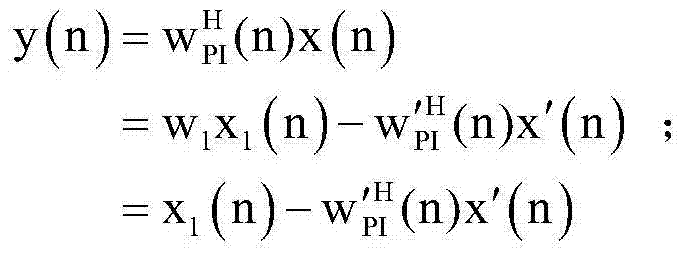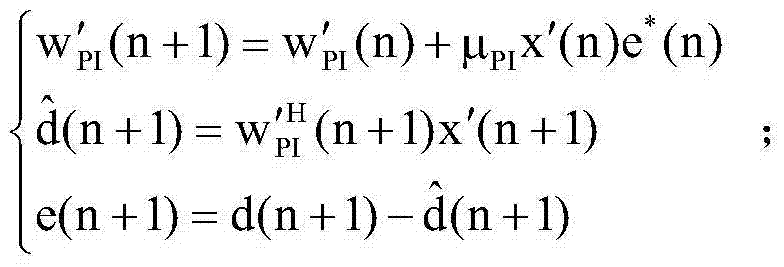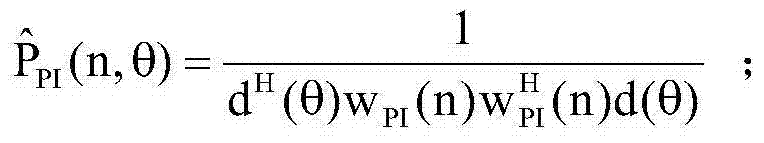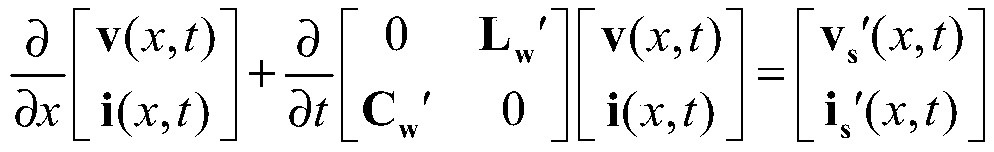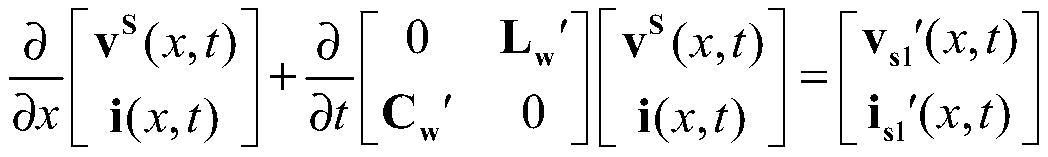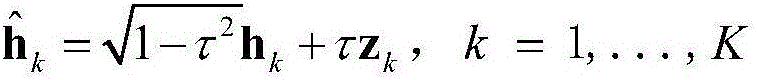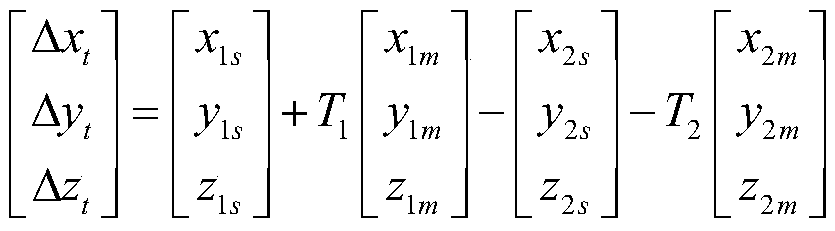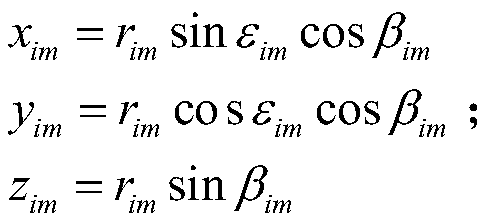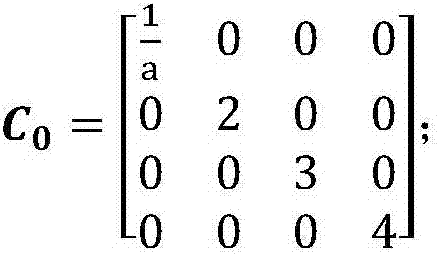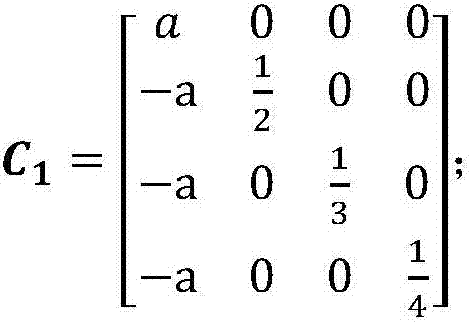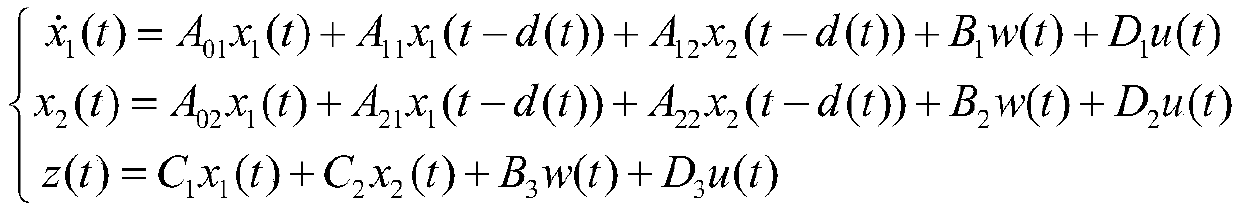Patents
Literature
59 results about "Matrix inverse" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The so-called invertible matrix theorem is major result in linear algebra which associates the existence of a matrix inverse with a number of other equivalent properties. A matrix possessing an inverse is called nonsingular, or invertible.
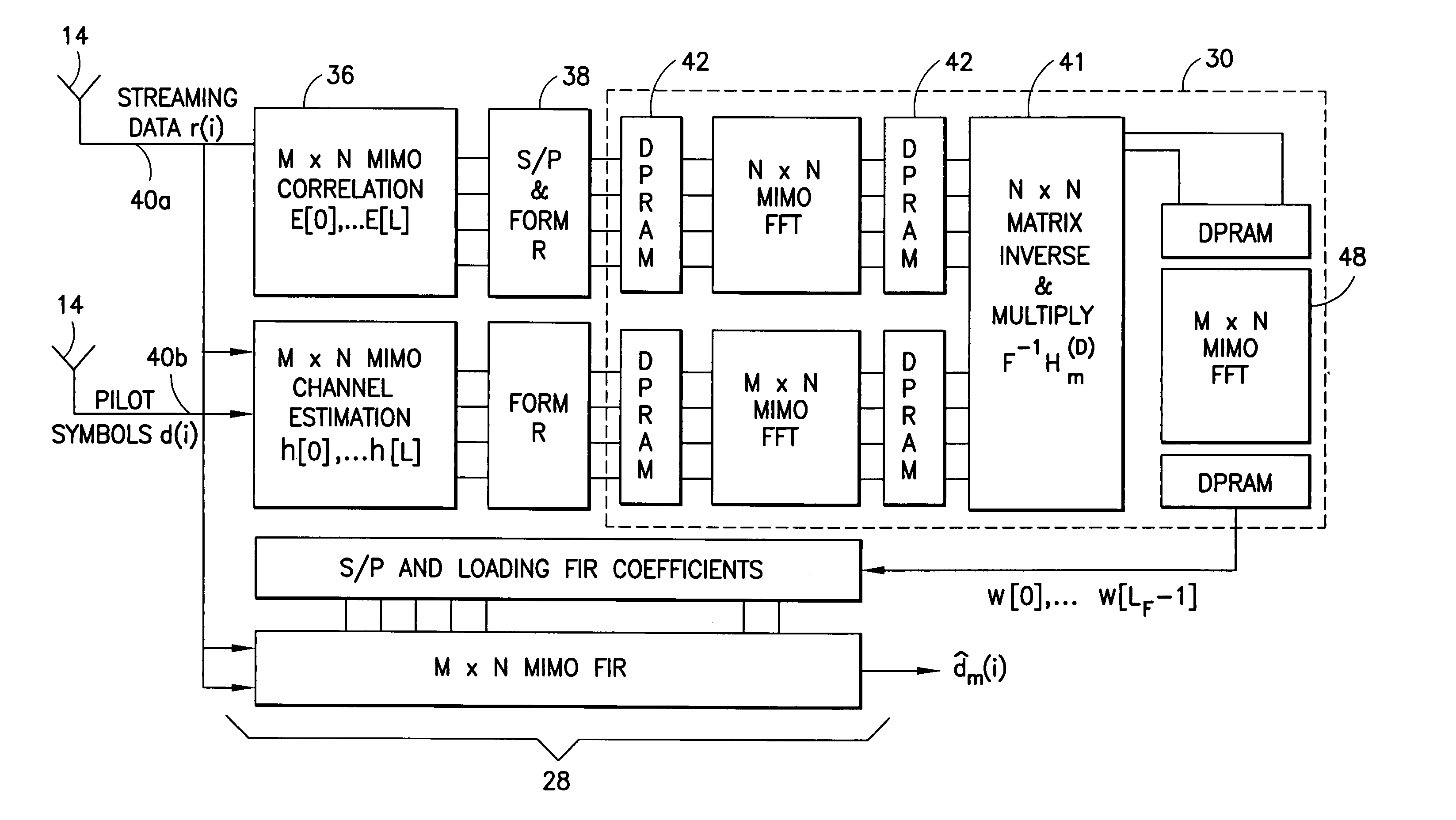
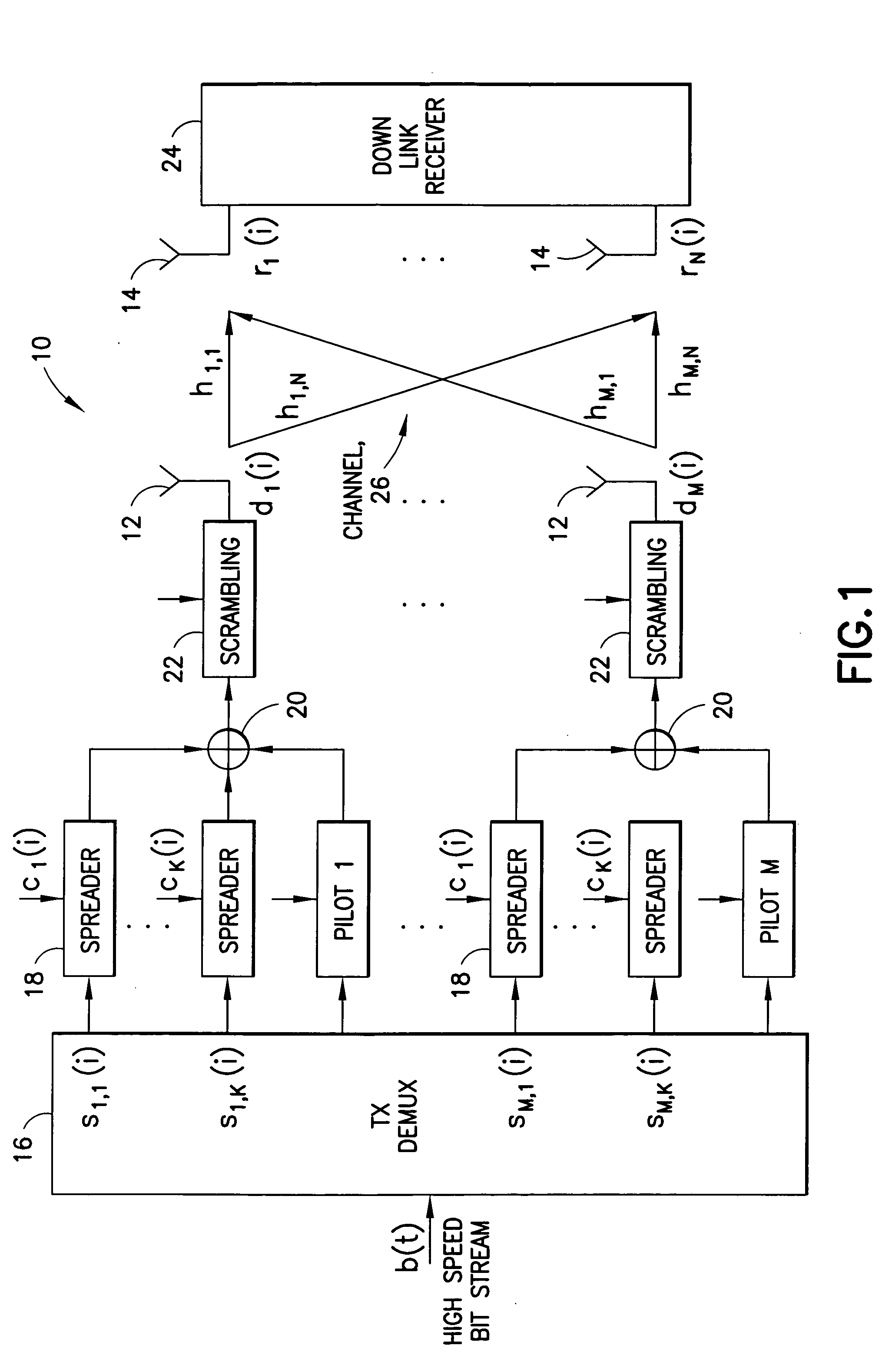
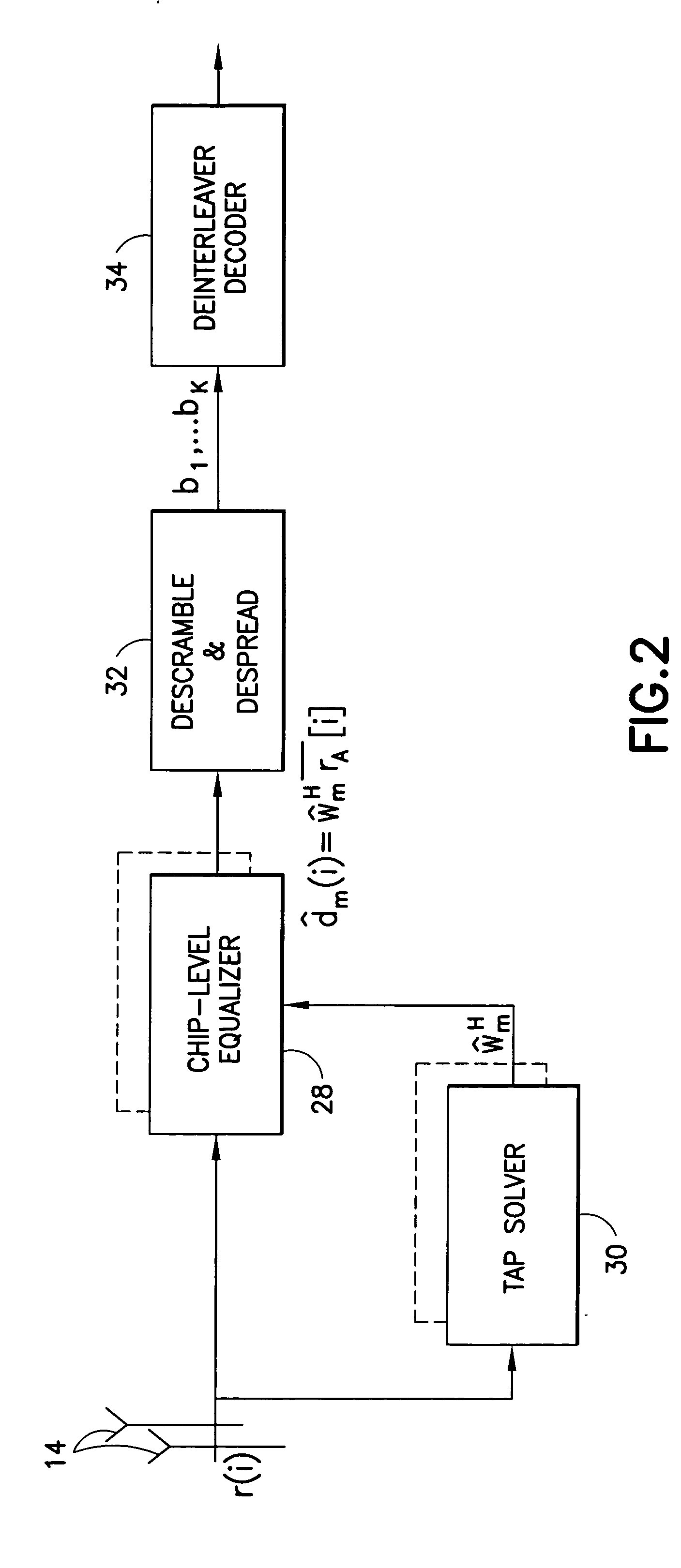
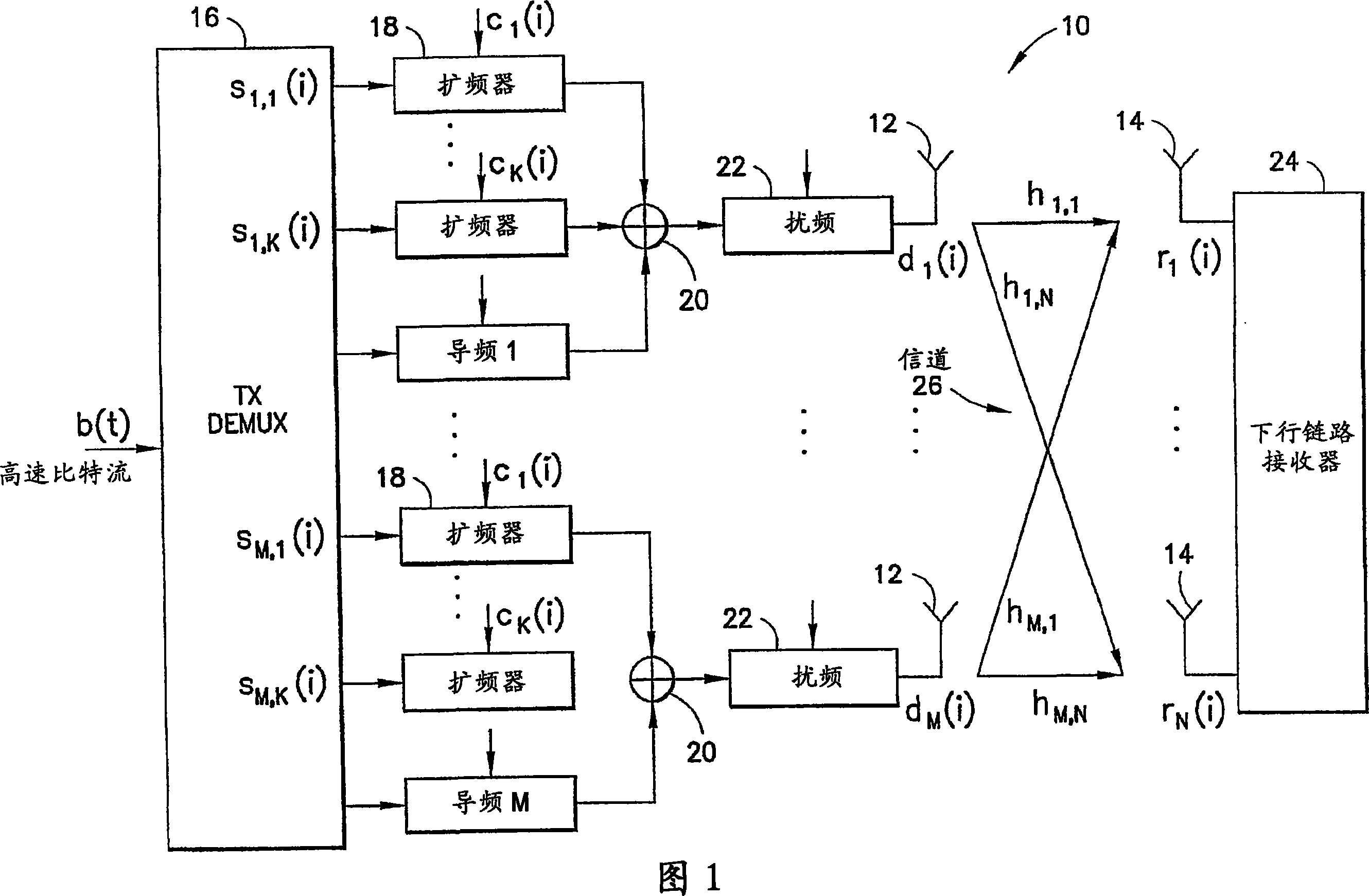
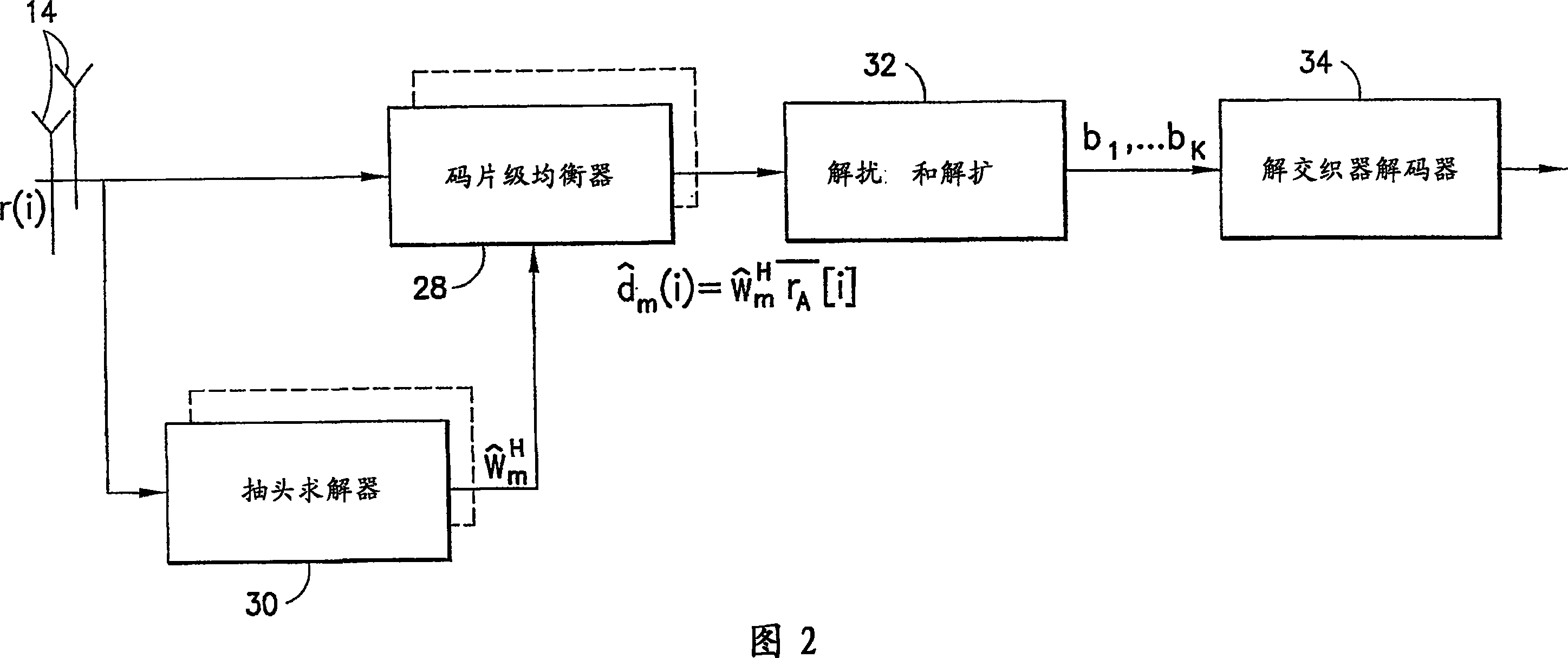
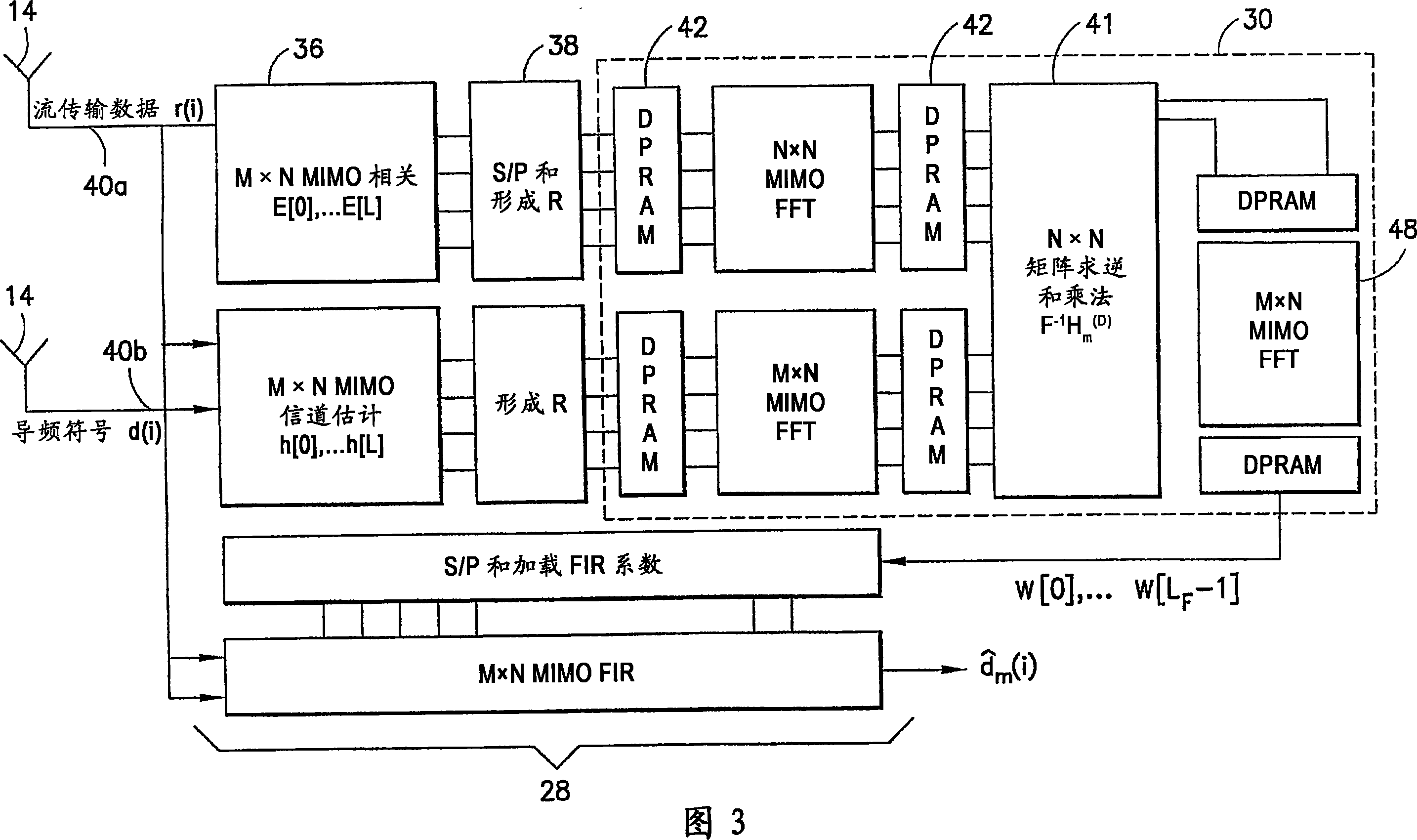
Reduced parallel and pipelined high-order MIMO LMMSE receiver architecture
ActiveUS20060109891A1Reduce complexityReduce the numberMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsFast Fourier transformRound complexity
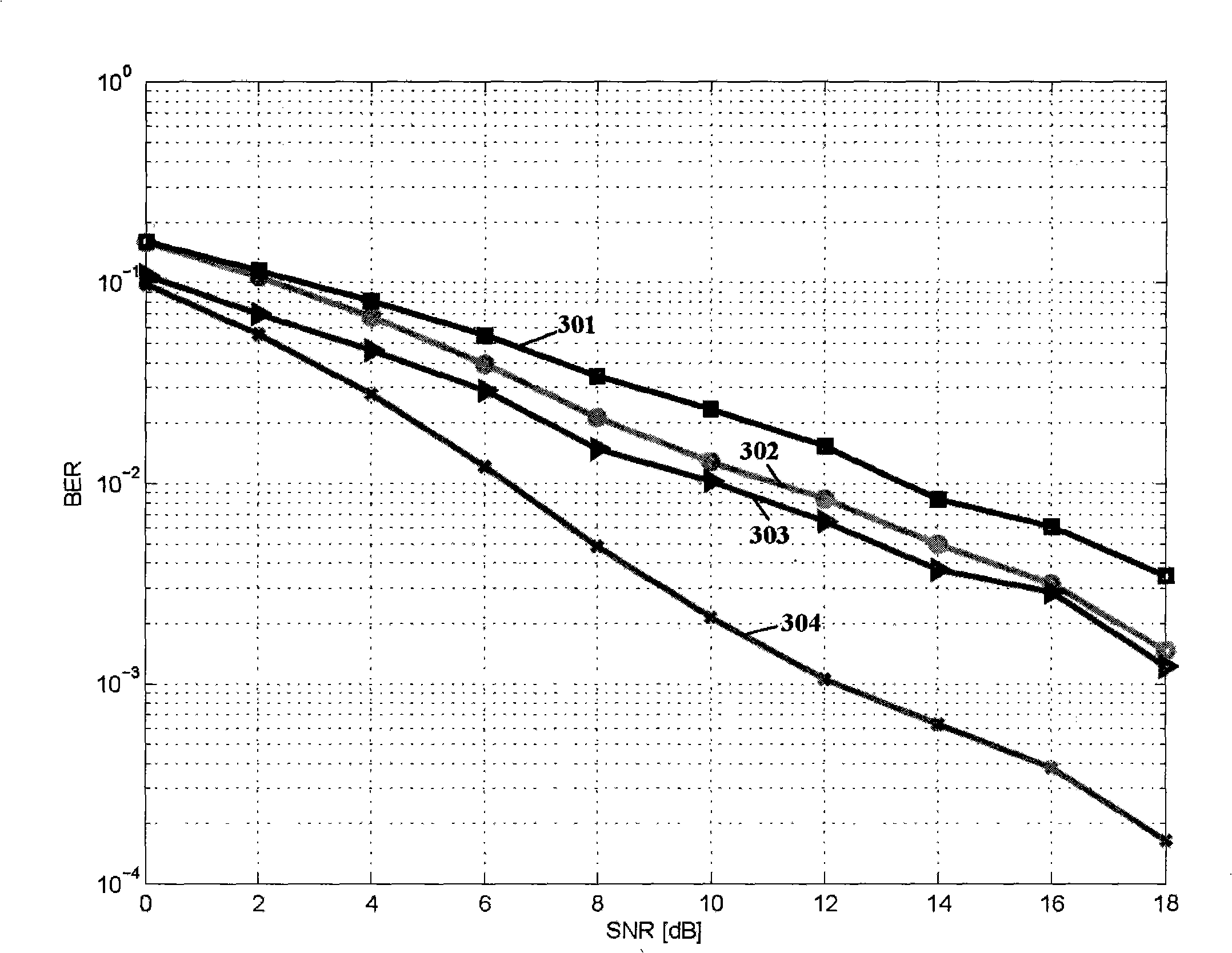
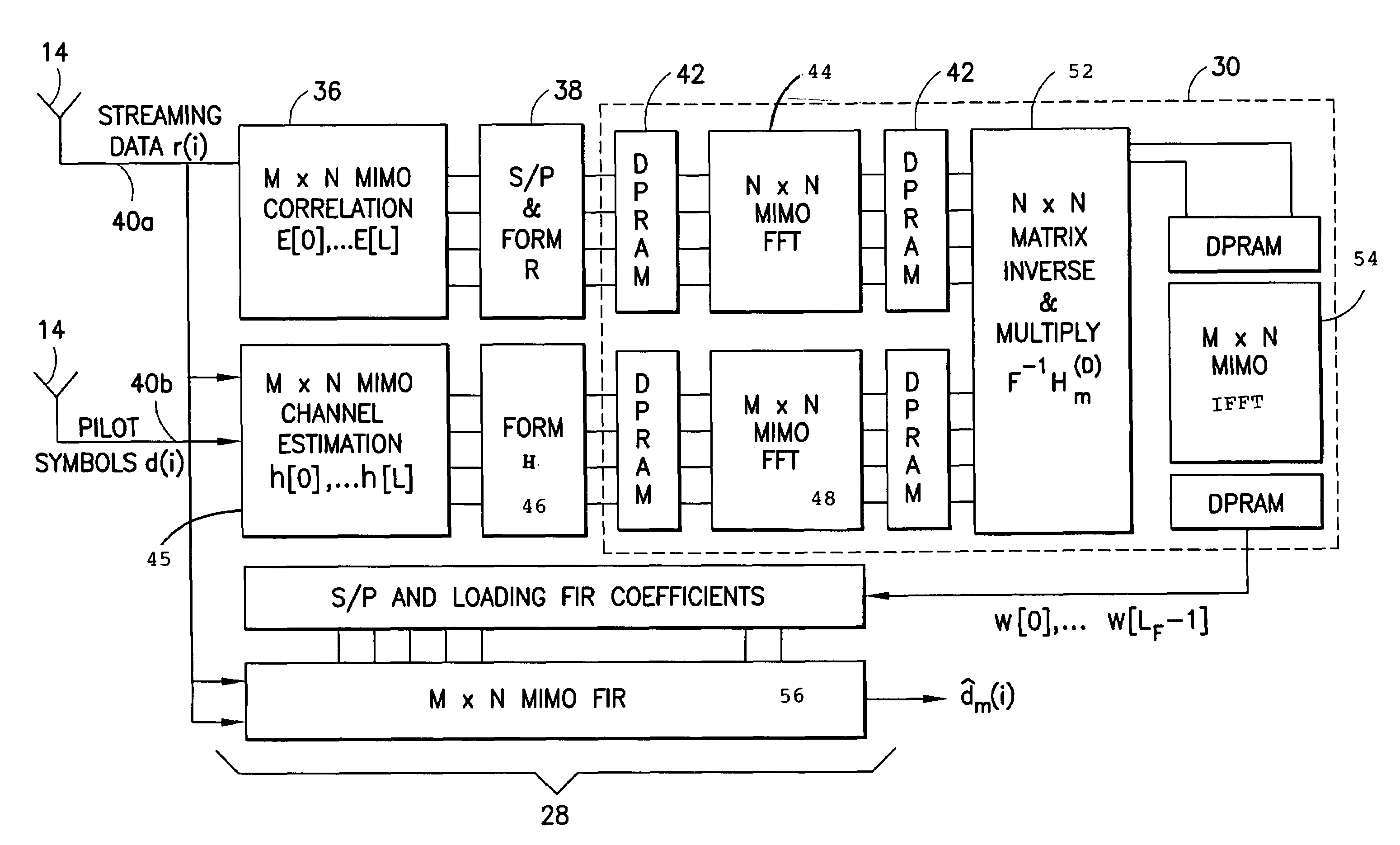
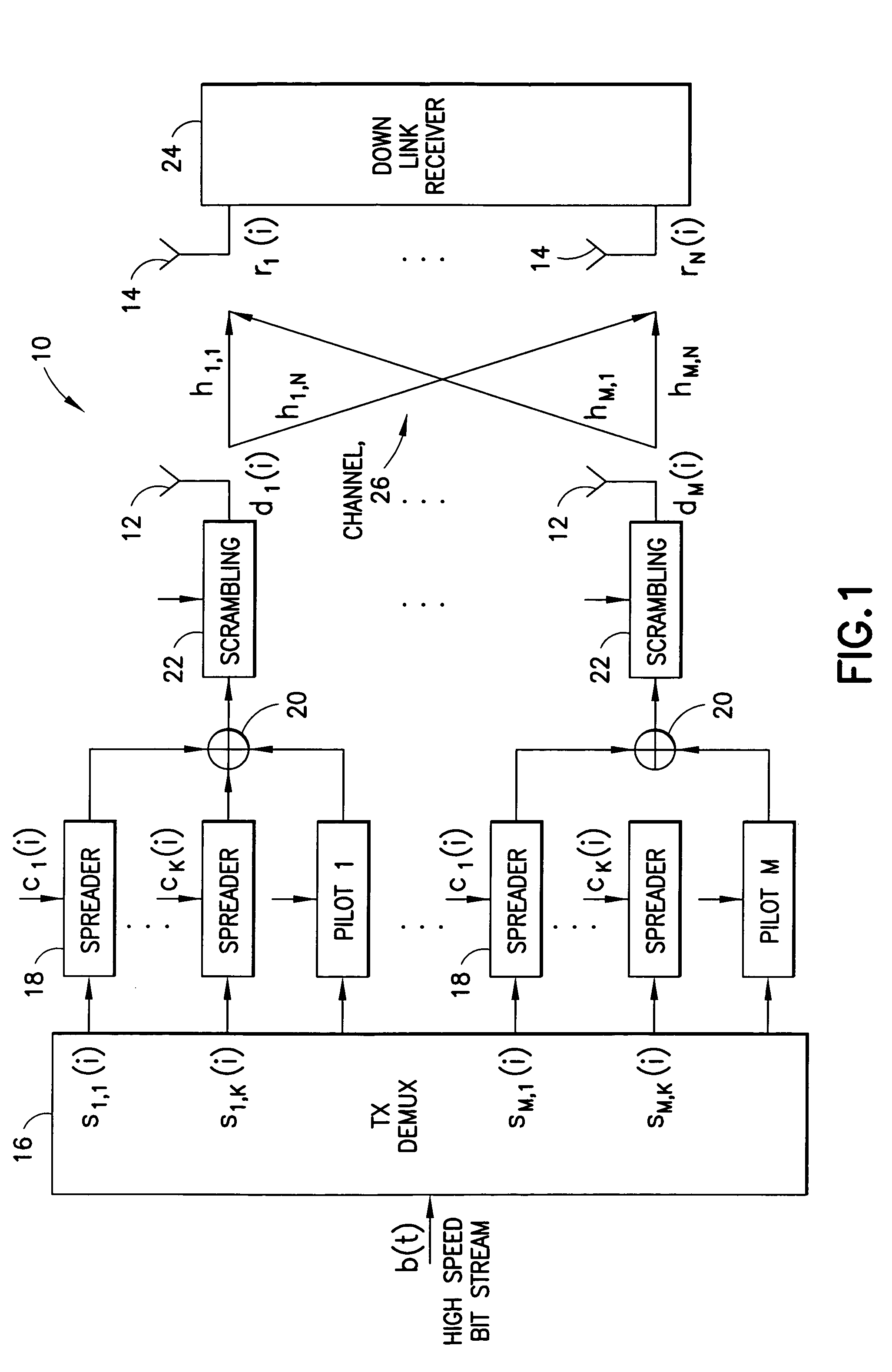
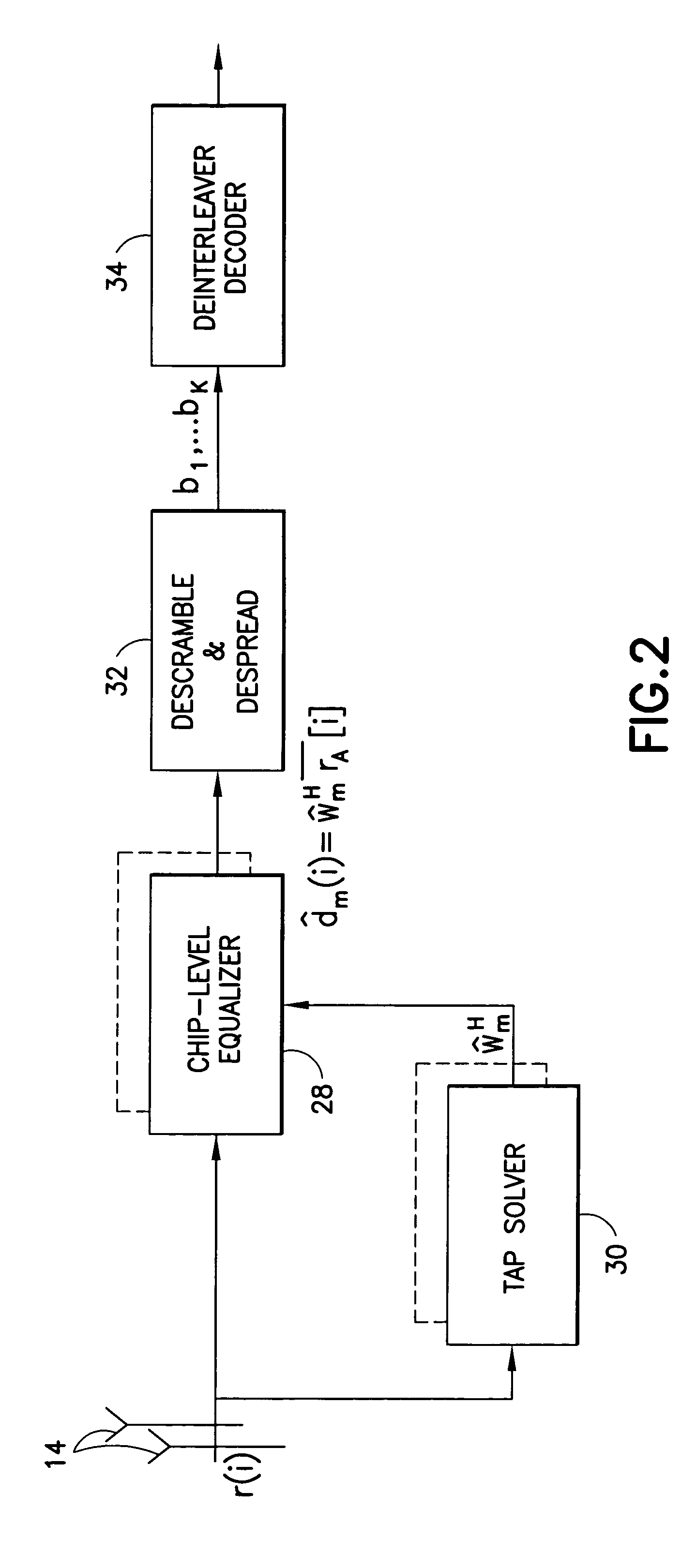
Disclosed is a LMMSE receiver that restores orthogonality of spreading codes in the downlink channel for a spread spectrum signal received over N receive antennas. The FFT-based chip equalizer tap solver reduces the direct matrix inverse of the prior art to the inverse of some submatrices of size N×N with the dimension of the receive antennas, and most efficiently reduces matrix inverses to no larger than 2×2. Complexity is further reduced over a conventional Fast Fourier Transform approach by Hermitian optimization to the inverse of submatrices and tree pruning. For a receiver with N=4 or N=2 with double oversampling, the resulting 4×4 matrices are partitioned into 2×2 block sub-matrices, inverted, and rebuilt into a 4×4 matrix. Common computations are found and repeated computations are eliminated to improve efficiency. Generic design architecture is derived from the special design blocks to eliminate redundancies in complex operations. Optimally, the architecture is parallel and pipelined.
Owner:VIVO MOBILE COMM CO LTD
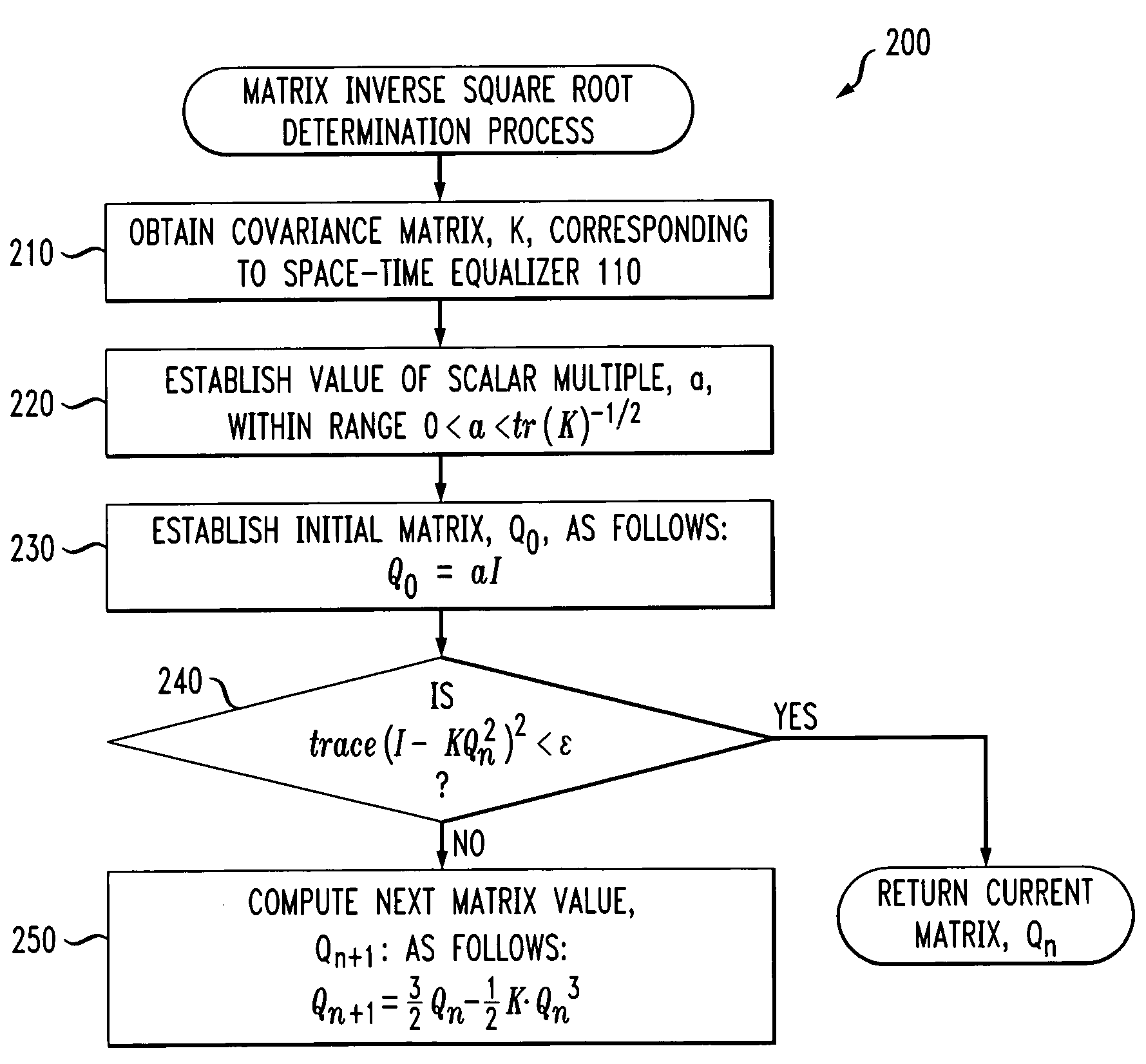
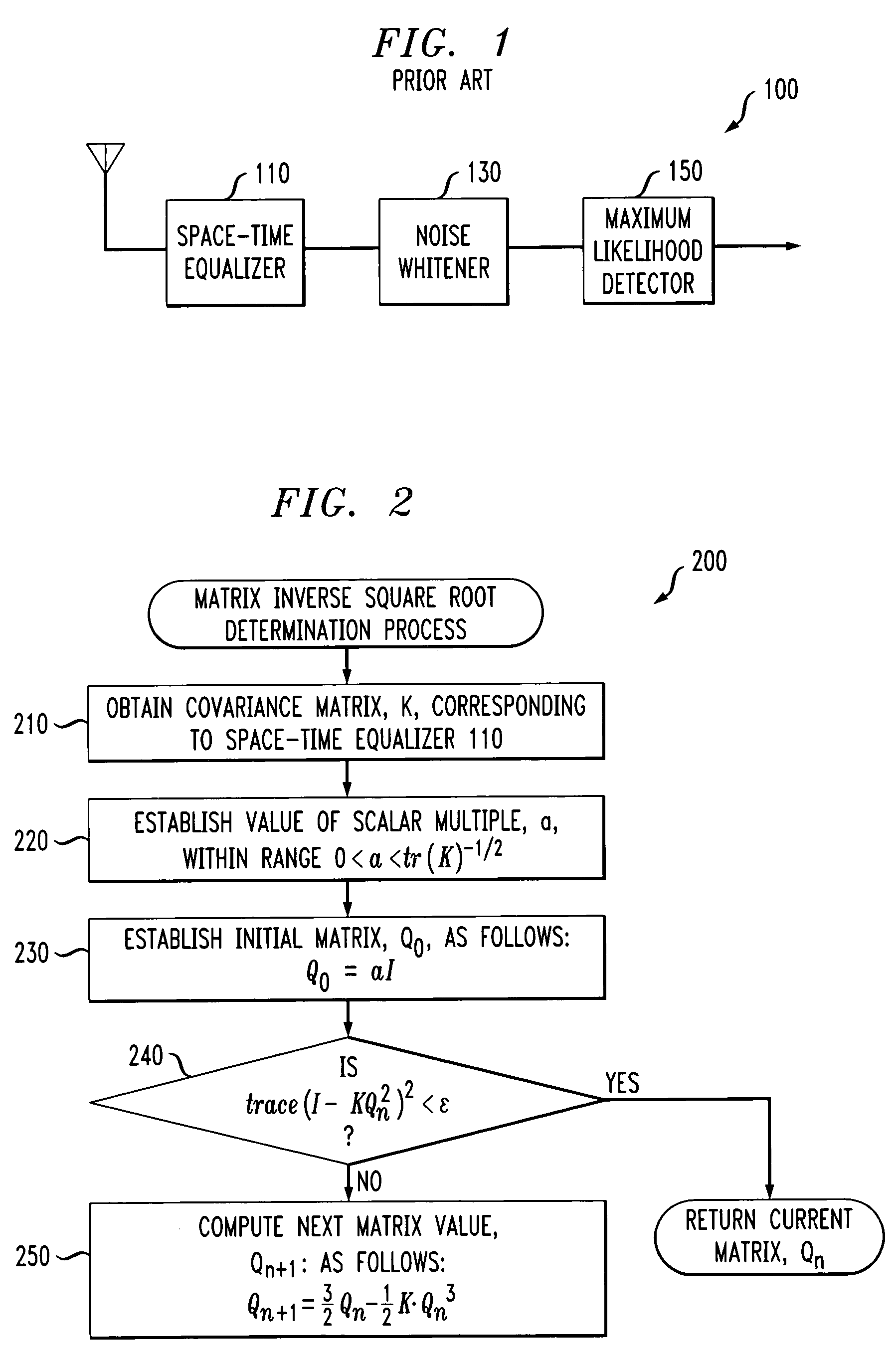
Method and apparatus for determining an inverse square root of a given positive-definite hermitian matrix
Generally, a method and apparatus are provided for computing a matrix inverse square root of a given positive-definite Hermitian matrix, K. The disclosed technique for computing an inverse square root of a matrix may be implemented, for example, by the noise whitener of a MIMO receiver. Conventional noise whitening algorithms whiten a non-white vector, X, by applying a matrix, Q, to X, such that the resulting vector, Y, equal to Q·X, is a white vector. Thus, the noise whitening algorithms attempt to identify a matrix, Q, that when multiplied by the non-white vector, will convert the vector to a white vector. The disclosed iterative algorithm determines the matrix, Q, given the covariance matrix, K. The disclosed matrix inverse square root determination process initially establishes an initial matrix, Q0, by multiplying an identity matrix by a scalar value and then continues to iterate and compute another value of the matrix, Qn+1, until a convergence threshold is satisfied. The disclosed iterative algorithm only requires multiplication and addition operations and allows incremental updates when the covariance matrix, K, changes.
Owner:LGS INNOVATIONS +1
Detection method and apparatus for multiple-input multiple-output single-carrier block transmission system
ActiveUS20120327757A1Improve performanceReduce complexityMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsQR decompositionTransfer system
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Sound beam forming method based on iterative algorithm
InactiveCN103944624AOne less inversion operationPrevent inversionSpatial transmit diversityMatrix inverseOptimal weight
The invention relates to the technology of sound and self-adaptive beam forming processing. A sound beam forming method based on the iterative algorithm is provided for solving the mismatching problem of array guiding vectors on the background of highly desired signals in the prior art. The sound beam forming method comprises the first step of working out the weight of the PI algorithm through a PI spectrum, the second step of reconstructing an interference noise covariance matrix out of the possible empty domain range of the desired signals according to the PI spectrum and the PI algorithm, and the last step of calculating the optimal weight of a beam forming device according to the reconstructed interference noise covariance matrix and repeatedly executing the PI algorithm, and the optimal weight vector of the beam forming device is updated. The interference noise covariance matrix is reconstructed based on the LMS iteration power inversion algorithm, and accordingly the matrix inverse operation in the traditional algorithm is directly avoided.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Matrix inverse operation method
InactiveCN105426345AImplement the inverse operationMeet performance needsComplex mathematical operationsMatrix inverseLU decomposition
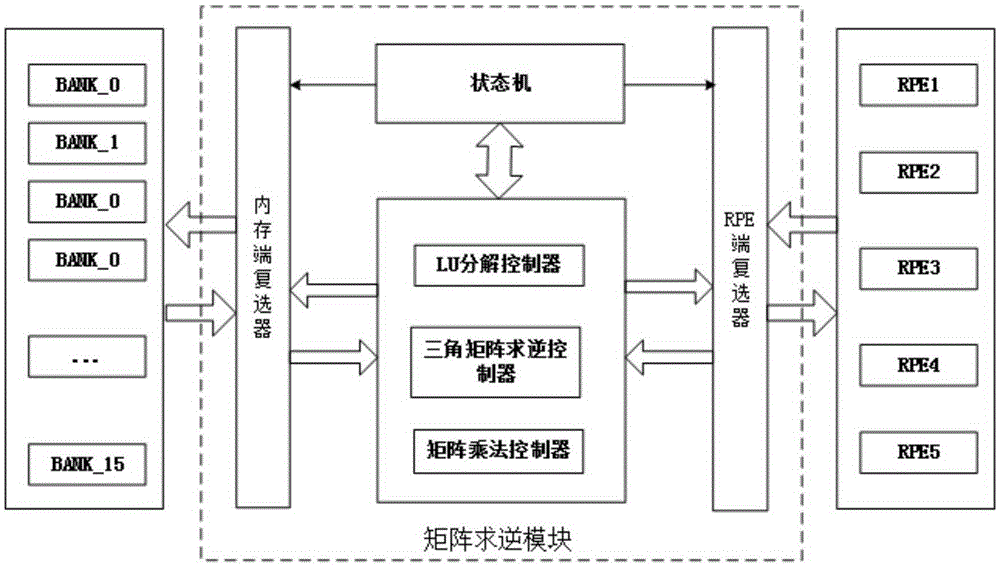
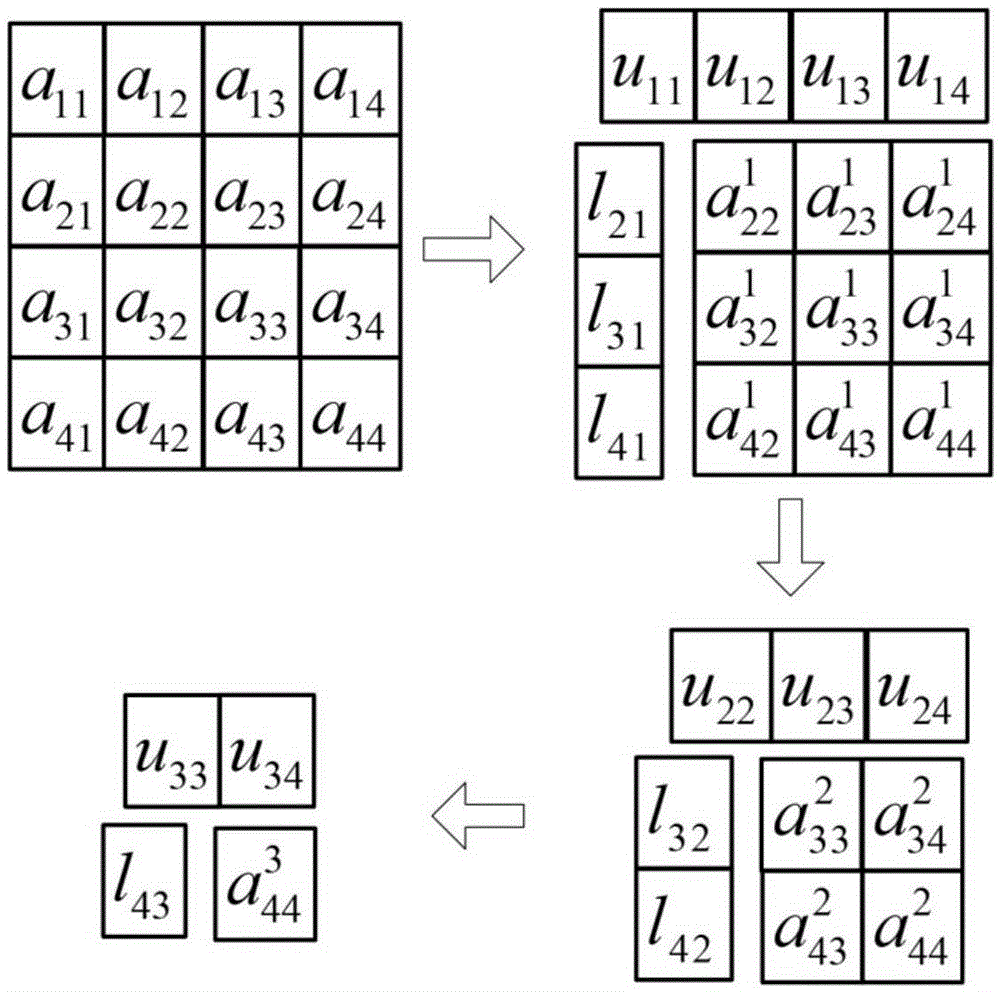
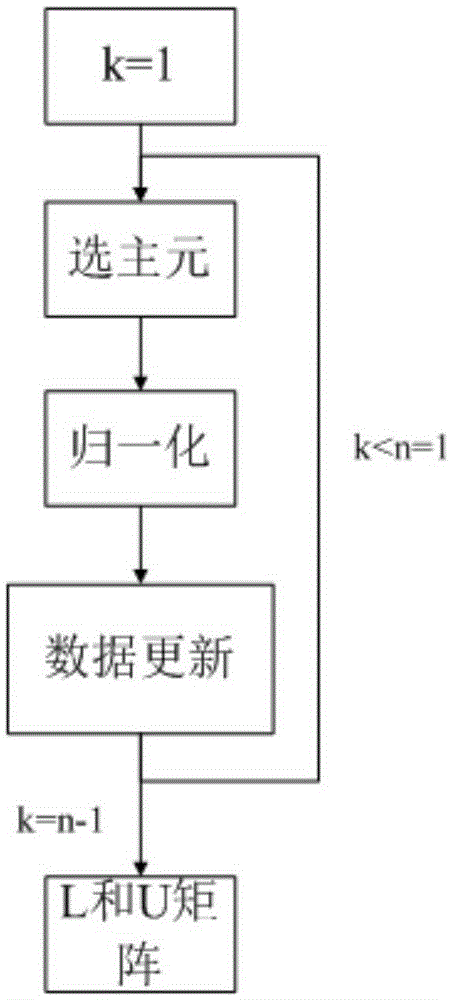
The invention relates to a matrix inverse operation method. The method comprises the steps of 1, conducting column pivoting LU decomposition, wherein a source matrix A is decomposed into a unit lower triangular matrix L, an upper triangular matrix U and a permutation matrix P according to the formula PA=LU; 2, conducting triangular matrix inversion, wherein the inverse matrix L-1 of the matrix L is obtained through matrix inversion, and matrix inversion is conducted on the transposed matrix of the matrix U and then transposition is conducted to obtain U-1; 3, finally conducting matrix multiplication, wherein the matrix U-1 and the matrix L-1 are multiplied, and column transformation is conducted on the matrix multiplication result according to the permutation matrix P to obtain a source matrix A-1. The method has the advantages that by using the column pivoting LU decomposition algorithm, the time complexity of the matrix inversion algorithm is effectively reduced, parallelizability of matrix inversion operation is improved, time for matrix inversion operation is shortened, matrix inversion operation of any order can be conducted, and the number of hardware resources can be increased or reduced according to count requirements of operation so that practical application requirements can be better met.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Rotor non-trial-weight dynamic balancing method suitable for distributed unbalance
InactiveCN103592081AImprove efficiencyReduce vibrationStatic/dynamic balance measurementAutomatic controlDynamic models
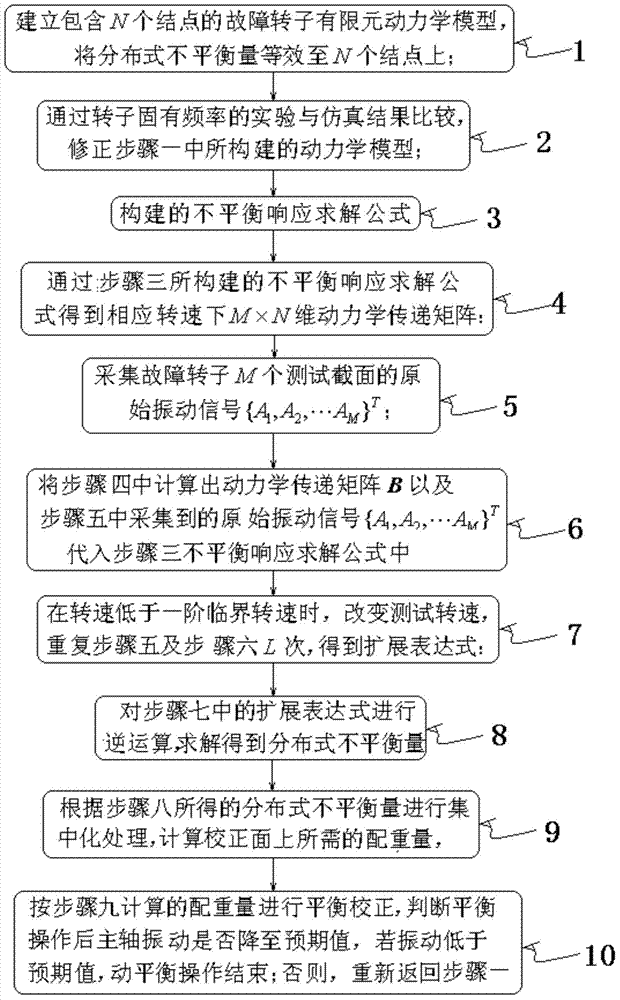
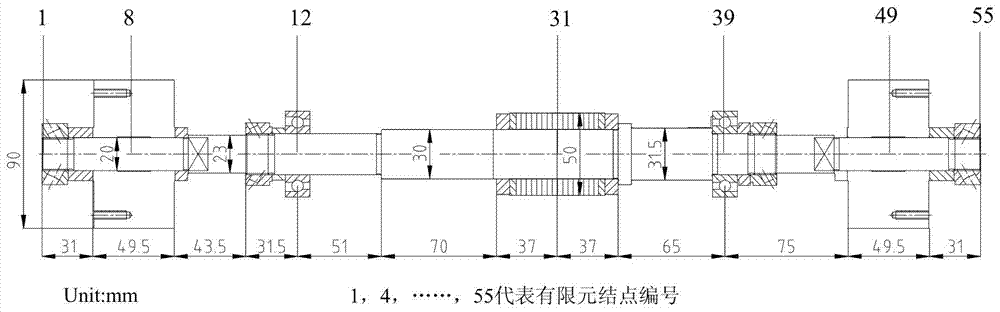
The invention discloses a rotor non-trial-weight dynamic balancing method suitable for distributed unbalance. The method includes the steps that firstly, on the basis of an established rotor finite element dynamic model, correction of the dynamic model is achieved through experiments and simulation, and then finite element node stress is used for describing the distributed unbalance of a rotor; secondly, dimensions of a dynamic transfer matrix in a describing equation of the distributed unbalance are extended through increase of the test rotating speed, reversibility of the transfer matrix is achieved, and then solution of the distributed unbalance is achieved through matrix inverse operation; finally, precise dynamic balance of the rotor is achieved through a concentrated correction method of the distributed unbalance. According to the rotor non-trial-weight dynamic balancing method suitable for the distributed unbalance, the distributed unbalance can be recognized integrally, and the dynamic balance precision is improved; no test weight is needed in the dynamic balance process, dynamic balance can be completed with the only requirement that the speed is lower than a critical rotating speed, safety of dynamic balance operation is guaranteed, and the requirements of the high-speed rotor are met; the dynamic balance process is concise, and automatic control of computers is achieved conveniently.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
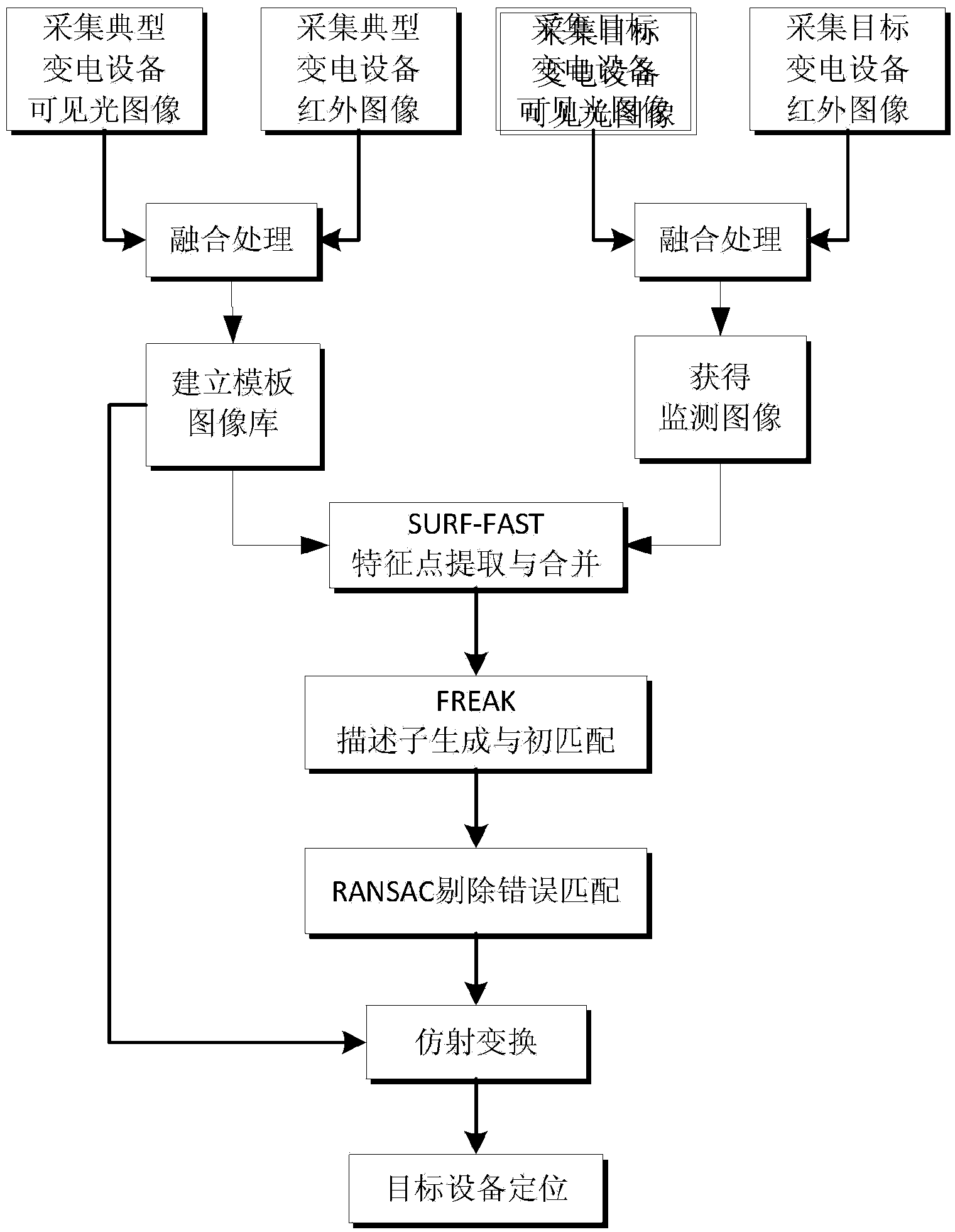
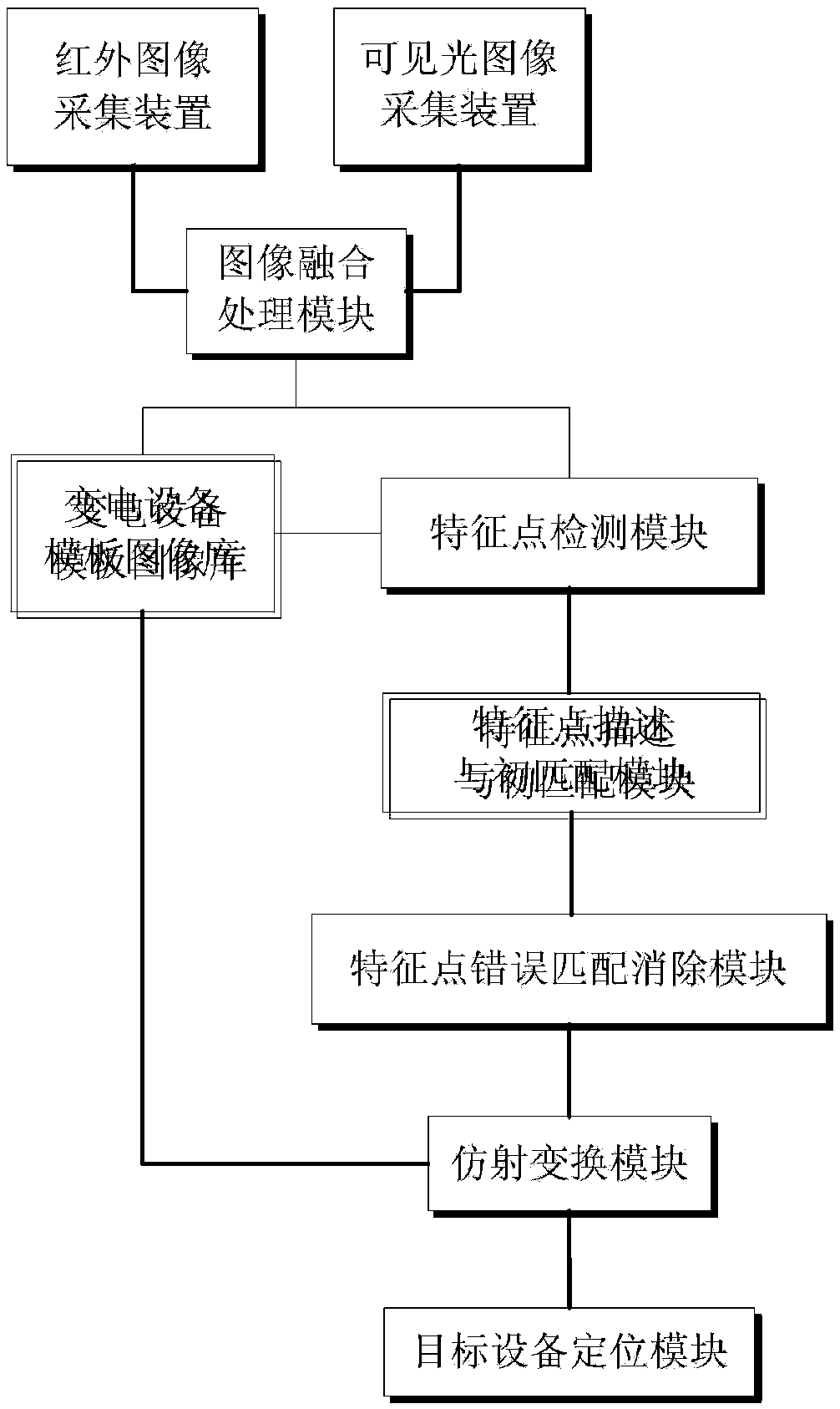
Method and device for positioning power transformation equipment on basis of infrared and visible image fusion
ActiveCN104361314AAutomatic and accurate positioningFault detection objectiveCharacter and pattern recognitionMatrix inverseComputer module
The invention belongs to the field of operating condition maintenance of power transmission and transformation equipment, and particularly relates to a method and a device for positioning power transformation equipment on basis of infrared and visible image fusion. The method includes: acquiring and fusing infrared and visible images of typical power transformation equipment and target power transformation equipment to obtain template images and monitoring images, detecting feature points according to the SURF (speed up robust feature)-FAST combinational algorithm, generating binary descriptors according to the FREAK (fast retina keypoint) algorithm and performing primary matching, and eliminating wrong matches according to the RANSAC (random sample consensus) algorithm; obtaining an affine transformation matrix by means of matrix inverse operation; performing affine transformation to obtain positions of the template images in the monitoring images, and positioning a recognition area of the target power transformation equipment. The device for positioning the power transformation equipment comprises an infrared image acquirer, a visible image acquirer, an image fusion processing module, a power transformation equipment template image base, a feature point detection module, a feature point description and primary matching module, a feature point wrong match eliminating module, an affine transformation module and a target equipment positioning module.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
Method for eliminating serial interference in multi-input multi-output system
InactiveCN101409604ASimplified Computational ComplexitySpatial transmit diversityError prevention/detection by diversity receptionPrecodingMulti input
The invention discloses a successive interference cancellation method in a multiple input and multiple output system, comprising QR ordering and decomposition are carried out on a channel transmission matrix based on householder transformation to obtain an upper triangular matrix R, and according to the matrix R, precoding successive interference cancellation is executed on all the transmit signals, or the successive interference cancellation is executed on the received signal. As the matrix R is the upper triangular matrix, the successive interference cancellation can be sequentially executed on all the transmit signals by utilizing the characteristics of the upper triangular matrix, thus avoiding determining the successive detection sequence in a way using VBLAST for matrix inverse or pseudo-inverse, and further simplifying the computational complexity of the successive interference cancellation and improving the performance of signal detection.
Owner:TD TECH COMM TECH LTD
Reduced parallel and pipelined high-order MIMO LMMSE receiver architecture
ActiveUS7492815B2Reduce complexityReduce the numberMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsFast Fourier transformRound complexity
Disclosed is a LMMSE receiver that restores orthogonality of spreading codes in the downlink channel for a spread spectrum signal received over N receive antennas. The FFT-based chip equalizer tap solver reduces the direct matrix inverse of the prior art to the inverse of some submatrices of size N×N with the dimension of the receive antennas, and most efficiently reduces matrix inverses to no larger than 2×2. Complexity is further reduced over a conventional Fast Fourier Transform approach by Hermitian optimization to the inverse of submatrices and tree pruning. For a receiver with N=4 or N=2 with double oversampling, the resulting 4×4 matrices are partitioned into 2×2 block sub-matrices, inverted, and rebuilt into a 4×4 matrix. Common computations are found and repeated computations are eliminated to improve efficiency. Generic design architecture is derived from the special design blocks to eliminate redundancies in complex operations. Optimally, the architecture is parallel and pipelined.
Owner:VIVO MOBILE COMM CO LTD
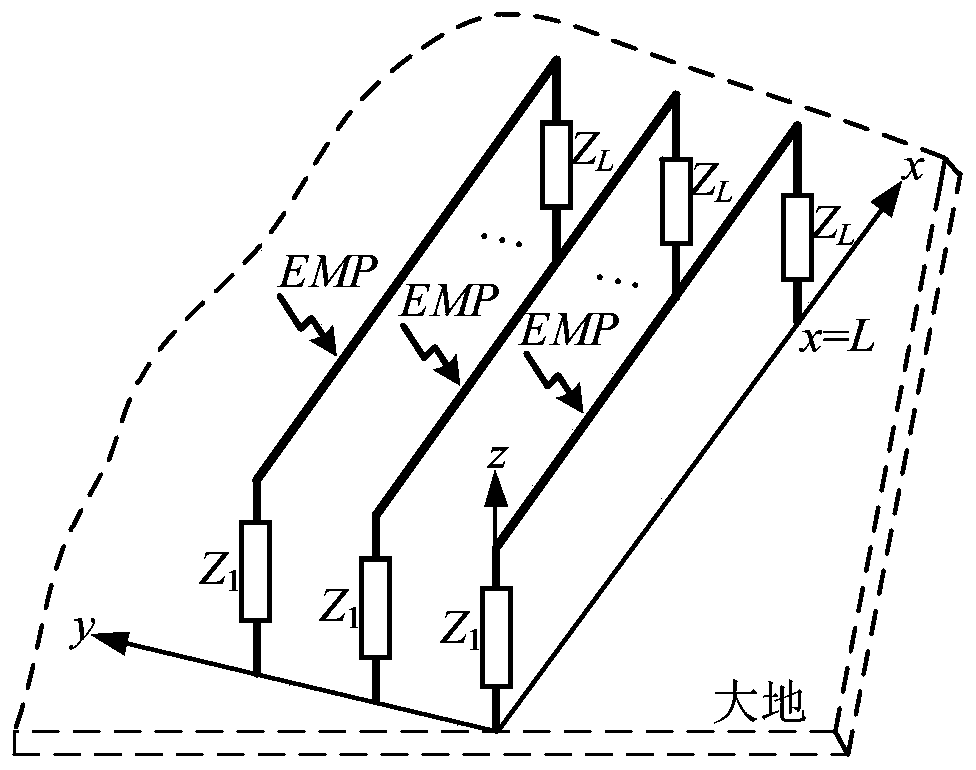
Waveform relaxation iteration-based rapid modeling method for electromagnetic pulse response of a time domain multi-conductor transmission line
ActiveCN109783768AImprove computing efficiencyComplex mathematical operationsElectrical conductorWave equation
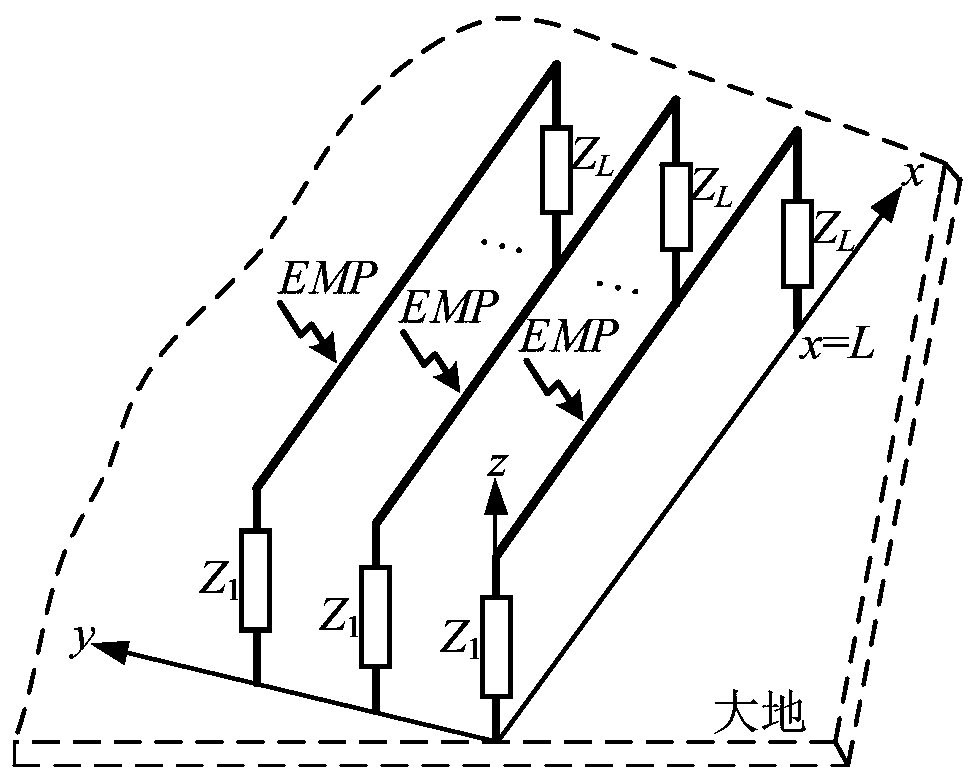
The invention discloses a waveform relaxation iteration-based rapid modeling method for electromagnetic pulse response of a time domain multi-conductor transmission line. According to the method, a time domain calculation model for solving coupling of the electromagnetic pulse to the multi-conductor transmission line based on a waveform relaxation algorithm and analytical iteration is establishedin a time domain; A combined voltage wave equation and a BLT supermatrix equation are used; the mutual coupling influence between the transmission lines is equivalent to virtual excitation sources which are continuously distributed on the transmission lines; An analytical expression of voltage and current responses along a transmission line is deduced and given, large-scale matrix inverse operation is converted into a series of iteration processes, meanwhile, each iteration step can give an analytical solution, time-consuming numerical integration is avoided, and the calculation efficiency isimproved.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
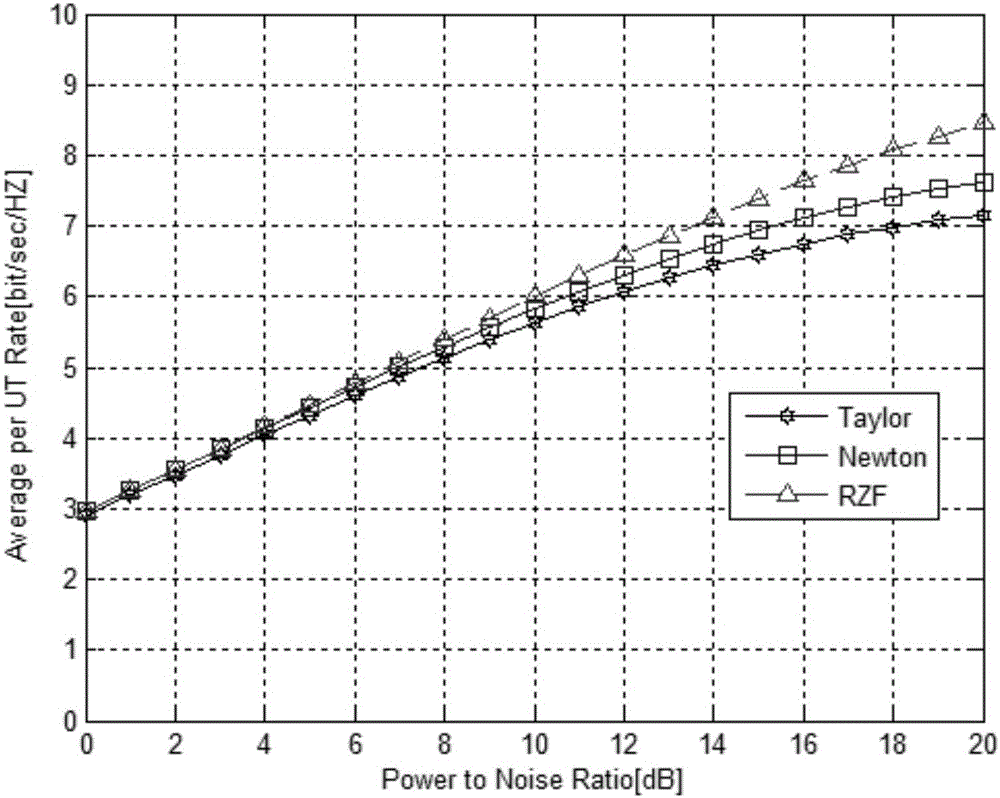
Large-scale MIMO (Multiple Input Multiple Output) precoding method based on improved newton iteration method
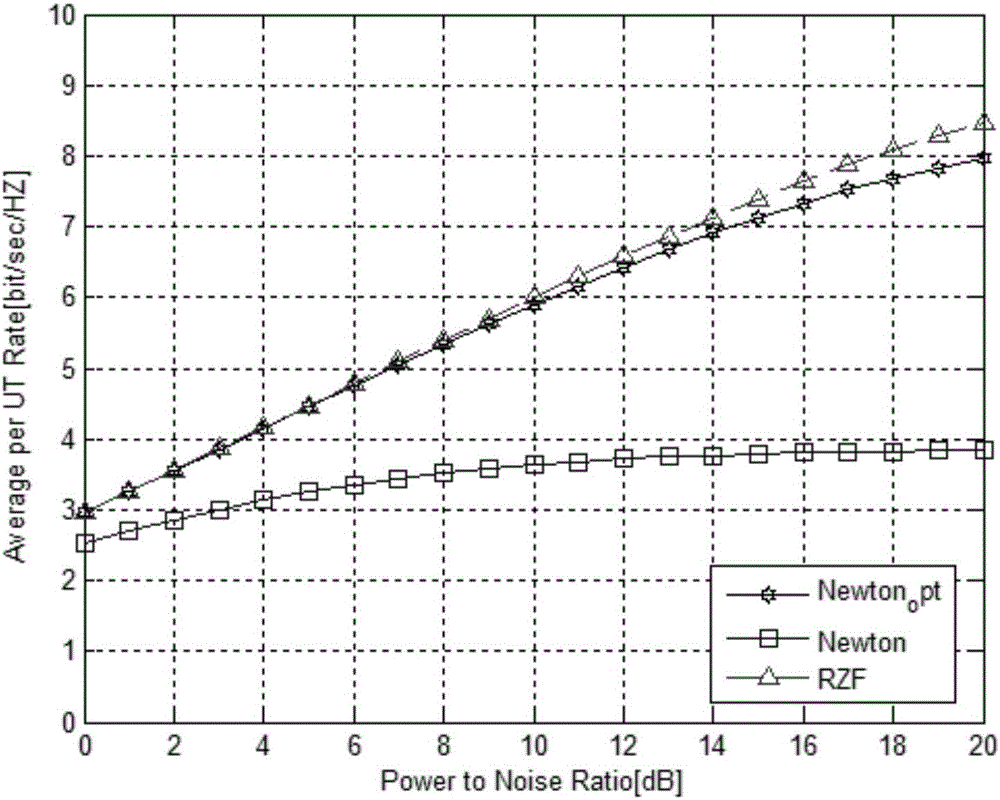
The invention discloses a large-scale MIMO (Multiple Input Multiple Output) precoding method based on an improved newton iteration method. The method comprises the following steps of firstly estimating a channel matrix, and calculating an RZF precoding expression through the obtained channel matrix; then adopting the newton iteration method for estimating an inverse matrix in an RZF precoding algorithm, and converting matrix inverse operation into matrix addition and matrix multiplication operation; finally utilizing an obtained precoding matrix for precoding a sending signal. The improved newton iteration method is characterized by building a high-order iteration formula, transforming a characteristic value located near 0 to closer to 1 , and remaining a characteristic value near 1 unchanged, so that the convergence rate of newton iteration is accelerated. An experimental result shows that when the iteration times exceeds four times, the performance of a traditional newton iteration method is superior to an inverse matrix estimation algorithm based on taylor series expansion. When the iteration times is 2, the improved newton iteration optimization algorithm can acquire around 95 percent of RZF precoding average client arrival rate.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
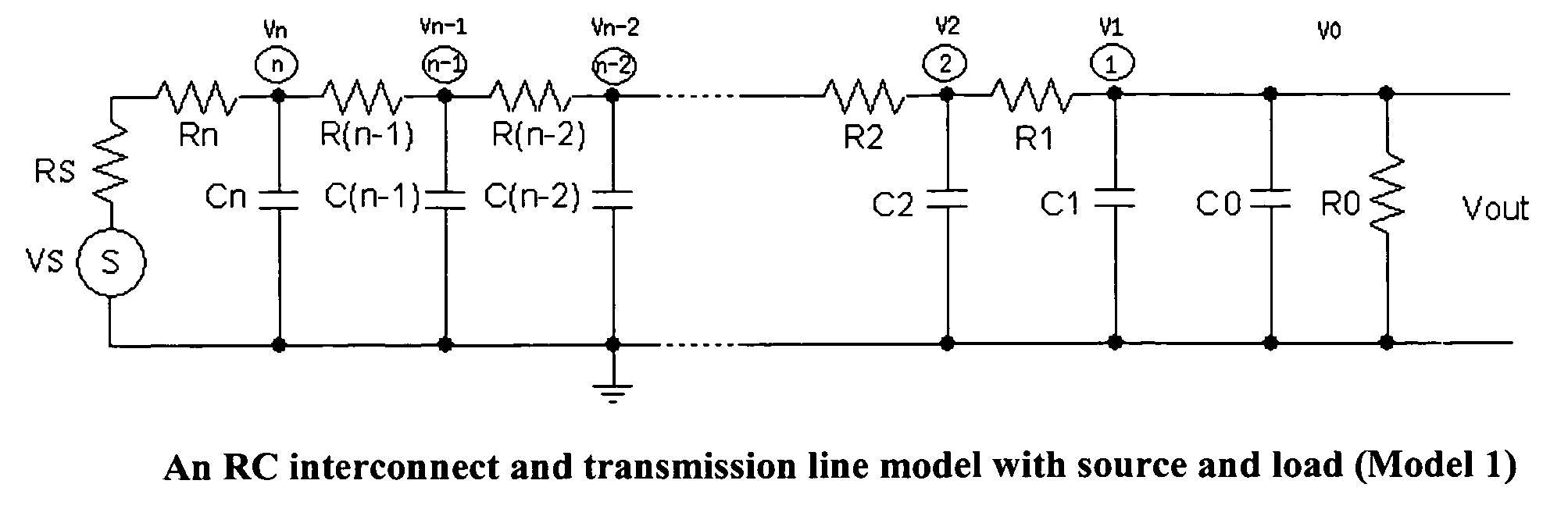
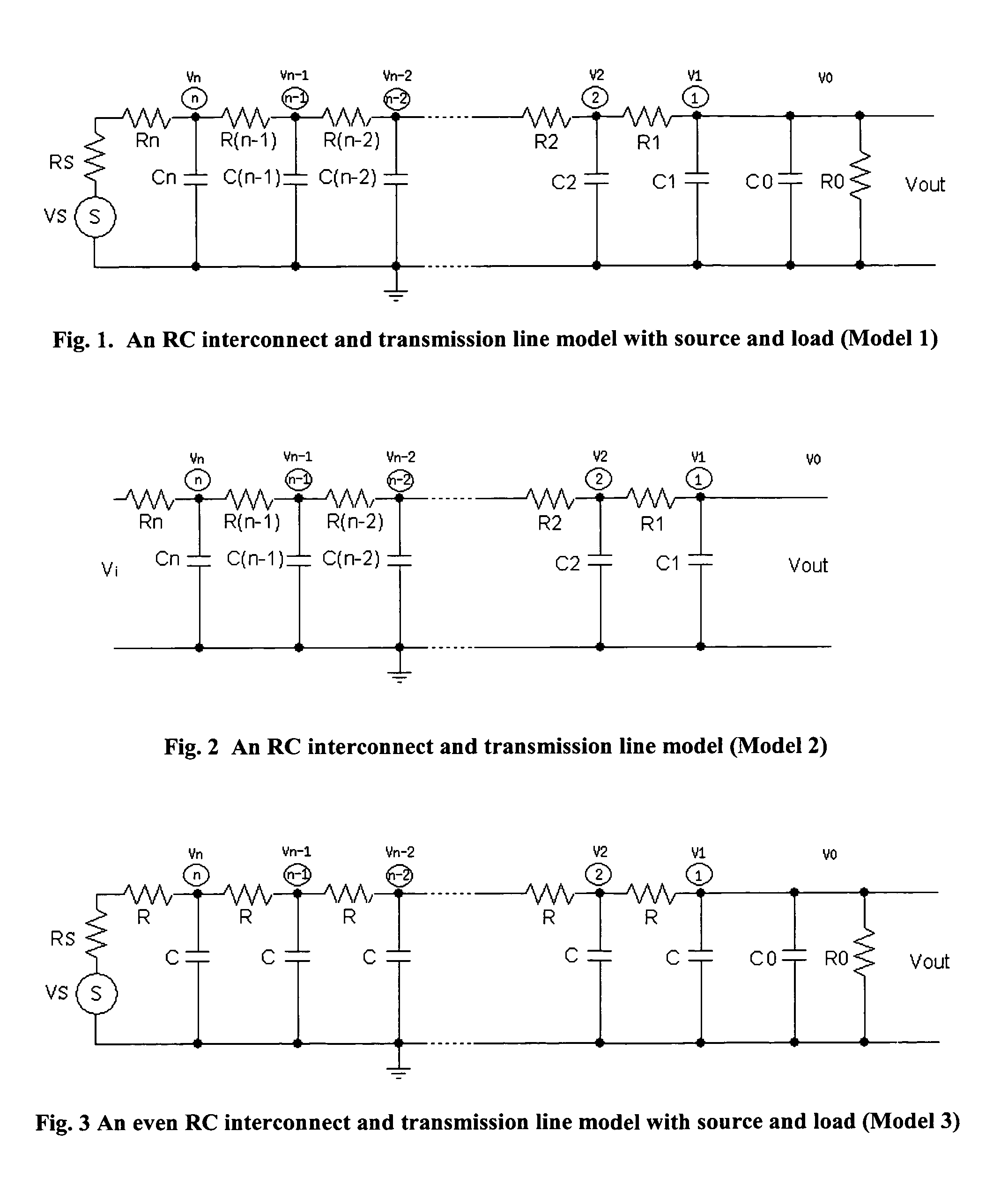
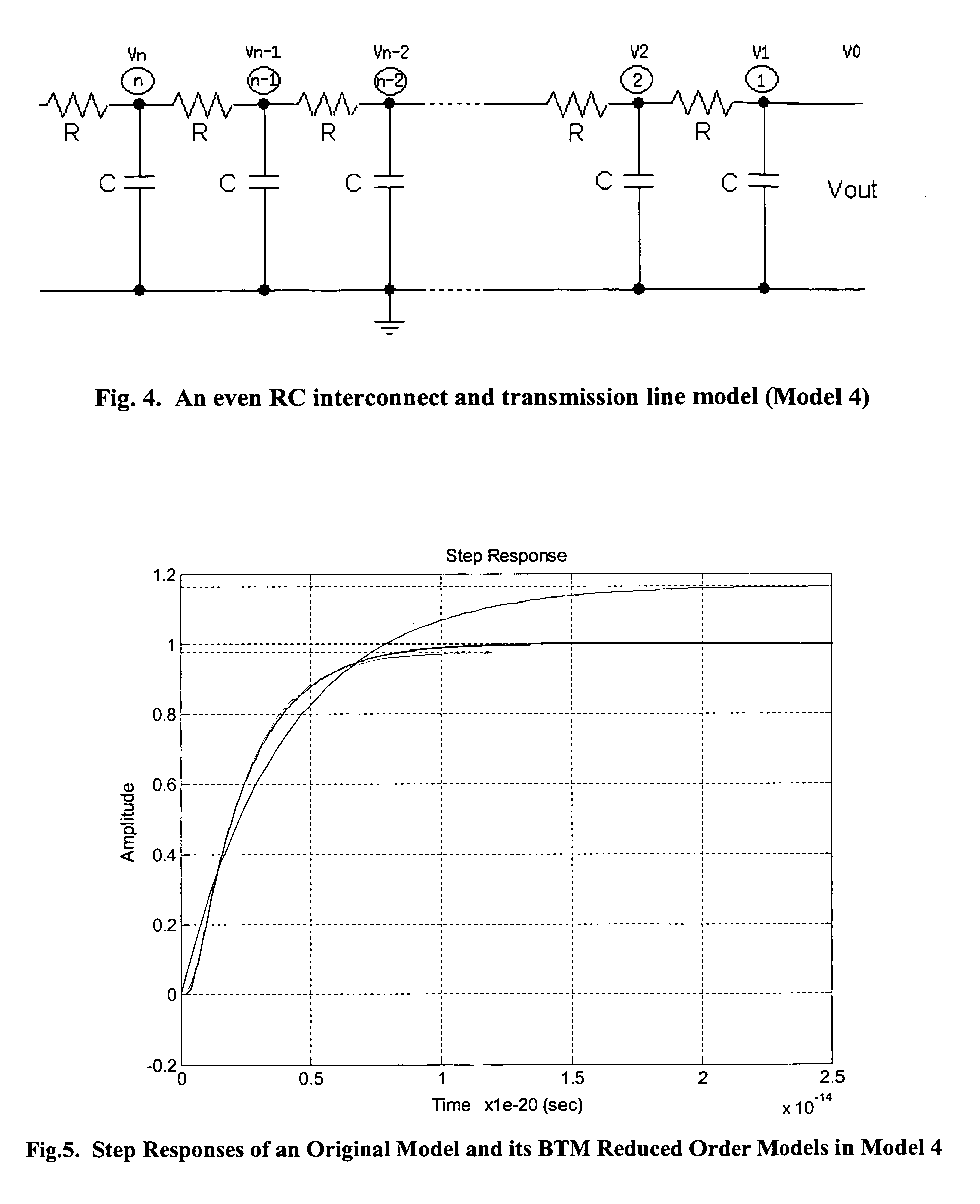
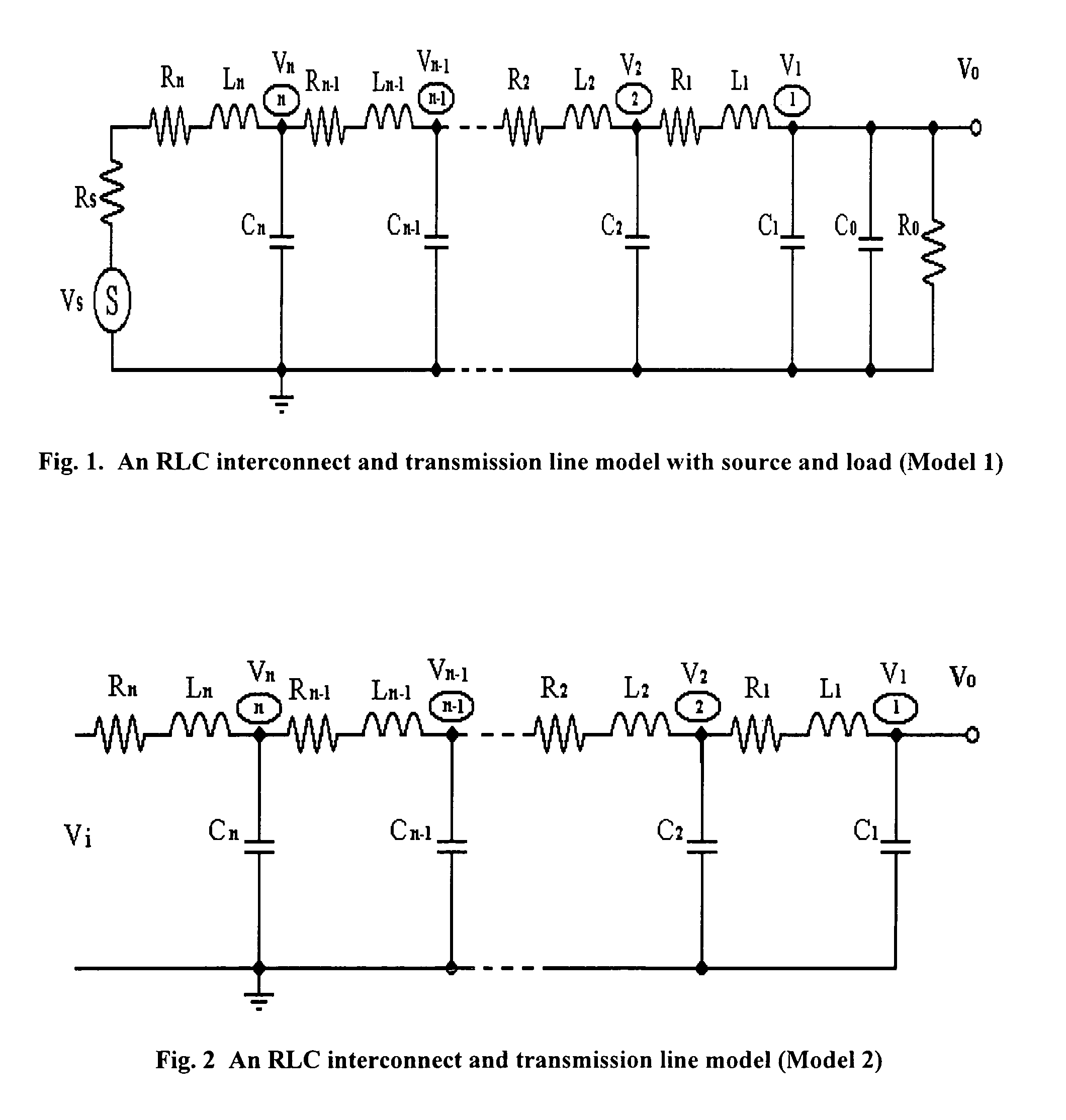
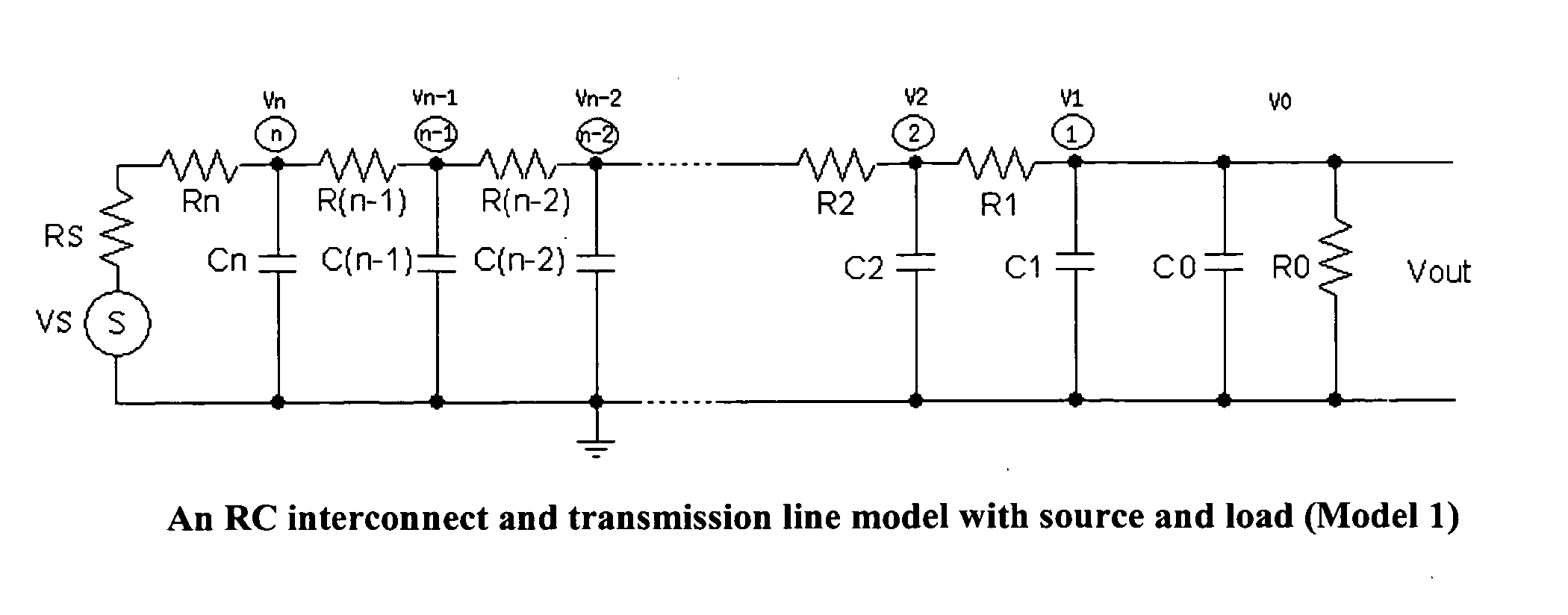
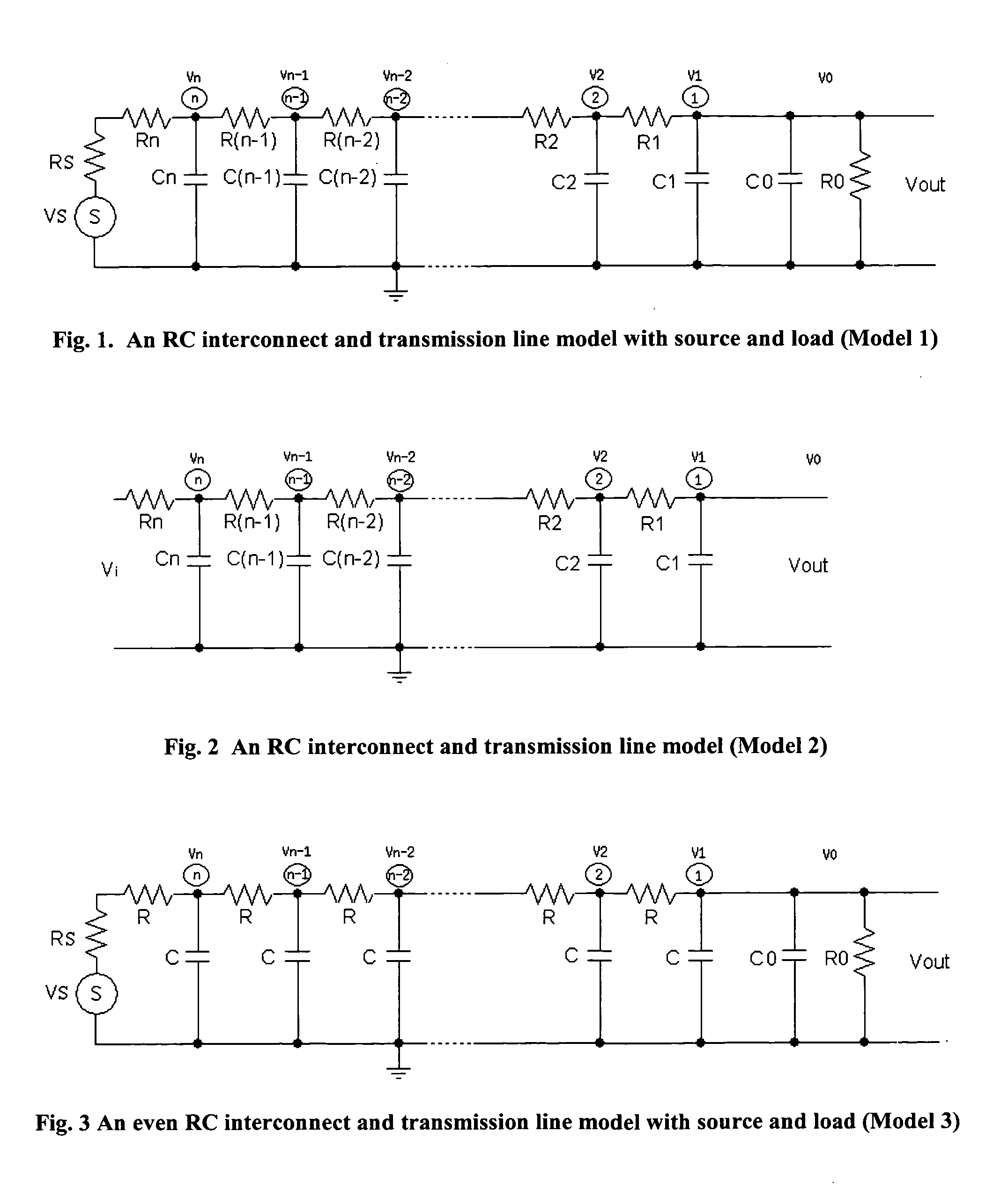
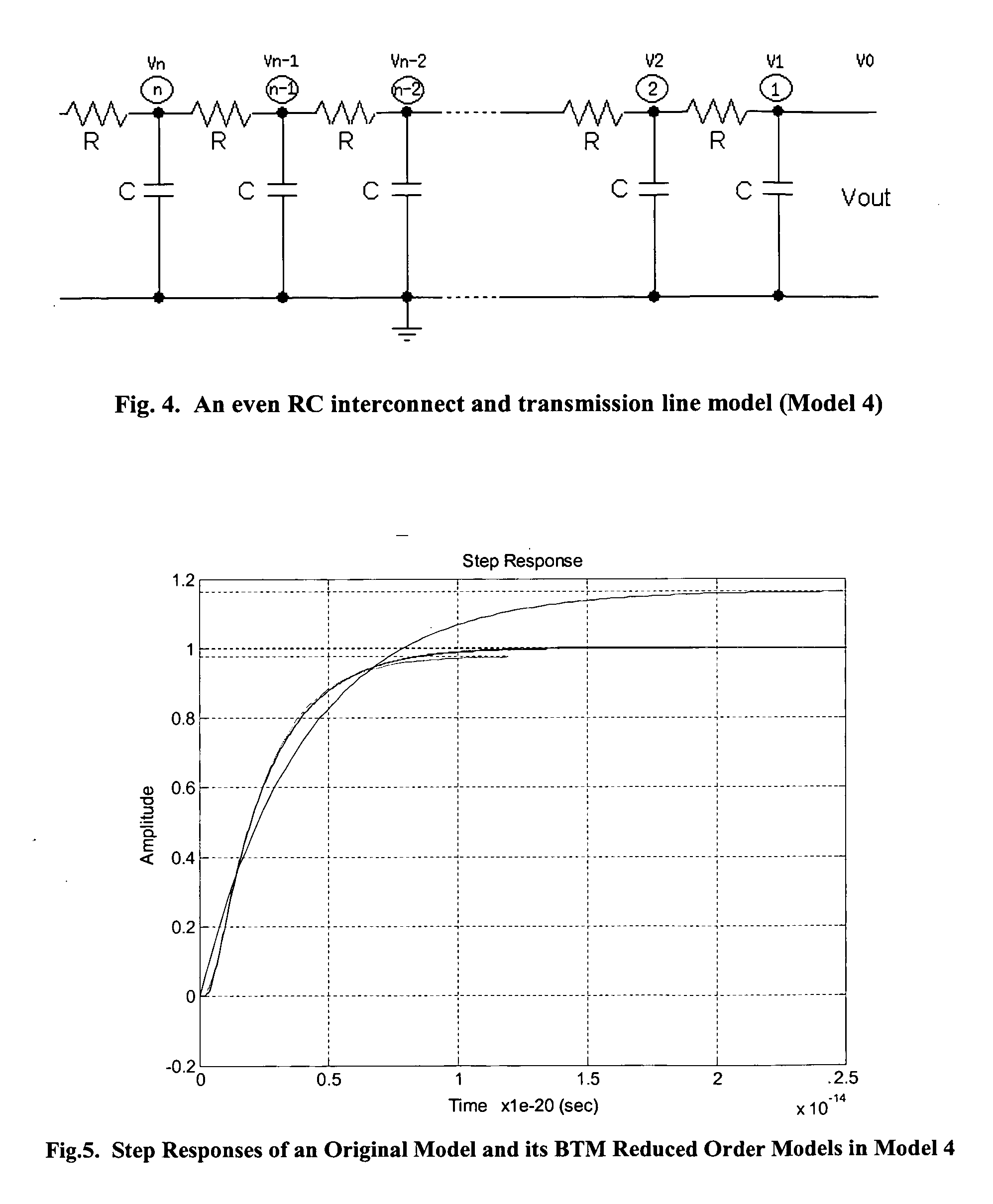
Methods to generate state space models by closed forms and transfer functions by recursive algorithms for RC interconnect and transmission line and their model reduction and simulations
ActiveUS7124388B2Accurate captureImprove stabilityComputation using non-denominational number representationProgram controlComputation complexityMatrix inverse
Owner:BEN SHENG TECH
Reduced parallel and pipelined high-order mimo lmmse receiver architecture
Disclosed is a LMMSE receiver that restores orthogonality of spreading codes in the downlink channel for a spread spectrum signal received over N receive antennas. The FFT-based chip equalizer tap solver reduces the direct matrix inverse of the prior art to the inverse of some submatrices of size NxN with the dimension of the receive antennas, and most efficiently reduces matrix inverses to no larger than 2x2. Complexity is further reduced over a conventional Fast Fourier Transform approach by Hermitian optimization to the inverse of submatrices and tree pruning. For a receiver with N=4 or N=2 with double oversampling, the resulting 4x4 matrices are partitioned into 2x2 block sub-matrices, inverted, and rebuilt into a 4x4 matrix. Common computations are found and repeated computations are eliminated to improve efficiency. Generic design architecture is derived from the special design blocks to eliminate redundancies in complex operations. Optimally, the architecture is parallel and pipelined.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
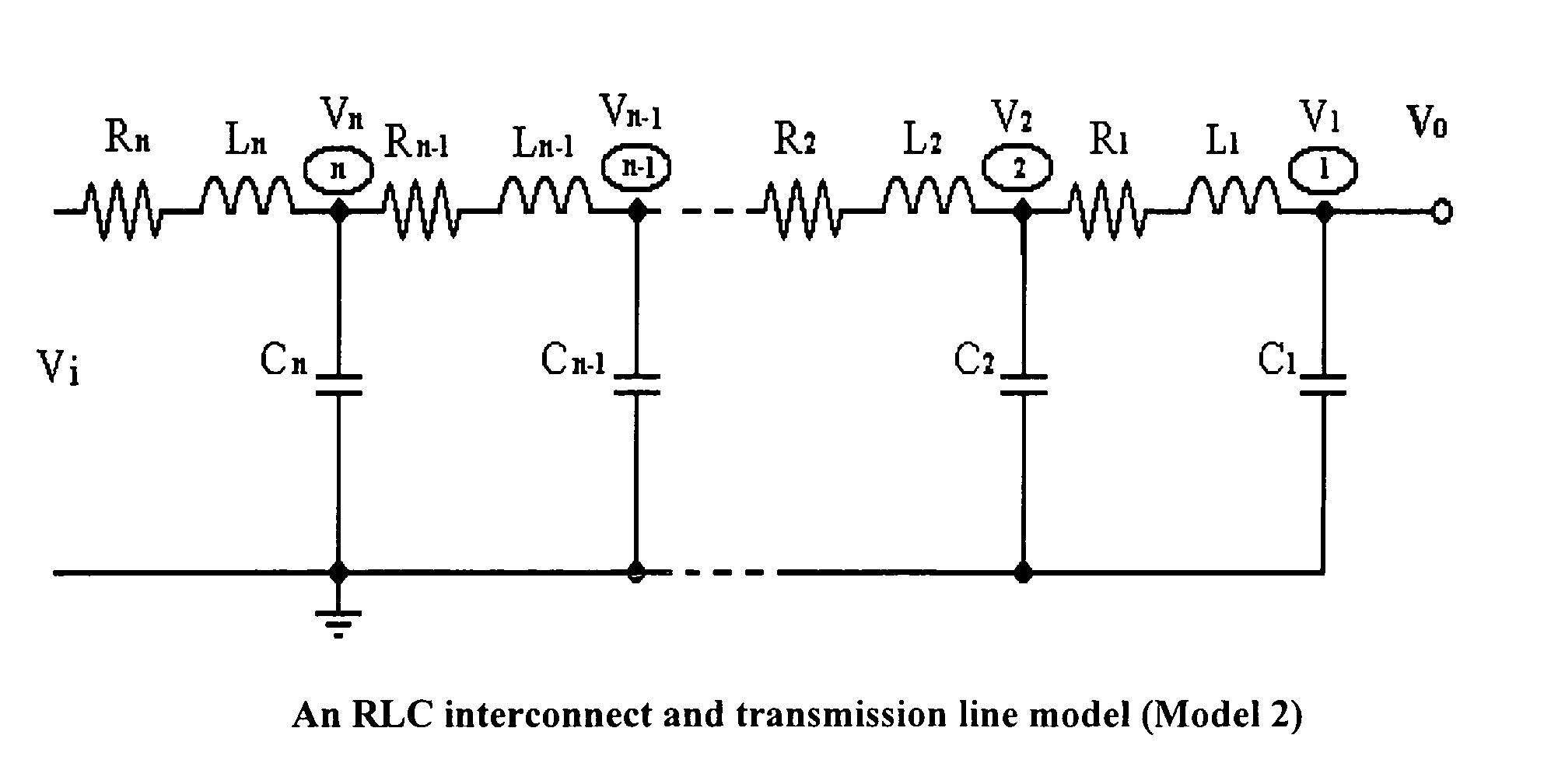
Methods to generate state space models by closed forms and transfer functions by recursive algorithms for RLC interconnect and transmission line and their model reduction and simulations
ActiveUS7251791B2Accurate captureImprove stabilityComputation using non-denominational number representationComputer aided designComputation complexityMatrix inverse
There is provided a set of methods with the exact accuracy to effectively calculate the 2n-th order state space models of RLC distributed interconnect and transmission line in closed forms in time domain and transfer functions by recursive algorithms in frequency domain, where their RLC components can be evenly distributed or variously valued. The main features include simplicity and accuracy of the said closed forms of the state space models {A,B,C,D} without involving matrix inverse and matrix multiplication operations, effectiveness and accuracy of the said recursive algorithms of the transfer functions, dramatic reduction of the calculation complexity to O(n2) for the state space models, simulation methodology, and practice of various model reductions and their optimization. For evenly distributed RLC interconnect and transmission line, the said closed form of state space model has its computation complexity of only a fixed constant, i.e., O(1).
Owner:BEN SHENG TECH
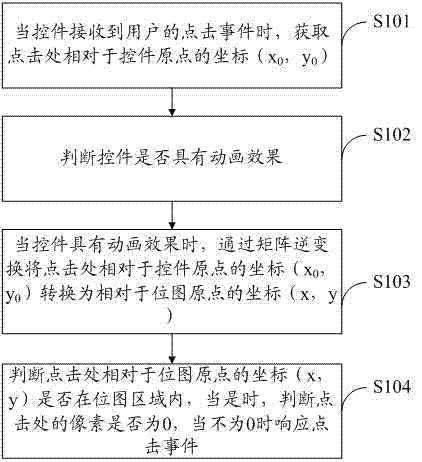
Control clicking event processing method and system
InactiveCN103543923AImprove user experienceImprove processing accuracyInput/output processes for data processingPattern recognitionMatrix inverse
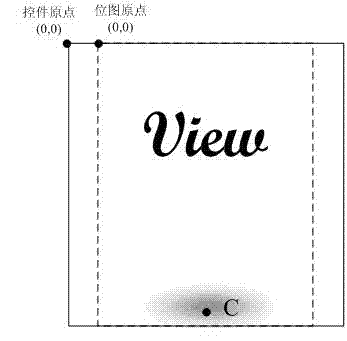
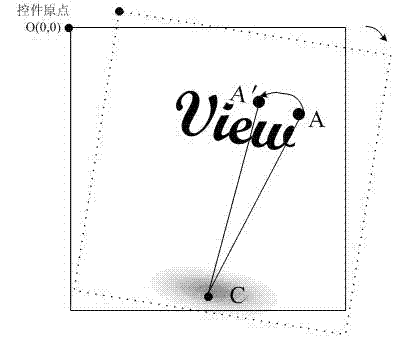
The invention discloses a control clicking event processing method and system. The method comprises the following steps: when a control receives a clicking event by a user, a coordinate (x0, y0) relative to a control origin at the clicking position is acquired; whether the control has an animation effect is judged; when the control has the animation effect, the coordinate (x0, y0) relative to the control origin at the clicking position is converted into a coordinate (x, y) relative to a bitmap origin through matrix inverse transformation; whether the coordinate (x, y) relative to the bitmap origin at the clicking position is in a bitmap area is judged, if yes, whether the pixel value of the coordinate at the clicking position is 0 is judged, and a response to the clicking event is conducted when the pixel value of the coordinate at the clicking position is not 0.
Owner:TCL CORPORATION
Plane type camera calibration method
ActiveCN103854271AImprove stabilityHigh distortion resistanceImage analysisComputation complexityMatrix inverse
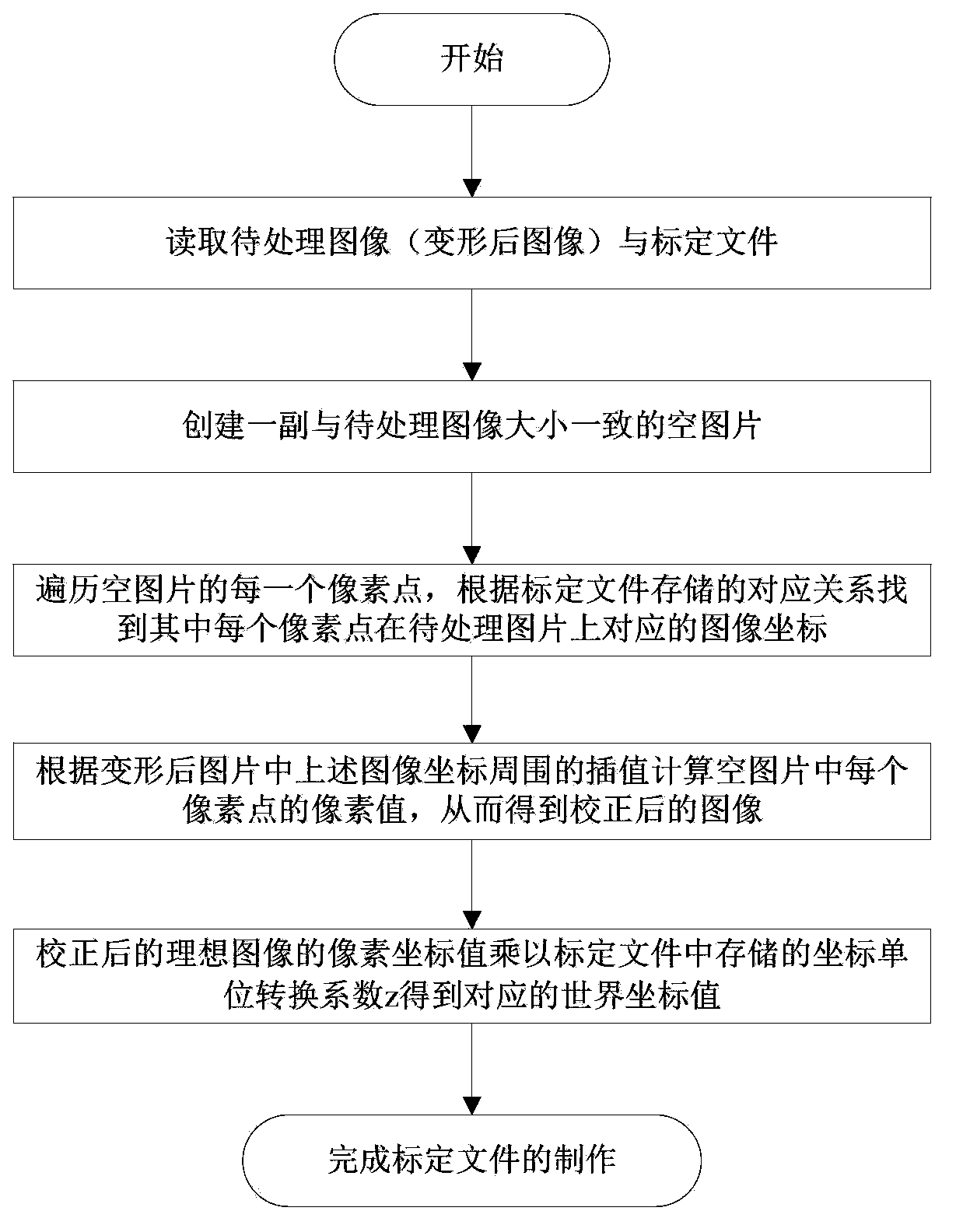
The invention discloses a plane type camera calibration method, comprising steps of estimating positions of characteristic points on an image before deformation and calculating interpolation relation between the pixel point in the image and the subdivision triangle peak where the pixel point is positioned, utilizing the pixel coordinate of the deformed characteristic point to calculate the corresponding position of each pixel point of the image before deformation on the deformed image according to the interpolation relation, and utilizing the pixel value interpolation of the deformed pixel points adjacent to the corresponding position to calculate to obtain the image pixel value to finish the image correction. The invention utilizes the local linear inner interpolation to replace the polynomial fitting which is finished by higher order matrix inverse. Compared with the prior art, the invention has lower calculation complexity, higher stability and higher deformation resistance on the premise that the image correction effect and the calibration calculation accuracy are guaranteed.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Frequency domain multi-conductor transmission line electromagnetic pulse response rapid modeling method based on waveform relaxation iteration
PendingCN109783919AReduce computational efficiencyImprove computing efficiencySpecial data processing applicationsElectrical conductorWave equation
The invention discloses a frequency domain multi-conductor transmission line electromagnetic pulse response rapid modeling method based on waveform relaxation iteration. A frequency domain calculationmodel for solving coupling of the electromagnetic pulse to the multi-conductor transmission line based on a waveform relaxation algorithm and analytical iteration is established in the frequency domain; A combined voltage wave equation and a BLT supermatrix equation are used; the mutual coupling influence between the transmission lines is equivalent to virtual excitation sources which are continuously distributed on the transmission lines; An analytical expression of voltage and current responses along a transmission line is deduced and given, large-scale matrix inverse operation is convertedinto a series of iteration processes, meanwhile, each iteration step can give an analytical solution, time-consuming numerical integration is avoided, and the calculation efficiency is improved.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Flexible magnetic levitation bearing rotator rigidity damping identification method
The invention discloses a flexible magnetic levitation bearing rotary rigidity damping identification method, and belongs to the technical field of magnetic levitation bearing dynamic feature identification. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, acquiring two groups of independent magnetic levitation bearing rotor system rotation responses, namely, responses added with unbalance masses and responses not added with any unbalance mass; acquiring amplitude and phase data of two groups of independent responses by first-order Fourier series fitting; subtracting corresponding amplitude and phase data from the two groups of responses to eliminate interference force influence in the rotating process of a magnetic levitation bearing rotor subsystem; calculating amplitude and phase data from which the interference force influence is eliminated through a matrix inverse transformation recognition algorithm to obtain a magnetic levitation bearing rigidity damping dynamic feature. Compared with the prior art, the method has the advantages of high resolving accuracy and high interference resistance, is suitable for rigidity rotors below a bending critical rotation speed, and is suitable for flexible rotors over a bending critical rotation speed.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Equation set solver based on memristor linear neural network and operation method of equation set solver
ActiveCN111460365AReduce power consumptionIntegrated reductionBiological neural network modelsComplex mathematical operationsCircuit complexityMatrix inverse
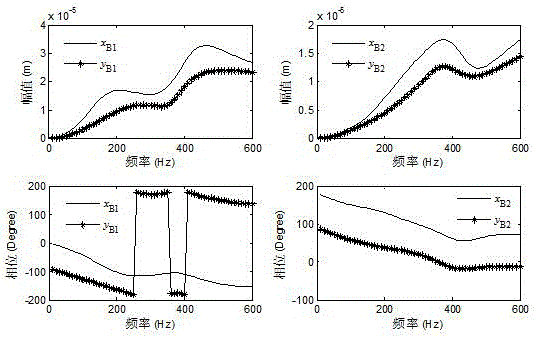
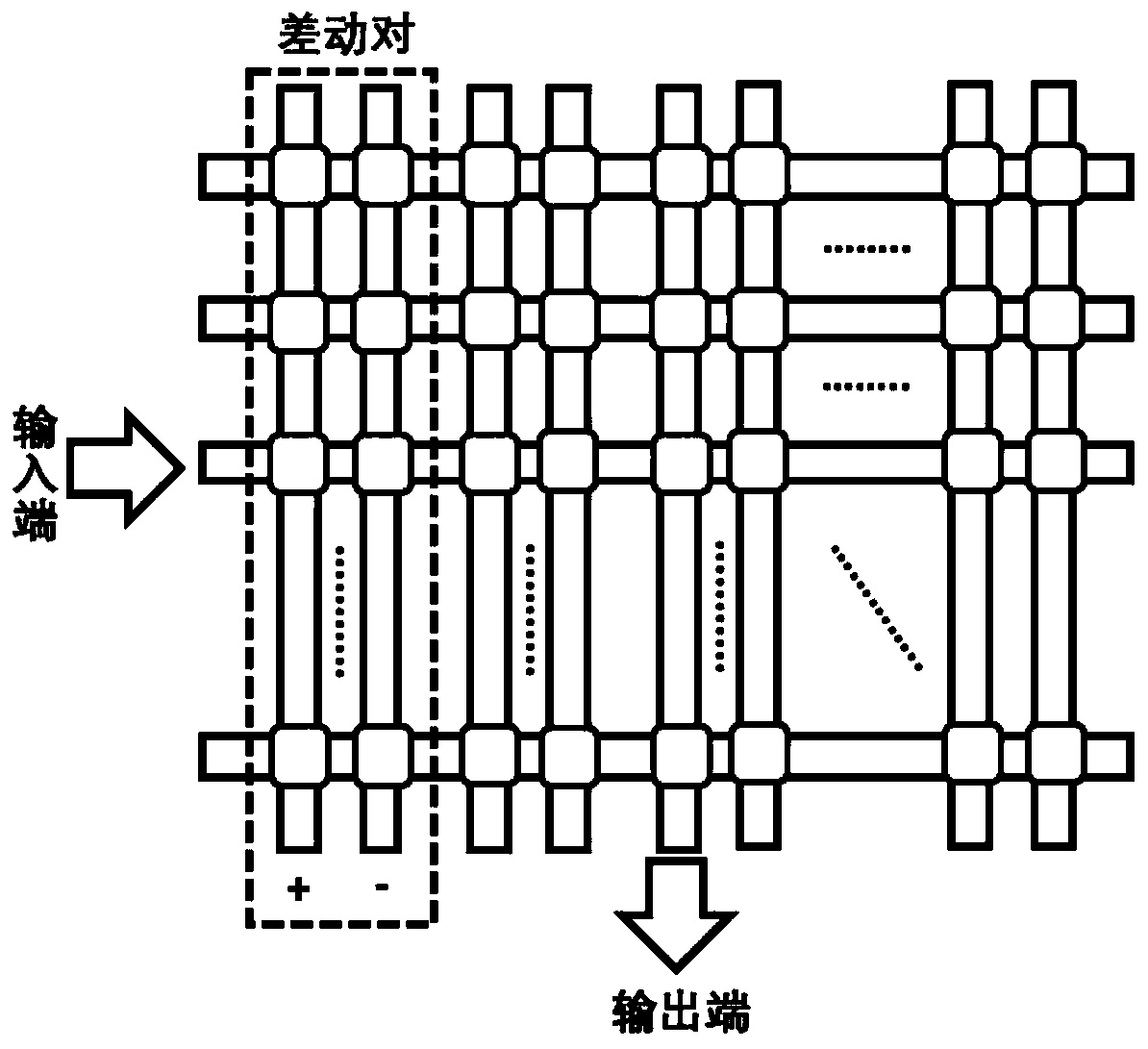
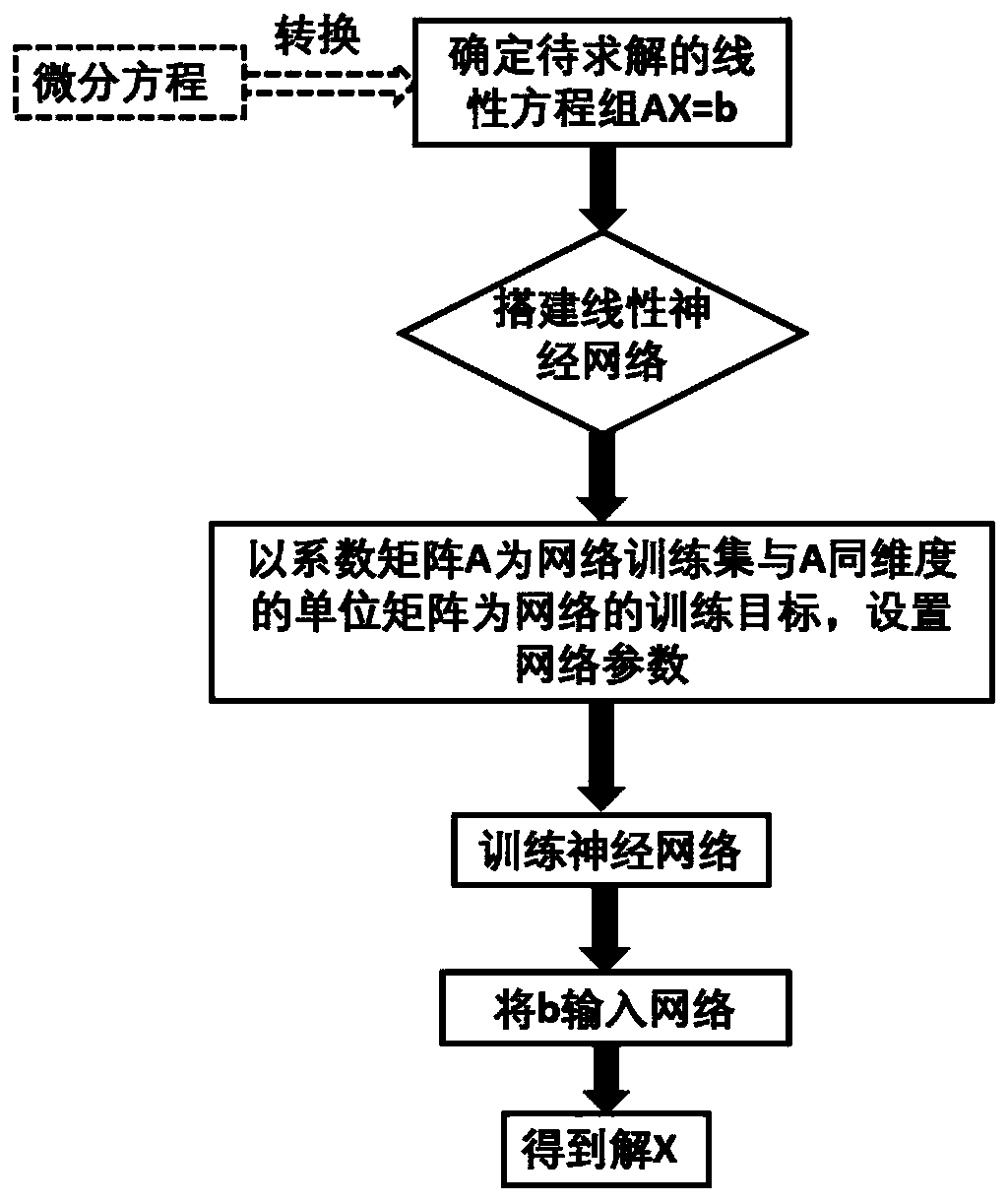
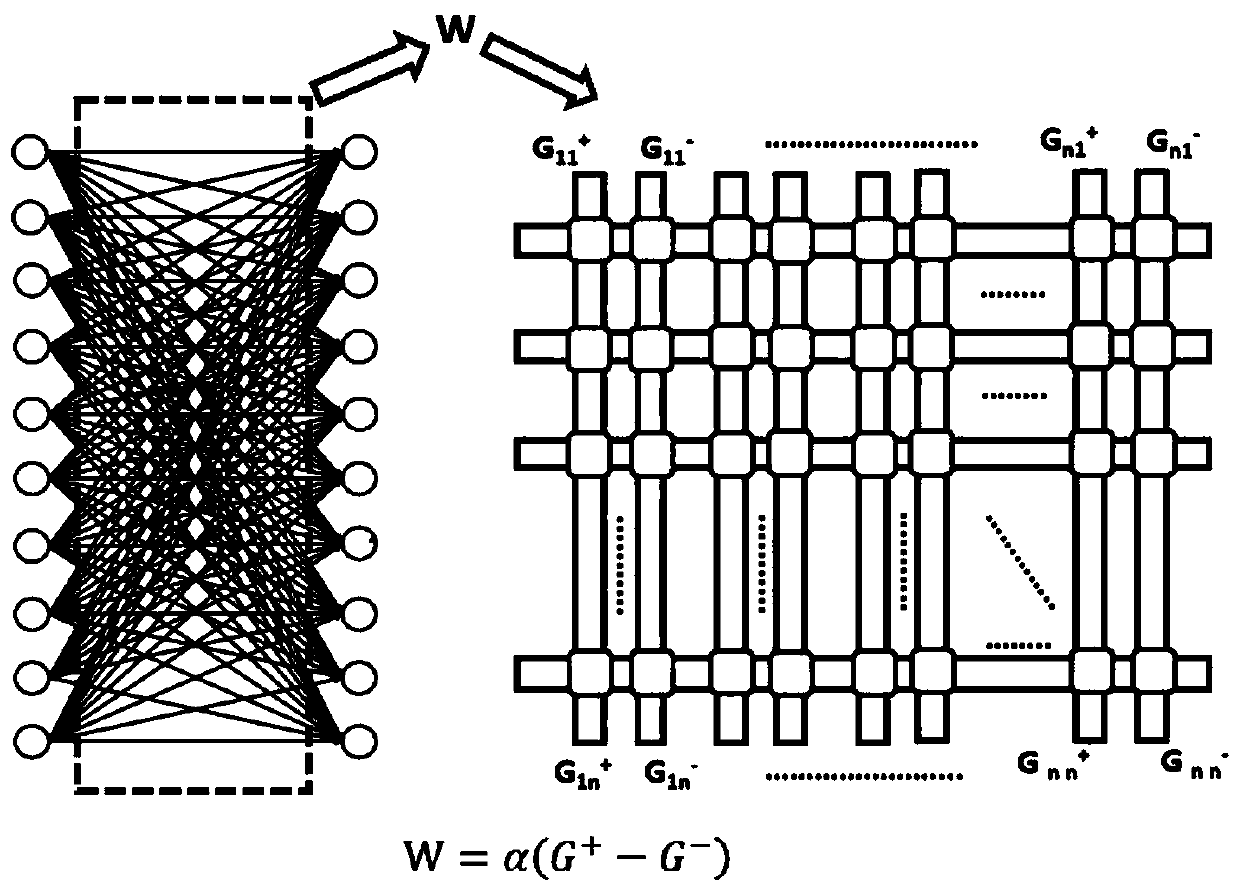
The invention discloses an equation set solver based on a memristor linear neural network and an operation method of the equation set solver. The solver comprises a digital-to-analog conversion module, a memristor array, a current subtraction circuit, an analog-to-digital conversion module, a comparison module and a conductivity modulation module, the memristor serves as a neural synapse of the neural network, analog vector-matrix multiplication operation is executed, the training process of the memristor linear neural network is completed, and finally an equation set is solved. According to the invention, the matrix inverse of the coefficient matrix is solved in the training process of solving the neural network; when differential equation is solved, only one training process is needed; the numerical solution can be expanded to the whole time domain through iteration, the circuit complexity is reduced, the process of one data transmission is reduced, and the circuit consumption is reduced. Compared with the traditional process of solving a linear equation set by using a computer, the circuit has the advantages that the time complexity can be effectively reduced, the fusion of storage and calculation can be realized, the operation energy consumption and time can be greatly saved, and the reliability is high.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
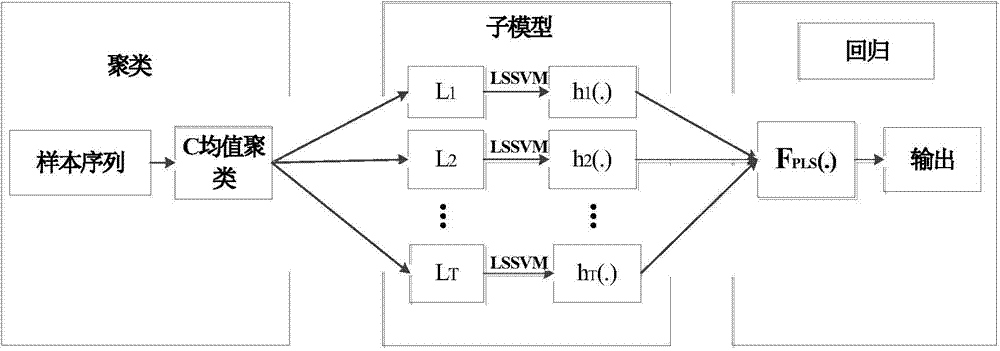
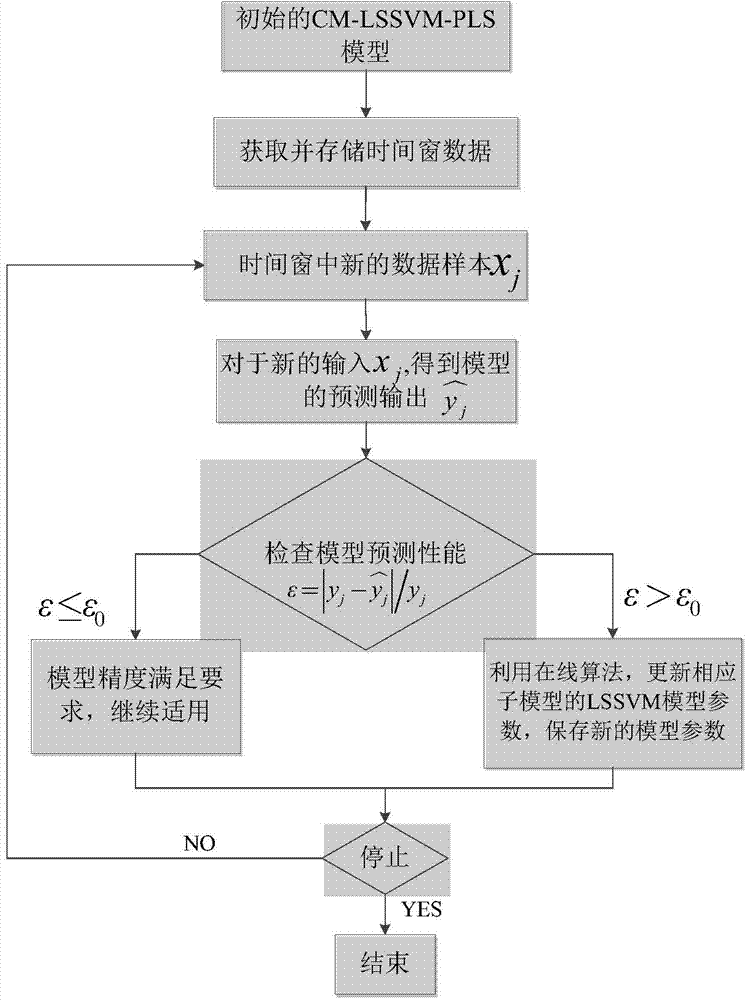
Online soft measurement method
InactiveCN104765955AReal-time online valueHigh precisionSpecial data processing applicationsReal-time dataMatrix inverse
The invention provides an online soft measurement method. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring operating data as a sample sequence; building a CM-LSSVM-PLS online soft measurement predicting model to train the model; using a model prediction measured value, and dynamically updating the model if a prediction error does not meet the requirements. According to the online soft measurement method provided by the invention, the measured value can be predicted by a CM-LSSVM-PLS method, the prediction precision can be improved, and the modeling time can be reduced; furthermore, the prediction precision can be further improved by dynamically updating the model; meanwhile, the matrix inverse operation can be carried out by a simple matrix, an algorithm is relatively simple, a result can be quickly calculated, and the model can be ensured to be applicable to online monitoring requirements; in addition, the soft measurement system is driven by real-time data, the model can be continuously updated according to the real-time data, and the online soft measurement method has the advantages of being likely to acquire data, low in extra hardware investment, high in model prediction precision, strong in self-adaption and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
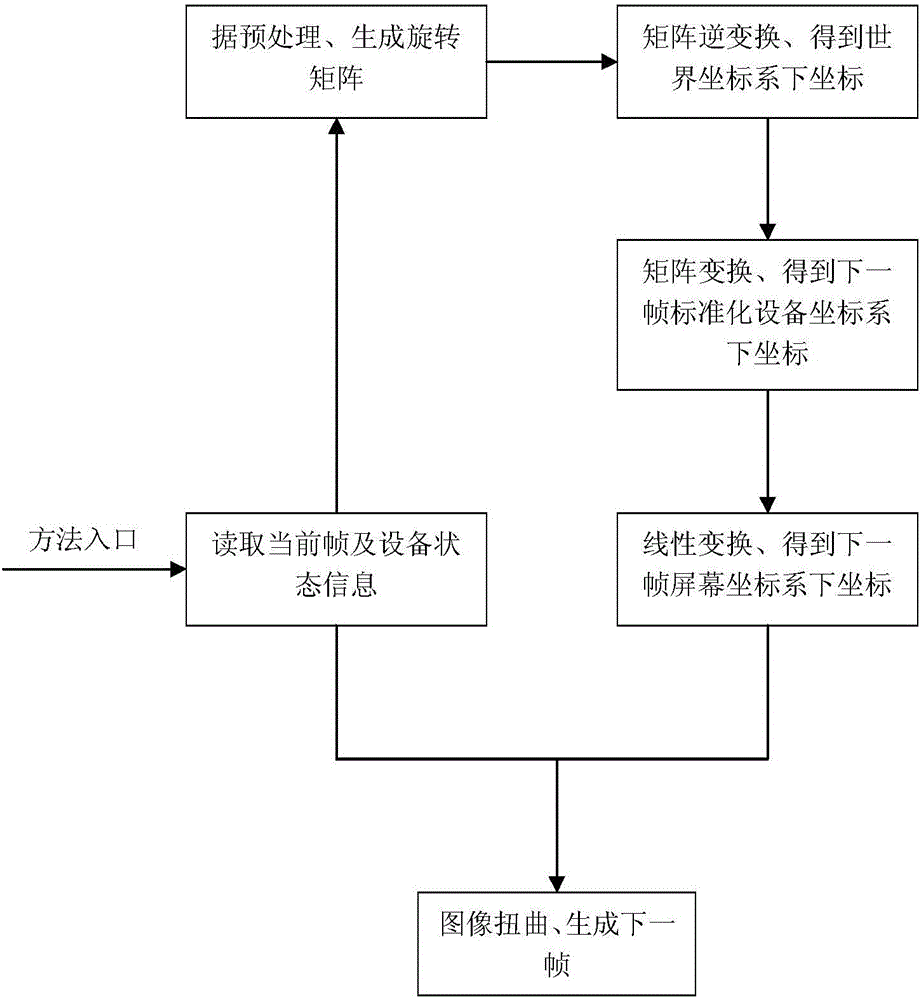
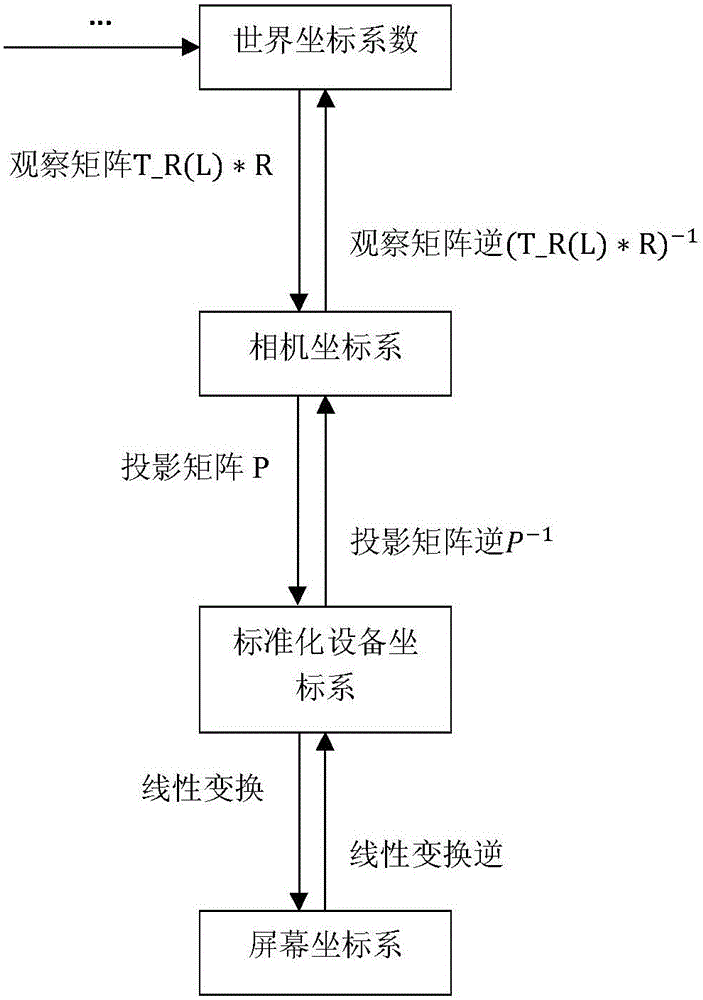
Image distortion method based on matrix inverse operation in virtual reality (VR) mobile end
ActiveCN106204418AReduce jitterImprove experienceGeometric image transformation3D-image renderingMatrix inverseFrame time
The invention discloses an image distortion method based on matrix inverse operation in a virtual reality (VR) mobile end. The method comprises the following steps: 1, reading a current frame and an equipment state; 2, converting coordinates under a screen coordinate system at current-frame time into coordinates under a standard equipment system at the current-frame time; 3, according to the coordinates under the standard equipment coordinate system at the current-frame time, obtaining coordinates in a world coordinate system; 4, according to the coordinates in the world coordinate system, obtaining coordinates under the standard equipment coordinate system at corresponding next-frame time; 5,performing linear transformation on the coordinates under the standard equipment coordinate system at the next-frame time so as to finally obtain coordinates under the screen coordinate system through the transformation; and 6, endowing the coordinates under the screen coordinate system at the corresponding next-frame time with pixel RGB values of the coordinates under the screen coordinate system at each current-frame time so as to obtain a final distortion image. The method is a method for generating intermediate frames in VR, can effectively reduce jittering in a VR game, and improves user experience.
Owner:NANJING RUIYUE INFORMATION TECH
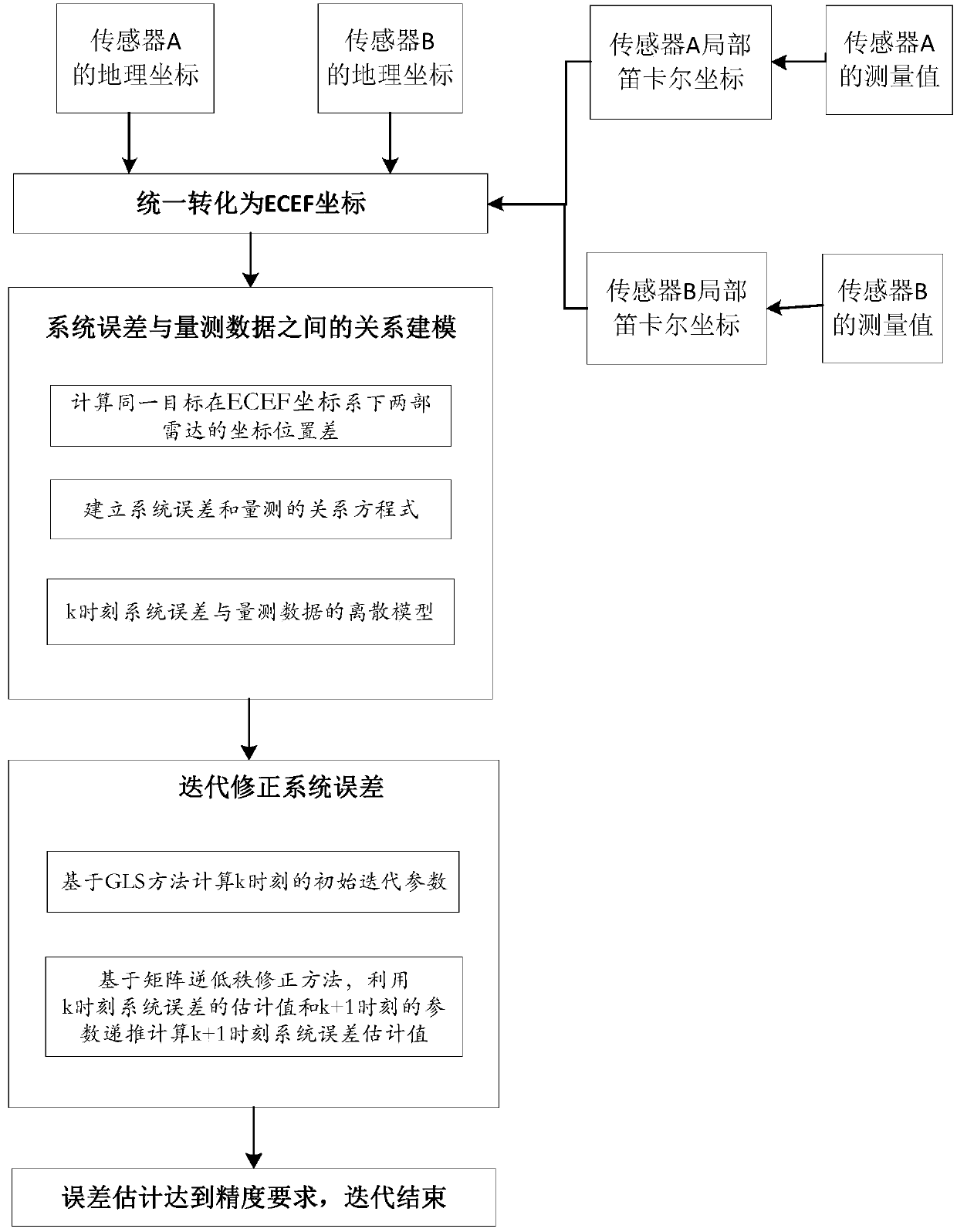
Multi-sensor system error registration method and system based on recursion correction
ActiveCN109782240AGuaranteed robustnessGuaranteed convergence speedWave based measurement systemsMatrix inverseModel parameters
The invention provides a multi-sensor system error registration method and system based on recursive correction. The method comprises the steps: building a discretization model of a system error estimation equation according to the position difference, obtained by two radars, of the same target in a geographic coordinate system and the relation equation of system errors and measurement; calculating an initial iteration parameter of the discretization model at the initial estimation moment by utilizing a generalized least square algorithm, then obtaining a recursion model of system error estimation at the current moment by correcting an error estimation value at the previous moment based on a matrix inverse low-rank correction method, and carrying out error registration on the multi-sensorsystem through iteration by using the recursion model. By applying the scheme, the problems that a large amount of data needs to be stored, data accumulation is waited, the calculated amount is large,the real-time performance is poor, repeated work exists and the like in traditional registration based on the GLS method can be solved, and meanwhile the convergence speed of the registration methodand the robustness to model parameters can be guaranteed.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF ELECTRONICS SYST ENG
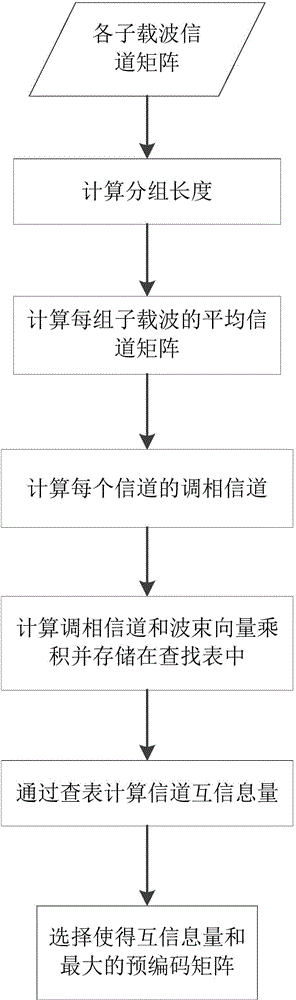
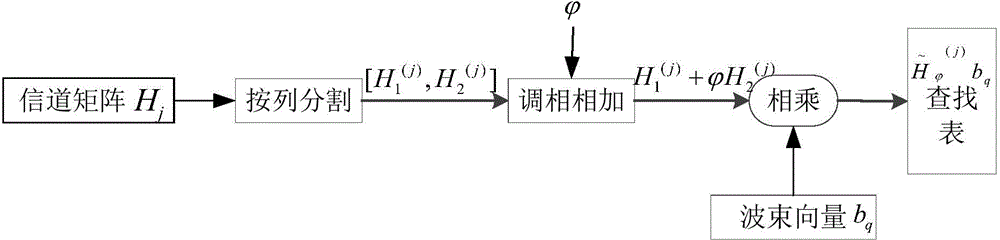
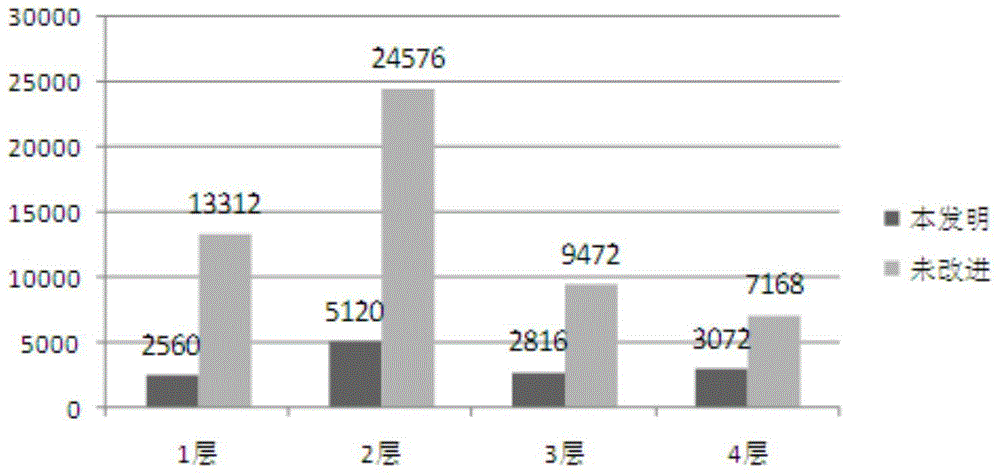
LTE-A double codebook pre-coding selection method based on wave beam operation and group average
ActiveCN104883215AEnsure consistencyReduce computational complexitySpatial transmit diversityComputation complexityMatrix inverse
The invention discloses an LTE-A double codebook pre-coding selection method based on wave beam operation and group average. Aiming at double codebook pre-coding adopted in 1 to 4 transmission layers in an LTE-A8 antenna spatial multiplexing mode, taking mutual information maximization as a rule and through traversing wave beam vectors and phase modulating parameters and storing products of phase modulating channels and wave beams, the calculation of mutual information can be acquired through table look-up and a problem of a large amount of repeated calculation in pre-encoding matrix selection in the prior art is solved. According to the invention, the thought of group average is adopted for grouping subcarriers of the whole bandwidth and mutual information amount is calculated by utilizing the average value of the channels, so that the number of the channels requiring calculation is reduced substantially. Under a premise of not losing pre-coding performance, frequencies of complex multiplication, addition and matrix inverse operation are reduced and calculation complexity is reduced.
Owner:上海瀚芯实业发展合伙企业(有限合伙)
Methods to generate state space models by closed forms and transfer functions by recursive algorithms for RC interconnect and transmission line and their model reduction and simulations
ActiveUS20050160382A1Accurate captureComputationally efficientComputation using non-denominational number representationProgram controlComputation complexityMatrix inverse
There is provided a set of methods with the exact accuracy to effectively calculate the n-th order state space models of RC distributed interconnect and transmission line in closed forms in time domain and transfer functions by recursive algorithms in frequency domain, where their RC components can be evenly distributed or variously valued. The main features include simplicity and accuracy of the said closed forms of the state space models {A,B,C,D} without involving matrix inverse and matrix multiplication operations, effectiveness and accuracy of the said recursive algorithms of the transfer functions, dramatic reduction of the calculation complexity to O(n) for the state space models, simulation methodology, and practice of various model reductions and their optimization. For evenly distributed RC interconnect and transmission line, the said closed form of state space model has its computation complexity of only a fixed constant, i.e., O(l).
Owner:BEN SHENG TECH
Methods for multi-user MIMO wireless communication using approximation of zero-forcing beamforming matrix
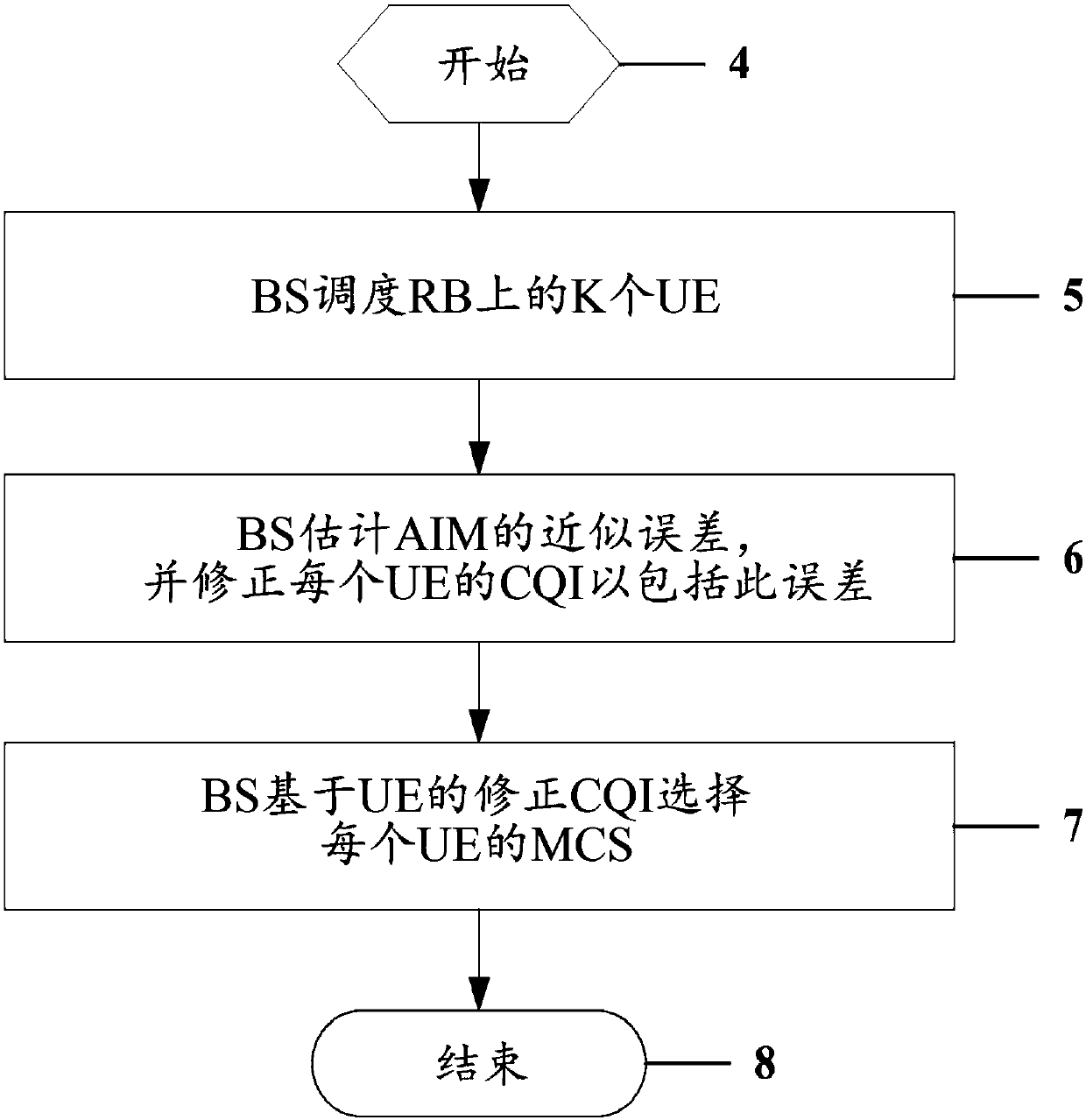
ActiveCN107005291ASpatial transmit diversityChannel coding adaptationPresent methodCommunications system
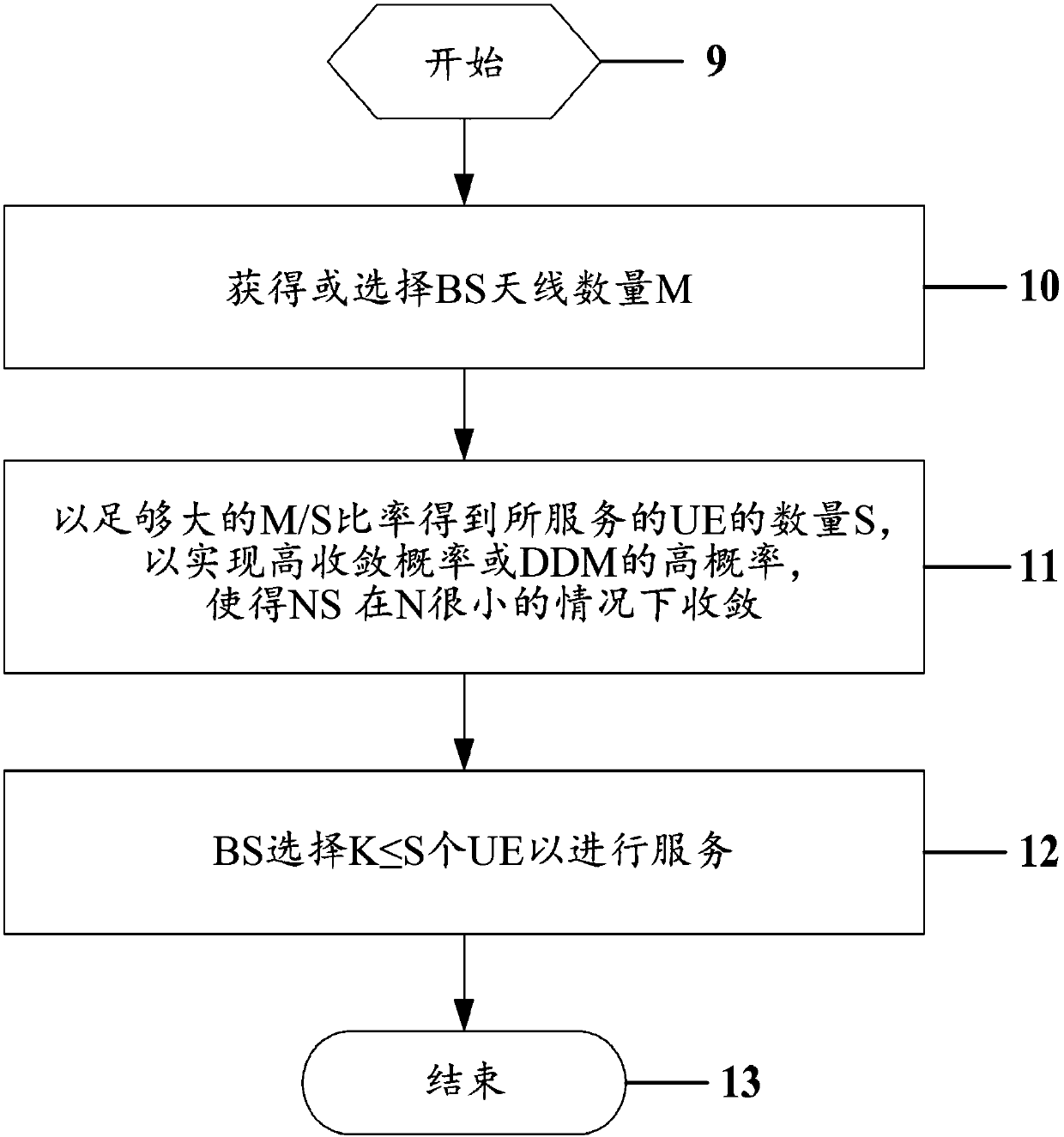
This invention presents methods for signal detection and transmission in MU-MIMO wireless communication systems, for inverse matrix approximation error calculation, for adaptively selecting the number of multiplexed UEs in a MU-MIMO group, for adaptively choosing a modulation and channel coding scheme appropriate for the quality of MU-MIMO channels with the approximation error of matrix inverse being incorporated.
Owner:LIANG PING
A soft in and soft out detection method capable of reducing the complexity
InactiveCN101056161AReduce complexityReduce the number of matrix inversionsError prevention/detection by diversity receptionMatrix inverseCovariance matrix
The present invention provides a soft-inlet-soft-outlet detecting method which can reduce the complexity through replacing the instantaneous covariance matrix by the average of the emitting symbol vector covariance matrix, namely one of said average channel values is used to replace the channel value of the whole region. Thus, Nt*T*F of matrix inverses are simplified to form one matrix inverse. In the present invention, only one time of matrix inverse is required in a high correlation channel region, and the complexity of the system is reduced greatly without any losing.
Owner:SHANGHAI RES CENT FOR WIRELESS COMM
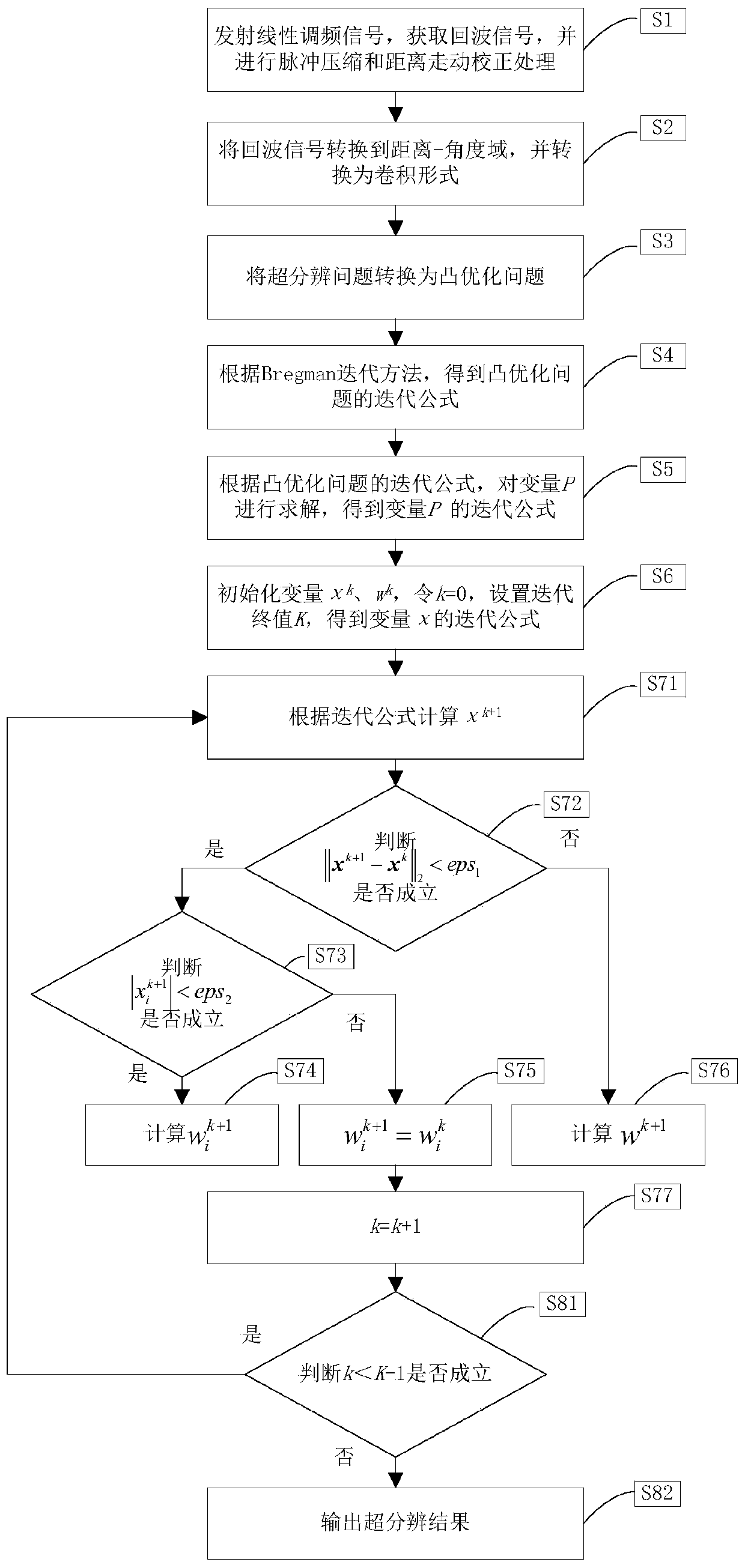
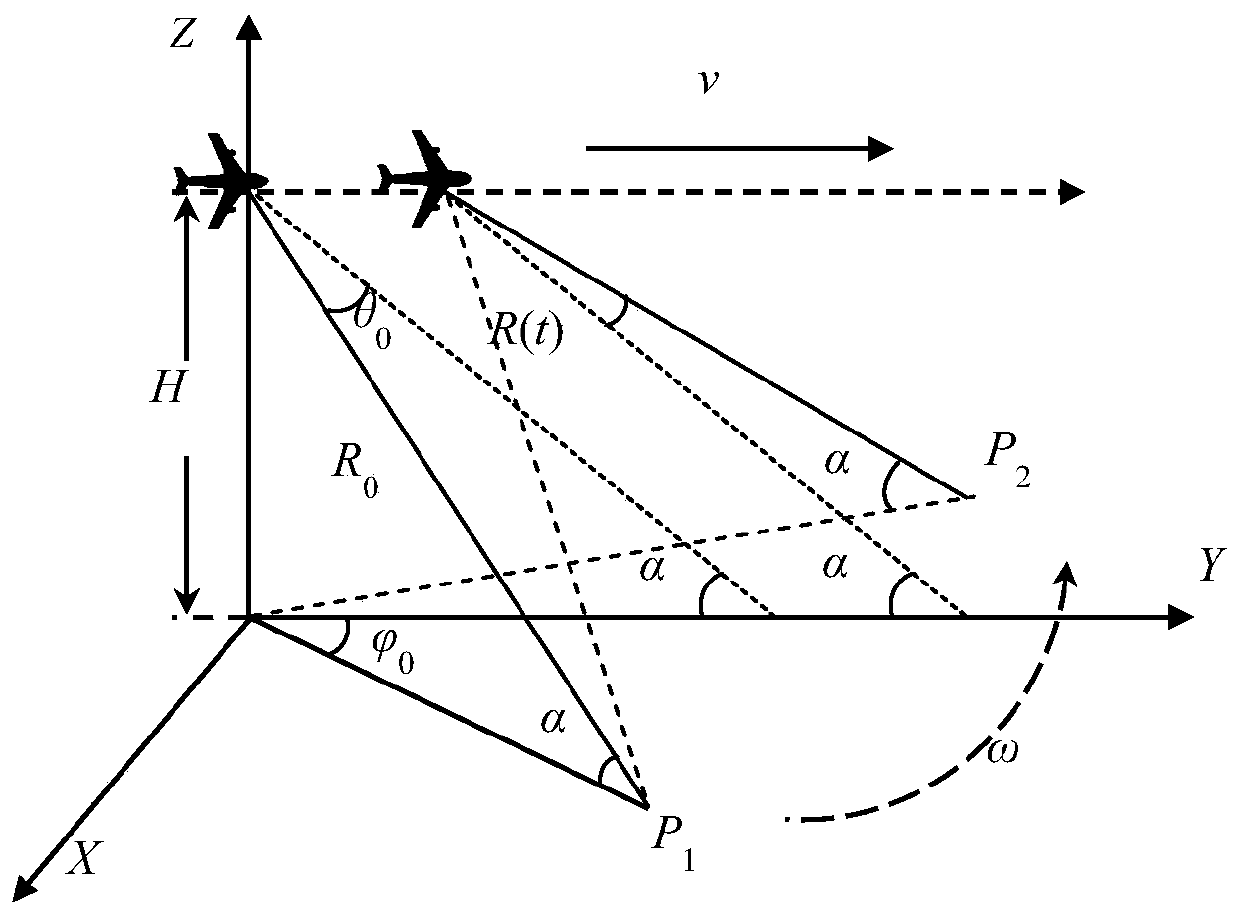
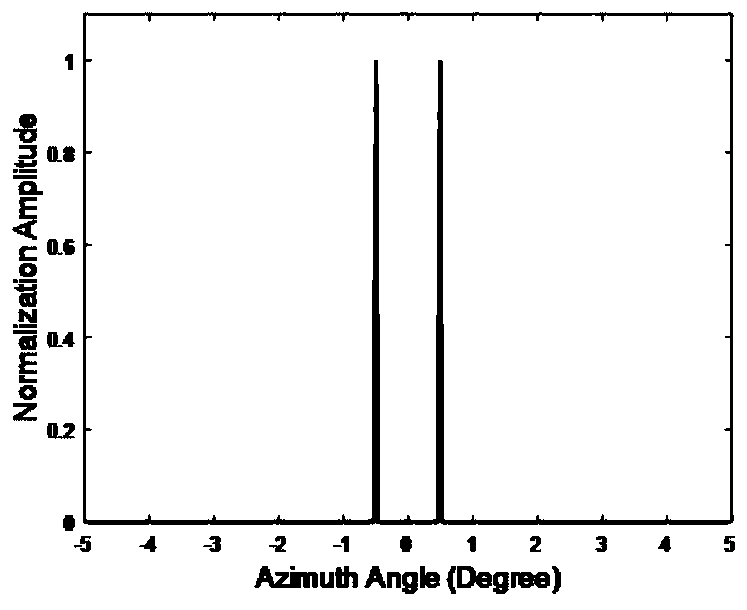
Scanning radar forward-looking imaging orientation super-resolution method
ActiveCN110109097AAvoid inverse operationsSuppress noiseRadio wave reradiation/reflectionMatrix inverseMaximum a posteriori estimation
The invention provides a scanning radar forward-looking imaging orientation super-resolution method, and belongs to the field of radar imaging. The scanning radar forward-looking imaging orientation super-resolution method aims to solve the problem that radar forward-looking imaging orientation resolution is low, and the azimuth resolution of radar forward-looking imaging is improved through a Bayesian deconvolution method. According to the scanning radar forward-looking imaging orientation super-resolution method, firstly noise obeys complex Gaussian distribution, and a target obeys laplace distribution; then under a Bayesian framework, a super-resolution problem is transformed to a convex optimization problem based on maximum a posteriori estimation; and finally the convex optimization problem is evaluated through an LBWK (linearized Bregman with kicking ) arithmetic, and azimuth super-resolution imaging is achieved. According to the scanning radar forward-looking imaging orientationsuper-resolution method, the creation is that priori distribution of the target and the noise is introduced, the matrix inverse operation is avoided in the calculating process, noise amplifying is effectively restrained, time consumption caused by the inverse operation is lowered, and thus better super-resolution performance is achieved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
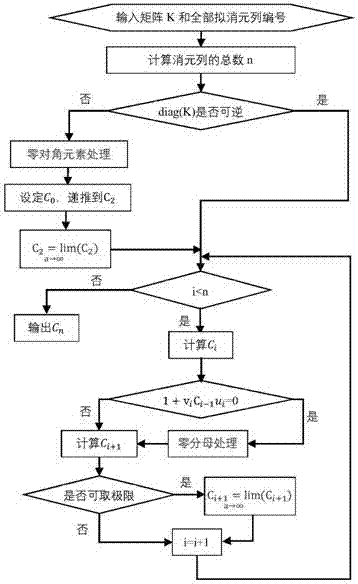
Method for processing zero denominator condition of matrix inversion lemma, and method for recursively solving inverse matrix level by level
The invention discloses a processing method for overcoming a zero denominator condition of a matrix inversion lemma through limit operation, and a method for recursively solving an inverse matrix level by level. The method comprises the main steps of firstly, decomposing any n-order invertible matrix K into a sum of a diagonal element matrix diag(K) and n rank-1 matrixes, defined in the specification, wherein ui is an ith column of the matrix (ki,i is set to be 0), vi is an n-dimensional row vector (the rest are equal to 0 except vi(i) is equal to 1); secondly, according to a recursion formula defined in the specification, performing calculation, wherein i is greater than or equal to 1 and less than or equal to n, C0 is equal to diag(K)<-1>, and Cn is equal to K<-1>; in the calculation, when an element ki,i of diag(K) is equal to 0, assuming a formula defined in the specification firstly, performing recursion twice, and defining C2=lima->infinity(C2); and in the calculation, when the condition of 1+vi.Ci-1.ui=0 occurs, assuming a formula defined in the specification firstly, performing recursion and defining Ci+1=lima->infinity(Ci+1). According to the recursion method, inverse of a Hilbert matrix can be accurately solved; a Gauss-Jordan elimination process can be realized by left multiplication of an elimination matrix and an original matrix; and in combination with a condensable selection freedom degree of elementary matrix transformation, the elimination matrix is used for preprocessing a finite element stiffness matrix, so that a condition number can be greatly reduced.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
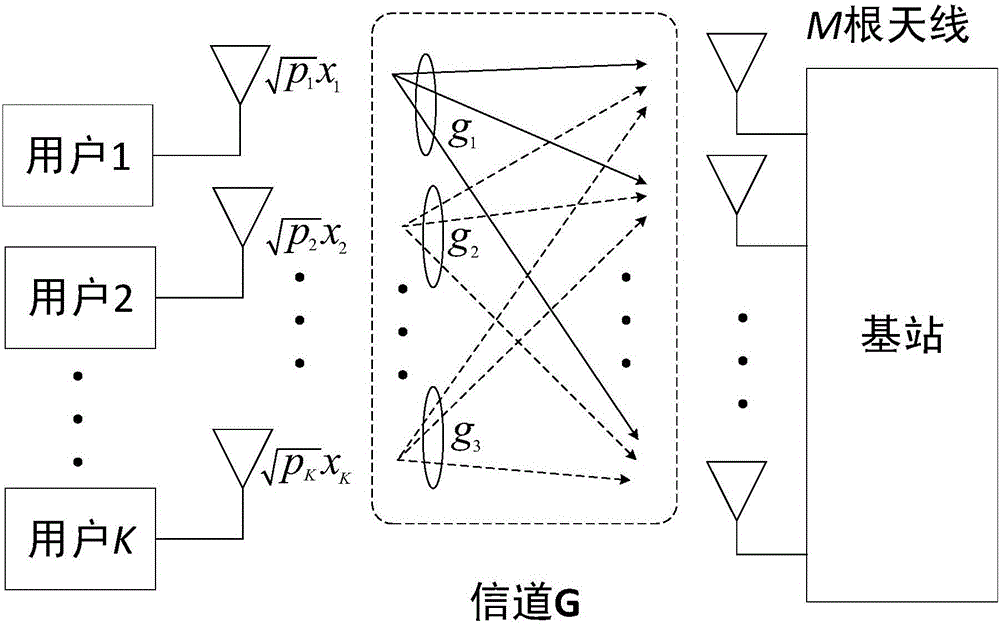
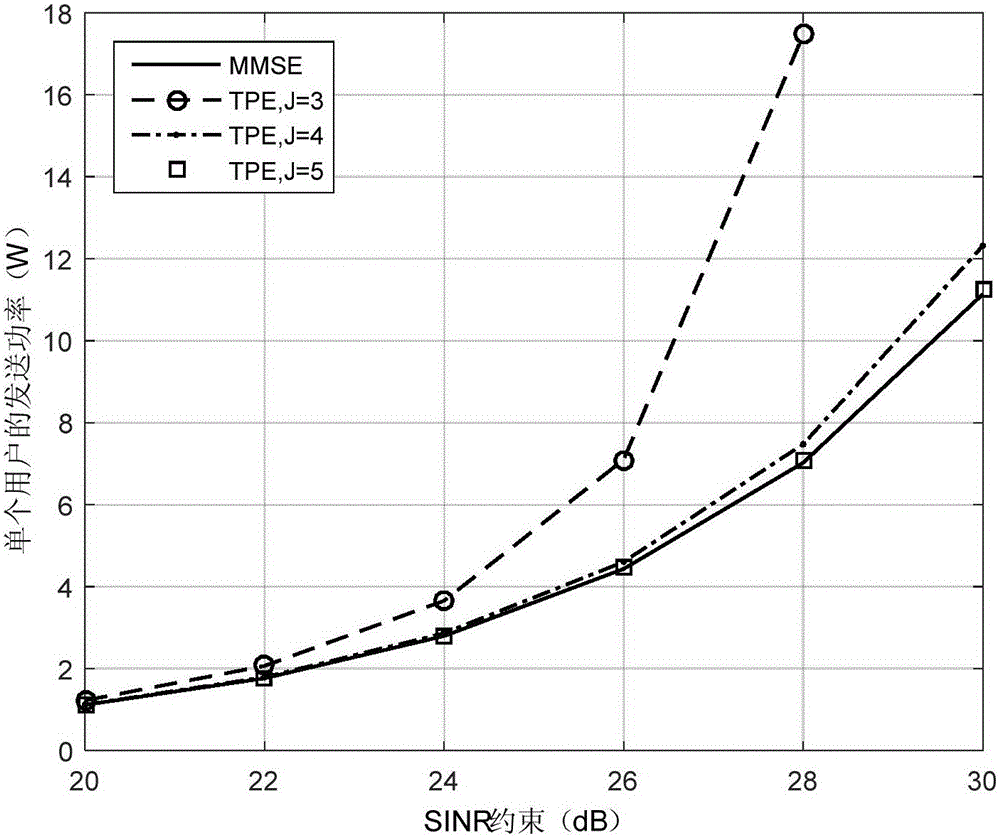
Power control method for uplink large-scale MIMO (Multiple Input Multiple Output) system based on low complexity receiver
ActiveCN105744613AIncreased complexityReduce complexityPower managementSpatial transmit diversityChannel state informationMatrix inverse
The invention discloses a power control method for an uplink large-scale MIMO (Multiple Input Multiple Output) system based on a low complexity receiver. The power control method comprises the following steps: in the uplink large-scale MIMO system, adopting a truncated polynomial (TPE) receiver, and taking a truncated polynomial as an inverse matrix in a minimum mean square error (MMSE) receiver; and acquiring statistical channel state information by a base station, and using an iterative algorithm to perform joint optimization on a multinomial coefficient of the TPE receiver and an uplink transmitting power of a user. The power control method for the uplink large-scale MIMO system based on the low complexity receiver provided by the invention effectively avoids a large dimensional matrix inverse operation of the MMSE receiver and reduces the complexity, and the performance can be approximated to the MMSE receiver.
Owner:上海瀚芯实业发展合伙企业(有限合伙)
Time delay correlation H-infinity control method for linear singular system with uncertain time delay
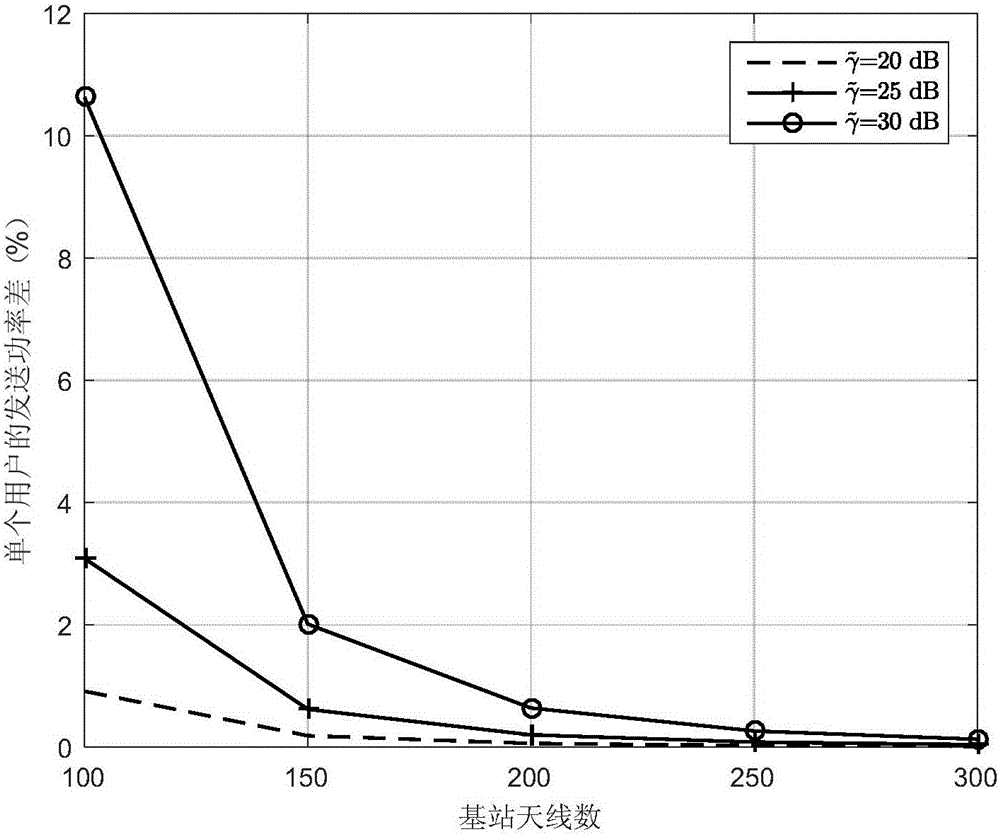
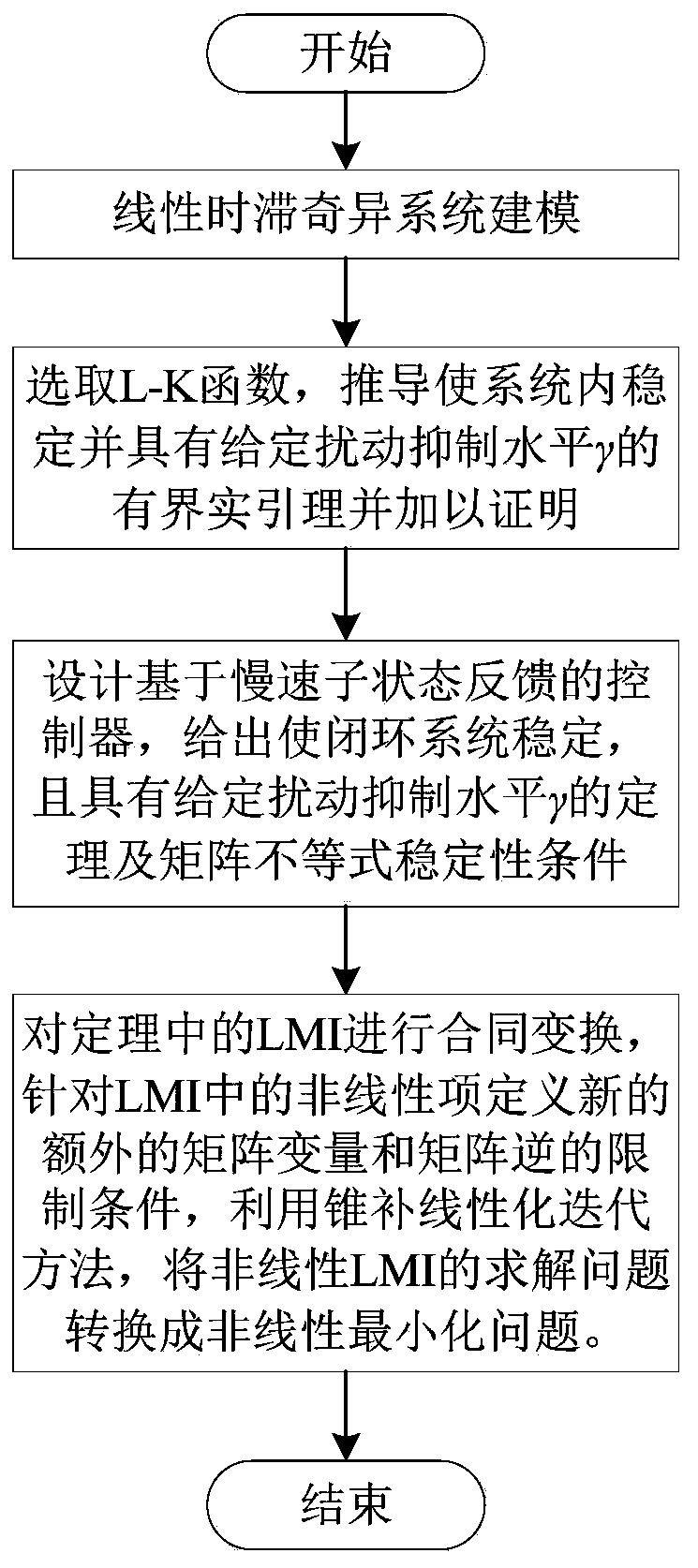
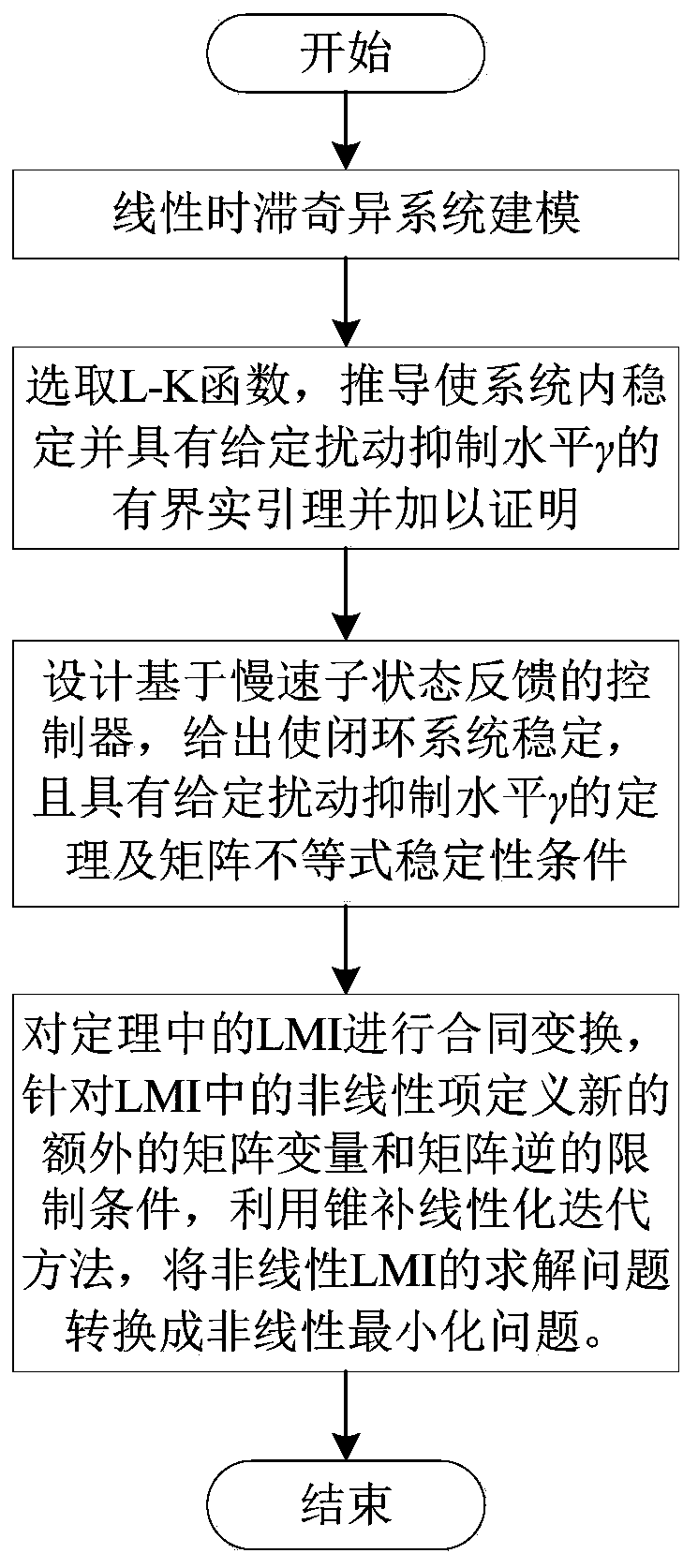
The invention aims to provide a time delay correlation H-infinity control method for a linear singular system with uncertain time delay. The method comprises the following steps: giving a state spacedescription of the linear singular system with the uncertain time delay; selecting a Lyapunov-Krasovskii function, and deriving and proving a bounded real lemma and an LMI inequality which enable thesystem to be stable and have a given H-infinity disturbance suppression level gamma by utilizing a method of combining an improved free weight and the Lyapunov-Krasovskii function; designing a non-memory controller u(t) = Kx1 (t) based on slow sub-state feedback, and giving a matrix inequality condition which enables a closed-loop system to be stable and contains nonlinearity; performing contracttransformation on the matrix inequality condition; defining new extra matrix variables and matrix inverse limiting conditions for nonlinear terms in a matrix inequality, and using a cone compensationlinearization iteration method to convert a solving problem of the nonlinear matrix inequality into a nonlinear minimization problem, so that an obtained result has a given disturbance suppression level gamma while ensuring the stability of a closed-loop system.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com