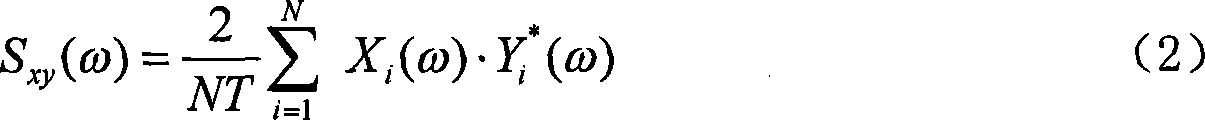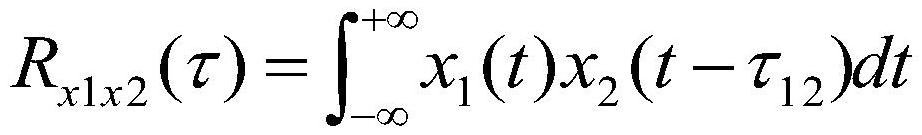Patents
Literature
132 results about "Cross-spectrum" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
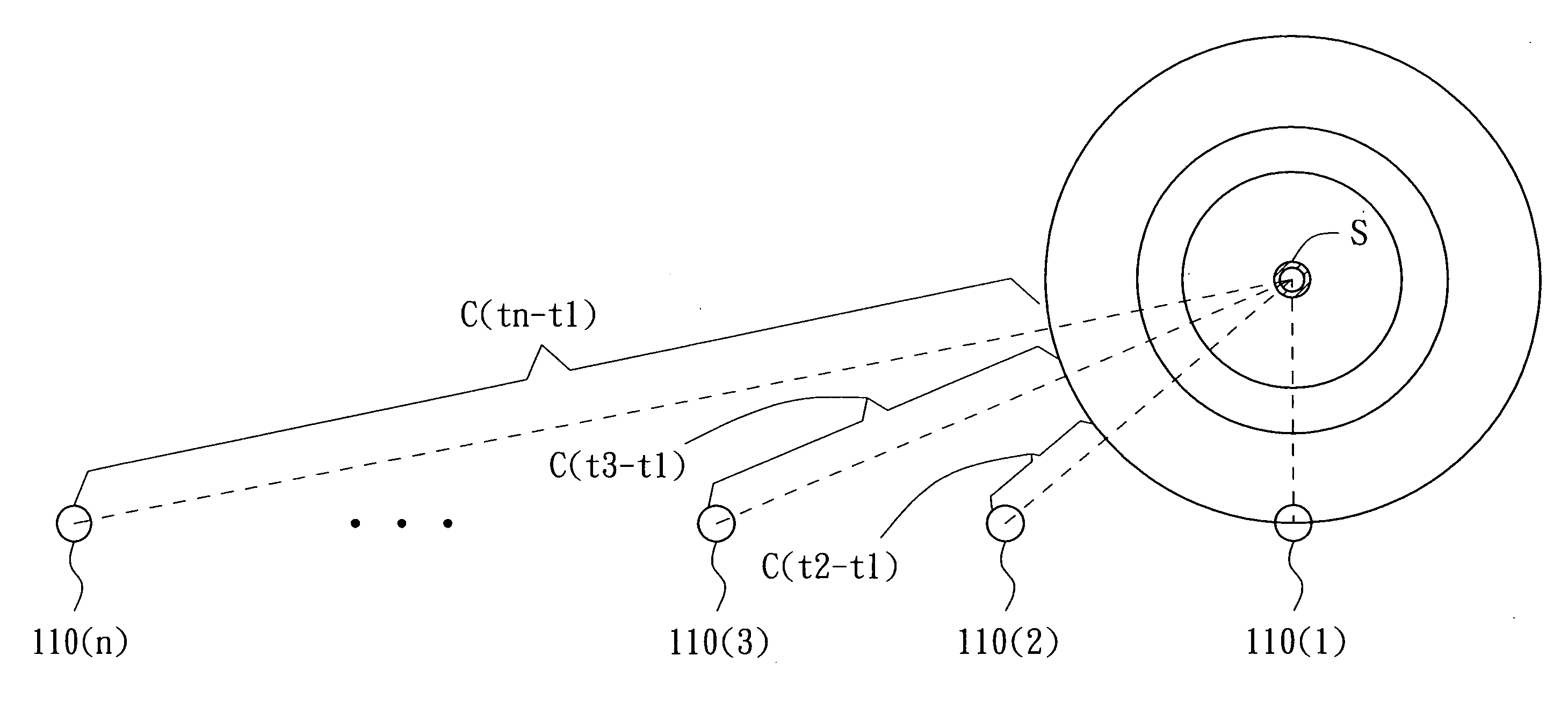
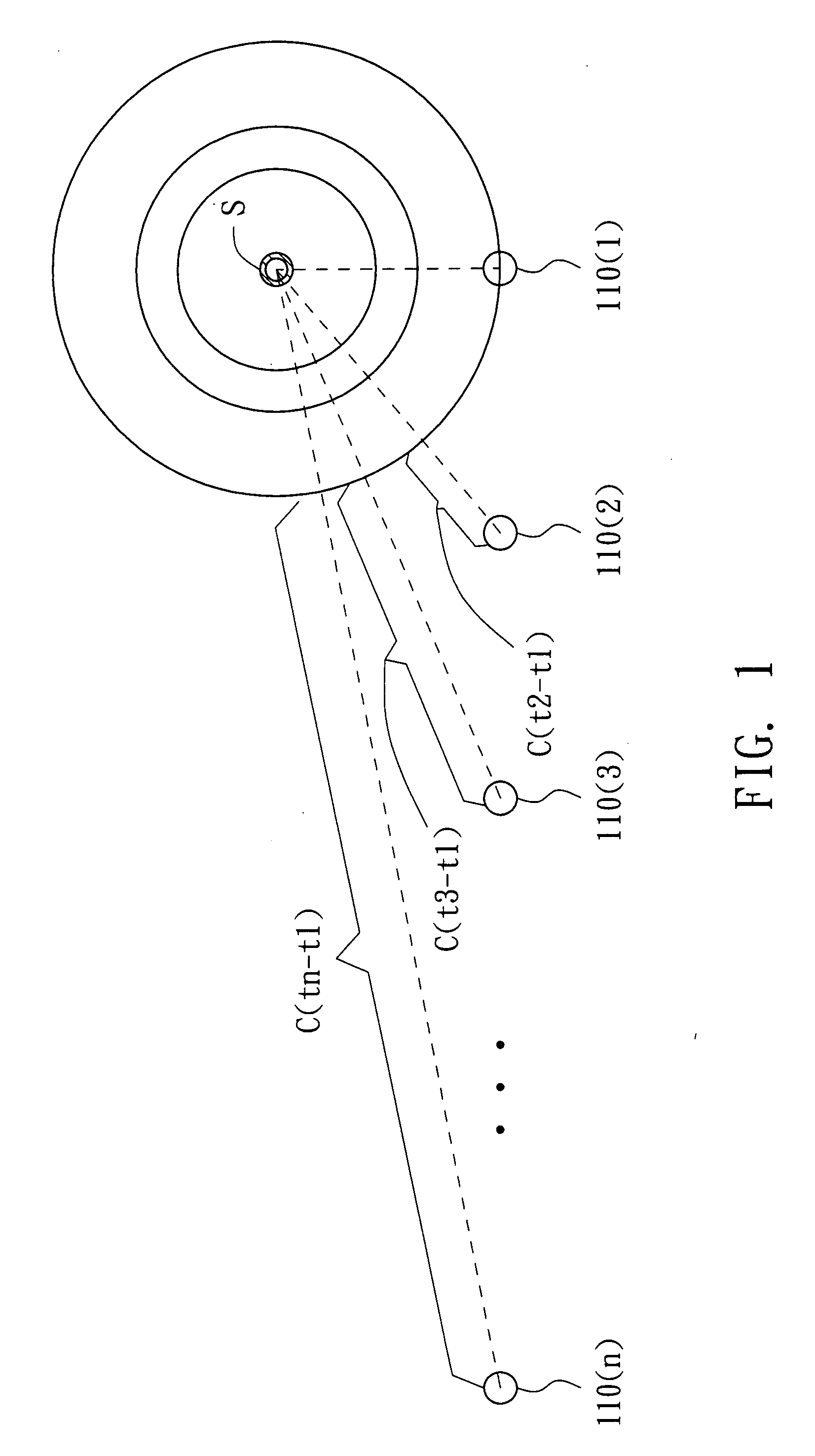
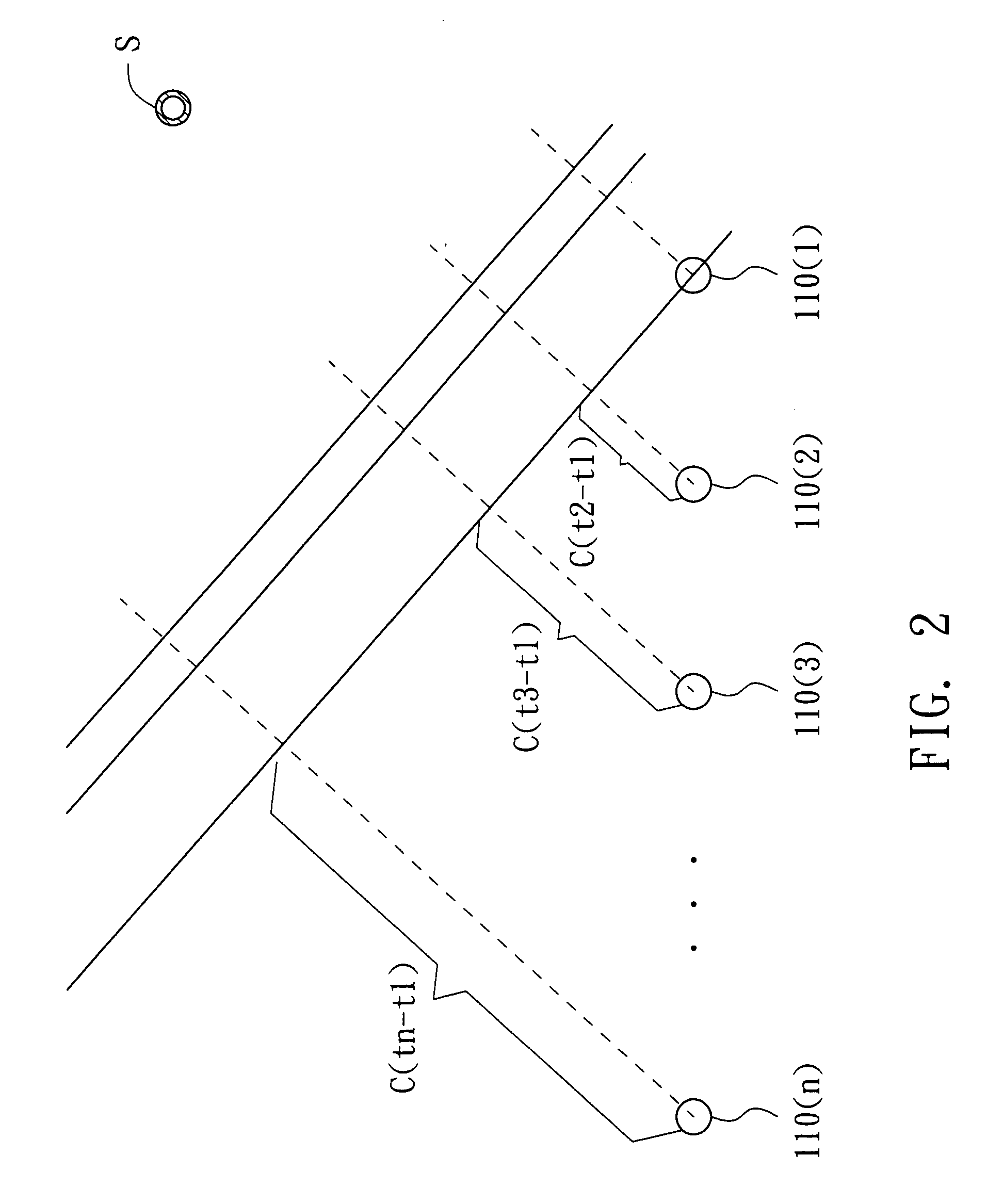
In time series analysis, the cross-spectrum is used as part of a frequency domain analysis of the cross-correlation or cross-covariance between two time series.
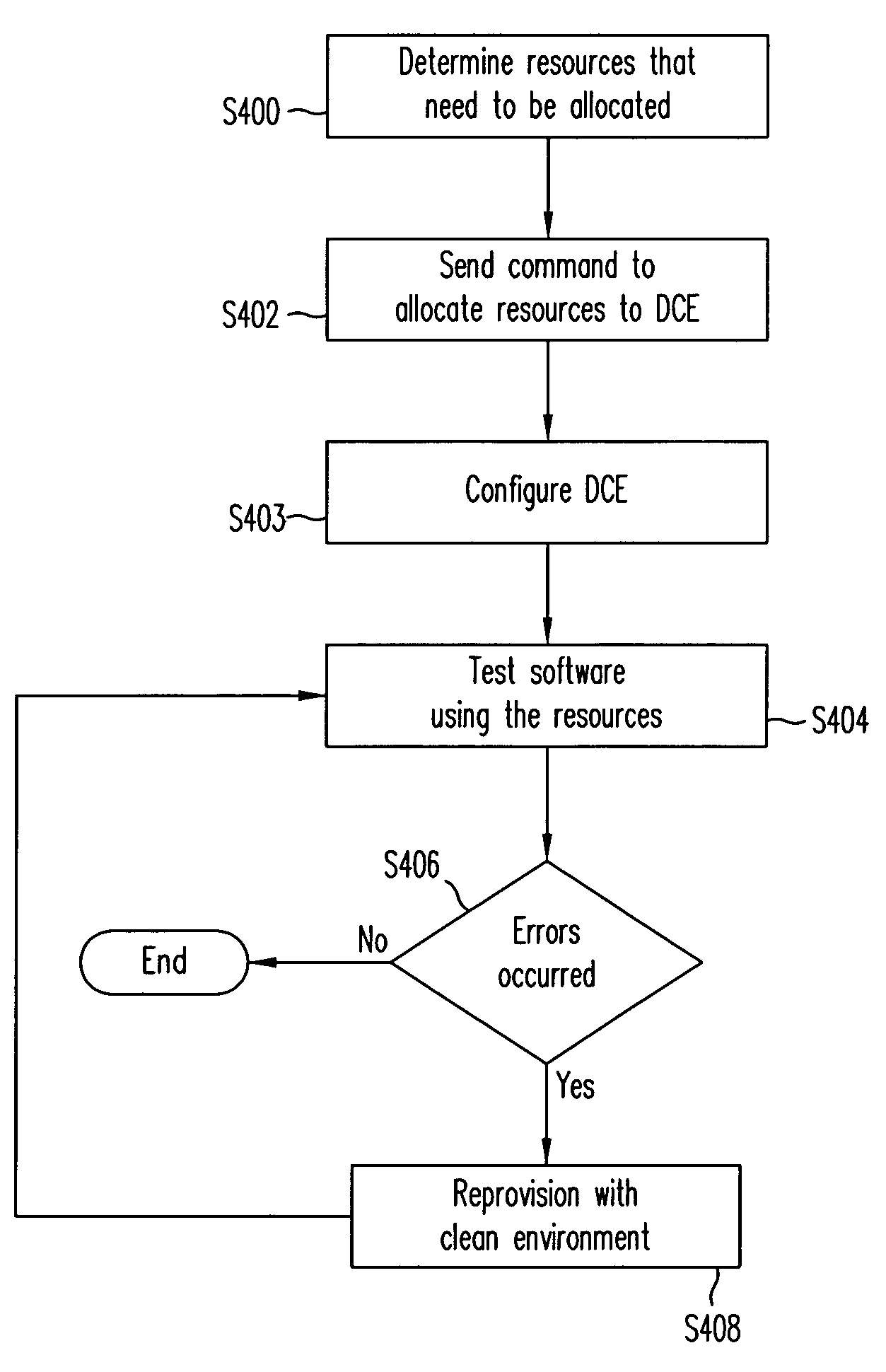
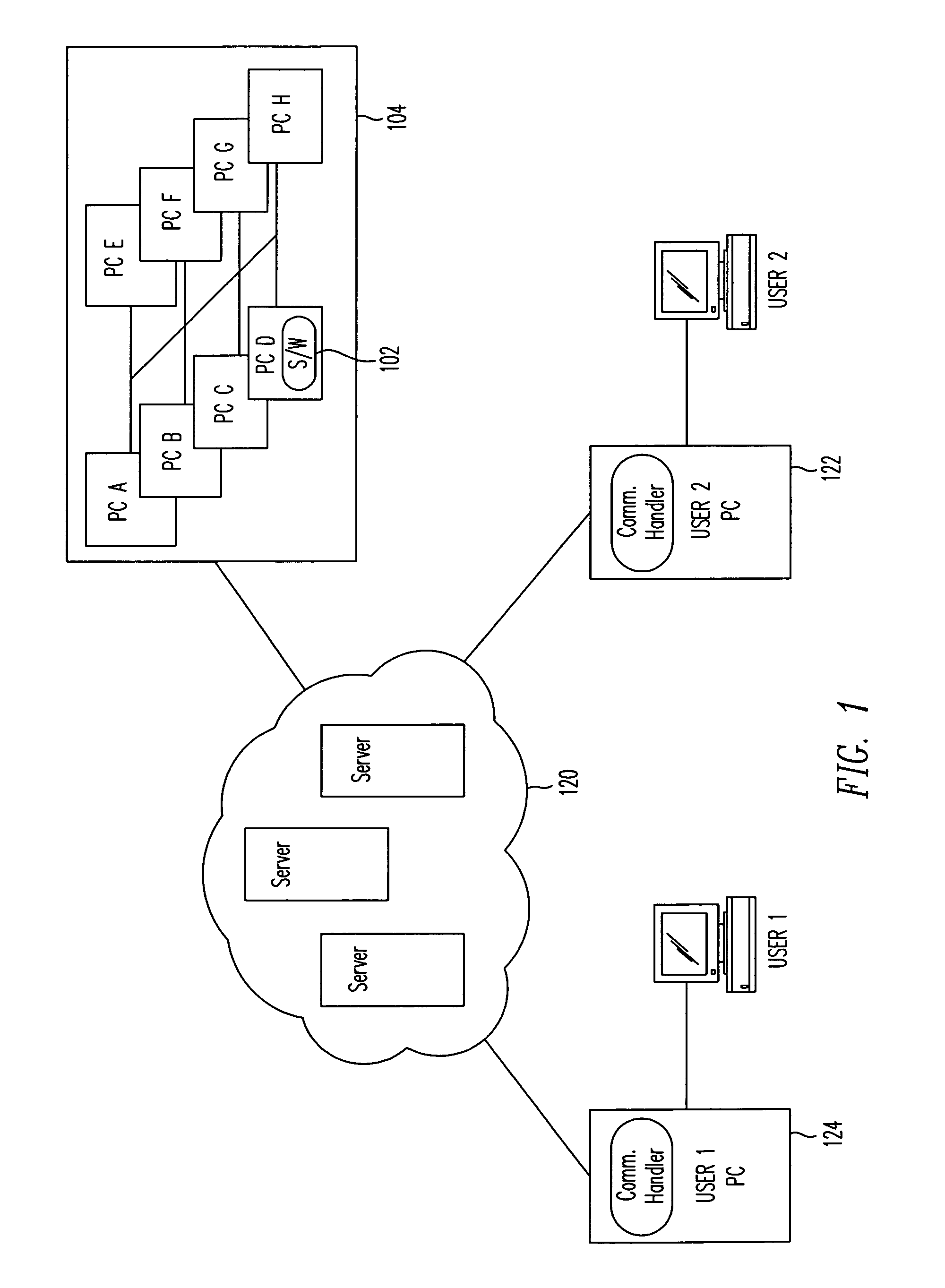
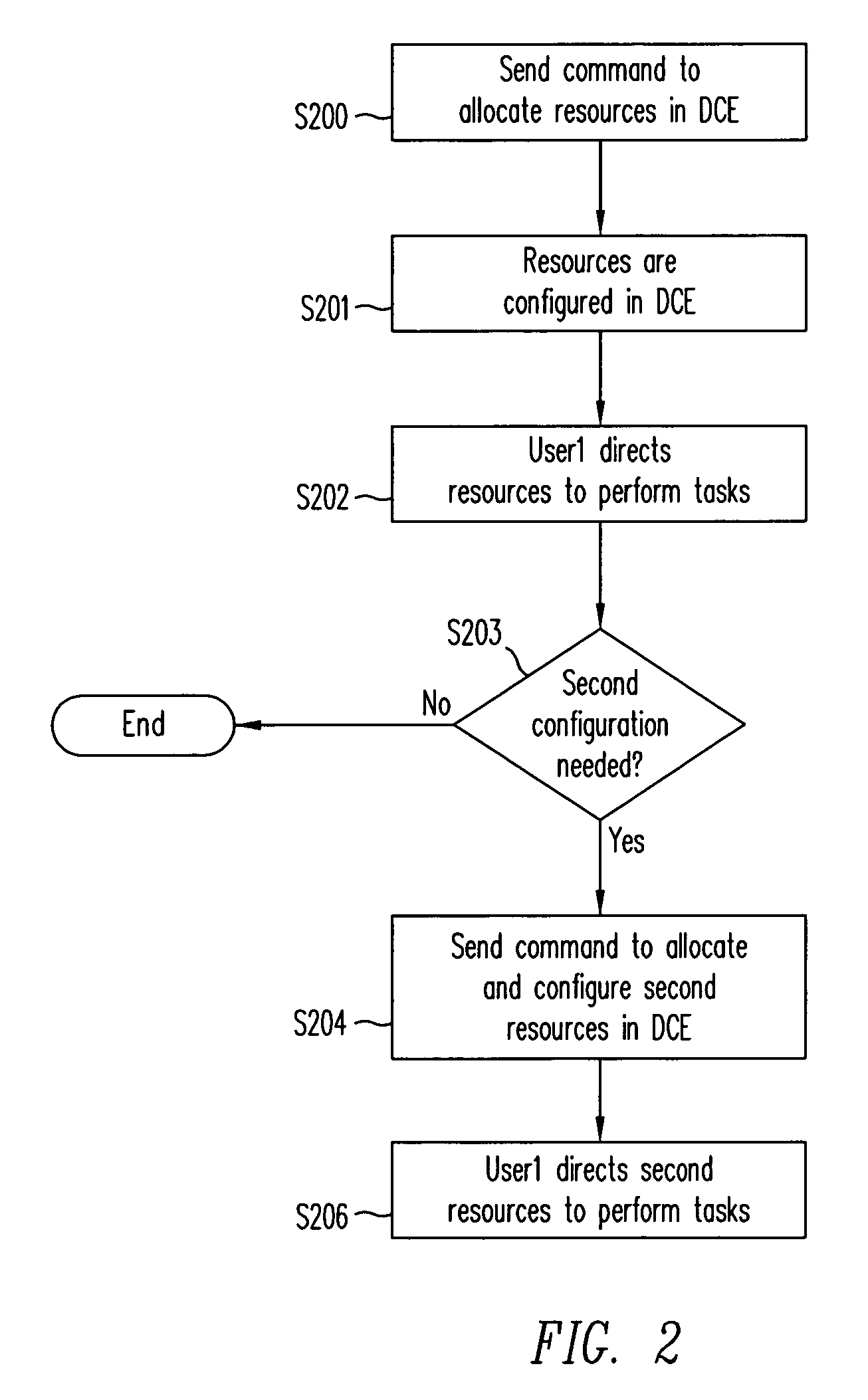
Cross-spectrum application model for dynamic computing environments in software lifecycle
Dynamic Computing Environments (DCEs) are used throughout phases of a software lifecycle. The DCE is configured through a remote user for a phase in the lifecycle. The DCE is then configured according to the command. The user then uses the DCE to fulfill the requirements of the phase. When the phase is completed, a command from the remote user is sent to configure the DCE for another phase. Once the DCE is re-configured, the user uses the DCE to fulfill the requirements of the phase.
Owner:SYMANTEC OPERATING CORP
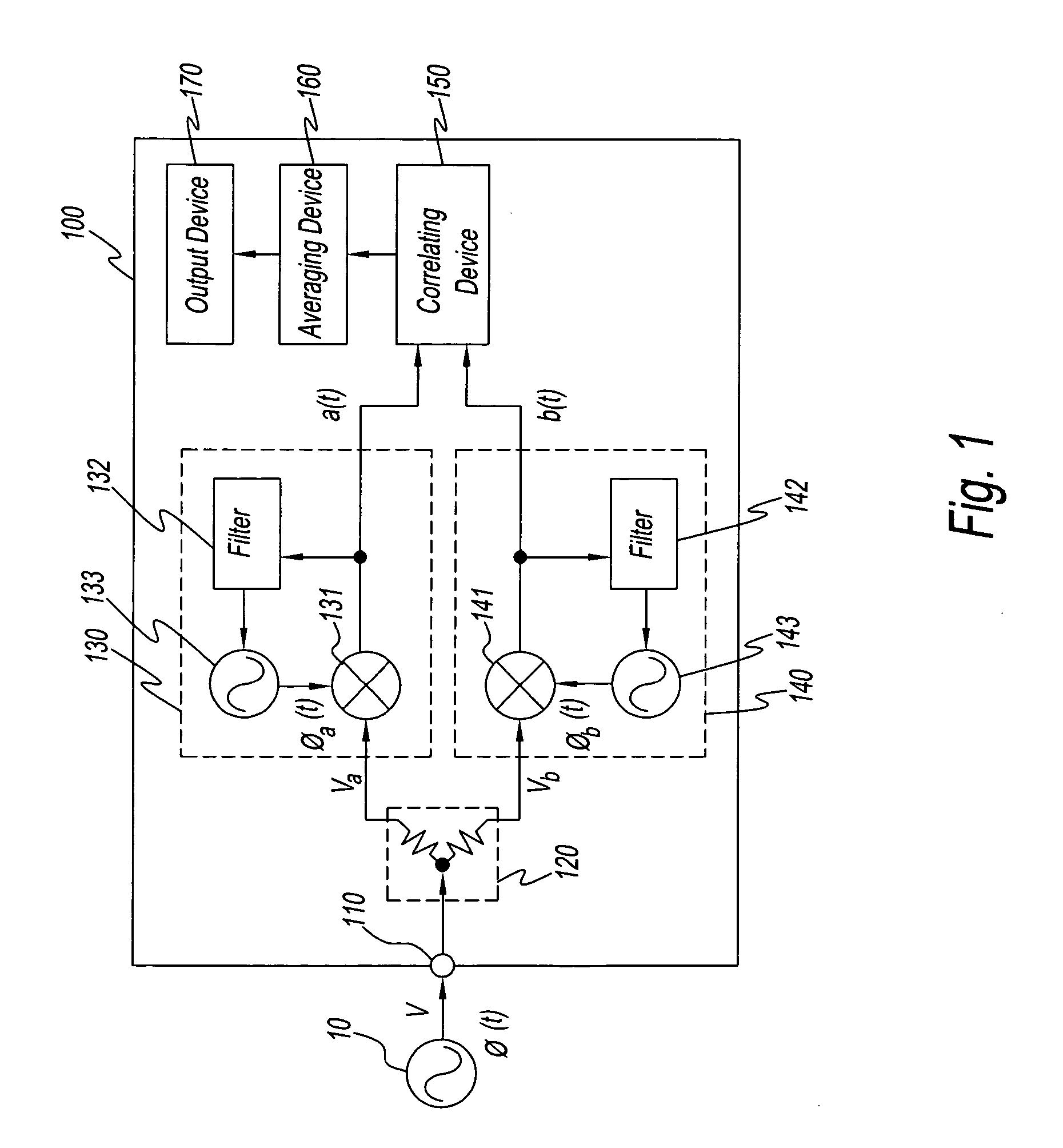
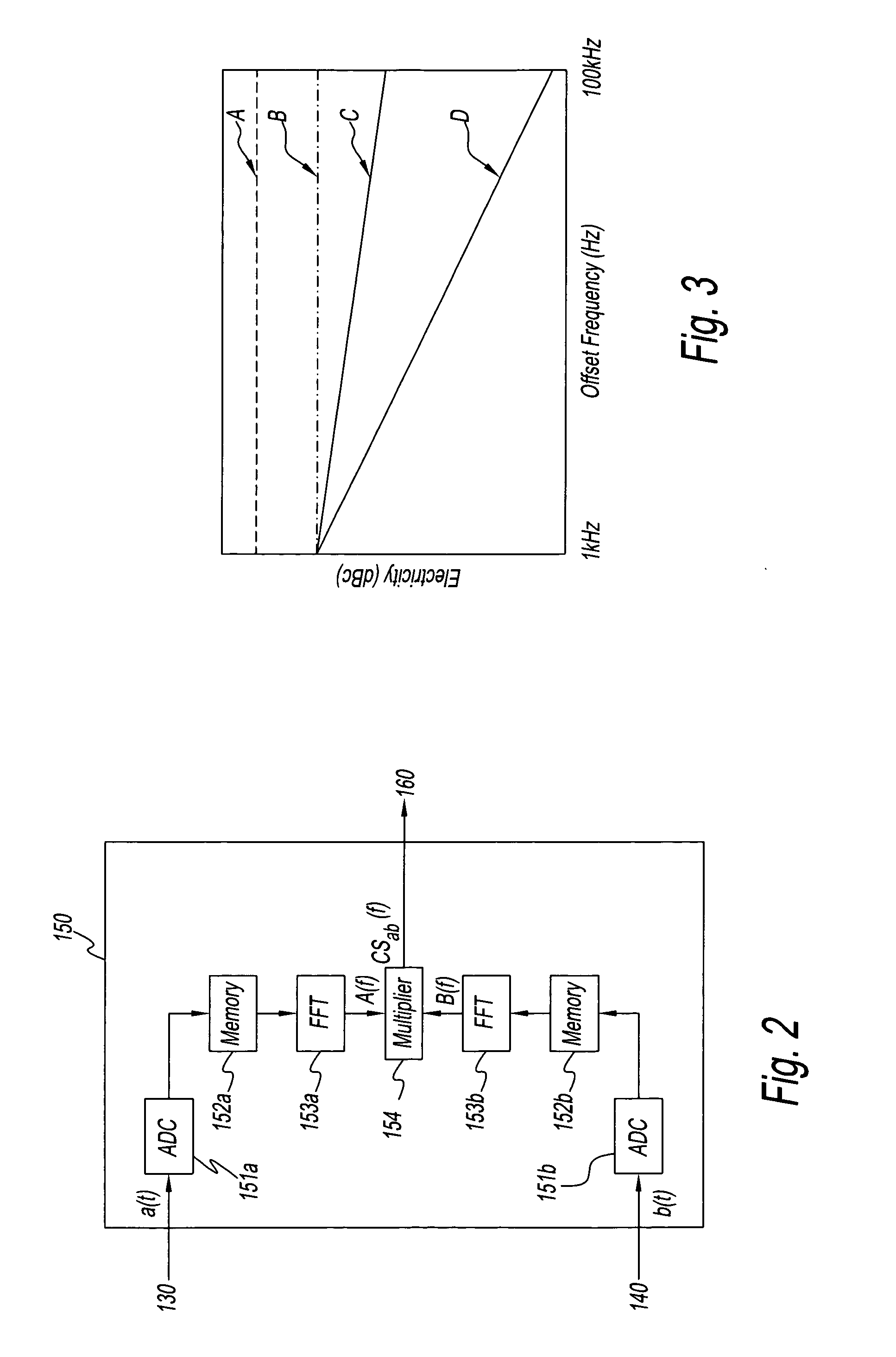
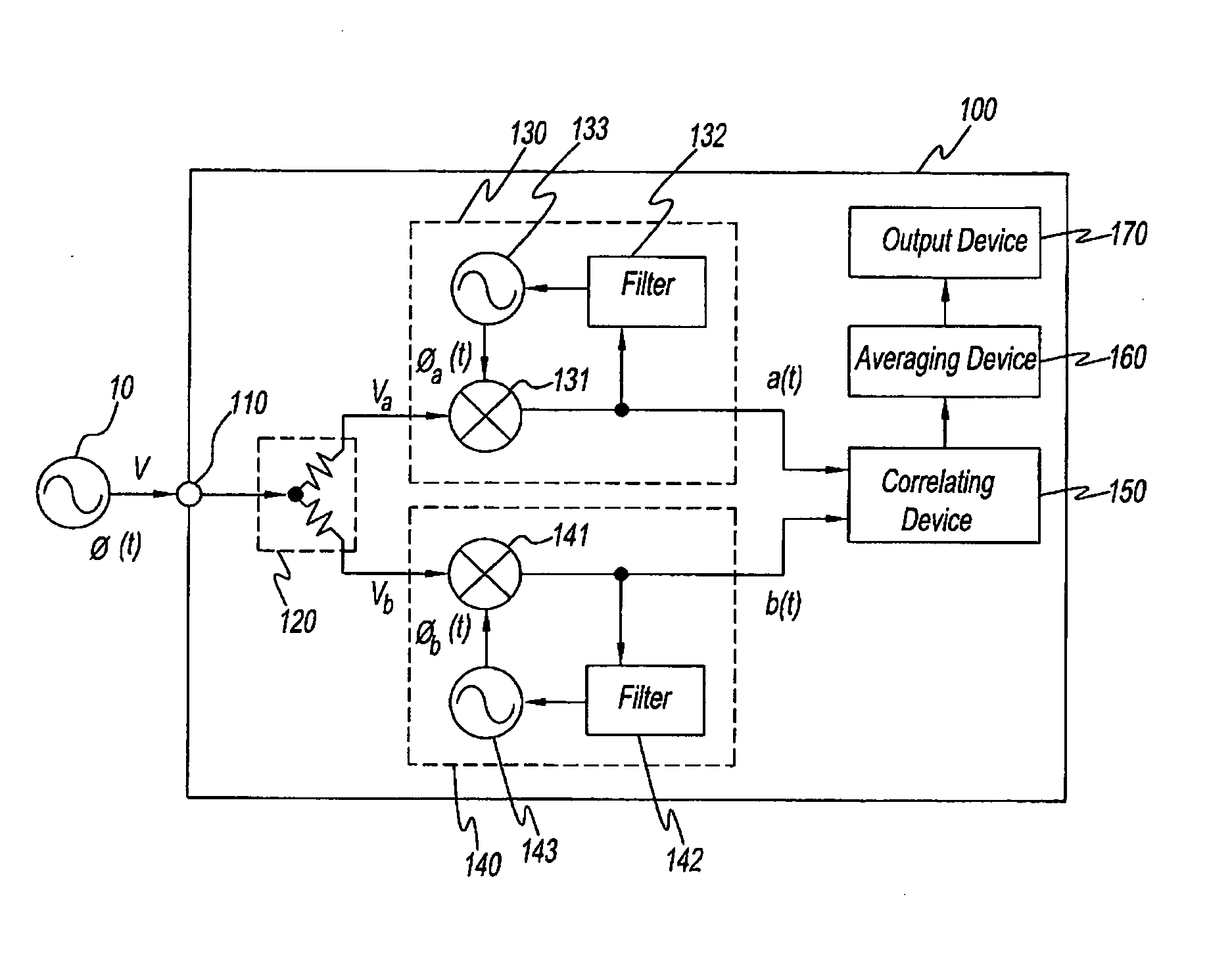
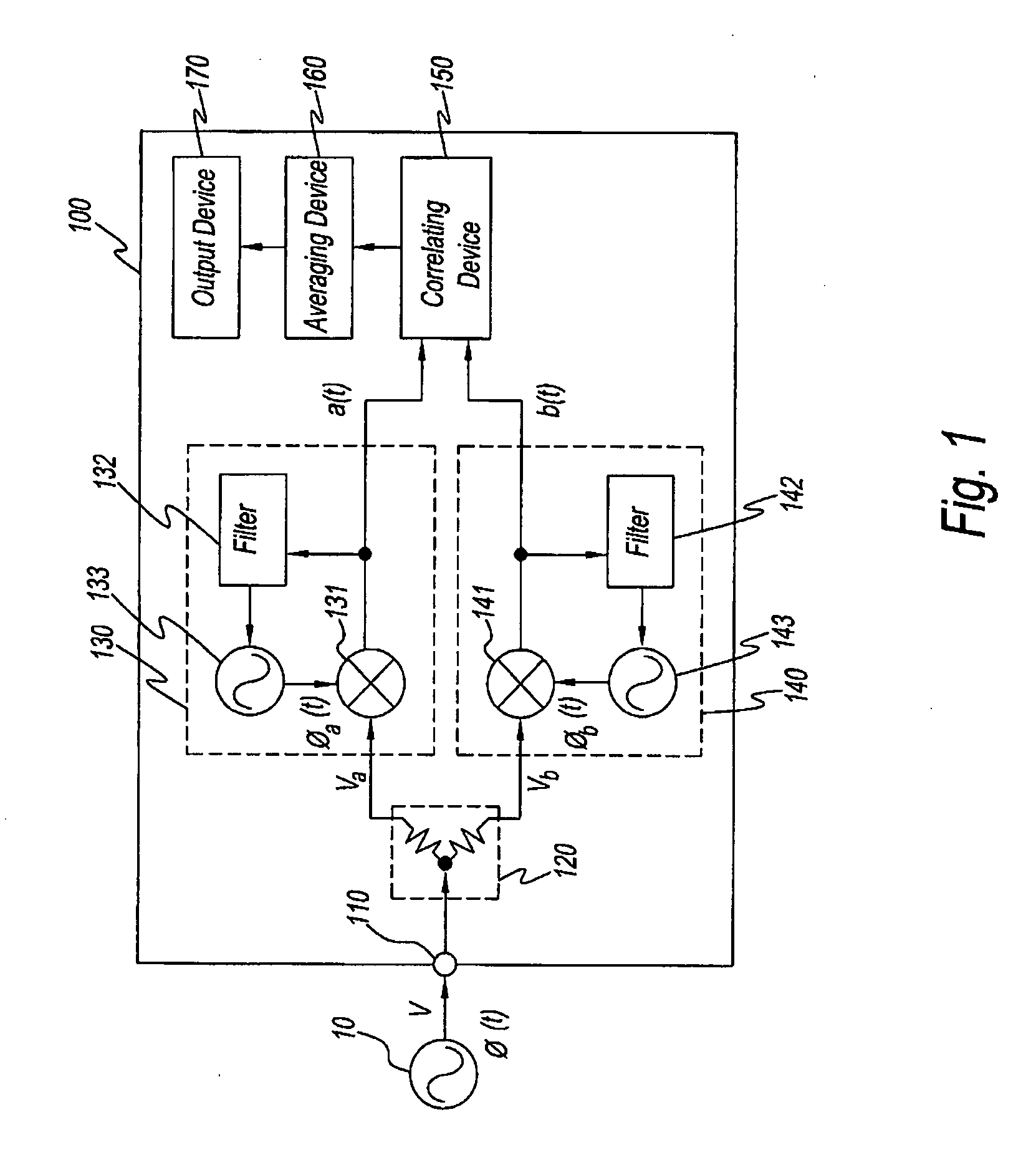
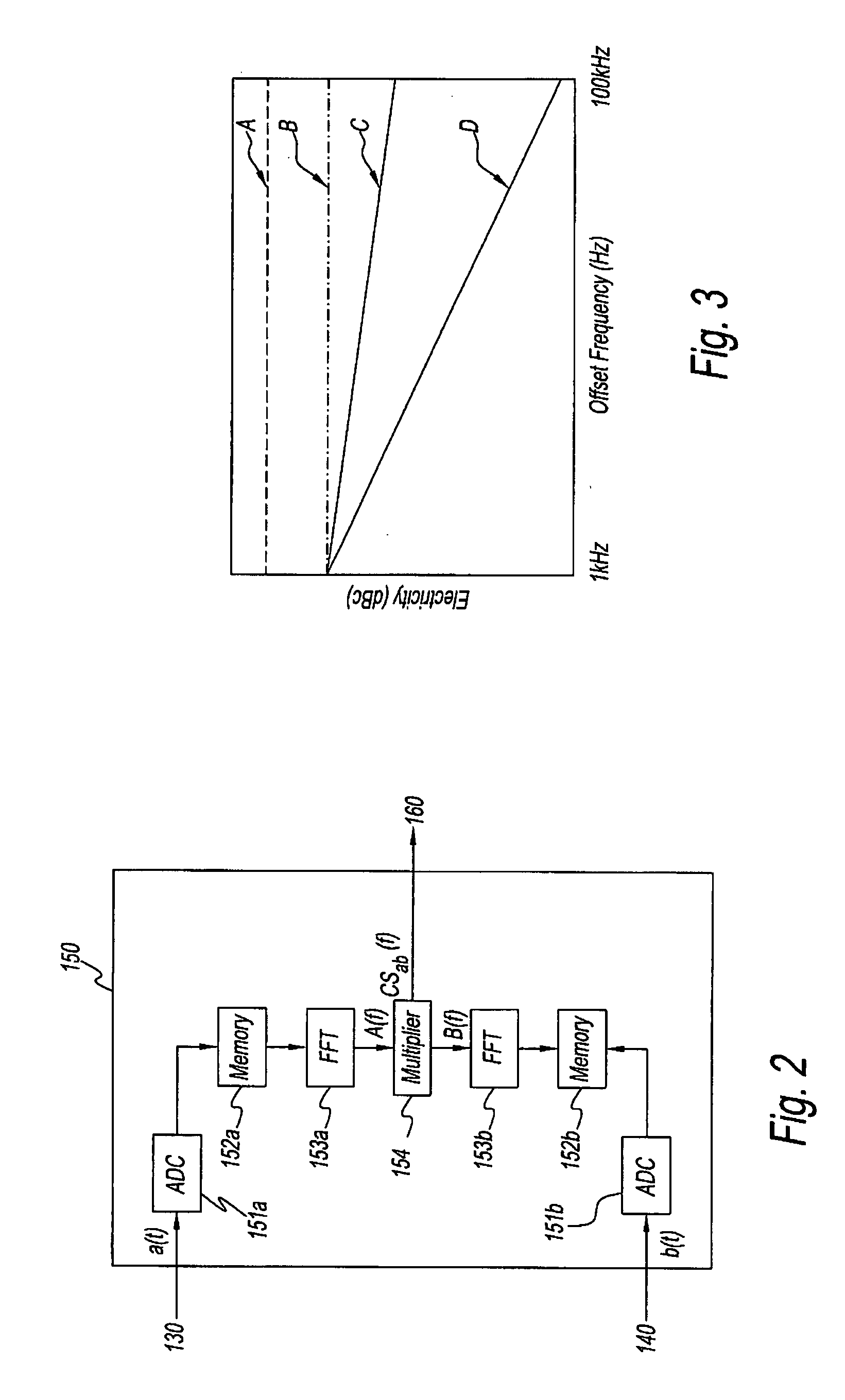
Method and an apparatus for measuring phase noise
InactiveUS20050238094A1Increase the number of timesLower Level RequirementsSpectral/fourier analysisNoise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementPhase noiseFrequency spectrum
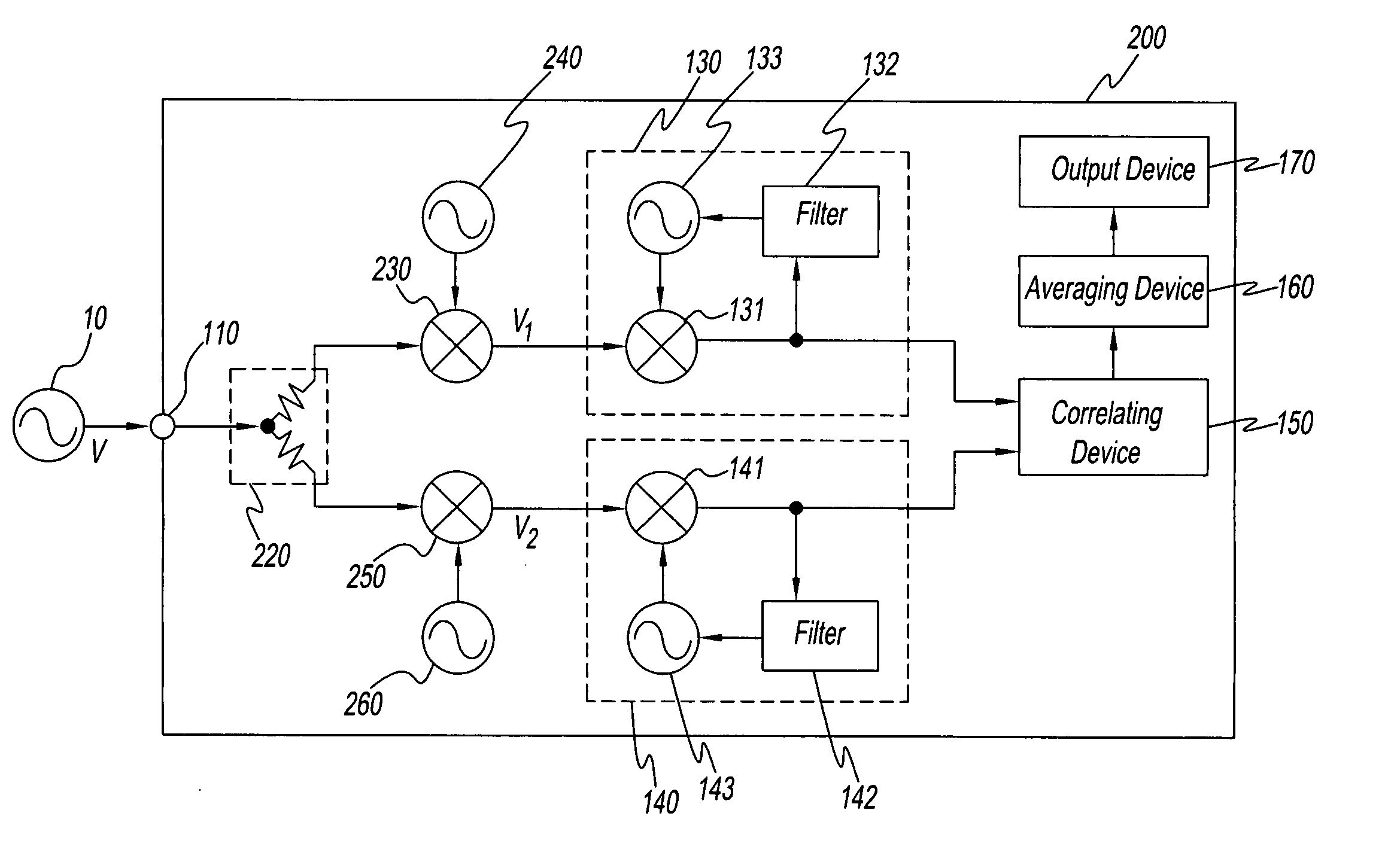
A method measuring the phase noise of signals under test by generating first phase signals representing the phase of signals under test using first local signals generated while referring to first reference signals, generating second phase signals representing the phase of signals under test using second local signals generated while referring to second reference signals having a frequency different from that of the first reference signals, and finding the cross correlation or cross spectrum between the first phase signals and second phase signals. The apparatus of the present invention measures the phase noise of signals under test using this method.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
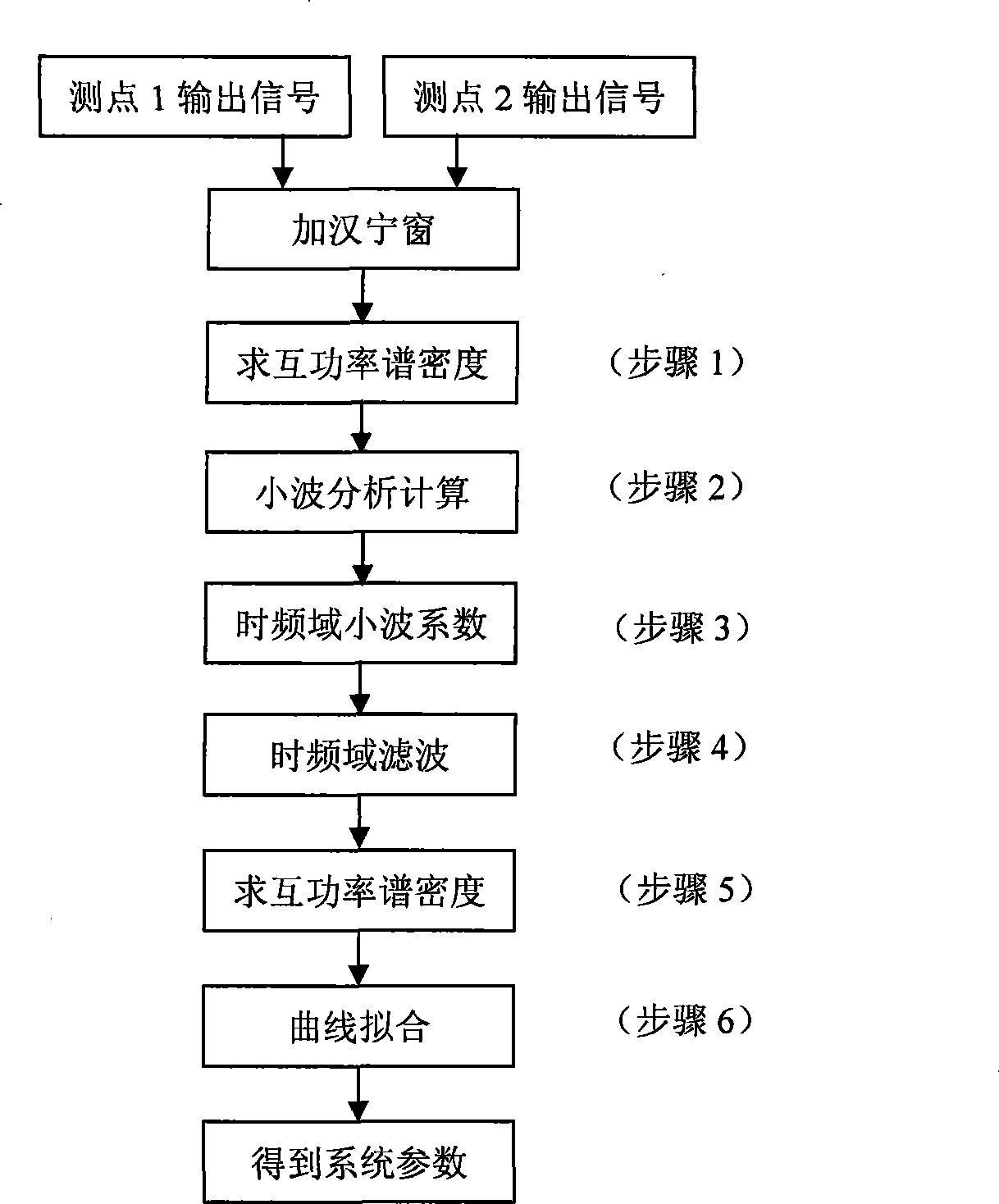
Acquiring system eigenfunction and signal feature value method
InactiveCN101158623AStructural/machines measurementFrequency analysisFourier transform on finite groupsCurve fitting
A method of catching systematic eigenfunctions and signal eigenvalues under the condition of only response output available belongs to the parametric recognition technique in dynamic test field. The technique is a method of adopting cross spectral density functions of each response point instead of frequency response functions to perform time-frequency filtering and the parametric recognition of frequency domain, and includes the following steps: (1) carrying out analytic calculation of the cross spectral density functions of different metering signal of output points; (2) analyzing and calculating the nonorthogonal wavelets in the time-frequency domain according to the cross spectral calculating result; (3) inversing the fourier transformation to gain the time-frequency analyse coefficient; (4) adding a rectangular window to perform the time-frequency filtering; (5) calculating the cross spectrum of the output signal after filtering as the systematic function for recognition; (6) performing curvefitting to obtain the systematic parameter; the technique improves the recognition precision of the systematic parameters, precisely recognizes modal parameters, is simple and convenient, and is suitable for the dynamic analyses, the performance verification and the failure diagnosis of large civil engineering establishments such as large and complex mechanical equipments under operation status, high-rise buildings, bridges, etc.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Sound source localization system and sound source localization method
ActiveUS20080247566A1Improve processing speedReduced Power RequirementsPosition fixationTransducer casings/cabinets/supportsTime domainSound sources
A sound source localization system and a sound source localization method. The sound source localization system includes sound capturing devices and an arithmetic unit. The sound capturing devices sense a sound source to output time domain signals. The arithmetic unit transforms the time domain signals into frequency domain signals, performs a cross spectrum process according to the frequency domain signals to determine time differences of arrival, and locates the sound source according to the time differences of arrival and locations of the sound capturing devices.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Device and method for detecting high sound pressure-phase shifting characteristic of microphone
ActiveCN102655628ASolving the Calibration Problem of Sensitivity Nonlinear Phase ShiftImplement Feedback ControlElectrical apparatusSound sourcesPhase difference
The invention provides a device and a method for detecting a high sound pressure-phase shifting characteristic of a microphone. A variable-section closed space is formed by an equal-phase coupling cavity, a variable-section reflection end cover, a standing wave tube and a bottom reflection end cover; a loudspeaker in the standing wave tube is connected with a power amplifier; the power amplifier is connected with a signal source; the signal source is connected with a computer; a reference microphone and a calibrated microphone are respectively arranged on the side wall of the equal-phase coupling cavity and are connected with a signal amplifier; and the signal amplifier is connected with the computer. The method comprises the following steps of: controlling the signal source by the computer, and driving the loudspeaker in the standing wave tube to send a sound wave signal by the power amplifier; and performing cross-spectrum analysis on a signal which is acquired by the reference microphone and the calibrated microphone, so as to obtain a phase difference of the calibrated microphone relative to the reference sensor under a certain condition. A sound source has high sound pressure of 94 to 160 decibels according to a standing wave sound field theory, and the distortion degree is less than 1 percent; and therefore, the phase shifting characteristic of the phase sensitivity of the microphone is calibrated under a high sound pressure environment.
Owner:BEIJING AEROSPACE INST FOR METROLOGY & MEASUREMENT TECH +1
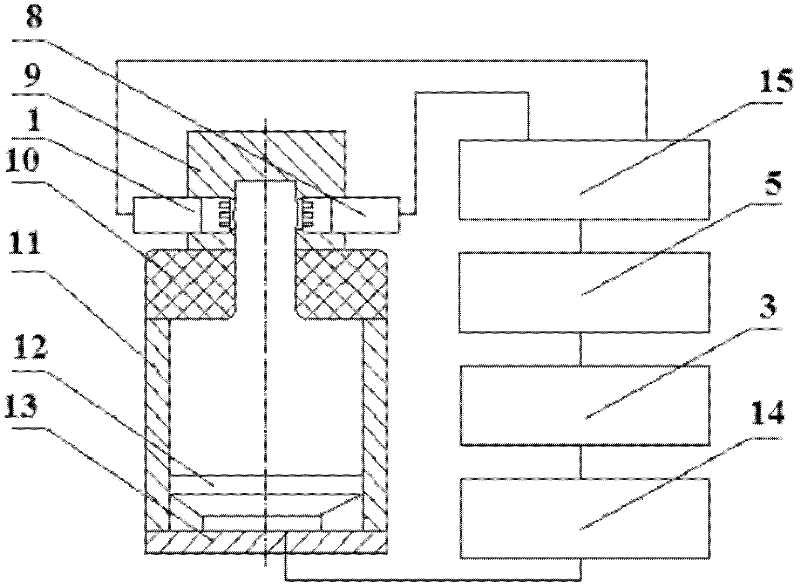
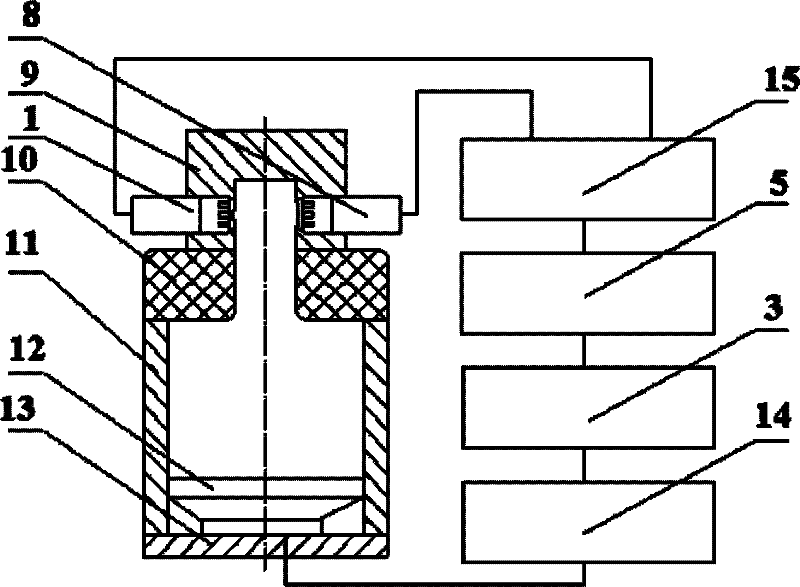
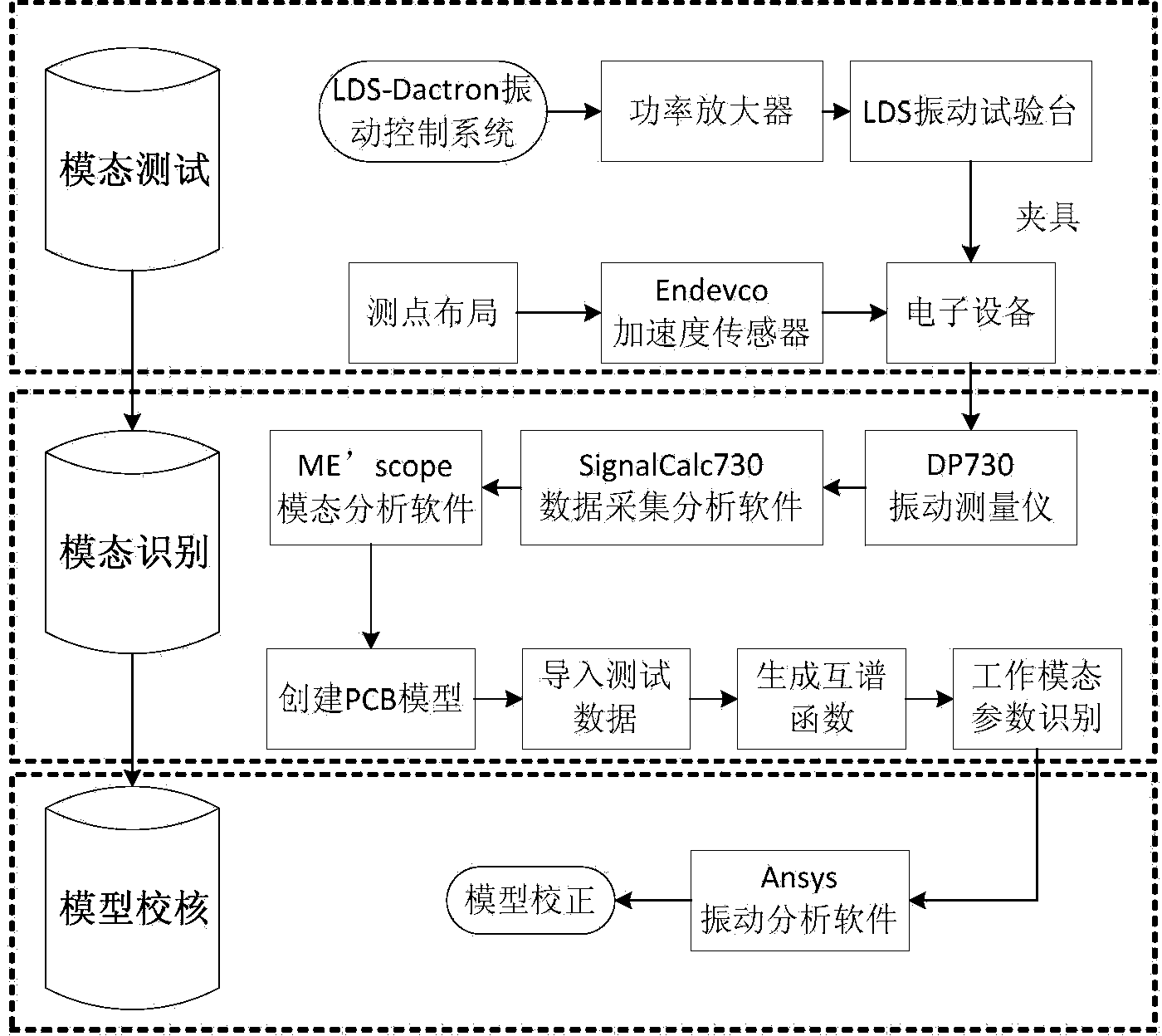
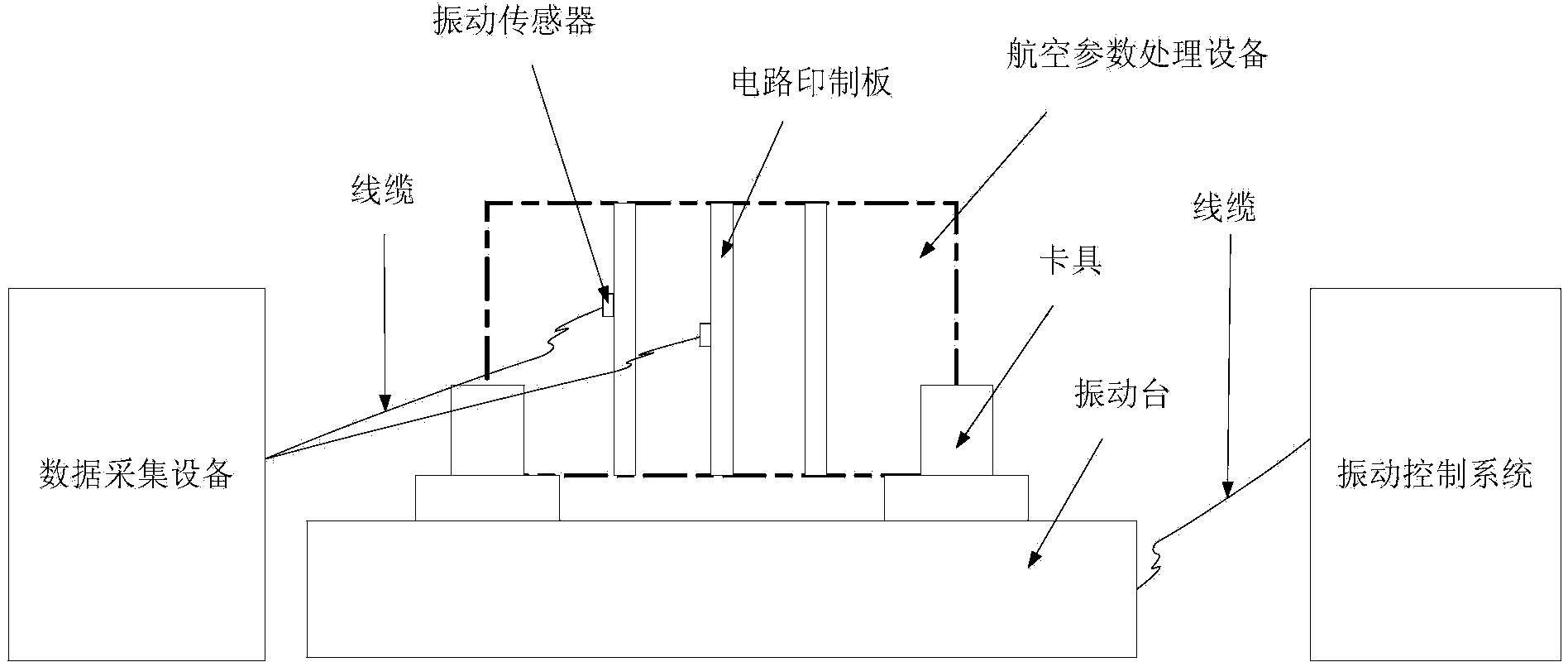
Avionic device operating modal measuring method for vibration finite element model correction
ActiveCN103983412ASpeed up the development processSave testing timeVibration testingModal testingElement model
The invention provides an avionic device operating modal measuring method for vibration finite element model correction. The method includes the following steps that firstly, response test points are arranged, and piezoelectric acceleration transducers are pasted, wherein the n response test points are arranged on a circuit board, and the piezoelectric acceleration transducers are pasted on the response test points respectively; secondly, an avionic device and a test device are installed, and an operating modal test platform is built; thirdly, time domain response data of the avionic device under the random vibration condition are acquired; fourthly, data processing is conducted through modal recognition software, and operating modal parameters of the avionic device are acquired. Through the steps, an avionic device operating modal measuring system for vibration finite element model correction is established, and the overall process from generation of random vibration signals to acquisition of the time domain response data and from generation of a time domain response data sample and a cross-spectrum function to recognition of the operating modal parameters of the avionic device is finished. According to the method, online modal recognition is achieved, and test time is saved and test cost is reduced.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
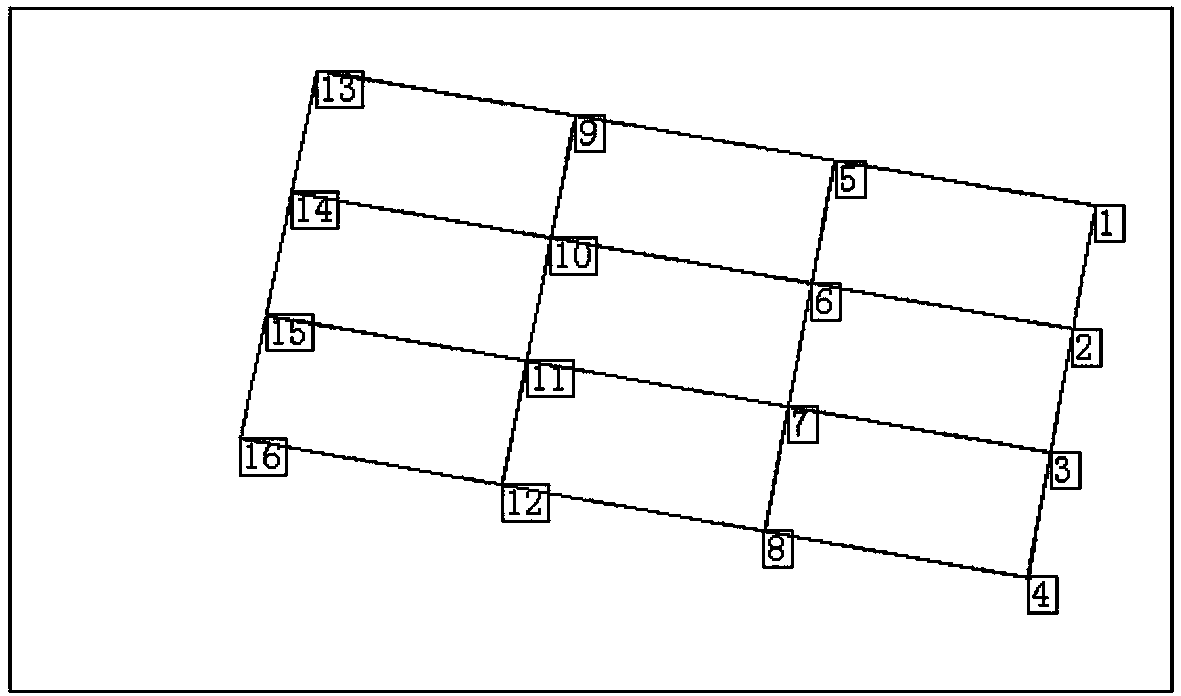
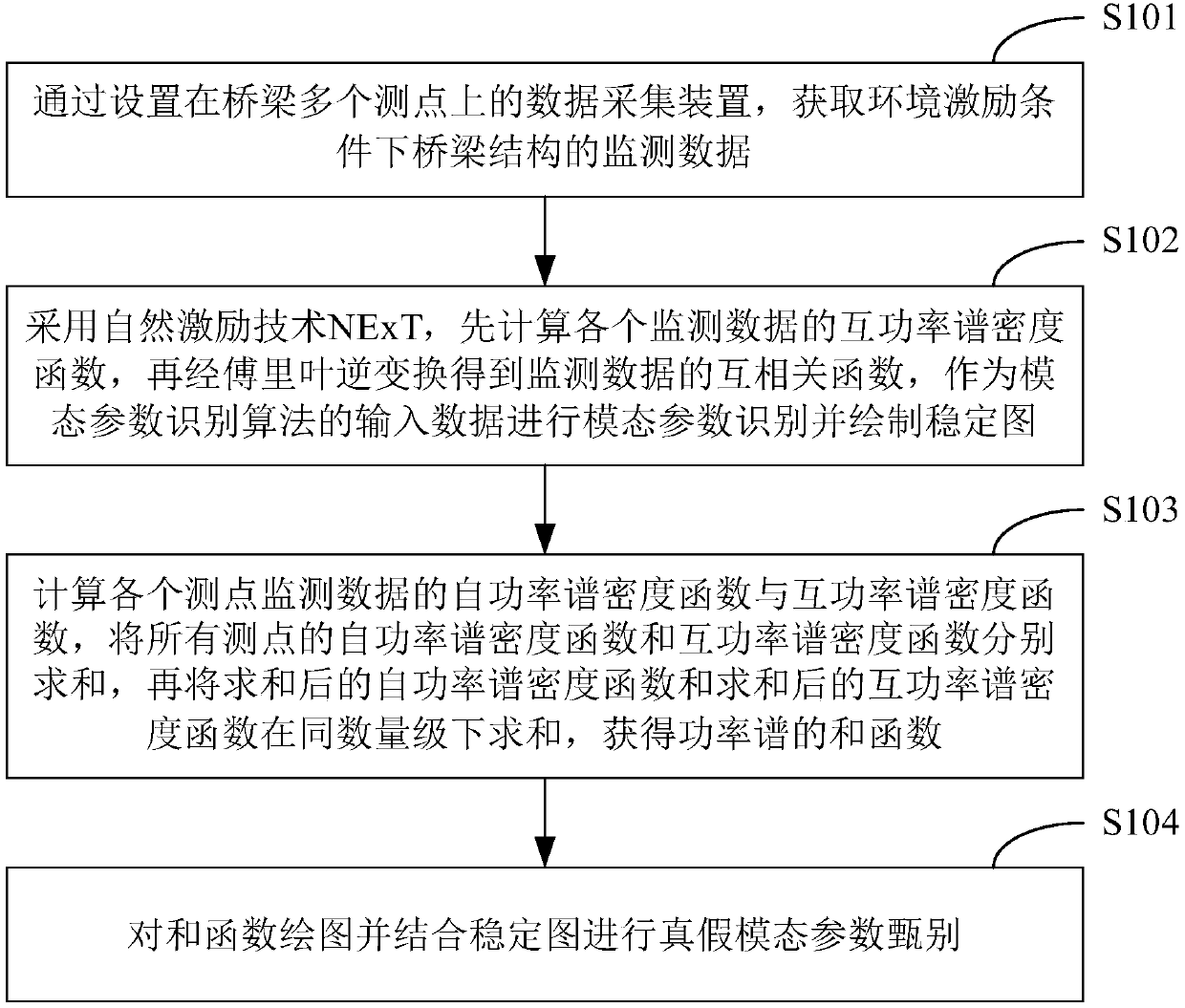
Bridge structure modal parameter authenticity and falsity discrimination method and terminal device
InactiveCN108318129AImprove discrimination accuracySubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementTerminal equipmentCorrelation function
The invention belongs to the bridge monitoring technical field and provides a bridge structure modal parameter authenticity and falsity discrimination method and a terminal device. The method includesthe following steps that: the monitoring data of the structure of a bridge under an environmental excitation condition are obtained through data acquisition devices disposed in a plurality of measuring points of the bridge; the NExT (natural excitation technique) is adopted, at first, the cross power spectrum density function of the monitoring data is calculated, and Fourier inverse transformation is performed on the cross power spectrum density function, so that the cross-correlation function of the monitoring data is obtained, the cross-correlation function is adopted as the input data of amodal parameter identification algorithm, so that modal parameter identification can be carried out, and a stability diagram can be drawn; the auto-power spectrum density function and cross-power spectrum density function of the monitoring data of the measuring points are calculated, the auto-power spectra and cross-power spectra of all the measuring points are summated, and the auto-spectra andthe cross spectra are summated in the same order of magnitude, so that the sum function of the power spectra can be obtained; and a diagram of the sum function, and true and false modal parameters canbe discriminated according to the stability diagram of the sum function. According to the method, the stability diagram method and a power spectrum summation peak method are combined to perform bridge structure modal parameter authenticity and falsity discrimination, so that discrimination accuracy can be improved.
Owner:SHIJIAZHUANG TIEDAO UNIV
Method and an apparatus for measuring noise
InactiveUS20070225927A1Increase the number of timesReduce measurement noiseSpectral/fourier analysisNoise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementFrequency spectrumPhase noise
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
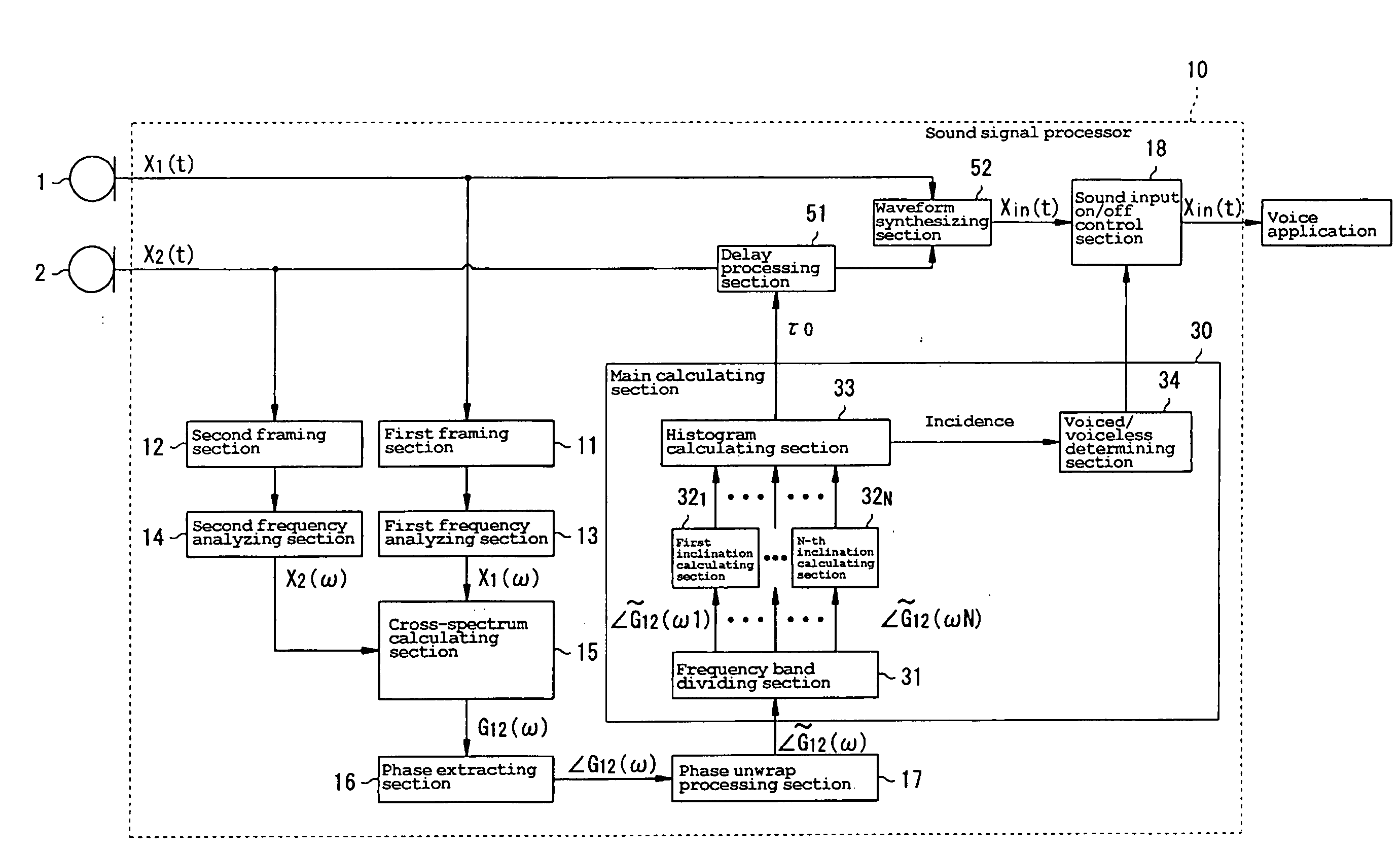
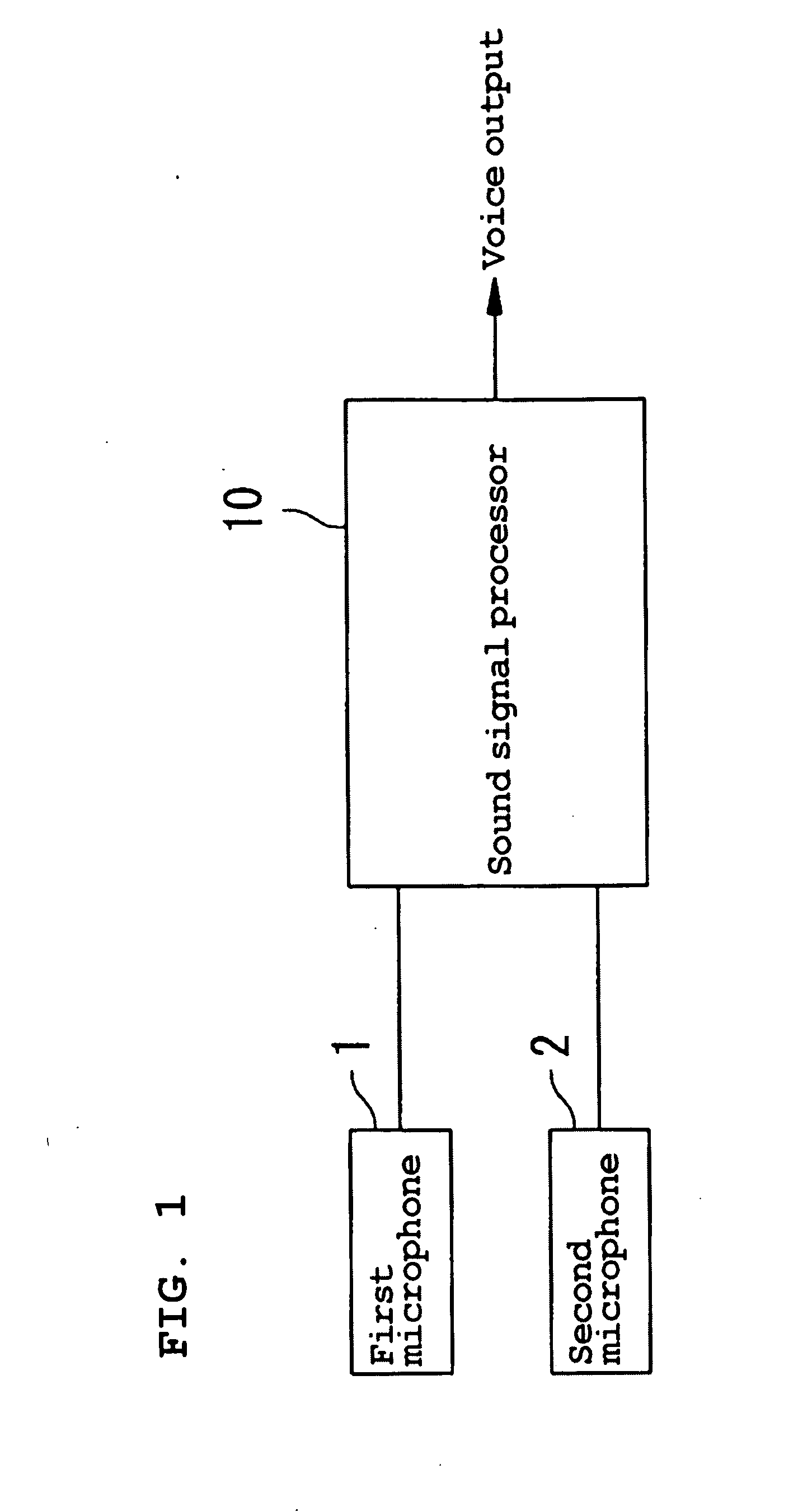
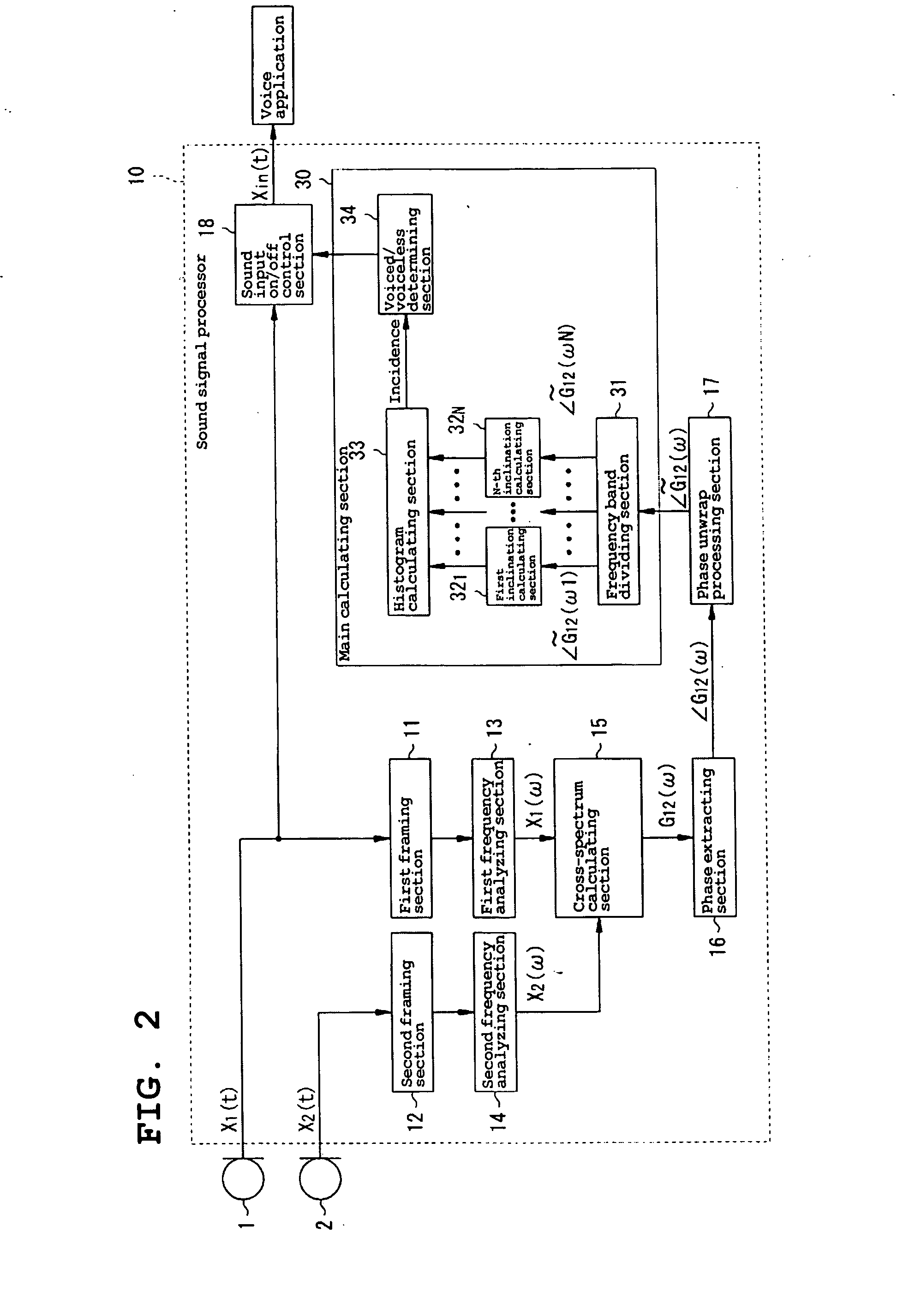
Method For Detecting Target Sound, Method For Detecting Delay Time In Signal Input, And Sound Signal Processor
InactiveUS20080120100A1Highly resistant to environmental fluctuationSpeech recognitionDelayed timeComputer science
A sound signal processor includes first and second framing sections, first and second frequency analyzing sections, and a cross-spectrum calculating sections, for detecting the phase of a cross-spectrum between the sound signals input to first and second microphones, a phase extracting sections, a phase unwrap processing sections, a frequency band dividing section, and first through N-th inclination calculating sections, for detecting the inclinations of the phase of the cross-spectrum detected by the cross-spectrum calculating section with respect to the frequency, and a histogram calculating section and a voiced / voiceless determining section, for detecting a speech section in the sound received by the first and second microphones based on the inclination with respect to the frequency detected by the first through N-th inclination calculating sections.
Owner:YAMAHA MOTOR CO LTD +1
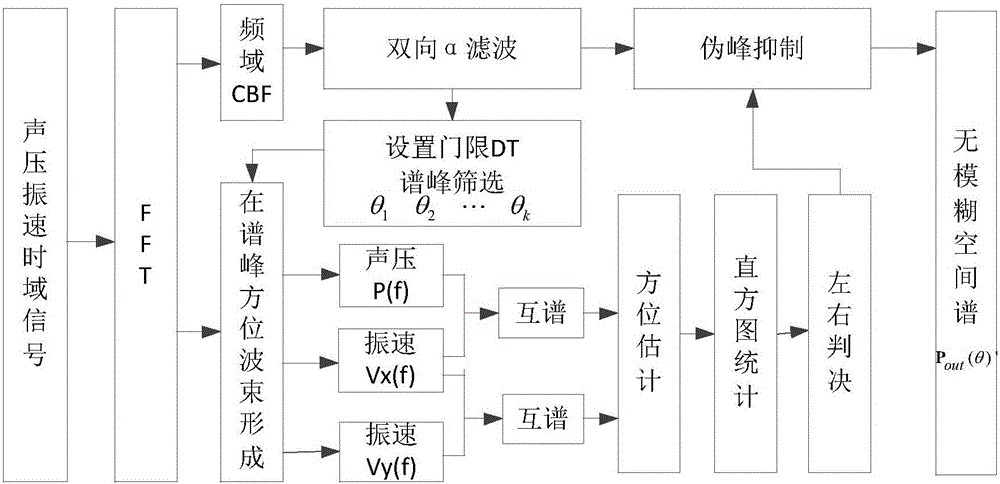
Sound pressure and vibration velocity cross spectrum method-based vector array port and starboard discrimination method
ActiveCN106066468AOvercome ambiguityImprove weak target detection abilityDirection/deviation determination systemsAmbiguityKnowledge Field
The invention belongs to the underwater sound direction-finding field and relates to a sound pressure and vibration velocity cross-spectrum method-based vector array port and starboard discrimination method. The method includes the following steps that: step (1) after received sound pressure signals are converted into frequency-domain signals, frequency-domain broadband conventional beamforming processing is carried out on the frequency-domain signals, so that an original spatial spectrum matrix can be obtained, wherein the spatial spectrum matrix is a matrix of an outputted spatial spectrum type; step (2) bidirectional one-order recursive filtering processing is performed on the obtained original spatial spectrum matrix, so that a smoothed spatial spectrum can be obtained; and step (3) according to the smooth spatial spectrum, DT decibels are increased based on the smooth spatial spectrum, so that a threshold for spectral peak screening can be obtained. According to the method of the invention, peak screening is carried out on the spatial spectrum; direction estimation is carried out on signals in a spectral peak range; subtractive suppression is carried out on pseudo peak measurement through comparing an estimated result with a spectral peak position; and therefore, the problem of port-starboard ambiguity under a low signal-to-noise ratio can be solved, and weak target detection under a homogeneous noise background can be improved.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
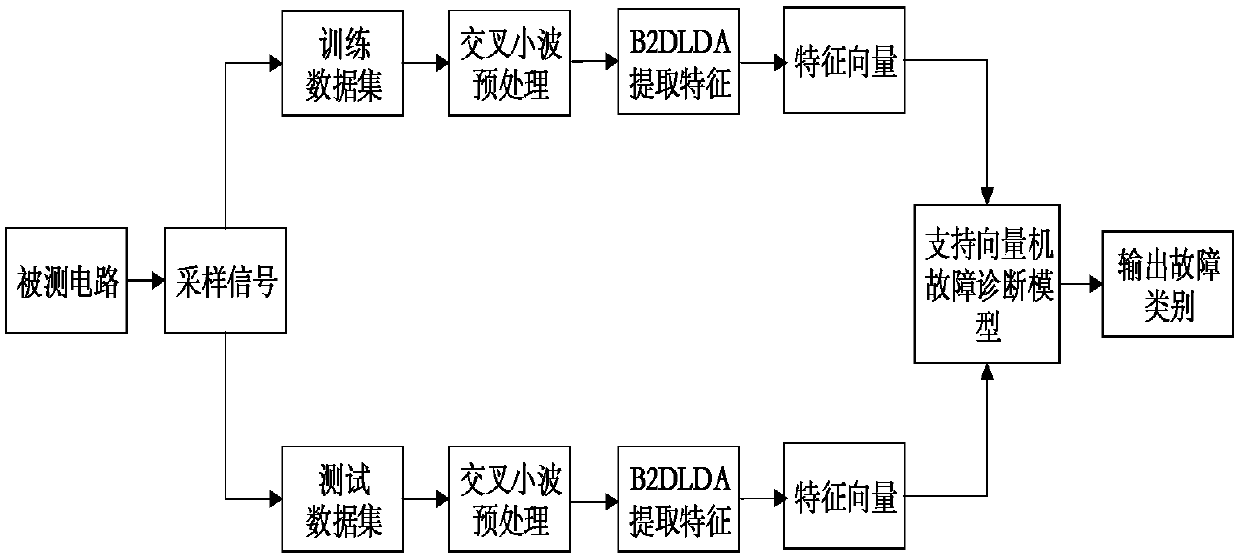
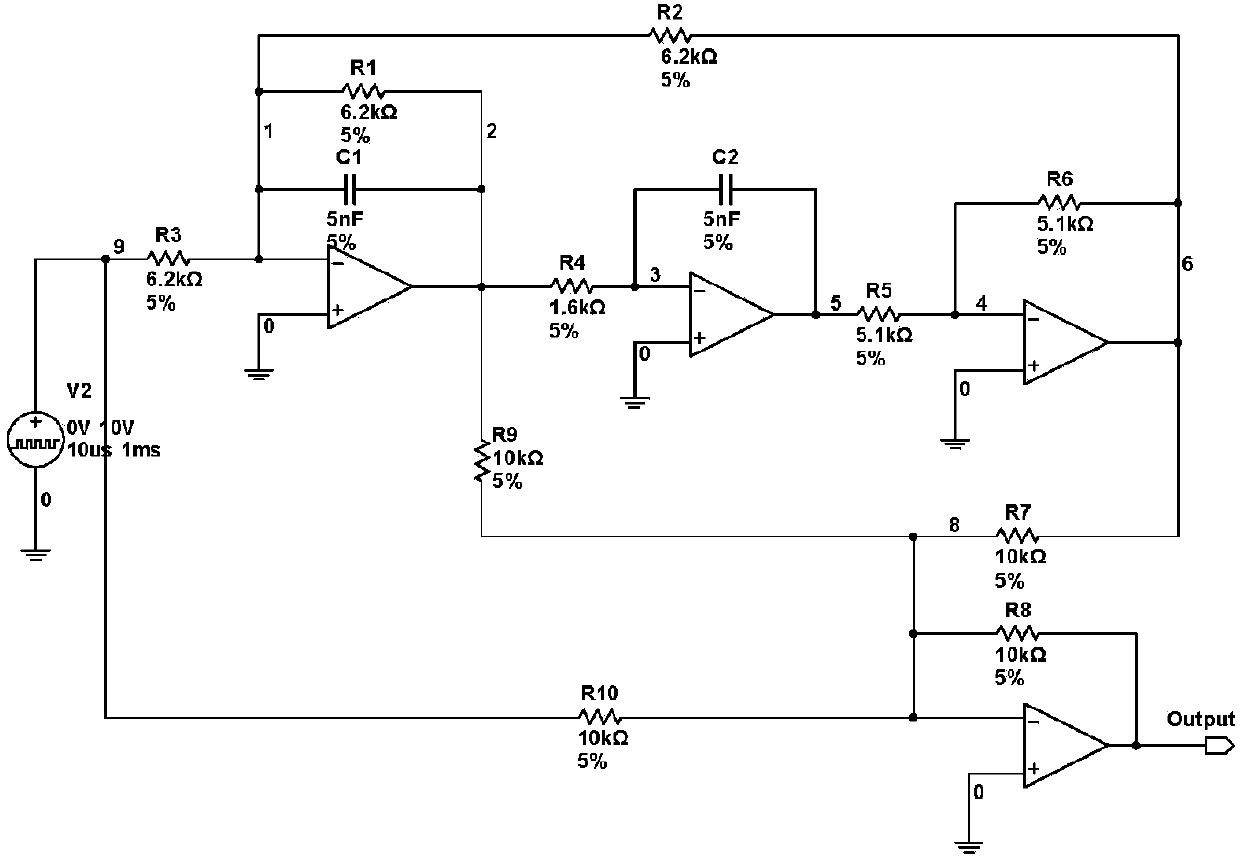
An analog circuit fault diagnosis method based on cross-wavelet characteristics
ActiveCN107894564AFast and accurate fault classificationAccurate fault diagnosisAnalog circuit testingSpecial data processing applicationsOriginal dataTime domain response
The invention provides an analog circuit fault diagnosis method based on cross-wavelet characteristics. The method comprises the following steps: inputting an excitation signal to a tested analog circuit, collecting time-domain response output signals and constructing an original data sample set; dividing the original data sample set into a training sample set and a test sample set; carrying out cross wavelet decomposition on the training sample set and the test sample set to obtain a wavelet cross spectrum of the training sample set and the test sample set; carrying out processing on the wavelet cross spectrum of the training sample set and the test sample set through bidirectional two-dimensional linear discriminant analysis, and extracting fault feature vectors of the training sample set and the test sample set; submitting the fault feature vectors of the training sample set to a support vector machine for training an SVM classifier, and constructing a support vector machine fault diagnosis model; and inputting the fault feature vectors of the test sample set to the model and carrying out fault classification. The method can effectively identify the fault of the analog circuit,and obviously improve fault diagnosis precision of the analog circuit.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
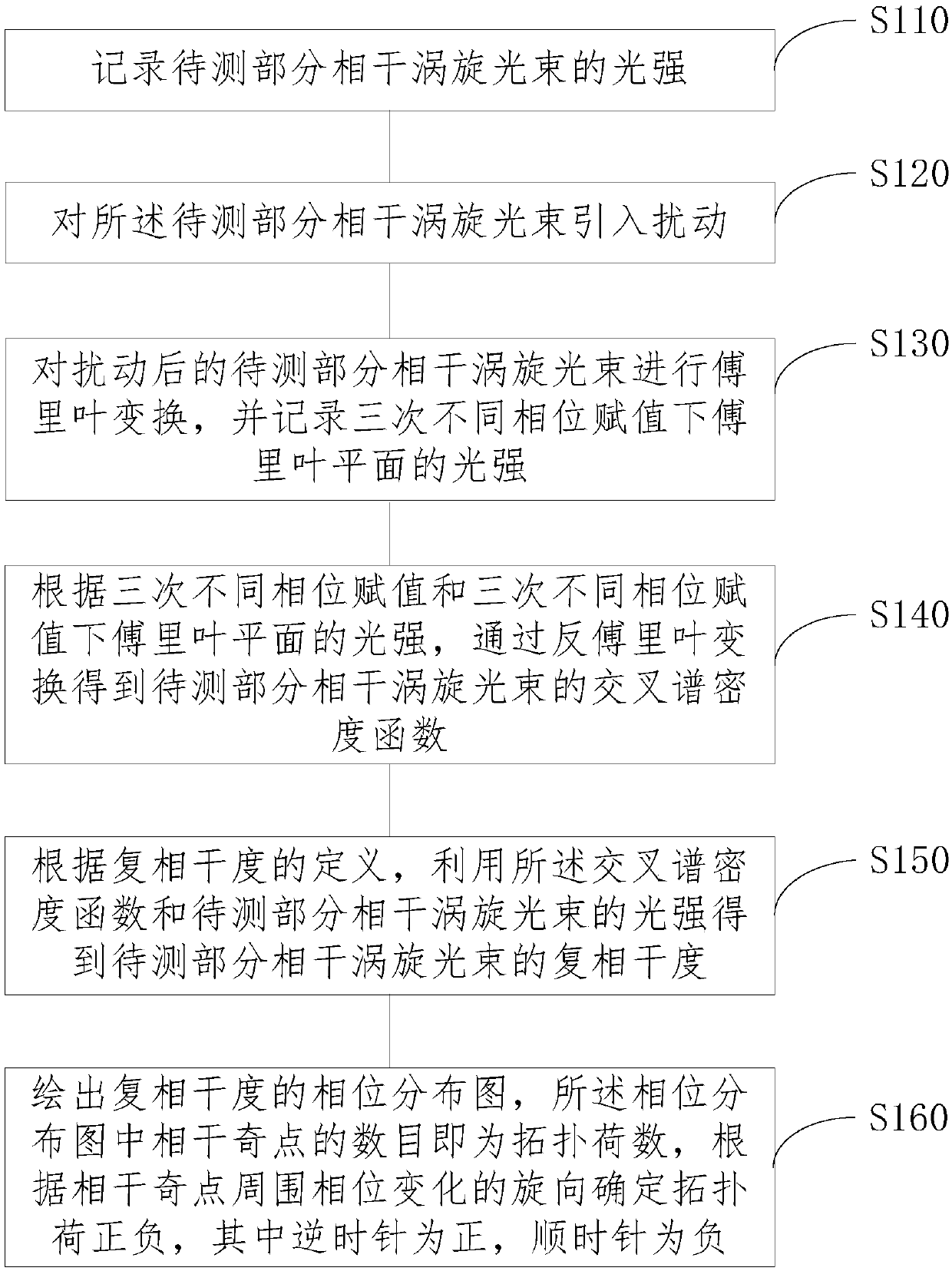
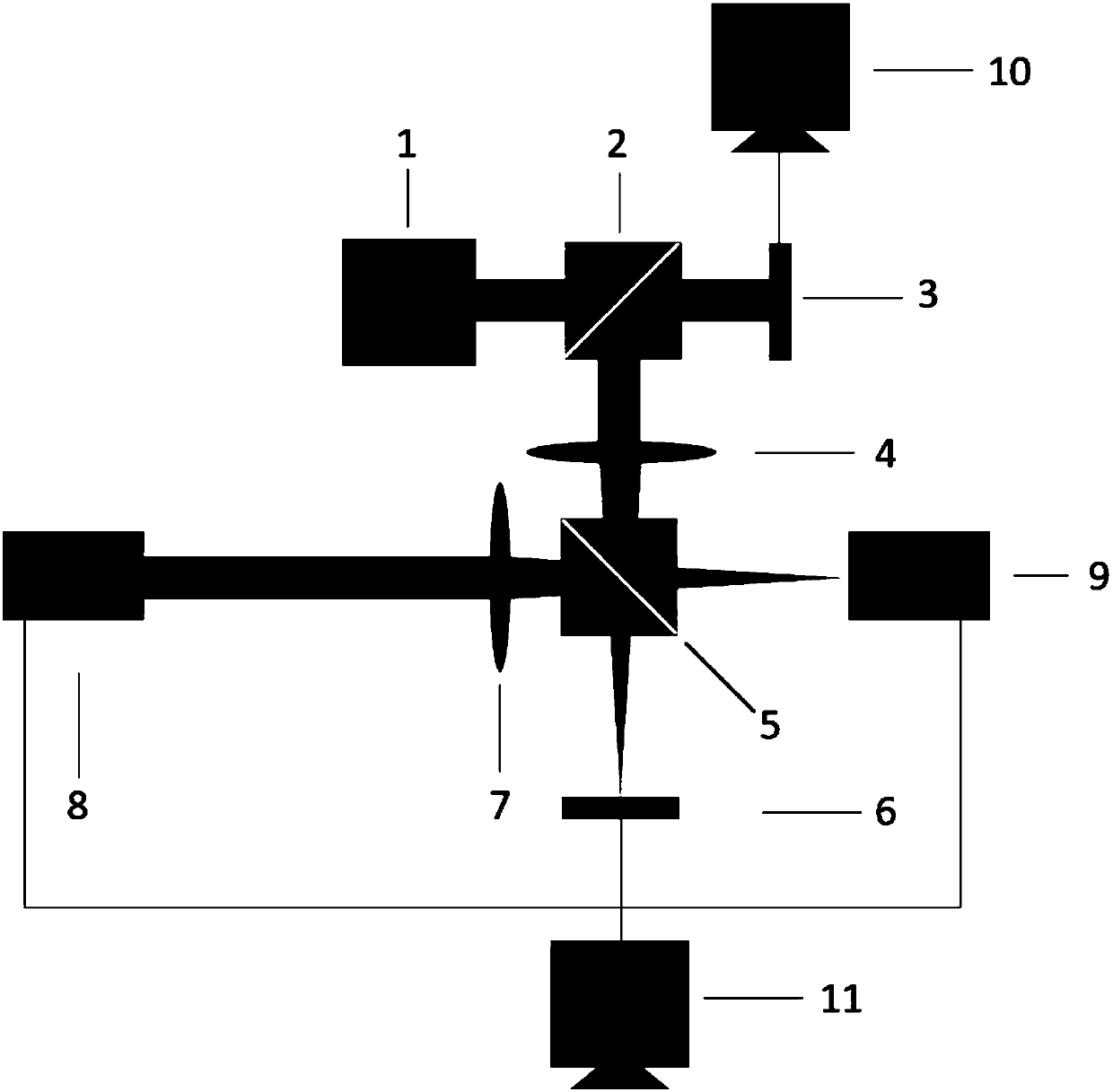
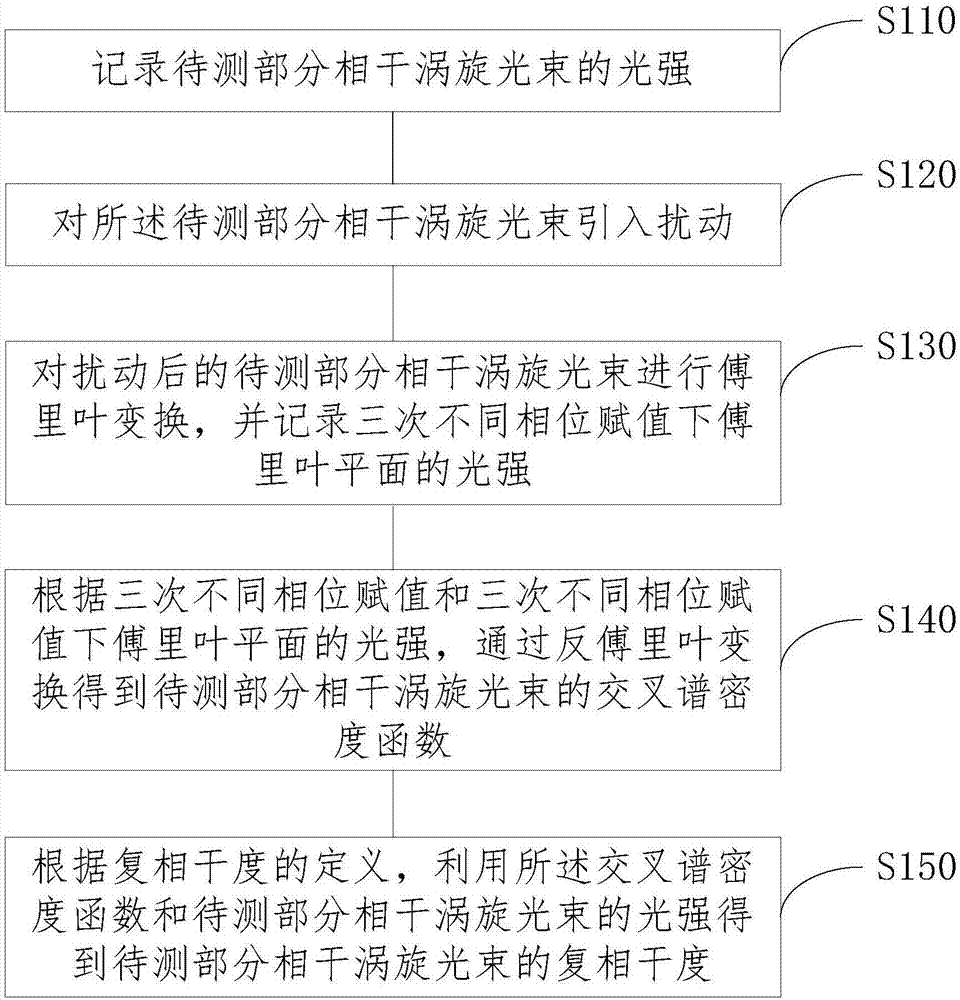
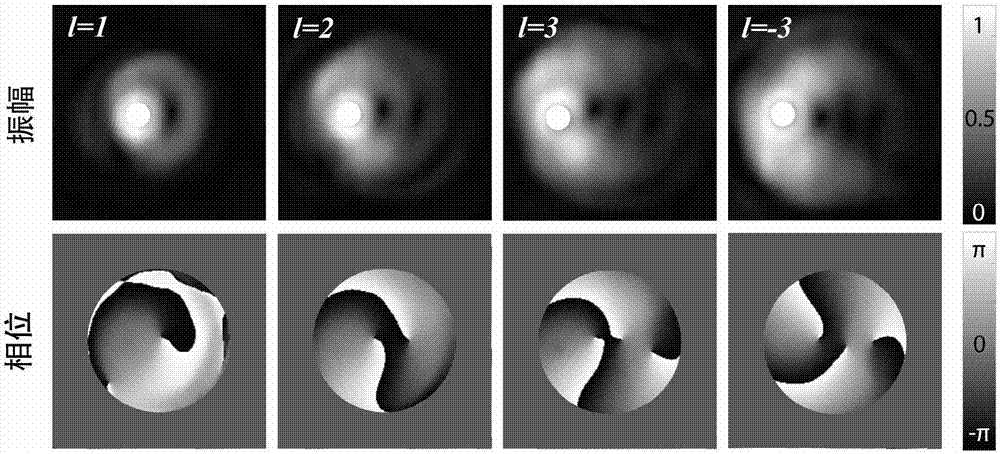
Method and system for measuring number of topological charges of partially coherent vortex beam and whether topological charges are positive or negative
The invention discloses a method and a system for measuring the number of the topological charges of a partially coherent vortex beam and whether the topological charges are positive or negative. Themethod includes the following steps: recording the light intensity of a to-be-measured partially coherent vortex beam; introducing three disturbances of different phase assignments to the to-be-measured partially coherent vortex beam; carrying out Fourier transformation on the to-be-measured partially coherent vortex beam after disturbance, and recording the light intensity of the Fourier plane after the three different phase assignments; getting a cross spectrum density function of the to-be-measured partially coherent vortex beam through inverse Fourier transformation according to the threedifferent phase assignments and the light intensity of the Fourier plane under the three different phase assignments; getting the complex coherent degree of the to-be-measured partially coherent vortex beam according to the cross spectrum density function and the light intensity of the to-be-measured partially coherent vortex beam; and drawing a phase distribution map of the complex coherent degree, wherein the number of coherent singular points in the phase distribution map is the number of topological charges, whether the topological charges are positive or negative is determined according to the rotation direction of phase change around the coherent singular points, the topological charges are positive if the rotation direction is anticlockwise, and the topological charges are negativeif the rotation direction is clockwise.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
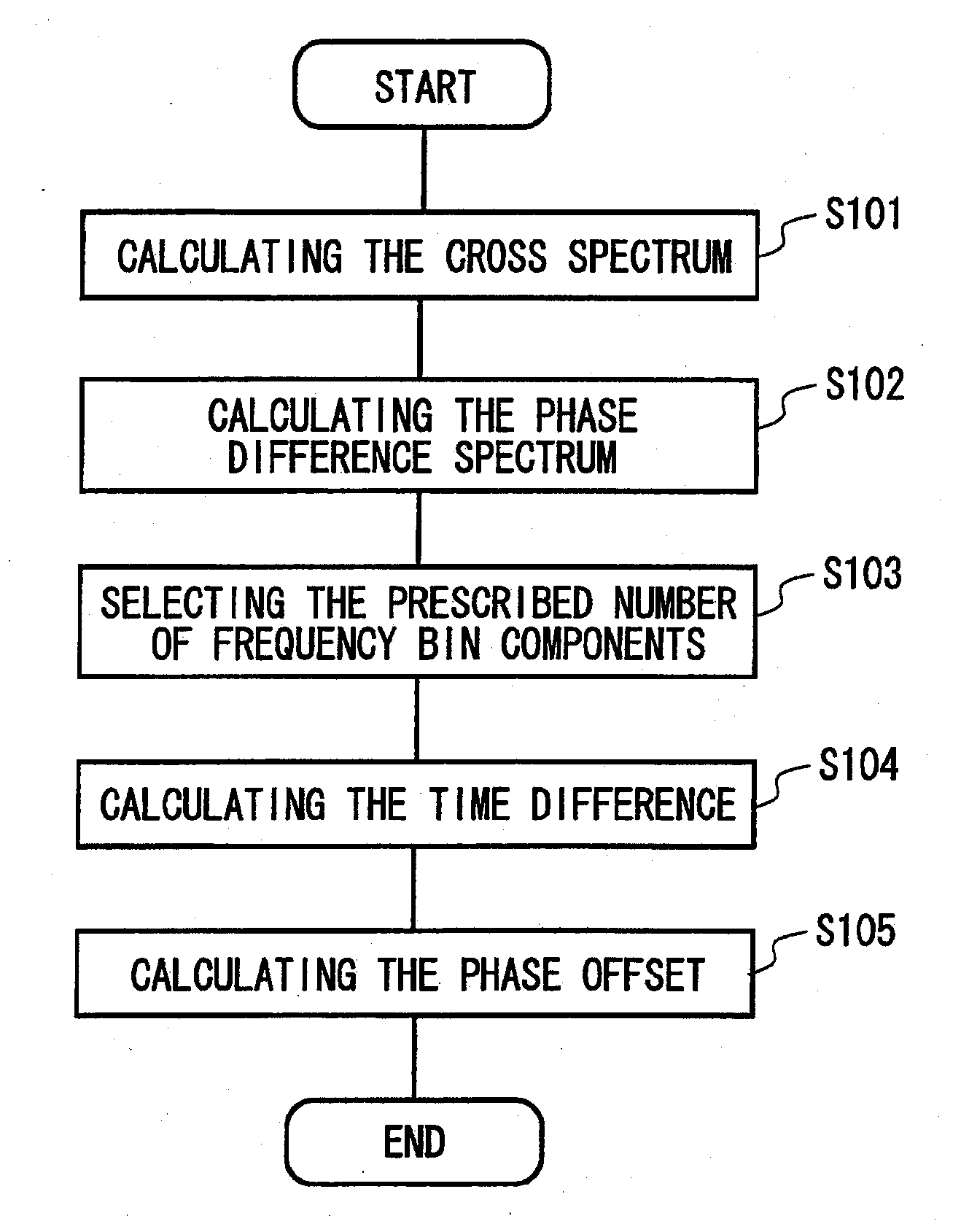
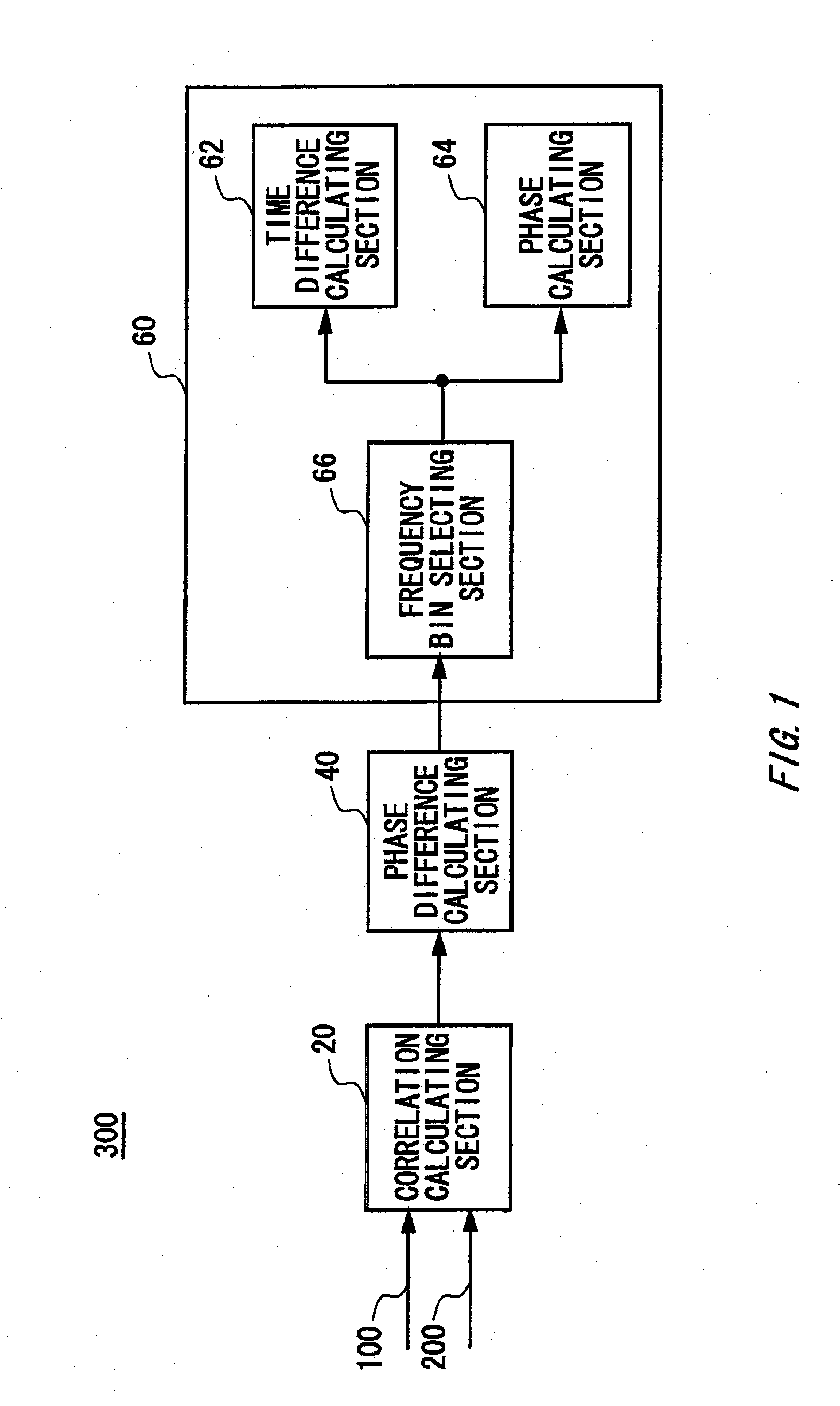
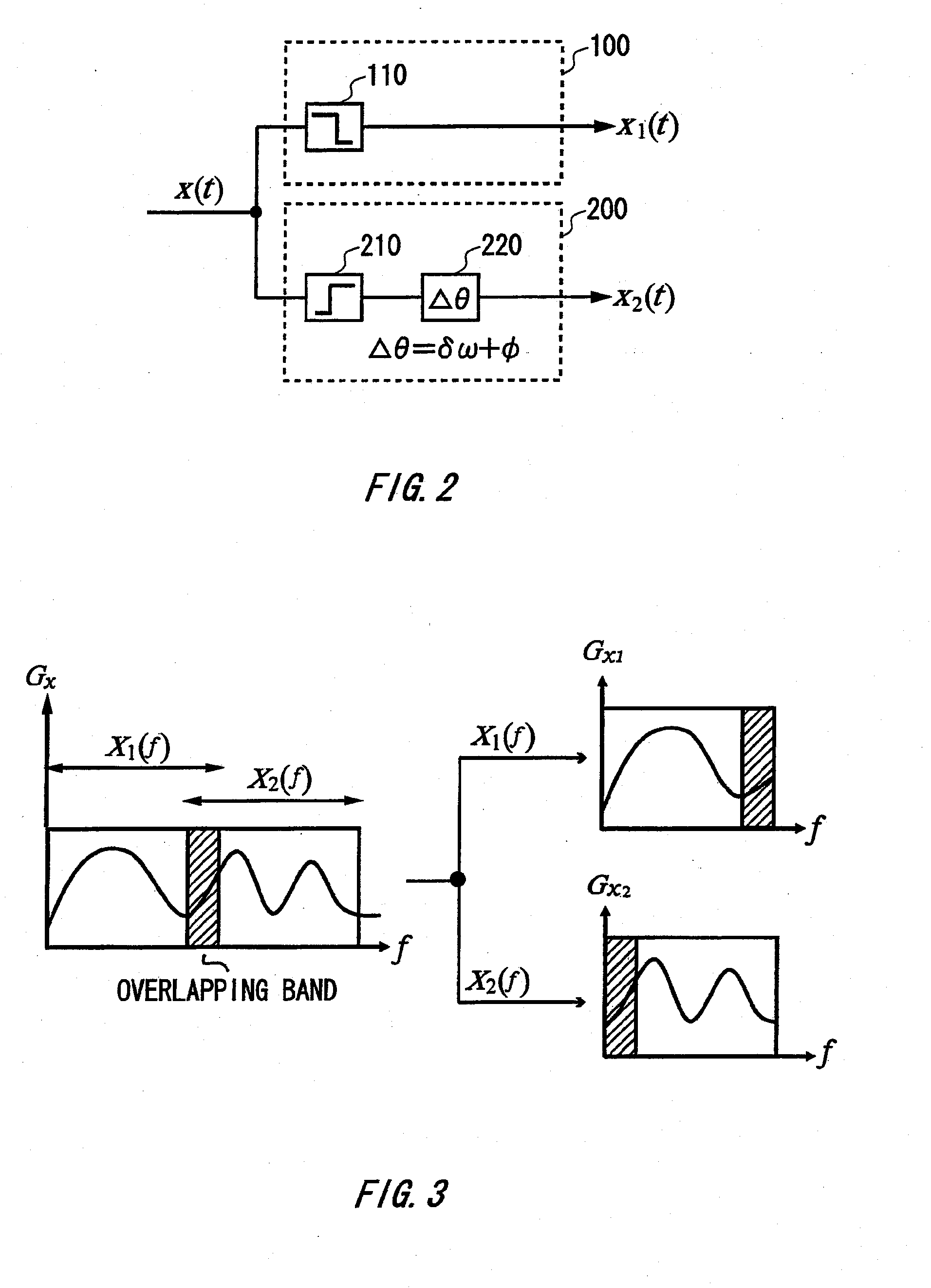
Detecting apparatus, calculating apparatus, measurement apparatus, detecting method, calculating method, transmission system, program, and recording medium
Provided is a detection apparatus that detects a phase alignment error between transmission signals transmitted on different channels, comprising a correlation calculating section that calculates a cross-spectrum between the transmission signals based on a result of a measurement of the transmission signals transmitted in the channels; a phase difference calculating section that calculates a phase difference spectrum between the transmission signals based on the cross-spectrum calculated by the correlation calculating section; and a detecting section that detects a difference between transmission times of the transmission signals transmitted on the different channels and a phase offset between the transmission signals, based on the phase difference spectrum calculated by the phase difference calculating section.
Owner:ADVANTEST CORP
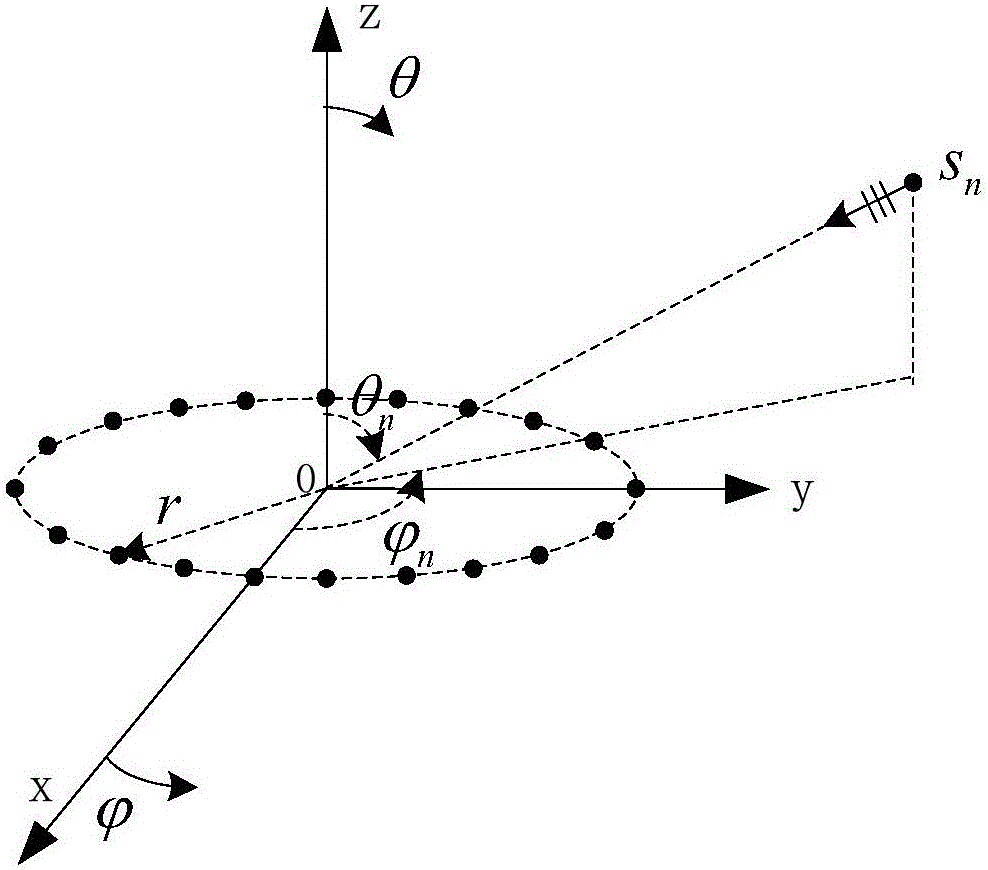
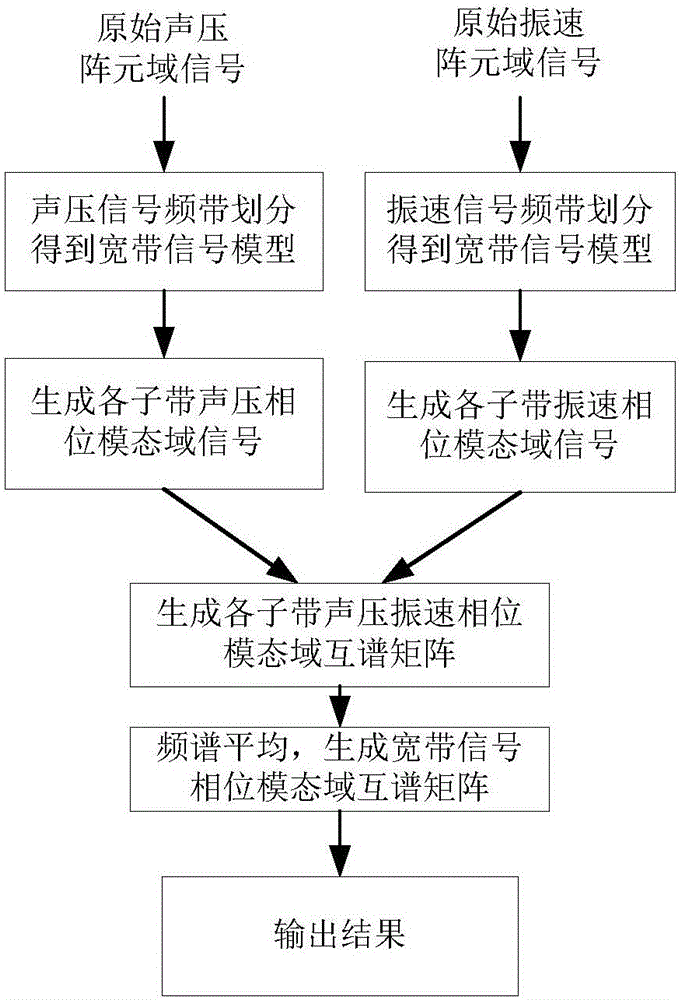
Acoustic vector circular array broadband coherent signal source direction-of-arrival estimation method
ActiveCN106249244ADecoherenceImplementing the Orientation Estimation ProblemAcoustic wave reradiationSound pressureFocus area
The invention provides an acoustic vector circular array broadband coherent signal source direction-of-arrival estimation method. Received data is divided into L sub-segments, and the DFT transform of the J point of every sub-segment is carried out, and 3M*1 dimensional array sample data of every sub-segment is acquired, and therefore the broadband data model of the acoustic vector circular array is acquired. A preprocessing matrix Tp(fi), a preprocessing matrix Tvr (fi), and a preprocessing matrix Tv phi (fi) are used to transform the acoustic vector circular array from an element domain into a phase modal domain, and a sub-segment receiving data cross spectrum matrix Repv (fi) is acquired in the phase modal domain. The cross spectrum matrix Repv of the acoustic vector circular array broadband signals is acquired by adopting a frequency domain average method. The direction-of-arrival estimation is carried out by adopting a sub-space processing method, and therefore a direction-of-arrival of a target is acquired. Sound pressure vibration velocity combination signal processing is realized in the phase modal domain, and therefore a strong noise suppression capability is provided, and a broadband coherent signal source estimation problem is realized. An initial focusing area is not required to be determined during designing of a focusing matrix, and direction-of-arrival estimation errors caused by the initial focusing area of the focusing matrix are overcome.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Cross-spectrum generalized inverse beam forming method based on cross spectrum optimization
ActiveCN107153172ATake advantage of noise immunityPosition fixationGeneralized inverseClassical mechanics
The invention discloses a cross-spectrum generalized inverse beam forming method based on cross-spectrum optimization. Firstly, a steering matrix is constructed based on the traditional generalized inverse beam formation. Secondly, an acoustic pressure cross-spectrum matrix is optimized through a linear optimization method. Finally, through the obtained steering matrix and the optimized acoustic pressure cross-spectrum matrix and according to the traditional idea of cross-spectrum matrix beam formation, a novel cross-spectrum generalized inverse beam forming algorithm based on an optimized cross-spectrum matrix is constructed. The algorithm can make full use of the anti-noise performance of cross-spectrum beam formation based on cross-spectrum optimization while taking advantage of high resolution of generalized inverse beam formation.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
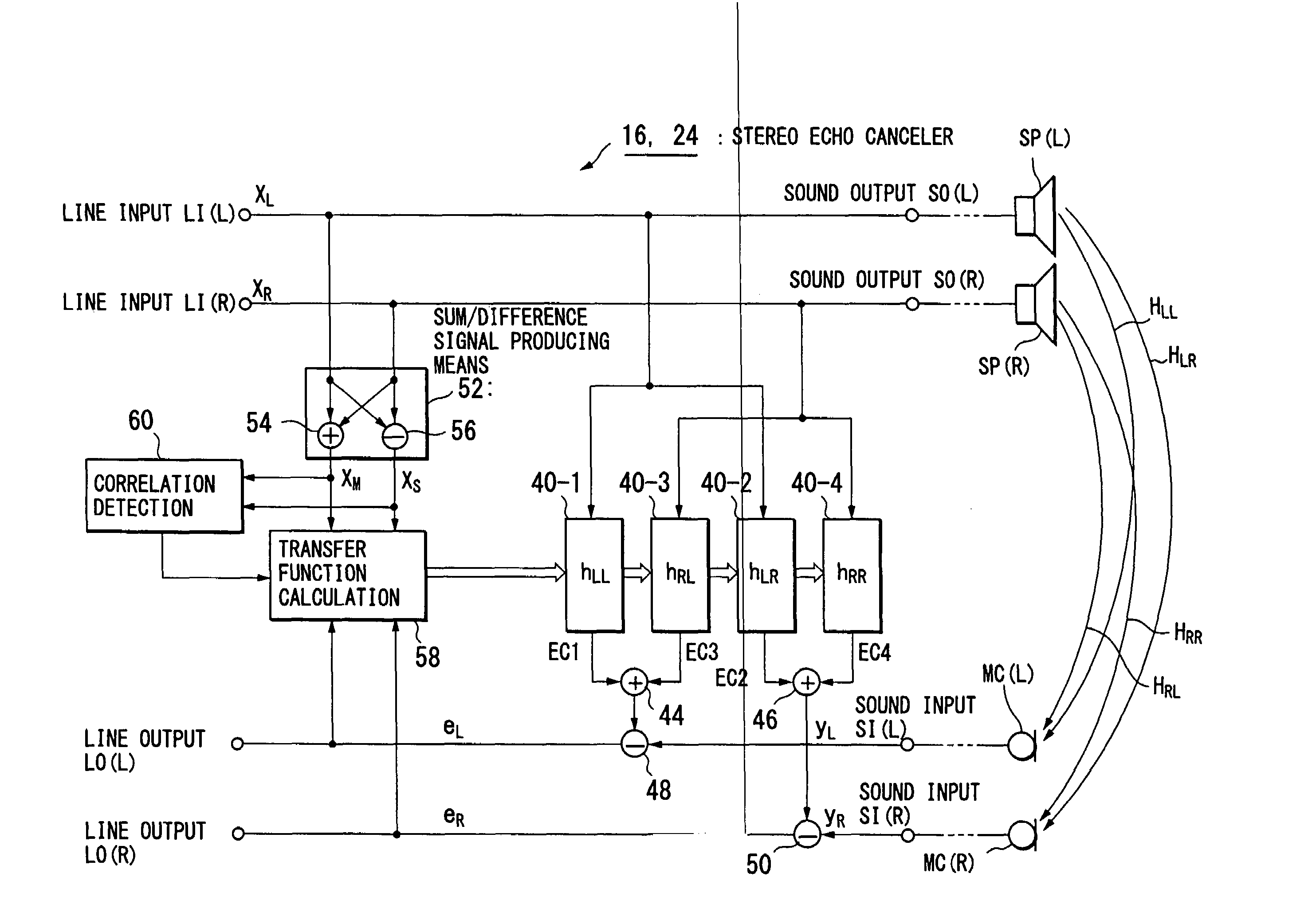
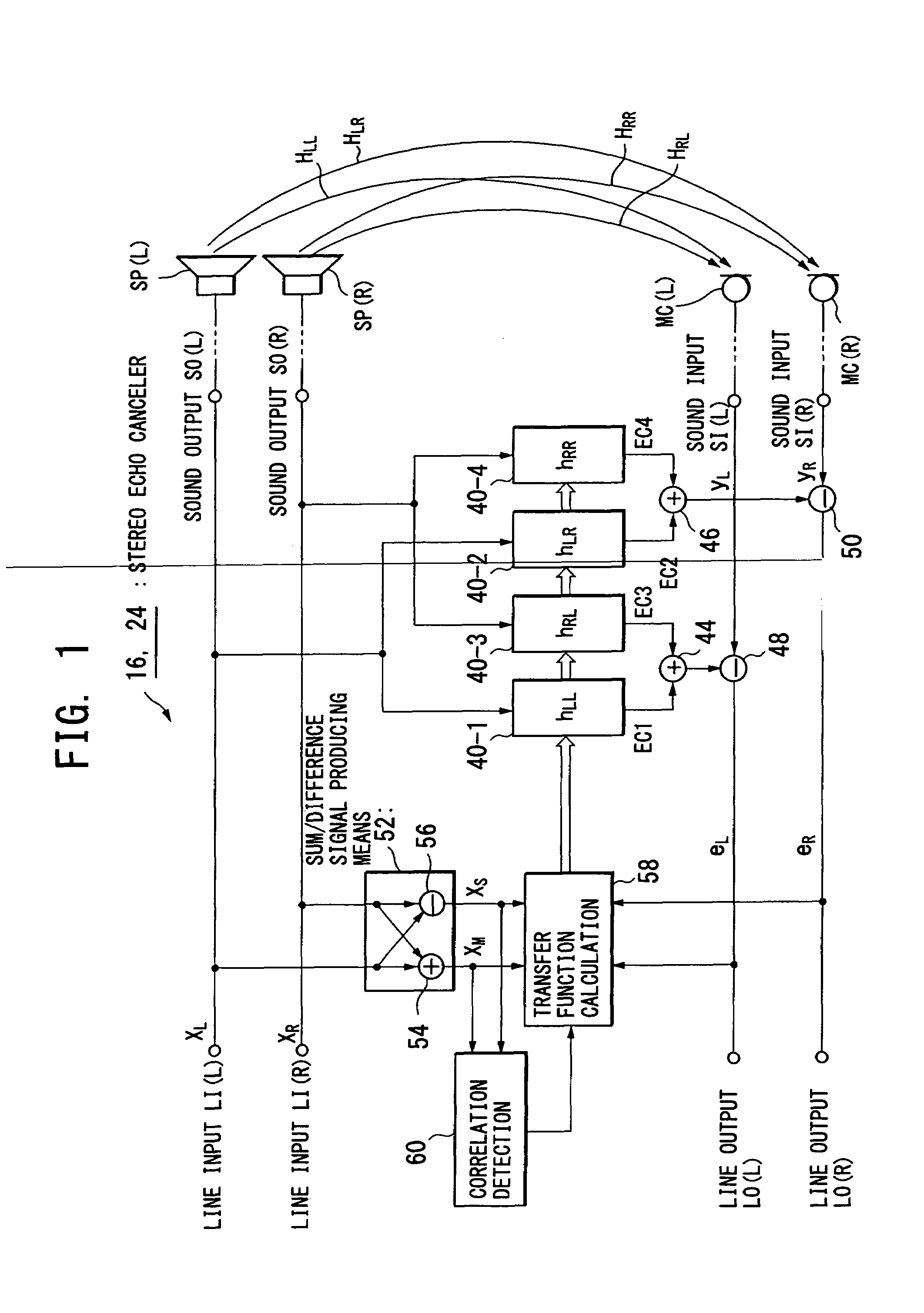
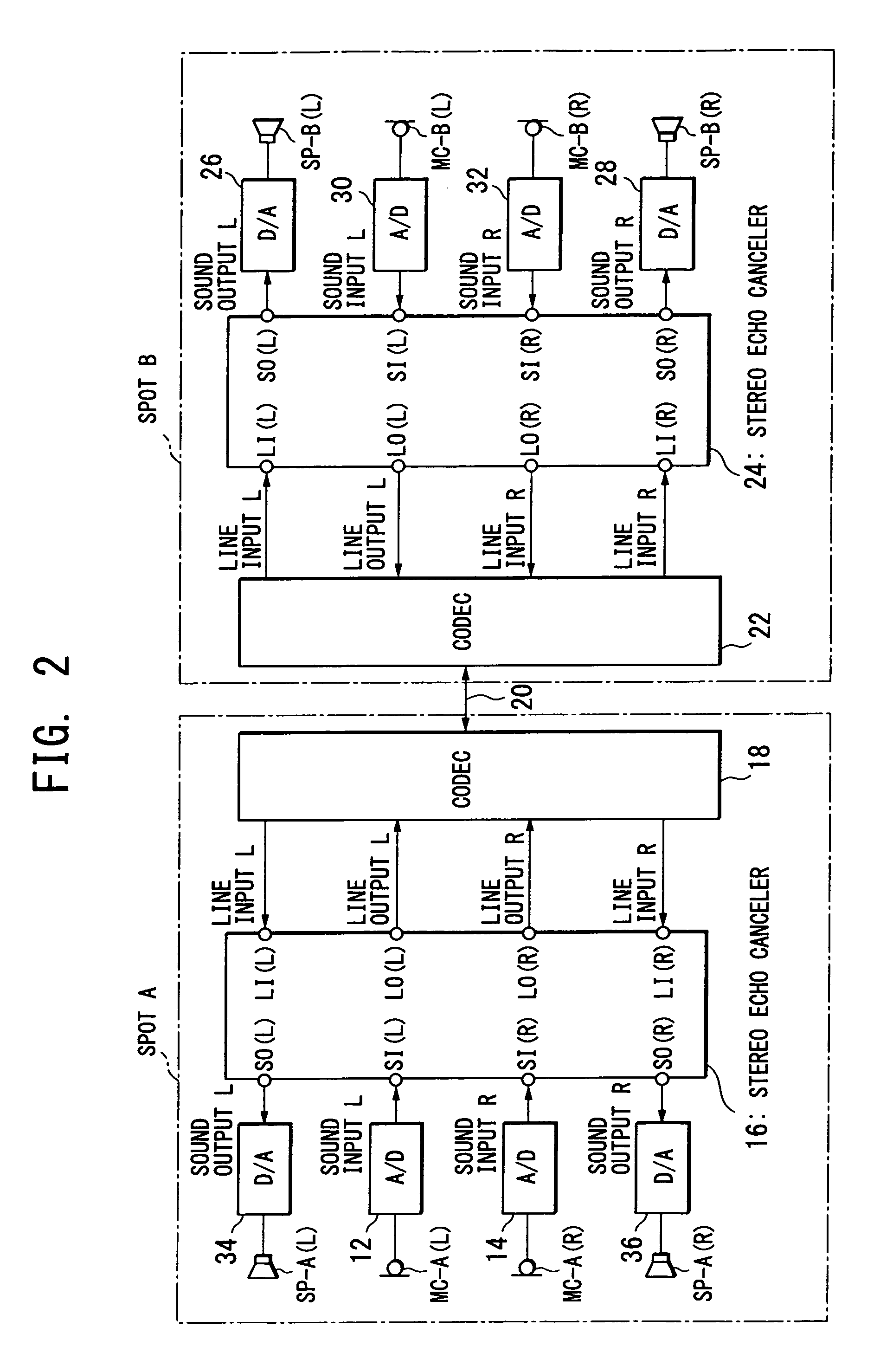
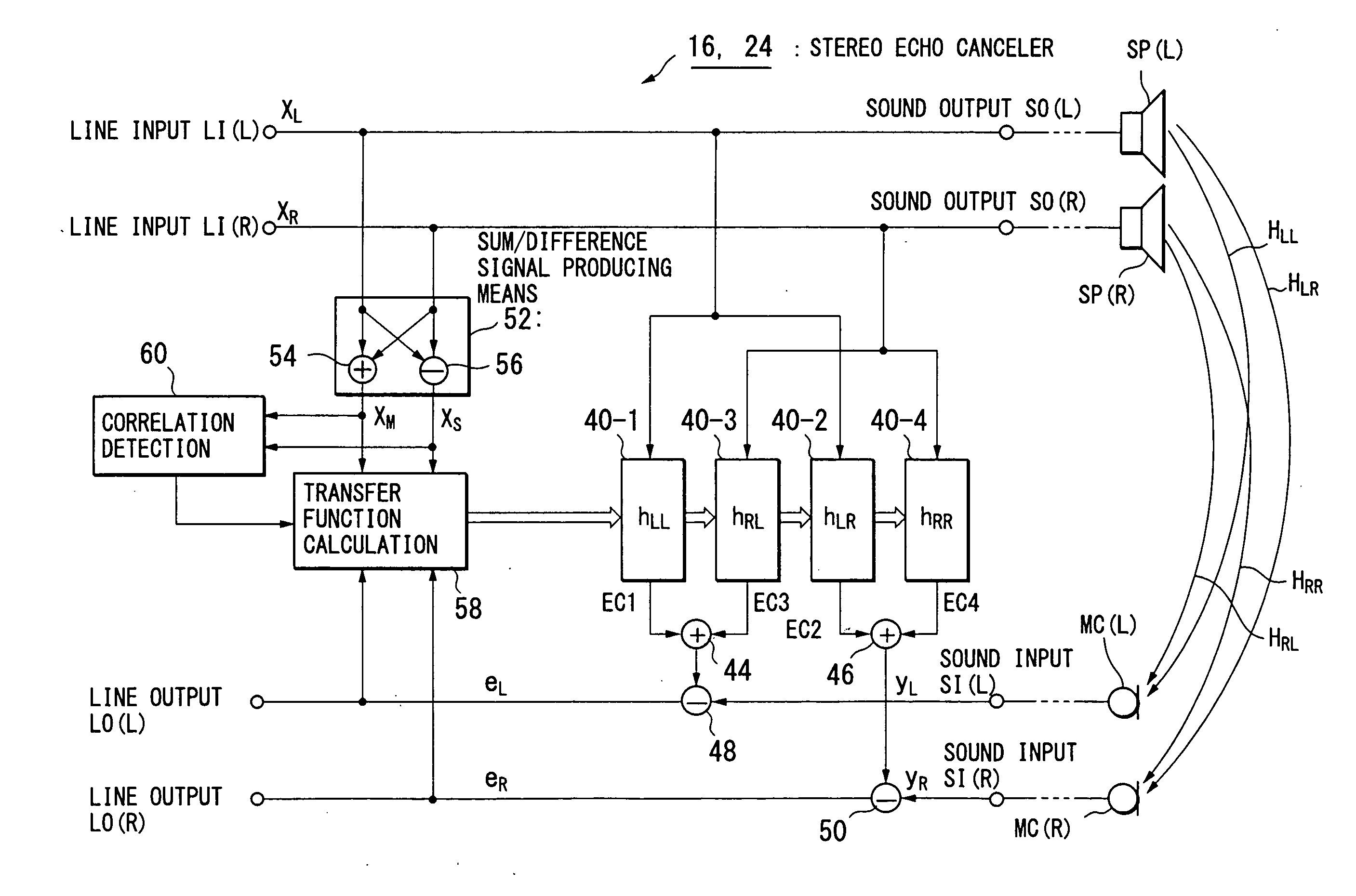
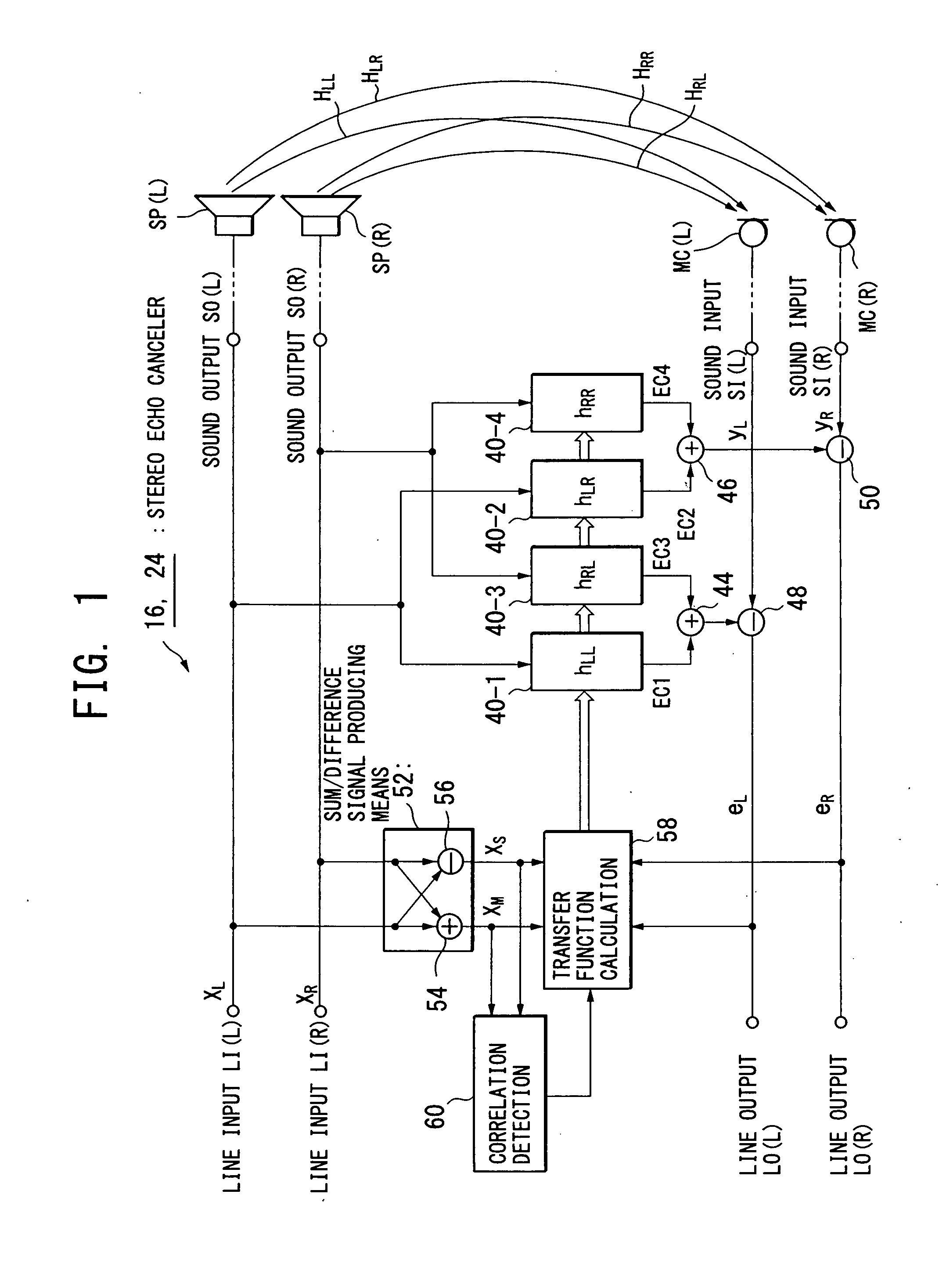
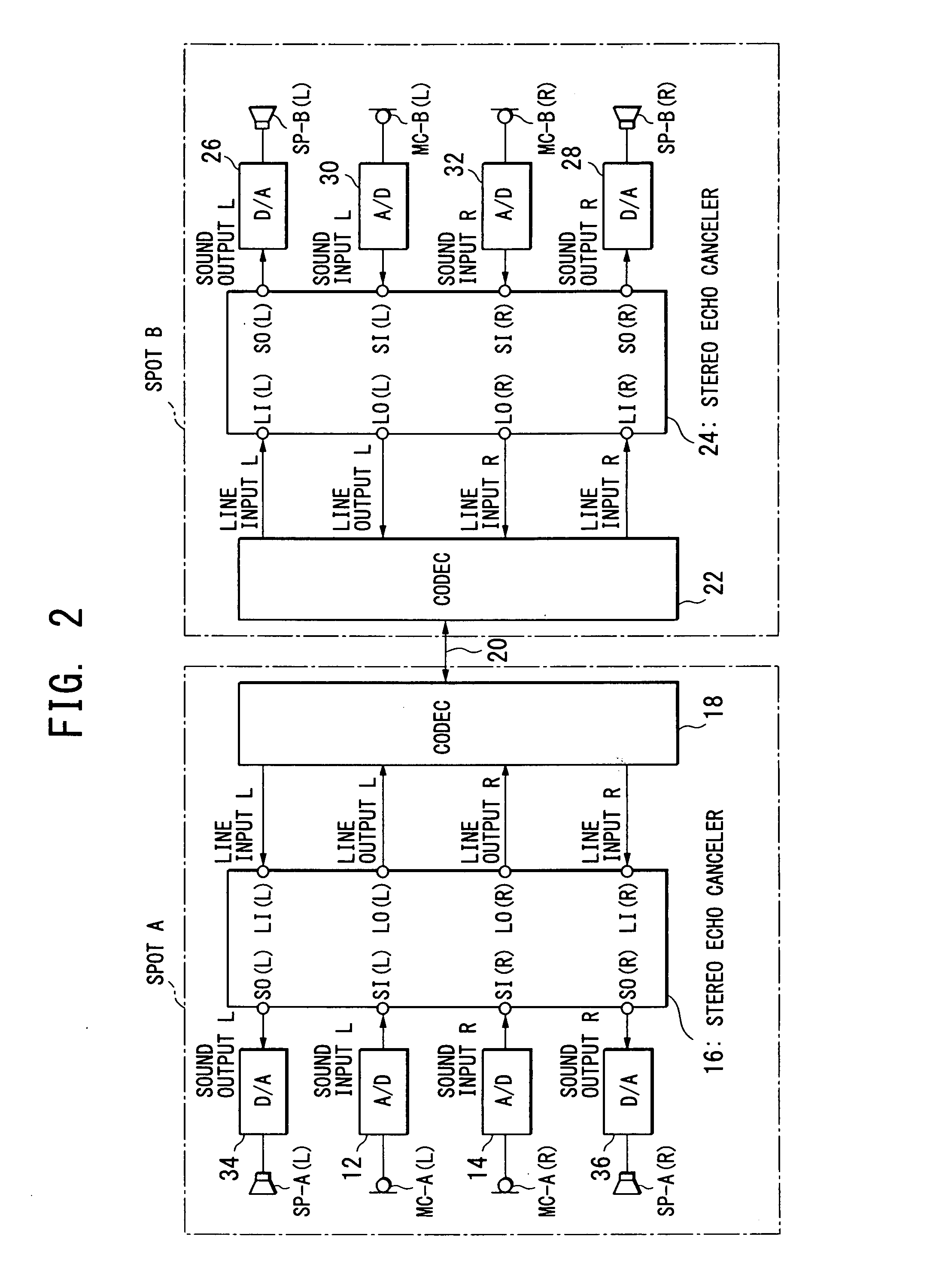
Multi-channel echo cancel method, multi-channel sound transfer method, stereo echo canceller, stereo sound transfer apparatus and transfer function calculation apparatus
InactiveUS7403609B2Reduce correlationTwo-way loud-speaking telephone systemsSpecial service for subscribersFourier transform on finite groupsLoudspeaker
Owner:YAMAHA CORP
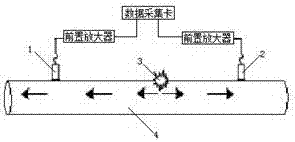
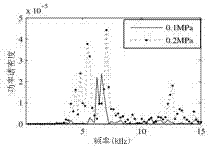
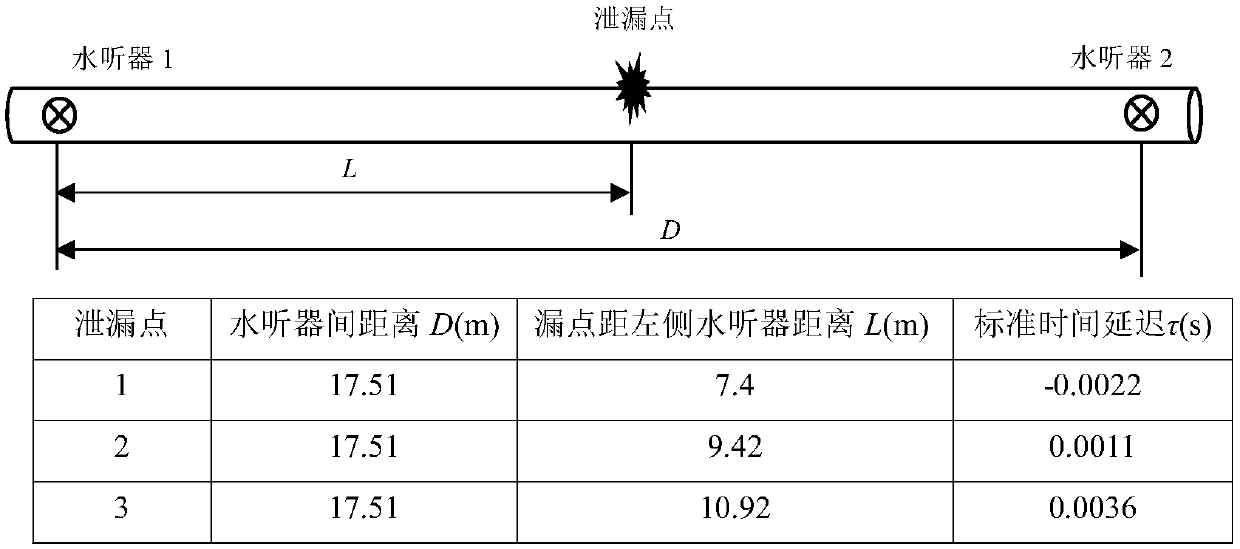
Gas pipeline leakage acoustic emission positioning method
InactiveCN106907577AReduce mistakesHigh positioning accuracyPipeline systemsAcoustic emissionEngineering
The invention discloses a gas pipeline leakage acoustic emission positioning method, and relates to the technical field of gas pipeline fault diagnosis. According to the gas pipeline leakage acoustic emission positioning method, leakage points can be positioned by detecting gas pipeline leakage acoustic emission, detection signals collected by sensors are subjected to cross-spectrum Gaussian window processing, single and small-dispersion modal compositions in leakage source signals are extracted, and the position of a leakage source can be positioned through a cross-correlation function of the sensors. By the adoption of the positioning method, multi-modal guided wave interference is reduced, positioning errors of the leakage source are lowered, positional accuracy of the leakage source is improved, and working efficiency of gas pipeline maintenance is also improved. According to the positioning method, a LabVIEW development platform is adopted for designing a gas pipeline leakage acoustic emission detecting and positioning virtual system, the selected single modal compositions can be extracted by selecting window parameters, and therefore operation is easy and applicability is high.
Owner:广西壮族自治区气象技术装备中心
Tetrahedral array three-dimensional passive direction finding method for underwater glider
ActiveCN109991567AOvercoming only two-dimensional direction angle can be measuredOvercome the disadvantages of ambiguity in direction finding, starboard and starboardDirection/deviation determination systemsRectangular coordinatesPhase difference
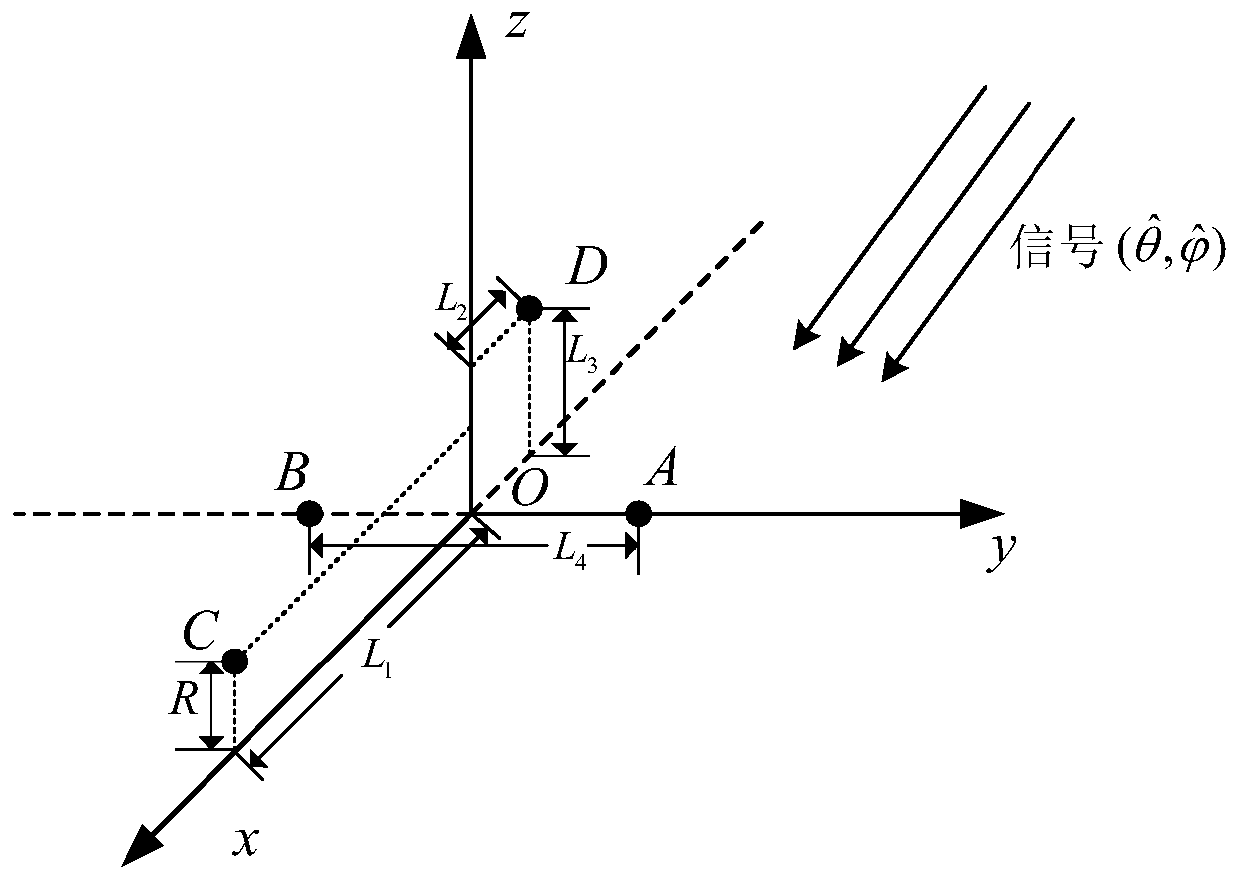
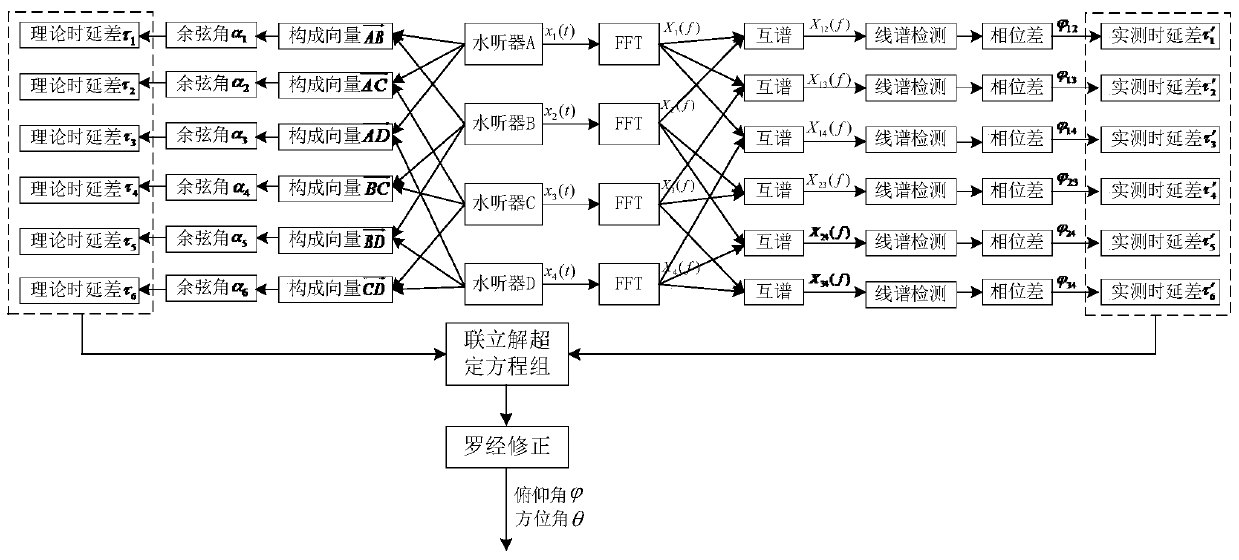
The invention discloses a tetrahedral array three-dimensional passive direction finding method for an underwater glider, and belongs to the field of detection signal processing. An underwater glider platform cannot perform three-dimensional direction finding on underwater line spectrum sound signals. Four hydrophones are combined in pairs into vectors, in a rectangular coordinate system, of combinations; a theoretical time delay difference of a signal, corresponding to a cosine included angle formed by each vector and an incident wave direction vector, reaching the two hydrophones is calculated; the received signals of the hydrophones are converted into frequency domain signals, cross spectrum calculation results of the frequency domain signals are subjected to modulo averaging to obtain across spectrum amplitude spectrum average value, and then signal frequencies are detected through line spectrum detection; a phase difference of the line spectrum signals of each group of the hydrophones is obtained through the signal frequencies; an actually measured time delay difference is obtained by the line spectrum frequency and the phase difference of the line spectrum signals; two time delay differences are correspondingly simultaneous to obtain a signal incidence direction vector in a carrier coordinate system; and a binary equation set is solved to obtain an azimuth angle and a pitch angle in a geodetic coordinate system. The three-dimensional azimuth angle of a target in the geodetic coordinate system can be measured. In addition, the direction finding process is simple.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Multi-channel high-repetition-frequency large-dynamic-range distance and speed measurement laser radar method and device
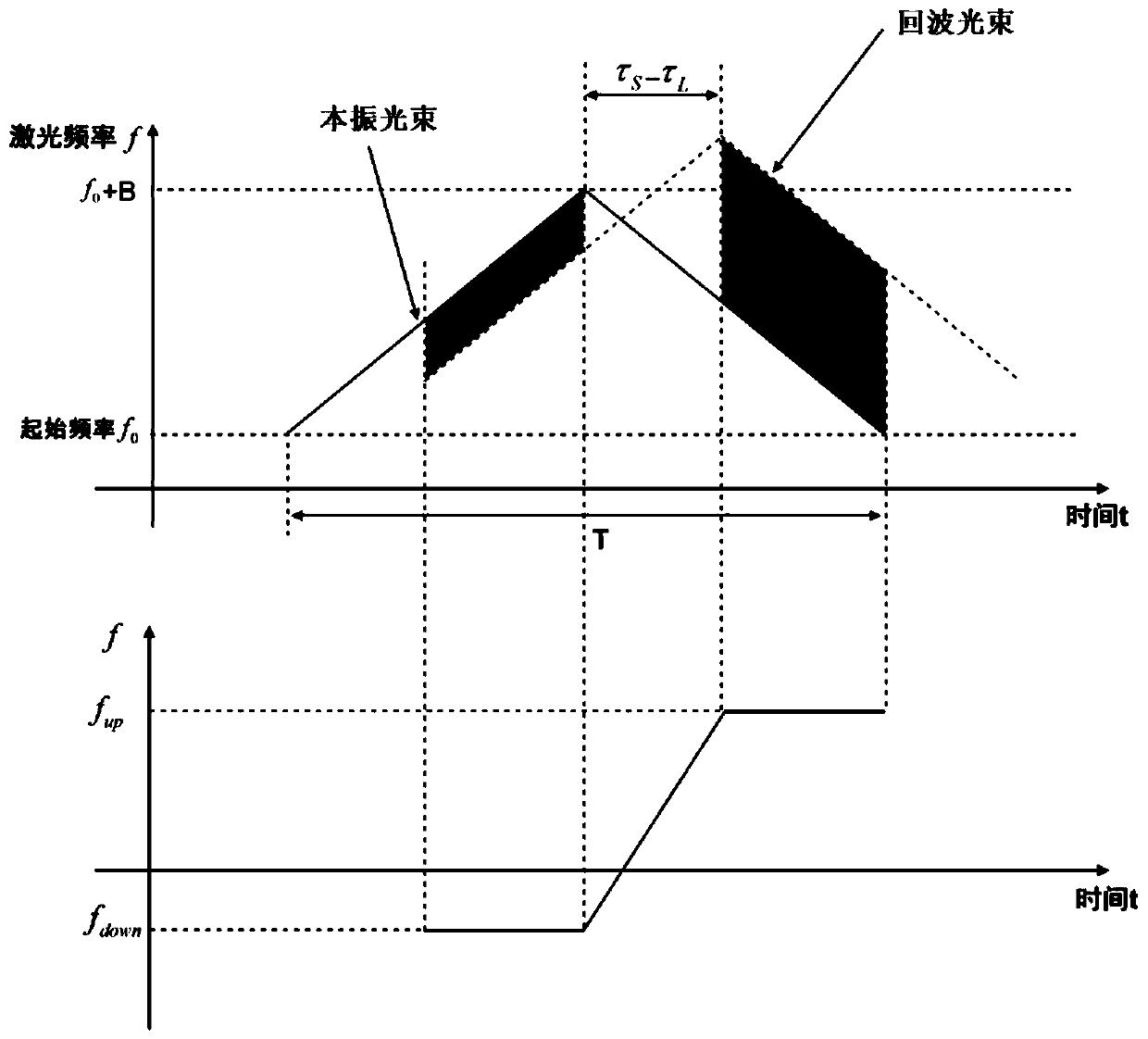
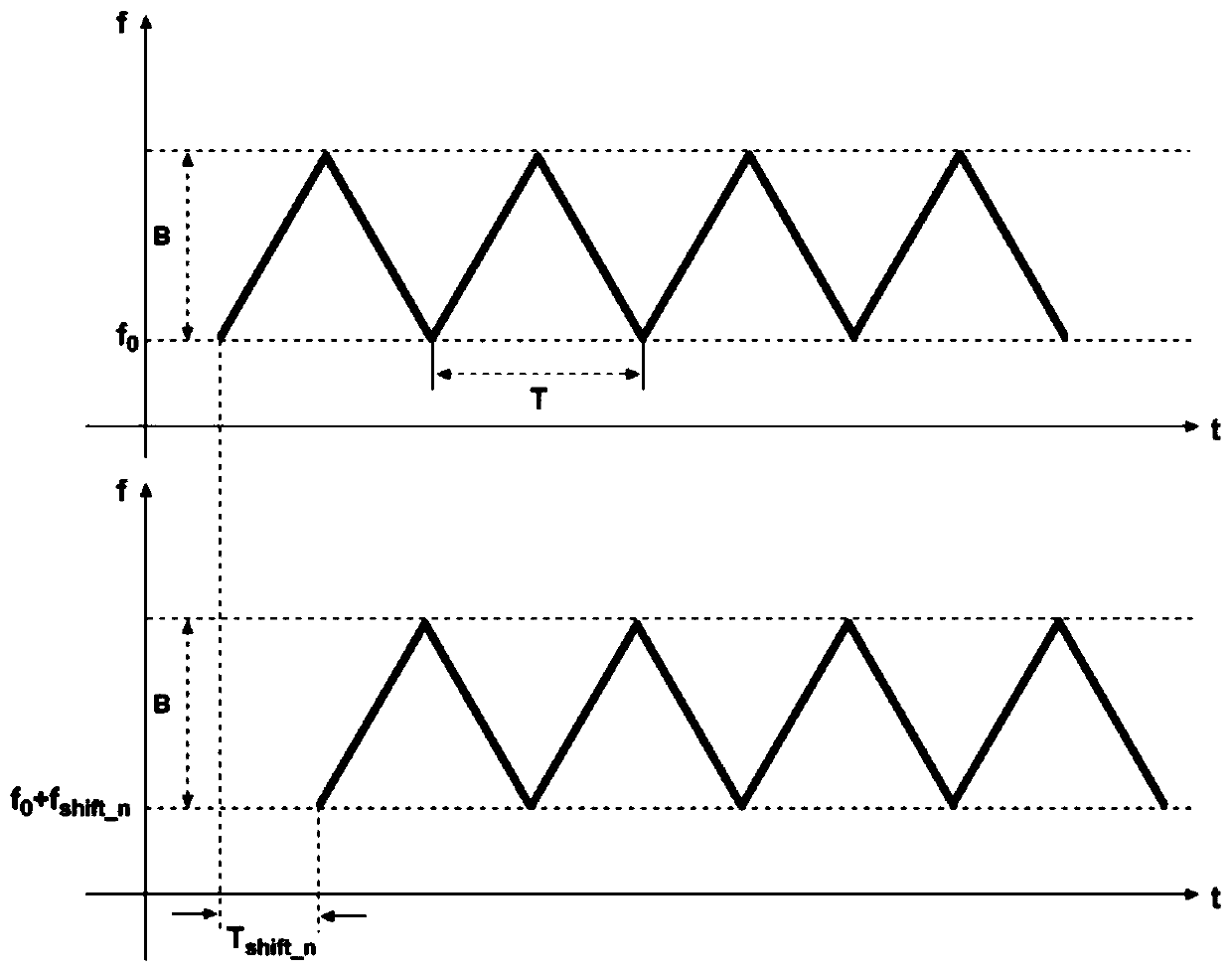
ActiveCN111337902AAchieve matchingAchieving Parallel Synchronized MeasurementsElectromagnetic wave reradiationBeam splitterIntermediate frequency
The invention discloses a multi-channel high-repetition-frequency large-dynamic-range distance measurement and speed measurement laser radar method and device. A laser light source generates a light beam, the light beam is divided into output light beams of N channels through a beam splitter, broadband linear frequency modulation is carried out on the output light beams of each channel, and then aphase modulator is driven after phase shift of different amplitudes, so that the output light beams of each channel have different time delays; the laser beam is divided into a local oscillation light beam and an emission light beam through a beam splitter; the N transmitting light beams are transmitted to a target in parallel and echo light beams of the target are received, coherent light mixingis carried out on the signals and corresponding local oscillation light beams, intermediate frequency signals containing target distance and speed information are obtained, parallel fast Fourier transform and cross-spectrum processing are carried out on sampling data of the intermediate frequency signals, parallel synchronous measurement of the target distance and speed is achieved, and finally merging output of point cloud images of N channels is achieved through a main control computer. The device can effectively overcome distance measurement ambiguity, and has the advantages of high repetition frequency, large dynamic distance measurement range, high resolution, high precision, high reliability, small size, light weight and the like.
Owner:孙建锋
Continuous spectrum signal target automatic detection method based on single vector subsurface buoy
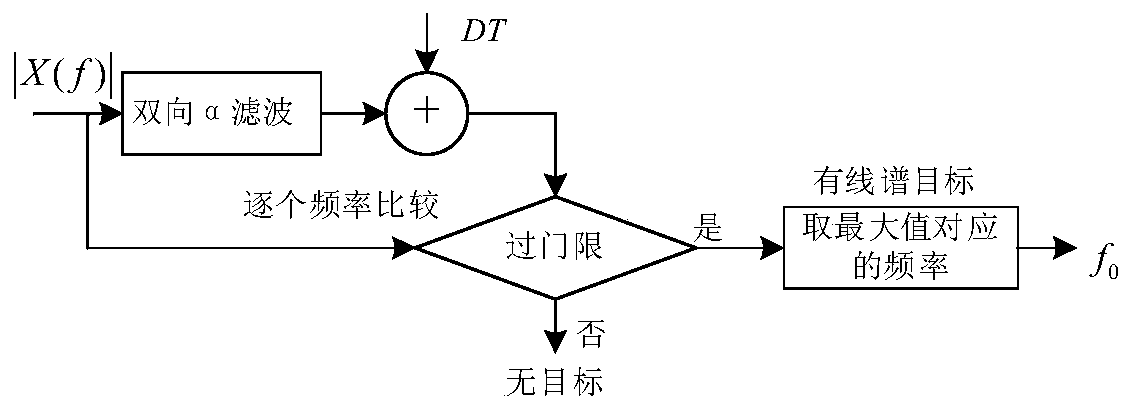
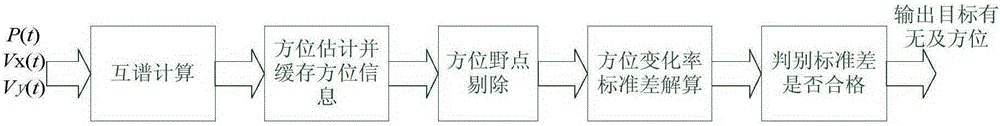
ActiveCN105182345ANo false alarmStable azimuth outputAcoustic wave reradiationCross-spectrumHistogram
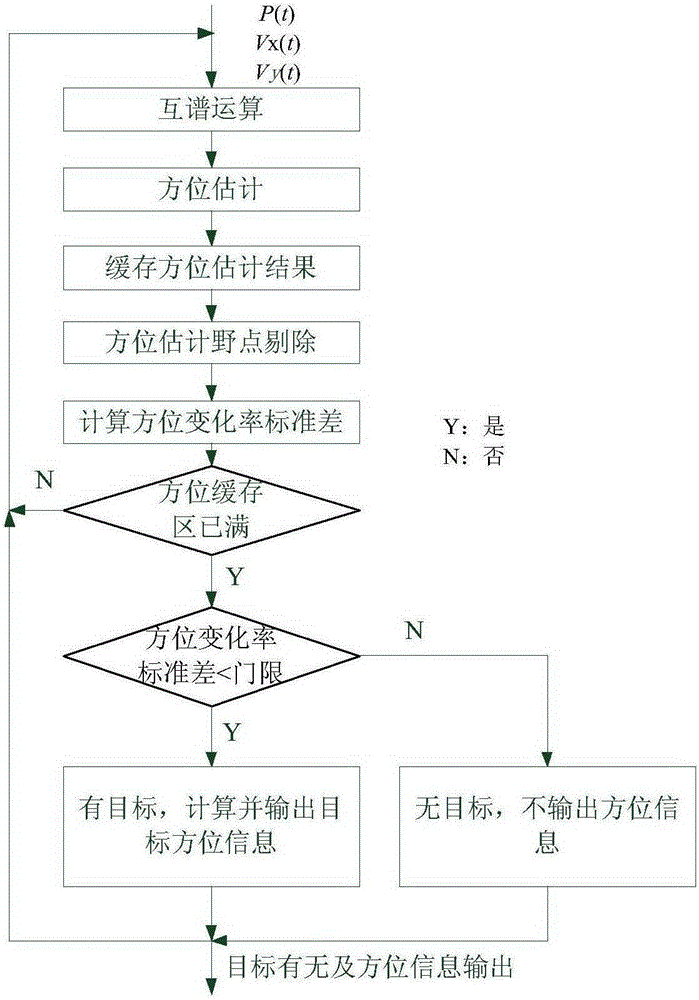
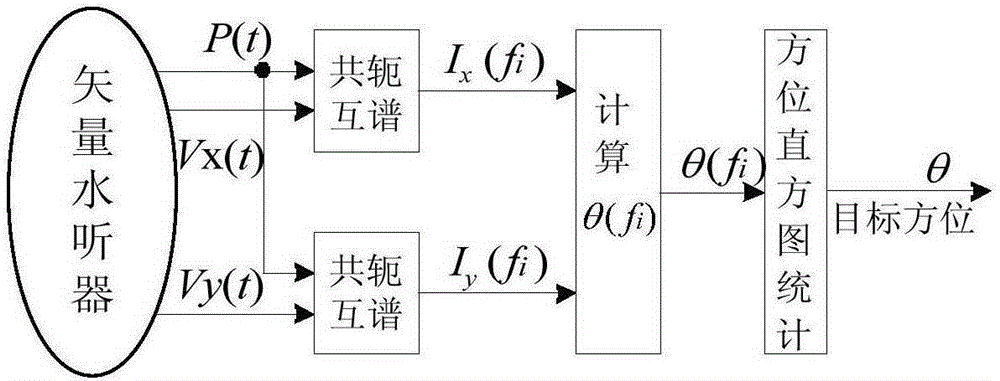
The invention provides a continuous spectrum signal target automatic detection method based on a single vector subsurface buoy. Firstly, a vector hydrophone sound pressure channel signal P(t) is taken, and cross-spectrum operation is carried out on the P(t), a Vx(t) and a Vy(t); secondly, a cross-spectrum histogram statistical method is used for continuous spectrum target bearing estimation; thirdly, jump points in a bearing cache array theta(n) are rejected, and bearing points with a stable measurement value are kept; fourthly, the bearing cache array theta(n) after the jump points are rejected in the third step is used for calculating a bearing change rate array delta theta(n), and a bearing change rate standard difference thetastd is further solved; and fifthly, a threshold thetastdDT for the bearing change rate standard difference is set, and whether the bearing change rate standard difference meets a threshold requirement is judged. The method of the invention is applied to a signal processing field, and the problems that the detection threshold is hard to determine in the existing energy detection method, and an energy detection method is easily disturbed can be solved.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Underwater target depth measuring method adopting passive vertical double-vector hydrophones
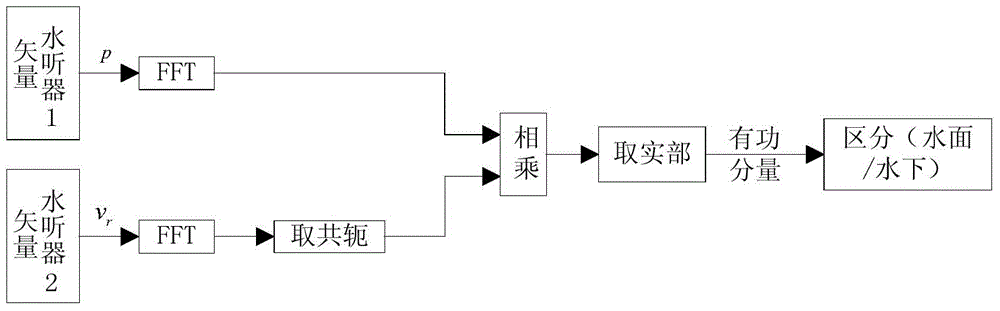
ActiveCN104091048ASolving Depth Determination ProblemsSpecial data processing applicationsAcoustic wave reradiationHydrophoneTwo-vector
The invention discloses an underwater target depth measuring method adopting passive vertical double-vector hydrophones. The method comprises the steps as follows: the two vector hydrophones which are perpendicularly arranged in water are used for receiving a sound pressure signal and a horizontal vibration velocity signal respectively; the laying depths of the two hydrophones can be obtained through calculation; the received sound pressure signal and horizontal vibration velocity signal are subjected to cross spectrum calculation; and the depth measurement is performed according to a symbol of an active component PHVCA obtained through the cross spectrum calculation, if the symbol is negative, the target is the surface ship, and if the symbol is positive, the target is the underwater target. According to the invention, the laying depths of the passive vertical double-vector hydrophones can be calculated, and the problem about the depth measurement of the underwater target is solved by the PHVCA.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
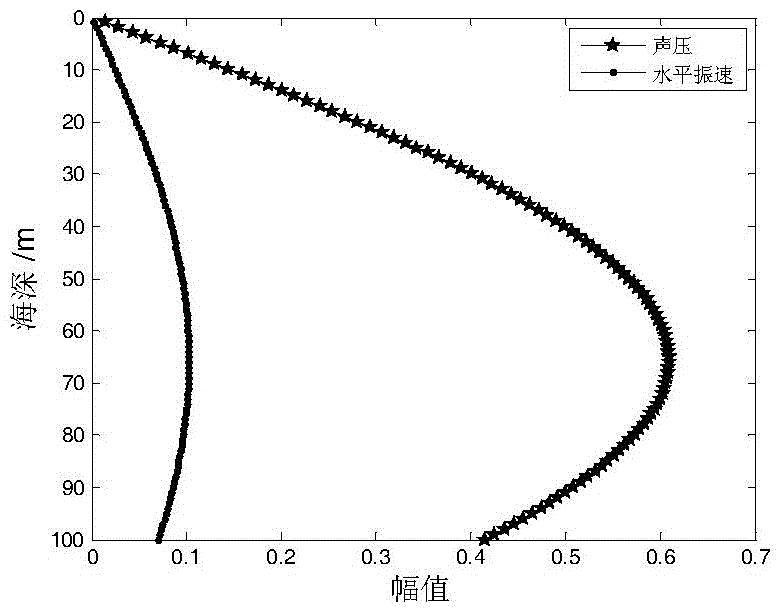
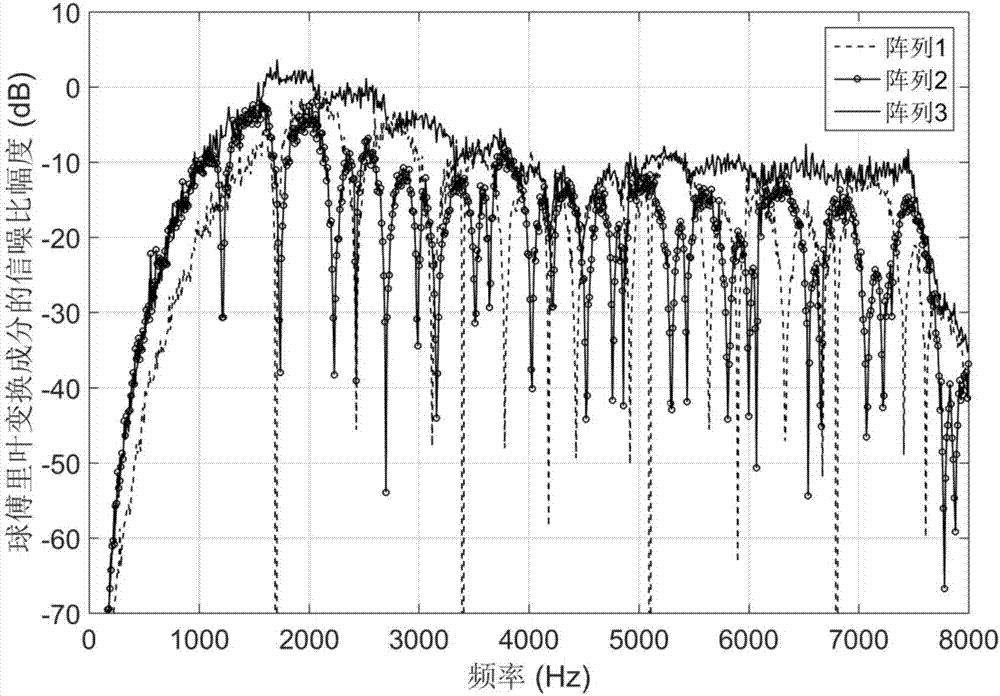
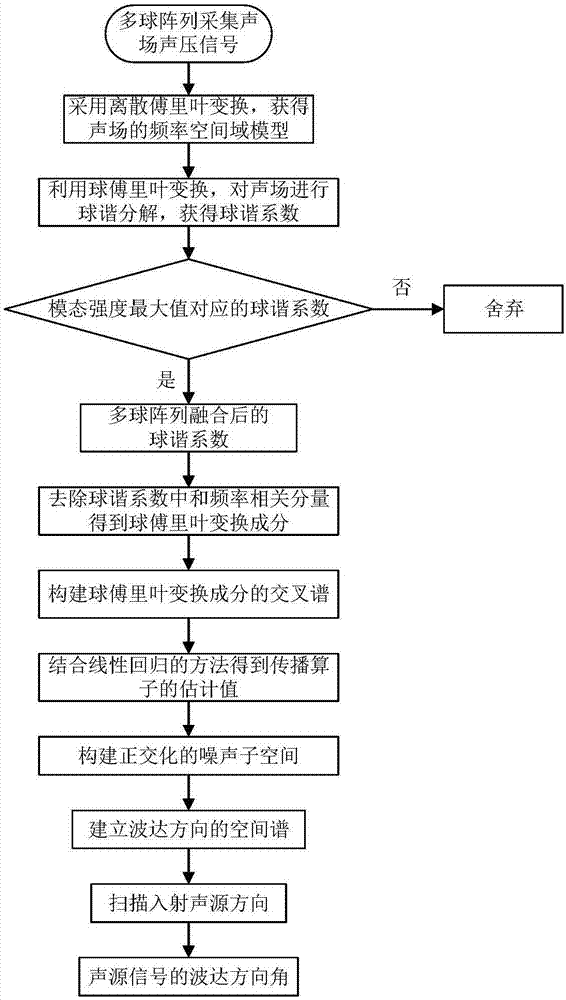
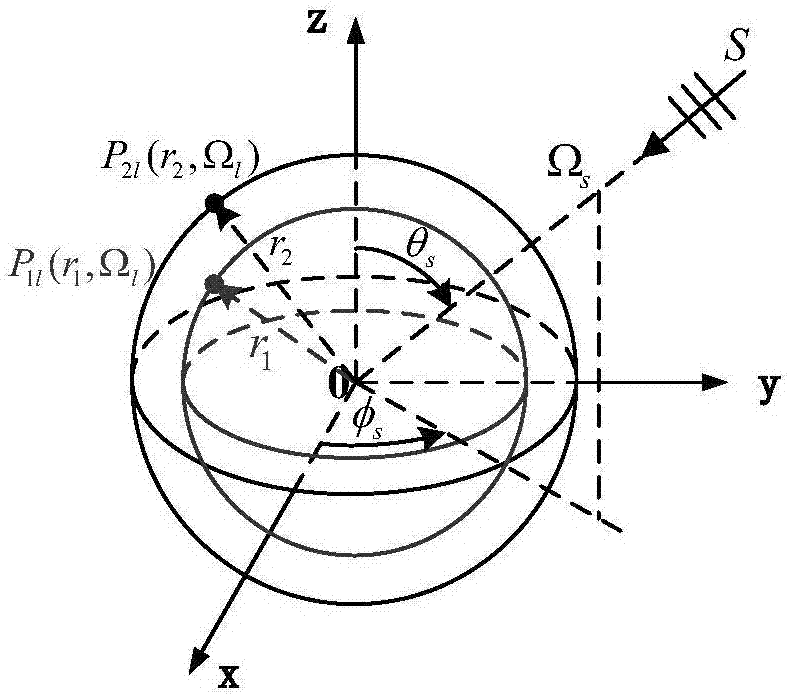
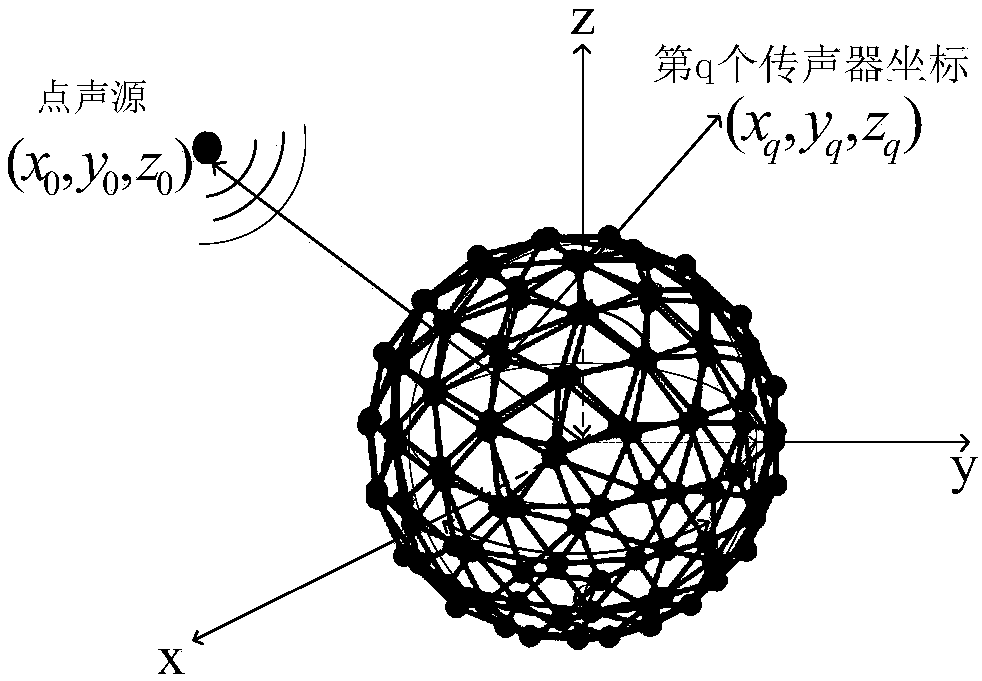
Multi-spherical array multiband sound source rapid orientation method
The invention discloses a multi-spherical array multiband sound source rapid orientation method, and belongs to the technical field of sound source orientation and detection. A frequency space domainmodel of a multi-spherical array sound field is established based on discrete Fourier transform; a spherical harmonic domain model of the multi-spherical array sound field is constructed based on spherical Fourier transform; the spherical harmonic coefficient corresponding to the maximum modal intensity of each spherical harmonic order is selected so as to obtain the spherical harmonic coefficientafter fusion of the multi-spherical array; the frequency-dependent component of the spherical harmonic coefficient is removed and the spherical Fourier transform component only including the angle-dependent component is obtained; the cross spectrum of the spherical Fourier transform component is constructed, the spherical Fourier transform component or the cross spectrum thereof are blocked and the estimation value of the propagator is obtained through combination of the linear regression method; an orthogonalized noise subspace is constructed based on the estimation value of the propagator,and the spatial spectrum of the direction of arrival is obtained by using mutual orthogonalization of the signal and the noise; and the incident sound source direction is scanned, and the sound sourcedirection corresponding to the maximum peak in the spatial spectrum is the direction-of-arrival angle of the sound source.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Sound source imaging method based on microphone array
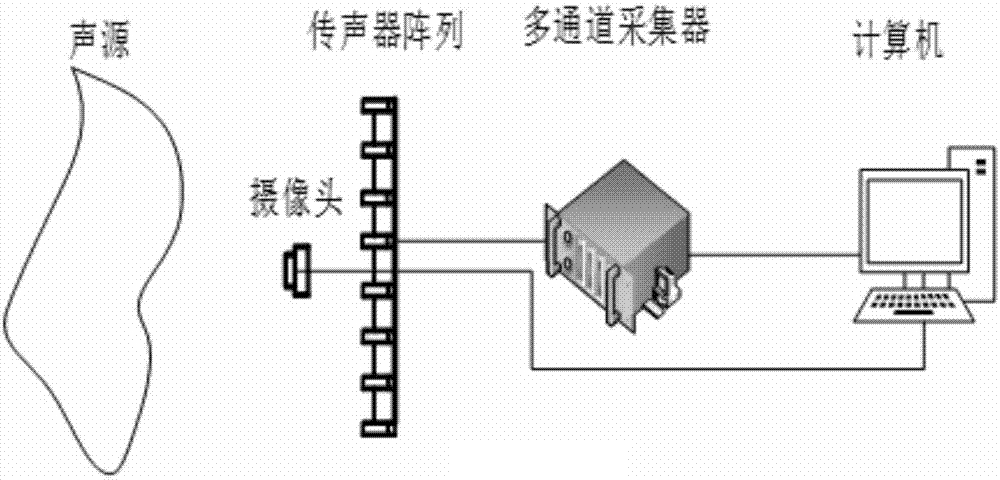
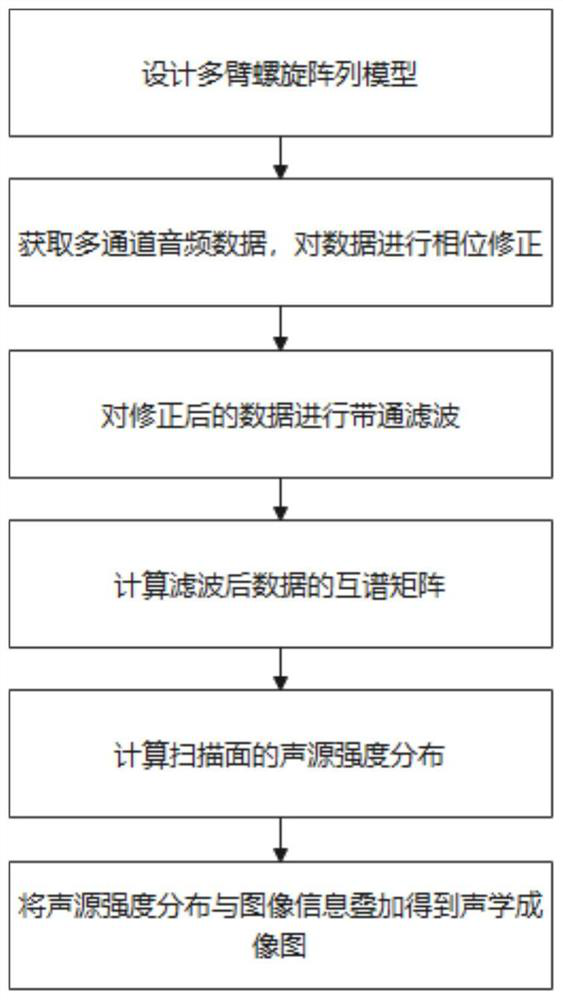
PendingCN113176538ARealize visualizationImaging Intuition and ImagePosition fixationPhase correctionSound sources
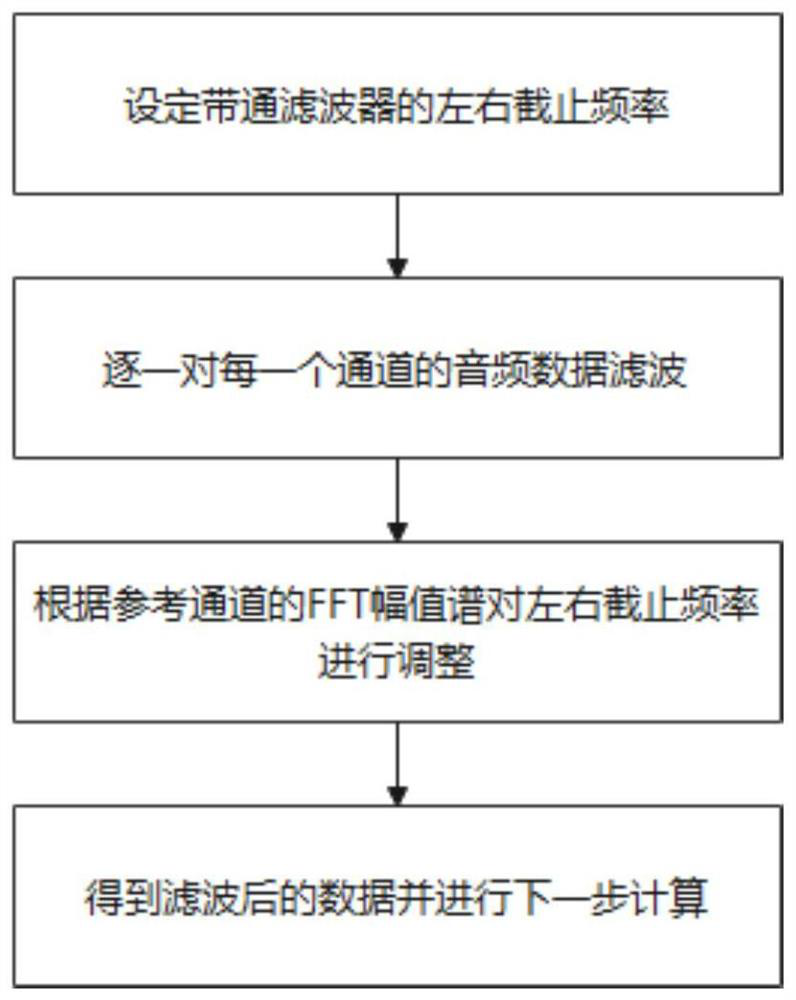
The invention provides a sound source imaging method based on a microphone array, and the method comprises the following steps: S1, forming a multi-channel microphone array through a multi-arm spiral array, and enabling the number of channels to be N; S2, collecting original audio data of N channels through a microphone array; S3, performing phase correction on the original audio data; S4, processing the corrected audio data to obtain a complex matrix R '; S5, determining coordinates of each point on the scanning surface according to the coordinates of the microphone array; S6, calculating a guide vector from the scanning surface to the array surface, and obtaining a sound source intensity distribution diagram of the scanning surface according to the cross-spectrum matrix R; and S7, carrying out superposition processing on the sound source intensity distribution diagram and the video image to obtain a real-time acoustic imaging diagram. The problem that the positioning result of the existing sound source positioning method is easily interfered by external factors is solved through audio data correction and video superposition.
Owner:HANGZHOU AIHUA INSTR
Multi-channel echo cancel method, multi-channel sound transfer method, stereo echo canceller, stereo sound transfer apparatus and transfer function calculation apparatus
InactiveUS20070258578A1Speed up the convergence processKeep for a long timeTwo-way loud-speaking telephone systemsSpecial service for subscribersTransfer systemVocal tract
Stereo sound signals are reproduced directly from loudspeakers (SP(L), SP(R)). By using a sum signal and a difference signal of the stereo sound signals as a reference signal, and according to a cross spectrum calculation of the reference signal with a microphone-collected sound signal, calculation is performed to obtain transfer functions of four sound transfer systems between the loudspeakers (SP(L), SP(R)) and microphones (MC(L), MC(R)). The transfer functions obtained are subjected to inverse Fourier transform to obtain impulse responses, which are set in filter means (40-1 to 40-4) to create echo cancel signals and perform echo canceling. This solves the problem of an indefinite coefficient in the echo cancel technique of a multi-channel sound signal.
Owner:YAMAHA CORP
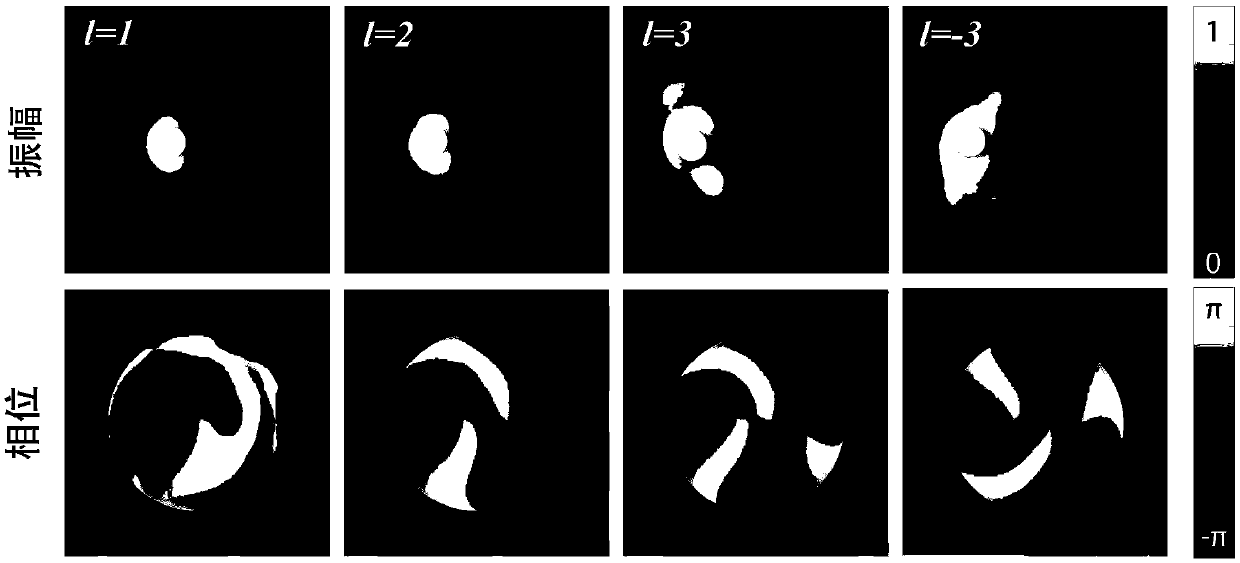
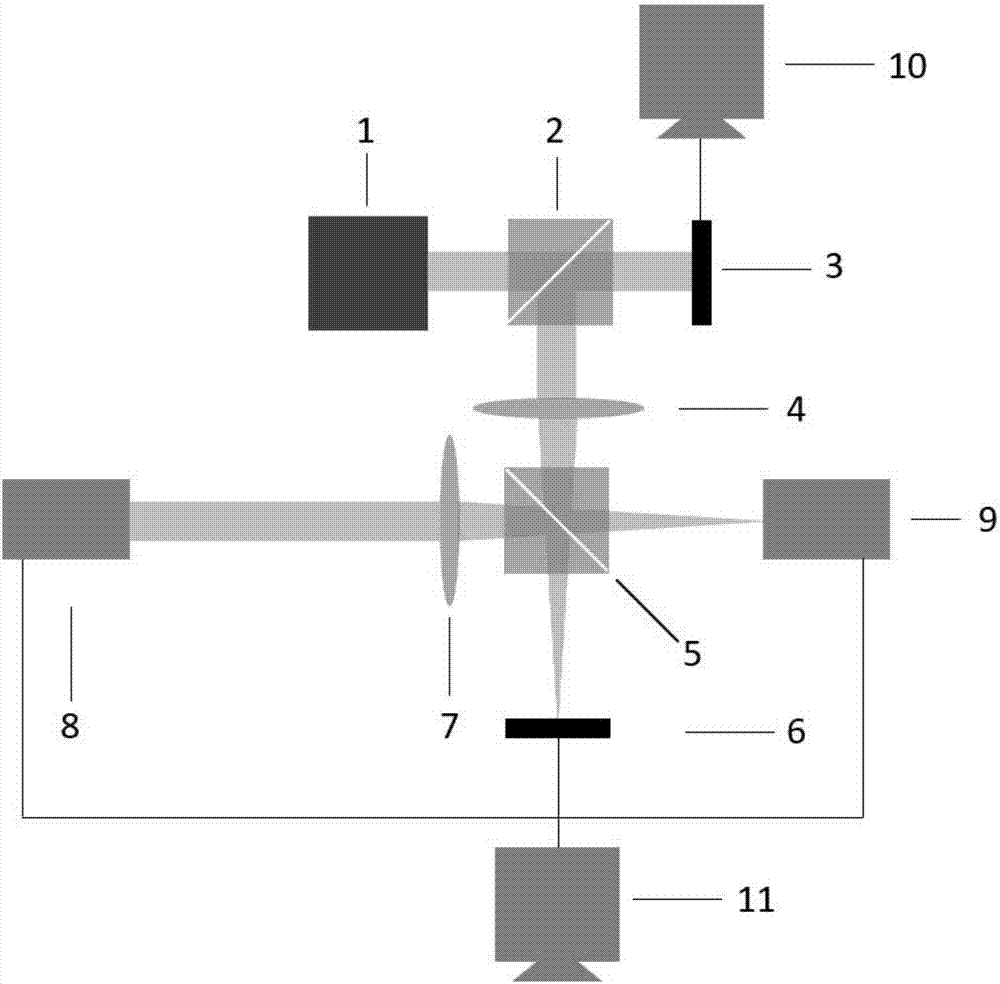
Method and system for measuring complex coherence degrees of partially coherent vortex light beams
The invention discloses a method and a system for measuring complex coherence degrees of partially coherent vortex light beams. The method includes recording the light intensity of the to-be-measuredpartially coherent vortex light beams; introducing disturbance with cubic different phase assigned values into the to-be-measured partially coherent vortex light beams; carrying out Fourier transformation on the disturbed to-be-measured partially coherent vortex light beams and recording the light intensity of Fourier planes under the conditions of the cubic different phase assigned values; carrying out inverse Fourier transformation according to the cubic different phase assigned values and the light intensity of the Fourier planes under the conditions of the cubic different phase assigned values to obtain cross-spectrum density functions of the to-be-measured partially coherent vortex light beams; acquiring the complex coherence degrees of the to-be-measured partially coherent vortex light beams by the aid of the cross-spectrum density functions and the light intensity of the to-be-measured partially coherent vortex light beams. The method and the system have the advantages that coherent singular points can be directly observed from phase distribution graphs of the complex coherent degrees, accordingly, topological charge number magnitude and positive-negative information of theto-be-measured partially coherent vortex light beams can be obtained, and the method and the system have important significance in the fields of laser processing, optical tweezers, atom cooling and the like.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
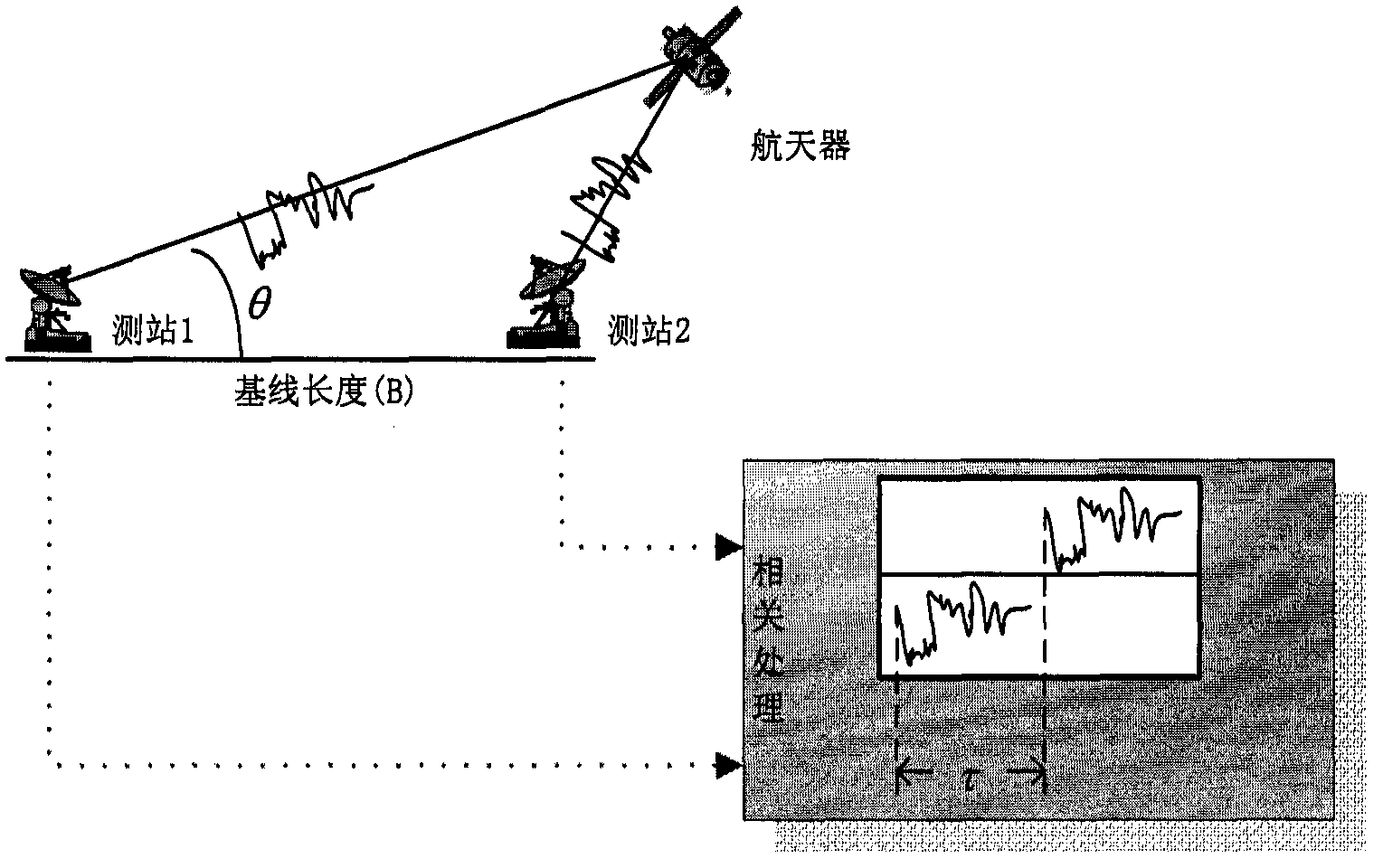
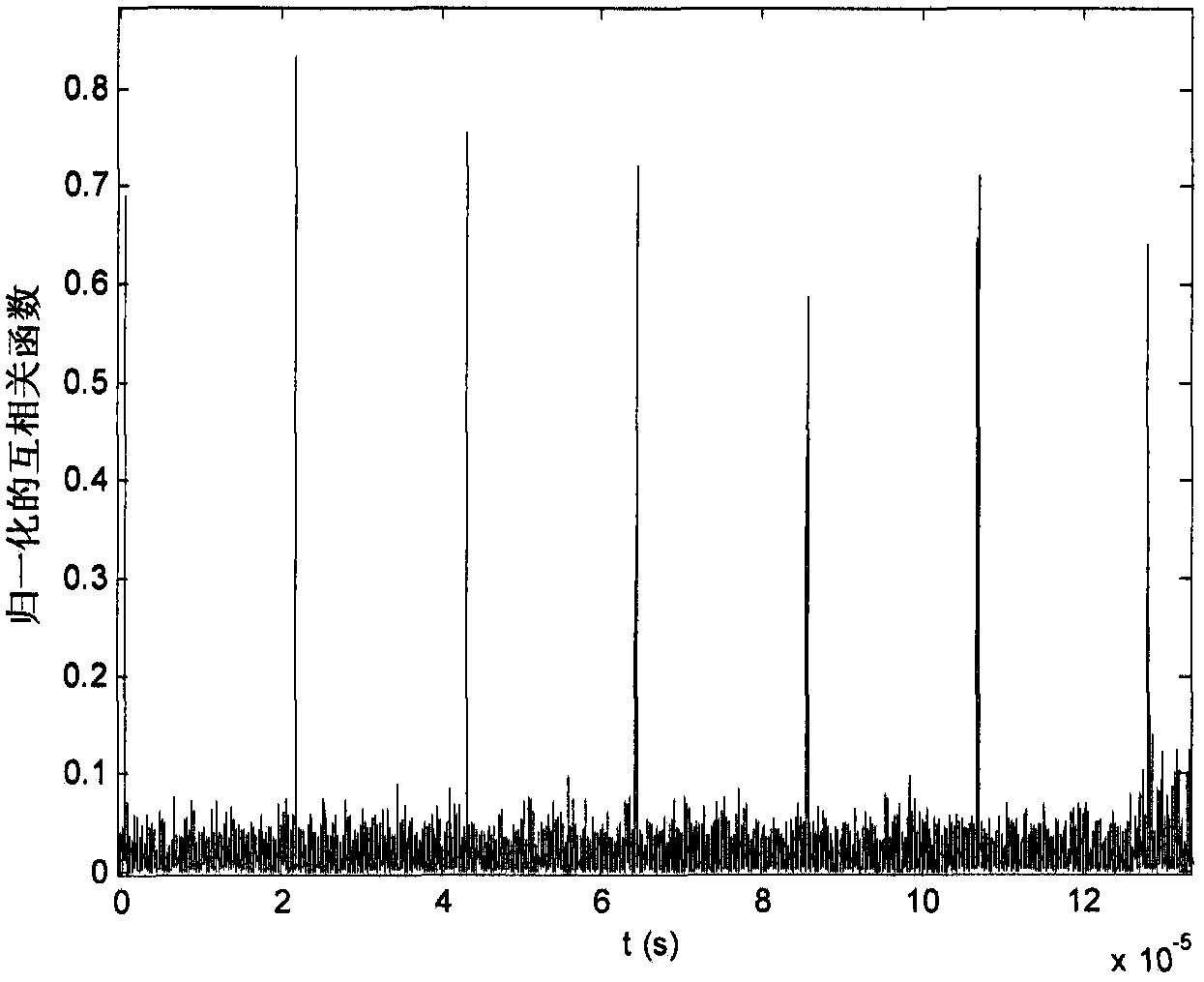
A Very Long Baseline Interferometry Processing Method Based on Digital Signals
InactiveCN105659869BImplementation Latency EstimationInstruments for comonautical navigationSatellite radio beaconingTime delaysAmbiguity
The invention discloses a very long baseline interferometry processing method based on digital transmission signals. The method is to obtain the part whose time delay is less than one cross-correlation period of digital transmission signals. The specific steps are as follows: 1) Receive signals through two stations The time-domain cross-correlation of the time domain to obtain the time delay of the integer sampling interval; 2) After the compensation of the integer sampling interval delay of the two received signals, the streak rate search is carried out to obtain the time delay rate of the two signals; 3) The integer sampling interval of the two signals is obtained Sampling interval time delay and fringe rate compensation, using cross-spectrum phase to calculate time delay less than one sampling interval. Then the whole-period ambiguity is estimated using the rough relative positional relationship between the spacecraft and the station. Based on the above processing, the required time delay from the spacecraft signal to the two stations can be obtained. In the case that no special VLBI beacon signal is received and no real-time a priori model is available, the present invention utilizes the most frequently broadcast data transmission signal of the spacecraft to carry out independent VLBI processing, and realizes the time delay estimation of the spacecraft arriving at the ground station .
Owner:BEIJING AEROSPACE CONTROL CENT
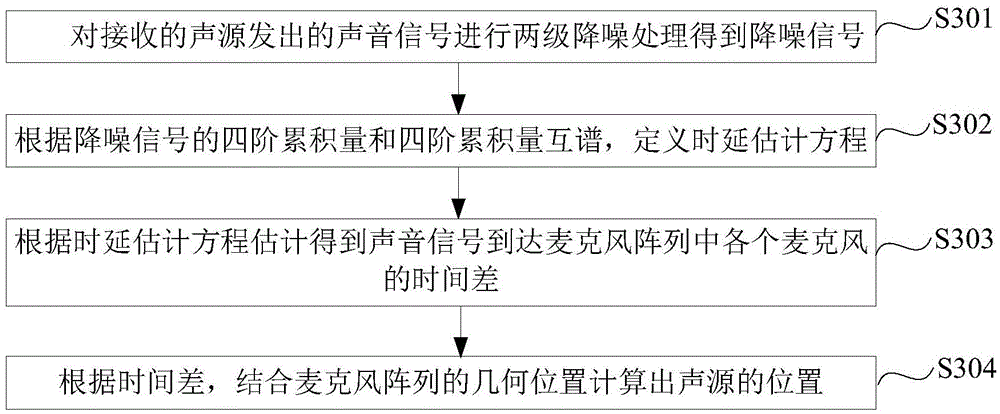
Sound source positioning method and apparatus and time delay estimation method and apparatus
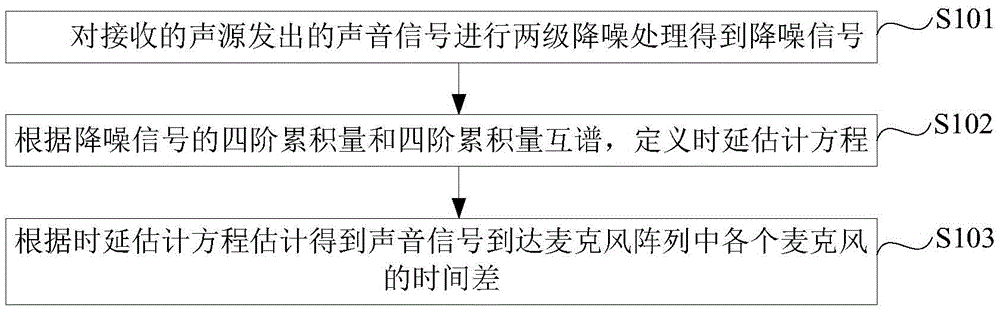
InactiveCN105609112AOvercoming the problem of increased positioning errorReduce noiseSpeech analysisPosition fixationSound sourcesPeak value
The application provides a sound source positioning method and apparatus and a time delay estimation method and apparatus. The time delay estimation method comprises: two-stage noise reduction processing is carried out on a received acoustical signal sent by a sound source to obtain a noise reduction signal; according to a four-order cumulant and a four-order cumulant cross spectrum of the noise reduction signal, a time delay estimation equation is defined; and according to the time delay estimation equation, time differences of arrival of acoustical signal at all microphones in a microphone array are estimated and obtained. According to the time delay estimation method, with the two-stage noise reduction processing and the four-order cumulant cross spectrum, influences of the noises and the interference are reduced; the time delay can be estimated accurately; and a problem that the sound source positioning error is increased due to the confused peak value around the acoustical signal delay and the Gaussian noise pollution influence according to the time-domain high-order statistics method and the generalized cross correlation-spectrum weight method can be solved.
Owner:北京爱宾果科技有限公司
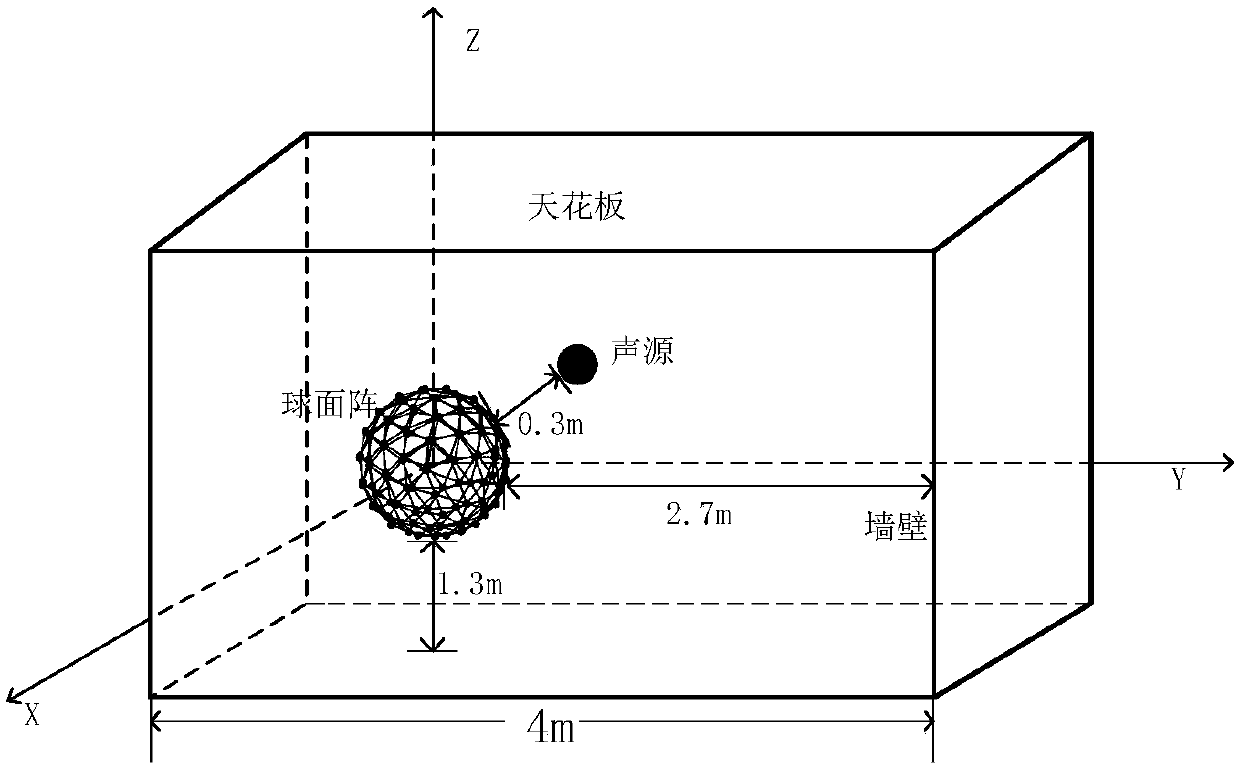
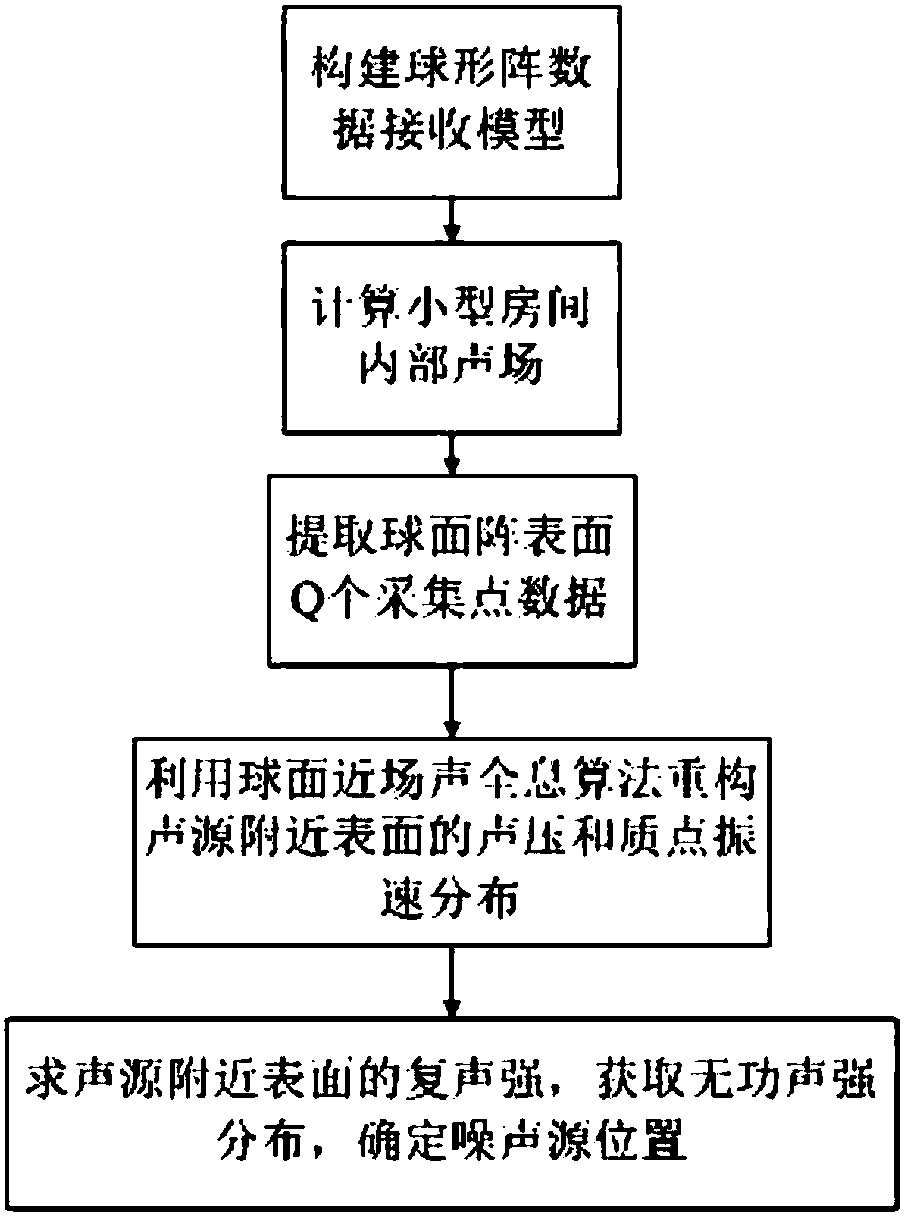
Indoor noise source localization method based on spherical surface near-field acoustic holography reconstructing reactive sound intensity
ActiveCN108051800AEliminate the effects ofEffective positioningUsing reradiationSound sourcesArray element
The invention discloses an indoor noise source localization method based on spherical surface near-field acoustic holography reconstructing reactive sound intensity. The method comprises the followingsteps: (1) calculating a three-dimensional spatial sound field data radiated by a mechanical sound source inside a regular small room; (2) using a spherical microphone array with Q array elements toacquire a sound pressure signal radiated from the target sound source to the three-dimensional space; (3) subjecting the Q pieces of microphone data of the spherical array and the first microphone data to cross spectrum analysis separately to obtain the frequency-domain complex sound pressure of the entire spherical array; (4) using a spherical near-field acoustic holographic algorithm to reconstruct the sound pressure and the mass point vibration velocity of the sound source surface; and (5) using the complex sound pressure and the mass point vibration velocity to reconstruct the surface complex sound intensity near the sound source to extract the reactive sound intensity; and determining the location of the indoor noise source by the reactive sound intensity distribution. Compared with the prior art, the method utilizes a fact that the reactive sound intensity is powerful in the near-field region of the sound source to eliminate the influence of indoor reverberation environment and effectively locate the indoor noise source.
Owner:GUIZHOU AEROSPACE INST OF MEASURING & TESTING TECH
Water supply pipeline multi-leakage point sound positioning method based on iterative recursion
ActiveCN108731886AImplement Adaptive EstimationSuppression of Signal Delay Estimation EffectsDetection of fluid at leakage pointPipeline systemsPhase spectrumPower spectral analysis
The invention discloses a water supply pipeline multi-leakage point sound positioning method based on iterative recursion. The method mainly comprises two parts of leakage sound signal cross spectrumphase spectrum calculation and multi-leakage source iteration estimation. Firstly, cross-power spectrum analysis is carried out for collected multi-leakage point sound signals, and the signal cross spectrum phase spectrum and corresponding frequency point distribution are determined. In the multi-leakage source iterative estimation process, the signals are firstly subjected to generalized cross-correlation time delay estimation, a linear change line group of the signal cross spectrum phase spectrum is determined according to the time delay estimation value, and frequency points associated withleakage points are determined through utilizing the linear change line group step by step. Estimation of the next leakage point is realized through removing the frequency points associated with the previous leakage point in the signals, and the number and the position of the pipeline leakage points are estimated through multiple times of iterative recursion calculation.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Target motion location method based on underwater acoustic detection
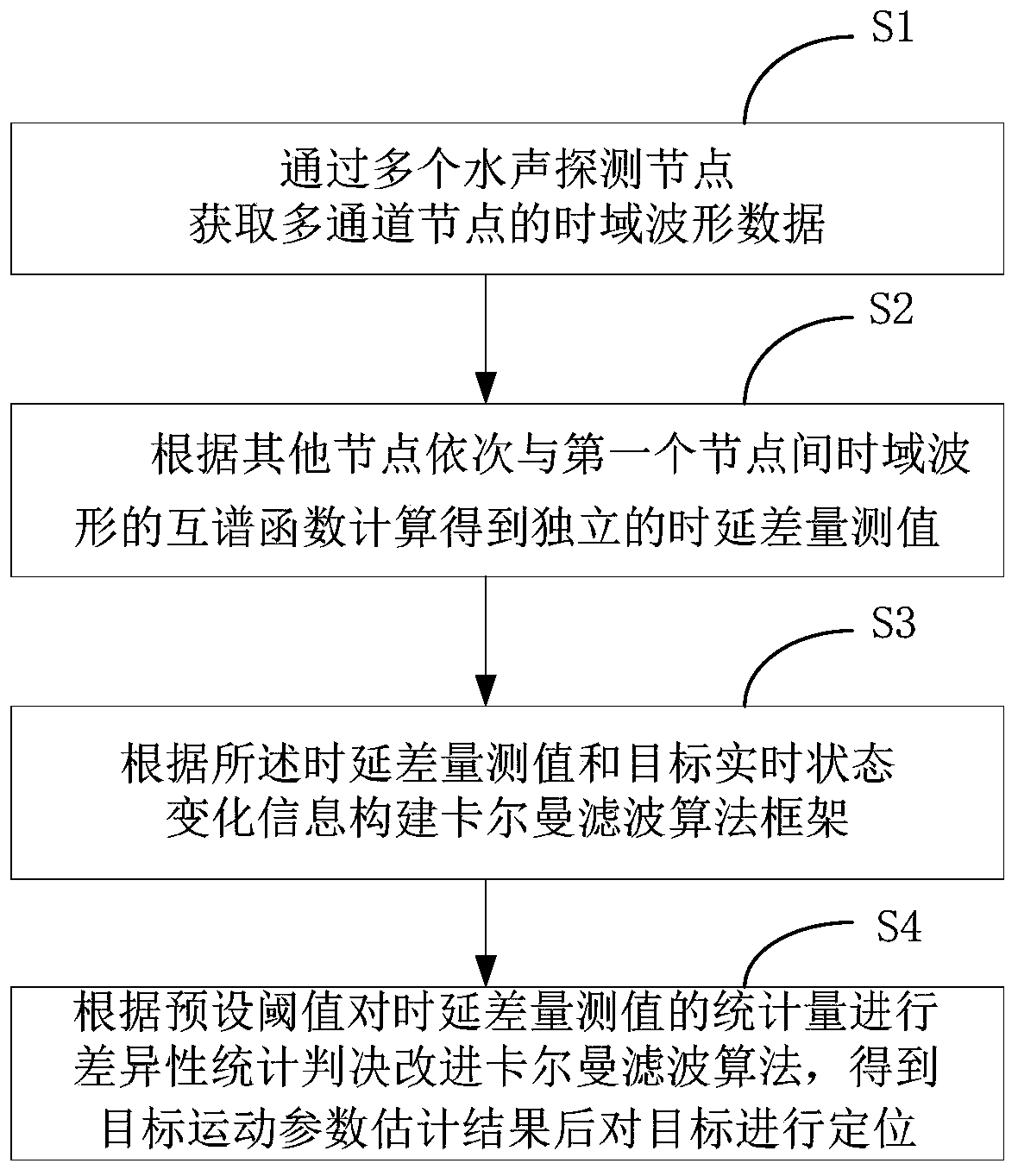
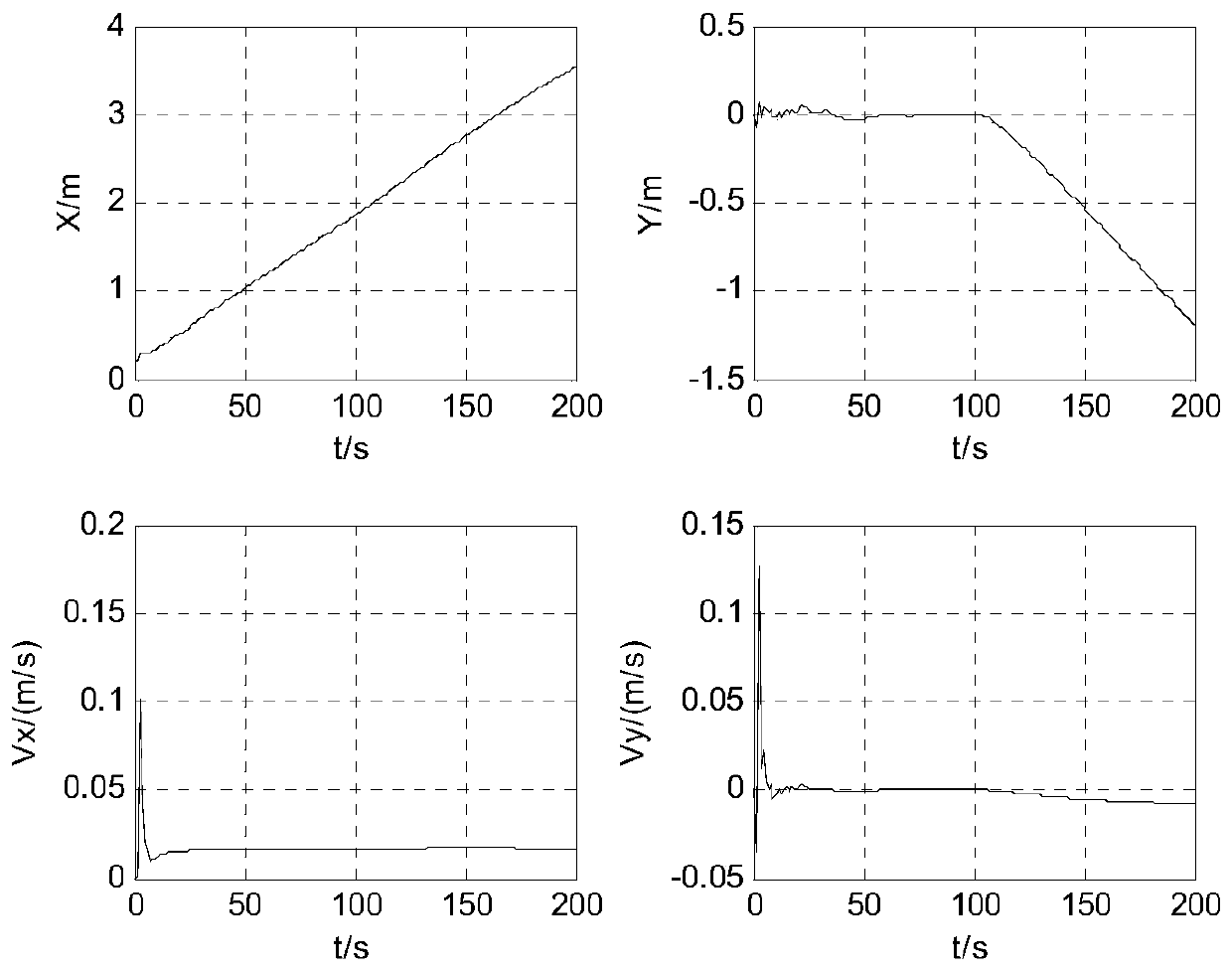
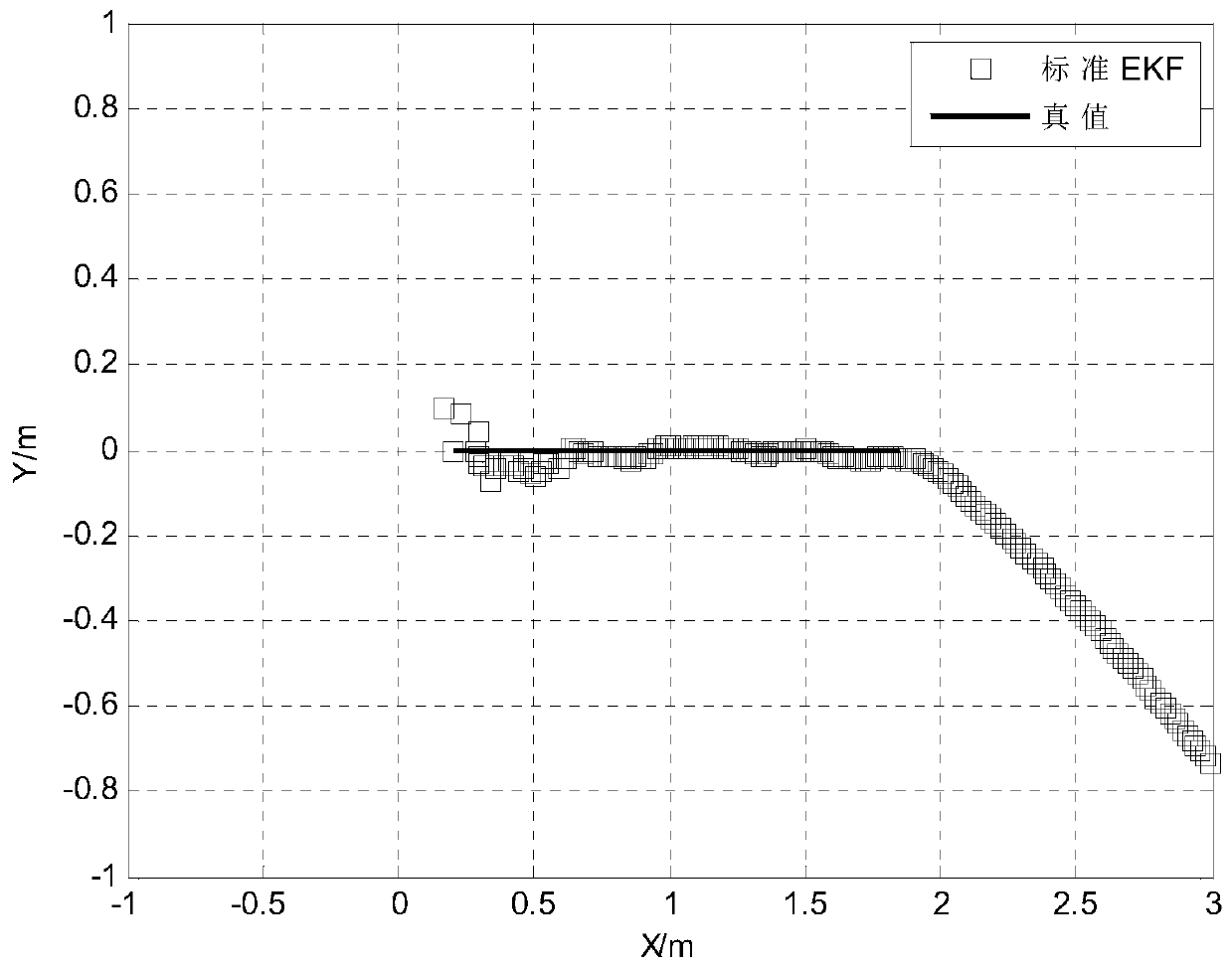
ActiveCN110286357ARealize real-time positioningPosition fixationAcoustic wave reradiationPattern recognitionCovariance matrix
The invention relates to a target motion location method based on underwater acoustic detection, and belongs to the technical field of target location. The method comprises the following steps: S1, acquiring the time domain waveform data of multi-channel nodes through a plurality of underwater acoustic detection nodes; S2, calculating the time delay difference measurement value according to the cross spectrum function of the time domain waveform between the other nodes and the first node in turn; S3, constructing a Kalman filtering algorithm framework according to the time delay difference measurement value and the target real-time state change information; and S4, performing the difference statistic decision on the statistics of the time delay difference measurement value according to the preset threshold value to improve the Kalman filter algorithm so as to obtain the estimation result of the target motion parameters and then locate the target. The TDONA measurement information and the extended Kalman filtering algorithm are utilized to obtain the target state information in real time, and the information is applied to modify the covariance matrix to quickly realize the target motion parameter estimation so as to better adapt to the motion parameter estimation in the case of high target maneuvering to locate the target motion.
Owner:36TH RES INST OF CETC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com