Finite-dimension eigen frequency domain analysis method for optical imaging system
An optical imaging system and frequency domain analysis technology, applied in complex mathematical operations, special data processing applications, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as the inability to obtain numerical calculation results and the inability to use computer numerical calculations
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0032] The technical solution of the present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings, but it is not limited thereto. Any modification or equivalent replacement of the technical solution of the present invention without departing from the spirit and scope of the technical solution of the present invention should be covered by the present invention. within the scope of protection.
[0033] The present invention provides a finite-dimensional eigenfrequency domain analysis method for an optical imaging system, and the specific steps are as follows:
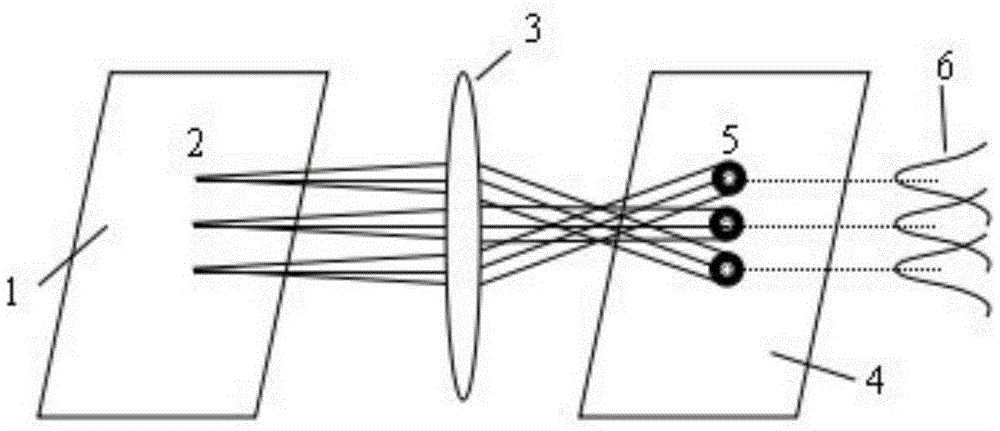
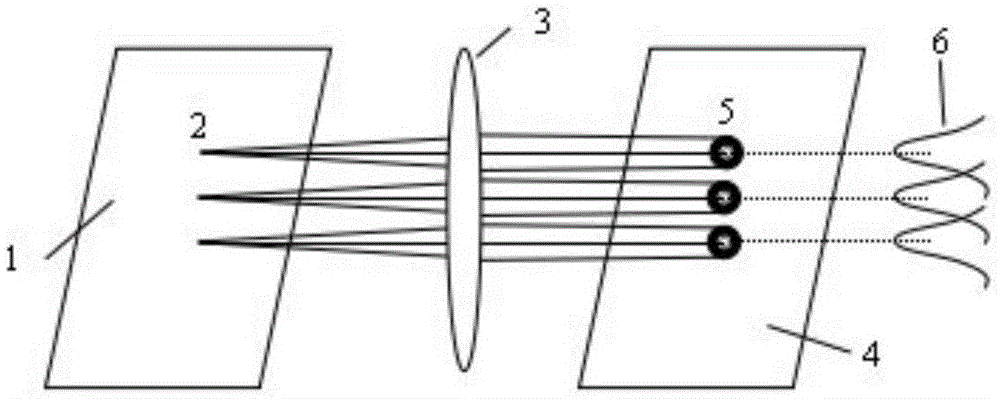
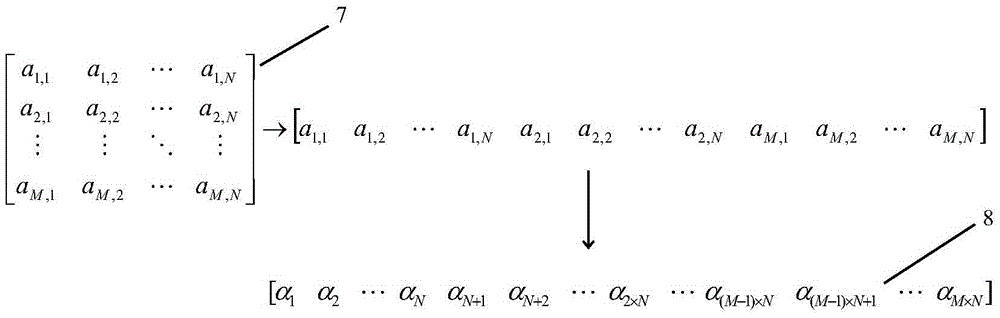
[0034] The first step: construction of two-dimensional light intensity transmission matrix.
[0035] 1) Construction of two-dimensional light intensity transmission matrix in the case of two-dimensional spatial domain imaging
[0036] The content of this part is similar to the principles described in the first and second steps in the specific implementations of CN104574315A and CN104360...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com