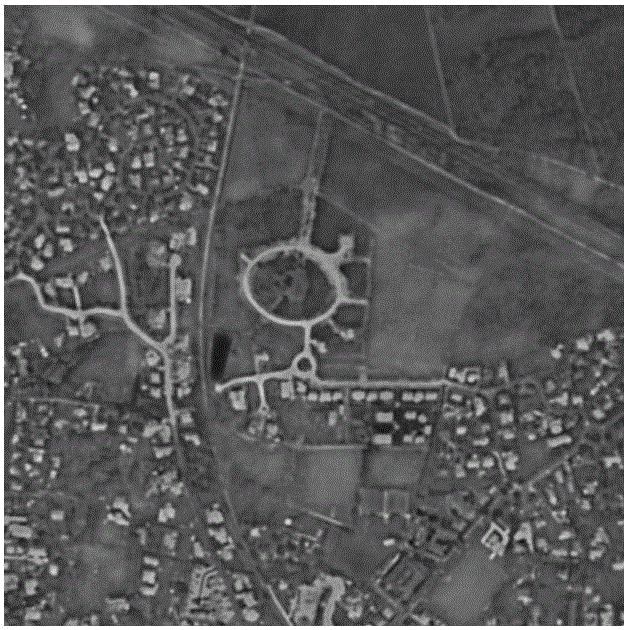
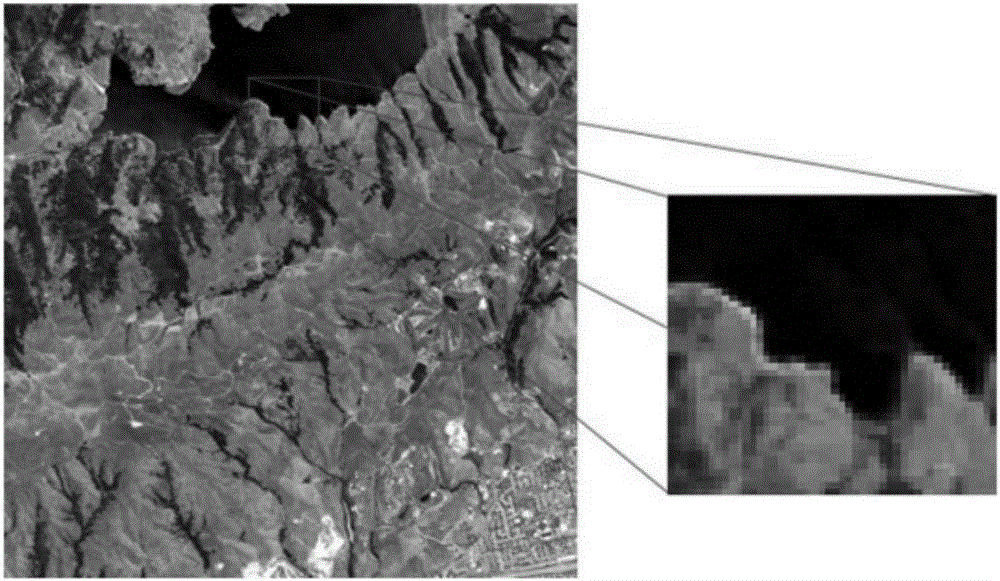
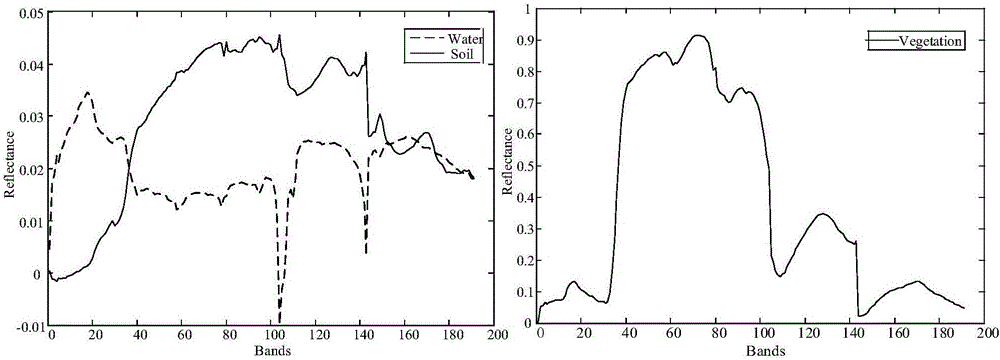
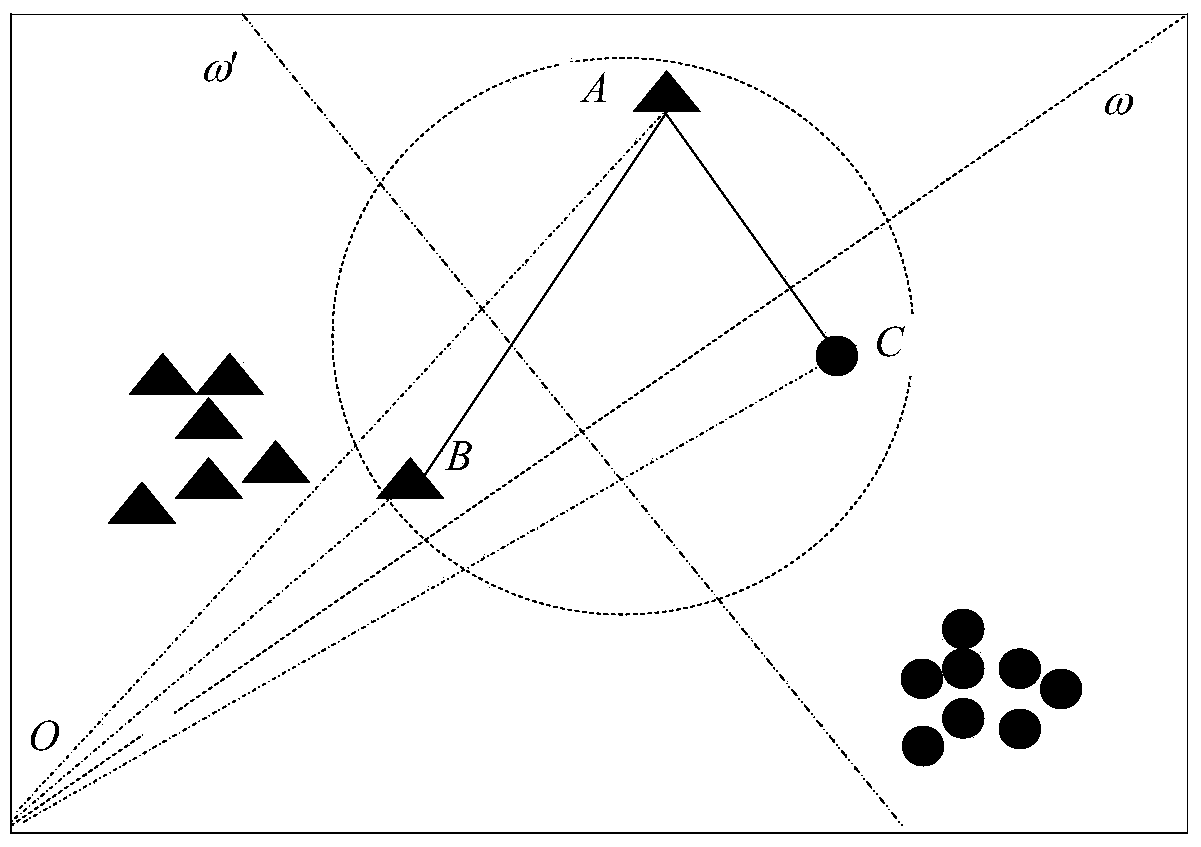
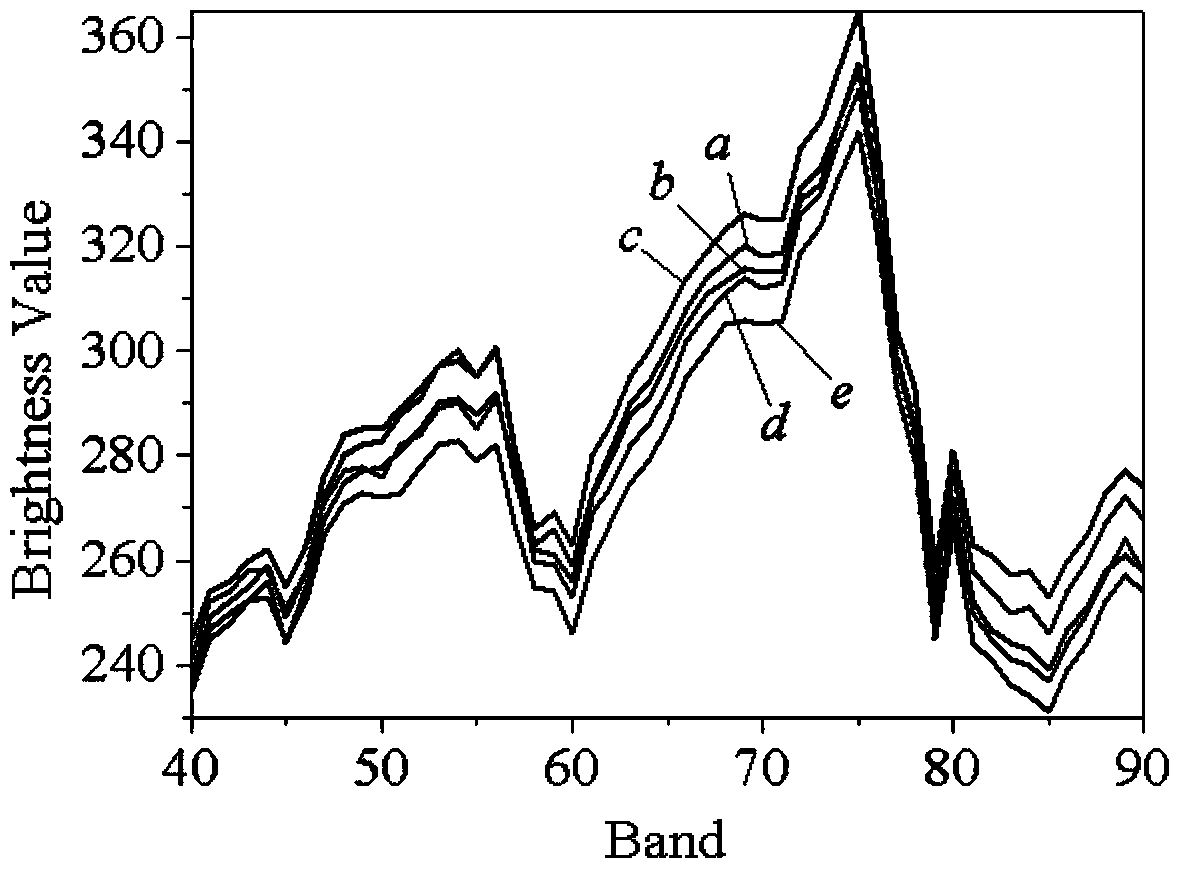
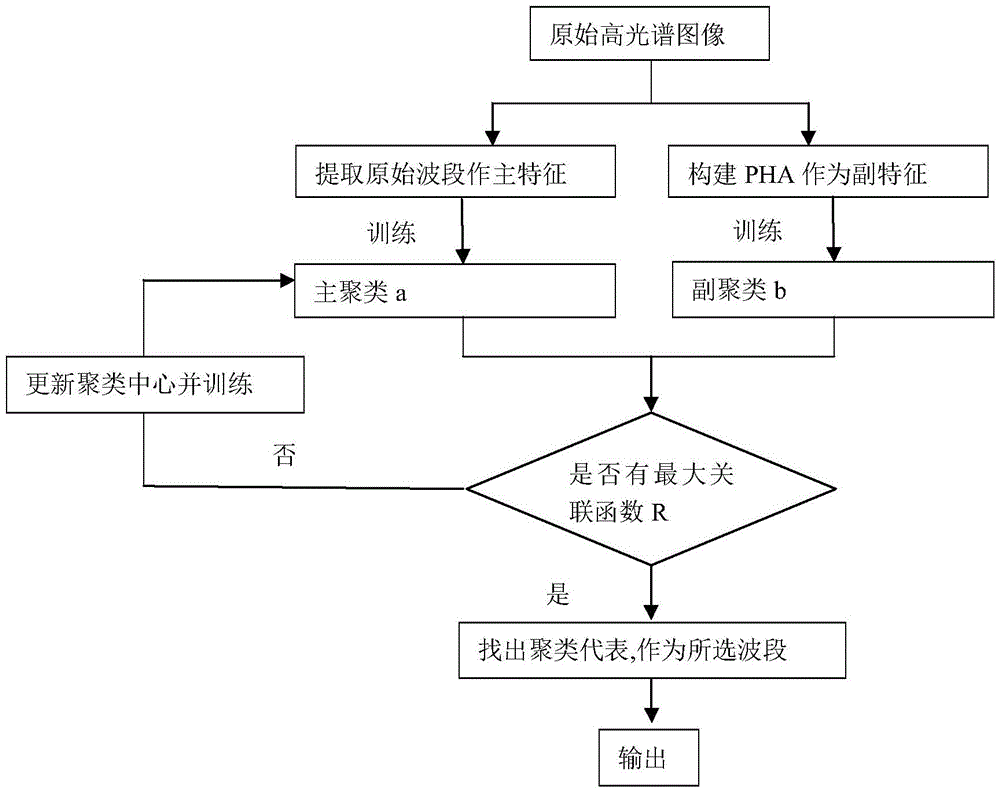
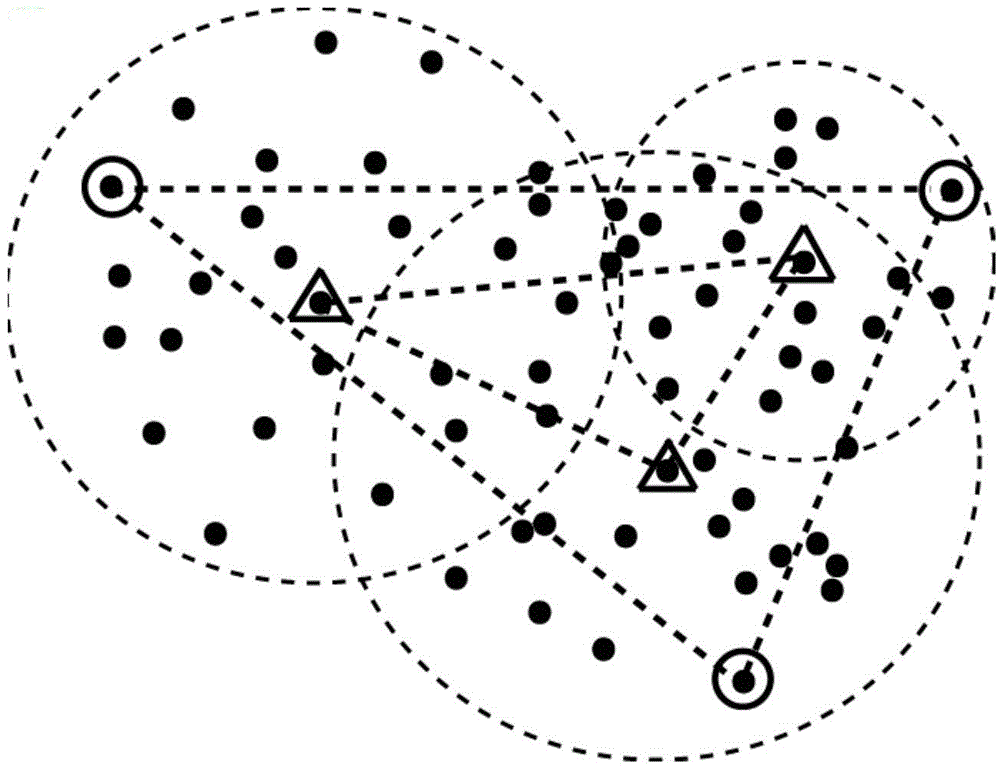
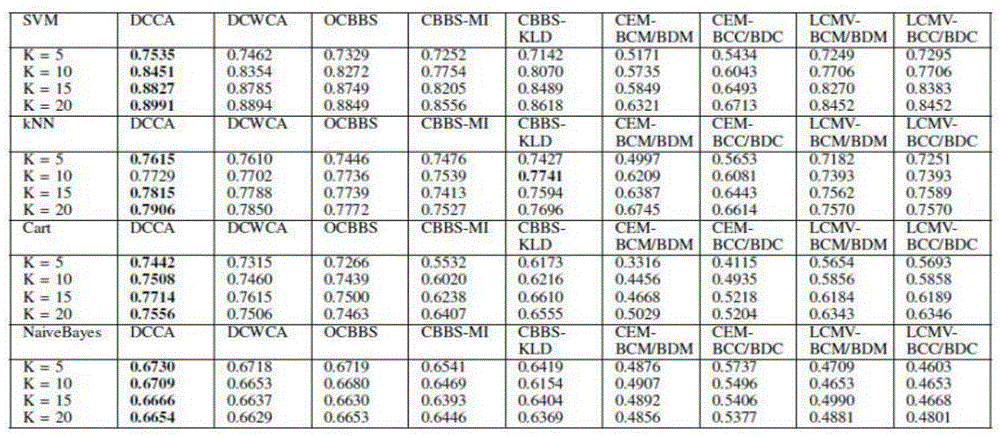
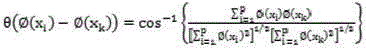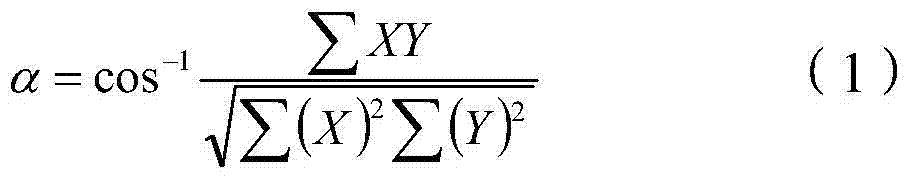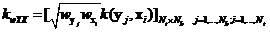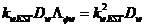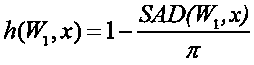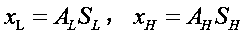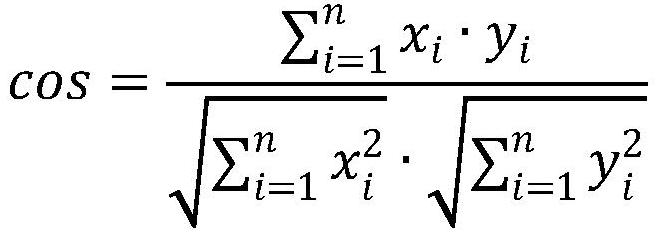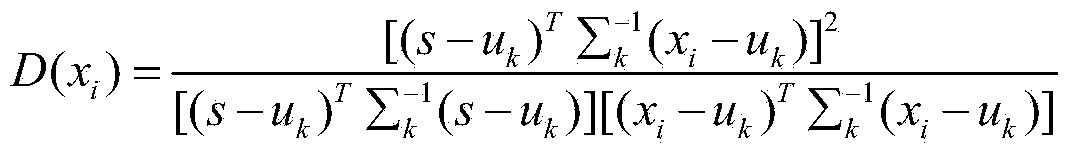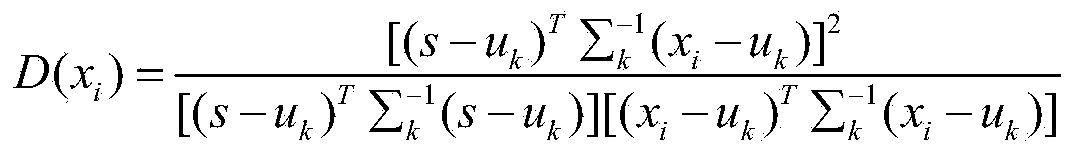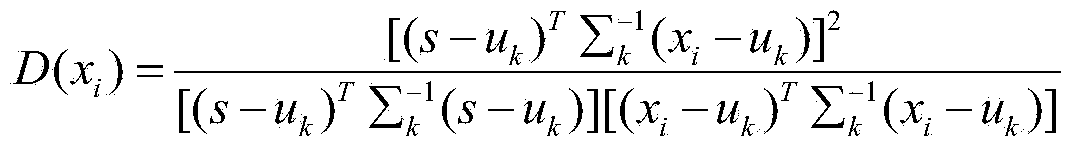Patents
Literature
127 results about "Spectral angle" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Spectral mixture process conditioned by spatially-smooth partitioning
InactiveUS20050047663A1Accurate global labelingImprove global labelingScene recognitionClassification methodsEnergy functional
A method that facilitates identification of features in a scene enables enhanced detail to be displayed. One embodiment incorporates a multi-grid Gibbs-based algorithm to partition sets of endmembers of an image into smaller sets upon which spatial consistency is imposed. At each site within an imaged scene, not necessarily a site entirely within one of the small sets, the parameters of a linear mixture model are estimated based on the small set of endmembers in the partition associated with that site. An, enhanced spectral mixing process (SMP) is then computed. One embodiment employs a simulated annealing method of partitioning hyperspectral imagery, initialized by a supervised classification method to provide spatially smooth class labeling for terrain mapping applications. One estimate of the model is a Gibbs distribution defined over a symmetric spatial neighborhood system that is based on an energy function characterizing spectral disparities in both Euclidean distance and spectral angle.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
Method and device for Hyperspectral image semi-supervised classification
ActiveCN103150580AAvoid choosing difficult questionsAvoid misclassification problemsCharacter and pattern recognitionClassification methodsHyperspectral image classification
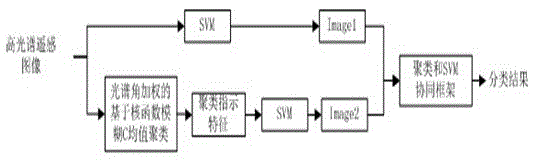
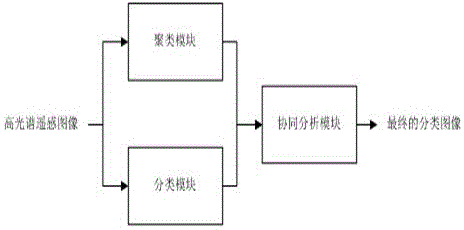
The invention relates to a method and a device for remote-sensed hyperspectral image classification. The method comprises the following steps of step 1: carrying out spectral angle weighted clustering based on kernel function vague C mean value on the hyperspectral image to obtain clustered indication characteristics; step 2: carrying out support vector machine (SVM) semi-supervised classification on the hyperspectral image to obtain a first classified image Image 1, and carrying out the SVM semi-supervised classification on the clustered indication characteristics to obtain a second calssified image Image 2; and step 3: establishing a clustering and SVM cooperation framework, inserting classification results of the Image 1 and the Image 2 into the clustering and SVM cooperation framework to be cooperatively analyzed so as to obtain a final hyperspectral classified image. The device comprises a clustering module, a classification module and a cooperative analysis module. The method and device for the hyperspectral image semi-supervised classification are feasible, capable of performing high-precise clustering and SVM-cooperative.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Semi-supervision and classification method for hyper-spectral remote sensing images based on local stream type learning composition
InactiveCN104408466AResponse nonlinear relationshipReduce the role of classificationCharacter and pattern recognitionSensing dataClassification methods
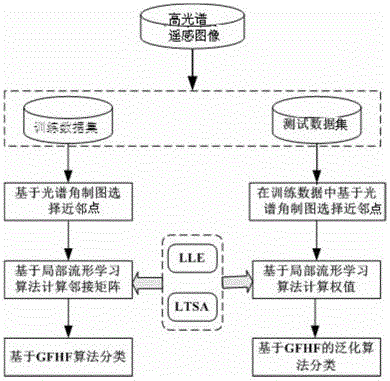
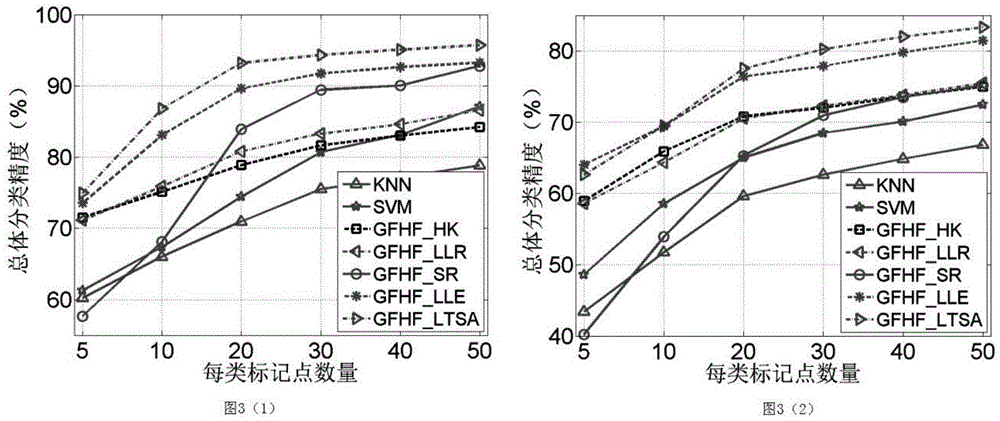
The invention discloses a semi-supervision and classification method for hyper-spectral remote sensing images based on local stream type learning composition. The method comprises the steps: (1) preparing a training sample set, including a small amount of marked data and a large number of non-marked data; (2) choosing k nearest neighbor points for each sample point in the training sample set based on the distance measurement method of spectral angle mapping; utilizing a local stream type learning algorithm to obtain weights among connecting points in a graphic structure and calculating a graphic adjacency matrix to obtain the corresponding graphic structure; classifying the non-marked data based on the graphic adjacency matrix and a GFHF algorithm; and (3) classifying other data points in the images by using a GFHF generalized algorithm. Two widely applied algorithms, including a local stream type learning dimension-reduction algorithm and a semi-supervision and classification algorithm, are contacted by a graph and are better applicable to classify a plurality of hyper-spectral remote sensing data, so that the classification precision of the hyper-spectral remote sensing images can be improved remarkably.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (WUHAN)
Remote sensing image alteration detection method
ActiveCN105405133ARobust change detection resultsHigh precisionImage enhancementImage analysisExpectation–maximization algorithmModel parameters
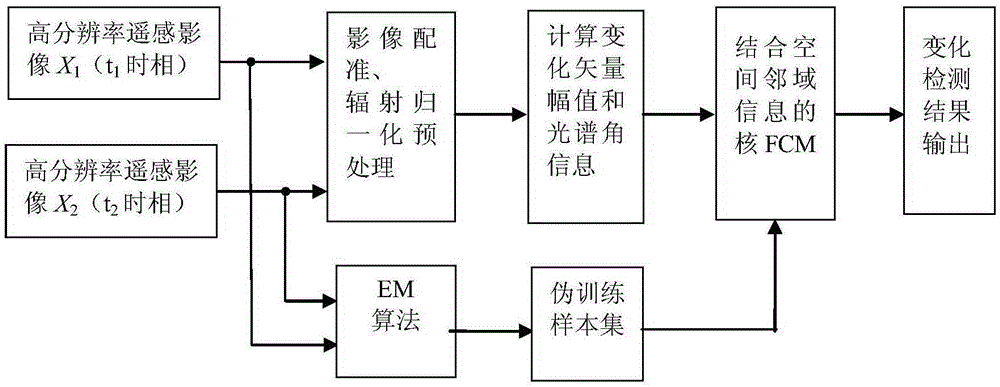
The invention discloses a remote sensing image alteration detection method comprising the steps that two time phase high-resolution optical remote sensing images X1 and X2 are obtained; image registration is performed on X1 and X2; radiation normalization correction is performed on X1 and X2 by utilizing a multivariate alteration detection method; alteration vector amplitude XM and spectral angle information XSA are respectively calculated according to X1 and X2 after radiation normalization correction; an optimal segmentation threshold T is calculated by utilizing the Bayes theory and an expectation maximization algorithm according to the XM; a pseudo training sample area is selected according to T and XM; XM and XSA are combined to act as input of a core FCM, and optimal model parameter value selection is performed on a core FCM combining spatial neighborhood information model according to the pseudo training sample area; and the alteration area and the non-alteration area of the optical remote sensing images are determined by adopting the method of core FCM combining spatial neighborhood information according to the selected optimal model parameter values. The remote sensing image alteration detection method is more robust and higher in precision.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Method for intelligently identifying mineral information based on spectral information
InactiveCN101916377AOvercoming featureOvercome environmental problemsCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionLength wave
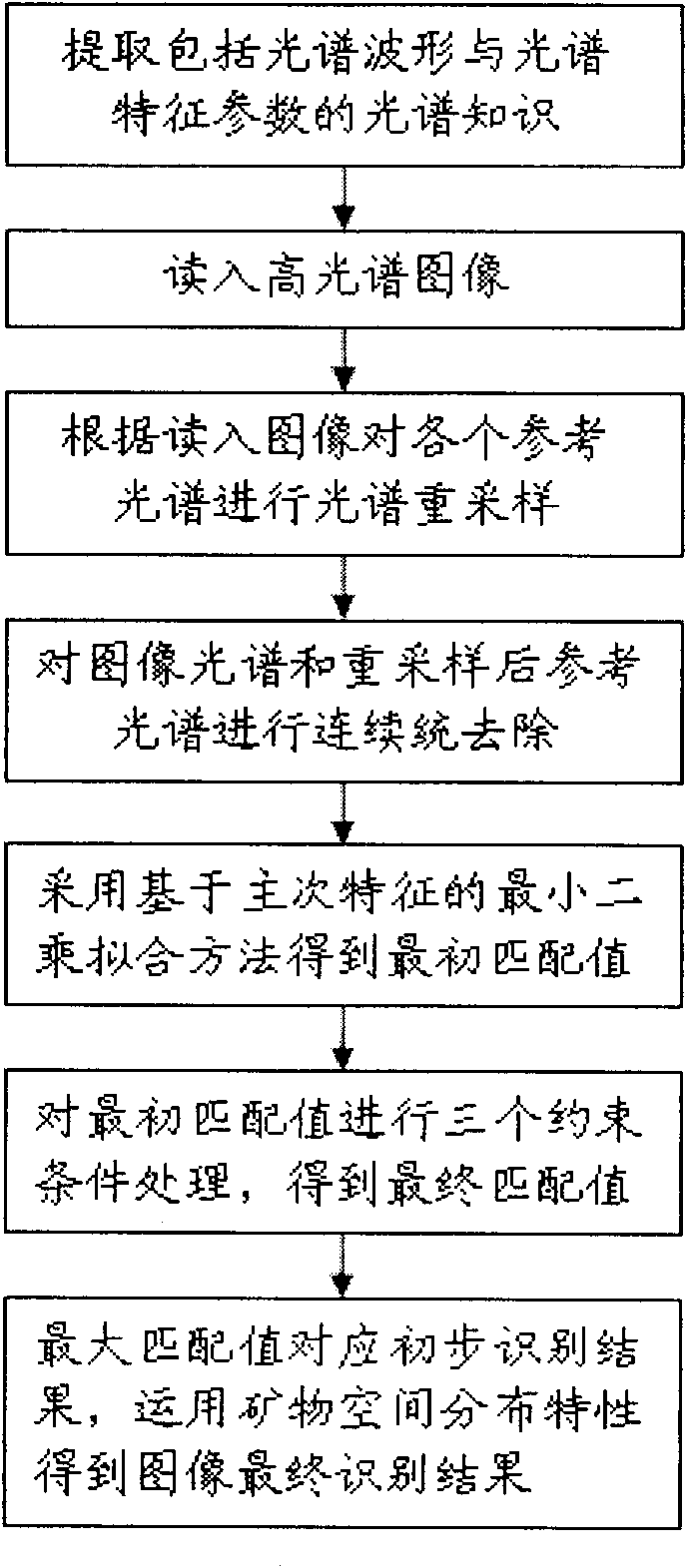
The invention discloses a method for intelligently identifying mineral information based on spectral information. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) extracting the spectral information comprising spectral waveform and spectral characteristic parameters; (2) reading in hyperspectral image data; (3) resampling each reference spectrum according to the wavelength of the image spectrum; (4) removing continuum of the image spectrum and the resampled reference spectrum; (5) performing least square fitting on the image spectrum and each reference spectrum processed by the step (4) at a primary absorption characteristic band and a secondary absorption characteristic band to obtain an initial matching value; (6) performing three kinds of constraint processing, namely matching of spectral angle at a characteristic band, judging of existence of specific absorption characteristic and setting of a reflectivity threshold value of the characteristic band, on the initial matching value to obtain the final matching value; and (7) obtaining the final identification result of the hyperspectral image by using the constraint of spatial distribution continuity of a mineral, wherein the reference spectrum corresponding to the maximum matching value in the final matching values obtained by the step (6) is a preliminary identification result of a pixel.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Spectral angle and Euclidean distance based remote-sensing image classification method
ActiveCN104751166AImprove classification accuracyGuaranteed classification efficiencyCharacter and pattern recognitionOptimal weightClassification methods
The invention is applicable to the field of remote-sensing image classification and provides a spectral angle and Euclidean distance based remote-sensing image classification method. The spectral angle and Euclidean distance based remote-sensing image classification method comprises the steps of preprocessing remote-sensing images to filter out noise; screening effective information for classification; segmenting the remote-sensing images into multiple homogenous image map spots serving as minimum research units; calculating mean values and variances of training samples at all wave bands; calculating mean values and variances of testing samples at all wave bands; further calculating Euclidean distances and spectral angles; determining the comprehensive similarity as the sum of weights of the spectral angles and the Euclidean distances and determining weights; calculating the comprehensive similarity of classification objects and surface features to enable the type of the surface features with minimum comprehensive similarity to serve as the final type of the classification objects. The spectral angle and Euclidean distance based remote-sensing image classification method integrates the advantages of two classifiers, achieves complementation of different classification methods, determines optimal weight through verification at minimum intervals, effectively improves classification accuracy, ensures classification efficiency, achieves algorithm automation and is high in classification efficiency.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
SAM weighted KEST hyperspectral anomaly detection algorithm
The invention discloses an SAM weighted KEST hyperspectral anomaly detection algorithm (SKEST). The method includes the steps: firstly, deducing the SKEST algorithm; and secondly, calculating the SKEST value of each image element in a hyperspectral image by the aid of a double-rectangular window, performing threshold segmentation and detecting abnormal points. In the SKEST algorithm, based on the KEST (kernel Eigen space separation transformation) algorithm, a weight factor is introduced into each sample in a DCOR (difference correlation) matrix of a high-dimensional Eigen space detection point neighborhood by means of SAM (spectral angle mapper) measurement, and the weight factor of each sample depends on an included angle between the spectral vector of the sample and a data center of the detection window. Therefore, abnormal data in the detection window are suppressed, the contribution of main compositional data is highlighted, and the DCOR matrix can more effectively describe target and background data distribution difference. Besides, the SAM is robust to spectral energy, and by the aid of a radial basis function, the SKEST algorithm considers both spectral energy difference and spectral curve shape difference of signals, and accordingly conforms to hyperspectral data characteristics more effectively.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
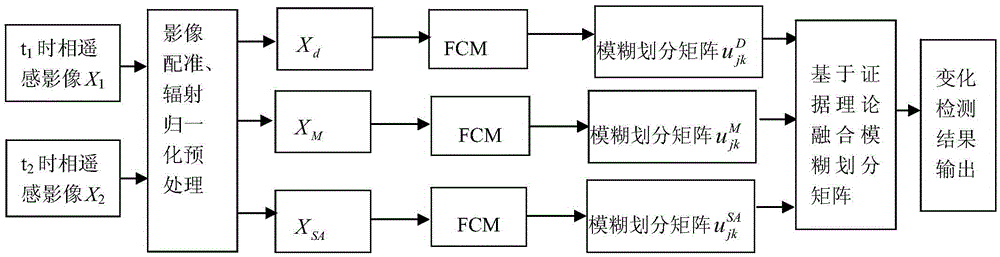
Multi-temporal remote sensing image change detection method based on FCM and evidence theory
ActiveCN105551031ARemove uncertaintyReliable resultsImage enhancementImage analysisComputer scienceChange detection
The invention discloses a multi-temporal remote sensing image change detection method based on FCM and the evidence theory, and the method is characterized in that the method comprises the steps: firstly solving the corresponding band difference of remote sensing images at two time phases, the amplitude values of variable vectors of the two time phases, and the cosine values of spectrum inclined angles of the two time phases; secondly taking the above values as the input of the FCM, and respectively obtaining a corresponding fuzzy division matrix, and enabling the fuzzy degree of each type of fuzzy division matrixes to serve as a quality function of the evidence theory; finally carrying out the fusion of the above three division matrixes through employing the evidence theory, obtaining a new fuzzy division matrix, and obtaining the final change detection result according to the above. The beneficial effects of the invention are that the method is based on the FCM and the D-S evidence theory, achieves the fusion of the band difference, the amplitude values of variable vectors and the cosine values of spectrum inclined angles through employing the evidence theory, inputs the above values into the FCM model and obtains a detection result, eliminates the uncertainty in change detection through the detection result, and enables the result of change detection to be more reliable and robust.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
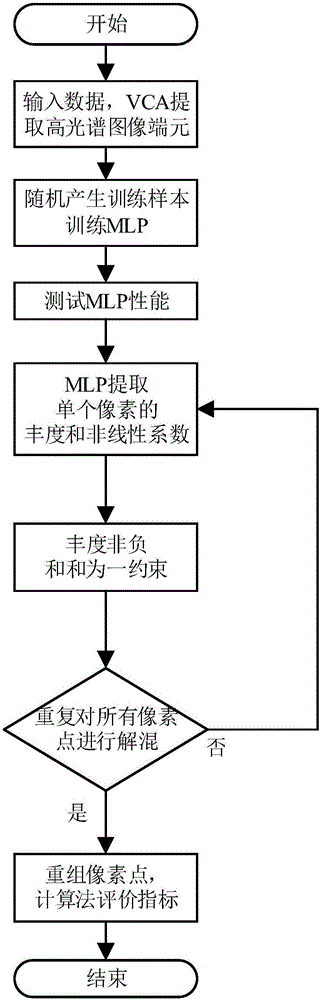
Hyperspectral image nonlinearity solution blending method based on neural network
InactiveCN105975912AAchieve accurate classificationEffective interpretationGeometric image transformationScene recognitionAngular distanceImaging data
The invention belongs to the image processing technology field and provides a hyperspectral image nonlinearity solution blending method based on a neural network. By using the method, corresponding work of extracting an end member and acquiring end member abundance and a nonlinear coefficient can be effectively completed so that a solution blending effect is further increased. The method comprises the following steps of (1) inputting hyperspectral image data; (2) randomly generating a sufficient number of training samples and testing samples; (3) using the trained multilayer perceptron neural network to extract abundance and a nonlinear coefficient of a single pixel point in a hyperspectral image; (4) making the acquired abundance satisfy a corresponding constraint condition; (5) repeatedly carrying out solution blending on all the pixel points in the image and then stopping calculation; otherwise, returning to the step (3); and (6) evaluating the performance of the algorithm by calculating a reconstruction error and a spectral angle distance. The method is mainly used for image processing.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
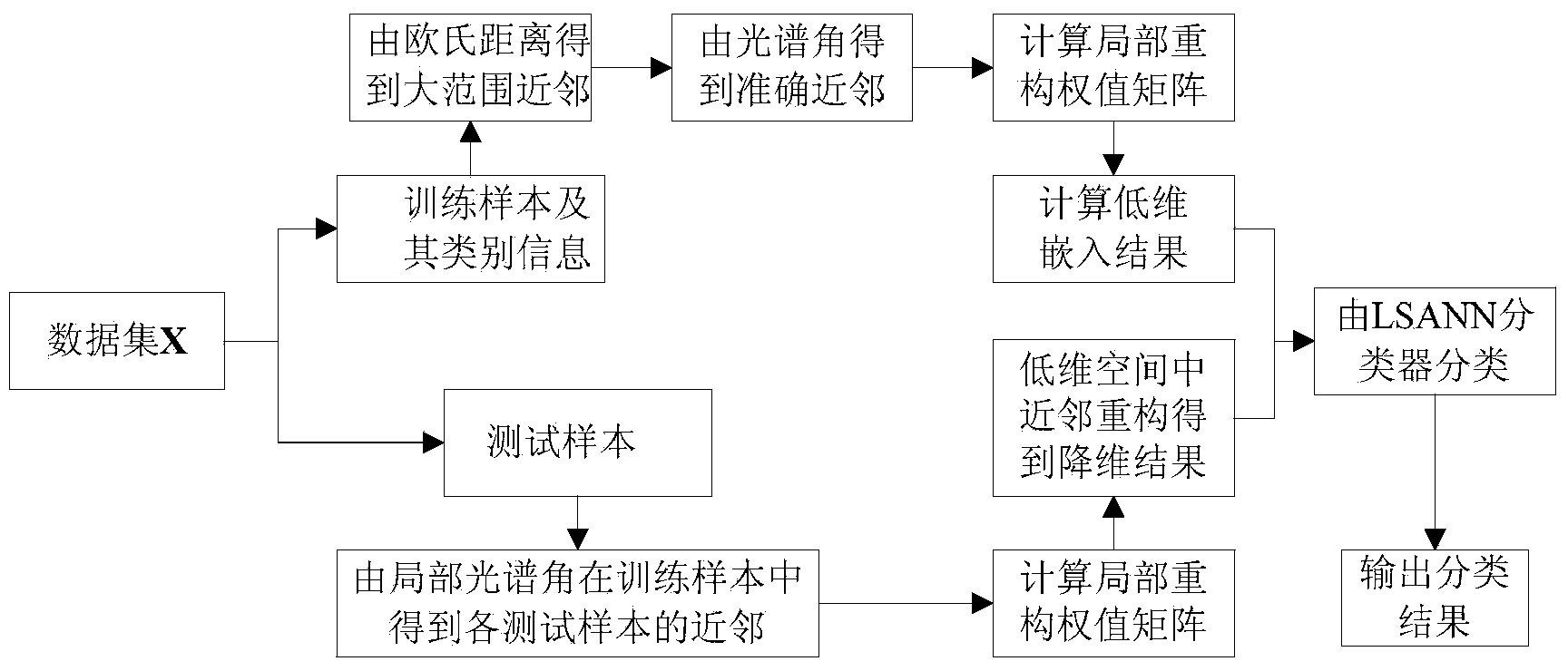
Hyperspectral remote sensing image classification method based on manifold neighbor measurement through local spectral angles
InactiveCN103729651AEfficient extractionImprove classification effectCharacter and pattern recognitionClassification methodsHigh dimensional
The invention discloses a hyperspectral remote sensing image classification method based on manifold neighbor measurement through local spectral angles. A wide range of neighbors are obtained through the traditional Euclidean distance, accurate neighbors are obtained through spectral angles, the local reconstruction is performed through the neighbors and the reconstruction error is minimized, the local reconstruction mode maintains unchanged in the low dimensional space, the reconstruction error is minimized, and accordingly internal identification characteristics in high dimensional data can be extracted. During classification, neighbors of a new sample are obtained through the traditional Euclidean distance, spectral angles between the new sample and the neighbors are calculated, and the new sample is classified as the class with the smallest spectral angles. According to the hyperspectral remote sensing image classification method based on the manifold neighbor measurement through the local spectral angles, the identification characteristics can be effectively extracted, the classification result is accurate, and the feature classification effect on a hyperspectral remote sensing image is good.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
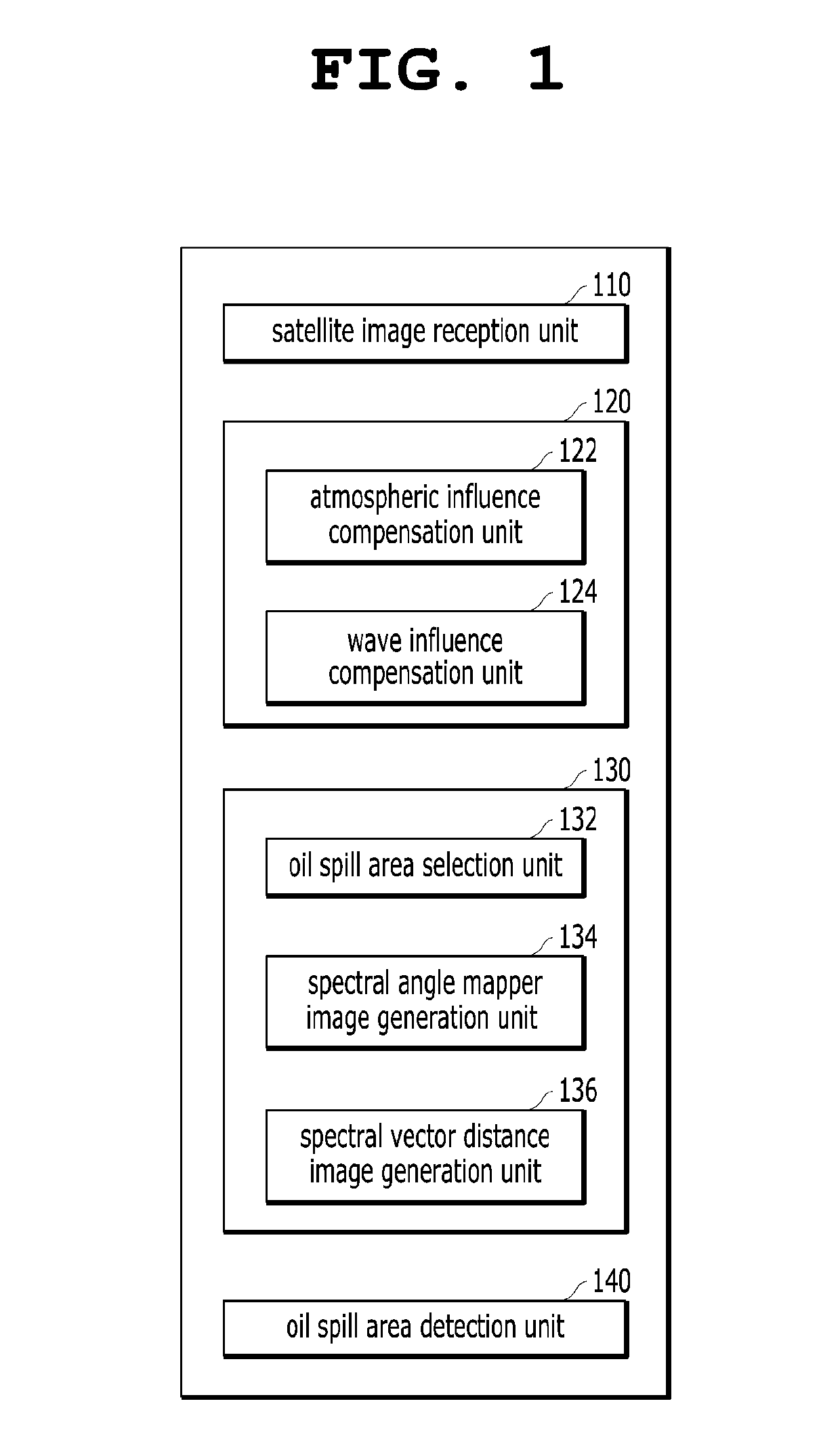
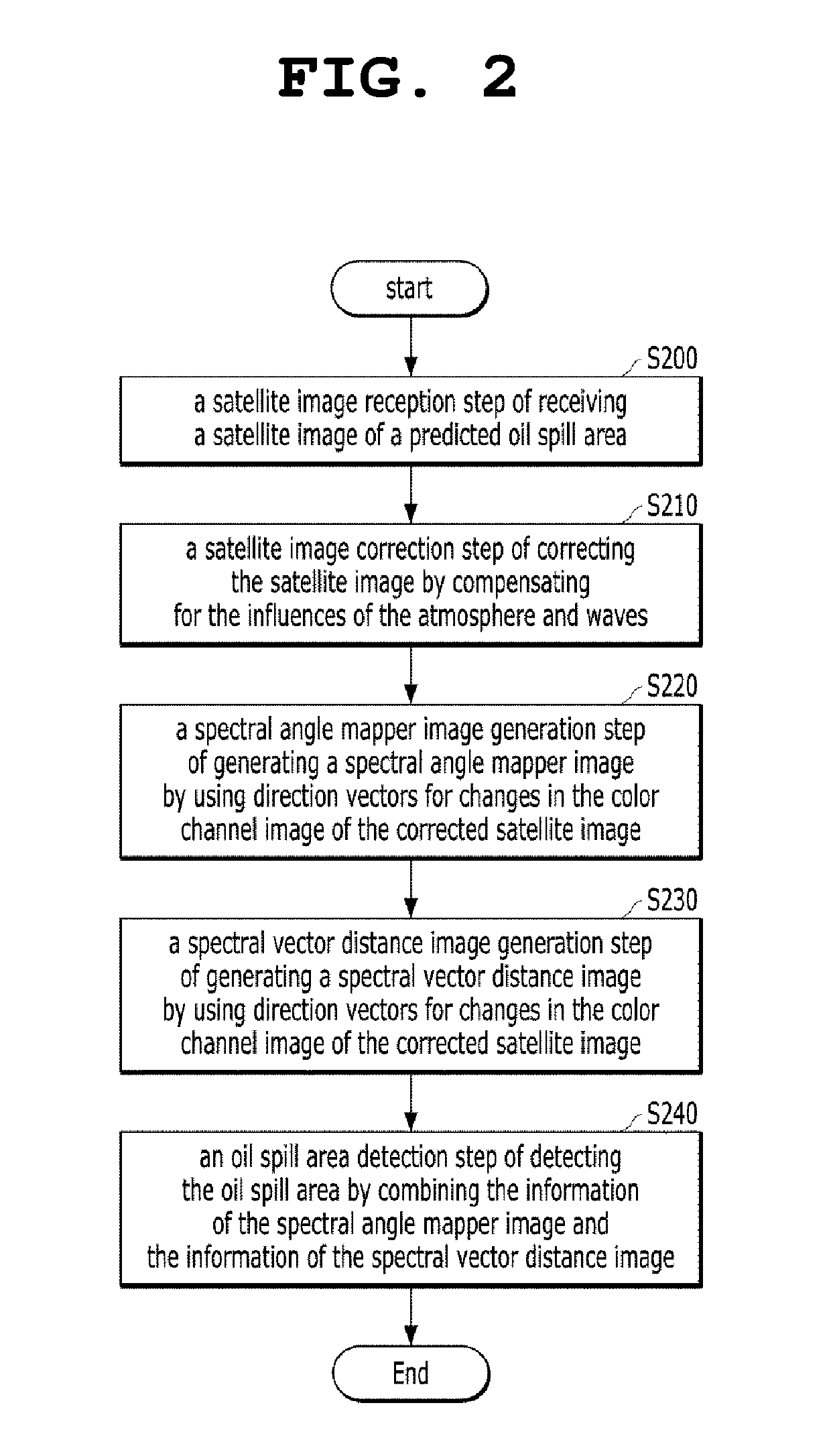
Apparatus and method for detecting oil spill by using satellite image
ActiveUS20190122369A1Accurately determinedEnsure high efficiency and accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisSpectral vectorSatellite image
The present invention relates to an apparatus and method for detecting an oil spill by using a satellite image, an apparatus for detecting an oil spill by using a satellite image, the apparatus including: a satellite image reception unit configured to receive a satellite image of a predicted oil spill area; a satellite image correction unit configured to correct the satellite image by compensating for the influences of the atmosphere and waves; a spectral angle mapper image generation unit configured to generate a spectral angle mapper image; a spectral vector distance image generation unit configured to generate a spectral vector distance image; and an oil spill area detection unit configured to derive the range of the oil spill area by combining the spectral angle mapper image and the spectral vector distance image together.
Owner:UNIV OF SEOUL IND COOP FOUND
Hyperspectral anomaly detection method based on spectrum-preserving sparse auto-encoder
InactiveCN111461087AImprove learning abilitySuppress interferenceScene recognitionNeural architecturesActivation functionAnomaly detection
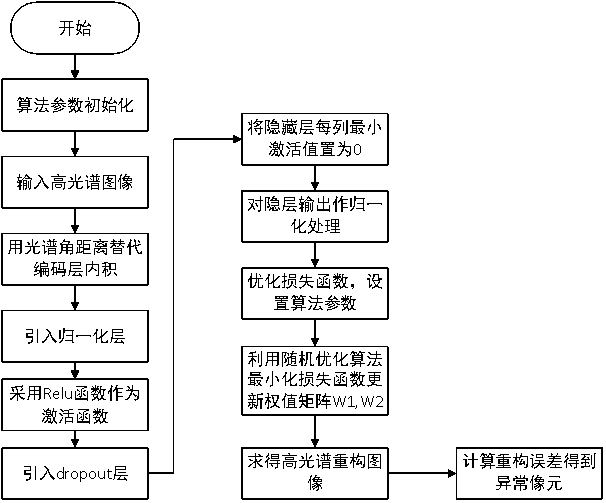
The invention discloses a hyperspectral image anomaly detection method based on a spectrum-preserving sparse auto-encoder. The hyperspectral image anomaly detection method comprises the following steps: solving a wavelet coefficient of hyperspectral data; constructing a wavelet self-encoding network of linear unmixing constraint, replacing an inner product of an encoding layer with a spectral angular distance, selecting a Relu function as an activation function of the encoding layer, introducing a normalization layer and a dropout layer, adding a penalty term and a regularization term into a loss function, and constructing a network based on the spectral-preserving sparse self-encoder; and inputting the hyperspectral data to be measured into the sparse auto-encoder network, setting networkparameters, performing unmixing operation on the network parameters to obtain background end metadata, and calculating a reconstruction error to obtain required abnormal target data. Rapid and accurate abnormal target detection can be carried out on the hyperspectral image.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
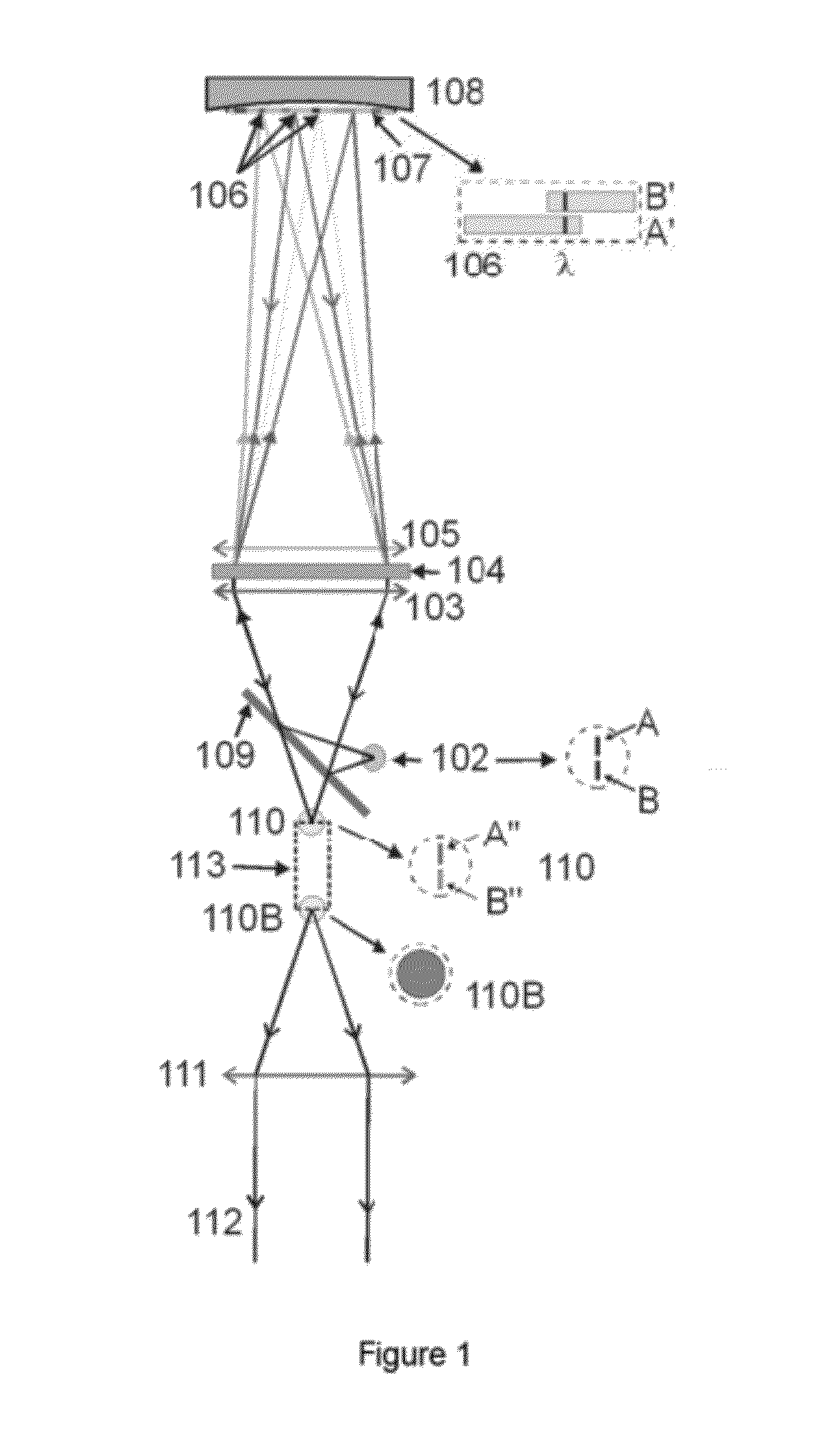
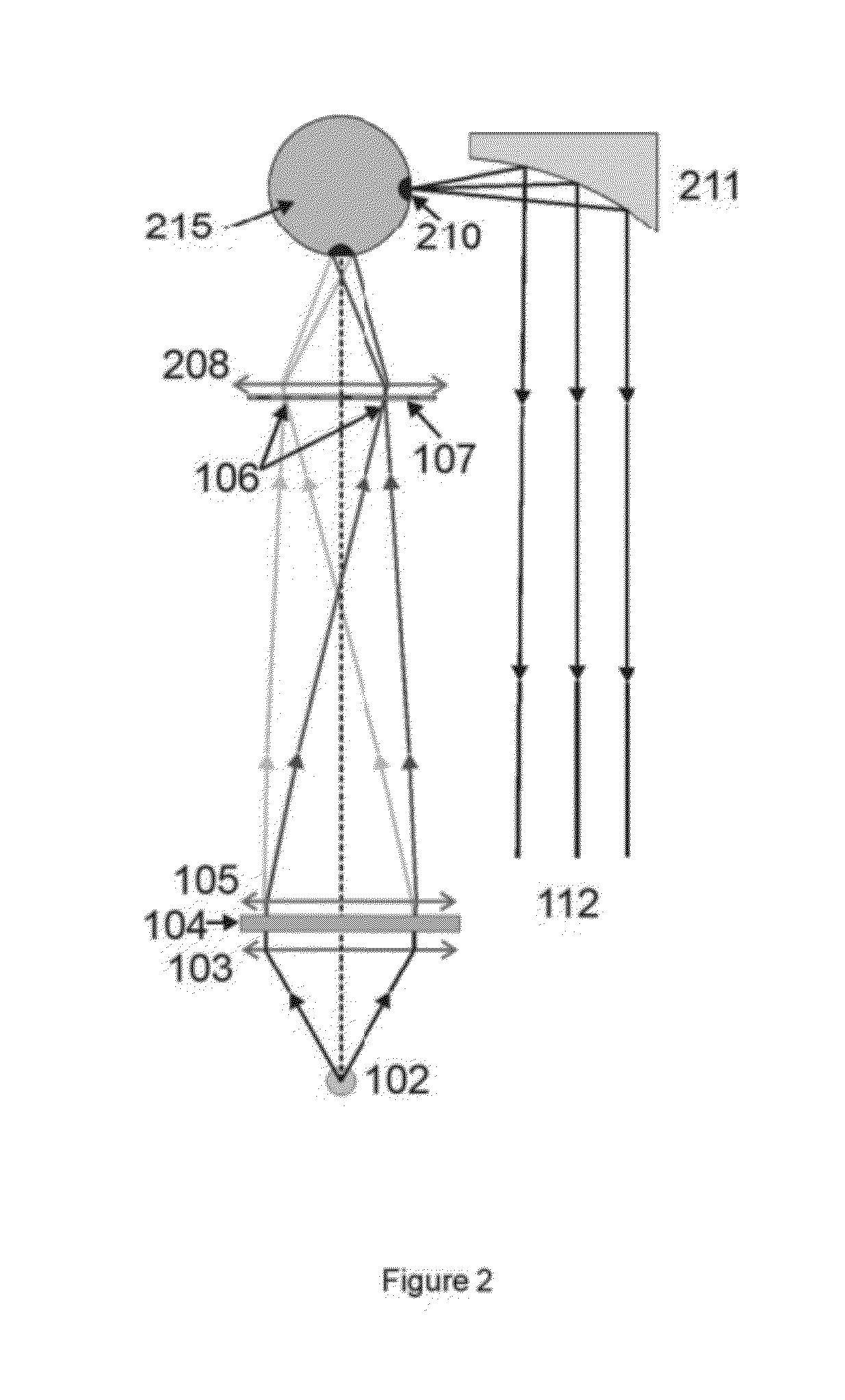
Variable-spectrum solar simulator
InactiveUS20120057324A1Facilitating characterisation of photovoltaicImprove versatilityElectrical apparatusElectric lighting sourcesControl systemLight beam
The invention relates to a variable-spectrum solar simulator for characterising photovoltaic systems. The simulator can be used to obtain a spectrum adjusted to the solar spectrum, both for a standard spectrum or a real spectrum adjusted to local irradiation conditions. The simulator also allows the spatial-angular characteristics of the sun to be reproduced. The invention comprises: a broad-spectrum light source, the flux from which is emitted through an aperture; an optical system which collimates the primary source; a system which disperses the beam chromatically; an optical system which forms an image of the dispersed primary source at a given position, at which a spatial mask is placed in order to filter the received irradiance spectrally; an optical system which captures the filtered spectrum and returns, mixes and concentrates same in a secondary source with the desired spectral, angular, and spatial characteristics; an optical system which collimates the secondary source such that it reproduces the angular characteristics of the sun; and a control system.
Owner:ABENGOA SOLAR NEW TECH SA
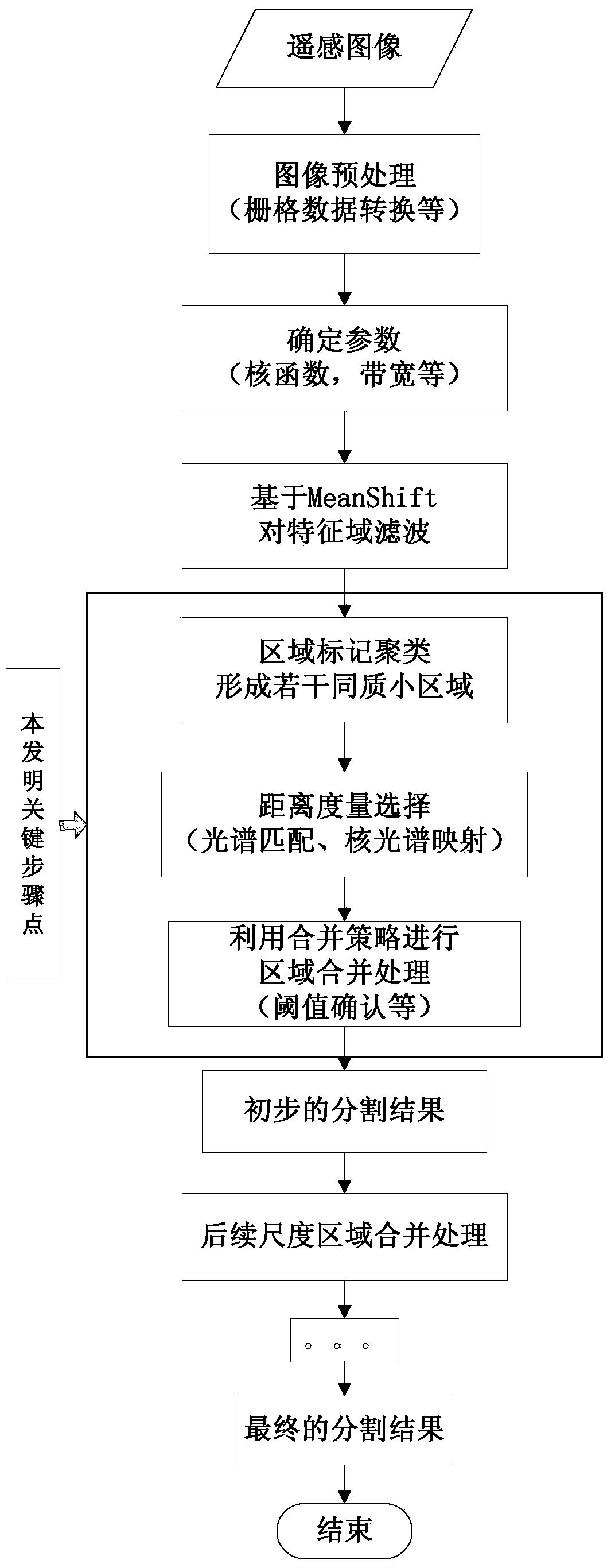
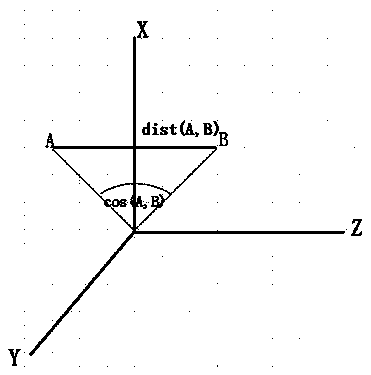
MeanShift based high-resolution remote sensing image segmentation distance measurement optimization method
InactiveCN104200458AAccurate calculationGood for judging similarityImage analysisImage segmentationComputer vision
The invention discloses a MeanShift based distance measurement optimization method in high-resolution remote sensing image segmentation during area merging. According to the MeanShift based high-resolution remote sensing image segmentation distance measurement optimization method, remote sending image data characteristics are fully considered, traditional Euclidean distance is replaced by spectrum matching distance measurement, specifically, spectrum angle matching measurement, spectral similarity measurement and Kernel mapping spectrum matching measurement, and the segmentation result is accurate.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Optical remote sensing image vegetation and water body information automatic extraction method
ActiveCN112131946ARealize fully automatic extractionAdaptableCharacter and pattern recognitionWater resource assessmentSensing dataVegetation Index
The invention discloses an optical remote sensing image vegetation and water body information automatic extraction method comprising the following steps: obtaining an optical remote sensing data sample, and randomly extracting 10% of the optical remote sensing data sample as a sample subset; calculating normalized vegetation indexes and normalized water indexes of all the samples in the sample subset, obtaining a general characteristic spectrum to execute supervised classification based on a minimum spectral angle on all the samples in the sample subset, and recording vegetation types, water body types and the sizes of the minimum spectral angles corresponding to other types at the same time; taking the minimum first 50% of samples in the minimum spectral angles, performing k-means unsupervised classification based on the minimum Euclidean distance on the first 50% of samples, obtaining 10 characteristic spectrums for each type, totally 30 characteristic spectrums, and performing supervised classification based on the minimum Euclidean distance pixel by pixel on the global image to obtain an extraction result of vegetation and water. Any prior sample is not needed for supporting from beginning to end, manual intervention is avoided, and full-automatic extraction of vegetation and water body information is achieved.
Owner:长沙银汉空间科技有限公司
Super-resolution reconstruction method of hyperspectral image based on coupled dictionary and spatial transformation estimation
ActiveCN106780345ALower usage limitSuper resolution effect is goodGeometric image transformationColor imageImage resolution
The invention discloses a super-resolution reconstruction method of hyperspectral image based on coupled dictionary and spatial transformation estimation, which is used for solving the existing technical problem of low precision reconstruction of the prior hyperspectral image super-resolution reconstruction method. The hyperspectral image is first linearly unmixed by a spectral unmixing theory. The corresponding spectral dictionary is obtained. The sparse representation theory is used to establish the hyperspectral reconstruction model of hyperspectral image based on coupled dictionary. The spatial transformation matrix between the image and the true color image is a regular term, and reduces the use limit of the algorithm. Then, the improved PALM algorithm is used for solving the model, and the hyperspectral image after super-resolution reconstruction is obtained. Though testing, the results show that the accuracy indexes such as the root-mean-square error RMSE and the spectral angle match SAM are higher than those of the background technology hyperspectral image super-resolution reconstruction method, and have better super-resolution effect when the spatial super-resolution is 32 times.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Urban green land soil moisture content detection method
PendingCN112577906ARealization of moisture content detectionThe method is simple and practicalColor/spectral properties measurementsSample plotVegetation
The invention discloses an urban green land soil moisture content detection method. The method comprises steps of preprocessing yperspectral data and panchromatic images; setting a sample plot, and measuring the moisture content of the sample; obtaining a vegetation area and a non-vegetation area through image segmentation and contour recognition, and selecting a bare soil sample of the non-vegetation area to obtain an end member spectrum curve of bare soil; extracting an exposed soil distribution area; utilizing the thermal infrared data to respectively establish inversion models for the plant coverage area and the bare soil area, and calculating constant values in the inversion models and inversion area soil moisture content in combination with the measured values. According to the method, image segmentation, contour recognition and spectral angle classification are combined, a vegetation coverage area and an exposed soil area are distinguished, two soil moisture content models are established, the soil moisture content of the urban greenbelt can be indirectly and directly detected, the adopted method is convenient and practical, large-area soil moisture content detection can beachieved, compared with most soil moisture content determination methods, the method is faster, more accurate and more comprehensive.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACADEMY OF LANDSCAPE ARCHITECTURE SCI & PLANNING
Hyperspectral image target detection method based on variational self-coding network
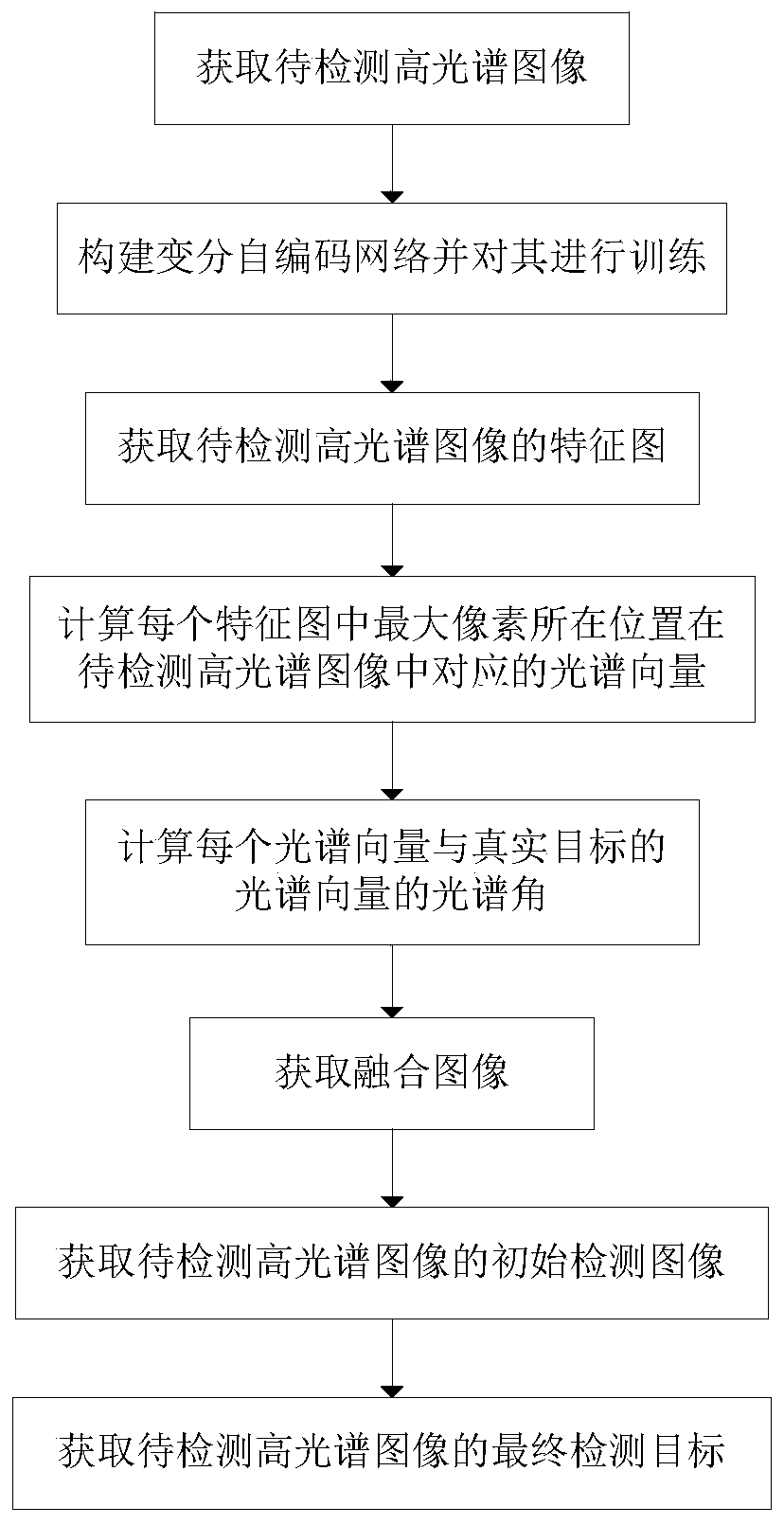
ActiveCN110008948ASolve the low detection accuracyImprove detection accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisSpectral vectorMaximum Pixel
The invention provides a hyperspectral image target detection method based on a variational self-coding network, which mainly solves the technical problem of low detection precision in the prior art,and comprises the following steps of: obtaining a to-be-detected hyperspectral image and a real spectral vector of a to-be-detected target; constructing a variational self-coding network, and trainingthe variational self-coding network; obtaining a feature map of the to-be-detected hyperspectral image; calculating a spectral vector corresponding to the position of the maximum pixel value in eachfeature map in the to-be-detected hyperspectral image; calculating a spectral angle between each spectral vector and a real spectral vector; obtaining a fusion image; obtaining an initial detection image of the to-be-detected hyperspectral image; and obtaining a final detection target of the to-be-detected hyperspectral image. According to the method, the frequency band interference in the hyperspectral image can be reduced, redundant information is reduced, a target and a complex background in the hyperspectral image are better distinguished, the detection precision of a target point is improved, and meanwhile, the complexity of data processing is reduced.
Owner:陕西丝路天图卫星科技有限公司
On-orbit hyperspectral sensor radiation and spectral calibration parameter simultaneous inversion method
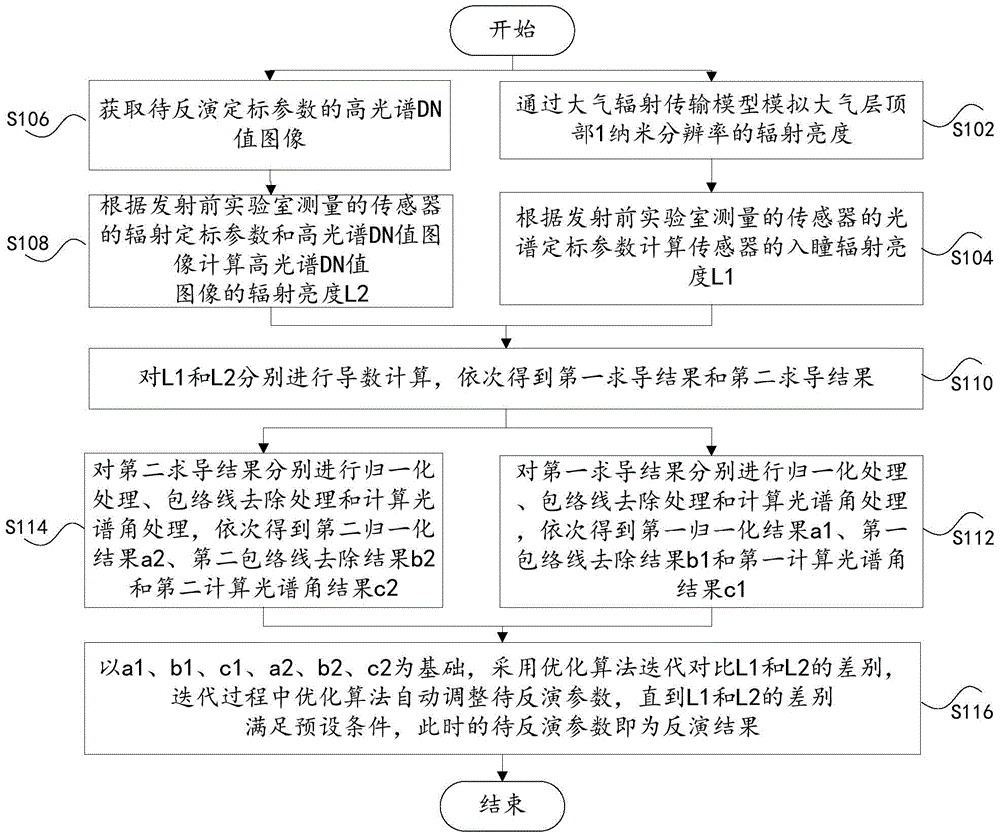
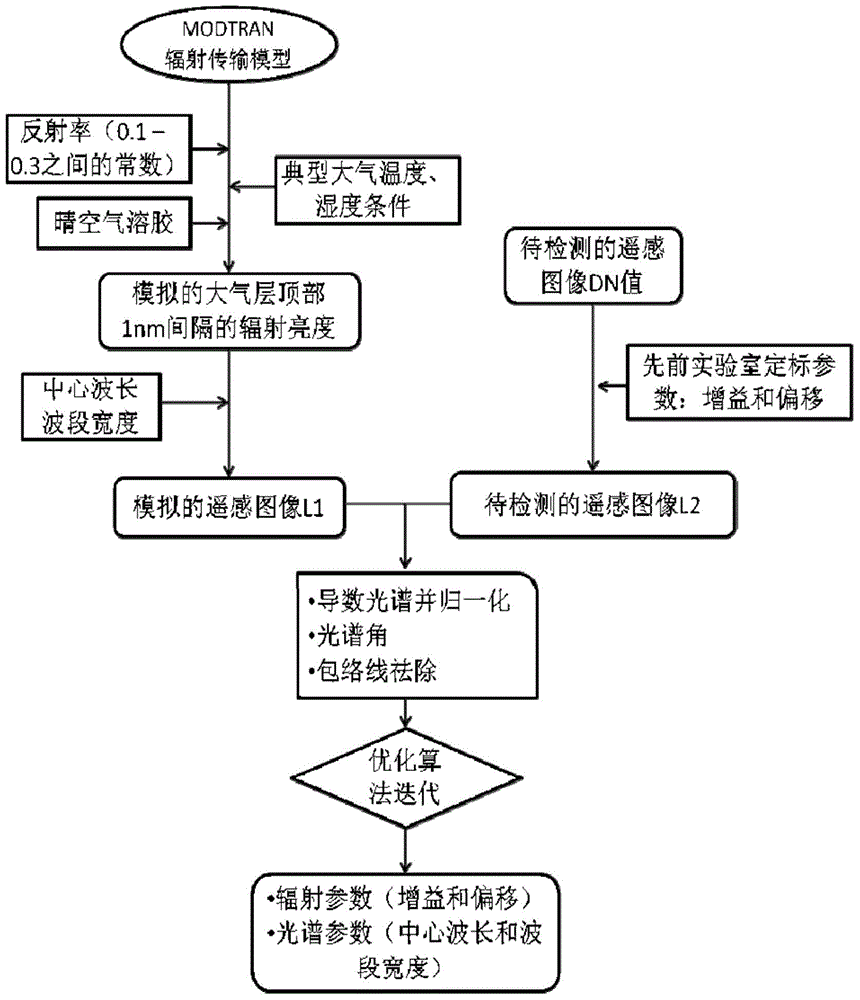
The invention discloses an on-orbit hyperspectral sensor radiation and spectral calibration parameter simultaneous inversion method. The method comprises the steps that an atmospheric radiation transfer model is used to simulate the radiance of 1 nanometer resolution at the top of atmosphere; by taking a spectral calibration parameter before launching as an initial value, the spectral calibration parameter is constantly adjusted through an optimization algorithm, and corresponding sensor entrance pupil radiance L1 is calculated; the hyperspectral DN value image of a calibration parameter to be inversed is acquired; according to a radiation calibration parameter before launching and the hyperspectral DN value image, corresponding radiance L2 is calculated; derivative calculation is carried out on L1 and L2, and normalization, envelope removing and spectral angle calculation are respectively carried out on two derivation results; based on processing results, the optimization algorithm is used to carry out iterative comparison on difference between L1 and L2 until optimization meets preconditions, and the parameter to be inversed is an inversion result. According to the invention, simultaneous inversion of the on-orbit hyperspectral sensor radiation calibration parameter and the spectral calibration parameter is realized.
Owner:INST OF REMOTE SENSING & DIGITAL EARTH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
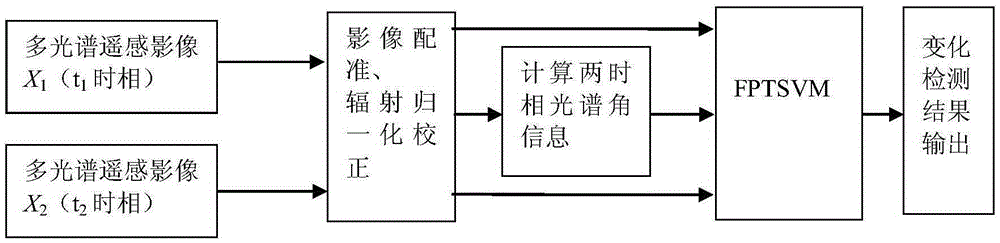
Method for semi-supervised detection on changes in remote sensing images
InactiveCN105354845AImprove classification accuracyImprove classification speedImage enhancementImage analysisComputer scienceHistogram
The present invention discloses a method for semi-supervised detection on changes in remote sensing images. The method comprises: acquiring original optical remote sensing images of two time phases; performing image registration on the original optical remote sensing images; using a histogram adjustment method to perform radiation normalization correction on the remote sensing images having undergone the image registration; calculating spectral angle information according to the remote sensing images having undergone the radiation normalization correction; combining the remote sensing images having undergone the radiation normalization correction with the spectral angle information, and using the combination as input of an FPTSVM; learning by means of an FPTSVM method, and constantly adjusting a classification hyperplane of an SVM until a designated number of learning iterations is reached; and determining a changing area and a non-changing area of the images by using a final classification hyperplane. The method provided by the present invention can increase speed and accuracy of detection on changes.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Multi-temporal remote sensing image change detection method based on fusion strategy and FCM
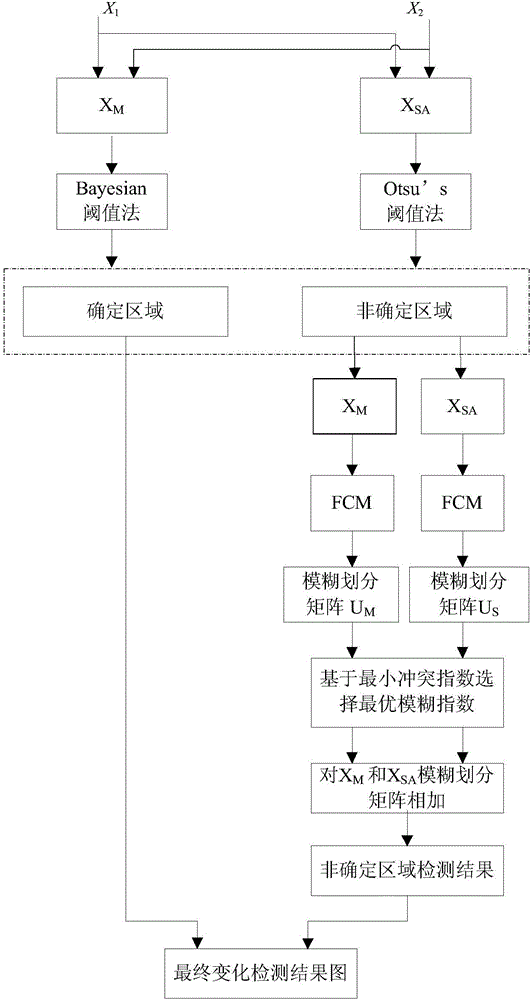
InactiveCN106384352AReliable test resultsRobustImage enhancementImage analysisMatrix additionSpectral angle
The invention discloses a multi-temporal remote sensing images change detection method based on fusion strategy and FCM, and the method comprises the steps: a detection range can be divided into a determined region and an undetermined region according to a change vector amplitude of multi-temporal remote sensing images and a multi-temporal spectral angle map; in the undetermined region, the change vector amplitude and SAM information are fused based on fuzzy division matrix addition; results of the determined region and the undetermined region are combined to obtain a final change detection result; wherein a fuzzy index in an FCM objective function in the undetermined region can be selected according to conflict indexes of MCV and SAM in the undetermined region to obtain a change detection result which is more stable and has higher precision than before. According to the invention, the change detection region is divided into the determined region and the undetermined region, detection results of two regions can be separately acquired through adopting a fusion strategy, so that the change detection results can be more reliable and more stable than before.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Accumulated snow identification method and system for synchronous satellite remote-sensing sequence images
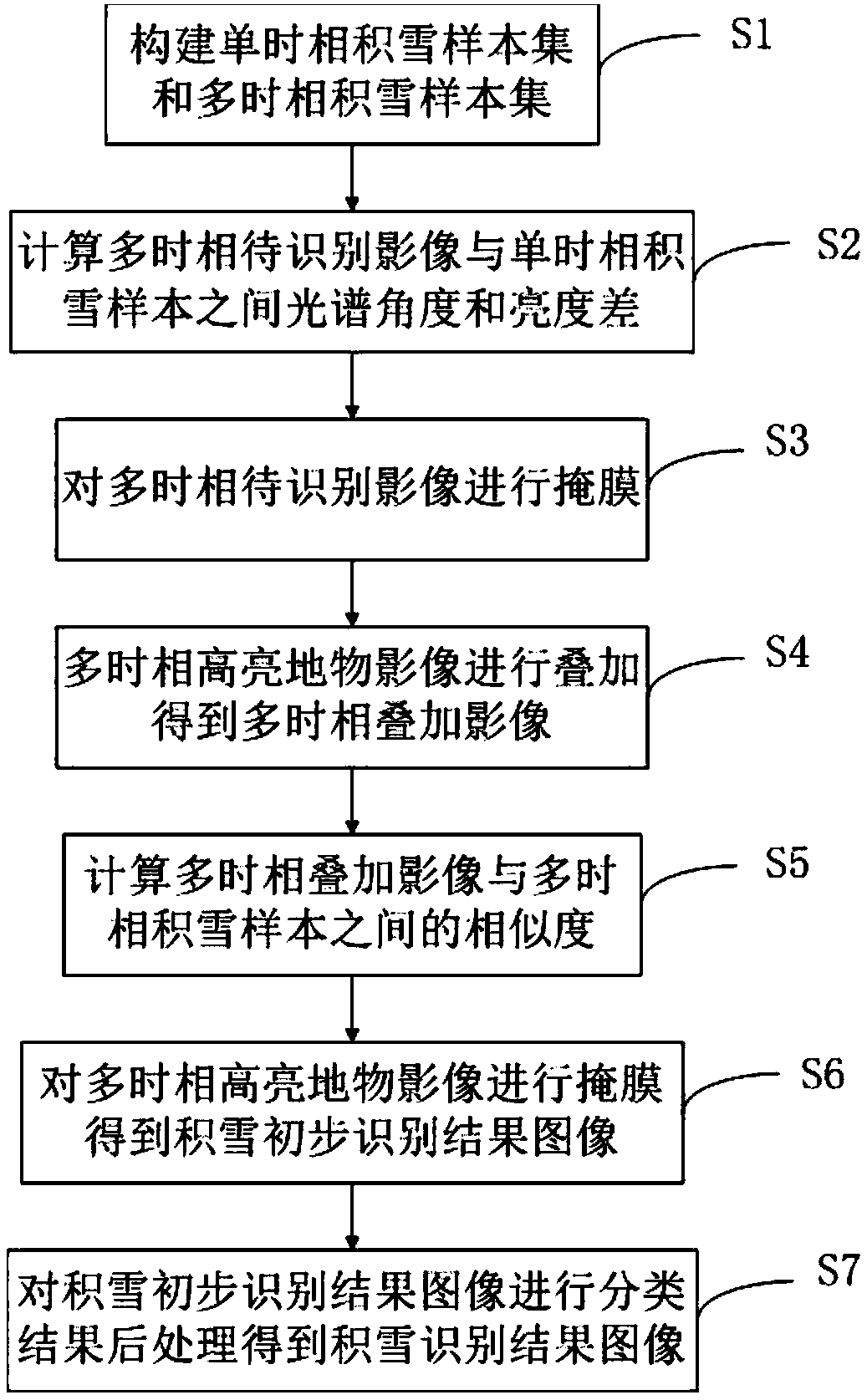
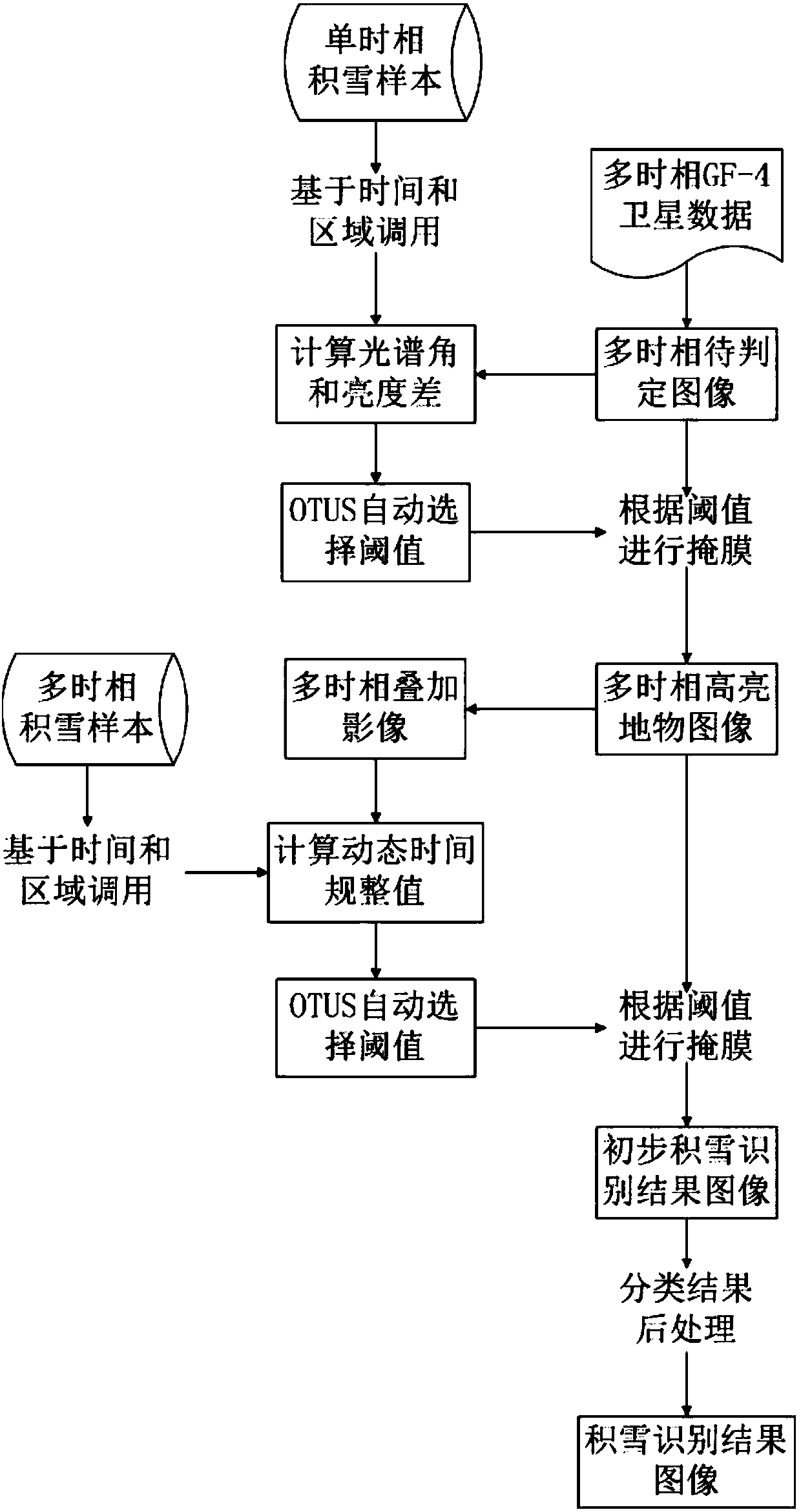
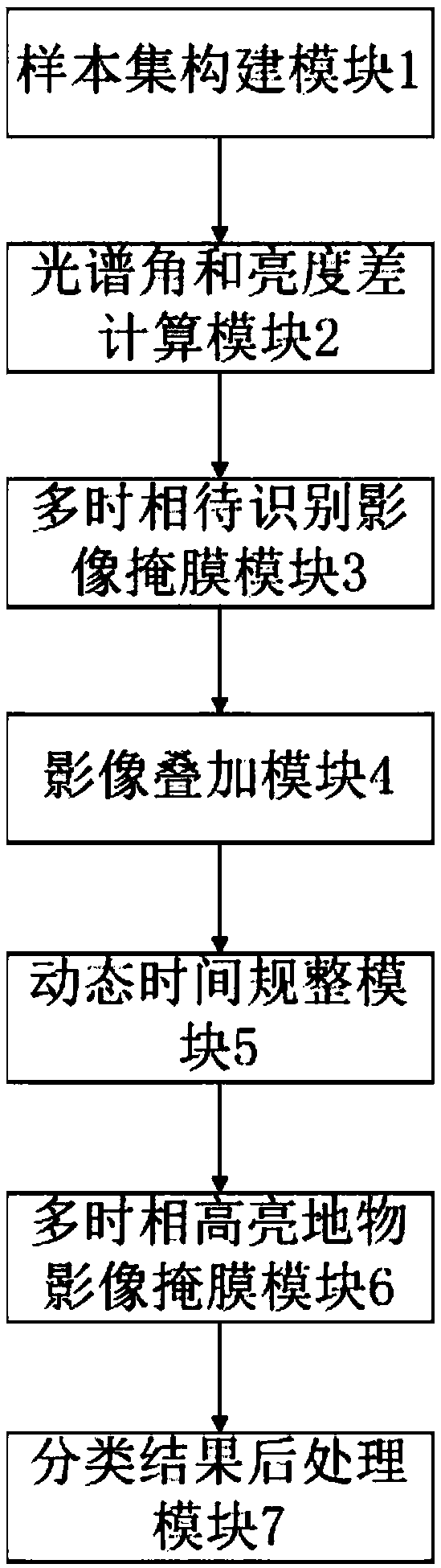
ActiveCN107066989ATake full advantage of multi-temporal featuresNo need to affectScene recognitionSpectral angleBrightness perception
The invention discloses an accumulated snow identification method and a system for synchronous satellite remote-sensing sequence images. Specifically, the method comprises the steps of calculating a spectral angle of a to-be-identified multi-temporal image relative to a single-temporal accumulated snow sample, and calculating the luminance difference between the to-be-identified multi-temporal image and the single-temporal accumulated snow sample; based on the spectral angle and the luminance difference, subjecting the to-be-identified multi-temporal image to mask treatment and generating a multi-temporal high-brightness object image; calculating a dynamic time warping value, and subjecting the multi-temporal high-brightness object image to mask treatment based on the dynamic time warping value so as to generate an accumulated snow preliminary identification result image; based on the accumulated snow preliminary identification result image, obtaining an accumulated snow identification result image by conducting the classification result post-processing method. In this way, the multi-temporal characteristics of synchronous satellite remote-sensing sequence images are fully utilized, while the influence of clouds is eliminated without any short-wave infrared waveband. Therefore, the accumulated snow in synchronous satellite remote-sensing sequence images can be rapidly and accurately identified.
Owner:INST OF REMOTE SENSING & DIGITAL EARTH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Hyperspectral remote sensing image classification method and device, equipment and storage medium
PendingCN112766227AHigh precisionImprove recognition accuracyScene recognitionEuclidean distanceRemote sensing
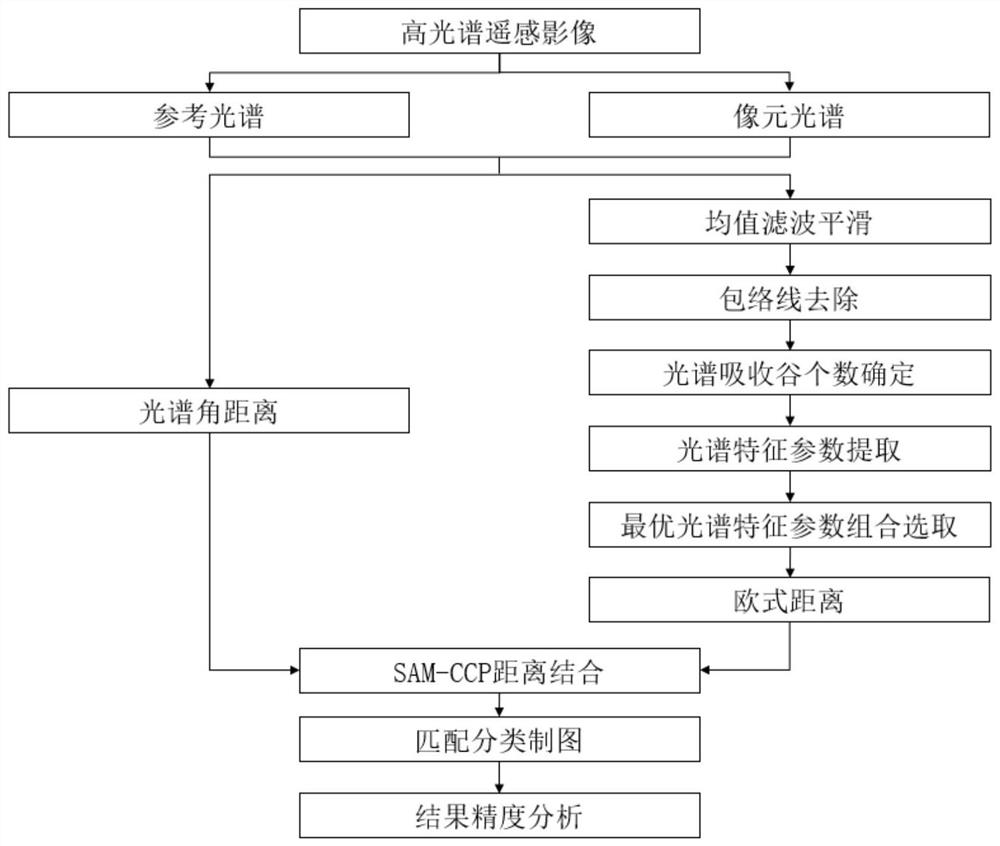
The invention provides a hyperspectral remote sensing image classification method, apparatus and device, and a storage medium. The method comprises the following steps: respectively obtaining a reference spectrum of each ground feature type and a pixel spectrum of each pixel from an original hyperspectral remote sensing image; calculating to obtain a spectral angular distance between the pixel spectrum and the reference spectrum; calculating the Euclidean distance of the optimal spectral characteristic parameter combination between the pixel spectrum and the reference spectrum; combining the spectral angular distance with the Euclidean distance to obtain a final matching distance between the pixel spectrum and the reference spectrum; and according to the final matching distance, judging a ground feature type to which each pixel in the image belongs, outputting a classification result graph of the original hyperspectral remote sensing image based on the ground feature type to which the pixel belongs, and carrying out precision evaluation on the classification result graph. According to the method, the spectral angular distance based on the overall characteristics of the spectrum and the combined characteristic parameter Euclidean distance which highlights the local detail characteristics of the spectrum are combined, so that the classification precision of the hyperspectral remote sensing image is improved.
Owner:WUHAN CENT CHINA GEOLOGICAL SURVEY CENT SOUTH CHINA INNOVATION CENT FOR GEOSCIENCES +1
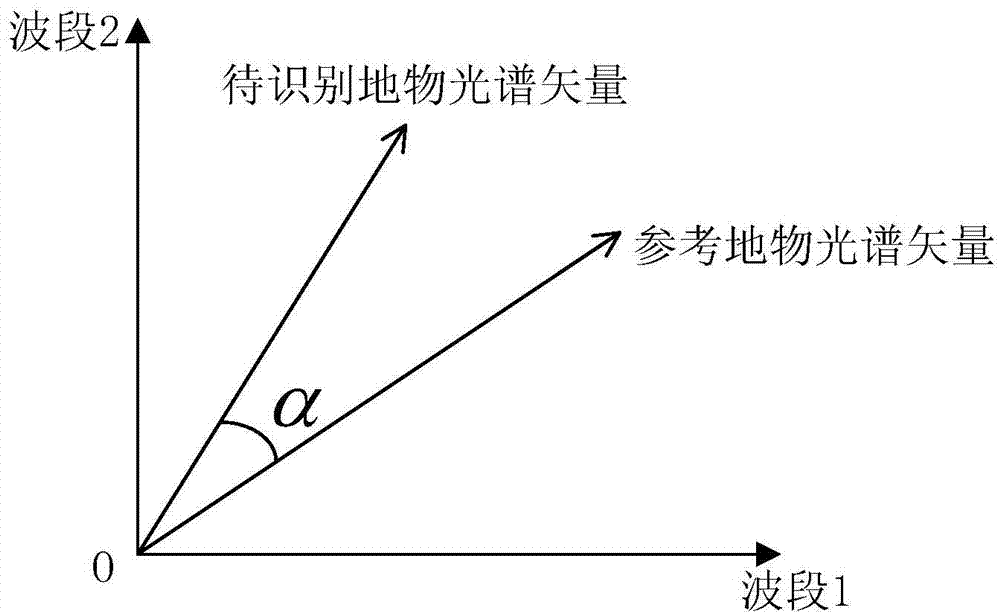
Spectral angle mapping method aiming at ground object spectrum uncertainty
ActiveCN103926203AHigh precisionOvercoming the effects of uncertaintyColor/spectral properties measurementsEuclidean vectorComputer science
The invention discloses a spectral angle mapping method aiming at ground object spectrum uncertainty. The method comprises the following steps of acquiring a test spectrum and a reference spectrum; calculating a spectrum difference by utilizing the test spectrum and the reference spectrum, and constructing a spectrum difference vector according to the spectrum difference, wherein the dimension of the spectrum difference vector is the same as that of a vector of the test spectrum, and the magnitude of each component of the spectrum difference vector is equal to that of the vector of the test spectrum; calculating a spectral angle between the test spectrum and the reference spectrum under a ground object spectrum uncertainty condition by utilizing the spectrum difference vector; and performing spectral angle mapping according to the spectral angle. According to the method, the spectral angle between the test spectrum and the reference spectrum is acquired under the ground object spectrum uncertainty condition by utilizing the spectrum difference, and the spectral angle mapping is performed according to the obtained spectral angle, so that the influence of ground object spectrum uncertainty is eliminated, the ground object recognition accuracy is improved, and the method is relatively high in applicability to the ground object spectrum uncertainty.
Owner:INST OF REMOTE SENSING & DIGITAL EARTH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
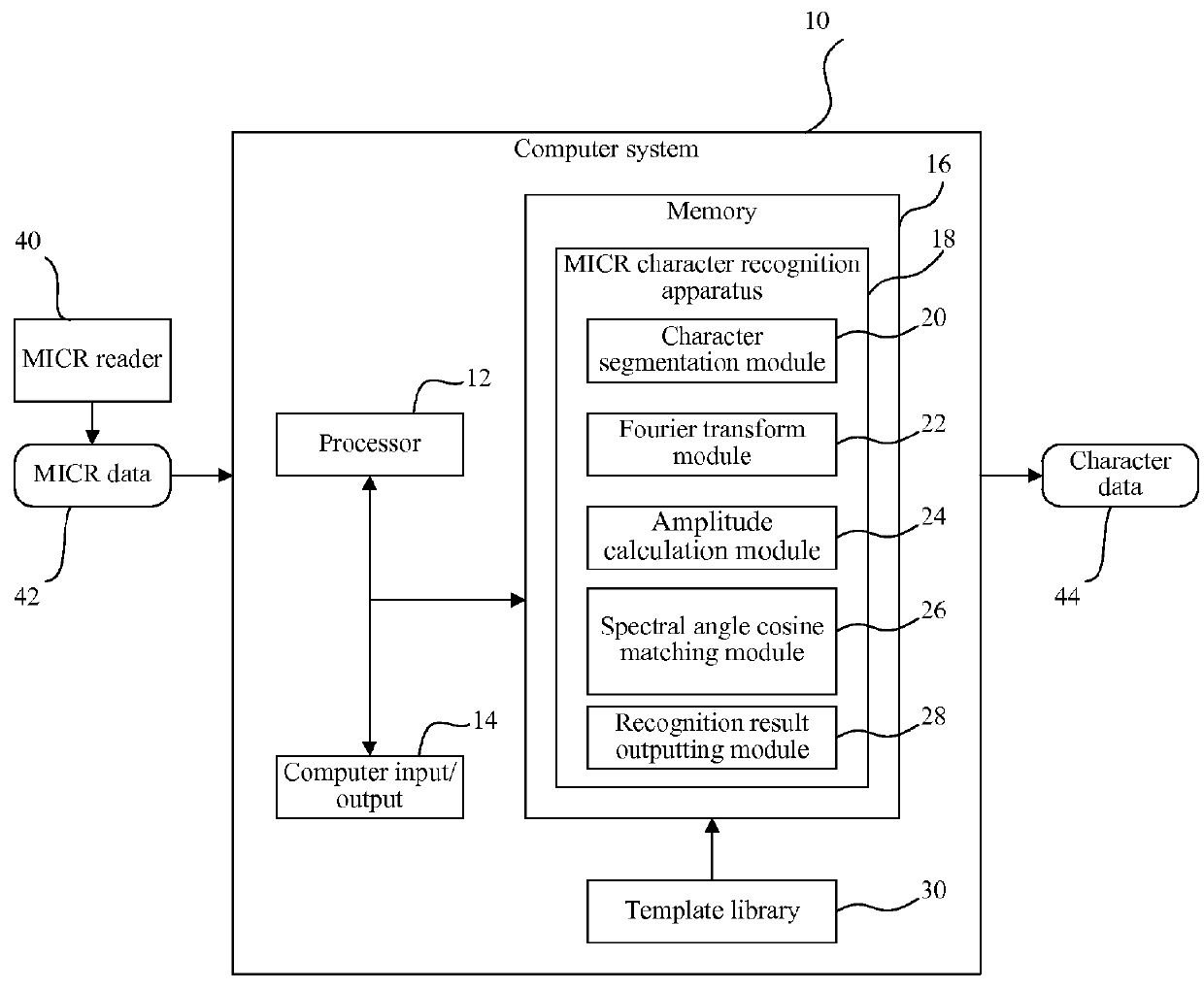
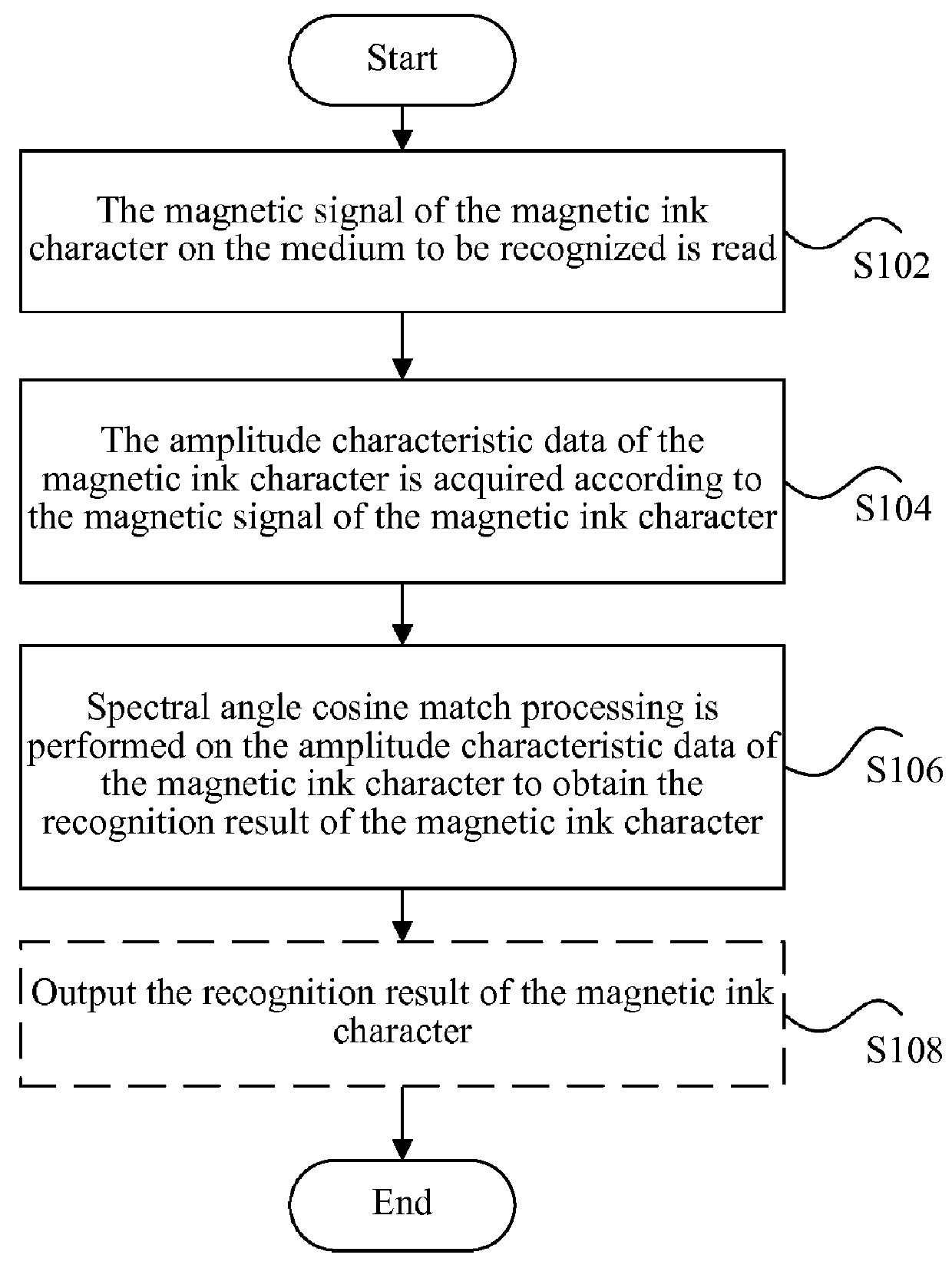
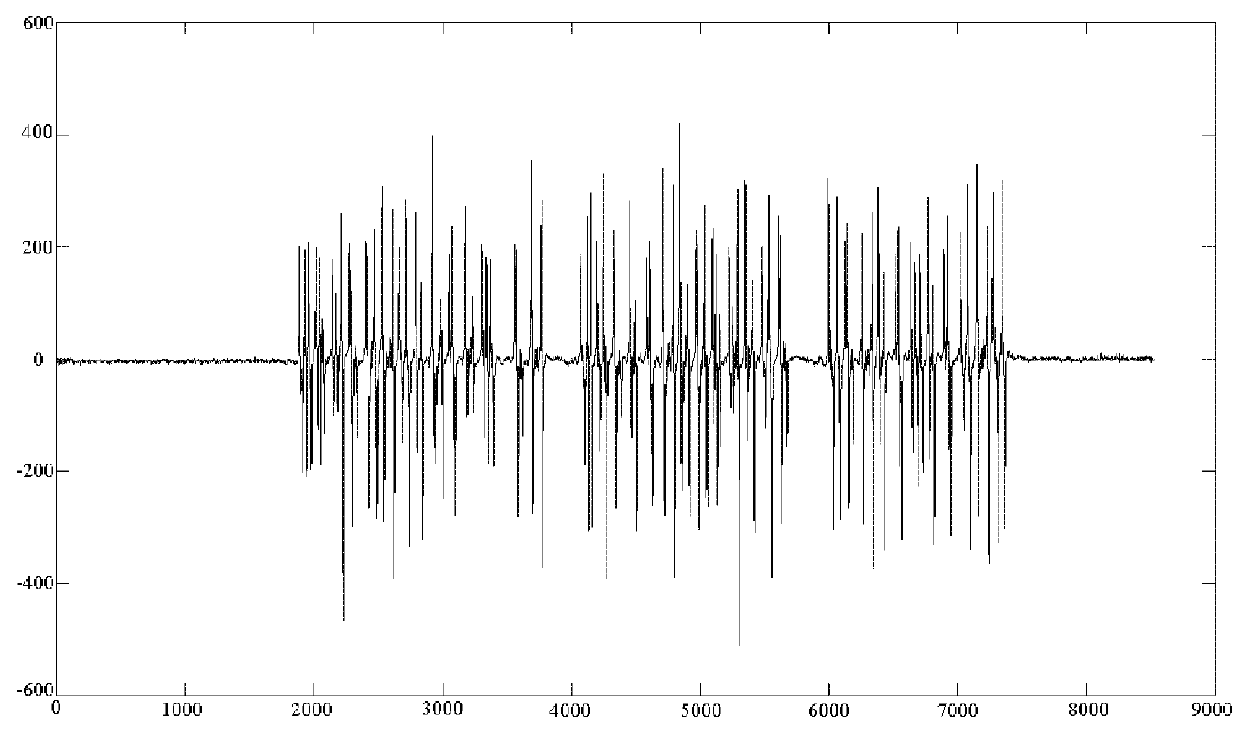
Method, apparatus and system for recognizing magnetic ink character
ActiveUS20130071005A1Lower requirementImprove recognition rateCharacter and pattern recognitionPresent methodFeature data
Disclosed are a magnetic ink character recognition method, apparatus and system. The method includes: reading a magnetic signal of a magnetic ink character on a medium to be recognized; acquiring the amplitude characteristic data of the magnetic ink character according to the magnetic signal thereof; and performing spectral angle cosine match processing on the amplitude characteristic data of the magnetic ink character to obtain the recognition result of the magnetic ink character. The present method can reduce the stability requirements on the magnetic signal and improve the recognition rate of the magnetic signal.
Owner:SHANDONG NEW BEIYANG INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
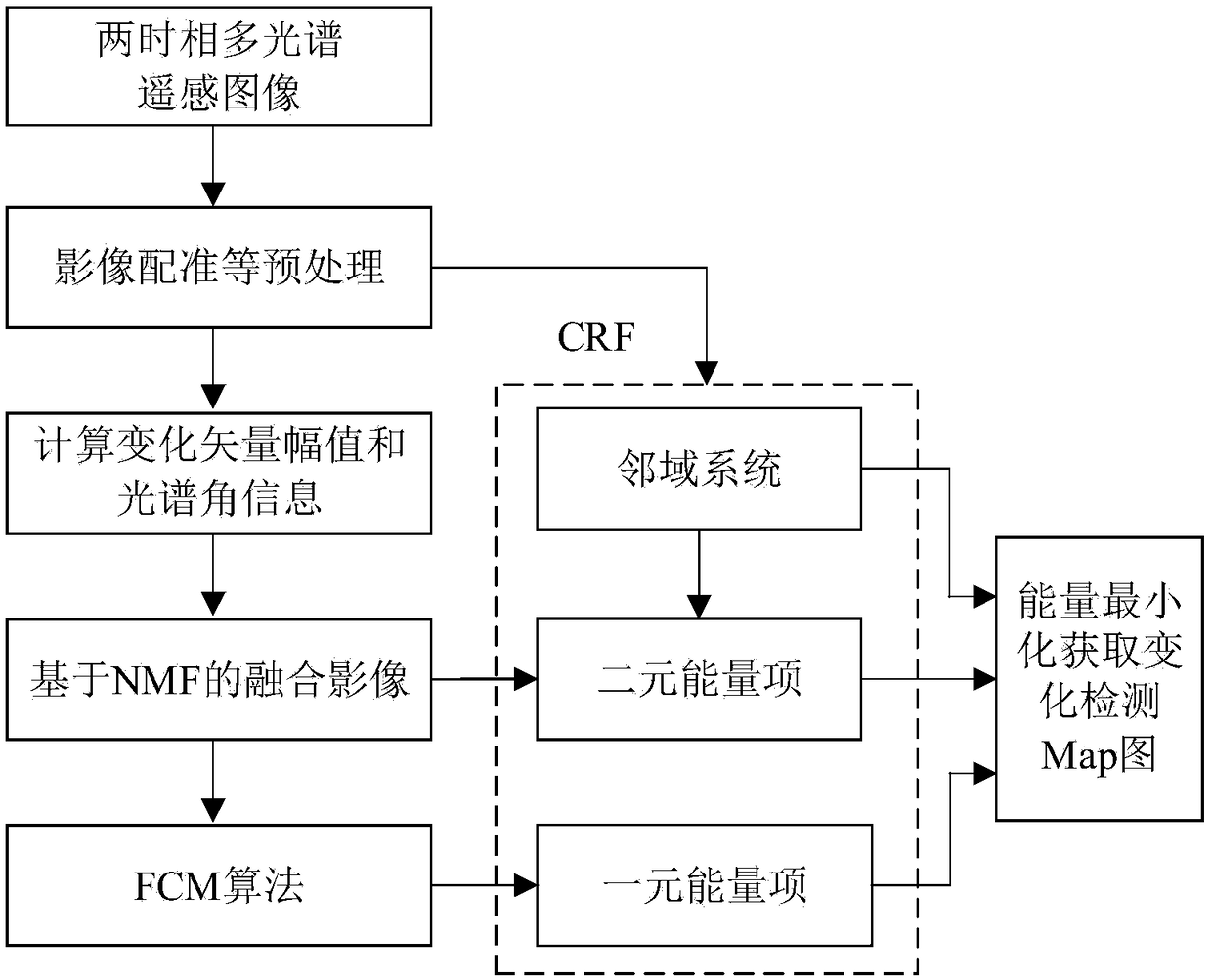
Multi-temporal multi-spectral remote sensing image change detection method and system
ActiveCN109242832AHigh precisionEasy to describeImage enhancementImage analysisMatrix decompositionEnergy minimization
The invention discloses a multi-temporal multi-spectral remote sensing image change detection method and system. Firstly, the method utilizes non-negative matrix decomposition to fuse the change vector amplitude of the multi-temporal remote sensing image and the spectral angle mapping map of the multi-temporal phase to obtain a new difference image. Then, the FCM algorithm is used to obtain the unitary energy terms of CRF for the difference images. Secondly, according to the neighborhood and difference images, the binary energy terms of CRF are obtained. Finally, the final change detection result is obtained by minimizing the energy of CRF with the cyclic reliability propagation algorithm. The invention can better depict the relationship between neighborhoods of images, and improves the accuracy of change detection. Change detection results are more reliable and more robust.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Hyperspectral image waveband selection method based on biclustering and neighborhood analysis
ActiveCN105989592AHigh precisionImprove clustering accuracyImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionCluster algorithmHyperspectral image classification
The invention provides a hyperspectral image waveband selection method based on biclustering and a neighborhood analysis. The method comprises the following steps of extracting a dual-spectral angle characteristic and a hyperspectral-image original wave band; clustering the characteristic; clustering the acquired characteristics respectively and then constructing connection between two clustering results; according to the acquired wave band clustering results, selecting one representative from each cluster, and simultaneously considering a specificity of each representative and expressivity of each representative in the corresponding cluster so as to deciding a cluster representative, which means that the final wave band is selected; and using the acquired wave band to carry out hyperspectral image classification. In the invention, a bicharacteristic idea is provided, and a limitation that a wave band gray value is only used as a spectral characteristic in a traditional cluster algorithm is overcome so that wave band selection precision is increased.
Owner:XI'AN INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Robust background estimation method-based local target detection method for hyperspectral image
ActiveCN104346812AEasy to detectReliable estimateImage analysisScene recognitionEstimation methodsComputer science
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
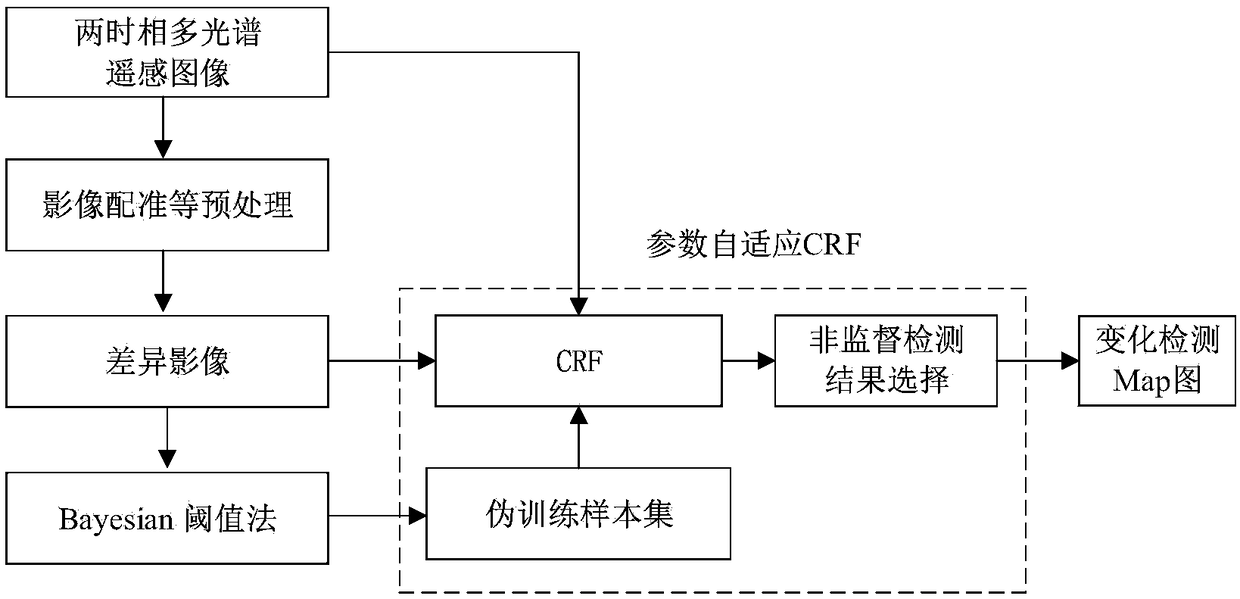
Remote sensing image change detection method and system based on conditional random field
ActiveCN109191503AEasy to describeReliable results for change detectionImage enhancementImage analysisConditional random fieldEnergy minimization
The invention discloses a remote sensing image change detection method and system based on a conditional random field. The method comprises the following steps: calculating the change vector amplitudeof a remote sensing image; according to the amplitude of the change vector, using the FCM algorithm to obtain the one-dimensional energy term of CRF; obtaining the binary energy terms of CRF from theneighborhood of each node, spectral angle information and the amplitude of the change vector of the remote sensing image; obtaining the change detection results by minimizing the energy of CRF usingthe cyclic reliability propagation algorithm. The regularization parameters of CRF energy function are selected by the pseudo-training sample set in the detection process, and the corresponding finalchange detection results are obtained under the optimal regularization parameters. The invention can make the result of the change detection more reliable and more robust, and improves the precision of the change detection.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
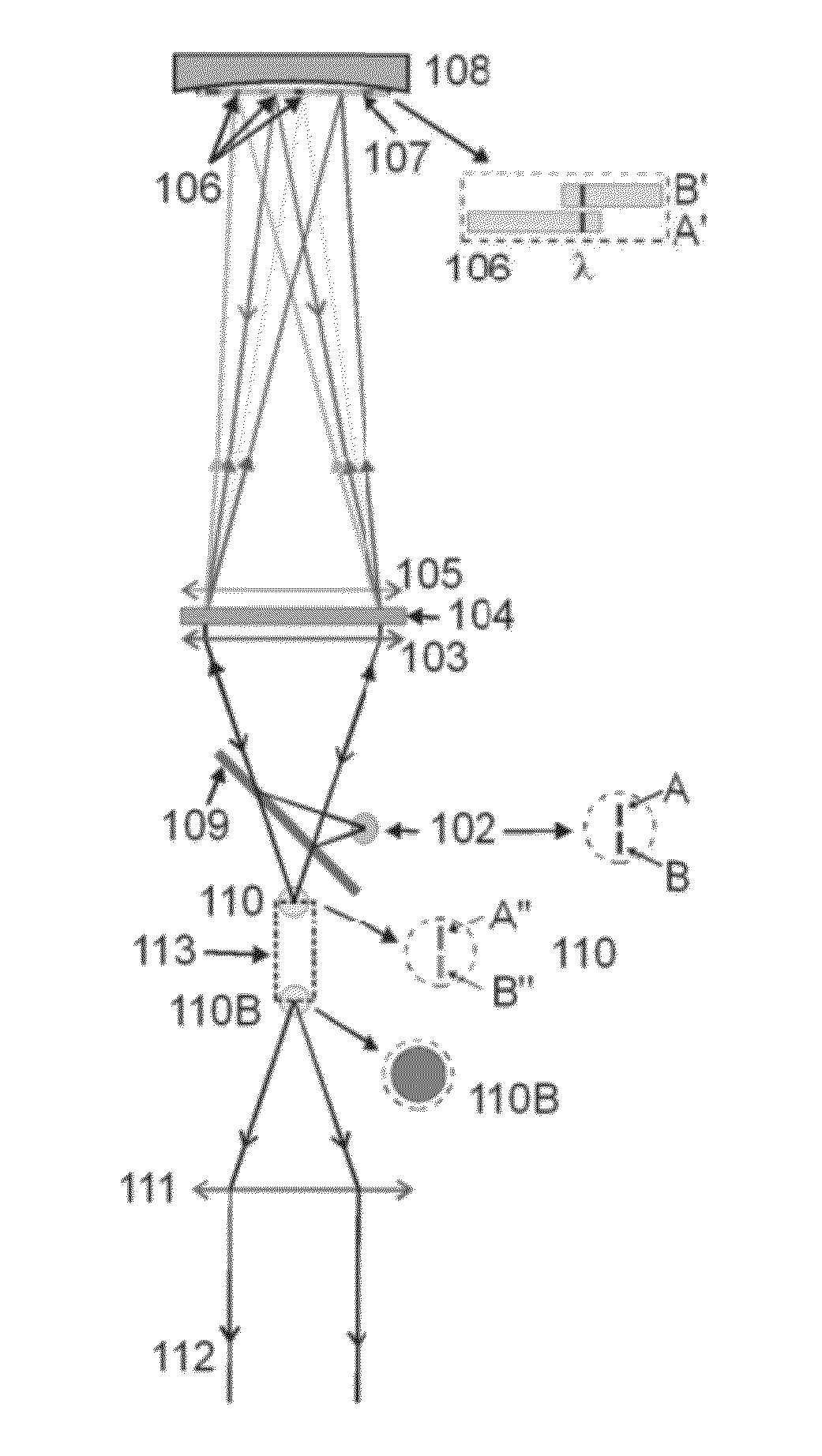
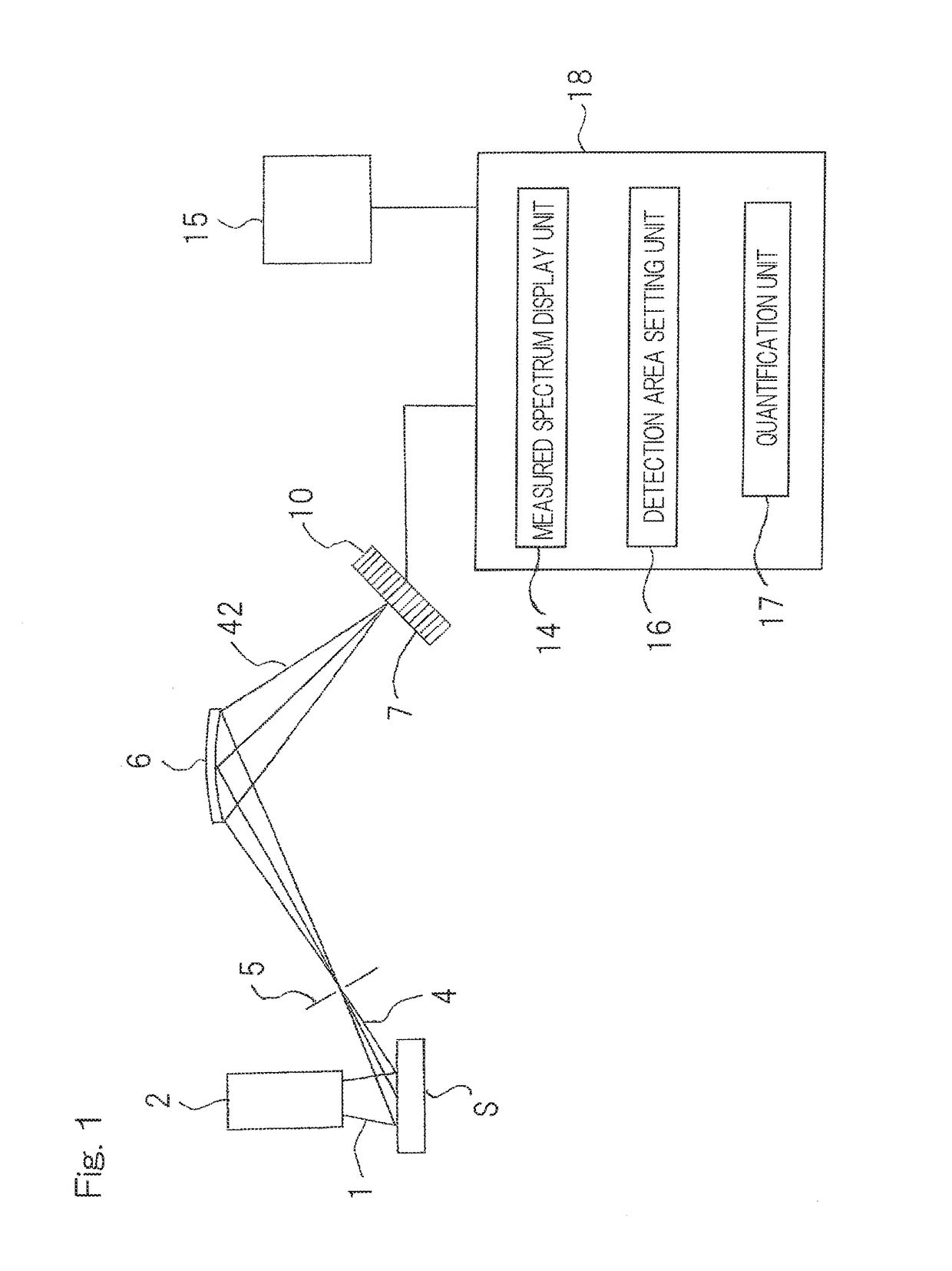
Wavelength dispersive x-ray fluorescence spectrometer and x-ray fluorescence analyzing method using the same
ActiveUS20190072504A1Low costExtension of timeMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationSoft x rayDisplay device
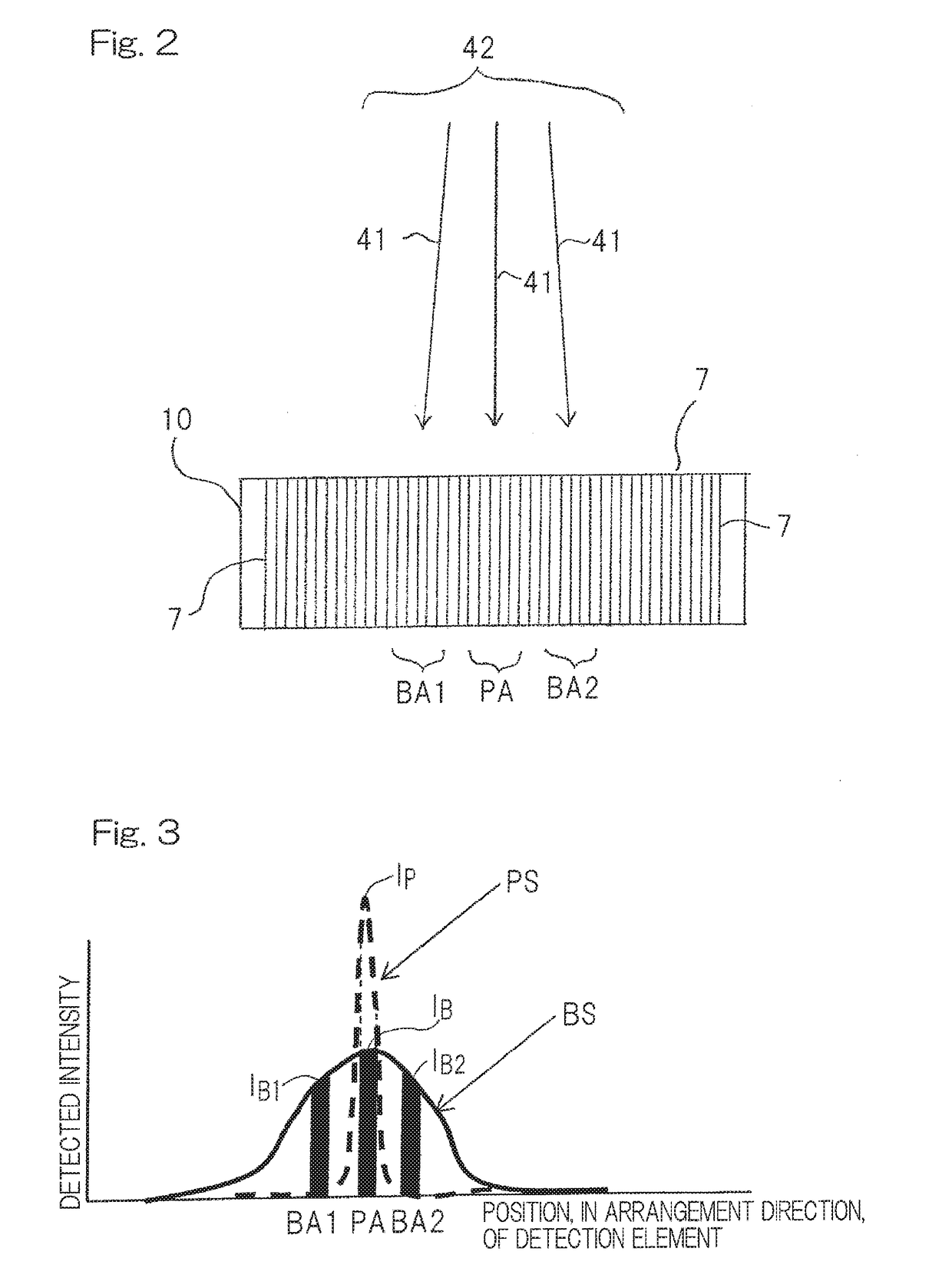
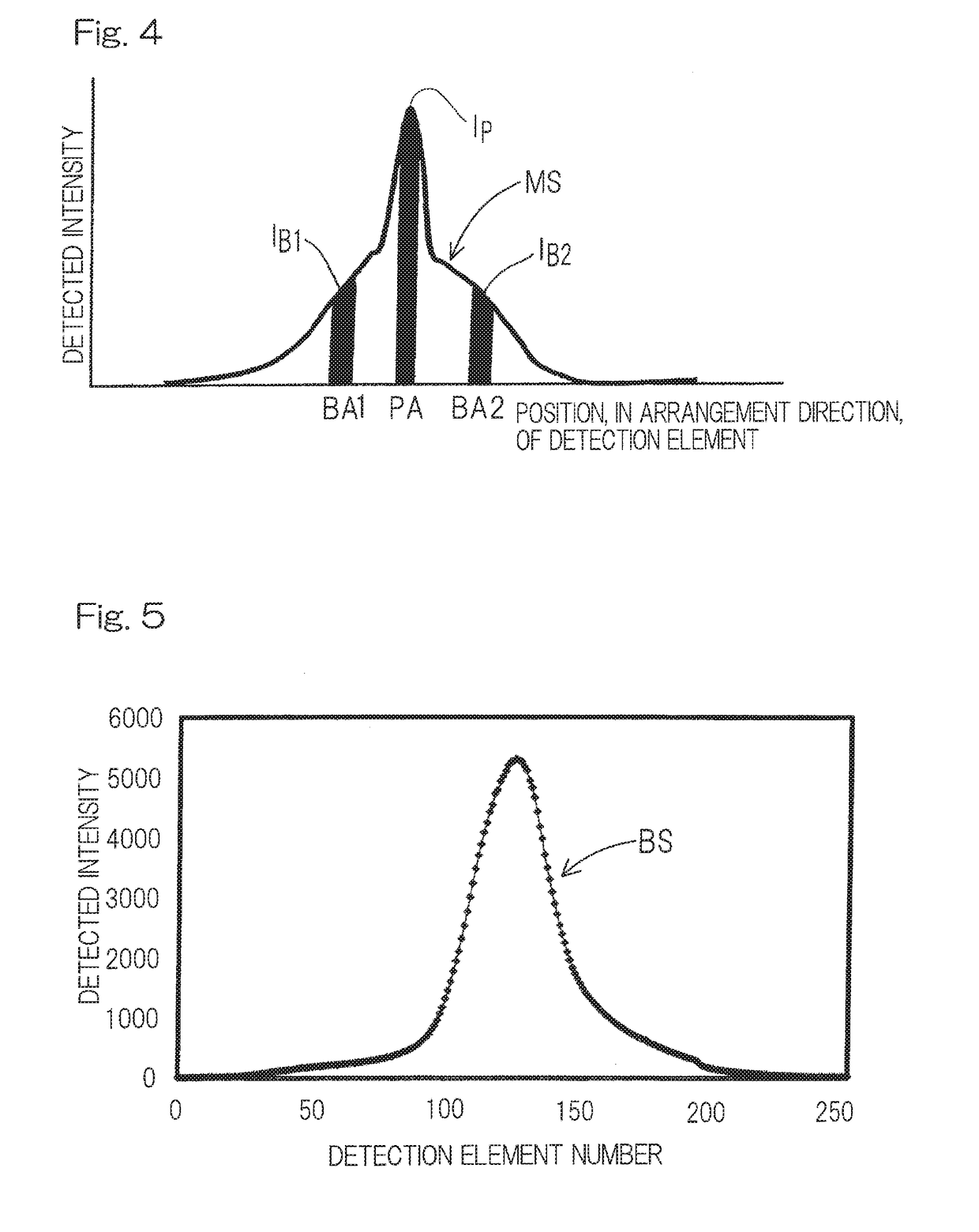
A wavelength dispersive X-ray fluorescence spectrometer of the present invention includes: a position sensitive detector (10) configured to detect intensities of secondary X-rays (41) at different spectral angles, by using detection elements (7) corresponding to the secondary X-rays (41) at different spectral angles; a measured spectrum display unit (14) configured to display a relationship between a position, in an arrangement direction, of each detection element (7), and a detected intensity by the detection element (7), as a measured spectrum, on a display (15); a detection area setting unit (16) configured to be set a peak area and a background area; and a quantification unit (17) configured to calculate, as a net intensity, an intensity of the fluorescent X-rays to be measured, based on a peak intensity in the peak area, a background intensity in the background area, and a background correction coefficient, and to perform quantitative analysis.
Owner:RIGAKU CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com