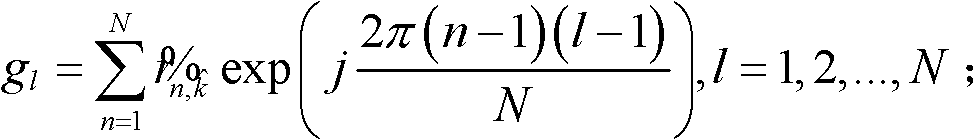Patents
Literature
677 results about "Multiple pulse" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Multiple Pulse, LIDAR Based 3-D Imaging
ActiveUS20170219695A1Minimize impactOptical rangefindersElectromagnetic wave reradiationLight beamPulse sequence
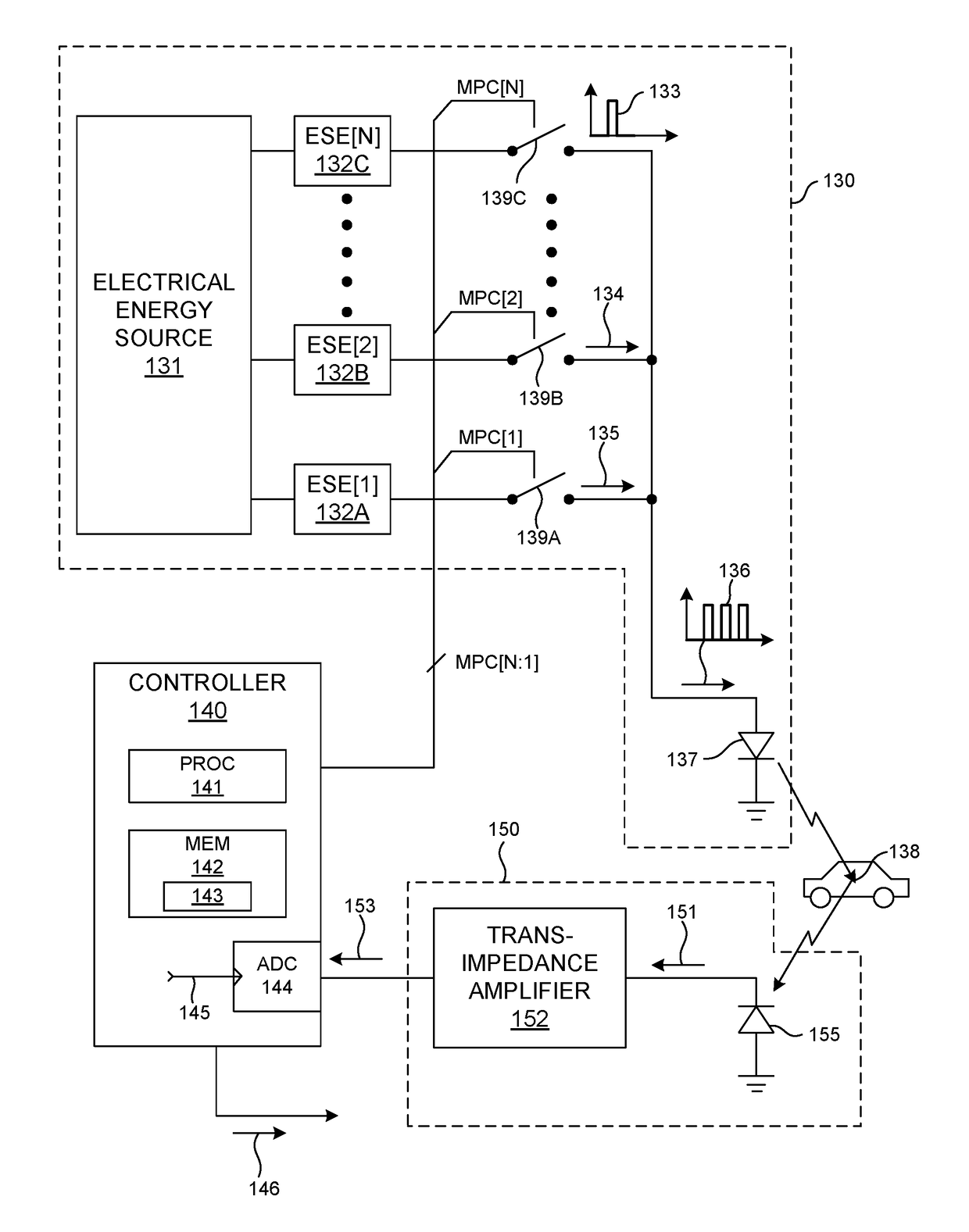
Methods and systems for performing multiple pulse LIDAR measurements are presented herein. In one aspect, each LIDAR measurement beam illuminates a location in a three dimensional environment with a sequence of multiple pulses of illumination light. Light reflected from the location is detected by a photosensitive detector of the LIDAR system during a measurement window having a duration that is greater than or equal to the time of flight of light from the LIDAR system out to the programmed range of the LIDAR system, and back. The pulses in a measurement pulse sequence can vary in magnitude and duration. Furthermore, the delay between pulses and the number of pulses in each measurement pulse sequence can also be varied. In some embodiments, the multi-pulse illumination beam is encoded and the return measurement pulse sequence is decoded to distinguish the measurement pulse sequence from exogenous signals.
Owner:VELODYNE LIDAR USA INC
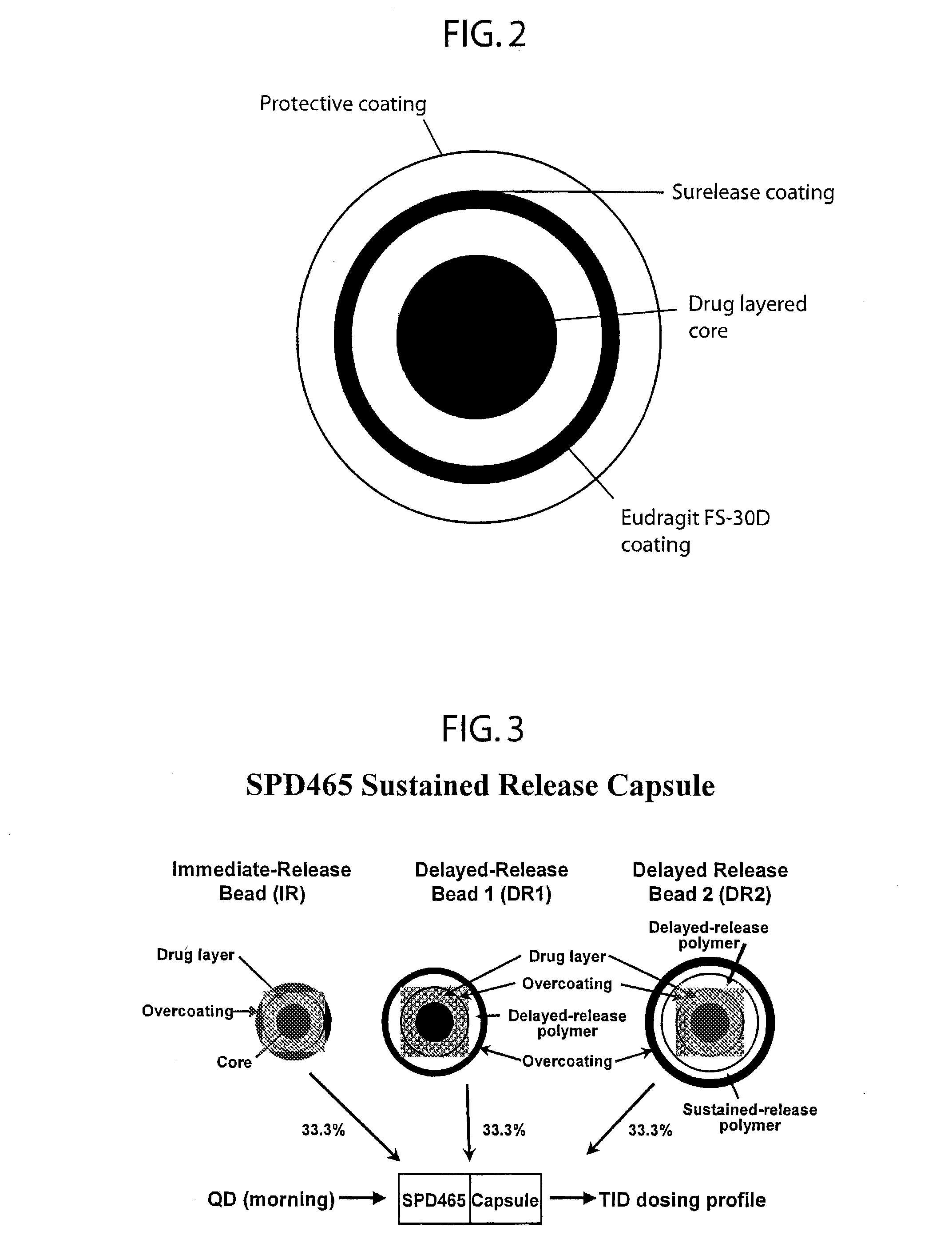
Controlled dose drug delivery system
ActiveUS20070264323A1Meet needsReduce the amount requiredOrganic active ingredientsBiocideImmediate releaseDose delivery
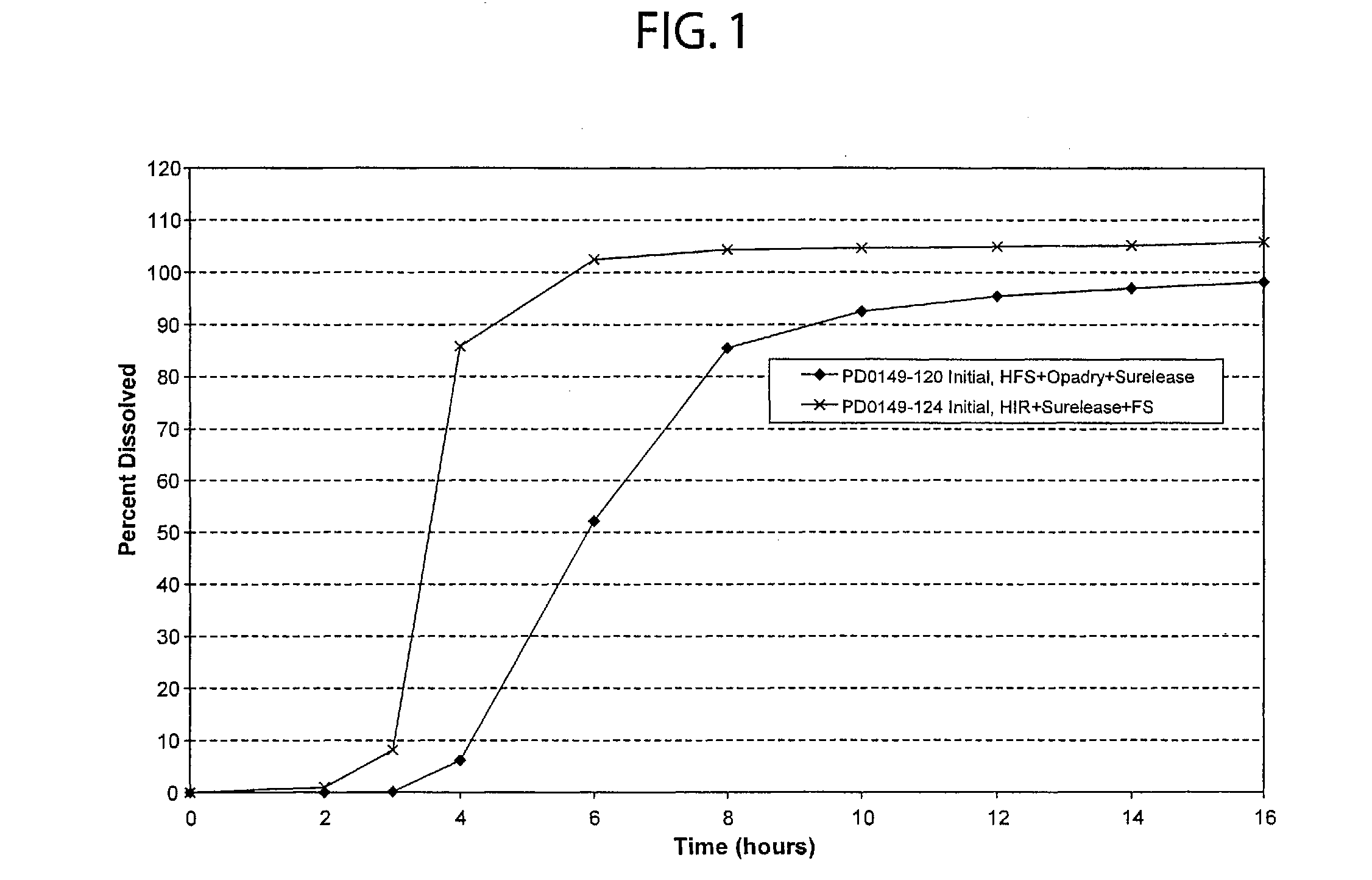
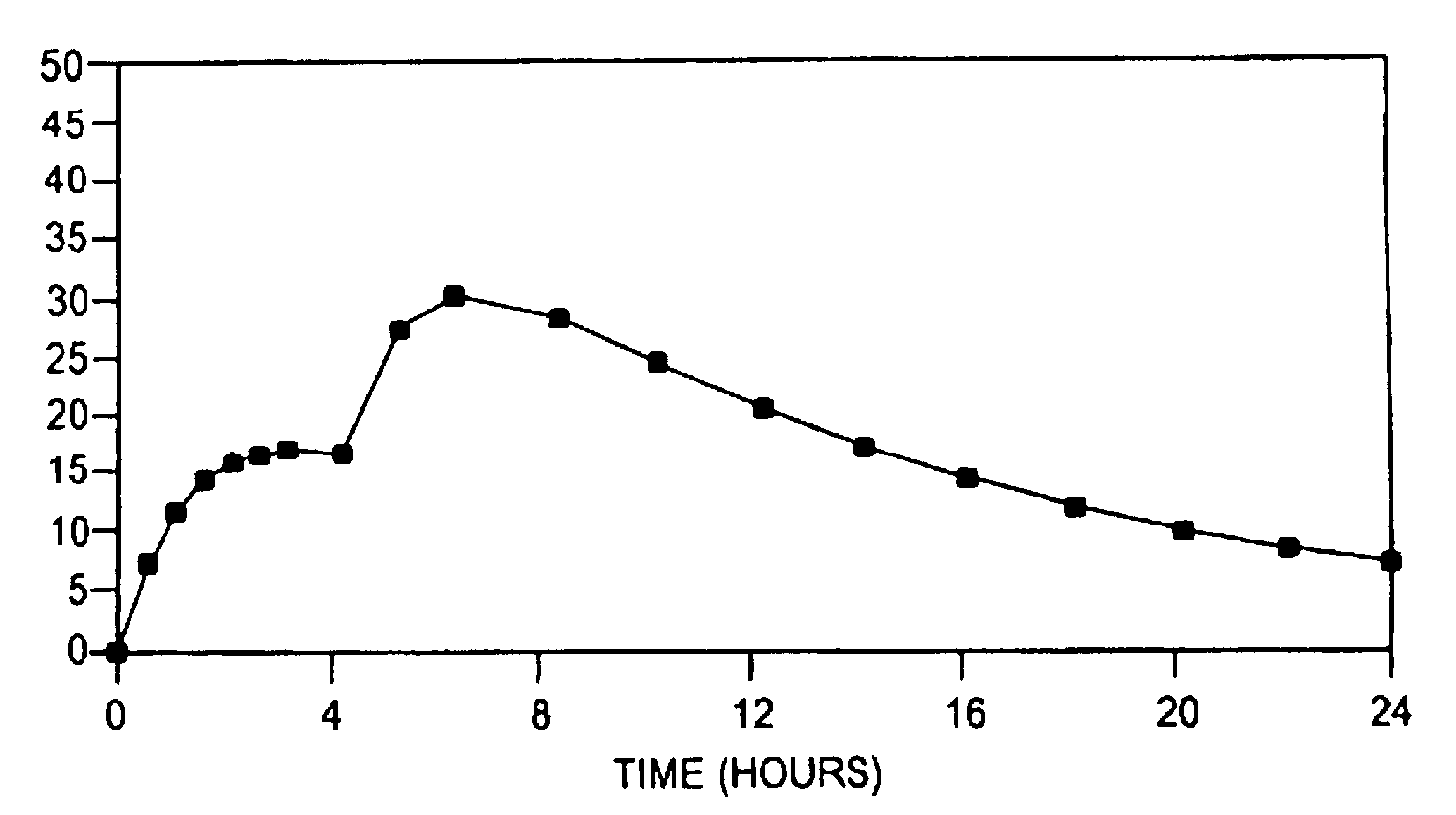
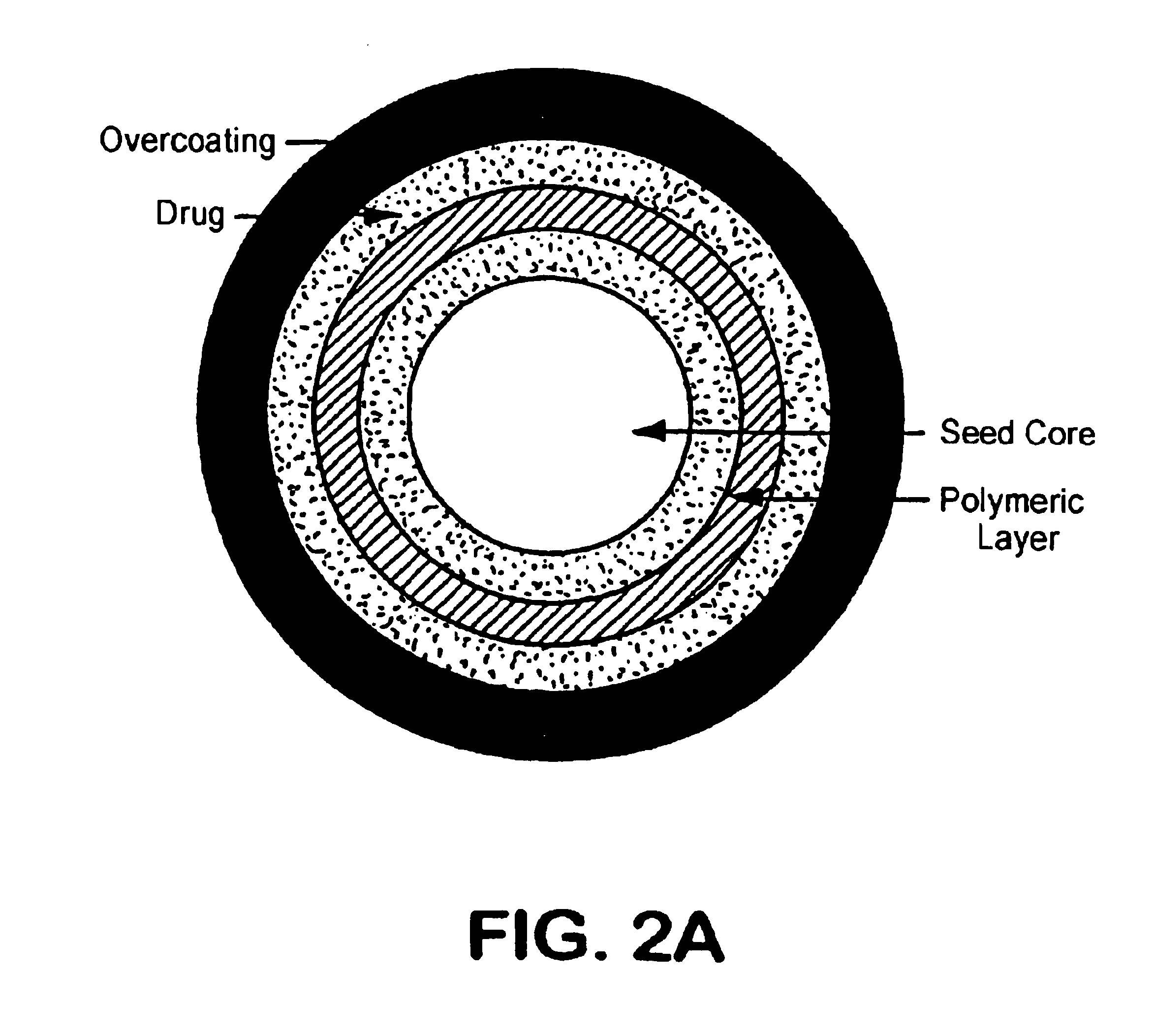
A multiple pulsed dose drug delivery system for pharmaceutically active amphetamine salts, comprising a pharmaceutically active amphetamine salt covered with an immediate-release coating and a pharmaceutically active amphetamine salt covered with an enteric coating wherein the immediate release coating and the enteric coating provide for multiple pulsed dose delivery of the pharmaceutically active amphetamine salt. The product can be composed of either one or a number of beads in a dosage form, including either capsule, tablet, or sachet method for administering the beads.
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD
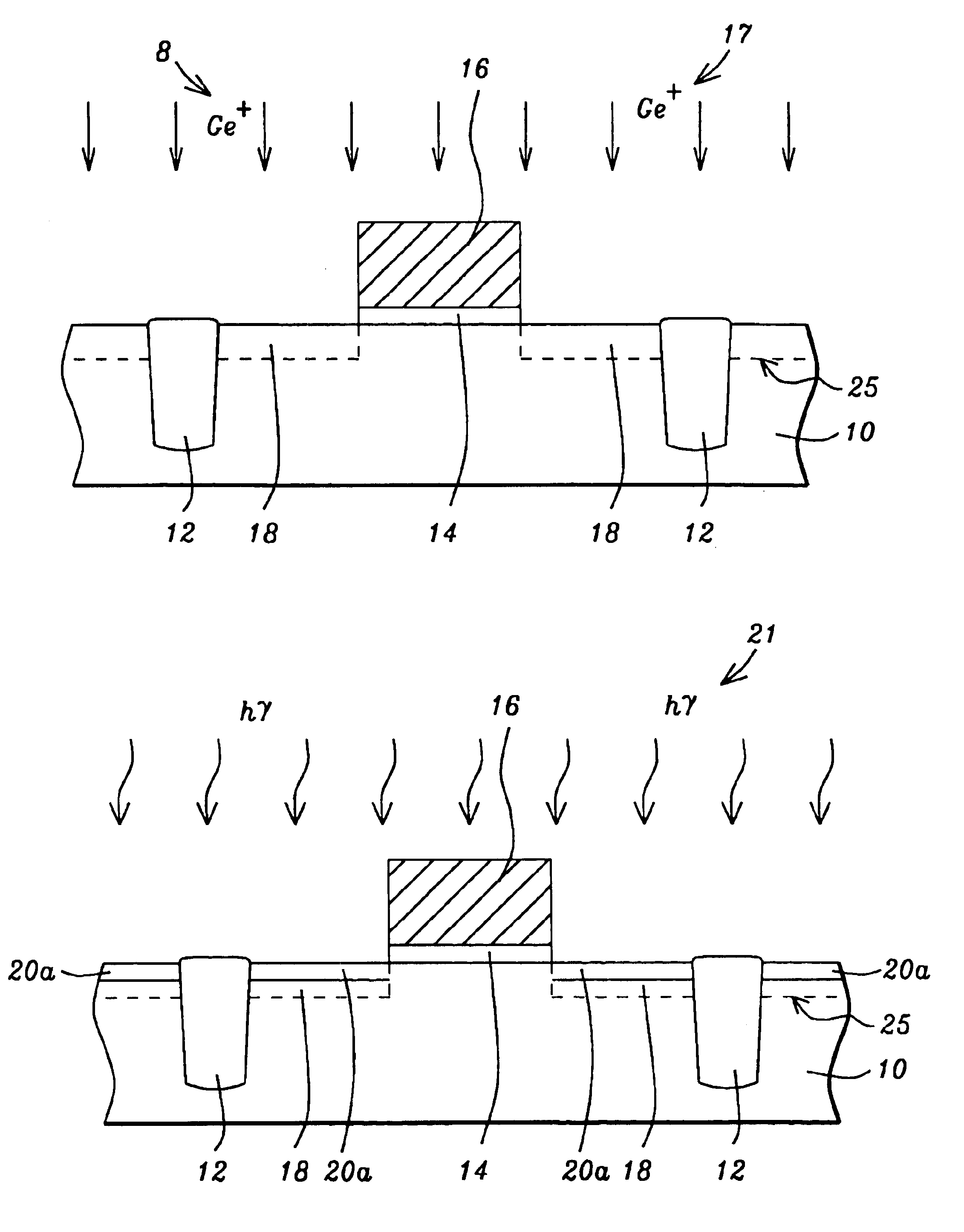
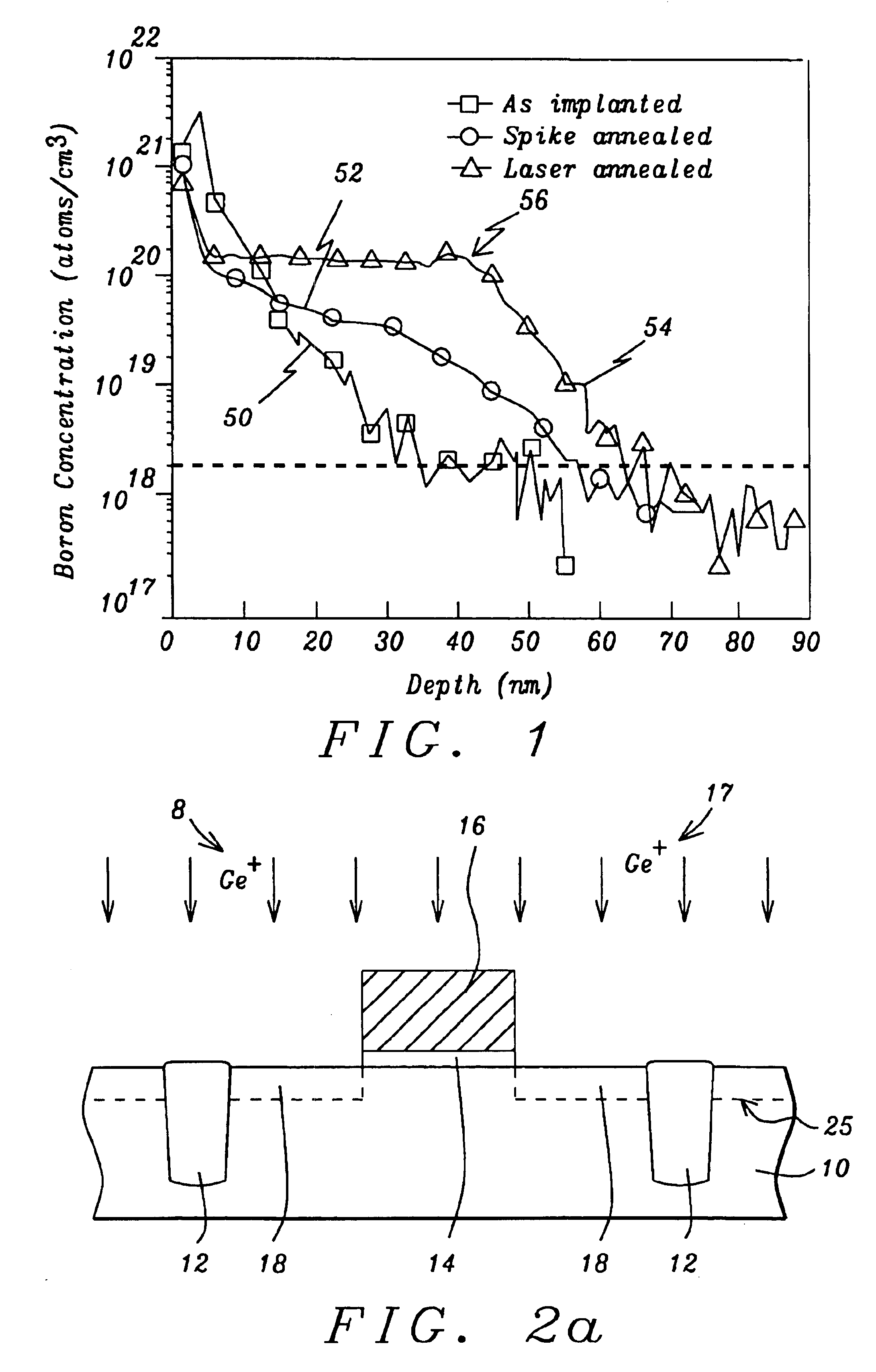
Method of multiple pulse laser annealing to activate ultra-shallow junctions
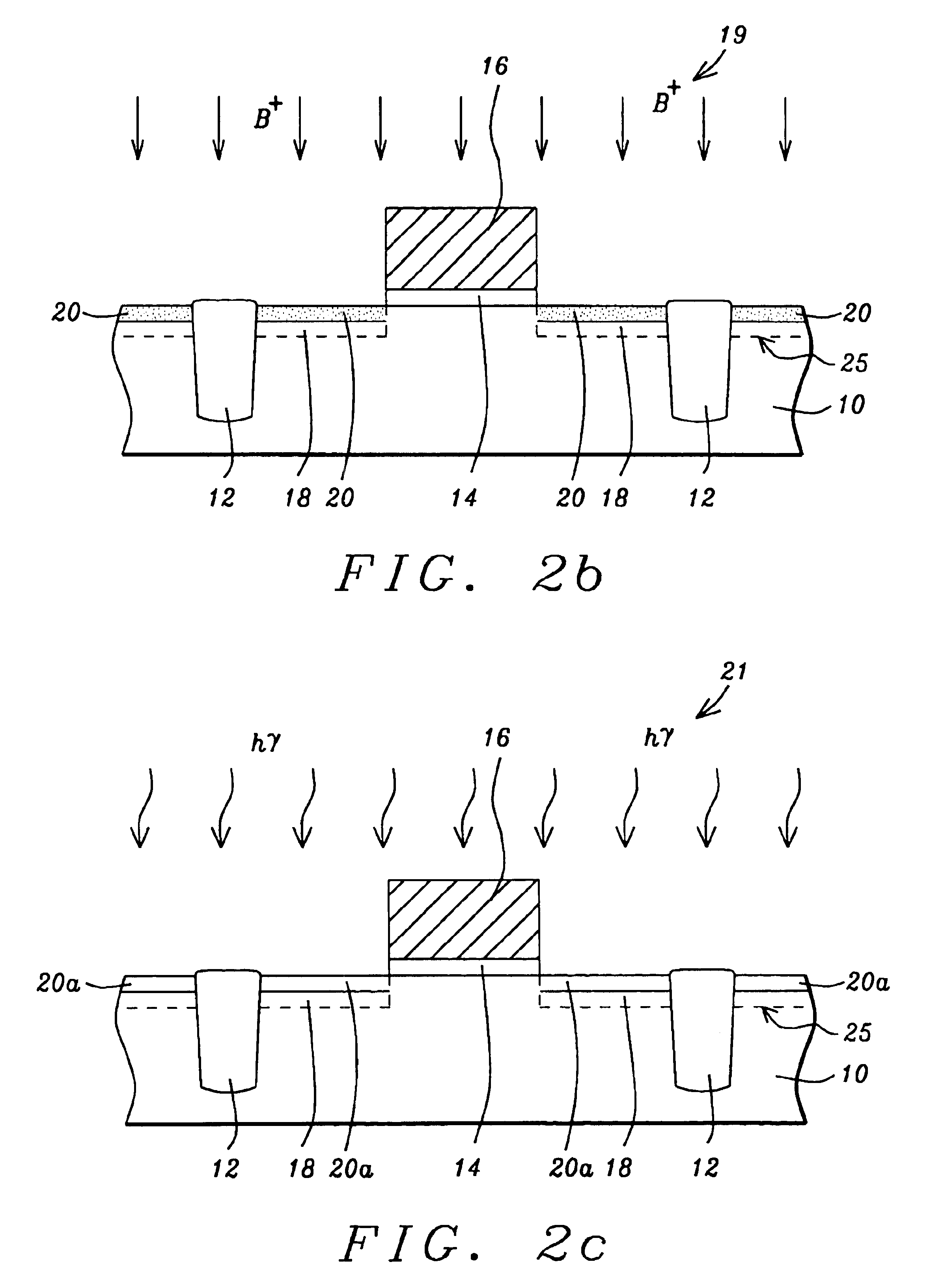
A method for forming a highly activated ultra shallow ion implanted semiconductive elements for use in sub-tenth micron MOSFET technology is described. A key feature of the method is the ability to activate the implanted impurity to a highly active state without permitting the dopant to diffuse further to deepen the junction. A selected single crystalline silicon active region is first amorphized by implanting a heavy ion such as silicon or germanium. A semiconductive impurity for example boron is then implanted and activated by pulsed laser annealing whereby the pulse fluence, frequency, and duration are chosen to maintain the amorphized region just below it's melting temperature. It is found that just below the melting temperature there is sufficient local ion mobility to secure the dopant into active positions within the silicon matrix to achieve a high degree of activation with essentially no change in concentration profile. The selection of the proper laser annealing parameters is optimized by observation of the reduction of sheet resistance and concentration profile as measured on a test site. Application of the method is applied to forming a MOS FET and a CMOS device. The additional processing steps required by the invention are applied simultaneously to both n-channel and p-channel devices of the CMOS device pair.
Owner:CHARTERED SEMICONDUCTOR MANUFACTURING
Pulsed processing semiconductor heating methods using combinations of heating sources
InactiveUS6951996B2Heating fastIncrease temperatureMuffle furnacesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPulse parameterEngineering
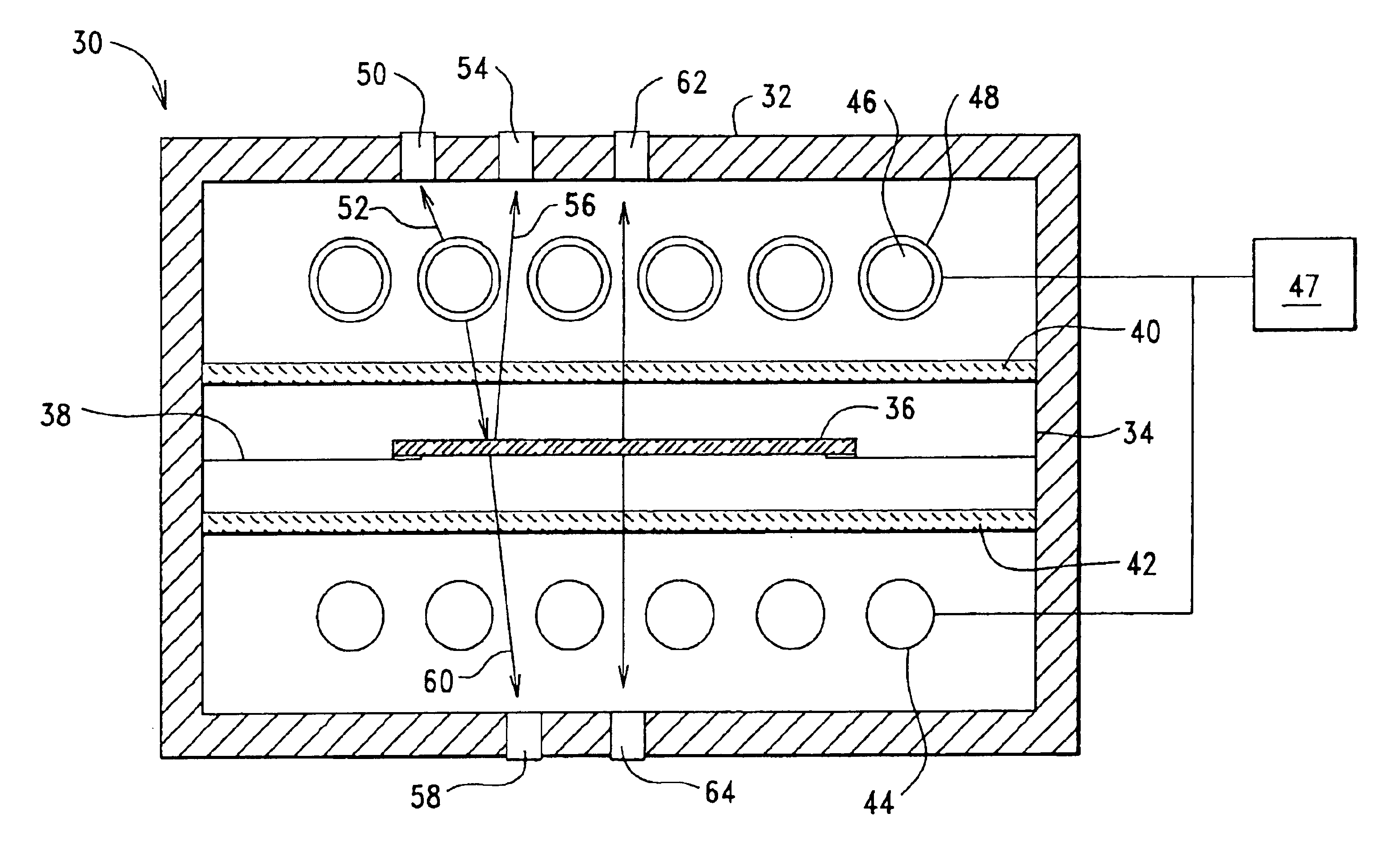
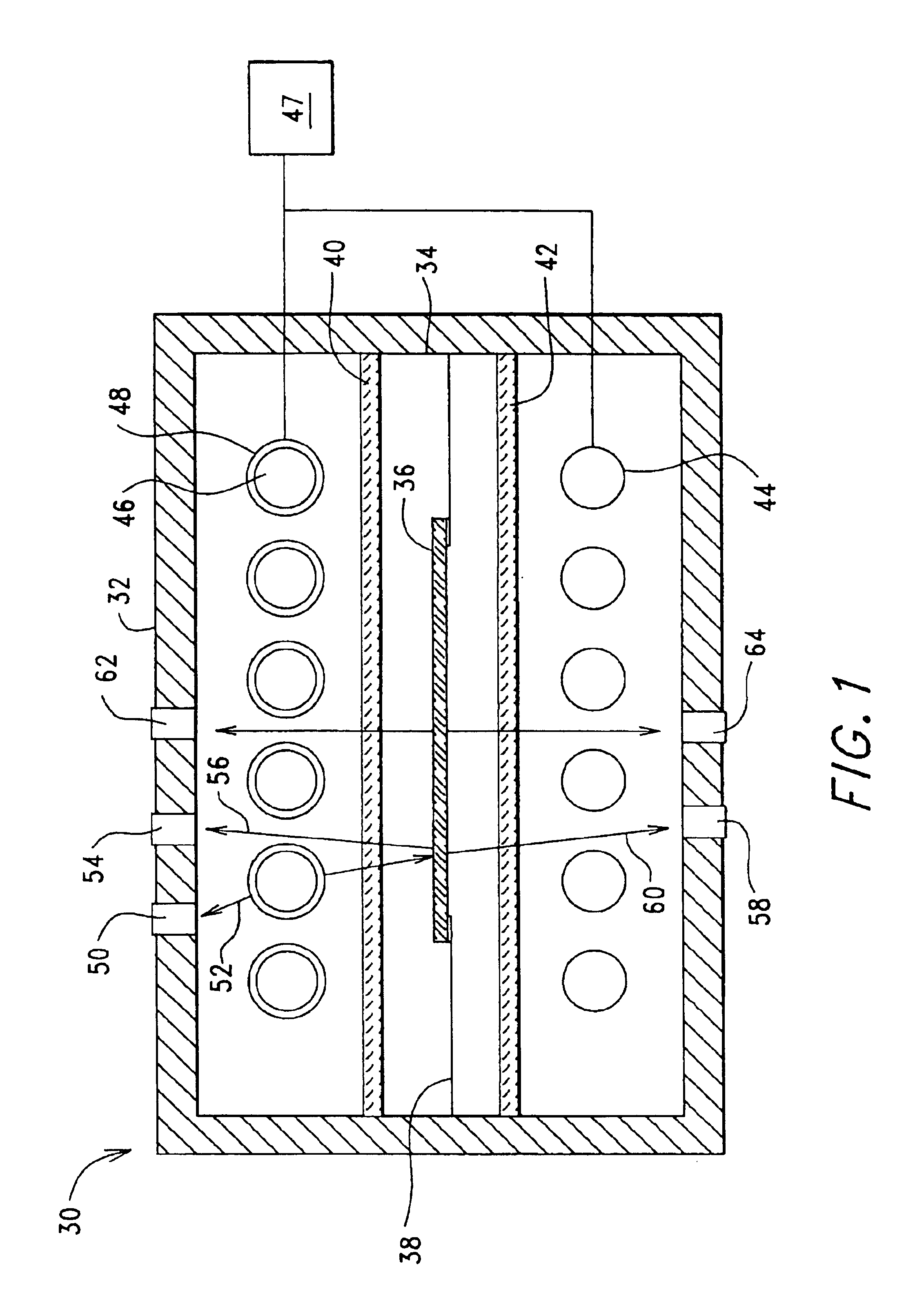
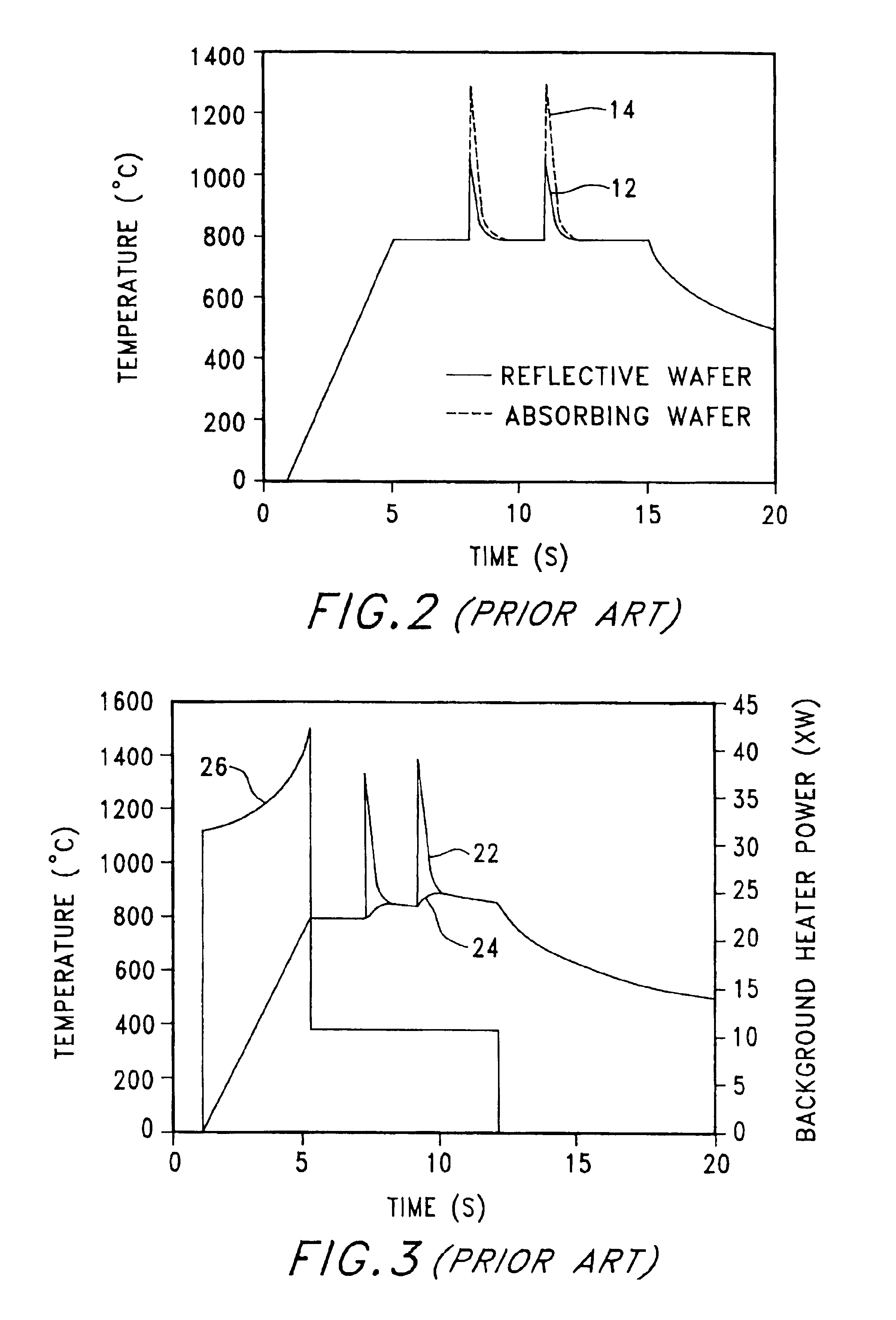
Pulsed processing methods and systems for heating objects such as semiconductor substrates feature process control for multi-pulse processing of a single substrate, or single or multi-pulse processing of different substrates having different physical properties. Heat is applied a controllable way to the object during a background heating mode, thereby selectively heating the object to at least generally produce a temperature rise throughout the object during background heating. A first surface of the object is heated in a pulsed heating mode by subjecting it to at least a first pulse of energy. Background heating is controlled in timed relation to the first pulse. A first temperature response of the object to the first energy pulse may be sensed and used to establish at least a second set of pulse parameters for at least a second energy pulse to at least partially produce a target condition.
Owner:MATTSON TECHNOLOGY +1
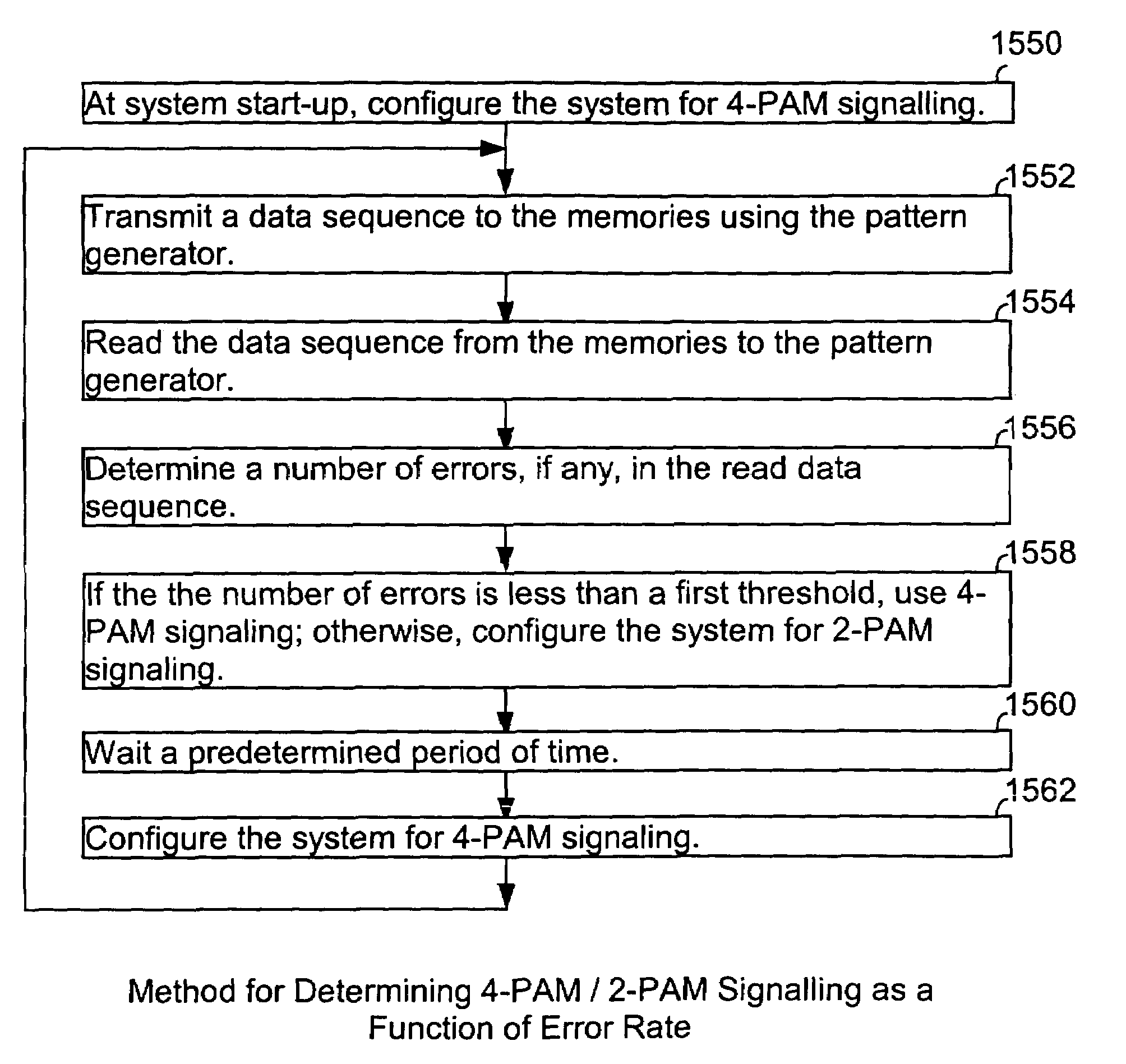
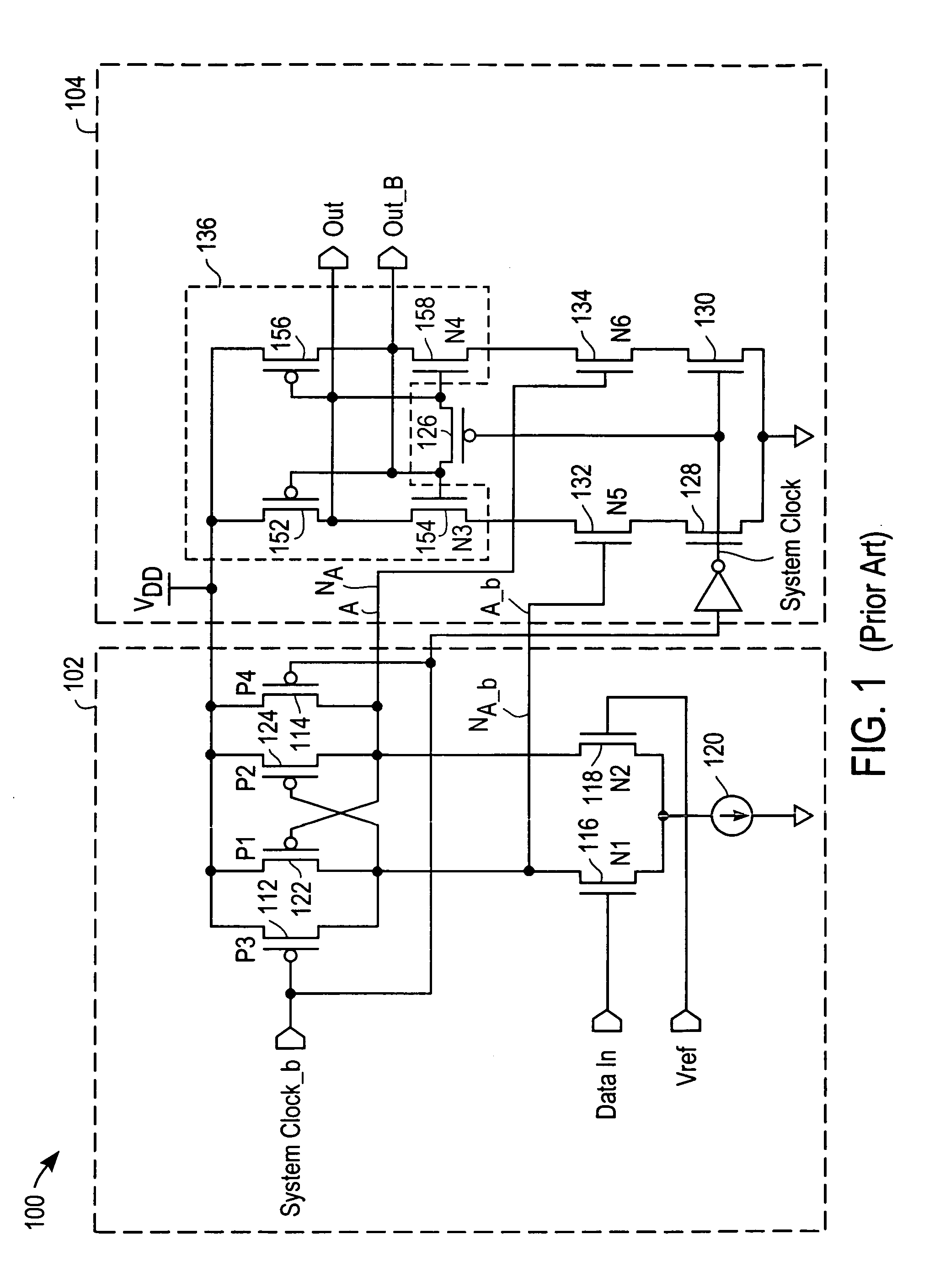
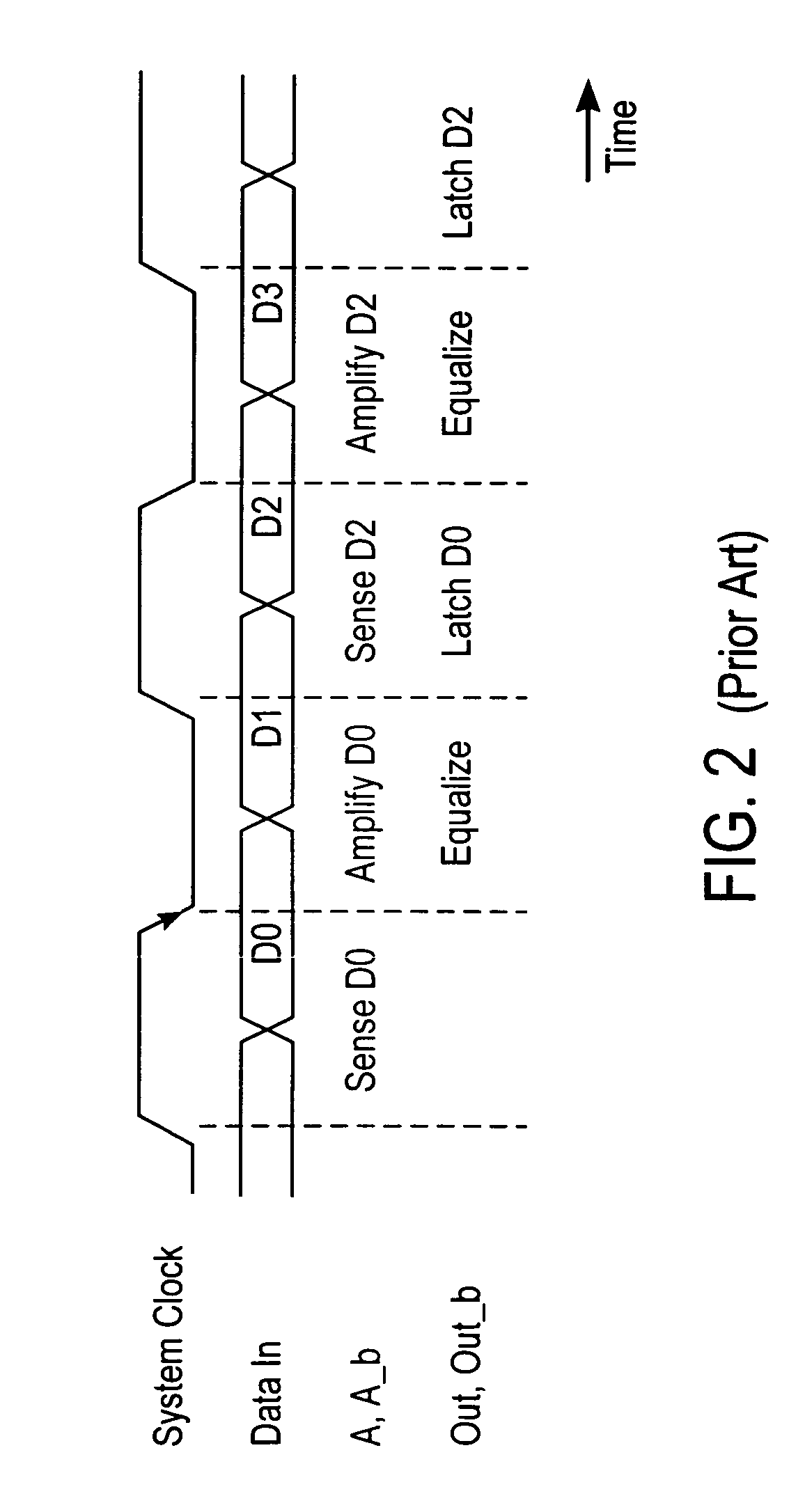
Low latency multi-level communication interface
InactiveUS7124221B1Reduce static power consumptionWide input common mode rangePulse modulation television signal transmissionElectric analogue storesCommunication interfaceLeast significant bit
A memory system uses multiple pulse amplitude modulation (multi-PAM) output drivers and receivers to send and receive multi-PAM sigsnals. A multi-PAM signal has more than two voltage levels, with each data interval now transmitting a “symbol” at one of the valid voltage levels. In one embodiment, a symbol represents two or more bits. The multi-PAM output driver drives an output symbol onto a signal line. The output symbol represents at least two bits that include a most significant bit (MSB) and a least significant bit (LSB). The multi-PAM receiver receives the output symbol from the signal line and determines the MSB and the LSB.
Owner:RAMBUS INC
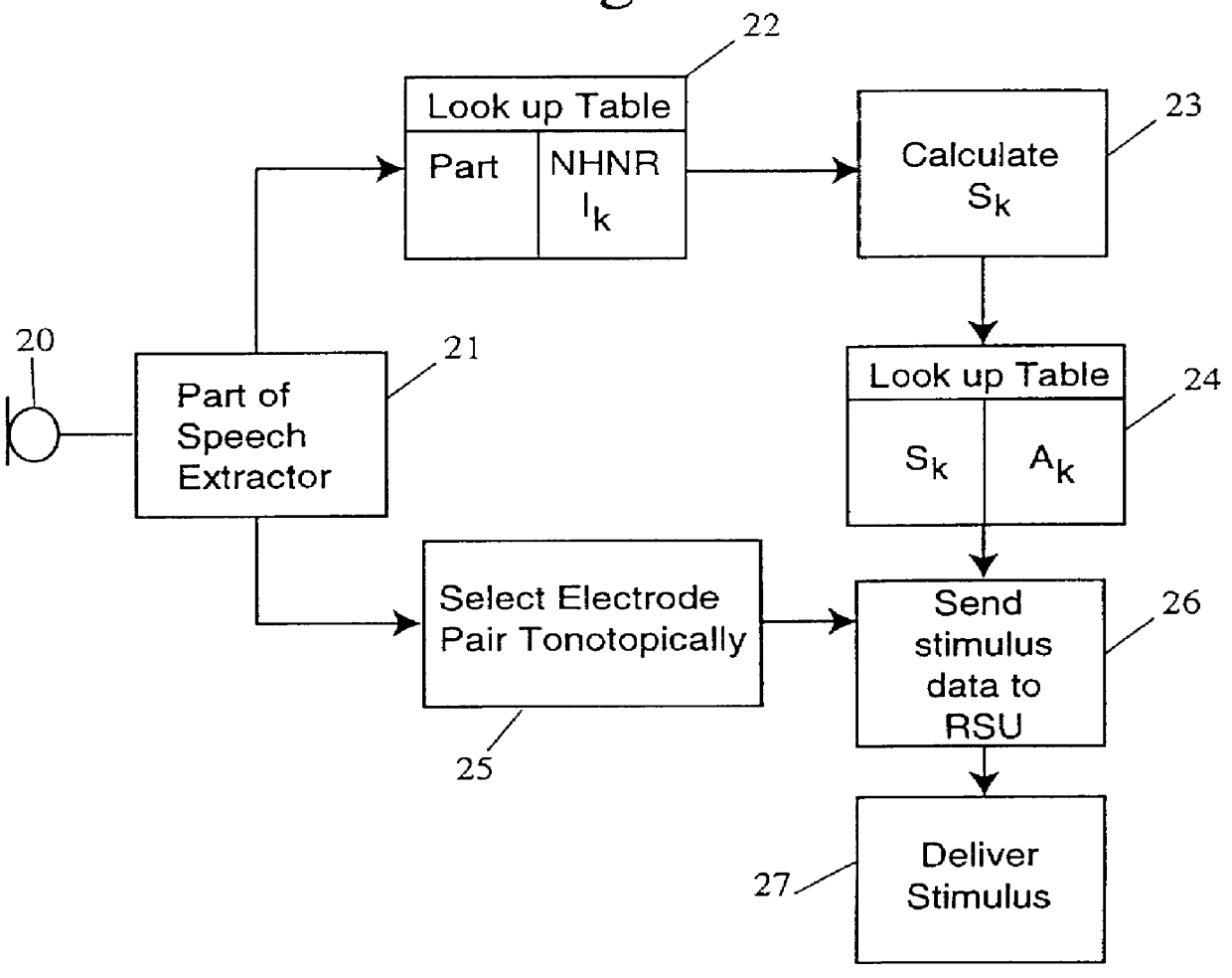
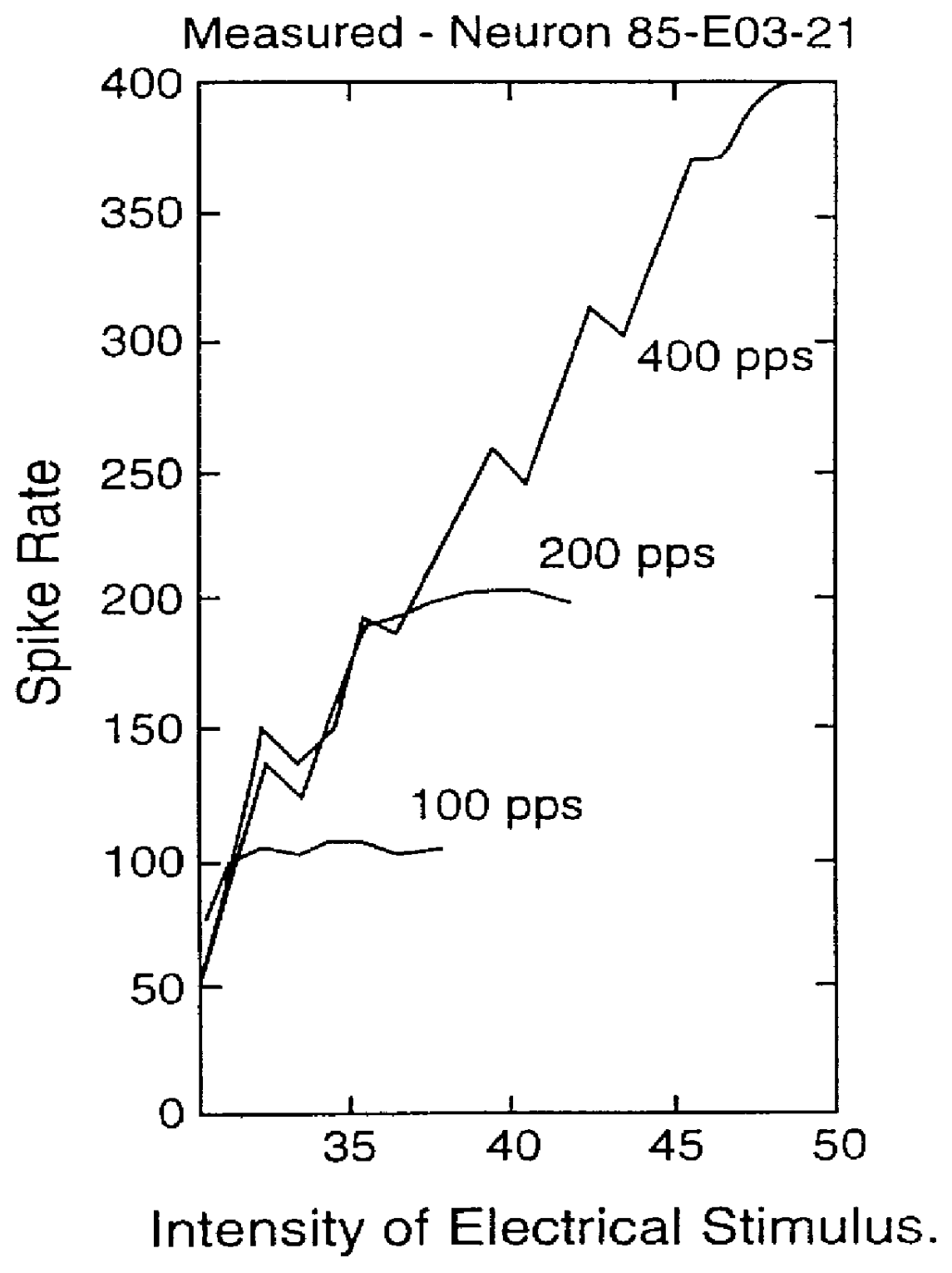
Multiple pulse stimulation
InactiveUS6064913AEasy to produceElectrotherapyArtificial respirationCochlear implantationTime domain response
A stimulation strategy for cochlear implants seeks to approximate the time domain response of a patient's neural system to electrical stimuli, to the time domain response of a normal hearing person to a corresponding acoustic stimulus. The strategy is designed to induce in the neurons of a patient a time domain response to an acoustic signal which is similar to, or approximates the time domain response induced by the normal processes in a healthy person. Various implementations are disclosed.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MELBOURNE
Efficient charge transferring in CMOS imagers
ActiveUS20070045681A1Improve dynamic rangeTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesCMOSEngineering
Methods for operating a pixel cell include efficient transferring of photo-charges using multiple pulses to a transistor transfer gate during a charge integration period for an associated photosensor. The pixel cell can be operated with efficient transfer characteristics in either normal or high dynamic range (HDR) mode. The high dynamic range can be realized by either operating an optional HDR transistor or by fluctuating the voltage applied to a reset gate.
Owner:APTINA IMAGING CORP
Ultra-wideband radar system using sub-band coded pulses
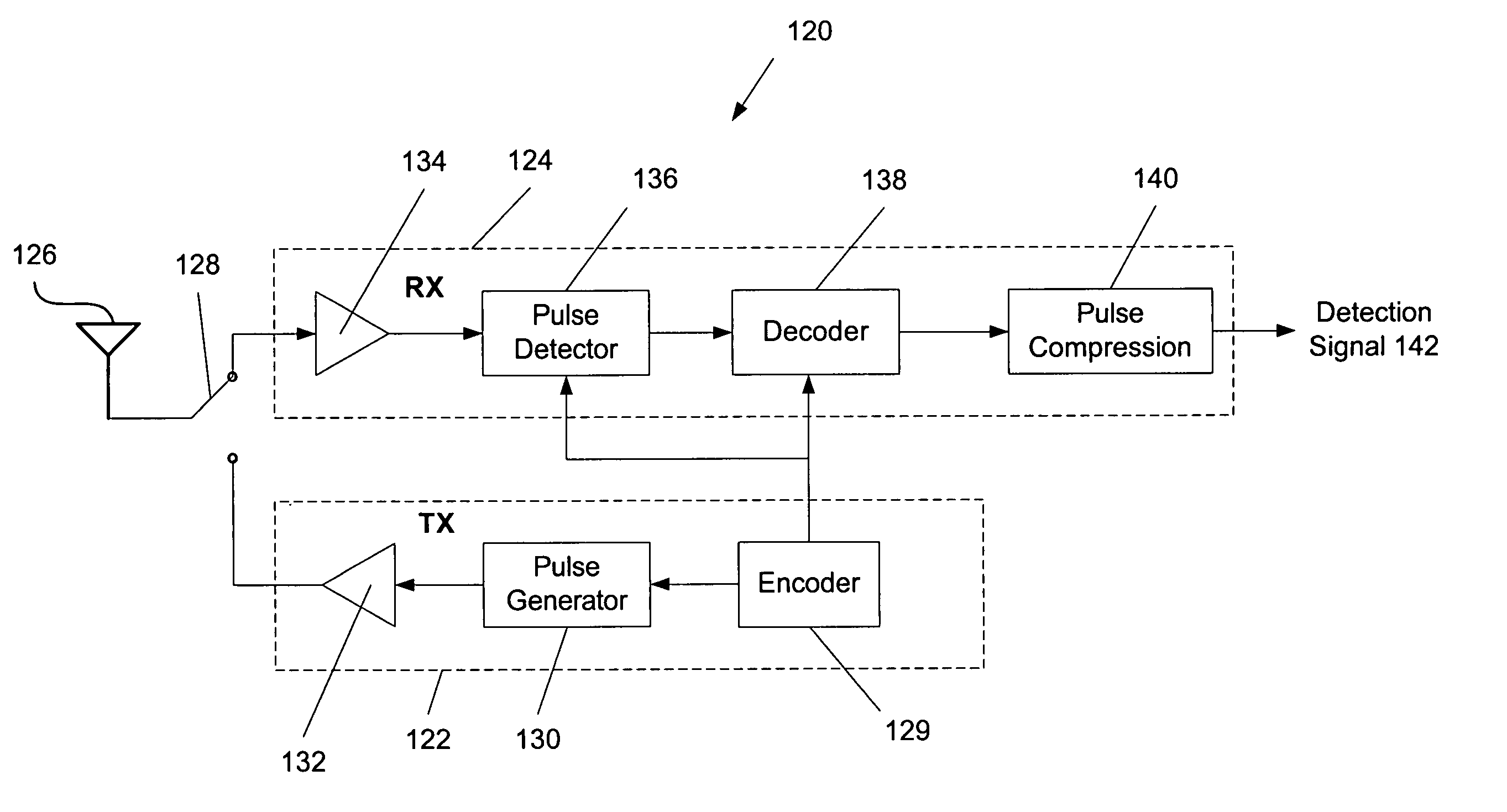
Methods and apparatus are provided for radar systems using multiple pulses that are shorter than the expected range delay extent of the target to be imaged. In one implementation, a method for performing radar includes the steps of: transmitting a plurality of pulses, each pulse having a different center frequency and a time duration shorter than an expected range delay extent of a target, wherein a total bandwidth is defined by a bandwidth occupied by the plurality of pulses; receiving reflections of the plurality of pulses; and performing pulse compression on the received pulse reflections to generate a detection signal having a radar resolution approximately equivalent to the transmission and reception of a single pulse having the total bandwidth. In preferred form, the pulses comprise ultrawideband (UWB) pulses each occupying a sub-band of the overall system bandwidth.
Owner:GENERAL ATOMICS
Increasing measurement rate in time of flight measurement apparatuses
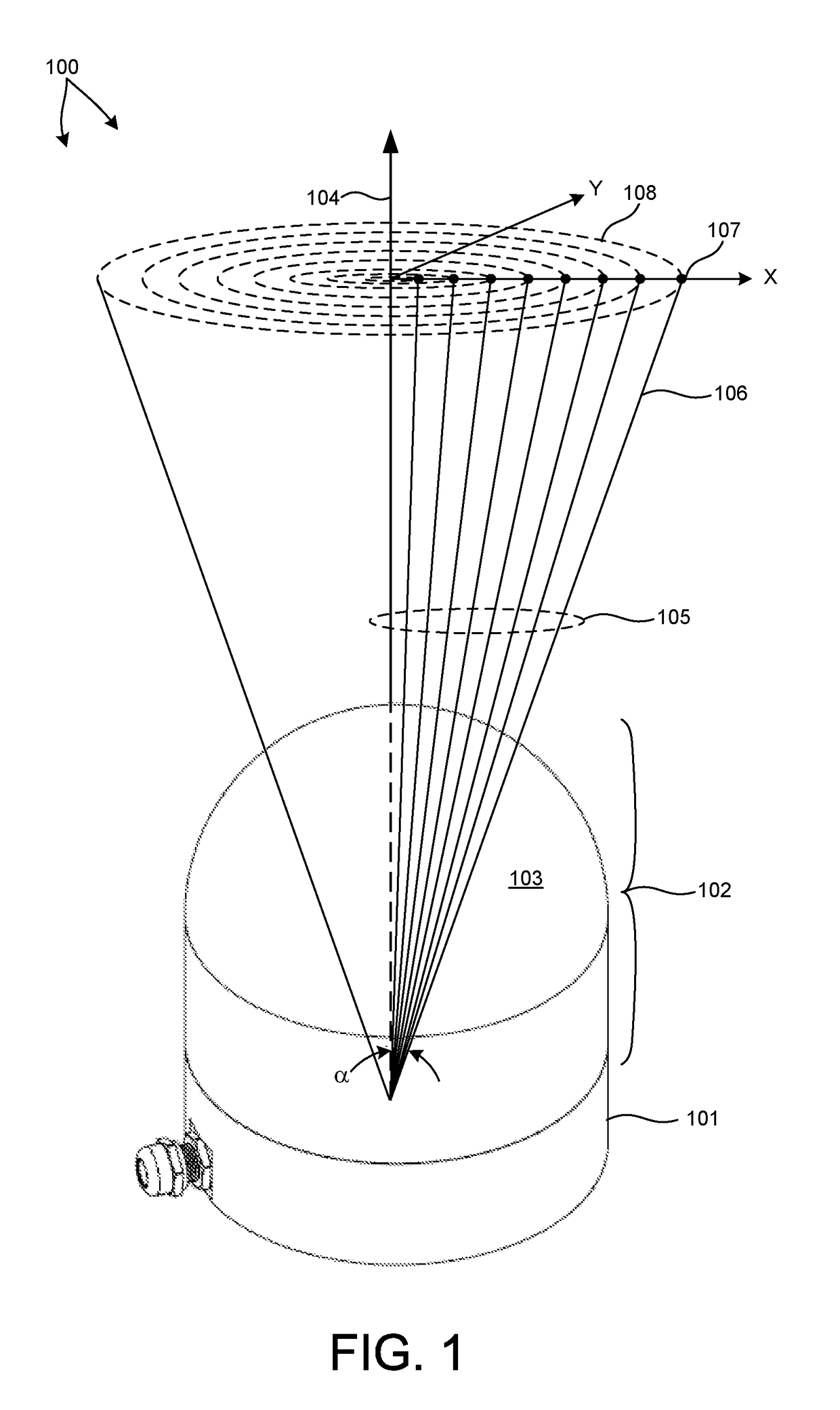
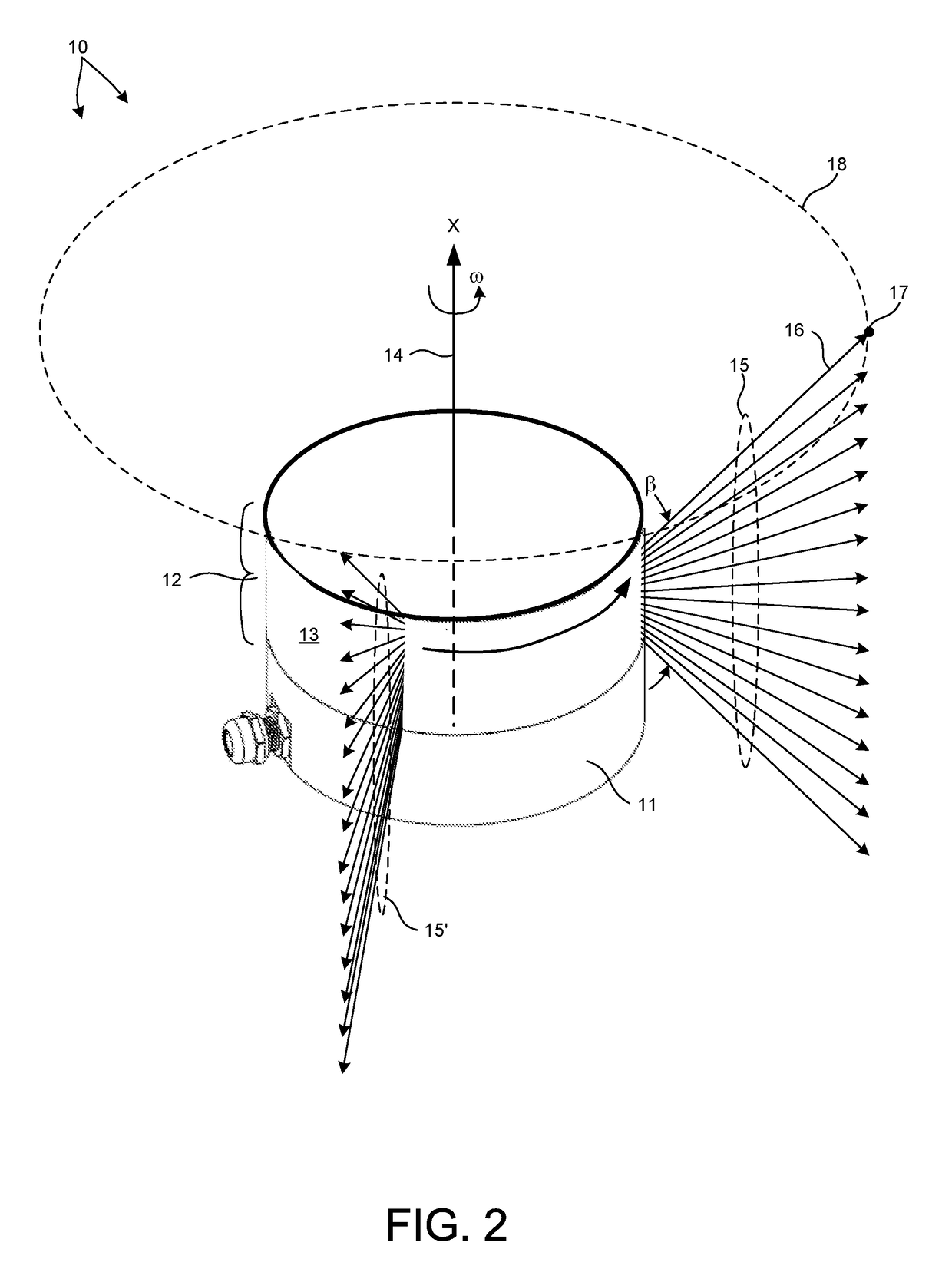
An apparatus for measuring distance to a surface is disclosed. The apparatus transmits at least one subsequent pulse of light prior to receiving a reflection of a previously sent pulse of light. Thus, multiple pulses of light are in-flight at a given time. The embodiments are applicable to terrain mapping, bathymetry, seismology, detecting faults, biomass measurement, wind speed measurement, temperature calculation, traffic speed measurement, military target identification, surface to air rangefinding, high definition survey, close range photogrammetry, atmospheric composition, meteorology, distance measurement, as well as many other applications. Examples of such apparatuses include laser ranging systems, such as light detection and ranging (LIDAR) systems, and laser scanners. Data received from the apparatus by a data processing unit can be used to create a data model, such as a point cloud, digital surface model or digital terrain model describing the surface, terrain, and / or objects.
Owner:LEICA GEOSYSTEMS AG
Method and apparatus to increase throughput of processes using pulsed radiation sources
ActiveUS20050247683A1Reduced strengthWelding/soldering/cutting articlesMetal working apparatusLithography processLithographic artist
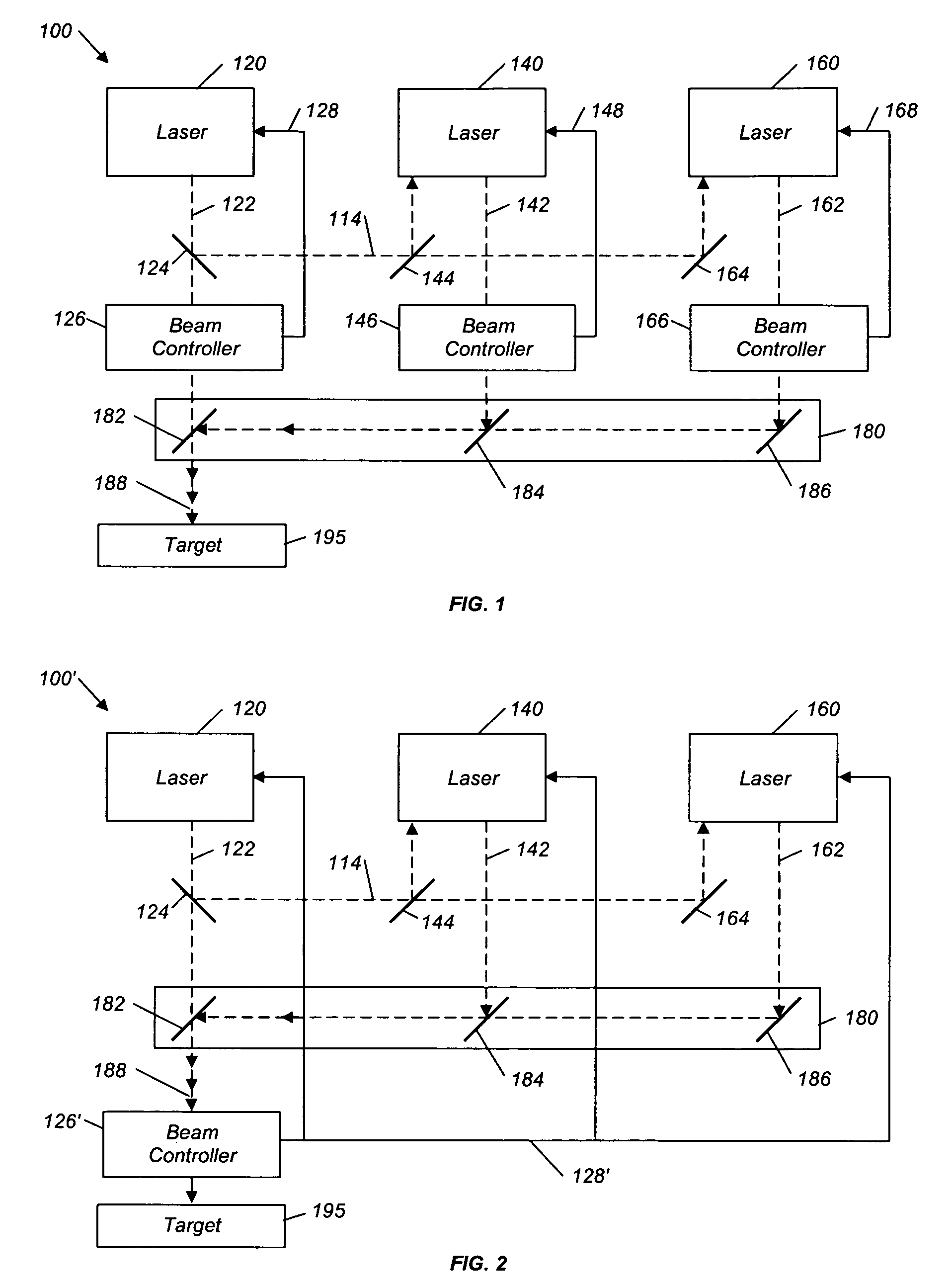
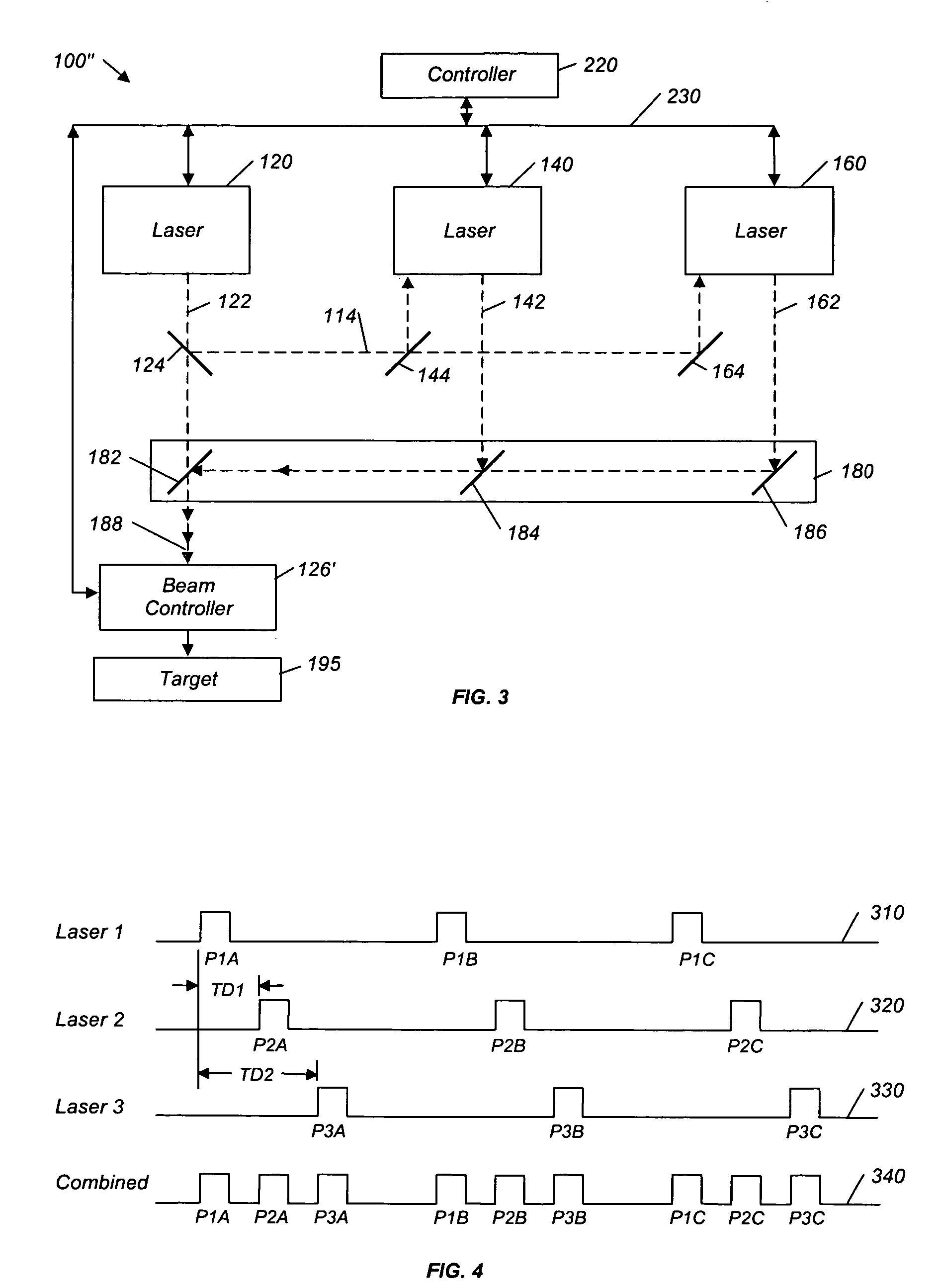
A material processing system and method is disclosed for processing materials such as amorphous silicon in an annealing processes and lithography processes on a silicon wafer, as well as ablation processes. A first laser generates periodic pulses of radiation along a beam path directed at the target material. Similarly, at least one additional laser generates periodic pulses. A beam aligner redirects the beam path of the at least one additional laser, such that the beam from the at least one additional laser is directed at the target along a path colinear with the first laser's beam path. As a result, all the lasers are directed at the target along the same combined beam path. The periodic pulses of the at least one additional laser are delayed relative to the first laser such that multiple pulses impinge on the target within a single pulse cycle of any given laser.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Controlled irreversible electroporation
Electrical pulses are applied to tissue in a manner which destroys targeted cells such as cancerous cells while sparing non-targeted cells such as nerve cells. The electrical pulses are controlled within ranges for voltage, wattage and duration of application. Multiple pulses or groups of pulses may be applied to obtain a desired result while maintaining any temperature increase below a level which destroys cells.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
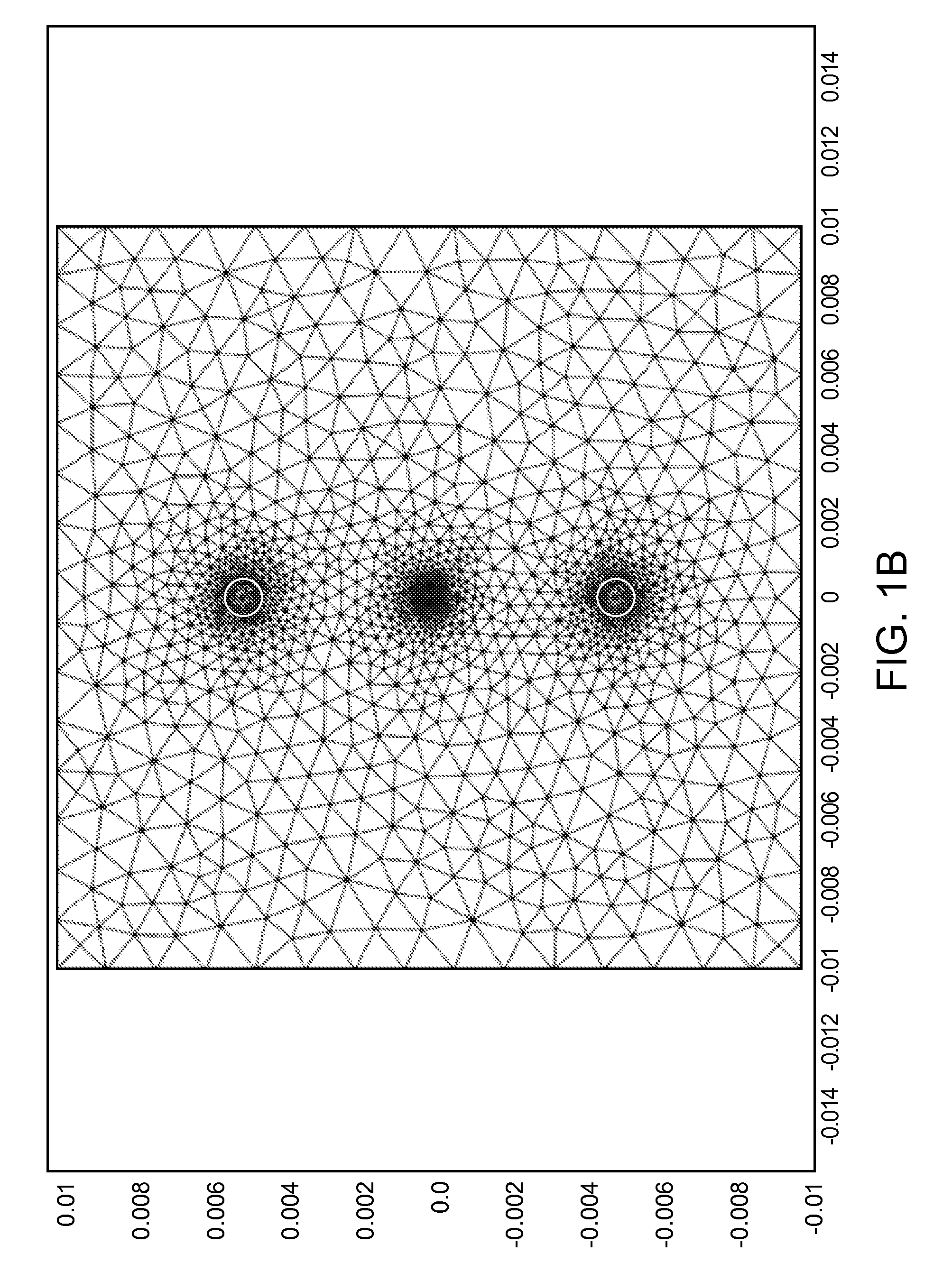
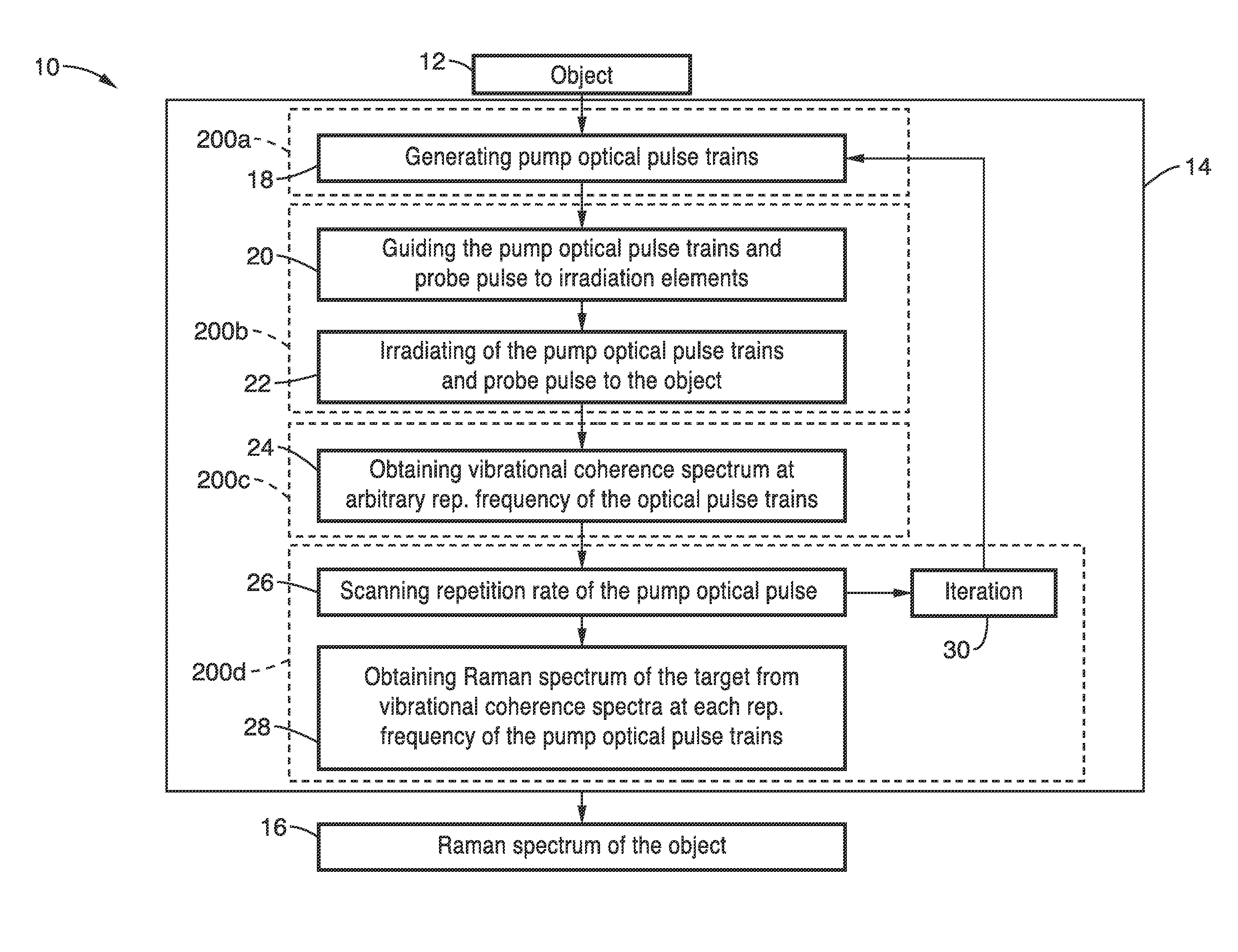
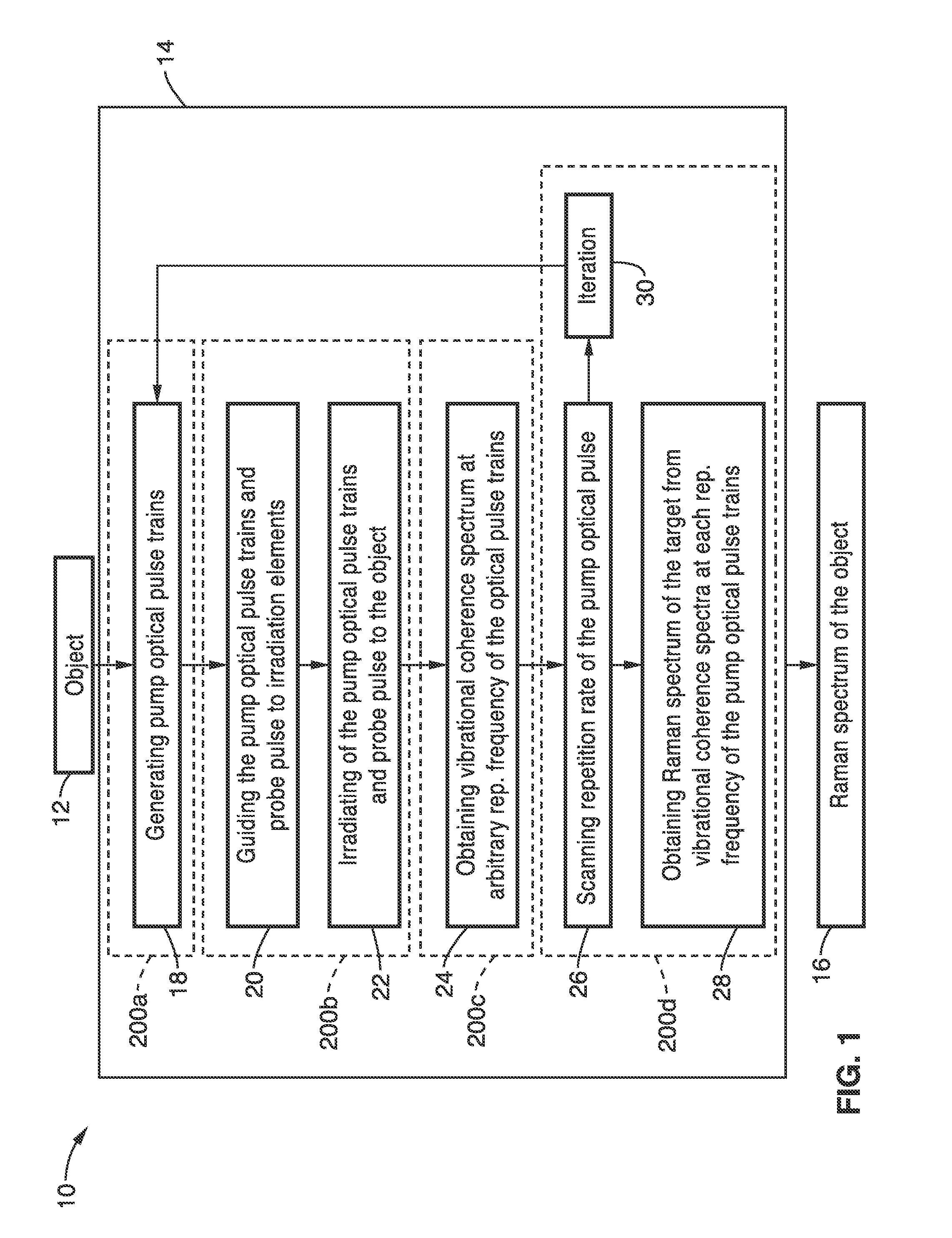
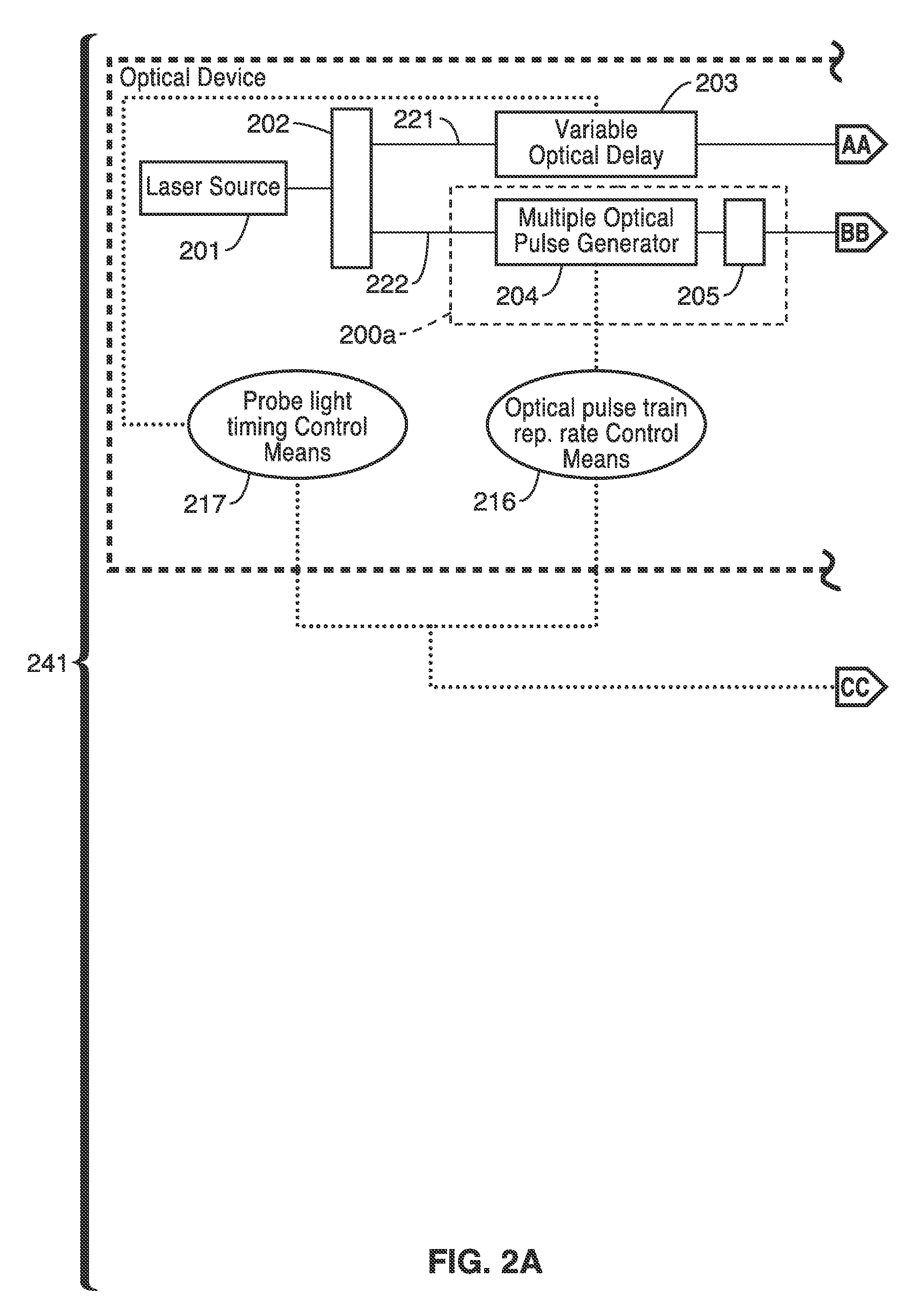
Apparatus and method for multiple-pulse impulsive stimulated raman spectroscopy
Spectroscopic measurements are described based on light-molecule interaction in response to a resonant rate optical pulse train so that a Raman spectrum is reflected containing at least two types of vibrational mode information (e.g., vibrational frequency, and vibrational phase relaxation) on the molecules comprising the object. A pump optical pulse train generation means is configured for generating an optical pulse train having an arbitrary repetition rate which is directed through irradiation means to the sample object. Light from the sample object is collected and vibrational coherence is detected for the sample object. The sample is tested across a plurality of different repetition frequencies. The detected information can be compared with data from other known samples from within a database when analyzing the information collected.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP +1
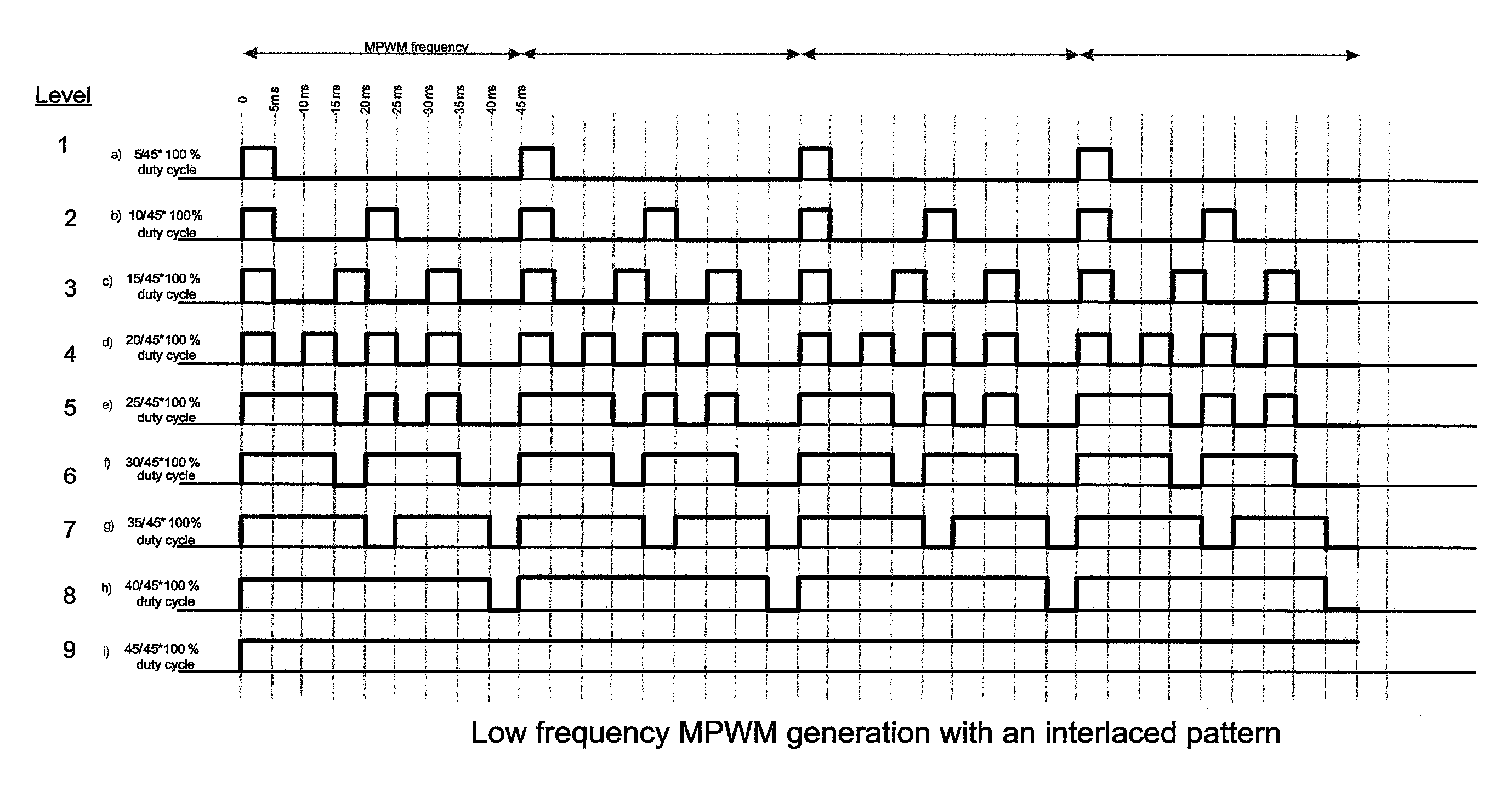
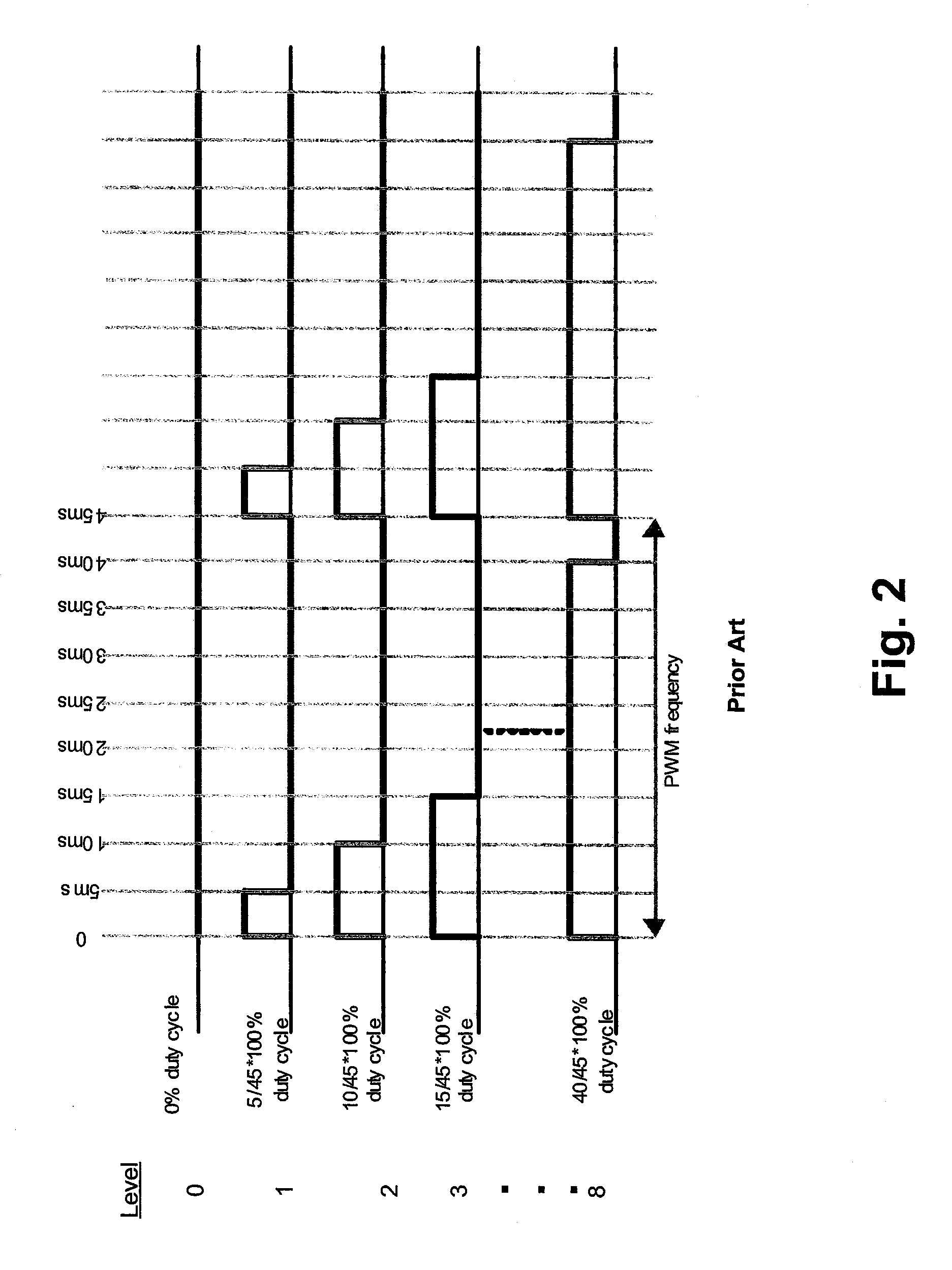
Multiple pulse width modulation
A method of generating a MPWM signal for a portable device such as a cellular telephone. For a first duty cycle that includes a MPWM frequency having N magnitude levels, the method generates a first waveform comprising a first and a second On pulse during a first MPWM frequency period. The first and second On pulses are separated by an Off period.
Owner:IMMERSION CORPORATION
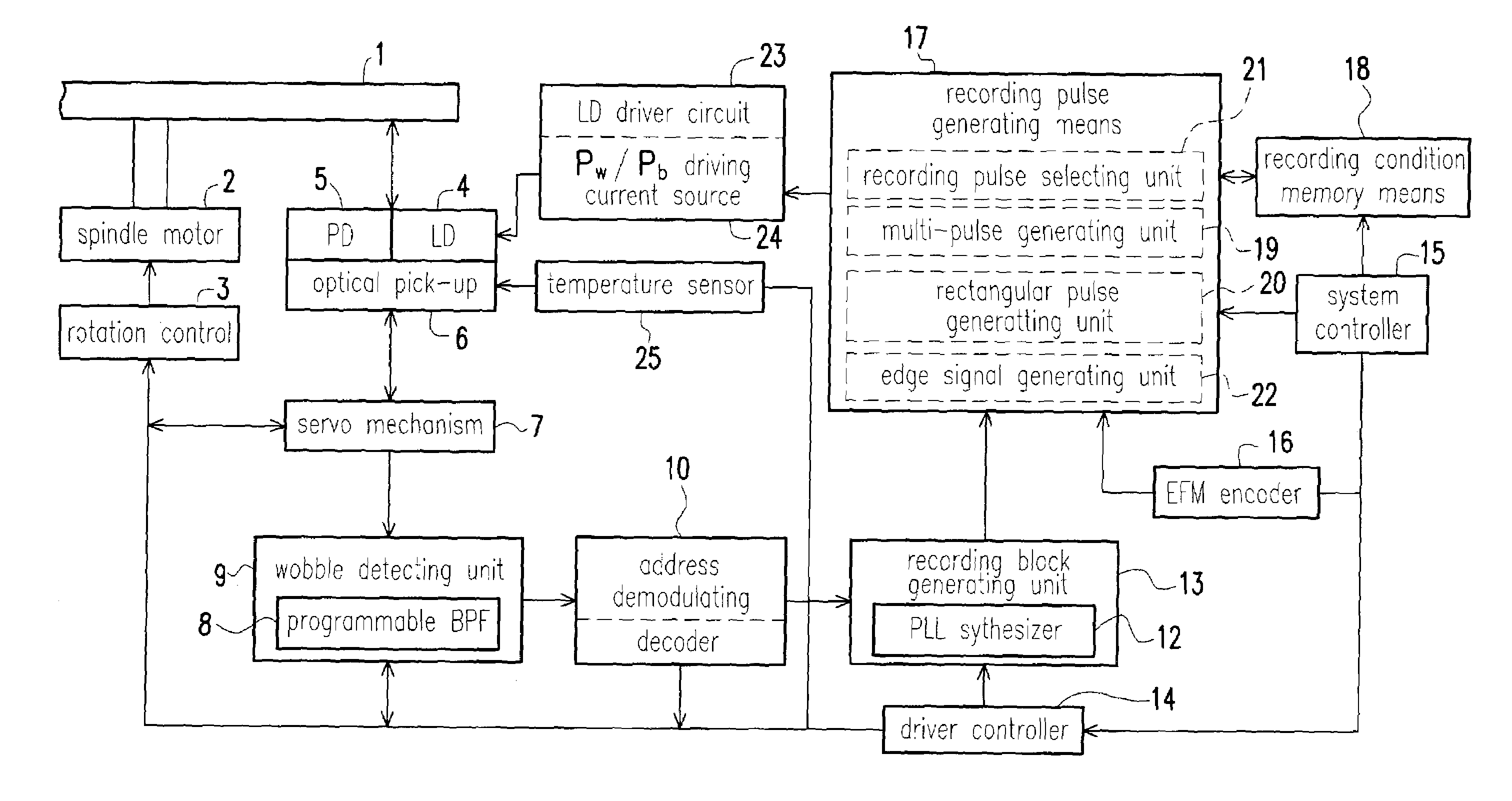
Information recording device
ActiveUS7006419B2Reduction in inabilityQuality improvementRecording strategiesTelevision system detailsLaser lightLight emission
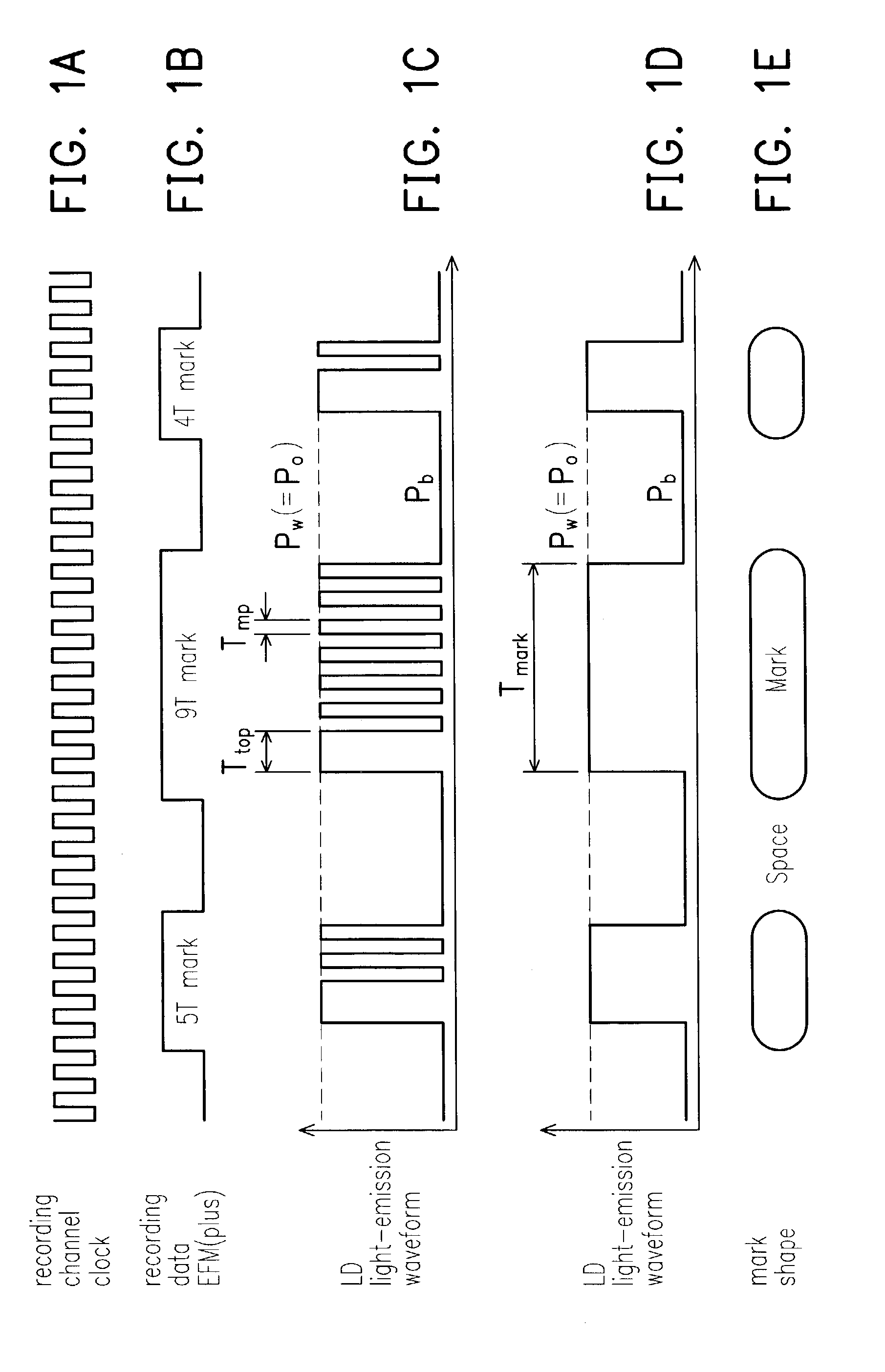
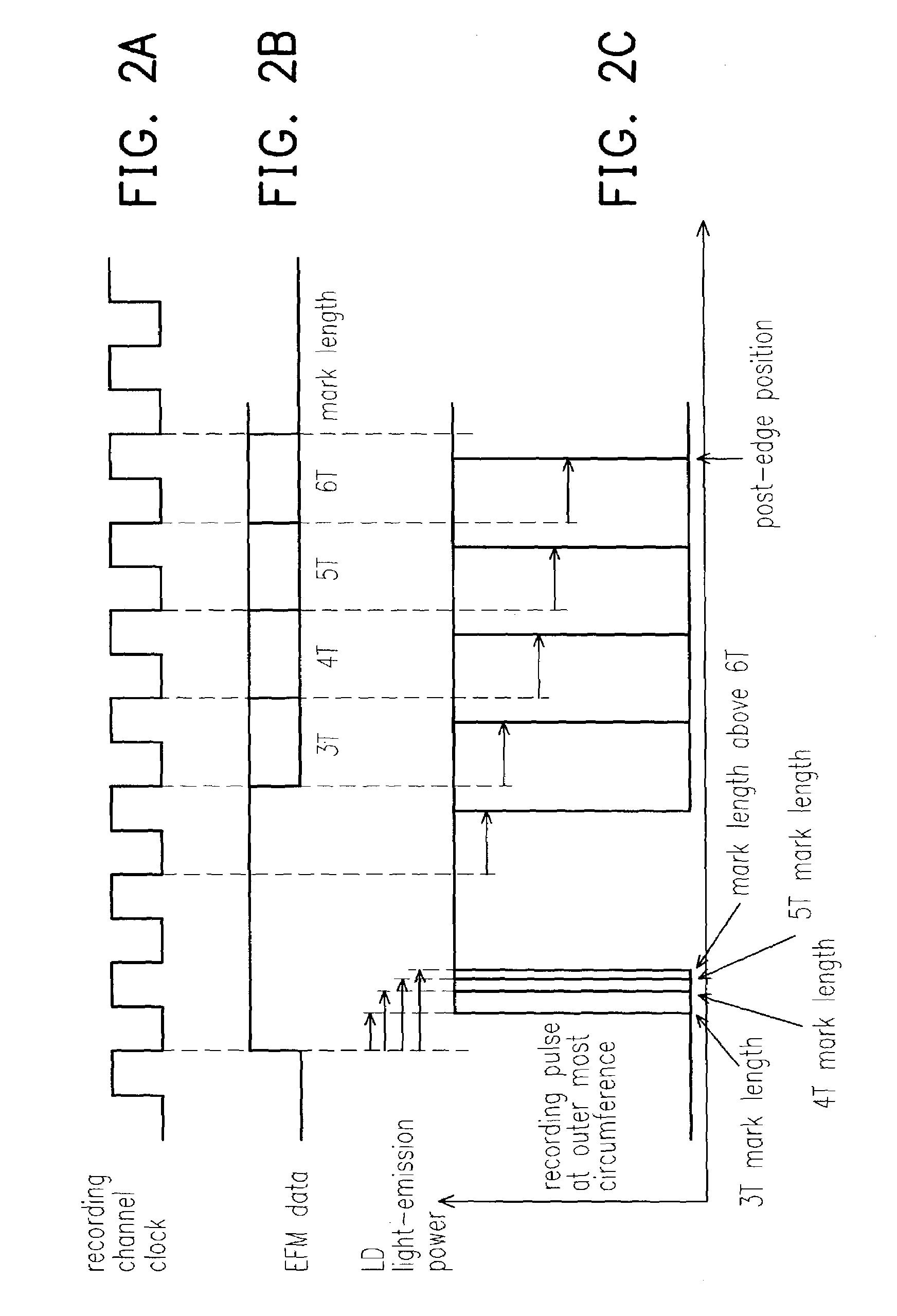
An information recording device comprising at least a recording pulse generating means and a recording pulse selecting means capable of generating various multi-pulses each of which is a combination of a leading heating pulse and a succeeding heating pulse, and rectangular pulses each of which is a single pulse, as a recording pulse, is disclosed. The recording pulse selecting means switches and selects among the multi-pulses and the rectangular pulses according to a recording condition, and then causes a light emission of a laser light source through a light source driving means. Even though in a high recording linear velocity recording condition that is insufficient in power for the recommended multi-pulse recording, a very low recording power can still be used by switching to the rectangular pulse recording, so as to achieve a recording with a much higher recording speed. In addition, good recording marks can be formed without exceeding a maximum allowable recording power.
Owner:RICOH KK
Systems and methods for determining depth using shuttered light pulses
Systems and methods are presented that use light sensors and computing devices to compute the depth of an object using shuttered light pulses. In one embodiment, depth is determined as follows: A light emitter emits a pulse of light that is directed toward an object. The pulse is reflected off the object and travels toward a beam splitter. The beam splitter splits the reflected pulse into multiple pulses, with each pulse directed to a shuttered sensor with a different shutter location. The shuttered sensors measure the integrated intensity of the light, and these values are used to determine the depth of the object. A method is presented which calibrates a system that has an arbitrary number of shutters and enables the system to determine the depth of an object, even in the presence of ambient illumination and scattered light.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
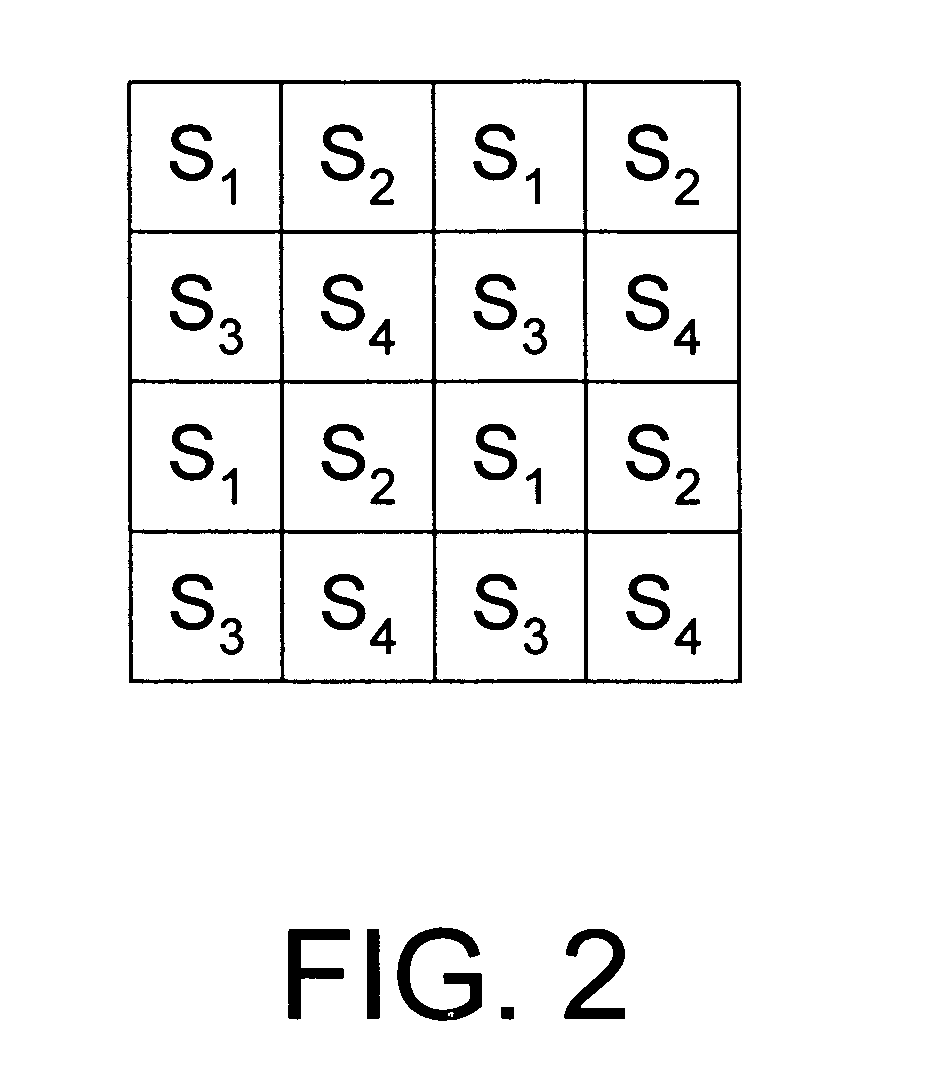
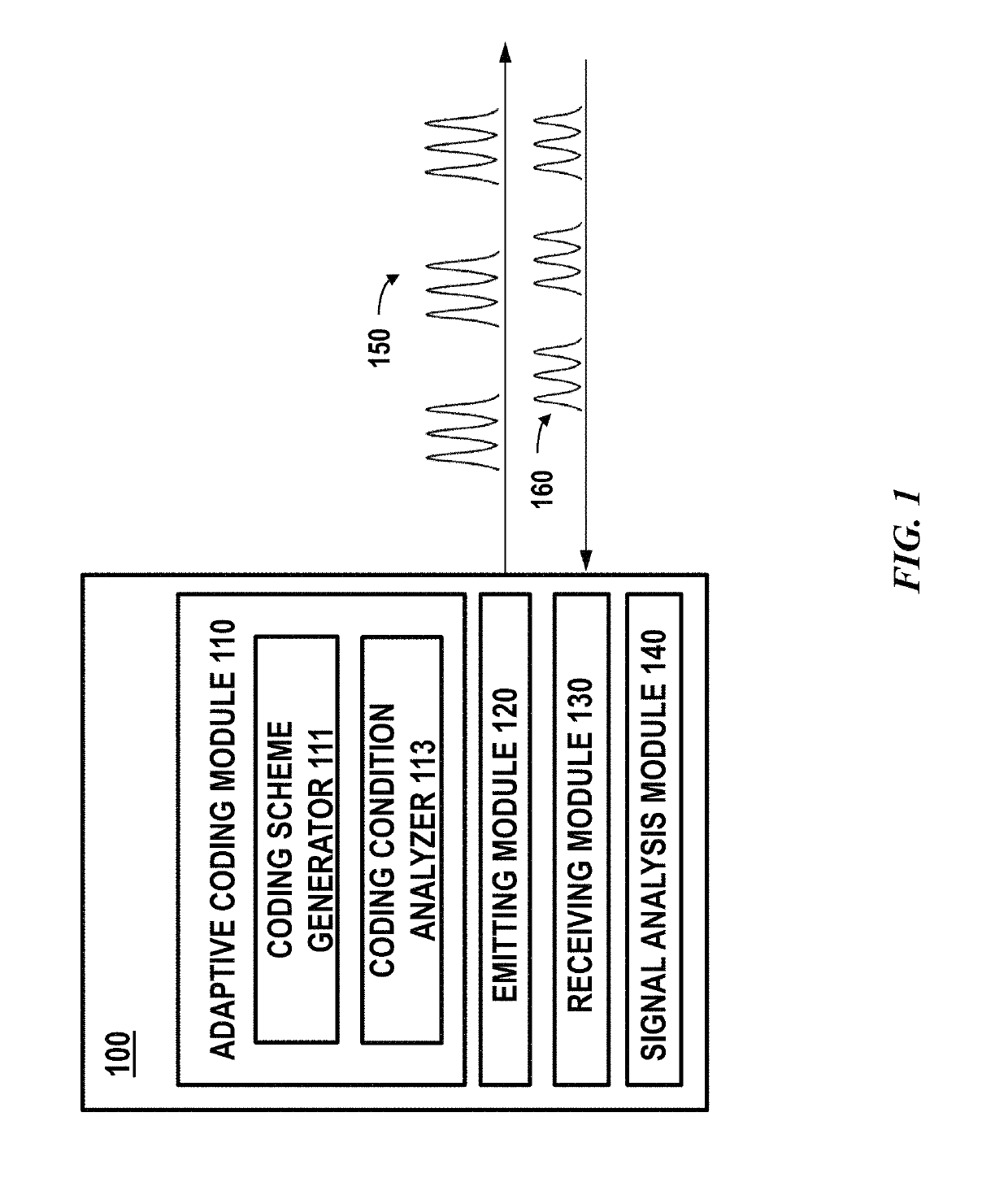
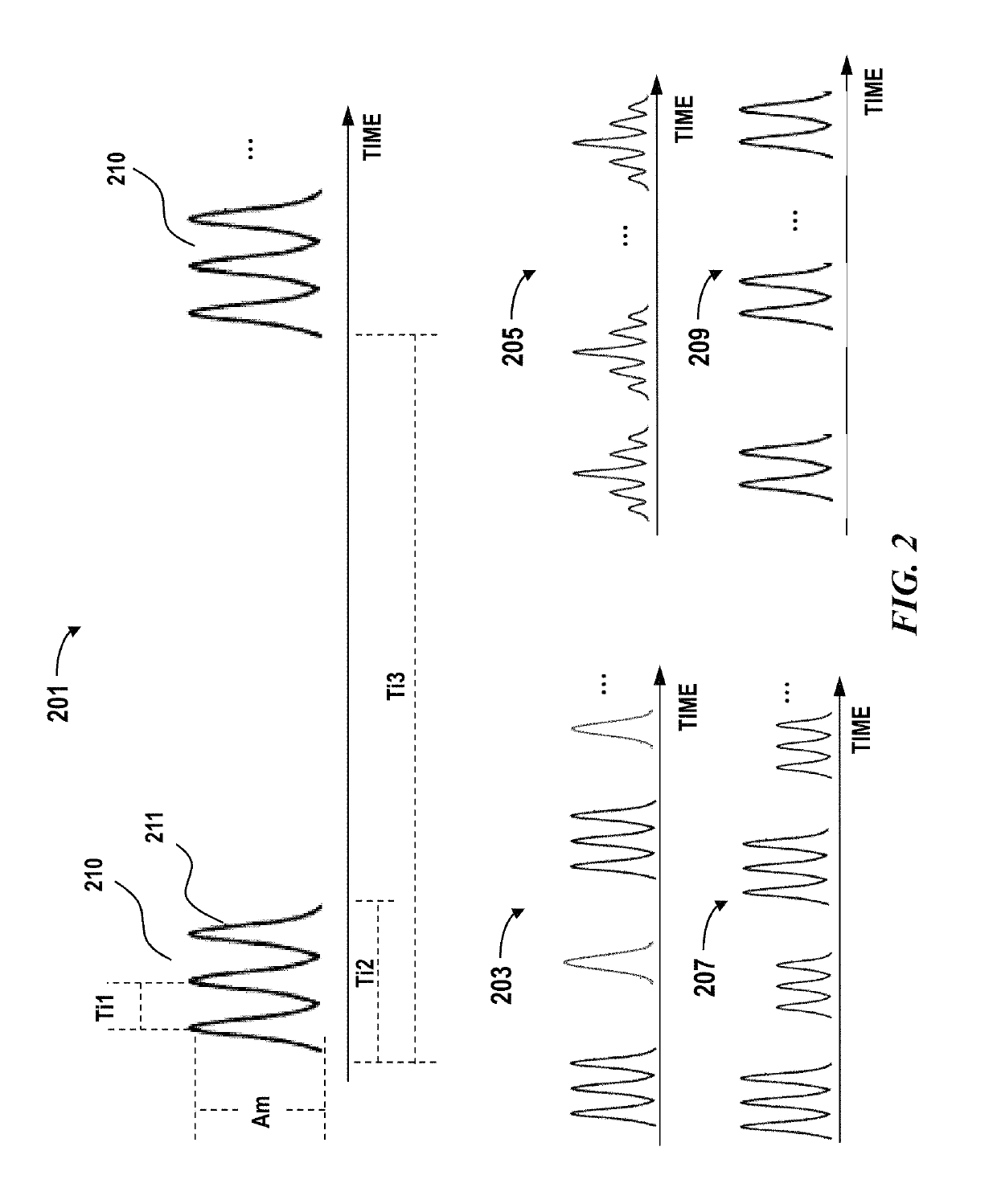
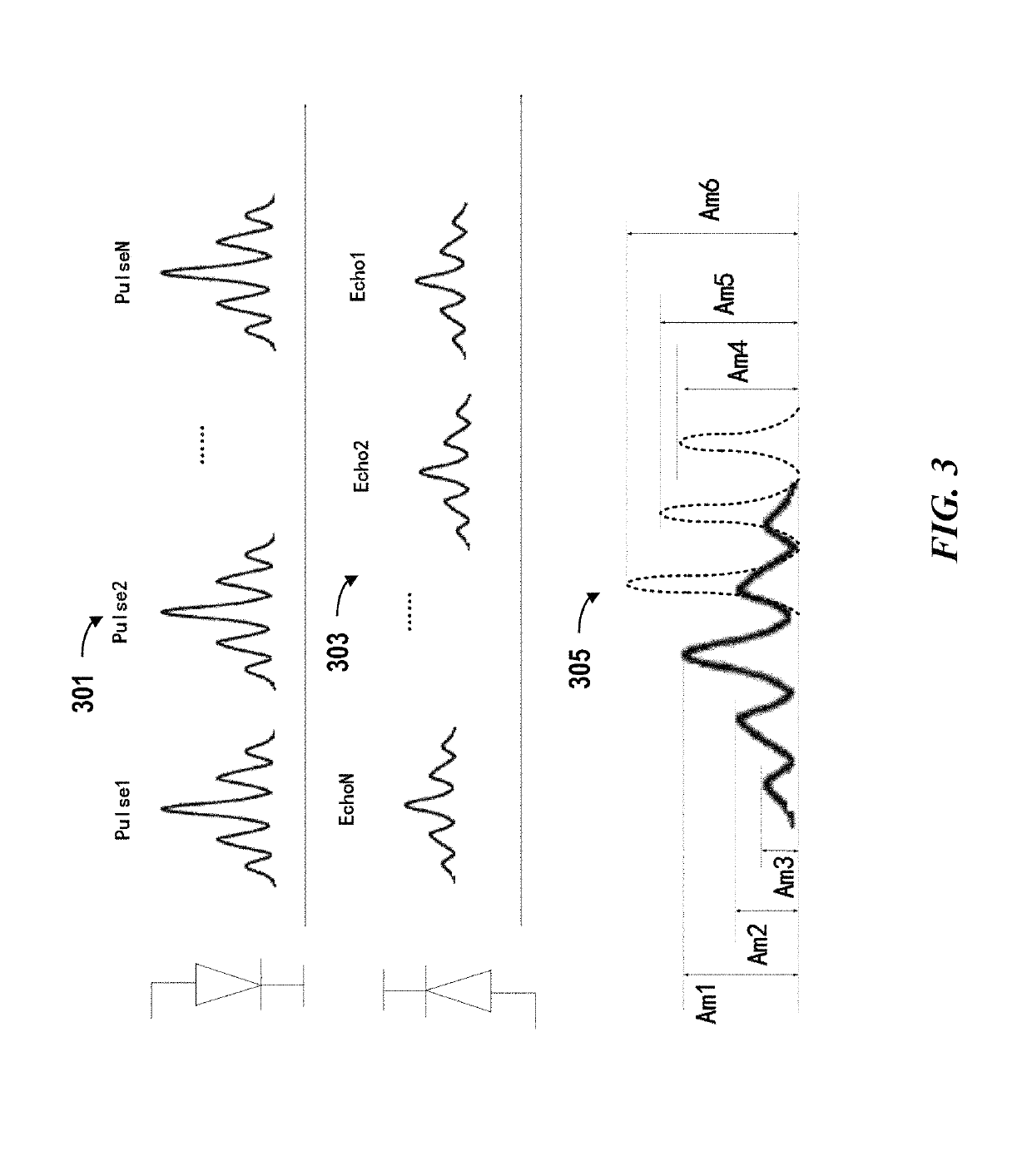
Adaptive coding for lidar systems
ActiveUS10466342B1Avoid cross-talk across different channels and/or interferenceImproved resistance to environmental noiseOptical rangefindersElectromagnetic wave reradiationAdaptive encodingAtmospheric sciences
A Lidar system is provided. The Lidar system comprise: a light source configured to emit a multi-pulse sequence to measure a distance between the Lidar system and a location in a three-dimensional environment, and the multi-pulse sequence comprises multiple pulses having a temporal profile; a photosensitive detector configured to detect light pulses from the three-dimensional environment; and one or more processors configured to: determine a coding scheme comprising the temporal profile, wherein the coding scheme is determined dynamically based on one or more real-time conditions including an environment condition, a condition of the Lidar system or a signal environment condition; and calculate the distance based on a time of flight of a sequence of detected light pulses, wherein the time of flight is determined by determining a match between the sequence of detected light pulses and the temporal profile.
Owner:HESAI TECH CO LTD
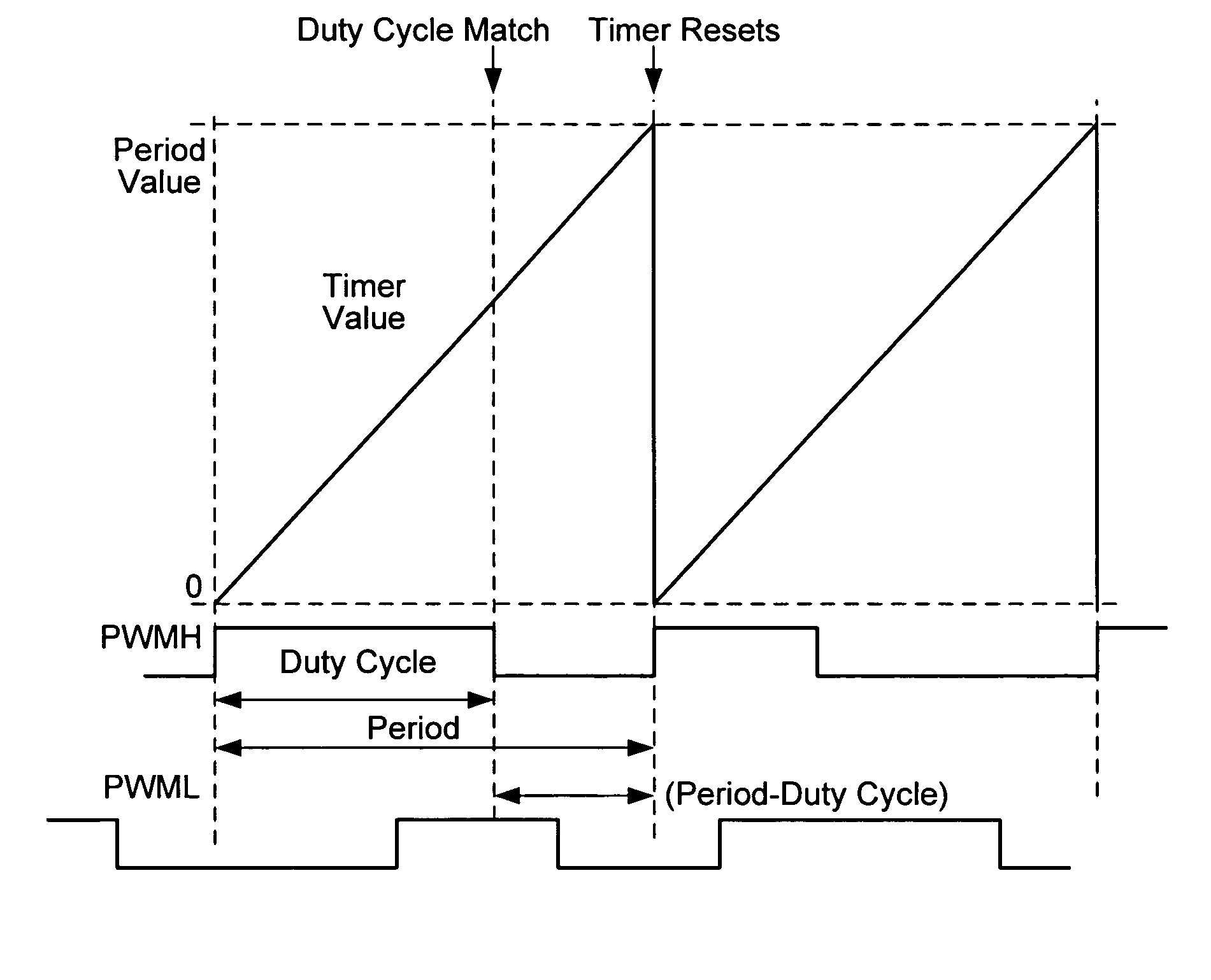
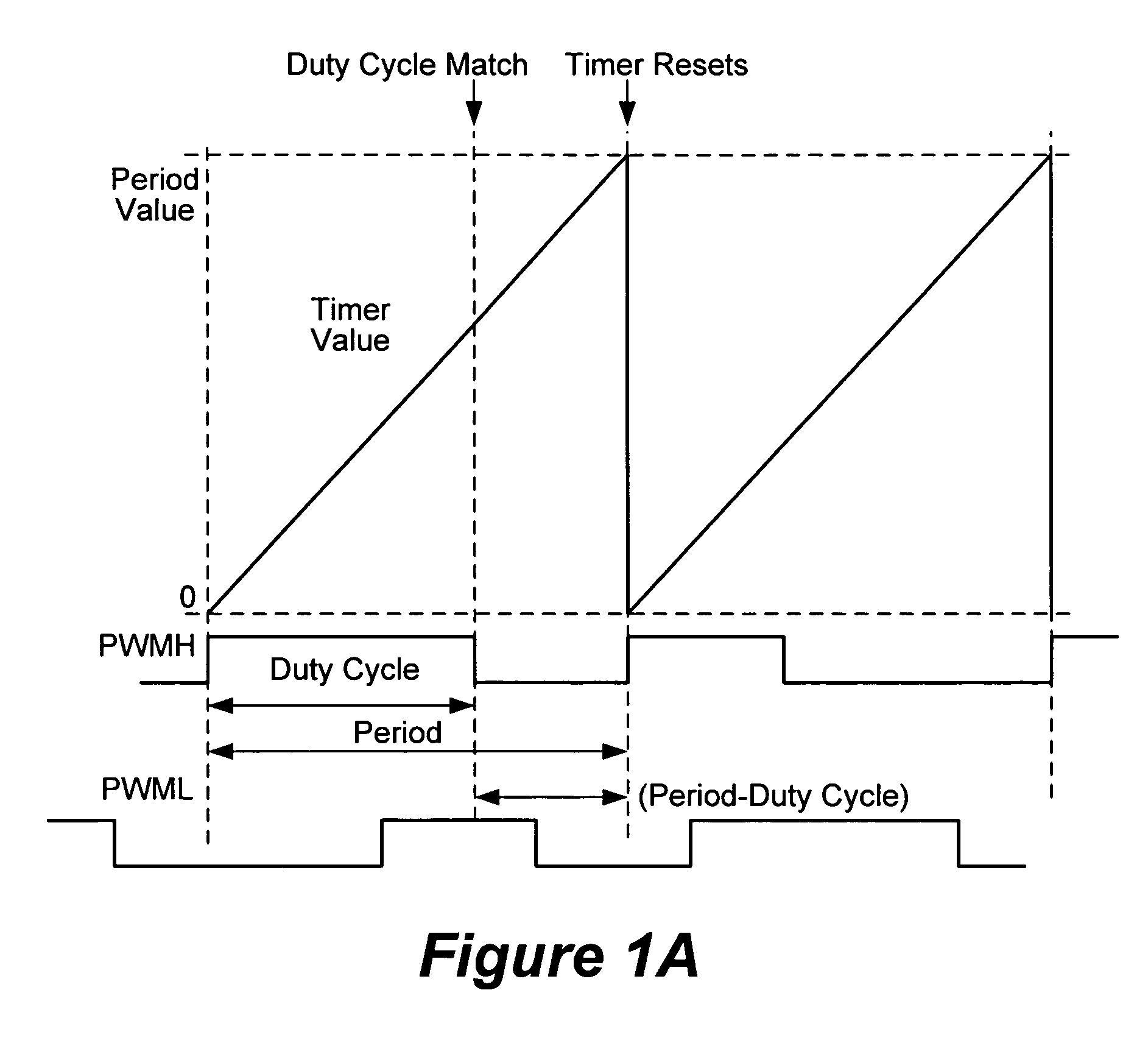
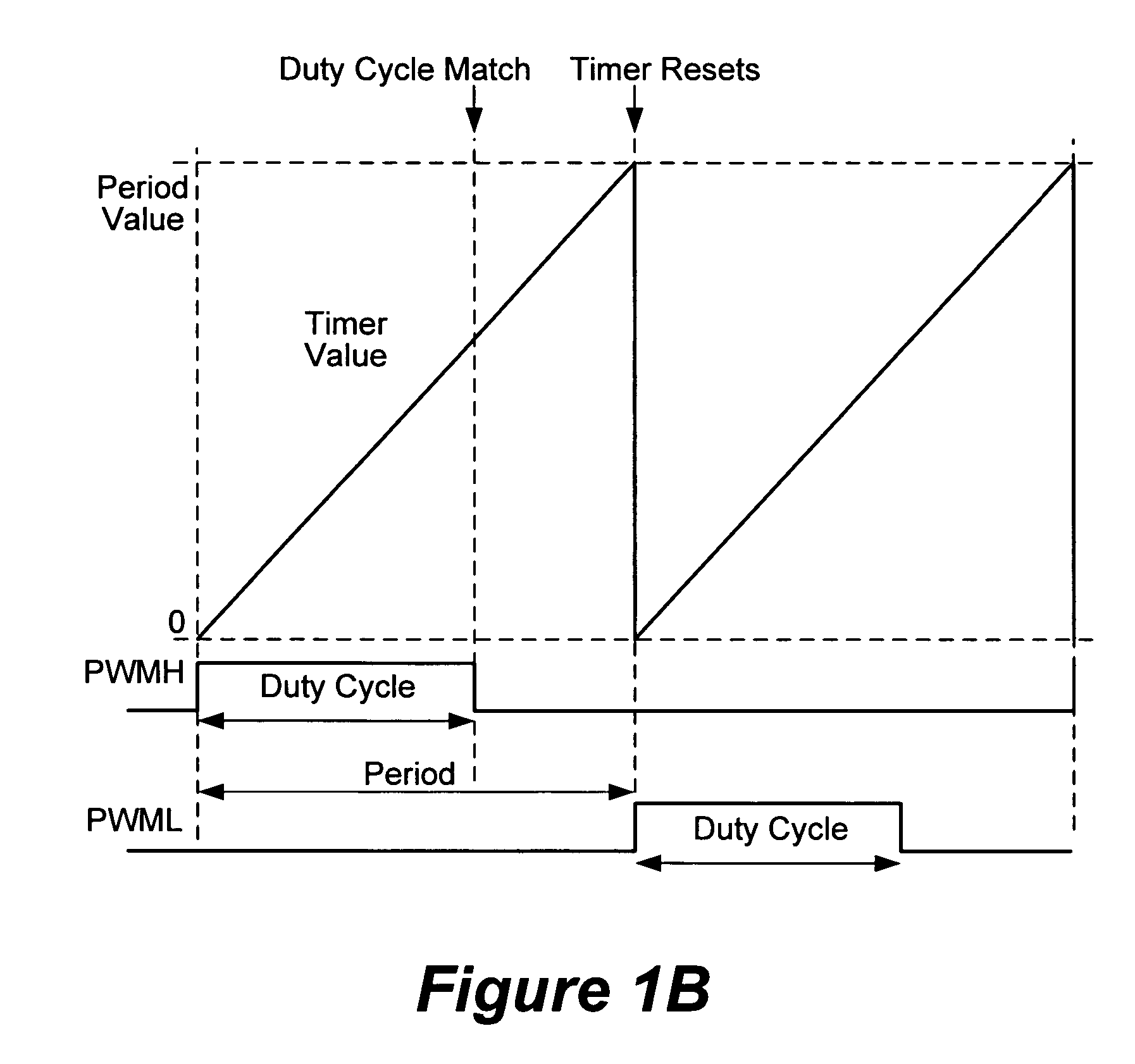
Digital processor with pulse width modulation module having dynamically adjustable phase offset capability, high speed operation and simultaneous update of multiple pulse width modulation duty cycle registers
ActiveUS20060064609A1Increase speedHigh resolution performanceRecord information storageDuration/width modulated pulse demodulationPush pullSwitching frequency
A pulse width modulation (PWM) generator featuring very high speed and high resolution capability and the ability to generate standard complementary PWM, push-pull PWM, variable offset PWM, multiphase PWM, current limit PWM, current reset PWM, and independent time base PWM while further providing automatic triggering for an analog-to-digital conversion (ADC) module that is precisely timed relative to the PWM signals. Applications include control of a switching power supply that requires very high speed operation to obtain high resolution at high switching frequencies, and the ability to vary the phase relationships among the PWM output signals driving the power supply power components. A single PWM duty cycle register may be used for updating any and / or all PWM generators at once to reduce the workload of a digital processor as compared to updating multiple duty cycle registers.
Owner:MICROCHIP TECH INC
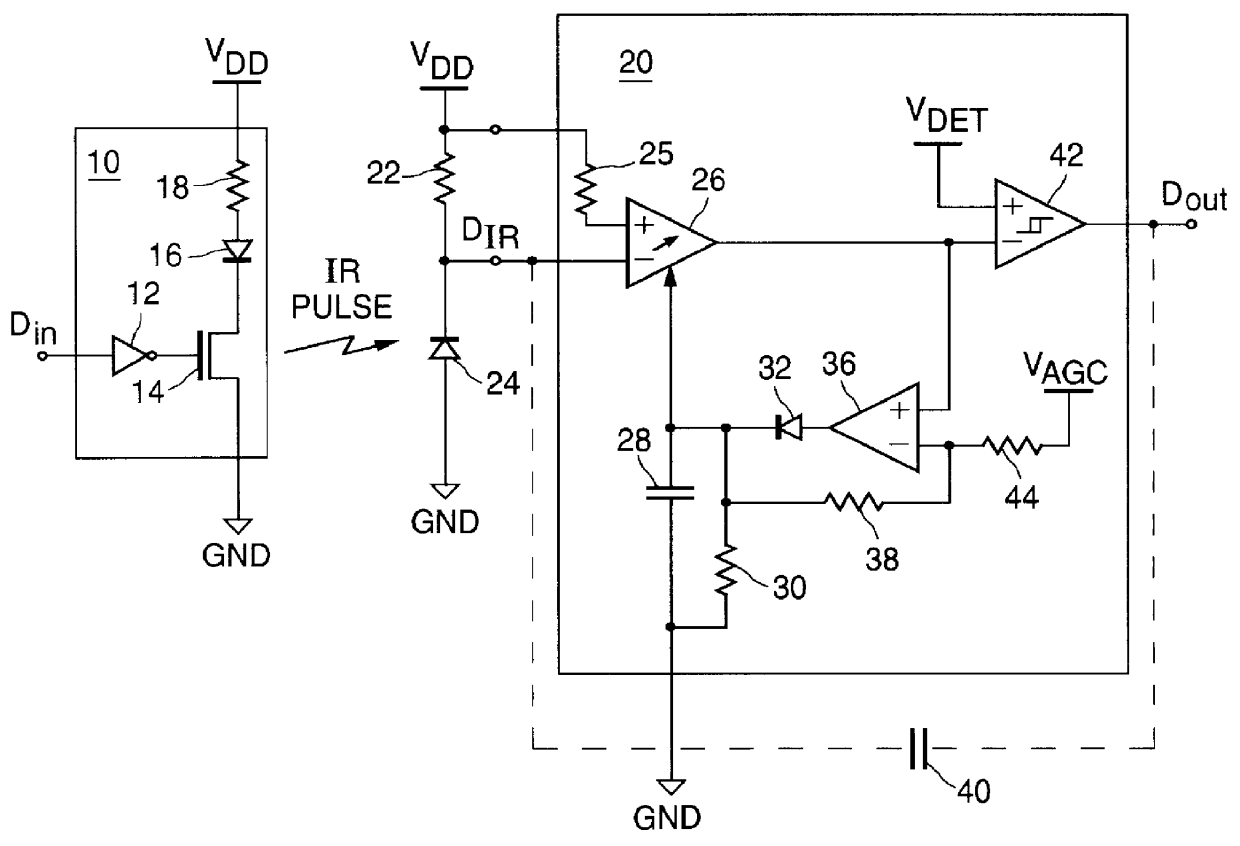
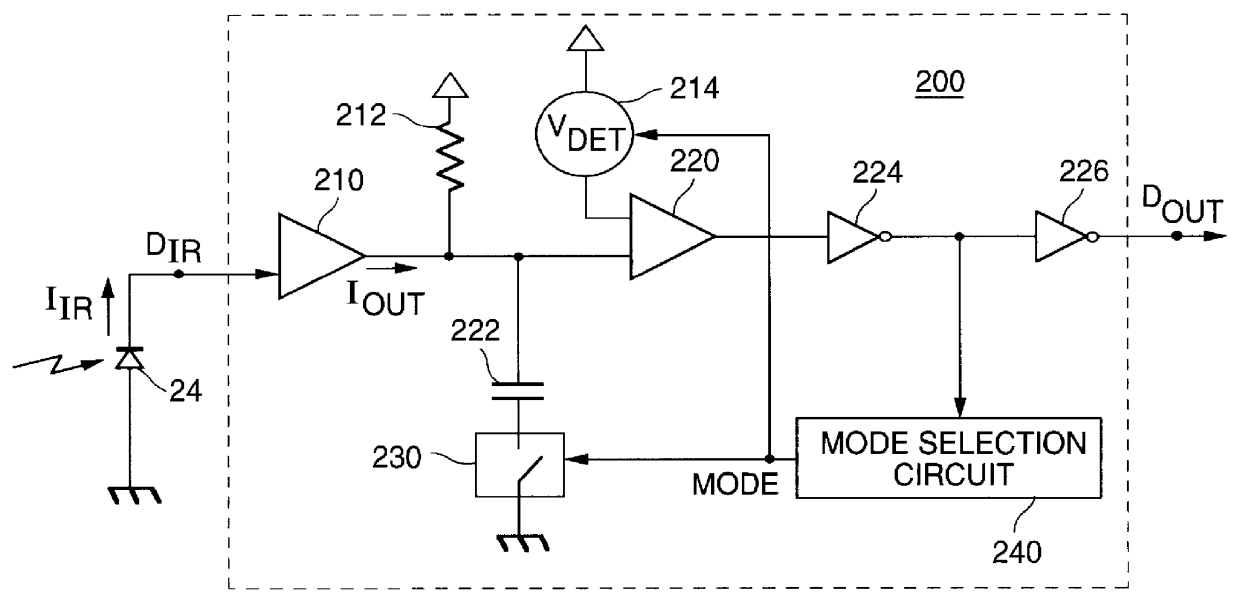
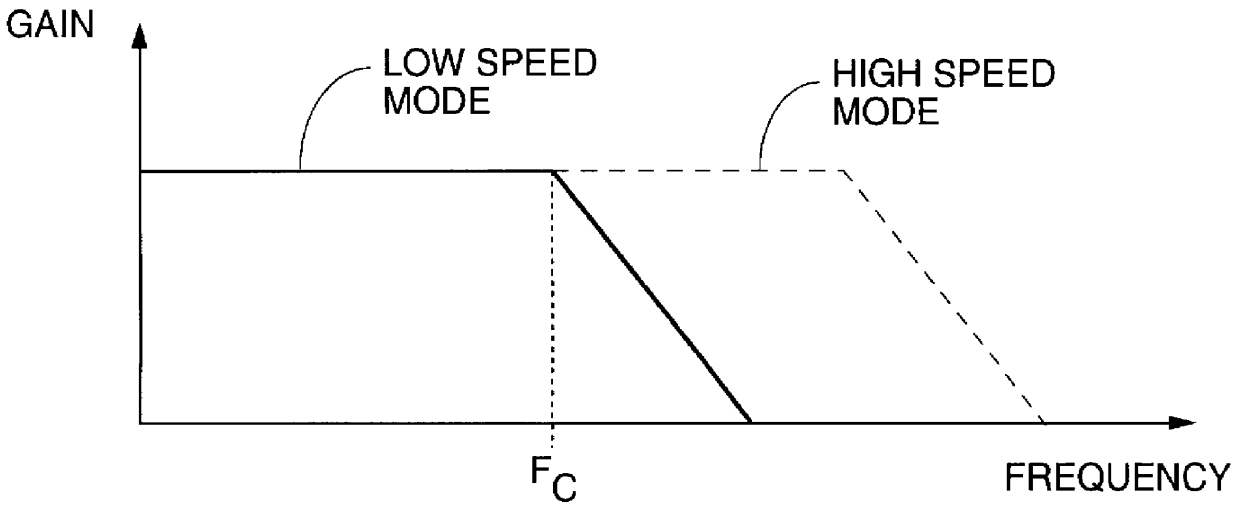
Apparatus and method for automatic mode selection in a communications receiver
InactiveUS6118829ADc level restoring means or bias distort correctionAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesInput amplifierMultiple pulse
A method and apparatus are shown for automatically adjusting a response bandwidth and input sensitivity of a communications receiver responsive to a frequency of a received data signal. The response bandwidth is adjusted by switching a low pass filter into a receive path of the receiver when the received data signal is a low speed data signal and switching the low pass filter out of the receive path when the received data signal is a high speed data signal. The input sensitivity is adjusted by either changing a detection threshold of a comparator in the receive path or varying a gain of an input amplifier in the receive path. The high speed data signal is discerned when the low pass filter limits the response bandwidth of the receiver by a mode selection circuit which examines the duration of multiple pulses in a pulse train in the received data signal.
Owner:HANGER SOLUTIONS LLC
Processes for forming layers for electronic devices using heating elements
InactiveUS20060141135A1Less time to heatLow costSolid-state devicesCoatingsMultiple pulseEngineering
A process for forming an electronic device includes placing a substrate adjacent to a heating element and a deposition source, wherein the deposition source lies between the substrate and the heating element. In one embodiment, the process also includes sending a multiple pulsed signal to the heating element such that the heating element is on and off for a plurality of times. In another embodiment, the process also includes sending a signal to the heating element and depositing a layer over the substrate. Either or both processes further includes depositing a layer over the substrate. Depositing occurs as a result of sending the multiple pulsed signal to the heating element. The layer includes a material from the deposition source.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
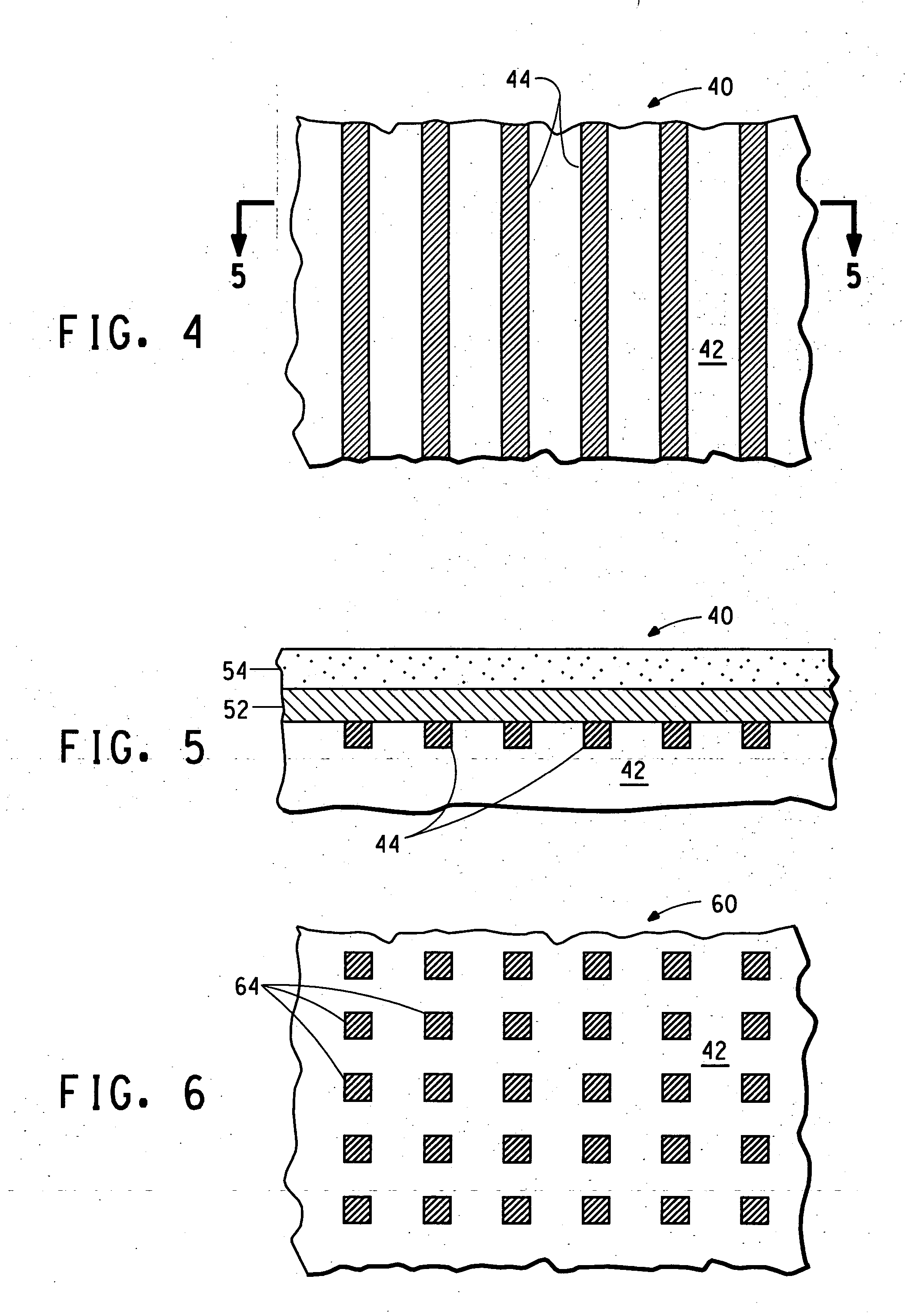
Method for cleaning and polishing steel-plantinum alloys
ActiveUS20050145508A1Enhanced chemical processingImprove radiopacityStentsElectrolysis componentsSulfurAlloy
A method of cleaning and polishing an alloy comprising at least one noble metal and at least one non-noble metal, the method including the steps of submerging said alloy in an electrolytic acidic bath comprising at least one chelating or complexing agent including sulfur, and applying a multiple pulse periodic reverse waveform, and articles cleaned and / or polished thereby.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
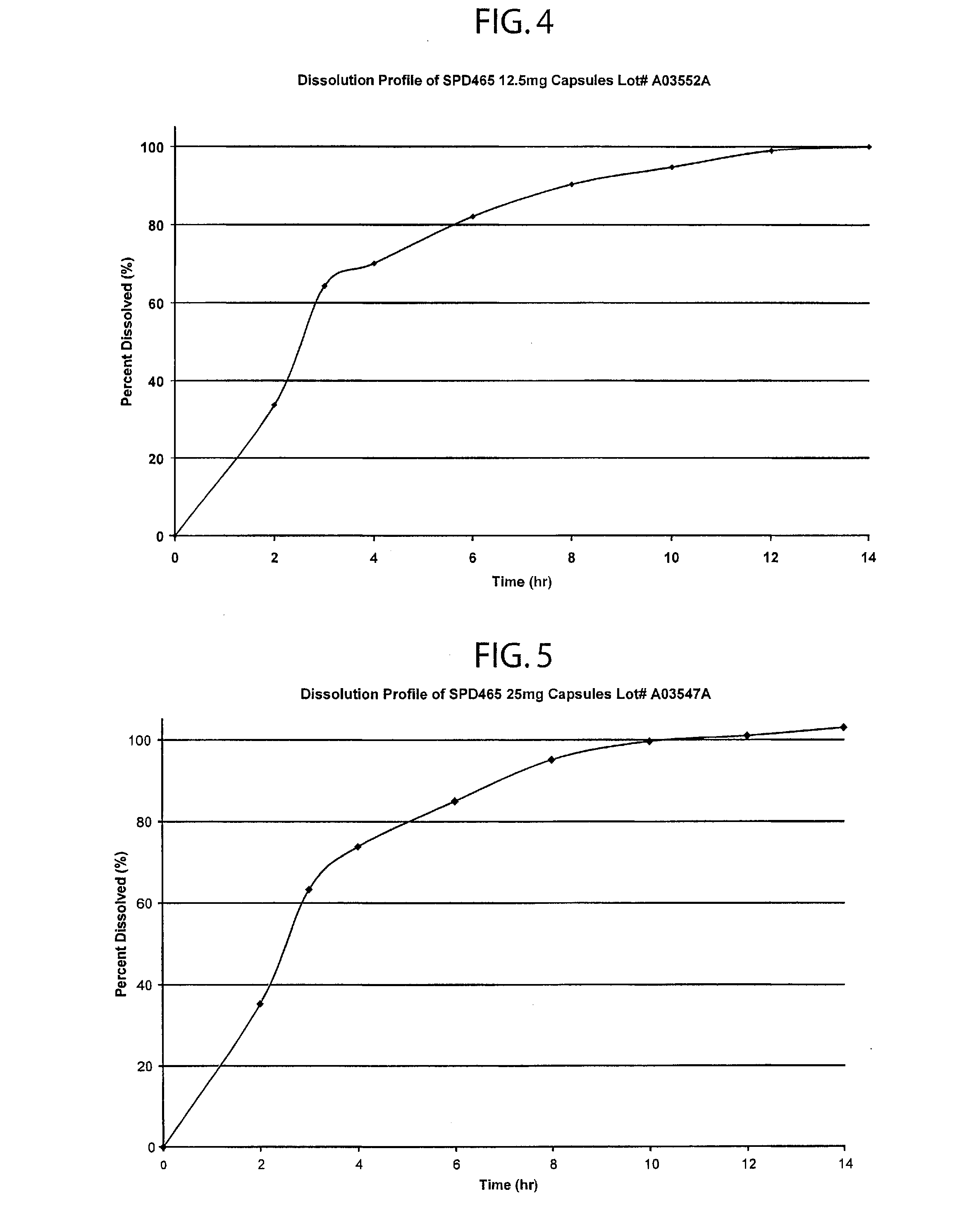
Oral pulsed dose drug delivery system
InactiveUSRE41148E1Prolonged delayed release timeDelayed release timeBiocideOrganic active ingredientsImmediate releaseDosing drugs
A multiple pulsed dose drug delivery system for pharmaceutically active amphetamine salts, comprising an immediate-release component and an enteric delayed-release component wherein (1) the enteric release coating has a defined minimum thickness and / or (2) there is a protective layer between the pharmaceutically active amphetamine salt and the enteric release coating and / or (3) there is a protective layer over the enteric release coating. The product can be composed of either one or a number of beads in a dosage form, including either capsule, tablet, or sachet method for administering the beads.
Owner:SHIRE PLC
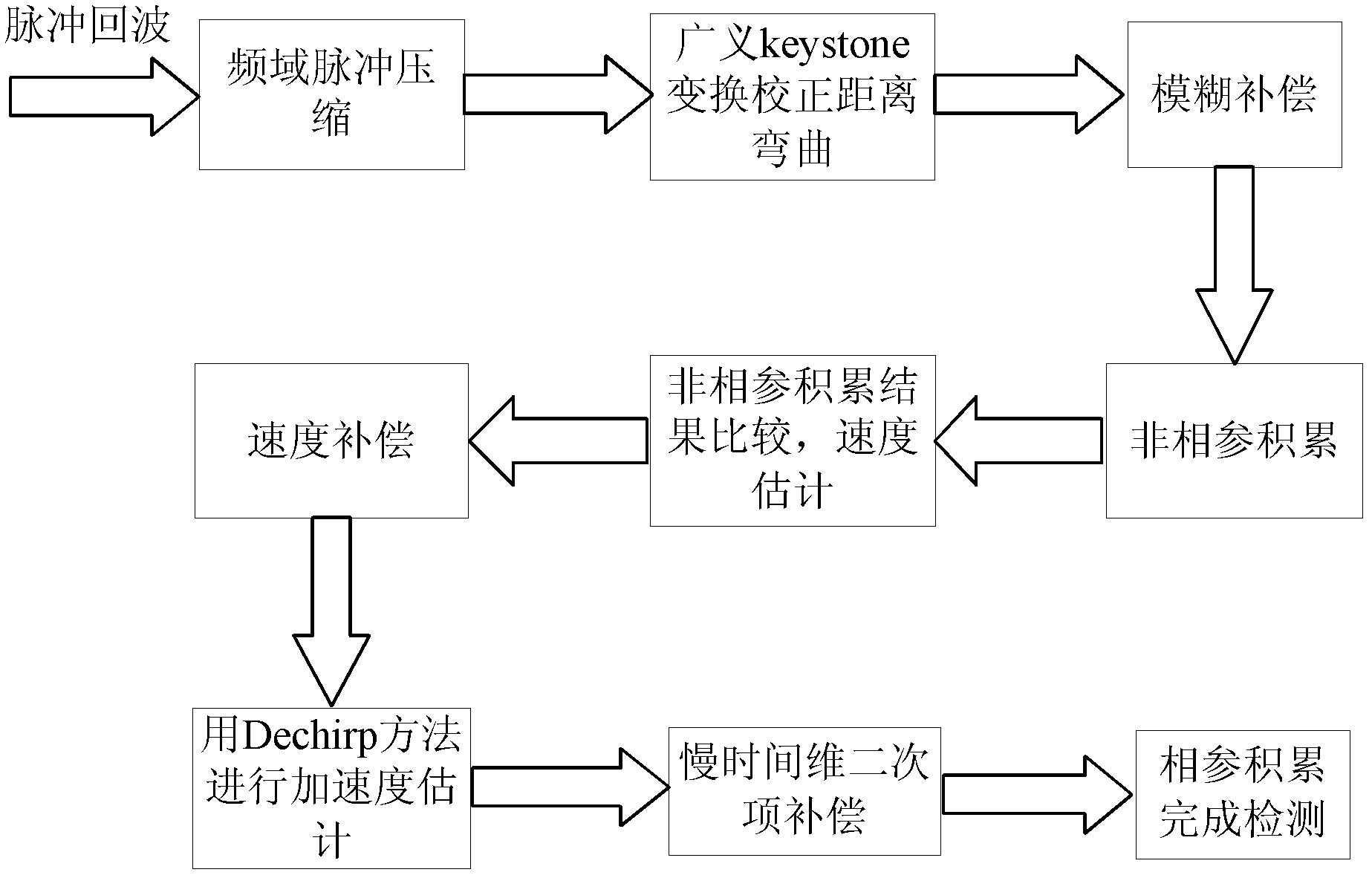
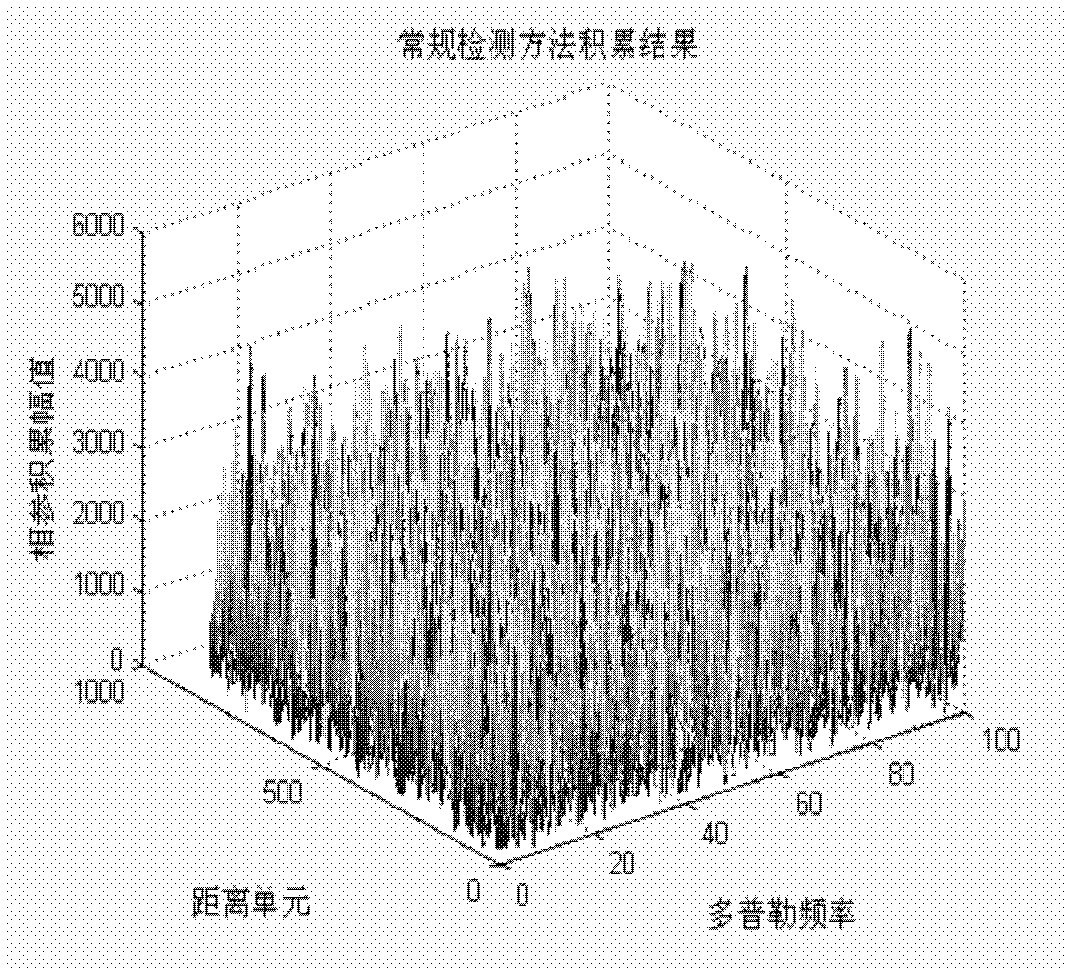
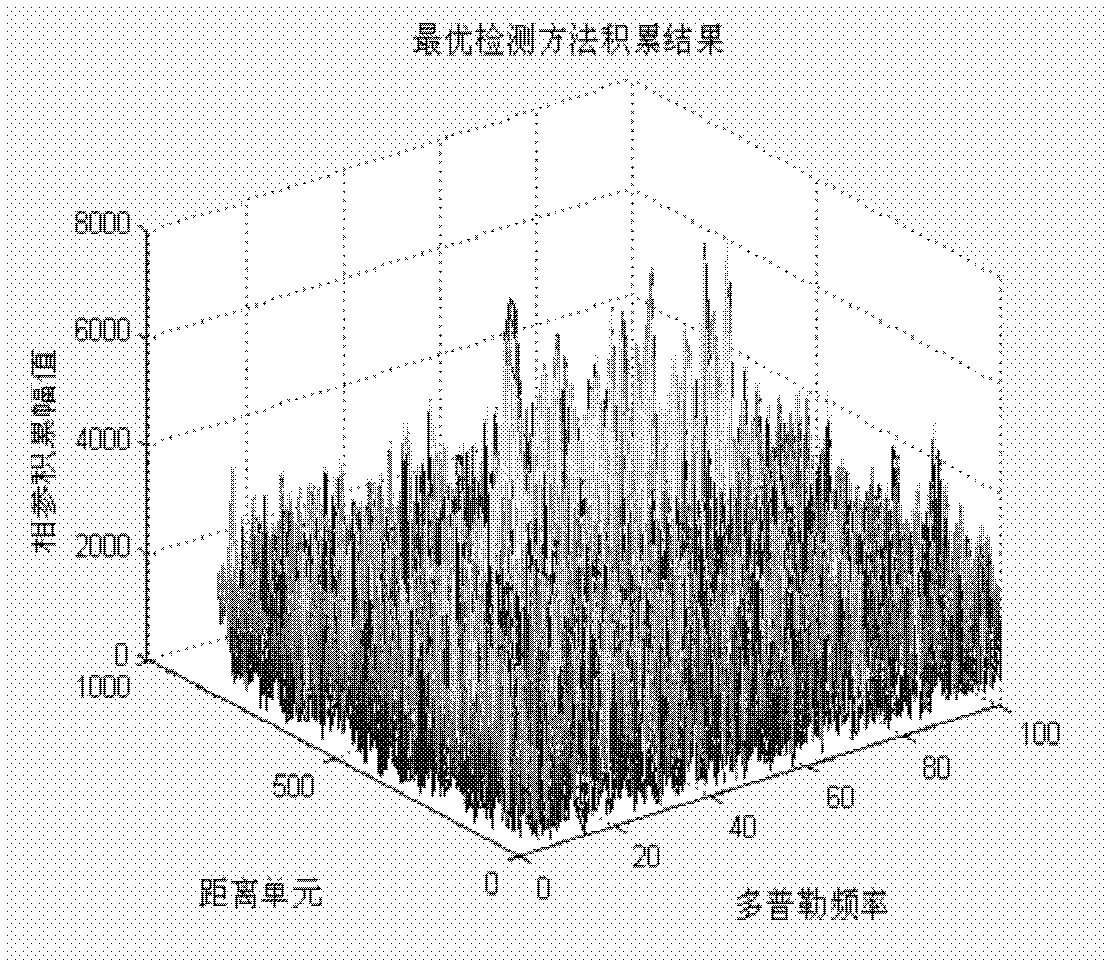
Radar detection method based on generalized keystone transformation and non-coherent accumulation
The invention discloses a radar detection method based on generalized keystone transformation and non-coherent accumulation, wherein the method mainly solves the detection problem of a high speed and highly accelerated target in a strong Gaussian white noise background. The method is implemented by the following steps: (1) generating radar target multiple-pulse echoes with Gaussian white noise added, and performing frequency domain pulse compression; (2) correcting range curvature of the pulse-compressed echoes by using the generalized keystone transformation; (3) performing fuzzy compensation on the curvature-corrected echoes by using a fuzzy factor; (4) performing non-coherent accumulation on the fuzzy-compensated echoes, and performing velocity compensation and slow time dimensional quadratic term compensation on the echoes by using a target velocity obtained in the non-coherent accumulation; (5) performing coherent accumulation on the slow time dimensional quadratic term compensated echoes to obtain the target to be detected. The method provided in the invention can eliminate effects of the range curvature and migration of the echoes on energy accumulation, can reduce computation of velocity search, and can be used in the detection of the target in the strong Gaussian white noise background.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
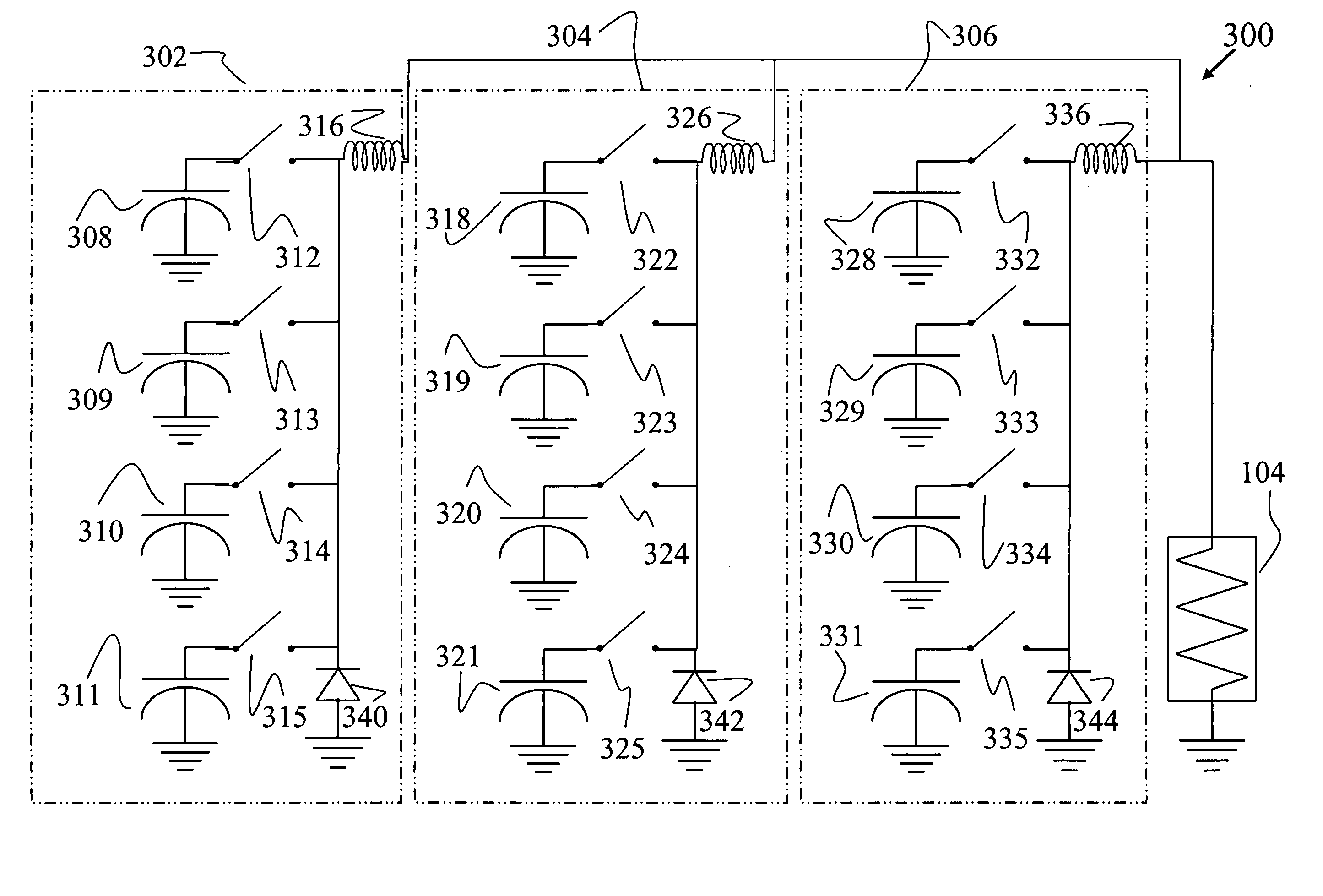
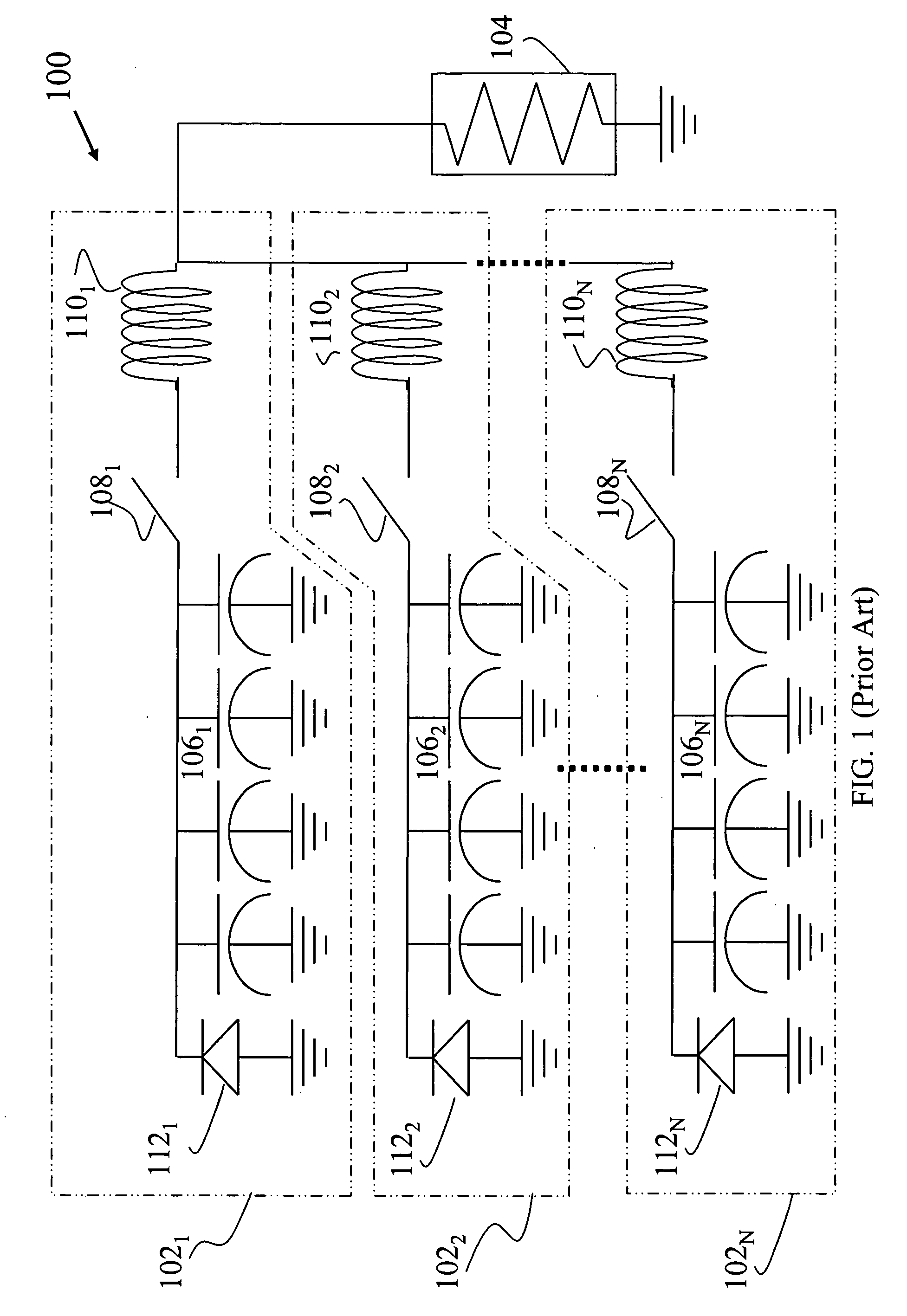
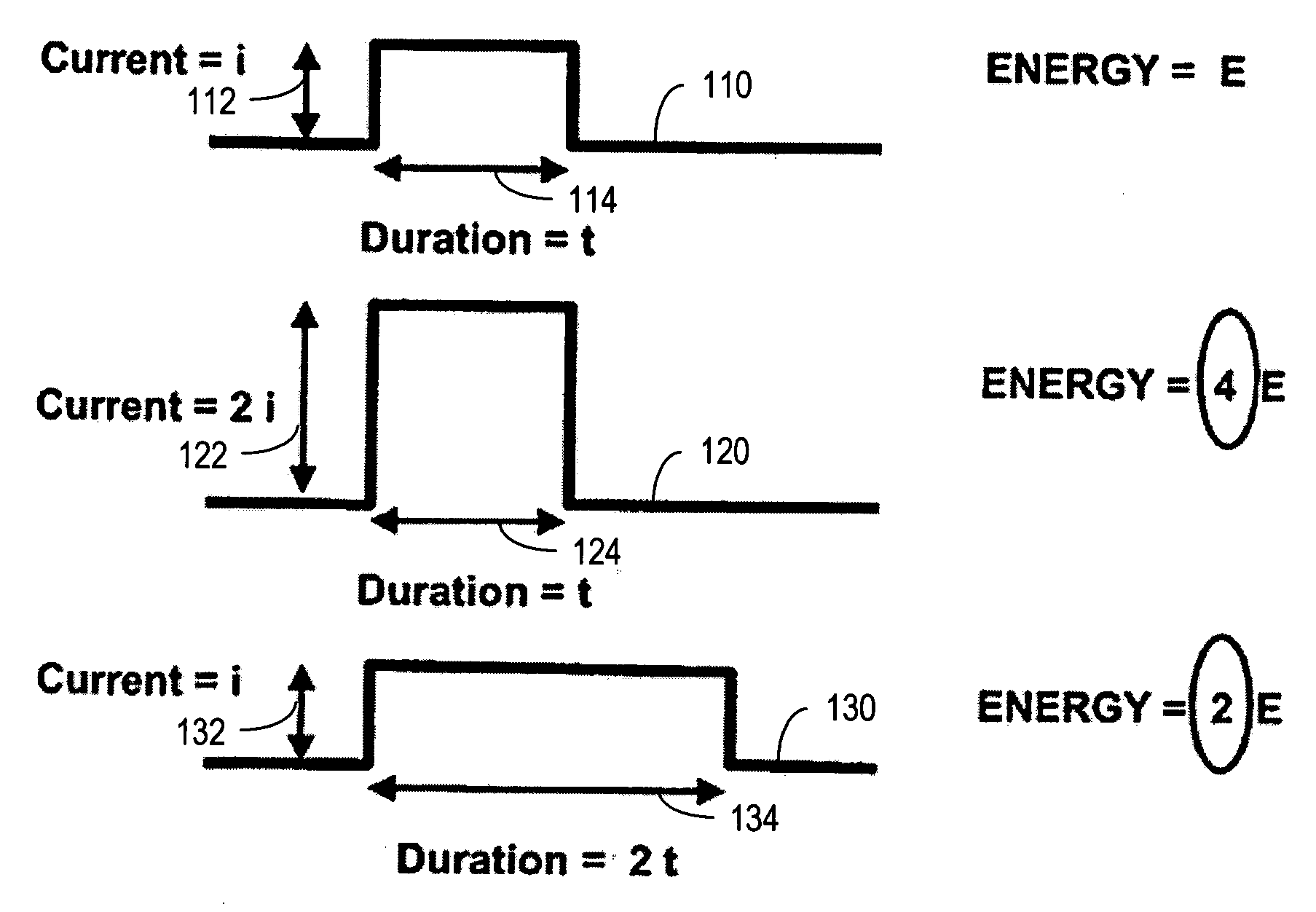
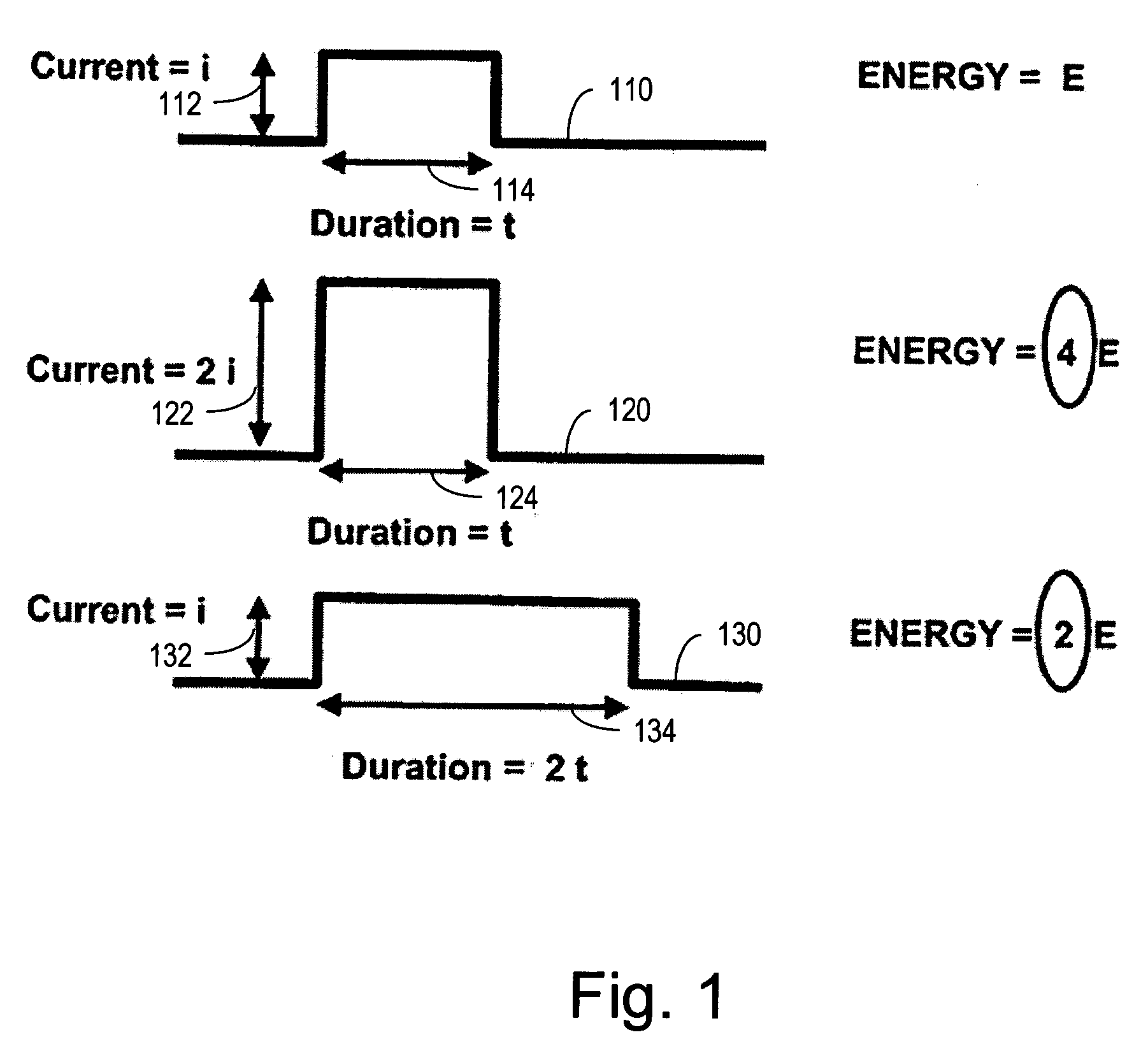
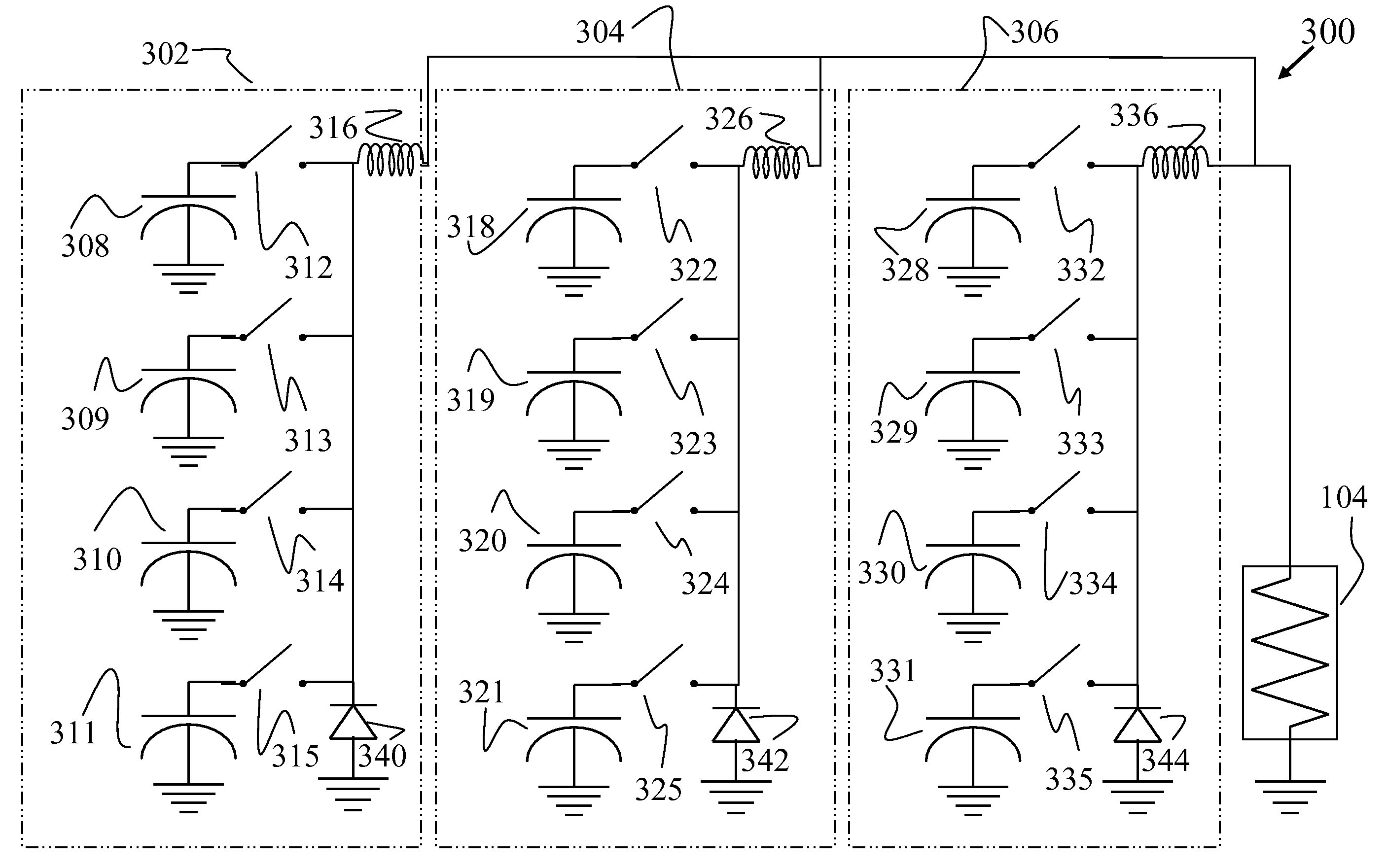
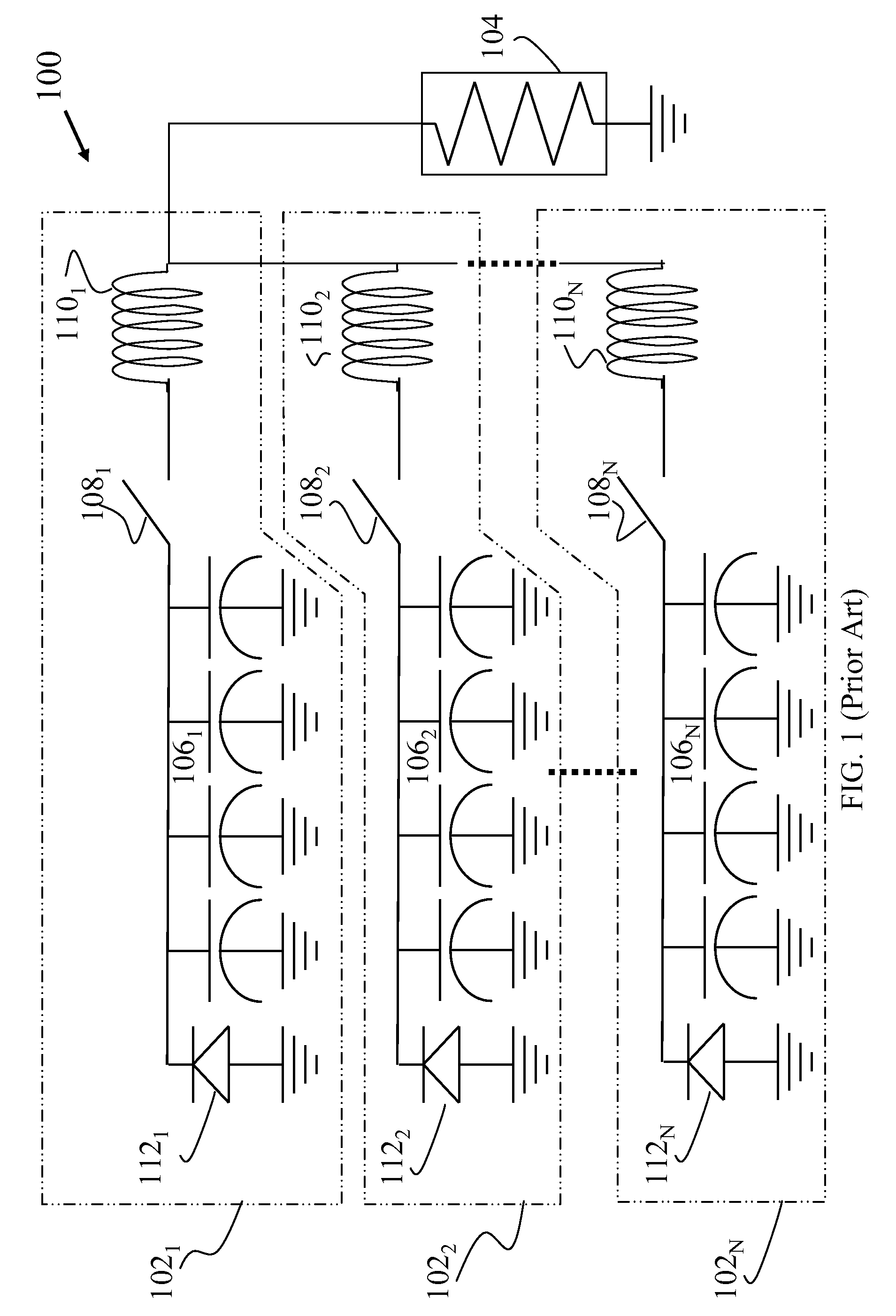
Capacitor pulse forming network with multiple pulse inductors
ActiveUS20050168195A1Shaping characteristicReduce quality problemsDc network circuit arrangementsBatteries circuit arrangementsPulse forming networkEngineering
Capacitor based pulse forming networks and related methods are provided which require fewer inductors are that pulsed more frequently to provide a smaller, lower mass, and lower inductance pulse forming network having better pulse shaping characteristics than conventional pulse forming networks. In one implementation, the invention can be characterized as a capacitor based pulse forming network comprising a plurality of inductors adapted to be coupled to a load, a plurality of capacitor units, and a plurality of switches. Each switch couples a respective capacitor unit to a respective inductor, wherein multiple capacitor units are coupled to each inductor by separate switches. The plurality of switches are adapted to non-simultaneously discharge the multiple capacitor units to provide non-simultaneous pulses through a given inductor to the load and not through other inductors. The non-simultaneous pulses form at least a portion of an output pulse waveform to the load.
Owner:GENERAL ATOMICS
Multi-fuelling an engine
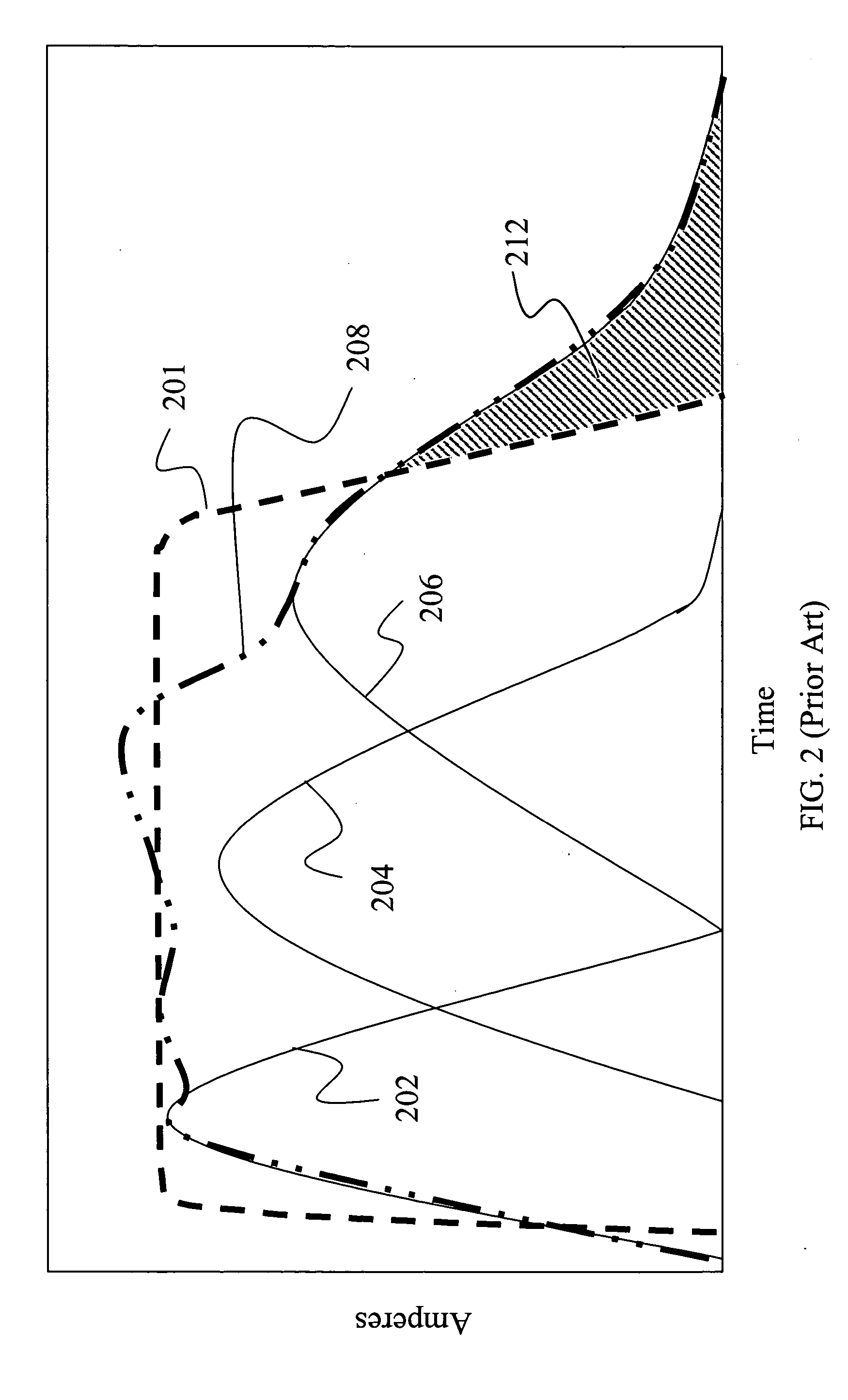
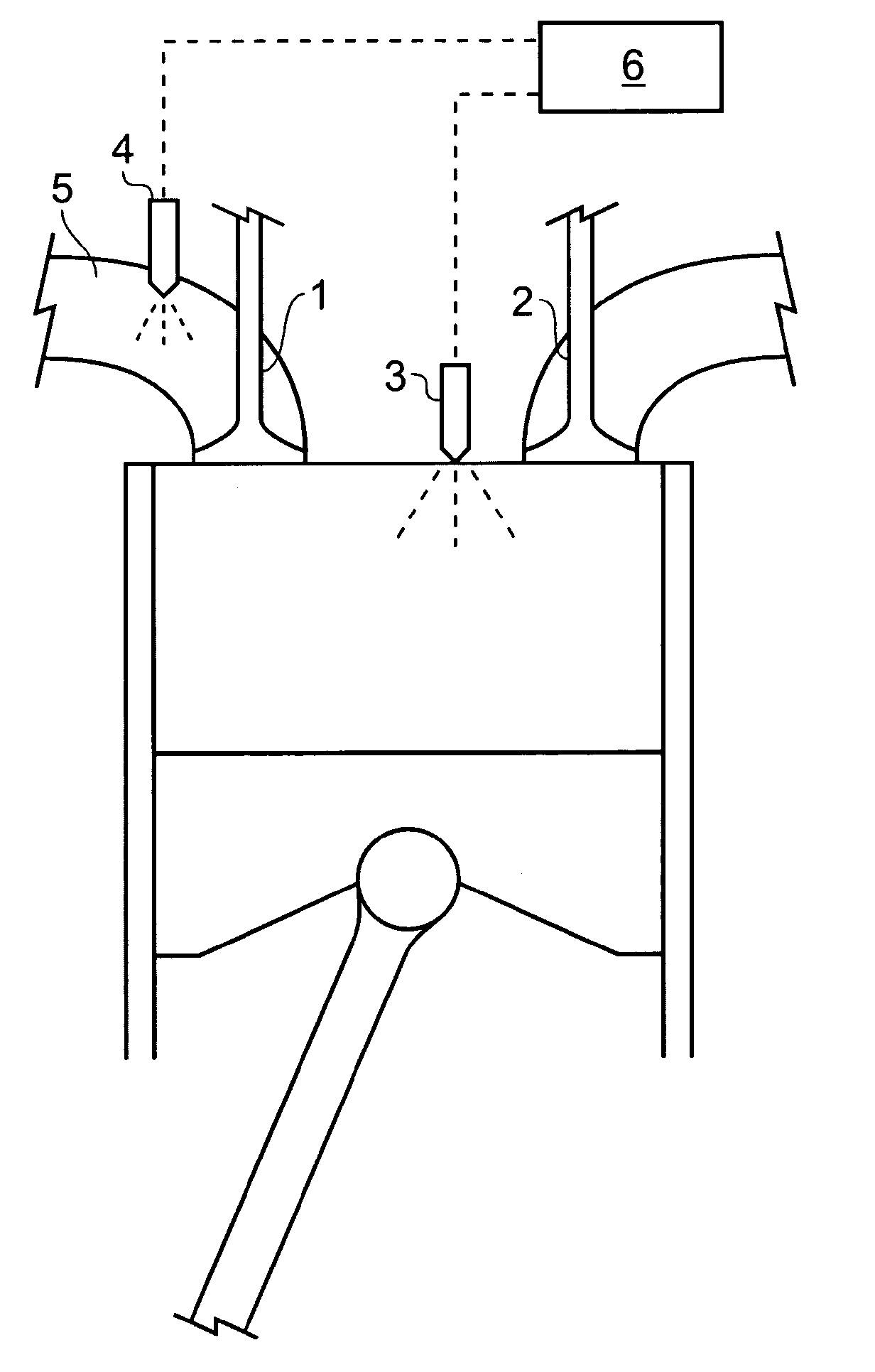
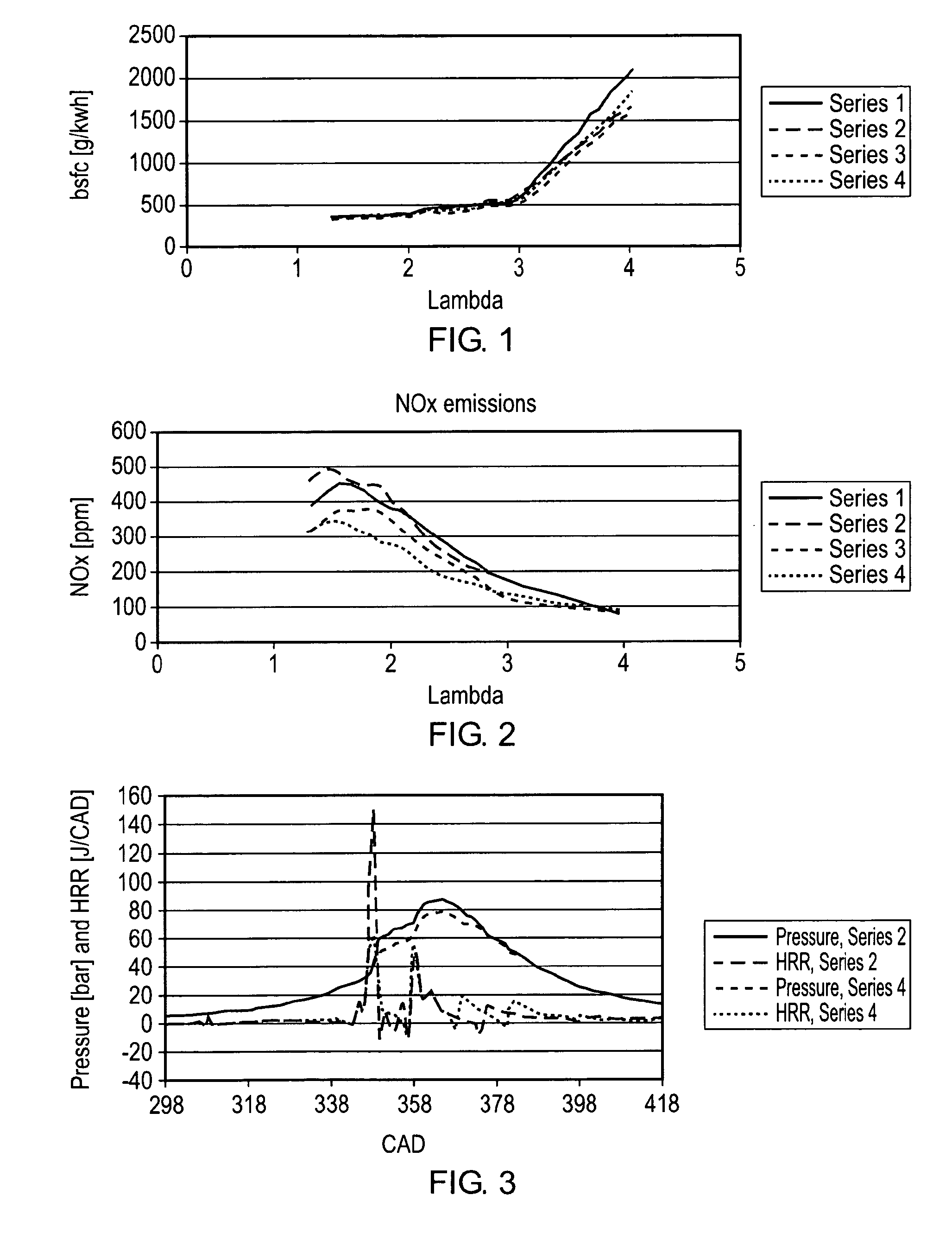
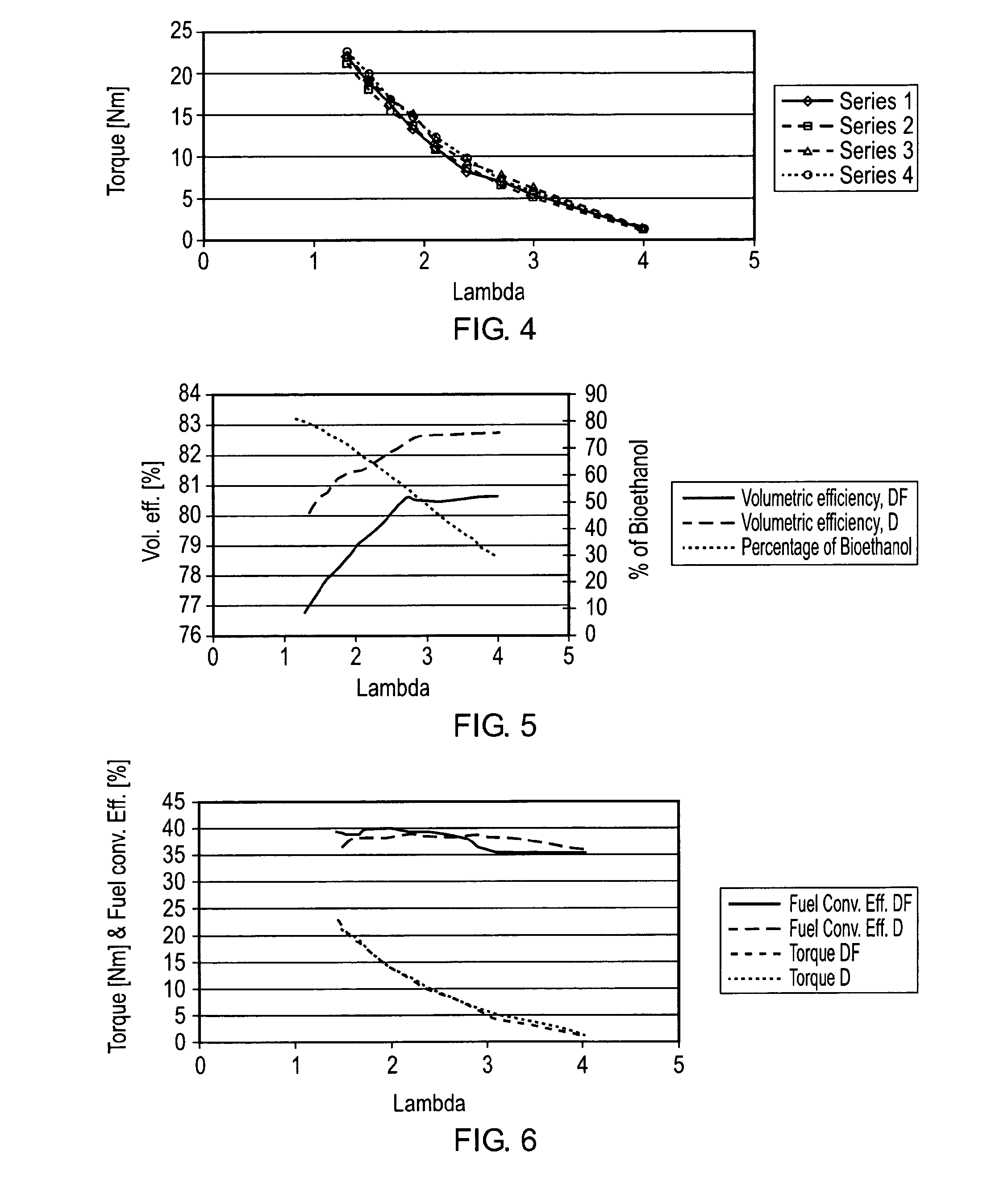
InactiveUS20110088654A1Reduce NOxReduce soot emissionsElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesBiodieselCombustion chamber
A compression ignition engine is supplied with a first fuel in a flow of air and a second fuel is injected into the combustion chamber. The first fuel comprises a more volatile fuel than diesel such as ethanol, LPG or other combustible gas; the second fuel comprises diesel or biodiesel; and the second fuel is injected in multiple pulses in each ignition cycle with the first pulse acting as a pilot pulse to trigger ignition, and the timing of the second pulse being such as to modify the temperature through evaporation of the second fuel and thereby reduce the combustion temperature and mitigate knock susceptibility. Preferably the pilot pulse is followed by a single further pulse of the second fuel in the ignition cycle. The engine may be controlled to operate in two different modes, one mode for light and medium load conditions when there is only a pilot pulse injection of the second fuel which reduces NOx and soot emissions, and the other mode for higher load conditions when there is a pilot pulse injection followed by a main pulse injection of the second fuel. The first fuel may comprise bioethanol and or one or more of the following: ethanol, butanol, propanol, lpg, natural gas, hydrogen.
Owner:G VOLUTION
Broadband radar detection method based on weighted sequence statistics and multiple-pulse coherence accumulation
InactiveCN102426354ARealize detectionSuppress clutterWave based measurement systemsRadar detectionMatched filter
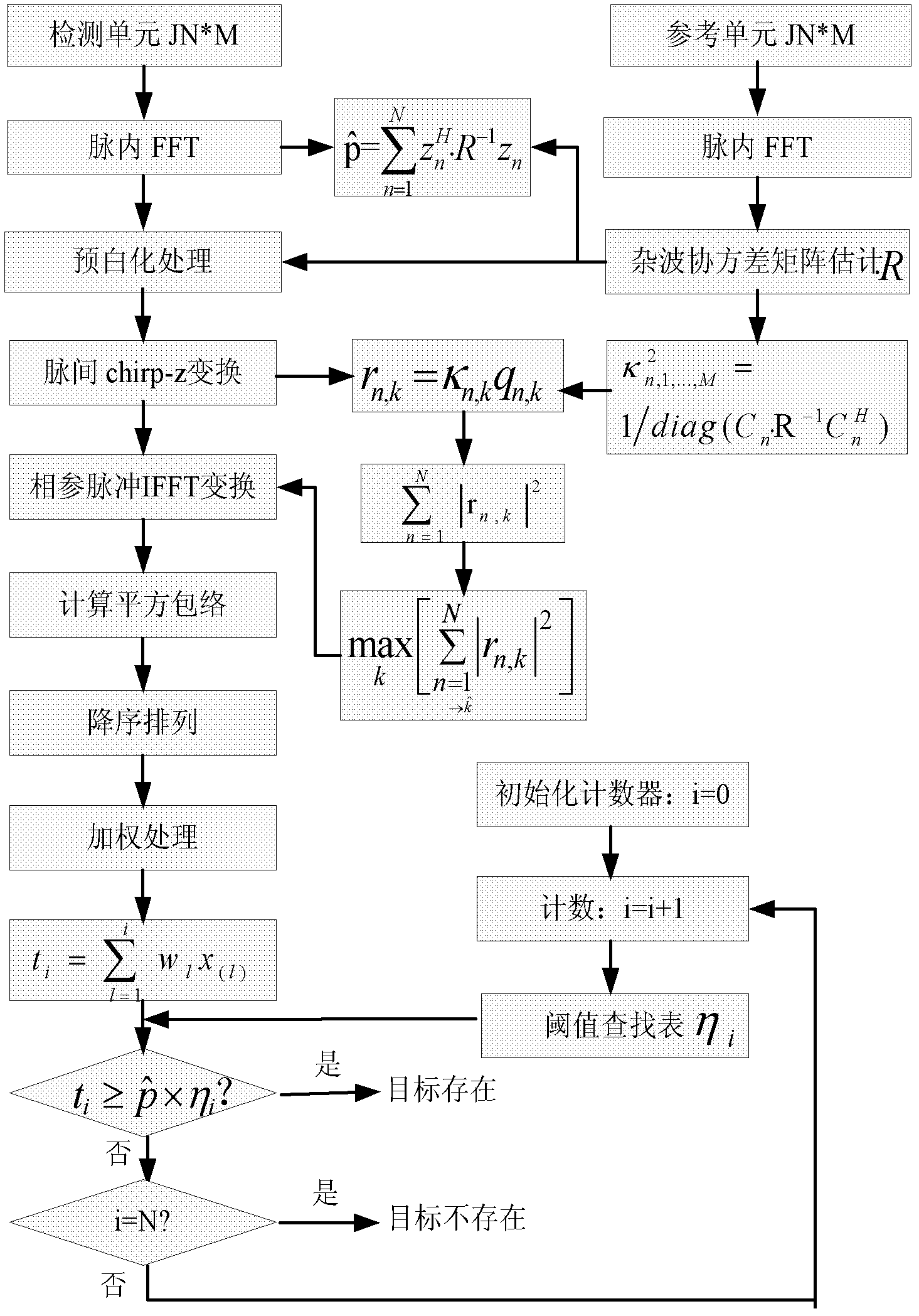
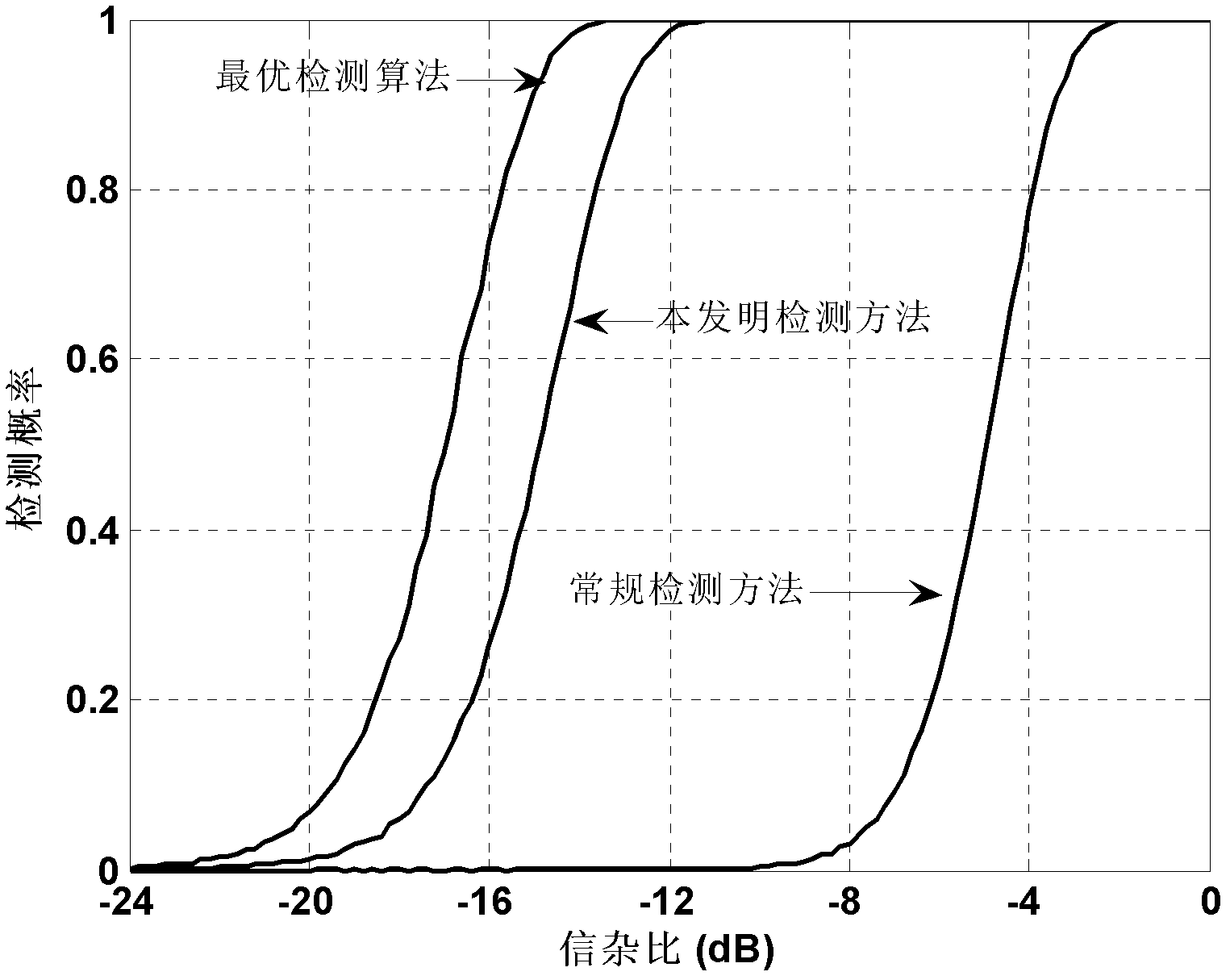
The invention discloses a broadband radar detection method based on weighted sequence statistics and multiple-pulse coherence accumulation. The method can be used to mainly solve a detection problem under an unknown scene of a high-speed moving target space distribution state. The method is characterize by: generating broadband radar target multipulse echo with clutter and performing FFT to the echo along a distance domain; calculating a clutter normalization covariance matrix; performing prewhitening processing and chirp-z transformation to distance frequency domain data; estimating a target speed and performing phase-coherent accumulation; performing IFFT to the pulse which is performed with the phase-coherent accumulation; calculating each distance unit square envelope of the pulse and performing descending order; carrying out weighted processing to the data after being performed with the descending order; initializing a counter; calculating the adaptive matched filter energy accumulation of a counting distance unit; detecting whether the target exists according to a threshold. By using the method of the invention, the clutter can be effectively inhibited. Migration through resolution cell of the echo can be corrected. Through descending-order weighted processing, the radar can rapidly detect the target under the unknown target space distribution state.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Ion trap mass spectrometer
ActiveCN102884608AImprove acquisitionPerfectly compatibleStability-of-path spectrometersTime-of-flight spectrometersTime–frequency analysisMass analyzer
The application relates to an ion trap mass spectrometer. An apparatus 41 and operation method are provided for an electrostatic trap mass spectrometer with measuring frequency of multiple isochronous ionic oscillations. For improving throughput and space charge capacity, the trap is substantially extended in one Z-direction forming a reproduced two-dimensional field. Multiple geometries are provided for trap Z-extension. The throughput of the analysis is improved by multiplexing electrostatic traps. The frequency analysis is accelerated by the shortening of ion packets and either by Wavelet-fit analysis of the image current signal or by using a time- of-flight detector for sampling a small portion of ions per oscillation. Multiple pulsed converters are suggested for optimal ion injection into electrostatic traps.
Owner:LECO CORPORATION
Rotating Machinery Condition Monitoring Using Position Sensor
ActiveUS20120126738A1Motor/generator/converter stoppersDC motor speed/torque controlWave shapePosition domain
Continuous monitoring and fault diagnosis of rotating machinery during variable speed operation is performed using only a position feedback signal. The position sensor generates a periodic waveform having multiple pulses per revolution of the machine. A circuit is included to detect, for example, a zero crossing or edge of the periodic waveform. At each detected zero crossing or edge, the time and position of the event is stored in memory. Other data, such as the current in the motor, may also be sampled and stored in memory. Because the sampled data is triggered by repeated feature of the position feedback signal, the sampled data is in a stationary reference frame in the position domain. Frequency analysis is performed on the sampled data, and the frequency components present in either the sampled signal are analyzed to identify the presence of a fault in the rotating machinery.
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
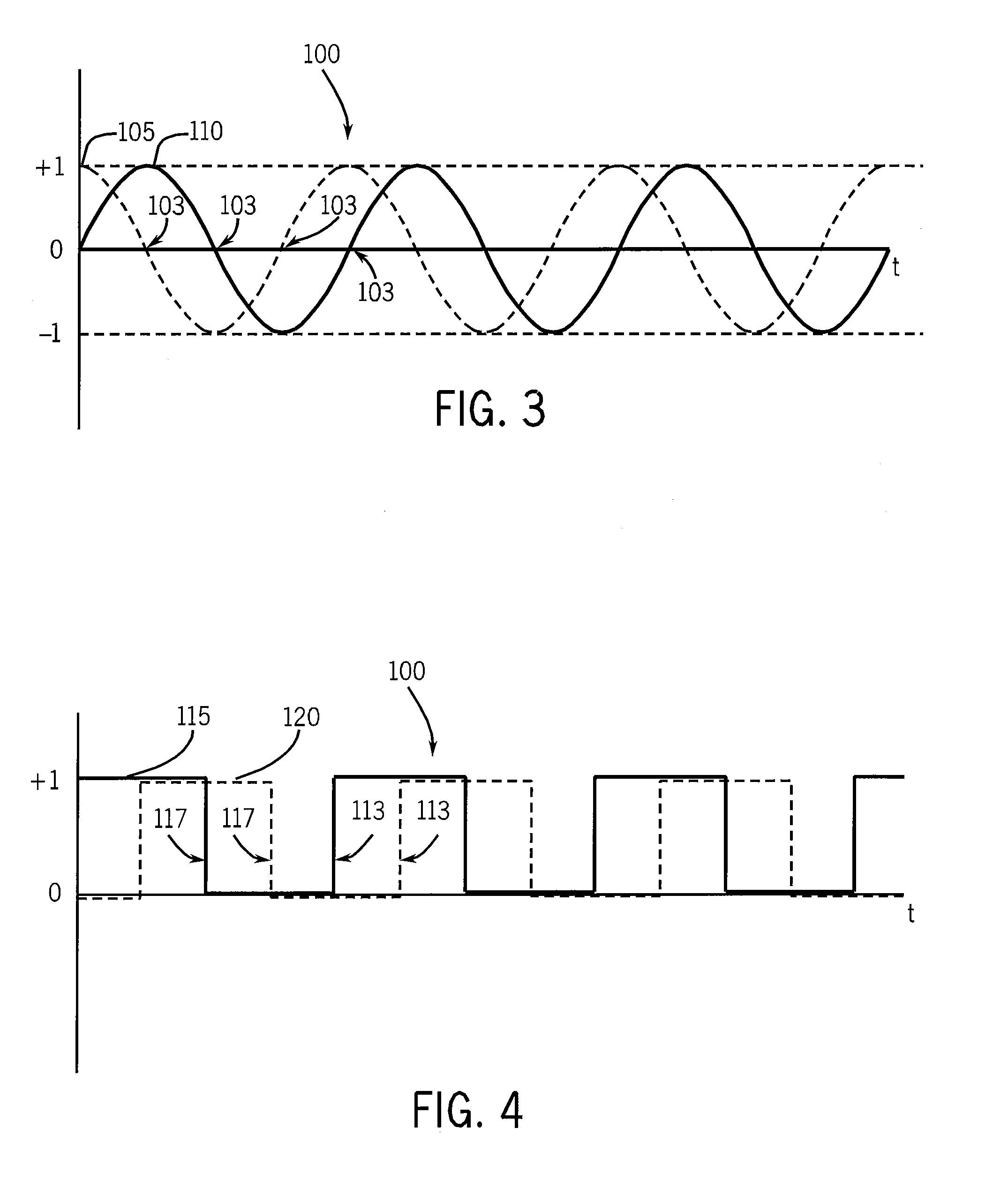
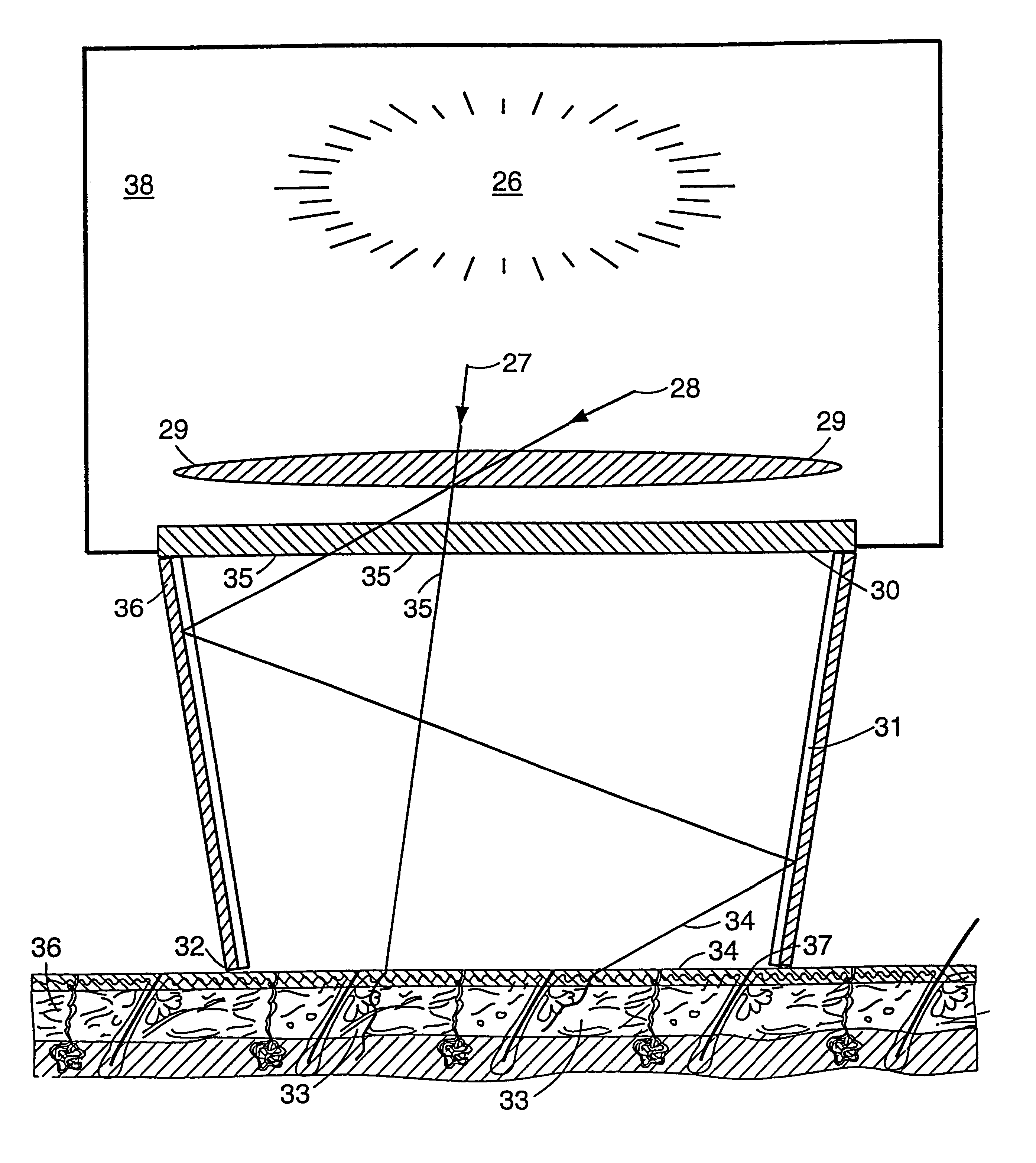
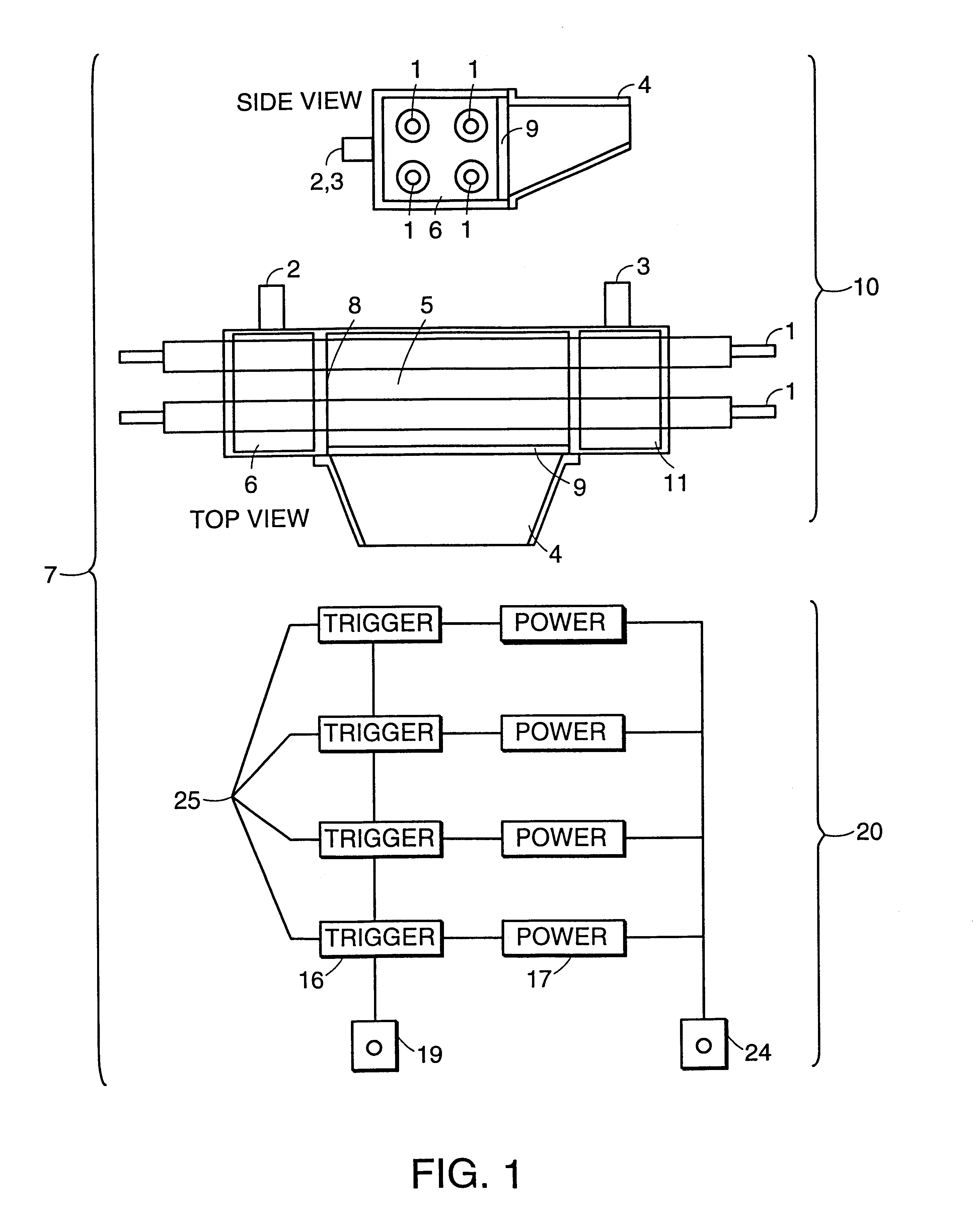
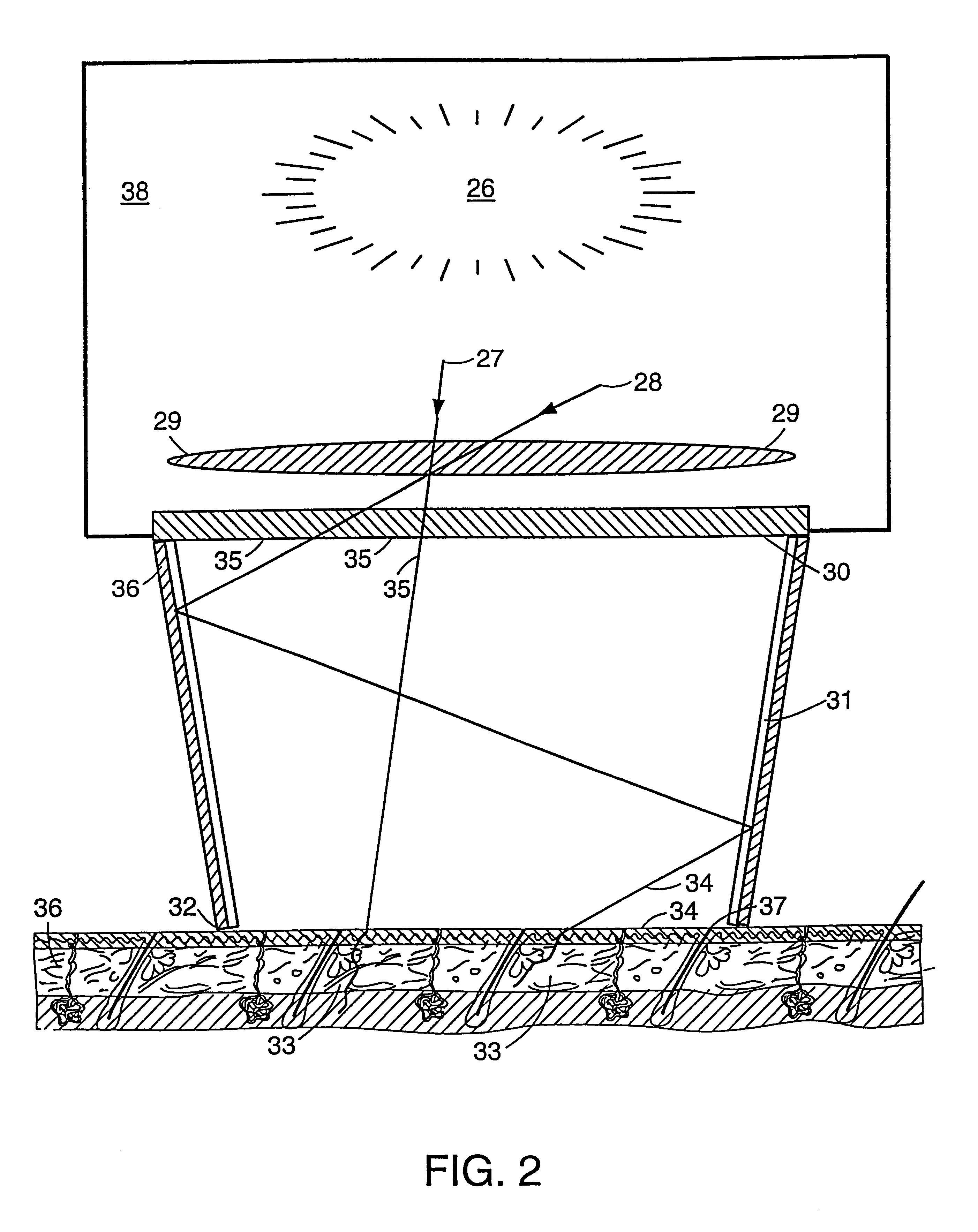
Multiple pulse photo-dermatological device
InactiveUS6595986B2Lesions be quite smallIncrease collagenDiagnosticsSurgical instrument detailsHair growthLength wave
Method and apparatus to cause the cessation of hair growth on a specific area of the body and for the treatment of unwanted dermatological conditions. The area of treatment is exposed to a particular pattern and wavelength of light generated by multiple flashlamps, which allow simultaneous, overlap, or consecutive firing. Controlling the intensity of light, the output wavelength and the delay between pulses allow treatment to be adjusted to different skin conditions and hair types. Skin damage is virtually eliminated by the length and characteristic shape of the individual pulse of light.
Owner:ZIAN MEDICAL
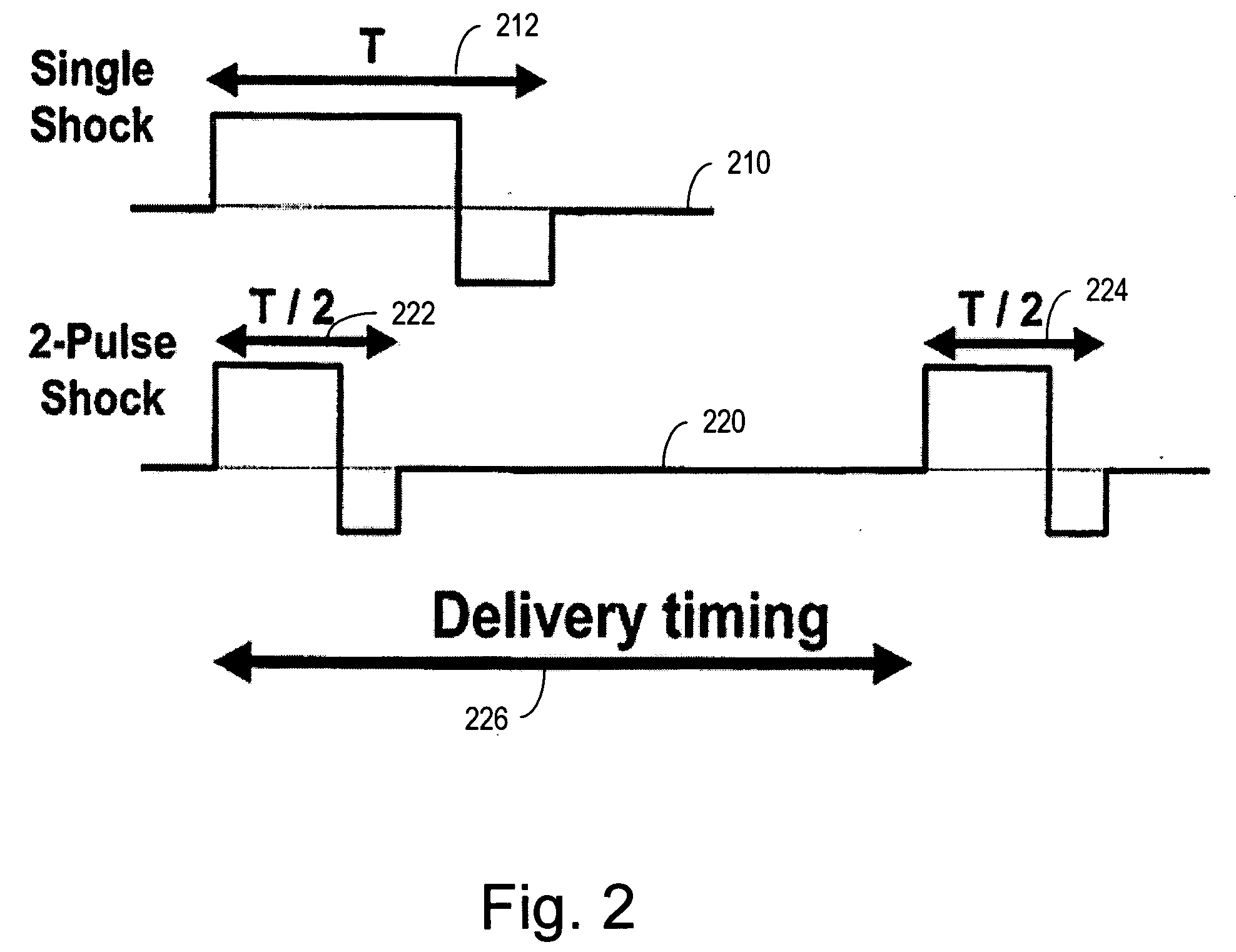
Multiple pulse defibrillation for subcutaneous implantable cardiac devices
Cardiac stimulation methods and systems provide for multiple pulse defibrillation, and involve sensing a fibrillation event, determining a fibrillation cycle length associated with the fibrillation event, and delivering a plurality of defibrillation pulses to treat the fibrillation event. Defibrillation pulses are delivered using a combination of subcutaneous non-intrathoracic electrodes. Delivery of each defibrillation waveform subsequent to a first defibrillation waveform is separated in time by a delay associated with the fibrillation cycle length. Delays between defibrillation waveform delivery may be associated with a percentage of the fibrillation cycle length.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Capacitor Pulse Forming Network with Multiple Pulse Inductors
InactiveUS20060290399A1Shaping characteristicReduce quality problemsDc network circuit arrangementsSecondary cells charging/dischargingCapacitancePulse forming network
Capacitor based pulse forming networks and methods are provided which require fewer inductors are that pulsed more frequently to provide a smaller, lower mass, and lower inductance pulse forming network having better pulse shaping characteristics than conventional pulse forming networks. In one implementation, the invention can be characterized as a capacitor based pulse forming network comprising a plurality of inductors adapted to be coupled to a load, a plurality of capacitor units, and a plurality of switches. Each switch couples a respective capacitor unit to a respective inductor, wherein multiple capacitor units are coupled to each inductor by separate switches. The plurality of switches are adapted to non-simultaneously discharge at least some of the multiple capacitor units to provide non-simultaneous pulses through a given inductor to the load and not through other inductors. The non-simultaneous pulses form at least a portion of an output pulse waveform to the load.
Owner:GENERAL ATOMICS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com