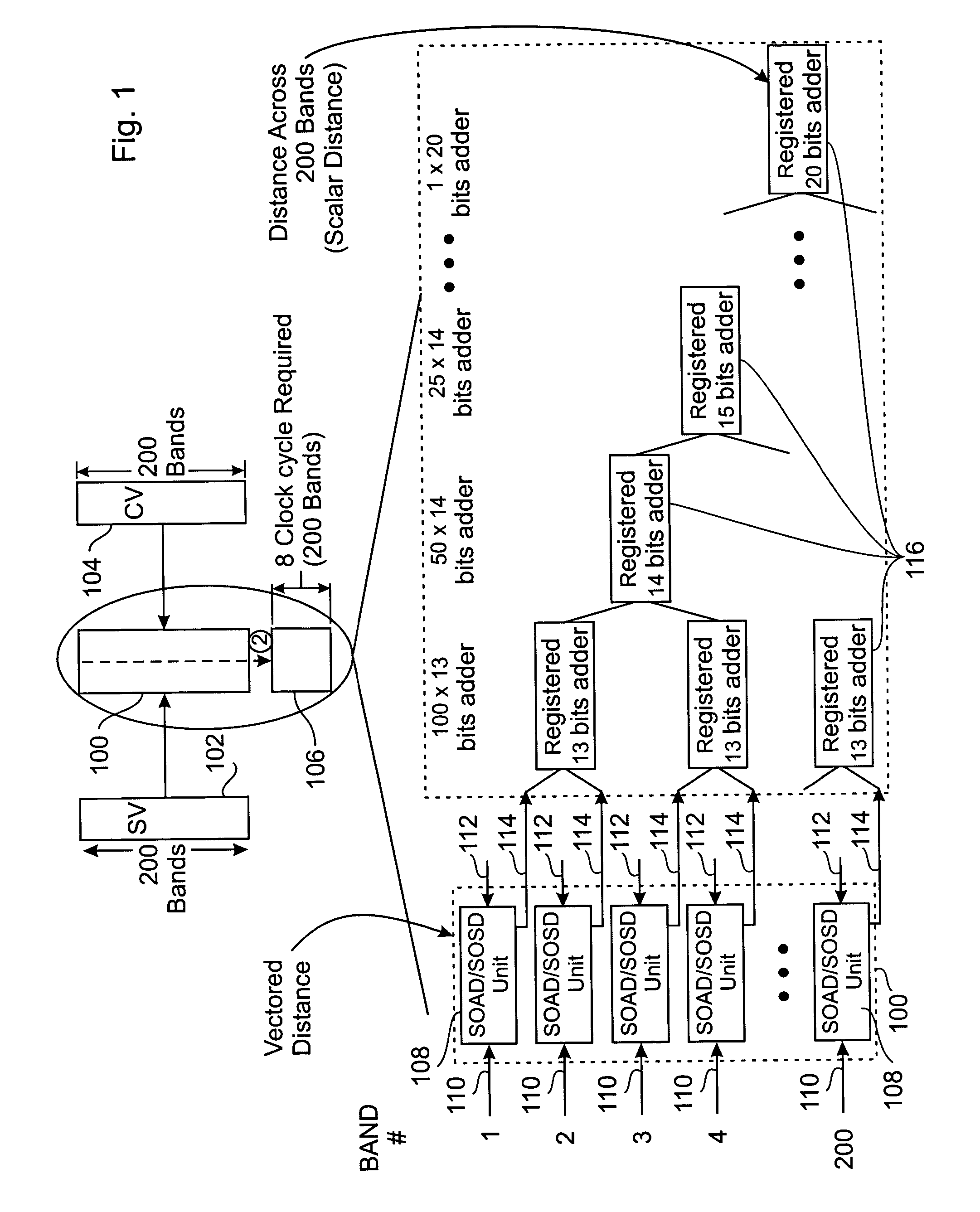
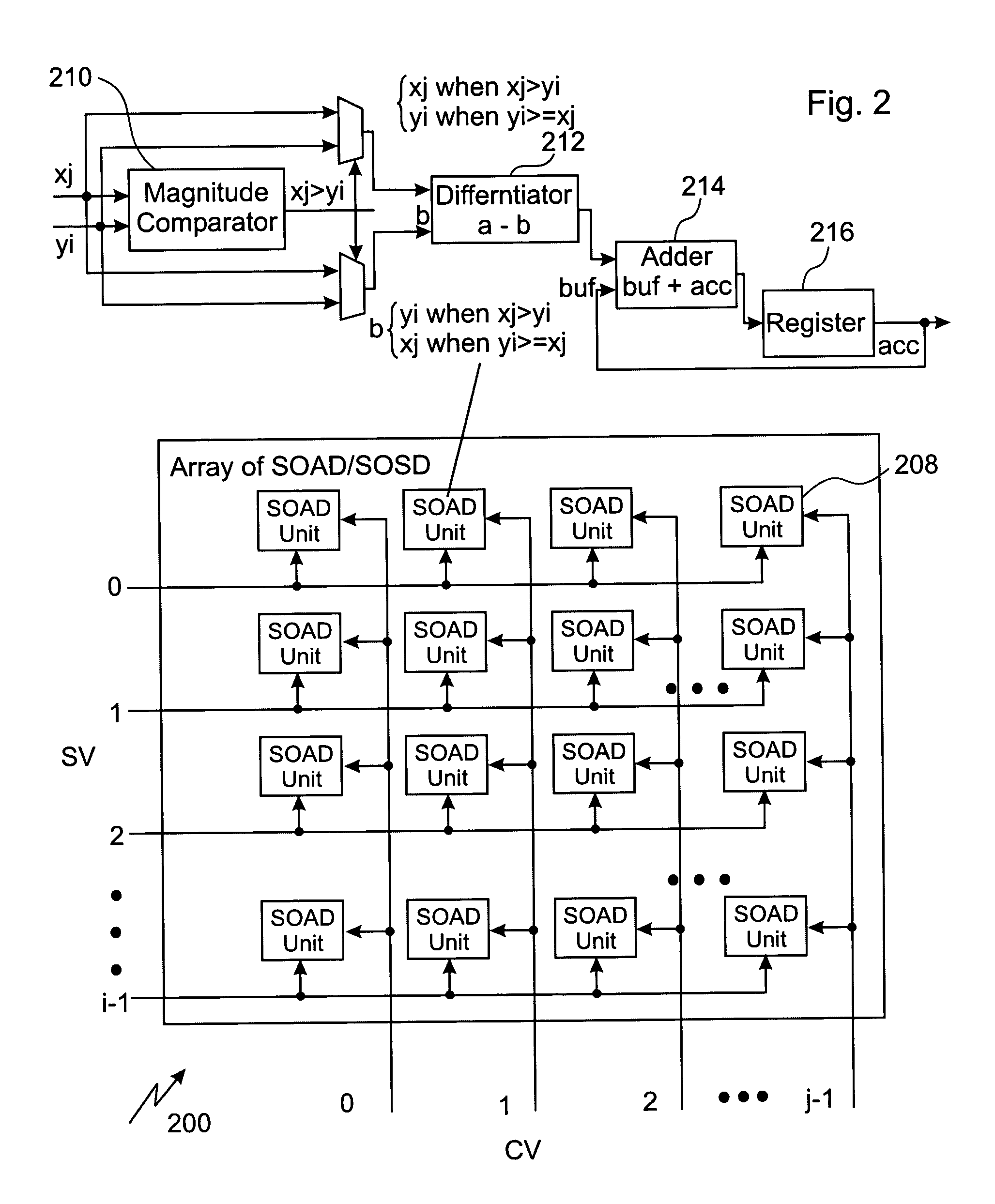
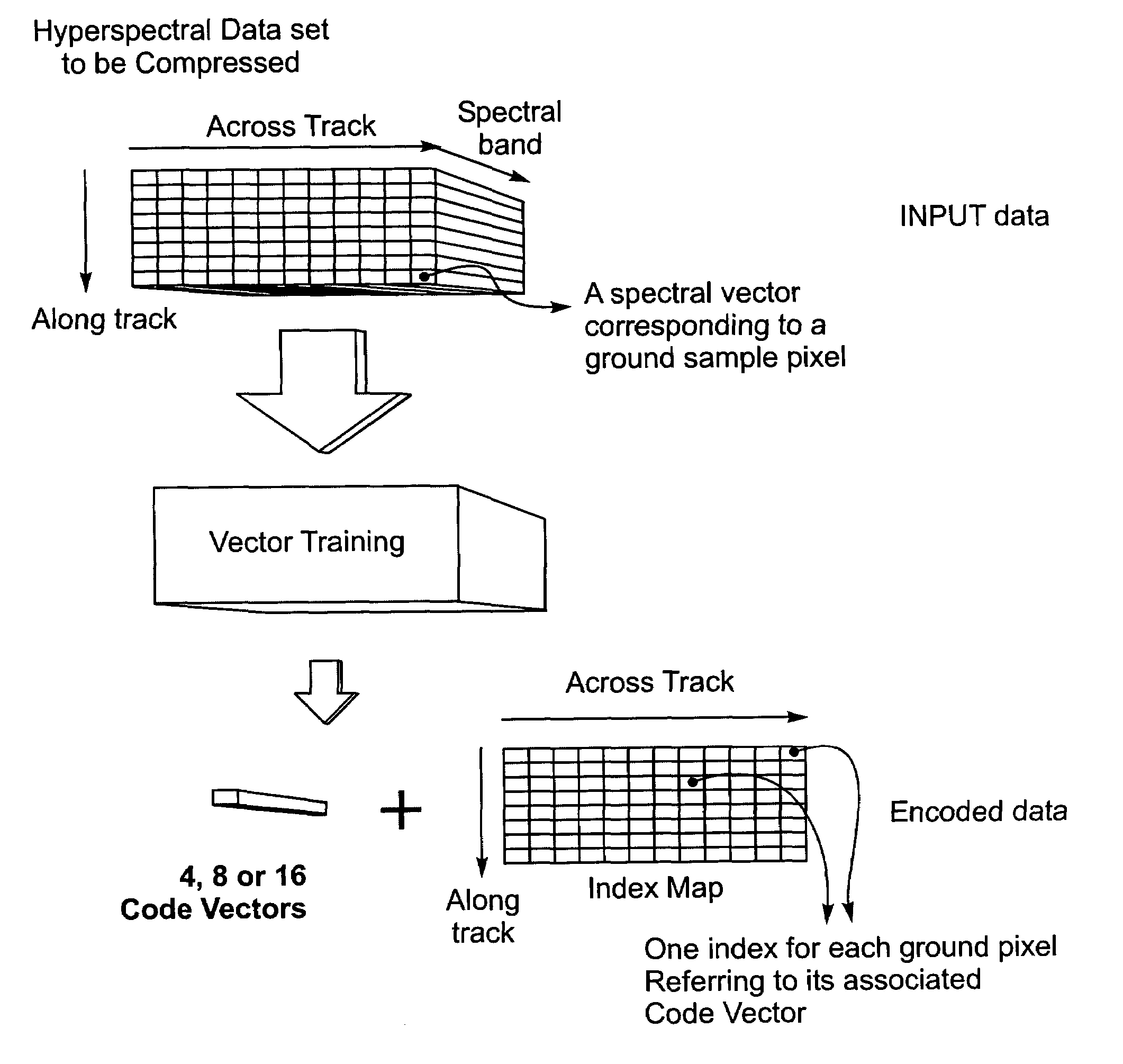
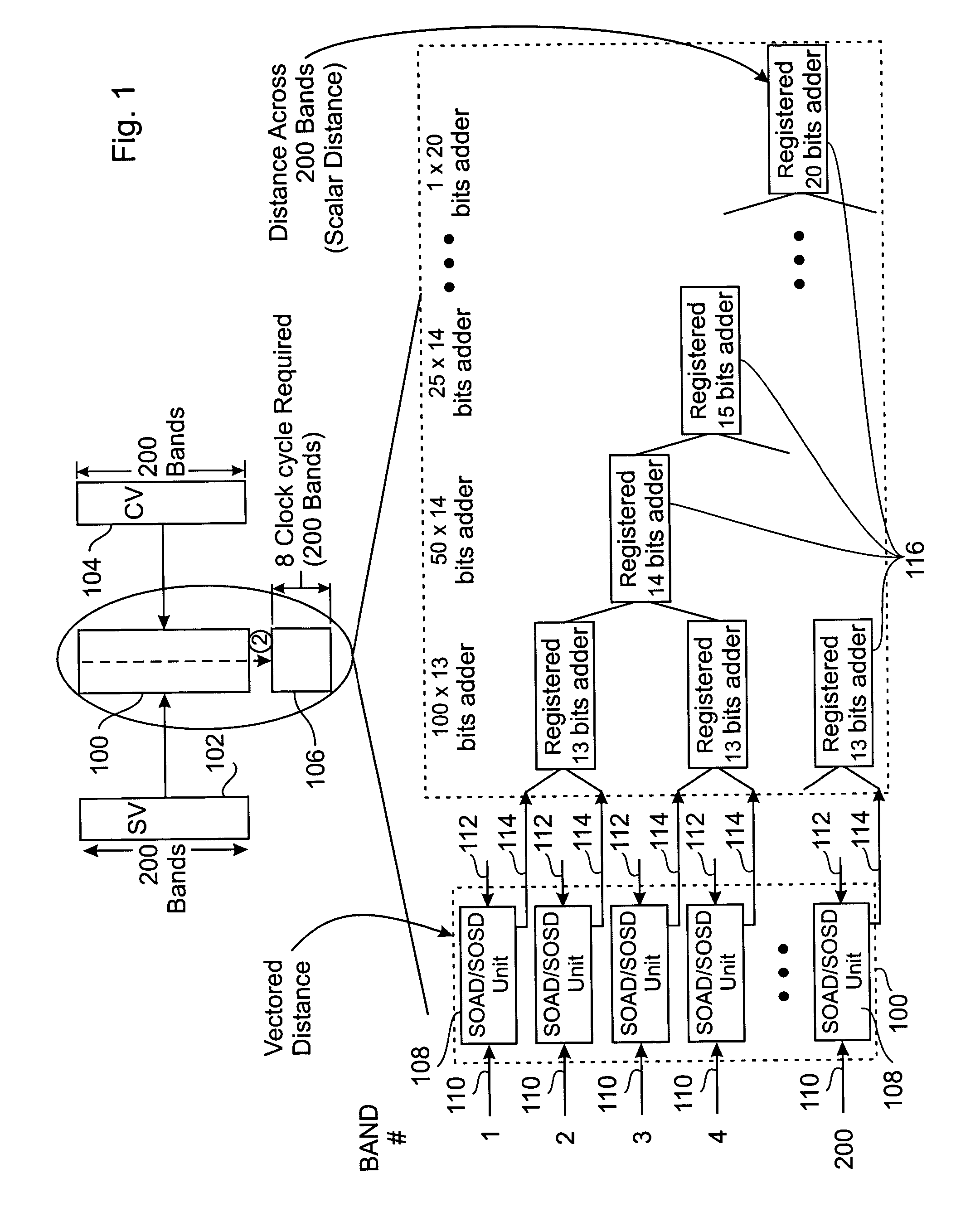
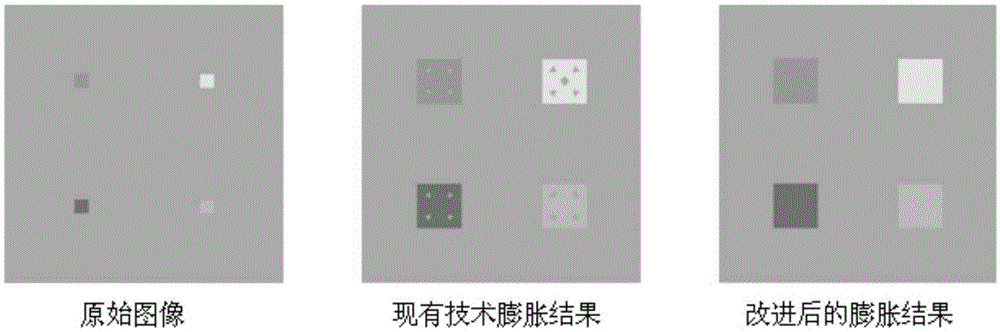
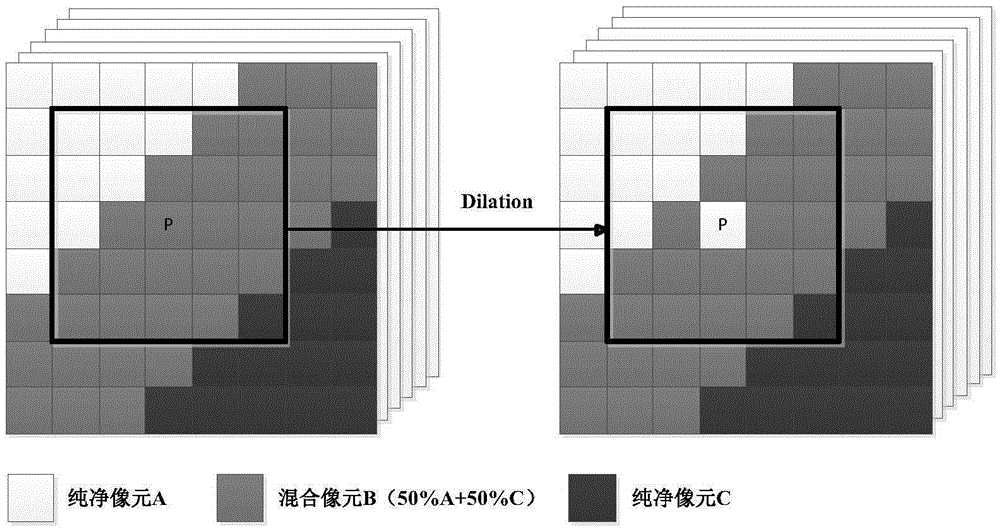
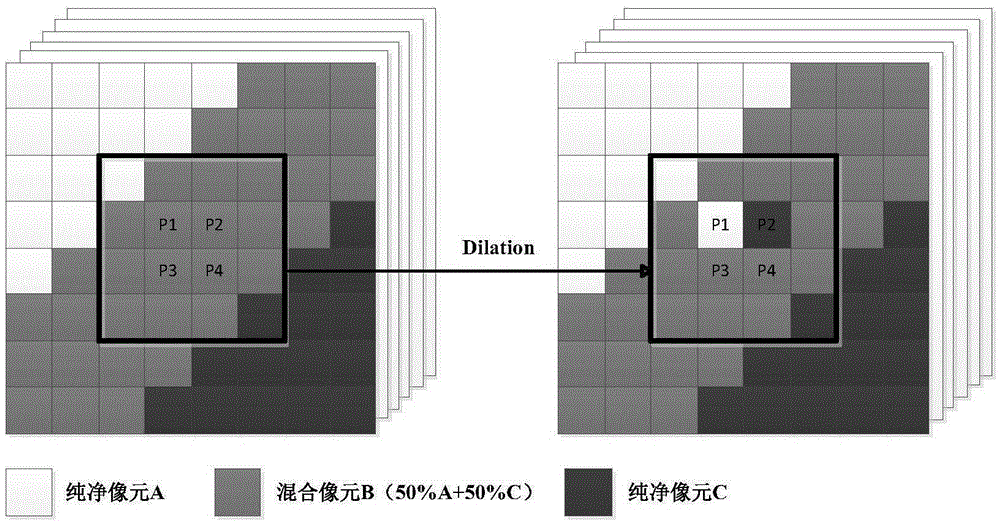
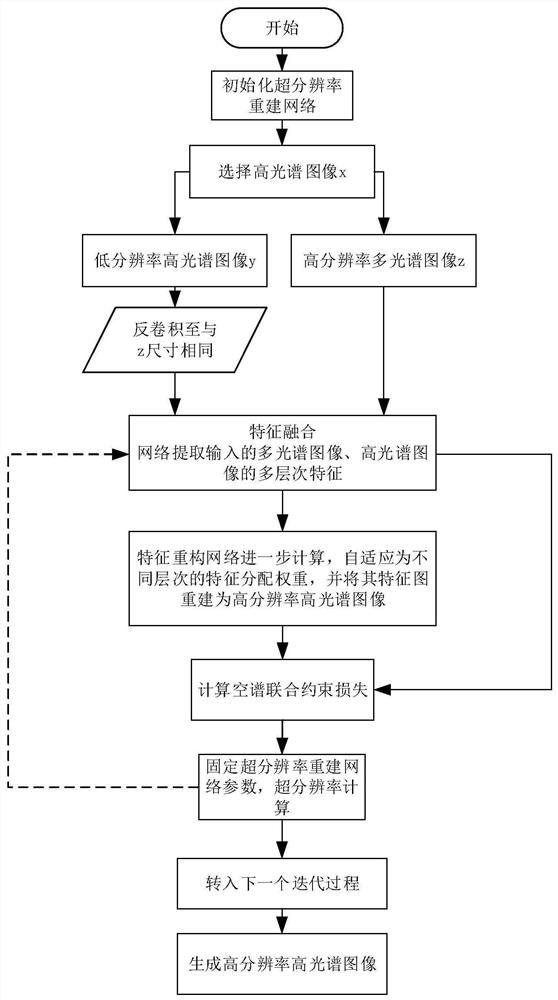
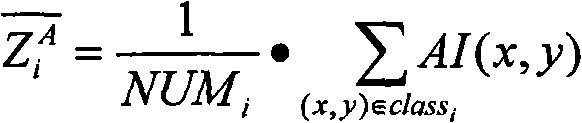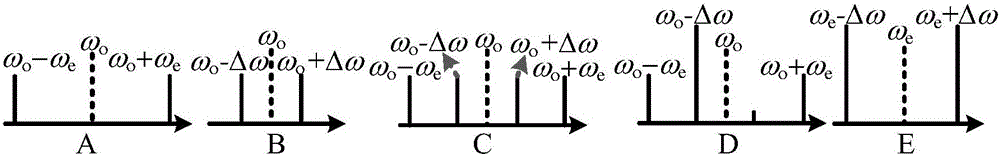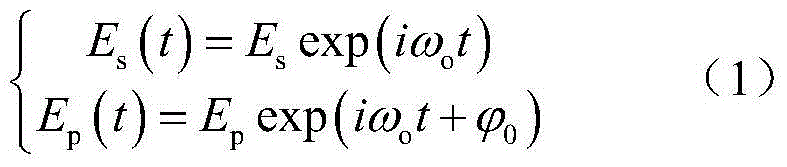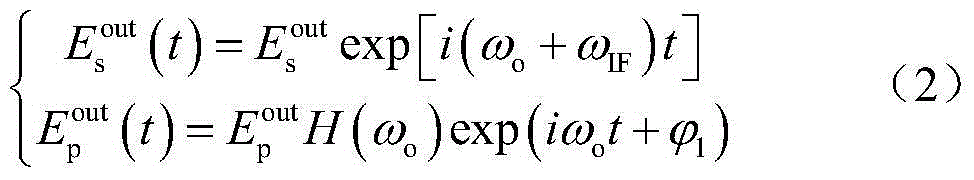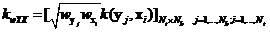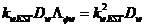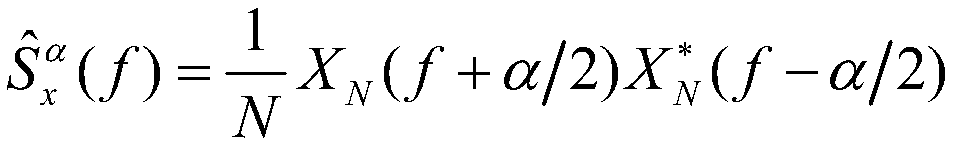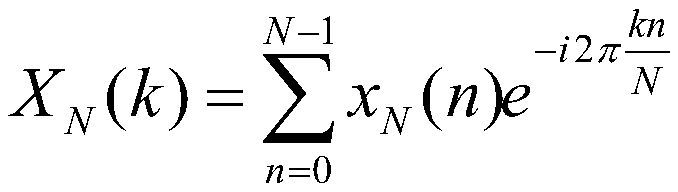Patents
Literature
96 results about "Spectral vector" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Spectral bio-imaging data for cell classification using internal reference
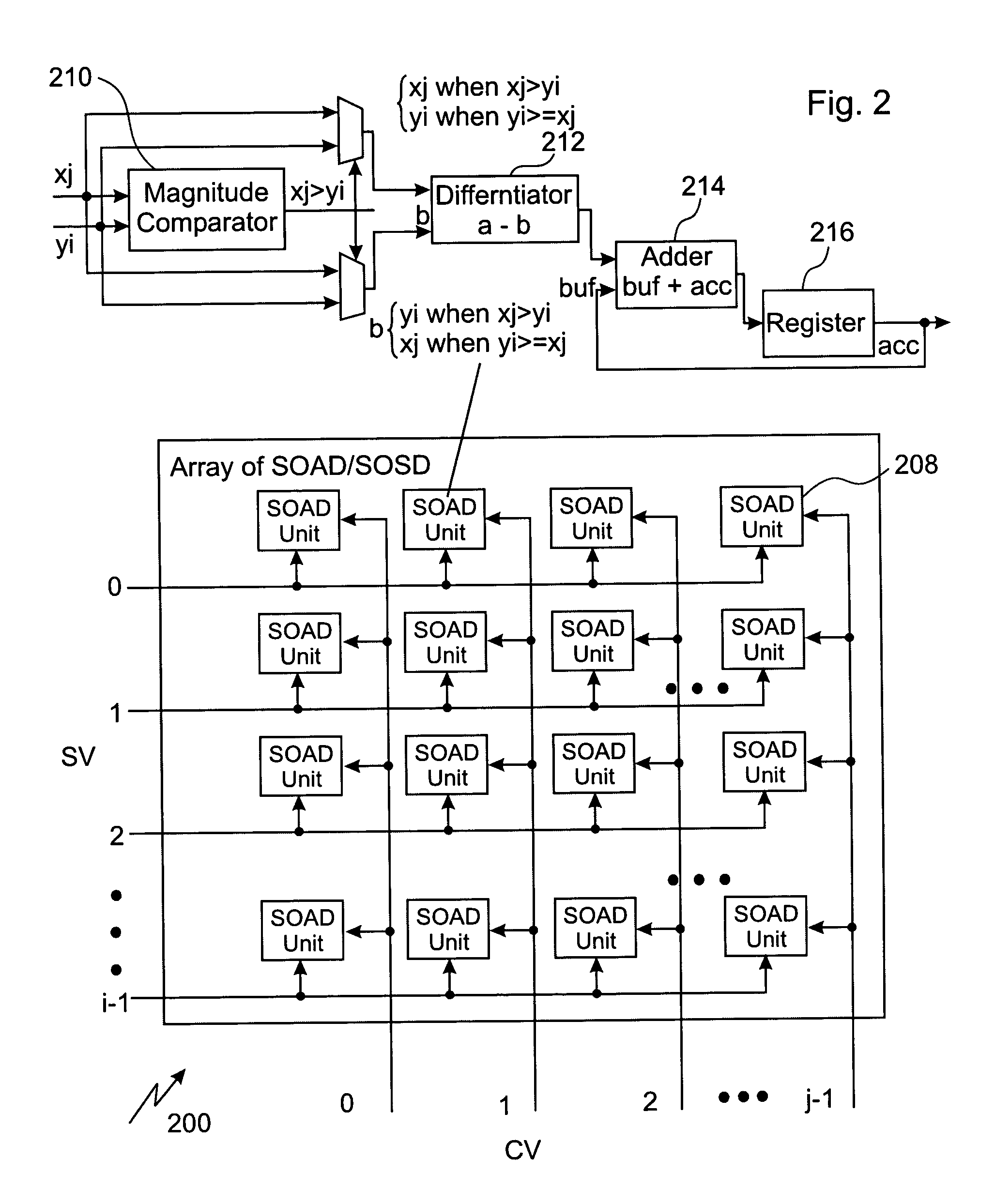
InactiveUS6690817B1Improve throughputReduced measurement timeRaman/scattering spectroscopyInterferometric spectrometrySpectral vectorConstant component
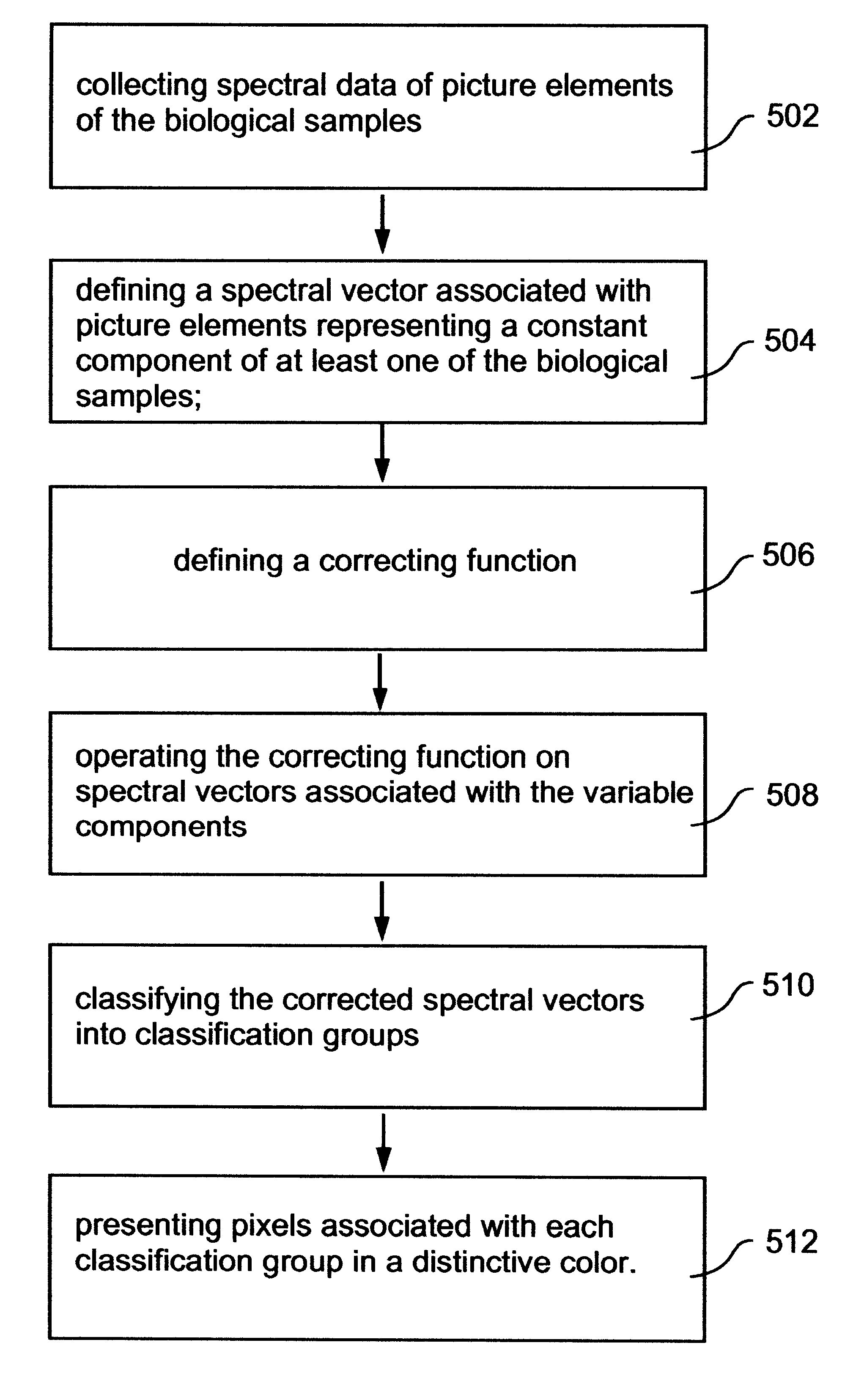
A method of spectral-morphometric analysis of biological samples, the biological samples including substantially constant components and suspected variable components, the method is effected by following the steps of (a) using a spectral data collection device for collecting spectral data of picture elements of the biological samples; (b) defining a spectral vector associated with picture elements representing a constant component of at least one of the biological samples; (c) using the spectral vector for defining a correcting function being selected such that when operated on spectral vectors associated with picture elements representing other constant components, spectral vectors of the other constant components are modified to substantially resemble the spectral vector; (d) operating the correcting function on spectral vectors associated with at least the variable components for obtaining corrected spectral vectors thereof; and (e) classifying the corrected spectral vectors into classification groups.
Owner:APPLIED SPECTRAL IMAGING
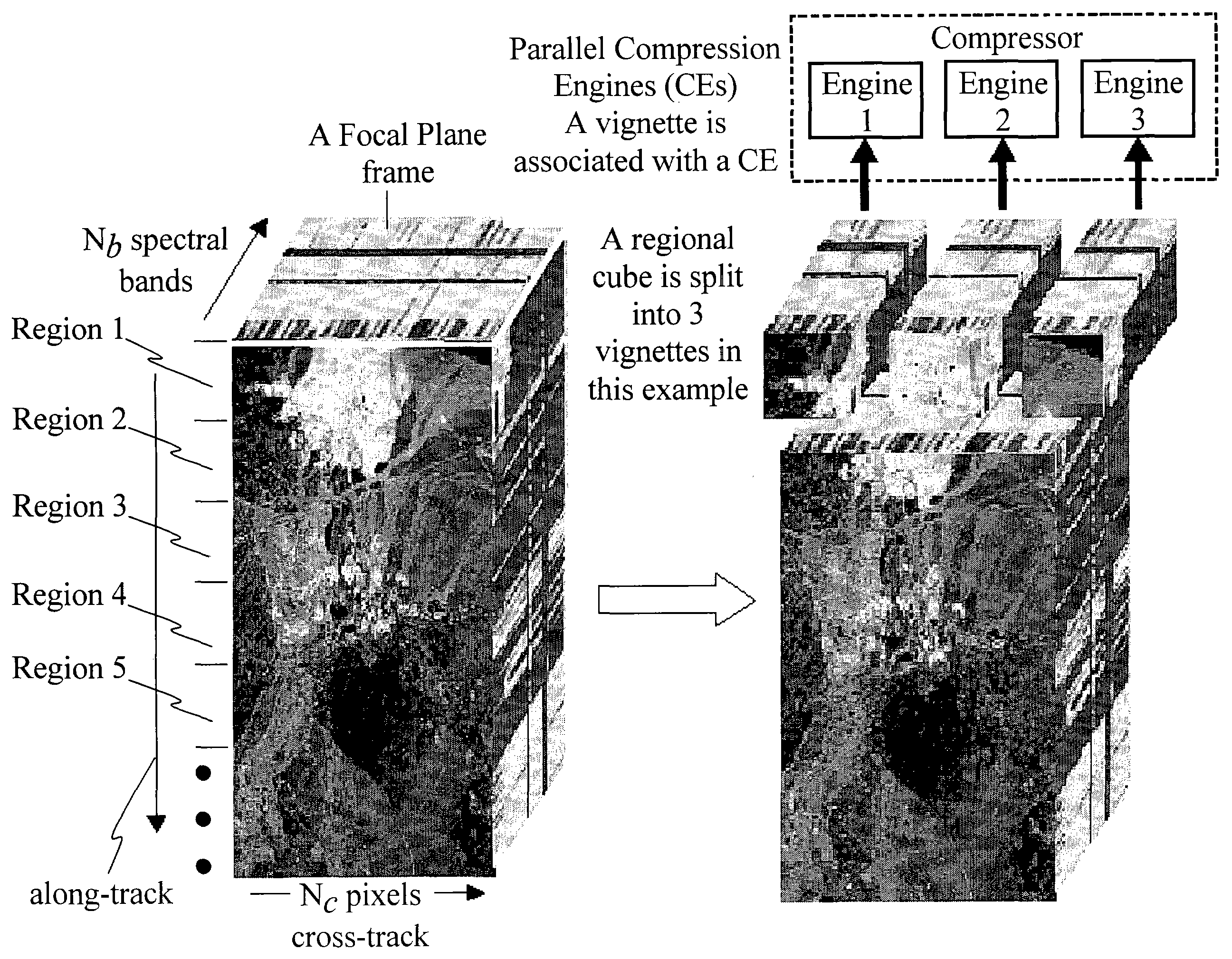
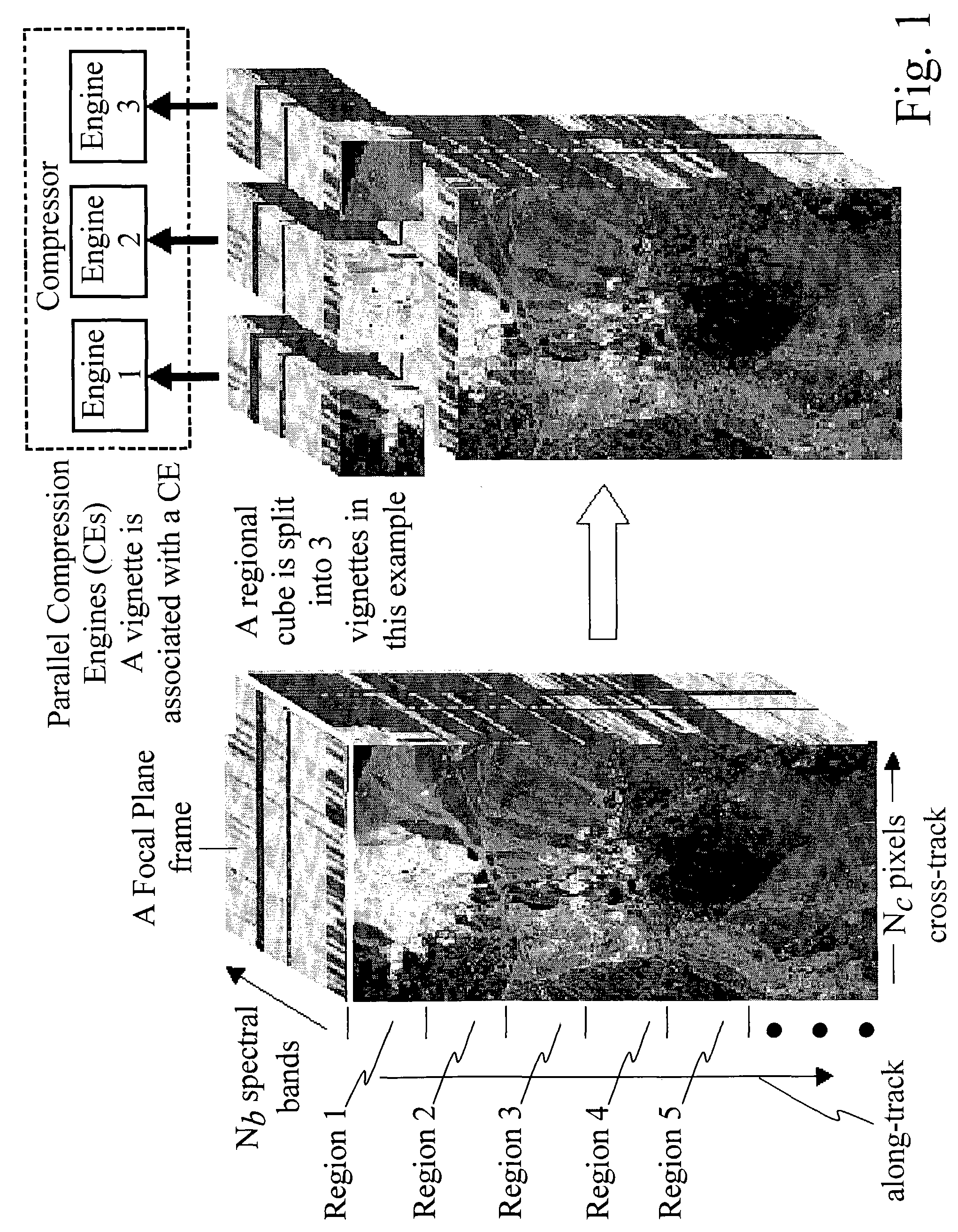
Data compression engines and real-time wideband compressor for multi-dimensional data
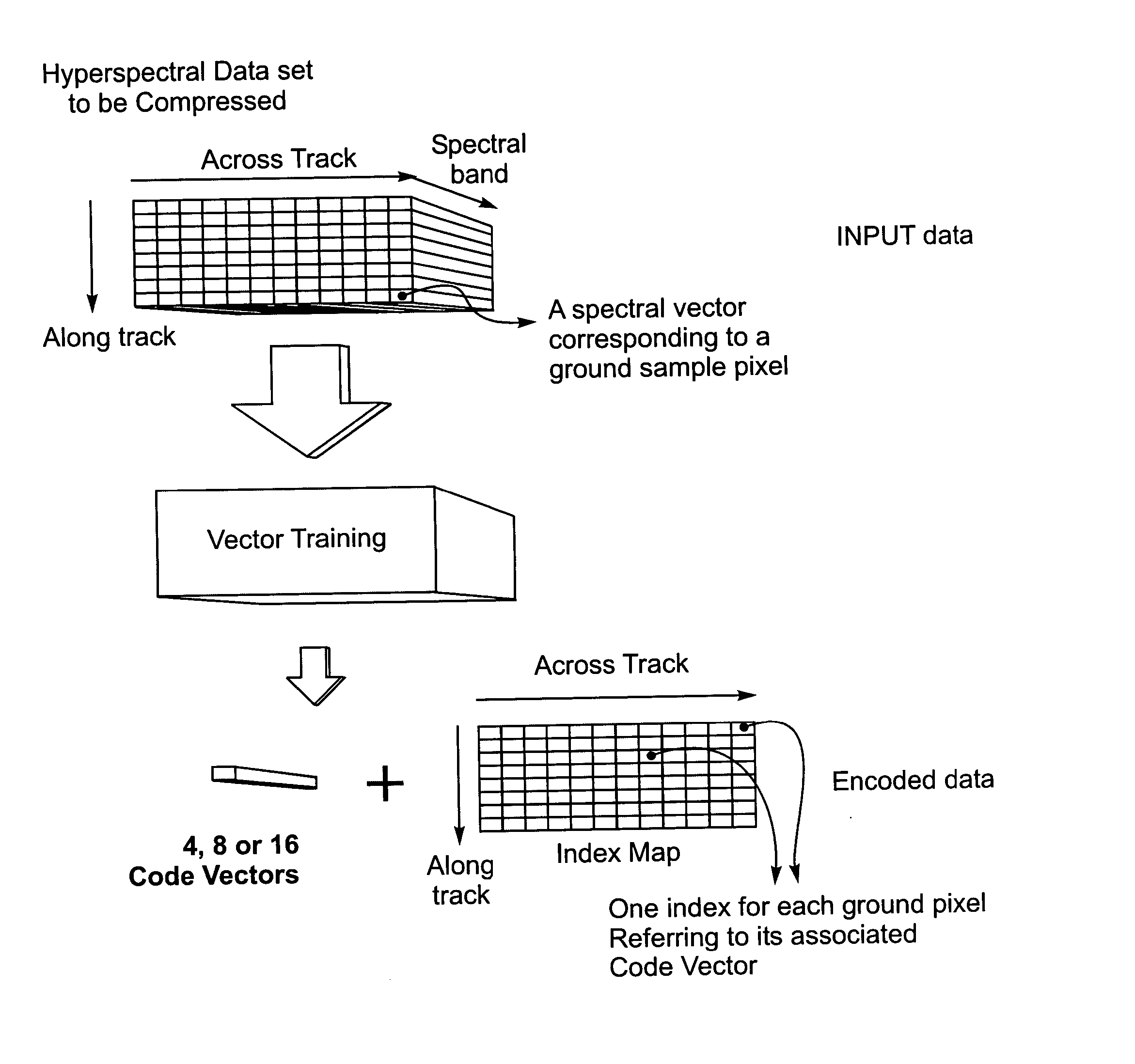
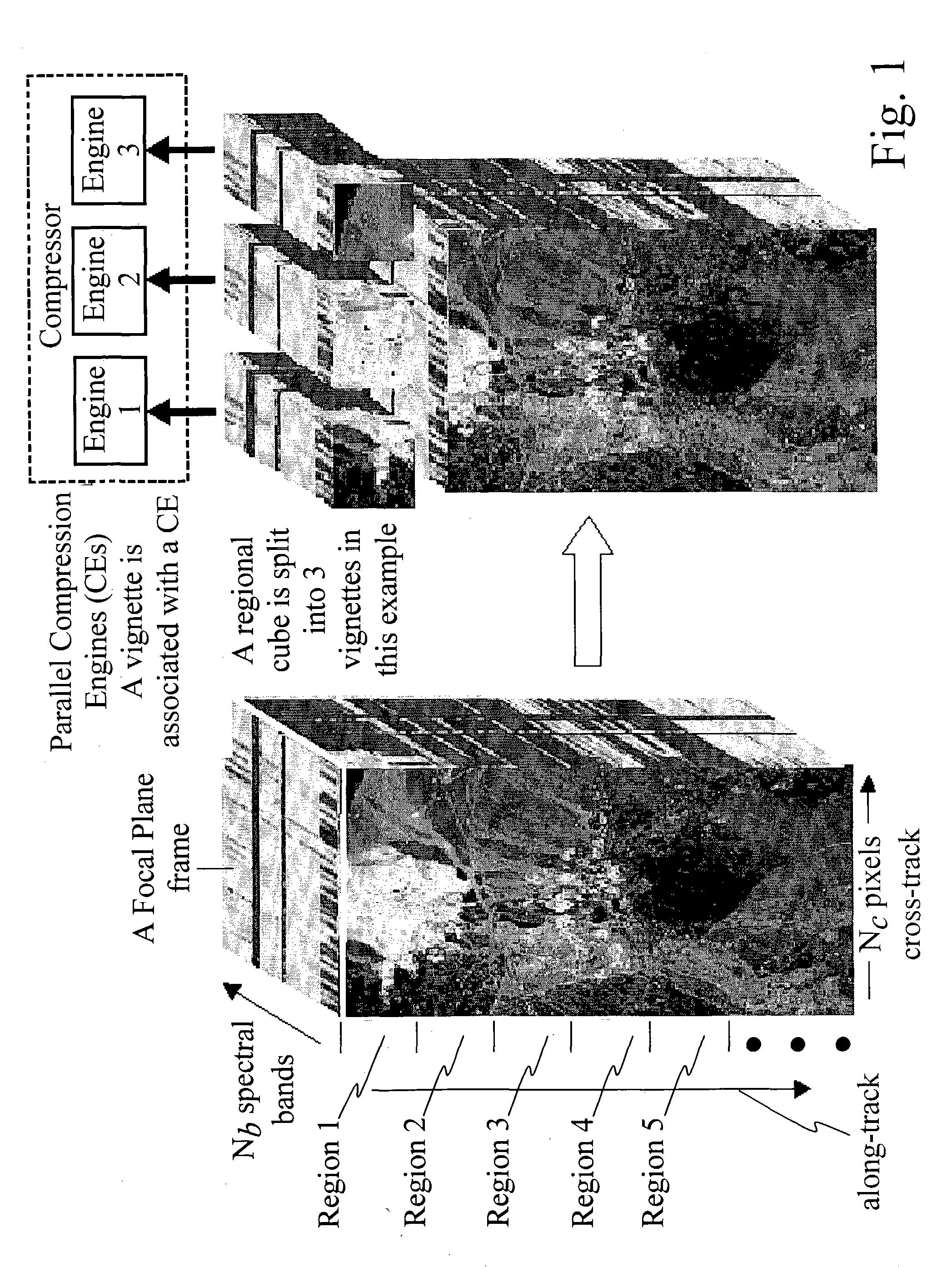
The present invention relates to a real-time wideband compressor for multi-dimensional data. The compressor comprises a plurality of compression engines for simultaneously compressing a plurality of data subsets of a set of input data vectors and providing compressed data thereof using one of SAMVQ or HSOCVQ data compression. Each compression engine comprises an along spectral vectors codevector trainer as well as an across spectral bands codevector trainer. The compression engines are programmable to perform either along spectral vectors codevector training or across spectral bands codevector training in combination with one of the SAMVQ or HSOCVQ techniques without changing hardware. The compressor further comprises a network switch for partitioning the set of input data vectors into the plurality of data subsets, for providing each of the plurality of data subsets to one of the plurality of compression engines, and for transmitting the compressed data. The real-time wideband compressor is highly advantageous in, for example, space applications by programmable enabling performance of different techniques of codevector training as well as different techniques of VQ. Furthermore, after the compression process is started the compression process is performed autonomously without external communication.
Owner:CANADIAN SPACE AGENCY
Data compression engines and real-time wideband compressor for multi-dimensional data
The present invention relates to a real-time wideband compressor for multi-dimensional data. The compressor comprises a plurality of compression engines for simultaneously compressing a plurality of data subsets of a set of input data vectors and providing compressed data thereof using one of SAMVQ or HSOCVQ data compression. Each compression engine comprises an along spectral vectors codevector trainer as well as an across spectral bands codevector trainer. The compression engines are programmable to perform either along spectral vectors codevector training or across spectral bands codevector training in combination with one of the SAMVQ or HSOCVQ techniques without changing hardware. The compressor further comprises a network switch for partitioning the set of input data vectors into the plurality of data subsets, for providing each of the plurality of data subsets to one of the plurality of compression engines, and for transmitting the compressed data. The real-time wideband compressor is highly advantageous in, for example, space applications by programmable enabling performance of different techniques of codevector training as well as different techniques of VQ. Furthermore, after the compression process is started the compression process is performed autonomously without external communication.
Owner:CANADIAN SPACE AGENCY
Hyperspectral remote sensing image classification method based on attention mechanism and convolution neural network
InactiveCN109376804AEnhance important featuresImprove featuresCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesPrincipal component analysisClassification methods
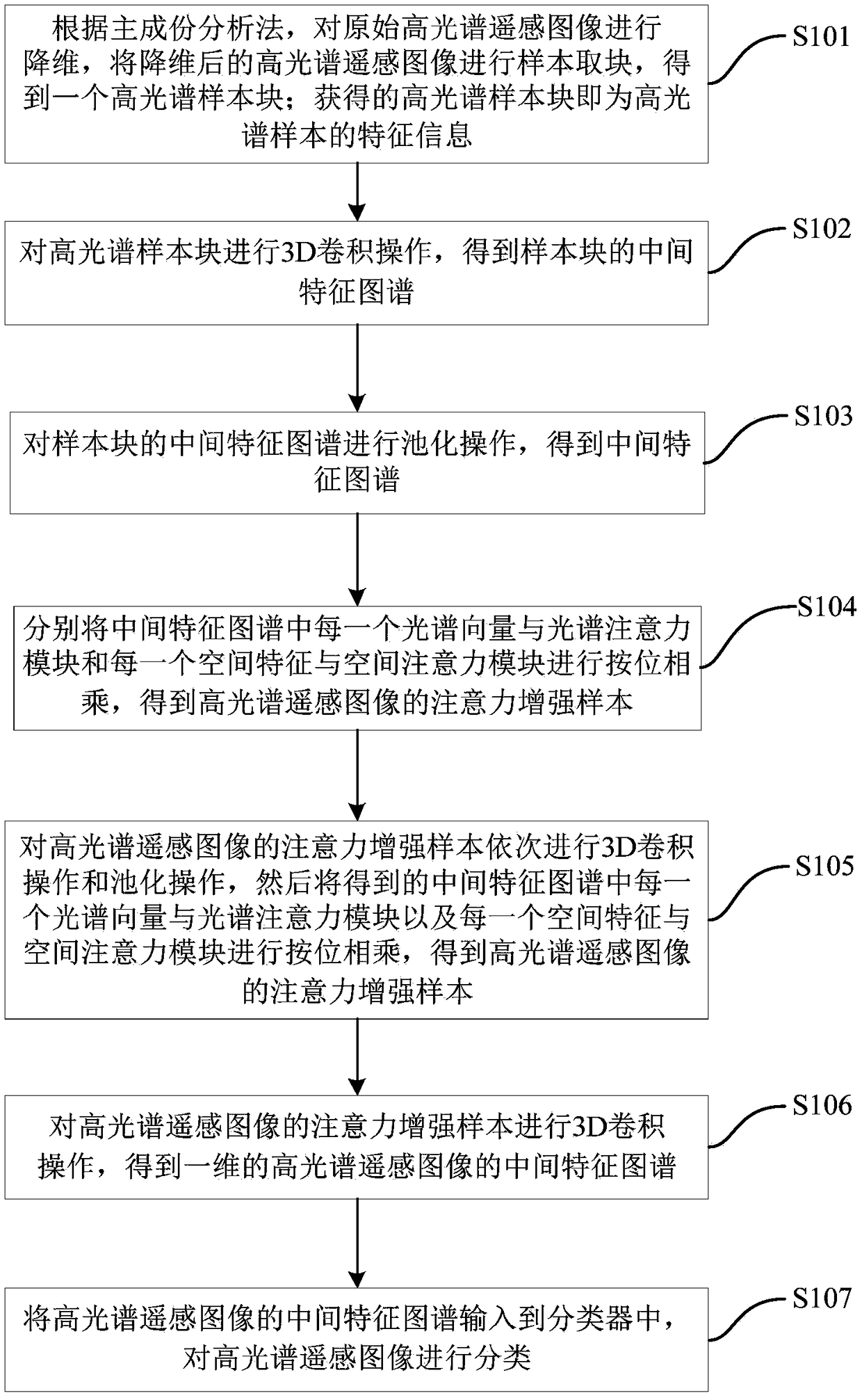
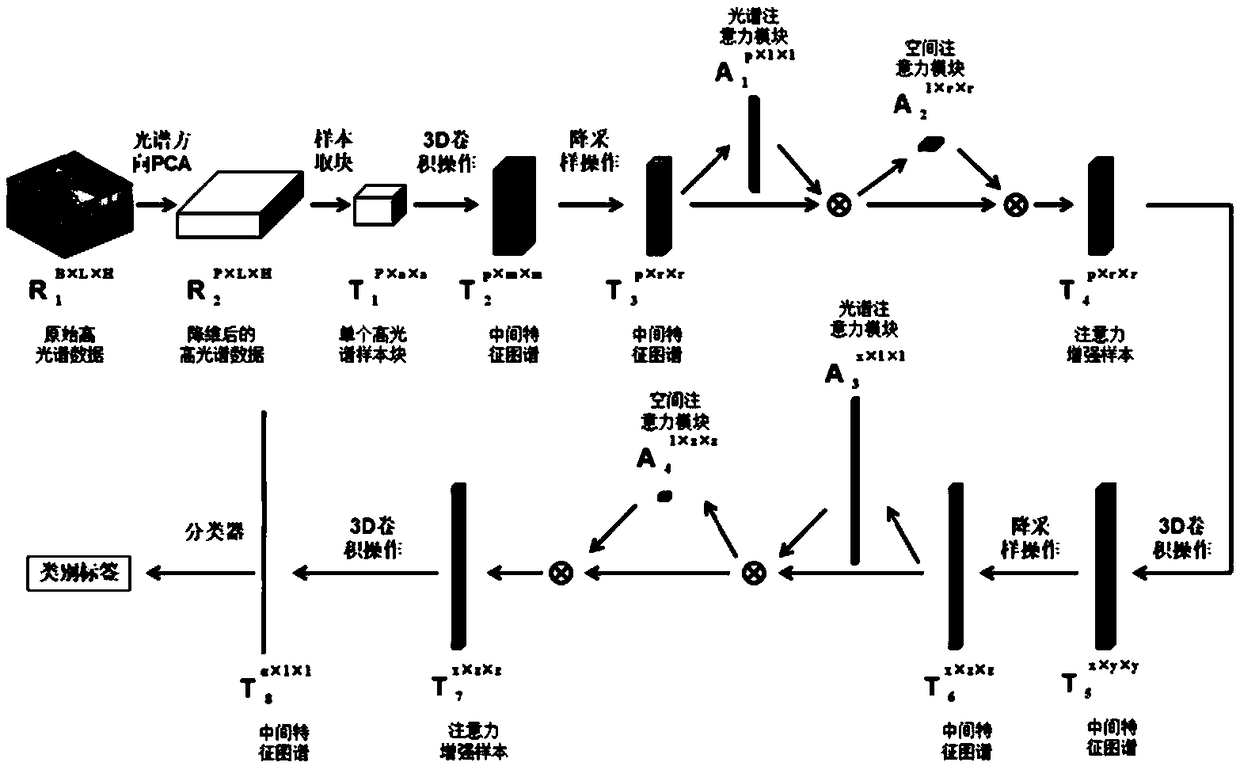
The invention provides a Hyperspectral remote sensing image classification method based on attention mechanism and convolution neural network.featuring that that original hyperspectral remote sensingimage is reduced in dimension by principal component analysis, and the reduce hyperspectral data is sampled into blocks. After that, 3D convolution and pooling operations are carried out to obtain theintermediate feature map. Then, each spectral vector of the intermediate feature is multiplied with the spectral attention module and each spatial feature is multiplied with the spatial attention module to obtain an attention enhancement sample. After that, the convolution operation and attention enhancement operation are performed again. Then the intermediate feature map obtained by 3D convolution operation is inputted into the classifier for classification. The invention has the advantages that the classification cost is reduced, the classification performance is improved, the adaptive feature thinning is realized through the extraction and enhancement of the sample features, and the classification accuracy of the hyperspectral remote sensing image is further improved.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (WUHAN)
Fusion method of multispectral remote sensing images with different spatial resolutions
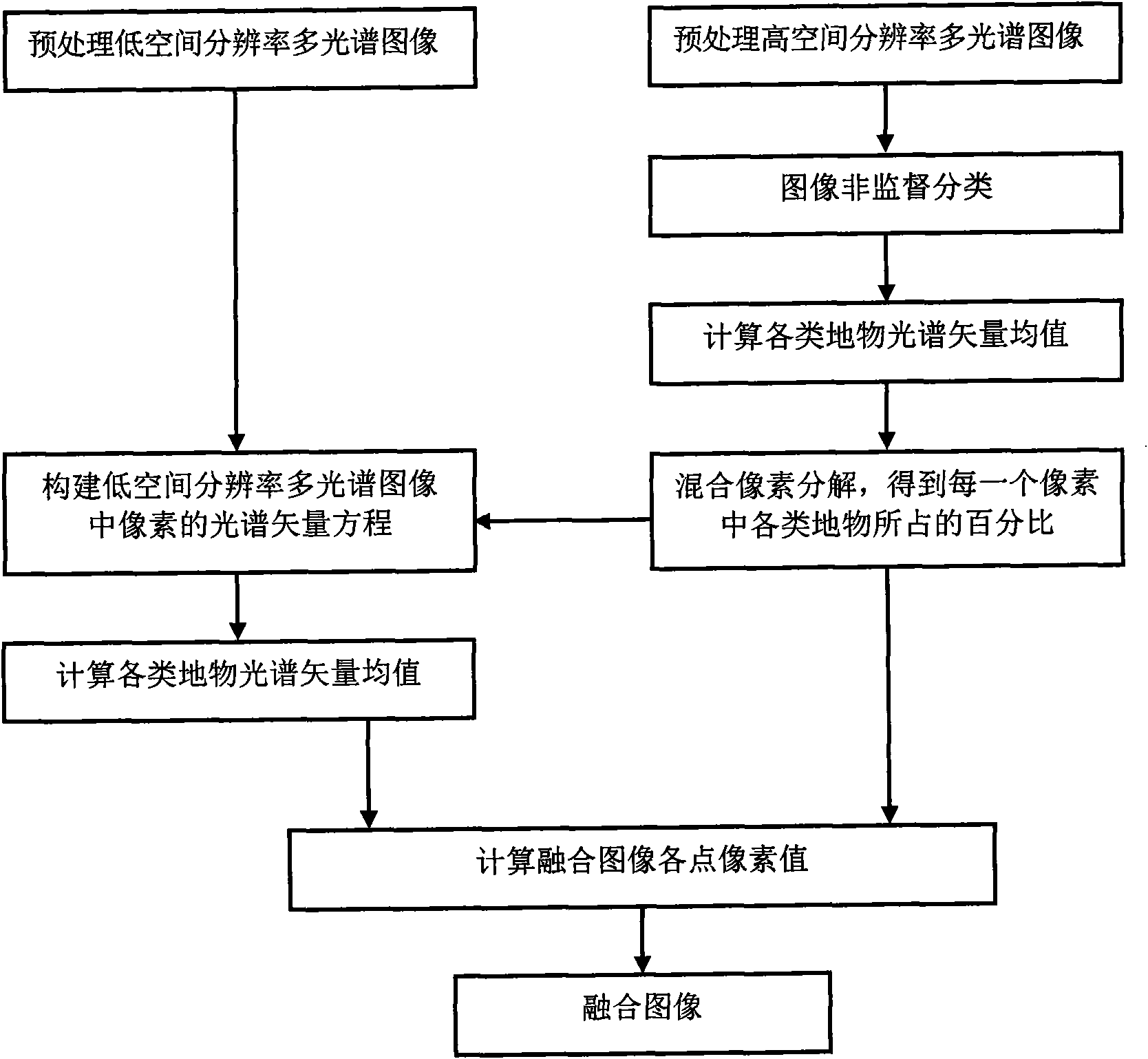
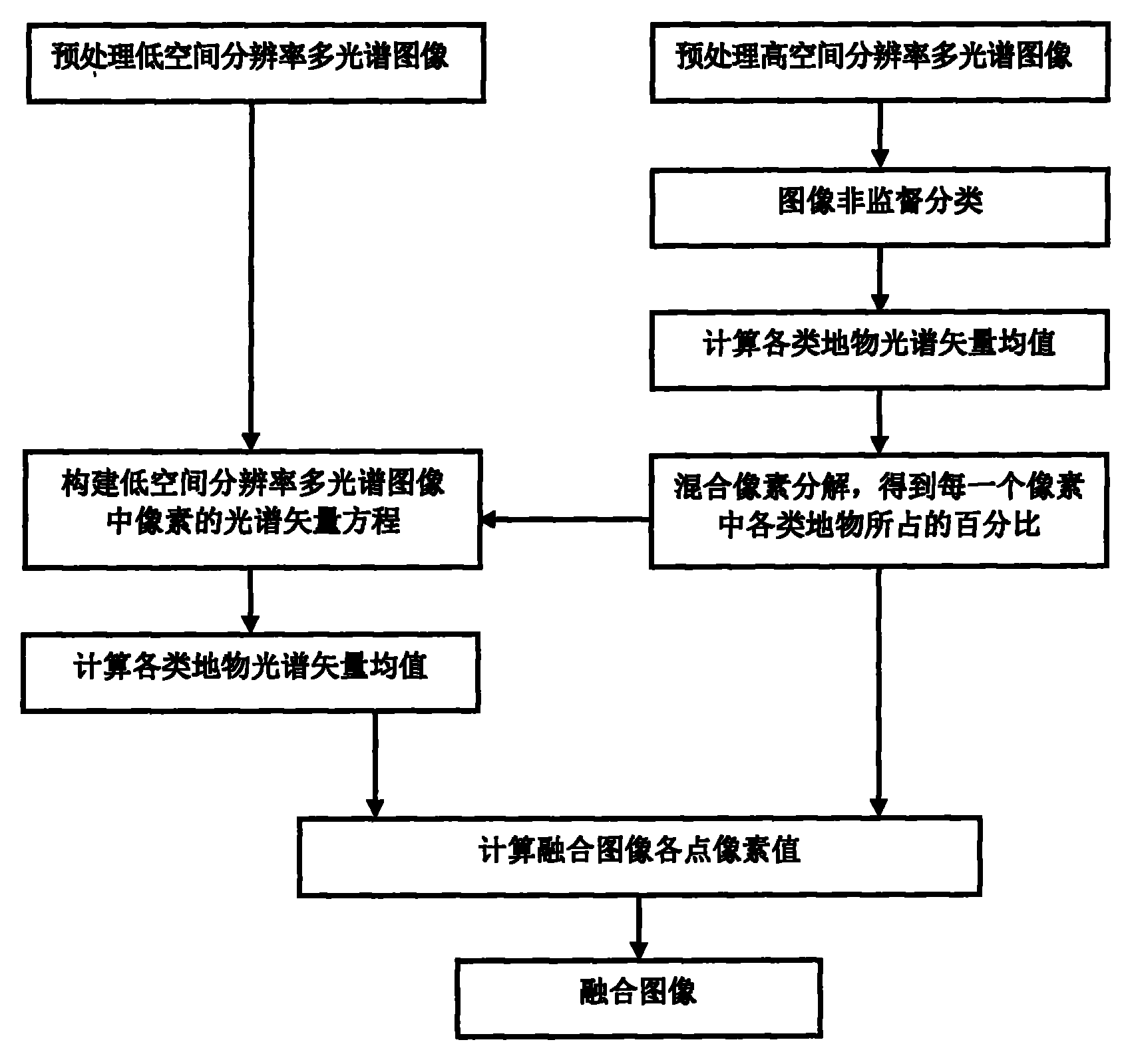
The invention belongs to the field of remote sensing image processing, and particularly relates to a fusion method of multispectral remote sensing images with different spatial resolutions. The method comprises the steps of dividing the multispectral image with high spatial resolution into n types of surface features, calculating the spectral vector mean value of all types of the surface features in the multispectral image with high spatial resolution, then conducting mixed pixel decomposition on the multispectral image with high spatial resolution, showing the multispectral image with low spatial resolution by the percent of all types of surface features in each pixel of the multispectral image with high spatial resolution, solving the spectral vector mean value of all types of the surface features in the multispectral image with low spatial resolution, and finally calculating the pixel value of each pixel of a fused image and generating the fused image. The method can fuse the multispectral image with high spatial resolution and the multispectral image with low spatial resolution, and enable the image fused to be sharper.
Owner:BEIJING RES INST OF URANIUM GEOLOGY
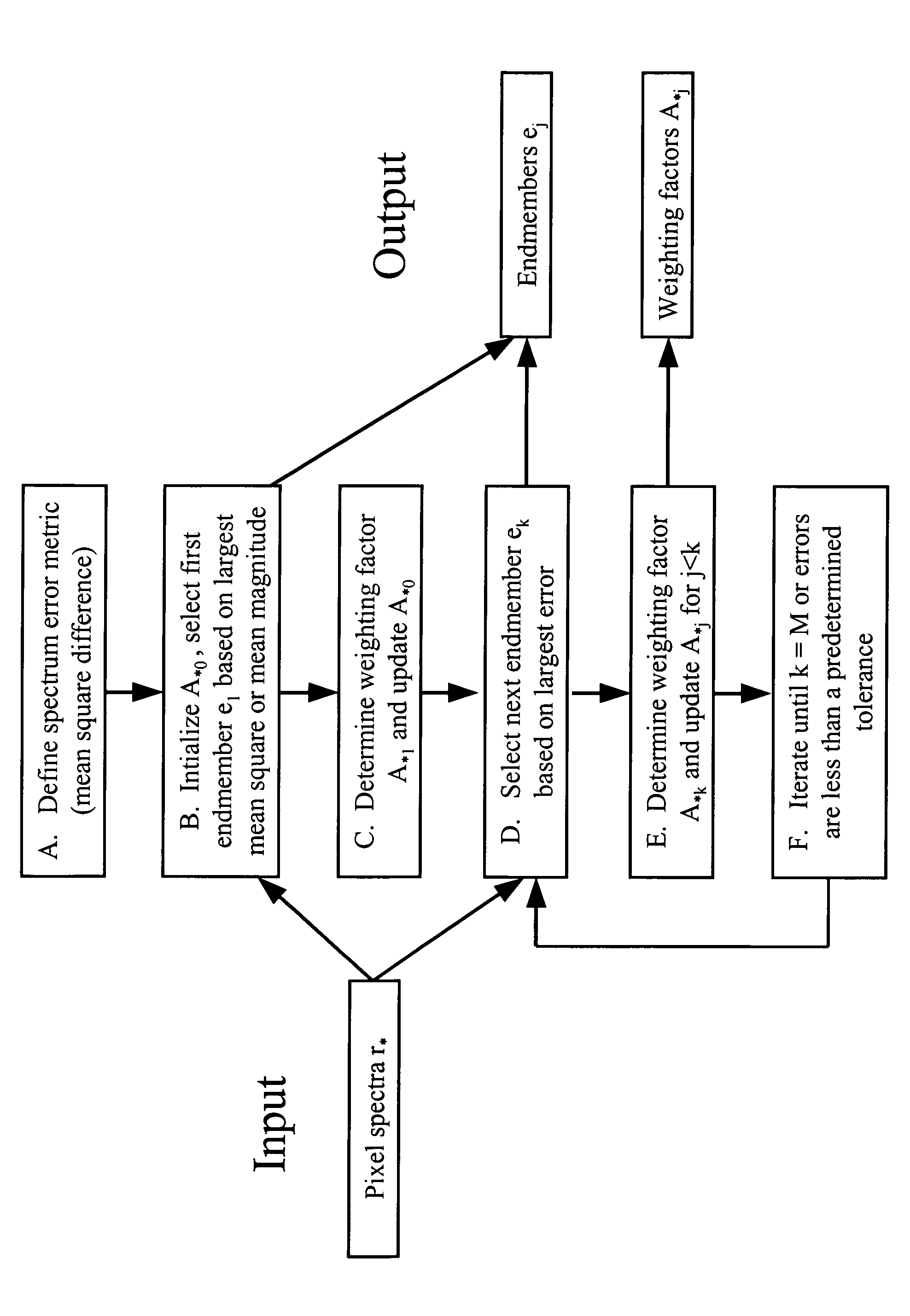
Process for finding endmembers in a data set
ActiveUS7680337B2Extended transfer timeRadiation pyrometryMaterial analysis by optical meansPattern recognitionData set
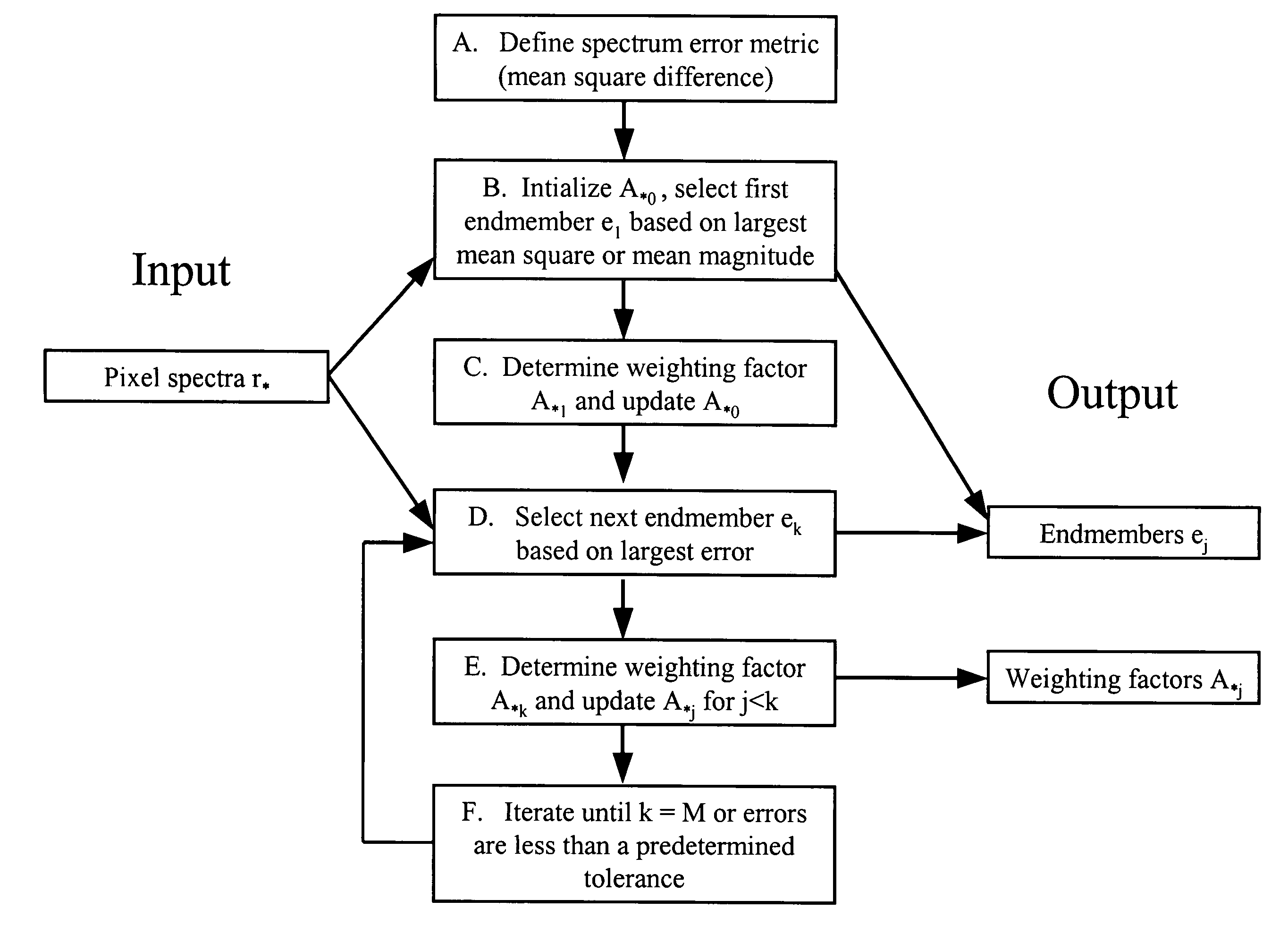
The invention provides a method for identifying one or more materials in a scene by determining a set of spectral vectors, called endmembers, from a data set comprised of spectra from the image data, and matching the set of endmembers to predefined library materials. The image data of the scene is captured with a sensor, and comprises a plurality of spectra. The method applies an iterative mathematical criterion, termed residual minimization, to find the endmembers. The first endmember may be selected based on the largest mean square value or the largest mean magnitude value. Subsequent endmembers are determined by calculating weighting factors, such that the weighting factors are non-negative and the calculated vector differences, or residuals, generate the smallest error metric. The error metric is dependent upon the vector difference between two spectra in the image data set, and may be the mean squared vector difference between two spectra.
Owner:SPECTRAL SCI
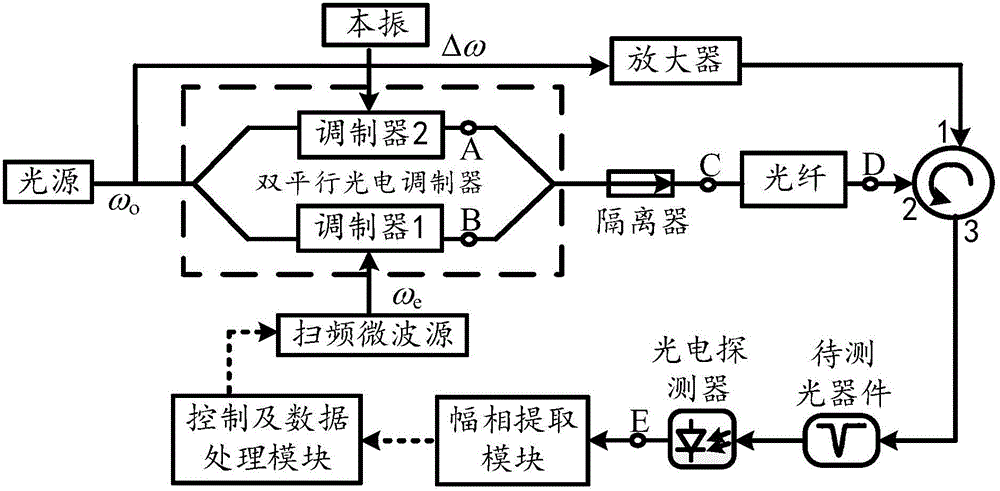
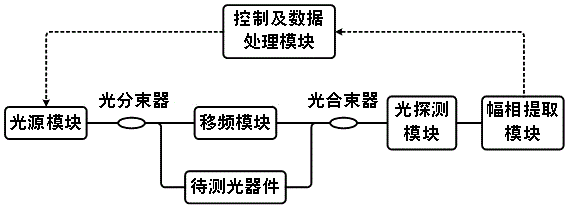
Optical device spectrum response measurement method and measurement device based on double sideband modulation and stimulated Brillouin scattering effect
ActiveCN105910797AExpand sweep rangeImprove sweeping efficiencyTesting optical propertiesTesting fibre optics/optical waveguide devicesFrequency spectrumSpectral response
The invention discloses an optical device spectrum response measurement method based on double sideband modulation and stimulated Brillouin scattering effect, comprising steps of dividing an optical carrier wave which is outputted by a light source into two paths, performing frequency-beating in a photoelectric detector by a scanning frequency double sideband signal and a carrier having the frequency shifted after the signal passes through the optical device to be detected, obtaining two radio frequency signals which have two different frequencies and carry spectral response information of the optical device to be detected at the scanning frequency double sideband signal frequency position, using a radio frequency amplitude phase extraction module to respectively extract amplitude phase information of two radio frequency signals to obtain an amplitude-frequency response and a phase frequency response of the optical device to be detected at the optical detection signal frequency, changing the wavelength of the optical detection signal and repeating the above process to obtain the spectral vector response information of the optical device to be detected. The invention also discloses an optical device spectrum response measurement device based on the double sideband modulation. Compared with the prior art, the optical device spectrum response measurement method and measurement device greatly improve the measurement range and the measurement efficiency.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
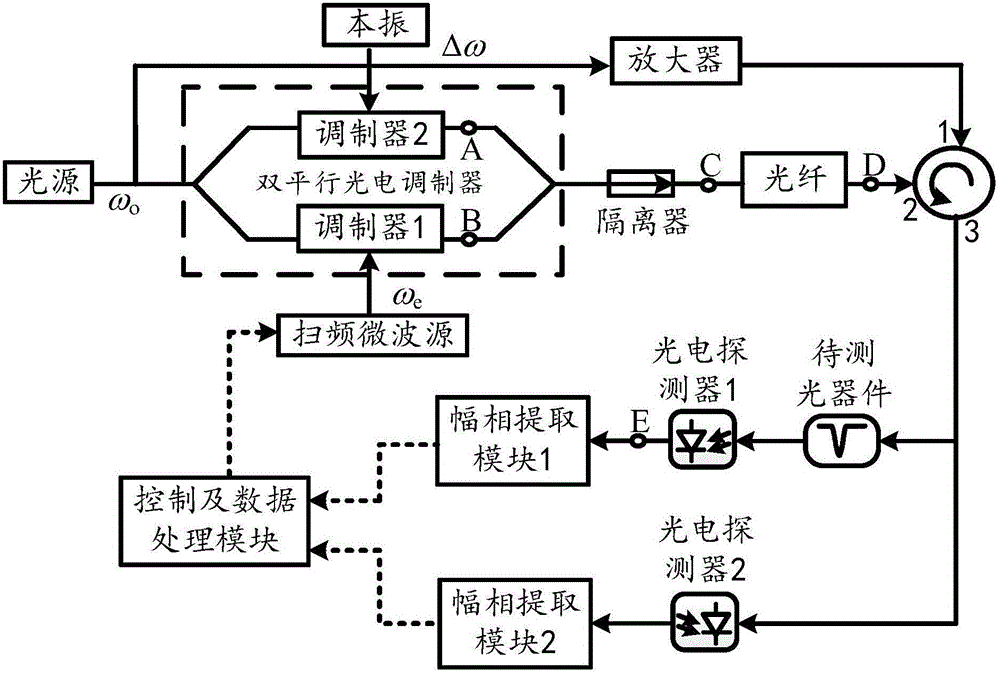
Spectral response measurement method and system of optical device
ActiveCN103954356AAchieving Amplitude-Frequency ResponseRealize the measurement of phase-frequency responseSpectrum investigationSpectral responseOptical measurements
The invention discloses a spectral response measurement method of an optical device and belongs to the technical field of optical measurement. According to the method, optical detection signals of the single wavelength are divided into two paths, frequency shifting with the fixed frequency shifting amount is carried out on one path of signals, and the other path of signals pass through the optical device to be detected; then frequency beat is carried out on the two paths of light, and radio-frequency signals carrying the spectral response information of the optical device to be detected at the optical detection signal frequency positions are obtained; a radio-frequency amplitude phase extraction device with the same working efficiency and the frequency shifting amount is used for extracting the amplitude phase information of the radio-frequency signals, and the amplitude frequency response and phase frequency response of the optical device to be detected at the optical detection signal frequency positions are obtained; the wavelength of the optical detection signals is changed, the process is carried out repeatedly, and the spectral vector response information of the optical device to be detected is obtained. The invention further discloses a spectral response measurement system of the optical device. Compared with the prior art, the spectral response measurement method and system of the optical device have the advantages of being capable of achieving the high-precision measurement of the amplitude frequency response and phase frequency response of the optical device and greatly lowering cost at the same time.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
SAM weighted KEST hyperspectral anomaly detection algorithm
The invention discloses an SAM weighted KEST hyperspectral anomaly detection algorithm (SKEST). The method includes the steps: firstly, deducing the SKEST algorithm; and secondly, calculating the SKEST value of each image element in a hyperspectral image by the aid of a double-rectangular window, performing threshold segmentation and detecting abnormal points. In the SKEST algorithm, based on the KEST (kernel Eigen space separation transformation) algorithm, a weight factor is introduced into each sample in a DCOR (difference correlation) matrix of a high-dimensional Eigen space detection point neighborhood by means of SAM (spectral angle mapper) measurement, and the weight factor of each sample depends on an included angle between the spectral vector of the sample and a data center of the detection window. Therefore, abnormal data in the detection window are suppressed, the contribution of main compositional data is highlighted, and the DCOR matrix can more effectively describe target and background data distribution difference. Besides, the SAM is robust to spectral energy, and by the aid of a radial basis function, the SKEST algorithm considers both spectral energy difference and spectral curve shape difference of signals, and accordingly conforms to hyperspectral data characteristics more effectively.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
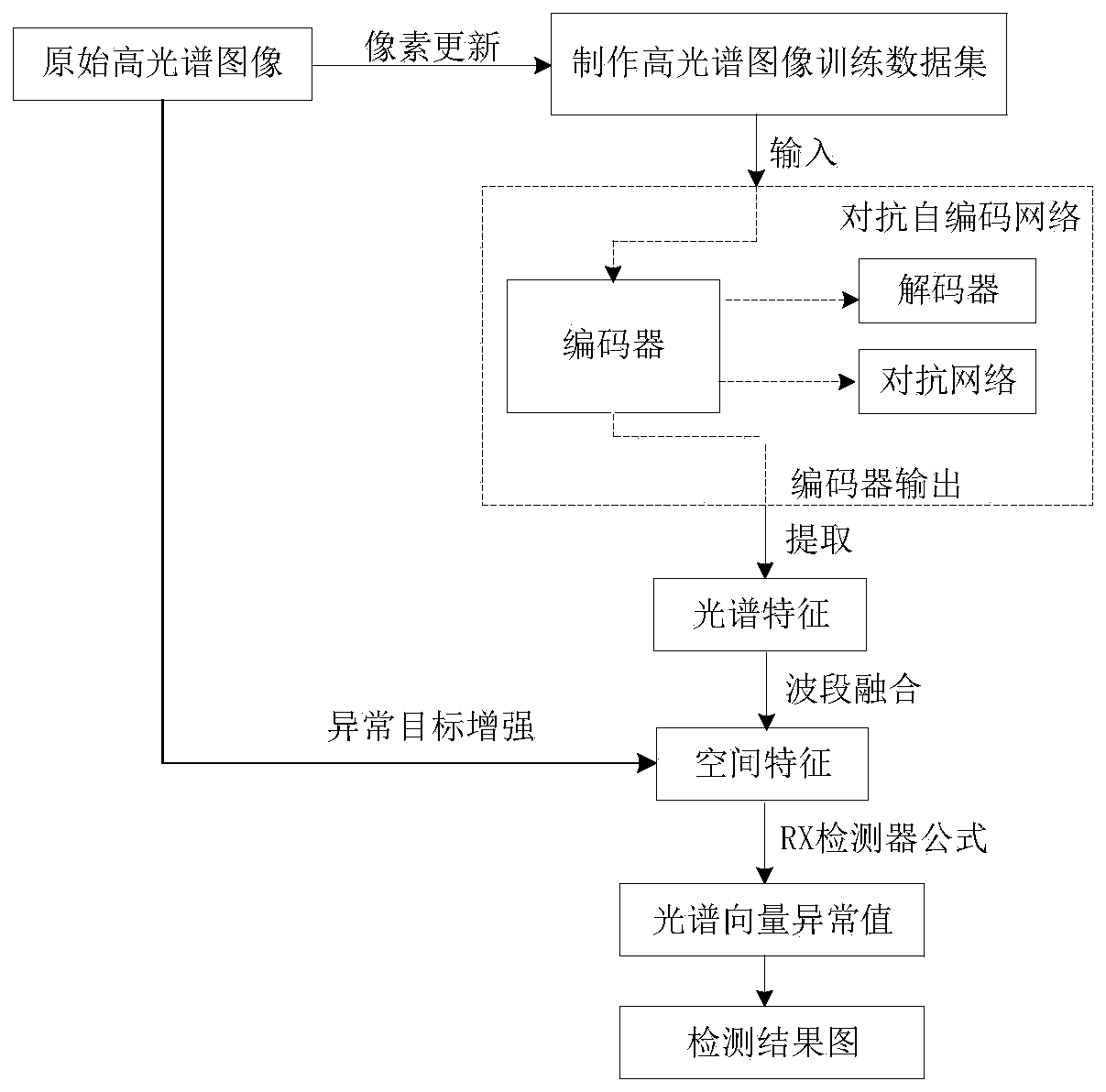
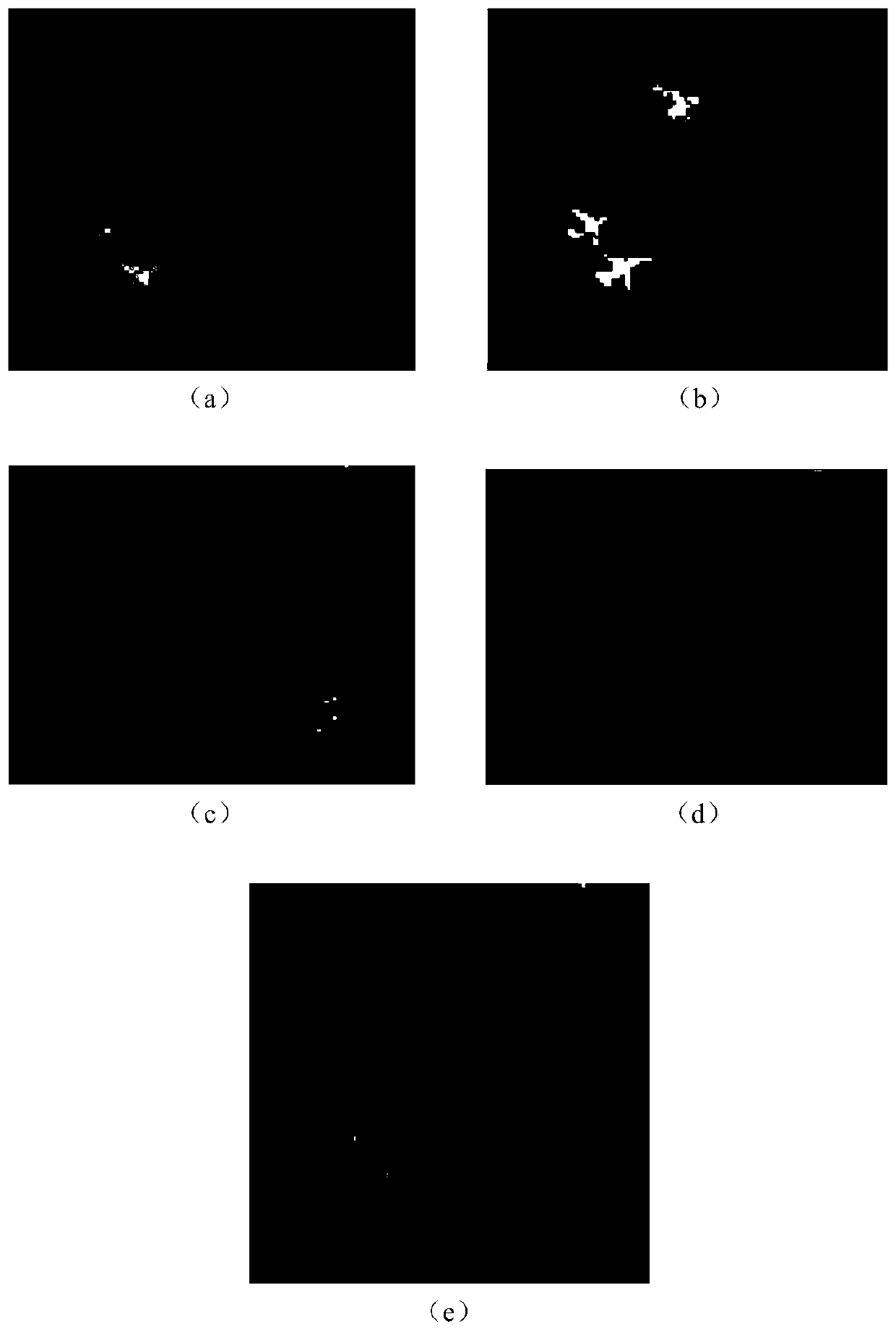
A hyperspectral anomaly detection method based on an adversarial self-coding network
ActiveCN109949278AReduce the number of bandsSimple calculationImage analysisImage codingData setAnomaly detection
The invention discloses a hyperspectral image anomaly detection method based on an adversarial self-coding network, and mainly solves the problems of complex calculation and low detection precision inthe prior art. The implementation scheme comprises the following steps of: 1) manufacturing a hyperspectral image training data set by using a pixel updating method; 2) inputting the training data set into a generative adversarial network for training, and extracting spectral characteristics of the training data set; 3) processing the spectral features by using a waveband fusion and attribute filtering method to obtain spatial features of the training data set; 4) enhancing an abnormal target in the original hyperspectral image by utilizing spatial characteristics; 5) calculating an abnormalvalue of the hyperspectral image spectral vector after the abnormal target is enhanced by using an RX detector formula; According to the method, richer potential information in the hyperspectral imagecan be obtained, the difference between an abnormal target and a complex background in the image is increased, the method has the advantages of being simple in calculation and high in detection precision, and the method can be used for detecting the abnormal target in the hyperspectral image.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
High-spectral ship detection method based on combination of spatial and spectral information
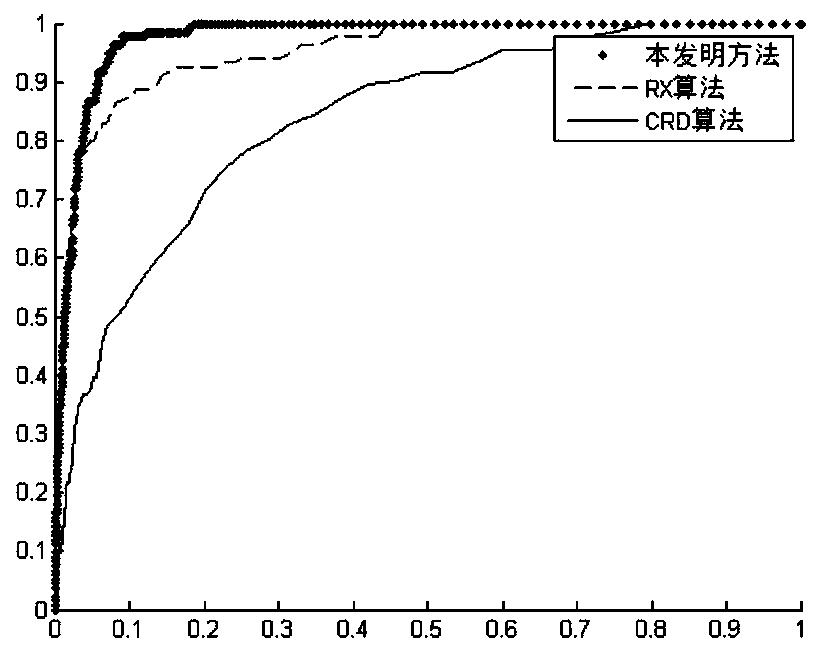
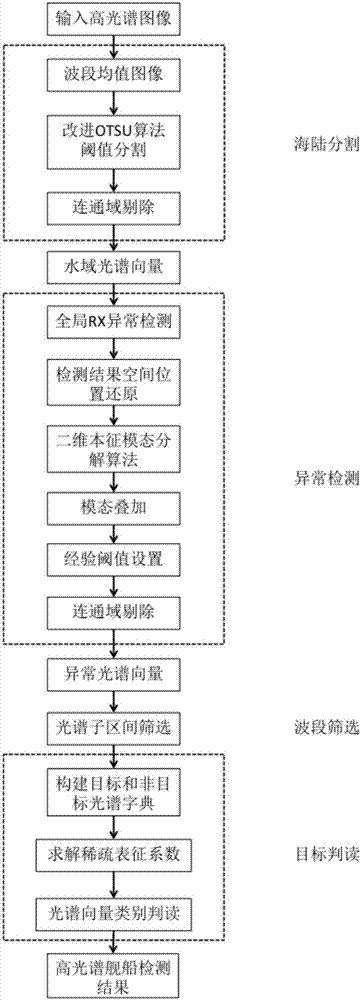
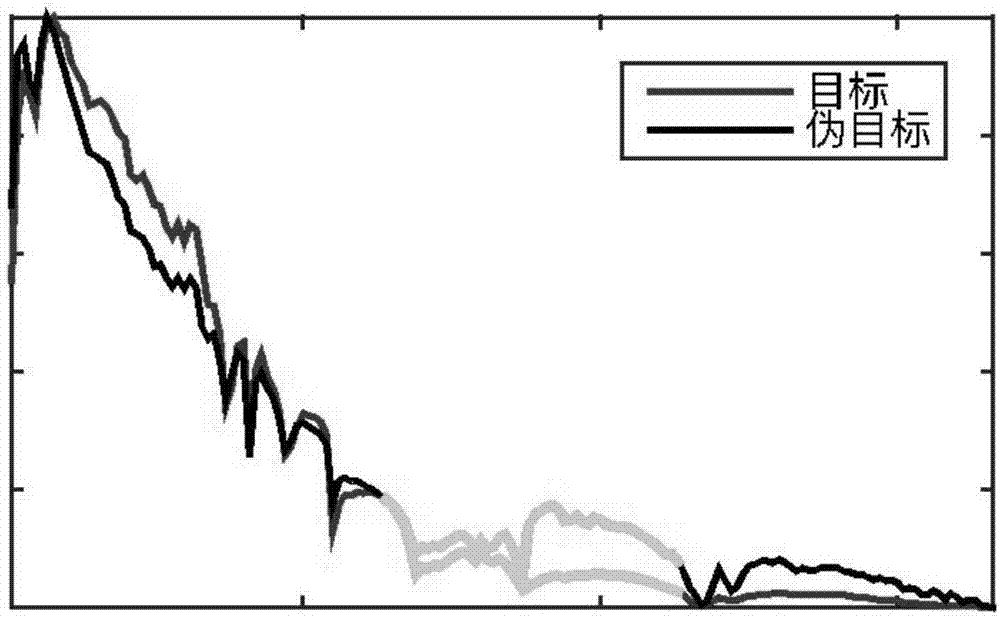
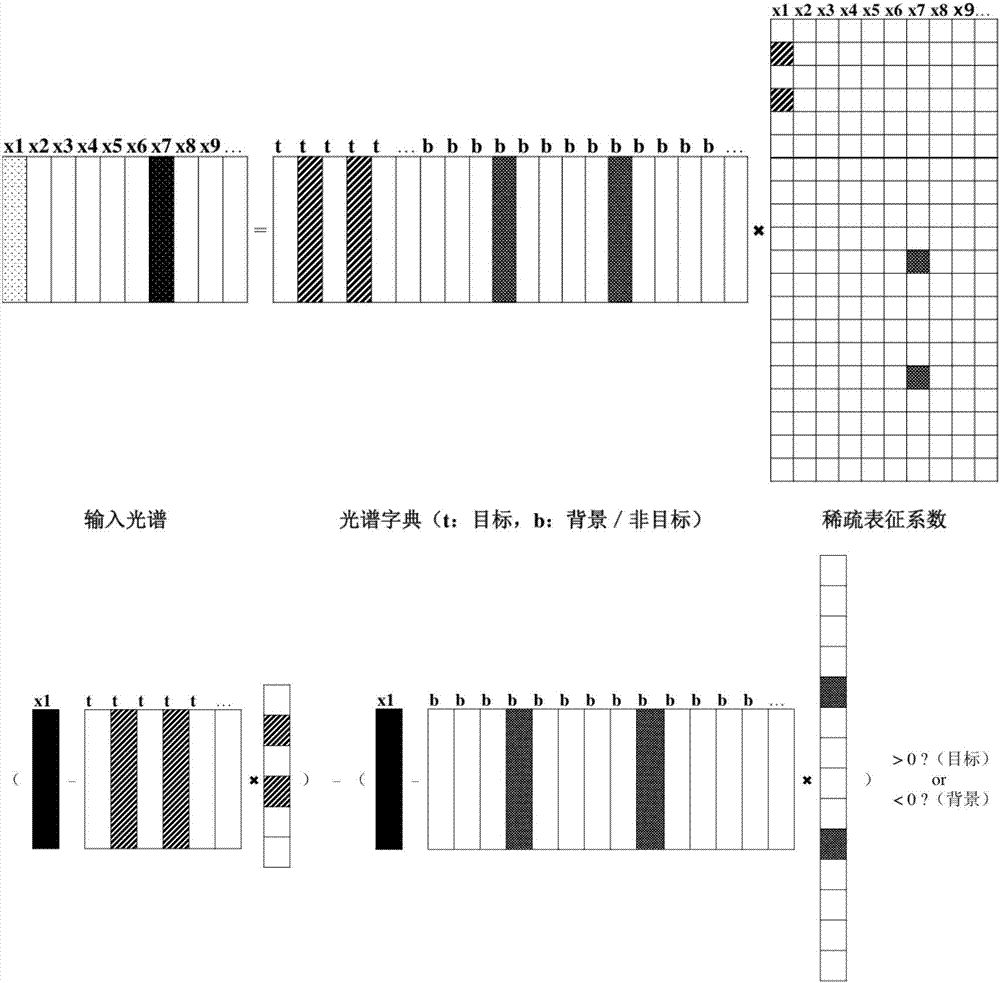
ActiveCN106886760AImprove accuracyReduce false alarm rateScene recognitionSpectral vectorScreening method
The invention provides a high-spectral ship detection method based on combination of spatial and spectral information, and the method can be used to solve the problems in accuracy and false alarm in ship object detection in a present ship detection method. A monitoring-free spectral subinterval screening method based on inter-class variation is related to, and the monitoring-free spectral waveband screening method is accurate, rapid and highly robust. Relative stability of a water domain is added to threshold segmentation, interference of a non water area of relatively low brightness value in a detection result is weakened greatly, a sea-land segmentation result of high accuracy can be obtained, and the method is simple, rapid and adaptive. Space features of an RX abnormal detection result are enhanced, namely, a 2D intrinsic mode is used to decompose a reconstruction image, and the method is self-adaptive and relies on structure of data itself. According to the method, the spectral feature of a substance is used to analyze main materials of the substance, and all spectrums can be obtained by linear combination of spectral vectors in a spectrum dictionary.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Method and system for compressing a continuous data flow in real-time using cluster successive approximation multi-stage vector quantization (SAMVQ)
InactiveUS20050002584A1Increase the compression ratioReduce Image ArtifactsSpeech analysisImage codingImaging qualityImage Artifact
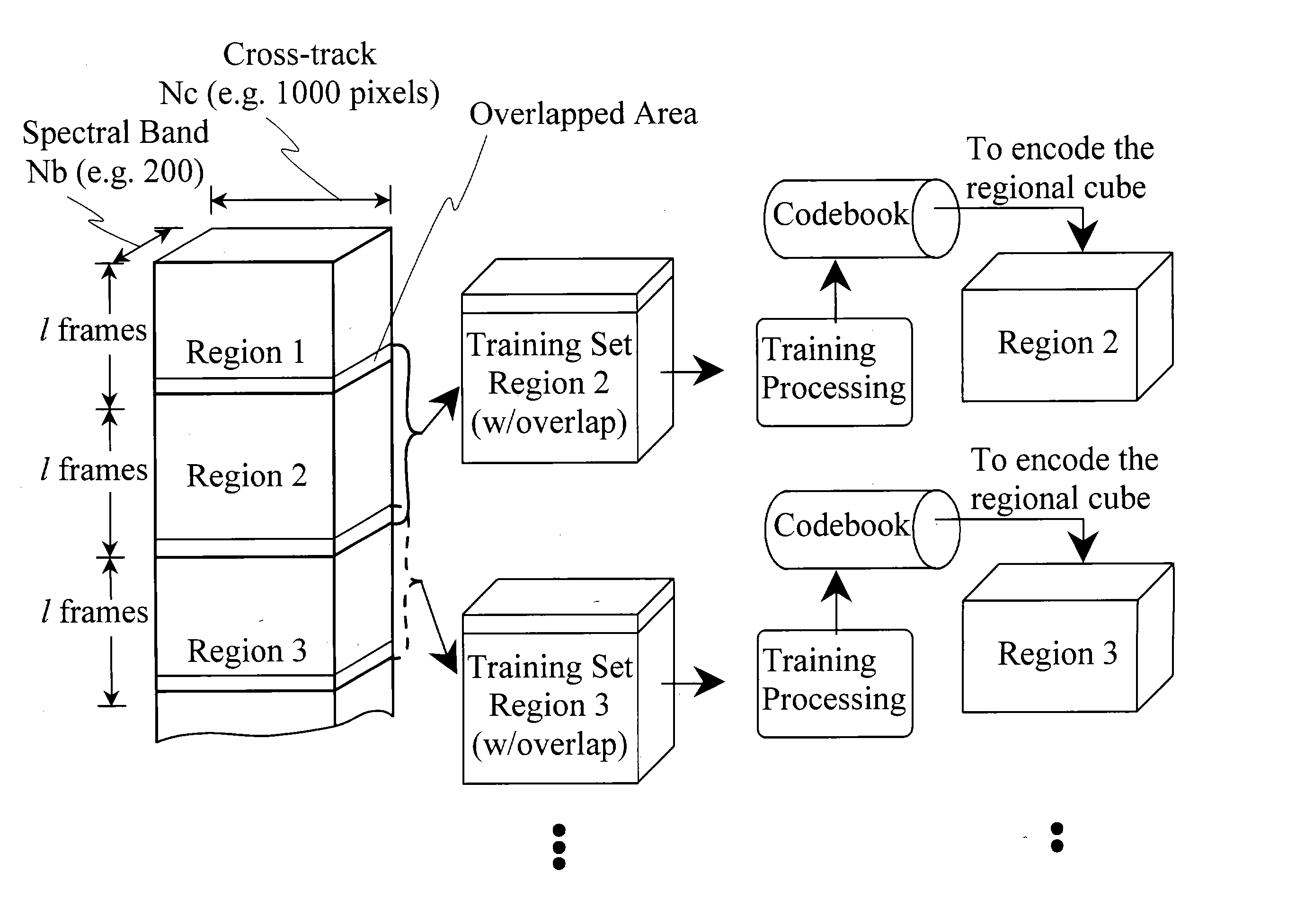
The present invention relates to a method and system for compressing a continuous data flow in real-time based on lossy compression. In real-time data compression, a series of multi-dimensional data subsets acquired in a given period of time are treated as a regional data cube for the purpose of dividing a continuous series of data subsets into a plurality of data cubes. In a first embodiment implementation of parallel processing using a plurality of compression engines is facilitated by separating a data cube into a plurality of clusters comprising similar spectral vectors. By separating the data cube into clusters of similar spectral vectors no artificial spatial boundaries are introduced substantially improving image quality. Furthermore, the spectral vectors within a cluster are more easily compressed due to their similarity. In a second embodiment a predetermined number of 2D focal plane frames in a boundary area of a previous regional data cube close to a current regional data cube are included in a training set used for codevector training for the current region. Therefore, no artificial boundary occurs between the two adjacent regions when codevectors trained in this way are used for codebook generation and encoding of the spectral vectors of the current regional data cube substantially reducing image artifacts between adjacent regions. A remedy for the single bit error problem is provided in a third embodiment. Full redundancy of compressed data for a regional data cube is obtained by combining the previous regional data cube and the current regional data cube for codebook training. In order to obtain redundancy for the index map, the codebook is used to encode the current regional data cube as well as the previous regional data cube producing a baseline index map for the current regional data cube and a redundant index map for the previous regional data cube. Therefore, full redundancy for a regional data cube is provided allowing restoration of a regional data cube if its codebook and / or index map are corrupted or lost due to single bit errors.
Owner:CANADIAN SPACE AGENCY
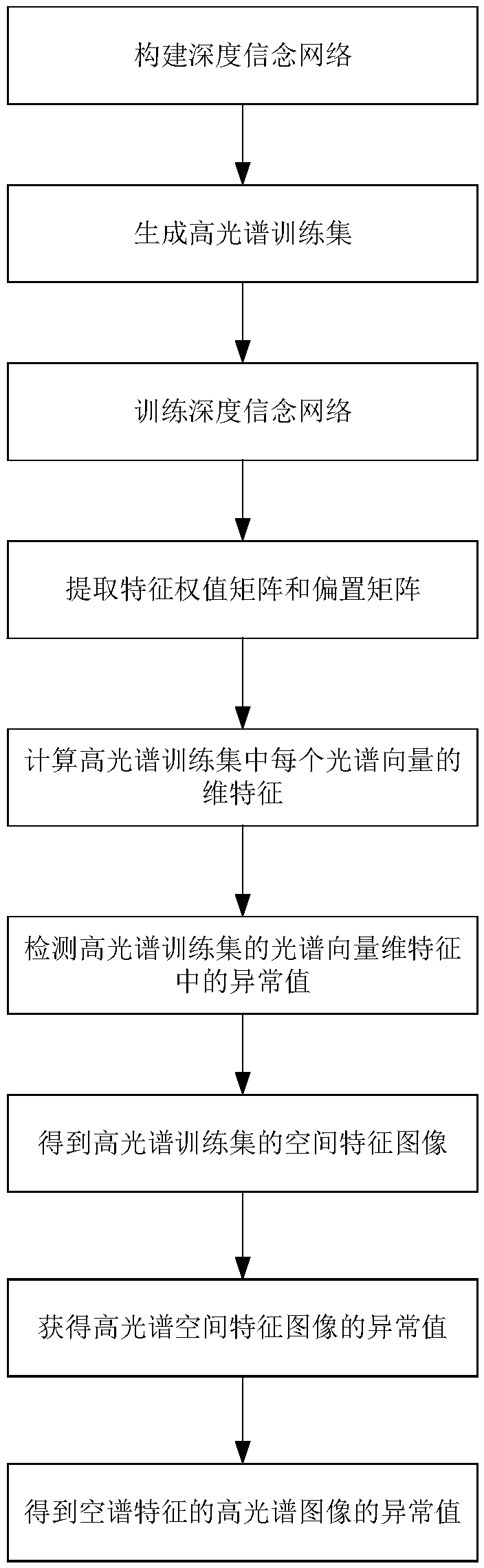
Hyperspectral image anomaly detection method based on joint extraction of spatial-spectral characteristics
ActiveCN109493338AEasy to distinguishReduce false detection rateImage enhancementImage analysisDeep belief networkAnomaly detection
The invention discloses a hyperspectral image anomaly detection method based on joint extraction of spatial-spectral characteristics, and mainly solves the problem that in the prior art, there are many missed detection anomaly points. The method comprises the following specific steps: (1) constructing a deep belief network; (2) generating a hyperspectral training set; (3) training a deep belief network; (4) extracting a feature weight matrix and a bias matrix; (5) calculating the dimensional characteristics of each spectral vector in the hyperspectral training set; (6) detecting an abnormal value of the spectral vector dimension of the hyperspectral training set; (7) obtaining a spatial feature image of the hyperspectral training set; (7) obtaining a spatial feature image of the hyperspectral training set; and (8) obtaining an abnormal value of the hyperspectral image with the spatial spectrum characteristic. The hyperspectral image detection method can extract spectral characteristicsand spatial characteristics, can better distinguish abnormity and complex backgrounds in the hyperspectral image, and has the advantages of less detection result false detection abnormity and less detection result missed detection abnormity.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
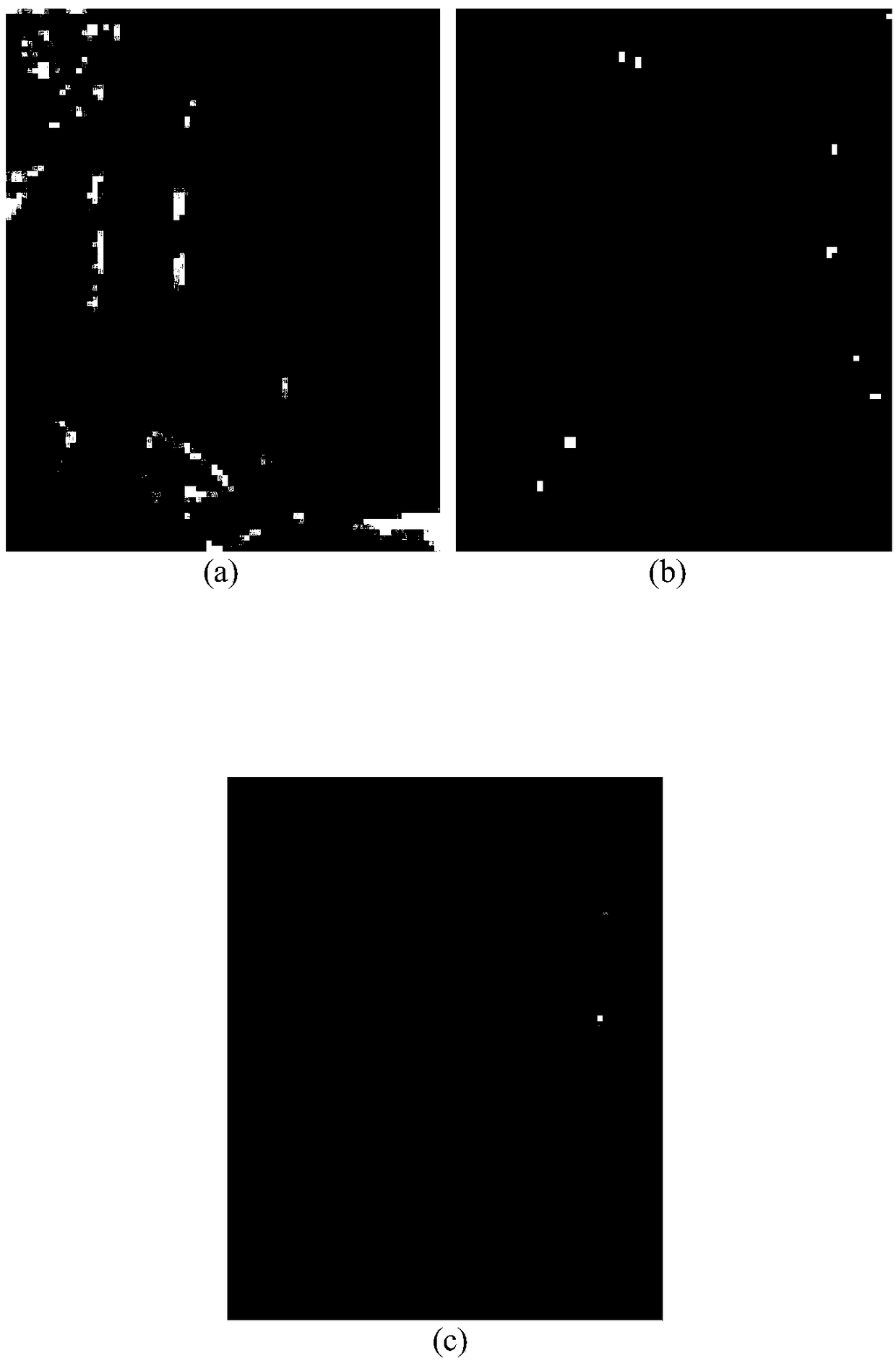
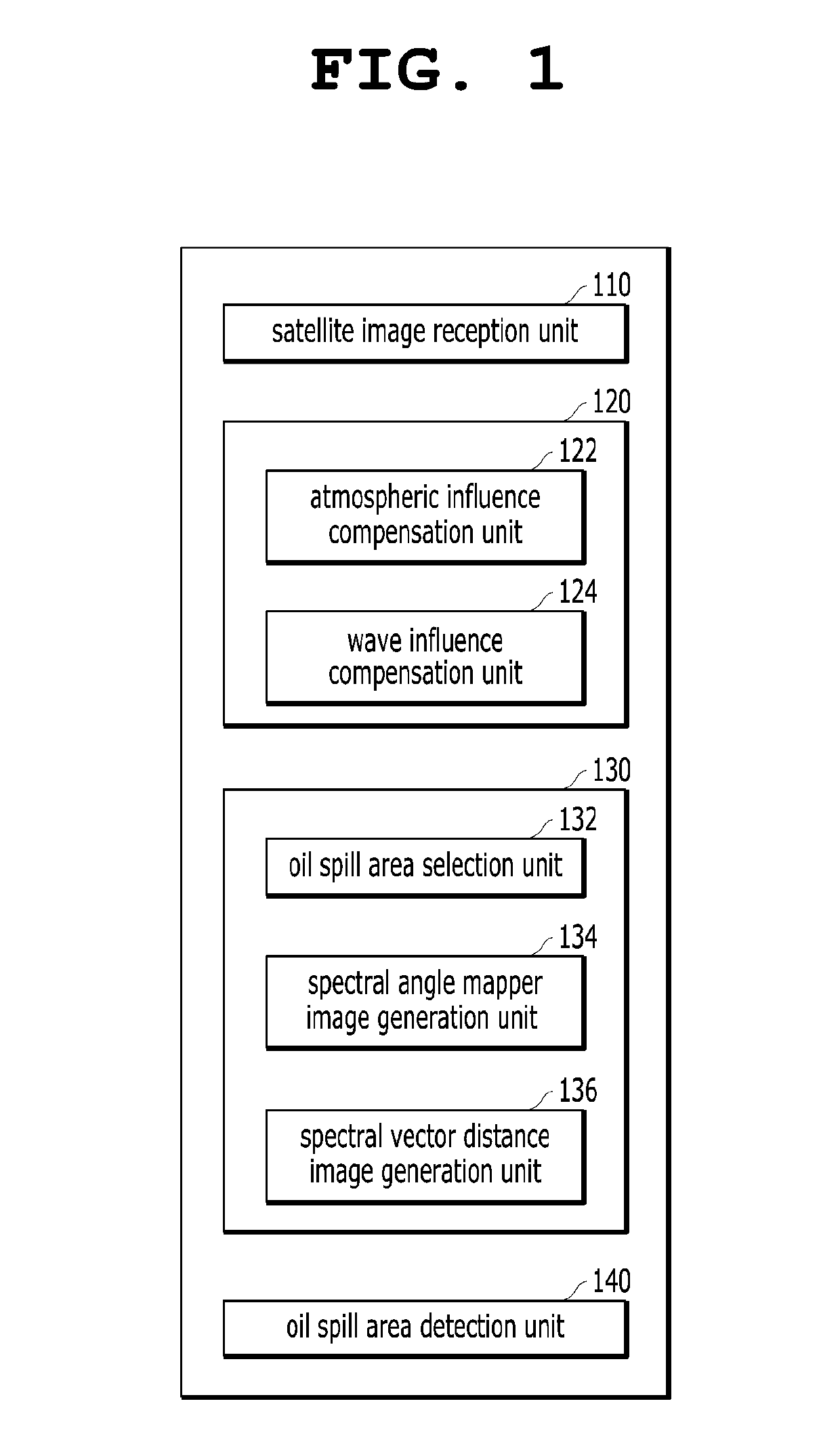
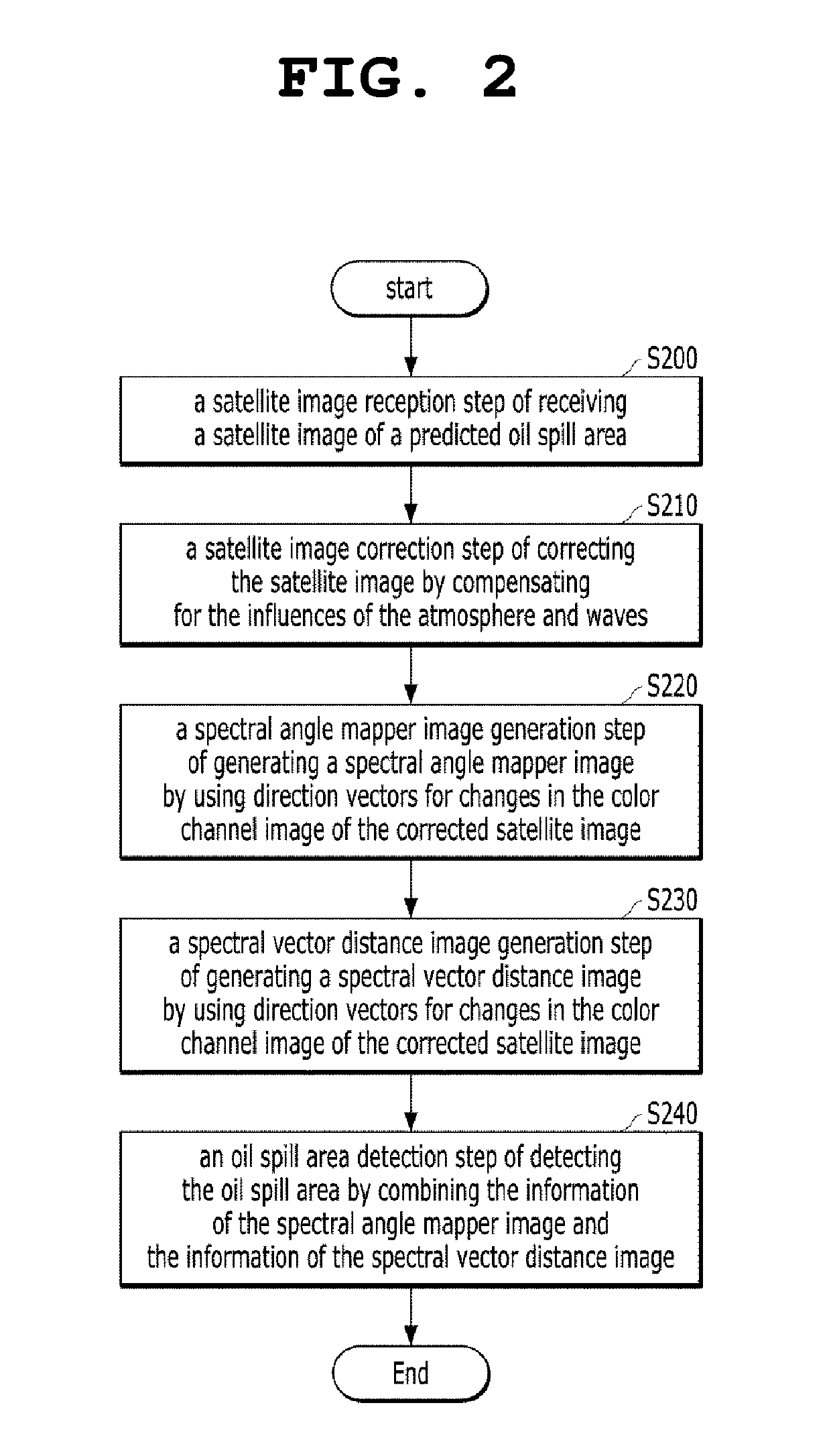
Apparatus and method for detecting oil spill by using satellite image
ActiveUS20190122369A1Accurately determinedEnsure high efficiency and accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisSpectral vectorSatellite image
The present invention relates to an apparatus and method for detecting an oil spill by using a satellite image, an apparatus for detecting an oil spill by using a satellite image, the apparatus including: a satellite image reception unit configured to receive a satellite image of a predicted oil spill area; a satellite image correction unit configured to correct the satellite image by compensating for the influences of the atmosphere and waves; a spectral angle mapper image generation unit configured to generate a spectral angle mapper image; a spectral vector distance image generation unit configured to generate a spectral vector distance image; and an oil spill area detection unit configured to derive the range of the oil spill area by combining the spectral angle mapper image and the spectral vector distance image together.
Owner:UNIV OF SEOUL IND COOP FOUND
Projection structure sparse coding-based hyperspectral image classification method
ActiveCN104866871AEasy to handleCutting costsCharacter and pattern recognitionHat matrixState of art
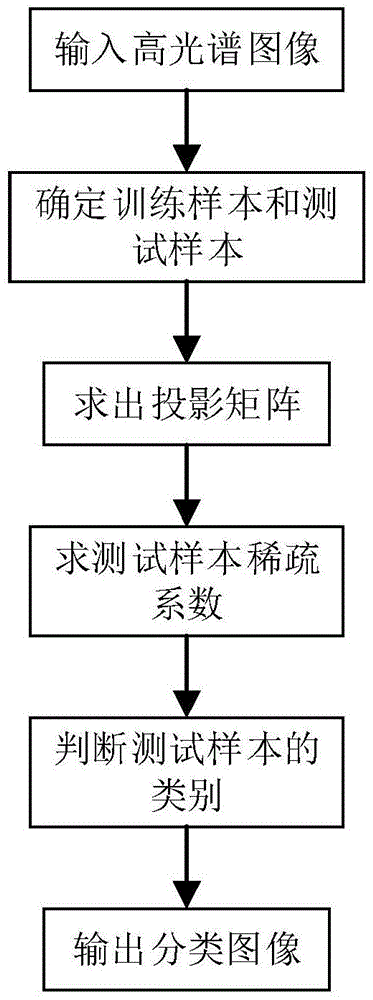
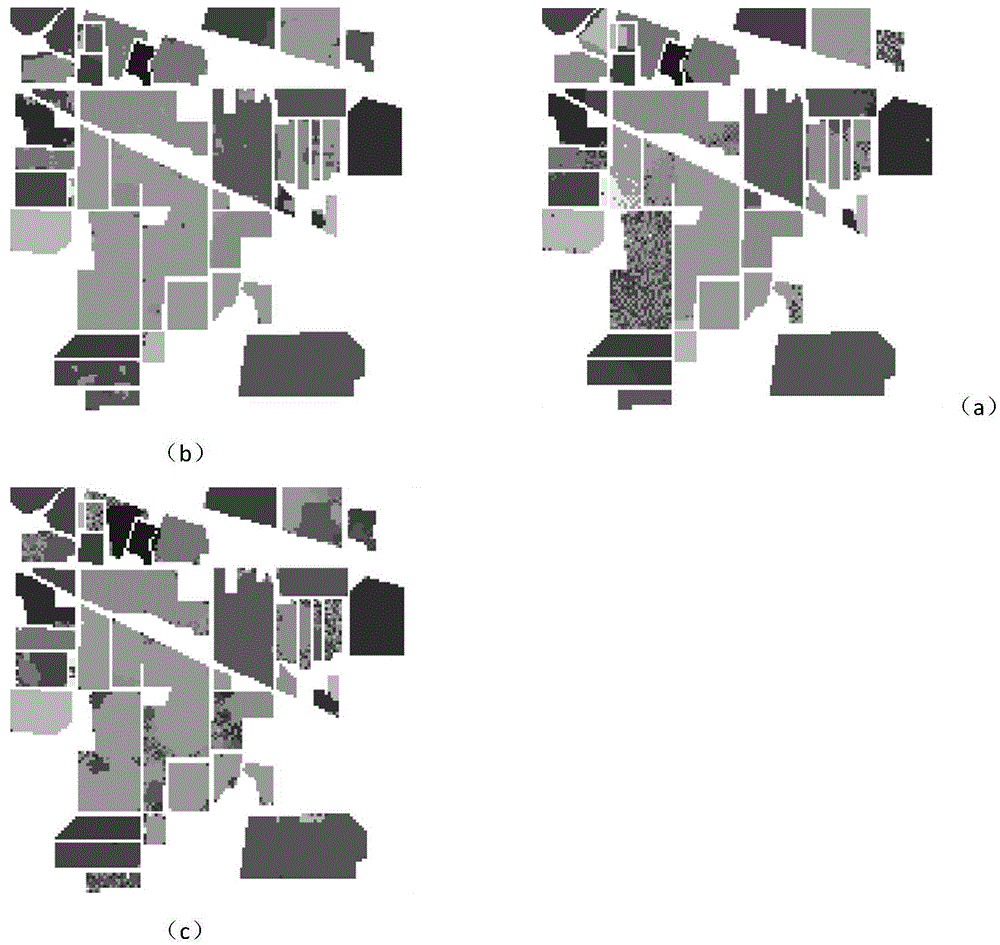
The invention discloses a projection structure sparse coding-based hyperspectral image classification method, which mainly solves the problem that in the prior art, neighborhood information of a hyperspectral image can not be effectively used for classification. The method comprises the realizing steps of: (1) reading in hyperspectral image data; (2) determining a training sample set and a test sample set in spectral vectors with labels of the hyperspectral image; (3) solving a projection matrix according to the training sample set; (4) according to the projection matrix of training samples of the hyperspectral image, solving a sparse coefficient of the test sample set; (5) according to the projection matrix and the sparse coefficient of the test sample set, judging a test sample by using an error judgment function, thus obtaining a surface feature category label of the test sample. The method has the advantages of high classification precision, small processing expenditure cost of high dimensional data and usage for surface feature differentiation of the hyperspectral image.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Decomposition method for mixed pixels of hyperspectral image
The present invention discloses a decomposition method for mixed pixels of a hyperspectral image. According to the method, in a process of using an NMF algorithm to decompose the mixed pixels, an SC-SVM algorithm is adopted to solve the quantity of end members and spectral vectors in the mixed pixels, the quantity of the end members can be actively recognized and the spectral vectors of the end members can be marked by the SC-SVM algorithm, thereby solving a basis matrix from the NMF algorithm; and a coefficient matrix (abundance matrix) is calculated by a non-negative matrix decomposition algorithm, gradual iteration to convergence is carried out by minimizing an objective function to calculate a wanted result, and finally achieve a purpose of decomposition of the mixed pixels.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Method and system for compressing a continuous data flow in real-time using cluster successive approximation multi-stage vector quantization (SAMVQ)
InactiveUS7551785B2Increase the compression ratioReduce Image ArtifactsImage codingCharacter and pattern recognitionImaging qualityMultidimensional data
Owner:CANADIAN SPACE AGENCY
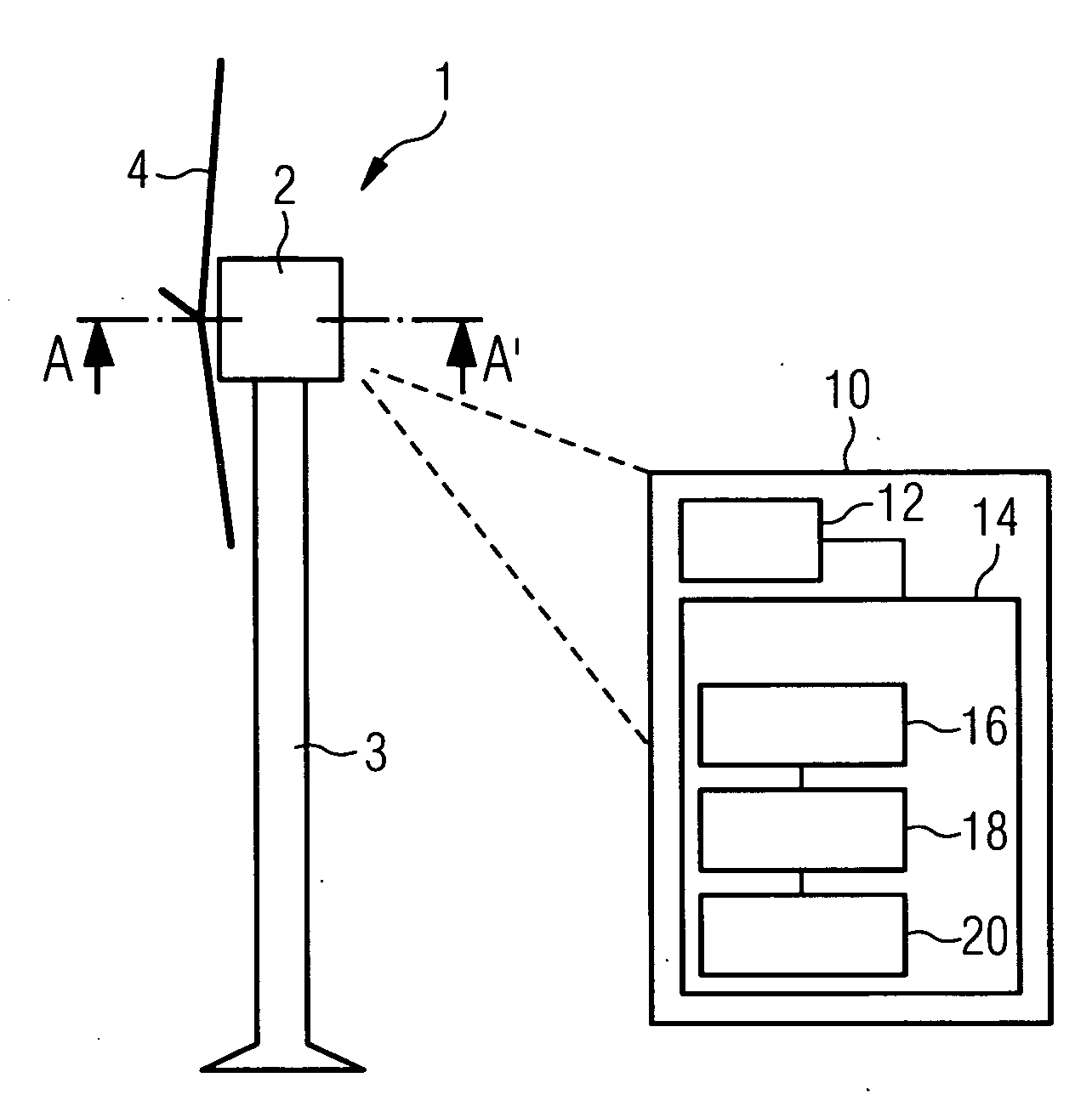
Apparatus and method for determining a resonant frequency of a wind turbine tower
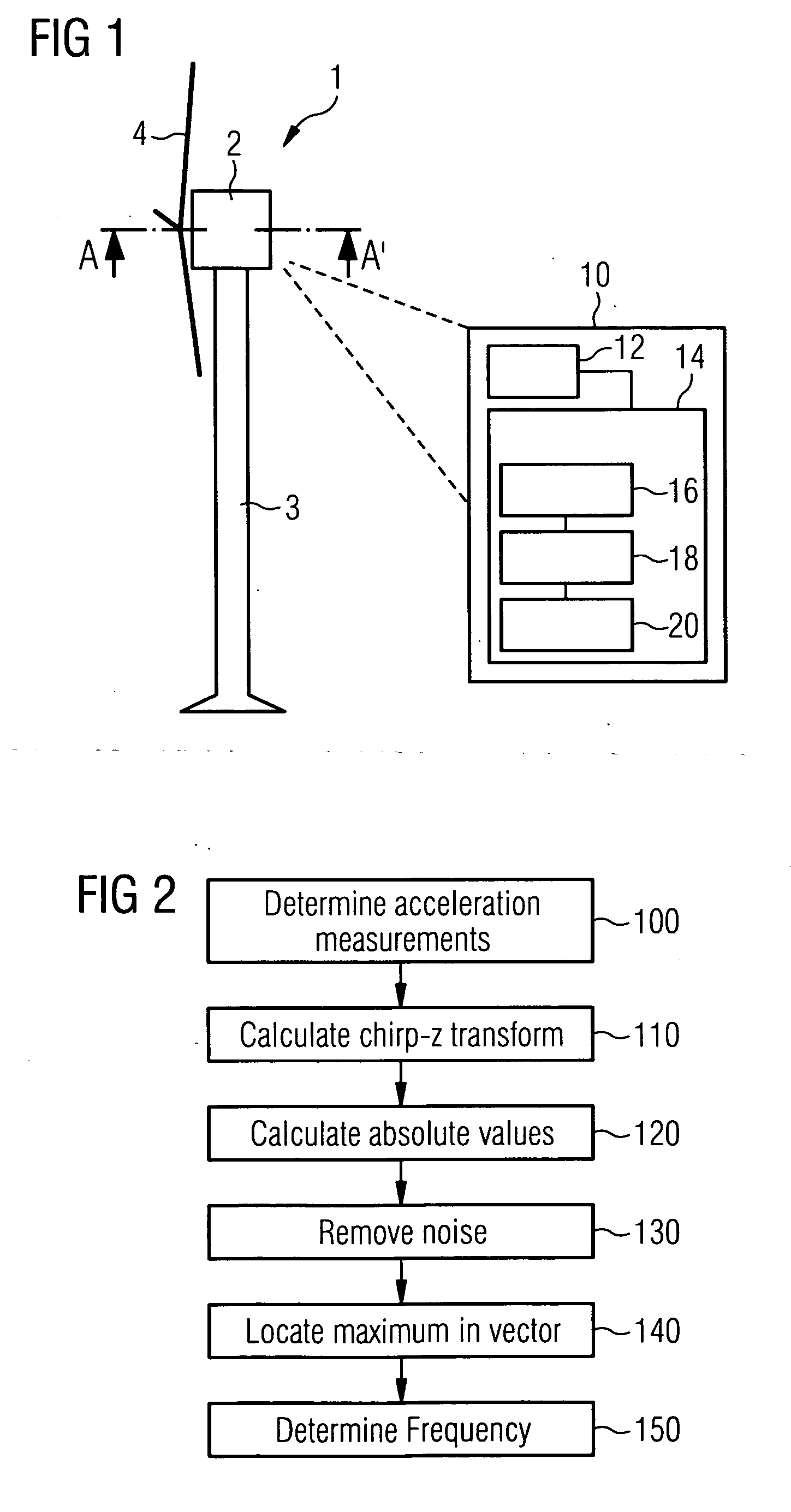
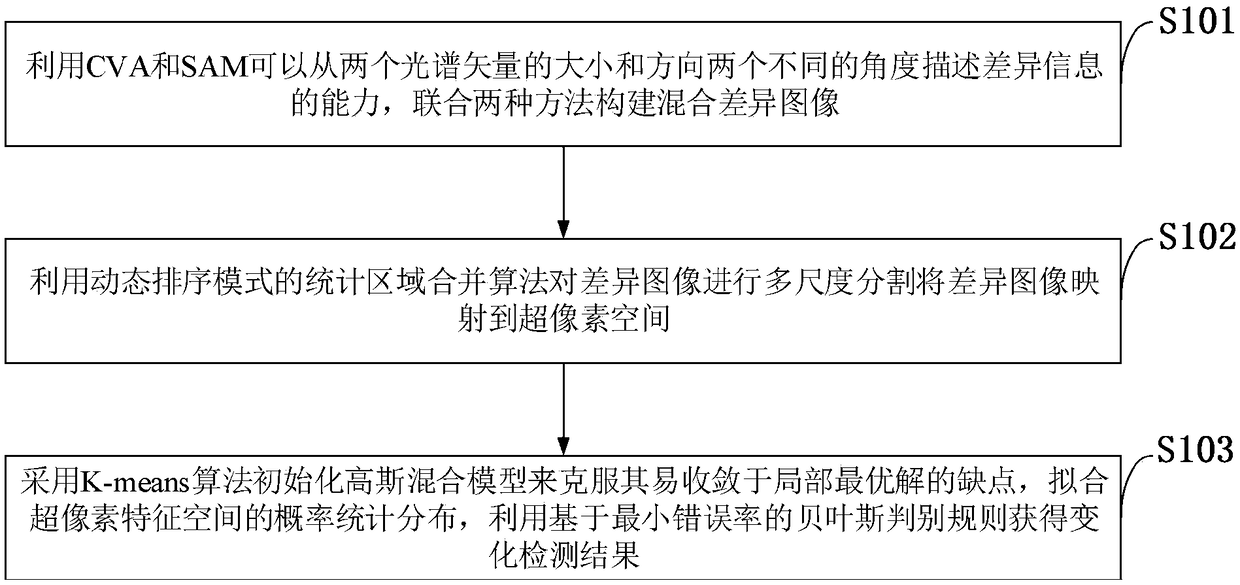
ActiveUS20090230682A1Efficiently determining resonant frequencyImprove accuracyLevel controlWind motor controlRotational axisFrequency spectrum
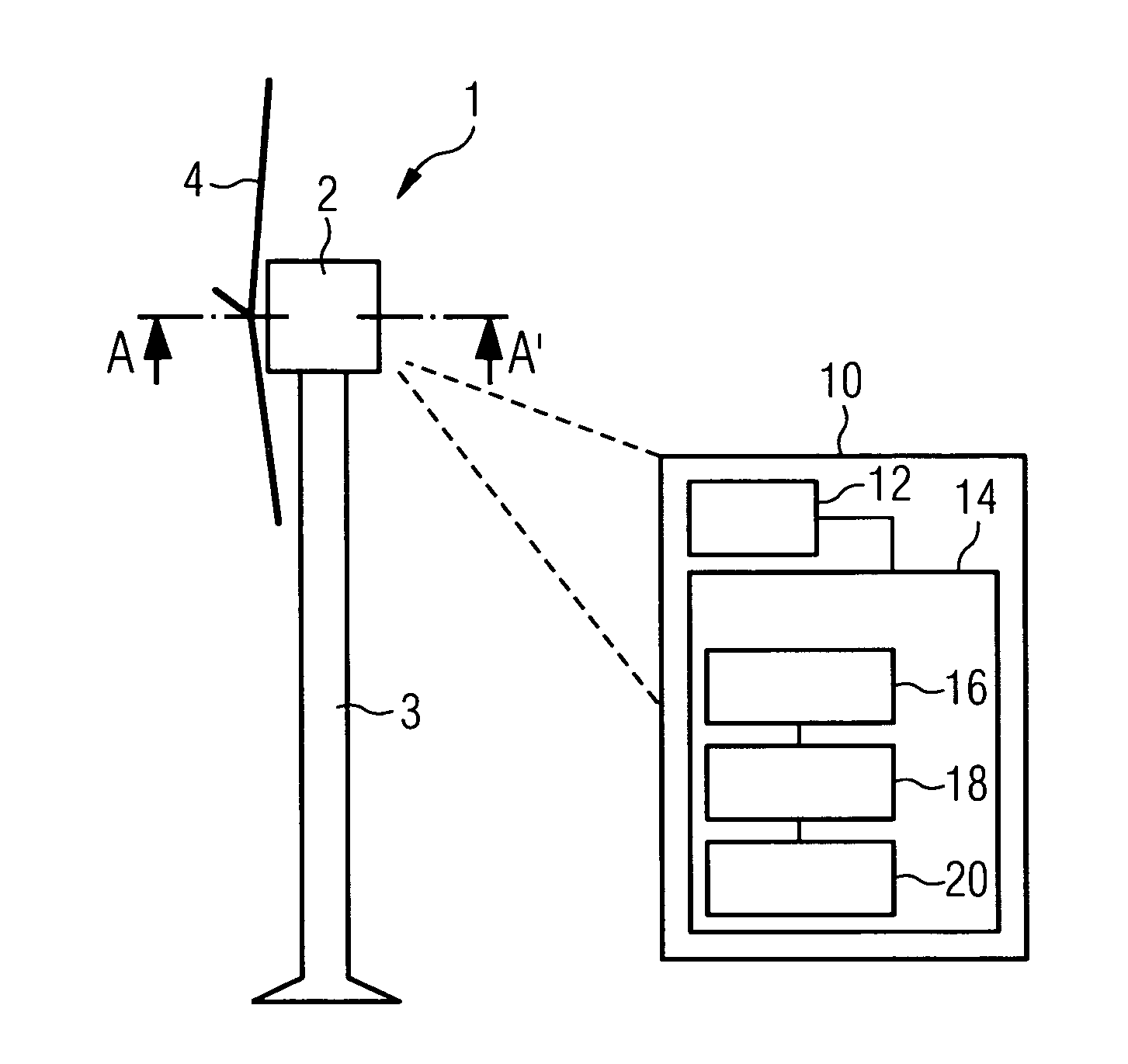
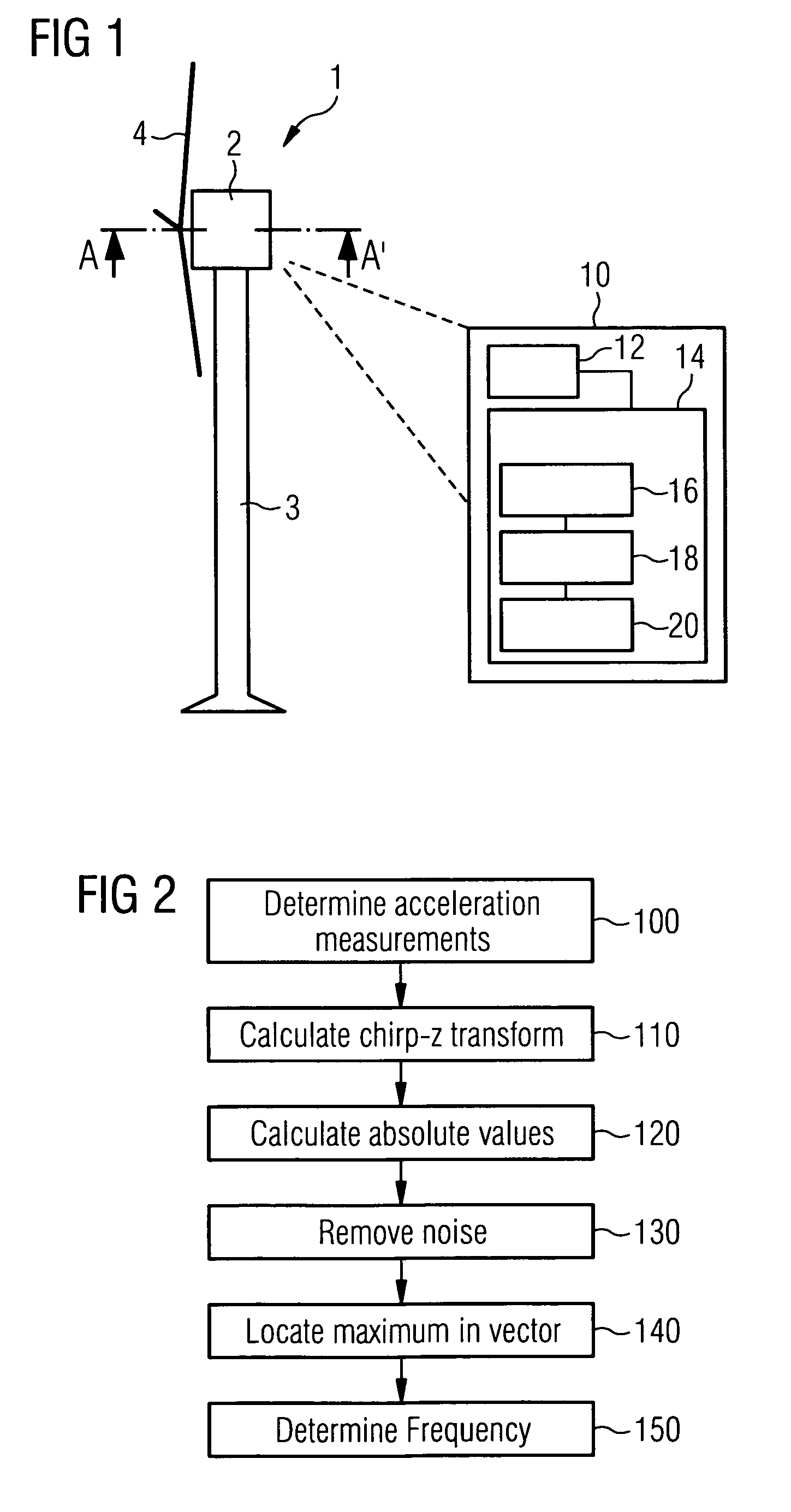
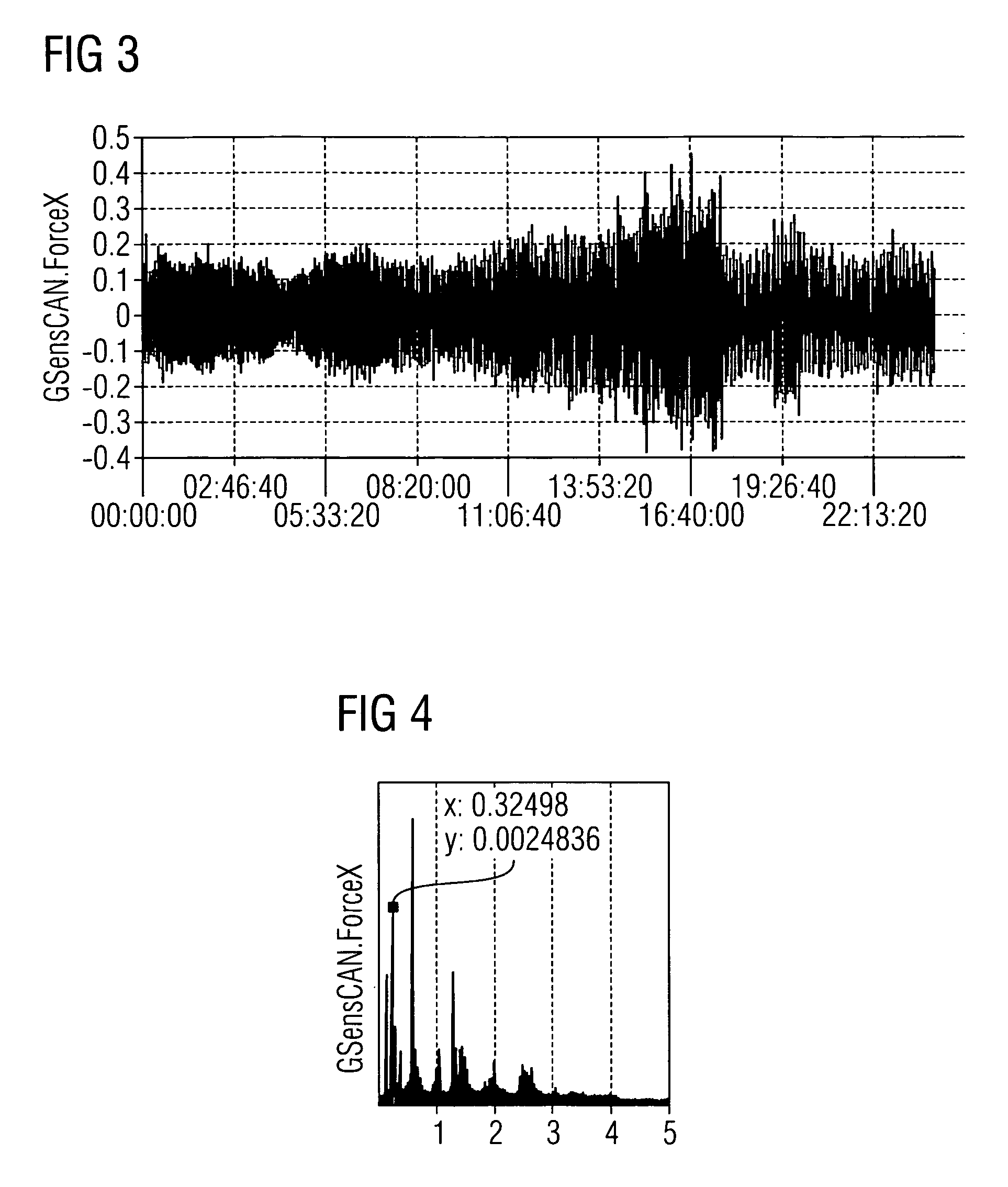
An apparatus for determining a resonant frequency of a wind turbine tower is provided. The apparatus includes a processing unit configured to receive an acceleration measurement value, the acceleration measurement value representative of the acceleration of the wind turbine tower in the direction parallel to a rotor rotational axis of the wind turbine and / or in the direction perpendicular to both the rotor rotational axis and the tower axis of the wind turbine. The apparatus includes a memory configured to store a series of acceleration measurement values, and the processing unit includes a Fourier transform module configured to calculate a spectral vector based on calculating a convolution-based fast Fourier transform of the series of acceleration measurement values, and includes a resonant frequency calculation module configured to calculate the tower resonant frequency based on the calculated spectral vector.
Owner:SIEMENS GAMESA RENEWABLE ENERGY AS
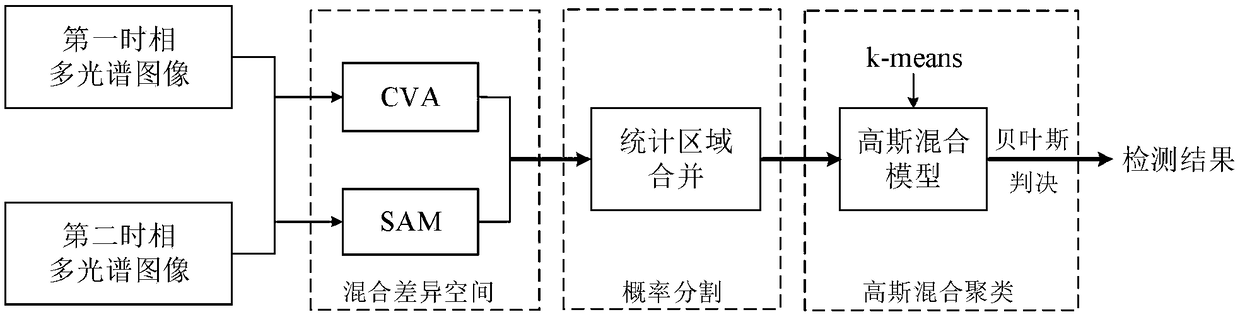
Multi-spectral image change detection method based on probability segmentation and Gaussian mixture clustering
ActiveCN109446894AHigh precisionReduce computational complexityScene recognitionMerge algorithmCharacteristic space
The invention belongs to the technical field of electronic equipment identification method or device, and discloses a multi-spectral image change detection method based on probability segmentation andGaussian mixture clustering. The method comprises the steps of firstly, inputting two original multi-spectral images of the same region and different time, and constructing the mixed difference imageHDS by CVA and SAM; secondly, segmenting the difference image into super-pixel space by using statistical region merging algorithm, and finally, using a K-Means algorithm to initialize Gaussian mixture model to overcome its shortcomings of convergence to local optimal solution, fitting the probability distribution of super-pixel feature space, and obtaining the change detection results by using Bayesian discriminant rule based on minimum error rate. The invention makes better use of the amplitude change information and the angle change information of the spectral vector, obtains the local structure characteristic of the image by using the super pixel segmentation, and effectively improves the detection accuracy of the change region in the SAR image.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Apparatus and method for determining a resonant frequency of a wind turbine tower
An apparatus for determining a resonant frequency of a wind turbine tower is provided. The apparatus includes a processing unit configured to receive an acceleration measurement value, the acceleration measurement value representative of the acceleration of the wind turbine tower in the direction parallel to a rotor rotational axis of the wind turbine and / or in the direction perpendicular to both the rotor rotational axis and the tower axis of the wind turbine. The apparatus includes a memory configured to store a series of acceleration measurement values, and the processing unit includes a Fourier transform module configured to calculate a spectral vector based on calculating a convolution-based fast Fourier transform of the series of acceleration measurement values, and includes a resonant frequency calculation module configured to calculate the tower resonant frequency based on the calculated spectral vector.
Owner:SIEMENS GAMESA RENEWABLE ENERGY AS
Jagged Doppler frequency shift selection method for DDMA waveform
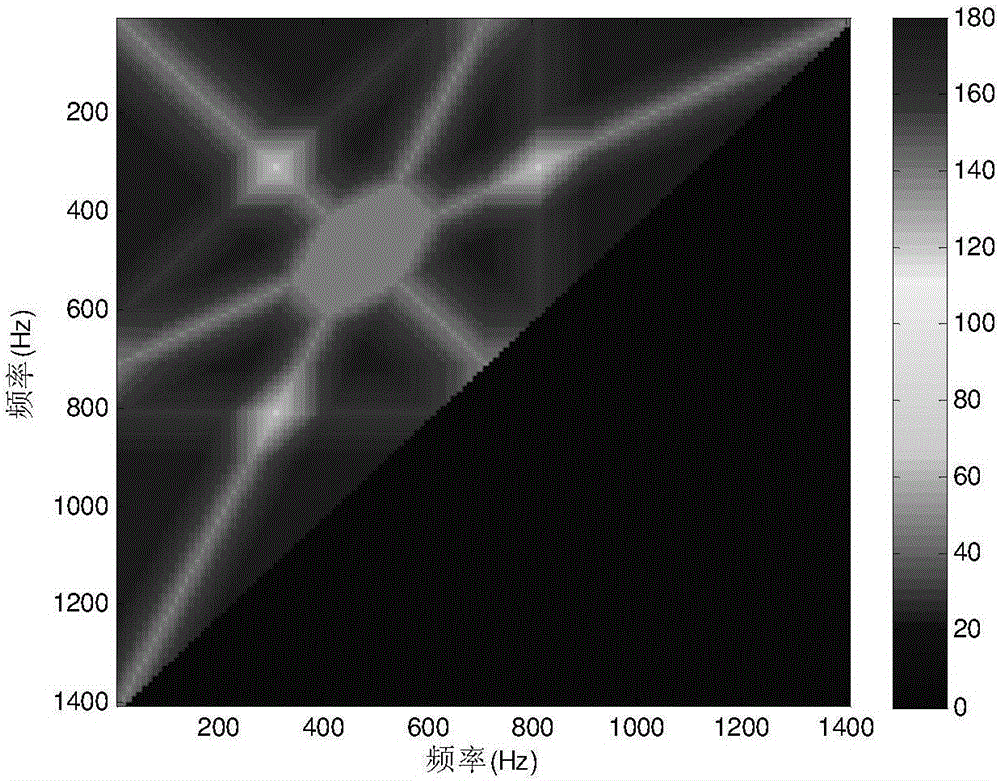
ActiveCN106054138AAvoid blind speedDoppler Frequency Offset FreeWave based measurement systemsWave shapeSpectral vector
The invention belongs to the technical field of radar, and discloses a jagged Doppler frequency shift selection method for DDMA waveform. The method comprises the following steps: determining the number of discrete points in a non-fuzzy Doppler scope and the Doppler frequency shift resolution; calculating the number of clutter Doppler points and the number of times of search, and constructing a Doppler frequency shift matrix; for each element of the Doppler frequency shift matrix, taking the coordinate thereof as the Doppler frequency shift number of a corresponding transmission channel, constructing a corresponding Doppler spectral vector after determining that the transmission channel is in the non-fuzzy Doppler scope, getting a synthetic Doppler spectral vector, and setting the element as the length of a non-overlapping clutter range in the synthetic Doppler spectral vector; and searching the maximum element in the Doppler frequency shift matrix, and calculating the optimal Doppler frequency shift corresponding to each transmission channel according to the coordinate of the maximum element. Through the method, the requirement on high-pulse repetition frequency of DDMA waveform is reduced, and the blind speed problem of a target during application of DDMA waveform is relieved effectively.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Hyperspectral image target detection method based on variational self-coding network
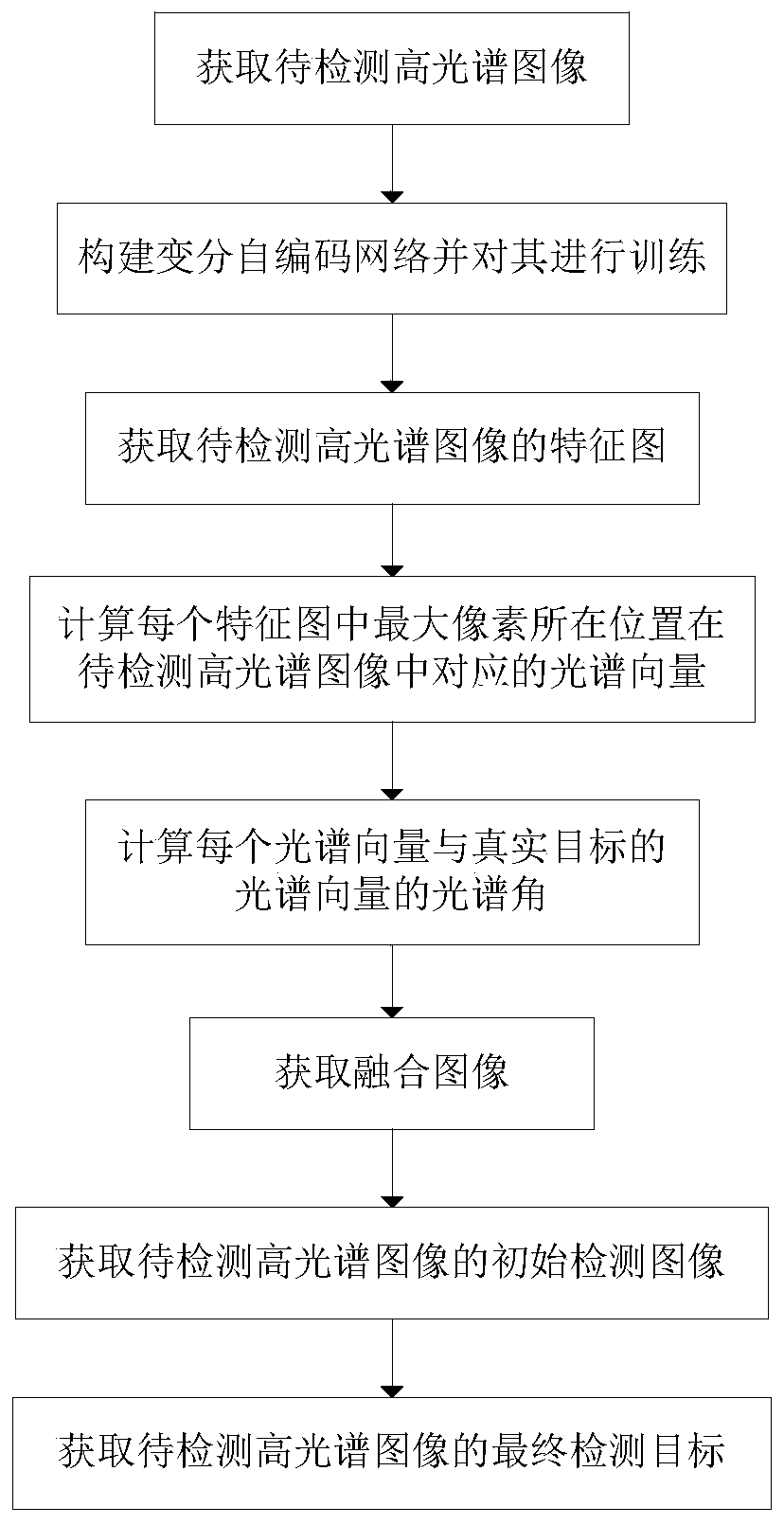
ActiveCN110008948ASolve the low detection accuracyImprove detection accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisSpectral vectorMaximum Pixel
The invention provides a hyperspectral image target detection method based on a variational self-coding network, which mainly solves the technical problem of low detection precision in the prior art,and comprises the following steps of: obtaining a to-be-detected hyperspectral image and a real spectral vector of a to-be-detected target; constructing a variational self-coding network, and trainingthe variational self-coding network; obtaining a feature map of the to-be-detected hyperspectral image; calculating a spectral vector corresponding to the position of the maximum pixel value in eachfeature map in the to-be-detected hyperspectral image; calculating a spectral angle between each spectral vector and a real spectral vector; obtaining a fusion image; obtaining an initial detection image of the to-be-detected hyperspectral image; and obtaining a final detection target of the to-be-detected hyperspectral image. According to the method, the frequency band interference in the hyperspectral image can be reduced, redundant information is reduced, a target and a complex background in the hyperspectral image are better distinguished, the detection precision of a target point is improved, and meanwhile, the complexity of data processing is reduced.
Owner:陕西丝路天图卫星科技有限公司
Hyper-spectral image ground object recognition method based on sparse kernel representation (SKR)
ActiveCN102324047BImprove recognition accuracyQuick identificationCharacter and pattern recognitionDiscriminantTest sample
The invention discloses a hyper-spectral image ground object recognition method based on a sparse kernel representation (SKR), which mainly solves the defects that the recognition time is long and the recognition accuracy is not high when the dimensions of a sample are decreased to be low in the existing method. The method comprises the recognition steps of: firstly, using the spectral vectors ofknown tags in a hyper-spectral image as a dictionary for sparse coding, wherein the spectral vectors of the known tags are arranged by classifications and the spectral vector samples of all unknown tags form a test sample set; secondary, using a neighbor method to construct a central sample matrix, respectively mapping test samples and the dictionary to a feature space by constructing a sparse kernel function to obtain the mapped dictionary and the mapped test samples, and conducting line normalization to the mapped dictionary; and finally using the normalized dictionary to conduct sparse coding to the mapped test samples and judging the classifications of the test samples through an error discriminant. The hyper-spectral image ground object recognition method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the recognition accuracy can be ensured to be high, the ground object recognition of the hyper-spectral image can be completed rapidly at the same time and the subsequent processing of the recognized ground objects is facilitated.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
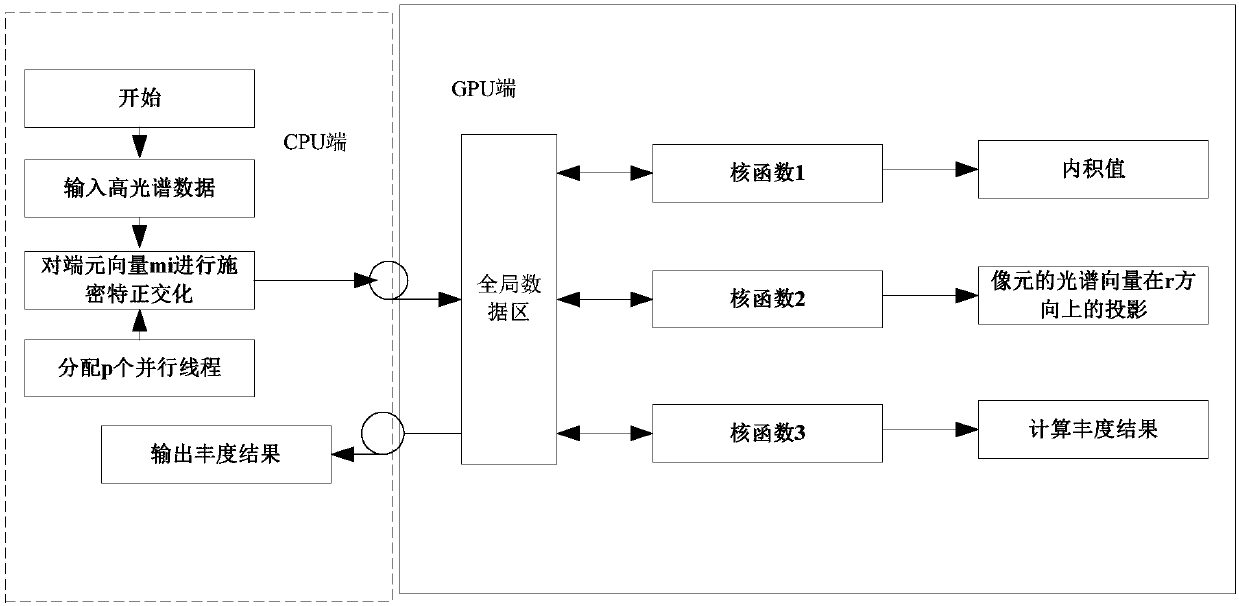
GPU-based parallel realizing method of abundance estimation algorithm
InactiveCN107644393AImprove operational efficiencyProcessor architectures/configurationSpectral vectorOrthogonal basis
The invention discloses a GPU-based parallel realizing method of an abundance estimation algorithm. The GPU-based parallel realizing method comprises the steps of: 1, storing hyperspectral mixed pixeldata H to a GPU end; 2, acquiring end element vectors m, and allocating the acquired end element vectors m to p parallel threads on a CPU side one by one; 3, acquiring vectors m<~> which correspond to the end element vectors m and are orthogonal in a vector space [m<1>, m<2>, ..., m<i-1>]; 4, acquiring an orthogonal basis corresponding to an end element set M, and calculating a corresponding inner product value; 5, calculating projection of a spectral vector of each pixel in a d<~T> direction; 6, and calculating an abundance result alpha p corresponding to each end element mp, andstoring the abundance result alpha p to the GPU end. According to the GPU-based parallel realizing method, the abundance value is calculated by adopting a GPU parallel processing kernel function, theparallel mechanism runs much faster than on the traditional CPU serial mechanism, and the operating efficiency of real-time abundance estimation is greatly improved.
Owner:DALIAN MARITIME UNIVERSITY
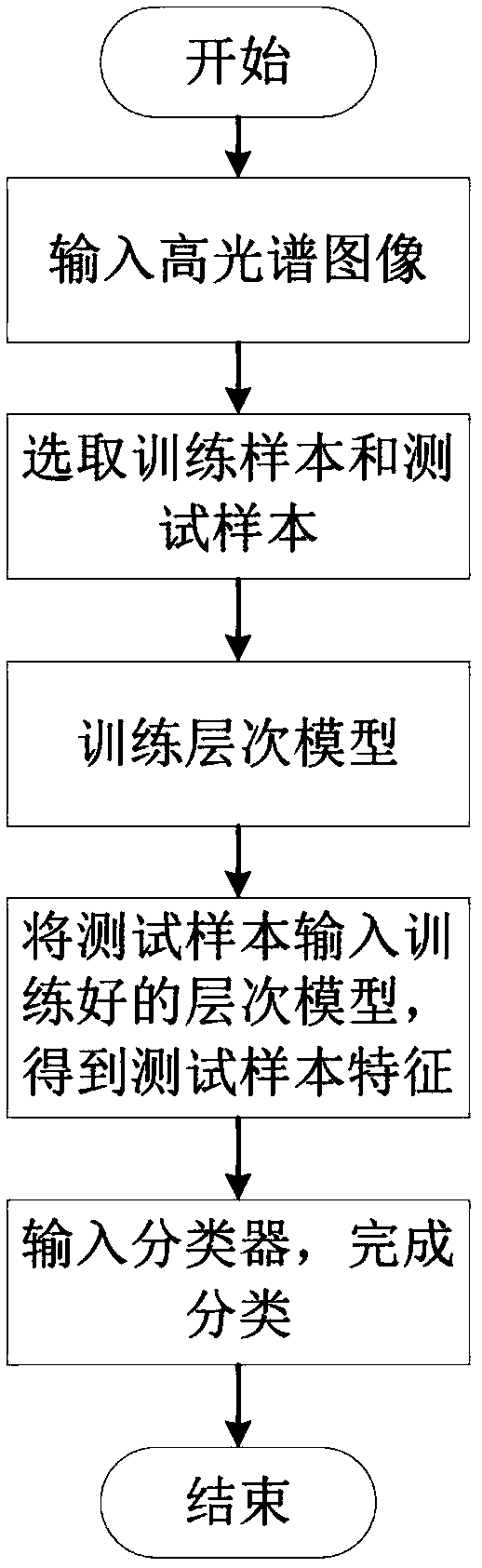
Hyperspectral image classification method and system based on correlation entropy principle
ActiveCN109034213ASpectral feature abstractionThe classification result is accurateCharacter and pattern recognitionSmall sampleEuclidean vector
The invention provides a hyperspectral image classification method and a system based on the correlation entropy principle. Firstly, the input image is preprocessed so that the element values of all spectral vectors are between 0 and 1; secondly, a small number of samples are selected as training samples, and the spatial features of hyperspectral images are extracted by using the designed hierarchical model of fusion dimension reduction method and correlation entropy principle. Then, the spatial spectrum characteristics of the test samples are learned by using the trained hierarchical structure. Finally, the characteristics of the test samples are input into the KNN classifier to get the class label. The invention fully combines the spectral and spatial characteristics of the hyperspectraldata by using the correlation entropy principle; by using the hierarchical model of the invention, more abstract spatial spectrum features can be obtained; due to the characteristics of LDA, the invention has small sample complexity, and only a small number of training samples are needed to obtain a better classification result, so the invention is more conducive to practical application.
Owner:HUAZHONG NORMAL UNIV
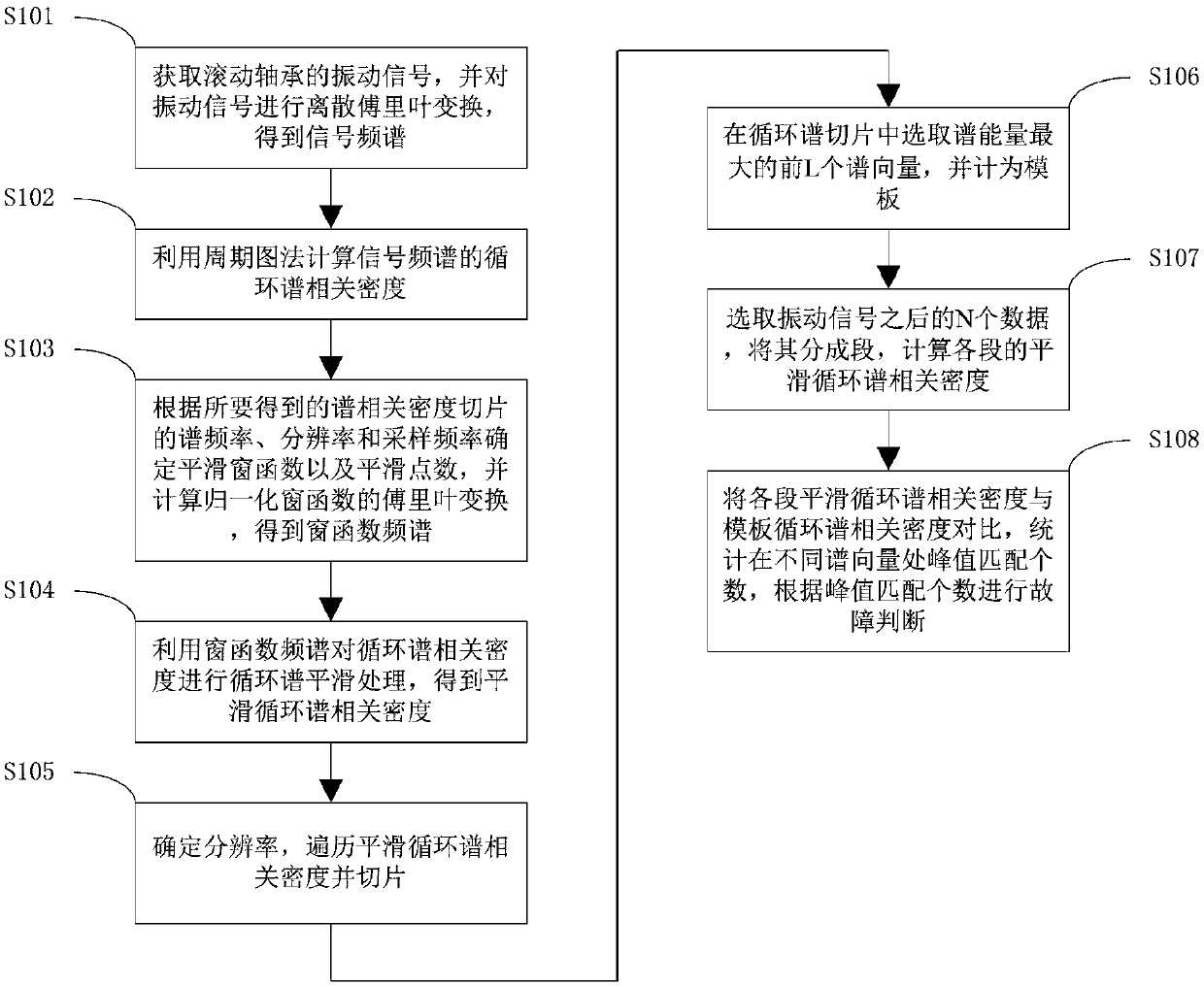
Rolling bearing fault real-time monitoring method
InactiveCN109580224AAccurate fault detectionSuppress stationary noiseMachine bearings testingFrequency spectrumSpectral vector
The invention relates to the technical field of bearing fault monitoring, and provides a rolling bearing fault real-time monitoring method. A rolling bearing vibration signal x<N>(n) is acquired, anddiscrete Fourier transformation is conducted to obtain a signal frequency spectrum X<N>(k); cycle-spectrum relative density (please see the specification) of the signal frequency spectrum X<N>(k) is calculated; a smoothing window function and a smoothing point M are determined, Fourier transform of a normalization windowing function is calculated, and thus a window function frequency spectrum W<N>(f) is obtained; cycle-spectrum smoothing processing is conducted on the cycle-spectrum relative density (please see the specification), and thus smoothing cycle-spectrum relative density (please seethe specification) is obtained; a resolution ratio is determined, the smoothing cycle-spectrum relative density (please see the specification) is traversed, and slicing is conducted; the first L spectral vectors with maximum spectrum energy are selected from cycle-spectrum slices and are regarded as a template; N data after the vibration signal x<N>(n) are selected and divided into K sections, andthe smoothing cycle-spectrum relative density (please see the specification) of the each section is calculated; the smoothing cycle-spectrum relative density (please see the specification) of the each section is compared with the cycle-spectrum relative density (please see the specification) of the template, peak matching number O at the different spectrum vectors is counted, and fault judgment is conducted according to the peak matching number O.
Owner:北京谛声科技有限责任公司
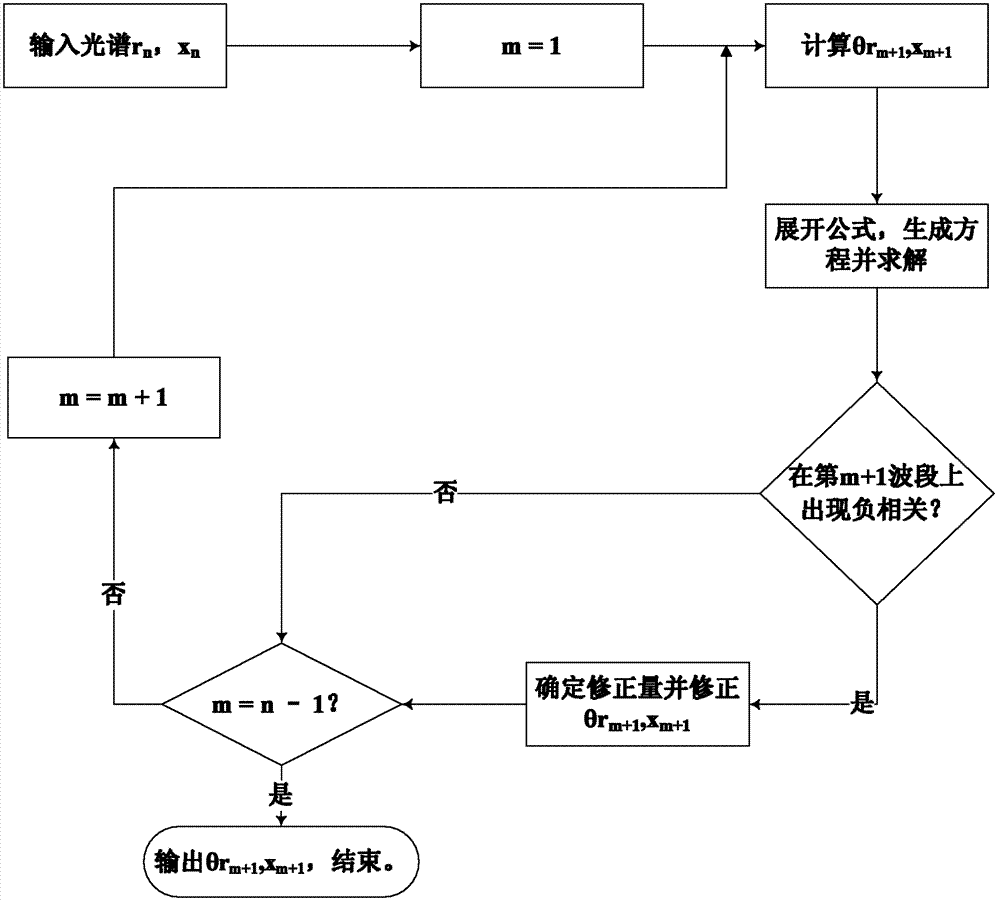
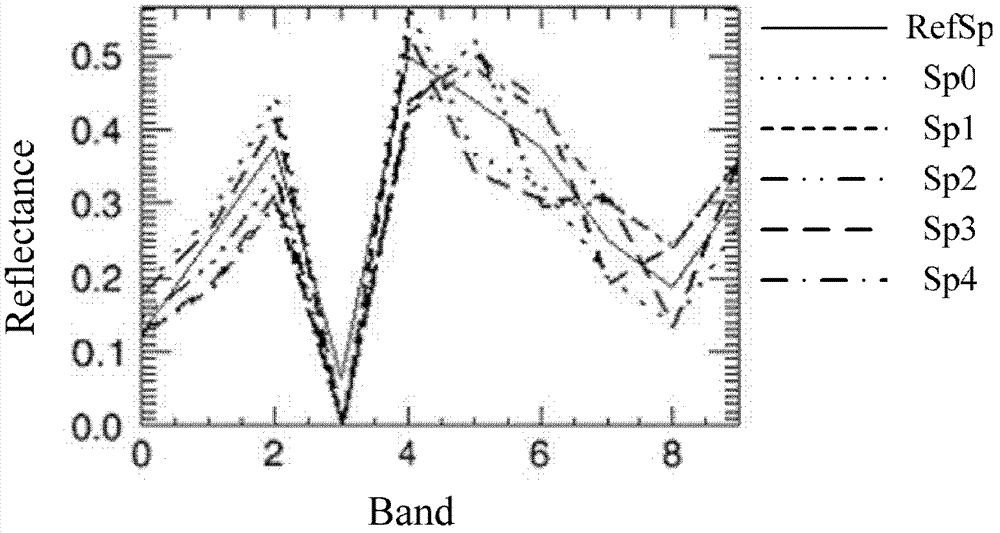
Spectral angle mapping method used for correcting negative correlation of hyperspectral remote sensing image by wavebands
InactiveCN102708544AEffective Stretch SeparabilityImprove classification accuracyImage enhancementSpectral curveSpectral bands
The invention provides a spectral angle mapping method used for correcting the negative correlation by wavebands, which is technically characterized in that: the traditional spectral angle is calculated, the value of the newly added spectral bands is used as the independent variable, the existence of the negative correlation on each newly added spectral band is judged, and the newly added spectral band with the negative correlation is provided with correction parameters. The spectral angle mapping method provided by the invention aims to solve the problem that the traditional spectral angle mapping method can not distinguish the negative correlation of spectrums so that the spectral curves with different characteristics are classified into the same category relative to a certain reference spectrum. The experiments proves that: due to the adoption of the spectral angle mapping method provided by the invention, the separability of the spectrums is improved effectively, and the spectral vectors which can not be separated by using the traditional spectral angle mapping method can be separated by stages according to the difference of the generated negative-correlation wavebands. The spectral angle mapping method provided by the invention laids a foundation for the subsequent hyperspectral remote sensing image classification, the target identification and the like.
Owner:南通久茂工贸有限公司 +1
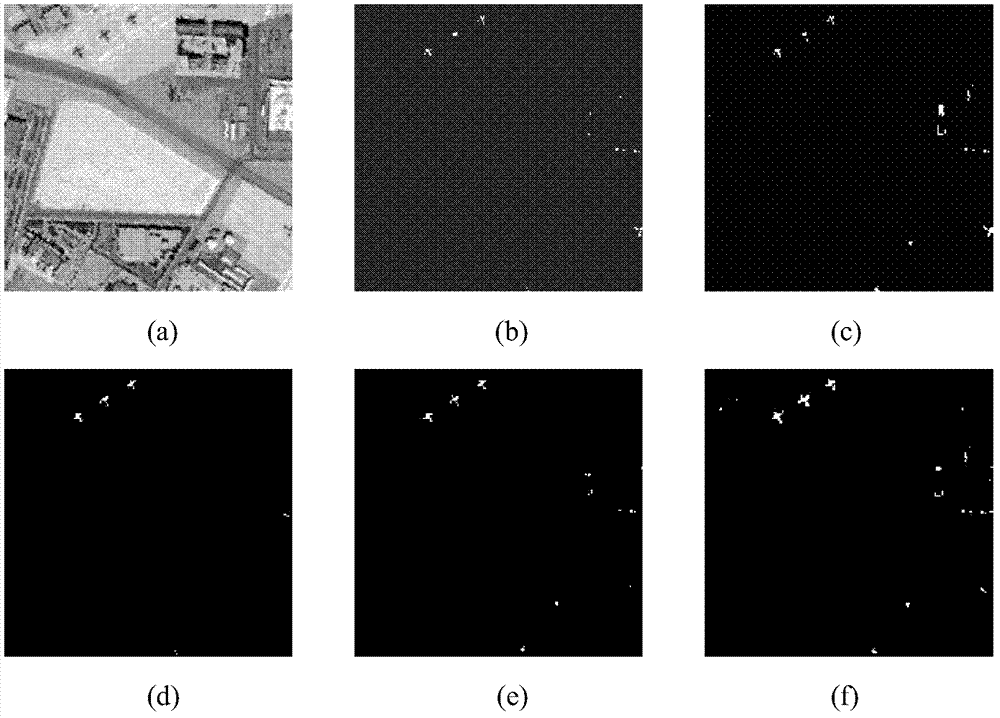
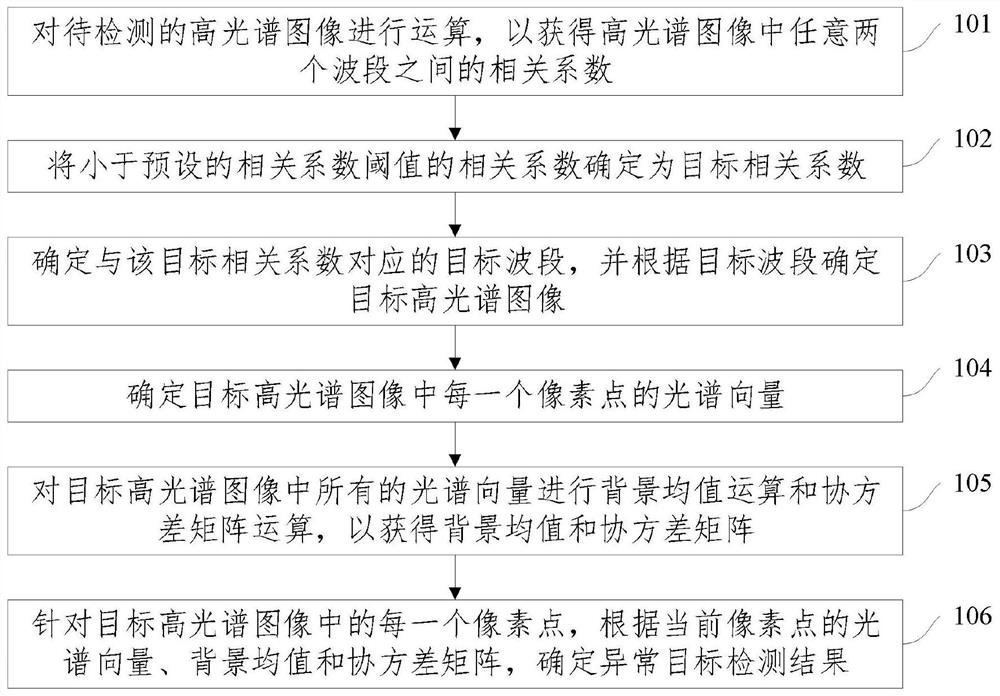
Abnormal target detection method and device and computer readable medium
PendingCN112163523AImprove detection accuracyReduce processing difficultyScene recognitionCorrelation coefficientSpectral vector
The invention relates to an abnormal target detection method and device and a computer readable medium, and the method comprises the steps: carrying out the operation of a to-be-detected hyperspectralimage, so as to obtain a correlation coefficient between any two wavebands in the hyperspectral image; determining the correlation coefficient smaller than a preset correlation coefficient thresholdas a target correlation coefficient; determining a target waveband corresponding to the target correlation coefficient, and determining a target hyperspectral image according to the target waveband; determining a spectral vector of each pixel point in the target hyperspectral image; performing background mean value operation and covariance matrix operation on all spectral vectors in the target hyperspectral image to obtain a background mean value and a covariance matrix; and for each pixel point in the target hyperspectral image, determining an abnormal target detection result according to thespectral vector, the background mean value and the covariance matrix of the current pixel point. According to the method, the detection precision of the abnormal target can be improved.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF ENVIRONMENTAL FEATURES
Automated morphological endmember extraction based hyperspectral image data unmixing method
ActiveCN105427319AImprove clarityAvoid lossImage enhancementImage analysisSpectral vectorStructuring element
The invention relates to an automated morphological endmember extraction based hyperspectral image data unmixing method and belongs to the technical field of image data processing. According to the method, calculation is performed by utilizing a reference spectral vector to obtain an image element with highest mixing degree in a whole image, and based on this, a morphological operator is improved; an original structural element is improved with a new MEI calculation method; a structural element of an odd size is replaced with a structural element of an even size; and four candidate endmembers are selected from each structural element, so that possible information loss is effectively avoided, the accuracy of data processing is further improved, and finally the definition of the image obtained after data processing is improved; and the automated morphological endmember extraction based hyperspectral image data unmixing method is quite simple and convenient to implement.
Owner:CHONGQING BIO NEWVISION MEDICAL EQUIP LTD
Image super-resolution reconstruction method and system based on channel constraint multi-feature fusion
PendingCN113744136AImprove multi-level feature expression abilityFully integratedGeometric image transformationCharacter and pattern recognitionHigh spatial resolutionSpectral vector
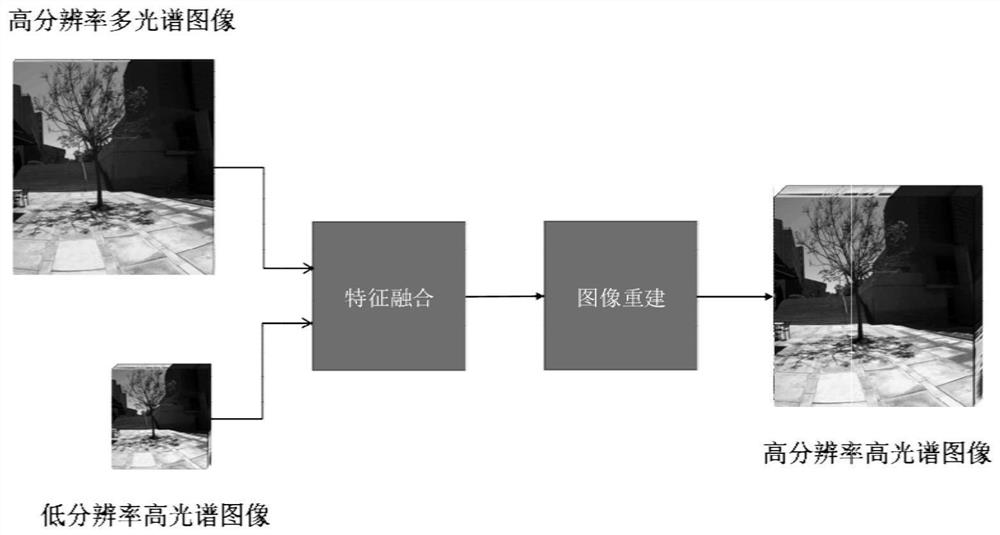
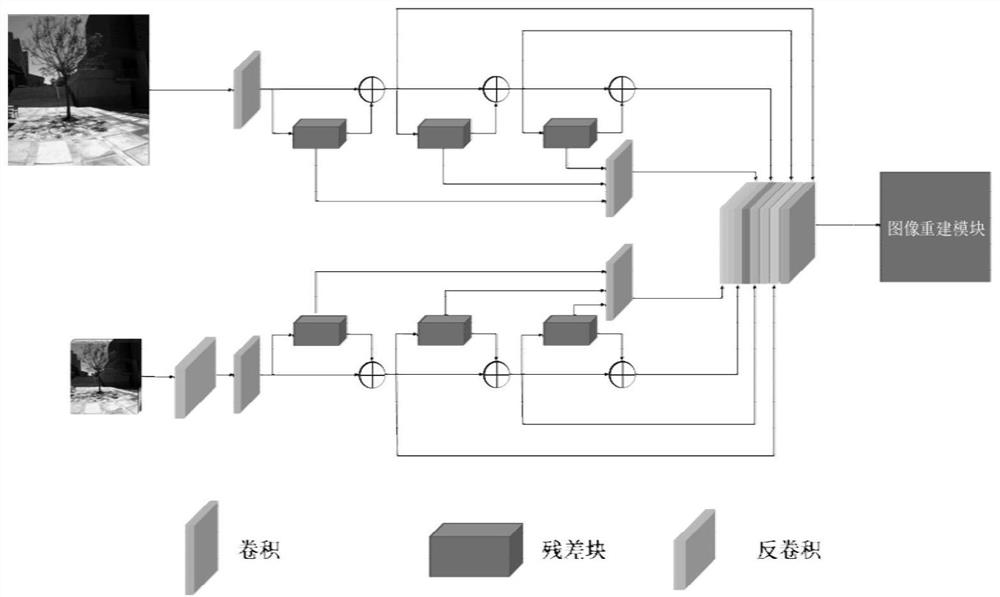
The invention discloses an image super-resolution reconstruction method and system based on channel constraint multi-feature fusion, and belongs to the field of super-resolution image reconstruction. The method comprises the steps: acquiring high-spatial-resolution hyperspectral image pairs, low-spatial-resolution hyperspectral image pairs and high-spatial-resolution multispectral image pairs in the same scene to construct a training set; constructing a double-channel super-resolution network, wherein the system comprises: a feature extraction module which is used for extracting spatial-spectral features from low-spatial-resolution hyperspectral and high-spatial-resolution multispectral images in the same scene at the same time, a feature fusion module which is used for fusing the spatial information of the multispectral images and the spectral information of the hyperspectral images in the same scene, and an image reconstruction module which is used for reconstructing to obtain a reconstructed image; training the network until the change rule of each element in the corresponding spectral vectors of the reconstructed image and the original image is consistent; and acquiring a low-spatial-resolution hyperspectral image and a high-spatial-resolution multispectral image in a scene to be reconstructed, and inputting the image into the trained network to obtain a reconstructed super-resolution hyperspectral image.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com