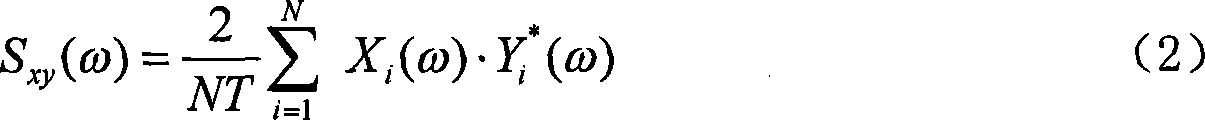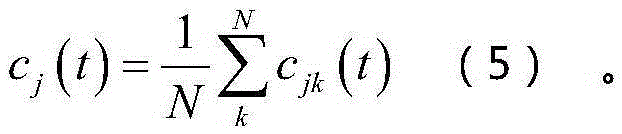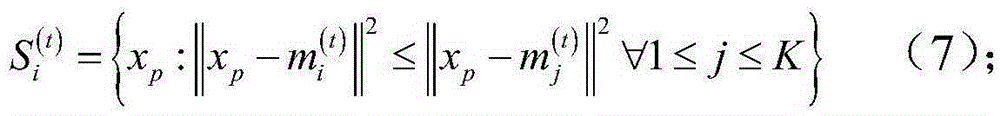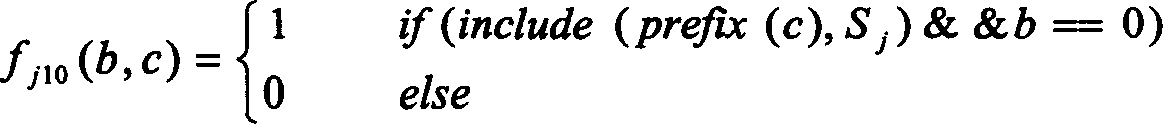Patents
Literature
42 results about "Eigenfunction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In mathematics, an eigenfunction of a linear operator D defined on some function space is any non-zero function f in that space that, when acted upon by D, is only multiplied by some scaling factor called an eigenvalue. As an equation, this condition can be written as Df=λf for some scalar eigenvalue λ. The solutions to this equation may also be subject to boundary conditions that limit the allowable eigenvalues and eigenfunctions.
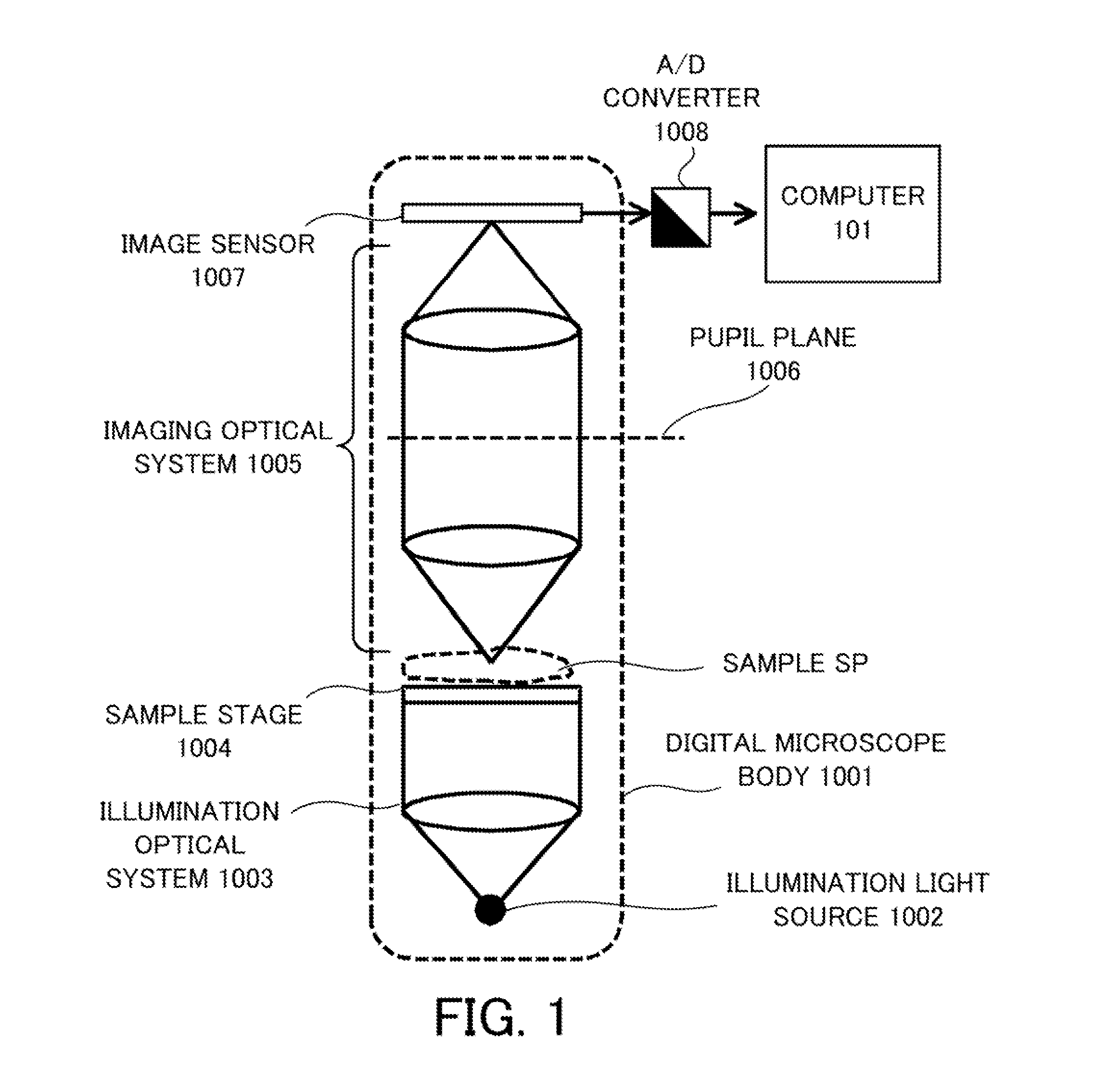
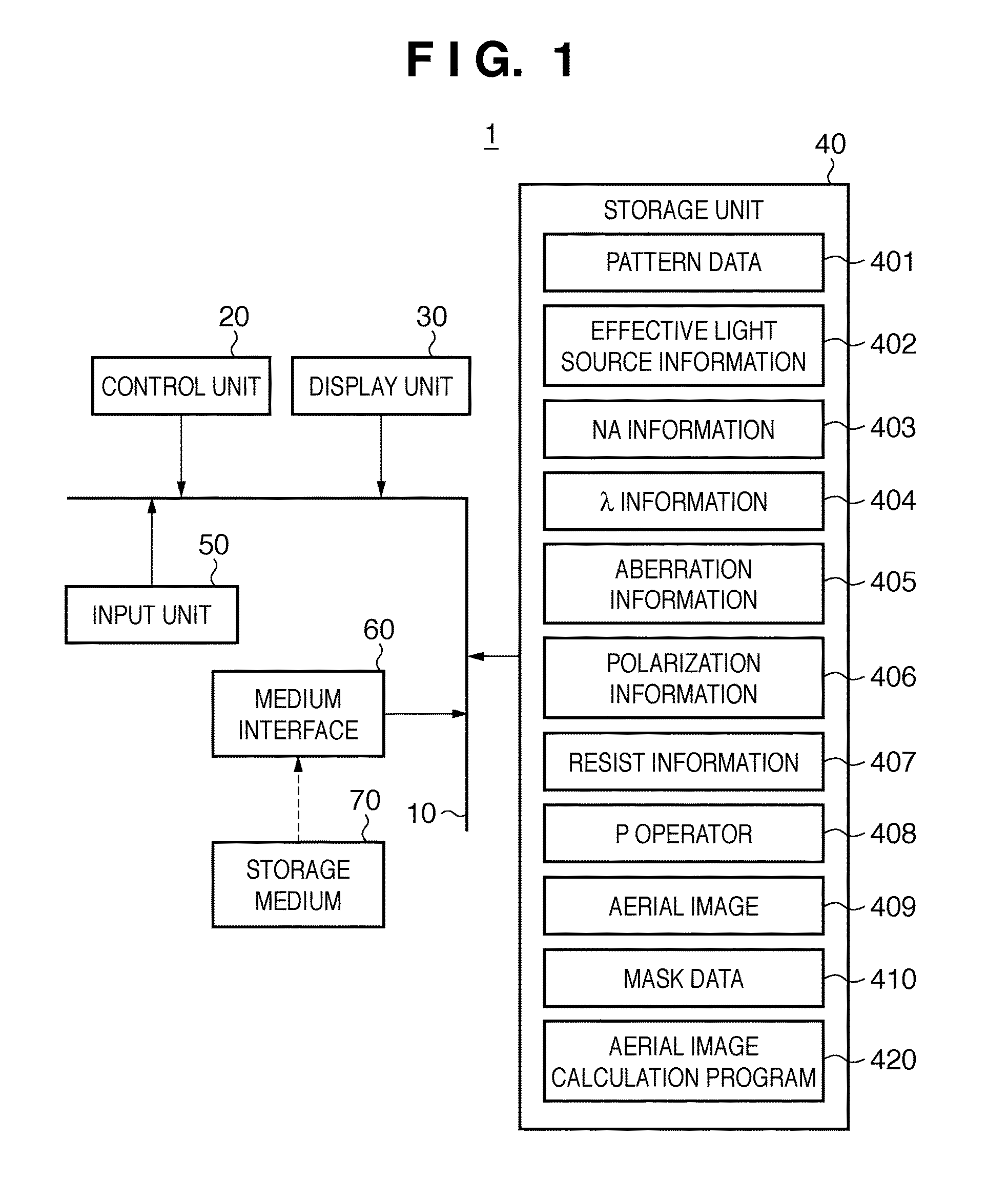
Fast model-based optical proximity correction
InactiveUS7079223B2Method is fastPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusResistDecomposition
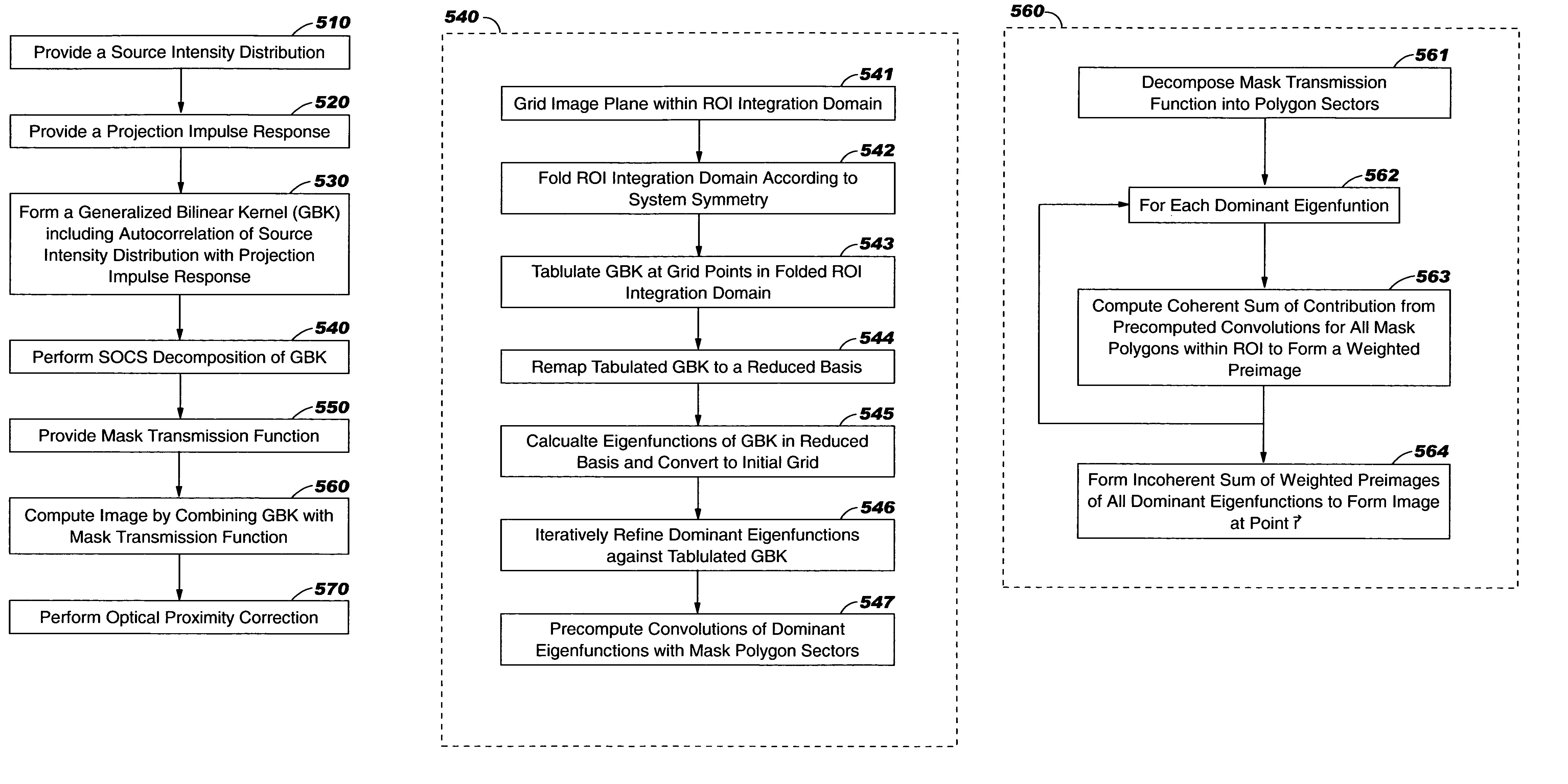
A method and system is provided for computing lithographic images that may take into account non-scalar effects such as lens birefringence, resist stack effects, tailored source polarizations, and blur effects of the mask and the resist. A generalized bilinear kernel is formed, which is independent of the mask transmission function, and which may then be treated using a decomposition to allow rapid computation of an image that includes such non-scalar effects. Weighted pre-images may be formed from a coherent sum of pre-computed convolutions of the dominant eigenfunctions of the generalized bilinear kernel with the appropriate mask polygon sectors. The image at a point may be formed from the incoherent sum of the weighted pre-images over all of the dominant eigenfunctions of the generalized bilinear kernel. The resulting image can then be used to perform model-based optical proximity correction (MBOPC).
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Acquiring system eigenfunction and signal feature value method
InactiveCN101158623AStructural/machines measurementFrequency analysisFourier transform on finite groupsCurve fitting
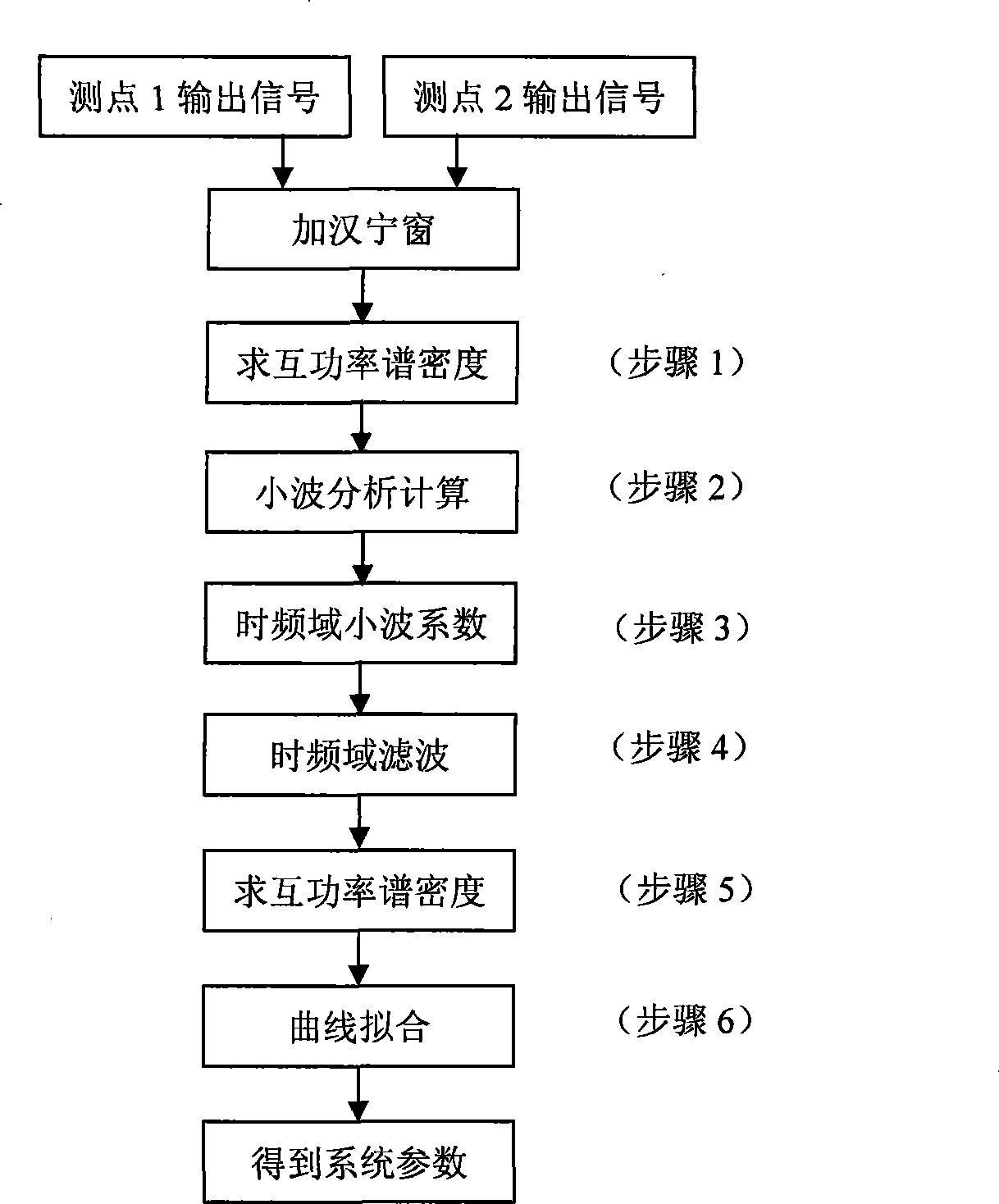
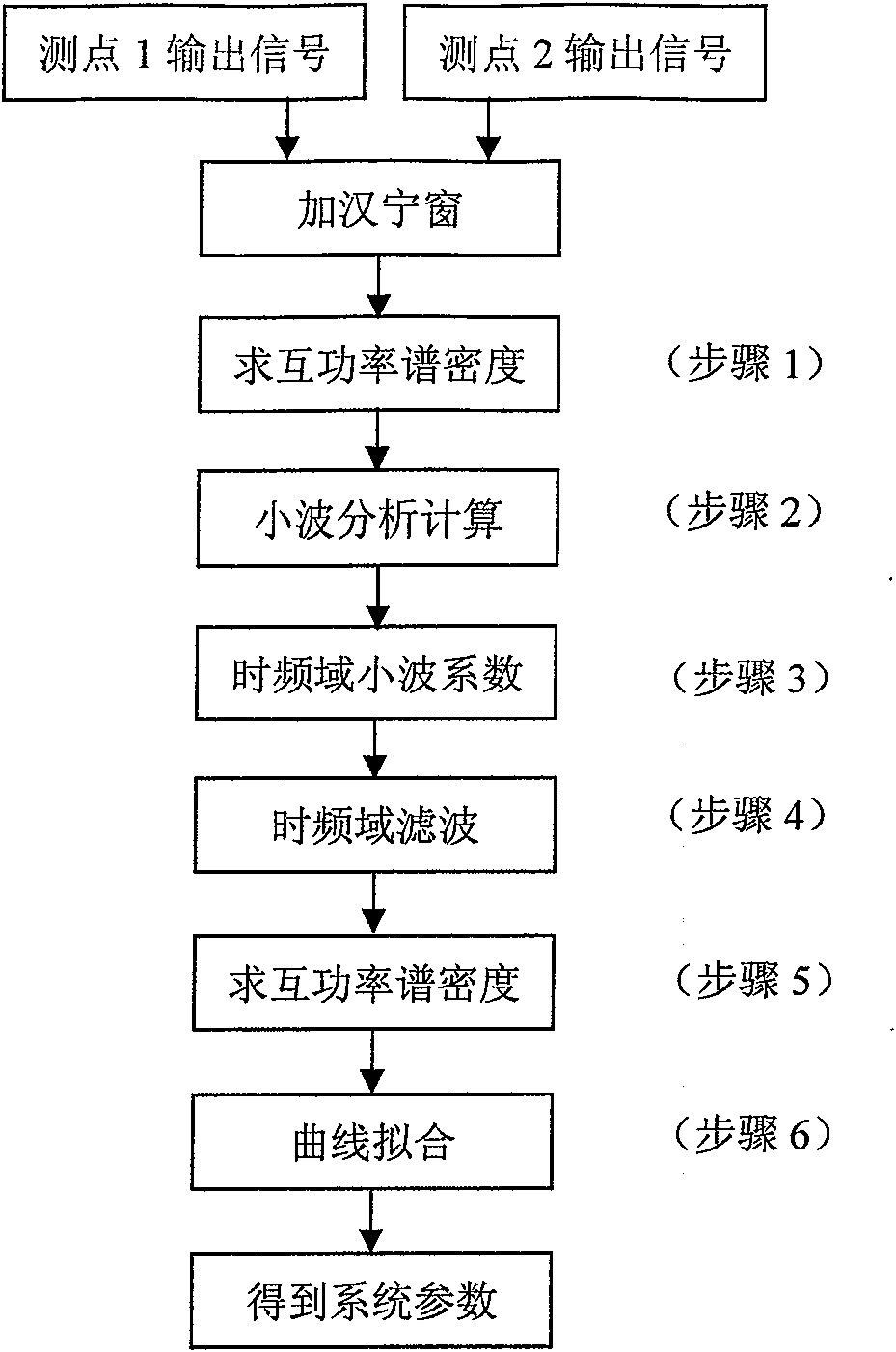
A method of catching systematic eigenfunctions and signal eigenvalues under the condition of only response output available belongs to the parametric recognition technique in dynamic test field. The technique is a method of adopting cross spectral density functions of each response point instead of frequency response functions to perform time-frequency filtering and the parametric recognition of frequency domain, and includes the following steps: (1) carrying out analytic calculation of the cross spectral density functions of different metering signal of output points; (2) analyzing and calculating the nonorthogonal wavelets in the time-frequency domain according to the cross spectral calculating result; (3) inversing the fourier transformation to gain the time-frequency analyse coefficient; (4) adding a rectangular window to perform the time-frequency filtering; (5) calculating the cross spectrum of the output signal after filtering as the systematic function for recognition; (6) performing curvefitting to obtain the systematic parameter; the technique improves the recognition precision of the systematic parameters, precisely recognizes modal parameters, is simple and convenient, and is suitable for the dynamic analyses, the performance verification and the failure diagnosis of large civil engineering establishments such as large and complex mechanical equipments under operation status, high-rise buildings, bridges, etc.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Methods, systems, and computer program products for analyzing cardiovascular sounds using eigen functions
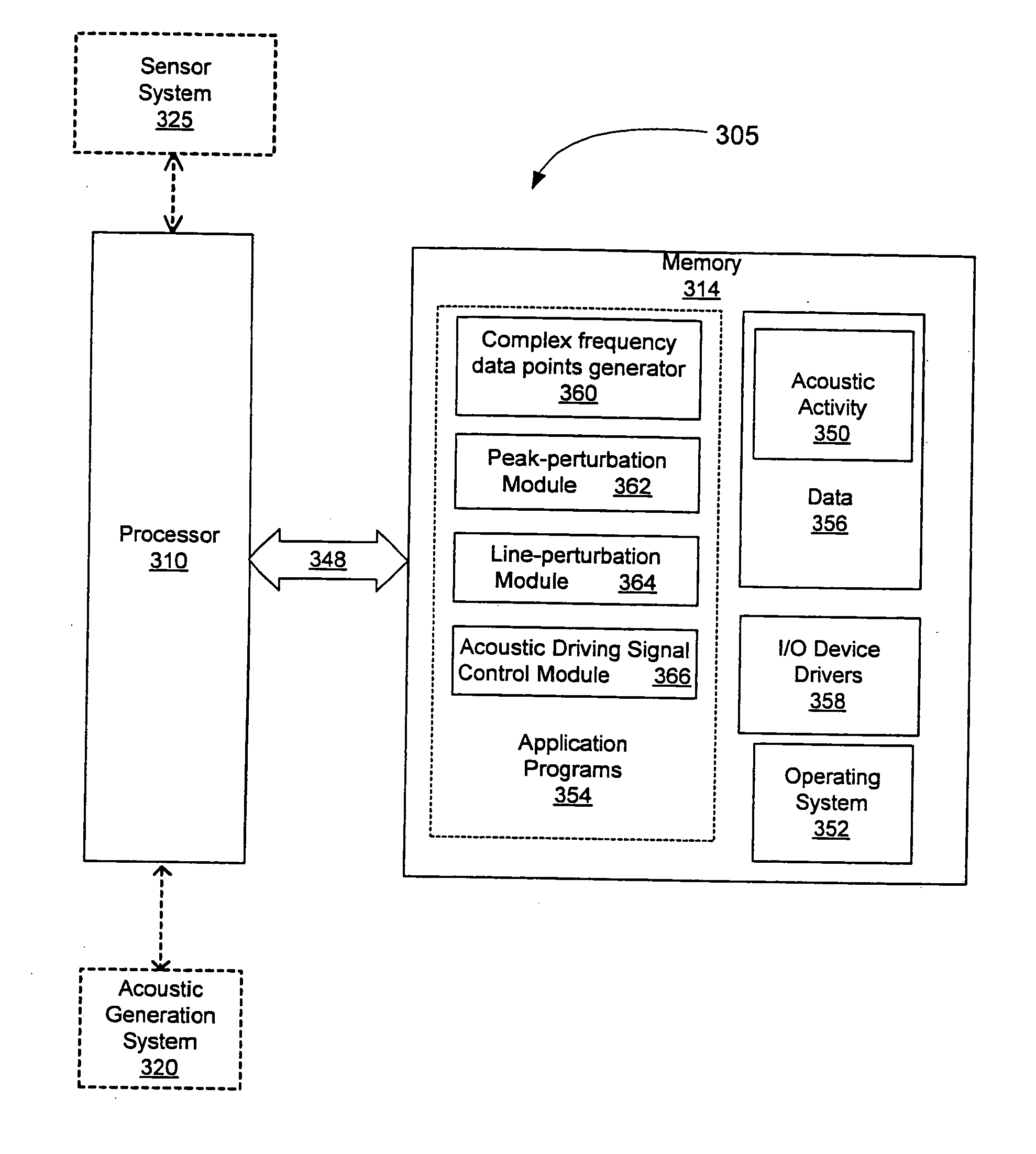
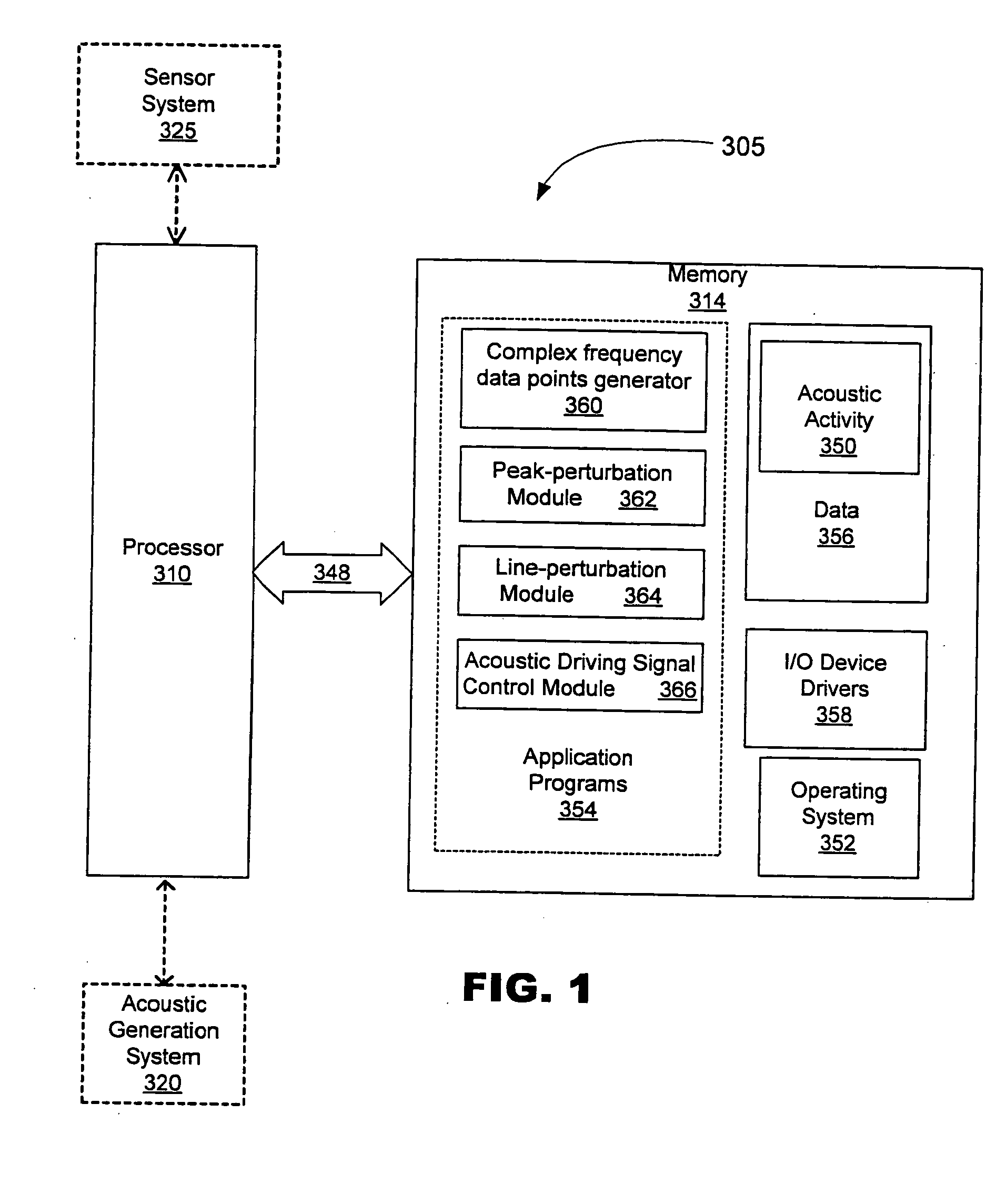
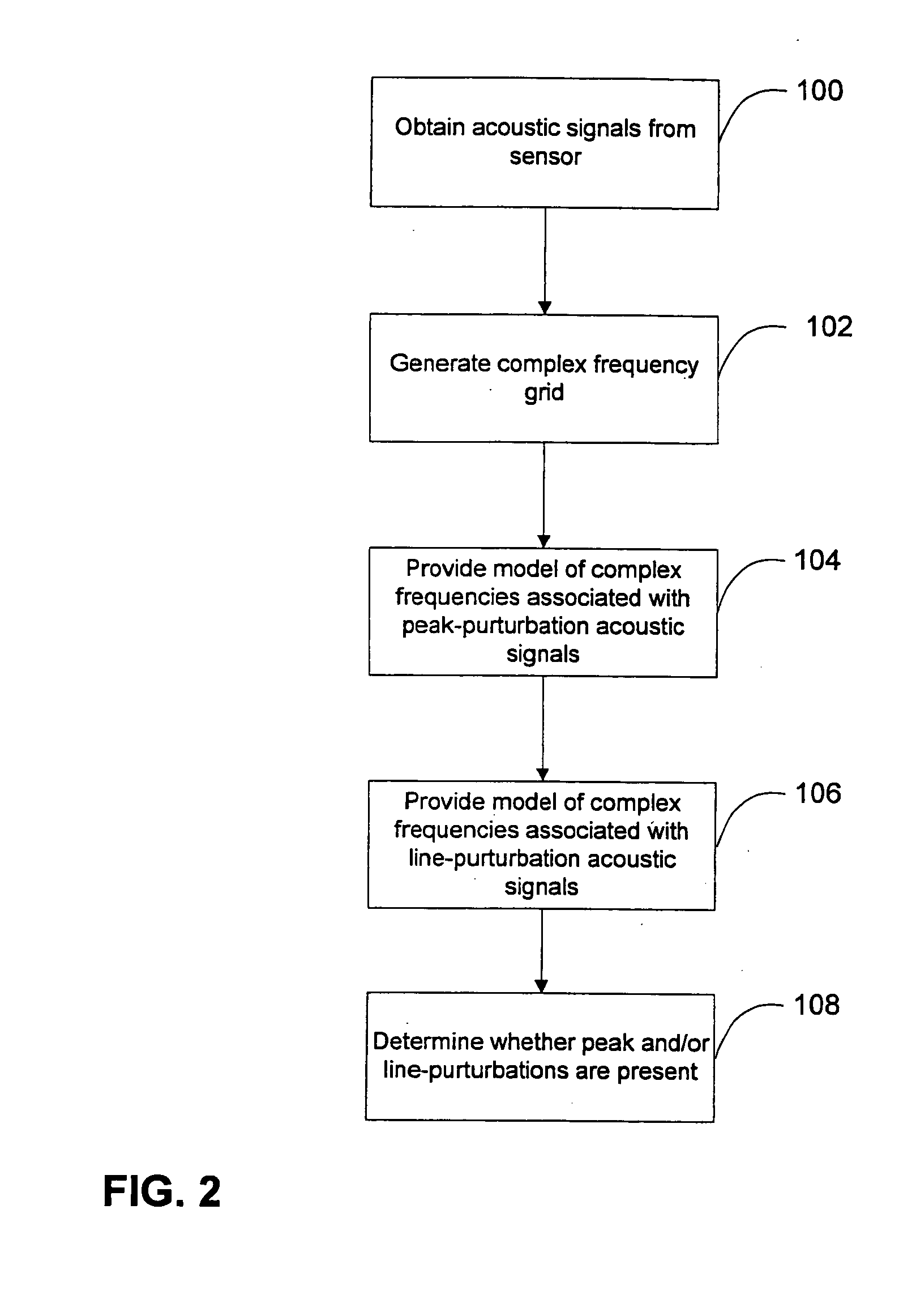
Non-invasive methods for detecting arterial disease in vivo include obtaining acoustic signals from a sensor held on an external body region proximate an artery. A complex frequency grid of frequencies and associated lifetimes of the obtained acoustic signals is generated. A predictive model of complex frequencies associated with peak-perturbation acoustic signals attributed to boundary perturbations in vivo that occur with early stage arterial disease is provided. A predictive model of complex frequencies associated with line-perturbation acoustic signals attributed to boundary perturbations in vivo that occur with later stage arterial disease and thickening of arterial junctions is also provided. It is determined whether peak and / or line-perturbation acoustic signals of the predictive models are present to detect whether the subject has arterial disease.
Owner:EAST CAROLINA UNIVERISTY
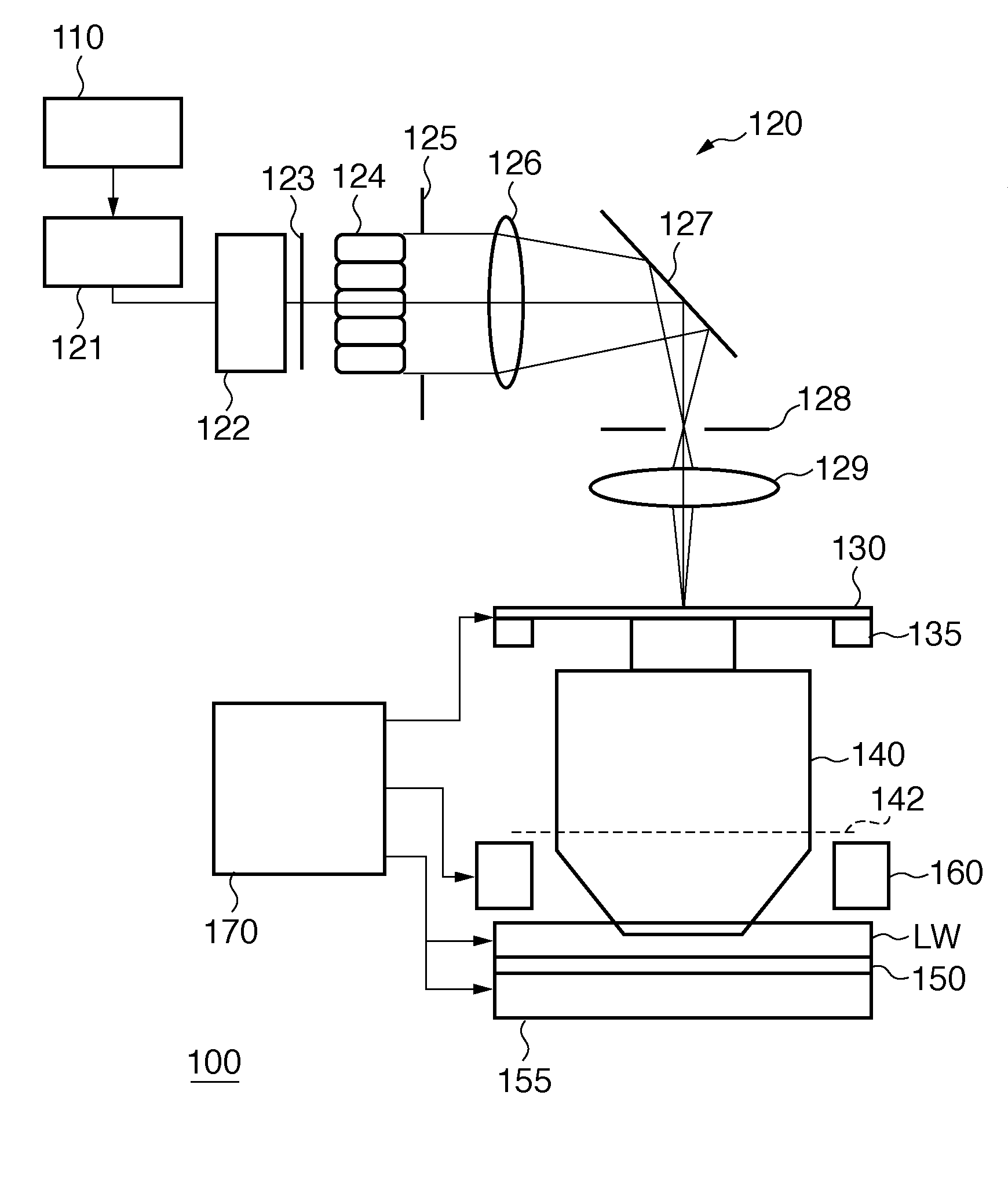
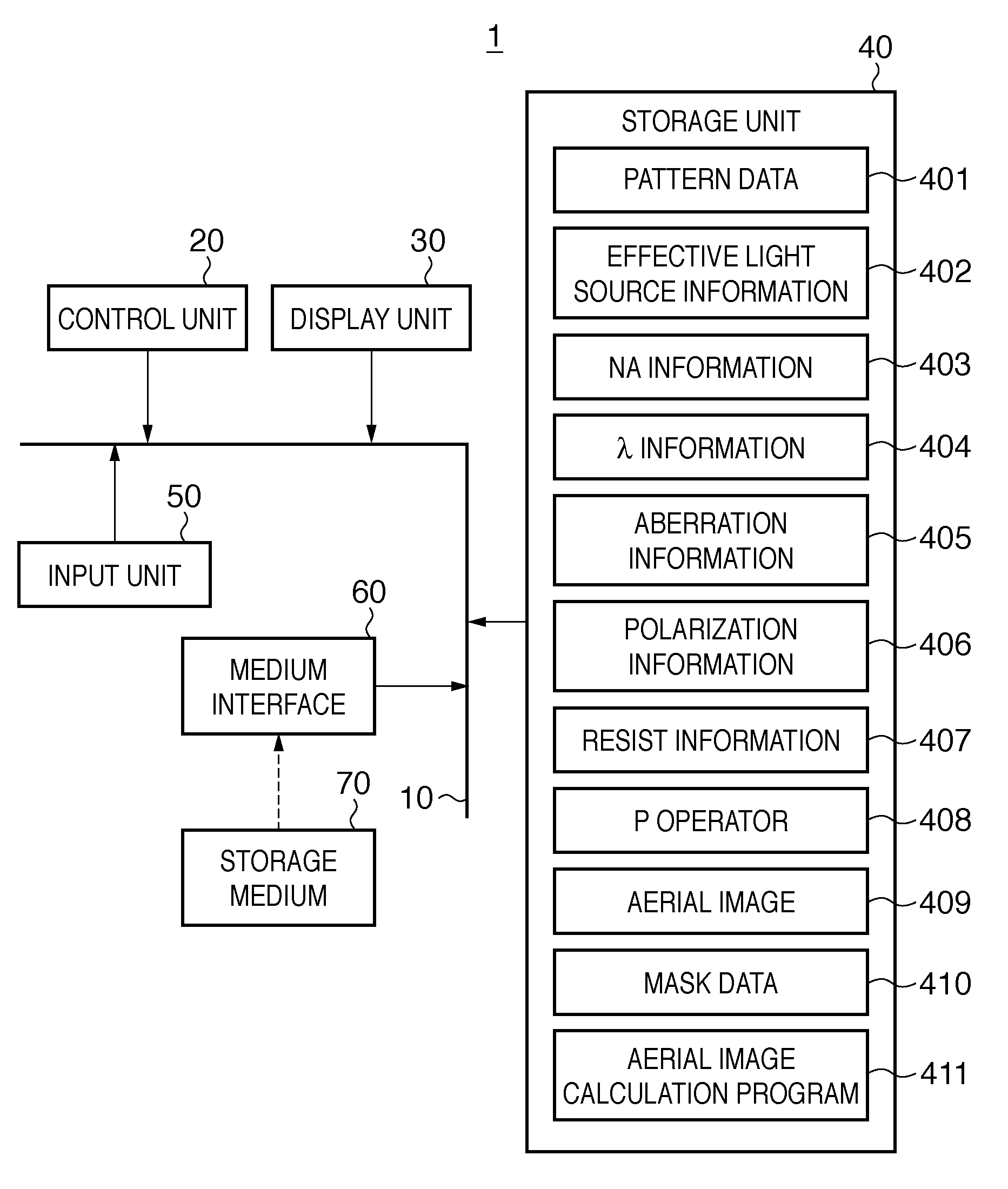
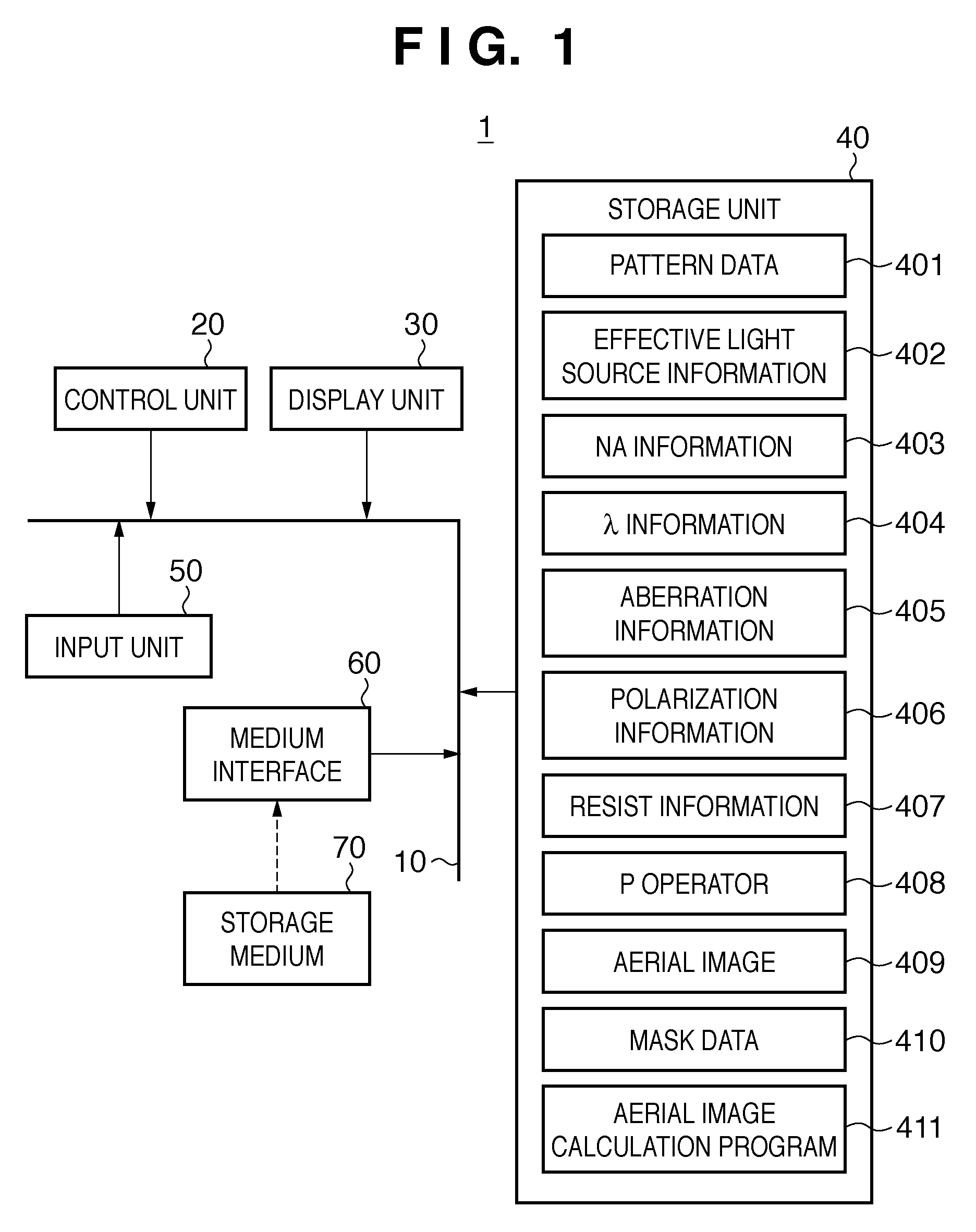
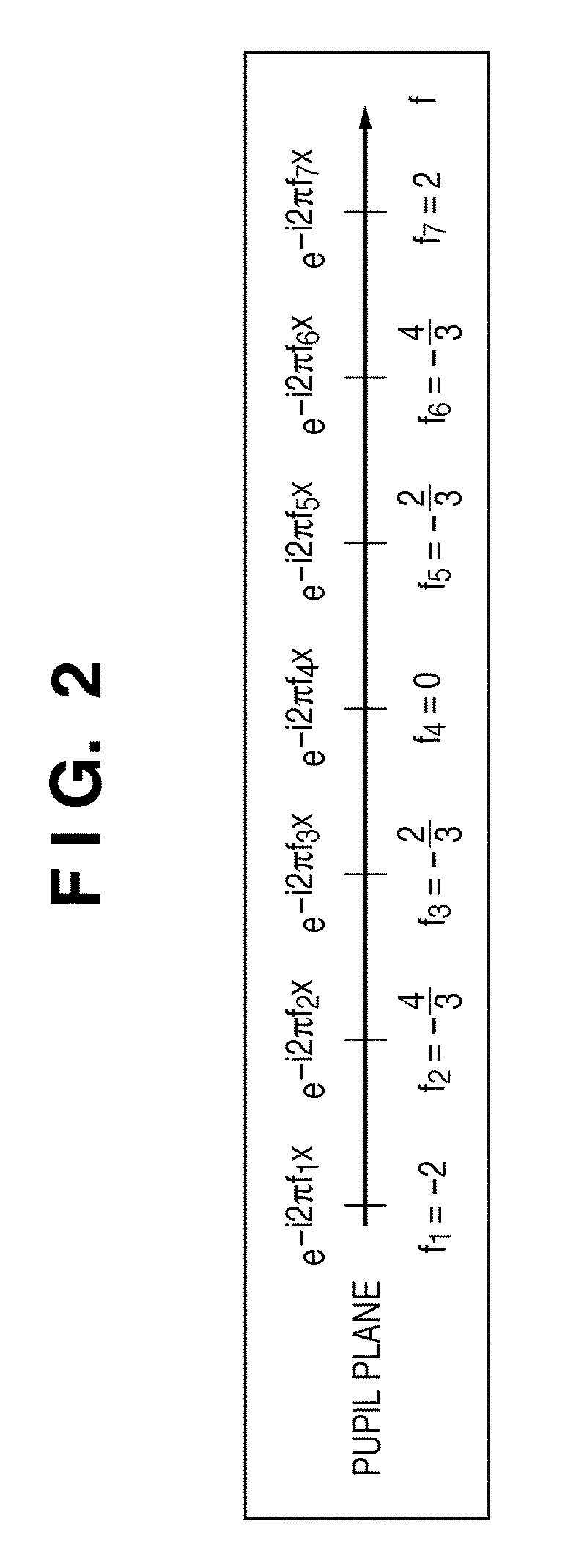
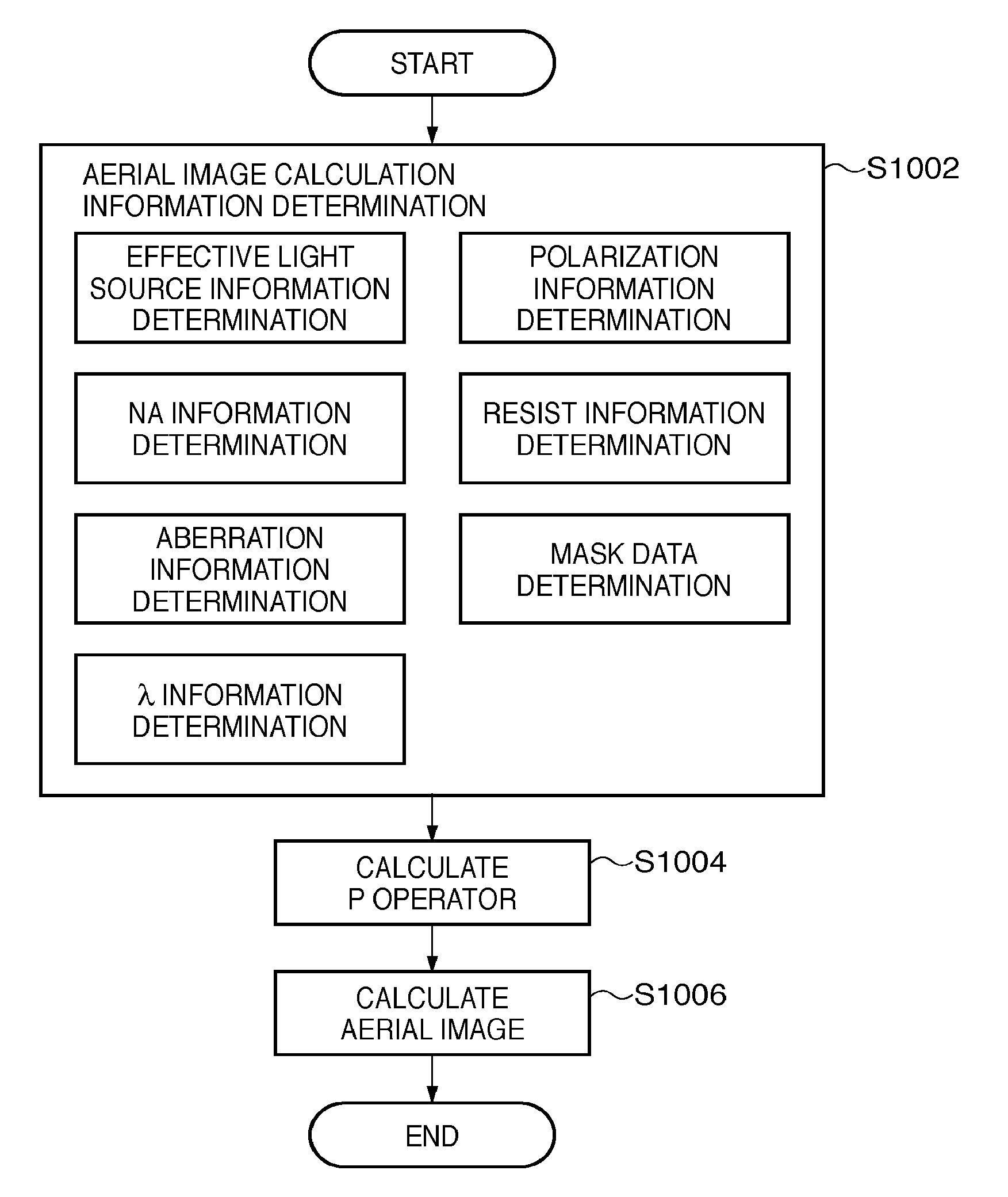
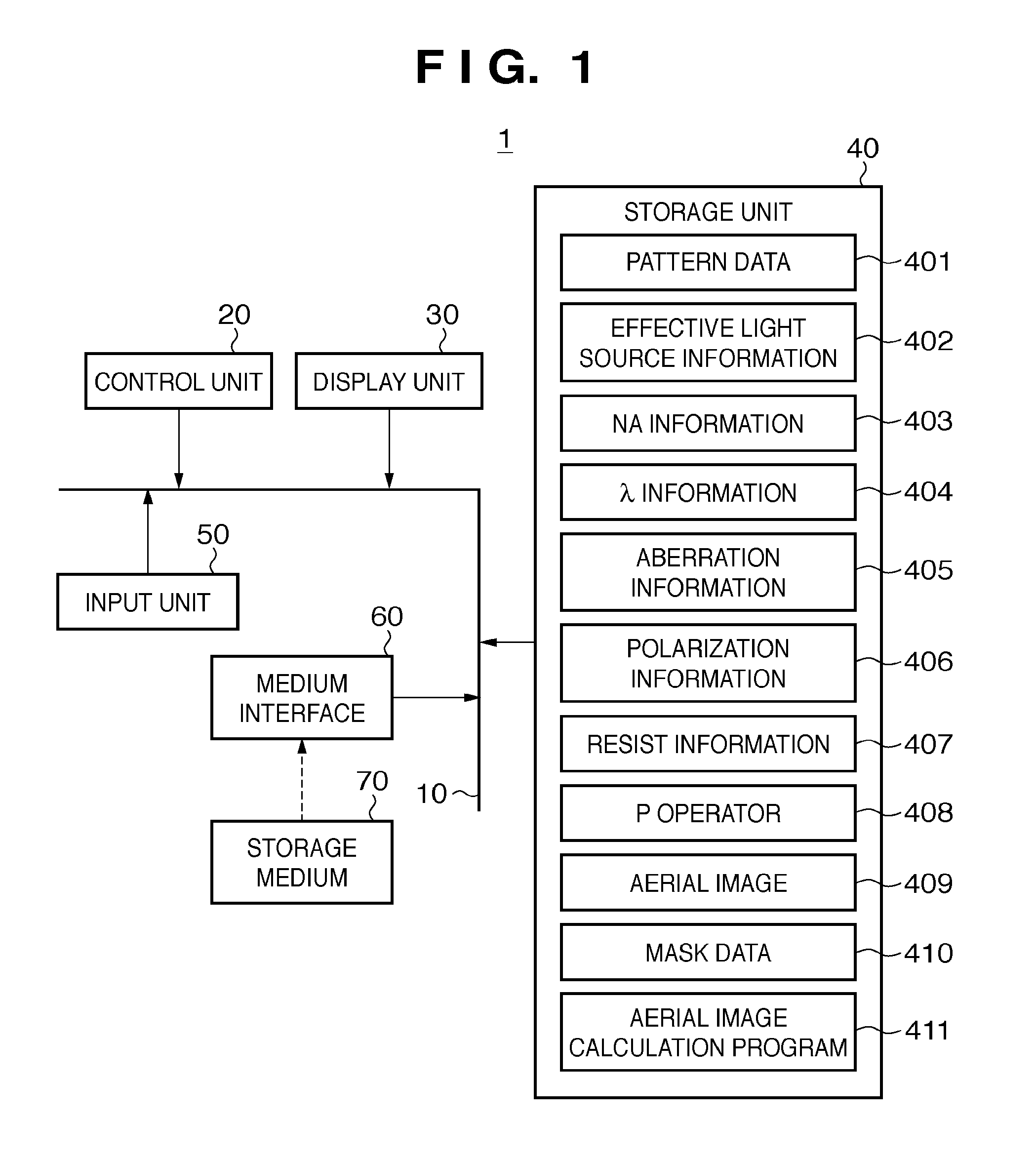
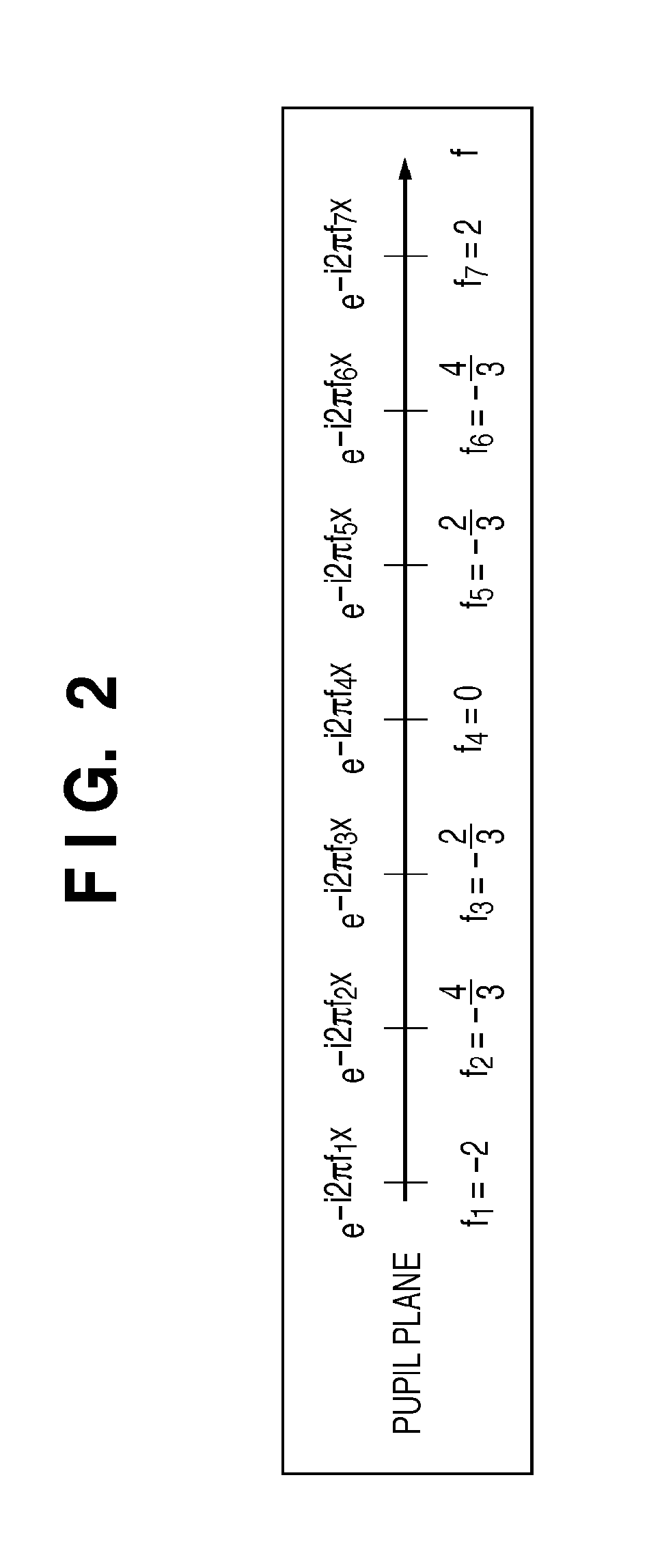
Calculation method, generation method, program, exposure method, and mask fabrication method
ActiveUS20090091736A1Short timeSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusSingular value decompositionPupil function
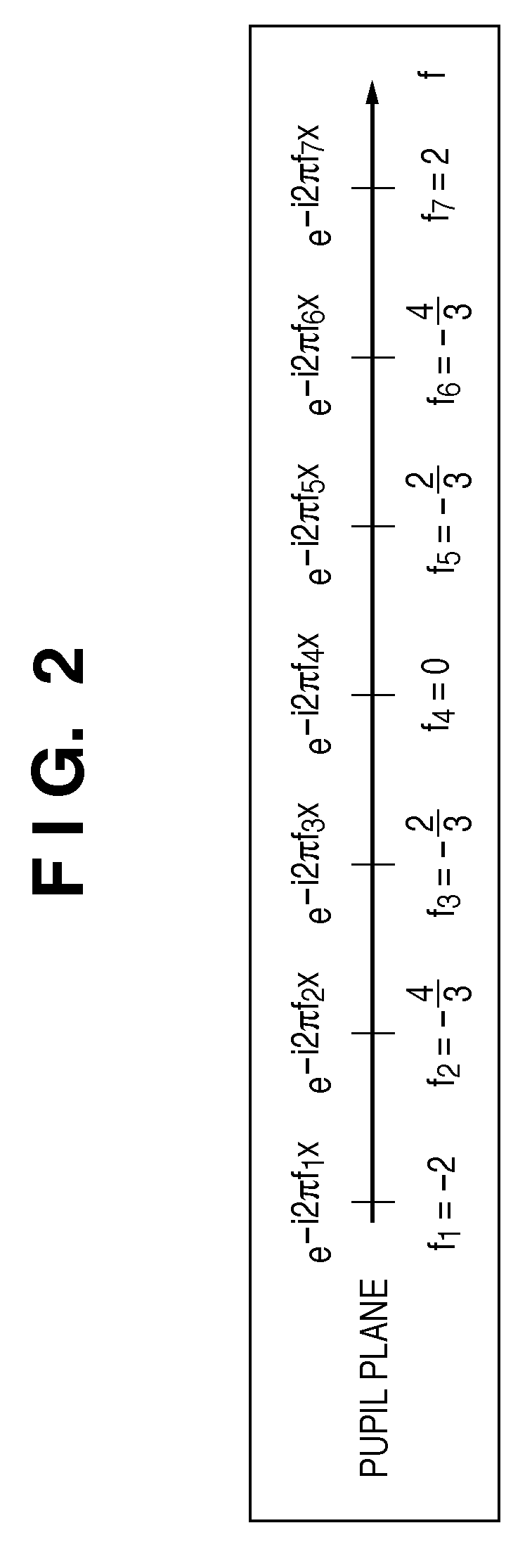
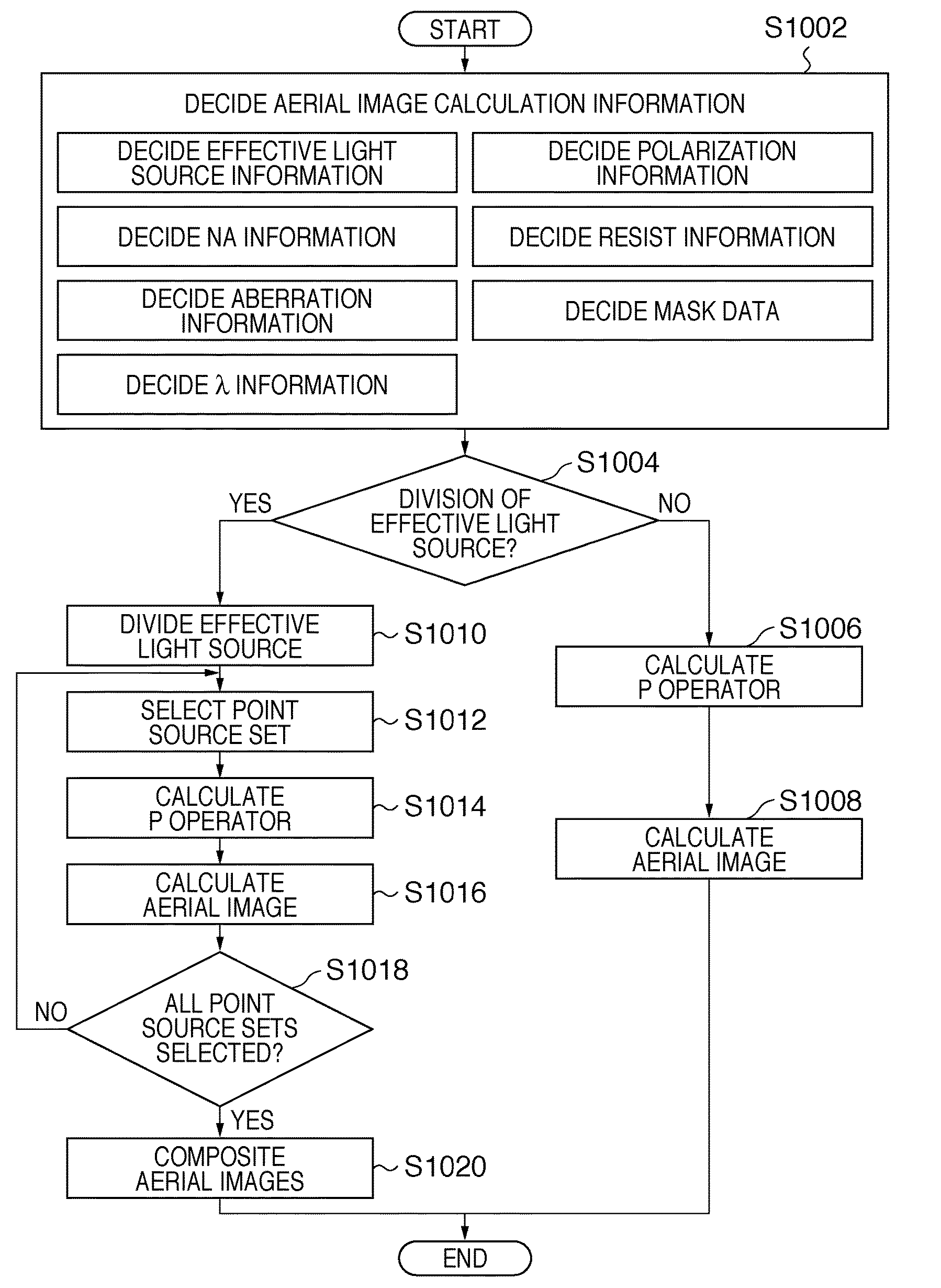
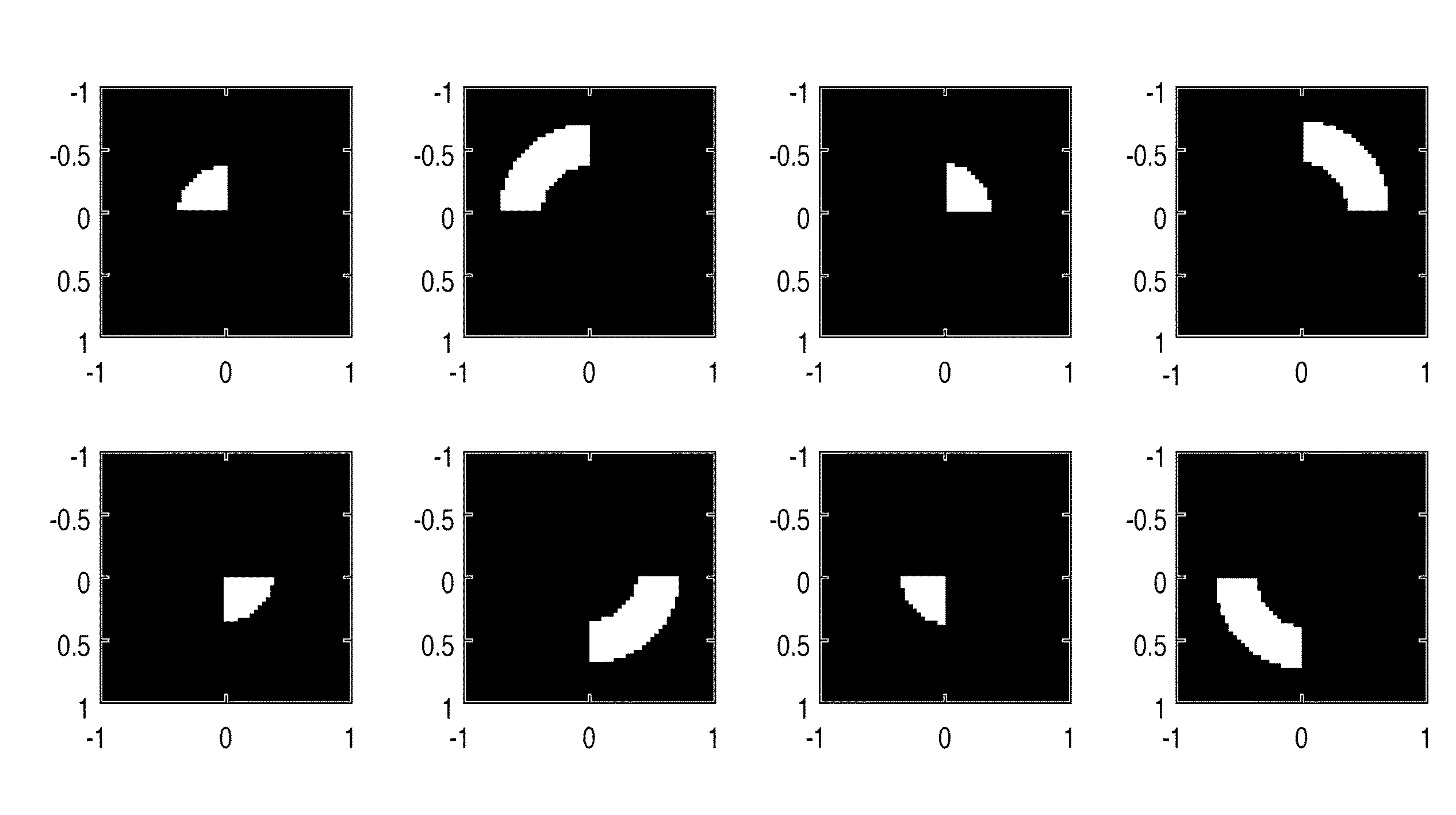
The present invention provides a calculation method of calculating, by a computer, a light intensity distribution formed on an image plane of a projection optical system, comprising a step of dividing an effective light source formed on a pupil plane of the projection optical system into a plurality of point sources, a step of shifting a pupil function describing a pupil of the projection optical system for each of the plurality of point sources in accordance with positions thereof, thereby generating a plurality of shifted pupil functions, a step of defining a matrix including the plurality of pupil functions, a step of performing singular value decomposition of the matrix, thereby calculating an eigenvalue and an eigenfunction, and a step of calculating the light intensity distribution, based on a distribution of the light diffracted by the pattern of the mask, and the eigenvalue and the eigenfunction.
Owner:CANON KK
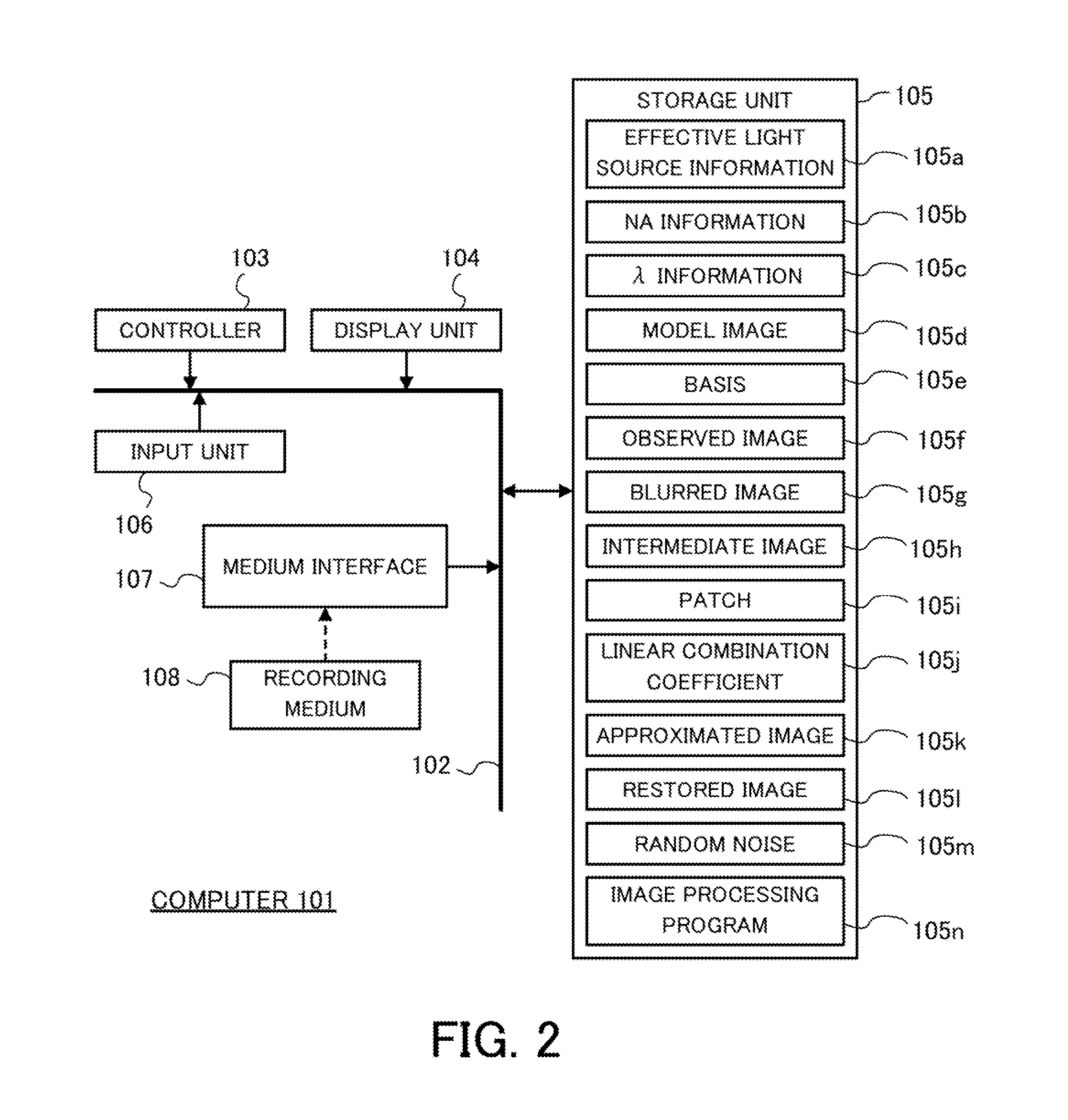
Image restoration method, image restoration apparatus, and image-pickup apparatus
InactiveUS20140055595A1Remove blurImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionMaximum eigenvalue
A method includes performing an approximate partially coherent imaging operation for elements of a first basis generated from a model image having no noise and no blur, and generating based upon the first basis a second basis that is blurred, the approximate partially coherent imaging operation being expressed by a convolution integral on an eigenfunction corresponding to a maximum eigenvalue of a Kernel matrix and each element of the first basis, generating an intermediate image in which each pixel value of the observed image that has been denoised is replaced with its square root, and obtaining a restored image by approximating each of a plurality of patches that are set to entirely cover the intermediate image, using a linear combination of elements of the first basis and linear combination coefficients obtained when each patch is approximated by a linear combination of elements of the second basis.
Owner:CANON KK
Calculation program, and exposure method for calculating light intensity distribution formed on image plane
ActiveUS8059262B2Short timeSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusSingular value decompositionPupil function
The present invention provides a calculation method of calculating, by a computer, a light intensity distribution formed on an image plane of a projection optical system, comprising a step of dividing an effective light source formed on a pupil plane of the projection optical system into a plurality of point sources, a step of shifting a pupil function describing a pupil of the projection optical system for each of the plurality of point sources in accordance with positions thereof, thereby generating a plurality of shifted pupil functions, a step of defining a matrix including the plurality of pupil functions, a step of performing singular value decomposition of the matrix, thereby calculating an eigenvalue and an eigenfunction, and a step of calculating the light intensity distribution, based on a distribution of the light diffracted by the pattern of the mask, and the eigenvalue and the eigenfunction.
Owner:CANON KK
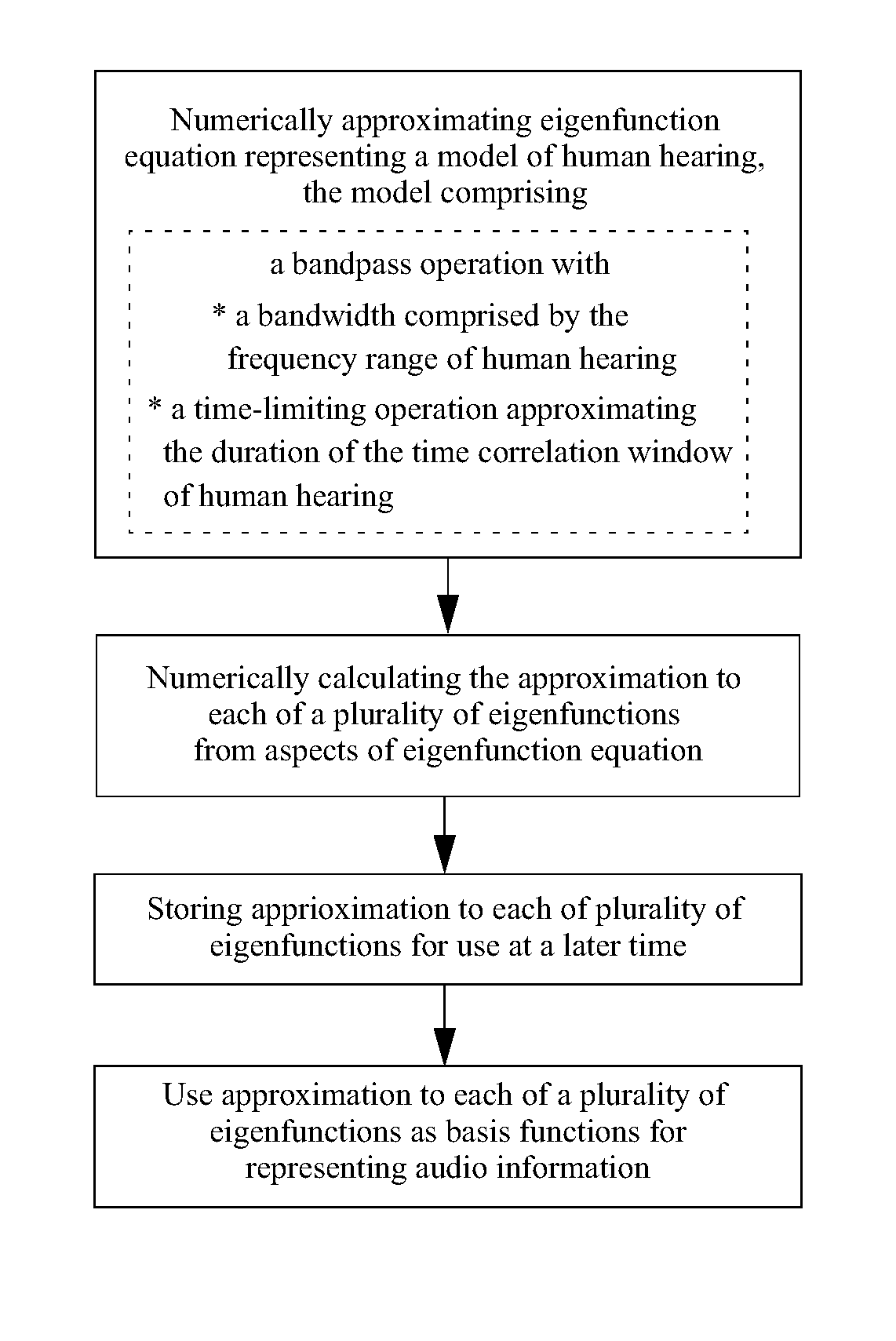
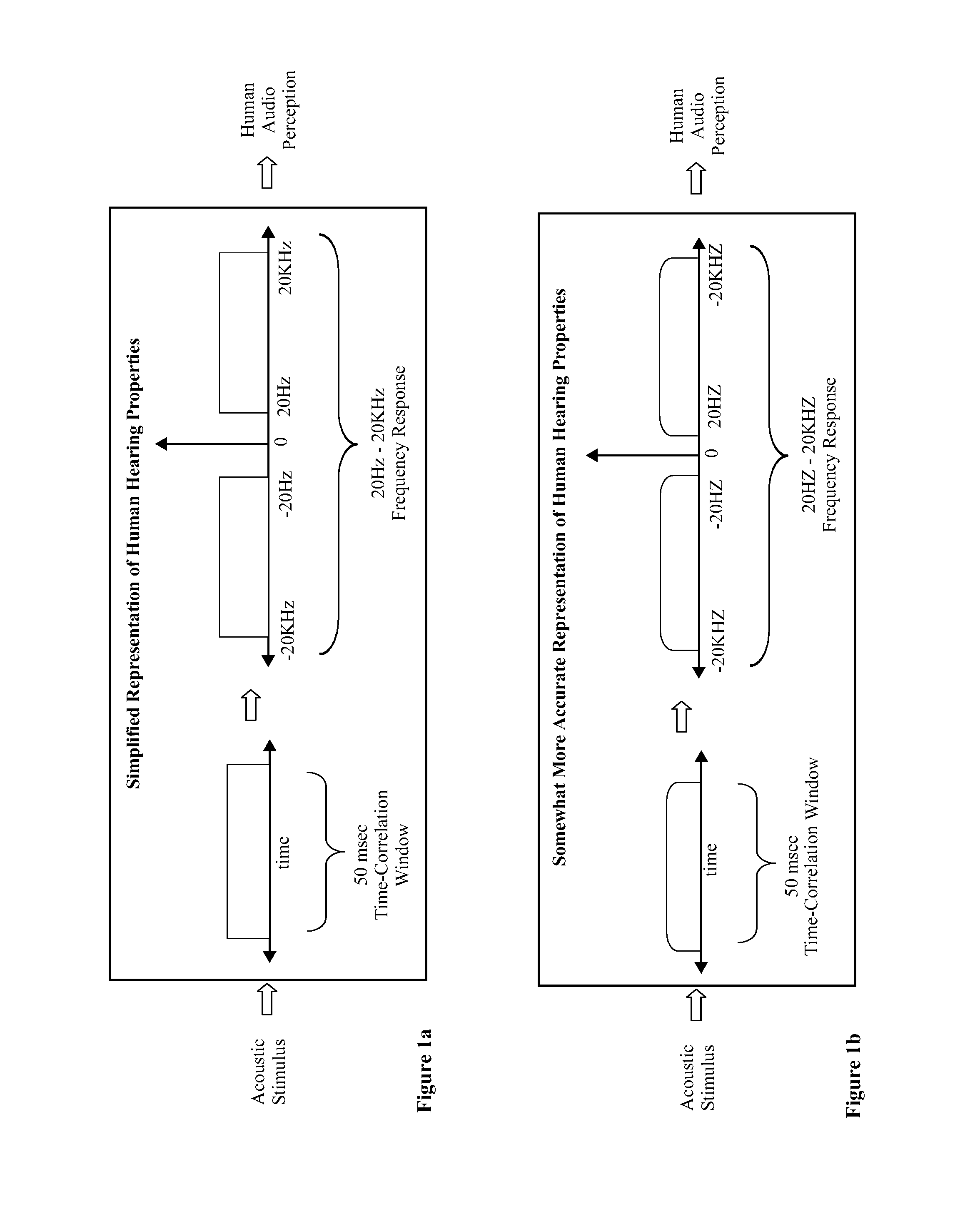
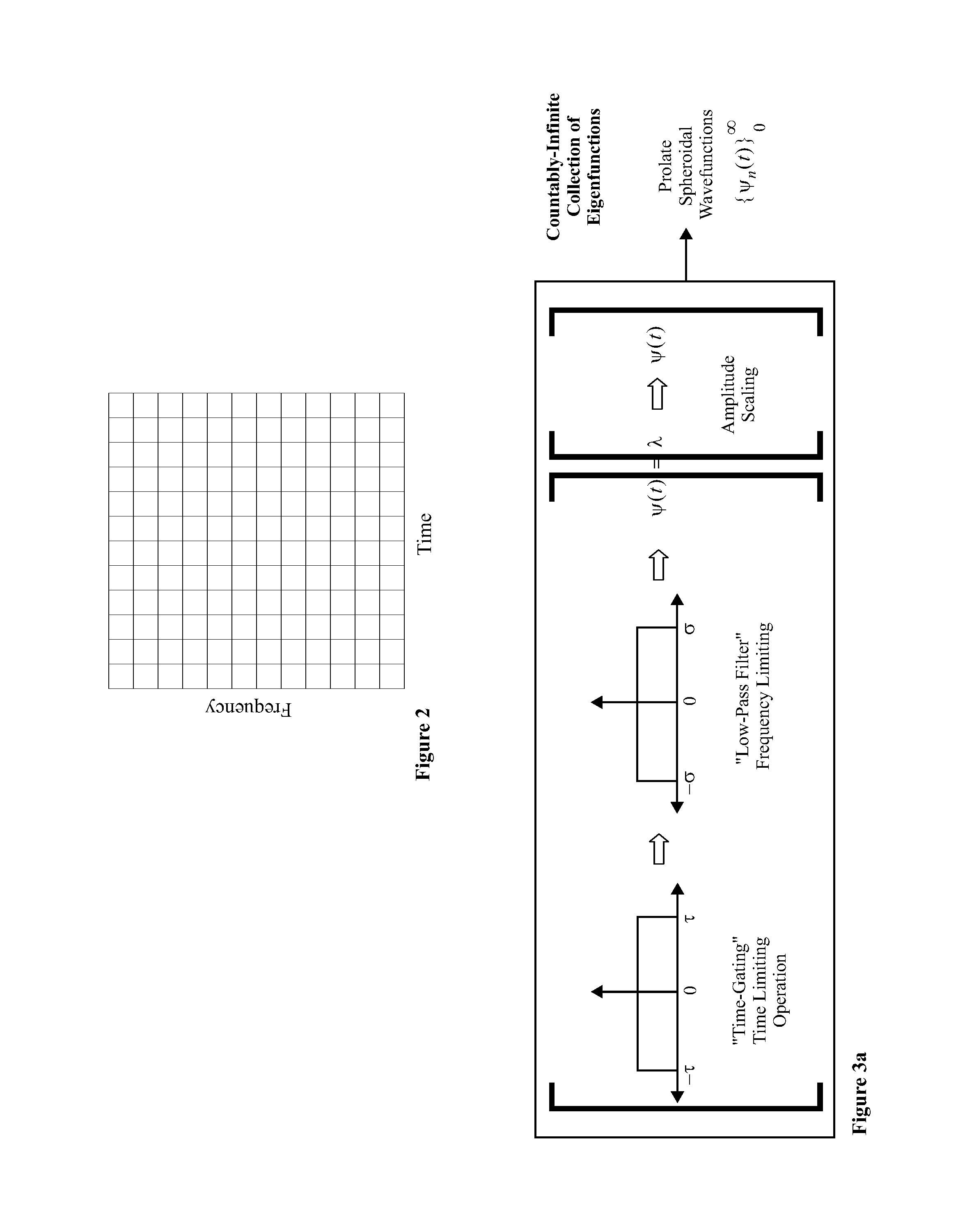
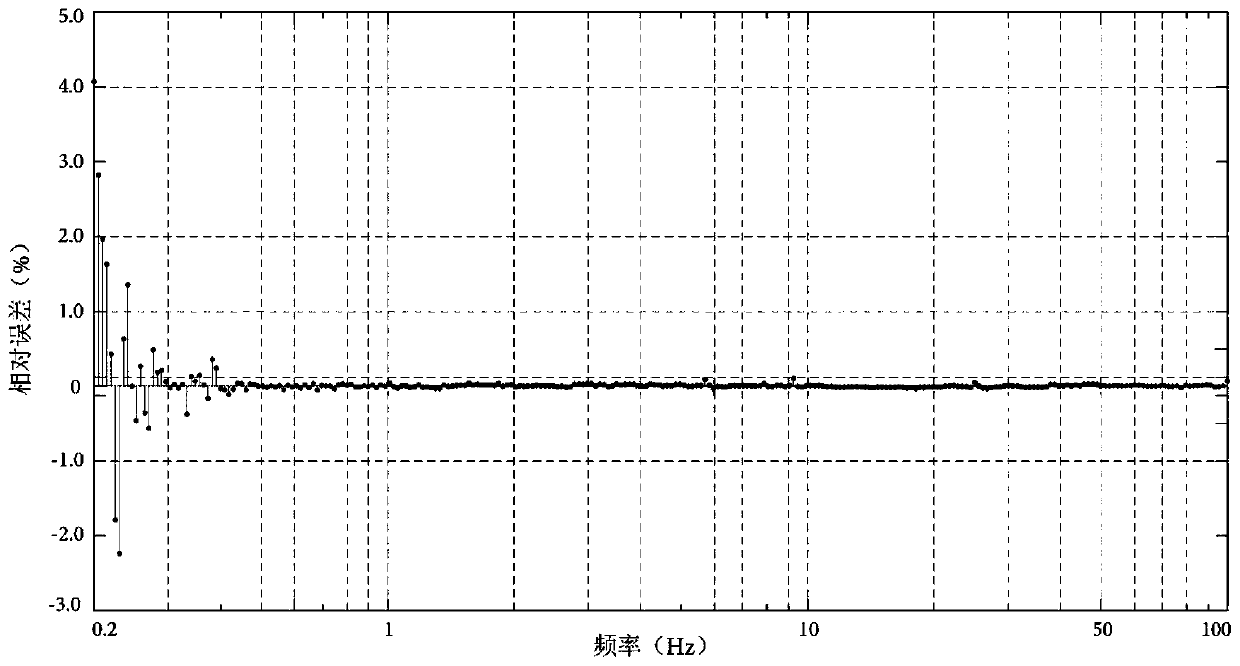
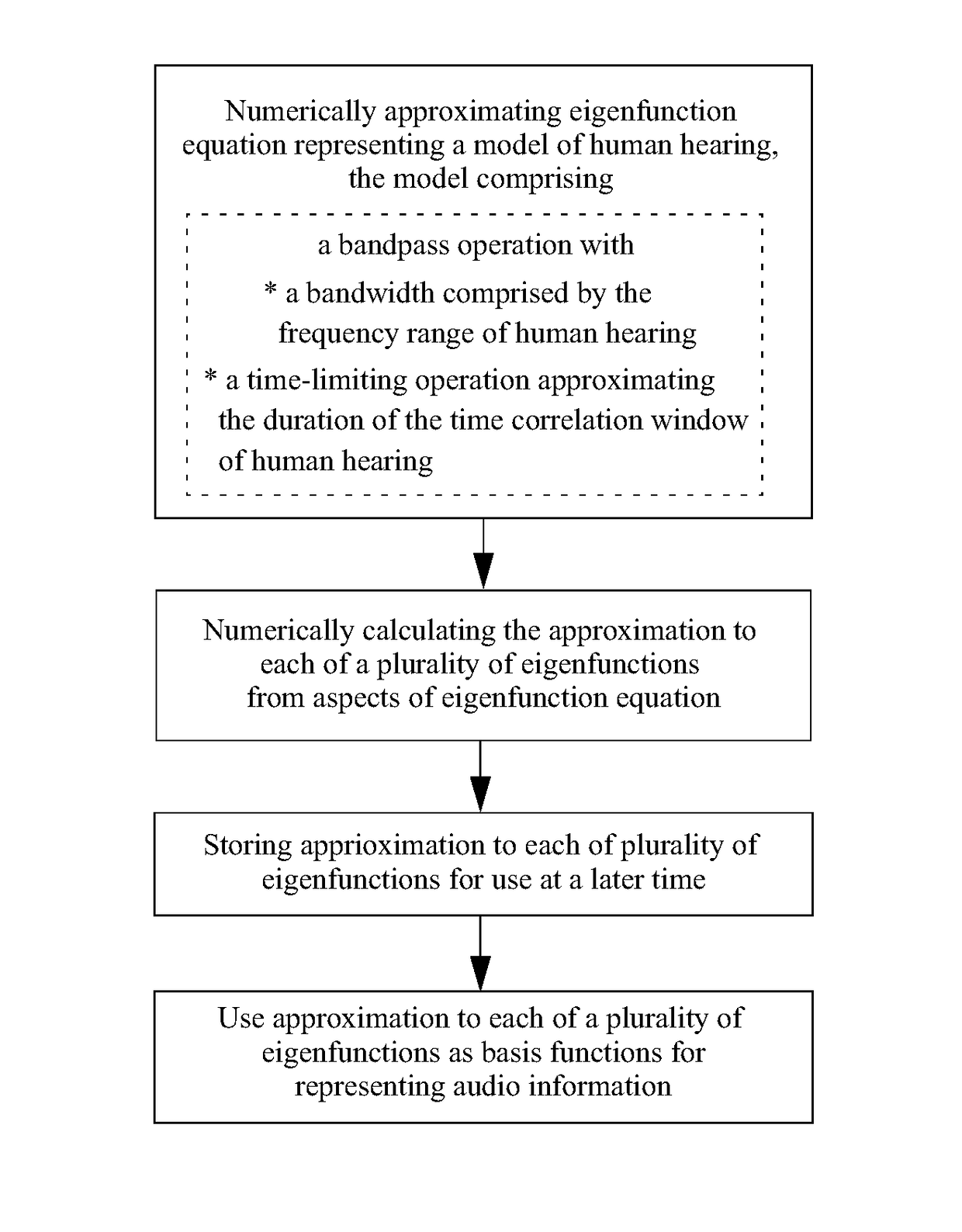
Auditory eigenfunction systems and methods
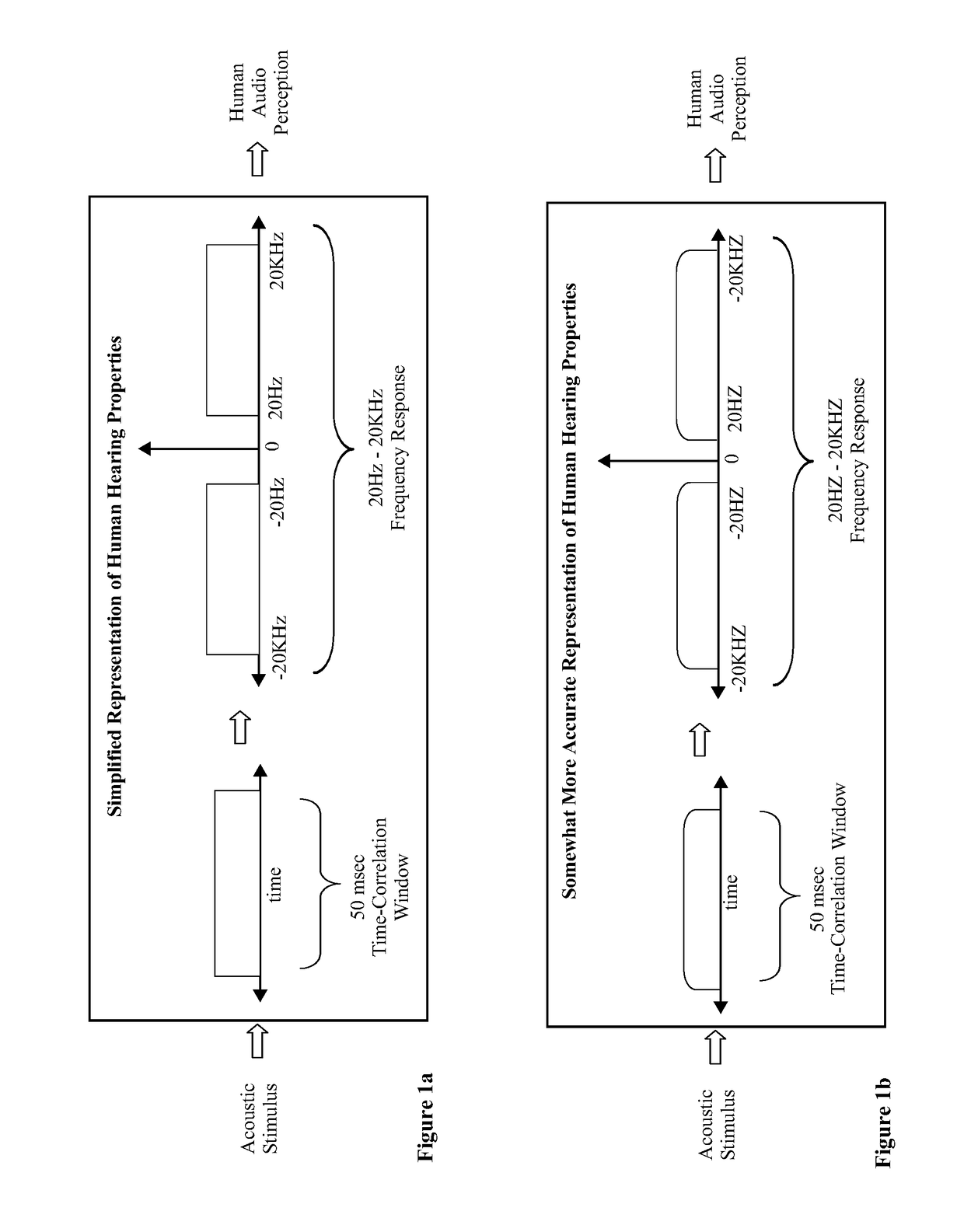
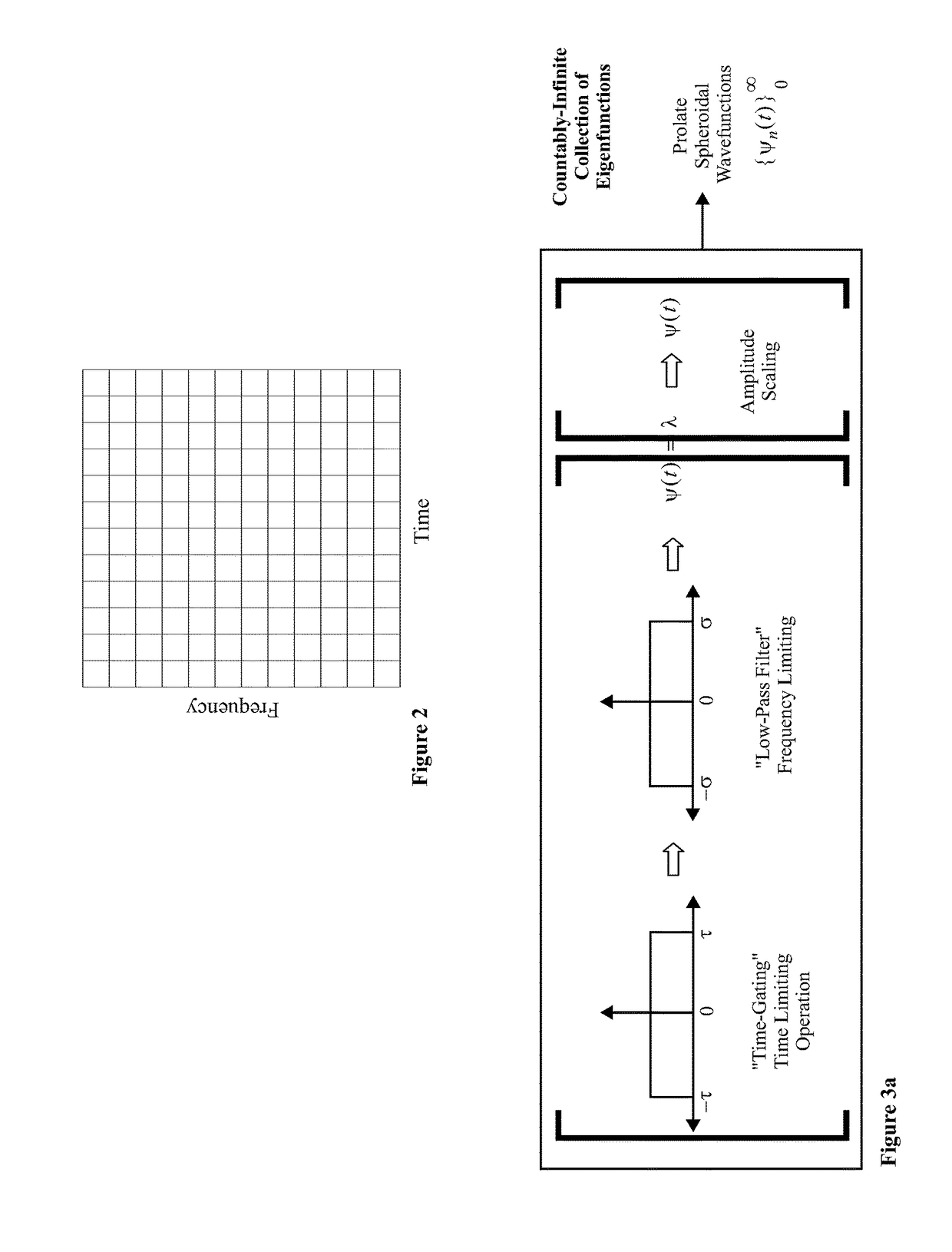
A computer numerical processing method for representing audio information for use in conjunction with human hearing is described. The method comprises approximating an eigenfunction equation representing a model of human hearing, calculating the approximation to each of a plurality of eigenfunctions from at least one aspect of the eigenfunction equation, and storing the approximation to each of a plurality of eigenfunctions for use at a later time. The approximation to each of a plurality of eigenfunctions represents audio information. The model of human hearing includes a bandpass operation with a bandwidth having the frequency range of human hearing and a time-limiting operation approximating the time duration correlation window of human hearing.
Owner:NRI R&D PATENT LICENSING LLC
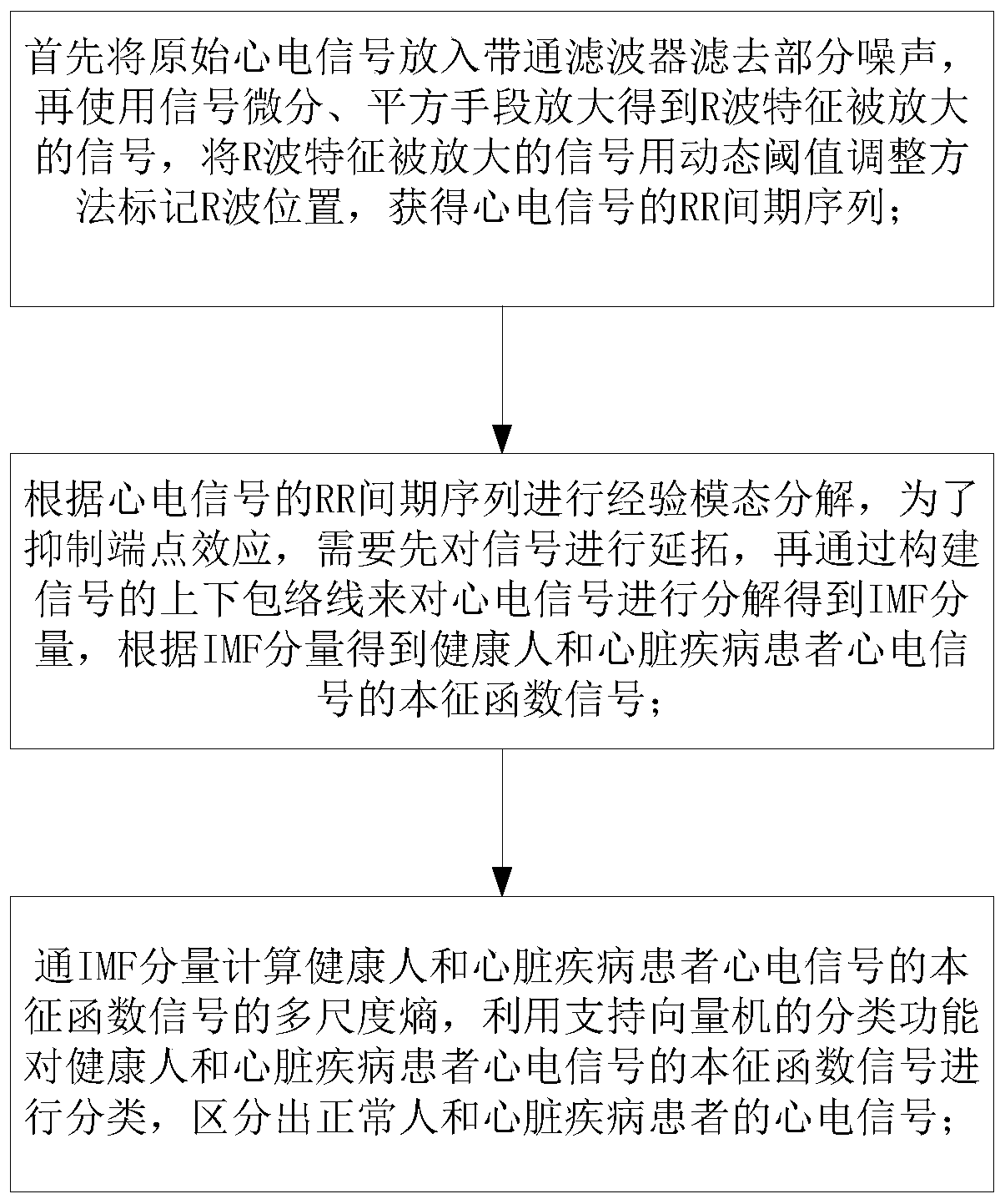
Method for detecting heart diseases based on multi-scale entropy
InactiveCN109998527AMeasure healthReflect frequency characteristicsDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsDiseaseEcg signal
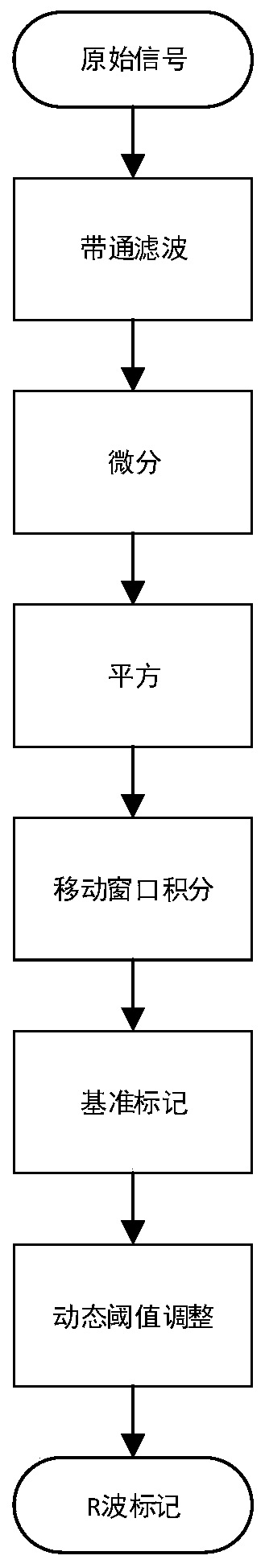
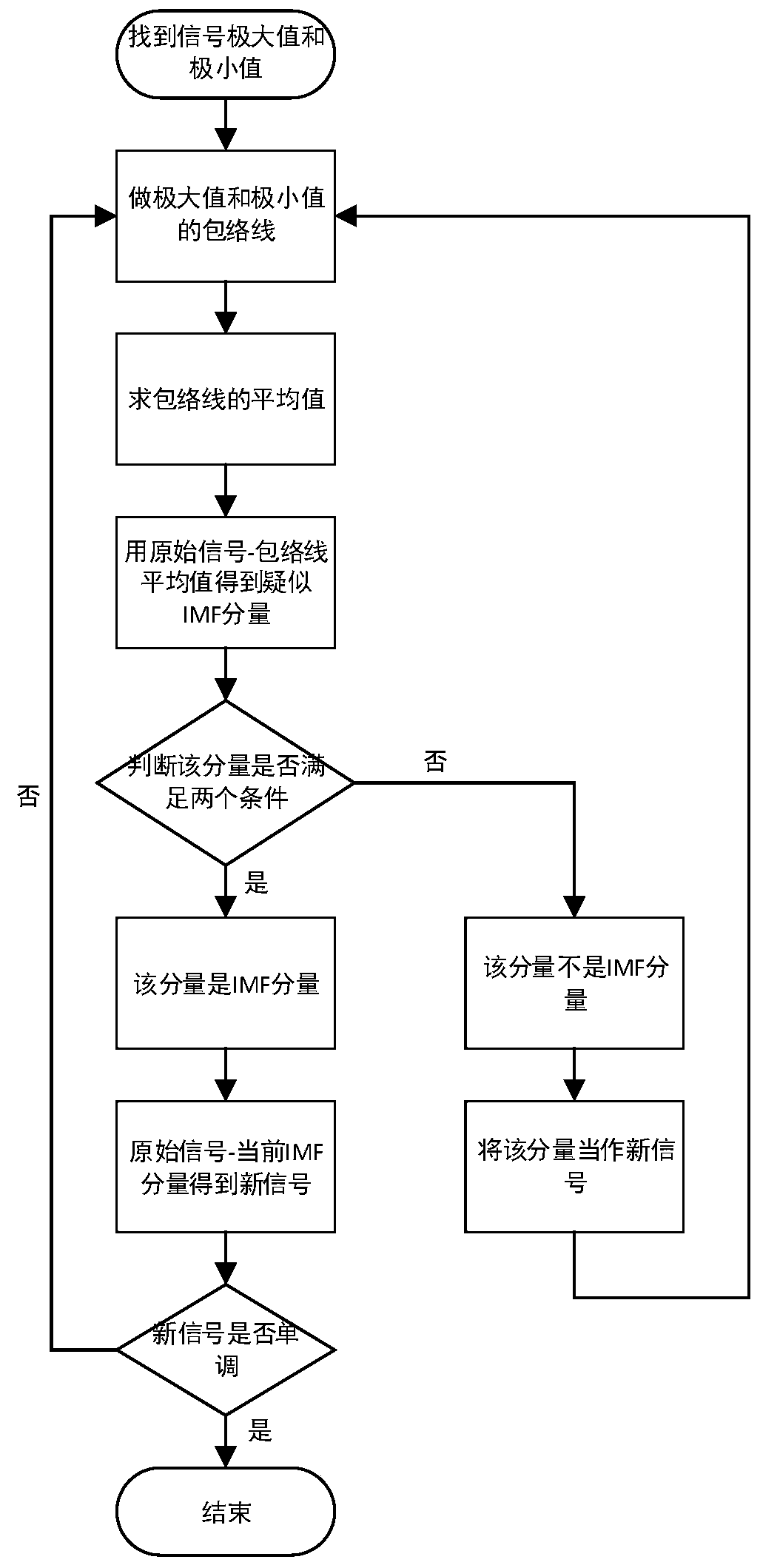
The invention provides a method for detecting heart diseases based on multi-scale entropy. Firstly, original electrocardiosignals are put into a band-pass filter to filter away partial noise, then amplification is carried out by using signal differentiation and square methods to obtain magnified signals of R wave features, an R wave position is marked by using a dynamic threshold adjusting method,and RR interphase sequences of the electrocardiosignals are obtained; according to the RR interphase sequences of the electrocardiosignals, empirical mode decomposition is carried out, the signals are extended, then the electrocardiosignals are decomposed by constructing upper and lower envelope lines of the signals to obtain IMF components, and eigenfunction signals of the electrocardiosignals of healthy persons and patients with the heart diseases are obtained; the multi-scale entropy of the eigenfunction signals is calculated through the IMF components, the eigenfunction signals of the electrocardiosignals of the healthy persons and the patients with the heart diseases are classified by using a classification function of a support vector machine, and the electrocardiosignals of the healthy persons and the patients with the heart diseases are distinguished. The method for detecting the heart diseases based on the multi-scale entropy can timely detect the healthy condition of the heart and is conductive to knowing disease principles.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV OF TECH
Computer readable medium and exposure method
InactiveUS20100053580A1Short timeSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDigital computer detailsSingular value decompositionPupil function
A computer readable medium containing computer-executable instructions which cause a computer to execute processing steps that calculate a light intensity distribution formed on an image plane of a projection optical system. When executed, the medium causes a computer to execute the steps of dividing an effective light source into the plurality of areas, generating, for each of the plurality of areas, a plurality of shifted pupil functions by shifting a pupil function in accordance with a position of each of divided point sources, defining, for each of the plurality of areas, a matrix including the plurality of pupil functions, calculating, for each of the plurality of areas, eigenvalues and eigenfunctions by performing singular value decomposition of the matrix, and calculating, for each of the plurality of areas, the light intensity distribution based on a diffracted light distribution from the mask and the eigenvalues and the eigenfunctions.
Owner:CANON KK
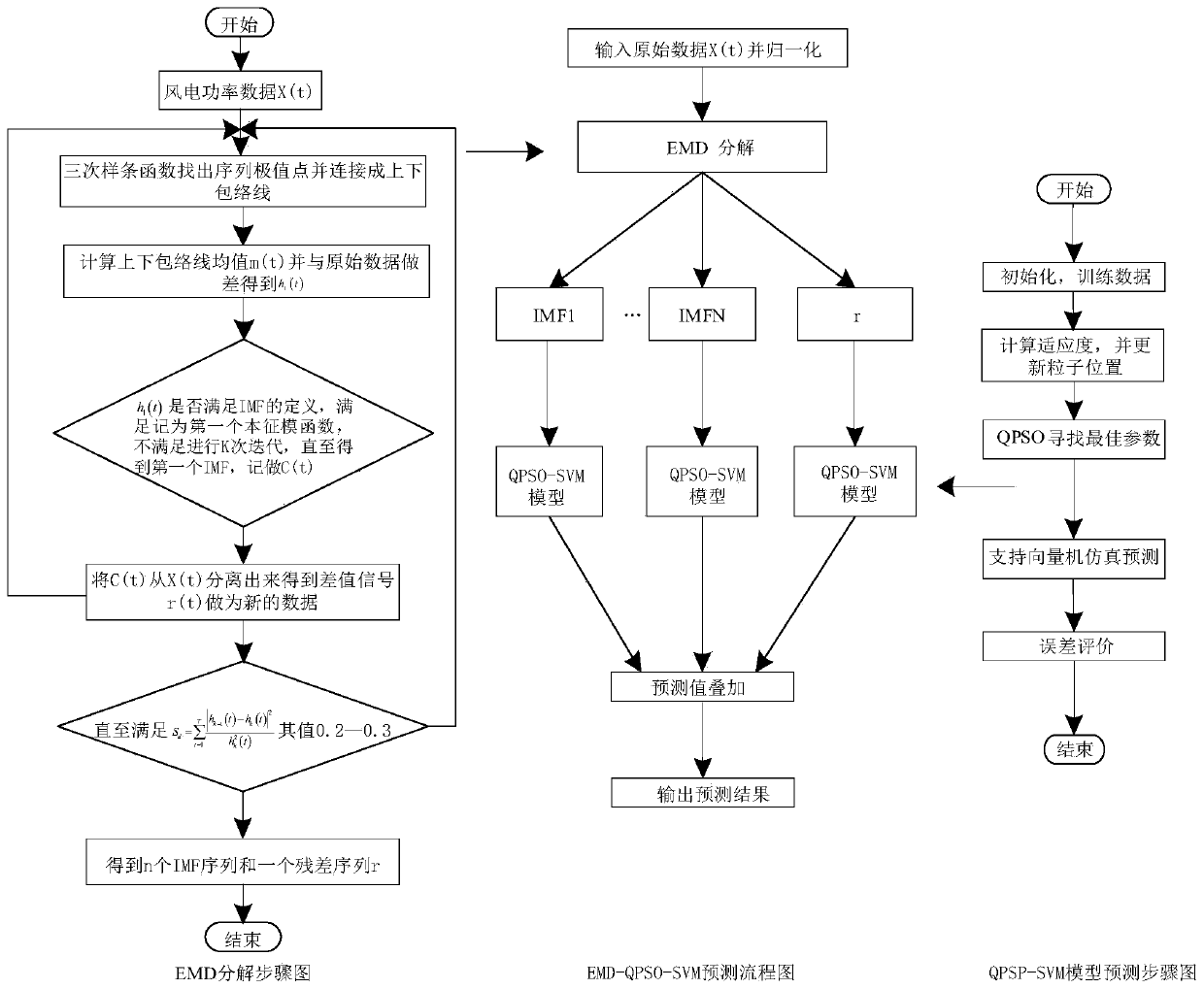
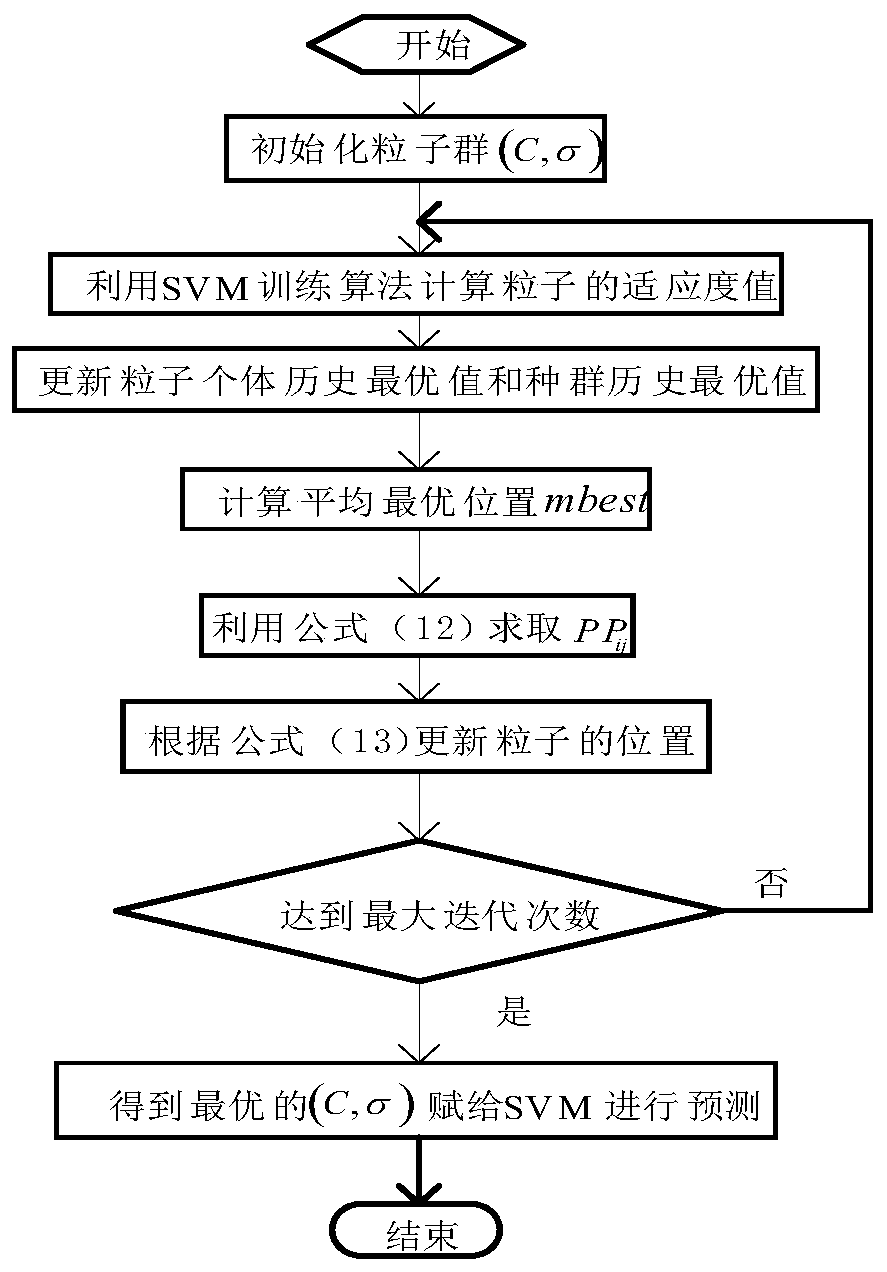
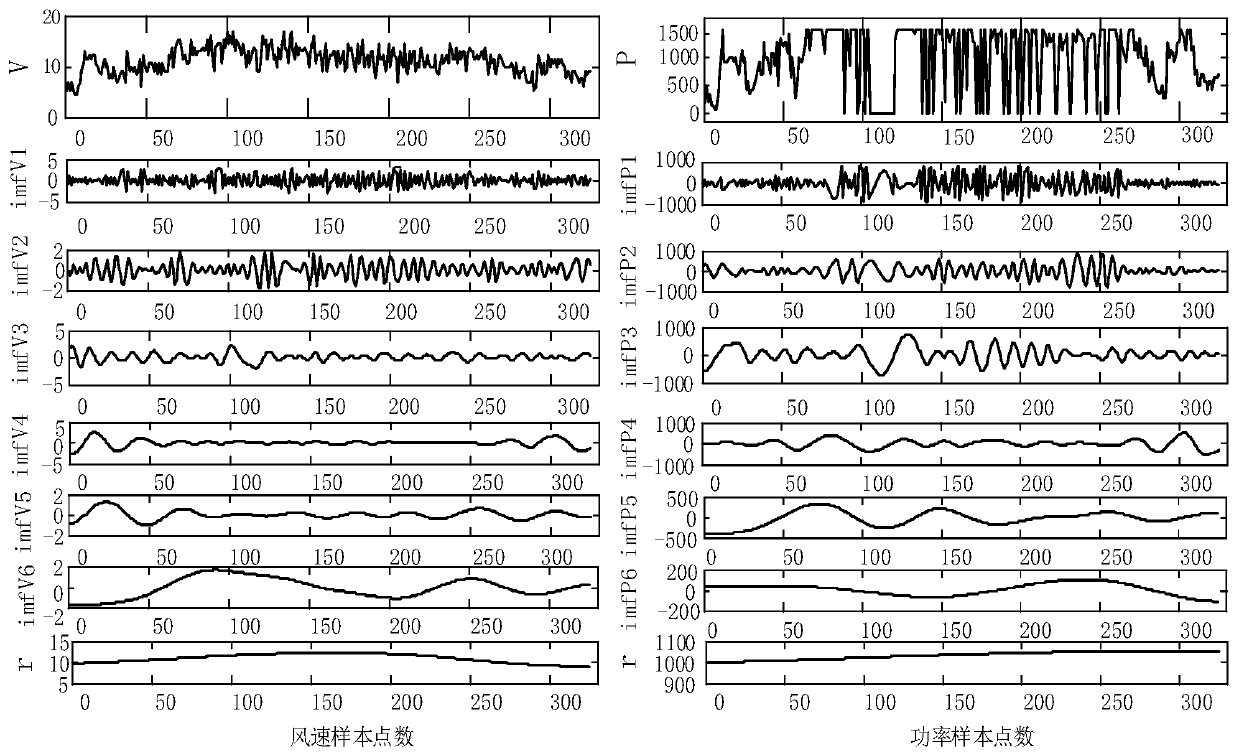
Ultra-short-term wind power combination prediction method based on support vector machine
PendingCN110263971AExpand the solution spaceImprove the situation where excessive local errors are prone to occurForecastingInformation technology support systemRobustificationDecomposition
The invention discloses an ultra-short-term wind power combination prediction method based on a support vector machine, and the method comprises the steps: firstly carrying out the linear interpolation replacement of to-be-processed wind power historical data according to the data of an adjacent time period, and carrying out the normalization of the preprocessed data; secondly, decomposing the processed wind power data into an eigenfunction sequence and a residual error sequence by using empirical mode decomposition; secondly, establishing a quantum particle swarm-support vector machine model for the eigenfunction sequence and the residual sequence obtained by decomposition, and performing training optimization to obtain a predicted value of each sequence; and finally, superposing the prediction values of the sequences to obtain a final wind power prediction value, and carrying out error evaluation analysis. Compared with a support vector machine direct prediction result or a result without data feature decomposition, the prediction result of the method is improved, and meanwhile the situation that local errors are too large does not occur. Compared with an existing wind power prediction scheme, the method is higher in robustness, higher in calculation speed, less in data requirement and better in prediction effectThe invention discloses an ultra-short-term wind power combination prediction method based on a support vector machine, and the method comprises the steps: carrying out the linear interpolation replacement of to-be-processed wind power historical data according to the data of an adjacent time period, and carrying out the normalization of the preprocessed data; secondly, decomposing the processed wind power data into a cost characteristic function sequence and a residual sequence by utilizing empirical mode decomposition; secondly, establishing a quantum particle swarm-residual sequence for the intrinsic function sequence and the residual sequence obtained by decomposition; carrying out training optimization on the support vector machine model to obtain a predicted value of each sequence; and finally, superposing the predicted values of the sequences to obtain a final wind power predicted value, and carrying out error evaluation analysis. Compared with a result of direct prediction of a support vector machine or no data feature decomposition, the prediction result of the method is improved, and meanwhile, the situation of overlarge local error does not occur. Compared with an existing wind power prediction scheme, the method is higher in robustness, higher in calculation speed, less in data demand and better in prediction effect.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF TECH
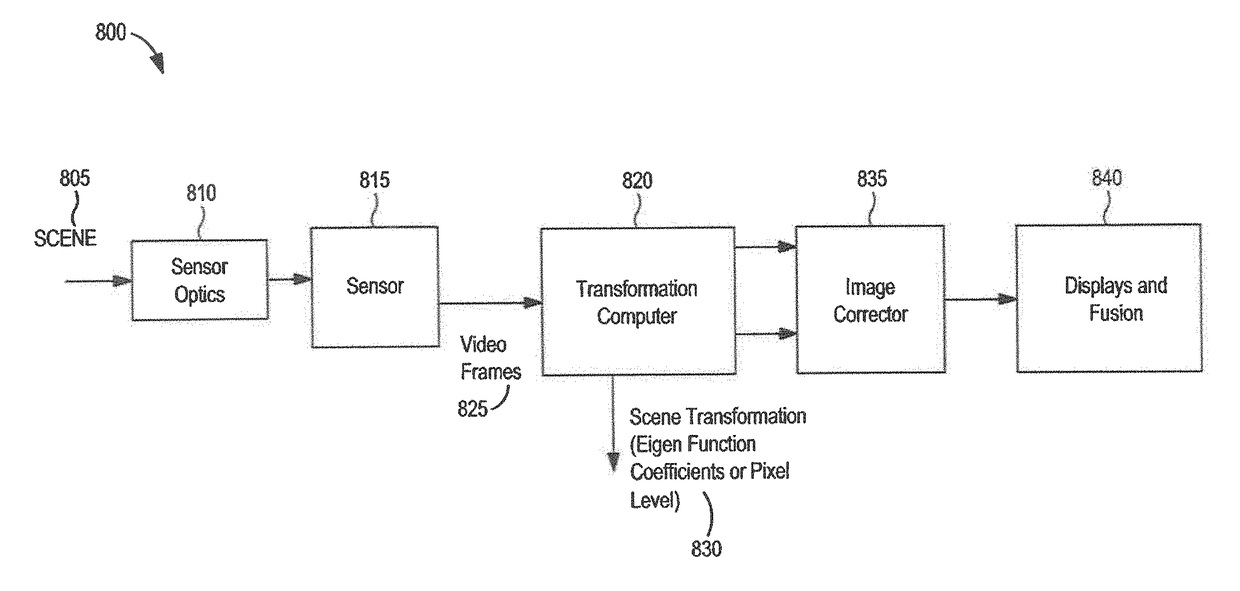
Self correcting adaptive low light optical payload
ActiveUS20170332017A1Reduce underexposureReduce weightTelevision system detailsImage analysisSpectral bandsRelative motion
Methods and systems are disclosed for compensating for image motion induced by a relative motion between an imaging platform and a scene. During an exposure period, frames of the scene may be captured respectively in multiple spectral bands, where one of the spectral bands has a lower light level than the first spectral band, and contemporaneous frames include a nearly identical induced image motion. Image eigenfunctions are utilized to estimate the induced image motion from the higher SNR spectral band, and compensate in each of the multiple bands.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
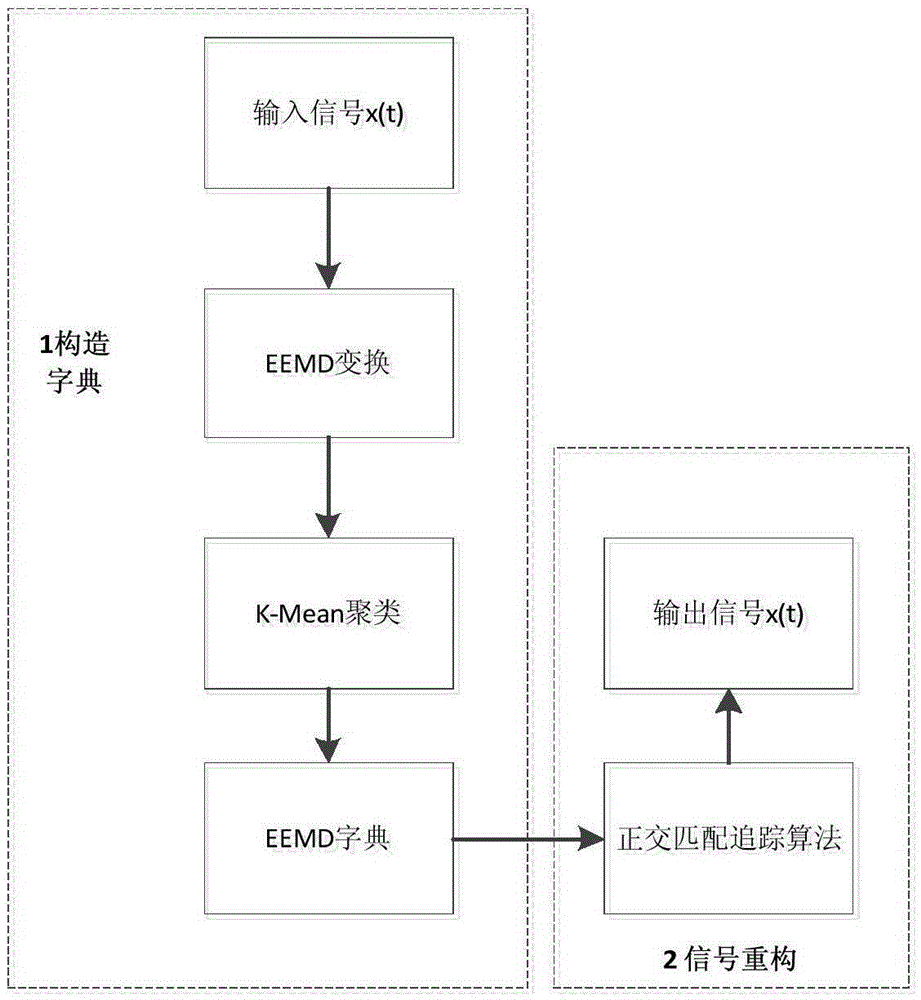
EEMD-based compressive sensing method
InactiveCN105406872AIncrease the compression ratioImprove accuracyCode conversionPattern recognitionInformation processing
The invention discloses an EEMD-based compressive sensing method which is a novel information processing method, overcomes the defects in the conventional signal compressing process, and can compress information and reconstruct a source signal to the maximum extent. The EEMD-based compressive sensing method comprises the following steps: separating out a signal eigenfunction according to an EEMD method, reconstructing an over-complete dictionary by adopting a K-mean cluster, and then reconstructing a sparse signal according to an orthogonal matching pursuit algorithm.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Calculation method, generation method, program, exposure method, and mask fabrication method
ActiveUS20120019805A1Short timeSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusSingular value decompositionPupil function
The present invention provides a calculation method of calculating, by a computer, a light intensity distribution formed on an image plane of a projection optical system, comprising a step of dividing an effective light source formed on a pupil plane of the projection optical system into a plurality of point sources, a step of shifting a pupil function describing a pupil of the projection optical system for each of the plurality of point sources in accordance with positions thereof, thereby generating a plurality of shifted pupil functions, a step of defining a matrix including the plurality of pupil functions, a step of performing singular value decomposition of the matrix, thereby calculating an eigenvalue and an eigenfunction, and a step of calculating the light intensity distribution, based on a distribution of the light diffracted by the pattern of the mask, and the eigenvalue and the eigenfunction.
Owner:CANON KK
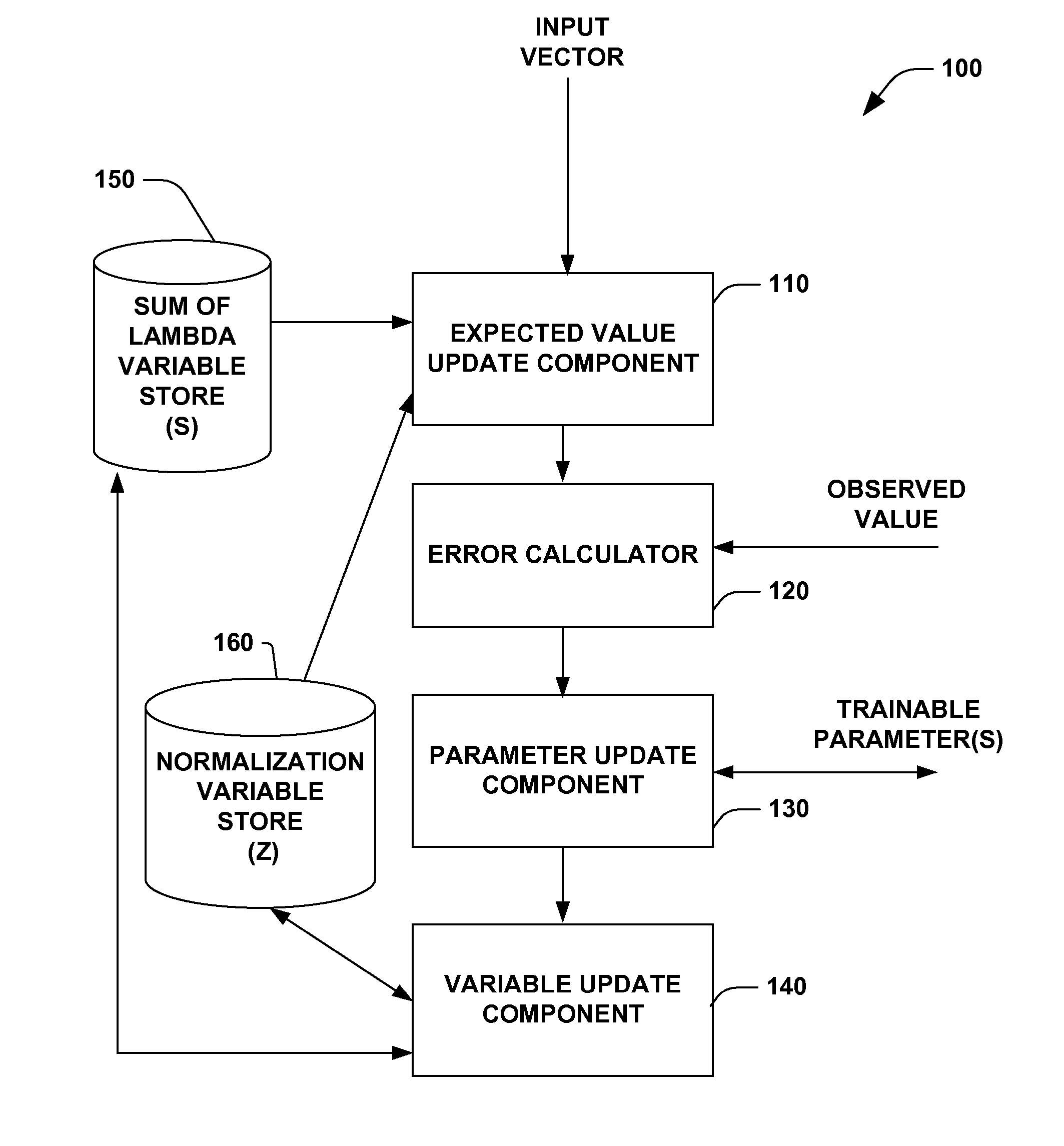
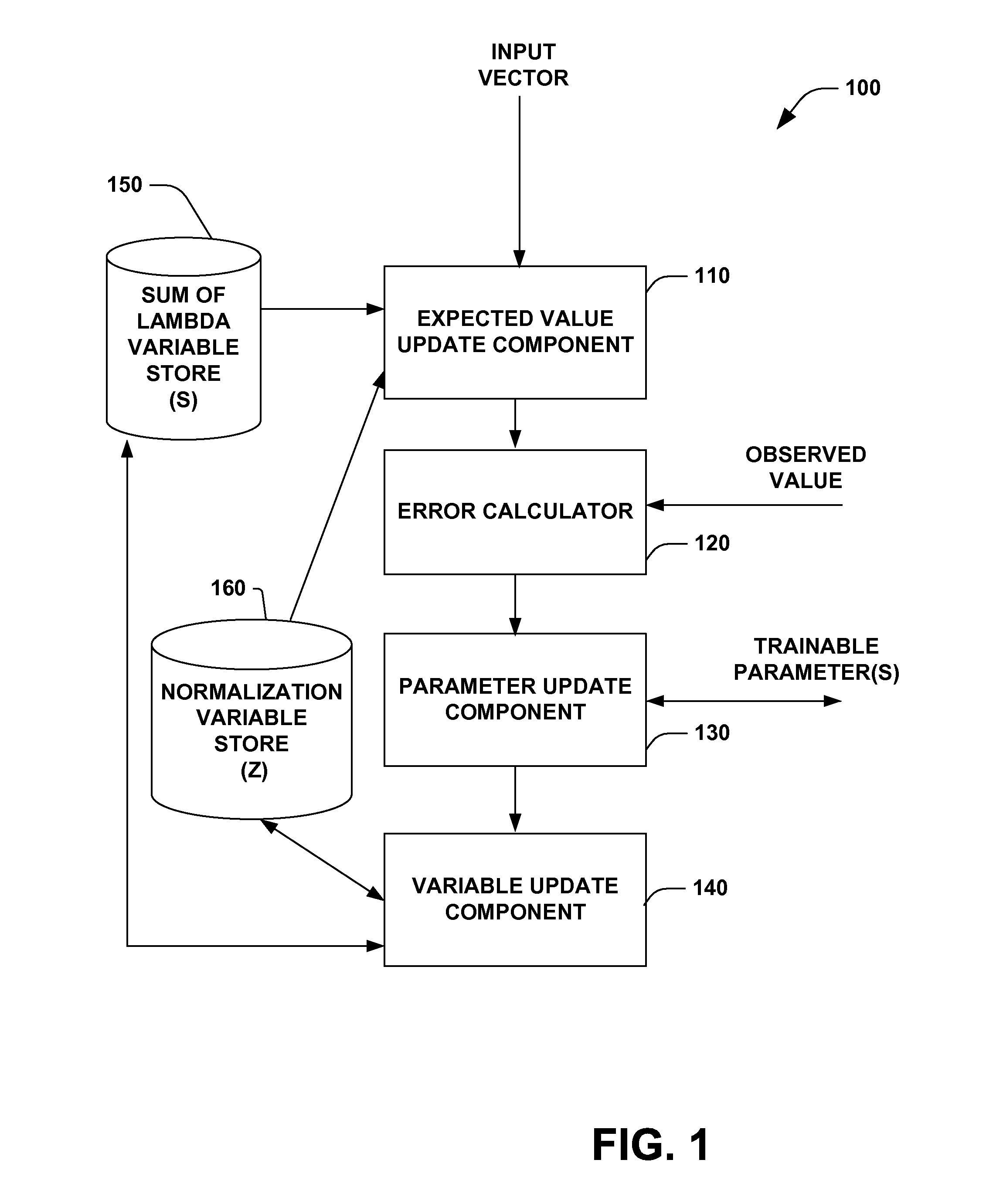
Sequential conditional generalized iterative scaling
InactiveUS20070022069A1Raise the possibilityIncrease speedDigital computer detailsSpeech recognitionGeneralized iterative scalingCalculation error
A system and method facilitating training machine learning systems utilizing sequential conditional generalized iterative scaling is provided. The invention includes an expected value update component that modifies an expected value based, at least in part, upon a feature function of an input vector and an output value, a sum of lambda variable and a normalization variable. The invention further includes an error calculator that calculates an error based, at least in part, upon the expected value and an observed value. The invention also includes a parameter update component that modifies a trainable parameter based, at least in part, upon the error. A variable update component that updates at least one of the sum of lambda variable and the normalization variable based, at least in part, upon the error is also provided.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Sentence boundary identification method in spoken language dialogue
InactiveCN1570923ASolve problems with manageable sentencesSpecial data processing applicationsSpoken languageEigenfunction
A kind of sentence dividing method based on bi-directional N-gram model and Maximum Entrpy model. This method comprises training and dividing. The training process comprises: obtaining the spoken language material library, preprocessing the spoken language material library, for example replacement; counting the n term co-appear frequency of n-gram model; estimating the n term positive dependence probability and n term negative dependence probability; obtaining the n term positive and negative dependence probability database; setting the eigenfunction of Maximum Entropy model; circulating account the eigenfunction parameter, obtaining eigenfunction parameter database. This method is a kind of purely statistical method. The operation only needs a background spoken language material library that doesn't need further dividing or labeling.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Distance-dependent spectra with uniform sampling spectrometry
InactiveUS8903670B2Flexible and robust realizationEvenly spacedDirection finders using radio wavesVoltage-current phase angleDigital signal processingPhase difference
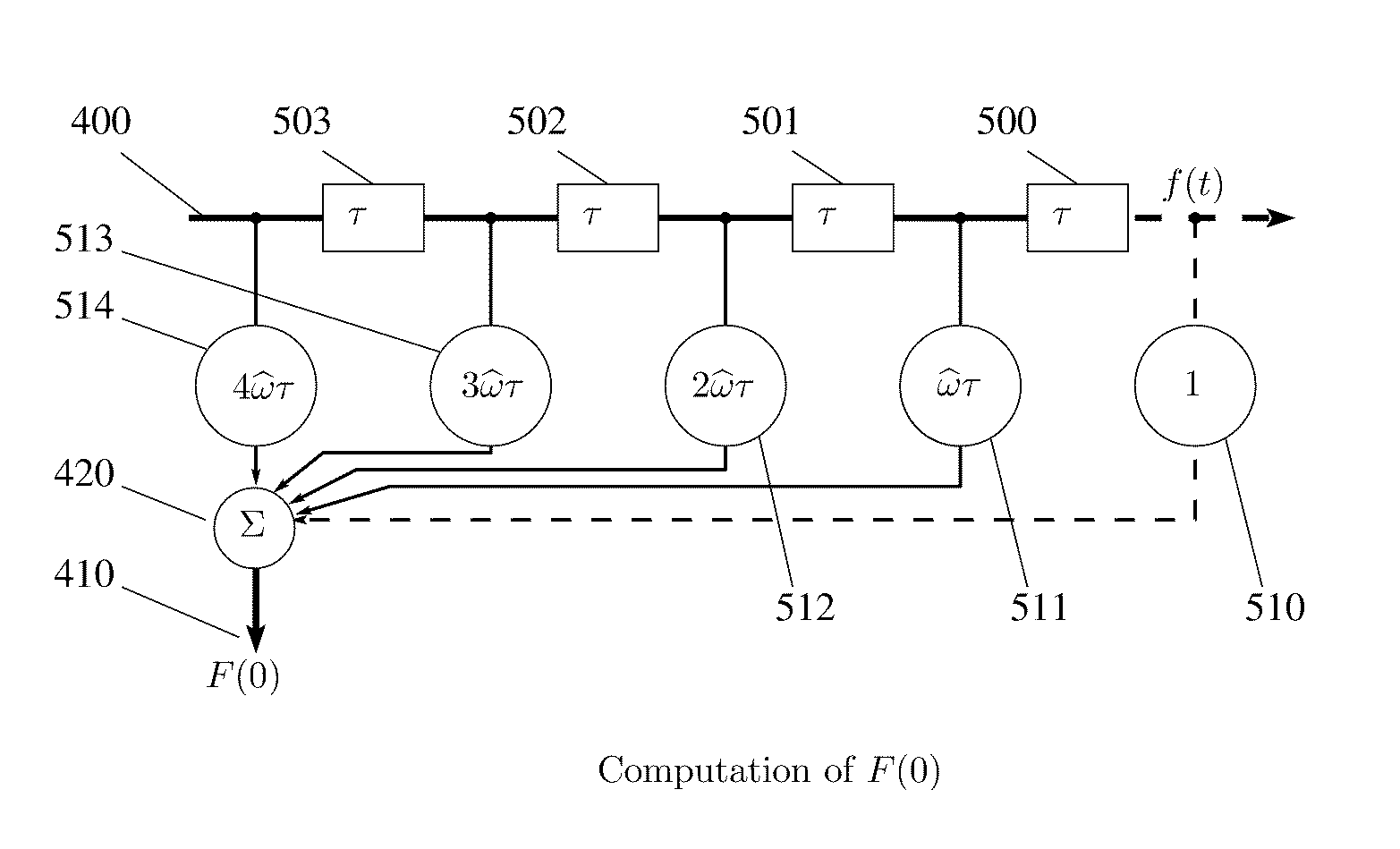
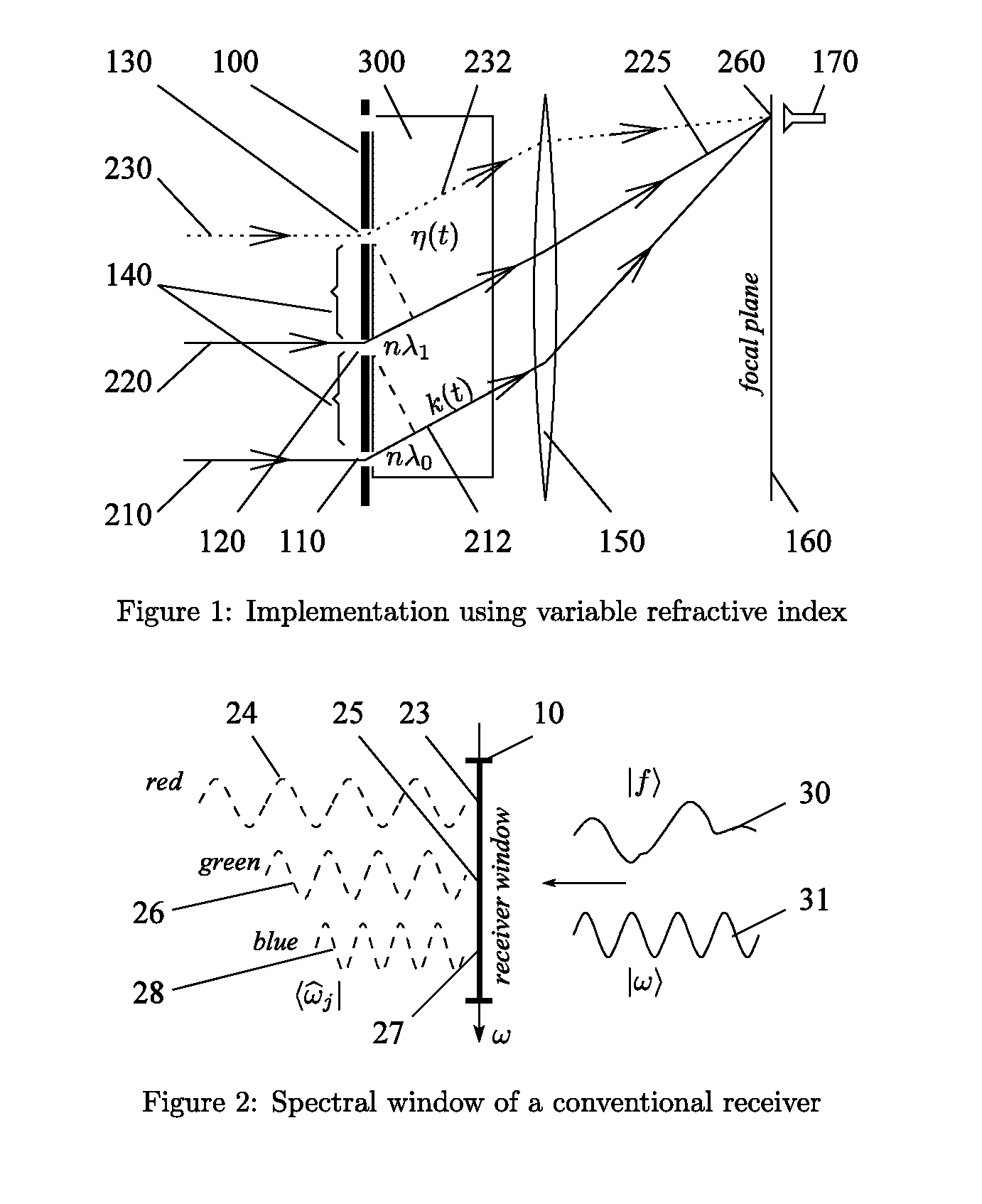
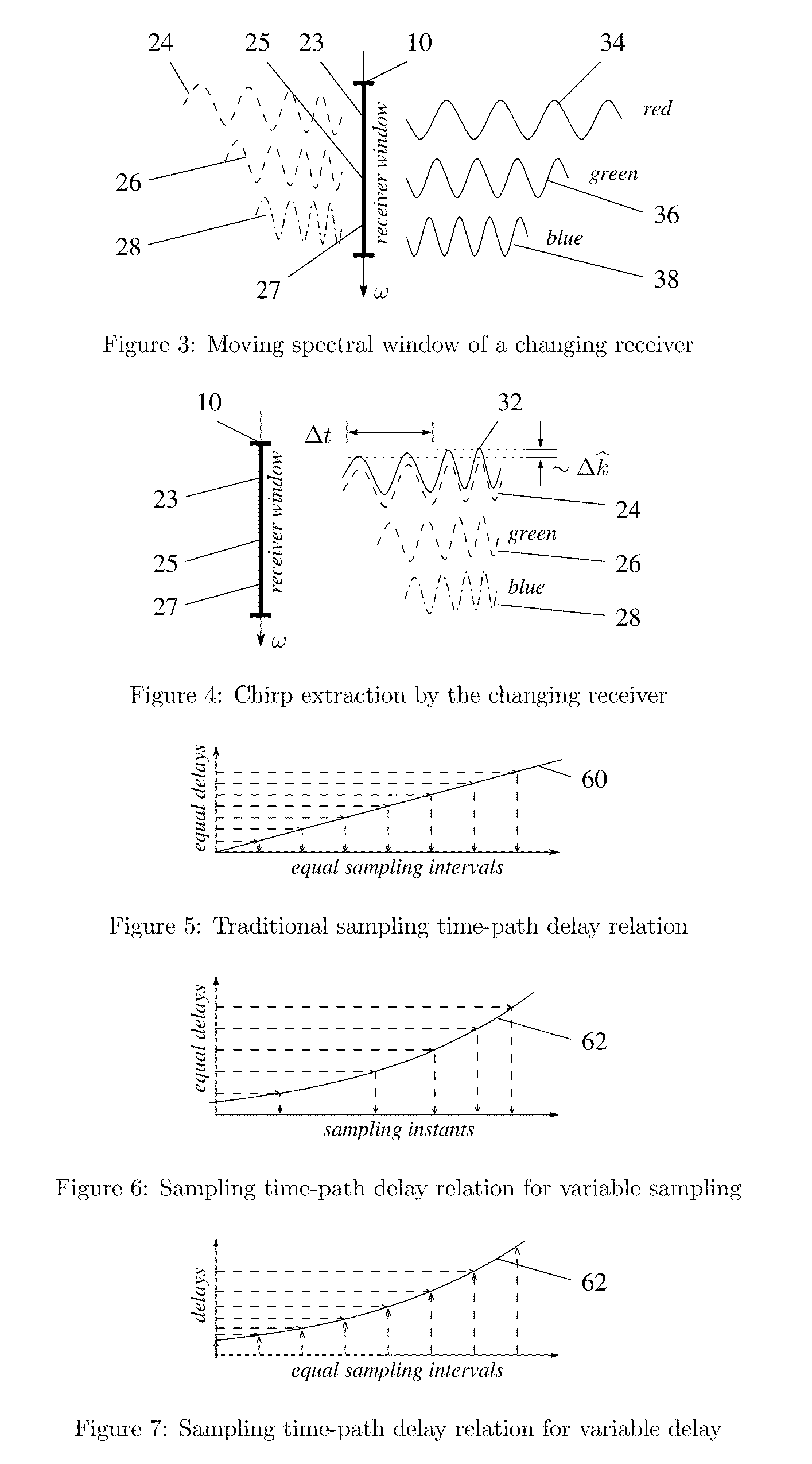
In a receiver of electromagnetic or other waves, scaling of received frequencies in proportion to the respective source distances, so as to reveal the source distances and permit isolation of signals from a particular source by simple spectral filtering. Phase differences between transmitted frequencies due to the common source path lead to chirp eigenfunctions registering in the receiver as scaled frequencies. The chirps are extracted by implementing exponentially varying path delays in autocorrelators and diffractive spectrometers say using a medium with variable refractive index. Analogous exponentially varying phase shifts are applied to successive samples in the kernel of discrete Fourier transform implementations. Advantage lies in enabling distance-dependent frequency scaling in autocorrelation spectroscopy, as well as in conventional diffractive or refractive spectrometers or digital signal processing with uniform sampling.
Owner:GURUPRASAD VENKATA
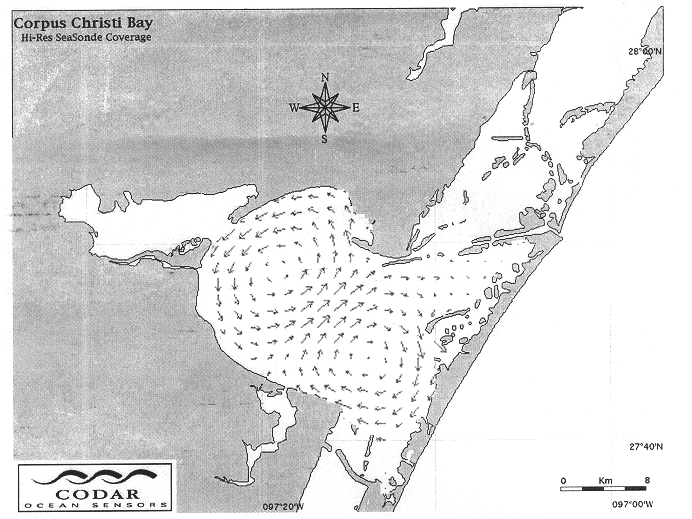
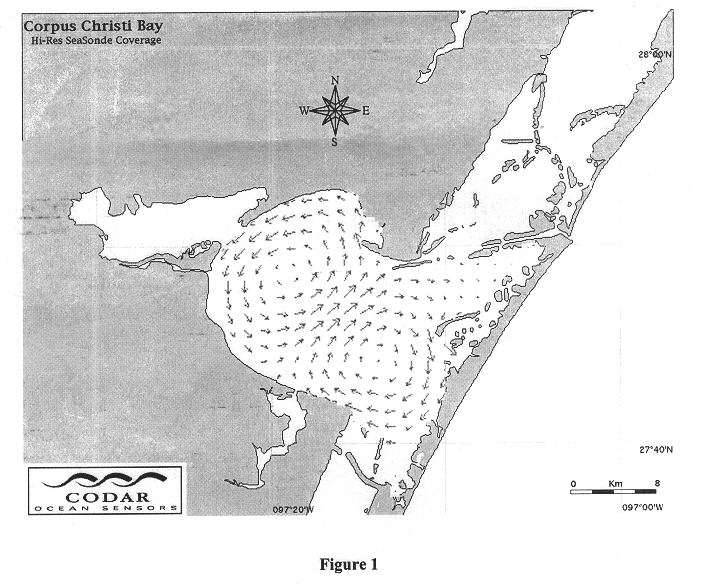
Synthesis of total surface current vector maps by fitting normal modes to single-site HF radar data
InactiveUS6590523B2Easy to useReduce complexityRadio wave reradiation/reflectionICT adaptationData setNormal mode
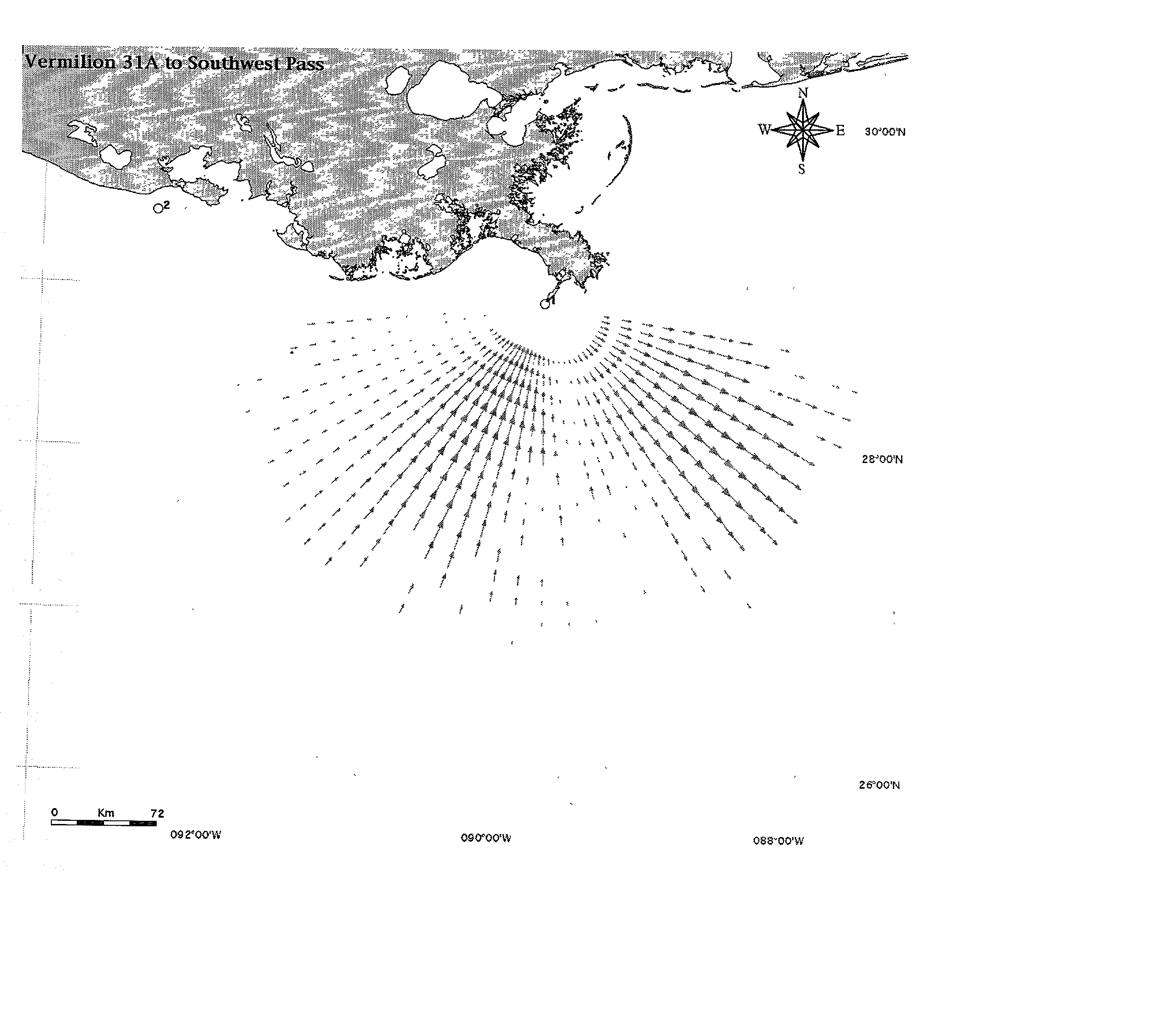
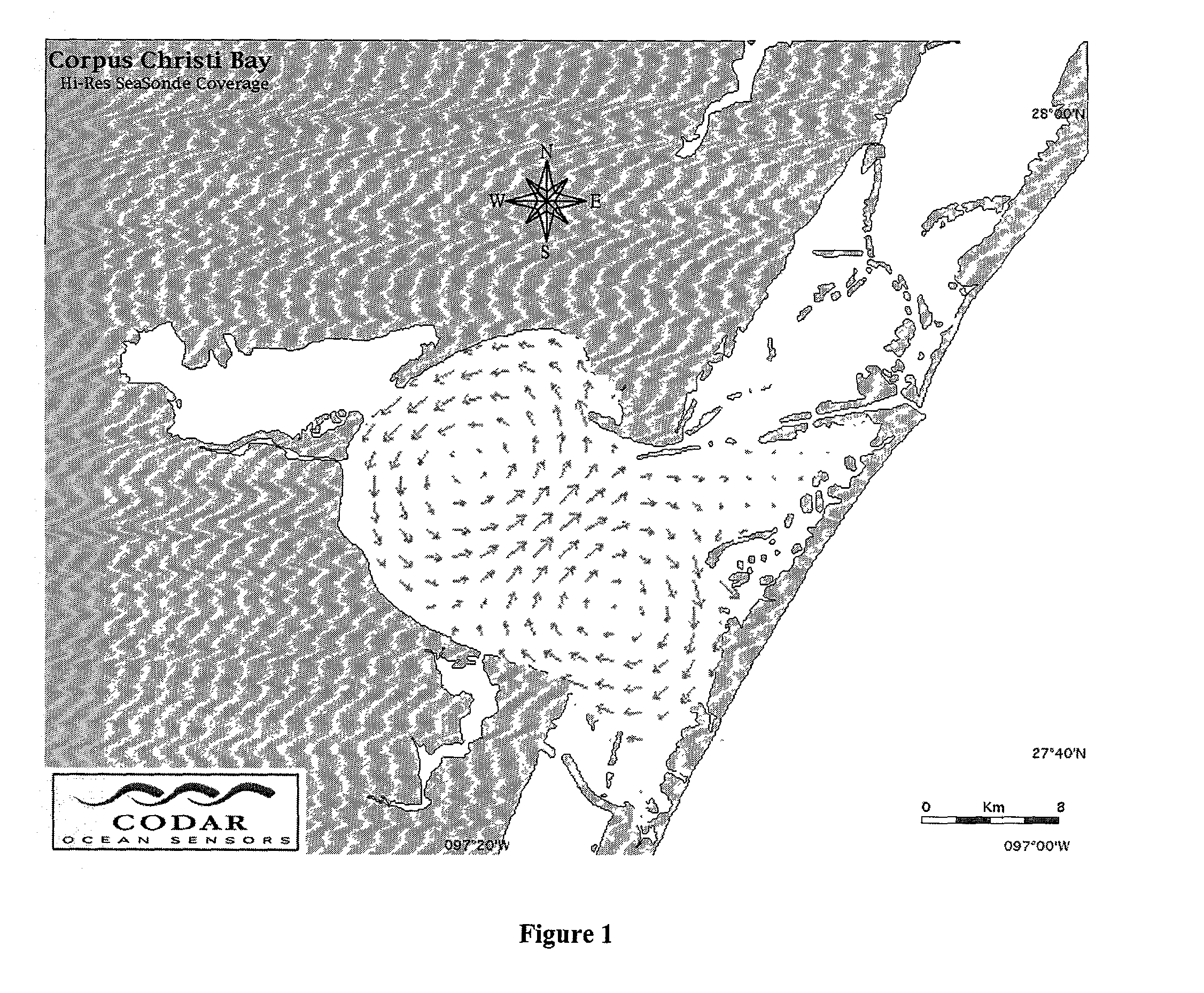
Systems and methods are described for synthesis of total surface current vector maps by fitting normal modes to radar data. A method includes extracting a scalar data set from a radar signal from a radar. Velocity components are calculated from the radar signal. The velocity components are fitted to a set of scalar eigenfunctions and eigenvalues to simultaneously solve for the best set of normal modes and the corresponding set of constants. The corresponding set of constants represent a corresponding set of amplitudes. The set of constants and the set of normal modes are used to create a two dimensional vector field used in creating a total vector map.
Owner:CODAR OCEAN SENSORS LTD
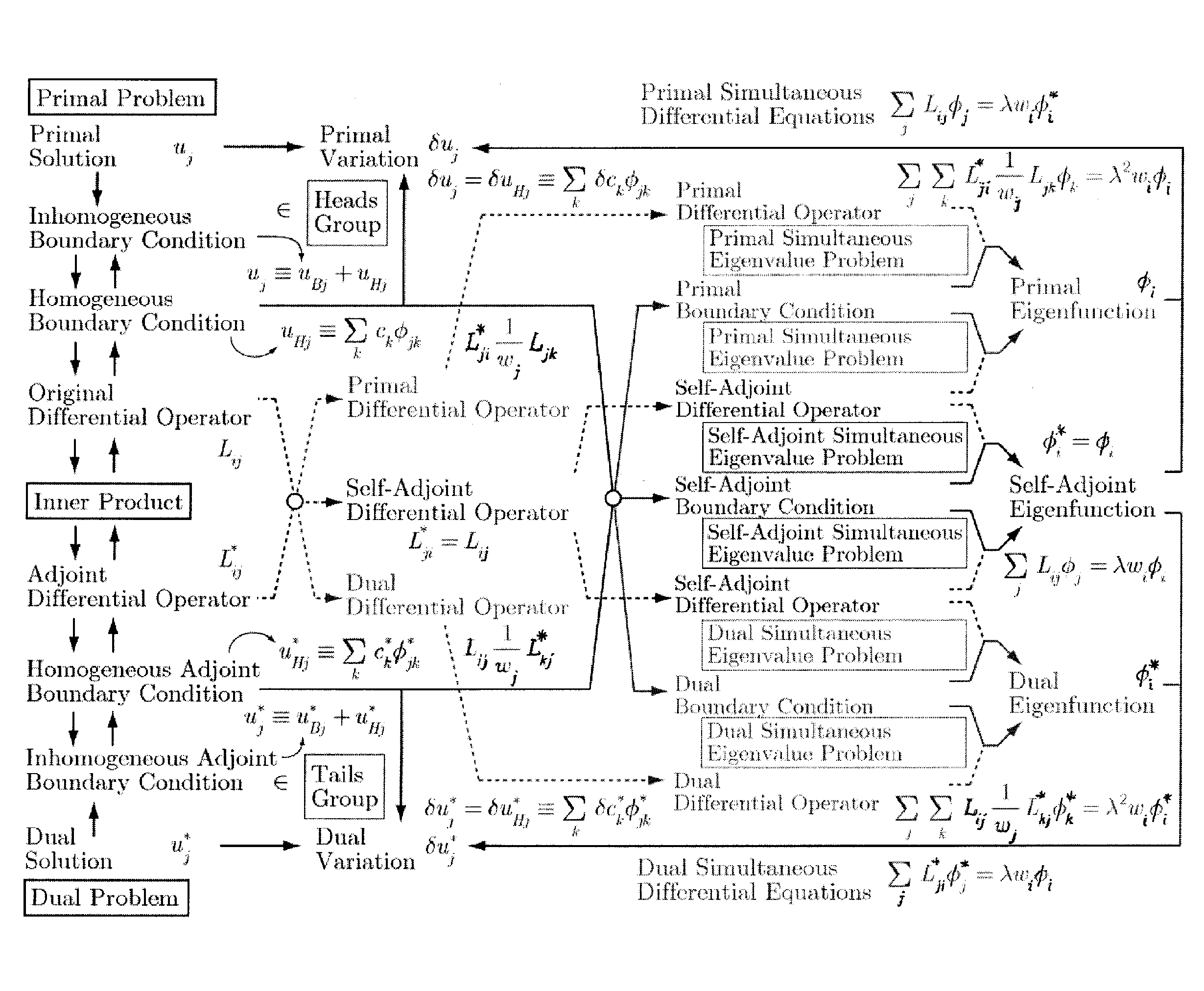
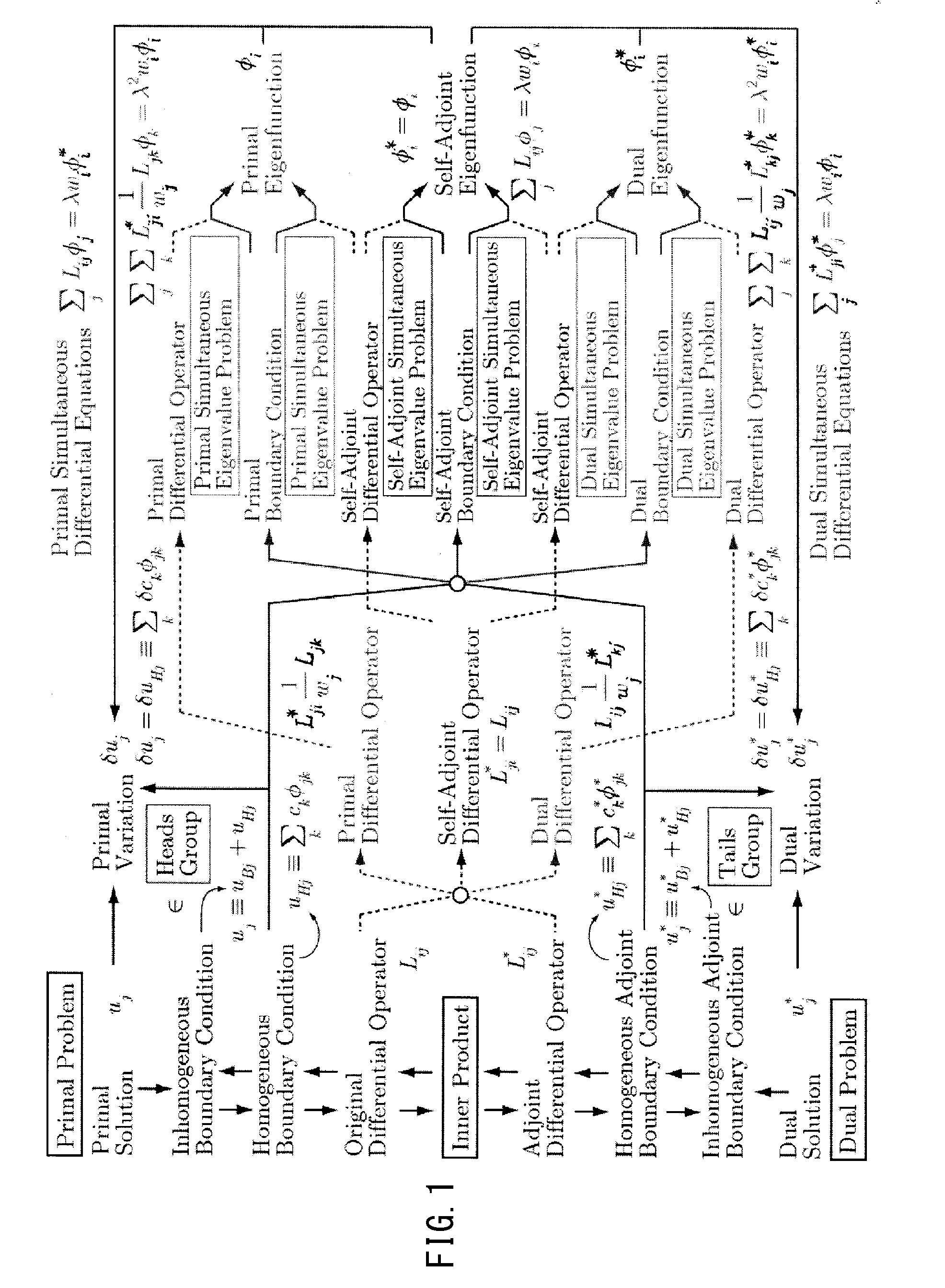
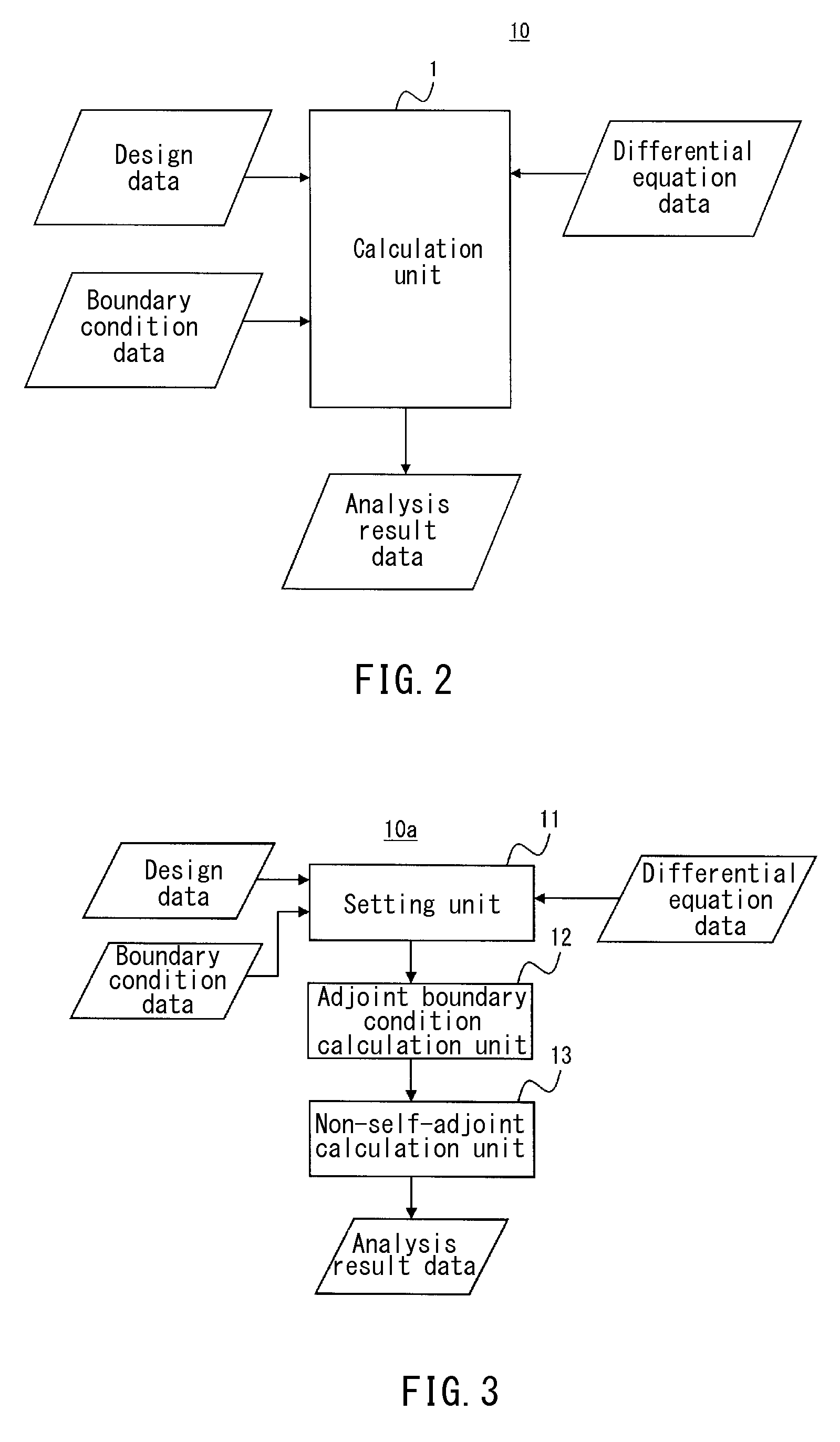
Analyzer, analysis method, and analysis program
InactiveUS20140379314A1Design optimisation/simulationCAD numerical modellingComputational physicsAnalysis method
The present invention enables calculation of a solution of a non-self-adjoint problem represented by simultaneous differential equations. An analysis device includes: a setting unit that sets an original differential operator of an analysis object and a boundary condition of variables; an adjoint boundary condition calculation unit that calculates an adjoint boundary condition from the boundary condition; and a non-self-adjoint calculation unit that calculates a primal differential operator and a dual differential operator from the original differential operator, and determines a primal eigenfunction and a dual eigenfunction by using primal simultaneous differential equations and dual simultaneous differential equations, as well as the boundary condition and the adjoint boundary condition, thereby calculating a solution of simultaneous differential equations.
Owner:OSAKA UNIV
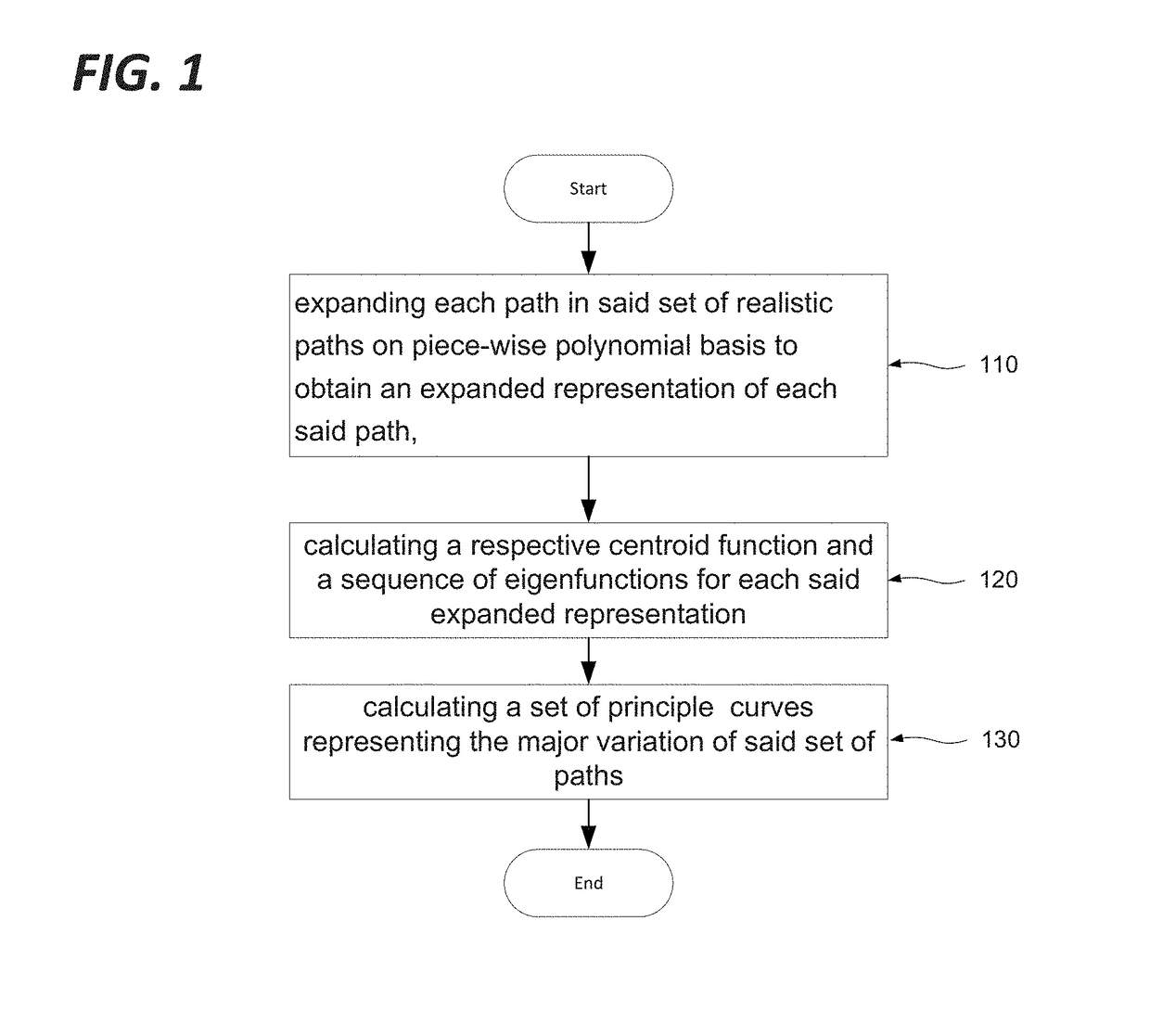
Random path generation upon functional decomposition
A method of defining a path model from a set of realistic paths is provided, where each path in the set of realistic paths is expanded on piece-wise polynomial basis, and a respective centroid function and sequence of eigenfunctions calculated for each expanded representation. A set of principle paths representing the major variation of this set of paths is obtained describing the variations of the set of realistic paths with respect to the centroid. The path model thus comprises a linear combination of said principle paths. The path model may be used as the basis for the generation of new curves having similar characteristics to the original set of realistic paths.
Owner:FRENCH CIVIL AVIATION UNIVERSITY
Synthesis of total surface current vector maps by fitting normal modes to single-site HF radar data
InactiveUS20030038744A1Easy to useReduce complexityICT adaptationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionData setNormal mode
Systems and methods are described for synthesis of total surface current vector maps by fitting normal modes to radar data. A method includes extracting a scalar data set from a radar signal from a radar. Velocity components are calculated from the radar signal. The velocity components are fitted to a set of scalar eigenfunctions and eigenvalues to simultaneously solve for the best set of normal modes and the corresponding set of constants. The corresponding set of constants represent a corresponding set of amplitudes. The set of constants and the set of normal modes are used to create a two dimensional vector field used in creating a total vector map.
Owner:CODAR OCEAN SENSORS LTD
Method and system for accurately and effectively solving eigenstate of large sparse matrix
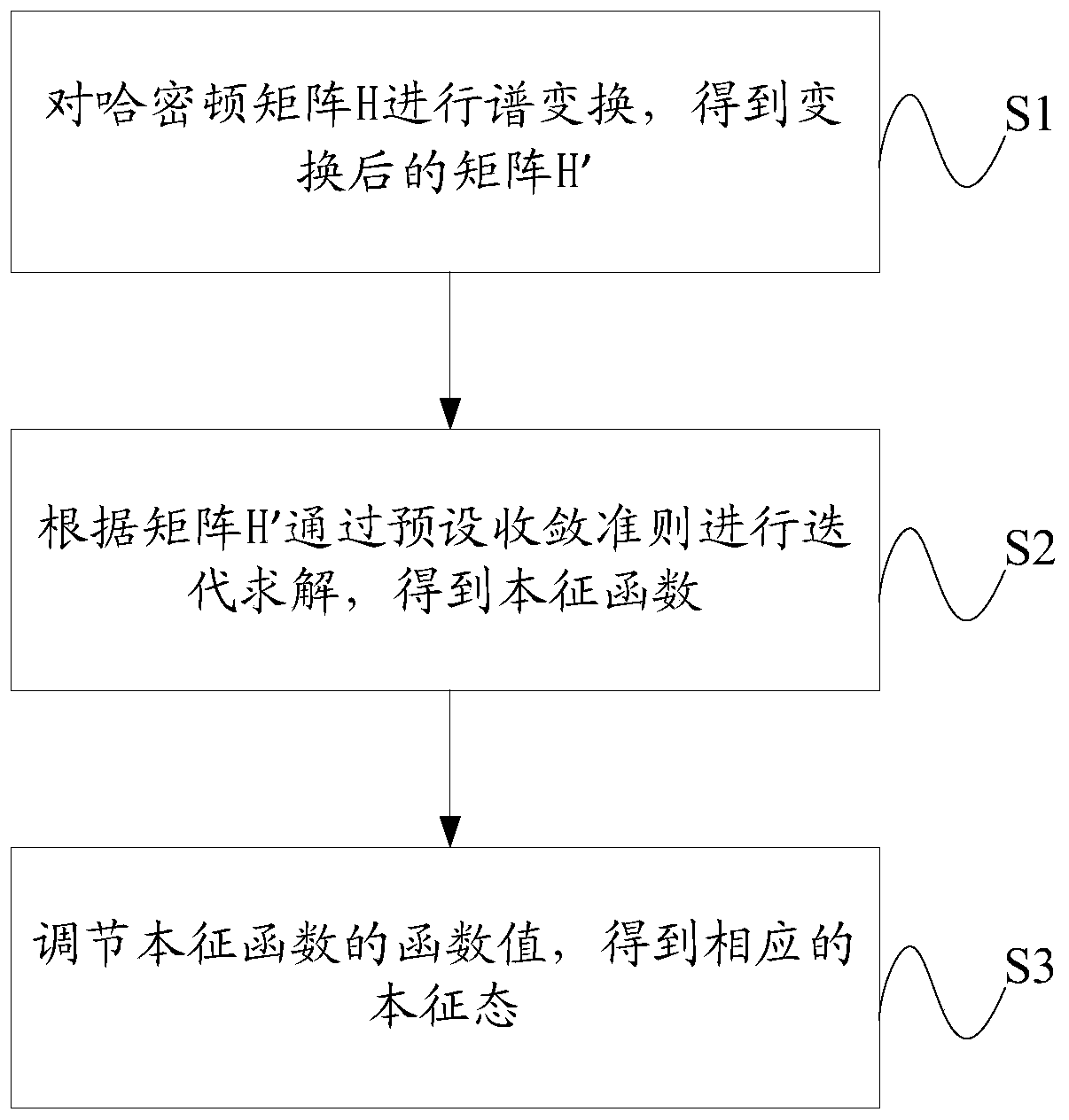
PendingCN111046333AImprove iterative solution efficiencyReduce dependenceComplex mathematical operationsAlgorithmSpectral transformation
The invention discloses a method and system for accurately and effectively solving the eigenstate of a large sparse matrix. The method comprises the steps: firstly enabling an original matrix H to beconverted into H' in a mode of spectral transformation, carrying out the psi'through an eigenfunction psi, and precisely giving the eigenvalue and the eigenfunction of the original matrix H through the quick solving of the psi'. According to the method, the solving of the eigenstate is an iterative solving process; according to the method, after an initial parameter is given, self-adjustment is carried out for iterative solving, on one hand, the dependence of the solving process on the initial value is reduced, on the other hand, the convergence rate is increased, the iterative solving efficiency of the matrix is greatly improved, universality is achieved for the bound state and the continuous state in the Hamiltonian quantity, and the method achieves the efficient and quick effects.
Owner:JIAXING UNIV
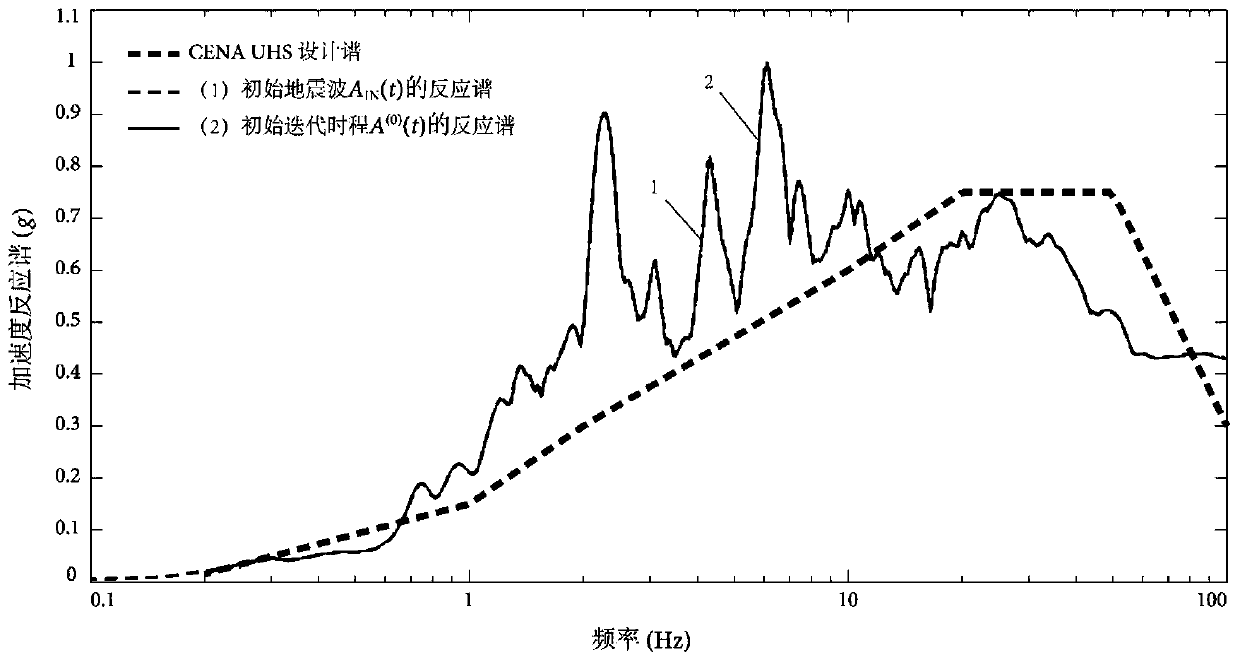
Method for adjusting influence matrix accurately matched with seismic wave and target response spectrum
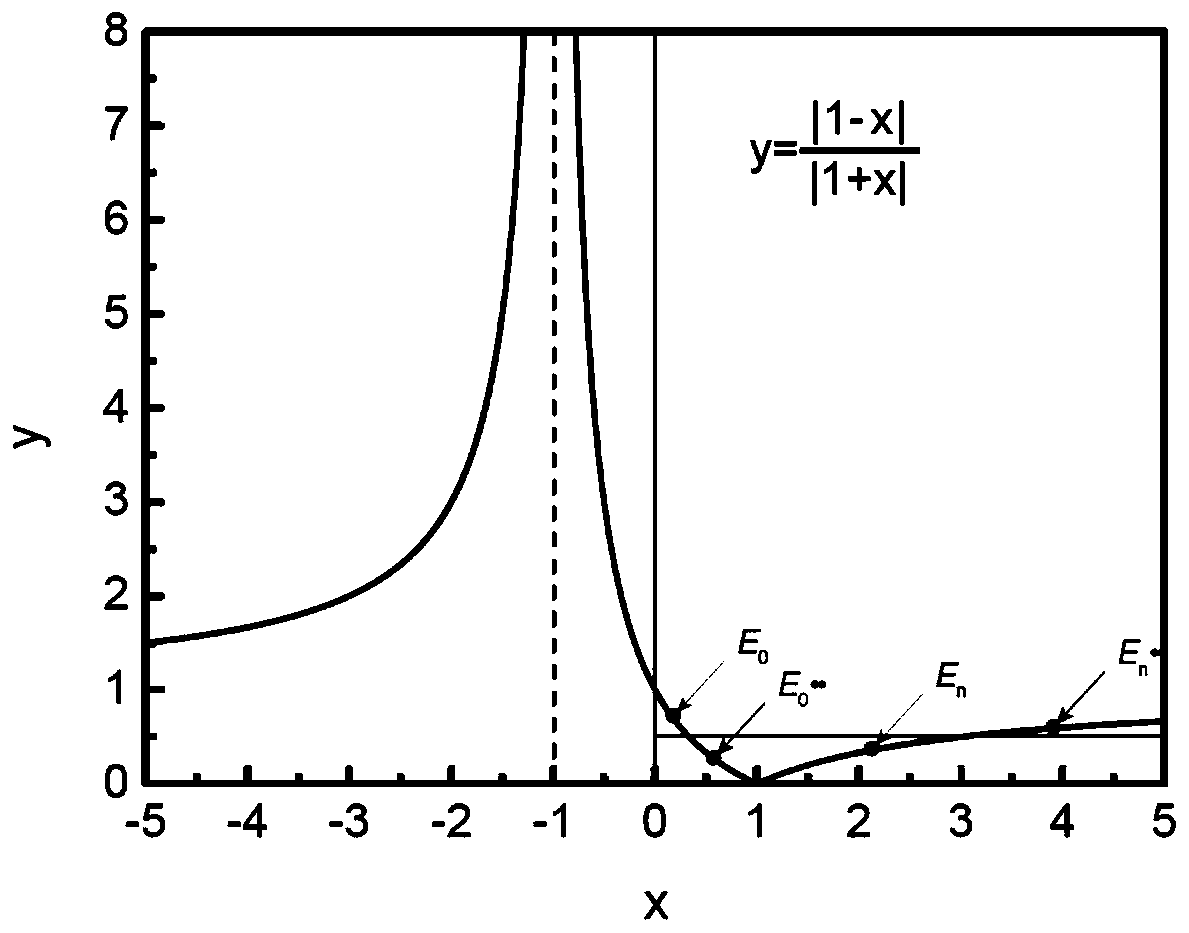
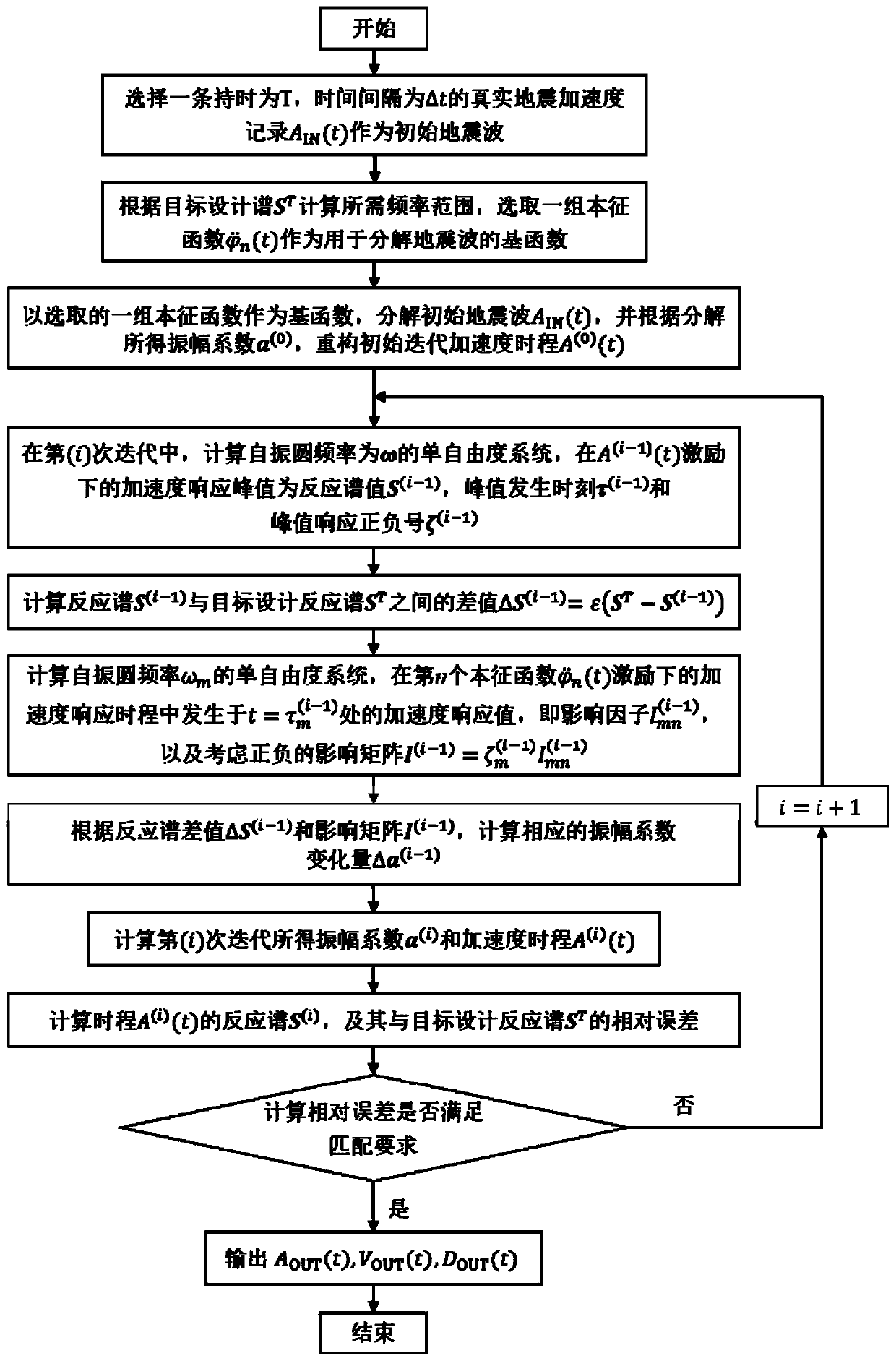
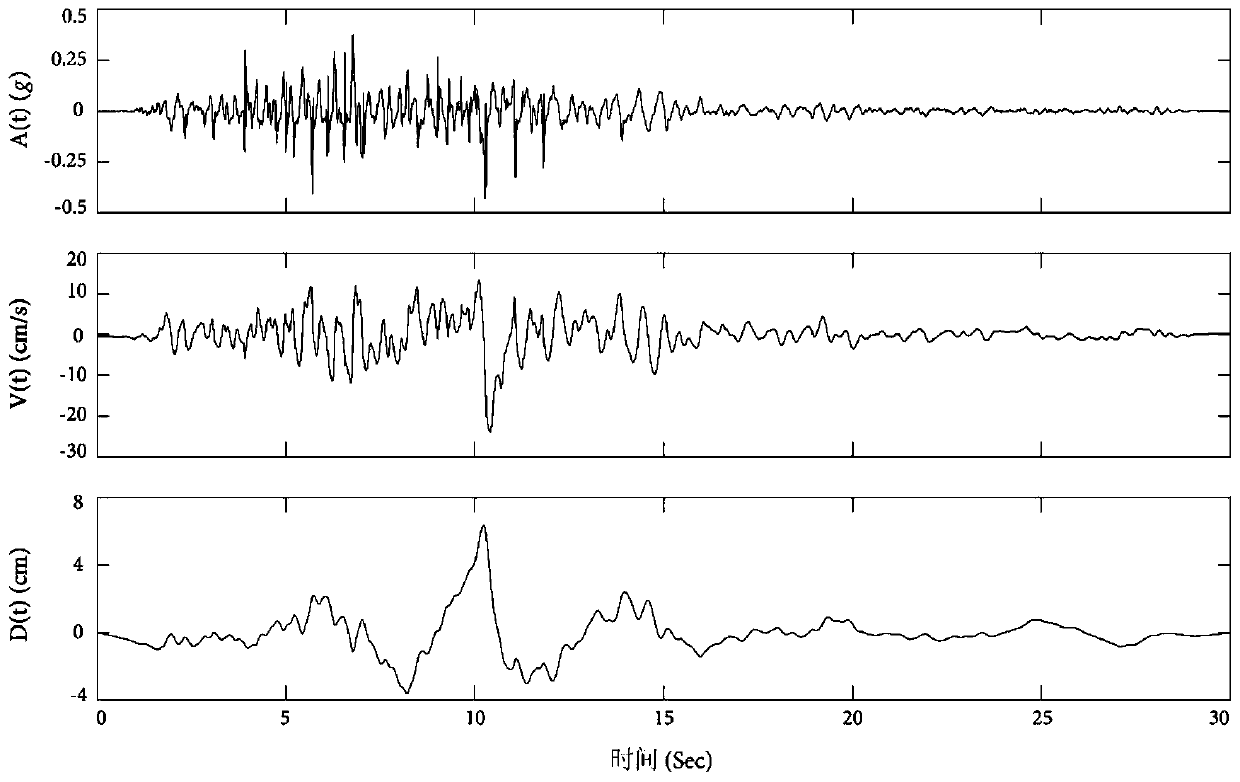
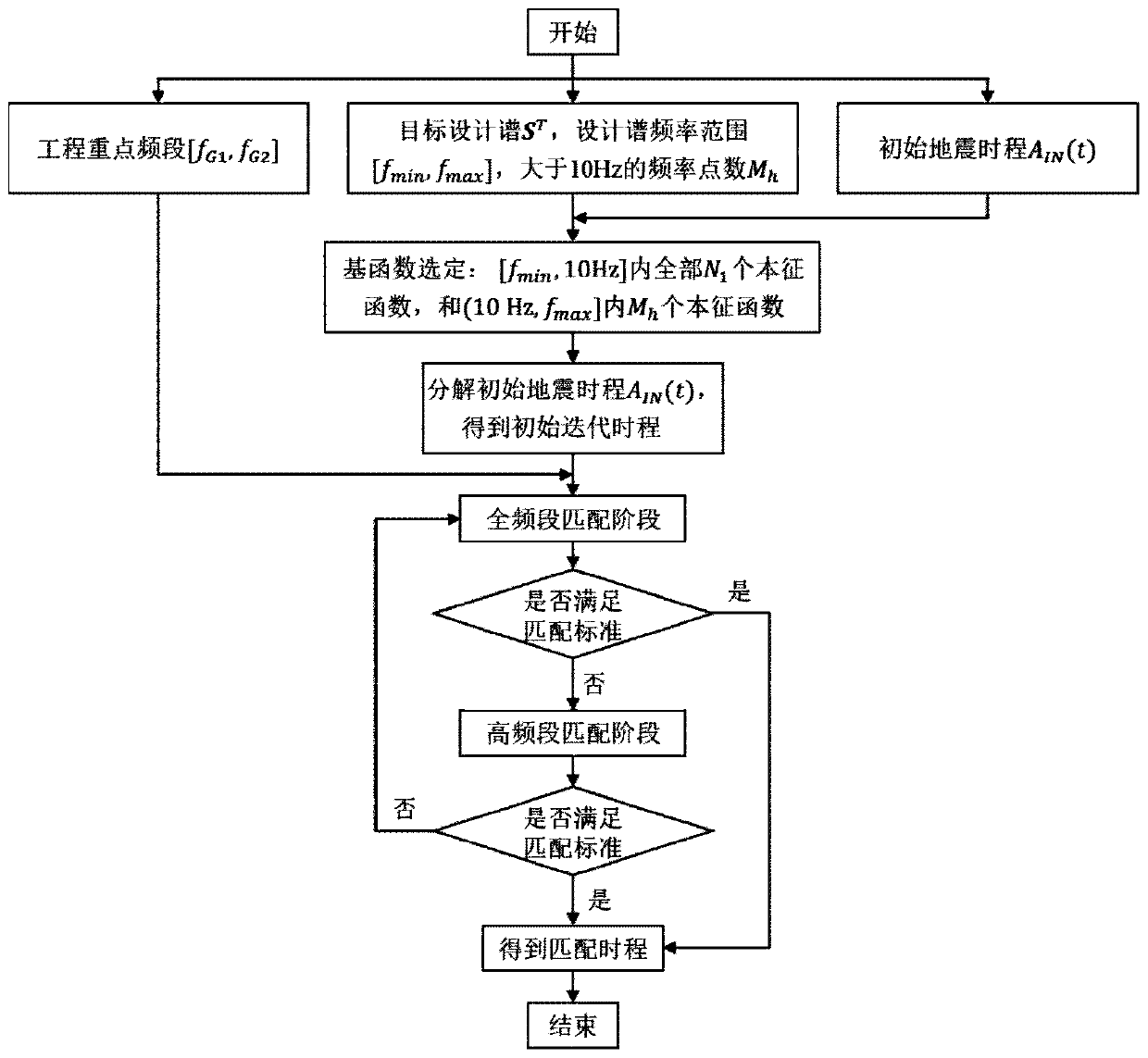
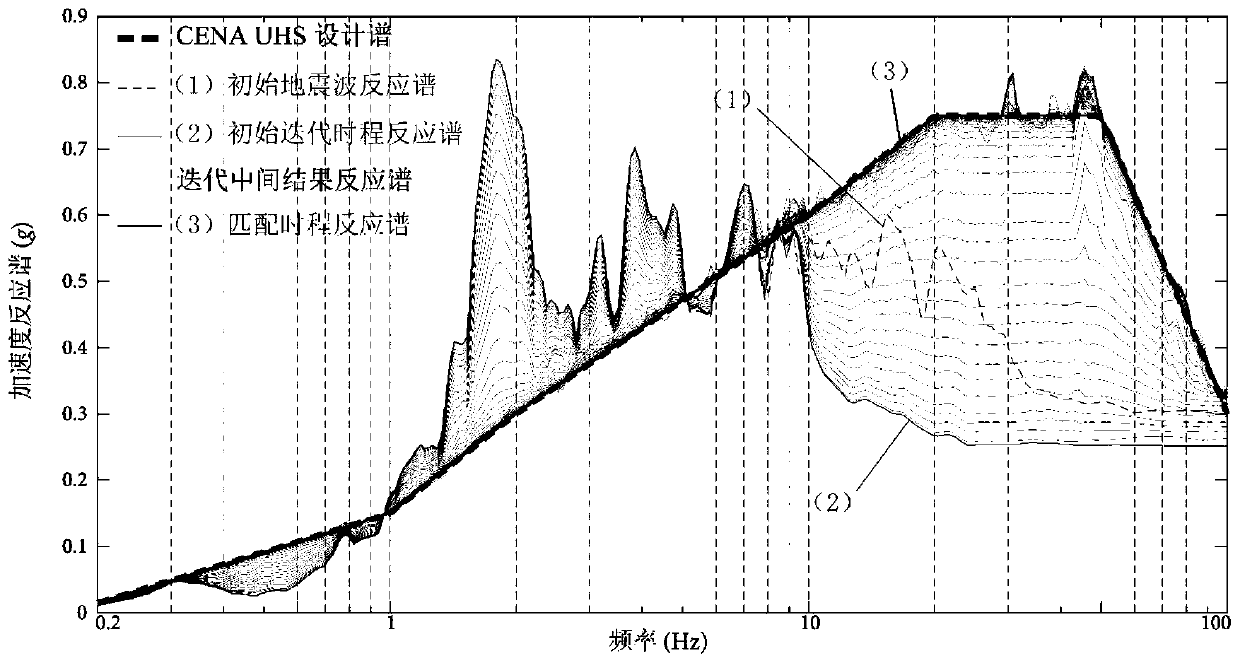
ActiveCN110020400AImprove matchImprove computing efficiencyVibration testingComplex mathematical operationsTarget ResponseIntrinsic function
The invention discloses a method for adjusting an influence matrix of accurate matching of seismic waves and a target response spectrum. The method comprises introducing an intrinsic function of a six-order differential equation to decompose initial seismic waves; obtaining initial amplitude coefficients in one-to-one correspondence with the intrinsic functions; in each time of iterative computation, calculating the response spectrum of the seismic wave reconstructed by the intrinsic function by using the Duhamel integral; calculating the contribution value of each intrinsic function to the reaction spectrum at each calculation frequency. The method has the advantages that the contribution of each intrinsic function to the calculation of the reaction spectrum can be adjusted by adjusting the amplitude coefficient of the intrinsic function, so that the calculation of the reaction spectrum is uniformly and consistently close to the standard reaction spectrum in each iteration calculation, and the purpose of matching the calculation of the reaction spectrum with the target design reaction spectrum is finally achieved. According to the method, the iteration process is monotonous and convergent, so that the time-history dynamic response analysis result of the important engineering structure has high precision and reliability, and the discreteness and the time consumption are remarkably reduced.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
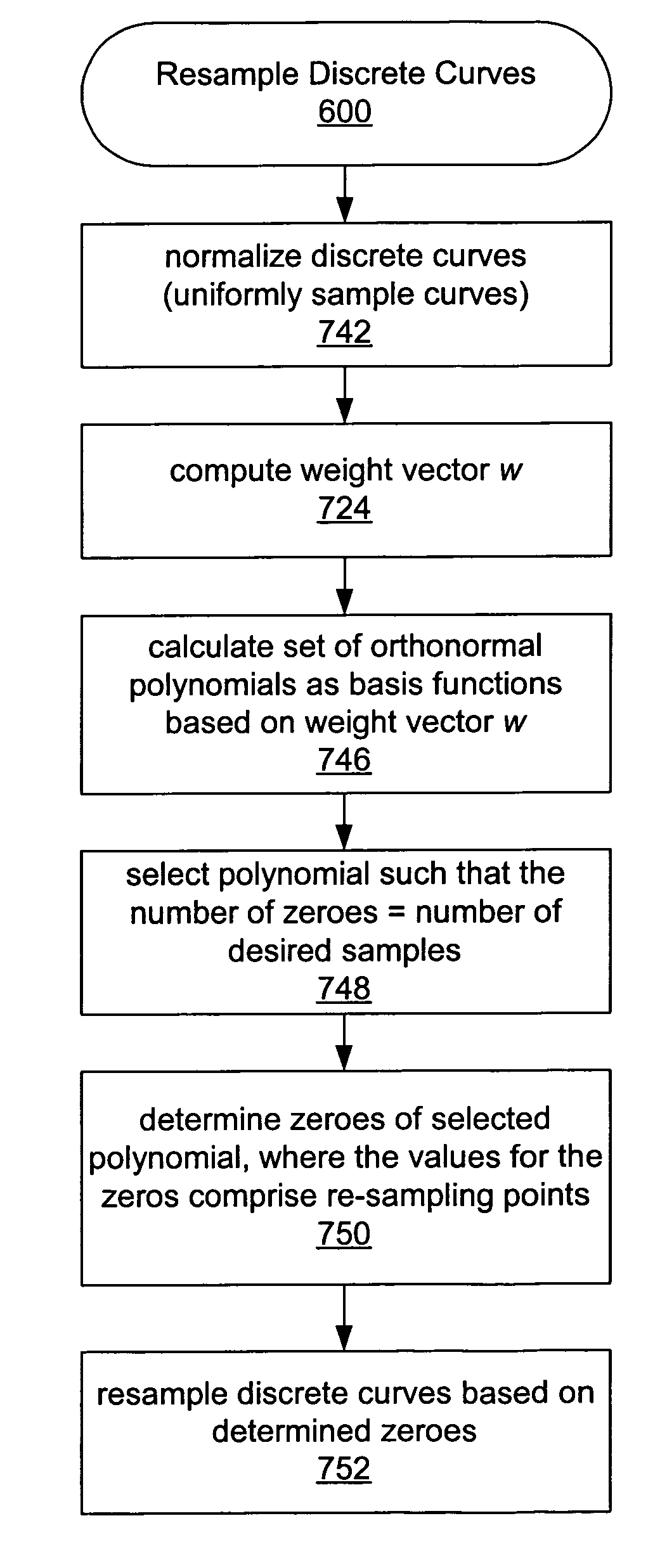
Efficient re-sampling of discrete curves
ActiveUS7120301B2Small sample sizeEfficiently re-sampleCharacter and pattern recognitionData setCurve matching
System and method for re-sampling discrete curves, thereby efficiently characterizing point sets or curves in a space. The method may also provide improved means for mapping point sets or curves to new point sets or curves for curve matching. A weight vector or function is determined based on a plurality of discrete curves, e.g., from one or more template data sets or images. The weight function enhances differences between weighted discrete curves. A set of orthonormal polynomials is determined based on the computed weight function, where the set of orthonormal polynomials comprises a set of orthogonal eigenfunctions of a Sturm-Liouville differential equation. Values for a plurality of zeros for one of the set of orthonormal polynomials is determined that comprise resampling points for the plurality of discrete curves. Each of the plurality of discrete curves is resampled based on the determined values of the plurality of zeros.
Owner:NATIONAL INSTRUMENTS
System for optimization of method for determining material properties at finding materials having defined properties and optimization of method for determining material properties at finding materials having defined properties
InactiveUS20160188771A1Chemical property predictionComputation using non-denominational number representationMagnetic susceptibilityLinearity
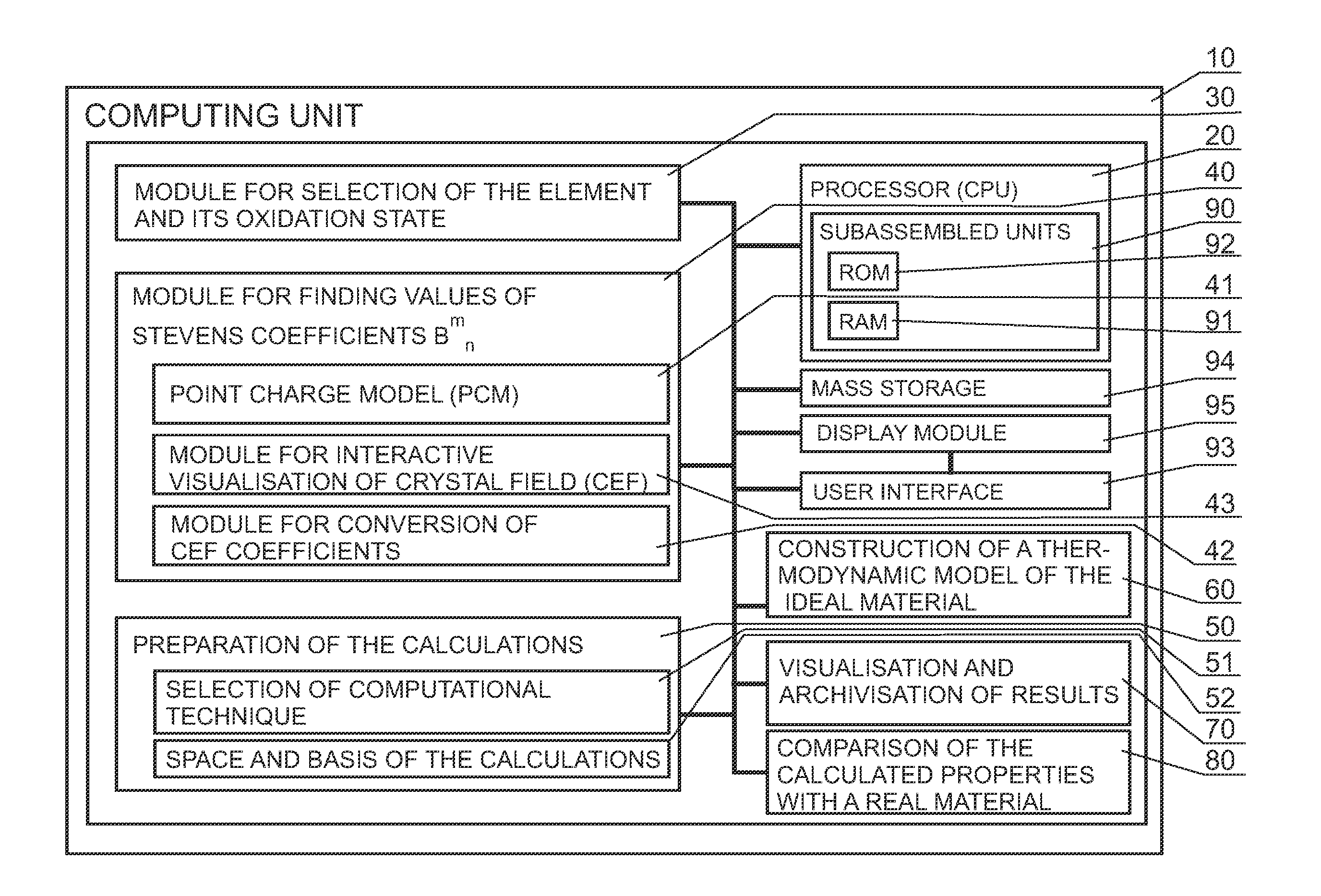
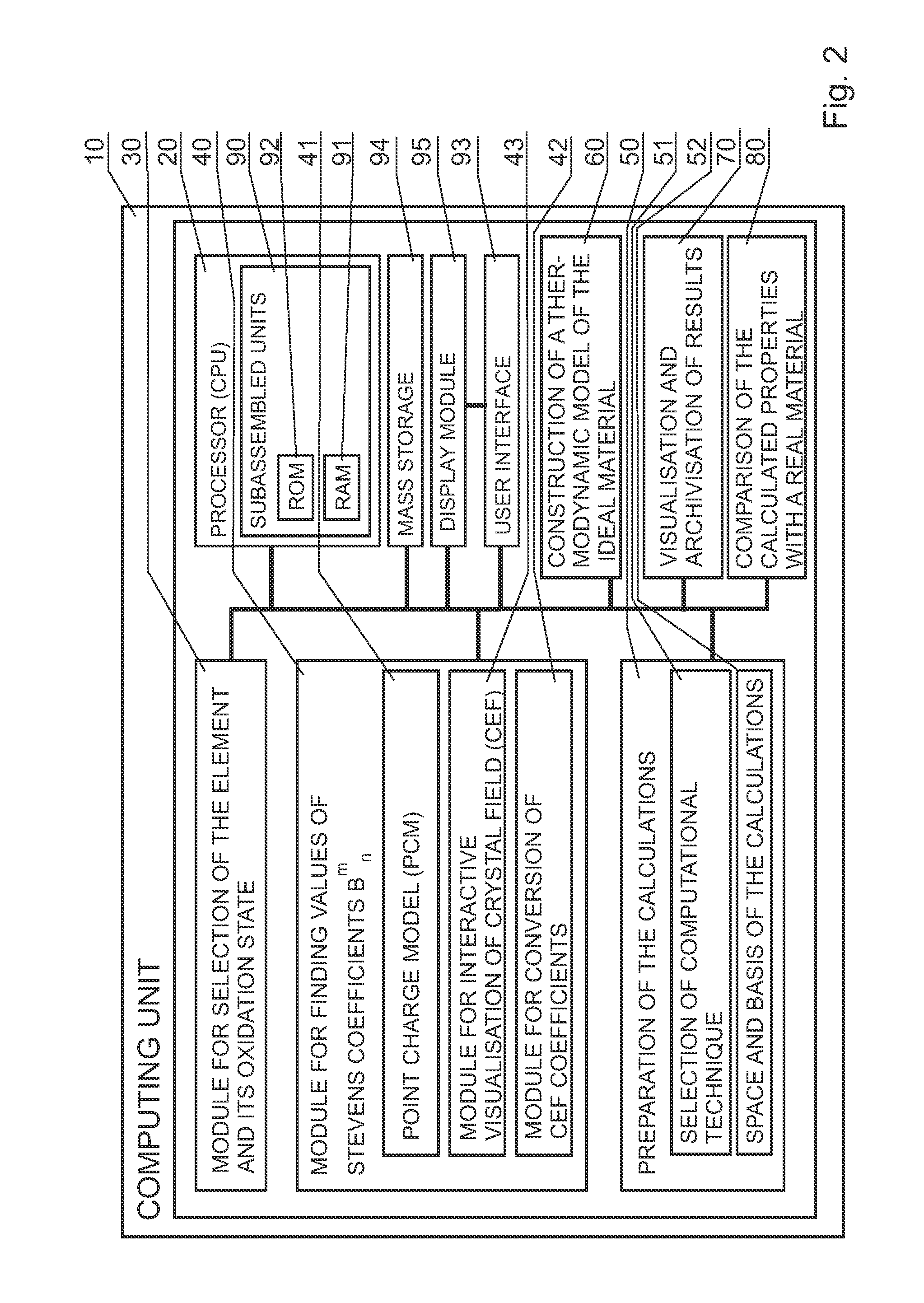
In a system for optimization of method for determining material properties when searching for materials having defined properties, comprising a computing unit with a processor and a device for presentation of data and calculation results, and with access to data on materials, and a testing unit carrying out tests on real materials and communicating with the computing unit, the computing unit having a module (60) for construction of a model of an ideal material, which comprises a module (64) for calculation of complete sets of pairs of the energy eigenvalues Ei (i=1 . . . n) and eigenfunctions being linear combinations of basis vectors, and a module (68) for calculation of courses of temperature dependencies of free energy, internal energy, entropy, magnetic susceptibility, calculated for a field applied along (x and z) or (x, y and z) directions, and Schottky specific heat in order to determine the calorimetric, electron and magnetic properties of a material containing ions in the defined environment of the Crystal Electric Field (CEF).
Owner:WLADYSLAW WLODARCZYK IGLOO
Method for acquiring system eigenfunction and signal feature value
InactiveCN100554917CStructural/machines measurementFrequency analysisTime–frequency analysisFourier transform on finite groups
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
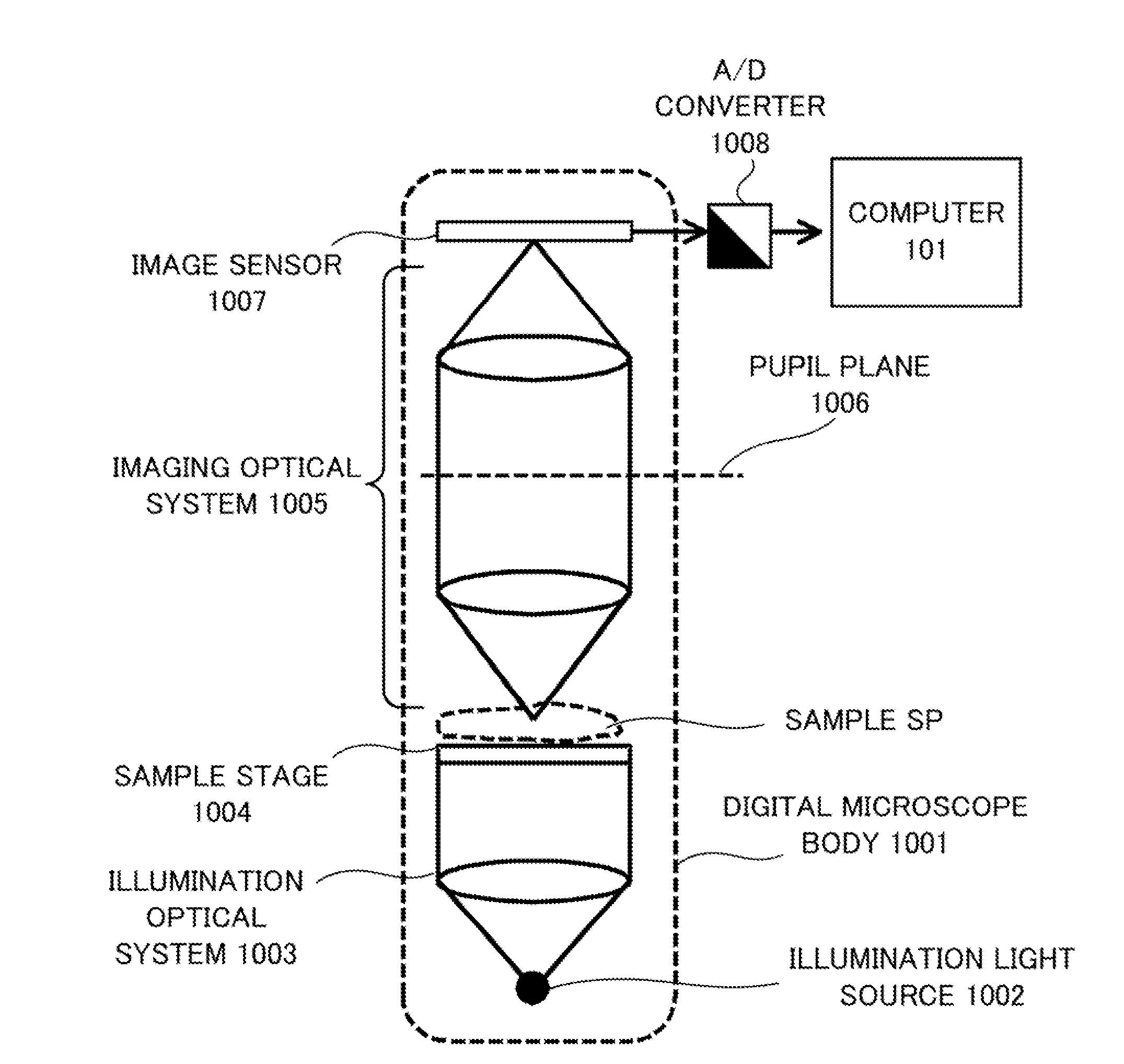
Finite-dimension eigen frequency domain analysis method for optical imaging system
The invention discloses a finite-dimension eigen frequency domain analysis method for an optical imaging system. The finite-dimension eigen frequency domain analysis method comprises the following steps: a first step: solving a two-dimensional light intensity transmission matrix of an optical system according to a PSF matrix and a one-dimensional object vector of the optical system; a second step: solving a characteristic value vector of the two-dimensional light intensity transmission matrix by using a QR decomposition method, and solving an eigen function vector group of the two-dimensional light intensity transmission matrix by using a power method; and a third step: solving object and image finite-dimension eigen spectral vectors by means of the object vector, an image vector and the eigen function vector group. The finite-dimension eigen frequency domain analysis method for the optical imaging system is used for overcoming the defects of the Fourier optical frequency-domain imaging analysis method in theory and numeral value calculation, providing the solving method of the object and image eigen spectral vectors and realizing that the object eigen spectral vector multiplying by the characteristic value vector of the optical imaging system is equal to the image eigen spectral vector.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Computer readable medium and exposure method
InactiveUS8411253B2Short timeSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDigital computer detailsSingular value decompositionPupil function
Owner:CANON KK
Self correcting adaptive low light optical payload
ActiveUS10341565B2Reduce contrastHigh rateTelevision system detailsImage analysisSpectral bandsRelative motion
Methods and systems are disclosed for compensating for image motion induced by a relative motion between an imaging platform and a scene. During an exposure period, frames of the scene may be captured respectively in multiple spectral bands, where one of the spectral bands has a lower light level than the first spectral band, and contemporaneous frames include a nearly identical induced image motion. Image eigenfunctions are utilized to estimate the induced image motion from the higher SNR spectral band, and compensate in each of the multiple bands.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Improved influence matrix method for high-low frequency band alternation and target spectrum matching
ActiveCN110069836AReduce dimensionalityImprove matching accuracyGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationEigen frequencyMatrix method
The invention discloses an improved influence matrix method for high-low frequency band alternation and target spectrum matching, which comprises the following steps: all intrinsic functions are selected in a low frequency band and intrinsic functions of which the intrinsic frequencies are in one-to-one correspondence with frequency calculation points of a target spectrum in a high frequency bandas a group of primary functions to decompose seismic waves, so that the dimension of an influence matrix is greatly reduced; the influence of different frequency components on each other and the difference of contribution values to the target spectrum are considered, and the reaction spectrum is gradually close to the target design spectrum within the full frequency range by alternately adjustingthe amplitude coefficients of the full-band and high-band intrinsic functions, so that a very good matching effect can be achieved within the key attention frequency range of a project. The method overcomes the defects that in an existing response spectrum matching influence matrix method, the influence matrix dimension is large in the iteration process, the calculation efficiency is low, and different requirements of high frequency bands and low frequency bands cannot be met at the same time. Therefore, the dynamic time-history response analysis efficiency of the important engineering structure is greatly improved, and the precision and reliability are high.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Auditory eigenfunction systems and methods
An “auditory eigenfunction” approach is provided for auditory language design, implementation, and rendering optimized for human auditory perception. The auditory eigenfunctions employed approximate solutions to an eigenfunction equation representing a model of human hearing, wherein the model comprises a frequency domain bandpass operation with a approximating the frequency range of human hearing and a time-limiting operation in the time domain approximating the time duration correlation window of human hearing. The method can be used to implement entirely new auditory languages, or modification to existing auditory languages, which are in various ways performance optimized for human auditory perception, either with or without the constraints of human vocal-tract rendering. The method can also be used, for example, to implement traditional speech synthesis, and can be useful in speech synthesis involving rapid phoneme production. The method could also be used to implement various other types of user machine interfaces.
Owner:NRI R&D PATENT LICENSING LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com