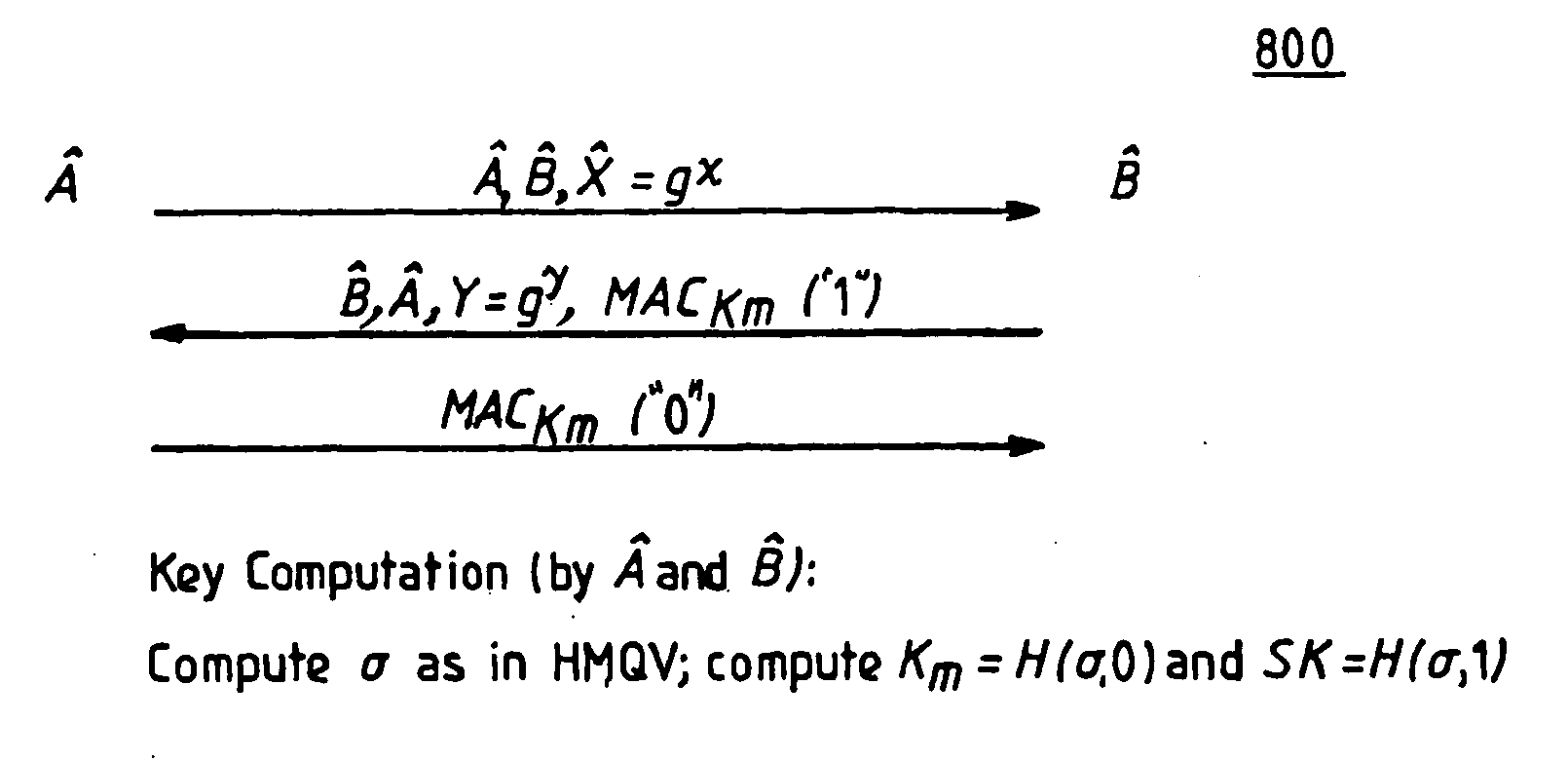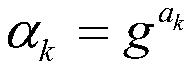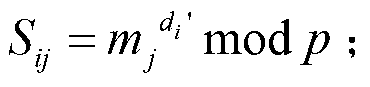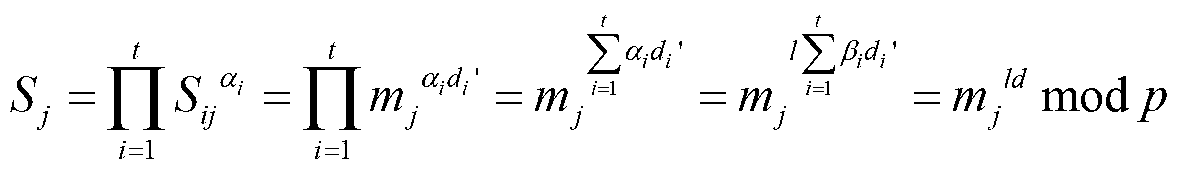Patents
Literature
320 results about "Secret share" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
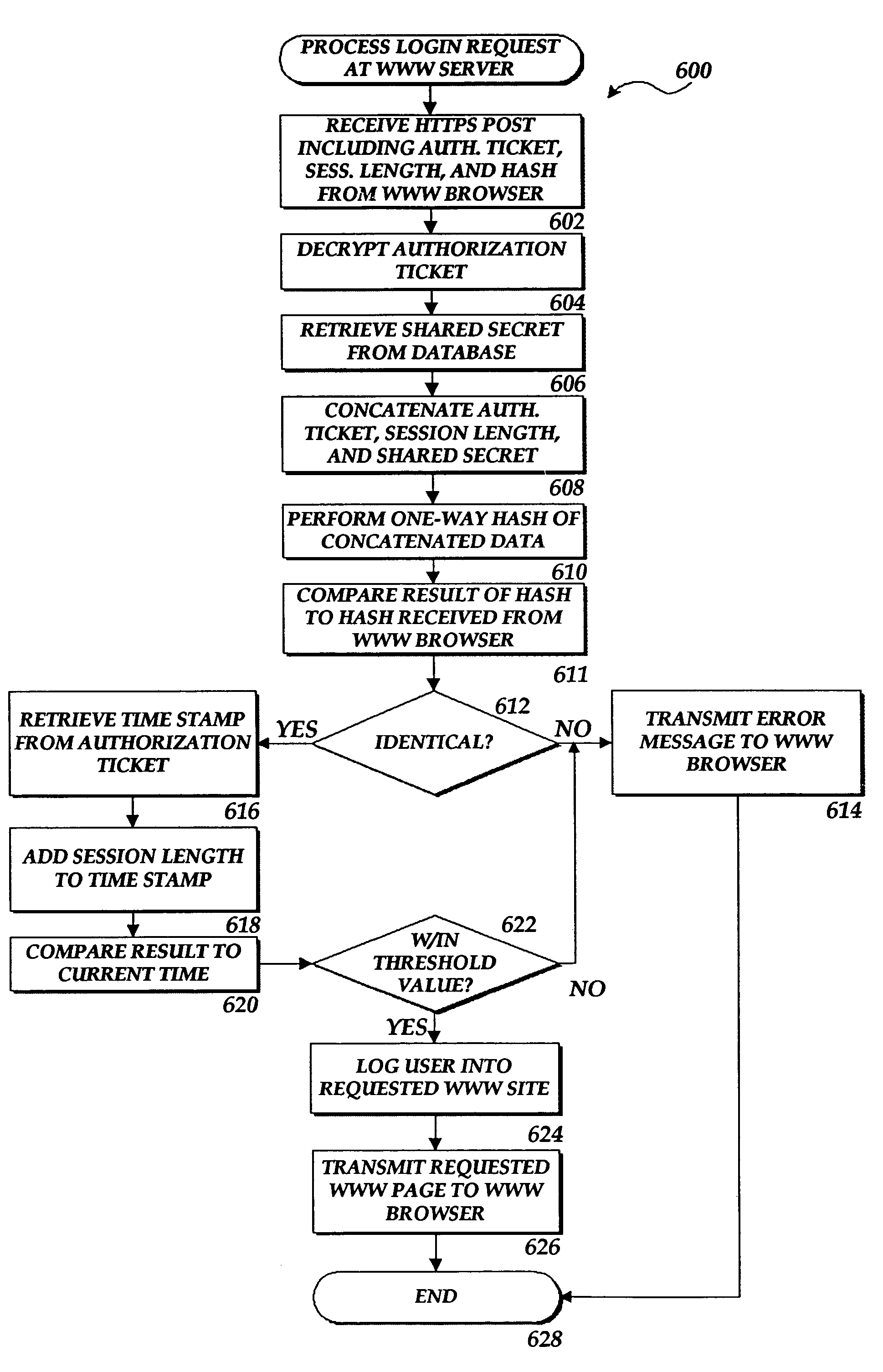
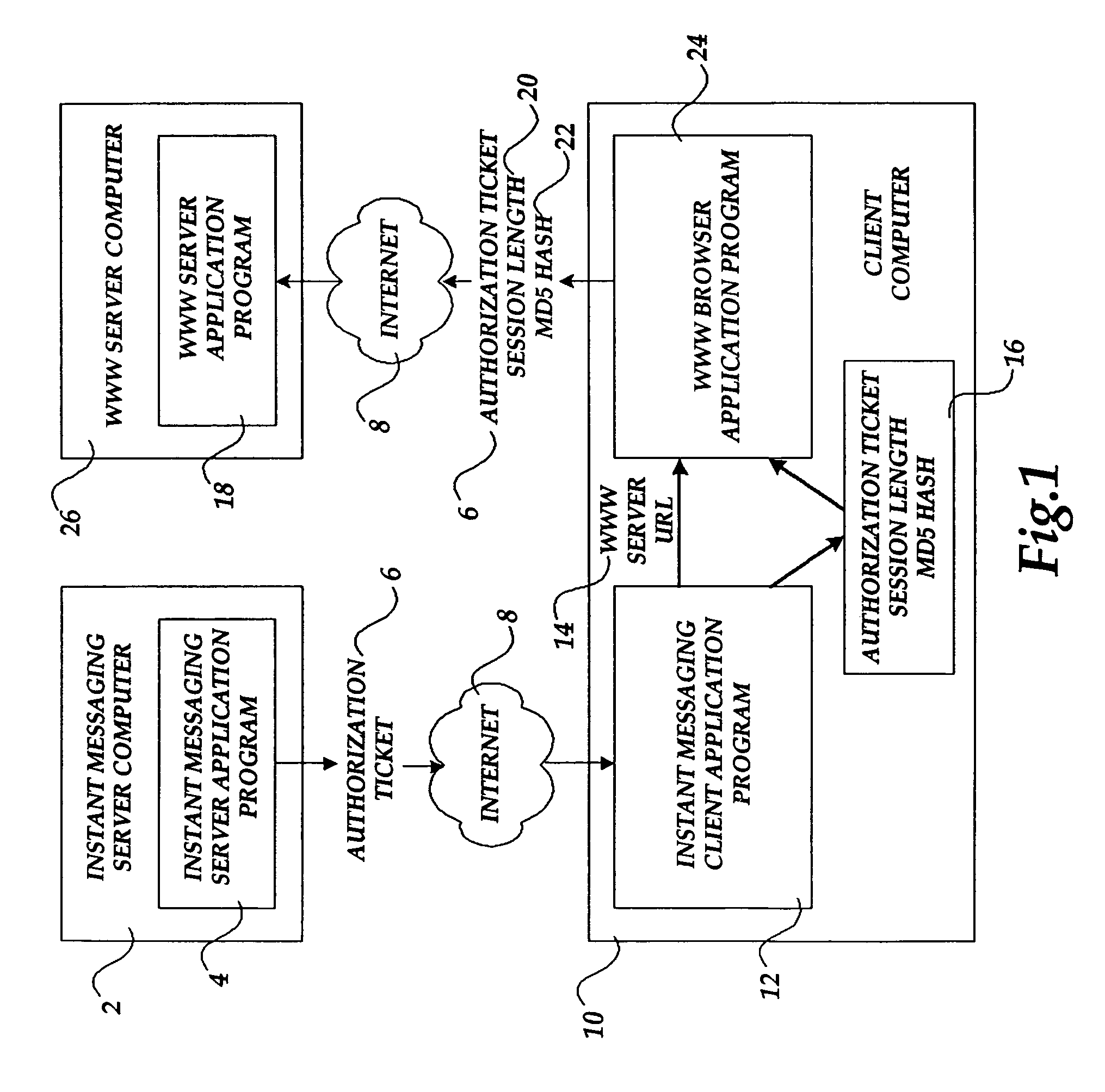
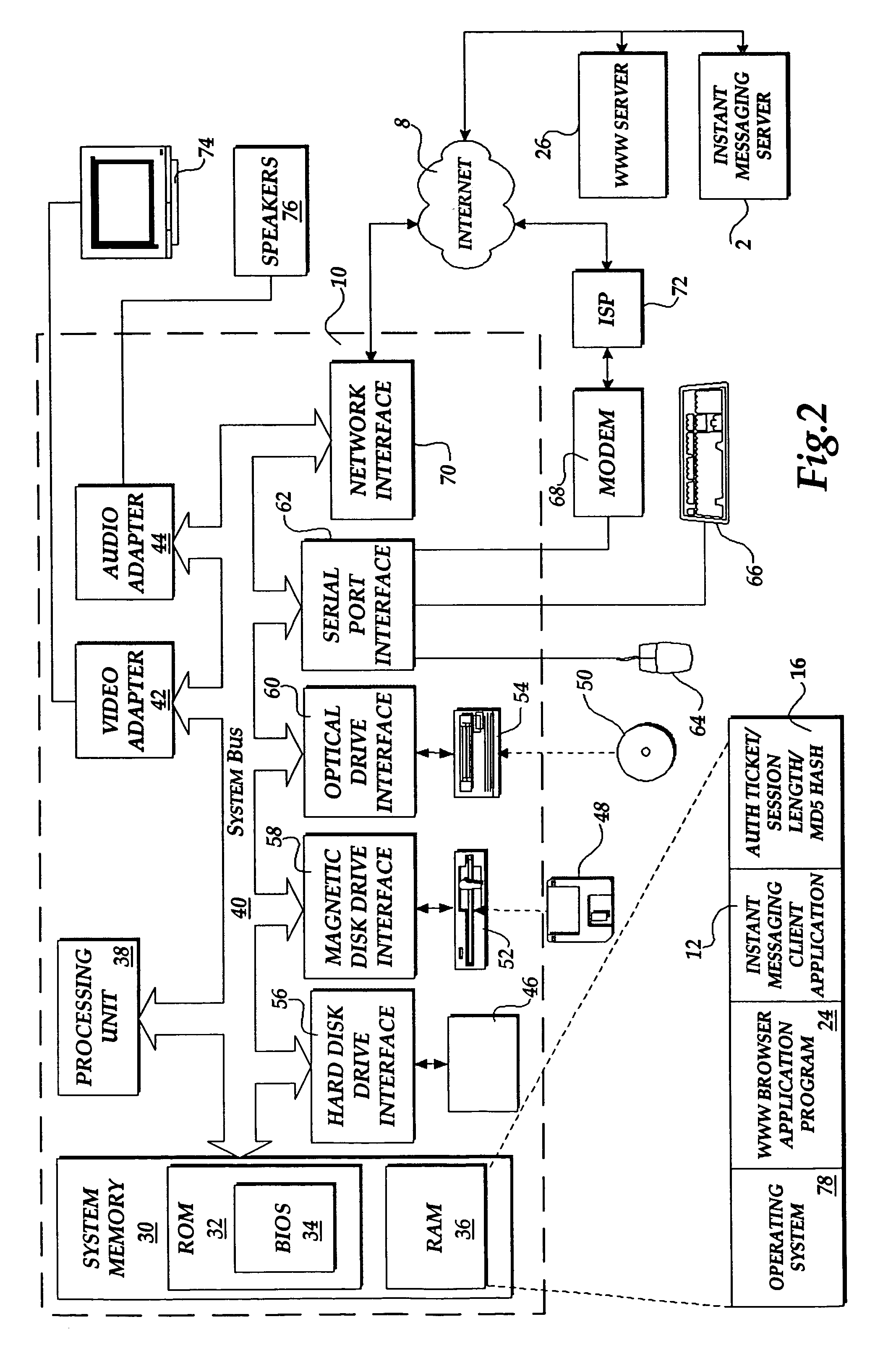
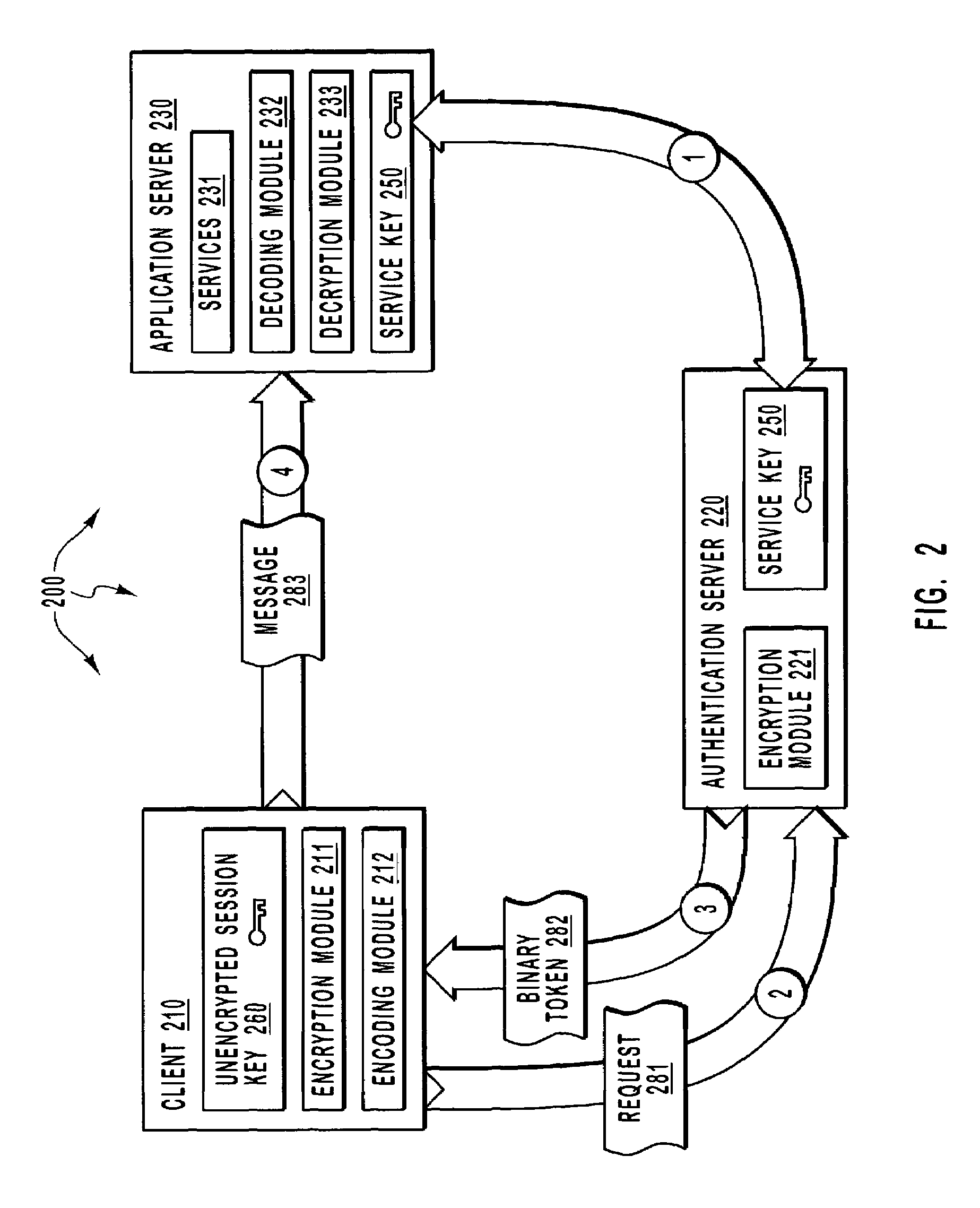
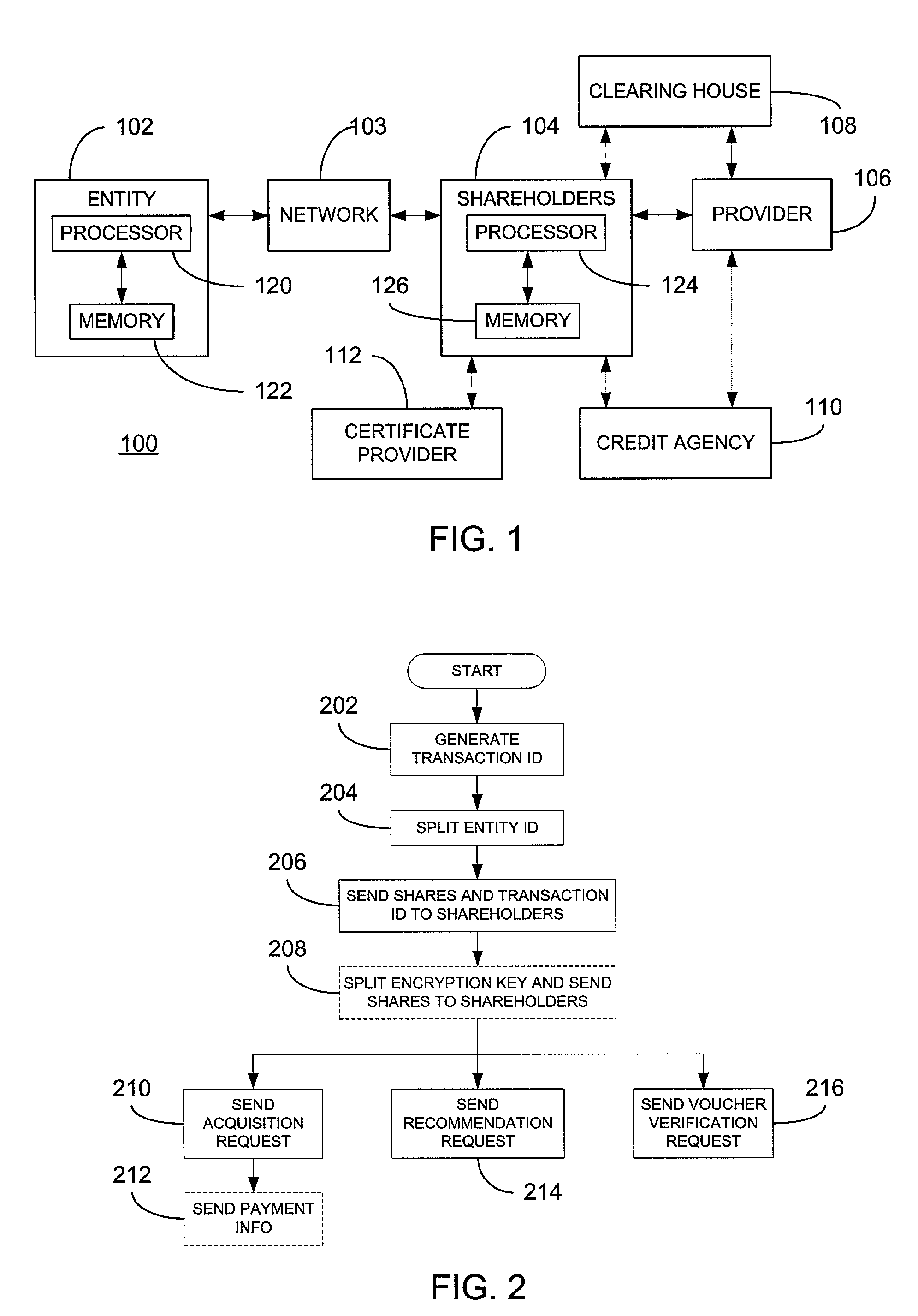
Method and system for authorizing a client computer to access a server computer
InactiveUS7089585B1Key distribution for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsAuthorization certificateHash function
The present invention includes a client computer, a first server computer, and a second server computer. The first server provides an authorization ticket containing a time stamp to the client computer when the client computer is authorized to access the first server. An elapsed time counter is started at the client computer when access is provided to the first server. When a request is received at the client computer to access the second server, the client computer determines the session length based upon the elapsed time counter. The client computer calculates a hash value for the authorization ticket, the session length, and a secret shared with the second server computer. The client computer transmits a login request to the second server including the authorization ticket, the session length, and the hash. The second server decrypts the authorization ticket and retrieves a copy of the shared secret. The second server executes a hash function on the authorization ticket, the session length, and the shared secret. The second server then compares the computed hash to the hash value received from the second client application. If the two hash values are identical, the second server retrieves the time stamp from the authorization ticket and adds the session length to the time stamp. The second server then compares the resulting value to the current time. If the resulting value and the current time are within a preset threshold value, the client computer is provided.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
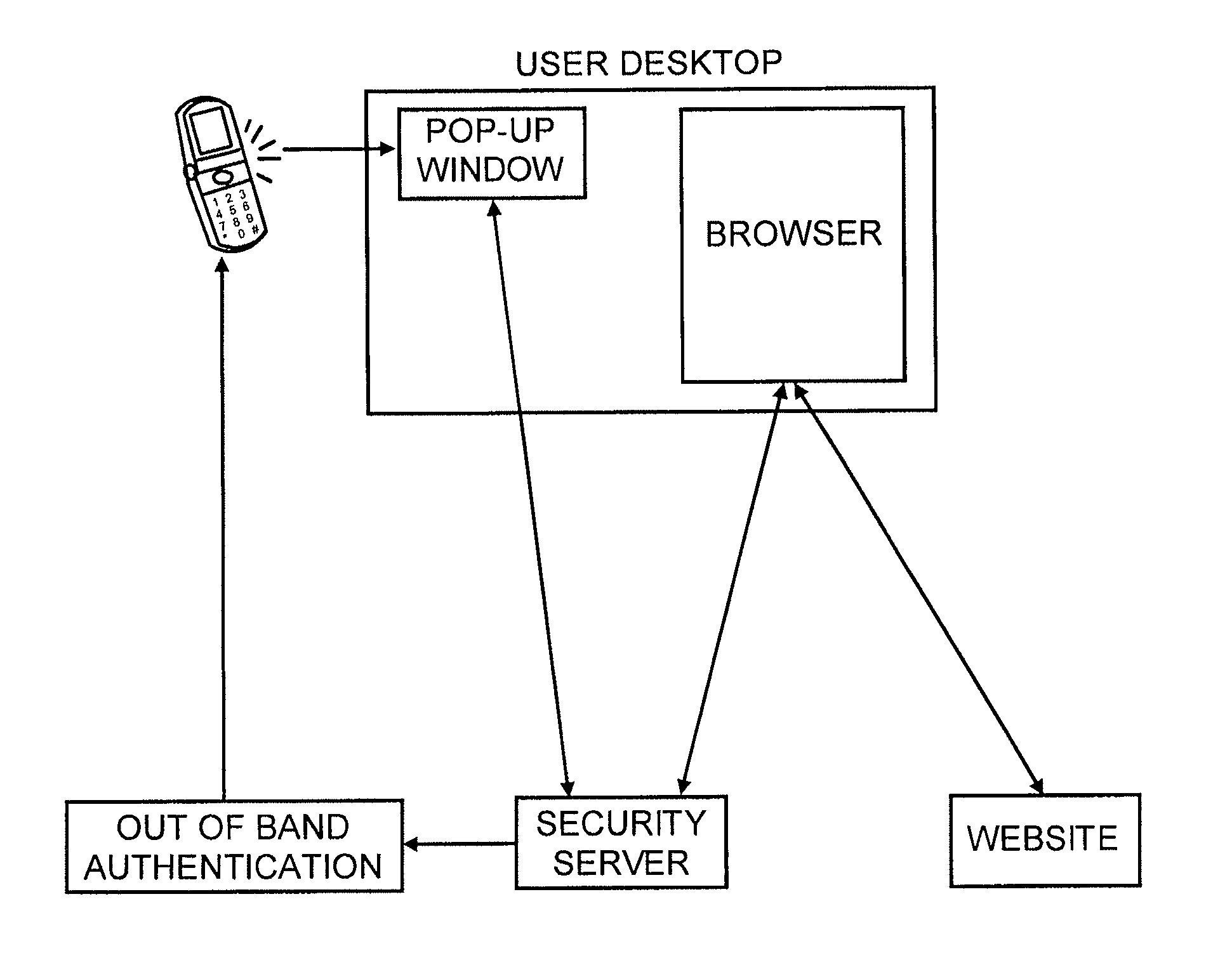
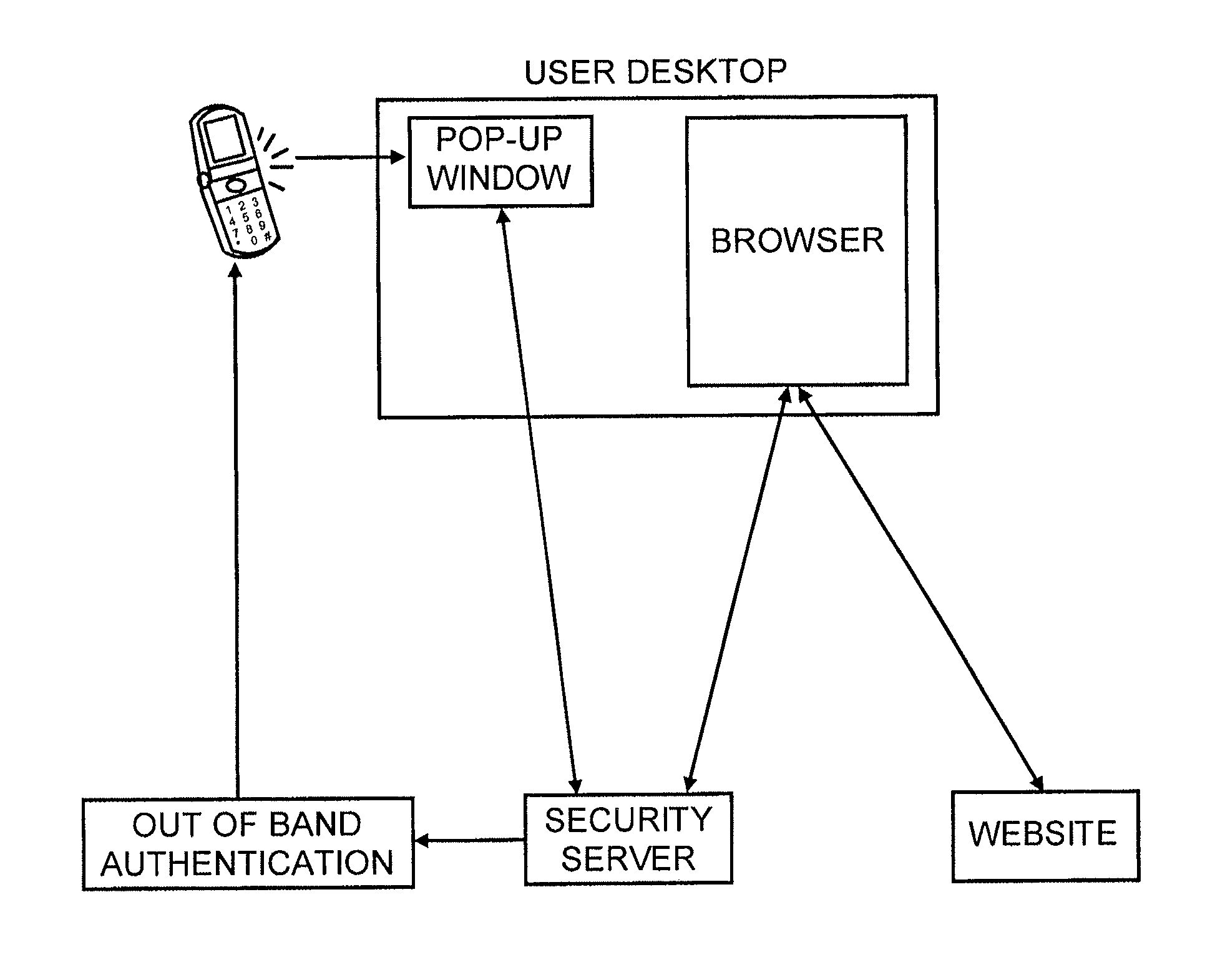
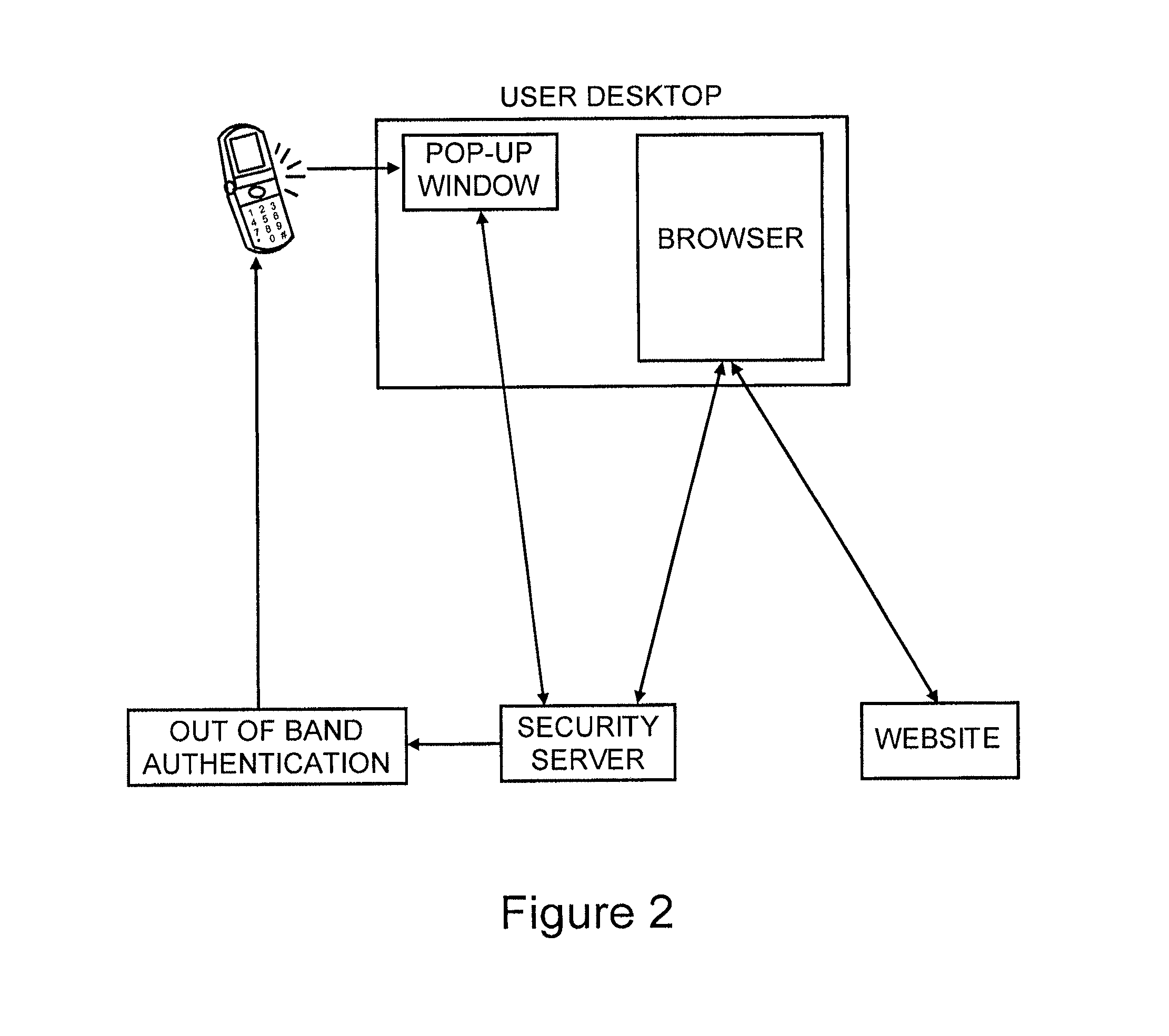
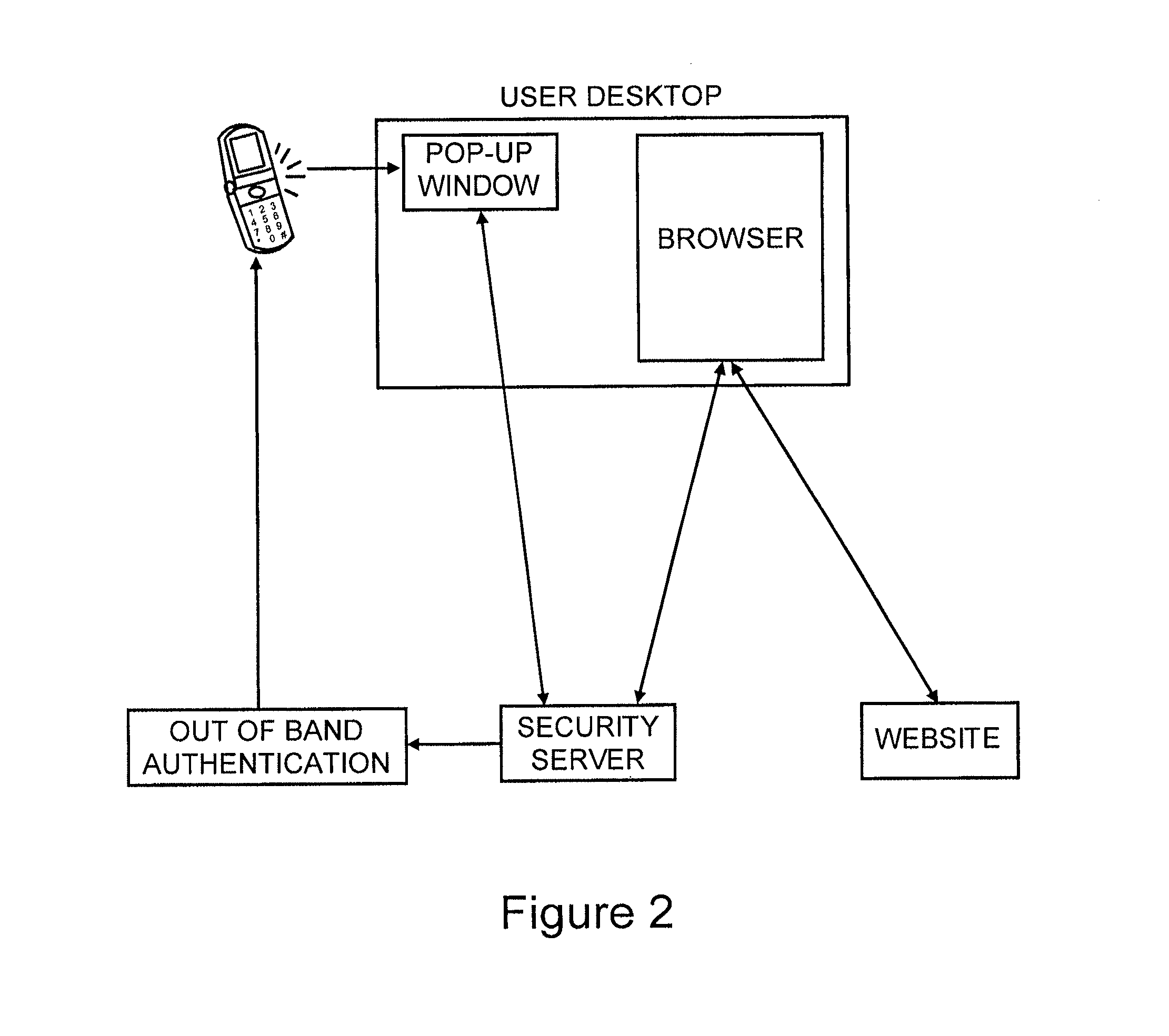
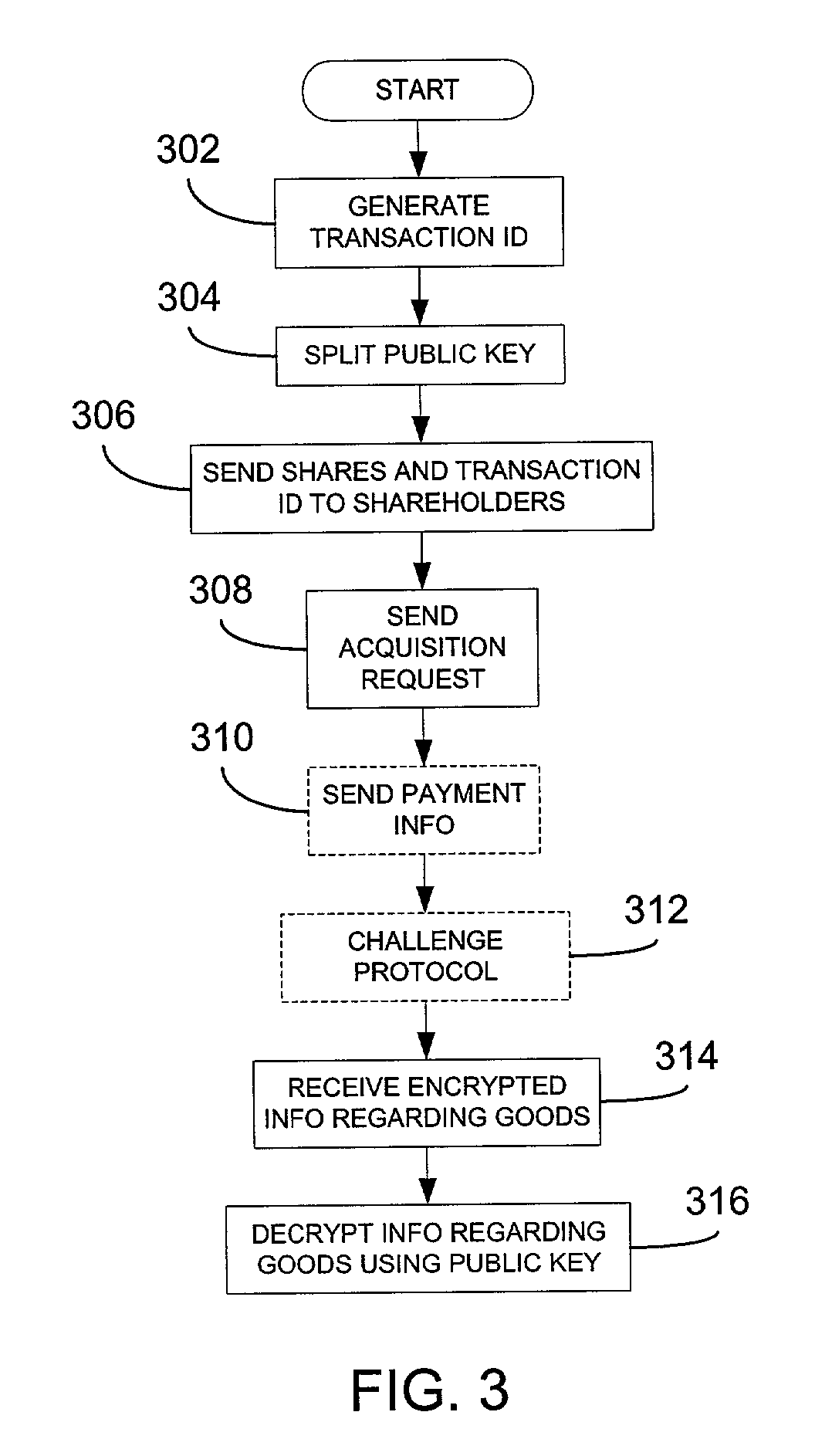
Method for secure user and transaction authentication and risk management
ActiveUS8806592B2Compromising usabilityCompromising costDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationSecret shareOne-time password
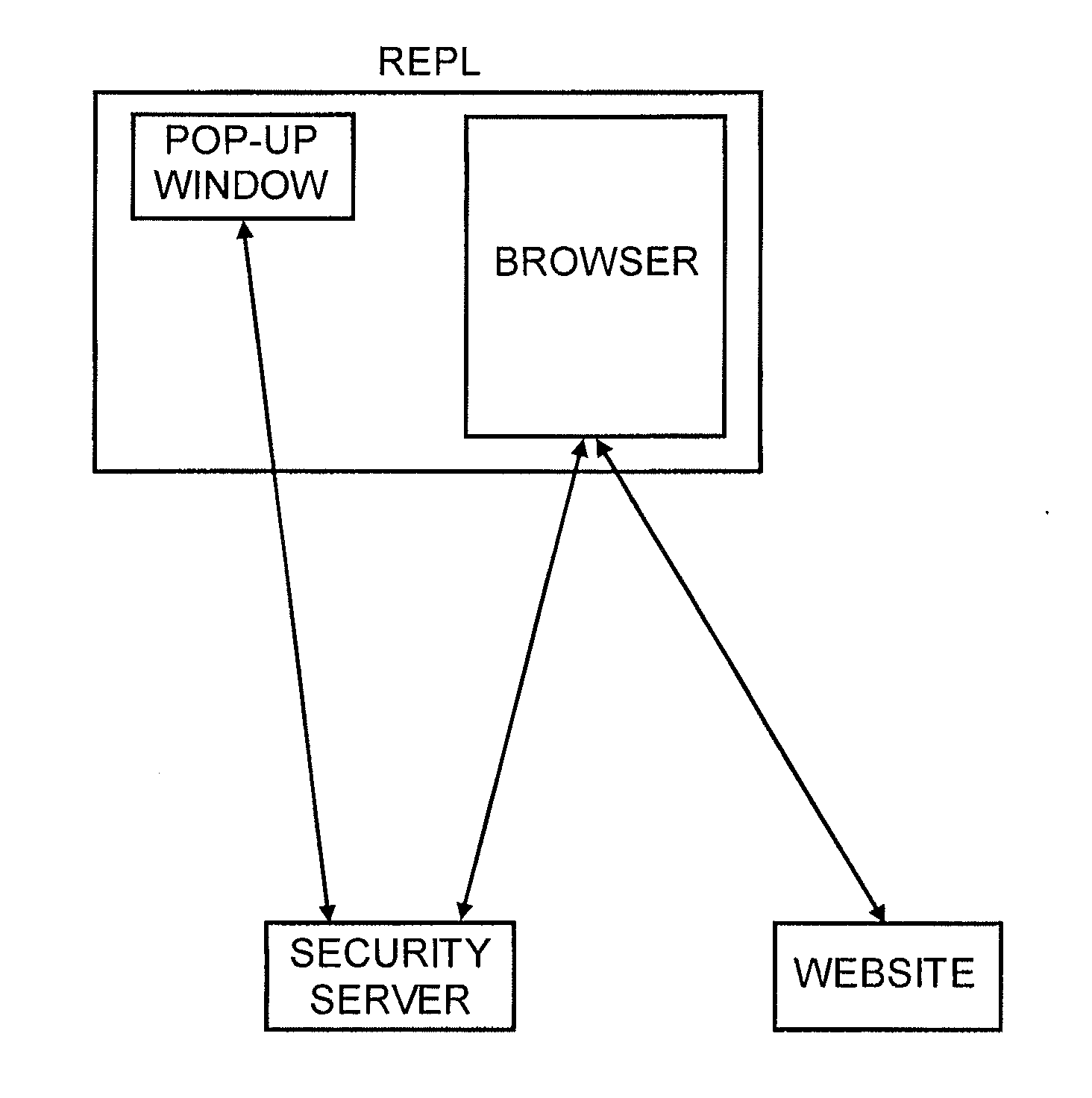
To provide a user signature on a network transaction, a security server receives transaction information representing a transaction between a network user and a network site, such as a website, directly from the network site. The security server calculates a one-time-password based on the received transaction information and a secret shared by the security server and the network site, but not by the user. The security server transmits the calculated one-time-password for application as the user's signature on the transaction. The one-time-password is independently calculable by the network site based on the shared secret.
Owner:PAYFONE
Network Security System
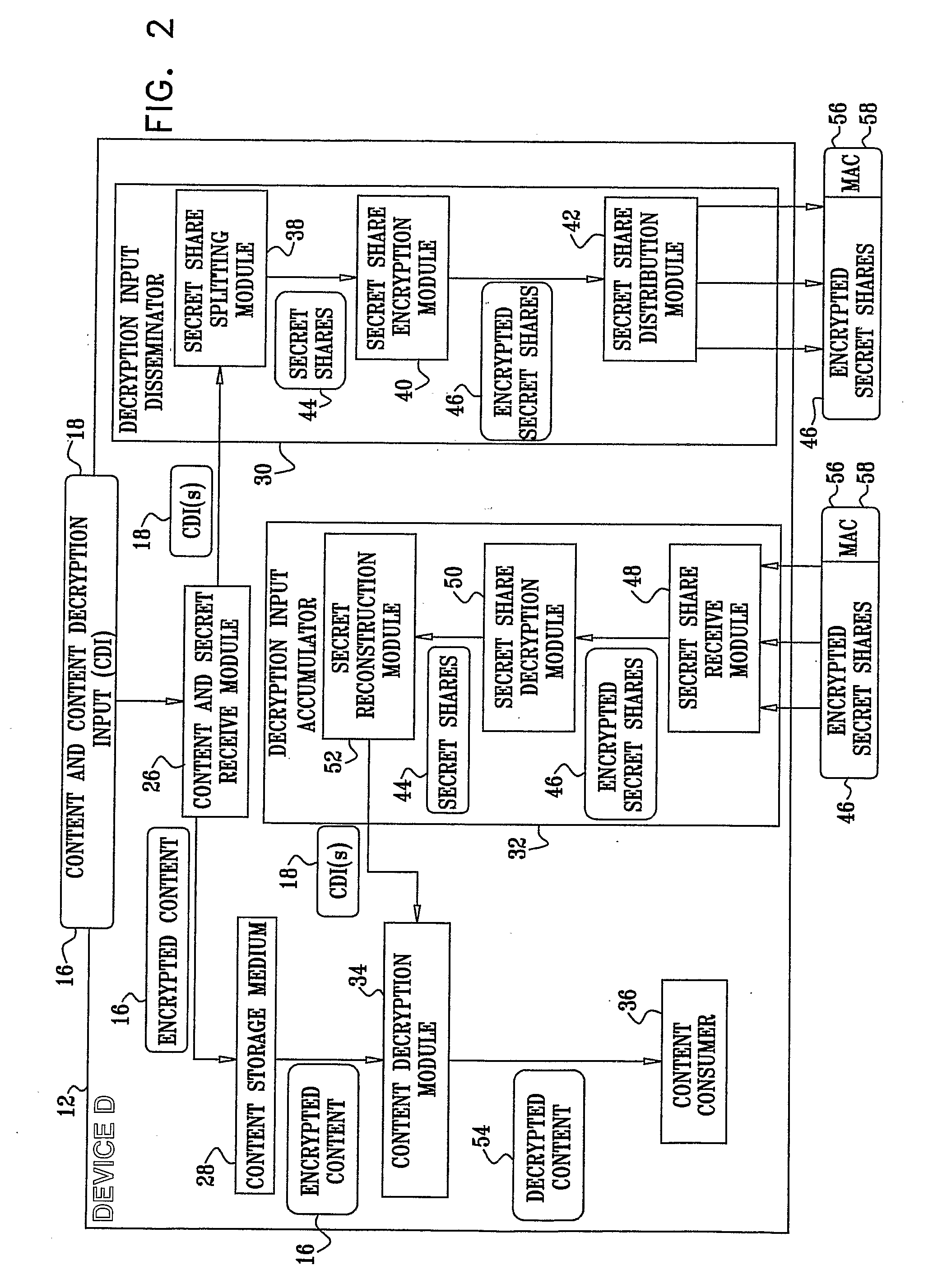
InactiveUS20090077379A1Limited accessSynchronising transmission/receiving encryption devicesUser identity/authority verificationComputer hardwareSecret share
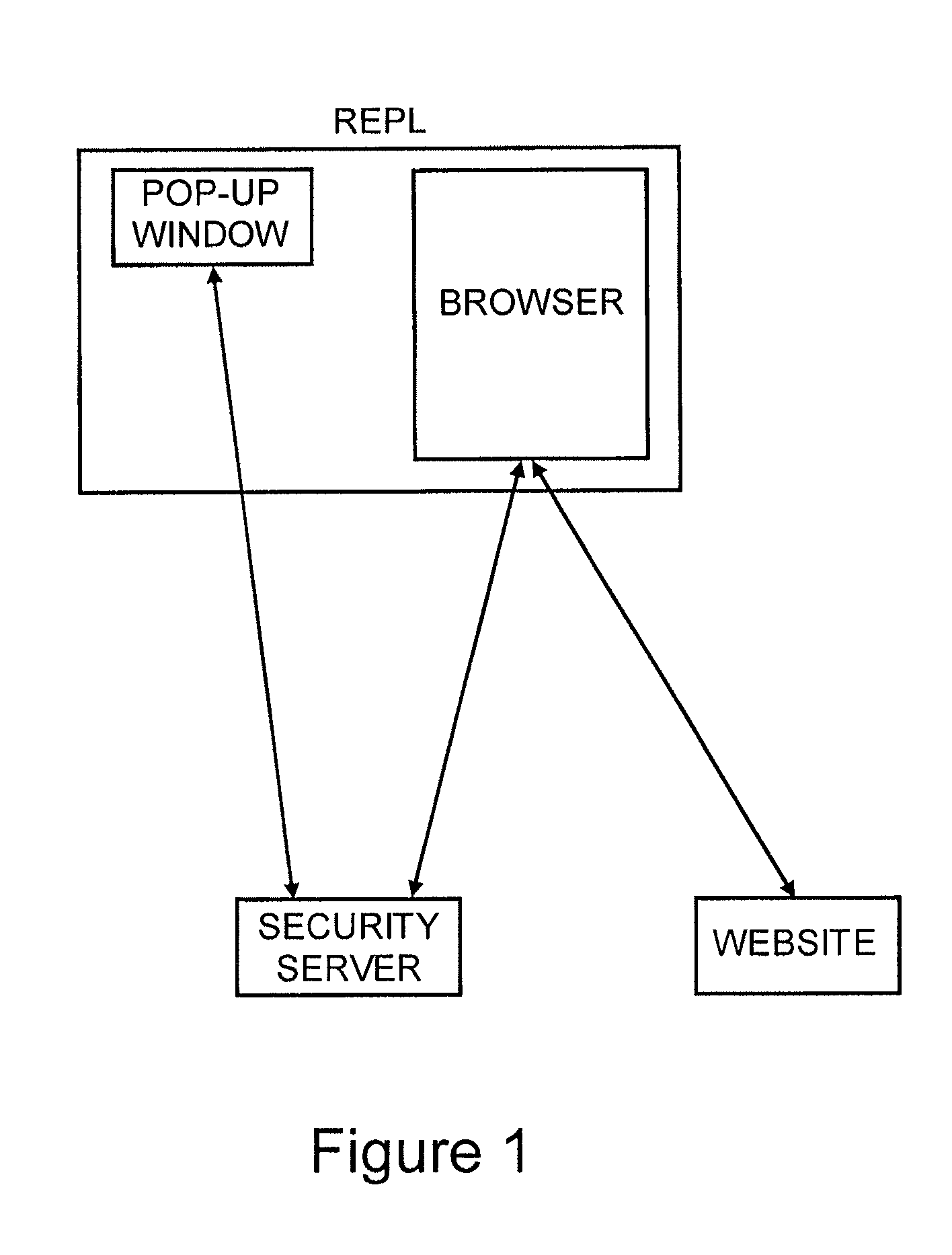
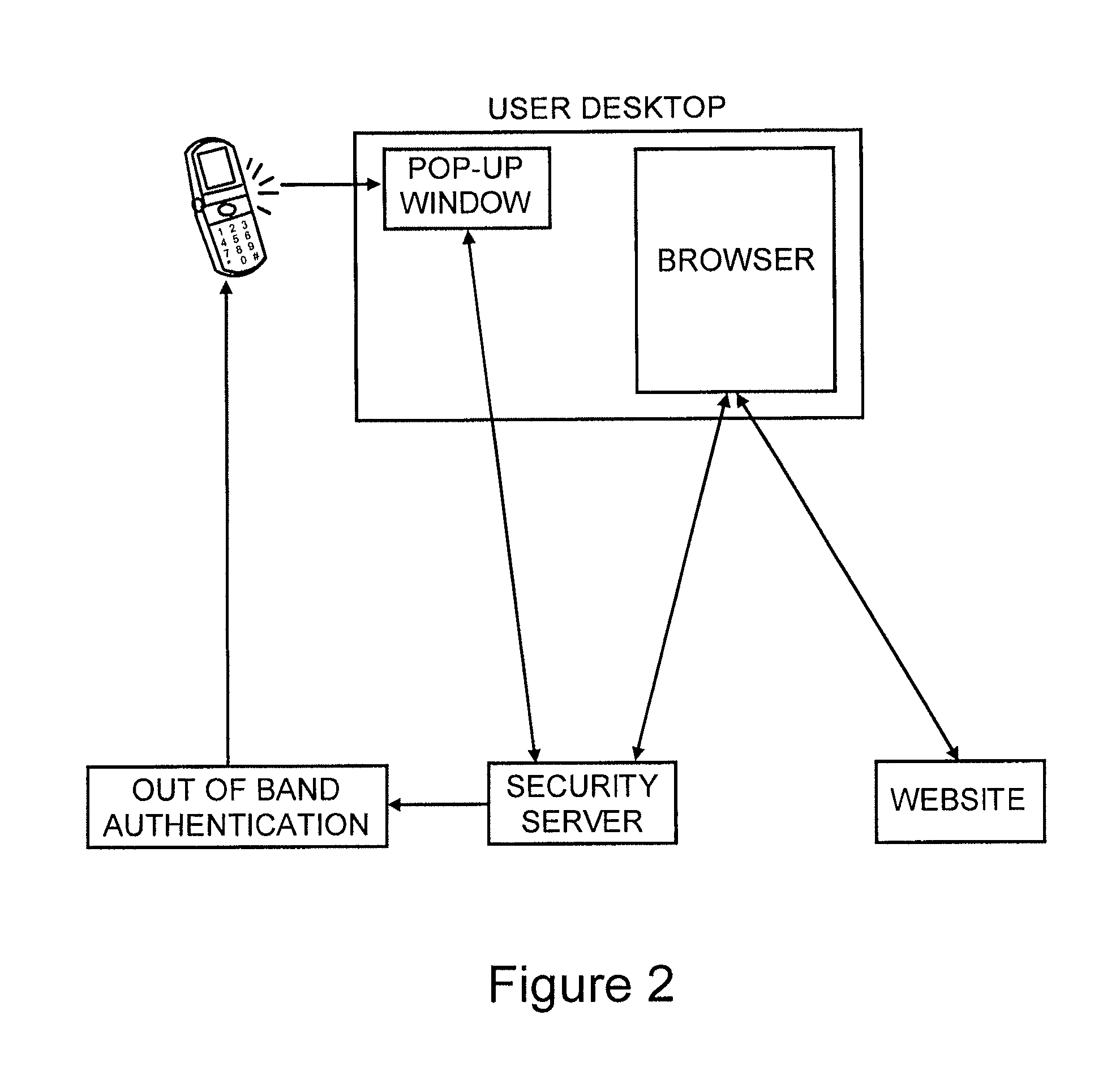
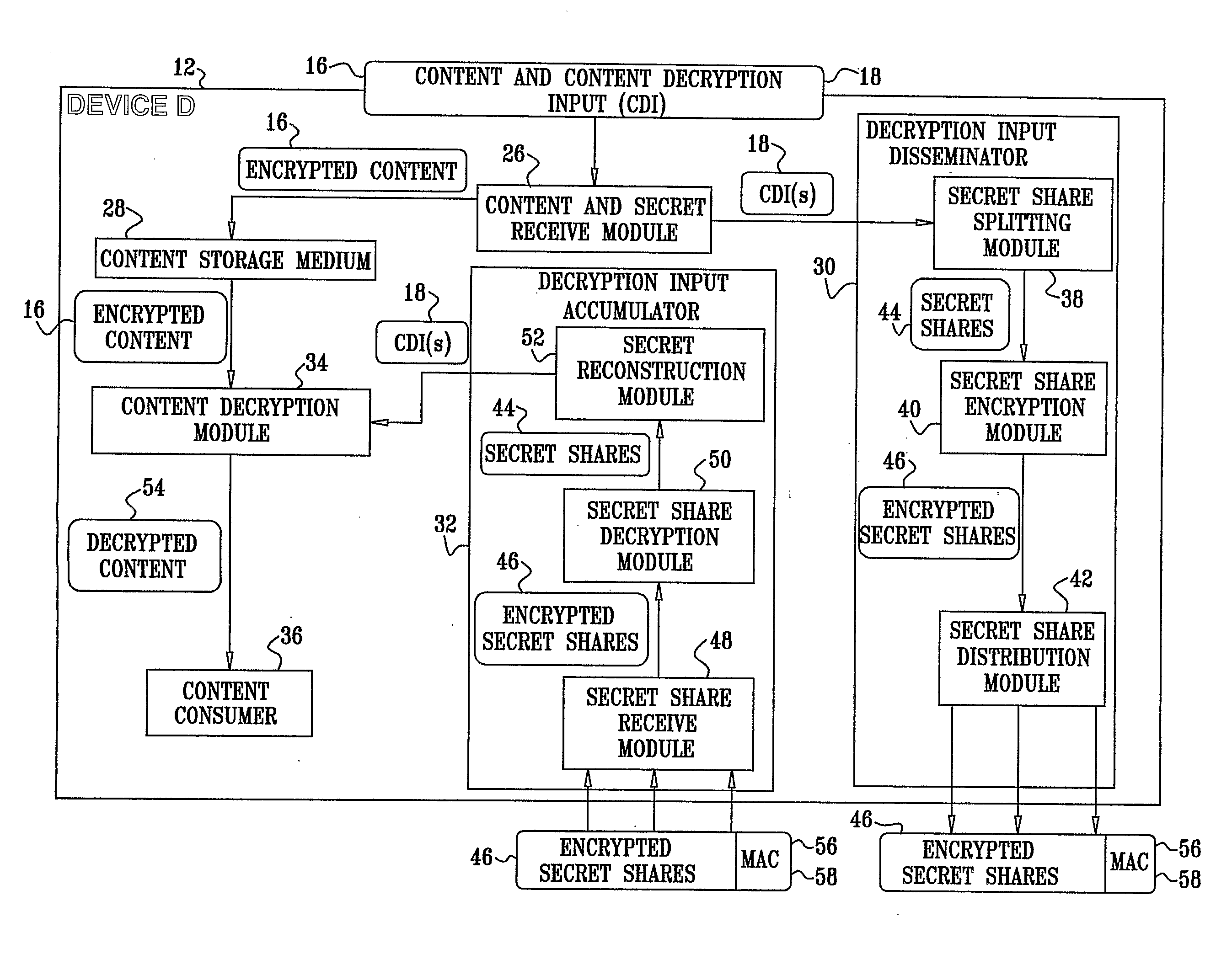
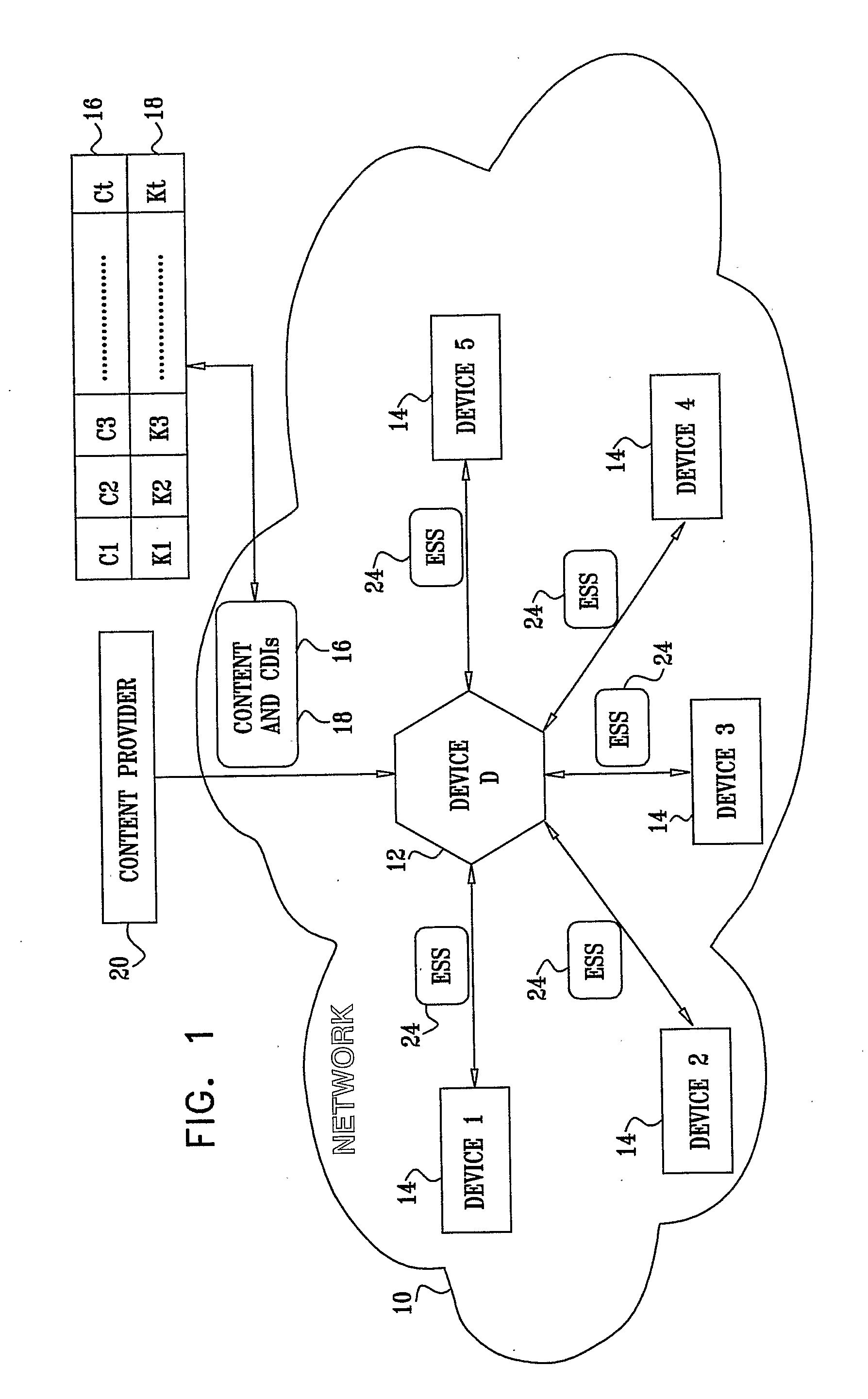
A system for restricting access to encrypted content stored in a consuming device (12) which is part of a network (10) including other devices (14), the system including a content storage medium to store the encrypted content, a secret-share distribution module to distribute secret-shares to the other devices (14), a secret-share receive module to receive the secret-shares from the other devices (14), a secret reconstruction module to form a content decryption input from the secret-shares received by the secret-share receive module, a content decryption module to receive the encrypted content from the content storage medium and the content decryption input from the secret reconstruction module and decrypt the encrypted content using the content decryption input thereby rendering decrypted content, and a content consumer to use the decrypted content, wherein the secret shares distributed to the other devices (14) are in an encrypted format for decryption by the consuming device (12) or the other devices (14).
Owner:CISCO TECH INC +1
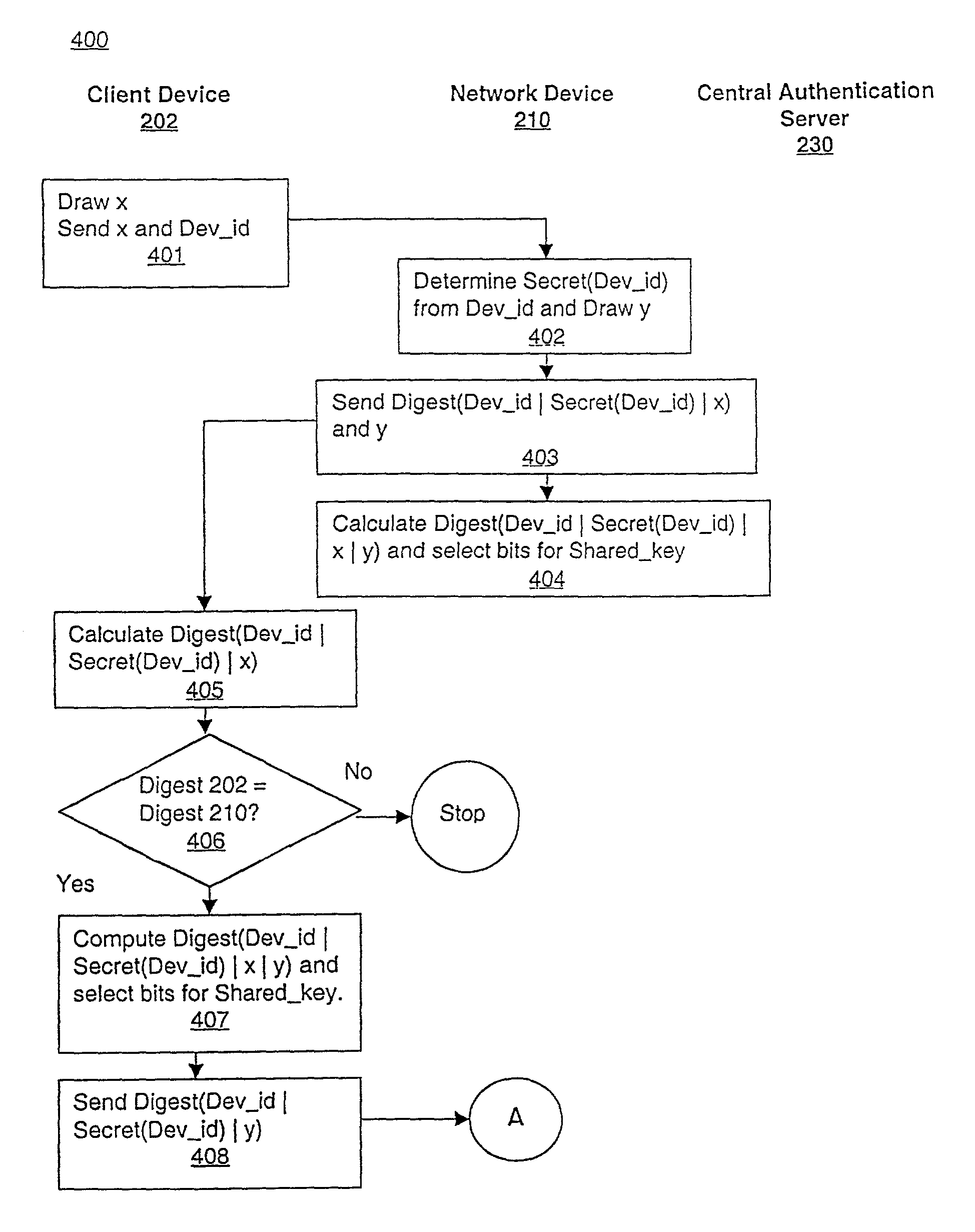
Scheme for device and user authentication with key distribution in a wireless network
ActiveUS7350076B1Reduction in marketLarge processing capabilityRandom number generatorsUser identity/authority verificationWeb authenticationSecret share
In a computer network, a method of mutually authenticating a client device and a network interface, authenticating a user to the network and exchanging encryption keys. In one embodiment, the method comprises authenticating the client device at the local network device point, with which the client device exchanges an encryption key and then the user is authenticated by a central authentication server. In another embodiment, the method comprises authenticating the client device at the central authentication server, with which the client device exchanges a key which is passed to the network device with a secret shared between the central authentication server and the network device. In this embodiment, the user is also authenticated at the central authentication server.
Owner:VALTRUS INNOVATIONS LTD +1
Method for Voting with Secret Shares in a Distributed System
ActiveUS20110022883A1Eliminate pointLess reliableKey distribution for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsFailoverSecret share
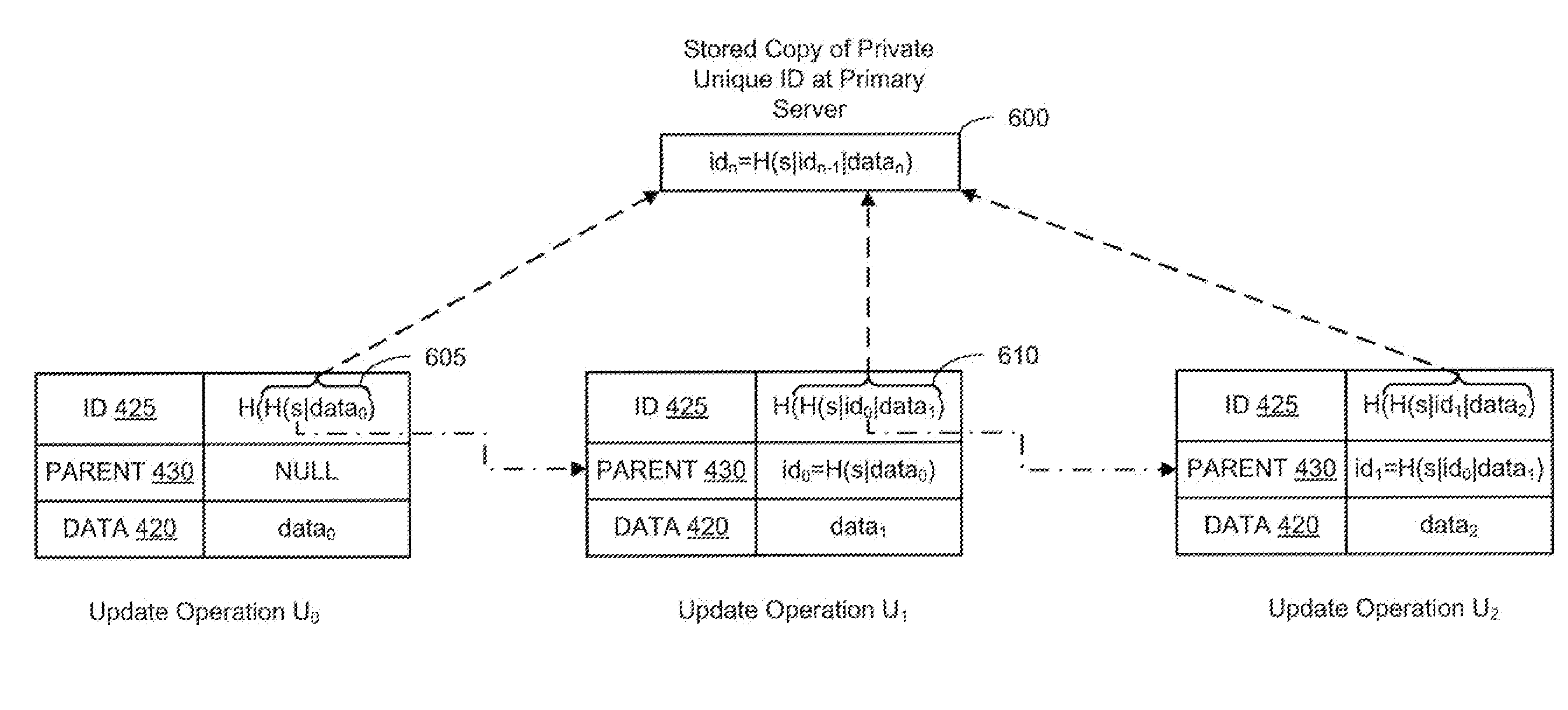
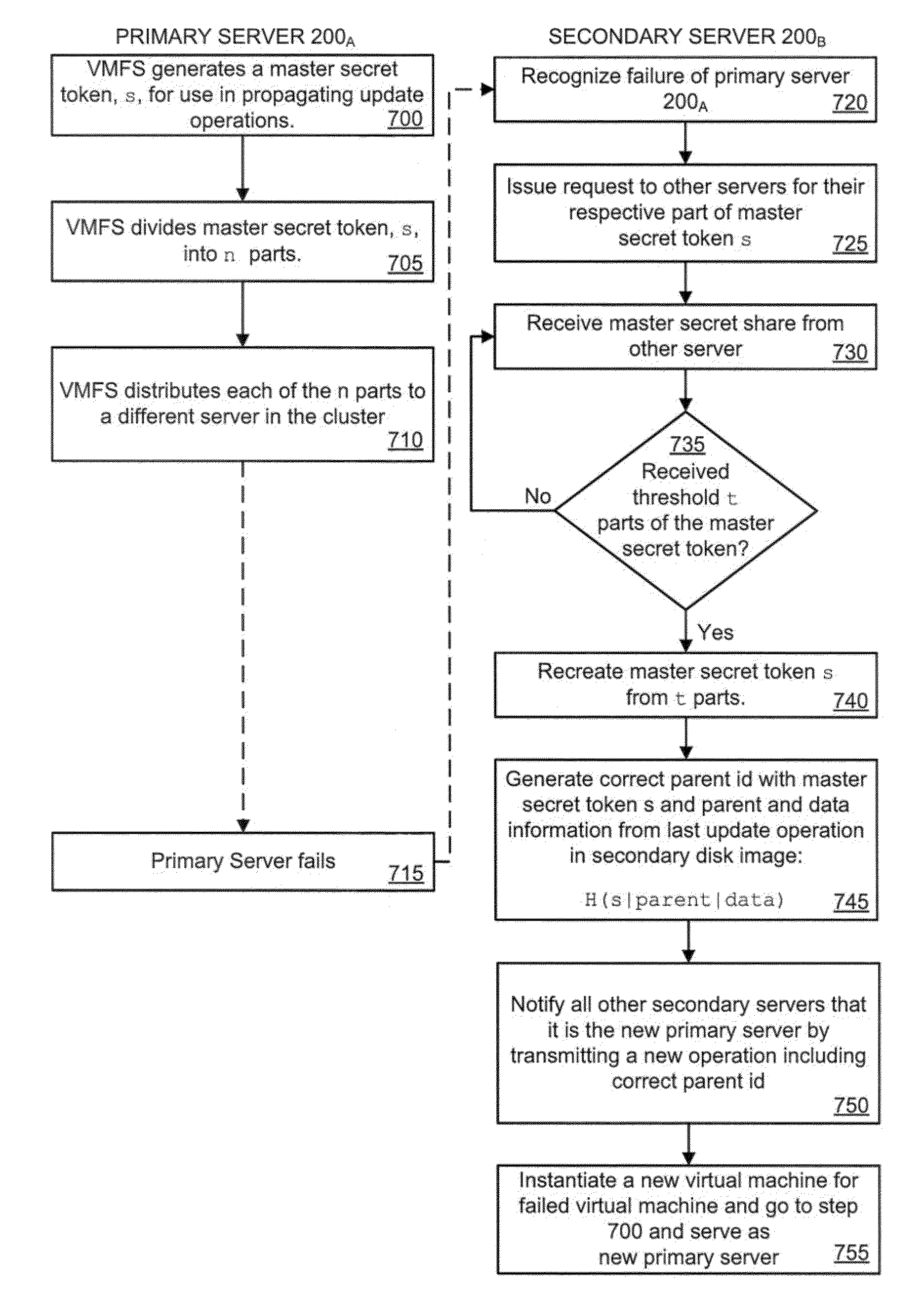
A replicated decentralized storage system comprises a plurality of servers that locally store disk images for locally running virtual machines as well as disk images, for failover purposes, for remotely running virtual machines. To ensure that disk images stored for failover purposes are properly replicated upon an update of the disk image on the server running the virtual machine, a hash of a unique value known only to the server running the virtual machine is used to verify the origin of update operations that have been transmitted by the server to the other servers storing replications of the disk image for failover purposes. If verified, the update operations are added to such failover disk images. To enable the replicated decentralized system to recover from a failure of the primary server, the master secret is subdivided into parts and distributed to other servers in the cluster. Upon a failure of the primary server, a secondary server receives a threshold number of the parts and is able to recreate the master secret and failover virtual machines that were running in the failed primary server.
Owner:VMWARE INC
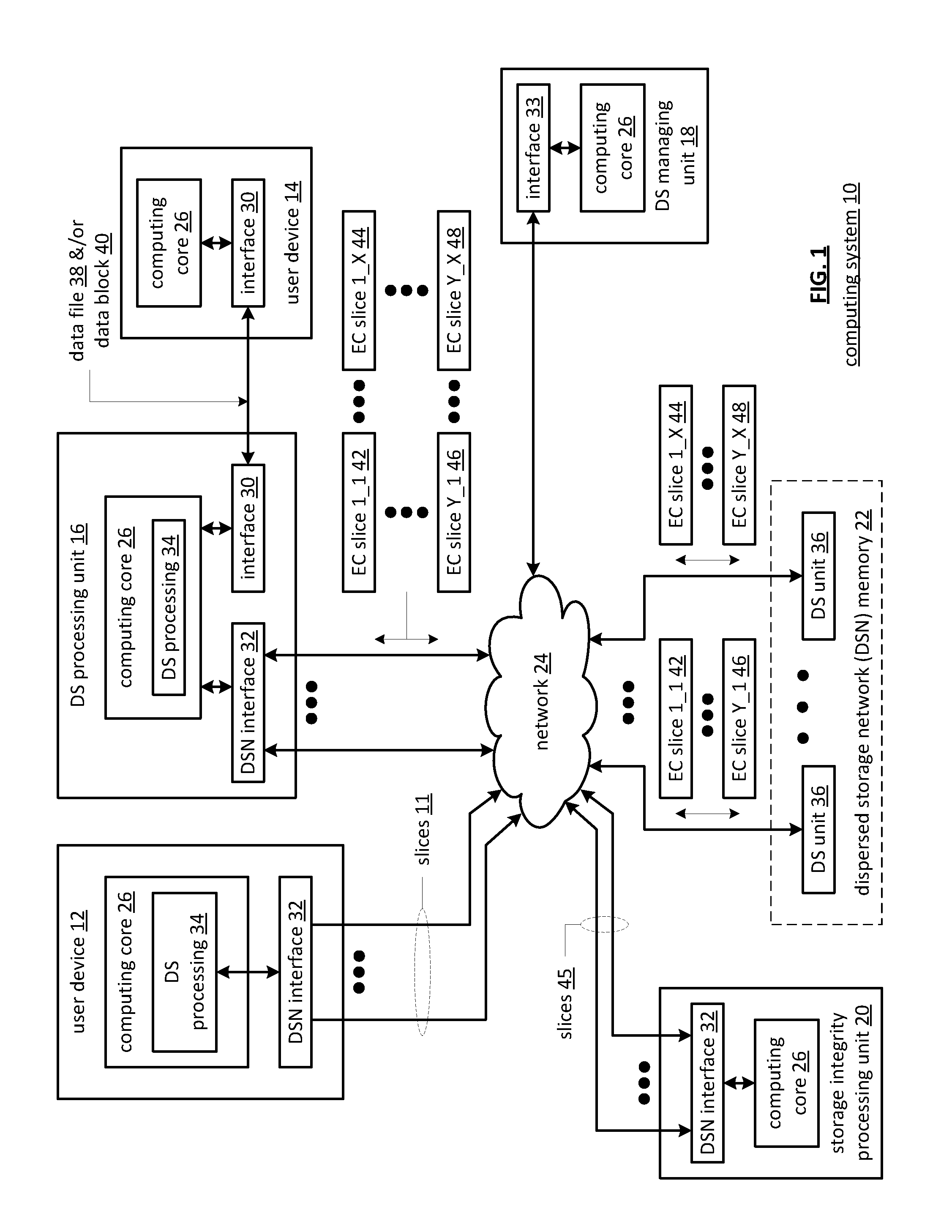
Dispersed storage network data slice integrity verification
InactiveUS20110126295A1Digital data information retrievalError detection/correctionData segmentSecret share
A method begins with a processing module issuing a retrieval request, receiving secret shares of a set of secret shares to produce received secret shares, and receiving encoded data slices of a set of encoded data slices. The method continues with the processing module decoding the received secret shares to recapture a message authentication key when a threshold number of the secret shares is received. The method continues with the processing module identifying a received encoded data slice of the received encoded data slices having an authentication code associated therewith when a threshold number of the encoded data slices is received. The method continues with the processing module verifying the authentication code based on the message authentication key and the received encoded data slice. The method continues with the processing module decoding the received encoded data slices to recapture a data segment when the authentication code is verified.
Owner:PURE STORAGE
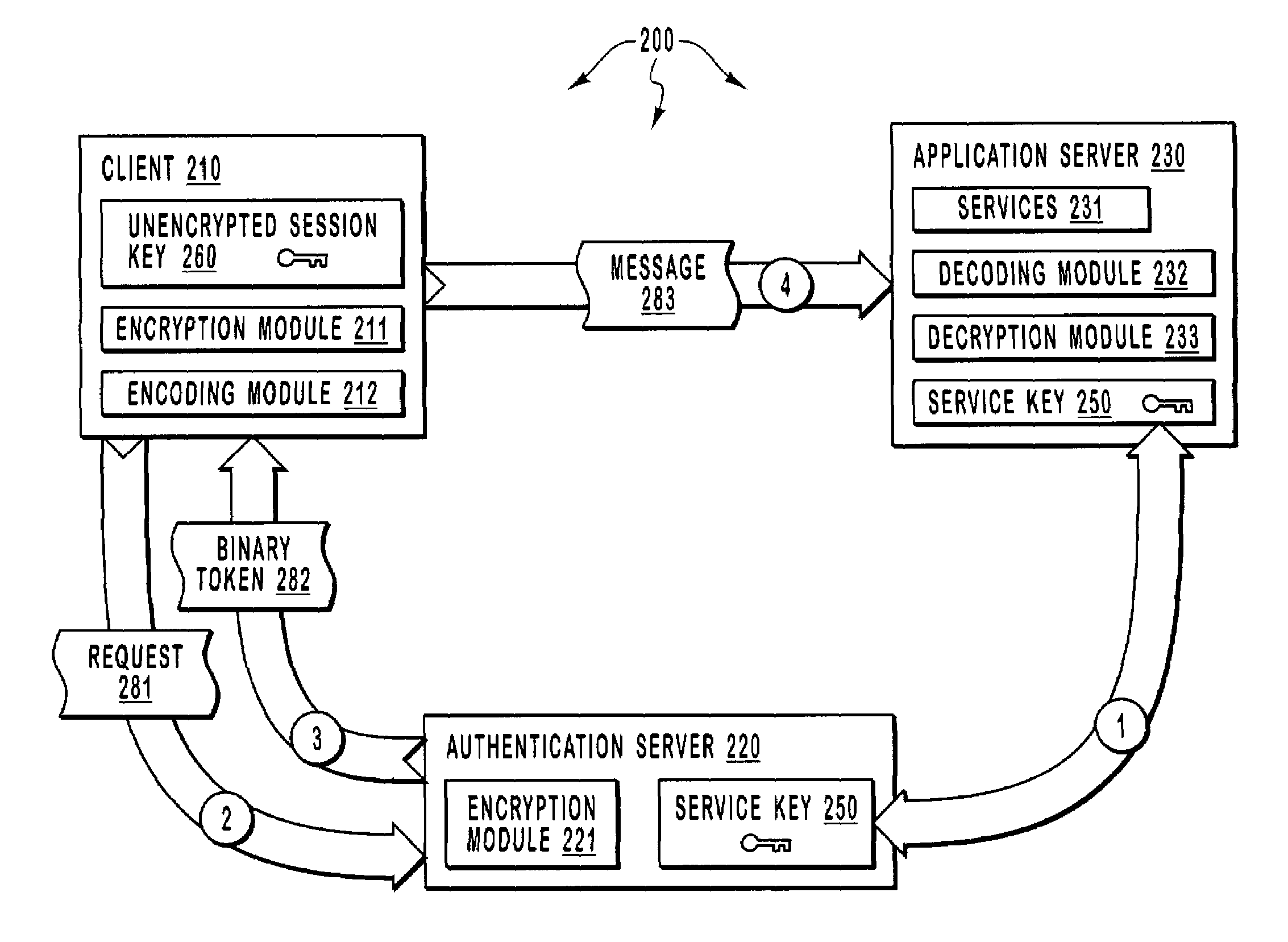
Using atomic messaging to increase the security of transferring data across a network
ActiveUS7305548B2Save resourcesImprove securityPublic key for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationSecret shareNetworked Transport of RTCM via Internet Protocol
A client sends a request to an authentication server requesting access to a service at an application server. The authentication server returns a token containing an encrypted version of a session key that was encrypted using a secret shared between the authentication server and the application server. The client encrypts application data using a corresponding unencrypted version of the session key and text-encodes both the encrypted application data and the encrypted version of the session key. The text-encoded application and text-encoded encrypted version of the session key are both included in a message and sent to the application server. The application server decrypts the encrypted version of the session key using the shared secret so as to reveal the unencrypted version of the session key. The application server then decrypts the encrypted application data using the revealed unencrypted version of the session key.
Owner:ZHIGU HLDG
Method and structure for challenge-response signatures and high-performance secure diffie-hellman protocols
InactiveUS20060179319A1Improve securityUser identity/authority verificationPayment architectureSecret shareChallenge response
Owner:IBM CORP
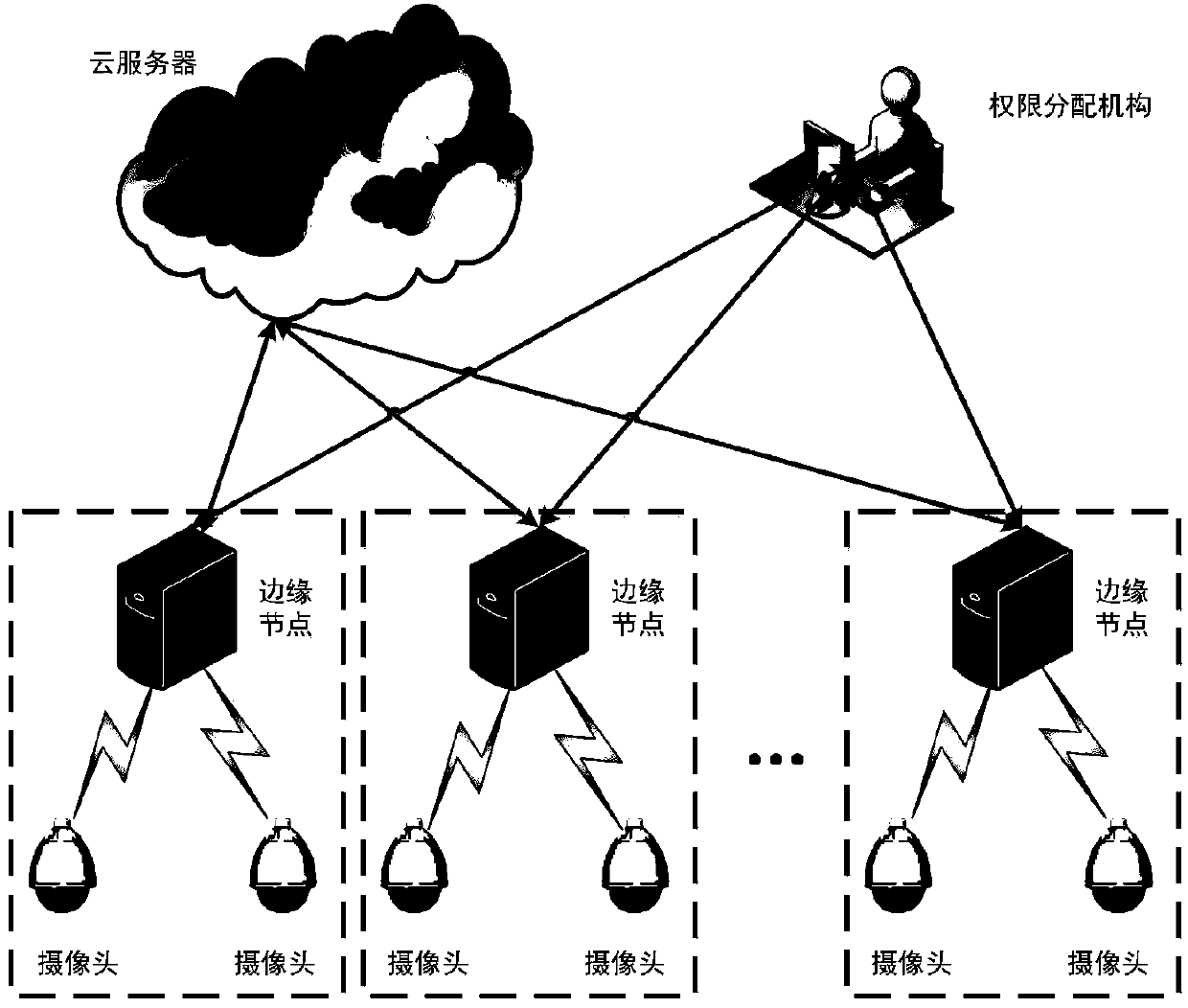
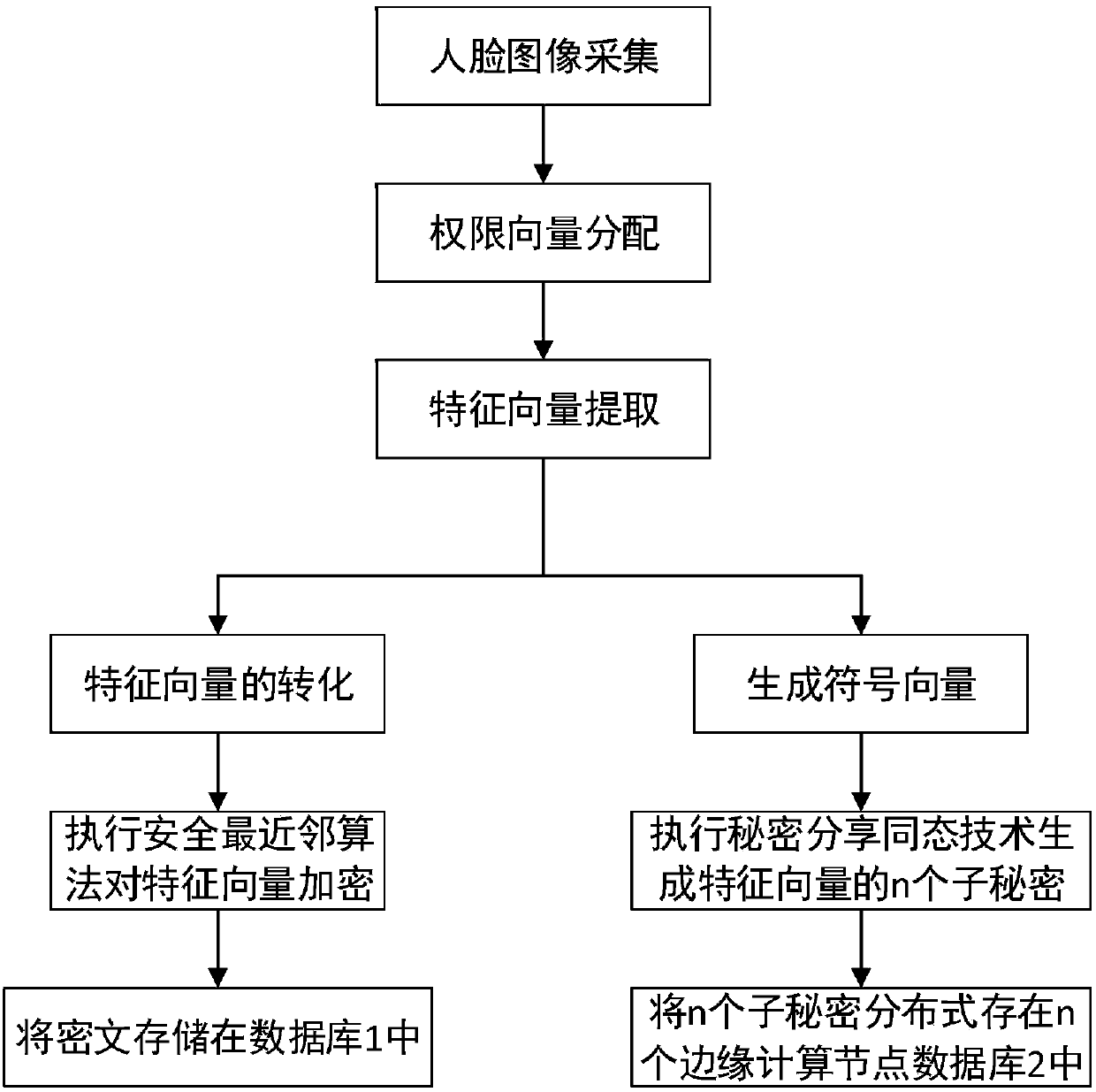
Privacy protection method in face authentication system based on edge calculation
ActiveCN108446680APrivacy protectionProtect face recognition functionCharacter and pattern recognitionTransmissionPlaintextFault tolerance
The invention belongs to the technical field of privacy protection in cloud computing and discloses a privacy protection method in face authentication system based on edge calculation. The method comprises the steps that: a camera collects a face image and uploads the face image to a connected edge computing node, an authority assigning mechanism sends a permission vector Li of a user to the edgecomputing node after collecting user face information, an edge computing device carries out feature extraction on a face image of a user requesting registration to obtain a feature vector by using a method based on a deep convolutional neural network, a safe nearest neighbor algorithm is performed to encrypt the feature vector of a registered user, and a secret sharing homomorphic algorithm is performed and n sub-secrets are generated according to the feature vector and are distributively stored in n edge computing devices. The direct upload of sensitive data to a cloud server is avoided, theprivacy of the face data is protected, and the fault tolerance of a system is improved. Results prove that the accuracy of face recognition under a ciphertext of the present invention is completely equal to the accuracy of face recognition under a plaintext.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Resilient secret sharing cloud based architecture for data vault
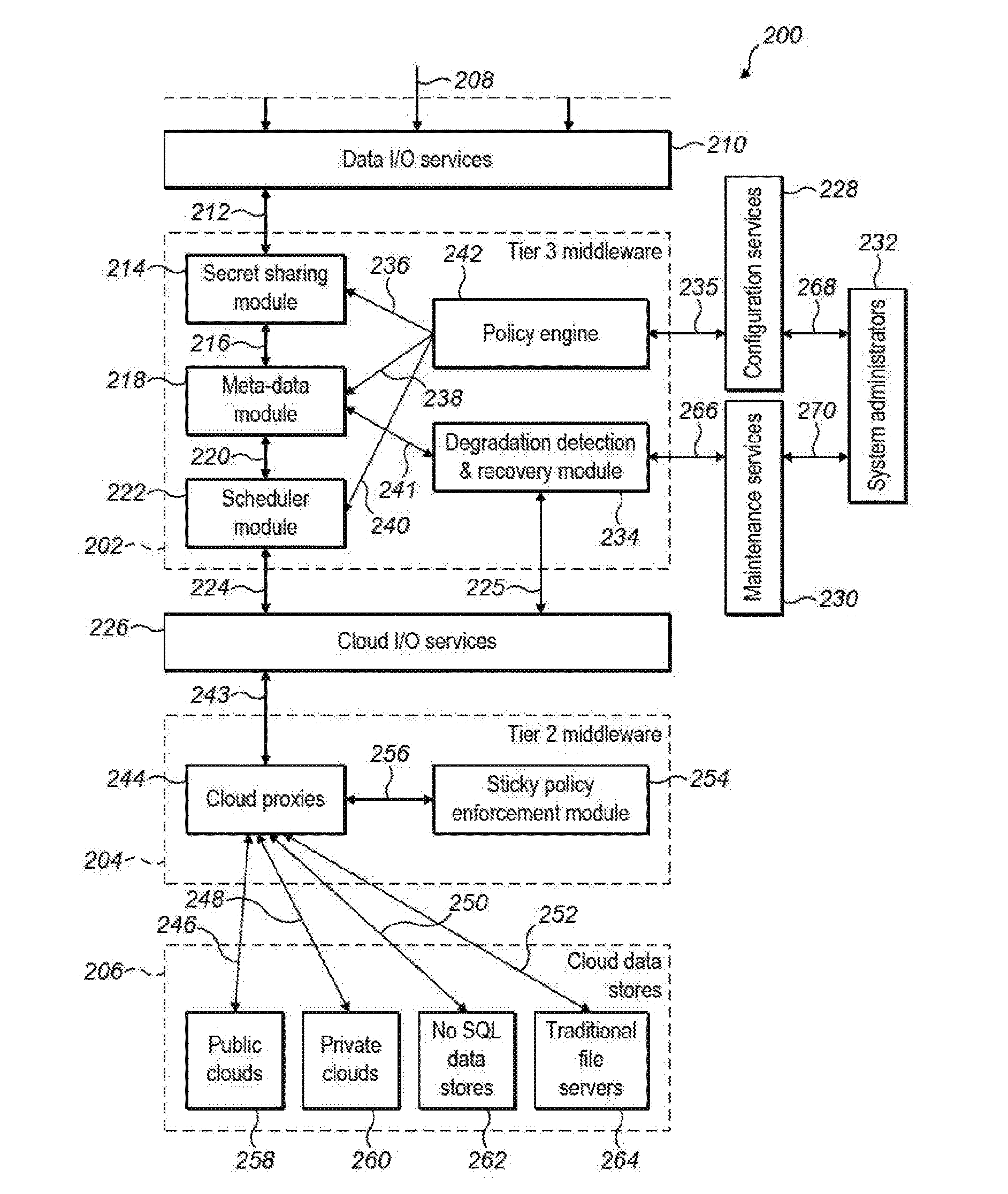
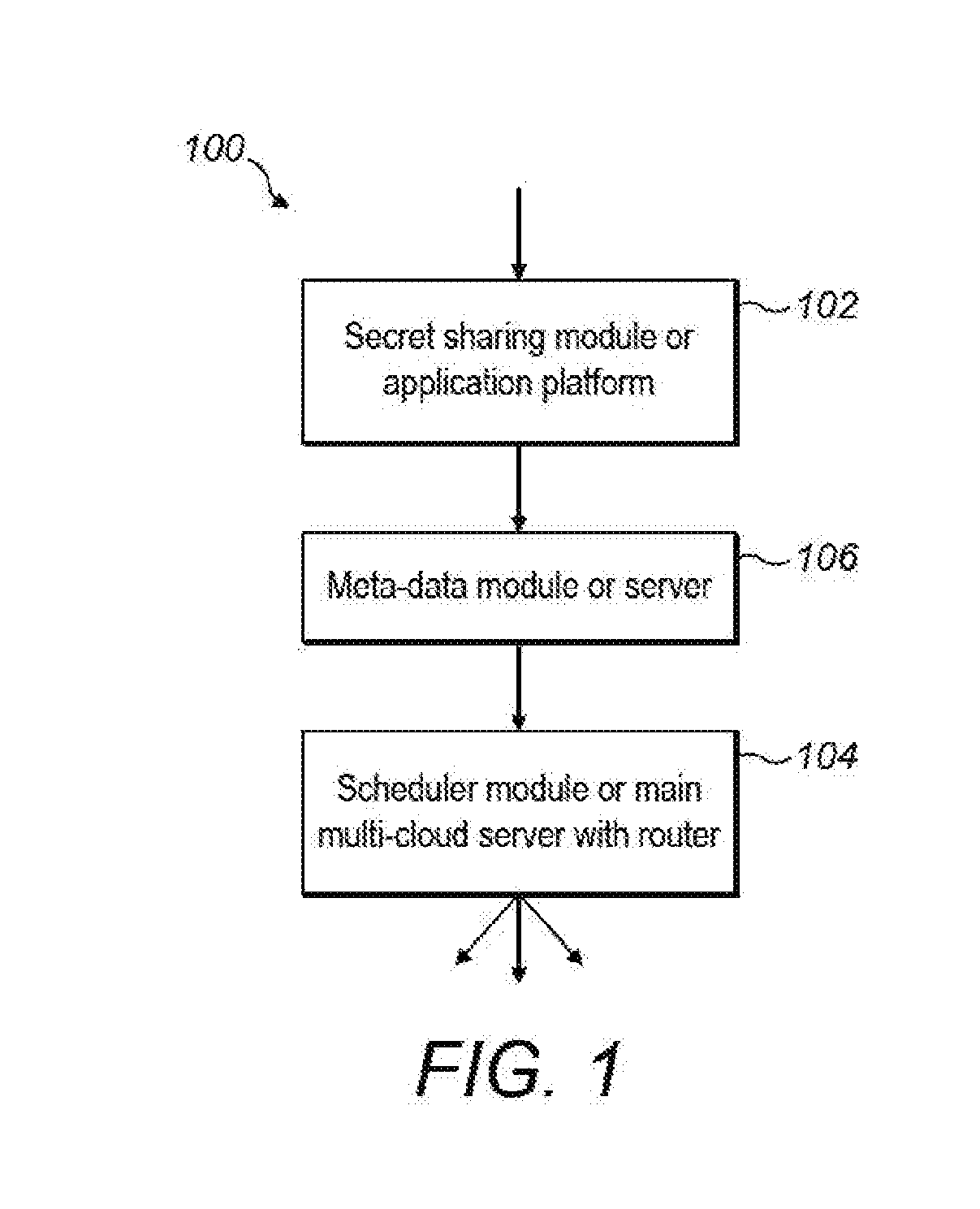
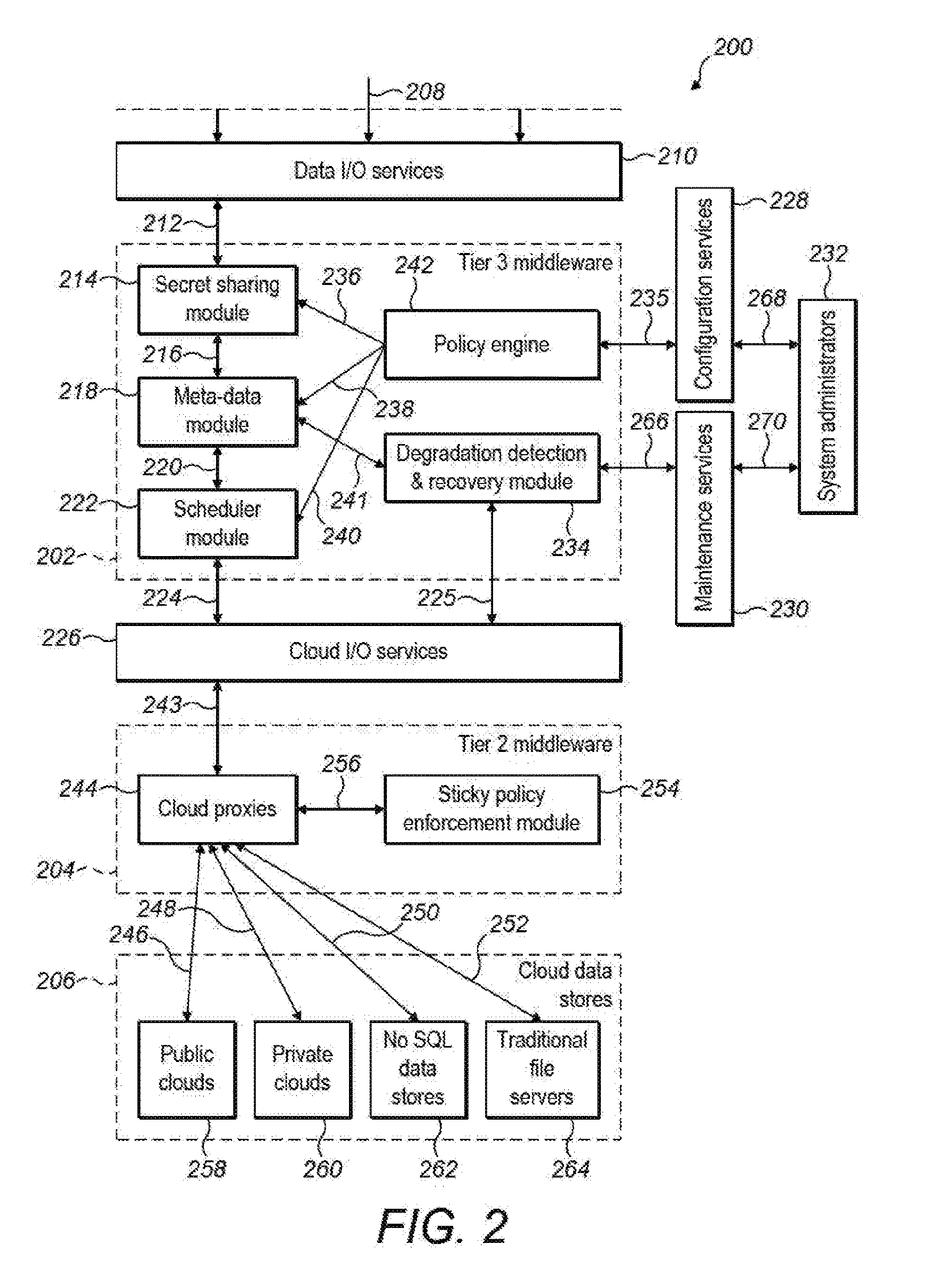
InactiveUS20170005797A1Increase choiceKey distribution for secure communicationMultiple keys/algorithms usageSecret shareComputer network
A method of securely storing data including: providing, within a secure data storage system, a plurality of secret sharing methods for selection and identifying a striping policy for storage of the data, in accordance with input preferences. The data can be split into N secret shares according to a secret sharing method, the selection being determined by the striping policy, wherein a threshold number, T, of such shares is sufficient to recover the data, where T is less than N, generating metadata associated with the data, the metadata identifying the selected secret sharing method and storing the metadata within the secure data storage system and writing the secret shares to storage that includes storage outside the secure data storage system, such that, when at least T shares are retrieved, the metadata can be recalled to identify the selected secret sharing method for recovery of the data.
Owner:LEADING SOFTWARE LTD
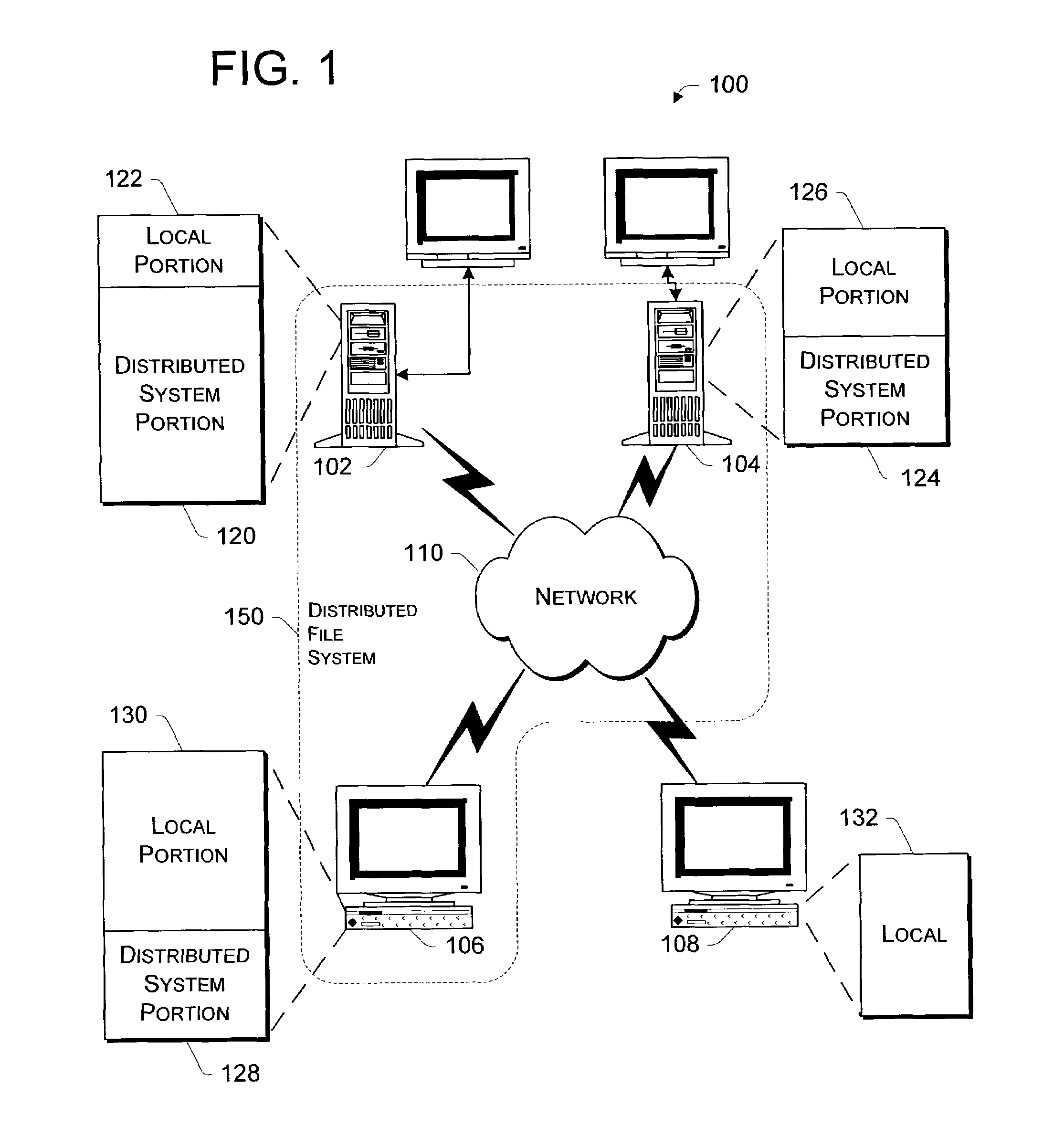
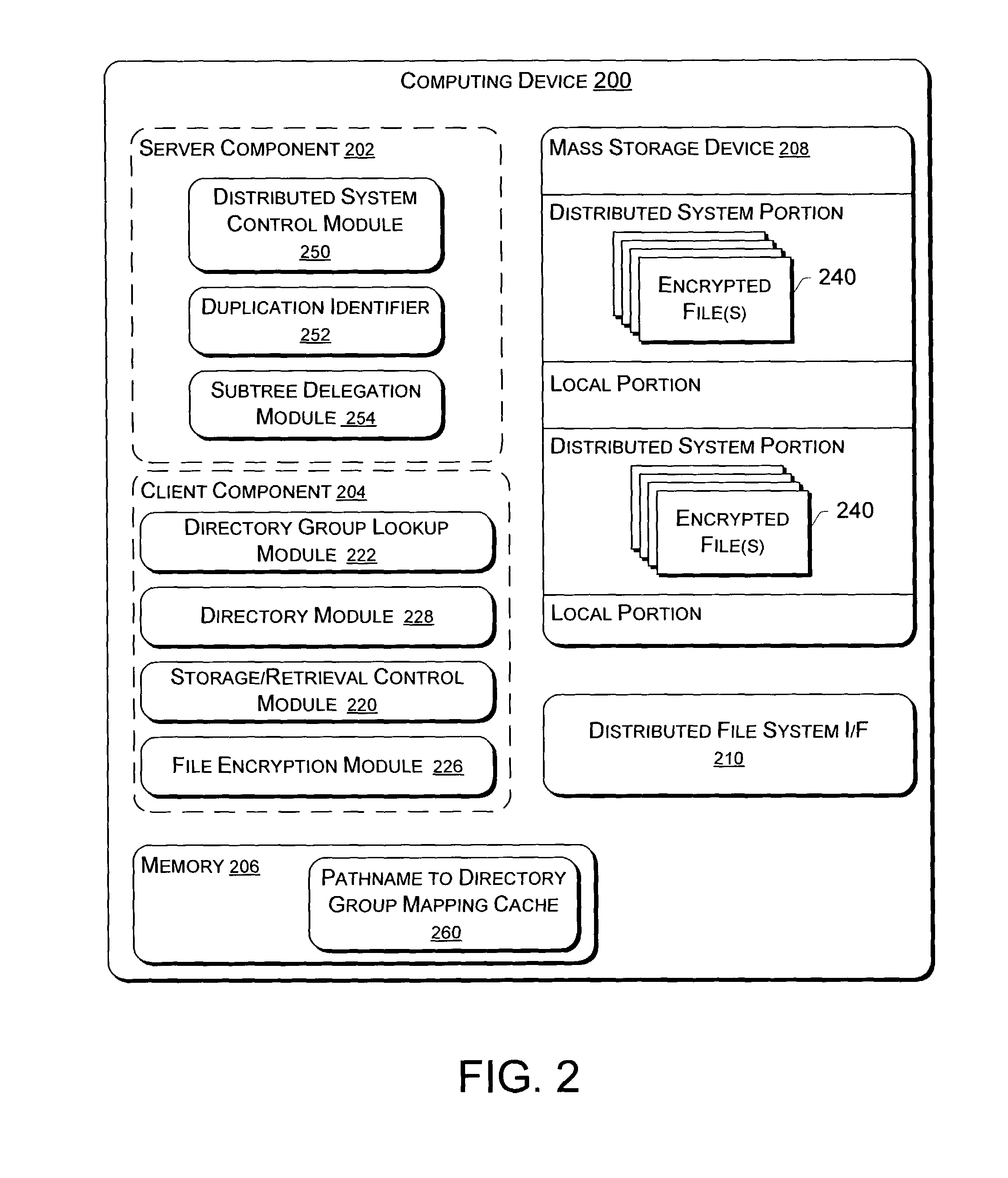
Secure recovery in a serverless distributed file system
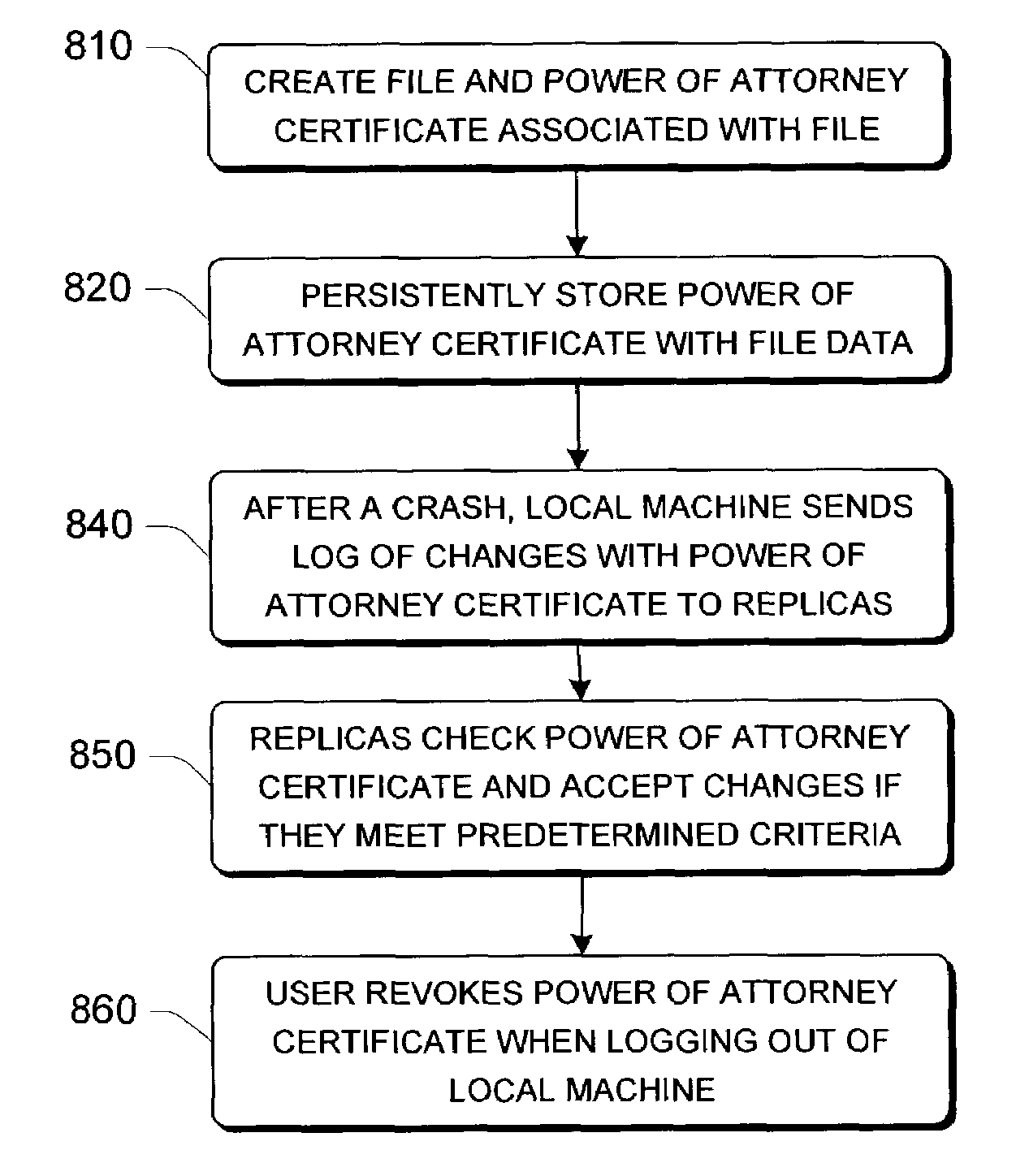
InactiveUS7428751B2Avoid selectionDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationSecret shareDistributed File System
Systems and methods for secure file writes after a catastrophic event are allowed over an unauthenticated channel in a serverless distributed file system if an authenticator accompanies the secure file writes. The authenticator can be a power-of-attorney certificate with time limitations, a vector of message authenticated code, or a single message authenticator with secured with a secret shared among members of the serverless distributed file system. The serverless distributed file system includes at least 3f+1 participating computer members, with f representing a number of faults tolerable by the system. The group requires at least one authenticator for file creation and file uploads. Any changes to files stored among the members can be made over an unauthenticated channel if the file changes are secured by the authenticator and the group is able to verify the authenticator.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Connection authorization with a privileged access
InactiveUS20130067542A1Secure transmissionConnection securityDigital data processing detailsMultiple digital computer combinationsClient-sideSecret share
Owner:AETHERPAL
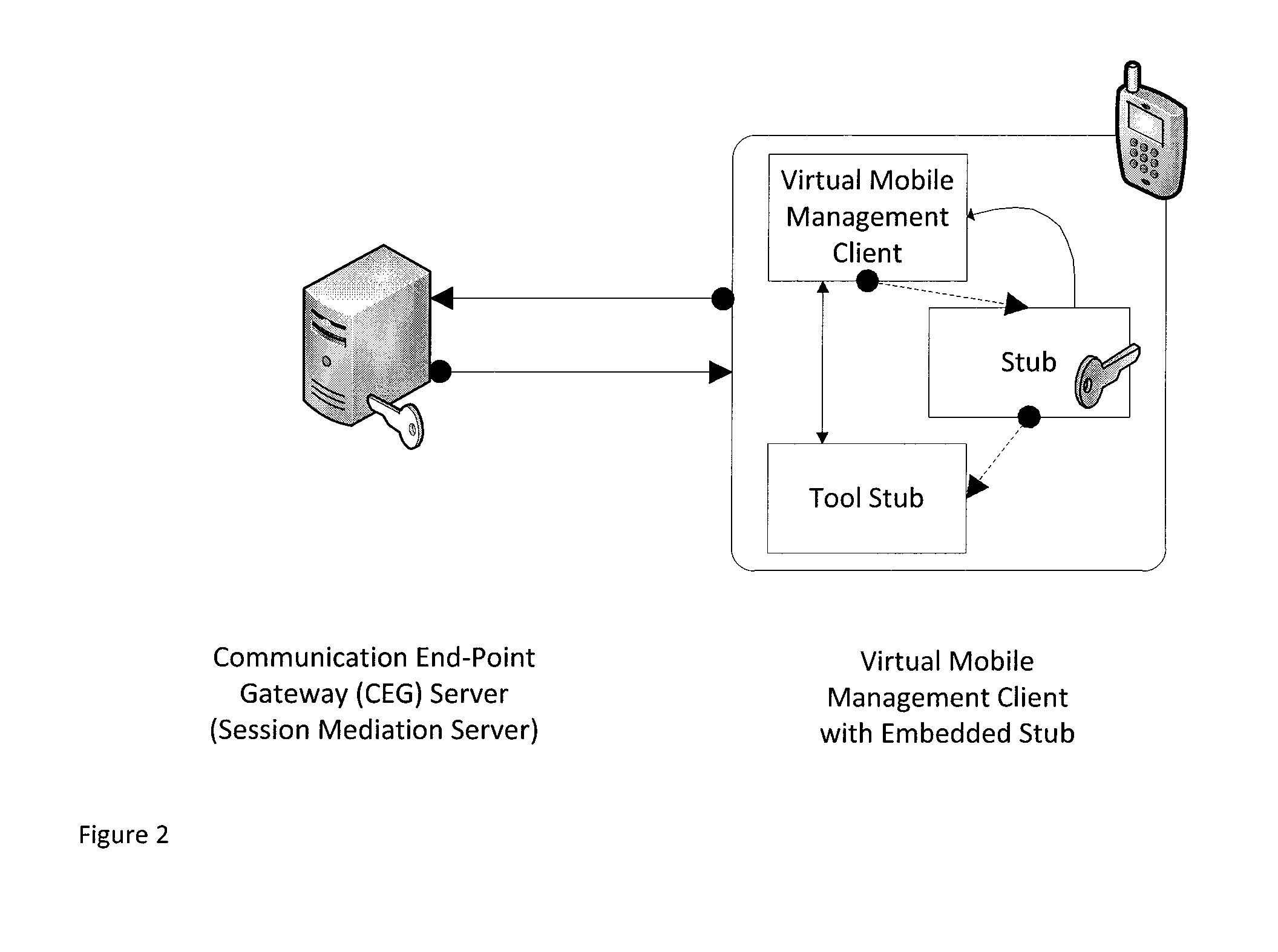
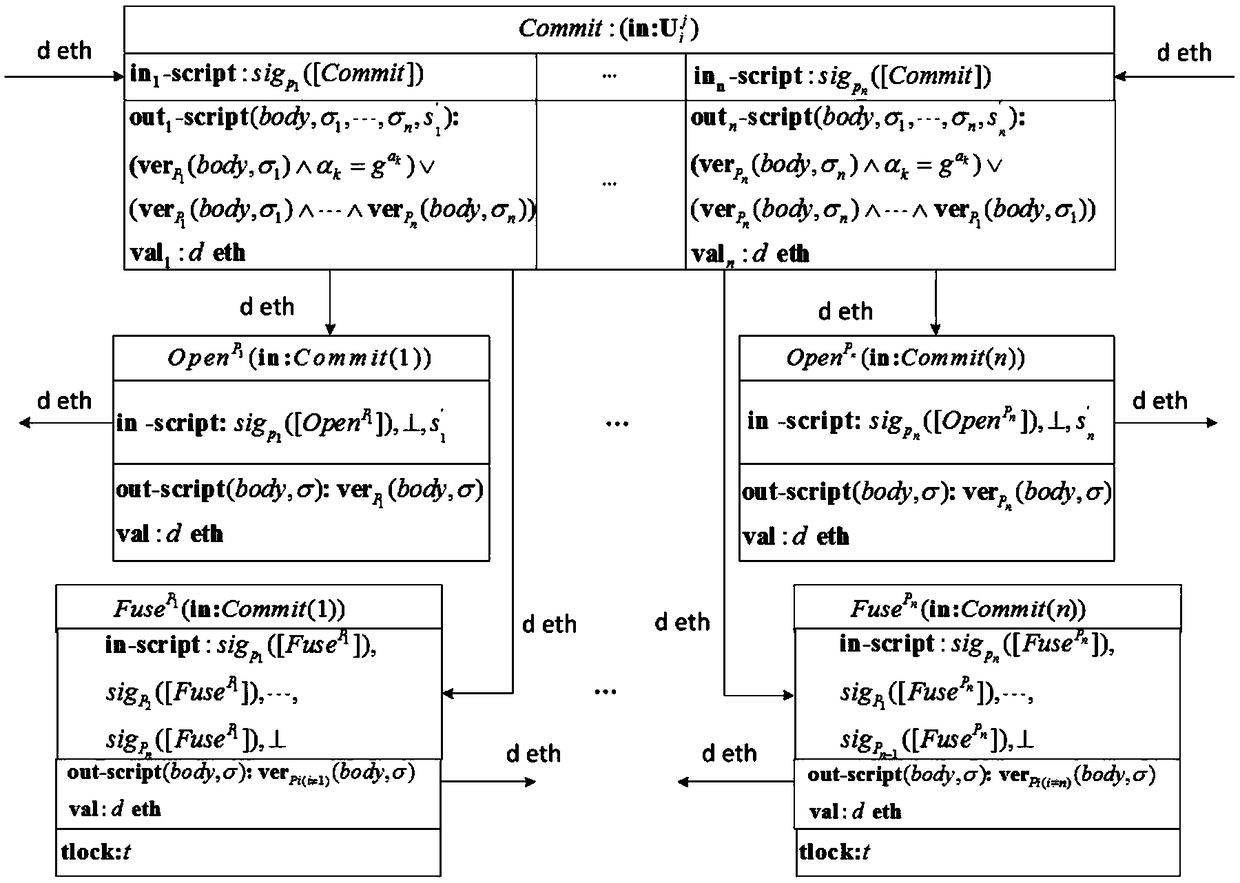
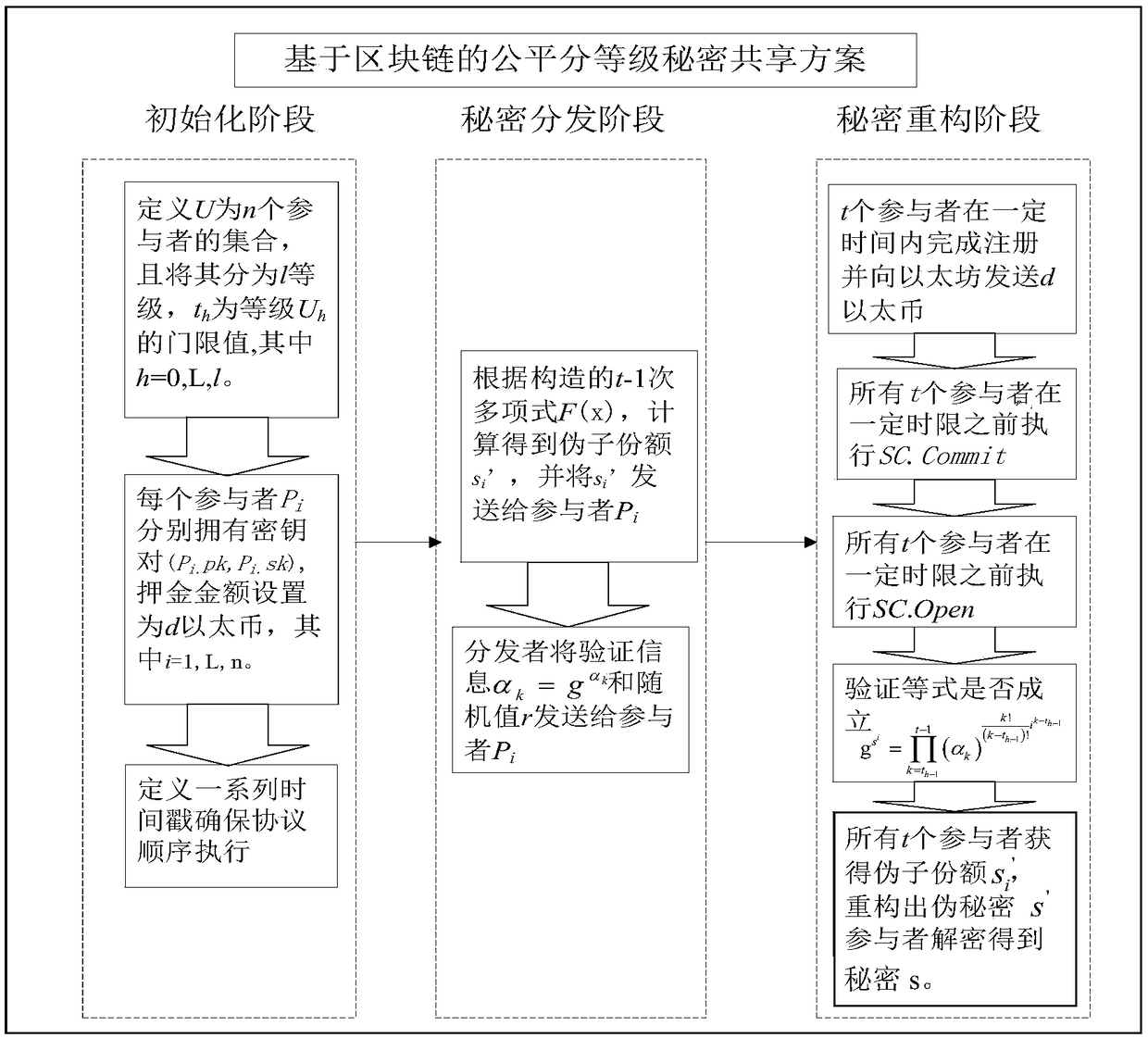
Secret sharing method and apparatus based on block chain system
ActiveCN109120398AKey distribution for secure communicationProtocol authorisationSecret shareUser privacy
The invention relates to a secret sharing method and apparatus based on a block chain system. The secret sharing method and apparatus based on a block chain system includes the steps: constructing a polynomial by using known secret shares, constructing pseudo sub-shares and verification information by using the polynomial, generating random values according to the secret shares and the pseudo sub-shares, and distributing the pseudo sub-shares, the verification information and the random values to secret participants; waiting for the secret participants to make a commitment protocol on the secret shares in the block chain system, and after all the secret participants complete the commitment protocol, waiting for the secret participants to disclose their respective pseudo sub shares in the block chain system; after the secret participants disclose the pseudo sub-shares, substituting the pseudo sub-shares and the verification information into a set verification equation, and when the verification equation is established, determining that the disclosed pseudo sub-shares to be correct; and after all the pseudo sub-shares are correct, obtaining the shared secret by means of the disclosedpseudo sub-shares and the random values. Therefore, the secret sharing method and apparatus based on a block chain system can avoid the user privacy leakage problem, can guarantee the fairness of secret sharing, and can enhance the security of secret sharing.
Owner:HENAN NORMAL UNIV
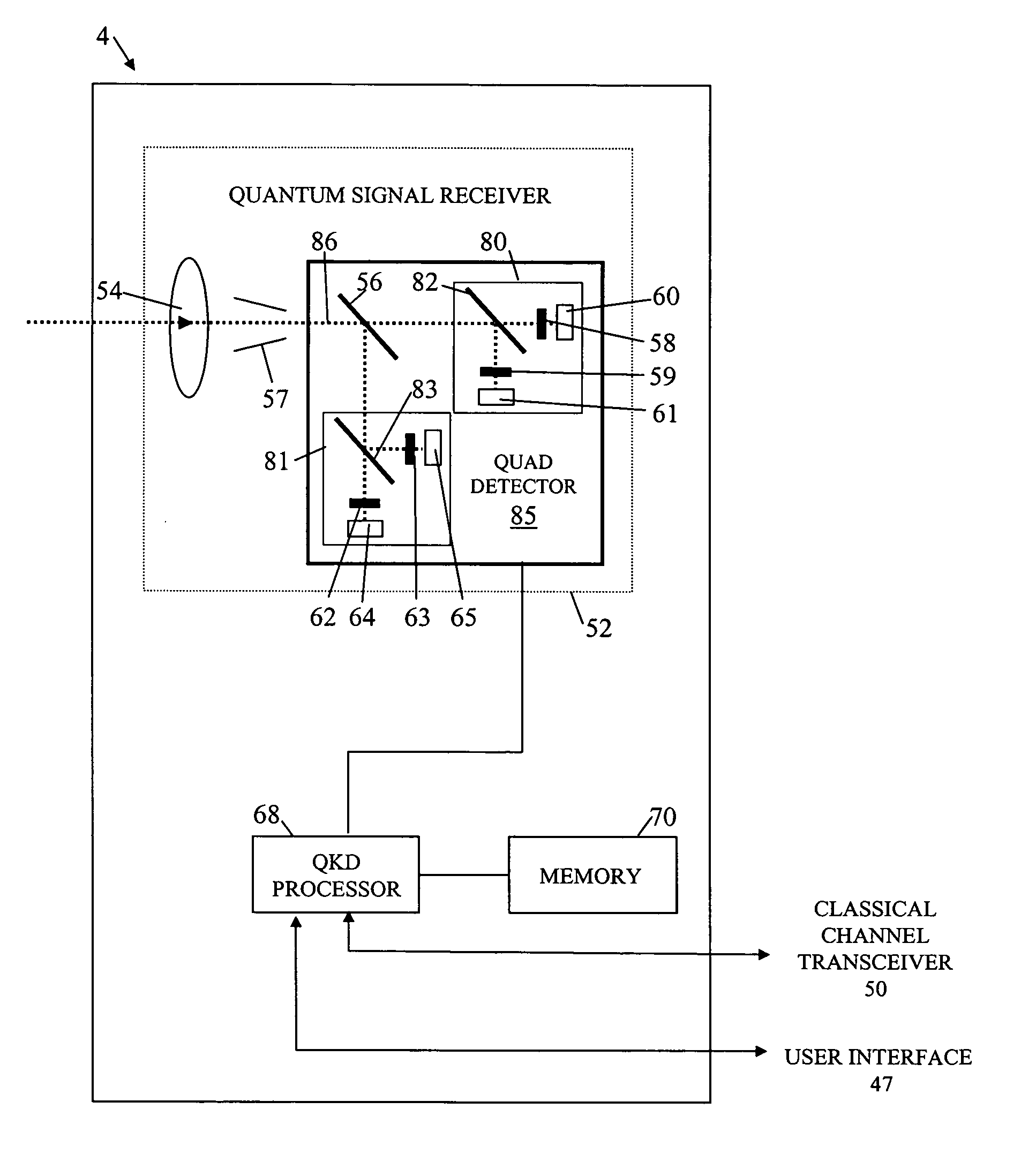
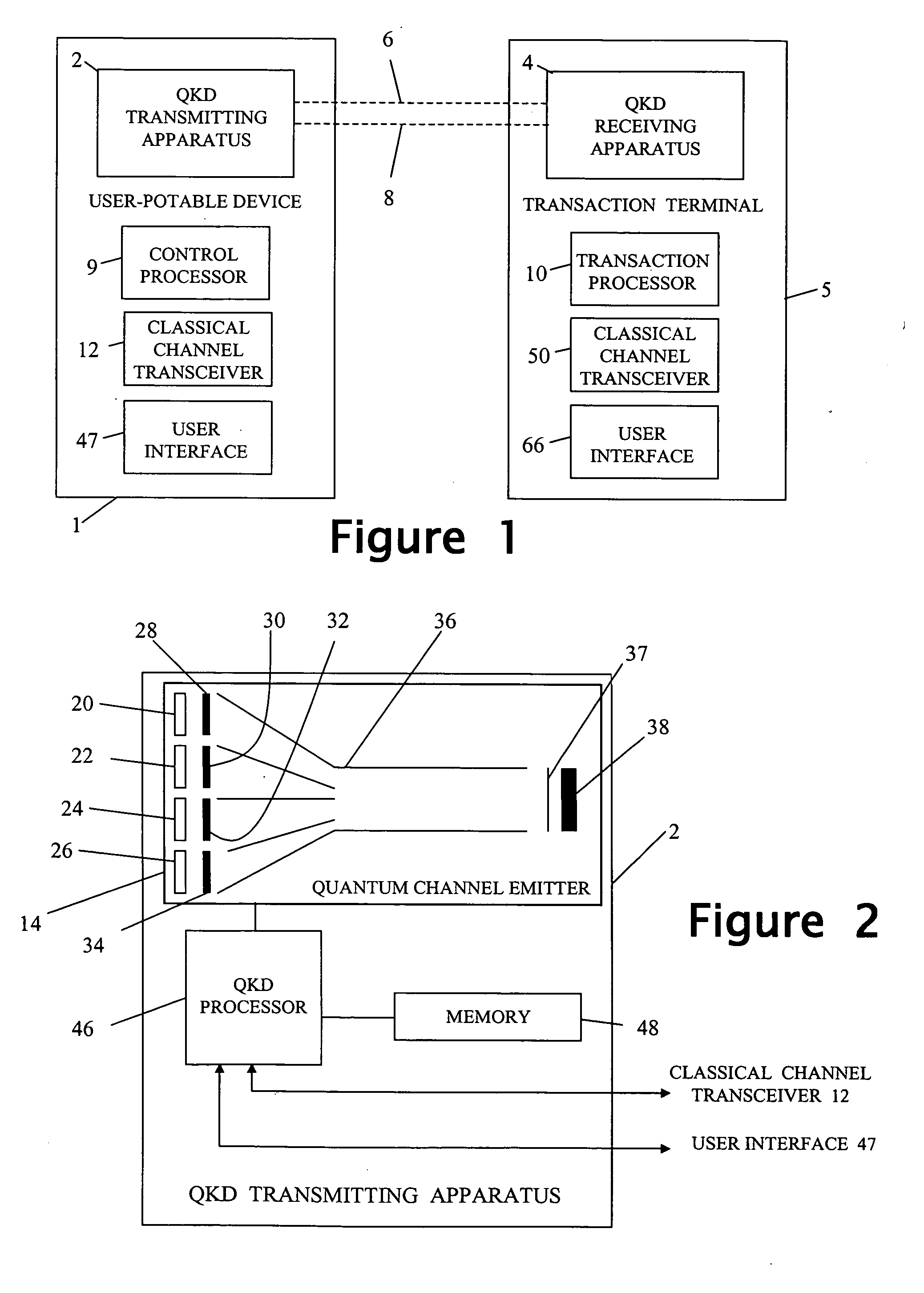
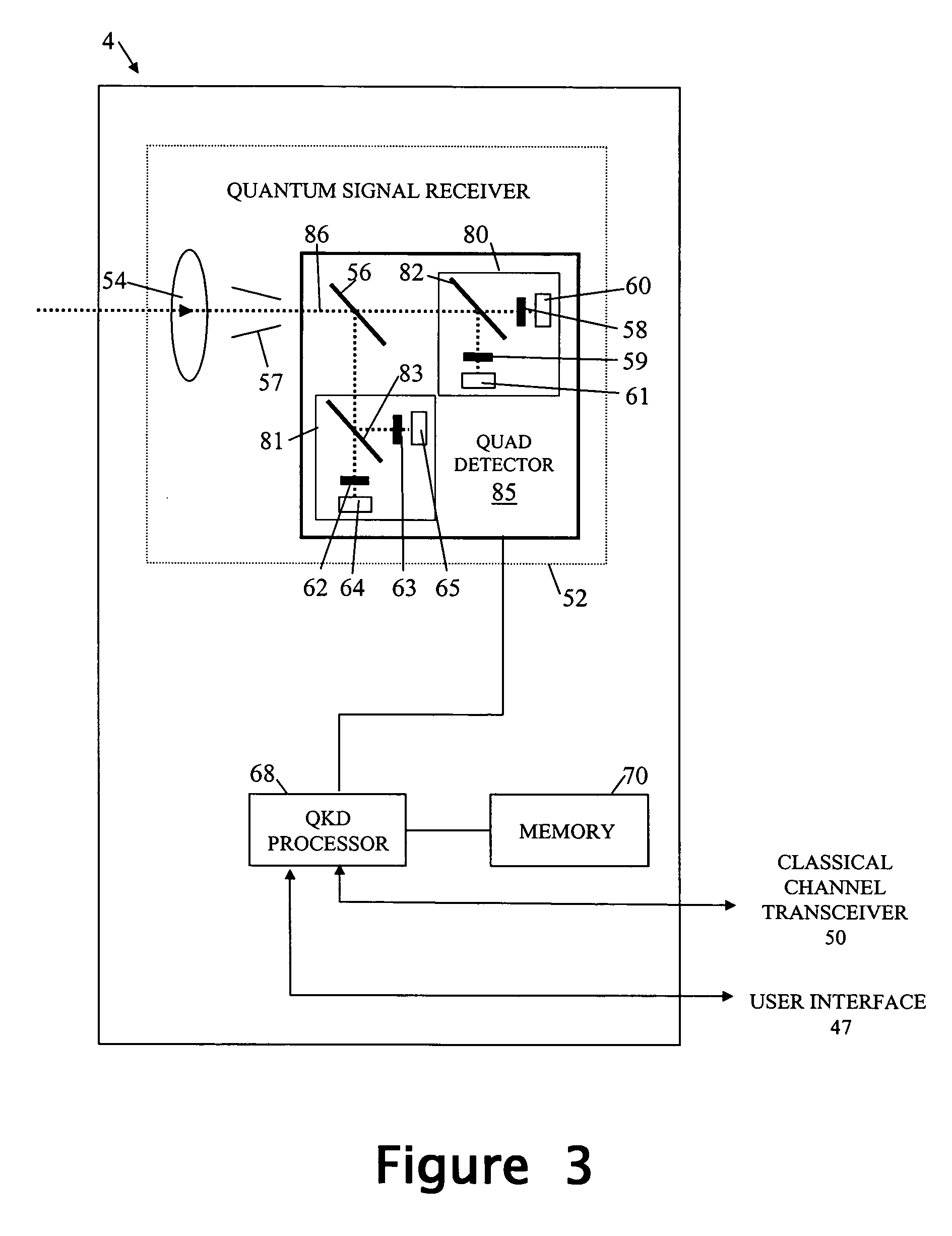
Secure transaction method and transaction terminal for use in implementing such method
InactiveUS20070016534A1Digital data processing detailsLine-of-sight transmissionComputer hardwareRandom materials
A secure transaction method is provided for publicly-accessible transaction terminals. The method uses quantum key distribution (QKD) between a hand-portable QKD device and a complimentary QKD apparatus incorporated the transaction terminal. After the QKD device has been brought up to the transaction terminal, the QKD device and the complimentary QKD apparatus of the terminal are is used to provide the device and terminal with new secret shared random material. The new secret shared random material is then used to establish a secure classical communication channel between the device and transaction terminal for conducting a transaction. An ATM terminal and POS terminal that use quantum key distribution are also disclosed.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
High-Precision Privacy-Preserving Real-Valued Function Evaluation
InactiveUS20200304293A1Reduced memory storage requirementImprove accuracyKey distribution for secure communicationNeural architecturesPlaintextSecret share
A method for performing privacy-preserving or secure multi-party computations enables multiple parties to collaborate to produce a shared result while preserving the privacy of input data contributed by individual parties. The method can produce a result with a specified high degree of precision or accuracy in relation to an exactly accurate plaintext (non-privacy-preserving) computation of the result, without unduly burdensome amounts of inter-party communication. The multi-party computations can include a Fourier series approximation of a continuous function or an approximation of a continuous function using trigonometric polynomials, for example, in training a machine learning classifier using secret shared input data. The multi-party computations can include a secret share reduction that transforms an instance of computed secret shared data stored in floating-point representation into an equivalent, equivalently precise, and equivalently secure instance of computed secret shared data having a reduced memory storage requirement.
Owner:INPHER INC
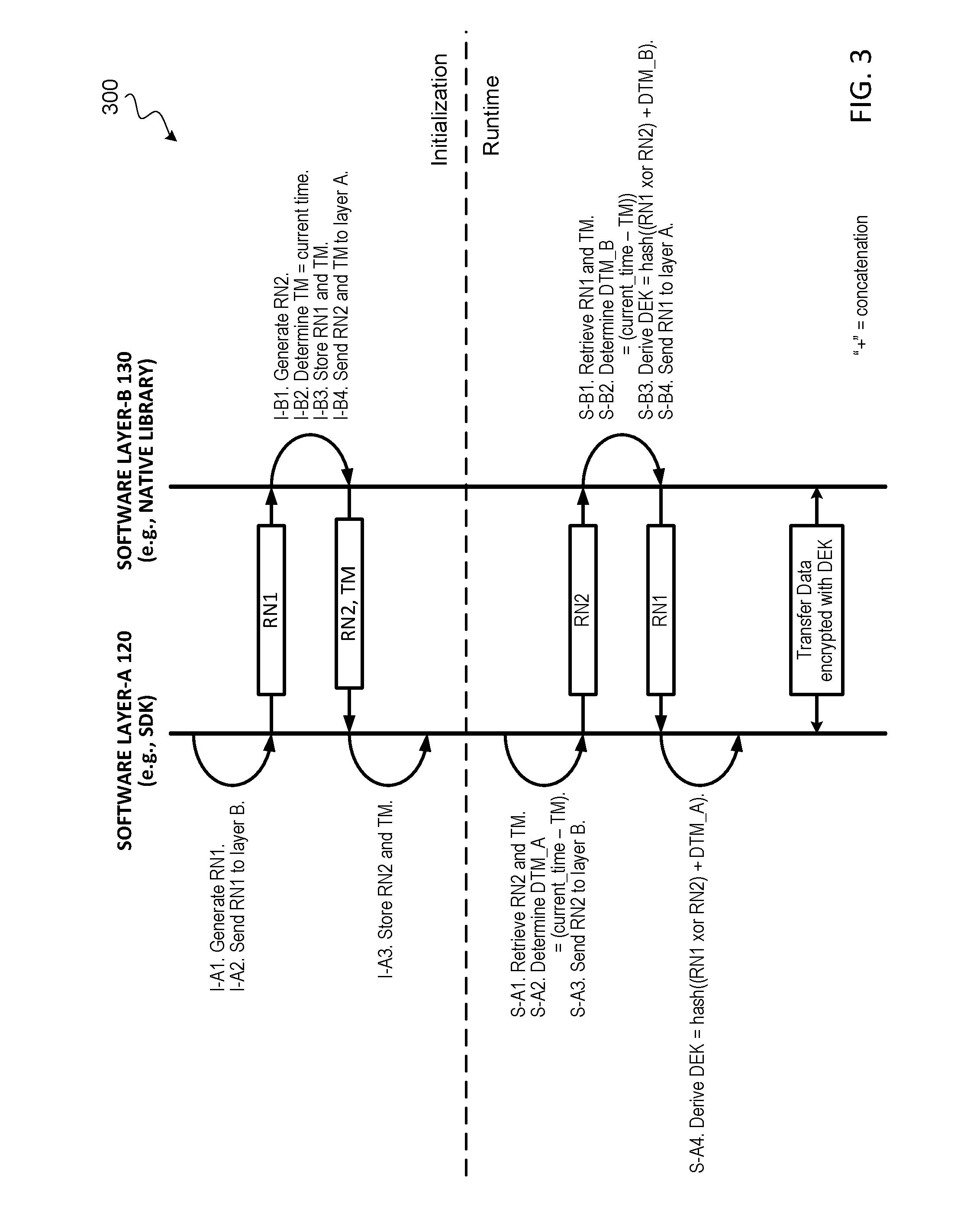
Mutual authentication of software layers
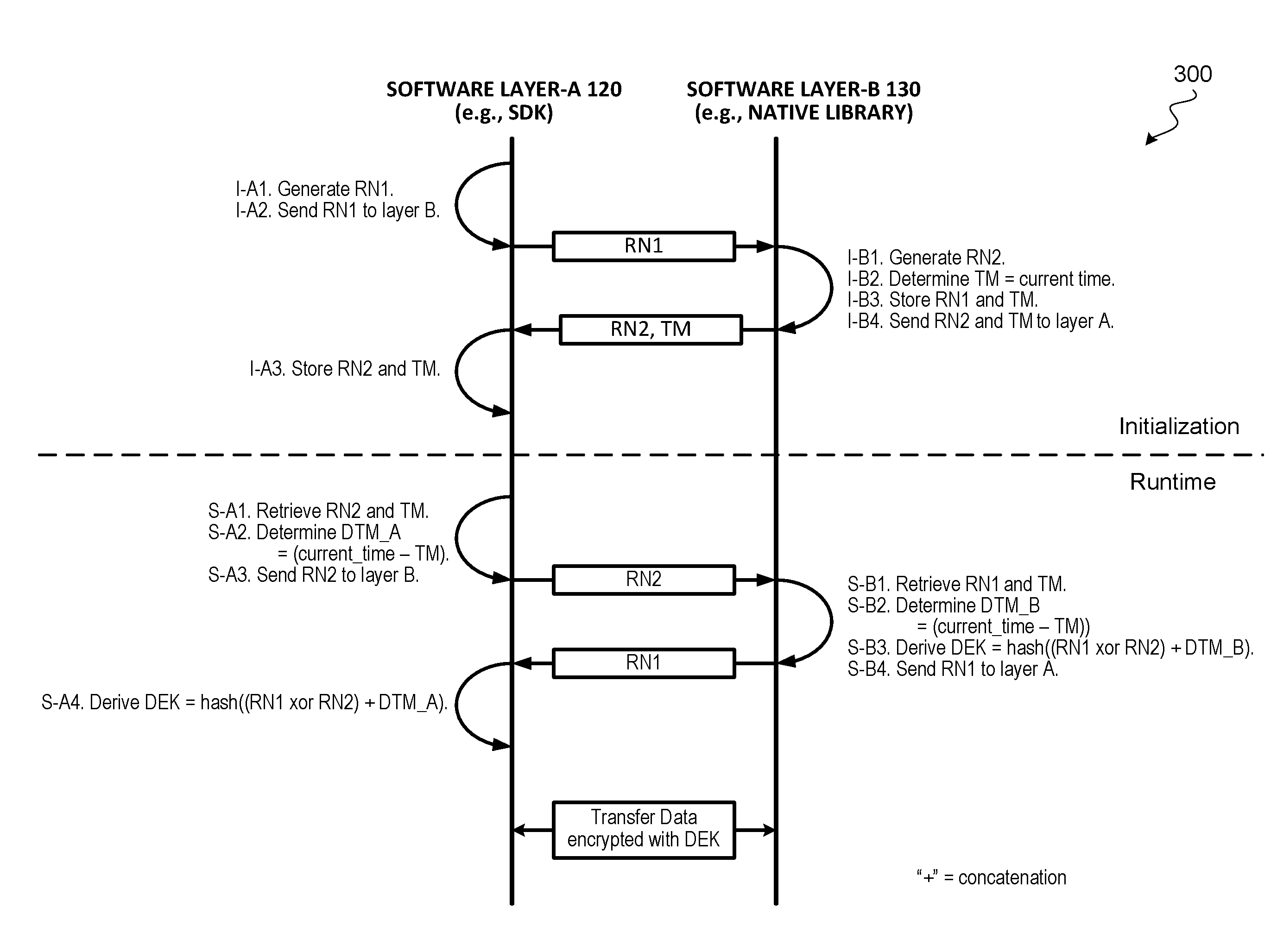
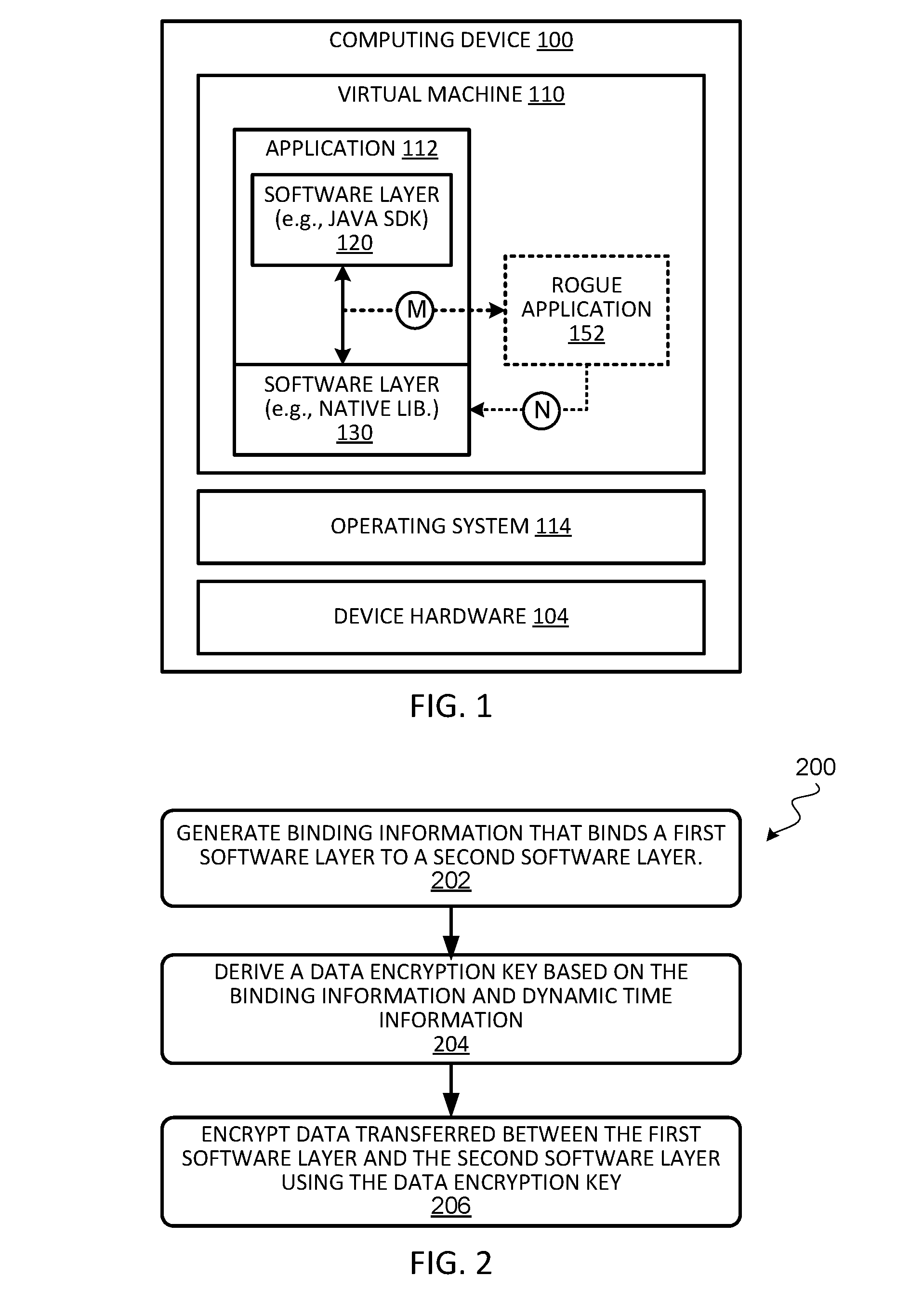
ActiveUS20160267280A1Digital data protectionDigital data authenticationComputer hardwareTime information
Techniques for establishing mutual authentication of software layers of an application are described. During initialization of the application, the software layers execute a binding algorithm to exchange secrets to bind the software layers to one another. During subsequent runtime of the software application, the software layers execute a runtime key derivation algorithm to combine the secrets shared during initialization with dynamic time information to generate a data encryption key. The software layers can then securely transfer data with each other by encrypting and decrypting data exchanged between the software layers using the dynamically generated data encryption key.
Owner:VISA INT SERVICE ASSOC
Method for secure user and transaction authentication and risk management
ActiveUS8789153B2Compromising usabilityCompromising costDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationSecret shareOne-time password
Owner:PAYFONE
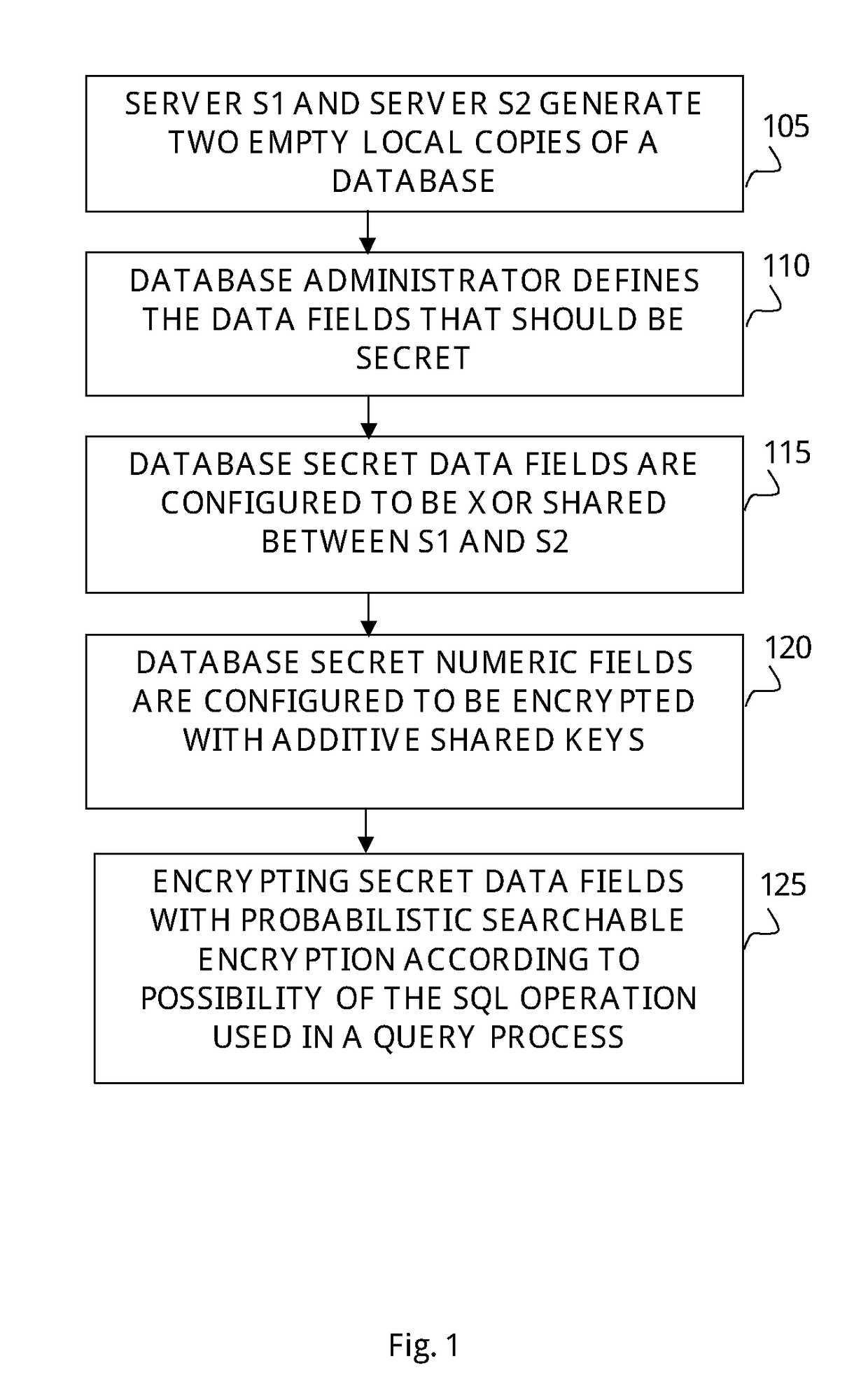
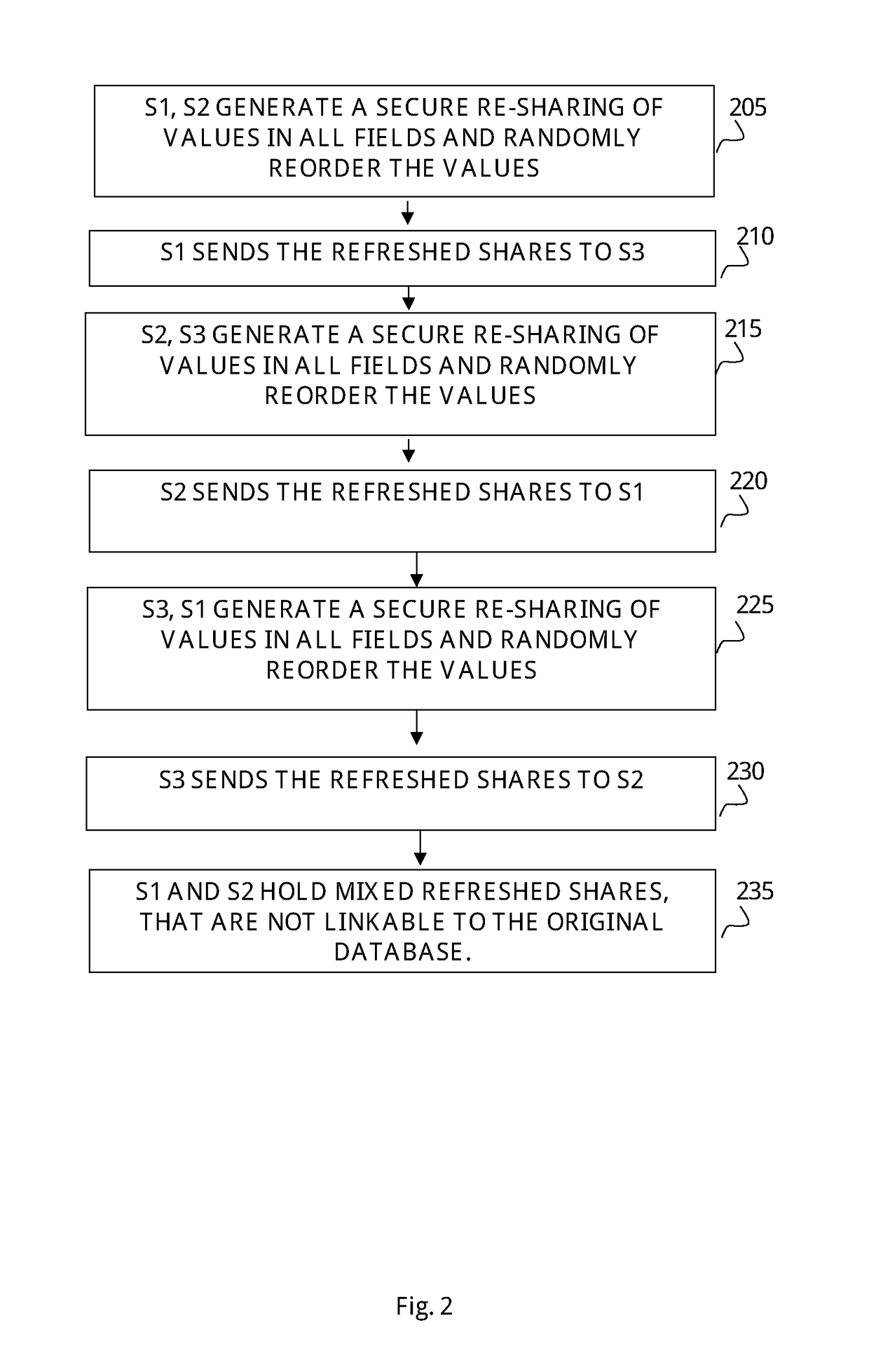
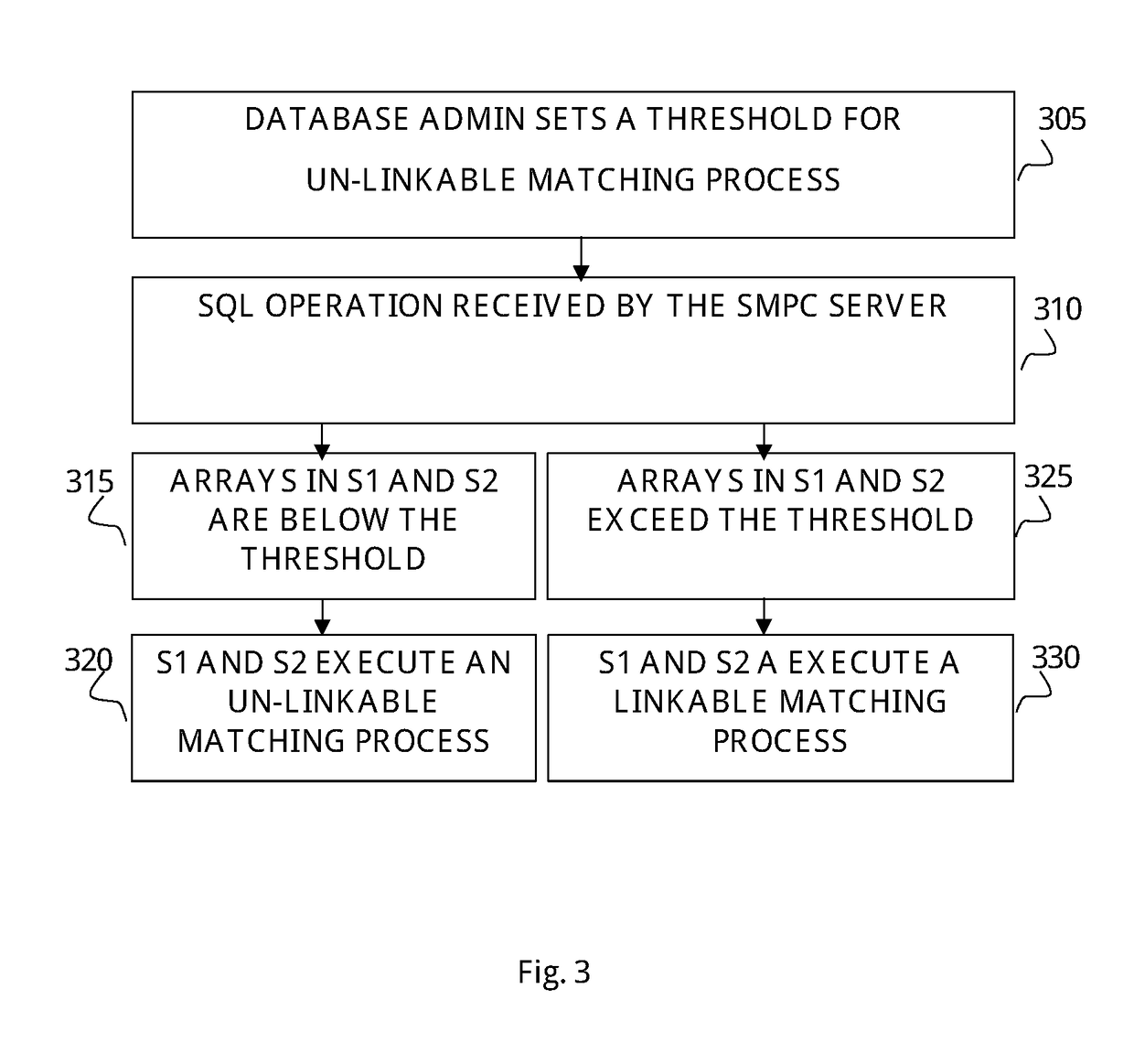
Securing SQL based databases with cryptographic protocols
ActiveUS20180357427A1Prevent leakageKey distribution for secure communicationDigital data information retrievalSecret shareData field
The subject matter discloses a method operated on a computerizing system comprising generating two secret shares of at least some of the data fields in a database, loading data fields of the database into two database copies, wherein one secret share of the two secret shares is loaded into one database copy and another secret share of the two secret shares is loaded into another database copy, receiving a request to perform a query in the database, processing said query on the database copies, wherein the database fields employed by the query process and the query results remain secret during processing, and revealing the secret query results.
Owner:COINBASE IL RD LTD
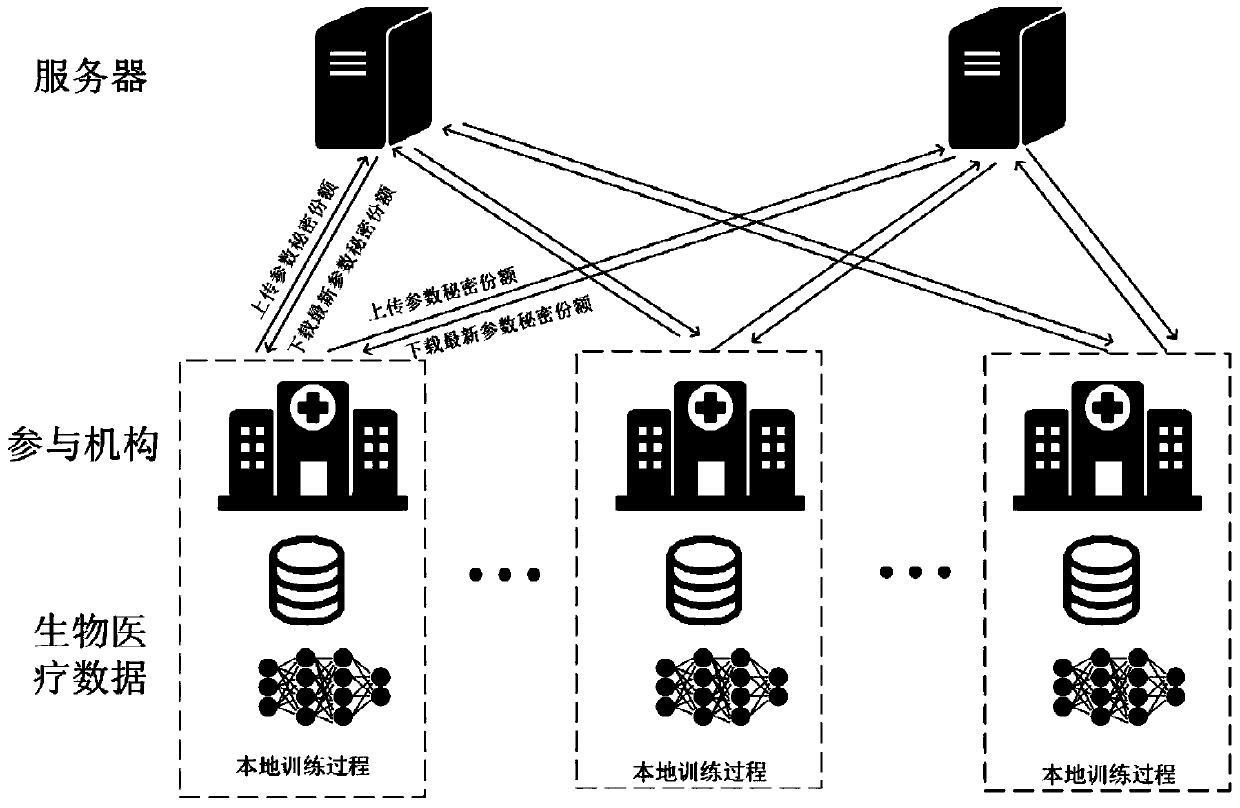
Data sharing method based on collaborative deep learning
InactiveCN109977694AGuaranteed data privacyDefense against aggressive behaviorDigital data protectionSecret shareModel parameters
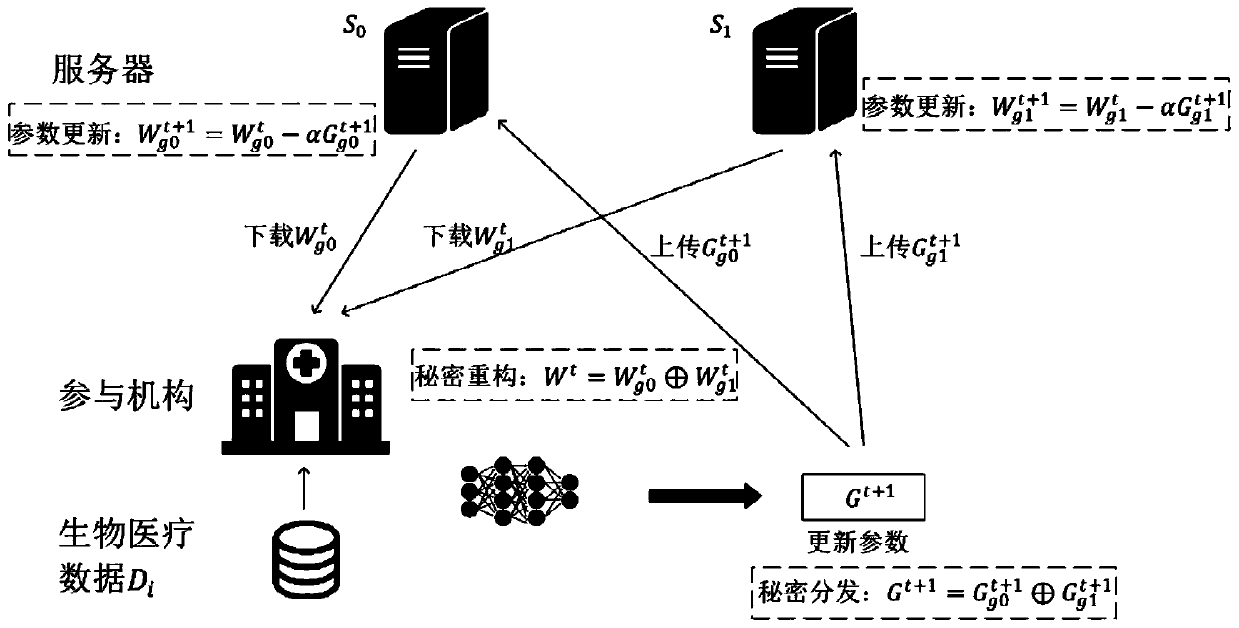
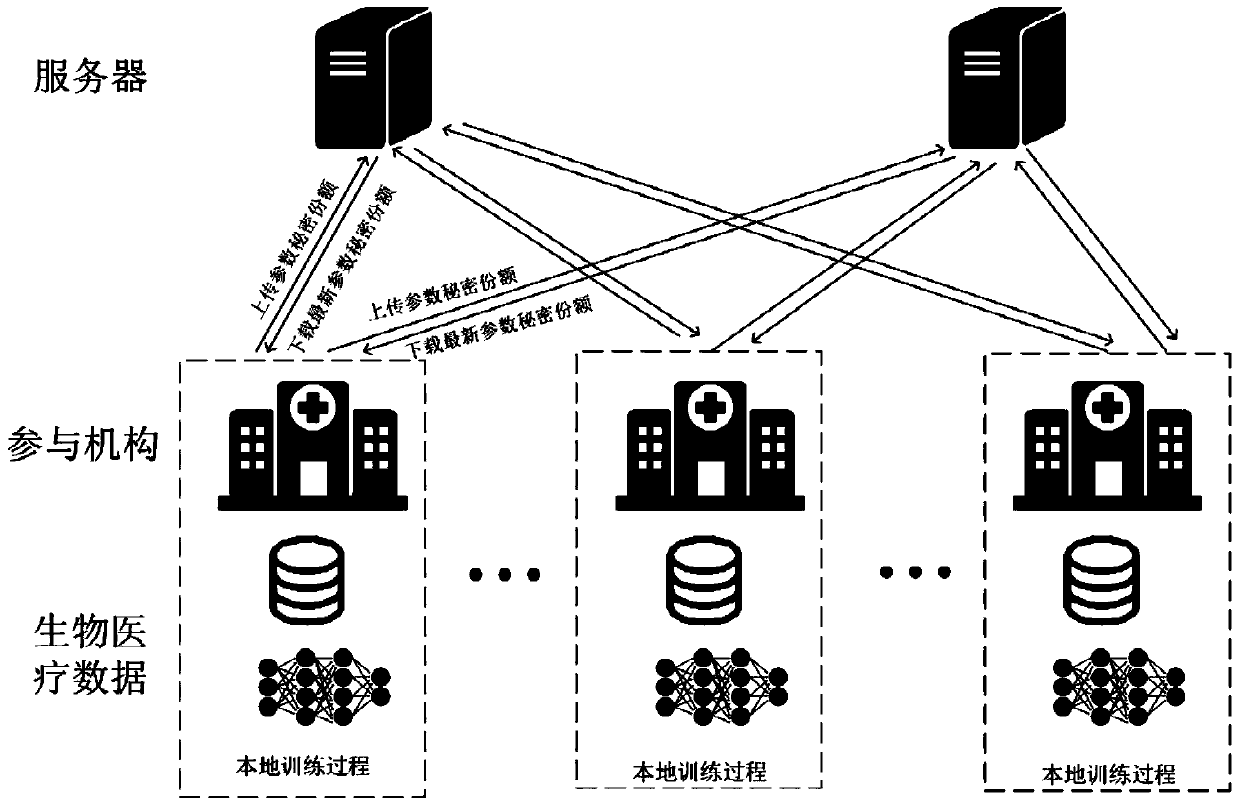
The invention discloses a data sharing method based on collaborative deep learning. The system comprises two servers and a plurality of participation mechanisms. Each participation mechanism has biomedical data in the same format. The server is responsible for updating and maintaining the model parameters uploaded by the participation mechanism; each participation mechanism only needs to downloadthe latest parameter secret share from the two servers. Secrete reconstruction and recovery are carried out locally to obtain a latest parameter; and then deep learning model training is carried out locally by utilizing the parameters and private biomedical data of the two servers, the updated model parameters are split into two secret shares through a secret sharing scheme after training is completed, and the two servers carry out parameter updating operation on the secret shares respectively for downloading of the participating institutions. The cooperative deep learning method and the secret sharing scheme are used, data privacy in the biomedical data sharing process is protected, and great significance is achieved for promoting sharing of biomedical data.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Method for secure user and transaction authentication and risk management
ActiveUS20110185405A1Compromising usabilityCompromising costDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationSecret shareOne-time password
To provide a user signature on a network transaction, a security server receives transaction information representing a transaction between a network user and a network site, such as a website. The security server calculates a one-time-password based on the received transaction information and a secret shared by the security server and the network site, but not by the user. The security server transmits the calculated one-time-password for application as the user's signature on the transaction. The one-time-password is independently calculable by the network site based on the shared secret.
Owner:PAYFONE
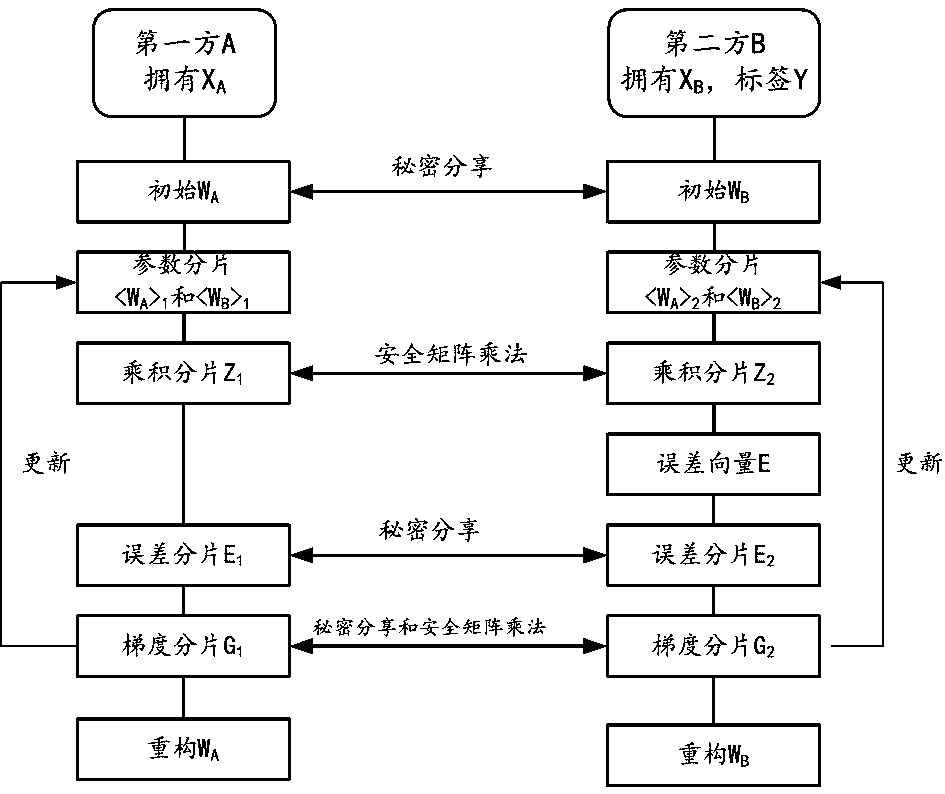
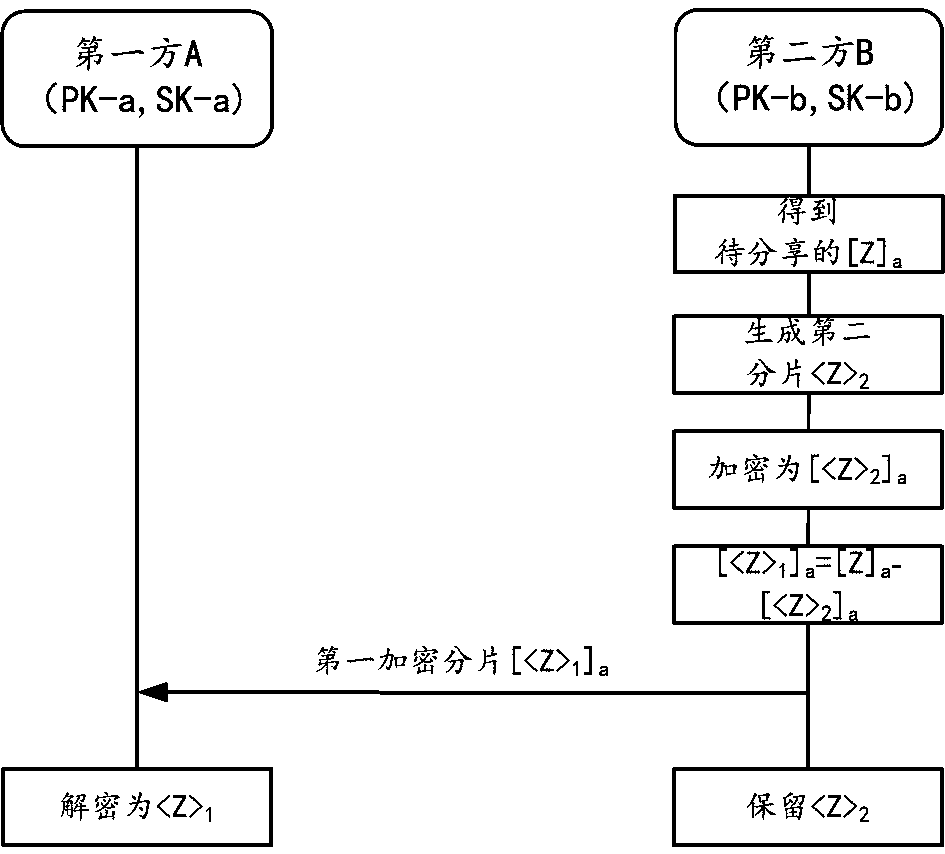
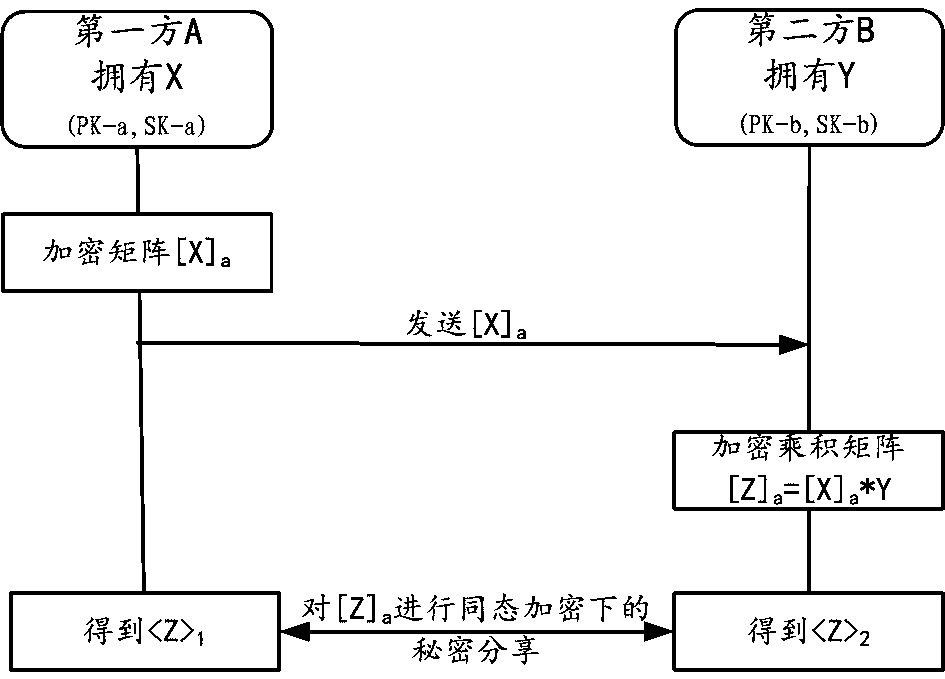
Method and device for jointly training service prediction model by two parties for protecting data privacy
ActiveCN111160573AImprove securityComputer security arrangementsMachine learningSecret shareIteration process
The embodiment of the invention provides a method and device for jointly training a service prediction model by two parties for protecting data privacy. The two parties respectively have a part of feature data. In the model iteration process, the two parties obtain encrypted fragments of the product result of the total feature matrix X and the total parameter matrix W through safety matrix multiplication; the two encrypted fragments are summarized by a second party with the label to obtain an encrypted product result Z; the second party obtains an encrypted error E based on the product resultZ and the encrypted label Y, and carries out secret sharing under homomorphic encryption. Therefore, the two parties respectively obtain error fragments. Then the two parties obtain corresponding gradient fragments through secret sharing and security matrix multiplication based on the error fragments and respective feature matrixes; and then, the first party updates the parameter fragments maintained by the first party by utilizing the gradient fragments of the first party, and the second party updates the parameter fragments maintained by the second party by utilizing the gradient fragments of the second party. Therefore, safe joint training for protecting data privacy is realized.
Owner:ALIPAY (HANGZHOU) INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
Fair and rational multi-secret sharing method for honest participants
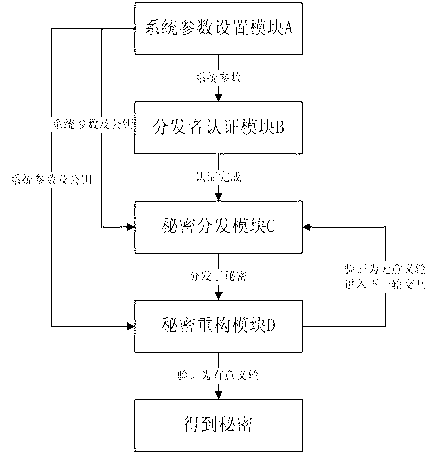
InactiveCN103259650AAddress inequitiesMany secrets to shareKey distribution for secure communicationSecret shareSystem parameters
The invention provides a fair and rational multi-secret sharing method for honest participants. The method relates to a system parameter setting module, a distributor authentication module, a secret distributing module and a secret reconstructing module, wherein the system parameter setting module generates public parameters of a system and public keys of distributors and the participants, the public parameters are transmitted to the other modules, the distributor authentication module authenticates the distributors according to a bit commitment agreement, the secret distributing module mainly relates to that the distributors distribute sub-secrets to the corresponding participants, the secrets reconstructing module is mainly used for authenticating accuracy of the sub-secrets, deleting the participants having deceit behaviors from an assembly of the participants that reconstruct secrets and reconstructing the secrets by judging whether the secrets are meaningful. If new secrets need to be shared, just parameters and commitment values which are chosen randomly need to be publicized. According to the solution, the unfair problem to the honest participants is solved, and multi-secret sharing can be effectively achieved.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Anonymous transactions based on distributed processing
ActiveUS7187772B2Key distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationSecret shareComputer security
Owner:HTC CORP
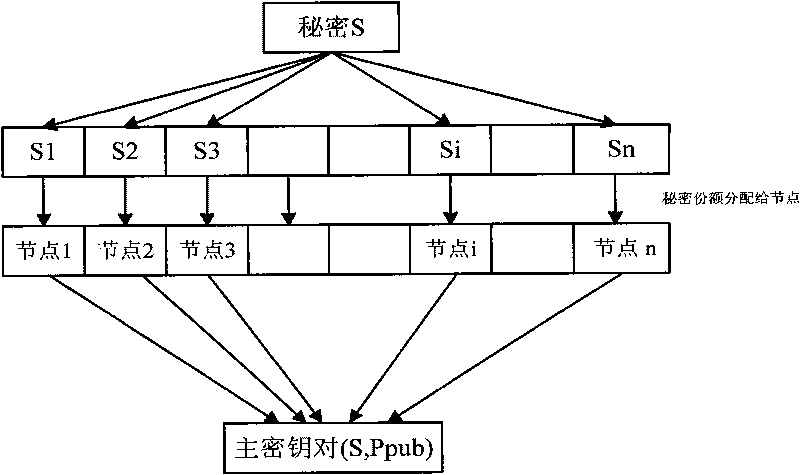
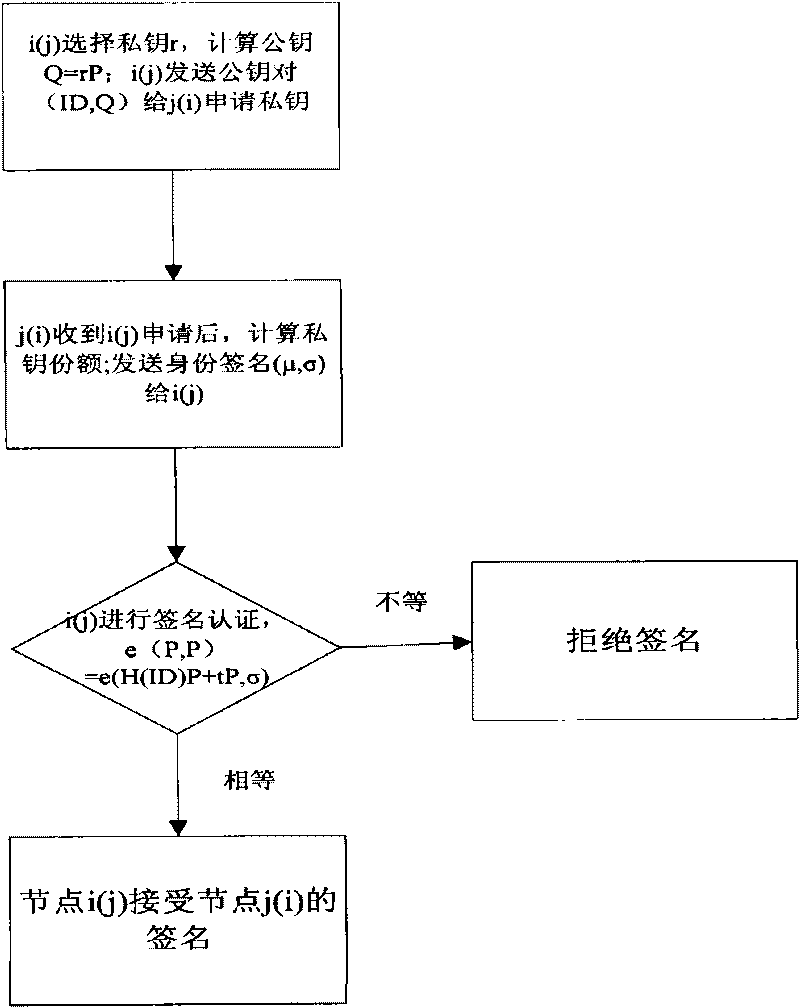
Method for managing dispersed keys based on identities in wireless sensor network
InactiveCN101711027AAvoid joiningImplement two-way authenticationSecurity arrangementSecret shareTime segment
The invention discloses a method for managing dispersed keys based on identities I a wireless sensor network, which comprises the following steps: 1, initializing system parameters, and setting the parameters to obtain master keys and master key pairs of the system parameters and a system; 2, performing two-way authentication on nodes in the system, and after the master keys are adduced by the system and when a node i applies for an encrypted key, acquiring the encrypted key from a node mastering system secret shares, and verifying the validity of the node i first; and 3, setting a key service life to realize the updating of communication group keys, and defining that the node i has a system secret share of sjt' at the beginning of a time period t, and has the system secret share of sjt after the updating. In the process of establishing communication keys, the method adopts a signature two-way authentication process to verify the validity of the node i first, namely to verify whether the node i is a legal node of the network so as to prevent malicious nodes from being added in; besides, for a secrete share sent by a response node j, the node i is also required to verify a signature and detect the validity so as to realize the two-way authentication and effectively improve the security.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
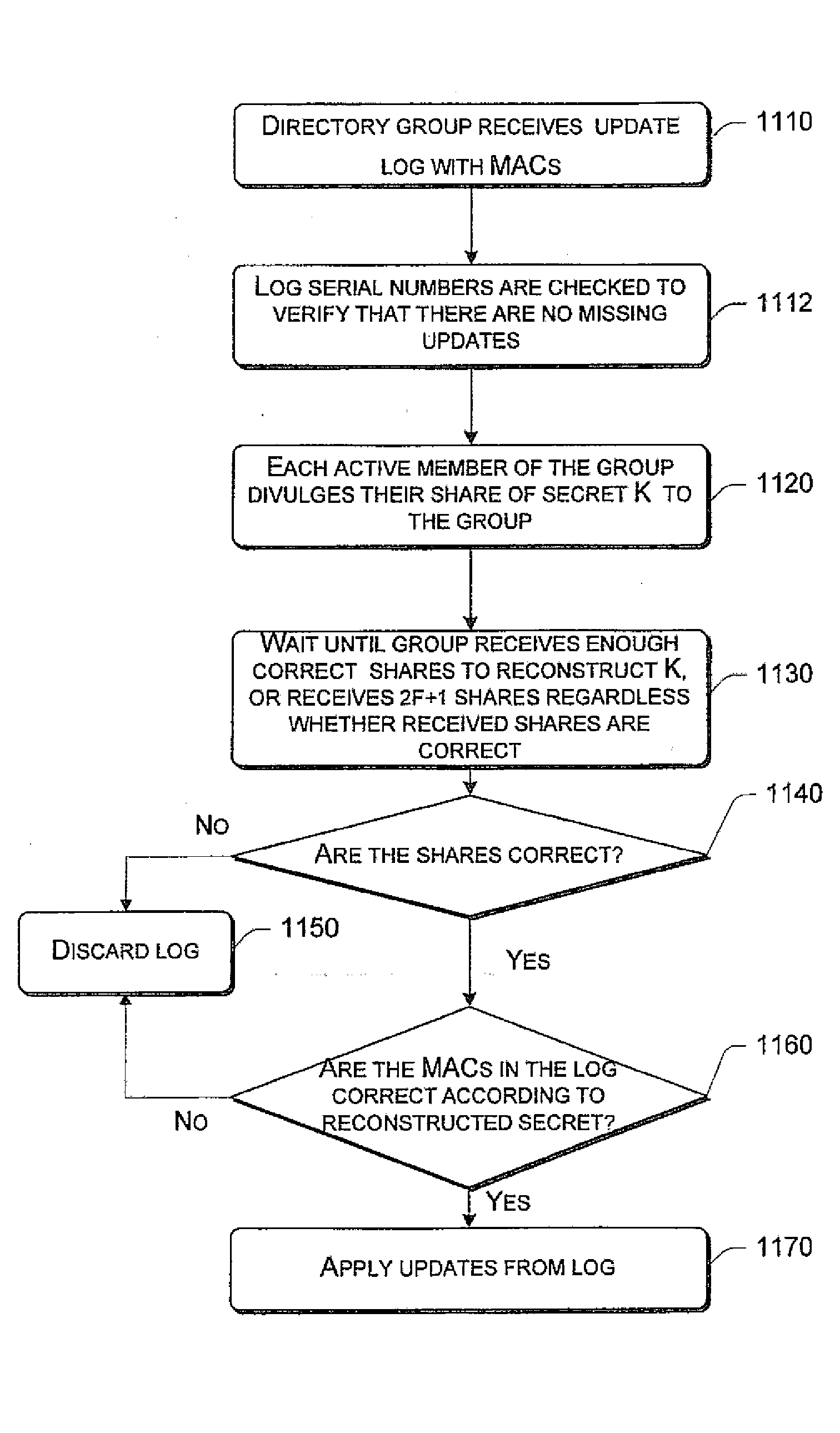
Method for voting with secret shares in a distributed system
ActiveUS8234518B2Eliminate pointLess reliableKey distribution for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsFailoverSecret share
A replicated decentralized storage system comprises a plurality of servers that locally store disk images for locally running virtual machines as well as disk images, for failover purposes, for remotely running virtual machines. To ensure that disk images stored for failover purposes are properly replicated upon an update of the disk image on the server running the virtual machine, a hash of a unique value known only to the server running the virtual machine is used to verify the origin of update operations that have been transmitted by the server to the other servers storing replications of the disk image for failover purposes. If verified, the update operations are added to such failover disk images. To enable the replicated decentralized system to recover from a failure of the primary server, the master secret is subdivided into parts and distributed to other servers in the cluster. Upon a failure of the primary server, a secondary server receives a threshold number of the parts and is able to recreate the master secret and failover virtual machines that were running in the failed primary server.
Owner:VMWARE INC
General protocol for proactively secure computation
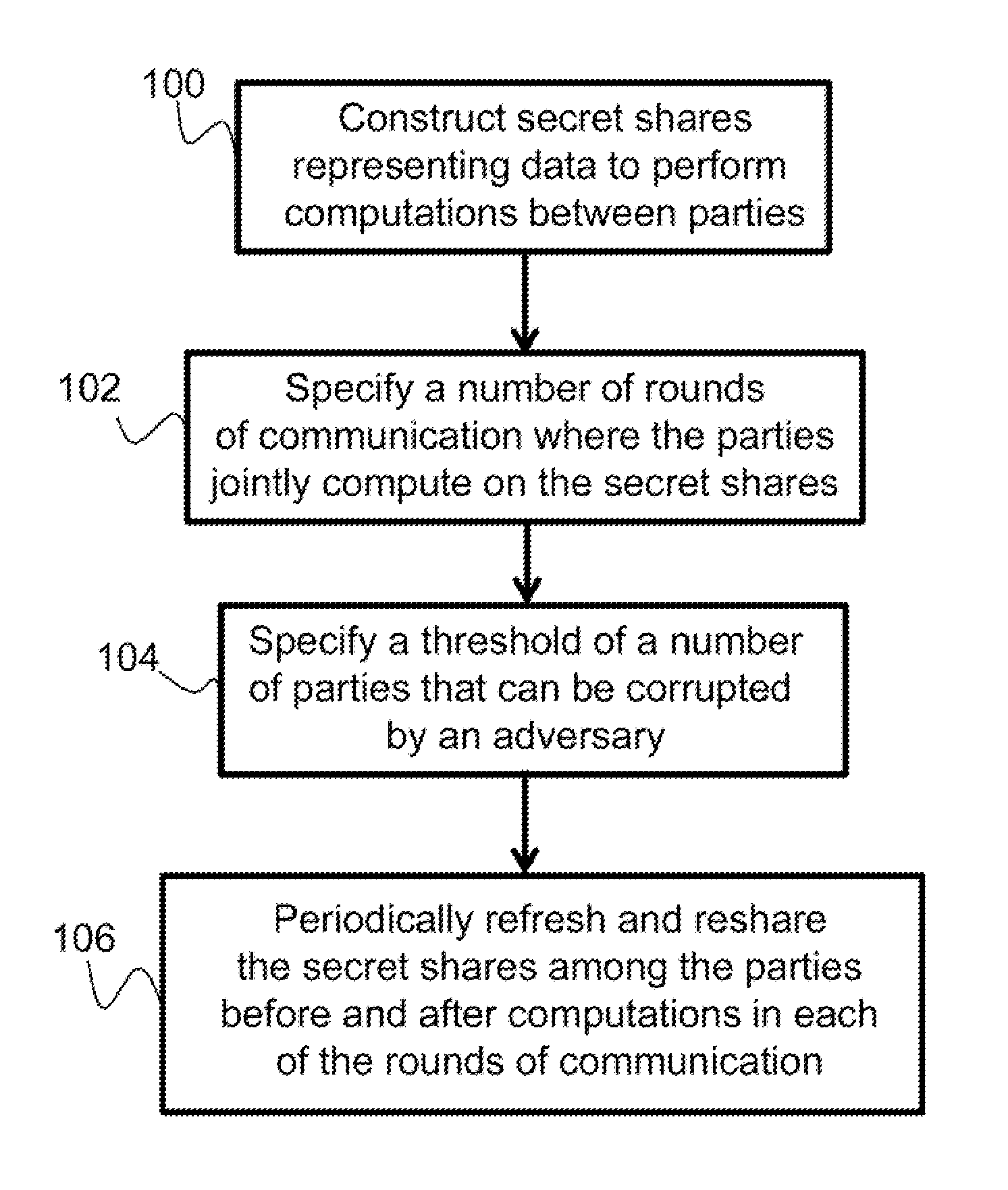
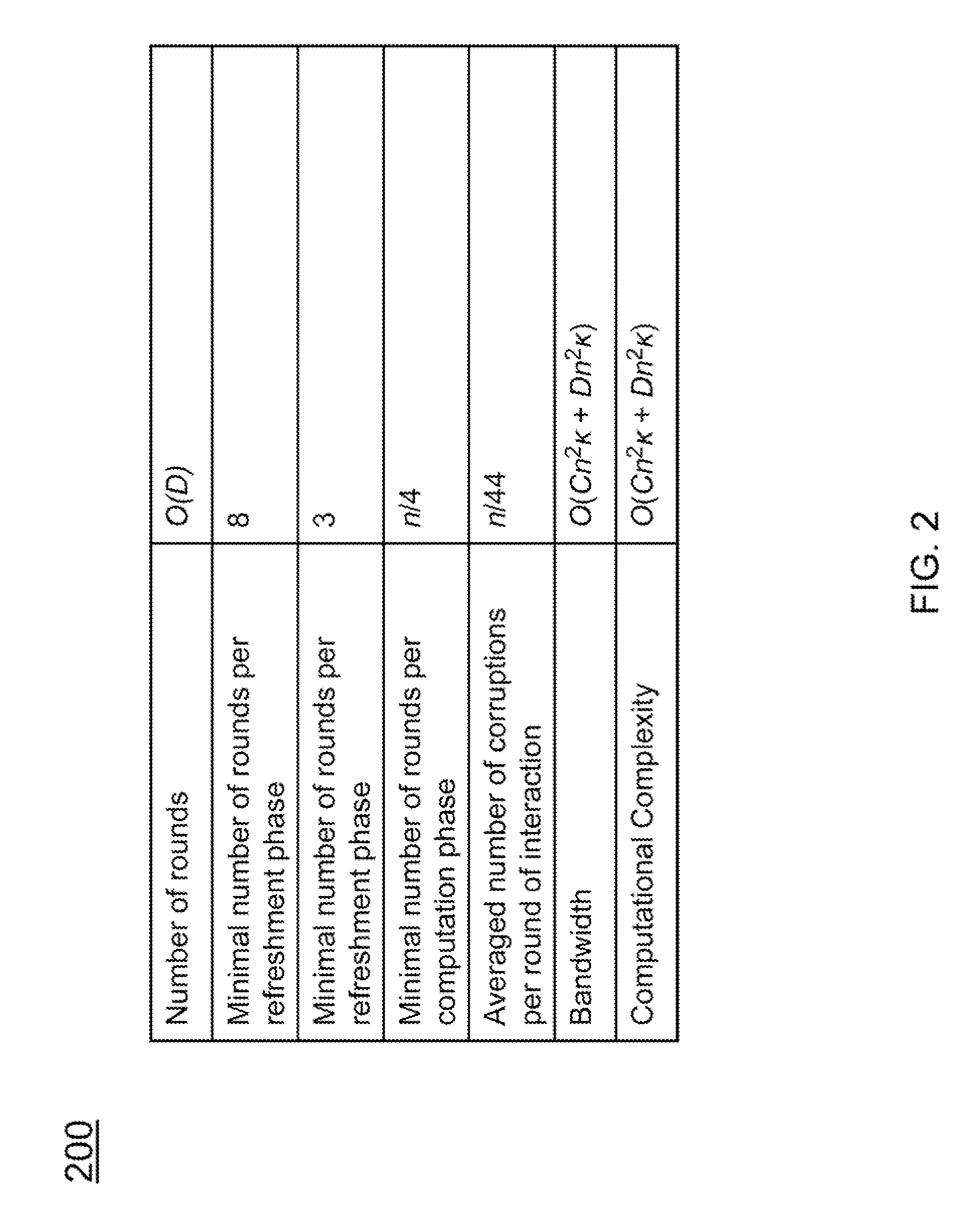
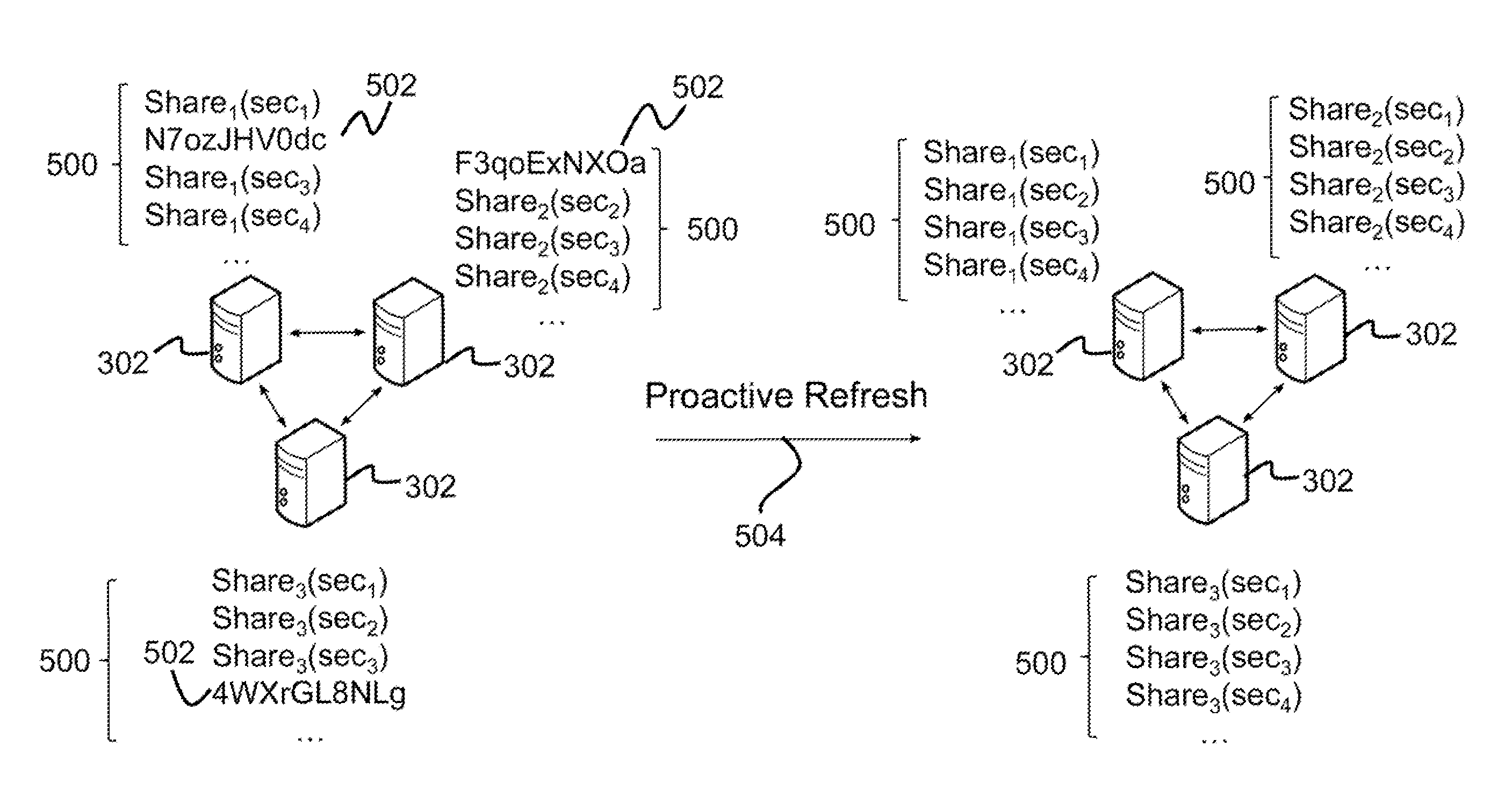
ActiveUS9449177B1Key distribution for secure communicationDigital data protectionSecret shareSecure multi-party computation
Described is a system for proactively secure multi-party computation (MPC). Secret shares representing data are constructed to perform computations between a plurality of parties modeled as probabilistic polynomial-time interactive turing machines. A number of rounds of communication where the plurality of parties jointly compute on the secret shares is specified. Additionally, a threshold of a number of the plurality of parties that can be corrupted by an adversary is specified. The secret shares are periodicially refreshed and reshared among the plurality of parties before and after computations in each of the rounds of communication. The data the secret shares represent is proactively secured.
Owner:HRL LAB
Method for secure and resilient distributed generation of elliptic curve digital signature algorithm (ECDSA) based digital signatures with proactive security
ActiveUS9489522B1User identity/authority verificationDigital data protectionActive safetySecret share
Described is system for generation of elliptic curve digital signature algorithm (ECDSA) based digital signatures. A Secret-Share protocol is initialized between a client and a set of servers to share a set of shares of a private key s among the set of servers. The set of servers initializes a protocol to generate a digital signature on a message using the set of shares of the private key s without reconstructing or revealing the private key s. The set of servers periodically initializes a Secret-Redistribute protocol on each share of the private key s to re-randomize the set of shares. A Secret-Open protocol is initialized to reveal the private key s to an intended recipient, wherein the private key s is used to compute the digital signature.
Owner:HRL LAB
Secure recovery in a serverless distributed file system
InactiveUS20090019288A1Avoid selectionDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationSecret shareDistributed File System
Systems and methods for secure file writes after a catastrophic event are allowed over an unauthenticated channel in a serverless distributed file system if an authenticator accompanies the secure file writes. The authenticator can be a power-of-attorney certificate with time limitations, a vector of message authenticated code, or a single message authenticator with secured with a secret shared among members of the serverless distributed file system. The serverless distributed file system includes at least 3f+1 participating computer members, with f representing a number of faults tolerable by the system. The group requires at least one authenticator for file creation and file uploads. Any changes to files stored among the members can be made over an unauthenticated channel if the file changes are secured by the authenticator and the group is able to verify the authenticator.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
System and method to share a guest version of rights between devices
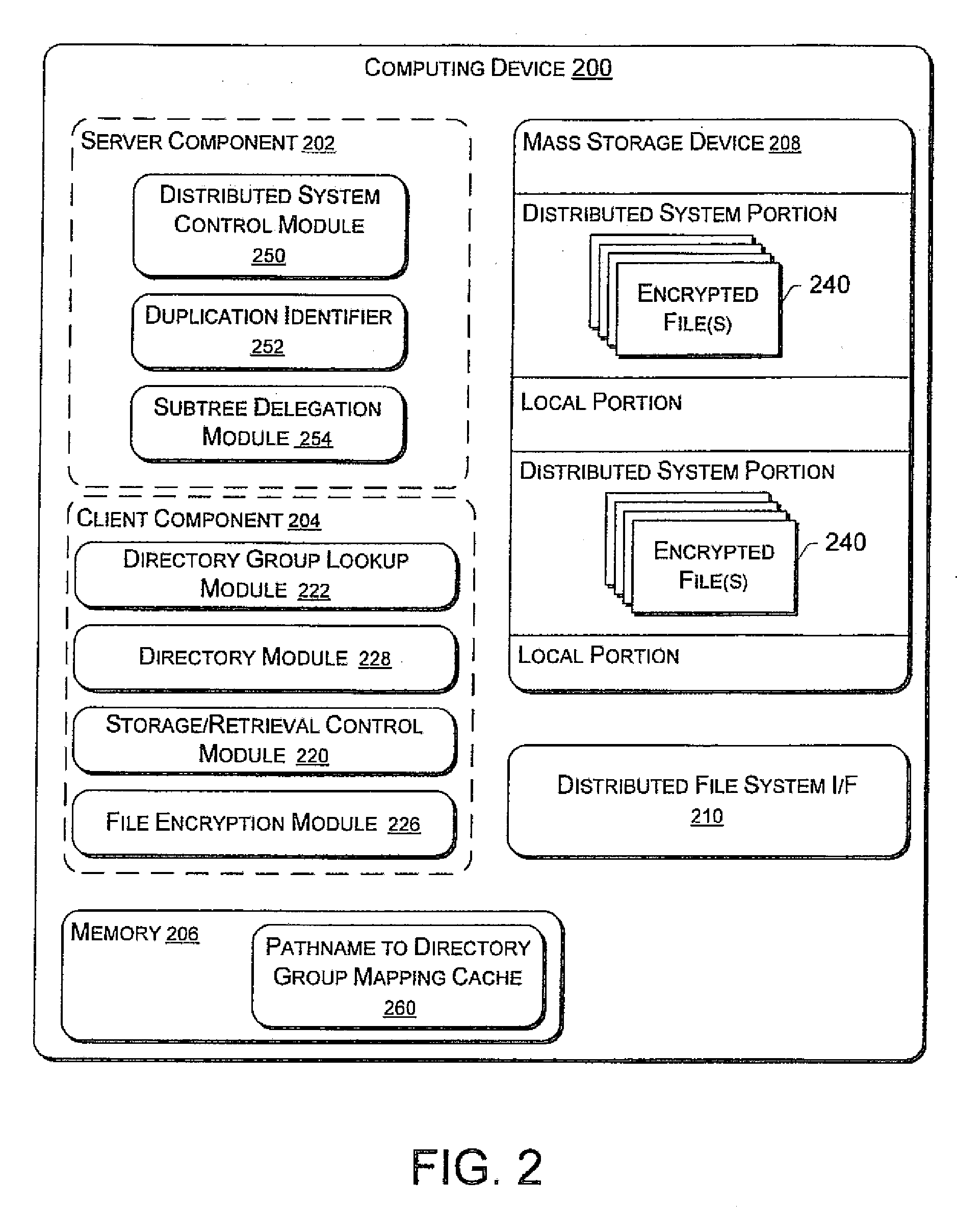
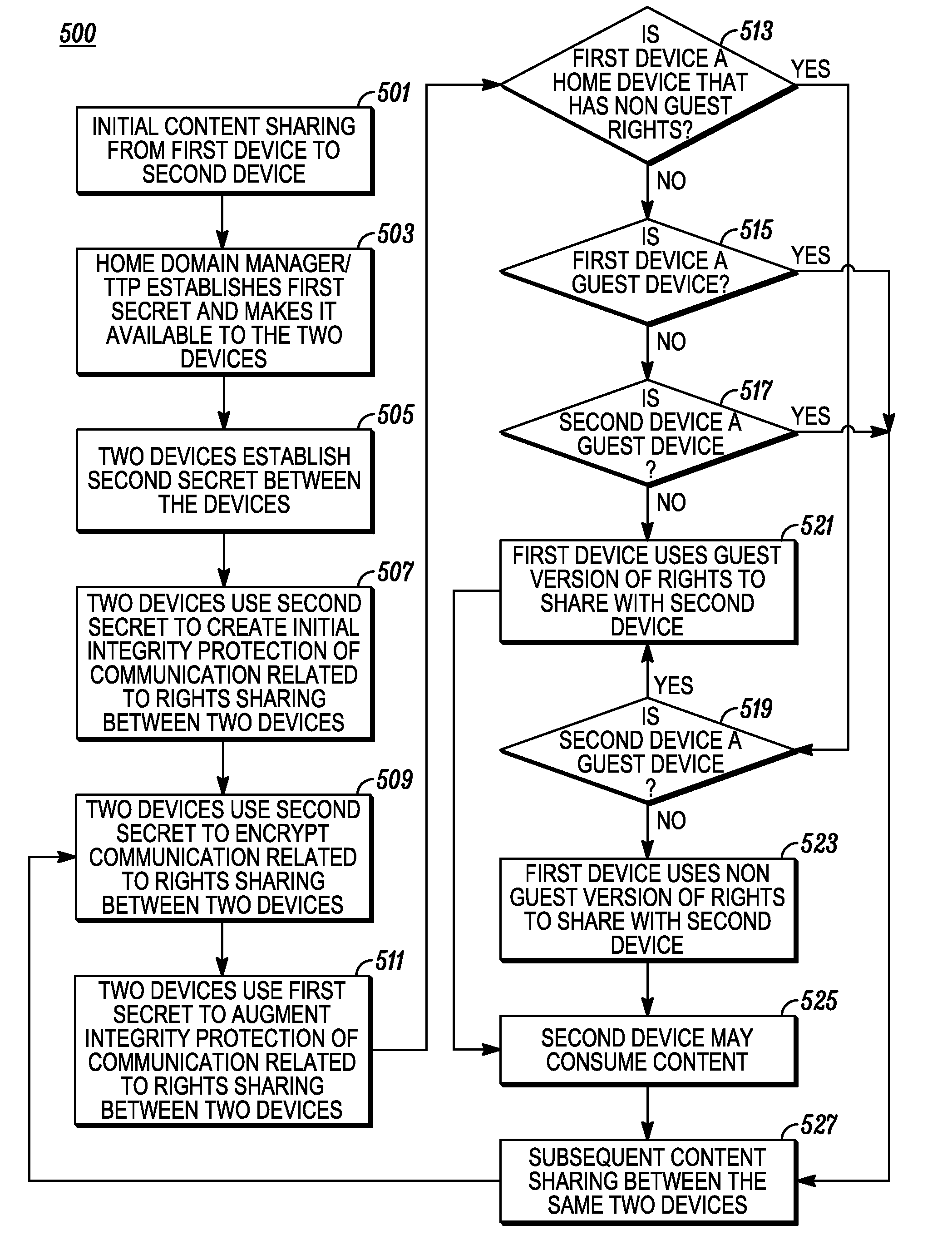
InactiveUS20080313085A1Program/content distribution protectionSecuring communicationSecret shareData integrity
A method to share a guest version of rights between two devices is described. For one embodiment, a non-guest rights object may be converted to a guest rights object by withholding certain information when conducting a secure transfer or sharing of rights. For another embodiment, rights issuers that issue rights for content create two digitally signed rights objects where one rights object may reference the other rights object. For yet another embodiment, a rights issuer's digital signature may be used to ensure source and data integrity of a guest rights object and prevent counterfeiting of guest rights objects. For still another embodiment, a secret shared between the rights issuer and a device, or a set of devices, to which a rights object is cryptographically bound.
Owner:MOTOROLA MOBILITY LLC
Method and system for authenticating and preserving the integrity of communication, secured by secret sharing
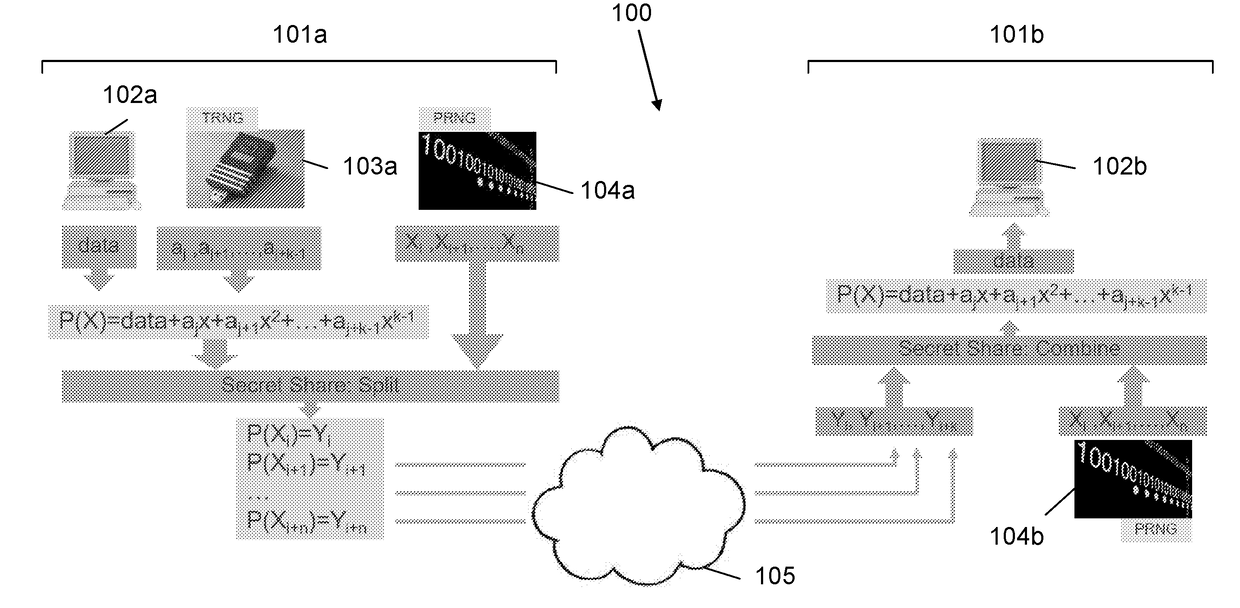
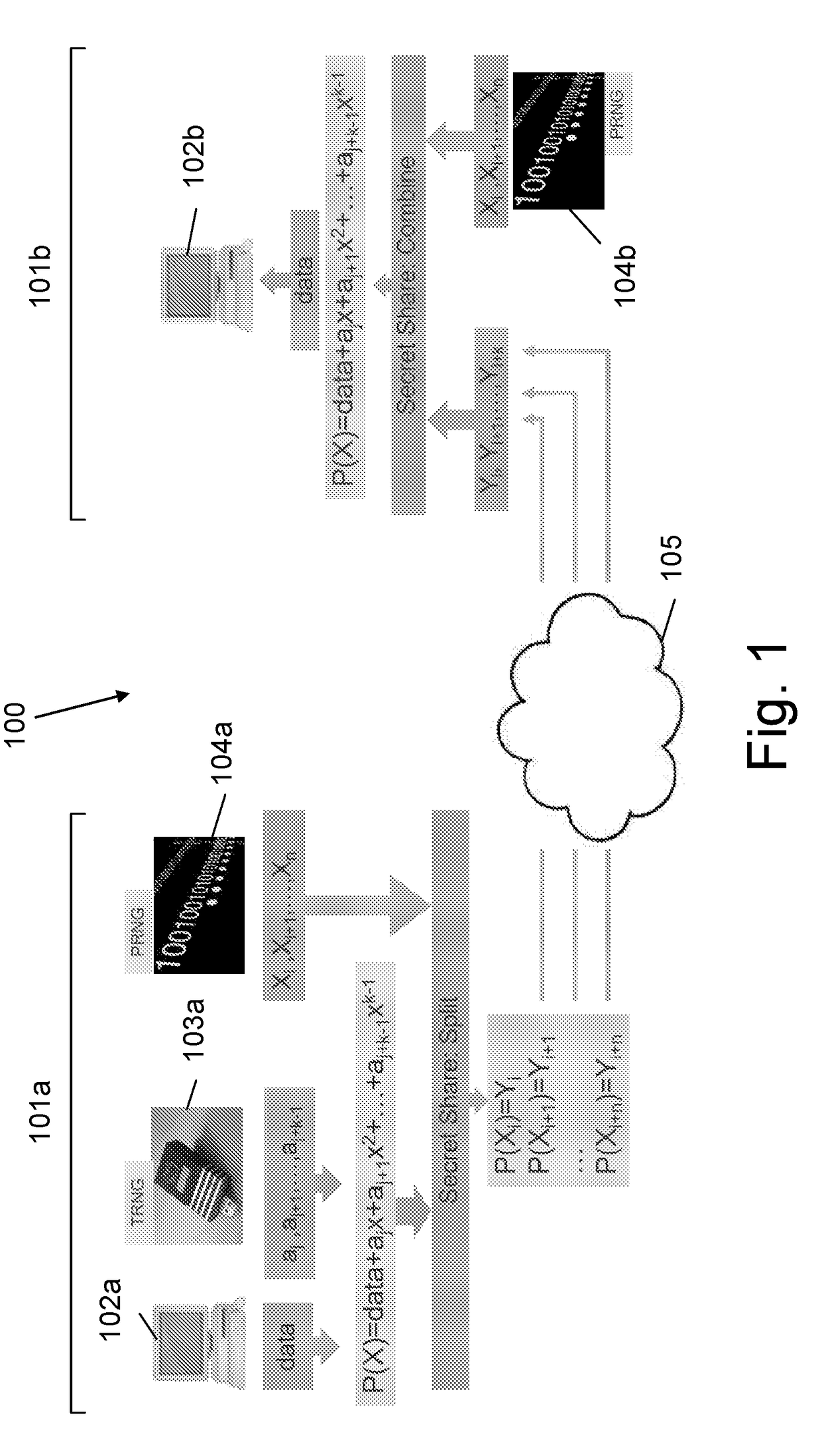
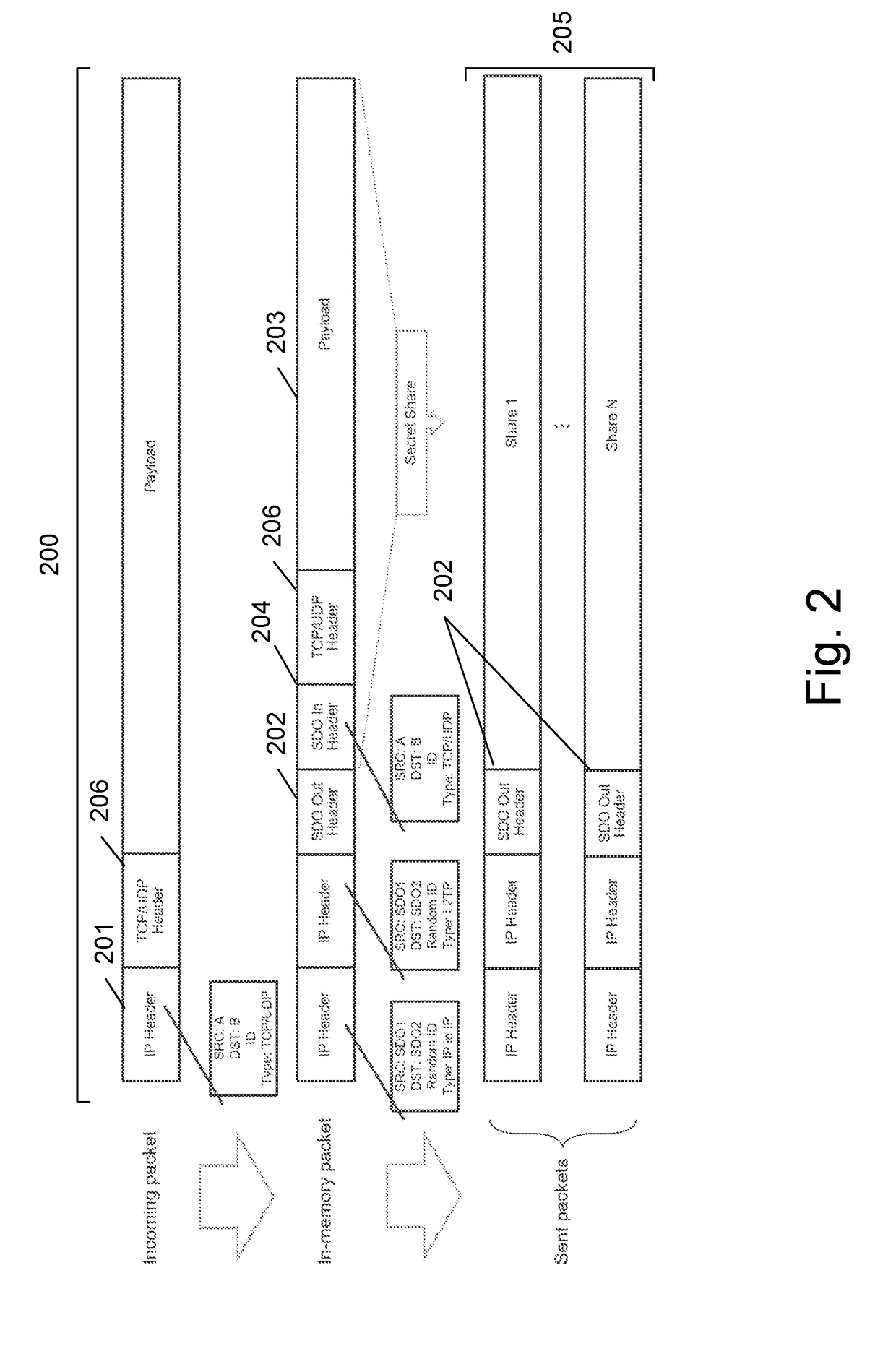
ActiveUS20180241548A1Key distribution for secure communicationRandom number generatorsSecure communicationSecret share
A system and method for providing secure communication between a source and a destination that is secured by secret sharing, during a vulnerability window in which all secret shares are collected in one or more points along the communication paths. Accordingly, during the regular operation of the communication protocol, a common random secret OTP is created by sending random bits from the sender to the receiver and the source is allowed to perform bitwise XOR operation between the information to be sent and the common random secret OTP, prior to using secret sharing. The results of the bitwise XOR operation are sent to the destination using secret sharing and the destination reconstructs the random secret and decrypts the received data, using the common established random secret. The common random secret is based on polynomial randomization being transferred from the source to the destination using secret sharing. The coefficients of a selected polynomial are randomly chosen at the sender side and are known both to the sender and the receiver. An x value is selected for each set of chosen coefficients, for which there is a corresponding y value. Pairs of x and y values transmitted from the sender to the receiver, where each pair represents a secret share. The transfer of polynomial randomization is repeated for every bit / byte or for any group of bits of the message to be transmitted, while in each time randomly choosing a different set of coefficients. At the end, the destination decrypts the message by collecting all shares being pairs of the received x and y values and reconstructs the selected polynomial from all collected shares.
Owner:SECRET DOUBLE OCTOPUS LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com