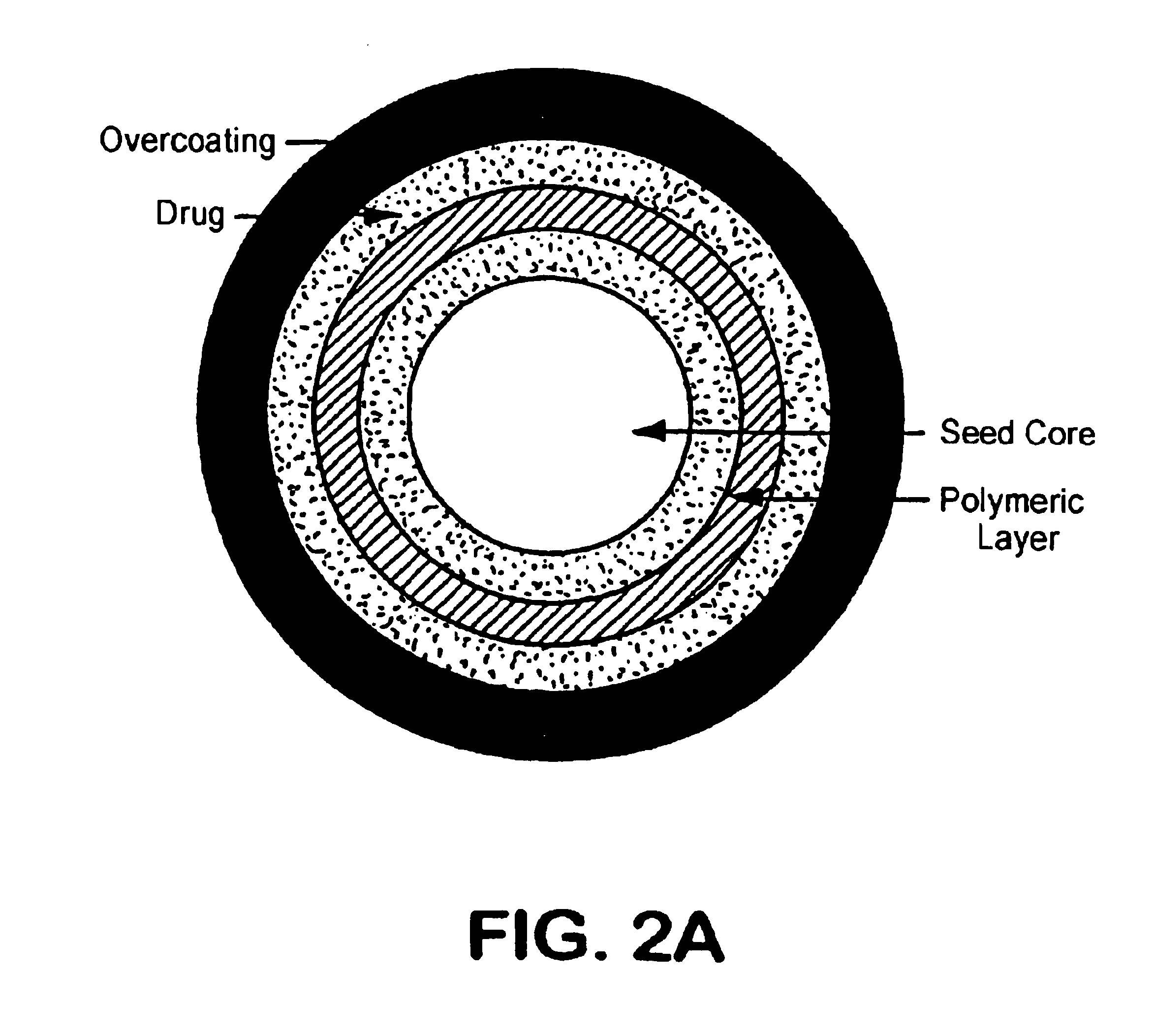
Oral pulsed dose drug delivery system
a drug delivery and pulsed dose technology, applied in the direction of biocide, microcapsules, drug compositions, etc., can solve the problems of time-consuming and difficult to optimize drug layering or core making for multiple unit systems, and the timing of sustained release delivery is not suitable, so as to reduce the ph value of the environment, prolong the delay the effect of release time and delay the release tim
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Immediate Release Formulation
[0092]The following formulation was used to layer the drug onto sugar spheres. Nonpareil seeds (30 / 35 mesh, Paulaur Corp., NJ), 6.8 kg were put into a FLM-15 fluid bed processor with a 9″ Wurster column and fluidized at 60° C. The suspension of mixed amphetamine salts (MAS) with 1% HPMC E5 Premium (Dow Chemical) as a binder was sprayed onto the seed under suitable conditions. Almost no agglomeration and no fines were observed with a yield of at least 98%. The drug-loaded cores were used to test enteric coatings and sustained release coatings.
[0093]
TABLE 1IngredientsAmount (%)Nonpareil seed88.00mixed amphetamine salts11.40METHOCEL ® E5 Premium0.60Water**removed during processing
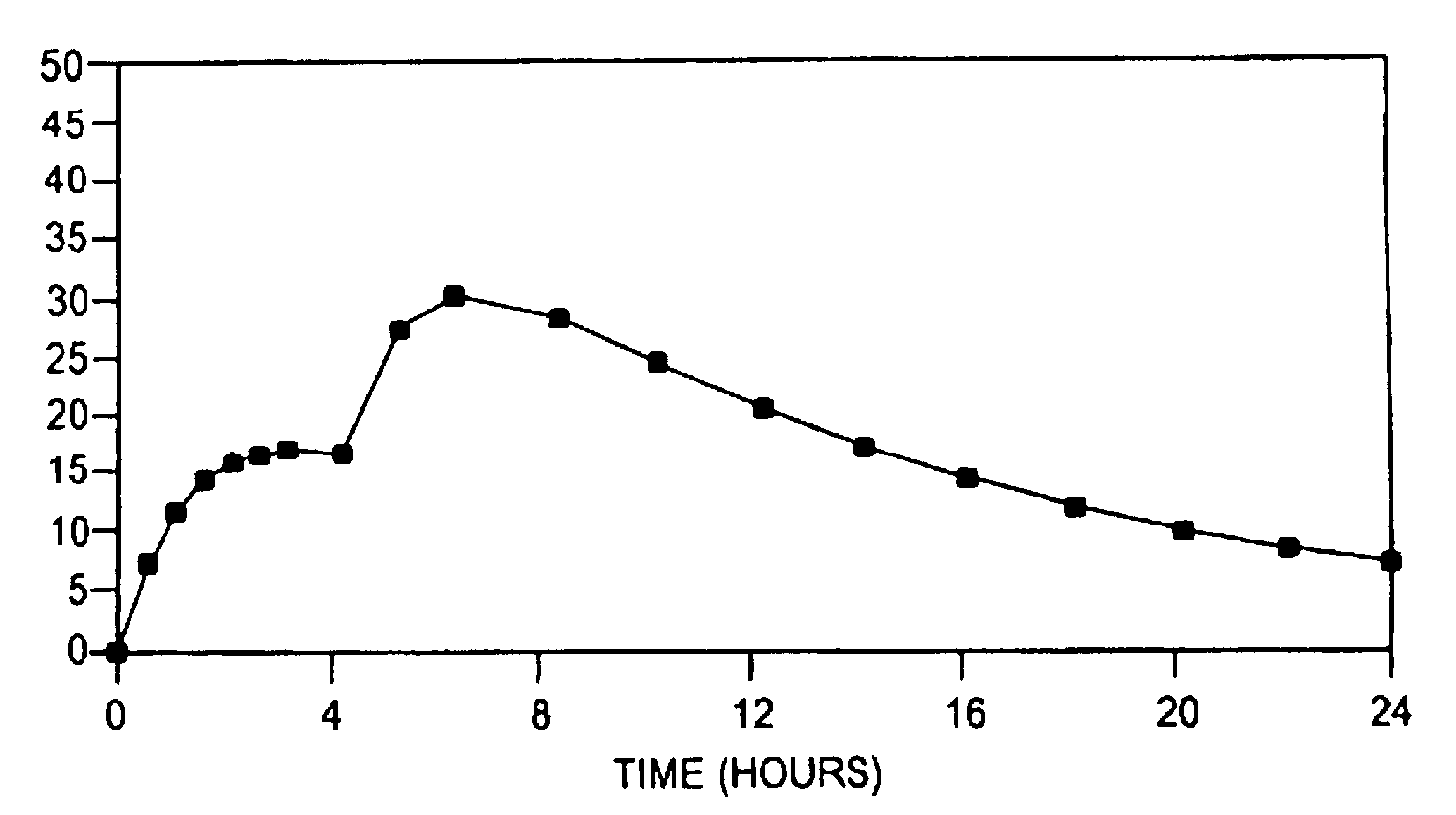
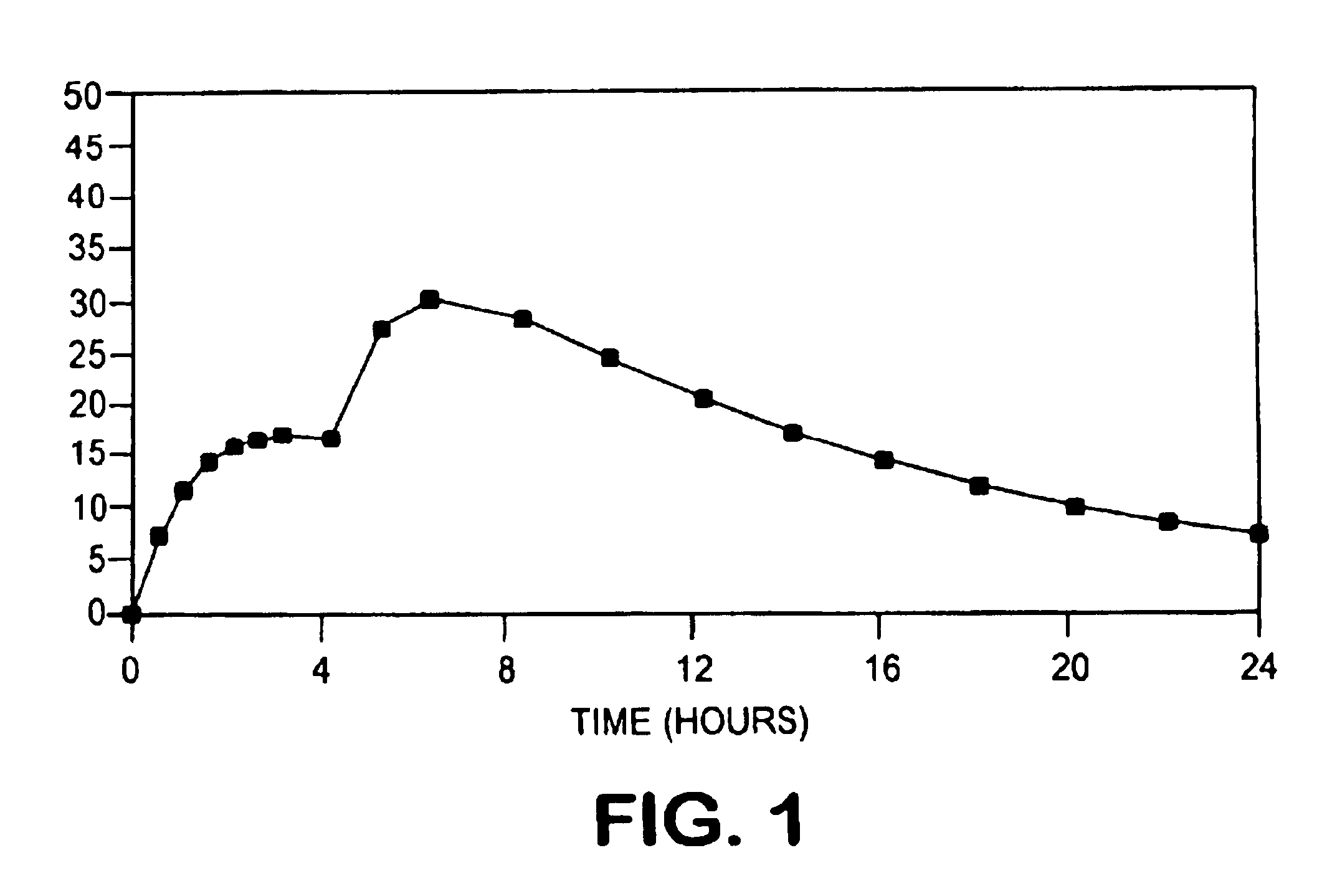
[0094]The drug release profile of the drug-loaded pellets of this example is shown in FIG. 3.
example 2
[0095]The following formulation was used to coat the mixed amphetamine salts loaded (MASL) pellets from Example 1 with the EUDRAGIT® L 30D-55 (Rohm Pharma, Germany) coating dispersion. 2 kg of MASL pellets were loaded into a fluid bed processor with a reduced Wurster column equipped with a precision coater (MP 2 / 3, Niro Inc) (see Examples 3 and 4). The coating dispersion was prepared by dispersing Triethyl citrate, Talc and EUDRAGIT® L 30D-55 into water and mixing for at least 30 minutes. Under suitable fluidization conditions, the coating dispersion was sprayed onto the fluidized MASL pellets. The spraying was continued until the targeted coating level was achieved (20 μ) . The coated pellets were dried at 30-35° C. for 5 minutes before stopping the process. The enteric coated PPAMASL pellets were tested at different pH buffers by a USP paddle method. The drug content was analyzed using HPLC. The results showed that the enteric coating delayed the drug release from the coated pell...
example 3
[0098]The following formulation was used to coat the MASL pellets from Example 1 with the EUDRAGIT® 4110D (Rohm Pharma, Germany) coating dispersion. MASL pellets (2 kg) were loaded in a fluid bed processor with a reduced Wurster column (GPGC-15, Glatt). The coating dispersion was prepared by dispersing Triethyl citrate, Talc and EUDRAGIT® 4110D into water and mixing for at least 30 minutes. Under suitable fluidization conditions, the coating dispersion was sprayed onto the fluidized MASL pellets. The spraying was continued until the targeted coating level was achieved. The coated pellets were dried at 30-35° C. for 5 minutes before stopping the process. The enteric coated MASL pellets were tested using a USP paddle method at different pH buffers. The drug content was analyzed using HPLC. The enteric coating delayed the drug release for several hours from the coated pellets until the pH value reached 6.8 or higher, as shown below in Table 3. (Reference #AR98125-3)
[0099]
...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com