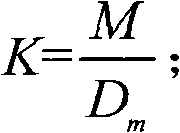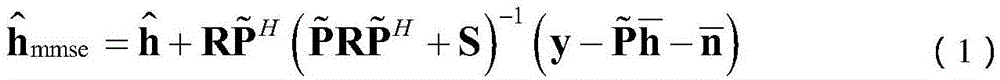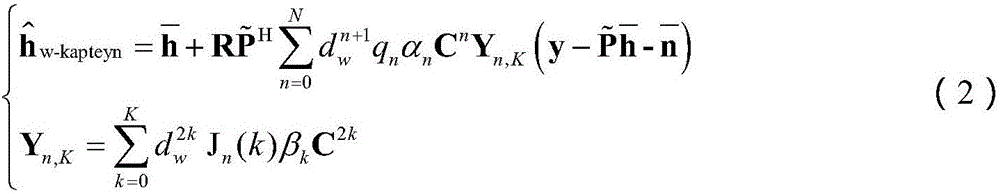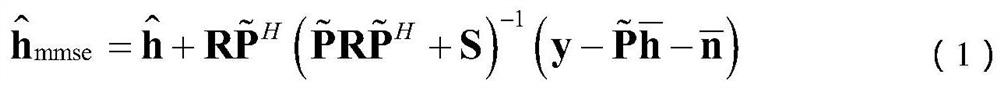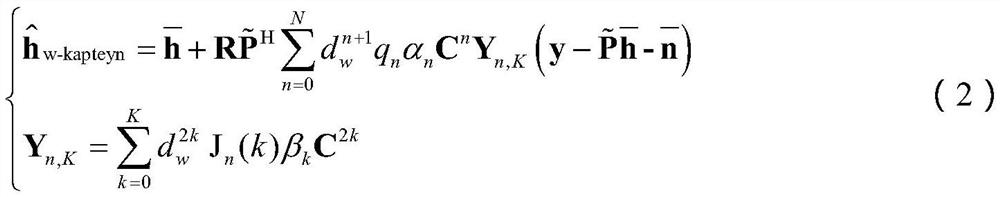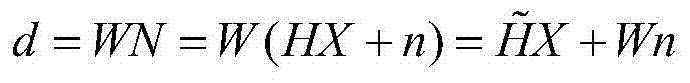Patents
Literature
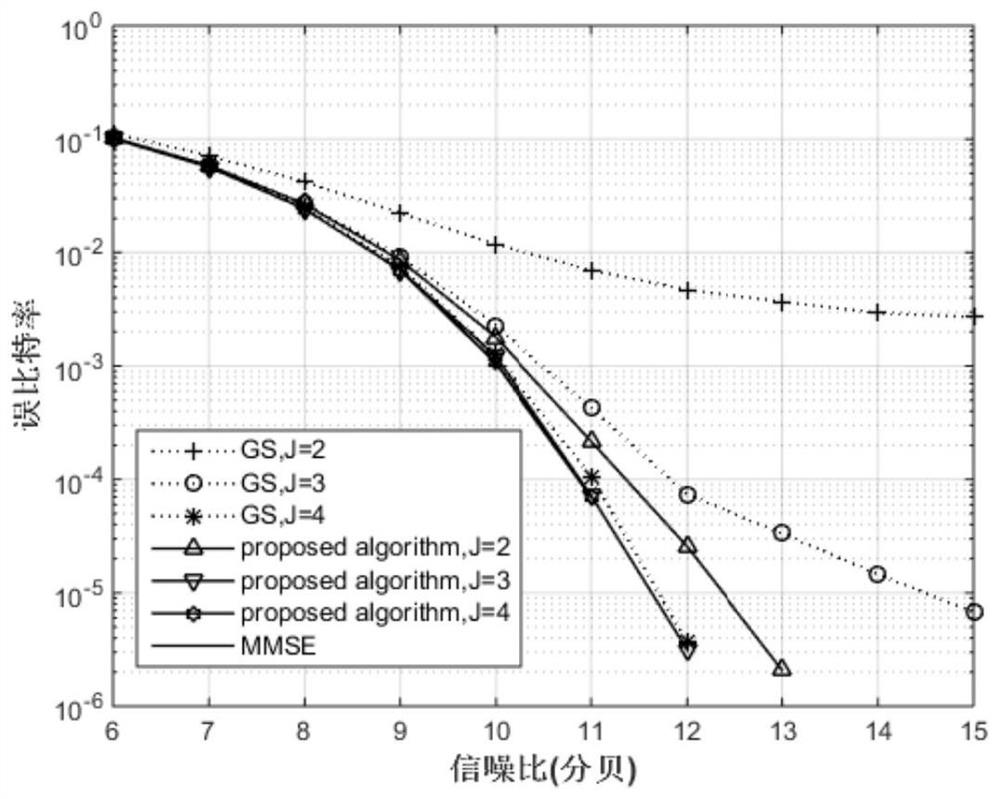
44 results about "Matrix addition" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
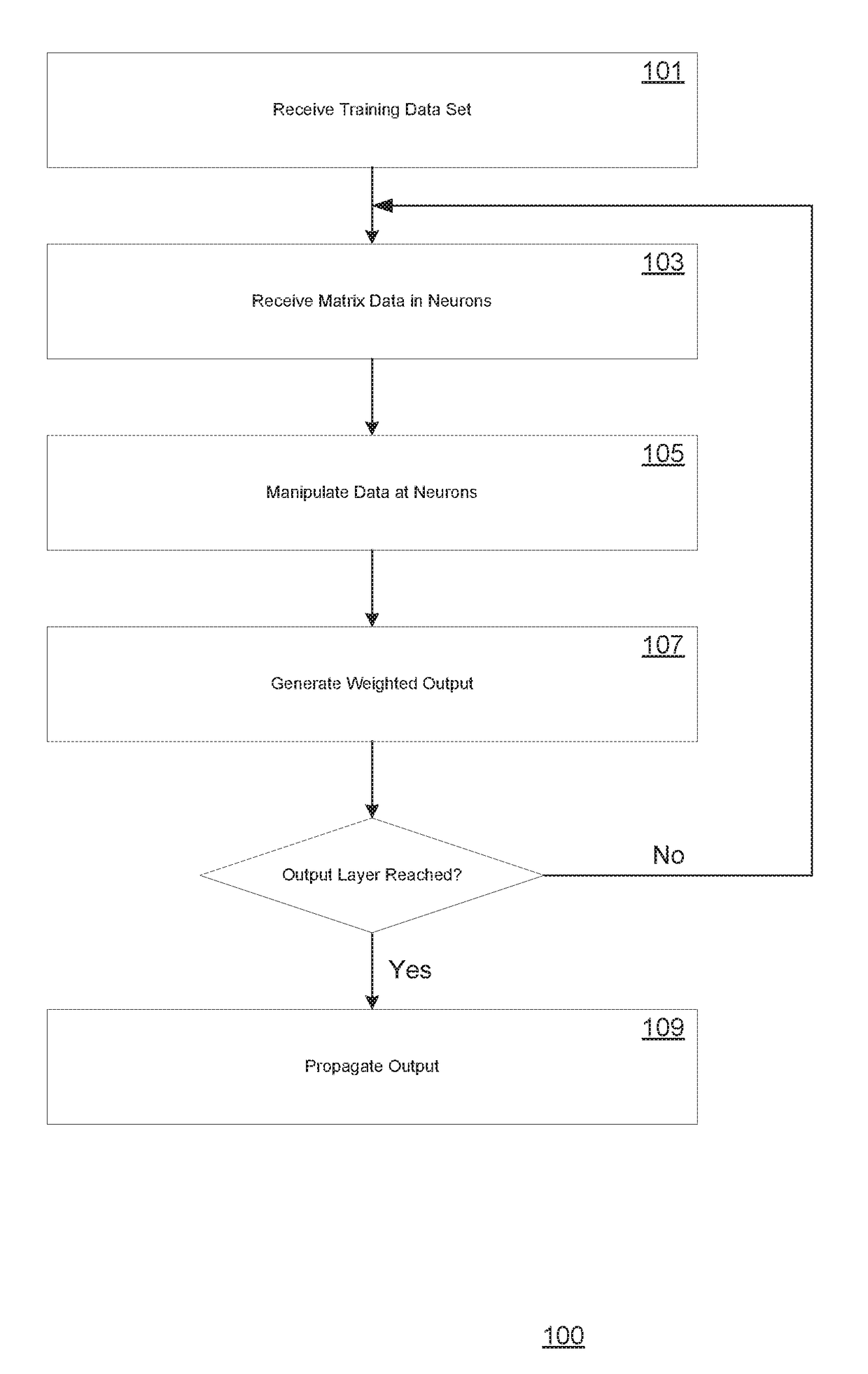
In mathematics, matrix addition is the operation of adding two matrices by adding the corresponding entries together. However, there are other operations which could also be considered as a kind of addition for matrices, the direct sum and the Kronecker sum.
Tensor processing using low precision format
PendingUS20170372202A1Accelerated trainingOperation accuracyNeural architecturesPhysical realisationMatrix additionAlgorithm
Aspects of the present invention are directed to computer-implemented techniques for improving the training of artificial neural networks using a reduced precision (e.g., float16) data format. Embodiments of the present invention rescale tensor values prior to performing matrix operations (such as matrix multiplication or matrix addition) to prevent overflow and underflow. To preserve accuracy throughout the performance of the matrix operations, the scale factors are defined using a novel data format to represent tensors, wherein a matrix is represented by the tuple X, where X=(a, v[.]), wherein a is a float scale factor and v[.] are scaled values stored in the float16 format. The value of any element X[i] according to this data format would be equal to a*v[i].
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
Radar device
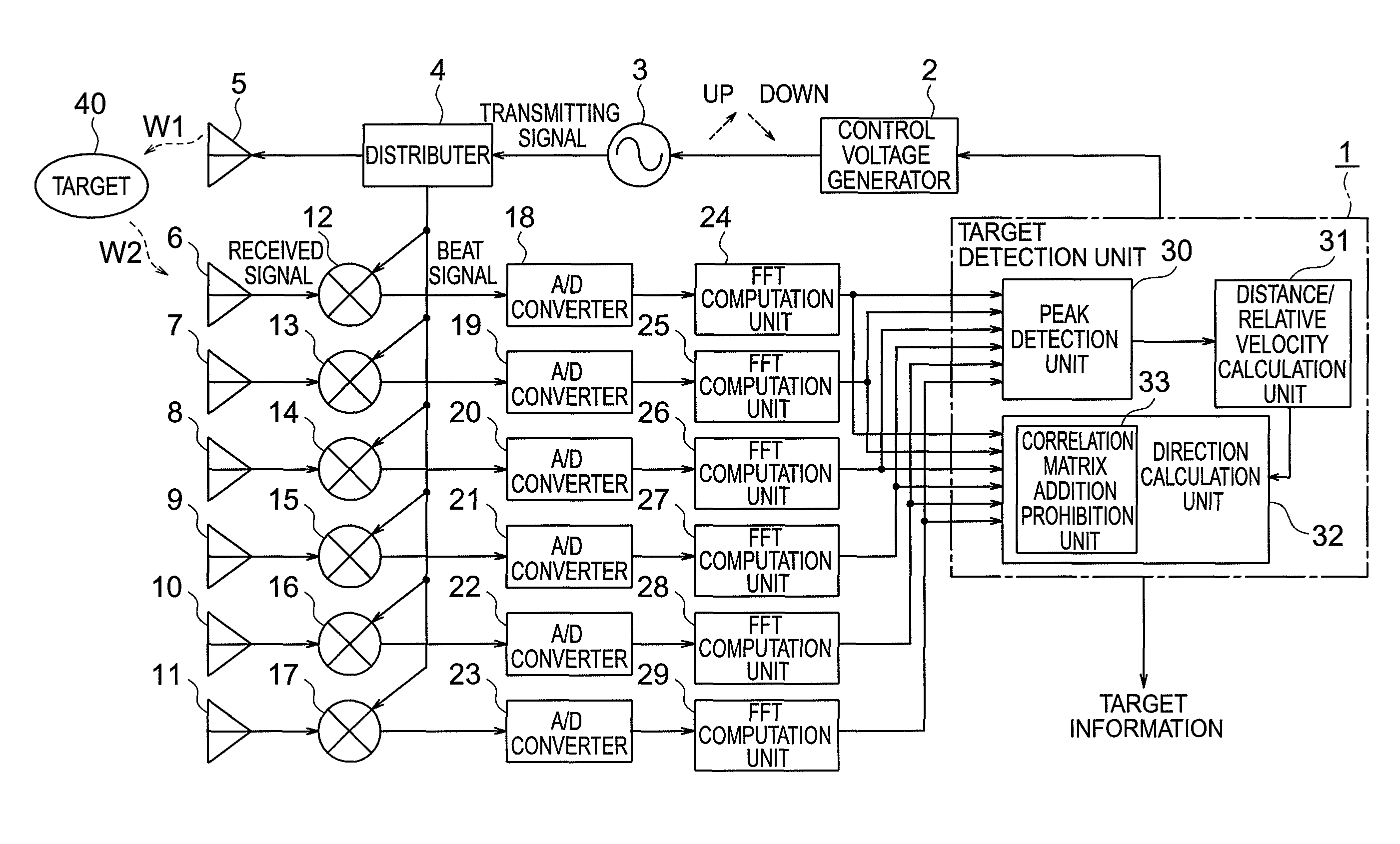
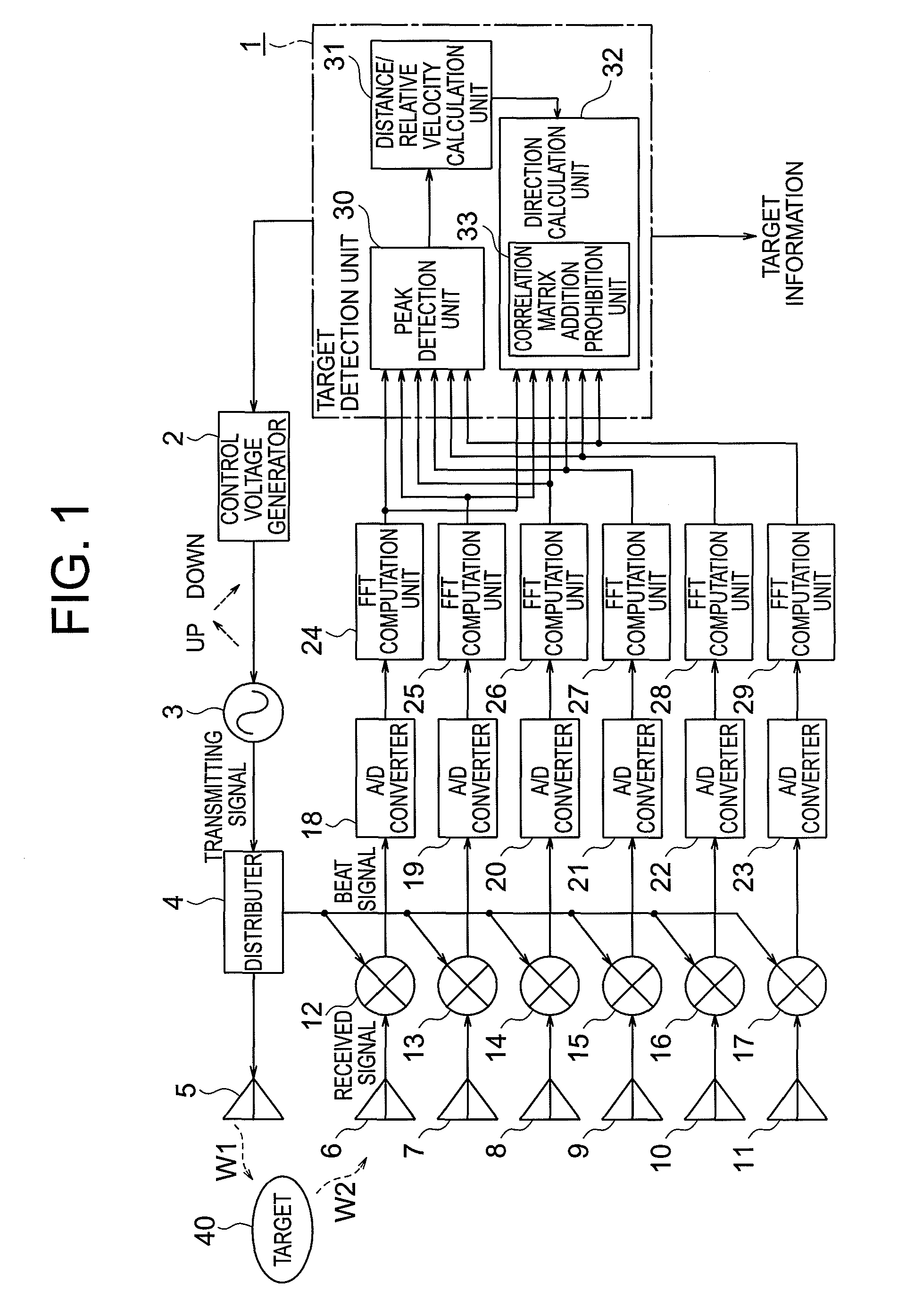
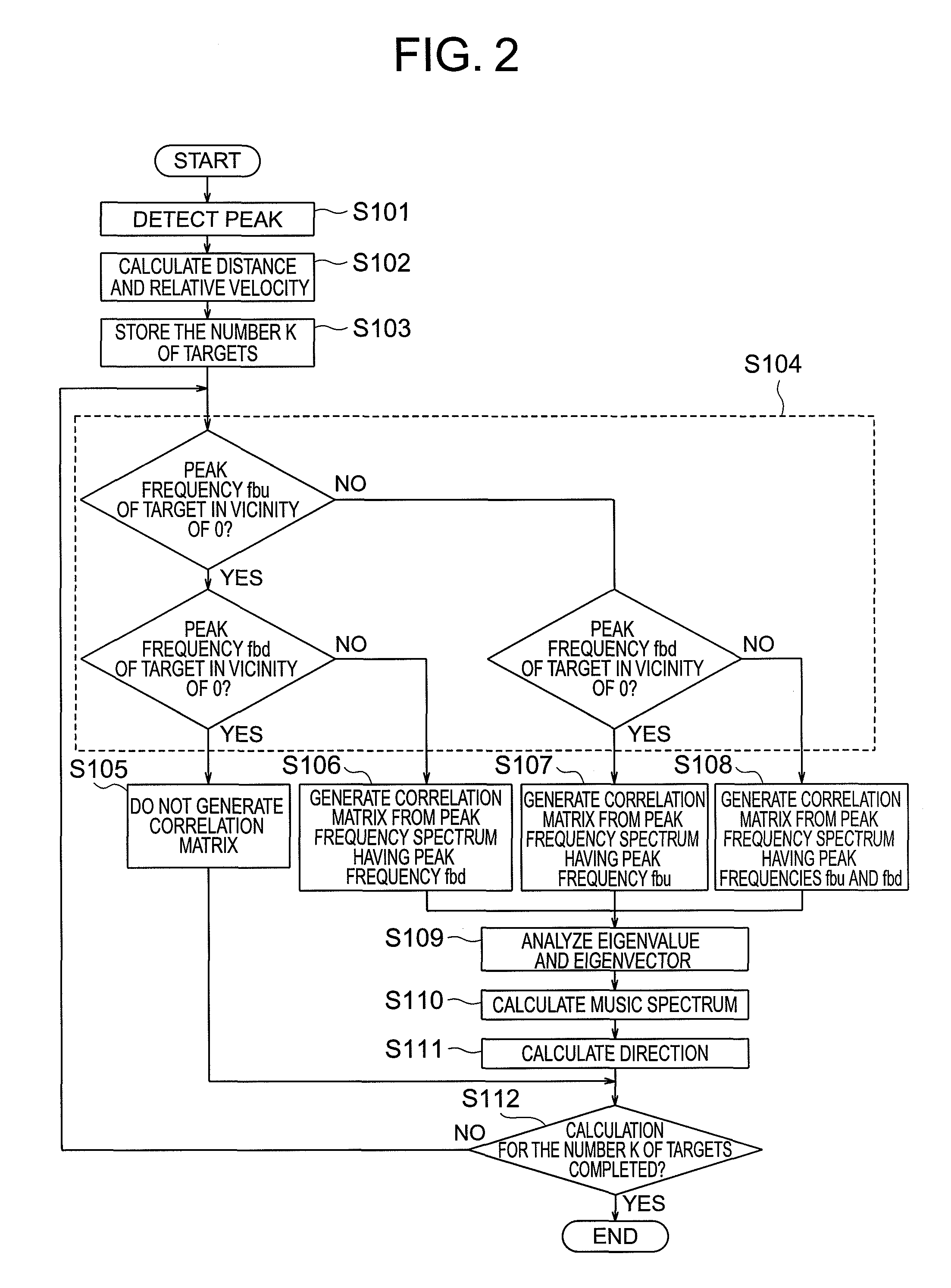
ActiveUS8102309B2Accurate calculationMulti-channel direction-finding systems using radio wavesRadio wave reradiation/reflectionMatrix additionFrequency spectrum
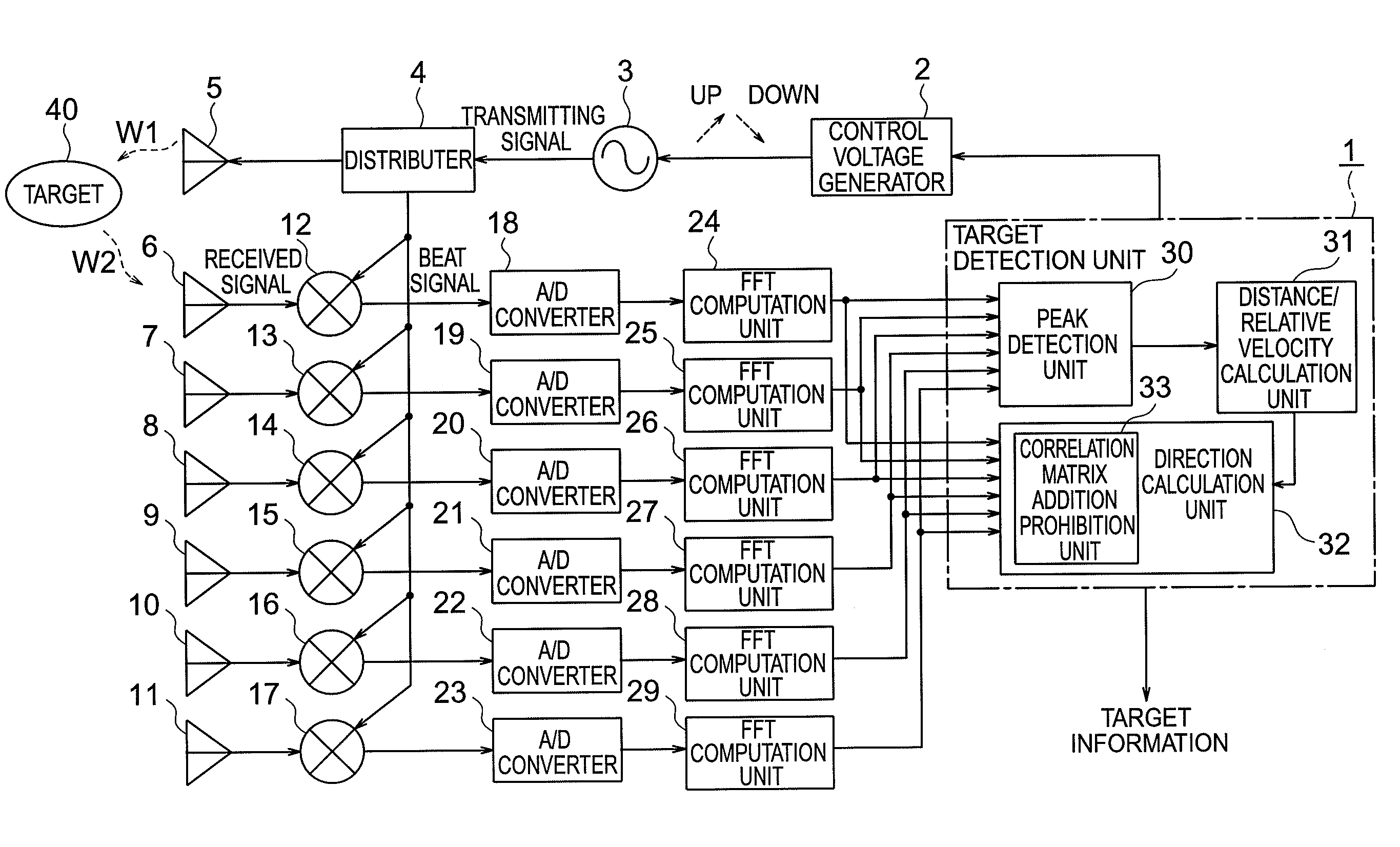
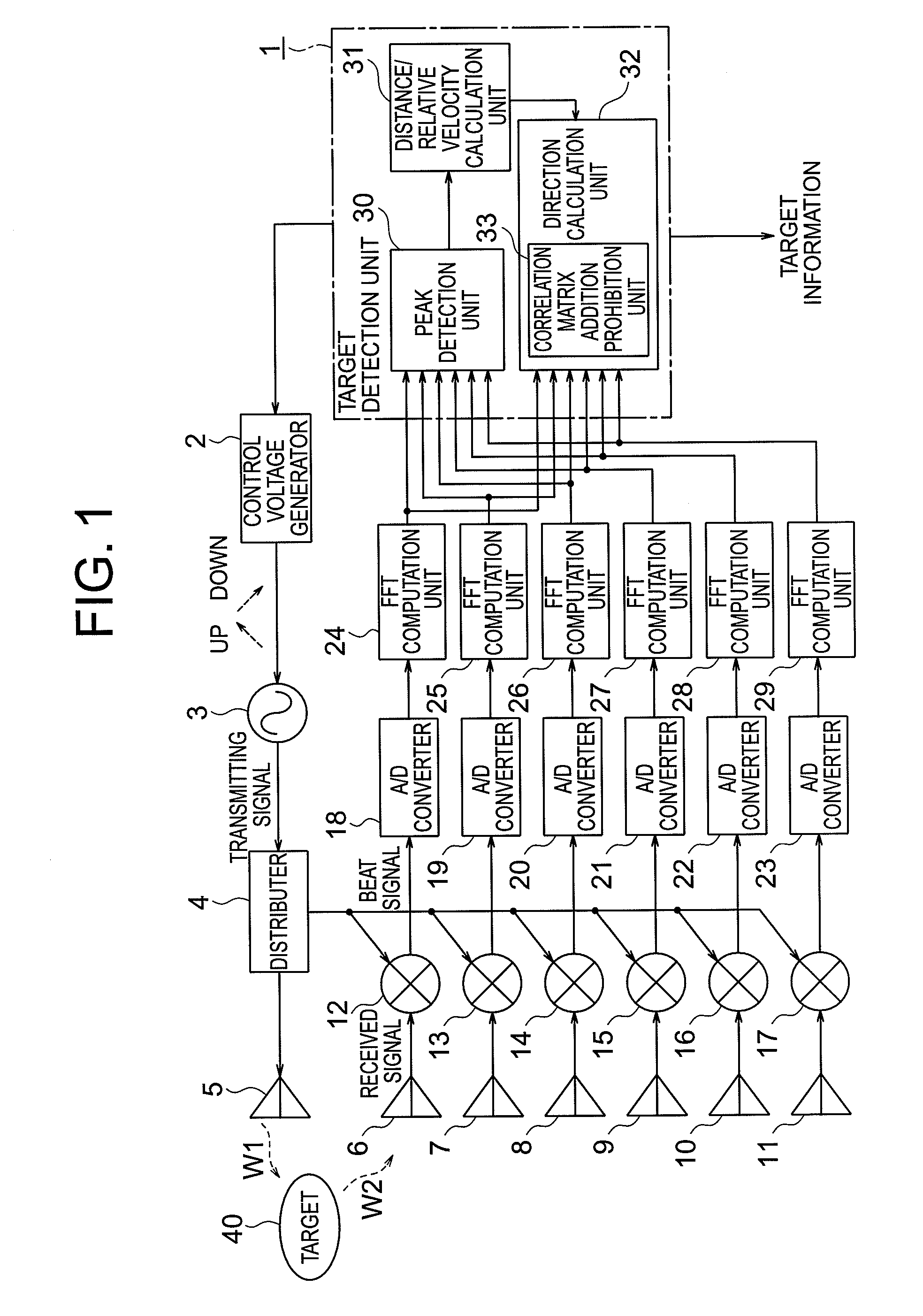
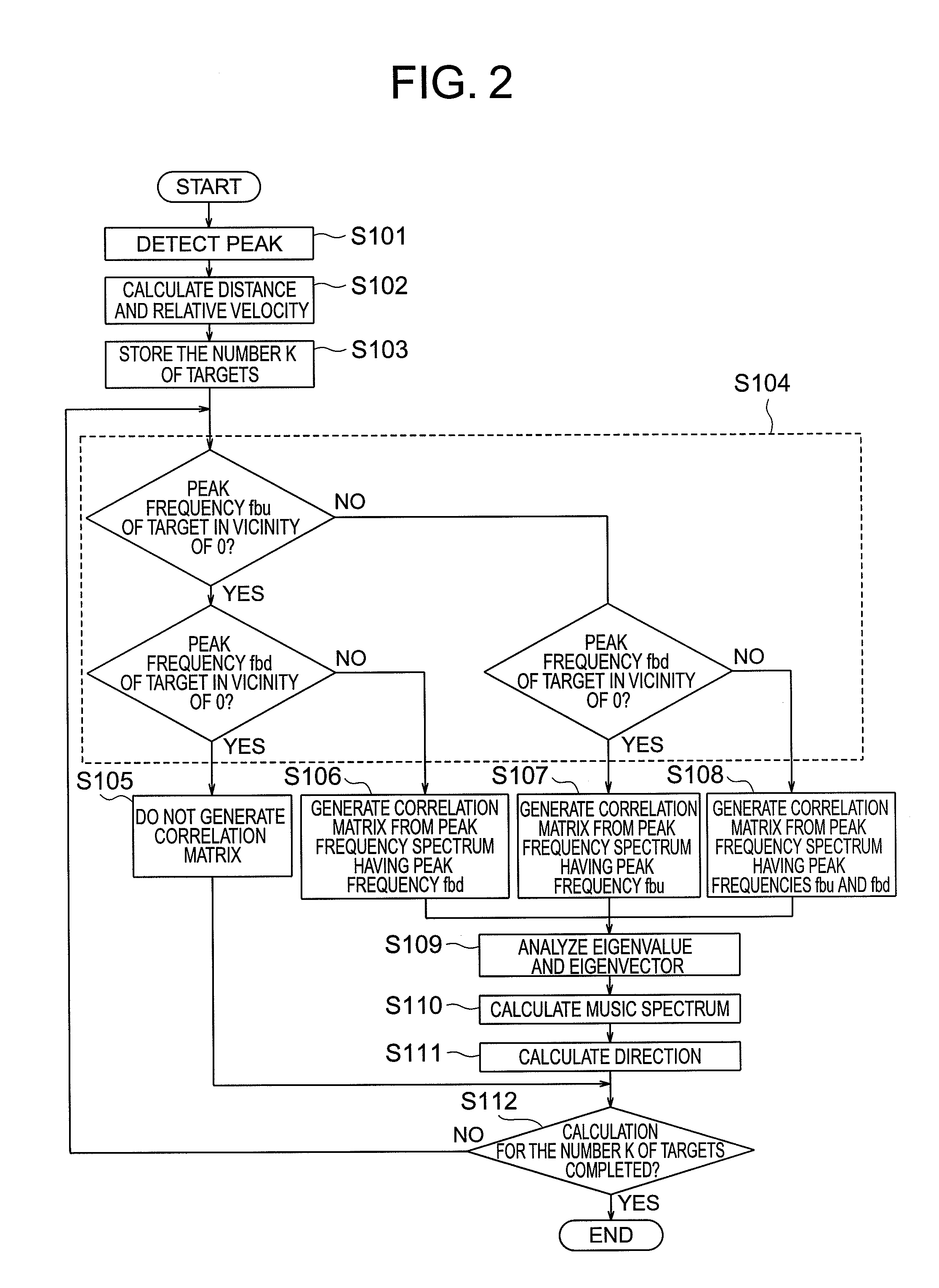
Provided is a radar device capable of accurately calculating directions and the number of targets. A direction calculation unit includes a correlation matrix addition prohibition unit that prohibits, when a peak frequency in a plurality of modulation periods of a target is in the vicinity of 0, addition of a correlation matrix generated from a peak frequency spectrum having the peak frequency in the vicinity of 0, and calculates the direction of the target on the basis of a summed correlation matrix in which correlation matrices generated from peak frequency spectra having peak frequencies out of the vicinity of 0.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
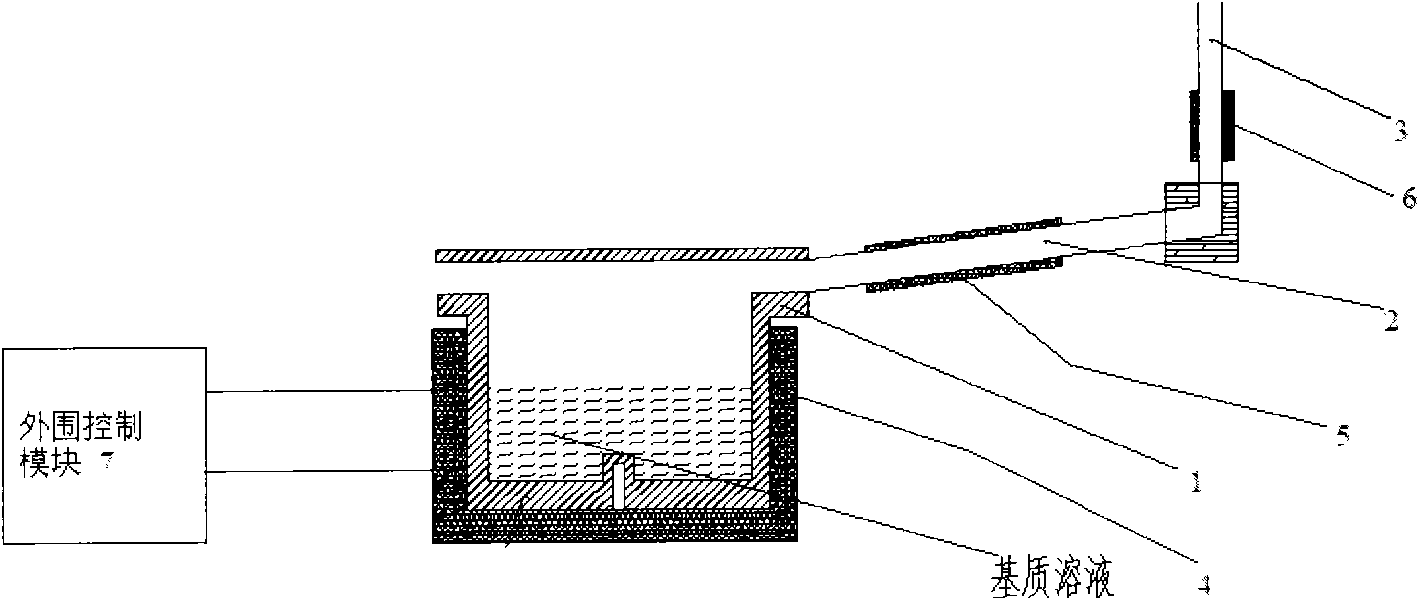
Matrix addition system for mass spectrum analysis
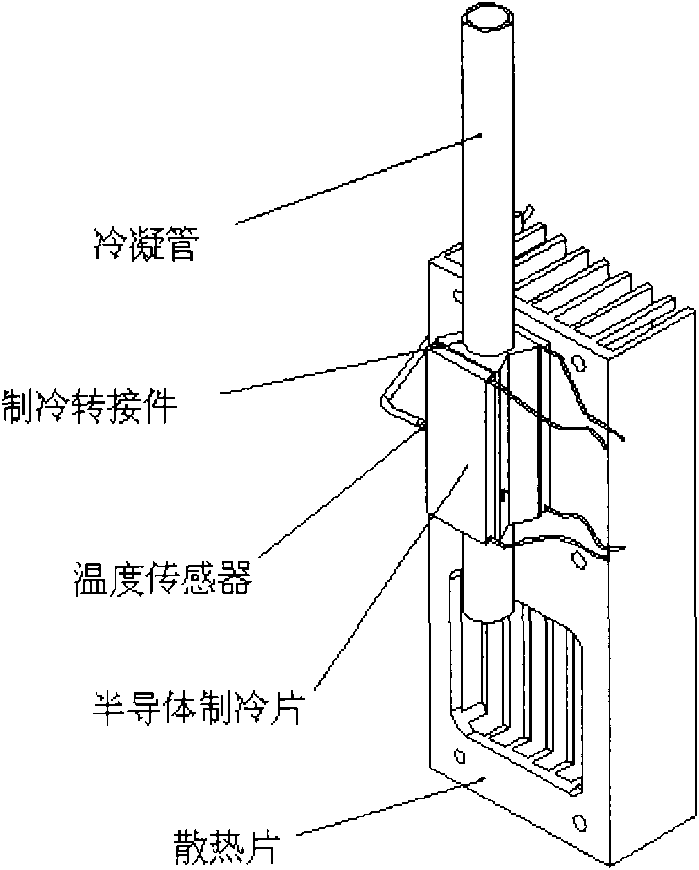
The invention discloses a matrix addition system for mass spectrum analysis, comprising a heating bath, a thermal saturated pipe, a condenser pipe and a peripheral control module, wherein the heating bath is used for containing a matrix solution; a first heating band is fixed outside the heating bath; the thermal saturated pipe is connected with the heating bath; a second heating band is fixed outside the thermal saturated pipe and used for providing appropriate temperature for a mixed gas of aerosol particles and a matrix so that the aerosol particles and the matrix are better bonded together; the condenser pipe is connected with the thermal saturated pipe; a refrigeration sheet is fixed outside the condenser pipe and used for condensing a gas exhausted from the thermal saturated pipe to enable the vaporous matrix, which is not attached to the aerosol particles, to be liquefied and reflow to the heating bath so as to obtain the aerosol particles attached with the matrix on an outlet of the condenser pipe; and the peripheral control module is respectively connected with the first heating band, the second heating band and the refrigeration sheet and used for regulating and displaying the set temperature and the current temperature of the heating bath, the thermal saturated pipe and the condenser pipe.
Owner:北京汇丰隆经济技术开发有限公司
Radar device
ActiveUS20100134343A1Exact numberAccurate calculationMulti-channel direction-finding systems using radio wavesRadio wave reradiation/reflectionMatrix additionFrequency spectrum
Provided is a radar device capable of accurately calculating directions and the number of targets. A direction calculation unit includes a correlation matrix addition prohibition unit that prohibits, when a peak frequency in a plurality of modulation periods of a target is in the vicinity of 0, addition of a correlation matrix generated from a peak frequency spectrum having the peak frequency in the vicinity of 0, and calculates the direction of the target on the basis of a summed correlation matrix in which correlation matrices generated from peak frequency spectra having peak frequencies out of the vicinity of 0.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Large-scale MIMO (Multiple Input Multiple Output) precoding method based on improved newton iteration method
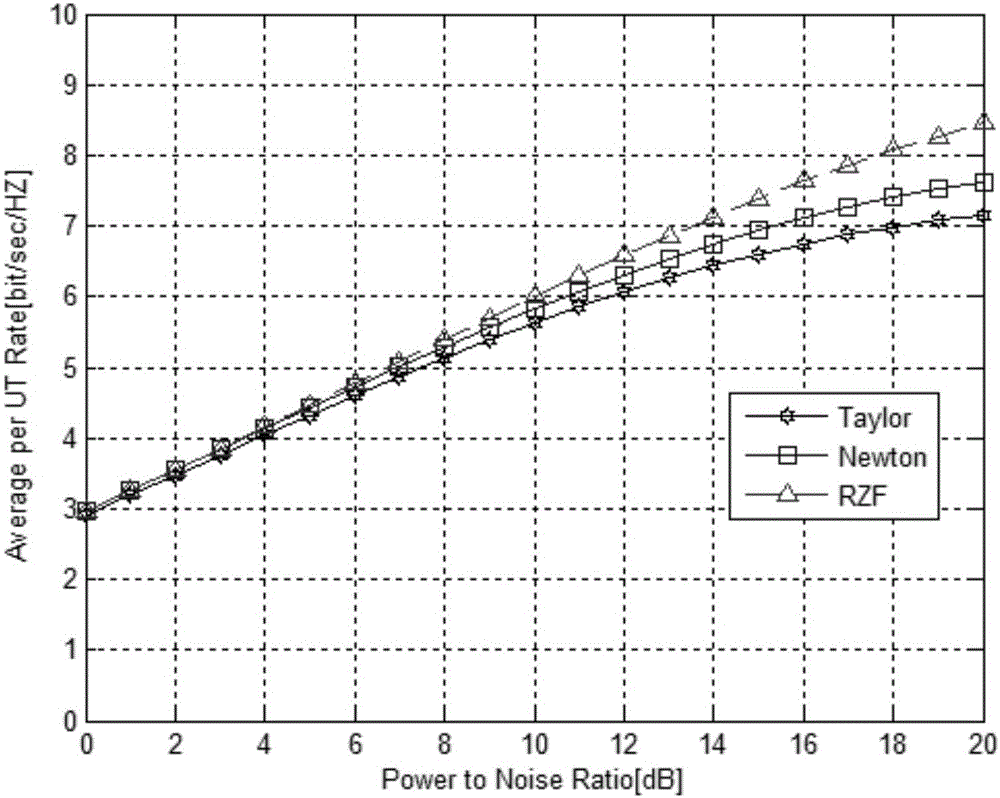
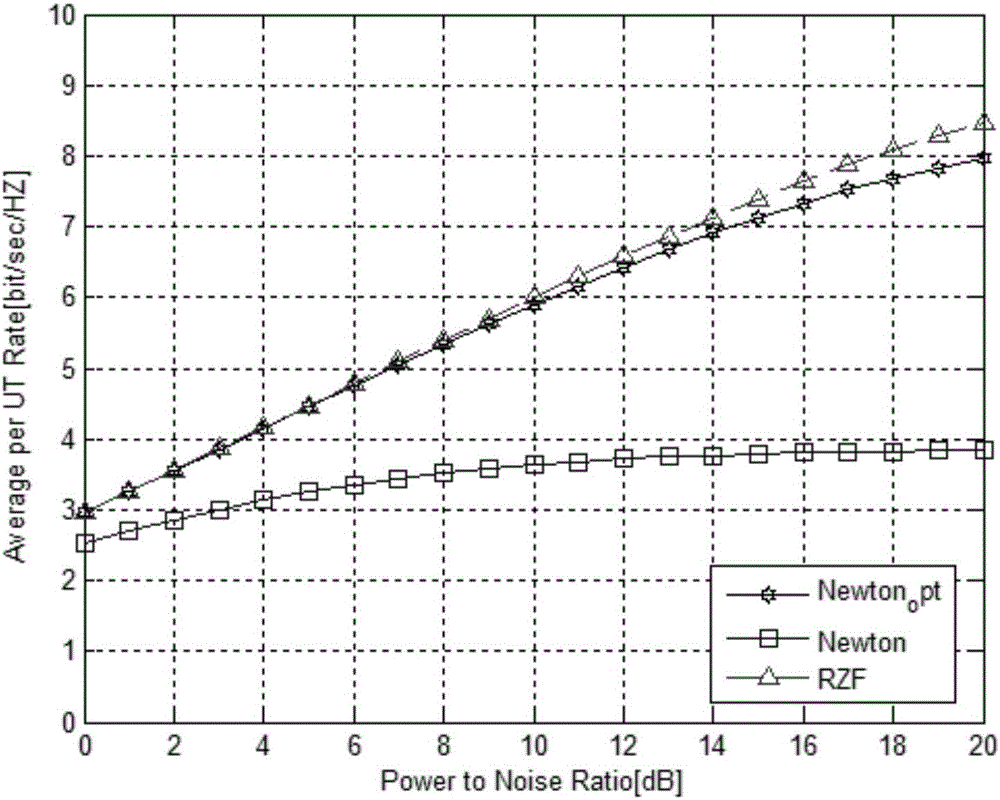
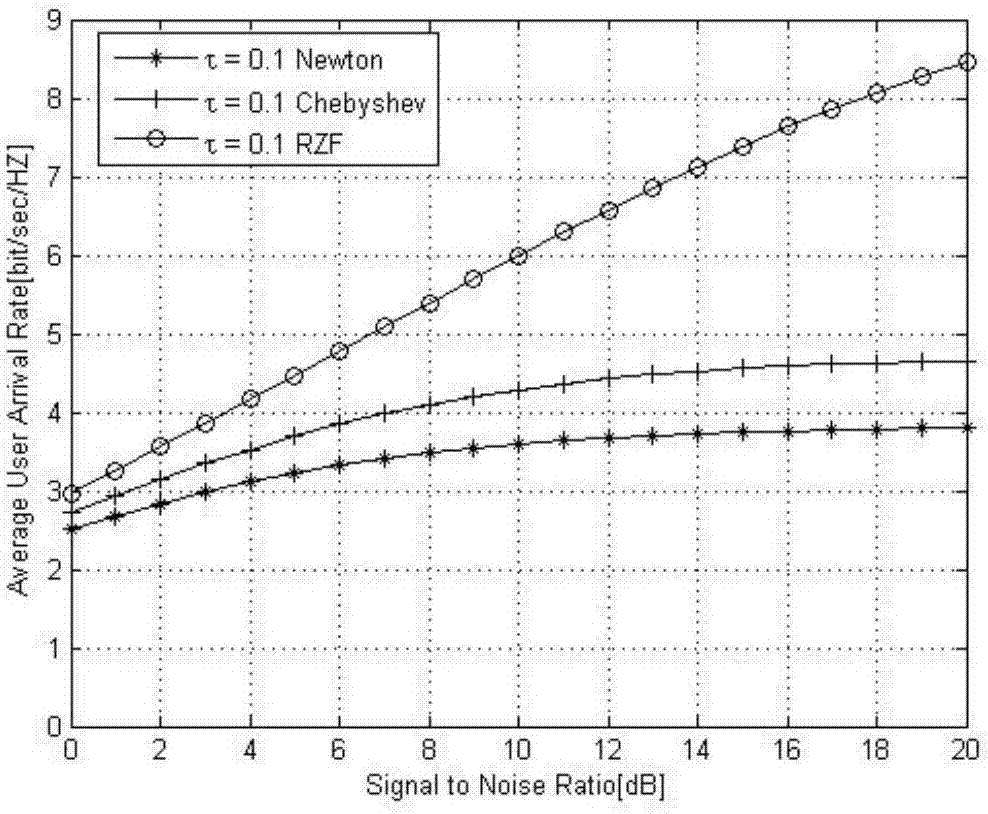
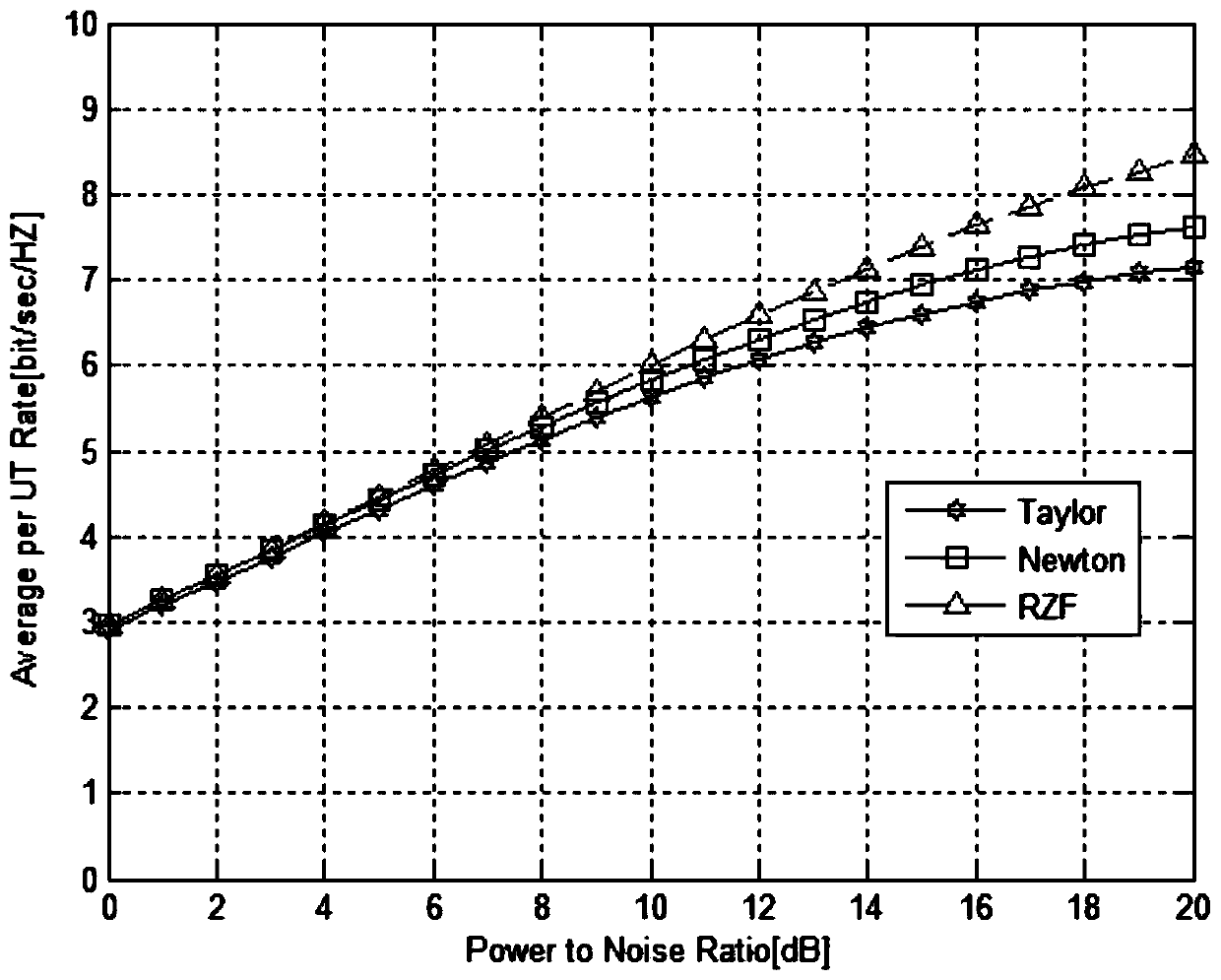
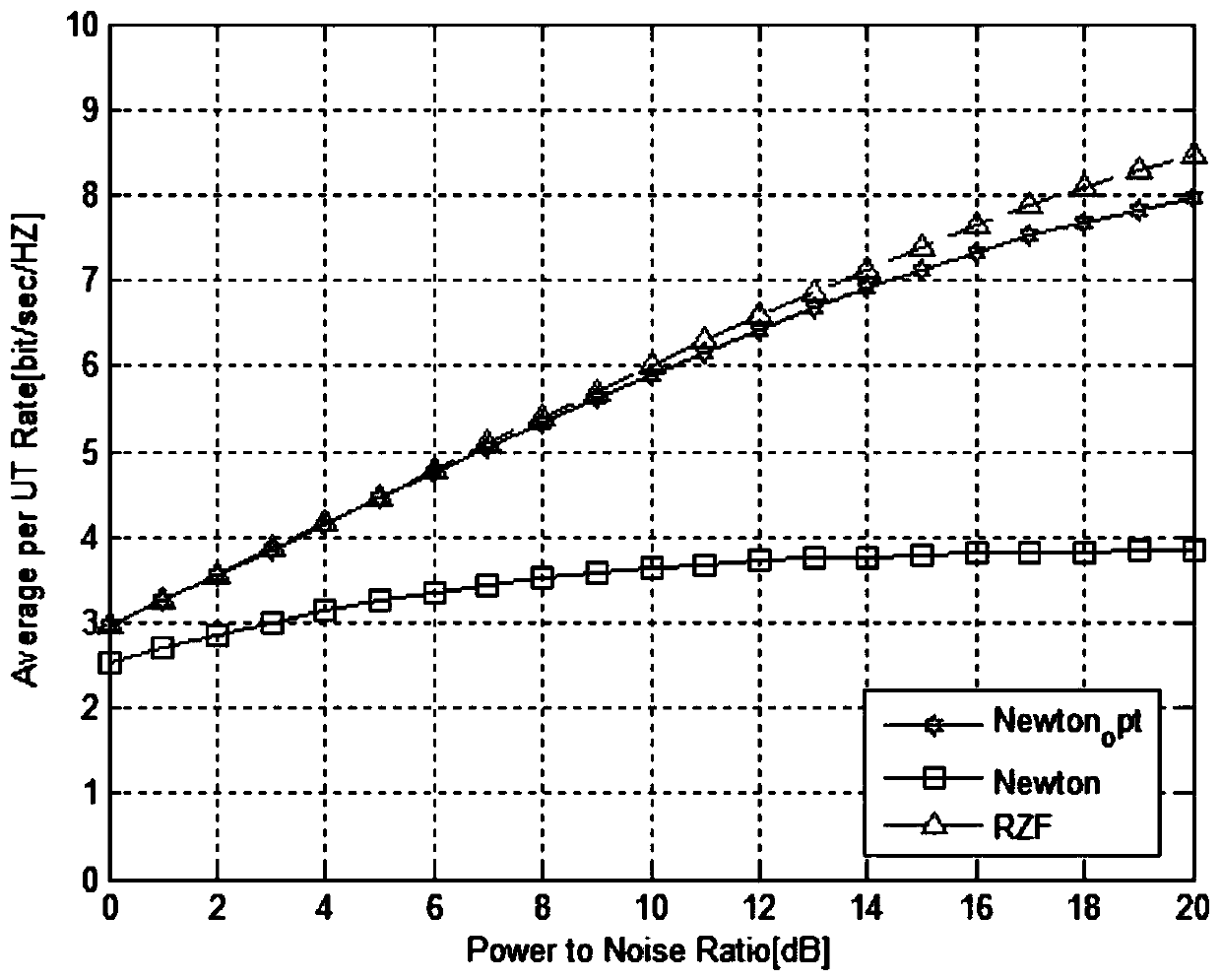
The invention discloses a large-scale MIMO (Multiple Input Multiple Output) precoding method based on an improved newton iteration method. The method comprises the following steps of firstly estimating a channel matrix, and calculating an RZF precoding expression through the obtained channel matrix; then adopting the newton iteration method for estimating an inverse matrix in an RZF precoding algorithm, and converting matrix inverse operation into matrix addition and matrix multiplication operation; finally utilizing an obtained precoding matrix for precoding a sending signal. The improved newton iteration method is characterized by building a high-order iteration formula, transforming a characteristic value located near 0 to closer to 1 , and remaining a characteristic value near 1 unchanged, so that the convergence rate of newton iteration is accelerated. An experimental result shows that when the iteration times exceeds four times, the performance of a traditional newton iteration method is superior to an inverse matrix estimation algorithm based on taylor series expansion. When the iteration times is 2, the improved newton iteration optimization algorithm can acquire around 95 percent of RZF precoding average client arrival rate.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Large-scale MIMO signal detection method based on Jacobi iteration
ActiveCN109245804AFast convergenceFast convergence rateSpatial transmit diversityMatrix additionComputation complexity
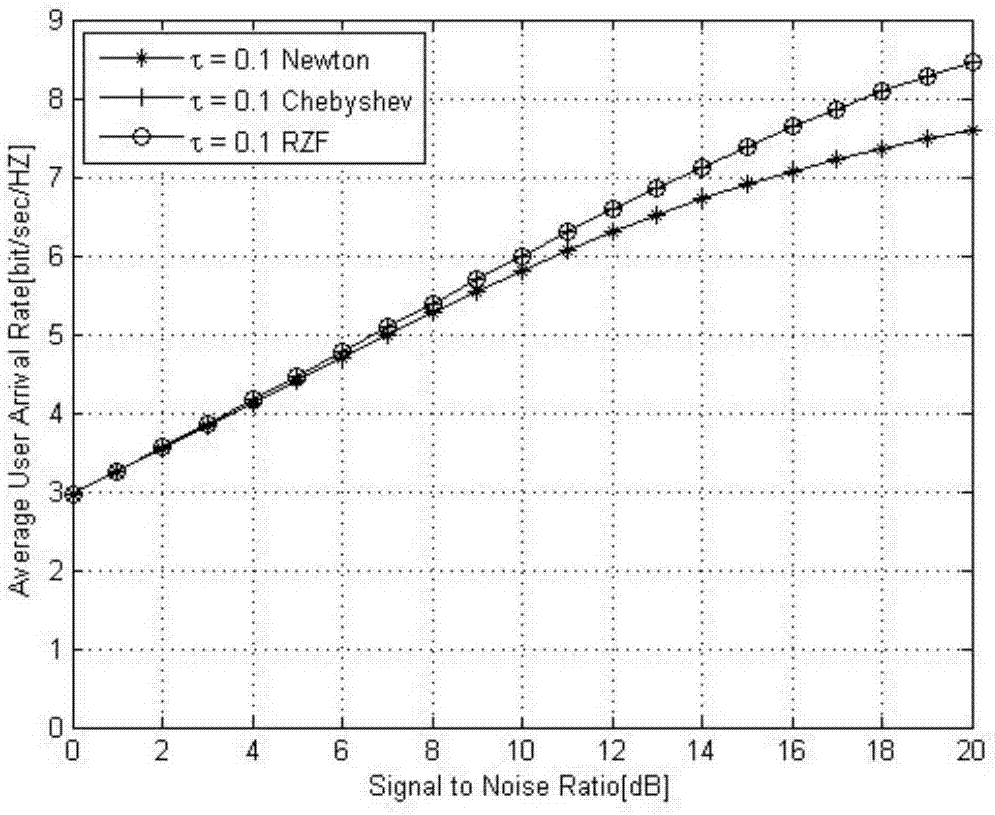
The invention discloses a large-scale MIMO signal detection method based on Jacobi iteration, and belongs to the technical field of wireless communication. The method comprises the steps: converting amatrix inversion process into an iteration process of matrix multiplication and matrix addition, providing the search direction for a Jacobi algorithm through a gradient algorithm and an overall correction acceleration method, and determining a correction coefficient of an iteration equation. According to the invention, the method performs the estimation of a high-dimensional matrix inversion process through an improved Jacobi iteration method, and converts the matrix inversion process into the iteration process of matrix multiplication and matrix addition, thereby greatly reducing the computing complexity. The gradient algorithm and the overall correction acceleration method are used for providing the search directions for the Jacobi algorithm and determining the correction coefficient of the iteration equation, thereby enabling the iteration convergence to be better, and enabling the convergence speed to be higher.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method and device for checking model feature significance based on multi-party security calculation
ActiveCN110889447AEnsure safetyFeature salience realizationCharacter and pattern recognitionDigital data protectionMatrix additionSecret share
The embodiment of the invention provides a method and device for checking the feature significance of a linear regression model based on multi-party security calculation. The method is executed by equipment of a first data holder in a plurality of data holders. N samples and model parameters of the model are jointly stored in respective devices of a plurality of data owners. The method comprises the steps of jointly executing matrix addition and matrix multiplication based on secret sharing with devices of other data owners to obtain an error quadratic sum of the N samples; jointly executing matrix addition and / or matrix multiplication based on secret sharing with other data holder equipment to obtain the value of the jth item on the diagonal line of the first matrix; calculating a secondnumerical value corresponding to the jth t test value; and executing matrix addition based on secret sharing in combination with equipment of other data owners to obtain the jth t test value, so as todetermine the significance of the corresponding characteristics of the linear regression model based on the jth t test value.
Owner:ALIPAY (HANGZHOU) INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
Large-scale MIMO pre-coding method based on Chebyshev iterative method
InactiveCN107359920AReduce complexityReduce the number of iterationsRadio transmissionChannel state informationMatrix addition
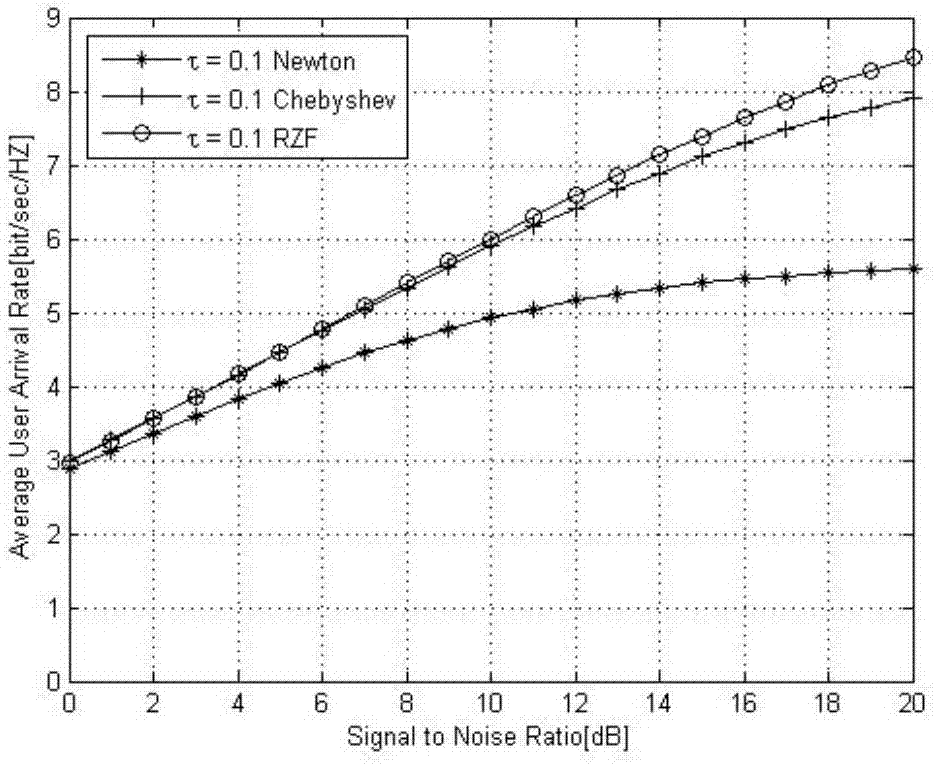
The invention discloses a large-scale MIMO pre-coding method based on a Chebyshev iterative method. The method comprises the following steps that firstly, a base station estimates a channel matrix through obtained channel state information and computes an expression of RZF precoding according to the obtained channel matrix; secondly, the base station adopts the Chebyshev iterative method to carry out iterative estimation on an inverse matrix in an RZF precoding matrix and transforms a process of solving the inverse matrix into matrix addition and matrix multiplication; and lastly, the base station utilizes the obtained precoding matrix to carry out precoding on a transmitting signal. The experimental result shows that the Chebyshev RZF precoding algorithm can obtain an average user arrival rate approximate to the RZF precoding algorithm under the same initial conditions through two iterations, and the computation complexity is low. When the same average user arrival rate is obtained, the complexity of the Chebyshev RZF precoding algorithm is smaller than that of a Newton RZF precoding algorithm, and the rate of convergence is faster.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Flink based large-scale matrix parallelization computing method
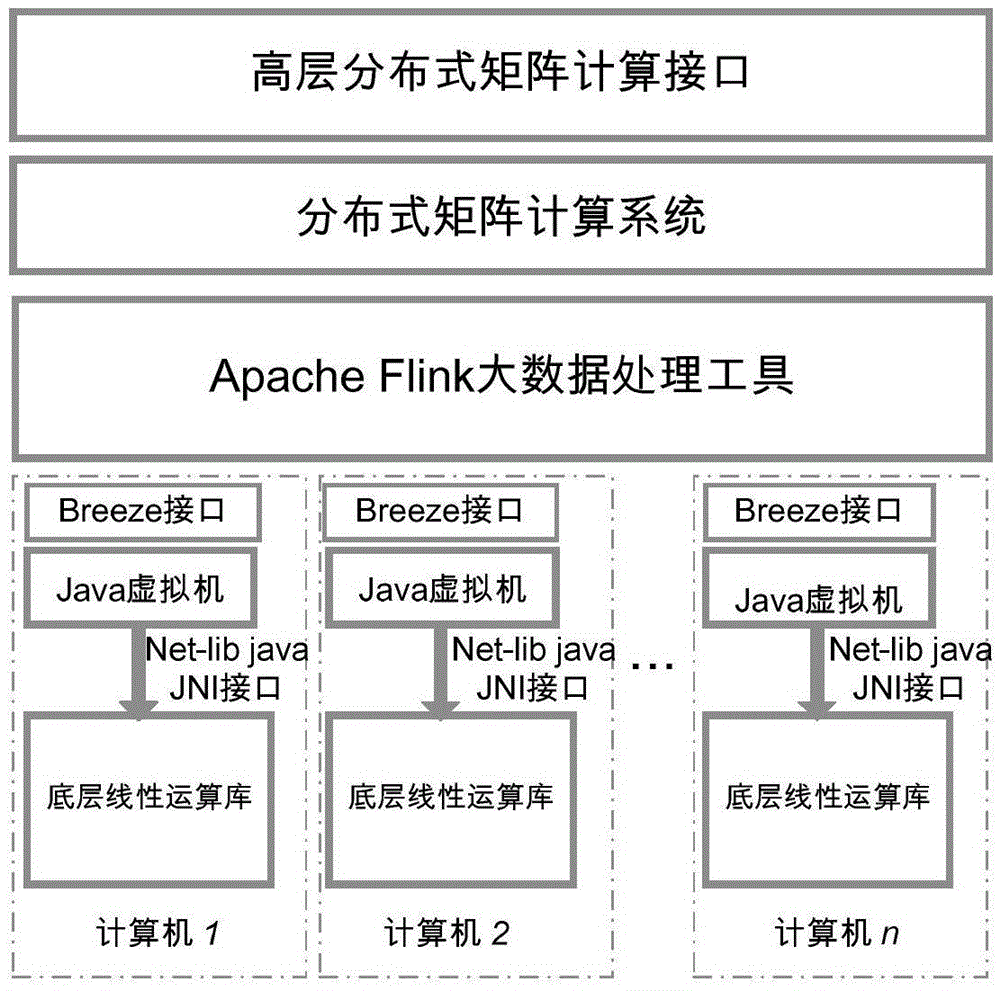
InactiveCN105608056ARealize computingImprove the efficiency of multiplicationComplex mathematical operationsMatrix additionAlgorithm
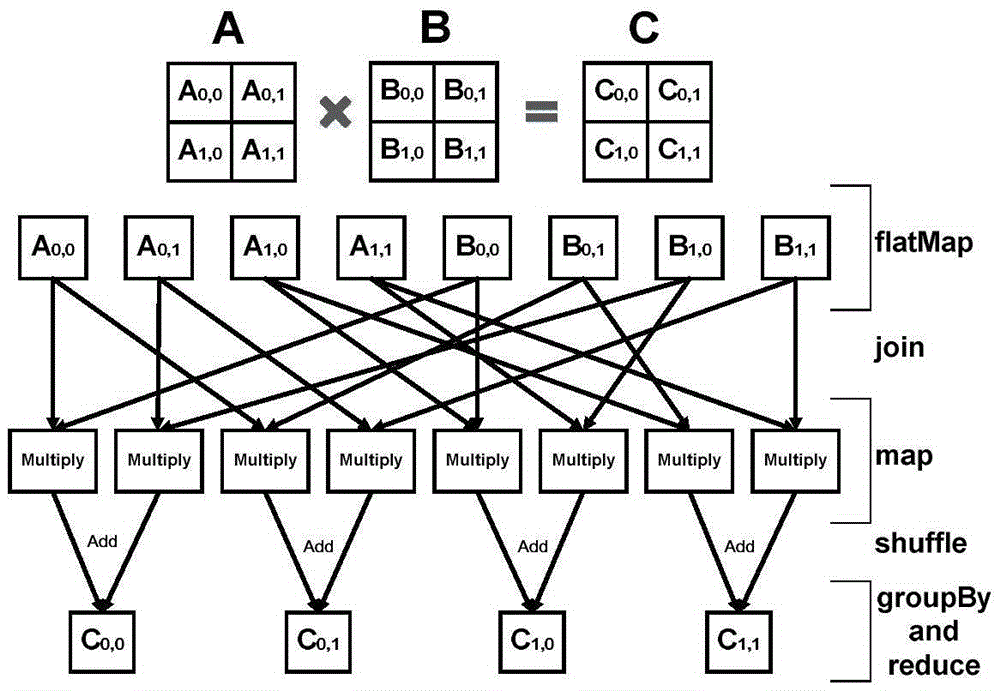
The invention discloses a Flink based large-scale matrix parallelization computing method. The method mainly comprises the following steps: storing large-scale matrix data by utilizing FlinkDataSet and accelerating matrix calculation by adopting BLAS during matrix calculation in a single computer; designing and realizing a series of matrix operations of matrix addition, subtraction and the like; and designing a parallelization scheme and designing three optimization means in combination with Flink and algorithm characteristics for improving the performance of matrix multiplication operation of different shapes, wherein the matrix multiplication includes square block division mode based matrix block multiplication, CARMA division mode based matrix block multiplication and broadcast mode based matrix block multiplication. According to the method, the problem that conventional large-scale matrix calculation in a single computer has high overhead and even cannot be executed is solved; and the method has very high expandability.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Noise-suppression infrared image digital detail enhancement method
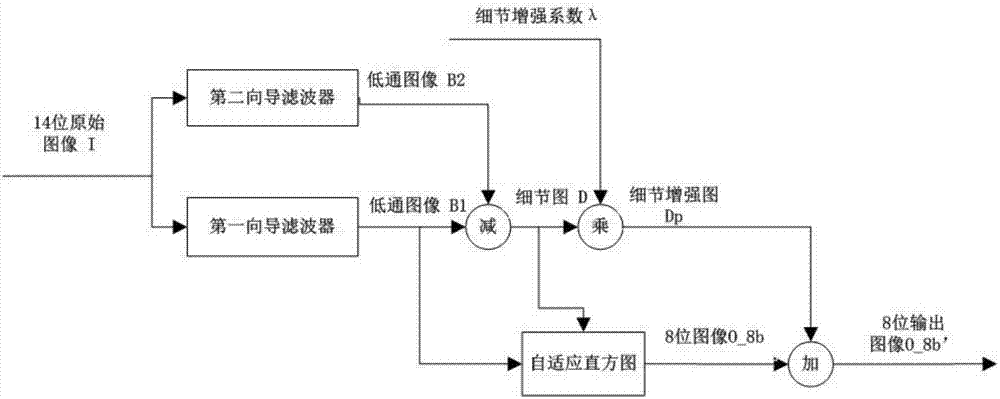
InactiveCN107464229ASuppress noiseDigital detail enhancementImage enhancementImage analysisMatrix additionNoise suppression
The invention belongs to the technical field of infrared image display processing, and particularly relates to a high-dynamic rage infrared image digital detail enhancement method with noise suppression ability. The infrared image digital detail enhancement method comprises the following steps of: respectively filtering a 14-bit original image by using two wizard filters with different smooth scale coefficients; obtaining detail images through matrix subtraction; and adding the detail image with a converted 8-bit image through matrix addition. According to the method, noises of infrared images can be effectively suppressed and digital details can be enhanced.
Owner:TIANJIN XITONG ELECTRONICS EQUIP CO LTD
Tensor processing using low precision format
PendingCN107526709ALarge dynamic rangeNeural architecturesPhysical realisationMatrix additionAlgorithm
The invention relates to tensor processing using low precision format. Aspects of the present invention are directed to computer-implemented techniques for improving the training of artificial neural networks using a reduced precision (e.g., float16) data format. Embodiments of the present invention rescale tensor values prior to performing matrix operations (such as matrix multiplication or matrix addition) to prevent overflow and underflow. To preserve accuracy throughout the performance of the matrix operations, the scale factors are defined using a novel data format to represent tensors, wherein a matrix is represented by the tuple X, where X=(a, v[.]), wherein a is a float scale factor and v[.] are scaled values stored in the float16 format. The value of any element X[i] according to this data format would be equal to a*v[i].
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
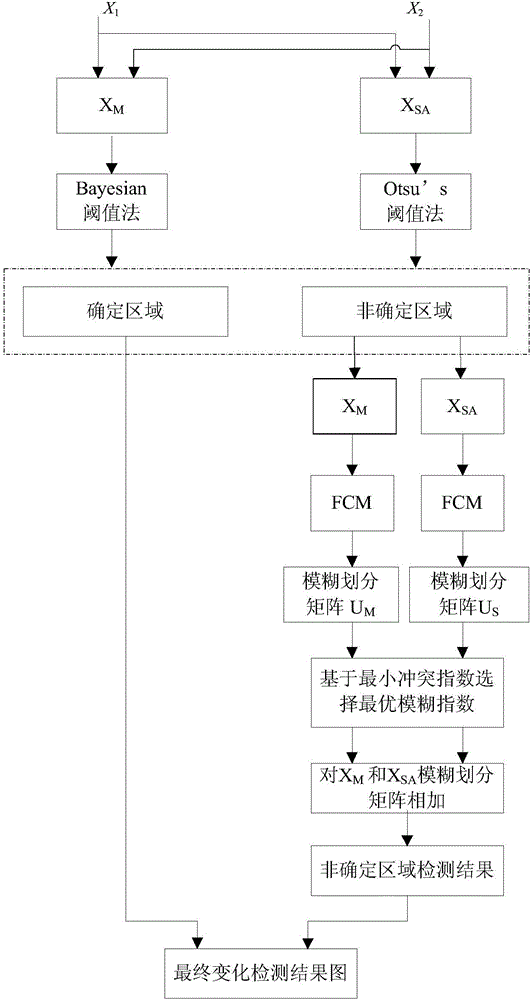
Multi-temporal remote sensing image change detection method based on fusion strategy and FCM
InactiveCN106384352AReliable test resultsRobustImage enhancementImage analysisMatrix additionSpectral angle
The invention discloses a multi-temporal remote sensing images change detection method based on fusion strategy and FCM, and the method comprises the steps: a detection range can be divided into a determined region and an undetermined region according to a change vector amplitude of multi-temporal remote sensing images and a multi-temporal spectral angle map; in the undetermined region, the change vector amplitude and SAM information are fused based on fuzzy division matrix addition; results of the determined region and the undetermined region are combined to obtain a final change detection result; wherein a fuzzy index in an FCM objective function in the undetermined region can be selected according to conflict indexes of MCV and SAM in the undetermined region to obtain a change detection result which is more stable and has higher precision than before. According to the invention, the change detection region is divided into the determined region and the undetermined region, detection results of two regions can be separately acquired through adopting a fusion strategy, so that the change detection results can be more reliable and more stable than before.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Data processing method for wireless sensor real-time monitoring system based on compressive sensing
InactiveCN102802199AMeet the requirements of smaller memory nodesSolve storage overflowNetwork traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesMatrix additionMonitoring system
The invention discloses a data processing method for a wireless sensor real-time monitoring system based on compressive sensing. A measurement matrix constructing mode in the compressive sensing is changed, a Gaussian random matrix is replaced by a two-dimensional random matrix, the original measurement matrix is subjected to block operation, and the position with the element value of 1 in a sparse two-dimensional matrix is determined by using a coordinate position matrix, so that the dimension of a reduction matrix is greatly reduced; and meanwhile, the original matrix multiplication is converted into matrix addition operation, the operation speed is increased, and the obvious effects are that due to the algorithm improvement, the compressive sensing algorithm can be realized in actual application, the requirement that a general wireless sensor node has low memory is met, the calculation amount is reduced, the problems that the storage of the sensor overflows and the calculation time is long are solved, and the data monitoring real-time property of the system is improved.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Deep learning-based single-image de-fogging method
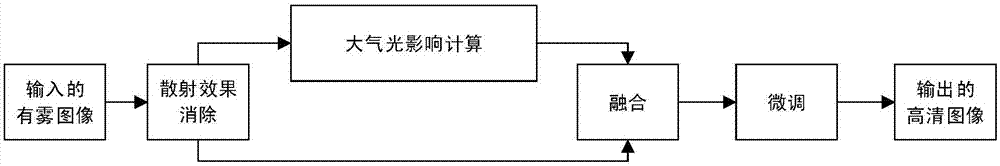
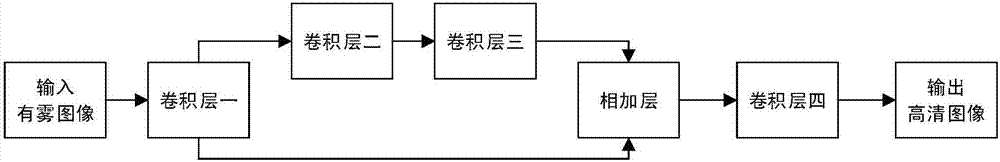
ActiveCN107451967AGood fog removal effectSubjective visual clarityImage enhancementMatrix additionImaging processing
The invention discloses a deep learning-based single-image de-fogging method and belongs to the image processing field. According to the method of the invention, a formula J(x,y)=I(x,y)1 / T(x,y)+A(1-1 / T(x,y) is inferred through transformation according to the formula I(x,y)=T(x,y)J(x,y)+(1-T(x,y))A; and a deep convolution neural network technique is adopted to obtain a high-definition J(x, y). The method of the invention has a good de-fogging effect. According to the method of the invention, matrix addition operation is adopted, so that the processing speed of the method is high.
Owner:PEKING UNIV SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
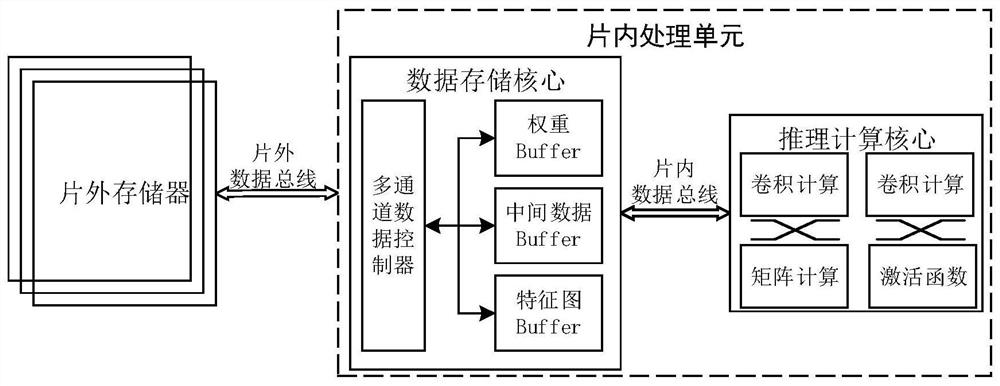
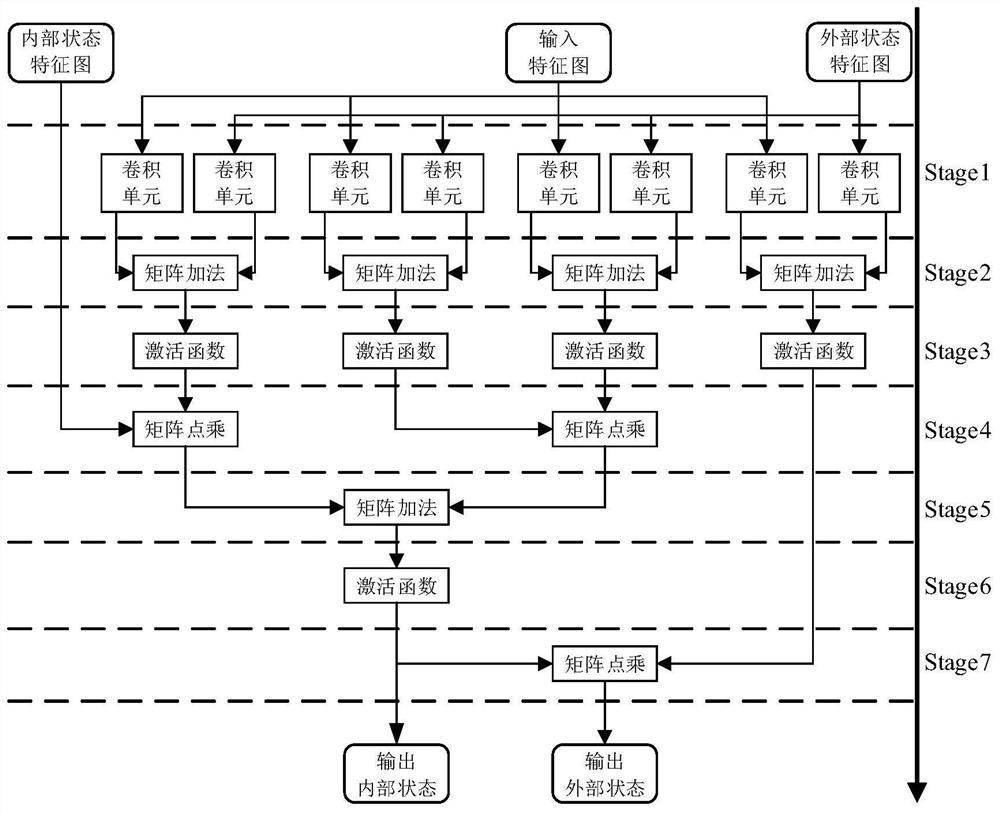
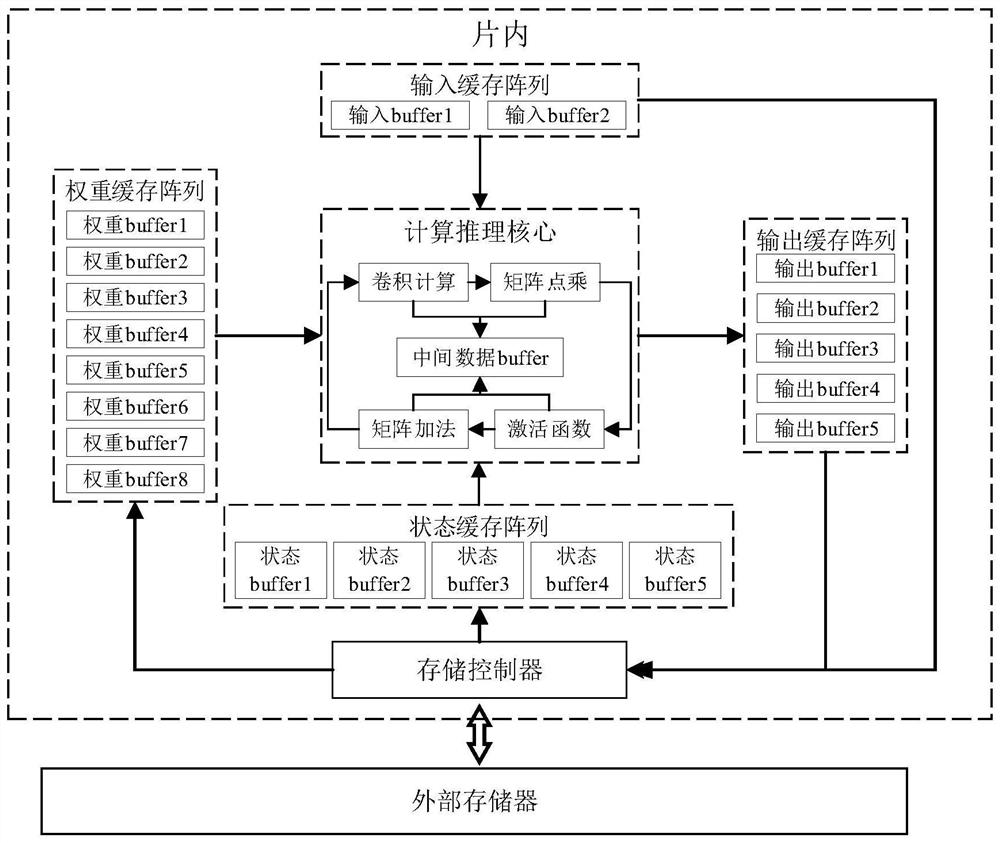
Hardware acceleration system for LSTM (Long Short Term Memory) network model
ActiveCN113191488AImprove parallelismReduce processing latencyNeural architecturesPhysical realisationActivation functionTerm memory
The invention discloses a hardware acceleration system for an LSTM network model, and belongs to the technical field of deep learning hardware acceleration. The invention discloses a hardware acceleration system for a deep learning long short-term memory (LSTM) network model. The hardware acceleration system comprises a network reasoning calculation core and a network data storage core. The network reasoning calculation core is used as a calculation accelerator of an LSTM network model, calculation units are deployed according to the network model, and calculation acceleration of the calculation units such as convolution operation, matrix dot multiplication, matrix addition and an activation function is achieved; and the network data storage core serves as a data cache and interaction controller of an LSTM network model, deploys an on-chip cache unit according to the network model, and realizes a data interaction link between the computing core and an off-chip memory. According to the invention, the calculation parallelism of the LSTM network model is improved, the processing delay is reduced, the memory access time is shortened, and the memory access efficiency is improved.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
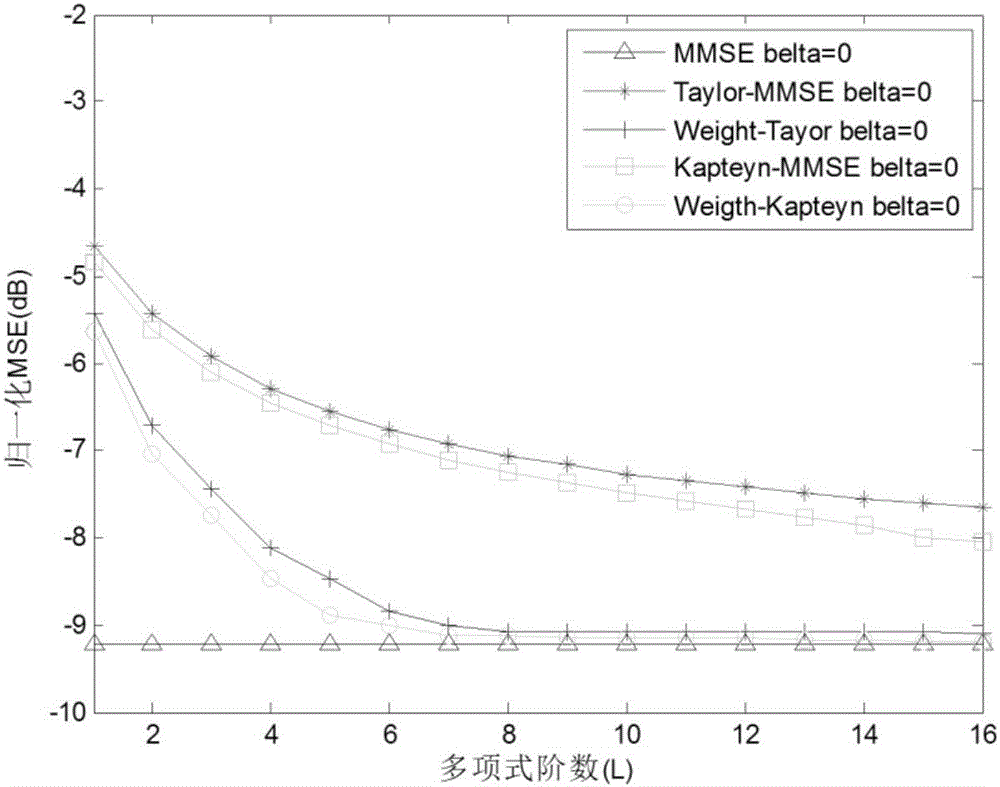
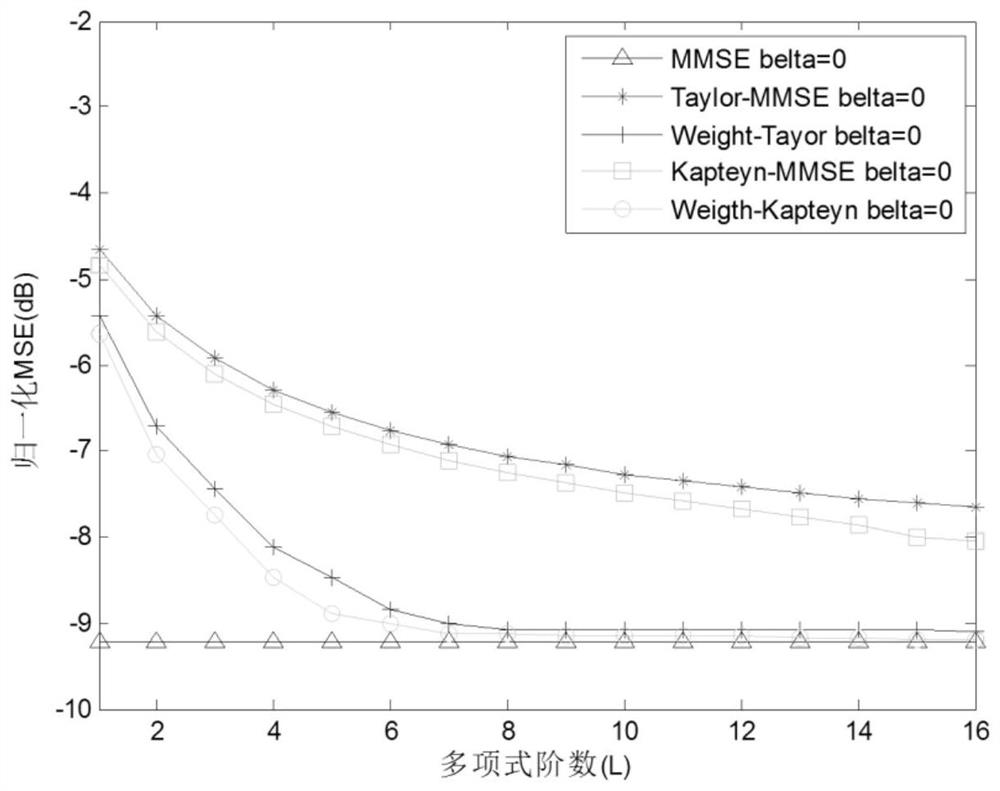
Large-scale MIMO low-complexity channel estimation method based on weighted Kapetyn grade number expansion
ActiveCN106817155AImprove accuracyFast convergenceRadio transmissionChannel estimationComputation complexityCovariance
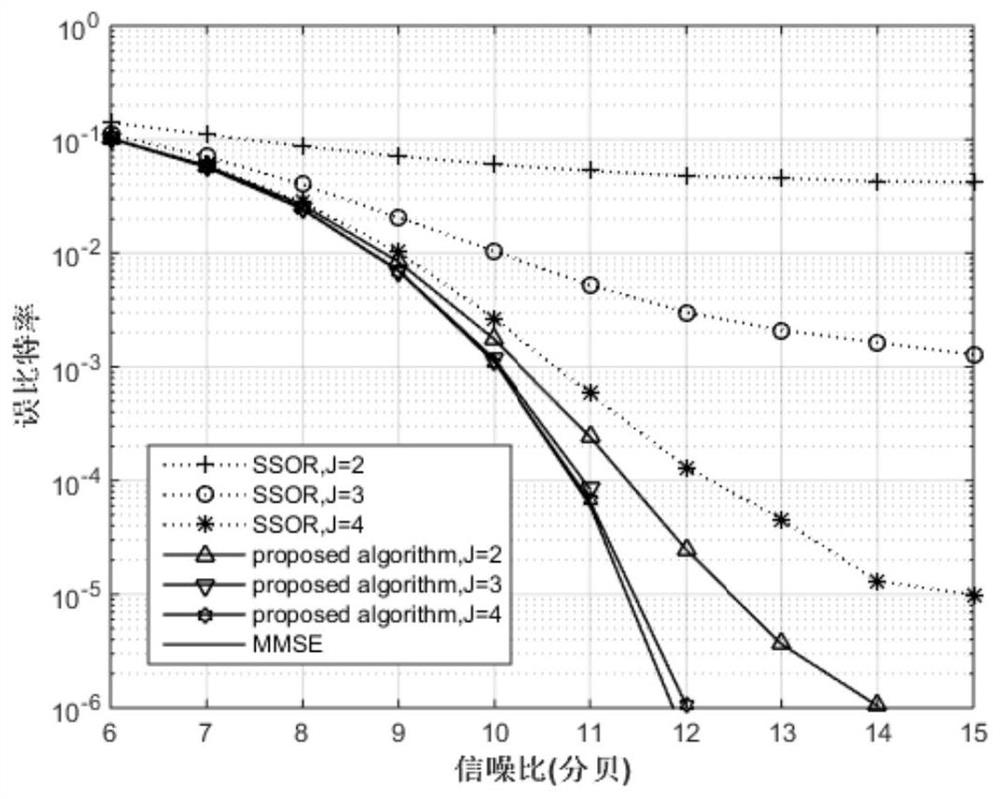
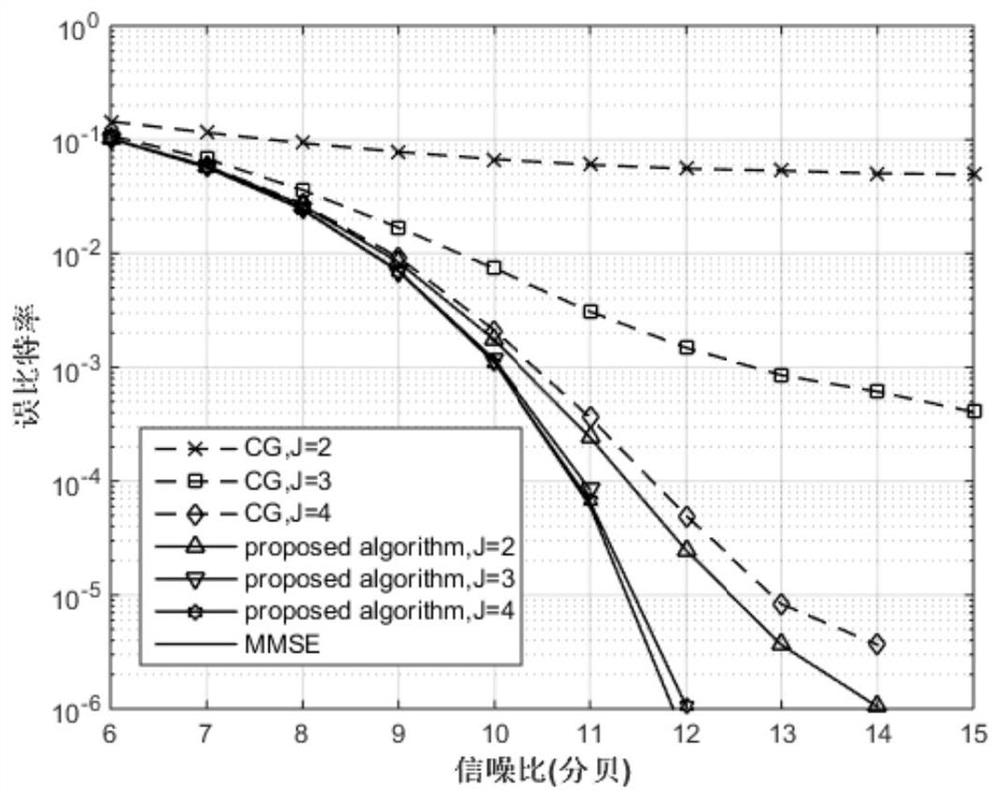
The invention discloses a large-scale MIMO low-complexity channel estimation method based on weighted Kapetyn grade number expansion. Firstly a Kapetyn grade number expansion method is utilized for performing approximate expansion on a channel covariance inverse matrix in a Bayesian-MMSE channel estimation expression. A matrix inversion operation is converted to matrix multiplication and matrix addition operations. Then a weighting manner is performed on each coefficient of a polynomial for optimizing polynomial expansion, establishing a model for solving weighting coefficient vectors alpha and beta for minimizing an estimated mean square error, and estimating the channel matrix by means of solving results of alpha and beta. Experiment results represent a fact that an MSE which is obtained through the channel estimation method based on a weighted Kapetyn grade number expansion is convergent to an MMSE method along with order number increase of the polynomial, and furthermore calculation complexity of the channel estimation method is lower than that of the MMSE method. Compared with a traditional Taylor-MMSE and Kapetyn grade number expansion channel estimation method, the channel estimation method based on the weighted Kapetyn grade number has higher convergence speed to the MMSE method.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
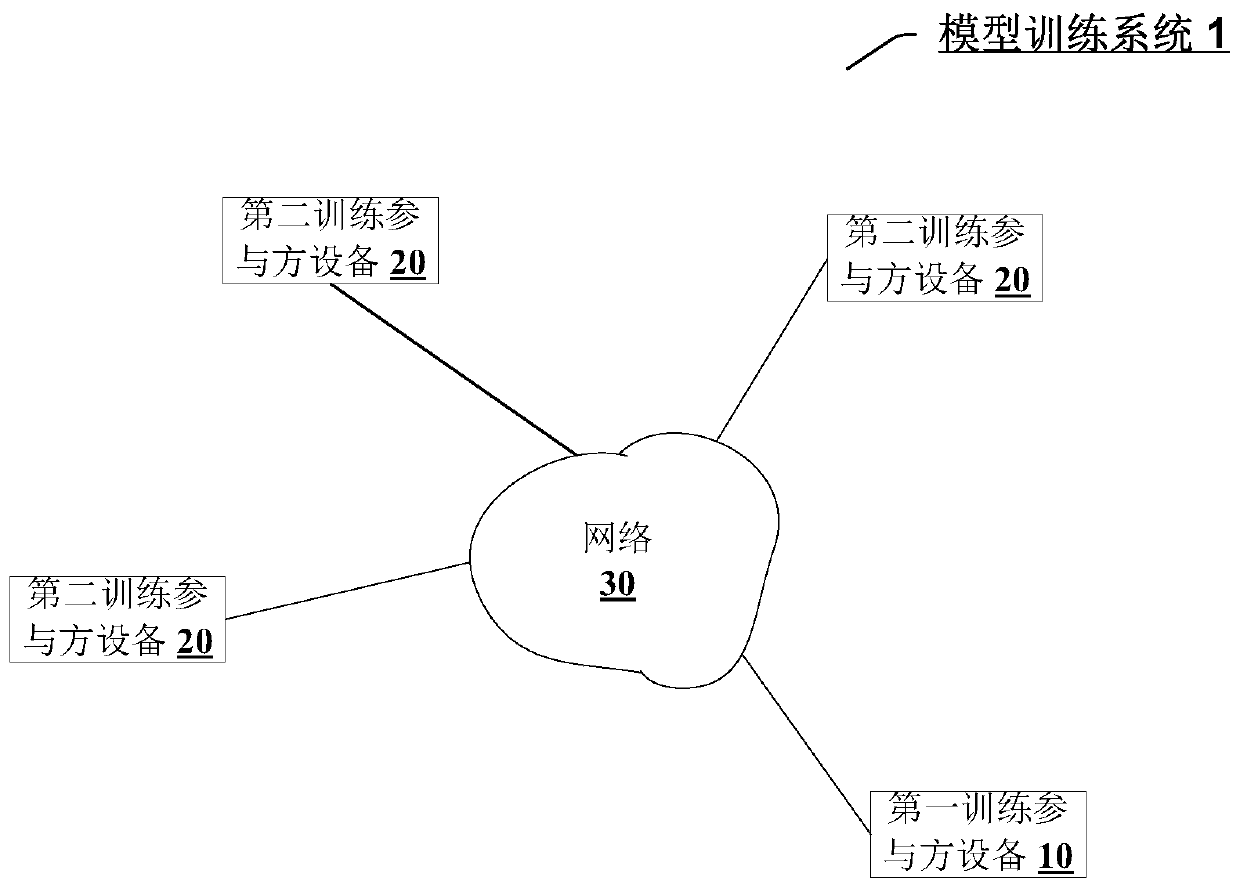
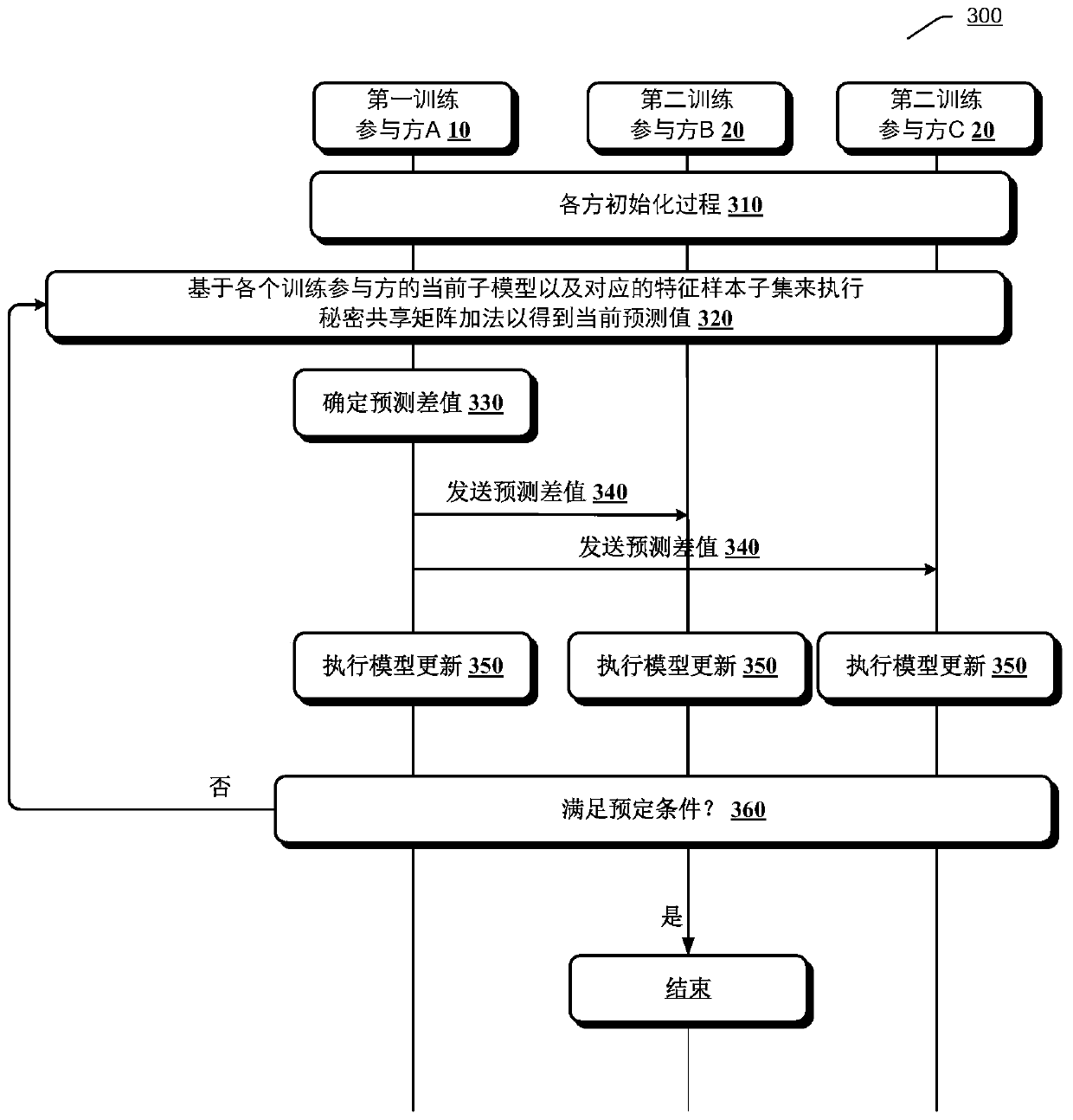
Model training method, device and system
ActiveCN111523673AImprove training efficiencyKernel methodsInference methodsMatrix additionEngineering
The invention provides a method and a device for training a linear / logistic regression model. The method comprises the steps of: executing the following iterative processes till a preset condition ismet: acquiring a current prediction value of the linear / logistic regression model through employing secret sharing matrix addition based on a current sub-model of each training participant and a corresponding feature sample subset; determining a prediction difference value between the current prediction value and a corresponding mark value, and transmitting the prediction difference value to eachsecond training participant so as to update the respective current sub-model at each second training participant; and updating the current sub-model of the first training participant based on the current sub-model of the first training participant and the product of the corresponding feature sample subset and the determined prediction difference. When the iteration process is not finished, the updated current sub-model of each training participant is used as the current sub-model of the next iterative process. According to the method, the model training efficiency can be improved under the condition of ensuring the data security of each party.
Owner:ADVANCED NEW TECH CO LTD
Error correction for length compatible polar codes for memory systems
PendingCN114696839ACode conversionError correction/detection using linear codesMatrix additionBinary multiplier
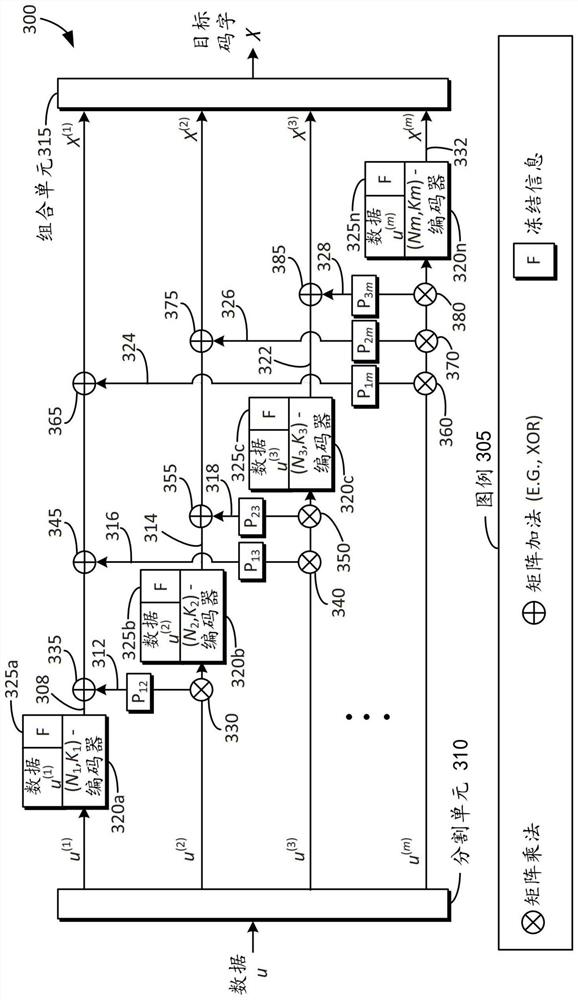
Inventive aspects include a polar code encoding system including a segmentation unit for receiving and segmenting input data into segmented input data units. The encoder encodes the divided input data units and generates encoded divided input data units. The multiplier unit performs matrix multiplication on the divided input data unit and the generator matrix, and generates a matrix product. The adder unit performs a matrix addition on the encoded divided input data unit and the matrix product. A combining unit combines the output of the encoder into a target codeword X. The target codeword X may be a codeword X of length N, where N = N1 + N2 +... + Nm, where each of N1, N2 to Nm is a power of two (2).
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
A large-scale MIMO precoding method based on the improved Newton iteration method
The invention discloses a large-scale MIMO (Multiple Input Multiple Output) precoding method based on an improved newton iteration method. The method comprises the following steps of firstly estimating a channel matrix, and calculating an RZF precoding expression through the obtained channel matrix; then adopting the newton iteration method for estimating an inverse matrix in an RZF precoding algorithm, and converting matrix inverse operation into matrix addition and matrix multiplication operation; finally utilizing an obtained precoding matrix for precoding a sending signal. The improved newton iteration method is characterized by building a high-order iteration formula, transforming a characteristic value located near 0 to closer to 1 , and remaining a characteristic value near 1 unchanged, so that the convergence rate of newton iteration is accelerated. An experimental result shows that when the iteration times exceeds four times, the performance of a traditional newton iteration method is superior to an inverse matrix estimation algorithm based on taylor series expansion. When the iteration times is 2, the improved newton iteration optimization algorithm can acquire around 95 percent of RZF precoding average client arrival rate.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
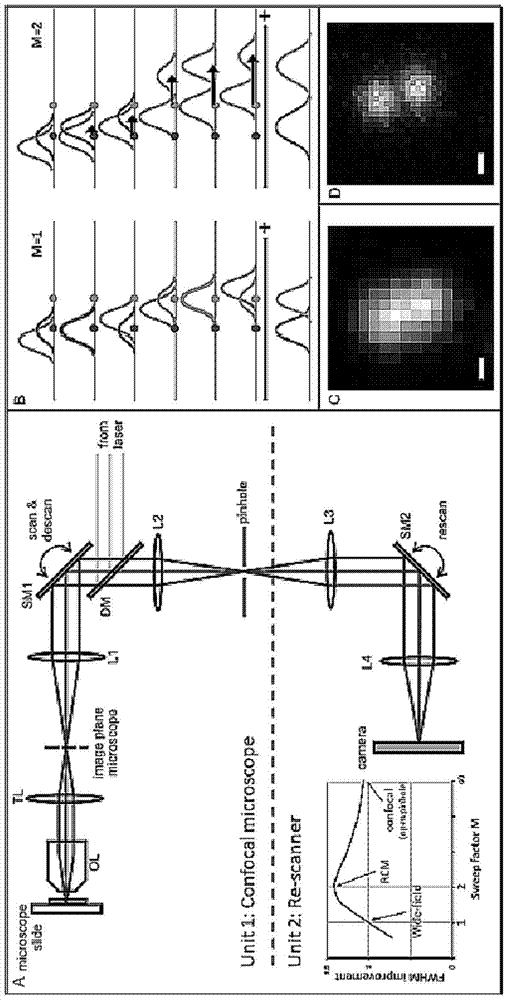
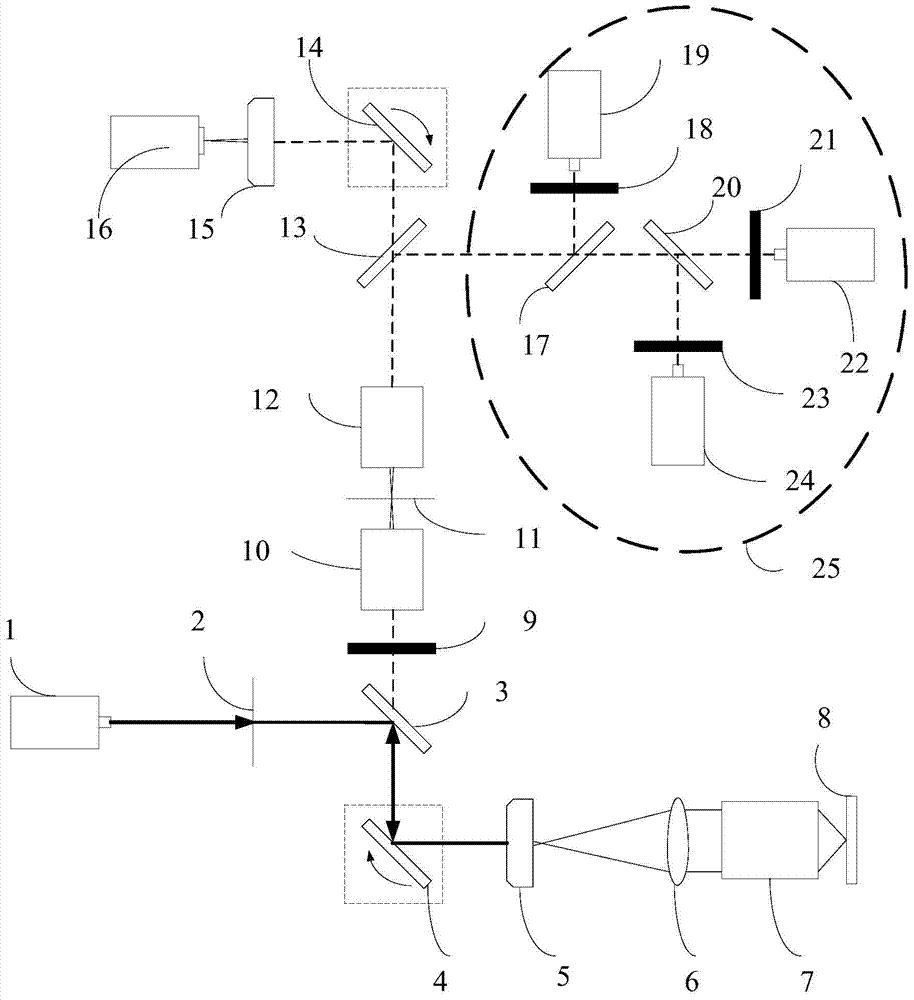
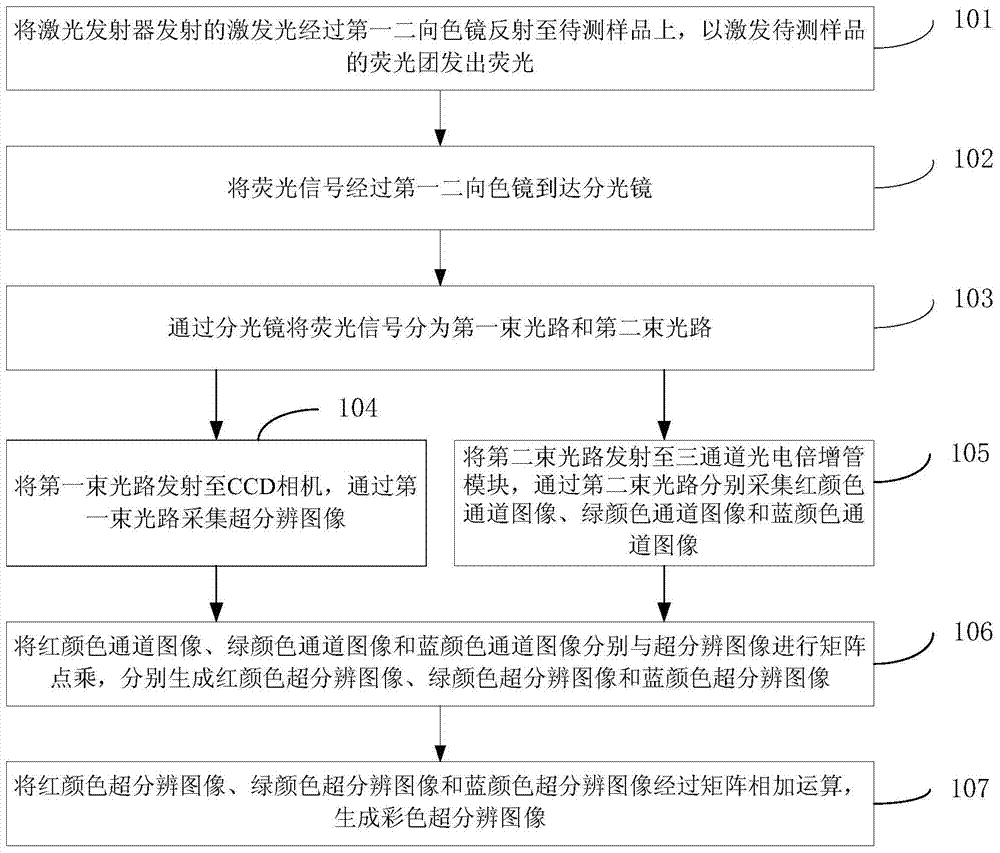
A color super-resolution imaging device and method
ActiveCN105136756BAcquisition speed is fastFluorescent signal enhancementFluorescence/phosphorescenceColor imageDot matrix
The invention provides a color super-resolution imaging device and method, and relates to the technical field of microscopic imaging. The method includes: dividing the fluorescence signal of the sample to be tested through a first dichroic mirror to a beam splitter and dividing it into a first beam path and a second beam path; transmitting the first beam path to a CCD camera to collect a super-resolution image; The second beam path is emitted to the three-channel photomultiplier tube module, and the three color channel images of red, green and blue are collected respectively; the red, green, and blue color channel images are respectively subjected to matrix dot product with the super-resolution image to generate the red color respectively. The super-resolution image, the green color super-resolution image and the blue color super-resolution image; the red color super-resolution image, the green color super-resolution image and the blue color super-resolution image are subjected to matrix addition operation to generate a color super-resolution image. The invention solves the problems of low signal acquisition rate and efficiency existing in the current secondary scanning super-resolution microscopy technology.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
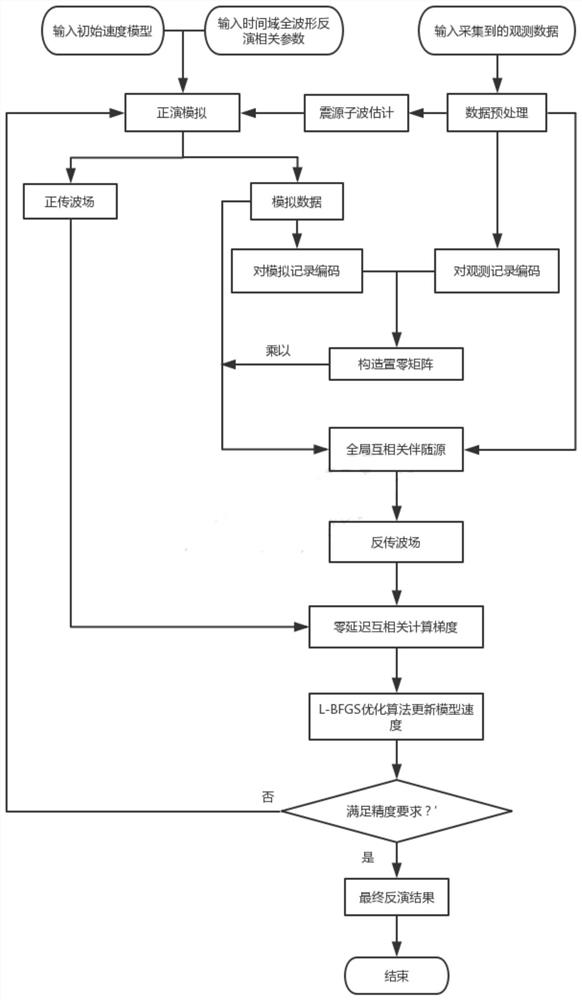
Time Domain Full Waveform Inversion Method Based on Amplitude Incremental Coding
InactiveCN111239806BReduce the effect of gradientsDoes not significantly increase computation timeSeismic signal processingTime domainMatrix addition
The present invention proposes a time-domain full-waveform inversion method based on amplitude incremental coding. By performing amplitude incremental coding on each sampling point of the simulated data and observation data and adding the amplitude polarity as a constraint, the same Data with different amplitude increments at time points; after encoding, construct a zero-setting matrix, multiply the matrix by the simulated data to set the data that causes cycle jumps to zero, thereby reducing the influence of this part of the data on the gradient; a part of the data After zeroing, the amplitude information of the original data is destroyed; in order to reduce the dependence of the inversion on the amplitude information and highlight the role of the phase information, a global cross-correlation objective function is used. The difference between this method and the traditional method lies in the encoding calculation and zeroing calculation of the simulated data and observation data, while the encoding calculation is simply matrix addition, subtraction, multiplication and division, which will not significantly increase the calculation time of the full waveform inversion. Comparing with the traditional full waveform inversion, the calculation efficiency is not reduced.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Large-scale multi-operation floating point matrix calculation acceleration implementation method and device
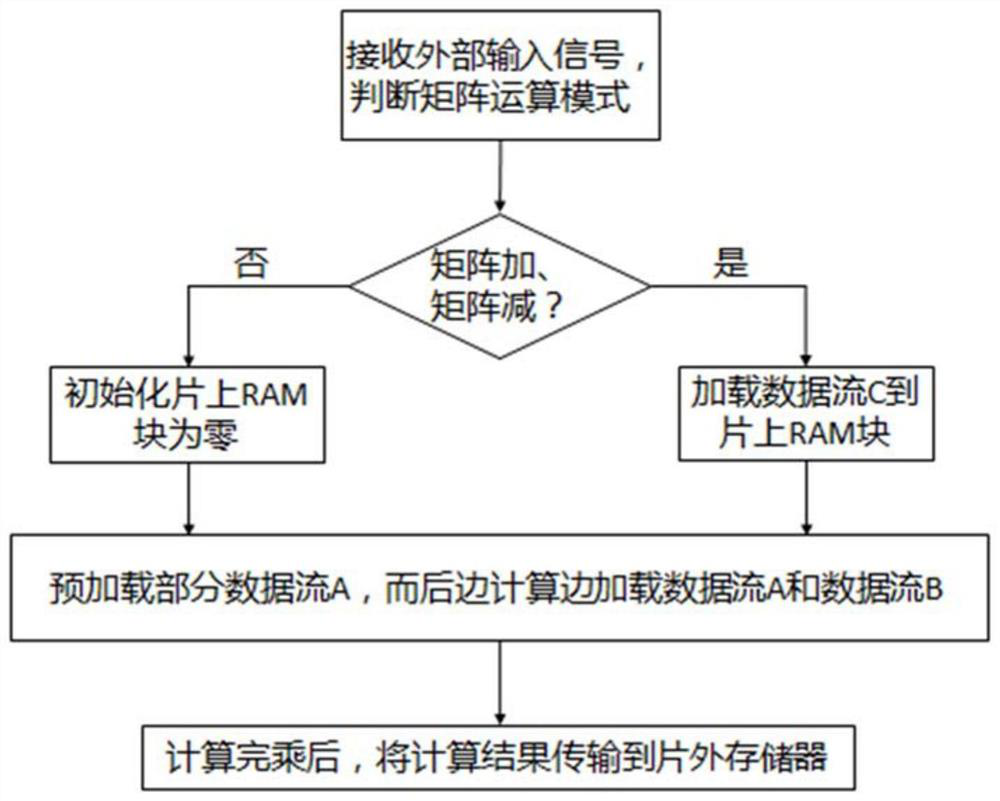
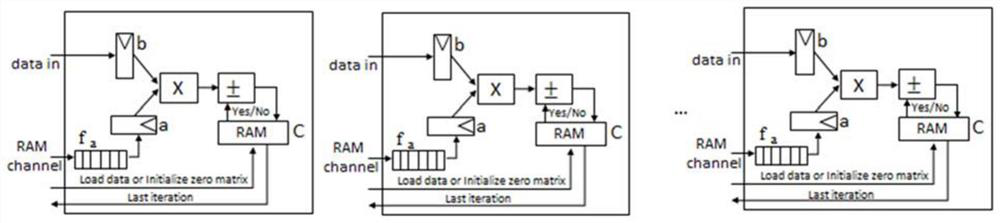
PendingCN114218524AImprove reusabilityFlexible useDigital data processing detailsComplex mathematical operationsMatrix additionData stream
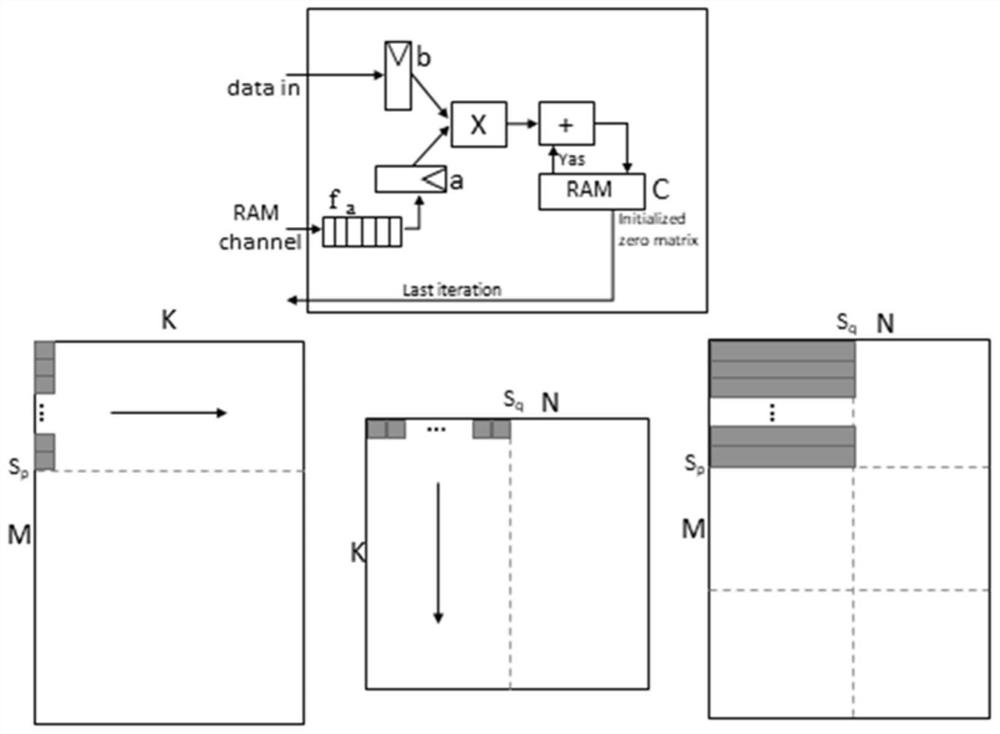
The invention discloses a large-scale multi-operation floating point matrix calculation acceleration implementation method, which comprises the following steps: S1, receiving an external input signal and judging a matrix operation mode according to an operation type of a to-be-processed matrix: when the operation mode is matrix addition and matrix subtraction, turning to execute a step S3, and when the operation mode is matrix subtraction, turning to execute a step S4; when the operation mode is matrix multiplication, matrix-vector multiplication and matrix-scalar multiplication, turning to execute the step S2; s2, initializing an on-chip RAM (Random Access Memory) to be zero, and turning to execute a step S4; s3, the data source C is loaded into the on-chip RAM through the RAM channel, and the step S4 is executed; s4, pre-loading a part of the data stream A through an RAM channel, and loading the data stream A and the data stream B while calculating; s5, after calculation is completed, a calculation result is transmitted to the off-chip memory. The device is used for implementing the method. The method has the advantages of low storage requirement, high calculation efficiency, high reusability, wide application range and the like.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH +1
Device and method for executing matrix addition/subtraction operation
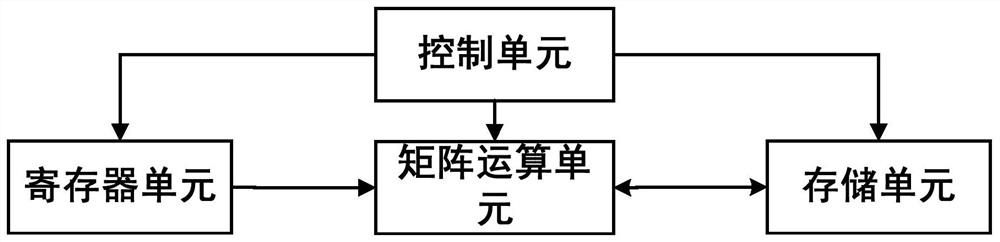
PendingCN111857819ANeural architecturesComplex mathematical operationsComputer hardwareMatrix addition
The invention provides a device for executing matrix addition and subtraction operation, and the device is characterized in that the device comprises: a storage unit which is used for storing matrix data related to a matrix operation instruction; the register unit that is used for storing scalar data related to the matrix operation instruction; the control unit that is used for decoding the matrixoperation instruction and controlling the operation process of the matrix operation instruction; the matrix operation unit that is used for carrying out matrix addition and subtraction operation on an input matrix according to the decoded matrix operation instruction, wherein the matrix operation unit is a customized hardware circuit. The invention further provides a method for executing matrix addition and subtraction.
Owner:CAMBRICON TECH CO LTD
An arbitrary order Kalman filtering system
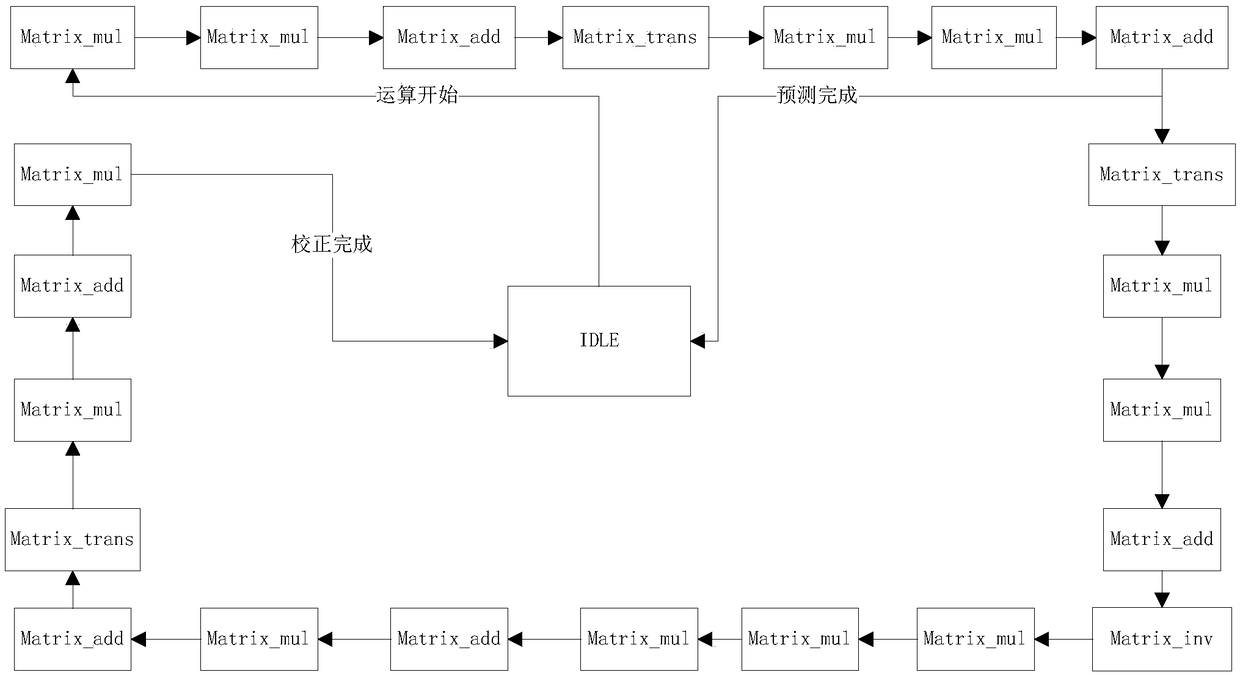
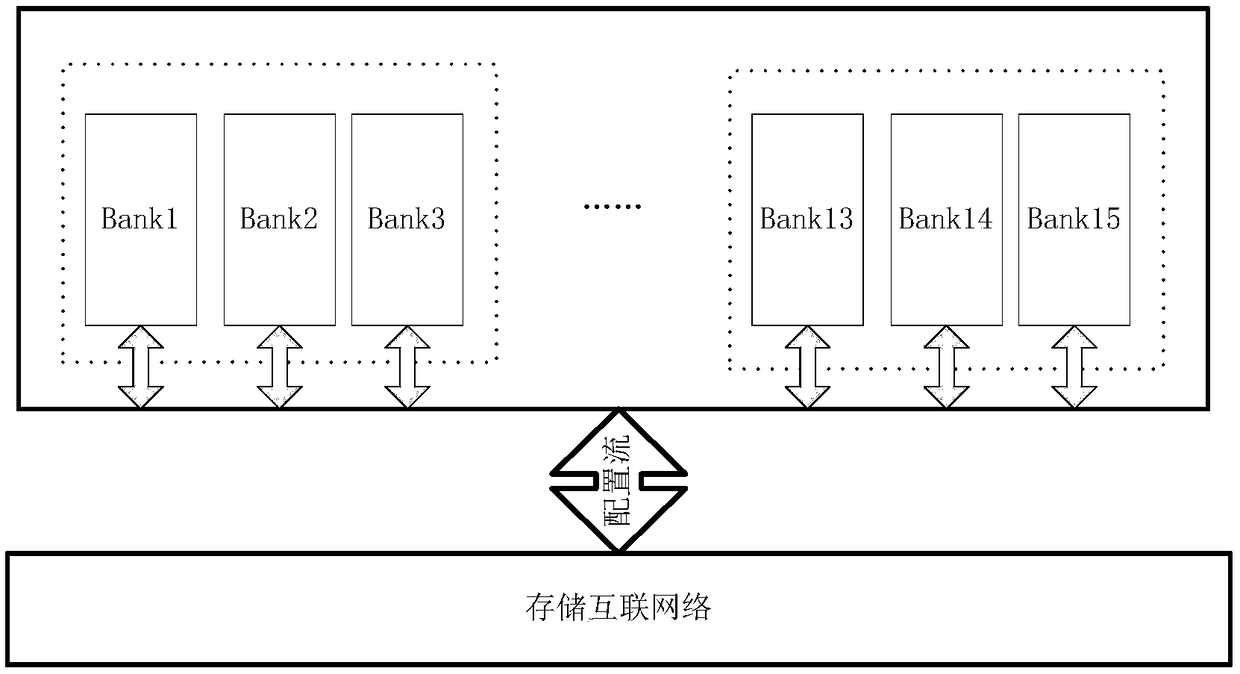
InactiveCN109376332AImprove reuse rateWide range of applicationsDigital data processing detailsComplex mathematical operationsSystems designParallel computing
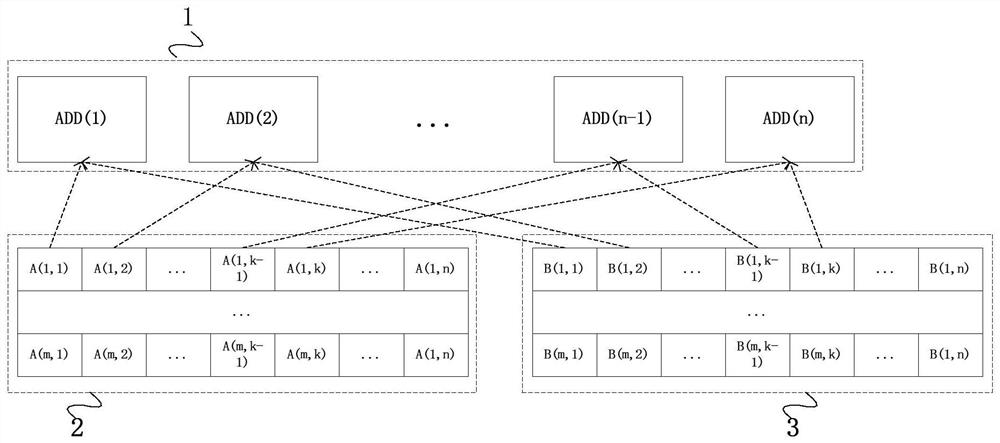
The invention relates to an arbitrary-order Kalman filtering system, comprising: a configurable memory array comprising a plurality of memory banks, wherein the memory banks are globally shared; a configurable computing array, including single-precision floating-point number multiplier, a single-precision floating-point number adder and a single-precision floating-point number divider; a matrix basic operation module, completing matrix addition, matrix subtraction, matrix transposition and matrix inversion; and the global configurable computing array is shared by time-sharing multiplexing; a state machine, according to the recurrence equation of the Kalman filter algorithm, the matrix basic operation module is called step by step, the intermediate result of the matrix basic operation module is stored in the memory array, and then the intermediate result is called according to the recurrence equation. The invention multiplexes the computing resource array and the storage resource arraythrough time-sharing and folding mode, thereby effectively reducing resources and area, and reducing power consumption. Multi-path parallel method is used to design the basic matrix operation, which can effectively improve the real-time performance and data processing ability of the system design.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Large-Scale MIMO Signal Detection Method Based on Jacobian Iteration
ActiveCN109245804BFast convergenceFast convergence rateSpatial transmit diversityMatrix additionComputation complexity
The invention discloses a large-scale MIMO signal detection method based on Jacobi iteration, and belongs to the technical field of wireless communication. The method comprises the steps: converting amatrix inversion process into an iteration process of matrix multiplication and matrix addition, providing the search direction for a Jacobi algorithm through a gradient algorithm and an overall correction acceleration method, and determining a correction coefficient of an iteration equation. According to the invention, the method performs the estimation of a high-dimensional matrix inversion process through an improved Jacobi iteration method, and converts the matrix inversion process into the iteration process of matrix multiplication and matrix addition, thereby greatly reducing the computing complexity. The gradient algorithm and the overall correction acceleration method are used for providing the search directions for the Jacobi algorithm and determining the correction coefficient of the iteration equation, thereby enabling the iteration convergence to be better, and enabling the convergence speed to be higher.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
A continuous rolling self-calibration and self-alignment method for an inertial platform under a static base
InactiveCN107270905BImprove navigation accuracyStrong benefitsNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsRolloverCubature kalman filter
Belonging to the technical field of inertial navigation, the invention in particular relates to an inertial platform continuous roll self-calibration and self-alignment method under a static base. The method firstly adopts an inertial device input shaft as the reference to establish a systematic coordinate system, then on the basis of an inertial platform working principle, an inertial platform attitude angle is employed as the intermediate quantity to establish a system dynamics model and an observation model, and then a platform matrix addition scheme needed by inertial platform self-calibration and self-alignment is designed through observability analysis, finally the platform attitude angle and various error coefficients of the platform are selected as the state variables of the system, and autonomous calibration and alignment of the inertial platform can be realized through reduced cubature Kalman filter. The method provided by the invention can change the existing calibration and alignment modes of the inertial platform, simplifies the inertial platform self-calibration and self-alignment process, weakens the strong coupling between system calibration and alignment, and provides the basic theory and technical support for improving the inertial platform actual use precision.
Owner:INHALE HYPERSONIC TECH RES CENT UNIT 63820 OF PLA
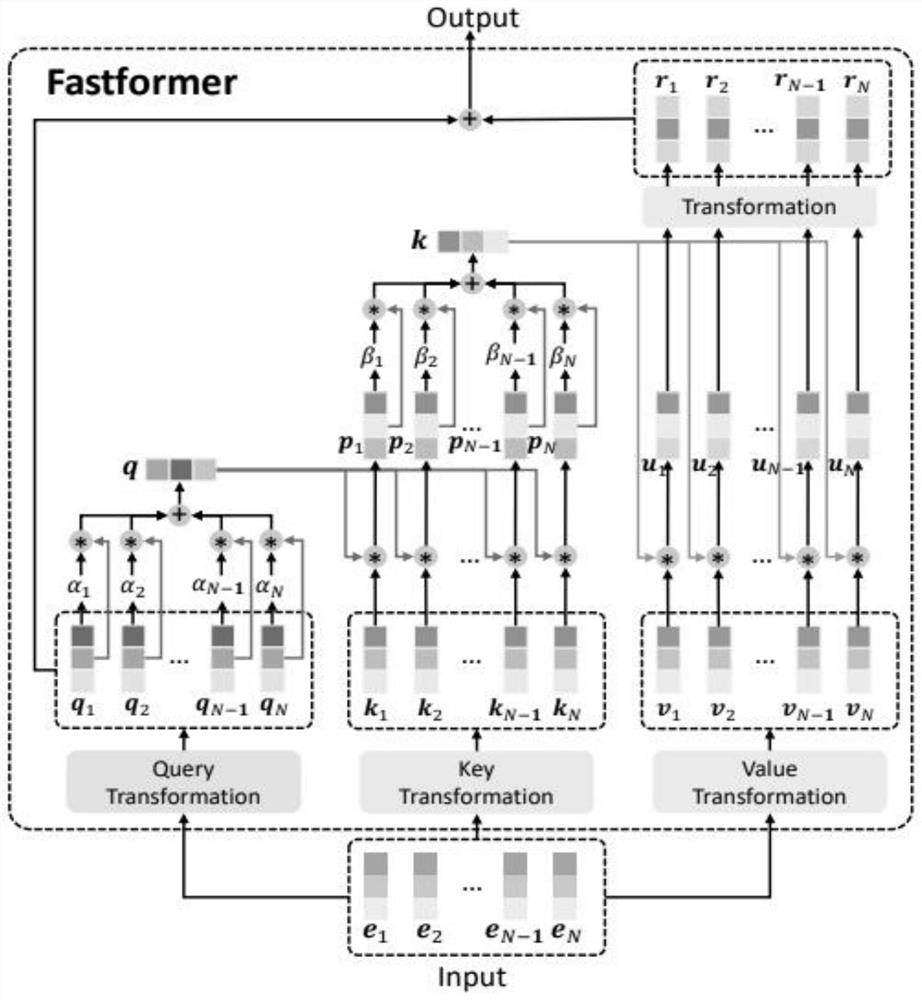
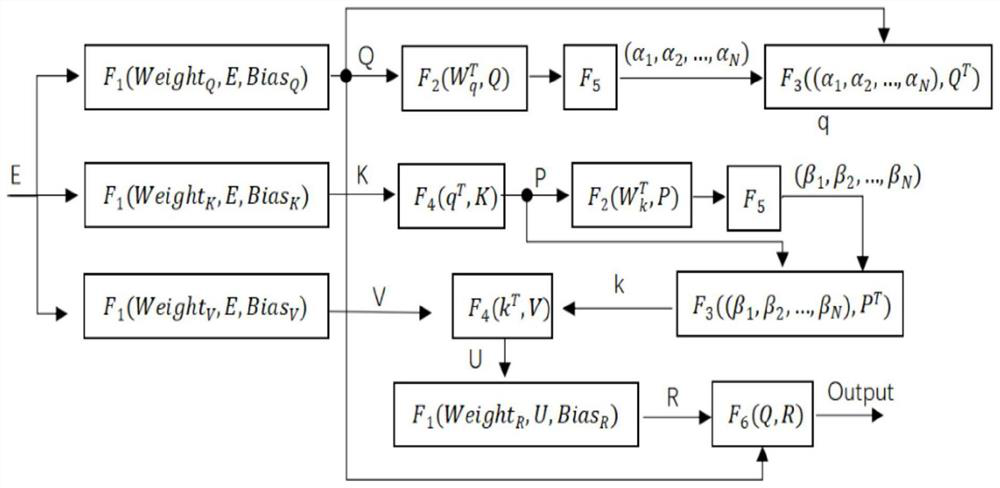
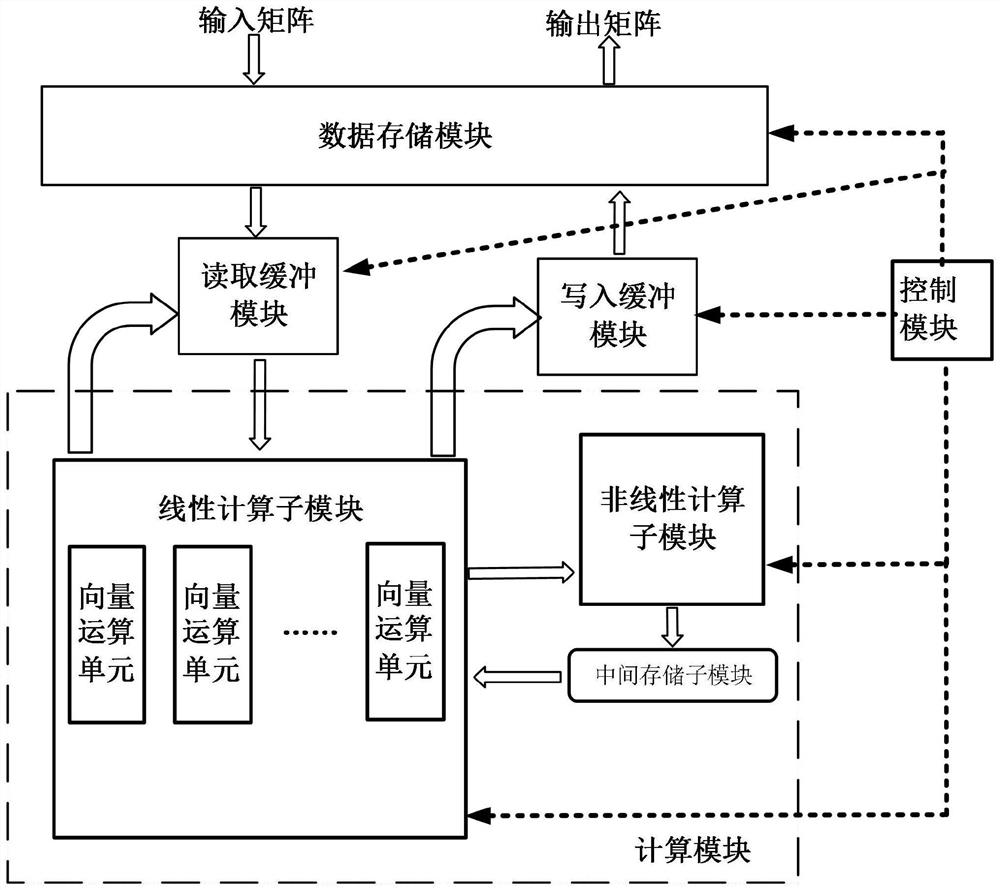
Hardware architecture applied to Fastform neural network and calculation method thereof
PendingCN114330682AIncrease computing speedImprove computing efficiencyPhysical realisationComplex mathematical operationsComputer hardwareMatrix addition
The invention discloses a hardware architecture applied to a Fastform neural network and a calculation method of the hardware architecture. The hardware architecture comprises a data storage module, a reading buffer module, a writing buffer module, a calculation module and a control module; wherein the control module is used for controlling the hardware architecture to execute calculation operation, and the calculation module comprises a linear calculation sub-module, a nonlinear calculation sub-module and an intermediate storage sub-module; the linear calculation module comprises a plurality of vector calculation units and is used for executing linear operation including vector matrix multiplication, matrix addition and element-by-element product, and the nonlinear submodule is used for executing normalized exponential function operation. According to the hardware architecture and the computing method thereof, the computing speed and efficiency of the Fastform neural network can be effectively improved.
Owner:南京风兴科技有限公司
A large-scale MIMO low-complexity channel estimation method based on weighted kapetyn series expansion
ActiveCN106817155BImprove accuracyFast convergenceRadio transmissionChannel estimationMatrix additionComputation complexity
The invention discloses a large-scale MIMO low-complexity channel estimation method based on weighted Kapetyn grade number expansion. Firstly a Kapetyn grade number expansion method is utilized for performing approximate expansion on a channel covariance inverse matrix in a Bayesian-MMSE channel estimation expression. A matrix inversion operation is converted to matrix multiplication and matrix addition operations. Then a weighting manner is performed on each coefficient of a polynomial for optimizing polynomial expansion, establishing a model for solving weighting coefficient vectors alpha and beta for minimizing an estimated mean square error, and estimating the channel matrix by means of solving results of alpha and beta. Experiment results represent a fact that an MSE which is obtained through the channel estimation method based on a weighted Kapetyn grade number expansion is convergent to an MMSE method along with order number increase of the polynomial, and furthermore calculation complexity of the channel estimation method is lower than that of the MMSE method. Compared with a traditional Taylor-MMSE and Kapetyn grade number expansion channel estimation method, the channel estimation method based on the weighted Kapetyn grade number has higher convergence speed to the MMSE method.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
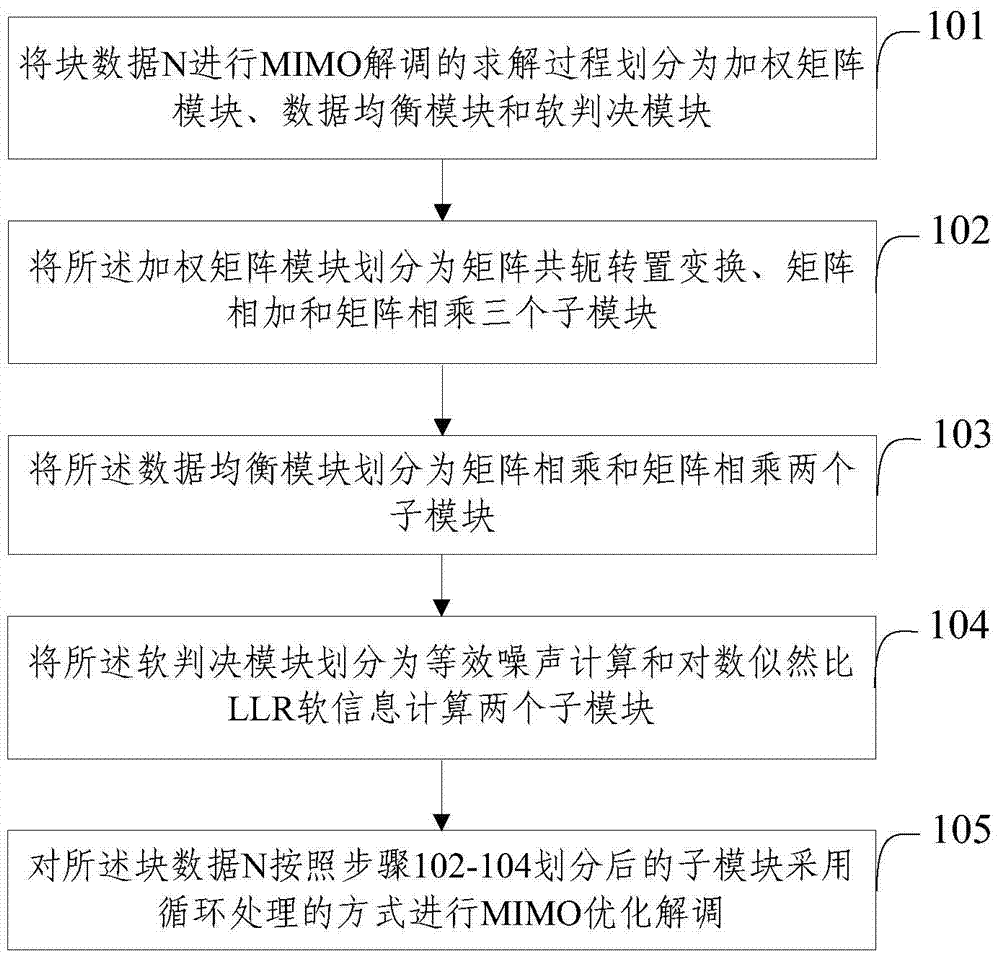
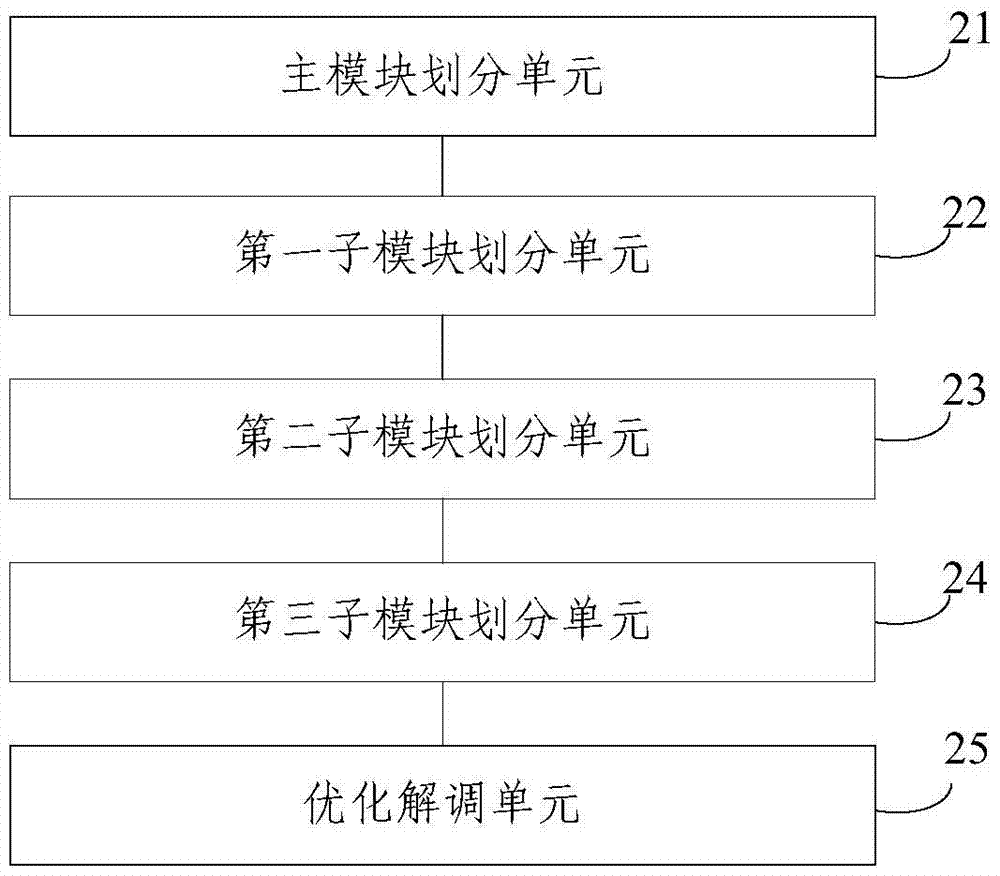
A space-time optimization method and system for multiple-input multiple-output MIMO demodulation
ActiveCN104270329BImprove resource utilizationReduce clock cyclesTransmitter/receiver shaping networksMatrix additionConjugate transpose
The invention provides an MIMO demodulation space-time optimization method and system. The method comprises the steps that S1, the solution process of carrying out MIMO demodulation on block data N is divided into a weighting matrix module, a data balance module and a soft-decision module; S2, the weighting matrix module is divided into three sub-modules including the matrix conjugate transpose conversion sub-module, the matrix addition sub-module and the matrix multiplication sub-module; S3, the data balance module is divided into two matrix multiplication sub-modules; S4, the soft-decision module is divided into the two sub-modules including the equivalent noise calculation sub-module and the log-likelihood ratio soft information calculation sub-module; S5, MIMO optimized demodulation is carried out on the block data N according to the sub-modules divided in the steps S2 to S4 by adopting a circulation processing mode. The MIMO demodulation space-time optimization method and system solve the problem that the space and time utilization rate of a DSP chip in a 4*4 MIMO demodulation system based on a TMS320C66x type multi-core DSP is low.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
SLAM (Simultaneous Localization and Mapping) back-end optimization-oriented Schur elimination accelerator
ActiveCN113177877AMeet computing performanceFulfil requirementsImage memory managementProcessor architectures/configurationSimultaneous localization and mappingMatrix addition
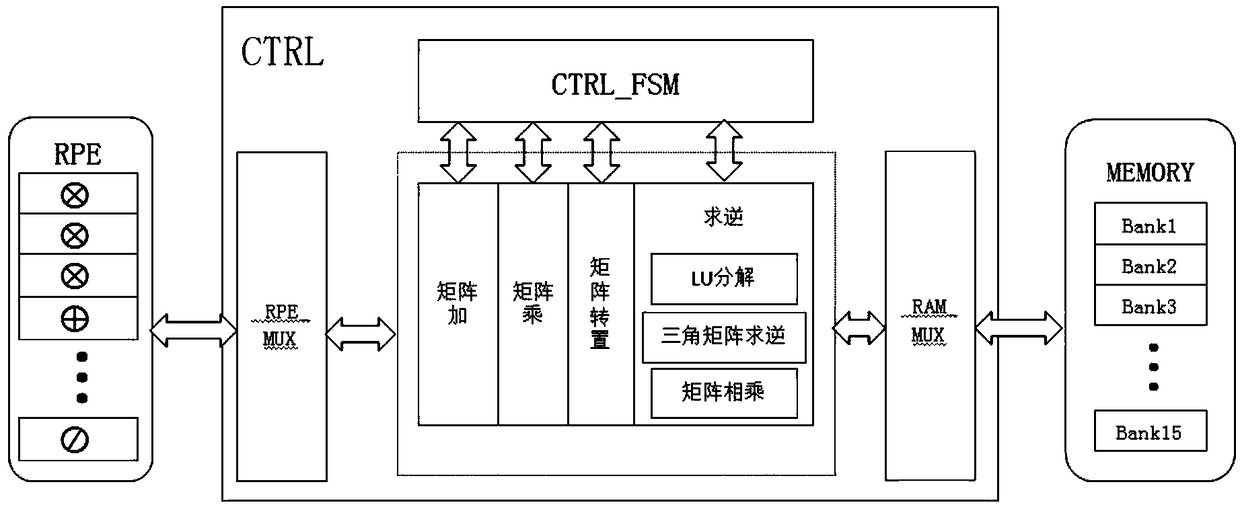
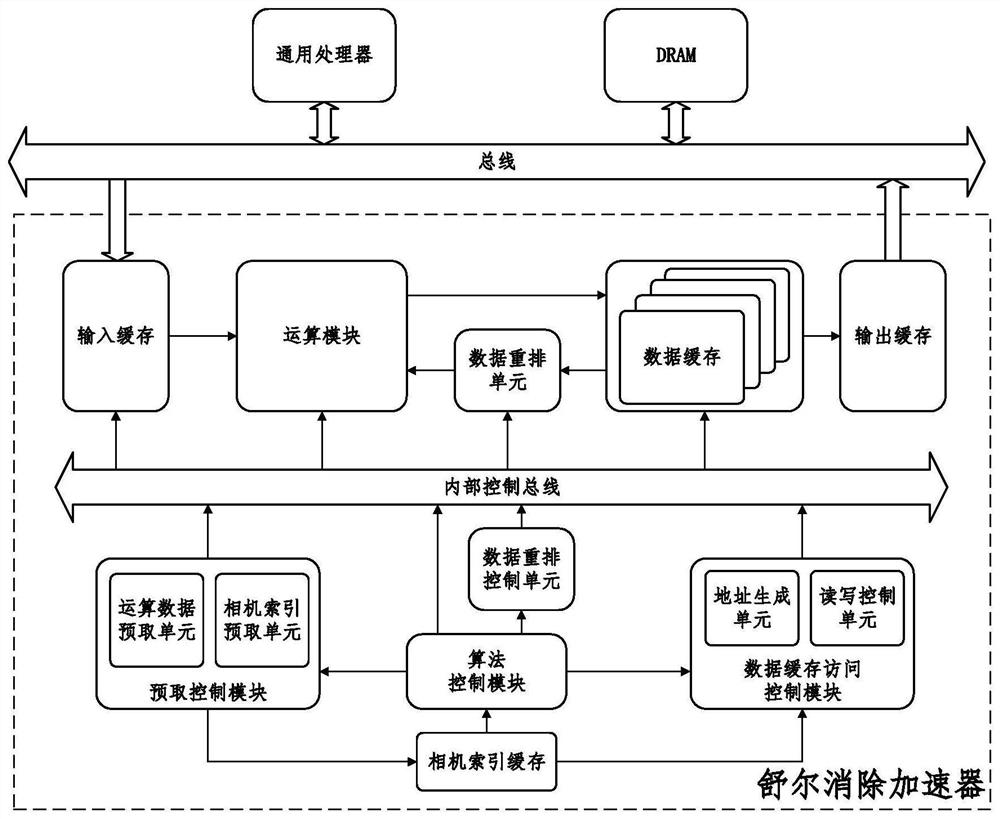
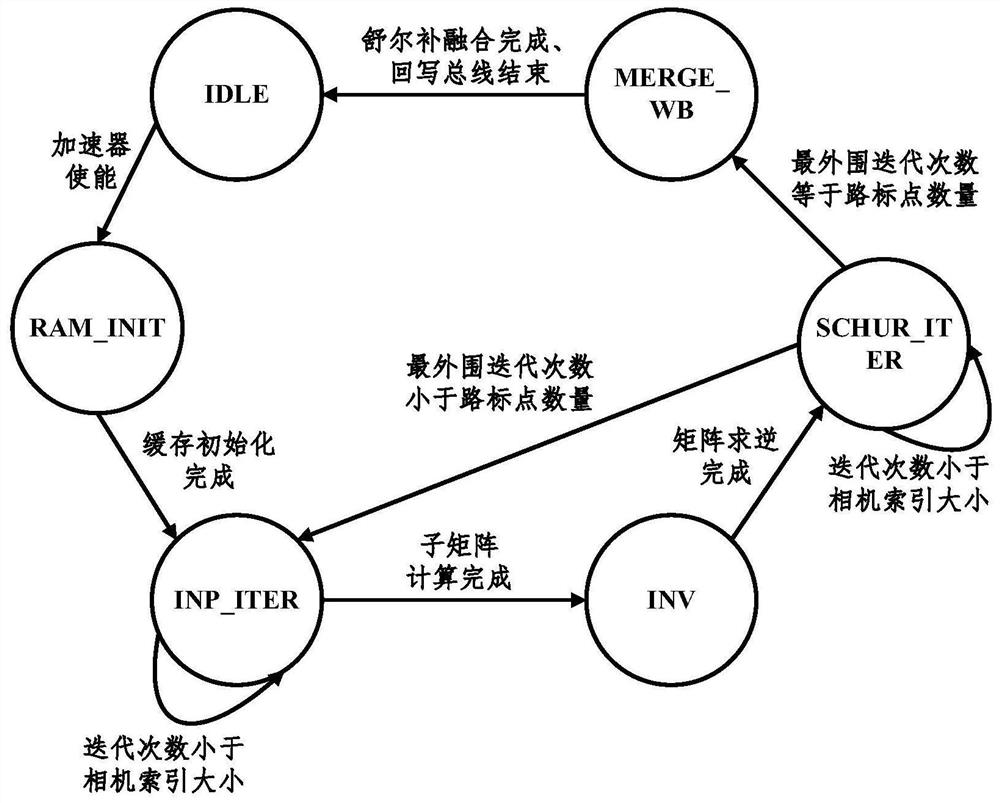
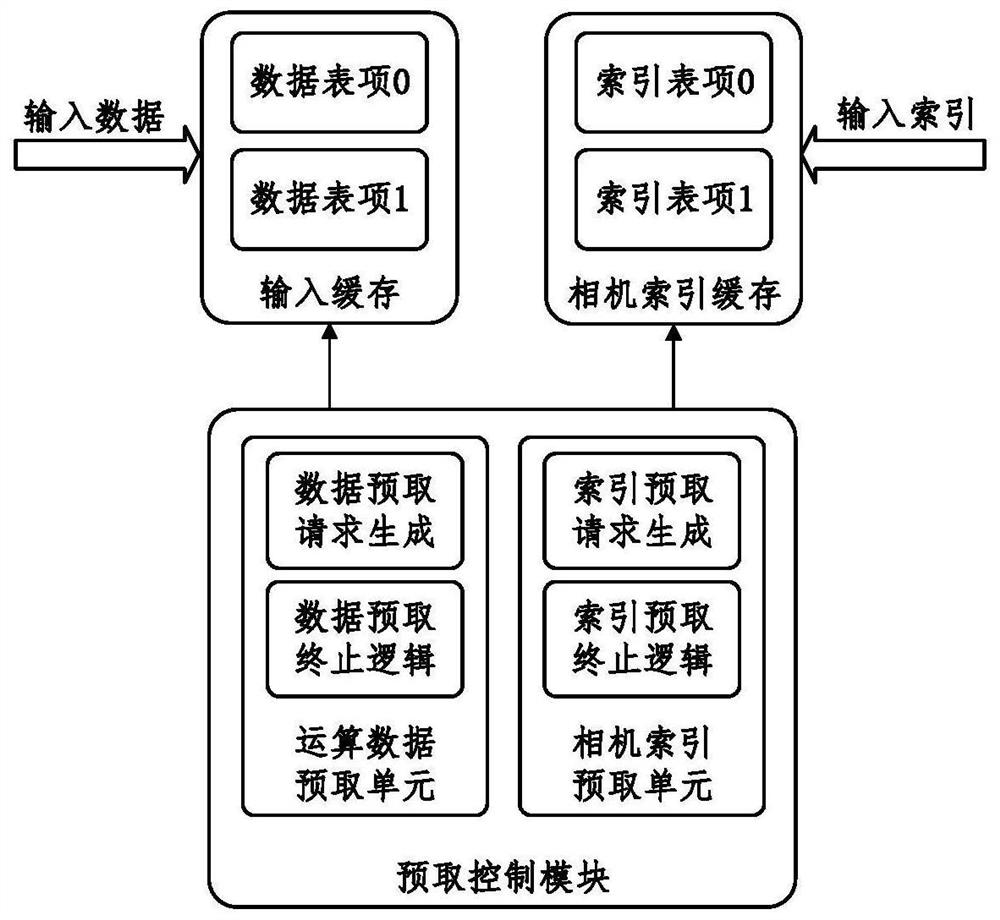
A SLAM rear-end optimization-oriented Schur elimination accelerator comprises an algorithm control module used for completing maintenance of a control signal; a prefetching control module used for completing prefetching operation of input projection error data and Jacobian matrix data; a data cache access control module used for completing address generation and read-write requests of data cache, including address maintenance of different matrix data and advanced initiation of read requests; an operation module used for completing matrix multiplication, matrix inversion, matrix addition and subtraction and matrix and constant multiplication; a data rearrangement and control unit used for completing data recombination; an input and output caching unit used for completing advanced caching of prefetch input and data caching during output; and a data caching unit used for completing caching of intermediate data in the operation process. According to the accelerator, hardware acceleration is carried out on the Schur elimination process by proposing an FPGA accelerator scheme, so that a traditional embedded platform can execute the BA optimization process with higher performance.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com