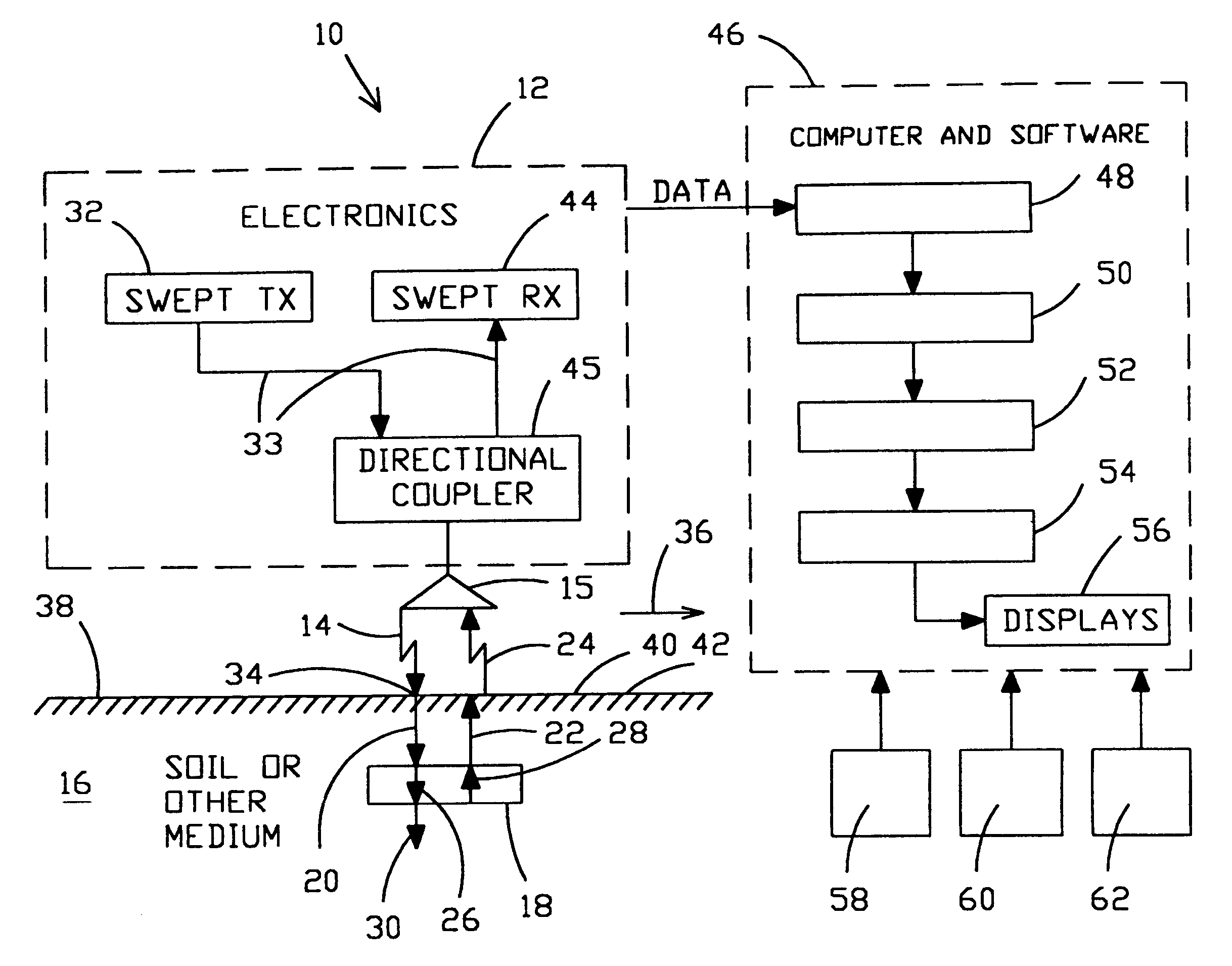
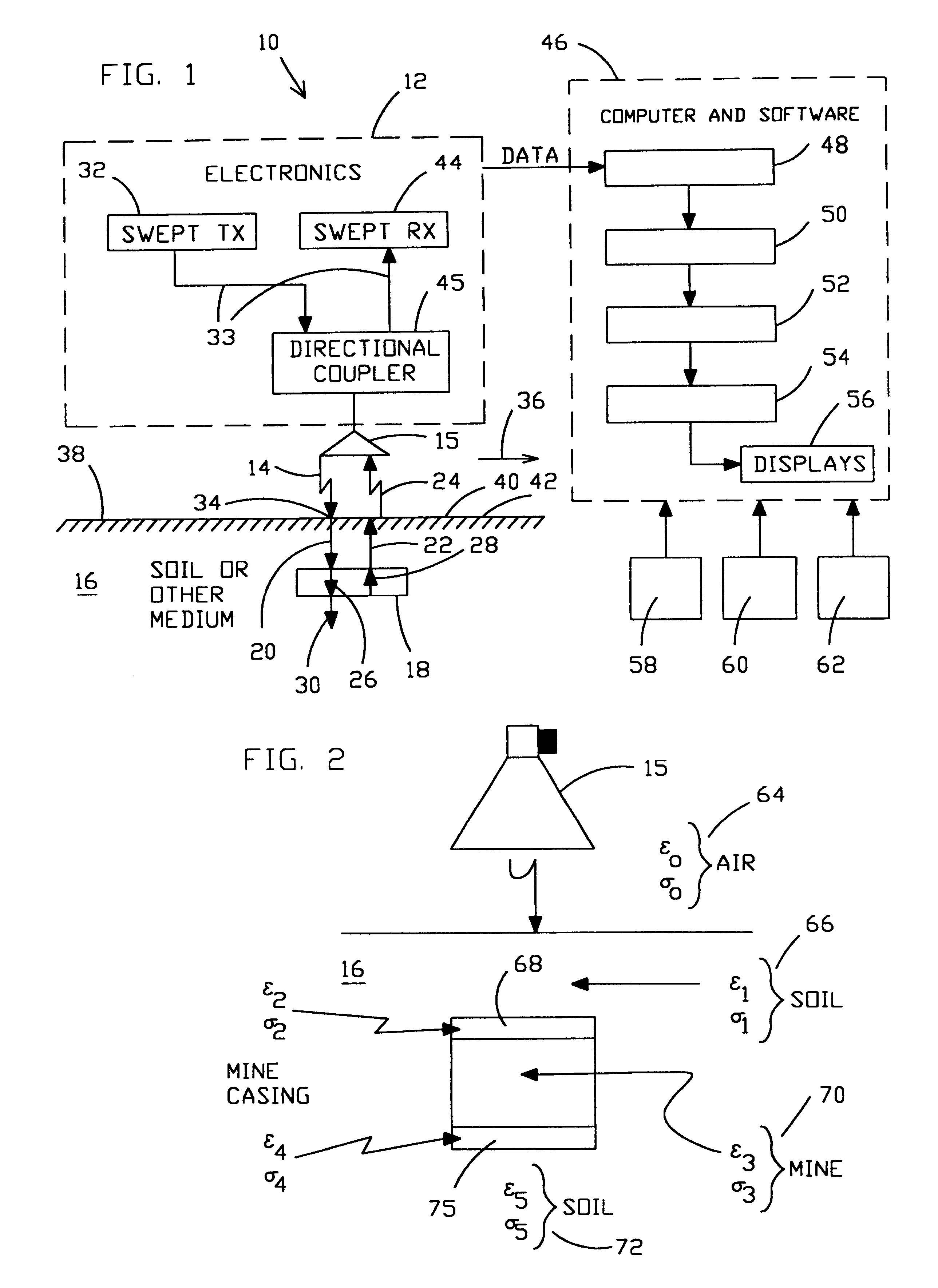
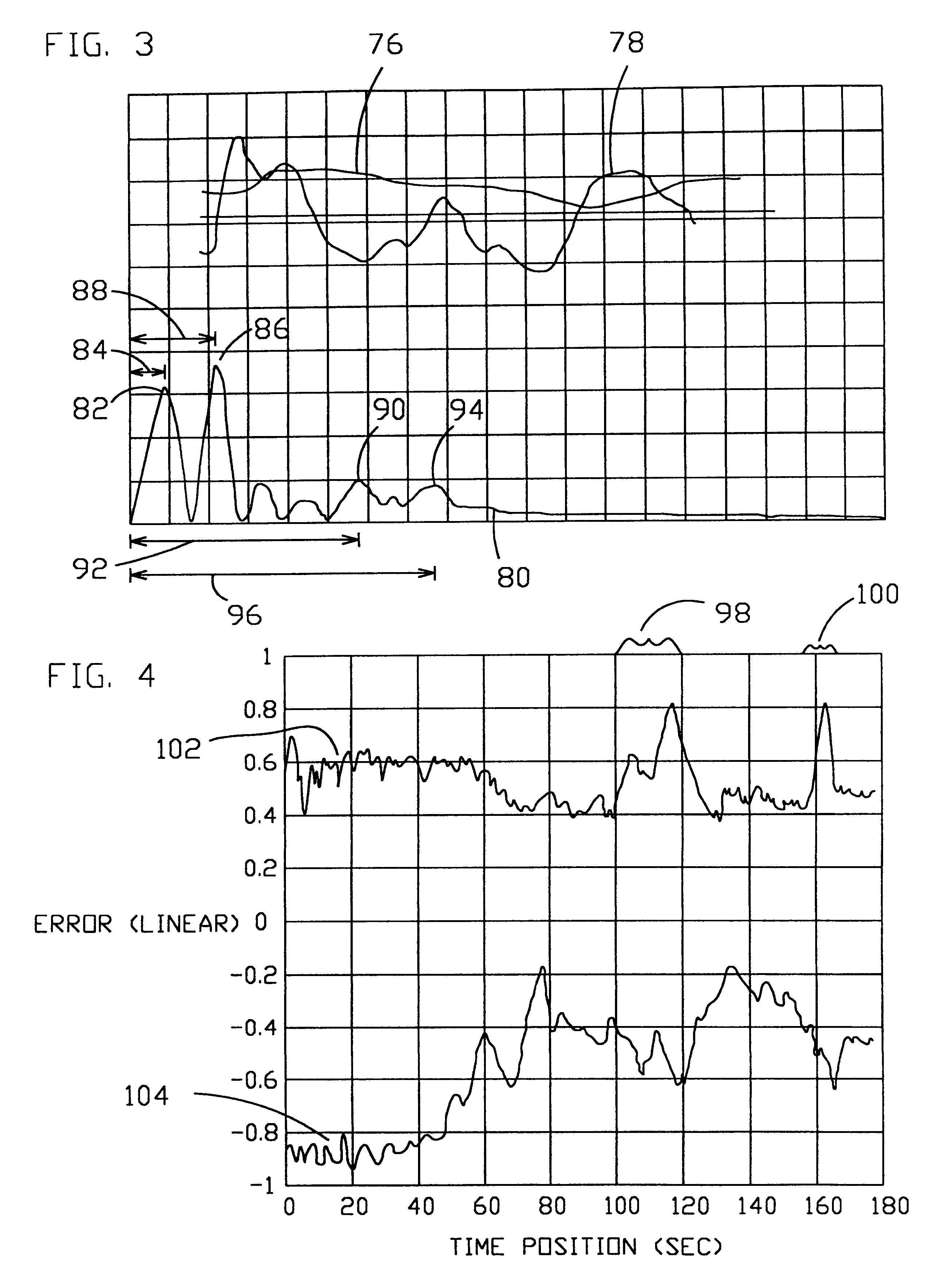
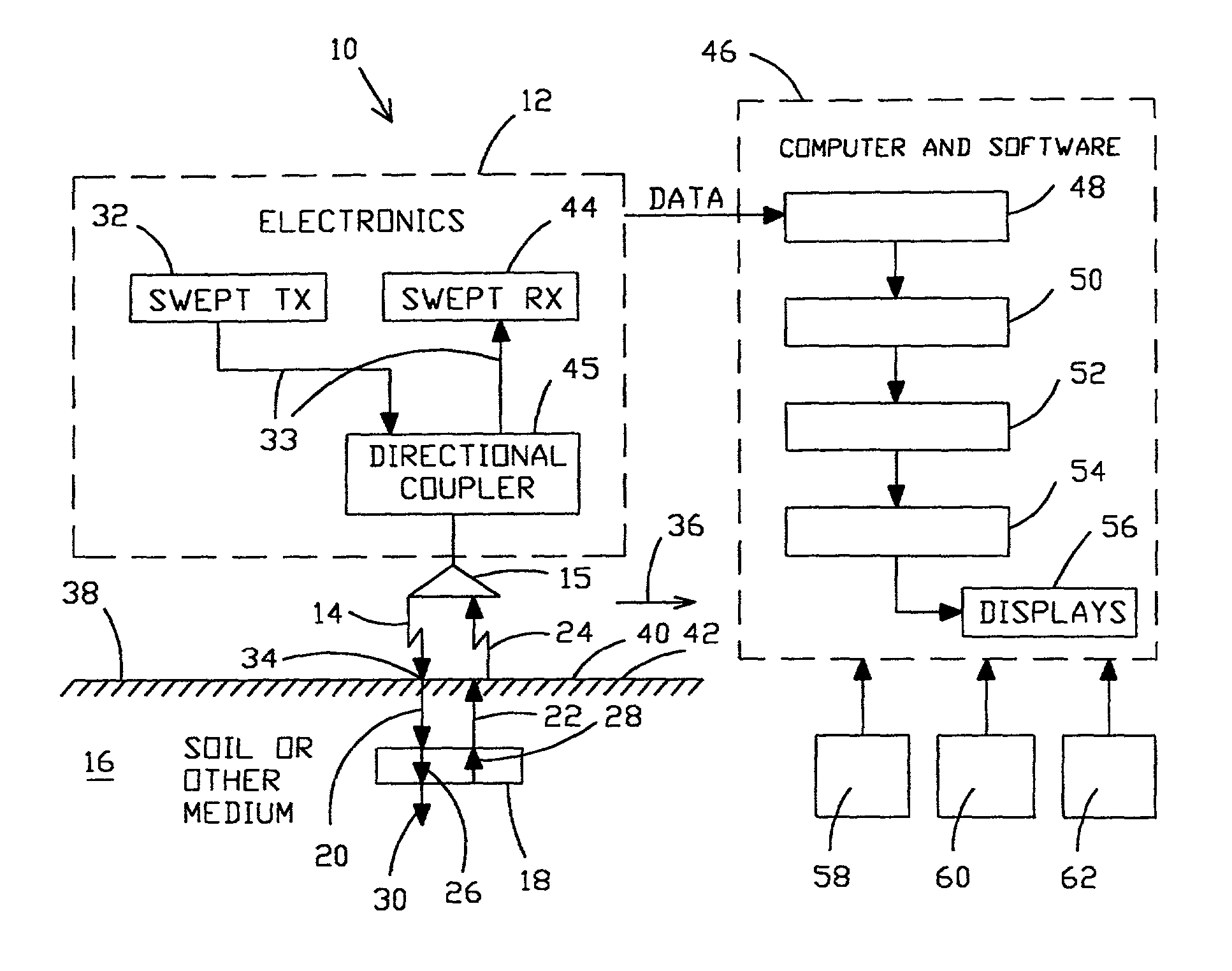
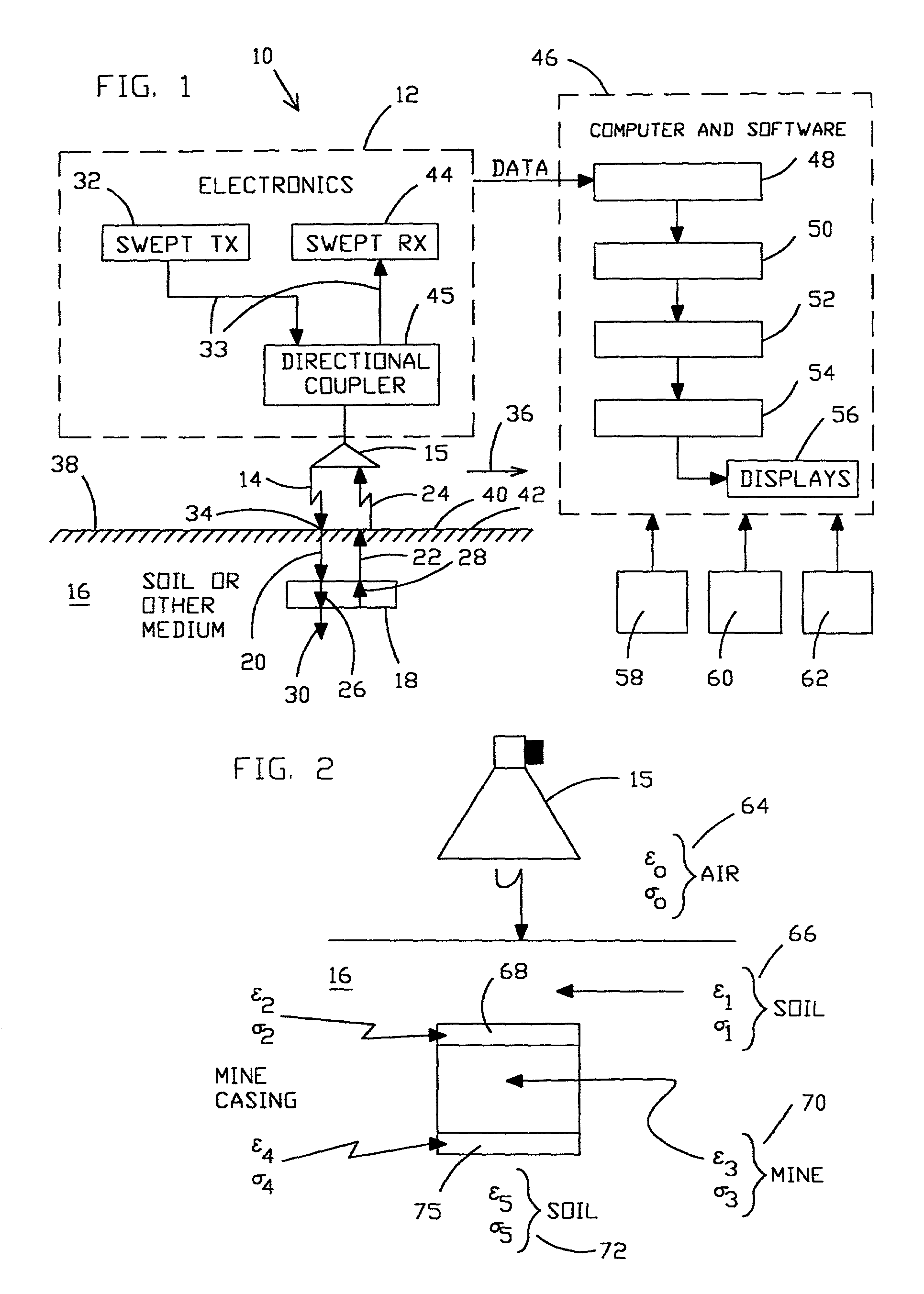
Method for locating a concealed object
InactiveUS6501414B2Accurate detectionEnhance and preserve resolutionDefence devicesDetection using electromagnetic wavesTime delaysComplex filter
Apparatus and methods are disclosed for detecting anomalies in microwave penetrable material that may be used for locating plastic mines or pipes underneath the ground. A transmitter is positioned at a plurality of different positions above the ground. A microwave signal is transmitted that is stepped over a plurality of frequencies. At each position, a plurality of reflections are received corresponding to each of the plurality of frequencies that were transmitted. A complex target vector may be produced at each position that contains complex values corresponding to magnitude, phase, and time delay for each of the plurality of reflections received at that location. A complex reference data vector may be produced, either based on predetermined values or based on data from the received plurality of reflections. A comparison is made between the complex target vector and the complex reference data vector to produce a channel vector. In one embodiment, an operator may be applied to the channel vector such as a complex filter matrix or to add a complex conjugate. A response signal is produced and anomalies are detected by variations in the response signal with respect to the plurality of positions.
Owner:NASA
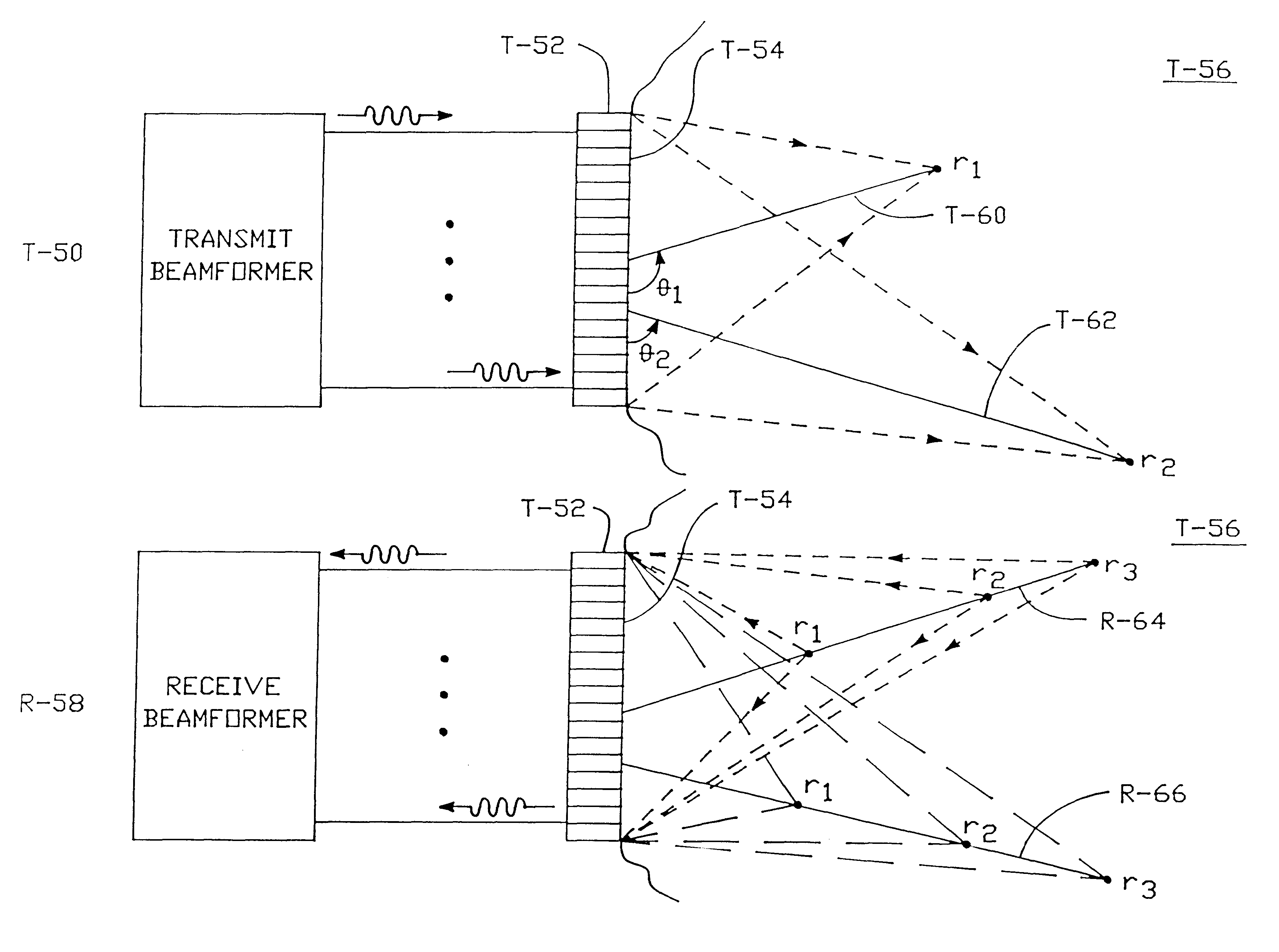
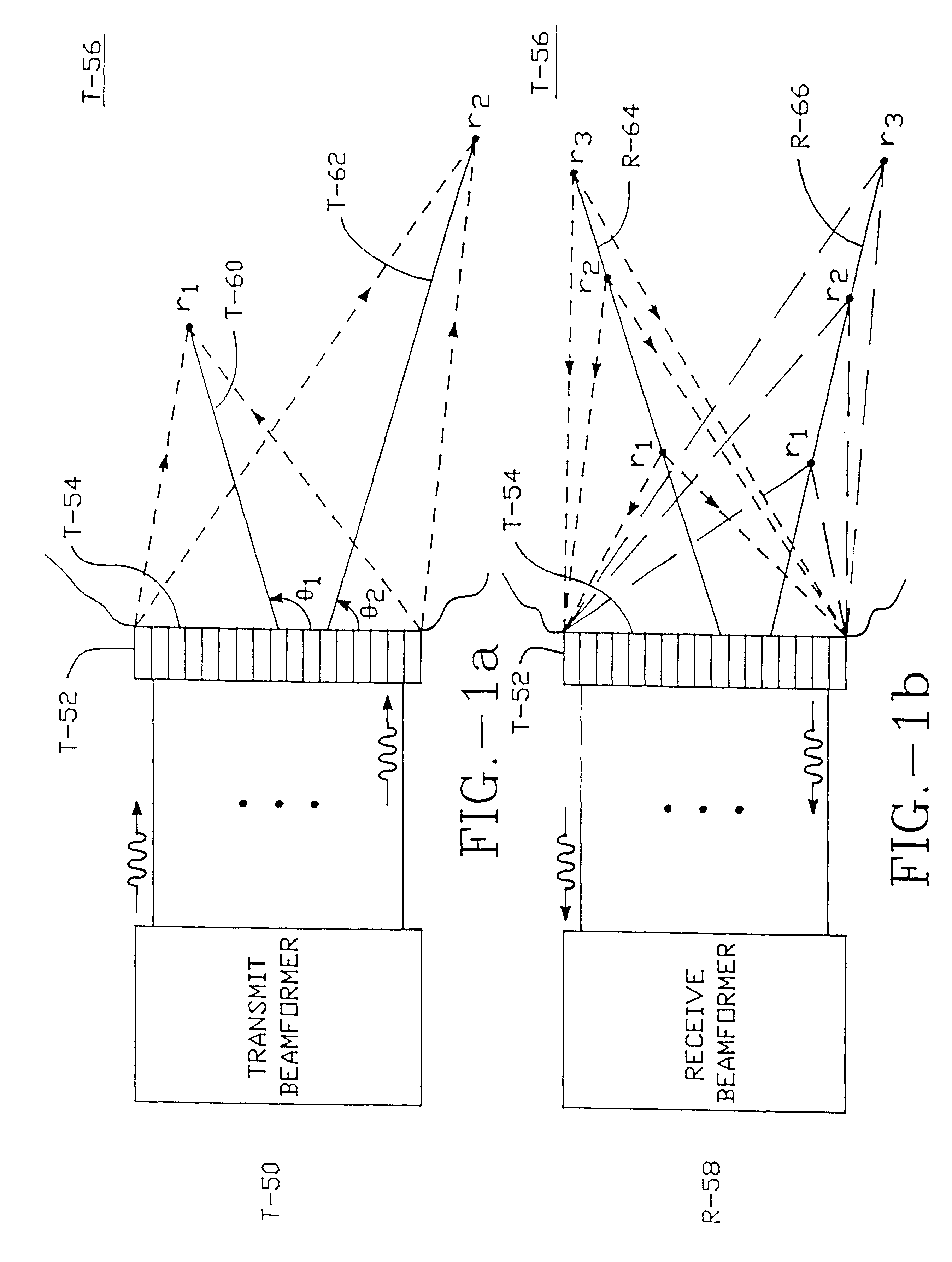
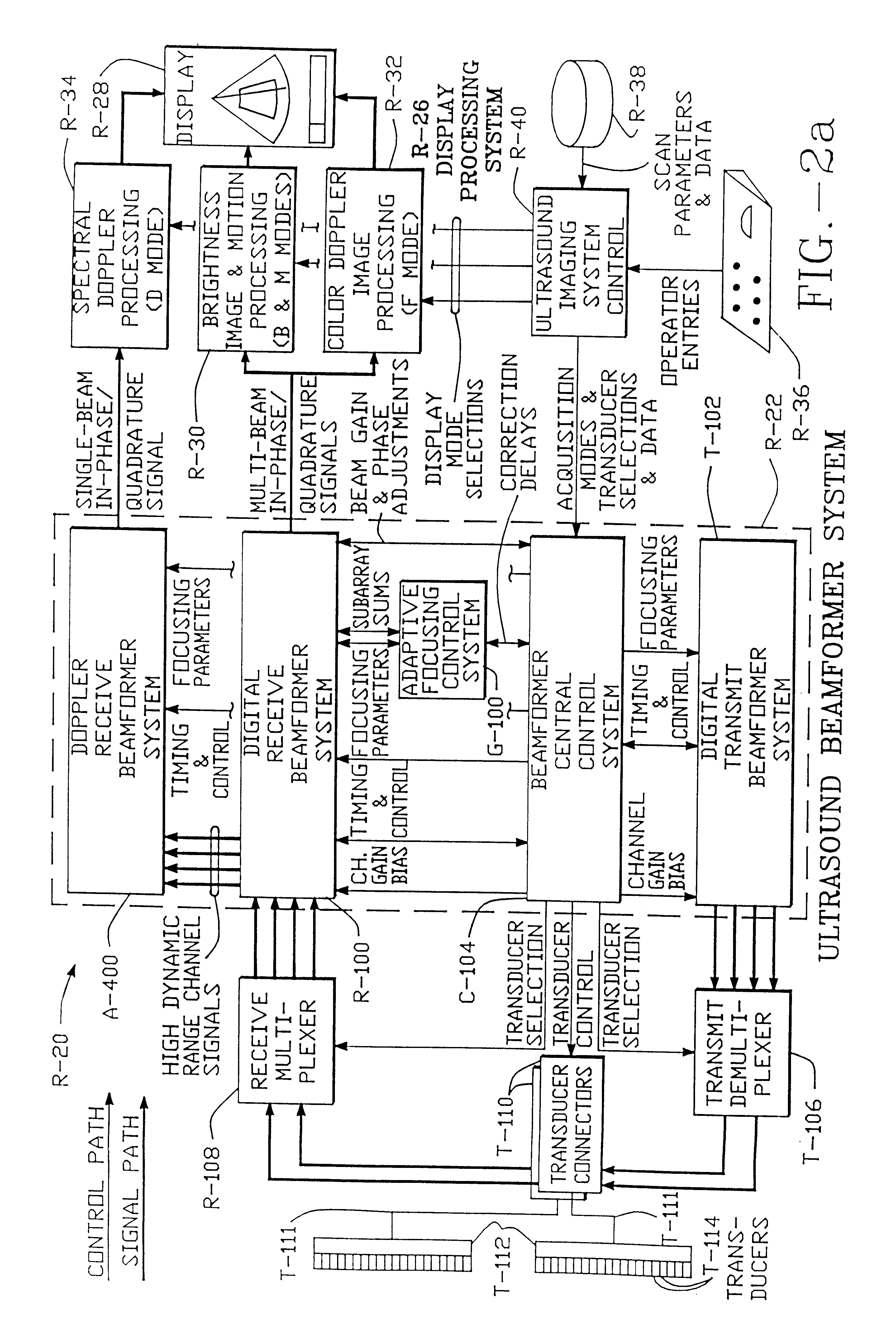
Method and apparatus for transmit beamformer system
InactiveUS6363033B1Improve programmabilityMaximum flexibilityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsProcessing detected response signalTrade offsApodization
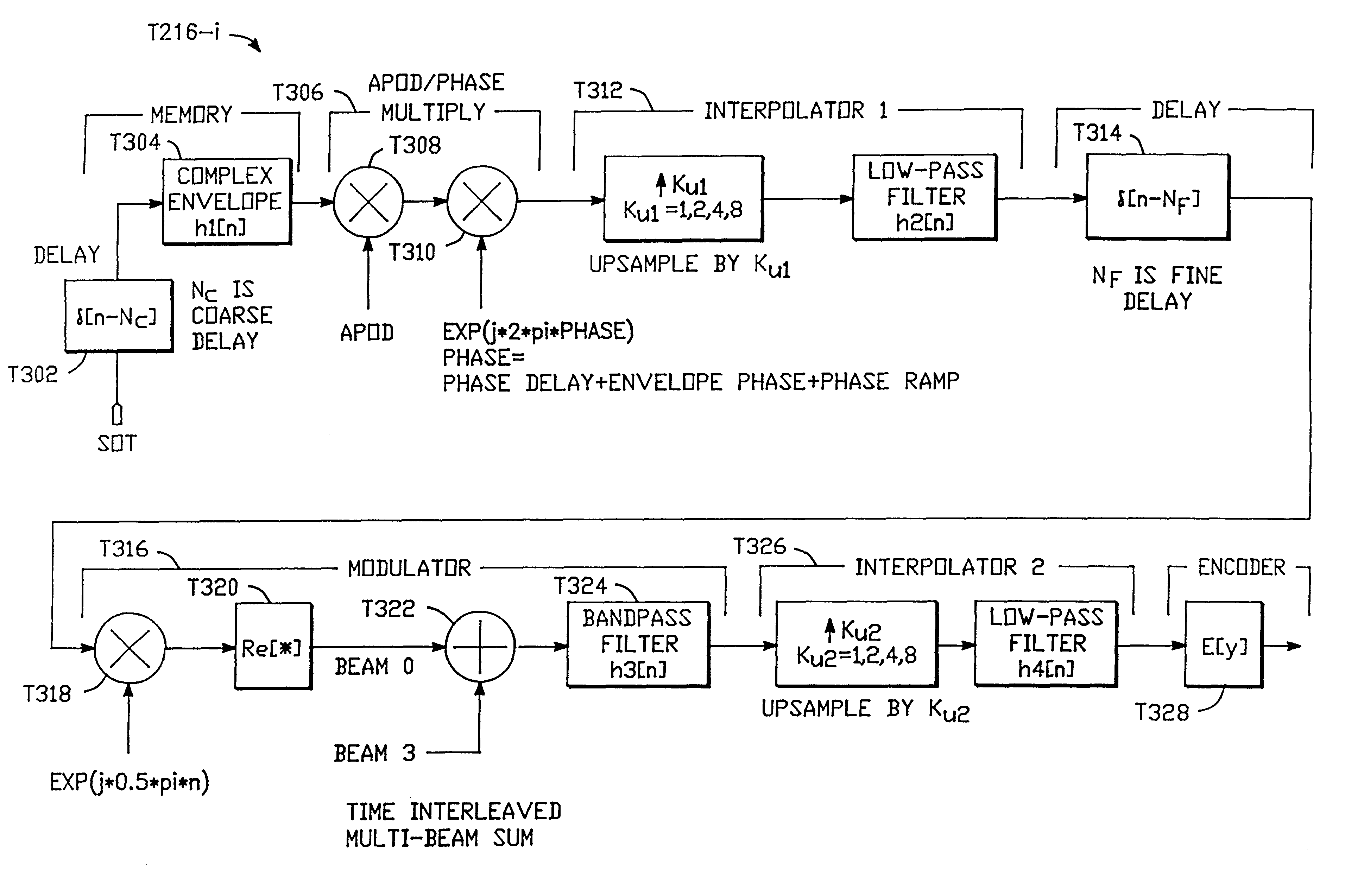
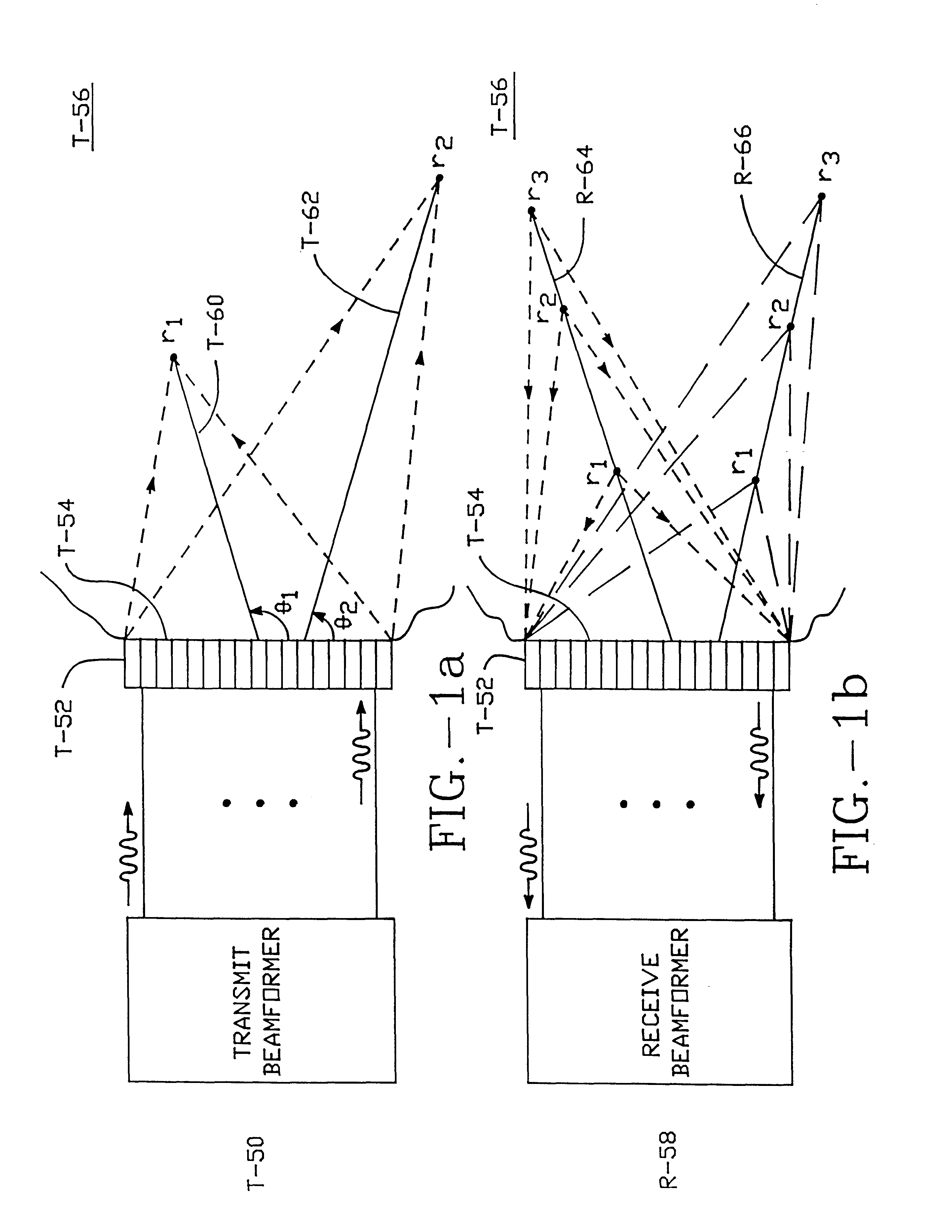
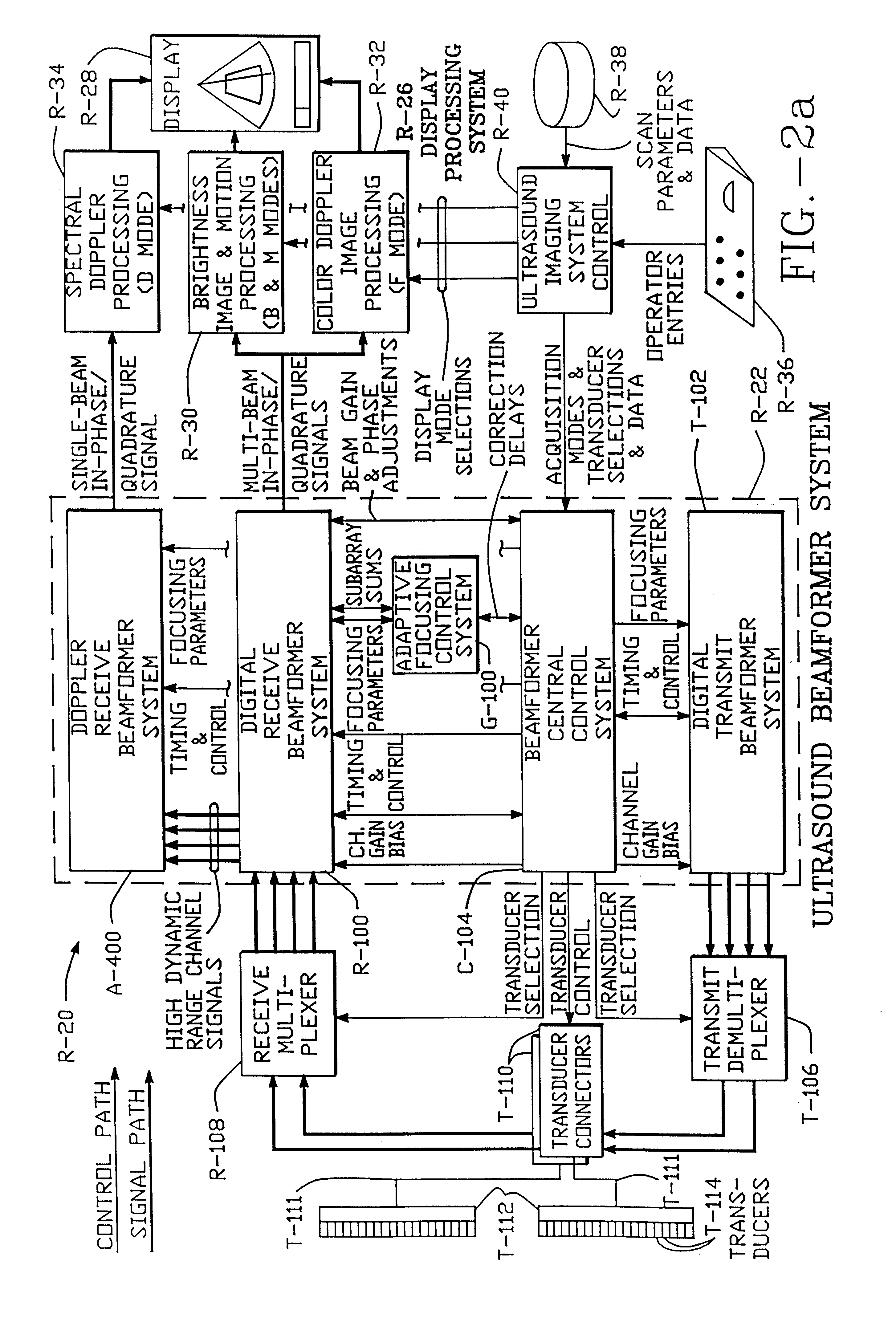
A digital transmit beamformer system with multiple beam transmit capability has a plurality of multi-channel transmitters, each channel with a source of sampled, complex-valued initial waveform information representative of the ultimate desired waveform to be applied to one or more corresponding transducer elements for each beam. Each multi-channel transmitter applies beamformation delays and apodization to each channel's respective initial waveform information digitally, digitally modulates the information by a carrier frequency, and interpolates the information to the DAC sample rate for conversion to an analog signal and application to the associated transducer element(s). The beamformer transmitters can be programmed per channel and per beam with carrier frequency, delay, apodization and calibration values, For pulsed wave operation, pulse waveform parameters can be specified to the beamformer transmitters on a per firing basis, without degrading the scan frame rate to non-useful diagnostic levels. Waveform parameters can be specified to the transmitters by an external central control system which is responsible for higher level flexibility, such as scan formats, focusing depths and fields of view. The transmit pulse delay specified per-channel to each transmitter is applied in at least two components: a focusing time delay component and a focusing phase component. The carrier frequency can be specified for each transmit beam, to any desired frequency within a substantially continuous predefined range of frequencies, and a beam-interleaved signal processing path permits operation in any of several predefined processing modes, which define different parameter sets in a trade-off among (1) the number of beams produced; (2) per-beam initial waveform sample interval; and (3) transmit frequency.
Owner:ACUSON
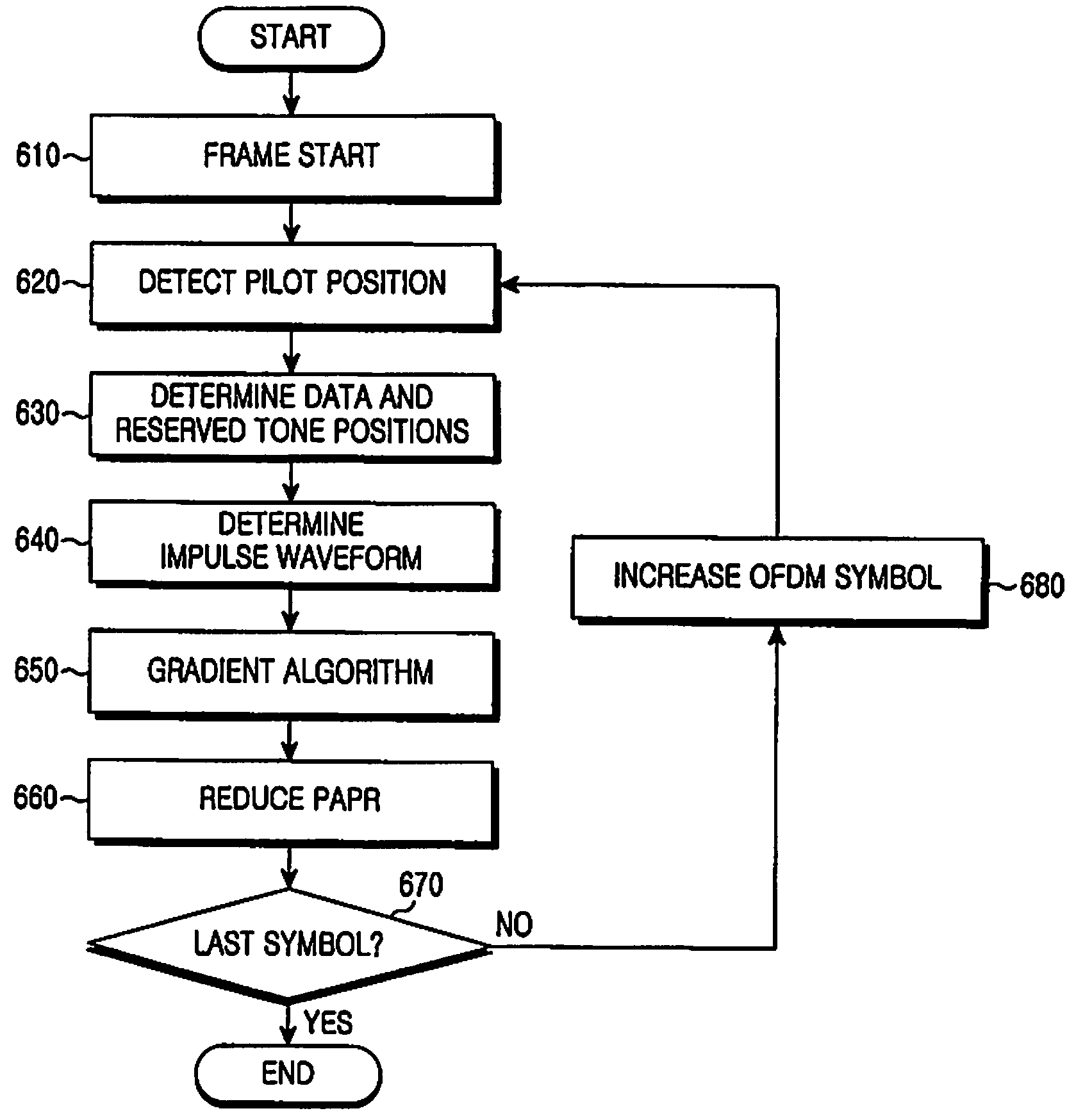
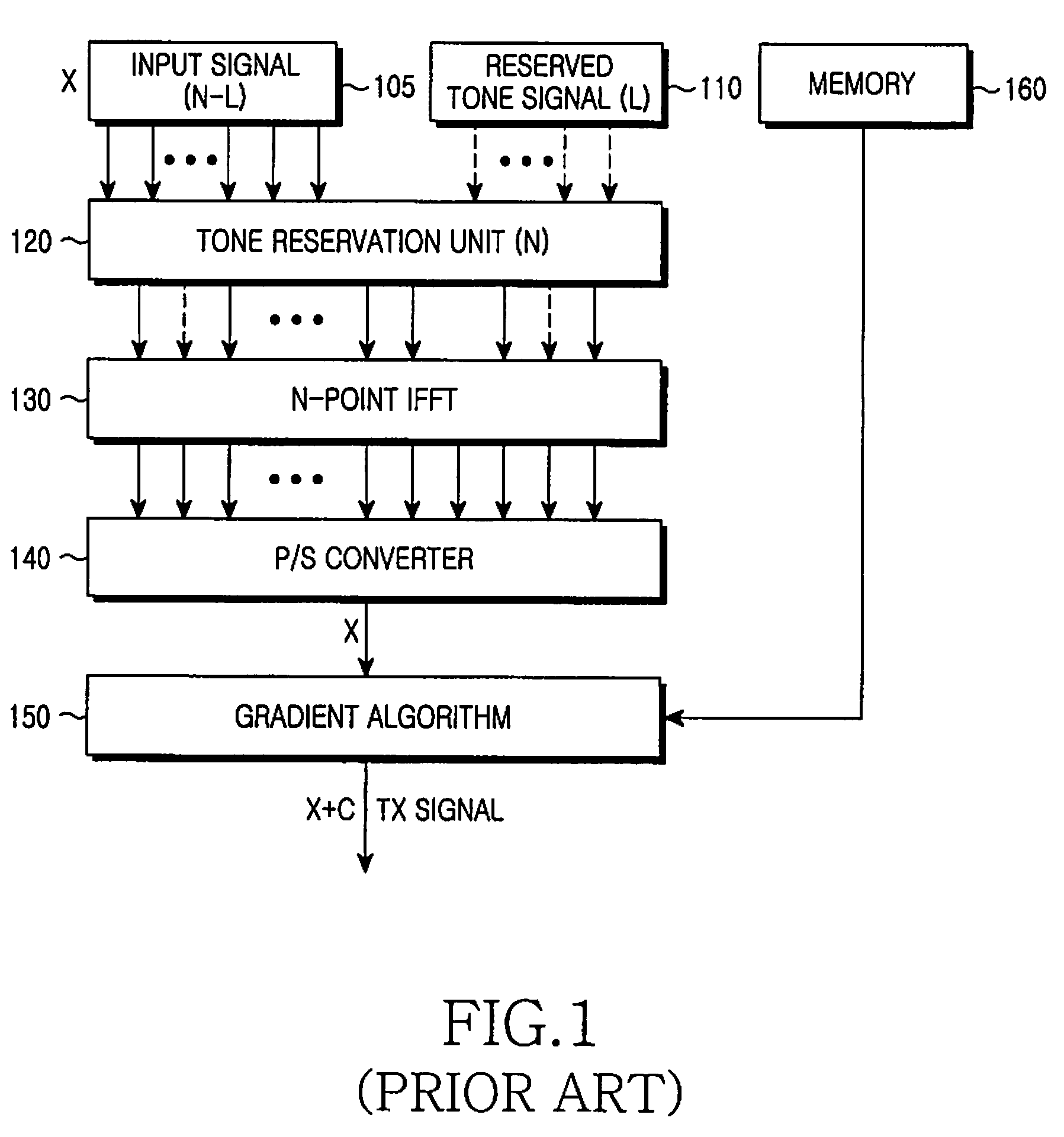
Apparatus and method for reducing peak to average power ratio in an orthogonal frequency division multiplexing system
ActiveUS20080298490A1Avoid collisionSecret communicationMulti-frequency code systemsCommunications systemComplex valued
A method for reducing a Peak to Average Power Ratio (PAPR) using reserved tones in a transmission apparatus of an Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) communication system is provided. The method includes detecting a subcarrier spacing interval and the number of spaced symbols based on a predetermined pilot pattern upon signal reception, and determining positions of shifted reserved tones obtained by shifting positions of reserved tones allocated to a predetermined symbol during the number of the spaced symbols at intervals of the spacing interval; determining an impulse waveform obtained by rotating a phase of a complex value of an impulse stored in a memory, using the determined positions of frequency-domain reserved tones of each symbol; calculating a subtrahend for a PAPR of an output signal using the phase-rotated impulse waveform; and reducing a PAPR of an input signal by performing a gradient algorithm using the phase-rotated impulse waveform.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
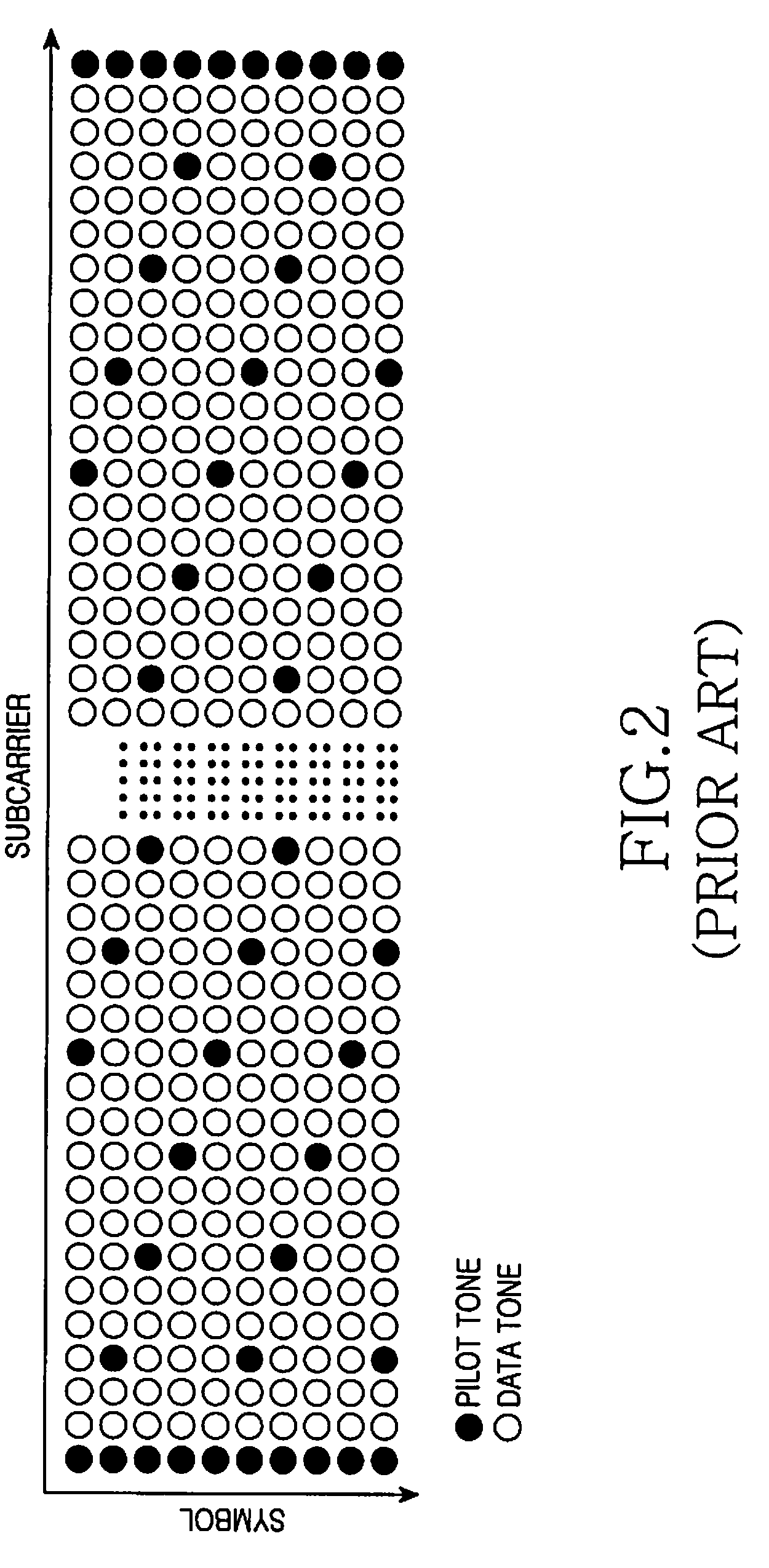
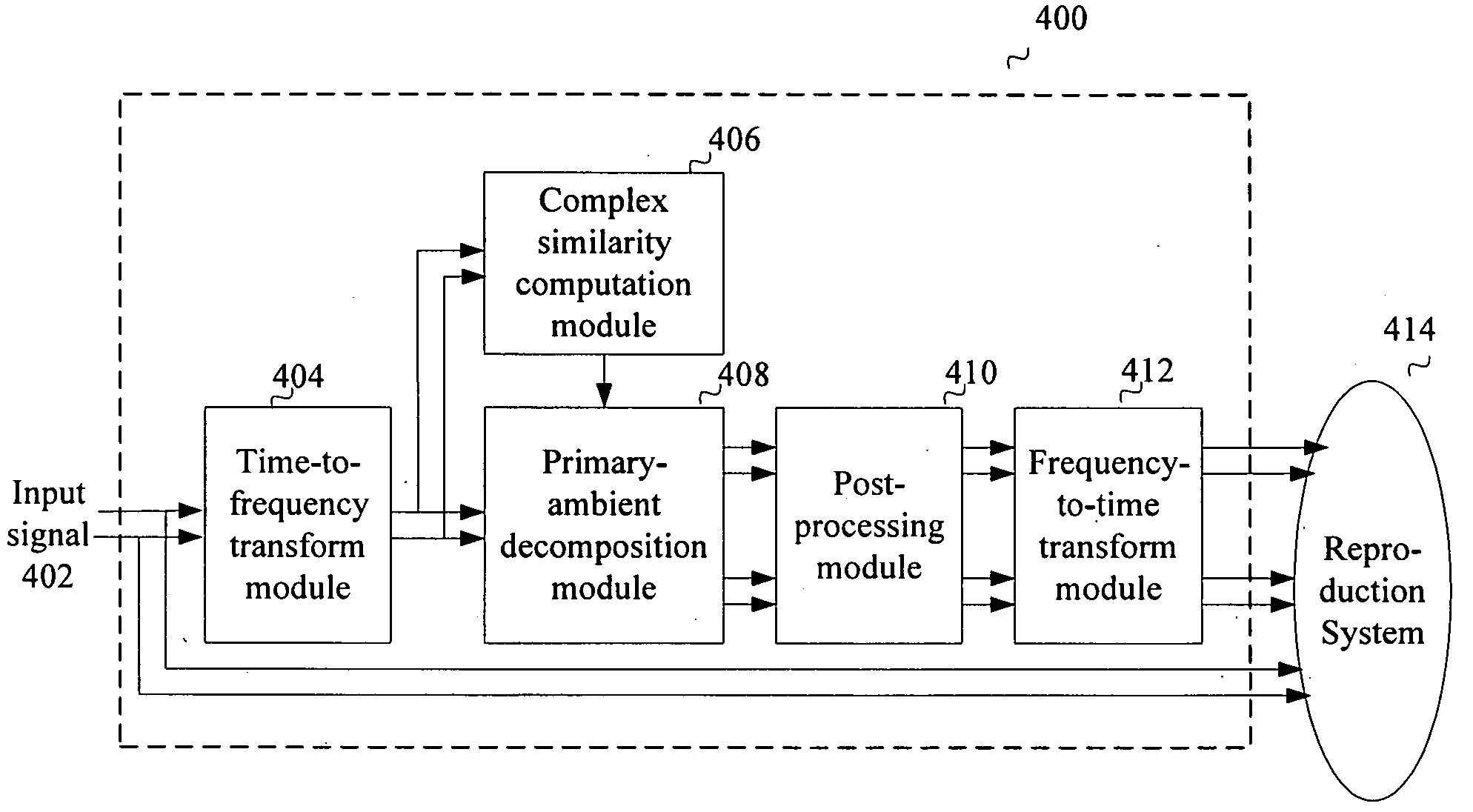
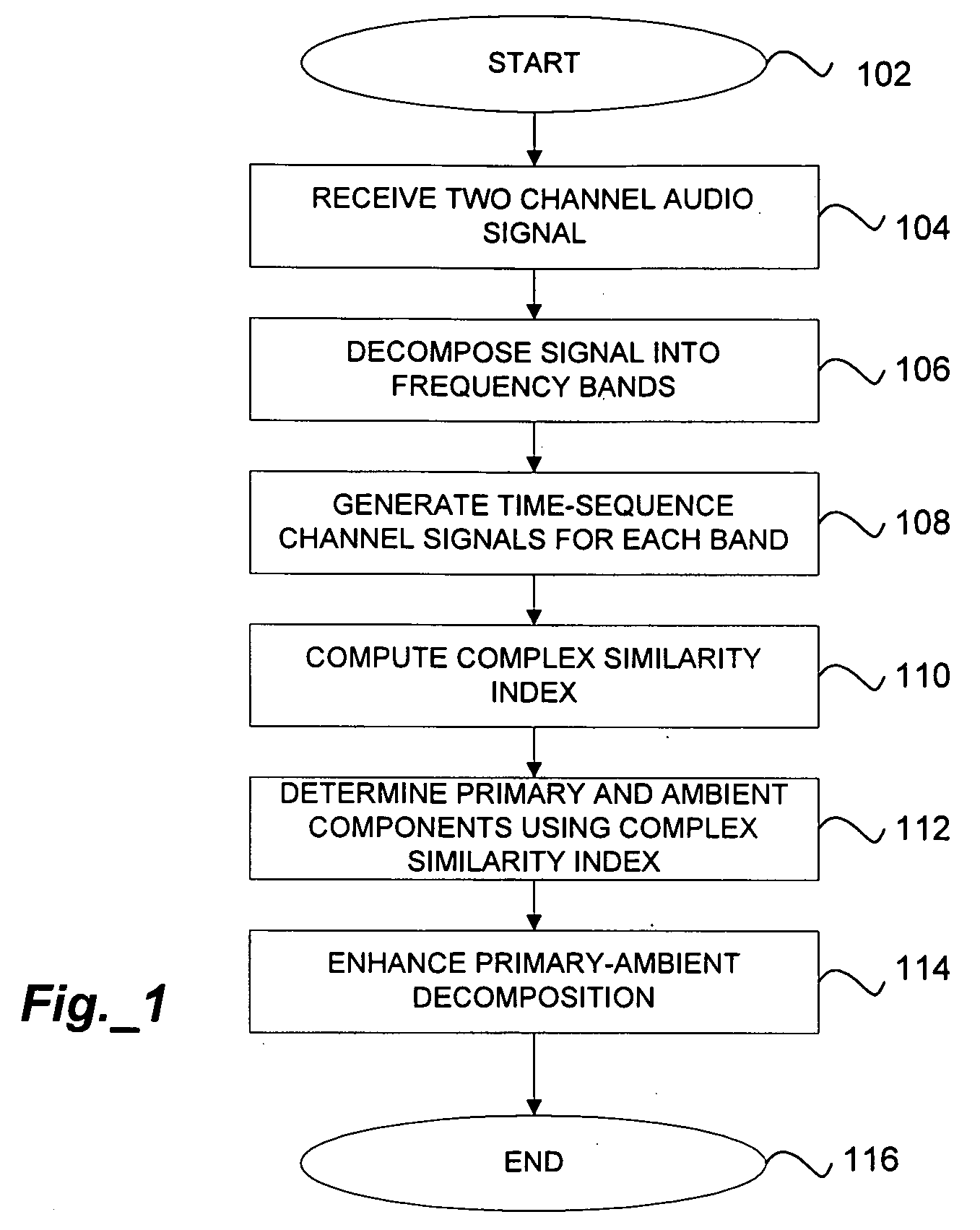
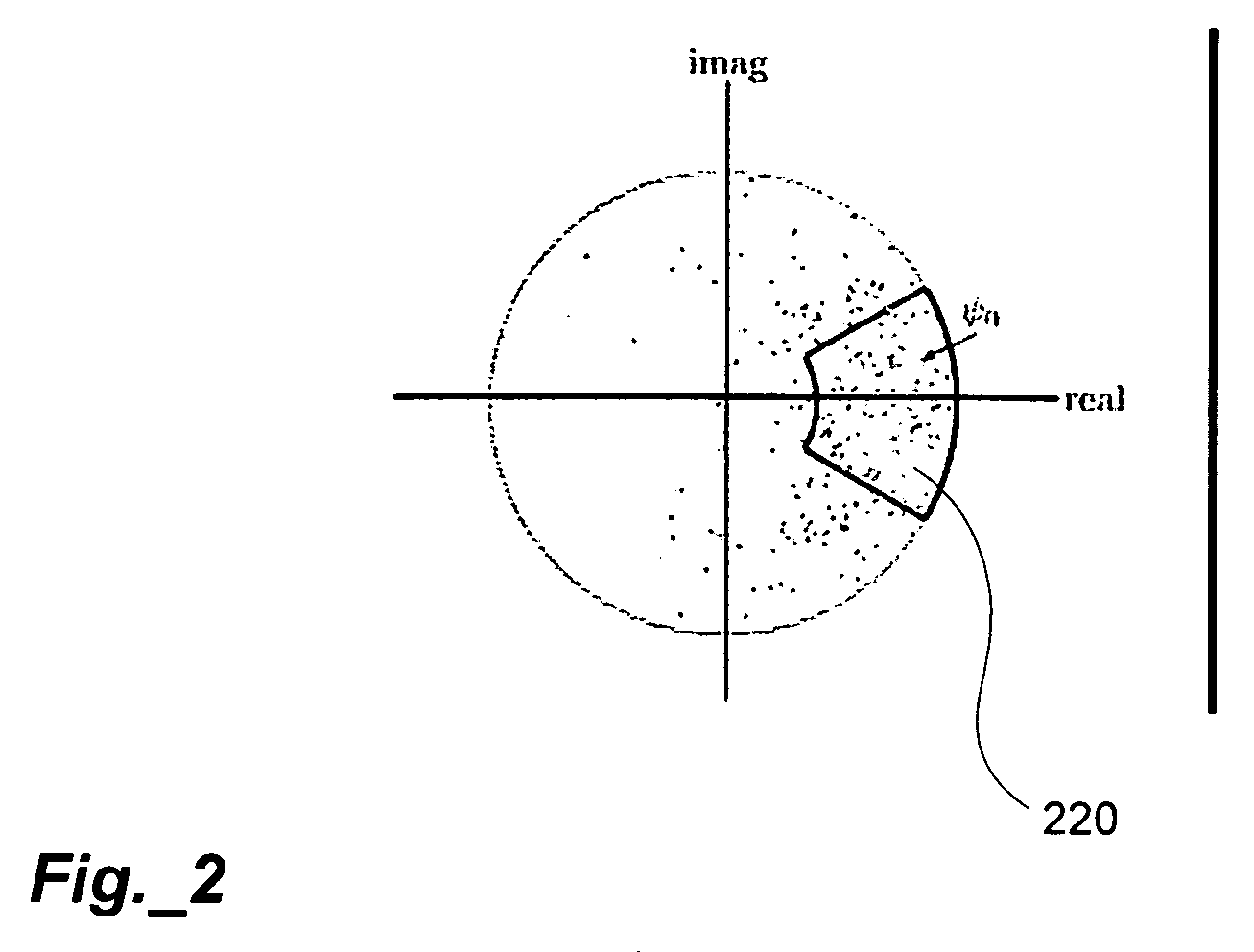
Primary-Ambient Decomposition of Stereo Audio Signals Using a Complex Similarity Index
ActiveUS20090198356A1Avoid artifactsPromote decompositionSpeech analysisBroadcast circuit arrangementsDecompositionAudio frequency
An audio signal is processed to derive primary and ambient components of the signal. The signal is first transformed to generate frequency-domain subband signals. Primary and ambient components are separated by comparing frequency subband content using a complex-valued similarity metric, wherein one of the primary and ambient components is determined to be the residual after the other is identified using the similarity metric.
Owner:CREATIVE TECH CORP
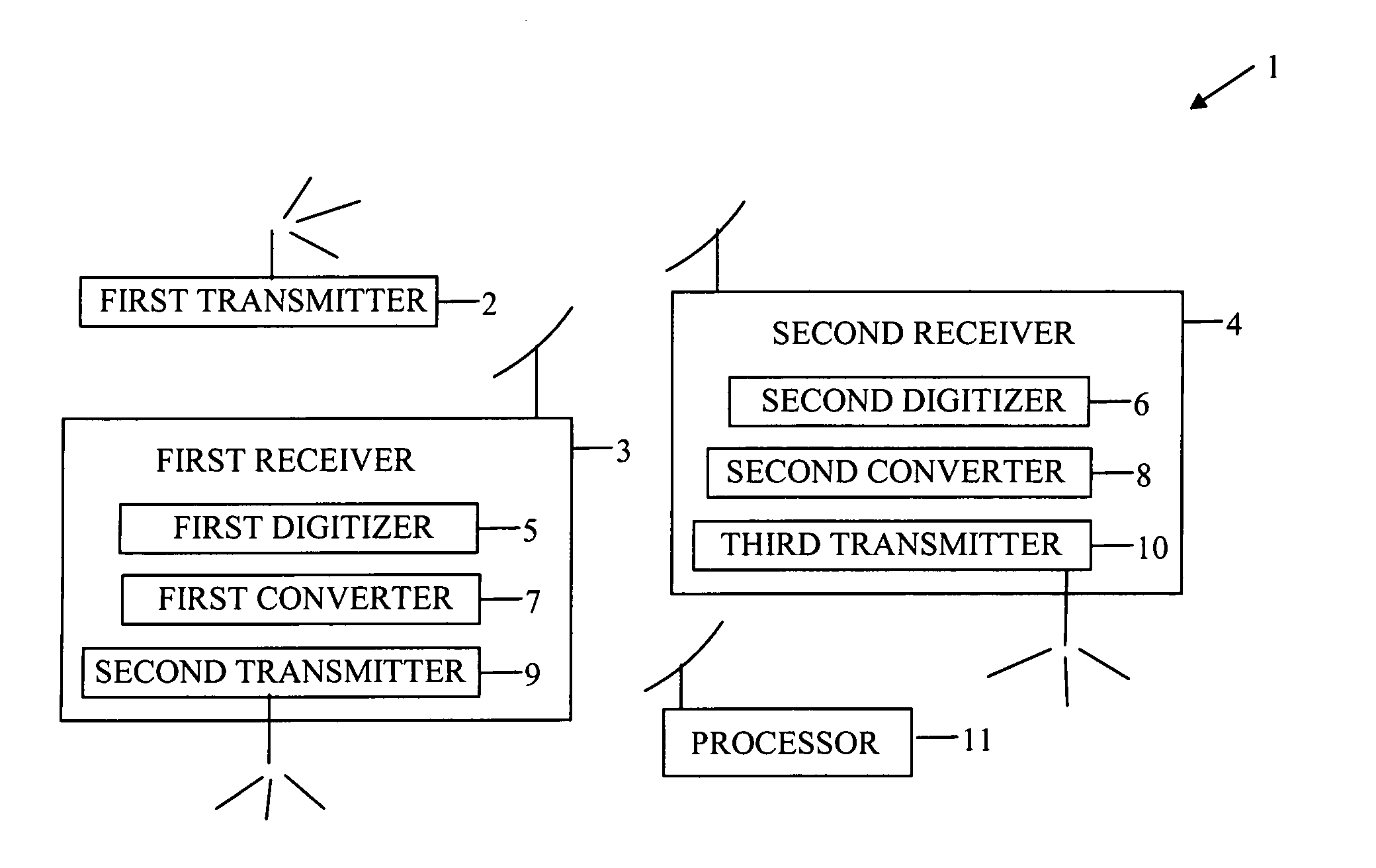
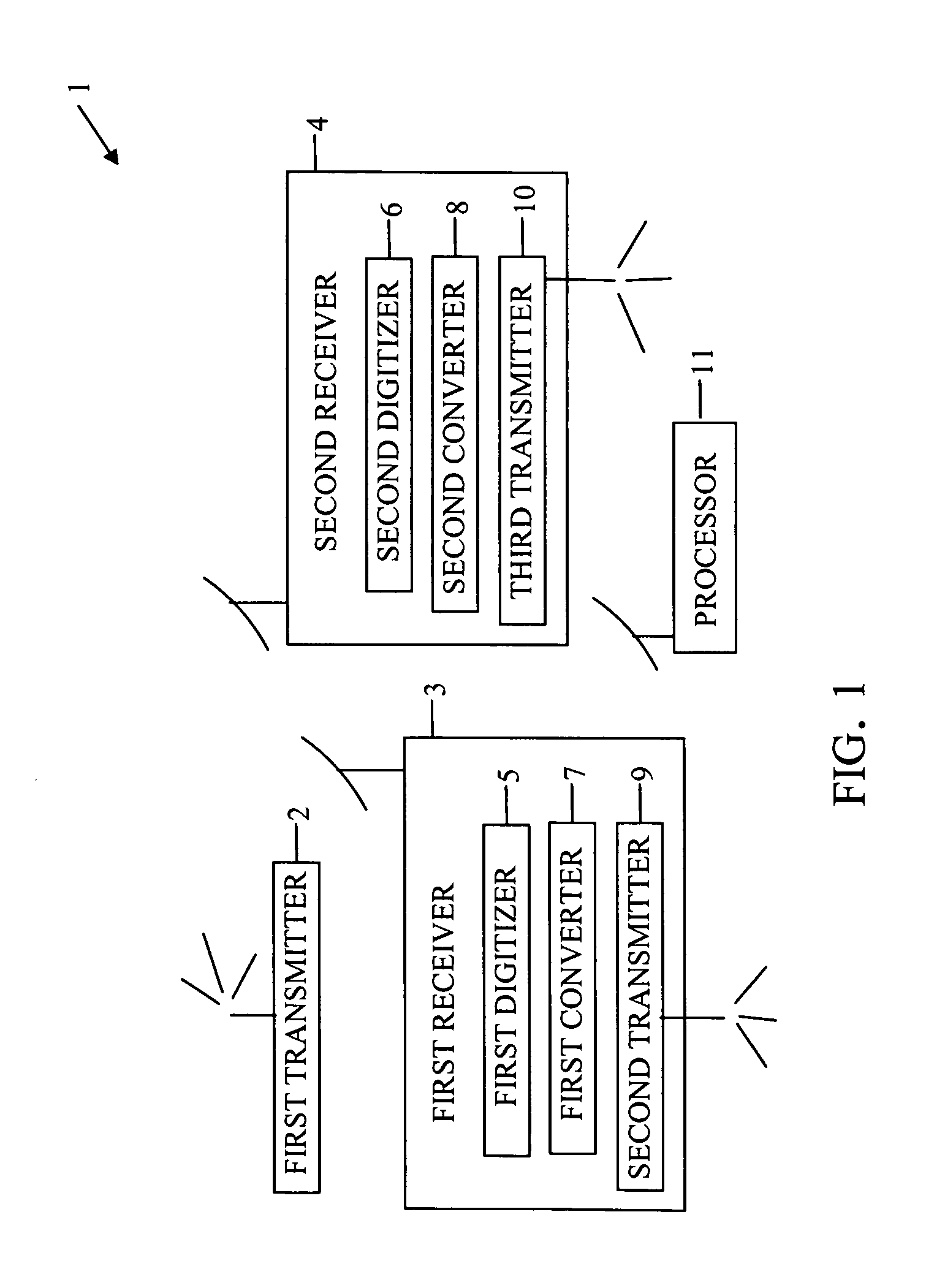
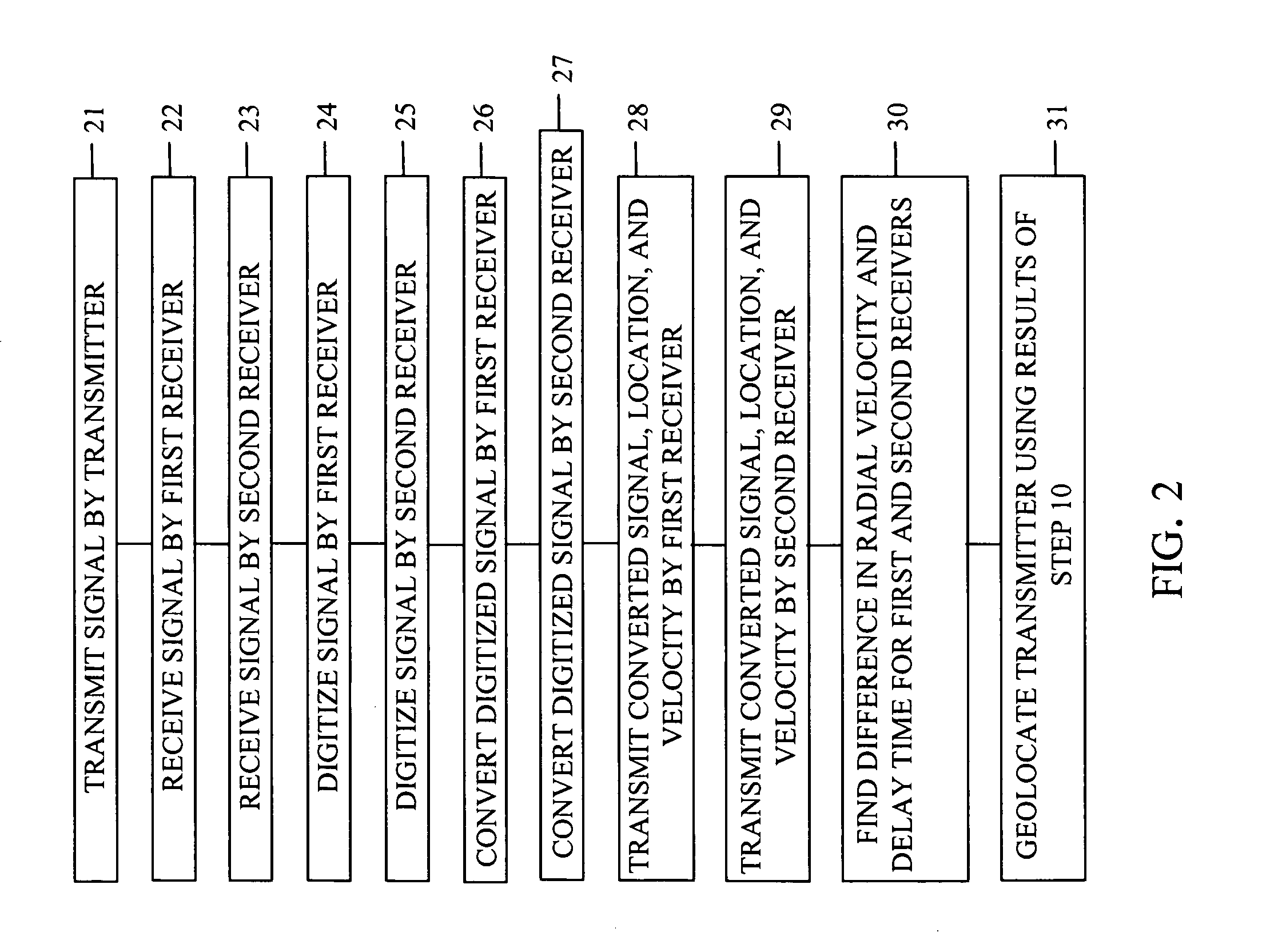
Device for and method of geolocation
ActiveUS7893875B1More precisionDirection finders using radio wavesPosition fixationGeolocationEngineering
A device and method of geolocating a transmitter. First and second receivers, in motion, receive a signal from the transmitter. Digitizers in the receivers digitize the signal. Converters in the receivers for converting the digitized signals to complex-valued signals. Transmitters on the receivers transmit their digitized signals, locations, and velocities at the time the signal was received to a processor. A central processing unit on the processor determines a difference in radial velocities of the receivers relative to the transmitter. The difference in radial velocities and delay time between the signals received at the receivers are used to geolocate the transmitter.
Owner:NATIONAL SECURITY AGENCY
Method for locating a concealed object
InactiveUS20020175849A1Defence devicesDetection using electromagnetic wavesComplex filterMicrowave signals
Apparatus and methods are disclosed for detecting anomalies in microwave penetrable material that may be used for locating plastic mines or pipes underneath the ground. A transmitter is positioned at a plurality of different positions above the ground. A microwave signal is transmitted that is stepped over a plurality of frequencies. At each position, a plurality of reflections are received corresponding to each of the plurality of frequencies that were transmitted. A complex target vector may be produced at each position that contains complex values corresponding to magnitude, phase, and time delay for each of the plurality of reflections received at that location. A complex reference data vector may be produced, either based on predetermined values or based on data from the received plurality of reflections. A comparison is made between the complex target vector and the complex reference data vector to produce a channel vector. In one embodiment, an operator may be applied to the channel vector such as a complex filter matrix or to add a complex conjugate. A response signal is produced and anomalies are detected by variations in the response signal with respect to the plurality of positions.
Owner:NASA
Method and apparatus using coordinate interleaving to increase diversity in a MIMO system
InactiveUS7409001B2Increase diversityModulated-carrier systemsPolarisation/directional diversityAs elementEngineering
A method to increase diversity in MIMO fading channels interleaves coordinates of complex symbol(s) in a transmission frame after encoding and modulating. Specifically, an input signal is encoded and modulated into a codeword, jointly across at least two pipes, said pipes having space, time, frequency, or other nature, wherein the codeword spans a frame and is defined as at least one complex symbol whose complex values are all those to be transmitted during all channel uses covered by the frame. Each of the complex symbols have a first and second coordinate. After modulating, which may be combined with encoding in a signal space encoder, the coordinates are interleaved. In modulation, the complex symbols (typically two dimensional) may arise as elements of a multidimensional (typically greater than two dimensions) signal constellation, in which case those multidimensional constellation coordinates are the ones that are interleaved in the frame. The frame carrying the interleaved coordinates is transmitted by the first and at least second antennas, possible opposed sub-frames of the overall frame being transmitted separately by opposed antennas. A coset selector is used in some embodiments to maximize a minimum Hamming distance, and / or a minimum Euclidean distance, between coordinates within a coset to control diversity and / or coding gain. In some embodiments, the operation of the encoder and modulator is such as to maximize a minimum coordinate-wise Hamming distance, and / or a minimum Euclidean distance, between allowable codewords, and / or to provide additional structure for the allowable codewords. A method, transmitter, system, and mobile station are described.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Communication through multiplexed one-dimensional optical signals
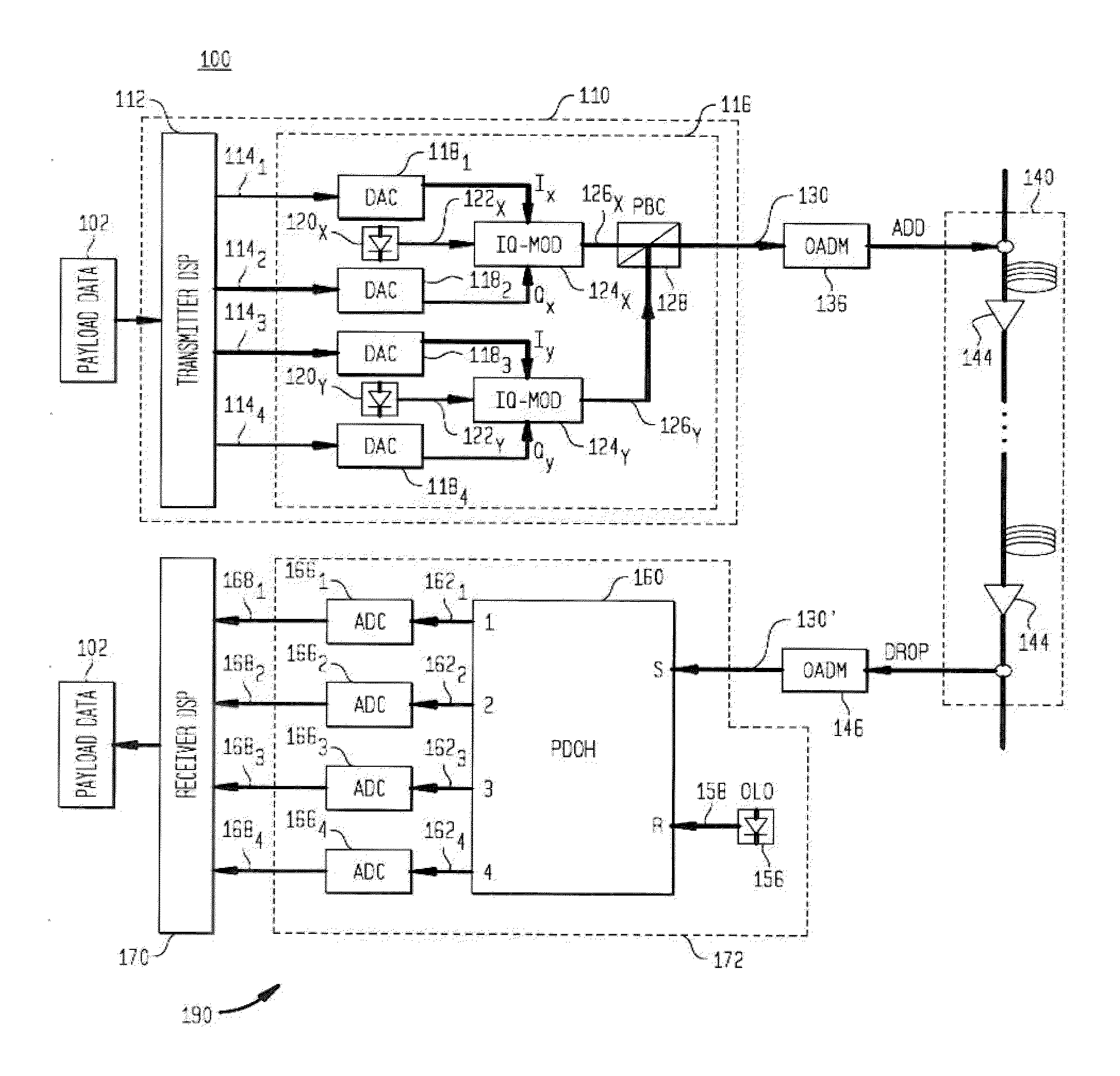
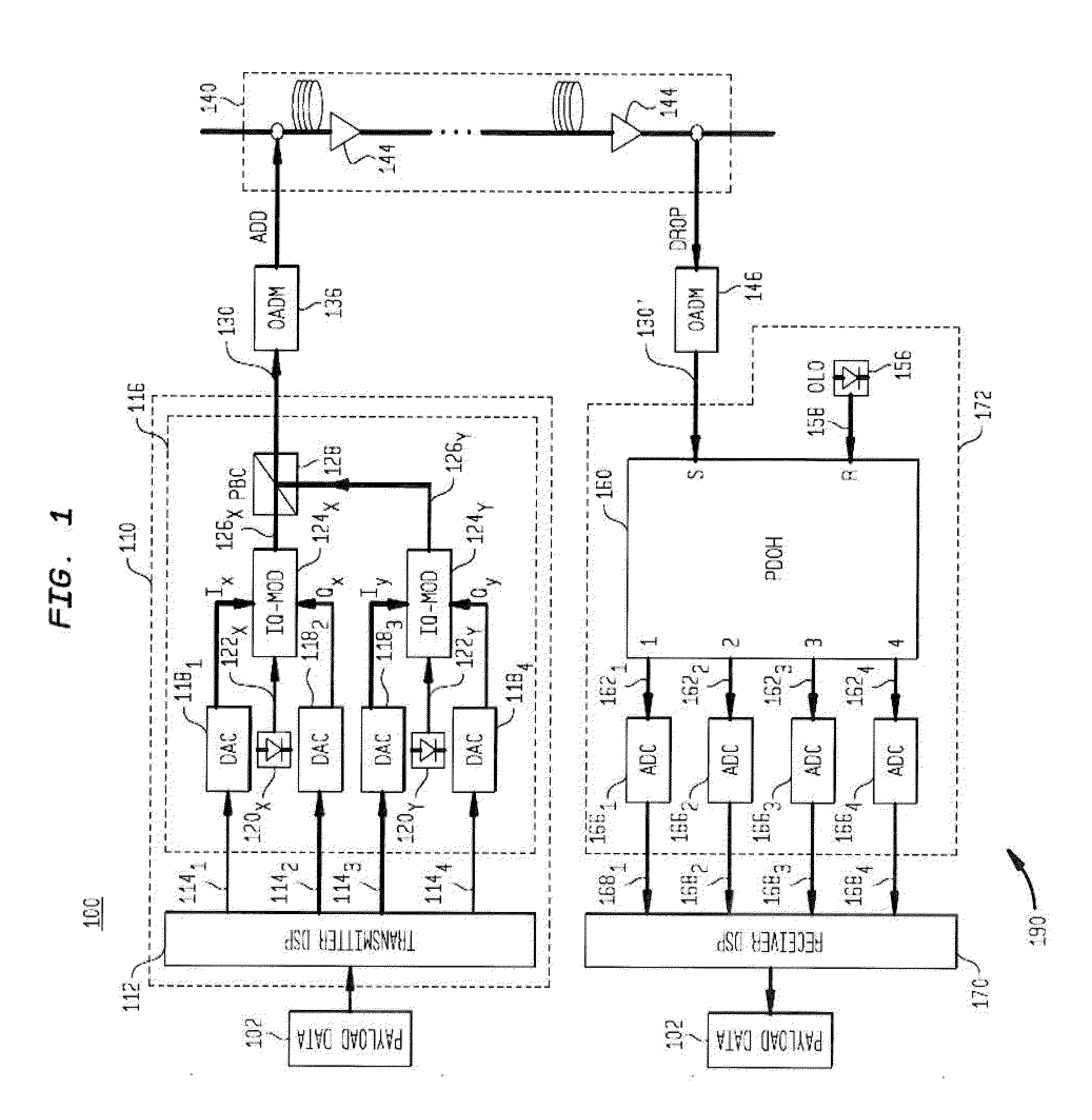
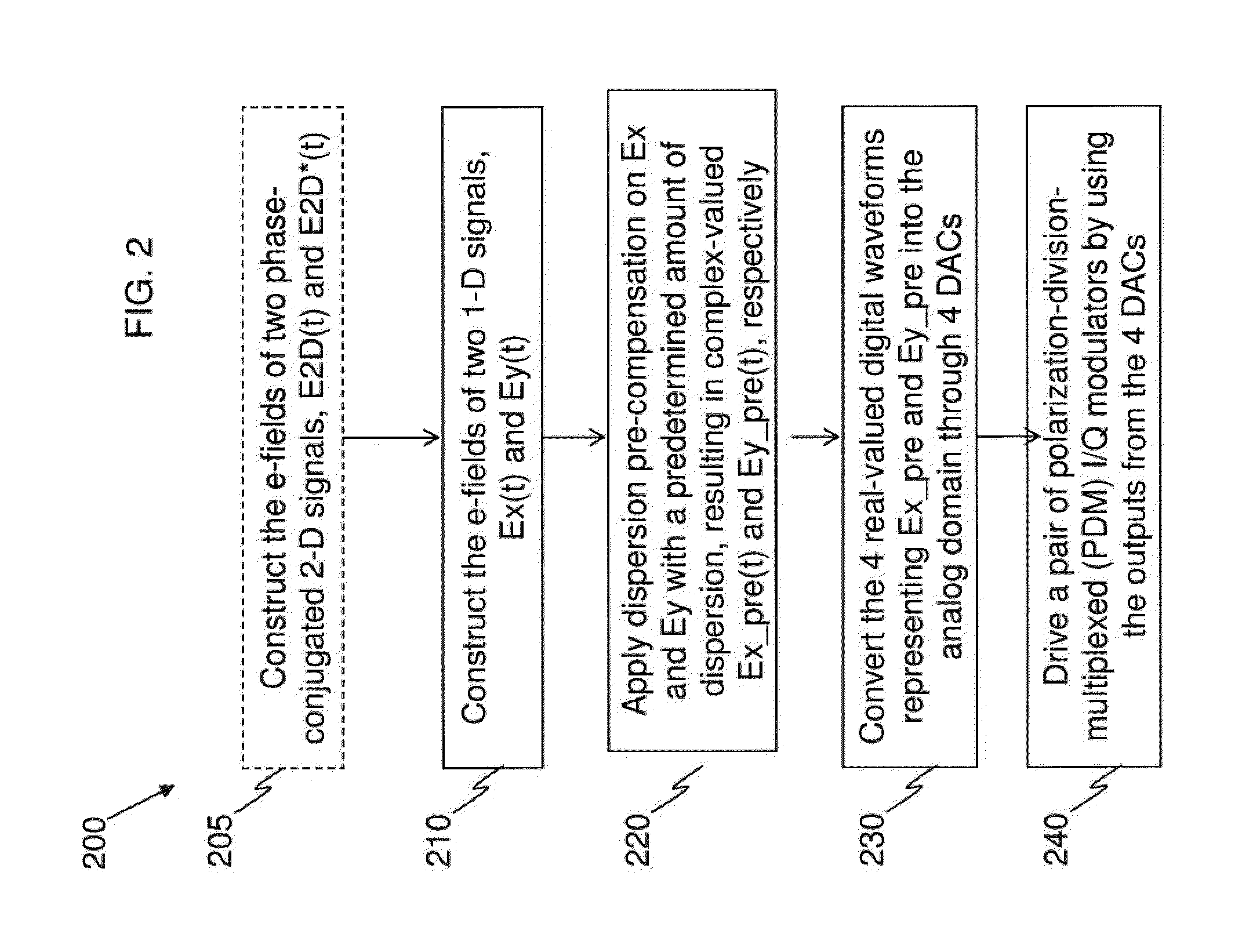
ActiveUS20130136449A1Effectively cancellingImprove signal qualityPolarisation multiplex systemsDistortion/dispersion eliminationMultiplexingCarrier signal
An example apparatus comprises an optical transmitter which includes a first processor and at least two optical modulators. The first processor is configured to generate a first electronic representation for each of at least two optical signals for carrying payload data modulated according to a one-dimensional (1-D) modulation format, and to induce on respective ones of the first electronic representations an amount of dispersion that depends on a power-weighted accumulated dispersion (ADPW) of a transmission link through which the at least two optical signals are to be transmitted thereby generating complex-valued electronic representations of pre-dispersion-compensated optical signals. Each of the at least two optical modulators modulate a respective analog version corresponding to a respective one of the complex-valued electronic representations onto a polarization of an optical carrier.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
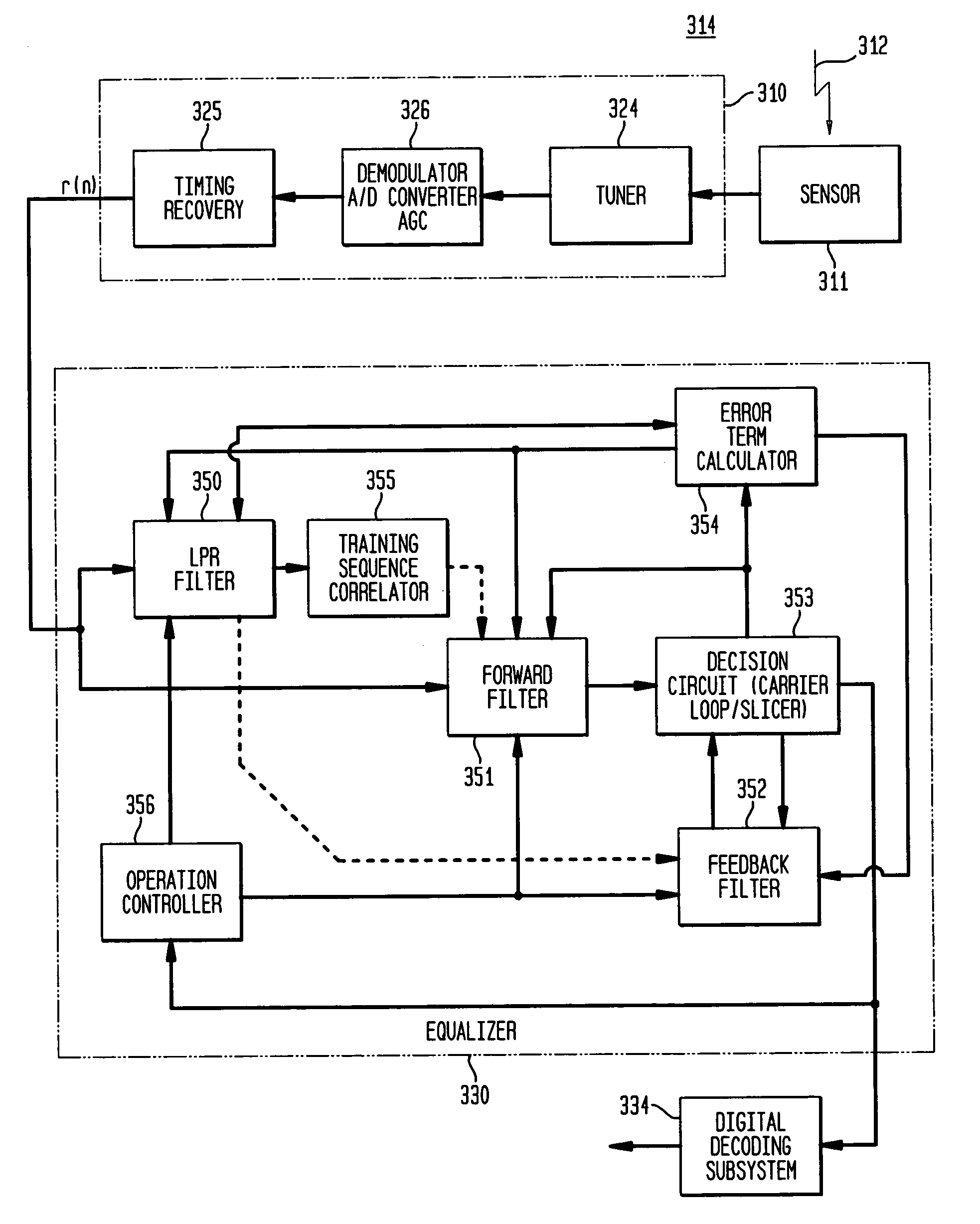
Linear prediction based initialization of a single-axis blind equalizer for VSB signals
ActiveUS7027500B1Minimize output powerMultiple-port networksTelevision system detailsImpulse frequencyEqualization
A single-axis receiver processing, for example, complex vestigial sideband modulated signals with an equalizer with forward and feedback filters. Forward and feedback filters have parameters that are initialized and adapted to steady state operation. Adaptive equalization employs linear predictive filtering and error term generation based on various cost criteria. Adaptive equalization includes recursive update of parameters for forward and feedback filtering as operation changes between linear and decision-feedback equalization of either single or multi-channel signals. An adaptive, linear predictive filter generates real-valued parameters that are employed to set the parameters of the feedback filter. In an initialization mode, filter parameters are set via a linear prediction filter to approximate the inverse of the channel's impulse / frequency response and a constant modulus error term for adaptation of the filter parameters. In an acquisition mode, equalization is as linear equalization with a constant modulus error term, and possibly other error terms in combination, for adaptation of the filter parameters. In a tracking mode, equalization is as decision feedback equalization with decision-directed error terms for adaptation of the filter parameters. For some equalizer configurations, feedback filtering is applied to real-valued decisions corresponding to complex-valued received data, and includes real-part extraction of the error term employed for recursive update of filtering parameters. Where a training sequence is available to the receiver, initial parameters for forward filtering are estimated by correlation of the received signal with the training sequence.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Method and apparatus using coordinate interleaving to increase diversity in a MIMO system
InactiveUS20060034381A1Increase diversityPolarisation/directional diversityPhase-modulated carrier systemsAs elementEngineering
A method to increase diversity in MIMO fading channels interleaves coordinates of complex symbol(s) in a transmission frame after encoding and modulating. Specifically, an input signal is encoded and modulated into a codeword, jointly across at least two pipes, said pipes having space, time, frequency, or other nature, wherein the codeword spans a frame and is defined as at least one complex symbol whose complex values are all those to be transmitted during all channel uses covered by the frame. Each of the complex symbols have a first and second coordinate. After modulating, which may be combined with encoding in a signal space encoder, the coordinates are interleaved. In modulation, the complex symbols (typically two dimensional) may arise as elements of a multidimensional (typically greater than two dimensions) signal constellation, in which case those multidimensional constellation coordinates are the ones that are interleaved in the frame. The frame carrying the interleaved coordinates is transmitted by the first and at least second antennas, possible opposed sub-frames of the overall frame being transmitted separately by opposed antennas. A coset selector is used in some embodiments to maximize a minimum Hamming distance, and / or a minimum Euclidean distance, between coordinates within a coset to control diversity and / or coding gain. In some embodiments, the operation of the encoder and modulator is such as to maximize a minimum coordinate-wise Hamming distance, and / or a minimum Euclidean distance, between allowable codewords, and / or to provide additional structure for the allowable codewords. A method, transmitter, system, and mobile station are described.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Downlink broadcasting by sequential transmissions from a communication station having an antenna array
InactiveUS7299071B1Acceptable performanceLow powerSpatial transmit diversityPolarisation/directional diversityTime segmentAntenna element
This invention relates to a method and apparatus for transmitting a downlink signal from a communication station to one or more subscriber units to achieve a desired radiation level over a desired sector (e.g., everywhere), the communication station including an array of antenna elements and one or more signal processors programmed (in the case of programmable signal processors) to weight the downlink signal according to one of a sequence of complex valued weight vectors. The method includes sequentially repeating transmitting the downlink signal, each repetition with a different weight vector from the sequence until all weight vectors in the sequence have been transmitted with. The sequence is designed for achieving the desired radiation level during at least one of the repetitions. In this way, every user in the desired region is transmitted to in the time period.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Method and apparatus for transmit beamformer system
InactiveUS6172939B1Improve abilitiesImprove programmabilityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsProcessing detected response signalEngineeringTrade offs
A digital transmit beamformer system with multiple beam transmit capability has a plurality of multi-channel transmitters, each channel with a source of sampled, complex-valued initial waveform information representative of the ultimate desired waveform to be applied to one or more corresponding transducer elements for each beam. Each multi-channel transmitter applies beamformation delays and apodization to each channel's respective initial waveform information digitally, digitally modulates the information by a carrier frequency, and interpolates the information to the DAC sample rate for conversion to an analog signal and application to the associated transducer element(s). The beamformer transmitters can be programmed per channel and per beam with carrier frequency, delay, apodization and calibration values. For pulsed wave operation, pulse waveform parameters can be specified to the beamformer transmitters on a per firing basis, without degrading the scan frame rate to non-useful diagnostic levels. Waveform parameters can be specified to the transmitters by an external central control system which is responsible for higher level flexibility, such as scan formats, focusing depths and fields of view. The transmit pulse delay specified per-channel to each transmitter is applied in at least two components: a focusing time delay component and a focusing phase component. The carrier frequency can be specified for each transmit beam, to any desired frequency within a substantially continuous predefined range of frequencies, and a beam-interleaved signal processing path permits operation in any of several predefined processing modes, which define different parameter sets in a trade-off among (1) the number of beams produced; (2) per-beam initial waveform sample interval; and (3) transmit frequency.
Owner:ACUSON
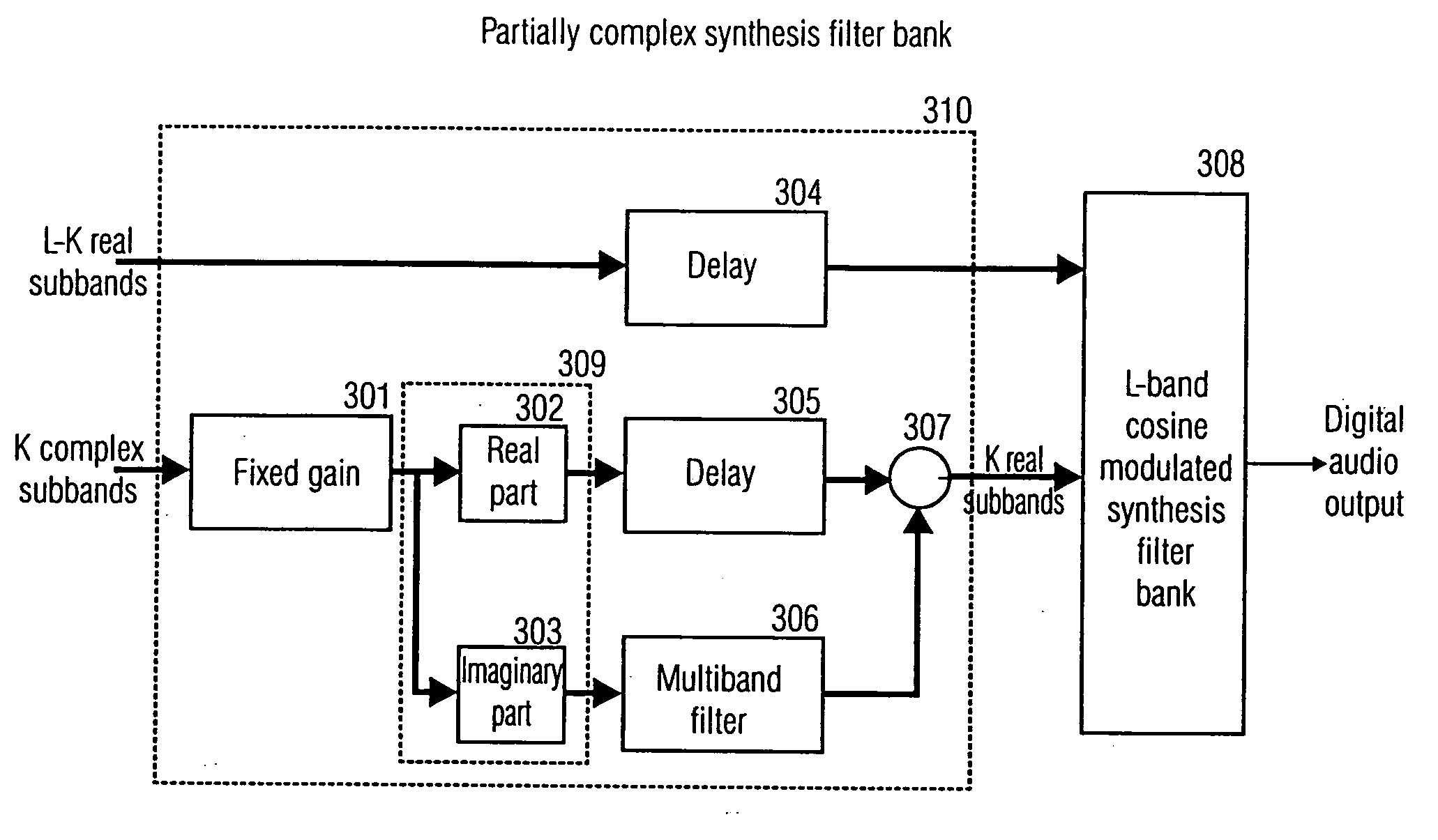
Partially complex modulated filter bank
ActiveUS20070100612A1Reduce signalingQuality improvementDigital technique networkSpeech analysisEngineeringFilter bank
An apparatus for processing a plurality of real-valued subband signals using a first real-valued subband signal and a second real-valued subband signal to provide at least a complex-valued subband signal comprises a multiband filter for providing an intermediate real-valued subband signal and a calculator for providing the complex-valued subband signal by combining a real-valued subband signal from the plurality of real-valued subband signals and the intermediate subband signal.
Owner:DOLBY INT AB
Interactive spacetime constraints: wiggly splines
Animation techniques for producing physically-realistic animation while providing the interactivity and control desired by animators. Techniques are provided specifying animation for motion problems that give rise to quadratic optimization functions solvable with linear systems of equations. The resultant splines generalize traditional splines to encompass oscillatory solutions. These problems can be solved at full frame rates, giving animators a keyframe animation tool. Such a formulation is able to address a wide range of oscillatory phenomena while retaining the interactive performance and predictability of traditional splines. The splines may be complex-valued.
Owner:PIXAR ANIMATION
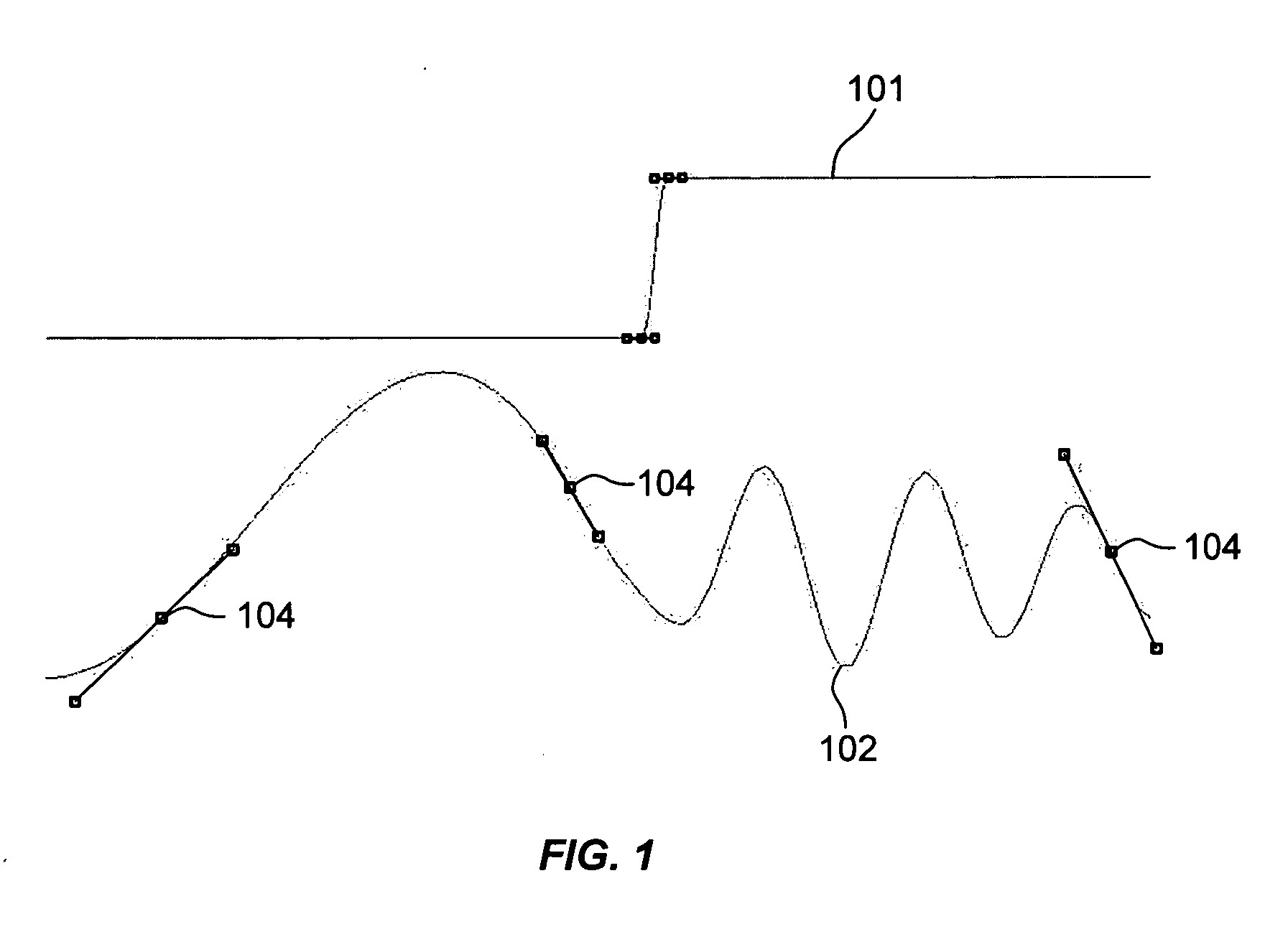
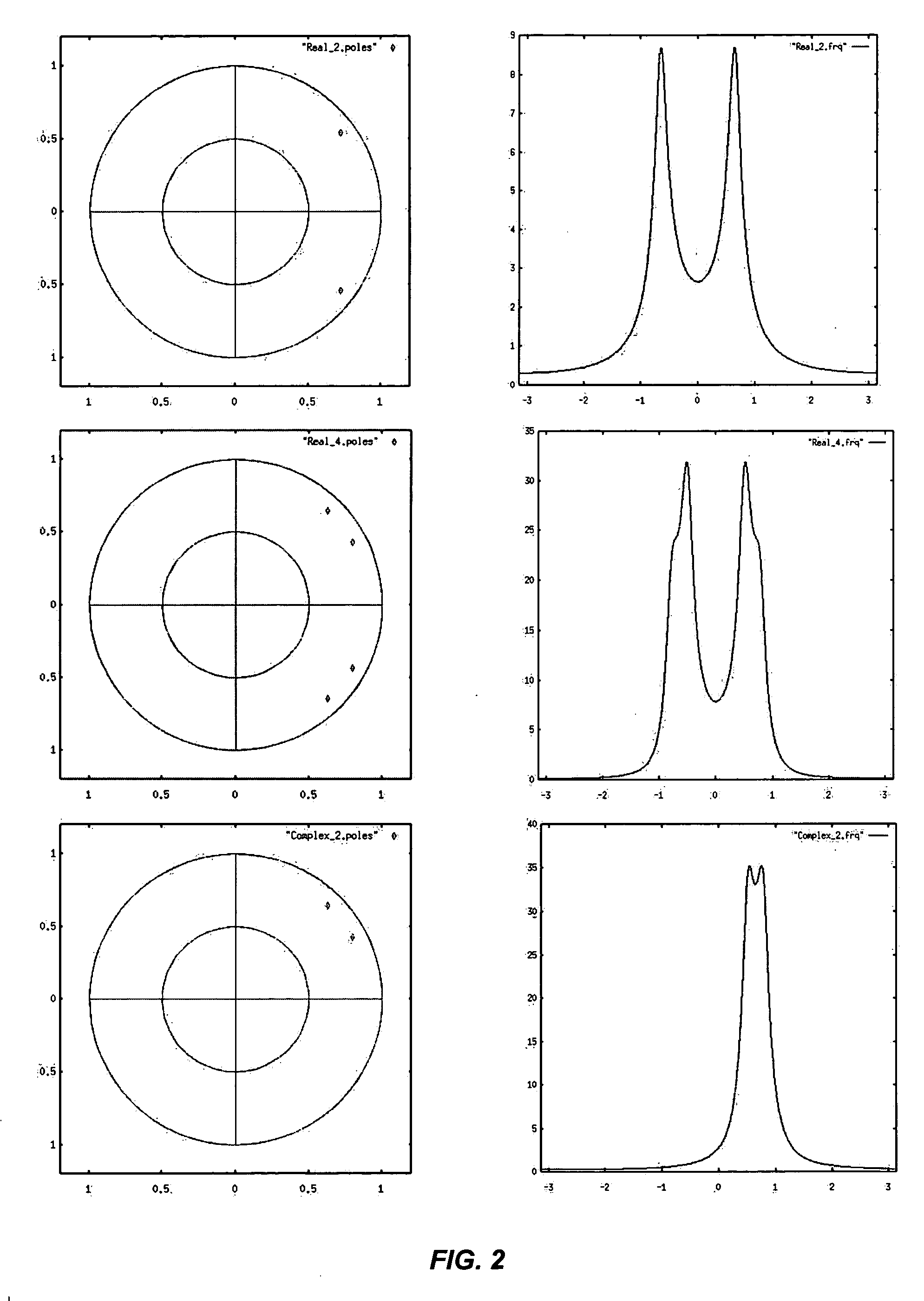
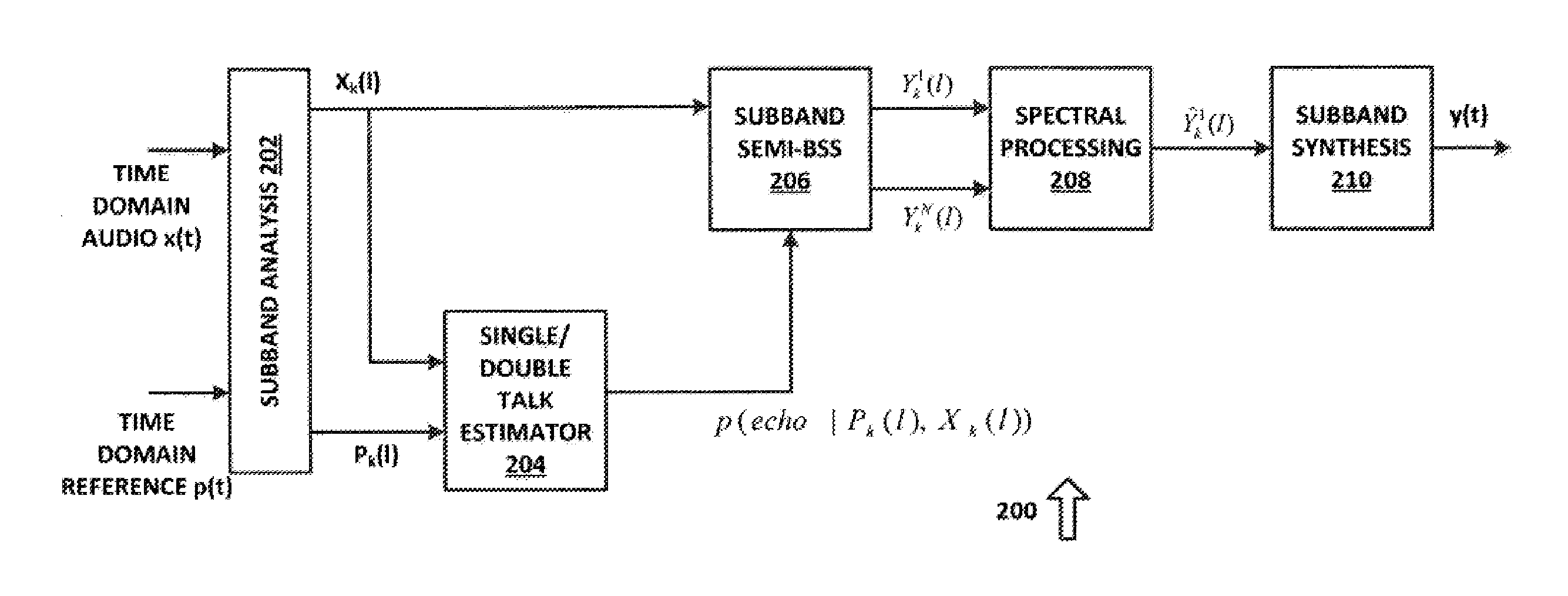
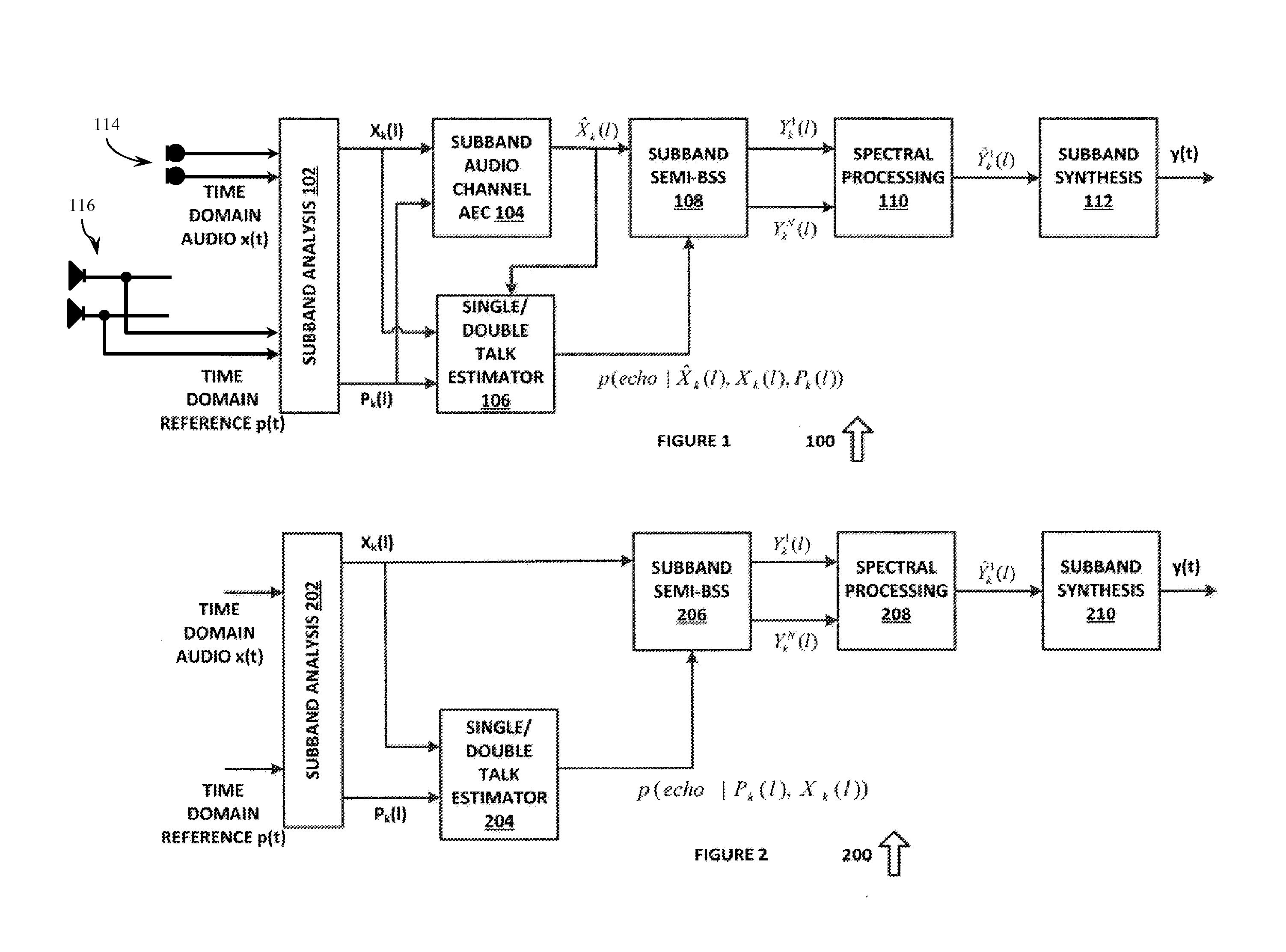
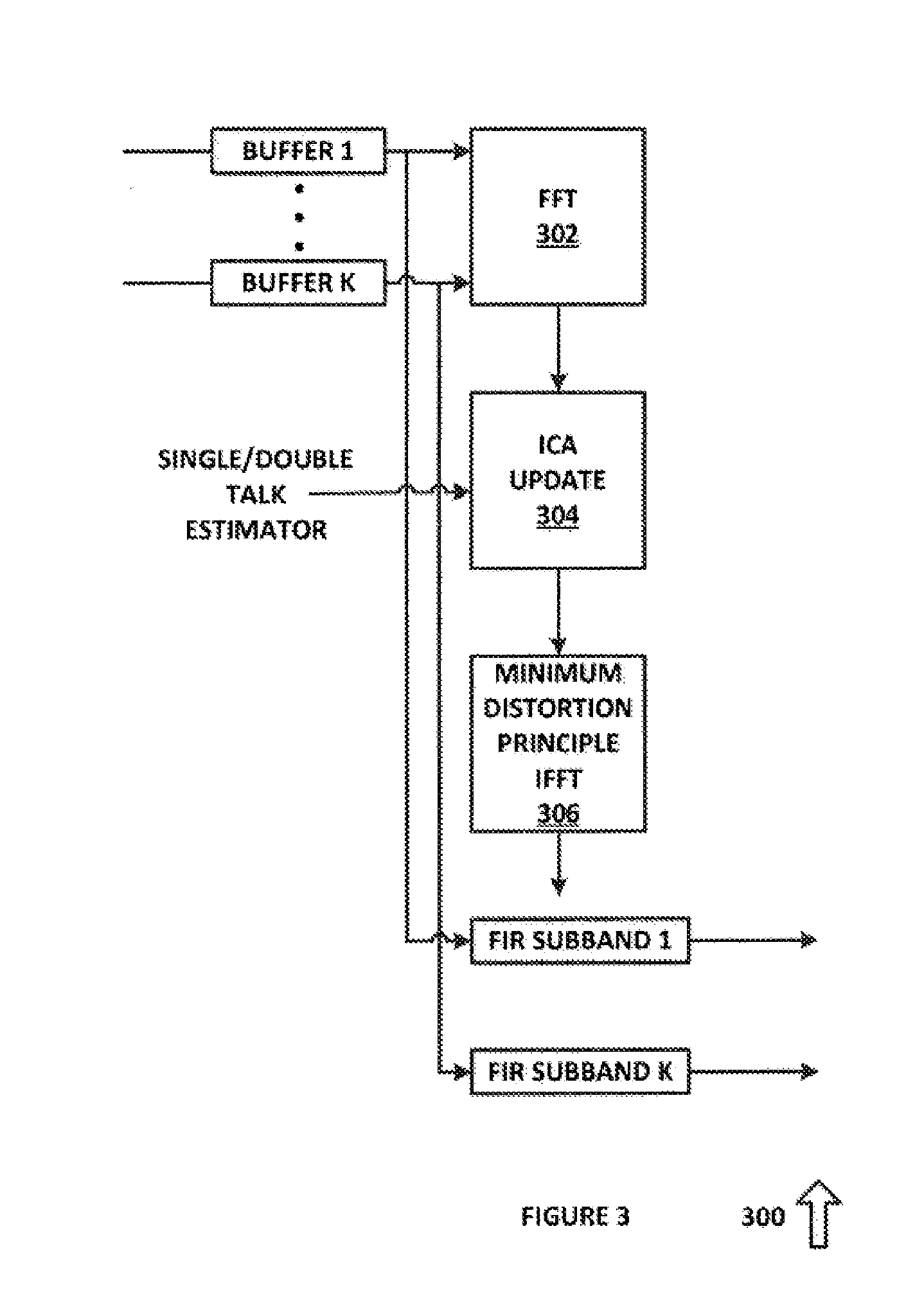
Robust acoustic echo cancellation for loosely paired devices based on semi-blind multichannel demixing
A method for echo cancellation in multichannel audio signals includes receiving a plurality of time-domain signals, including multichannel audio signals and at least one reference signal, transforming the time-domain signals to K under-sampled complex-valued subband signals using an analysis filter bank, and performing, for each of the K under-sampled complex-value subband signals, linear echo cancellation of the reference signal from each channel using an acoustic echo canceller. A probability of acoustic echo dominance is produced using a single-double talk estimator, and a semi-blind multichannel source separation is performed based on the probability and independent component analysis (“ICA”) to decompose the audio signals into a near-end source signal and a residual echoes using subband semi-blind source separation. The residual echo components are removed from the near-end source signal using a spectral filter bank, and the subband audio signals are reconstructed to a multichannel time-domain audio signal using a subband synthesis filter.
Owner:SYNAPTICS INC
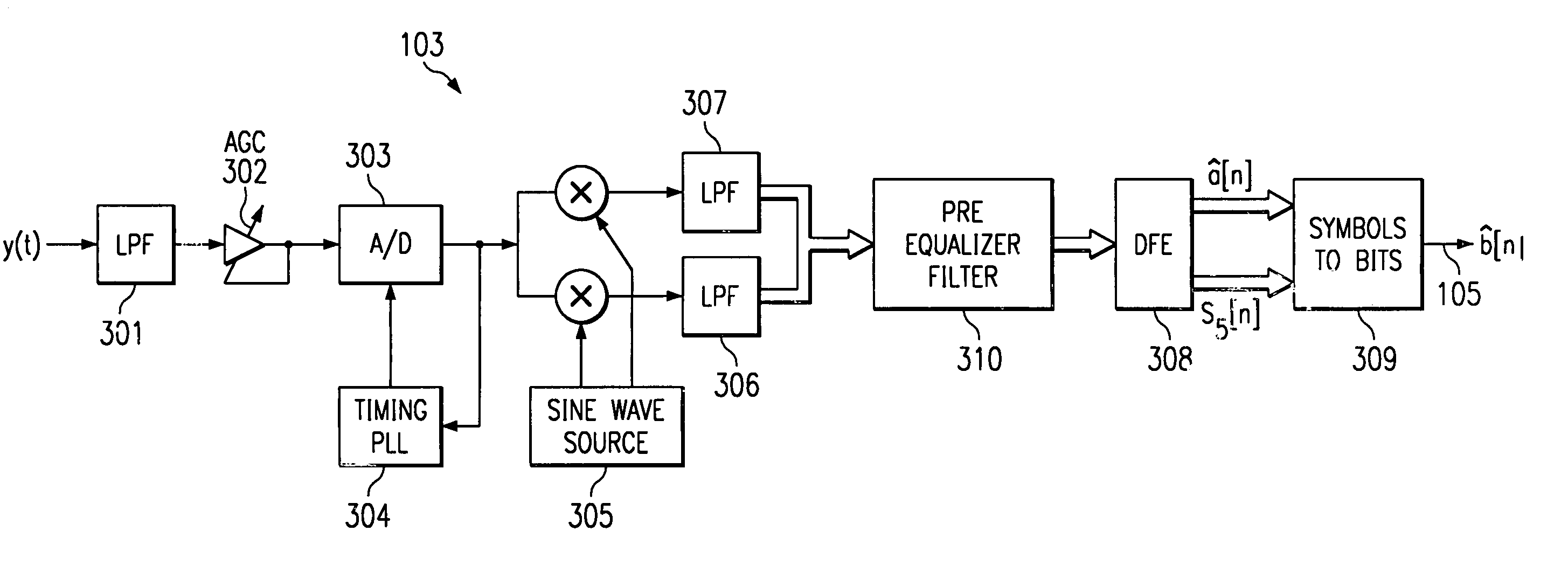
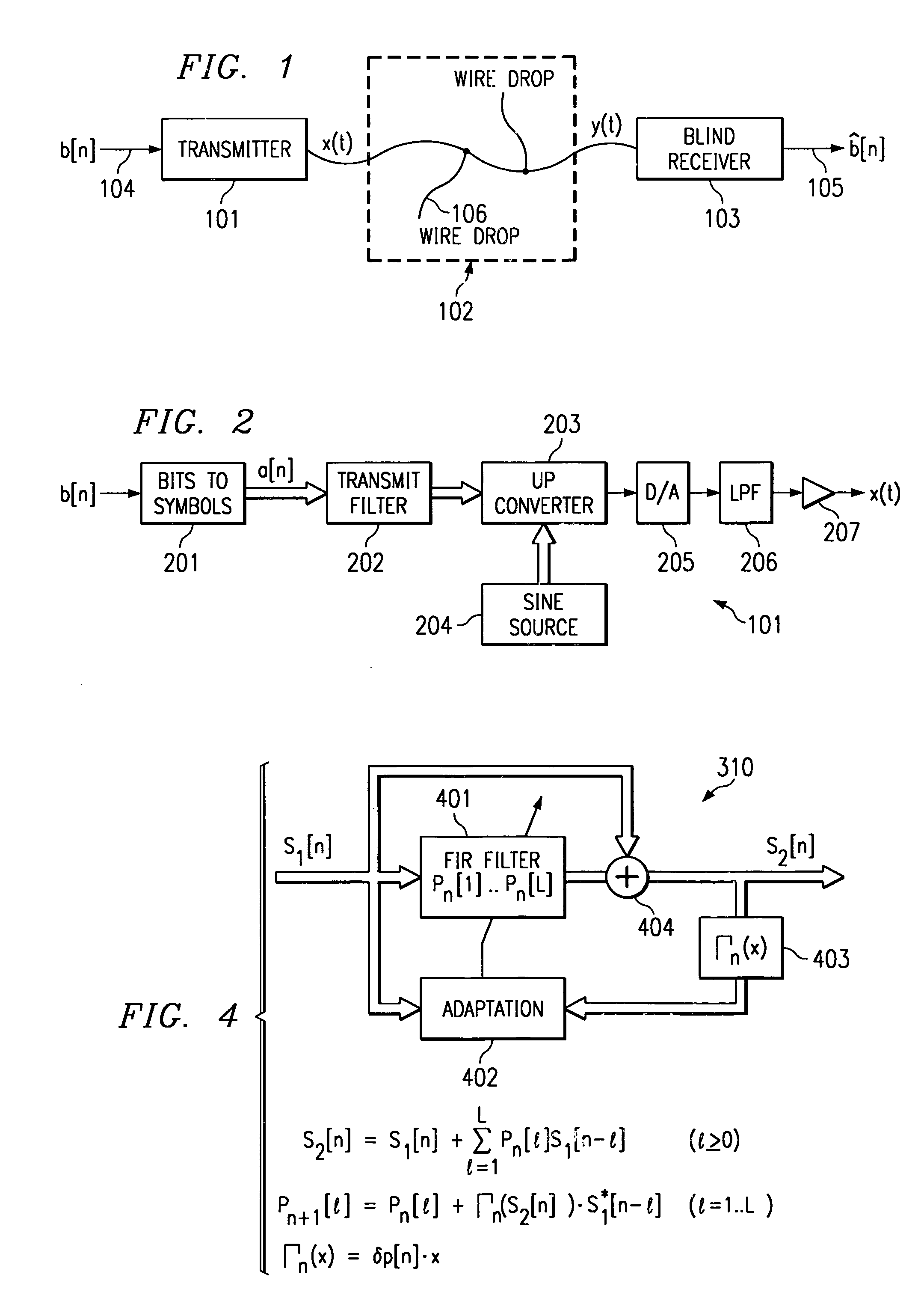
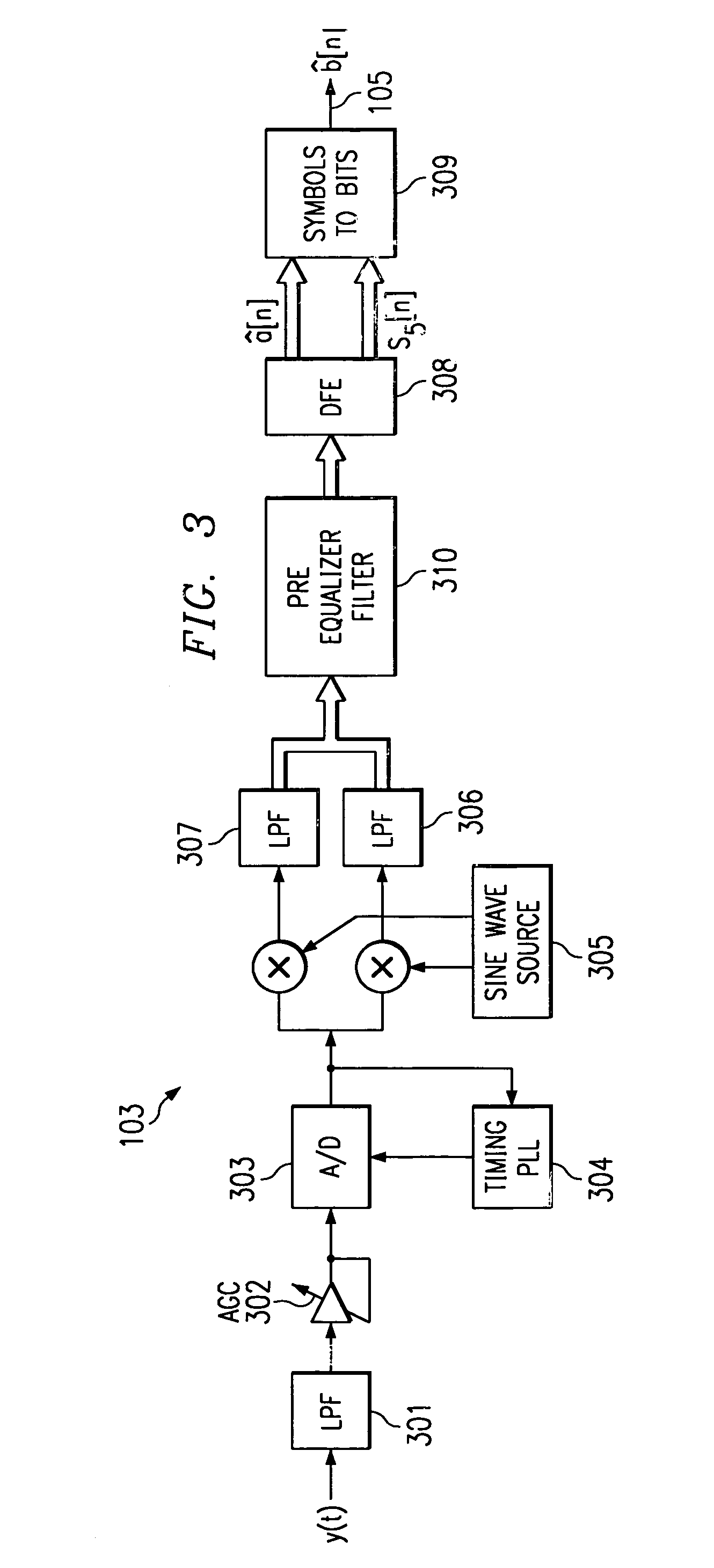
Blind DFE and phase correction
InactiveUS6952444B1Reduce eigen value spread correlationInterfere with removalMultiple-port networksError preventionPhase correctionAdaptive filter
The digital communications receiver receives an analog signal, modulated with digital information. The receiver converts the analogue signal to a digital signal, and demodulates the digital signal to recover the complex valued components of the transmitted digital signal. The complex valued components are low pass filtered and passed through an adaptive pre-equalizer filter, to reduce eigen value spread. The filtered complex valued signal is then subject to a decision feedback equalization, which operates using a series of adaptive filters additionally to remove artifacts of inter-symbol interference. The resulting filtered and equalized complex valued signal is the converted to a digital signal to recover the digital information.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC +1
Adaptive Complex Gain Predistorter for a Transmitter
ActiveUS20100035554A1Resonant long antennasPower amplifiersLinear regionIn-phase and quadrature components
Symbols are transmitted in a Cartesian transmitter by pre-distorting an input signal X having in-phase and quadrature components using a first compensation lookup table operable to hold complex valued entries to carry out in-phase and quadrature compensation pre-distortion with respect to the input signal to form a pre-distorted signal Z. The pre-distorted signal Z is processed to form an output signal Y using a nonlinear element. A complex gain normalization parameter adaptively updated to reflect varying gain of a linear region of the nonlinear element. A normalized feed back signal {tilde over (Y)} is formed using the adaptively updated complex gain normalization parameter. The first compensation lookup table is updated based on the pre-distorted input signal Z and the adaptively normalized feedback signal {tilde over (Y)}.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
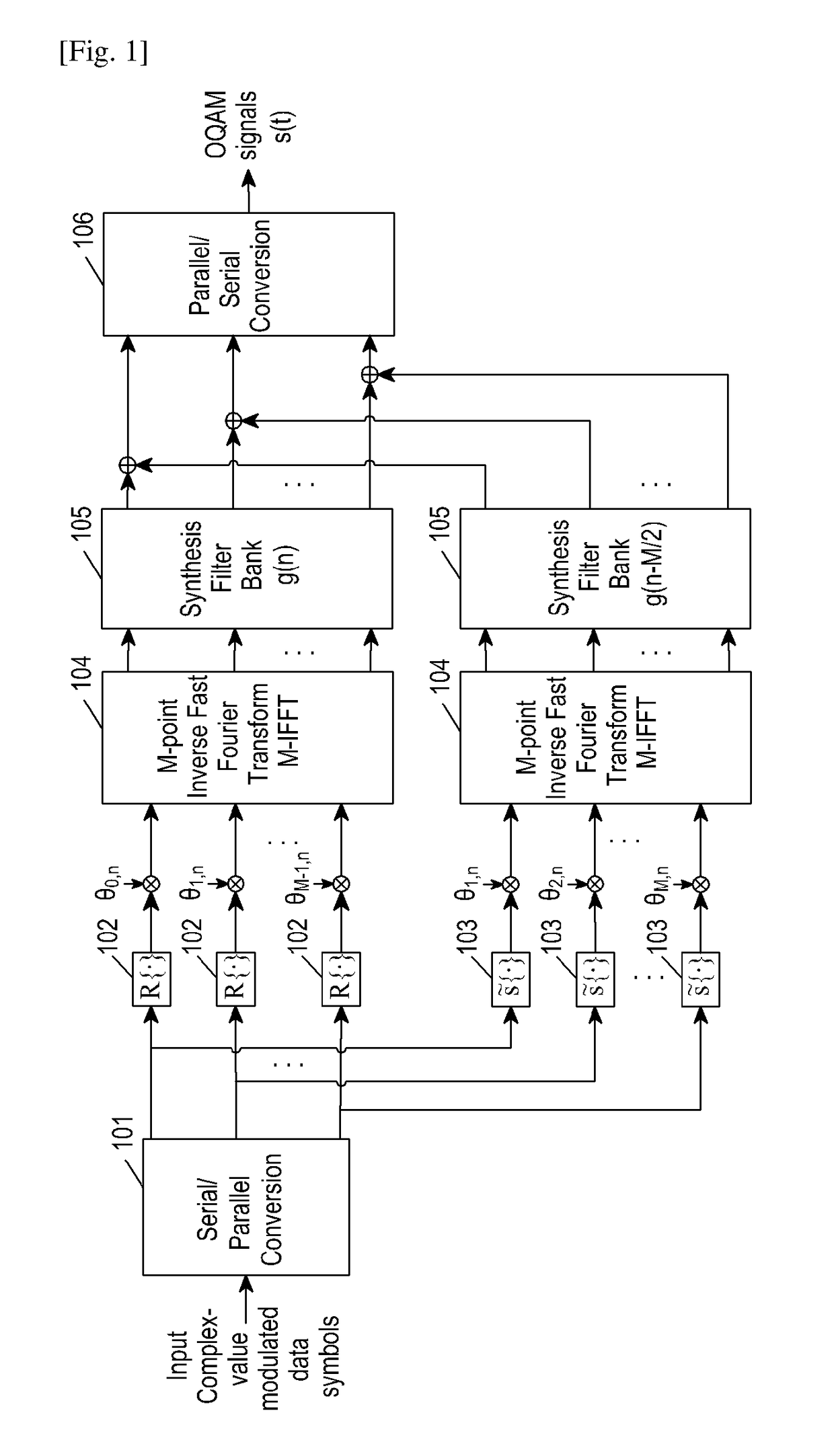
Method and apparatus for generating, transmitting and receiving signals based on filter bank in wireless communication system
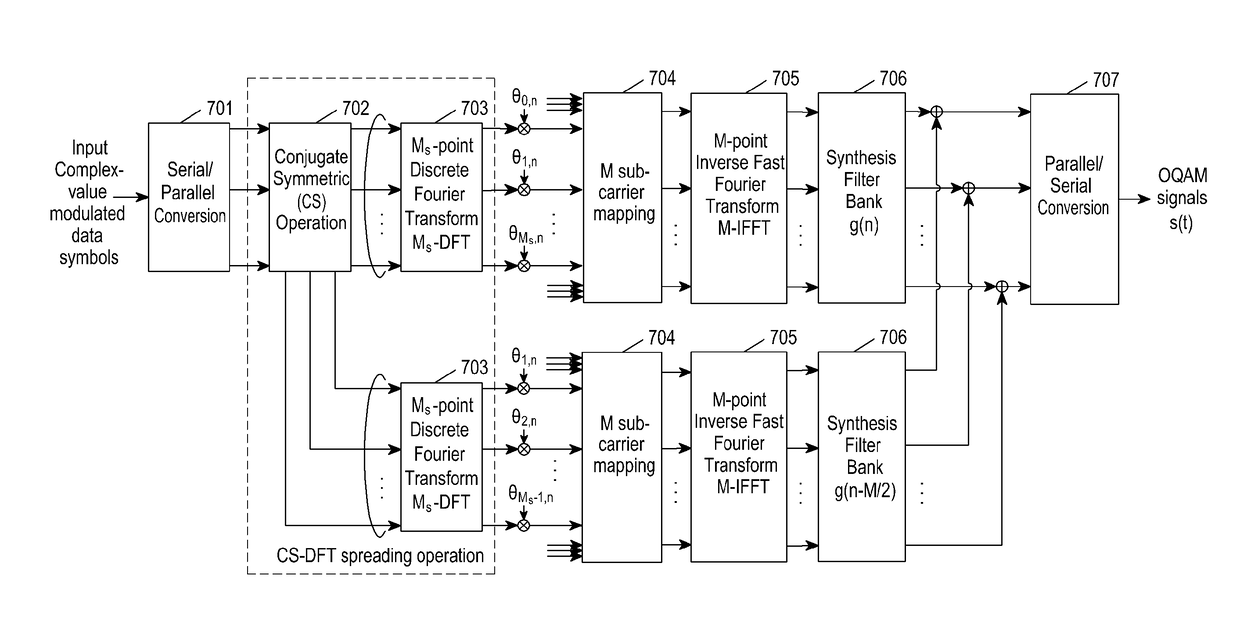
ActiveUS20170134203A1Comparable performanceMaintenance characteristicRadio transmissionMulti-frequency code systemsCommunications systemData stream
The present disclosure relates to a communication method and system for converging a 5G communication system for supporting higher data rates beyond a 4G system with a technology for IoT. The present disclosure may be applied to intelligent services based on the 5G communication technology and the IoT-related technology, such as smart home, smart building, smart city, smart car, connected car, health care, digital education, smart retail, security and safety services. The present application discloses a method and device for transmitting and receiving signals based on a filter bank. The device comprises: a CS-DFT spreading unit for generating two data flows by applying a CS-DFT spreading operation to a first complex-value data flow input thereto; a sub-carrier mapping unit for mapping each of the two data flows to corresponding sub-carriers; and an OQAM modulator for generating OQAM signals by applying an OQAM operation to the data flows mapped on sub-carriers.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
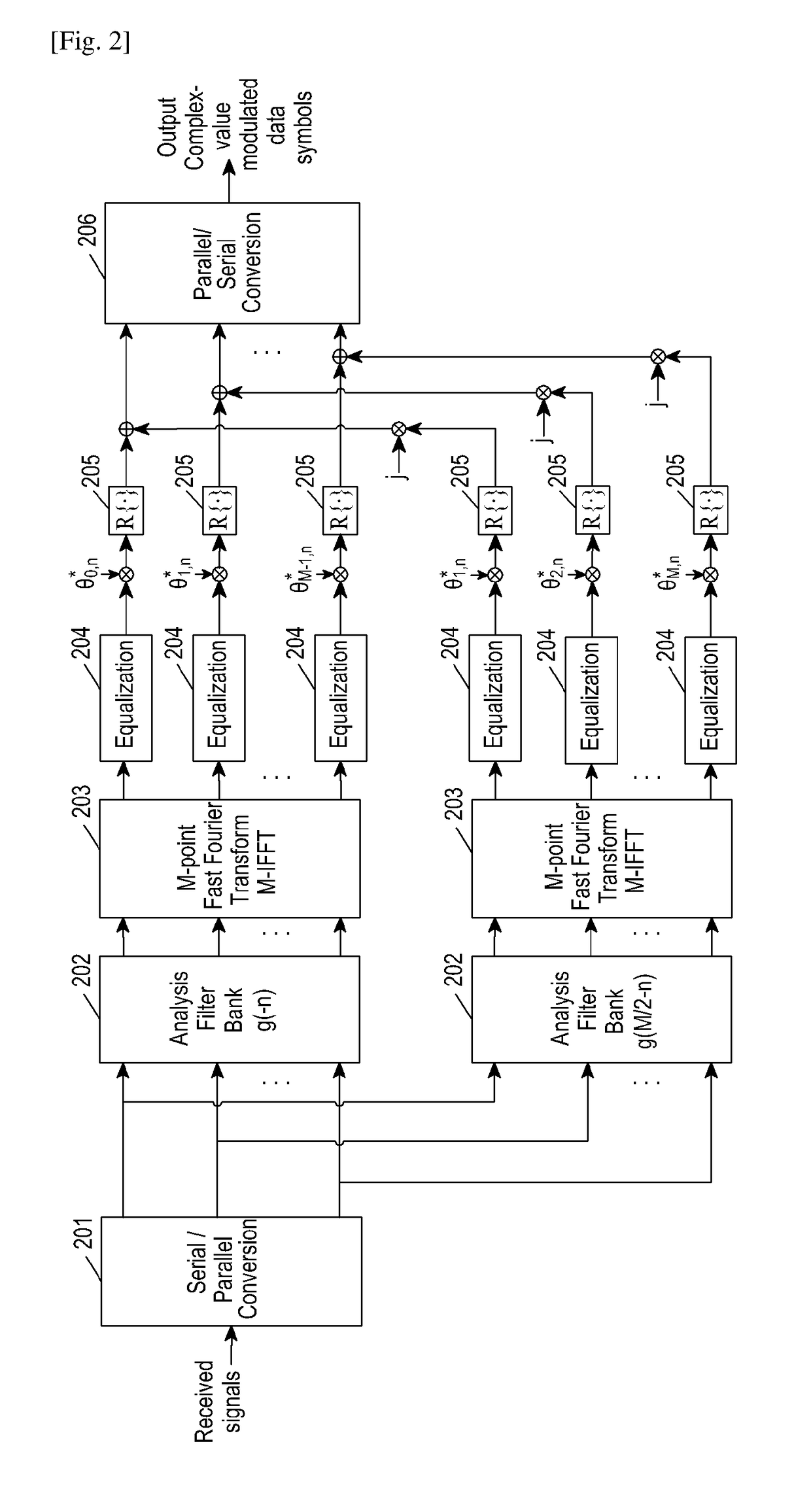
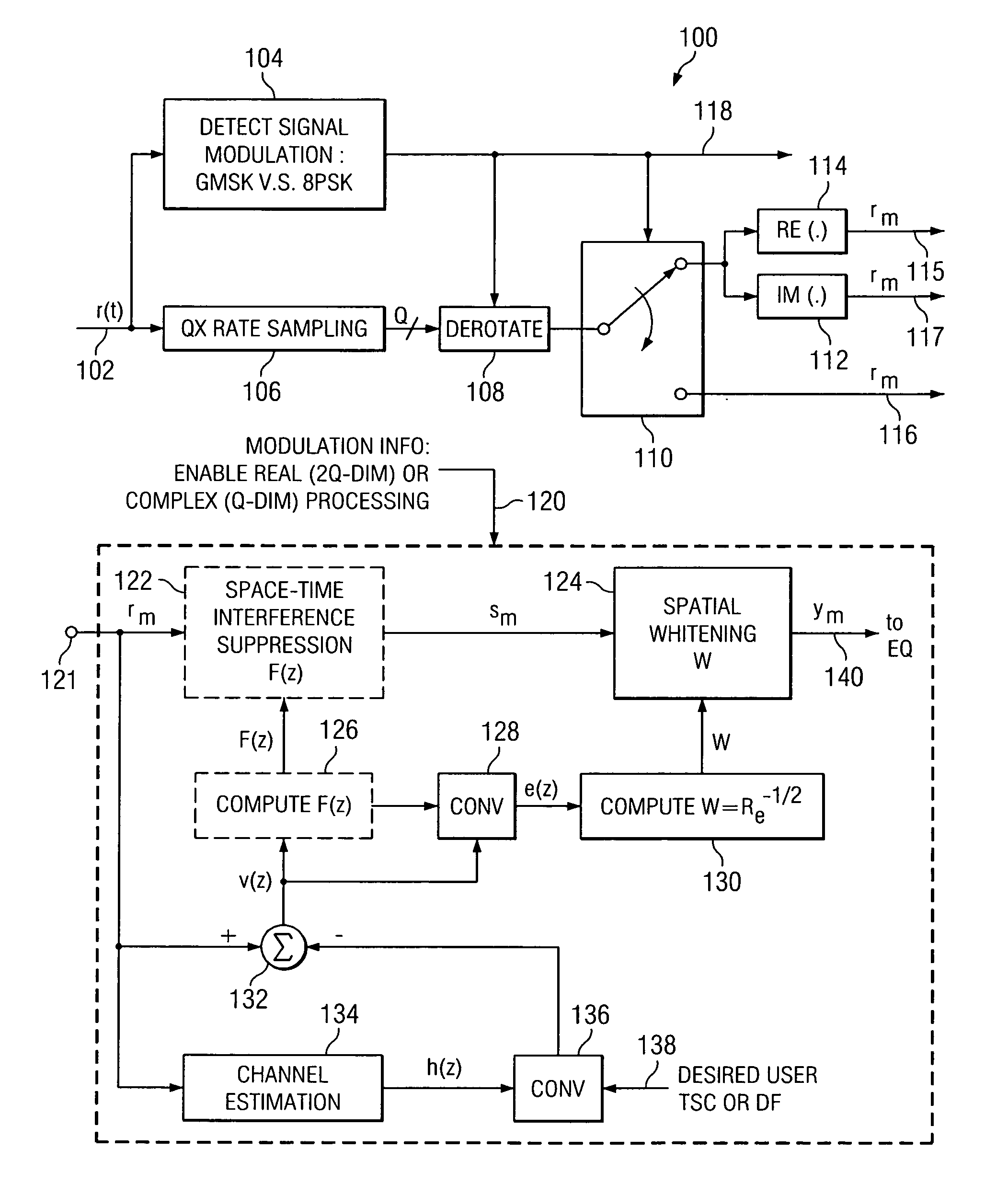
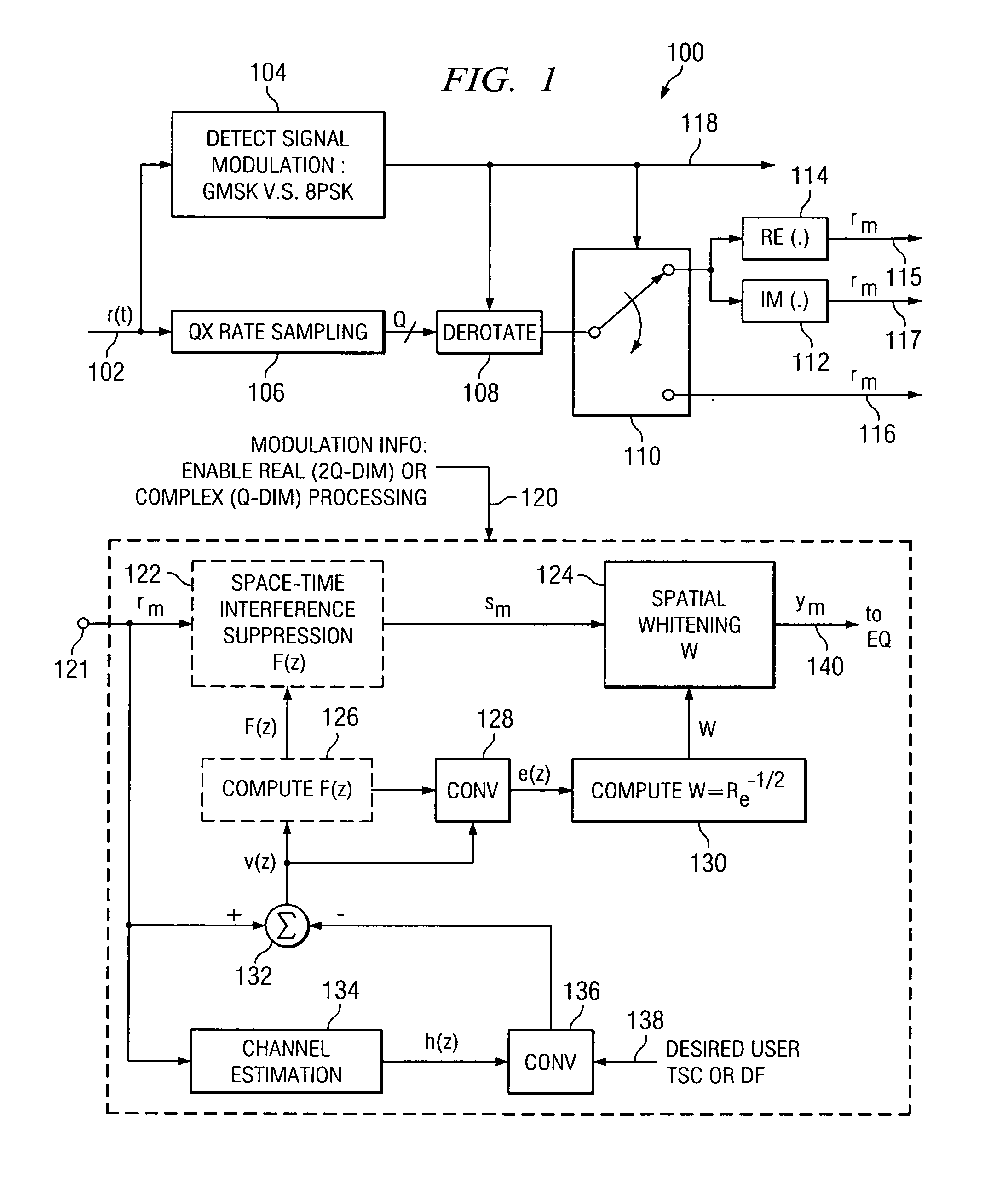
Linear interference cancellation receiver for edge systems
A method for providing interference suppression in a communication device includes receiving a signal, determining if the received signal comprises a Gaussian Minimum Shift Keying (GMSK) or an 8 phase shift keying (8PSK) signal. Over sampling and inphase and quadrature phase separation with real-valued signal processing on the received signal is performed whenever the received signal is determined to be a GMSK signal. Oversampling with complex-valued signal processing on the received signal is performed whenever the received signal is determined to be an 8PSK signal. A receiver is also disclosed that provides for interference suppression.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Residual frequency error estimation in an OFDM receiver
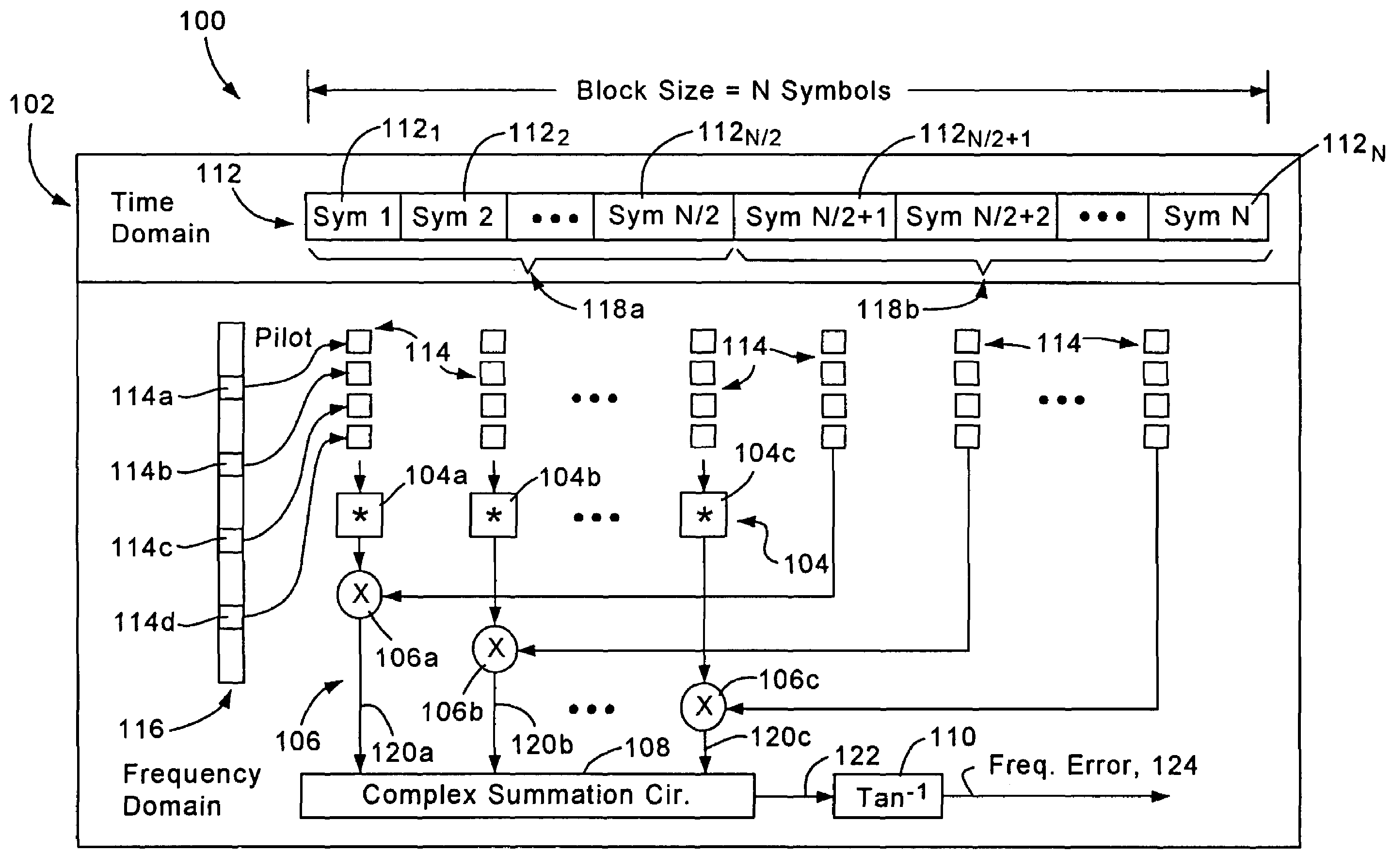
ActiveUS7292527B2Accurate estimatePrecise elimination of frequency errorMultiplex system selection arrangementsSpecial service provision for substationSymbol of a differential operatorComplex valued
An OFDM receiver configured for measuring frequency error based on comparing prescribed pilot tones from a prescribed group of consecutive symbols in a received OFDM signal. A complex conjugate generator is configured for generating complex conjugates of the prescribed pilot tones of a first subgroup of the consecutive symbols. A multiplier is configured for generating a complex pilot product, for each symbol subgroup position, by multiplying the pilot tones of a second subgroup symbol at the corresponding symbol subgroup position with the respective complex conjugates of the first subgroup symbol at the corresponding symbol subgroup position. A complex summation circuit sums the complex pilot products of the symbol subgroup positions to obtain an accumulated complex value. A error calculator calculates the frequency error from the accumulated complex value for use in correcting frequency offset.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
Driving Techniques for Phased-Array Systems
ActiveUS20180166063A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMechanical vibrations separationPhased arrayComputer science
Various techniques for driving phased array systems are described, specifically intended for acoustic phased arrays with applications to mid-air haptics, parametric audio, acoustic levitation and acoustic imaging, including a system: 1) that is capable of mitigating the effect of the changes in the air to provide a consistent haptic experience; 2) that produces trap points in air; 3) that defines phased-array optimization in terms of vectors for the production of more consistent haptic effects; 4) that defines one or more control points or regions in space via a controlled acoustic field; 5) that uses a reduced representation method for the construction of acoustic basis functions; 6) that performs efficient evaluation of complex-valued functions for a large quantity of throughput; 7) that generates a Krylov sub-space of a matrix; and 8) that maximizes an objective described by different control points and / or regions to those used to create the acoustic basis functions.
Owner:ULTRAHAPTICS IP LTD
Method, system, and computer program product for executing SIMD instruction for flexible FFT butterfly
InactiveUS20050071403A1Reduce in quantityDigital computer detailsProgram controlModem deviceControl register
An FFT butterfly instruction based on single instruction multiple data (“SIMD”) technique is executed to reduce the number of cycles for software to perform FFT butterfly operations. The FFT butterfly instruction can implement one or more instances of the FFT butterfly operation (e.g., non-SIMD, 2-way SIMD, 4-way SIMD, etc.), at once, each instance operating over a set of complex values. A control register or variant opcode controls the behavior of the FFT butterfly operation. The contents of the control register or the variant opcode can be altered to configure the butterfly behavior to suit specific circumstances. The FFT butterfly instruction can be used in the software on a processor in a chip-set implementing the central-office modem end of a DSL link. The FFT butterfly instruction can also be used in other contexts where an FFT function is performed (and / or where an FFT butterfly operation is used) including systems that do not implement DSL or DMT.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
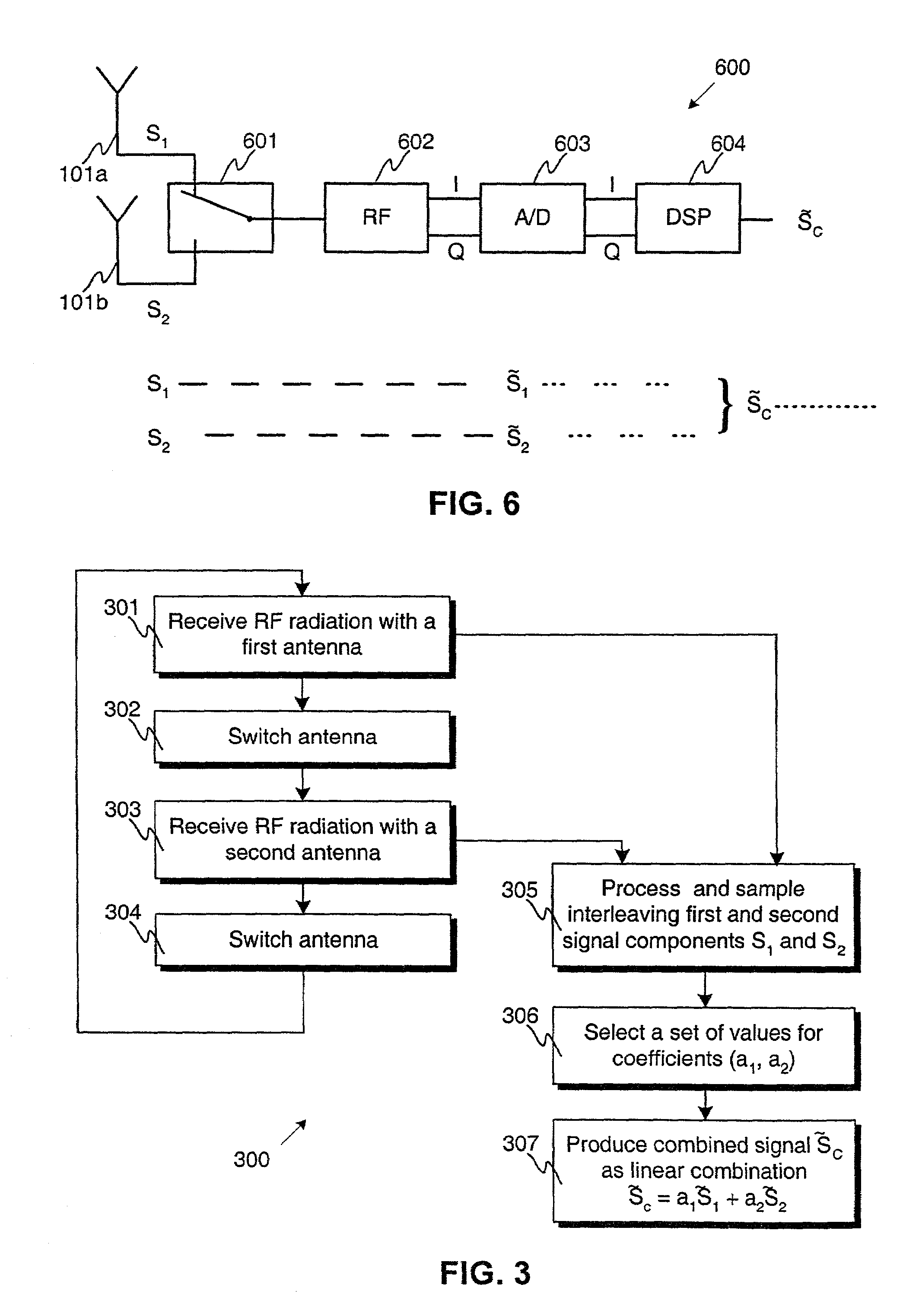
Method for receiving radio frequency signal and a receiver device
ActiveUS7171175B2Maintain good propertiesEasy to produceSpatial transmit diversityPolarisation/directional diversityRadio frequency signalComplex valued
In a method (300) for receiving a radio signal, there are steps of: receiving (301, 303) first and second received signal components by use of first and second antennas having different properties; processing (305) a received signal component to produce a sampled signal component; producing (307) at least one combined signal, which is a linear combination of at least two sampled signal components; and selecting (306) at least one set of complex values for coefficients of the linear combination so that a quality of a combined signal is at least equal to the quality of that sampled signal component having the best quality. Furthermore, the antennas are alternately connected (302, 304) via a switching element to radio frequency means so that received signal components are interleaving and so that first and second parts of a certain piece of transmitted information are received with the first and second antennas, respectively. A corresponding receiver device is also presented.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
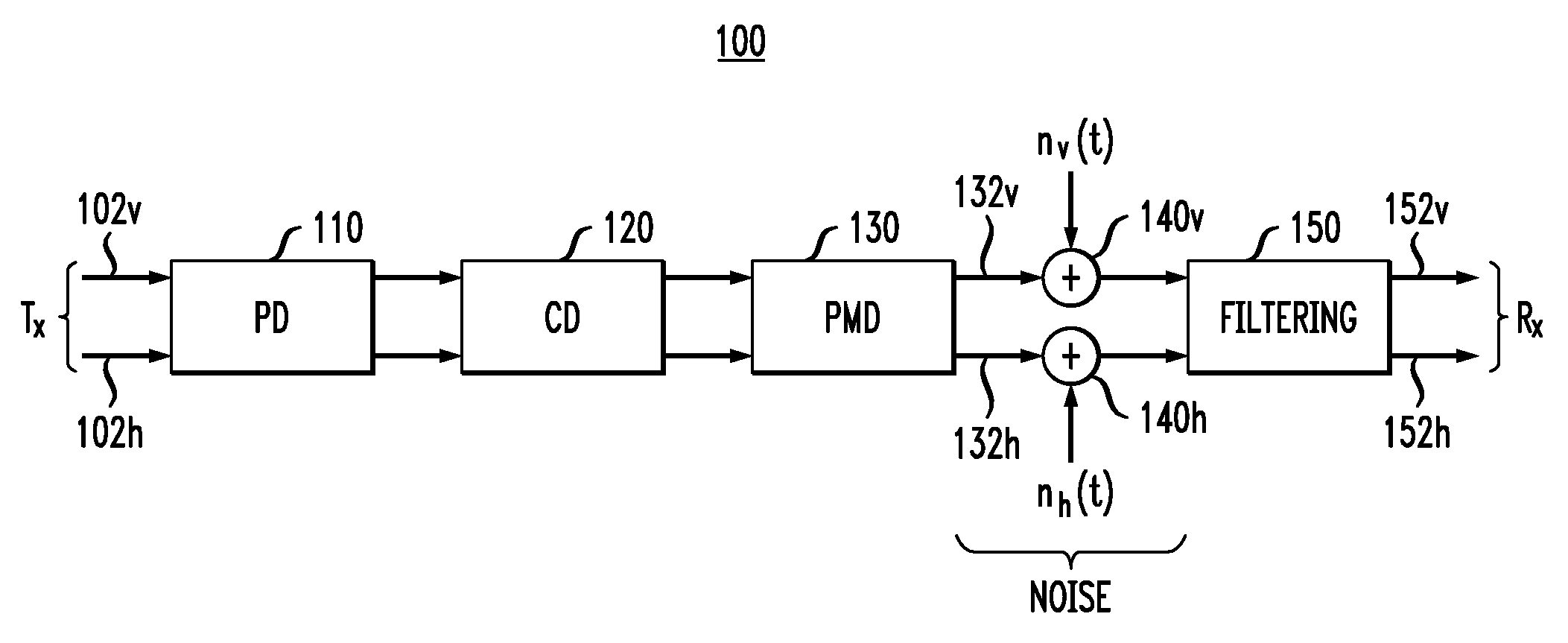
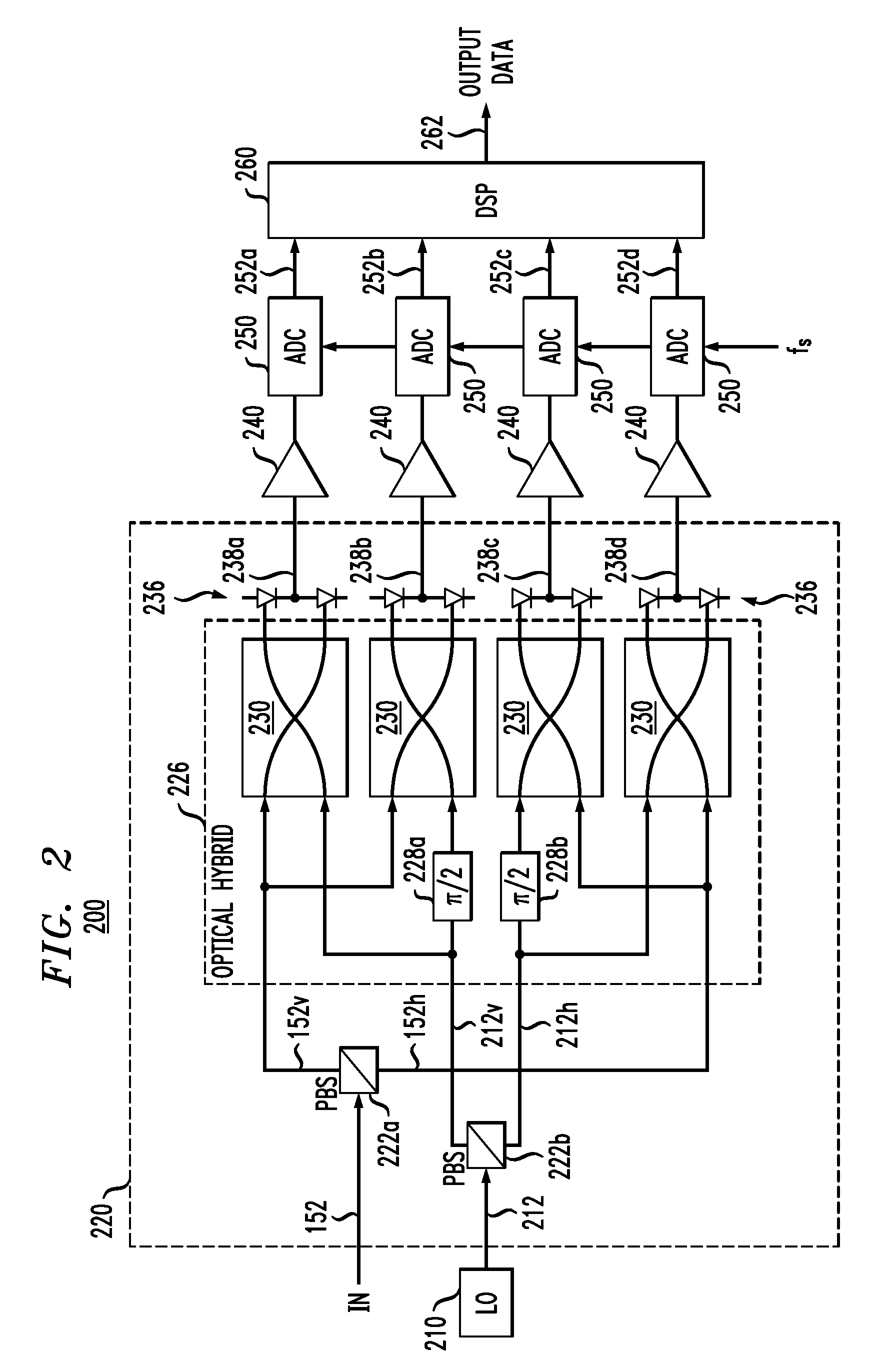
Polarization tracking and signal equalization for optical receivers configured for on-off keying or pulse amplitude modulation signaling
According to one embodiment, an optical receiver adapted to recover OOK or PAM data carried by a modulated optical carrier has an optical detector adapted to produce a sequence of vector pairs having first and second digital vectors indicative of complex values of first and second polarization components, respectively, of the modulated optical carrier at a corresponding sampling time. The optical receiver also has a digital processor that is connected to receive the sequence and is adapted to perform a rotation on each pair in a manner that tends to compensate for polarization rotation produced by transmitting the modulated optical carrier from an optical transmitter thereof to the optical receiver. The digital processor is further adapted to estimate values of the OOK or PAM data encoded onto each of the first and second polarization components based on the vectors produced by the rotation in a manner responsive to values of energy errors in the estimated values.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
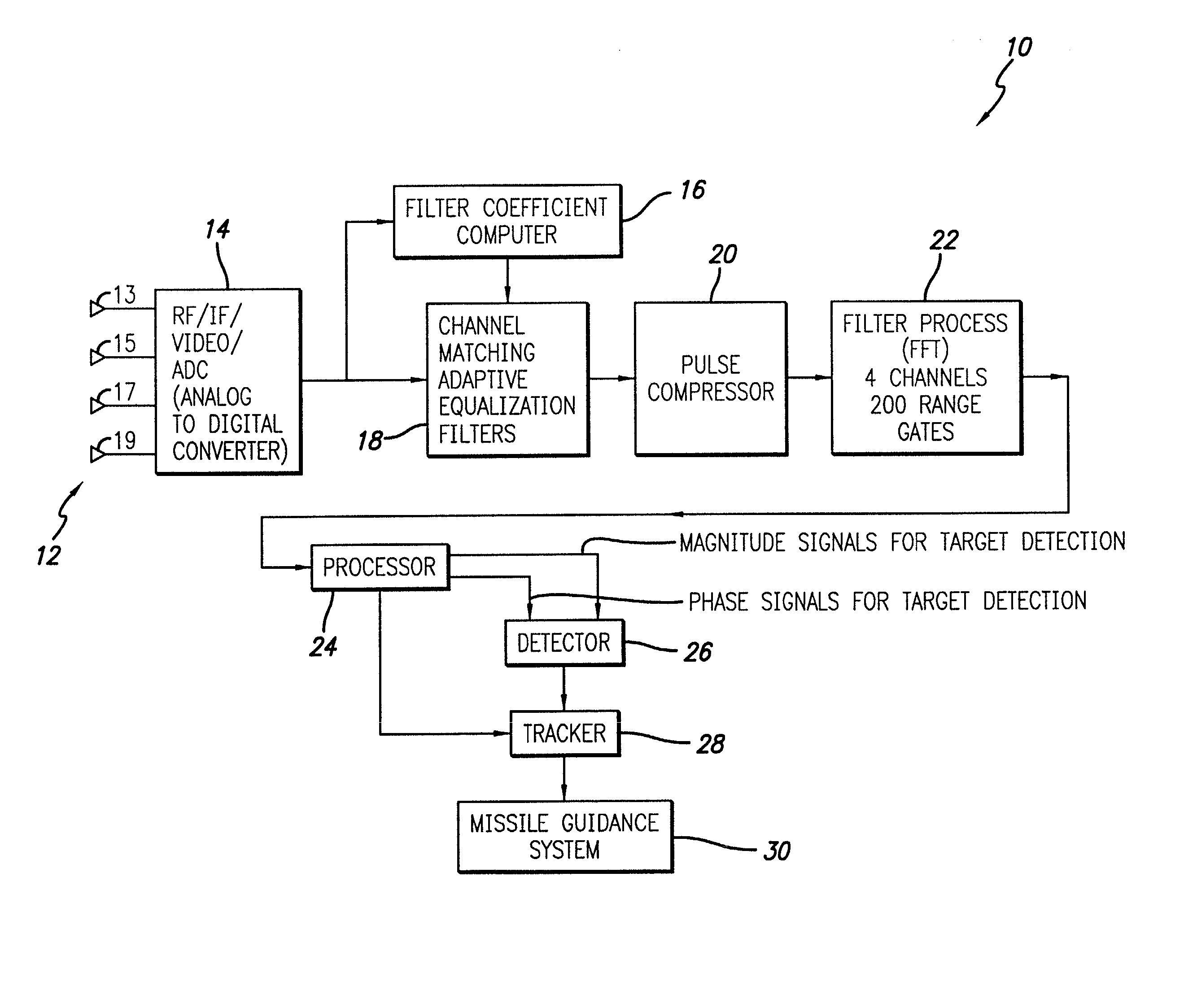
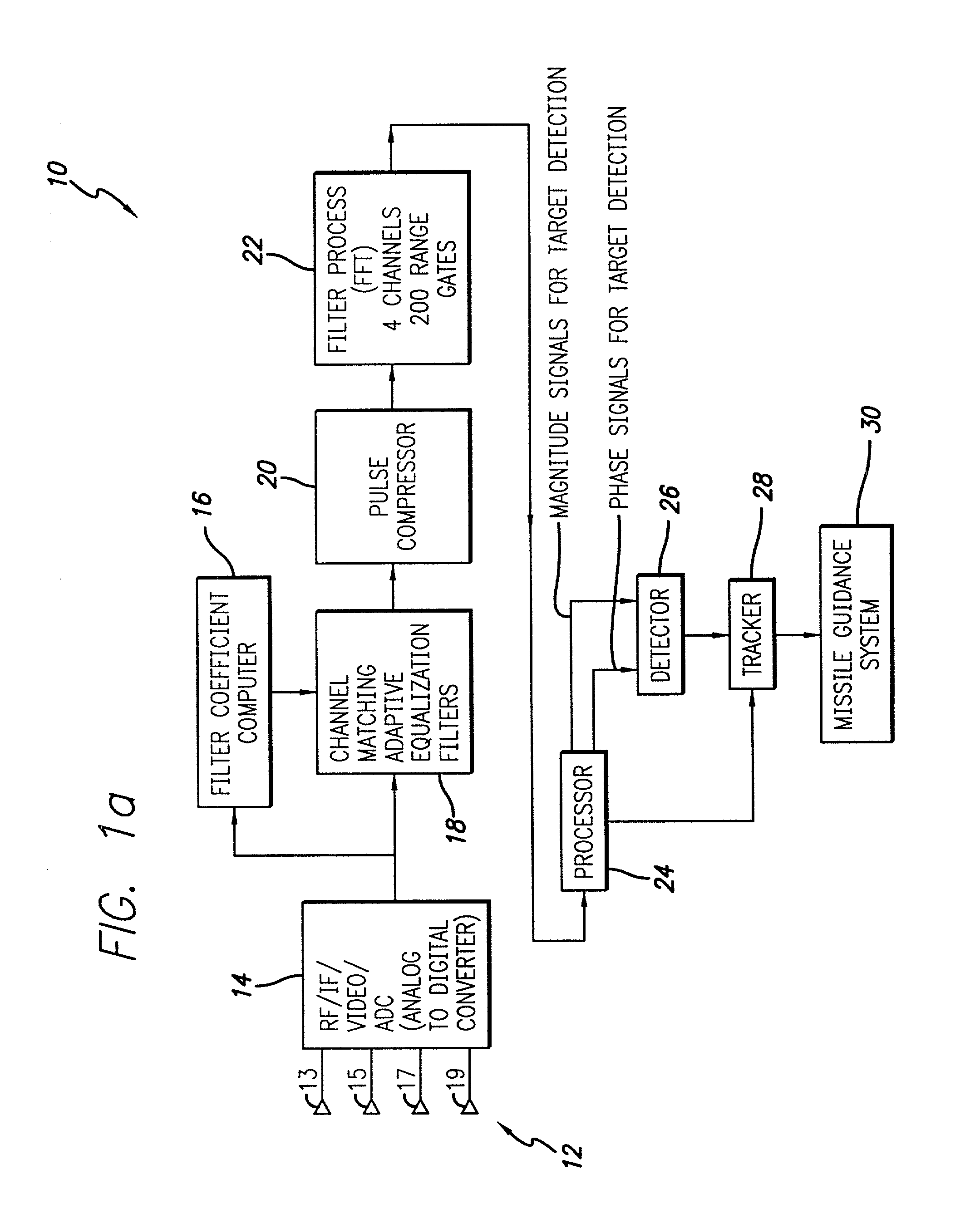
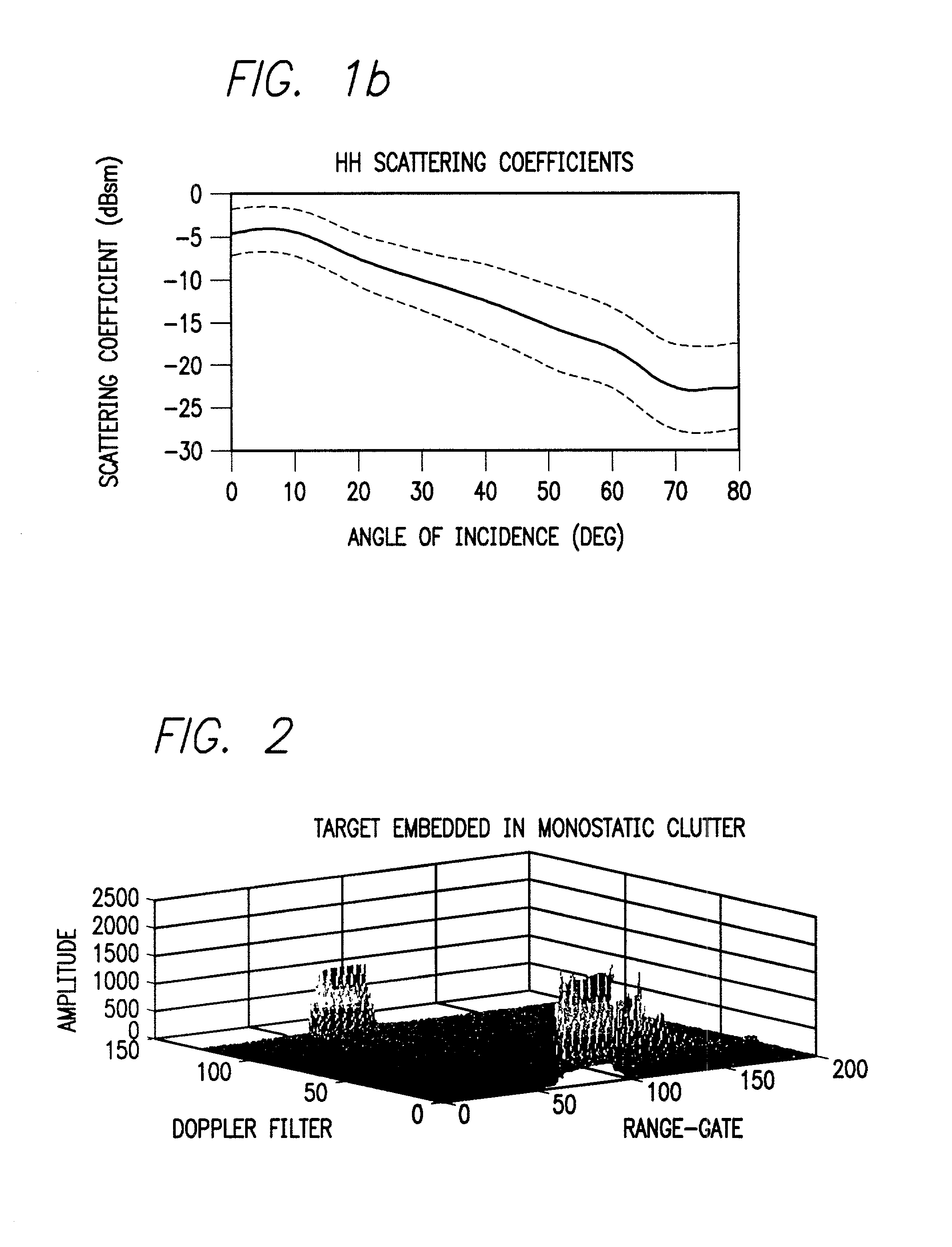
System and method for detecting and estimating the direction of near-stationary targets in monostatic clutter using phase information
InactiveUS20030189512A1Optical rangefindersHeight/levelling measurementElectromagnetic pulseComplex valued
A system and method for detecting a target. The inventive method includes the steps of receiving a complex return signal of an electromagnetic pulse having a real and an imaginary component; extracting from the imaginary component information representative of the phase component of the return signal; and utilizing the phase component to detect the target. Specifically, the phase components are those found from the complex range-Doppler map. More specific embodiments further include the steps of determining a power spectral density of the phase component of the return signal; performing a cross-correlation of power spectral density of the phase component of the return signal between different antenna-subarray (quadrant channels); and averaging the cross-correlated power spectral density of the low frequency components. In an alternative embodiment, the cross-correlation is performed on the phase component of the range-Doppler map directly. This signal can then be averaged to potentially provide improved detection of targets. The cross-correlations of the power spectral densities derived from the complex valued range-Doppler map are then used to detect the target in the presence of monostatic clutter. An additional teaching relates to a utilization of the phase component to ascertain a direction of the target and thereby effect target tracking as well as target detection.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
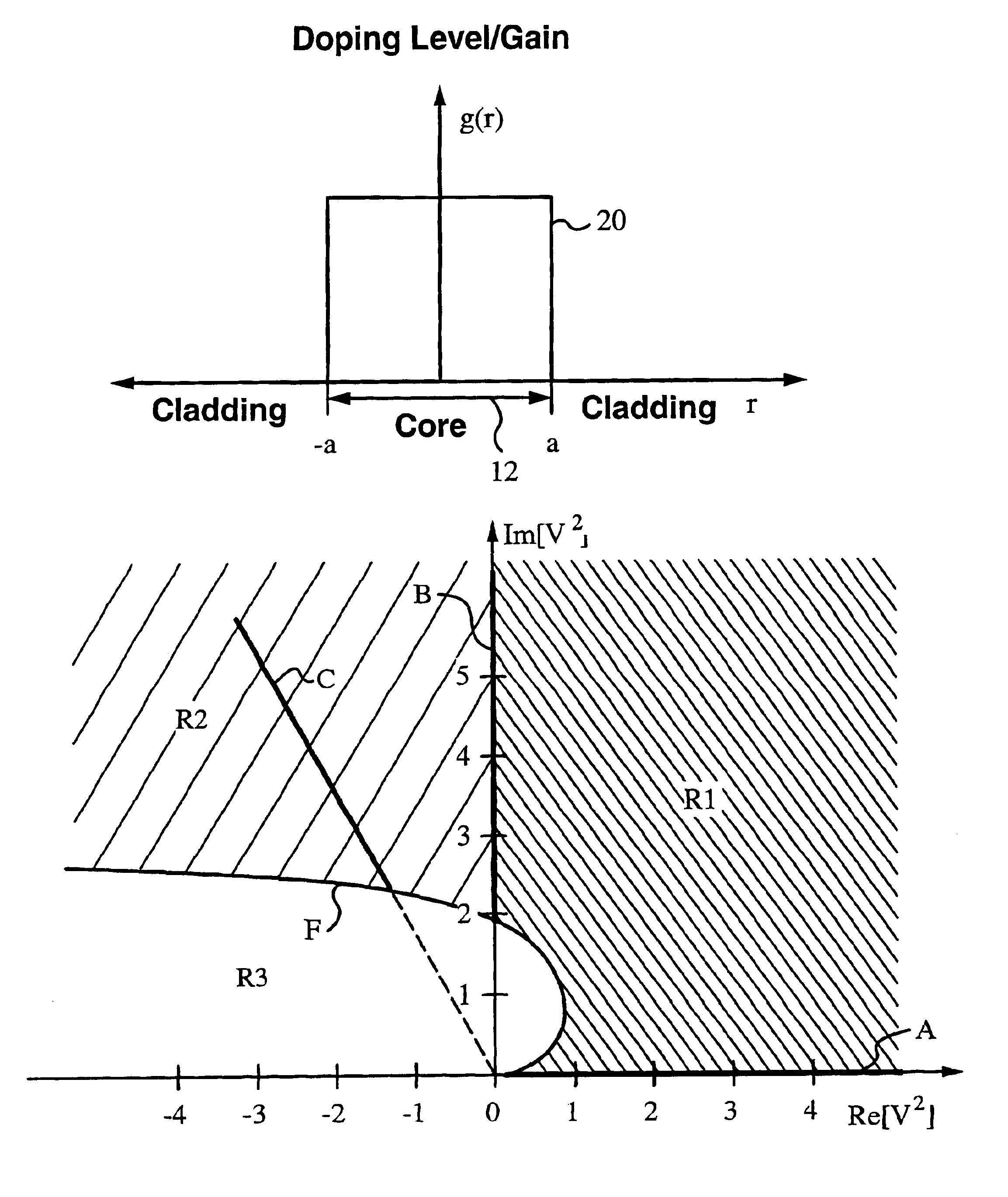
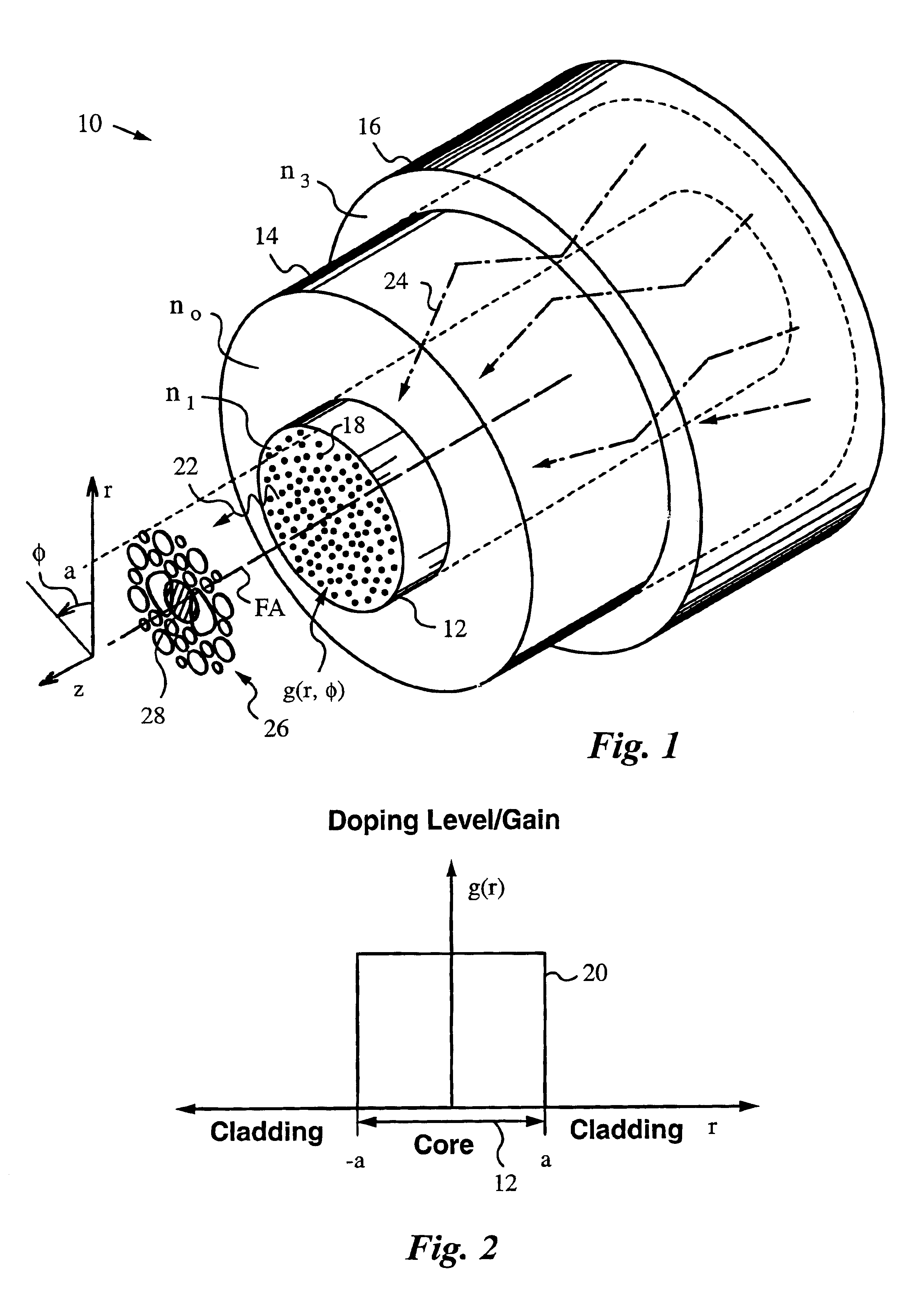
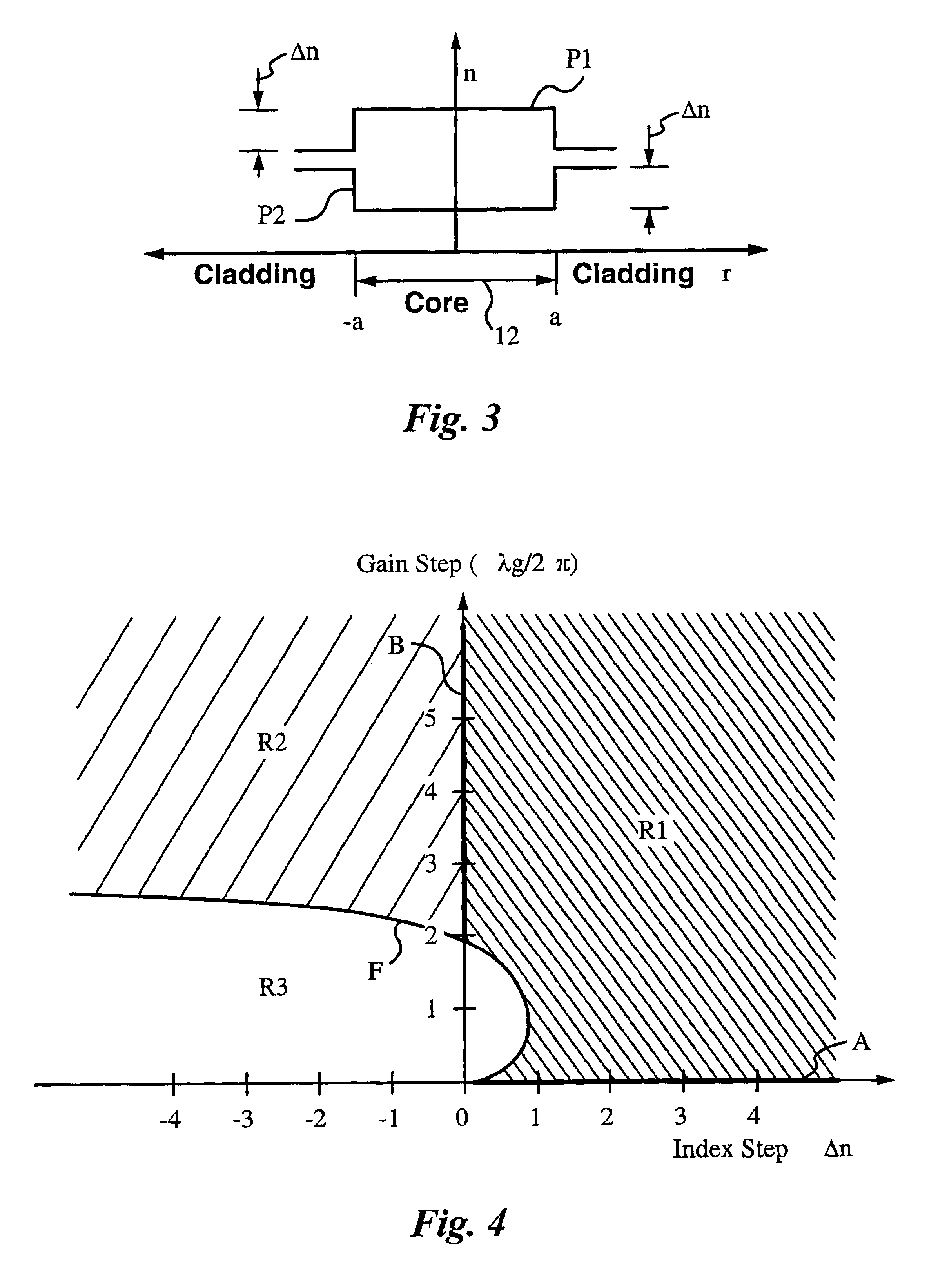
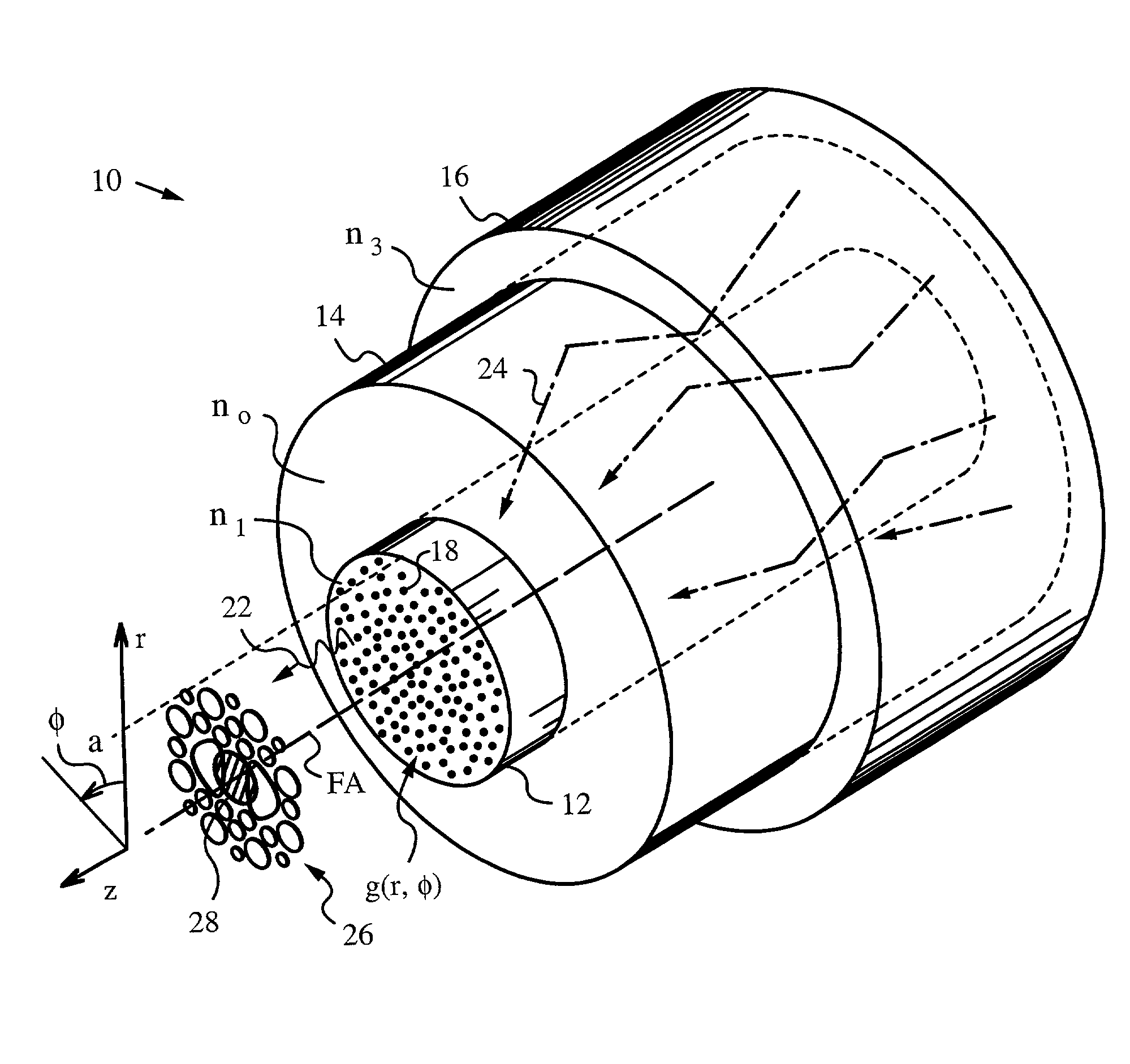
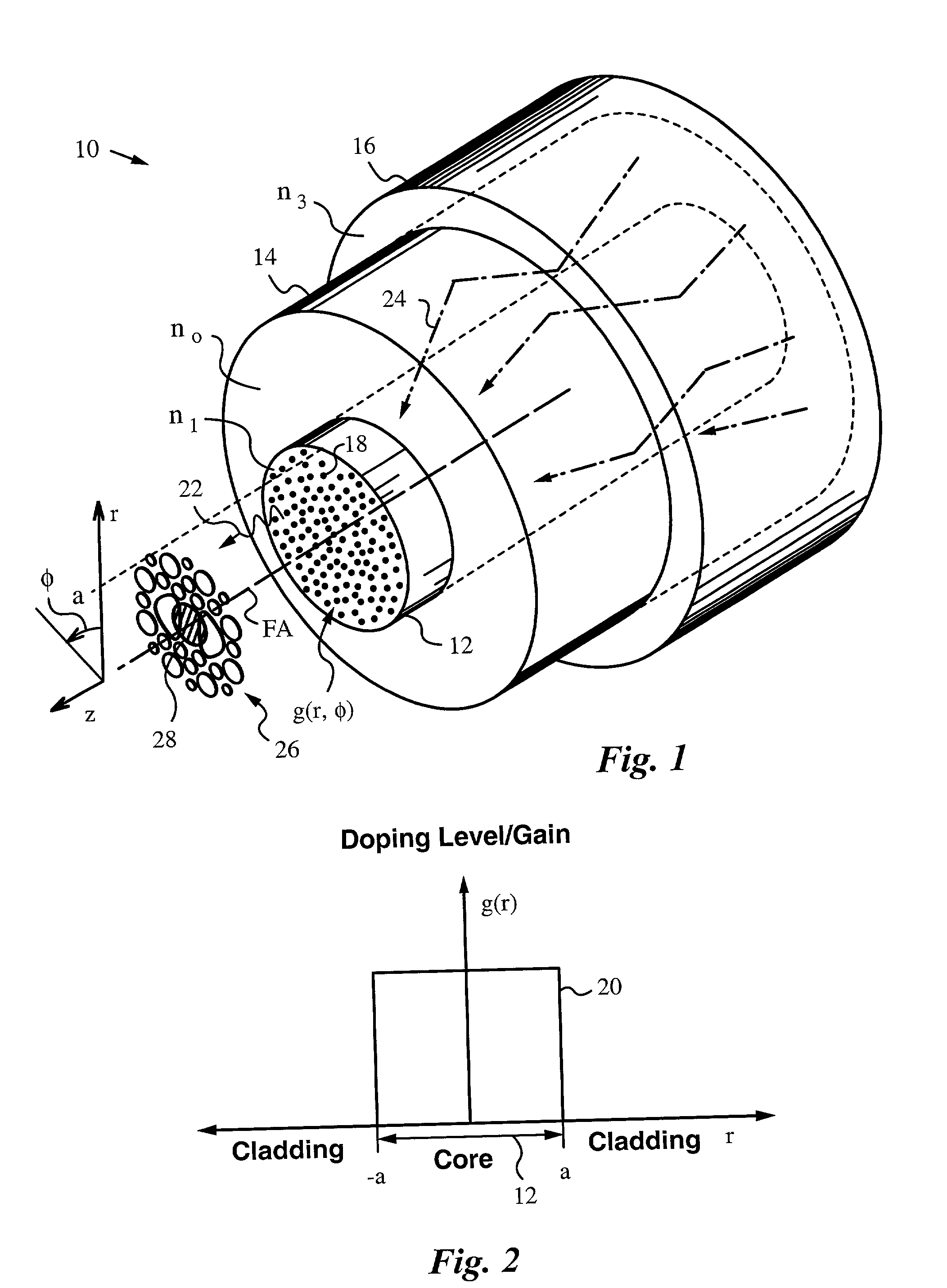
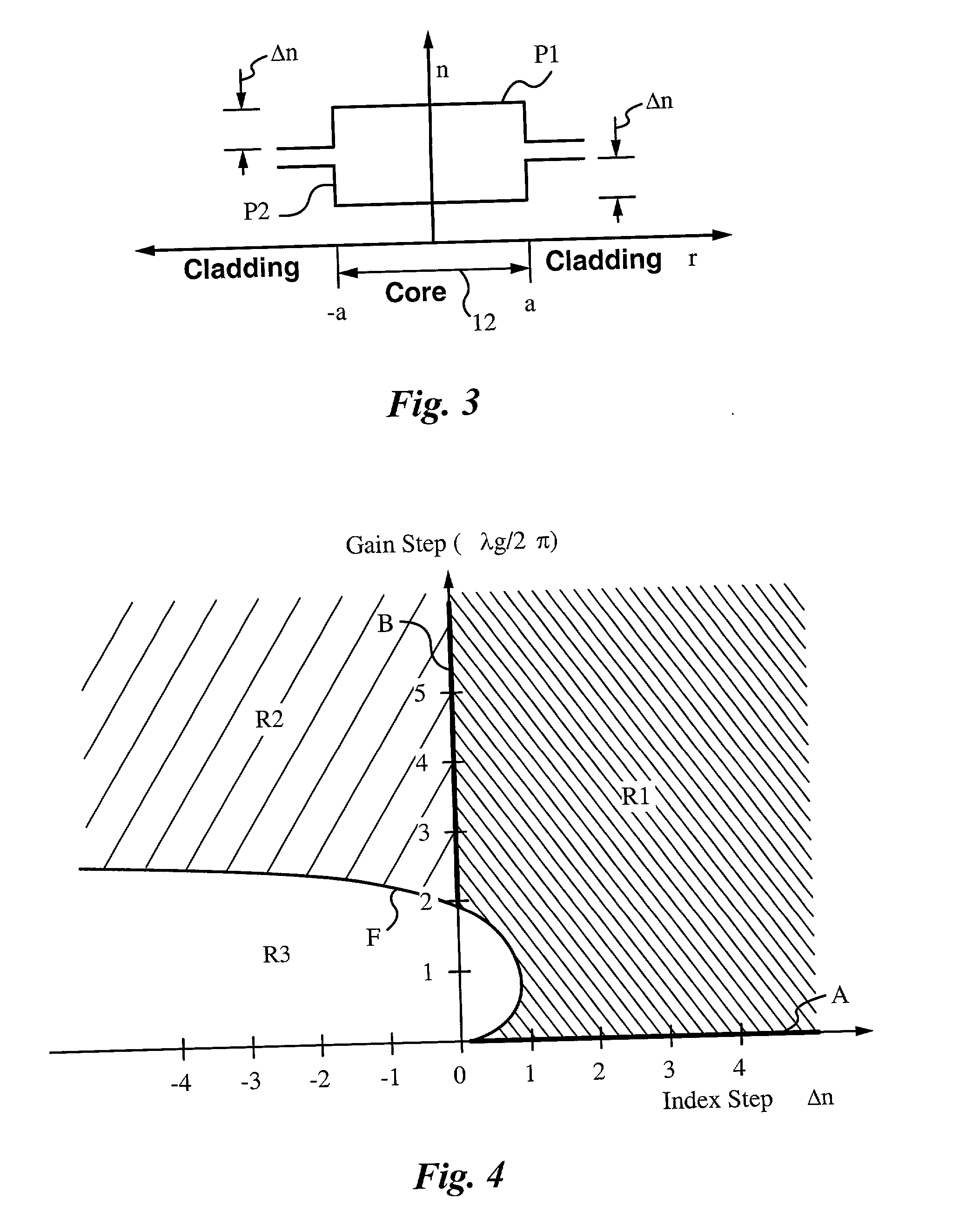
Fiber lasers having a complex-valued Vc-parameter for gain-guiding
InactiveUS6751388B2Laser using scattering effectsOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingDopantRadiation mode
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Fiber lasers having a complex-valued Vc-parameter for gain-guiding
InactiveUS20030031442A1Easy to useLowering indexLaser using scattering effectsOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingDopantRadiation mode
The instant invention concerns optical fibers that have complex-valued Vc-parameters due to gain g established by active dopants that are doped into the fiber core in accordance with a doping profile. In particular, the doping levels are very high, such that the gain g makes a sufficiently large contribution to an imaginary part of the complex-valued Vc-parameter to define at least one gain-guided mode, e.g., the fundamental mode or several low-order modes of radiation in the optical fiber. The fiber does not require any index-guiding effects to a single mode or just a few of the lowest-order modes in large cross-section cores having diameters in the range from 50 mum to 500 mum in diameter and yield kilowatt level output power. The fiber may, in addition to gain-guiding, take advantage of a refractive index profile to provide for index-guiding or index-antiguiding effects in addition to gain-guiding.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
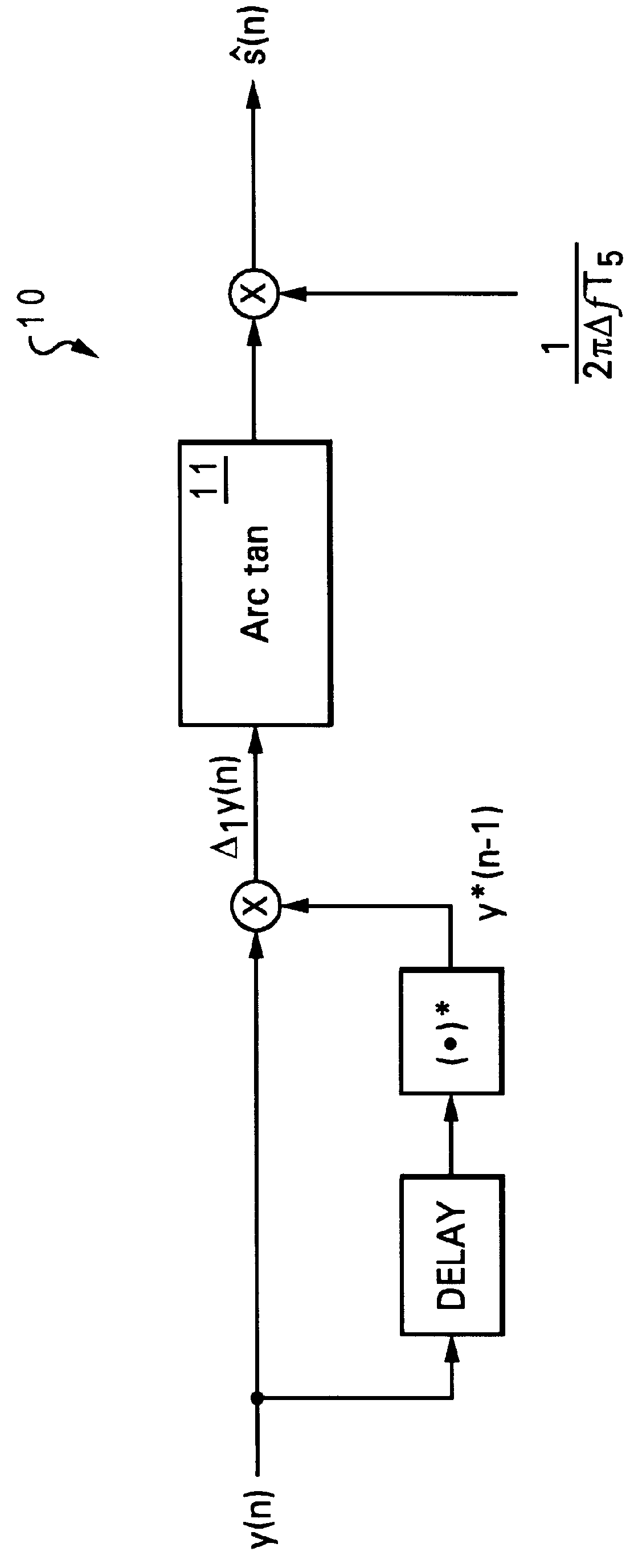
Method and apparatus for demodulating digital frequency modulation (FM) signals
InactiveUS6031418AFrequency/rate-modulated pulse demodulationFrequency-modulated carrier systemsComplex valuedPulse-frequency modulation
A method for demodulating digital frequency modulation (FM) signals is disclosed. A group of complex-valued discrete-time FM signal samples is initially received. A corresponding first complex product for each of the complex-valued discrete-time FM signal samples is computed, and a corresponding second complex product for each of the first complex values of the complex-valued discrete-time FM signal samples is computed. Subsequently, an inverse tangent of the second complex products are computed to yield an angle for each of the second complex values, wherein each of the angles represents a second-order difference of a phase of the complex-valued discrete-time FM signal samples. Finally, a digital integration is performed to obtain a first-order difference of the phase of the complex-valued discrete-time FM signal samples.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
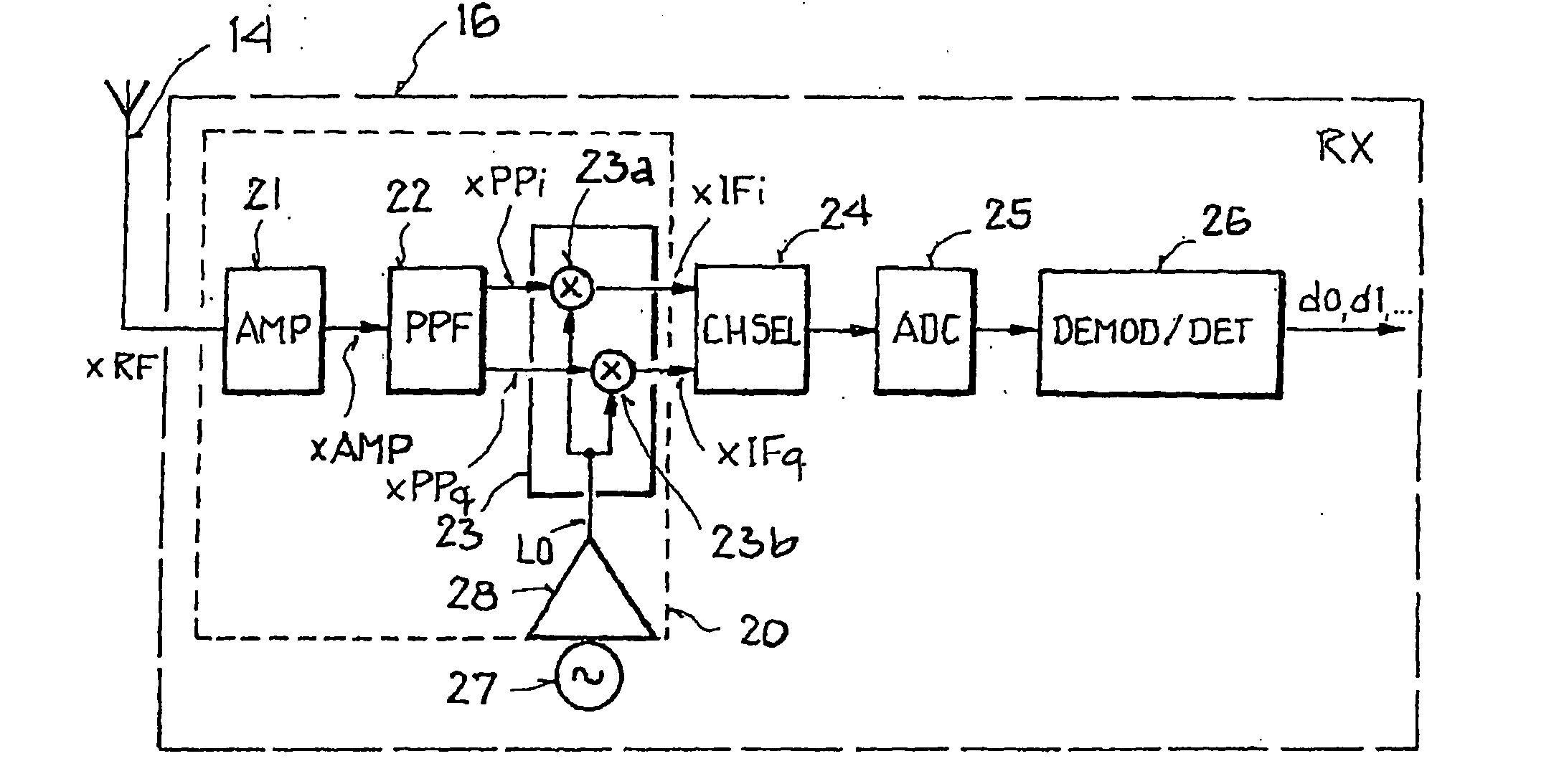
Integrated circuit arrangement for converting a high-frequency bandpass signal to a low-frequency quadrature signal
InactiveUS20070177693A1Energy-efficient and powerful transmitting/receivingRealized cost-effectivelyModulation transferencePhase-modulated carrier systemsLocal oscillator signalAudio power amplifier
An integrated circuit arrangement is provided for converting a high-frequency bandpass signal to a low-frequency quadrature signal with a first in-phase component and a first quadrature-phase component, which has: an amplifier arrangement, which is designed to generate an amplified signal and has a first amplifier stage for amplifying the high-frequency bandpass signal, a mixer unit with a first mixer to provide the first in-phase component and a second mixer to provide the first quadrature-phase component, and a driver amplifier, which is designed to generate a local oscillator signal. According to the invention, between the amplifier arrangement and the mixer unit a polyphase filter is disposed, which converts the amplified signal to a complex-valued polyphase signal with a second in-phase component and a second quadrature phase component. Furthermore, according to the invention each mixer is connected to the driver amplifier, and the first mixer is designed to multiply the second in-phase component by the local oscillator signal, and the second mixer is designed to multiply the second quadrature-phase component by the local oscillator signal.
Owner:ATMEL AUTOMOTIVE
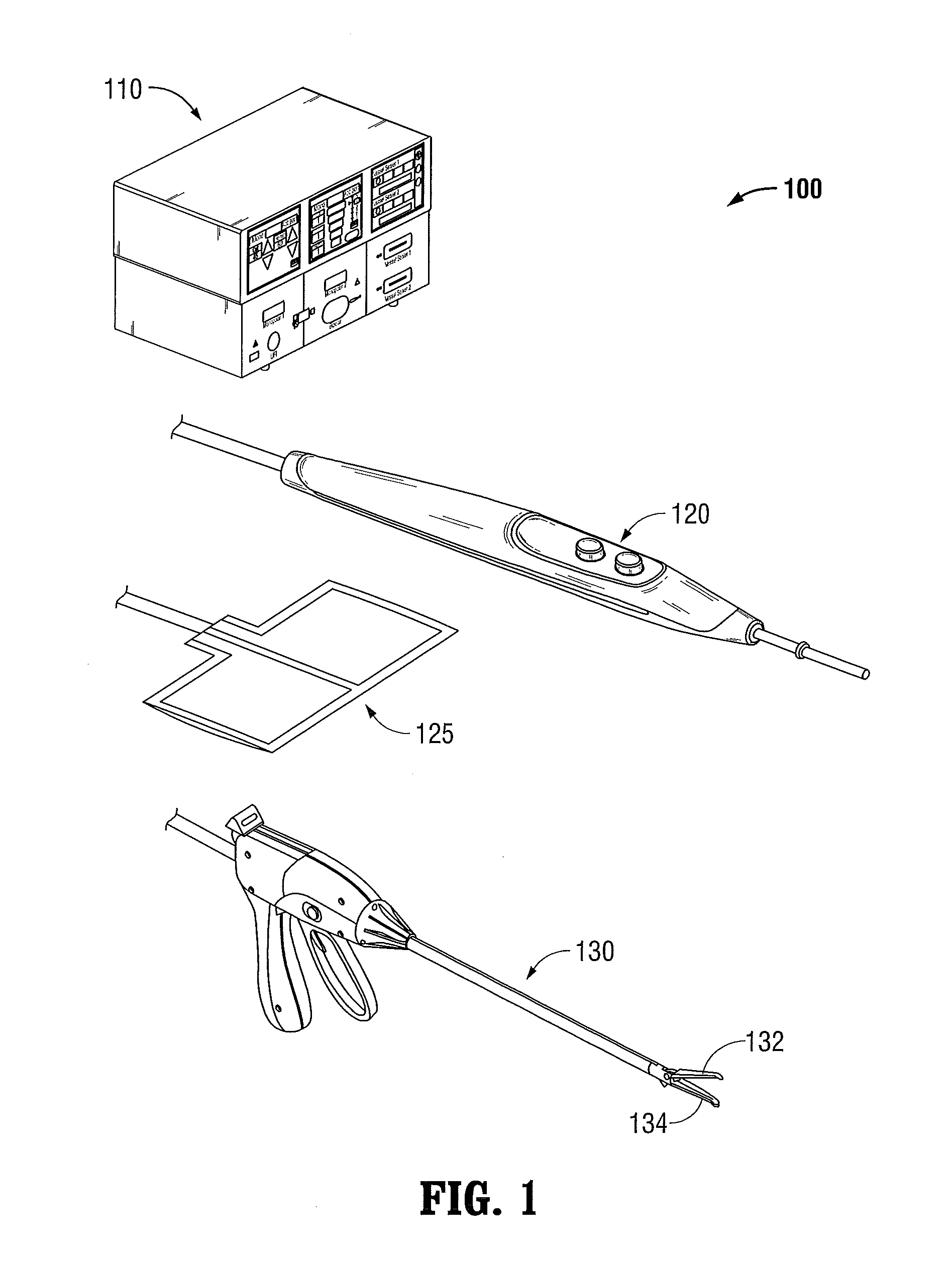
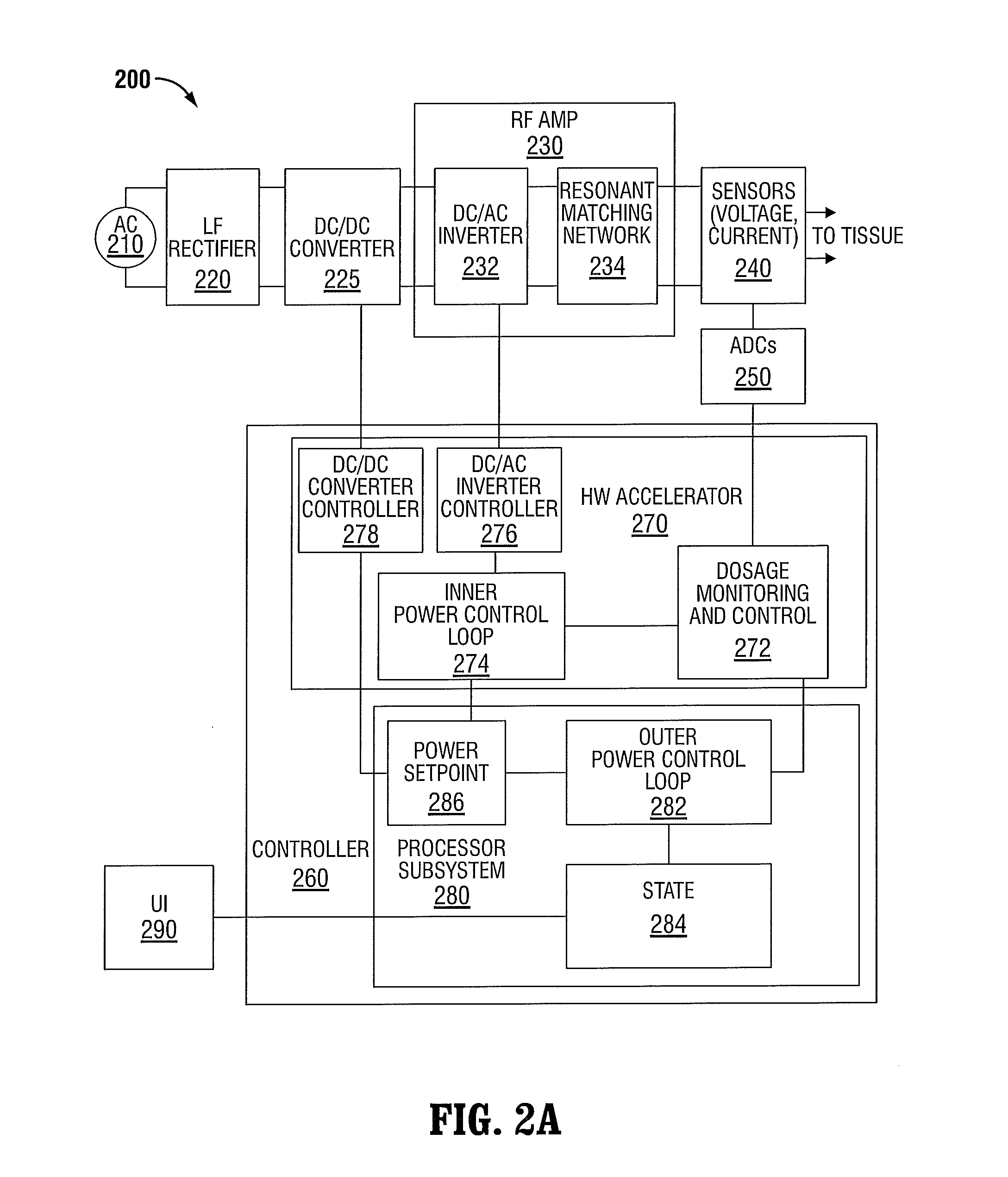
Systems and methods for narrowband real impedance control in electrosurgery
The electrosurgical systems and associated methods of the present disclosure perform narrowband real impedance control for precise treatment of tissue in electrosurgery. The electrosurgical systems include an electrosurgical generator that includes an output stage configured to generate electrosurgical energy to treat tissue, a plurality of sensors configured to sense voltage and current waveforms of the electrosurgical energy, and a controller coupled to the output stage to control the generated electrosurgical energy. The controller includes a signal processor that (1) determines a complex-valued voltage and a complex-valued current based on the voltage waveform and the current waveform sensed by the plurality of sensors using a plurality narrowband filters, and (2) calculates a real part of an impedance of the tissue using the complex-valued voltage and the complex-valued current. The controller also includes an output controller that controls the output stage based on the calculated real part of the impedance of the tissue.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com