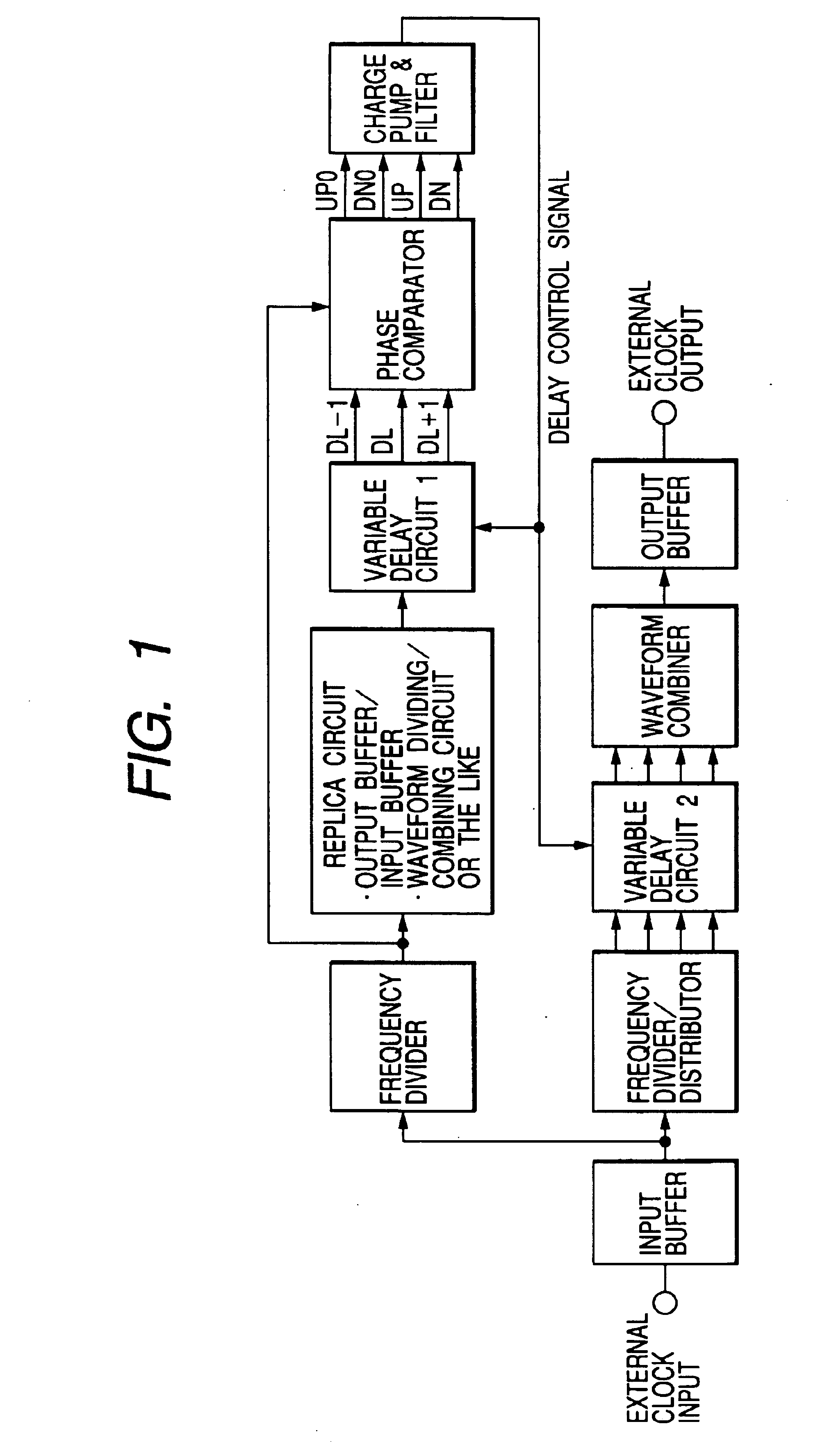
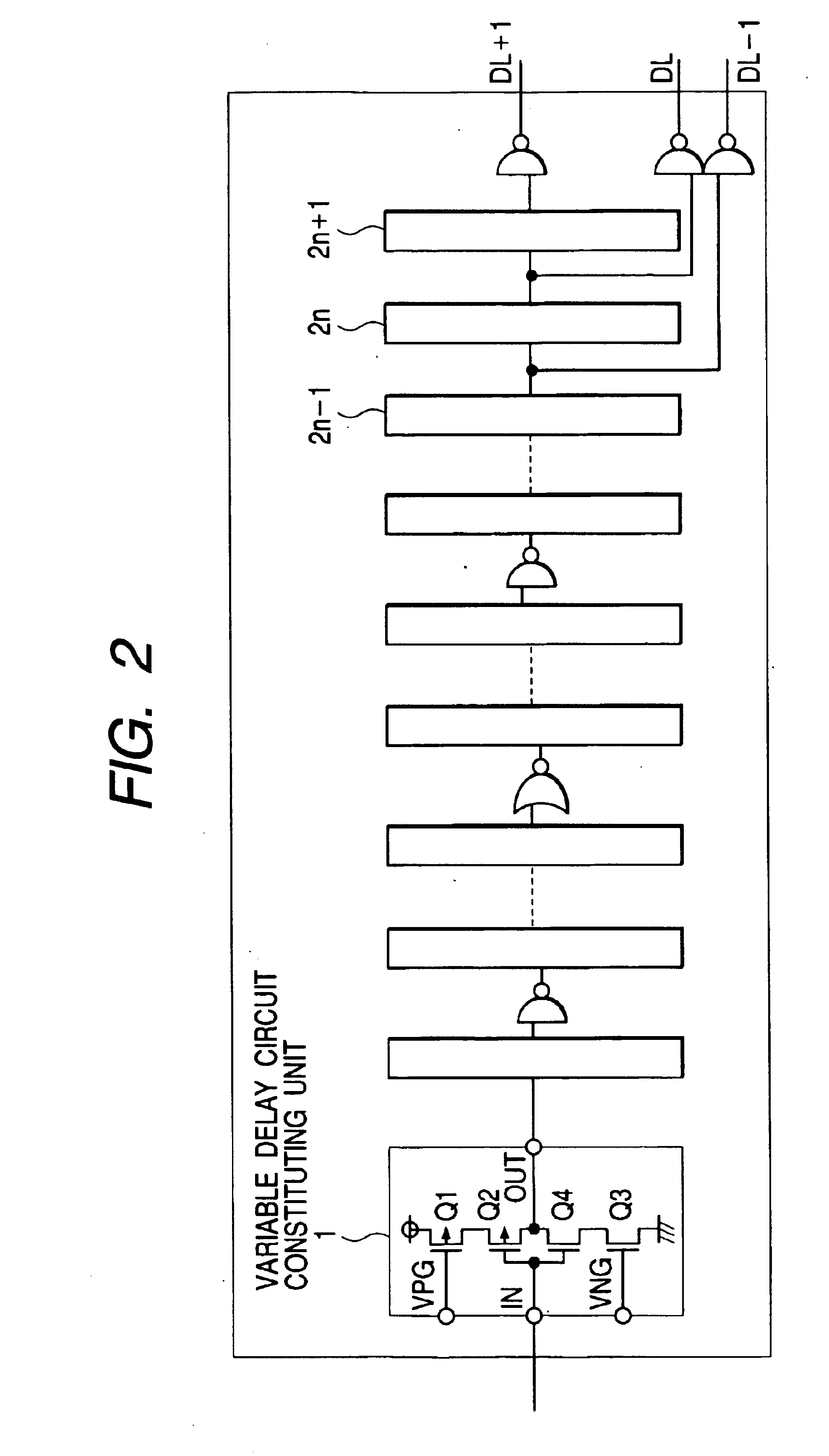
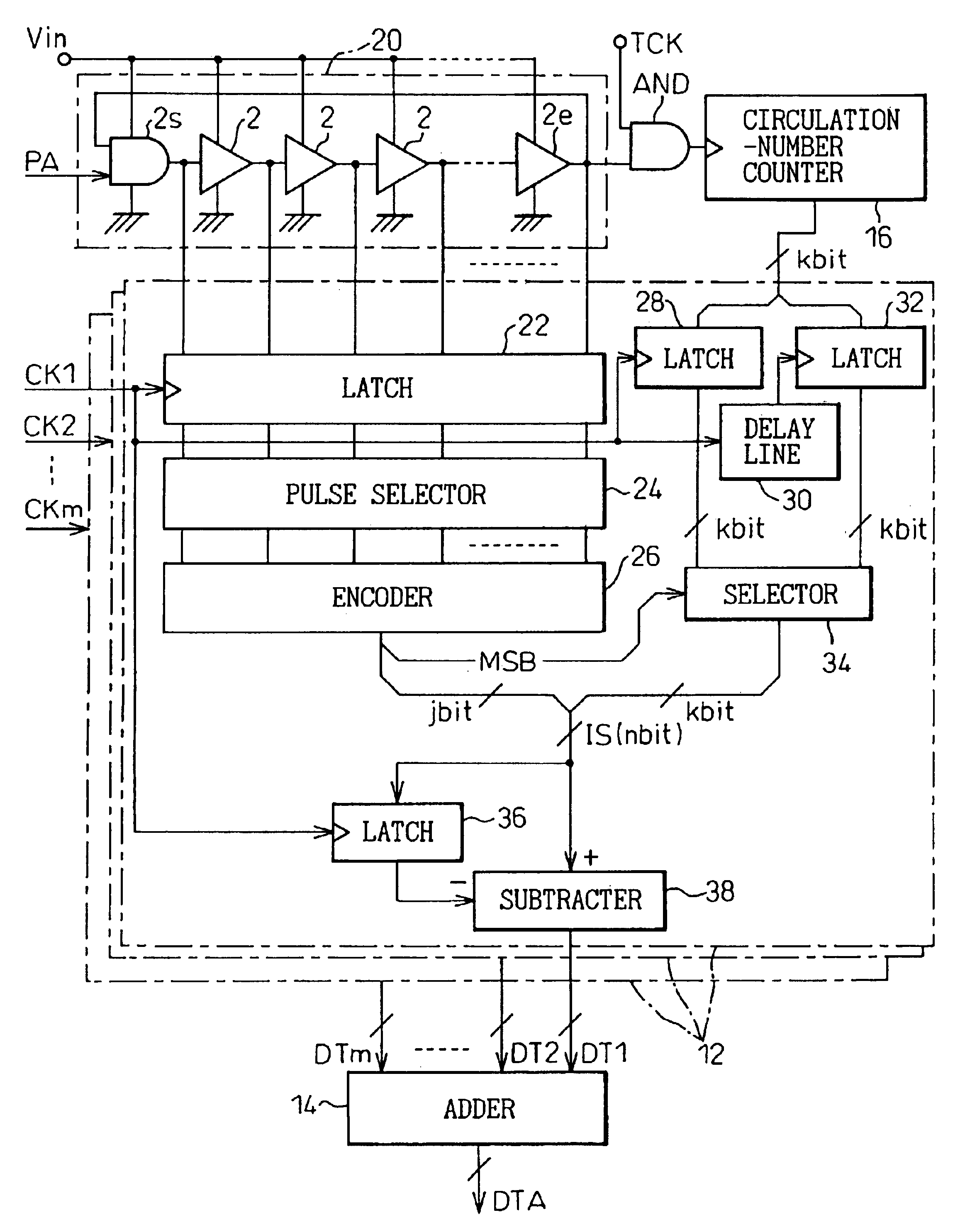
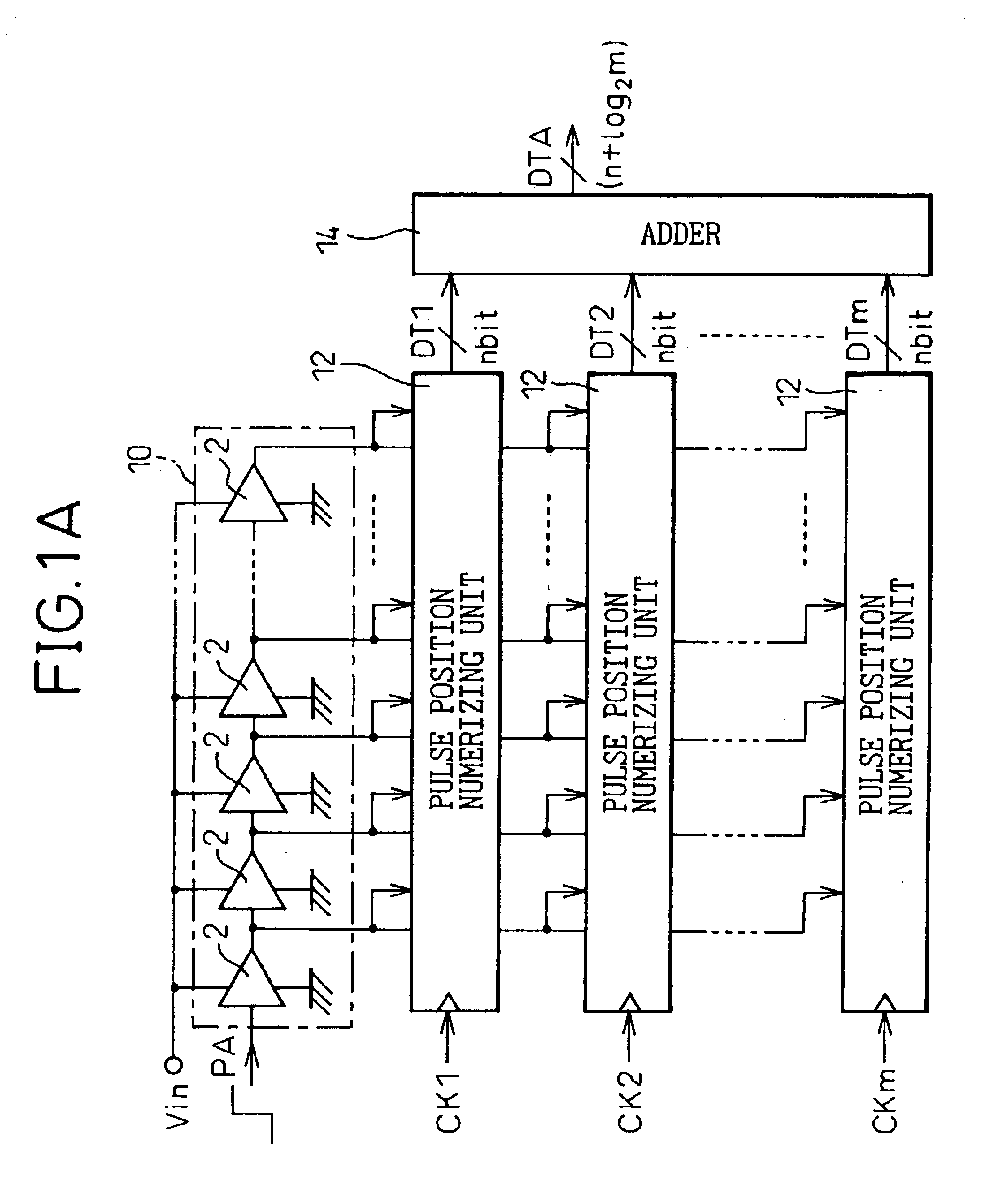
Patents
Literature
383 results about "Pulse delay" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
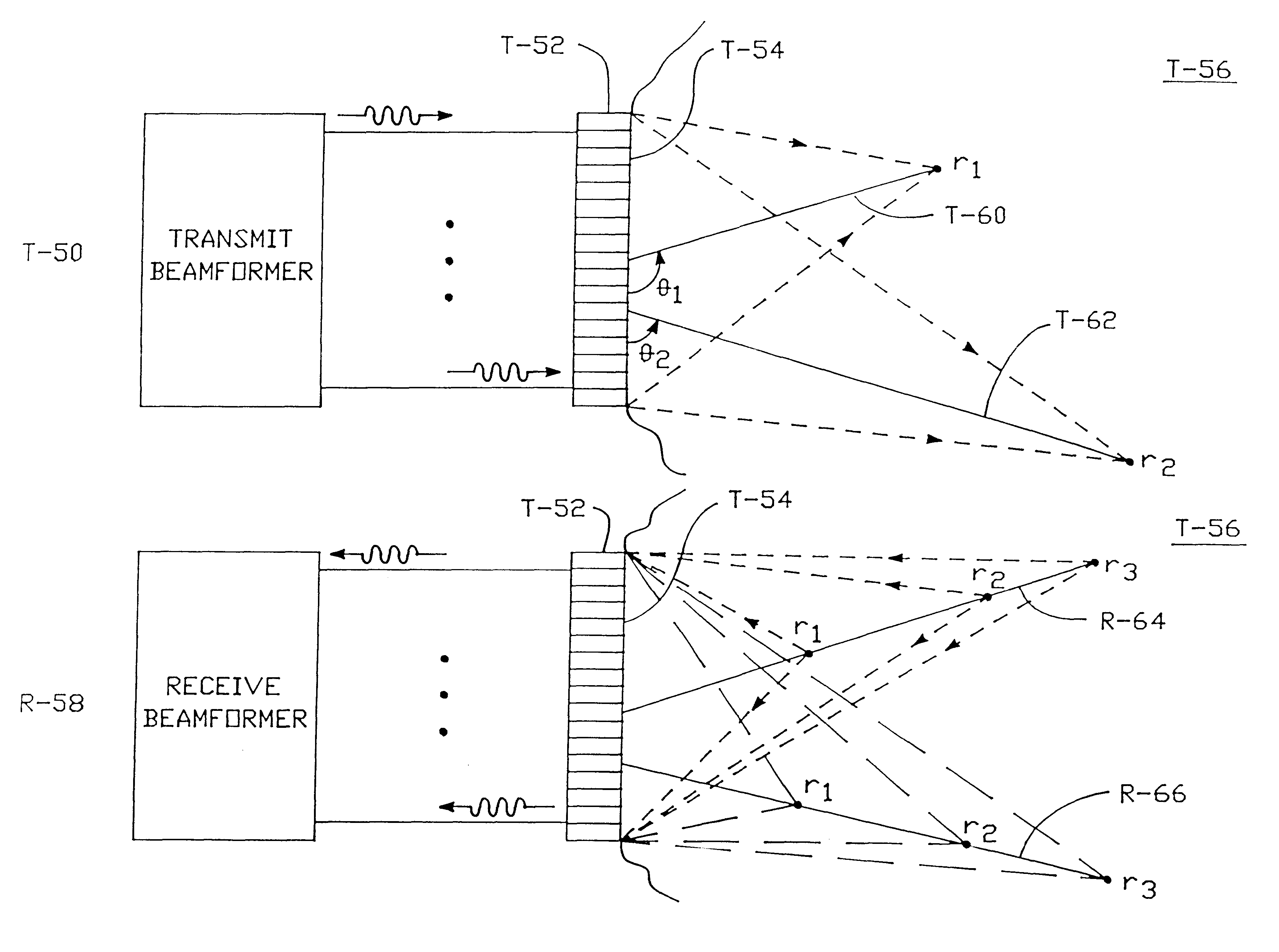
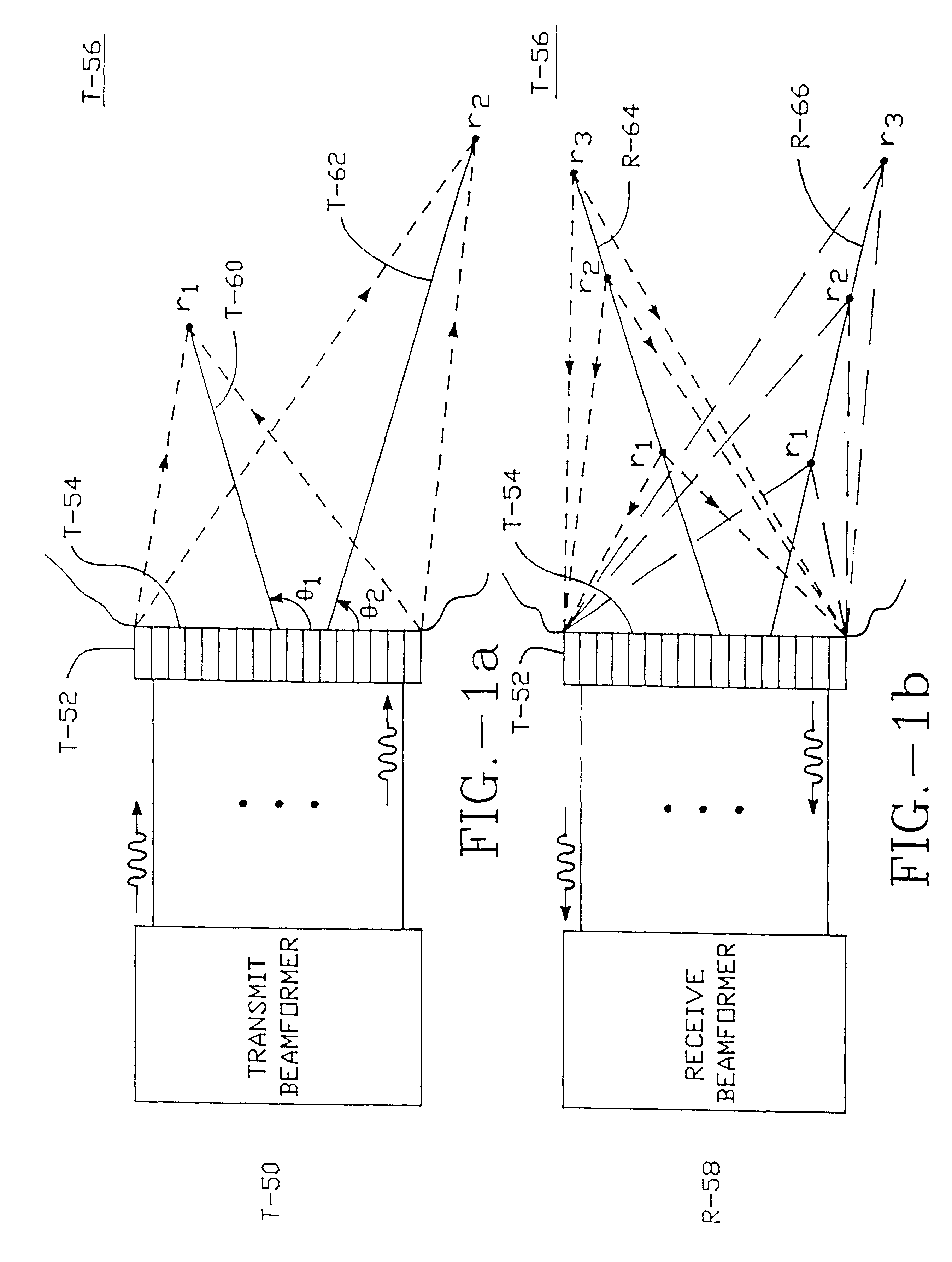
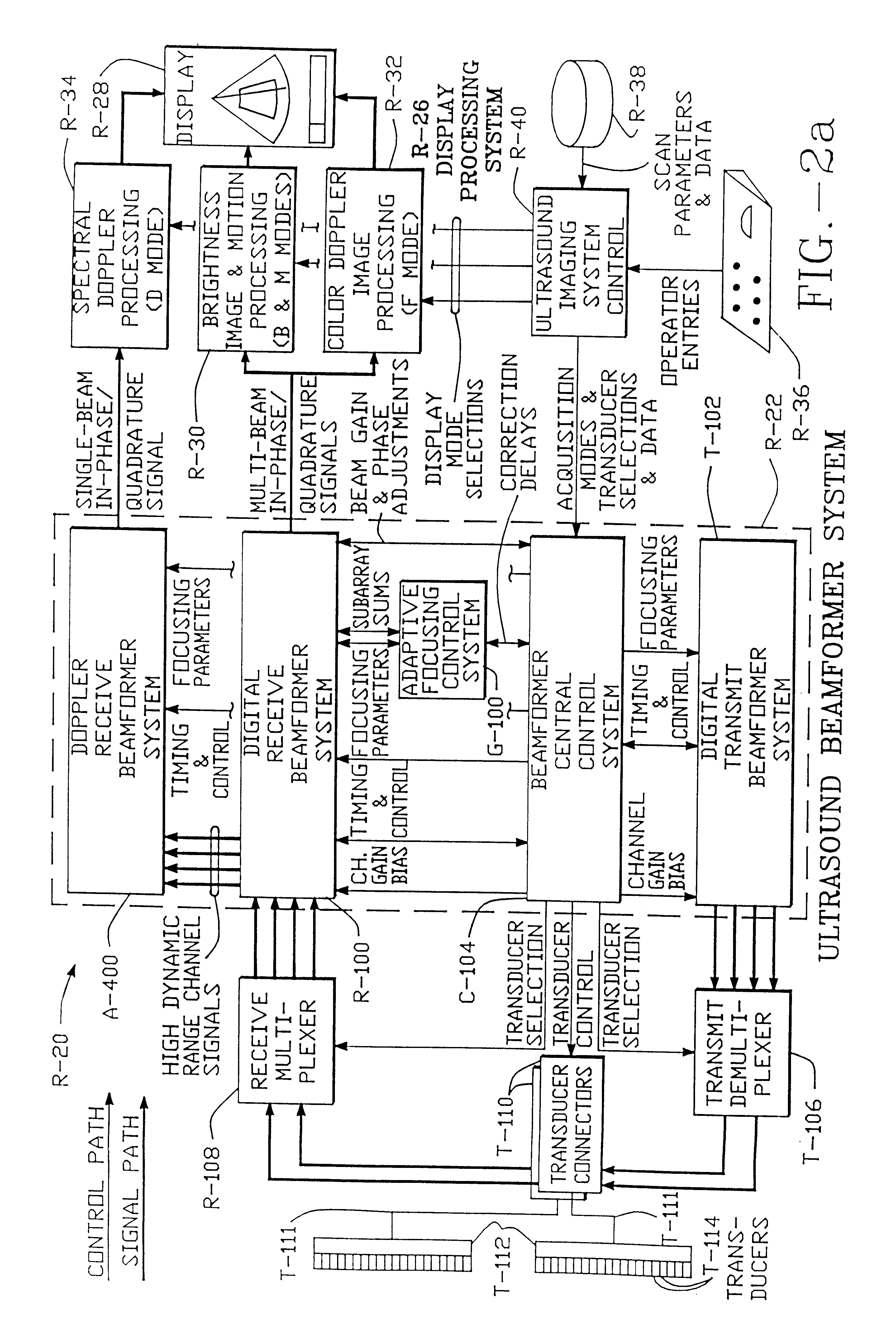
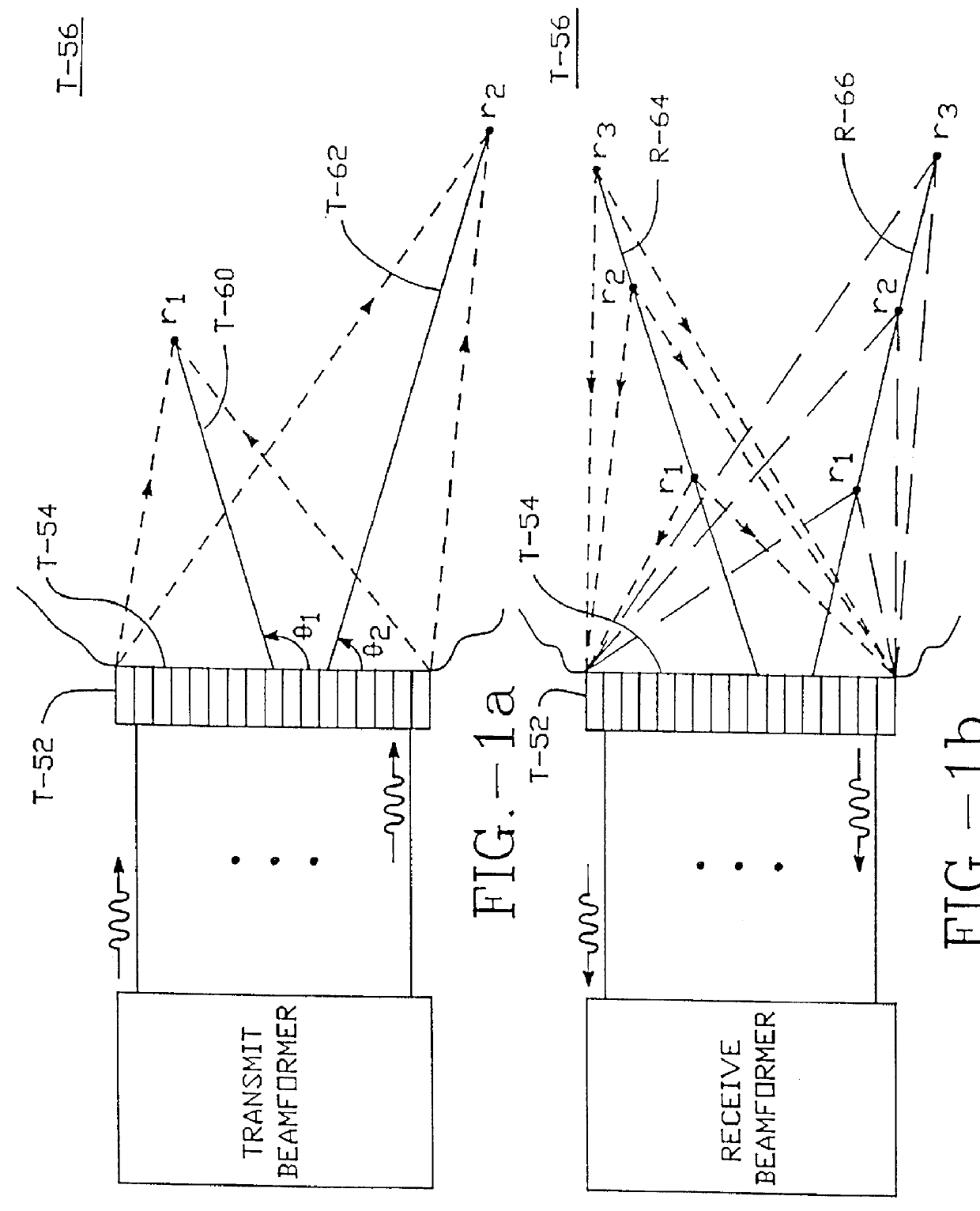
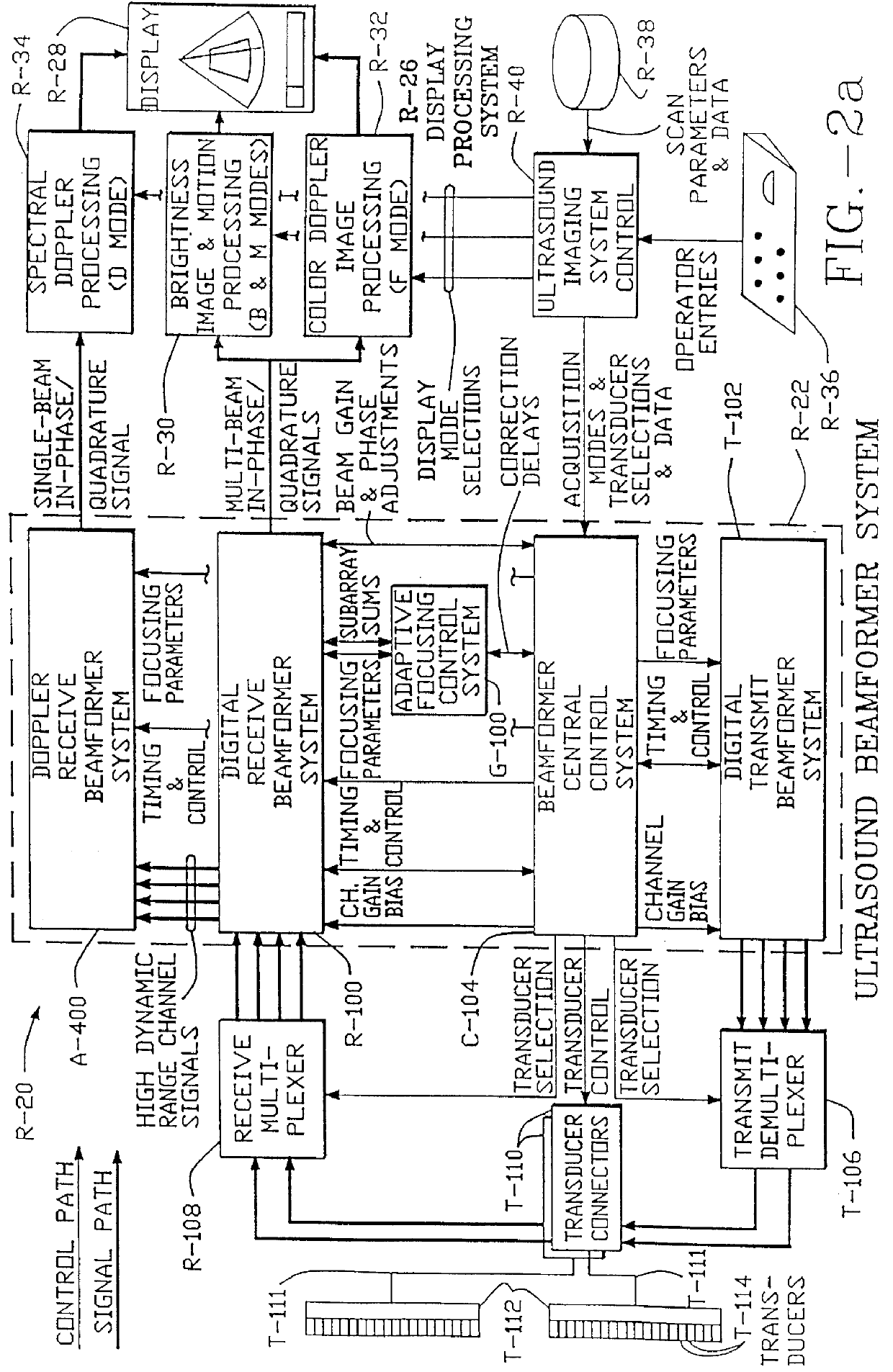
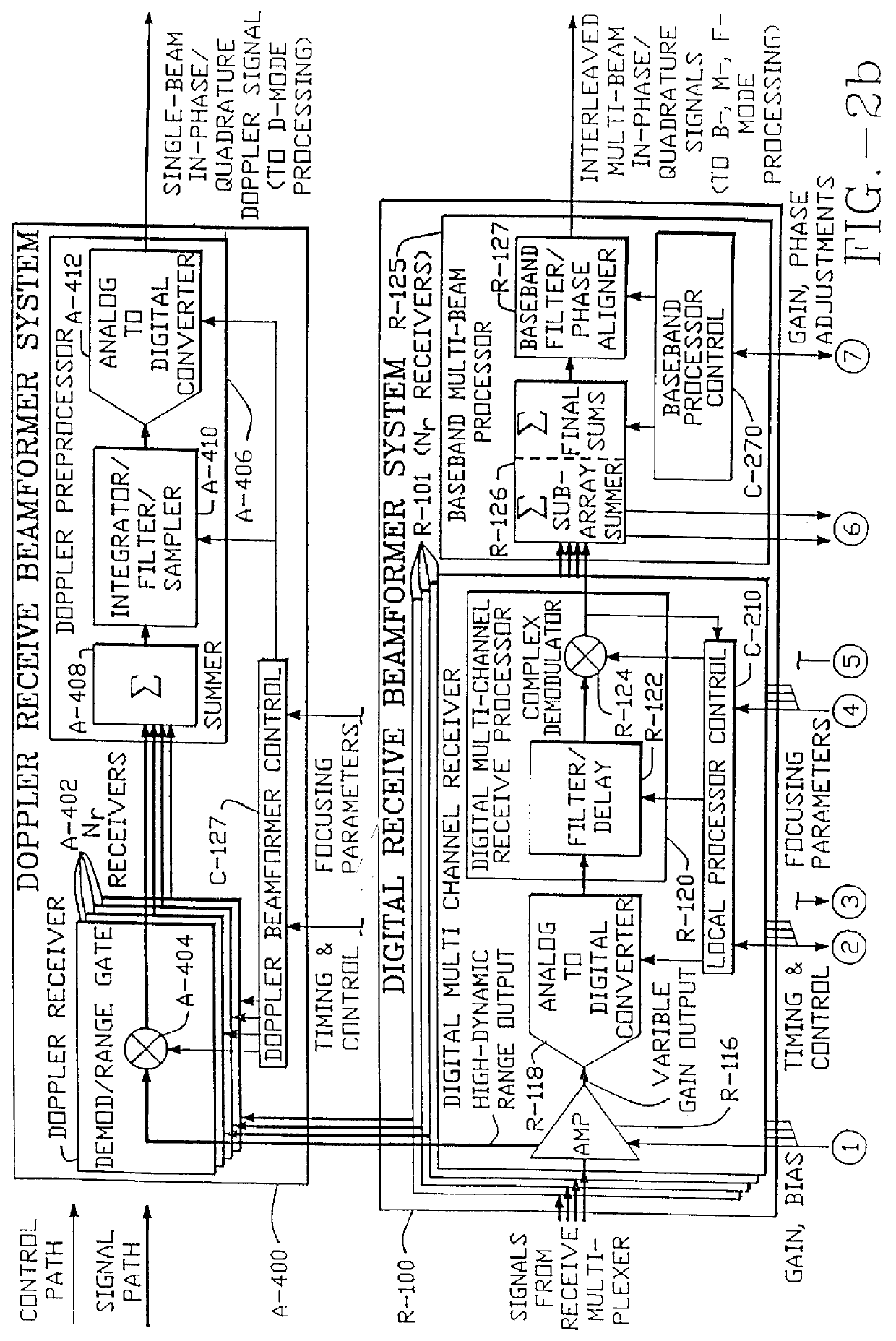
Method and apparatus for transmit beamformer system
InactiveUS6363033B1Improve programmabilityMaximum flexibilityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsProcessing detected response signalTrade offsApodization
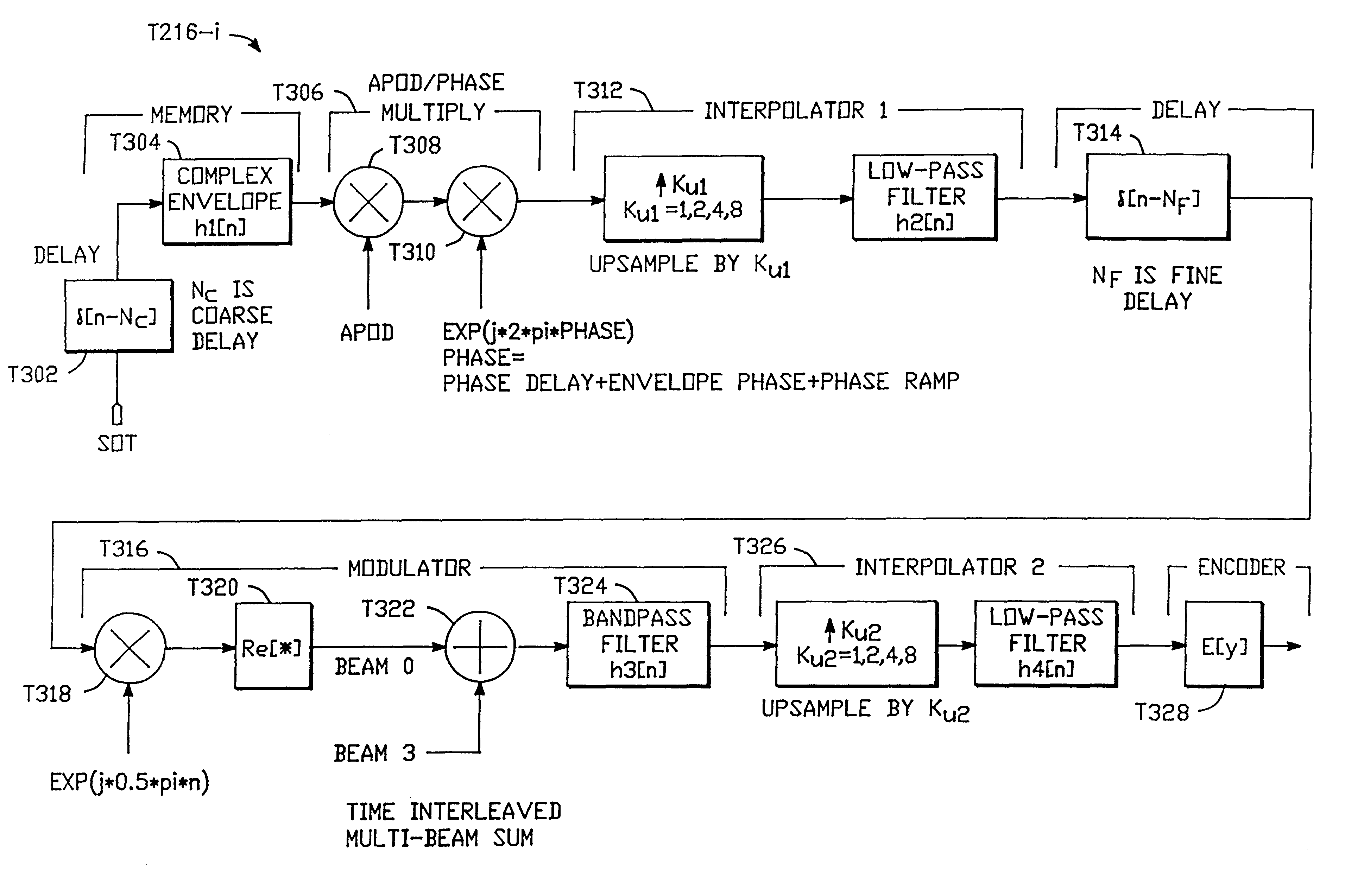
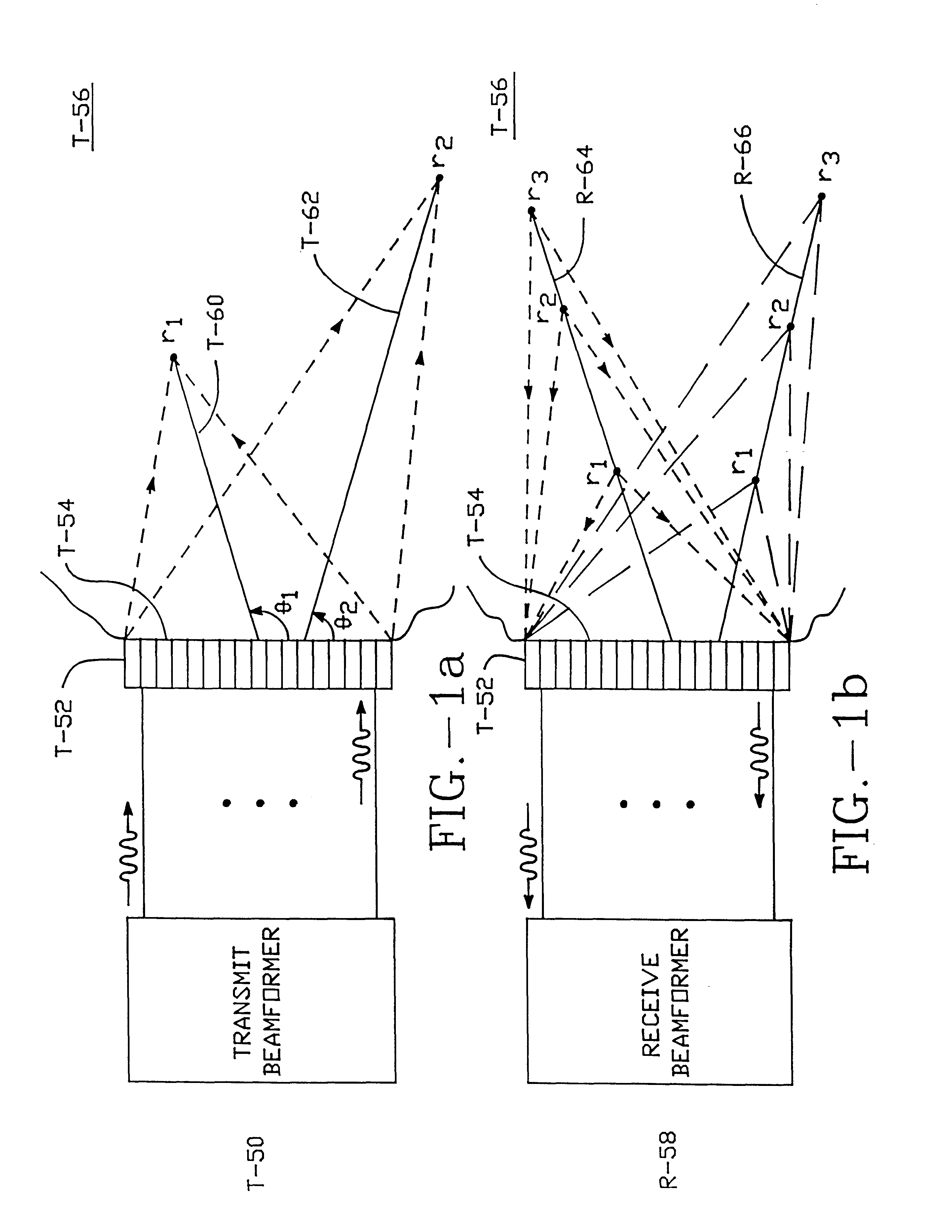
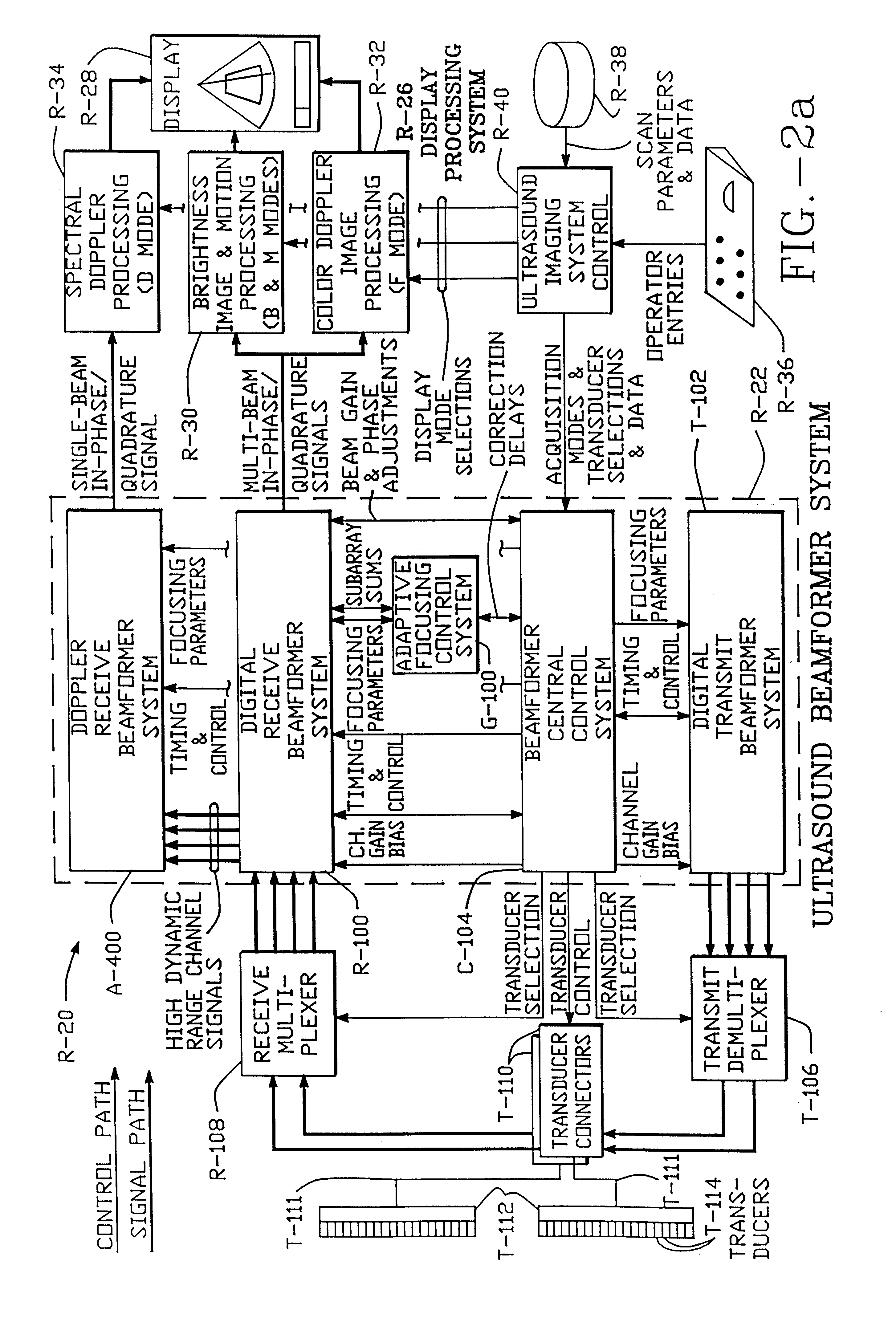
A digital transmit beamformer system with multiple beam transmit capability has a plurality of multi-channel transmitters, each channel with a source of sampled, complex-valued initial waveform information representative of the ultimate desired waveform to be applied to one or more corresponding transducer elements for each beam. Each multi-channel transmitter applies beamformation delays and apodization to each channel's respective initial waveform information digitally, digitally modulates the information by a carrier frequency, and interpolates the information to the DAC sample rate for conversion to an analog signal and application to the associated transducer element(s). The beamformer transmitters can be programmed per channel and per beam with carrier frequency, delay, apodization and calibration values, For pulsed wave operation, pulse waveform parameters can be specified to the beamformer transmitters on a per firing basis, without degrading the scan frame rate to non-useful diagnostic levels. Waveform parameters can be specified to the transmitters by an external central control system which is responsible for higher level flexibility, such as scan formats, focusing depths and fields of view. The transmit pulse delay specified per-channel to each transmitter is applied in at least two components: a focusing time delay component and a focusing phase component. The carrier frequency can be specified for each transmit beam, to any desired frequency within a substantially continuous predefined range of frequencies, and a beam-interleaved signal processing path permits operation in any of several predefined processing modes, which define different parameter sets in a trade-off among (1) the number of beams produced; (2) per-beam initial waveform sample interval; and (3) transmit frequency.
Owner:ACUSON
Method and apparatus for transmit beamformer system
InactiveUS6104673AImprove abilitiesImprove programmabilityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsProcessing detected response signalSoftware engineeringCarrier signal
A digital transmit beamformer system with multiple beam transmit capability has a plurality of multi-channel transmitters, each channel with a source of sampled, complex-valued initial waveform information representative of the ultimate desired waveform to be applied to one or more corresponding transducer elements for each beam. Each multi-channel transmitter applies beamformation delays and apodization to each channel's respective initial waveform information digitally, digitally modulates the information by a carrier frequency, and interpolates the information to the DAC sample rate for conversion to an analog signal and application to the associated transducer element(s). The beamformer transmitters can be programmed per channel and per beam with carrier frequency, delay, apodization and calibration values. For pulsed wave operation, pulse waveform parameters can be specified to the beamformer transmitters on a per firing basis, without degrading the scan frame rate to non-useful diagnostic levels. Waveform parameters can be specified to the transmitters by an external central control system which is responsible for higher level flexibility, such as scan formats, focusing depths and fields of view. The transmit pulse delay specified per-channel to each transmitter is applied in at least two components: a focusing time delay component and a focusing phase component. The carrier frequency can be specified for each transmit beam, to any desired frequency within a substantially continuous predefined range of frequencies, and a beam-interleaved signal processing path permits operation in any of several predefined processing modes, which define different parameter sets in a trade-off among (1) the number of beams produced; (2) per-beam initial waveform sample interval; and (3) transmit frequency.
Owner:ACUSON
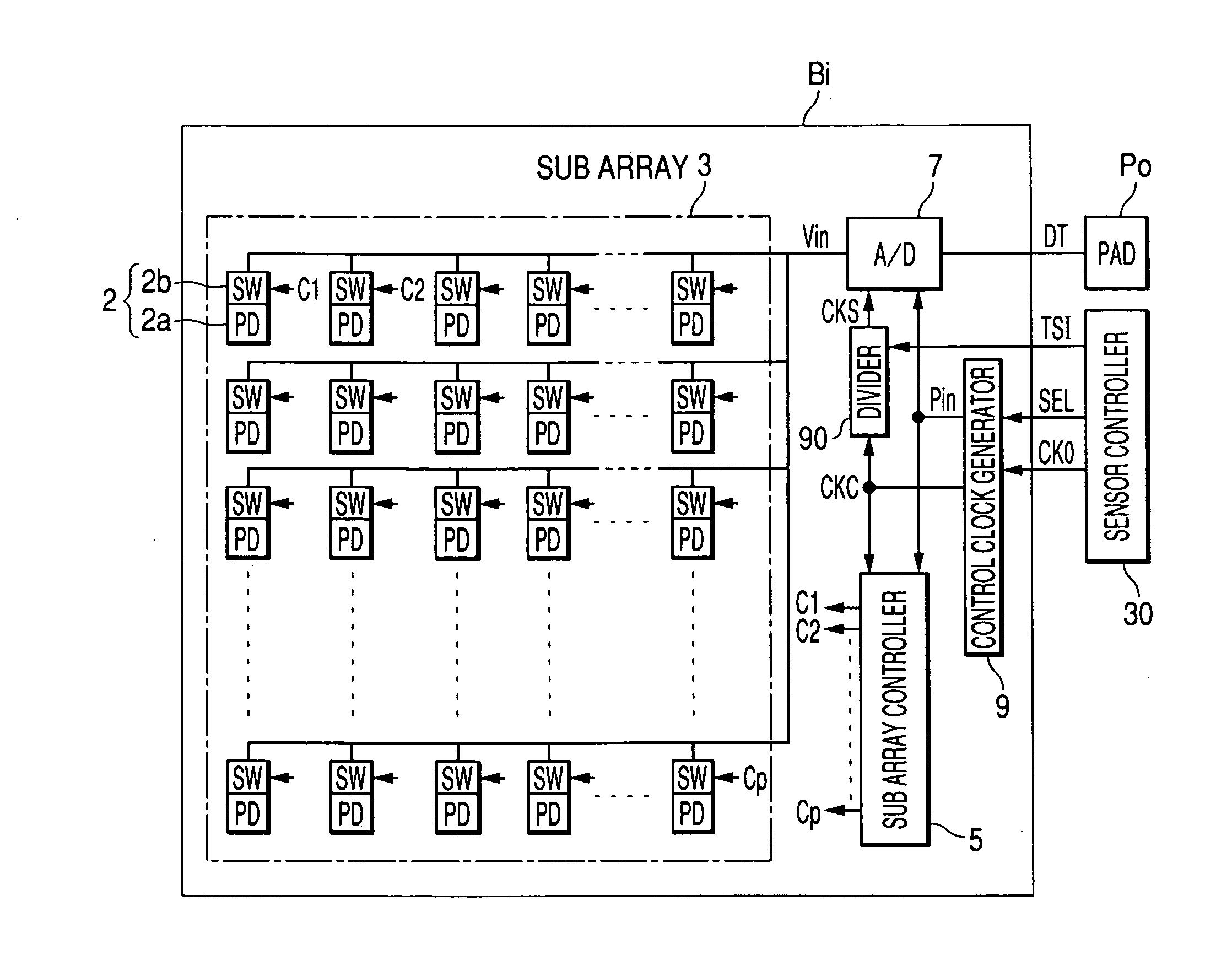
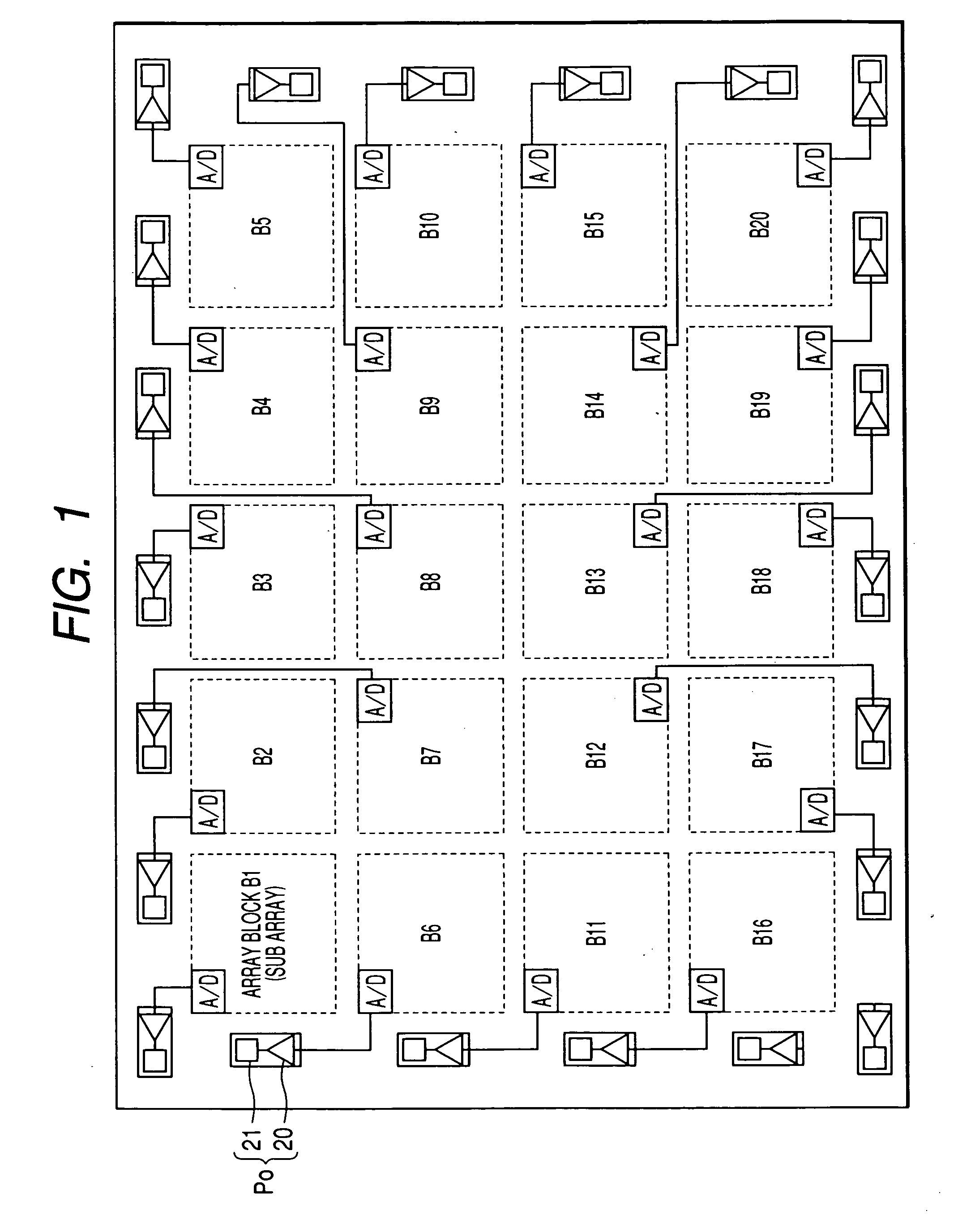
Image sensor and control method of the image sensor
ActiveUS20060243885A1Increase speedImprove accuracyTelevision system detailsElectric signal transmission systemsLight signalComputer science
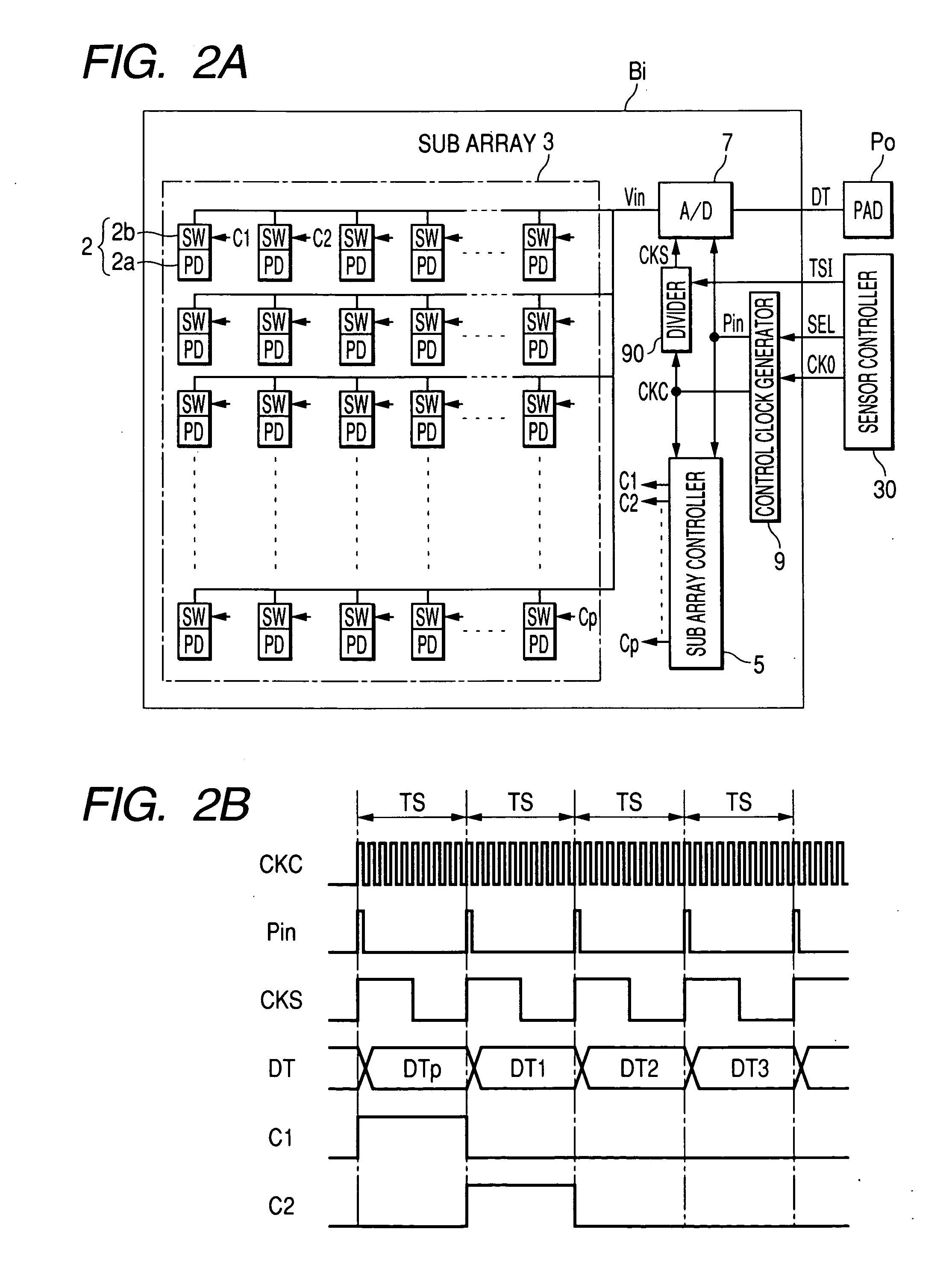
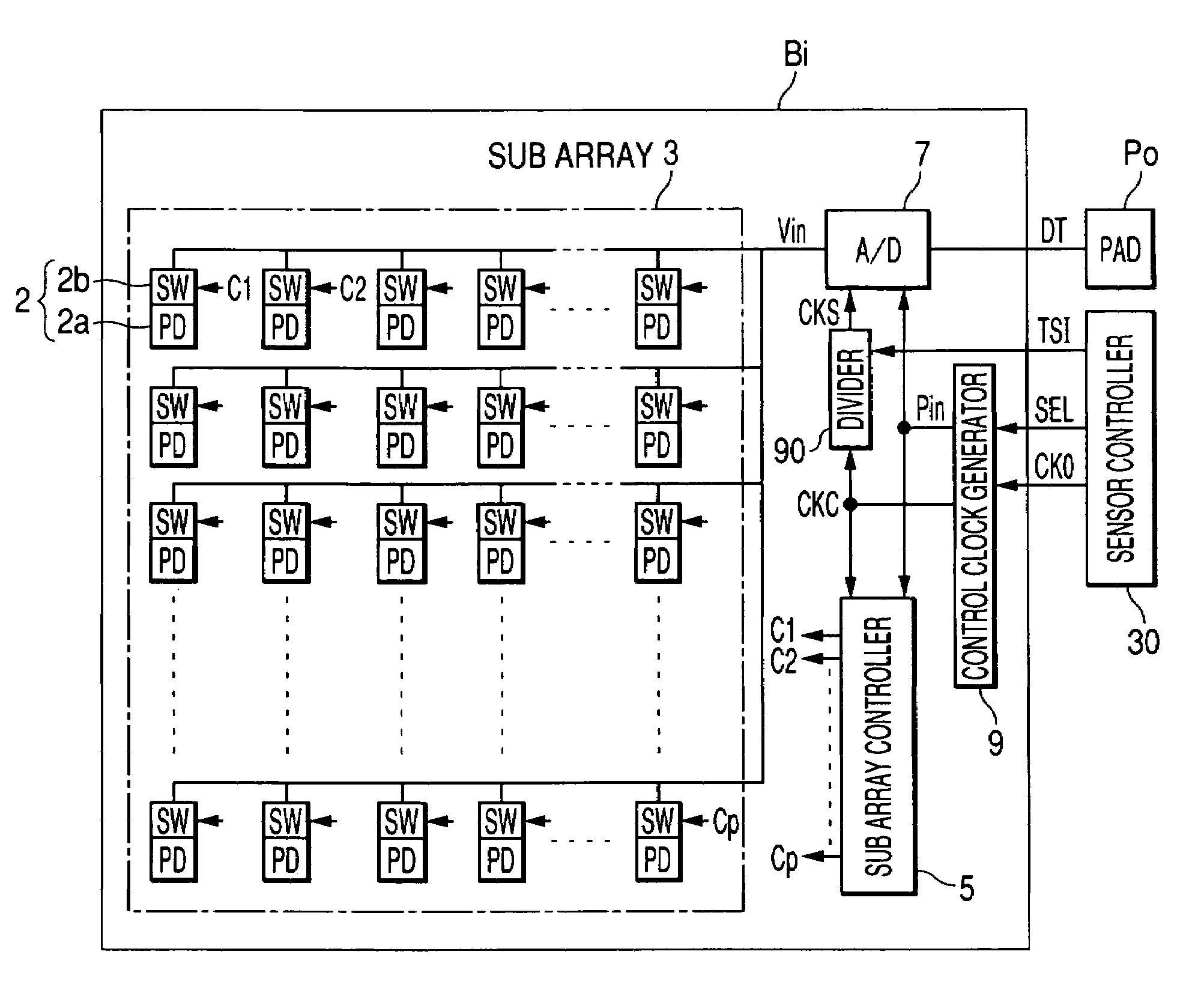
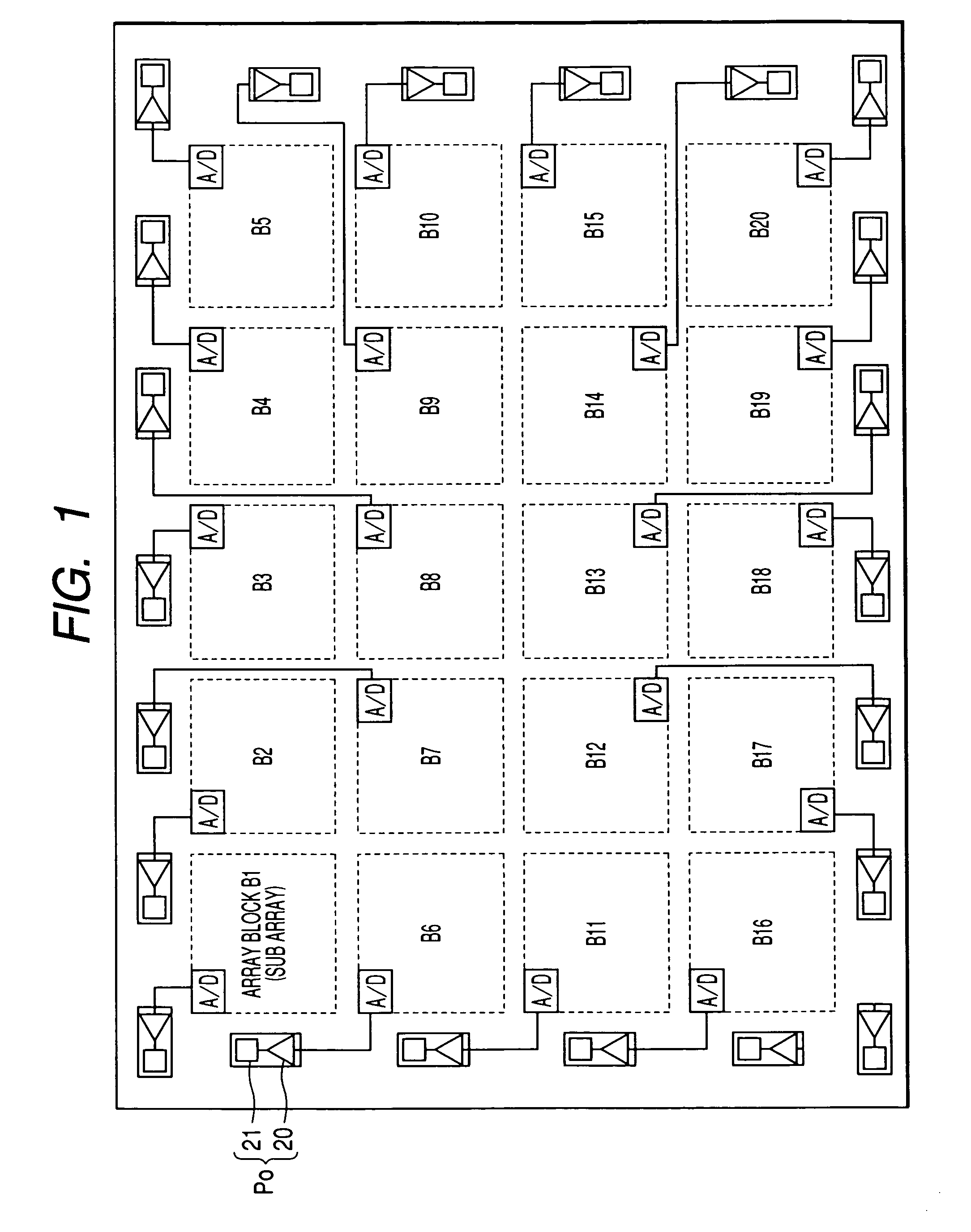
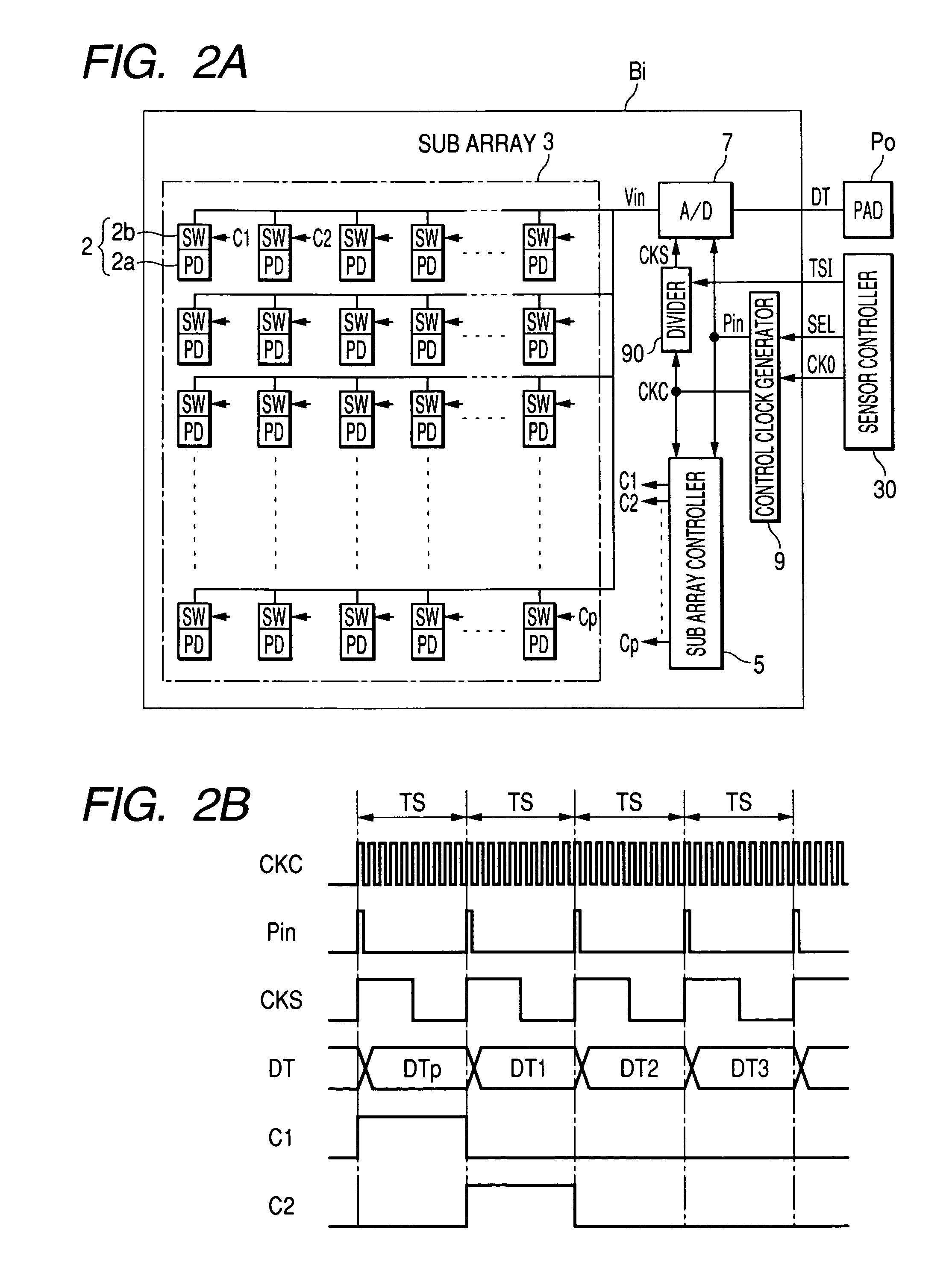
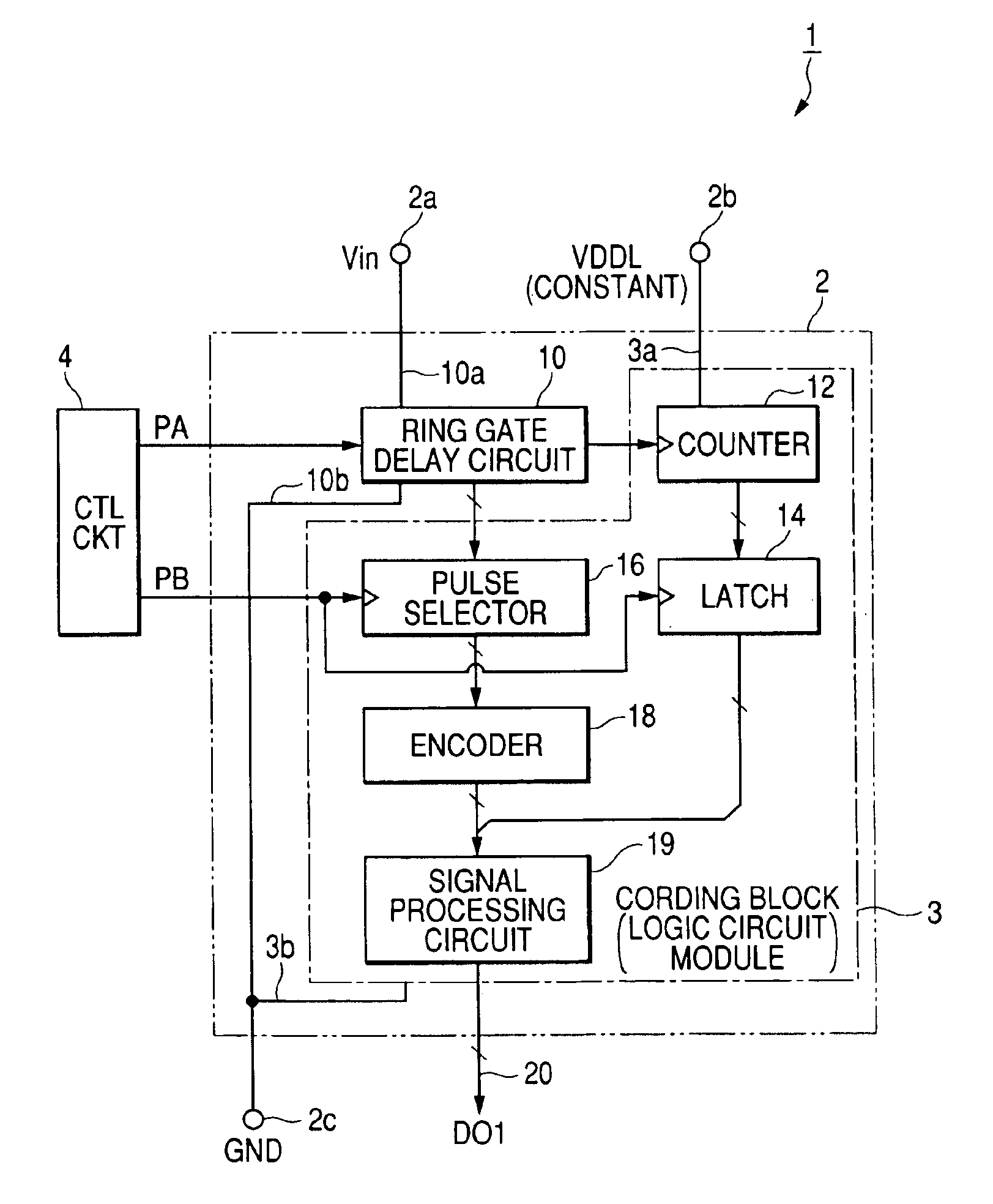
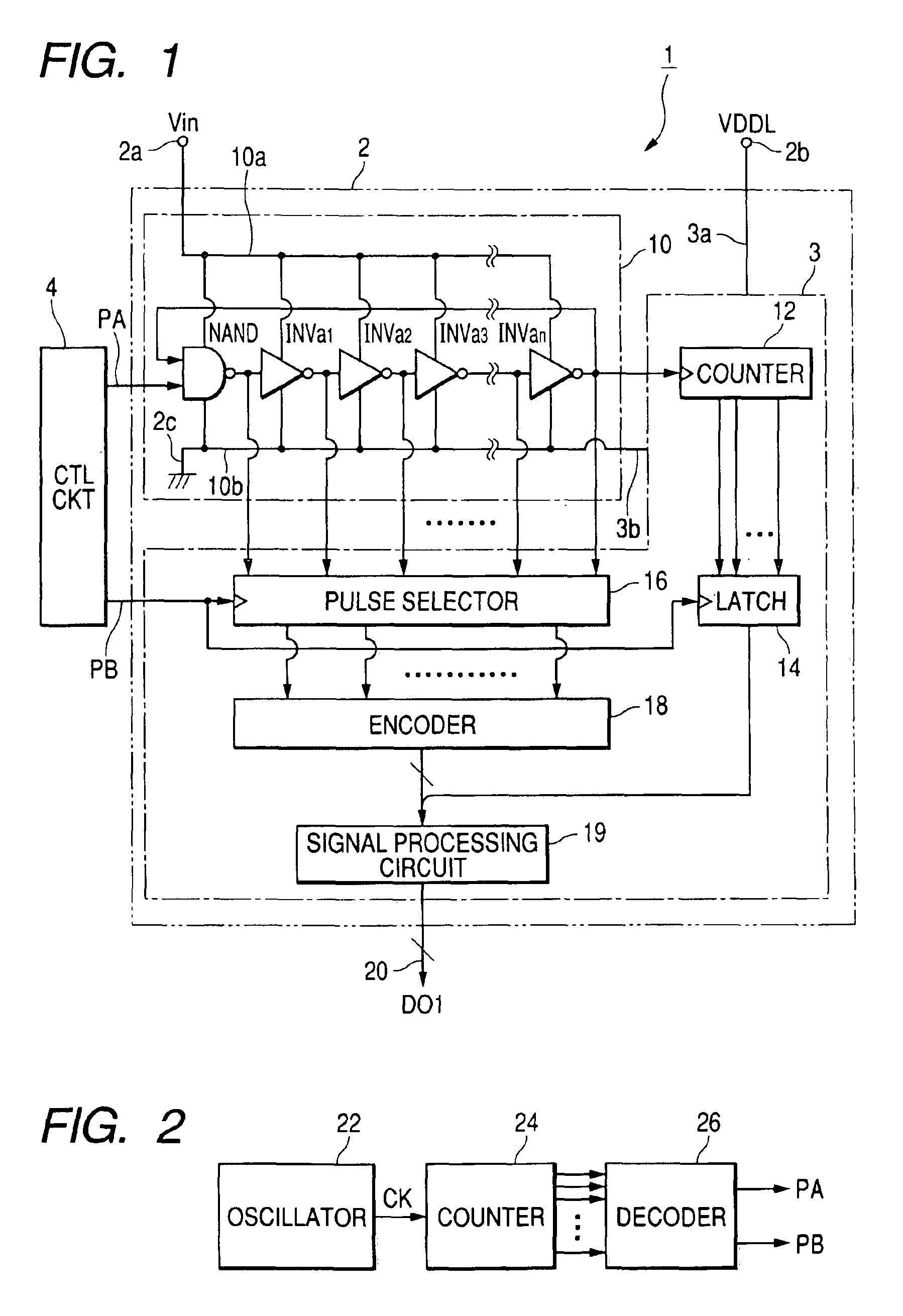
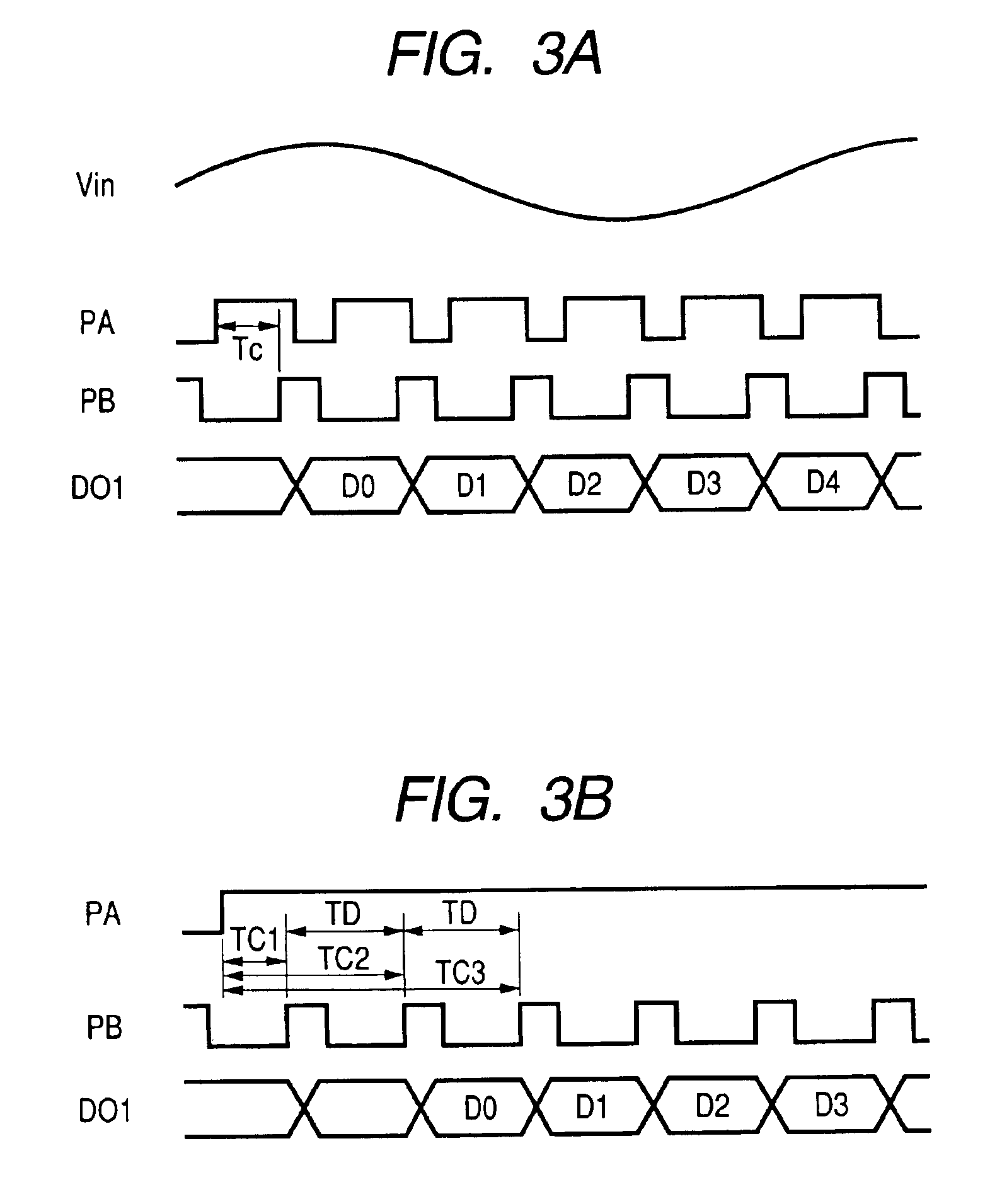
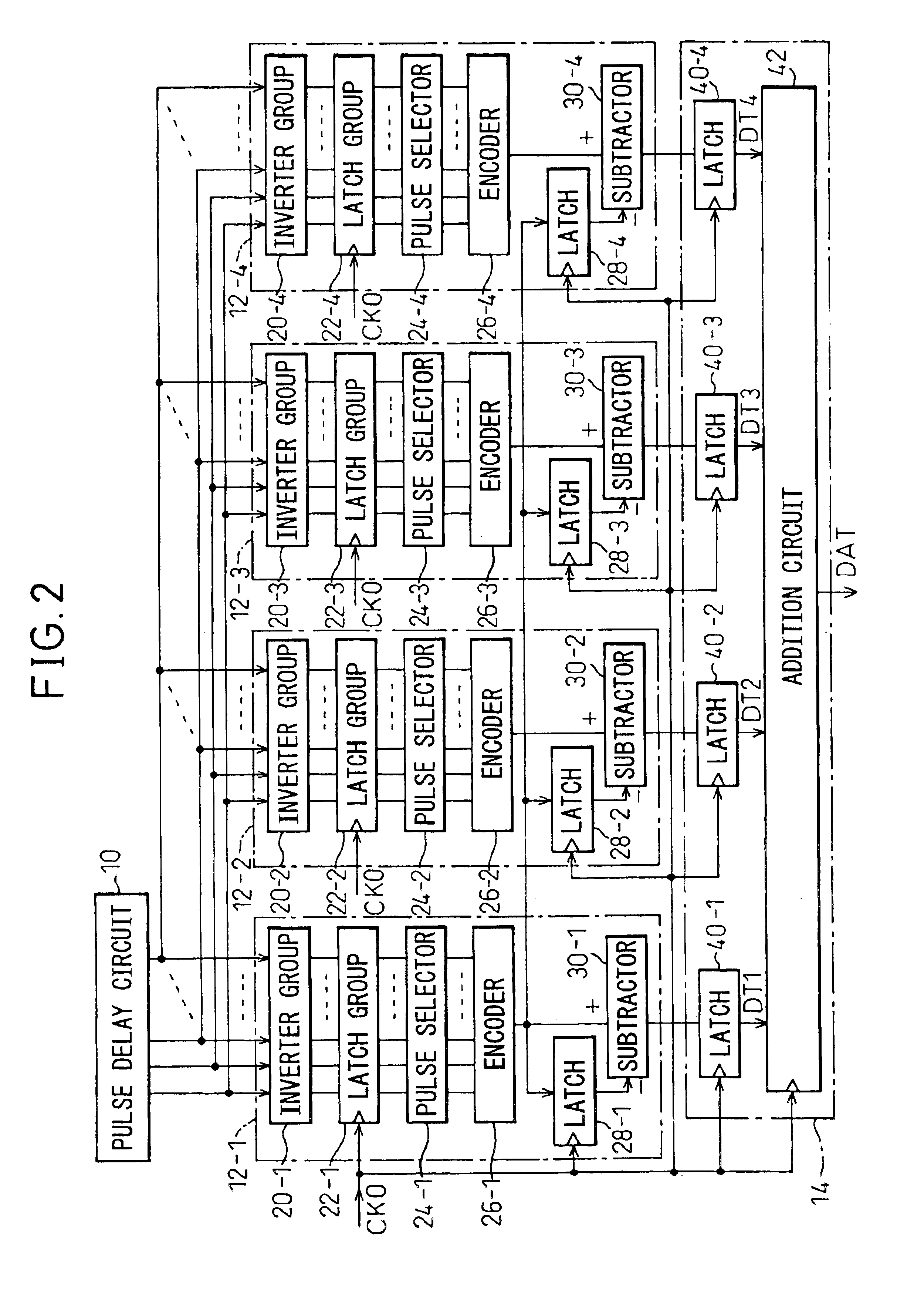
An image sensor has plural array blocks B1 to B20 arranged in a two dimensional (2D) arrangement. Each array block has a sub array and a corresponding analogue to digital (A / D) converter for performing an A / D conversion of light signals (or detection signals) output from the sub array. The sub array has plural picture element cells arranged in a 2D arrangement. Each A / D converter has a pulse delay circuit having delay units of plural stages connected in series. Each delay unit delays an input pulse by a delay time corresponding to a level of the light signals received from the sub array. A pulse delay type A / D converter is used as the A / D converter, which outputs the number of the delay units as an A / D conversion data item through which the input pulse passes for a measurement time period.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Method and apparatus for transmit beamformer system
InactiveUS6172939B1Improve abilitiesImprove programmabilityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsProcessing detected response signalEngineeringTrade offs
A digital transmit beamformer system with multiple beam transmit capability has a plurality of multi-channel transmitters, each channel with a source of sampled, complex-valued initial waveform information representative of the ultimate desired waveform to be applied to one or more corresponding transducer elements for each beam. Each multi-channel transmitter applies beamformation delays and apodization to each channel's respective initial waveform information digitally, digitally modulates the information by a carrier frequency, and interpolates the information to the DAC sample rate for conversion to an analog signal and application to the associated transducer element(s). The beamformer transmitters can be programmed per channel and per beam with carrier frequency, delay, apodization and calibration values. For pulsed wave operation, pulse waveform parameters can be specified to the beamformer transmitters on a per firing basis, without degrading the scan frame rate to non-useful diagnostic levels. Waveform parameters can be specified to the transmitters by an external central control system which is responsible for higher level flexibility, such as scan formats, focusing depths and fields of view. The transmit pulse delay specified per-channel to each transmitter is applied in at least two components: a focusing time delay component and a focusing phase component. The carrier frequency can be specified for each transmit beam, to any desired frequency within a substantially continuous predefined range of frequencies, and a beam-interleaved signal processing path permits operation in any of several predefined processing modes, which define different parameter sets in a trade-off among (1) the number of beams produced; (2) per-beam initial waveform sample interval; and (3) transmit frequency.
Owner:ACUSON
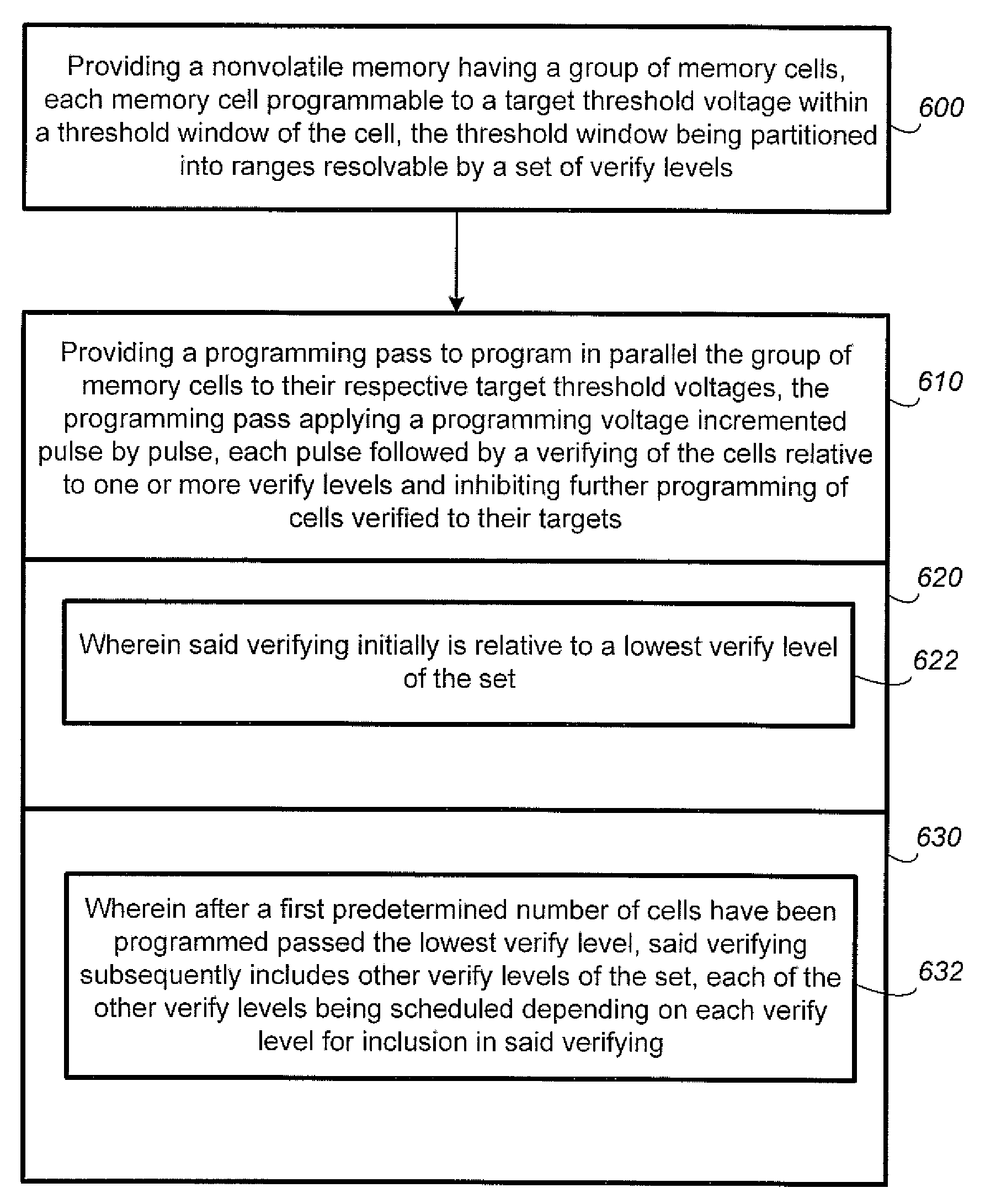
Nonvolatile Memory and Method With Reduced Program Verify by Ignoring Fastest and/or Slowest Programming Bits
ActiveUS20100091568A1Reduce in quantityRead-only memoriesDigital storagePulse delayNon-volatile memory
A group of non-volatile memory cells are programmed in a programming pass by a series of incremental programming pulses where each pulse is followed by a program-verify and possibly program-inhibition step. Performance is improved during the programming pass by delayed starting and prematurely terminating the various verify levels that demarcate the multiple memory states. This amounts to skipping the verifying and inhibiting steps of the fastest and slowest programming (fringe) cells of the group. A reference pulse is established when the fastest cells have all been program-verified relative to a first verify level. The starting of what verify level at what pulse will then be delayed relative to the reference pulse. Verifying stops for a given verify level when only a predetermined number of cells remain unverified relative to that given level. Any errors arising from over- or under-programming of the fringe cells are corrected by an error correction code.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
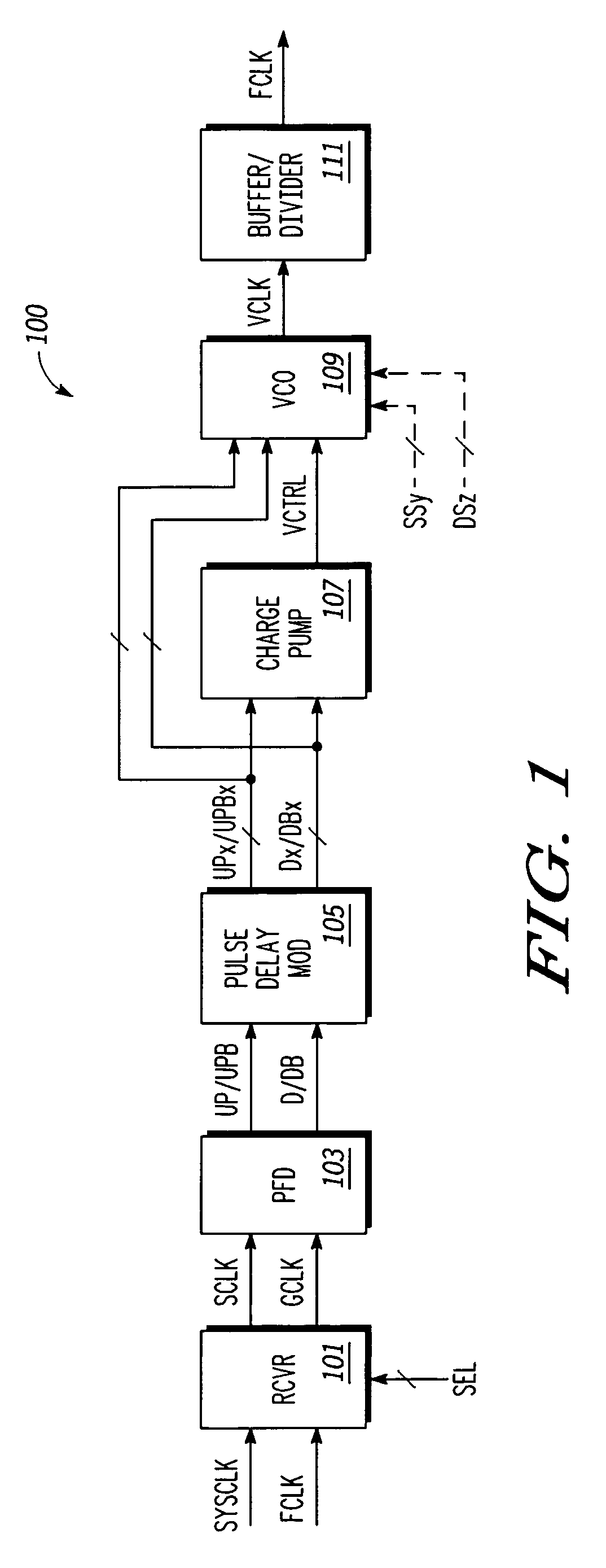
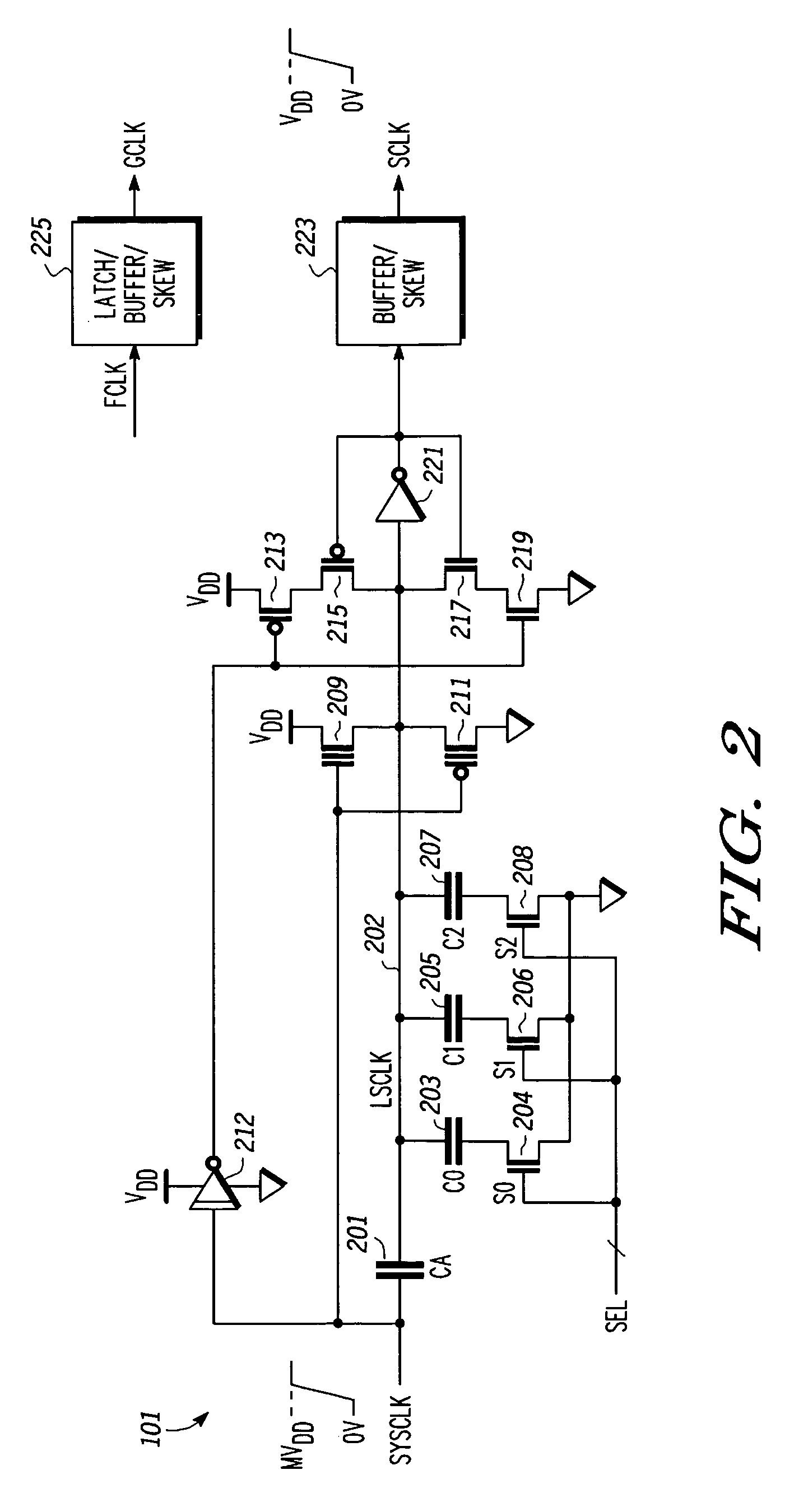
Synchronization circuit and synchronization method
InactiveUS6909312B2Simple structurePulse automatic controlSingle output arrangementsPhase synchronizationPulse delay
Phase synchronization is achieved by forming a first pulse to be synchronized with a reference pulse, a second pulse leading in phase for a certain period relative to said first pulse and a third pulse delayed in phase for a certain period from said first pulse; comparing said reference pulse with said first pulse in a first comparing; comparing said reference pulse with said second pulse and said third pulse in a second comparing; and forming a control voltage by giving priority to a comparison output of said second comparing with respect to a comparison output of said first comparing, matching the phase of said reference pulse with the phrase of said second pulse or said third pulse, and matching, after said matching of phases, the phrase of said reference pulse with the phase of said first pulse by forming said control, voltage from the comparison output of said first comparing.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
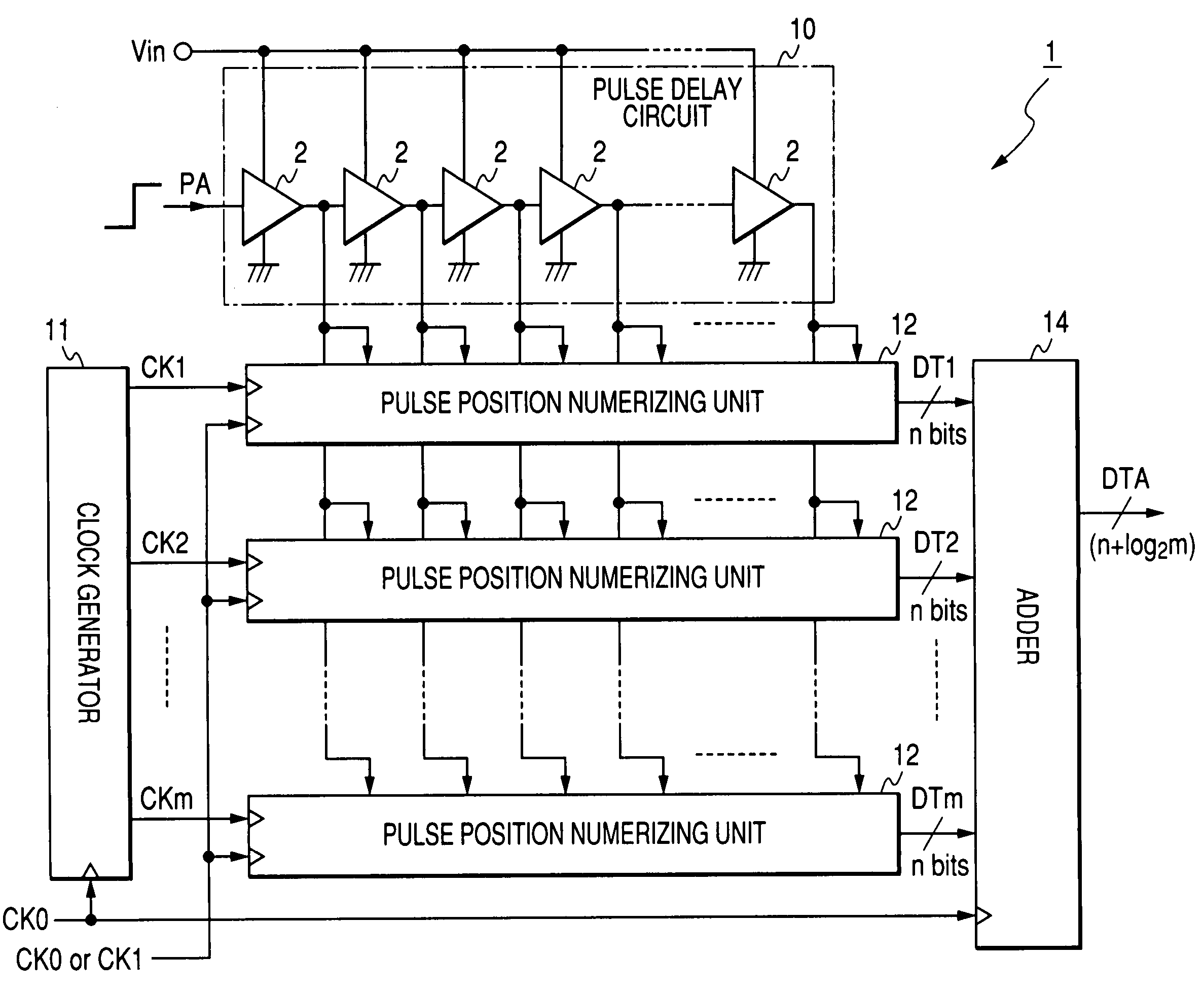
Analog-to-digital conversion method and device
InactiveUS6771202B2Improve accuracyShorten the timeElectric signal transmission systemsPulse generation by logic circuitsDelayed timeEngineering
Owner:DENSO CORP
Analog-to-digital conversion method and device
InactiveUS6850178B2High resolutionLarge driving voltageElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue-digital convertersDigital dataEngineering
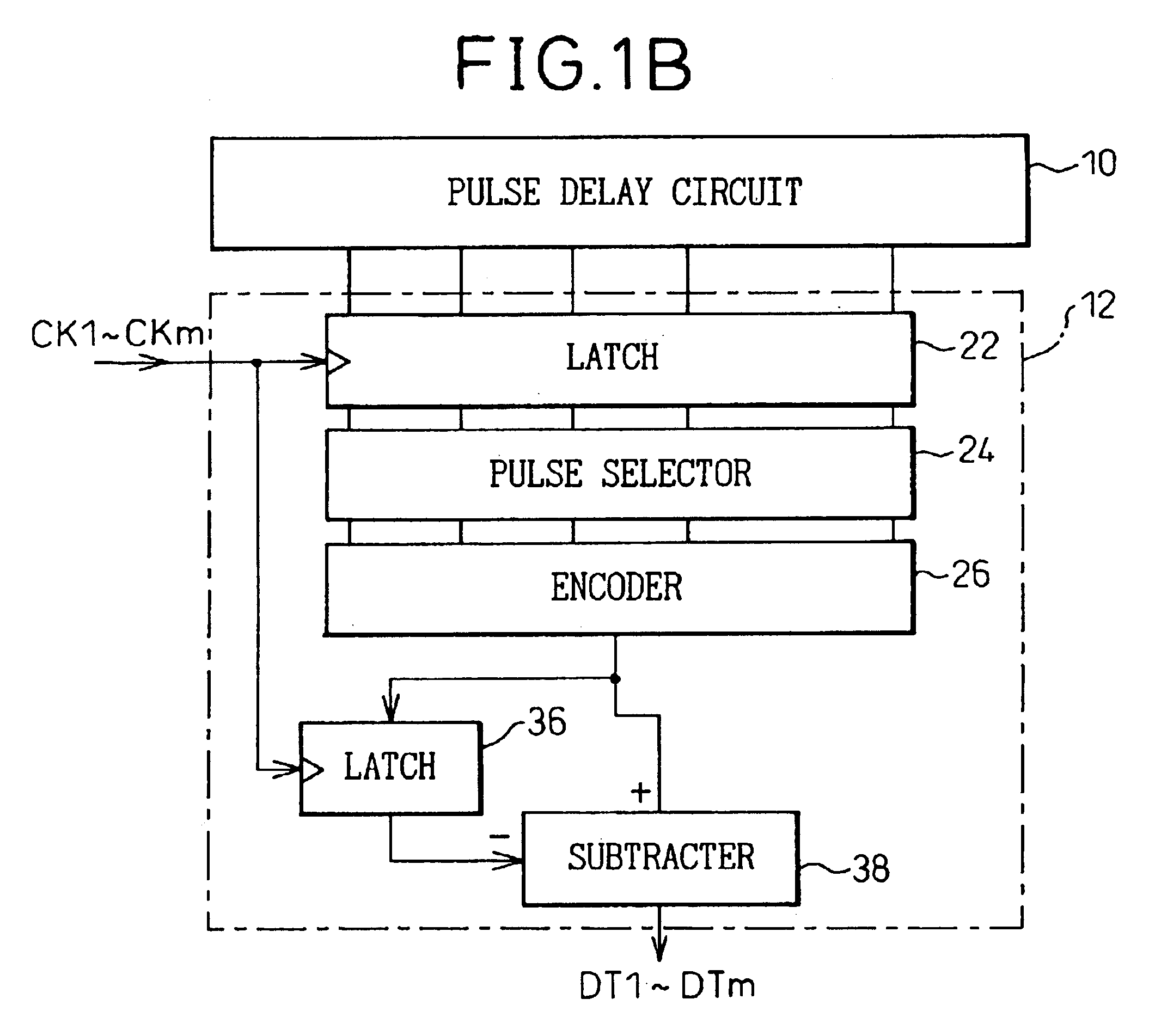
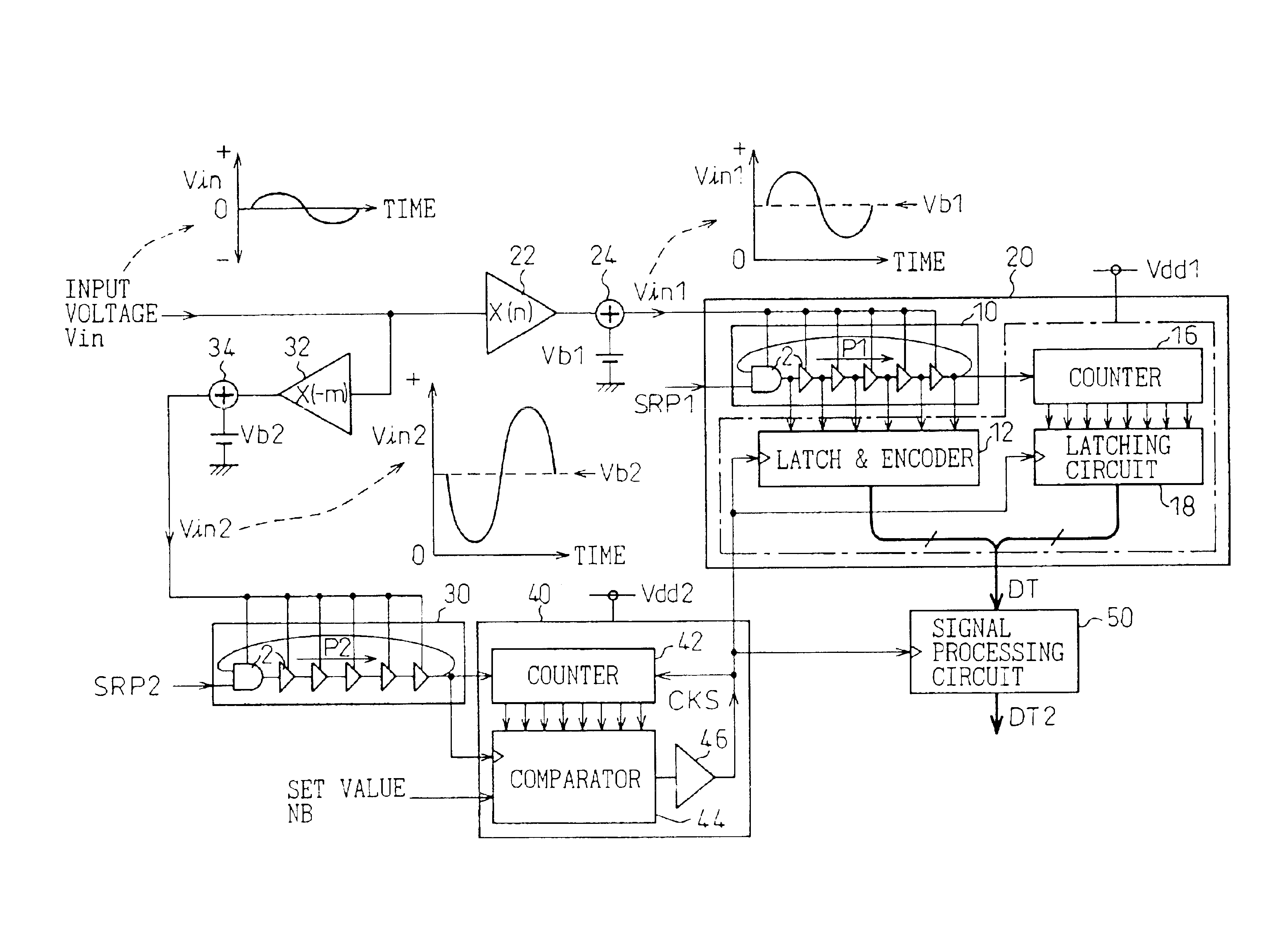
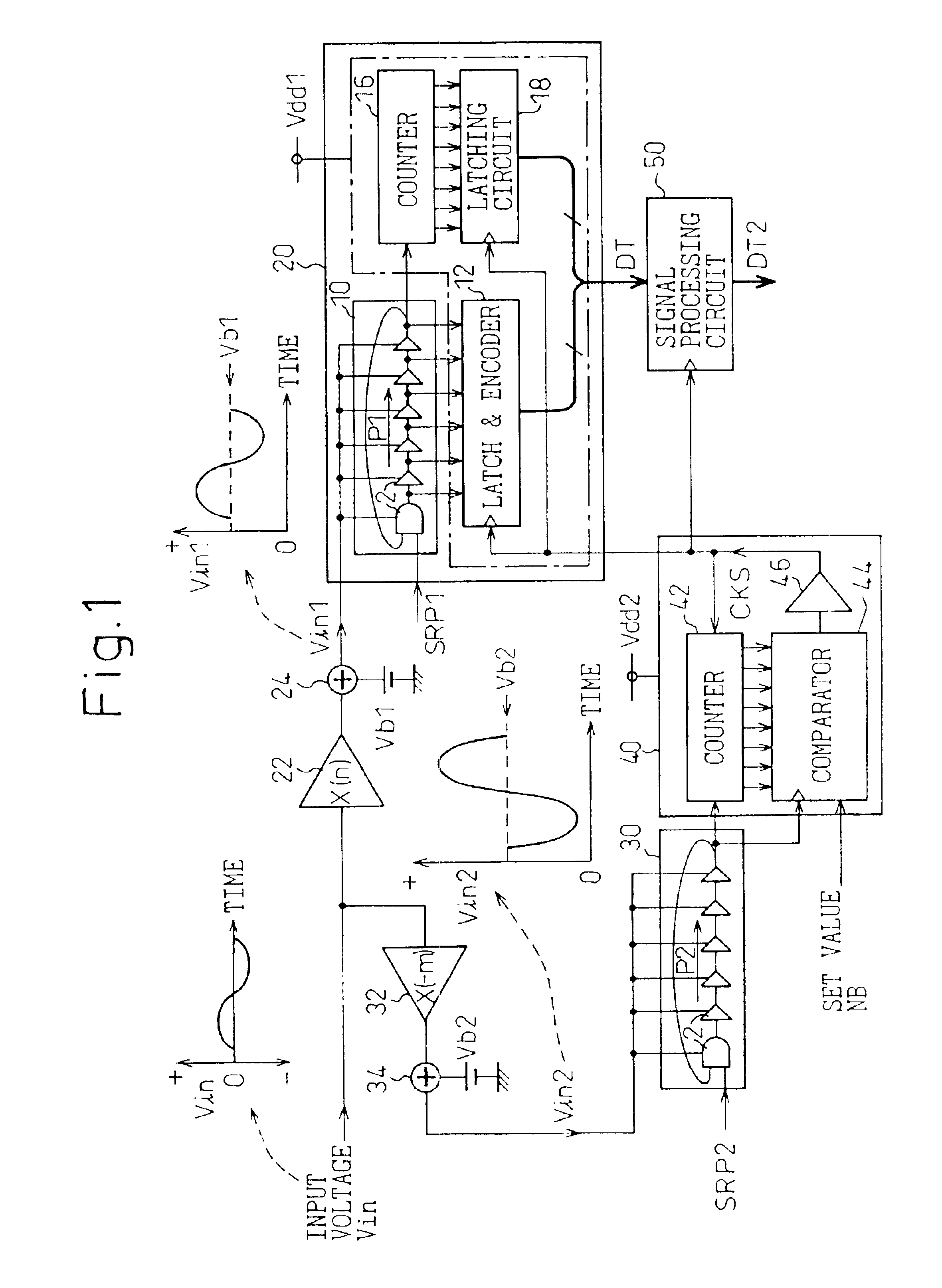
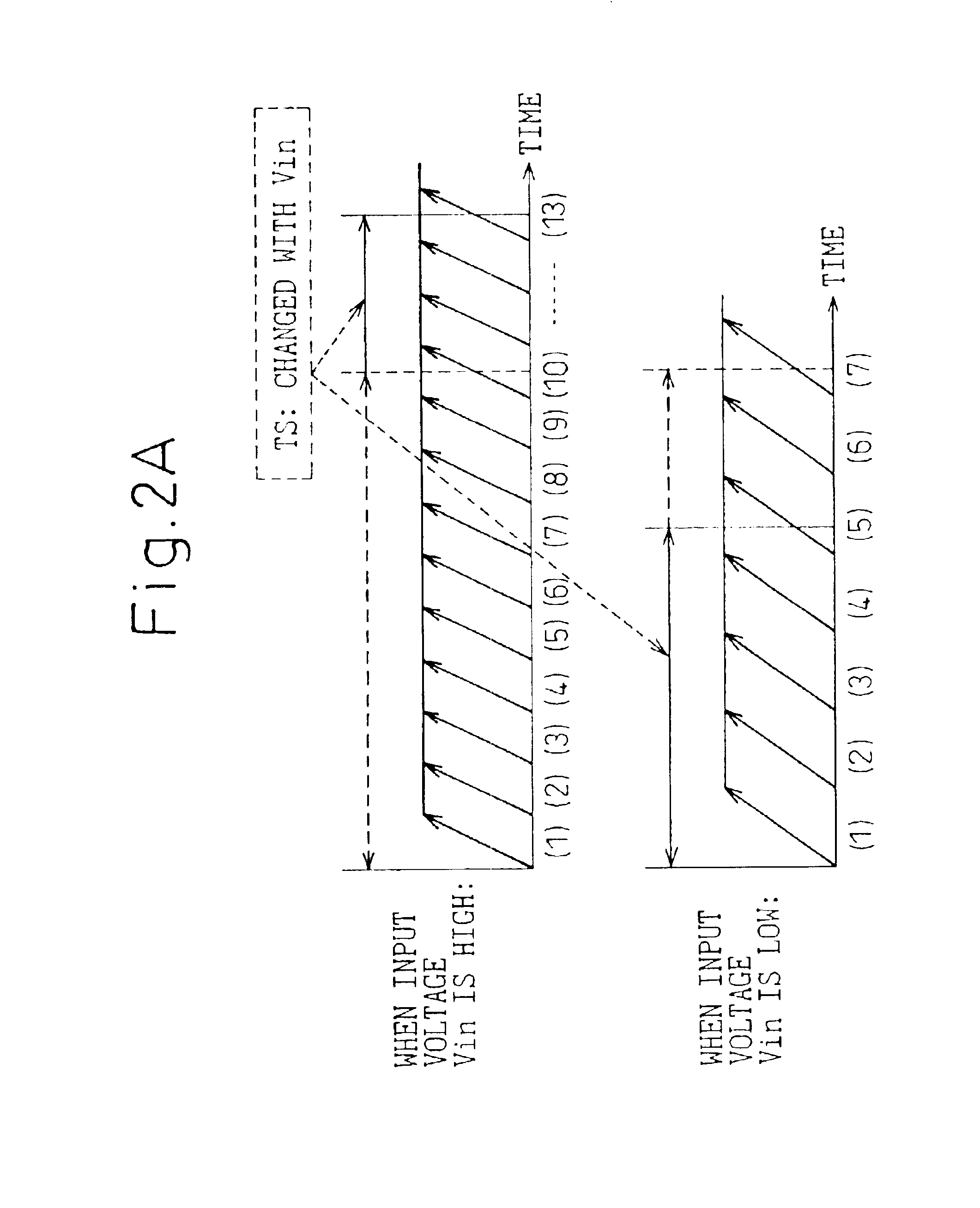
An analog-to-digital conversion device is provided that uses pulse delay circuits to convert an input voltage into numerical data and offers a high resolution in analog-to-digital conversion or a high analog-to-digital conversion rate. The analog-to-digital conversion device includes an analog-to-digital conversion unit having a pulse delay circuit composed of a plurality of delay units. The delay units are driven with a voltage produced by amplifying or shifting an input voltage. The number of delay units through which a pulse signal has passed during a predetermined sampling cycle is adopted as a digitized value of the input voltage. Herein, delay units constituting another pulse delay circuit are driven with a voltage produced by inversely amplifying or shifting the input voltage. Every time the number of delay units through which a pulse signal has passed within the pulse delay circuit reaches a predetermined value determined with a set value, a sampling signal is transferred to the analog-to-digital conversion unit.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Nonvolatile Memory And Method With Reduced Program Verify By Ignoring Fastest And/Or Slowest Programming Bits
ActiveUS20100091573A1Reduce in quantityReduce the numberRead-only memoriesDigital storageComputer scienceNon-volatile memory
A group of non-volatile memory cells are programmed in a programming pass by a series of incremental programming pulses where each pulse is followed by a program-verify and possibly program-inhibition step. Performance is improved during the programming pass by delayed starting and prematurely terminating the various verify levels that demarcate the multiple memory states. This amounts to skipping the verifying and inhibiting steps of the fastest and slowest programming (fringe) cells of the group. A reference pulse is established when the fastest cells have all been program-verified relative to a first verify level. The starting of what verify level at what pulse will then be delayed relative to the reference pulse. Verifying stops for a given verify level when only a predetermined number of cells remain unverified relative to that given level. Any errors arising from over- or under-programming of the fringe cells are corrected by an error correction code.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
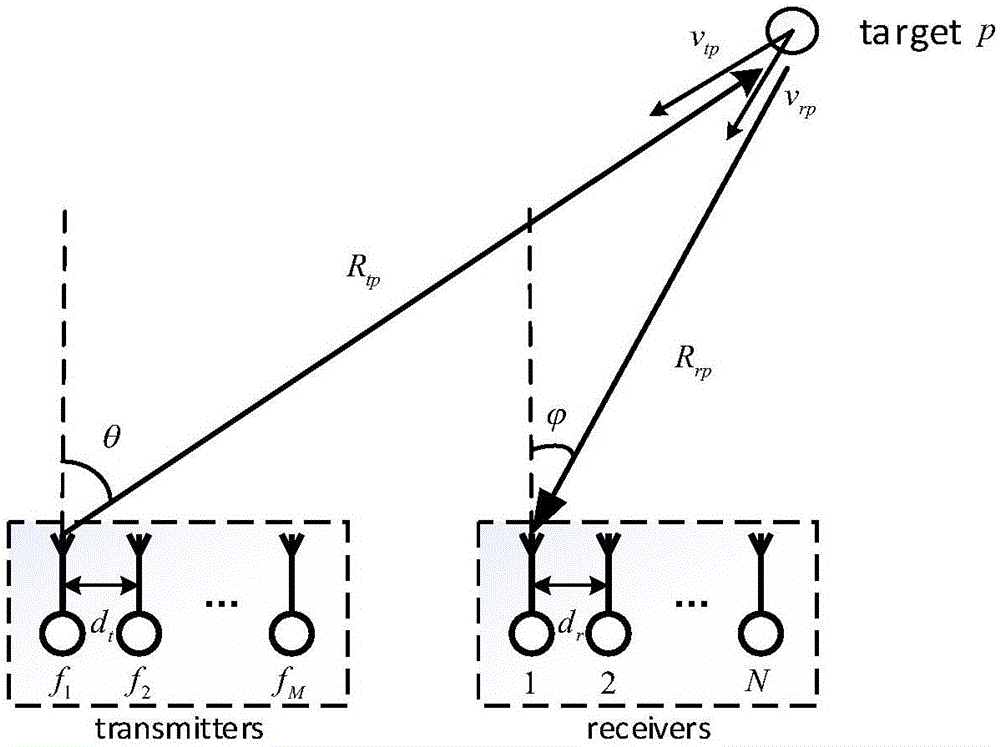
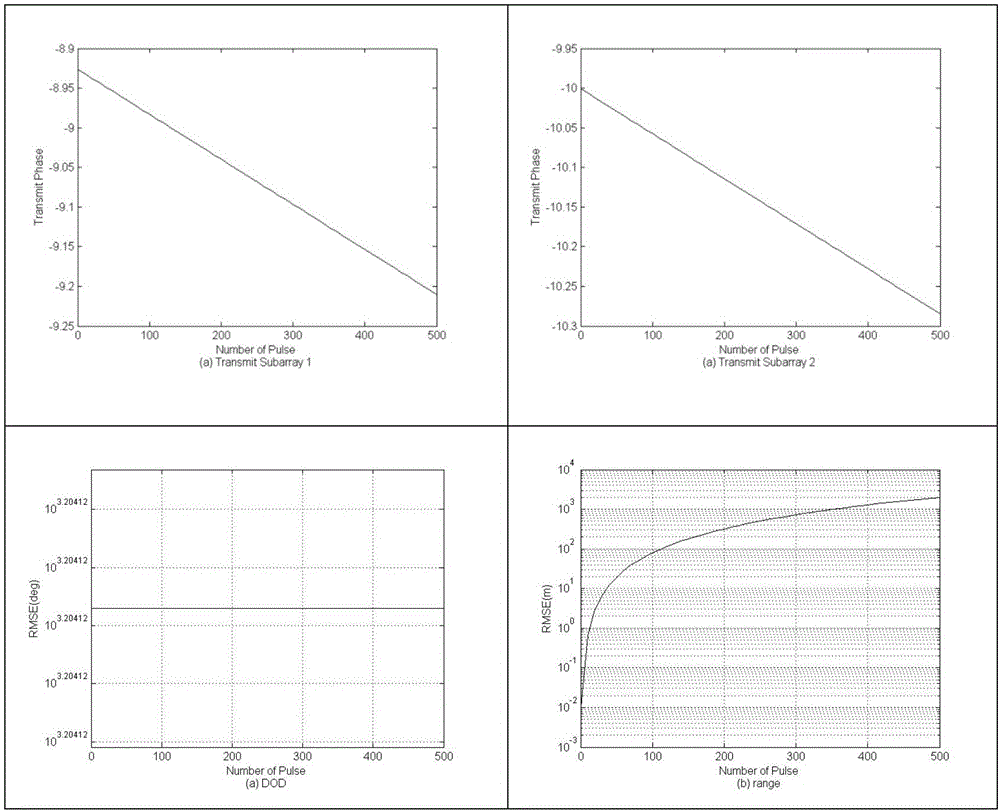
Multi-parameter combined estimation method based on bi-static FDA-MIMO radars
ActiveCN106353744AImprove estimation performanceSolve problems that are prone to ambiguityRadio wave reradiation/reflectionEstimation methodsMultiple signal classification
The invention relates to a multi-parameter combined estimation method based on bi-static FDA-MIMO radars. The method comprises the following steps: firstly designing a transmitting signal by utilizing characteristics of FDA and MIMO radars; carrying out matched filtering, vectorization and spatial smooth processing on a receiving signal; then estimating a combined steering vector and estimating a DOA and a speed parameter by utilizing an ESPRIT algorithm, and carrying out decoupling and parameter estimation on the DOD and distance information by combining characteristics of a transmitting waveform; and carrying out ambiguity resolution on a distance result estimated by utilizing an ESPRIT algorithm and combining a distance estimated by virtue of a pulse delay estimation algorithm, and carrying out ambiguity resolution on a speed by virtue of an MUSIC algorithm by combining signal characteristics of a large number of pulses. The method provided by the invention has the advantages that the problem that the distance and speed can not be accurately estimated under the condition of a single PRF can be effectively solved, and the estimation of the three-dimensional position and speed of a target can be realized; and a simulation result shows that the method provided by the invention has good estimation accuracy and stability.
Owner:THE PLA INFORMATION ENG UNIV
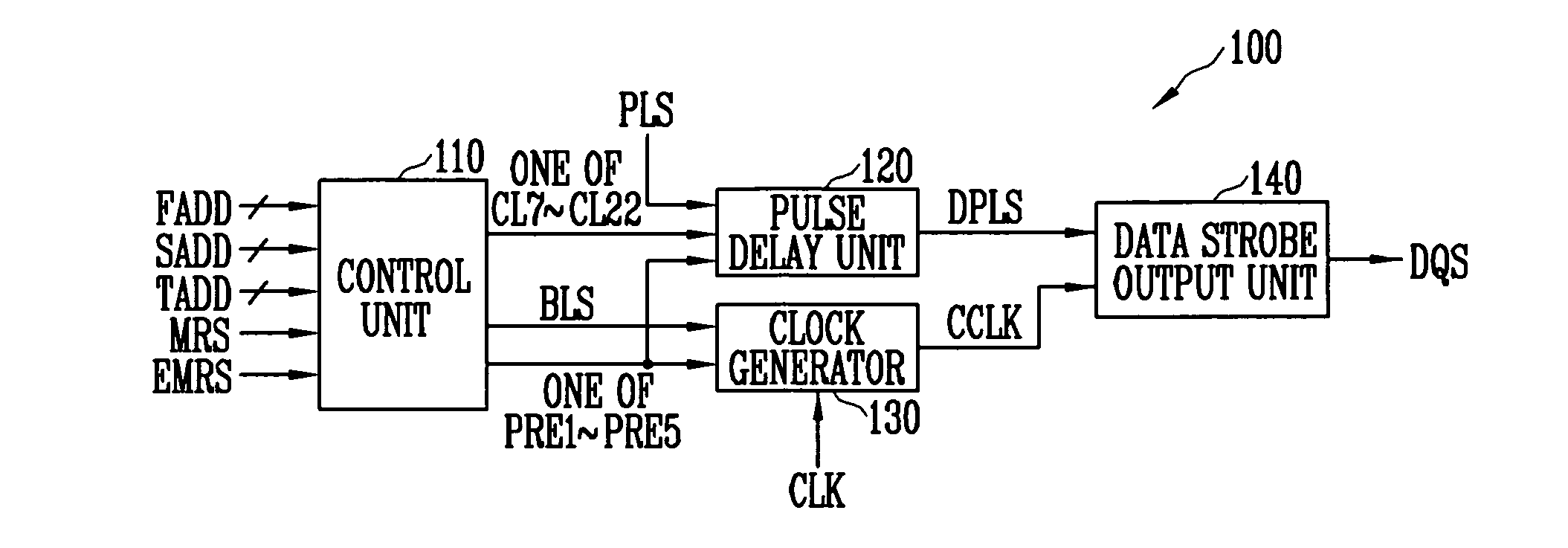
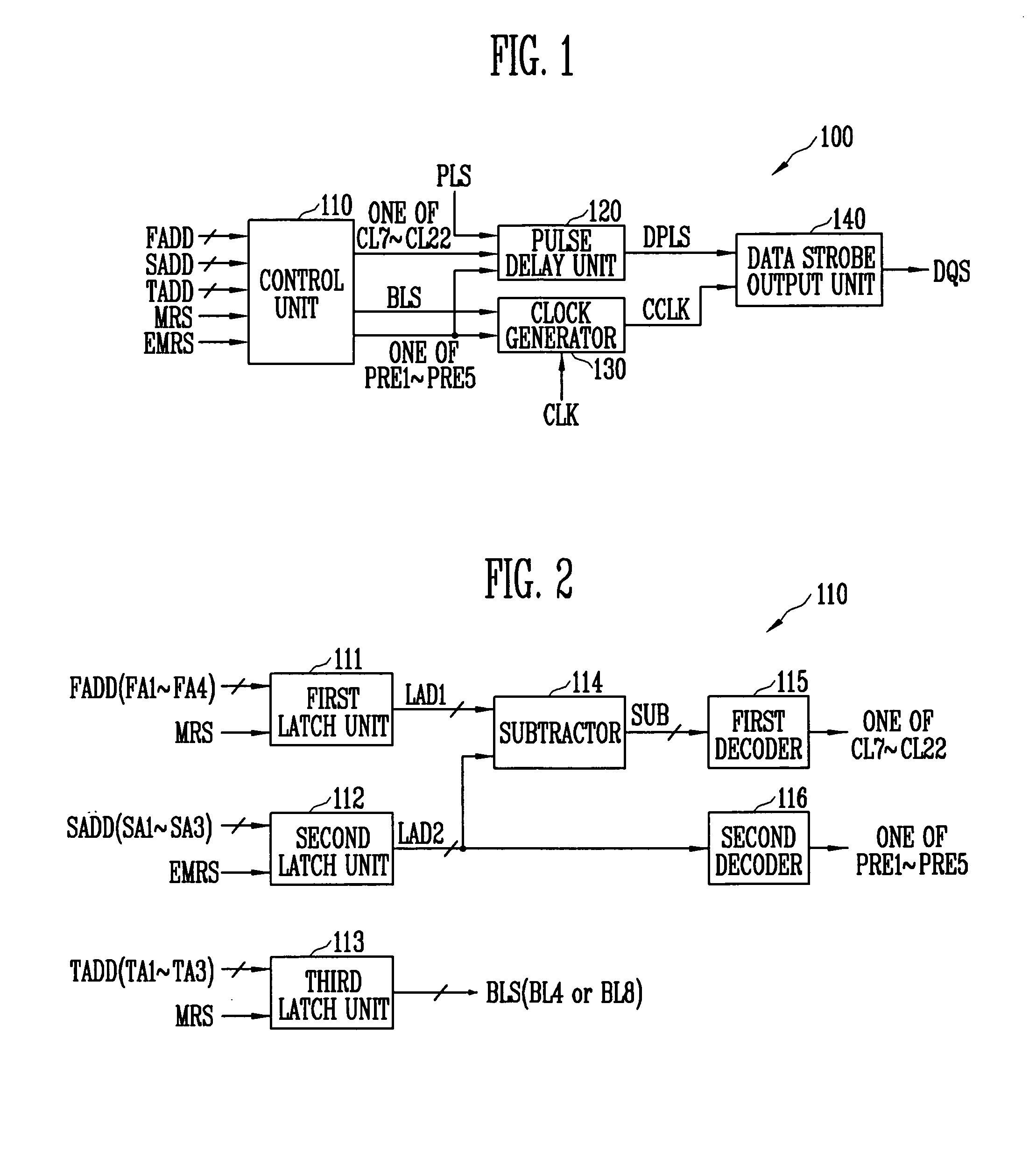
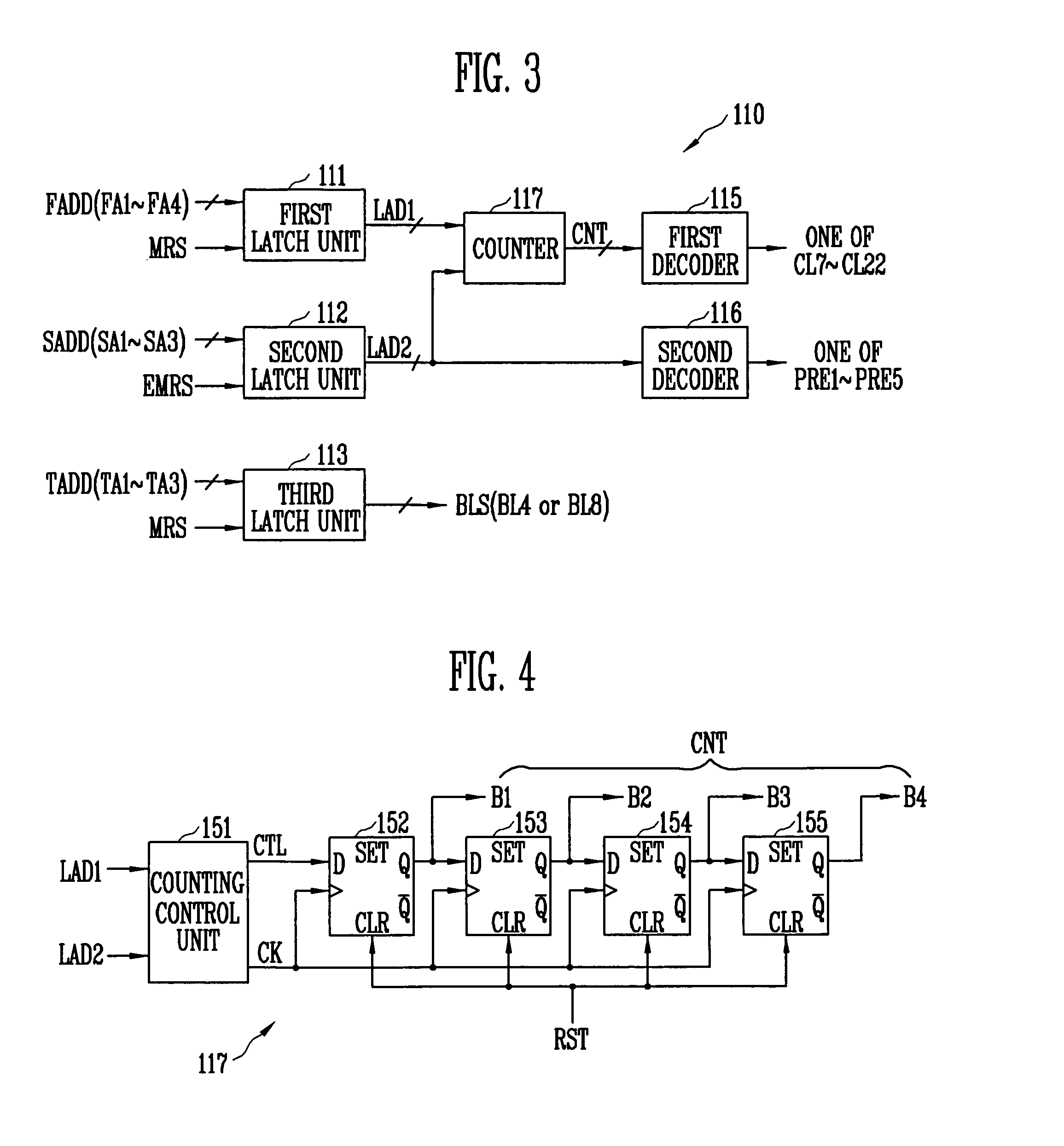
Data strobe signal generator for generating data strobe signal based on adjustable preamble value and semiconductor memory device with the same
InactiveUS20070291558A1Stabilized data output operationIncrease speedDigital storageHigh speed memoryControl signal
A data strobe signal generator according to the present invention includes a control unit, a pulse delay unit, a clock generator, and a data strobe output unit. The control unit generates a CAS latency signal and a preamble signal. The pulse delay unit delays a pulse signal for predetermined time and outputs a delayed pulse signal. The clock generator outputs a control clock signal. The data strobe output unit outputs a data strobe signal. The data strobe signal generator and the semiconductor memory device having the same according to the present invention generate a data strobe signal based on an adjustable preamble value, thereby ensuring the stabilized data output operation of a high-speed memory device.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
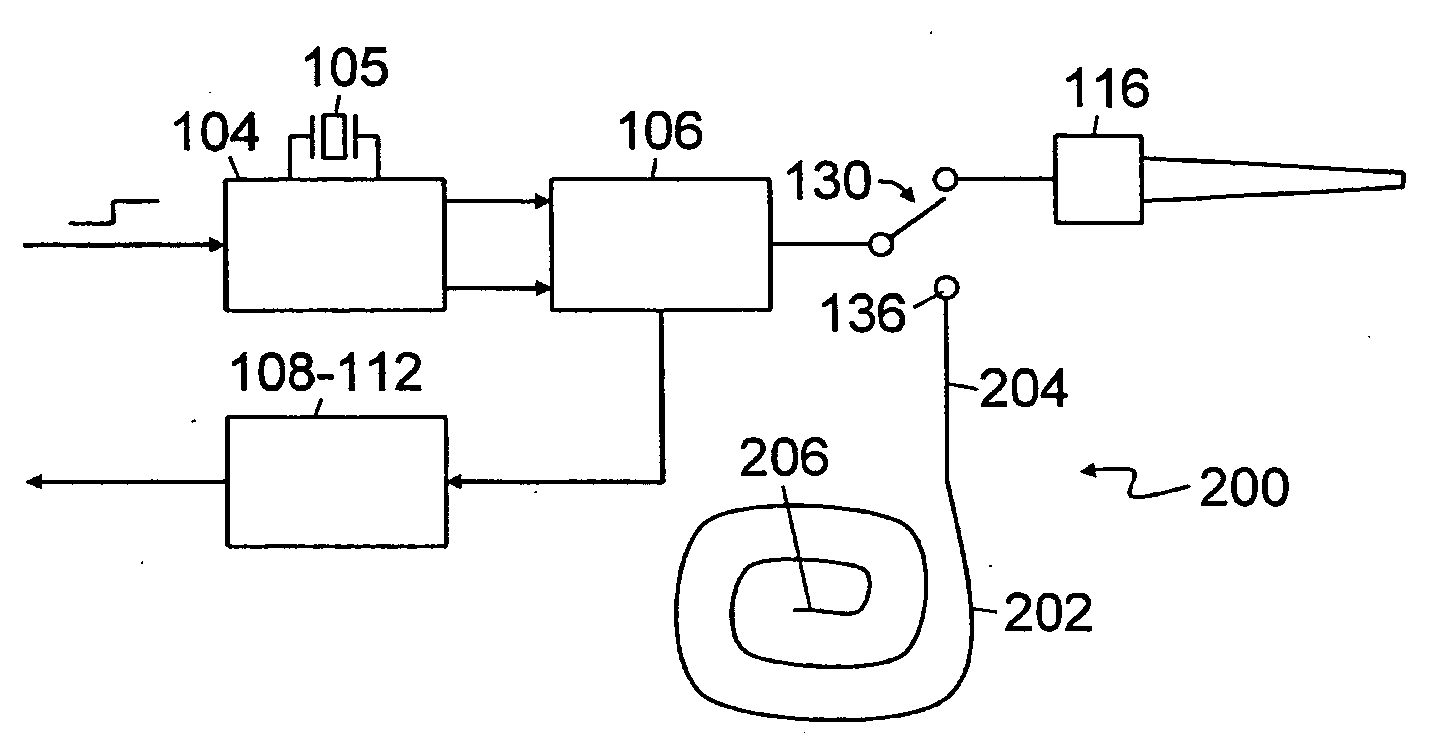
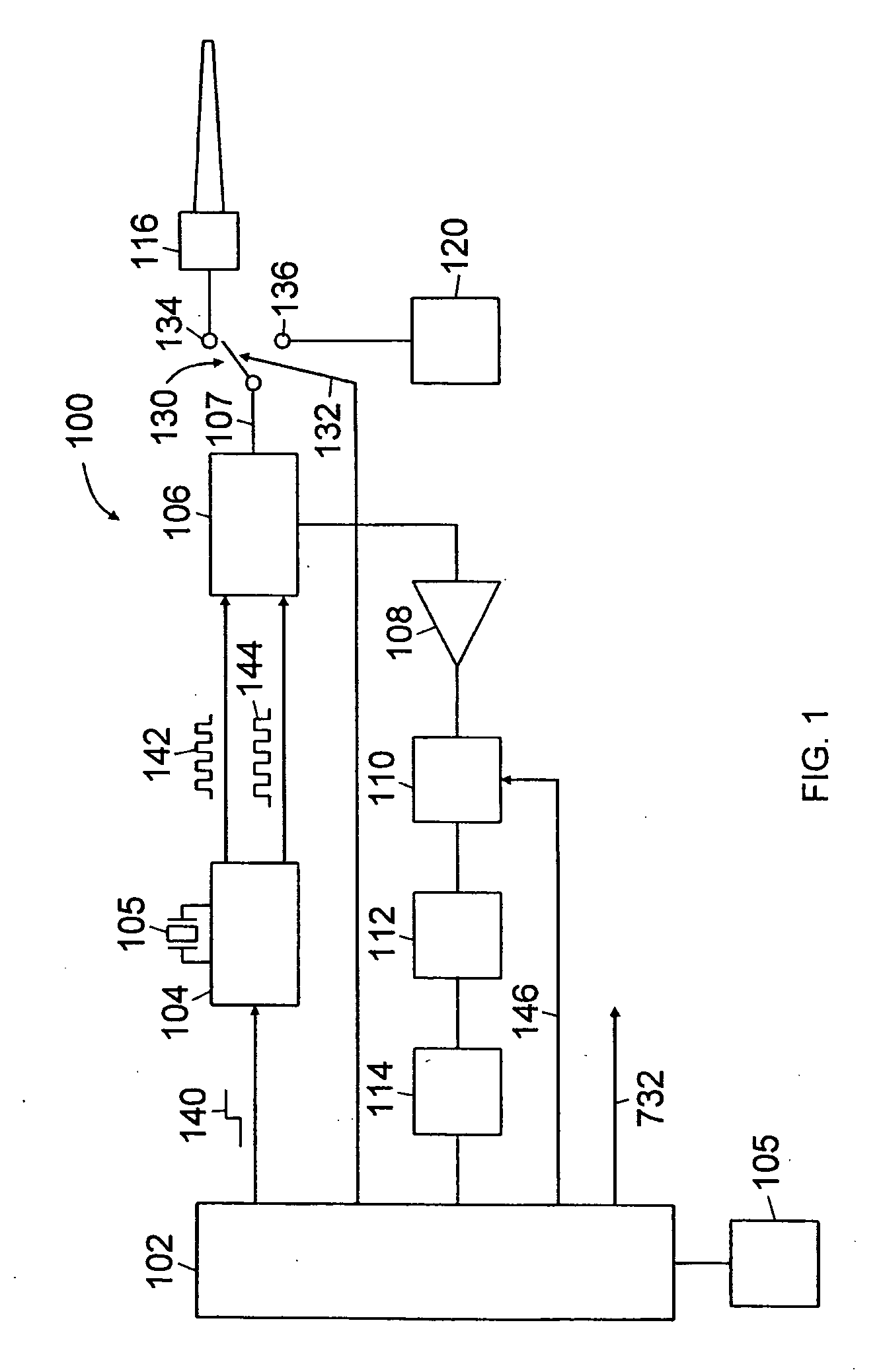
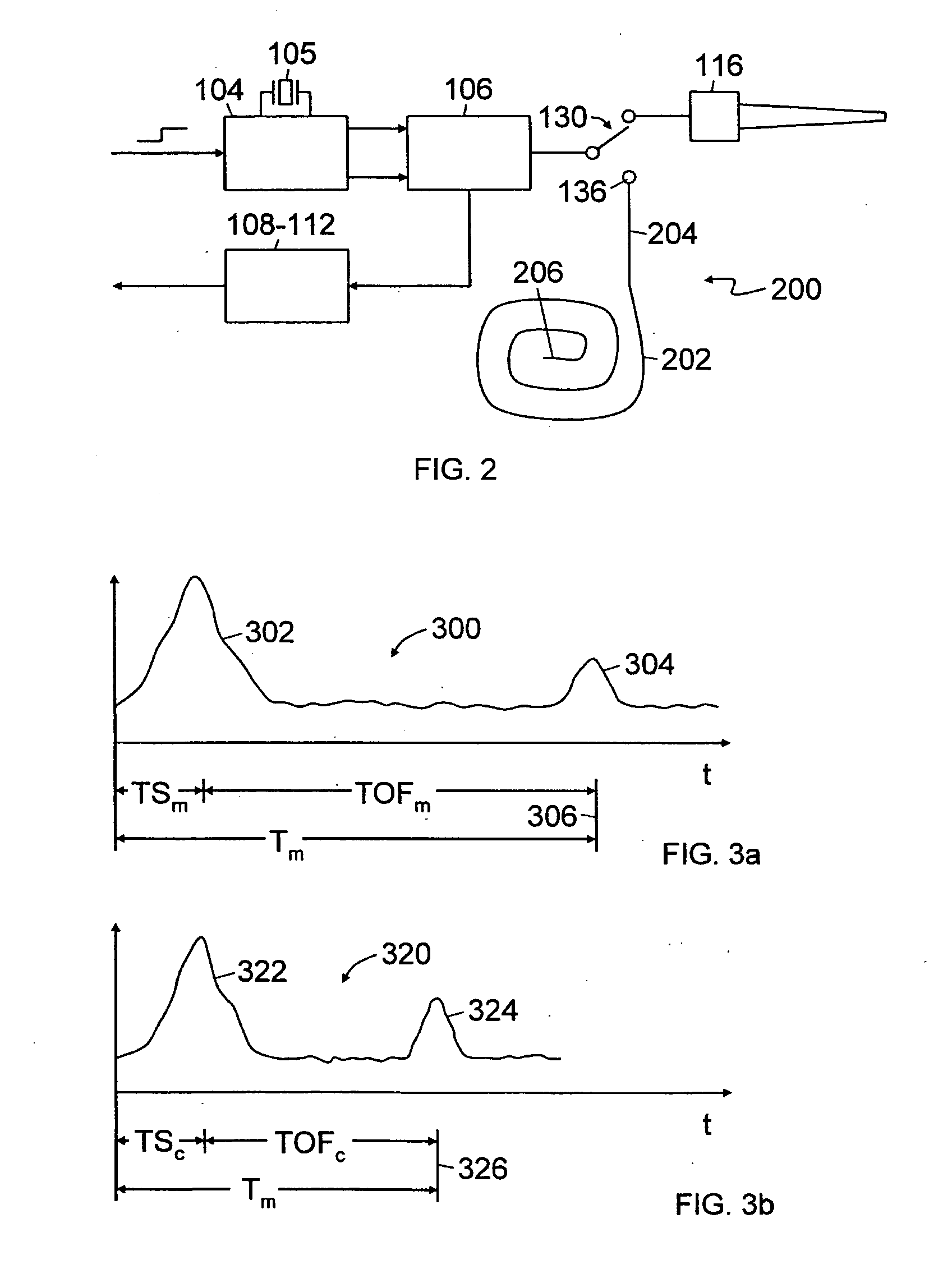
Time-of-flight-ranging system and method for calibrating such a system
An embedded calibration mechanism and method for a time-of-flight ranging system. The calibration mechanism (200) comprises a channel (202) having known characteristics. Periodically or as part of a calibration function, a pulse is transmitted through the calibration channel (202) and parameters such transmit pulse delay time and apparent velocity are determined. The calibration parameters or measurements are used to calibrate or compensate operation or measurements from the measurement channel.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Analog-to-digital conversion method and device
InactiveUS20030201927A1Improve accuracyShorten the timeElectric signal transmission systemsPulse generation by logic circuitsDelayed timePulse delay
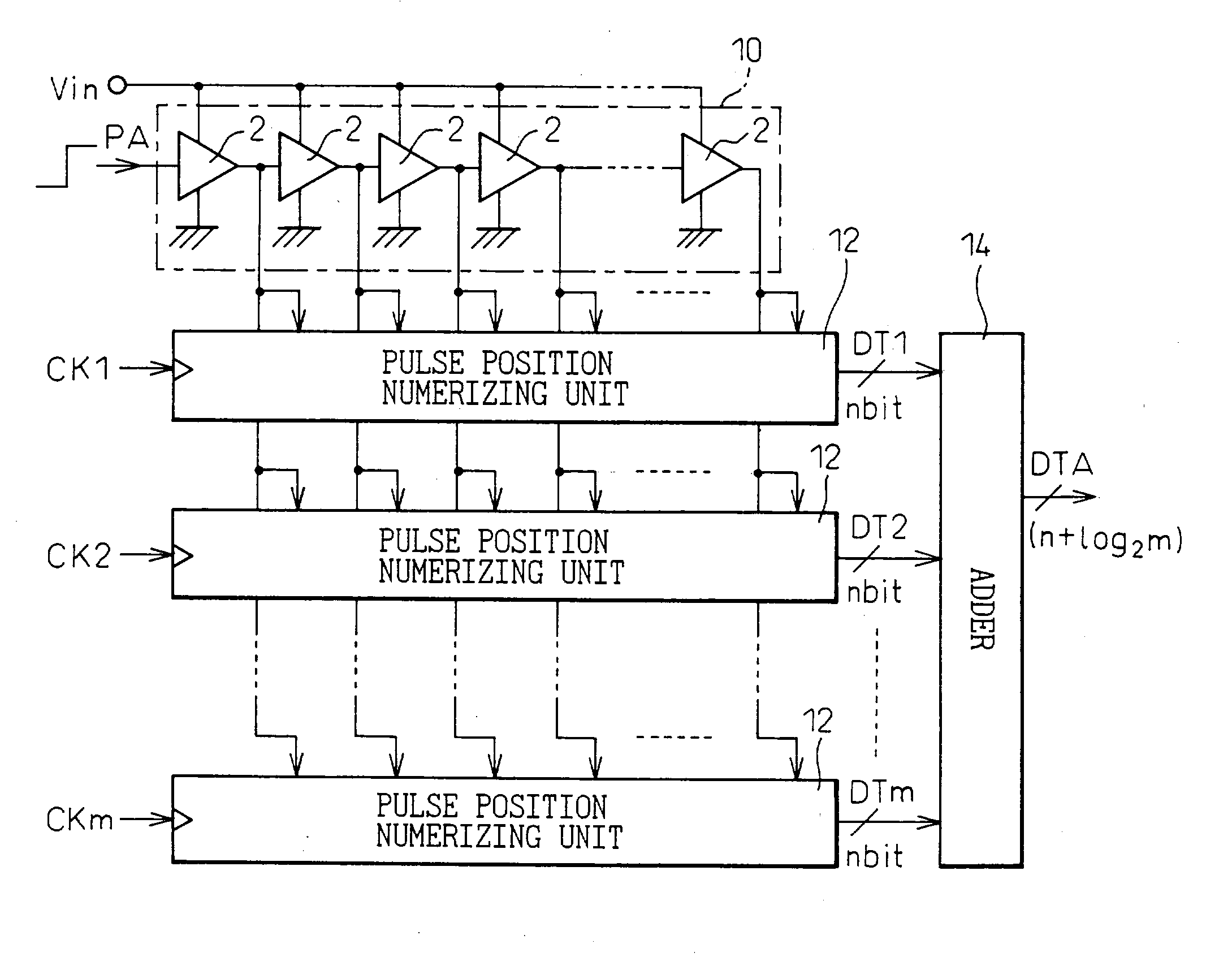
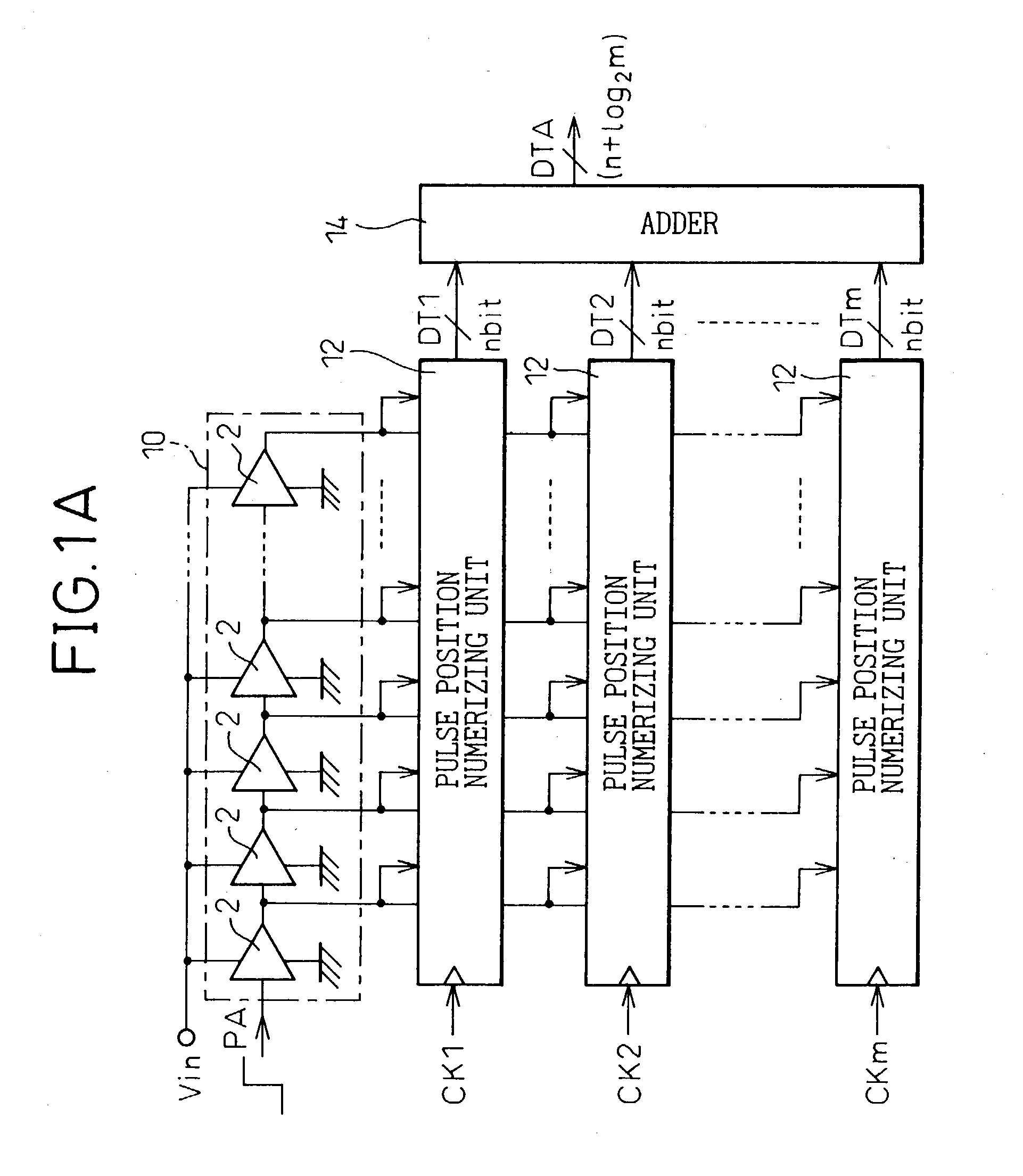
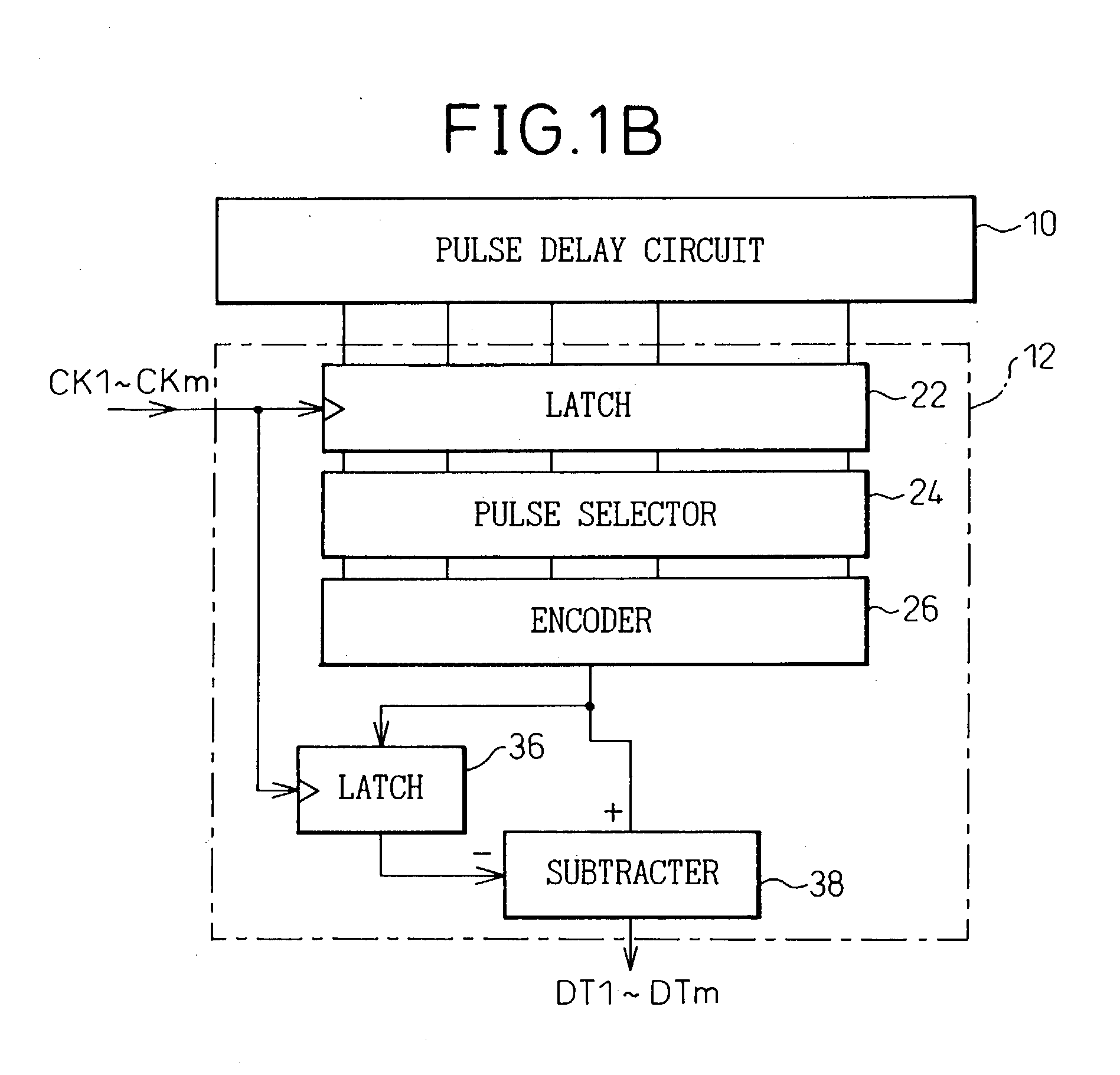
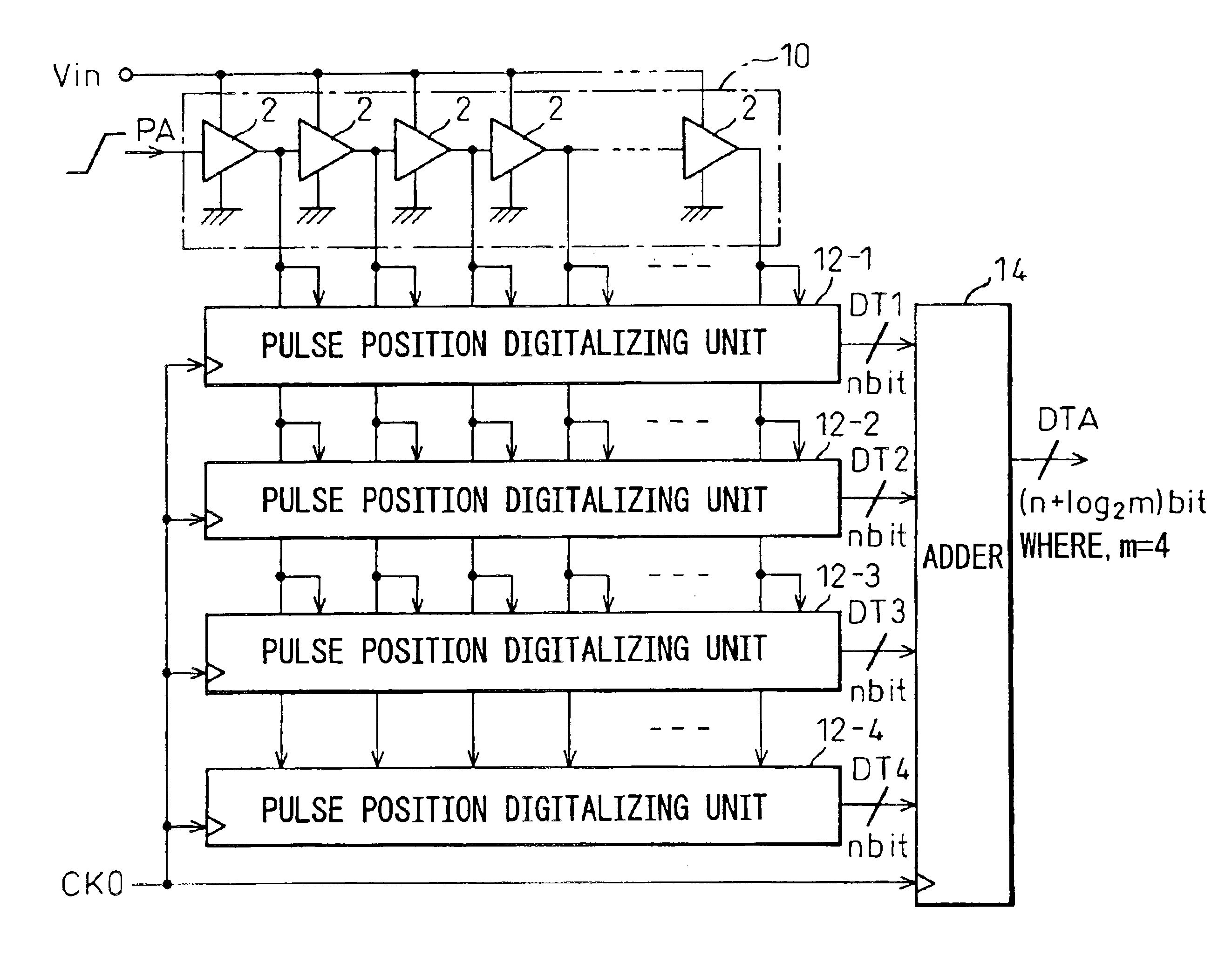
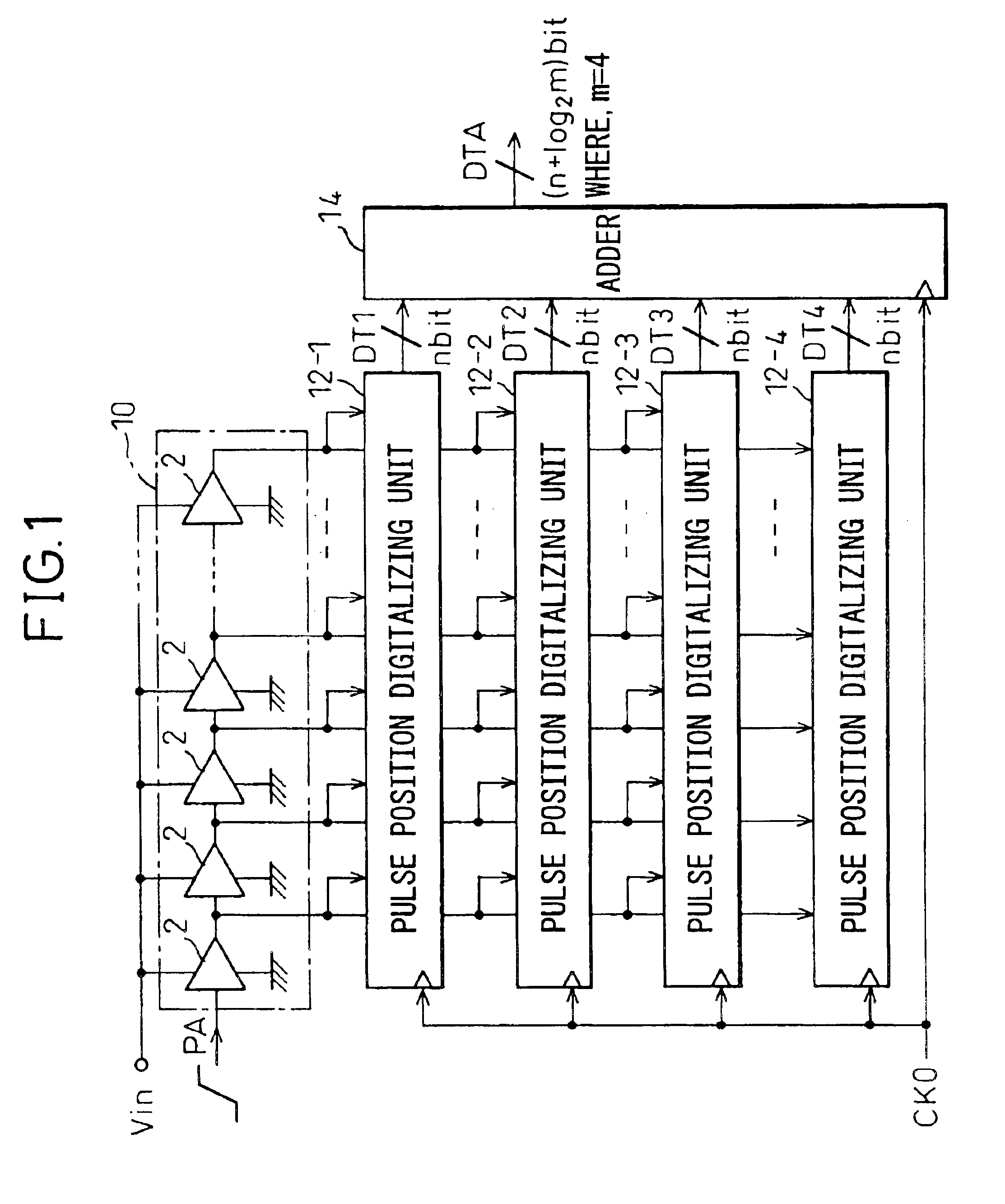
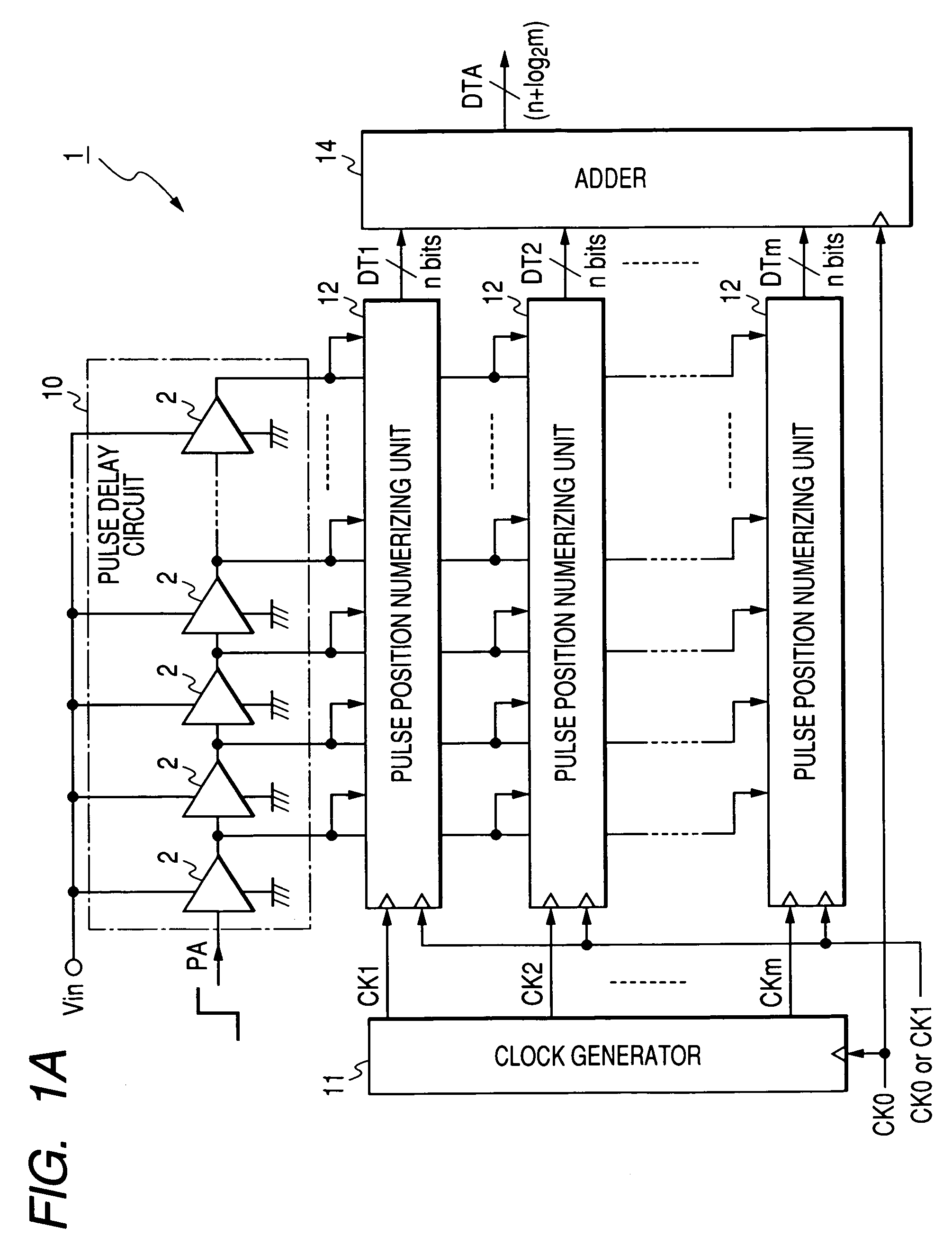
In a device for analog-to-digital converting an input signal, the input signal is applied to a plurality of delay units constituting a pulse delay circuit in order to change a delay time to be given by the delay units. The number of delay units through which a pulse signal has passed during one period of sampling clocks is numerically expressed. The A / D conversion device has a plurality of pulse position numerizing units that is used for A / D conversion. Sampling clocks of which the phases are different from one another are applied to the respective pulse position numerizing units. An adder summates numerical data items produced by the respective pulse position numerizing units so as to generate final numerical data representing a result of A / D conversion.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Image sensor and control method of the image sensor
ActiveUS7671313B2Increase speedImprove accuracyTelevision system detailsElectric signal transmission systemsBuck converterDelayed time
An image sensor has plural array blocks B1 to B20 arranged in a two dimensional (2D) arrangement. Each array block has a sub array and a corresponding analogue to digital (A / D) converter for performing an A / D conversion of light signals (or detection signals) output from the sub array. The sub array has plural picture element cells arranged in a 2D arrangement. Each A / D converter has a pulse delay circuit having delay units of plural stages connected in series. Each delay unit delays an input pulse by a delay time corresponding to a level of the light signals received from the sub array. A pulse delay type A / D converter is used as the A / D converter, which outputs the number of the delay units as an A / D conversion data item through which the input pulse passes for a measurement time period.
Owner:DENSO CORP
On-line in situ detecting method for infrared-ultraviolet double pulse laser induced breakdown spectroscopy
InactiveCN102507512ARealize fixed-point sampling detectionFlexible time optimizationAnalysis by material excitationSpectrographUltraviolet
The invention discloses an on-line in situ detecting method for an infrared-ultraviolet double pulse laser induced breakdown spectroscopy, which at least comprises the following steps of: A. setting a pulse delay time according to the sample excitation characteristics to control the time interval of two lasers; B. firstly outputting laser from an infrared waveband laser, long-distance collecting, adjusting and focusing on a position to be detected, and ablating the sample to generate plasma; C. outputting laser from an ultraviolet waveband laser after a delay time, long-distance collecting, adjusting and focusing on the same position, and exciting the plasma to reinforce a spectrum signal; D. receiving the spectrum signal through a long-distance spectrum collecting device, coupling the spectrum signal in an optical fiber, transmitting the spectrum signal to a spectrograph, and obtaining the spectrum data information through an assorted software; E. collecting the spectrum data, and obtaining a detection ingredient analysis result by a calibration-free correction analysis method.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Radar apparatus
InactiveUS20060187111A1High-resolution searchSuppress level changeRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadarSignal correlation
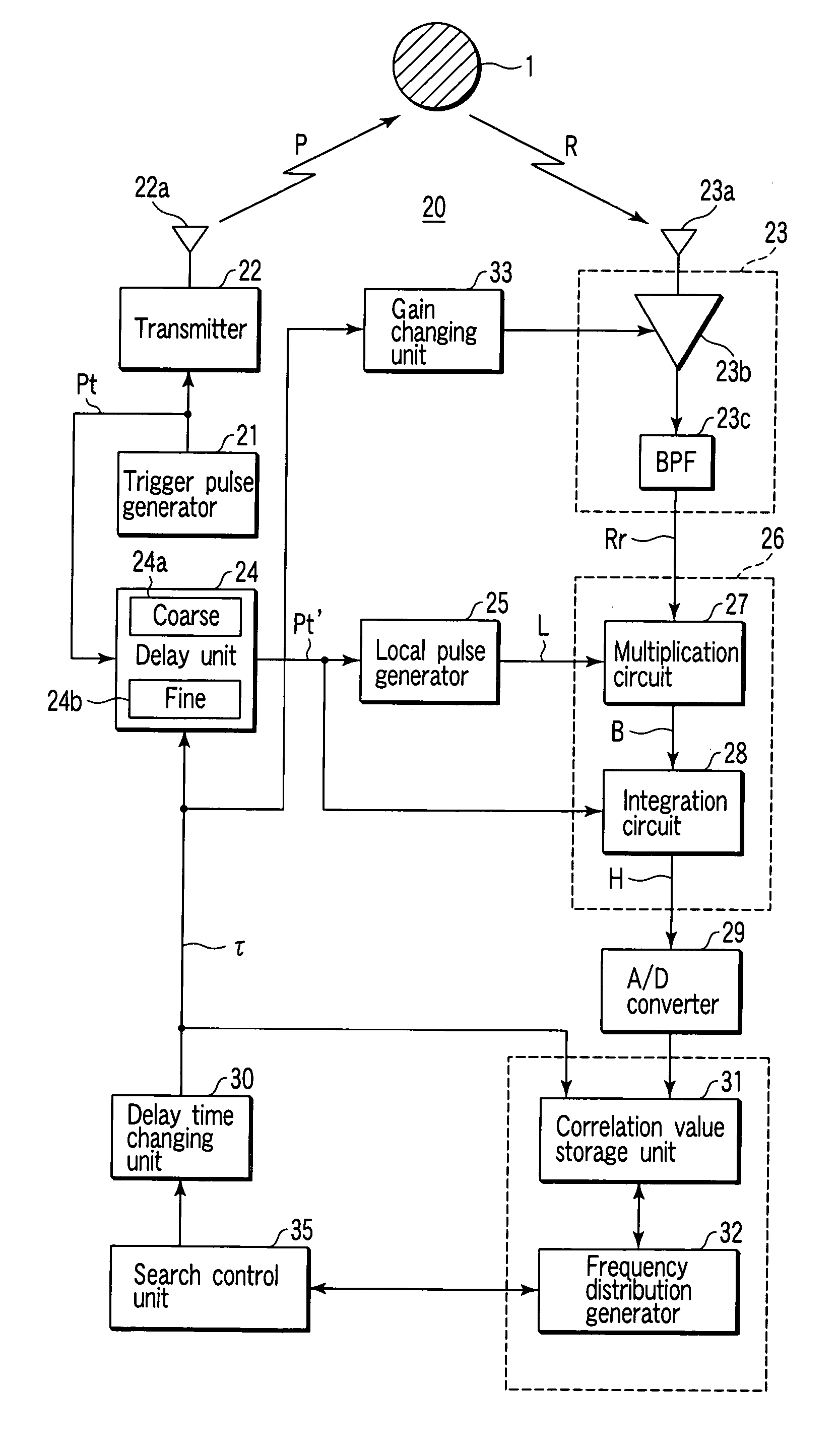
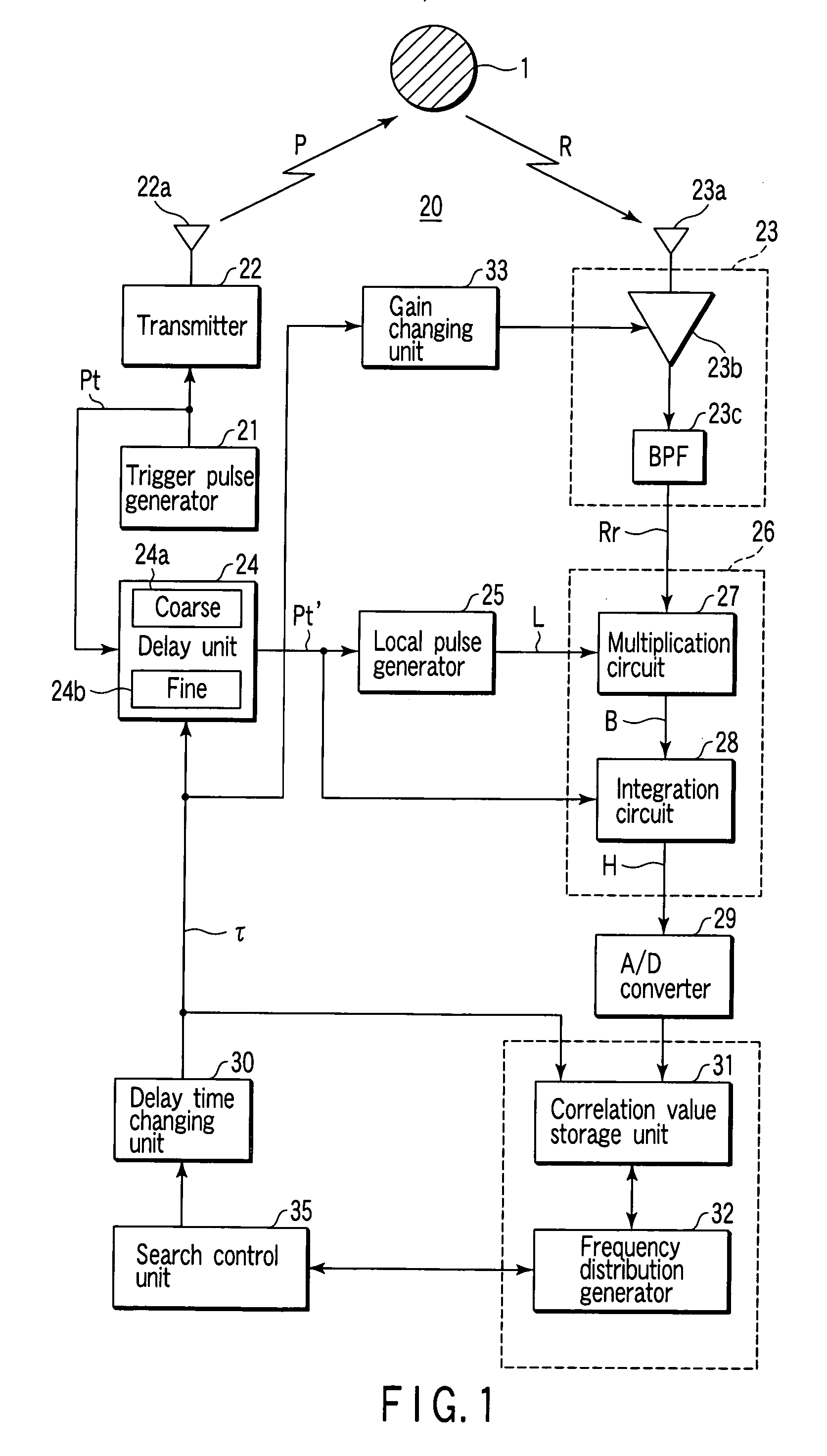
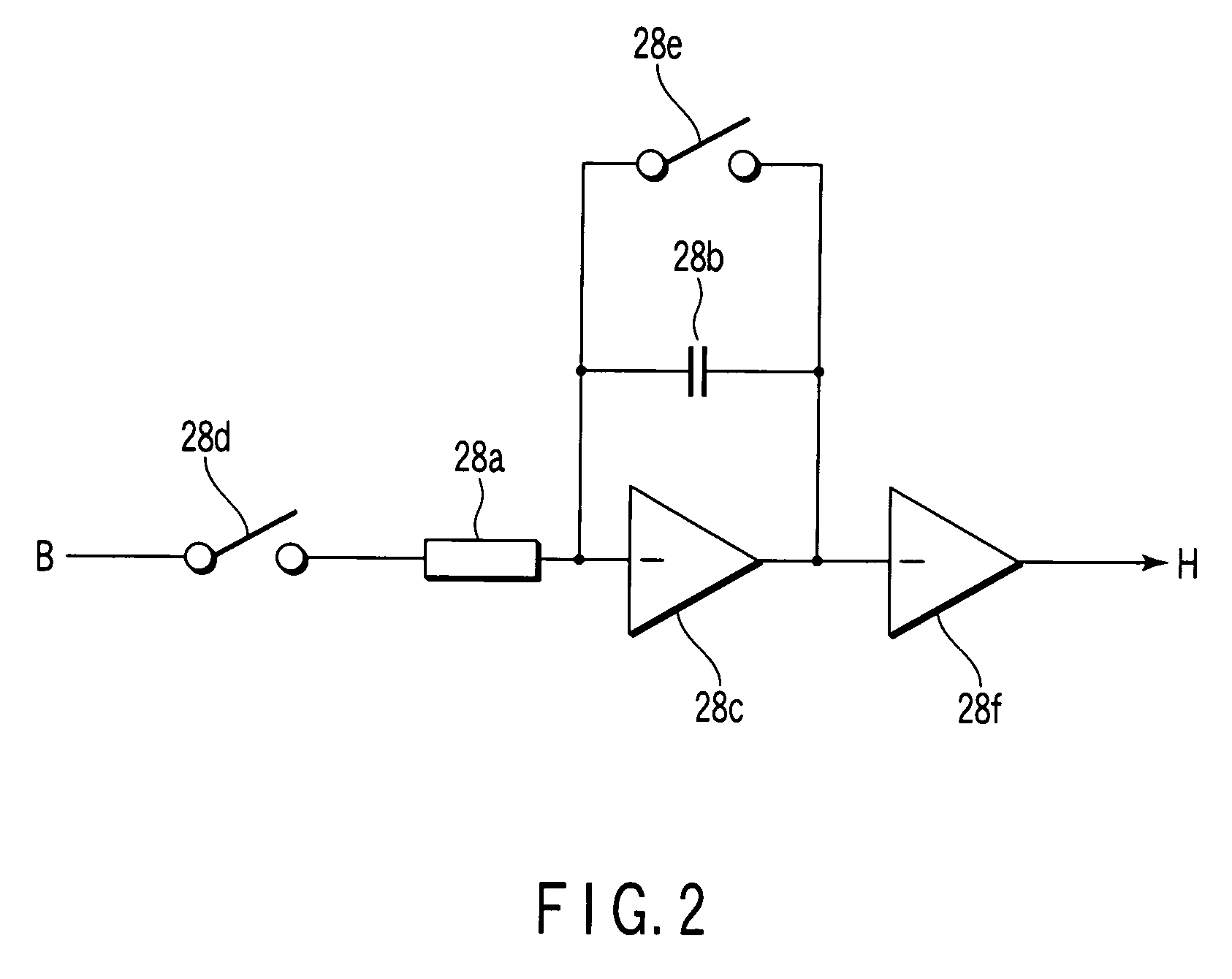
A transmitter emits into an intended search space a radar wave having a predetermined frequency pulse-modulated by a trigger pulse of a predetermined width. A receiver receives a reflected wave of the radar wave and outputs a receive signal. A local pulse generator outputs a local pulse signal having the predetermined frequency pulse-modulated by the trigger pulse delayed by the delay unit. A correlation value detector detects a strength correlation value between the receive signal and the local pulse signal. A delay time changing unit changes the delay time sequentially within a range of a predetermined period representing a generation period of the trigger pulse. A correlation value storage unit stores the strength correlation value detected for each delay time changed. A frequency distribution generator generates a frequency distribution of a stored correlation value against the delay time. A search control unit executes an analyzation for the intended search space based on a generated frequency distribution.
Owner:ANRITSU CORP +1
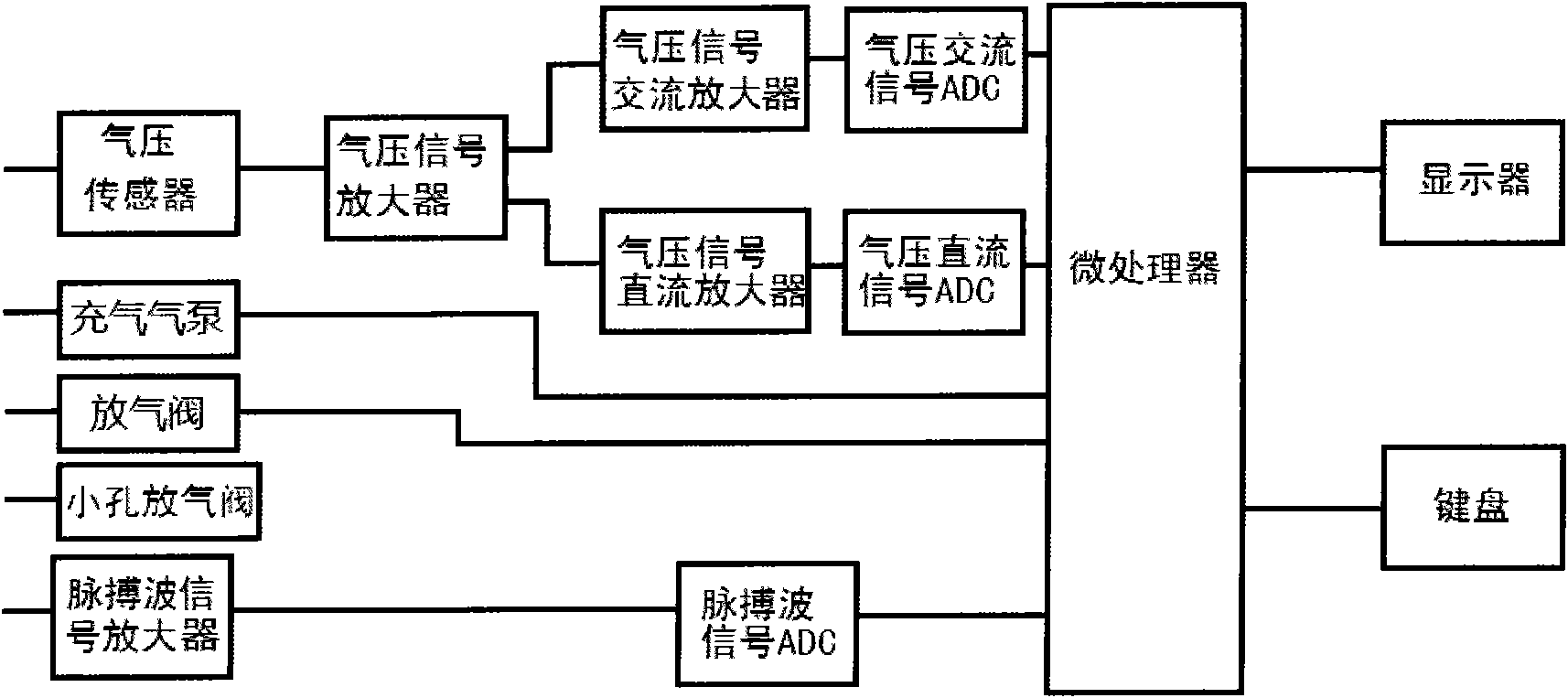
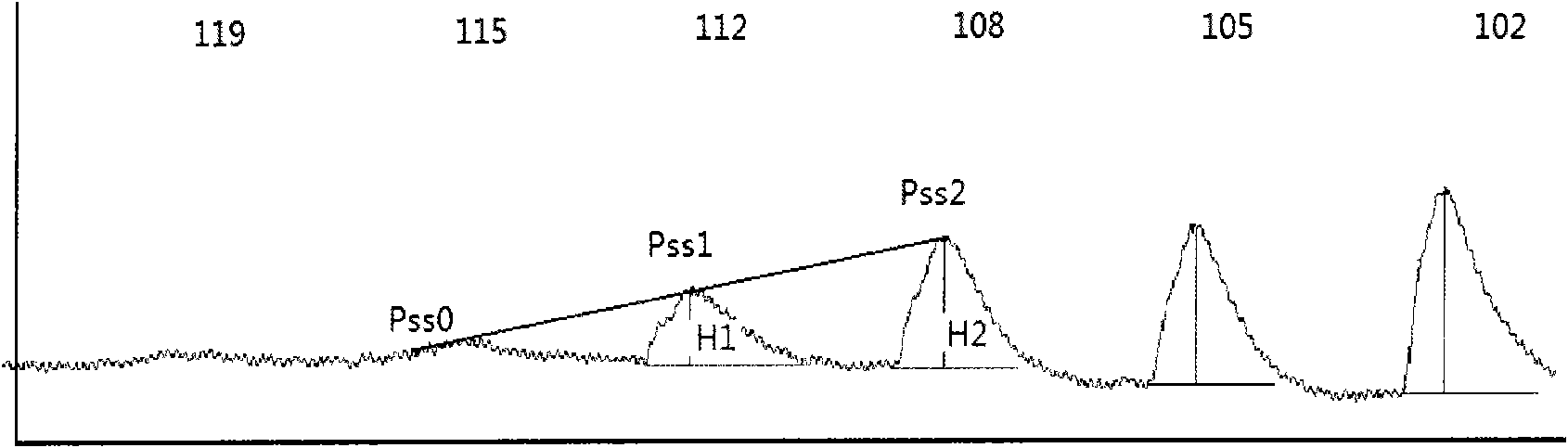
Non-invasive blood pressure measuring device and measuring method thereof
ActiveCN101912259AAccurate and non-invasive measurement of systolic blood pressureAvoid errorsDiagnostic signal processingEvaluation of blood vesselsContinuous measurementNon invasive
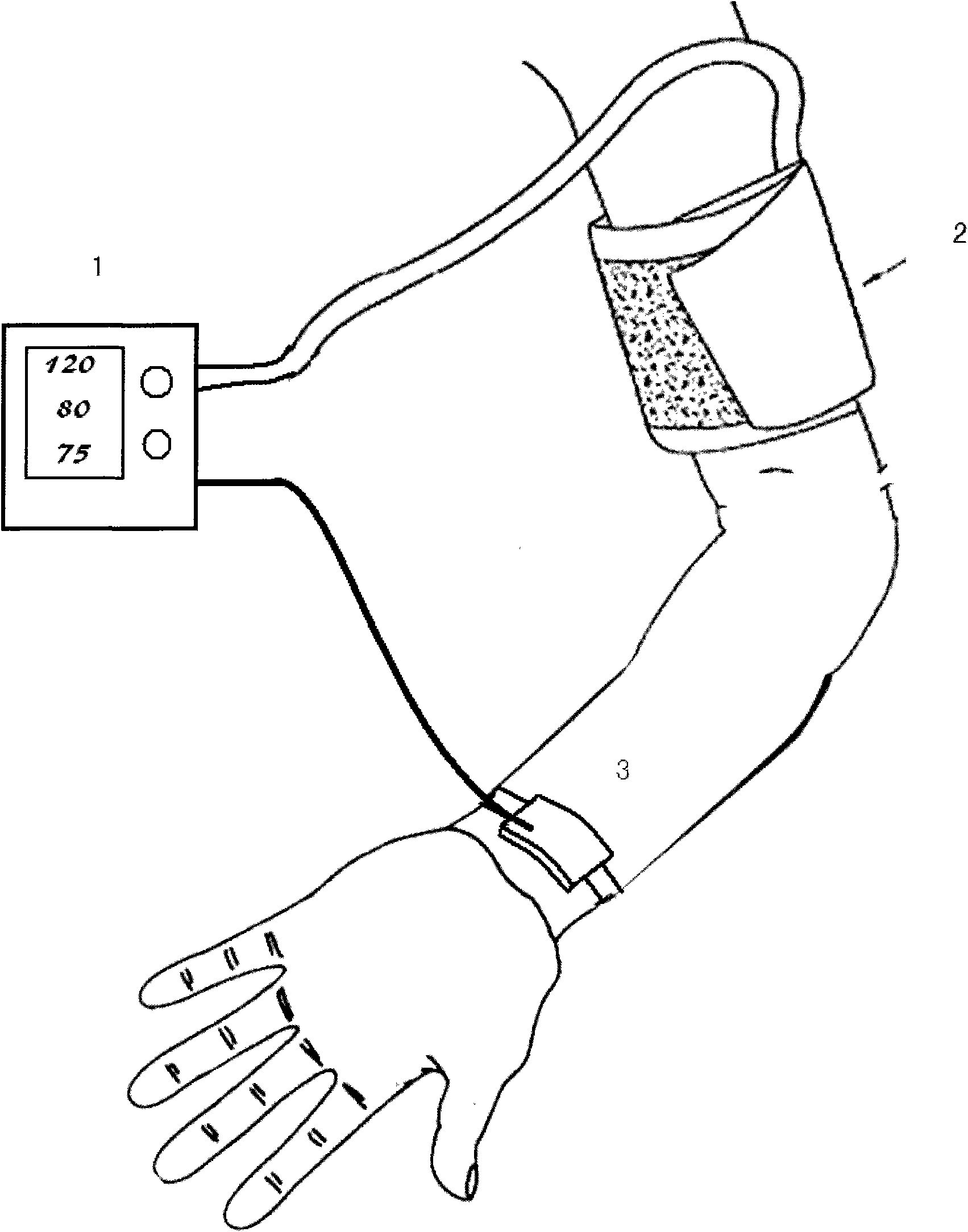
The invention provides a non-invasive blood pressure measuring device and a measuring method thereof. In the device, a main machine is provided with a microprocessor connected with an air pressure sensor; a pressurizing band is an inflatable sac-shaped band with air tubes, is connected with the air pressure sensor, is tied on a limb where the flowing of arterial blood of a measured person can be completely blocked after inflation, and is provided with a pulse wave detector which is fixed at a downstream position of the pressurizing band in the arterial blood flowing direction; and the microprocessor processes a plurality of pulse wave amplitudes detected by the pulse wave detector in the gradual increasing process from zero and corresponding pressurizing band pressure thereof in real time so as to determine the systolic pressure, and processes a plurality of pulse delay time in the process from variation to relative invariant of the delay time between the pulse wave and the corresponding pressure AC signal in real time so as to determine the diastolic pressure. The device converts discontinuous events to continuous measurement, avoids unavoidable possible errors caused by the discontinuity of cardiac impulse, and can accurately and non-invasively measure the systolic pressure and the diastolic pressure in blood pressure.
Owner:SHENZHEN RAYCOME HEALTH TECH
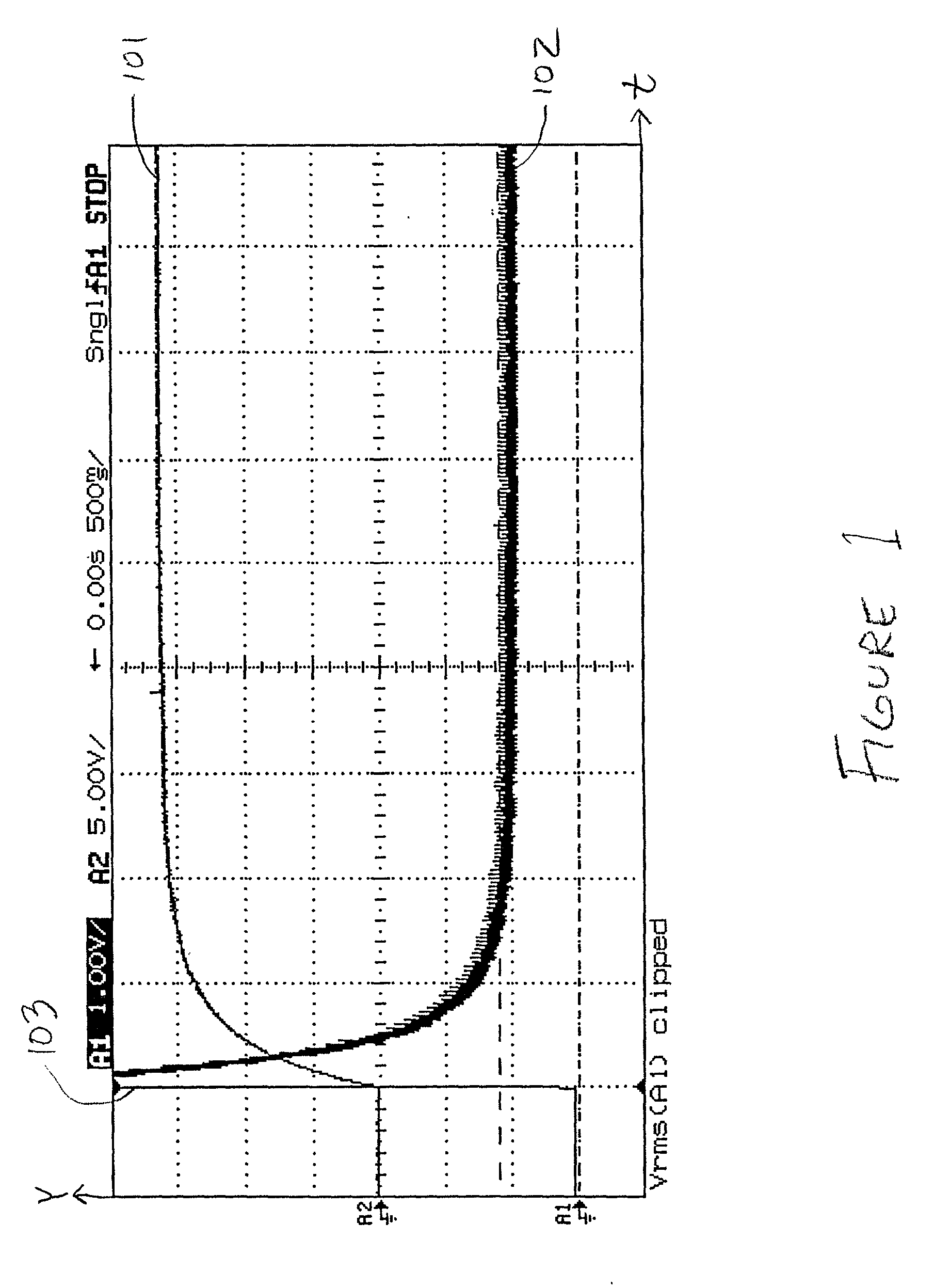
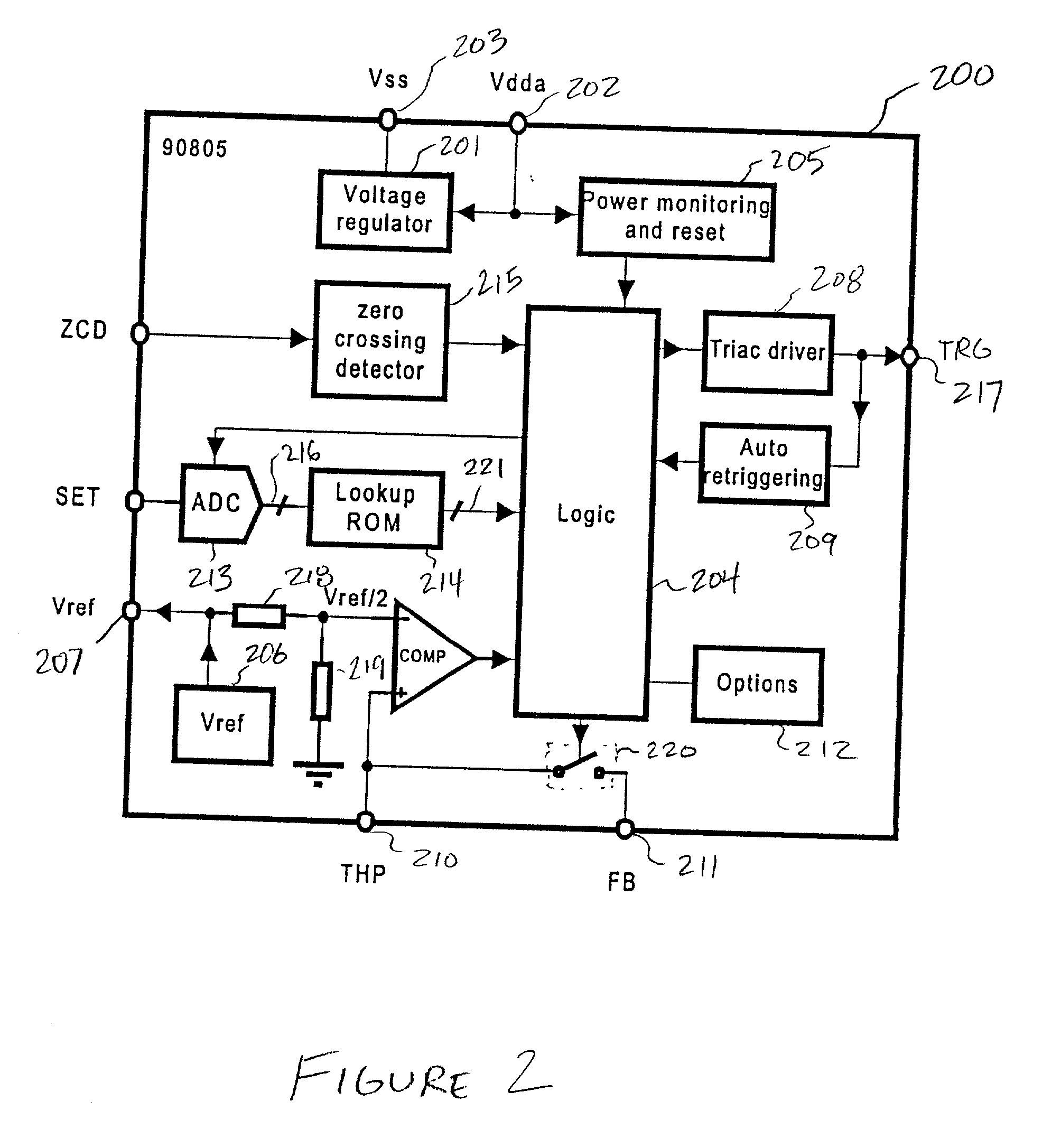
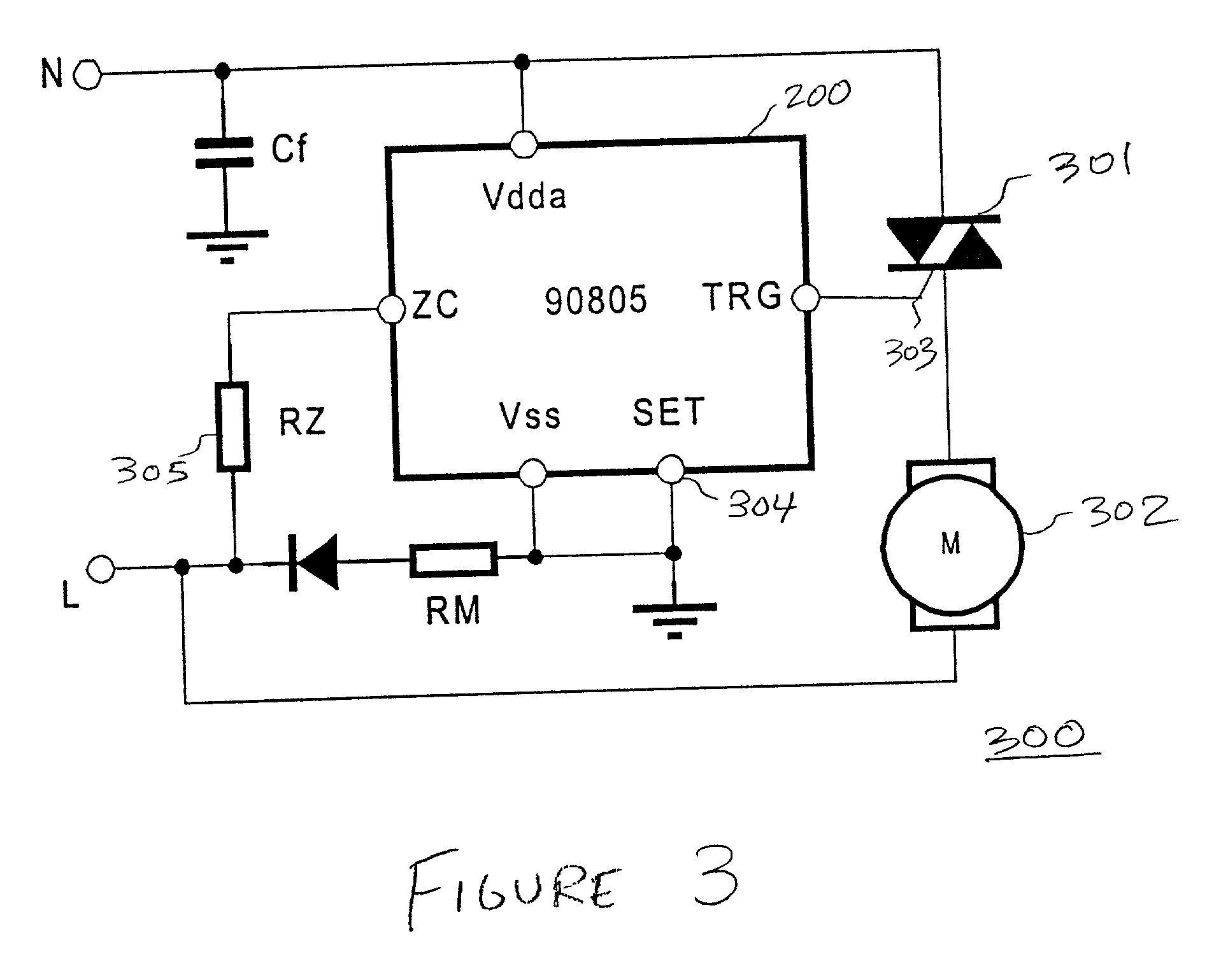
Triac controller having soft start speed regulation
InactiveUS20010028239A1Facilitate proper ignitionCurrent consumptionAc network voltage adjustmentElectric variable regulationDIACControl signal
A triac controller includes a triac driver that provides a triac control signal suitable for connection to a gate terminal of a triac, such that, when in a power-on condition, the control signal carries at least a first firing pulse during each half period of the alternating current power supply. A soft start subcircuit and a zero crossing detector directs the triac driver to produce the first firing pulse at a first firing pulse delay time after the zero crossing time. During a soft start operation the first firing pulse delay time varies monotonically with each successive half period from an initial delay time to a final delay time. An auto-retriggering subcircuit causes the triac driver to produce a second firing pulse at a predetermined retriggering delay time from an end of the first firing pulse if the triac is not in an on conduction state after the end of the first firing pulse during a same half period. The auto-retriggering subcircuit causes the triac driver to produce retriggering firing pulses periodically for so long as the triac is not in the on conduction state during the same half period; however, it is inhibited from causing the triac driver to produce retriggering firing pulses during a predetermined retriggering mask period at an end of the same half period. The soft start subcircuit includes a table specifying a plurality of predetermined first firing pulse delay values. A set signal is used to determine an index into the table. The plurality of predetermined first firing delay values is monotonically organized with respect to the index into the table, and a programmable rate variable determines a rate of change of the first firing delay values during a soft start operation.
Owner:MELEXIS NV
Device and method for enhancing atomic layer deposition by pulse-modulation radio frequency plasma
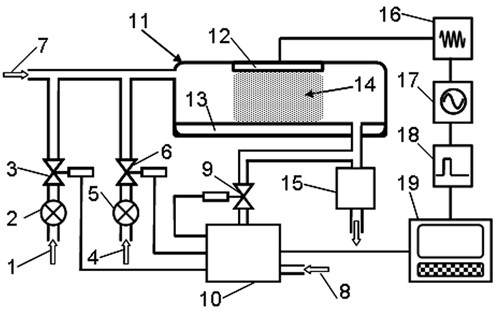
InactiveCN102127756AHigh activityIncrease the number of graftsChemical vapor deposition coatingIon bombardmentPhysical chemistry
The intention relates to a device and method for enhancing atomic layer deposition by pulse-modulation radio frequency plasma. The device comprises a vacuum reaction chamber, wherein a substrate is arranged at the inner bottom of the vacuum reaction chamber, and the vacuum reaction chamber is respectively connected with a vacuum mechanical pump and a precursor input pipeline. The device is characterized in that a plasma electrode is arranged at the inner top of the vacuum reaction chamber and is sequentially connected with a radio-frequency power matcher, a pulse modulation radio-frequency power supply and a pulse delay unit. In the method, plasma is generated by the pulse modulation radio-frequency power supply to assist deposition when at least one precursor is deposited. The device and method provided by the invention reduces the impact of ion bombardment on the deposited film during deposition process and prevents the temperature increase of the cavity during deposition process.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV +1
Analog to digital converter with a pulse delay circuit
ActiveUS6940443B2Reduce power consumptionElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue-digital convertersLogic gateAnalog-to-digital converter
An A / D converter has a pulse delay circuit including a plurality of inverting circuits to each of which an analog voltage signal is inputted through a first pair of power supply lines. Each of the inverting circuits has a first logic gate. The A / D converter has a logic circuit having a second logic gate and a second pair of power supply lines, the logic circuit operating based on a power supply voltage. At least one of a first range of a level of the voltage signal and a second range of the power supply voltage is set to prevent a tunneling current from flowing at least one of between the first paired power supply lines and between the second paired power supply lines when at least one of first and second logic gates operates.
Owner:DENSO CORP
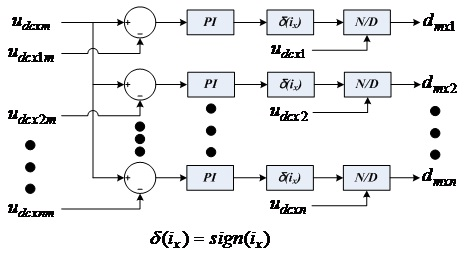
Auto disturbance rejection control technology-based direct-current busbar voltage control method of high-voltage chain-type STATCOM (Static Synchronous Compensator) power unit module
InactiveCN102324746ANo overshootQuick responseFlexible AC transmissionAc network voltage adjustmentDifferentiatorBusbar
The invention relates to an auto disturbance rejection control technology-based direct-current busbar voltage control method of a high-voltage chain-type STATCOM (Static Synchronous Compensator) power unit module. Capacitors at the direct-current side of a chain-type STATCOM are mutually independent; the individual unit module has direct-current capacitor loss difference, switch loss difference, drive pulse delay time difference, and the like in the running process; the voltage of the direct-current capacitor of each chain-type STATCOM unit module is unbalanced and has difference, so that harmonic contents of an output voltage and an output current of the chain-type STATCOM unit module are influenced, even the normal and safe operation of the chain-type STATCOM unit module is endangered. According to the method disclosed by the invention, an auto disturbance rejection controller does not need to judge the instantaneous current direction; after parameters are accurately set, the disturbance quantity contains active components with active fluctuation; and the auto disturbance controller can achieve the purposes of high response speed and no overshoot of voltage of the unit direct-current capacitors due to the existence of a tracking differentiator and a nonlinear controller.
Owner:JIANGSU WEIFAN INTELLIGENT ELECTRICAL TECH
A/D conversion method and apparatus
ActiveUS6879278B2Increase speedImprove accuracyElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue-digital convertersDelayed pulseDigital data
An A / D converter for driving a plurality of delay units forming a pulse delay circuit by an analog input signal Vin and digitalizing the number of delay units through which a pulse signal passes in the pulse delay circuit at predetermined timings, provided with a plurality of pulse position digitalizing units used for A / D conversion and inputting delay pulses from the delay units of the pulse delay circuit to the pulse position digitalizing units through an inverter group comprised of inverters with different inversion levels (switching threshold level) by different input timings. The digital data obtained by the pulse position digitalizing units are added by an adder.
Owner:DENSO CORP
New method for precisely measuring optical fiber length by adoption of vector network analyzer
ActiveCN104279959AMeasurement frequency range or phase measurement accuracy is superiorExcellent phase measurement accuracyUsing optical meansFiber chromatic dispersionInterference factor
The invention provides a new method for precisely measuring optical fiber length by adoption of a vector network analyzer. The vector network analyzer is introduced, the phase zero making technology is combined, and therefore the defects that a back scattering method is poor in measuring precision, many in interference factor of a pulse method, short in measuring distance and the like are overcome, and the shortcomings that a traditional phase shifting method is narrow in frequency measuring range of a phase meter and poor in phase measuring stability are overcome; in the long-distance transmission of optical fibers, due to widening of optical pulses caused by optical fiber dispersion, time amount of optical pulse delay is replaced with the phase variable quantity generated by measuring optical signals in transmission in the optical fibers, the accuracy value of the optical fiber length is calculated, and therefore the influence of the optical fiber dispersion on a measuring result of the optical fiber length is reduced.
Owner:THE 41ST INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GRP
Cardiac pulsed field ablation
A method for ablating tissue by applying at least one pulse train of pulsed-field energy. The method includes delivering a pulse train of energy having a predetermined frequency to cardiac tissue, thepulse train including at least 60 pulses, an inter-phase delay between 0 mus and 5 mus, an inter-pulse delay of at least 5 mus, and a pulse width of 5 mus.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
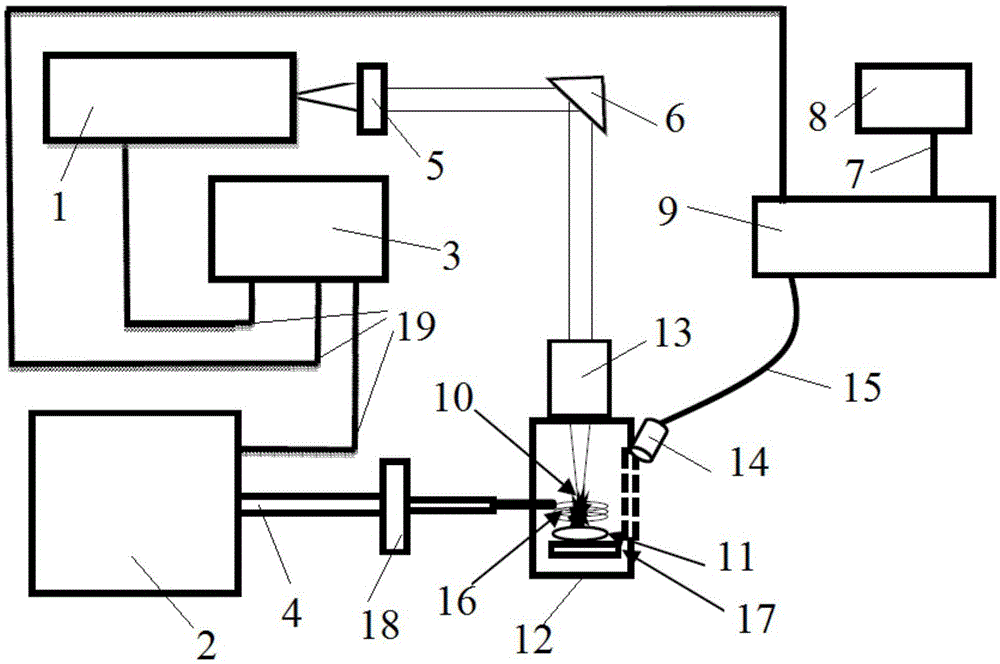
Multipulse laser-induced breakdown spectrum on-line detection system
The invention provides a multipulse laser-induced breakdown spectrum on-line detection system which comprises a pulse laser, an optical-path extending loop device, a second light-path guiding device, a light-path convergence device and a data detection system. The optical-path extending loop device comprises a light-path splitting device, a pulse delay device and a first light-path guiding device. The light-path splitting device is used for dividing pulse laser into first pulse laser and second pulse laser. The pulse delay device is used for increasing optical path of the second pulse laser. The first light-path guiding device is used for changing the light path of the second pulse laser with the increased optical path. The second light-path guiding device is used for changing the light path of the first pulse laser. The light-path convergence device is used for converging the first pulse laser and the second pulse laser with the increased optical path to a same specific light path. A pulse laser is adopted to generate multiple pulse lasers with different optical paths, and the multiple pulse lasers are focused on a same position on a sample to be detected.
Owner:ACAD OF OPTO ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Echo pulse delay generating device for pulse type radar test
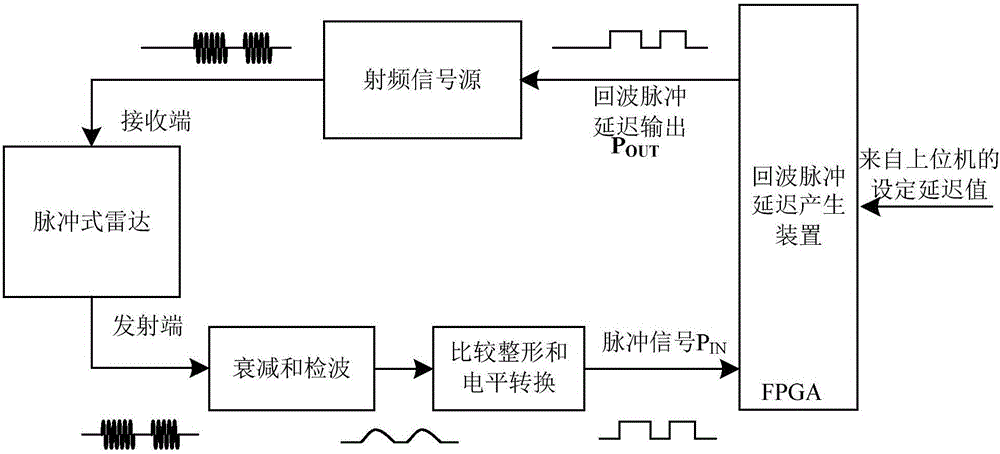
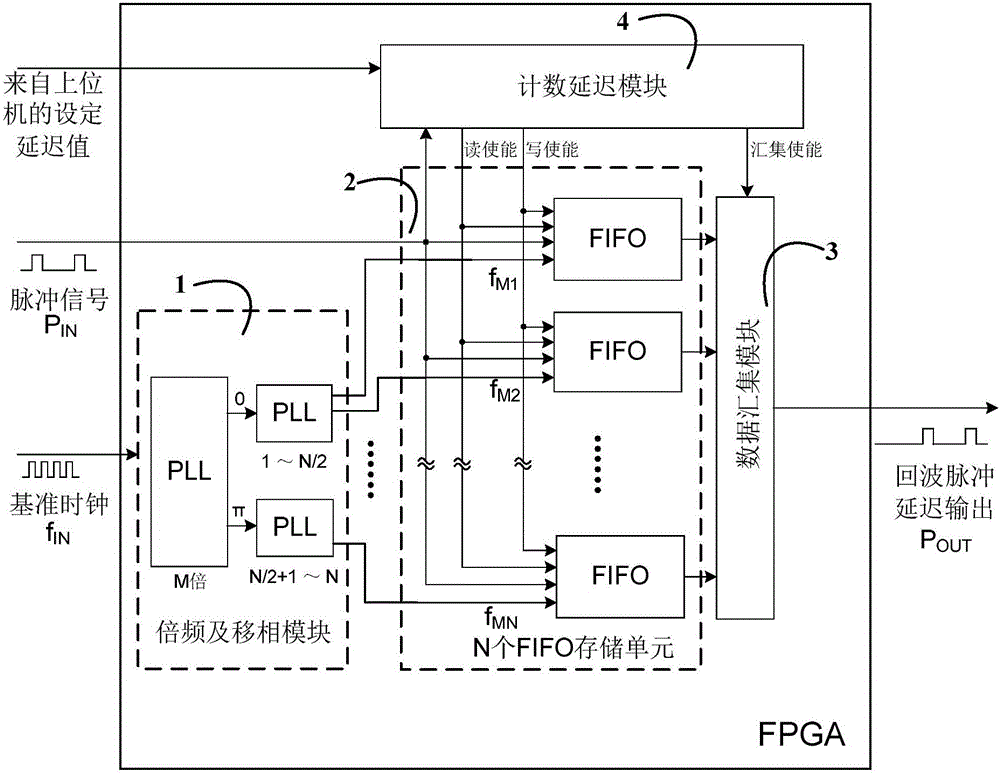
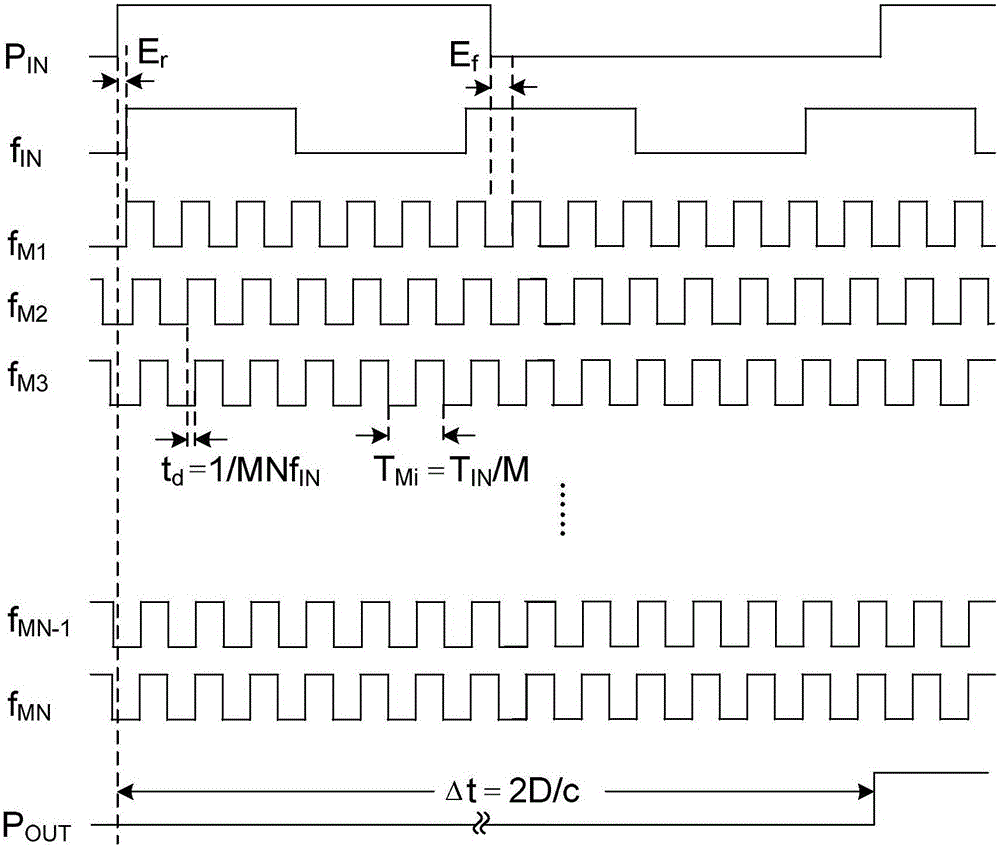
ActiveCN105676198AHighly integratedIncrease working frequencyWave based measurement systemsSignal delayPhase-locked loop
The invention discloses an echo pulse delay generating device for a pulse type radar test. A multi-channel phase-shifting clock is creatively utilized to perform high-speed equivalent interpolation sampling on pulse signals; a multi-channel FIFO storage unit is utilized to uninterruptedly store the pulse signals; an interpolation counting method is utilized to realize high-precision delay control output of the inputted pulse signals under a low clock frequency, and therefore, the requirement of back-end test equipment for the delay precision of echo pulse signals can be satisfied; and if a basic clock signal frequency is fIN, a phase-locked loop is utilized to perform M frequency multiplication and N-channel phase shifting, and therefore, equivalent sampling speed can be increased to MNfIN, and the time resolution of the sampled and stored pulse data can be increased by MN times, and thus, the control precision of delay output can be increased to 1 / MNfIN. Compared with a traditional pulse signal delay method, the device of the invention can carry out high-precision control output of pulse signal fixed delay and variable delay, so that flexible simulation of height or distance echo signals can be realized.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Fully programmable phase locked loop
ActiveUS7135934B2Pulse automatic controlPulse generation by logic circuitsControl signalCapacitor voltage
Owner:APPLE INC
Microwave-assisted laser-induced breakdown spectrum device
InactiveCN105486676AImprove signal-to-noise ratioImprove stabilityAnalysis by thermal excitationLaser-induced breakdown spectroscopyElectromagnetic field
The invention discloses a microwave-assisted laser-induced breakdown spectrum device which comprises a laser device, a microwave generator, a pulse delay generator, a collimation system, a spectrograph and an optical focusing system, wherein the laser device is firstly triggered by the pulse delay generator to emit a pulse type laser beam; the laser beam is collimated by the collimation system, and then the energy of the laser beam is focused on the surface of a sample through the optical focusing system; the laser beam and the sample interact with each other so as to generate high-temperature high-density plasma; and then the microwave generator is triggered by the pulse delay generator to emit a microwave pulse and the microwave pulse is controlled to stimulate the plasma again; under the effect of electromagnetic field, the electrons in the plasma are accelerated, so that sufficient kinetic energy is acquired for stimulating atoms and ions again; the electrons under the atom and ion stimulating state transit to lower energy level; during transition, a spectral signal is emitted, namely, a characteristic spectrum with specific wavelength is emitted; the spectrograph is triggered by the pulse delay generator again to collect the spectral signal.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Analogue to digital conversion device operable on different sampling clocks
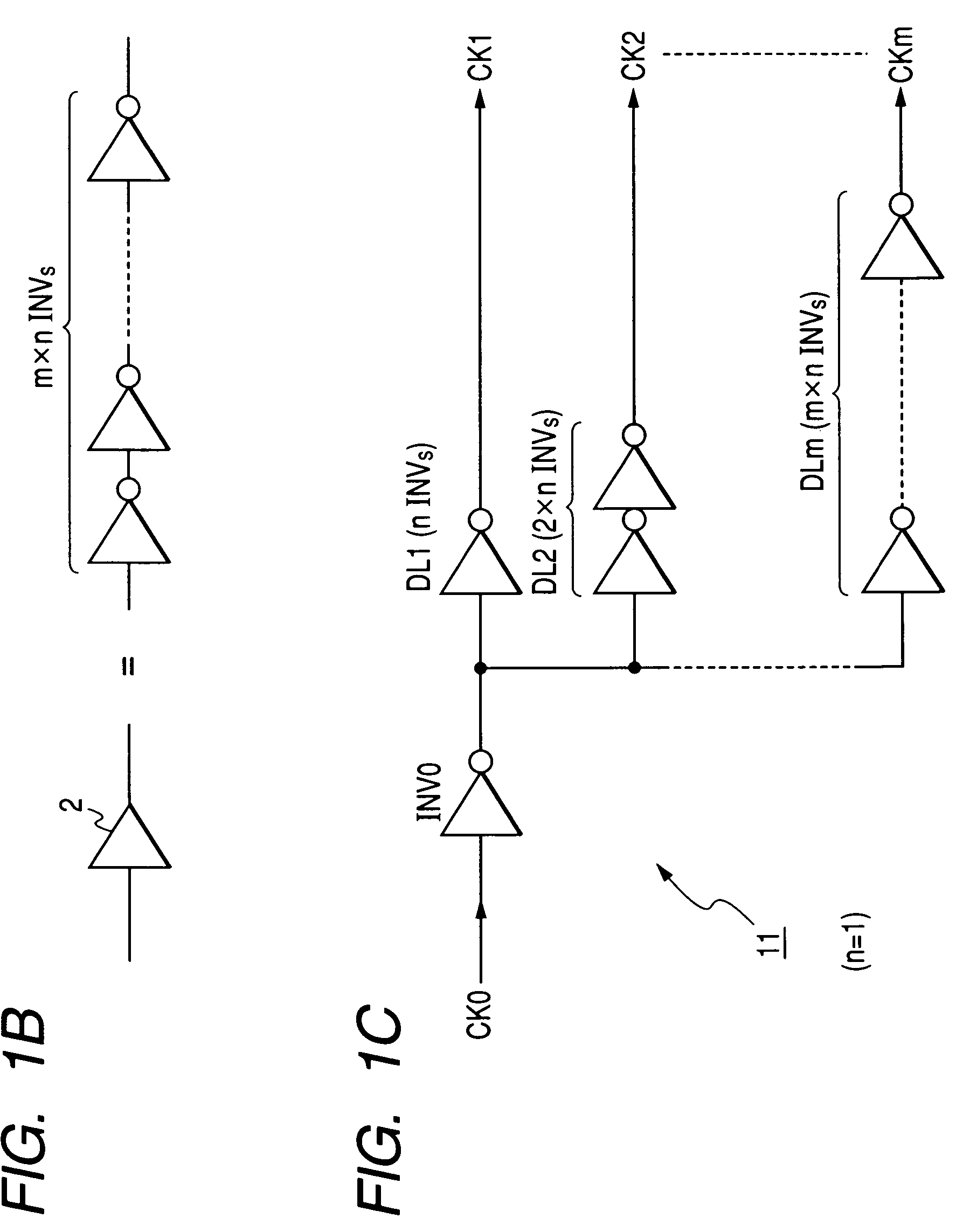
InactiveUS7268719B2High voltageAccurate dataElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue-digital convertersEngineeringClock generator
In an A / D conversion device, each delay unit in a pulse delay circuit has inverters INV of m×n stages (m, n are positive integers), a clock generator has m-delay lines, and each delay line has inverters INV of i×n stages (i=1, 2, . . . , and m). Those delay lines DL1 to DLm output sampling clocks CK1 to CKm. Each of those inverters INV has a same characteristic. In the A / D conversion device, the delay time in each of the delay lines DL1 to DLm is adjusted by the number of the inverters INV. It is thereby possible to provide the m-sampling clocks CK1 to CKm of a different phase ΔT with one another, namely whose phases are preciously shifted by ΔT with one another.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Pulse time synchronization system for quantum enhanced laser detection
ActiveCN106526575AHighly coherent propertiesReduce volumeWave based measurement systemsFiberSignal light
The invention provides a pulse time synchronization system for quantum enhanced laser detection. The system comprises a laser main light source (1), a delay unit (2), a time synchronization monitoring detector (3), a digital phase-locked unit (4), and a synchronous control unit (5). According to the system, the delay unit (2) is guided to carry out high precision optical pulse delay through the feedback signal of the digital phase-locked unit (4), a problem that the satisfaction of the time synchronization and maintenance of a pulse coherent characteristic at the same time in quantum enhanced laser detection by pump light, signal light and local-oscillator light are needed can be solved, the delay unit (2) adopts fiber or Fabry-Perot interference cavity to carry out fixed time delay modulation, the size is small, and the degree of integration is high.
Owner:BEIJING RES INST OF SPATIAL MECHANICAL & ELECTRICAL TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com