Patents
Literature
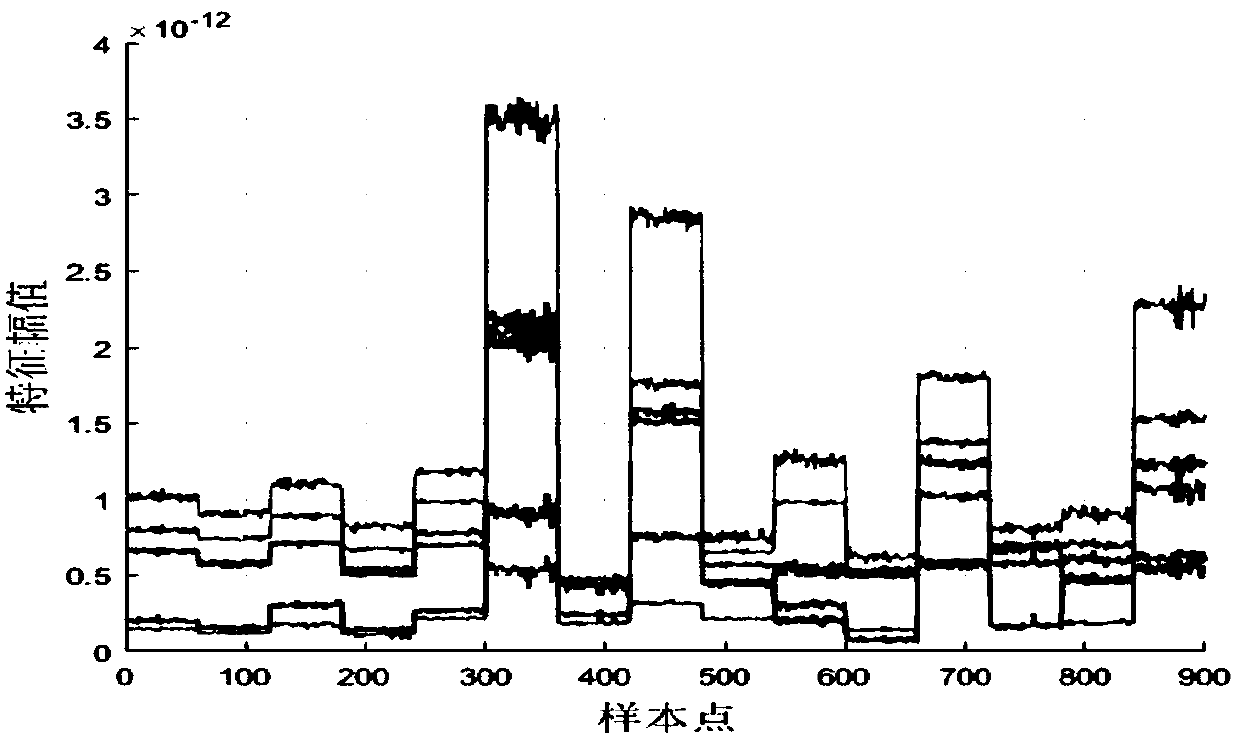
234 results about "Time domain response" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Time-Domain Response Analysis. The time-domain approach is a unified method for analyzing and designing systems modeled by either modern or classical approach.
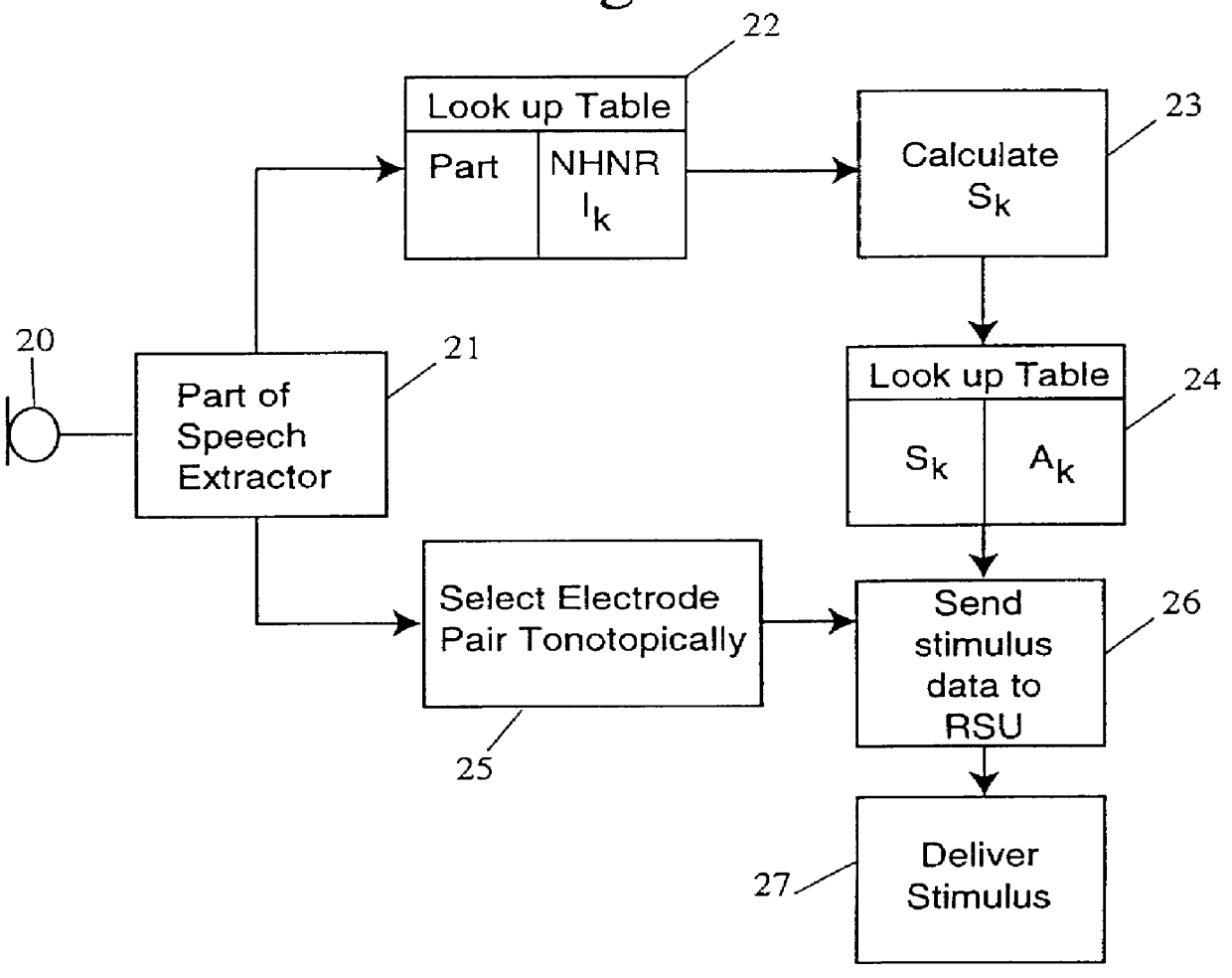
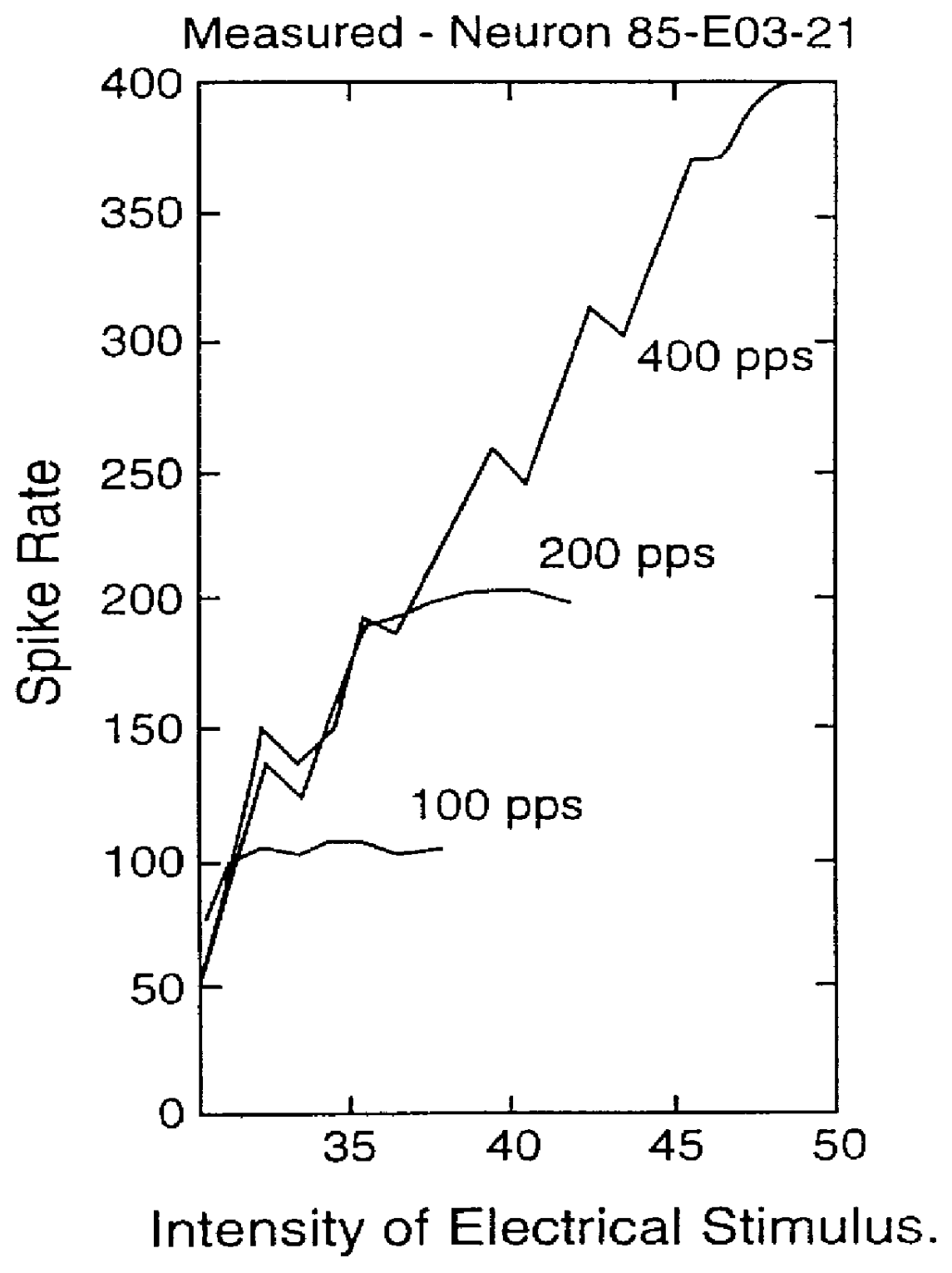
Multiple pulse stimulation
InactiveUS6064913AEasy to produceElectrotherapyArtificial respirationCochlear implantationTime domain response
A stimulation strategy for cochlear implants seeks to approximate the time domain response of a patient's neural system to electrical stimuli, to the time domain response of a normal hearing person to a corresponding acoustic stimulus. The strategy is designed to induce in the neurons of a patient a time domain response to an acoustic signal which is similar to, or approximates the time domain response induced by the normal processes in a healthy person. Various implementations are disclosed.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MELBOURNE
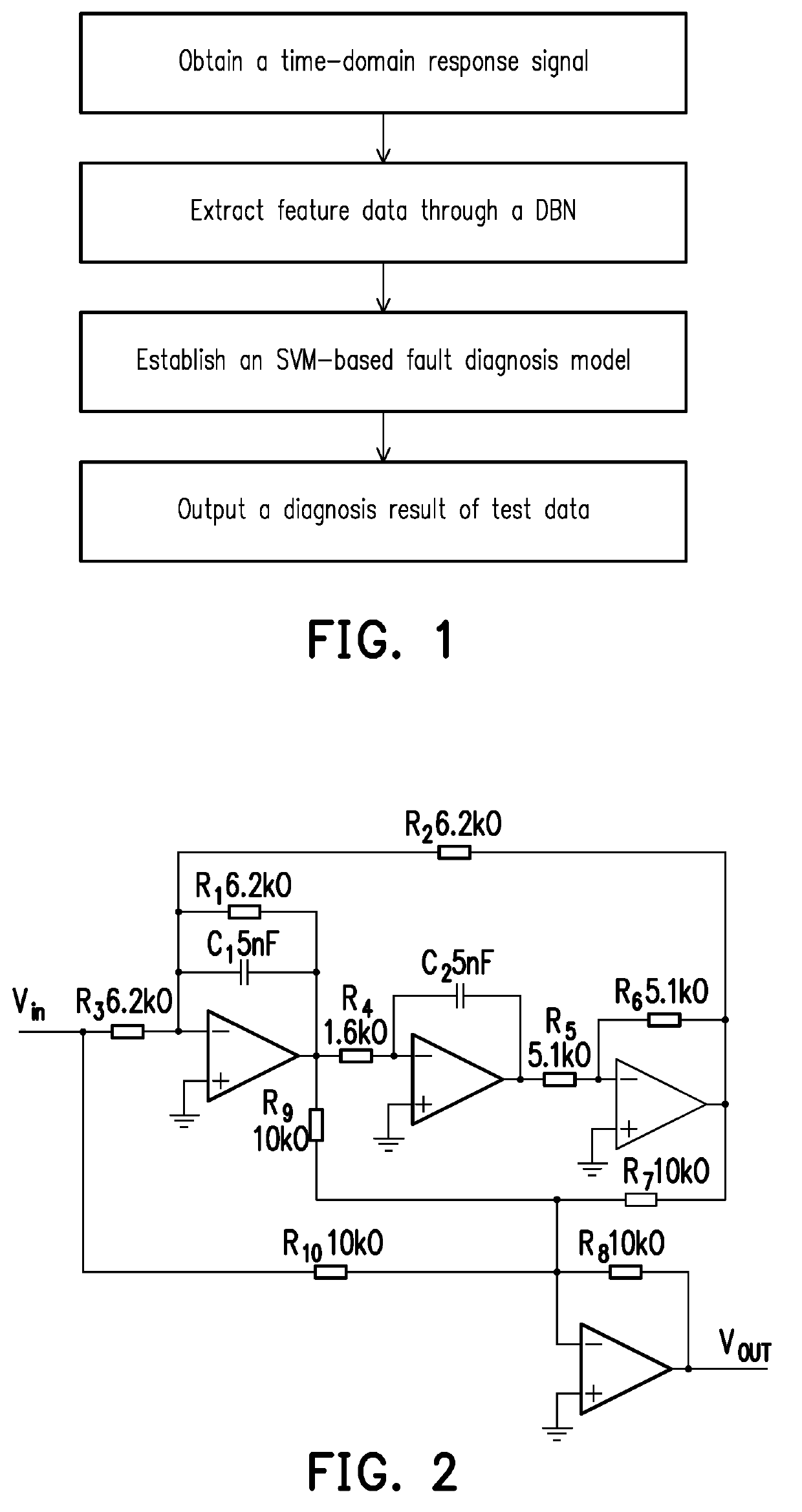
Deep belief network feature extraction-based analogue circuit fault diagnosis method
ActiveUS20190243735A1Improve feature extraction performanceImprove the extraction effectDetecting faulty hardware using neural networksAnalog circuit testingRestricted Boltzmann machineFeature extraction
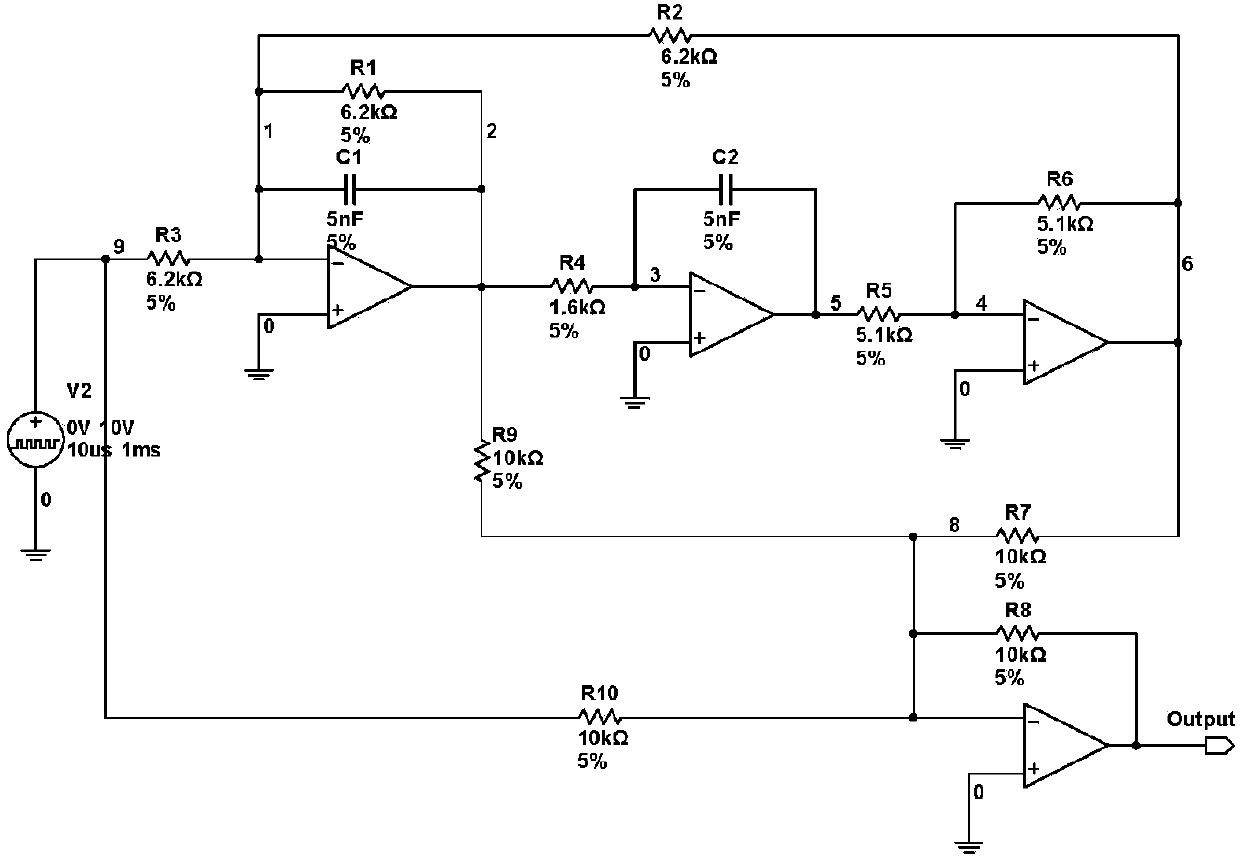
A Deep Belief Network (DBN) feature extraction-based analogue circuit fault diagnosis method comprises the following steps: a time-domain response signal of a tested analogue circuit is acquired, where the acquired time-domain response signal is an output voltage signal of the tested analogue circuit; DBN-based feature extraction is performed on the acquired voltage signal, wherein learning rates of restricted Boltzmann machines in a DBN are optimized and acquired by virtue of a quantum-behaved particle swarm optimization (QPSO); a support vector machine (SVM)-based fault diagnosis model is constructed, wherein a penalty factor and a width factor of an SVM are optimized and acquired by virtue of the QPSO; and feature data of test data are input into the SVM-based fault diagnosis model, and a fault diagnosis result is output, where the feature data of the test data is generated by performing the DBN-based feature extraction on the test data.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Synthetic circuit component and amplifier applications
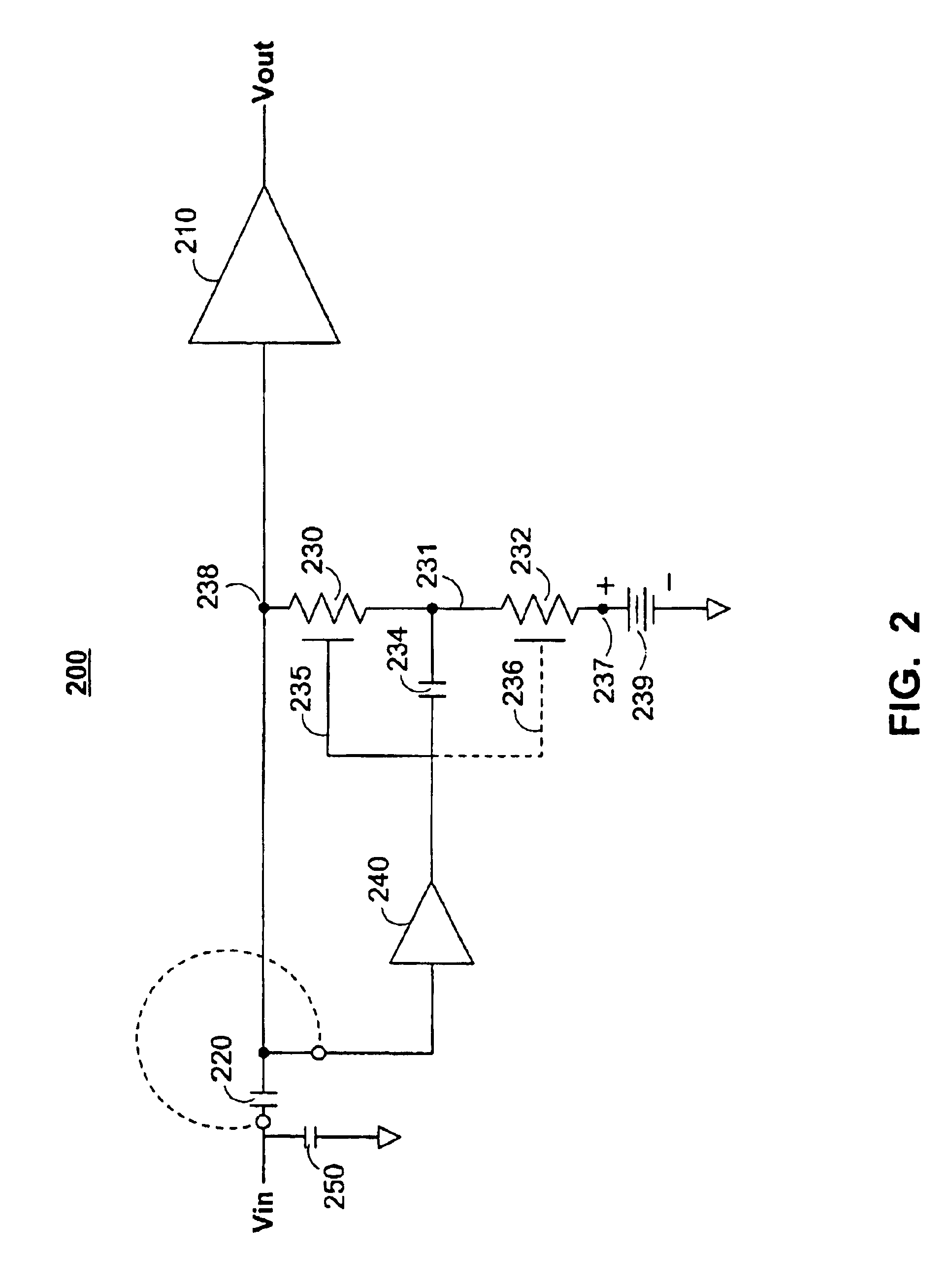
InactiveUS6879215B1Improve performanceImprove frequency responseNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsHigh frequency amplifiersAudio power amplifierParasitic capacitance
Synthetic circuit elements and amplifier applications for synthetic circuit elements are provided. The synthetic circuit elements disclosed herein may be configured to compensate for some or all of the parasitic capacitance normally associated with circuit elements disposed on a substrate providing a selectable impedance characteristic. Amplifier circuit constructed using such synthetic circuit elements exhibit improved performance characteristics such as improved recovery time, frequency response, and time domain response.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INT UNLTD
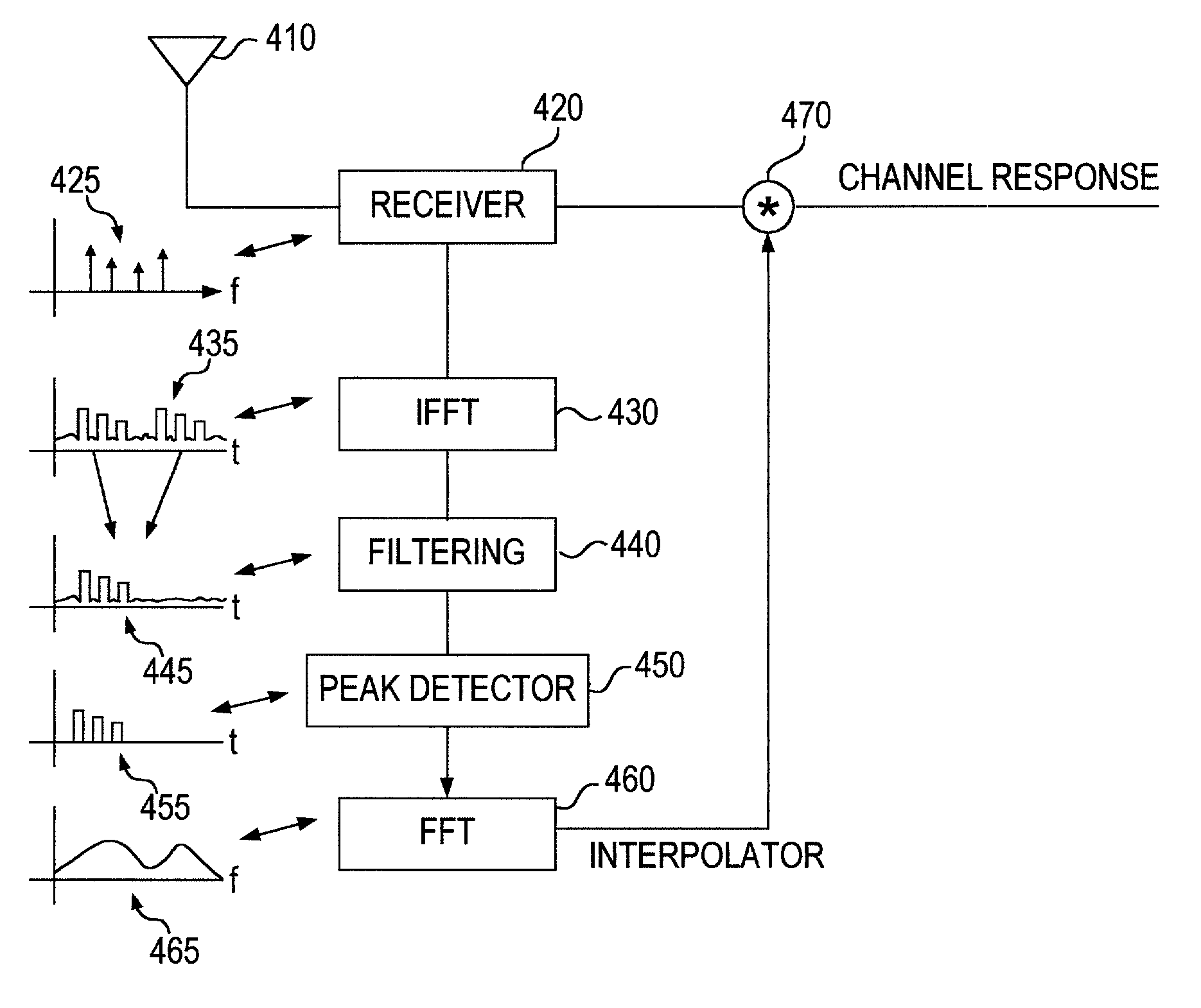
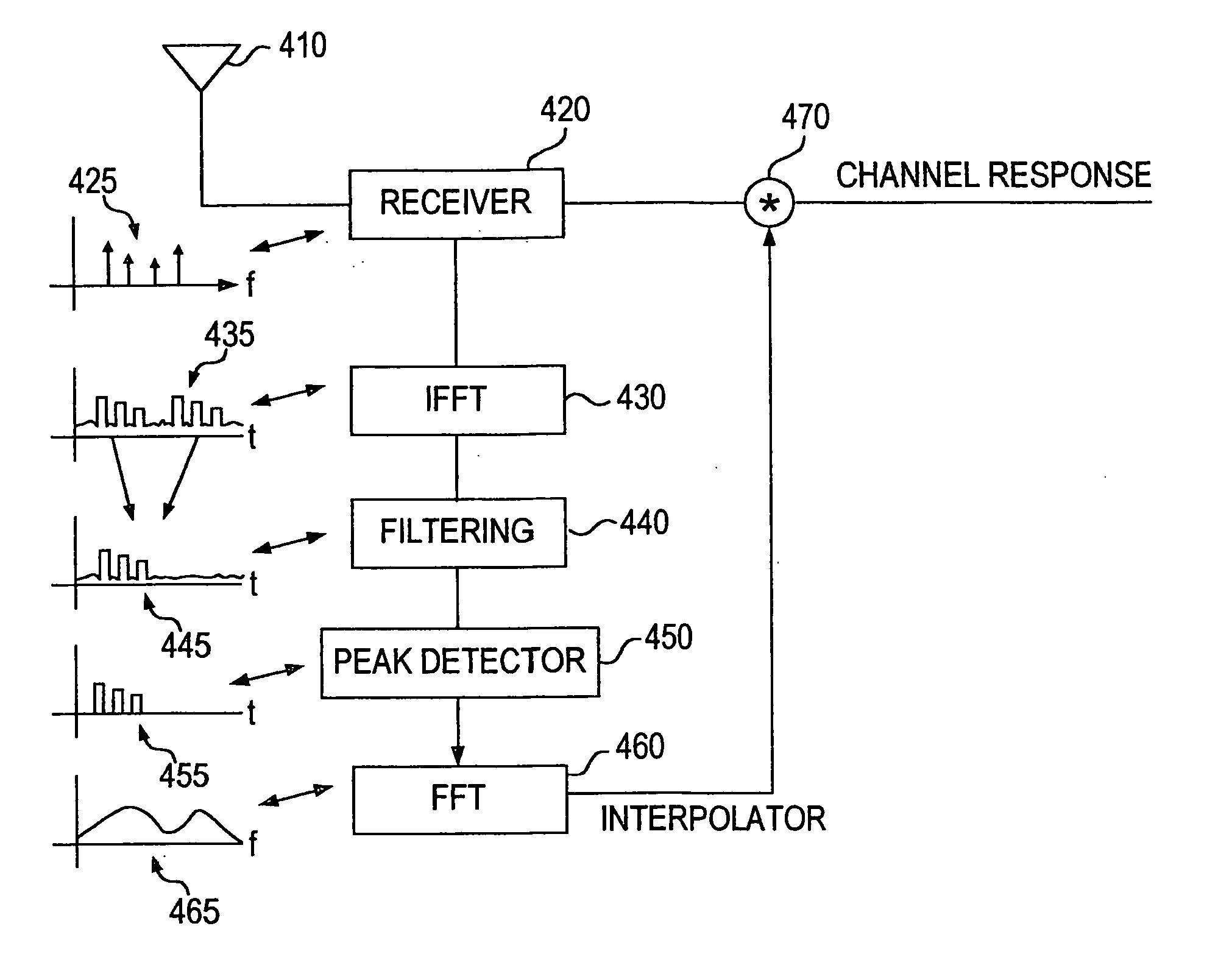
System and method for multiple signal carrier time domain channel estimation
The present invention provides a method of characterizing a frequency response of a transmission channel between a transceiver and a subscriber unit. The method includes once per predetermined interval of time, the transceiver transmitting a signal including multiple carriers, a plurality of the carriers including training symbols, a plurality of the carriers including information symbols. The subscriber unit generates frequency response estimates at the frequencies of the carriers including training symbols, each interval of time. The frequency response estimates are converted into a time domain response generating an impulse response once per interval of time. The impulse responses are filtered over a plurality of intervals of time. A channel profile is determined from the filtered impulse responses. The channel profile is converted to the frequency domain generating a channel interpolator. The characterized frequency response is generated from the channel interpolator and the frequency response estimates. The filtering can include averaging the impulse responses over a plurality of intervals of time, accumulating the impulse responses over a plurality of intervals of time, or weighted averaging of the impulse responses over a plurality of intervals of time. The weighted averaging can be dependent upon a phase error between the impulse responses, and / or an amplitude error between the impulse responses.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Novel analog circuit early fault diagnosis method
InactiveCN104198924AFacilitates early fault diagnosisImprove feature extractionAnalog circuit testingSpecial data processing applicationsFeature vectorLeast squares support vector machine
A novel analog circuit early fault diagnosis method includes the steps of (1) acquiring time domain response signals of an analog circuit and taking the time domain response signals as output voltage signals of the analog circuit; (2) performing wavelet transform to the acquired voltage signals; (3) performing fractal analysis to original signal patterns and wavelet sub patterns to generate wavelet fractal dimensions of different patterns; (4) performing kernel entropy component analysis to candidate feature vector data composed of the wavelet fractal dimensions to acquire low-dimension feature vector data; (5) creating a multi-class classifier of a least squares support vector machine, and optimally selecting penalty factor and width factor of the least squares support vector machine, which are used for distinguishing overlapped early fault categories, by a quantum-behaved particle swarm optimization algorithm; and (6) sending the low-dimension feature vector data into the multi-class classifier of the least squares support vector machine and then outputting early fault diagnosis results. The novel analog circuit early fault diagnosis method can effectively detect early faults of analog circuits.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
MIMO-OFDM system channel estimation method based on compressed sensing
ActiveCN104052691AImproved channel estimation resultsSmall distribution intervalBaseband system detailsMulti-frequency code systemsEstimation methodsGain coefficient
The invention provides an MIMO-OFDM system channel estimation method based on compressed sensing. The MIMO-OFDM system channel estimation method based on compressed sensing is mainly applied to channel estimation when a receiving terminal is provided with a two-dimensional antenna array. According to the MIMO-OFDM system channel estimation method based on compressed sensing, the time delay, incidence angle and gain of each path of a space channel are estimated in sequence, and channel estimation accuracy can be improved effectively. The MIMO-OFDM system channel estimation method based on compressed sensing comprises the following steps that 1, an initially-estimated value of a channel frequency domain response vector of each pilot frequency sub-carrier is obtained according to the least square criterion; 2, by means of the sparsity of the channel frequency domain response vectors in a time delay domain, the time delay of each path of the channel and an estimated value of a channel time domain response vector of each path of the channel are estimated on the basis of the compressed sensing theory; 3, by means of the sparsity of the channel time domain response vectors in a two-dimensional angle domain, the incidence angle of each path of the channel is estimated on the basis of the compressed sensing theory; 4, the gain coefficient of each path of the channel is estimated according to the least square criterion; 5, estimated values of channel frequency domain responses of all the sub-carriers and antennas are obtained.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Vector measurement method for passive intermodulation interference
ActiveCN103675448ASelf-intermodulation reductionNarrow down the measurement rangeSpectral/fourier analysisTransmitters monitoringLocal oscillator signalAudio power amplifier
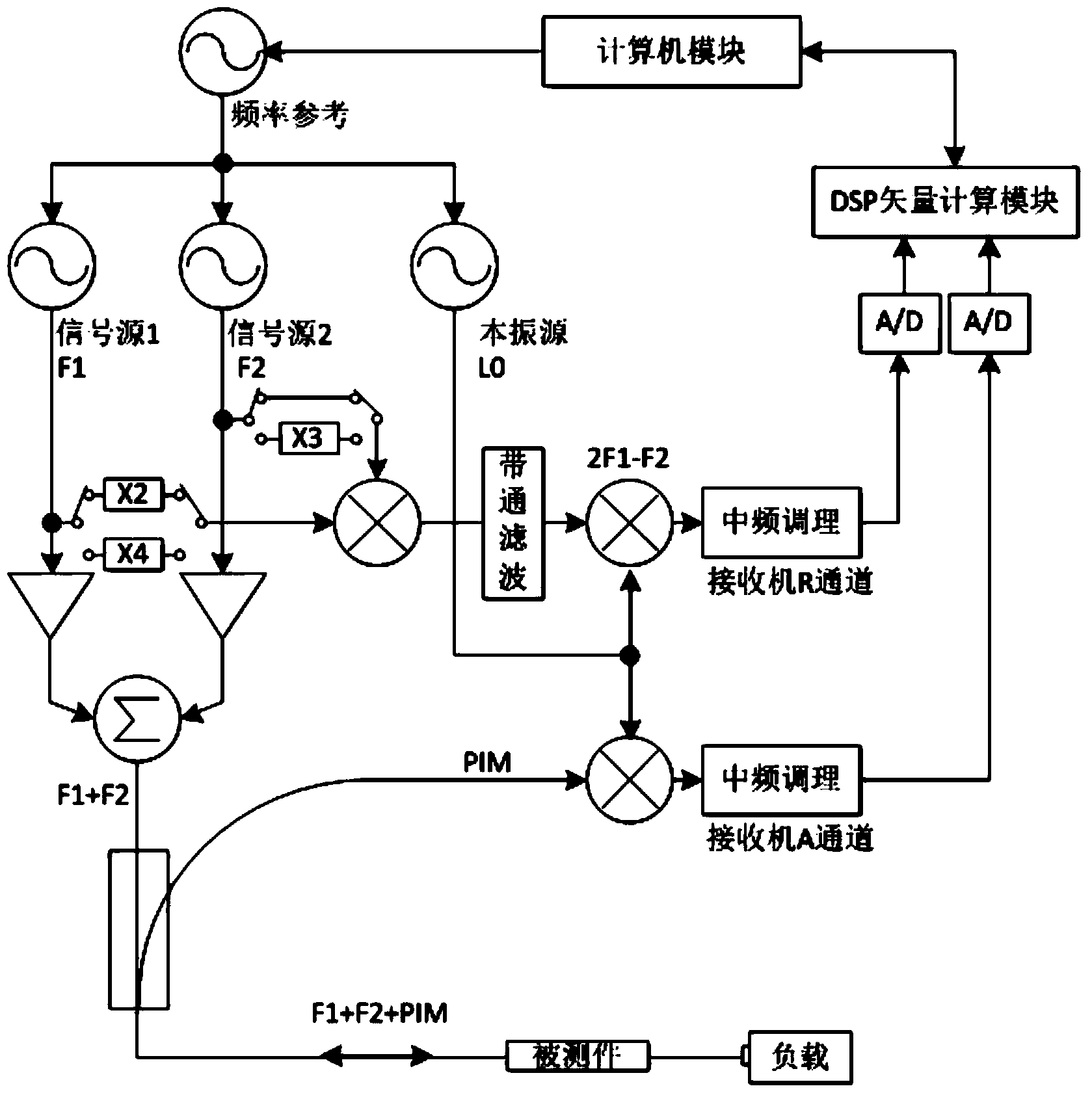
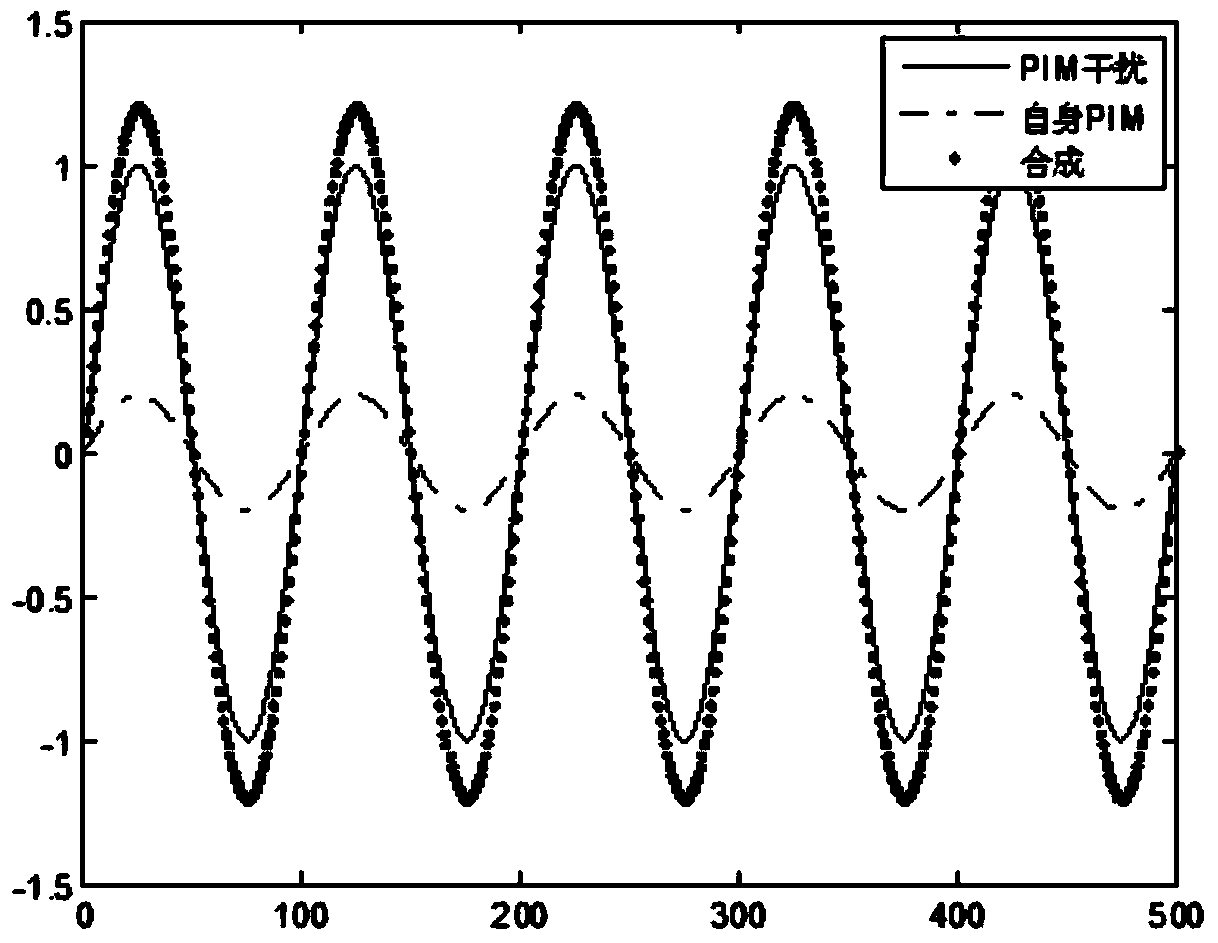
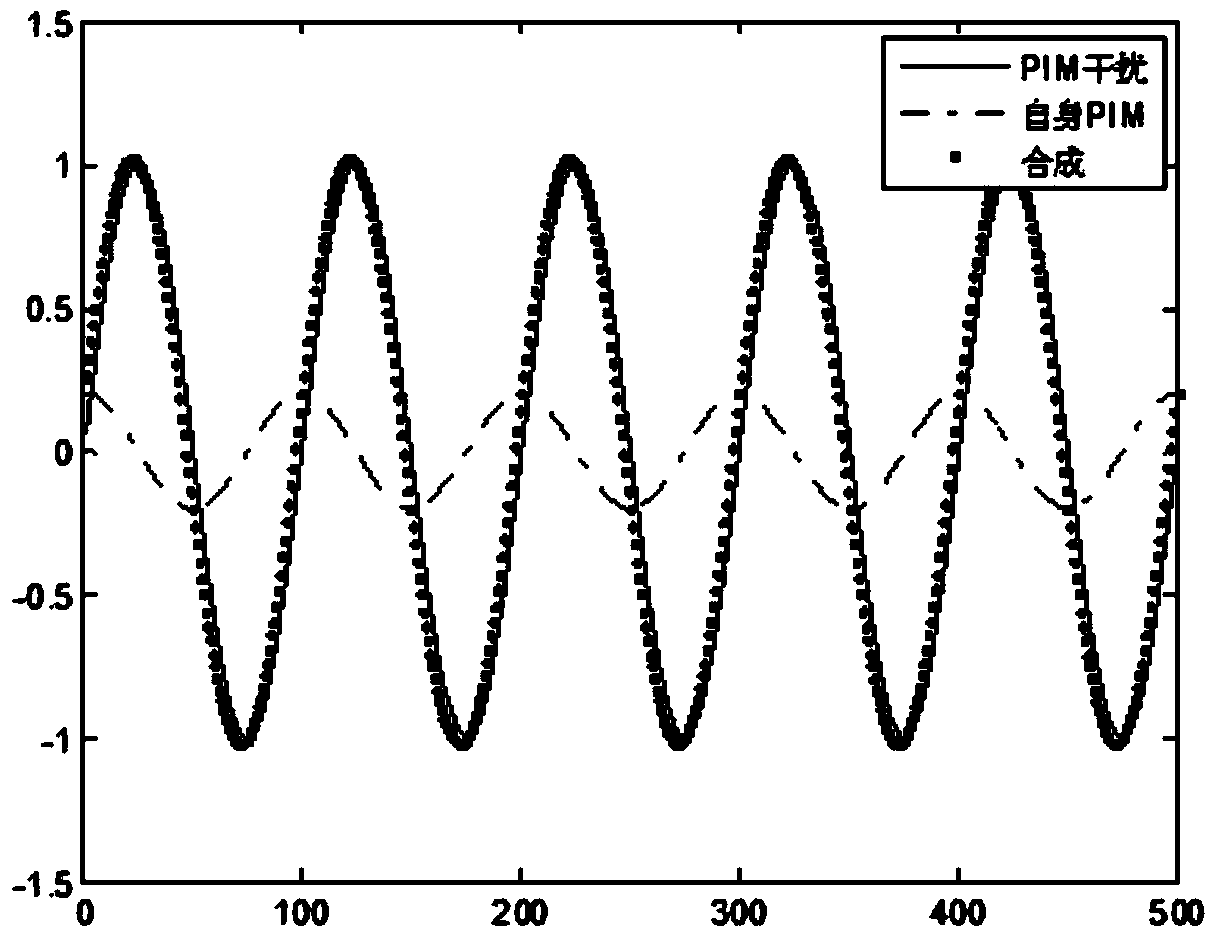
The invention provides a vector measurement method for passive intermodulation interference. The vector measurement method for the passive intermodulation interference comprises the steps that firstly a computer module adjusts the output frequency of a frequency reference unit, and a frequency reference signal is output; the frequency reference signal is used by a first signal source, a second signal source and a local oscillator source module after power division is conducted on the frequency reference signal, and then a testing signal with a frequency F1, a testing signal with a frequency F2 and a local oscillator signal L0 are generated; a part of the testing signal F1 and a part of the testing signal F2 are amplified by an amplifier module after power division is conducted on the testing signal F1 and the testing signal F2, then the signals are combined to generate a +43dBm dual-tone signal used for testing, reciprocal mixing is conducted on the other part of the testing signal F1 and the other part of the testing signal F2 after the other part of the testing signal F1 and the other part of the testing signal F2 pass through a frequency multiplication module, the frequency of an obtained signal is 2F1-F2 after filtering, and the signal is received by a reference receiver to serve as a PIM reference signal. By the adoption of the vector measurement method for the passive intermodulation interference, self-intermodulation and self-calibration of an instrument can be achieved, vector compensation for the self-intermodulation of the instrument can be achieved, the self-intermodulation of a system is greatly reduced, the measurement range of the system is widened, and the uncertainty of measurement is reduced; the time-frequency conversion technology can be directly adopted by a measurement result, and the time domain response to a PIM product can be observed.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRONIS TECH INSTR CO LTD
Channel estimation method and device based on OFDM (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing)
InactiveCN101808053AImprove the speed of estimationImprove estimation accuracyBaseband system detailsMulti-frequency code systemsSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Estimation methods
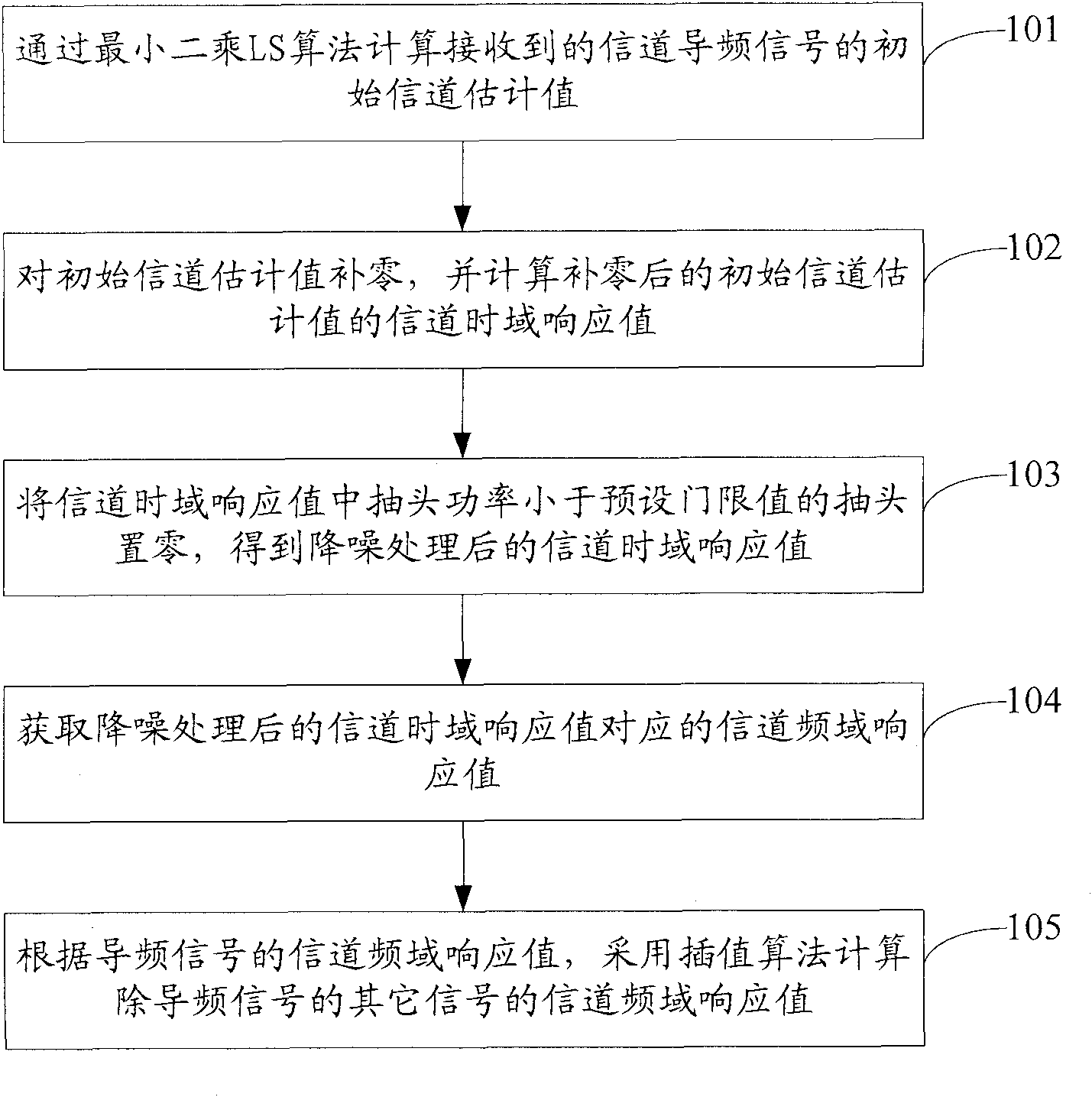
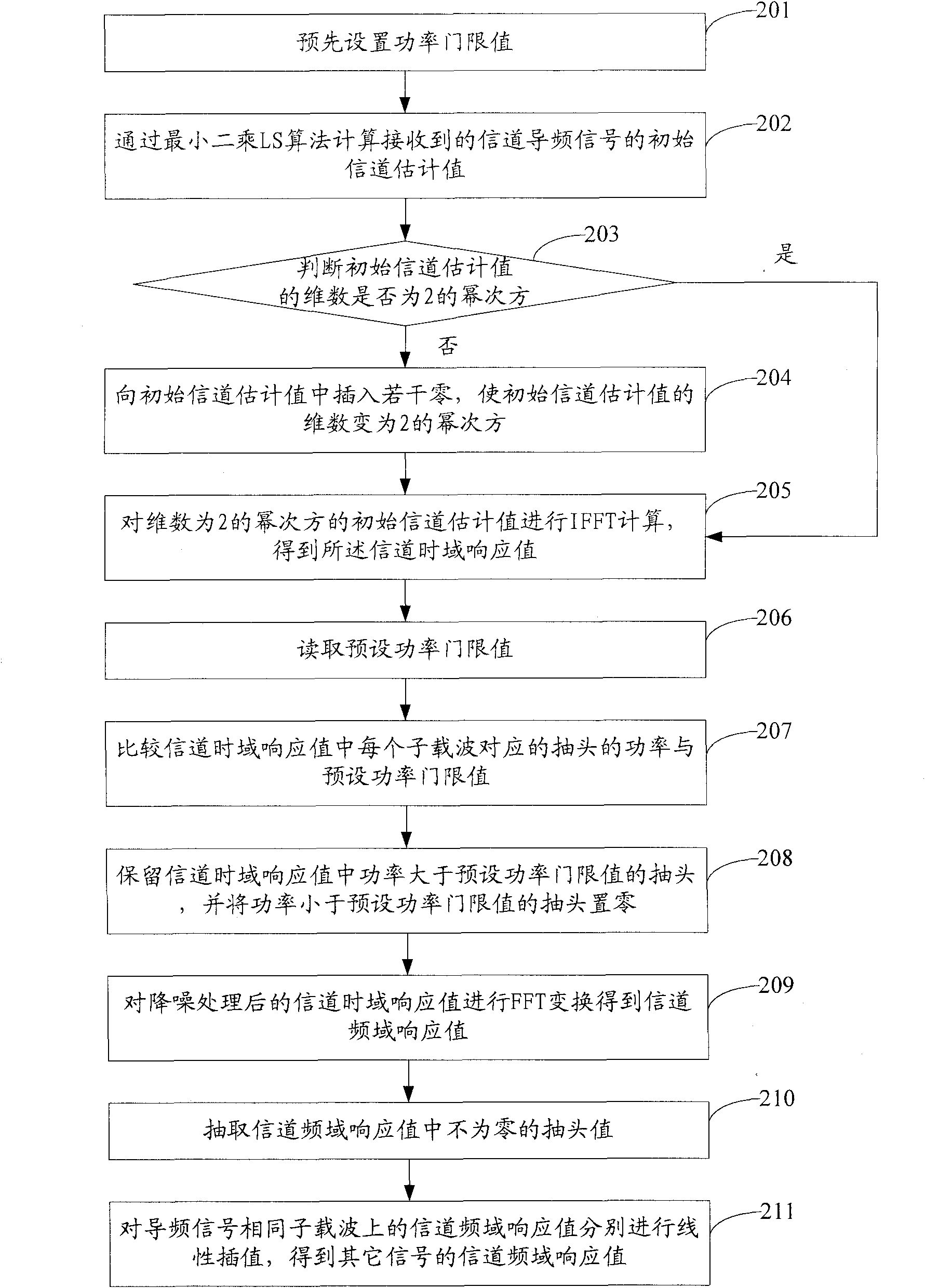
The embodiment of the invention discloses channel estimation method and device based on an OFDM (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing). The method comprises the following steps of: calculating an initial channel estimated value of received channel pilot signals by the least square (LS) algorithm; zeroizing the initial channel estimated value, and calculating the channel time domain response value of the zeroized initial channel estimated value; resetting taps of which the tap power is less than a preset threshold value in the channel time domain response value to obtain a denoised channel time domain response value; acquiring a channel frequency domain response value corresponding to the denoised channel time domain response value; and calculating the channel frequency domain response values of other signals except the pilot signals by the interpolation algorithm based on the channel frequency domain response value of the pilot signals. By denoising the channel time domain response based on the existing LS channel estimation, the embodiment of the invention improves the channel estimation accuracy of the OFDM system at a low signal-to-noise ratio, is easy to realize and correspondingly raises the speed of the channel estimation.
Owner:大唐联诚信息系统技术有限公司
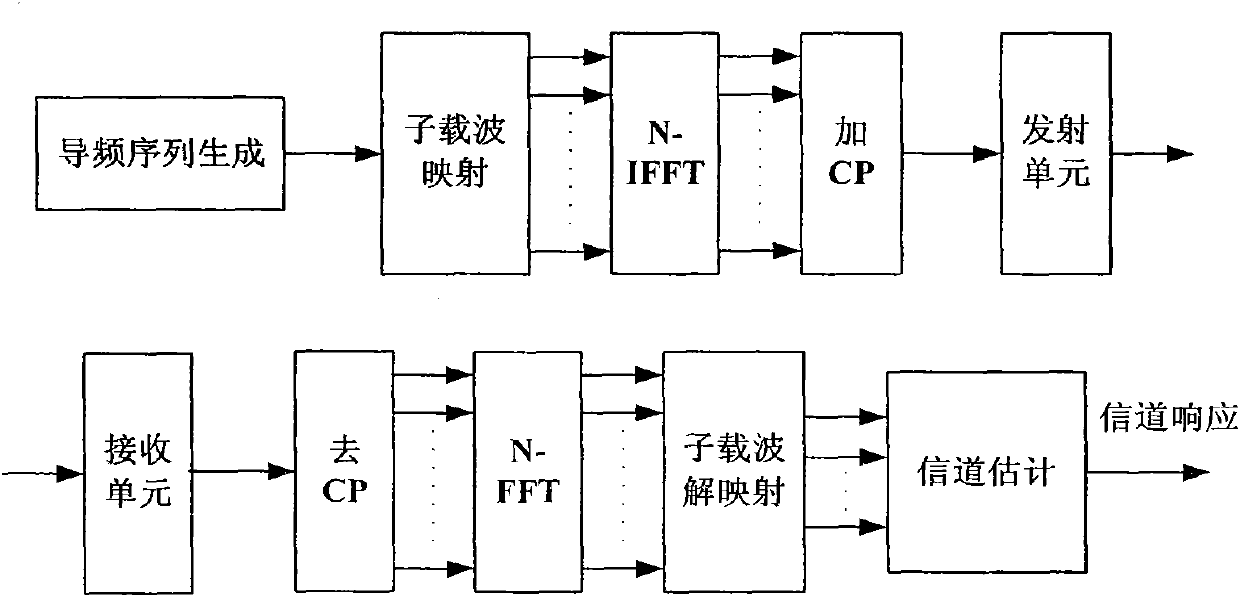
Method for pilot transmitting, channel estimation and noise power estimation in OFDM system
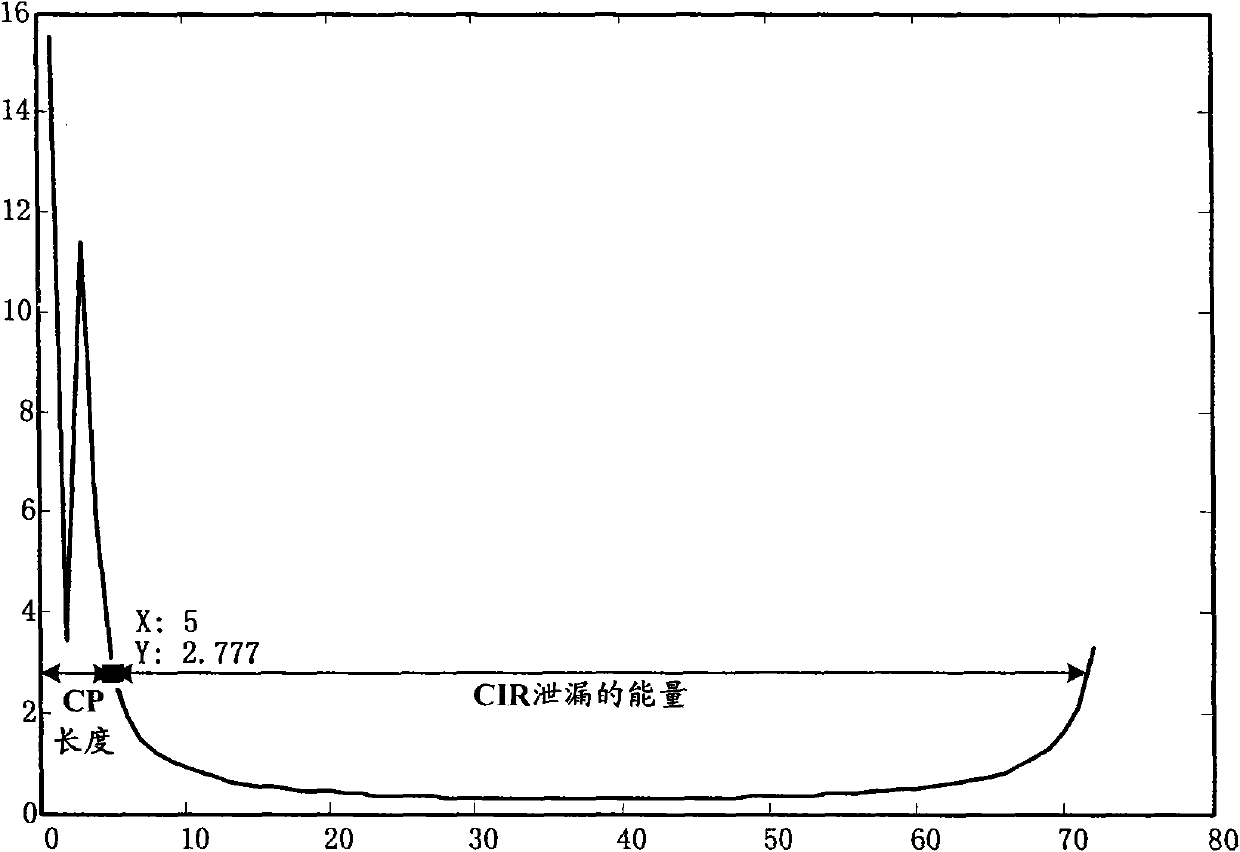
InactiveCN101557378ALeakage Energy ReductionReduce leakage energyMulti-frequency code systemsTransmitter/receiver shaping networksEstimation methodsTime domain response
The invention discloses a pilot signal transmitting method in an OFDM system, which is used for carrying out frequency domain windowing processing to pilot sequences and then transmitting. The invention also discloses a channel estimation method and a noise power estimation method, comprising the following steps of: receiving pilot signals processed by frequency domain windowing, carrying out channel estimation according to pilot sequences without windowing to determine an initial value HLS-W(k) of frequency domain channel response on each subcarrier corresponding to a user, and utilizing HLS-W(k) to determine corresponding channel time domain response hW(n); calculating signal power of channel time domain response with the index value of larger than NCP-W in the channel time domain response hW(n) as noise power of the system; setting the channel time domain response valve with the index value of larger than NCP-W in the channel time domain response hW(n) to be 0, completing denoising processing of channel estimation, carrying out Fourier transformation and dewindowing processing to CIR by denoising processing and obtaining the final frequency domain channel response of each subcarrier. The invention can improve accuracy of noise power estimation and channel estimation.
Owner:POTEVIO INFORMATION TECH
Detection method for damage of random vibration structure based on correlation function amplitude vector
InactiveCN1804612AShort test timeThe identification method is simpleAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesProcessing detected response signalFrequency spectrumMeasurement point
The invention relates to a method for testing random vibration structure damage based on cross-correlation function peak value vector. It uses the relation between the frequency respond function of the cross-correlation function of the two points respond signal of the vibration structure and the structure out-exiting frequency spectrum to collect the respond signal of a period times of a plurality of measuring points, it dose cross-correlation function computing to one point respond signal with other points respond signals, it uses the largest peak of each cross-correlation function to construct the cross-correlation function peak value vector, it compares the relative factor of the intact structure and the current structure cross-correlation function peak value vector to quote weather the structure is damaged, it analyzes the content change of the corresponding elements to ascertain the damaged location.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
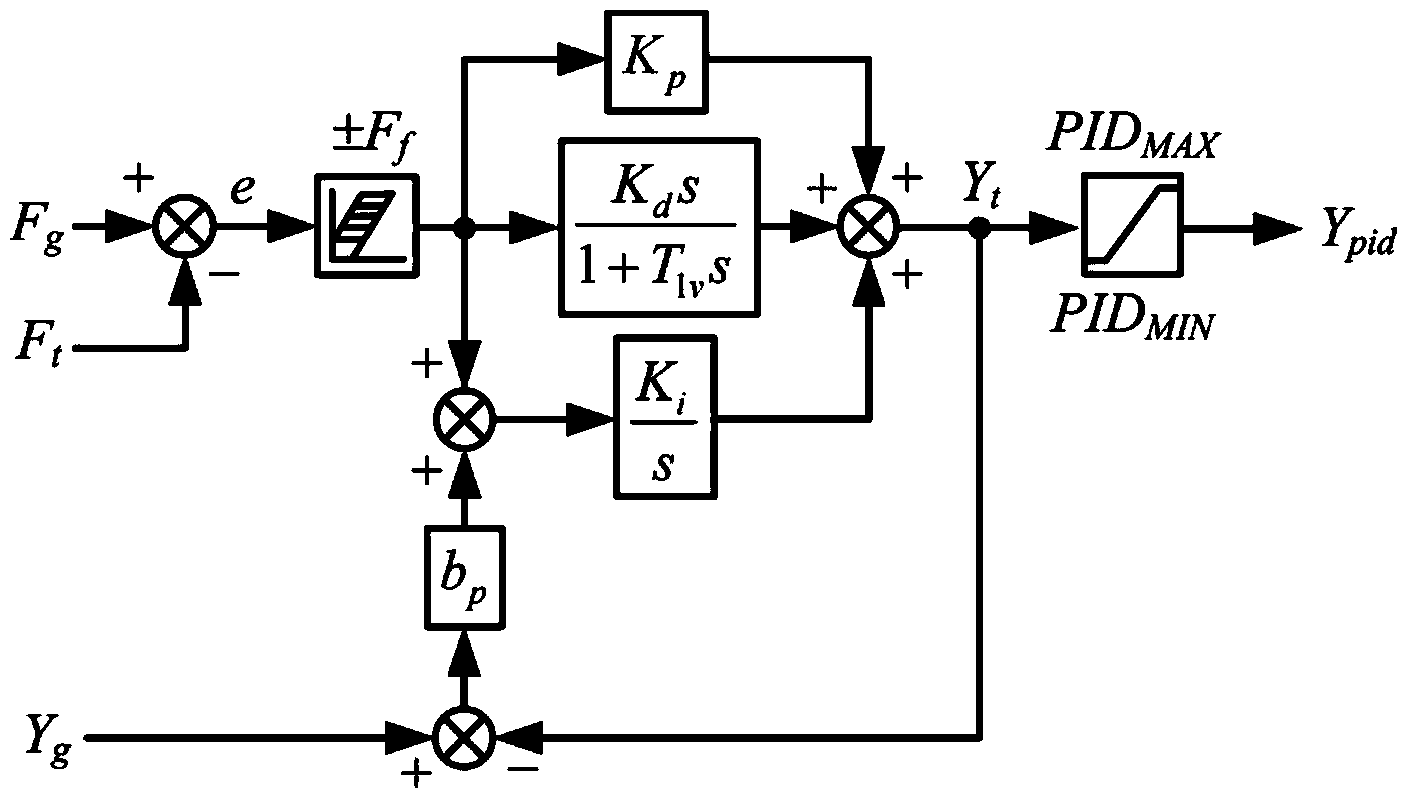
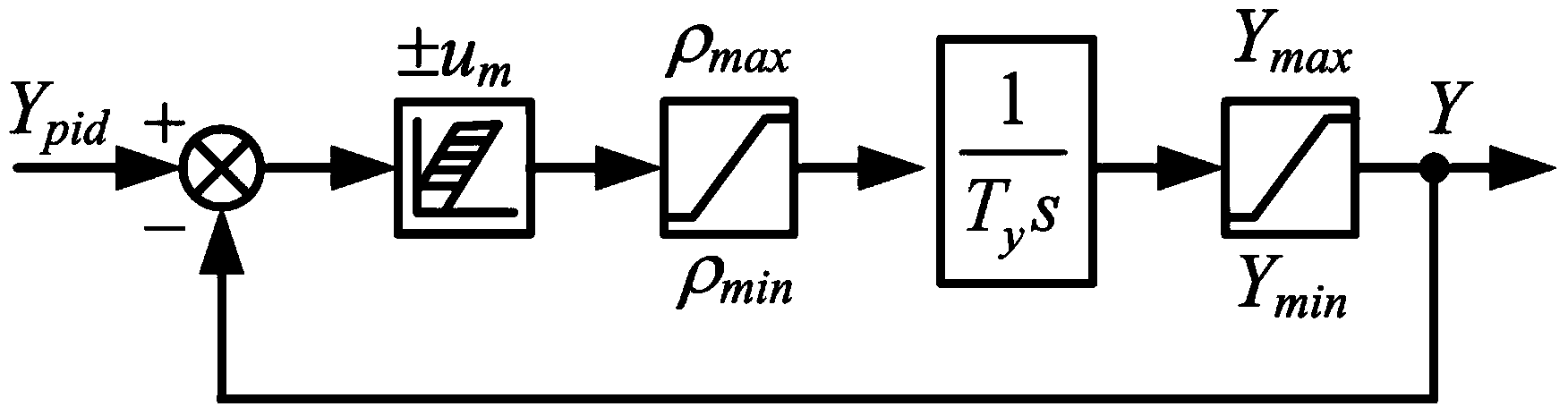
PID hydraulic turbine governor parameter optimization method based on multi-working-condition time domain response
InactiveCN103590969ASatisfied with dynamic characteristicsImprove robustnessHydro energy generationMachines/enginesOptimal controlField tests
The invention discloses a PID hydraulic turbine governor parameter optimization method based on multi-working-condition time domain response. The method includes the following steps that (1) a hydraulic turbine regulating system model is built, wherein the hydraulic turbine regulating system model particularly comprises a PID hydraulic turbine governor model, a hydraulic turbine-water diversion pipeline model and a generator model; (2) parameters of the hydraulic turbine regulating system model are obtained in a field test and parameter recognition mode; (3) a comprehensive fitness function based on multi-working-condition time domain response is designed, and the optimization objectives of finding out an optimum PID control parameter and enabling a comprehensive fitness function value to be minimum are determined; (4) the optimal PIC control parameter is obtained through an intelligent optimization algorithm. The control parameters obtained through the method enable a system to keep satisfying dynamic characteristics under different working conditions, and robustness of the system is enhanced.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
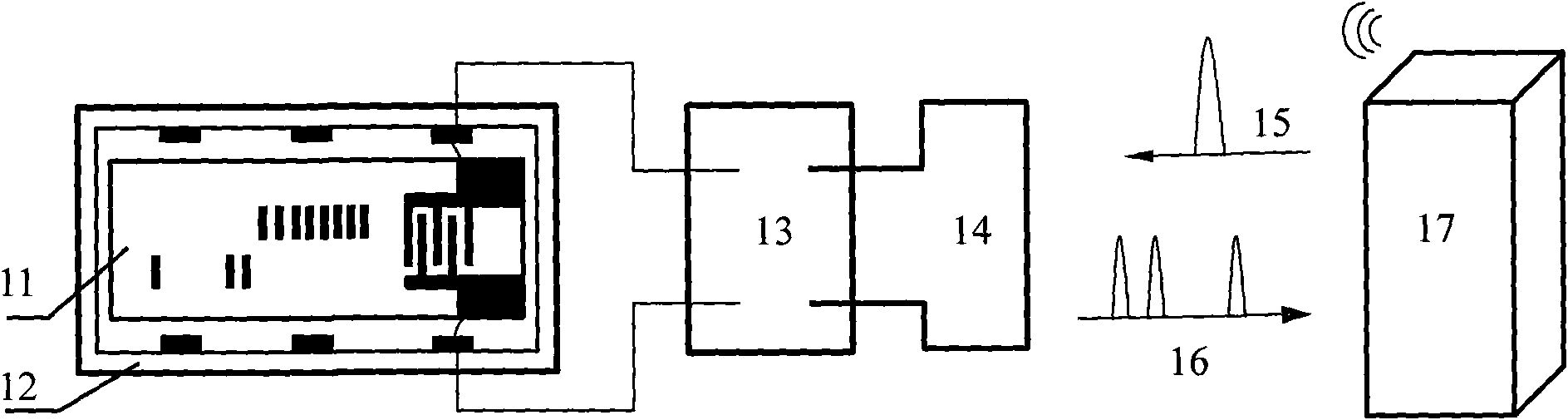
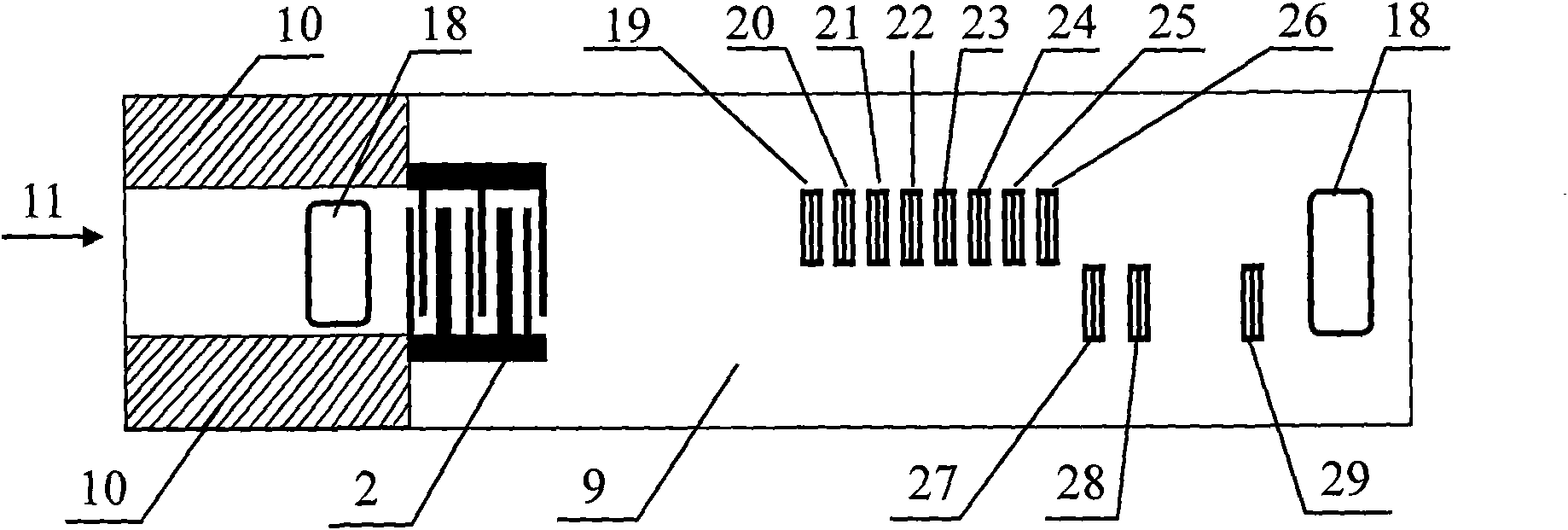
Integrated surface acoustic wave wireless temperature sensor
InactiveCN101644608AImproved signal-to-noise ratio performanceSpread suppression or even offsetThermometers using physical/chemical changesElectricityTime domain response
The invention relates to an integrated surface acoustic wave (SAW) wireless temperature sensor, comprising an interdigital transducer with an EWC / SPUDT structure and 11 reflectors with short-circuit gate structures, which are manufactured on a piezoelectric substrate, wherein, the EWC / SPUDT receives an electromagnetic wave signal transmitted from a wireless reading unit by a wireless antenna and transforms the signal into surface acoustic wave which is propagated along the reflectors on the surface of the piezoelectric substrate and is respectively reflected by the reflectors, the reflected acoustic wave is retransformed into the electromagnetic wave signal by an EWC / SPUDT2, the signal is returned to the wireless reading unit by the wireless antenna, and finally temperature detection is realized by evaluation on a phase change of time-domain response via a signal processing method. In the sensor, the 11 reflectors of a SAW reflection delay line are divided into two paths for reducing multiple reflection among the reflectors, wherein, 8 reflectors on one path are used for 8-bit electronic tags, and 3 reflectors on the other path are used for temperature detection; and a reflection peak of a time domain S11 with even response is obtained by adjusting electrode number of the reflectors.
Owner:INST OF ACOUSTICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
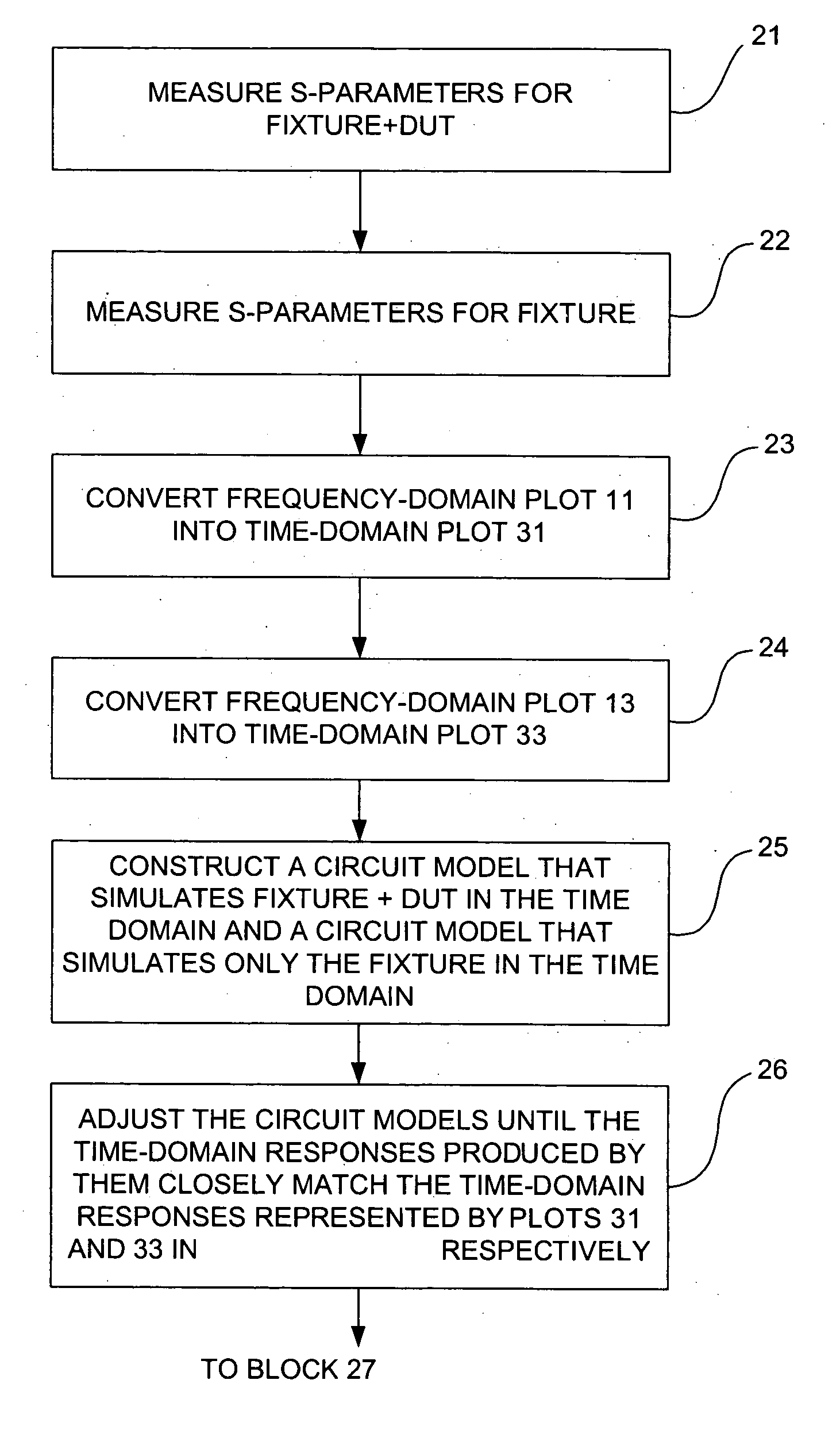
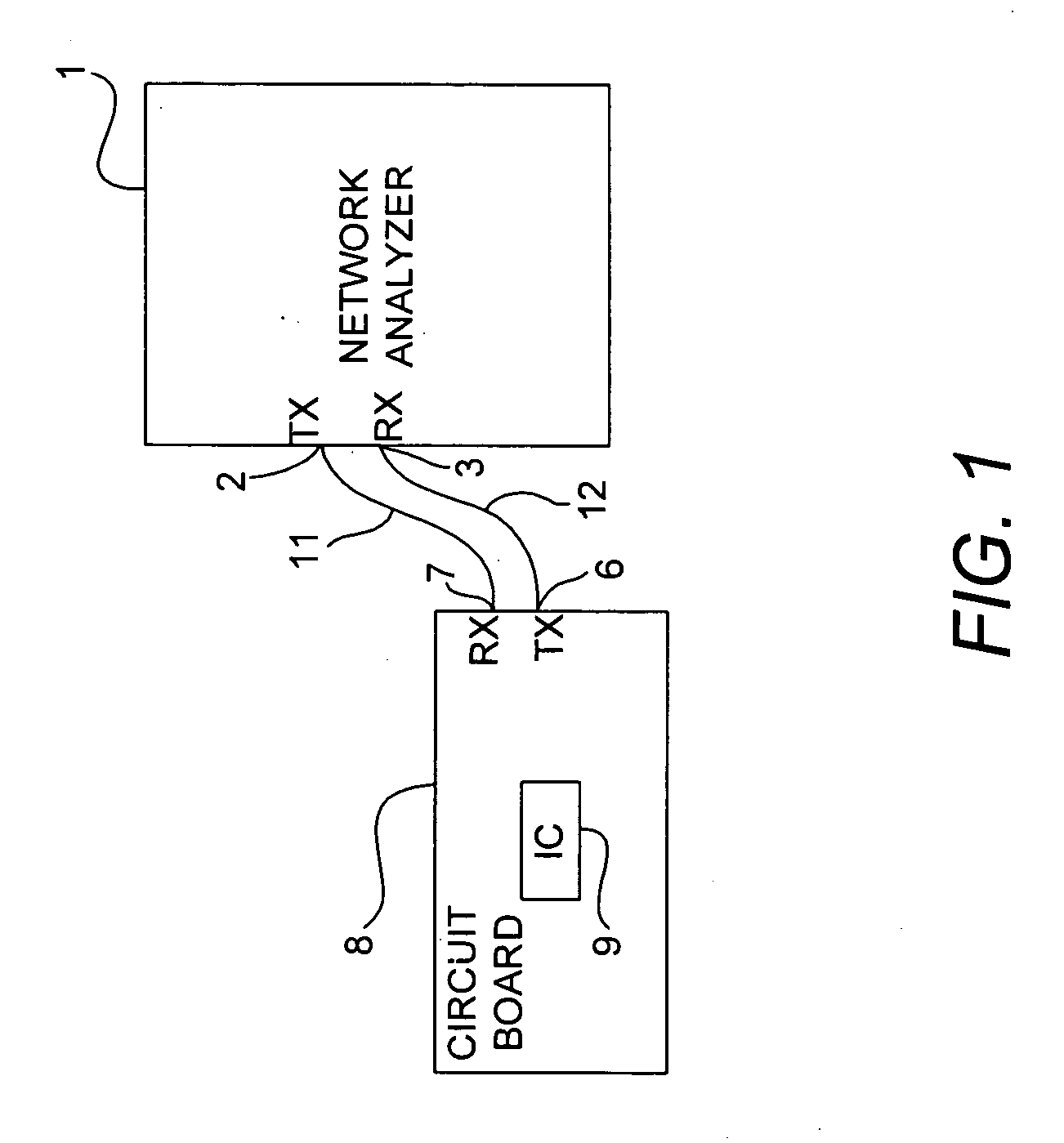
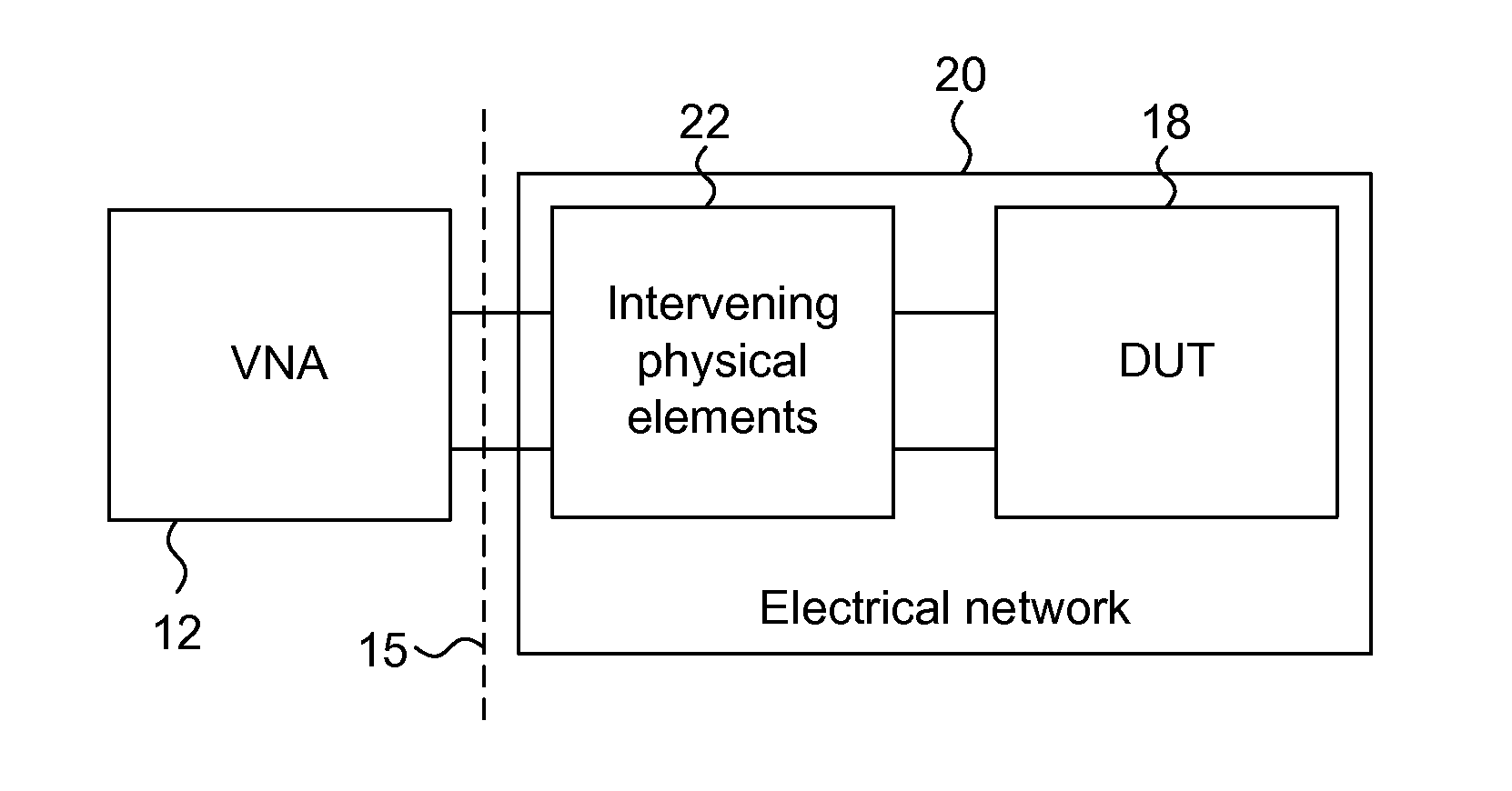
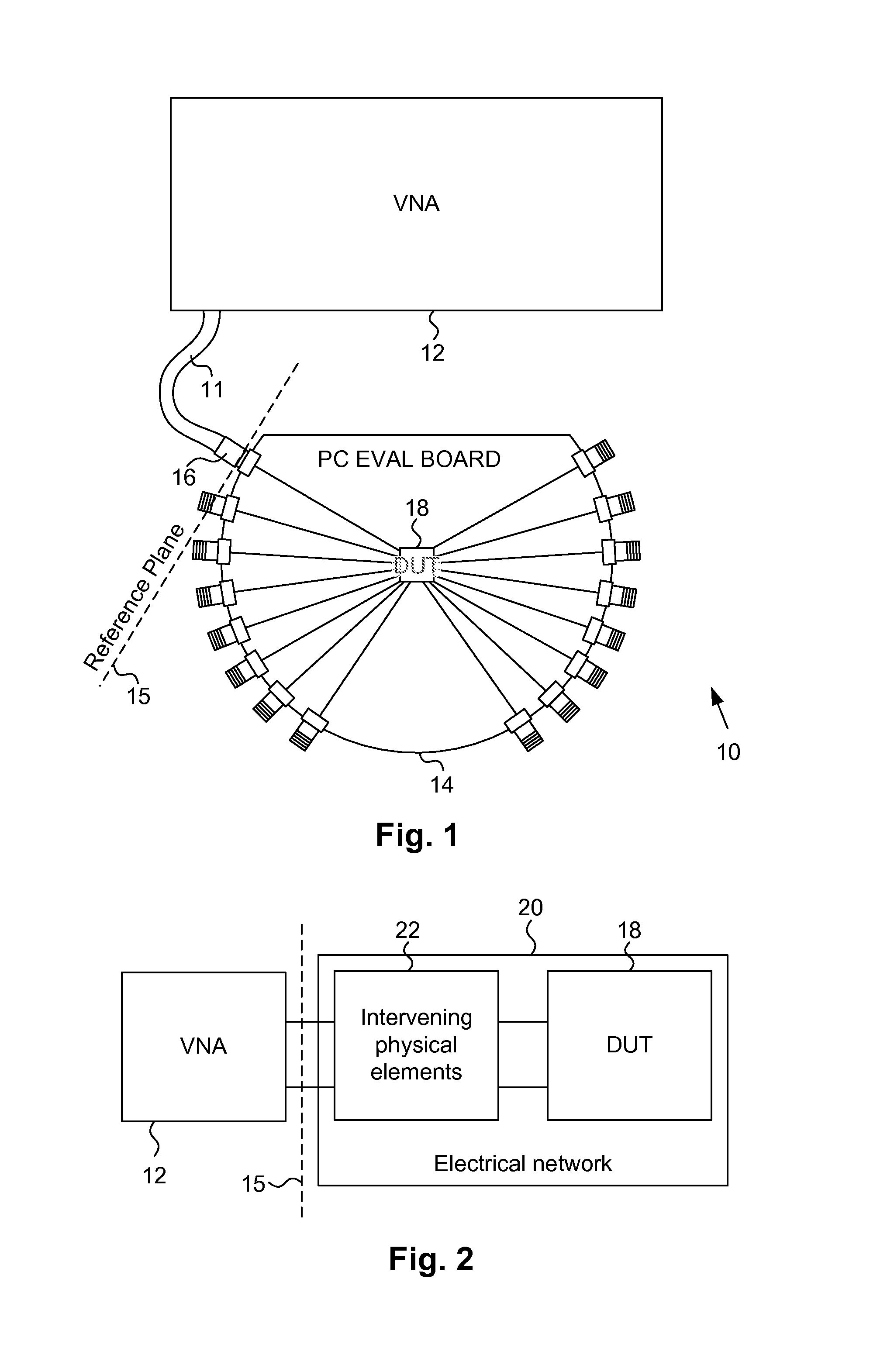
Method and apparatus for determining one or more s-parameters associated with a device under test (DUT)
InactiveUS20070073499A1Resistance/reactance/impedenceFrequency analysisEngineeringTime domain response
Frequency domain responses associated, respectively, with a fixture having a DUT connected to it and a fixture without the DUT are converted into respective time-domain responses that are then used to construct respective time-domain circuit models. The time-domain circuit model corresponding to the fixture by itself is subsequently de-embedded from the time-domain circuit model corresponding to the fixture and the DUT connected to it to obtain a time-domain circuit model for the DUT by itself. The time-domain circuit model for the DUT is operated over a range of frequencies as the frequency domain response is measured. The s-parameters for the DUT are then computer from the frequency domain response for the DUT.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Amplification forwarding cooperation treatment based broadband wireless sensing network channel estimation method
InactiveCN101136883AHigh precisionReduce complexityData switching by path configurationMulti-frequency code systemsMean squareEstimation methods
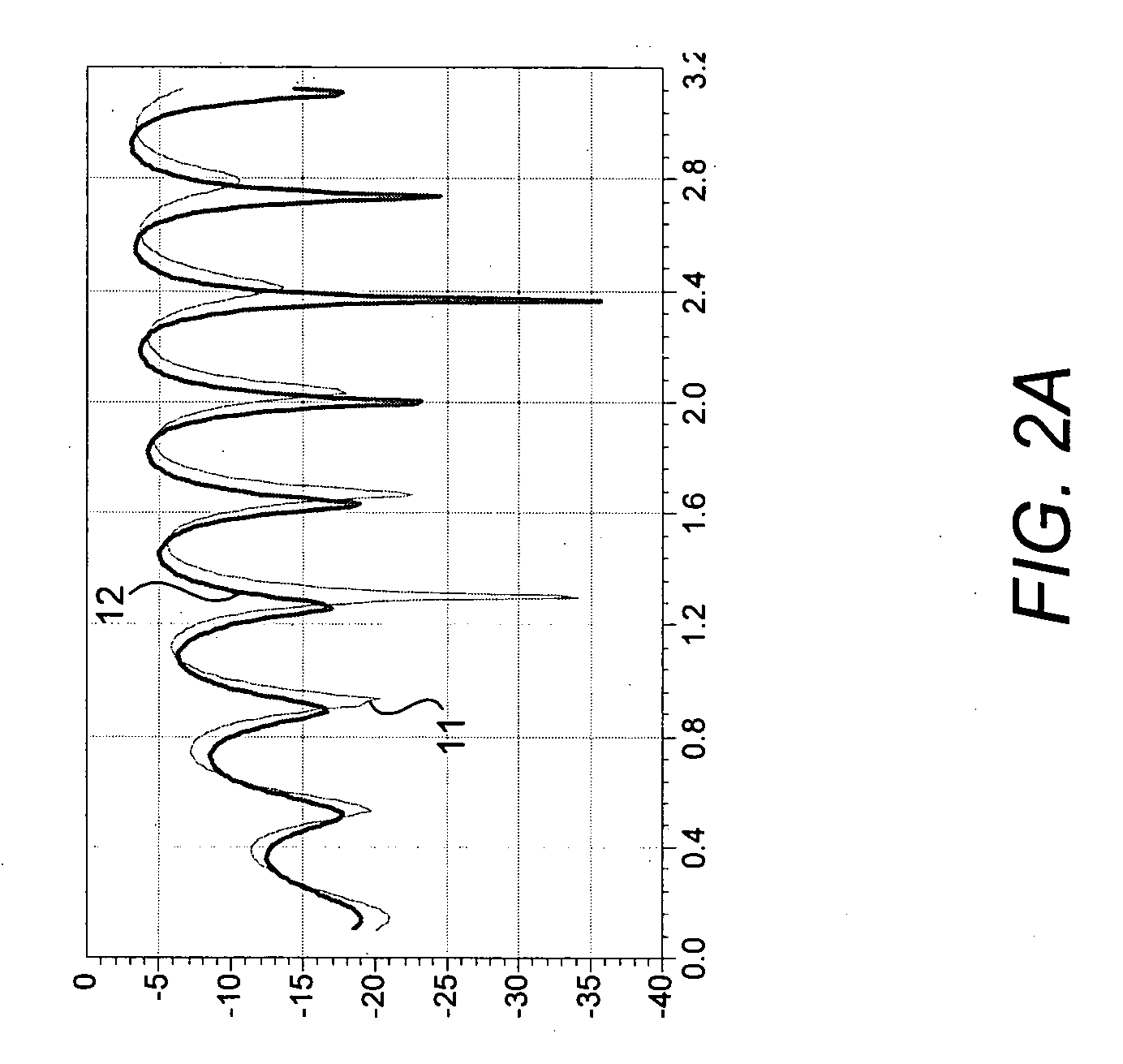
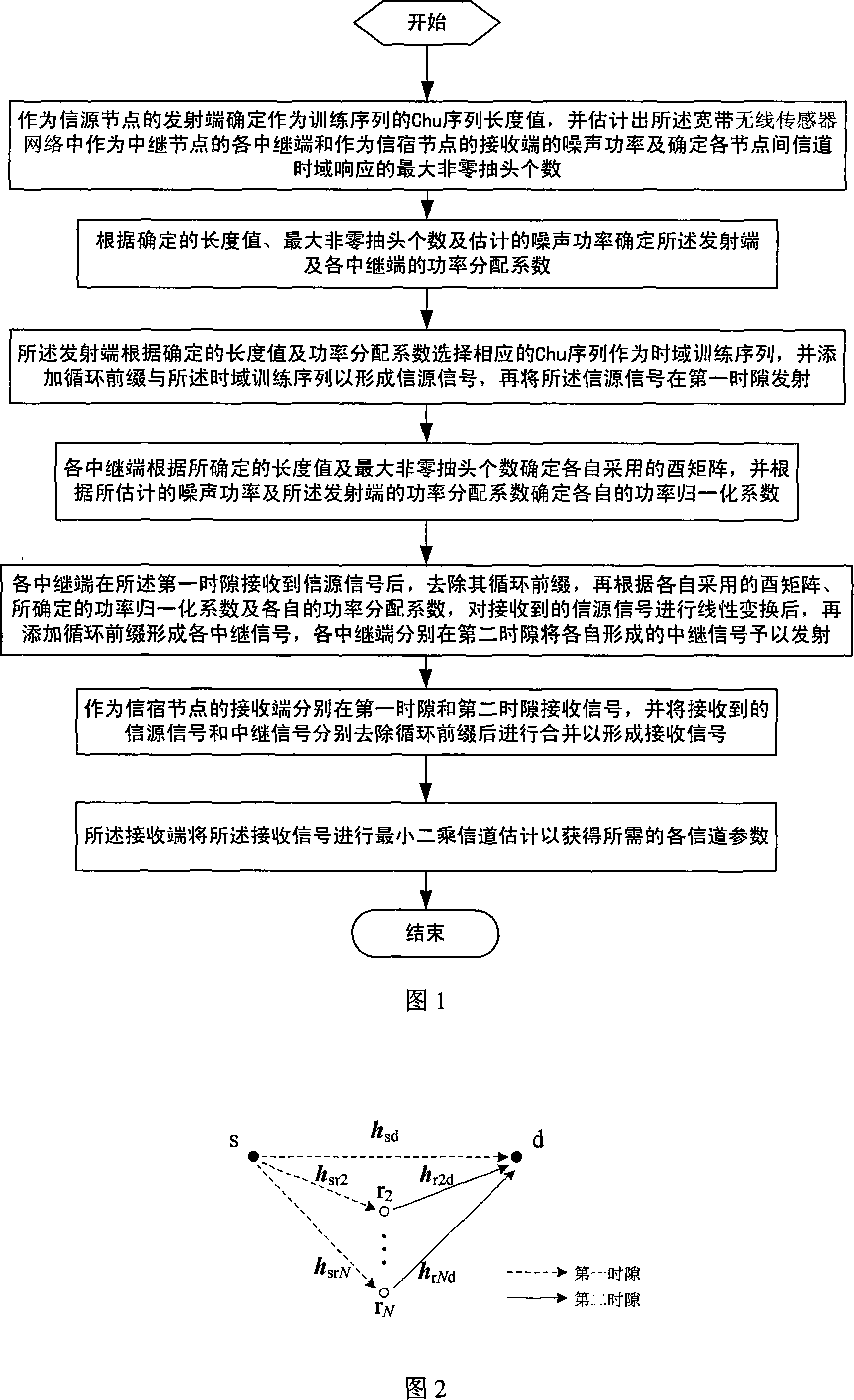
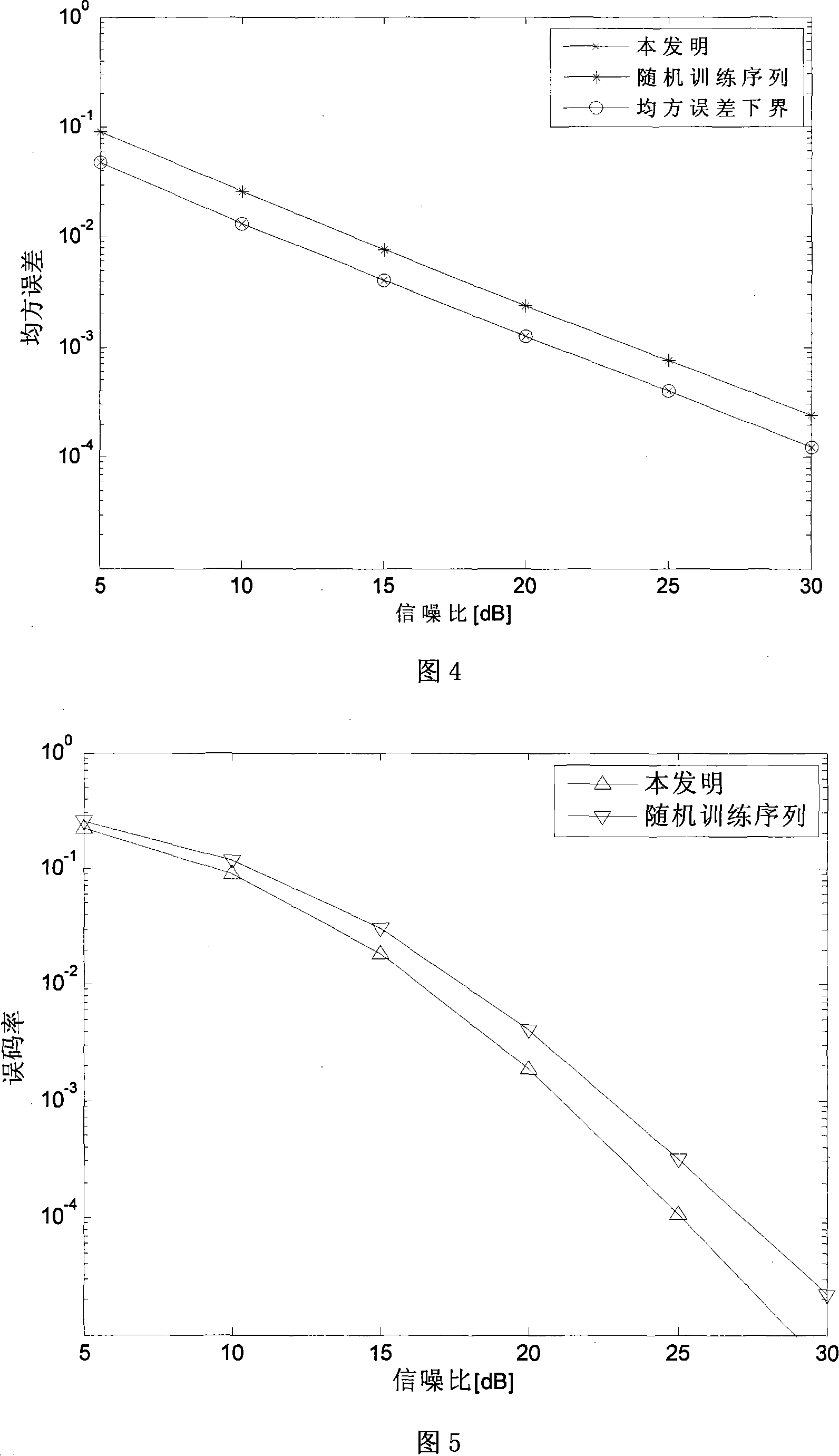
The method includes steps: transmitting end (TE) determines length value of Chu sequence as training sequence; estimating out noise power at each relay end and receiving end, and determining maximal number of nonzero tap in time domain response of channel between nodes, and determining power distribution coefficient (PDC) of each node; after determining value of length and PDC, and selecting corresponding Chu sequence and adding circular prefix (CP), TE carries out transmission at first time slot (TS); after receiving signal, each relay end carries out linear processing on the received signal based on PDC and unitary matrix, and then adds CP, and transmits them in second TS; the receiving end receives signals at first TS and second TS, and unites the received signals with CP being removed, further, carries out channel estimation (CE) by minimum mean-square value. Thus, the invention realizes CE in high precision and low complexity in cooperation comm containing multiple relay nodes.
Owner:JIAXING WIRELESS SENSOR NETWORKS CENT CAS
Simulation circuit fault diagnosis method on the basis of generalized multi-nuclear support vector machine
ActiveCN105548862AImprove classification accuracyEasy to classifyAnalog circuit testingCharacter and pattern recognitionSupport vector machineAlgorithm
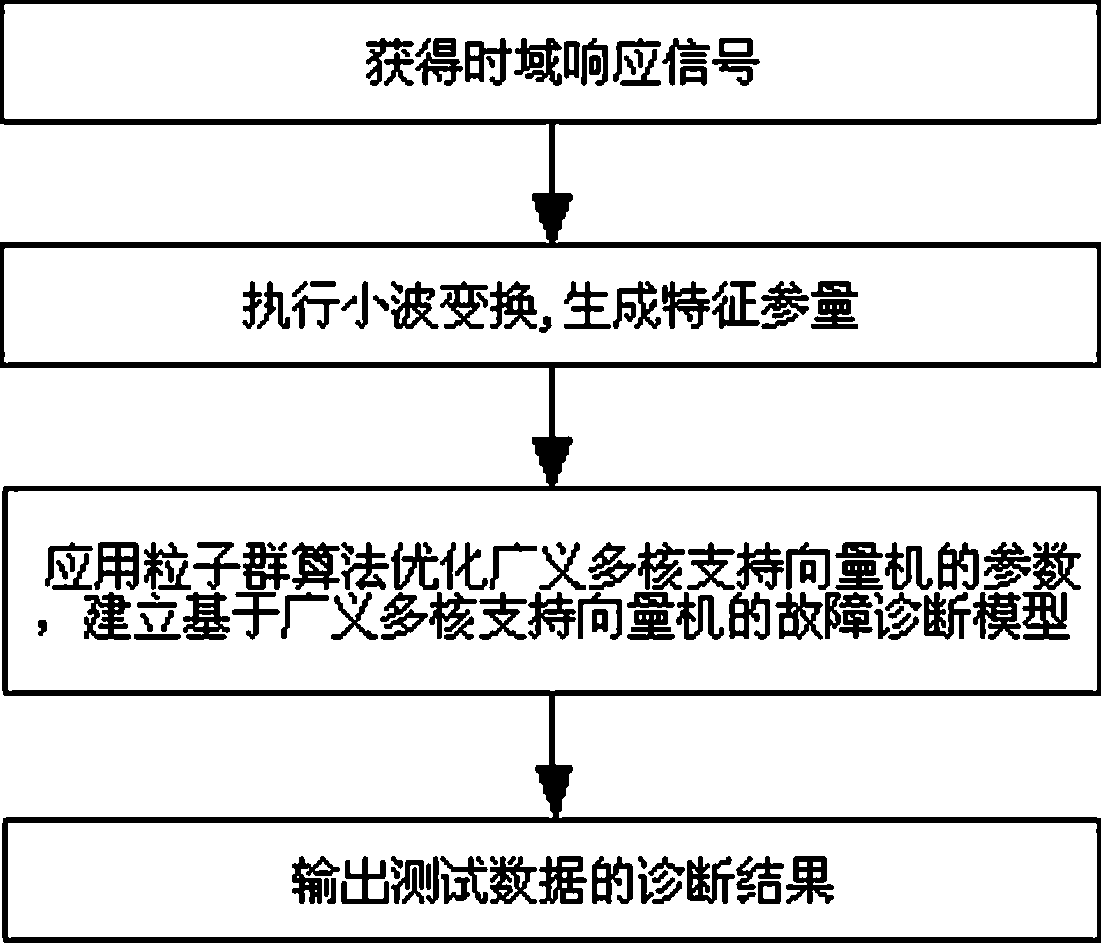
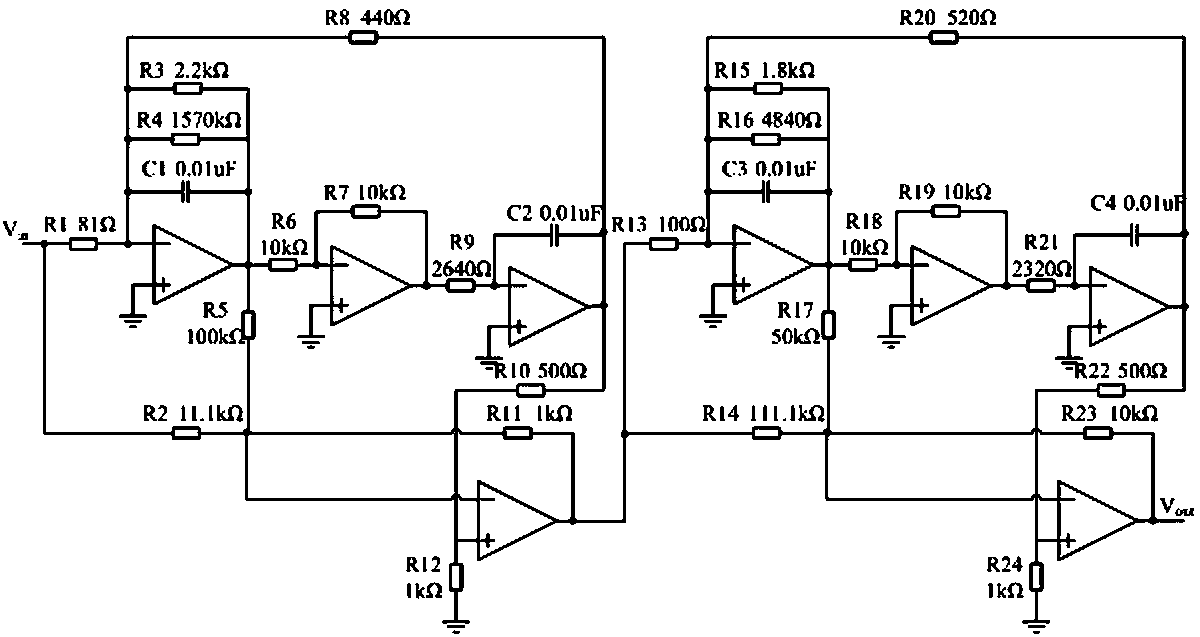
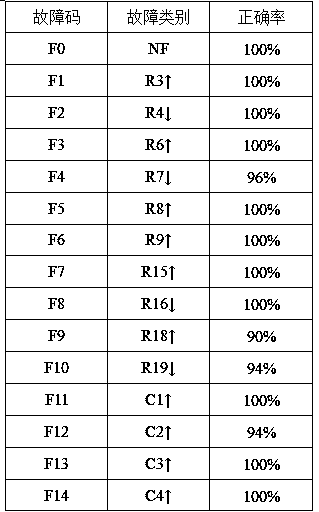
The present invention provides a simulation circuit fault diagnosis method on the basis of a generalized multi-nuclear support vector machine. The method comprises the following steps: (1) collecting time domain response signals of a simulation circuit, namely collecting output voltage signals of a simulation circuit; (2) performing Wavelet Transform of collected voltage signals, taking energy used for calculating wavelet and coefficients as characteristic parameters, wherein the set of all the characteristic parameters is sample data; (3) applying regularization parameters and trade-off parameters of a PSO optimization generalized multi-nuclear support vector machine based on the sample data, and constructing a fault diagnosis model on the basis of GMKL-SVM; (4) taking the constructed fault diagnosis model on the basis of GMKL-SVM as a classifier, and performing fault diagnosis of the simulation circuit. The classification performance of the GMKL-SVM is better than other classification algorithms, and the method for optimization GMKL-SVM parameters by applying PSO is better than a traditional method for obtaining parameters so as to efficiently detect element faults of a simulation circuit.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Integrated surface acoustic wave wireless pressure sensor applied to TPMS
InactiveCN101644616AImprove signal-to-noise ratioGood signal to noise ratioThermometers using physical/chemical changesTyre measurementsAdhesiveEngineering
The invention relates to an integrated surface acoustic wave wireless pressure sensor applied to a TPMS, comprising two SAW reflection delay lines which are encapsulated for integration with a JSR membrane by a nickel conducting cylinder and a conducting adhesive, and a matched network connected with a wireless antenna, wherein, the first SAW reflection delay line comprises a single-phase unidirectional energy converter for controlling electrode width, and 3 short-circuit gate reflectors applied to pressure detection; and the second SAW reflection delay line comprises 11 short-circuit gate reflectors, wherein, 8 reflector are used for 8-bit electronic tags, and the other 3 reflectors are used for temperature detection. In the sensor, an EWC / SPUDT receives an electromagnetic wave signal from a wireless reading unit by the wireless antenna and transforms the signal into an SAW signal which is propagated along the surface of a piezoelectric substrate and is respectively reflected by the reflectors, the reflected acoustic wave is retransformed into the electromagnetic wave signal by the EWC / SPUDT and is returned to the wireless reading unit by the wireless antenna, and finally temperature and pressure detection in a tire is realized at the same time by evaluation of a phase change of time-domain response via a signal processing method.
Owner:INST OF ACOUSTICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
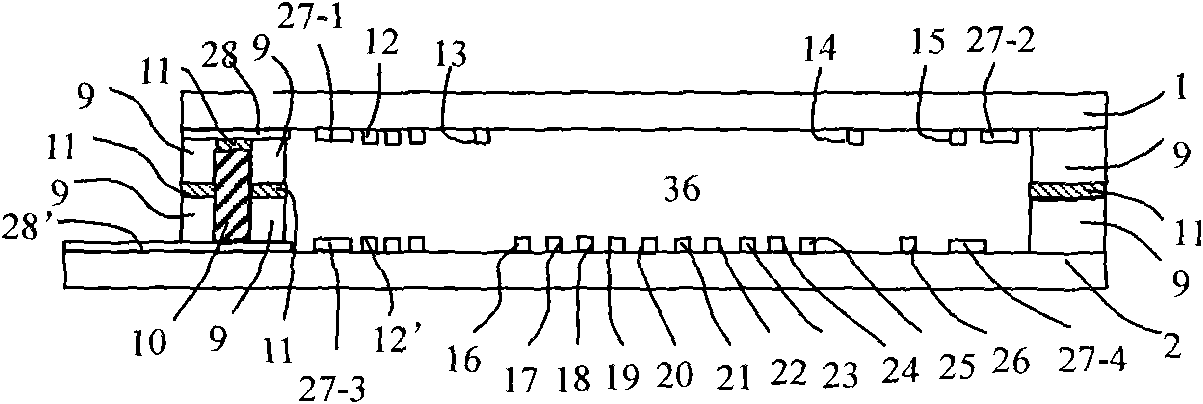
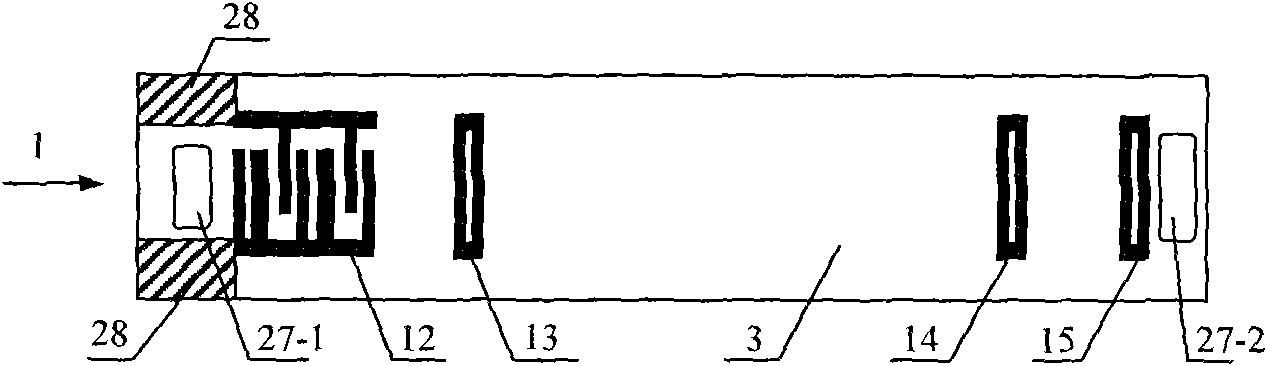
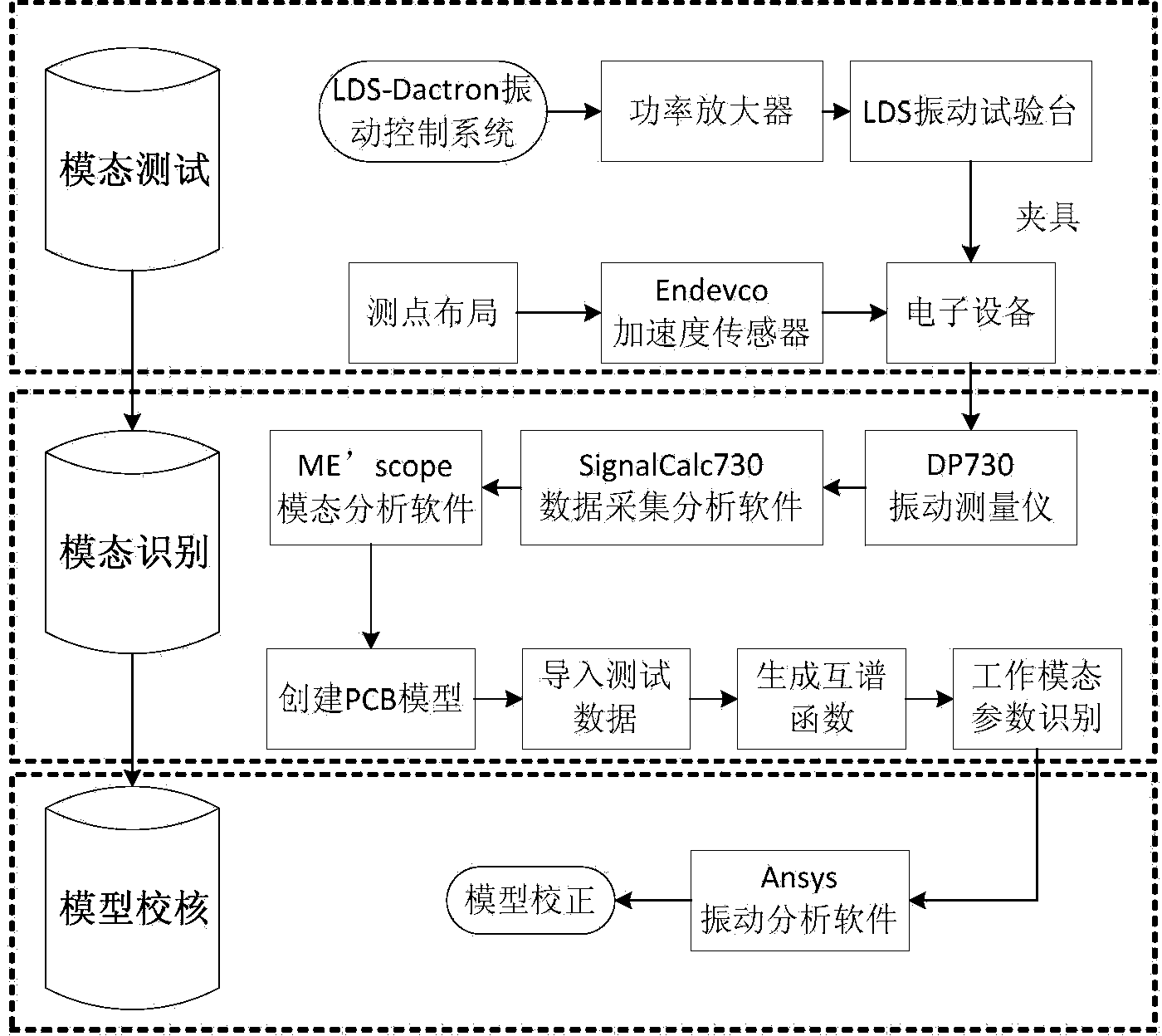
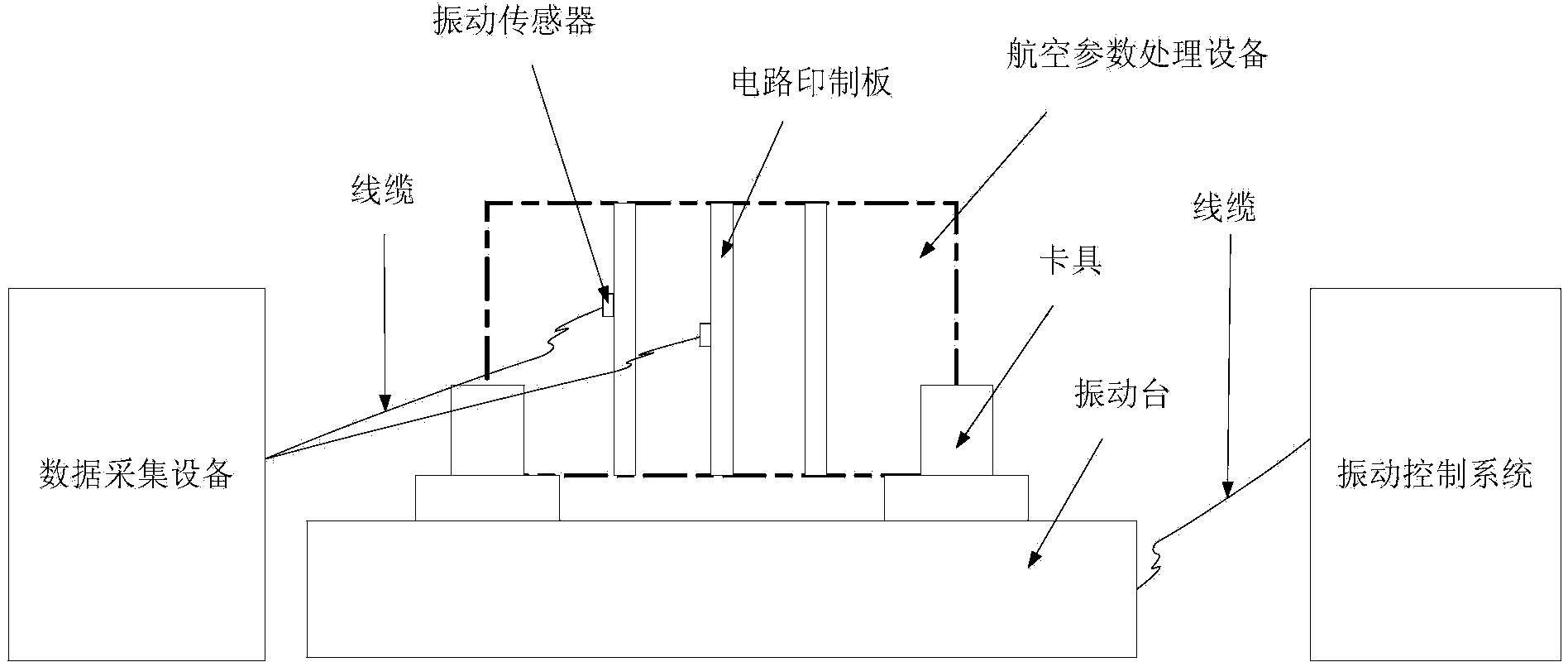
Avionic device operating modal measuring method for vibration finite element model correction
ActiveCN103983412ASpeed up the development processSave testing timeVibration testingModal testingElement model
The invention provides an avionic device operating modal measuring method for vibration finite element model correction. The method includes the following steps that firstly, response test points are arranged, and piezoelectric acceleration transducers are pasted, wherein the n response test points are arranged on a circuit board, and the piezoelectric acceleration transducers are pasted on the response test points respectively; secondly, an avionic device and a test device are installed, and an operating modal test platform is built; thirdly, time domain response data of the avionic device under the random vibration condition are acquired; fourthly, data processing is conducted through modal recognition software, and operating modal parameters of the avionic device are acquired. Through the steps, an avionic device operating modal measuring system for vibration finite element model correction is established, and the overall process from generation of random vibration signals to acquisition of the time domain response data and from generation of a time domain response data sample and a cross-spectrum function to recognition of the operating modal parameters of the avionic device is finished. According to the method, online modal recognition is achieved, and test time is saved and test cost is reduced.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
System and user interface for producing acoustic response predictions via a communications network
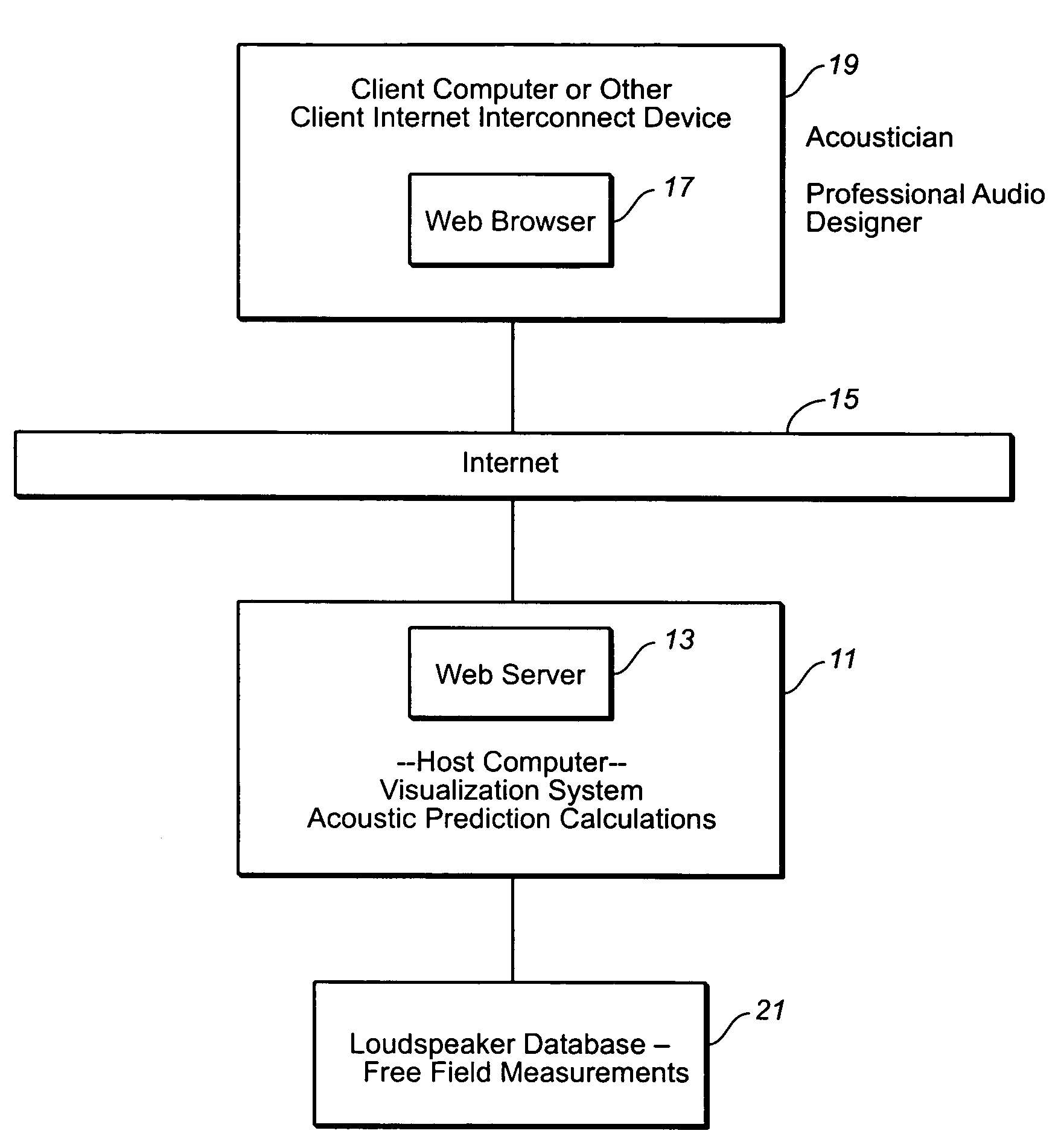
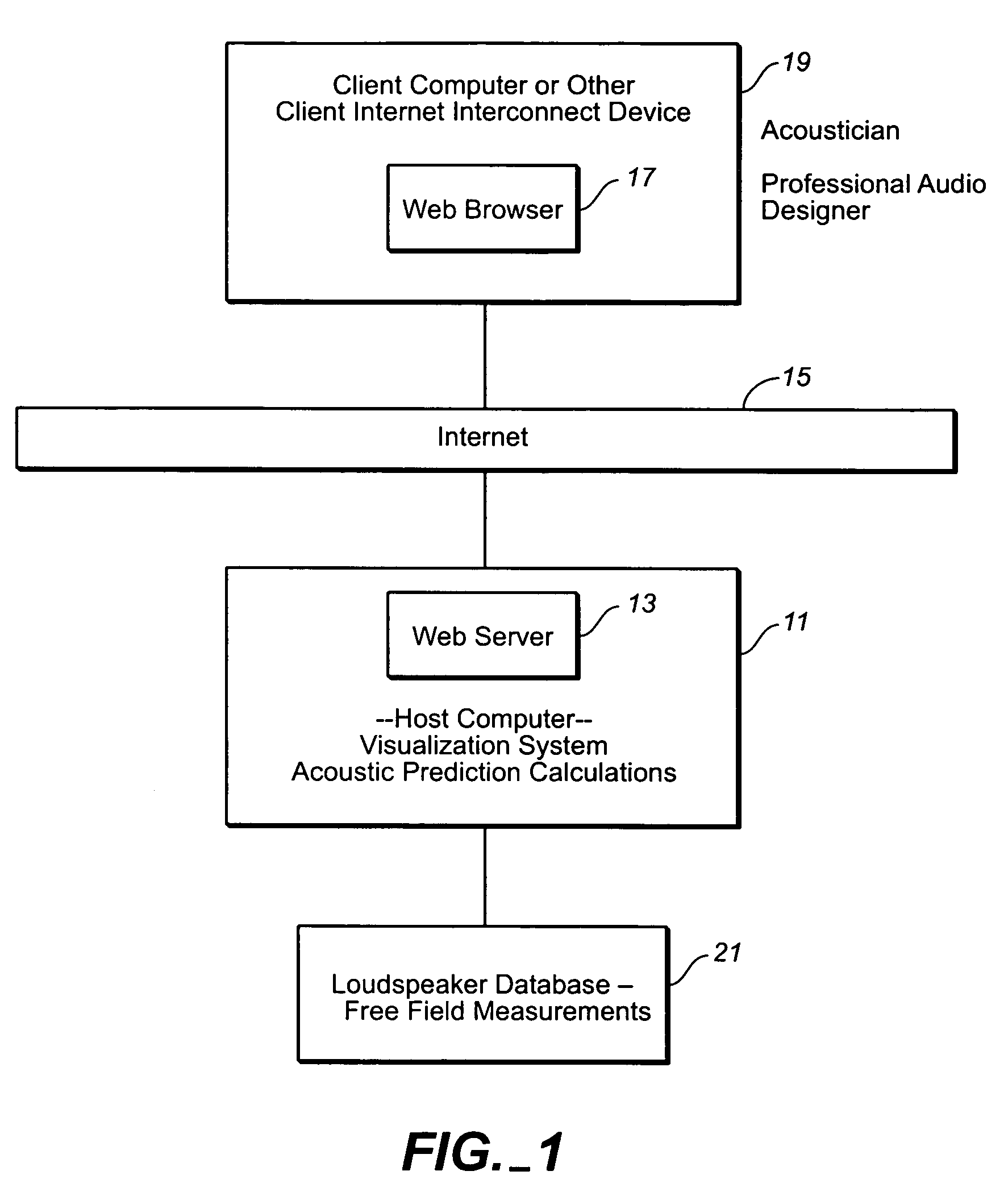
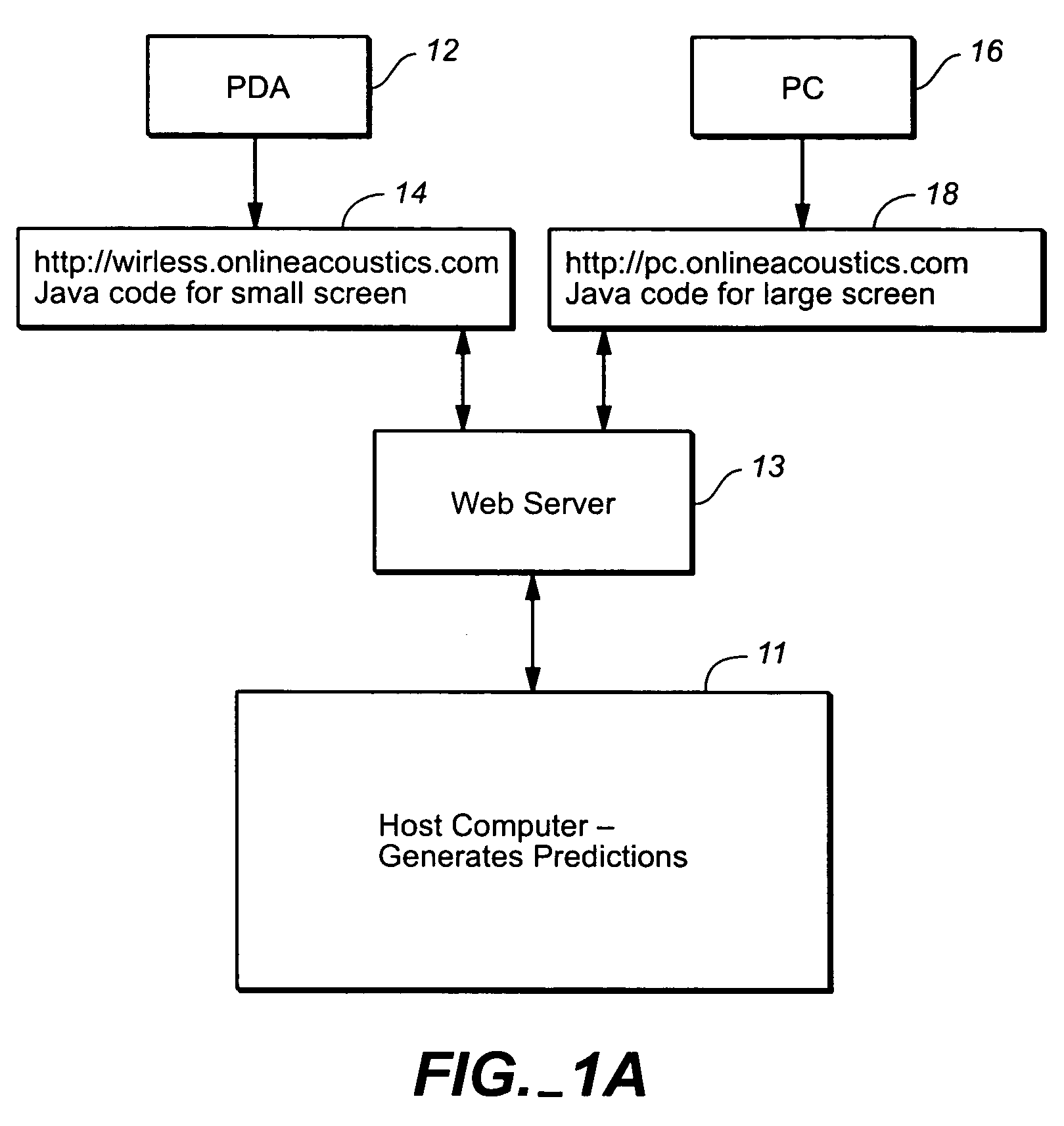
InactiveUS7069219B2Easy to handleMinimization requirementsElectrical transducersSpeech analysisThe InternetTime domain response
A web hosted system and user interface in a client-server architecture permits audio designers to perform acoustic prediction calculations from a thin client computer. A client computer or other Internet connect device having a display screen is used by an audio professional to access via the Internet a host computer which performs acoustic prediction calculations and returns results of the calculations to the client. The results of the calculations are returned in the form of data visualizations, such as an area view showing visualizations of sound pressure levels within a defined space, an impulse view showing the time domain response at a defined location, and / or a frequency domain view showing the frequency response at a defined location. Calculations are performed based on user-defined inputs, such as speaker type and location, sent to the host computer from the client computer and based on retrieval of loudspeaker data from one or more databases accessible by the host computer.
Owner:MEYER SOUND LABORATORIES
One-Port De-embedding Using Time Domain Substitution
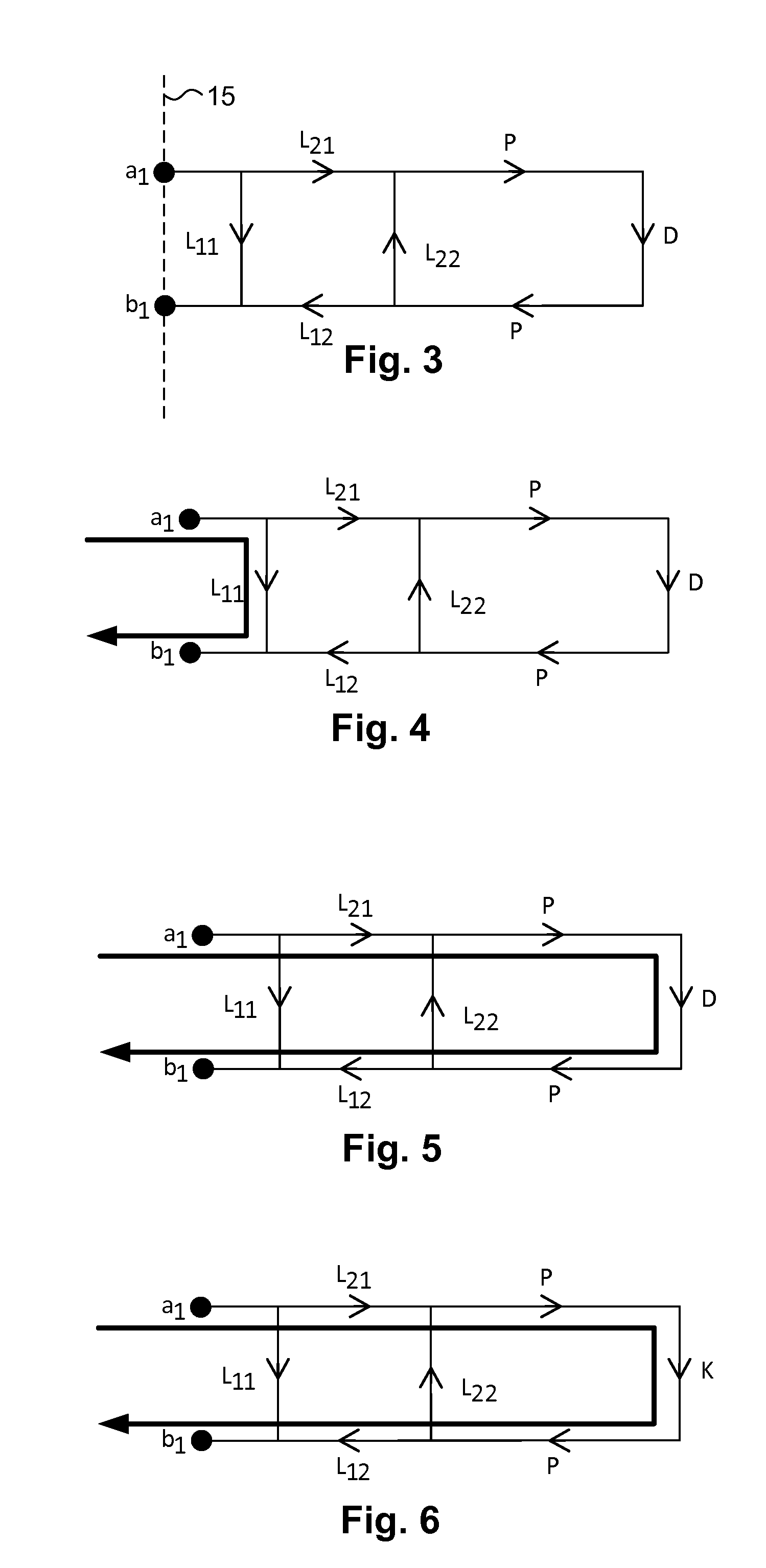
InactiveUS20110238383A1Readily and easily solvedAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceResistance/reactance/impedencePower gridTime domain response
A method is provided for de-embedding the S-parameter response of an electrical DUT embedded in an electrical network. The method comprises making first and second S-parameter measurements in the frequency domain at a port or measurement reference plane to the network containing the DUT. For the second measurement, a known impedance condition is created at the embedded location of the DUT. The first and second measurements are transformed to the time domain, and then gated to select portions of the time-domain-transformed responses that correspond to paths that include the DUT and known impedance condition, respectively. The gated time domain responses are then transformed back into the frequency domain, yielding first and second selected S-parameter measurement responses M1 and M2, respectively. A reflection S-parameter for the DUT is then determined as a function of the first and second selected S-parameter measurement responses and the known impedance condition.
Owner:CONSTANT WAVE
Surface acoustic wave electric current sensor
InactiveCN103954823AImprove temperature stabilityHigh detection sensitivityCurrent/voltage measurementVibrating membraneElectricity
Owner:INST OF ACOUSTICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Ultrasonic transducer and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN104722469AEfficient use ofImproved Time Domain ResponseMechanical vibrations separationUltrasonic sensorTransducer
The invention belongs to the technical field of transducers, and provides an ultrasonic transducer and a manufacturing method thereof. The ultrasonic transducer comprises a piezoelectric layer, a matching layer, a tuning layer and a backing layer. The piezoelectric layer is used for radiating ultrasonic wave signals forwards or backwards, and electrodes are plated on the two sides of the piezoelectric layer respectively. The matching layer is arranged at the front end of the piezoelectric layer and used for transmitting the ultrasonic wave signals radiated forwards. The tuning layer is arranged at the rear end of the piezoelectric layer located between the tuning layer and the matching layer. The backing layer is used for absorbing the ultrasonic wave signals radiated backwards by the piezoelectric layer and located on the side, deviating from the piezoelectric layer, of the tuning layer. Through arranging the tuning layer between the piezoelectric layer and the backing layer, the ultrasonic wave signals radiated backwards by the piezoelectric layer are effectively utilized, it is avoided that part of the ultrasonic wave signals enter the backing layer to be attenuated in a heat energy mode, meanwhile, the tuning layer is used for tuning pulse reverb of an ultrasonic probe, and therefore the time-domain response and frequency-domain response of the ultrasonic transducer are improved to a certain degree.
Owner:EDAN INSTR
Method for calculating vehicle interior noise
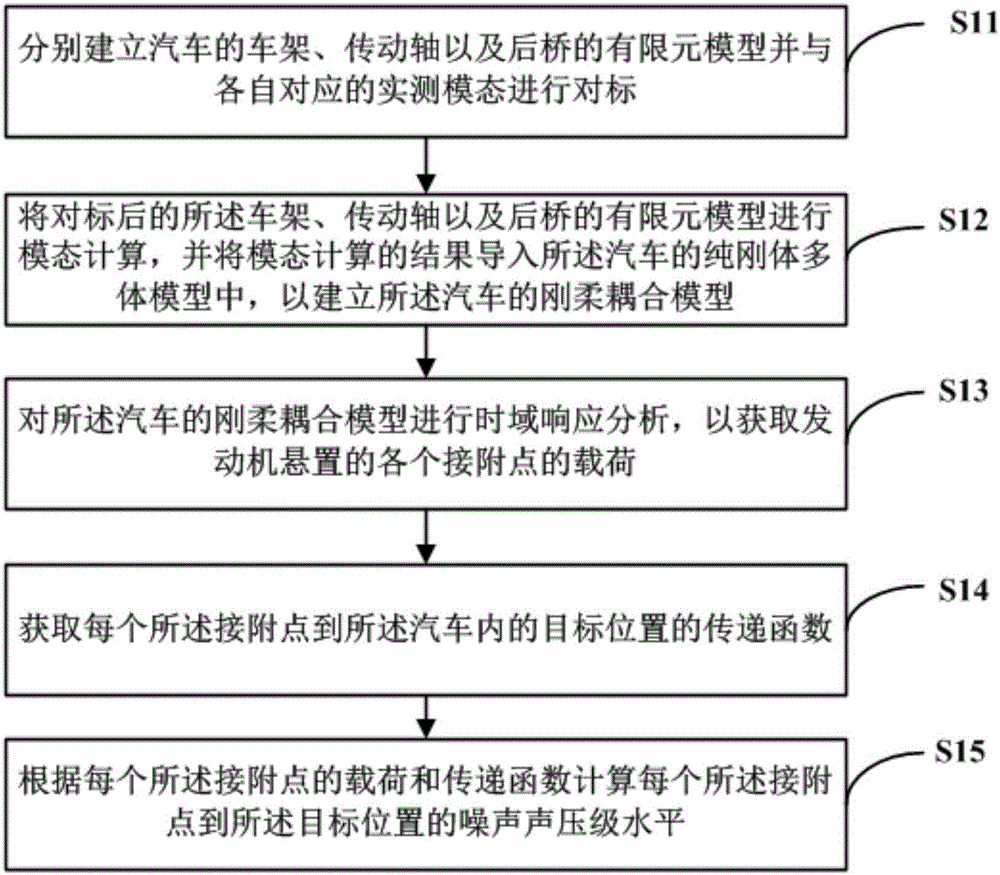
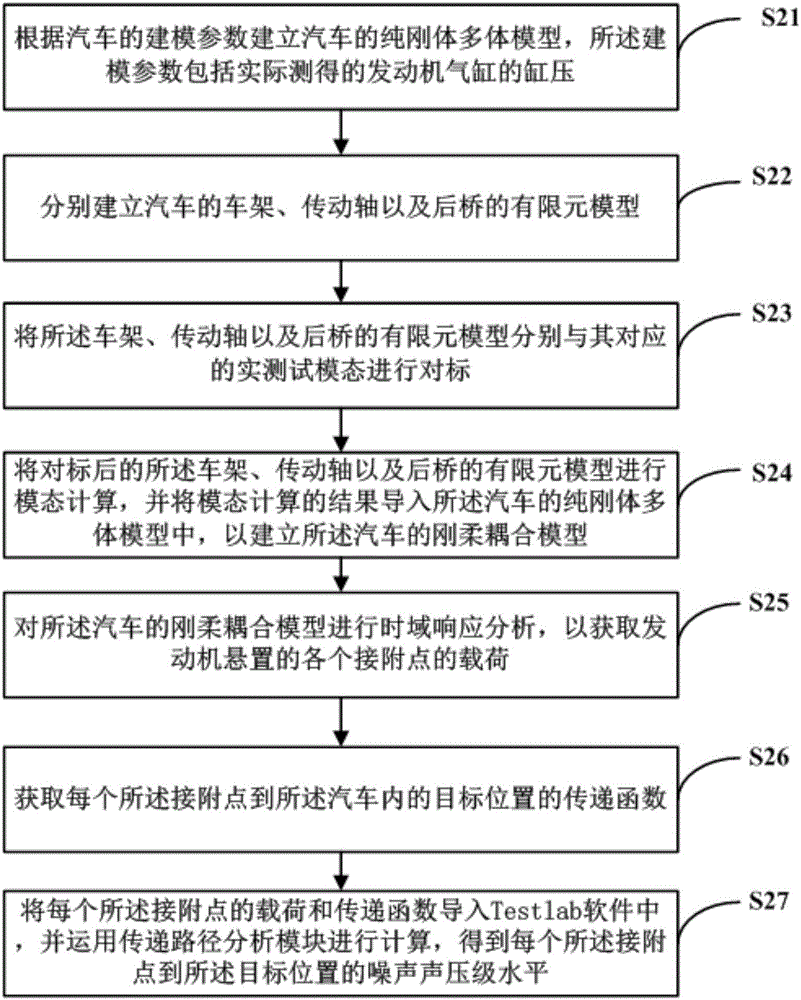
ActiveCN106845015AAccurate noise sound pressure levelGeometric CADSustainable transportationVehicle frameElement model
A method for calculating vehicle interior noise comprises steps as follows: finite element models of a vehicle frame, a transmission shaft and a rear axle of an automobile are established respectively, and benchmarking is performed between the finite element models and corresponding actually measured modes; modal calculation is performed on the finite element models of the vehicle frame, the transmission shaft and the rear axle after benchmarking, and modal calculation results are imported into a pure rigid multi-body model of a vehicle for establishment of a rigid-flexible coupled model; the rigid-flexible coupled model is subjected to time-domain response analysis, so that loads at connecting points during engine mounting are acquired; a transfer function from each connecting point to a target position in the vehicle is acquired; the noise pressure level from each connecting point to the target position is calculated according to the load of the corresponding connecting point and the corresponding transfer function. The accurate load data of each connecting point is extracted through the rigid-flexible coupled model of the vehicle, and the accurate noise pressure level in the vehicle is acquired in real time in the time domain of each connecting point during engine mounting in combination with the corresponding transfer function.
Owner:JIANGLING MOTORS
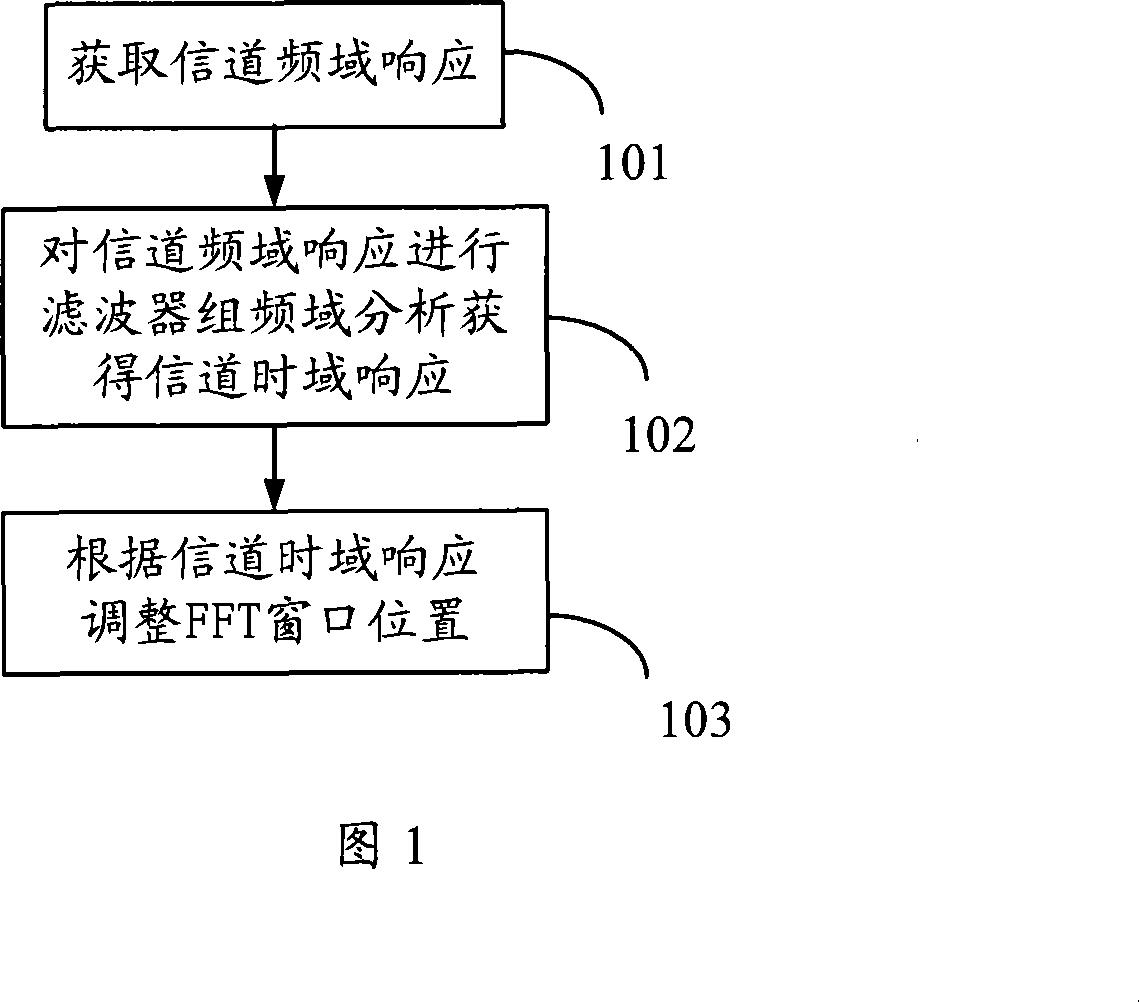
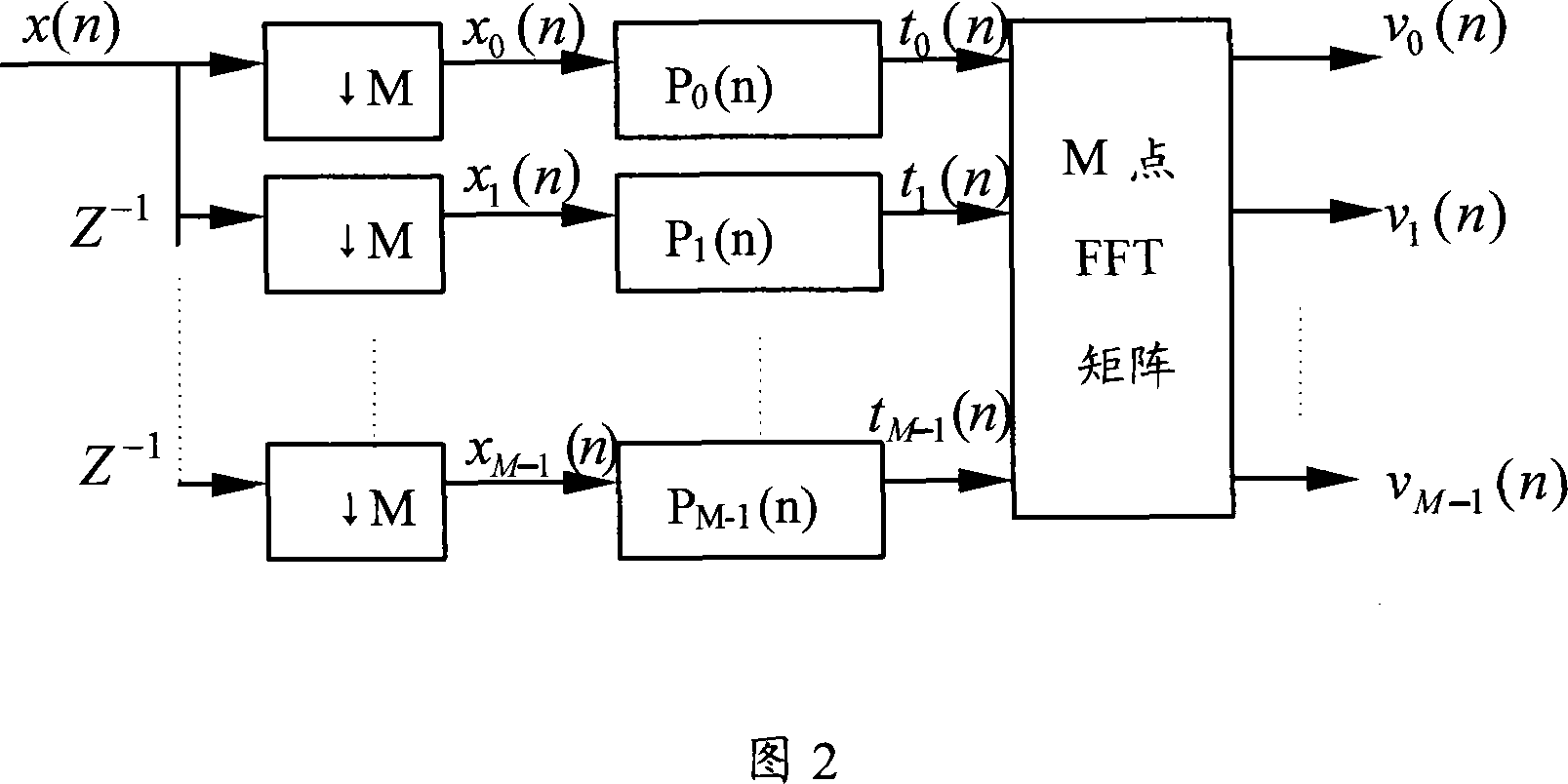
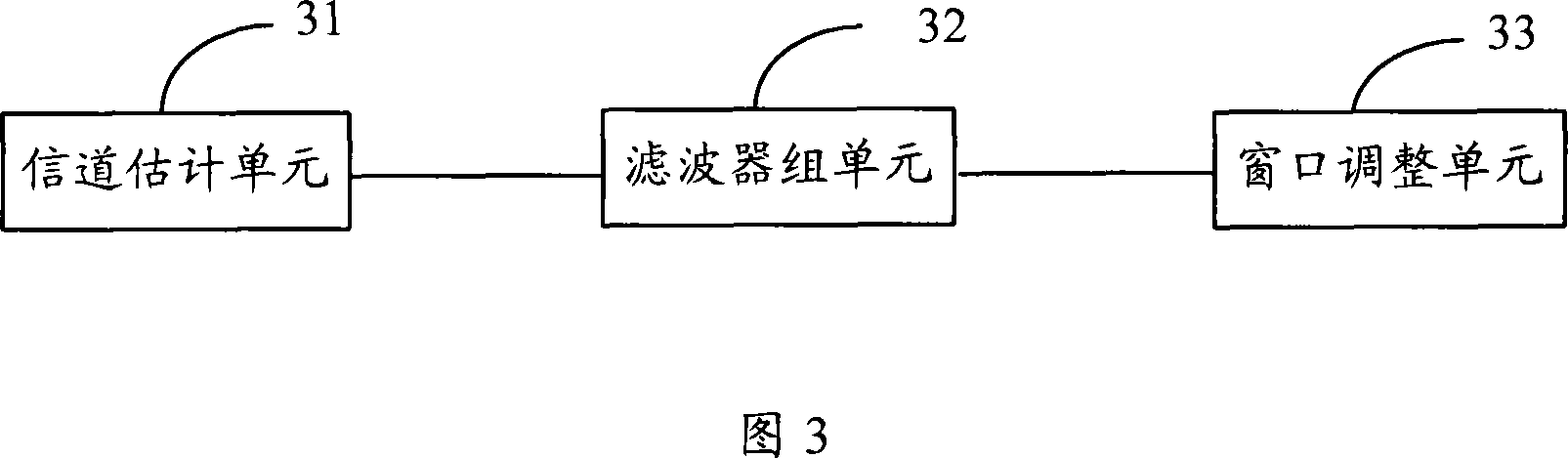
Method and device for getting channel time domain response, OFDM fine symbol synchronizing method and device
InactiveCN101068232AMeet the reliability requirements of fine synchronizationReduce operationMulti-frequency code systemsFast Fourier transformImage resolution
A method for obtaining time domain response of channel includes carrying out filter set treatment on channel frequency domain response corresponding to symbol of orthogonal frequency division multiplexing to obtain corresponding channel time domain response, setting resolution ratio of channel time domain response to be greater than time resolution ratio of channel time domain response obtained by using channel frequency domain as IFFT transform and regulating position of fast Fourier transform window according to said channel time domain response.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Equivalent time sampling system
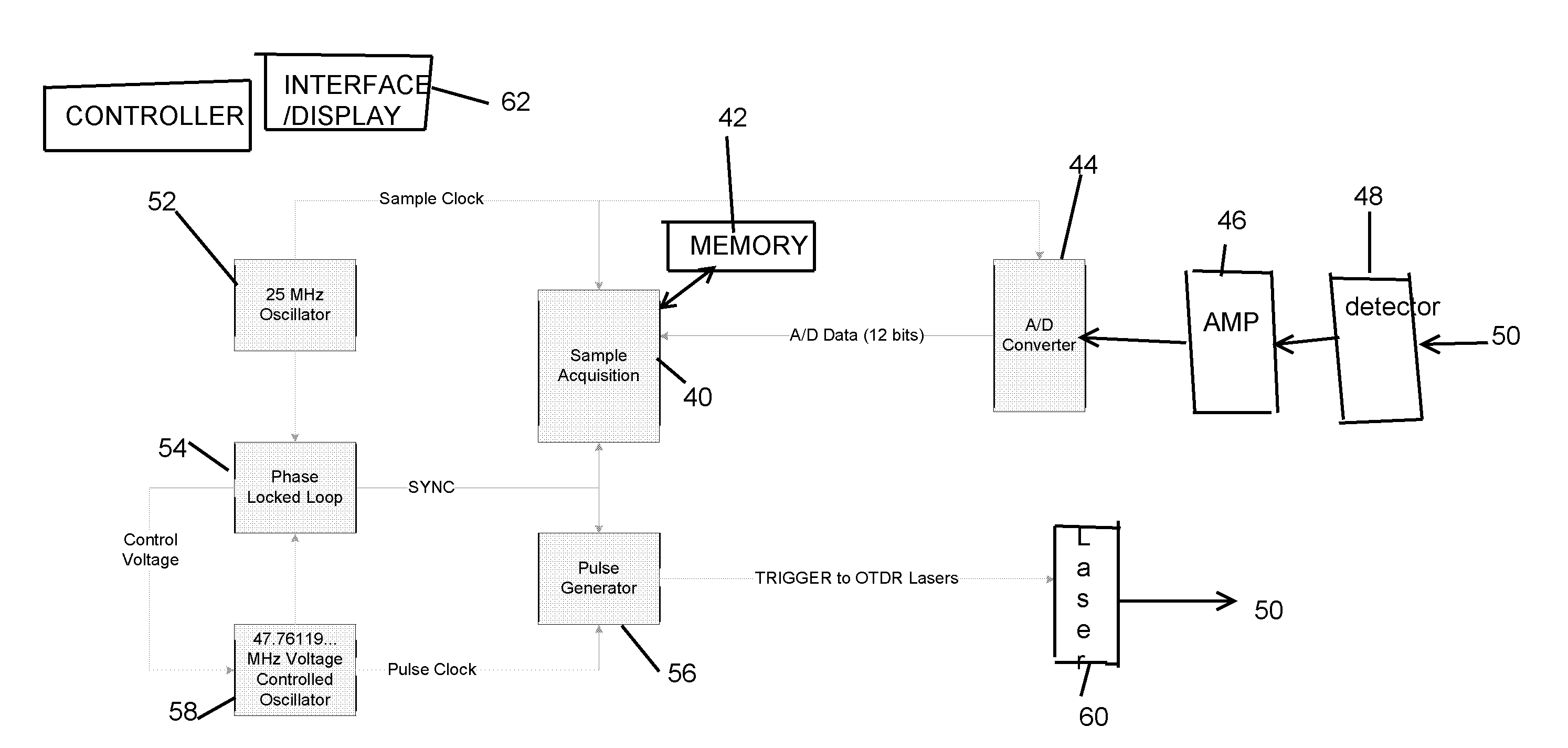
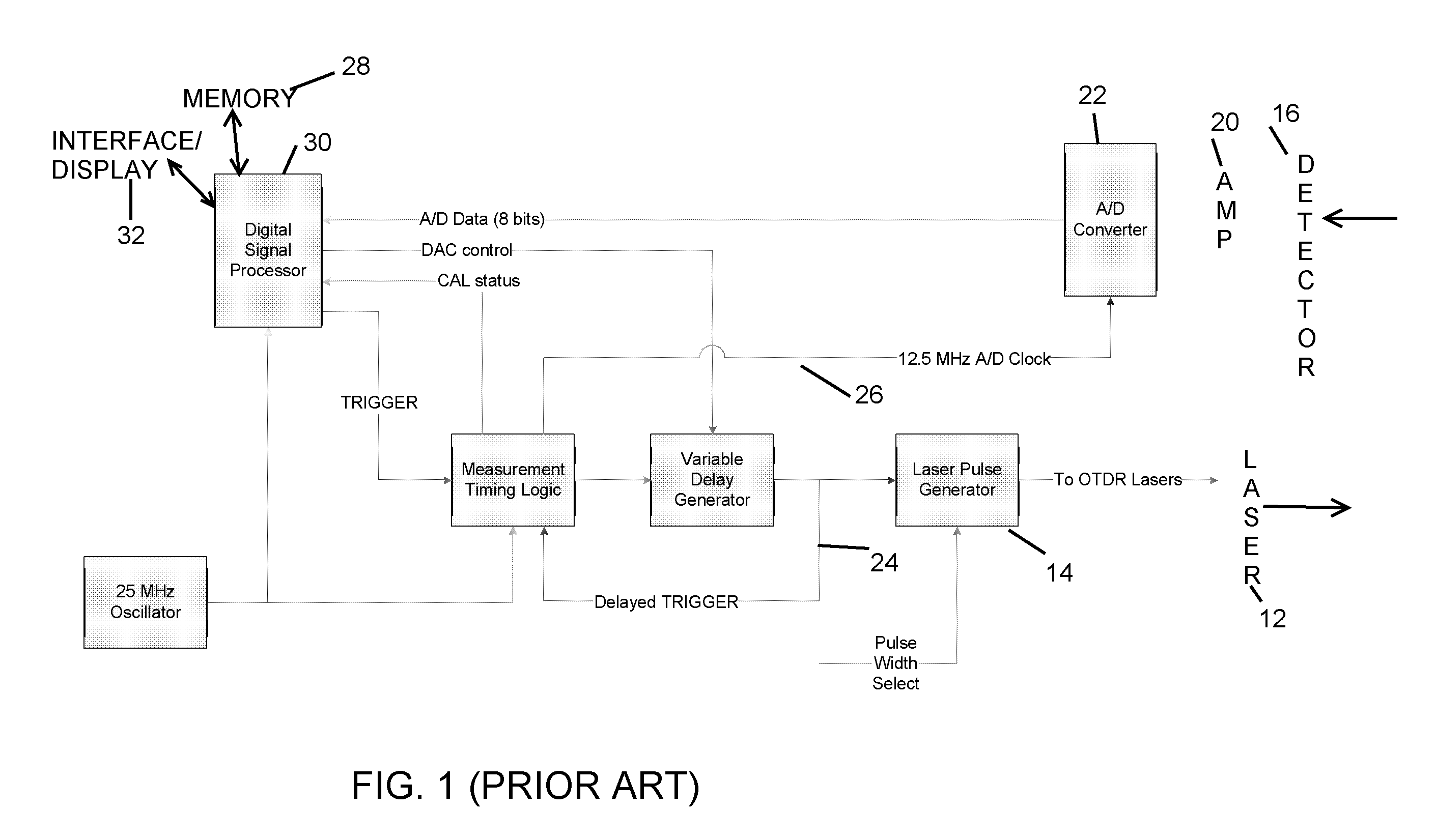
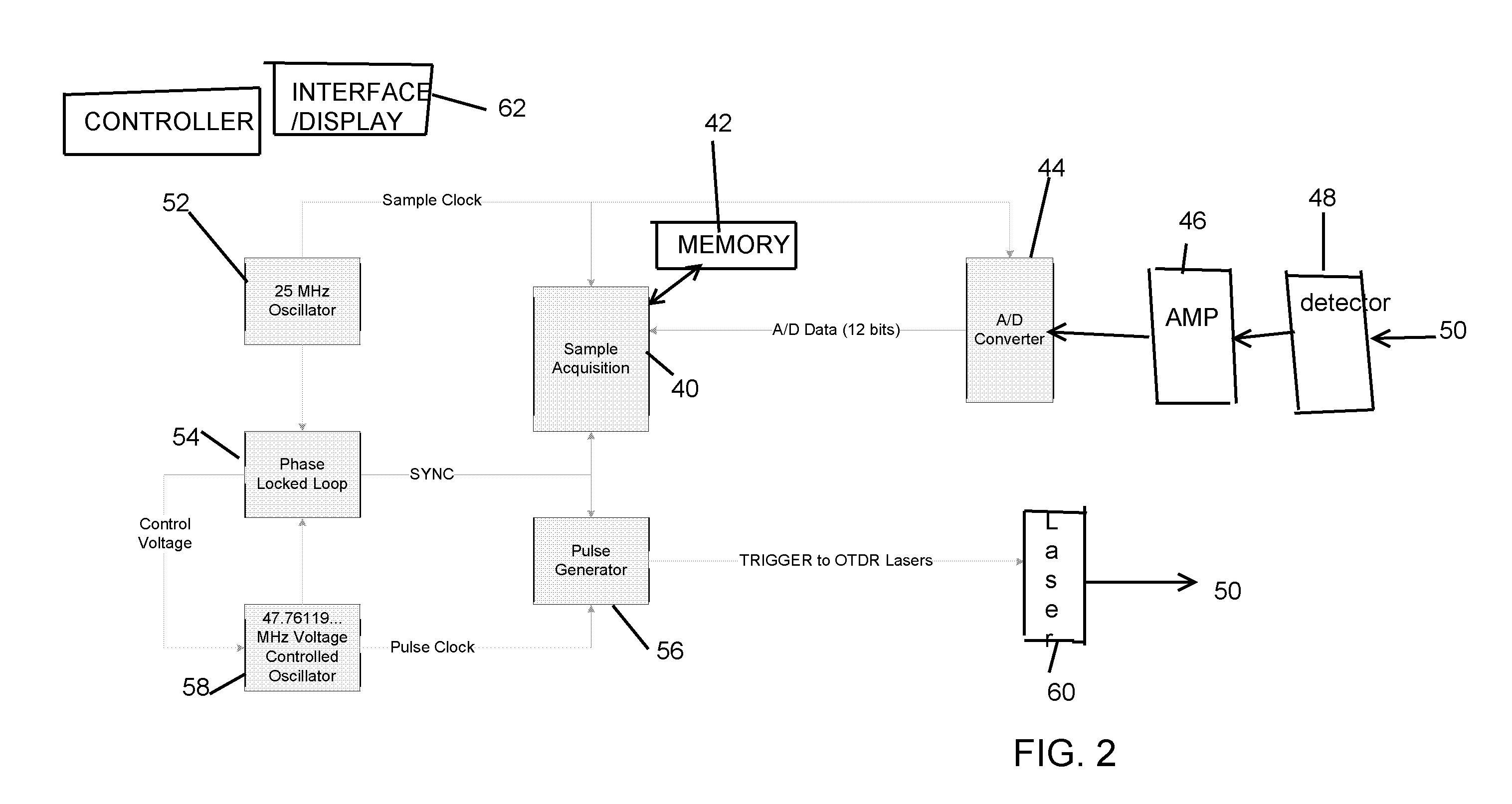
ActiveUS20080013079A1Material analysis by optical meansReflectometers detecting back-scattered light in time-domainTime-domain reflectometerClock rate
An equivalent time sampling system employs two clock frequency sources, phase locked, wherein an analog to digital converter sampling clock is derived from one source and a pulse generator clock is derived from the other. Choice of the clock frequencies determines minimum time step and the set of available time steps, and pulse repetition period determines the time step size, for equivalent time sampling. The system is suitably implemented in a time domain reflectometer, optical time domain reflectometry system, or other systems for obtaining time domain responses to a periodic stimulus of a system under test, with stimulus rate and the sampling intervals varying over a wide range.
Owner:JOHN FLUKE MFG CO INC
An analog circuit fault diagnosis method based on cross-wavelet characteristics
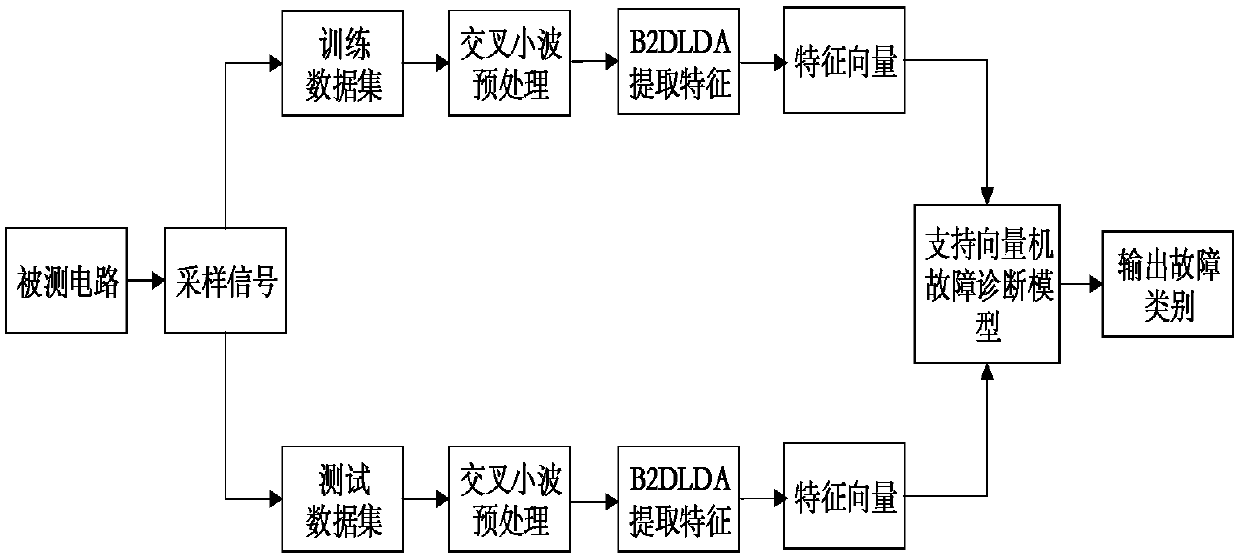
ActiveCN107894564AFast and accurate fault classificationAccurate fault diagnosisAnalog circuit testingSpecial data processing applicationsOriginal dataTime domain response
The invention provides an analog circuit fault diagnosis method based on cross-wavelet characteristics. The method comprises the following steps: inputting an excitation signal to a tested analog circuit, collecting time-domain response output signals and constructing an original data sample set; dividing the original data sample set into a training sample set and a test sample set; carrying out cross wavelet decomposition on the training sample set and the test sample set to obtain a wavelet cross spectrum of the training sample set and the test sample set; carrying out processing on the wavelet cross spectrum of the training sample set and the test sample set through bidirectional two-dimensional linear discriminant analysis, and extracting fault feature vectors of the training sample set and the test sample set; submitting the fault feature vectors of the training sample set to a support vector machine for training an SVM classifier, and constructing a support vector machine fault diagnosis model; and inputting the fault feature vectors of the test sample set to the model and carrying out fault classification. The method can effectively identify the fault of the analog circuit,and obviously improve fault diagnosis precision of the analog circuit.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
System and method for multiple signal carrier time domain channel estimation
InactiveUS20060188034A1Amplitude-modulated carrier systemsSecret communicationTransceiverCarrier signal
The present invention provides a method of characterizing a frequency response of a transmission channel between a transceiver and a subscriber unit. The method includes once per predetermined interval of time, the transceiver transmitting a signal including multiple carriers, a plurality of the carriers including training symbols, a plurality of the carriers including information symbols. The subscriber unit generates frequency response estimates at the frequencies of the carriers including training symbols, each interval of time. The frequency response estimates are converted into a time domain response generating an impulse response once per interval of time. The impulse responses are filtered over a plurality of intervals of time. A channel profile is determined from the filtered impulse responses. The channel profile is converted to the frequency domain generating a channel interpolator. The characterized frequency response is generated from the channel interpolator and the frequency response estimates. The filtering can include averaging the impulse responses over a plurality of intervals of time, accumulating the impulse responses over a plurality of intervals of time, or weighted averaging of the impulse responses over a plurality of intervals of time. The weighted averaging can be dependent upon a phase error between the impulse responses, and / or an amplitude error between the impulse responses.
Owner:INTEL CORP
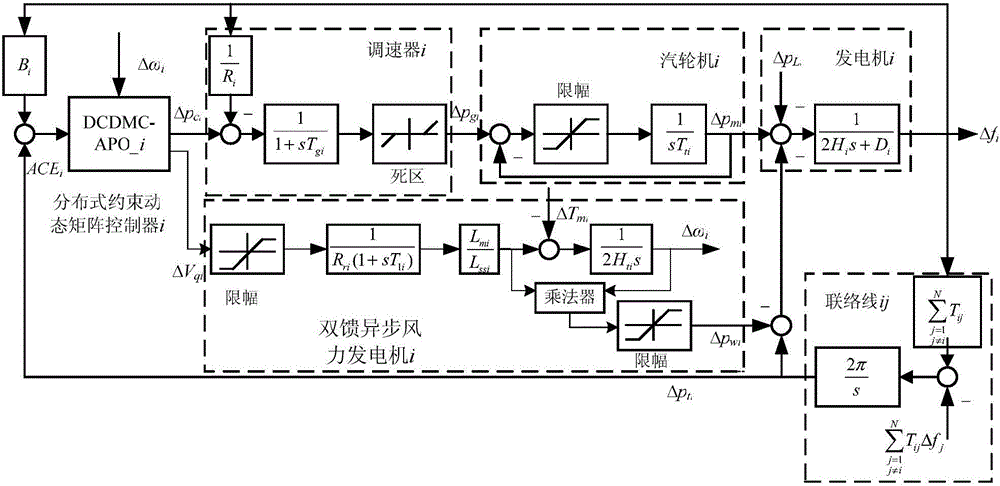
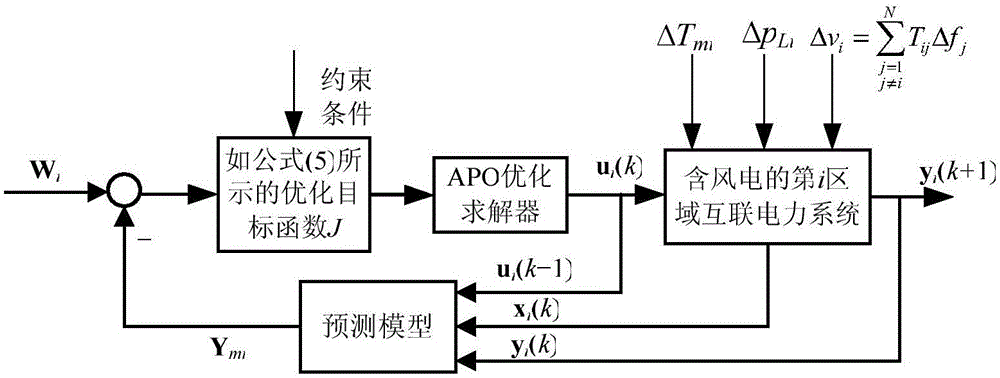
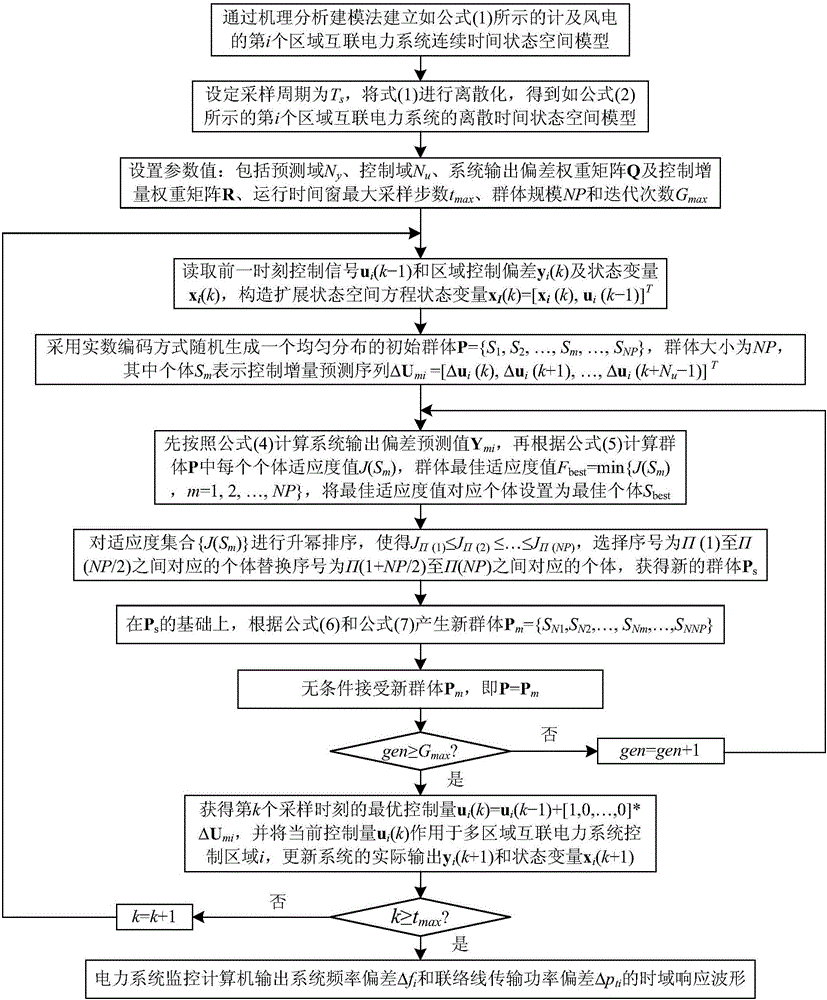
Distributed dynamic matrix frequency control method of interconnected power system considering wind power
ActiveCN106786677AShort adjustment timeSmall dynamic oscillation amplitudePower oscillations reduction/preventionElectric power systemAngular velocity
The invention discloses a distributed dynamic matrix frequency control method of interconnected power systems considering wind power, comprising the following steps: establishing a distributed discrete time state space model of the interconnected power systems considering the wind power based on a mechanism analysis modeling method and a discretization method, designing respective area control errors and quadratic control performance indexes weighted by a fan angular velocity output prediction deviation vector and a control increment prediction vector as rolling optimized objective functions, considering respective constraint conditions of a system output prediction deviation, a control prediction signal and an increment prediction signal, adopting a distributed constraint dynamic matrix control method based on a self-adaptive colony optimization strategy to realize load frequency coordinated optimization and control of the interconnected power systems in respective areas. Compared with the prior art, time domain response of load frequency of the interconnected power systems considering the wind power according to the invention has the advantages of faster regulation time, smaller dynamic oscillation amplitude, smaller steady-state error and higher robust performance.
Owner:WENZHOU UNIVERSITY
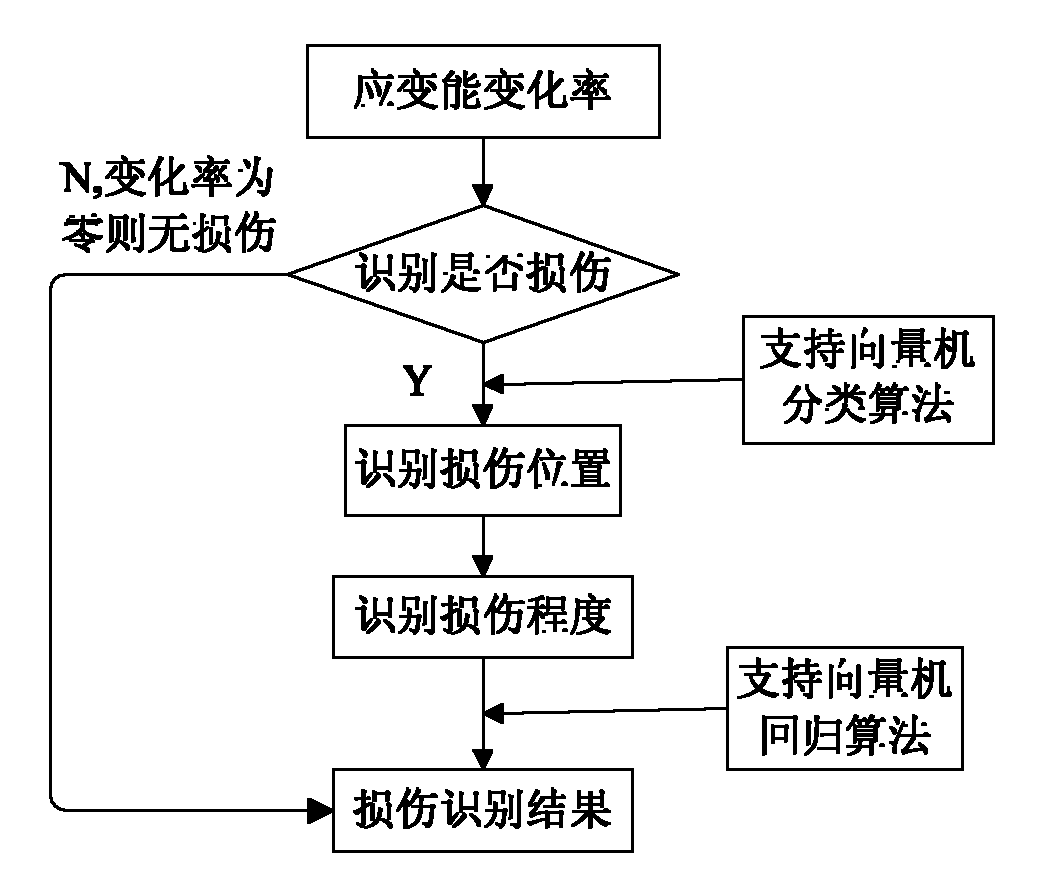
Blade fault diagnostic method based on strain energy response of wind-driven generator
InactiveCN102175449AAccurate diagnosisTimely brakingMachine part testingSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementWind drivenNacelle
The invention relates to a blade fault diagnostic method based on a strain energy response of a wind-driven generator, which comprises the following steps of: (1) obtaining the natural frequencies and the modes of the first M orders of the blade of a wind generator set by performing dynamic modeling and model analytical calculation to the wind generator set; (2) simulating the rotational excitation load of the blade through finite element calculation to the wind generator set to obtain strain energy time domain responses corresponding to the cabin sensor set points of the first M orders of the blade of the wind generator set, and then calculating strain energy frequency domain responses; and (3) obtaining the running state characteristic values of the blade of the wind generator set from the strain energy frequency domain responses corresponding to the cabin sensor set points of the first M orders of the blade of the wind generator set through the strain energy and the rate of change thereof and the method of a support vector machine, and then comparing to obtain a diagnostic result. The blade fault diagnostic method based on the strain energy response of the wind-driven generator related to the invention is simple and easy, high in sensitivity and accuracy and low in diagnostic cost, and can effectively improve the safety and reliability of the blade of the wind generator set and accurately perform fault point positioning, fault qualification and prediction for the blade.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
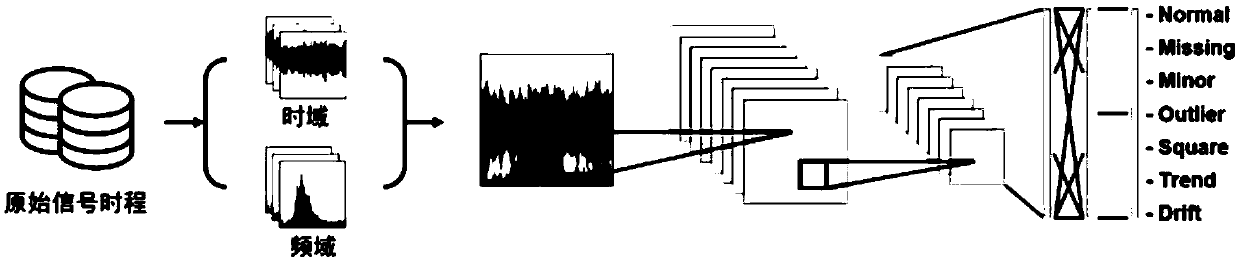
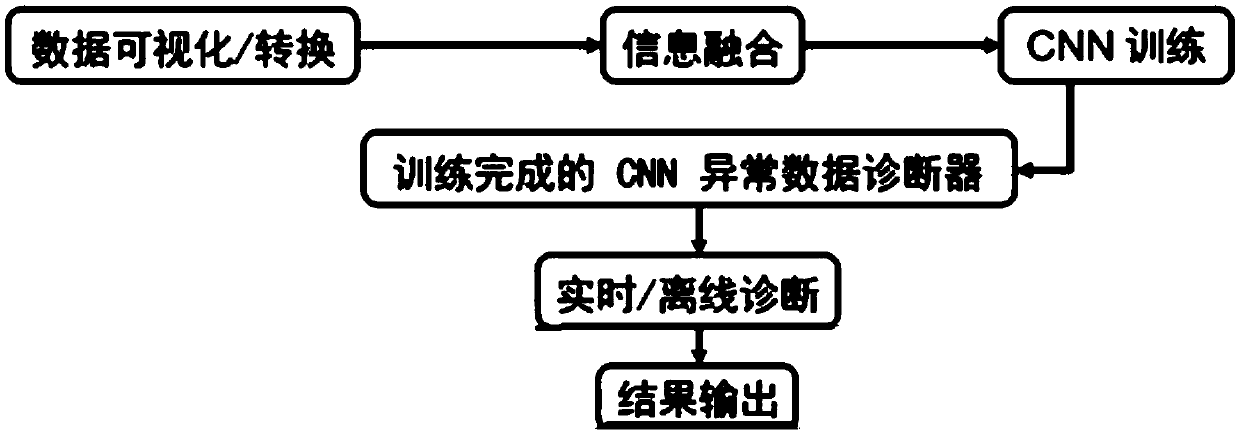
Structural health monitoring abnormal data diagnosis method based on computer vision and deep learning technology
ActiveCN108764601AImprove analysis efficiencyImprove reliabilityResourcesNeural architecturesData segmentPresent method
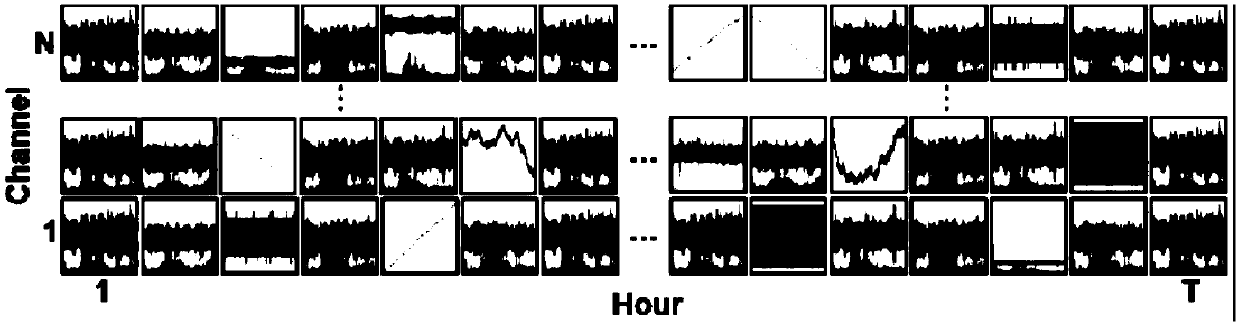
The invention provides a structural health monitoring abnormal data diagnosis method based on computer vision and deep learning technology, and aims at solving the problems of overtreatment and under-treatment due to the fact that the present method has difficulty to handle the situations with multiple abnormal patterns and the disadvantages of low degree of automation and high cost of manual expert intervention. The method comprises the steps that the monitoring data to be diagnosed are converted into the time domain response image data and the frequency domain response image data from the time sequent data through data visualization processing; a two-channel time-frequency response diagram is formed according to the time domain response image data and the frequency domain response imagedata corresponding to the same data segment; the samples are selected from the two-channel time-frequency response diagram and the abnormal type of the samples is marked so as to form a training set;the training set is inputted to a convolutional neural network model, and the trained model acts as the abnormal data diagnosis instrument; and the monitoring data to be diagnosed are inputted to theabnormal data diagnosis instrument so as to obtain the diagnosis result. The method is suitable for structural health data monitoring.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Optimal active time-reversal focusing method based on iterative least square/pre-filtering
ActiveCN101645264ARealize inverse filter focusing in time domainEliminate focus blurAdaptive networkSound producing devicesSound sourcesSonification
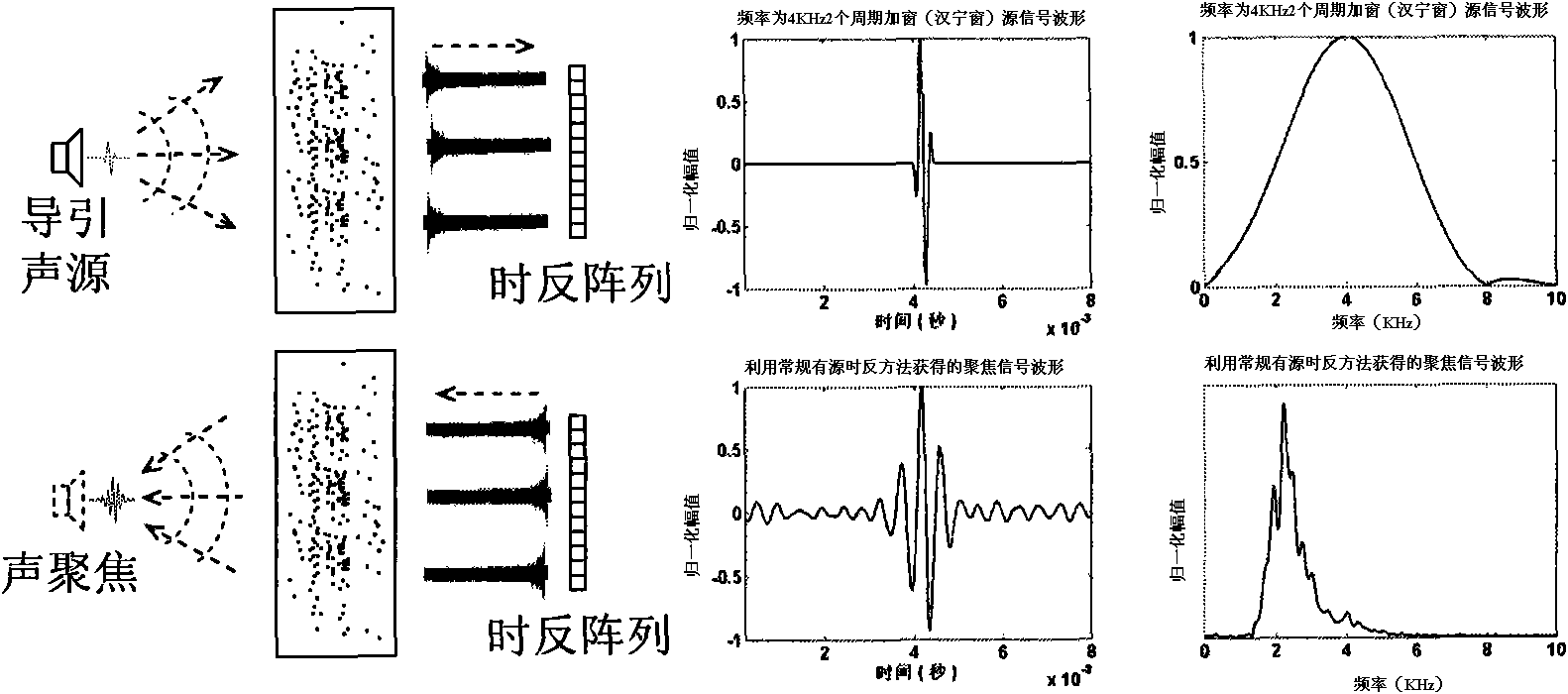
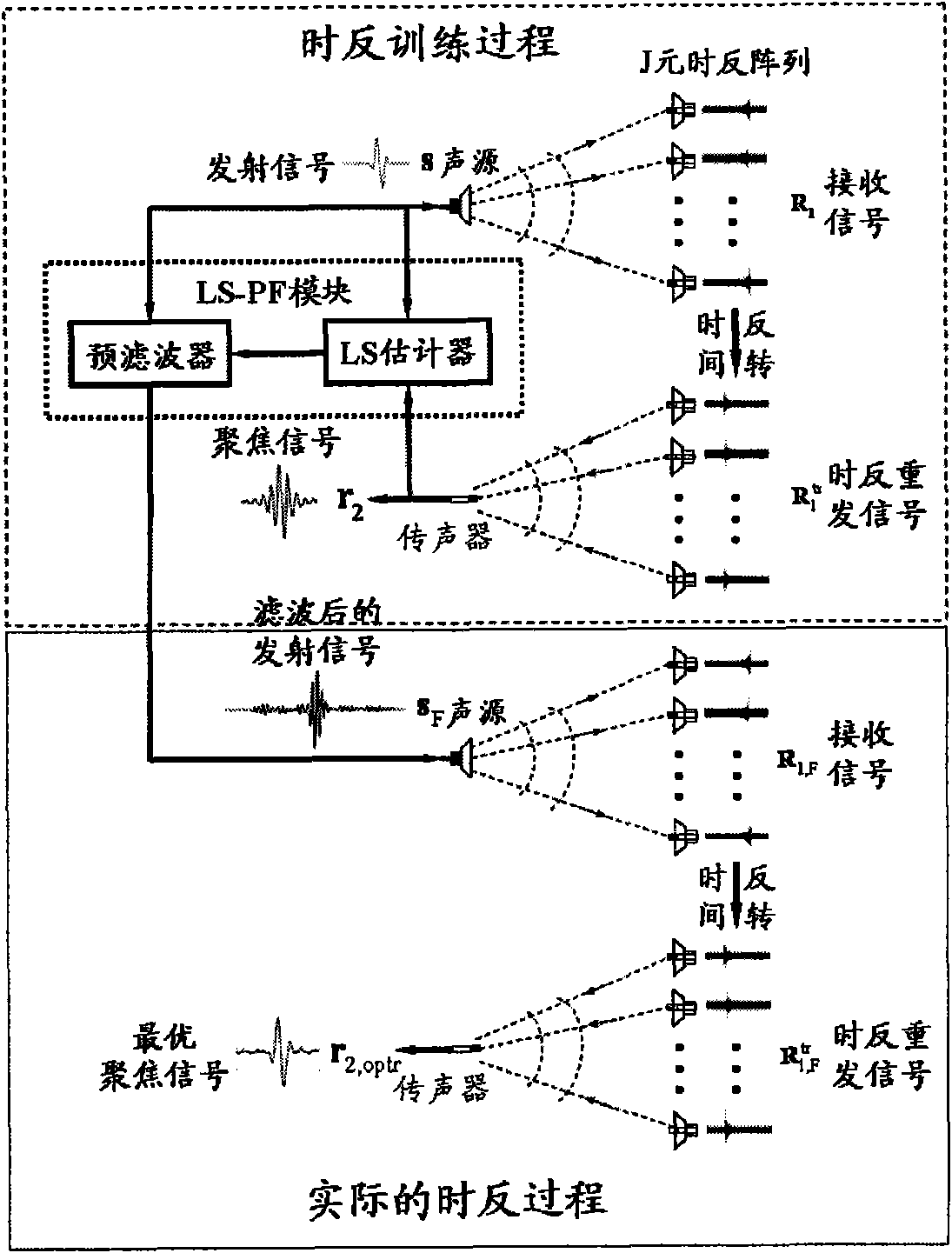
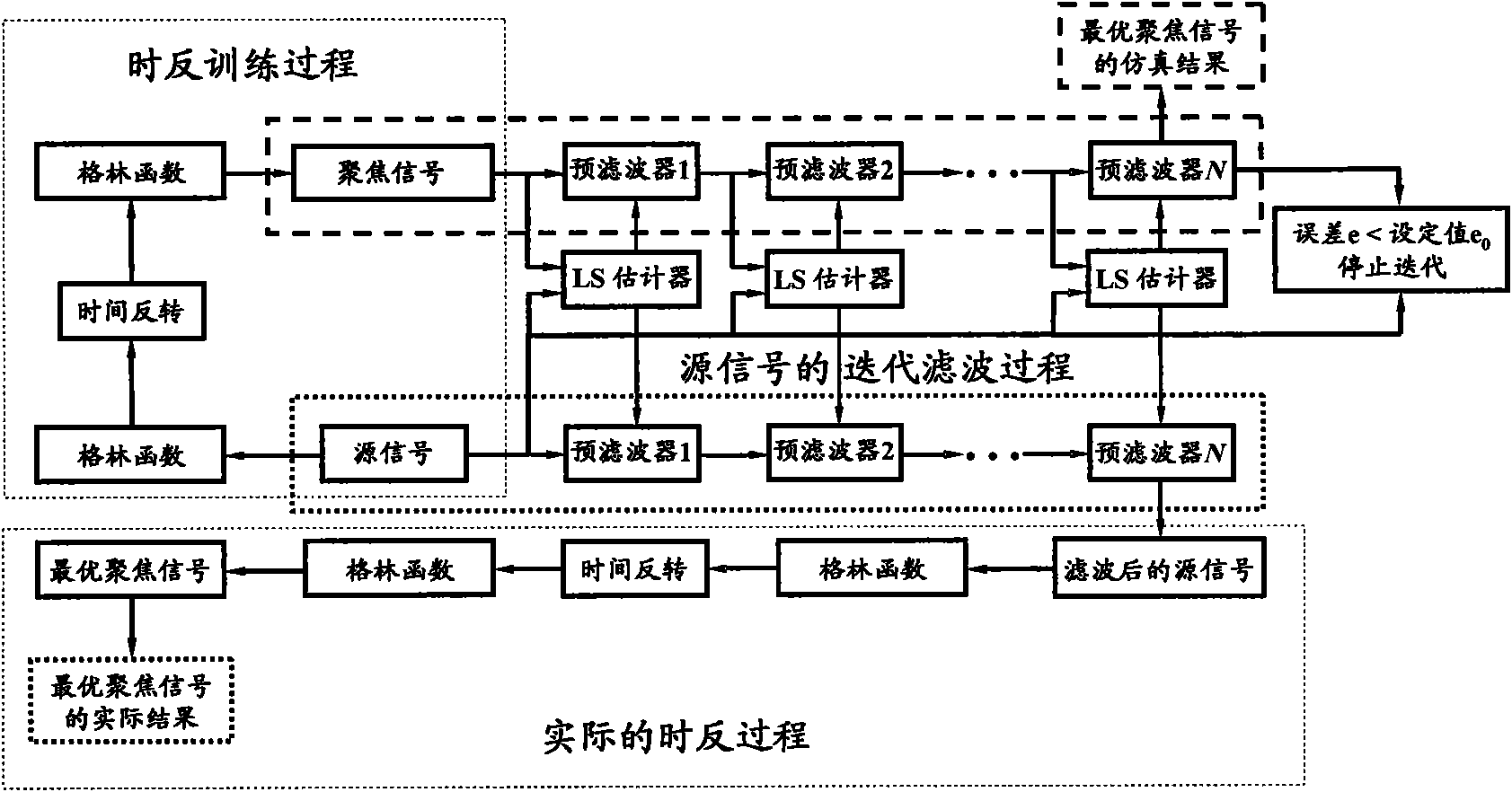
The invention relates to an optimal active time-reversal focusing method based on iterative least square / pre-filtering. The method comprises the following steps: 1) sending source signals by a guide sound source, and conducting the operations of receiving, time-reversal and re-sending by a time-reversal array according to the conventional active time-reversal process, so as to acquire focusing signals at the location point of the sound source, wherein the source signals are wideband pulse signals with the bandwidth being 20Hz to 200kHz and the frequency range being within an audible sound or ultrasound frequency band range; 2) estimating a plurality of cascaded pre-filter time-domain responses used for carrying out the filtration treatment on the source signals on the basis of the iterative least square rule by combining the source signals and the focusing signals; and 3) re-sending the pre-filtered source signals by the guide sound source, and carrying out the operations of receiving,time-reversal and re-sending by the time-reversal array according to the conventional time-reversal process, so as to acquire the optimal focusing signal waveform at the location of the sound source.The invention can achieve the inverse-filtering and focusing effects within the time domains and recover the waveform of the source signals within the focusing region; the invention allows the randomdistribution of array elements and the difference in the frequency response among the array elements; and the invention has high spatial resolution.
Owner:INST OF ACOUSTICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com